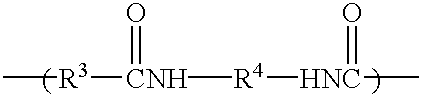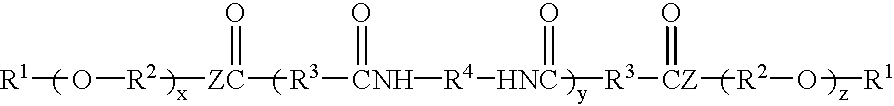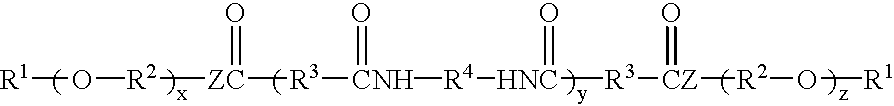Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
274results about "Candle ingredients" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
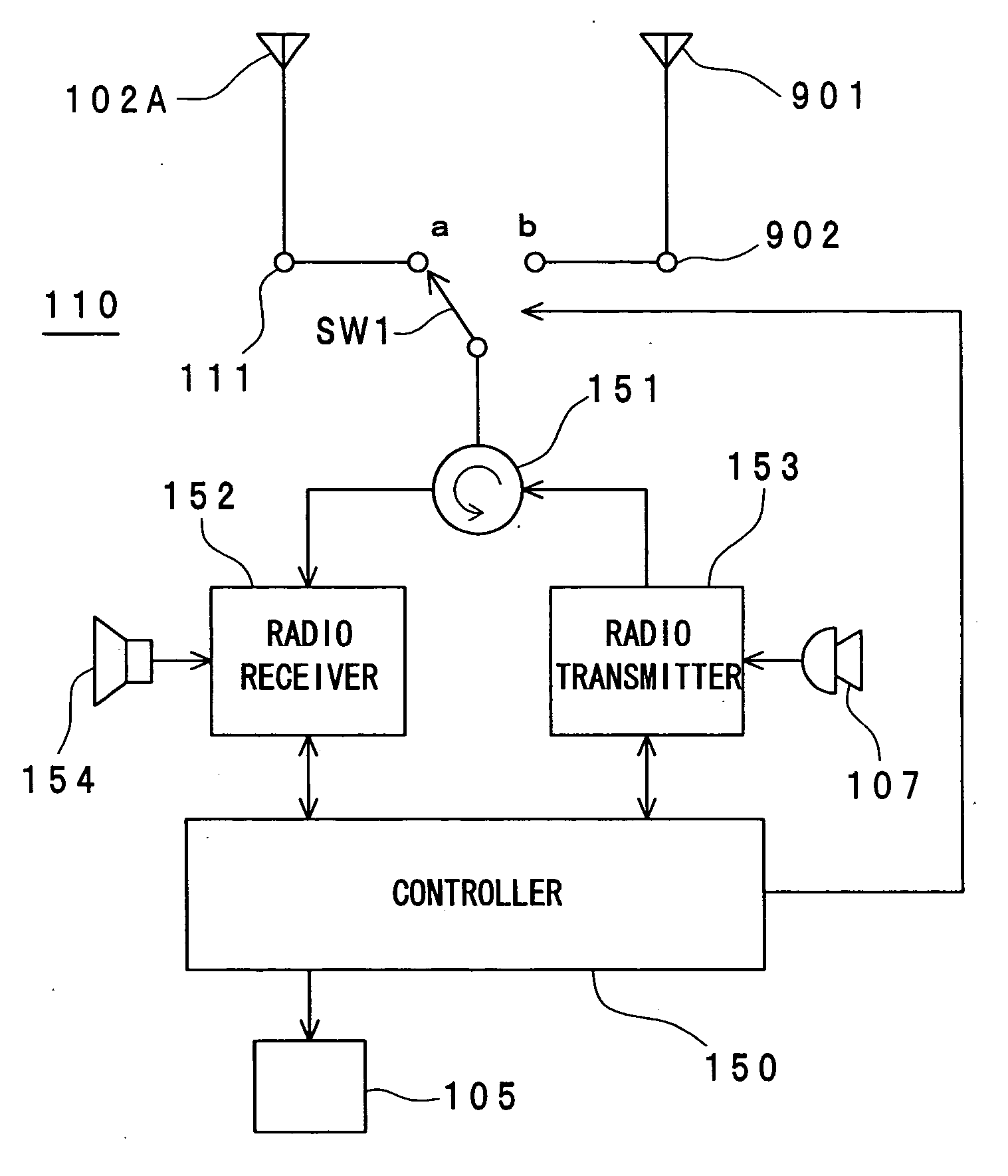
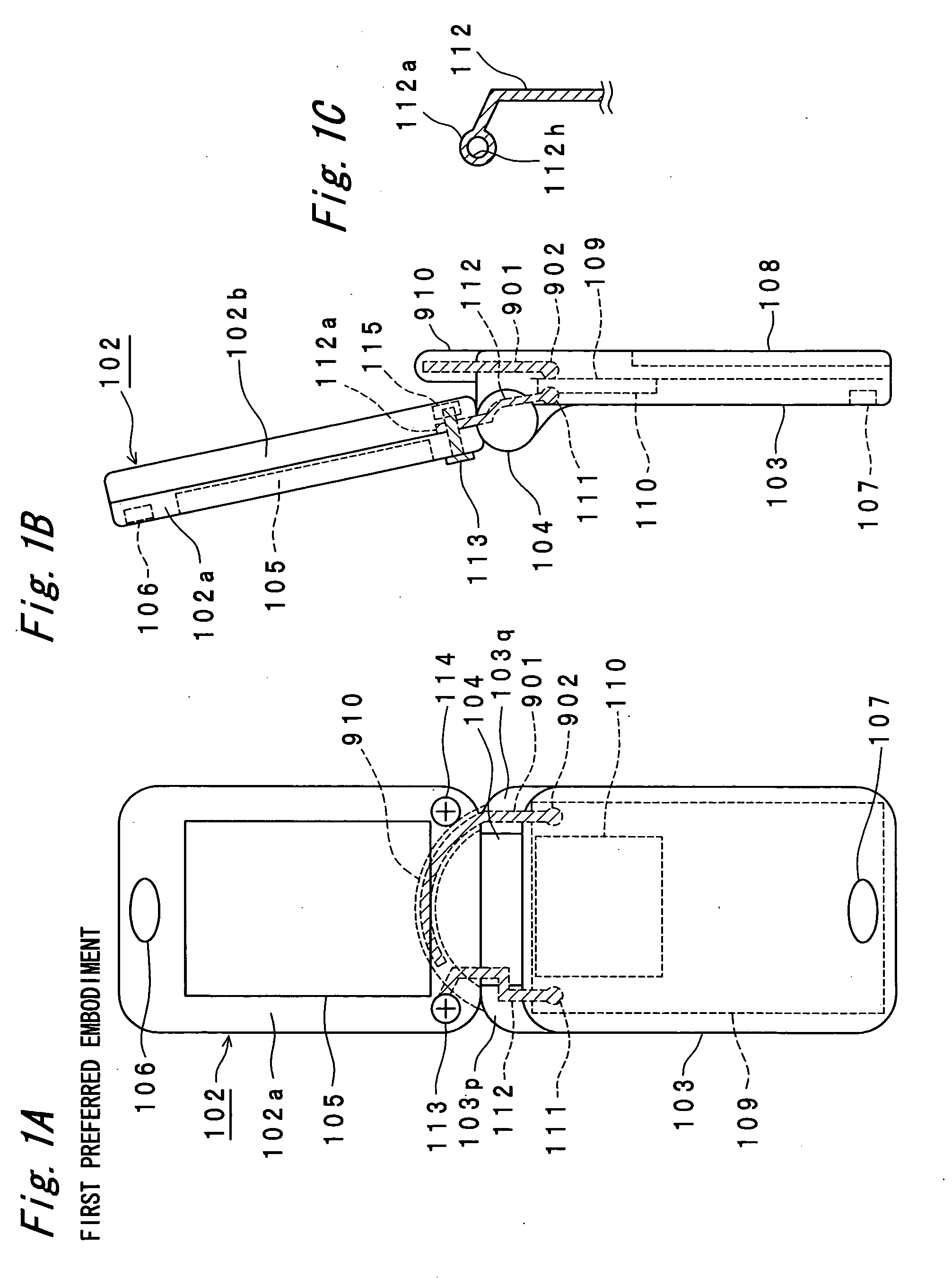
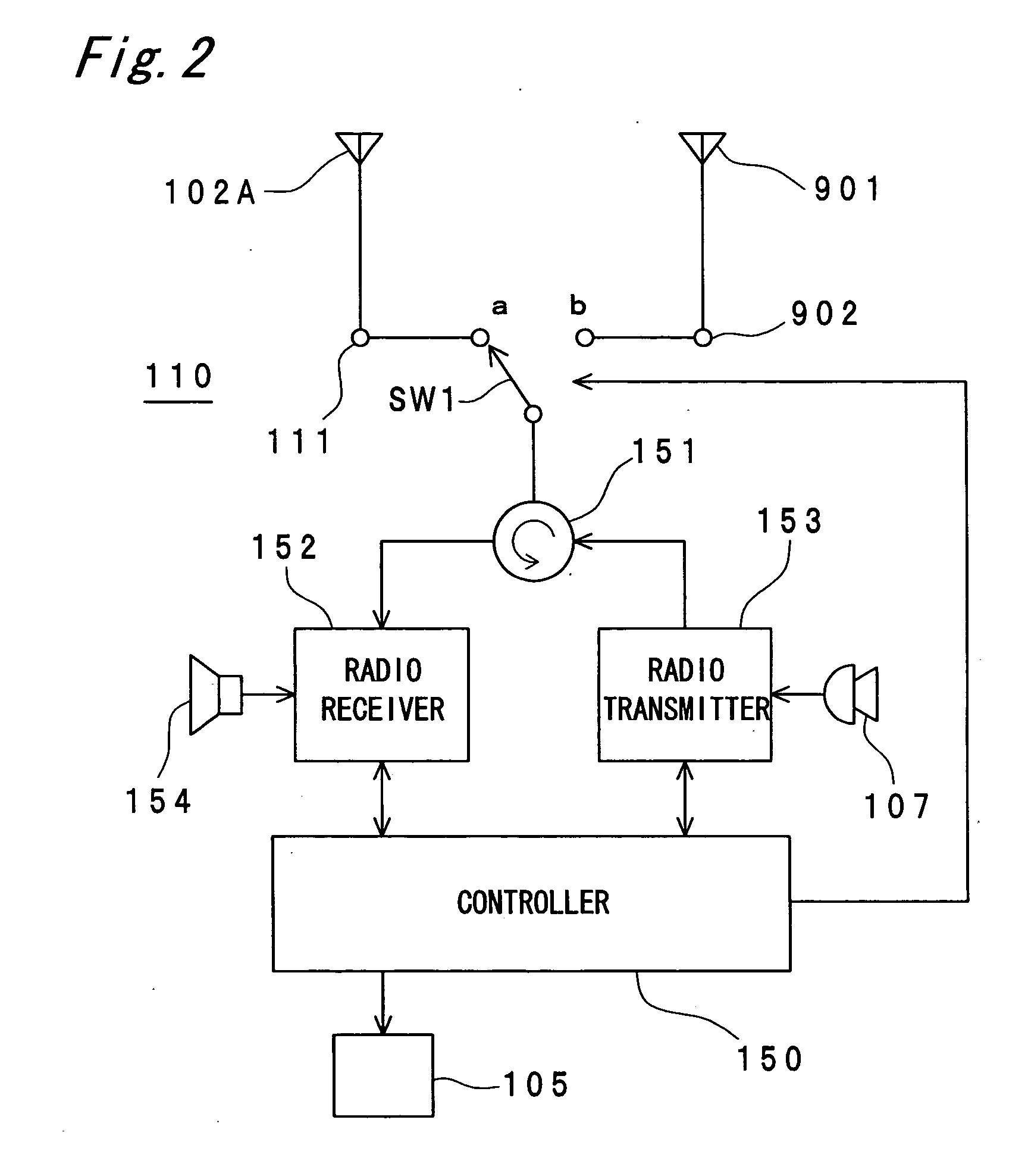
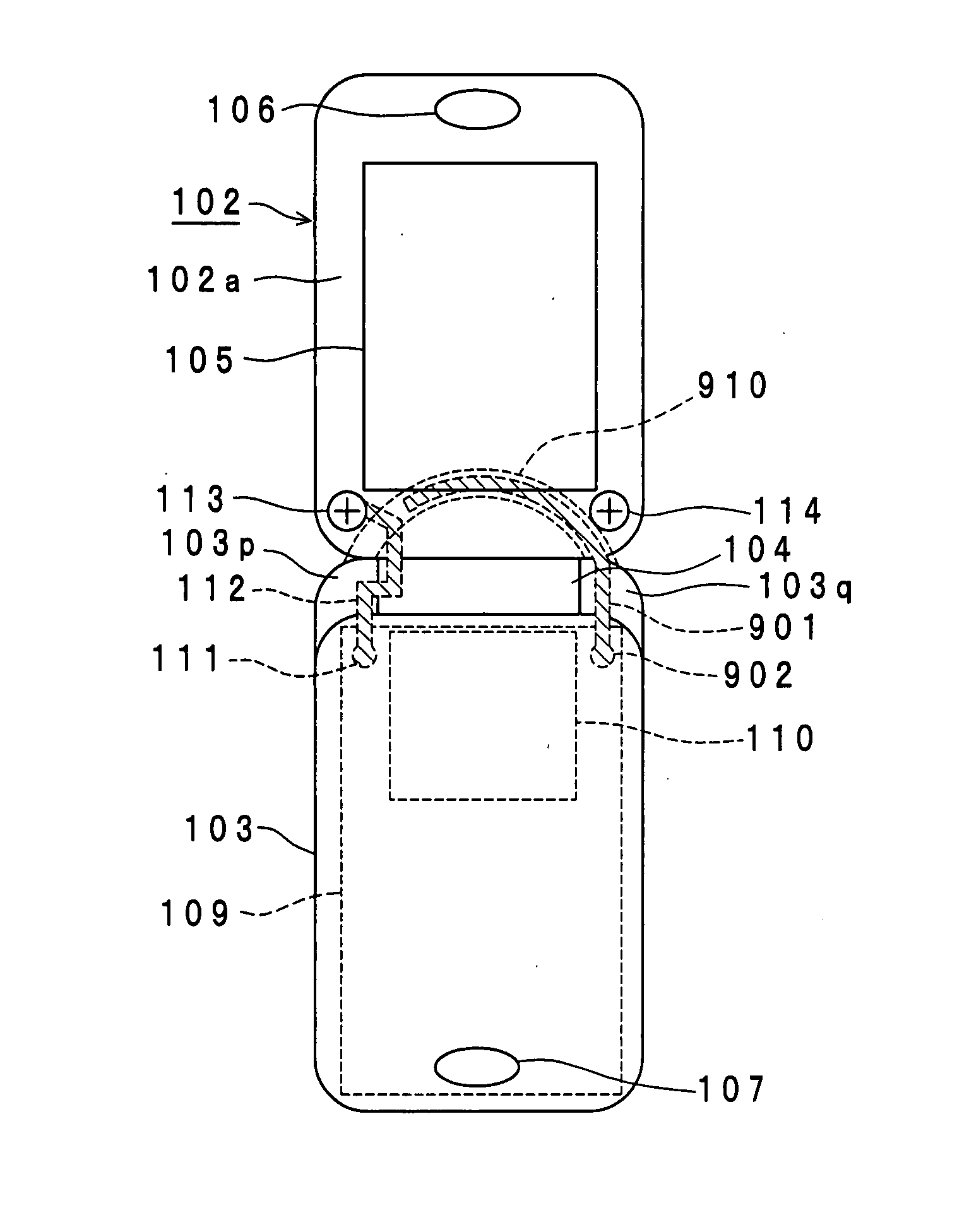
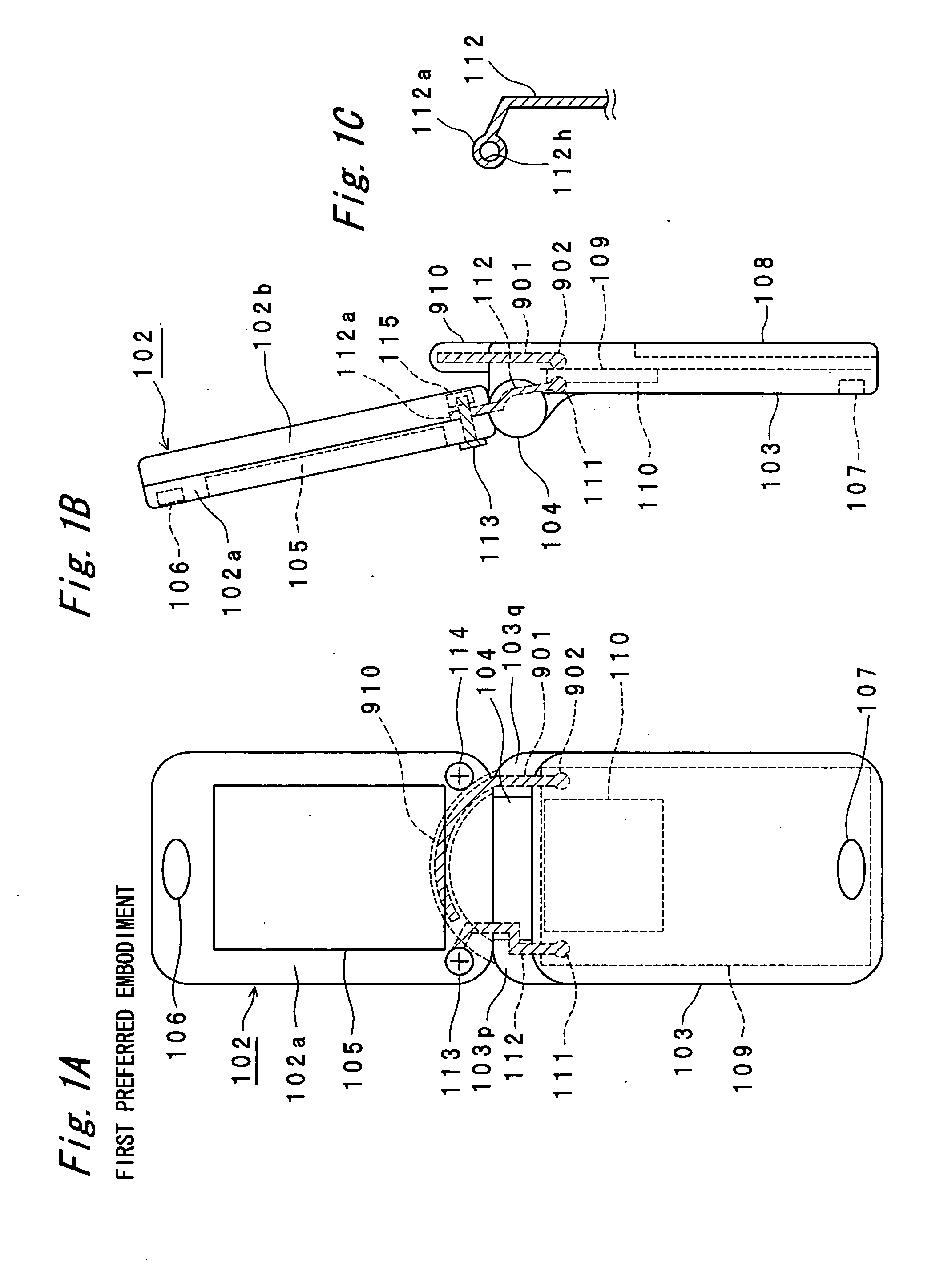
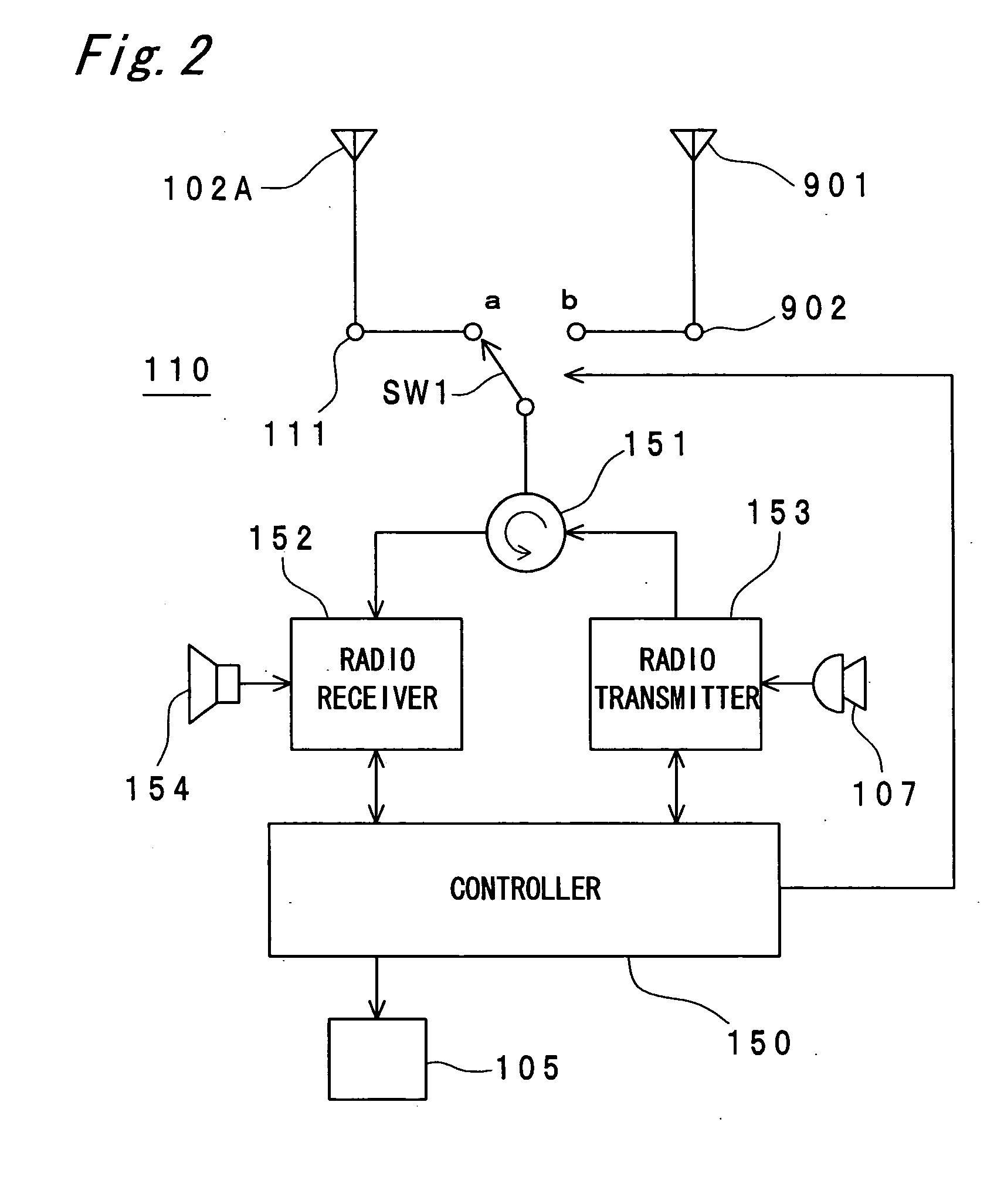
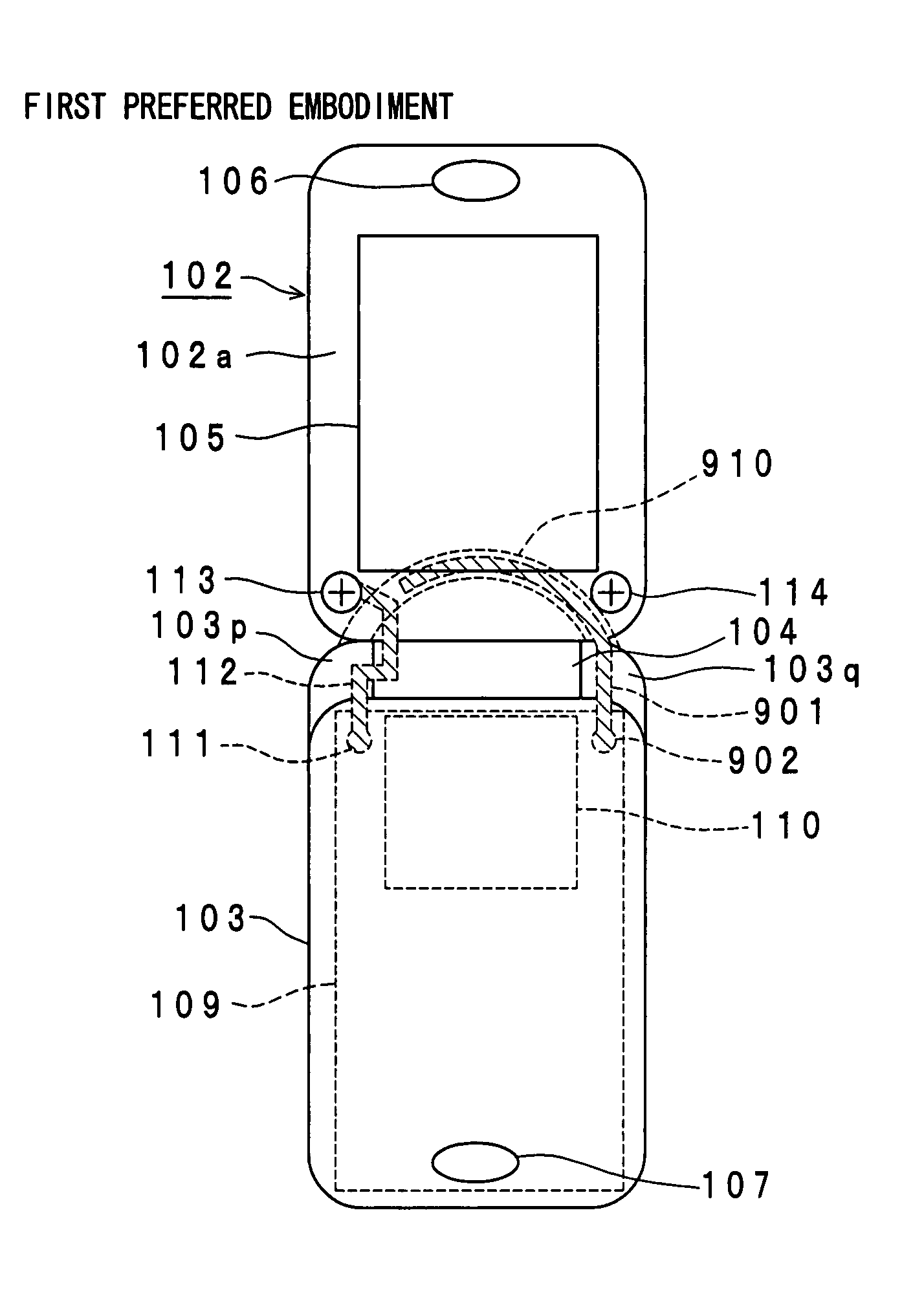
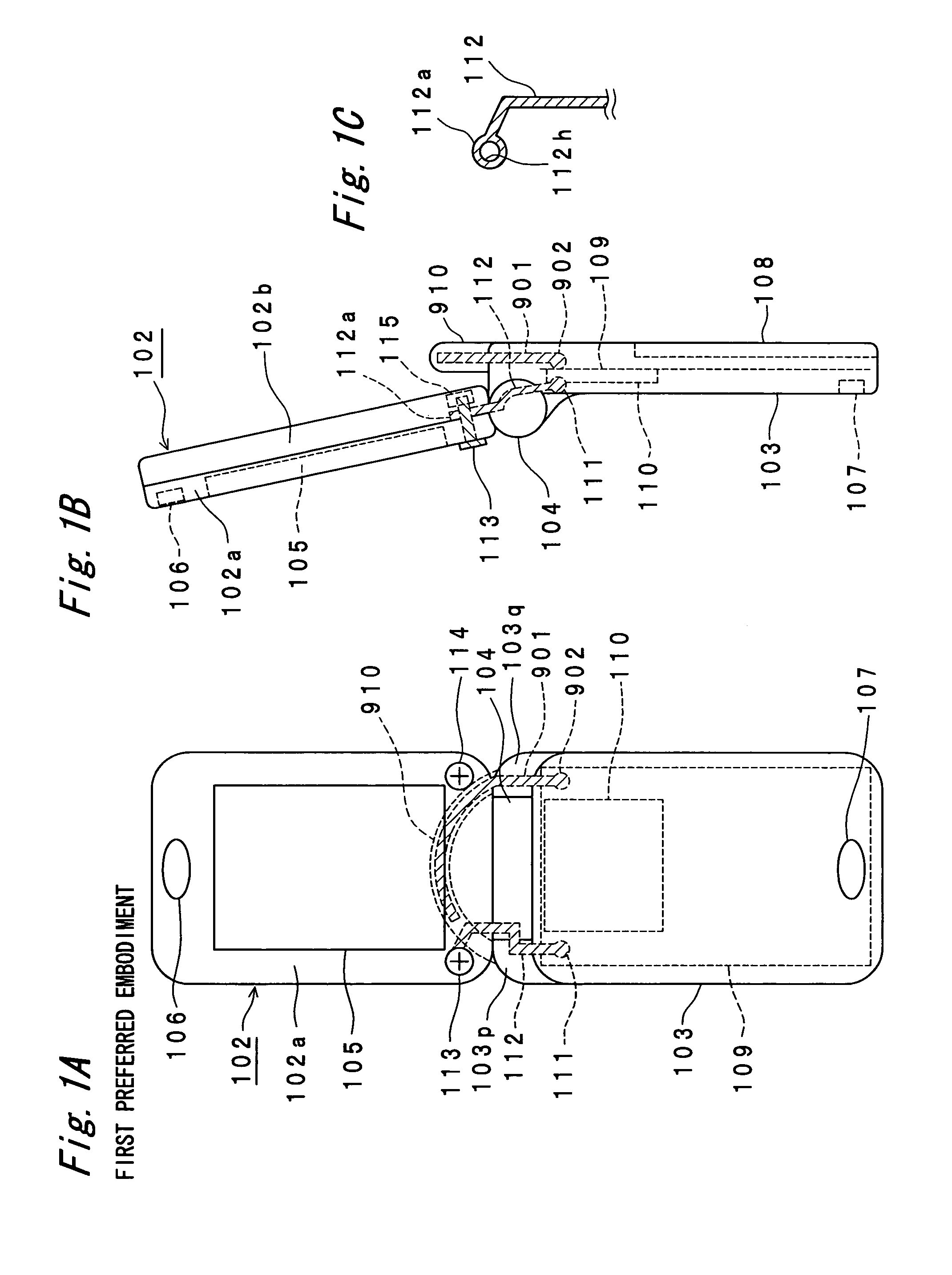
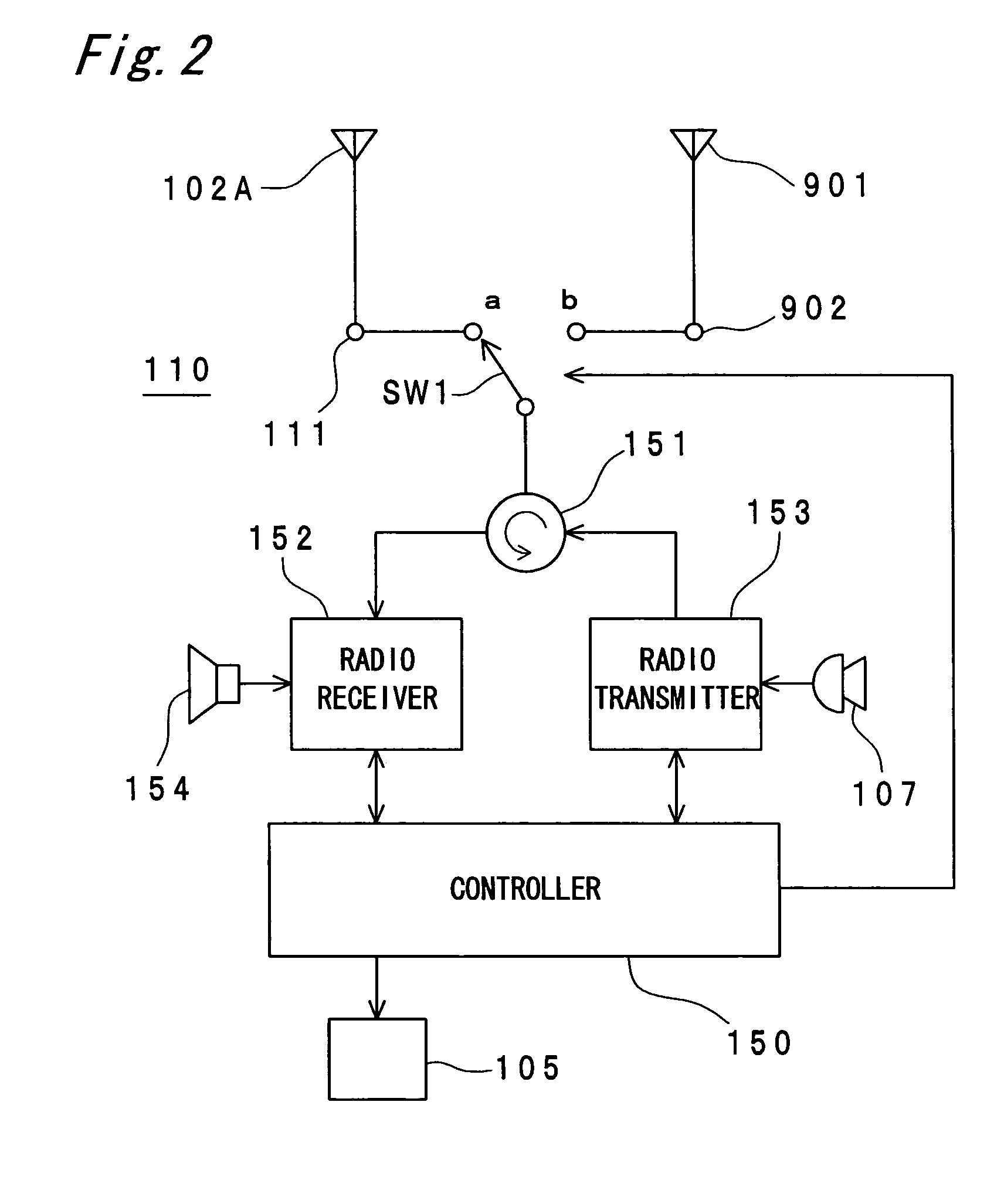
Portable radio communication apparatus provided with a boom portion and a part of housing operating as an antenna
ActiveUS20040219956A1Uniform processImprove featuresAntenna arraysSimultaneous aerial operationsElectrical conductorCantilever
In a portable radio communication apparatus including a housing, at least one part of at least one of the housing is formed as a housing electrical conductor portion by an electrically conductive material. The housing electrical conductor portion is connected with a radio communication circuit of the portable radio communication apparatus so as to operate as at least one part of an unbalanced type antenna of the radio communication circuit. Further, the portable radio communication apparatus further includes a boom portion coupled with the housing at least at two positions so as to provide at least one penetrating hole between the housing and the boom portion.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Portable radio communication apparatus provided with a part of housing operating as an antenna
