Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
699results about How to "Reduce aspect ratio" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
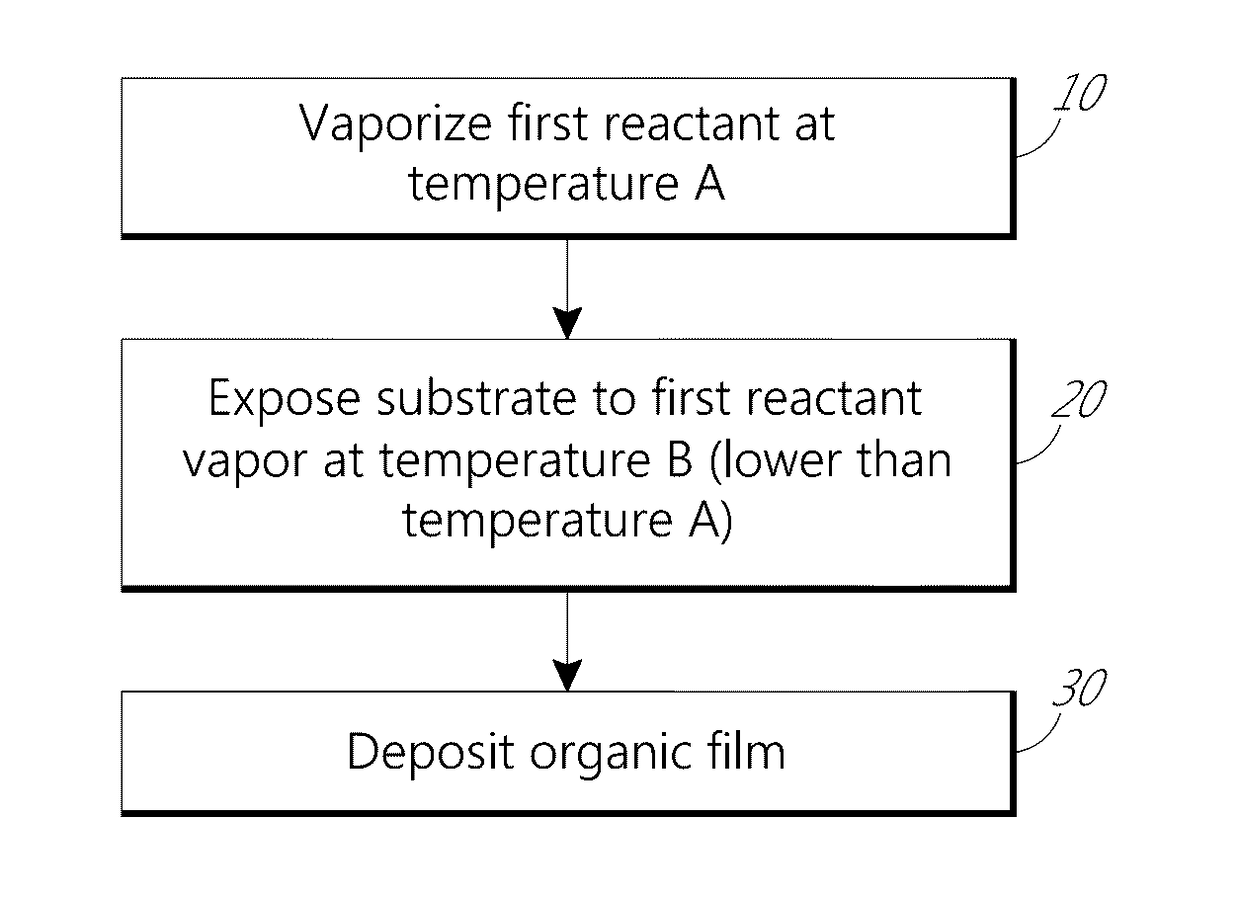
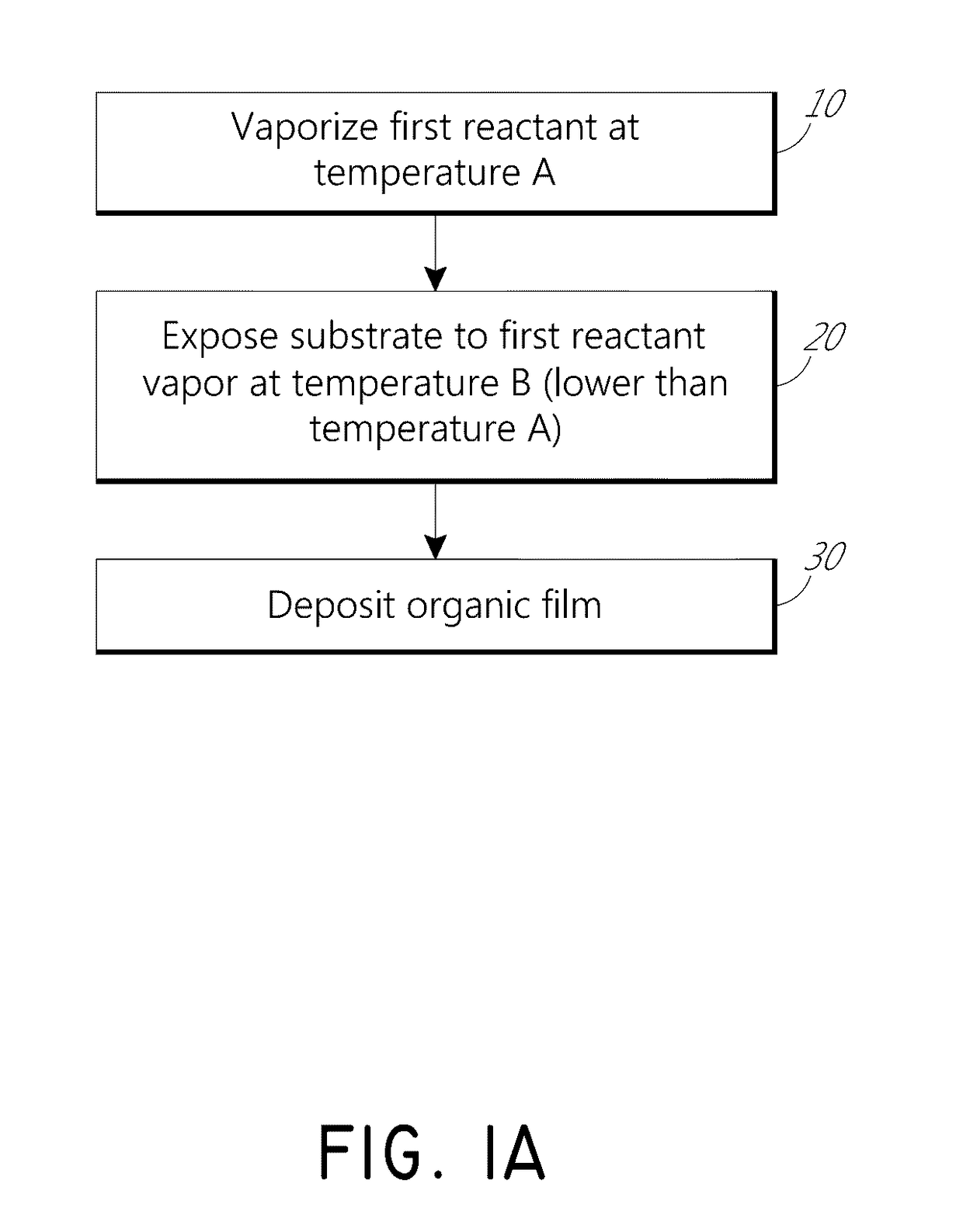
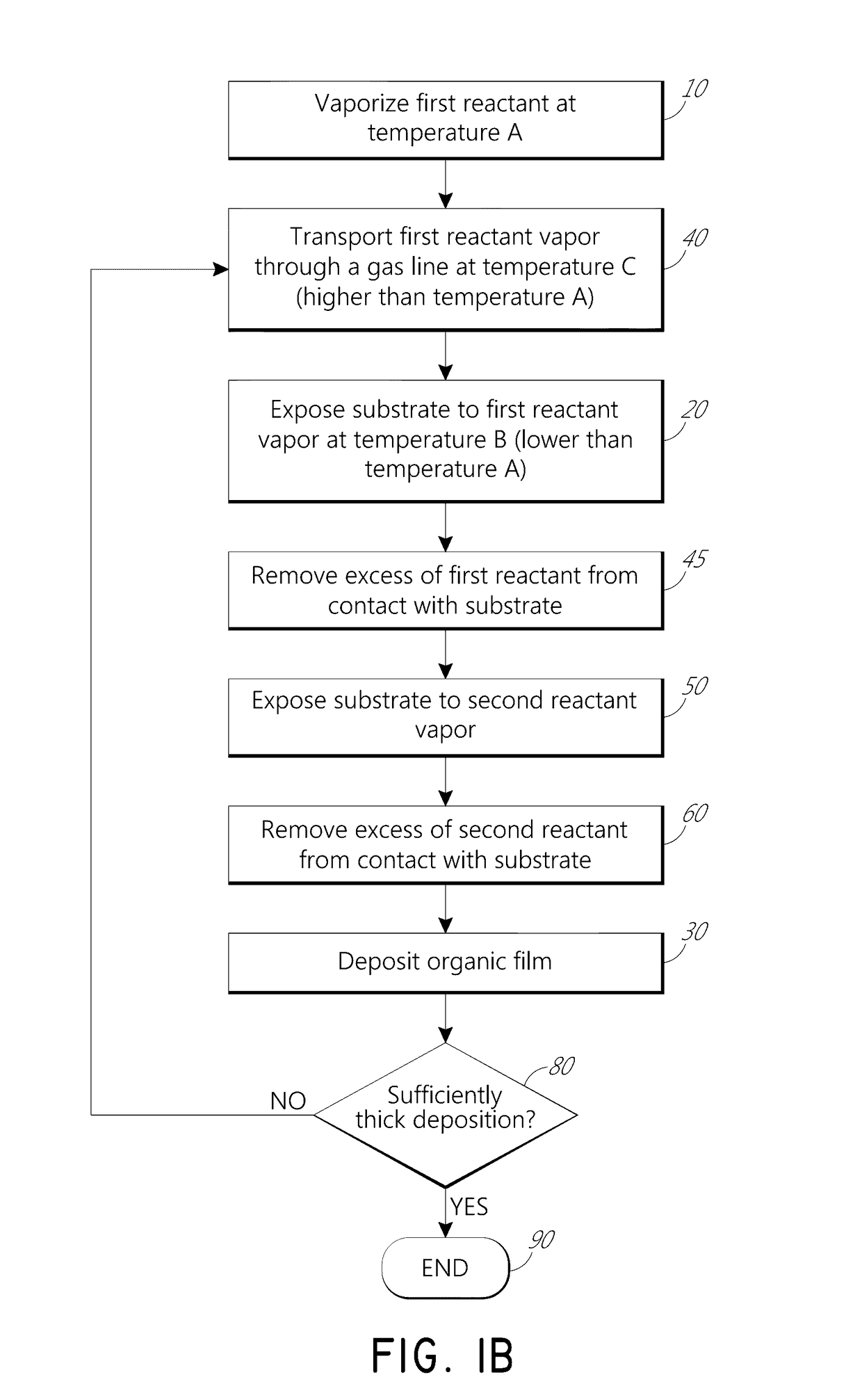
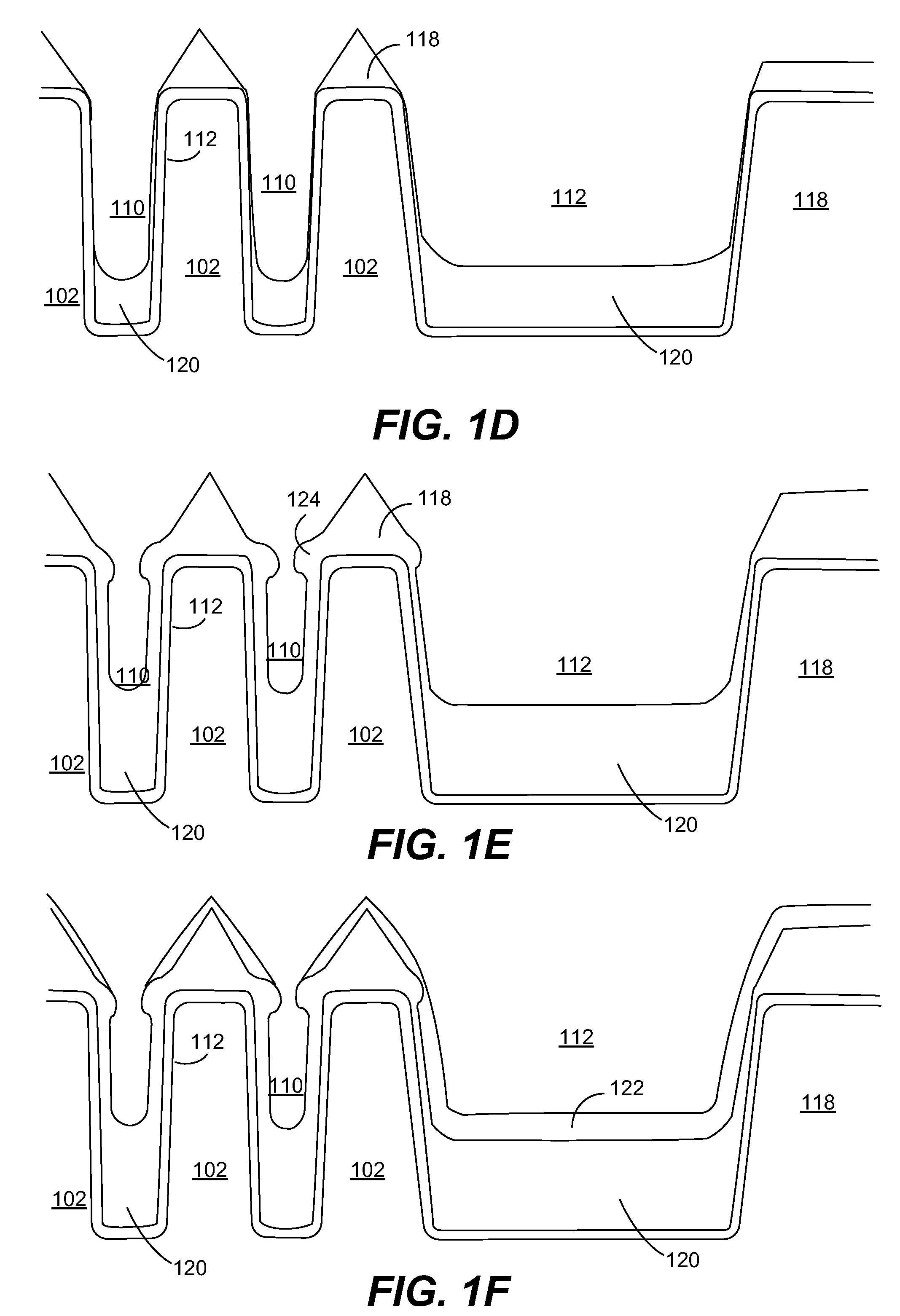
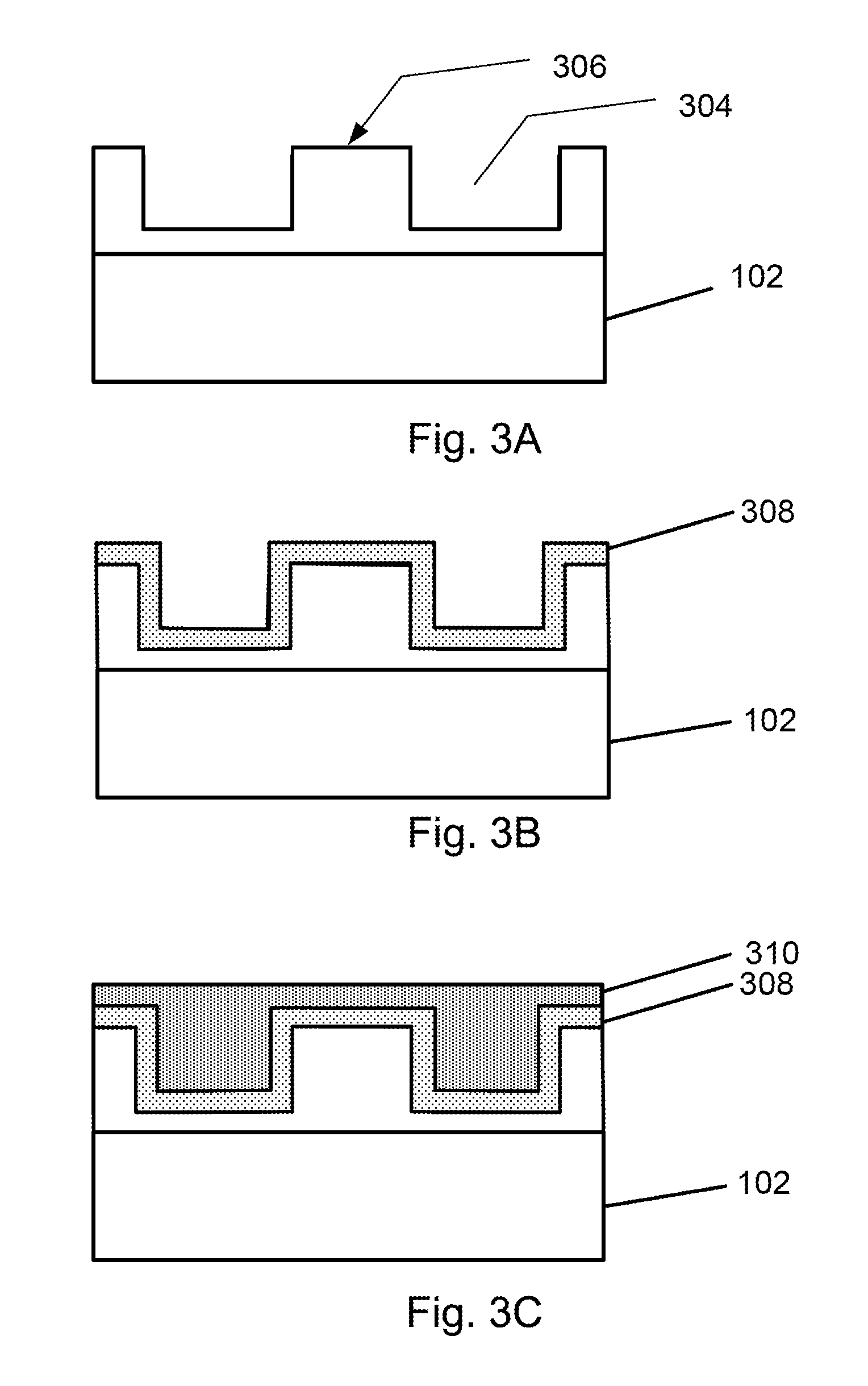
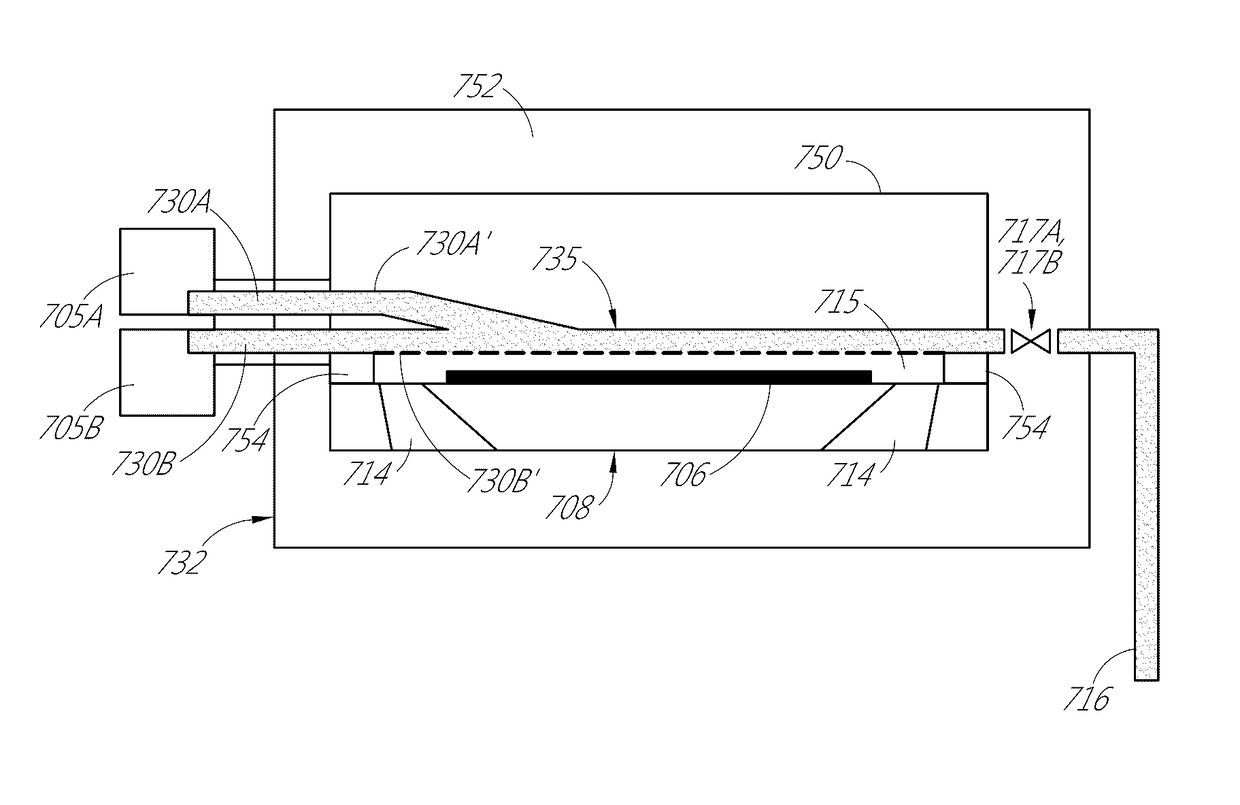
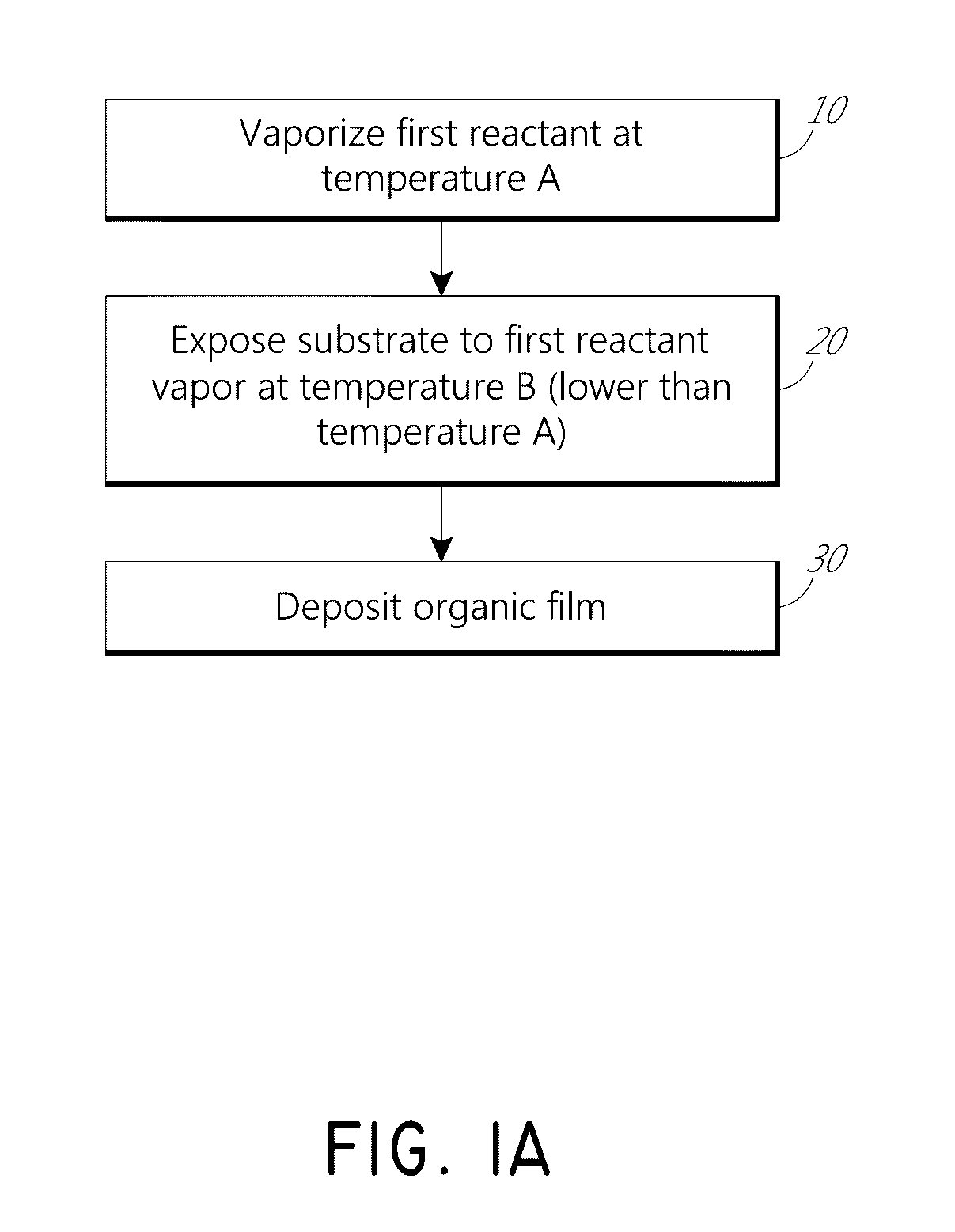
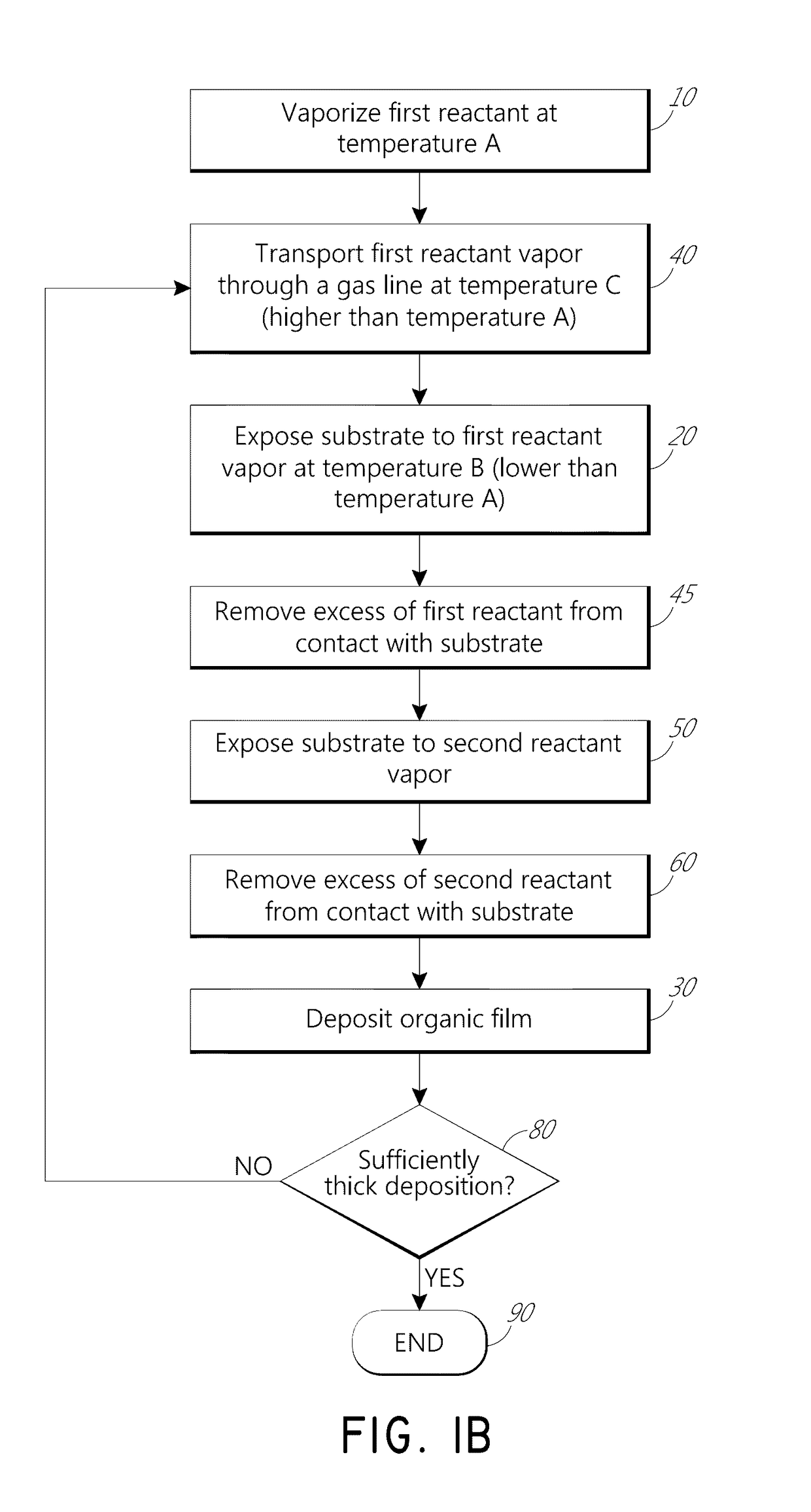
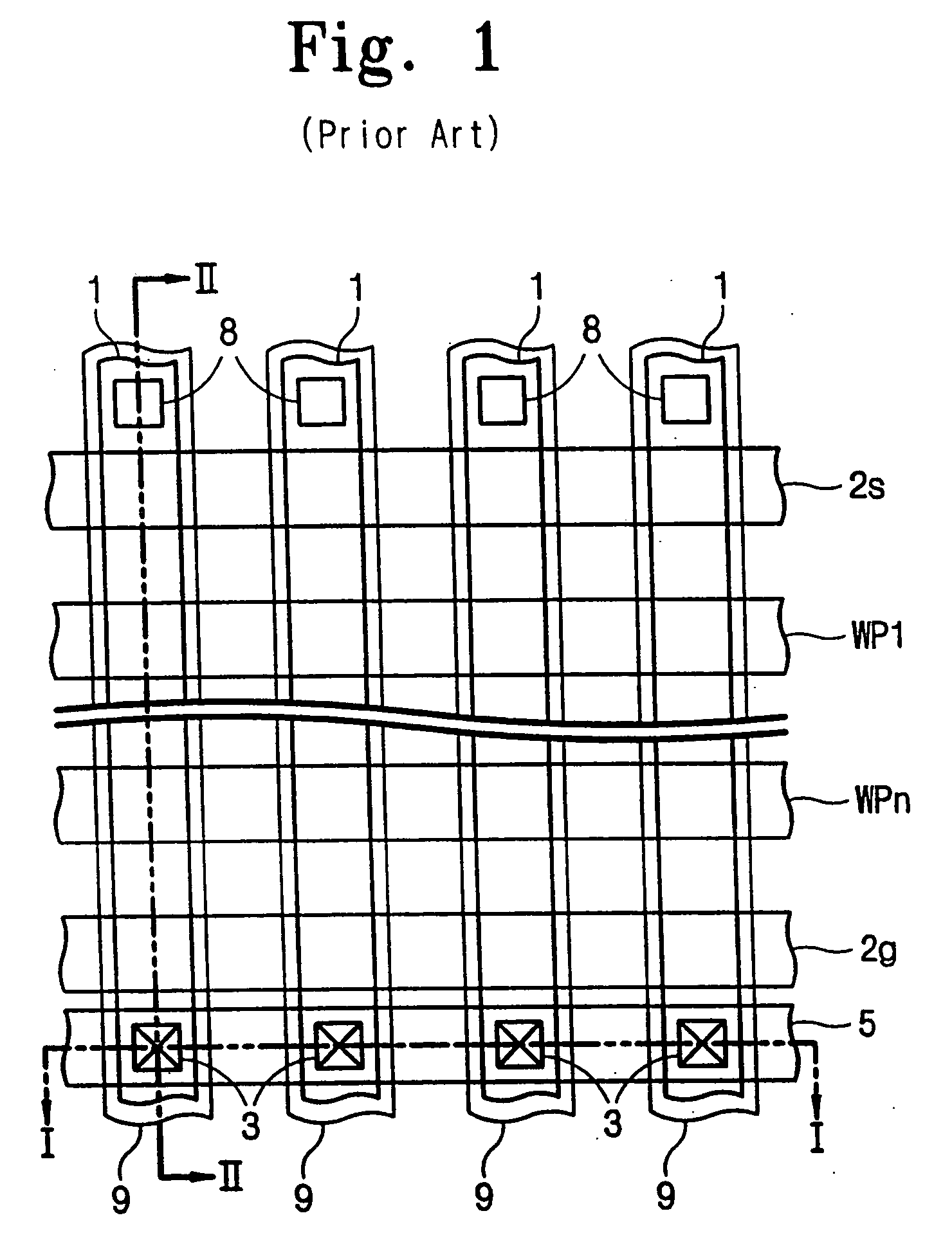
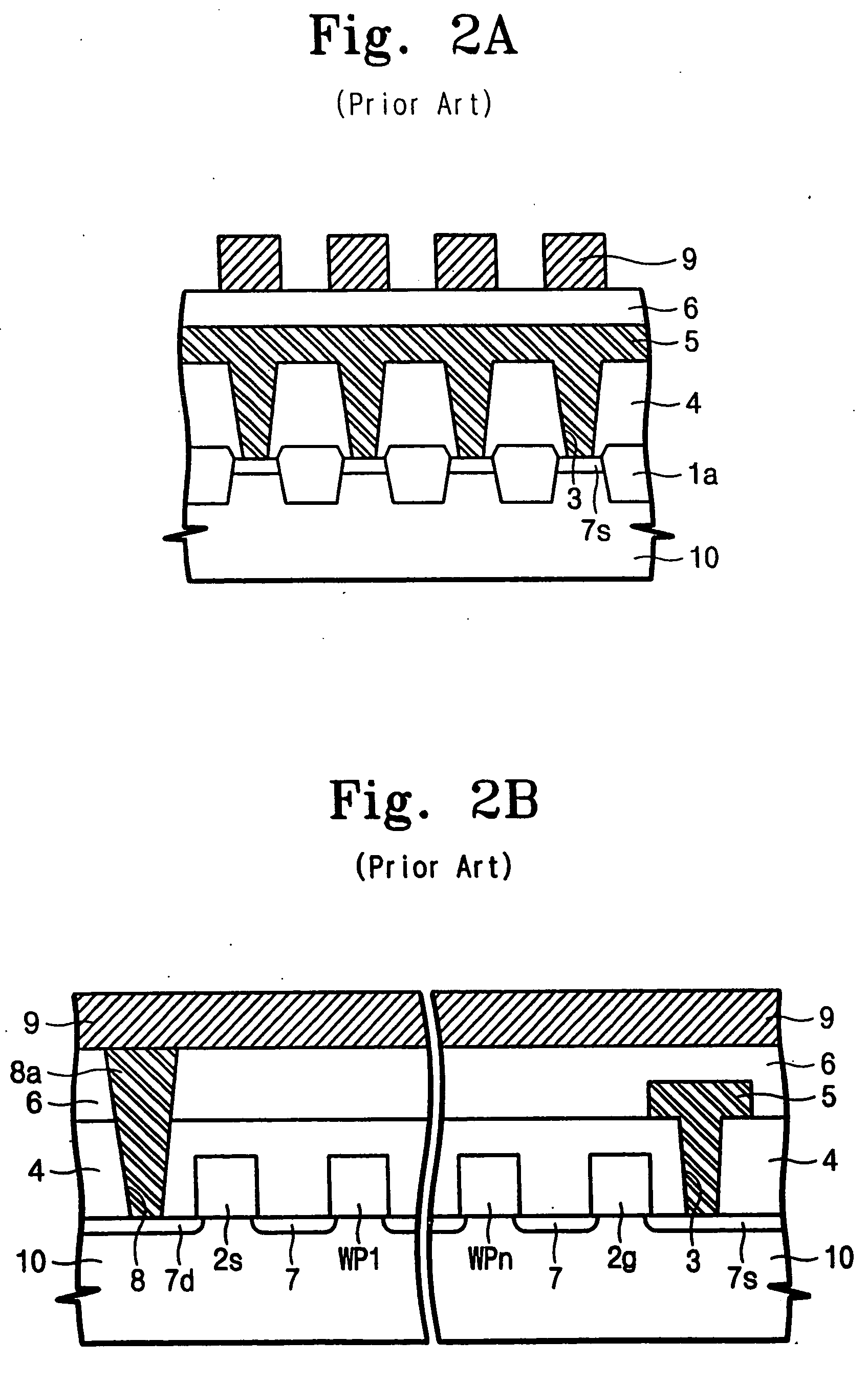
Vapor phase deposition of organic films
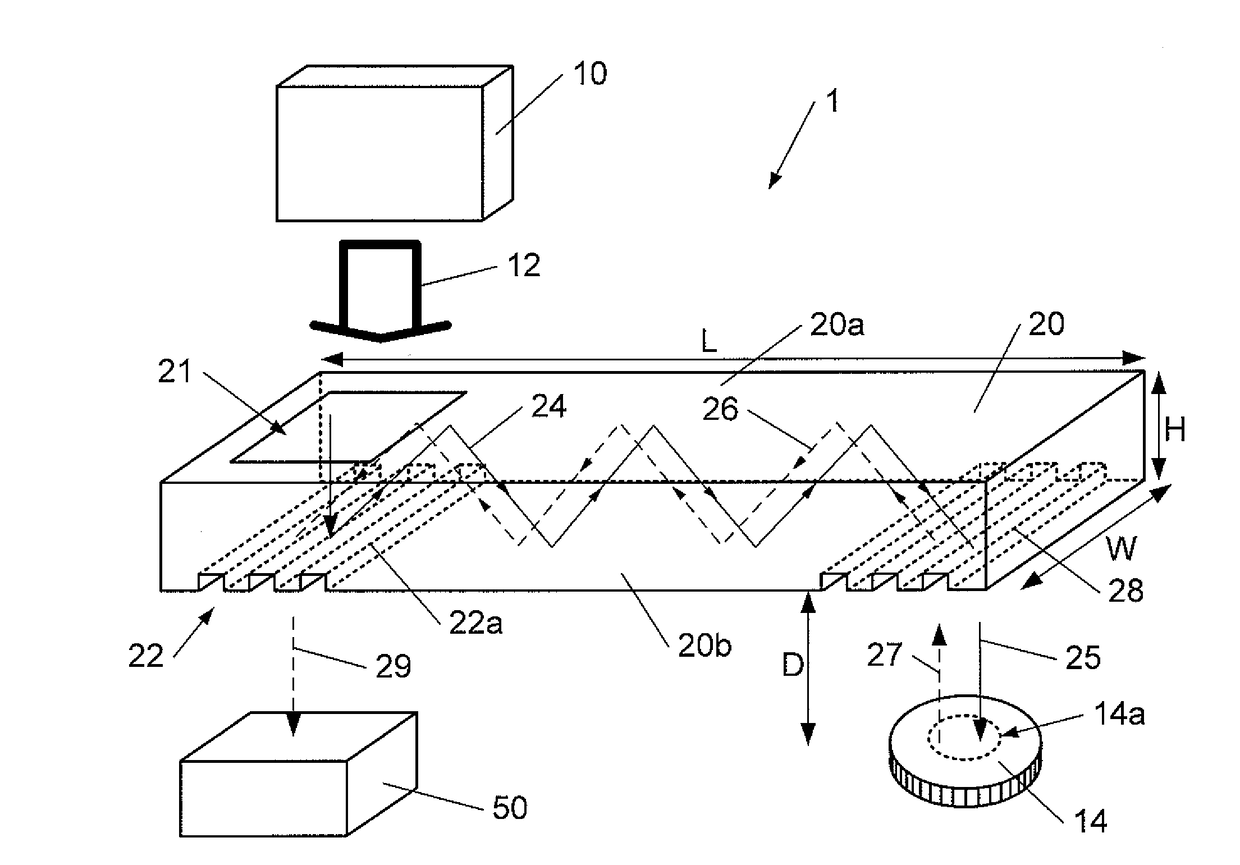
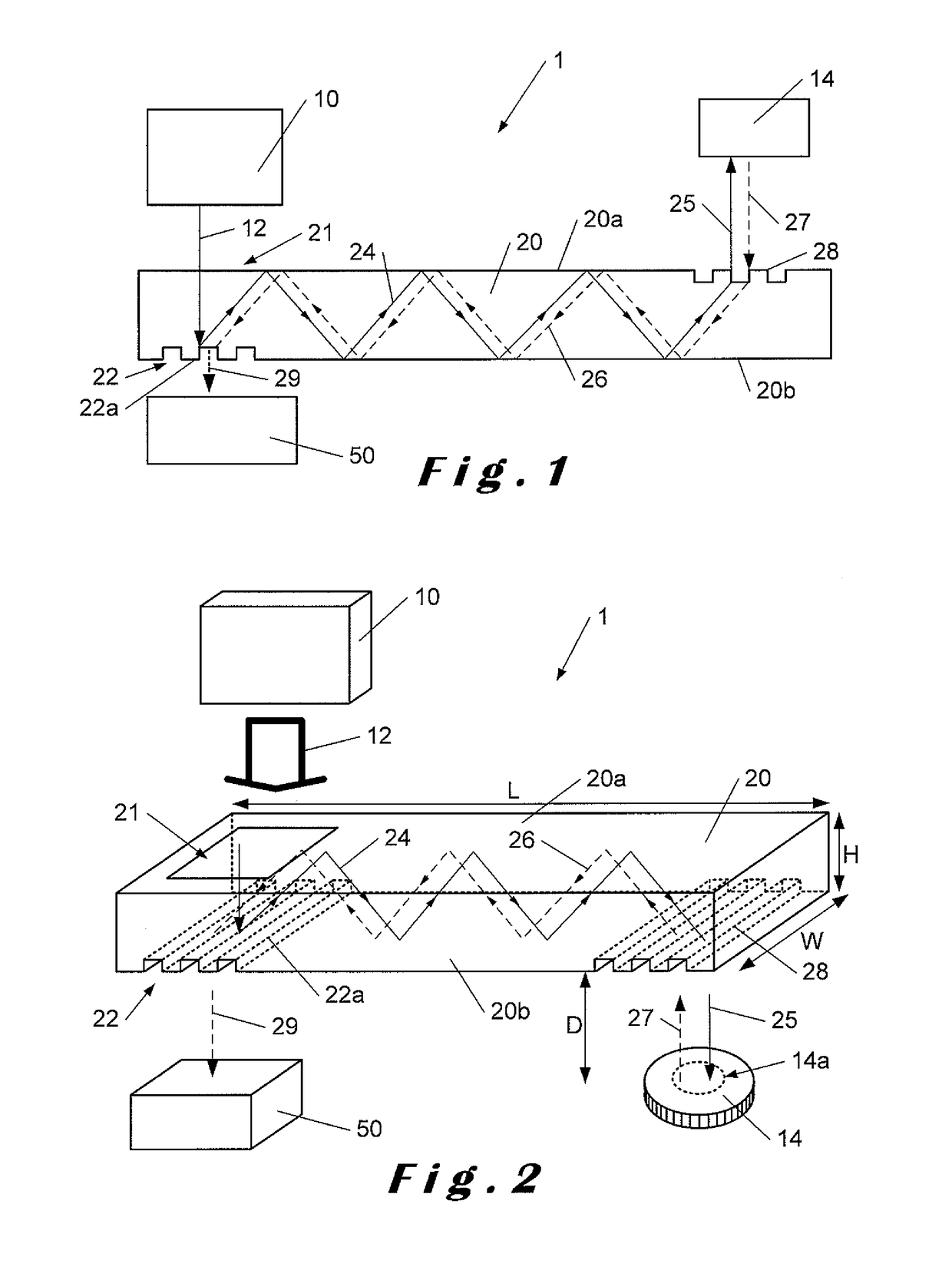
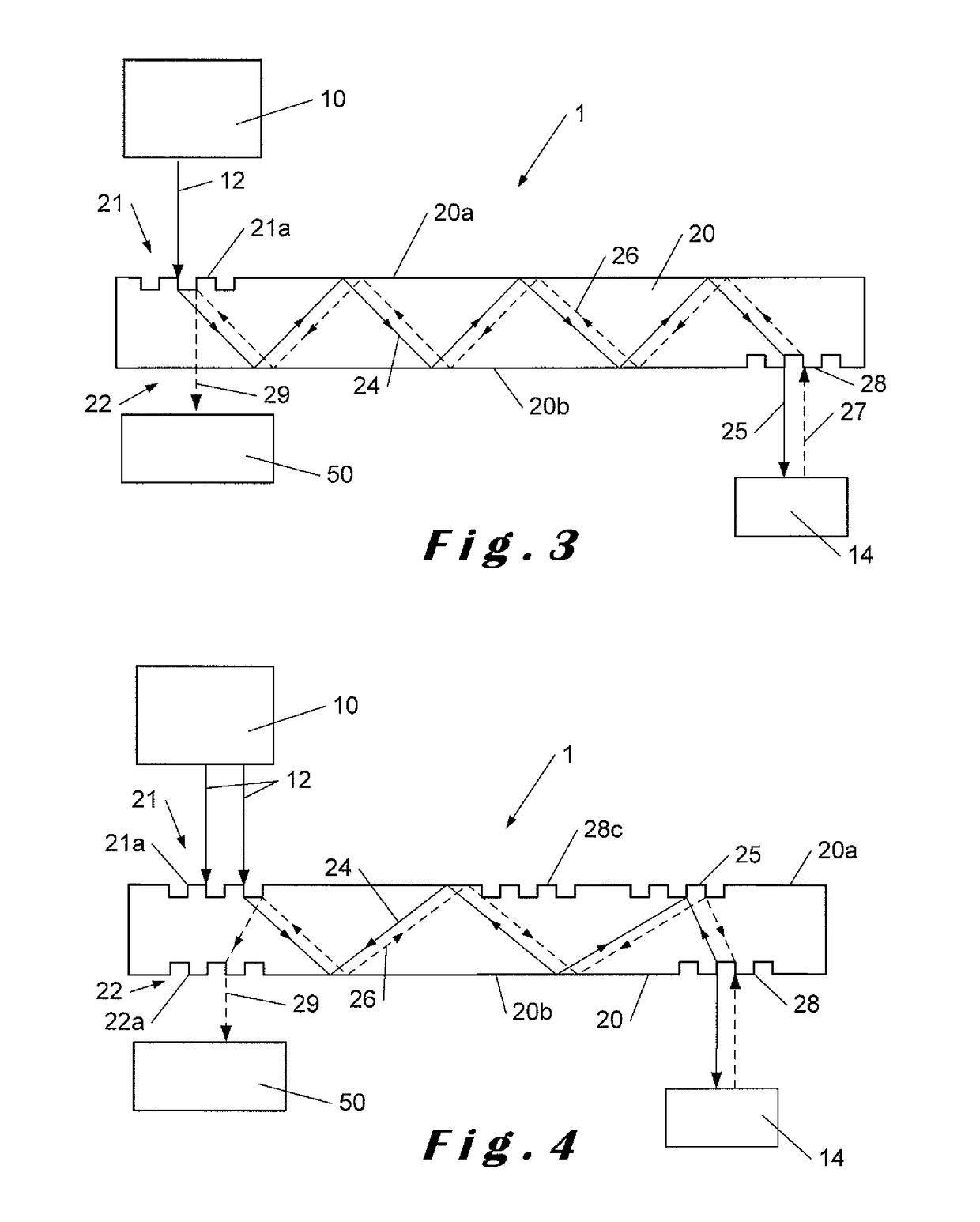
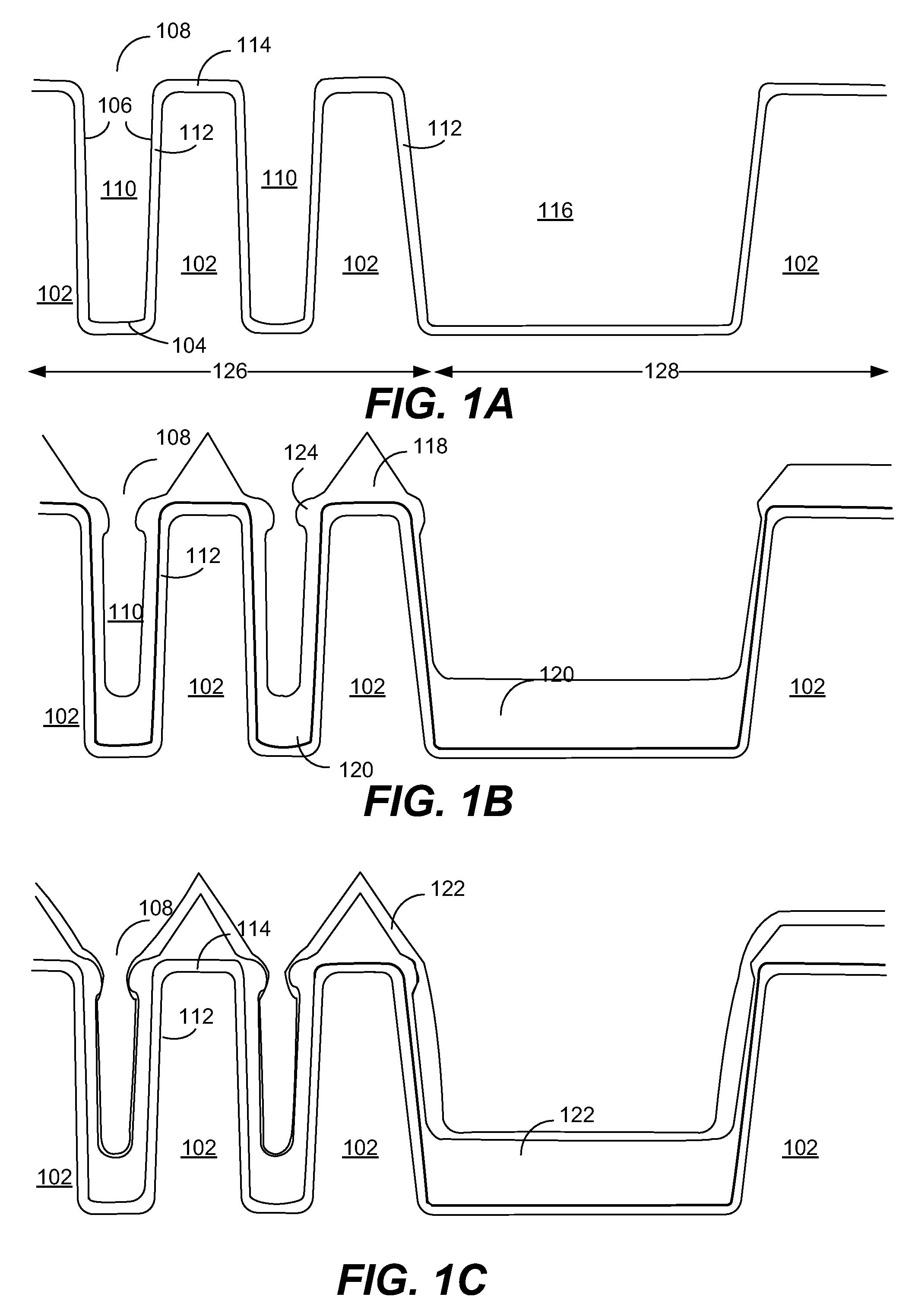
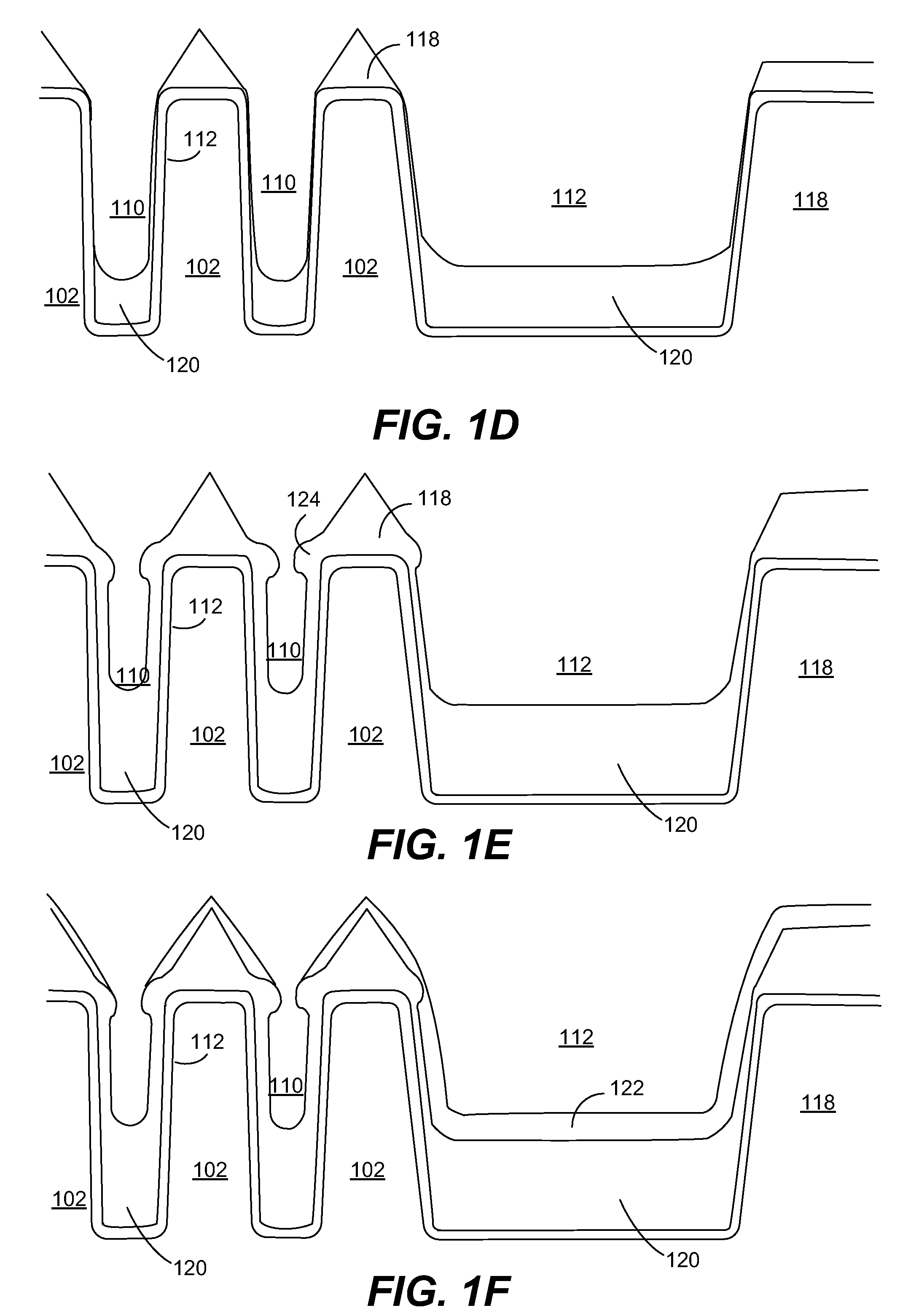
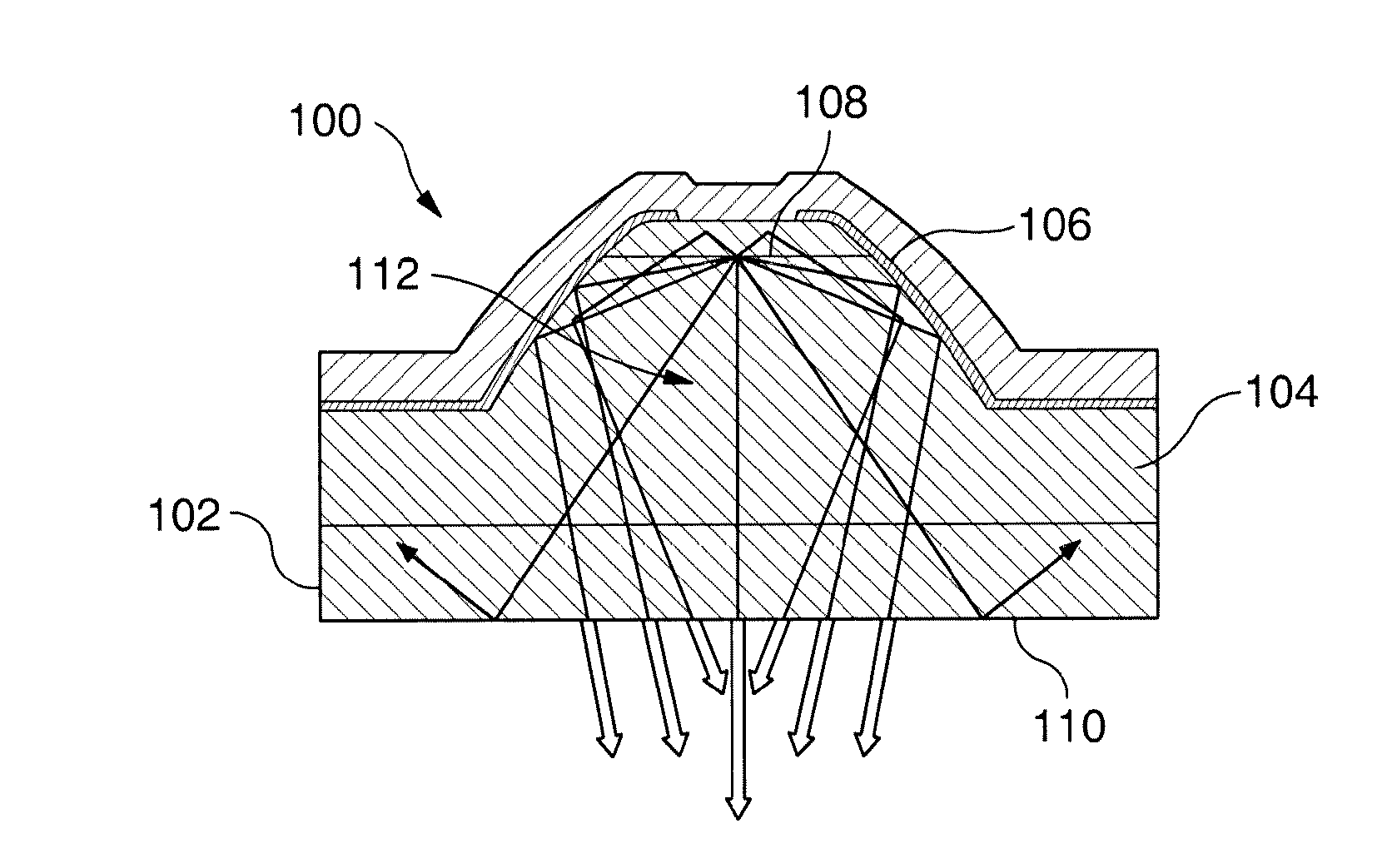
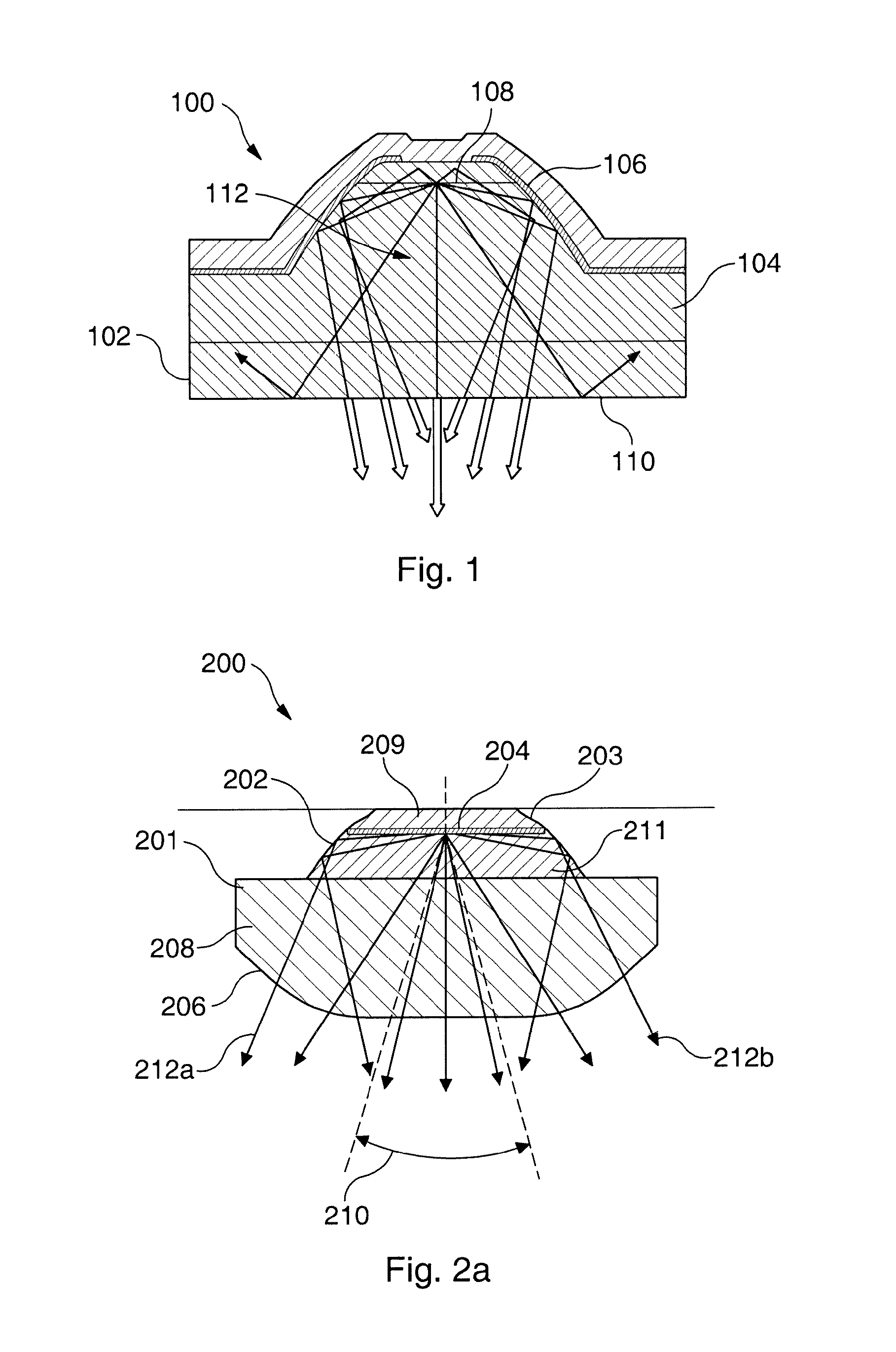
