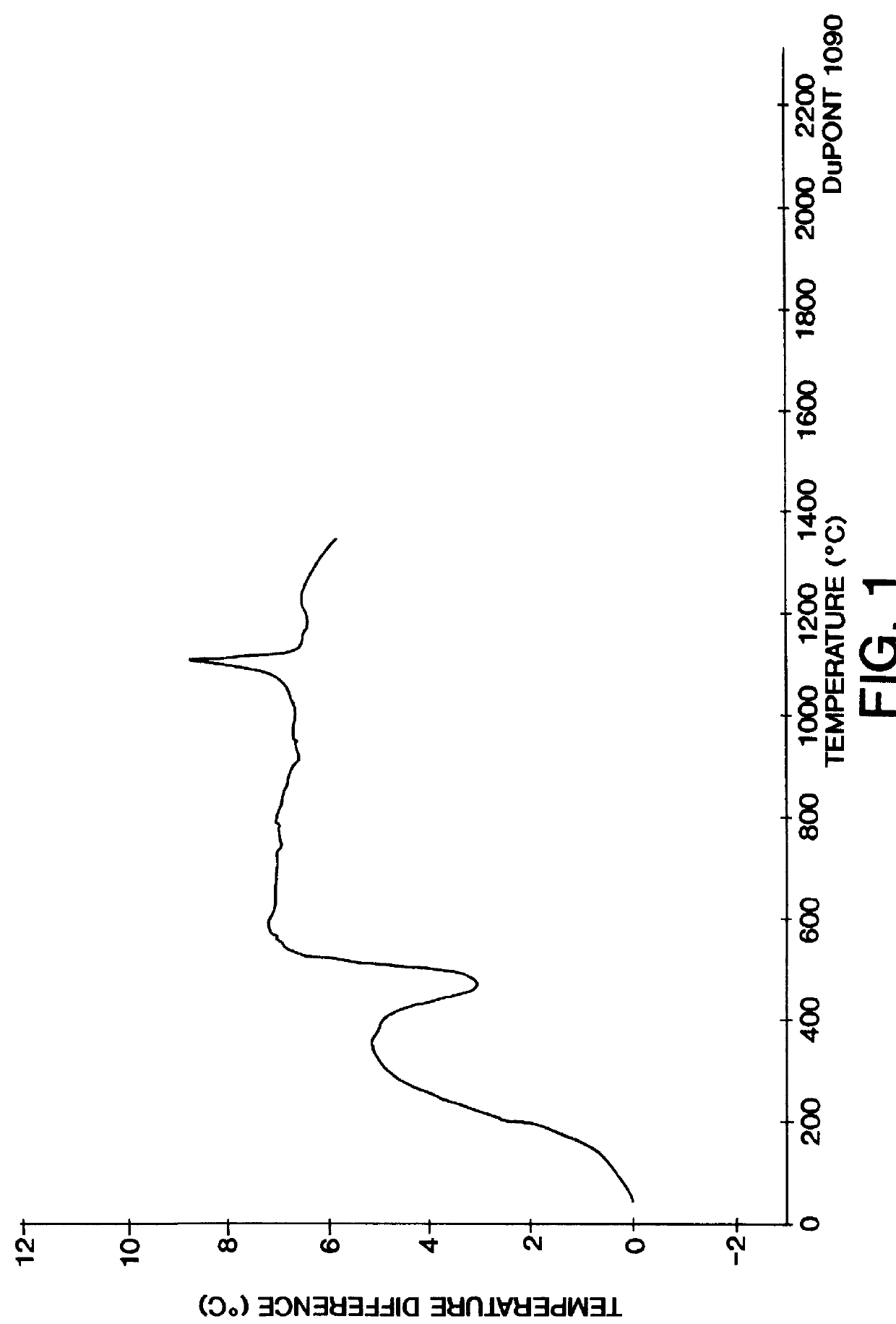
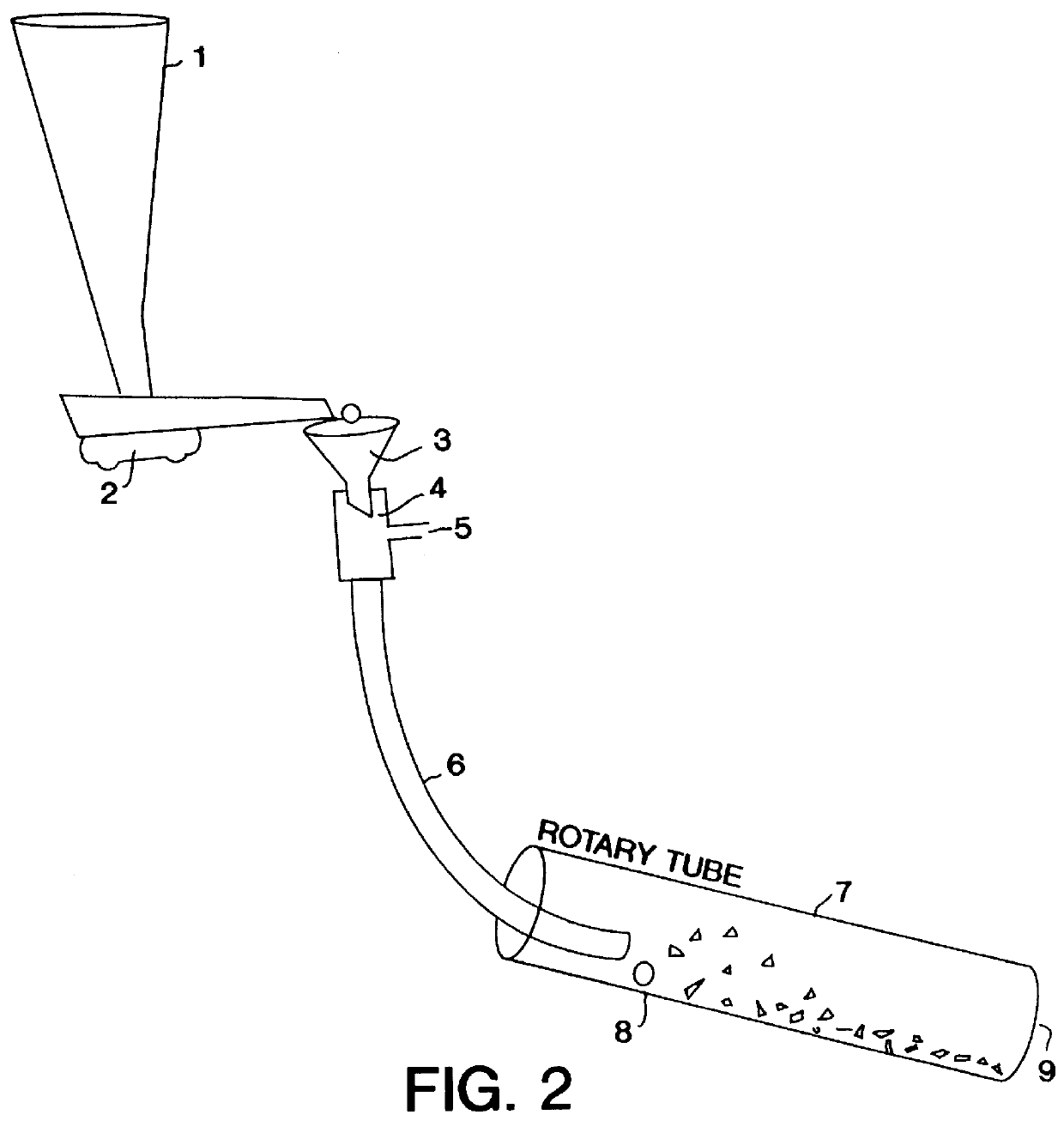
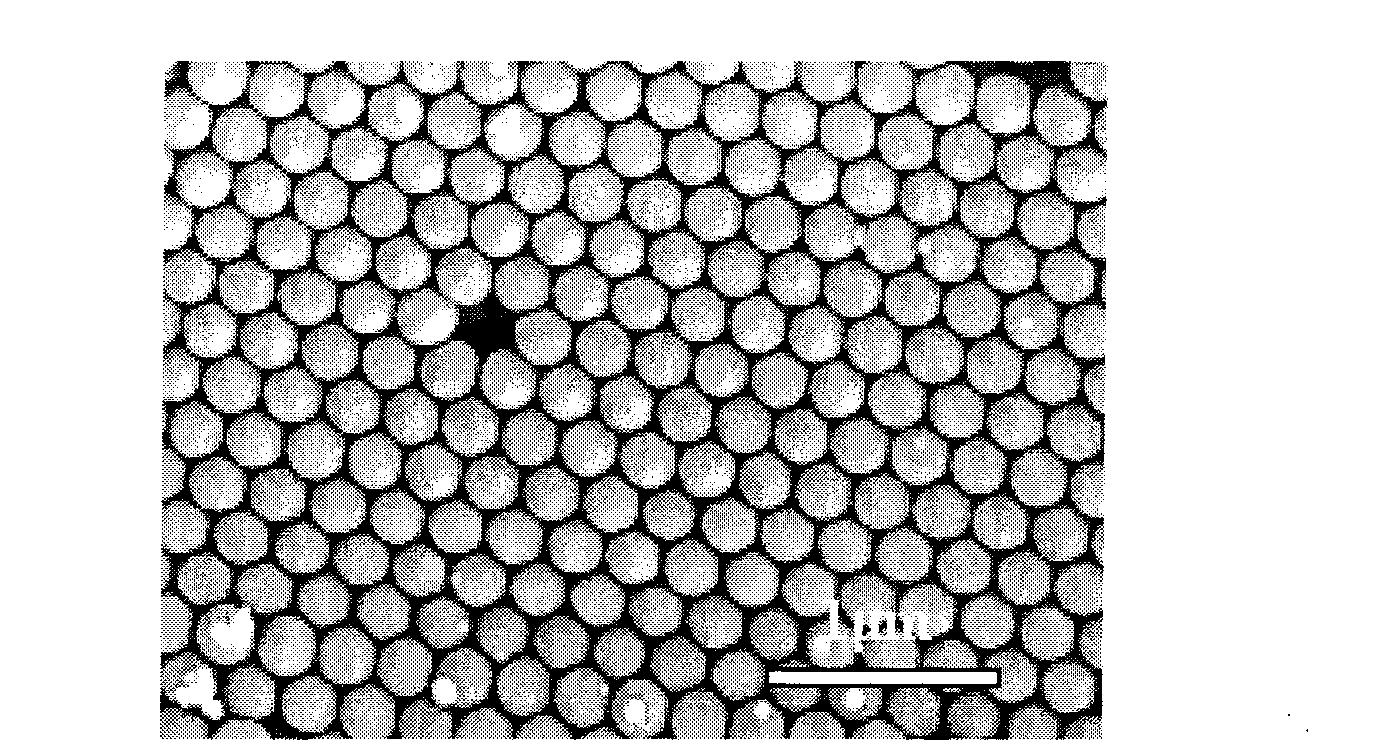
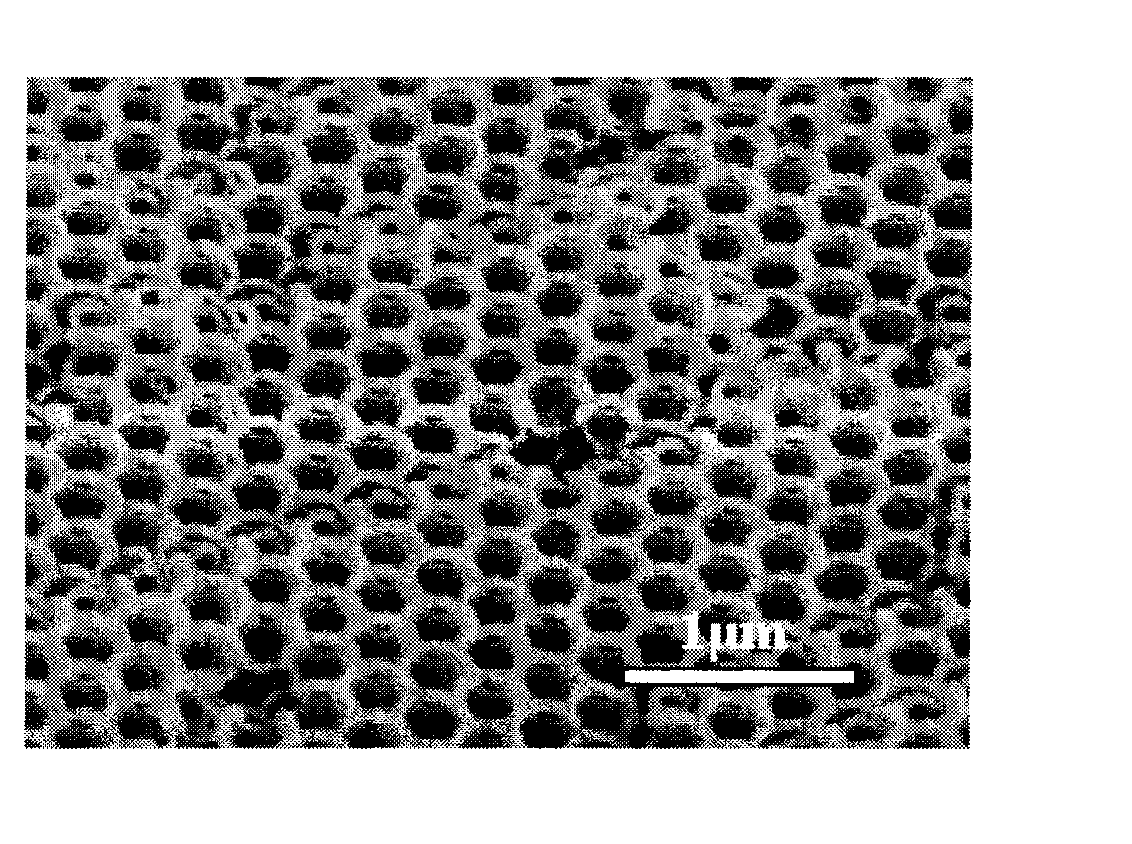
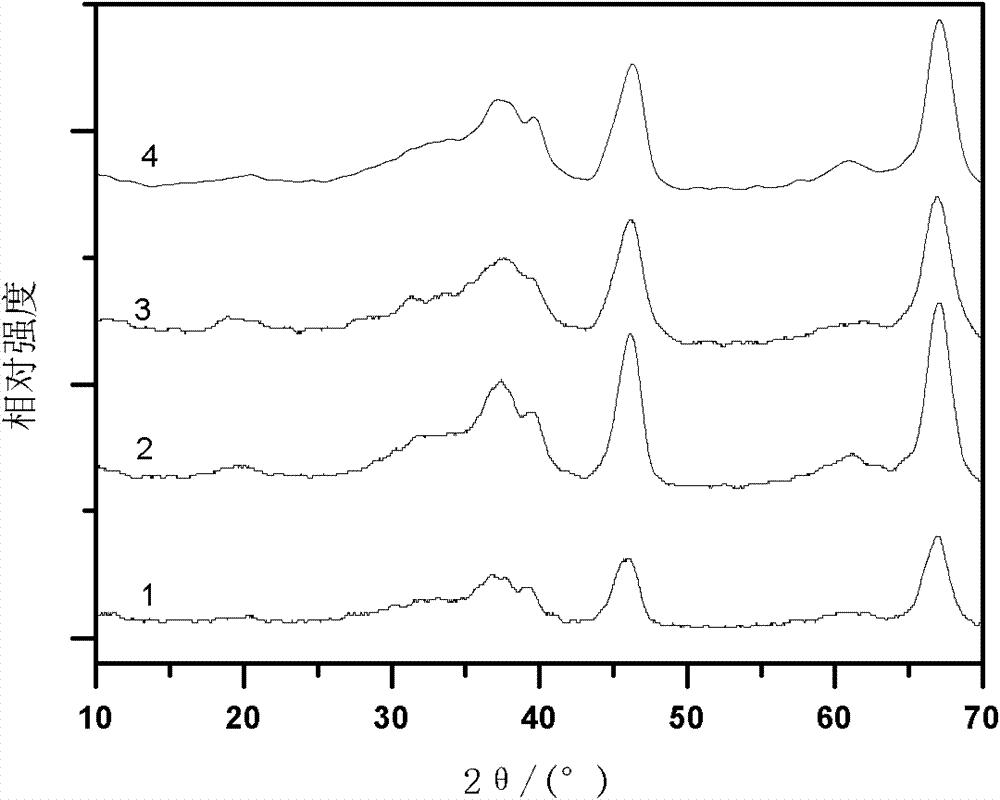
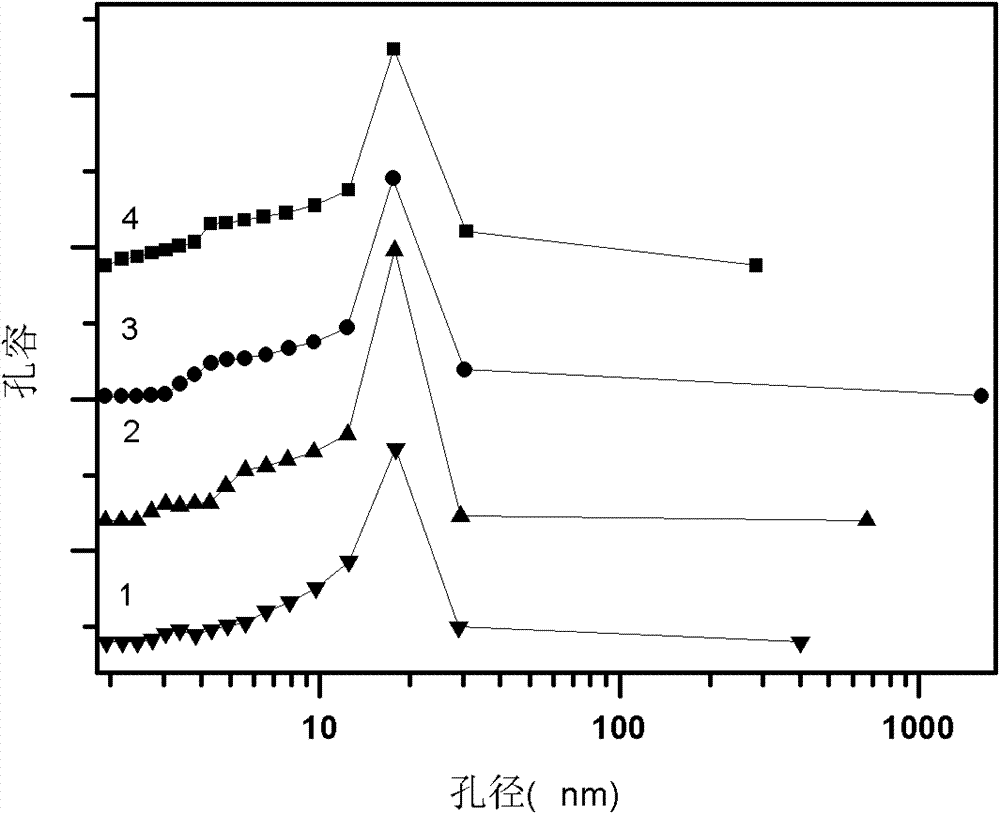
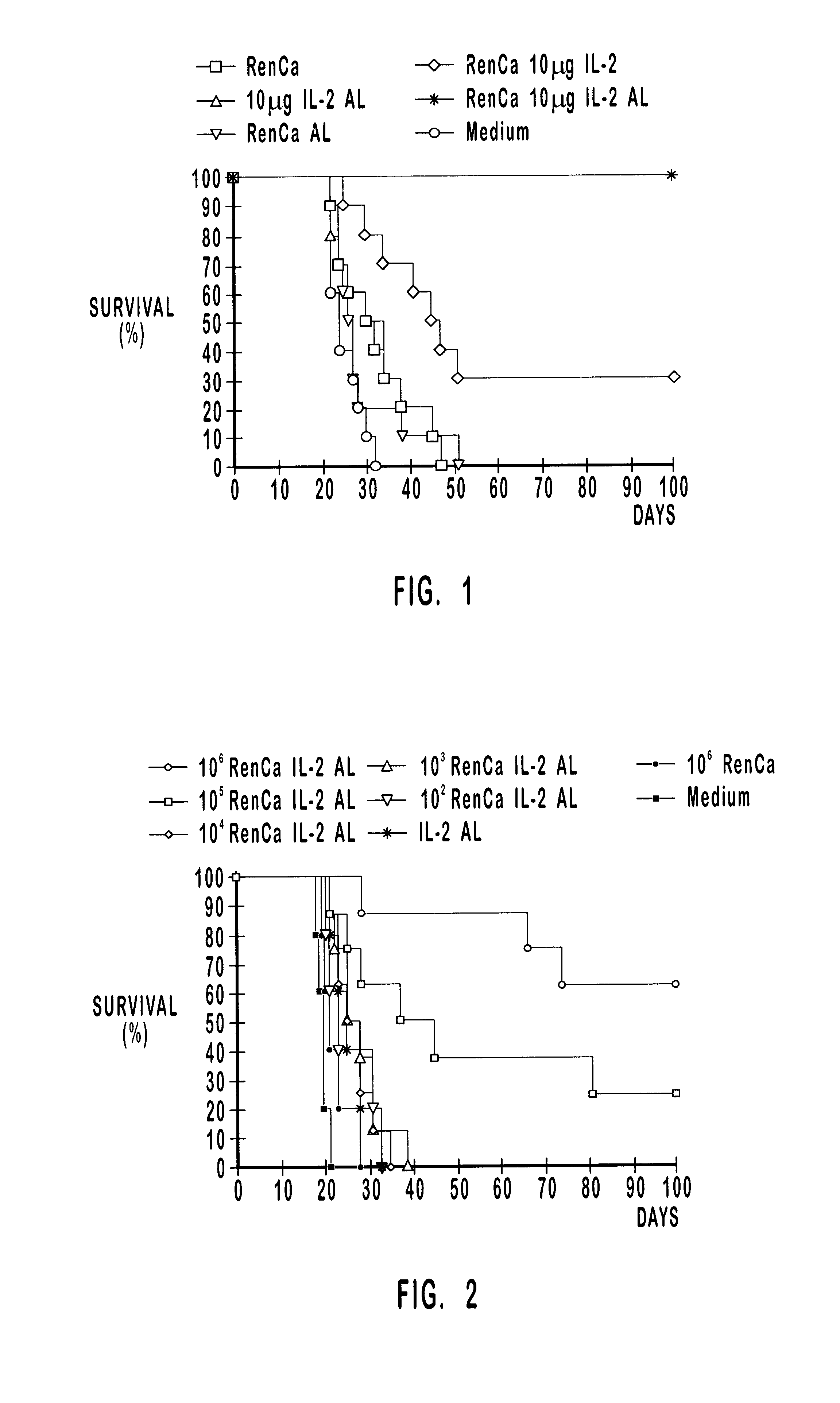
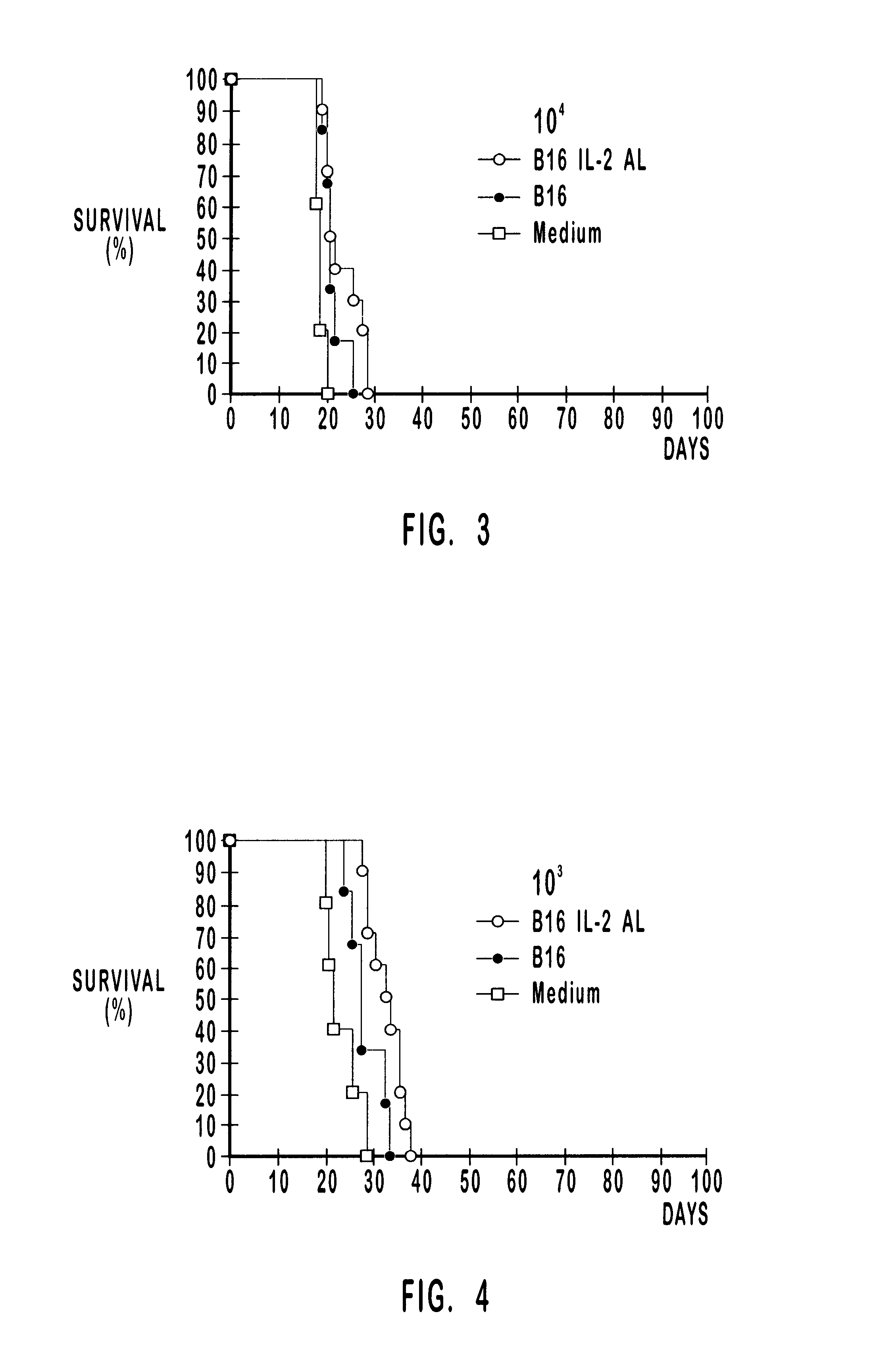
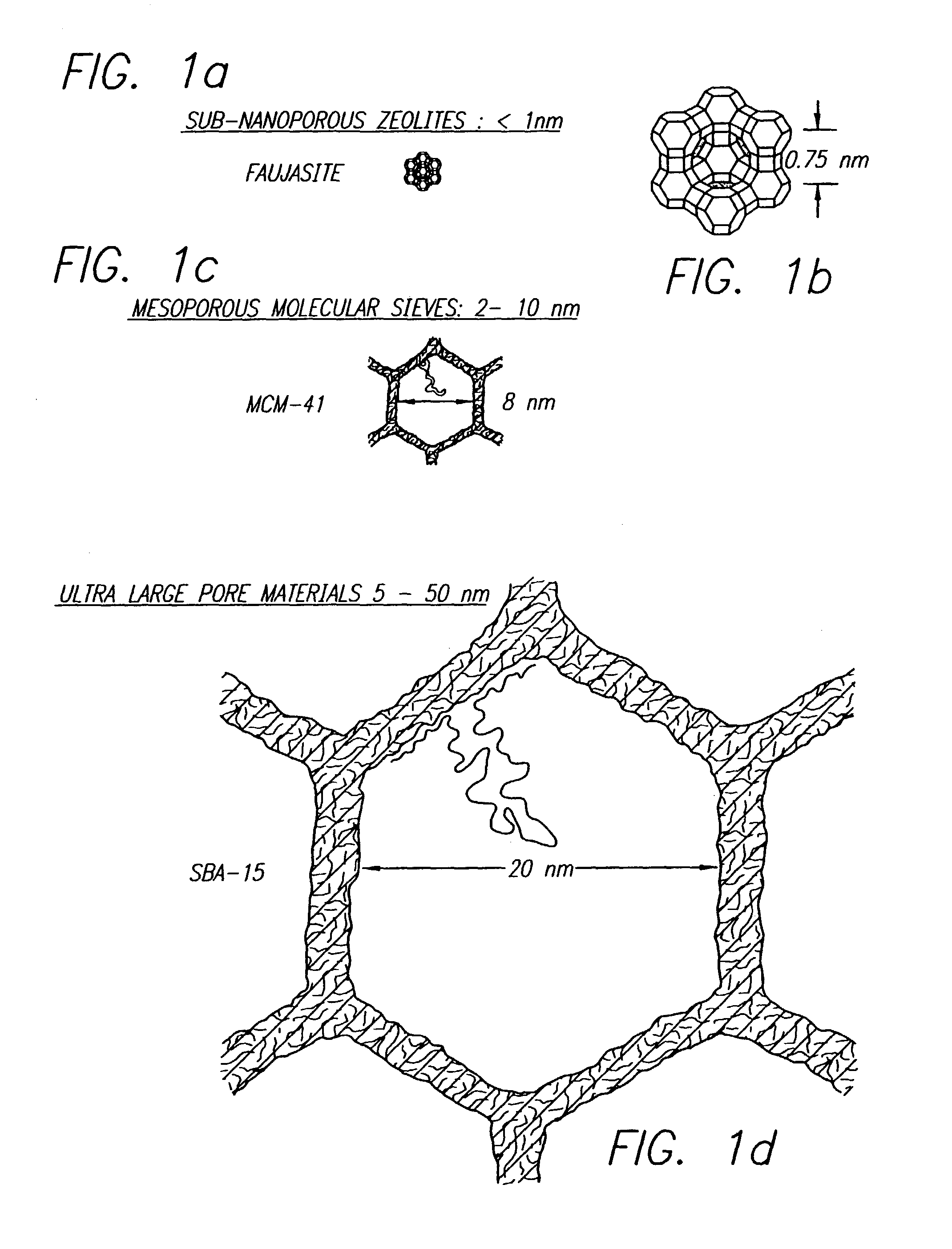
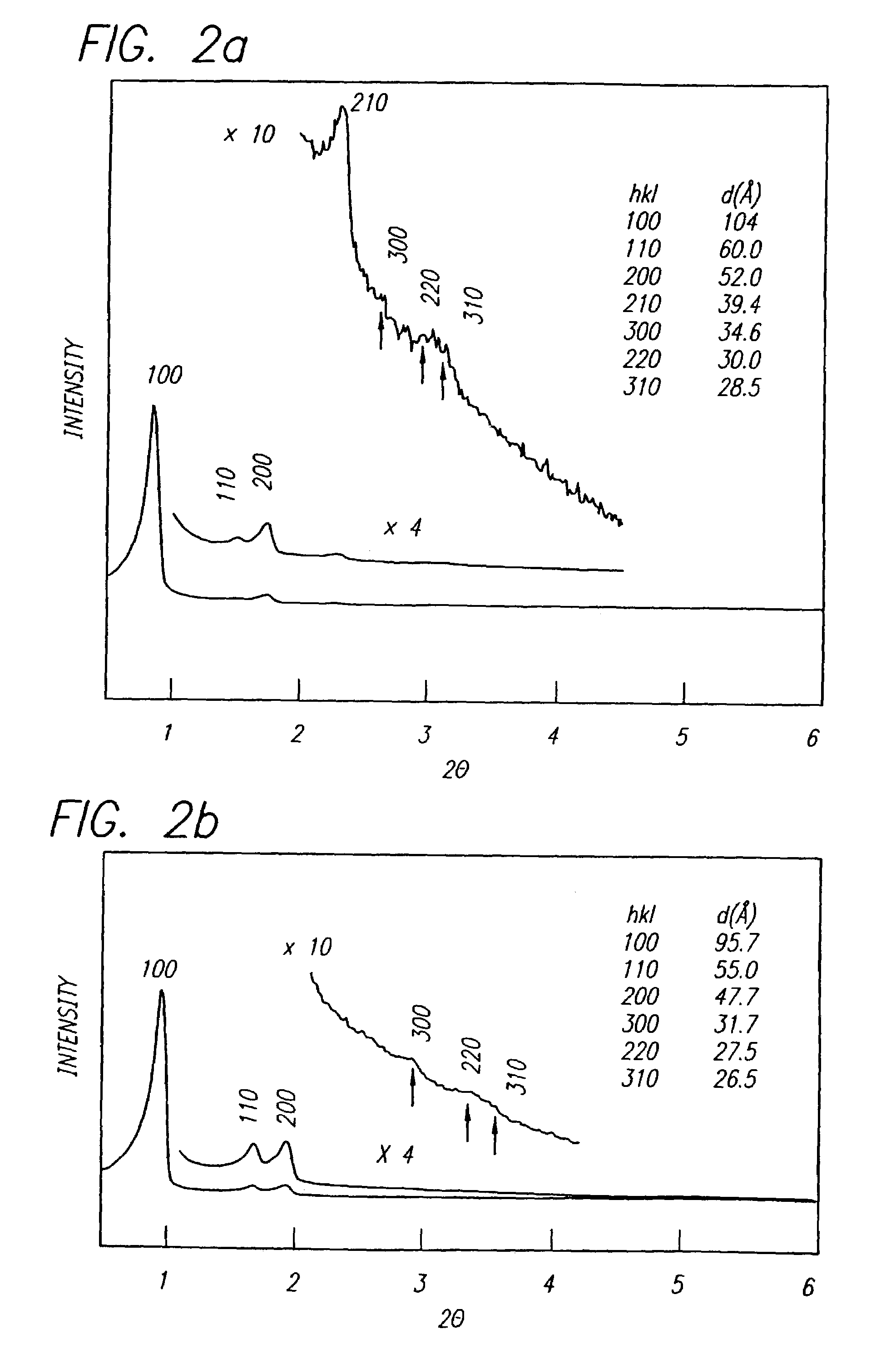
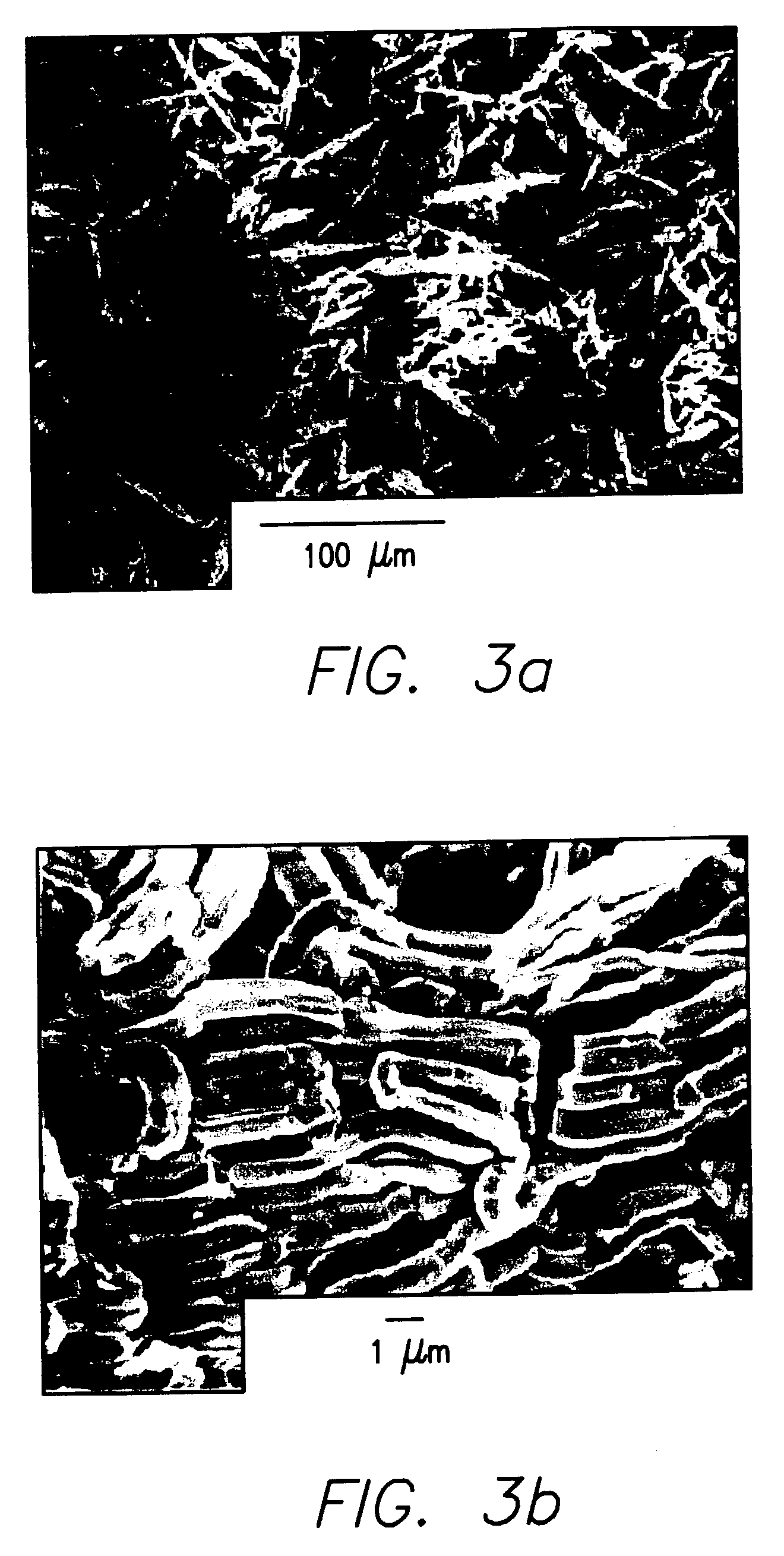
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
4159results about "Aluminium oxides/hydroxides" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
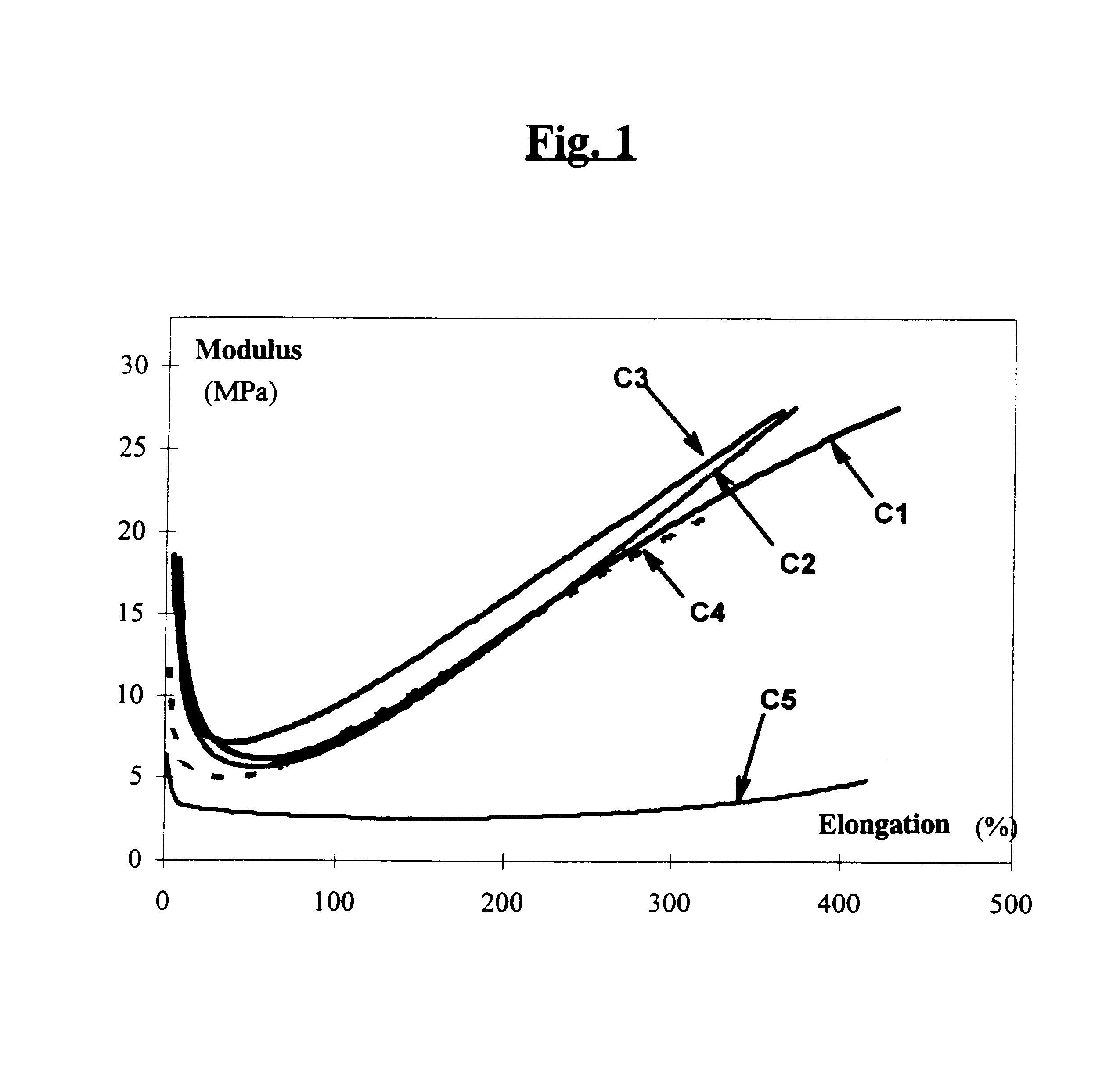
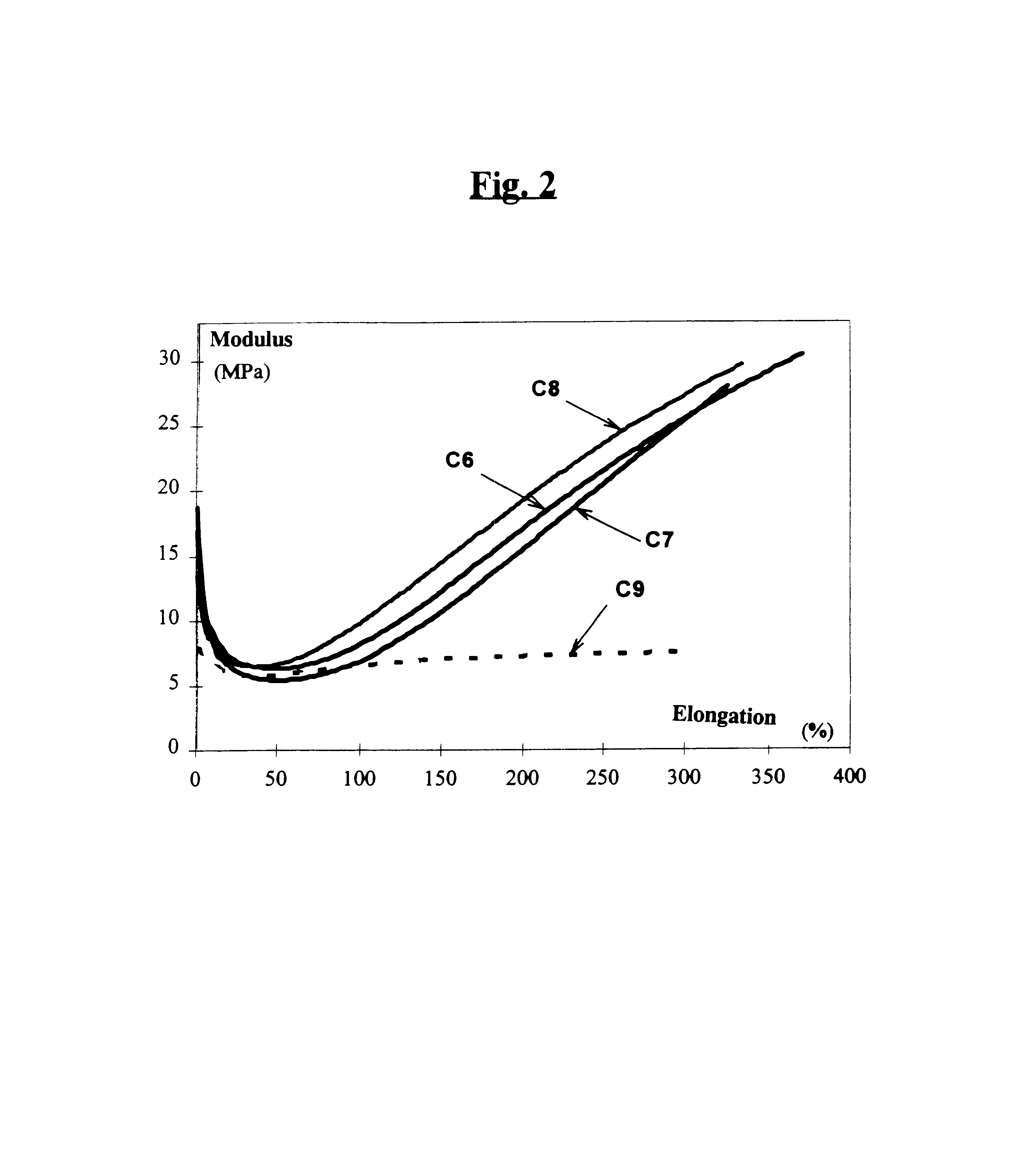
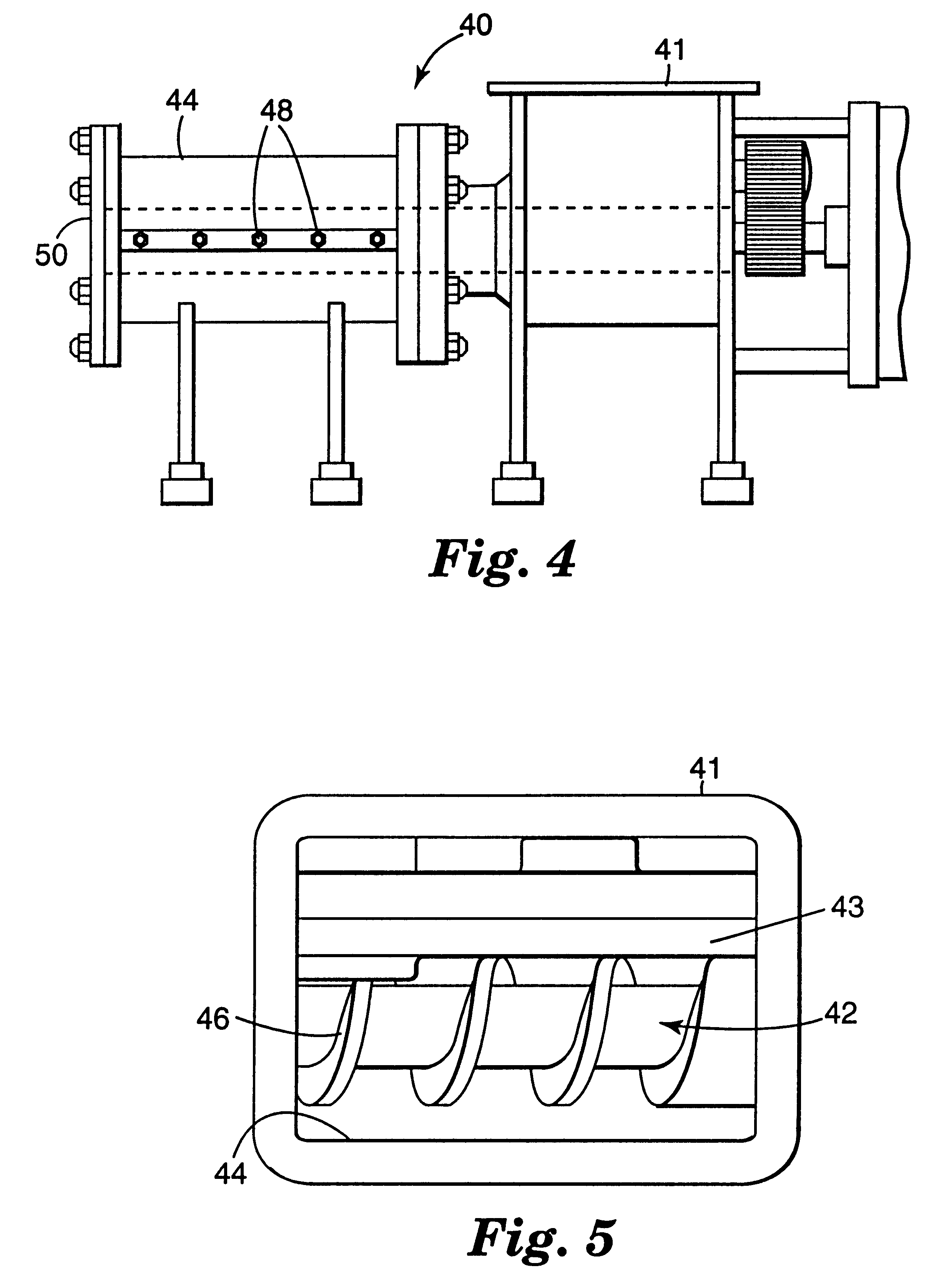
Reinforcing aluminum-based filler and rubber composition comprising such a filter
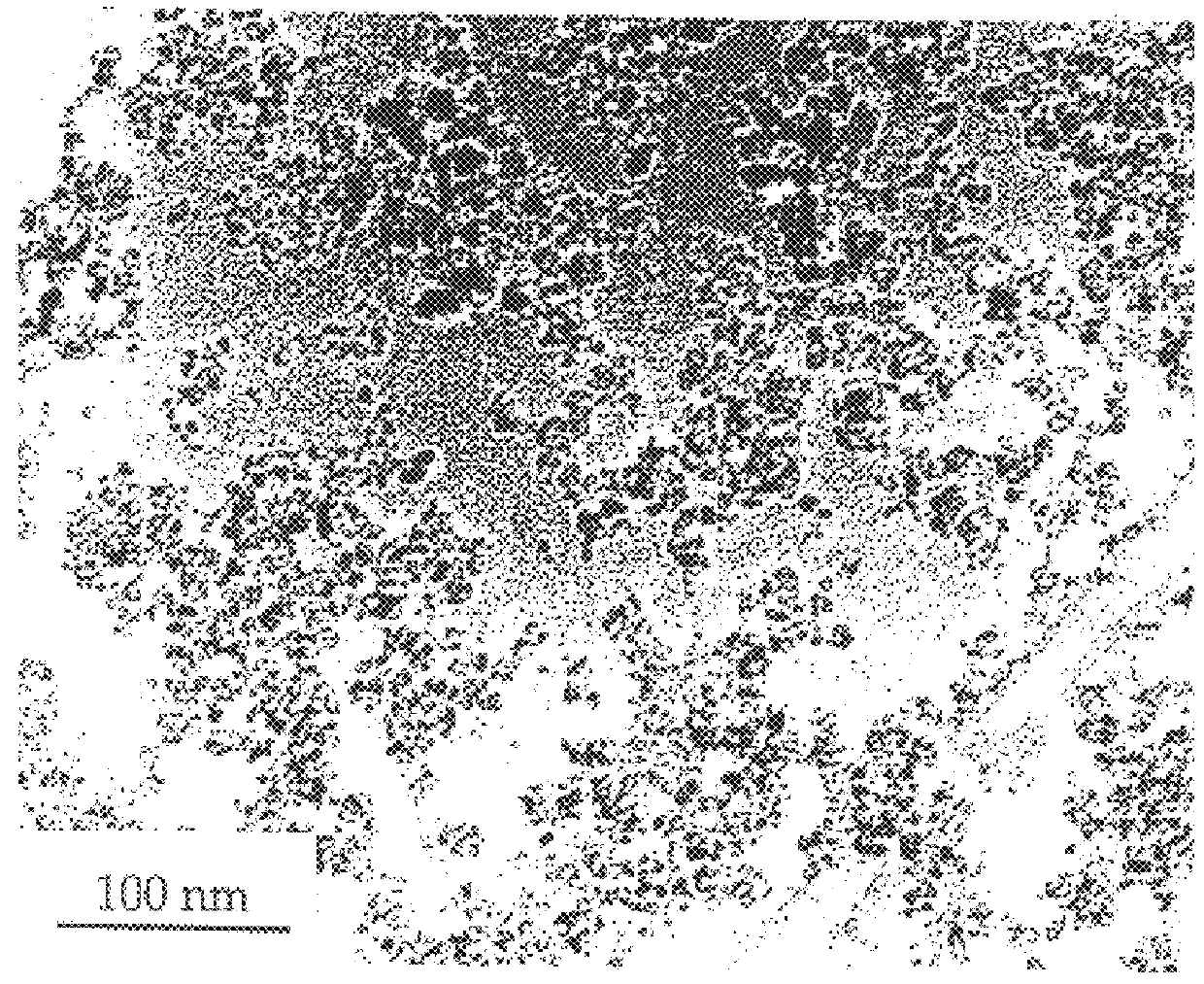
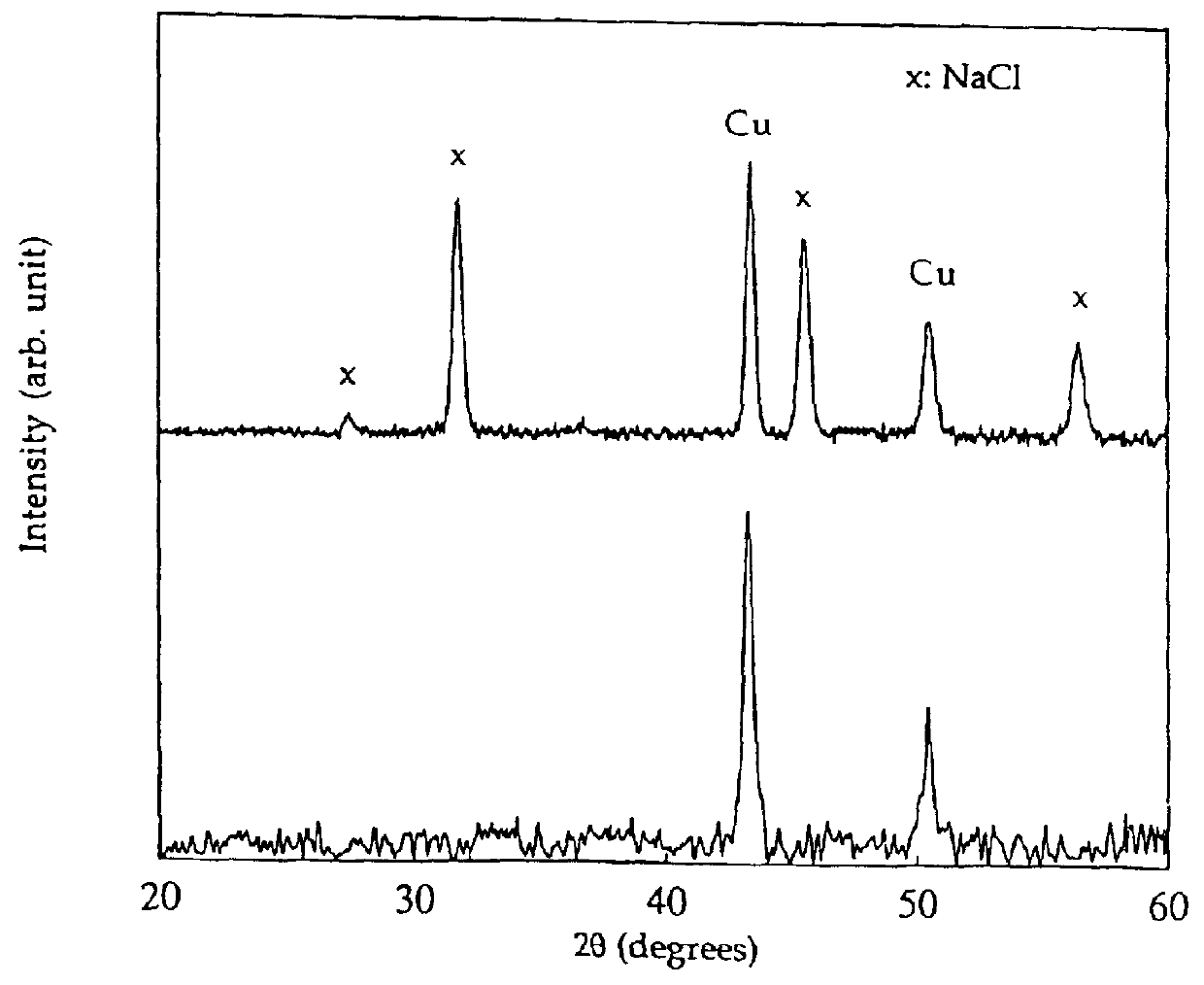
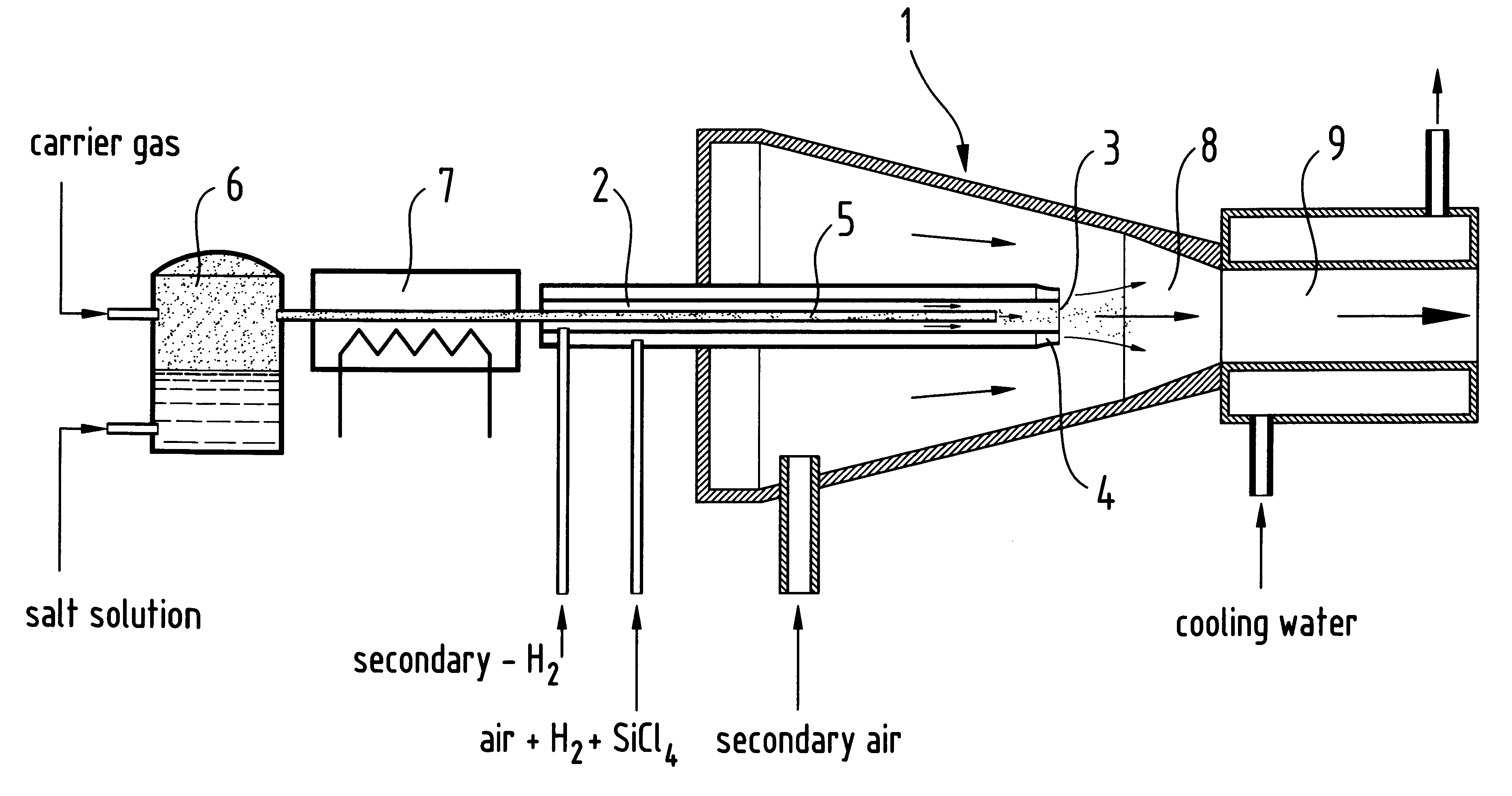
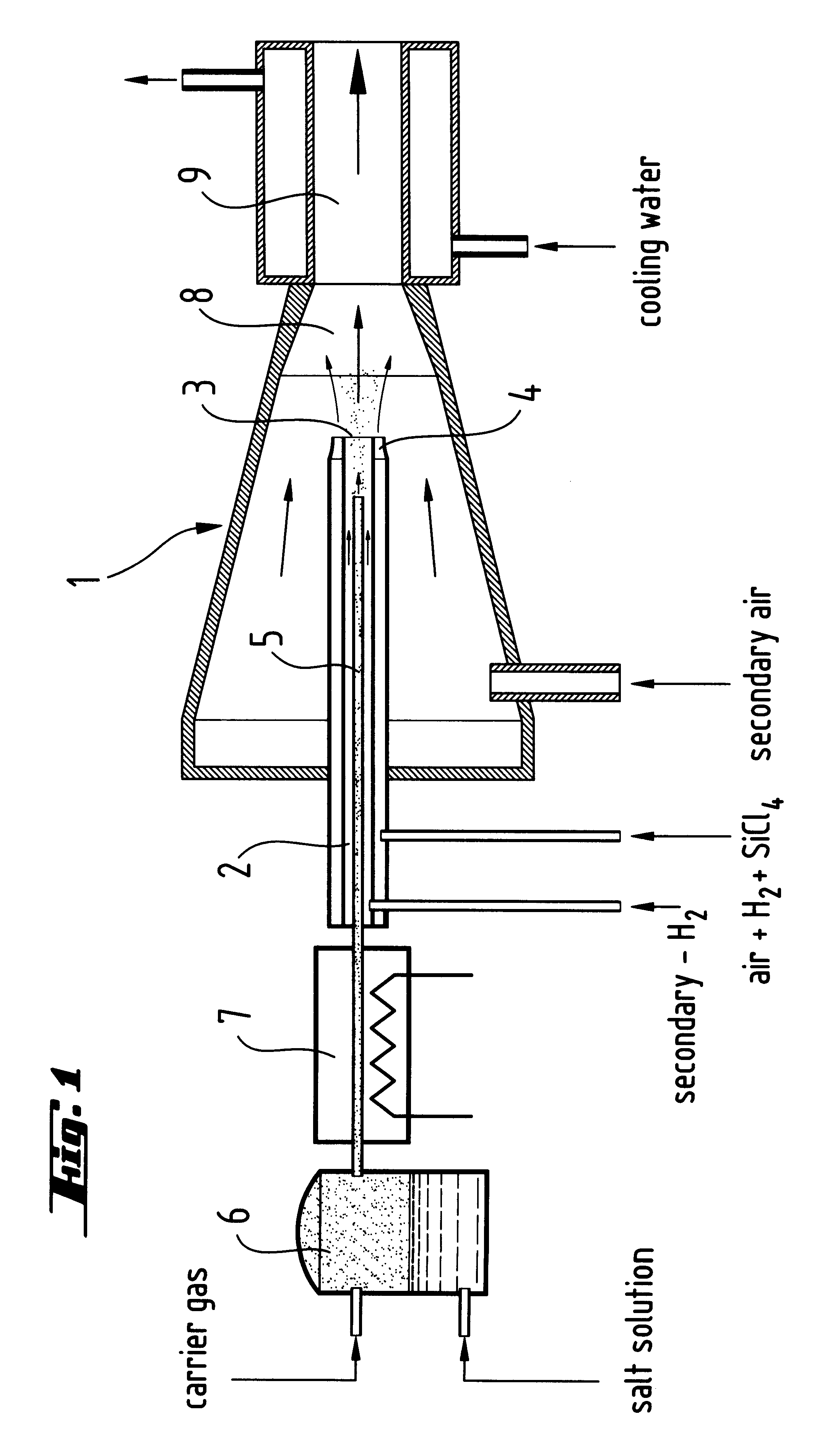
A reinforcing aluminum-based filler which can be used for reinforcing diene rubber compositions intended for the manufacture of tires, comprising an aluminum (oxide-)hydroxide corresponding, with the exception of any impurities and the water of hydration, to the general formula (a and b being real numbers):the specific BET surface area of which is between 30 and 400 m2 / g, the average particle size (by mass) dw of which is between 