ActiveUS20040227673A1High strengthThinner and lighter in weightSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsElectrical conductorEngineering
In a portable radio communication apparatus including a housing, at least one part of the housing is formed as a housing electrical conductor portion by an electrically conductive material. The housing electrical conductor portion is connected with a radio communication circuit of the portable radio communication apparatus so as to operate as at least one part of an unbalanced type antenna of the radio communication circuit.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Topical macqui berry formulation
InactiveUS20070065396A1High ORACImprove antioxidant capacityBiocideCosmetic preparationsMedicineOxygen radical absorbance capacity
The present invention provides a topical formulation and method of use where the formulation comprises macqui berry or a macqui berry extract containing anthocyanins having a very high oxygen radical absorbance capacity (ORAC). The formulation provides the macqui berry in a stabilized form which includes a glucuronide or glycuronide, a photostabilizing agent, encapsulation, or light -and / or air-blocking packaging.
Owner:TRACIE MARTYN INT
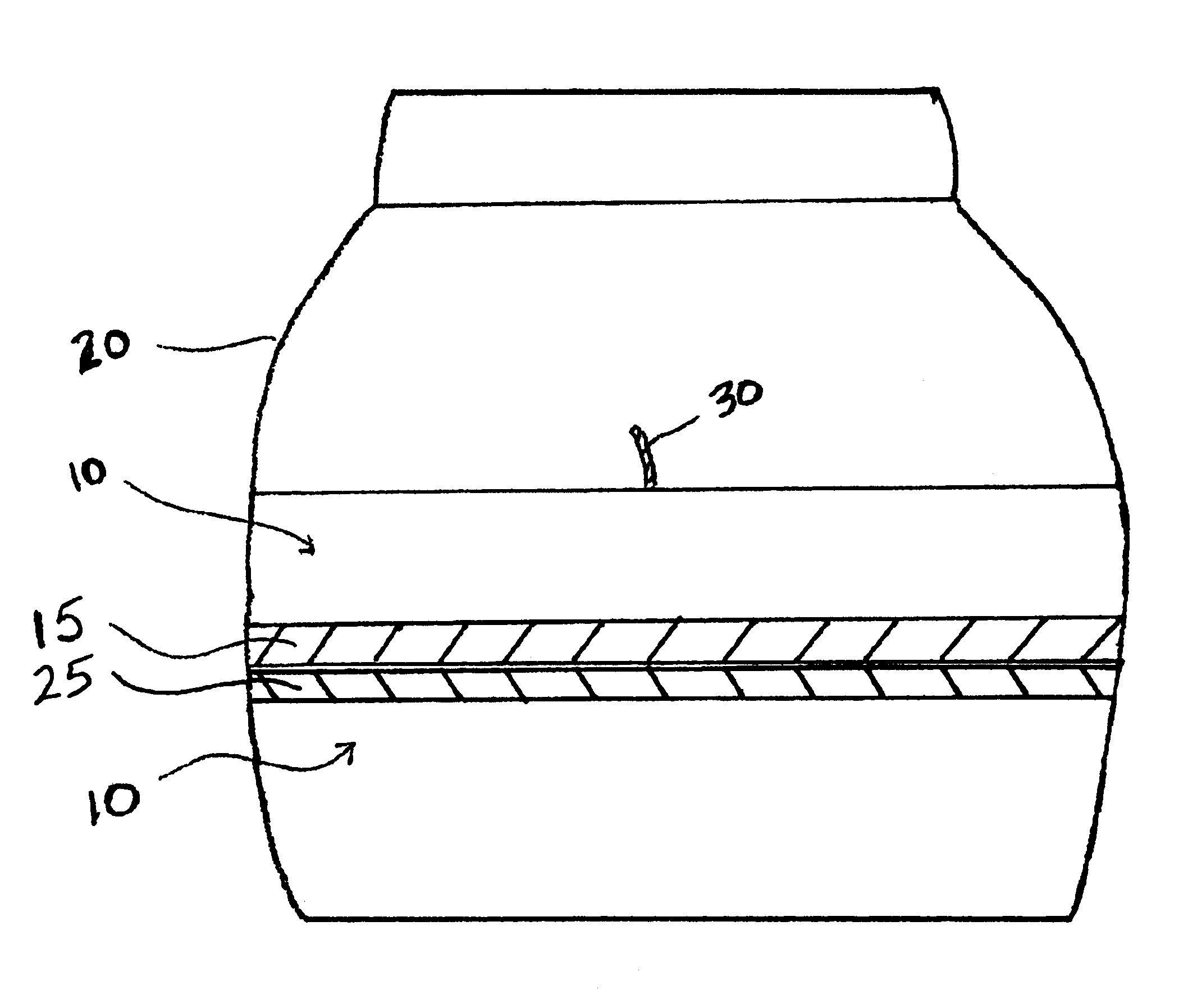
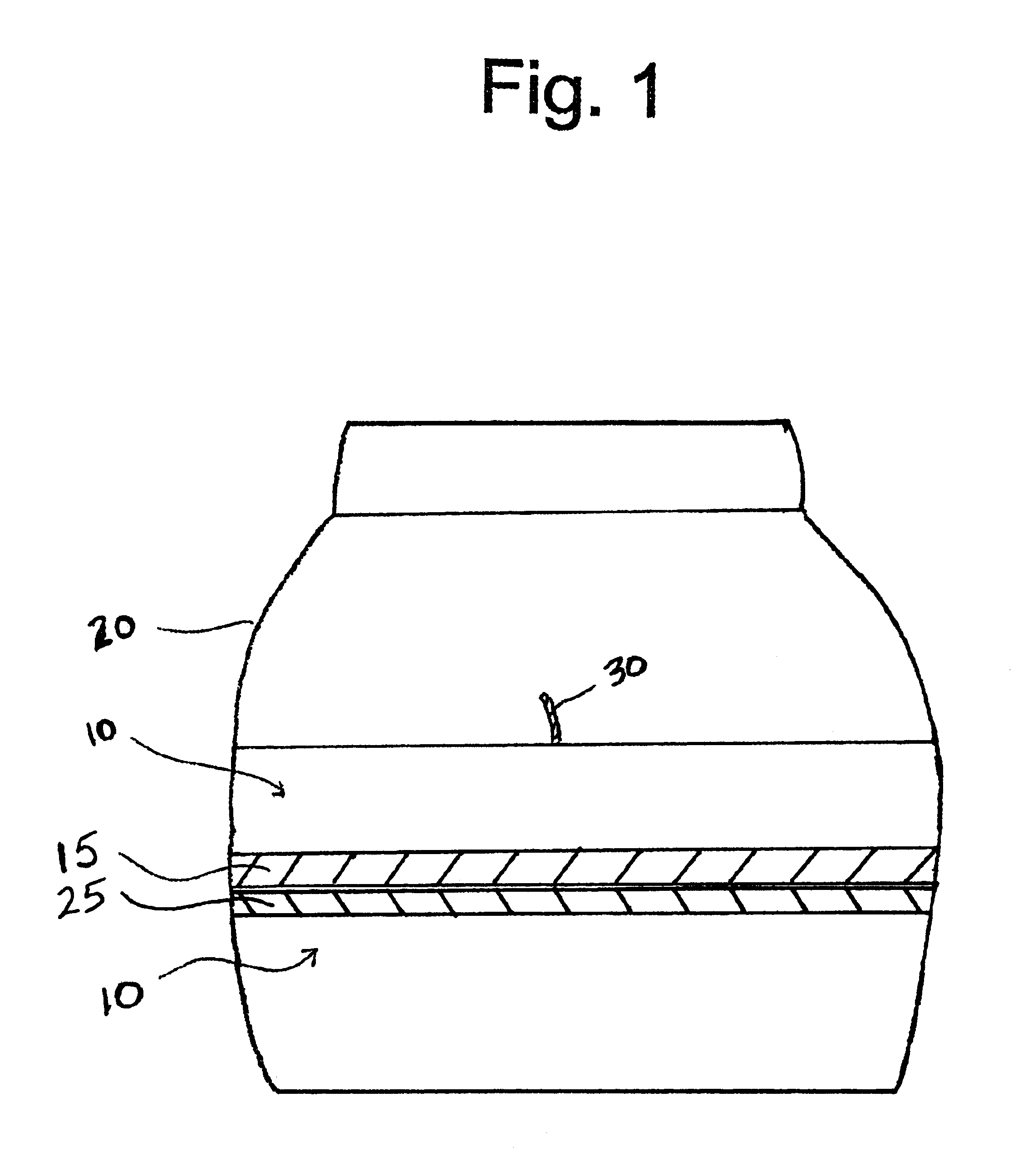
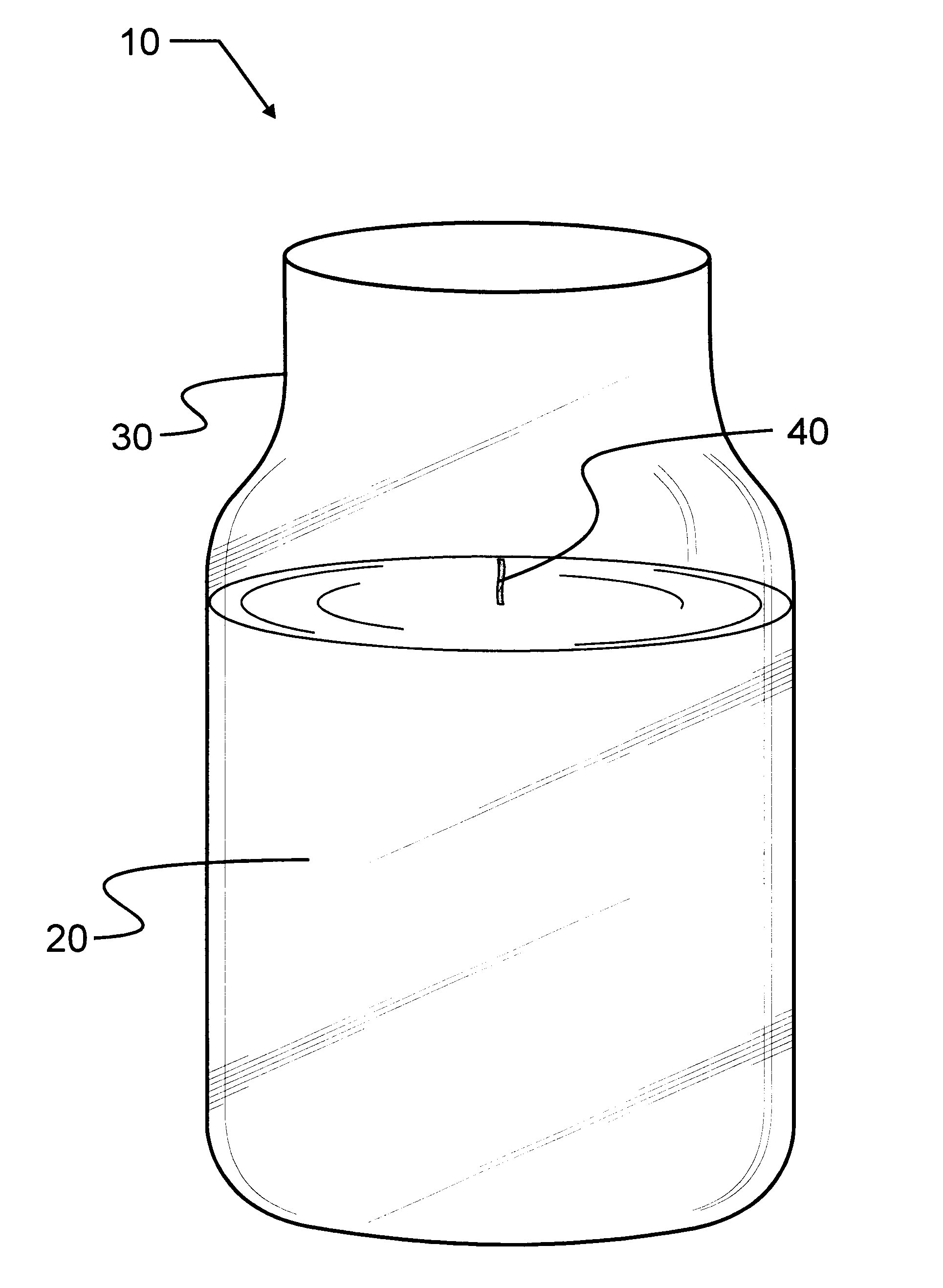
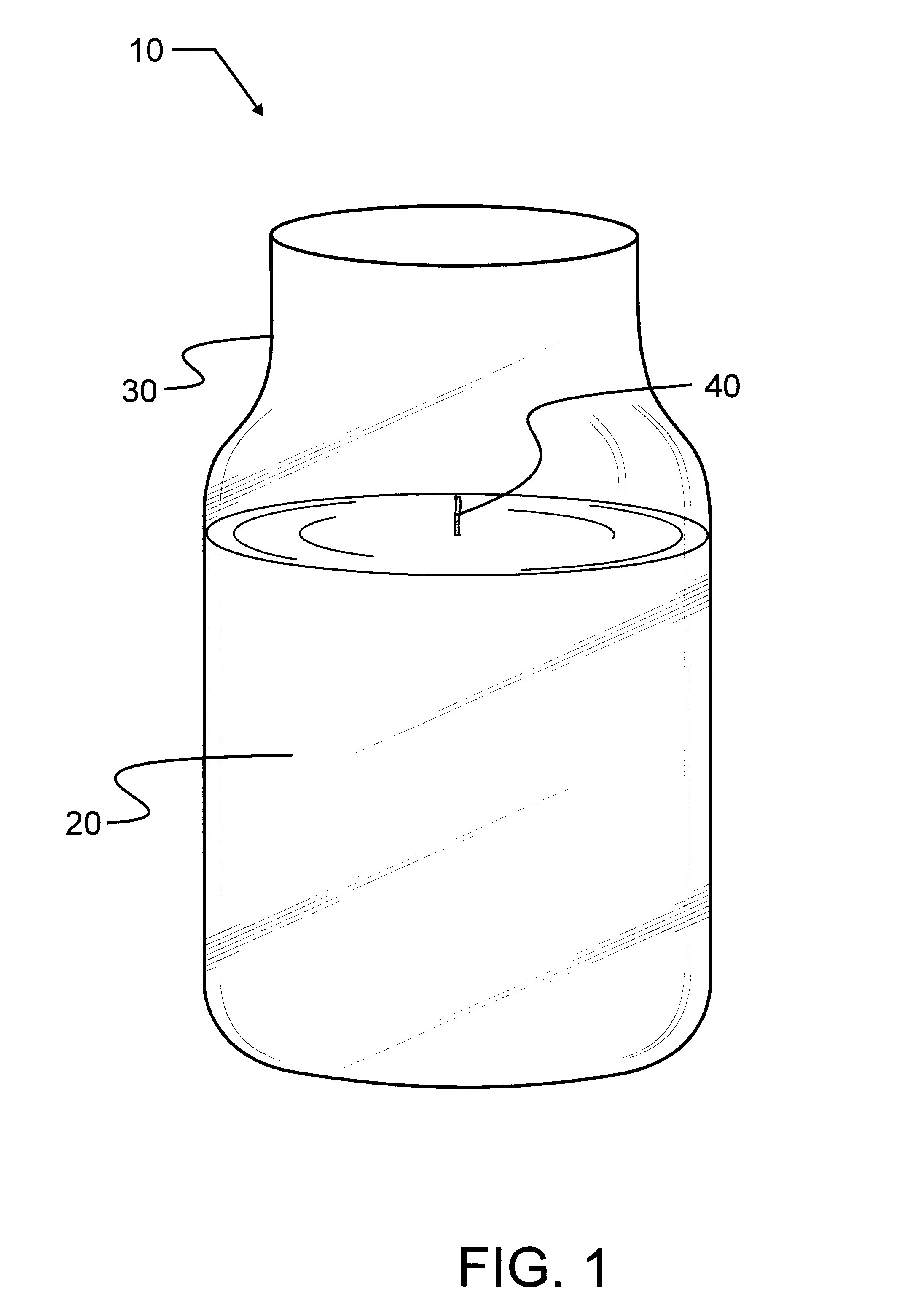
Vegetable oil candle
InactiveUS6730137B2Novel burning and fragrance characteristicBiofuelsSolid fuelsParaffin waxVegetable oil
