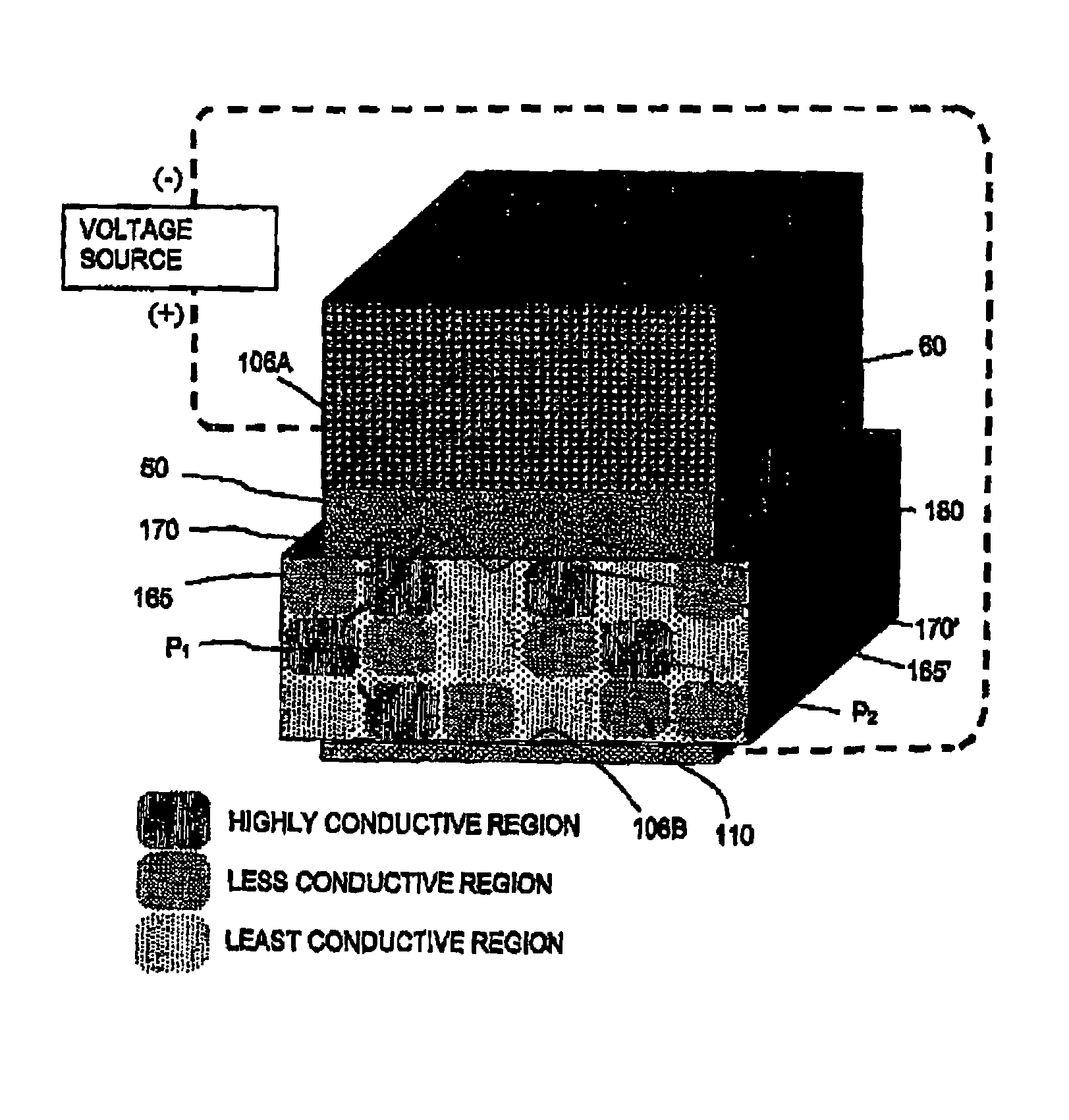
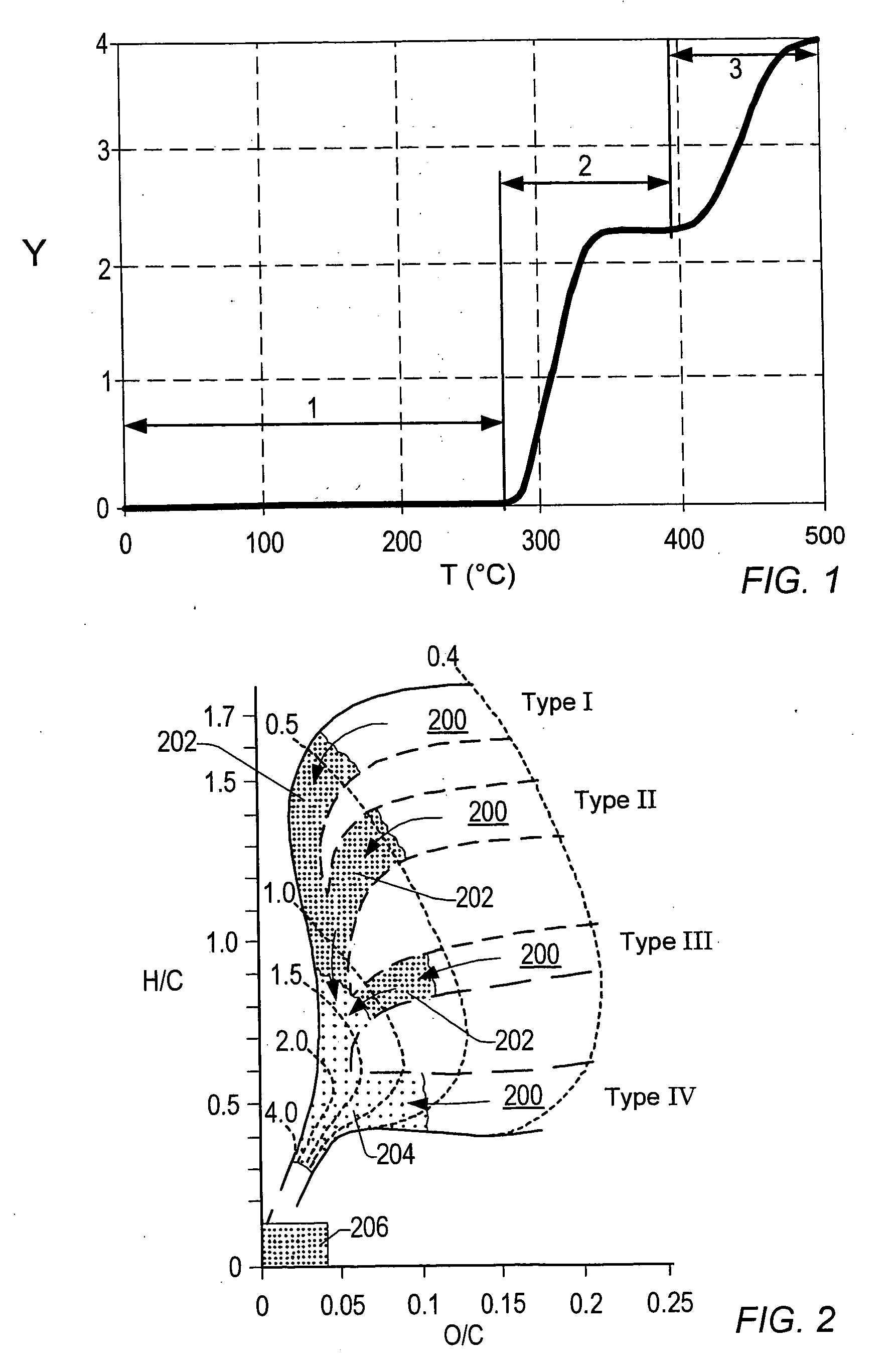
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
357results about "Dielectric heating" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
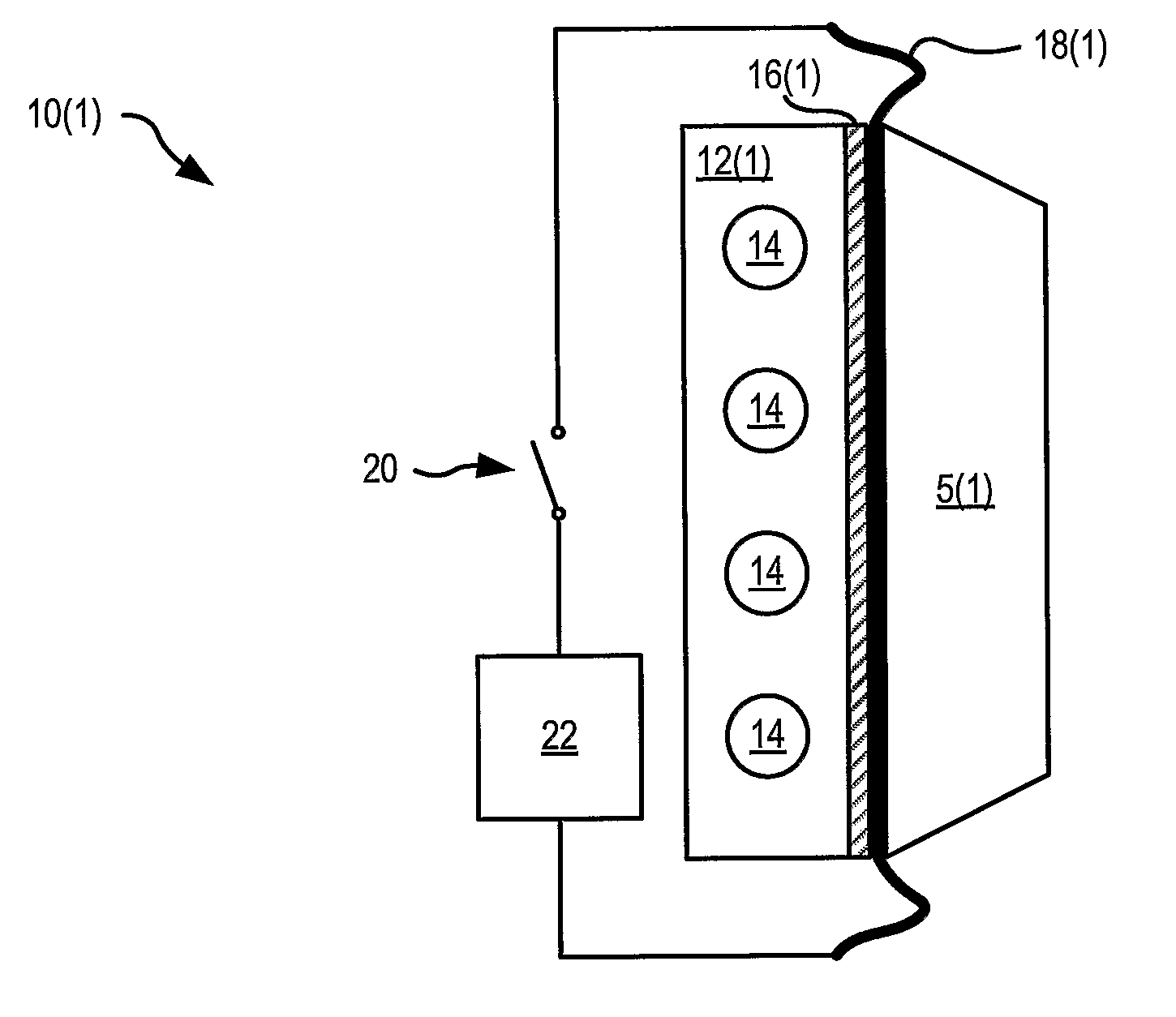
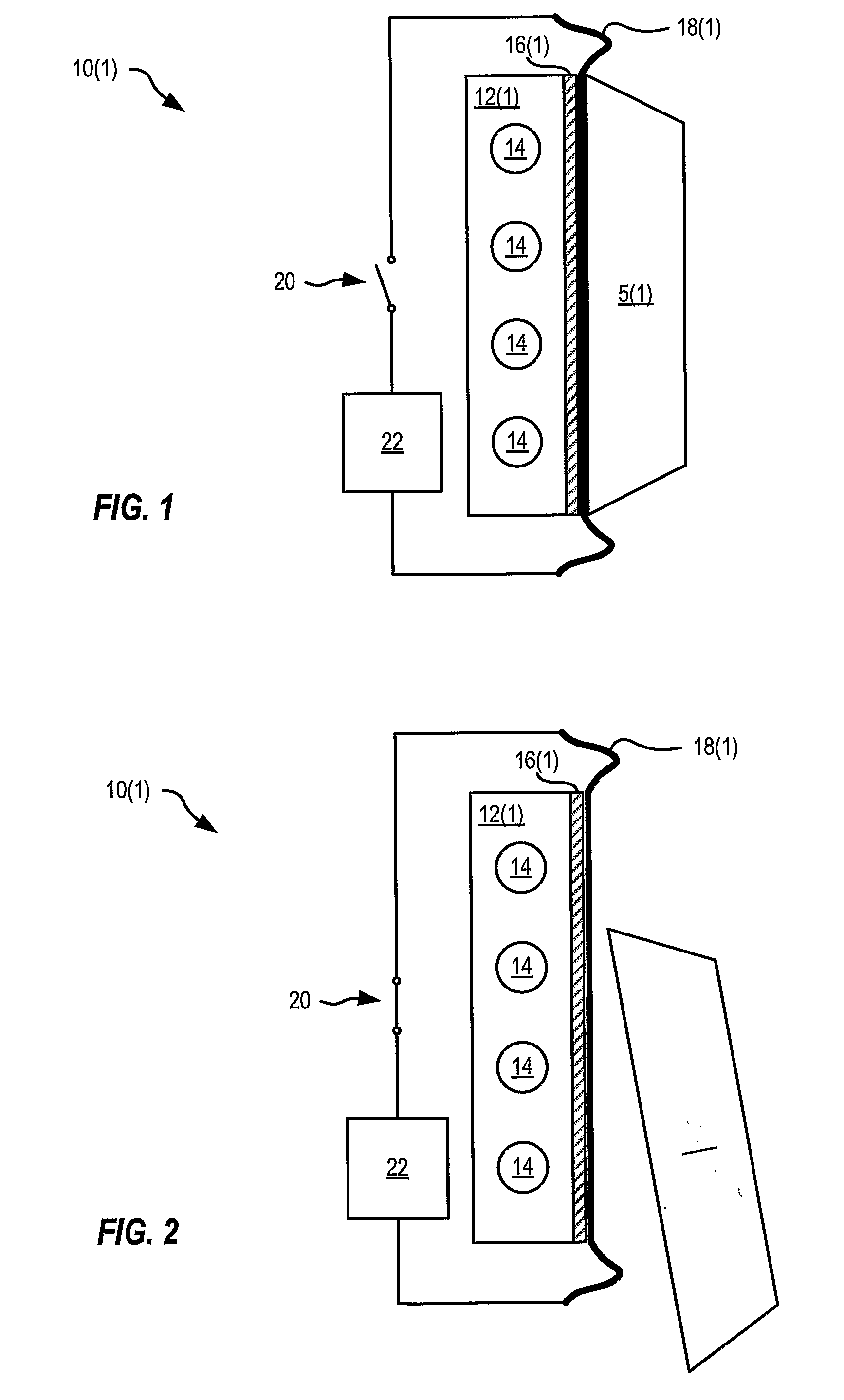
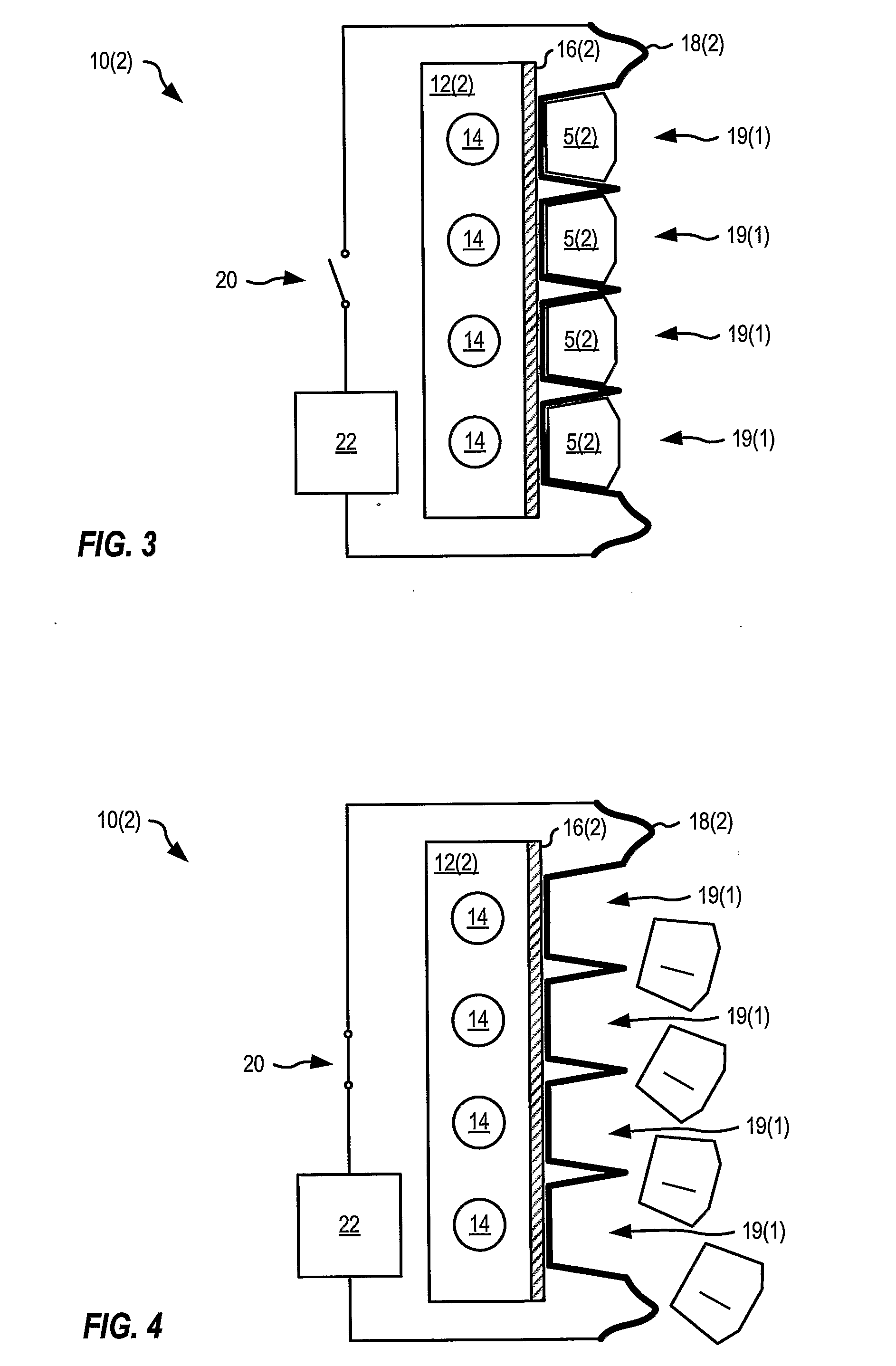
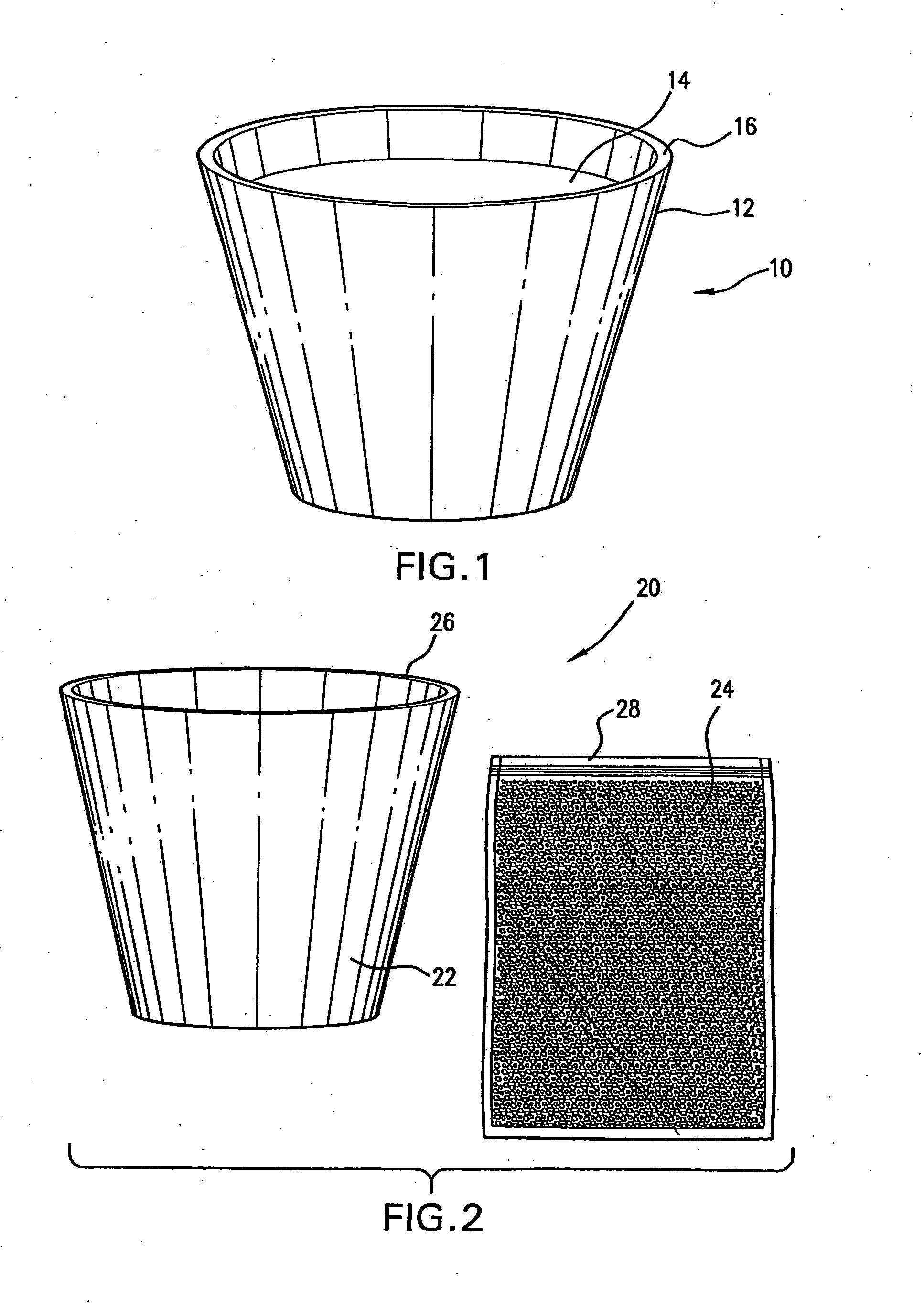
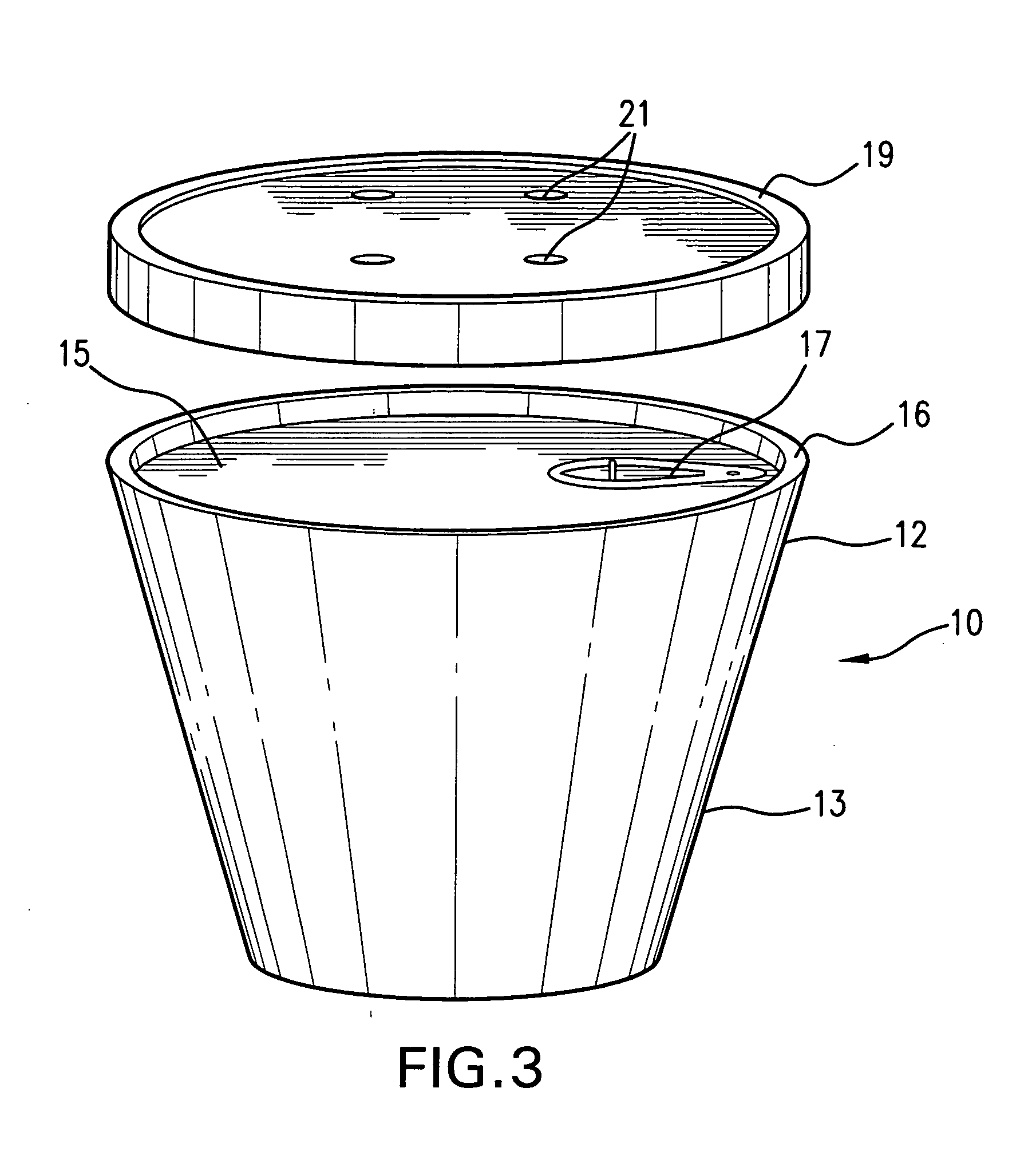
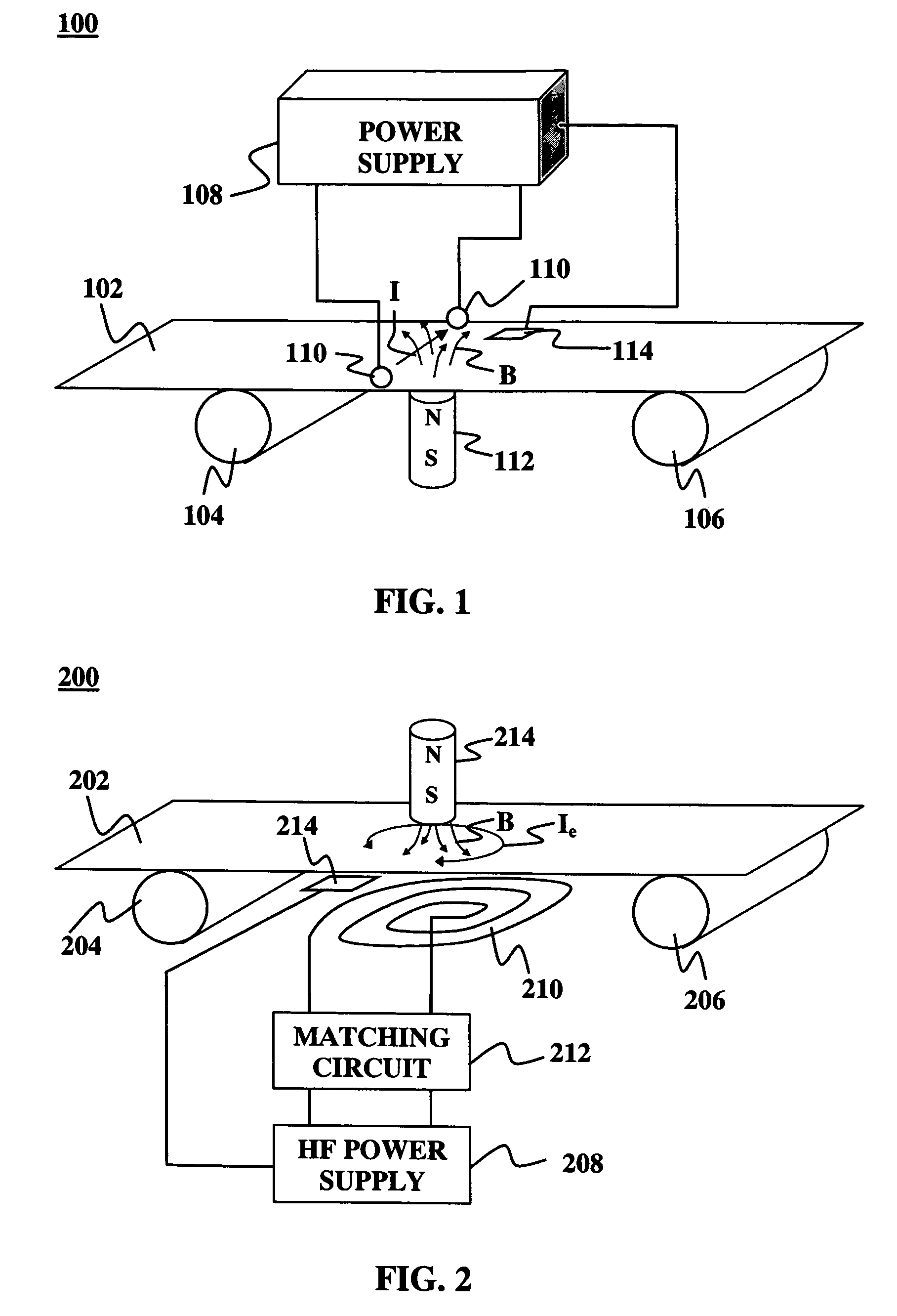
Surgical sealing surfaces and methods of use
ActiveUS7220951B2Fast transferHighly stable current-limitingDielectric heatingSurgical instruments for heatingOmni directionalSwitching time
Various embodiments provide compositions that exhibit positive temperature coefficient of resistance (PTCR) properties for use in thermal interactions with tissue—including thermal sensing and I2R current-limiting interactions. Embodiments also provide tissue-engaging surfaces having PTCR materials that provide very fast switching times between low resistance and high, current-limiting resistance. One embodiment provides a matrix for an electrosurgical energy delivery surface comprising a PTCR material and a heat exchange material disposed within an interior of the matrix. The PTCR material has a substantially conductive state and a substantially non-conductive state. The heat exchange material has a structure configured to have an omni-directional thermal diffusivity for exchanging heat with the PTCR material to cause rapid switching of the PTCR material between the conductive state and non-conductive state. Preferably, the structure comprises a graphite foam having an open cell configuration. The matrix can be carried by tissue contacting surfaces of various electrosurgical devices.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Subsurface electrical heaters using nitride insulation
Certain embodiments provide a heating system configurable to heat a subsurface formation. The system includes an electrical conductor configured to generate an electrically resistive heat output during application of electrical current to the electrical conductor. An electrical insulator at least partially surrounds the electrical conductor. The electrical insulator includes a nitride. A sheath at least partially surrounds the electrical insulator.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
