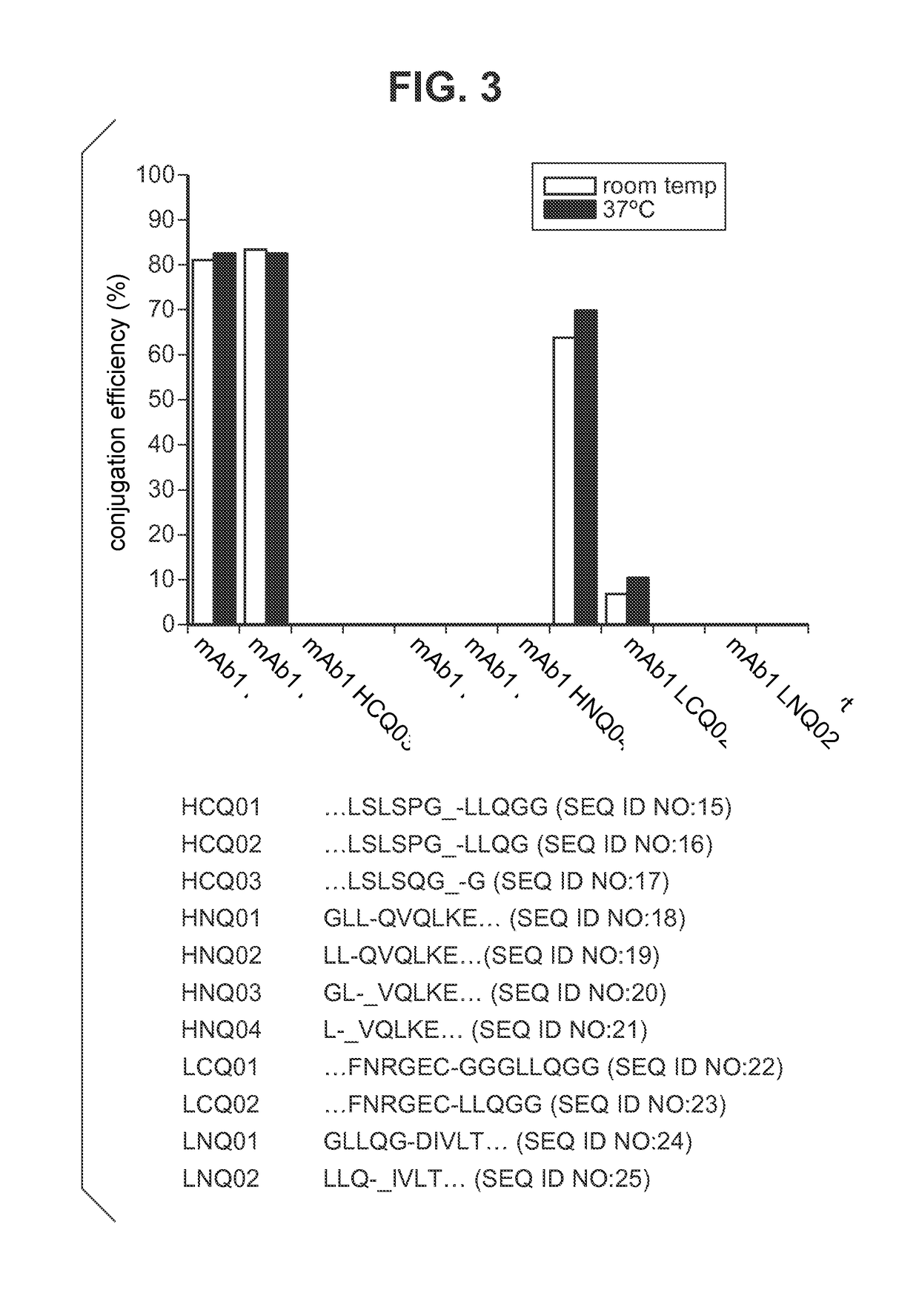
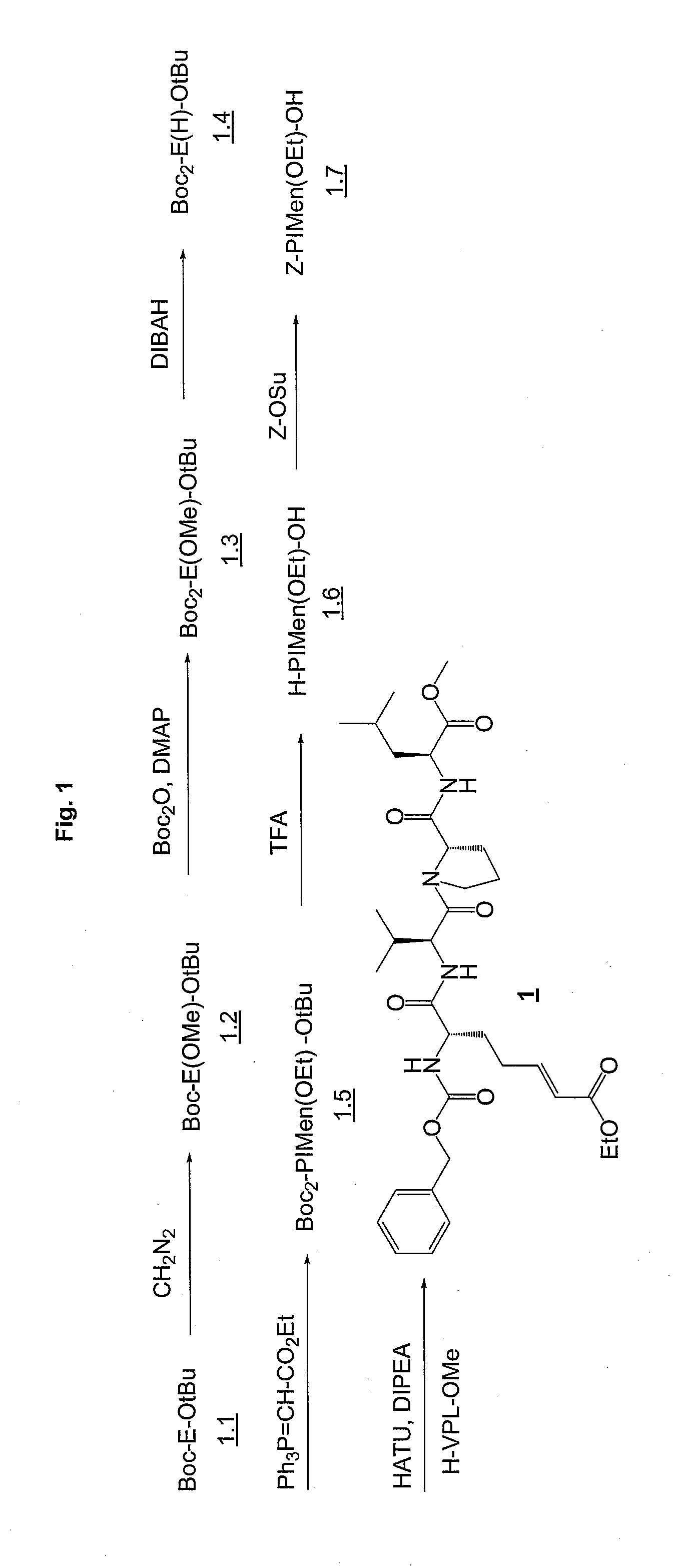
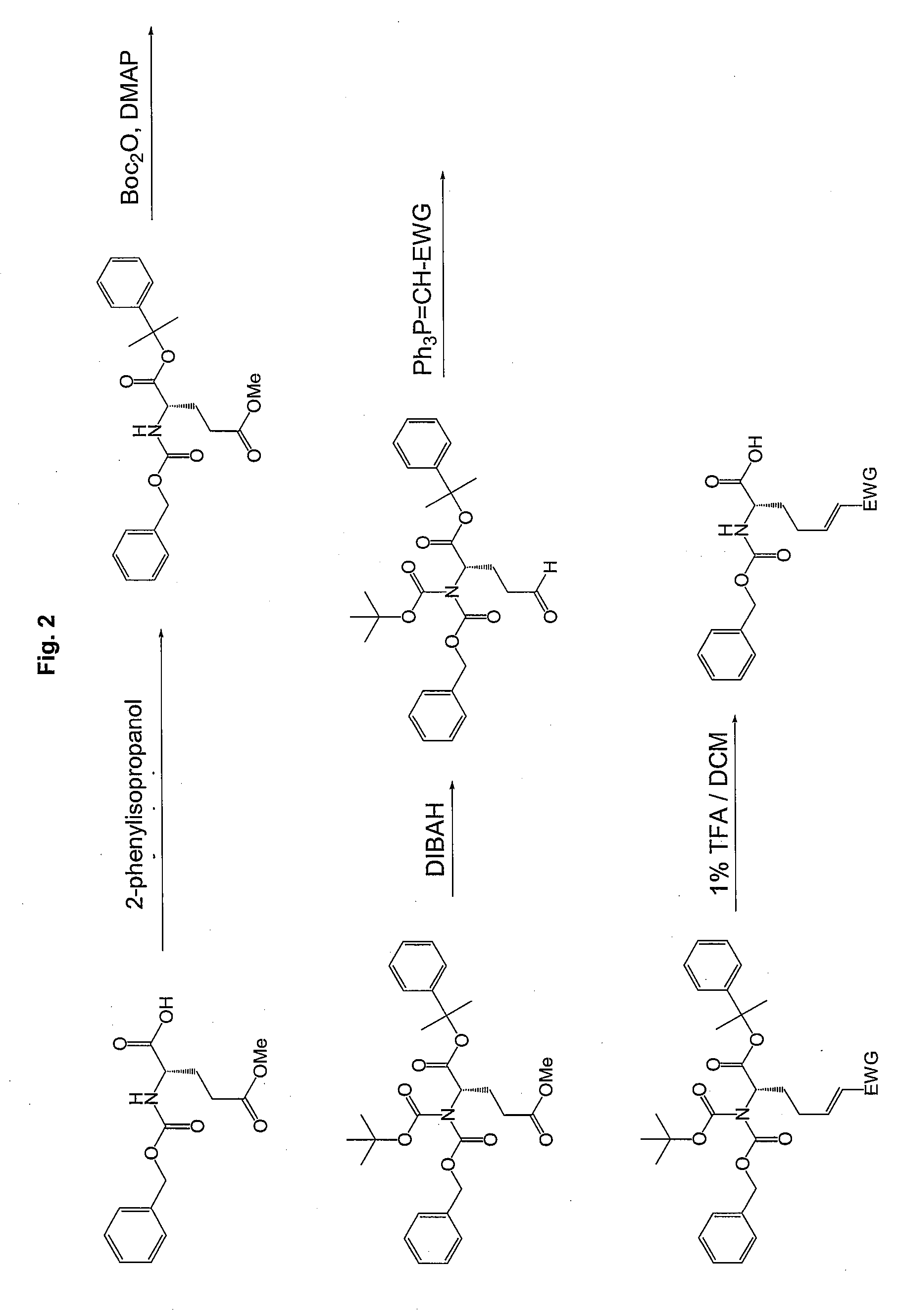
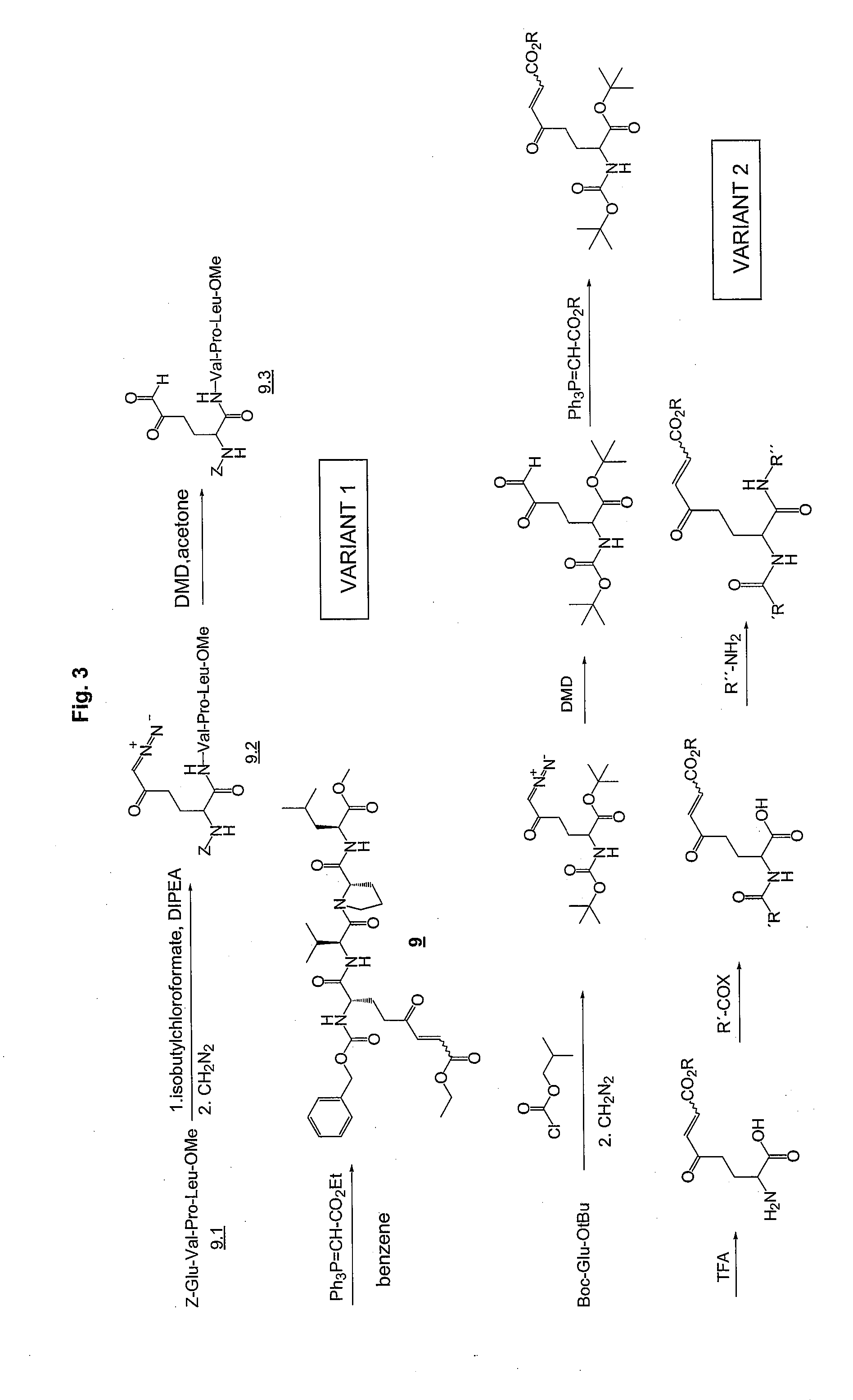
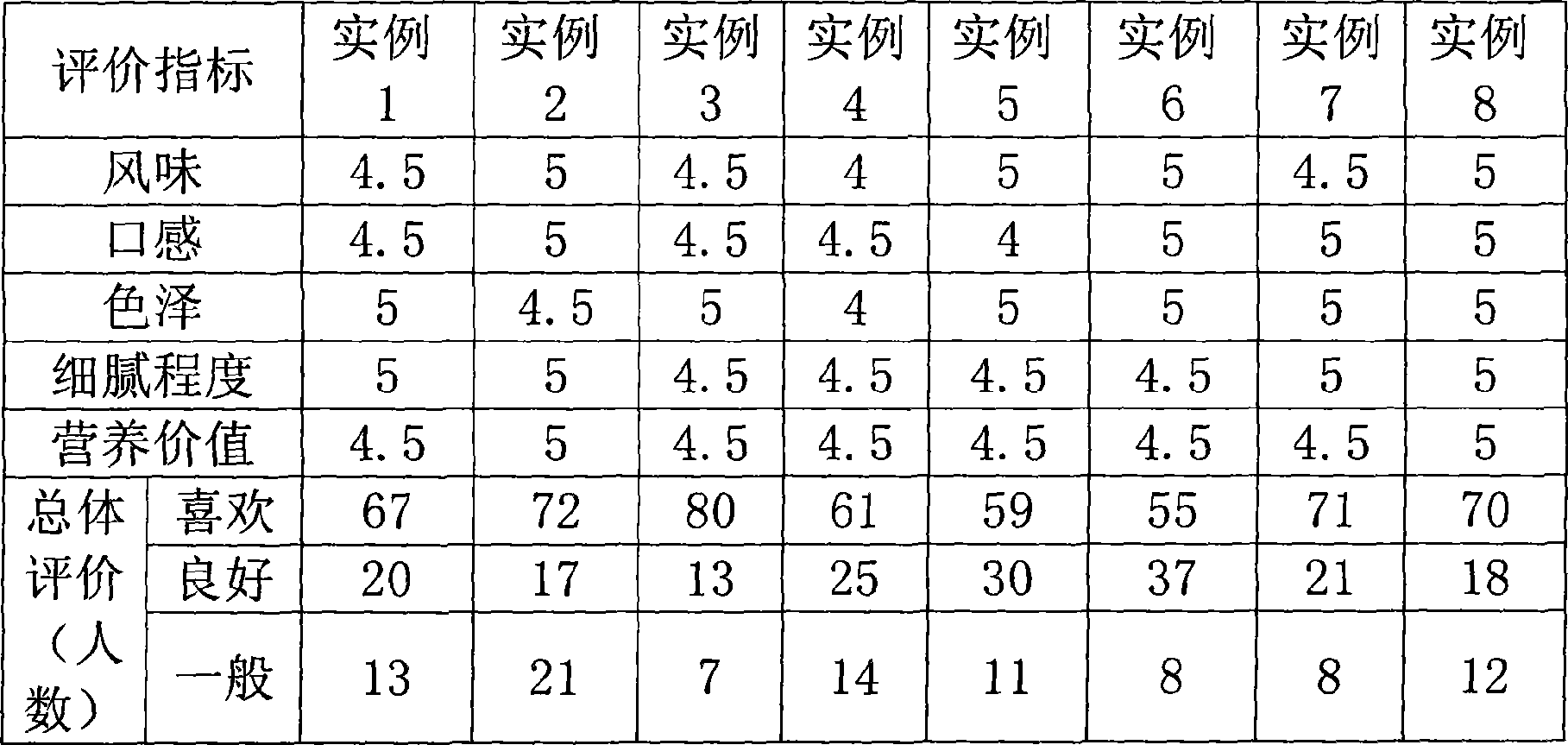
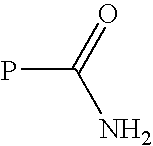
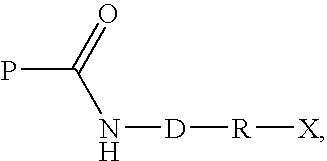
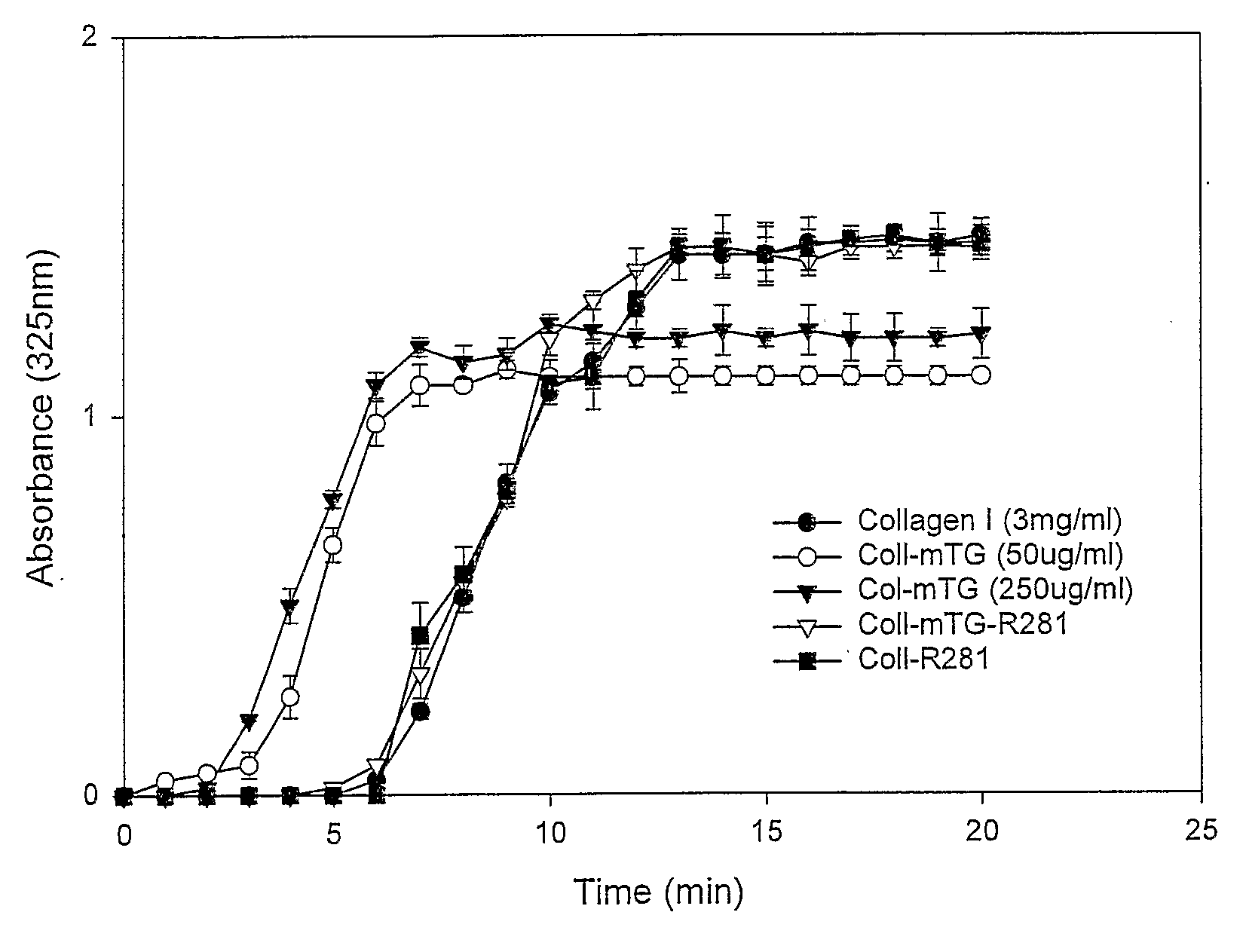
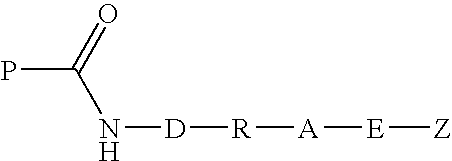Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
512 results about "Glutaminase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Glutaminase (EC 3.5.1.2, glutaminase I, L-glutaminase, glutamine aminohydrolase) is an amidohydrolase enzyme that generates glutamate from glutamine. Glutaminase has tissue-specific isoenzymes. Glutaminase has an important role in glial cells.