A candle composition has a paraffin wax mixture of a high melting point paraffin wax and a low melting point paraffin wax, and a hydrogenated vegetable oil that is present in a greater amount than the mixture of the varying grades of paraffin wax, and the vegetable oil contains no more than 0.15% free fatty acid, with the remainder being triglycerides. Candles of the composition have good burn characteristics, particularly good fragrance intensity and produce a unique crystallization effect after the first burn.
Owner:BEAUTYAVENUES
Soybean wax candles
InactiveUS6599334B1Increase profitWithout and crackingSolid fuelsCapillary burnersVegetable oilAlpha-olefin
A solid fuel candle which is highly adapted for use both in a container and also as a free-standing candle includes at least 85 percent hydrogenated soybean oil, approximately 0 to 4 percent synthetic wax composition, approximately 0 to 4 percent of a second hydrogenated vegetable or petroleum oil, approximately 0 to 10 percent fragrance or scent, and approximately 0 to 3 percent dye. The hydrogenated vegetable oil most preferably has an iodine value of approximately 50 and a melting point of approximately 125 degrees Fahrenheit, with a free fatty acid content of less than one-tenth of one percent. The synthetic wax composition is most preferably formed from alpha olefin monomers and oligomers under free radical conditions at relatively low pressures to yield a highly branched polymer wax having congealing and melting points lower than the starting alpha olefin material and a higher molecular weight.
Owner:ANDERSON JILL M
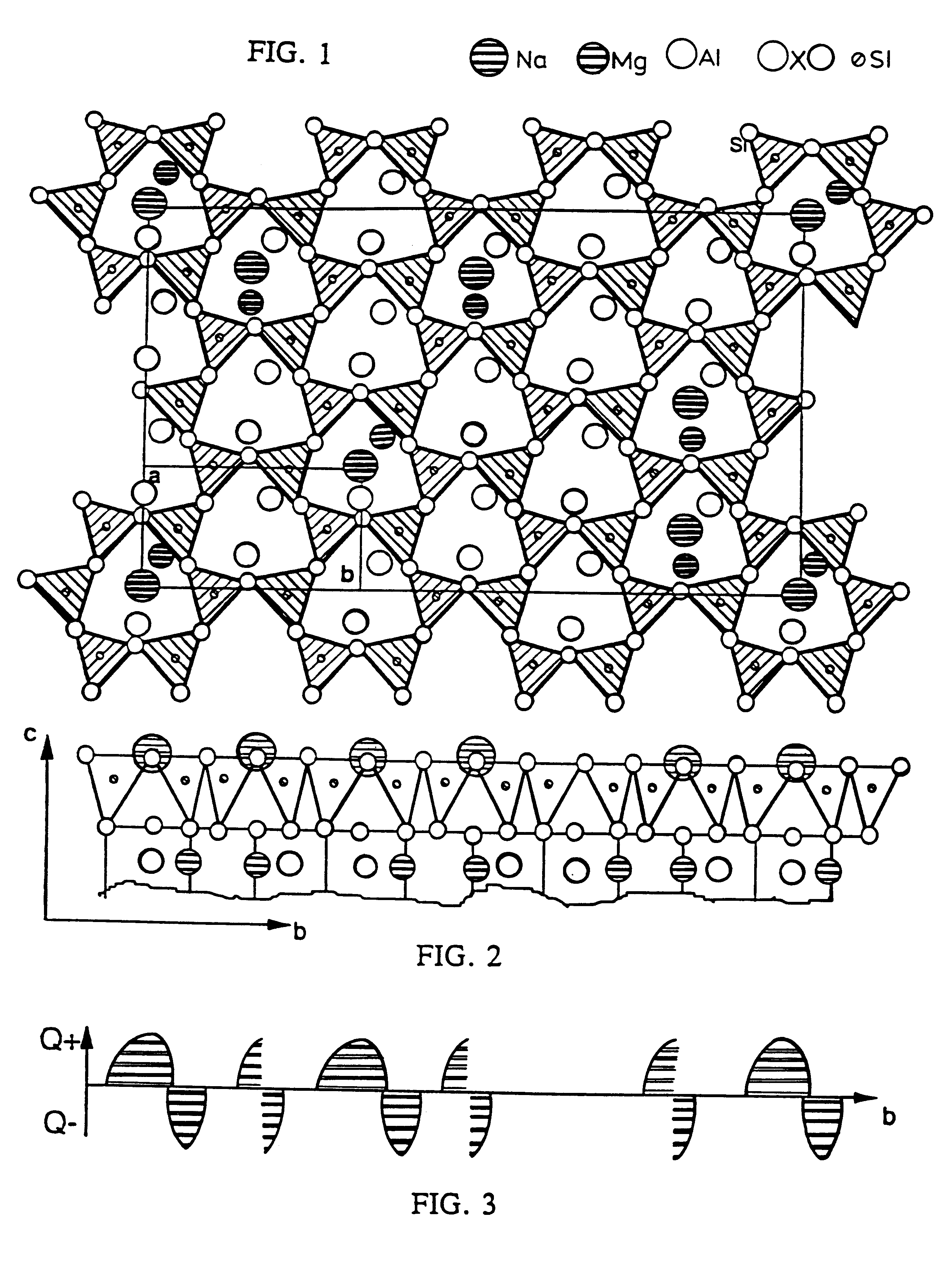