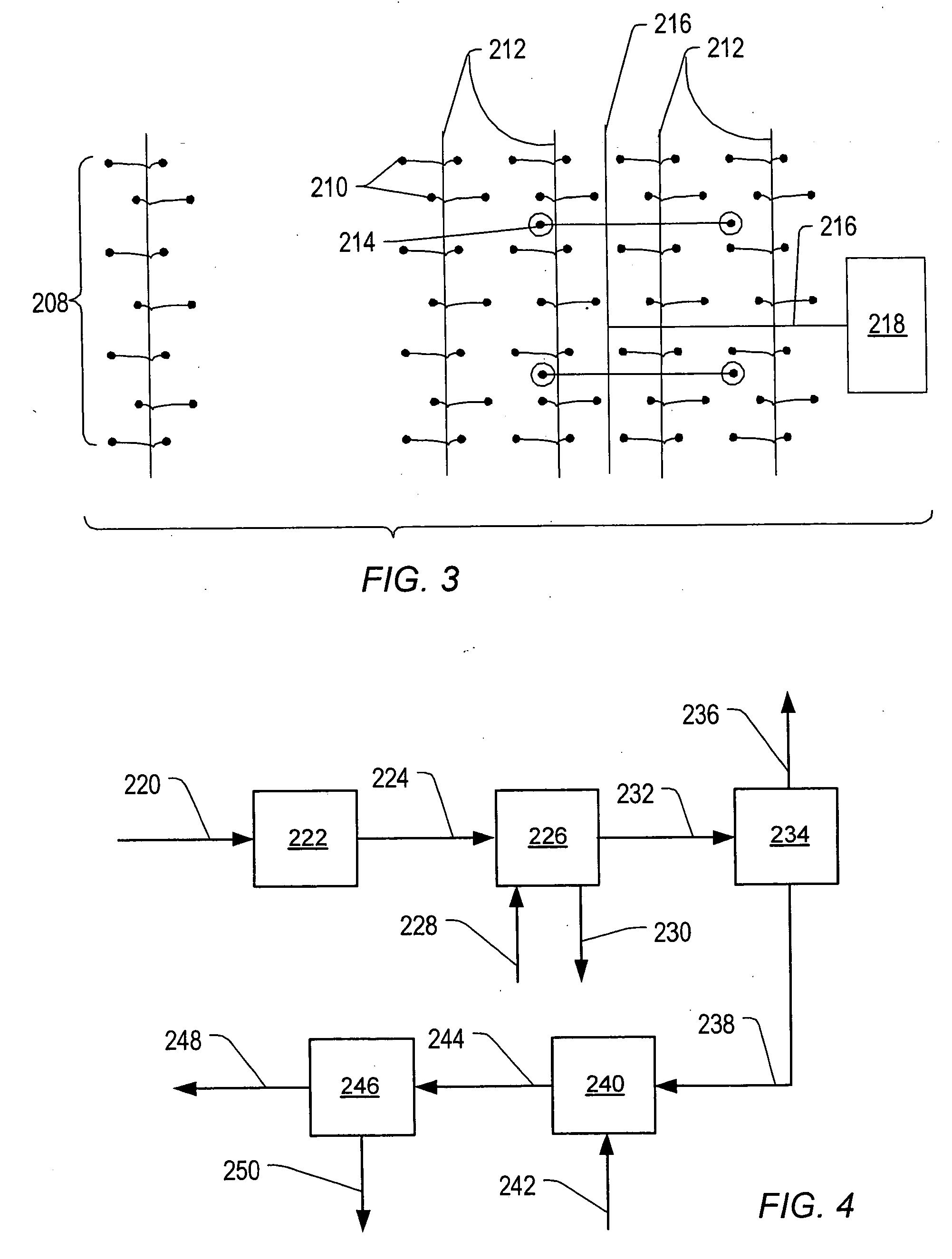
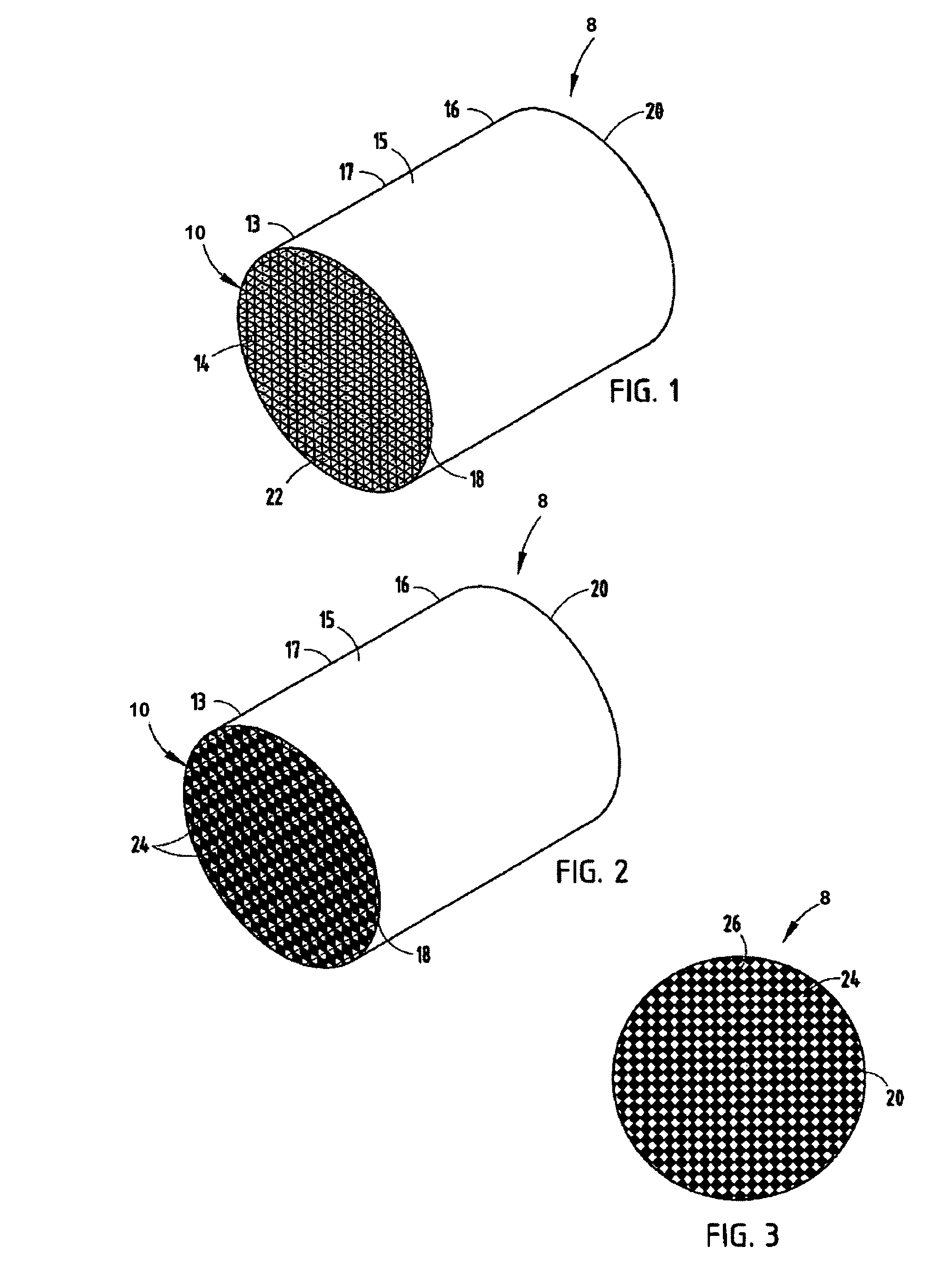
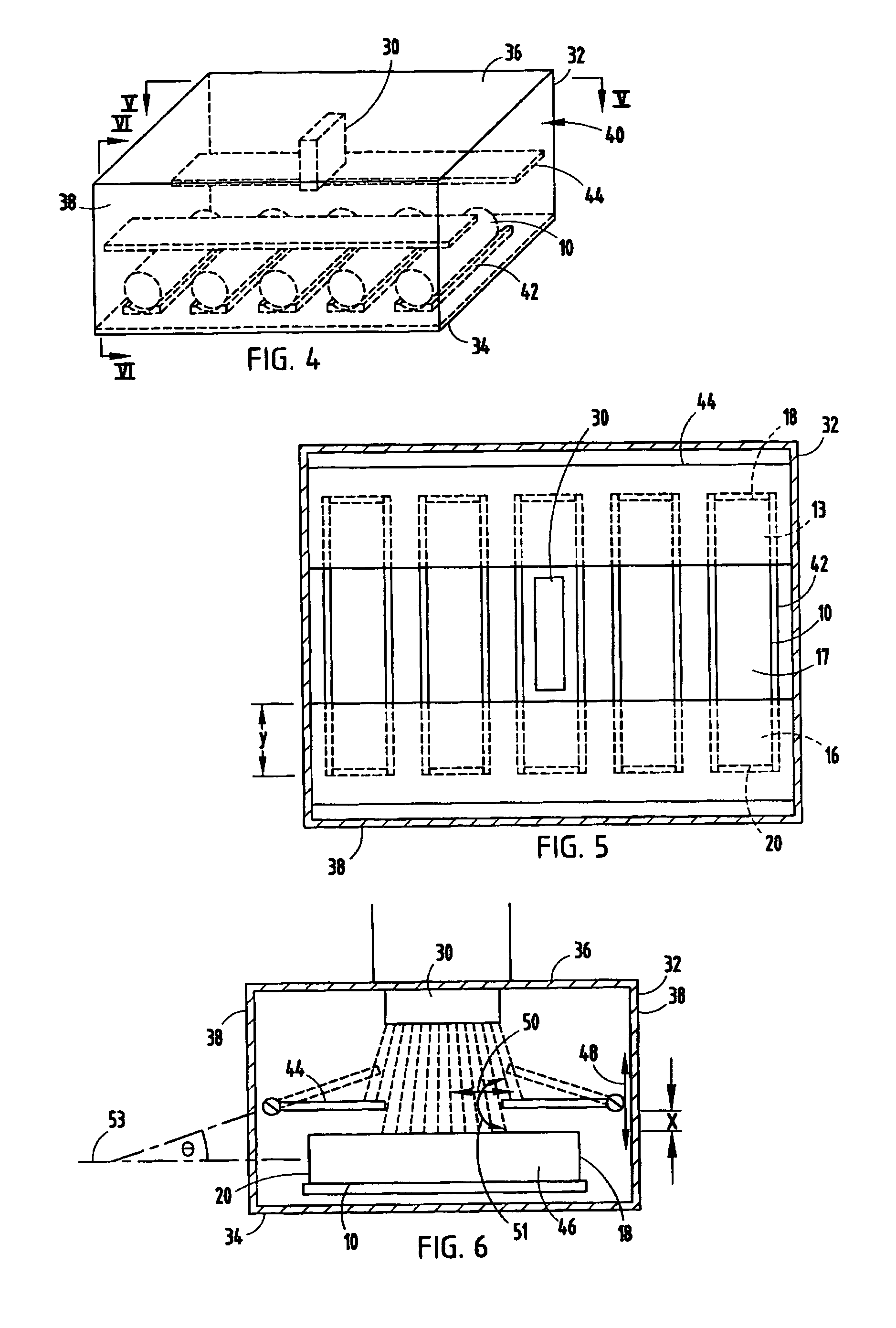
Method for Fabricating a Long-Range Ordered Periodic Array of Nano-Features, and Articles Comprising Same
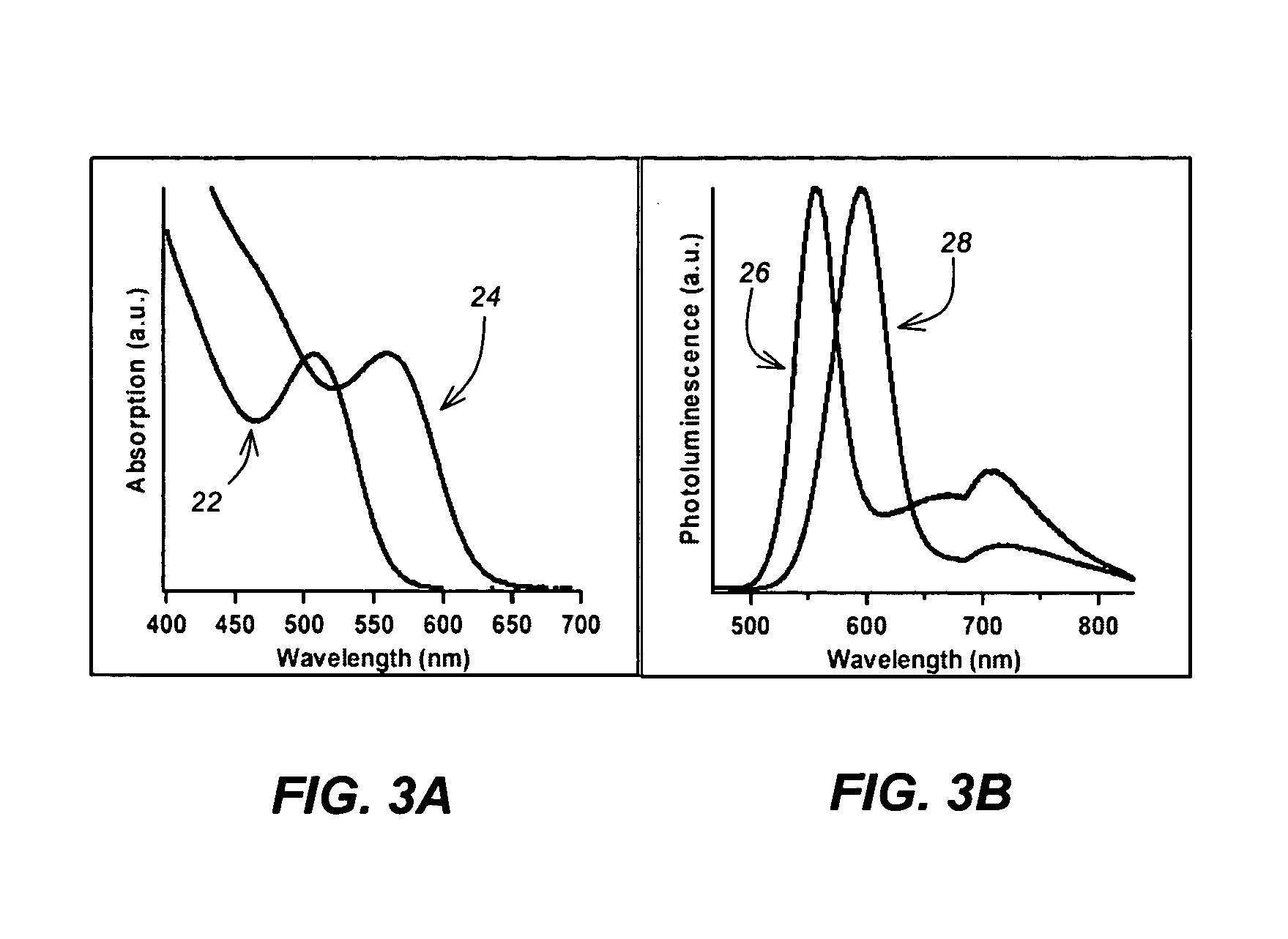
A long range, periodically ordered array of discrete nano-features (10), such as nano-islands, nano-particles, nano-wires, non-tubes, nano-pores, nano-composition-variations, and nano-device-components, are fabricated by propagation of a self-assembling array or nucleation and growth of periodically aligned nano-features. The propagation may be induced by a laterally or circularly moving heat source, a stationary heat source arranged at an edge of the material to be patterned (12), or a series of sequentially activated heaters or electrodes. Advantageously, the long-range periodic array of nano-features (10) may be utilized as a nano-mask or nano-implant master pattern for nano-fabrication of other nano-structures. In addition, the inventive long-range, periodically ordered arrays of nano-features are useful in a variety of nanoscale applications such as addressable memories or logic devices, ultra-high-density magnetic recording media, magnetic sensors, photonic devices, quantum computing devices, quantum luminescent devices, and efficient catalytic devices.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Material and method for three-dimensional modeling
InactiveUS6869559B2Improve thermal stabilityResists build-upDielectric heatingAdditive manufacturing apparatusThree dimensional modelResist
The present invention is a modeling technique wherein a three-dimensional model and its support structure are built by fused deposition modeling, using a thermoplastic blended material containing a polyphenylsulfone (PPSF) polymer and a polycarbonate (PC) polymer to form the model. The PPSF / PC blend exhibits good chemical resistance, thermal stability, and resists build-up in the nozzle of a three-dimensional modeling apparatus. Removal of the support structure from a completed model is facilitated by operating on the material while it is hot.