Compositions of hyaluronic acid and methods of use
InactiveUS20060094643A1Good curative effectLong lasting prophylacticBiocideSenses disorderDiseaseDrying mouth
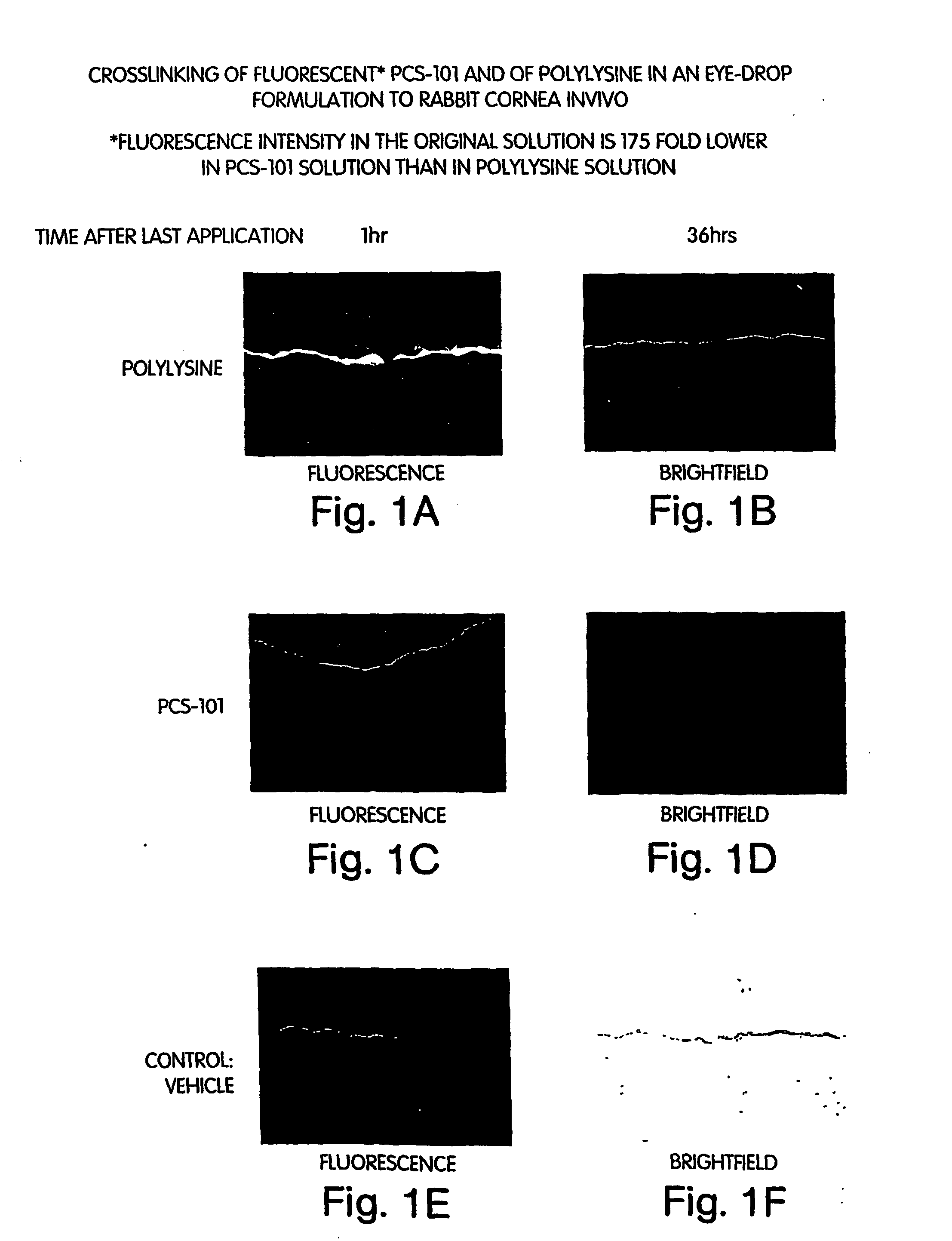
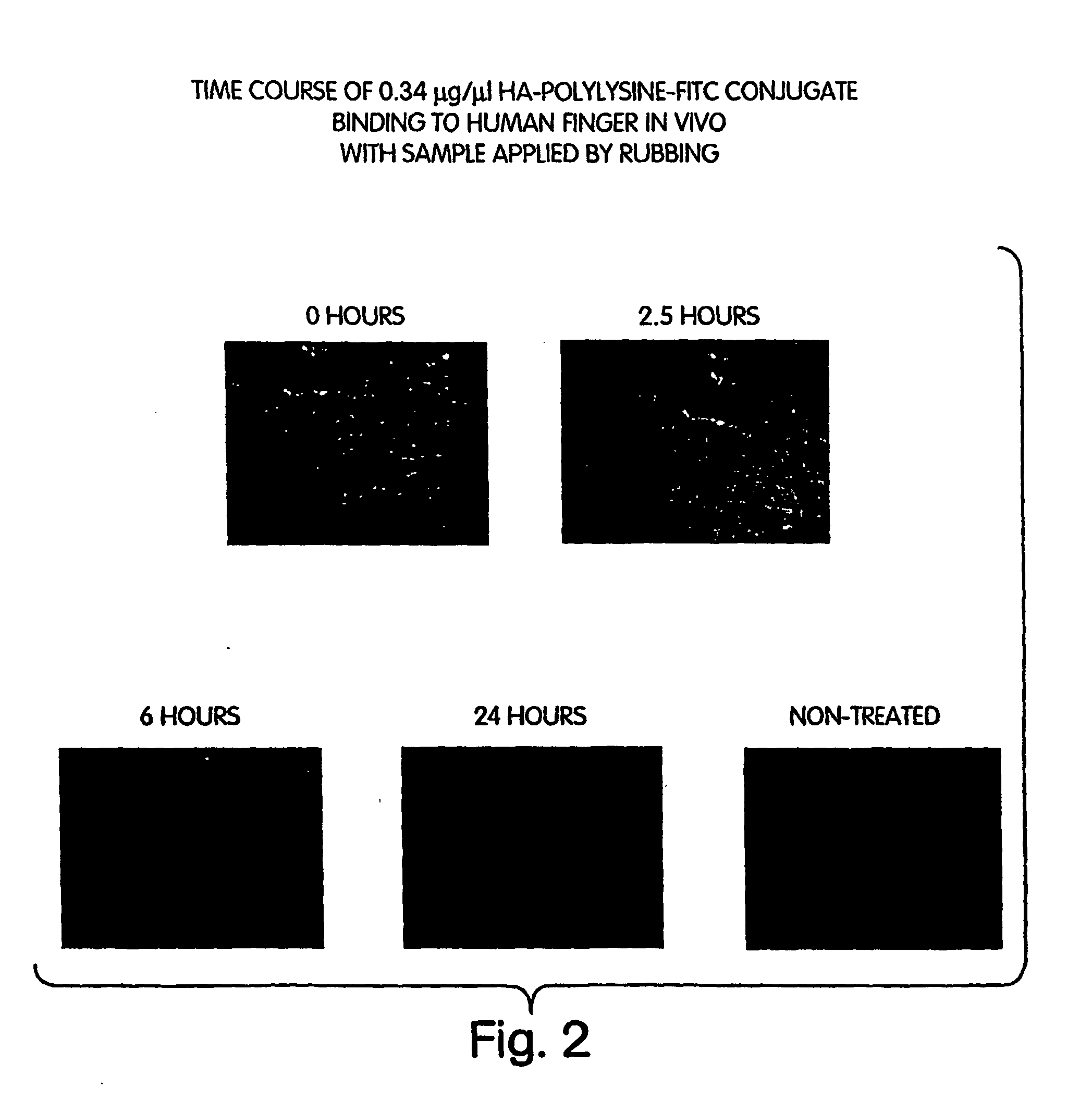
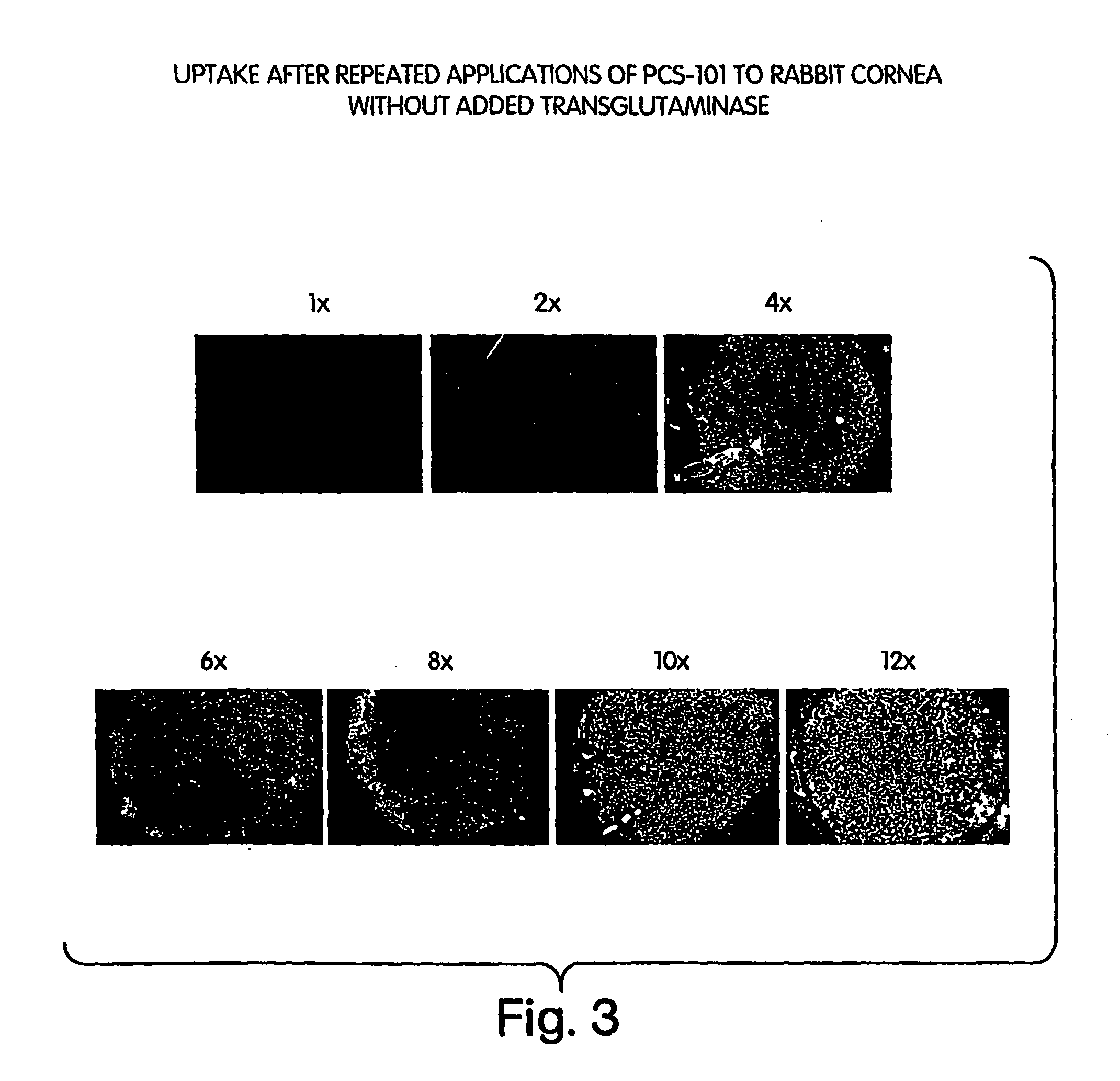
The invention provides compositions for the treatment of disorders characterized by dryness including dry eye and dry mouth. The compositions commonly comprise a conjugate of hyaluronic acid and polylysine. These conjugates are attached to affected body tissues or surfaces using transglutaminase, and preferably endogenous transglutaminase.
Owner:PERICOR SCI
Composition for stabilizing corneal tissue during or after orthokeratology lens wear
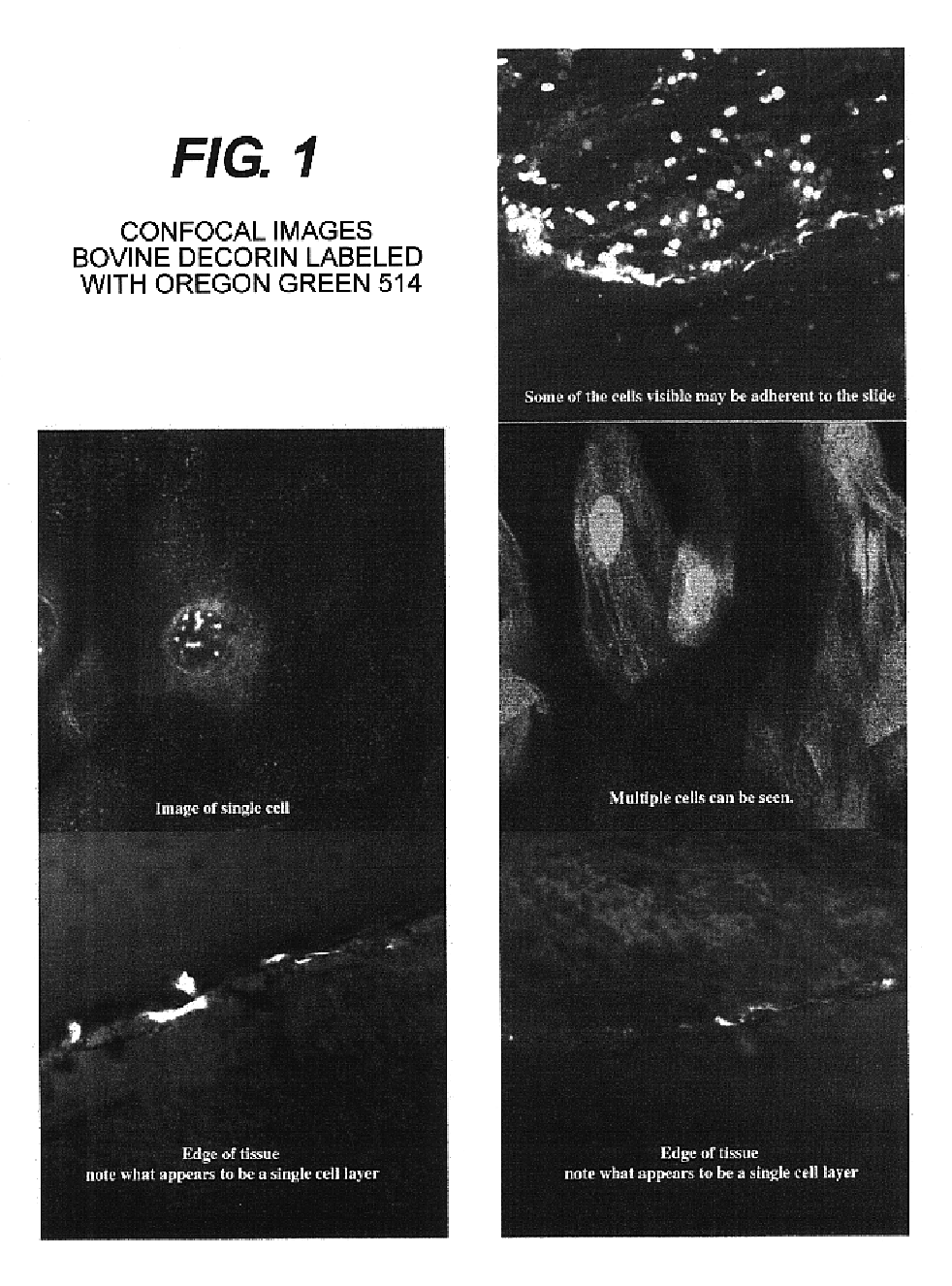
Two types of compositions having an eye-drop delivery system are used during or after an orthokeratology procedure to prevent or retard relaxation of corneal tissue back to the original anterior curvature of the cornea. Each composition functions independently from the others and is a different approach of preparing a stabilizing agent. The first composition is directed to a biologically compatible composition comprising fibril associated collagens with interrupted triple helices (FACITs) and / or small leucine-rich repeat proteoglycans (SLRPs). The fibril associated collagen family includes various types of collagens, such as type VI, type XX, type XII, and type XIV. The small leucine-rich repeat proteoglycans family includes decorin, keratocan, biglycan, epiphycan, lumican, mimecan, and fibromodulin. The second composition includes the enzyme found as a normal component of tissues, plasma, or epidermis, such as transglutaminase.
