Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
88 results about "Colloidal nanoparticles" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Colloidal nanoparticles are nanometer-sized particles that can be uniformly dispersed within a solution. Their capability to disperse is usually enabled by a layer of surfactants attached to their surface (Yin and Alivisatos, 2005).
Durable optical element
ActiveUS7074463B2Liquid crystal compositionsTelevision system detailsDisplay deviceColloidal nanoparticles
A durable optical film or element includes a polymerized structure having a microstructured surface and a plurality of surface modified colloidal nanoparticles of silica, zirconia, or mixtures thereof. Display devices including the durable microstructured film are also described.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Durable optical element
A durable optical film or element includes a polymerized structure having a microstructured surface and a plurality of surface modified colloidal nanoparticles of silica, zirconia, or mixtures thereof. Display devices including the durable microstructured film are also described.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Method for reducing odor using colloidal nanoparticles
InactiveUS20050084412A1Reduce odorMaterial nanotechnologyNon-fibrous pulp additionGramColloidal nanoparticles
A method for reducing odors is provided. In one embodiment, the method comprises contacting a substrate containing a thin coating of colloidal nanoparticles with an odorous compound. The colloidal nanoparticles have an average size of less than about 500 nanometers, a surface area of from about 50 to about 1000 square meters per gram, and a pore volume of less than about 0.5 milliliters per gram. The colloidal nanoparticles may adsorb at least about 25% of the odorous compound when contacted therewith.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
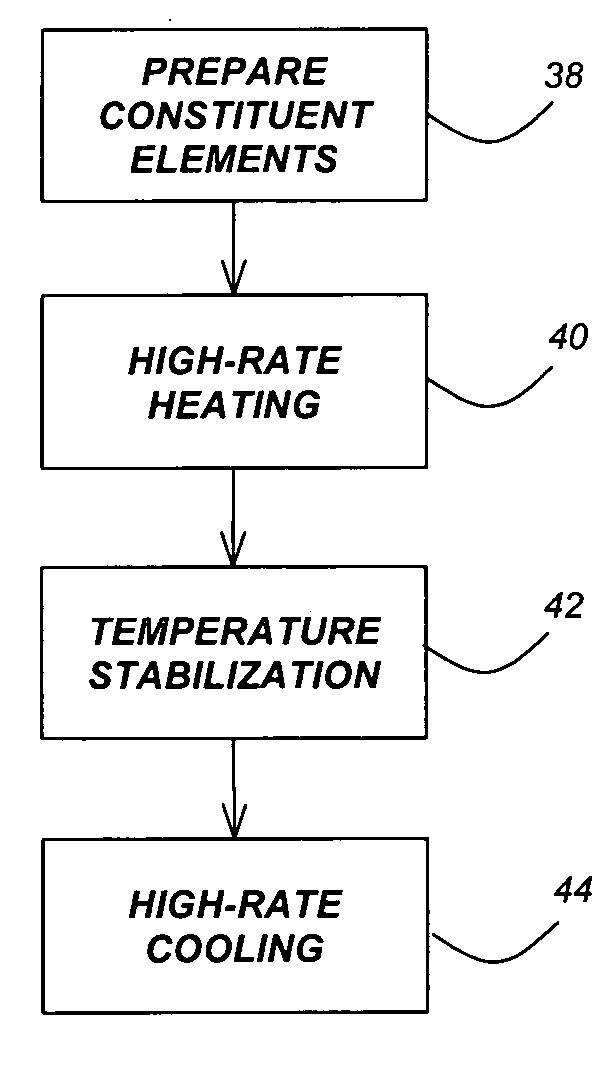
Method for synthesis of colloidal nanoparticles
InactiveUS20060061017A1High crystallinityLarge-scale, safe, convenient, reproducible, and energy-efficient productionDielectric heatingMaterial nanotechnologyContinuous flowColloidal nanoparticles
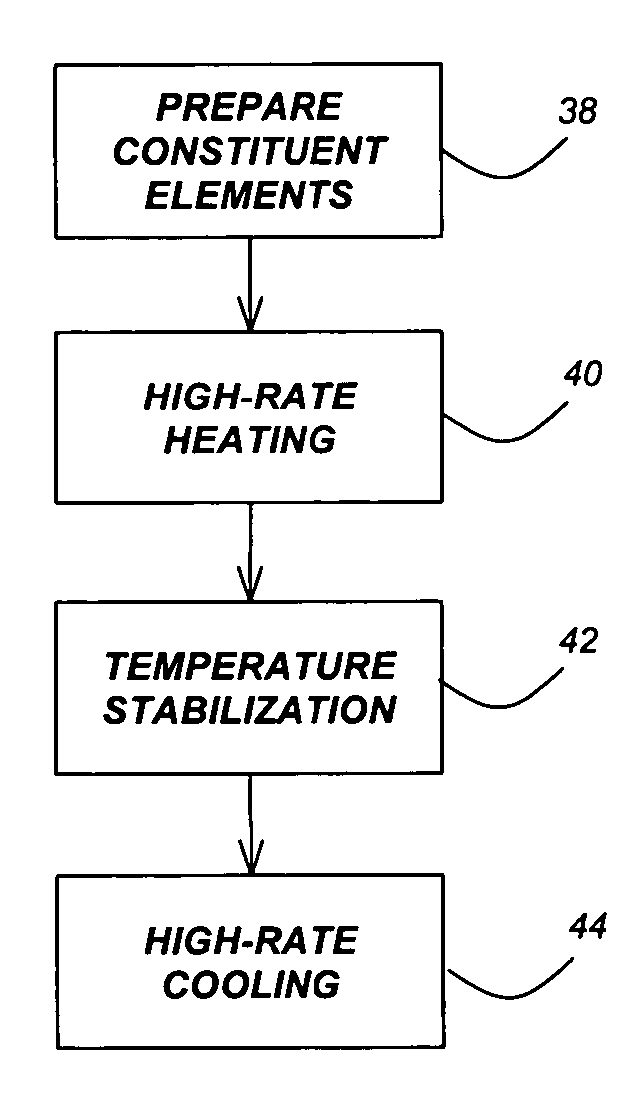
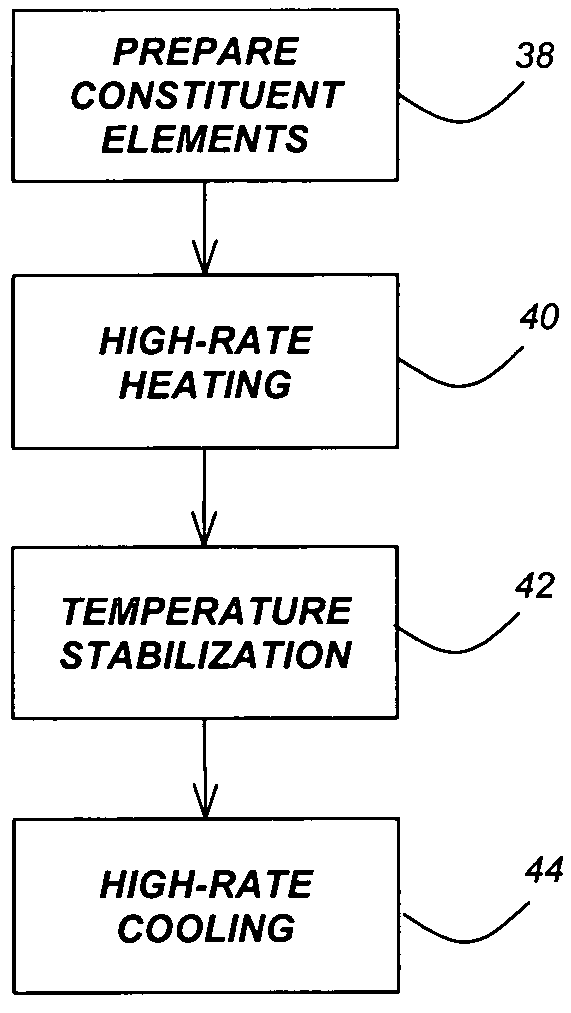
