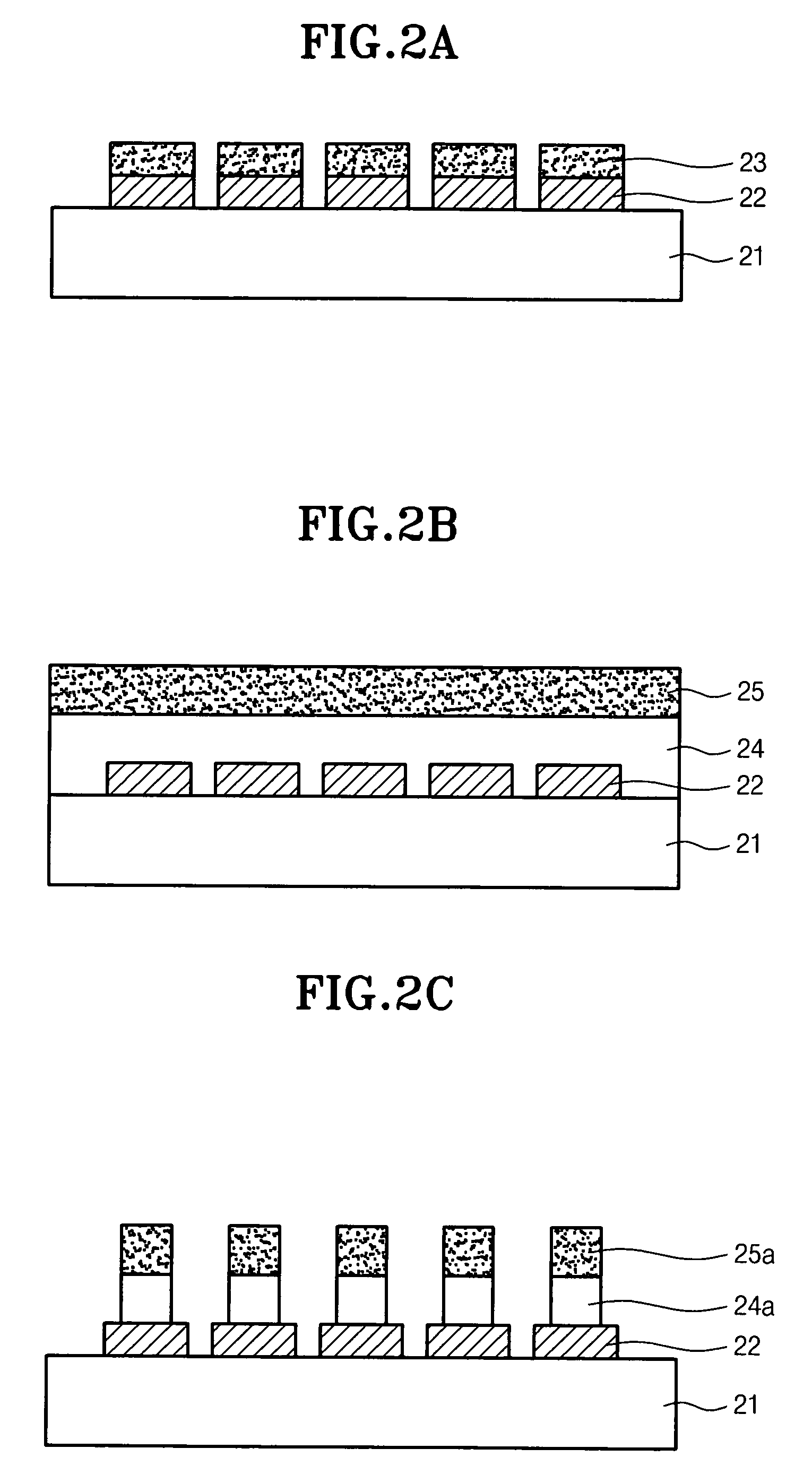
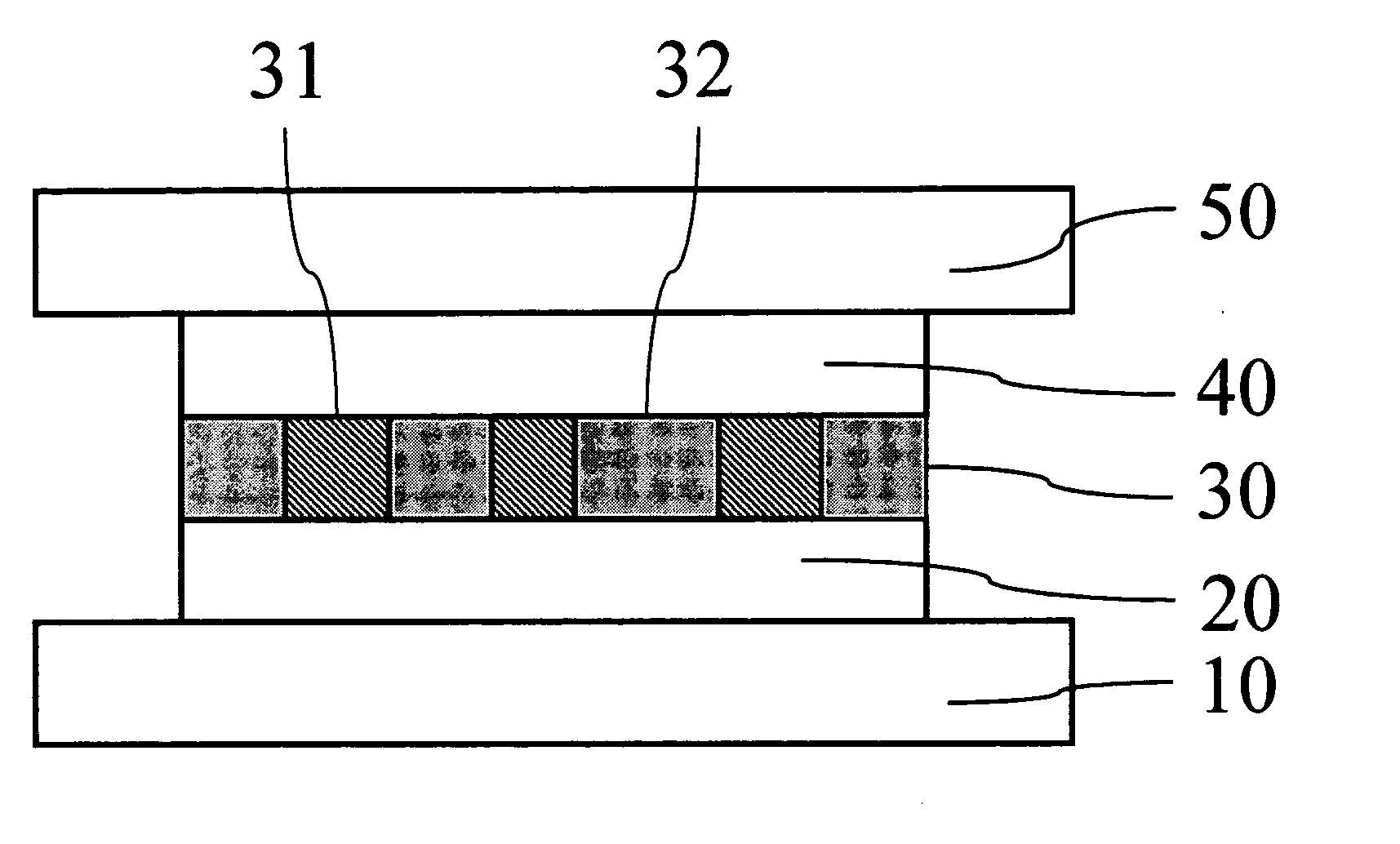
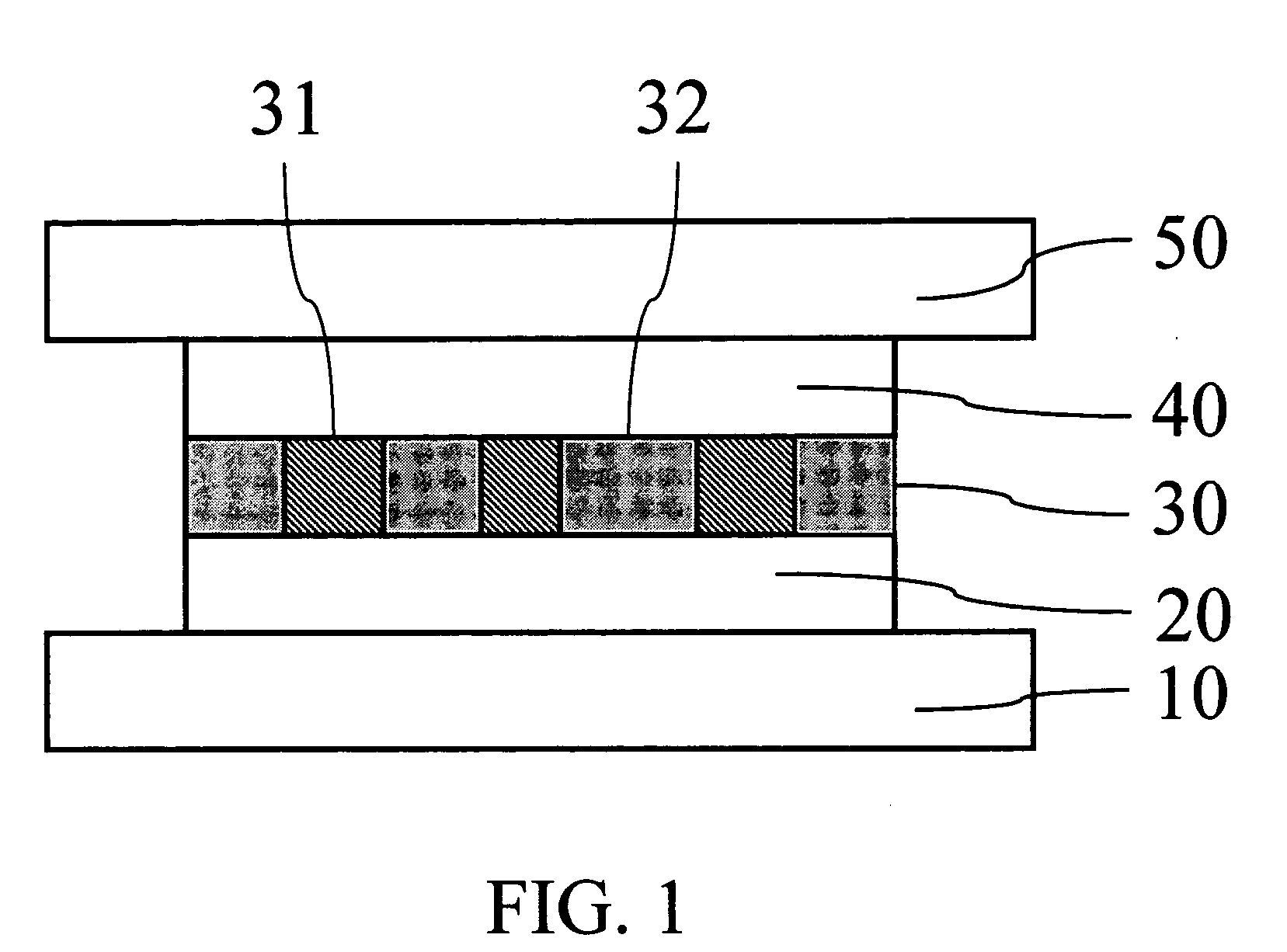
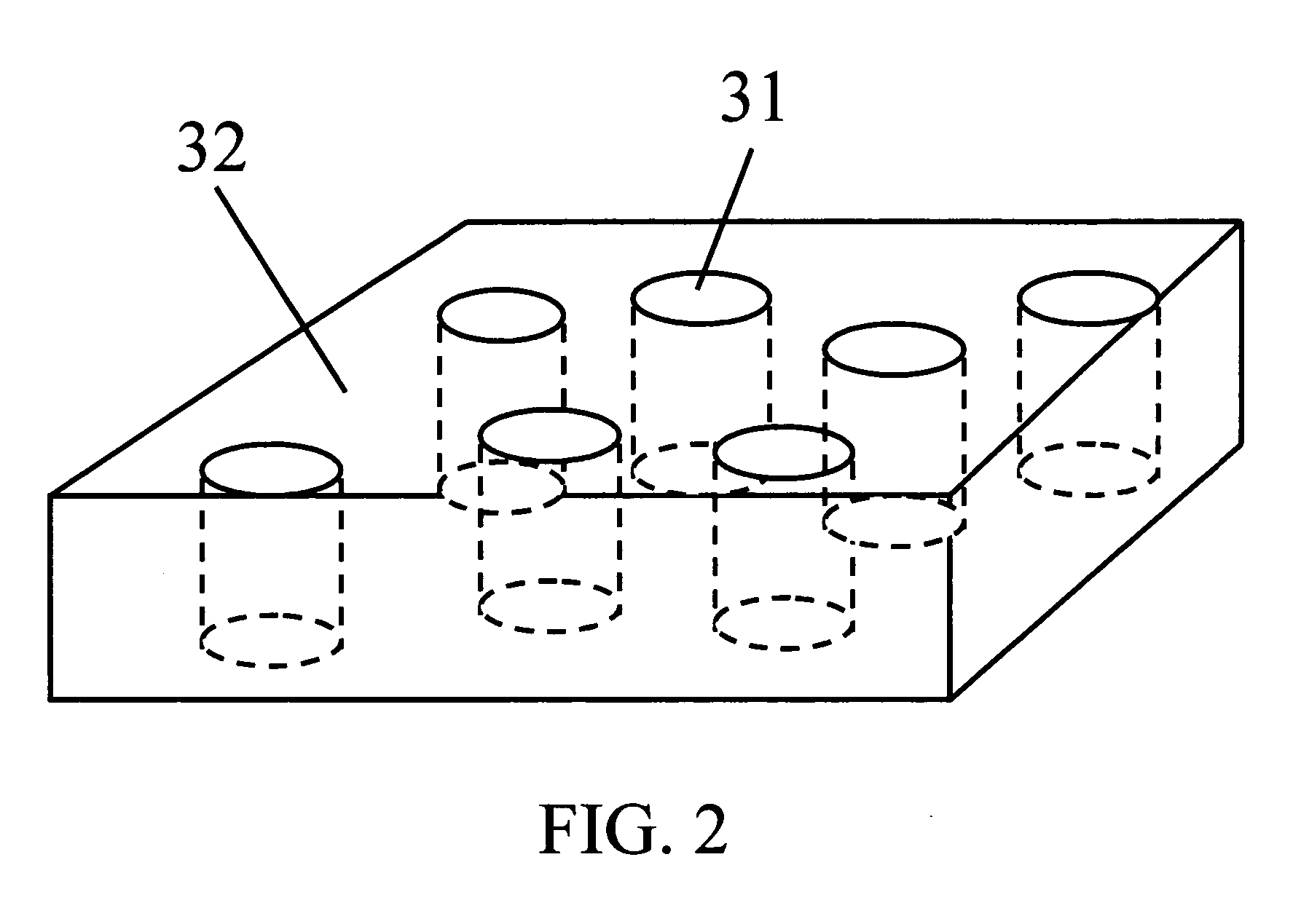
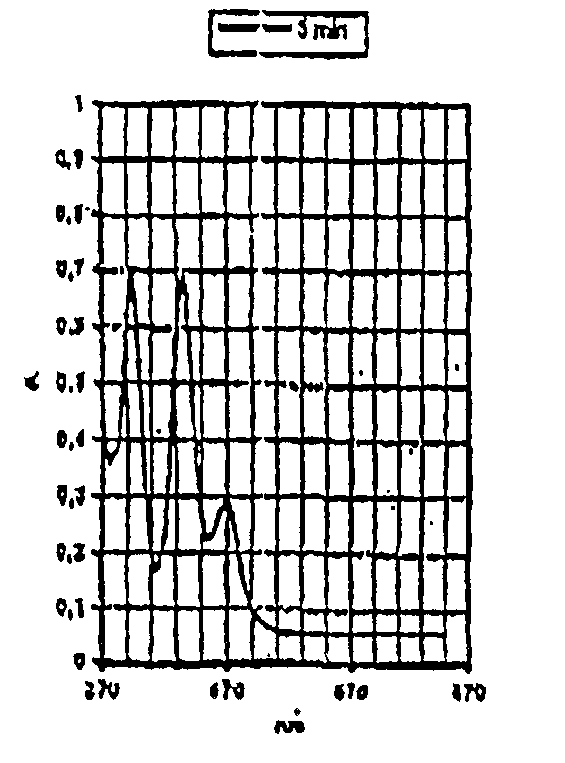
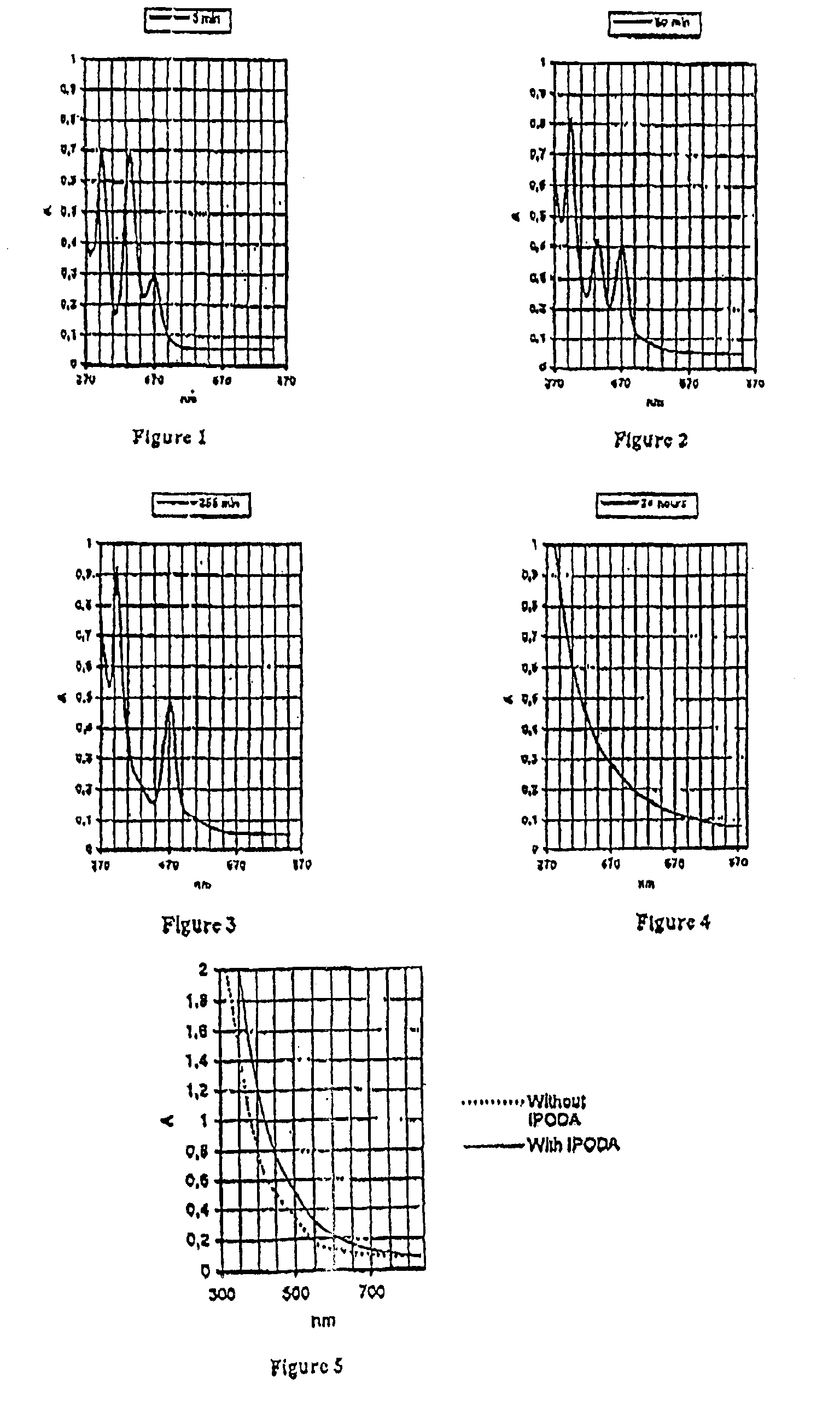
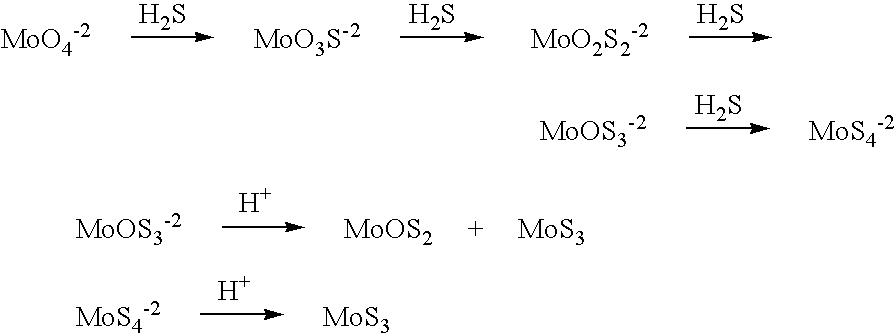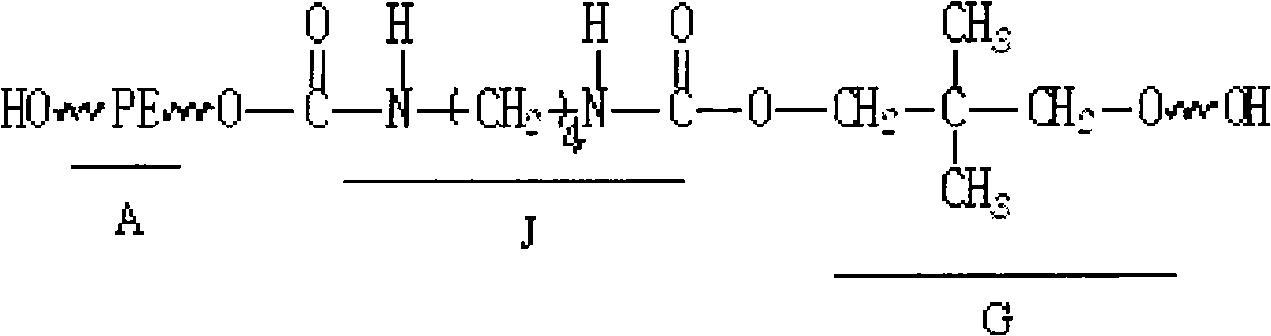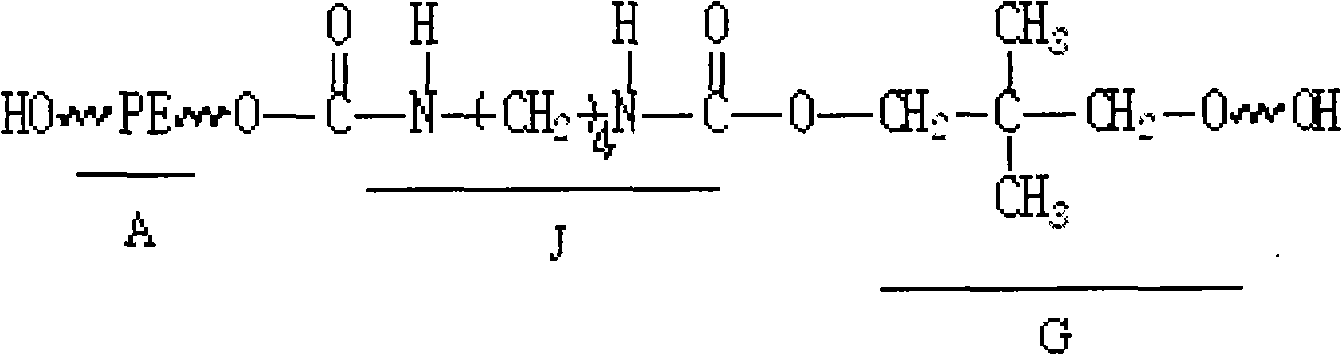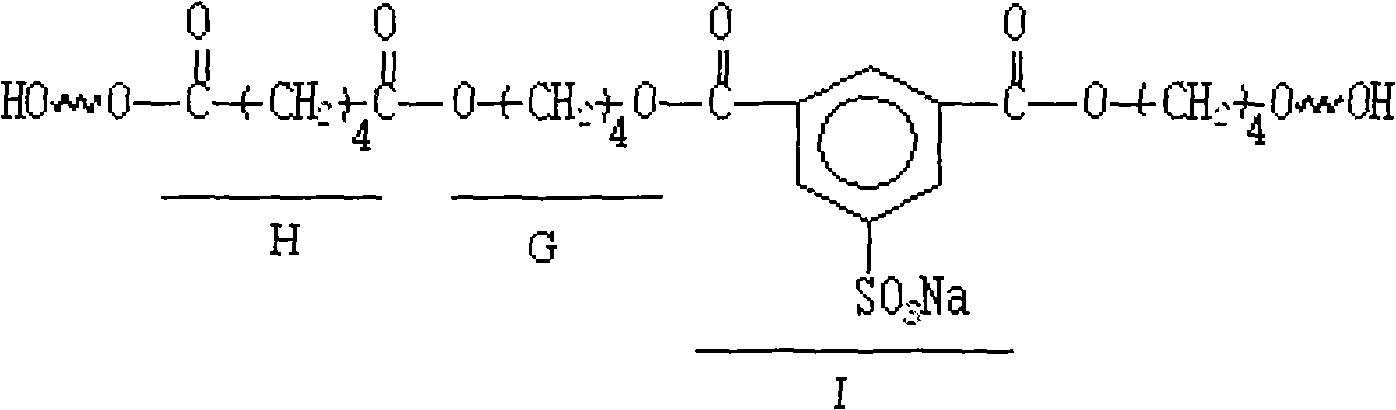Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
283 results about "Nano size" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The iPod nano® is yet another member of Apple Computer's venerable iPod® family. The model name was clearly chosen to focus attention on the diminutive size of the portable music player. This particular iPod® is certainly petite, and according to the tech specs from Apple's site, the dimensions are 3.5 x 1.6 x 0.27 inches (8.9 x 4.1 x 0.7 cm).
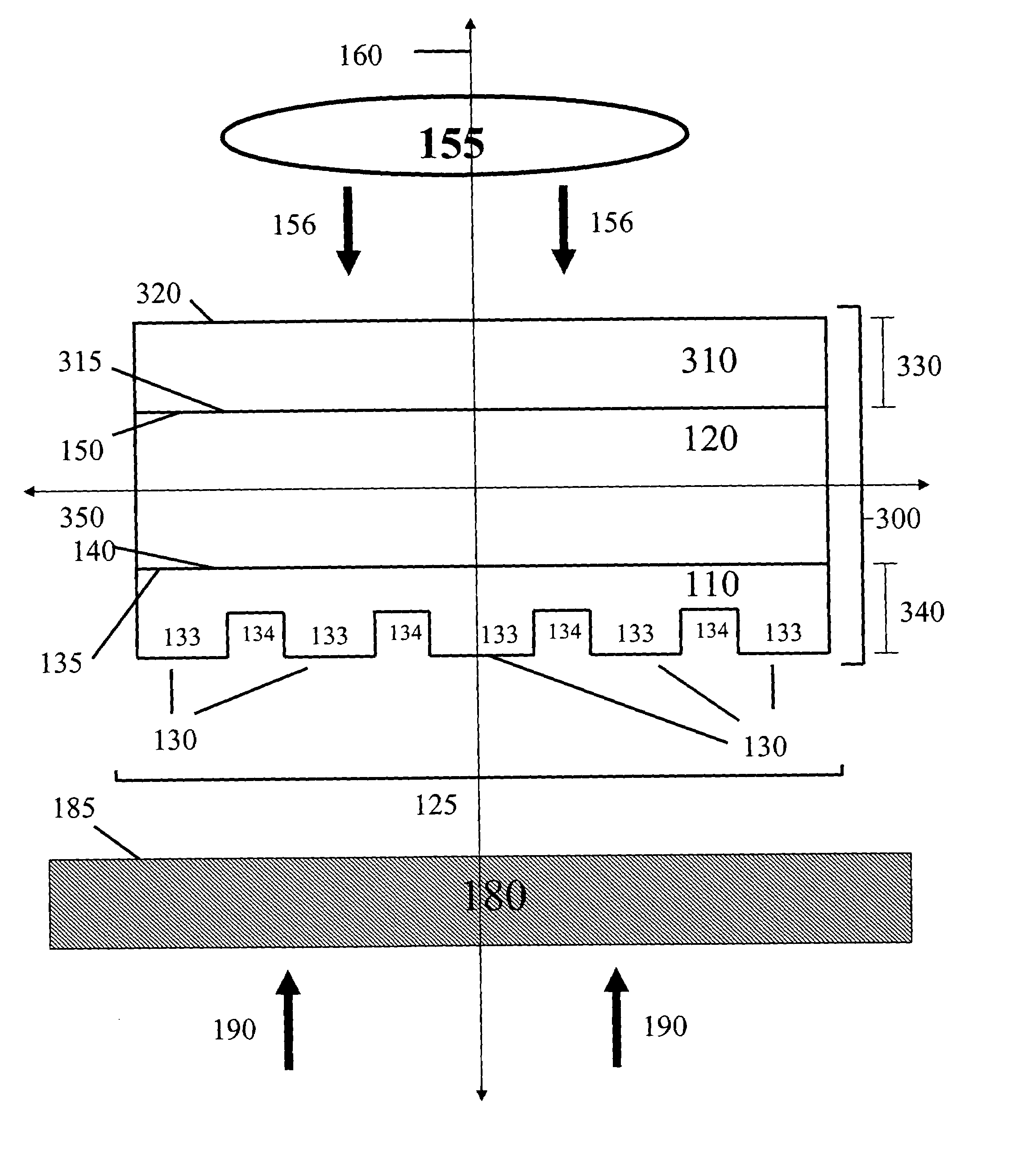
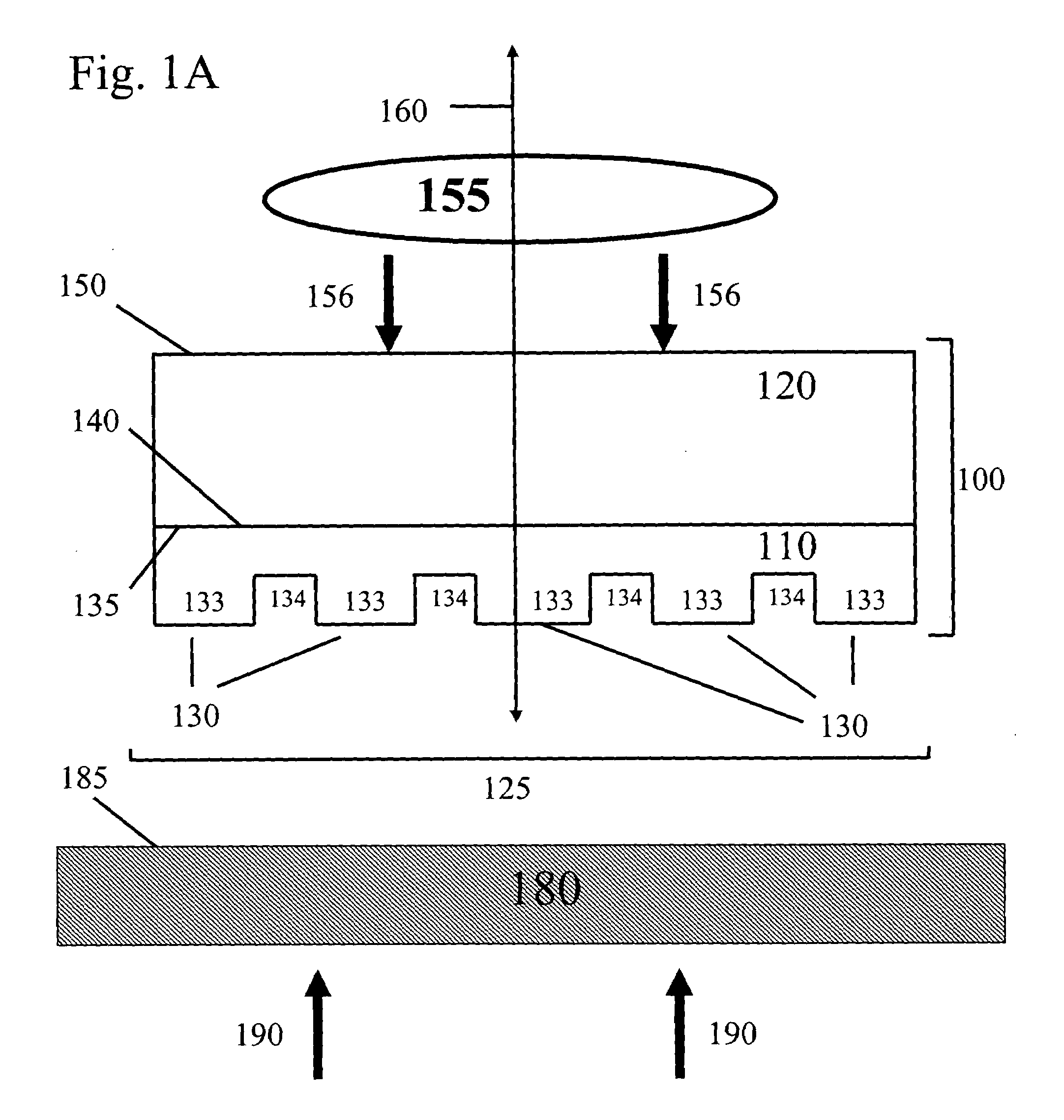
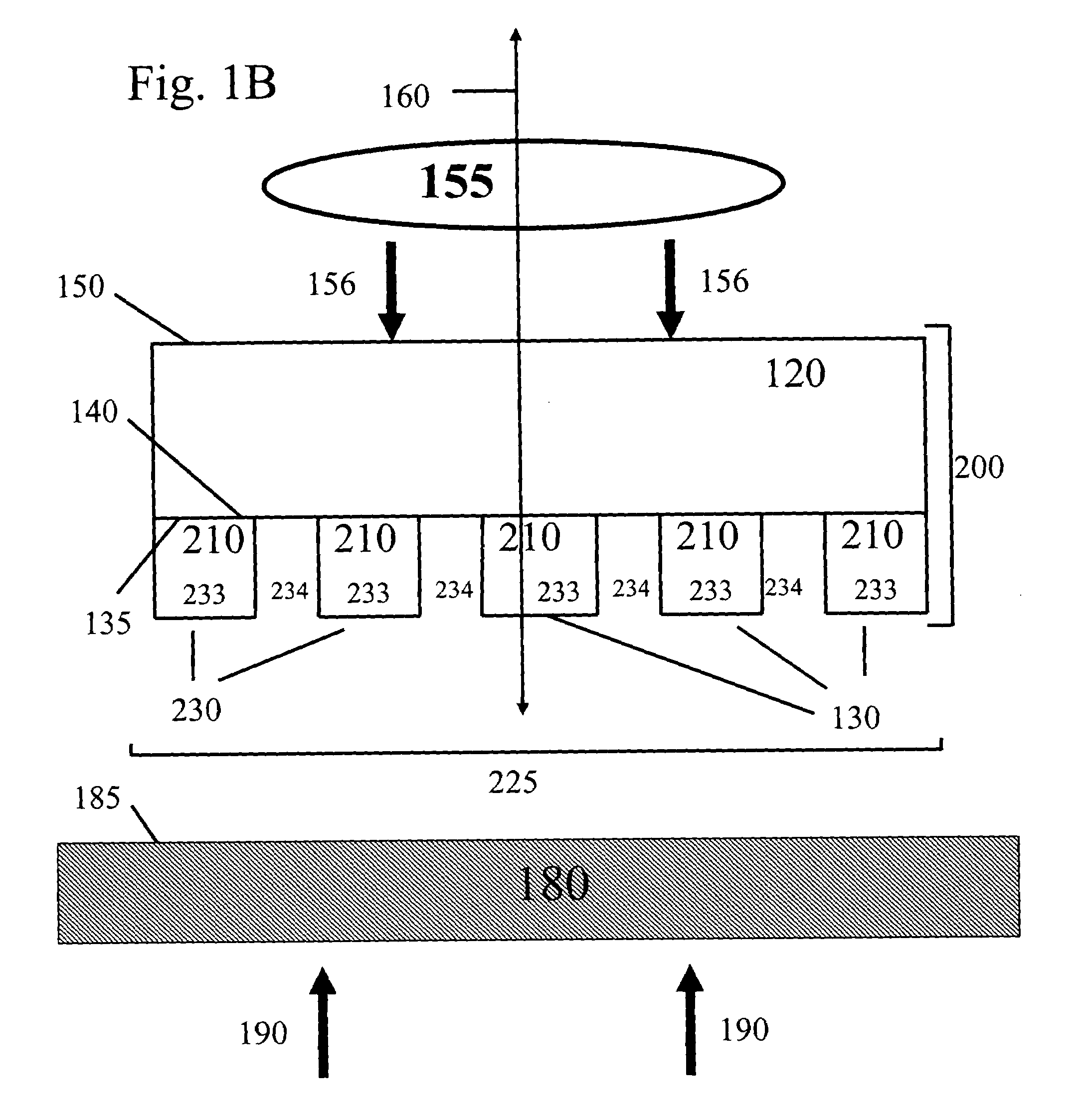
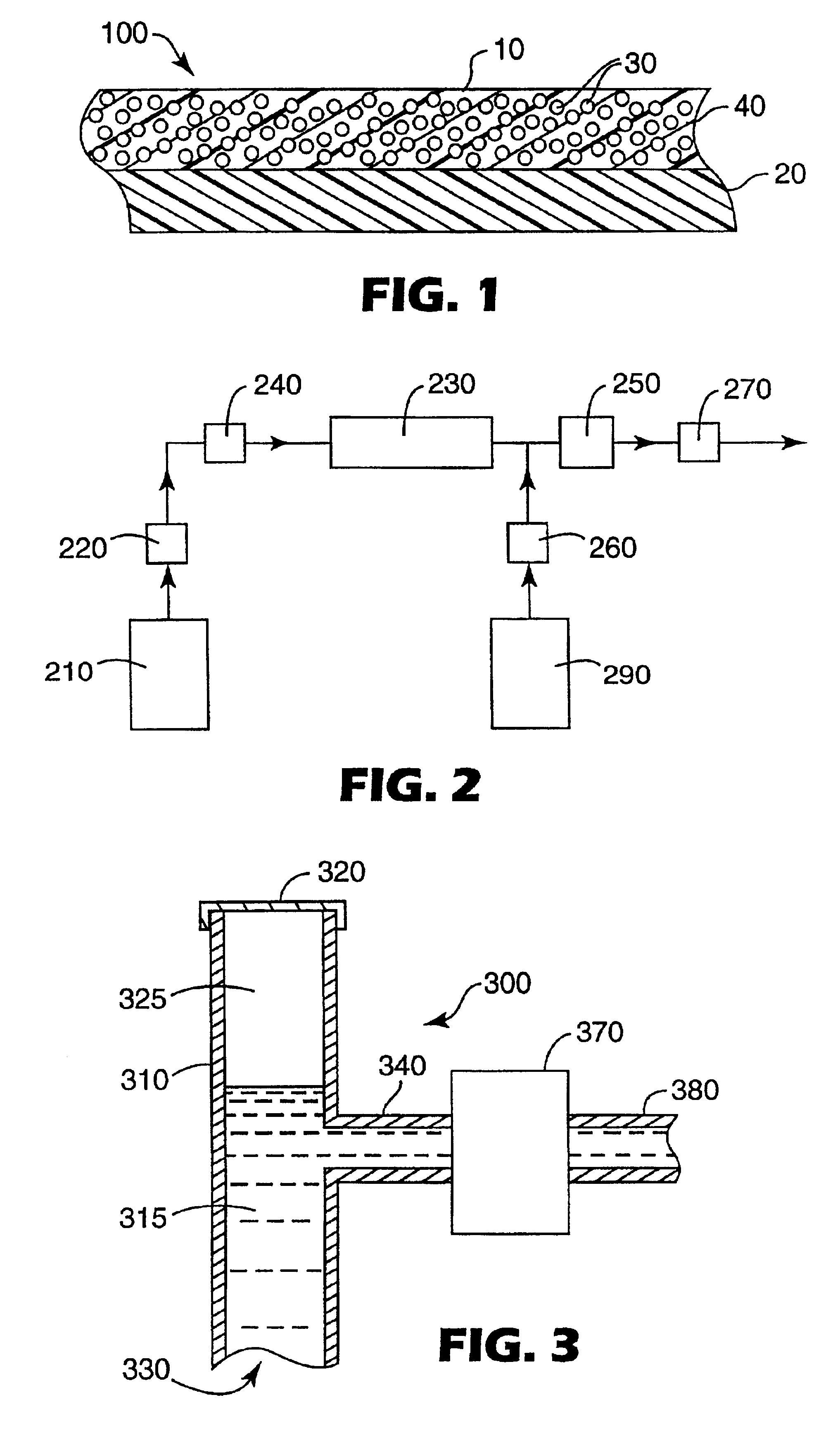
Composite patterning devices for soft lithography
ActiveUS7195733B2Improve fidelityIncrease resistanceMaterial nanotechnologyNanoinformaticsNano sizeYoung's modulus
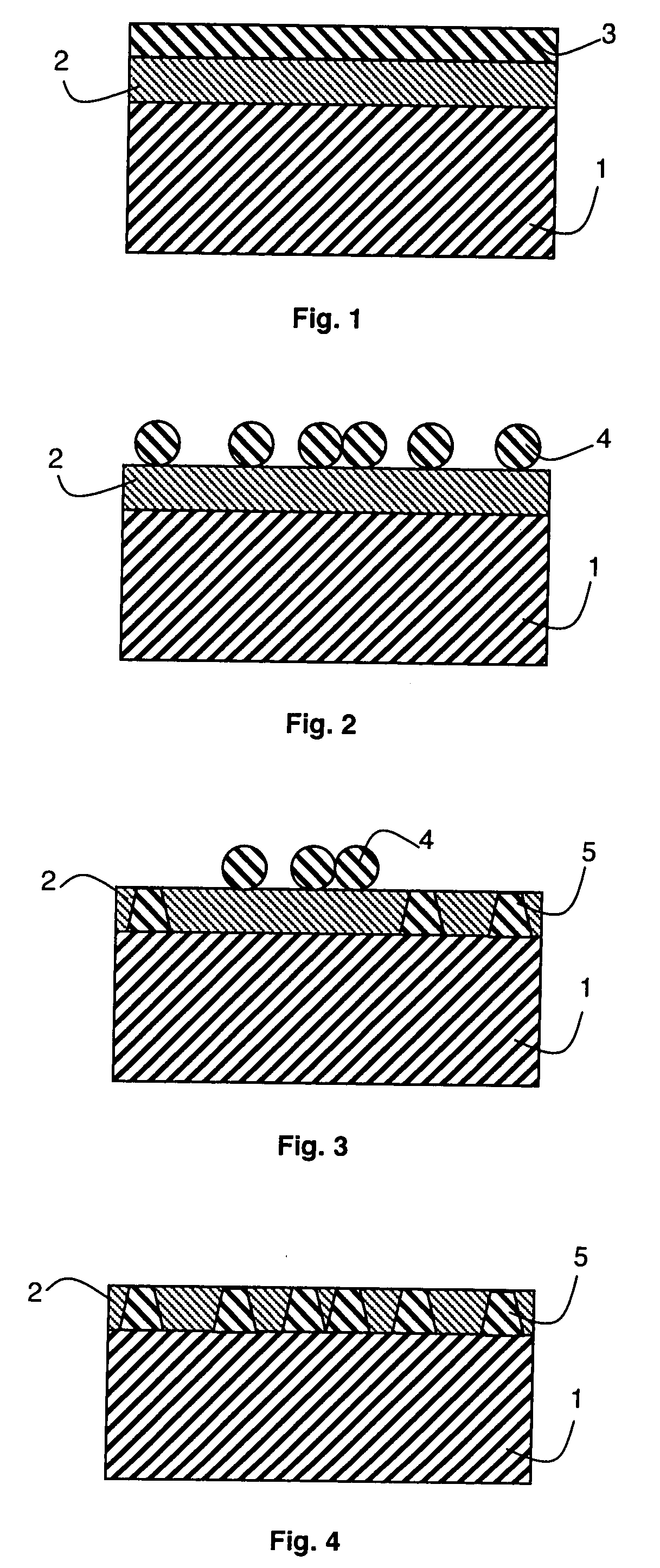
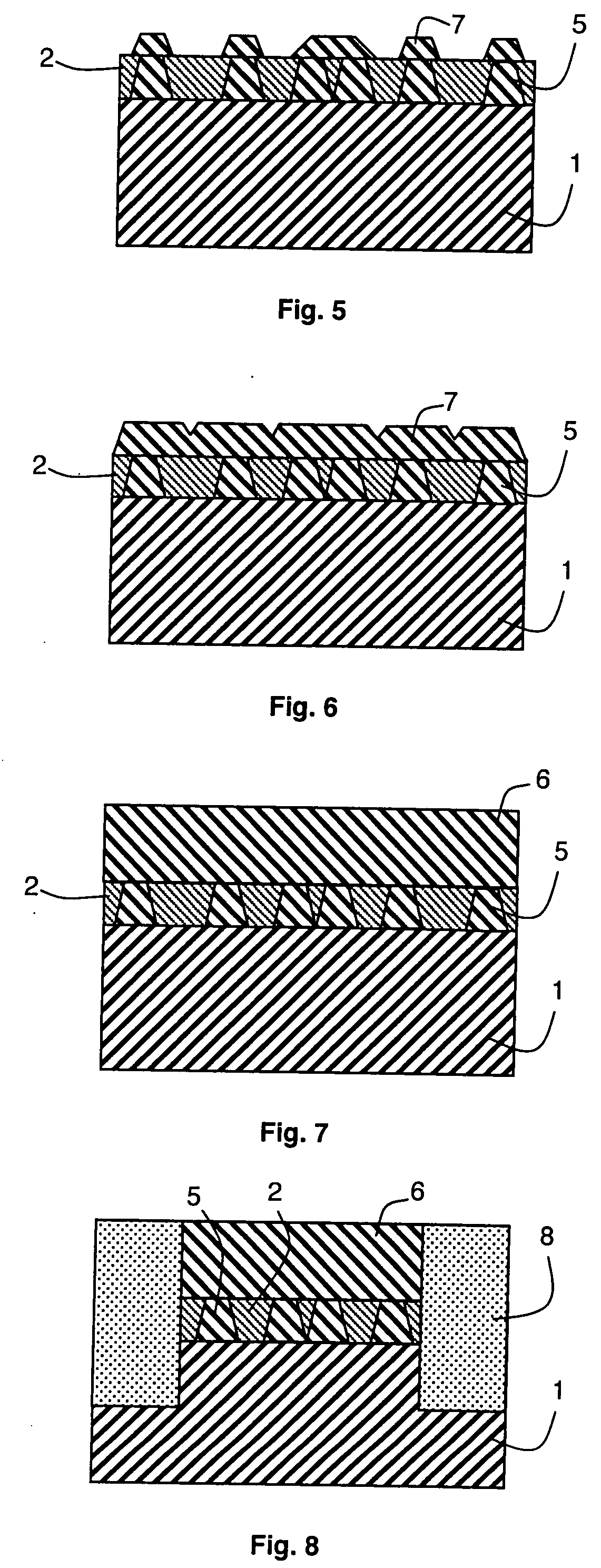
The present invention provides methods, devices and device components for fabricating patterns on substrate surfaces, particularly patterns comprising structures having microsized and / or nanosized features of selected lengths in one, two or three dimensions. The present invention provides composite patterning devices comprising a plurality of polymer layers each having selected mechanical properties, such as Young's Modulus and flexural rigidity, selected physical dimensions, such as thickness, surface area and relief pattern dimensions, and selected thermal properties, such as coefficients of thermal expansion, to provide high resolution patterning on a variety of substrate surfaces and surface morphologies.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Double-gate FinFET device and fabricating method thereof