Owner:EUCLID SYST CORP +2
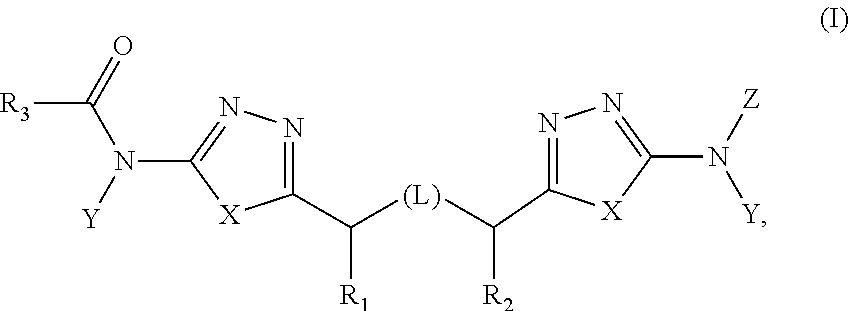
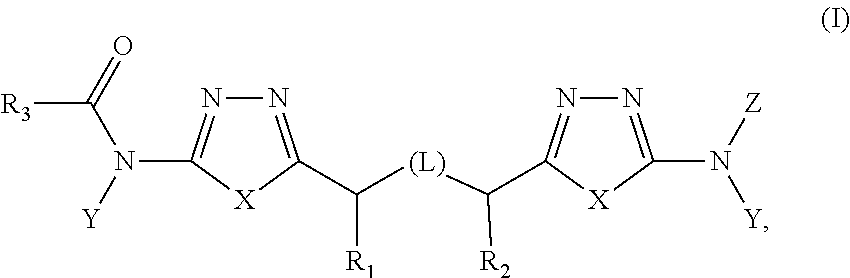
Heterocyclic inhibitors of glutaminase
Owner:CALITHERA BIOSCIENCES INC
G-csf site-specific mono-conjugates
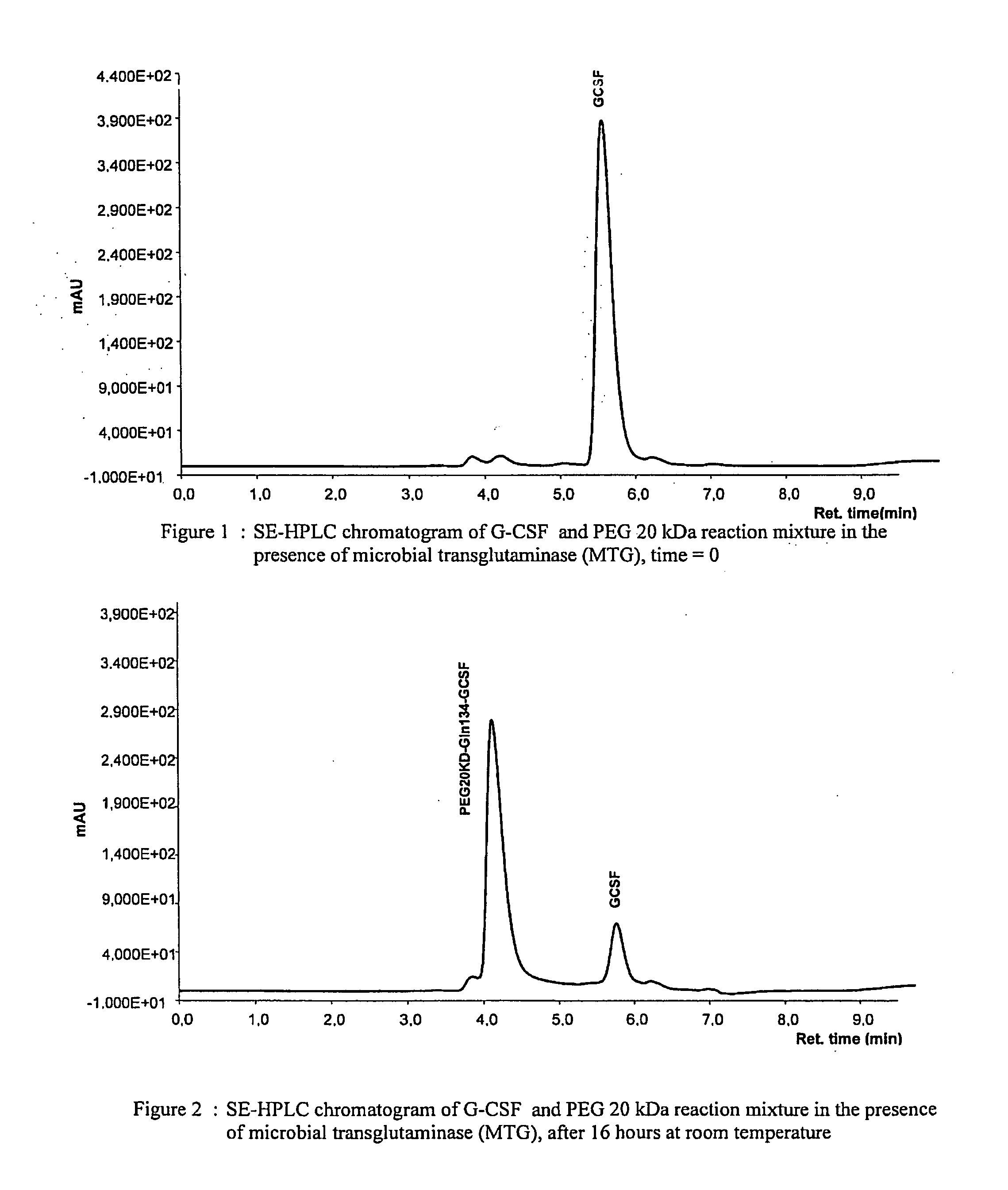
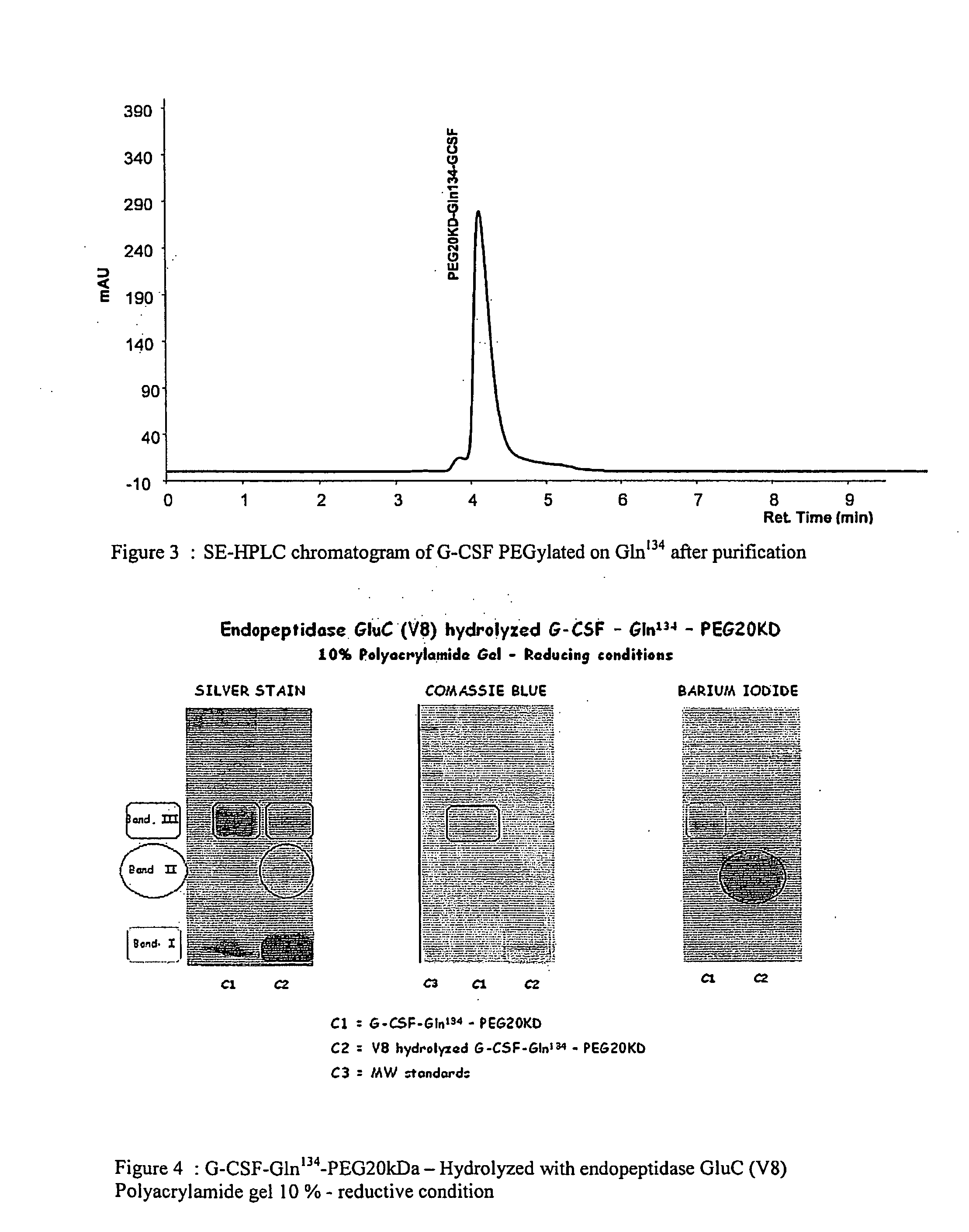
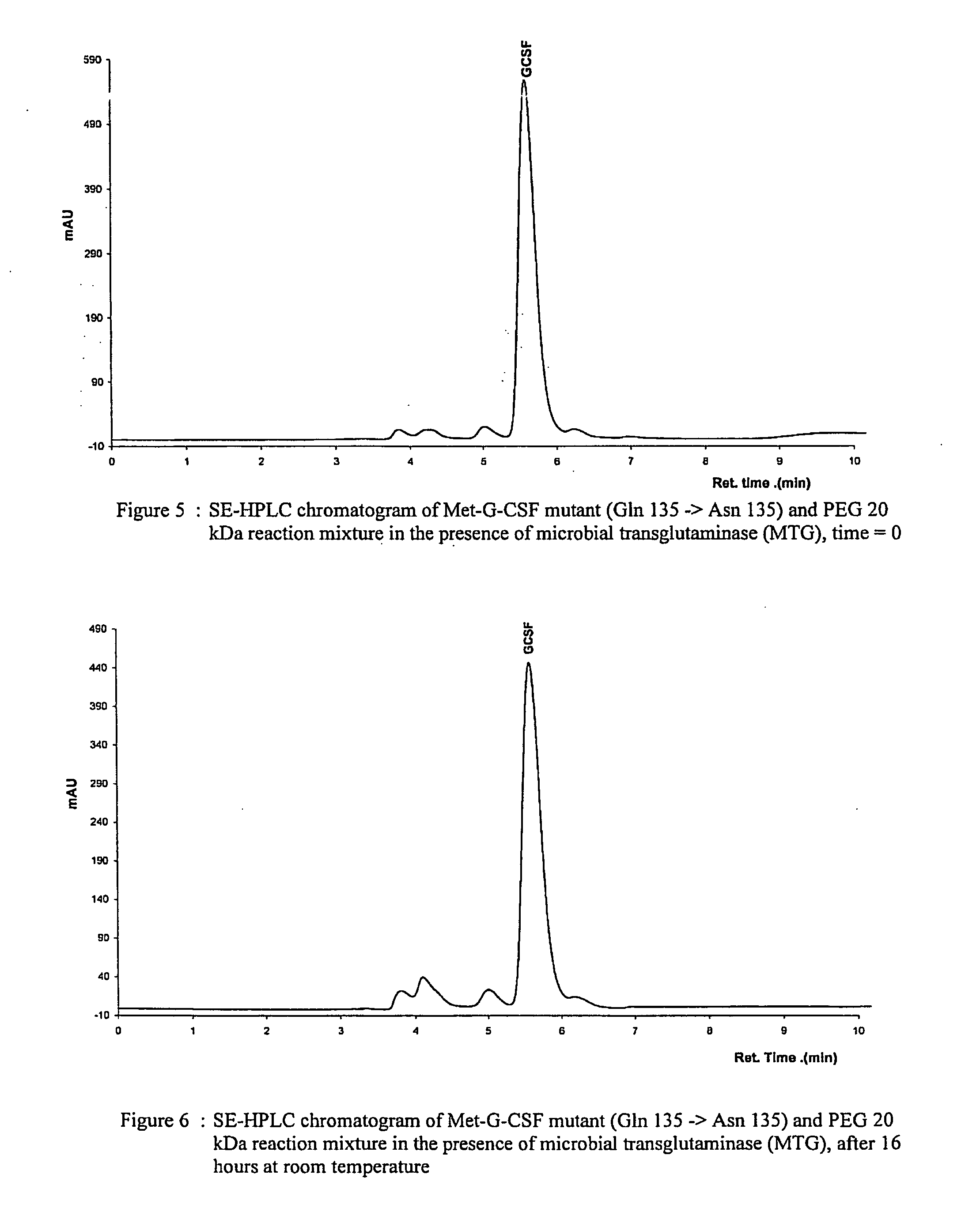
Novel site-specific mono-conjugates of Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) are hereby described, with analogues and derivatives thereof, which stimulate proliferation and differentiation of progenitor cells to mature neutrophiles. These conjugates have been obtained using transglutaminase to covalently and site-specifically bind a hydrophilic, non-immunogenic polymer to a single glutamine residue of the human G-CSF native sequence and analogues thereof. These novel site-specific mono-conjugated derivatives are recommended for therapeutic use since they are stable in solution and exhibit significant biological activity in vitro and a longer bloodstream half-life, as compared to the non-conjugated protein, with a consequent prolonged pharmacological activity.
