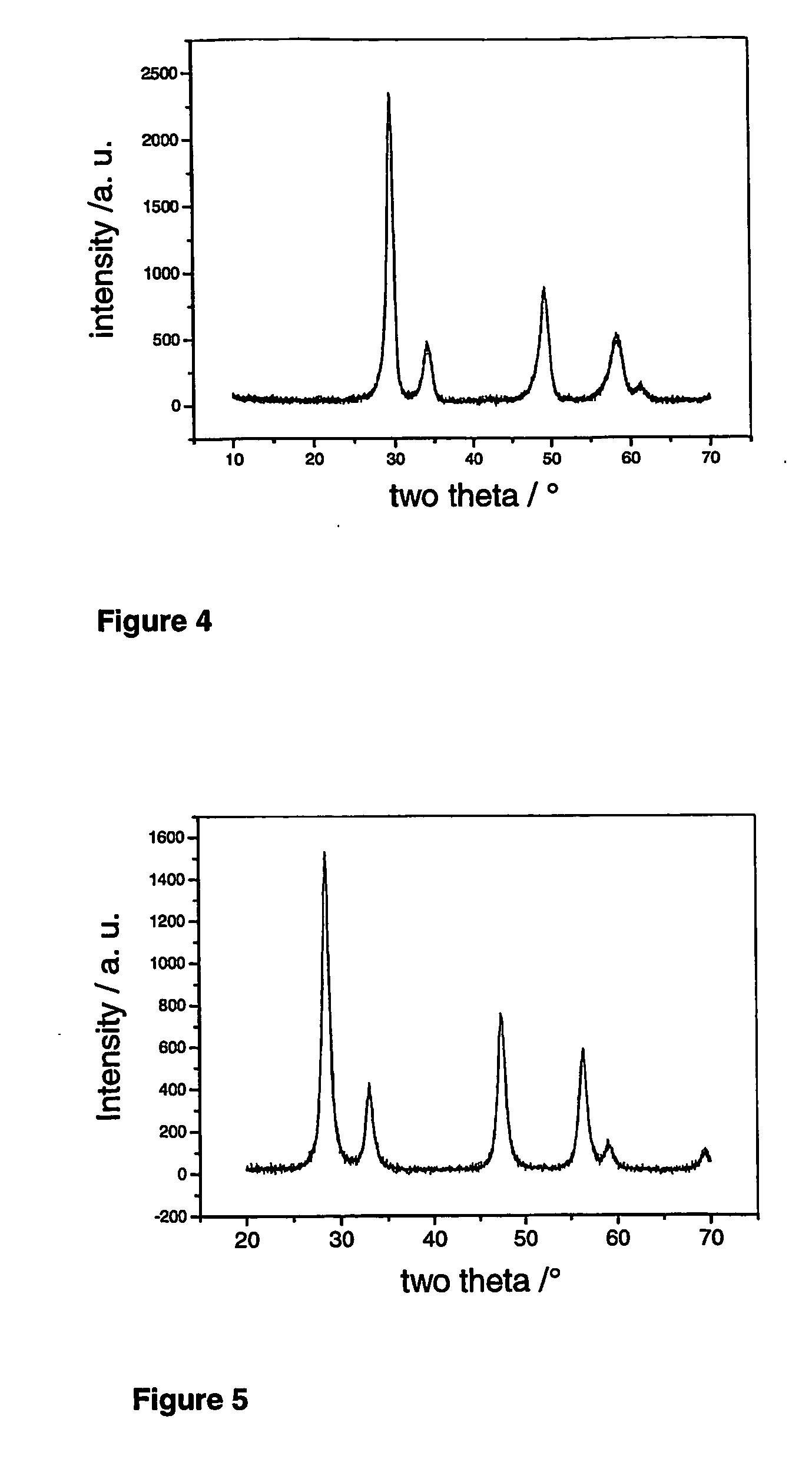
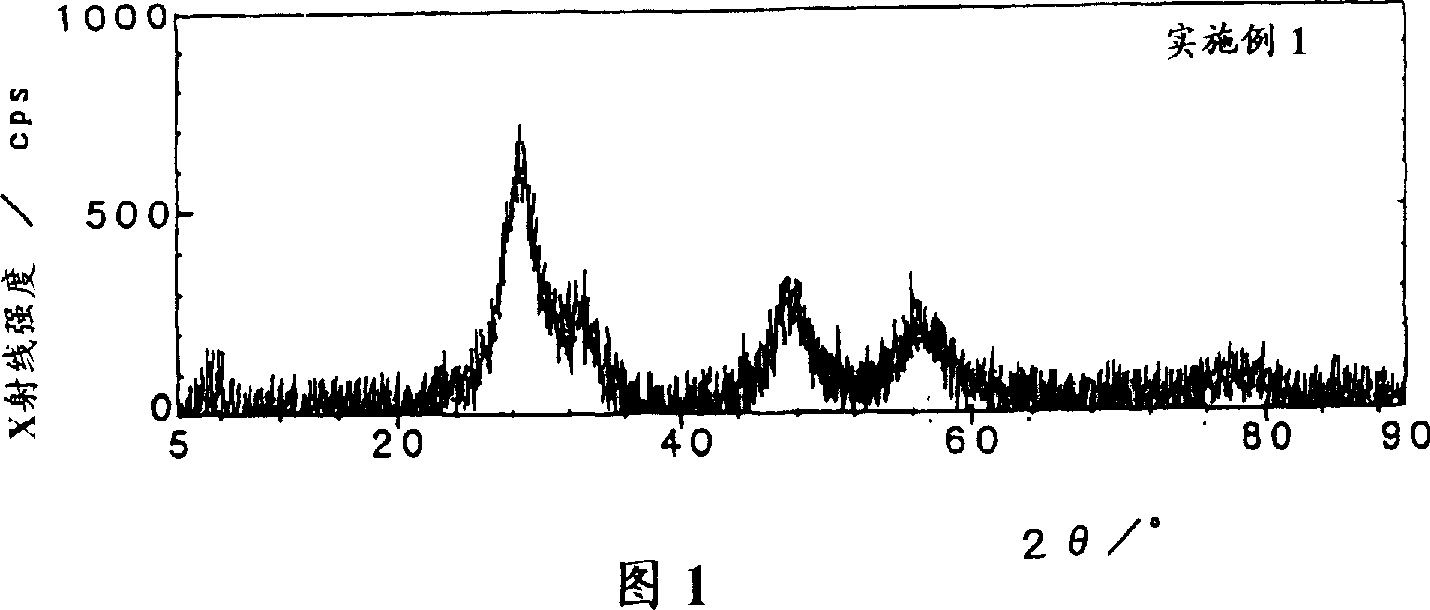
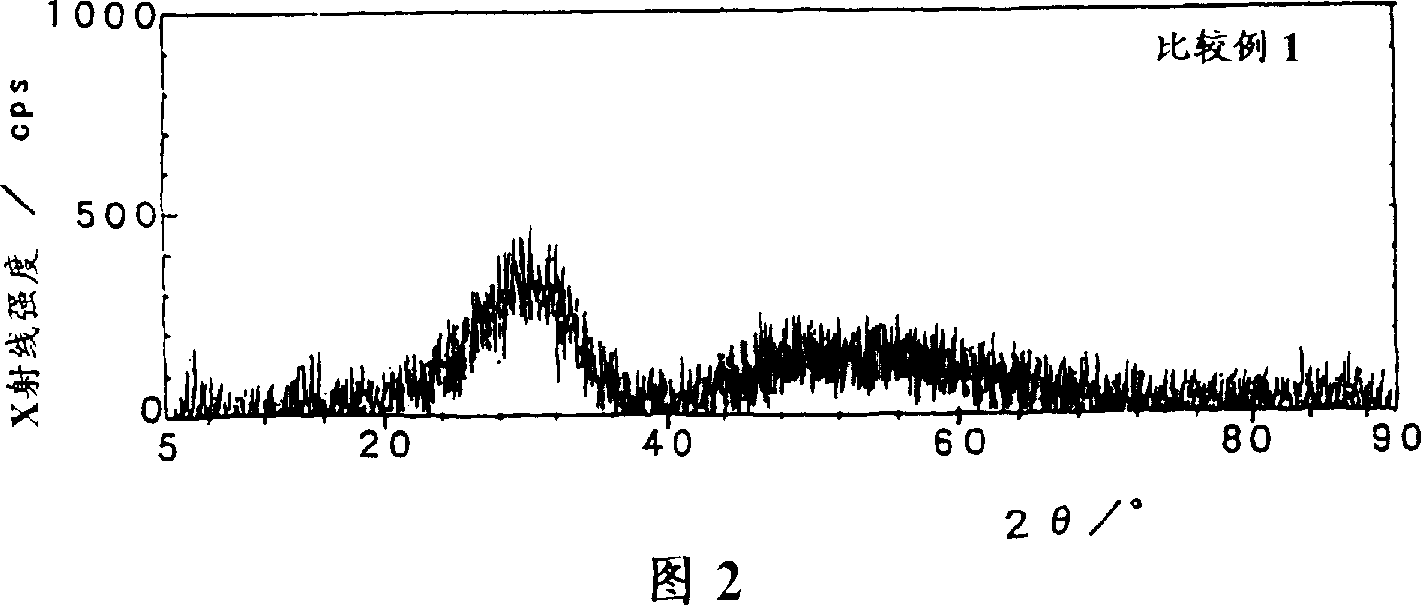
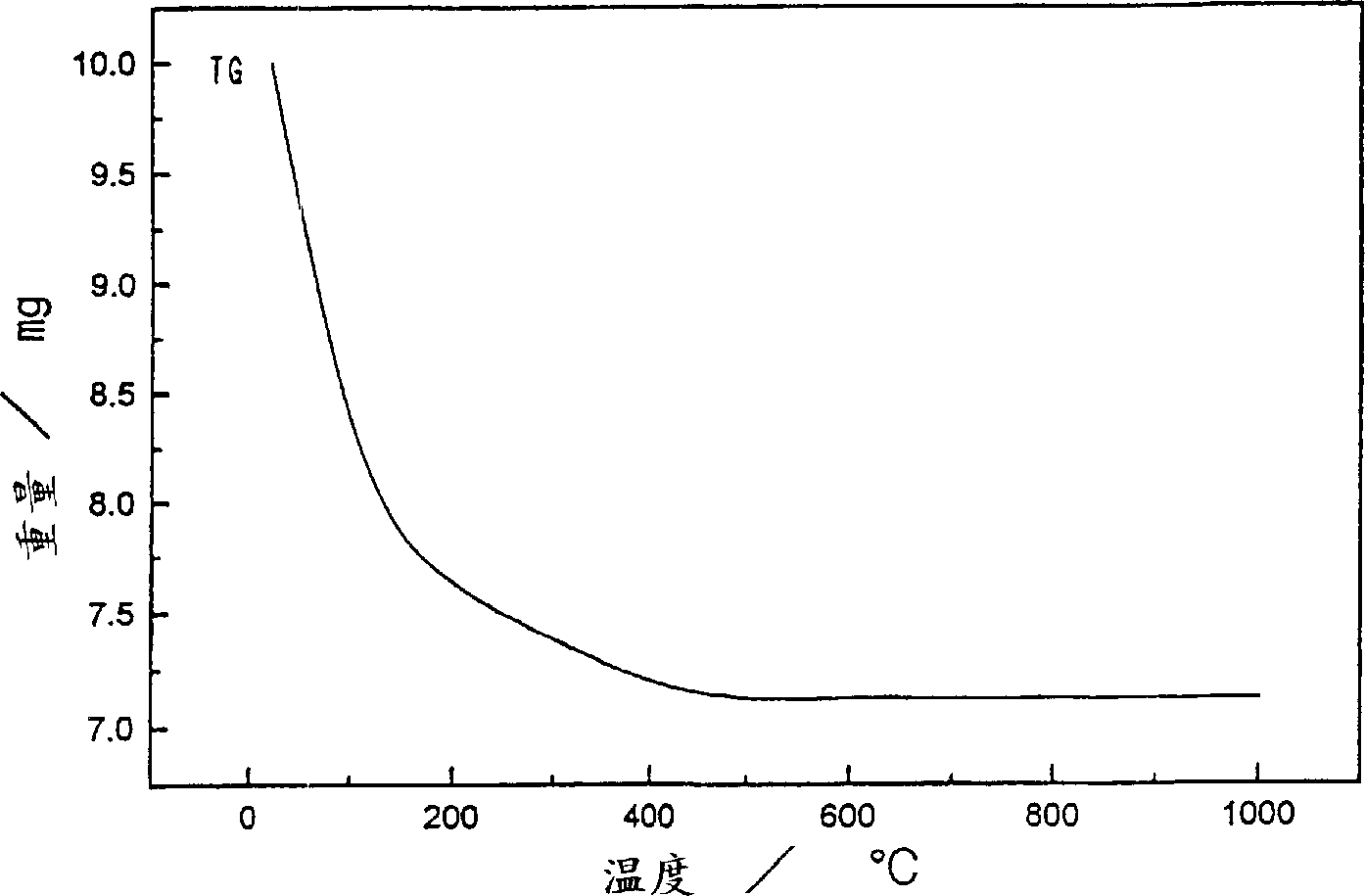
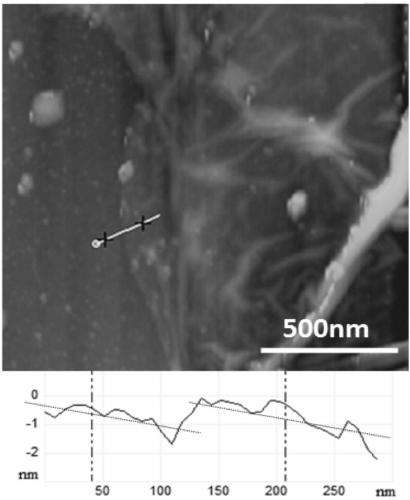
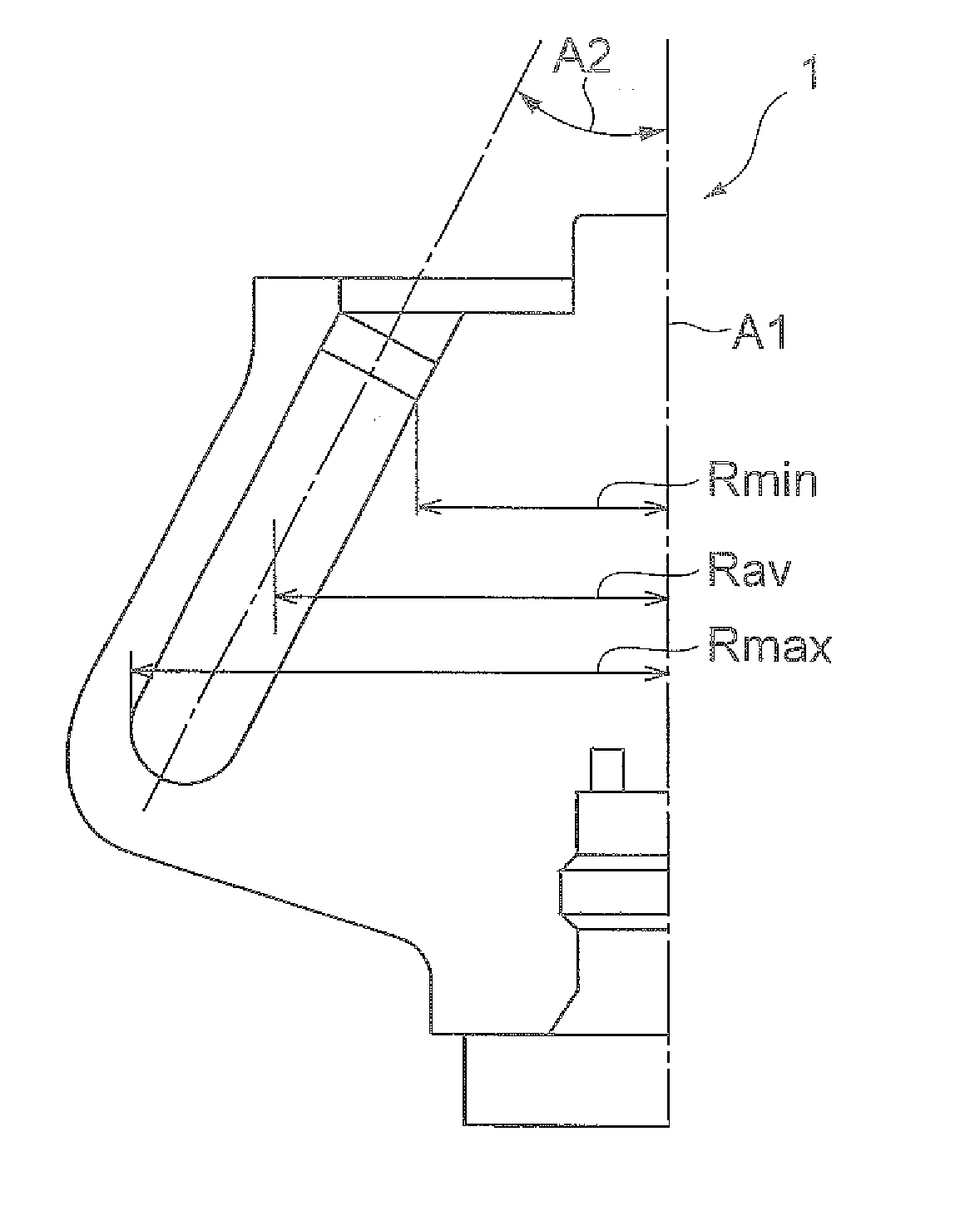
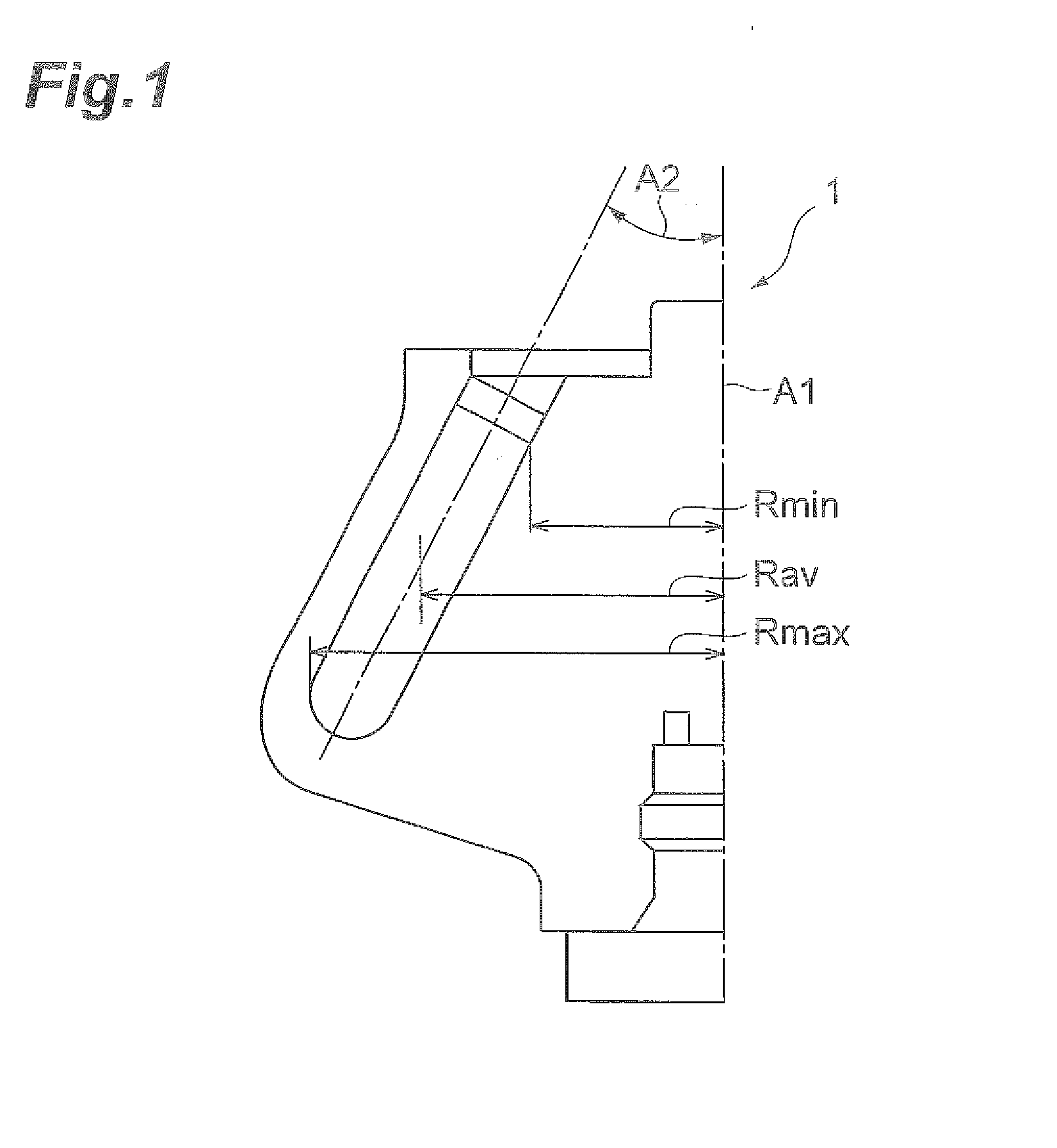
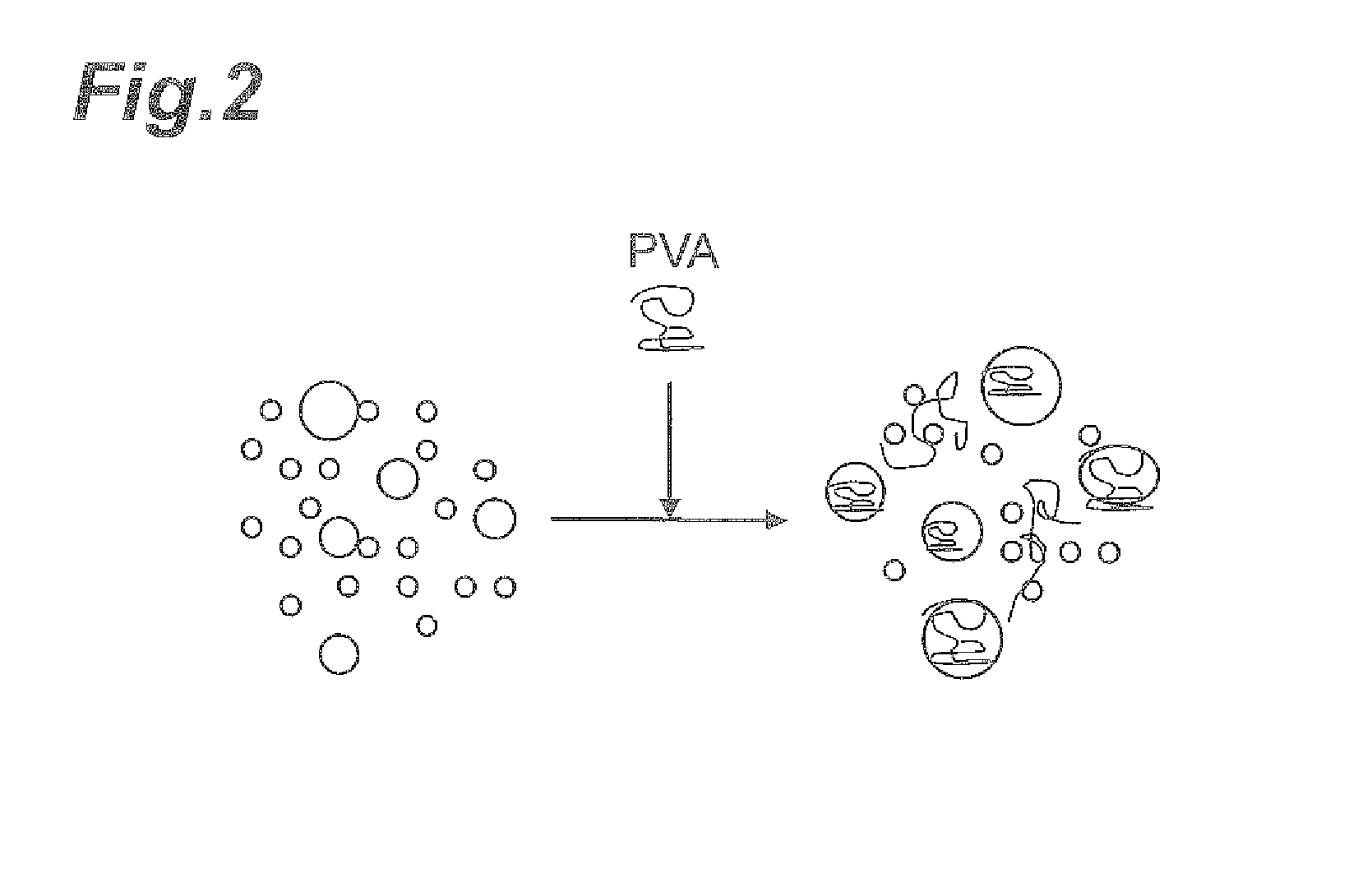