A method for synthesis of high quality colloidal nanoparticles using comprises a high heating rate process. Irradiation of single mode, high power, microwave is a particularly well suited technique to realize high quality semiconductor nanoparticles. The use of microwave radiation effectively automates the synthesis, and more importantly, permits the use of a continuous flow microwave reactor for commercial preparation of the high quality colloidal nanoparticles.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
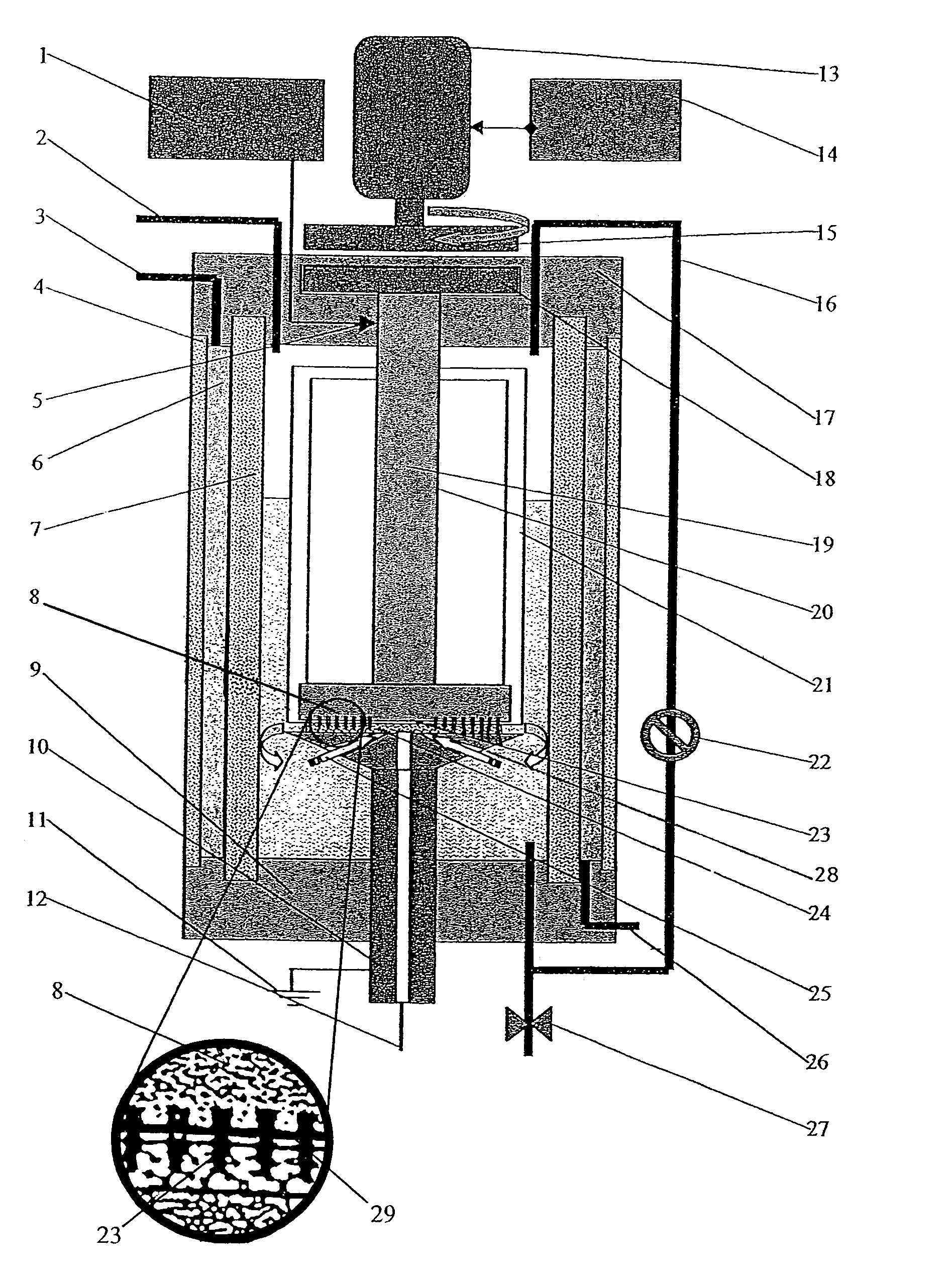
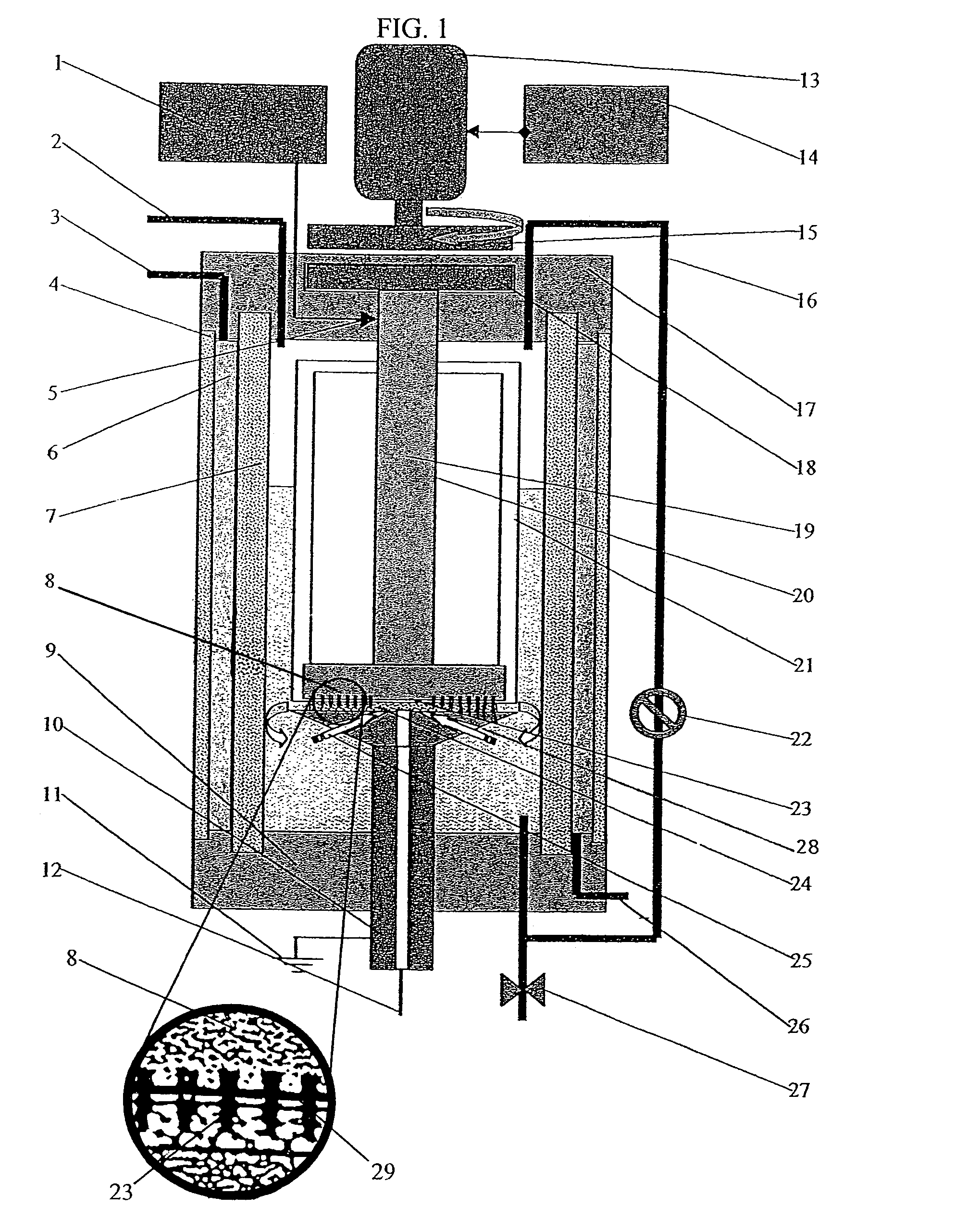
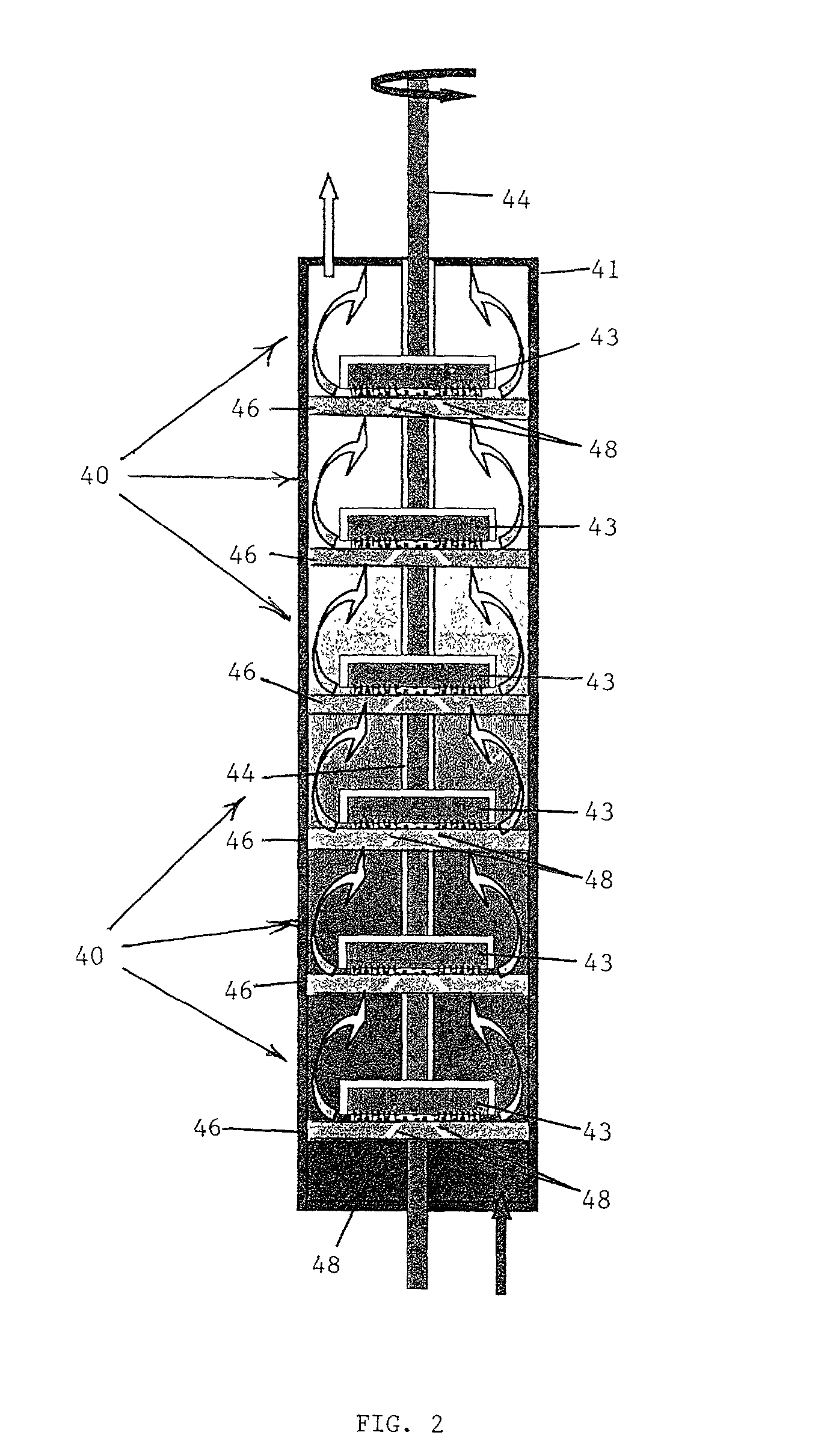
Method and apparatus for producing colloidal nanoparticles in a dense medium plasma
InactiveUS7128816B2Easy to convertEasily interchangeablePowder deliveryPhotography auxillary processesConductive materialsColloidal nanoparticles
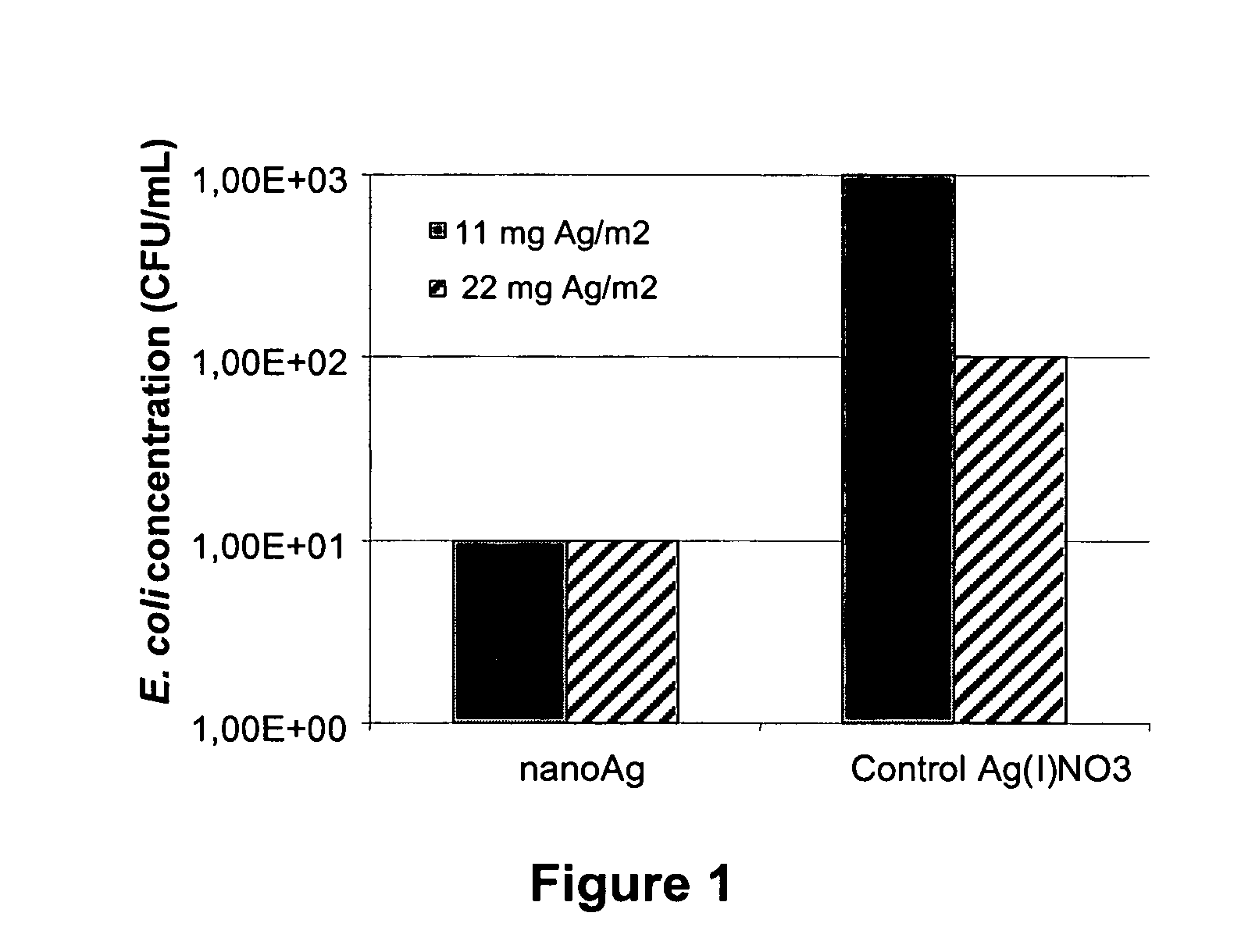
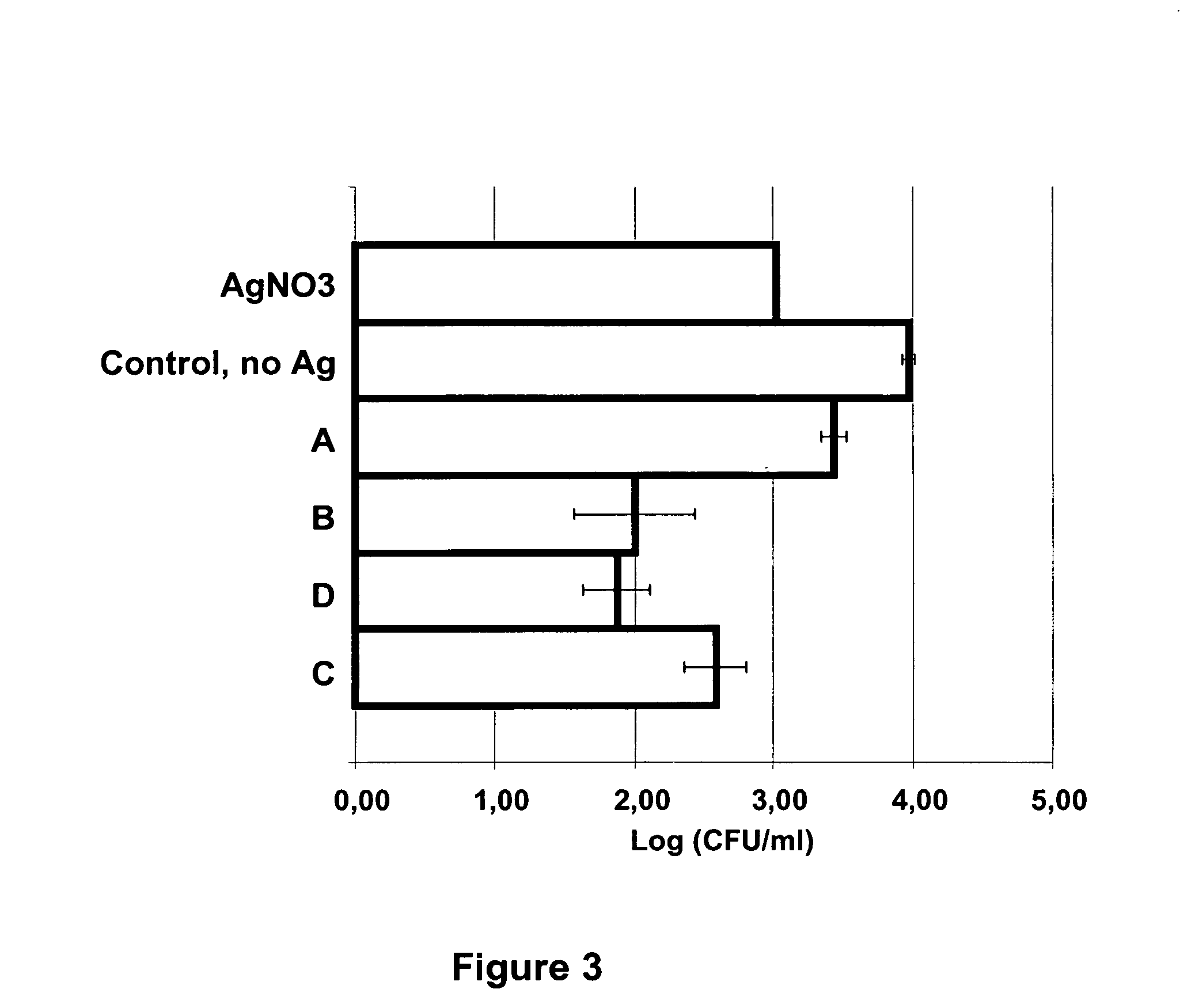
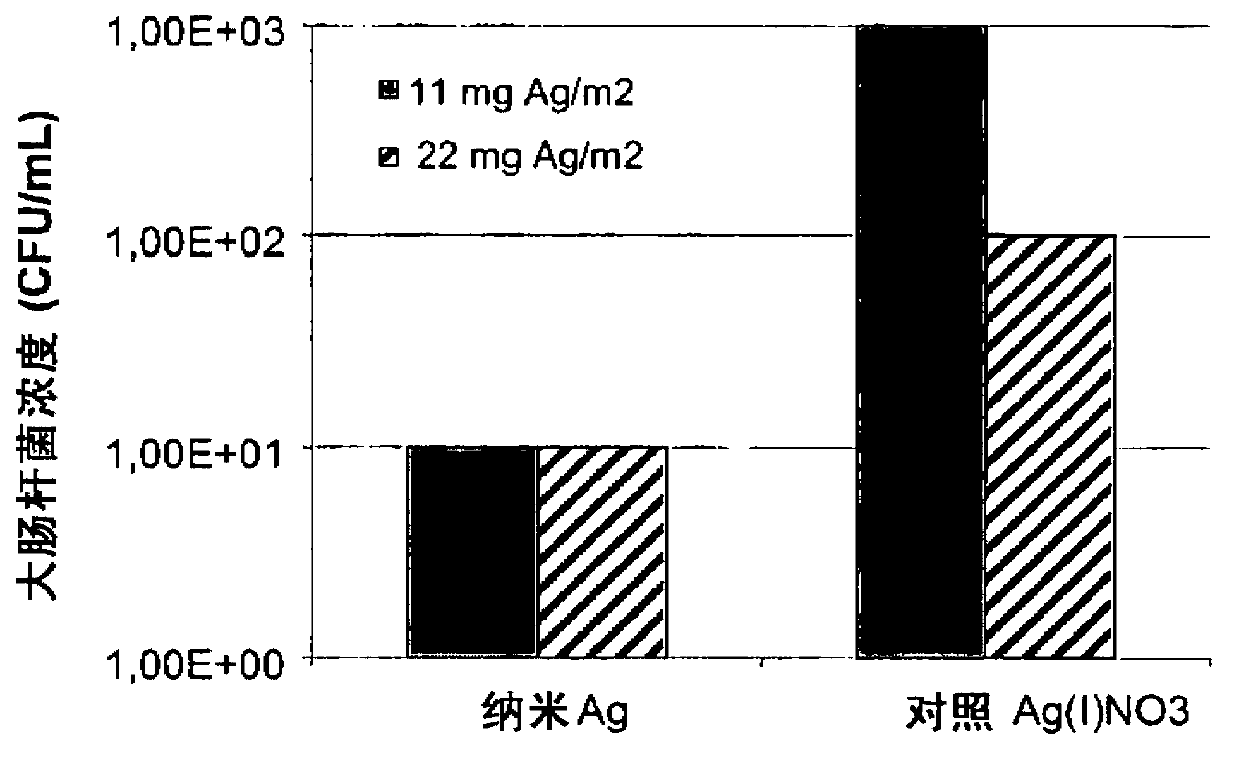
A method and apparatus is utilized for producing colloidal dispersions of nanoparticles of electrically conducting materials. The colloidal dispersions are produced in a dense media plasma reactor comprising at least one static electrode and at least one rotating electrode. The plasma reaction sputters off minute particles of the electrically conducting material from which the electrodes are made. Methods of using the colloidal dispersions thus made are also described. Colloidal dispersions of silver produced in this manner are highly effective for bactericidal purposes.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Microchemical method and apparatus for synthesis and coating of colloidal nanoparticles
InactiveUS20080087545A1Aggressive processing conditionsRealize the structureFlow mixersVolume/mass flow measurementCrystallographyBatch processing
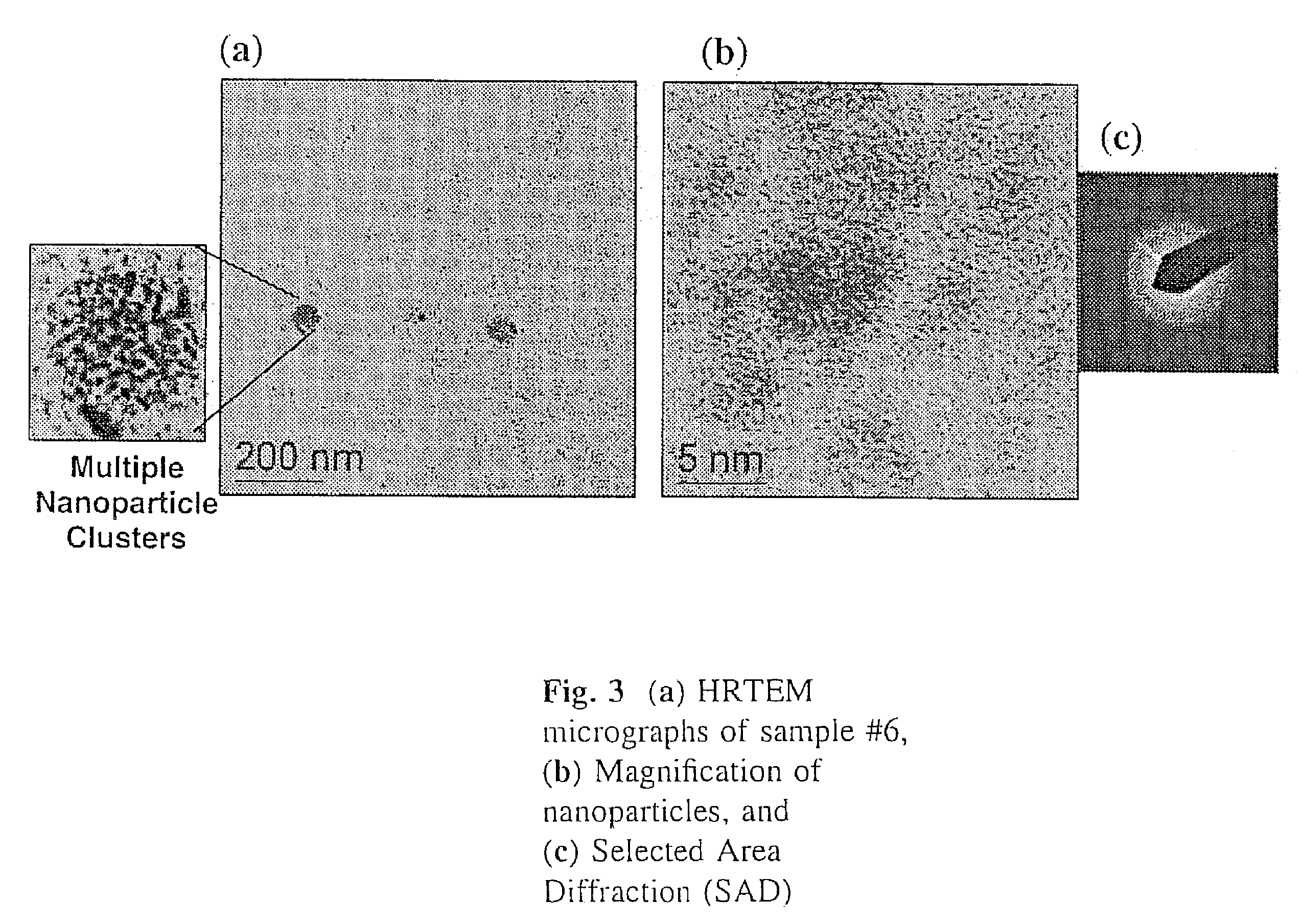
The present invention represents a radical departure from most conventional macro-scale batch processing methods employed to synthesize and coat colloidal nanoparticles. Synthesis and coating are in series and in-situ, obviating the need for numerous cumbersome, and often expensive intermediate-processing steps. In one embodiment, the invention is a method and apparatus for synthesizing colloidal nanoparticles. In another embodiment, the invention is a method and apparatus for enabling coating of colloidal nanoparticles using an electrophoretic switch for contacting and separating said colloid nanoparticles.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