ActiveUS20170100742A1Reduce aspect ratioLiquid surface applicatorsChemical vapor deposition coatingOrganic filmGas phase
Methods and apparatus for vapor deposition of an organic film are configured to vaporize an organic reactant at a first temperature, transport the vapor to a reaction chamber housing a substrate, and maintain the substrate at a lower temperature than the vaporization temperature. Alternating contact of the substrate with the organic reactant and a second reactant in a sequential deposition sequence can result in bottom-up filling of voids and trenches with organic film in a manner otherwise difficult to achieve.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
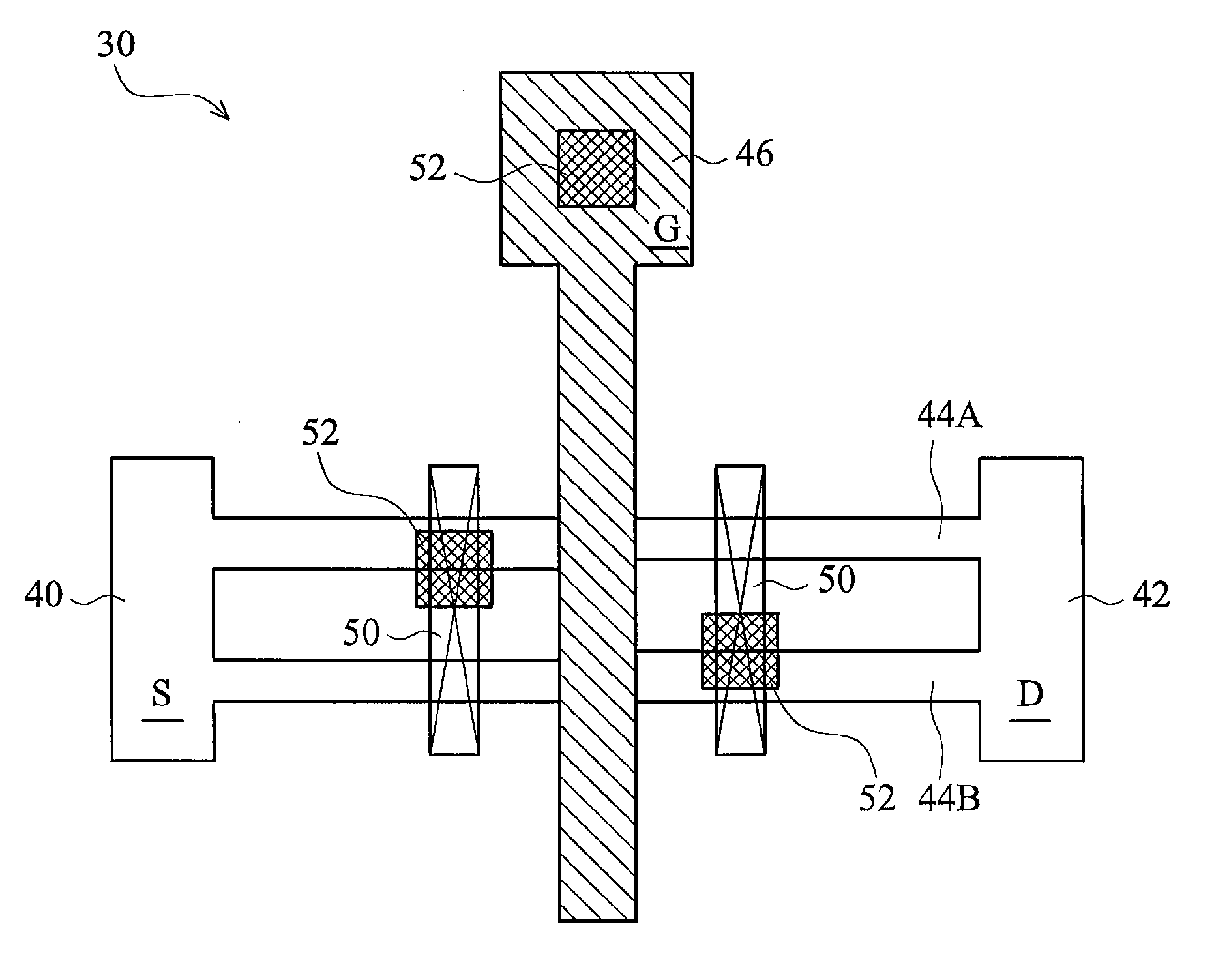
Semiconductor Device with Improved Contact Structure and Method of Forming Same
ActiveUS20090014796A1Reduce aspect ratioReduce contact densityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringDielectric layer