InactiveUS6885055B2Cost of wafer is decreasedImprove featuresTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsNano sizeFloating body effect
The present invention relates to double-gate FinFET devices and fabricating methods thereof. More particularly, the invention relates to an electrically stable double-gate FinFET device and the method of fabrication in which the Fin active region on a bulk silicon substrate where device channel and the body are to be formed has a nano-size width and is connected to the substrate and is formed with the shape of a wall along the channel length direction.The conventional double-gate MOS devices are fabricated using SOI wafers which are more expensive than bulk silicon wafers. It also has problems including the floating body effects, larger source / drain parasitic resistance, off-current increase, and deterioration in heat transfer to the substrate.
Owner:KIPB LLC
Method of manufacturing a phase change RAM device utilizing reduced phase change current
ActiveUS7332370B2Effectively lowering currentNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesNano sizePhase change
To effectively lower the current required for changing a phase of a phase change layer in a phase change RAM device, metal pads are formed on a semiconductor substrate, and an oxide layer is formed on the metal pads. Nano-sized copolymer patterns aligned with the metal pads covered by the oxide layer are formed on the oxide layer. The oxide layer is etched to form oxide layer patterns by using the nano-sized copolymer patterns as barrier. The nano-sized copolymer patterns are then removed. A nitride layer is deposited and then etched to expose the oxide layer patterns. The exposed oxide layer patterns are removed to form nano-sized holes exposing the metal pads. Bottom electrodes are then formed in the nano-sized holes. A phase change layer and a top electrode are formed on each of the bottom electrodes.