Exfoliated layered materials and nanocomposites comprising said exfoliated layered materials having water-insoluble oligomers or polymers adhered thereto
InactiveUS6228903B1Solve the lack of spaceIncreased energy requirementMaterial nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentOrganic solventOligomer
A phyllosilicate material is exfoliated by admixture of the phyllosilicate with water, and a solvent for a water-insoluble oligomer or polymer that is sorbed or electrostatically bonded to the inner surfaces of the phyllosilicate platelets after exfoliation of the phyllosilicate. Intercalation and exfoliation can be achieved via contact of the phyllosilicate with an organic solvent and water to electrostatically bond one or more polar moieties from the organic solvent to a metal cation on the platelet inner surfaces, so that after evaporation of the water used for intercalation of the organic solvent between phyllosilicate platelets, the platelets do not then collapse together, but remain exfoliated. After exfoliation of the phyllosilicate, the exfoliated platelets are contacted with a polymer / carrier composition that includes a water-insoluble polymer or water-insoluble oligomer, and a solvent for the water-insoluble polymer or oligomer. After exfoliating the phyllosilicate and prior to polymer contact, the individual phyllosilicate platelets are contacted with the polymer / carrier composition to sorb the water-insoluble polymer or water-insoluble oligomer onto one or both surfaces of the exfoliated phyllosilicate platelets and drive off the adhered solvent.
