Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
850results about How to "Increased process window" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
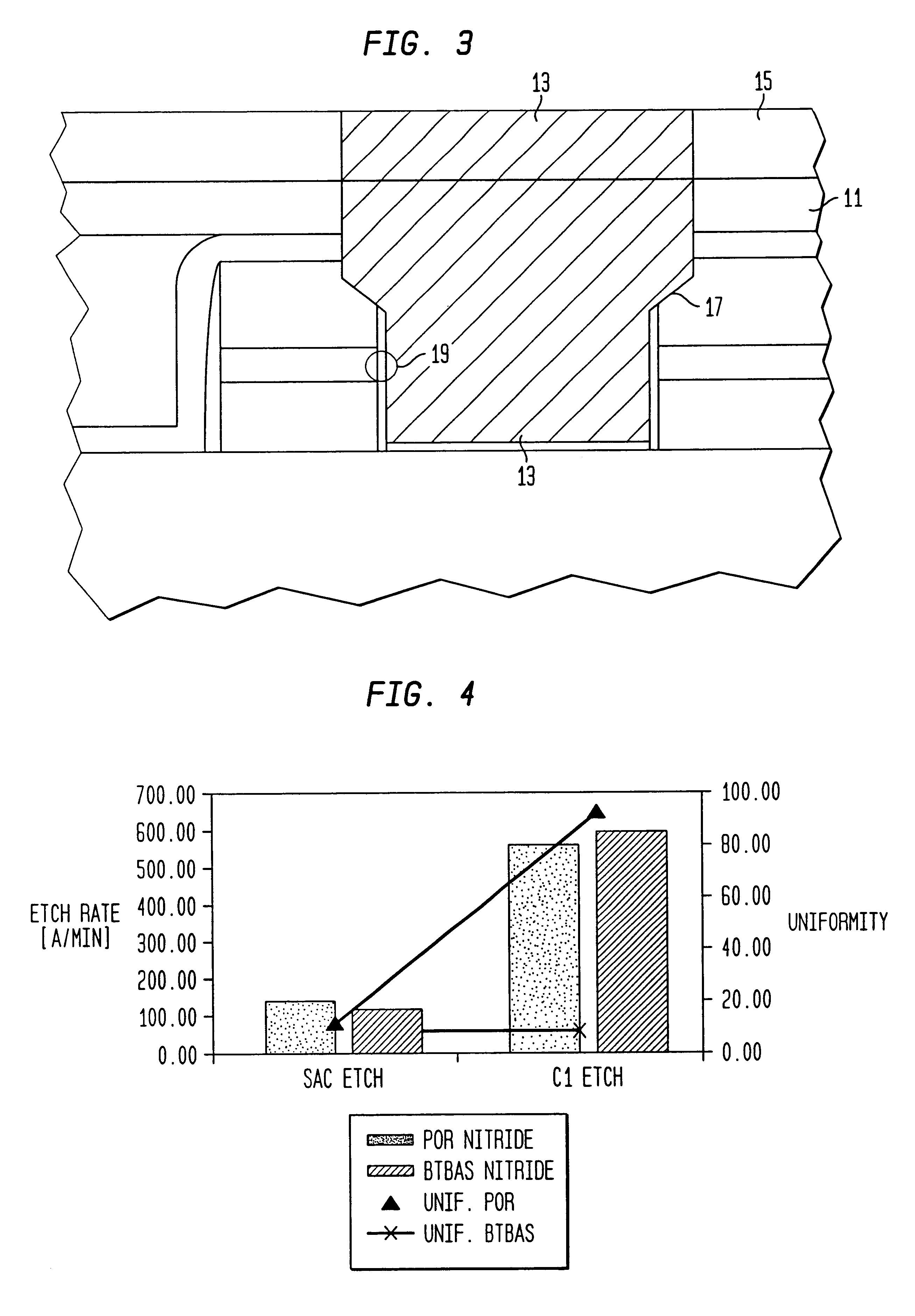
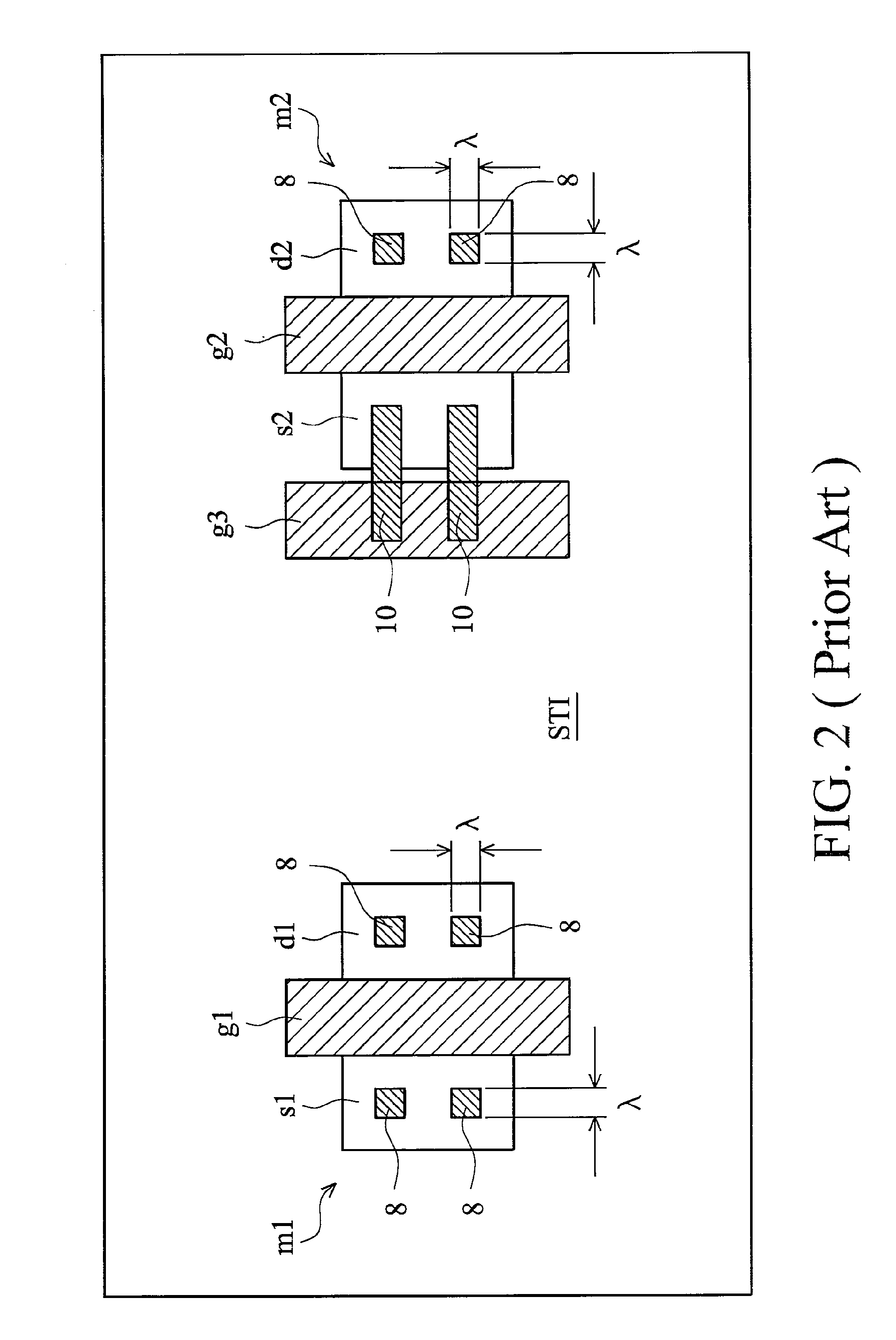
Method utilizing compensation features in semiconductor processing
InactiveUS7202148B2Increased process windowReduce depthRadiation applicationsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringFlare
A photolithography and etch process sequence includes a photomask having a pattern with compensation features that alleviate patterning variations due to the proximity effect and depth of focus concerns during photolithography. The compensation features may be disposed near isolated or outermost lines of a device pattern. A photoresist pattern is formed to include the compensation features and the pattern etched to form a corresponding etched pattern including the compensation features. After etching, a protection material is formed over the layer and a trim mask is used to form a further photoresist pattern over the protection material. A subsequent etching pattern etches the protection material and removes the compensation features and results in the device lines being formed unaffected by proximity effects. Flare dummies may additionally be added to the mask pattern to increase pattern density and assist in endpoint detection. Flare dummies, like the compensation features, are subsequently removed by a photolithography and etching process sequence.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Non-volatile memory
InactiveUS20080224202A1Improve stability and reliabilityLow working voltageTransistorSolid-state devicesIsolation layerEngineering
A non-volatile memory includes a substrate, a number of isolation layers, a number of active layers, a number of floating gates, a number of control gates and a number of doped regions. The active layers are disposed in the substrate between the isolation layers, and the top surface of the active layer is higher than that of the isolation layer. The active layers and the isolation layers are arranged in parallel to each other and extend in the first direction. The control gates are disposed in the substrate. The control gates are arranged in parallel and extend in the second direction which crosses the first direction. The floating gates are disposed between the active layers and the control gates. The doped regions are disposed in the active layers between the control gates.
Owner:POWERCHIP SEMICON CORP
Photoresist pattern trimming methods
ActiveUS20140186772A1Increased process windowSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotosensitive material processingResistPolymer science
Provided are methods of trimming a photoresist pattern. The methods comprise: (a) providing a semiconductor substrate; (b) forming a photoresist pattern on the substrate, wherein the photoresist pattern is formed from a chemically amplified photoresist composition comprising: a matrix polymer comprising an acid labile group; a photoacid generator; and a solvent; (c) coating a photoresist trimming composition on the substrate over the photoresist pattern, wherein the trimming composition comprises: a matrix polymer, an aromatic acid that is free of fluorine; and a solvent; (d) heating the coated substrate, thereby causing a change in polarity of the photoresist matrix polymer in a surface region of the photoresist pattern; and (e) contacting the photoresist pattern with a rinsing agent to remove the surface region of the photoresist pattern, thereby forming a trimmed photoresist pattern. The methods find particular applicability in the manufacture of semiconductor devices.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS LLC
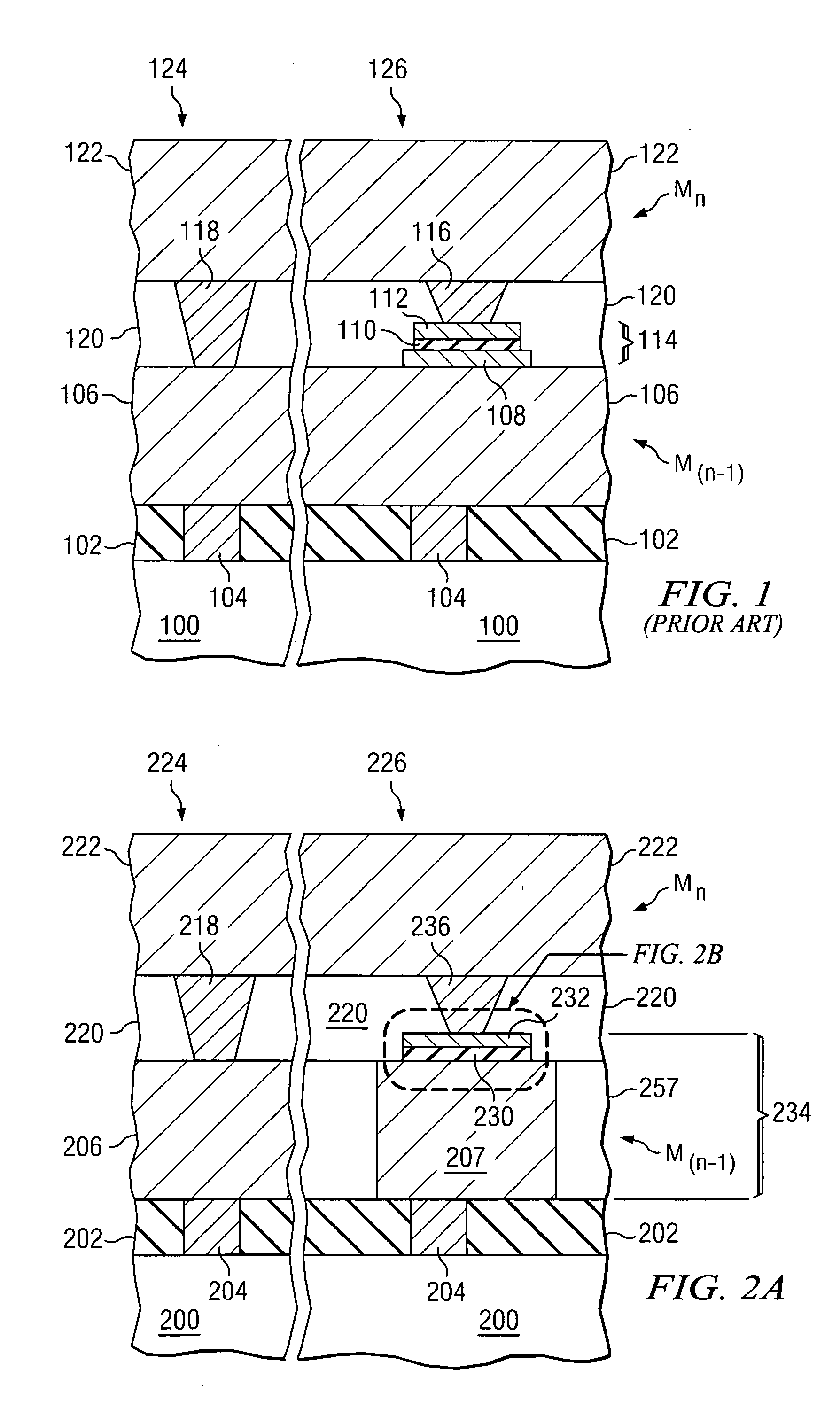
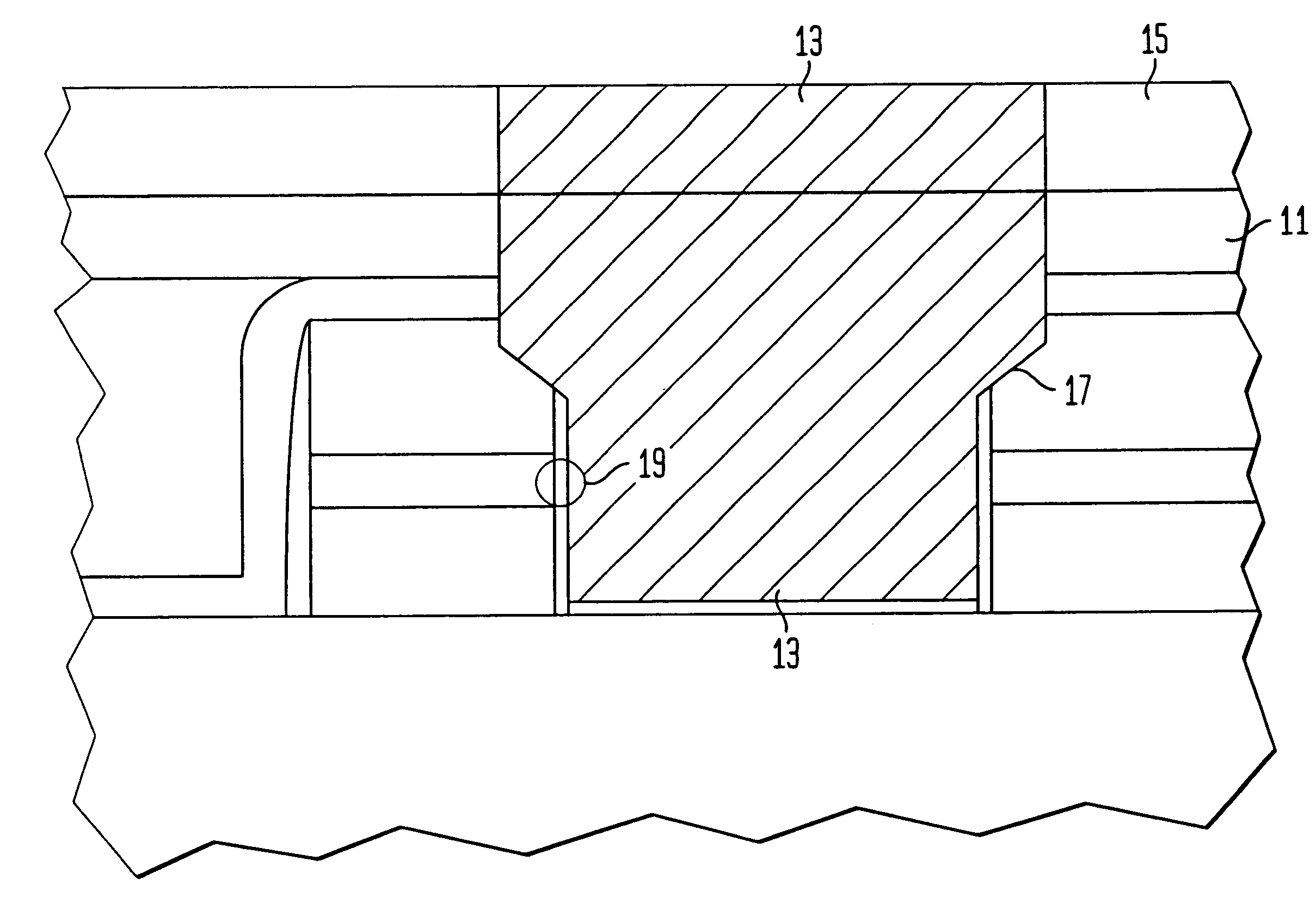
Semiconductor Device with Improved Contact Structure and Method of Forming Same
ActiveUS20090014796A1Reduce aspect ratioReduce contact densityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringDielectric layer
A contact structure includes a first contact formed in a first dielectric layer connecting to the source / drain region of a MOS transistor, and a second contact formed in a second dielectric layer connecting to a gate region of a MOS transistor or to a first contact. A butted contact structure abutting a source / drain region and a gate electrode includes a first contact formed in a first dielectric layer connecting to the source / drain region of a MOS transistor, and a second contact formed in a second dielectric layer with one end resting on the gate electrode and the other end in contact with the first contact.