Owner:BIO KER
Enzyme substrate for labeling of protein
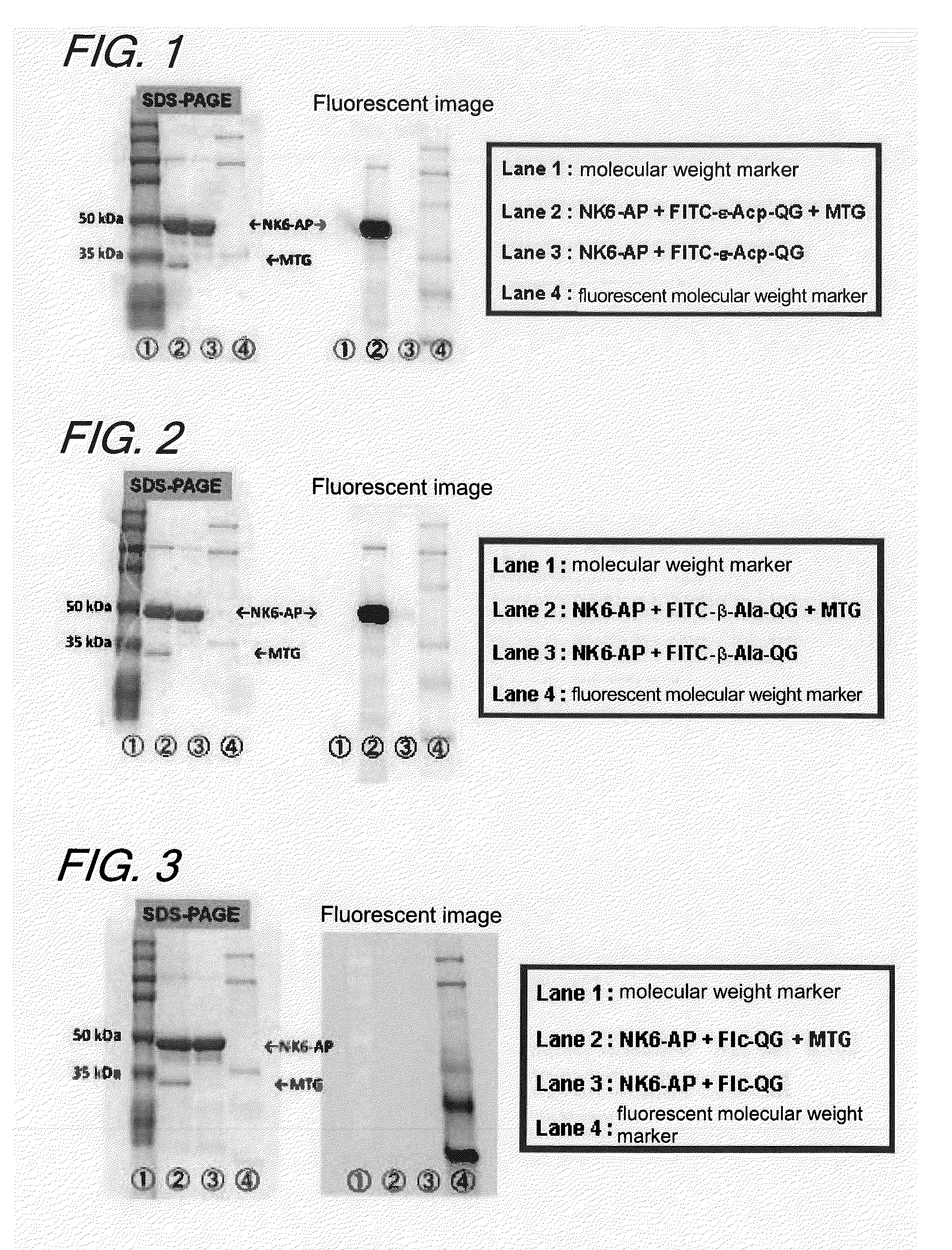
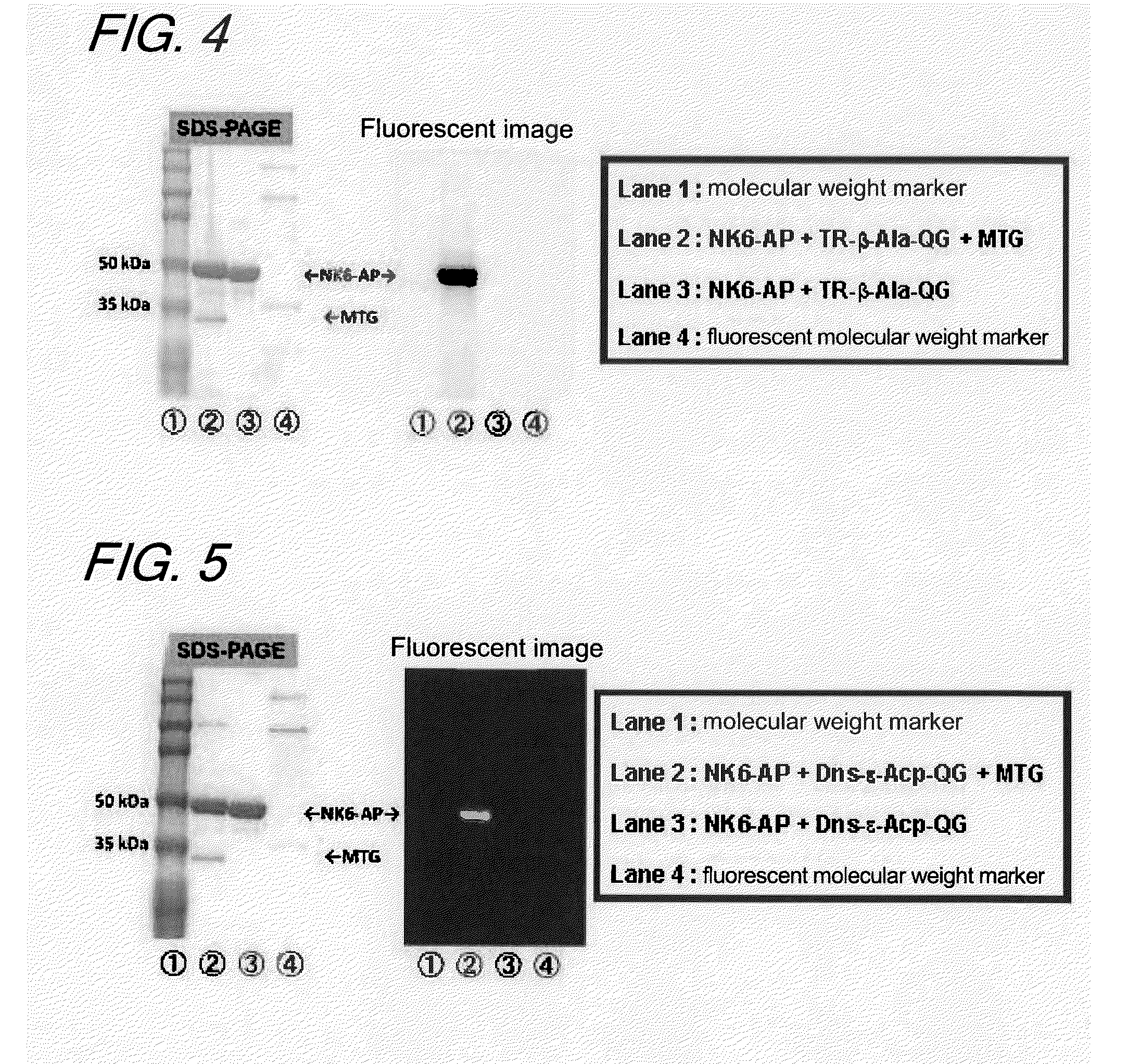
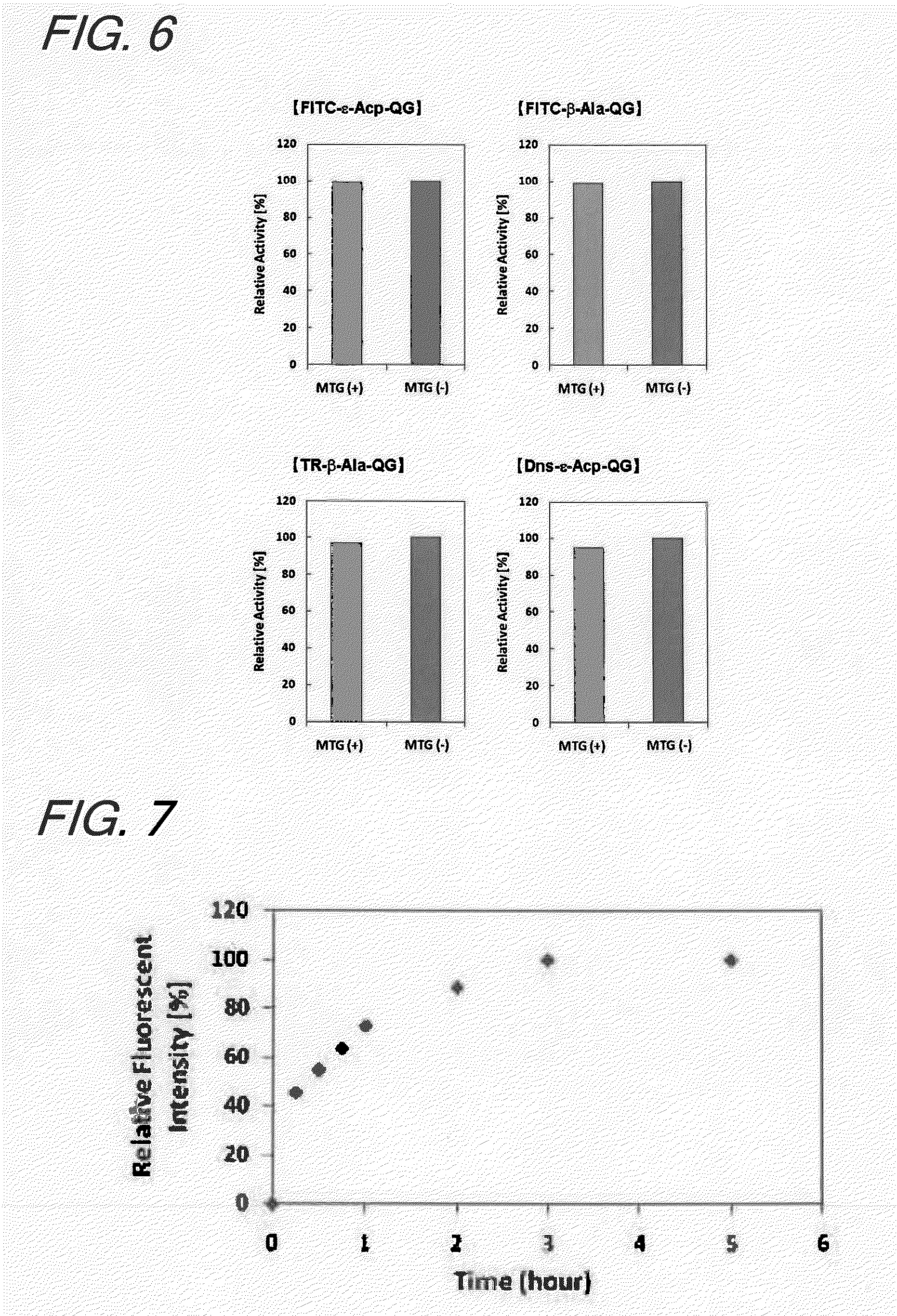
The present invention provides a substrate of TGase represented by (fluorescent group)-(linker)-(a portion containing a Gln residue capable of recognition by transglutaminase (TGase))-R, wherein the fluorescent group is fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC), Texas Red (TE) or dansyl (Dns) or a group derived therefrom; the linker is a group represented by —NH—(CH2)n—CO— (n is an integer of 1 to 6); the portion containing a Gln residue capable of recognition by TGase is a group derived from a peptide selected from among QG and the like; and R is a hydroxyl group, or biotin, nucleic acid, azide, alkyne, maleimide or cyclopentadiene, or a group derived therefrom.