20 and 400 nm and the disagglomeration rate, alpha, of which, measured via an ultrasound disagglomeration test at 100% power of a 600-watt ultrasonic probe, is greater than 5x10-3 mum-1 / s is provided. A rubber composition suitable for the manufacture of tires comprising said aluminum-based filler as reinforcing filler.
Owner:MICHELIN & CO CIE GEN DES ESTAB MICHELIN
Thermal oxide equivalent low temperature ALD oxide for dual purpose gate oxide and method for producing the same
ActiveUS10106892B1Nitrogen-metal/silicon/boron binary compoundsSolid-state devicesNitrideThermal oxide
Methods of forming conformal low temperature gate oxides on a HV I / O and a core logic and the resulting devices are provided. Embodiments include providing a HV I / O and core logic laterally separated on a Si substrate, each having a fin; forming a gate oxide layer over each fin and the Si substrate; forming a silicon oxy-nitride layer over the gate oxide layer; forming a sacrificial oxide layer over the silicon oxy-nitride layer; removing the sacrificial oxide and silicon oxy-nitride layers and thinning the gate oxide layer; forming a second gate oxide layer over the thinned gate oxide layer; forming a silicon oxy-nitride layer over the second gate oxide layer; removing the silicon oxy-nitride and second gate oxide layers over the core logic fin portion; forming an IL over the core logic fin portion; and forming a HfOx layer over the second silicon oxy-nitride layer and ILs.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