Owner:MOSAID TECH
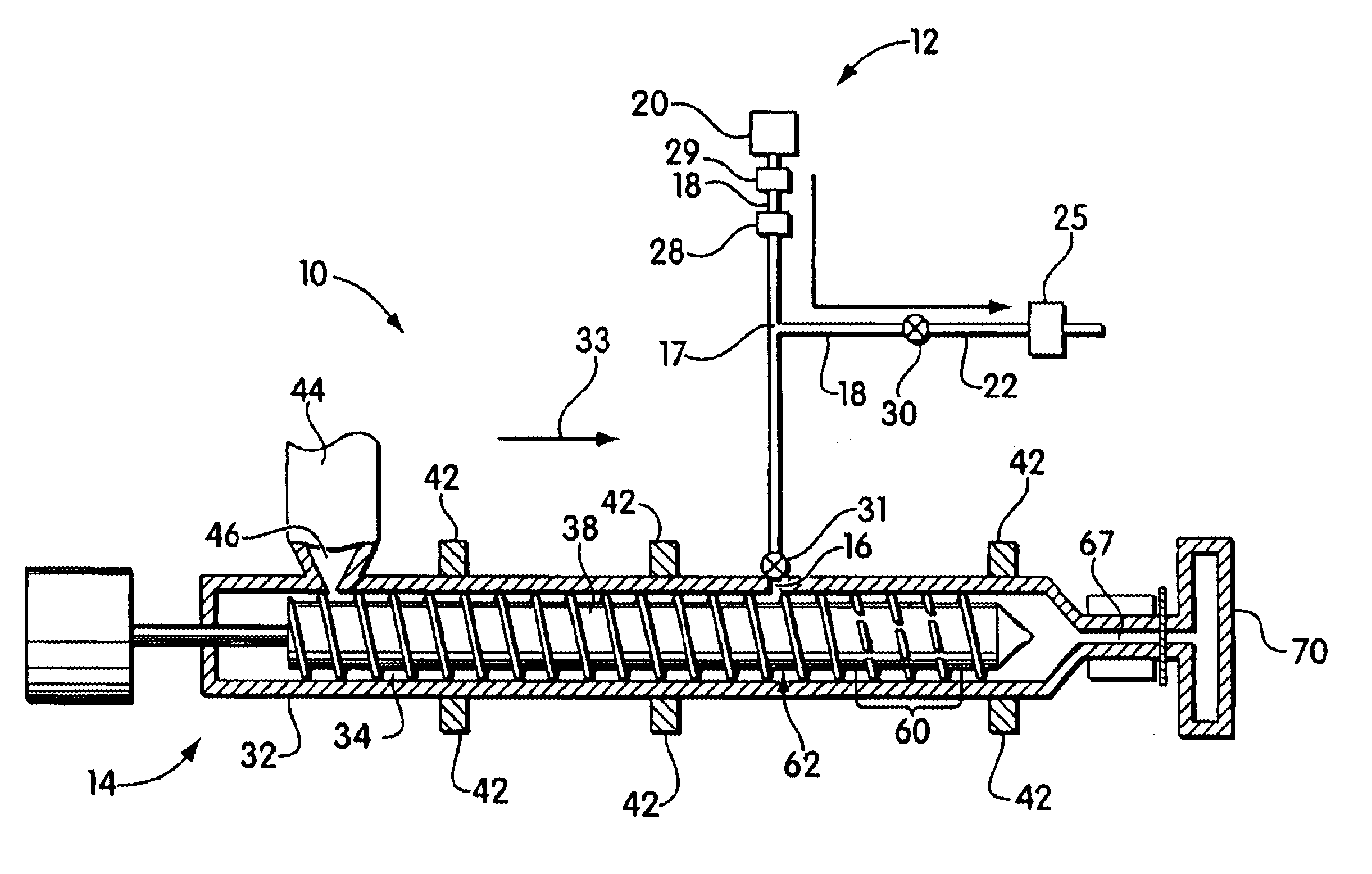
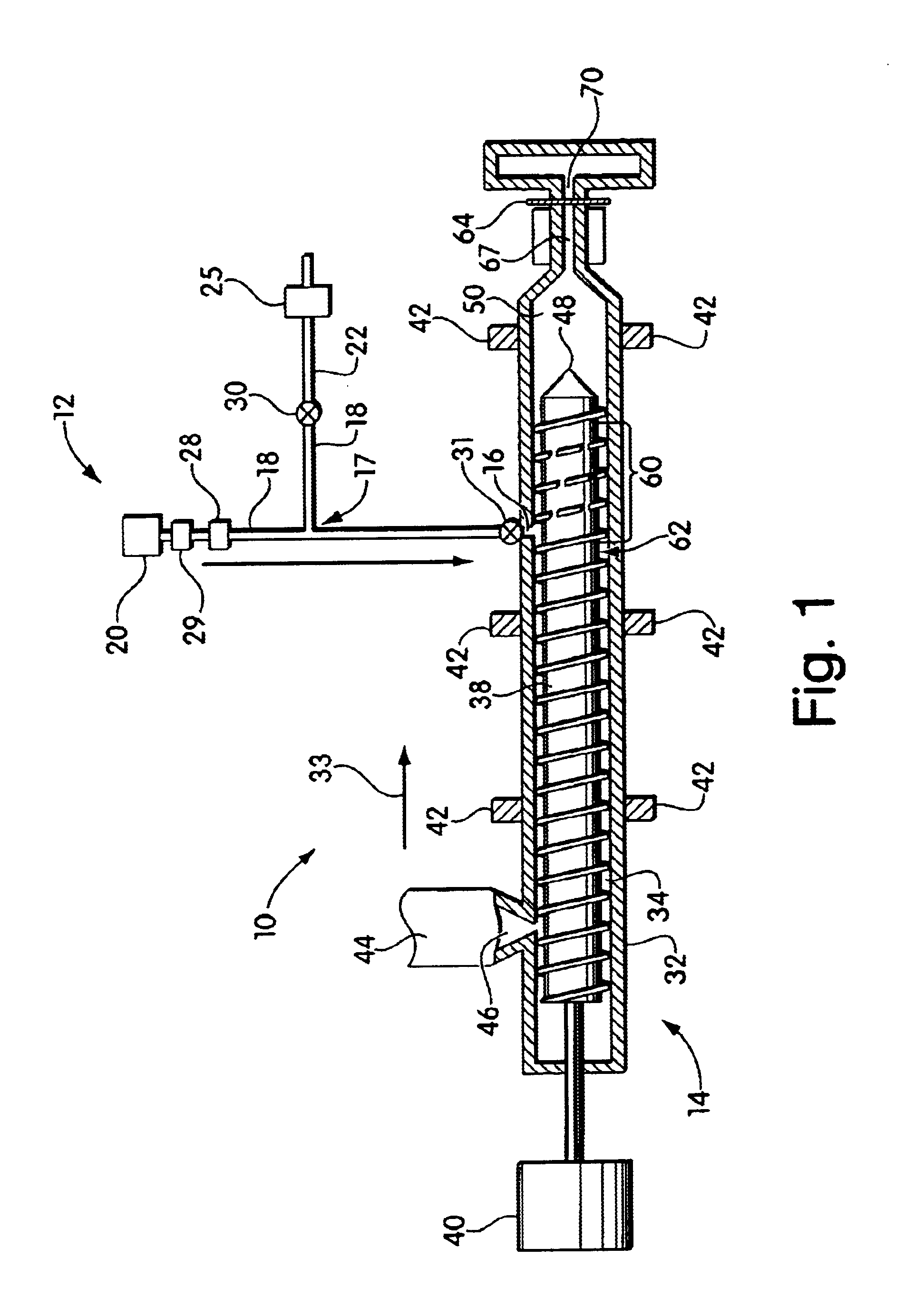
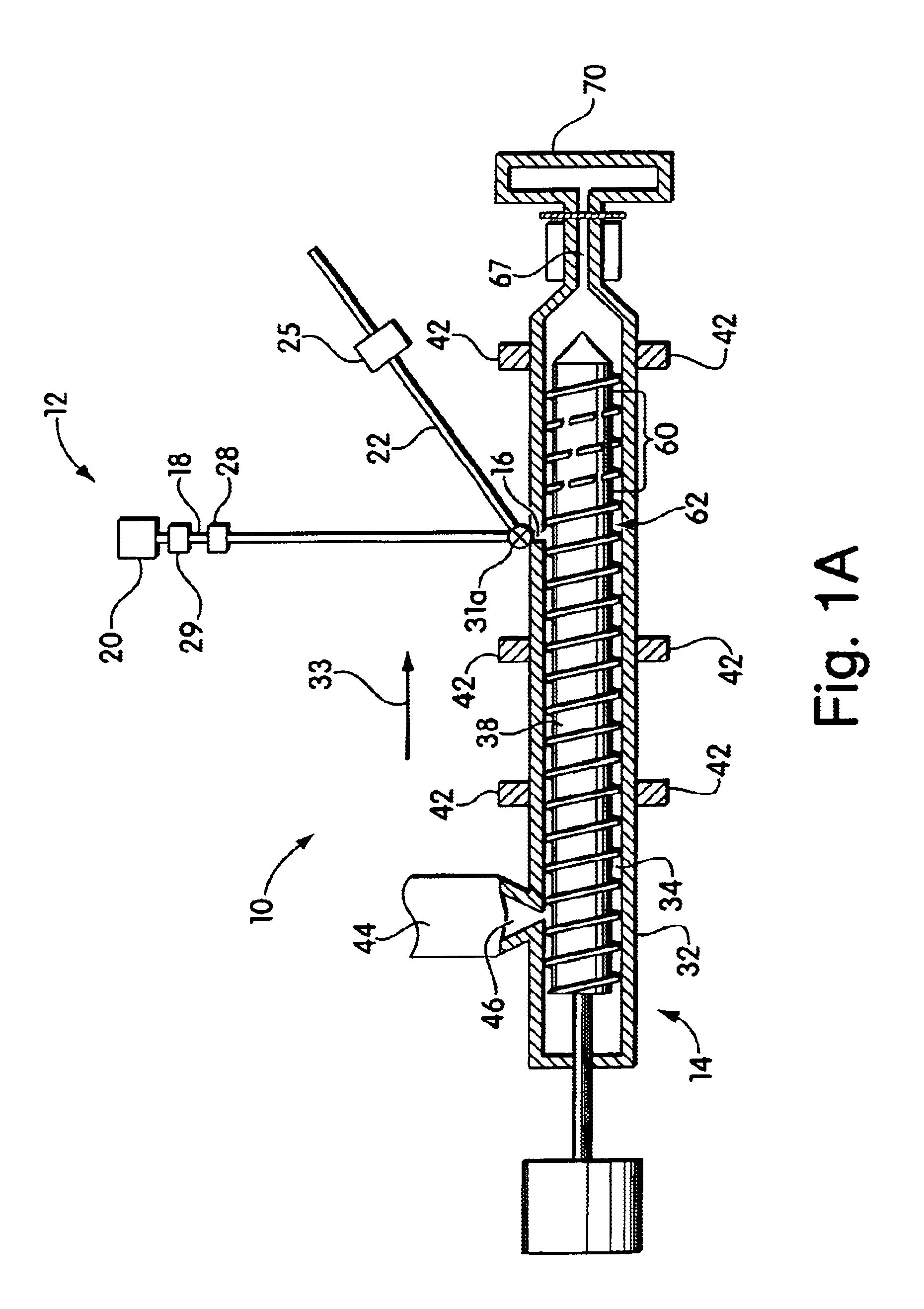
Blowing agent delivery system
InactiveUS6926507B2Easy to controlPrevents output inconsistencyAuxillary shaping apparatusFood shapingBlow moldingInjection molding machine
The invention provides a blowing agent delivery system for introducing a blowing agent into a polymeric foam processing system. The delivery system is designed to discontinuously introduce blowing agent from a continuous source into polymeric material within an extruder. The system, thus, may improve control over blowing agent delivery in discontinuous polymer processing systems such as injection molding or blow molding. In some embodiments, the blowing agent delivery system selectively directs blowing agent flow from the source to the extruder barrel, or through a bypassing passageway. In this manner, blowing agent may be continuously supplied by the source but discontinuously injected into the extruder barrel. During use, the delivery system may cause blowing agent to flow through the bypassing passageway, for example, when the screw stops plasticating polymeric material.
Owner:TREXEL
Modification of electrical properties of display cells for improving electrophoretic display performance
ActiveUS7504050B2Improve performanceIncreased process windowStatic indicating devicesConductive materialElectricityElectrophoresis
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Electrospinning in a controlled gaseous environment
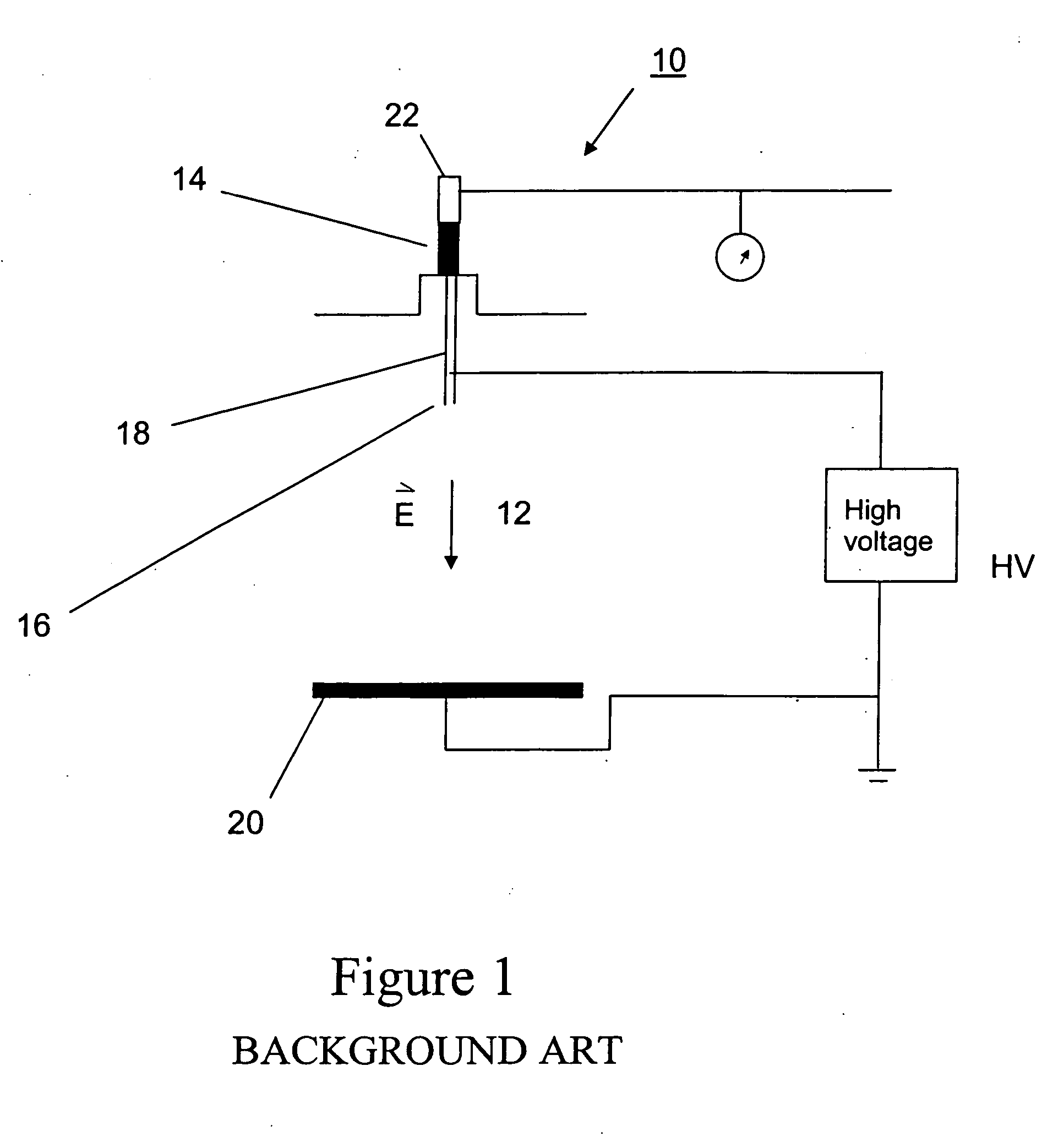
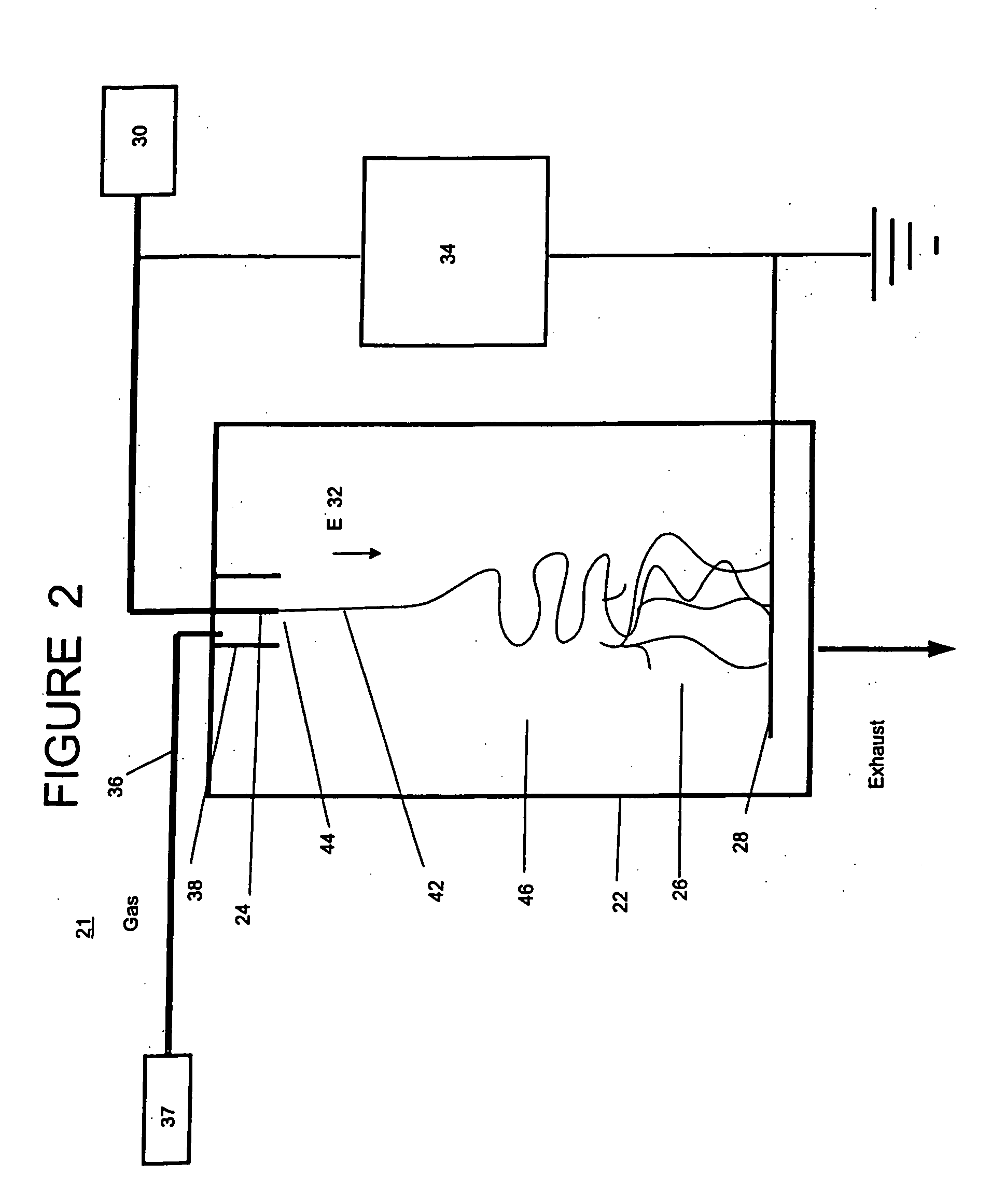
ActiveUS20050224999A1Increased process windowEasy to processDielectric heatingElectric discharge heatingFiberElectrospinning
Apparatus and method for producing fibrous materials in which the apparatus includes an extrusion element configured to electrospin a substance from which the fibers are to be composed by an electric field extraction of the substance from a tip of the extrusion element, a collector disposed from the extrusion element and configured to collect the fibers, a chamber enclosing the collector and the extrusion element, and a control mechanism configured to control a gaseous environment in which the fibers are to be electrospun. The method includes providing a substance from which the fibers are to be composed to a tip of an extrusion element, applying an electric field to the extrusion element in a direction of the tip, controlling a gaseous environment about where the fibers are to be electrospun, and electrospinning the substance from the tip of the extrusion element by an electric field extraction of the substance from the tip into the controlled gaseous environment.