Owner:STRATSYS INC
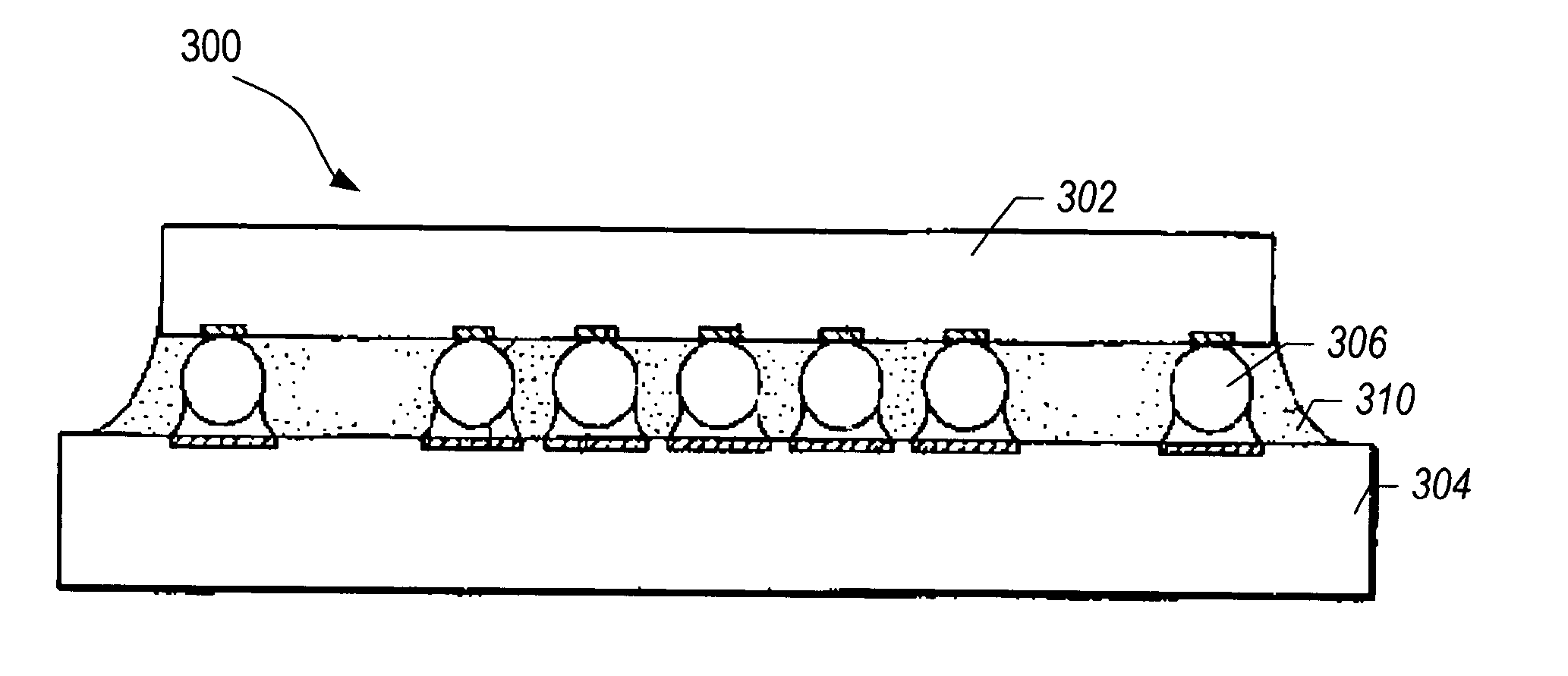
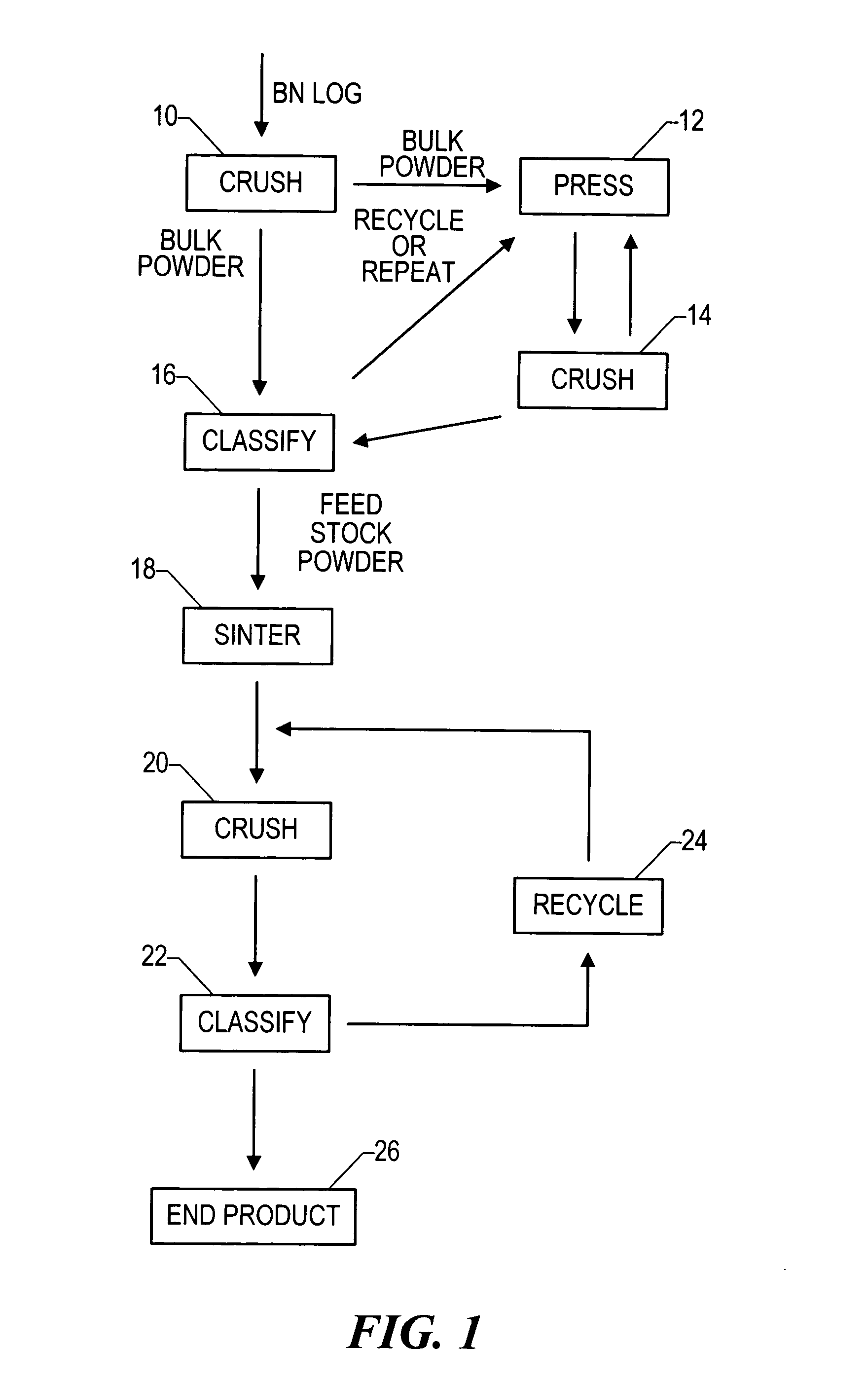
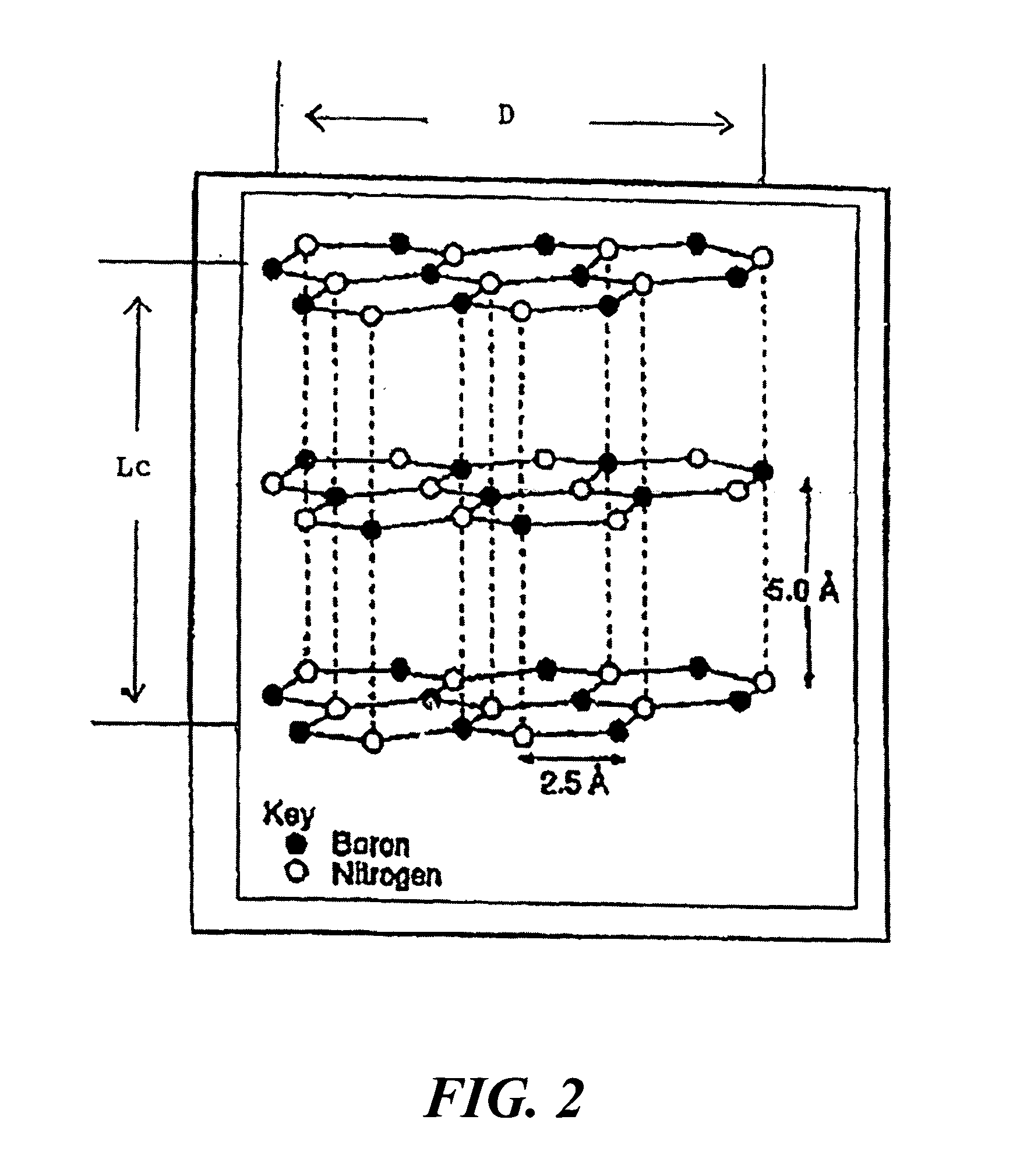
Boron nitride agglomerated powder
Novel boron nitride agglomerated powders are provided having controlled density and fracture strength features. In addition methods for producing same are provided. One method calls for providing a feedstock powder including boron nitride agglomerates, and heat treating the feedstock powder to form a heat treated boron nitride agglomerated powder. In one embodiment the feedstock powder has a controlled crystal size. In another, the feedstock powder is derived from a bulk source.
Owner:SAINT GOBAIN CERAMICS & PLASTICS INC
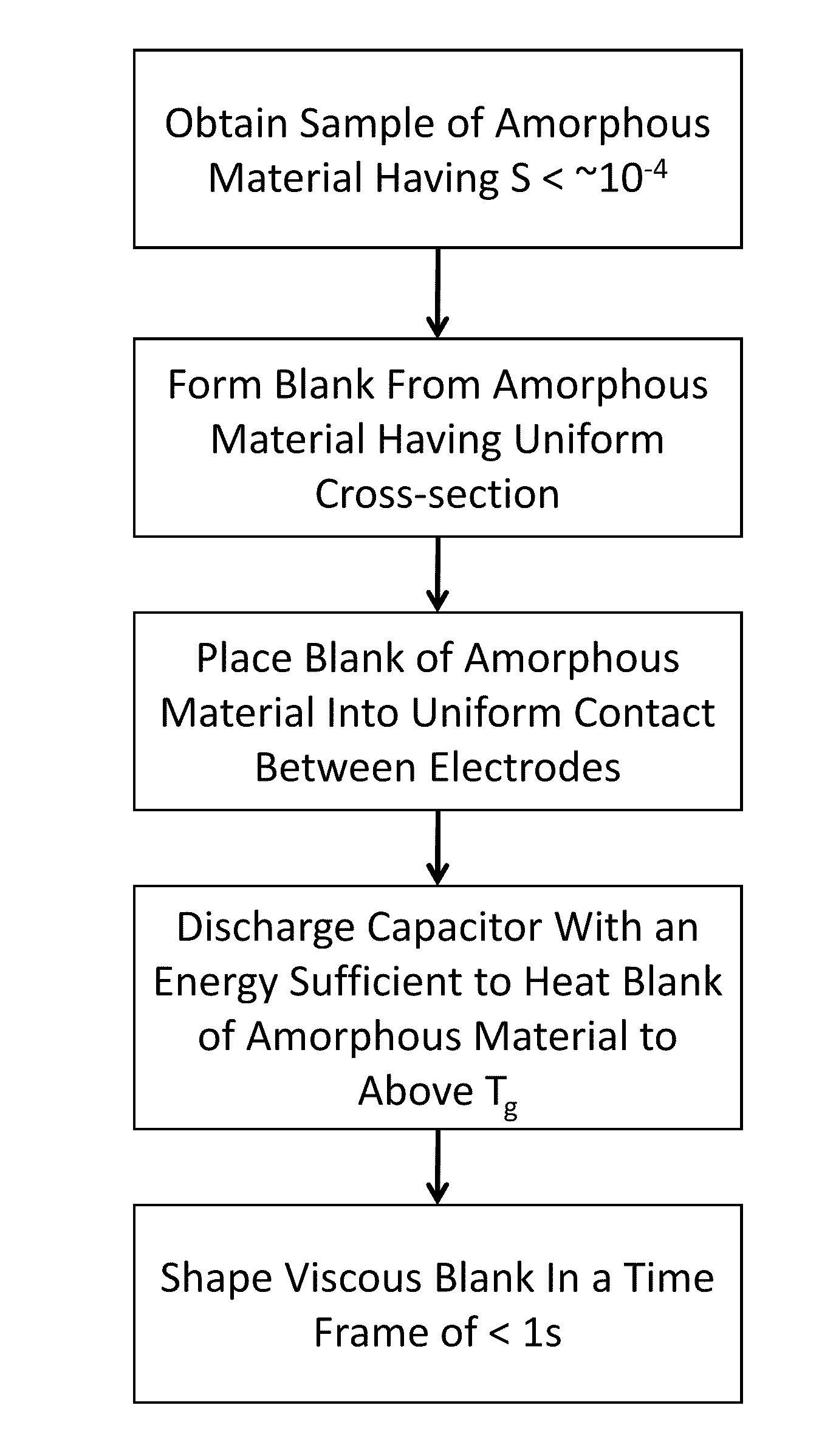
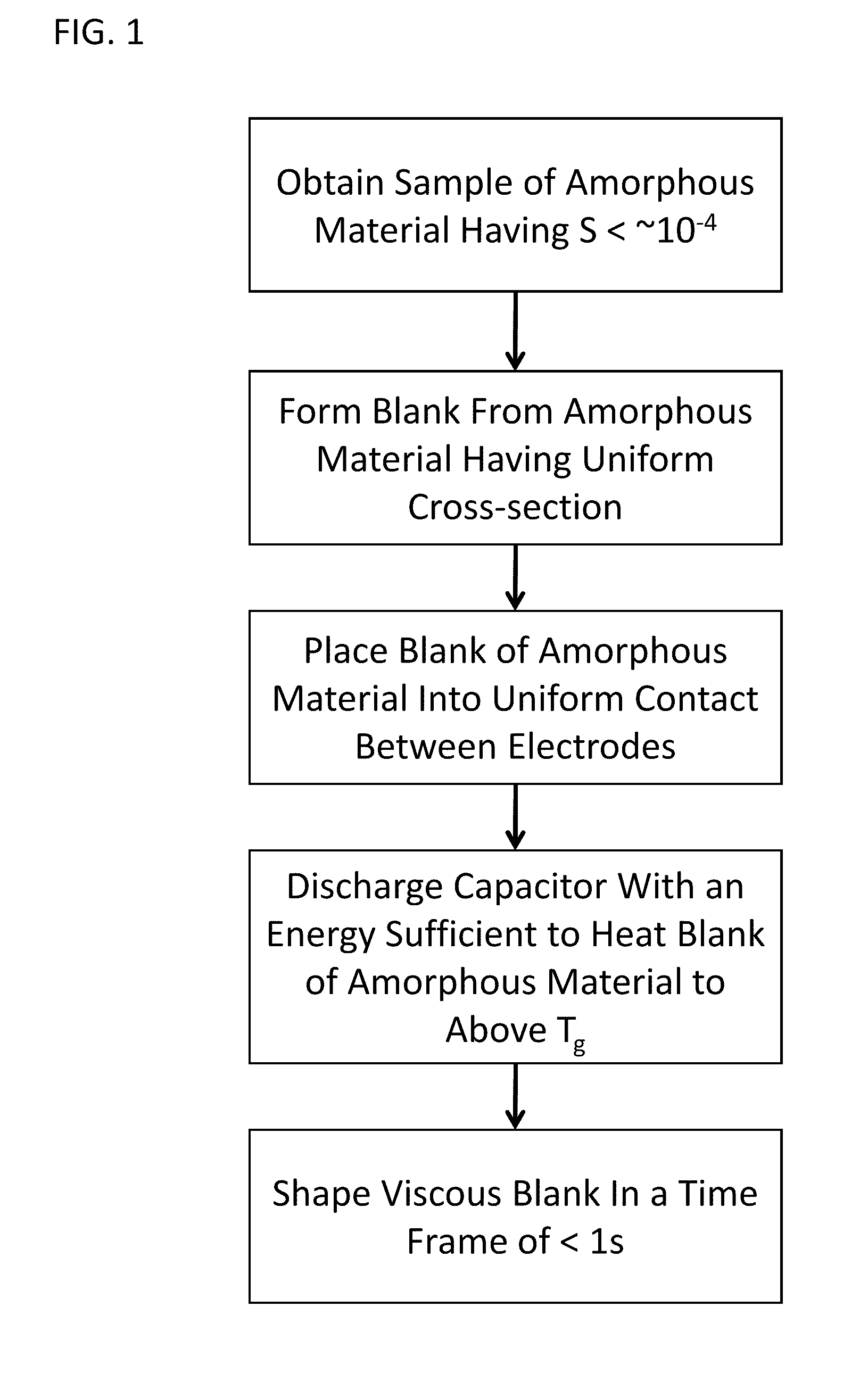
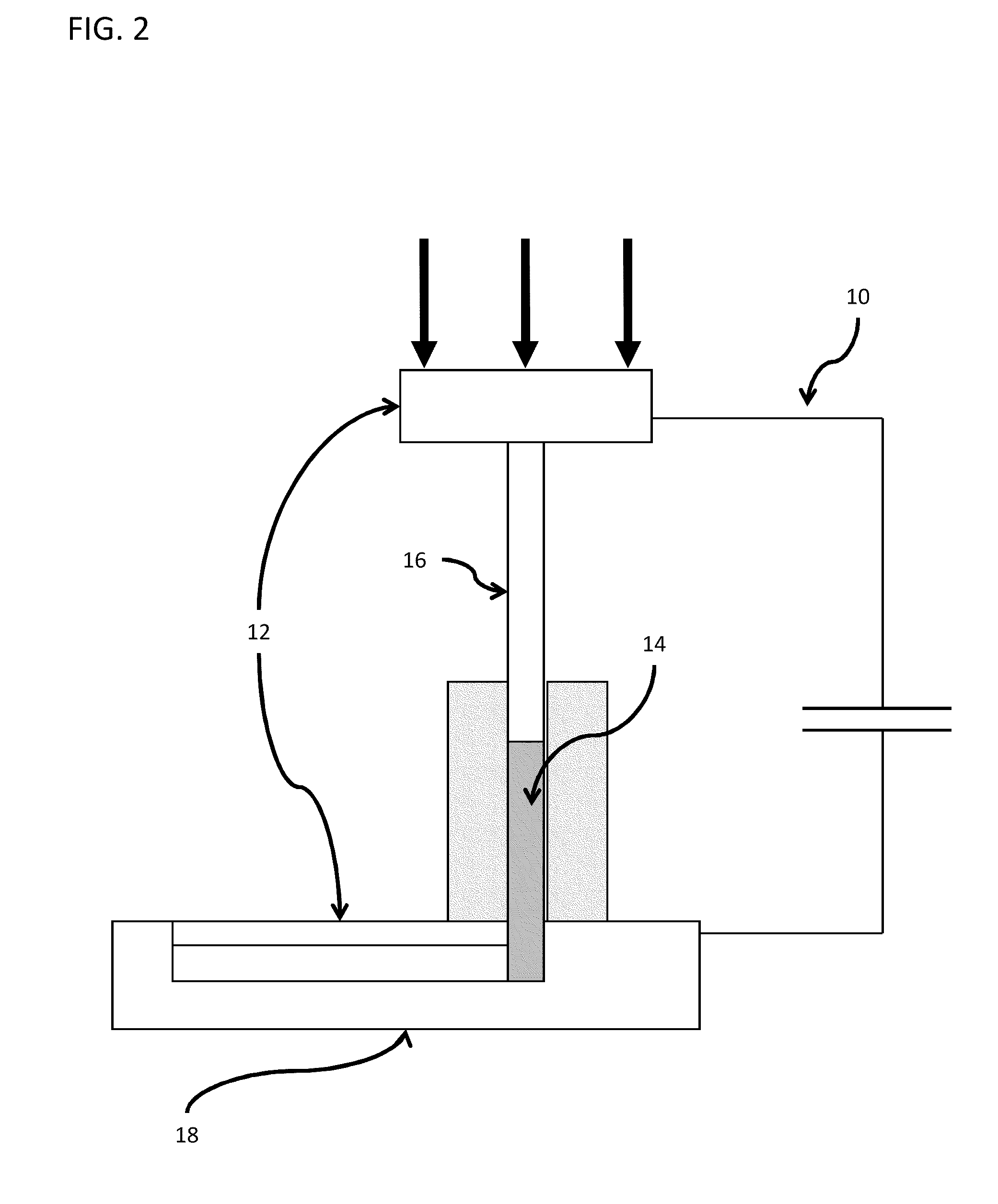
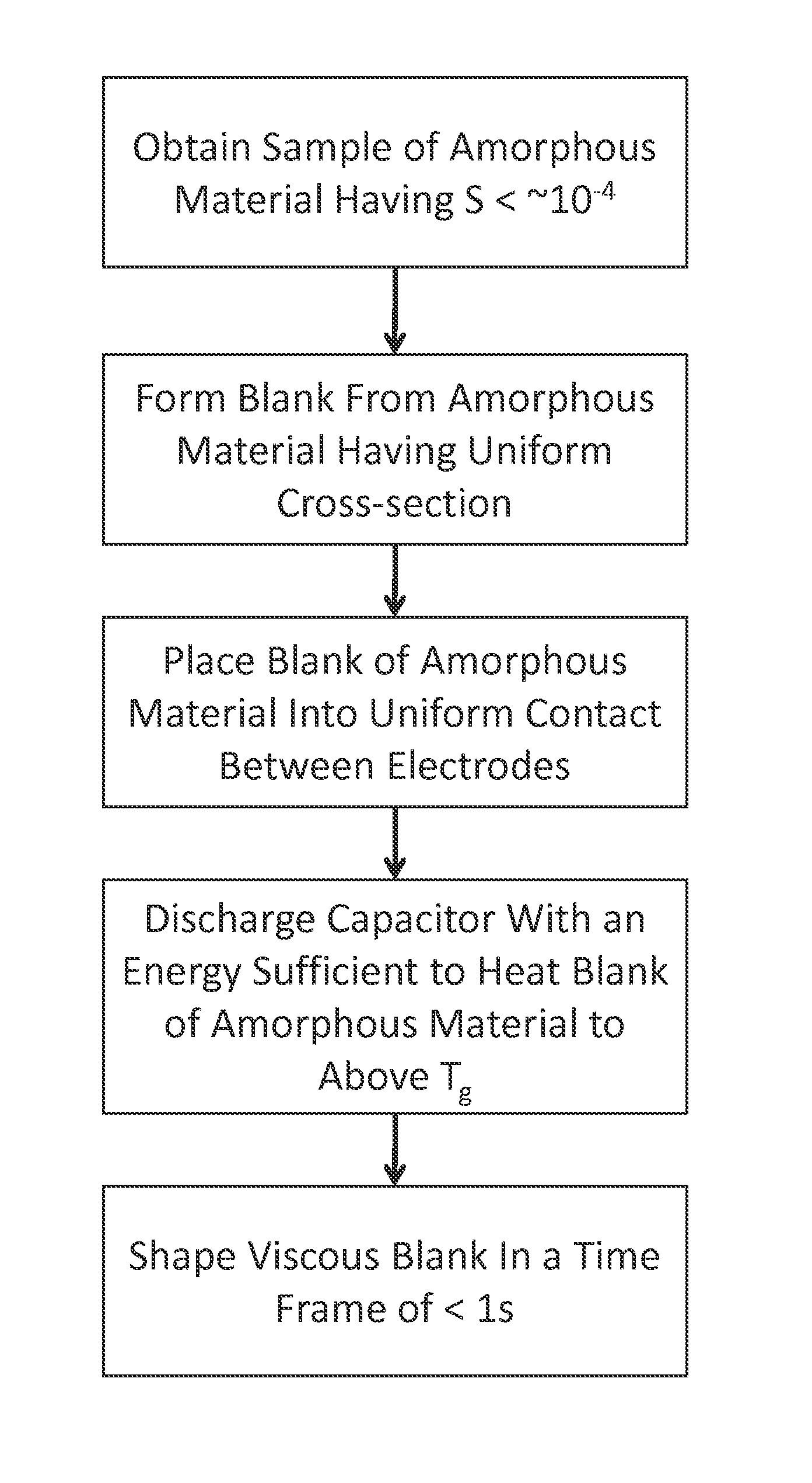
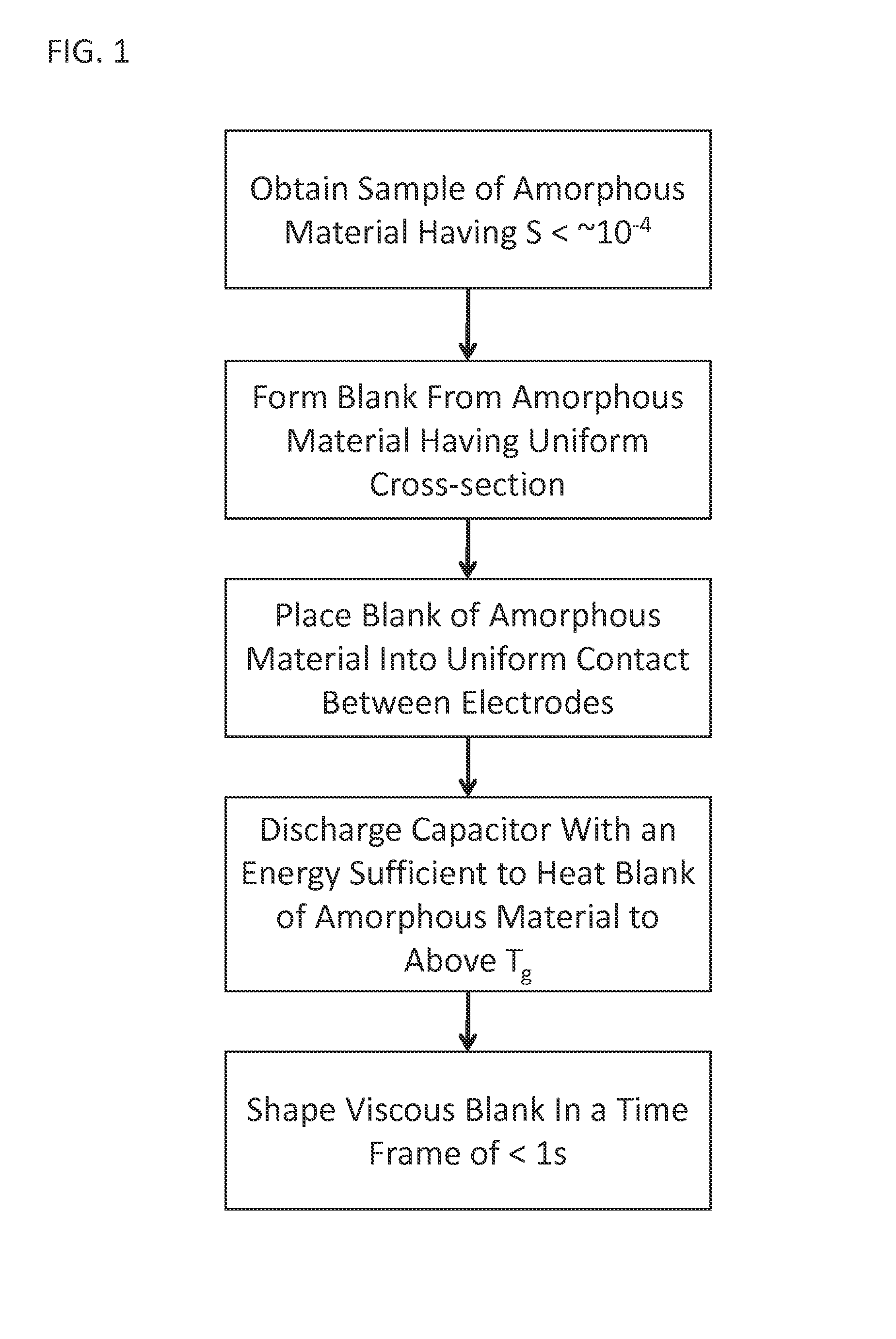
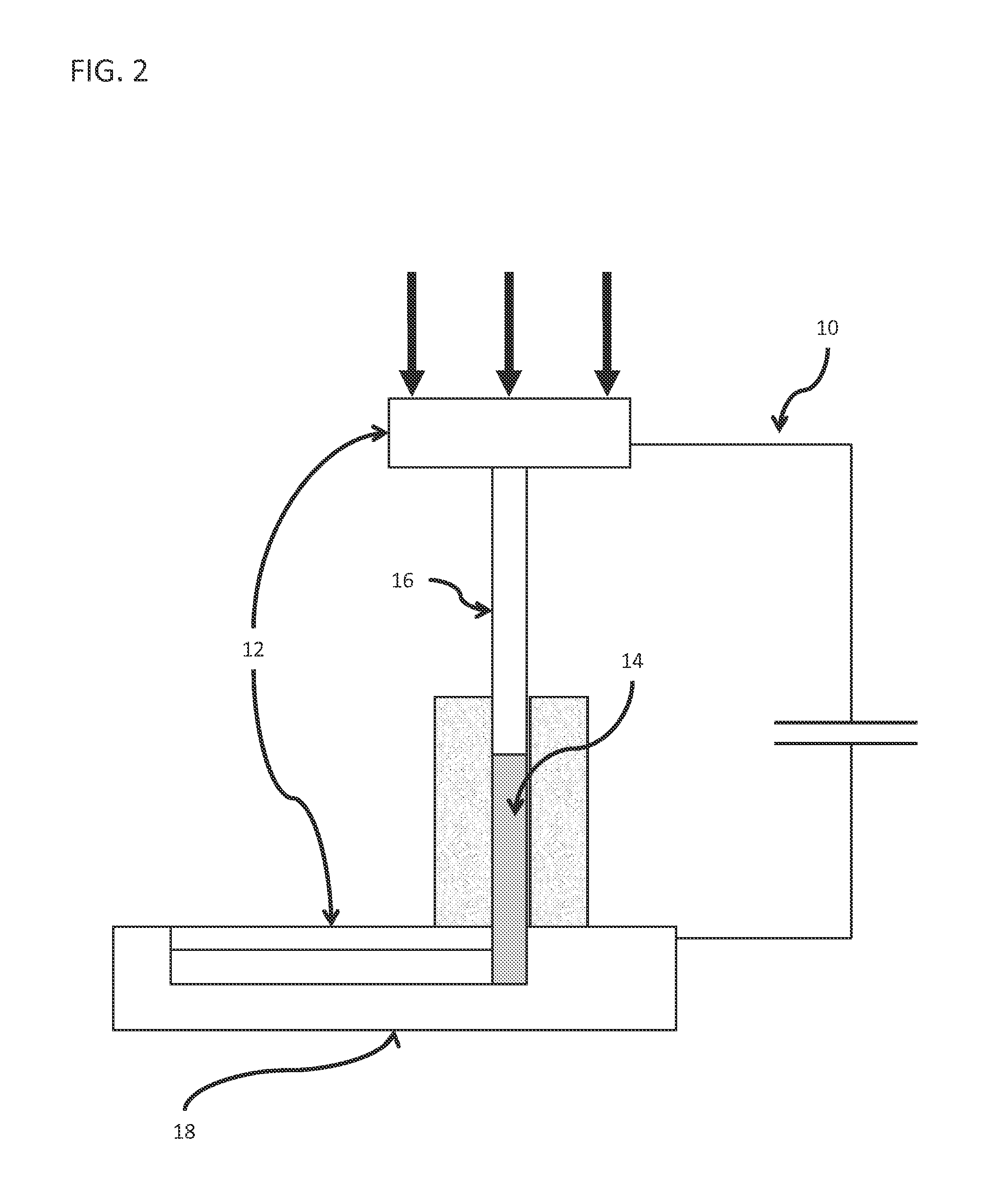
Forming of metallic glass by rapid capacitor discharge
ActiveUS20090236017A1Avoid failureAvoid thermal transport and development of thermalDielectric heatingShaping toolsAlloyGlass transition
An apparatus and method of uniformly heating, rheologically softening, and thermoplastically forming metallic glasses rapidly into a net shape using a rapid capacitor discharge forming (RCDF) tool are provided. The RCDF method utilizes the discharge of electrical energy stored in a capacitor to uniformly and rapidly heat a sample or charge of metallic glass alloy to a predetermined “process temperature” between the glass transition temperature of the amorphous material and the equilibrium melting point of the alloy in a time scale of several milliseconds or less. Once the sample is uniformly heated such that the entire sample block has a sufficiently low process viscosity it may be shaped into high quality amorphous bulk articles via any number of techniques including, for example, injection molding, dynamic forging, stamp forging, and blow molding in a time frame of less than 1 second.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
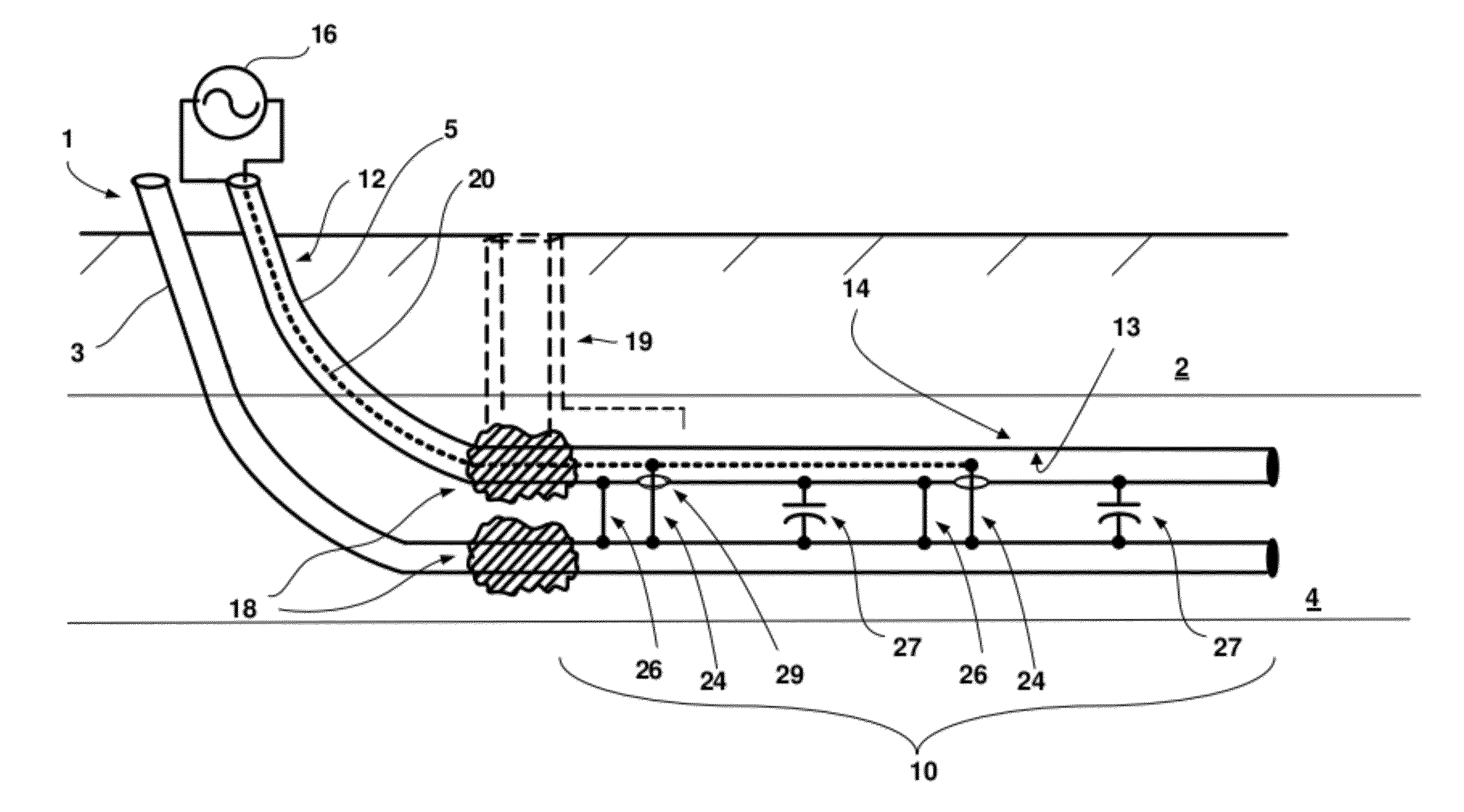
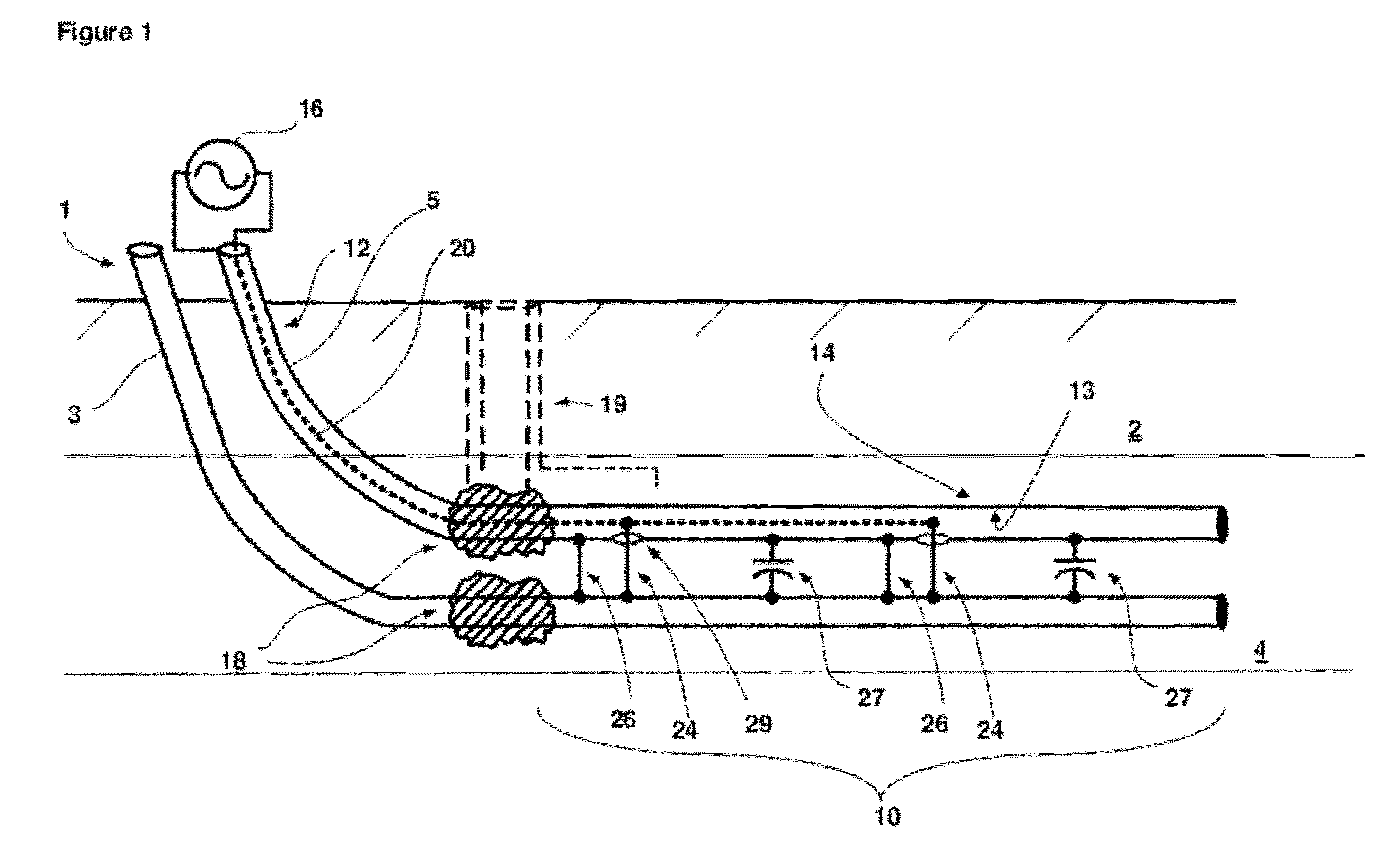
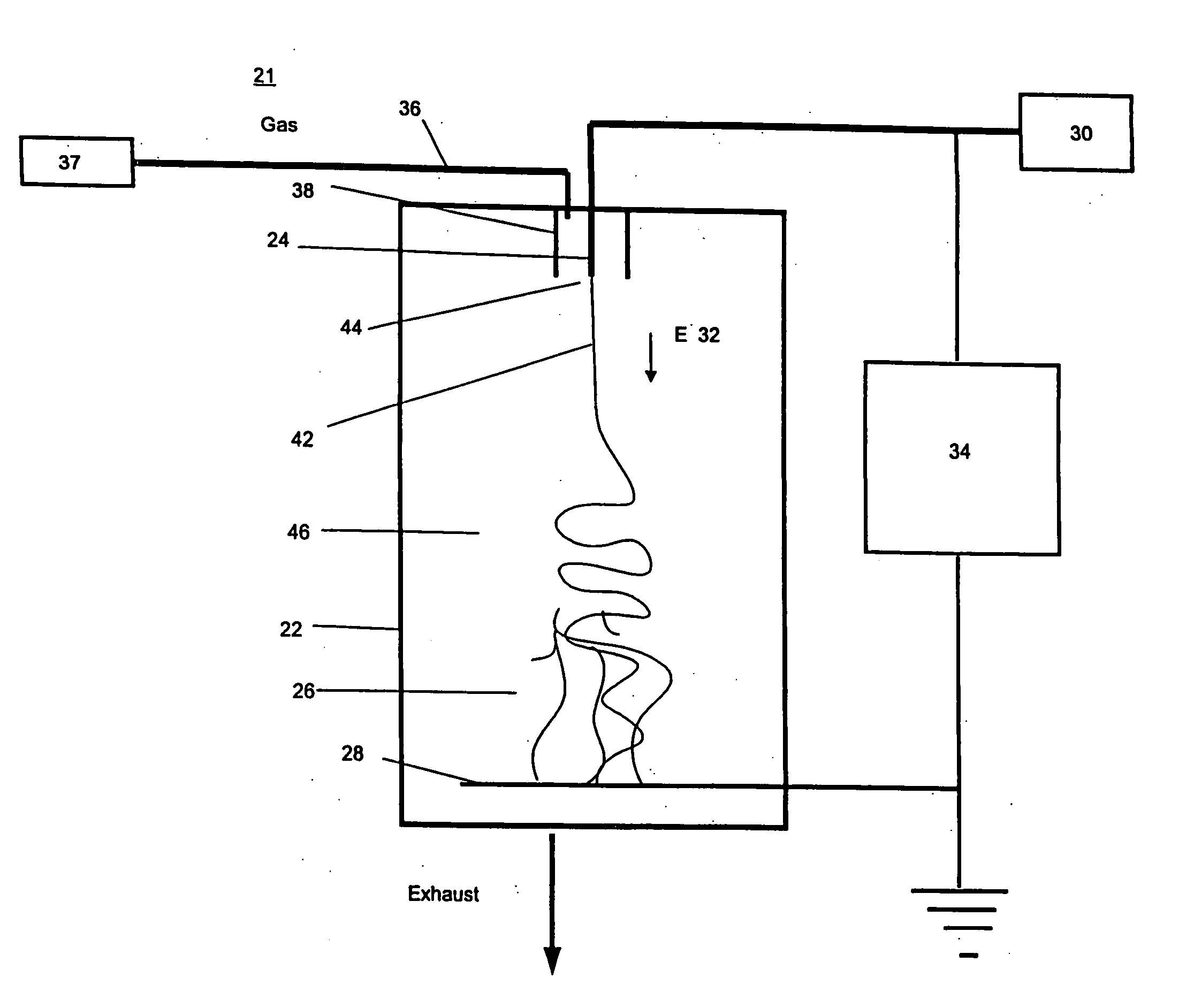
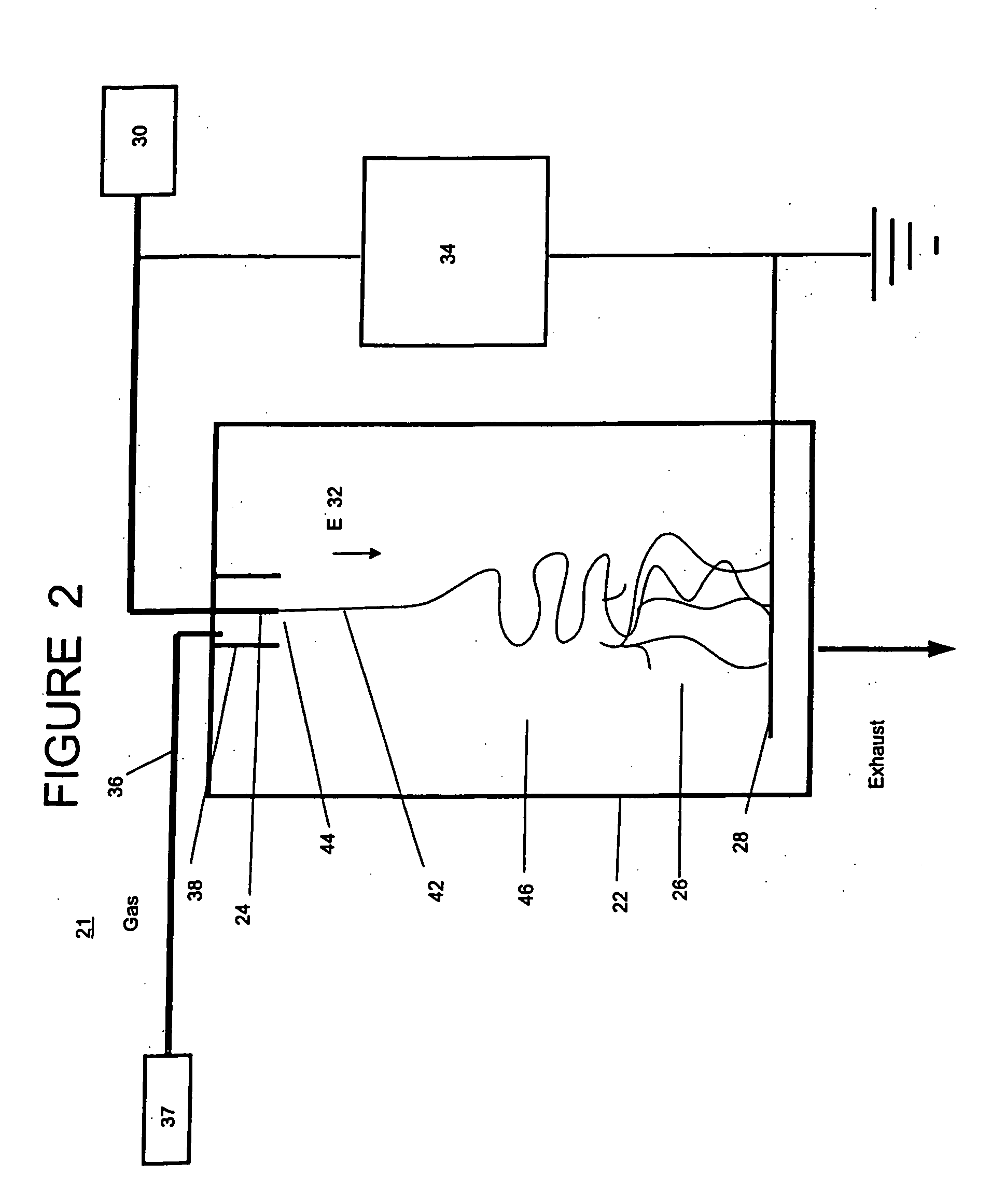
Radio frequency heat applicator for increased heavy oil recovery
A radio frequency applicator and method for heating a geological formation is disclosed. A radio frequency source configured to apply a differential mode signal is connected to a coaxial conductor including an outer conductor pipe and an inner conductor. The inner conductor is coupled to a second conductor pipe through one or more metal jumpers. One or more current chokes, such as a common mode choke or antenna balun, are installed around the outer conductor pipe and the second conductor pipe to concentrate electromagnetic radiation within a hydrocarbon formation. The outer conductor pipe and the second conductor pipe can be traditional well pipes for extracting hydrocarbons, such as a steam pipe and an extraction pipe of a steam assisted gravity drainage (SAGD) system. An apparatus and method for installing a current choke are also disclosed.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Methods of making orthodontic appliances