A contact structure includes a first contact formed in a first dielectric layer connecting to the source / drain region of a MOS transistor, and a second contact formed in a second dielectric layer connecting to a gate region of a MOS transistor or to a first contact. A butted contact structure abutting a source / drain region and a gate electrode includes a first contact formed in a first dielectric layer connecting to the source / drain region of a MOS transistor, and a second contact formed in a second dielectric layer with one end resting on the gate electrode and the other end in contact with the first contact.
Owner:MOSAID TECH
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20060261392A1Reduce the overall heightIncrease gap-fill marginTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsParasitic capacitanceSilicon oxide
Disclosed herein are a semiconductor device and a method of manufacturing the same that increases the reliability of these devices as size design limitations decrease. Generally, a first insulating film, and wiring, including conductive film patterns and second insulating film patterns are formed on a substrate. Third insulating film patterns including a silicon-oxide-based material are formed on sidewalls of the wiring, and contact patterns and spacers on the sidewalls thereof for defining contact hole regions are formed on the wiring. The contact holes contact surfaces of the third insulating film patterns and pass through the first insulating film. Thus, the thickness of a second insulating film pattern used in the wiring can be minimized, thereby increasing a gap-fill margin between the wiring. A parasitic capacitance between the wiring can be reduced because silicon oxide spacers with a low dielectric constant are formed on sidewalls of the wiring.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Pillar structure for memory device and method