Owner:RES TRIANGLE INST
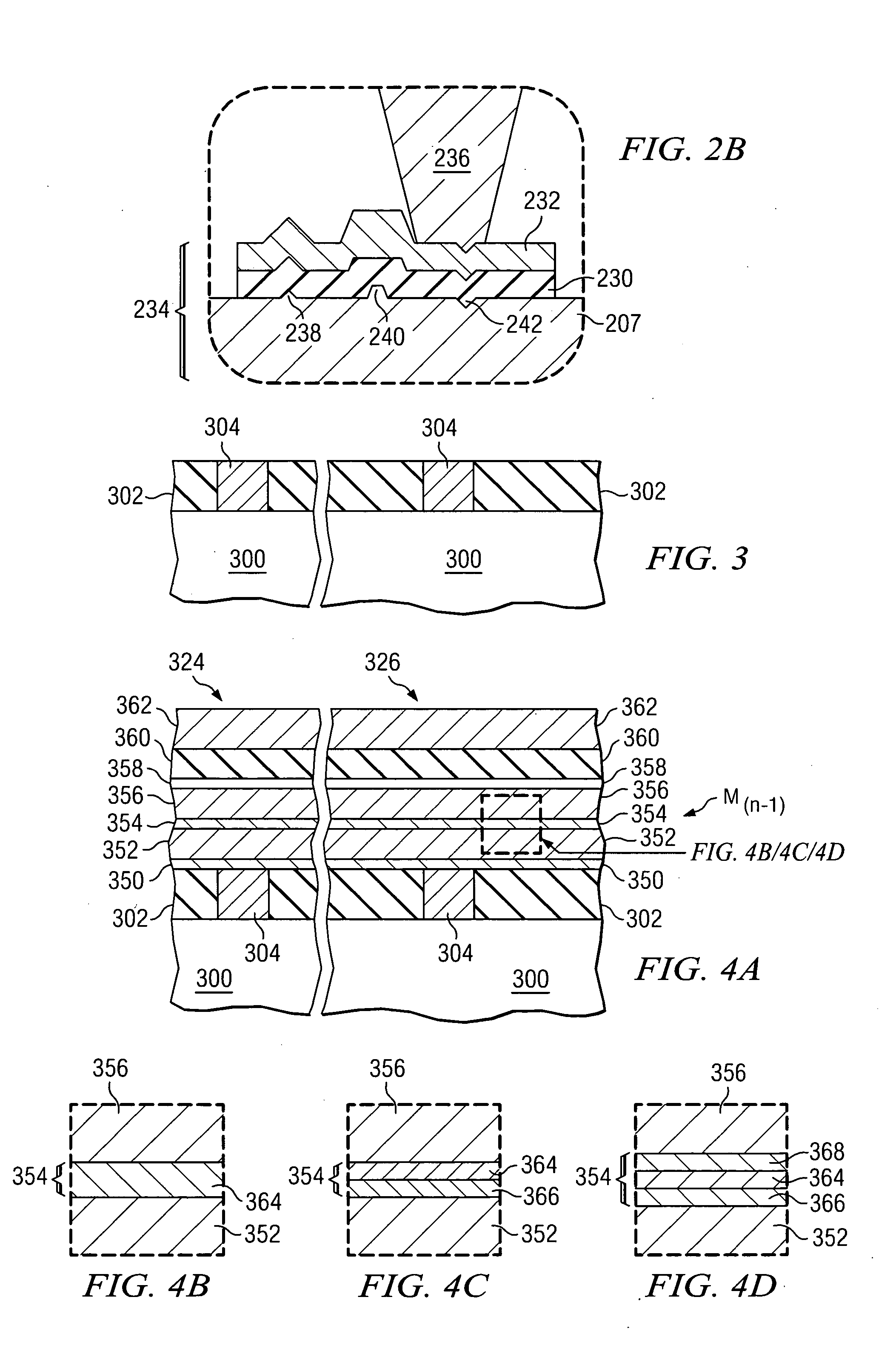
Method of forming a magnetic tunnel junction structure
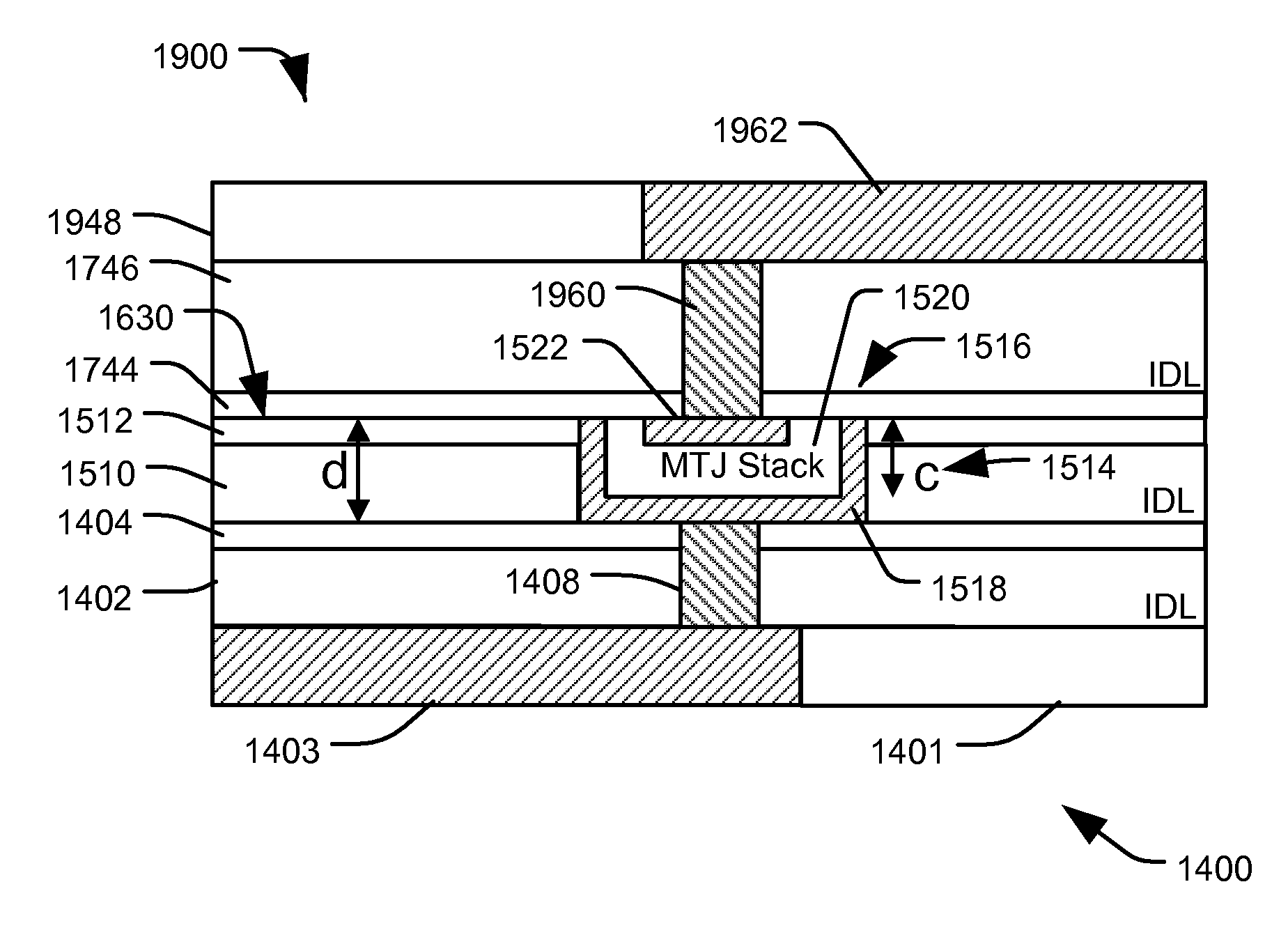
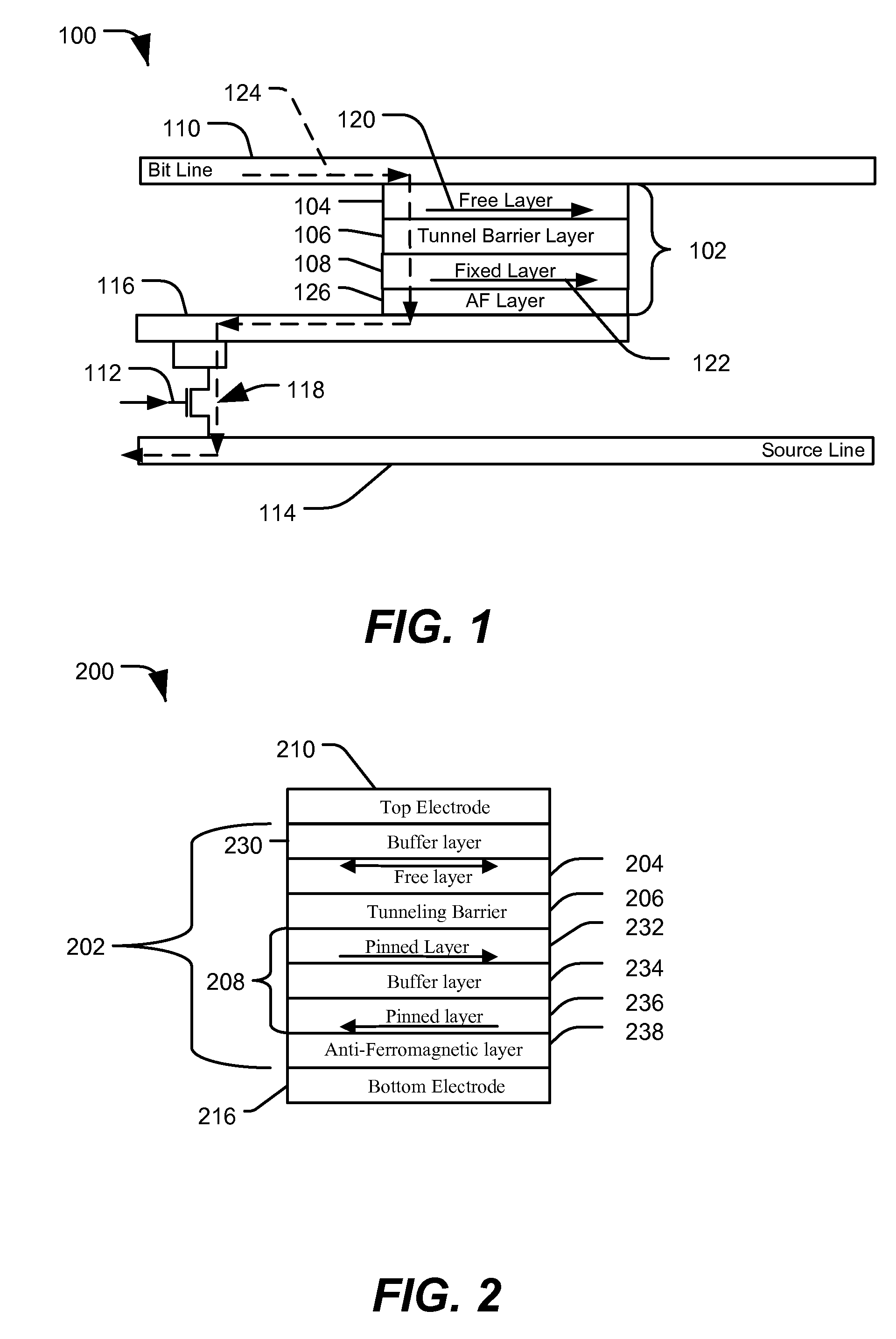
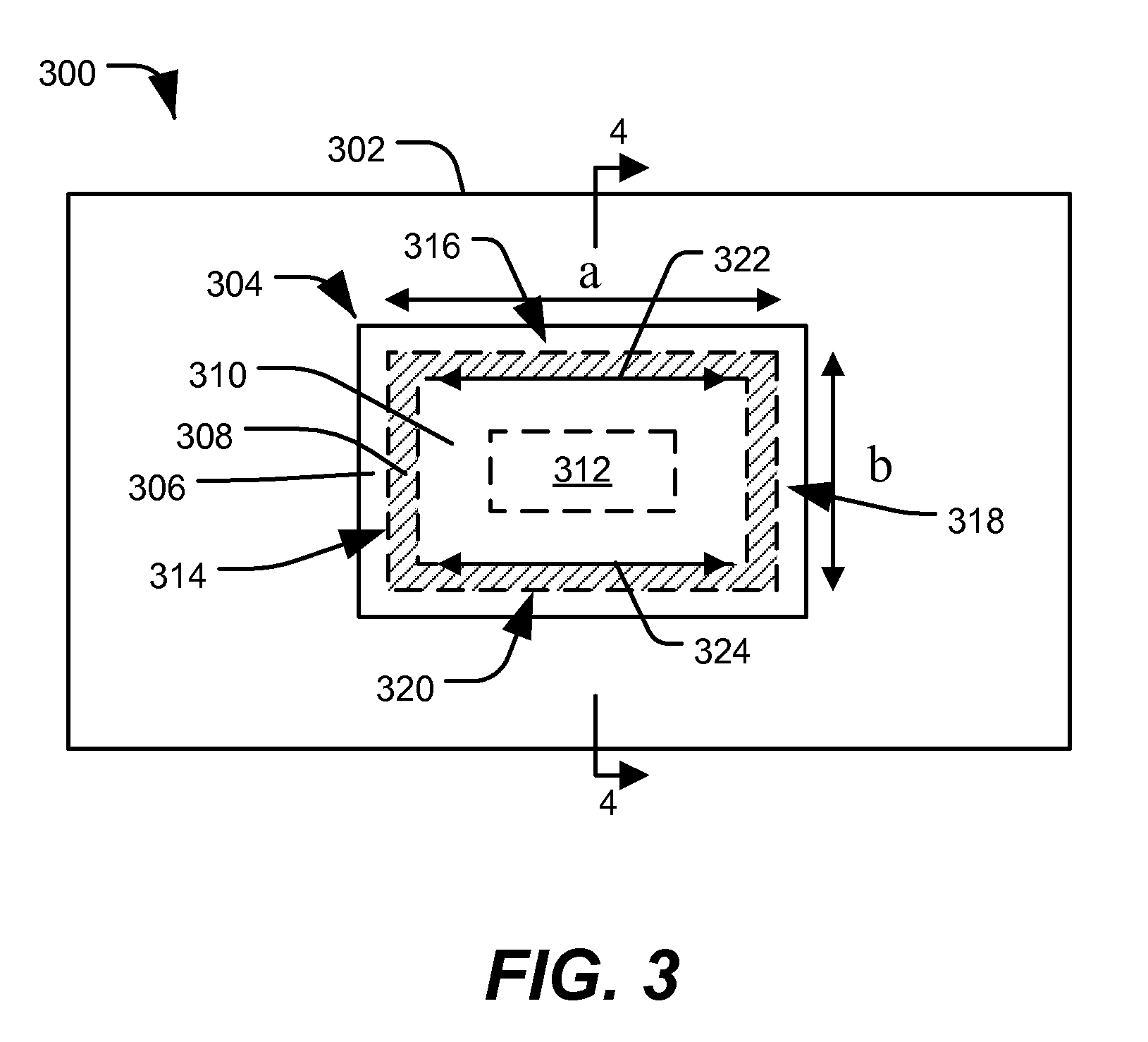
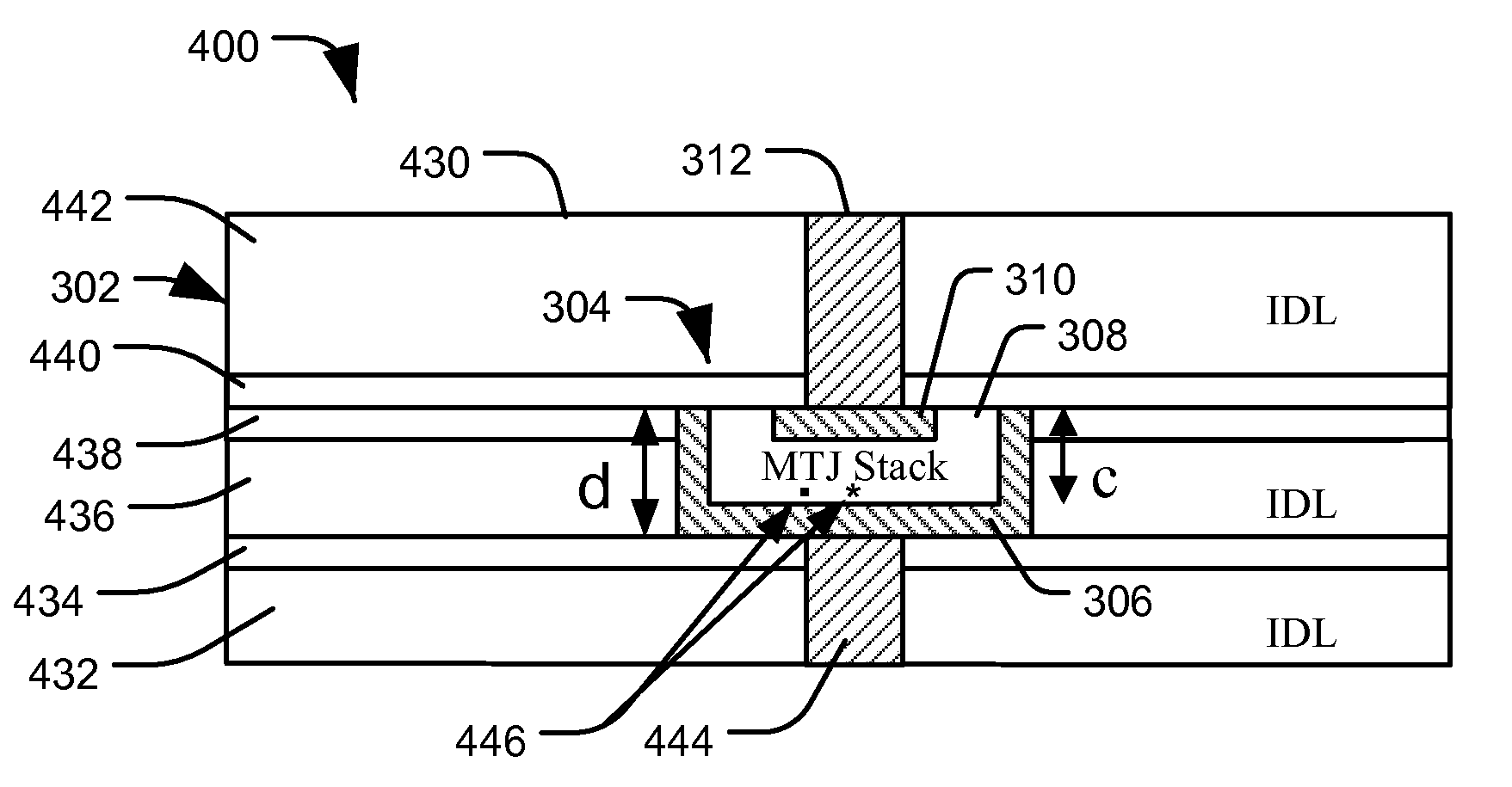
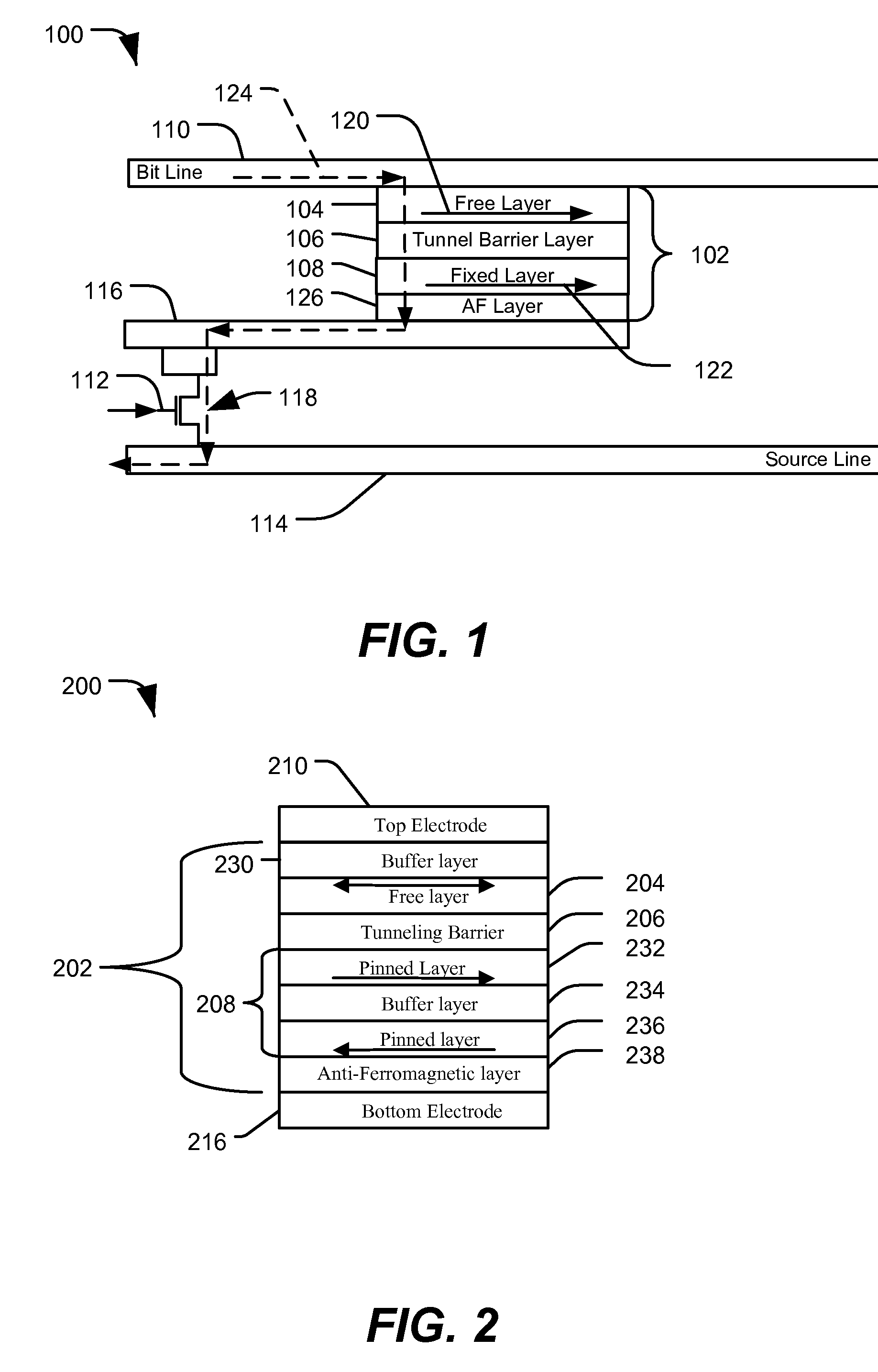
ActiveUS7579197B1Good etchingIncreased process windowMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringTunnel junction
In a particular illustrative embodiment, a method of forming a magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) device is disclosed that includes forming a trench in a substrate. The method further includes depositing a magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) structure within the trench. The MTJ structure includes a bottom electrode, a fixed layer, a tunnel barrier layer, a free layer, and a top electrode. The method also includes planarizing the MTJ structure. In a particular example, the MTJ structure is planarized using a Chemical Mechanical Planarization (CMP) process.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Photoresist pattern trimming methods
ActiveUS20130171825A1Increased process windowSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotosensitive material processingResistSolvent
Provided are methods of trimming photoresist patterns. The methods involve coating a photoresist trimming composition over a photoresist pattern, wherein the trimming composition includes a matrix polymer, a thermal acid generator and a solvent, the trimming composition being free of cross-linking agents. The coated semiconductor substrate is heated to generate an acid in the trimming composition from the thermal acid generator, thereby causing a change in polarity of the matrix polymer in a surface region of the photoresist pattern. The photoresist pattern is contacted with a developing solution to remove the surface region of the photoresist pattern. The methods find particular applicability in the formation of very fine lithographic features in the manufacture of semiconductor devices.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS LLC
Etch chamber with dual frequency biasing sources and a single frequency plasma generating source
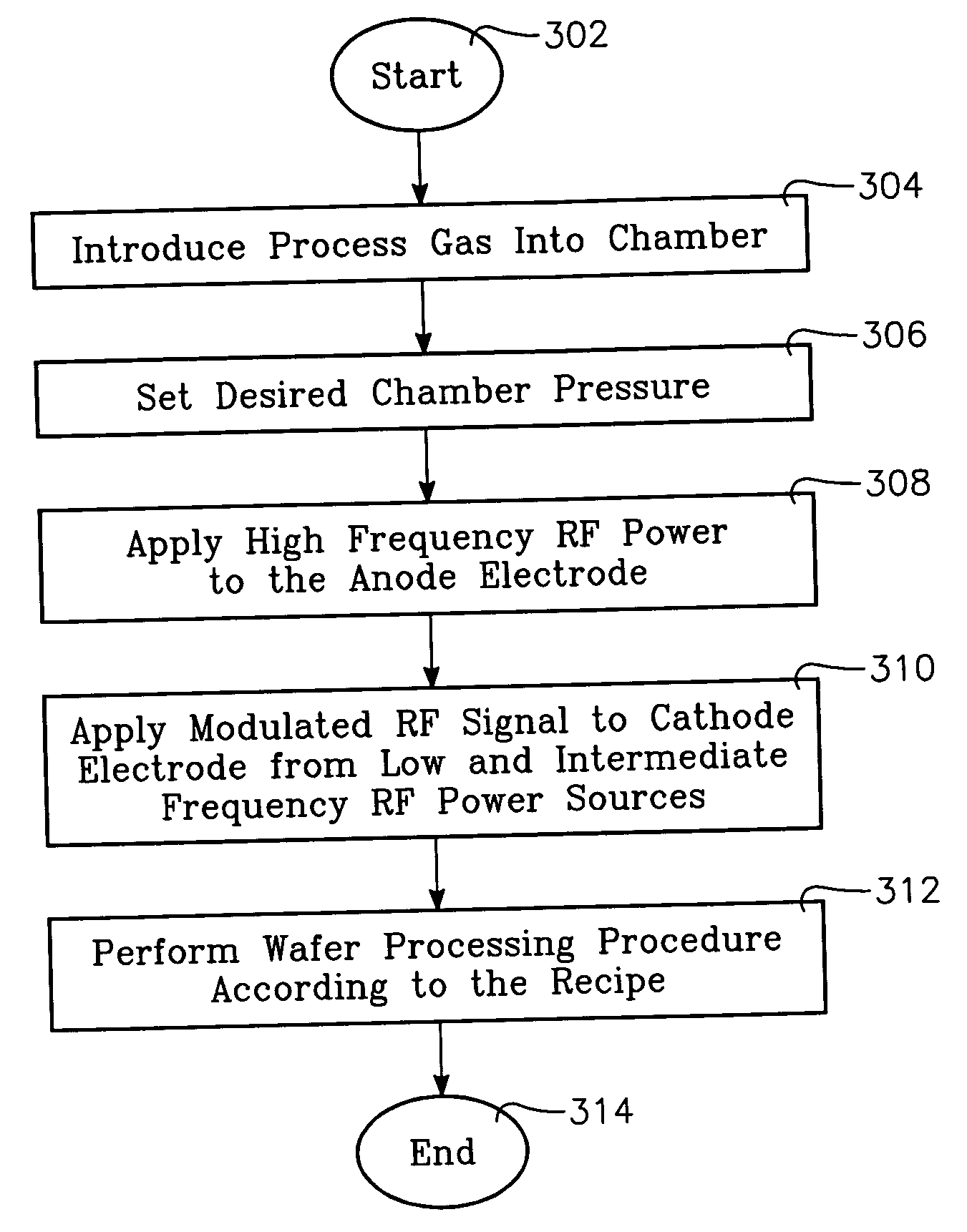
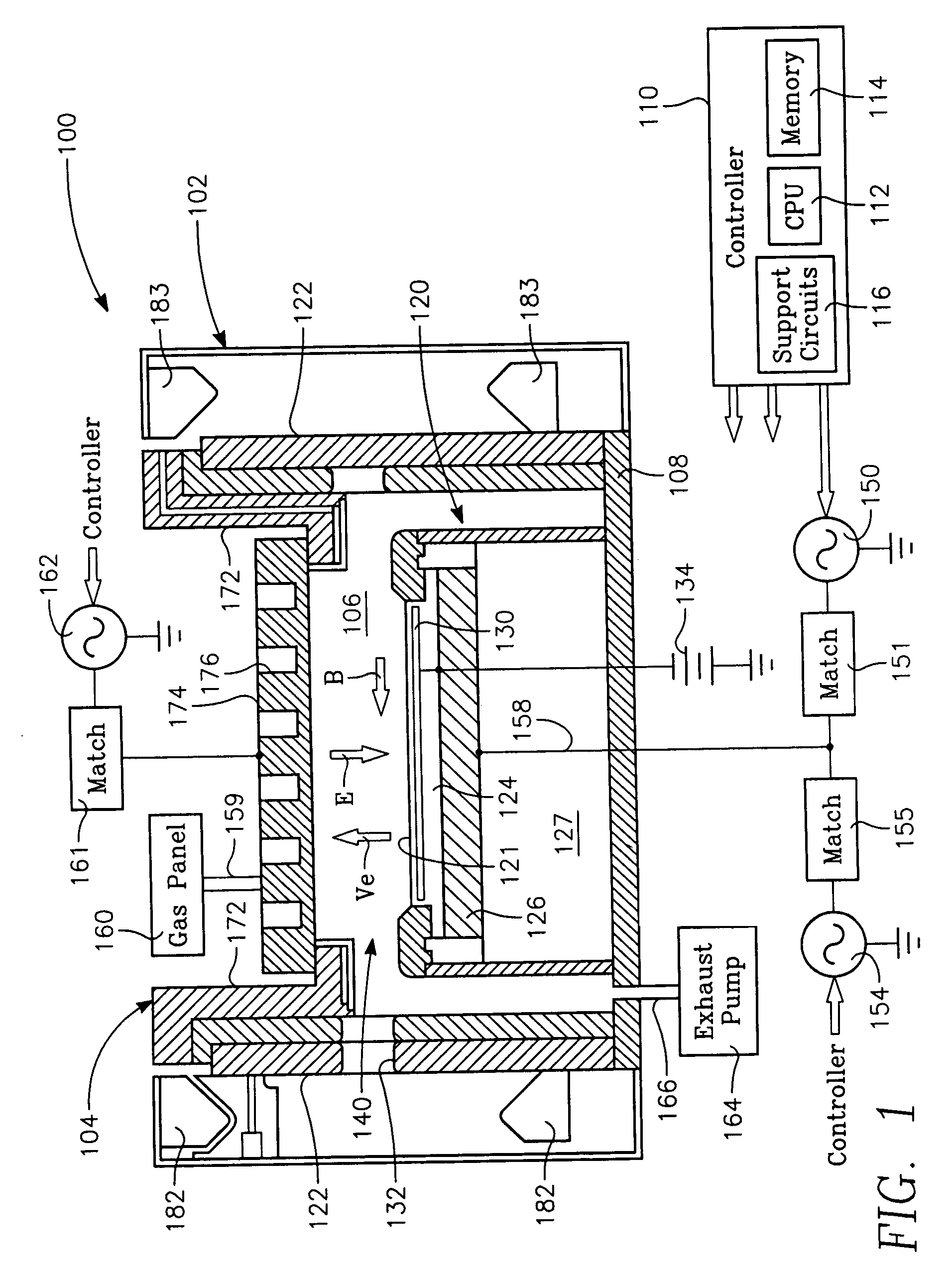
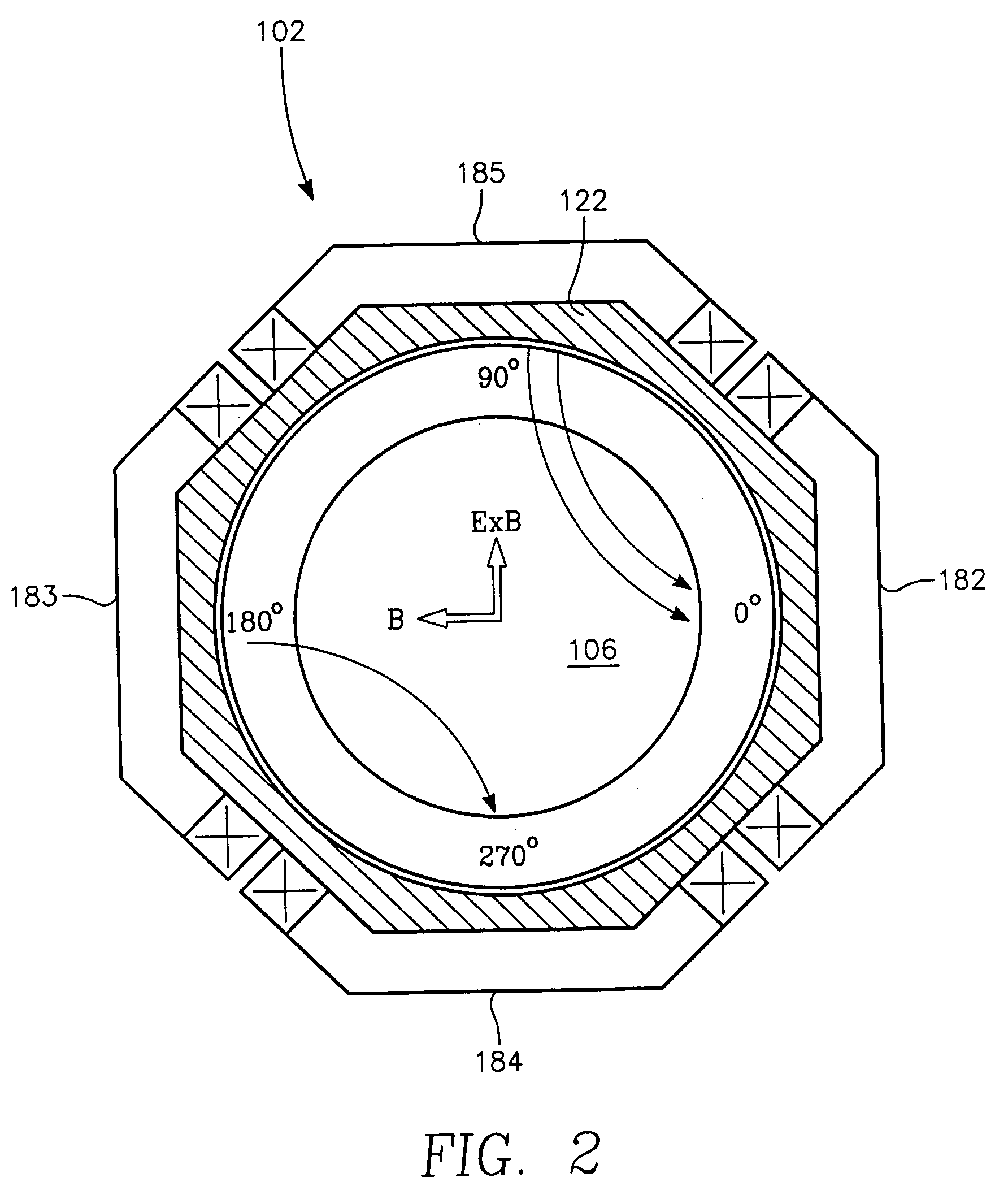
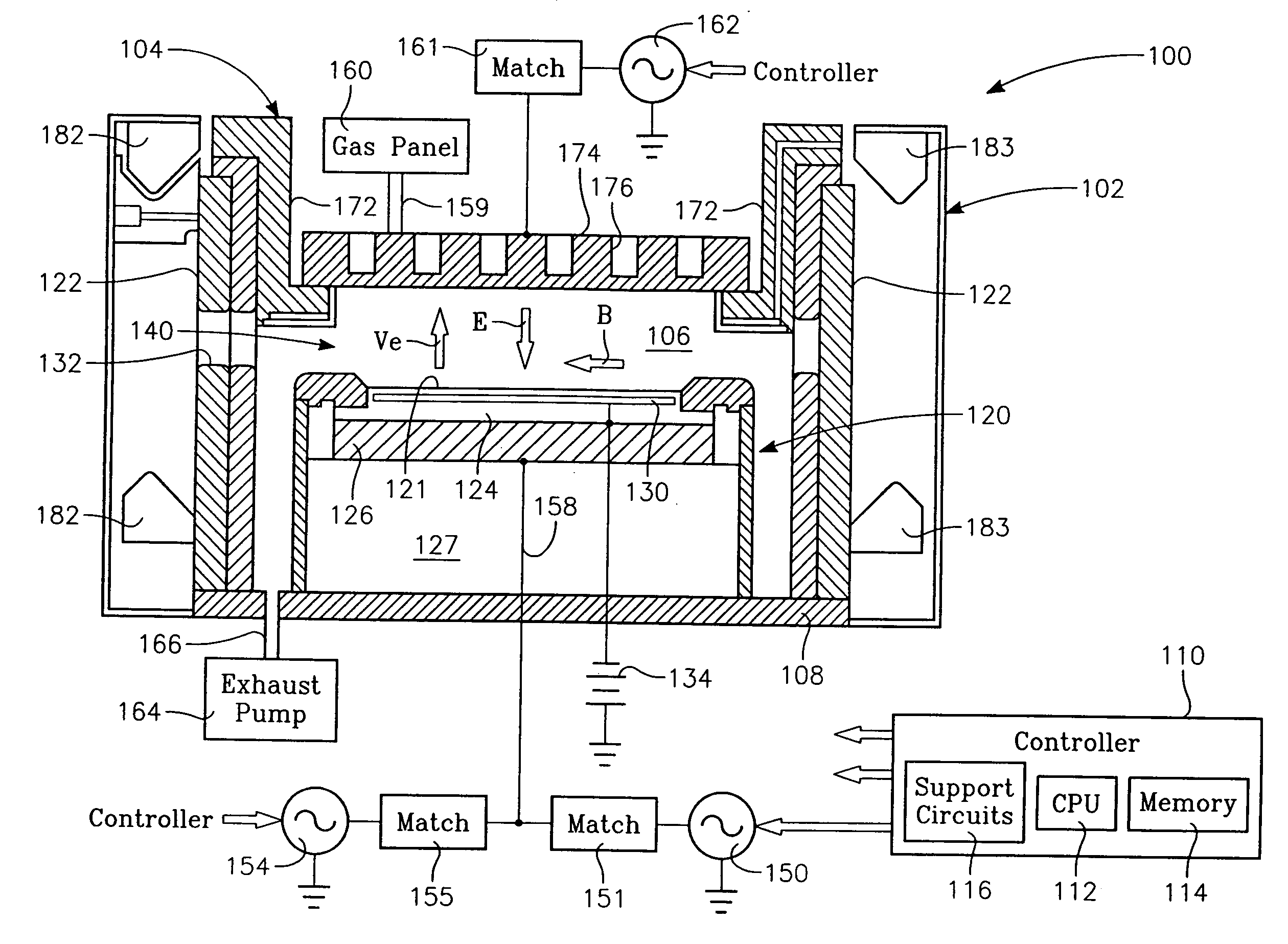
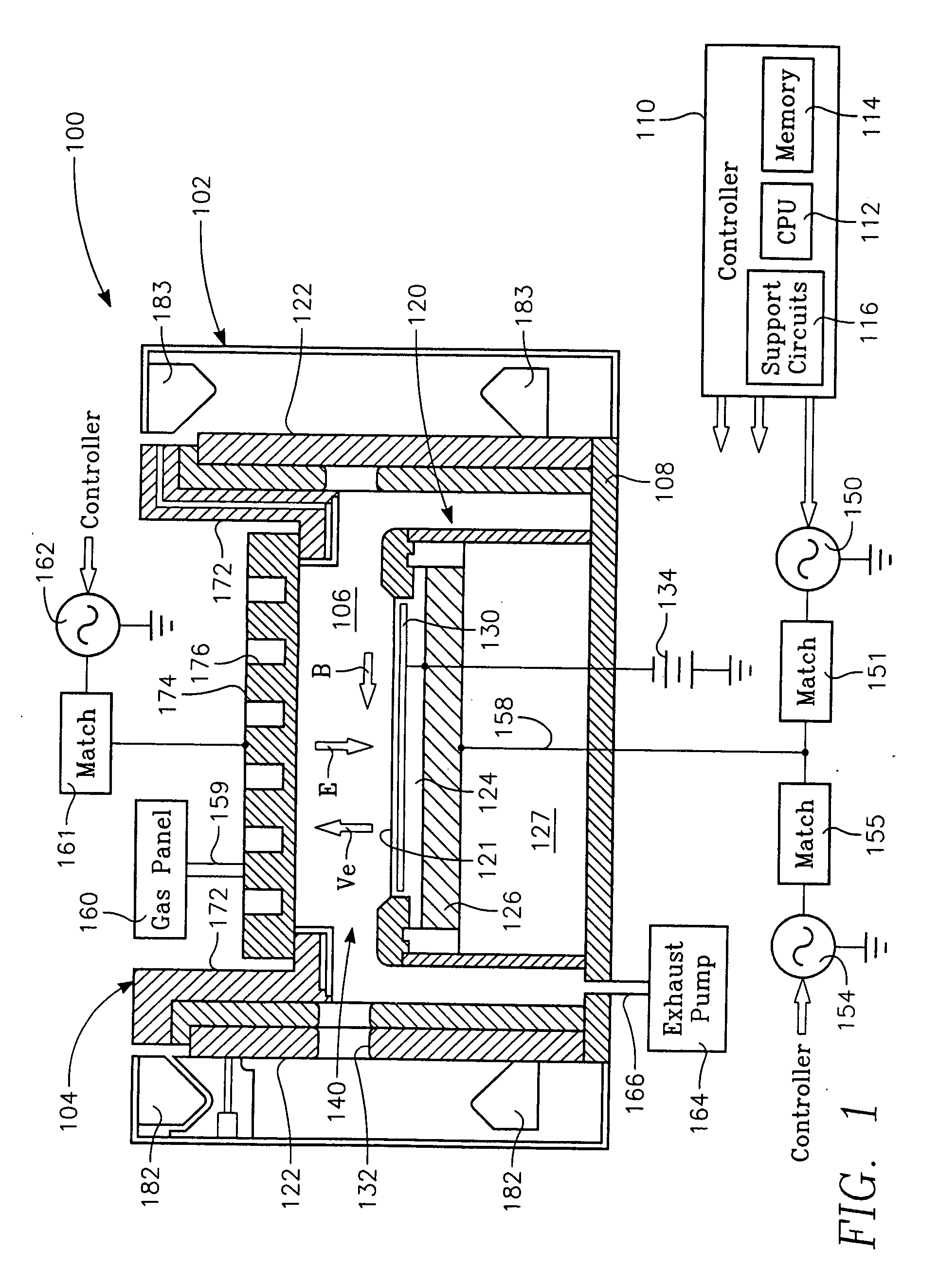
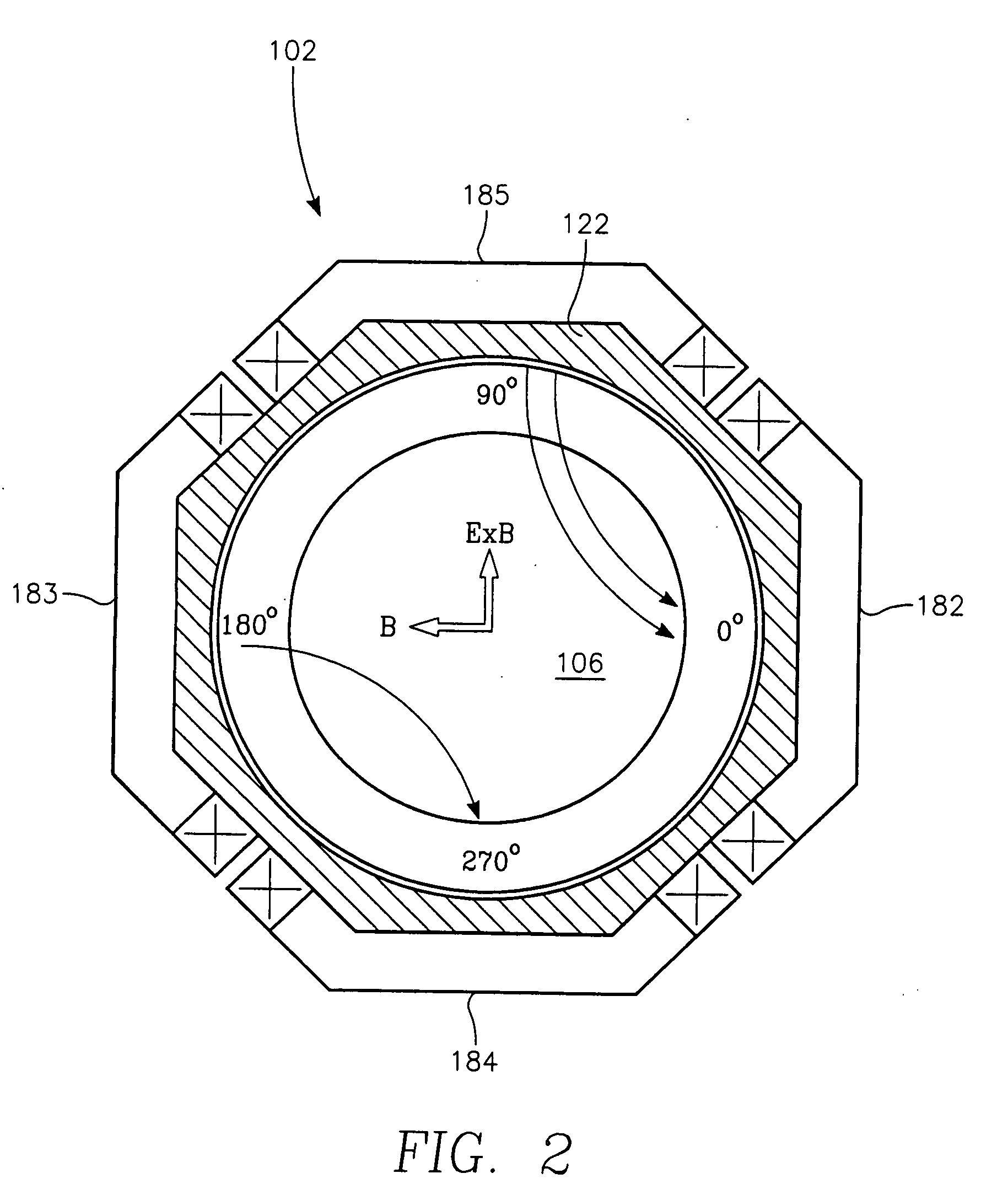
InactiveUS20060175015A1Increased process windowExpand coverageElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsDual frequencyHigh frequency power