Owner:AMCOL INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
Hydrocarbon-terminated polyether-polyamide block copolymers and uses thereof
A composition comprising (a) a resin composition comprising a block copolymer of the formula hydrocarbon-polyether-polyamide-polyether-hydrocarbon; and (b) a polar liquid. The block copolymer may be prepared by a process comprising reacting together reactants comprising dimer acid, diamine, and a polyether having termination at one end selected from amine, hydroxyl and carboxyl, and termination at another end selected from hydrocarbons. The polar liquid may be one or more of an aromatic liquid, a polar aprotic liquid, a ketone-containing liquid, an ester-containing liquid, an ether-containing liquid, an amide-containing liquid and a sulfoxide-containing liquid. The composition may be a gel at room temperature.
Owner:CRODA INT PLC
Vegetable oil candle
InactiveUS20030091949A1Novel burning and fragrance characteristicBiofuelsSolid fuelsParaffin waxVegetable oil
A candle composition has a paraffin wax mixture of a high melting point paraffin wax and a low melting point paraffin wax, and a hydrogenated vegetable oil that is present in a greater amount than the mixture of the varying grades of paraffin wax, and the vegetable oil contains no more than 0.15% free fatty acid, with the remainder being triglycerides. Candles of the composition have good burn characteristics, particularly good fragrance intensity and produce a unique crystallization effect after the first burn.
Owner:BEAUTYAVENUES
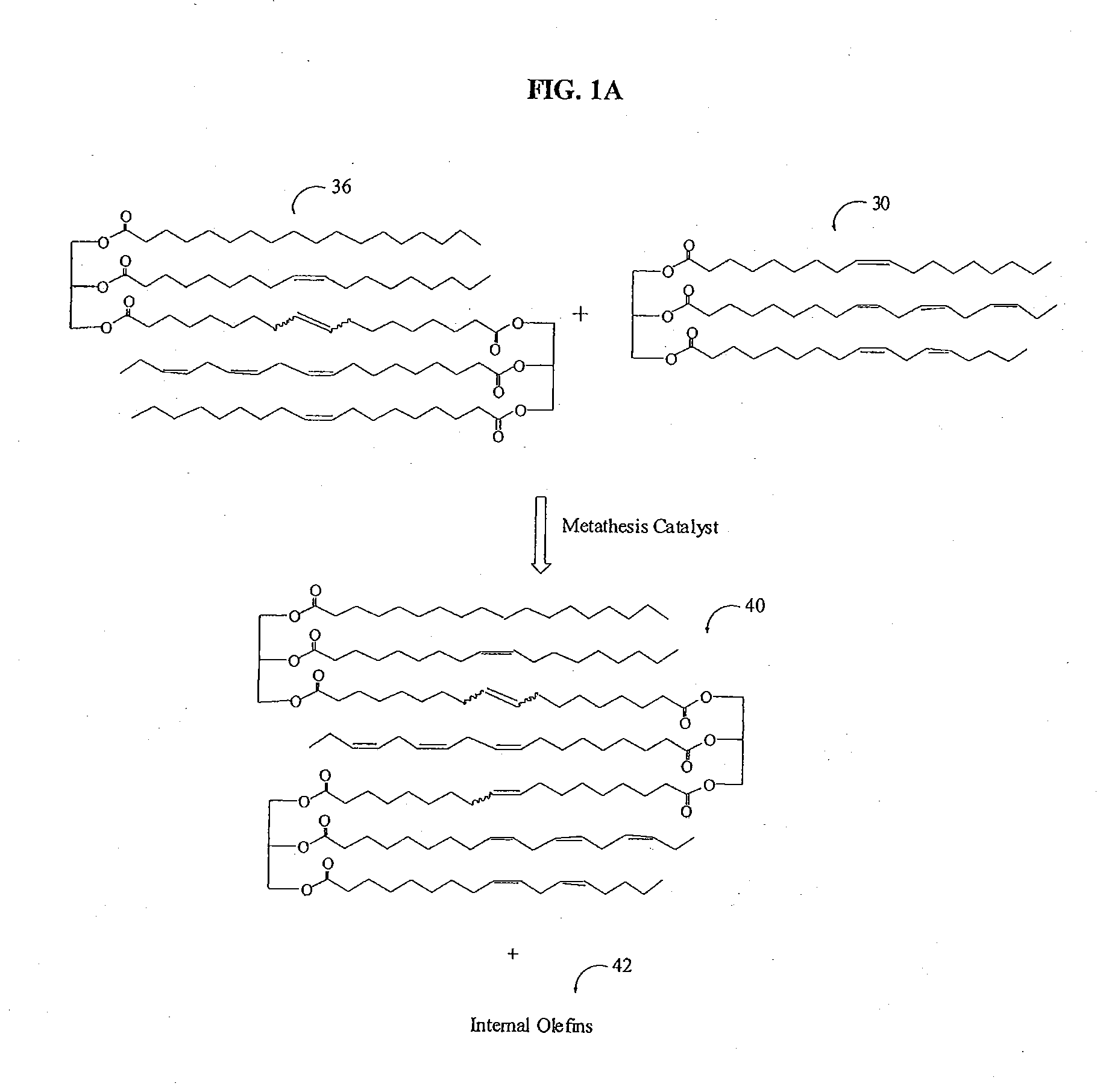
Process for producing a paraffin-based object and such an object
The invention relates to a process for producing a paraffin-based object, especially a candle, with a proportion of a perfume which exceeds 10% by weight, in which the perfume is dissolved in a solvent containing an organic ester, and the solution is in turn added to or disolved in paraffin.
Owner:SCHUMANN SASOL SOUTH AFRICA
Wax compositions comprising fatty ester poly(oxyalkylenated) colorants
This invention relates to wax formulations comprised of specific poly(oxyalkylenated) colorants having fatty ester terminal groups. Preferably the wax formulation is a candle. Such polymeric ester capped colorants provide excellent coloring, decreased migratory properties, and improved balanced burning characteristics over traditional candle colorants and dyestuffs. This invention also concerns methods of making the aforementioned colored candle formulations as well as other colored wax articles, such as crayons.
Owner:MILLIKEN & CO
Candlewax compositions with improved scent-throw
InactiveUS7588607B1Improve release of aromaPromote escapeSolid fuelsCapillary burnersPolymer scienceEngineering
A candlewax composition having improved scent-throw, and candles made from the composition, are provided. The candlewax composition includes at least a wax component and an antifoam agent. An effective amount of a scenting agent can be separately added by a candlemaker.
Owner:CAP DANIEL S
Wax compositions comprising alkenyl succinic anhydride-capped poly (oxyalkylenated) colorants
This invention relates to wax formulations comprised of specific poly(oxyalkylenated) colorants having alkenyl succinic anhydride (ASA) terminal groups. Preferably the wax formulation is a crayon. Such polymeric ASA-capped colorants provide excellent coloring, decreased migratory properties, and improved balanced burning characteristics over traditional crayon colorants, pigments, and dyestuffs. This invention also concerns methods of making the aforementioned colored crayon formulations as well as other colored wax articles, such as candles.