Owner:KYUSHU UNIV
Heterocyclic inhibitors of glutaminase
Owner:CALITHERA BIOSCIENCES INC
Heterocyclic inhibitors of glutaminase
ActiveUS20140050699A1Ultrasound therapyHeavy metal active ingredientsGlutaminaseCombinatorial chemistry
Owner:CALITHERA BIOSCIENCES INC
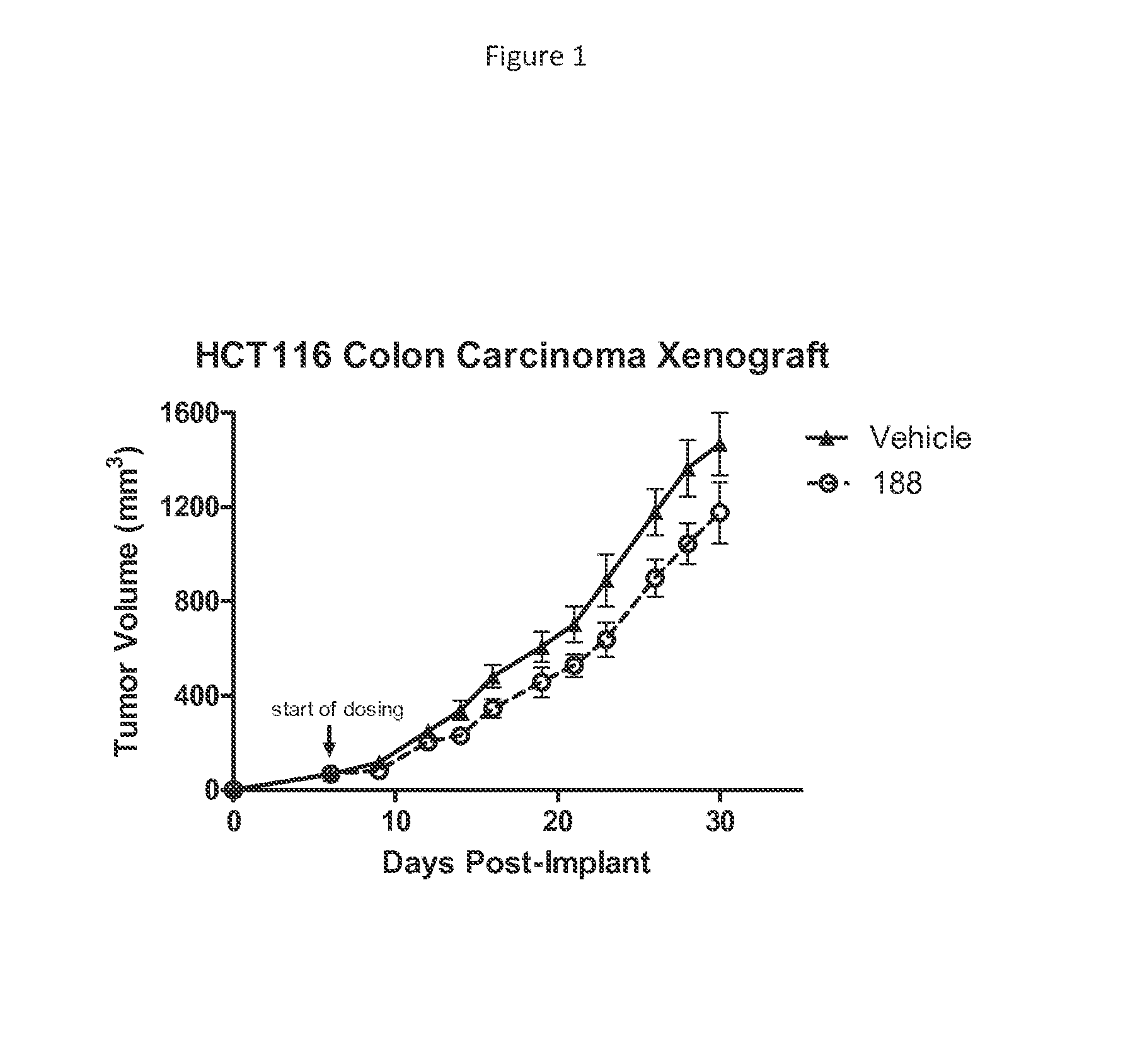
Treatment of cancer with heterocyclic inhibitors of glutaminase
InactiveUS20150004134A1Shrink tumorBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsGlutaminaseCombinatorial chemistry
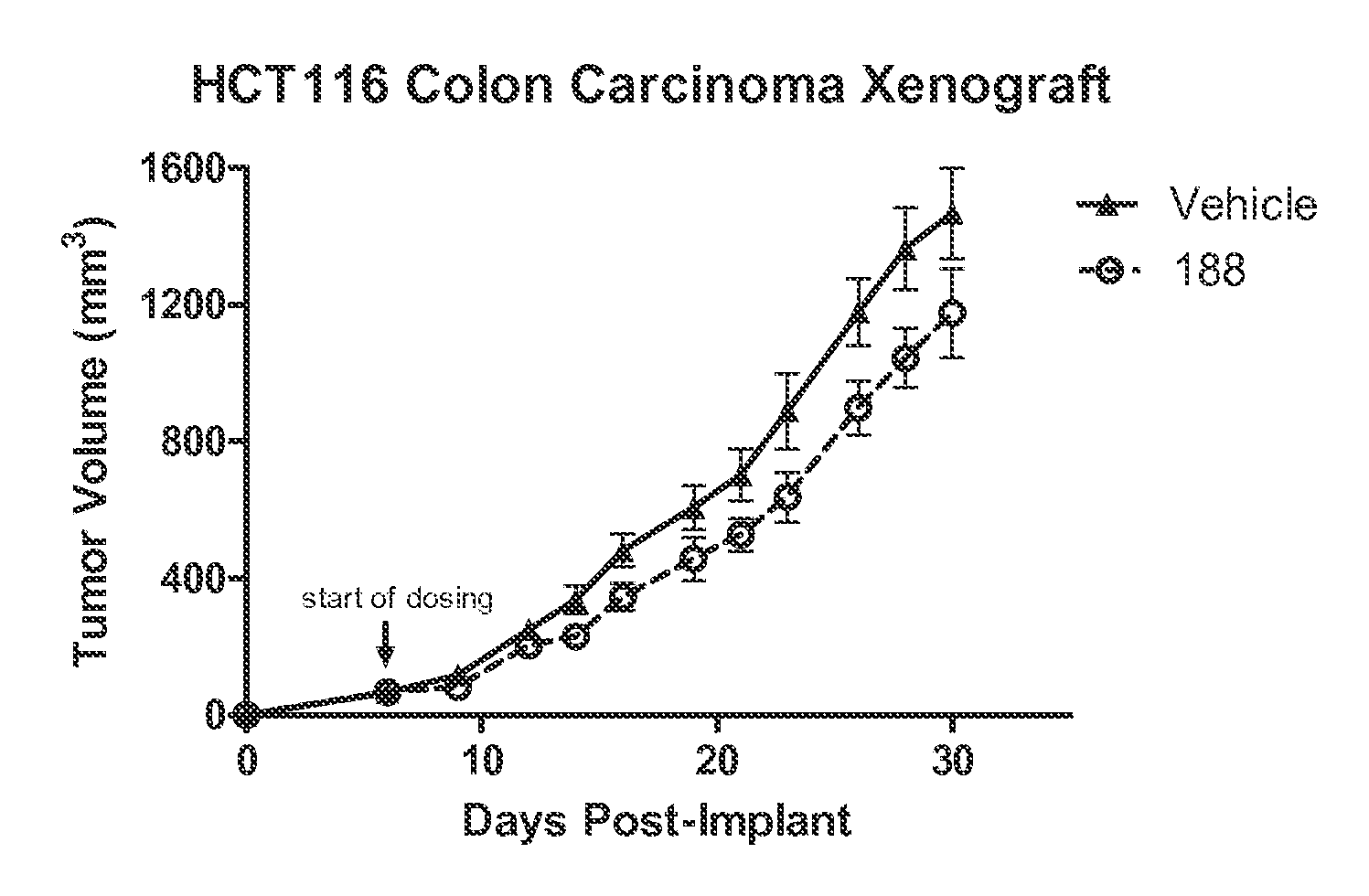
The invention relates to novel heterocyclic compounds and pharmaceutical preparations thereof. The invention further relates to methods of treating or preventing cancer using the novel heterocyclic compounds of the invention.
Owner:CALITHERA BIOSCIENCES INC
Methods for producing potato products
The present invention relates to methods for producing consumable products from potatoes, comprising: (a) treating a potato substance with an effective amount of one or more exogenous enzymes selected from the group consisting of an amyloglucosidase, glucose oxidase, laccase, lipase, maltogenic amylase, pectinase, pentosanase, protease, and transglutaminase, and (b) processing the enzyme-treated potato substance to produce a potato product. The invention also relates to consumable products obtained from potatoes by the methods of the present invention.
Owner:NOVO NORDISKBIOTECH INC
Heterocyclic glutaminase inhibitors
Owner:CALITHERA BIOSCIENCES INC
Gelatin-transglutaminase hemostatic dressings and sealants
An adhesive material for medical use comprising gelatin and a non-toxic cross-linking material such as transglutaminase. An optional embodiment of the invention includes dressings in which a layer of a transglutaminase is sandwiched between a first and second layer of gelatin. The hemostatic products are useful for the treatment of wounded tissue.