A method and apparatus for selectively controlling a plasma in a processing chamber during wafer processing. The method includes providing process gasses into the chamber over a wafer to be processed, and providing high frequency RF power to a plasma generating element and igniting the process gases into the plasma. Modulated RF power is coupled to a biasing element, and wafer processing is performed according to a particular processing recipe. The apparatus includes a biasing element disposed in the chamber and adapted to support a wafer, and a plasma generating element disposed over the biasing element and wafer. A first power source is coupled to the plasma generating element, and a second power source is coupled to the biasing element. A third power source is coupled to the biasing element, wherein the second and third power sources provide a modulated signal to the biasing element.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Flip chip package utilizing trace bump trace interconnection
ActiveUS20120032322A1Low costIncreased process windowSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringInterconnection
A flip chip package includes a substrate having a die attach surface; and a die mounted on the die attach surface with an active surface of the die facing the substrate, wherein the die is interconnected to the substrate via a plurality of copper pillar bumps on the active surface, wherein at least one of the plurality of copper pillar bumps has a bump width that is substantially equal to or smaller than a line width of a trace on the die attach surface of the substrate.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Method and system for laser processing targets of different types on a workpiece
InactiveUS20080067155A1Increased process windowSimple processLaser detailsWelding/soldering/cutting articlesLaser processingPulse shaping
A method and system for laser processing targets of different types on a workpiece are provided. The method includes setting a laser pulse width of one or more laser pulses to selectively provide one or more laser output pulses having one or more set pulse widths based on a first type of target to be processed. The method further includes setting a pulse shape of the one or more output pulses to selectively provide the one or more output pulses having the set pulse shape based on the types of targets to be processed. The method still further includes delivering the one or more output pulses having the one or more set pulse widths and the set pulse shape to at least one target of the first type. The method finally includes resetting the laser pulse width of one or more laser pulses to selectively provide one or more laser output pulses having one or more reset pulse widths based on a second type of target to be processed.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Superjunction device with improved ruggedness
ActiveUS20050082570A1Reduce dependenceEasy to chargeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialEngineering
An improved superjunction semiconductor device includes a charged balanced pylon in a body region, where a top of the pylon is large to create slight charge imbalance. A MOSgated structure is formed over the top of the pylon and designed to conduct current through the pylon. By increasing a dimension of the top of the pylon, the resulting device is less susceptible to variations in manufacturing tolerances to obtain a good breakdown voltage and improved device ruggedness.