Owner:MILLIKEN & CO
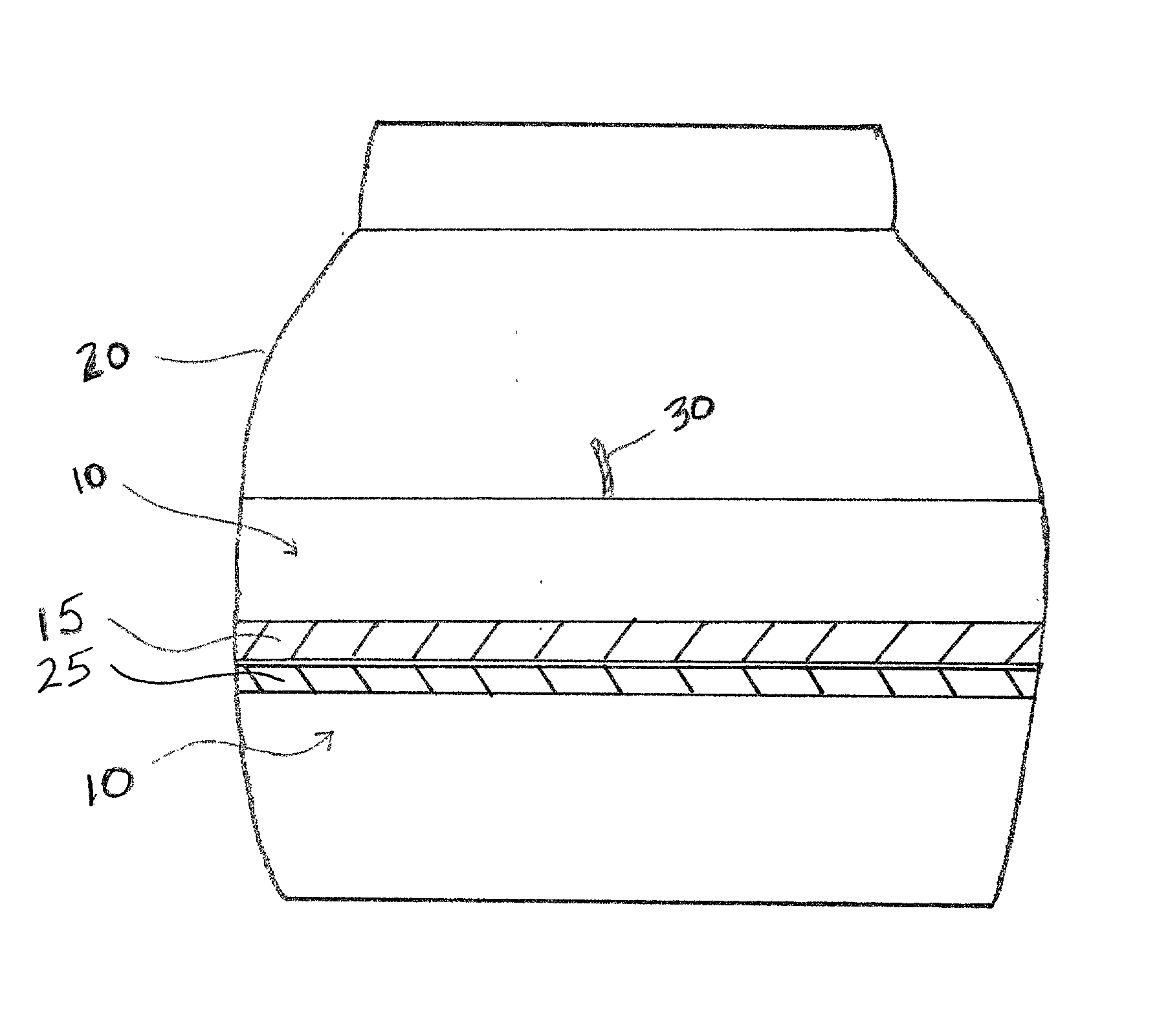
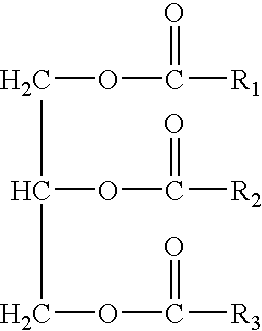
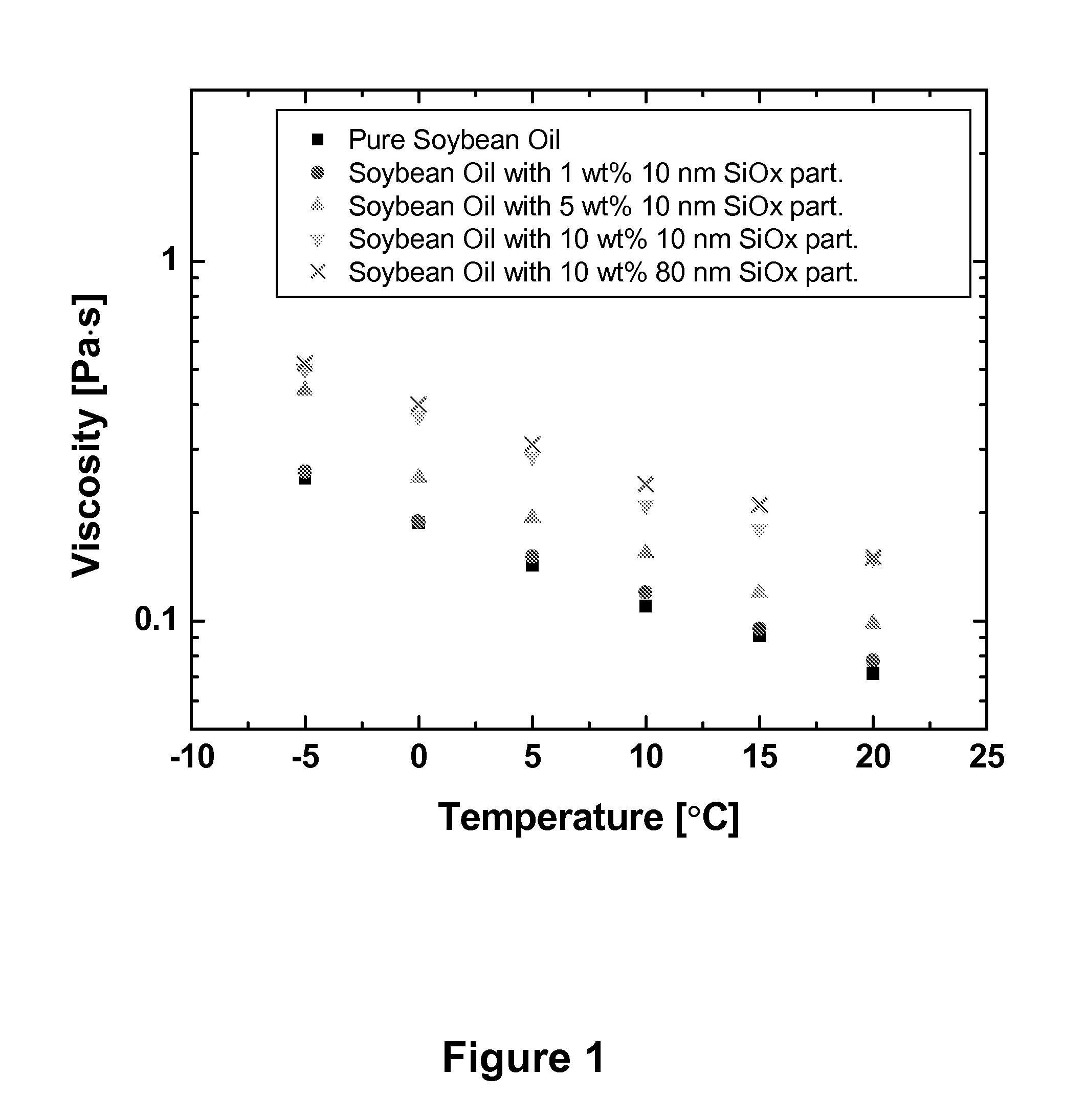
Nanoparticle modified lubricants and waxes with enhanced properties
InactiveUS20090053268A1Improve mechanical stabilityExtended shelf lifeCosmetic preparationsBiocideWaxVegetable oil
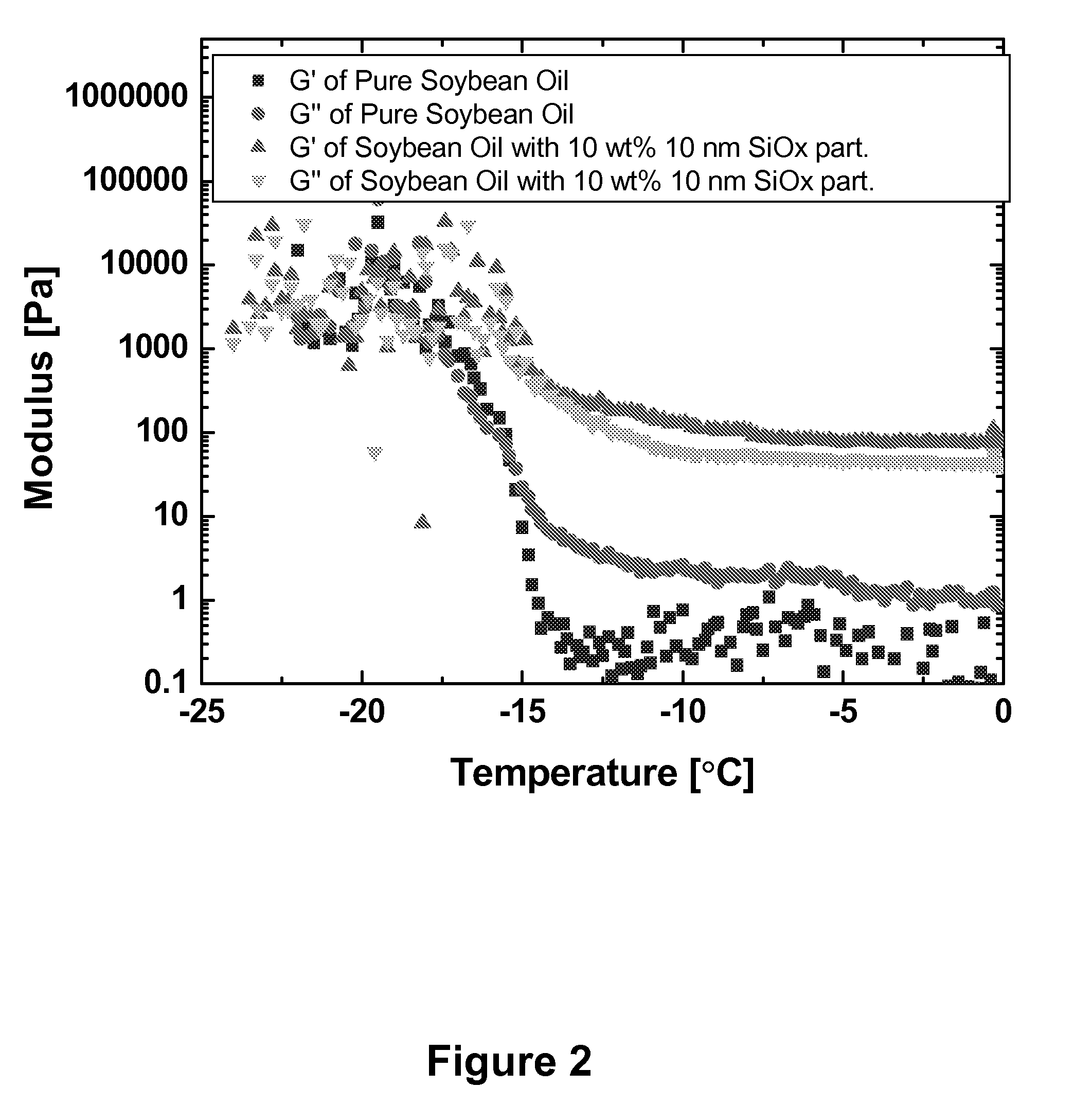
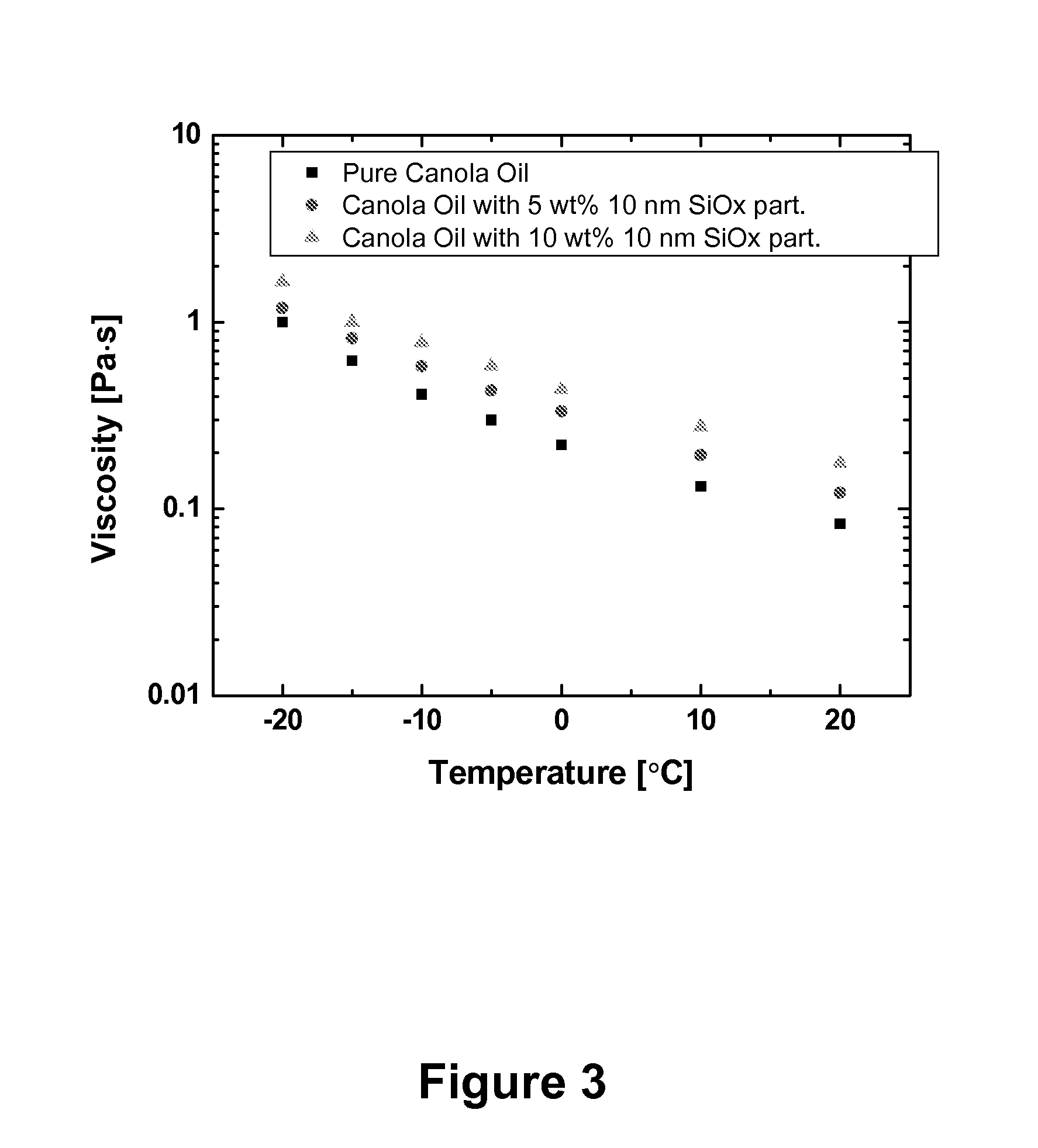
The present invention provides compositions and products, such as waxes and lubricants, comprising a plurality of nanoparticles dispersed in a continuous phase comprising a vegetable oil derived material, such as one or more vegetable oils or a synthetic product derived from one or more vegetable oils. Incorporation of nanoparticles in the present compositions is beneficial for providing mechanical, thermal and / or chemical properties useful for a selected product or product application. In some compositions of the present invention, for example, incorporation of the nanoparticle component provides compositions derived from one or more vegetable oils exhibiting enhanced mechanical stability, hardness, viscosity, thermal stability and mechanical strength.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Compression-molded vegetable wax-based candle
InactiveUS20070144058A1Burn cleanSuperior compressed candle productSolid fuelsCandle ingredientsParaffin waxCompression molding
Prilled wax particles are formed from a vegetable wax-based composition. After compression, a predominantly paraffin wax-based composition is optionally poured over the vegetable wax-based composition to form an encased candle. The method of the present invention offers the possibility to incorporate a high fragrance load to the candle.
Owner:CHEN QIN +4
Prilled waxes comprising small particles and smooth-sided compression candles made therefrom
Owner:CARGILL INC
Compression-molded vegetable wax-based candle
InactiveUS20050158679A1Simple methodBurn cleanCombustion using gaseous and pulverulent fuelCombustion using liquid and pulverulent fuelParaffin waxCompression molding
Prilled wax particles are formed from a vegetable wax-based composition. After compression, a predominantly paraffin wax-based composition is optionally poured over the vegetable wax-based composition to form an encased candle. The method of the present invention offers the possibility to incorporate a high fragrance load to the candle.
Owner:CHEN QIN +4
Candle refill kit and method of use
InactiveUS20100044924A1Processed easily and safelyQuality improvementDielectric heatingBagsWaxRefill Kit
A candle refill kit useful for preparing home made candles includes a disposable microwaveable container and a microwaveable candlewax composition. The candlewax composition is microwave heated in the microwaveable container to an elevated temperature sufficient to initiate pouring of the candlewax composition. The candlewax composition is then poured from the microwaveable container into a candle mold (to make a stand-alone candle) or a candle container (to make a container candle).
Owner:CAP DANIEL S
Vegetable lipid-based composition and candle
InactiveUS20070006522A1Risk minimizationMinimizes and eliminates useBiofuelsSolid fuelsWaxLipid formation
A vegetable lipid-based composition and candle comprised of a vegetable lipid component and a petroleum wax is described. The vegetable lipid component may include a triglyceride or a free fatty acid / triglyceride mixture. The vegetable lipid-based composition has properties that make it advantageous in candle production.