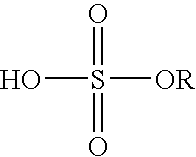Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
595results about "Rare earth metal oxides/hydroxides" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
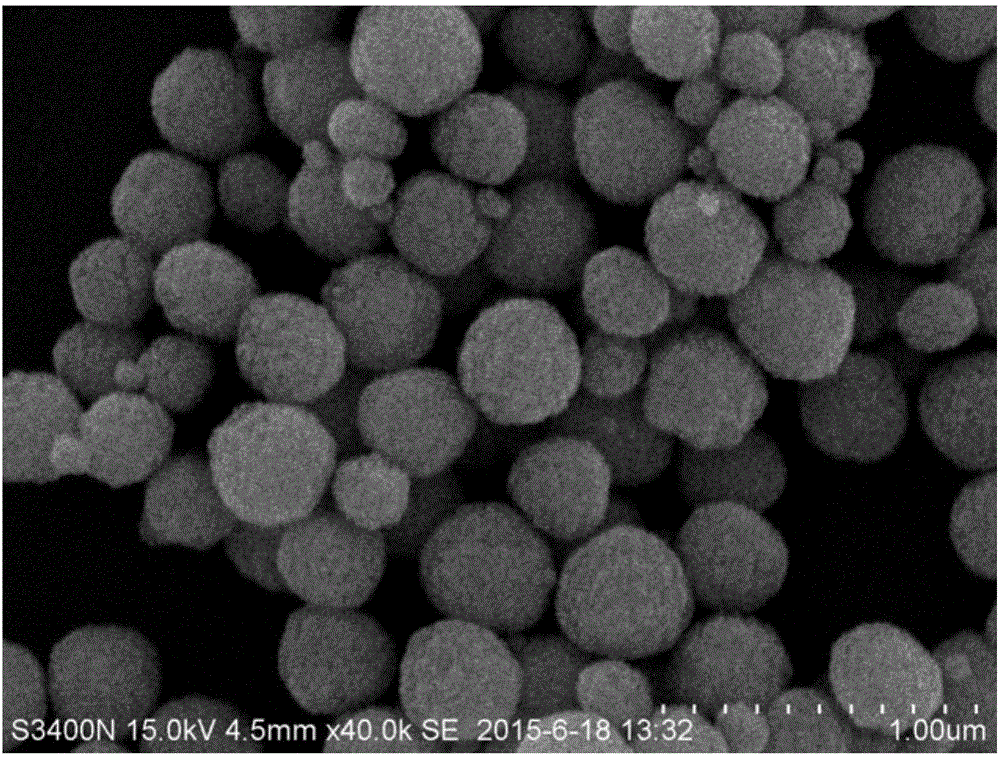
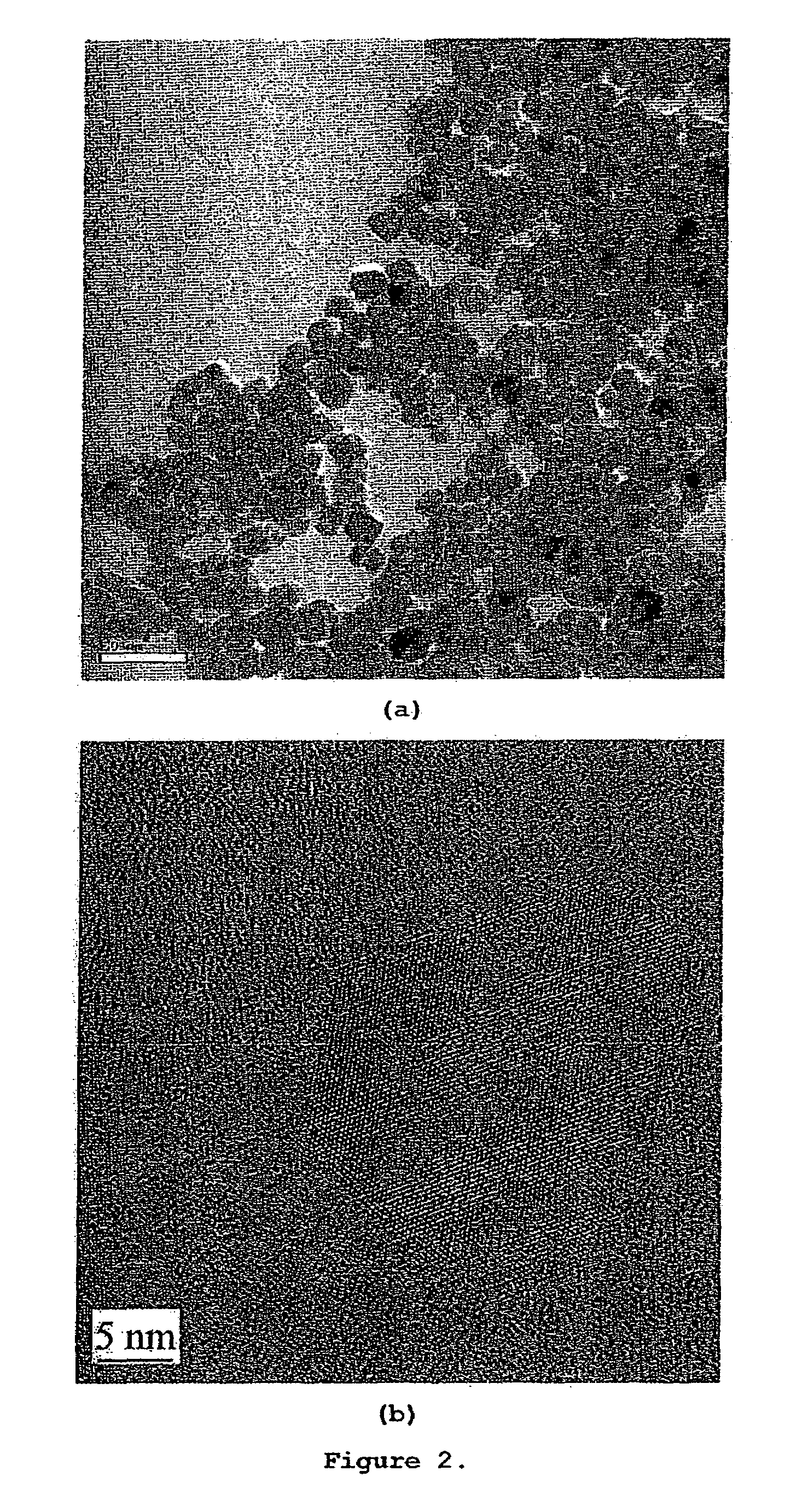
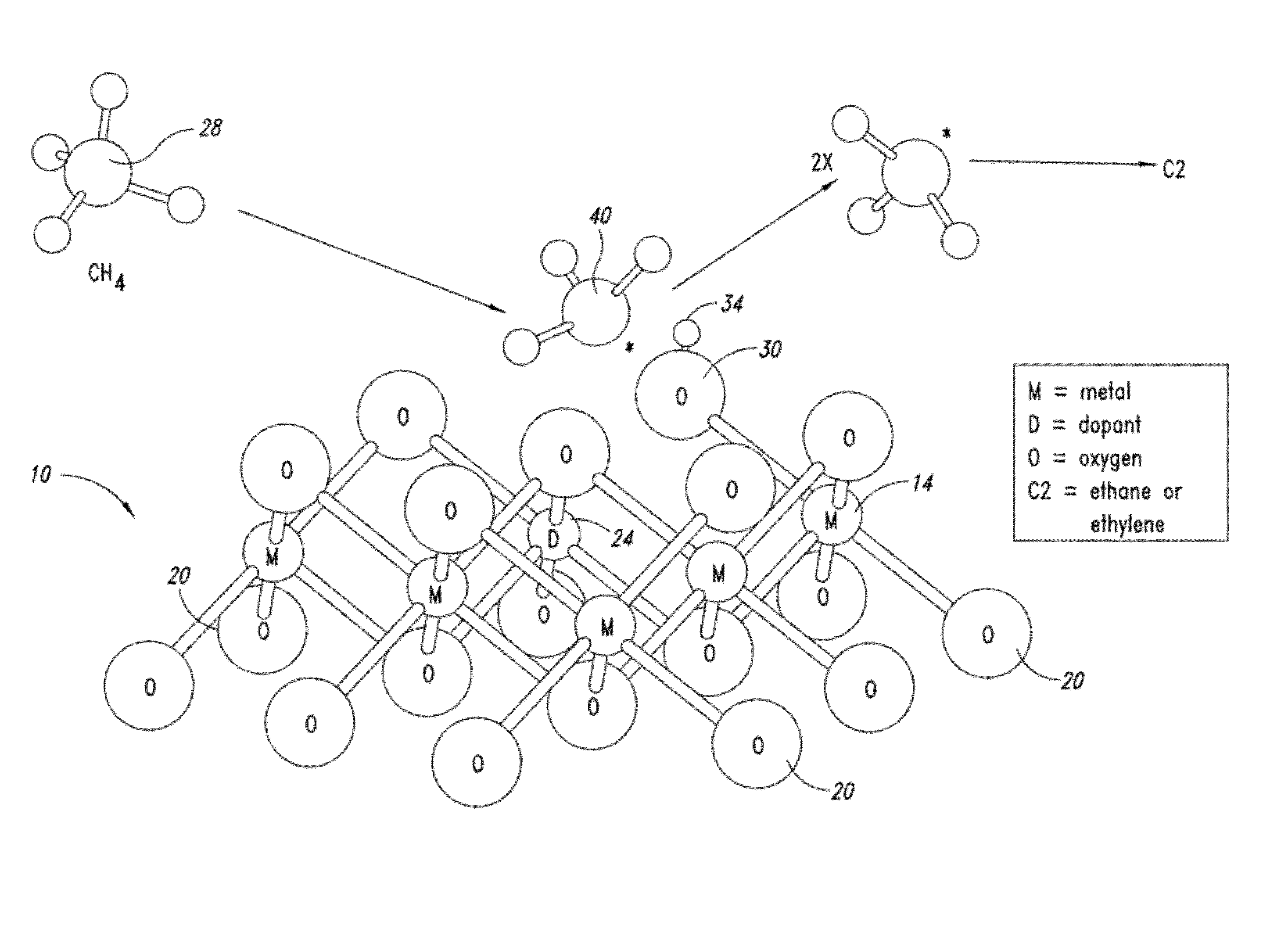
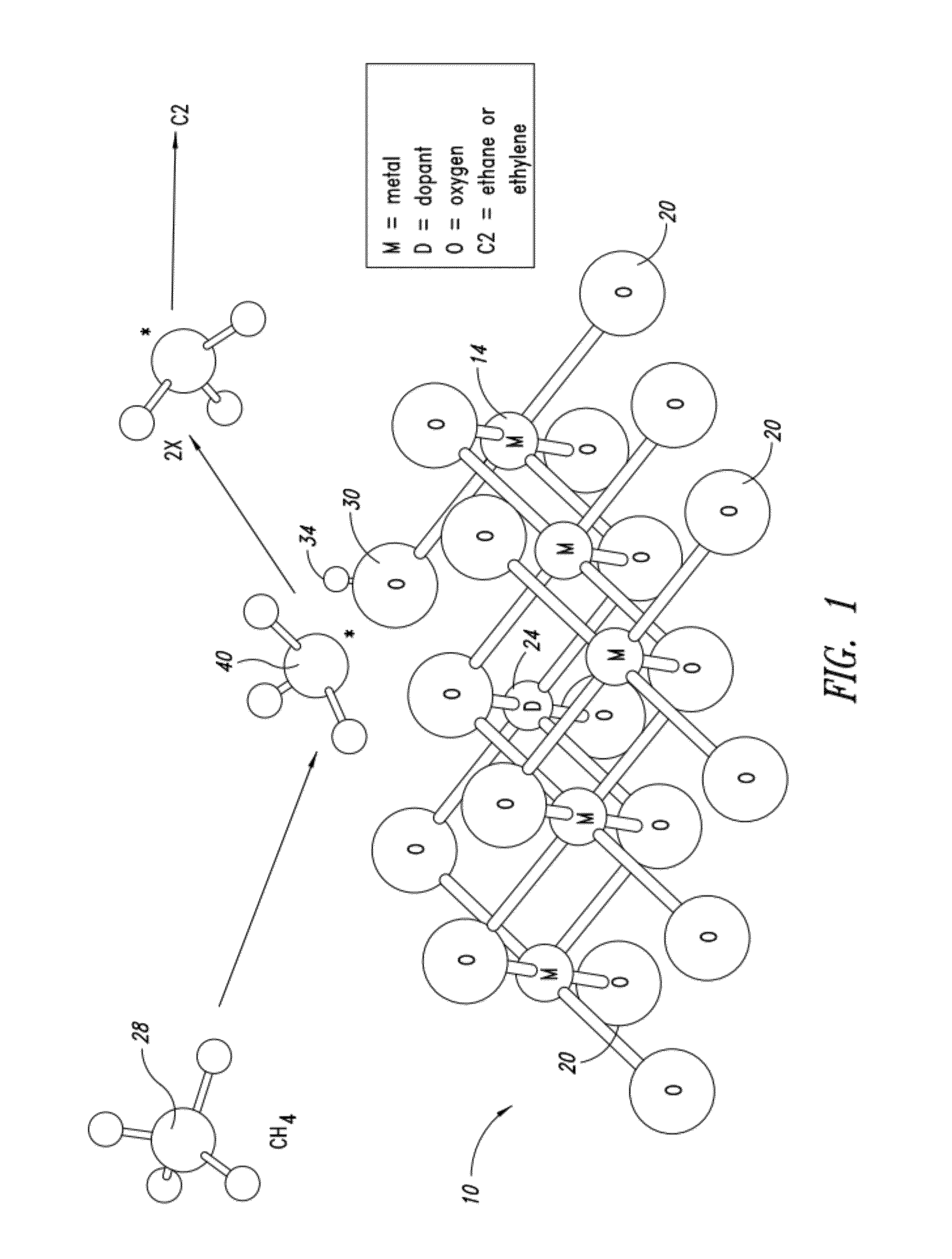