Owner:SILICONIX TECH C V
Gate structure and fabricating method thereof
ActiveUS20070104862A1Gate resistance be lowerLower gate resistancePretreated surfacesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
A gate structure comprising a substrate, a gate dielectric layer, a first conductive layer, a second conductive layer, a cap layer and a first insulating spacer is provided. The gate dielectric layer is disposed on the substrate. The first conductive layer is disposed on the gate dielectric layer and has an opening. Part of the second conductive layer is disposed in the opening. The second conductive layer has an extrusion that protrudes above the opening of the first conductive layer. The extrusion has a cross-sectional width less than the width of the second conductive layer inside the opening. The cap layer is disposed on the extrusion. The first insulating spacer is disposed on part of the first conductive layer and covers the sidewalls of the extrusion. The inclusion of the extrusion in the second conductive layer decreases the resistance of the gate structure and promotes the efficiency of the device.
Owner:PROMOS TECH INC
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20130062701A1Improve device qualityImprove processing yieldTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsInter layerDielectric layer
A manufacturing method of a semiconductor device includes the following steps. First, a substrate is provided. At least one sacrificial gate structure is formed on the substrate, at least one diffusion region is formed in the substrate at each of two sides of the sacrificial gate structure, and a first inter-layer dielectric layer is formed to cover the diffusion region. A gate recess is then formed in the sacrificial gate structure. A first diffusion contact hole is then formed in the first inter-layer dielectric layer and at least partially exposes the diffusion region. A metal layer is subsequently formed in the gate recess and the first diffusion contact hole.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Method of fabricating silicon nitride layer and method of fabricating semiconductor device
ActiveUS20070066022A1Increase the tensile stressIncrease currentTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingUV curingDevice material
A method of fabricating a silicon nitride layer is described. First, a substrate is provided. Then, a silicon nitride layer is formed on the substrate. The silicon nitride layer is UV-cured in an atmosphere lower than the standard atmospheric pressure. Through the UV curing treatment, the tensile stress of the silicon nitride layer is increased.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
High efficiency light-emitting diode and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20080157109A1Simple process conditionsIncreased process windowSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDiffusion barrierLight-emitting diode
A high efficiency light-emitting diode and a method for manufacturing the same are described. The high efficiency light-emitting diode comprises: a permanent substrate; a first contact metal layer and a second contact metal layer respectively deposed on two opposite surfaces of the permanent substrate; a bonding layer deposed on the second contact metal layer; a diffusion barrier layer deposed on the bonding layer, wherein the permanent substrate, the bonding layer and the diffusion barrier layer are electrically conductive; a reflective metal layer deposed on the diffusion barrier layer; a transparent conductive oxide layer deposed on the reflective metal layer; an illuminant epitaxial structure deposed on the transparent conductive oxide layer, wherein the illuminant epitaxial structure includes a first surface and a second surface opposite to the first surface; and a second conductivity type compound electrode pad deposed on the second surface of the illuminant epitaxial structure.
Owner:EPISTAR CORP
Computational Process Control
ActiveUS20120303151A1Achieving performance stabilityIncreased process windowPhotomechanical apparatusManufacturing data aquisition/processingMetrologyLithographic artist