Owner:INDIANA SOYBEAN BOARD
Low-soot, low-smoke renewable resource candle
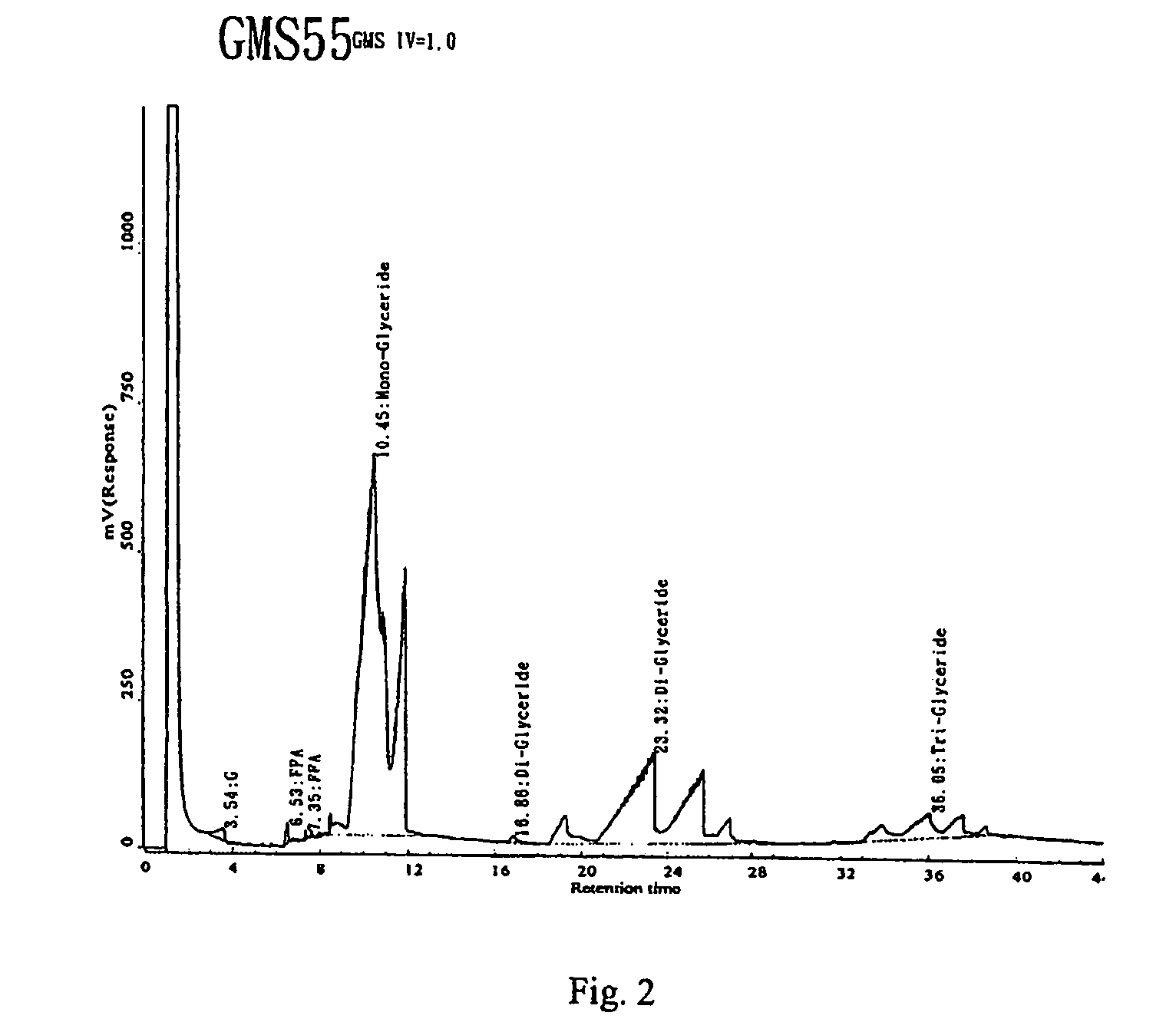
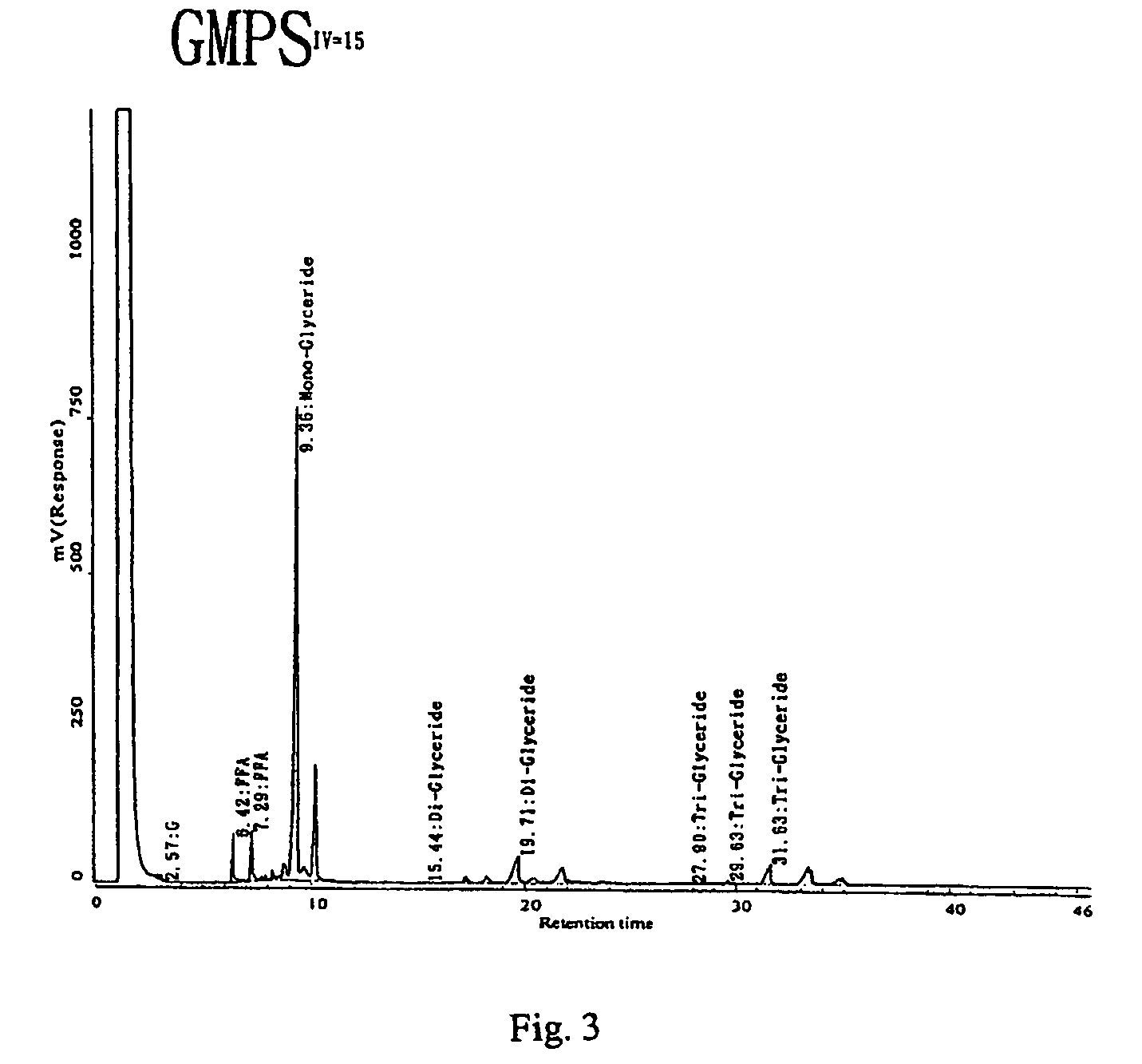
A low soot, low smoke candle that in one embodiment is made of renewable resource material such as plant source material. The candle may include plant source triglycerides and free fatty acids. The free fatty acids may be plant source or other source. Lower iodine value source materials provide highly saturated triglycerides and free fatty acids that in turn are low soot, low smoke. Iodine values of 10 or less down to 1 and 0.5 or less are taught. Use of agricultural “waste” material provides economically priced source material.
Owner:CLEANWAX
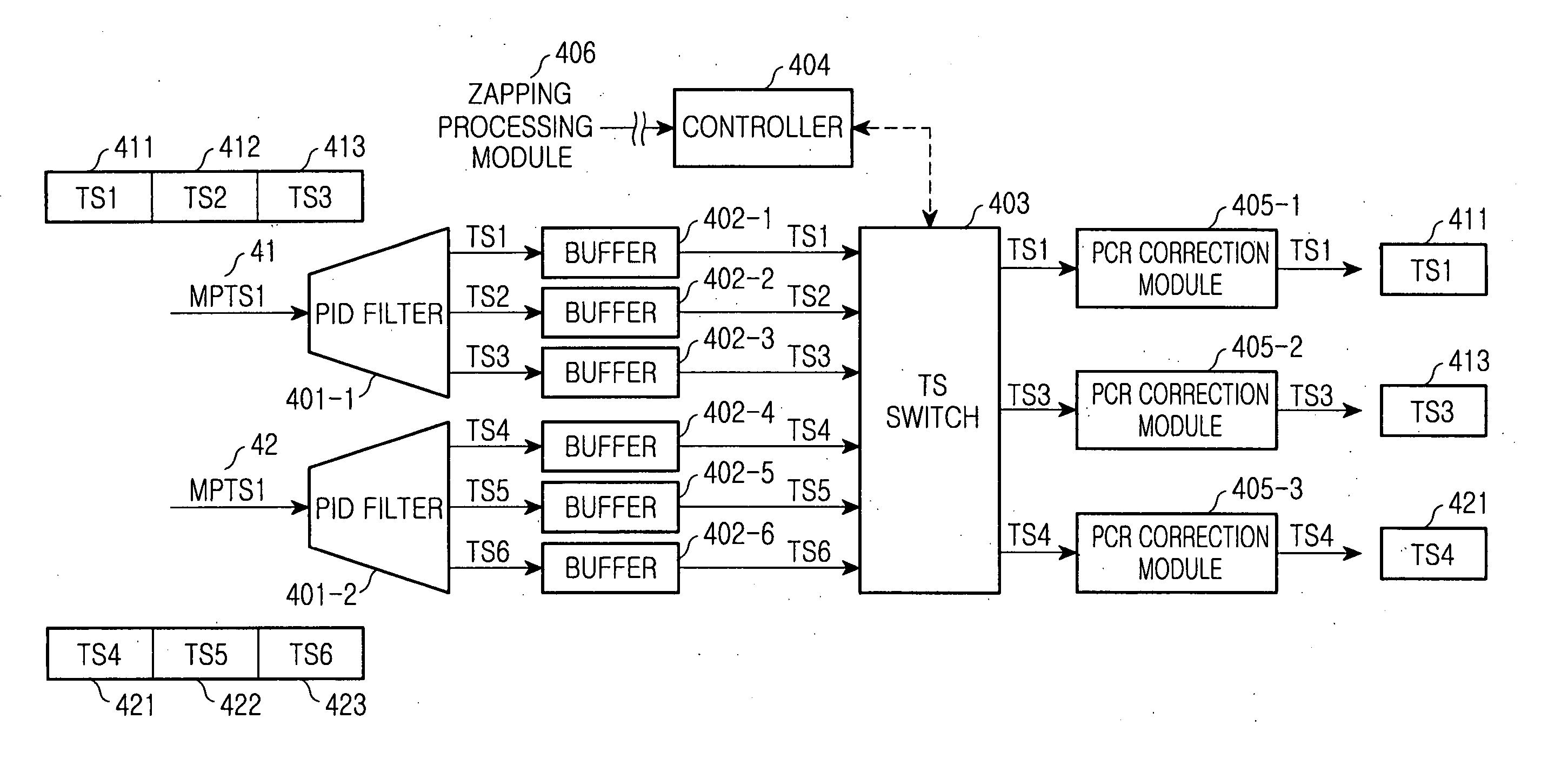
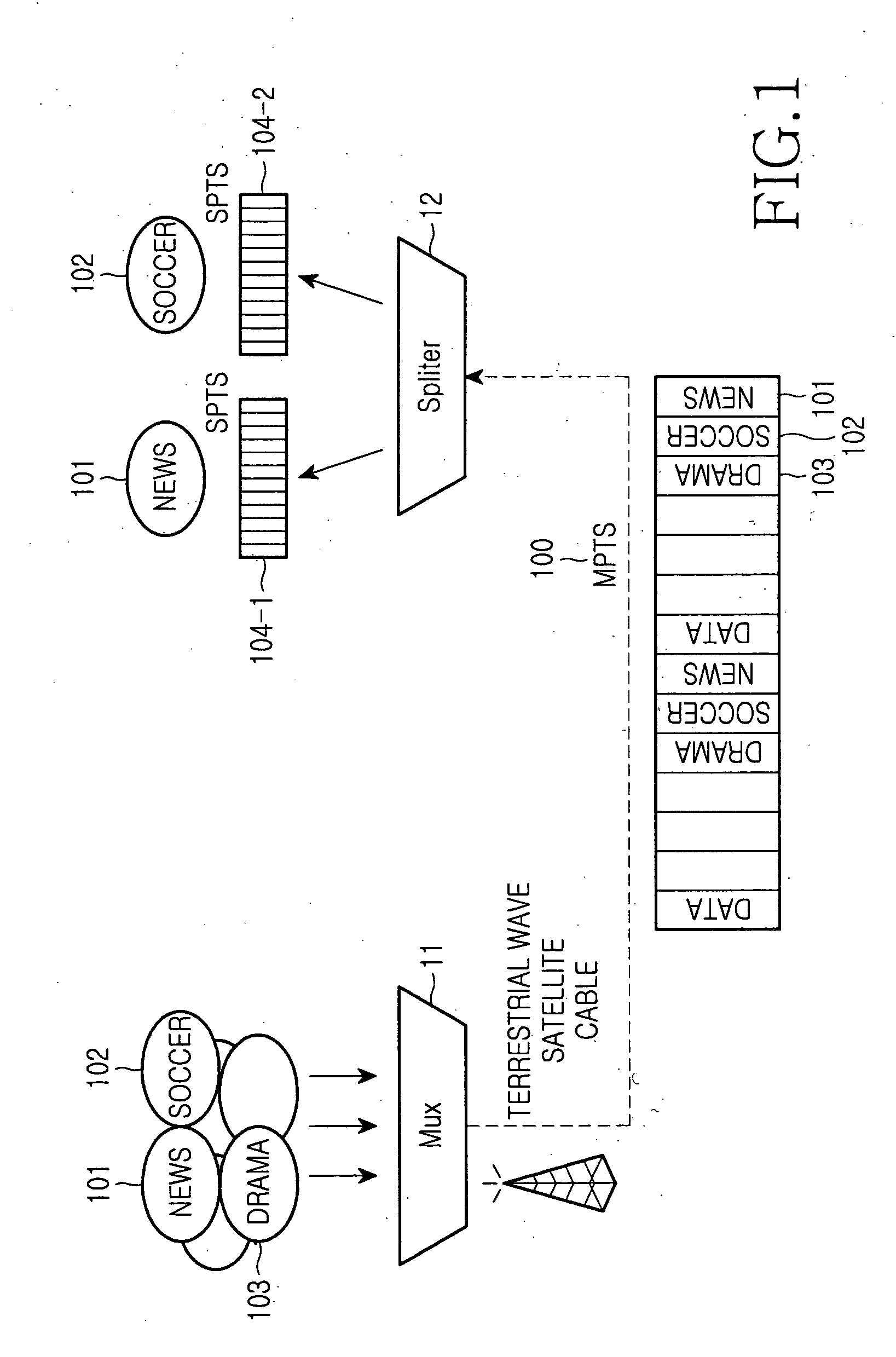
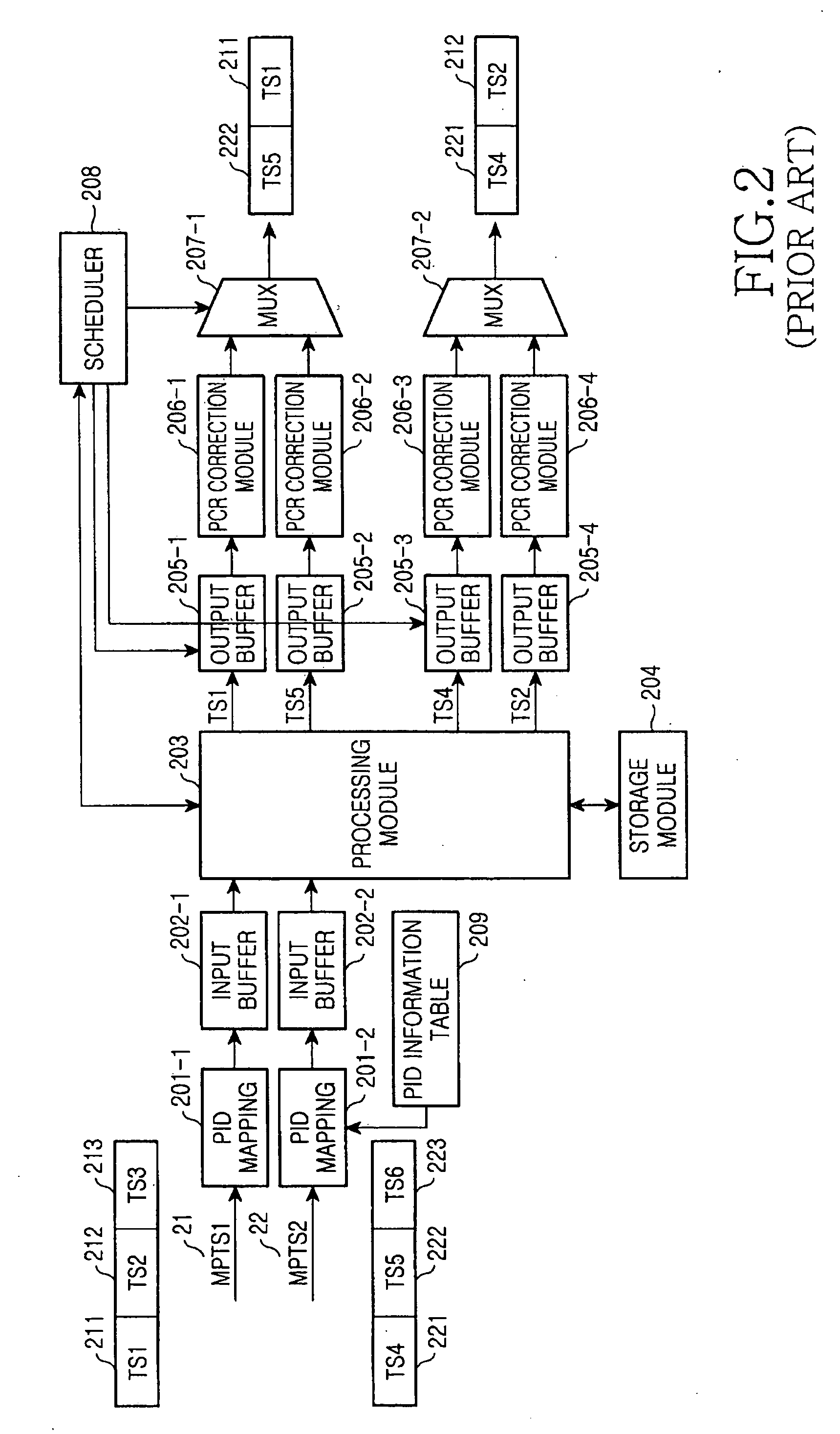
Broadcast splitter enabling selective transmission in real time
InactiveUS20060159093A1Improve good performanceMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexMultiplexingComputer science
Disclosed is a broadcast splitter enabling a selective transmission in real time. The broadcast splitter divides one multi-program transport stream (MPTS), which is obtained by multiplexing motion picture expert group-2 transport streams (MPEG-2TSs), into several single program transport streams (SPTSs). In particular, the broadcast splitter for MPEG-2TSs has a function of selecting a desired SPTS by performing a switching operation with respect to an MPTS in real-time without storing the MPTS when the MPTS is split into several SPTSs. Accordingly, it is possible to transmit MPTS signals in real time because desired TSs are extracted and delivered to output ports in real time by using a broadcast switch without storing the MPTS signals in a storage unit such as a RAM.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
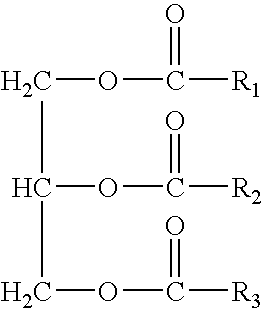
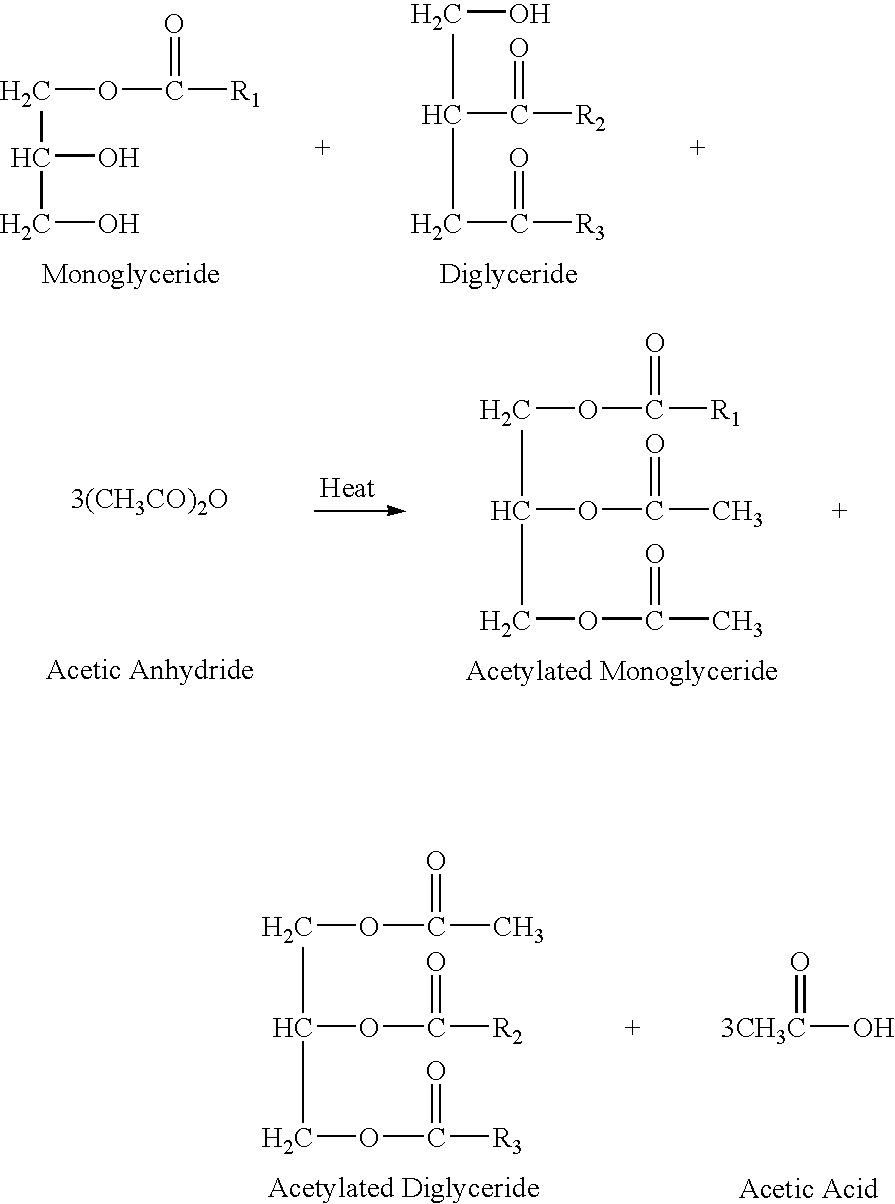
Acetylated wax compositions and articles containing them
InactiveUS7510584B2Increase flexibilityGood chemical stabilityCosmetic preparationsOrganic chemistryWaxDental flossing
A wax composition is provided having high melt temperature, flexibility, pliability and chemical stability. The wax composition includes an acetylated wax including an acetylated glyceride and, optionally, a plant-based wax. The wax composition is useful for candle wicks, dental floss, candle bodies and other articles where these properties are advantageous.
Owner:CAP DANIEL S
Vegetable lipid-based composition and candle
InactiveUS20080138753A1Quantity maximizationIncrease the cost of useBiofuelsSolid fuelsCandleChemistry
The present invention is a candle composition containing a vegetable lipid base component and a candle formed from the composition. The candle composition may contain up to 100 percent by weight of a vegetable lipid base component. The candle composition may further contain a plant derived crystal modifier.
Owner:INDIANA SOYBEAN BOARD
Vegetable lipid-based composition and candle
A vegetable lipid-based composition comprised of a vegetable lipid component and a petroleum wax is described. The vegetable lipid component may include a triglyceride or a free fatty acid / triglyceride mixture. The vegetable lipid-based composition has properties that make it advantageous in candle production.
Owner:INDIANA SOYBEAN BOARD
Additives and methods for reducing odor
Additives and methods for reducing or eliminating odor in oil based media. The additives comprise an essential oil, an essential oil component, or mixtures thereof.
Owner:ODOR MANAGEMENT
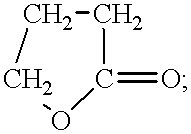
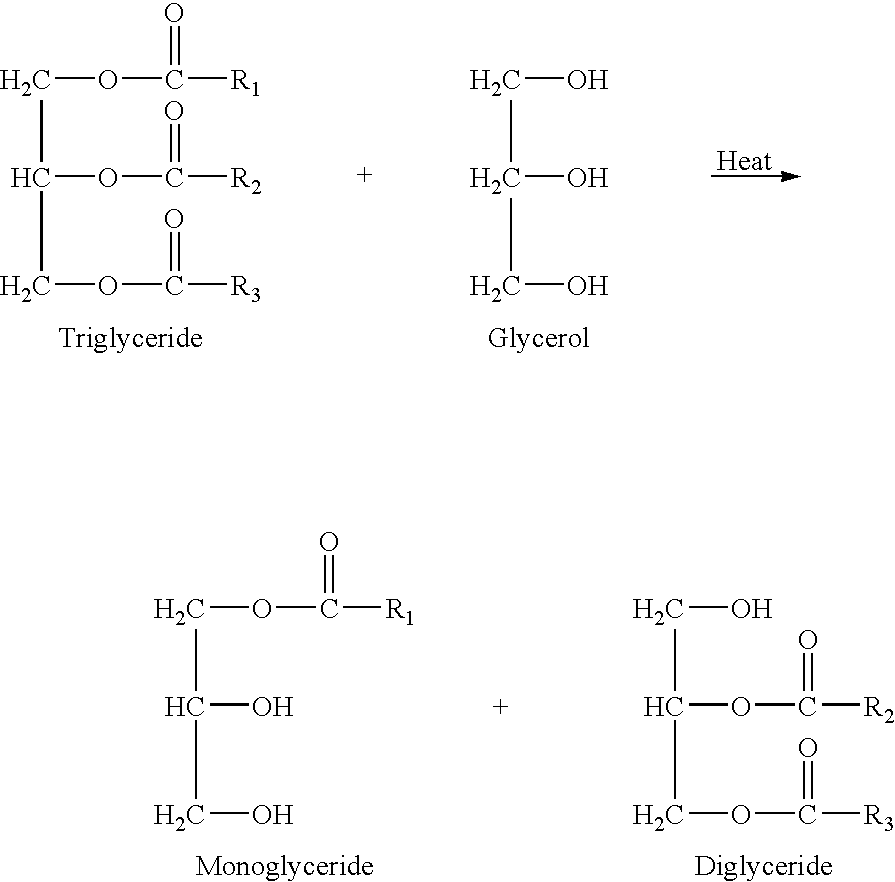
Partial acyl glyceride based biowaxes, biocandles prepared therefrom and their preparation