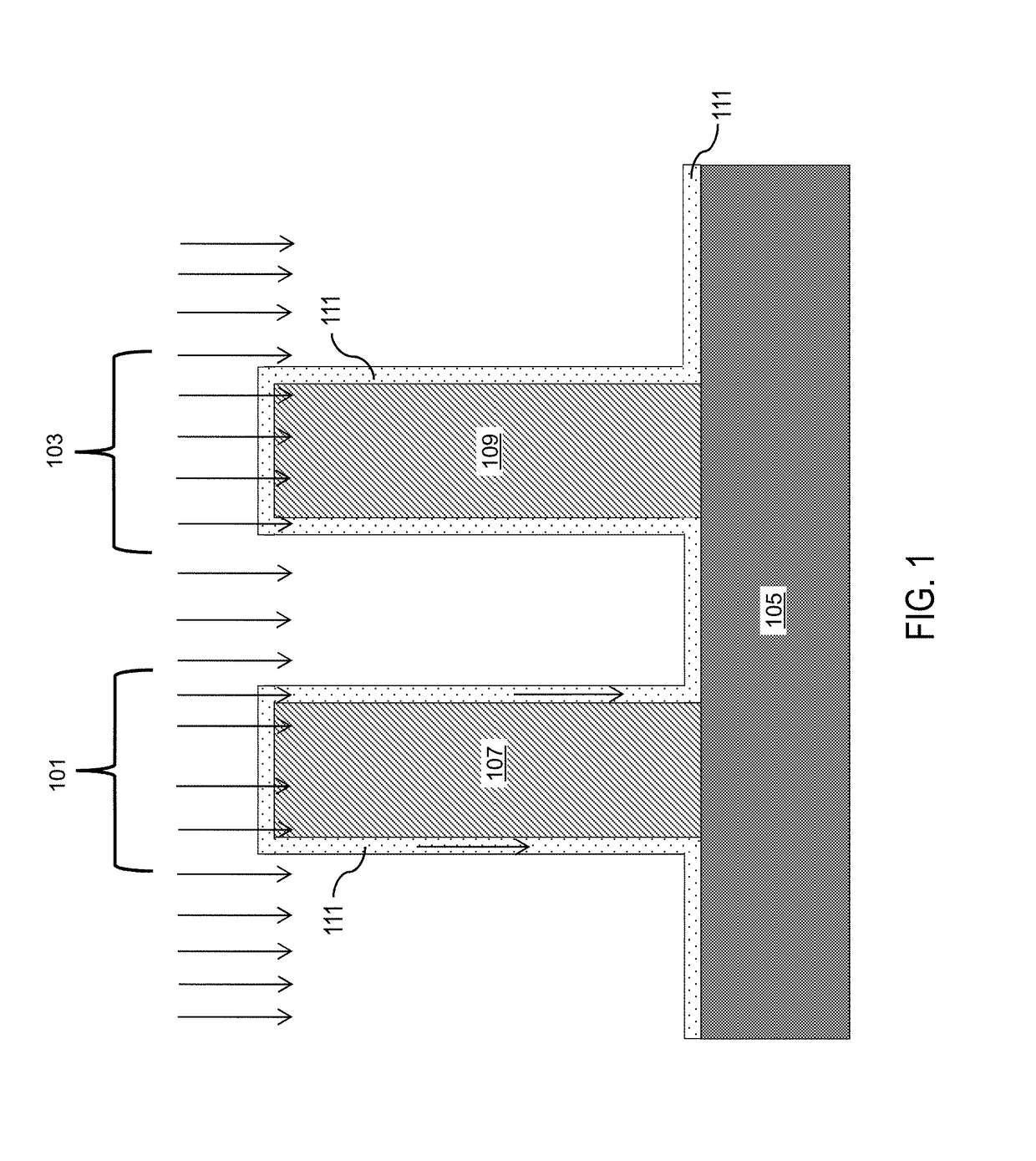
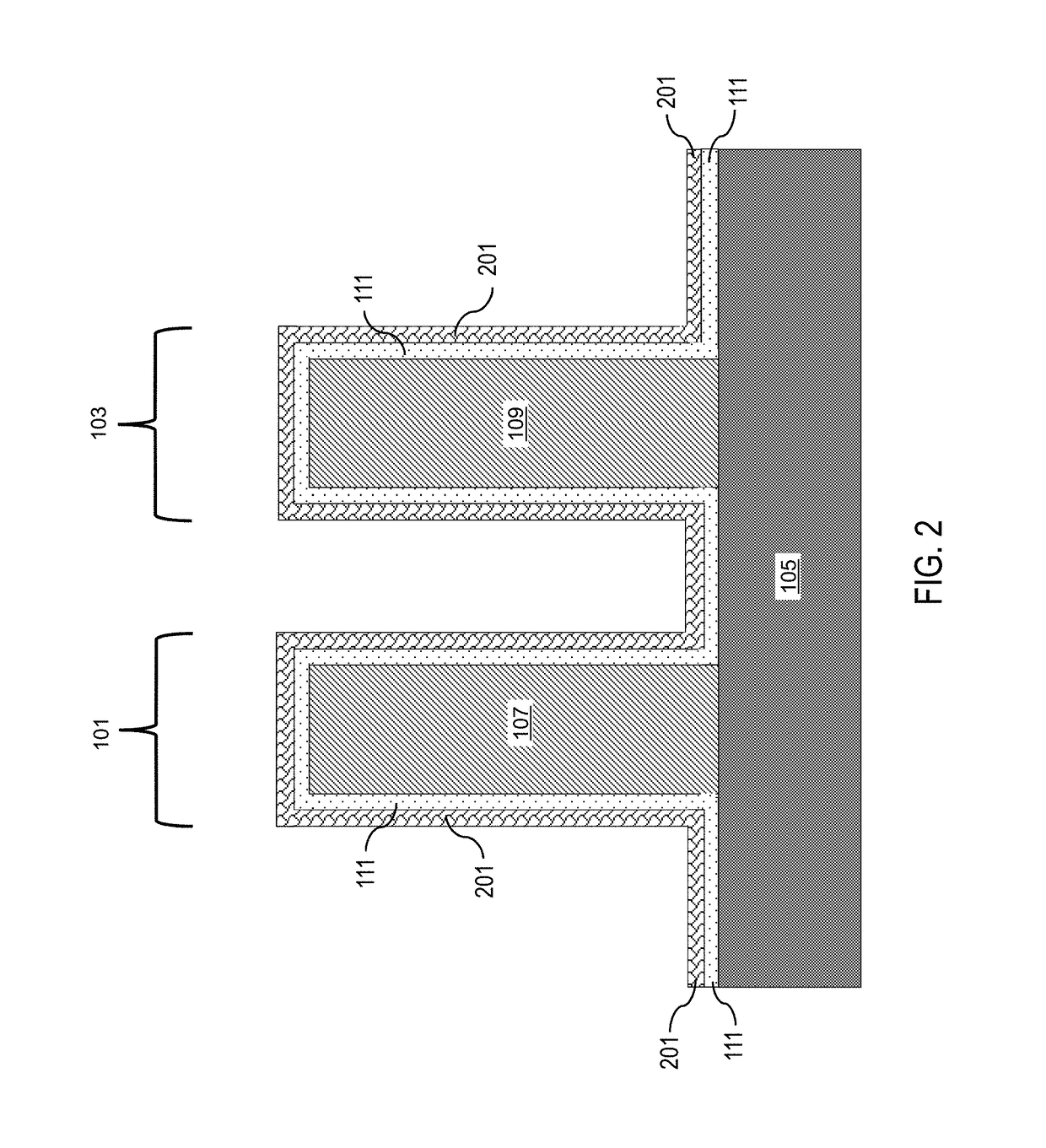
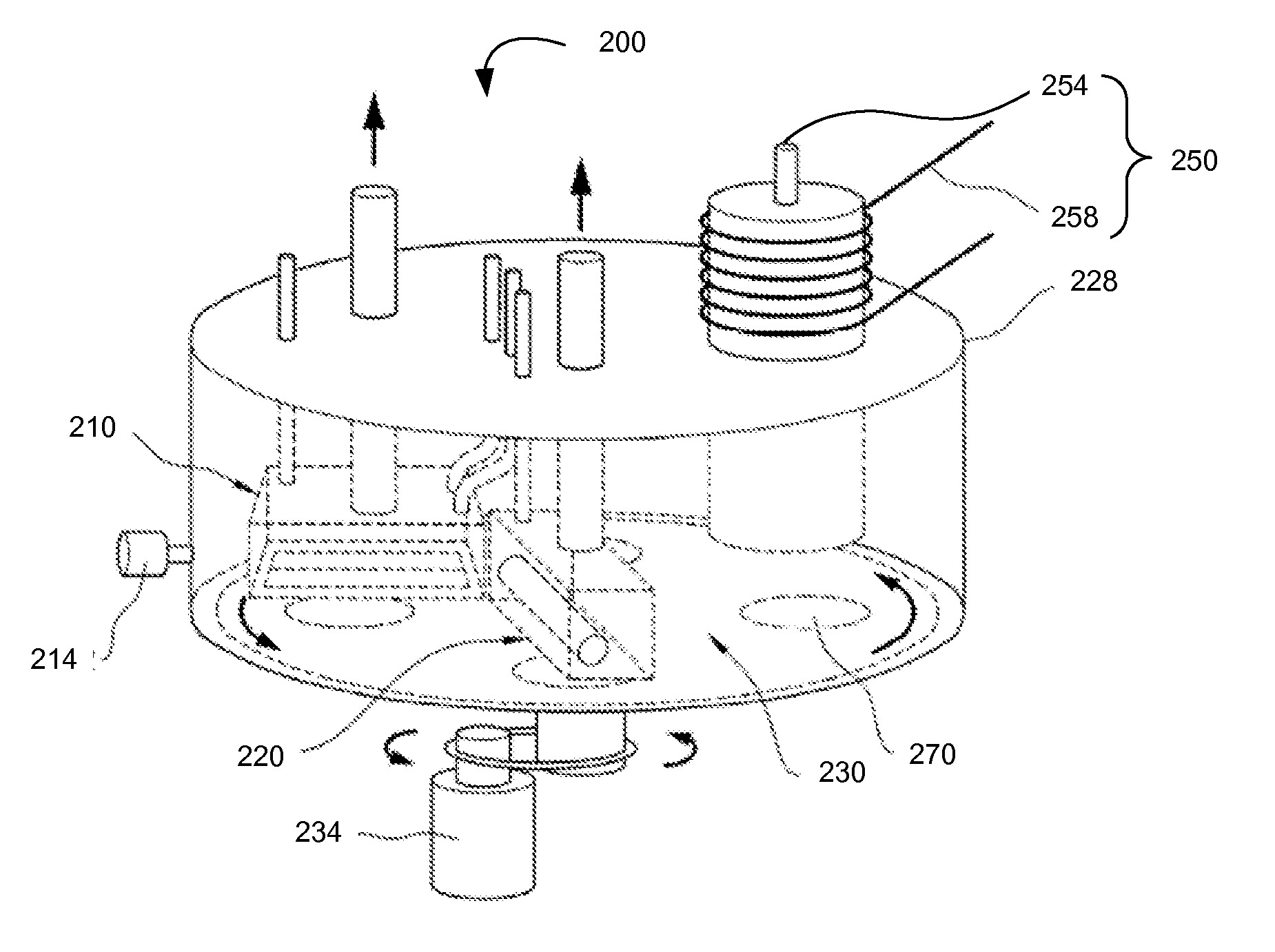
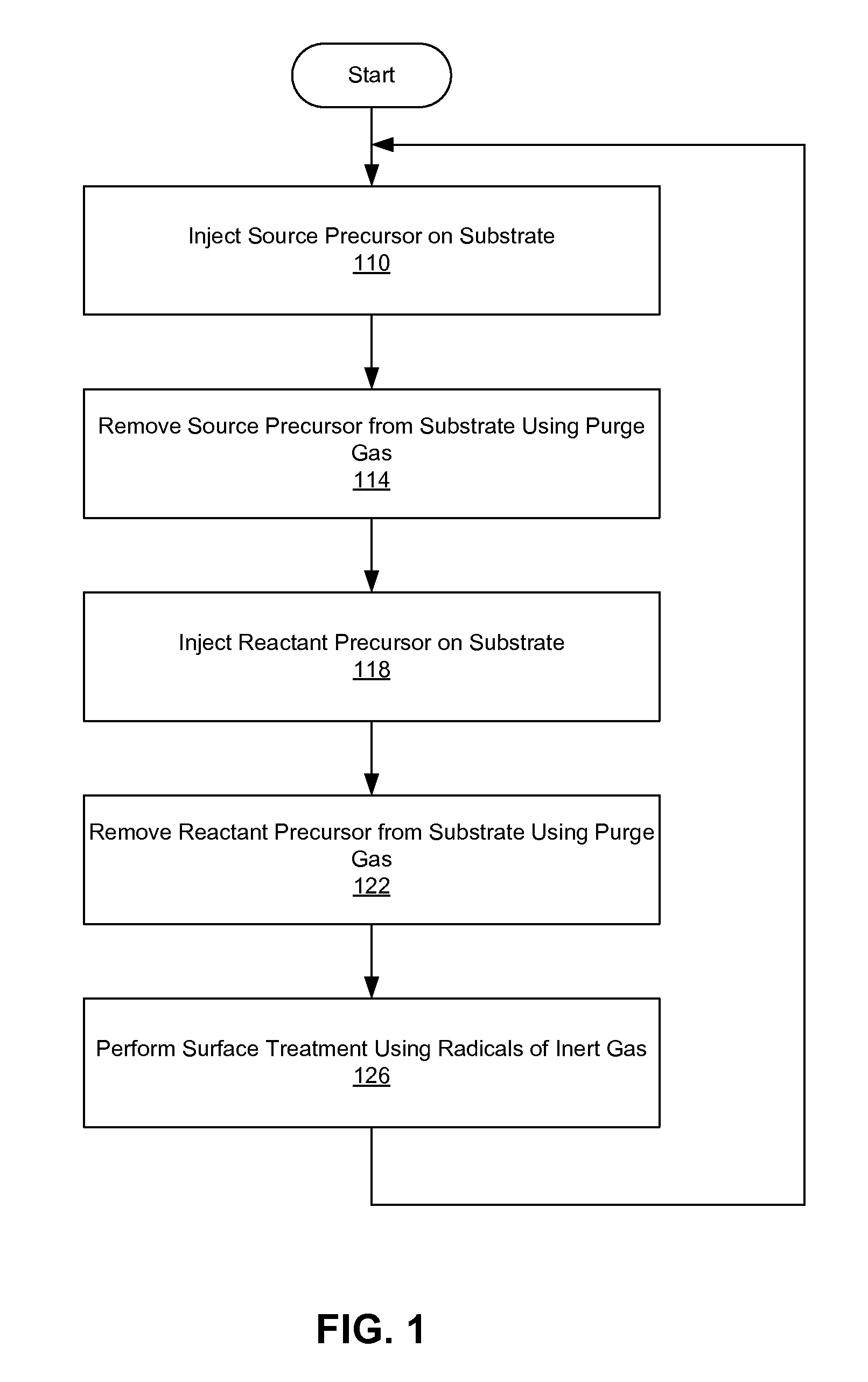
Treating Surface of Substrate Using Inert Gas Plasma in Atomic Layer Deposition
InactiveUS20120021252A1Increase deposition rateElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDangling bondGas plasma
Depositing one or more layers of material on a substrate using atomic layer deposition (ALD) followed by surface treating the substrate with radicals of inert gas before subjecting the substrate to further deposition of layers. The radicals of the inert gas appear to change the surface state of the deposited layer to a state more amenable to absorb subsequent source precursor molecules. The radicals of the inert gas disconnect bonding of molecules on the surface of the substrate, and render the molecules on the surface to have dangling bonds. The dangling bonds facilitate absorption of subsequently injected source precursor molecules into the surface. Exposure to the radicals of the inert gas thereby increases the deposition rate and improves the properties of the deposited layer.
Owner:VEECO ALD
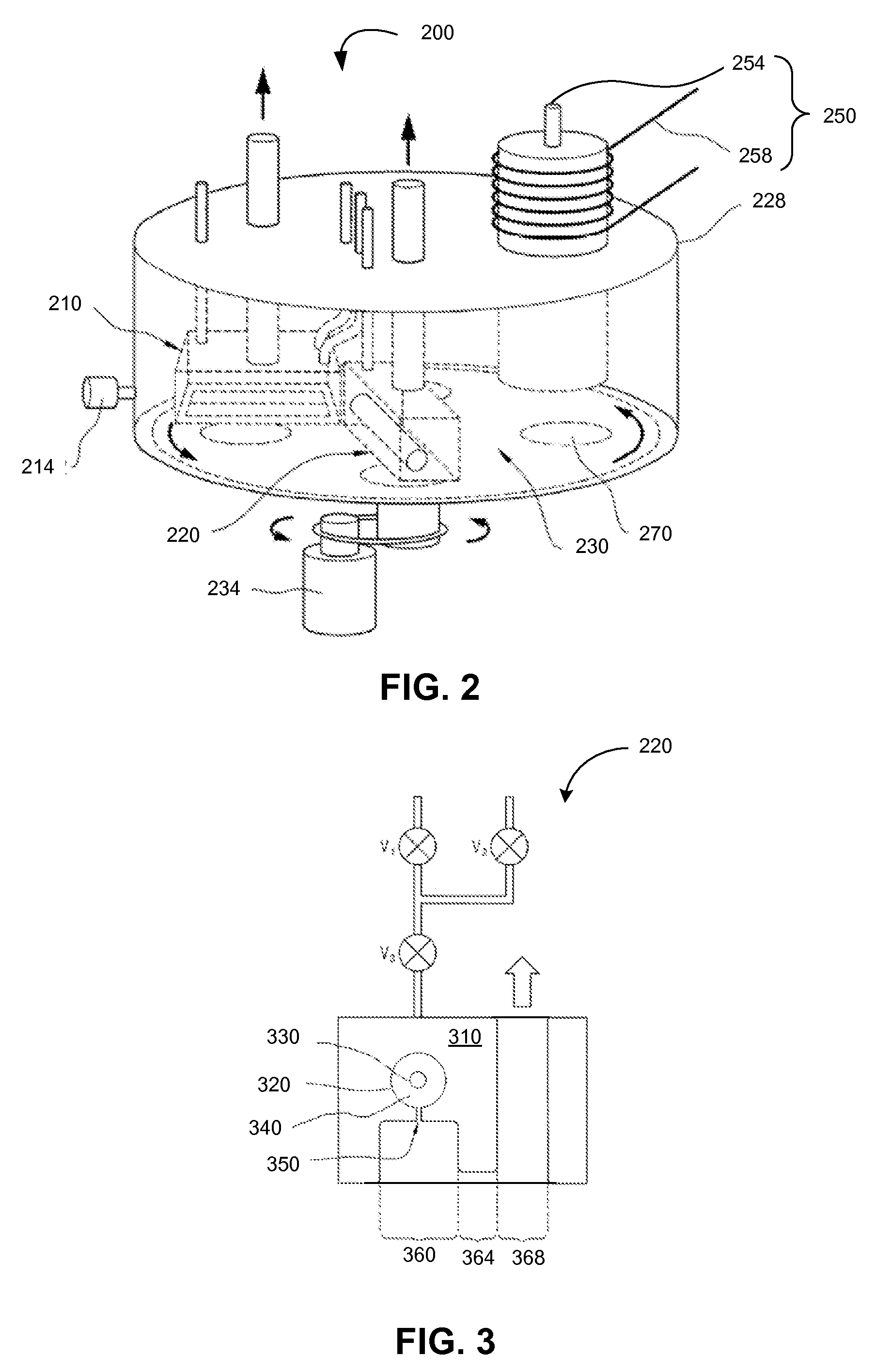
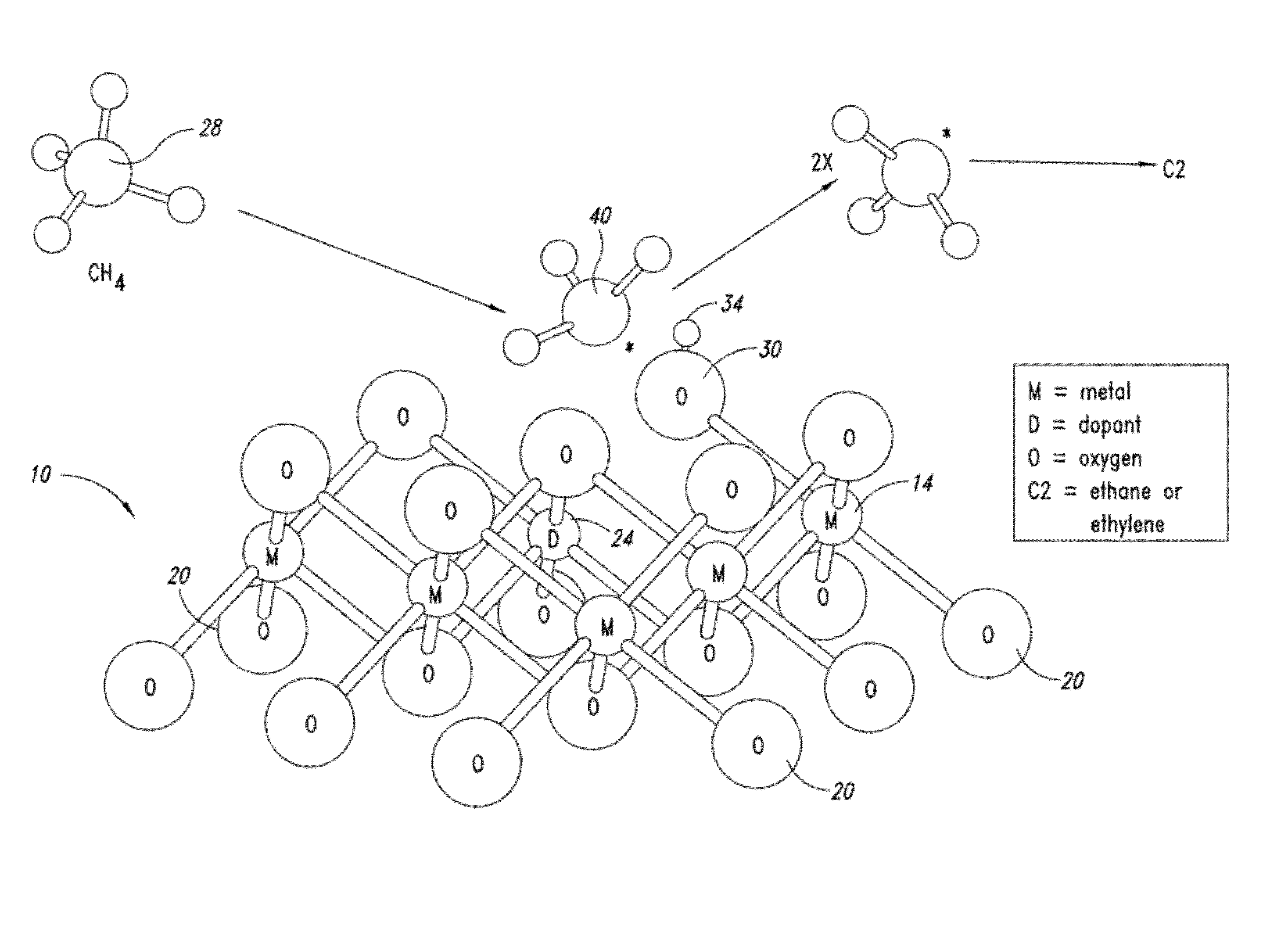
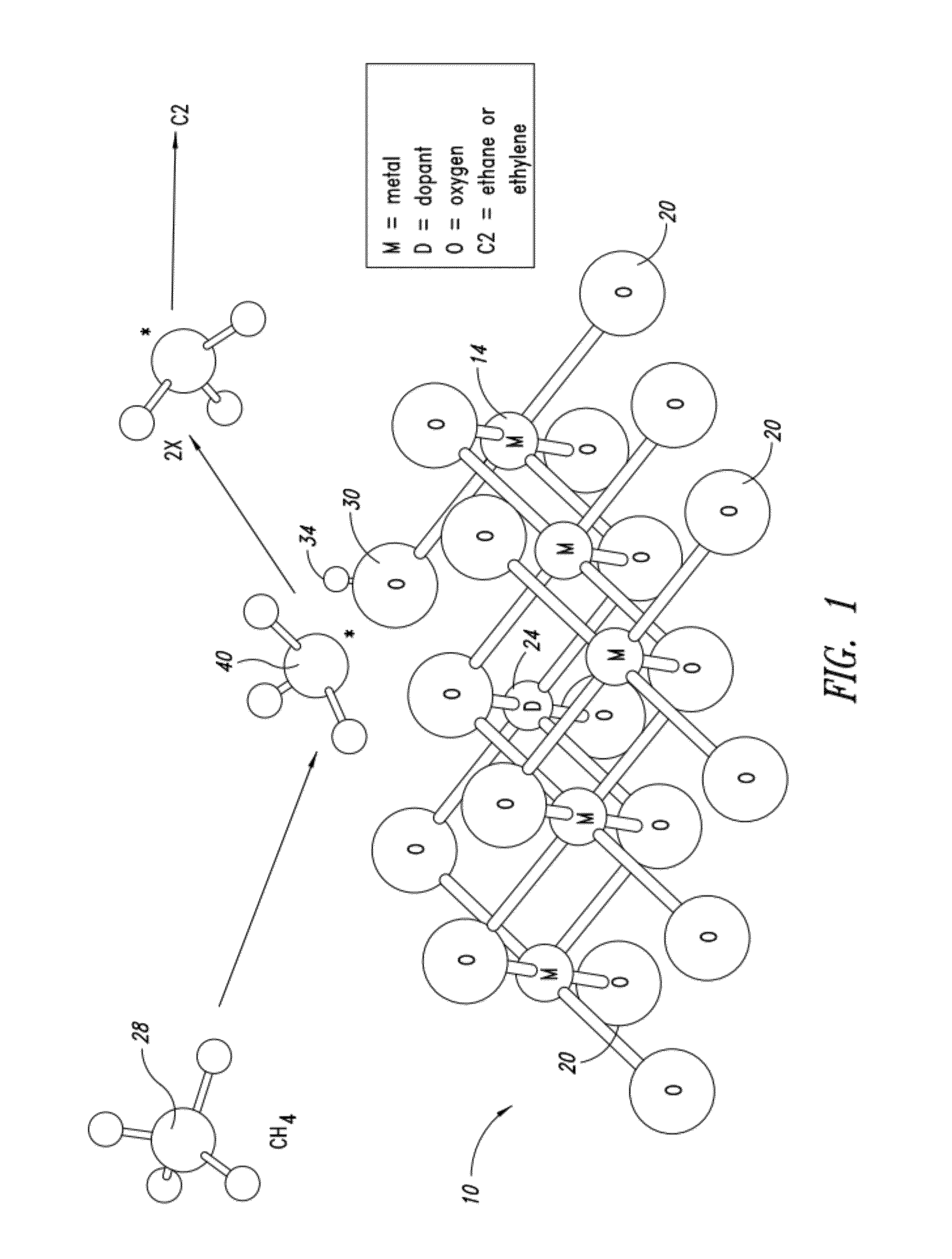