ActiveUS20110312151A1High densityWide rangeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingConductive materialsEngineering
A method of forming a memory device. The method provides a semiconductor substrate having a surface region. A first dielectric layer is formed overlying the surface region of the semiconductor substrate. A bottom wiring structure is formed overlying the first dielectric layer and a second dielectric material is formed overlying the top wiring structure. A bottom metal barrier material is formed to provide a metal-to-metal contact with the bottom wiring structure. The method forms a pillar structure by patterning and etching a material stack including the bottom metal barrier material, a contact material, a switching material, a conductive material, and a top barrier material. The pillar structure maintains a metal-to-metal contact with the bottom wiring structure regardless of the alignment of the pillar structure with the bottom wiring structure during etching. A top wiring structure is formed overlying the pillar structure at an angle to the bottom wiring structure.
Owner:CROSSBAR INC
Imaging system
InactiveUS20170205618A1Enhance imageImprove performanceMechanical apparatusPlanar/plate-like light guidesLight waveLight source
An imaging system suitable to provide an image of a surface portion of an object is disclosed. The system includes a light source arranged to provide a light beam, at least a first optical waveguide having a first face and having a second face opposite to the first face, the first face having an incoupling surface. The optical waveguide includes an outcoupling surface, a first diffraction grating arranged on the optical waveguide, and an imaging subsystem arranged to the outcoupling surface. The first diffraction grating is arranged to outcouple at least a fraction of the light beam.