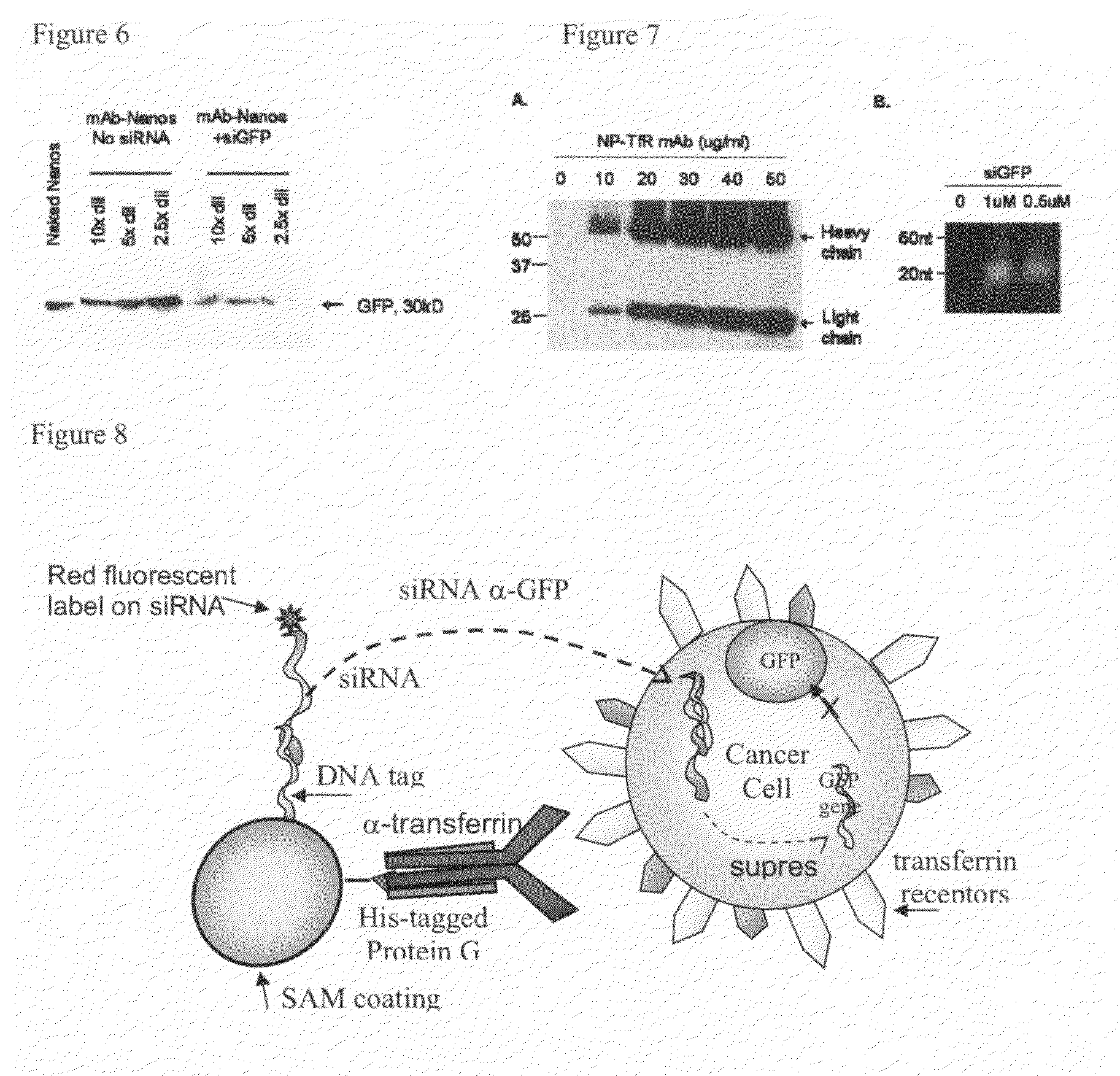
Method for treating cancer using interference RNA
InactiveUS20090148535A1Facilitate communicationPowder deliverySpecial deliveryProtein targetColloidal nanoparticles
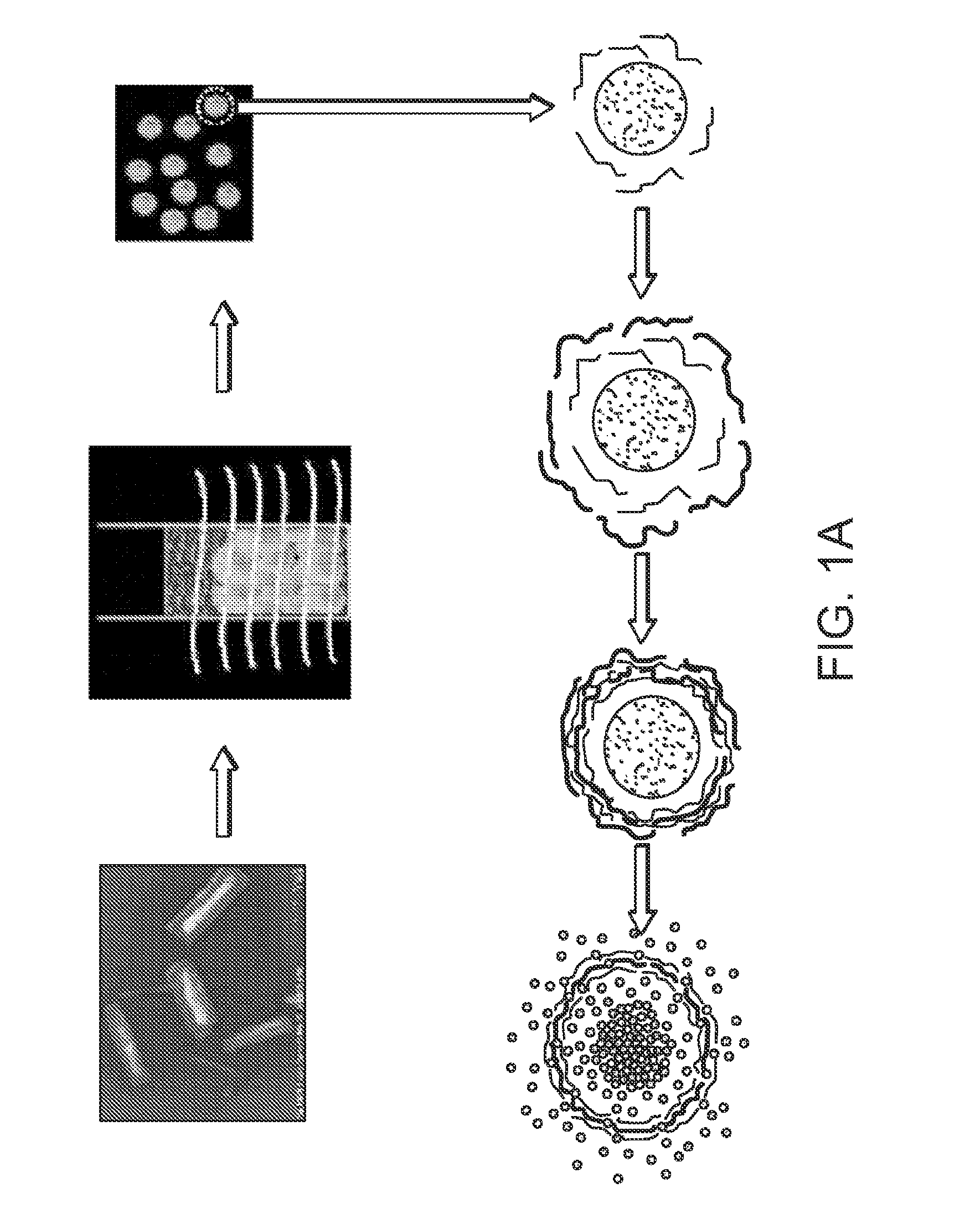
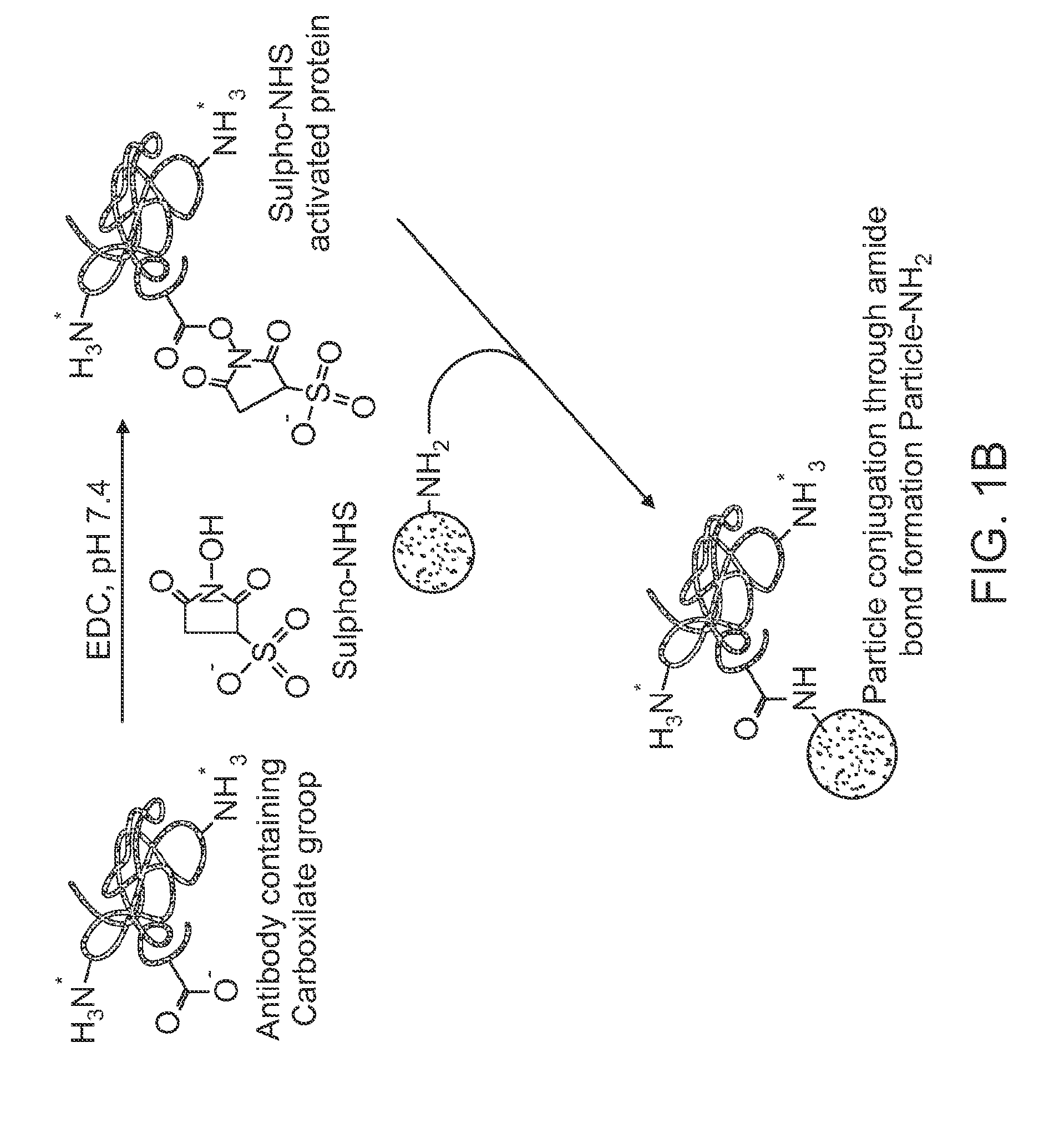
The present application discloses acolloidal nanoparticle that includes a therapeutic nucleic acid species and a targeting protein species attached via a coating on the nanoparticle that facilitates the specific attachment of both species.
Owner:MINERVA BIOTECH
Method for synthesis of colloidal nanoparticles
InactiveUS20060060998A1Large-scale, safe, convenient, reproducible, and energy-efficient productionHigh crystallinityDielectric heatingNanoinformaticsColloidal nanoparticlesContinuous flow
A method for synthesis of high quality colloidal nanoparticles using comprises a high heating rate process. Irradiation of single mode, high power, microwave is a particularly well suited technique to realize high quality semiconductor nanoparticles. The use of microwave radiation effectively automates the synthesis, and more importantly, permits the use of a continuous flow microwave reactor for commercial preparation of the high quality colloidal nanoparticles.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Core-Shell Nanocatalyst For High Temperature Reactions
The present invention provides a core-shell nanoparticle that includes a metal-oxide shell and a nanoparticle. Pores extend from an outer surface to an inner surface of the shell. The inner surface of the shell forms a void, which is filled by the nanoparticle. The pores allow gas to transfer from outside the shell to a surface of the nanoparticle. The present invention also provides a method of making a core-shell nanoparticle includes forming a metal-oxide shell on a colloidal nanoparticle, which forms a precursor core-shell nanoparticle. A capping agent is removed from the precursor core-shell nanoparticle, which produces the core-shell nanoparticle. The present invention also provides a method of using a nanocatalyst of the present invention includes providing the nanocatalyst, which is the core-shell nanoparticle. Reactants are introduced in a vicinity of the nanocatalyst, which produces a reaction that is facilitated or enhanced by the nanocatalyst.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Therapeutic stable nanoparticles