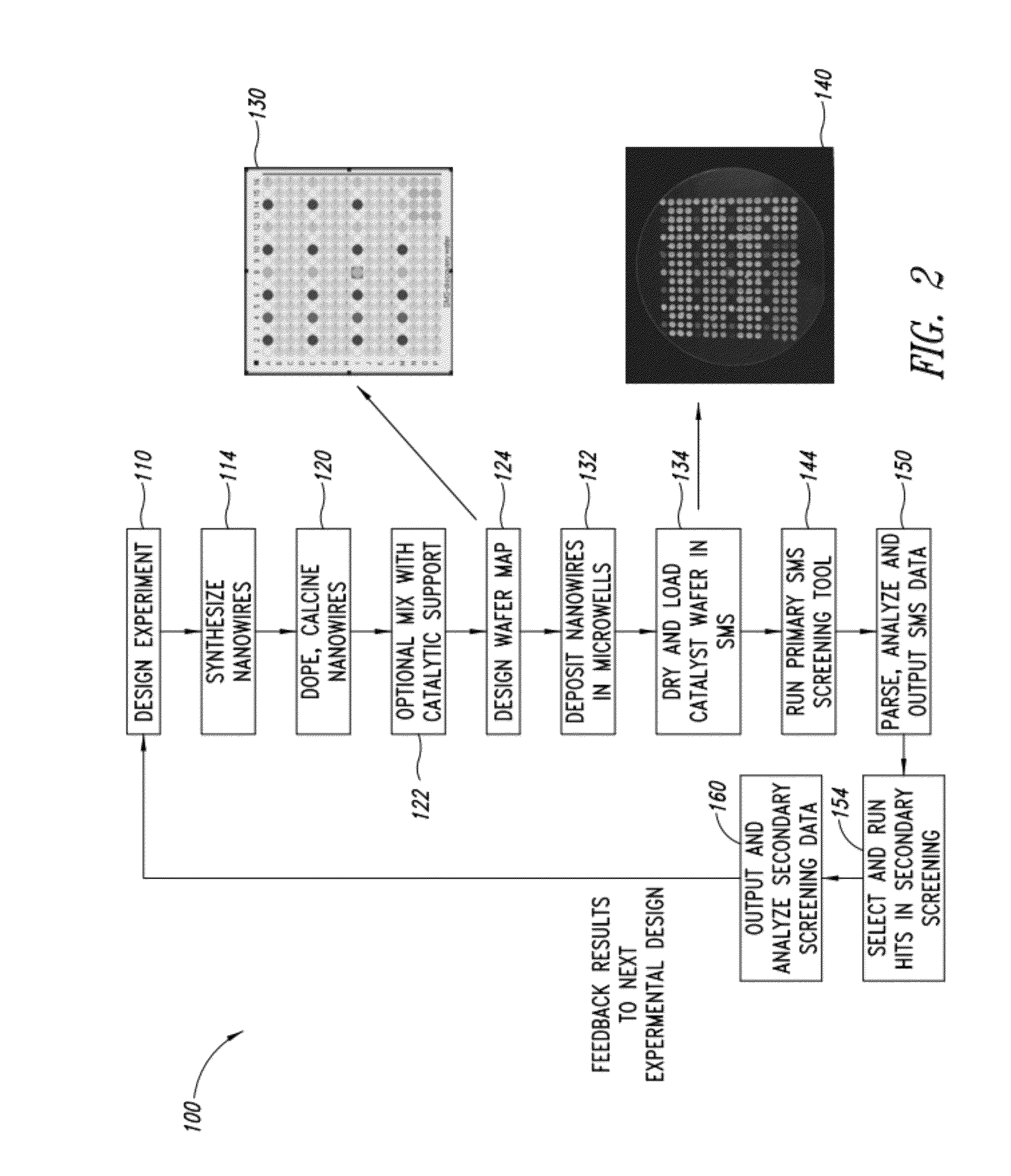
Nanowire catalysts
Nanowires useful as heterogeneous catalysts are provided. The nanowire catalysts are useful in a variety of catalytic reactions, for example, the oxidative coupling of methane to ethylene. Related methods for use and manufacture of the same are also disclosed.
Owner:SILURIA TECH INC
Process for preparing nanostructured materials of controlled surface chemistry
InactiveUS6669823B1Good dispersionReduce hydrolysis rateMaterial nanotechnologyMolten spray coatingCharge carrierNanostructured materials
A process to prepare stoichiometric-nanostructured materials comprising generating a plasma, forming an "active volume" through introduction of an oxidizing gas into the plasma, before the plasma is expanded into a field-free zone, either (1) in a region in close proximity to a zone of charge carrier generation, or (2) in a region of current conduction between field generating elements, including the surface of the field generation elements, and transferring energy from the plasma to a precursor material to form in the "active volume" at least one stoichiometric-nanostructured material and a vapor that may be condensed to form a stoichiometric-nanostructured material. The surface chemistry of the resulting nanostructured materials is substantially enhanced to yield dispersion stable materials with large zeta-potentials.