Owner:CSEM CENT SUISSE DELECTRONIQUE & DE MICROTECHNIQUE SA RECH & DEV
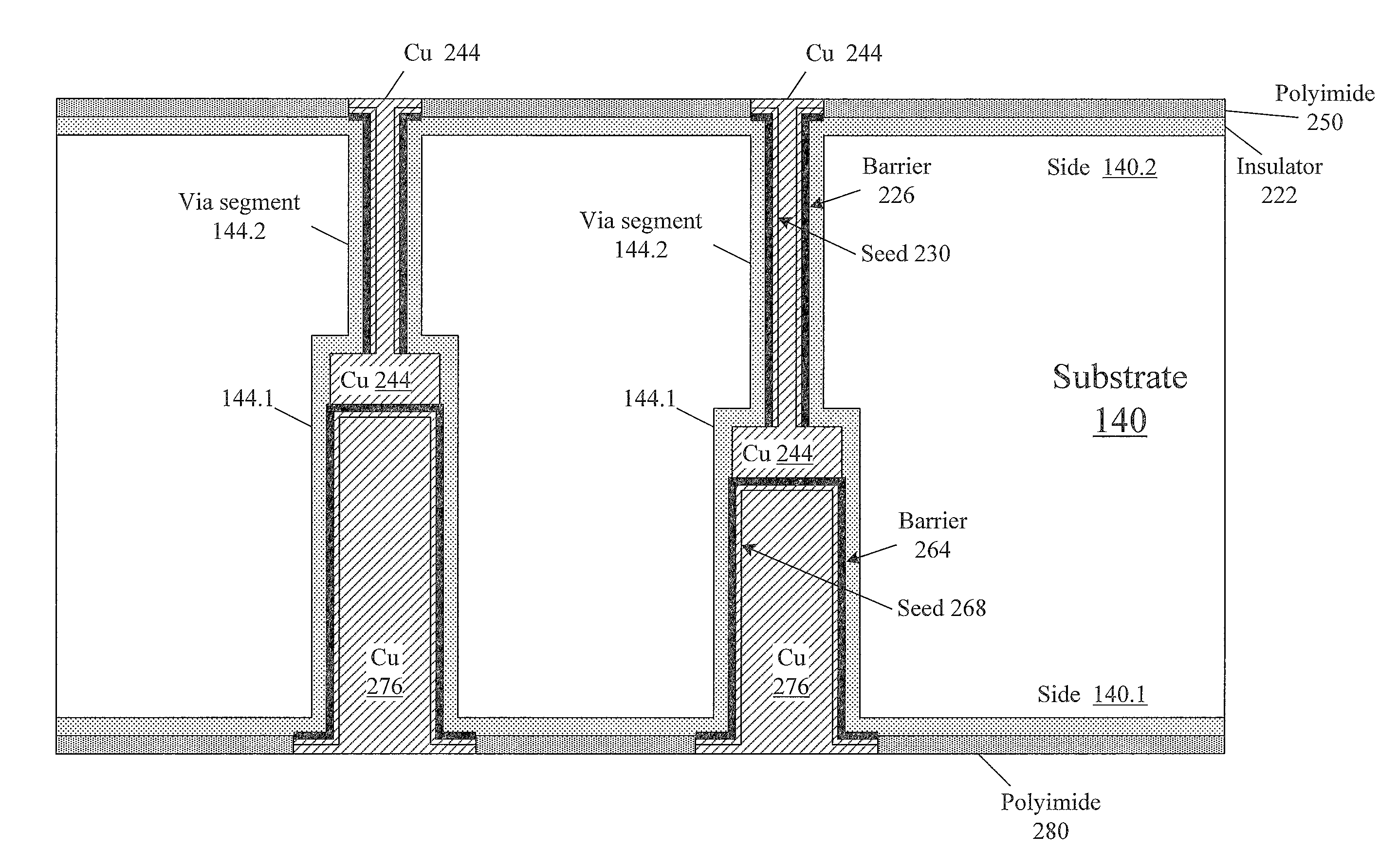
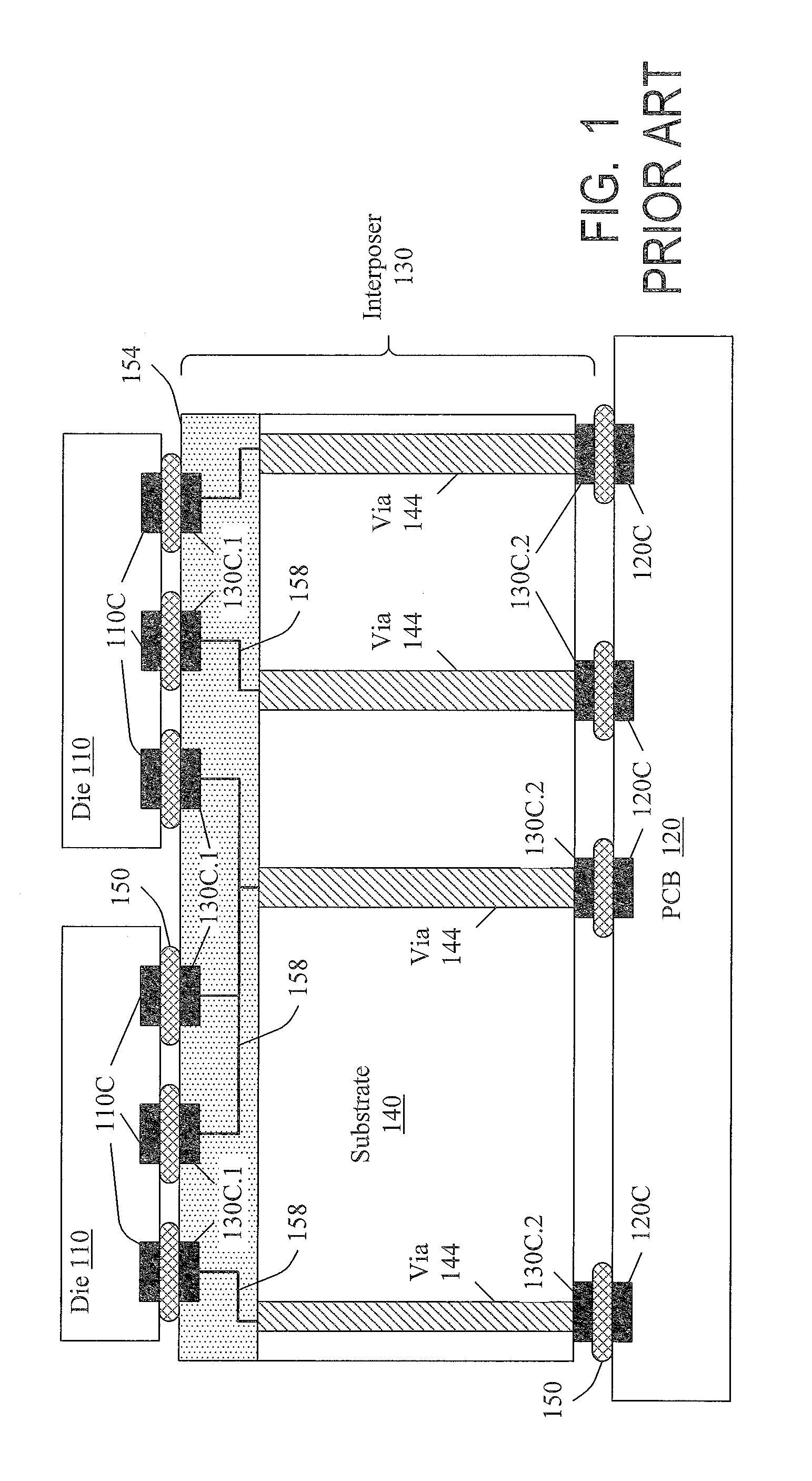
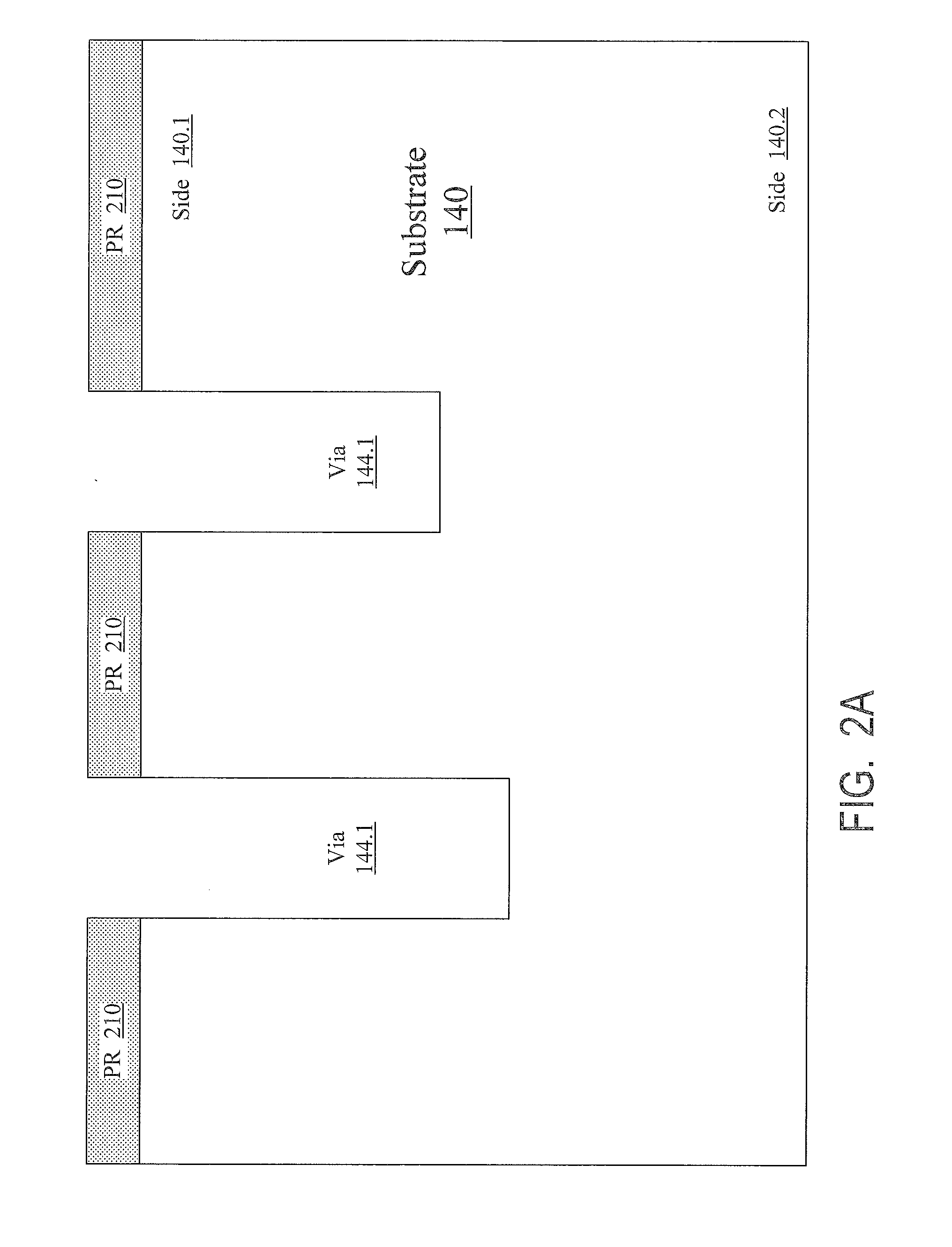
Substrates with through vias with conductive features for connection to integrated circuit elements, and methods for forming through vias in substrates
ActiveUS20120228778A1Reducing aspect ratio subjected to processingAspect ratioSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsEngineeringConductive materials
A through via (144) contains a conductor (244, 276) passing through a substrate (140) for connection to an integrated circuit element. The through via consists of two segments (144.1, 144.2) formed from respective different sides (140.1, 140.2) of the substrate and meeting inside the substrate. Each segment is shorter than the entire via, so via formation is facilitated. The second segment is etched after deposition of an etch stop layer (214) into the first segment. Due to the etch stop layer, the first segment's depth does not have to be rigidly controlled. The conductor is formed by separate depositions of conductive material into the via from each side of the substrate. From each side, the conductor is deposited to a shallower depth than the via depth, so the deposition is facilitated. Other embodiments are also provided.
Owner:INVENSAS CORP
Protective layer to enable damage free gap fill
ActiveUS8133797B2Improve throughputPlasma-enhanced chemical vapor depositionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingEtchingProtection layer
In-situ semiconductor process that can fill high aspect ratio (typically at least 6:1, for example 7:1 or higher), narrow width (typically sub 0.13 micron, for example 0.1 micron or less) gaps without damaging underlying features and little or no incidence of voids or weak spots is provided. A protective layer is deposited to protect underlying features in regions of the substrate having lower feature density so that unwanted material may be removed from regions of the substrate having higher feature density. This protective layer may deposits thicker on a low density feature than on a high density feature and may be deposited using a PECVD process or low sputter / deposition ratio HDP CVD process. This protective layer may also be a metallic oxide layer that is resistant to fluorine etching, such as zirconium oxide (ZrO2) or aluminum oxide (Al2O3).
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Spar with improved VIV performance
InactiveUS6092483AReduce VIVReduce aspect ratioShip vibration reductionBuoysAspect ratioMarine engineering
A method for reducing VIV is disclosed for a spar platform having a deck, a cylindrical hull having a buoyant tank assembly, a counterweight and an counterweight spacing structure. The overall aspect ratio of the hull is reduced by providing one or more abrupt changes in hull diameter below the waterline.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Latchable container system
InactiveUS20070095848A1Increase efficiencyIncrease safetyPackage recyclingCapsMechanical engineeringEngineering
A latching system including both apparatus and methods addresses the need for a reusable latch that is identical on either side of a container opening, thereby facilitating container manufacture. Also disclosed are apparatus and methods for assuring the quality of latchable container enclosed contents and enhancing the safety of container users by providing an unopened condition assurance element such as a tab that is removable from a reusable container latch. A novel latching system with a split insertion clement on a first latch side and unitary receptor element on a second latch side is also disclosed. A preferred embodiment involves an elastically obstructed latch as used on a squeeze-openable container.