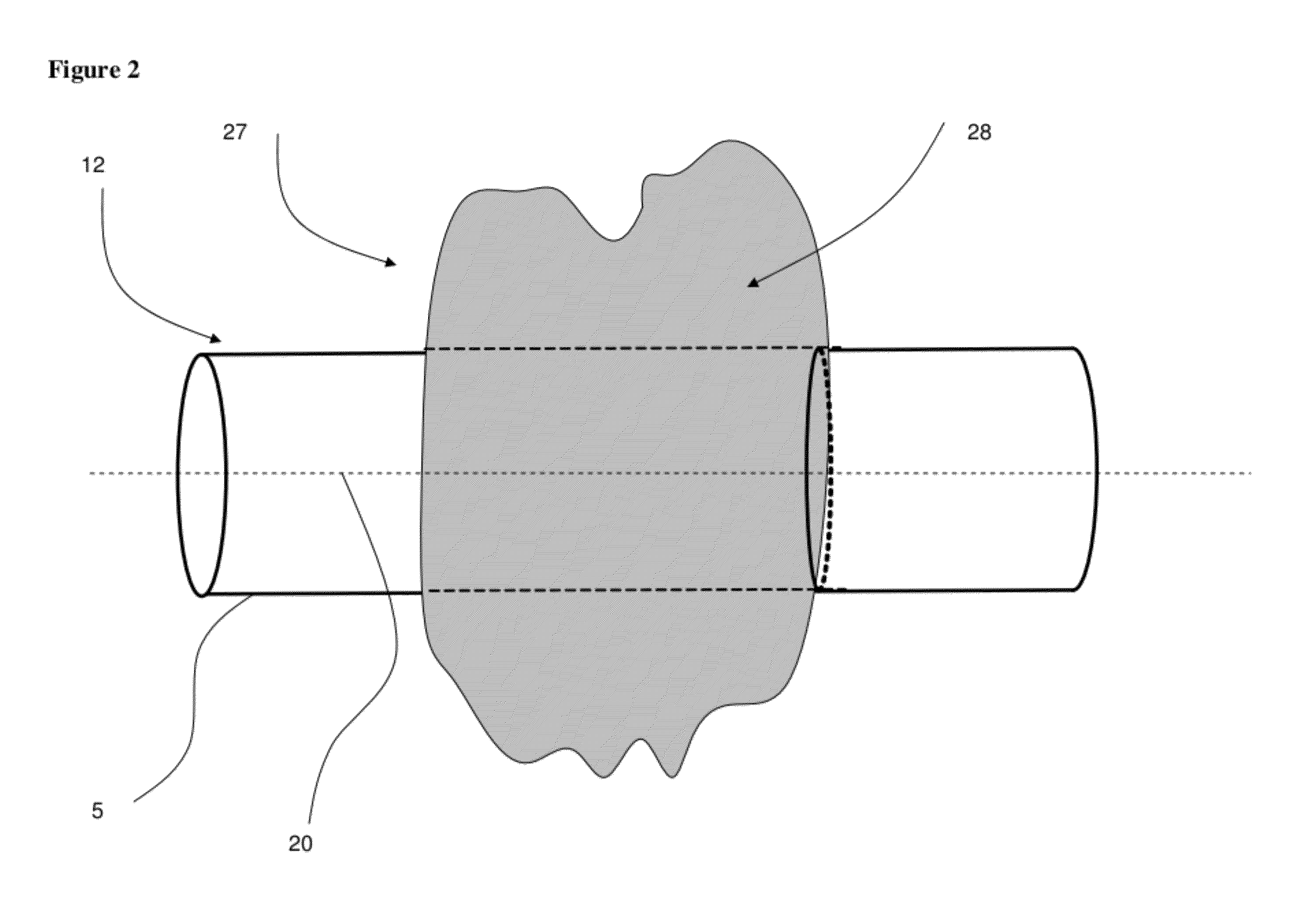
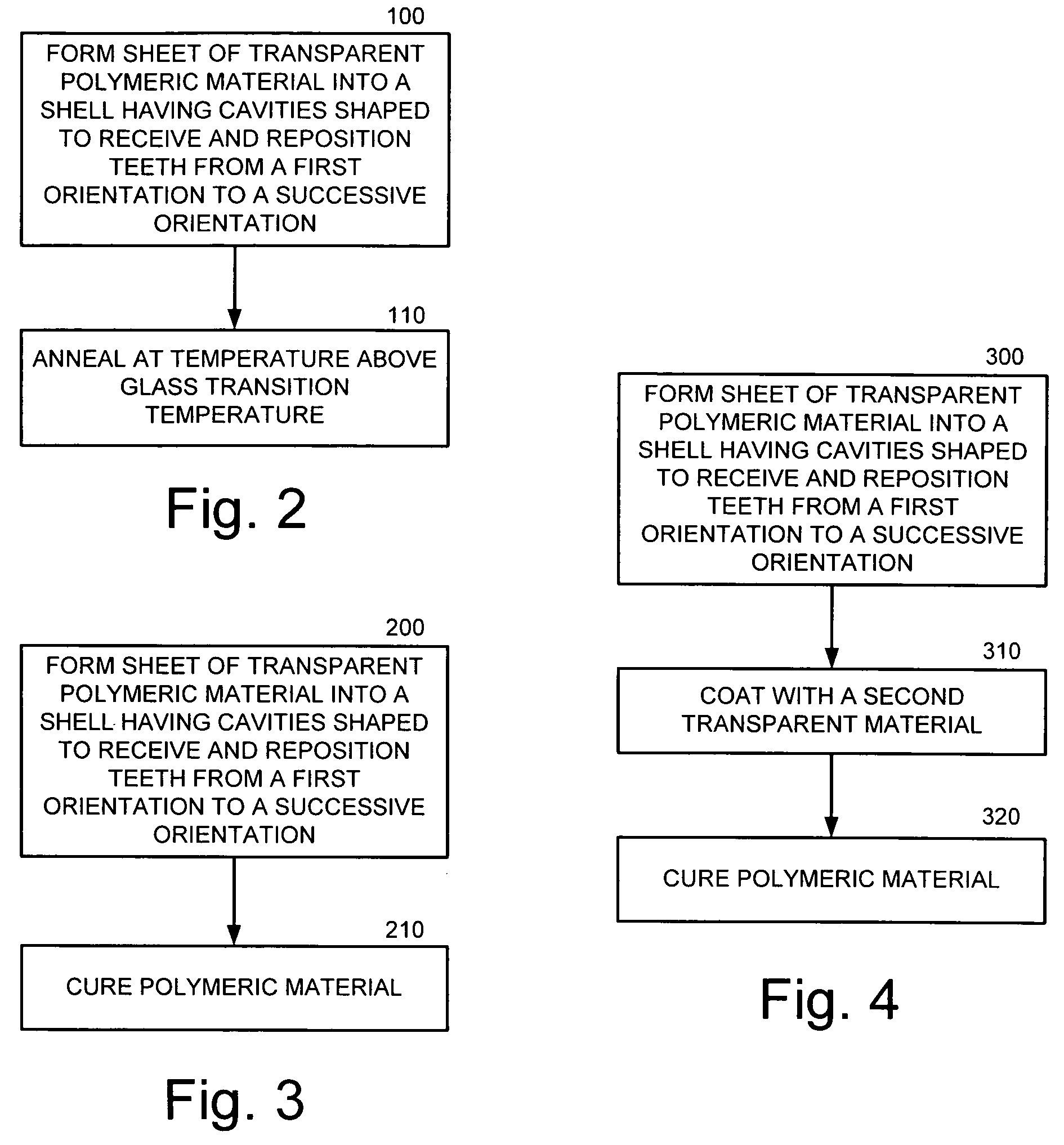
Methods of making a removable dental positioning appliance include forming a sheet of transparent crystalline polymeric material into a shell having cavities shaped to receive and reposition teeth from a first orientation to a successive orientation. The polymeric material may then be annealed at a temperature above its glass transition temperature or cured if a curable material to enhance characteristics of the polymeric material. The polymeric material may be coated with a second transparent material.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
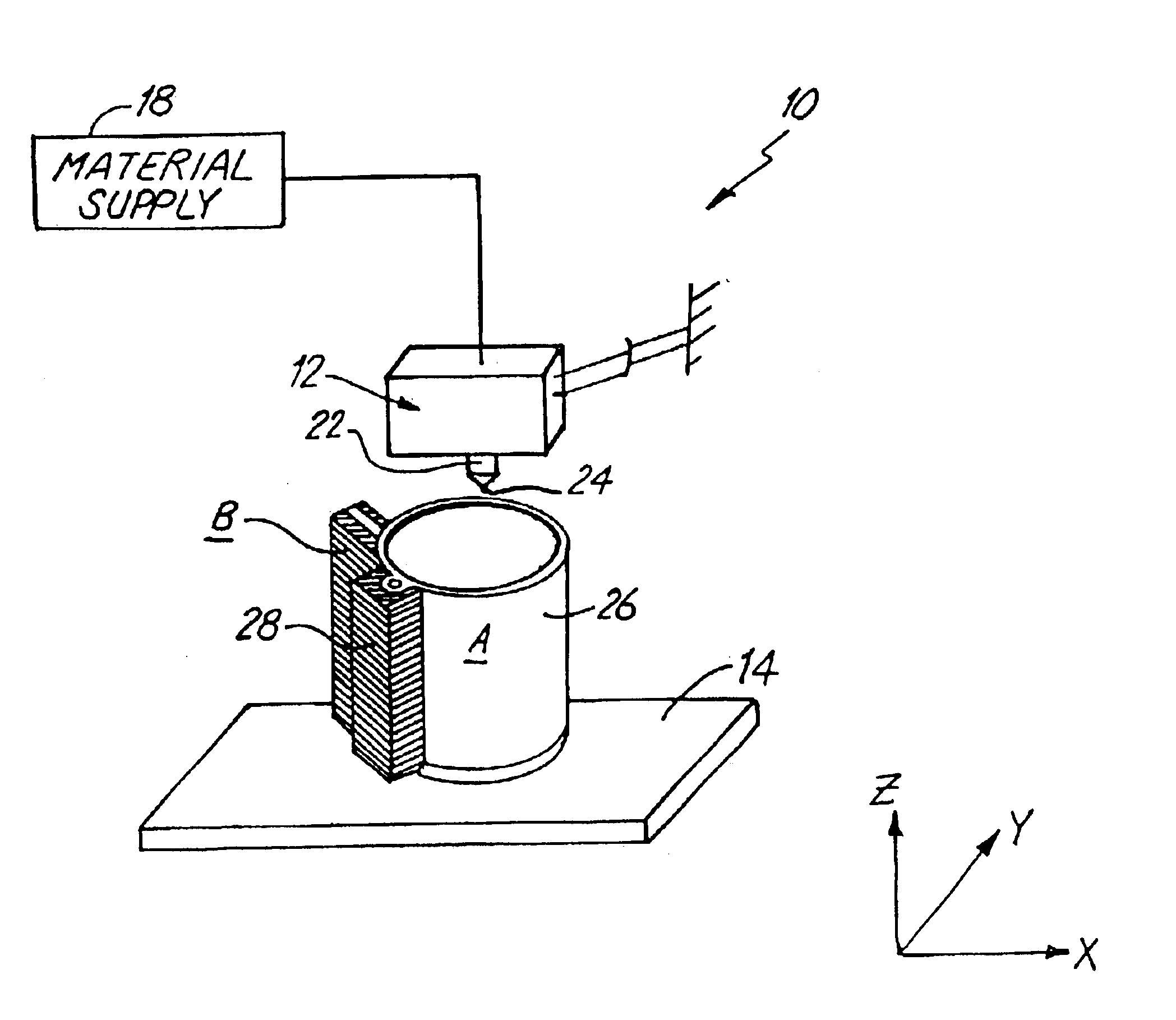
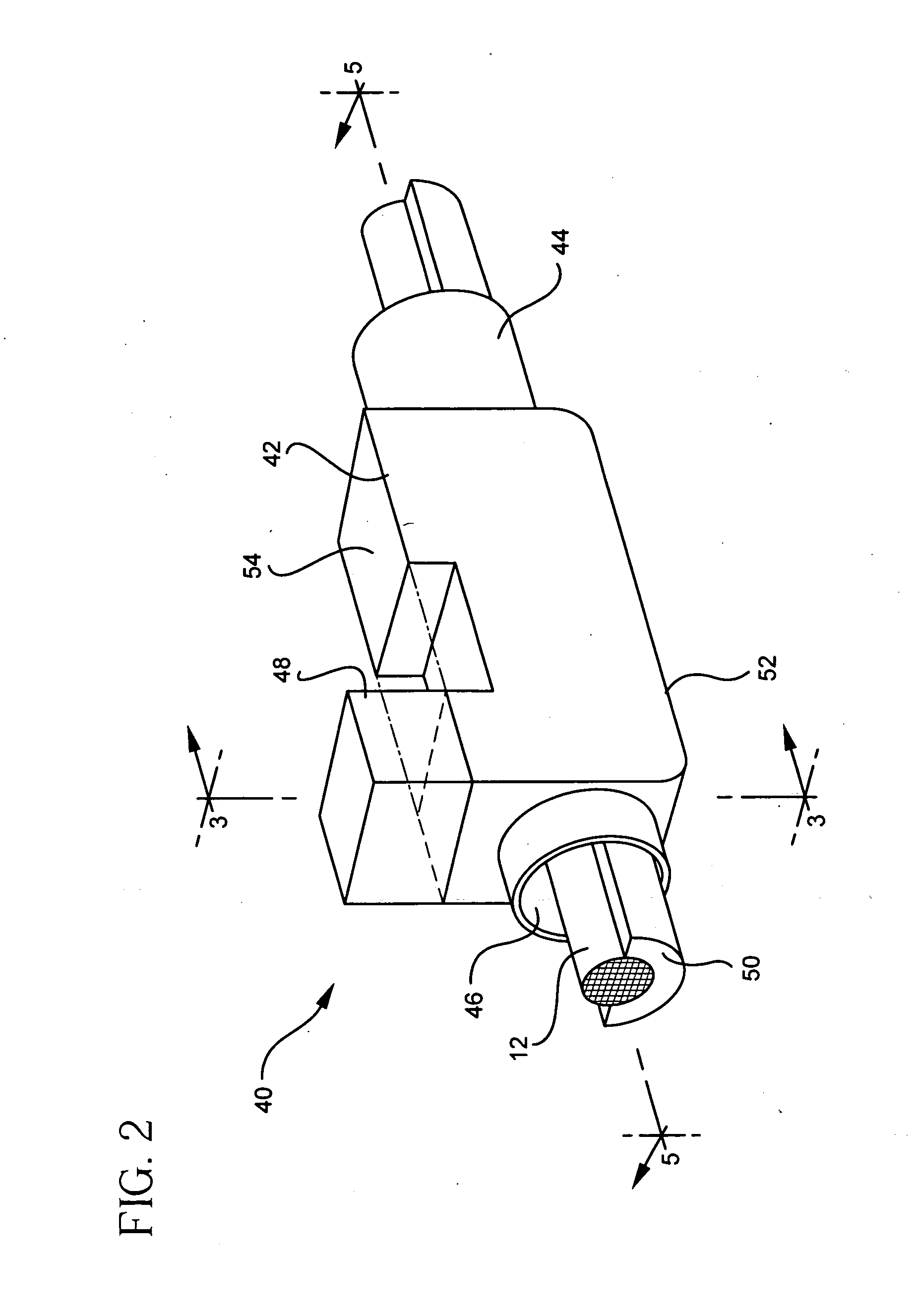
Method and apparatus for extruding polymers employing microwave energy
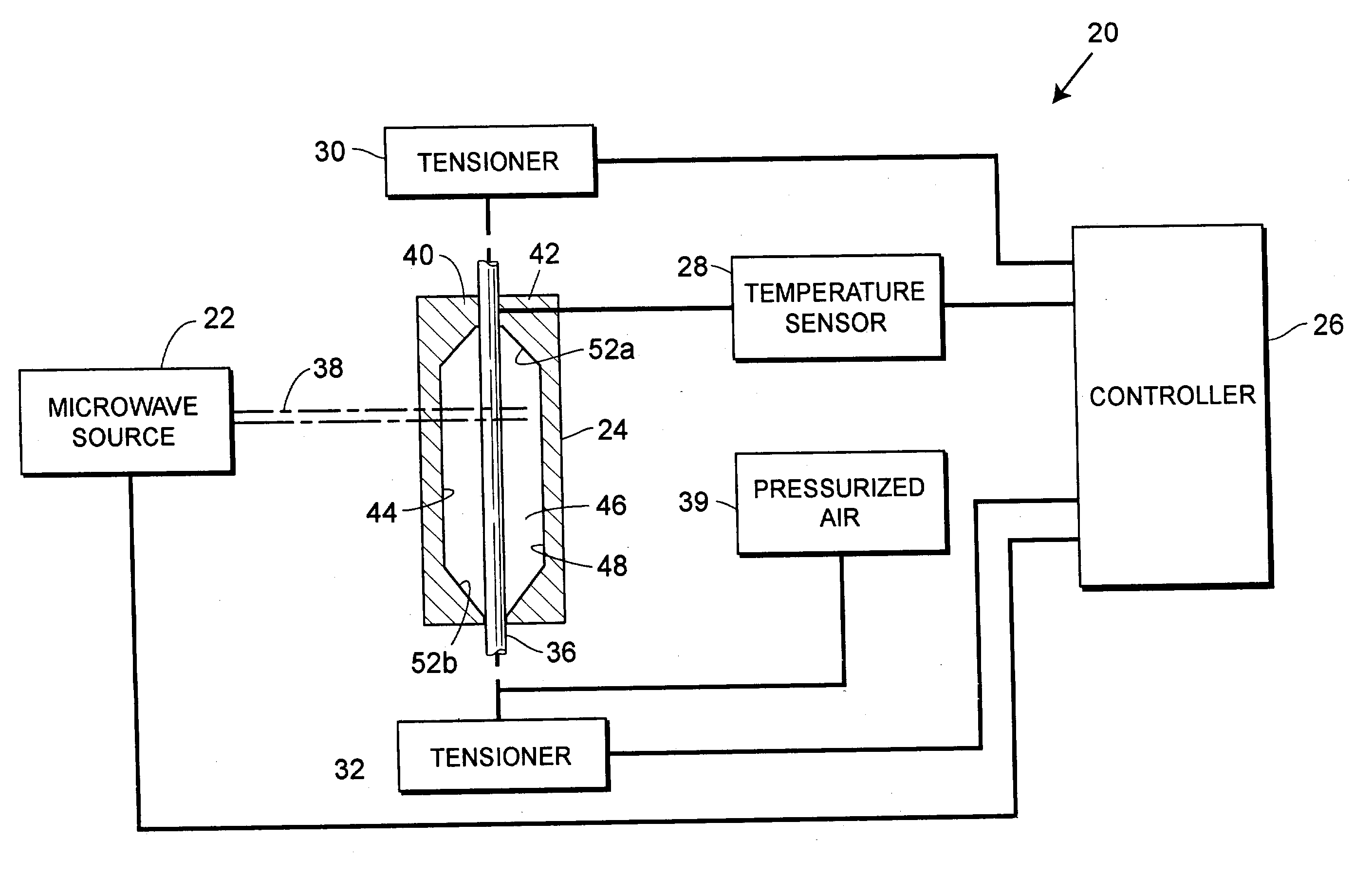
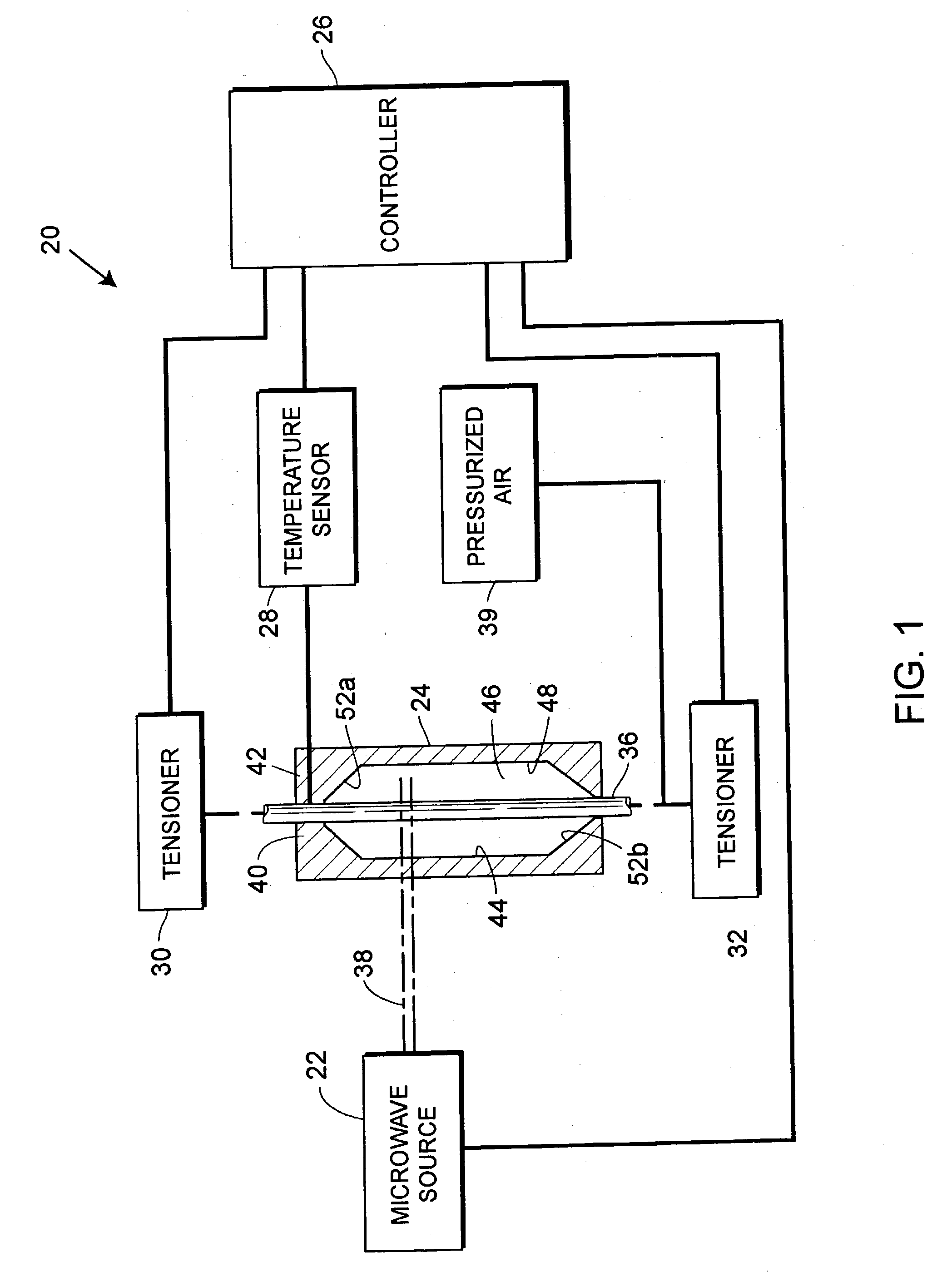
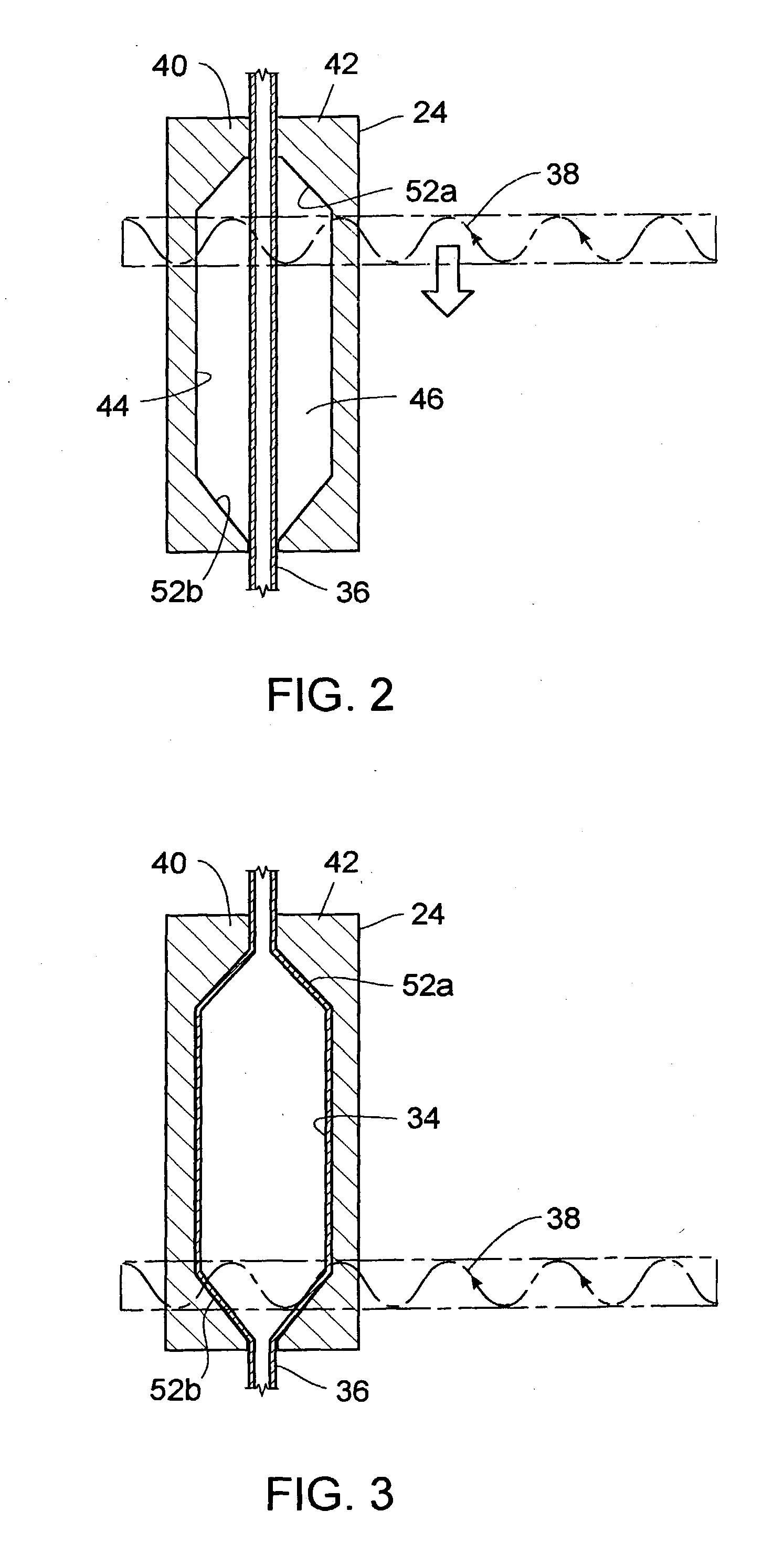
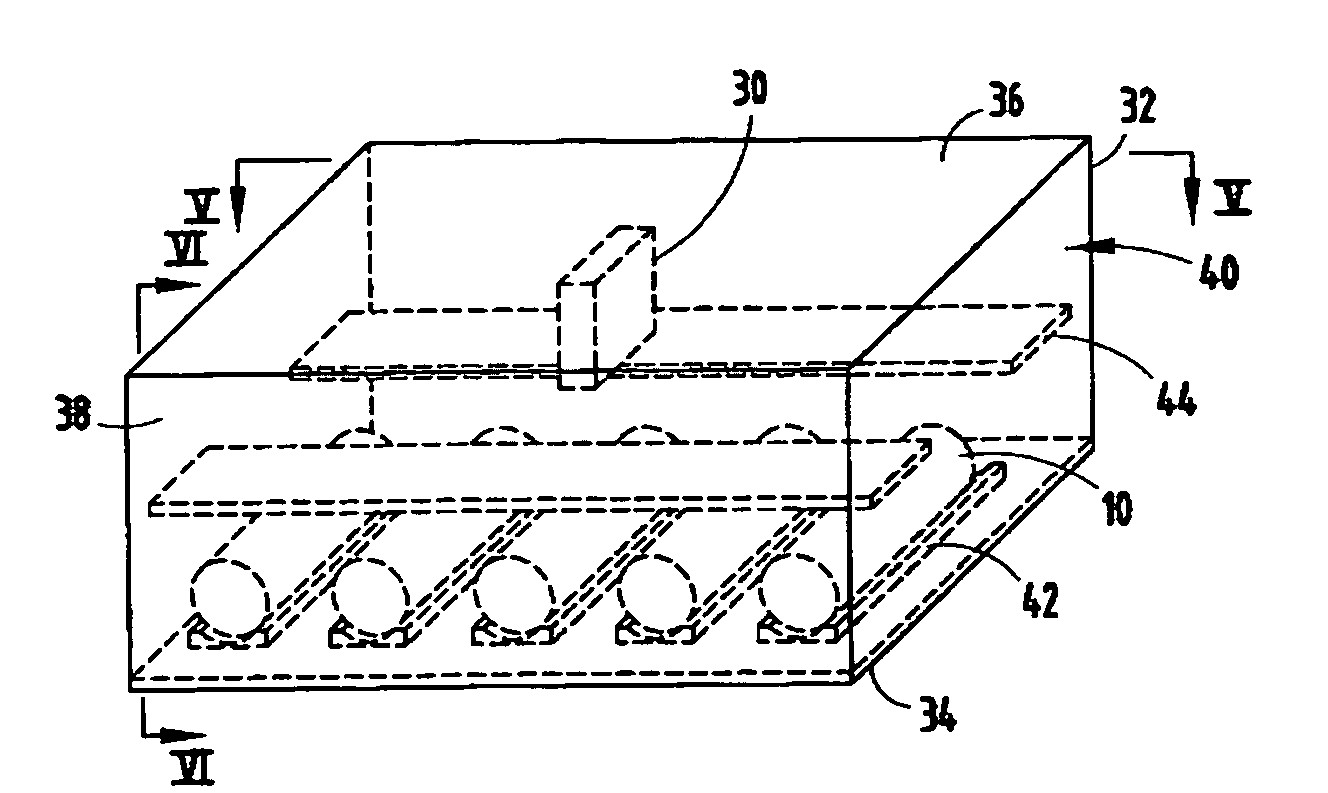
An apparatus and method for molding balloon catheters is disclosed. The balloon may be molded by providing a polymeric tube within a mold having an interior cavity in the shape of the desired balloon. Microwave energy, which may be generated by a gyrotron, may then be directed toward the mold, to heat the polymeric material without heating the mold. Once heated, pressurized fluid may be injected into the tube to blow the polymeric material against the interior cavity whereupon the material can cool to form the balloon or can be further heatset by additional microwave energy and be cooled to form the balloon. In accordance with one embodiment, microwave energy can also be used without a mold to form a medical device. A polymer extrusion apparatus is disclosed utilizing a microwave energy for heating polymer feedstock material within the extruder tip and die unit just prior to formation of the extrudate product. A cooling bath mechanism, which in one embodiment can also include a cooling tube member having a cooling medium forced therethrough, is also disclosed. An apparatus for preparing polymer disk members, to use as the polymer feedstock material for the microwave extrusion apparatus, is also disclosed. Apparatus for interconnecting and rotating the polymer disk members, the die tip, or the die, or any combination thereof, for creating angularity characteristics in the polymer extrudate, is also disclosed.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Microwave drying of ceramic structures