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Phase change memory with extra-small resistors
InactiveUS20060006472A1SmallImprove good performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesNano sizePhase-change memory
A phase change memory cell comprises of multiple resistors. In one design, the resistor layer is a layer with a plurality of resistors embedded in an insulator layer which is sandwiched between the electrodes. In the other design, a combination of a heater layer with a plurality of heaters and a layer of phase change material constitutes the resistor sandwiched a pair of electrodes. The resistor or heater can be easily made in nano-size.
Owner:JIANG HAI
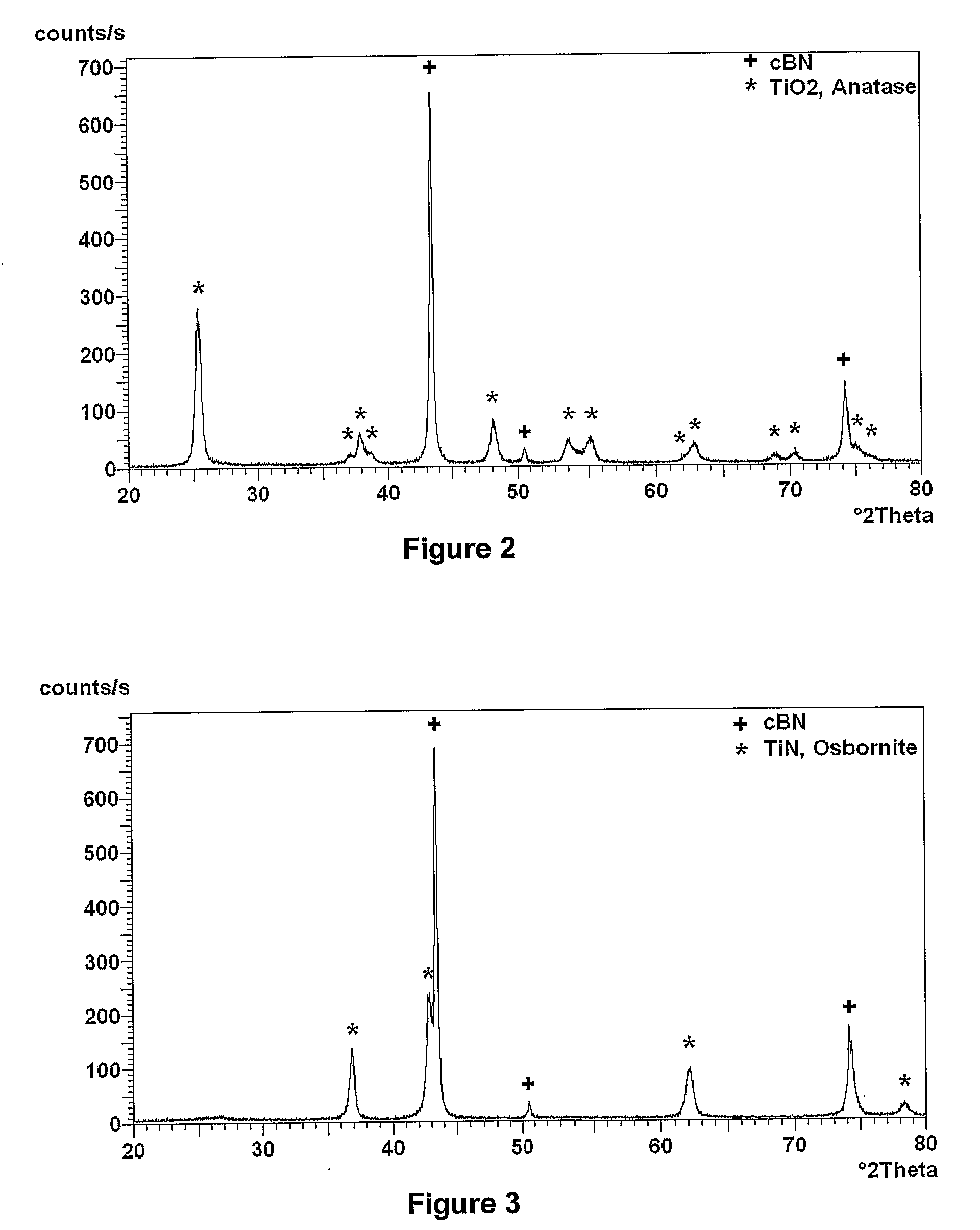
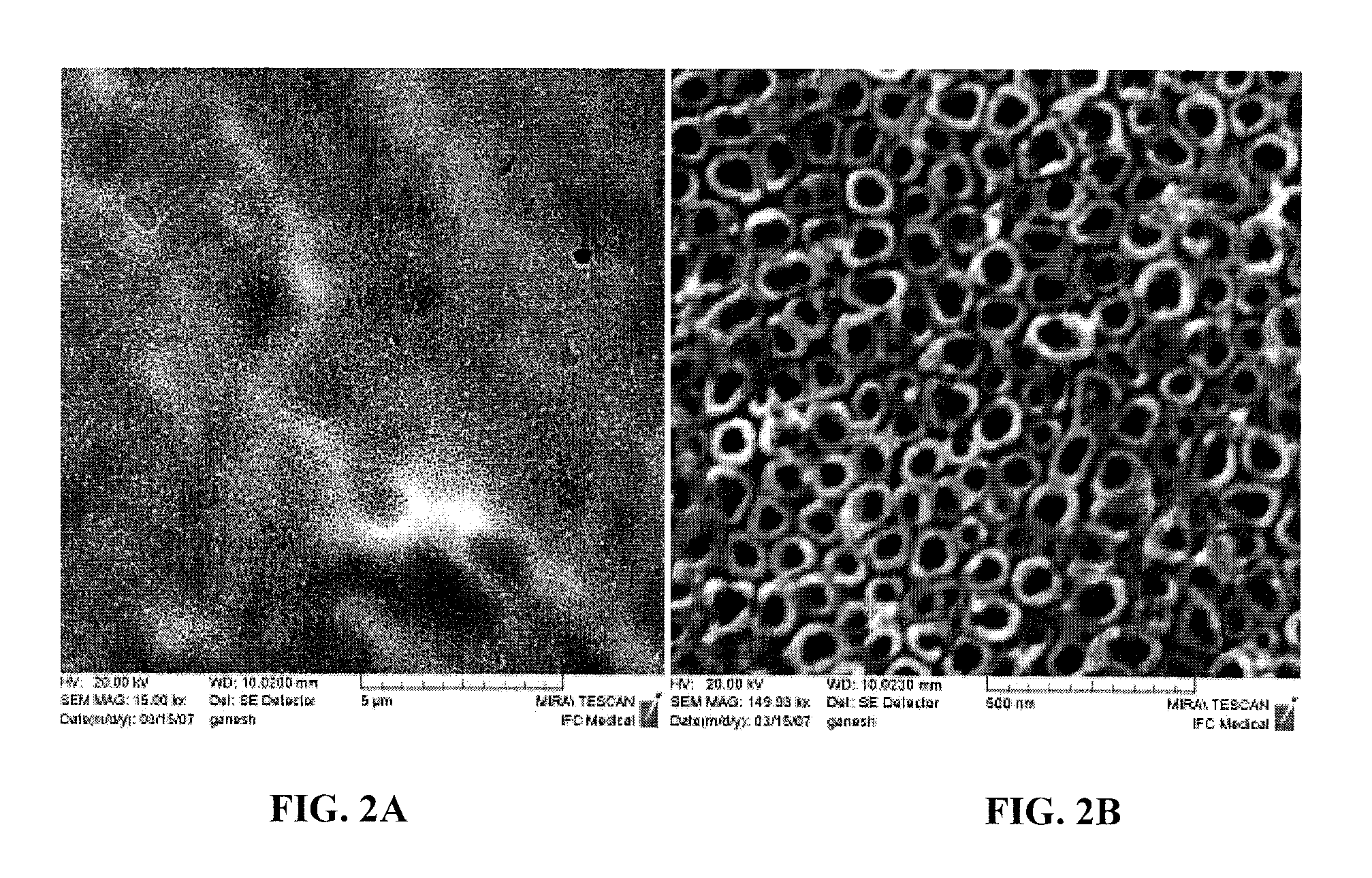
Polycrystalline abrasive compacts
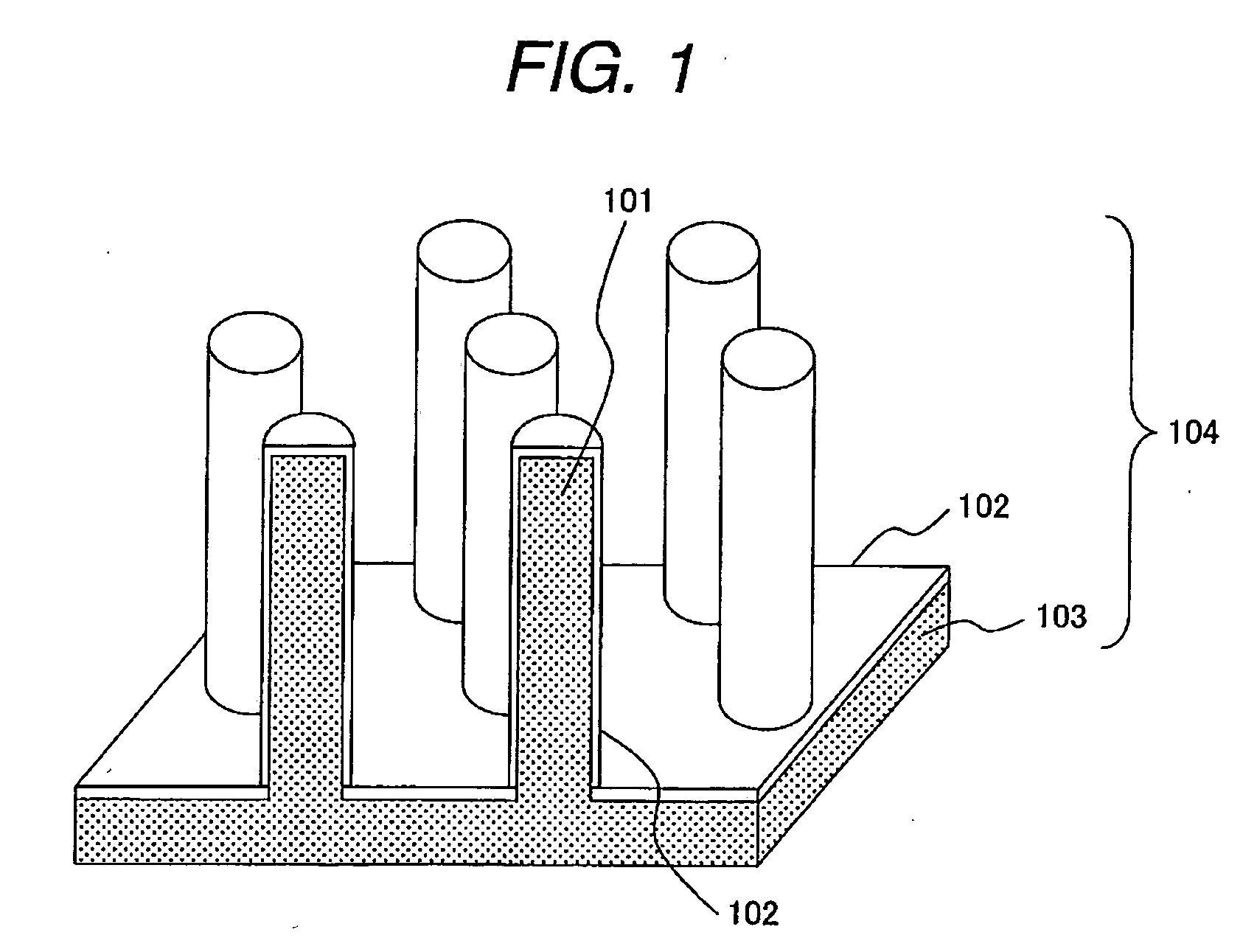
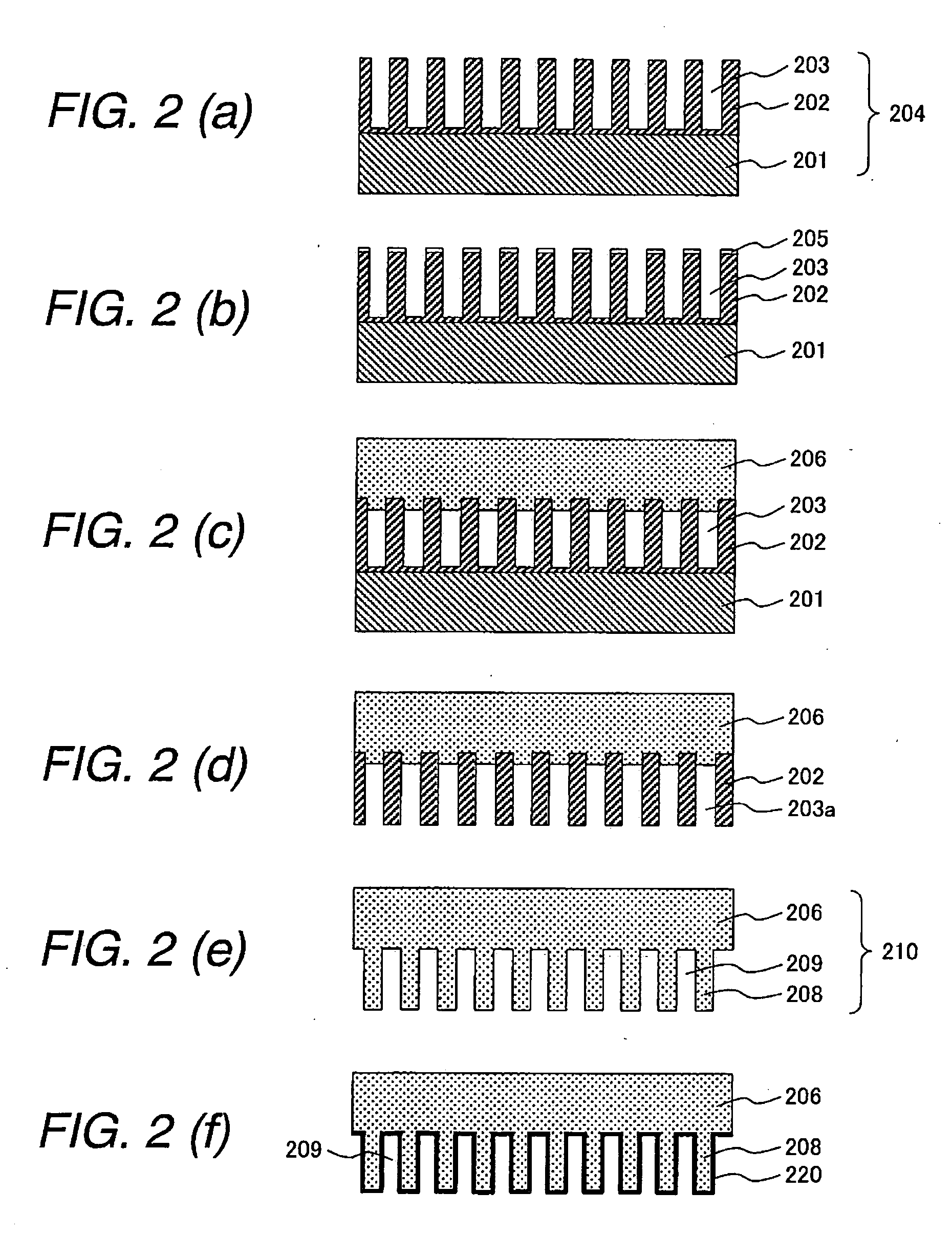
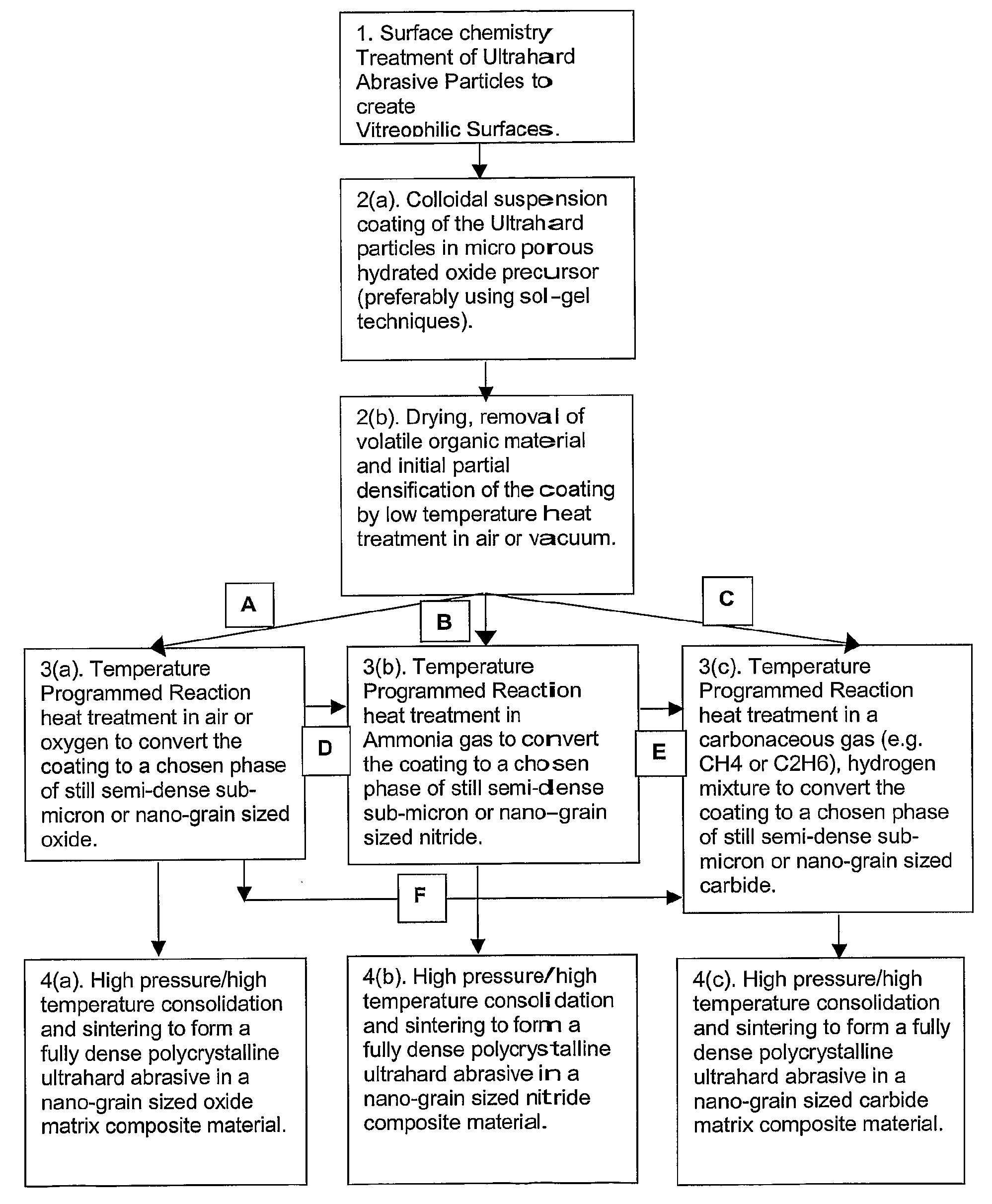
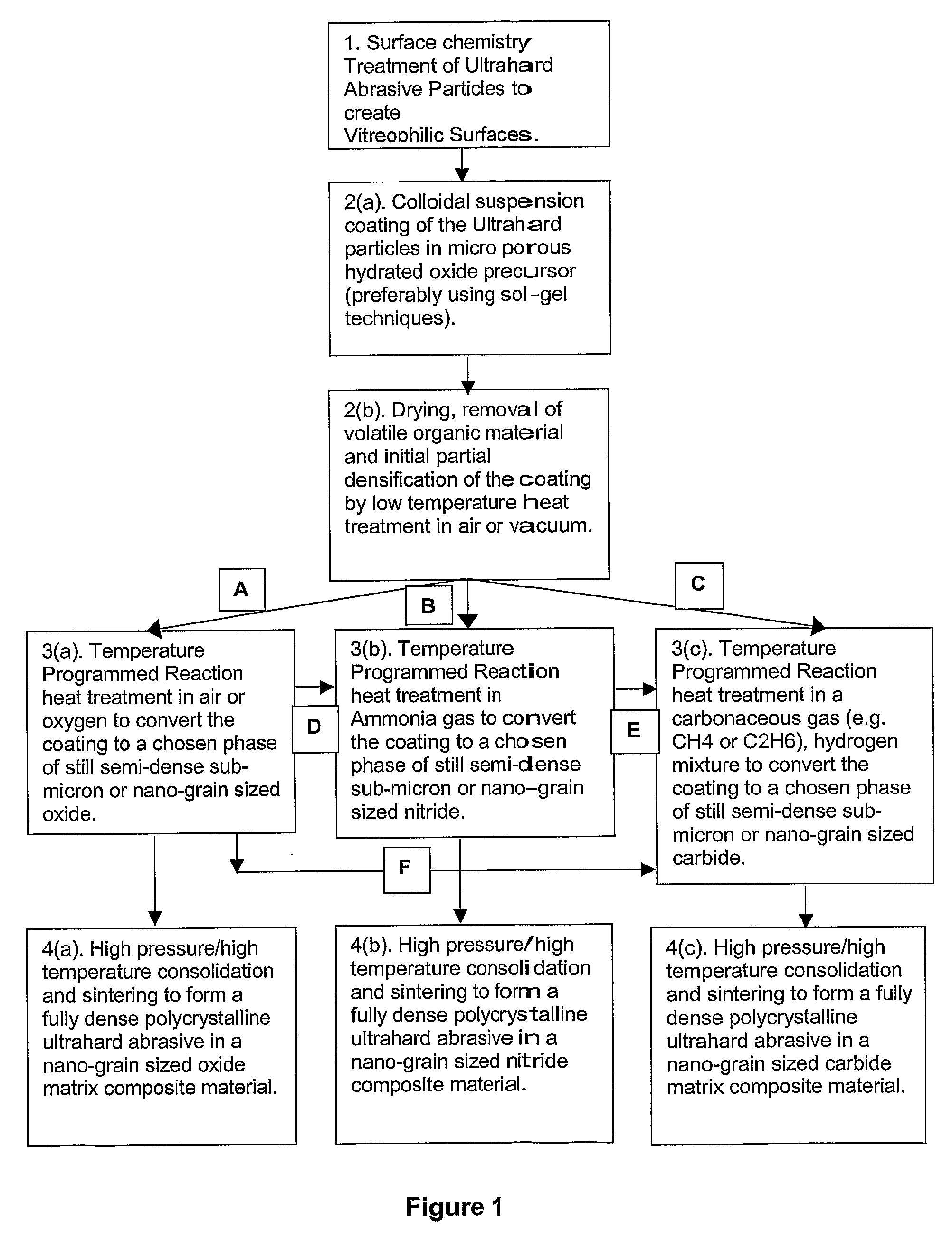
A method of manufacturing polycrystalline abrasive elements consisting of micron, sub-micron or nano-sized ultrahard abrasives dispersed in micron, sub-micron or nano-sized matrix materials. A plurality of ultrahard abrasive particles having vitreophilic surfaces are coated with a matrix precursor material in a refined colloidal process and then treated to render them suitable for sintering. The matrix precursor material can be converted to an oxide, nitride, carbide, oxynitride, oxycarbide, or carbonitride, or an elemental form thereof. The coated ultrahard abrasive particles are consolidated and sintered at a pressure and temperature at which they are crystallographically or thermodynamically stable.
Owner:ELEMENT SIX ABRASIVES +1