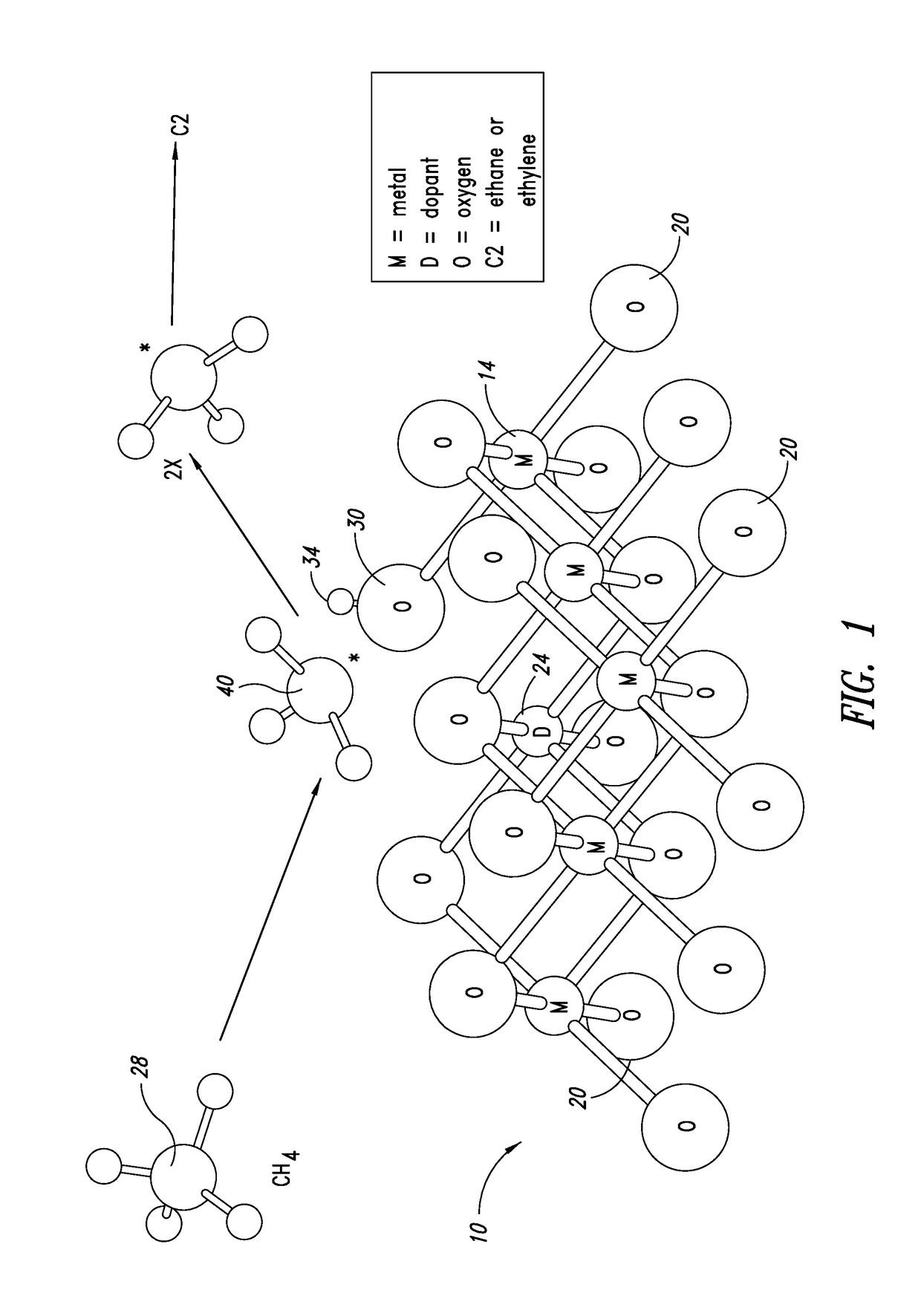
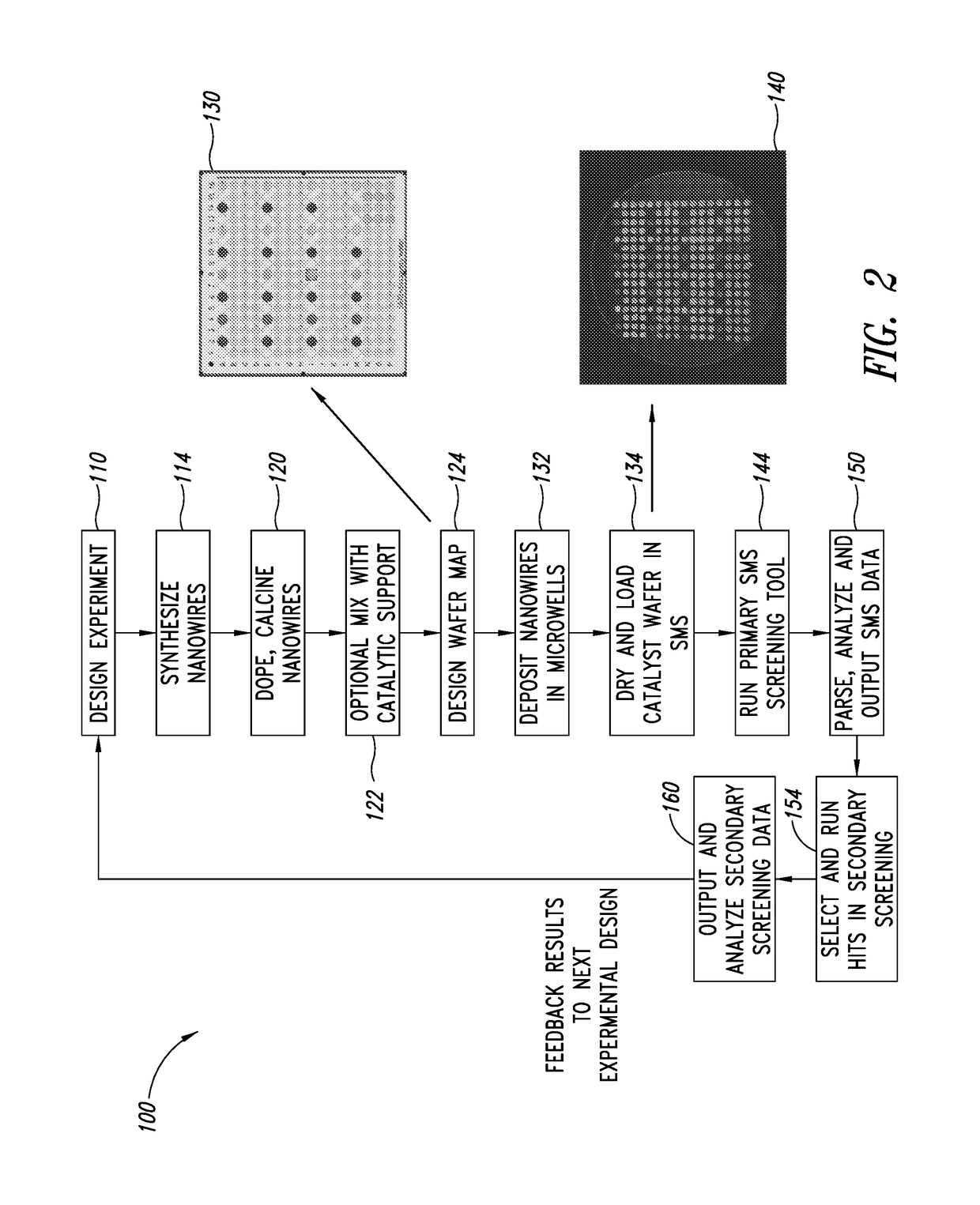
Nanowire catalysts
Nanowires useful as heterogeneous catalysts are provided. The nanowire catalysts are useful in a variety of catalytic reactions, for example, the oxidative coupling of methane to ethylene. Related methods for use and manufacture of the same are also disclosed.