ActiveUS7596885B2Dry evenlySimple structureDielectric heatingDrying solid materials with heatStructural degradationMetallurgy
Owner:CORNING INC
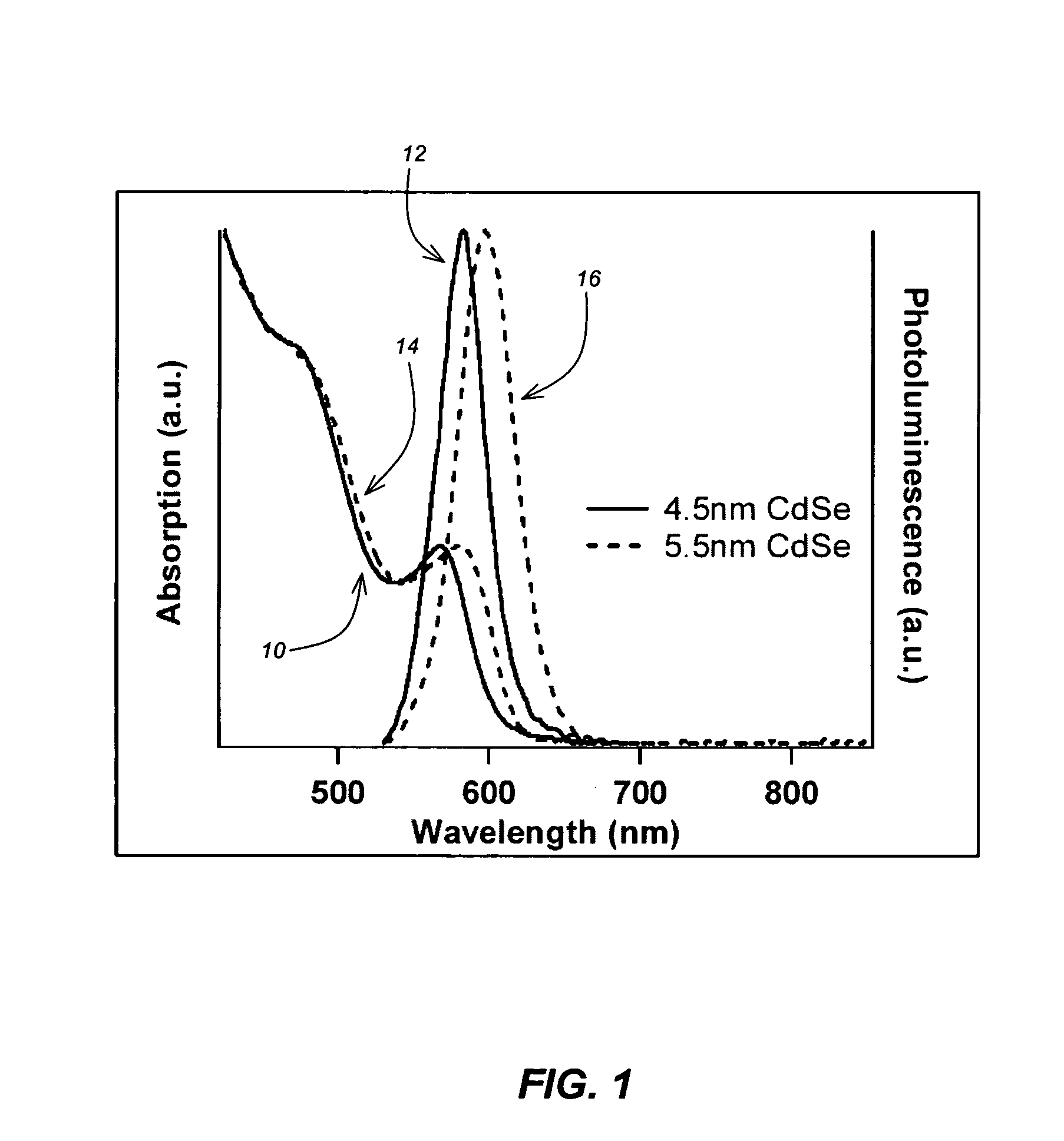
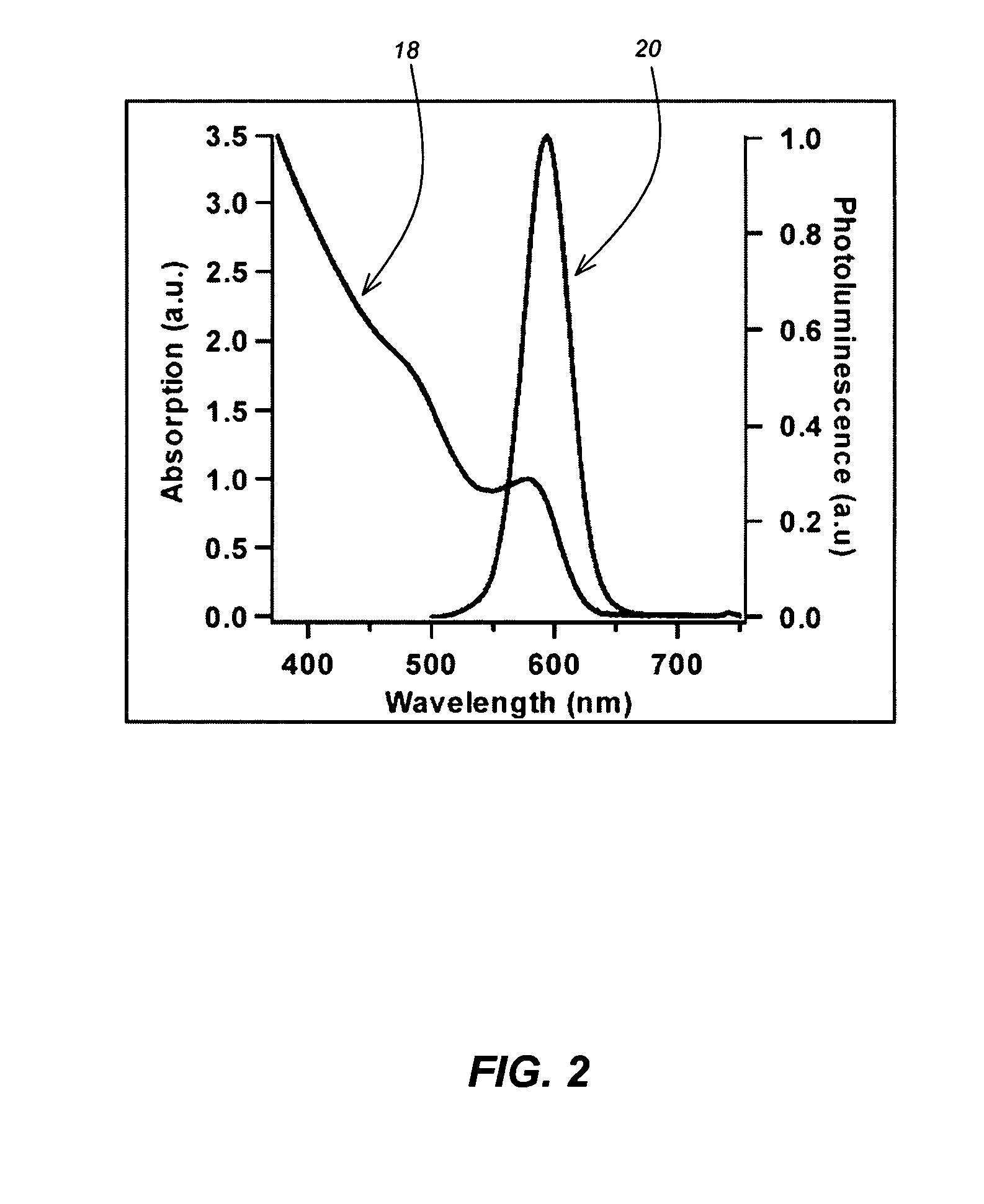
Method for synthesis of colloidal nanoparticles
InactiveUS20060061017A1High crystallinityLarge-scale, safe, convenient, reproducible, and energy-efficient productionDielectric heatingMaterial nanotechnologyContinuous flowColloidal nanoparticles
A method for synthesis of high quality colloidal nanoparticles using comprises a high heating rate process. Irradiation of single mode, high power, microwave is a particularly well suited technique to realize high quality semiconductor nanoparticles. The use of microwave radiation effectively automates the synthesis, and more importantly, permits the use of a continuous flow microwave reactor for commercial preparation of the high quality colloidal nanoparticles.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Electrospinning in a controlled gaseous environment
ActiveUS20050224999A1Increased process windowEasy to processDielectric heatingElectric discharge heatingFiberElectrospinning
Apparatus and method for producing fibrous materials in which the apparatus includes an extrusion element configured to electrospin a substance from which the fibers are to be composed by an electric field extraction of the substance from a tip of the extrusion element, a collector disposed from the extrusion element and configured to collect the fibers, a chamber enclosing the collector and the extrusion element, and a control mechanism configured to control a gaseous environment in which the fibers are to be electrospun. The method includes providing a substance from which the fibers are to be composed to a tip of an extrusion element, applying an electric field to the extrusion element in a direction of the tip, controlling a gaseous environment about where the fibers are to be electrospun, and electrospinning the substance from the tip of the extrusion element by an electric field extraction of the substance from the tip into the controlled gaseous environment.
Owner:RES TRIANGLE INST
Systems and methods for nanomaterial transfer
Systems and methods of nanomaterial transfer are described. A method of nanomaterial transfer involving fabricating a template and synthesizing nanomaterials on the template. Subsequently, the nanomaterials are transferred to a substrate by pressing the template onto the substrate. In some embodiments, the step of transferring the nanomaterials involves pressing the template onto the substrate such that the nanomaterials are embedded below a surface layer of the substrate. In some embodiments, the temperature of the plurality of nanomaterials is raised to assist the transfer of the nanomaterials to the substrate.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Drying jig, drying method of honeycomb molded body, and manufacturing method of honeycomb structured body