Electrode for use in electrochemical device, solid electrolyte/electrode assembly, and production method thereof
InactiveUS20070059584A1Resistance of electrodeHigh capacity densityMachining electrodesElectrolytic inorganic material coatingNano sizeNanometre
In an electrode in electrochemical device, particularly an anode lithium ion secondary battery, a cathode for use in alkali storage battery, an electrode for use in fuel cell, or a capacitor electrode, a metal structure has nano size micro-pillars is constructed with an electrode active material being formed on the surface of the metal structure. The metal structure having nano size micro-pillars can be formed, for example, by forming a metal layer as an electrode material by plating to the surface of a substrate having pores and then removing the substrate by dissolution, the metal filled in the pores of the substrate to form a group of micro-pillars. And the active material can be formed by depositing metal by plating. Since the active material is in direct contact with the conductive skeleton, the conducting agent for connecting the active materials to each other may not be added at all.
Owner:HITACHI CABLE
Micron nano material composite modified water-based adhesive
InactiveCN101210157ALow shrinkageImprove performanceMonocarboxylic acid ester polymer adhesivesNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesMicro nanoExtensibility
The invention relates to an aqueous binder which is compounded and modified by micro nano material. The modified aqueous binder of the invention adopts emulsion adhesive as matrix and micro-size and nano-size inorganic powder as modifier to prepare the compound and modified aqueous binder. The method of the invention can not only enhance the interface binding force of the aqueous binder, but also greatly improve the properties of water resistance, toughness and extensibility, leading comprehensive performance of the aqueous binder to be improved.