Owner:BARD SHANNON LTD
Edible packing membrane, and its preparing method and use
ActiveCN1743379ADoes not change appearanceNo change in flavorFood preparationNutritive valuesGenipin
The invention relates to food pachaging material, in particular edible packing film prepared from soybean protein isolate and glutin and its preparing method and use. The packing film is composed mainly of soybean protein isolate and glutin. Film solution for preparing the film is obtained by mixing two solutions of soybean protein isolate and glutin. The film solution contains soybean protein isolate, glutin, and further adding auxiliary haulages for improving film property, such as glycerin, crosslinking agnet (genipin,transglutaminase or alum), alkaline matter(sodium carbonate, sodium hydroxide).The film appearance is similar to plastic film, can be solved in 30-100deg.C water, and has certain nutritive value. The invention makes the best of advantage of glutin and soybean protein isolate, and obtains edible packing film with definite mechanical stength and low cost.
Owner:BAOTOU DONGBAO BIO TECH CO LTD
Engineered polypeptide conjugates and methods for making thereof using transglutaminase
ActiveUS9676871B2Improve bindingHybrid immunoglobulinsTripeptide ingredientsAntiendomysial antibodiesBispecific antibody
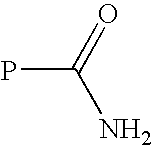
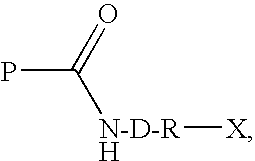
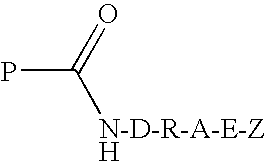
The present invention provides engineered polypeptide conjugates (e.g., antibody-drug-conjugates, toxin-(biocompatible polymer) conjugates, antibody-(biocompatible polymer) conjugates, and bispecific antibodies) comprising acyl donor glutamine-containing tags and amine donor agents. In one aspect, the invention provides an engineered Fc-containing polypeptide conjugate comprising the formula (Fc-containing polypeptide)-T-A, wherein T is an acyl donor glutamine-containing tag engineered at a specific site or comprises an endogenous glutamine made reactive by the Fc-containing polypeptide engineering, wherein A is an amine donor agent, and wherein the amine donor agent is site-specifically conjugated to the acyl donor glutamine-containing tag or the endogenous glutamine. The invention also provides methods of making engineered polypeptide conjugates using transglutaminase.
Owner:PFIZER INC RINAT NEUROSCIENCE CORP
Transglutaminase Mediated Conjugation of Peptides
InactiveUS20090264366A1Strong specificityImprove solubilityHormone peptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsChemical compoundGlutaminase
Methods for conjugating peptides are provided comprising i) reacting a peptide with a first compound comprising a functional group in the presence of a transglutaminase capable of incorporating said compound into the peptide to form a transaminated peptide, and ii) reacting said transaminated peptide with e.g. a functionalized polymer capable of reacting with the functional group incorporated in the peptide in the enzymatic reaction.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK HEALTH CARE AG
Recombinant bacillus subtilis and method for producing transglutaminase by utilizing recombinant bacillus substilis
InactiveCN102586167AReduce breakageSimplify the fermentation production processBacteriaTransferasesStreptoverticillium mobaraenseGlutaminase
The invention discloses a recombinant bacillus subtilis and a method for producing transglutaminase by utilizing the recombinant bacillus substilis. The recombinant bacillus subtilis is obtained by the following steps of: (1) by virtue of fusion PCR (polymerase chain reaction), connecting a P43 promoter and a signal peptide gene with a subtilisin-like protease gene, and converting a fusion PCR amplification product into bacillus subtilis WB800 to obtain bacillus subtilis B.subtilis WB800S; and (2) carrying out PCR amplification on streptoverticillium mobaraense transglutaminase protogene, andthen converting amplification product into the bacillus subtilis B.subtilis WB800S to obtain bacillus subtilis B.subtilis WB800S / proMTG. The bacillus subtilis B.subtilis WB800S / proMTG is fermented and purified to obtain soluble transglutaminase. By adopting the method disclosed by the invention, the transglutaminase with biological activity can be directly obtained in supernatant of fermentation liquor, fussy processes of breaking cells and activating proenzyme after purification are eliminated, and a fermentation production process is simplified.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH +1
Transglutaminase for inhibiting angiogenesis
InactiveUS7704943B2Improve stabilityExtend your lifeSenses disorderHydrolasesTissue transglutaminaseAngiogenesis growth factor
The present invention relates to use of a transglutaminase in the preparation of a medicament for inhibiting angiogenesis. Preferably, the transglutaminase is a human tissue transglutaminase. Advantageously, the medicament is for treating cancer, rheumatoid arthritis, retinopathy and / or psoriasis. Additionally, the invention relates to compositions comprising a transglutaminase in an amount sufficient to inhibit angiogenesis.
Owner:ASTON UNIV
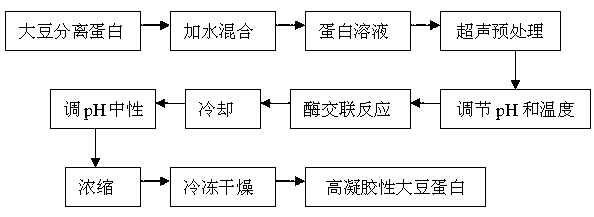
Preparation method of high-gelation soybean protein
InactiveCN102934731AReduce dosageImprove gel performanceVegetable proteins working-upProtein solutionFreeze-drying
The invention relates to a preparation method of a high-gelation soybean protein, and belongs to the technical field of soybean protein processing. The method comprises the following steps: (1) mixing soybean protein isolate and water to obtain a protein solution, and performing ultrasound preprocessing on the protein solution; and (2) adjusting the pH and temperature of the protein solution subjected to ultrasound preprocessing in the step (1), adding transglutaminase for cross linking reaction, cooling the product after cross linkage to room temperature, and then concentrating and freeze drying to obtain the high-gelation soybean protein. The method has the beneficial effects that the needed equipment is simple and safe to operate; the enzyme needed in production is small in amount, short in enzymolysis time, low in cost and environmentally-friendly; the obtained soybean protein is high in gel strength, and meanwhile the gel stability is good; and the application range of the soybean protein in foodstuff is expanded.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Hemostatic materials and dressing
ActiveUS8133484B2Unwanted immune responseHigh allergenicitySurgical adhesivesPeptide/protein ingredientsCross-linkGlutaminase
Owner:BARD SHANNON LTD
Transglutaminase soy fish and meat products and analogs thereof
This invention relates to a transglutaminase-coupled vegetable protein composition and a process for preparing said composition. Further, this invention relates to soy fish and meat products and analogs thereof and a process for making the same.
Owner:SOLAE LLC
Biological modifying and recombinant human growth hormone compound and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN1528787AEasy to maintain biological activityImprove biostabilityCarrier-bound/immobilised peptidesGrowth hormonesMonomethoxypolyethylene glycolHalf-life
The invention is a bio-modified recombinant growth hormone (rhGH) complex and preparing method, making glutamine residue-containing rhGH react with amino donor polyethylene glycol alkyl amine PEG or monomethoxypolyethylene glycol (mPEG) under the catalysis of transglutaminase (mTG), to make acylamide in gamma-bit of the glutamine residue and amino in primary amine bit of the amino donor form an amido bond, thus obtaining it, namely PEG-rhGH or Mpeg-rhGH. It has high biostability and long in vivo half life, applied to prepare permanent injection drugs or develop oral drugs.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
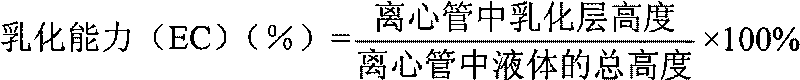
Preparation method of emulsified stable type soy isolate protein
InactiveCN102578365AImprove emulsion stabilityHigh activityVegetable proteins working-upProtein solutionFreeze-drying
The invention relates to a preparation method of emulsified stable type soy isolate protein and belongs to the field of process technology of soy protein. The preparation method comprises the main steps as follows: preparing a soy isolate protein solution with the ratio of deionized water to soy isolate protein used as a raw material being (5-25):1 w / w; fully hydrating, and then stirring and preheating at 40-60 DEG C; regulating pH to be 6.5-7.5; adding papain for enzymolysis to obtain a sample of different hydrolysis degrees; then killing enzyme for 5 min at 90 DEG C; cooling to room temperature; regulating pH to be neutral; centrifuging; taking supernate to carry out freeze drying or spray drying; preparing a sample solution with the ratio of deionized water to the sample of different hydrolysis degrees being (5-25):1 w / w; preheating at 30-50 DEG C; regulating pH to be 7.0; adding transglutaminase to start crosslinking; after 1h, heating for 5 min at 80 DEG C to inactivate the enzyme; cooling to room temperature; then regulating pH to be neutral; centrifuging; taking supernate; and performing freeze drying or spray drying to obtain the highly emulsified stable type soy isolate protein. The preparation method for the emulsified stable type soy isolate protein is economic and effective; and the emulsion stability of the soy protein is remarkably improved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Preparation method for improving gel hardness of fish balls
The invention relates to a preparation method for improving the gel hardness of fish balls, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of: separating fish meat by using a meat separator, removing fish bones and black films, putting fish fillets into 5 to 8 percent salt solution and soaking for 20 to 40 minutes with continuous stirring; putting the fish meat from which fishy smell is removed into clear water in an amount which is 4 to 6 times that of fish meat, slowly stirring for 8 to 10 minutes, repeatedly washing by using circulating water, dissolving 2 to 4 percent of salt in water, adding into minced fillets, milling for 2 to 4 minutes, adding 0.1 to 0.6 percent of transglutaminase (TGase), milling for 6 to 10 minutes, adding seasonings into the minced fillets, and milling for 1 to 4 minutes; adding 3 to 6 percent of wheat gluten into the minced fillets, and milling for 2 to 5 minutes; putting the minced fillets into a 0 DEG C refrigerator for 1 to 3 hours, forming by using a ball making machine, and ensuring that the weight of each ball is 7 to 15g; and heating the fish balls to the temperature of between 37 and 45 DEG C, keeping for 15 to 25 minutes, putting into a 70 to 85 DEG C water bath for 20 to 30 minutes, fishing out, quickly cooling, quickly freezing, and packaging. The fish balls prepared by the method have smooth and mellow appearance, smooth mouthfeel, high elasticity and rich nutrition.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Michael systems as transglutaminase inhibitors
ActiveUS20110229568A1High activityHigh selectivityOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderCombinatorial chemistryCoeliac disease
Described herein are peptide derivatives and peptidomimetics as inhibitors for transglutaminases, methods for their preparation, pharmaceutical compositions containing said compounds as well as uses of said transglutaminase inhibitors in particular for the treatment of coeliac disease and transglutaminase dependent diseases.