Owner:NANOPHASE TECH CORP
Nanosize electropositive fibrous adsorbent
InactiveUS6838005B2Improve the immunityEfficient precipitationIon-exchanger regenerationLoose filtering material filtersFiberParticulates
Aluminum hydroxide fibers approximately 2 nanometers in diameter and with surface areas ranging from 200 to 650 m2 / g have been fount to be highly electropositive. When dispersed in water they are able to attach to and retain electronegative particles. When combined into a composite filter with other fibers or particles they can filter bacteria and nano size particulates such as viruses and colloidal particles at high flux through the filter. Such filters can be used for purification and sterilization of water, biological, medical and pharmaceutical fluids, and as a collector / concentrator for detection and assay of mirobes and viruses. The alumina fibers are also capable of filtering sub-micron inorganic and metallic particles to produce ultra pure water. The fibers are suitable as a substrate for growth of cells. Macromolicules such as proteins may be separated from each other based on their electronegative charges.
Owner:ARGONIDE CORP
Method for making abrasive grain using impregnation, and abrasive articles
InactiveUS6206942B1High densityImprove performancePigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesAbrasive
Method for making alpha alumina-based abrasive grain, wherein during an impregnation step of the method, alpha alumina-based ceramic precursor particles conchoidally fracture. The abrasive grain can be incorporated into abrasive products such as coated abrasives, bonded abrasives, and non-woven abrasives.
Owner:3M CO
Process for the production of ultrafine powders of metal oxides
InactiveUS6503475B1Low costHigh yield rateAlkaline earth titanatesMaterial nanotechnologyDiluentBiological activation
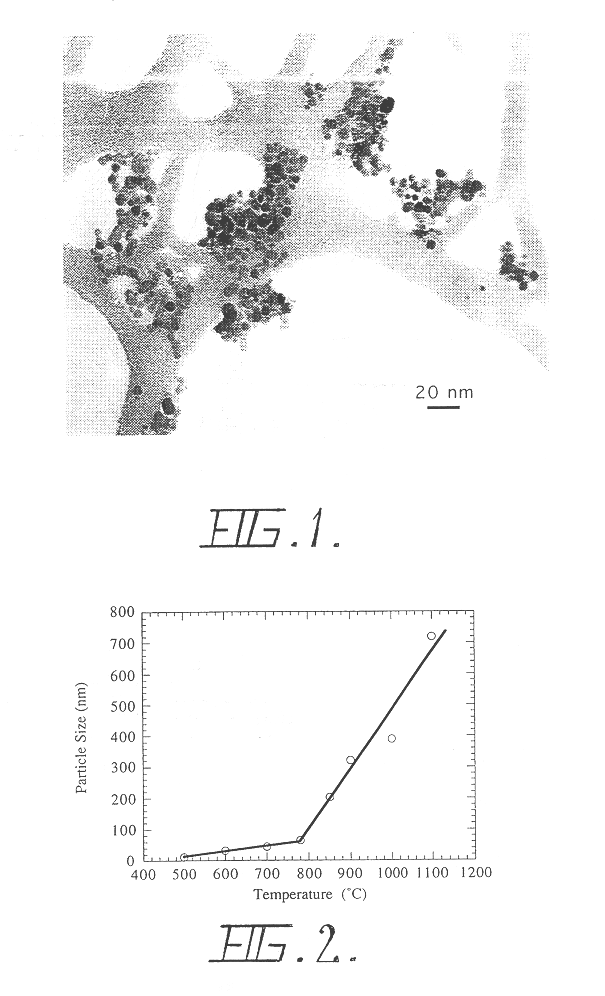
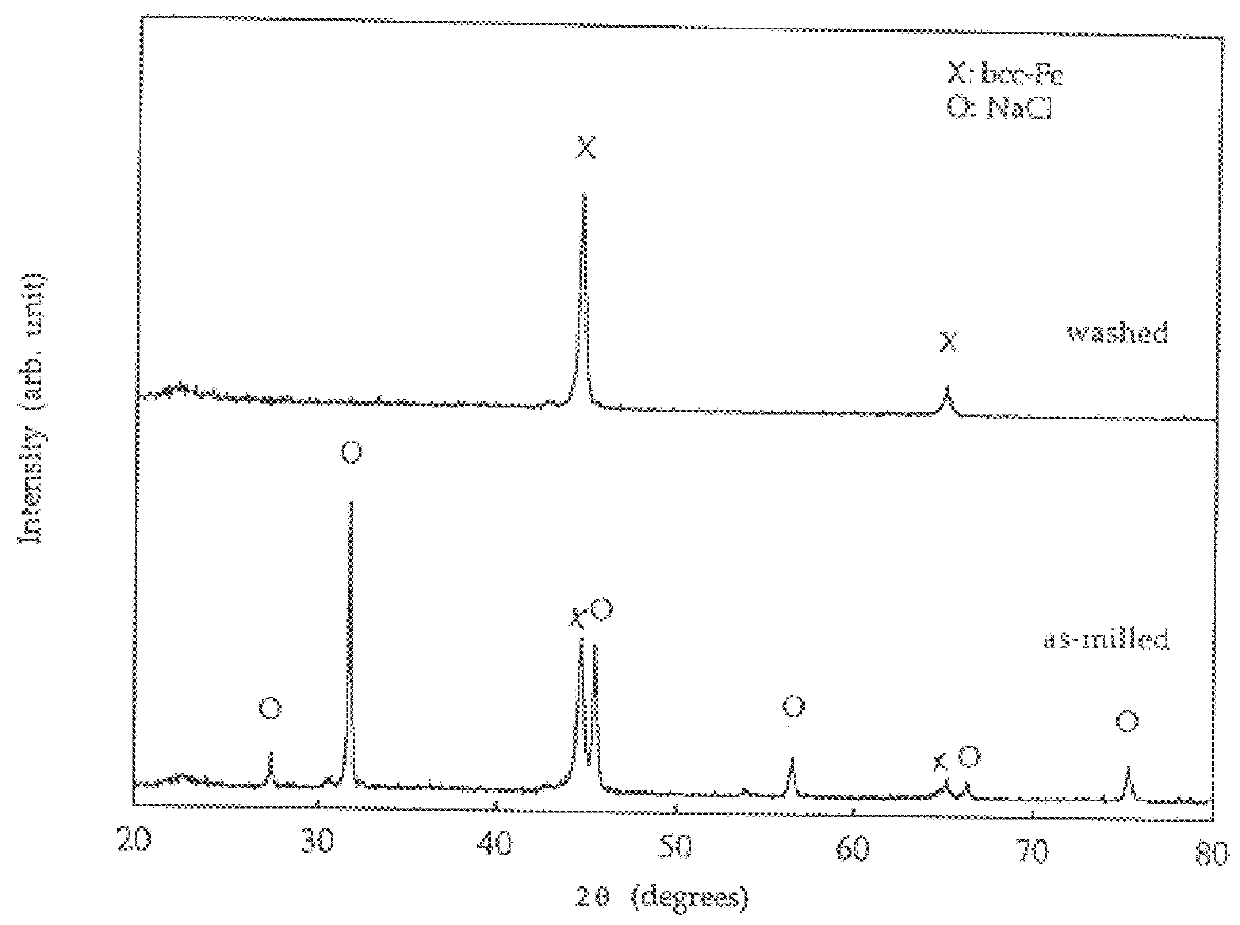
A process for the production of ultrafine powders that includes subjecting a mixture of precursor metal compound and a non-reactant diluent phase to mechanical milling whereby the process of mechanical activation reduces the microstructure of the mixture to the form of nano-sized grains of the metal compound uniformly dispersed in the diluent phase. The process also includes heat treating the mixture of nano-sized grains of the metal compound uniformly dispersed in the diluent phase to convert the nano-sized grains of the metal compound into a metal oxide phase. The process further includes removing the diluent phase such that the nano-sized grains of the metal oxide phase are left behind in the form of an ultrafine powder.
Owner:SAMSUNG CORNING PRECISION MATERIALS CO LTD +1
Process for abstracting earth silicon, oxide of alumina and gallium oxide from high-alumina flying ash
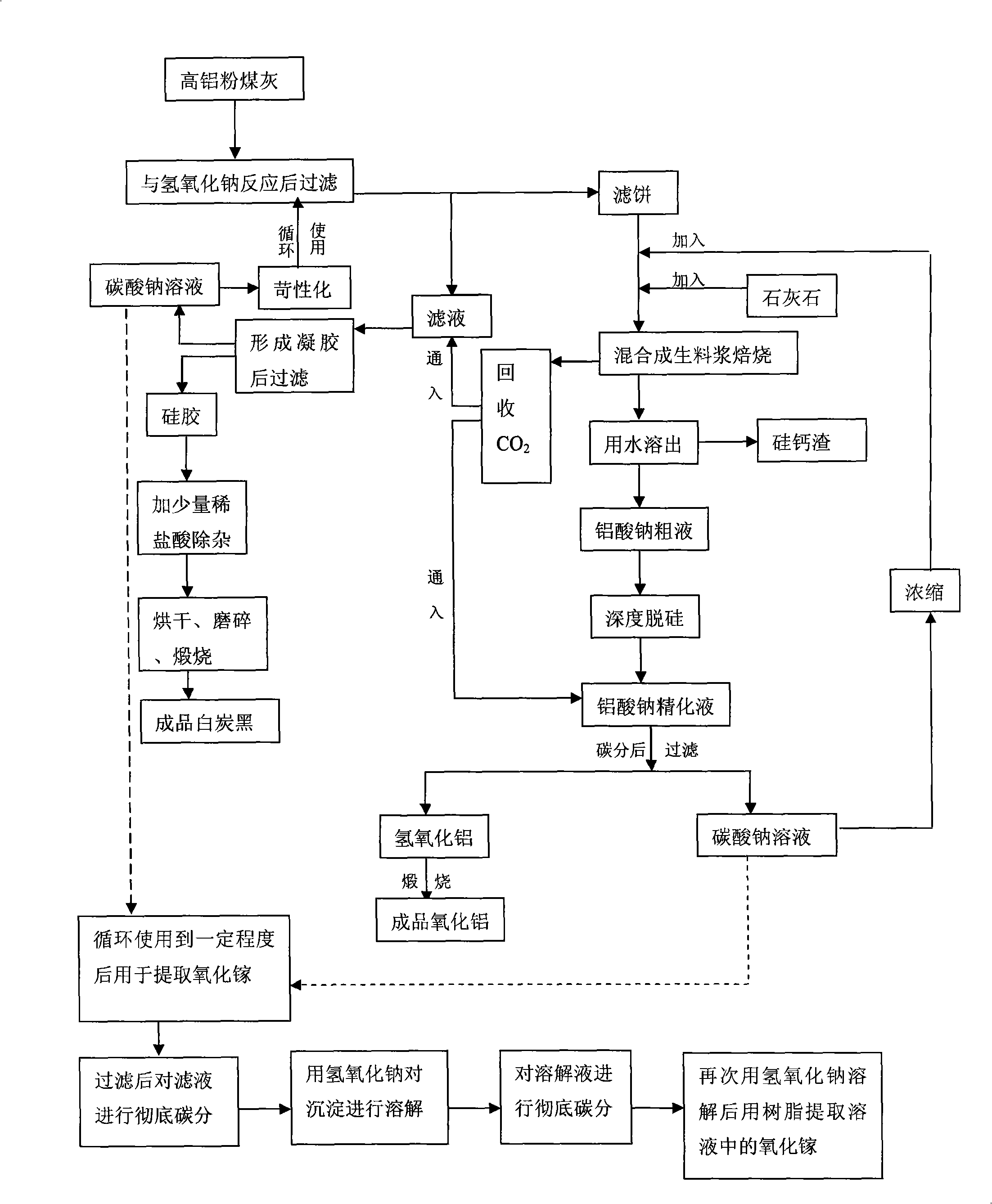
ActiveCN101284668AReduce the total massLow firing temperatureGallium/indium/thallium compoundsSilicon oxidesChemical industryFiltration
A method for extracting silicon dioxide, alumina and gallium oxide from high-alumina fly ash relates to the technology fields of environmental mineralogy and material, chemical industry and metallurgy. The method comprises the main steps as follows: causing the high-alumina fly ash to react with sodium hydroxide solution; filtering the solution; introducing CO2 to the filtrate for full gelation; cleaning, purifying, drying, grinding and calcining the silica gel after gel filtration to obtain finished white carbon black; adding limestone and a sodium carbonate solution into the filter mass after the reaction and filtration of the high-alumina fly ash and the sodium hydroxide solution; ball grinding the mixture into raw slurry; dissolving out the clinker obtained by baking the raw slurry; subjecting the filtrate to deep desiliconization to obtain sodium aluminate extraction liquid; filtrating the sodium aluminate extraction liquid after subjecting the sodium aluminate extraction liquid to carbon dioxide decomposition; baking the aluminum hydroxide after washing the filter mass to form the aluminum hydroxide product; and extracting the gallium oxide from the carbon dioxide decomposition mother solution and desiliconized solution. The method has the advantages of low material price, simple operating procedures, low investment, low production cost, low energy consumption and less slag.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Process for the production of ultrafine particles
A new, cost effective process for the production of ultrafine particles which is based on mechanically activated chemical reaction of a metal compound with a suitable reagent. The process involves subjecting a mixture of a metal compound and a suitable reagent to mechanical activation to increase the chemical reactivity of the reactants and / or reaction kinetics such that a chemical reaction can occur which produces a solid nano-phase substance. Concomitantly, a by-product phase is also formed. This by-product phase is removed so that the solid nano-phase substance is left behind in the form of ultrafine particles. During mechanical activation a composite structure is formed which consists of an intimate mixture of nano-sized grains of the nano-phase substance and the reaction by-product phase. The step of removing the by-product phase, following mechanical activation, may involve subjecting the composite structure to a suitable solvent which dissolves the by-product phase, while not reacting with the solid nano-phase substance. The process according to the invention may be used to form ultrafine metal powders as well as ultrafine ceramic powders. Advantages of the process include a significant degree of control over the size and size distribution of the ultrafine particles, and over the nature of interfaces created between the solid nano-phase substance and the reaction by-product phase.
Owner:WESTERN AUSTRALIA UNIV OF THE
Doped, pyrogenically prepared oxides
InactiveUS6328944B1Germanium dioxidePipe protection by thermal insulationDoped oxideAqueous solution
Doped, pyrogenically prepared oxides of metals and / or non-metals which are doped with one or more doping components in an amount of 0.00001 to 20 wt. %. The doping component may be a metal and / or non-metal or an oxide and / or a salt of a metal and / or a non-metal. The BET surface area of the doped oxide may be between 5 and 600 m2 / g. The doped pyrogenically prepared oxides of metals and / or non-metals are prepared by adding an aerosol which contains an aqueous solution of a metal and / or non-metal to the gas mixture during the flame hydrolysis of vaporizable compounds of metals and / or non-metals.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Method for quick-speed preparing aerogel by hydro-thermal synthesis at low cost
InactiveCN101456569AReduce surface tensionIntegrity guaranteedSilicaAlkali metal silicatesReaction temperatureHydrothermal synthesis
The invention discloses a method for preparing aerogel materials by combining hydrothermal synthesis technology and sol-gel technology. The prepared aerogel comprises one or more of alumina aerogel, silica aerogel, zirconia aerogel and titania aerogel. The method comprises the following steps: mixing a reactant and a structure-directing agent according to certain proportion, and adding a pH value control agent to adjust the pH value; sealing hydrothermal reaction equipment, heating the mixture to be between 50 and 280 DEG C, making the mixture stand for 0 to 72 hours, raising the temperature to be between 60 and 300 DEG C, and continuously reacting for 0.1 to 72 hours; and cooling gel, taking out the gel, drying the gel and obtaining the aerogel. Compared with the prior art, the method has low reaction temperature and pressure, small equipment investment and simple and controllable technology, reduces potential safety hazards, greatly improves the preparation speed of the aerogel, saves the production cost, and is favorable to realize commercial mass production.
Owner:纳诺科技有限公司 +1
Metal oxide processing methods and systems
InactiveUS20050074380A1Move quicklyIncrease load capacityCombination devicesTemperatue controlIndustrial gasBatch processing
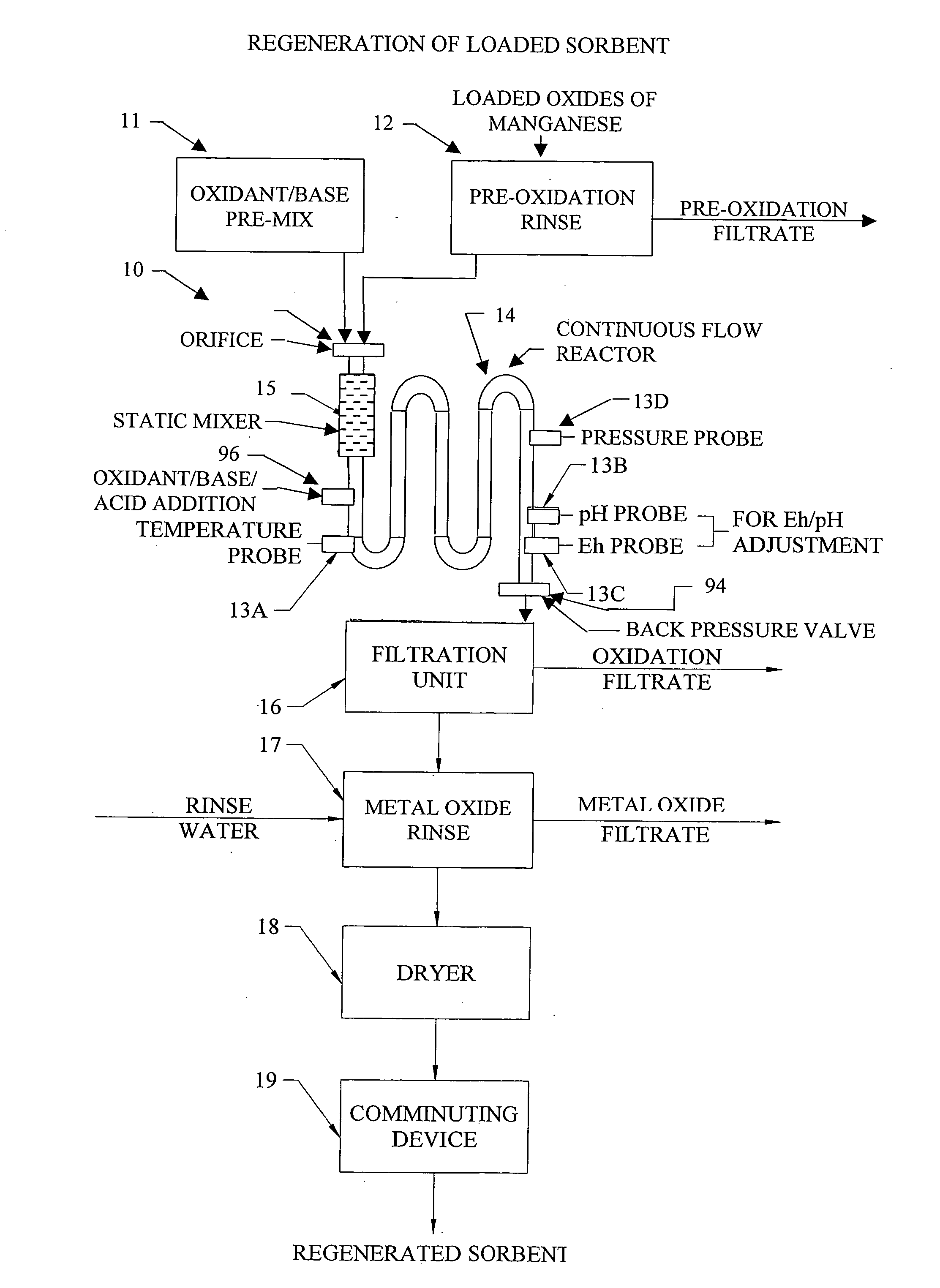
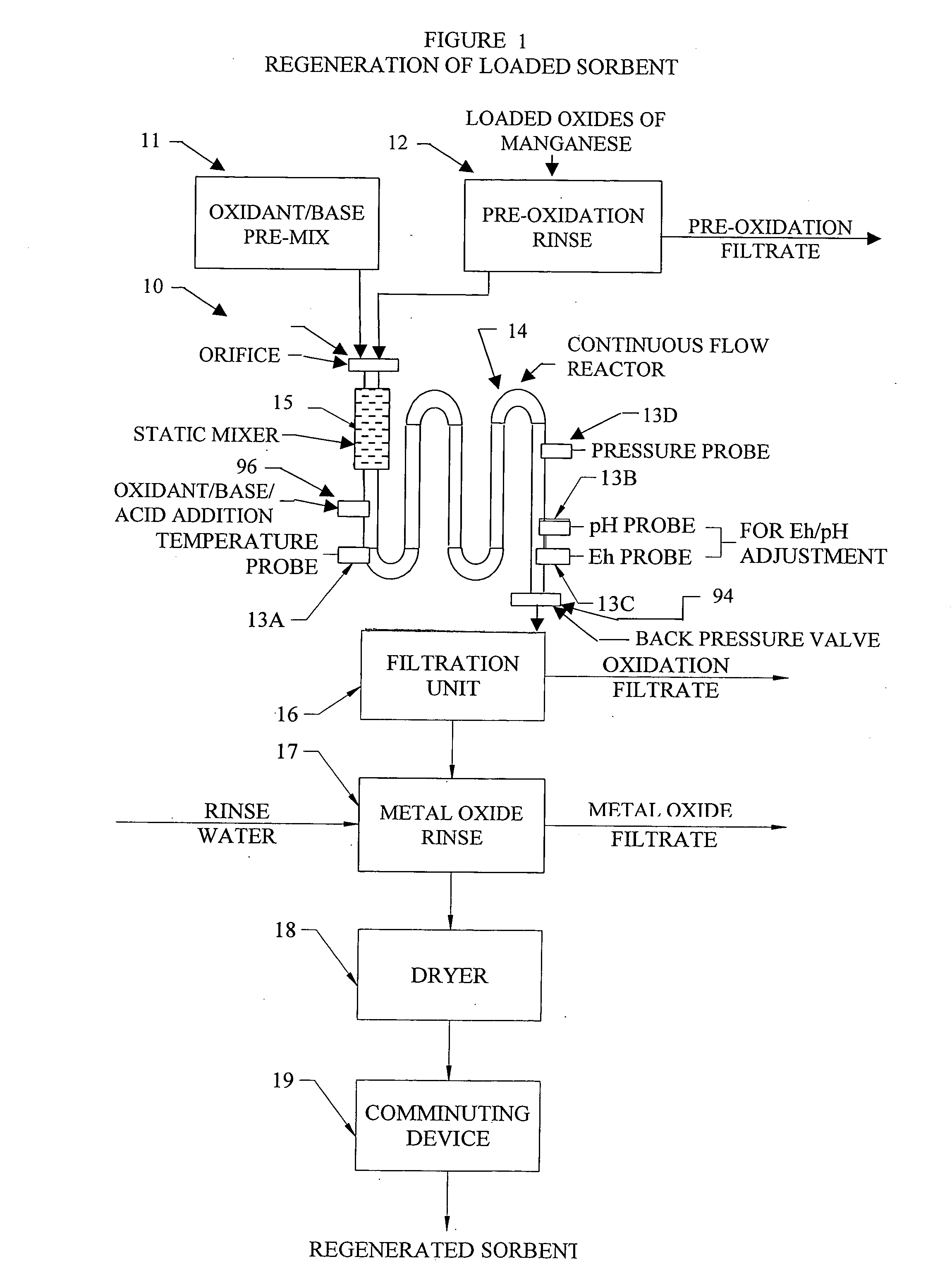
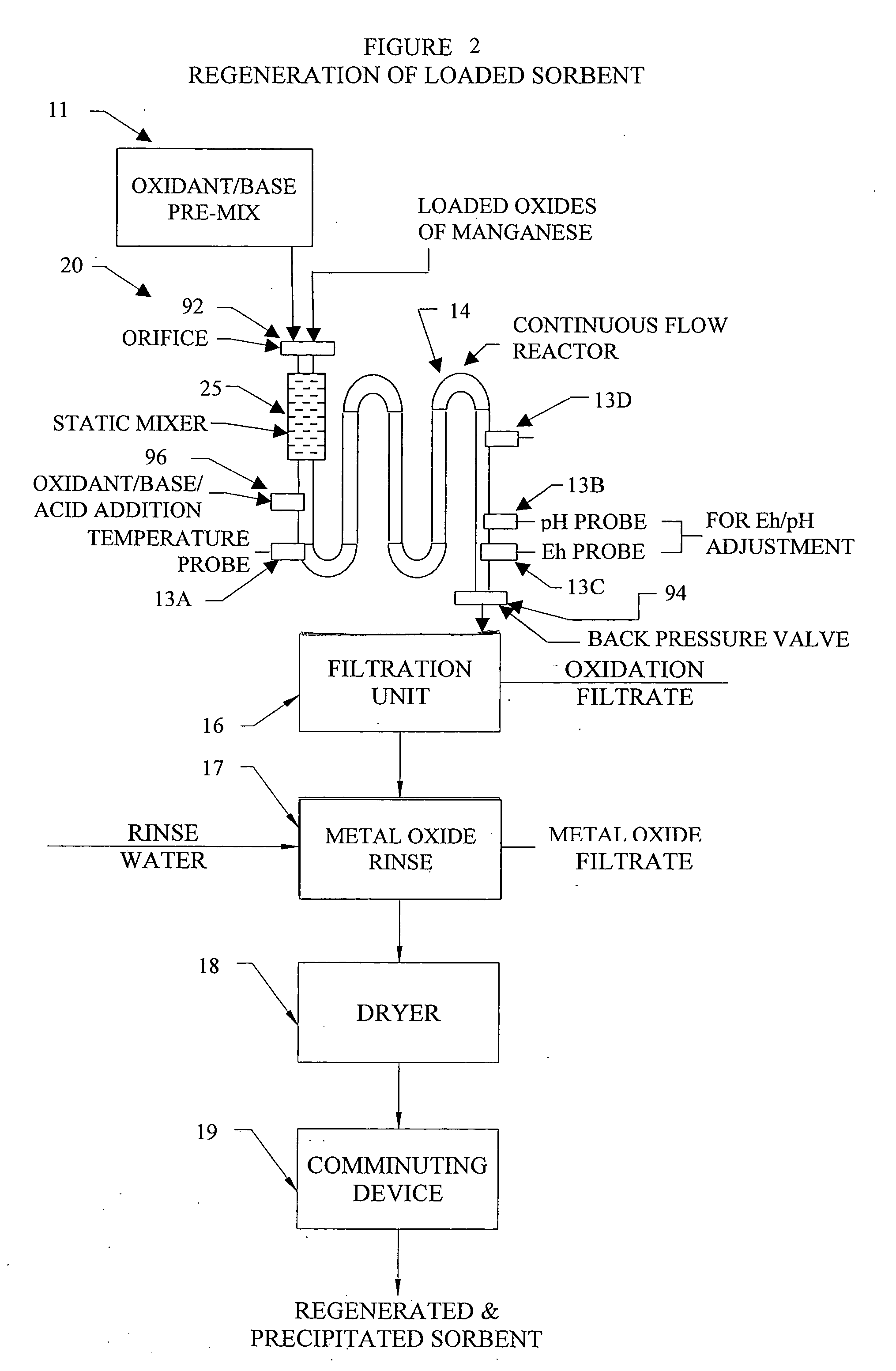
Methods and systems for processing metal oxides from metal containing solutions. Metal containing solutions are mixed with heated aqueous oxidizing solutions and processed in a continuous process reactor or batch processing system. Combinations of temperature, pressure, molarity, Eh value, and pH value of the mixed solution are monitored and adjusted so as to maintain solution conditions within a desired stability area during processing. This results in metal oxides having high or increased pollutant loading capacities and / or oxidation states. These metal oxides may be processed according to the invention to produce co-precipitated oxides of two or more metals, metal oxides incorporating foreign cations, metal oxides precipitated on active and inactive substrates, or combinations of any or all of these forms. Metal oxides thus produced are, amongst other uses; suitable for use as a sorbent for capturing or removing target pollutants from industrial gas streams or drinking water or aqueous streams or for personal protective respirators.