Owner:SILURIA TECH INC
Ceria-based mixed-metal oxide structure, including method of making and use
InactiveUS20030186805A1Increase surface areaSimple structureRare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesMaterial nanotechnologyPtru catalystCerium(IV) oxide
A homogeneous ceria-based mixed-metal oxide, useful as a catalyst support, a co-catalyst and / or a getter, is described. The mixed-metal oxide has a relatively large surface area per weight, typically exceeding 150 m<2> / g, a structure of nanocrystallites having diameters of less than 4 nm, and including pores larger than the nanocrystallites and having diameters in the range of 4 to about 9 nm. The ratio of the pore volumes, VP, to skeletal structure volumes, VS, is typically less than about 2.5, and the surface area per unit volume of the oxide material is greater than 320 m<2> / cm<3>, such that the structural morphology supports both a relatively low internal mass transfer resistance and large effective surface area for reaction activity of interest. The mixed metal oxide is made by co-precipitating a dilute metal salt solution containing the respective metals, which may include Zr, Hf, and / or other metal constituents in addition to Ce, replacing water in the co-precipitate with a water-miscible low surface-tension solvent, and relatively quickly drying and calcining the co-precipitate at moderate temperatures. A highly dispersive catalyst metal, such as Pt, may be loaded on the mixed metal oxide support from a catalyst-containing solution following a selected acid surface treatment of the oxide support. The mixed metal oxide, as catalyst support, co-catalyst or getter, is applied in various reactions, and particularly water gas shift and / or preferential oxidation reactions as associated with fuel processing systems, as for fuel cells and the like.
Owner:INT FUEL CELLS
Ceria-based mixed-metal oxide structure, including method of making and use
InactiveUS20030235526A1Increased internal surface areaHigh catalytic activityRare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesMaterial nanotechnologyRheniumFuel cells
A homogeneous ceria-based mixed-metal oxide, useful as a catalyst support, a co-catalyst and / or a getter has a relatively large surface area per weight, typically exceeding 150 m<2> / g, a structure of nanocrystallites having diameters of less than 4 nm, and including pores larger than the nanocrystallites and having diameters in the range of 4 to about 9 nm. The ratio of pore volumes, VP, to skeletal structure volumes, VS, is typically less than about 2.5, and the surface area per unit volume of the oxide material is greater than 320 m<2> / cm<3>, for low internal mass transfer resistance and large effective surface area for reaction activity. The mixed metal oxide is ceria-based, includes Zr and or Hf, and is made by a novel co-precipitation process. A highly dispersed catalyst metal, typically a noble metal such as Pt, may be loaded on to the mixed metal oxide support from a catalyst metal-containing solution following a selected acid surface treatment of the oxide support. Appropriate ratioing of the Ce and other metal constituents of the oxide support contribute to it retaining in a cubic phase and enhancing catalytic performance. Rhenium is preferably further loaded on to the mixed-metal oxide support and passivated, to increase the activity of the catalyst. The metal-loaded mixed-metal oxide catalyst is applied particularly in water gas shift reactions as associated with fuel processing systems, as for fuel cells.
Owner:AUDI AG
Direct-write deposition of phosphor powders
InactiveUS7476411B1Improve automationHigh resolution displayRare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesMaterial granulation and coatingApparent densityPhosphor
A liquid suspension of phosphor particles and method for depositing the liquid suspension. The suspension advantageously has a low viscosity with a high solids-loading of phosphor particles. The apparent density of the phosphor particles is well-controlled to enable the particles to be dispersed in the liquid vehicle. The suspension is useful in direct-write tools such as ink-jet devices.
Owner:SICPA HLDG SA
Turbine components with thermal barrier coatings
InactiveUS7226672B2Low thermal conductivityRare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesMolten spray coatingComposite ceramicSelf reinforced
A turbine component has a substrate formed from a ceramic material selected from the group consisting of a monolithic ceramic material and a composite ceramic material and a thermal barrier coating bonded to the substrate. In one embodiment, the ceramic material forming the substrate is selected from the group of silicon nitride and self-reinforced silicon nitride. In another embodiment, the ceramic material forming the substrate is selected from the group consisting of a silicon carbide-silicon carbide material and a carbon-carbon material. At least one bond coat layer may be interposed between the substrate and the thermal barrier coating.
Owner:RAYTHEON TECH CORP
Thermal barrier coating material
InactiveUS20060246226A1Rare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesLiquid surface applicatorsChemical compositionBond coating
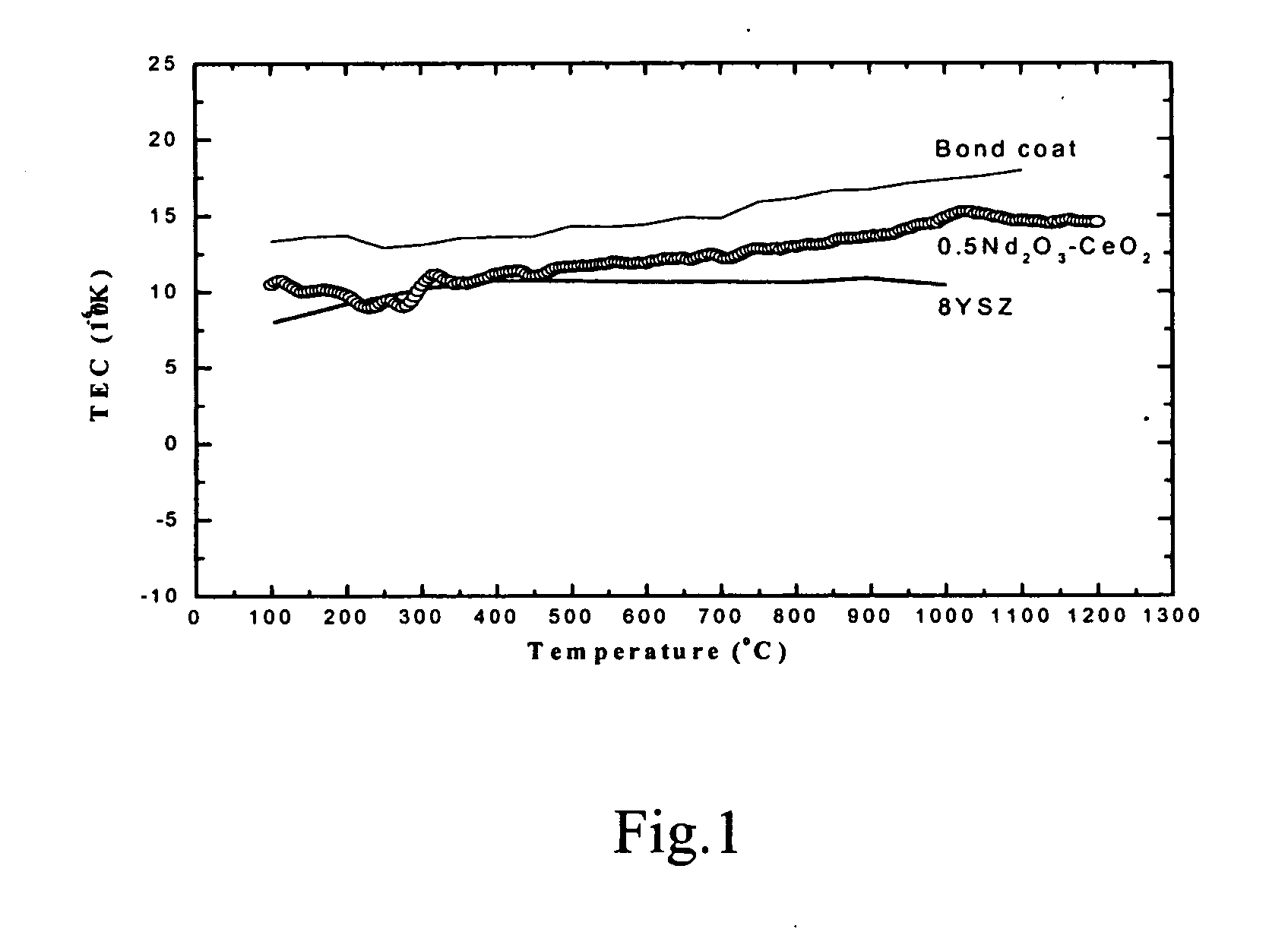
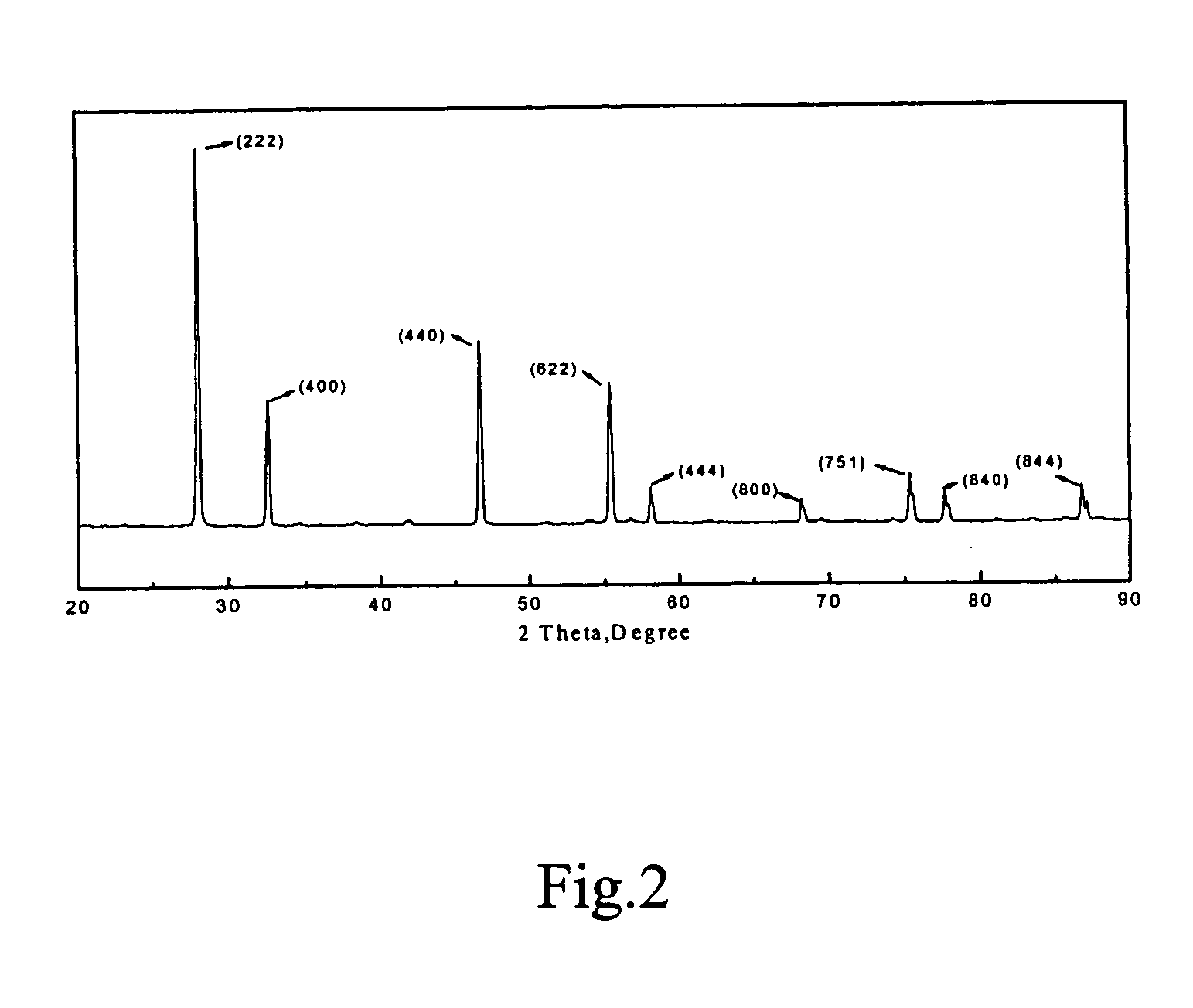
The present invention relates to a thermal barrier coating material having the chemical composition of (1−n)CeO2-nZrO2-0.5R2O3, where n is in the range of 0.9≧n≧0 and R is selected from a group consisting of Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb and combinations of at least two among them. It possesses a thermal expansion coefficient higher than 12×10−6 K−1 from ambient temperature up to 1200° C. and superior to those of the presently widely-used thermal barrier coating materials. Even if it is subjected to long time calcinations at 1400° C. or is quenched to room temperature, it can still maintain the stable crystal structure. In addition, its thermal expansion trend matches quite well with that of the bond coating alloy. This is beneficial to the elimination of thermal stress generated between the substrate and the ceramic top coating during the thermal cycle and can significantly improve the thermal shock resistance of the coating. The present invention further relates to a method for producing a thermal barrier coating material and a method for preparing a thermal barrier coating.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Ultrastable Particle-Stabilized Foams and Emulsions
ActiveUS20090325780A1Cheap methodLong-term stabilityRare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesMaterial nanotechnologySolubilityEmulsion
Described is a method to prepare wet foams exhibiting long-term stability wherein colloidal particles are used to stabilize the gas-liquid interface, said particles being initially inherently partially lyophobic particles or partially lyophobized particles having mean particle sizes from 1 nm to 20 μm. In one aspect, the partially lyophobized particles are prepared in-situ by treating initially hydrophilic particles with amphiphilic molecules of specific solubility in the liquid phase of the suspension.