Stable colloid nanoparticles comprising poorly soluble drugs are disclosed, as well as methods of making and methods of using such nanoparticles, e.g., as therapeutics and diagnostics.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV +1
Method for synthesis of colloidal nanoparticles
InactiveUS7615169B2Large-scale, safe, convenient, reproducible, and energy-efficient productionHigh crystallinityDielectric heatingMaterial nanotechnologyColloidal nanoparticlesContinuous flow
A method for synthesis of high quality colloidal nanoparticles using comprises a high heating rate process. Irradiation of single mode, high power, microwave is a particularly well suited technique to realize high quality semiconductor nanoparticles. The use of microwave radiation effectively automates the synthesis, and more importantly, permits the use of a continuous flow microwave reactor for commercial preparation of the high quality colloidal nanoparticles.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Photonic crystal humidity sensor and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102269693AQuick checkStrong water swelling performanceColor/spectral properties measurementsPhotonicsColloidal nanoparticles
The invention provides a photonic crystal humidity sensor comprising: a substrate which is polyacrylamide gel; a photonic crystal material cured in the substrate, wherein the photonic crystal material is superparamagnetic carbon-coated ferroferric oxide colloidal nanoparticles. The invention also provides a preparation method of the photonic crystal humidity sensor. In the photonic crystal humidity sensor provided by the invention, the polyacrylamide gel has strong water swelling performance, and has different absorptivity under different relative humidity; when ambient relative humidity changes, the absorptivity of the polyacrylamide gel changes, and thus the expansion rate of the polyacrylamide changes; therefore, the band gap of the photonic forbidden band of the photonic crystal material cured in the polyacrylamide gel changes, and finally the photonic crystal humidity sensor shows different colors with the change of the humidity.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method for synthesis of colloidal nanoparticles