Owner:郑旷宇
Polycrystalline Abrasive Materials and Method of Manufacture
ActiveUS20080115424A1Reduce the temperatureNanostructure manufactureOther chemical processesNitrogen oxidesNano size
A method of manufacturing polycrystalline abrasive elements consisting of micron, sub-micron or nano-sized ultrahard abrasives dispersed in micron, sub-micron or nano-sized matrix materials. A plurality of ultrahard abrasive particles having vitreophilic surfaces are coated with a matrix precursor material and then treated to render them suitable for sintering. The matrix precursor material can be converted to an oxide, nitride, carbide, oxynitride, oxycarbide, or carbonitride, or an elemental form thereof. The coated ultrahard abrasive particles are consolidated and sintcred at a pressure and temperature at which they are crystallographically or thermodynamically stable.
Owner:ELEMENT SIX TRADE MARKS LTD +2
Biocompatible Coated Nanostructured Titanium Surfaces
InactiveUS20100028387A1Promote bone growthStrong cell adhesionBiocideTetrapeptide ingredientsNano sizeCell adhesion
Bioactive molecules have been coated on nanotubular structured titanium substrates by molecular plasma deposition. The coatings promote cell adhesion and are particularly suited for orthopedic implants that provide improved bone cell adhesion and new tissue growth. Nanodimensional features on titanium substrates are engineered using electrochemical anodization techniques. The nanostructured surfaces provide superior support for a wide selection of polypeptide coatings.
Owner:METASCAPE
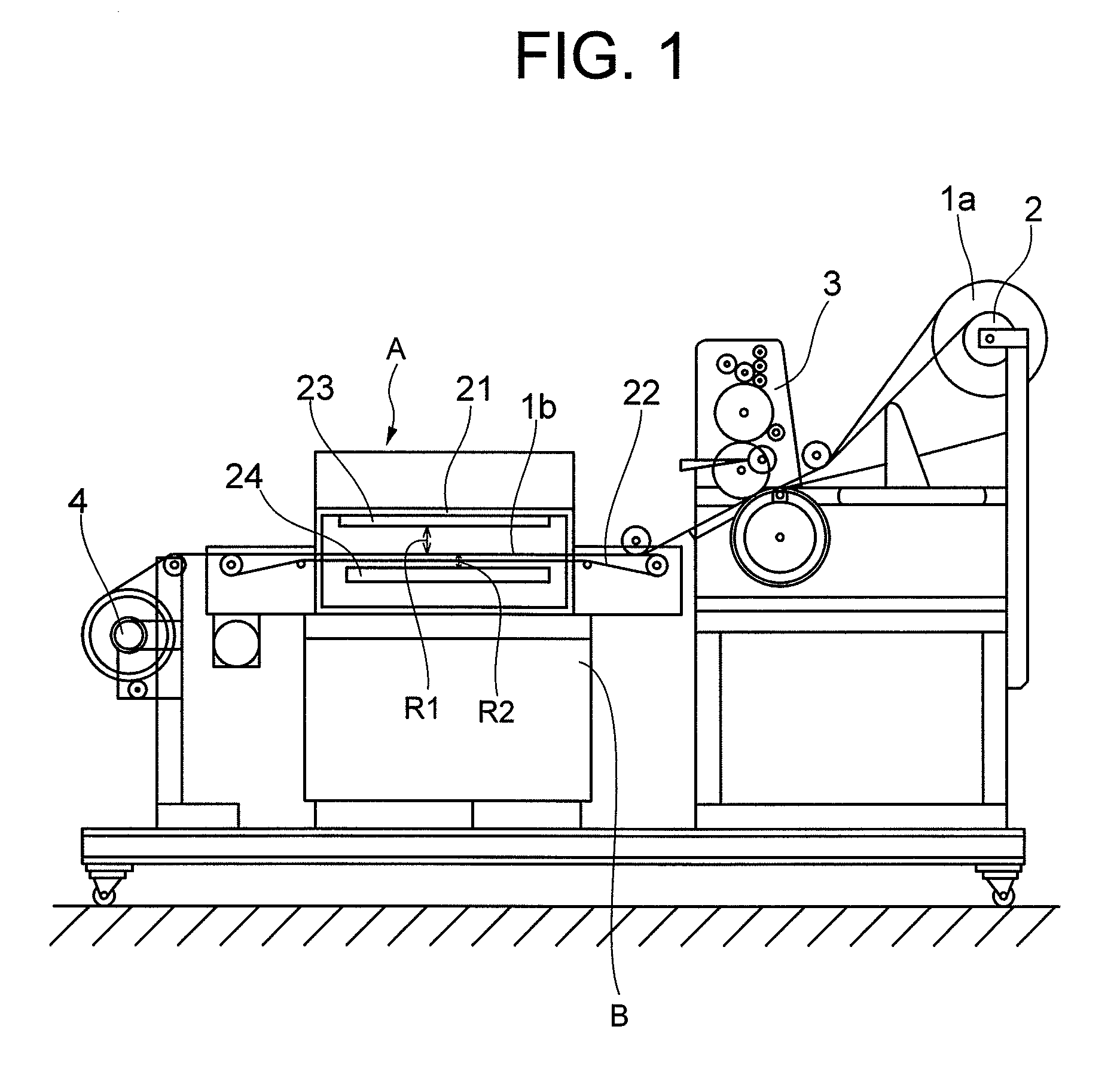
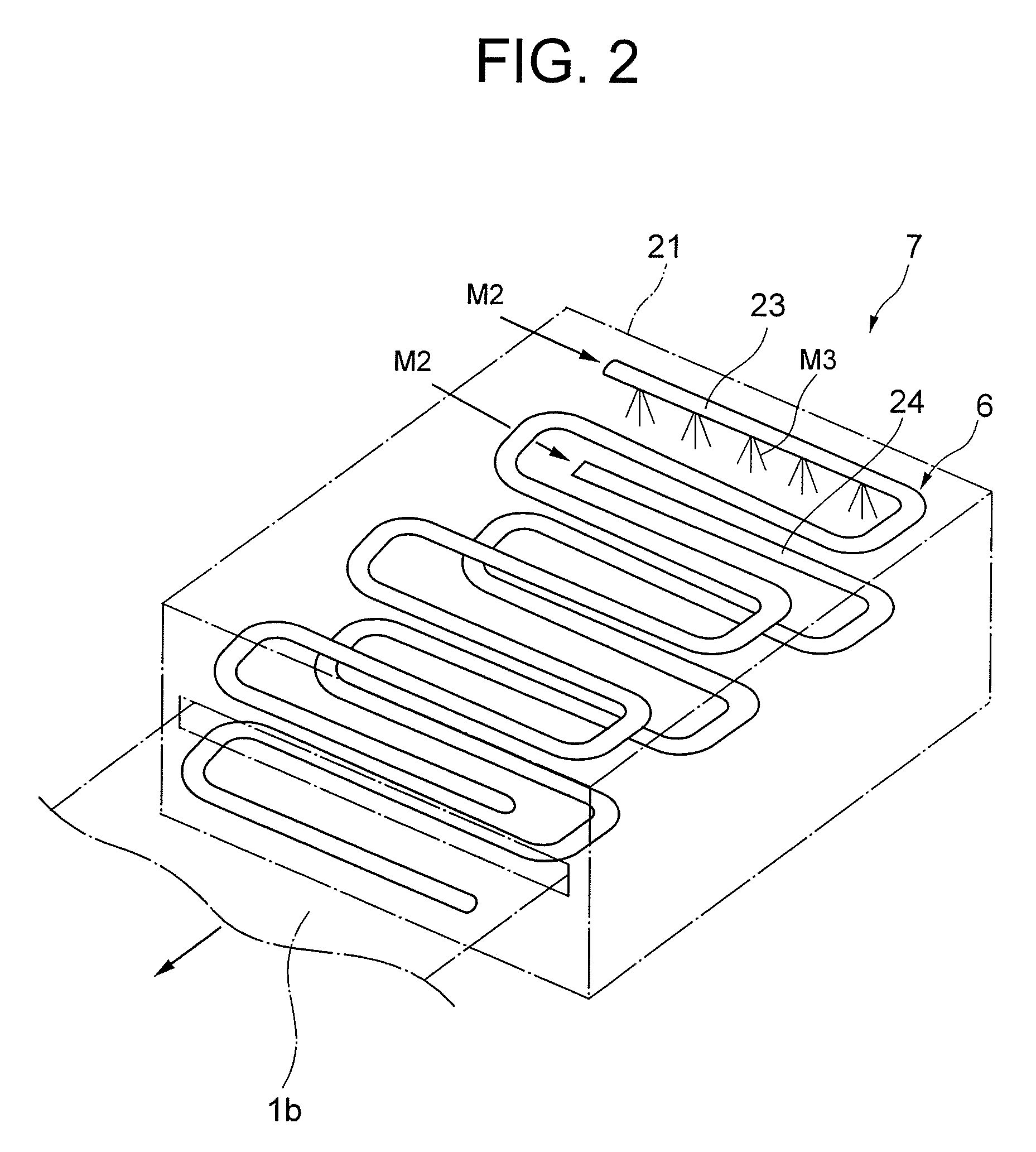
Method of drying printed material and apparatus therefor
InactiveUS20100192402A1Avoid stickingFast dryingDrying solid materials with heatDrying gas arrangementsFiberNano size
To carry out drying of printing ink with the use of Nano sized high-temperature dryness steam. Nano sized high-temperature dryness steam being clustered on Nano oder is generated and jetted to the print side of printed material so that the Nano sized high-temperature dryness steam imparts intramolecular vibrational energy to ink of the print side. Consequently, the Nano sized high-temperature dryness steam being clustered on Nano oder not only passes through fiber pores in the printed material but also collides with the ink of the print side. The Nano sized high-temperature dryness steam having collided with the ink of the print side imparts thermally excited energy as intramolecular vibrational energy to the ink containing polar molecules. The ink is dried by the intramolecular energy.
Owner:DAIDO SANGYO
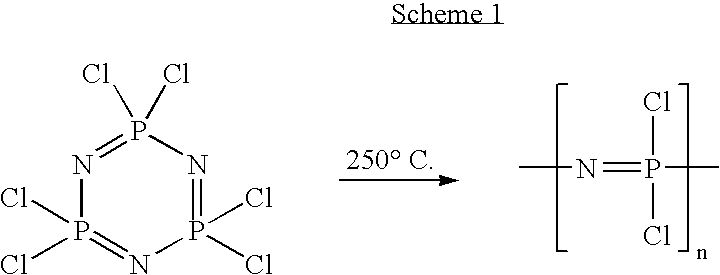
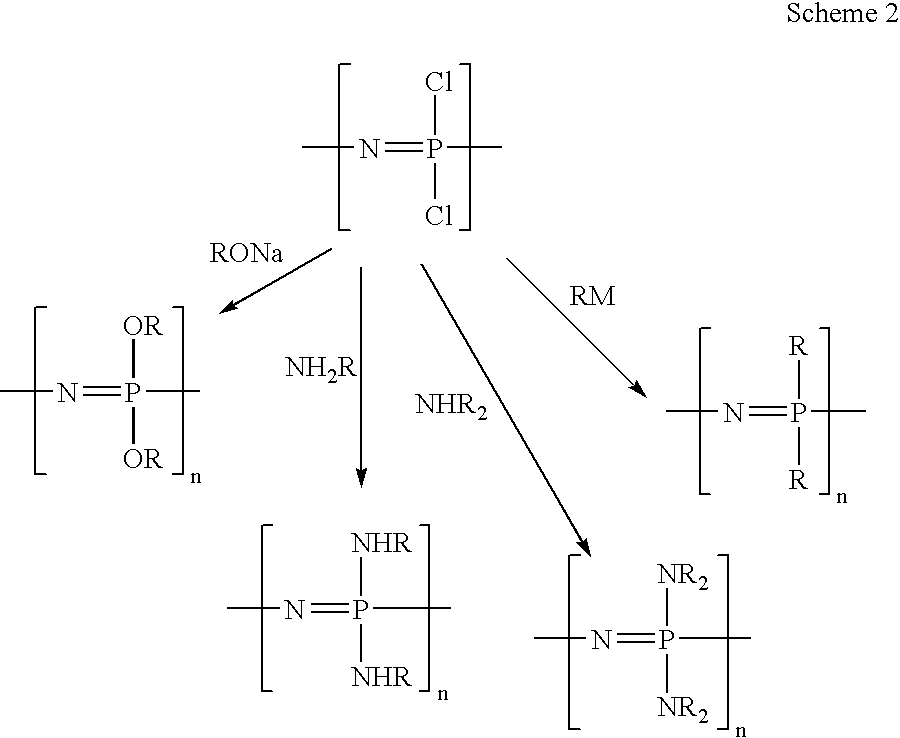
Polymeric nanofibers for tissue engineering and drug delivery
Polymeric nanofibers have been developed which are useful in a variety of medical and other applications, such as filtration devices, medical prosthesis, scaffolds for tissue engineering, wound dressings, controlled drug delivery systems, cosmetic skin masks, and protective clothing. These can be formed of any of a variety of different polymers, either non-degradable or degradable. In a preferred embodiment demonstrated in the following examples, nanofibers are formed of biodegradable and non biodegradable polyphosphazenes, their blends with other polyphosphazenes or with organic, inorganic / organometallic polymers as well as composite nanofibers of polyphosphazenes with nanosized particles such as hydroxyapatites.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
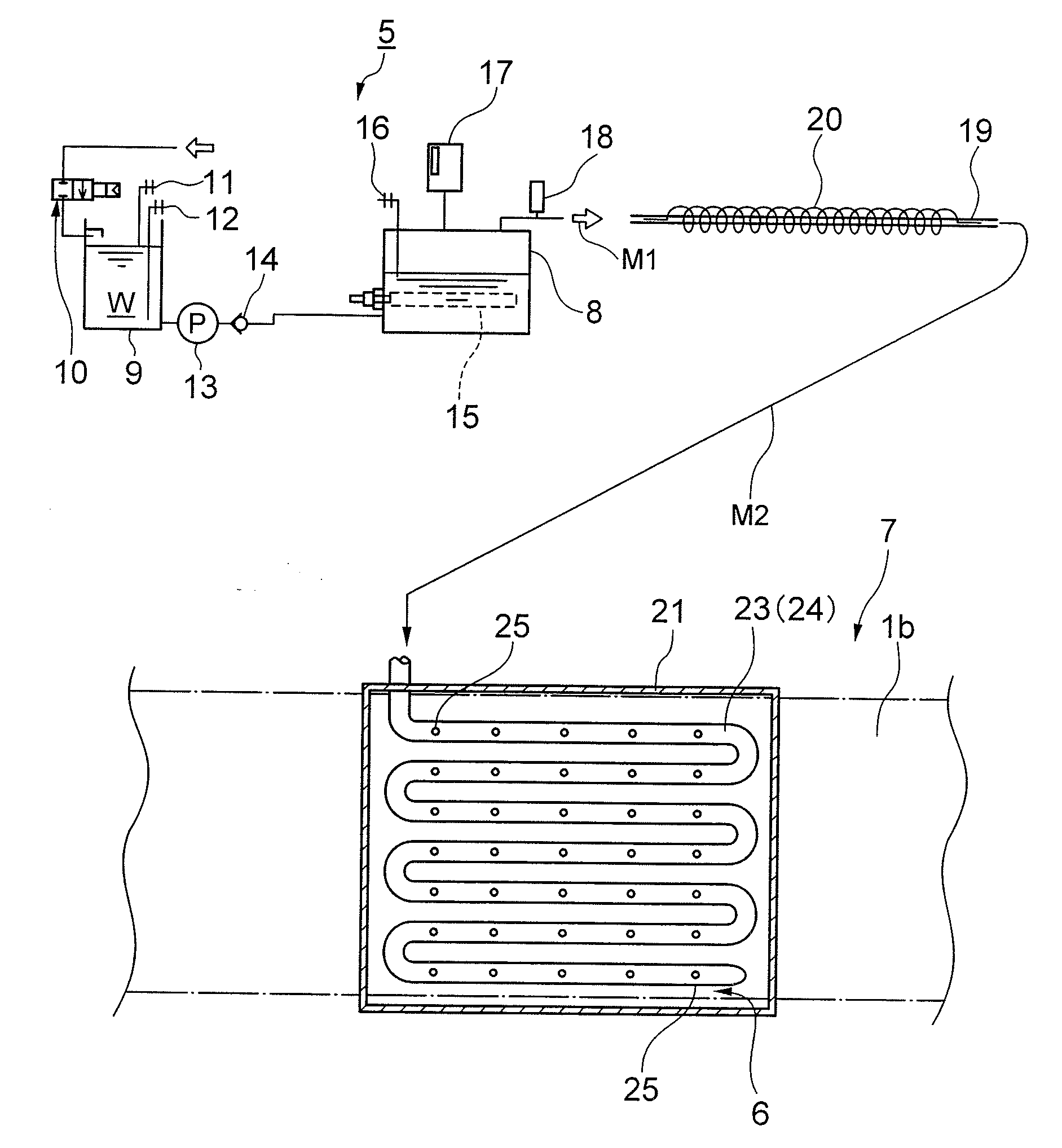
Refrigerator
InactiveUS20100223944A1Reduce adhesionEliminate growthBurnersFruit and vegetables preservationNano sizeEngineering
To provide a refrigerator including: a heat-insulating main body; a storage compartment defined in the heat-insulating main body; and a mist spray apparatus that sprays a fine mist into the storage compartment. The fine mist generated by the mist spray apparatus has a nano-size particle diameter and reduces microorganisms adhering to the inside of the storage compartment and to vegetable surfaces, the microorganisms including molds, bacteria, yeasts, and viruses.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Ultra low k (ULK) SiCOH film and method
InactiveUS7288292B2Improve mechanical propertiesHigh elastic modulusPigmenting treatmentSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsNano sizeGas phase
The present invention provides a multiphase, ultra low k film which exhibits improved elastic modulus and hardness as well as various methods for forming the same. The multiphase, ultra low k dielectric film includes atoms of Si, C, O and H, has a dielectric constant of about 2.4 or less, nanosized pores or voids, an elastic modulus of about 5 or greater and a hardness of about 0.7 or greater. A preferred multiphase, ultra low k dielectric film includes atoms of Si, C, O and H, has a dielectric constant of about 2.2 or less, nanosized pores or voids, an elastic modulus of about 3 or greater and a hardness of about 0.3 or greater. The multiphase, ultra low k film is prepared by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition in which one of the following alternatives is utilized: at least one precursor gas comprising siloxane molecules containing at least three Si—O bonds; or at least one precursor gas comprising molecules containing reactive groups that are sensitive to e-beam radiation. Electronic structures including the multiphase, ultra low k film are also disclosed.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Method of manufacturing a phase change RAM device utilizing reduced phase change current