Owner:ETH ZZURICH
Metal delivery system for nanoparticle manufacture
ActiveUS20060229197A1Improve productivityWell mixedRare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesMolten spray coating2-Ethylhexanoic acidMetallacarboxylic acid
Described is a method for the production of pure or mixed metal oxides, wherein at least one metal precursor that is a metal carboxylate with a mean carbon value per carboxylate group of at least 3, e.g. the 2-ethyl hexanoic acid salt, is formed into droplets and e.g. flame oxidized. The method is performed at viscosities prior to droplet formation of usually less than 40 mPa s, obtained by heating and / or addition of one or more low viscosity solvents with adequately high enthalpy.
Owner:ETH ZURICH THE SHORT NAME OF EID GENOSSISCHE TECHN HOCHSCHULE ZURICH
Production of ethylene with nanowire catalysts
ActiveUS10195603B2Thermal non-catalytic crackingRare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesNanowireOxidative coupling of methane
Nanowires useful as heterogeneous catalysts are provided. The nanowire catalysts are useful in a variety of catalytic reactions, for example, the oxidative coupling of methane to ethylene. Related methods for use and manufacture of the same are also disclosed.
Owner:SILURIA TECH INC
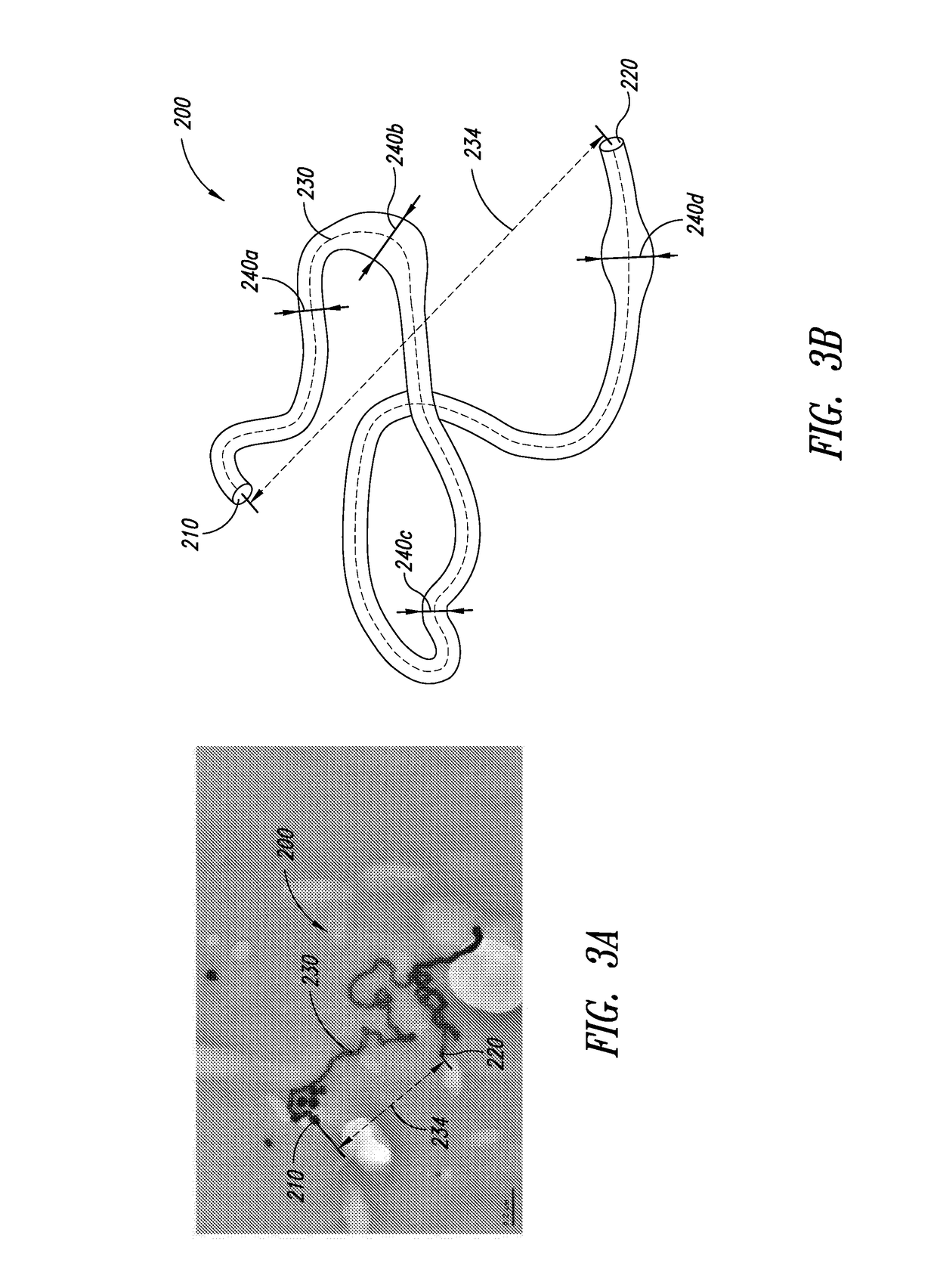
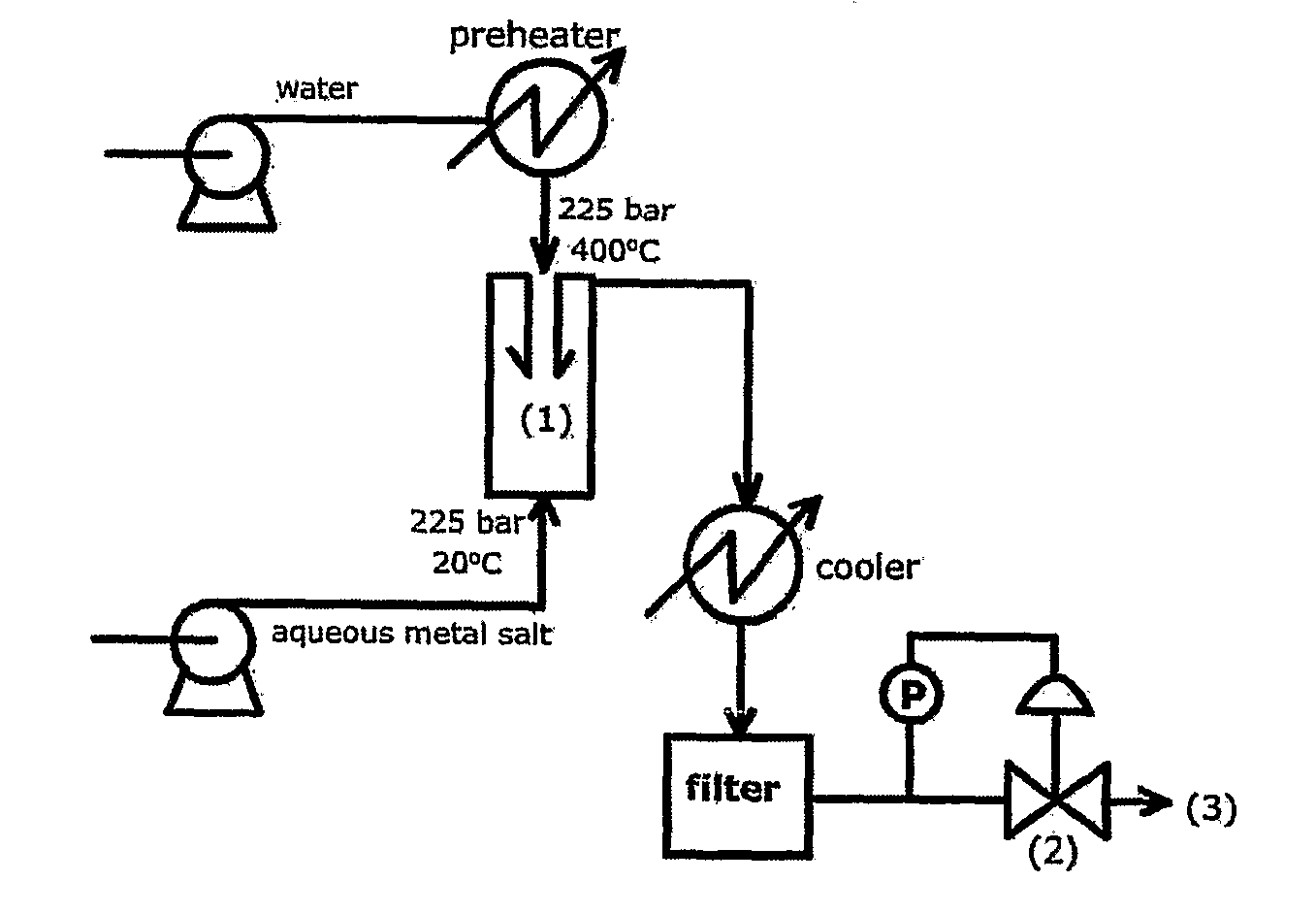
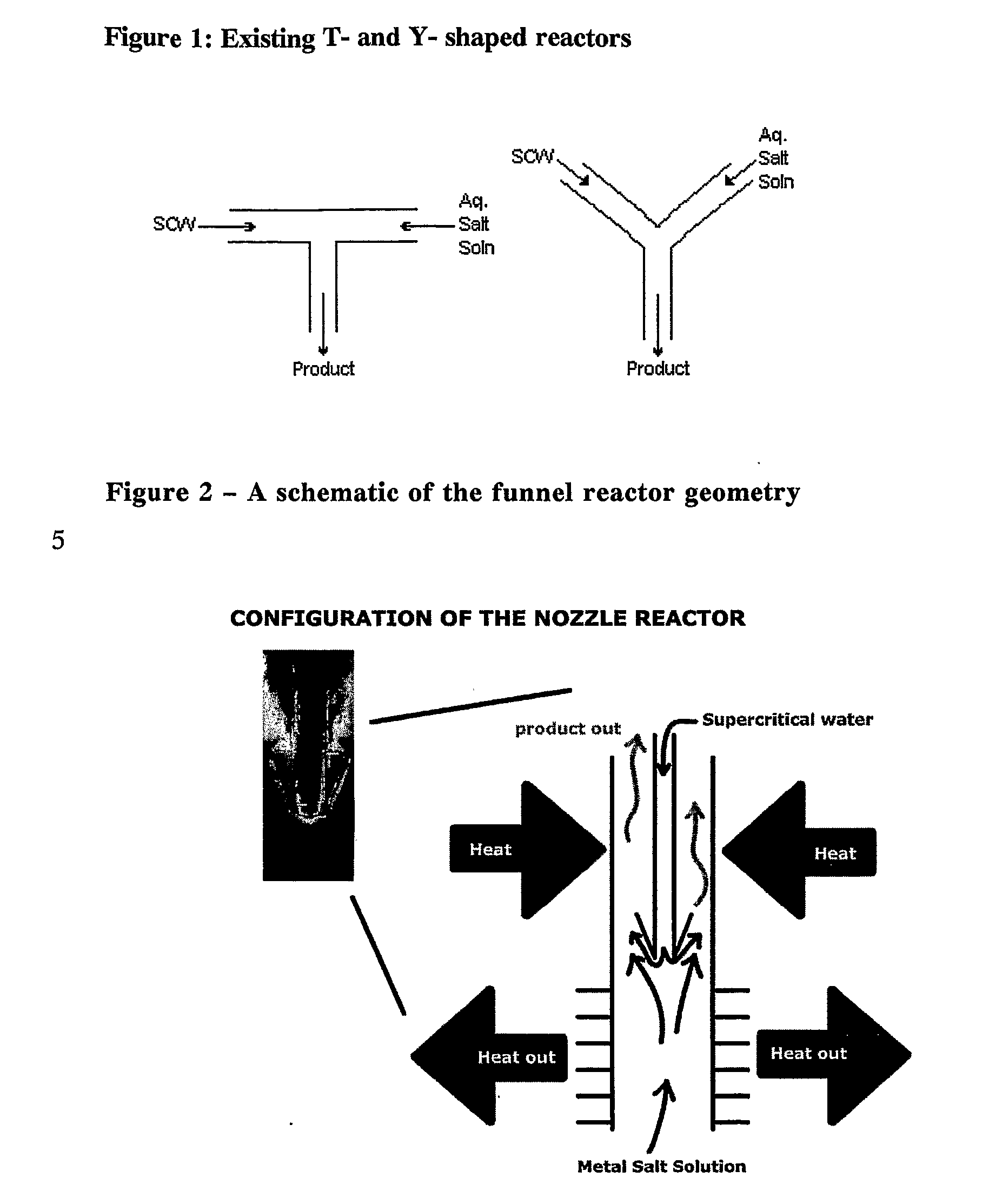
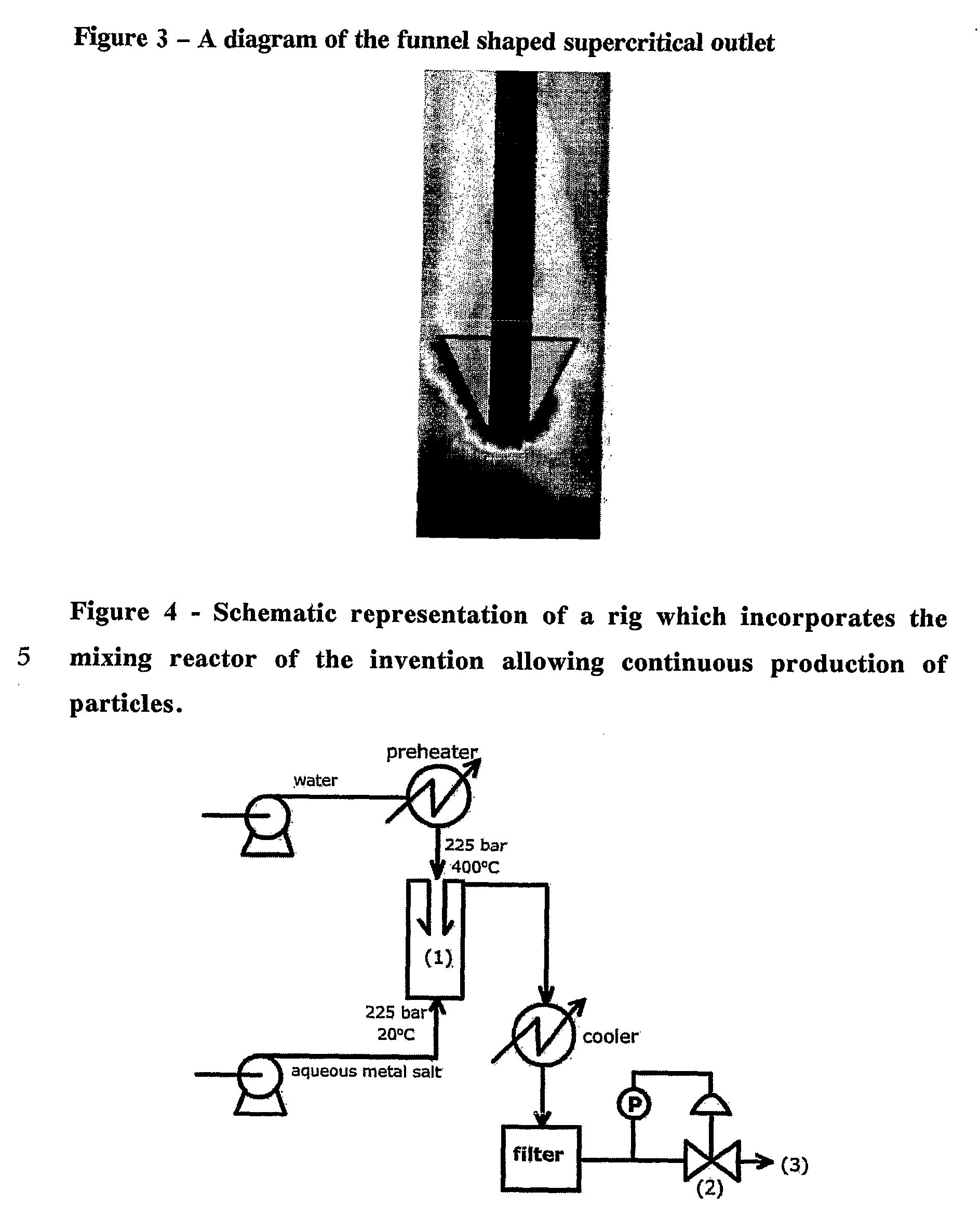
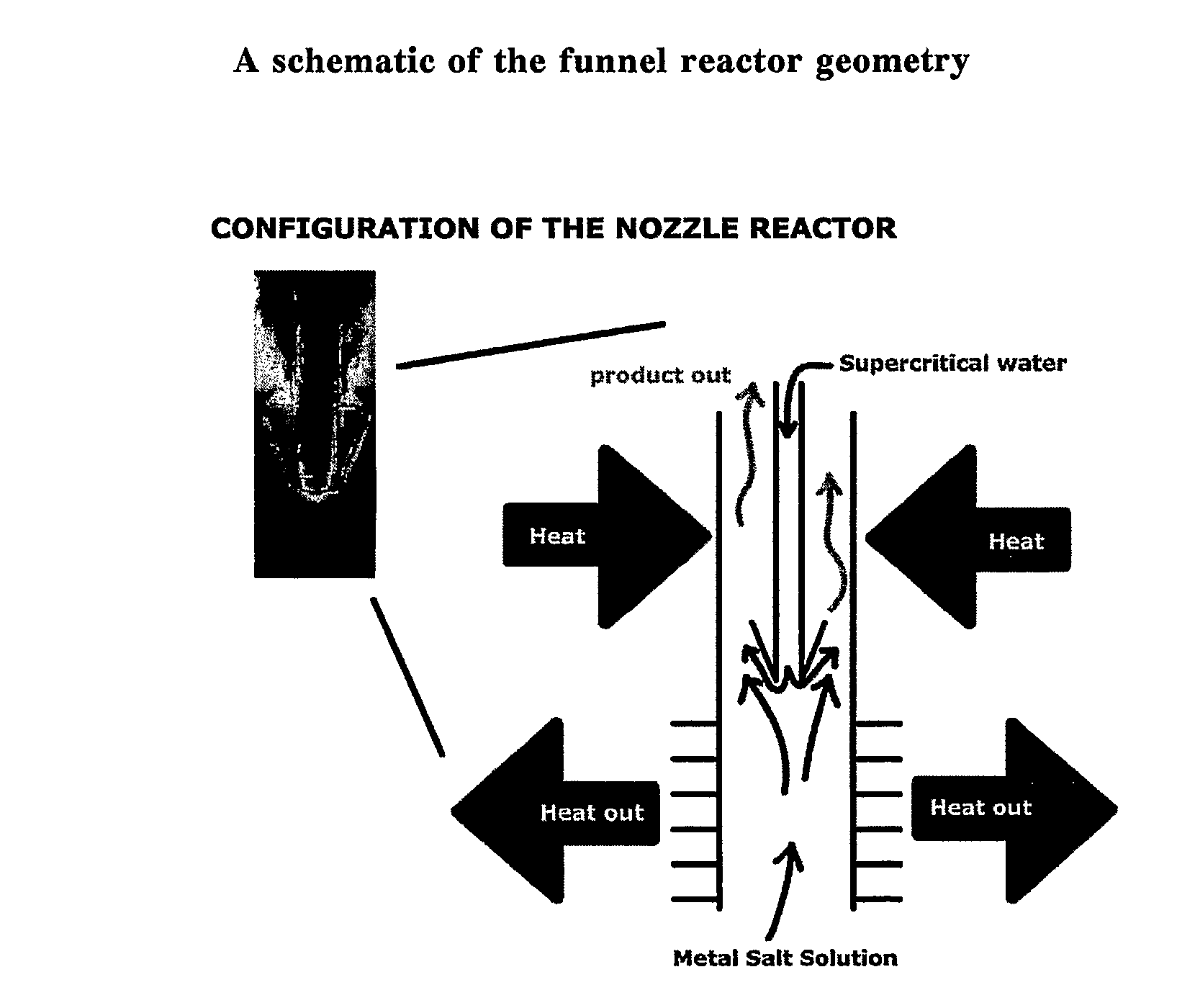
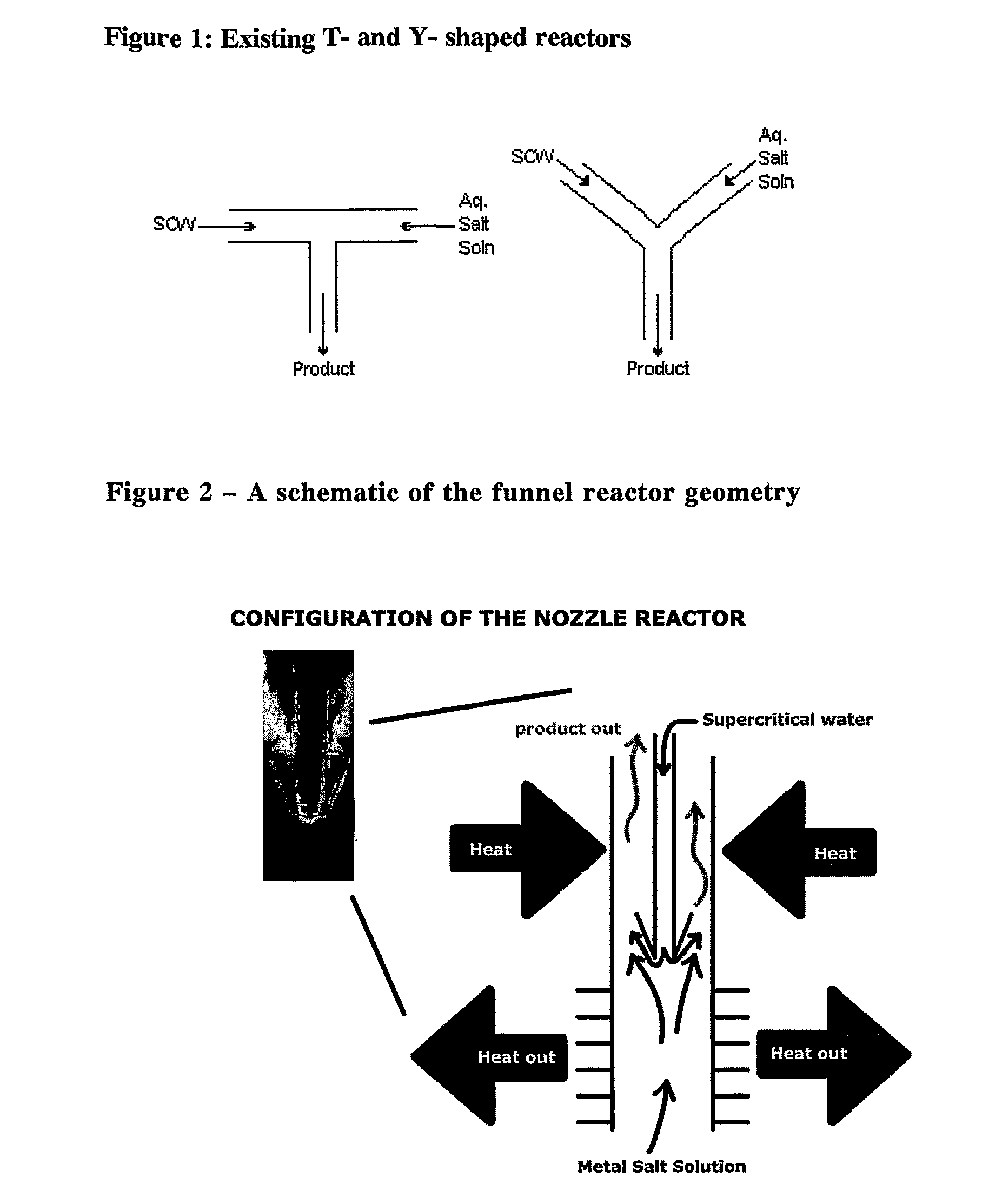
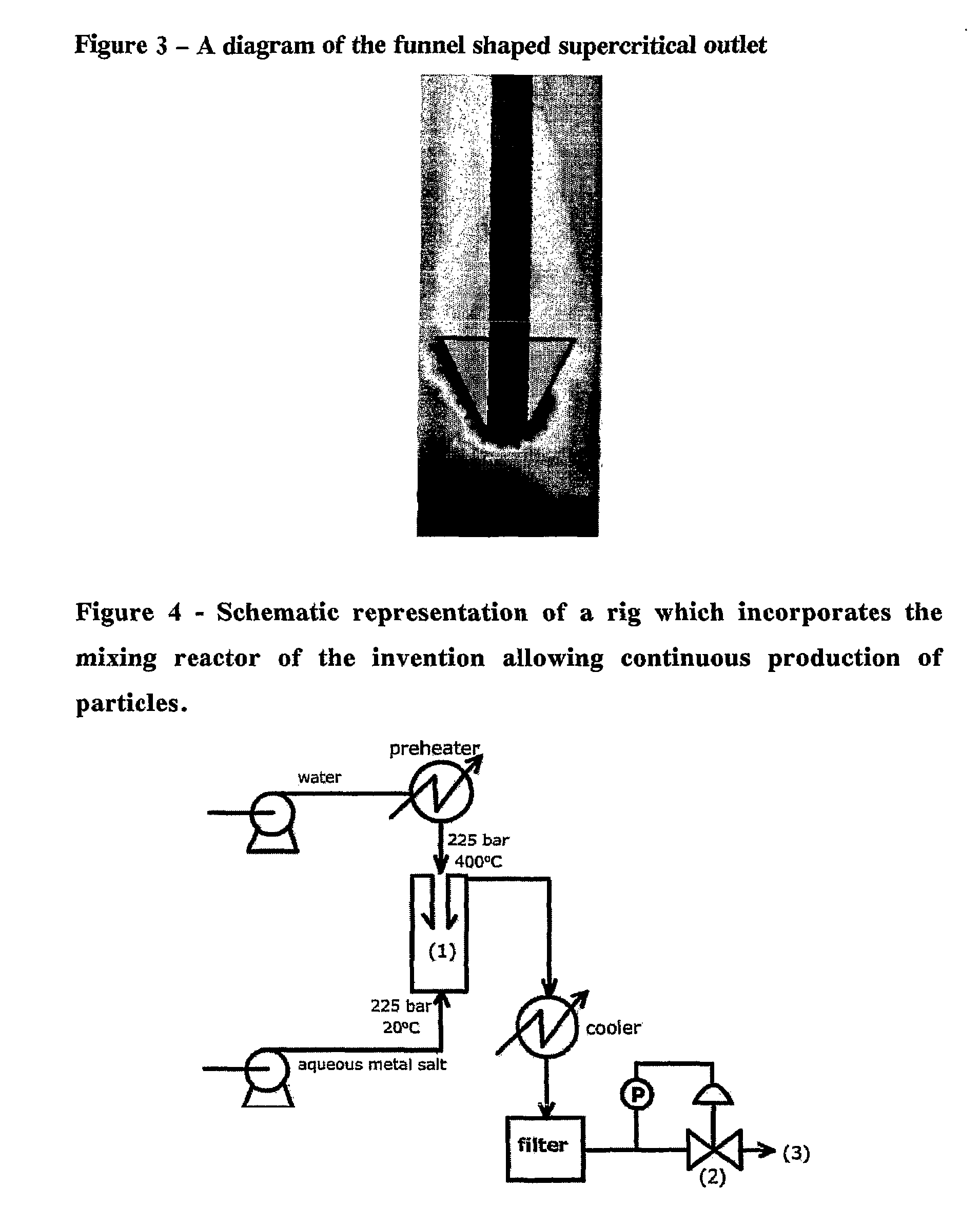
Counter Current Mixing Reactor
ActiveUS20070206435A1Minimize blockingEliminate mixingRare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesFlow mixersMetal oxide nanoparticlesReactor design
A mixing reactor for mixing efficiently streams of fluids of differing densities. In a preferred embodiment, one of the fluids is supercritical water, and the other is an aqueous salt solution. Thus, the reactor enables the production of metal oxide nanoparticles as a continuous process, without any risk of the reactor blocking due to the inefficient mixing inherent in existing reactor designs.