InactiveUS7575699B2Large-scale, safe, convenient, reproducible, and energy-efficient productionHigh crystallinityDielectric heatingNanoinformaticsColloidal nanoparticlesContinuous flow
A method for synthesis of high quality colloidal nanoparticles using comprises a high heating rate process. Irradiation of single mode, high power, microwave is a particularly well suited technique to realize high quality semiconductor nanoparticles. The use of microwave radiation effectively automates the synthesis, and more importantly, permits the use of a continuous flow microwave reactor for commercial preparation of the high quality colloidal nanoparticles.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
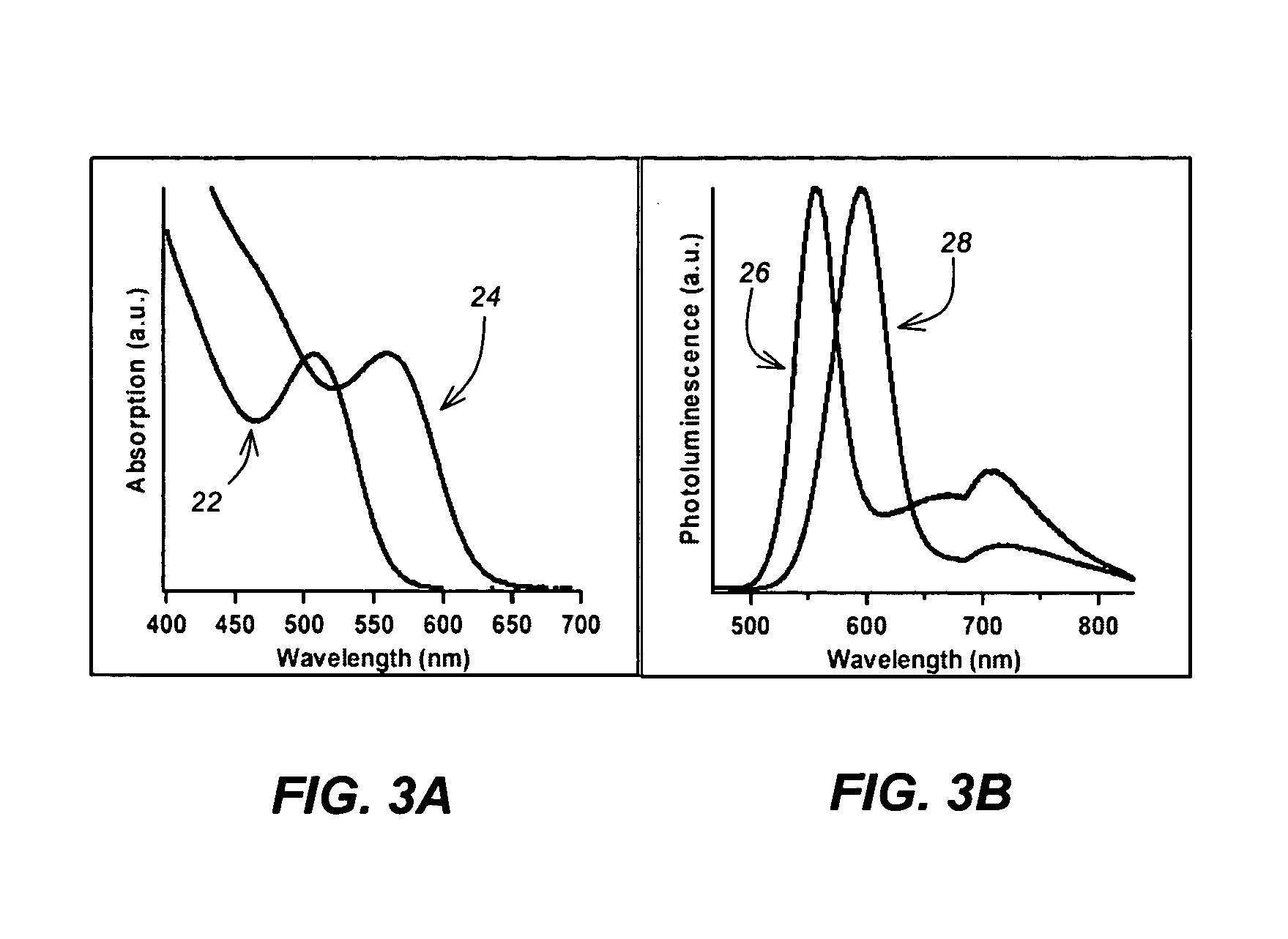
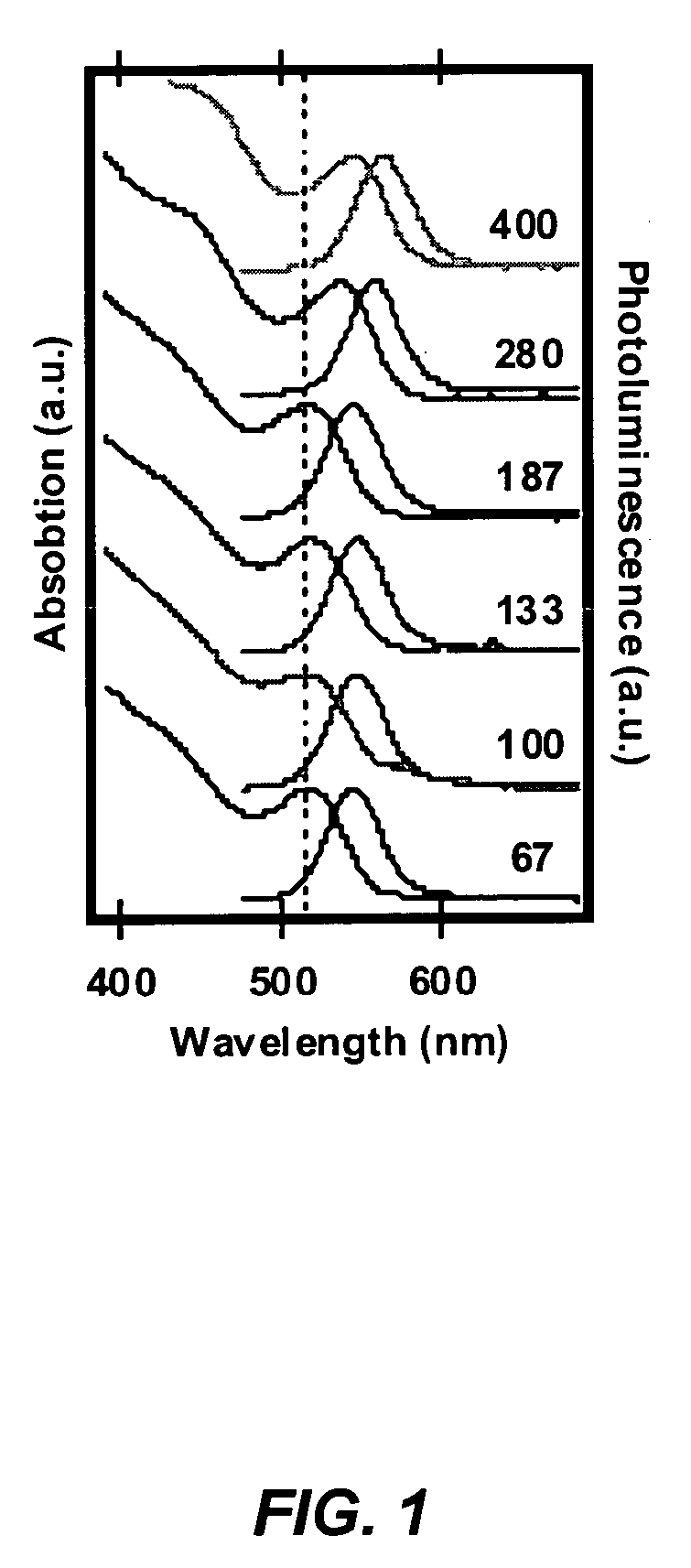
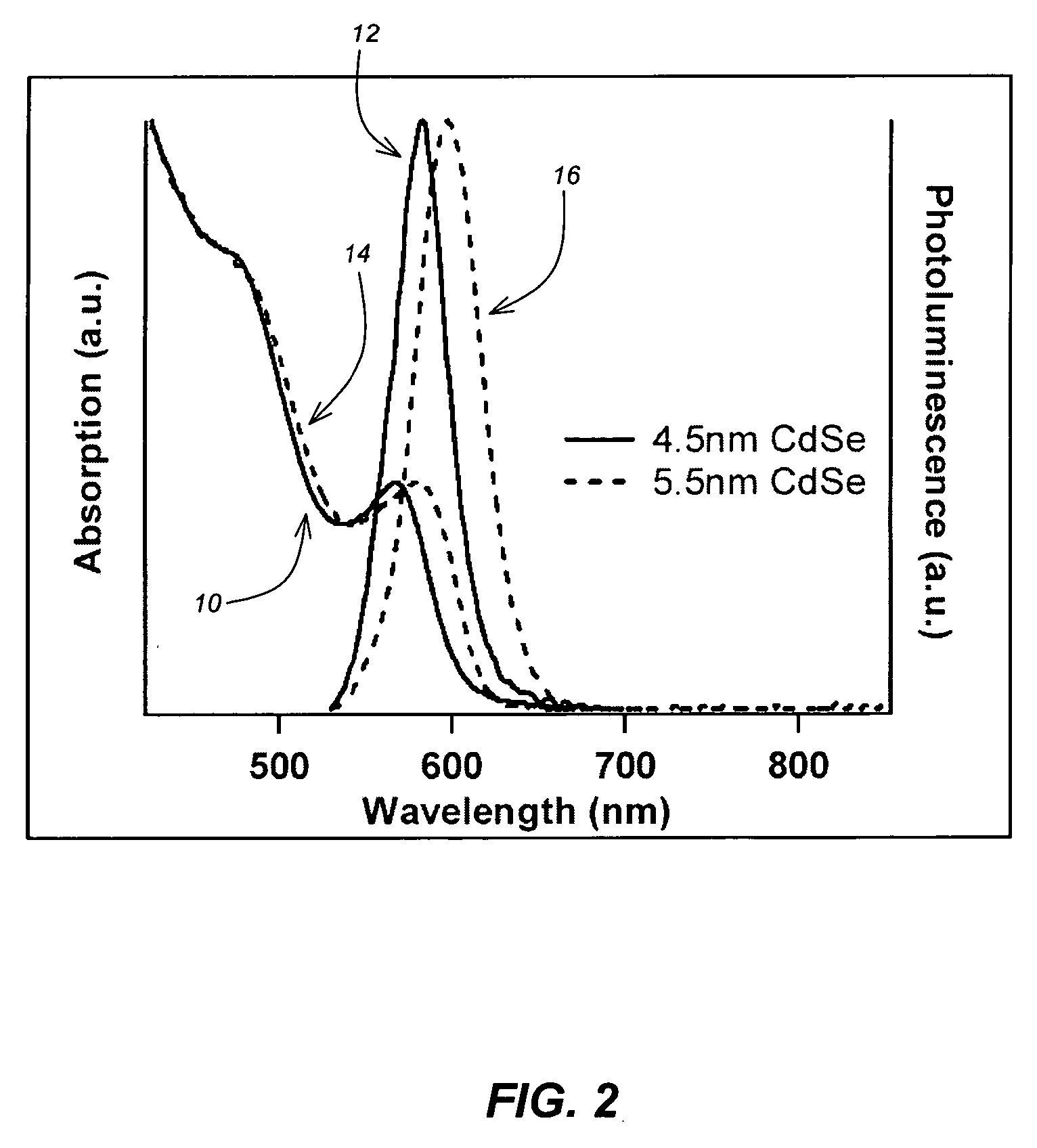
Rapid synthesis and size control of chalcopyrite-based semi-conductor nanoparticles using microwave irradiation
ActiveUS7892519B2Increases microscopic temperature of reactionImprove homogeneityNanotechPolycrystalline material growthChalcopyritePhotoluminescence
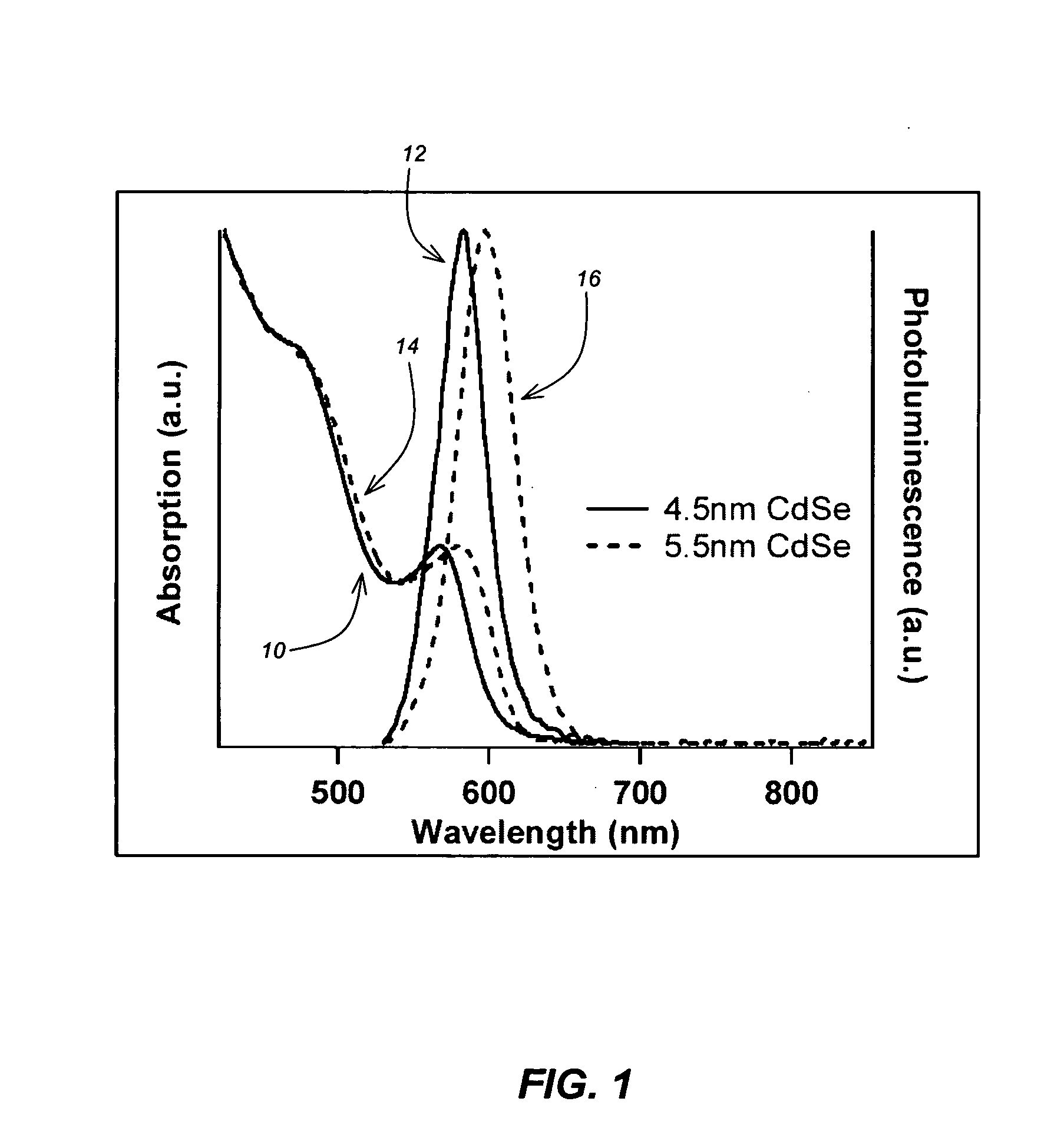
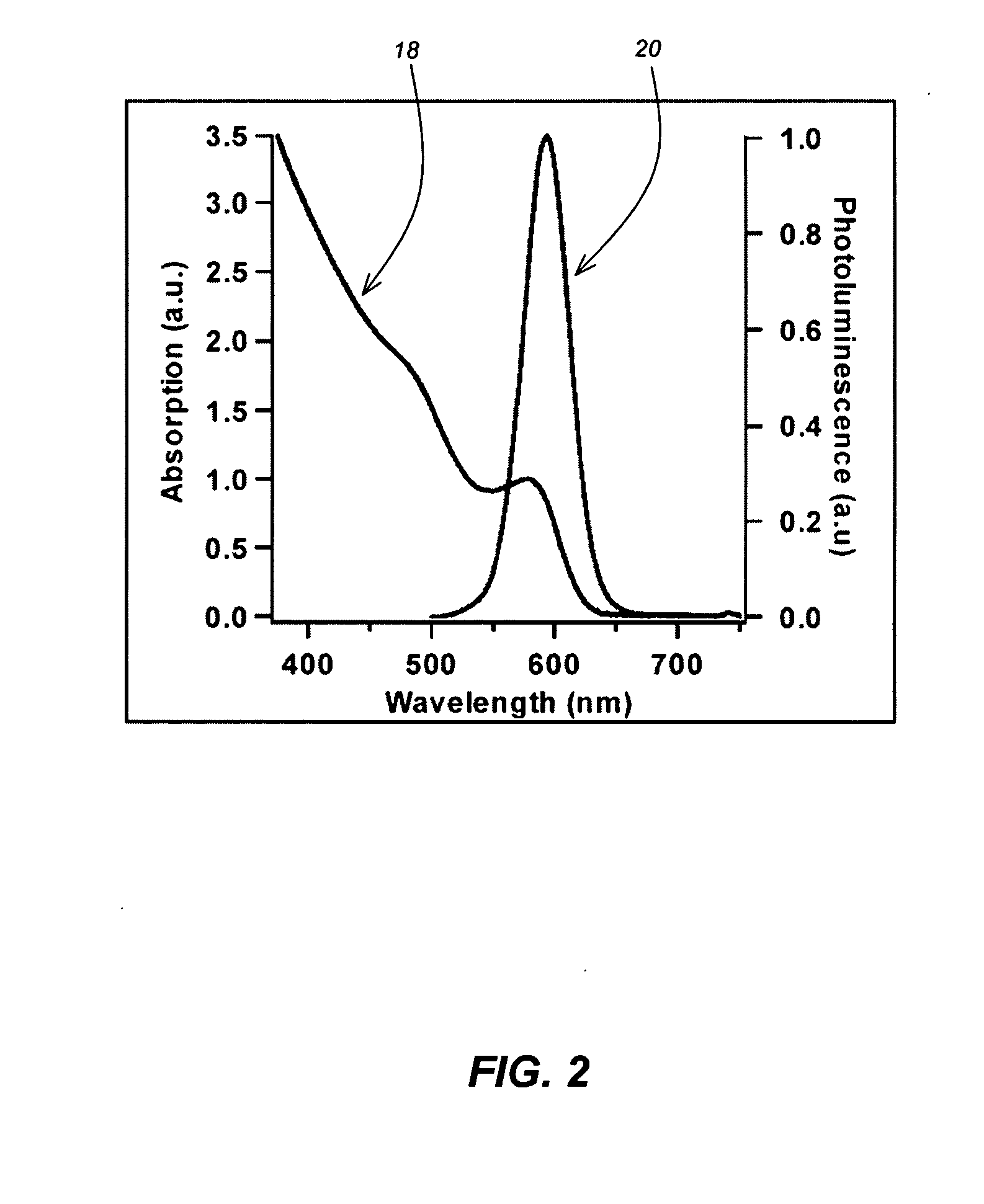
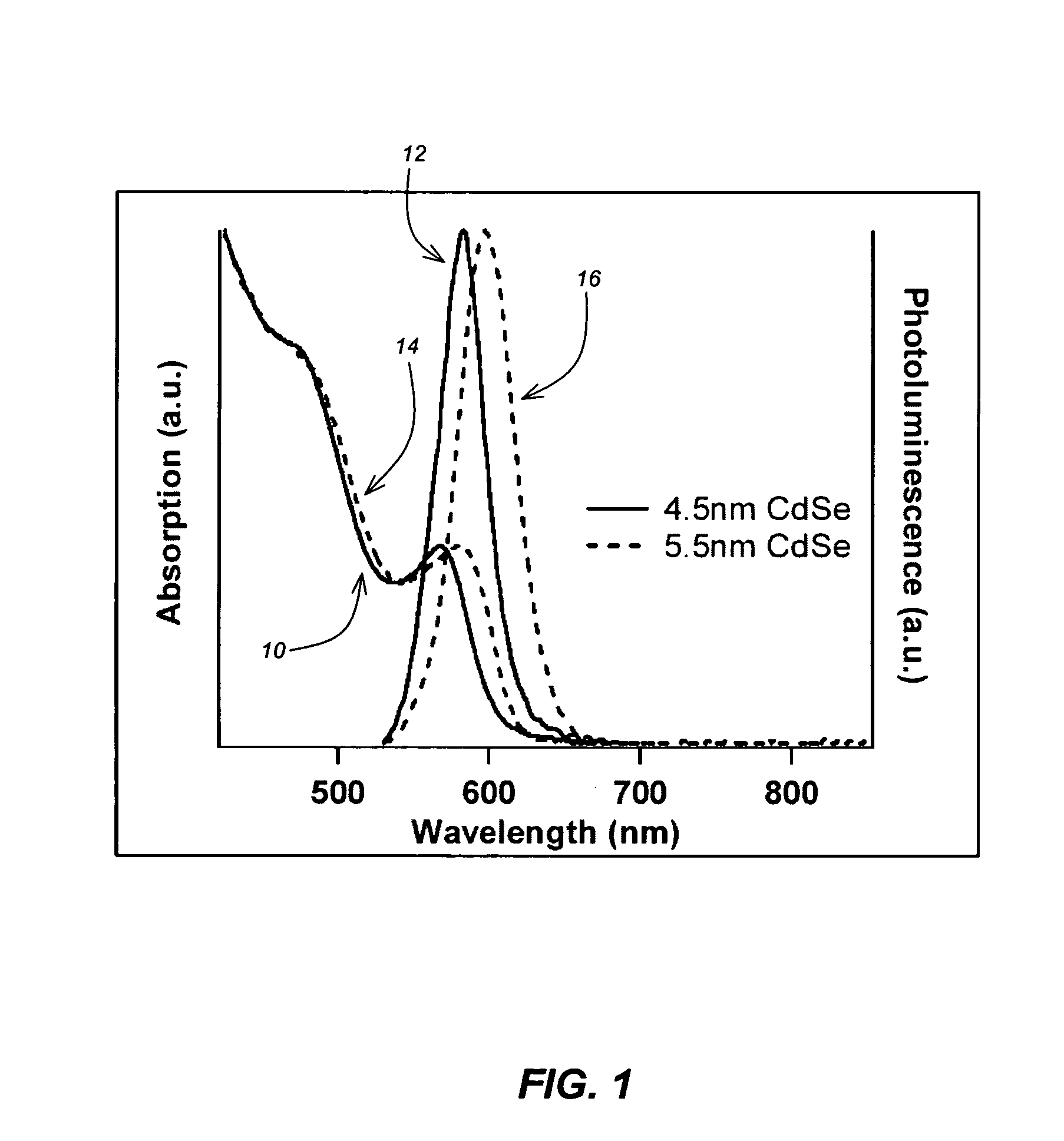
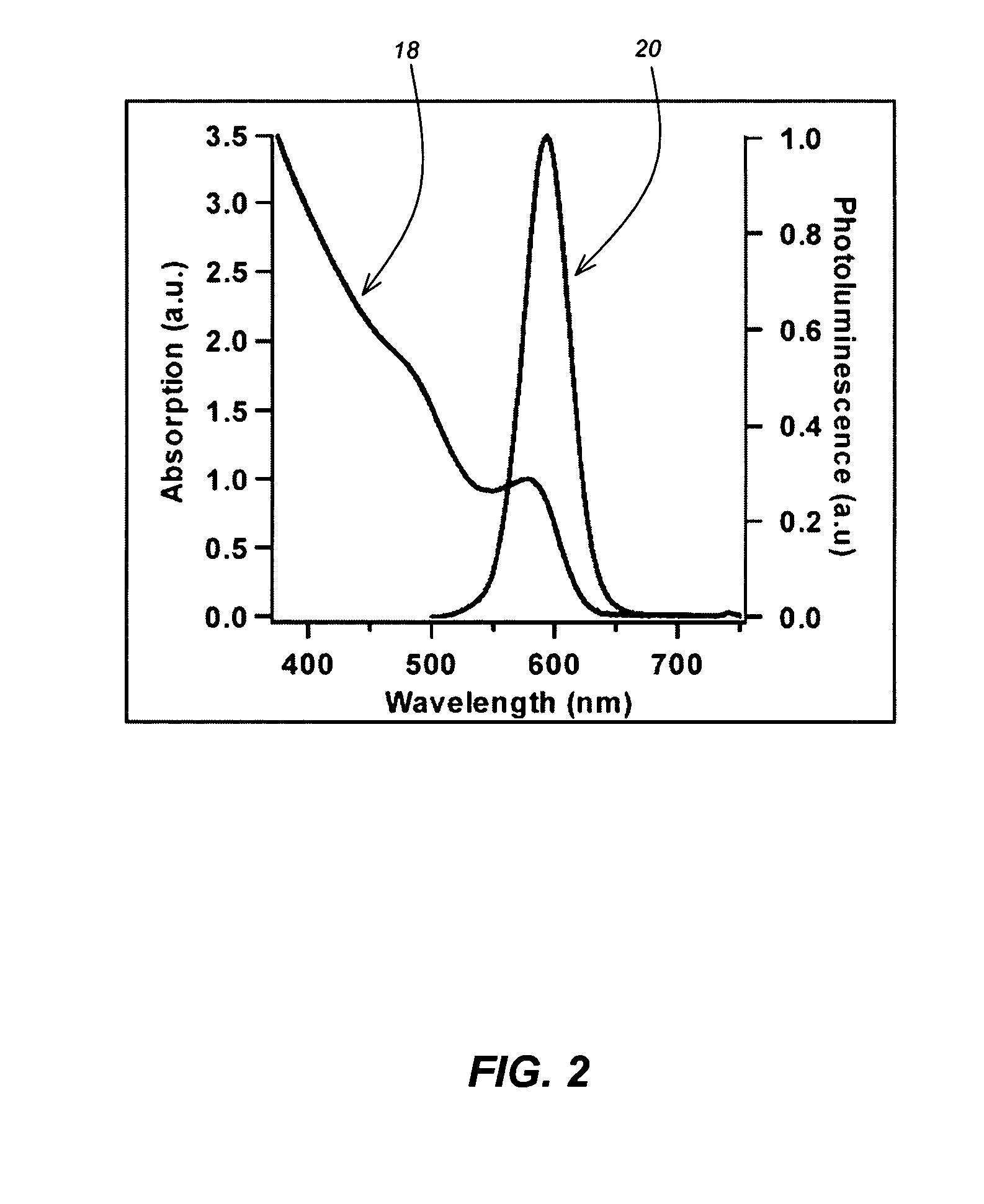
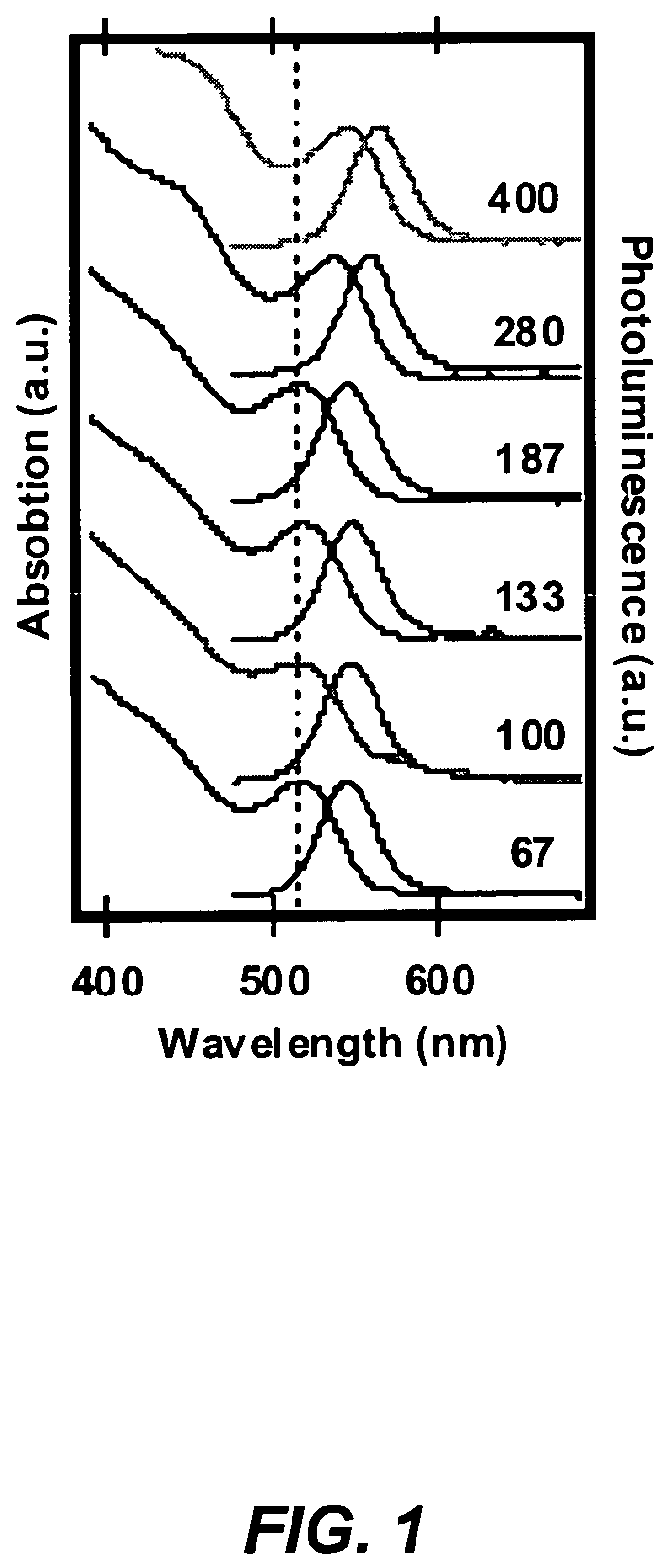
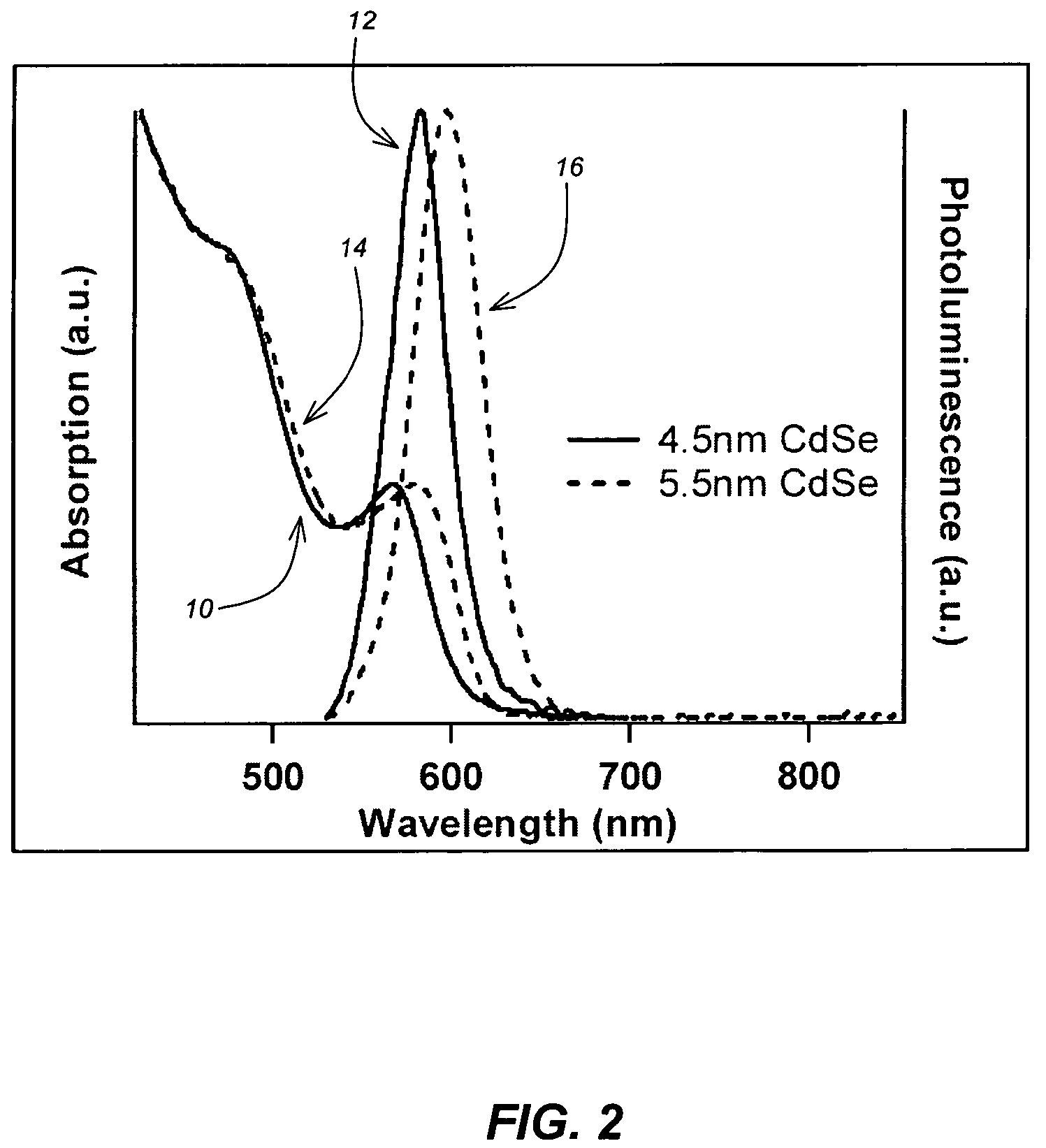
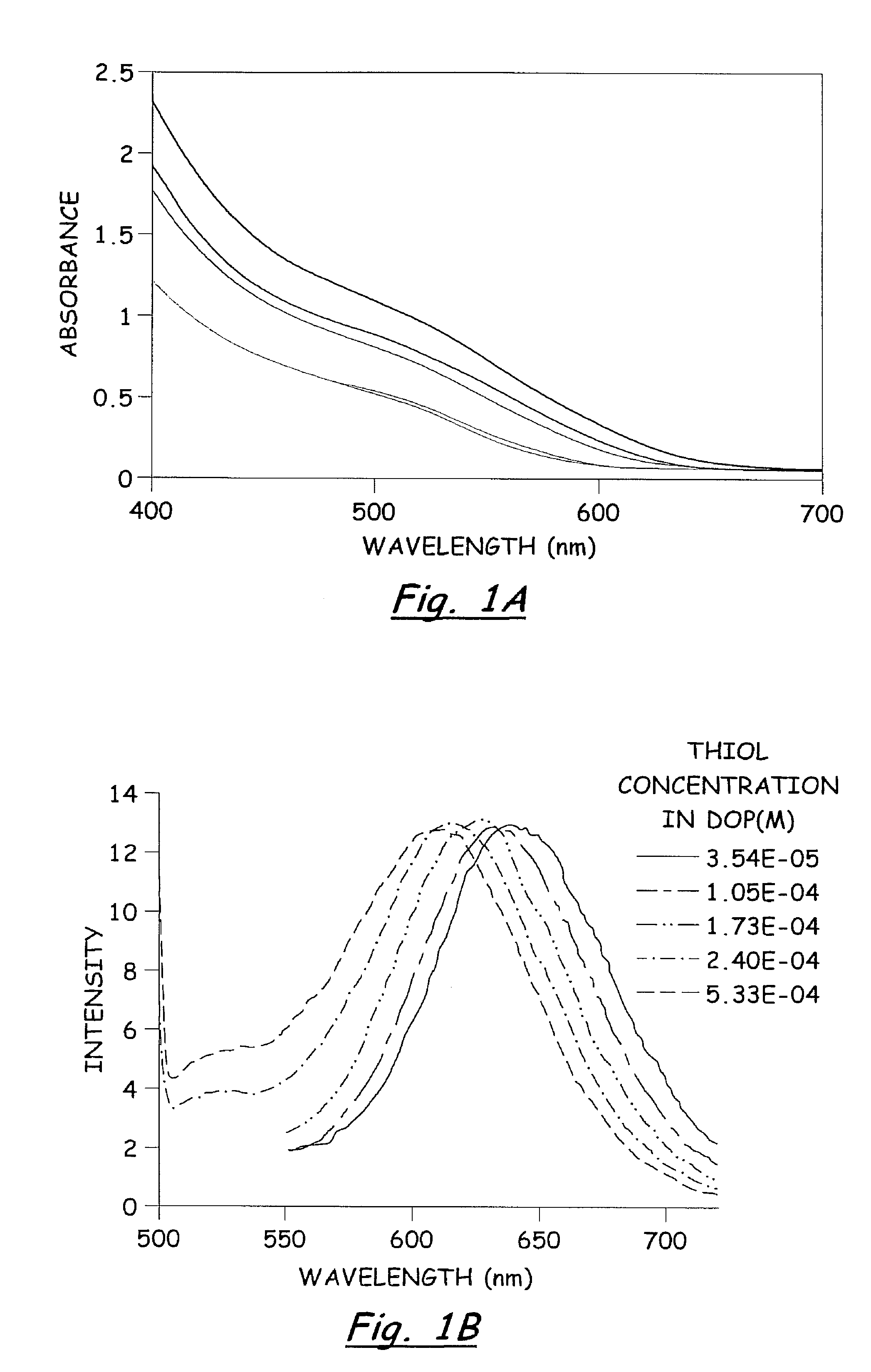
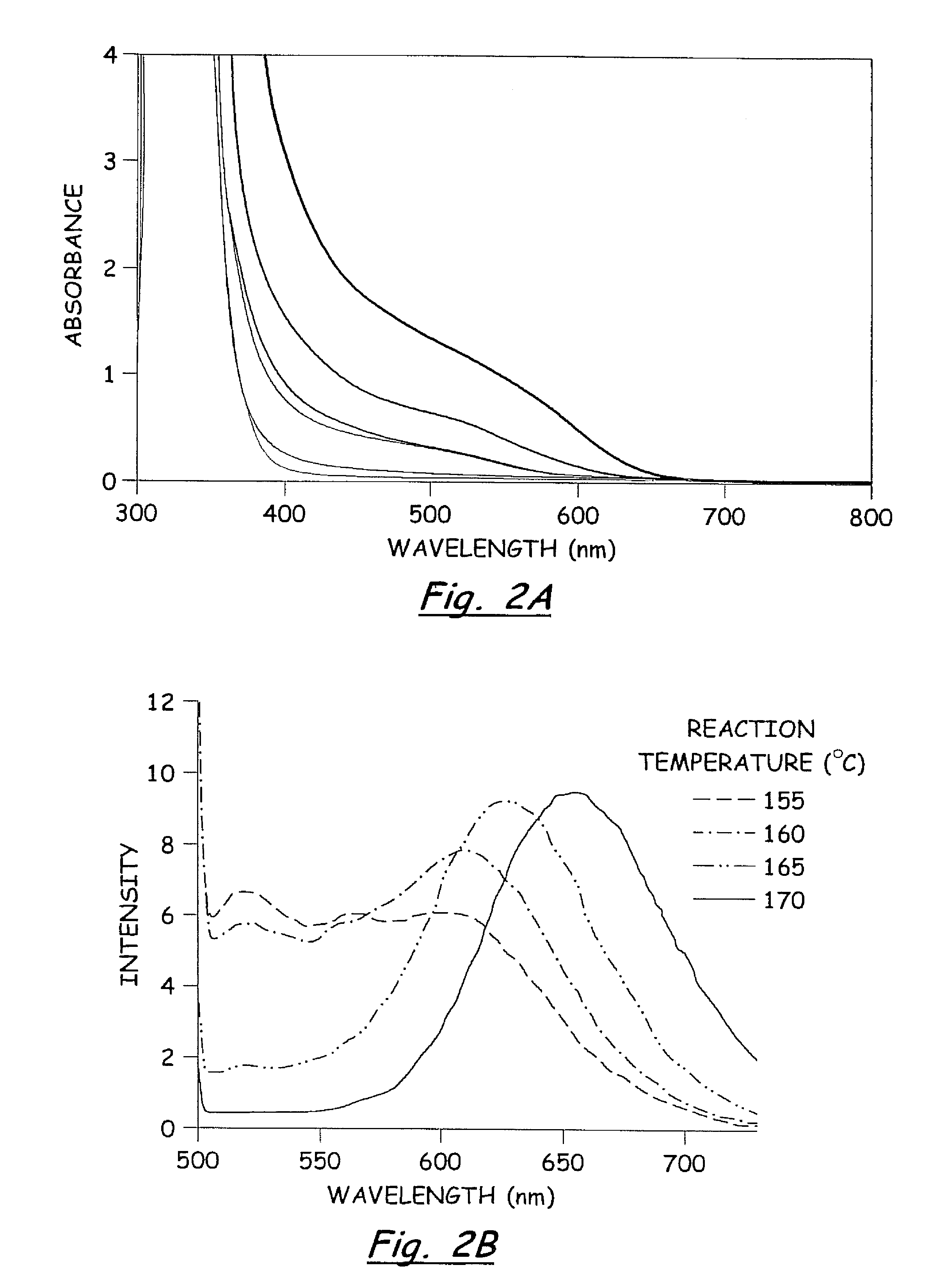
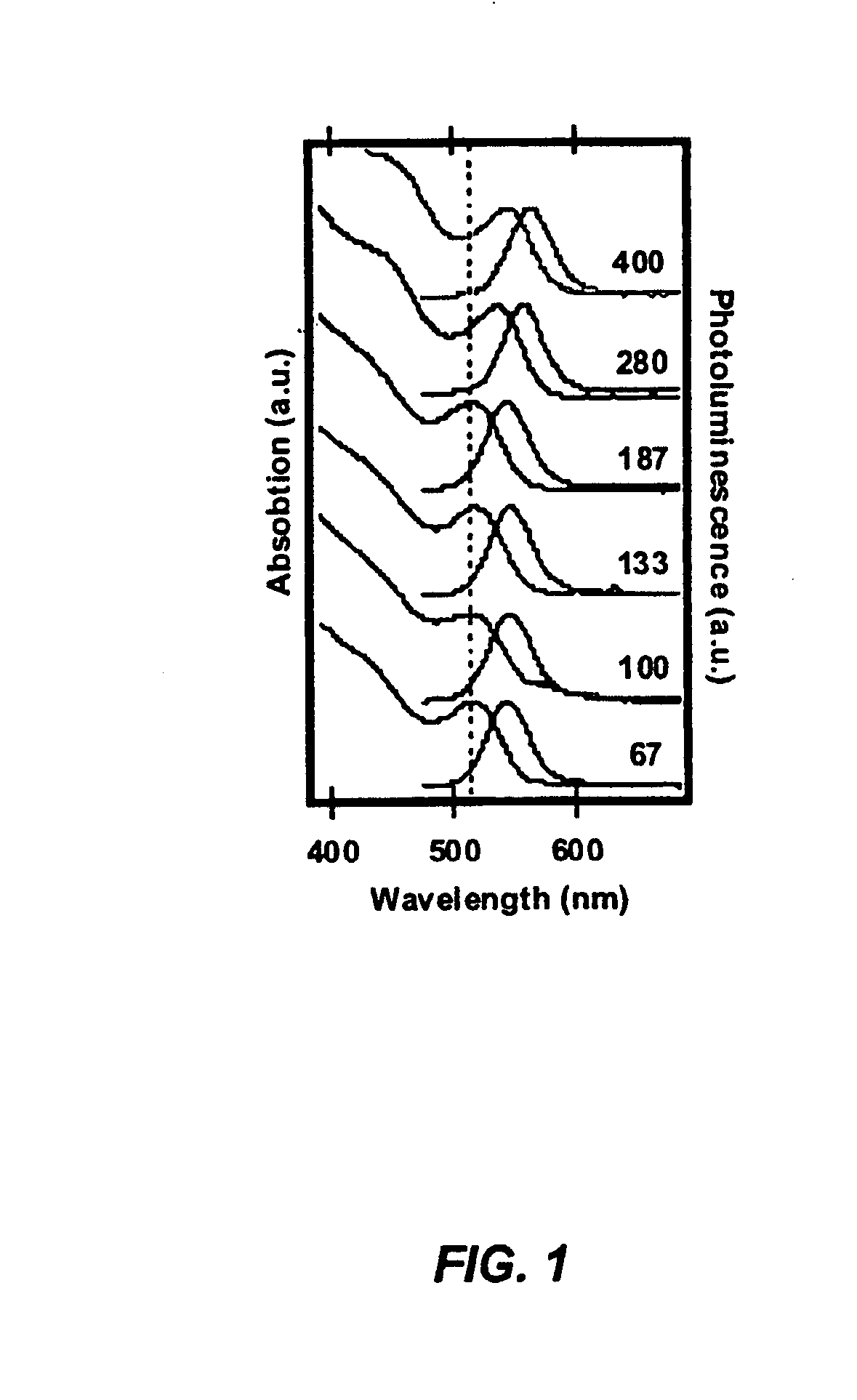
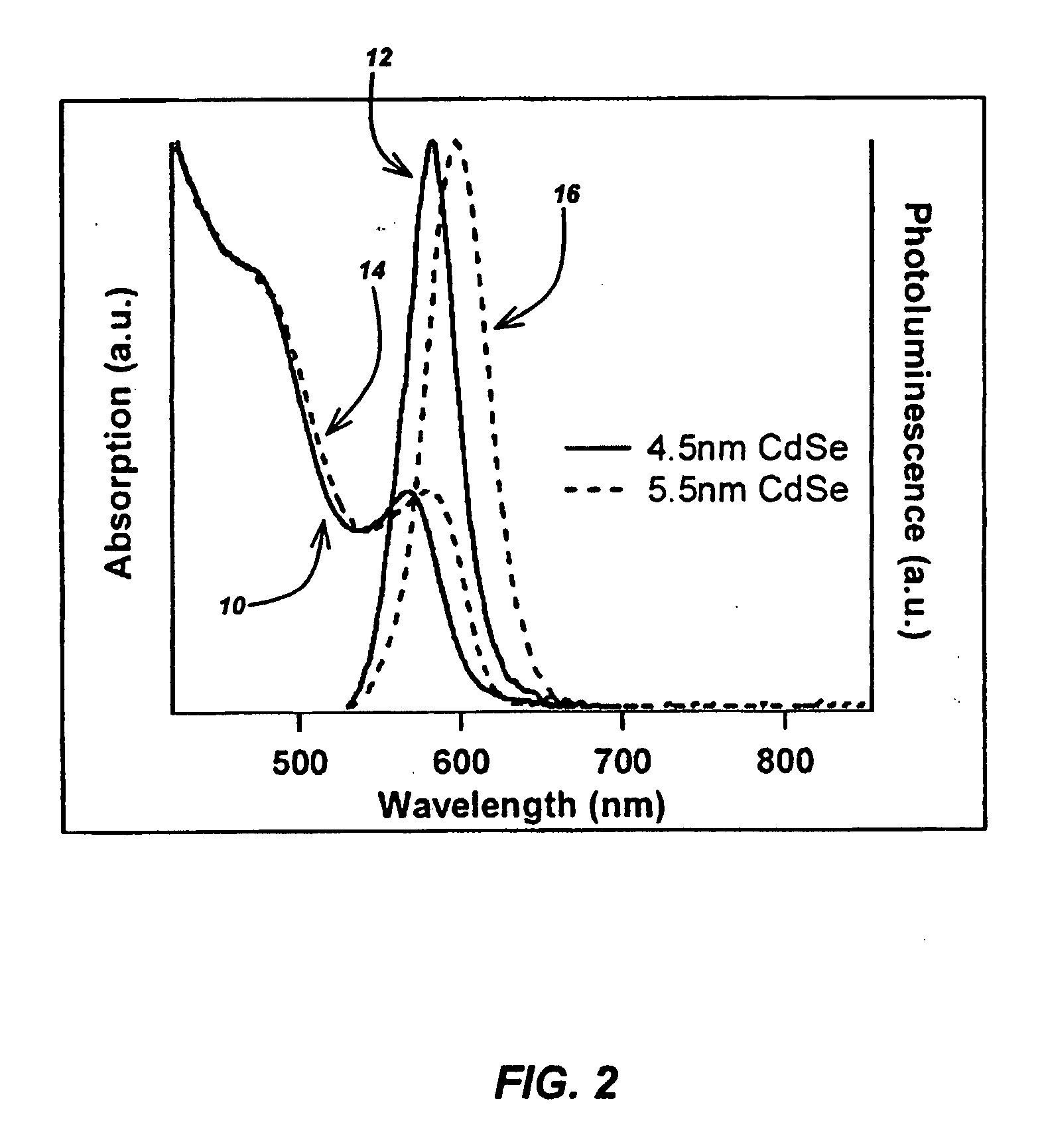
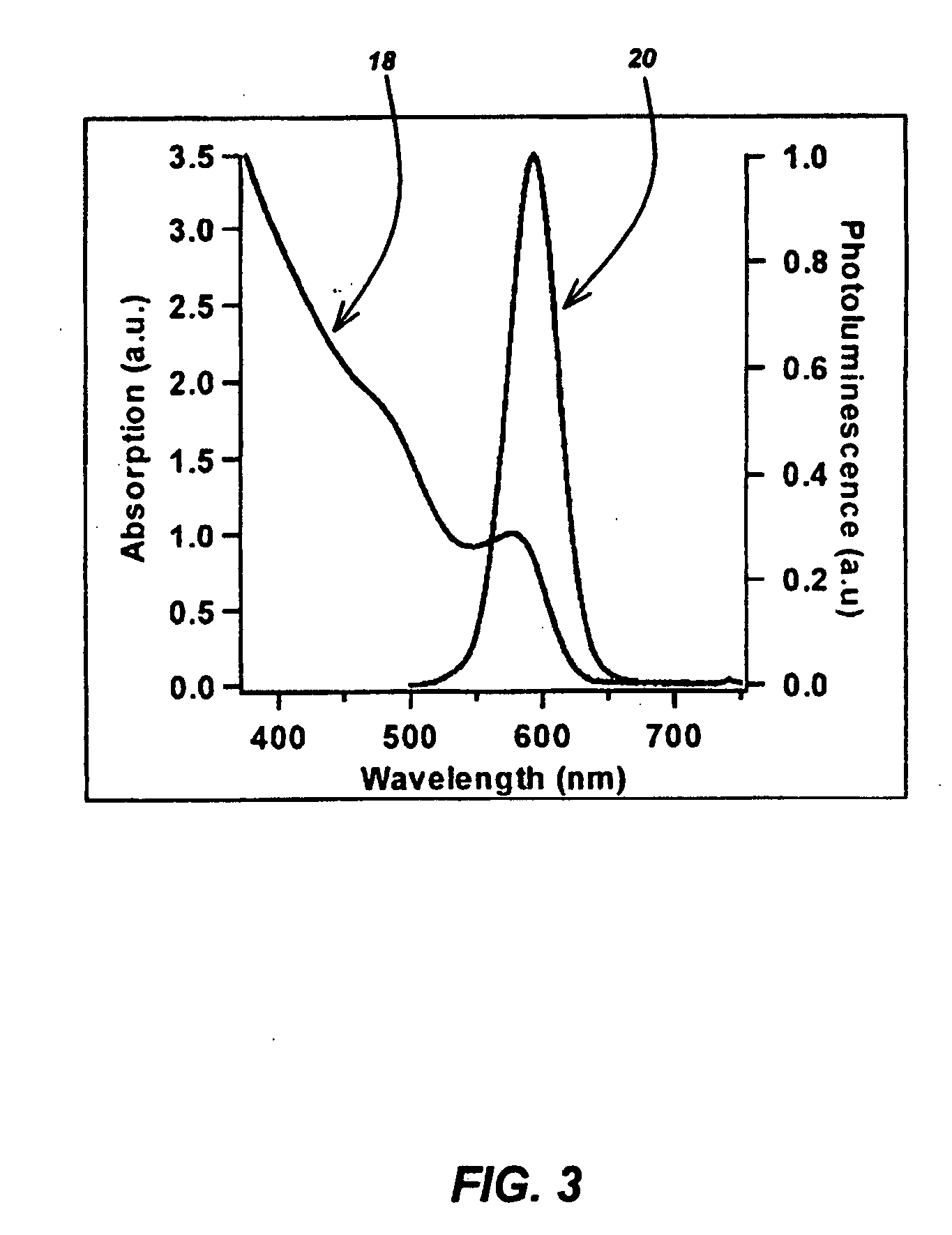
CuInS2 nanoparticles have been prepared from single source precursors via microwave irradiation. Also, CuInGaS2 alloy nanoparticles have been prepared. Microwave irradiation methods have allowed an increase in the efficiency of preparation of these materials by providing increased uniformity of heating and shorter reaction times. Nanoparticle growth has been controlled in the about 1 to 5 nm size range by variation of thiolated capping ligand concentrations as well as reaction temperatures and times. Investigation of the photophysical properties of the colloidal nanoparticles has been performed using electronic absorption and luminescence emission spectroscopy. Qualitative nanoparticles sizes have been determined from the photoluminescence (PL) data and compared to TEM images.