InactiveUS20080145808A1Promote healthy developmentImprove featuresSolid fuelsCapillary burnersWaxMedicine
The present invention relates to a biowax comprising a partial acyl glyceride selected from the group consisting of a monoacylglyceride, a diacylglyceride and the combination thereof. The present invention also relates to a biocandle comprising a biowax and a wick, and to a method of producing the same.
Owner:CHANT OIL
Candle body composition for colored flame candles and use thereof
The present invention discloses a novel candle body composition for colored flame candles, which can be directly press-molded or provided in any containers in a form of bulk materials and combined with a candle combustion wick to form a colored flame candle. The candle body composition according to the present invention is also suitable for DIY articles. Compared with conventional solid colored flame candles, the colored flame candle according to the present invention can be manufactured in a simple manner, with the heat shaping step being dispensed with and the problem of environmental pollution being largely avoided. Furthermore, the colored flame candle according to the present invention has a good ignition property, a pure and sharp flame and a high retention of flame, and is an environmentally friendly product.
Owner:JIANDE JIAXUAN ARTICLES
Candle composition
A candle composition containing non-hydrogenated oil and at least one of long-chain hydrocarbon and long-chain hydrocarbon derivatives. A candle composition having non-hydrogenated oil and a solidifying amount of congealing reagent. A candle composition having paraffin, non-hydrogenated oil, and a solidifying amount of a congealing reagent comprising petrolatum, oxidized petrolatum, oxidized long-chain hydrocarbons, or modified hydrocarbons. A process for making a candle composition is also provided, the process comprising mixing together a non-hydrogenated oil and a congealing amount of a congealing reagent, heating mixture to a temperature of 75-90° C., preferably 75-80° C., then cooling the mixture and pouring into a container.
Owner:PREMIER CANDLE CORP
Vegetable lipid-based composition and candle
The present invention is a candle composition containing a vegetable lipid base component and a candle formed from the composition. The candle composition may contain up to 100 percent by weight of a vegetable lipid base component. The candle composition may further contain a plant derived crystal modifier.
Owner:INDIANA SOYBEAN BOARD
Portable radio communication apparatus provided with a part of a housing operating as an antenna
InactiveUS7009567B2Low costReduce the numberSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsElectrical conductorEngineering
In a portable radio communication apparatus including a housing, at least one part of the housing is formed as a housing electrical conductor portion by an electrically conductive material. The housing electrical conductor portion is connected with a radio communication circuit of the portable radio communication apparatus so as to operate as at least one part of an unbalanced type antenna of the radio communication circuit.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Protection of fragrance in a wax candle using an antioxidant
InactiveUS7220288B2Outstanding propertyProtects the candle from fragrance discolorationSolid fuelsCandle ingredientsParaffin waxPolymer science
Disclosed is a fragranced wax candle and fragranced wax composition comprising paraffin wax, a fragrance containing an antioxidant, with or without vegetable wax and / or beeswax, saturated fatty acid, hindered amine, and an additive. Also disclosed is a method for incorporating an antioxidant into the fragranced candle wax composition.
Owner:SCENT2MARKET
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com