The present invention provides a number of innovations in the area of computational process control (CPC). CPC offers unique diagnostic capability during chip manufacturing cycle by analyzing temporal drift of a lithography apparatus / process, and provides a solution towards achieving performance stability of the lithography apparatus / process. Embodiments of the present invention enable optimized process windows and higher yields by keeping performance of a lithography apparatus and / or parameters of a lithography process substantially close to a pre-defined baseline condition. This is done by comparing the measured temporal drift to a baseline performance using a lithography process simulation model. Once in manufacturing, CPC optimizes a scanner for specific patterns or reticles by leveraging wafer metrology techniques and feedback loop, and monitors and controls, among other things, overlay and / or CD uniformity (CDU) performance over time to continuously maintain the system close to the baseline condition.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Technology for manufacturing interlaced back contact (IBC) crystalline silicon solar battery with ion implantation
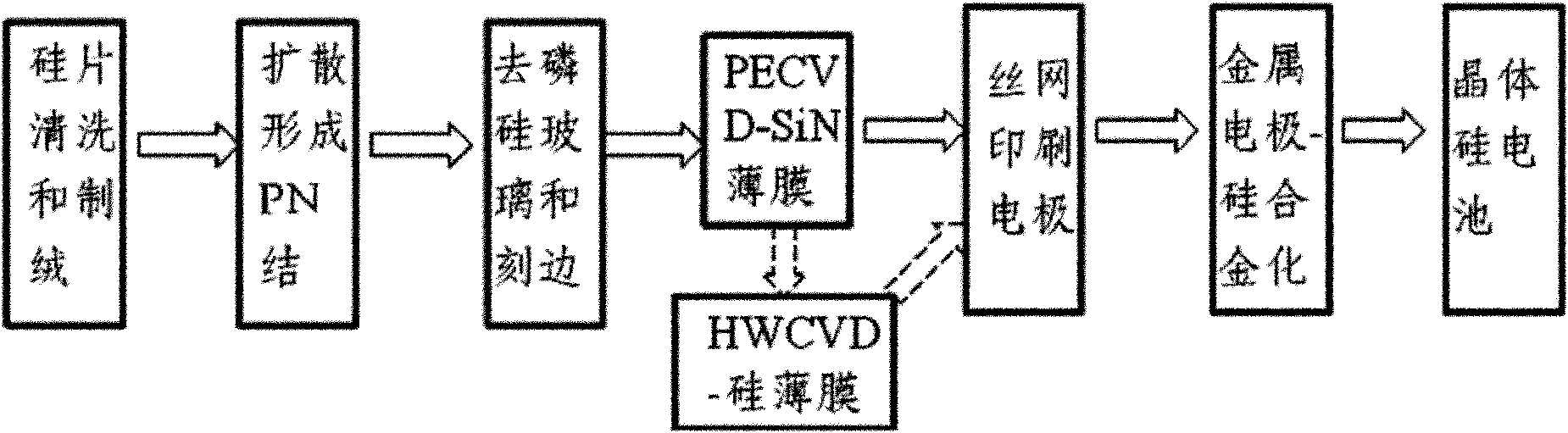
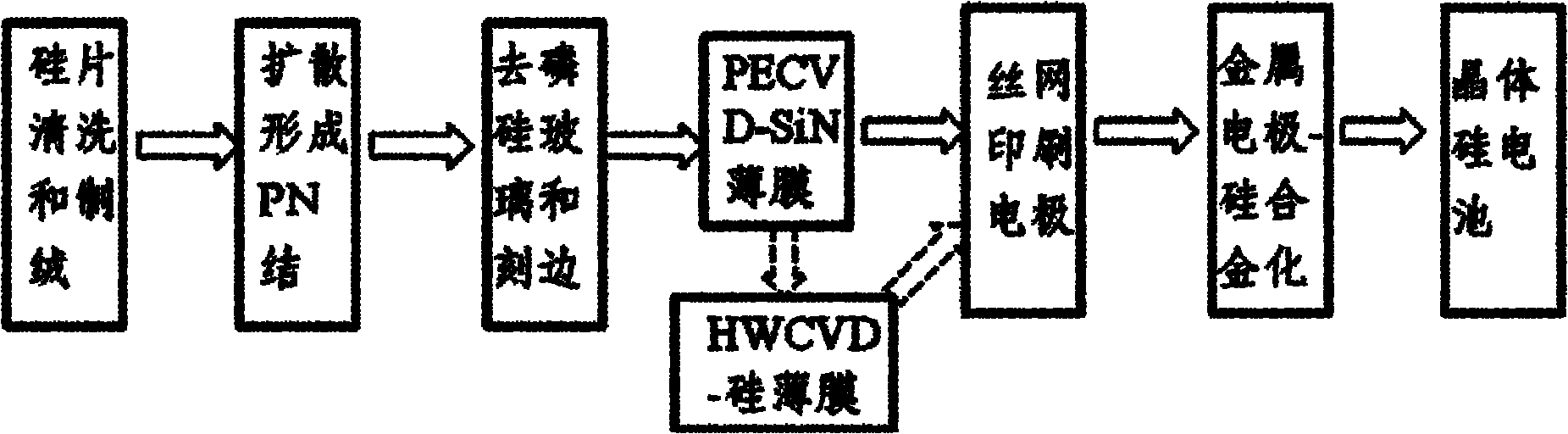
ActiveCN102222726ASimple preparation processHigh feasibilityFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesSilicon solar cellOptoelectronics
A technology for manufacturing an interlaced back contact (IBC) crystalline silicon solar battery with ion implantation comprises the following steps: (1) selecting a crystalline silicon base body to perform surface texturing; (2) forming a homotype doping layer having the same electrical property with the base body on the positive surface; (3) forming n+ doping regions and p+ doping regions interlaced to each other on the back surface of the crystalline silicon by the ion implantation; (4) insulating the n+ doping regions and the p+ doping regions on the back surface of the crystalline silicon base body; (5) performing annealing in order to eliminate crystalline damage caused by iron implantation to the crystalline silicon base body, and performing thermal oxidation to form a SiOx oxide layer; (6) forming a passive anti-reflecting film on the positive surface of a silicon chip; (7) forming a passive film on the back surface of the silicon chip; and (8) forming an emitter and a metal contact electrode of a base electrode on the back surface, and forming the ohmic contact of the metal electrode with the n+ doping regions and the p+ doping regions after one sintering. The method canaccurately control concentration, depth and position of the doping, and the technological process is simple, and easy to operate.
Owner:JA SOLAR TECH YANGZHOU
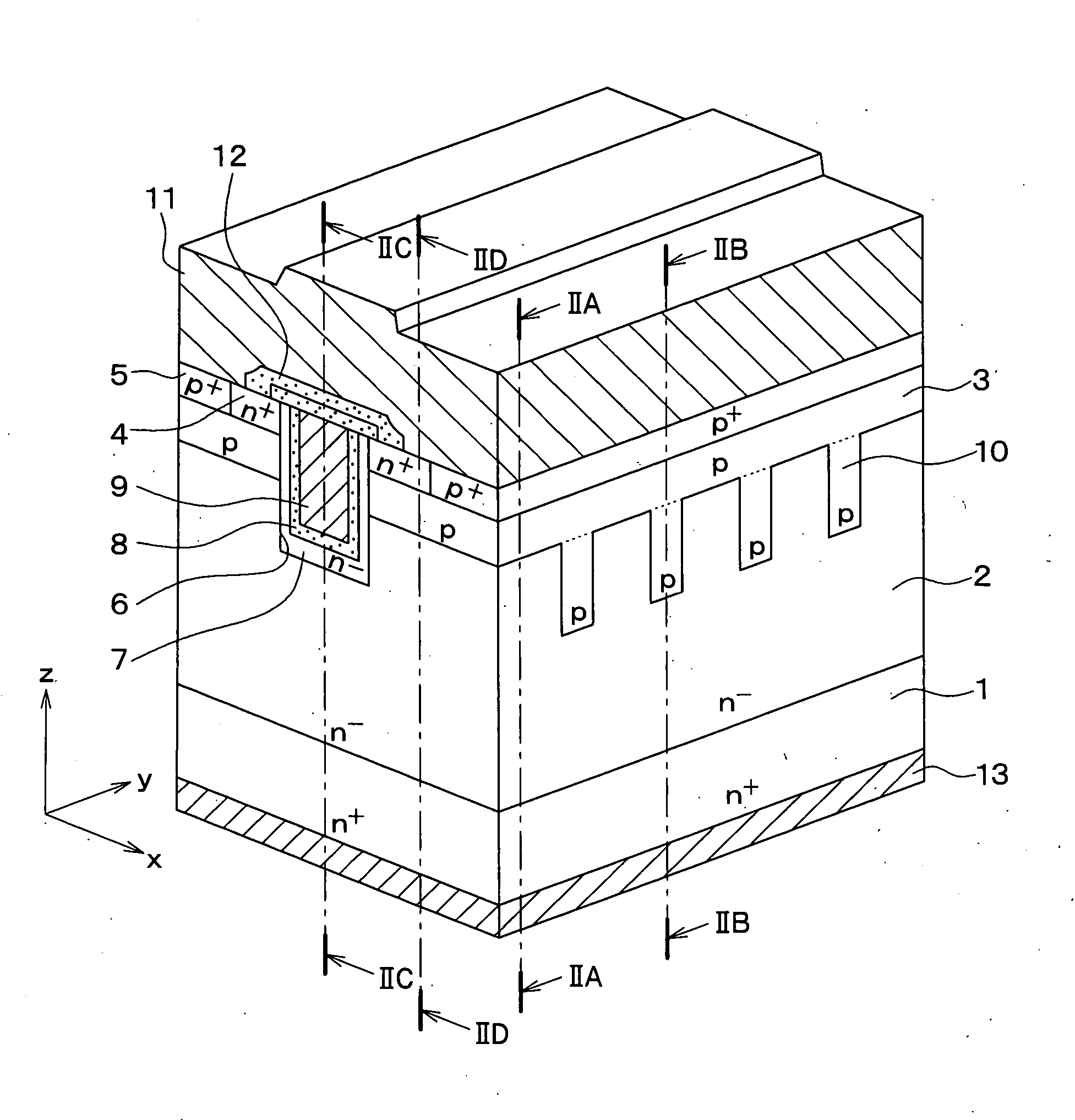
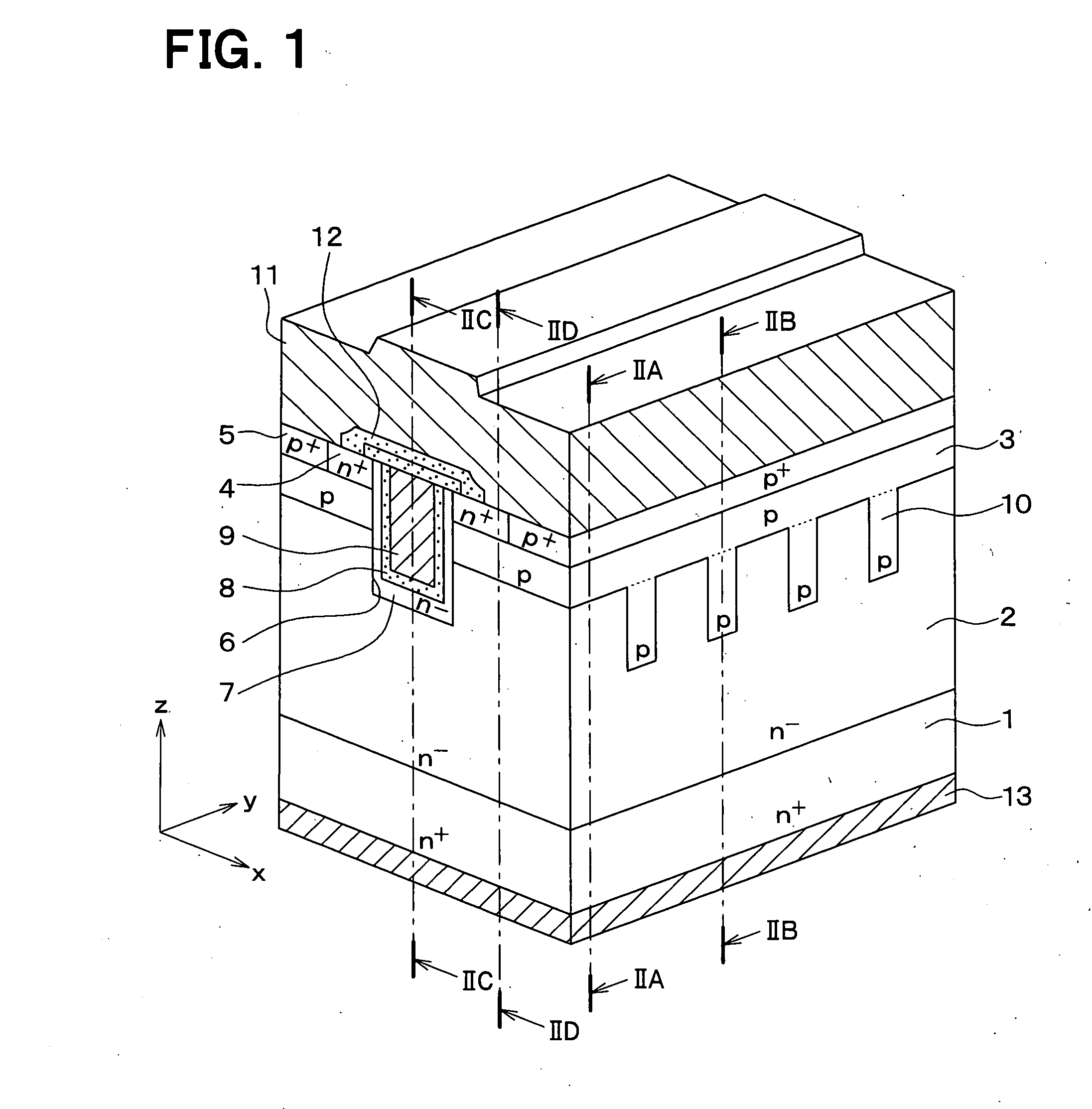
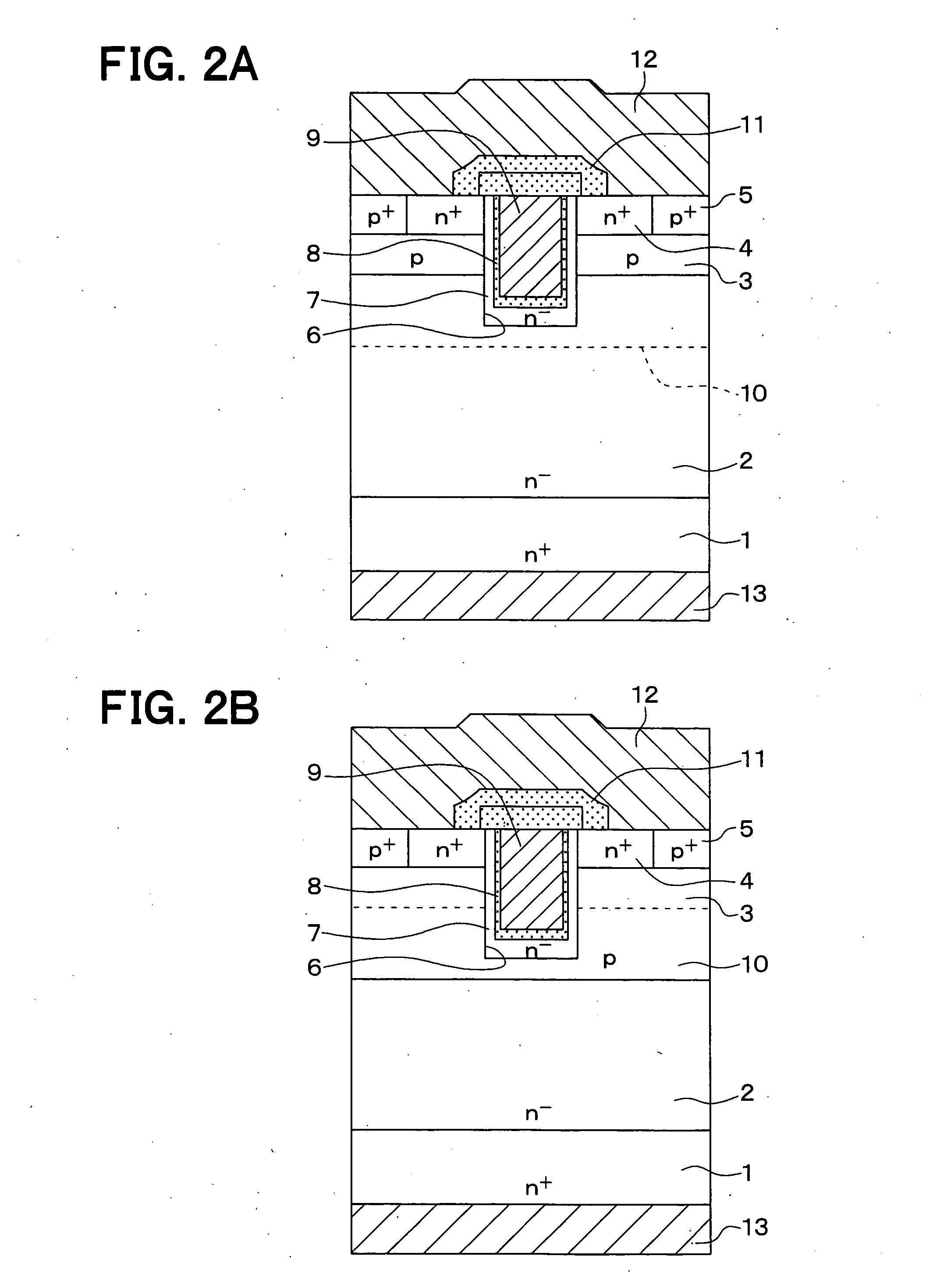
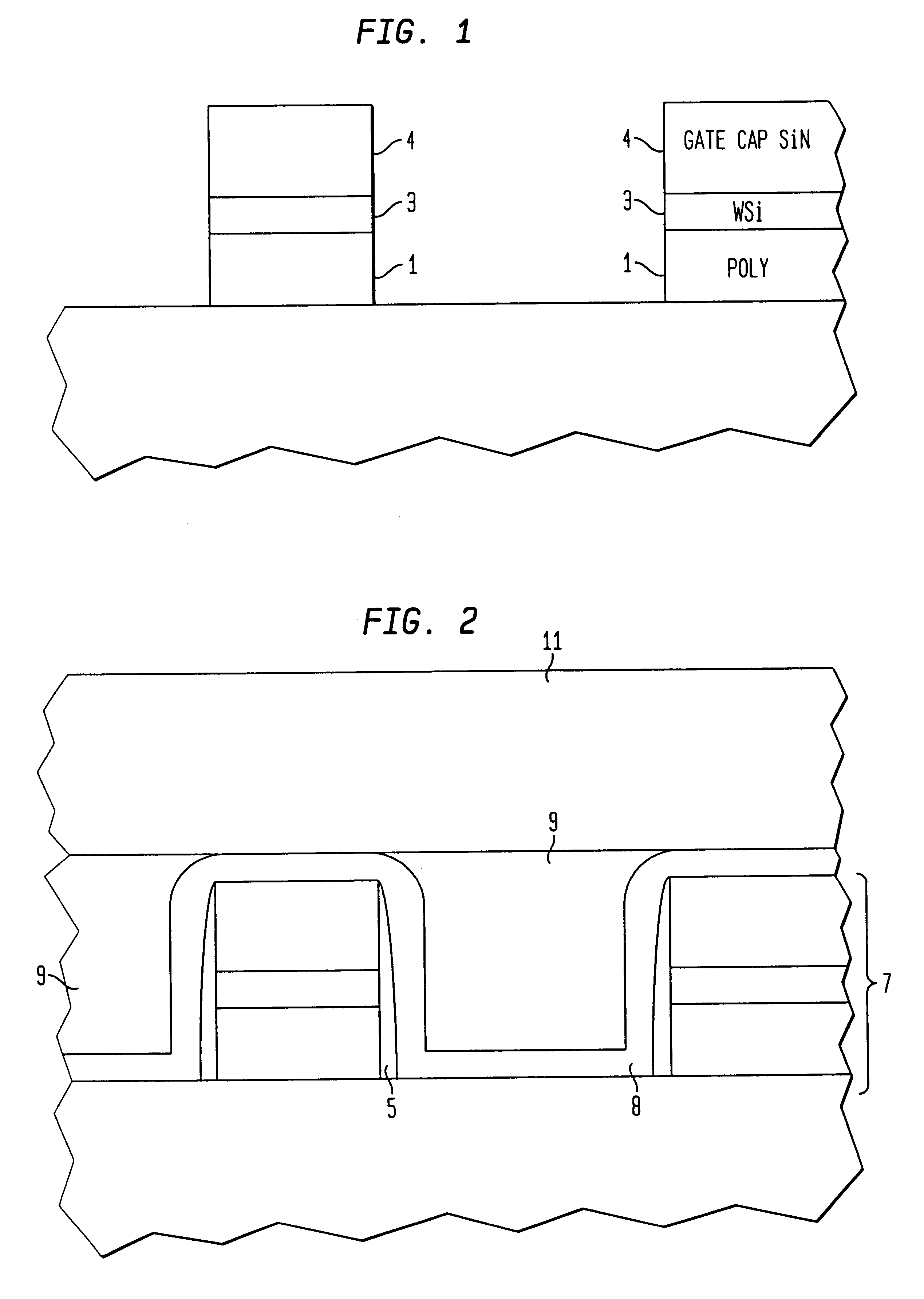
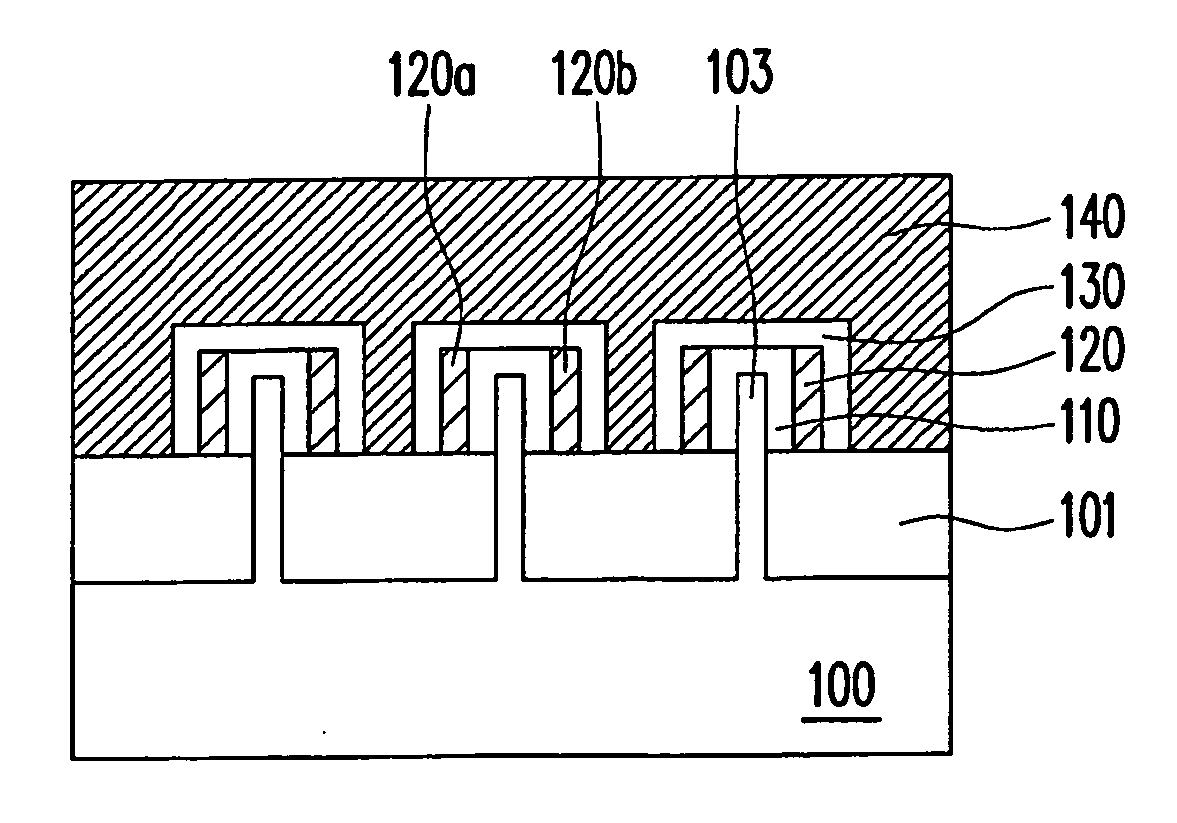
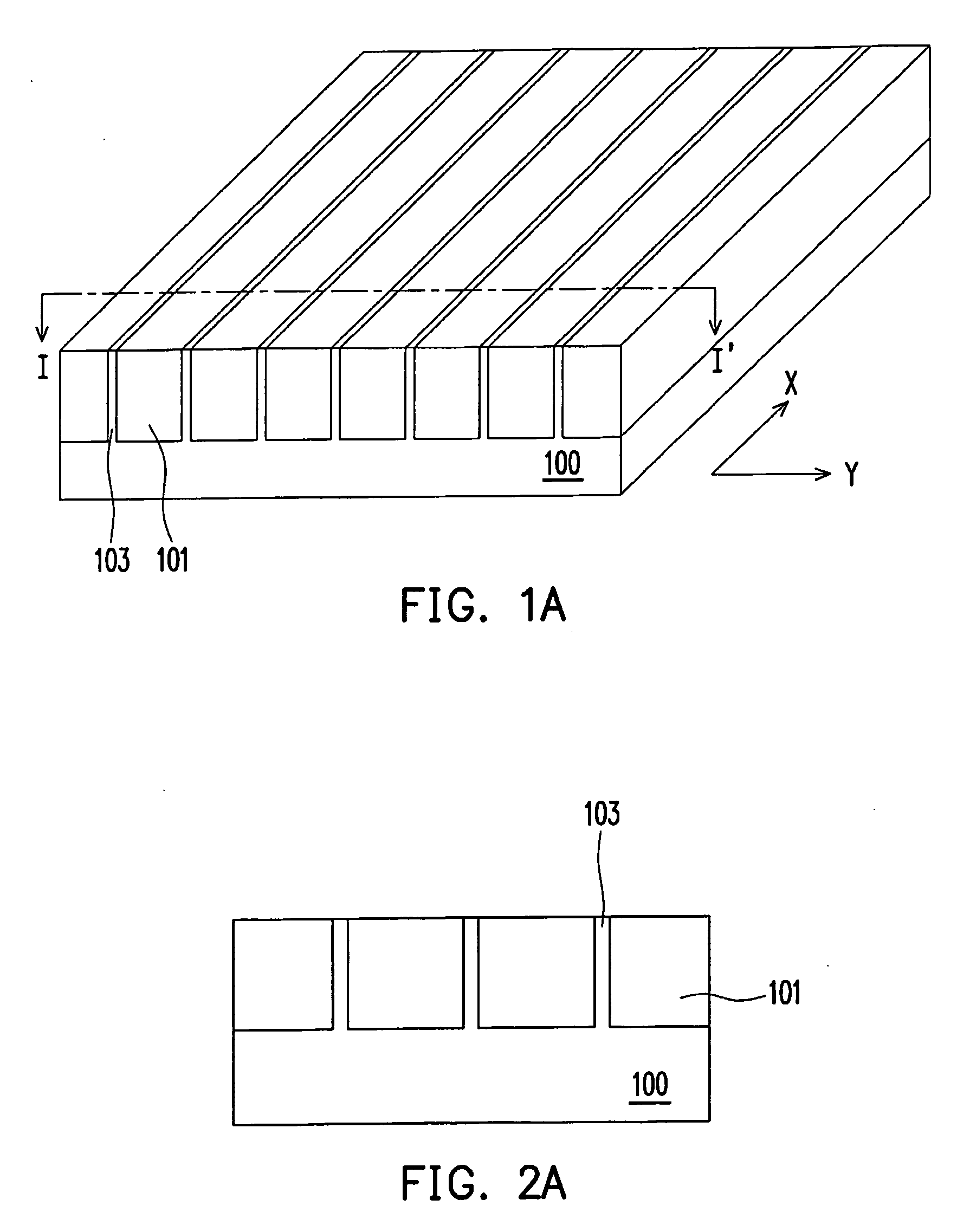
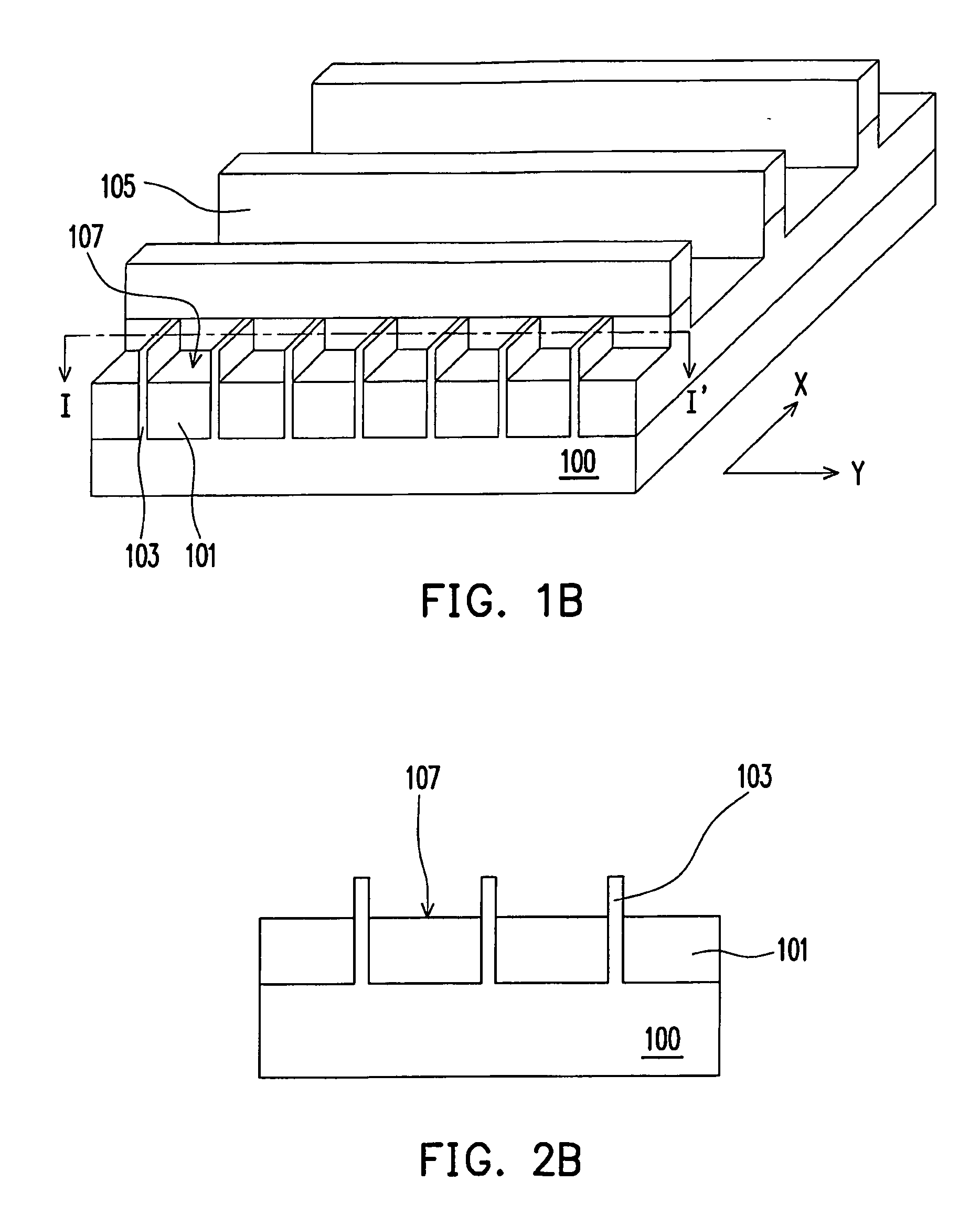
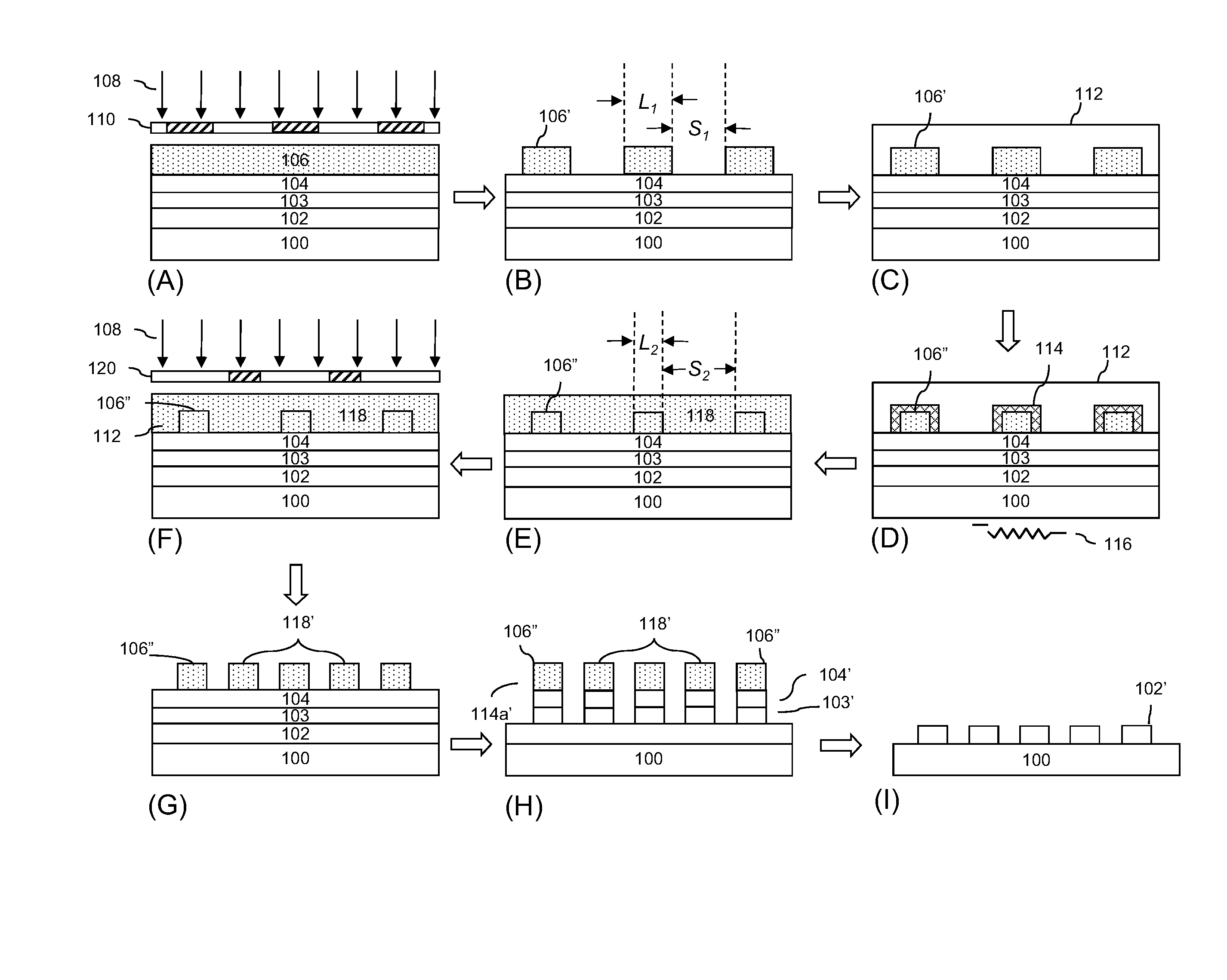
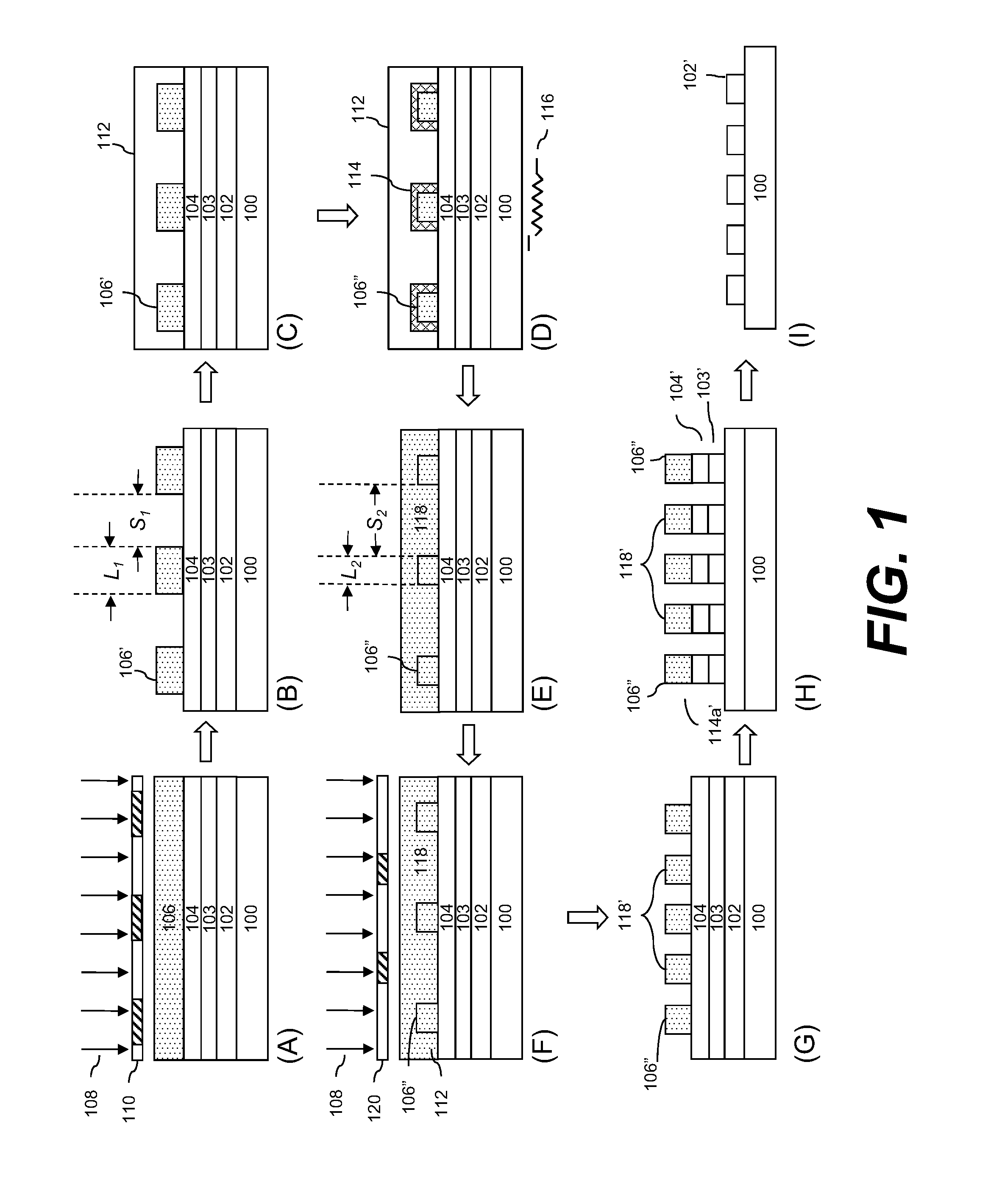
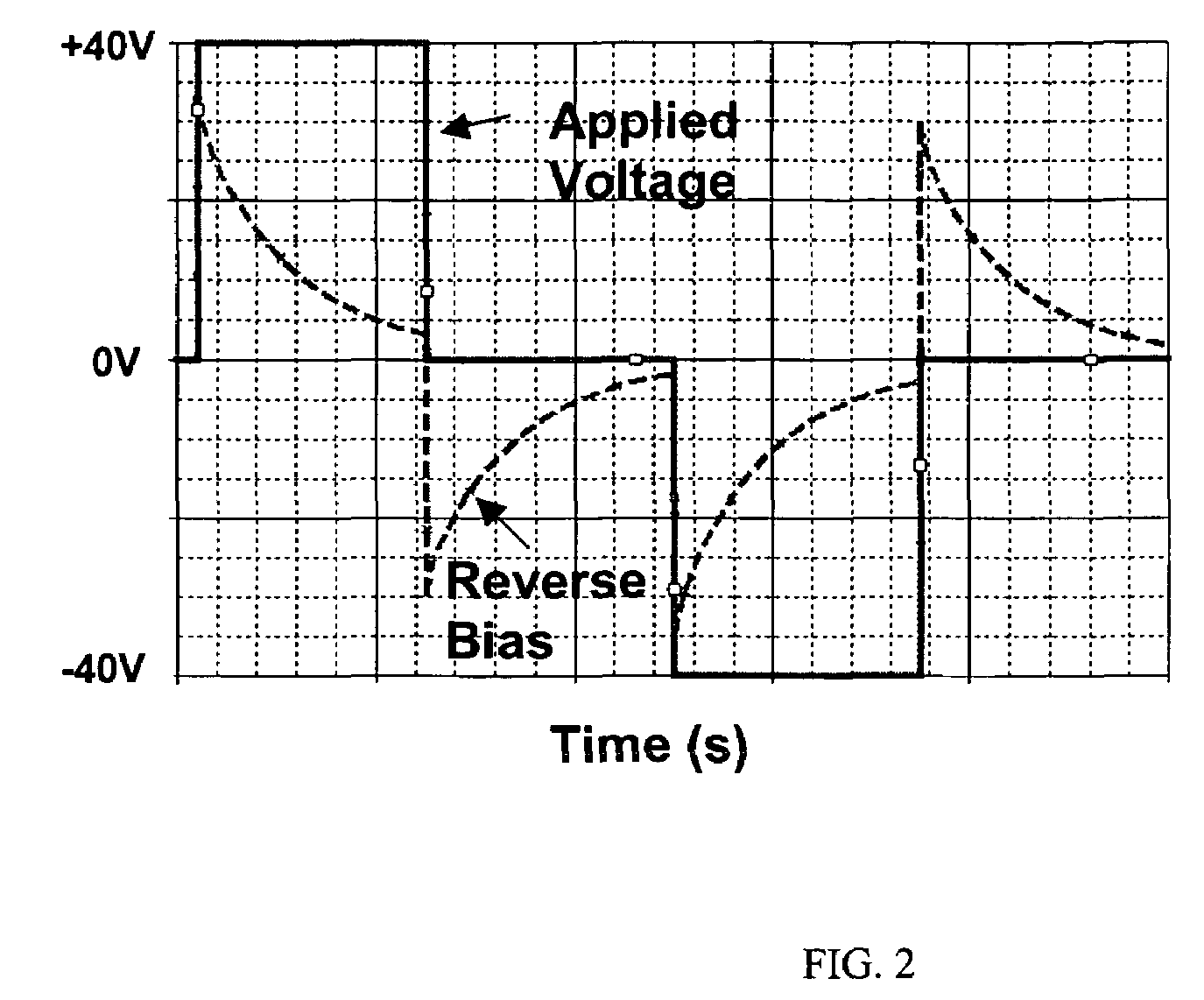
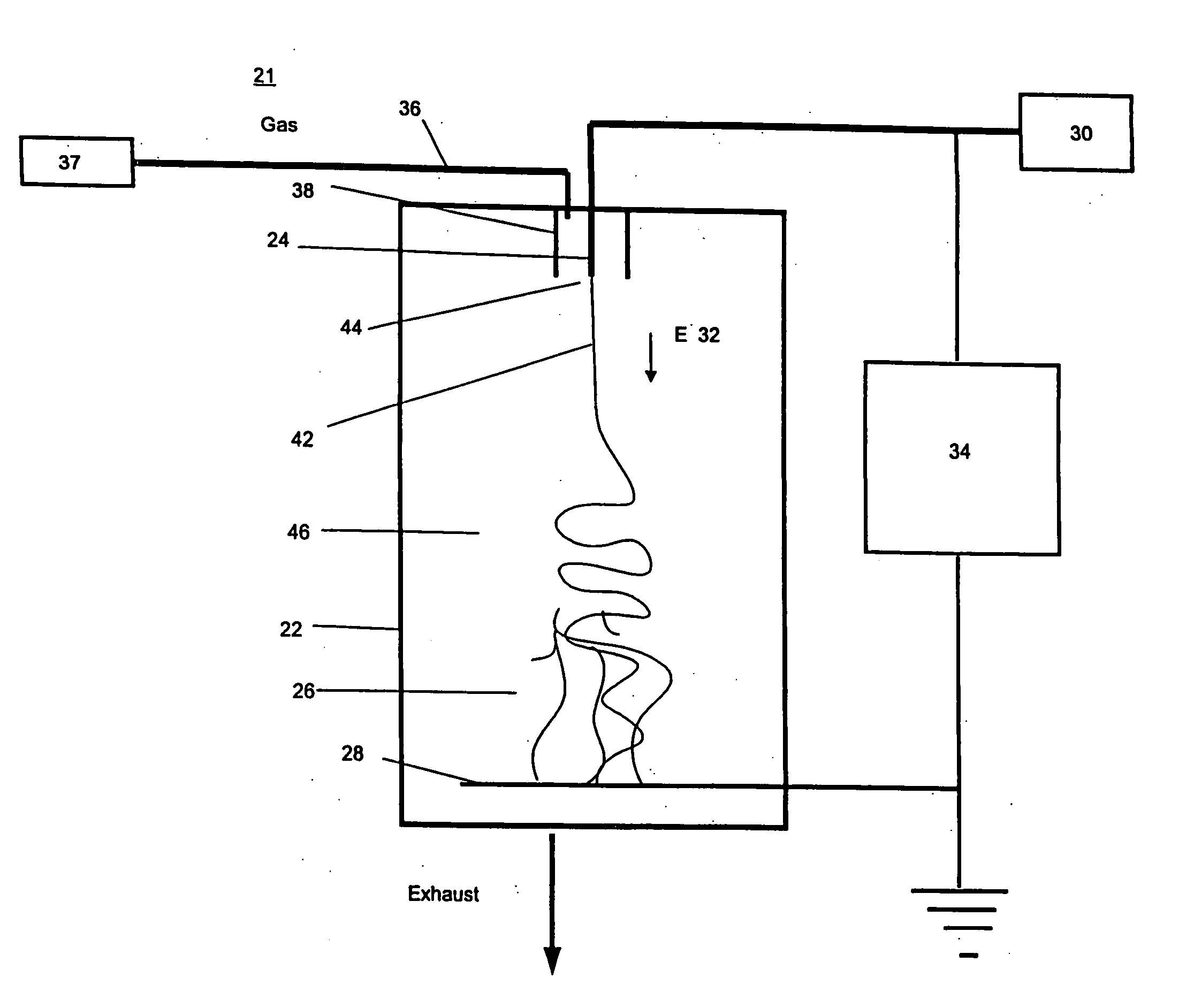
[method of fabricating polysilicon film]
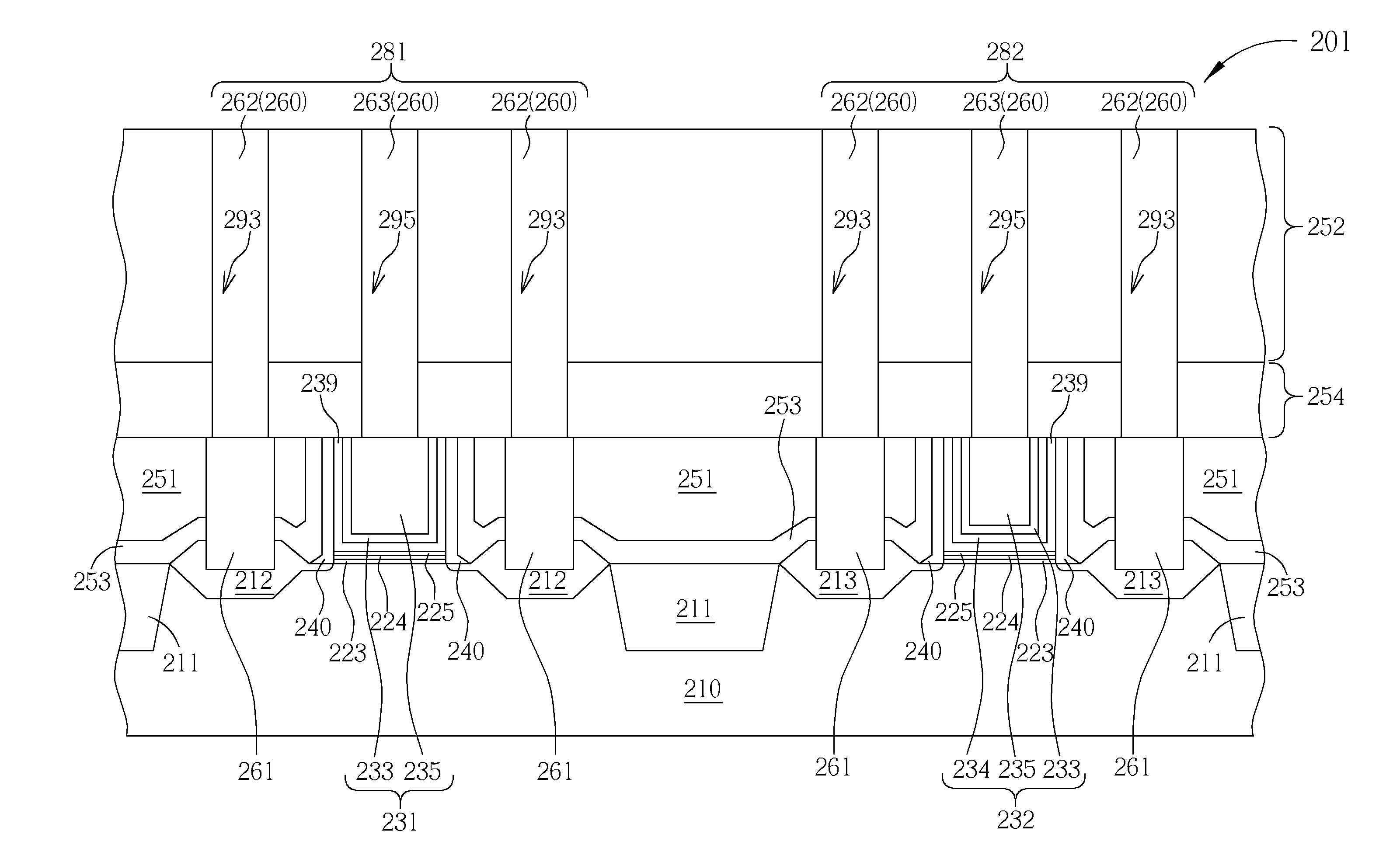
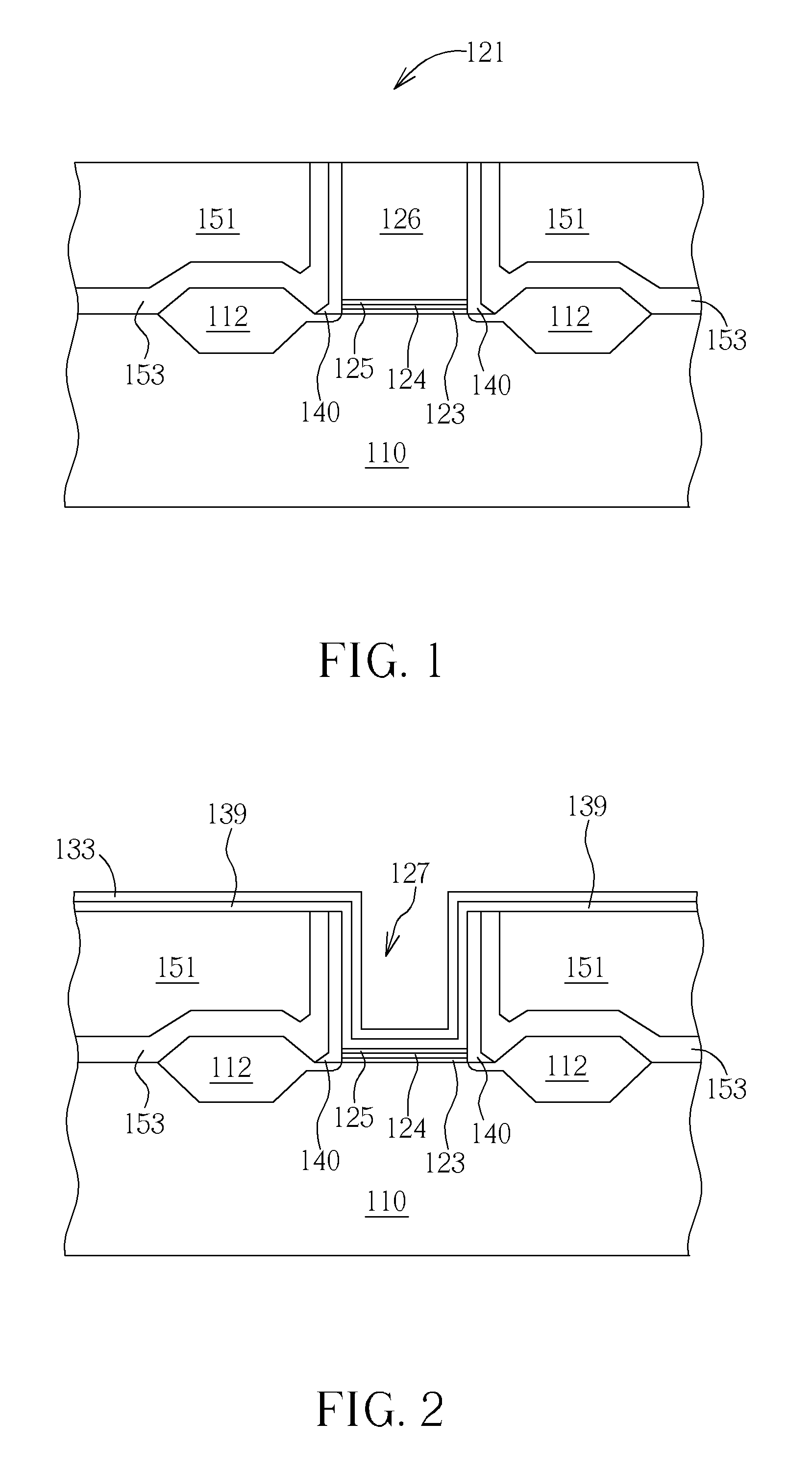
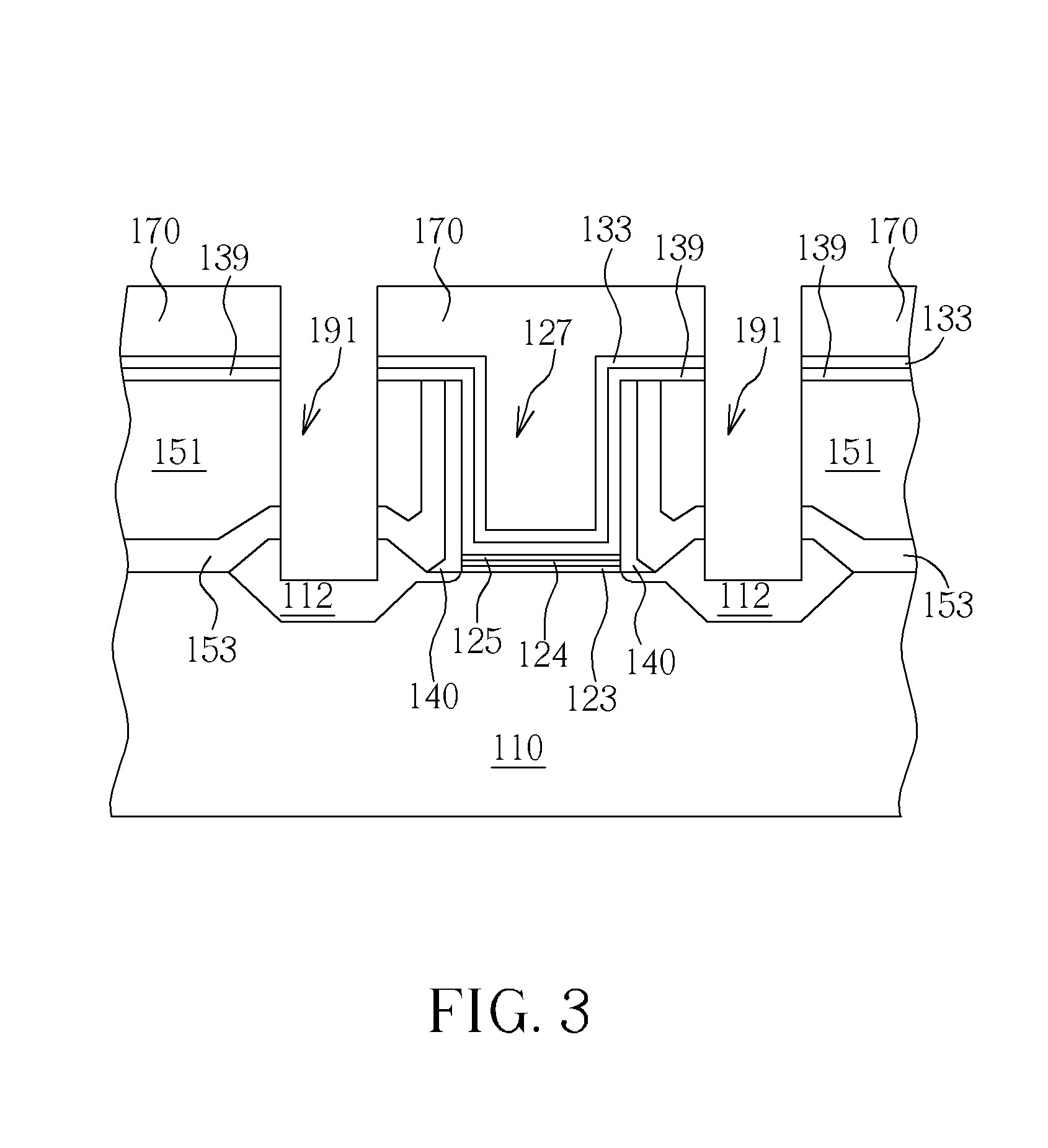
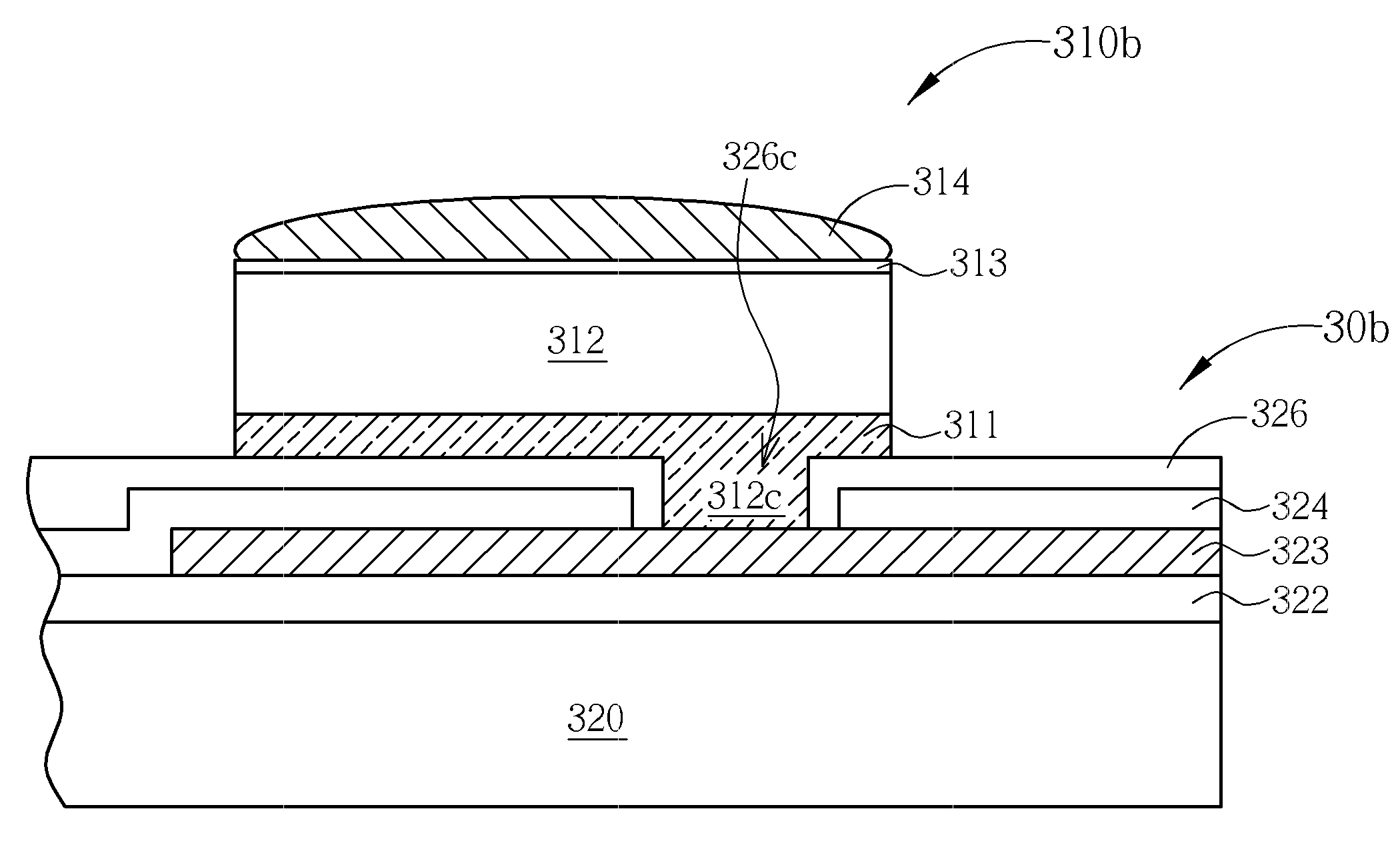
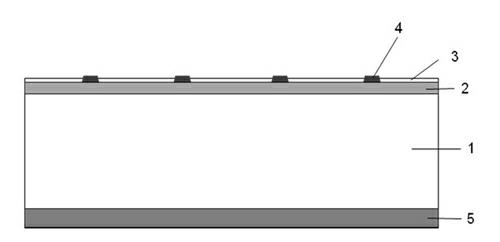
InactiveUS20050019994A1Improve throughputIncreased process windowSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAmorphous siliconOptoelectronics
A method of fabricating polycrystalline silicon layer of TFT is provided. The method includes sequentially forming an insulating layer, a first amorphous silicon layer, and a cap layer on a substrate. A laser annealing is performed to transform the first amorphous silicon layer to a first polycrystalline silicon layer, wherein at least one hole is formed in the amorphous silicon layer during the laser annealing process. Thereafter, the cap layer is removed. A portion of the insulating layer exposed within the hole is removed to form a second opening. A second amorphous silicon layer is formed over the first polycrystalline silicon layer filling the second opening. Finally a second annealing is performed to transform the second amorphous silicon layer to a second polycrystalline silicon layer.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
Method of forming a magnetic tunnel junction structure
ActiveUS20090227045A1Good etchingReduce erosionMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringTunnel junction