Owner:IDAHO STATE UNIVERSITY
Preparation of Diesel Oxidation Catalyst Via Deposition of Colloidal Nanoparticles
ActiveUS20140044627A1Good conditionReduce in quantityGas treatmentExhaust apparatusPtru catalystColloidal nanoparticles
The present invention relates to a process for preparing a catalyst, at least comprising the steps of adding a protecting agent to an aqueous solution of a metal precursor to give a mixture (M1), adding a reducing agent to mixture (M1) to give a mixture (M2), adding a support material to mixture (M2) to give a mixture (M3), adjusting the pH of mixture (M3), and separating the solid and liquid phase of mixture (M3). Furthermore, the present invention relates to the catalyst as such and its use as diesel oxidation catalyst.
Owner:BASF CORP
Colloidal photonic crystals using colloidal nanoparticles and method for preparation thereof
The present invention relates to colloidal photonic crystals using colloidal nanoparticles and a method for the preparation thereof, wherein by adding a viscoelastic material into a solution containing the colloidal nanoparticles when preparing the colloidal photonic crystals, a uniform volume contraction occurs due to the elasticity of the viscoelastic material even when a nonuniform volume contraction occurs while drying a dispersion medium in the colloidal solution. Thus, it is possible to prepare 2 or 3 dimensional colloidal photonic crystals of large scale with no defects in less time.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Colloidal photonic crystals using colloidal nanoparticles and method for preparation thereof
ActiveUS20070163486A1No surface defectsLess timeFrom gel statePolycrystalline material growthColloidal nanoparticlesColloidal particle
The present invention relates to colloidal photonic crystals using colloidal nanoparticles and a method for the preparation thereof, wherein by adding a viscoelastic material into a solution containing the colloidal nanoparticles when preparing the colloidal photonic crystals, a uniform volume contraction occurs due to the elasticity of the viscoelastic material even when a nonuniform volume contraction occurs while drying a dispersion medium in the colloidal solution. Thus, it is possible to prepare 2 or 3 dimensional colloidal photonic crystals of large scale with no defects in less time.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
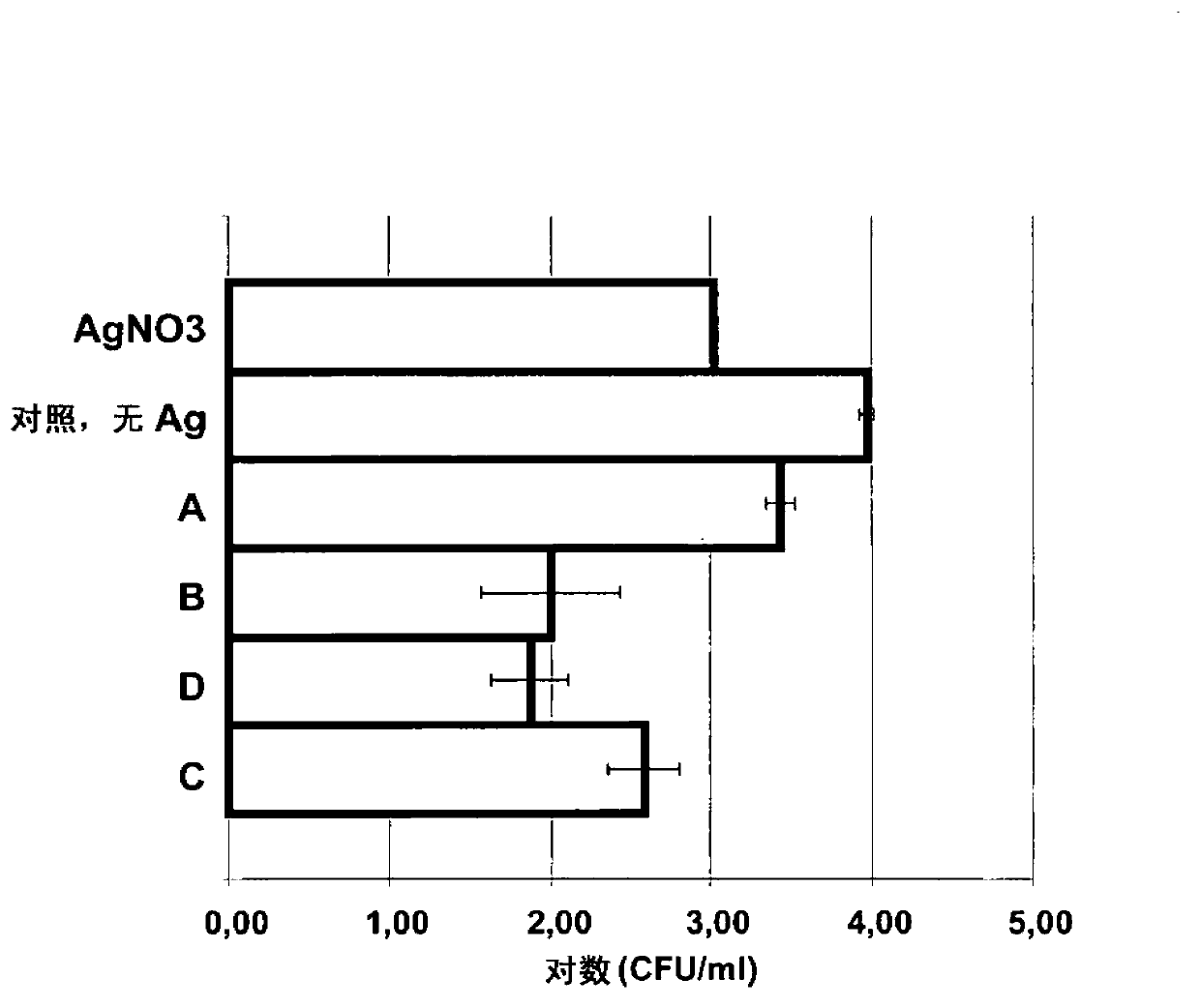
Method for producing metal nanoparticles
InactiveUS20090239280A1High reliability of resultsLow costAntibacterial agentsBiocidePlatinumColloidal nanoparticles
This invention provides a method for producing a composition comprising colloidal nanoparticles of metals including silver, gold, zinc, mercury, copper, palladium, platinum, or bismuth, by contacting a metal or metal compound with bacteria. An embodiment of the method comprises a step of incubating probiotic bacteria with an aqueous solution comprising at least 4 mM of a silver or gold salt. A resulting nanosilver-containing composition is useful as a highly efficient antimicrobial agent, for instance when impregnated onto a carrier, or an algicide agent or a herbicide agent.
Owner:JANSSEN PHARMA NV
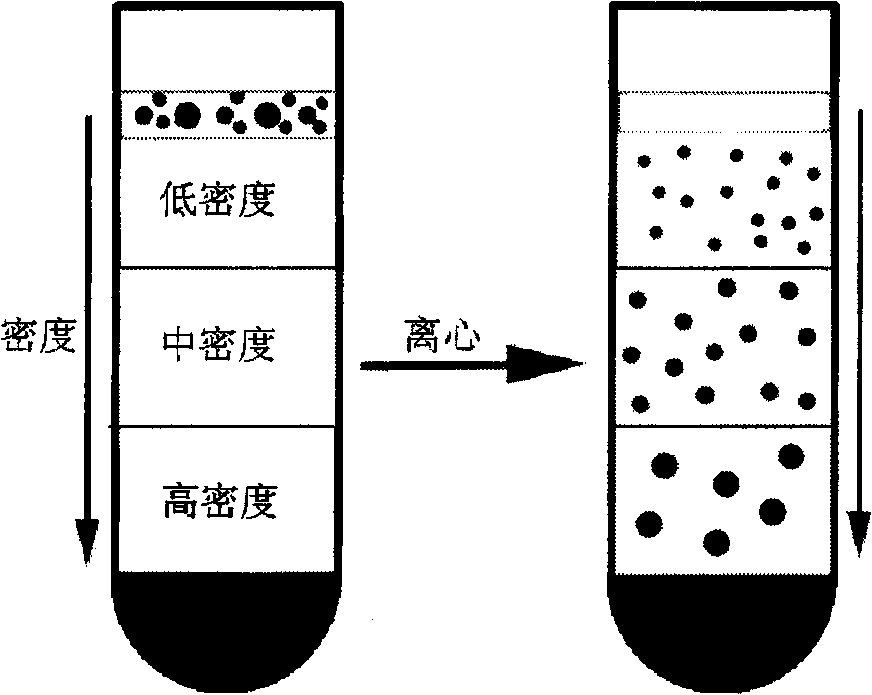
Method for separating nano-particles at water-phase density gradient centrifugation rate
InactiveCN101559401AEasy to separateWide range of separation sizesWet separationGradient centrifugationColloidal nanoparticles
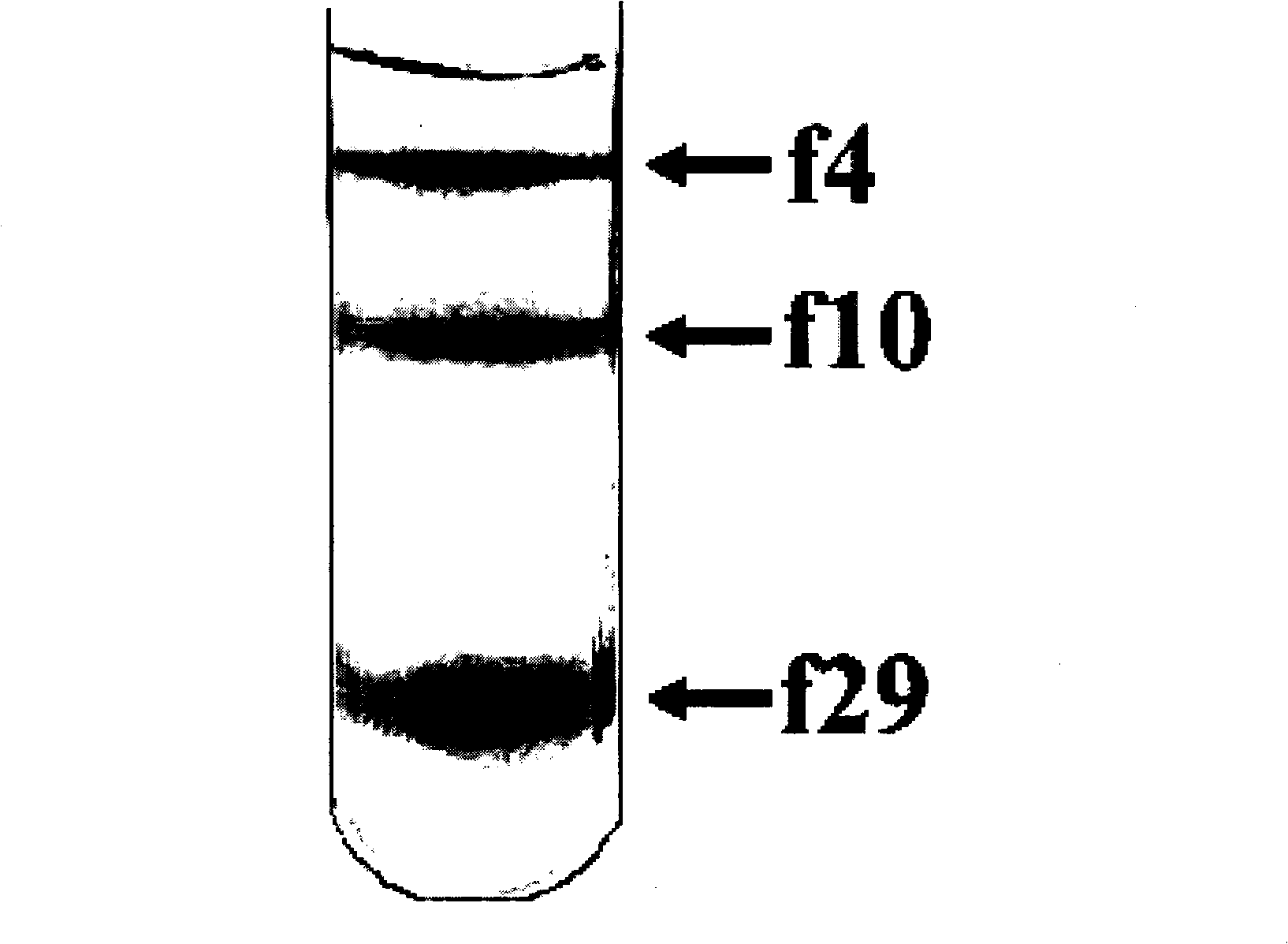
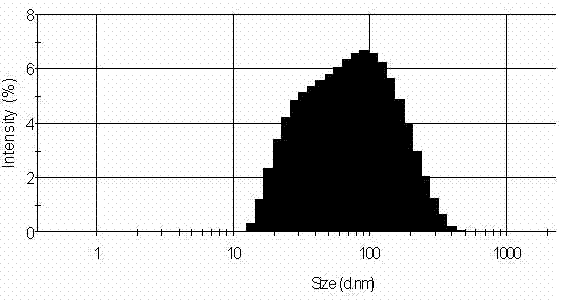
The invention relates to a method for separating nano-particles at a water-phase density gradient centrifugation rate, which mainly comprises the following steps: 1) preparing the nano-particles into a homogeneous transparent colloid nano-particle solution by means of ultrasound, stirring and the like; 2) preparing density gradient solutions with different mass percentage concentrations respectively; 3) adding certain amount of density gradient medium solutions with different concentrations into a centrifuge tube in turn to prepare a step-like or linear density gradient solution; and 4) adding the solution containing colloid nano-particles to the liquid surface of the density gradient solution slowly, and performing centrifugalization under certain condition. Because the colloid nano-particles with different sizes have different sedimentation rates in the density gradient solution and can be detained at different positions in the density gradient solution so as to achieve the effect of separation. The method has the advantages of simple method, quick separation, low cost, small influence on the stability and the purity of a sample, and the separation effect of certain section can be enhanced selectively by adjusting and controlling centrifugal parameters.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Stabilized Defoamers For Cementitious Compositions
ActiveUS20130281577A1Improved additive (admixture) formulation storage life spanIncreased freeze-thaw durabilitySpecial tyresWater dispersibleColloidal nanoparticles
The present invention discloses additive compositions, cementitious compositions, and methods for controlling air in cementitious compositions in which colloidal nano-particles are used for stabilizing a water-dispersible defoamer within a cement-dispersant-containing aqueous additive formulation for modifying hydratable cementitious compositions such as cement or concrete.