Owner:PROMETHEAN PARTICLES
Nano-scale metal oxyhalide and oxysulfide scintillation materials and methods for making same
InactiveUS20080241041A1Rare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesMaterial nanotechnologyEmulsionNanoparticle
Crystalline scintillator materials comprising nano-scale particles of metal oxides, metal oxyhalides and metal oxysulfides are provided. The nano-scale particles are less than 100 nm in size. Methods are provided for preparing the particles. In one method, used to form oxyhalides and oxysulfides, metal salts are dissolved in water, and then precipitated out as fine particles using an aqueous base. After the particles are separated from the solution, they are annealed under a flow of a water saturated hydrogen anion gas, such as HCl or H2S, to form the crystalline scintillator particles. The other methods take advantage of the characteristics of microemulsion solutions to control droplet size, and, thus, the particle size of the final nano-particles. For example, in one method, a first micro-emulsion containing metal salts if formed. The first micro-emulsion is mixed with an aqueous base in a second micro-emulsion to form the final nano-scale particles.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
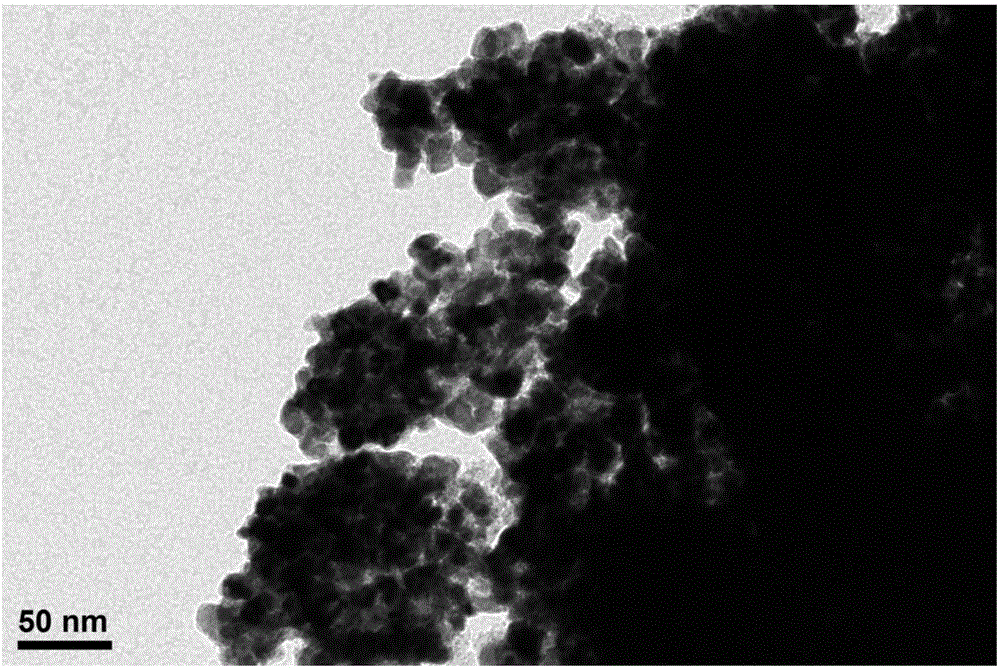
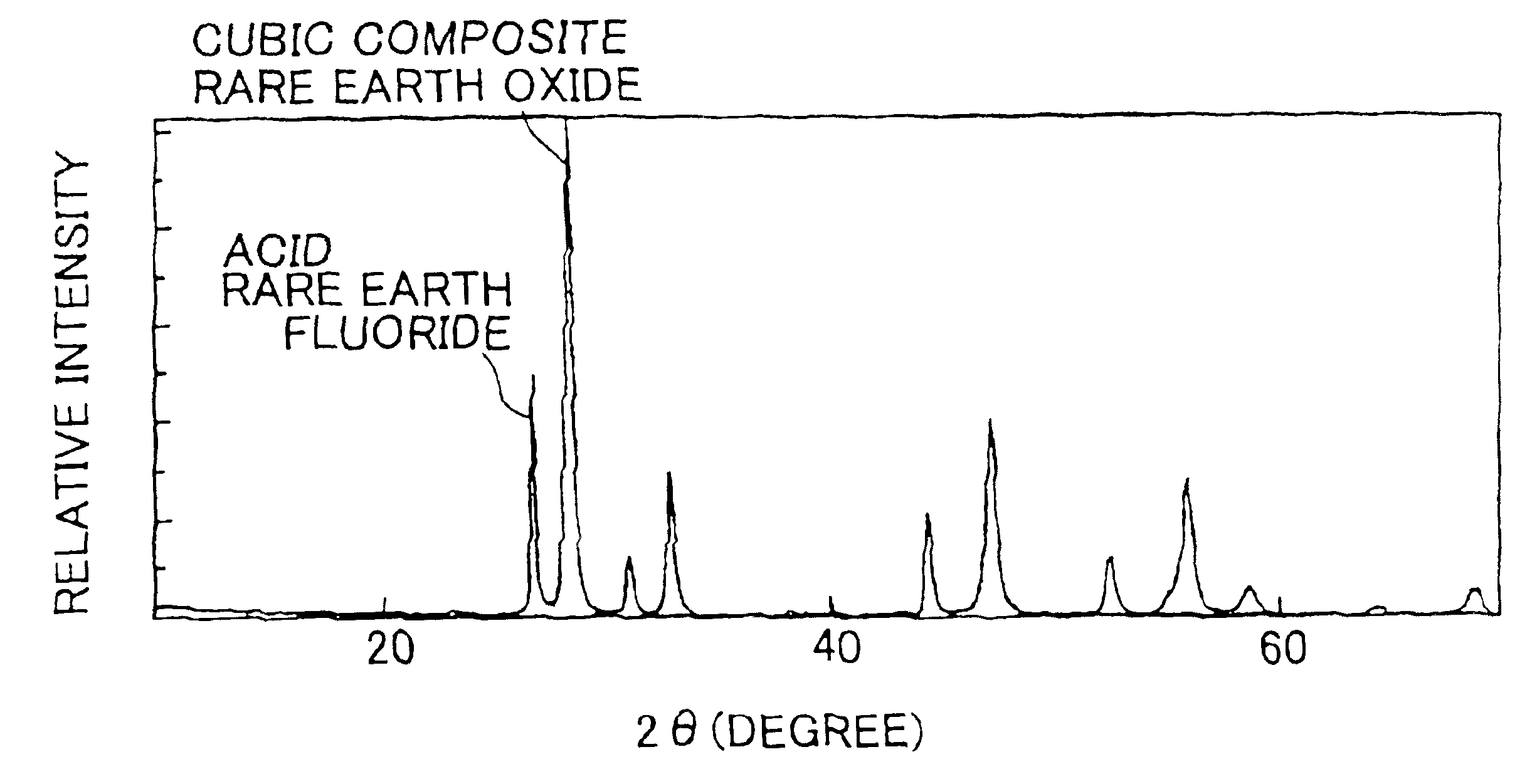
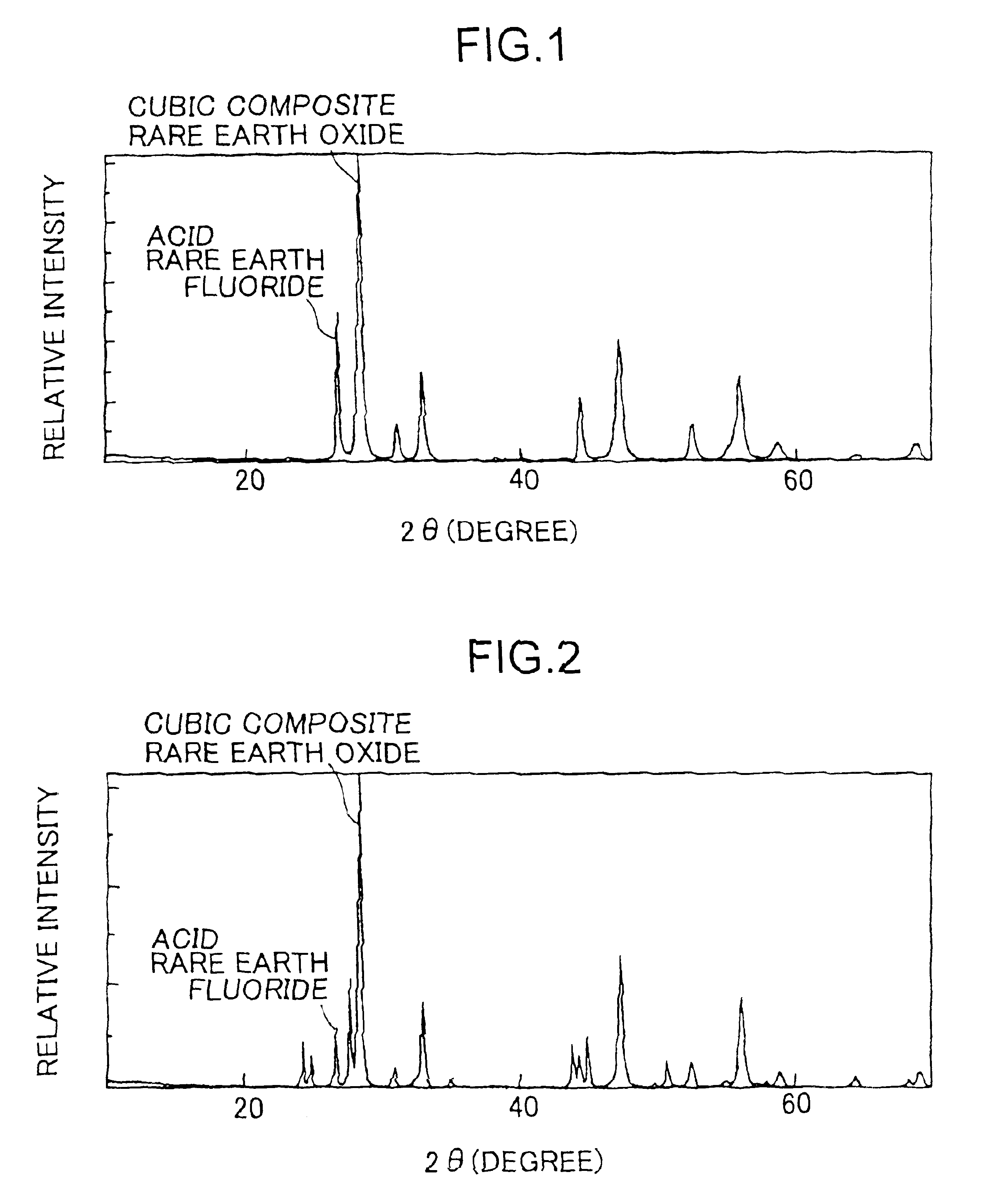
Mixed rare earth oxide, mixed rare earth fluoride, cerium-based abrasive using the materials and production processes thereof
InactiveCN101010402AReduce polishing rateRare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesOther chemical processesCeriumFluoride
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Method for recovering rare earth, aluminum and silicon from rare earth-containing aluminum and silicon wastes
ActiveCN106319218AReduce dosageEfficient separationRare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesRare earth metal chloridesAluminum IonAluminium hydroxide
The invention provides a method for recovering rare earth, aluminum and silicon from rare earth-containing aluminum and silicon wastes. The method comprises the following steps: 1, carrying out acid dipping on the rare earth-containing aluminum and silicon wastes by using an aqueous inorganic acid solution to obtain silicon-rich residues and an acid dipping solution containing rare earth ions and aluminum ions; 2, adding an alkaline substance to the acid dipping solution containing rare earth ions and aluminum ions to control the pH value of the acid dipping solution to be 3.5-5.2, and carrying out solid-liquid separation to obtain an aluminum hydroxide-containing precipitate and a rare earth-containing filtrate; and 3, reacting the aluminum hydroxide-containing precipitate with sodium hydroxide to obtain a sodium metaaluminate solution and aluminum and silicon residues, and using the rare earth-containing filtrate to prepare a rare earth compound product. Aluminum and rare earth are dissolved in the acid, segmented alkaline transfer is carried out, the aluminum ions are precipitated to obtain aluminum hydroxide and the rare earth ions which are separated from the aluminum hydroxide, and excess sodium hydroxide is added to convert aluminum hydroxide into the sodium metaaluminate solution, so simultaneous and high-efficiency recycling of the rare earth and aluminum is realized, the use amount of sodium hydroxide is greatly reduced, and the recovery cost is reduced.
Owner:GRIREM ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
Preparation method of superfine yttrium oxide doped tungsten composite precursor powder
ActiveCN106564927AImprove uniformityGuaranteed purityRare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesNanotechnologyAmmonium paratungstateDissolution
The invention relates to a preparation method of superfine yttrium oxide doped tungsten composite precursor powder. The preparation method comprises the steps: dissolving ammonium paratungstate, yttrium nitrate hexahydrate and a surfactant into water, and carrying out sufficient dispersion and dissolution through mechanical stirring and ultrasonic treatment to prepare a solution; adding concentrated HNO3 into the solution under stirring and ultrasonics to carry out precipitation reaction to form a suspension liquid; adding absolute ethyl alcohol into the suspension liquid to further react, filtering the reacted suspension liquid, and cleaning a precipitate by using absolute ethyl alcohol or distilled water; after drying the precipitate, grinding the precipitate to obtain composite powder, then, placing the composite powder into a tube furnace, and calcining the composite powder in a nitrogen or argon flow to obtain W-Y2O3 composite oxide powder; and carrying out two-step reduction in the tube furnace by using pure hydrogen to obtain the superfine yttrium oxide doped tungsten composite precursor powder. The average grain size of the powder reaches about 10nm, and the uniformity of the grain size is good. Meanwhile, Y2O3 is also uniformly doped, which provides a good basis for subsequent calcination for obtaining fine-grain compact tungsten-based alloy.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Oxidatively regenerable adsorbents for sulfur removal
InactiveUS20090065400A1Increase capacityHigh selectivityRare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesGold compoundsSorbentSulfur
Compositions and processes are disclosed for removing sulfur and sulfur compounds from hydrocarbon fuel feedstocks. The feedstock is contacted with a regenerable sorbent such as a compound of the formula TixCeyO2 where 0<x / y≦1 and where 0<x≦1 and 0<y≦1 capable of selectively adsorbing sulfur compounds present in the hydrocarbon feedstock at about 0° C. to about 100° C. such as at about 25° C.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Cerium-based abrasive, production process thereof
InactiveUS6986798B2High quality polishingSmall surface roughnessRare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesPigmenting treatmentRare-earth elementCerium
A mixed light rare earth compound which has been obtained by chemically removing medium-to-heavy rare earth elements, Nd and impurities other than rare earth elements from an ore containing rare earth elements is fired at 500 to 1100° C. to yield a mixed rare earth oxide. A cerium-based rare earth fluoride is added to the mixed rare earth oxide to obtain a mixture. The mixture is subjected to wet-pulverization, drying, firing, disintegration and classification to thereby yield a cerium-containing abrasive.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Mesoporous flower-shaped CeO2, as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN105731515AThe preparation process is matureEasy to operateRare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesMaterial nanotechnologyCeriumHigh pressure
The invention belongs to the technical field of water treatment, and relates to mesoporous flower-shaped CeO2, a preparation method thereof and an application thereof as mimic oxidase to degrade wastewater containing reactive light yellow. The mesoporous flower-shaped CeO2 is a hollow type crystal consisting of a plurality of small particles with an average particle diameter of 214 nm. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, by adopting CeCl3.7H2O as a cerium source, adopting urea as a precipitator and adopting PVP as a surfactant, preparing a CeO2 precursor under high pressure at a high temperature through a hydrothermal method; and roasting the precursor at a high temperature, thereby preparing a light yellow CeO2 nano material. According to the TMB chromogenic reaction, the prepared CeO2 has characteristics of mimic enzyme. The mesoporous flower-shaped CeO2 is used for reactive light yellow catalytic degradation reaction, so that the degradation rate of the reactive light yellow can be about 95% under the optimum proportion condition, and therefore, the mesoporous flower-shaped CeO2 has relatively good application prospects.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF AERONAUTICS
Chemical-mechanical planarization slurries and powders and methods for using same
InactiveUS20050081998A1High rateIncrease loadRare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesMaterial granulation and coatingSpherical morphologySlurry
Chemical-mechanical planarization slurries and methods for using the slurries wherein the slurry includes abrasive particles. The abrasive particles have a small particle size, narrow size distribution and a spherical morphology and the particles are substantially unagglomerated.
Owner:CABOT CORP
Composite zirconium-cerium oxide, process for the preparation thereof, and cocatalyst for cleaning exhaust gas
InactiveCN1241988ACheap manufacturingGood reproducibilityRare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesDispersed particle separationHeat resistanceCerium
A zirconium-cerium composite oxide having excellent heat resistance and being capable of maintaining its large specific surface area even when used under high-temperature conditions, which composite oxide contains zirconium and cerium at a weight ratio of 51 to 95:49 to 5 in terms of zircomium oxide and ceric oxide, the composite oxide having a specific surface area of not smaller than 50 m2 / g, wherein said composite oxide is capable of maintaining a specific surface area of not smaller than 20 m2 / g even after heating at 1100 DEG C. for 6 hours, a method for preparing the same, and a co-catalyst for purifying exhaust gas prepared with the composite oxide.