Owner:ZEDIRA GMBH
Instant cheese and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to an instant cheese and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps: using full-cream fresh milk as main material, pasteurizing the milk after being hydrolyzed through lactase, and concentrating the full-cream fresh milk to 35-40 percent of the original volume in vacuum. The preparation method of the instant cheese has the core points that transglutaminase is added at 35 DEG C, and milk proteins are linked to form a protein network under the action of the transglutaminase, thereby forming a uniform and stable gel system easily. Then, chymosin is added for promoting gel to form , and uniform, stable and delicate instant cheese can be obtained in a water bath for half hour at about 30 DEG C. The invention is simple and easy for operation, and can be used for development of various application products on the theoretical basis, including breakfast cereal cheese, jelly cheese and the like. Moreover, the instant cheese can meet the requirements of consumers for taste, texture, nutrition, and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Transglutaminase mediated conjugation of peptides
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Method for modification of rice protein and oryzenin with protein glutaminase
ActiveCN101861909AOvercome hydrolysisOvercoming the problem of partial denaturation of proteinsVegetable proteins working-upFreeze-dryingReaction temperature
The invention relates to a method for modification of rice protein and oryzenin with protein glutaminase, which comprises the following steps: adding the rice protein or oryzenin into a constant-temperature enzyme reactor with phosphate buffer solution while stirring to obtain protein dispersion solution with a certain substrate concentration; adding protein glutaminase to obtain a system with a certain proportion of enzyme and substrate, wherein the temperature of enzymatic reaction is 36-38 DEG C, the time of the enzymatic reaction is 0.1-48 hour(s), and the pH value of the enzymatic reaction is maintained 7.0; adding dialysis solution, i.e. acetic acid solution of 0.10mol / L, wherein the dialysis time is about 8 hours; and carrying out vacuum freeze-drying, thereby obtaining the product. The invention can improve the protein solubility of the rice protein or the oryzenin, and can also enhance the emulsification, foaming performance, gelation and other functional properties of the rice protein or the oryzenin.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Method for improving wool fire-retardancy with biological enzyme
InactiveCN101509193AConform to modern green environmental protection requirementsMild reaction conditionsBiochemical fibre treatmentAnimal fibresYarnBiotechnology
A method for improving flame retardance of wool by bioenzyme treatment is disclosed, belonging to the field of textile biotechnology. The invention utilizes a catalytic action of transglutaminase (MTG) to graft a type of compounds containing primary amino groups and a large number of phosphorus elements onto the wool so as to improve the flame retardance of the wool, the technological procedures comprise: pretreatment, treatment with a phosphoric finishing agent containing the MTG, water rinsing and drying. Wool yarns and fabrics treated by the inventive technology can not only be improved in the flame retardance, but also be enhanced in some other performances to a certain extent, in particularly the strength of the wool yarns and the fabrics is enhanced to play a role of powerful repair, which is outstandingly superior to other flame-retardant finishing agents or flame-retardant finishing technologies. In addition, in contrast to chemical finishing, the invention is healthier and more environmentally-friendly due to the employment of bioenzyme technique and the pollution-free treatment technology.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
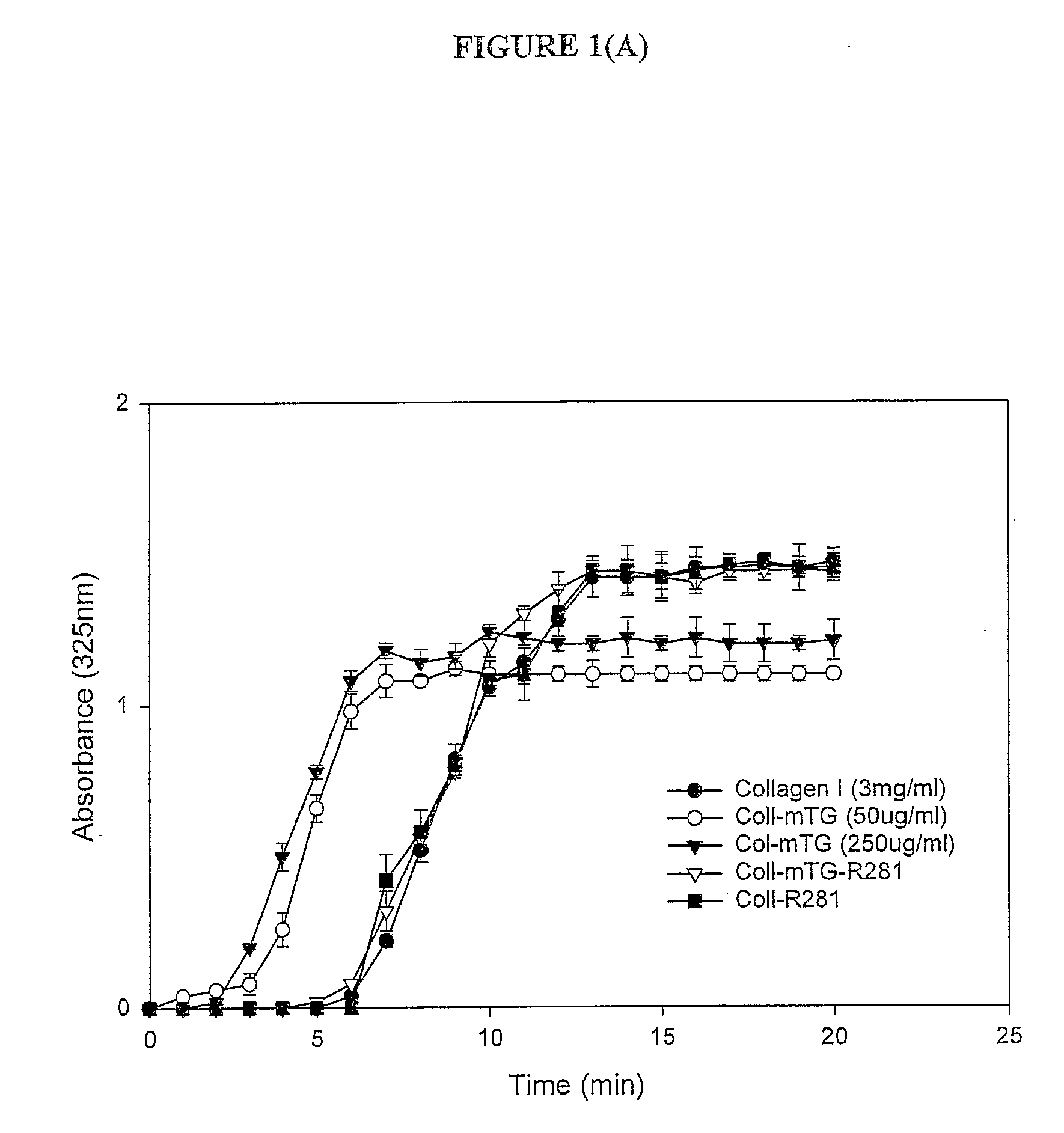
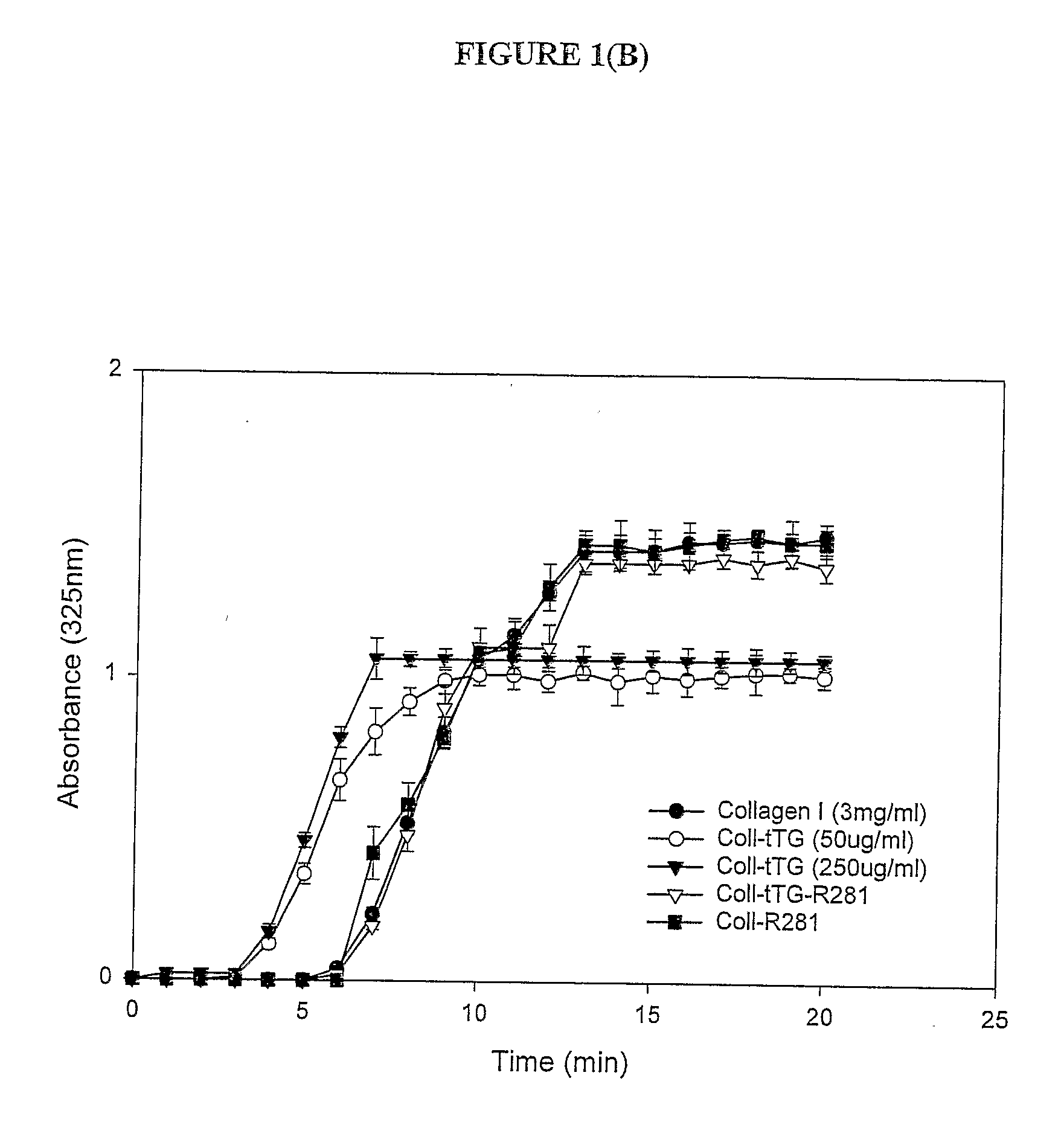
Transglutaminase Crosslinked Collagen Biomaterial for Medical Implant Materials
InactiveUS20080305517A1Enhanced ability to support cell attachment cellEnhanced ability to support attachmentBone implantTissue cultureCross-linkMicroorganism
The present invention provides a method for producing an improved biomaterial comprising treating a collagen biomaterial with a transglutaminase under conditions which permit the formation of cross-links within the collagen. Preferably, the transglutaminase is a tissue transglutaminase, a plasma transglutaminase or a microbial transglutaminase. In a preferred embodiment, the collagen biomaterial further comprises a cell adhesion factor, such as fibronectin. The invention further provides biomaterials obtainable by the methods of the invention, and medical implants and wound dressings comprising the same.
Owner:ASTON UNIV
Enzymatic-process method for improving emulsifying property and gelation property of pea protein
InactiveCN101703147AFunctional characteristics are not idealIncrease useVegetable proteins working-upFood industryPea protein
The invention provides an enzymatic-process method for improving emulsifying property and gelation property of pea protein, which belongs to the technical fields of agricultural-product deep processing and food industry. The invention relates to the modification of transglutaminase (also named glutamine transamine enzyme) to pea protein. The method takes pea protein as raw material and utilizes transglutaminase to modify the pea protein in different degrees so as to improve the emulsifying property and gelation property of the pea protein. A process of modifying the pea protein comprises the steps of mixing pulp, regulate pH, adding the transglutaminase, performing enzyme modification, concentrating, drying and obtaining modified pea protein. The method can obviously improve the emulsifying property and gelation property of the pea protein.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Edible protein/polysaccharide composite membrane and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105802249AWide variety of sourcesGood film formingFlexible coversWrappersCross-linkProtein solution
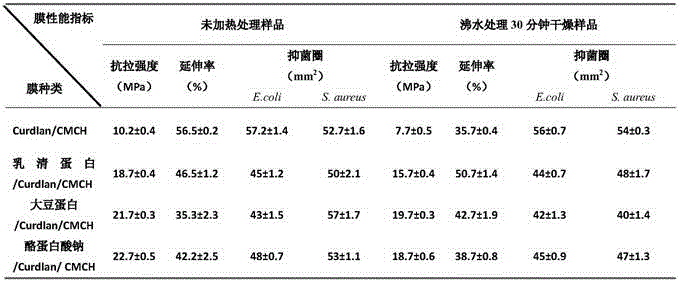
The invention discloses an edible protein / polysaccharide composite membrane and a preparation method and application thereof.The composite membrane is prepared through the method that a Curdlan solution, a carboxymethyl chitosan solution and plasticizer glycerinum are added into a protein solution including one of soybean protein, casein and whey protein, the pH value of the mixed liquid is adjusted to be 5-8; ultrasonic degassing is conducted, MTG is added, and membrane-forming liquid is acquired; the membrane-forming liquid is poured into a polyfluortetraethylene plate, a reaction is conducted for 30-60 minutes at the temperature of 55-65 DEG C, sizing and sterilization are conducted, 4-DEG C cooling is conducted for 10-20 minutes, drying is conducted under the conditions that RH is 30-50% and the temperature ranges from 20 DEG C to 30 DEG C, and then membrane uncovering is conducted.The heat stability of the membrane is improved by adding Curdlan into the common edible protein solution, chitosan is added so that the membrane can have the antibacterial performance, microorganism source transglutaminase is added to catalyze the protein and cross linking between the protein and chitosan, and the chemical performance of the membrane is improved.
Owner:TAIXING DONGSHENG FOOD TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com