Owner:GCP APPL TECH INC
Colloidal nanoparticles and apparatus for producing colloidal nanoparticles in a dense medium plasma
InactiveUS20070013317A1Easy to convertEasily interchangeableOther chemical processesElectric discharge tubesConductive materialsColloidal nanoparticles
An apparatus is utilized for producing colloidal dispersions of nanoparticles of electrically conducting materials. The colloidal dispersions are produced in a dense media plasma reactor comprising at least one static electrode and at least one rotating electrode. The plasma reaction sputters off minute particles of the electrically conducting material from which the electrodes are made. Methods of using the colloidal dispersions thus made are also described. Colloidal dispersions of silver produced in this manner are highly effective for bactericidal purposes.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Method for Synthesis of Colloidal Nanoparticles
InactiveUS20070264834A1Large-scale, safe, convenient, reproducible, and energy-efficient productionHigh crystallinityDielectric heatingNanoinformaticsSynthesis methodsContinuous flow
A method for synthesis of high quality colloidal nanoparticles using comprises a high heating rate process. Irradiation of single mode, high power, microwave is a particularly well suited technique to realize high quality semiconductor nanoparticles. The use of microwave radiation effectively automates the synthesis, and more importantly, permits the use of a continuous flow microwave reactor for commercial preparation of the high quality colloidal nanoparticles.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
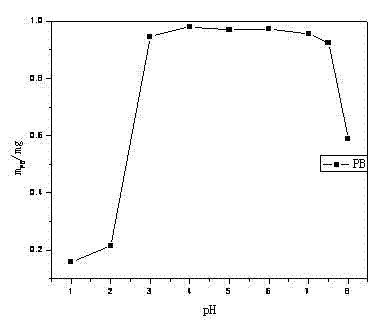
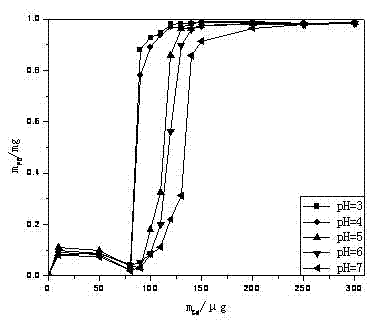
Method for recovering rare earth from low-concentration rare earth solution through prussian blue colloidal nanoparticles
InactiveCN102352448ASimple processLarge loading of rare earthWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisProcess efficiency improvementDialysis membranesRare earth ions
The invention relates to a method for recovering rare earth from low-concentration rare earth solution through prussian blue colloidal nanoparticles (PB-CNP). The method comprises the following steps: firstly synthesizing a stable PB-CNP colloidal solution, loading into a bag produced by a dialysis membrane, enabling a dialysis bag containing PB-CNP suspension to be in contact with rare earth material liquid (the pH value is 4-7), and enabling rare earth ions to pass through membrane holes to be in contact with the PB-CNP for being adsorbed. Dilute acid solution is used for desorbing the rareearth from the PB-CNP suspension which absorbs the rare earth ions, thereby achieving the purpose of recovering the rare earth. The PB-CNP suspension and the rare earth material liquid can also be arranged in different channels on the two sides of the membrane of a membrane component for flowing in a countercurrent way, thereby achieving the high-efficient enrichment effect. The method has the advantages of simple process, large rare earth loading amount, high rare earth recovery rate and the like, and can be widely used for the rare earth material liquid of rare earth mines and separation factories; and furthermore, by adopting the method, the rare earth ions in low-concentration rare earth wastewater can be completed removed and recovered, thereby having wide application prospects.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
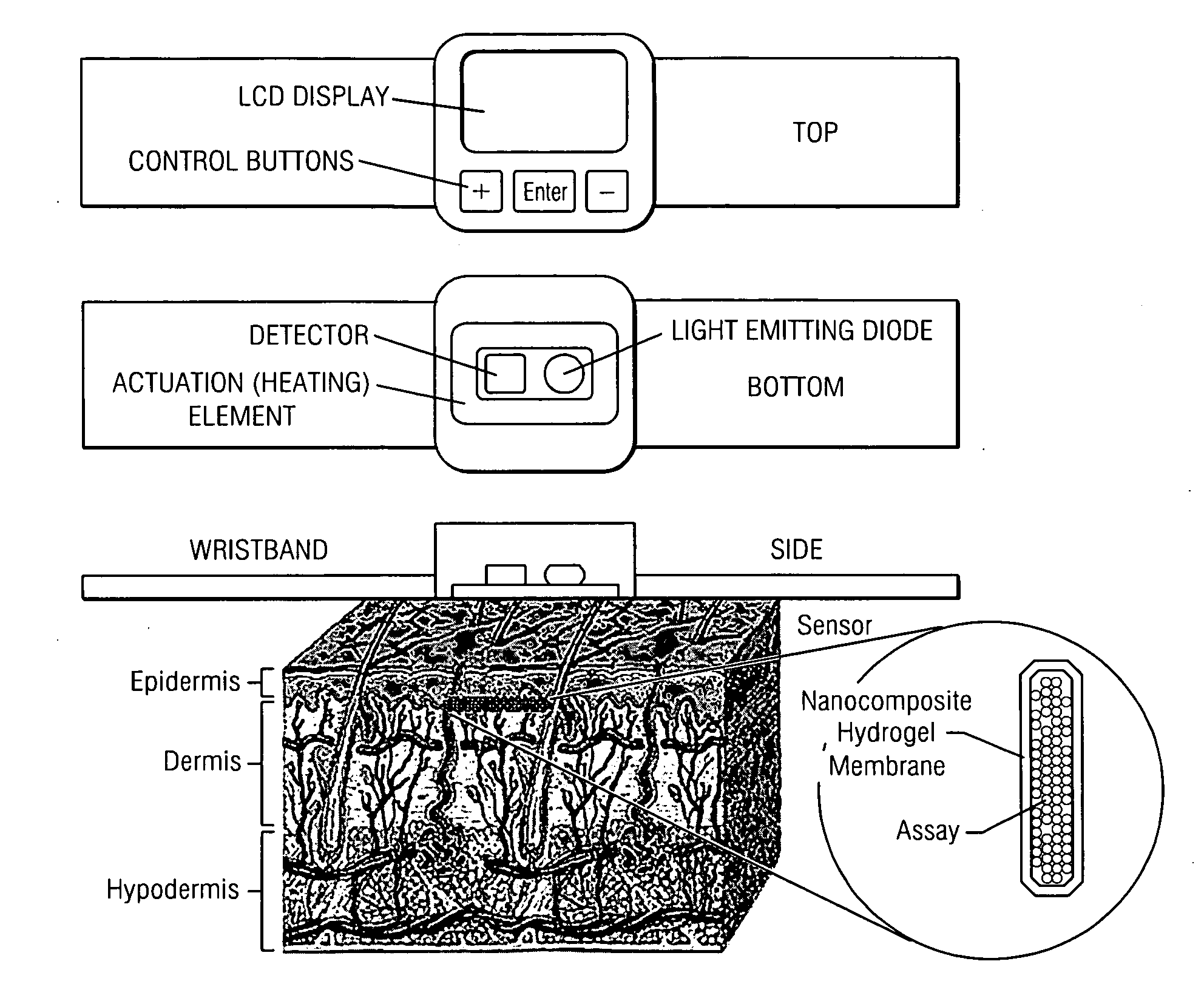
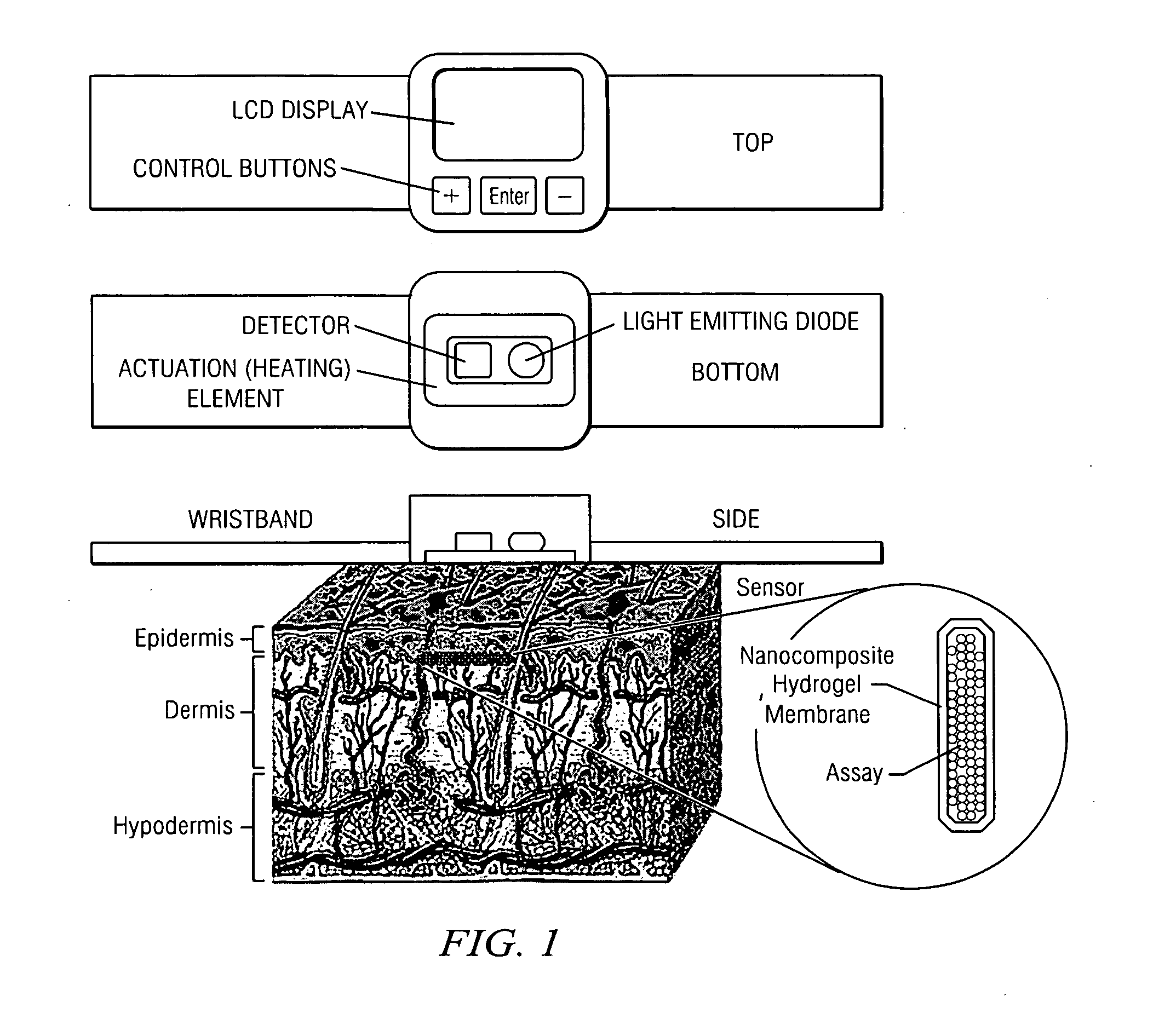
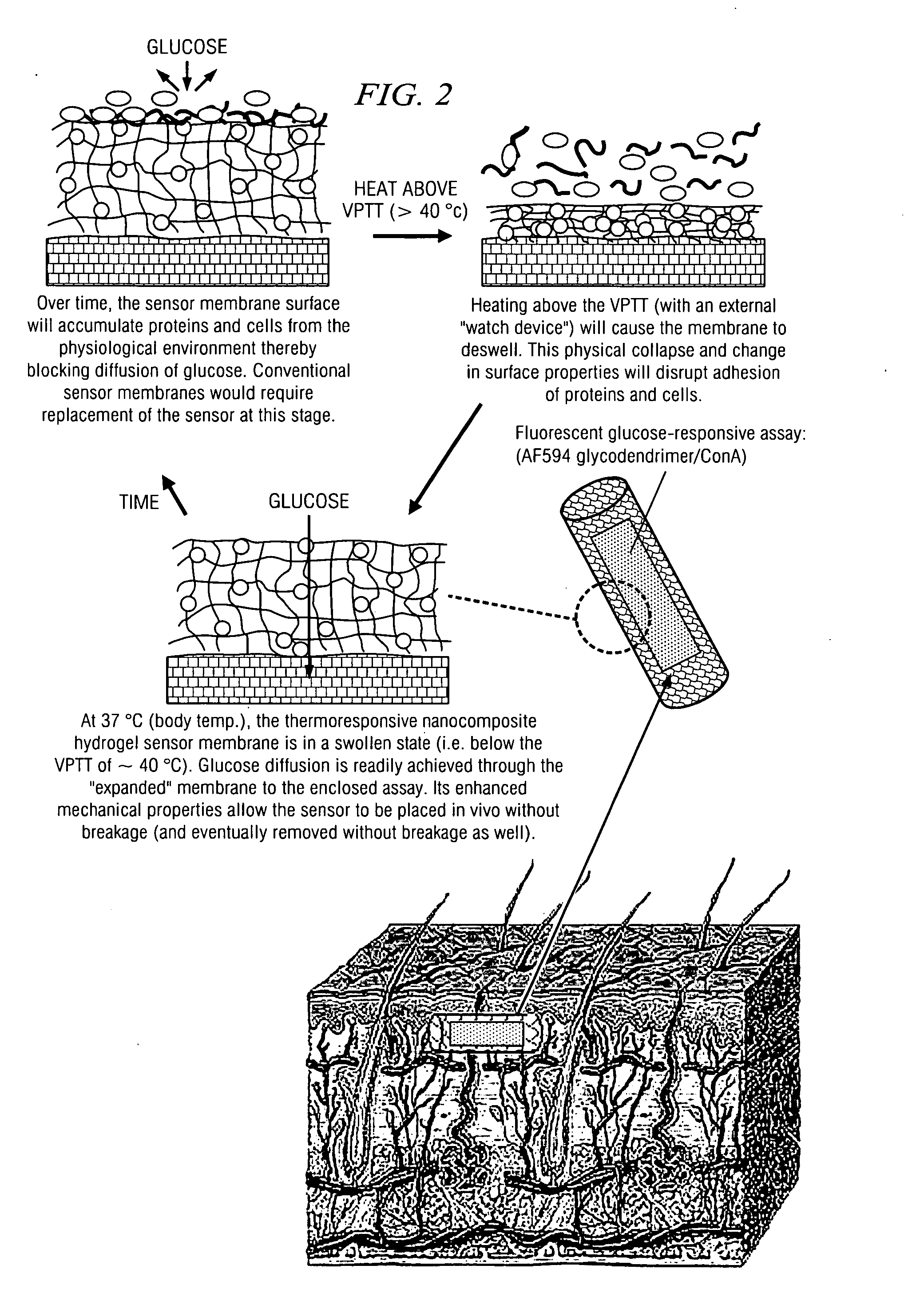
Self-Cleaning Membrane for Implantable Biosensors
InactiveUS20100056894A1Extended service lifeMinimized and eliminatedImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHydrogel swellingColloidal nanoparticles
The present disclosure relates, according to some embodiments, to compositions, devices, systems, and methods including and / or for preparing and / or using a thermoresponsive nanocomposite hydrogel. In some embodiments, the disclosure relates to methods of preparing a hydrogel including, for example, photochemically curing an aqueous solution of NIPAAm and copoly(dimethylsiloxane / methylvinylsiloxane) colloidal nanoparticles (˜219 nm). At temperatures above a volume phase transition temperature (VPTT) of ˜33-34° C., a hydrogel may deswell and become hydrophobic, while lowering the temperature below a VPTT may cause the hydrogel to swell and become hydrophilic.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
Preparation of Diesel Oxidation Catalyst Via Deposition of Colloidal Nanoparticles
InactiveUS20110033353A1Good conditionReduce in quantityNitrogen compoundsExhaust apparatusColloidal nanoparticlesAqueous solution
The present invention relates to a process for preparing a catalyst, at least comprising the steps of adding a protecting agent to an aqueous solution of a metal precursor to give a mixture (M1), adding a reducing agent to mixture (M1) to give a mixture (M2), adding a support material to mixture (M2) to give a mixture (M3), adjusting the pH of mixture (M3), and separating the solid and liquid phase of mixture (M3). Furthermore, the present invention relates to the catalyst as such and its use as diesel oxidation catalyst.
Owner:BASF CORP
Method for synthesizing monodisperse stable LDHs (layered double hydroxides) colloid nanocrystalline
InactiveCN102976373ANarrow size distributionMaterial nanotechnologyAluminium oxides/hydroxidesDispersityColloidal nanoparticles