InactiveUS20090079111A1Avoid separationPrevent openingDielectric heatingConfectioneryEngineeringCell wall
A drying jig of the present invention is a drying jig for a pillar-shaped honeycomb molded body having a large number of cells longitudinally placed in parallel with one another with a cell wall therebetween, comprising: a fixing member for preventing separation or opening of the drying jig; and a piling member which enables the drying jig to be piled up in multi stage at the time of drying.
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD
Apparatus, system and method for preventing biological contamination to materials during storage using pulsed electrical energy
InactiveUS20120034131A1Reduce and substantially eliminate undesirable organic contaminationDielectric heatingBacterial antigen ingredientsElectrical impulseContamination
A container having a main storage space for holding a matter, having an inlet / outlet opening and fitted with a PEF system. The PEF system comprises two or more electrodes disposed within said container and contacting the matter; and electric pulse source connected to the two or more electrodes and adapted to pass pulsed electric energy through the matter. The PEF system being activated to deliver a treatment protocol to the matter.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD +1
Pulse systems and methods for detaching ice
ActiveUS20090199569A1Increase temperatureDielectric heatingDe-icing equipmentsJet aeroplaneElectrical resistance and conductance
A pulse system for detaching ice includes a power supply for applying a high-power heating pulse to the interface between ice and an object such as a cold plate of an ice making system, an ice-container, a heat-exchanger, a refrigerator surface or an airplane wing. Pulse heating may be generated within a metal foil or resistive film disposed upon an object to be deiced, or a capillary tube proximate the object to be deiced. An interfacial layer of ice is melted and the ice is released from the object. A force, for example gravity, pressure of vaporization or mechanical scraping, removes the ice from the object.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
Non-Modal Interplate Microwave Heating System and Method of Heating
InactiveUS20110139773A1Maintain loadDielectric heatingPreparing sample for investigationEngineeringMicrowave applicator
Disclosed is a microwave heater and a method of heating. The microwave heater includes a non-modal interplate microwave applicator and may include a nonresonant enclosure. The non-modal interplate microwave applicator is configured to receive therein a load to be heated by microwaves radiated from the non-modal interplate microwave applicator.