In a particular illustrative embodiment, a method of forming a magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) device is disclosed that includes forming a trench in a substrate. The method further includes depositing a magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) structure within the trench. The MTJ structure includes a bottom electrode, a fixed layer, a tunnel barrier layer, a free layer, and a top electrode. The method also includes planarizing the MTJ structure. In a particular example, the MTJ structure is planarized using a Chemical Mechanical Planarization (CMP) process.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Preparation method of double-sided passivated crystalline silicon solar cell
InactiveCN101937944APrevent escapeAdjustable bandgapSemiconductor devicesP type siliconMicrocrystalline silicon
The invention discloses a preparation method of a double-sided passivated crystalline silicon solar cell, belonging to the technical field of photovoltaic power generation. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: firstly, respectively carrying out surface precleaning and surface texturing on P-shaped single crystal silicon and a polycrystalline silicon wafer by adopting an alkaline solution and an acid solution; secondly, diffusing by using phosphorus oxychloride as a diffusion source to form a PN junction; thirdly, removing a phosphosilicate glass on the surface of the silicon wafer by adopting a chemical wet method, and etching the edge of the silicon wafer by adopting a plasma; fourthly, preparing a silicon nitride film on the surface of an emitting region of a P-type silicon wafer by adopting a plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition method; fifthly, preparing a mixed phase film material of hydrogenated microcrystalline silicon and amorphous silicon by adopting a hot filament chemical vapor deposition method, depositing a film at one side of the P-type silicon wafer, and passivating the defects and a dangling bond on the surface of the P-type silicon wafer; and sixthly, sintering a screen printing back electrode and a screen printing positive electrode to form the solar cell. The invention lowers the probability of compounding photo-generated minority carriers on the back surface, enhances the long-wave light quantum efficiency and creates the conditions of transportation and collection of the photo-generated carriers.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Semiconductor device and fabricating method thereof
ActiveUS20130161754A1Process yield and quality may be enhanceImprove process windowTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWork functionContact hole
A manufacturing method of a semiconductor device includes the following steps. First, a substrate is provided. At least one gate trench and a first inter-layer dielectric layer are formed on the substrate. A work function metallic layer is then formed in the gate trench. A first contact hole is then formed in the first inter-layer dielectric layer. A main conductive layer is formed in the gate trench and the first contact hole simultaneously.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Etch chamber with dual frequency biasing sources and a single frequency plasma generating source
InactiveUS20070020937A1Increased process windowExpand coverageElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDual frequencyHigh frequency power
A method and apparatus for selectively controlling a plasma in a processing chamber during wafer processing. The method includes providing process gasses into the chamber over a wafer to be processed, and providing high frequency RF power to a plasma generating element and igniting the process gases into the plasma. Modulated RF power is coupled to a biasing element, and wafer processing is performed according to a particular processing recipe. The apparatus includes a biasing element disposed in the chamber and adapted to support a wafer, and a plasma generating element disposed over the biasing element and wafer. A first power source is coupled to the plasma generating element, and a second power source is coupled to the biasing element. A third power source is coupled to the biasing element, wherein the second and third power sources provide a modulated signal to the biasing element.