Owner:ENVIROSCRUB TECH CORP
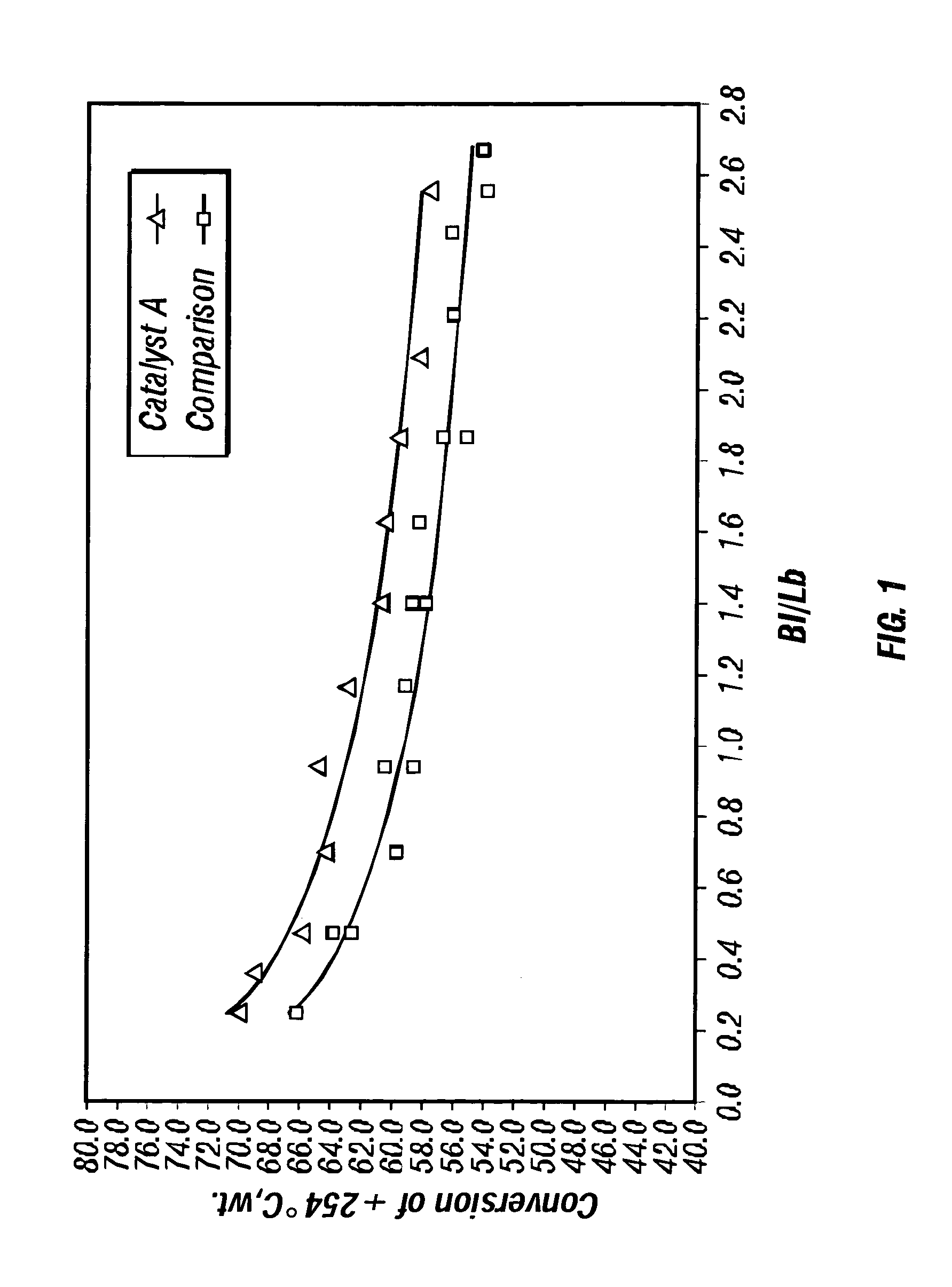
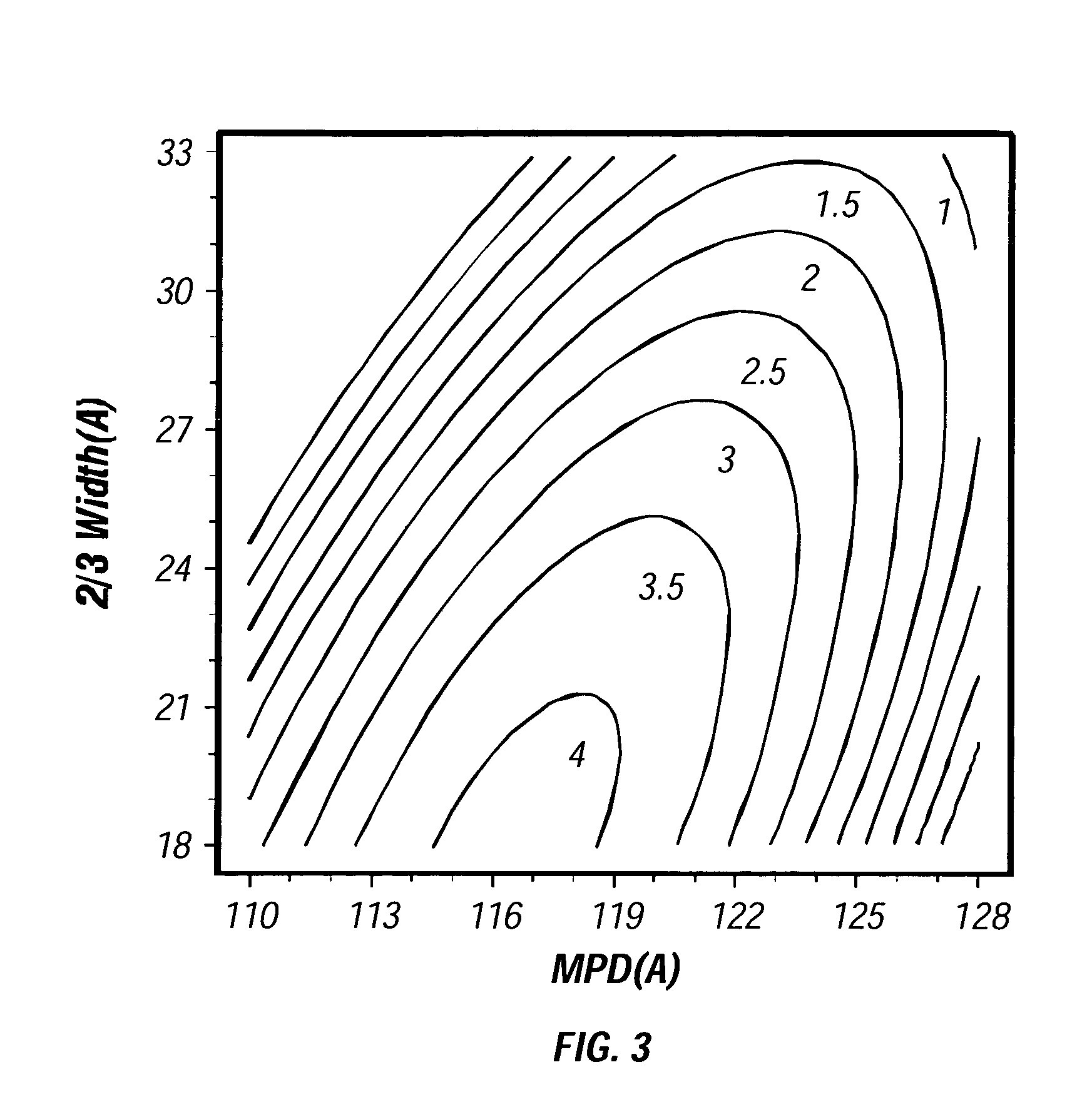
Process and catalyst for the hydroconversion of a heavy hydrocarbon feedstock
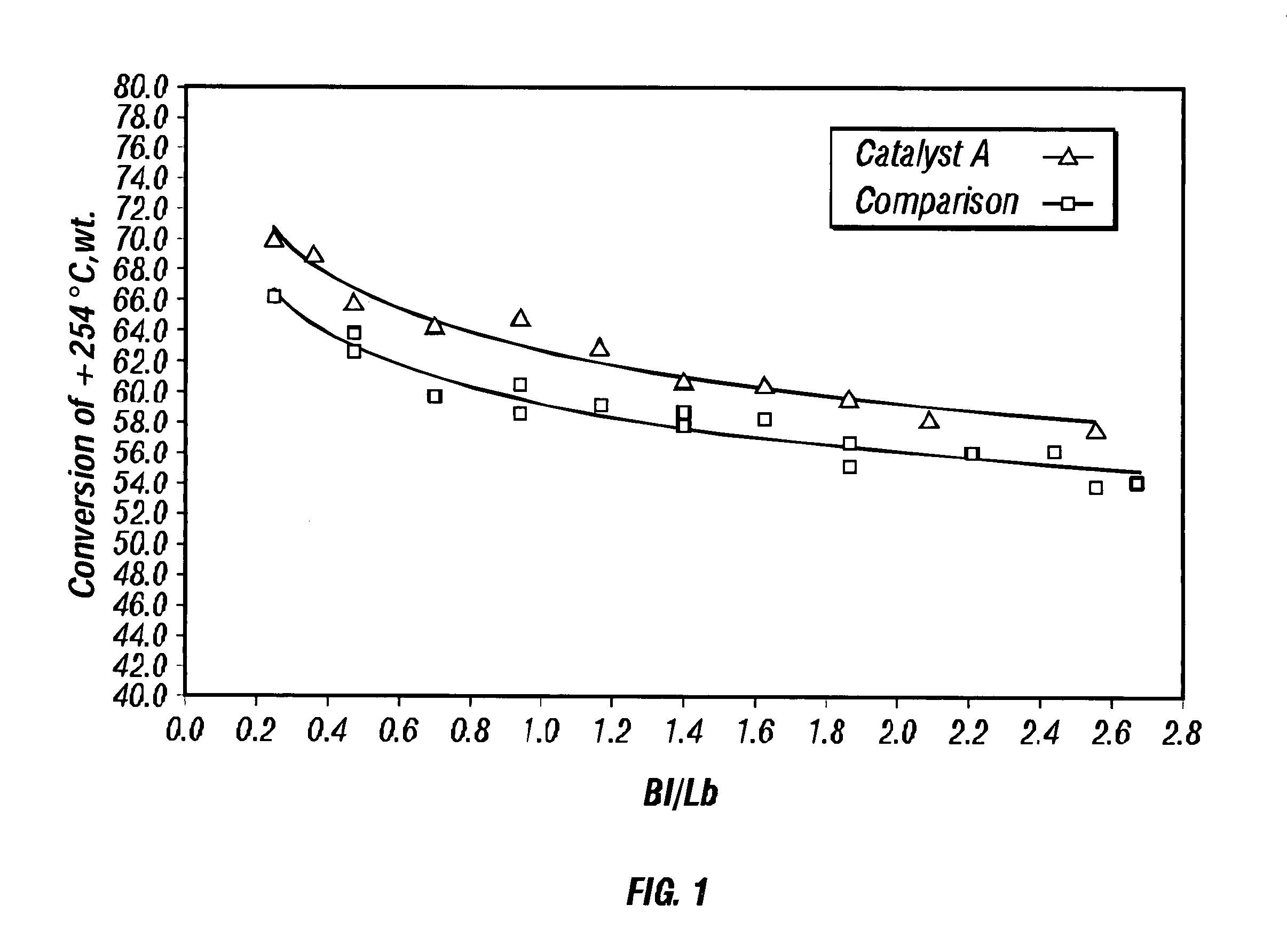
A method of hydroprocessing a heavy hydrocarbon feedstock using a hydroprocessing catalyst having specific properties making it effective in the hydroconversion of at least a portion of the heavy hydrocarbon feedstock to lighter hydrocarbons. The hydroprocessing catalyst comprises a Group VIB metal component (e.g., Cr, Mo, and W), a Group VIII metal component (e.g., Ni and Co) and, optionally, a potassium metal component that are supported on a support material comprising alumina. The alumina has novel physical properties that, in combination with the catalytic components, provide for the hydroprocessing catalyst. The hydroprocessing catalyst is particularly effective in the conversion of the heavy hydrocarbon feedstock. The alumina is characterized as having a high pore volume and a high surface area with a large proportion of the pore volume being present in the pores within a narrow pore diameter distribution about a narrowly defined range of median pore diameters. The support material preferably does not contain more than a small concentration of silica. The alumina component is preferably made by a specific method that provides for an alumina having the specific physical properties required for the hydroprocessing catalyst.
Owner:SHELL USA INC
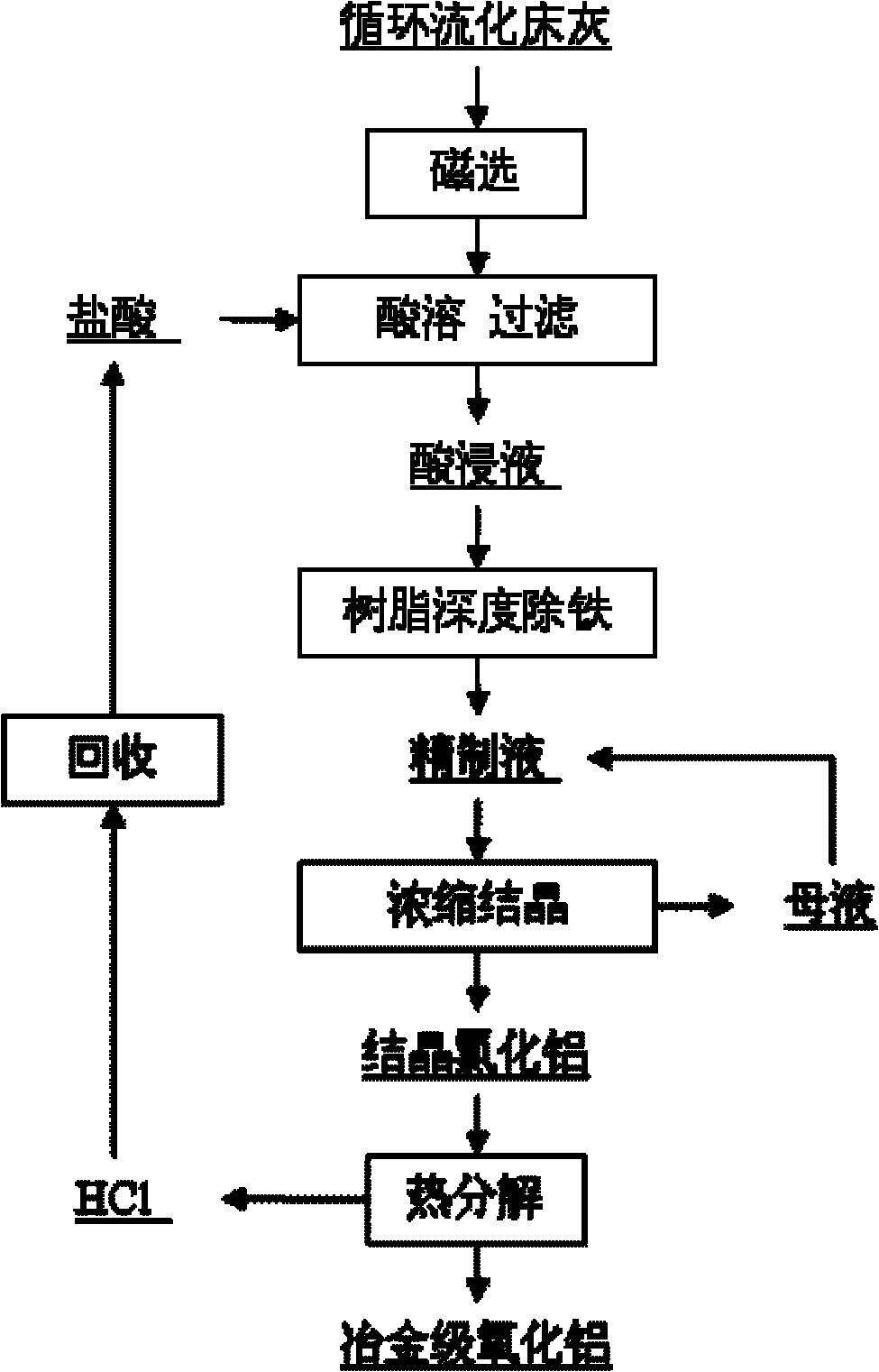
Method for preparing metallurgy-level aluminum oxide by using fluidized bed pulverized fuel ash
ActiveCN102145905AHigh extraction rateReduce manufacturing costSolid waste disposalTransportation and packagingAluminium chloridePulverized fuel ash
The invention discloses a method for preparing metallurgy-level aluminum oxide by using fluidized bed pulverized fuel ash as a raw material. The method comprises the following steps of: a) grinding the pulverized fuel ash, and removing iron by a wet magnetic separation method; b) reacting the pulverized fuel ash subjected to magnetic separation with hydrochloric acid to obtain hydrochloric acid immersion liquid; c) allowing the hydrochloric acid immersion liquid to pass through a large pore type cation resin column for further iron removal to obtain refined aluminum chloride solution; d) concentrating the refined aluminum chloride solution, and crystallizing to obtain an aluminum chloride crystal; and e) calcining the aluminum chloride crystal and decomposing to obtain the metallurgy-level aluminum oxide. The method has a simple process and an easily-controlled production process, and is high in aluminum oxide extraction efficiency, low in production cost and stable in product quality.
Owner:CHINA SHENHUA ENERGY CO LTD
Process and catalyst for the hydroconversion of a heavy hydrocarbon feedstock
A method of hydroprocessing a heavy hydrocarbon feedstock using a hydroprocessing catalyst having specific properties making it effective in the hydroconversion of at least a portion of the heavy hydrocarbon feedstock to lighter hydrocarbons. The hydroprocessing catalyst comprises a Group VIB metal component (e.g., Cr, Mo, and W), a Group VIII metal component (e.g., Ni and Co) and, optionally, a potassium metal component that are supported on a support material comprising alumina. The alumina has novel physical properties that, in combination with the catalytic components, provide for the hydroprocessing catalyst. The hydroprocessing catalyst is particularly effective in the conversion of the heavy hydrocarbon feedstock. The alumina is characterized as having a high pore volume and a high surface area with a large proportion of the pore volume being present in the pores within a narrow pore diameter distribution about a narrowly defined range of median pore diameters. The support material preferably does not contain more than a small concentration of silica. The alumina component is preferably made by a specific method that provides for an alumina having the specific physical properties required for the hydroprocessing catalyst.