Owner:DAKOAS
Non-thermal process for forming porous low dielectric constant films
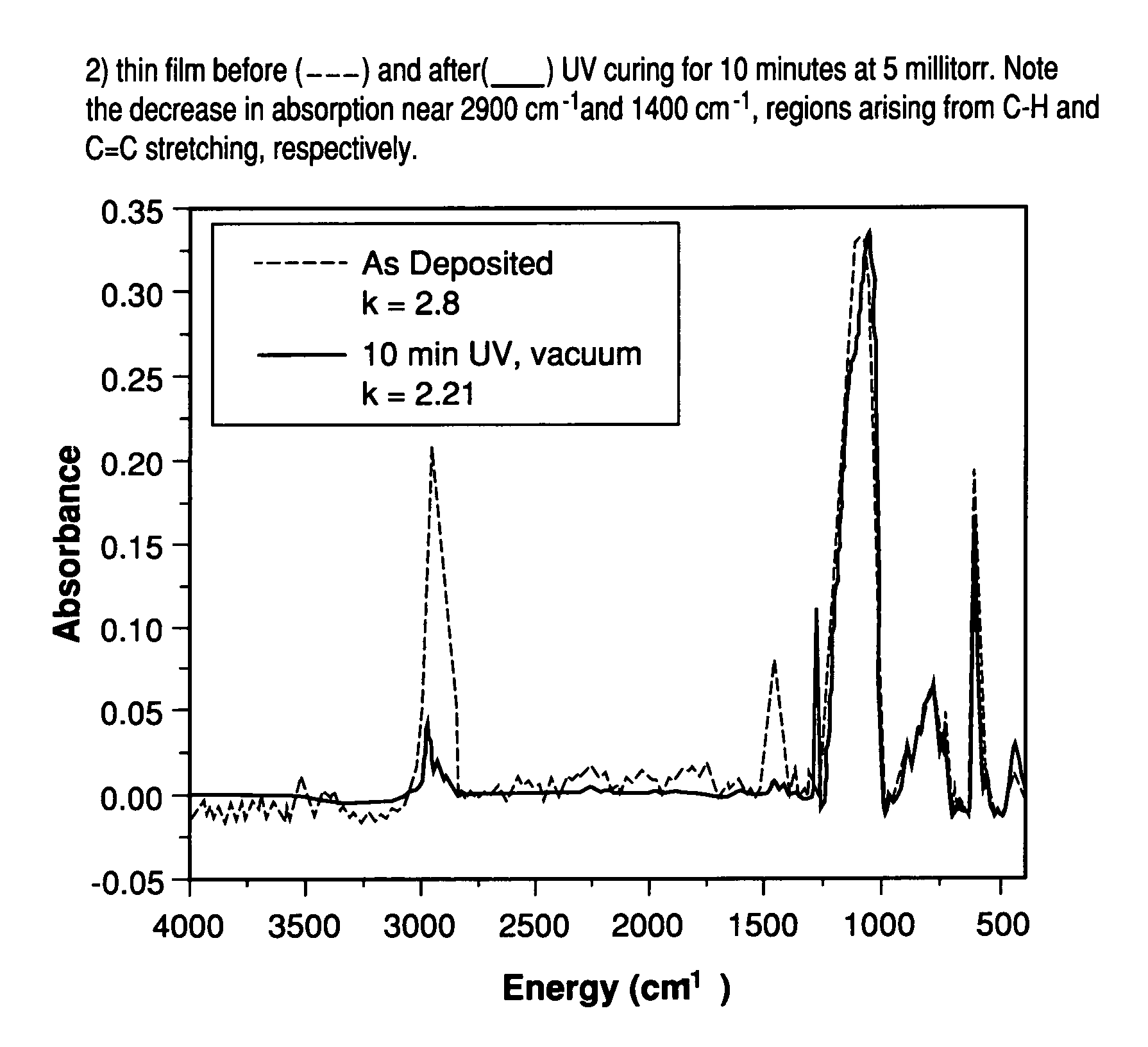
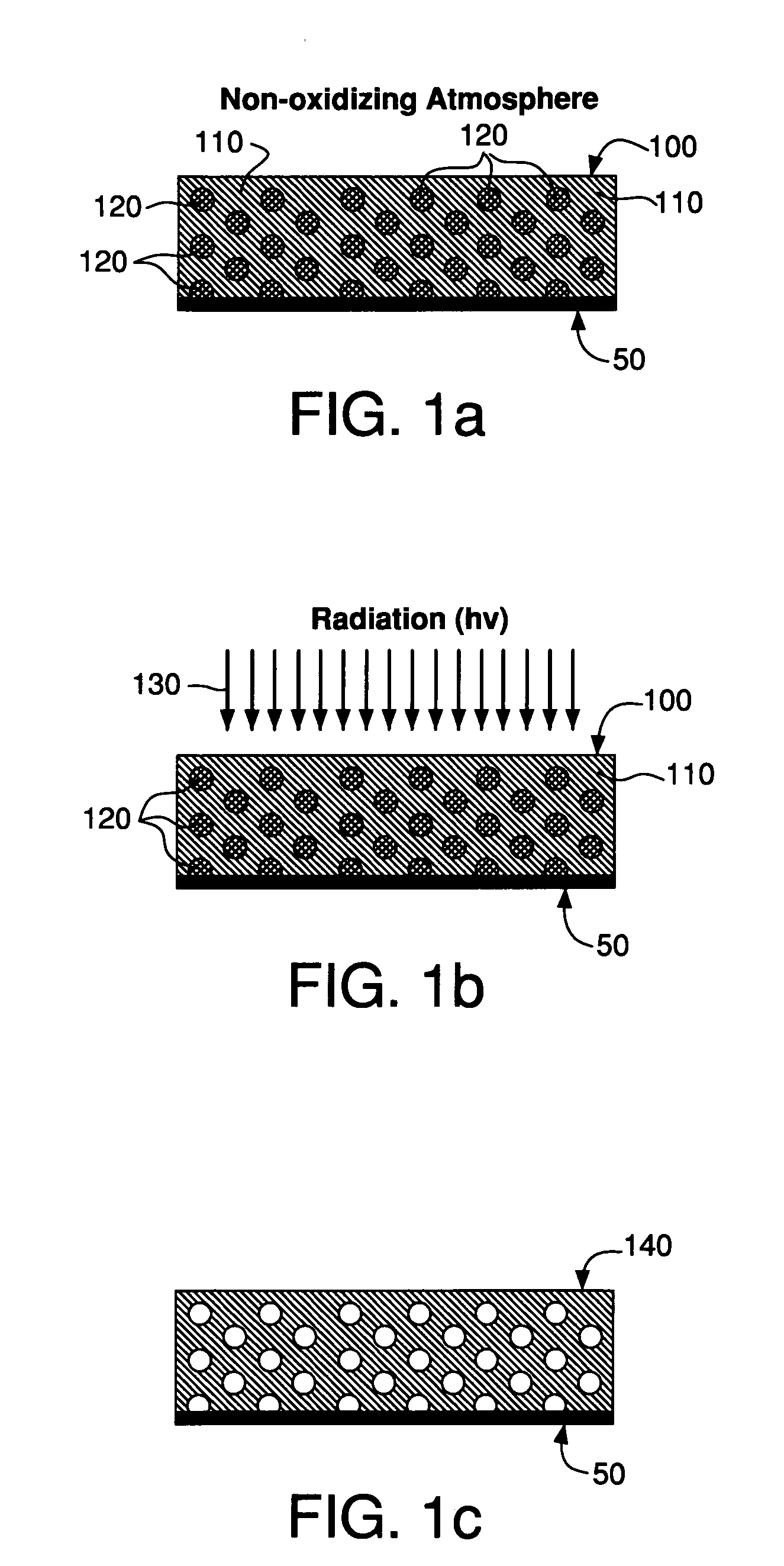
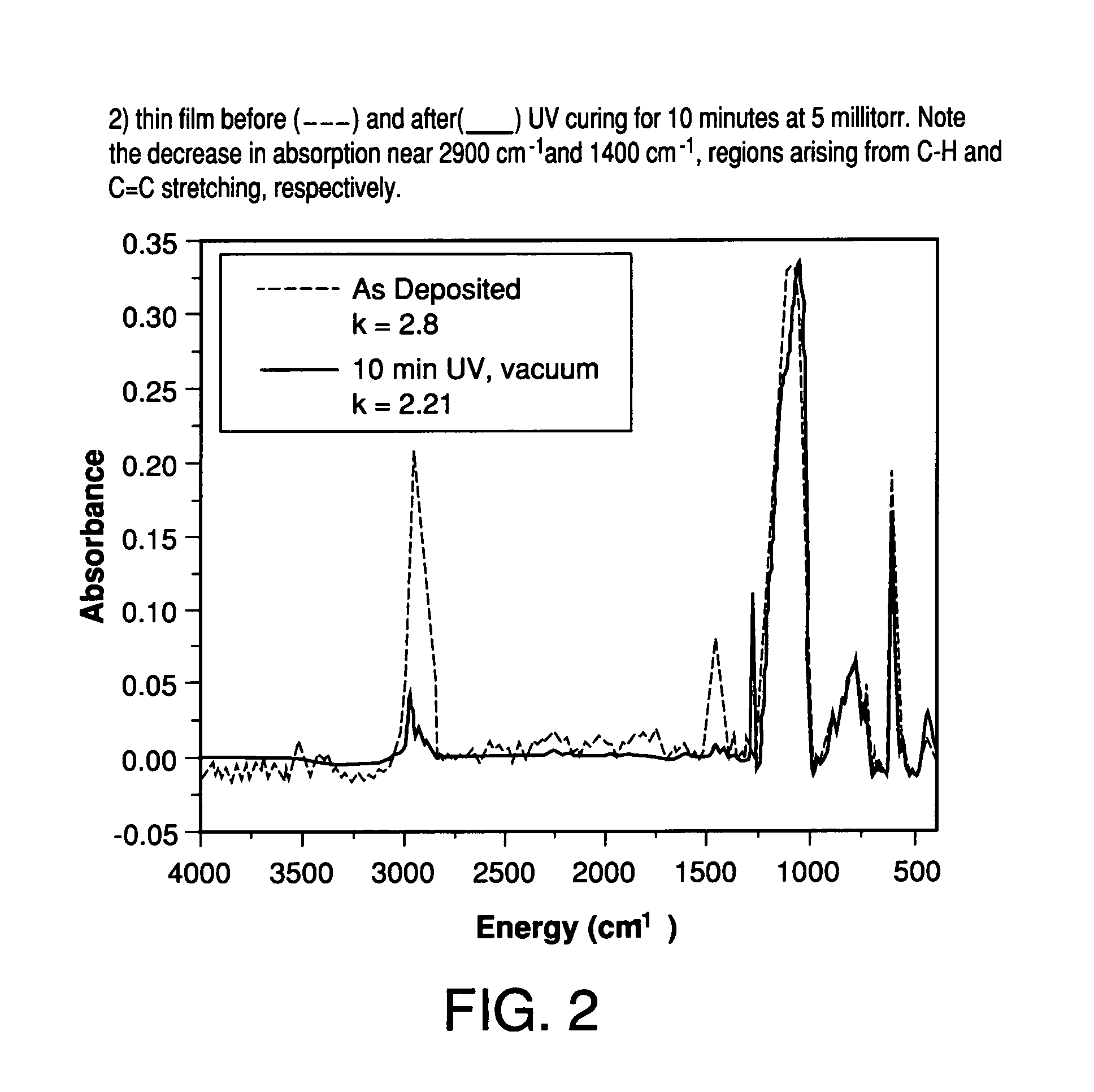
Low dielectric materials and films comprising same have been identified for improved performance when used as interlevel dielectrics in integrated circuits as well as methods for making same. In certain embodiments of the invention, there is provided a low-temperature process to remove at least a portion of at least one pore-forming phase within a multiphasic film thereby forming a porous film. The pore-forming phase may be removed via exposure to at least one energy source, preferably an ultraviolet light source, in a non-oxidizing atmosphere.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
Candle refill kit and method of use
InactiveUS20100044924A1Processed easily and safelyQuality improvementDielectric heatingBagsWaxRefill Kit
A candle refill kit useful for preparing home made candles includes a disposable microwaveable container and a microwaveable candlewax composition. The candlewax composition is microwave heated in the microwaveable container to an elevated temperature sufficient to initiate pouring of the candlewax composition. The candlewax composition is then poured from the microwaveable container into a candle mold (to make a stand-alone candle) or a candle container (to make a container candle).
Owner:CAP DANIEL S
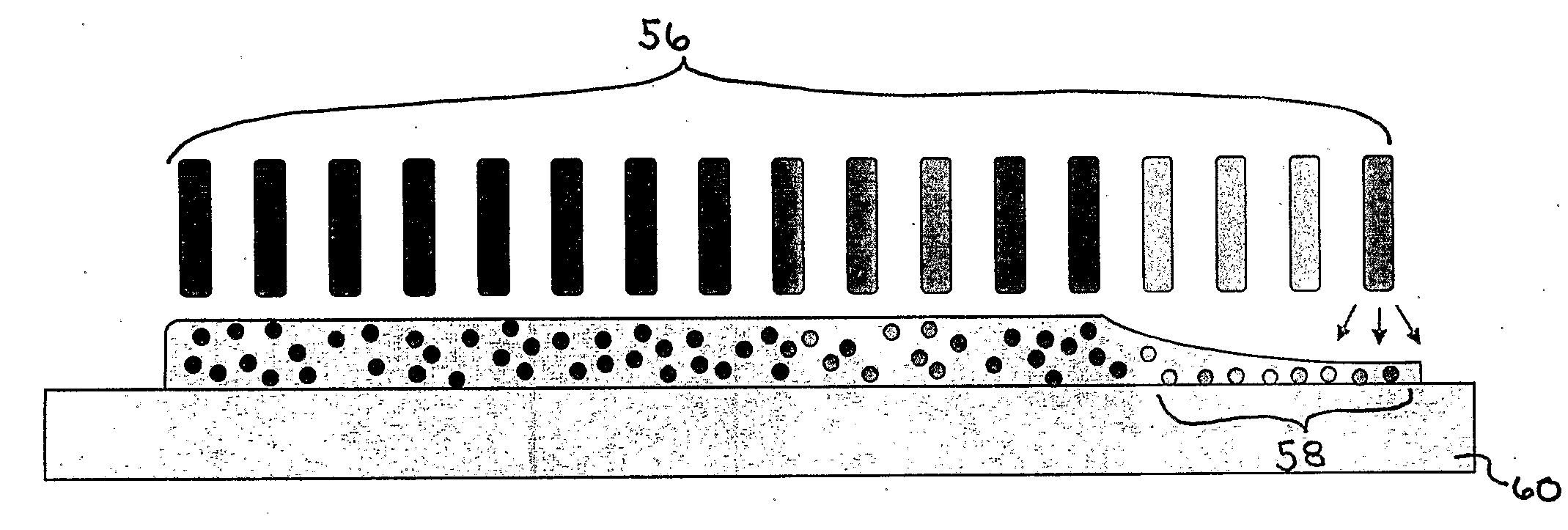
Microwave stiffening system for ceramic extrudates
InactiveUS20050093209A1Prevent saggingPreventing handling deformationDielectric heatingDrying solid materials with heatMicrowaveMetallurgy
An apparatus and method for stiffening an wet extruded ceramic body for improved handling prior to drying and firing. The ceramic body is formed from a plastically deformable material including inorganic raw materials, and organics, such as a binder having a thermal gel point. As the ceramic body log exits the extruder die it is passed through a microwave energy field to be heated to above the gelling point of the organic binder. The ceramic body then stiffens and can be easily handled without deformation.
Owner:CORNING INC
Sheet forming of metallic glass by rapid capacitor discharge
ActiveUS8613815B2Avoid thermal transport and development of thermalHeating evenlyDielectric heatingShaping toolsAlloyGlass transition
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Additive Manufacturing Microwave Systems And Methods
A system for manufacturing a 3-dimensional object comprises a print head that is configured and disposed for depositing one or more material layers in a prescribed manner on a printing table. At least one of the material layers comprises two or more materials. A source of microwave energy is disposed and configured for directing a beam of microwave energy toward the work-piece in a prescribed manner. A controller is operatively coupled to the print head and the source of microwave energy. The controller is configured for causing the print head to deposit the one or more material layers in the prescribed manner and for causing the source of microwave energy to direct the beam of microwave energy toward the work-piece in the prescribed manner. A method for manufacturing a 3-dimensional object comprises depositing one or more material layers in a prescribed manner on a printing table and directing a beam of microwave energy toward the work-piece in a prescribed manner.
Owner:ESCAPE DYNAMICS
Method for synthesis of colloidal nanoparticles
InactiveUS20060060998A1Large-scale, safe, convenient, reproducible, and energy-efficient productionHigh crystallinityDielectric heatingNanoinformaticsColloidal nanoparticlesContinuous flow
A method for synthesis of high quality colloidal nanoparticles using comprises a high heating rate process. Irradiation of single mode, high power, microwave is a particularly well suited technique to realize high quality semiconductor nanoparticles. The use of microwave radiation effectively automates the synthesis, and more importantly, permits the use of a continuous flow microwave reactor for commercial preparation of the high quality colloidal nanoparticles.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Plasma processing system with a new inductive antenna and hybrid coupling of electronagnetic power
An antenna adapted to apply a uniform electromagnetic field with high energy density to a volume of gas. The antenna includes an input node for receiving electrical energy and a first coil for radiating electromagnetic energy into the gas. The first coil is connected to the input node on one end thereof and is grounded on the opposite side to cause flux to flow in a first direction. A second coil is included for radiating electromagnetic energy into the gas. The second coil is also connected to the input node on one end thereof and grounded on the opposite side to flow in the first direction. Multiple number of coils can be added to form an antenna. In an illustrative application, the antenna is used in a plasma processing system comprising a vacuum chamber, a gas disposed within the vacuum chamber, and a dielectric disposed around the vacuum chamber. The inventive antenna is mounted around the dielectric tube and radiates electromagnetic energy into the gas. In a specific embodiment, the invention further includes a magnet disposed about the chamber in proximity to the antenna. When RF power is supplied to the antenna via an impedance matching network, the antenna radiates a uniform, dense electromagnetic wave into the gas creating plasma. The invention includes an electrically isolated electrode located on top of the source. When (RF) power is supplied to the electrode via on impedance matching network, the electrode creates an electrostatic force that pushes electrons back into plasma there by resulting in high plasma density.
Owner:BETHEL MATERIAL RES
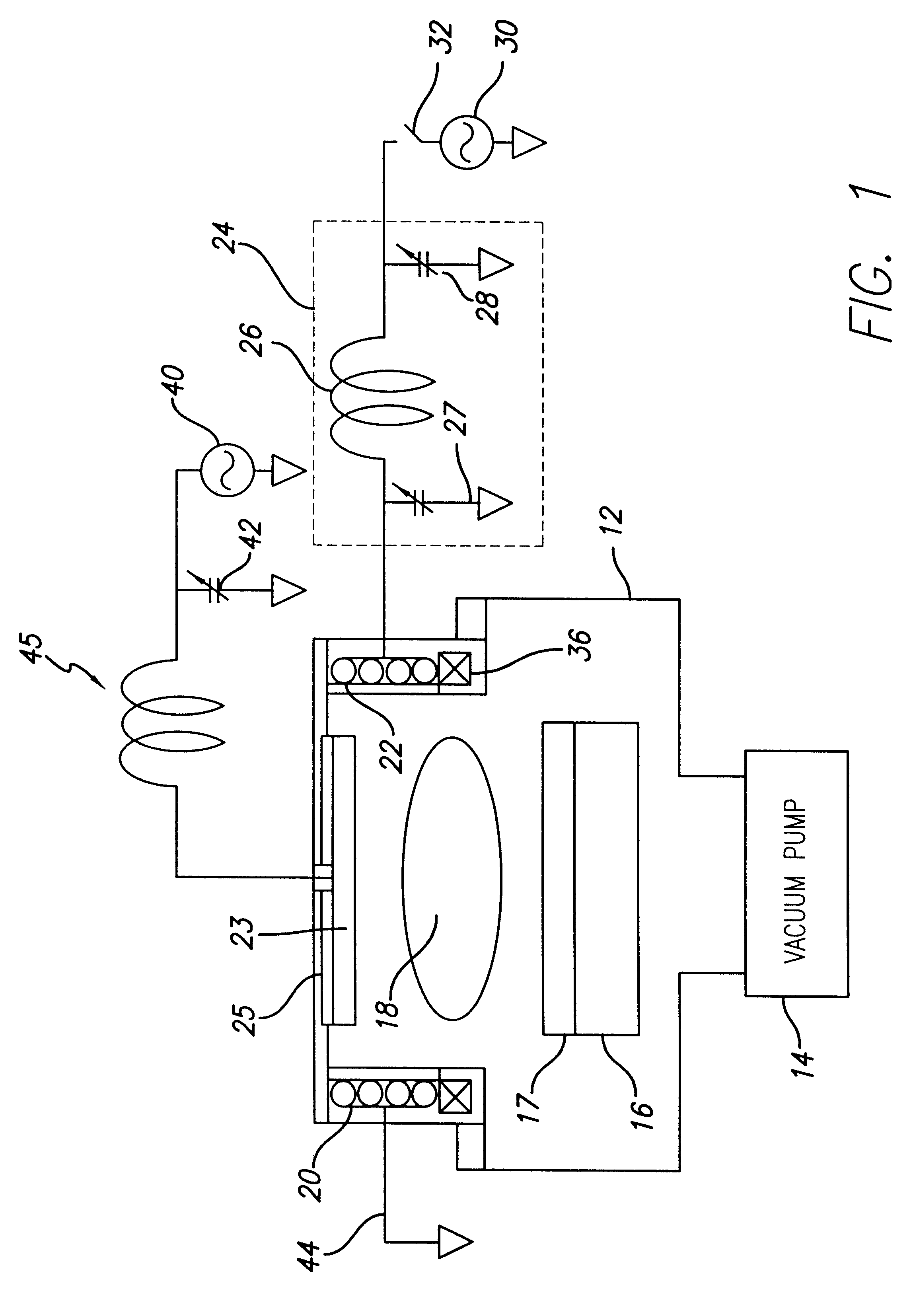
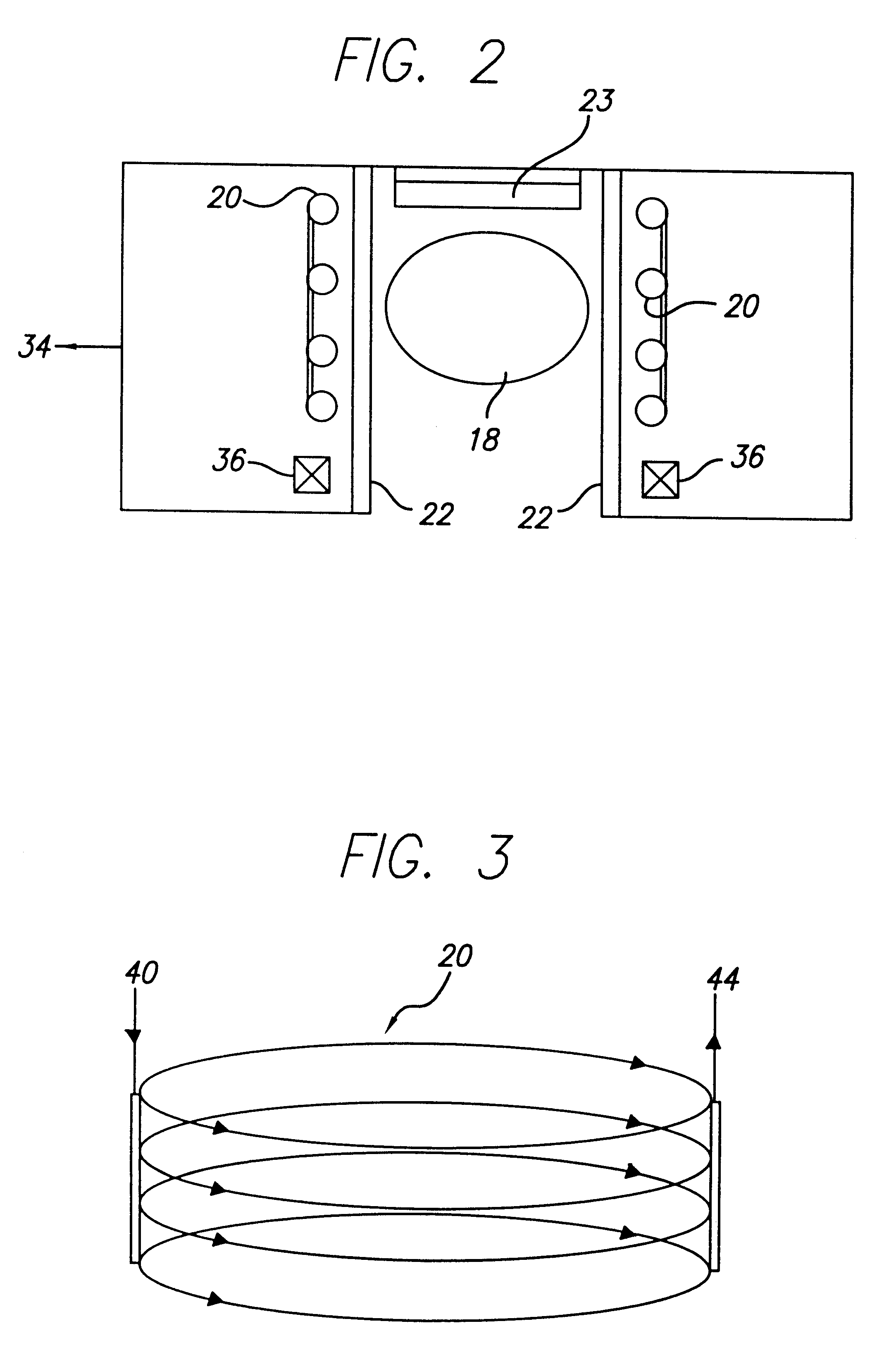
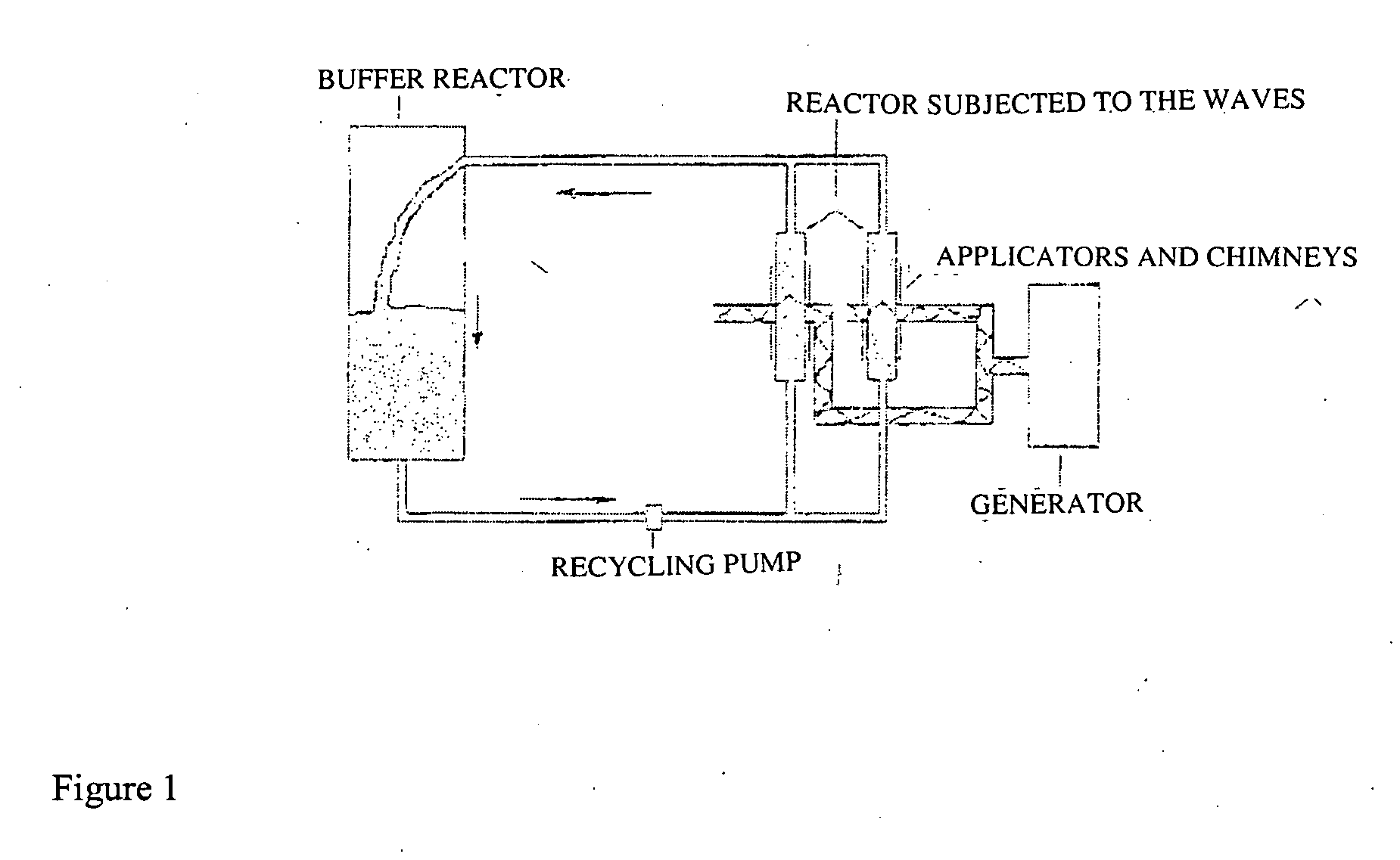
Chemical synthesis comprising heat treatment by intrmittent dielectric heating combined with a recycling system
InactiveUS20060228088A1Low costEfficient and rapid heat treatmentDielectric heatingBiofuelsChemical synthesisElectricity
This invention relates to the design of a process by intermittent dielectric heating combined with a recycling system. This process consists in subjecting reagents to electromagnetic waves selected in the frequencies ranging between 300 GHz and 3 MHz intermittently using a recycling system. This process enables the treatment of oils that are hardly absorbent as well as great investment savings. This process enables operation on different scales, whether in laboratories, on a semi-industrial or industrial scale, without forfeiting the advantages of continuous dielectric heating.