The invention relates to a preparation method for synthesizing relatively strict monodisperse stable LDHs (layered double hydroxides) colloid nanocrystalline. The preparation method mainly comprises the following steps of: 1, synthesizing the LDHs through a colloid mill to obtain white slurry, then centrifugally washing three times, transferring to a hydrothermal kettle, re-crystallizing to obtain a stable colloid solution; 2, respectively preparing density gradient medium solutions with different densities; 3, sequentially adding quantitative gradient solutions according to different densities in a centrifugal tube for preparing a step type density gradient solution; 4, slowly adding the prepared colloid solution on the liquid level of the density gradient solution, centrifuging under a certain condition; and 5, since colloid nano particles with different sizes have different sedimentation rates in the density gradient solutions, after centrifugation is stopped, the colloid nano particles remain in the gradient solutions with different densities, so that an effective method for preparing the monodisperse LDH nanocrystalline is provided. The high-monodispersity nano material has great potential application on the aspects of medicines, genetic vectors, polymer / LDHs biological nano composite materials, LDH films and the like.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
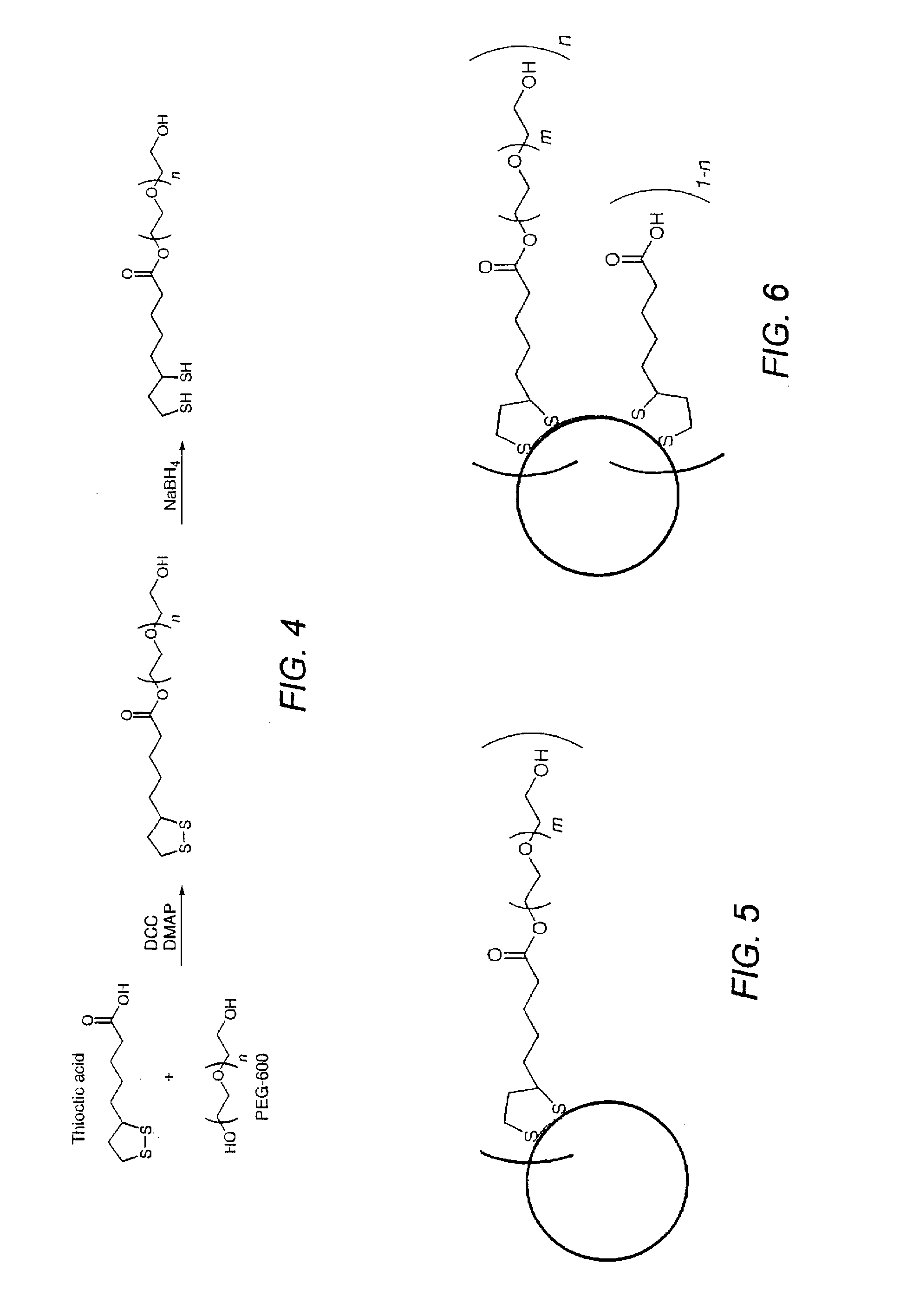
Field of modular multifunctional ligands
ActiveUS20070269904A1Wide pH stabilityRemain luminescentNanoinformaticsNanomedicineSolubilityQuantum dot
This invention pertains to a surface ligand; preparation of the ligand; colloidal nanoparticle, such as quantum dot bearing one or more of the ligand; and a bioconjugate characterized by a nanoparticle bearing one or more of the ligand conjugated to a biomolecule. The ligand is characterized by the presence of a first module containing atoms that can attach to an inorganic surface; a second module that imparts water-solubility to the ligand and to the inorganic surface that may be attached to the ligand; and a third module that contains a functional group that can, directly or indirectly, conjugate to a biomolecule. Order of the modules can be different and other modules and groups can be on the ligand. Preparation of the ligand includes the steps of reacting a compound having atoms that can attach to an inorganic surface with a water-solubilizing compound that imparts the property of water-solubility to the ligand and the inorganic surface to which it may be attached and purification thereof. Colloidal nanoparticle is characterized by an inorganic surface having attached to it one or more of the ligands. The colloidal bioconjugate is characterized by an inorganic surface having attached thereto one or more of the ligand wherein at least some of the ligand have a biomolecule conjugated thereto.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
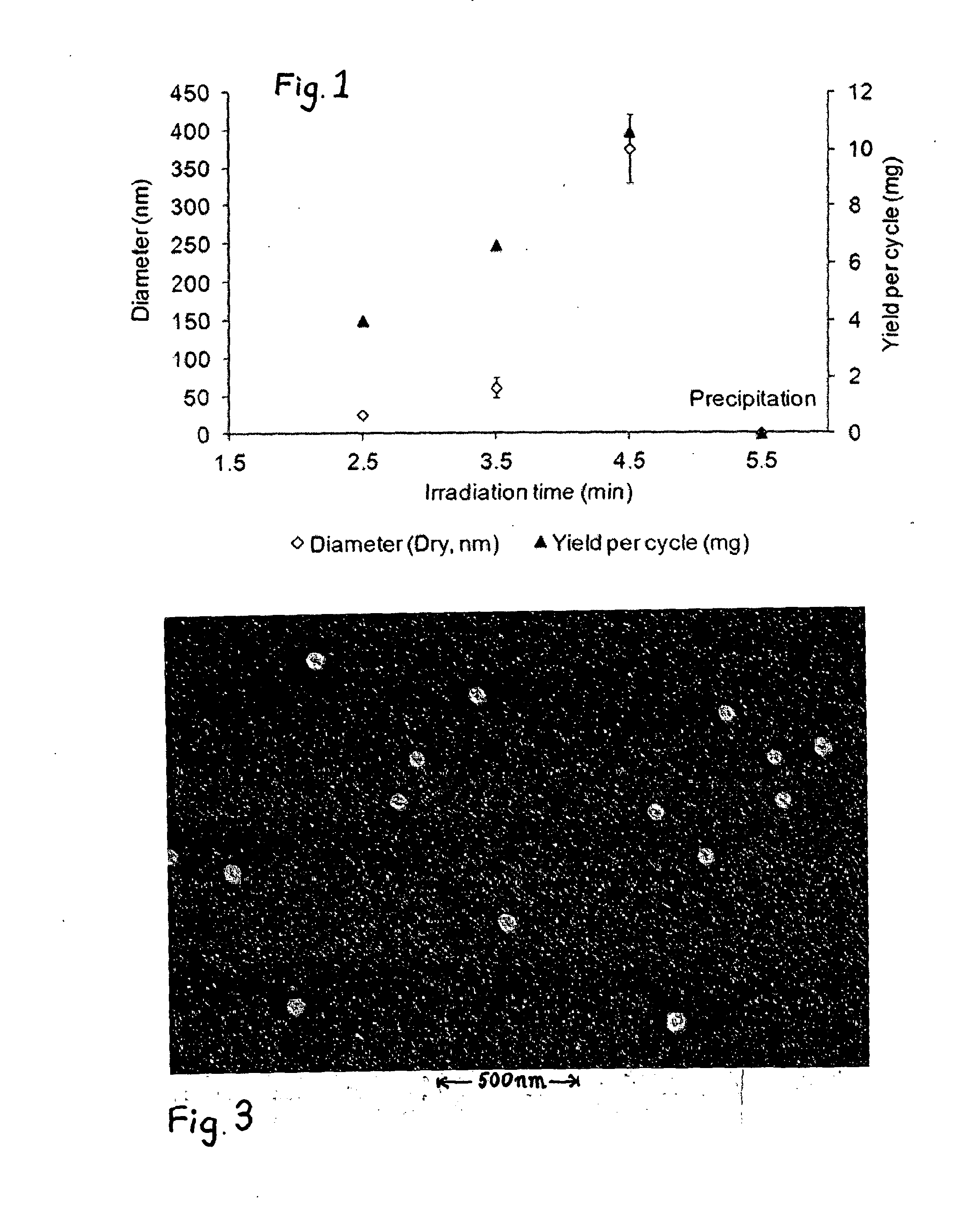
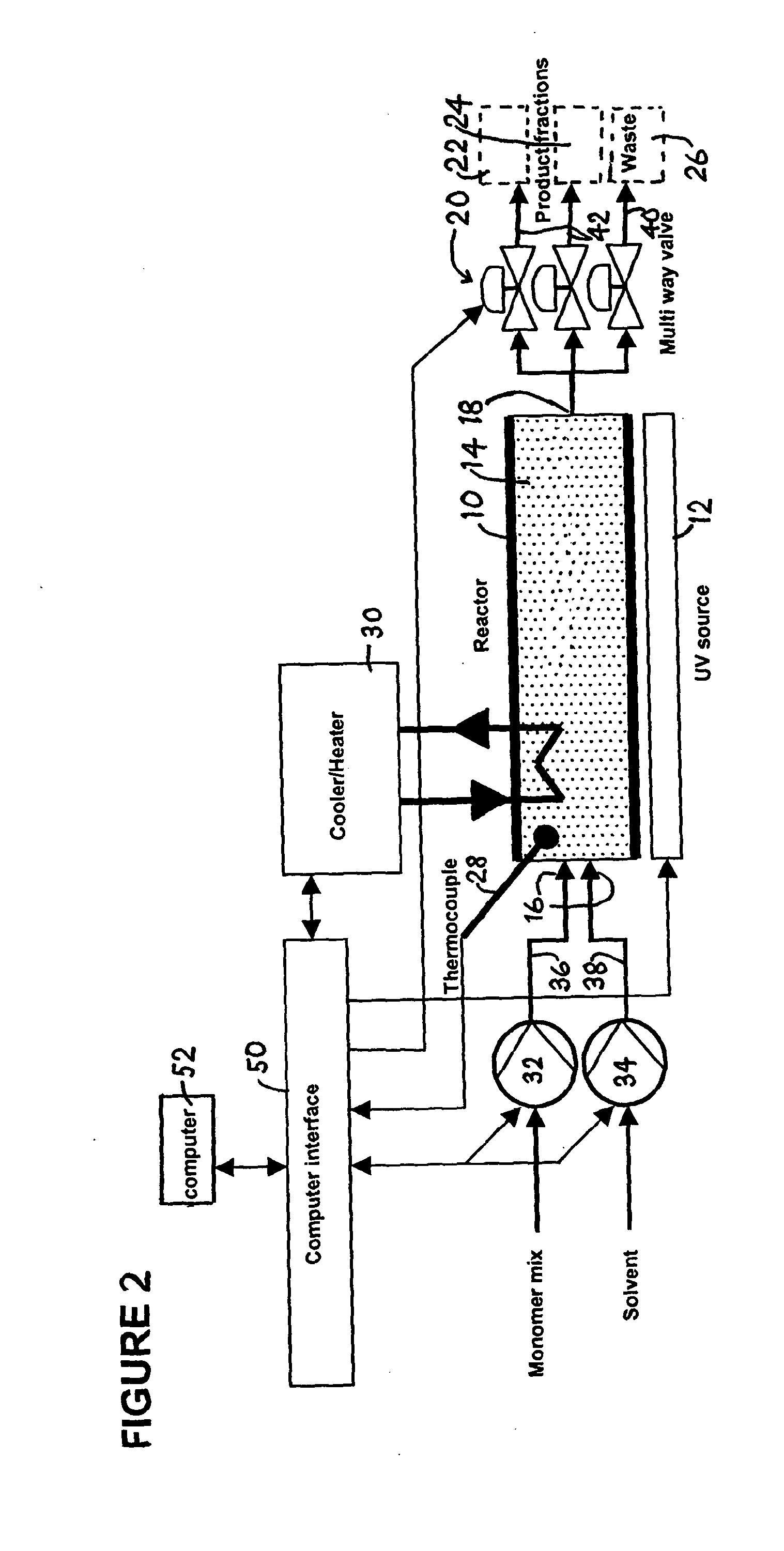
Photoreactor and Process for Preparing MIP Nanoparticles
InactiveUS20140228472A1Temperature controlMaterial nanotechnologyTemperatue controlColloidal nanoparticlesMolecularly imprinted polymer
Soluble or colloidal nanoparticles of molecularly imprinted polymer are produced reliably and consistently in a photoreactor with a reaction vessel (18) containing a solid phase (14) bearing immobilised template. Parameters such as temperature, fluid flows and irradiation time are controlled by a computer (52).
Owner:MIP DIAGNOSTICS LTD
Method for producing metal nanoparticles
InactiveCN102978241AGood size controlControllable distributionMicroorganism based processesFermentationPlatinumColloidal nanoparticles
This invention provides a method for producing a composition comprising colloidal nanoparticles of metals including silver, gold, zinc, mercury, copper, palladium, platinum, or bismuth, by contacting a metal or metal compound with bacteria. An embodiment of the method comprises a step of incubating probiotic bacteria with an aqueous solution comprising at least 4 mM of a silver or gold salt. A resulting nanosilver-containing composition is useful as a highly efficient antimicrobial agent, for instance when impregnated onto a carrier, or an algicide agent or a herbicide agent.
Owner:JANSSEN PHARMA NV
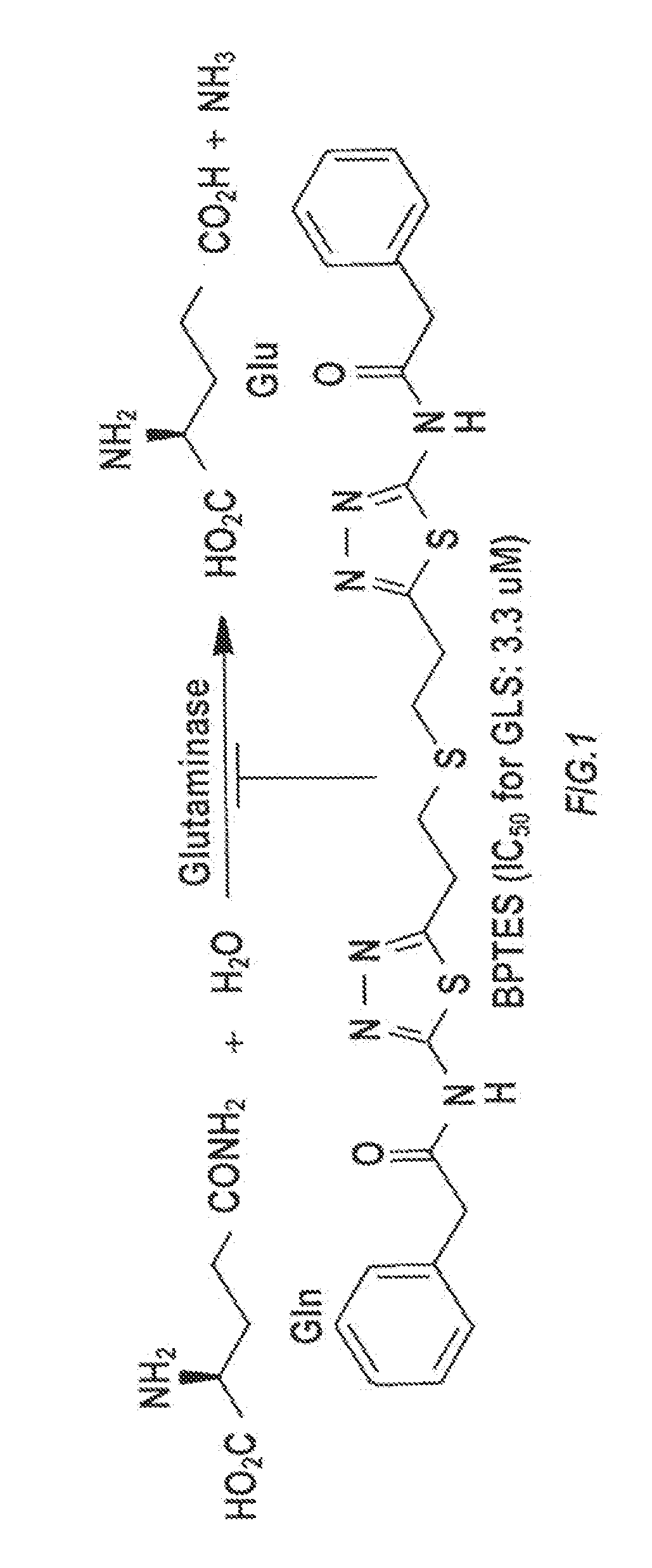
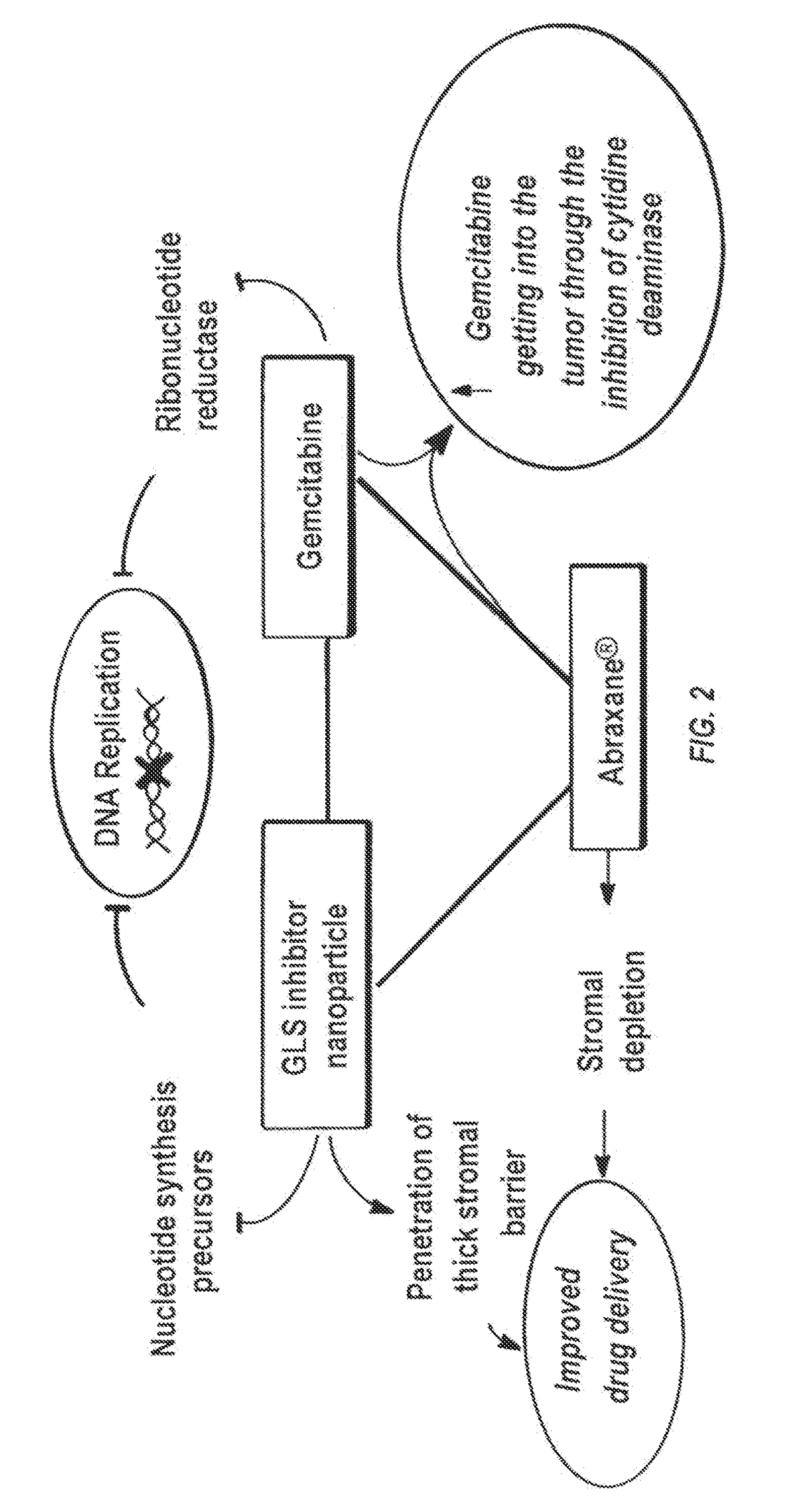
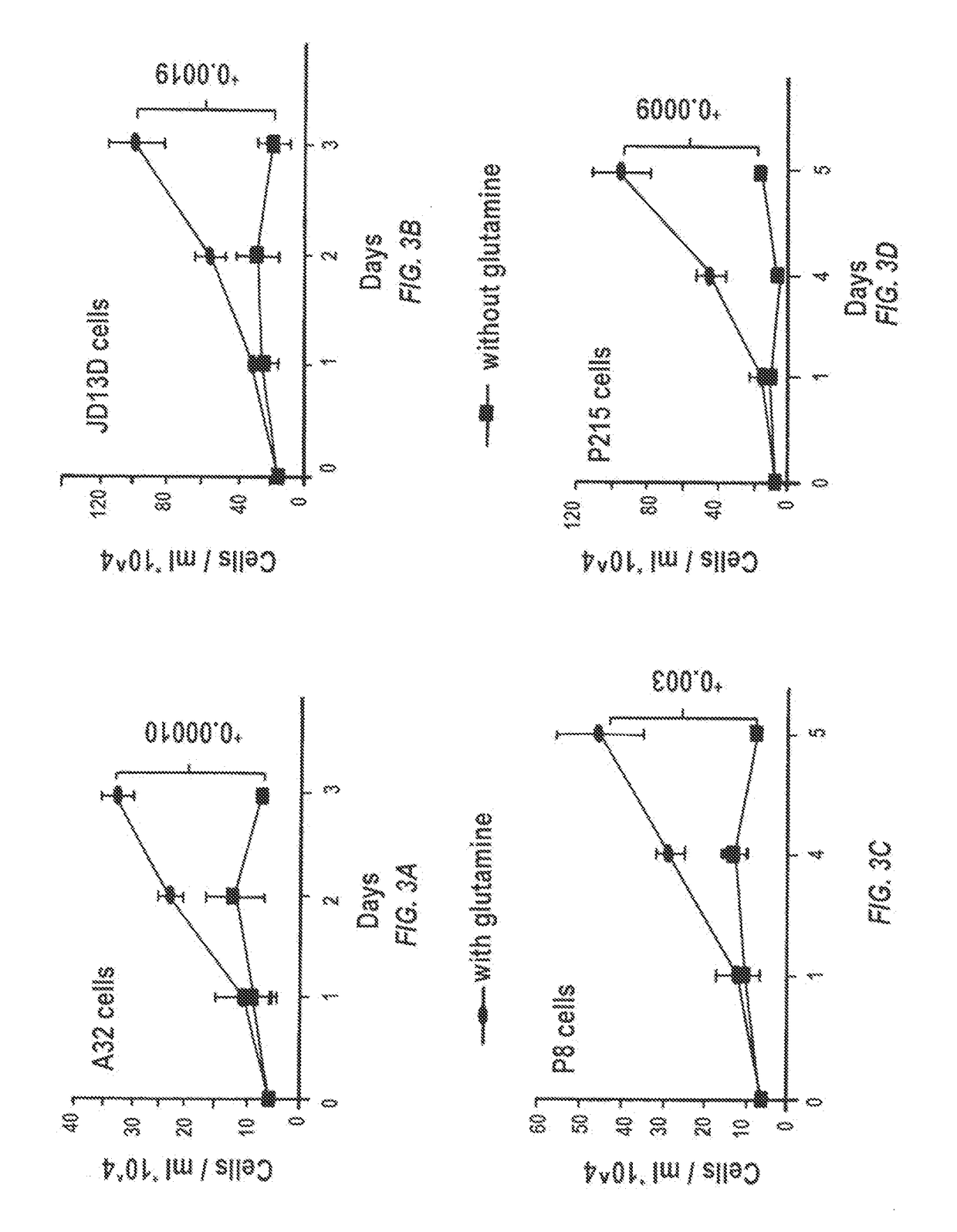
Glutaminase inhibitor discovery and nanoparticle-enhanced delivery for cancer therapy
ActiveUS20170209387A1Improve effectivenessEnhanced interactionOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryHigh concentrationHigh doses
Currently available glutaminase inhibitors are generally poorly soluble, metabolically unstable, and / or require high doses, which together reduce their efficacy and therapeutic index. These can be formulated into nanoparticles and delivered safely and effectively for treatment of pancreatic cancer and other glutamine addicted cancers. Studies demonstrate that nanoparticle delivery of BPTES, relative to use of BPTES alone, can be safely administered and provides dramatically improved tumor drug exposure, resulting in greater efficacy. GLS inhibitors can be administered in higher concentrations with sub-100 nm nanoparticles, since the nanoparticles package the drug into “soluble” colloidal nanoparticles, and the nanoparticles deliver higher drug exposure selectively to the tumors due to the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect. These factors result in sustained drug levels above the IC50 within the tumors for days, providing significantly enhanced efficacy compared to unencapsulated drug.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com