Owner:SHELL USA INC
Firing sol-gel alumina particles
InactiveUS6083622AImprove grinding performanceMaterial nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentMaterials scienceSol-gel
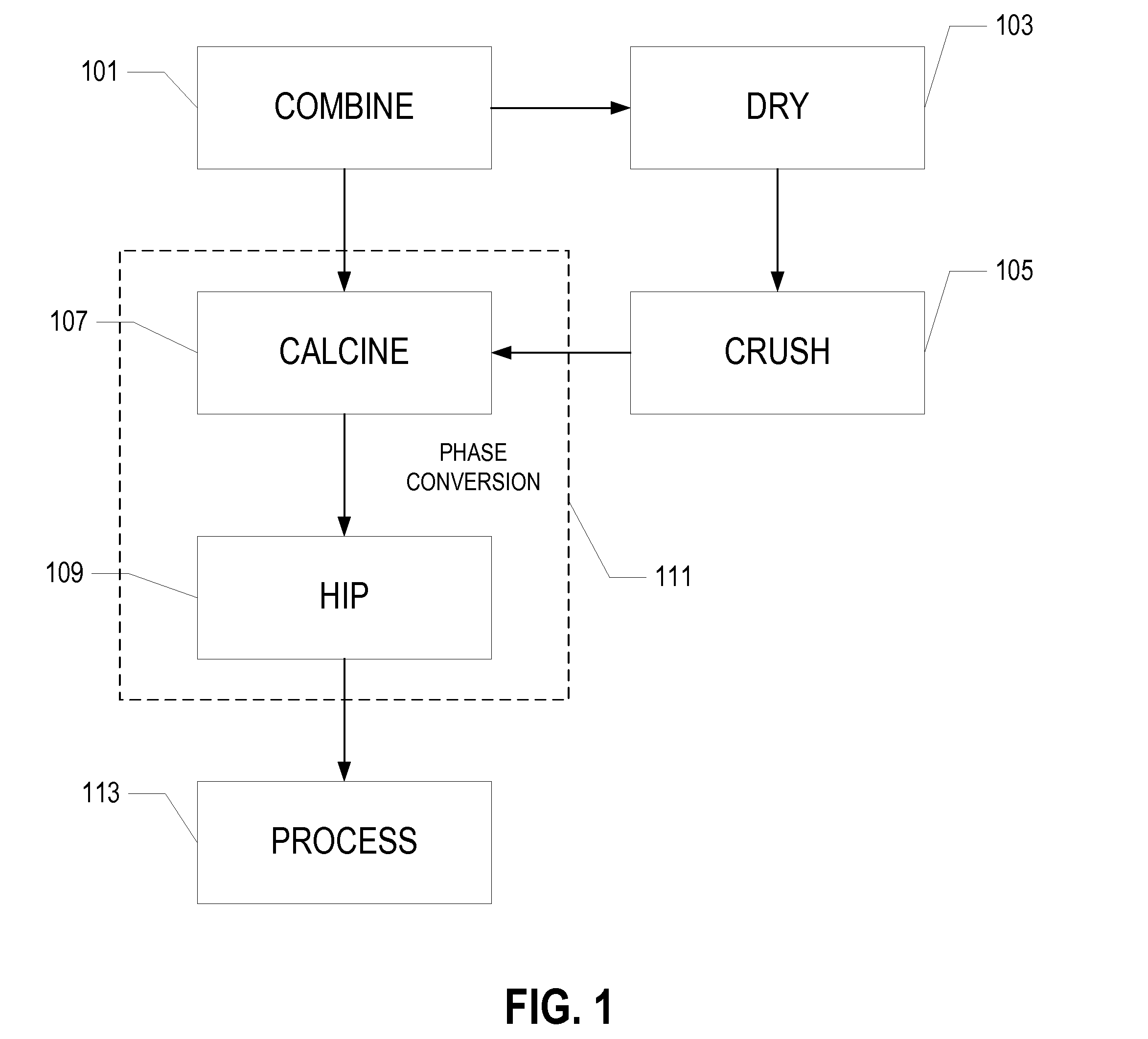
PCT No. PCT / US96 / 04137 Sec. 371 Date Oct. 31, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Oct. 31, 1997 PCT Filed Mar. 27, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 32226 PCT Pub. Date Oct. 17, 1996Sol-gel alumina that is dried but unfired can be explosively comminuted by feeding the dried gel into a furnace held at temperatures above those at which vaporizable materials are eliminated from the particles of gel. At suitably elevated temperatures the firing is sufficient to form fully densified alpha alumina particles of a size suitable for direct use as abrasive grits.
Owner:SAINT GOBAINNORTON INDAL CERAMICS
Three-dimensional ordered macroporous alumina and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102040235AHigh activityGood choiceOther chemical processesAluminium oxides/hydroxidesMicrosphereNetwork structure
The invention provides a three-dimensional ordered macroporous alumina and a preparation method thereof, wherein the method comprises the following steps of: assembling polymer microspheres which are singly dispersed to form a colloidal crystal template, filling the alumina sol which is prepared by means of a special method into the template, and drying and roasting to obtain macroporous alumina. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that the alumina sol and the compounding process of the alumina sol and the polymer microspheres can be controlled well, the network structure of the alumina sol is protected possibly, the alumina which is prepared by means of the method not only has three-dimensional ordered macroporous channels but also has a high specific surface area. Furthermore, the macropores within the material are communicated to the surrounding macropores by means of 12 small window holes, and the window holes are formed by sintering the template properly. The alumina prepared by means of the method provided by the invention is suitable for being used as a catalyst carrier of heavy oil and an adsorption and separation material of organic macromolecule. The alumina prepared by means of the method which is provided by the invention is suitable for improving the mass transfer capability of the material within the catalyst and is suitable for improving the activity and the selectivity of the catalyst during the application process as a catalyst carrier.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
High strength, nanoporous bodies reinforced with fibrous materials
ActiveUS7560062B2High modulusHigh strengthLayered productsOrnamental structuresFlexural strengthHigh intensity
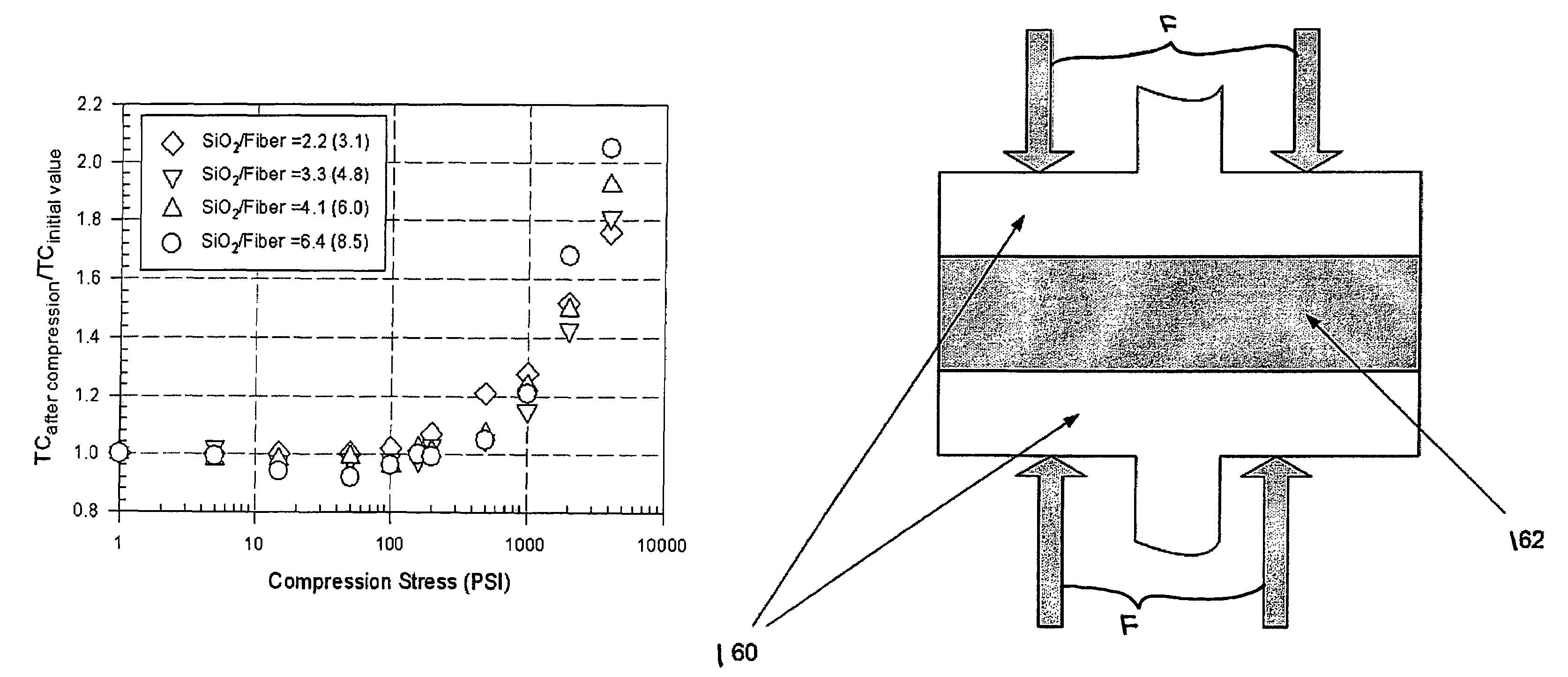
This invention discloses improvements that can be achieved in thermal or mechanical performance of aerogel composites via densification. Densified aerogels and aerogel composites can display higher compressive strength, modulus, flexural strength, and maintains or insubstantially increases the thermal conductivity relative to the pre-densified form. In the special case of fiber reinforced aerogel composites densification via mechanical compression can prove highly beneficial.
Owner:ASPEN AEROGELS INC
Mesoporous spherical alumina prepared by guiding of template and preparation method thereof
The invention provides mesoporous spherical alumina and a method for preparing the mesoporous spherical alumina by guiding of a template. By the adoption of an oil column forming method, the template with a guiding function is added into aluminum sol during the aluminum sol preparation process; and during the forming and aging processes of the aluminum sol, due to the existence of the template with the guiding function, a large number of meso-structures are prepared in alumina balls. The mesoporous spherical alumina has the following characteristics of: its specific surface is 150-300 m<2> / g; particle diameter is 0.1-5 mm; pore volume is 0.7-1.5 ml / g; holes, hole diameter of which is 2-40 nm, are greater than 97%; bulk density is 0.30-0.80g / cm<3>; and crushing strength is 70-250 N / granule. The mesoporous spherical alumina can be used as a catalyst or a catalyst carrier in the petrochemical industry and the industry of fine chemicals.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Alumina powder, process for producing the same and polishing composition
InactiveUS6440187B1High speed polishing propertyQuality improvementPigmenting treatmentMaterial nanotechnologyAlumina hydrateCrystal structure
Production of an alumina powder characterized by having a single or multiple crystal structure selected from the group consisting of gamma, delta and theta-forms, a primary particle size of 10 to 50 nm, a mean secondary particle size of 100 to 500 nm, and a granular primary particle shape, or an alumina powder characterized by having an a-form crystal structure, a primary particle size of 60 to 150 nm, a mean secondary particle size of 200 to 500 nm, and a granular primary particle shape, using as a raw material an alumina hydrate comprising rectangular plate-like primary particles having a boehmite structure and having a length of one side of 10 to 50 nm; and preparation of a polishing composition comprising the alumina powder, water and a polishing accelerator.
Owner:NISSAN CHEM IND LTD
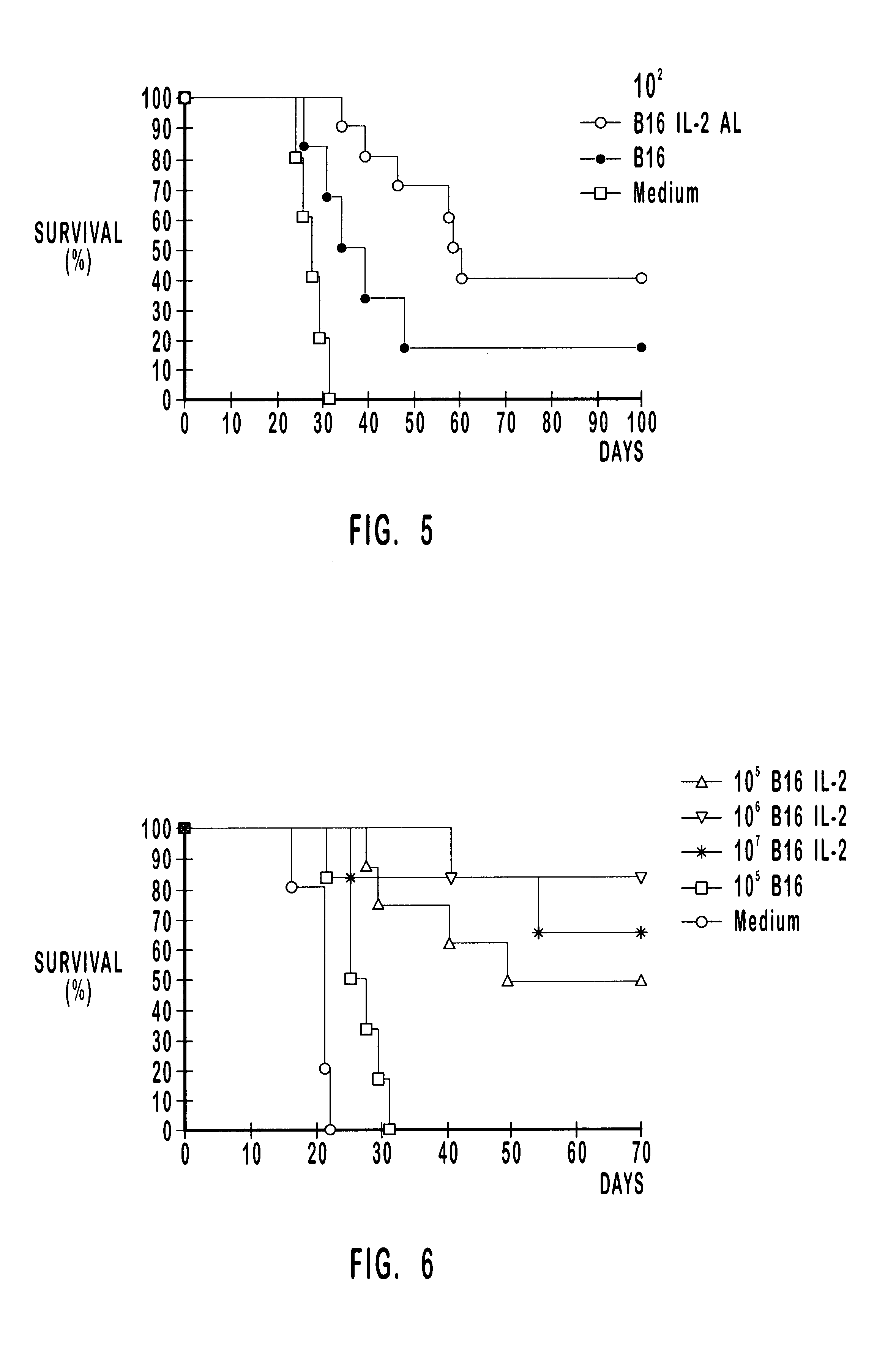
Compositions and methods for treatment of tumors and metastatic diseases
InactiveUS6406689B1Stimulate immune responseSimple and reliable to useBiocideSnake antigen ingredientsDiseaseActive immunization
Owner:FALKENBERG FR W
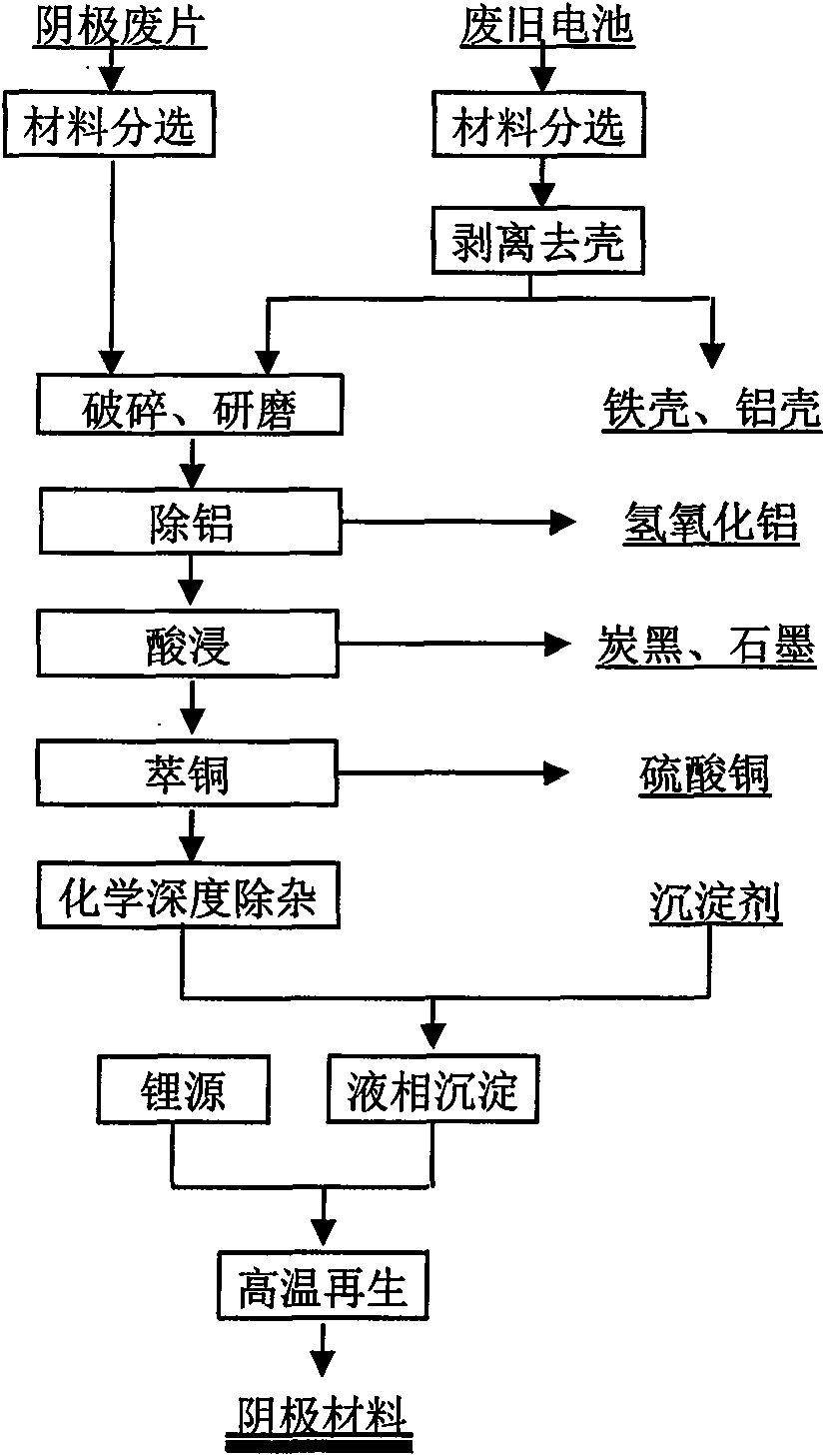
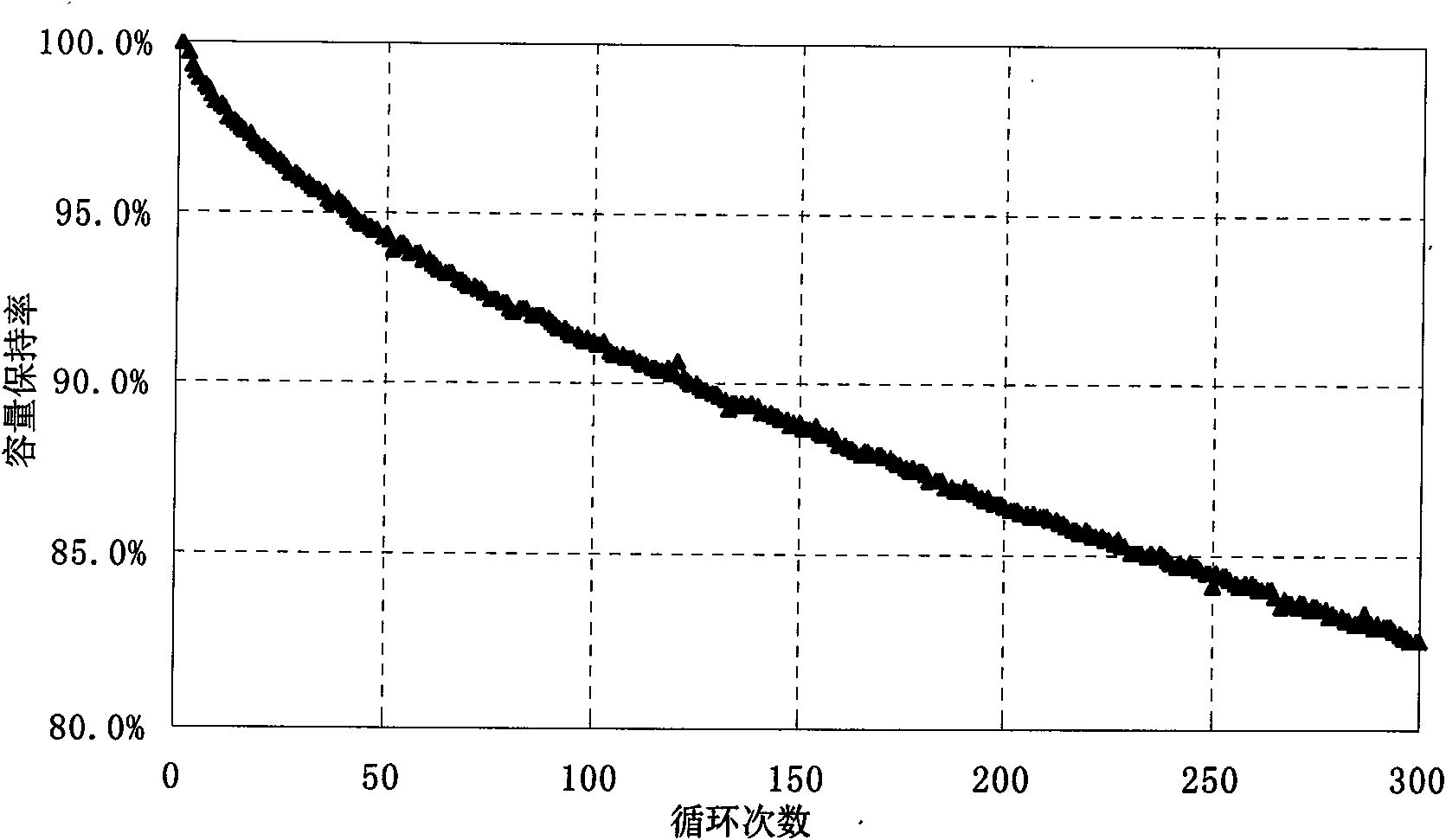
Method for recovering and recycling waste lithium ion battery cathode material
InactiveCN101555030AAchieve recyclingAchieve regenerationCobalt compoundsNickel compoundsEngineeringLithium-ion battery
The invention discloses a method for recovering and recycling waste lithium ion battery cathode material, belonging to the fields of lithium ion battery material preparation and recycling use of waste resources. The method has the technical proposal with the key points as follows: the recovered waste batteries are sorted, cathode waste material (after being sorted) which is stripped to remove the shell and generated in the production process of the lithium ion battery is directly crushed and ground, and then processed by the procedures such as aluminum removing, acid dipping, copper extracting, chemical purification and the like under different conditions, so that byproduct materials such as aluminum hydroxide, carbon black, graphite, copper sulphate and the like are generated; reaction products are added with precipitator with certain concentration for liquid-phase precipitation and then added with lithium source, so that cathode material can be generated in the high temperature environment. The technical proposal successfully realizes the valuable constituent recovery and cathode material regeneration of the waste lithium ion battery cathode material.
Owner:GUANGDONG BRUNP RECYCLING TECH
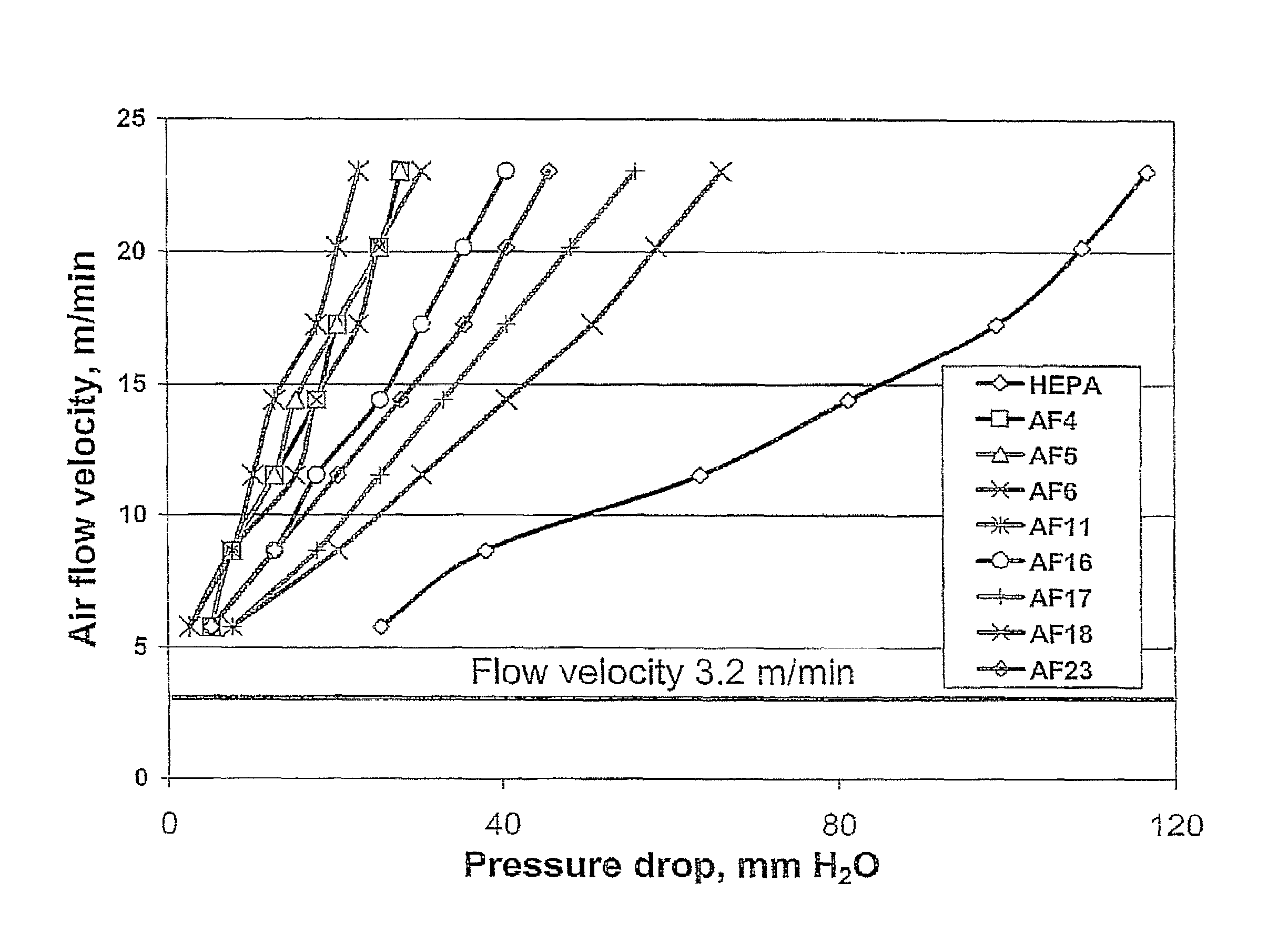
Catalyst carriers
The selectivity and activity of a silver-based olefin epoxidation catalyst is found to be a function of the pore size distribution in the alumina carrier on which it is deposited. Specifically it is found advantageous to provide a carrier which has a minimum of very large pores, (greater than 10 micrometers) and a water absorption of 35 to 55% and a surface area of at least 1.0 m2 / g. A method of making such carriers is also described.