ActiveUS20060281216A1Effectively lowering currentNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesNano sizePhase change
To effectively lower the current required for changing a phase of a phase change layer in a phase change RAM device, metal pads are formed on a semiconductor substrate, and an oxide layer is formed on the metal pads. Nano-sized copolymer patterns aligned with the metal pads covered by the oxide layer are formed on the oxide layer. The oxide layer is etched to form oxide layer patterns by using the nano-sized copolymer patterns as barrier. The nano-sized copolymer patterns are then removed. A nitride layer is deposited and then etched to expose the oxide layer patterns. The exposed oxide layer patterns are removed to form nano-sized holes exposing the metal pads. Bottom electrodes are then formed in the nano-sized holes. A phase change layer and a top electrode are formed on each of the bottom electrodes.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
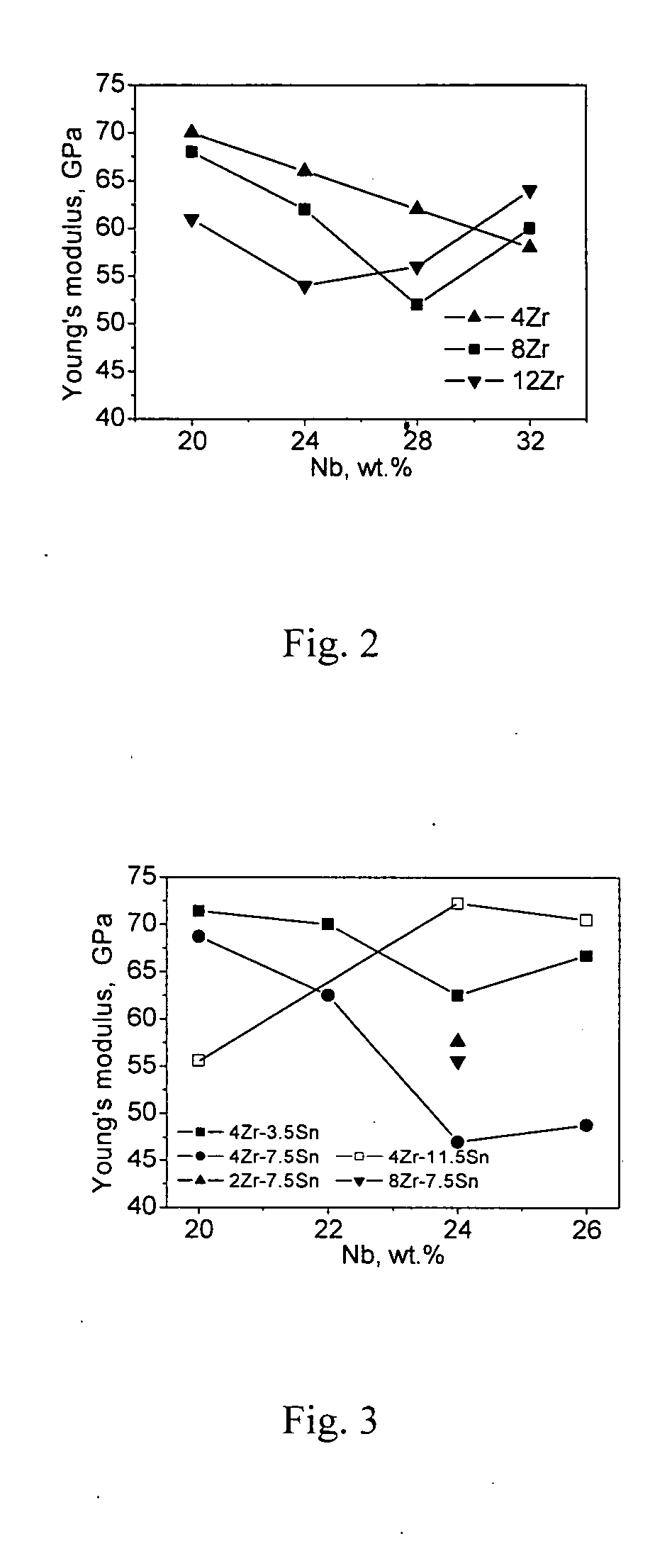
Titanium alloy with extra-low modulus and superelasticity and its producing method and processing thereof
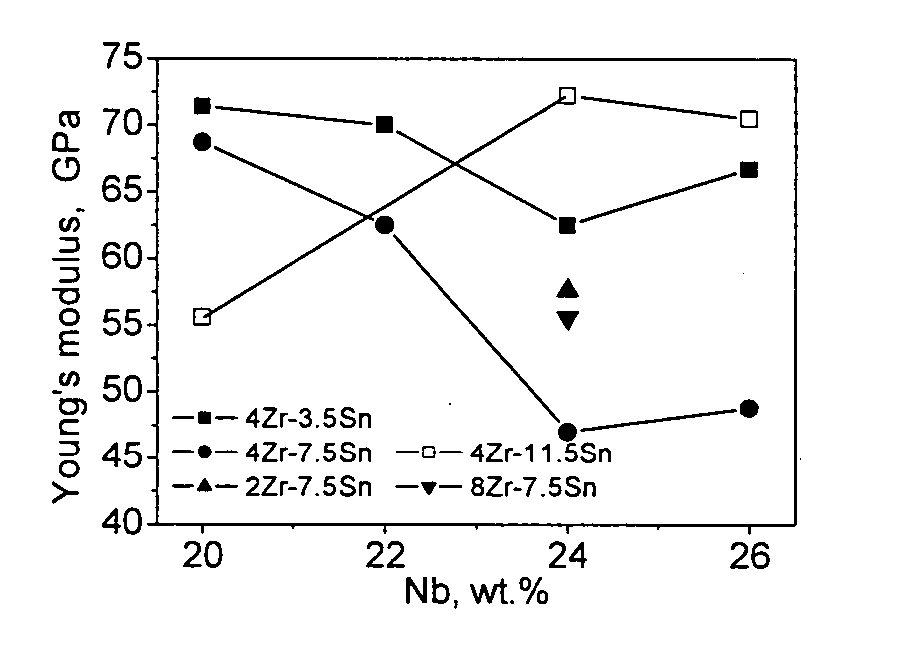
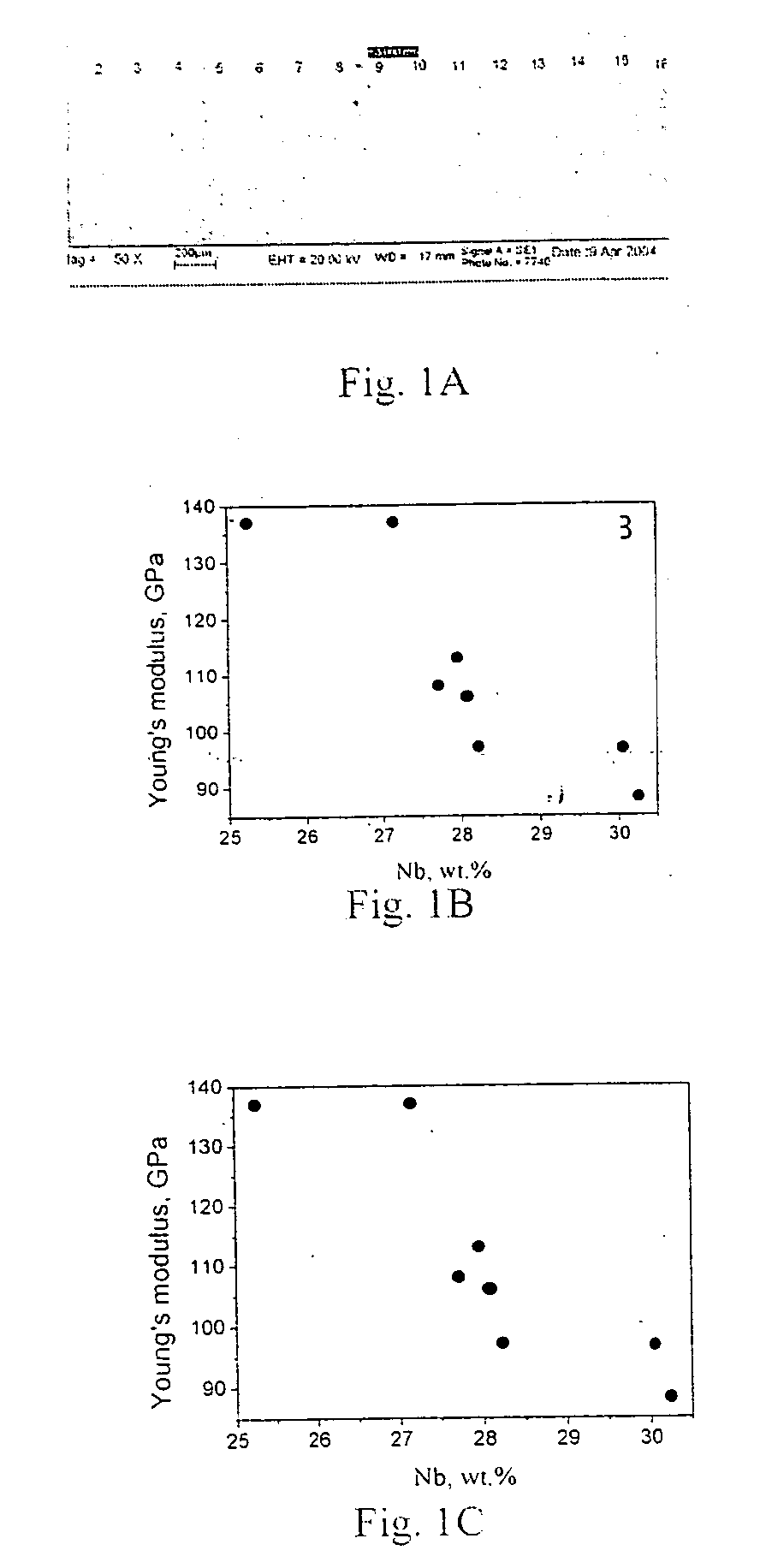
The patent provides the titanium alloy with extra-low modulus and superelasticity containing 20˜35 wt. % niobium, 2˜15 wt. % zirconium, balanced titanium and other unavoidable impurity elements. The advantages of the invention alloy are shown as follows: The invention titanium alloy has superior cold processing capacity and low work hardening rate; It can be severely deformed by cold rolling and cold drawing; It has superelasticity, shape memory effect, damping capacity, low modulus, high strength, good corrosion resistance and high biocompatibility; The invention titanium alloy can be made into nano-size materials by cold deformation and extra high strength can be achieved by heat treatment.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Nanoporous films and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20120000845A1Small sizeEfficient removalMaterial nanotechnologySemi-permeable membranesCoated membraneNano size
Provided is a carbon nanostructure-metal composite nanoporous film in which a carbon nanostructure-metal composite is coated on one surface or both surfaces of a membrane support having micro- or nano-sized pores. A method for manufacturing a carbon nanostructure-metal composite nanoporous film, includes: dispersing a carbon nanostructure-metal composite in a solvent at the presence of a surfactant and coating the carbon nanostructure-metal composite on one surface or both surfaces of a membrane support; and fusing the metal on the membrane support by heating the coated membrane support. The metal in carbon nanostructure-metal composite nanoporous film melts at a low temperature since a size of a metal of the carbon nanostructure-metal composite is several nm to several-hundred nm.
Owner:BIONEER
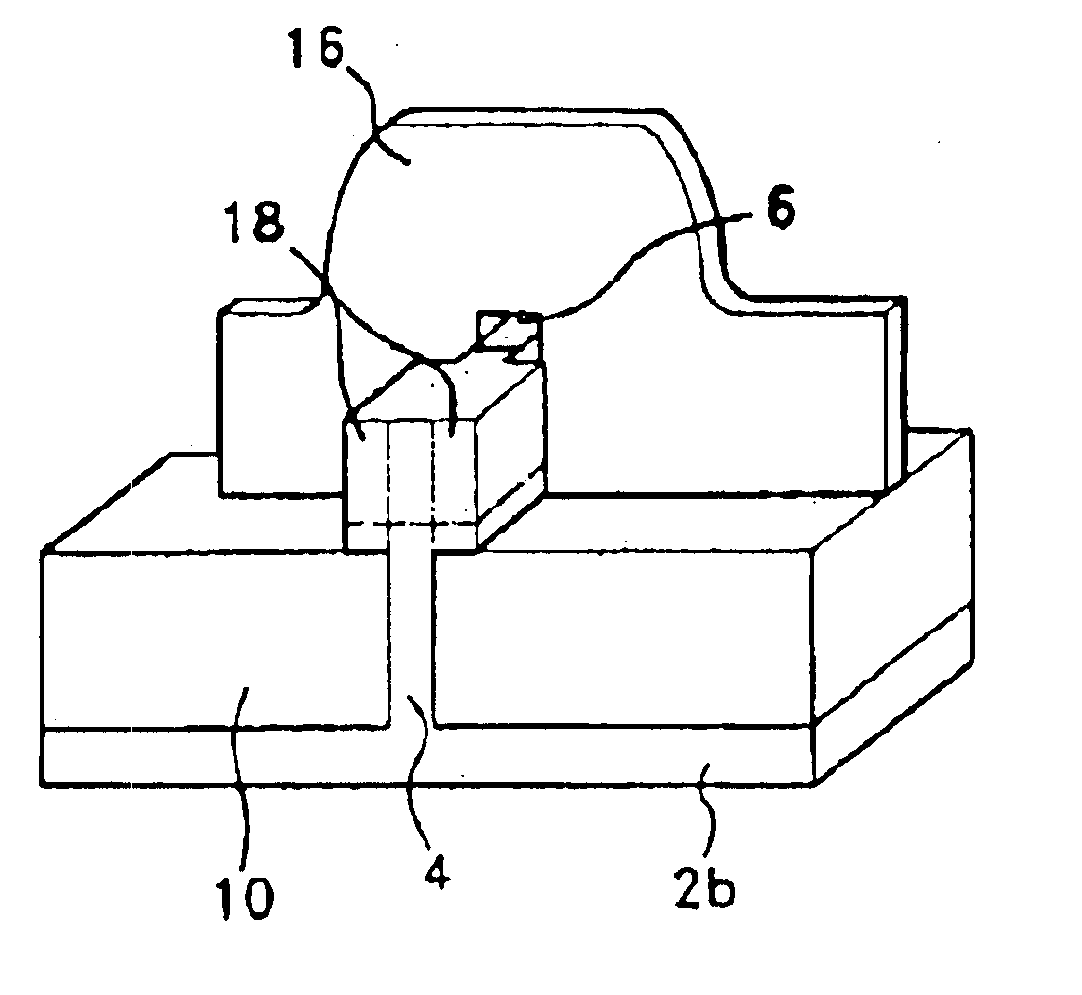
Method of producing a light-emitting diode comprising a nanostructured PN junction and diode thus obtained
InactiveUS20090072245A1Easy to produceNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesDopantSemiconductor materials
A nanostructured pn junction light-emitting diode is fabricated from a semi-conducting substrate doped by a first dopant and covered by a dielectric thin layer. An amorphous thin film formed by a semi-conducting material doped by a second dopant of opposite type to that of the first dopant is then deposited on the surface of the dielectric thin layer. The assembly then undergoes a thermal treatment designed to form, in the dielectric thin layer and from the amorphous thin film, a plurality of dots of nanometric size and made of semi-conducting material doped by the second dopant. The dots are designed to be in epitaxial relationship with the substrate to form a plurality of pn junctions of nanometric size. An additional thin layer is then formed by epitaxial growth from the dots.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
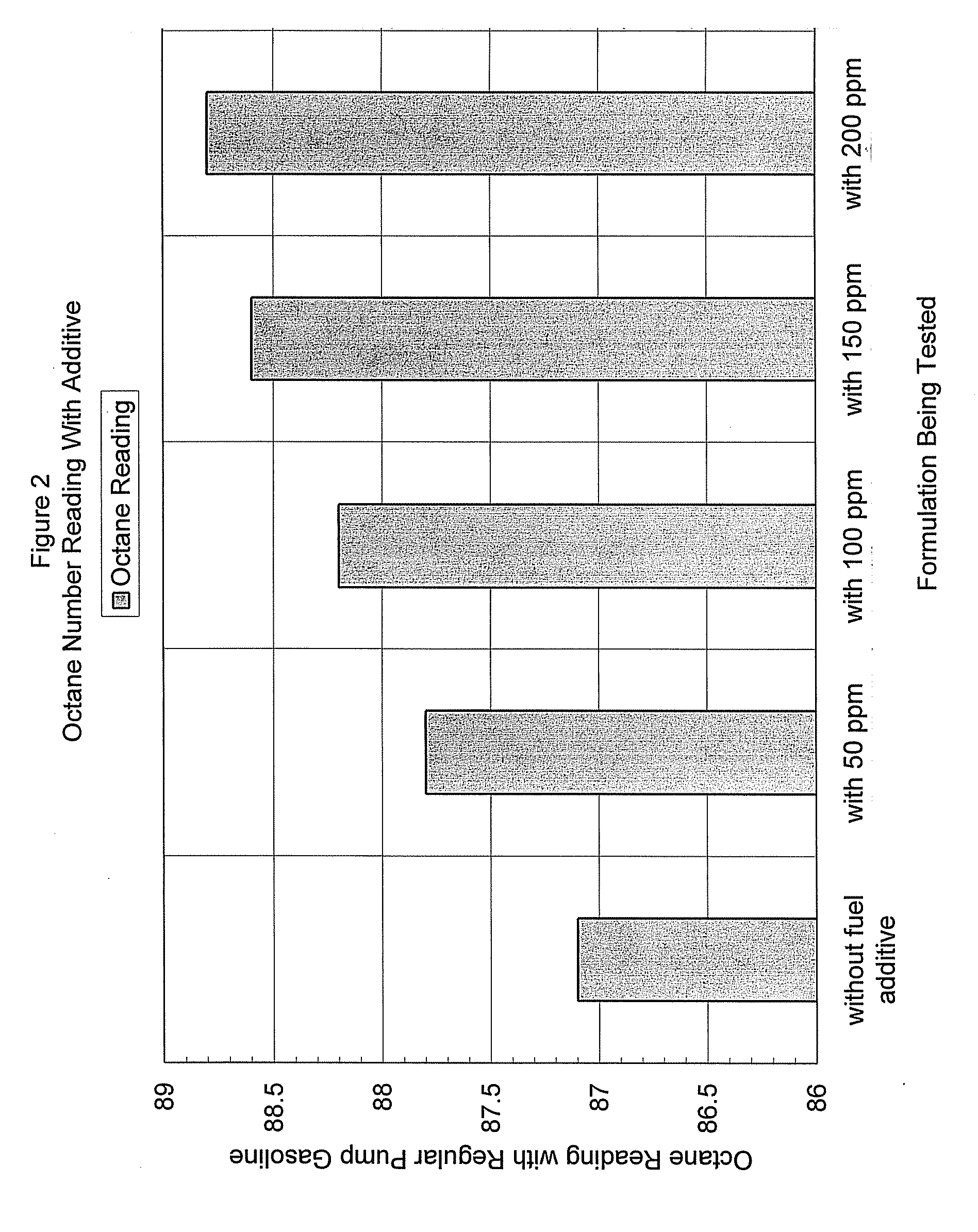
Nano-sized metal and metal oxide particles for more complete fuel combustion
InactiveUS20090000186A1Increase catalytic chemical oxidationPromote combustionLiquid carbonaceous fuelsFuel additivesNano sizeMetal particle
A fuel composition contains a liquid fuel and nano-sized metal particles or nano-sized metal oxide particles or combinations thereof. The nano-sized metal particles and nano-sized metal oxide particles can be used to either improve combustion or increase catalytic chemical oxidation of fuel.