Owner:SOLVAY SPECIAL CHEM JAPAN LTD
Rare earth fluoride spray powder and rare earth fluoride-sprayed article
InactiveUS20130122283A1Speed up the flowLow yieldRare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesMolten spray coatingRare-earth elementHalogen
A powder comprising rare earth element fluoride particles having an aspect ratio of up to 2, an average particle size of 10-100 m, a bulk density of 0.8-1.5 g / cm3, and a carbon content of 0.1-0.5 wt % is amenable to atmospheric plasma spraying. An article obtained by spraying the rare earth fluoride spray powder to a substrate undergoes few partial color changes and performs well even when used in a halogen gas plasma.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
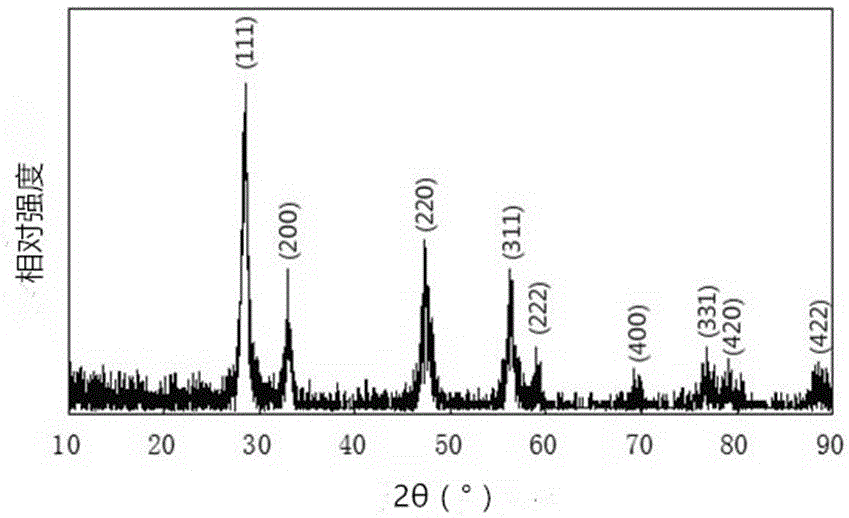
Preparation method of cerium oxide nanoparticles
ActiveCN108017081AParticle size controllableGood dispersionRare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesNanotechnologyNanoparticleCerium
The invention relates to a preparation method of cerium oxide nanoparticles and belongs to the field of rare earth oxide materials. The method comprises steps as follows: S1, cerium salt and a surfactant are prepared in the mass ratio being (1:1)-(1:5) and then mixed, the mixture is dissolved in water and stirred, and a clear solution is obtained; S2, the solution is continuously stirred, the pH value of a reaction solution is regulated to 7-10 with an alkaline solution; S3, the uniformly mixed solution is transferred to a reaction kettle for a hydrothermal reaction until the reaction is full;S4, a product obtained after the reaction is dried and ground, and cerium oxide powder is obtained. The preparation method adopts a simple process, and the prepared cerium oxide nanoparticles have controllable particle size and are uniform and stable.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Method for preparing two-dimensional inorganic nanomaterial by mechanical force intercalation stripping
InactiveCN109250693AImprove stripping efficiencyShort manufacturing timeRare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesNitrogen compoundsHigh energyCrystal structure
The invention relates to the technical field of inorganic nanomaterial preparation, and in particular, relates to a method for preparing a two-dimensional inorganic flaky nanomaterial by mechanical force intercalation stripping of a three-dimensional inorganic layered crystal material. With mixed metal halide as an intercalation and stripping medium, the purified layered inorganic crystal materialand the intercalation and stripping medium are subjected to solid-phase high-energy ball milling treatment together, mixed powder after ball milling treatment is washed with water to remove the intercalation and stripping medium, the three-dimensional layered material can be highly efficiently made into the corresponding two-dimensional flaky material. The method has universality for stripping ofthe inorganic non-metallic layered crystal material, has the advantages of simple preparation process, short production cycle, and high yield of the two-dimensional material, does not affect a crystal structure of the two-dimensional material, and the intercalation and stripping medium can be reused without causing environmental pollution.
Owner:深圳烯材科技有限公司
Slurry, polishing-solution set, polishing solution, substrate polishing method, and substrate
ActiveUS20150140904A1Increase ratingsGood storage stabilityRare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesOther chemical processesSlurryLength wave
A polishing liquid comprising an abrasive grain, an additive, and water, wherein the abrasive grain includes a hydroxide of a tetravalent metal element, produces absorbance of 1.00 or more and less than 1.50 for light having a wavelength of 400 nm in an aqueous dispersion having a content of the abrasive grain adjusted to 1.0 mass %, and produces a liquid phase having a content of a non-volatile component of 300 ppm or more when centrifuging an aqueous dispersion having a content of the abrasive grain adjusted to 1.0 mass % for 50 minutes at a centrifugal acceleration of 1.59×105 G.
Owner:RESONAC CORP
Counter current mixing reactor
ActiveUS7566436B2Minimize blockingRare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesFlow mixersMetal oxide nanoparticlesReactor design
Owner:PROMETHEAN PARTICLES
Preparation method of rare-earth-based fluorite type high-entropy oxide powder material
ActiveCN108946787AAchieving a stoichiometric ratioReduce energy consumptionRare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesMaterial nanotechnologySynthesis methodsRare earth
The invention discloses a preparation method of a rare-earth-based fluorite type high-entropy oxide powder material and belongs to the field of rare earth oxide powder materials. The method is a low-temperature combustion synthesis method and specifically comprises the following steps: taking rare earth nitride as a metal source and one or a mixture of more of urea, acetic acid, ammonium acetate,oxalic acid and glycine as fuel; and controlling the concentration of metal salt raw materials, types and adding amounts of the fuel, types and adding amounts of a combustion improver and an ignitionmanner to regulate and control properties including granularity, shapes and the like of rare-earth-based fluorite type high-entropy oxide powder. According to the preparation method disclosed by the invention, liquid-phase ingredients are adopted to ensure that a molecular level of the raw materials is uniform and a stoichiometric proportion of a product is realized; meanwhile, the preparation method has the advantages of energy source saving, high production efficiency, greenness and environment protection, no need of complicated post-treatment and the like; and the prepared rare earth oxidepowder has the advantages of high purity, small granularity and uniformity in distribution.
Owner:内蒙古广禾元纳米高科技有限公司
Spherical cerium dioxide
ActiveCN105948097AShort reaction timeSimple and fast operationRare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesCerium(IV) oxideThermal stability
The invention discloses a spherical cerium dioxide. The average particle size of spherical cerium dioxide is 50 nm-300 nm, and the specific surface area after roasting at 1000 DEG C is 1.5-20 m<2> / g, preferably, the specific surface area after roasting at 350 DEG C is 102-153 m<2> / g, and the specific surface area after roasting at 550 DEG C is 80-120 m<2> / g. The preparation method of the spherical cerium dioxide disclosed in the invention has short reaction time and simple operation, and is easy to control. Moreover, the prepared cerium dioxide is spherical and has regular shape, good degree of crystallization, high heat stability, and big specific surface area.
Owner:广州市威格林环保科技有限公司
Process for making nano-sized and micro-sized precipitate particles
ActiveUS7985388B2Increase shearShort timeRare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesSelenium/tellurium compundsMetal chalcogenidesReaction zone
There is disclosed a process of making nano-sized or micro-sized precipitate particles. The process comprising the steps of mixing, in a reaction zone, a metal salt solution with a precipitant solution to form a precipitate, said precipitate being at least one of a metal chalcogenide, metal hydroxide and metal oxide; and applying a shear force to said mixing solutions in said reaction zone during said mixing step, wherein said shear force and the conditions within said reaction zone form said nano-sized or micro-sized precipitate particles.
Owner:NANOMATERIALS TECH PTE
Preparation method of rare earth oxide and graphene nanocomposite material
ActiveCN106219590ASynthesis temperature is lowEasy to implementRare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesMaterial nanotechnologyGraphene nanocompositesRare earth
Provided is a preparation method of a rare earth oxide and graphene nanocomposite material. The method comprises the following steps that 1, an aqueous solution containing needed amount of rare earth nitrate is prepared according to the loading capacity of rare earth oxide on graphene and the preparation quantity of a target product and added into a certain volume of graphene oxide dispersing agent of which the concentration ranges from 0.5 g / L to 5 g / L; 2, an appropriate amount of organic fuel is added into the dispersing agent in the first step, stirring and ultrasound are conducted, and a uniform dispersing agent is obtained; 3, the dispersing agent in the first step is heated and concentrated to be thick, the heated and concentrated dispersing agent is put into a heating furnace of 300 DEG C-900 DEG C for ignition, and after burning is conducted, cooling is conducted to room temperature. The preparation method of the rare earth oxide and graphene nanocomposite material is low in synthesis temperature, short in time, easy to carry out and low in cost, a reducing agent does not need to be additionally added, and graphene oxide is subjected to self reduction to obtain graphene; meanwhile, rare earth oxide is small in particle size and uniform in size, and the uniform dispersibility on graphene is achieved. The preparation method of the rare earth oxide and graphene nanocomposite material is rapid, efficient, high in yield, green, environmentally friendly and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Preparation method of high-specific surface area micro-nano cerium dioxide
InactiveCN108238627ALarge specific surface areaMild conditionsRare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesNanotechnologyInorganic saltsMicro nano
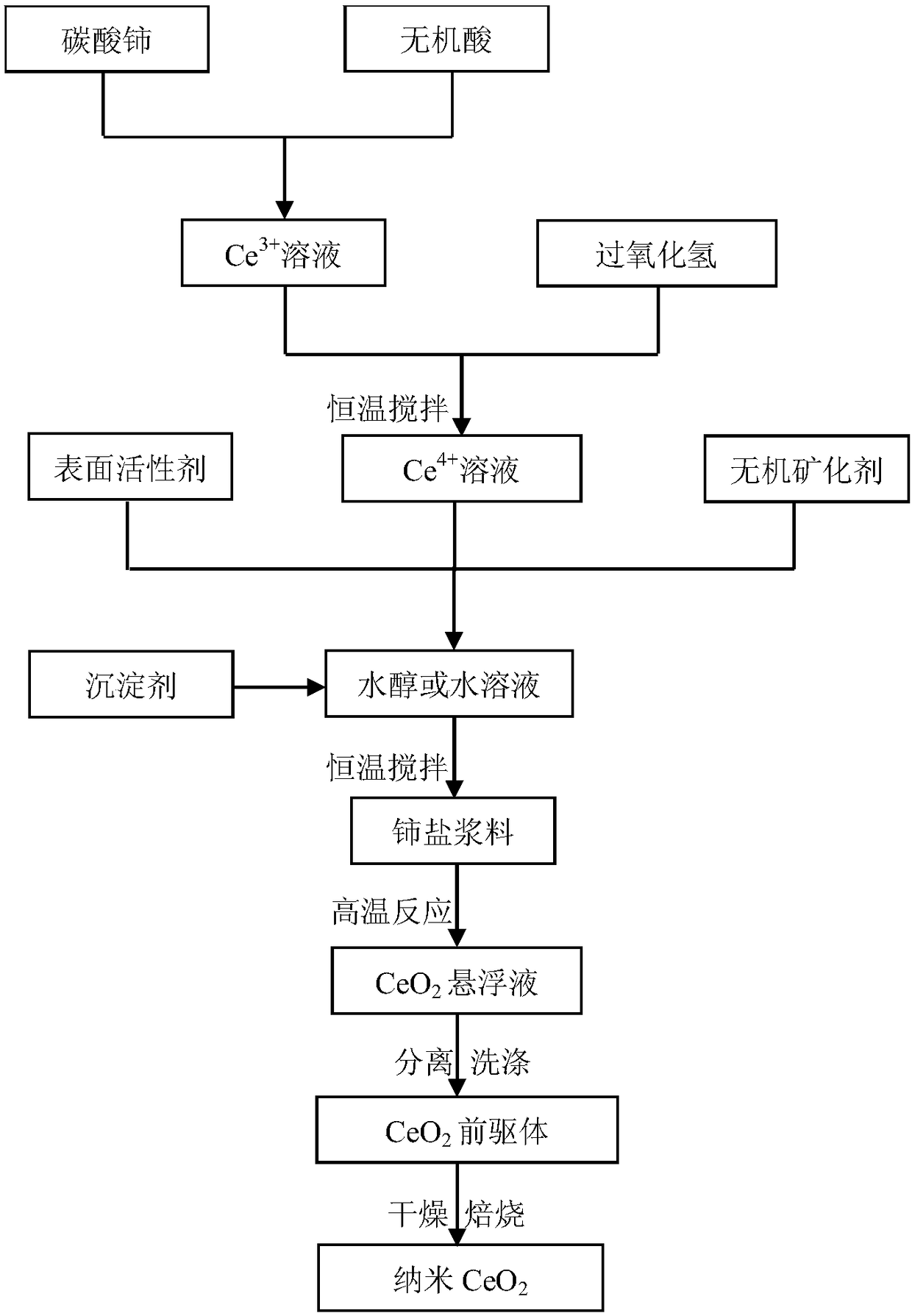
The invention discloses a preparation method of high-specific surface area micro-nano cerium dioxide. The preparation method comprises the steps of preparing a cerium-containing inorganic acid solution, adding an inorganic salt mineralization agent, a surfactant and hydrogen peroxide, stirring to obtain a cerium salt solution, dropwise adding a precipitator solution into the cerium salt solution,stirring at constant temperature to form cerium salt slurry, reacting by virtue of the cerium salt slurry at 80-95 DEG C for 2-24 hours, carrying out centrifugal washing, drying by virtue of a dryingtank, adequately grinding the dried material, and carrying out high-temperature roasting, so as to obtain high-specific surface area micro-nano cerium dioxide. Compared with a traditional hydrothermalmethod, the method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the reaction temperature is low, the conditions are mild, the operation is easy, prepared micro-nano cerium dioxide is high in specific surface area and small in particle size, and the industrial production is relatively easily realized.
Owner:NEIJIANG NORMAL UNIV +1
Synthetic method of metallic oxide nanospheres
ActiveCN108975391AControl water contentHydrolysis rate regulationRare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesMaterial nanotechnologyChemical reactionMicrosphere
The invention discloses a synthetic method of metallic oxide nanospheres. The synthetic method is characterized by taking microemulsion as a template, hydrolyzing metal alcoholate or organic metal salt in the microemulsion, and finally forming nanospheres. The reaction is capable of introducing matters which can react with each other to generate water into a microemulsion system under an anhydrouscondition, and the water content of the microemulsion system is controlled by controlling the speed of chemical reaction which is capable of generating water, so that effective control on the hydrolysis speed of the metal alcoholate or the organic metal salt can be realized; meanwhile, the micelle diameter of the microemulsion in the microemulsion system can be regulated, and the metallic oxide nanospheres are controllable in particle diameter and narrow in particle diameter distribution; the particle diameter of the metallic oxide nanospheres obtained by utilizing the technology is controllable within a range from 10 to 2000 nm, and the polydispersion index of the particle diameter of the metallic oxide nanospheres ranges from 1 to 5 percent. The synthetic method disclosed by the invention is simple in a synthetic process, easy to operate and good in repeatability and has a good application prospect.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING
Popular searches
Manganese oxides/hydroxides Hydrocarbon by hydrocarbon condensation Bulk chemical production Hydrocarbon oils treatment products Aluminium oxides/hydroxides Tungsten oxides/hydroxides Organic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalysts Heterogenous catalyst chemical elements Hydrocarbon preparation catalysts Catalyst activation/preparation
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com