Owner:SAINT-GOBAIN GLASS FRANCE
Drinking water filtration device
ActiveUS7390343B2Improve efficiencyLarge capacityMaterial nanotechnologyDispersed particle filtrationFiberHalogen
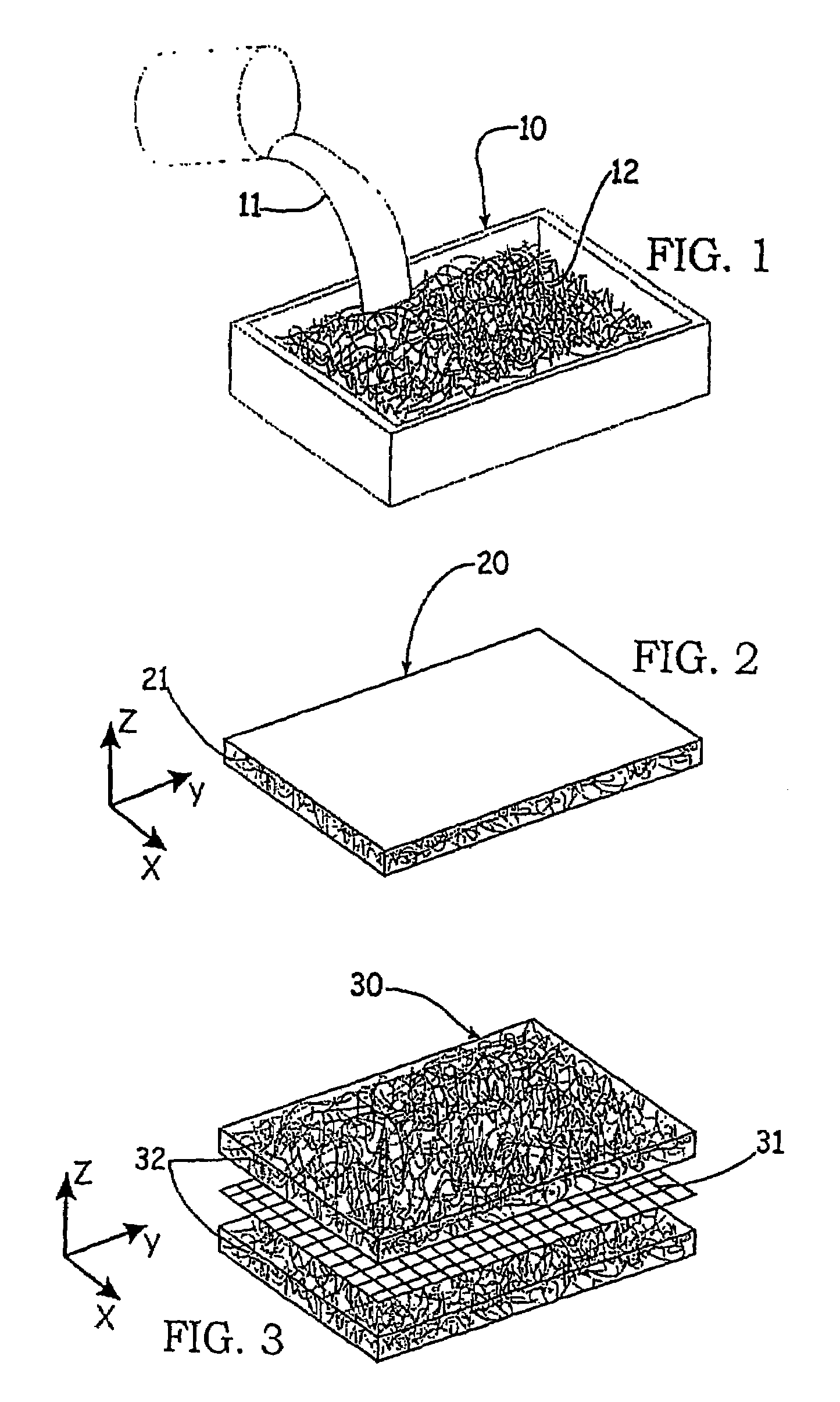
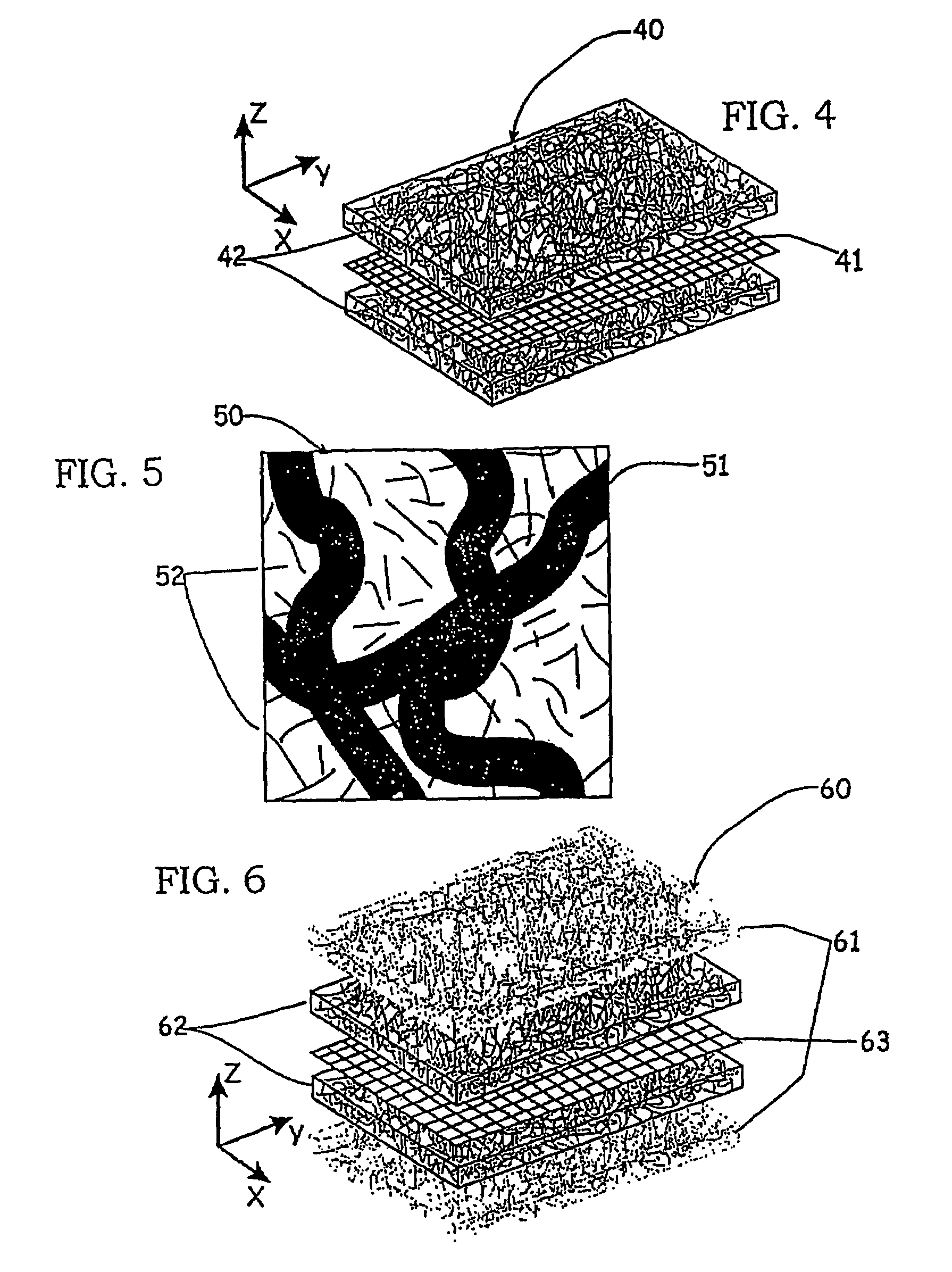
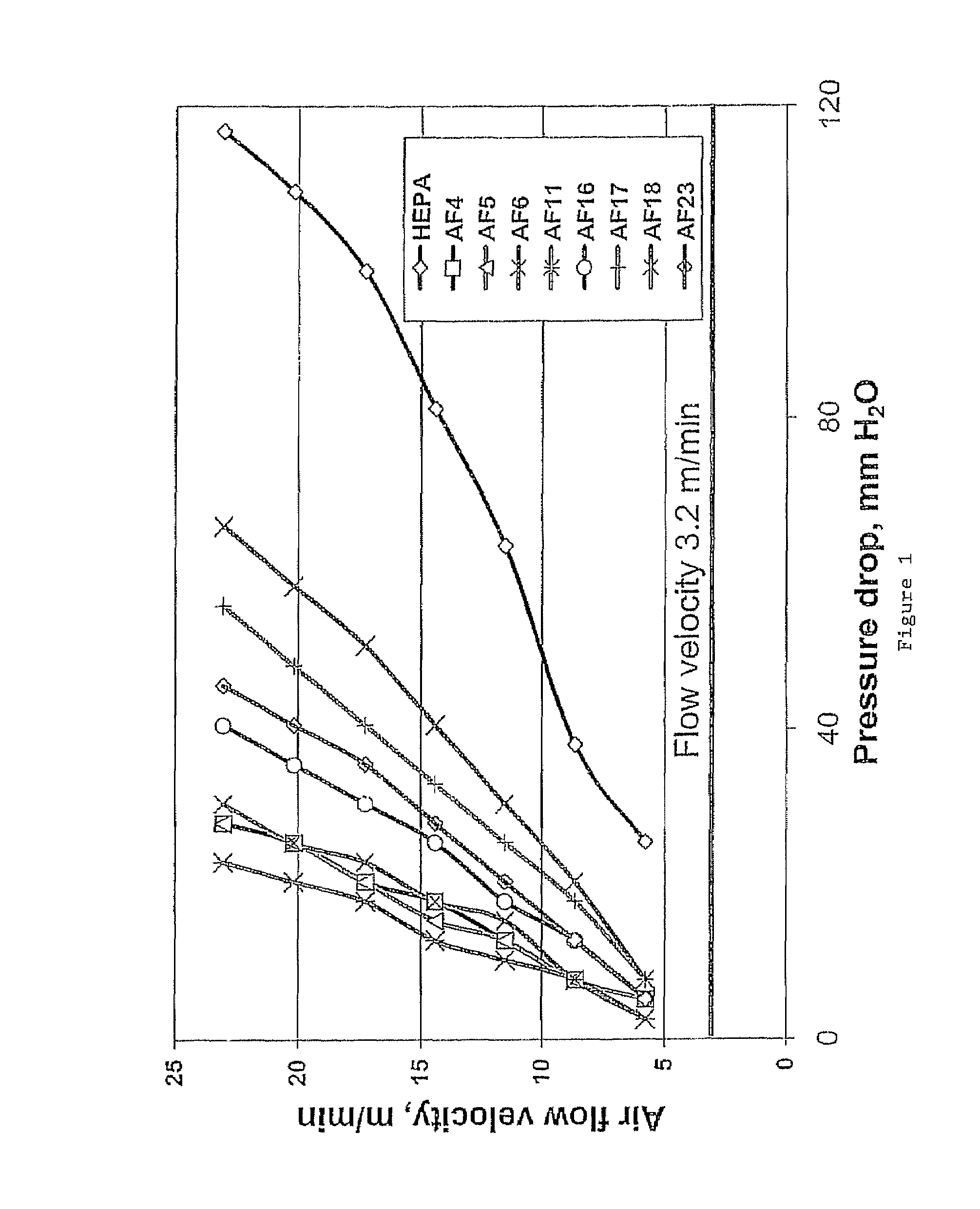
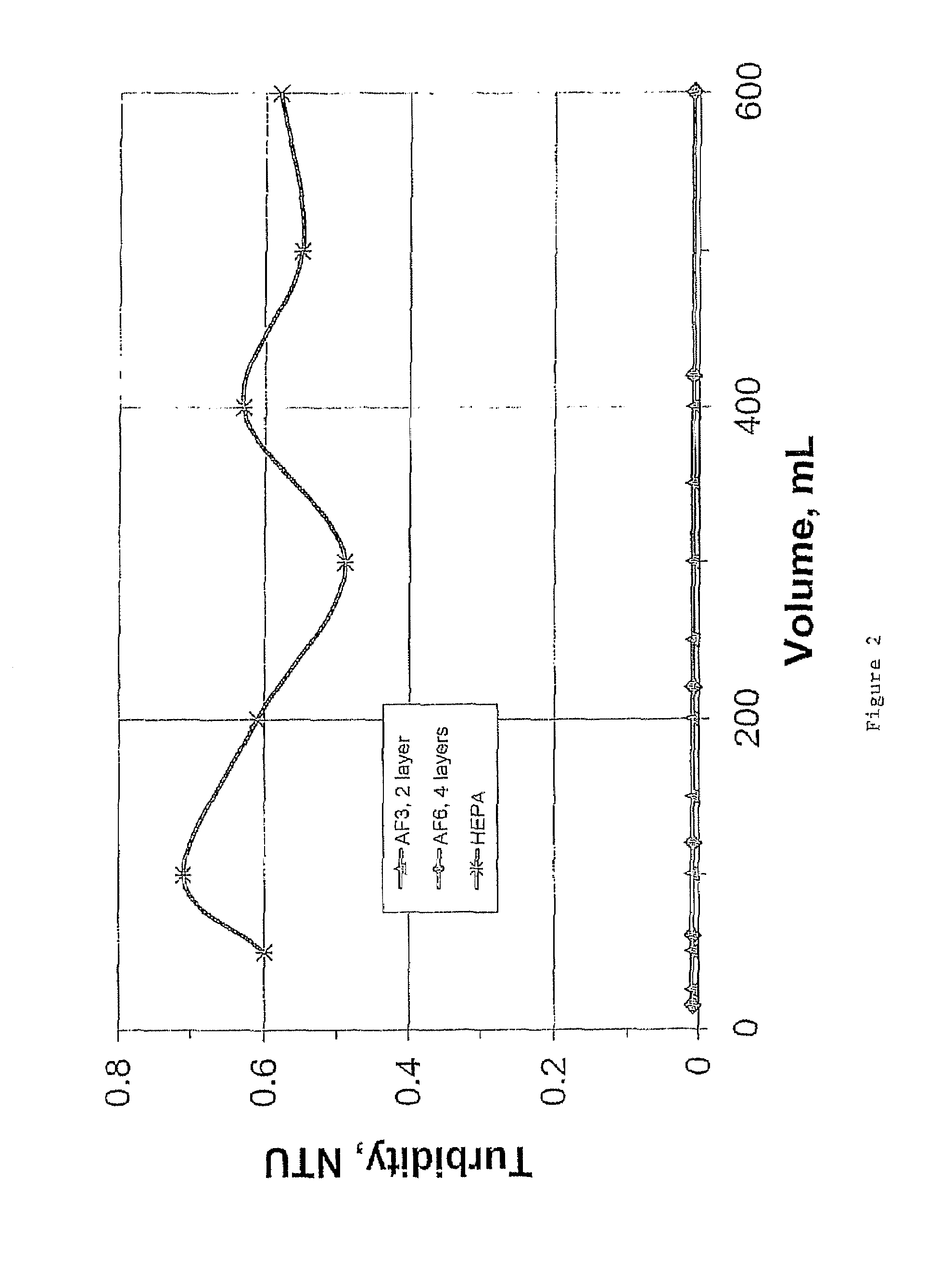
The invention is a device for purifying drinking water that has at least one fibrous structure. Preferably, there is an upstream and downstream fibrous structure. Each fibrous structure is a mixture of nano alumina fibers and second fibers arranged in a matrix to create asymmetric pores and to which fine, ultrafine, or nanosize particles are attached. Preferably, the device has an upstream antimicrobial for sterilization of retained microbes. The device is substantially more efficient at removing soluble contaminants such as halogens from a fluid stream than those previously available and is also able to retain turbidity, bacteria, and virus.
Owner:ARGONIDE CORP
Preparation method of alumina
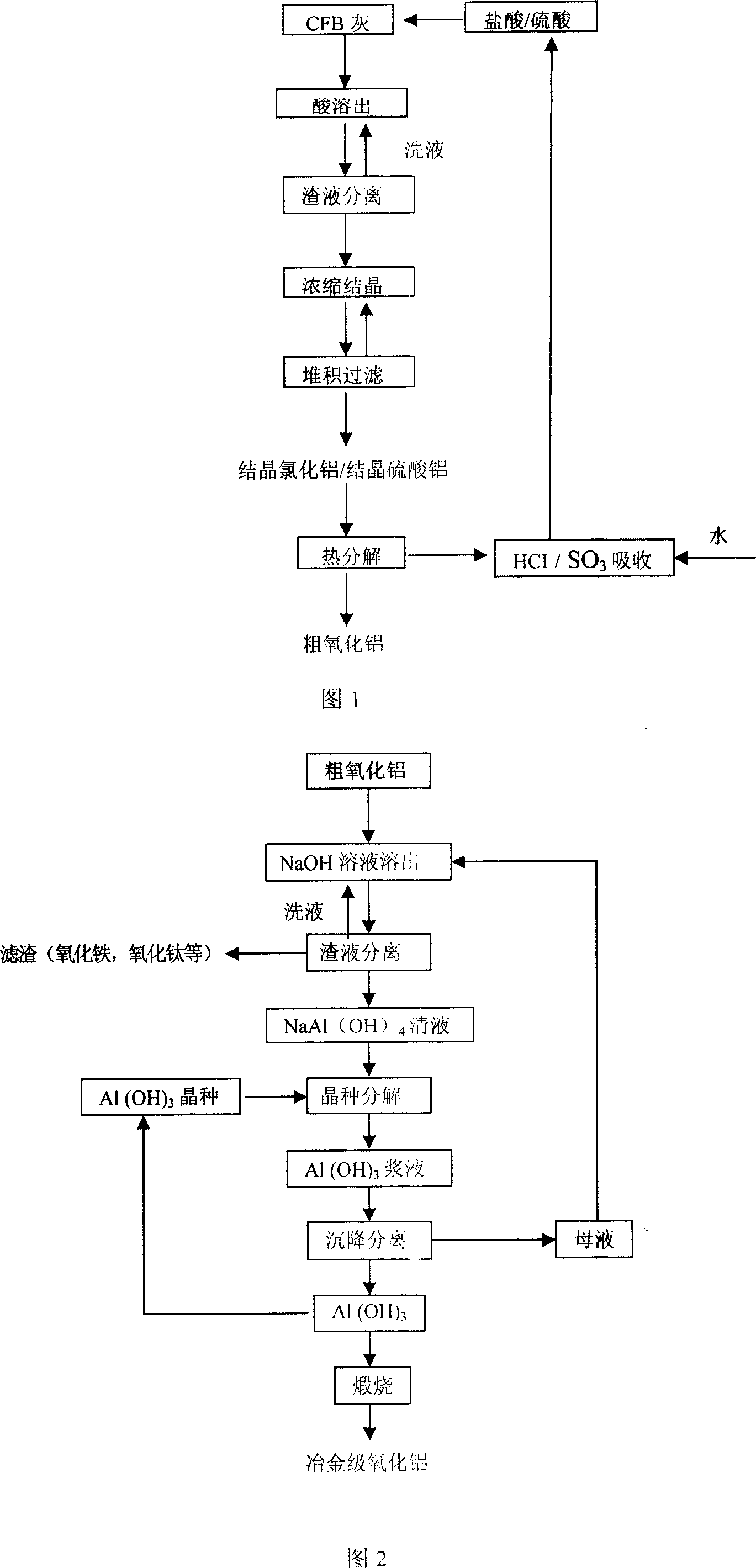
ActiveCN1927716AReduce pollutionReduce consumptionAluminium oxide/hydroxide preparationAluminium oxides/hydroxidesAluminium hydroxideDecomposition
The process of preparing alumina includes: the reaction of flyash from circular fluidizing bed and acid to obtain aluminum chloride solution, eliminating silicon impurity, concentrating to crystallize and heating to decompose and to obtain crude alumina product; reaction of crude alumina product and hot alkali solution to obtain sodium aluminate solution; eliminating iron, titanium and other impurity, adding aluminum hydroxide crystal seed into sodium aluminate solution for seed separating decomposition to obtain aluminum hydroxide precipitate; and final calcining aluminum hydroxide to obtain metallurgical alumina. The normal pressure process has no any cosolvent added, and the alumina product has Al2O3 content up to 98 %. The process has small sodium hydroxide consumption, reuse of most of sodium hydroxide, simple operation, low cost, low power consumption, capacity of reducing flyash pollution and other advantages.
Owner:SHENHUA ZHUNGER ENERGY
Ceramic particulate material and processes for forming same
InactiveUS20080176075A1Material nanotechnologyCeramic shaping apparatusImaging analysisMaterials science
Ceramic particulate material includes alumina particles, the particles having a specific surface area (SSA) not less than 15 m2 / g and not greater than 75 m2 / g and a sphericity quantified by at least one of (i) a mean roundness not less than 0.710 as measured by Roundness Correlation Image Analysis, and (ii) a concavity less than 20%, wherein concavity is the percent of alumina particles based on a sample of at least 100 particles, which have a concave outer peripheral portion that extends along a distance not less than 10% of d50 by TEM inspection, the concave outer peripheral portion having a negative radius of curvature as viewed from an interior of the particle
Owner:SAINT GOBAIN CERAMICS & PLASTICS INC
Spherical integral macroporous alumina and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102311134AHigh mechanical strengthSize is easy to controlAluminium oxides/hydroxidesMicrosphereSpherical shaped
The invention discloses spherical integral macroporous alumina and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: uniformly mixing polymer microspherical emulsion, alumina sol and a coagulant in a certain ratio, and dispersing the mixture in an oil phase to obtain W / O liquid drops; heating the miscible phase system to make the alumina sol in an aqueous phase gelatinized into spheres; separating out the formed gel microspheres from the oil phase; and ageing in an ammonia water medium, drying, and roasting to obtain the spherical integral macroporous alumina. The macropore size of the alumina is uniform and controllable in a range of less than 1 mu m, spherical particles have controllable size and high mechanical strength, and the forming process is simple and feasible, and is suitable for mass preparation.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Block copolymer processing for mesostructured inorganic oxide materials
InactiveUS7176245B2High BET surface areaIncrease surface areaMolecular-sieve and base-exchange compoundsCation exchangersMesoporous materialCopolymer
Owner:SBA MATERIALS
Method of preparing aluminum oxide from fly ash
ActiveCN1923695AHigh dissolution rateFewer separation stepsAluminium oxide/hydroxide preparationAluminium oxides/hydroxidesAluminium sulfateSlag
The invention discloses a preparing method of alumina through fly ash, which comprises the following steps: grinding fly ash; sintering; activating; stirring with H2SO4 evenly to sinter into dried slag; immersing through hot water; stripping aluminum sulfate; condensing; cooling to evolve aluminum sulfate; crystallizing; heating; dehydrating to obtain anhydrous aluminum sulfate; heating; decomposing to obtain gamma-Al2O3.
Owner:PINGSHUO INDAL
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com