Owner:JAMES K & MARY SANDERS FAMILY
Composition for coating organic electrode and method of manufacturing an organic conductive layer having excellent transparency using the composition
The present invention relates to a composition for coating an organic electrode and method of manufacturing an organic electrode having a excellent transparency using the composition comprising 3% to 20% by weight of a polyhydric alcohol, polyol or a mixture thereof, 5% to 10% by weight of a primary alcohol having C1 to C5, 5% to 25% by weight of a amide, sulfoxide or a mixed solvent thereof, 0.01% to 0.1% by weight of a surfactant and a aqueous solution of polyethylenedioxythiophene (PEDOT) conductive polymers having nano-sized particle in a remainder. The present invention indicates the excellent transparency that transmittance of organic conductive layer is more than 90% in the visible ray area and sheet resistance is 300 to 900 Ω / sq in case of coating. Therefore the present invention is capable of manufacturing the organic electrode such a electrode or a writing material of organic transistor, smart card, antenna, electrode of battery and fuel battery, capacitor using for PCB, inductor, electromagnetic wave cover and a sensor etc. as well as the transparency electrode using for display.
Owner:DPI SOLUTIONS INC
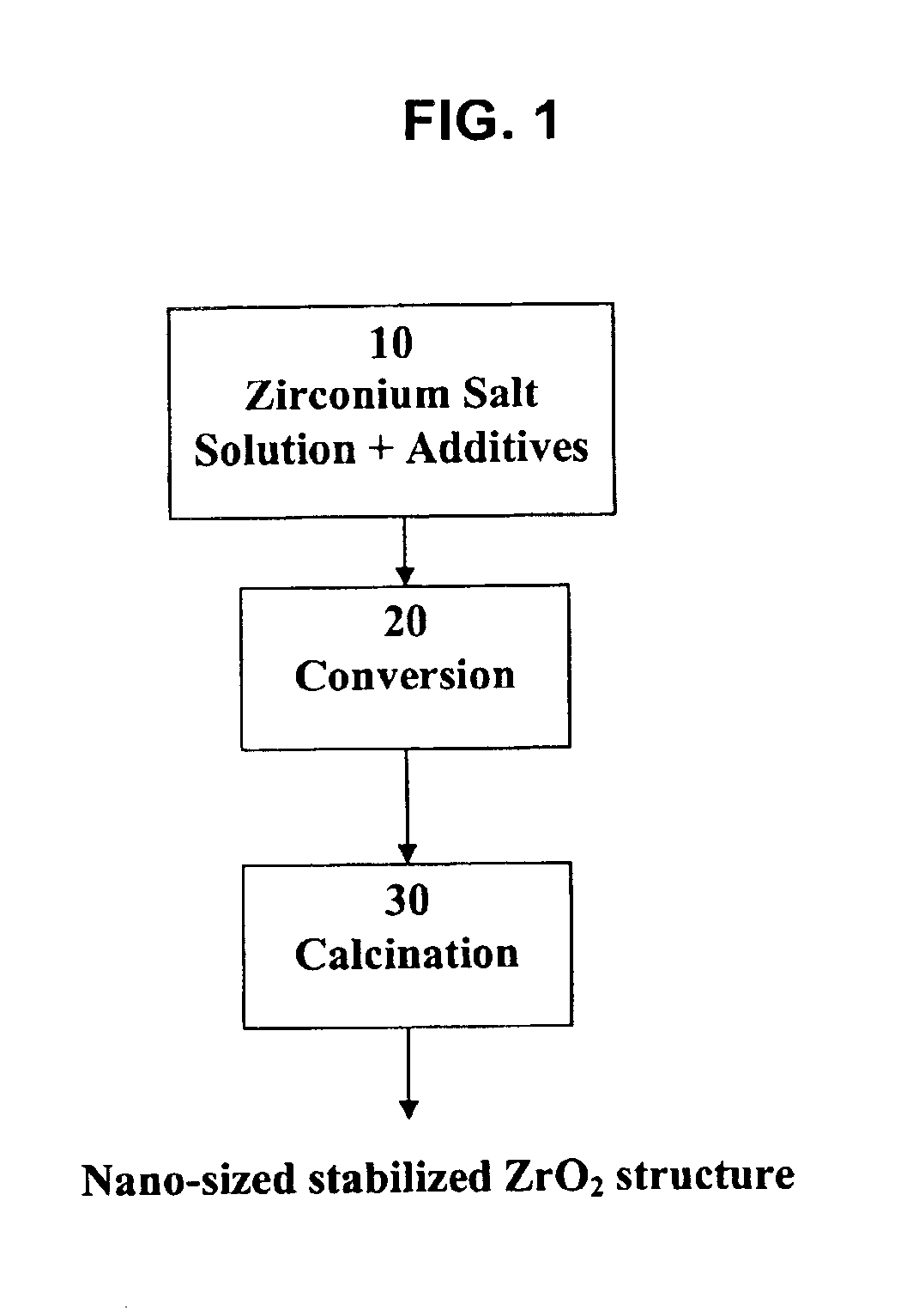
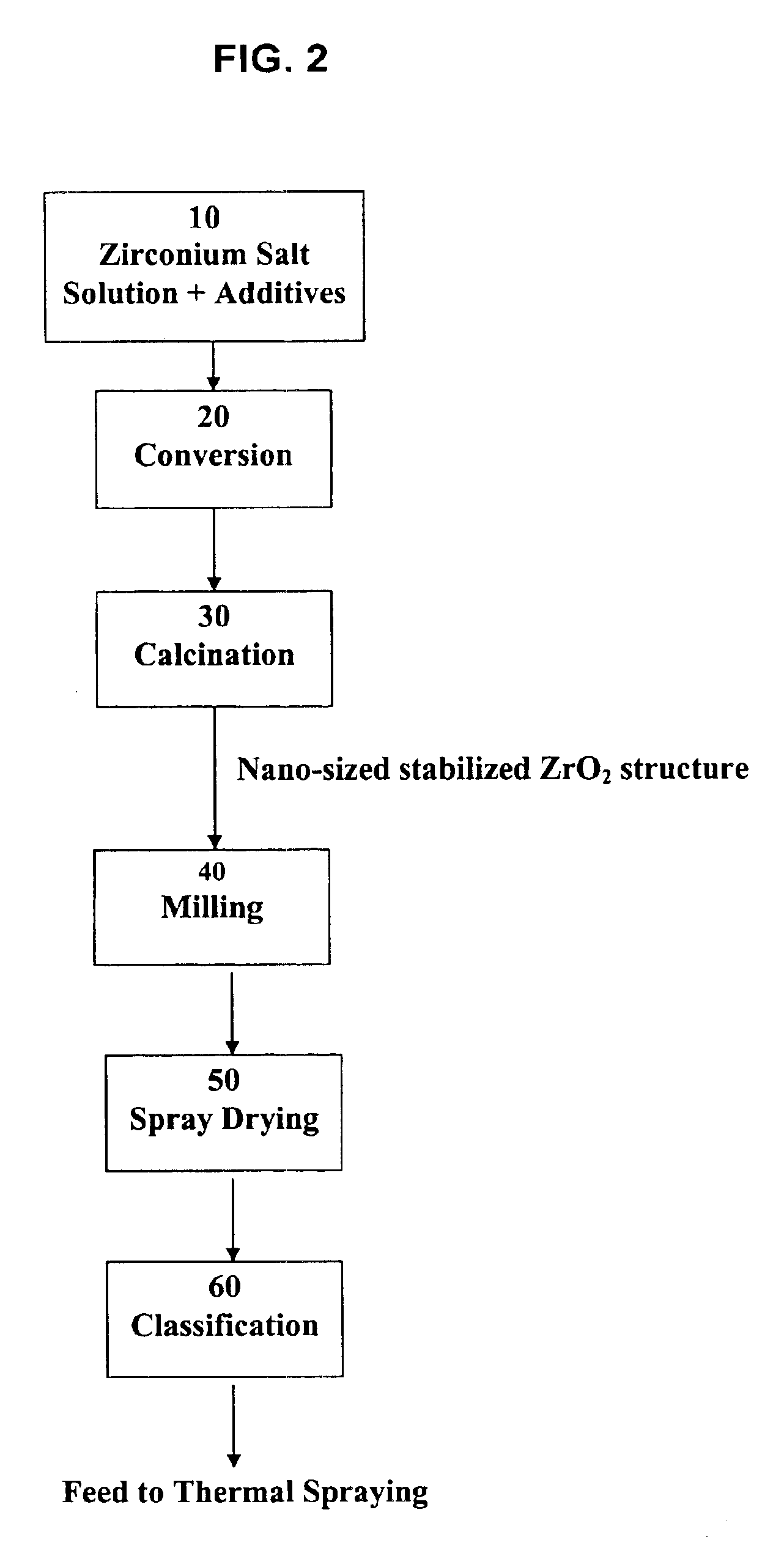
Process for making nano-sized stabilized zirconia
A process to produce stabilized zirconia from a solution of zirconium salt and a stabilizing agent. The zirconium salt may include zirconium oxysulfate, zirconium oxychloride, zirconium oxynitrate, zirconium nitrate, and other water-soluble zirconium salts. The stabilizing agent may include calcium, magnesium, yttrium salts of oxides and rare earth oxides. The process is conducted by evaporation of the solution above the boiling point of the solution but below the temperature where there is significant crystal growth. The evaporation step is followed by calcination to produce the desired nano-sized structure. Further processing by sintering may be applied to produce solid structures or by milling and classification to produce material for thermal spray coating.
Owner:ALTAIR NANOMATERIALS INC
Nanoparticles having a rutile-like crystalline phase and method of preparing same
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Method for preparing nano pore composite humidity adjusting material
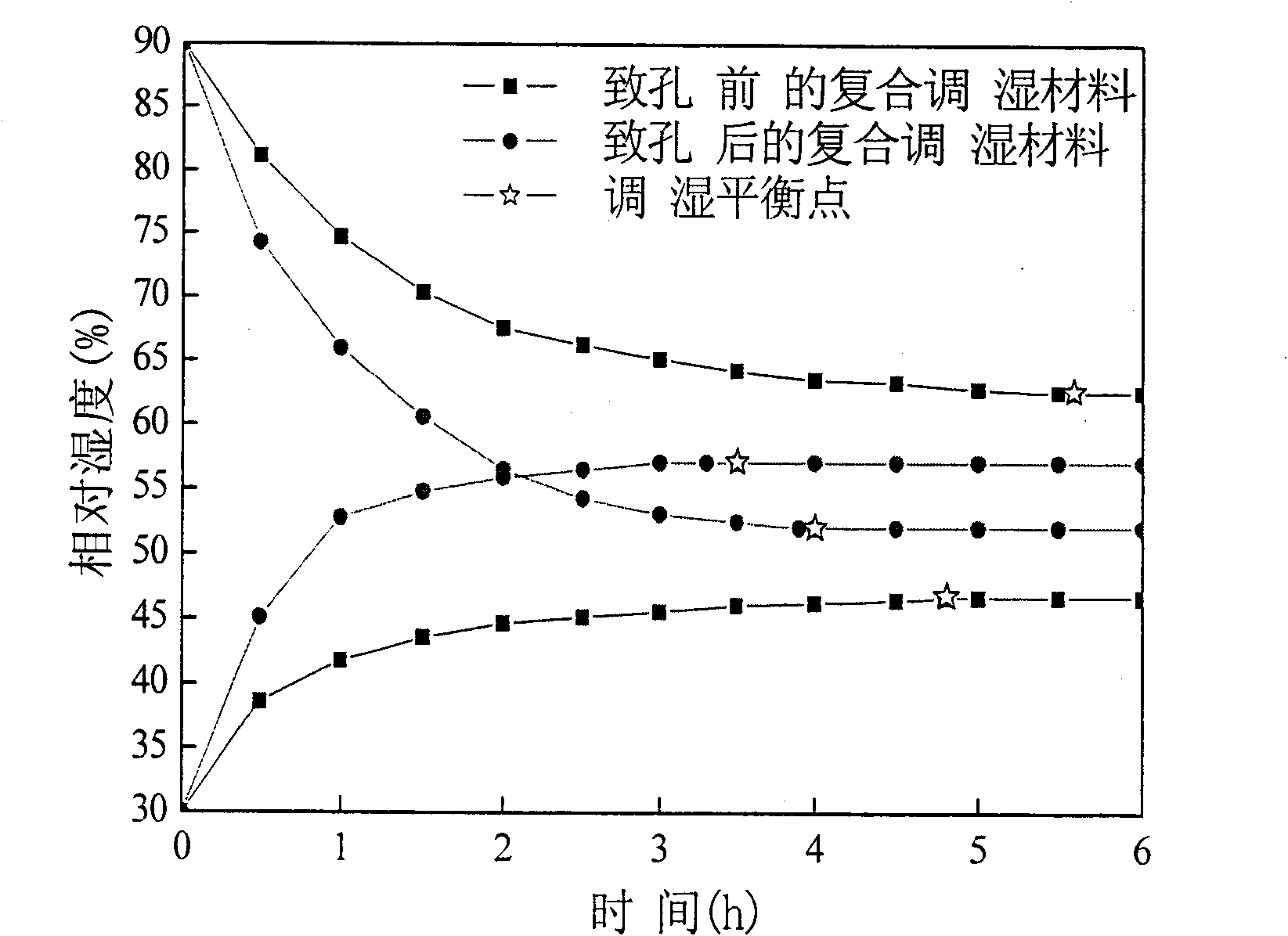
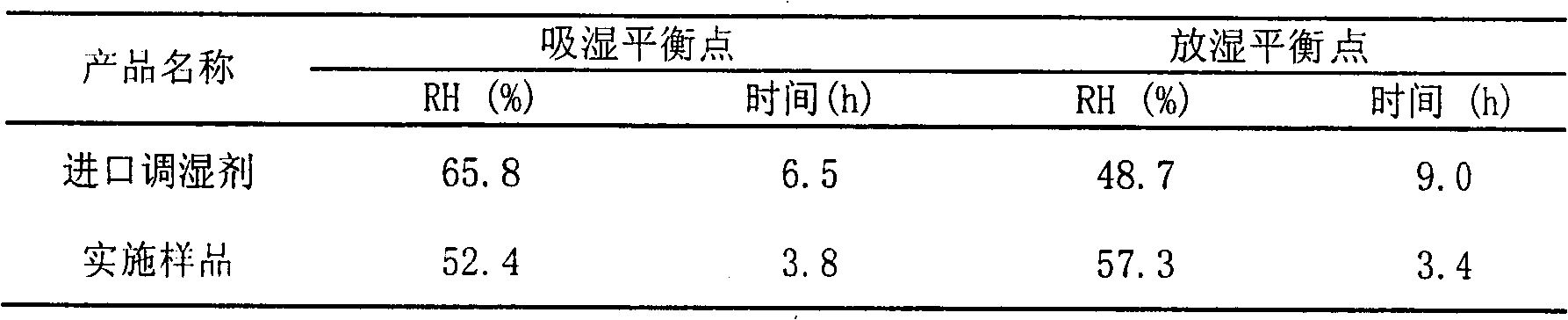
InactiveCN101928438AQuickly adjust relative humidityLarge moisture absorption capacityOther chemical processesHigh humidityNano size
The invention discloses a method for preparing a nano pore composite humidity adjusting material. An organic macromolecular material, a natural macromolecular material and an inorganic porous material are compounded into the humidity adjusting material by synthesis so as to absorb the advantages of various humidity adjusting materials and improve the wet capacity and humidity adjusting performance of the synthesized material; and a large amount of nano-scale pore structures are formed on the material through the synthesis process so as to further improve the humidity absorbing and discharging performance of a product. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that: 1) the material has high humidity absorbing and discharging capacity and high humidity absorbing and discharging response speed, and can efficiently and quickly adjust the relative humidity of a microenvironment; 2) the material is renewable and very convenient to reuse; 3) the production process and the production equipment are simple and easy for industrialization; and 4) the production process is environmentally-friendly.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
System and method for ammonia synthesis
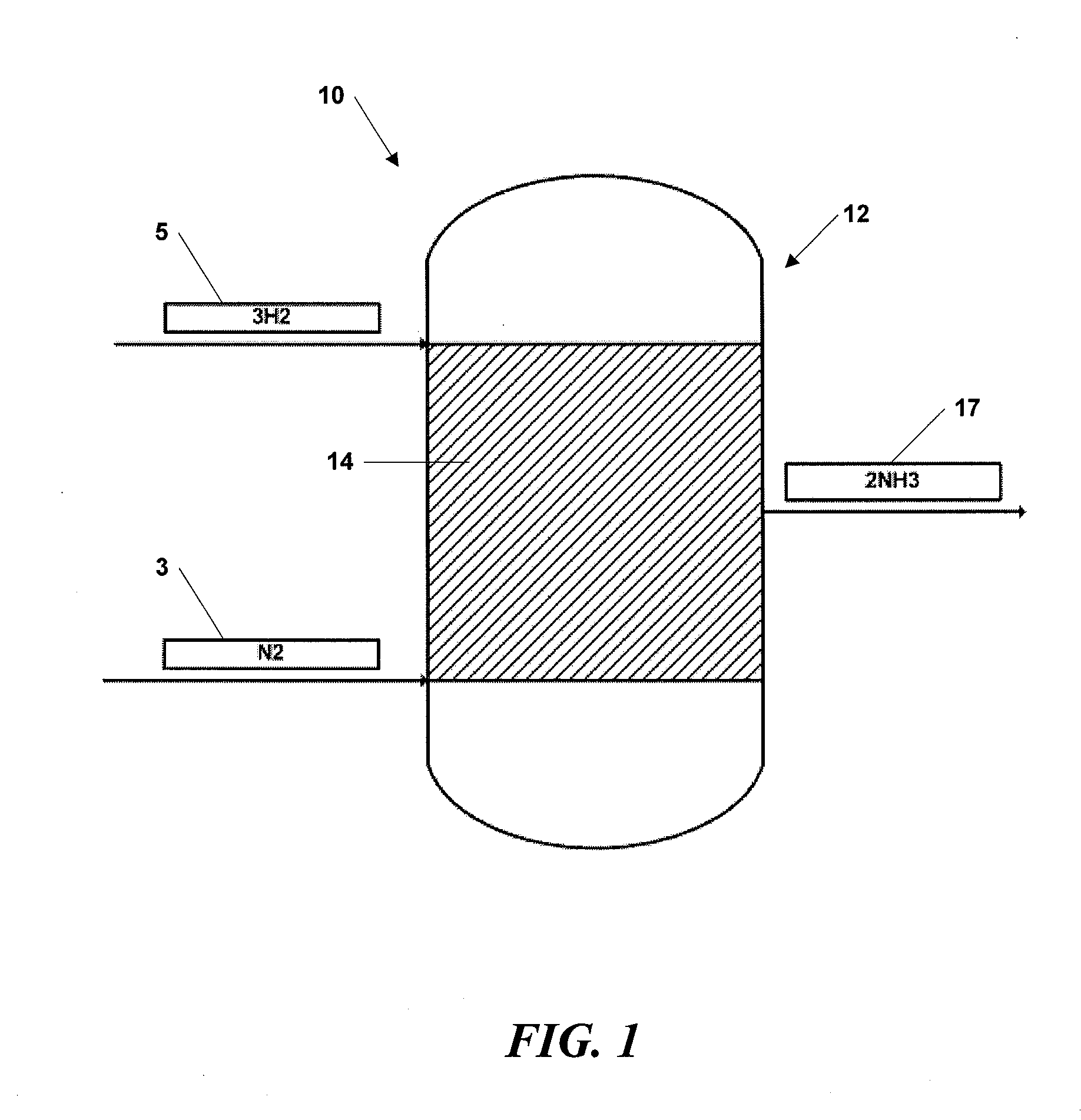
InactiveUS20090117014A1Reducing and eliminating sinteringFunction increaseBulk chemical productionAmmonia preparation/separationNano sizeHydrogen
Systems and methods are disclosed herein for synthesizing ammonia at mid- to low-pressures using nano-size metal or metal alloy catalyst particles. Hydrogen and nitrogen gases are passed through a system comprising, for example, a packed bed of supported nano-size iron or iron alloy catalyst particles having an optional oxide layer that form the catalyst.