Owner:ALDIVIA
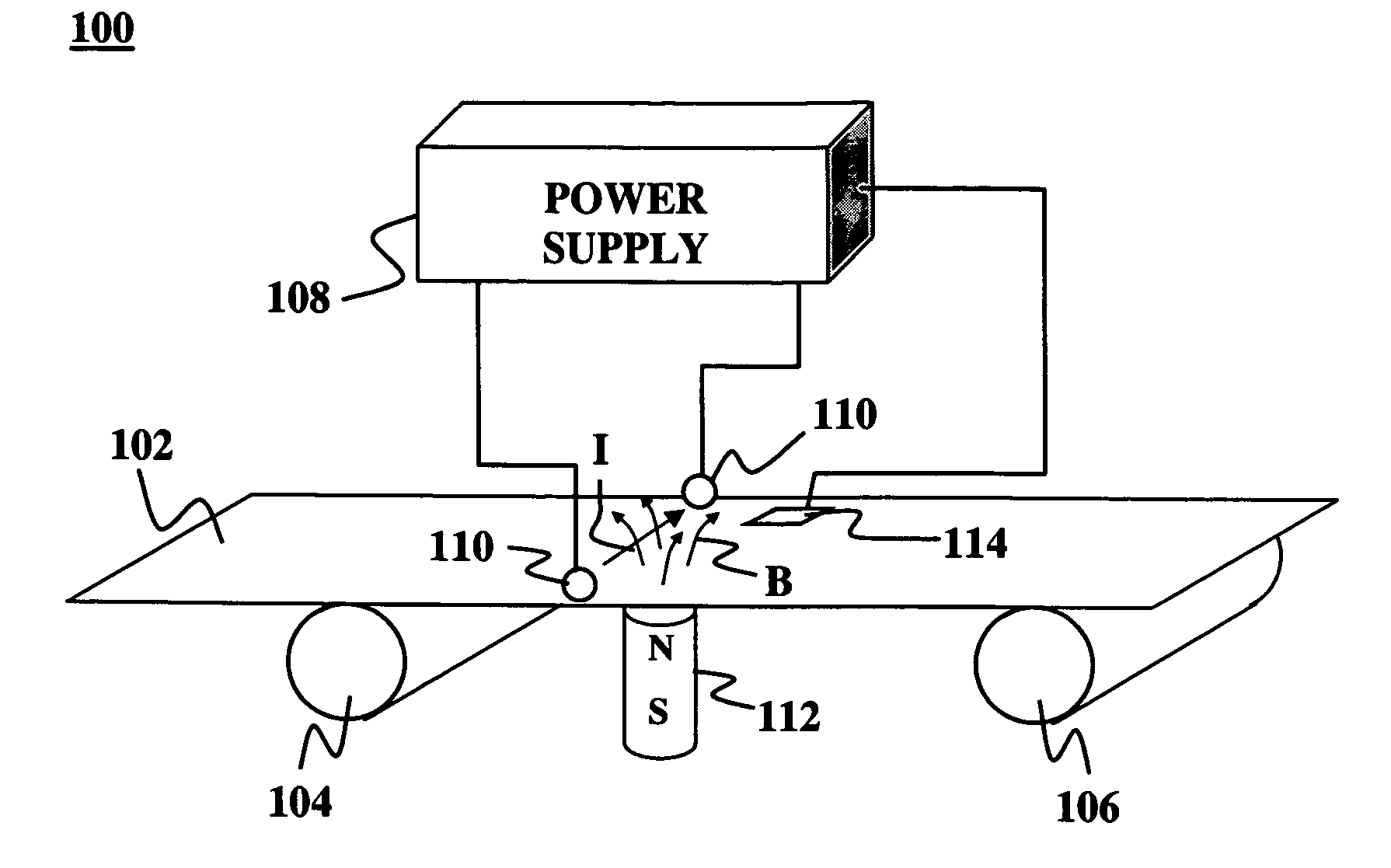
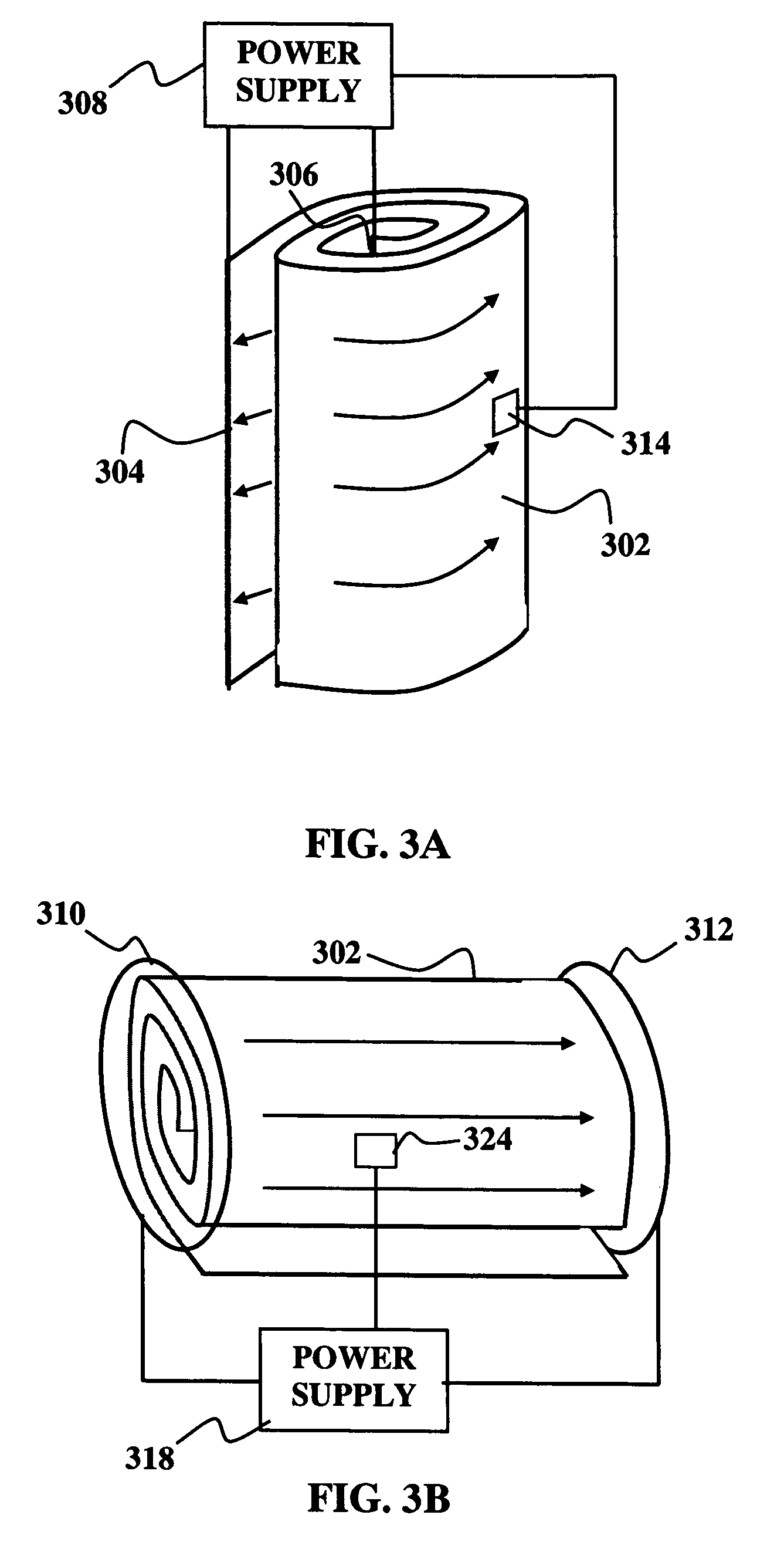
Uniform thermal processing by internal impedance heating of elongated substrates
An elongated substrate may be heated in a roll processing system. At least a portion of the elongated substrate is loaded into the roll processing system. A sufficient electrical current is caused to flow in the portion of the elongated substrate to heat the portion to a desired temperature. The heating may be either resistive or inductive. The roll processing system may be a roll-to-roll type where the substrate moves as a portion of it is heated. Alternatively, the substrate may be wound into a coiled substrate and the turns of the coil insulated against undesired electrical contact. The entire coiled substrate may then be heated either resistively or inductively.
Owner:AERIS CAPITAL SUSTAINABLE IP
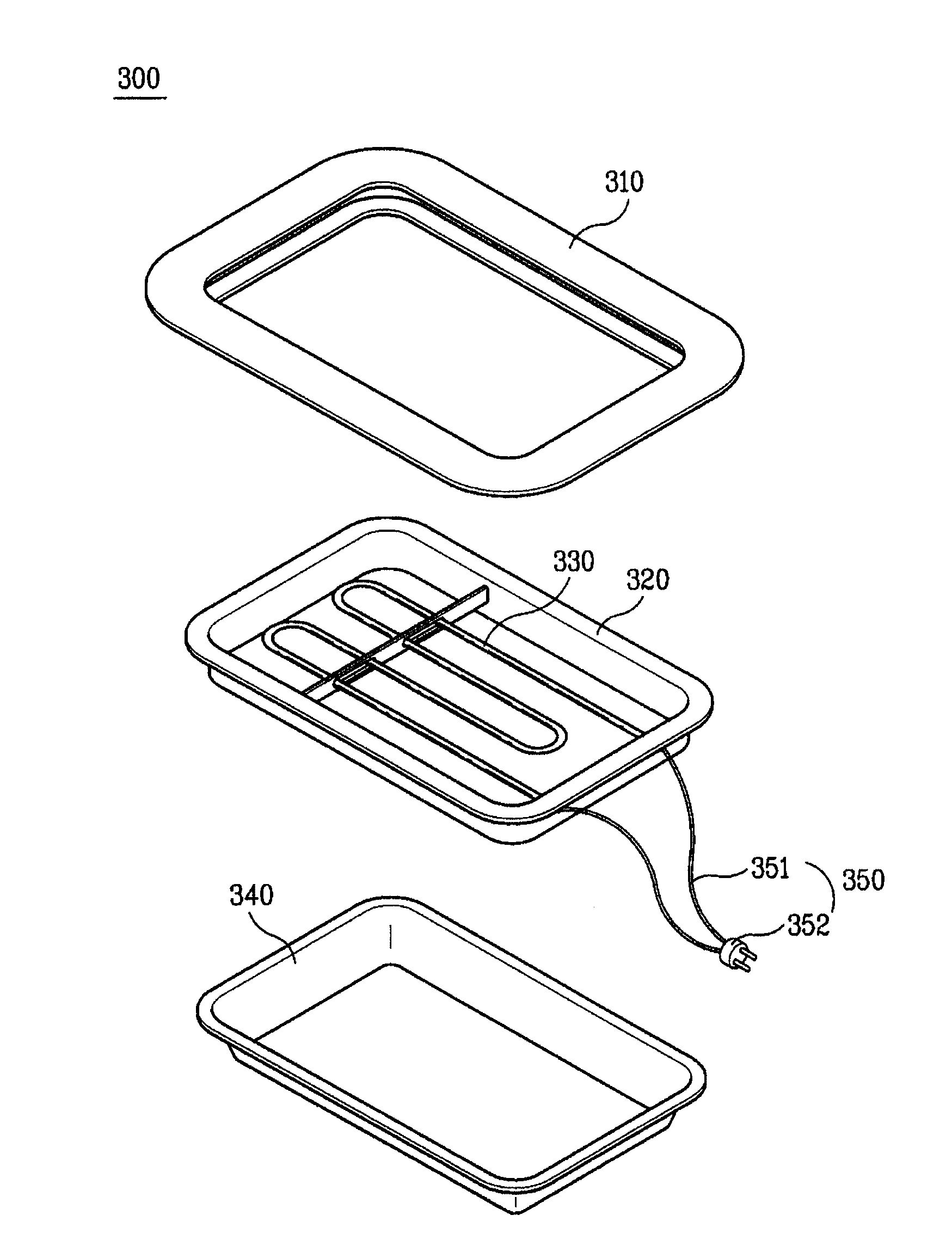
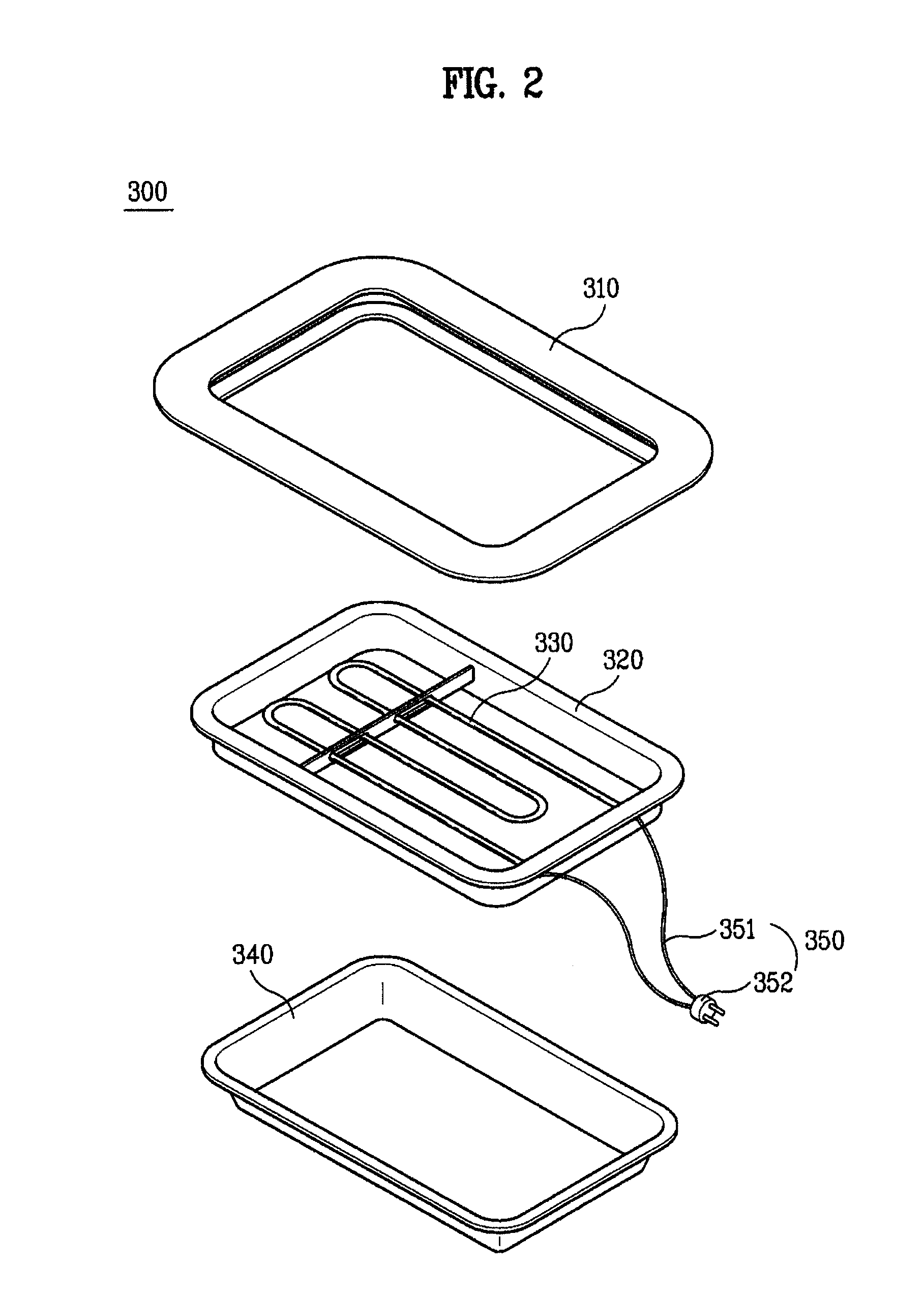
Cooking apparatus
ActiveUS7781702B2Easily and rapidlyImprove energy efficiencyDielectric heatingDomestic stoves or rangesMechanical engineeringEngineering
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Method for synthesis of colloidal nanoparticles
InactiveUS7615169B2Large-scale, safe, convenient, reproducible, and energy-efficient productionHigh crystallinityDielectric heatingMaterial nanotechnologyColloidal nanoparticlesContinuous flow
A method for synthesis of high quality colloidal nanoparticles using comprises a high heating rate process. Irradiation of single mode, high power, microwave is a particularly well suited technique to realize high quality semiconductor nanoparticles. The use of microwave radiation effectively automates the synthesis, and more importantly, permits the use of a continuous flow microwave reactor for commercial preparation of the high quality colloidal nanoparticles.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method of manufacturing embroidered surgical implants
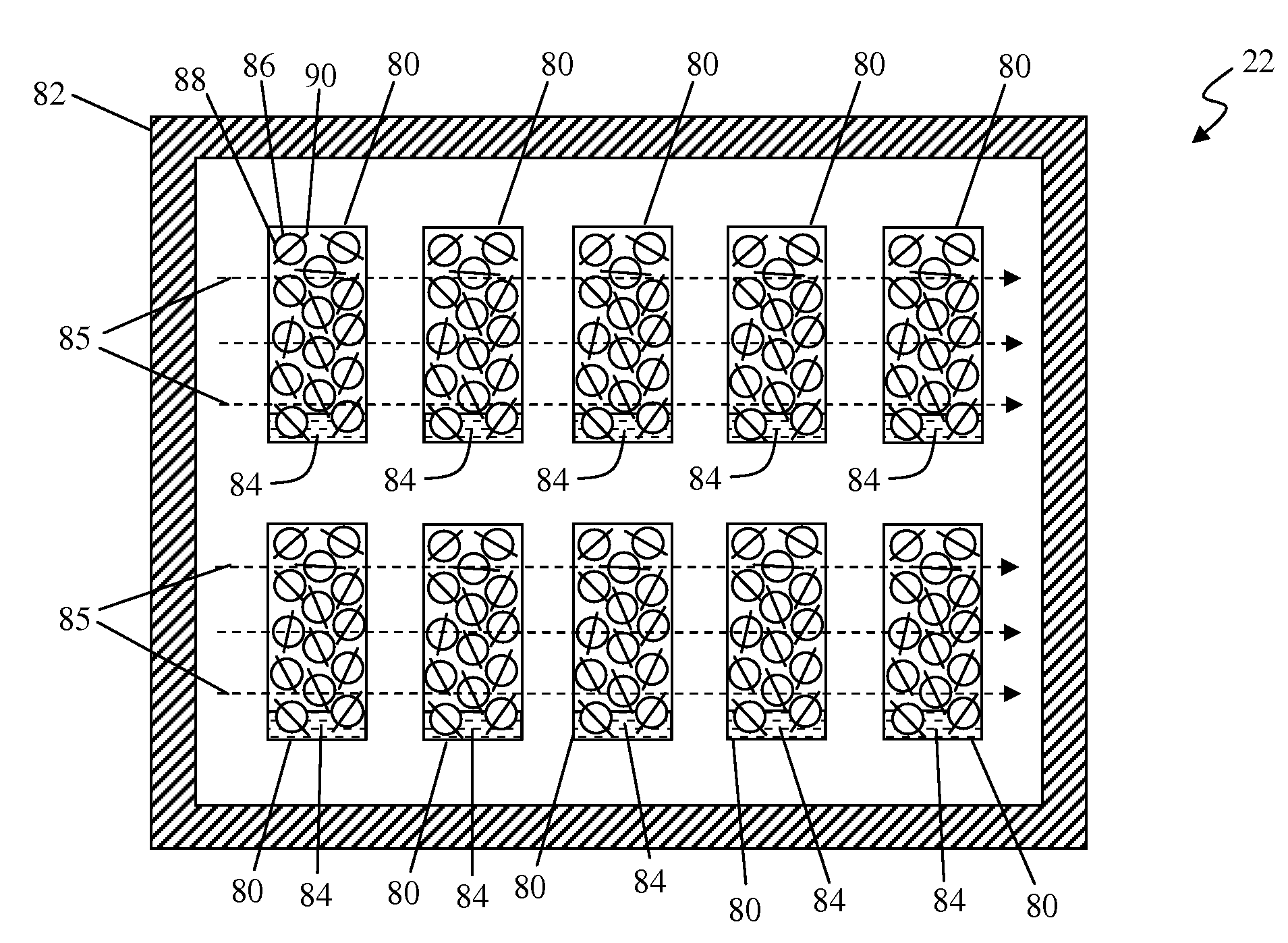
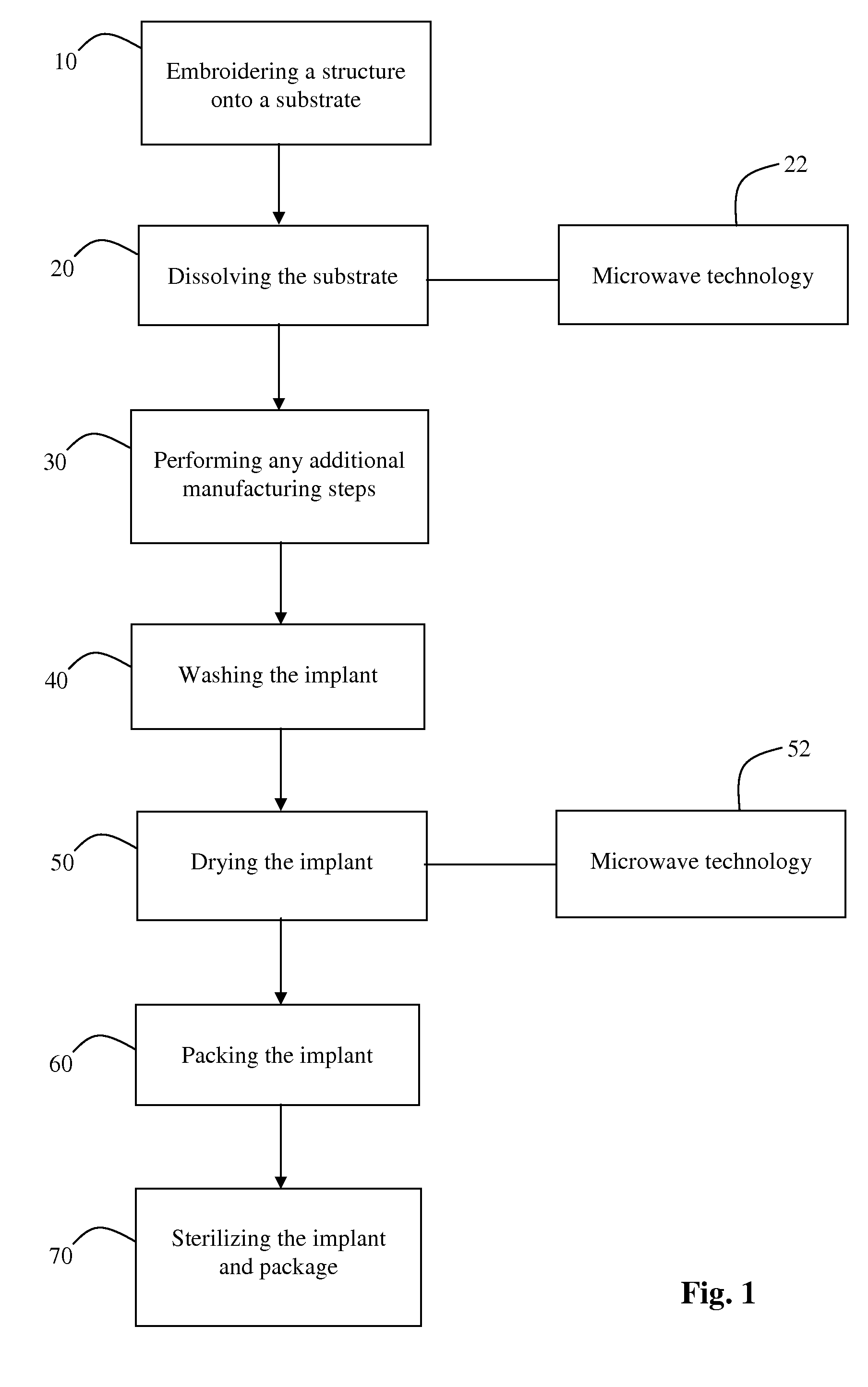
InactiveUS7713463B1Shorten the timeQuality improvementDielectric heatingProsthesisSurgical implantMicrowave technology
A method for applying microwave techniques to embroidered surgical implants including using microwave technology in the process of acetate removal and using microwave technology in the process of drying implants.
Owner:NUVASIVE
Apparatus and method for producing objects utilizing three-dimensional printing
InactiveUS20160096327A1Minimize warping and thermal stressImprove bindingDielectric heatingConfectioneryEngineering3 dimensional printing
A method and apparatus for the fabrication of an article made using a three-dimensional printing process. The invention includes depositing material from a print head onto a build plate located in a build chamber to form an article, heating ambient air in the build chamber to a first temperature which acts as a proper sink temperature for cooling of the article, and heating the build plate to a second temperature which is higher than the first temperature. The first and second temperatures are controlled to minimize warping and thermal stress of the article.
Owner:TE CONNECTIVITY CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com