Owner:CHEN JIN YUAN +2
Patterning method for OLEDs
ActiveUS8940568B2Increased process windowUltra-rapid growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOrganic layerOrganic vapor
Owner:UNIVERSAL DISPLAY
Determining Source Patterns for Use in Photolithography
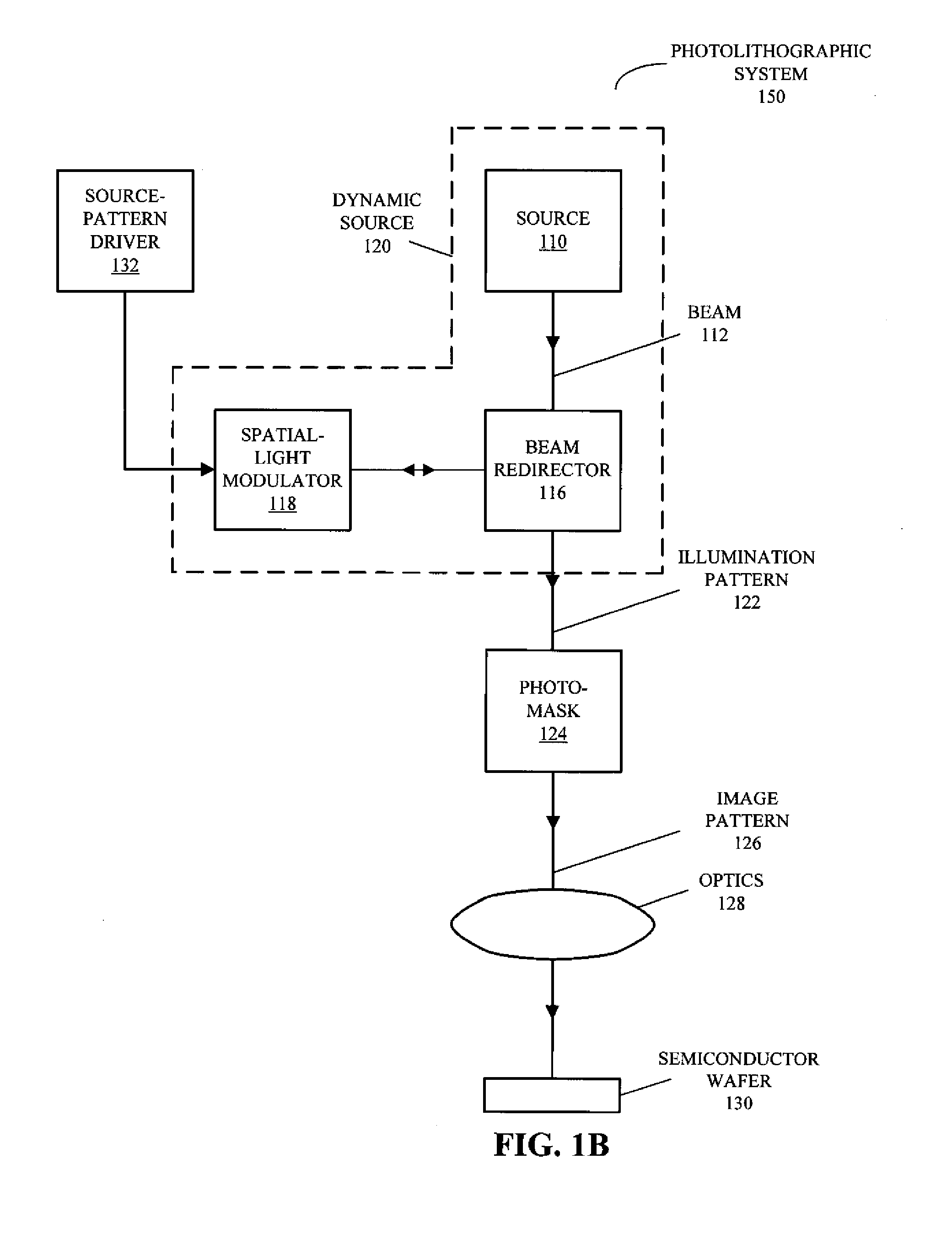
ActiveUS20110022994A1Increased process windowPhotomechanical apparatusOriginals for photomechanical treatmentPattern recognitionLithographic artist
Embodiments of a computer system, a process, a computer-program product (i.e., software), and a data structure or a file for use with the computer system are described. These embodiments may be used to determine or generate source patterns that define illumination patterns on photo-masks during a photolithographic process. Moreover, a given source pattern may be determined concurrently with an associated mask pattern (to which a given photo-mask corresponds) or sequentially (i.e., either the given source pattern may be determined before the associated mask pattern or vice versa.). During the determining, the given source pattern may be represented using one or more level-set functions. Additionally, the source pattern may be determined using an Inverse Lithography (ILT) calculation.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Method for manufacturing silicon carbide semicondutor device having trench gate structure
InactiveUS20090311839A1Increased process windowSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesTrench gateImpurity
A manufacturing method of a SiC device includes: forming a drift layer on a substrate having an orientation tilted from a predetermined orientation with an offset angle; obliquely implanting a second type impurity with a mask on the drift layer so that a deep layer is formed in the drift layer, wherein the impurity is implanted to cancel the offset angle; forming a base region on the deep layer and the drift layer; implanting a first type impurity on the base region so that a high impurity source region is formed; forming a trench having a bottom shallower than the deep layer on the source region to reach the drift layer; forming a gate electrode in the trench via a gate insulation film; forming a source electrode on the source region and the base region; and forming a drain electrode on the substrate.
Owner:DENSO CORP
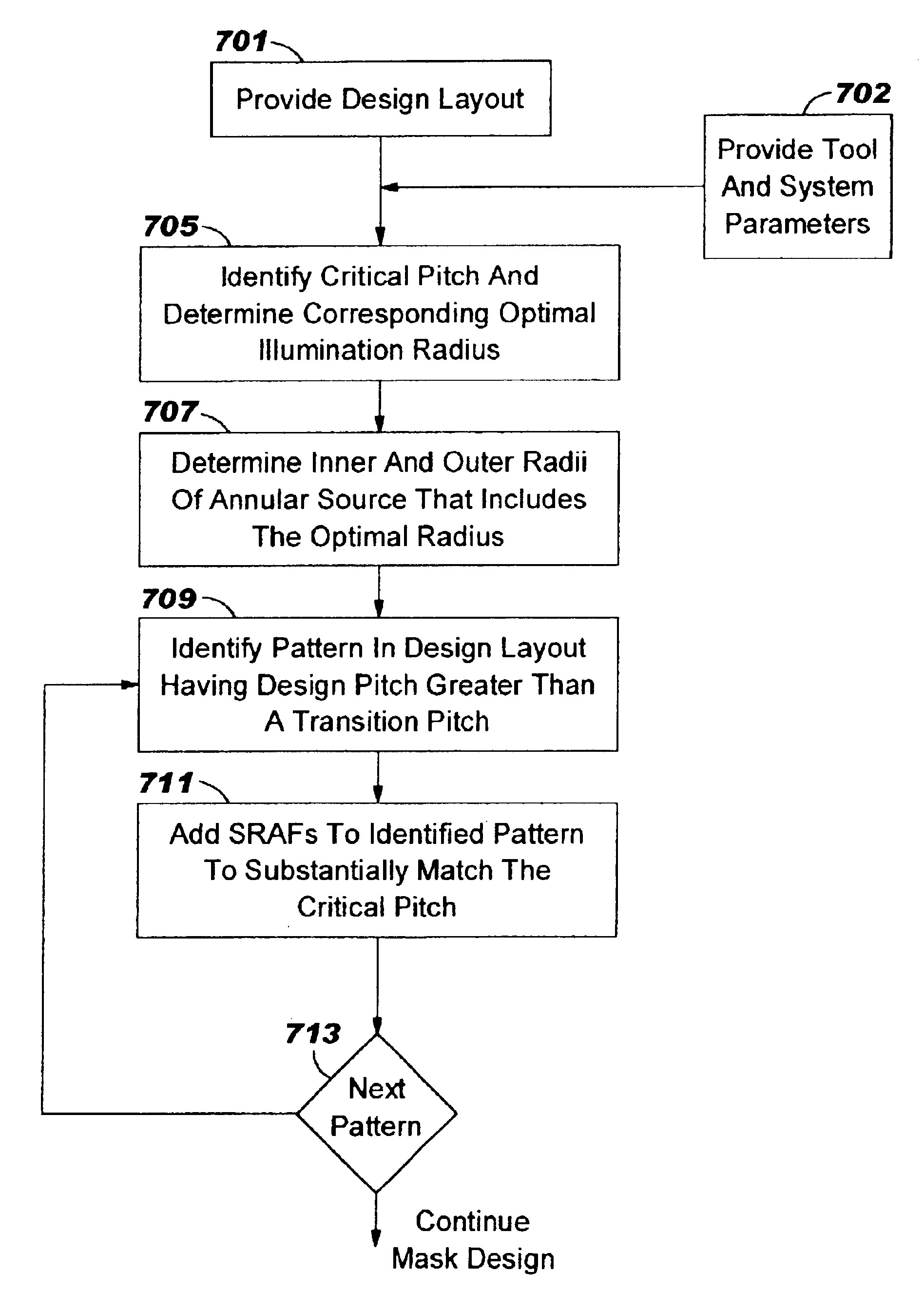
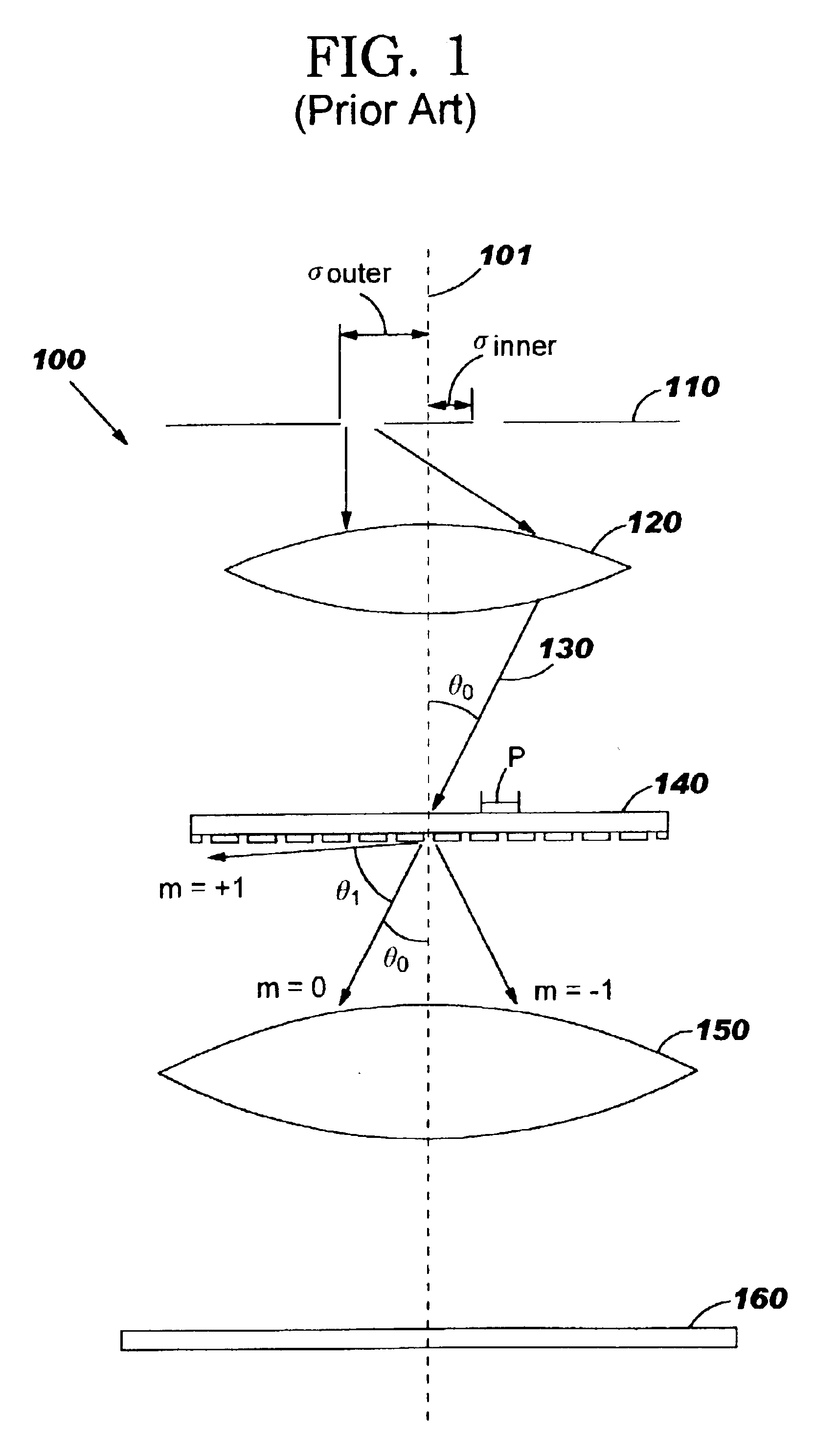
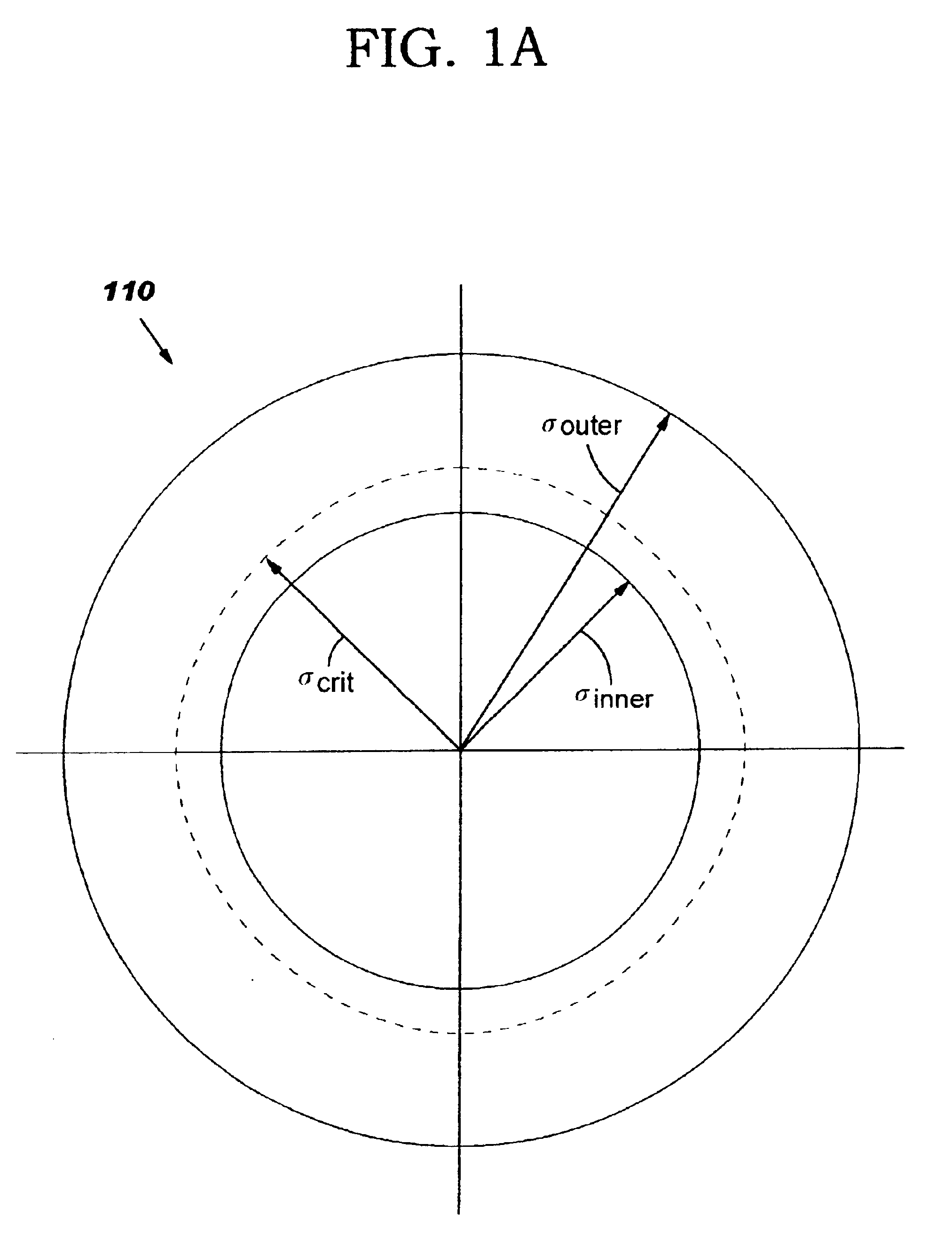
Pitch-based subresolution assist feature design
InactiveUS6964032B2Maximizes process windowFast and cost-effectivePhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringFeature design
A method of designing a mask for imaging an integrated circuit (IC) design layout is provided to efficiently configure subresolution assist features (SRAFs) corresponding to an optimally configured annular illumination source of a lithographic projection system. A critical pitch is identified for the IC design, and optimal inner and outer radial coordinates of an annular illumination source are determined so that the resulting image projected through the mask will be optimized for the full range of pitches in the design layout. A relationship is provided for determining an optimal inner radius and outer radius for the annular illumination source. The number and placement of SRAFs are added to the mask design so that the resulting range of pitches substantially correspond to the critical pitch. The method of configuring SRAFs so that the image will have optimal characteristics, such as good contrast and good depth of focus, is fast.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
MIM capacitor structure and method of fabrication
ActiveUS20050112836A1Reduce number of maskReduce processing costTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringMetal-insulator-metal
A method of forming a metal-insulator-metal (MIM) capacitor wherein a plate of a MIM capacitor is formed in the entire thickness of a metallization layer of a semiconductor device. At least one thin conductive material layer is disposed within the material of the metallization layer to reduce the surface roughness of the metallization layer, thus improving the reliability of the MIM capacitor. The thin conductive material layer may comprise TiN, TaN, or WN and may alternatively comprise a barrier layer disposed over or under the TiN, TaN, or WN. One plate of the MIM capacitor is patterned using the same mask that is used to pattern conductive lines in a metallization layer, thus reducing the number of masks that are required to manufacture the MIM capacitor.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Low temperature carbon rich oxy-nitride for improved RIE selectivity
InactiveUS6486015B1Minimize diffusionGood choiceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCarbonizationNitrogen oxide
Reactive ion etch (RIE) selectivity during etching of a feature nearby embedded structure is improved by using a silicon oxynitride layer formed with carbonization throughout layer.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
![[method of fabricating polysilicon film] [method of fabricating polysilicon film]](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/62be3fe2-94cc-44cd-a381-5c1ce28c1440/US20050019994A1-20050127-D00000.png)
![[method of fabricating polysilicon film] [method of fabricating polysilicon film]](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/62be3fe2-94cc-44cd-a381-5c1ce28c1440/US20050019994A1-20050127-D00001.png)
![[method of fabricating polysilicon film] [method of fabricating polysilicon film]](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/62be3fe2-94cc-44cd-a381-5c1ce28c1440/US20050019994A1-20050127-D00002.png)