Owner:BRICOLEUR PARTNERS LP
Nano inorganic composite fire-resisting agent for macromolecular material
InactiveCN1536000AAchieve flame retardancyTo achieve the purpose of smoking suppressionPolyesterNano size
The present invention relates to a nano inorganic composite fire-retardant for macromolecular material. It is composed of nano aluminium hydroxide, nano structure modified aluminium hydroxide or nano magnesium hydroxide and micro-size magnesium hydroxide and auxiliary fire retardant, in which the average grain size of nano aluminium hydroxide is less than or equal to 100 nano, the average grain size of nano structure modified aluminium hydroxide is less than or equal to 150 nano, the average grain size of nano magnesium hydroxide is less than or equal to 100 nano, the average grain size of micro-size magnesium hydroxide is 1-10 microns, and the mass ratio of nano-size inorganic fire retardant and micro-size magnesium hydroxide is 80:20 to 10:90, and the mas ratio of nano-size inorganic fire-retardant and micro-size magnesium hydroxide and auxiliary fire retardant is 100:10 to 100:30. It can be used in the fire-retarding composite materials of PE, PP, ABS, nylon, PC, PVC, EVA and polyester, etc.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH +1
Nanoparticle composition and process thereof
Owner:JAWAHARLAL NEHRU CENT FOR ADVANCED SCI RES
Nanosized particles of molybdenum sulfide and derivatives, method for its preparation and uses thereof as lubricant additive
InactiveUS6878676B1Prevent coagulationProvide solubility and stabilityGroup 1/11 element organic compoundsAdditivesNano sizeSulfur
A lubricant composition is disclosed that comprises: (a) a lubricant and (b) at least one molybdenum-containing compound in the form of surface-capped nanosized particles of the general formula: (Z)n(X—R)m wherein Z is an inorganic moiety comprising molybdenum and sulfur in the form of particles having dimensions in the range of from about 1 to about 100 nm; (X—R) is a surface-capping reagent wherein R is a C4 to C20 straight or branched-chain alkyl or alkylated cycloalkyl radical or radicals and X is a functional group capable of specific sorption and / or chemical interaction with molybdenum / sulfur moiety; n is the number of molecules of Z in the particles; m is an integer representing the amount of surface-capping reagents relative to a single particle; and the ratio of m to n is in the range of from about 1:1 to about 10:1.
Owner:CROMPTON CORP
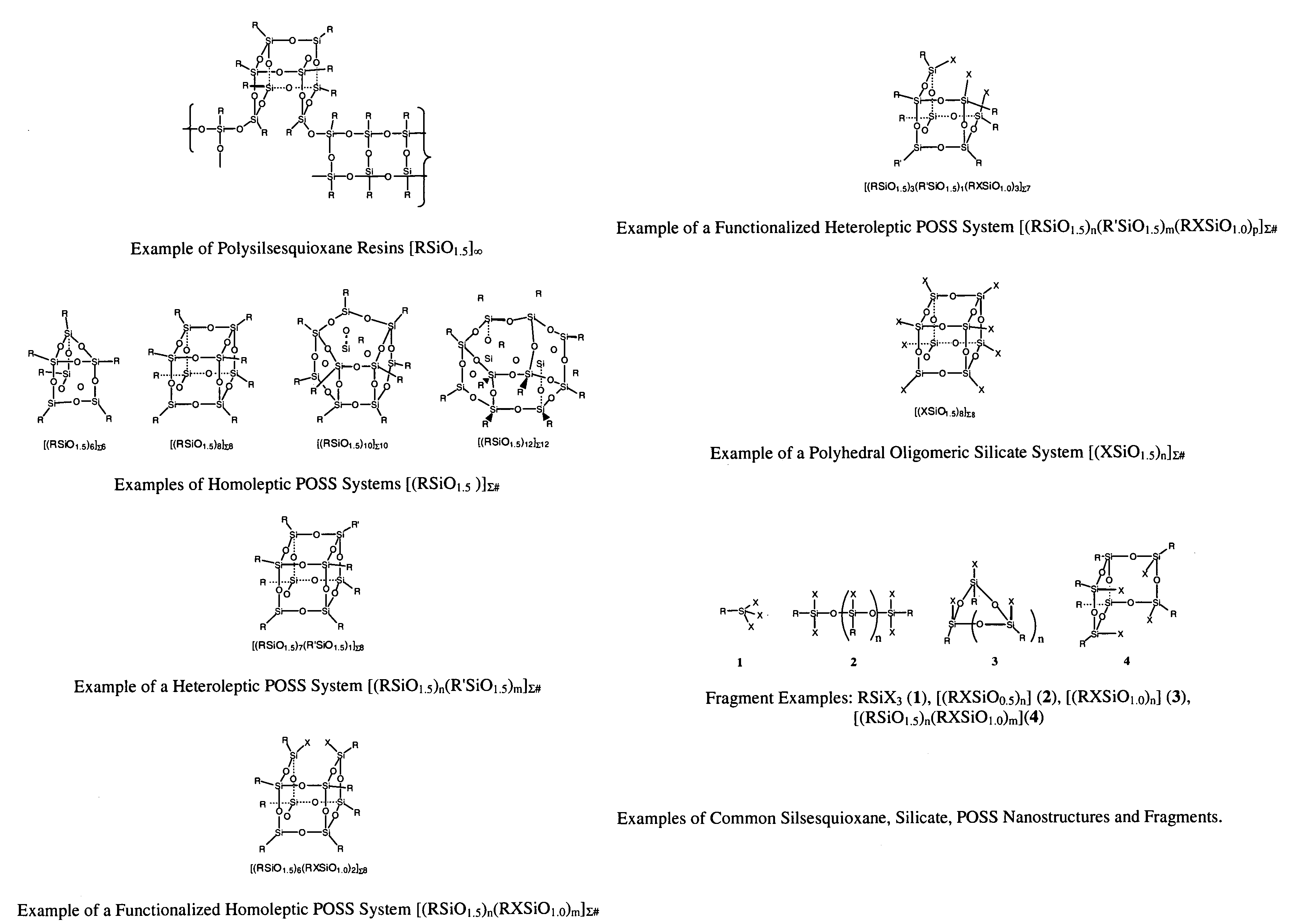
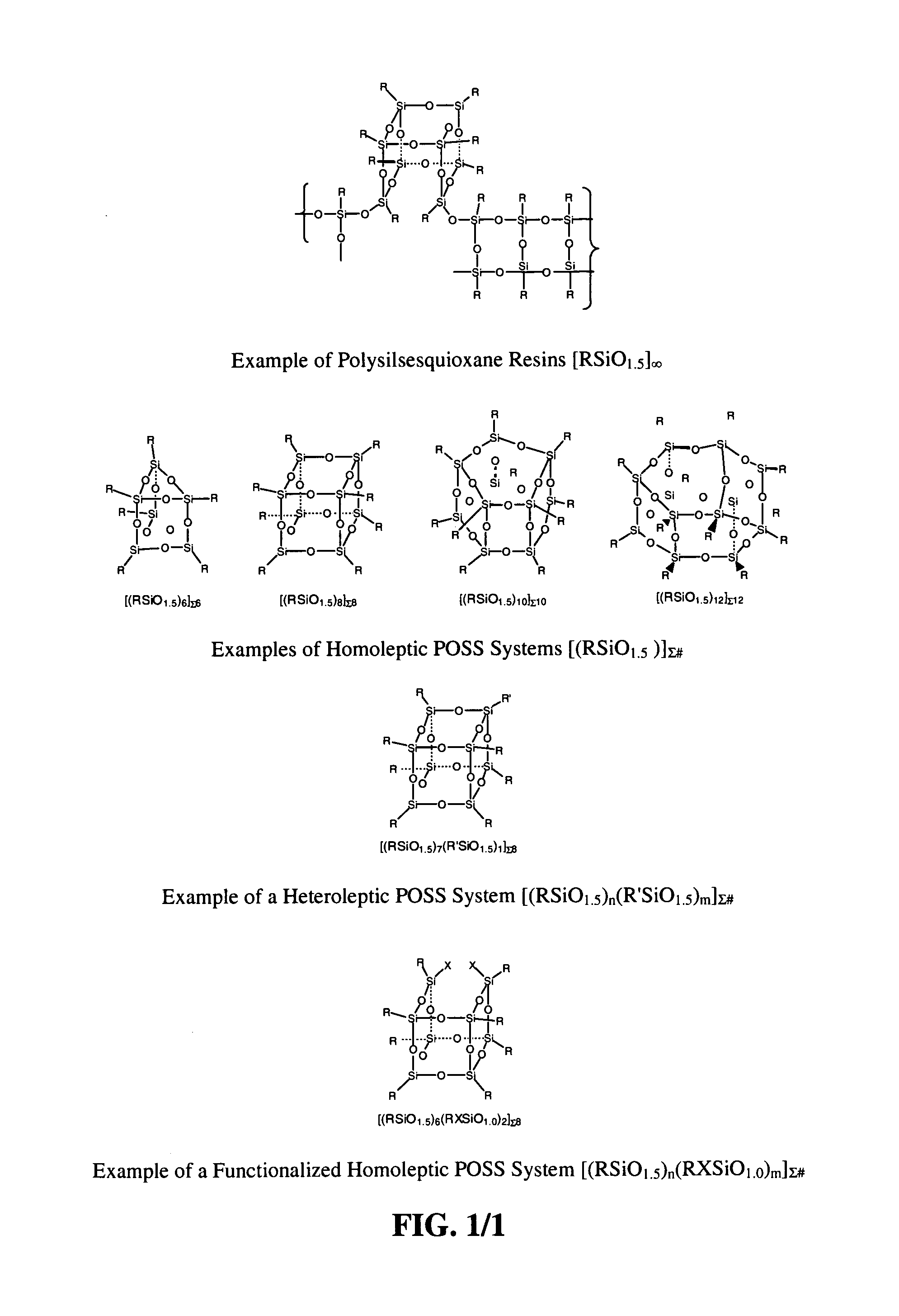
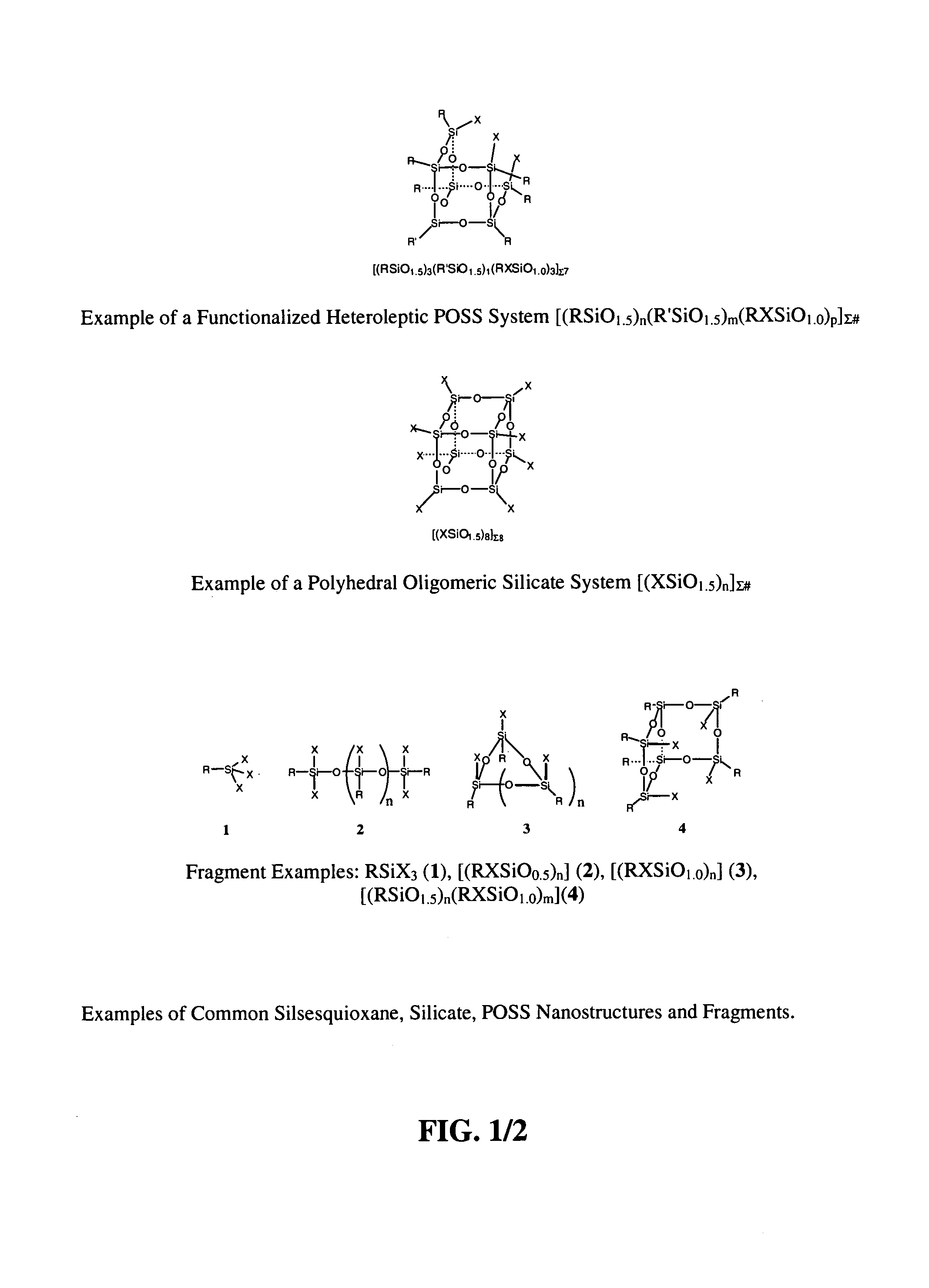
Lubrication via nanoscopic polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes
ActiveUS7217683B1Improve interface performanceIncrease frictionBearing componentsAdditivesNano sizeChemical potential
Nanoscale chemicals based on polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes (POSS) and polyhedral oligomeric silicates (POS) are taught as lubricants, mold release agents, and as additives to control the viscosity, lubrication, wear, and thermal properties of conventional lubricous materials. The precisely defined nanoscopic dimensions of POSS materials enable viscosity, miscibility, and thermal properties to be (increased) or reduced (decreased) as desired. A key feature to the successful tailoring of properties is the inherent thermal and chemical stability of the POSS / POS nanostructure and the ability to control its topology and chemical potential to match that of surfaces and other materials.
Owner:GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE AIR FORCE
Anisotropic conductive adhesive
InactiveUS20070213429A1Stable and reliableShort thermocompression bond timeNanostructure manufactureElectrically conductive adhesive connectionsThermal energyNano size
An anisotropic conductive adhesive that provides strong adhesion to metals and organic substrates to generate stable and reliable electric interconnects. The adhesive provides the benefits of short thermocompression bond time at low temperatures. The adhesive contains cationic curable resin, latent cationic catalyst that thermally cures the resin at high speeds and low temperatures, conductive filler, optionally a film forming thermoplastic solid resin and optionally nano size filler. The optional nano filler provides the benefit of reducing the coefficient of thermal energy mismatch, improving the adhesion strength and reducing the total heat of reaction for the system.
Owner:HENKEL KGAA
Nanoemulsions having reversible continuous and dispersed phases
A nanoemulsion having reversible continuous and dispersed phases. The nanoemulsion includes an aqueous phase and an oil phase, a weight ratio of the aqueous phase to the oil phase being 1:40-100:1. In the nanoemulsion, the aqueous phase is dispersed as nanosized droplets in the oil phase or the oil phase is dispersed as nanosized droplets in the aqueous phase. The aqueous phase contains water or a water solution and a water-soluble organic nanostructure stabilizer. The oil phase contains an oil or an oil solution, an organic gel thickener, and a hydrophilic surfactant having a hydrophilic-lipophilic balance value greater than 8.0. Also disclosed is a method for preparing the above-described nanoemulsion.
Owner:LG BIONANO LLC
Glass heat insulation paint of water-based hydroxyl polyurethane resin and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101633816AImprove performanceExcellent heat reflectionPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsWater basedPolyester
The invention discloses a glass heat insulation paint of water-based hydroxyl polyurethane resin and a preparation method thereof. The glass heat insulation paint is prepared by mixing the raw materials by weight percent: 15-76% of water-based hydroxyl polyurethane, 20-60% of nano sizing agent, 0.5-4.0% of water-based auxiliary agent, 0.50-3.0% of silane coupling agent and 3-18% of water-based curing agent; wherein the structural formula of the water-based hydroxyl polyurethane is shown above, A section is hydrophile type end hydroxyl polyester with the molecular number of 1-5; J section is polyisocyanate with the molecular number of 5-15; and the G section is dibastic alcohol with the molecular number of 5-10. The invention has the advantages of high transmission of light and thermal insulation, good water resistance, strong adhesive force when being coated on glass, and being not easy to fall off.
Owner:武汉双虎涂料股份有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com