Owner:INT MOLDED PACKAGING CORP
Biocompatible wire battery
ActiveUS20130034760A1Reliable and stable powerEasy to useFinal product manufactureSmall-sized cells cases/jacketsActive componentElectrochemistry
A rechargeable electrochemical battery in the form of a single or multi-stranded wire assembly may be utilized as a power source for any number of implantable or non-implantable medical devices. As the wire form battery may be scaled to micro size, it may be utilized to power medical devices that were traditionally non-active devices, but which may be enhanced with active components. The wire form battery may be cut to size for a particular application which provides the same open circuit voltage regardless of how the wire is ultimately configured and the length of the wire utilized. Although the battery is in wire form, various arrangements of the components within the battery are also possible.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
Pillar structure for memory device and method
ActiveUS8198144B2High densityHigh yieldSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingConductive materialsDielectric layer
A method of forming a memory device. The method provides a semiconductor substrate having a surface region. A first dielectric layer is formed overlying the surface region of the semiconductor substrate. A bottom wiring structure is formed overlying the first dielectric layer and a second dielectric material is formed overlying the top wiring structure. A bottom metal barrier material is formed to provide a metal-to-metal contact with the bottom wiring structure. The method forms a pillar structure by patterning and etching a material stack including the bottom metal barrier material, a contact material, a switching material, a conductive material, and a top barrier material. The pillar structure maintains a metal-to-metal contact with the bottom wiring structure regardless of the alignment of the pillar structure with the bottom wiring structure during etching. A top wiring structure is formed overlying the pillar structure at an angle to the bottom wiring structure.
Owner:CROSSBAR INC
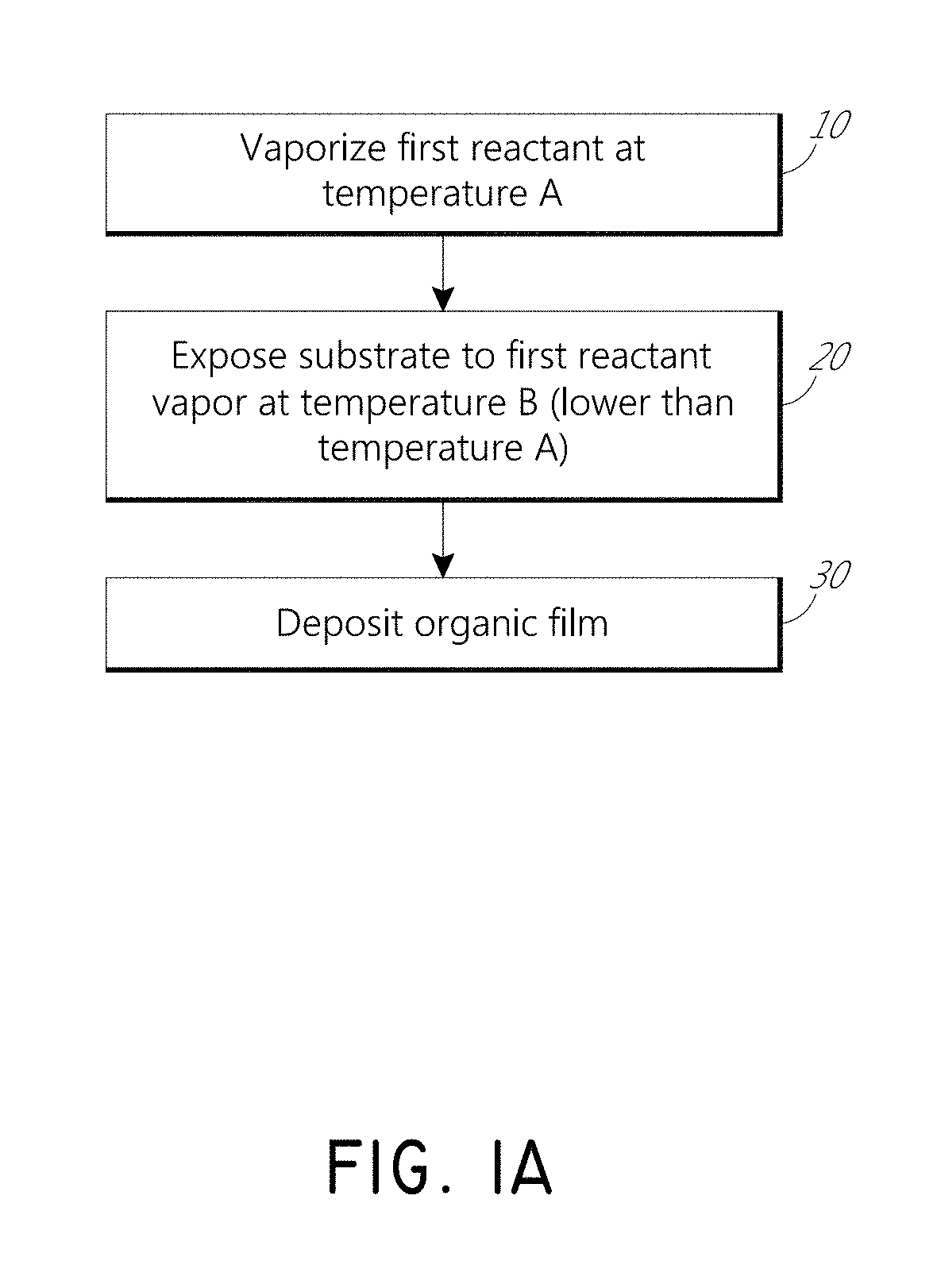
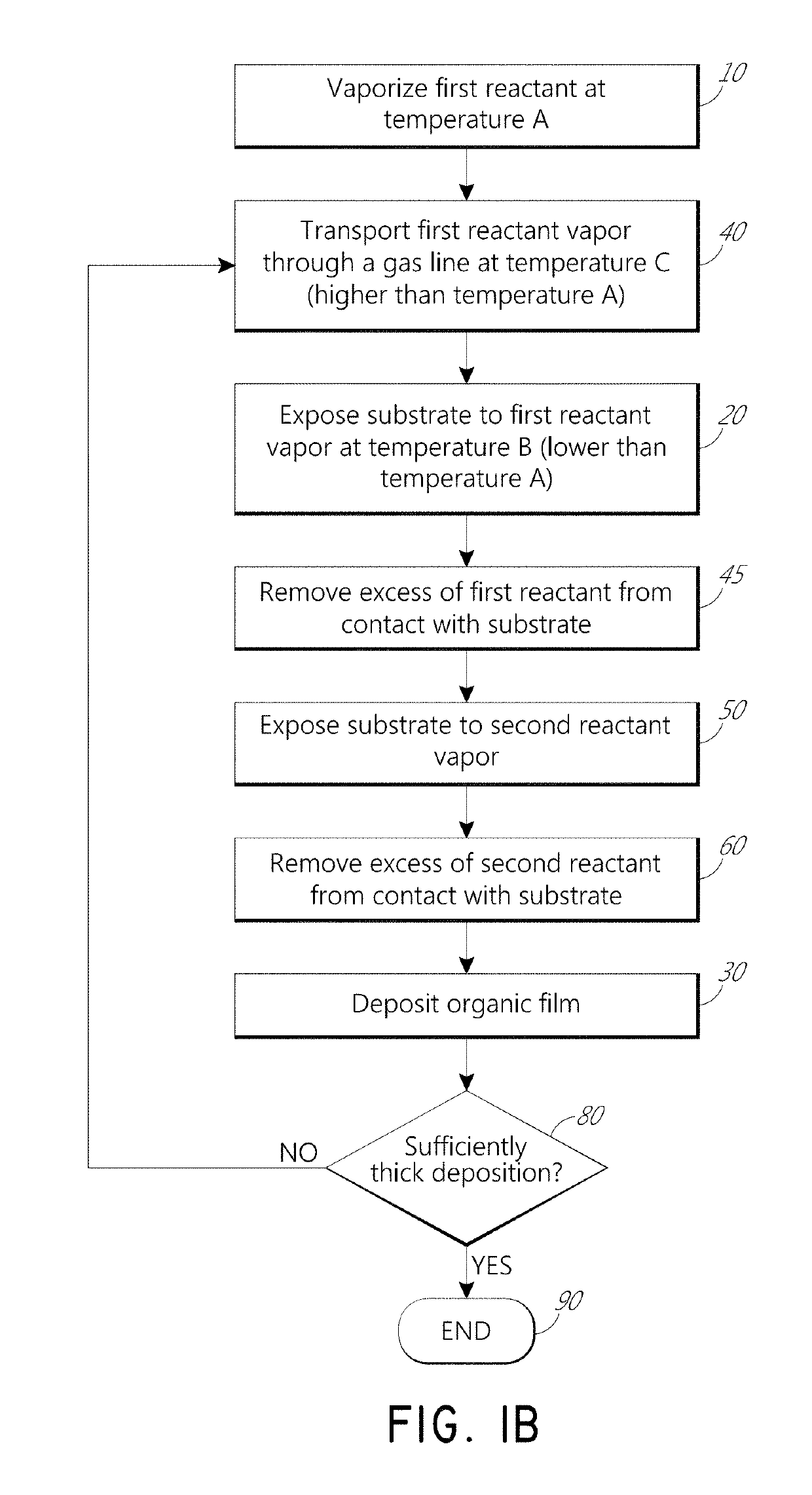
Vapor phase deposition of organic films
ActiveUS20170100743A1Reduce aspect ratioSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPretreated surfacesOrganic filmGas phase
Methods and apparatus for vapor deposition of an organic film are configured to vaporize an organic reactant at a first temperature, transport the vapor to a reaction chamber housing a substrate, and maintain the substrate at a lower temperature than the vaporization temperature. Alternating contact of the substrate with the organic reactant and a second reactant in a sequential deposition sequence can result in bottom-up filling of voids and trenches with organic film in a manner otherwise difficult to achieve. Deposition reactors conducive to depositing organic films are provided.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20060097314A1Reduce stepsHighly integratedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSub thresholdSubthreshold conduction
After an element isolation region is formed using a field-forming silicon nitride film, the silicon nitride film and a semiconductor substrate are patterned. Thereafter, the silicon nitride film and the semiconductor substrate are patterned, thereby forming a gate trench reaching the semiconductor substrate in an active region. Next, after a gate electrode is formed within a gate trench, the silicon nitride film is removed, thereby forming a contact hole. A contact plug is buried into this contact hole. Accordingly, a diffusion layer contact pattern becomes unnecessary, and the active region can be reduced. Because a gate electrode is buried in the gate trench, a gate length is increased, and a sub-threshold current can be reduced.
Owner:LONGITUDE LICENSING LTD
Method and apparatus for reducing aspect ratio dependent etching in time division multiplexed etch processes
ActiveUS20050287815A1Reduce decreaseReducing ARDESemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsEngineeringTime-division multiplexing
The present invention provides a method and an apparatus for reducing aspect ratio dependent etching that is observed when plasma etching deep trenches in a semiconductor substrate through an alternating deposition / etch process. A plurality of different sized features on the substrate are monitored in real time during the alternating deposition / etch process. Then, based on the information received from the monitor, at least one process parameter is adjusted in the alternating deposition / etch process to achieve equivalent etch depths of at least two different sized features on the substrate.
Owner:PLASMA THERM
Self aligned dual damascene method
InactiveUS6365504B1Increased process windowSmall line widthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingConductive materialsInterconnection
A method for fabricating an interconnection between a conductive line and a via plug on an insulating layer, comprises the steps of: forming a conductive line pattern on the insulating layer; etching the upper part of the insulating layer and forming a conductive line opening; forming conductive line spacers to provide better alignment between the conductive line and the via, to provide better control of a small via, and to help the metal to have better coverage effects in filling in the conductive line opening and the via; producing a via pattern on the insulating layer and the via pattern opening being substantially larger than the conductive line opening; etching the exposed lower part of the insulating layer by utilizing the conductive line spacers as an etching mask and forming a via hole; and filling the conductive line opening and the via hole with a conductive material and forming an interconnection of the conductive line and a via plug.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD +1
System for continuous growing of monocrystalline silicon
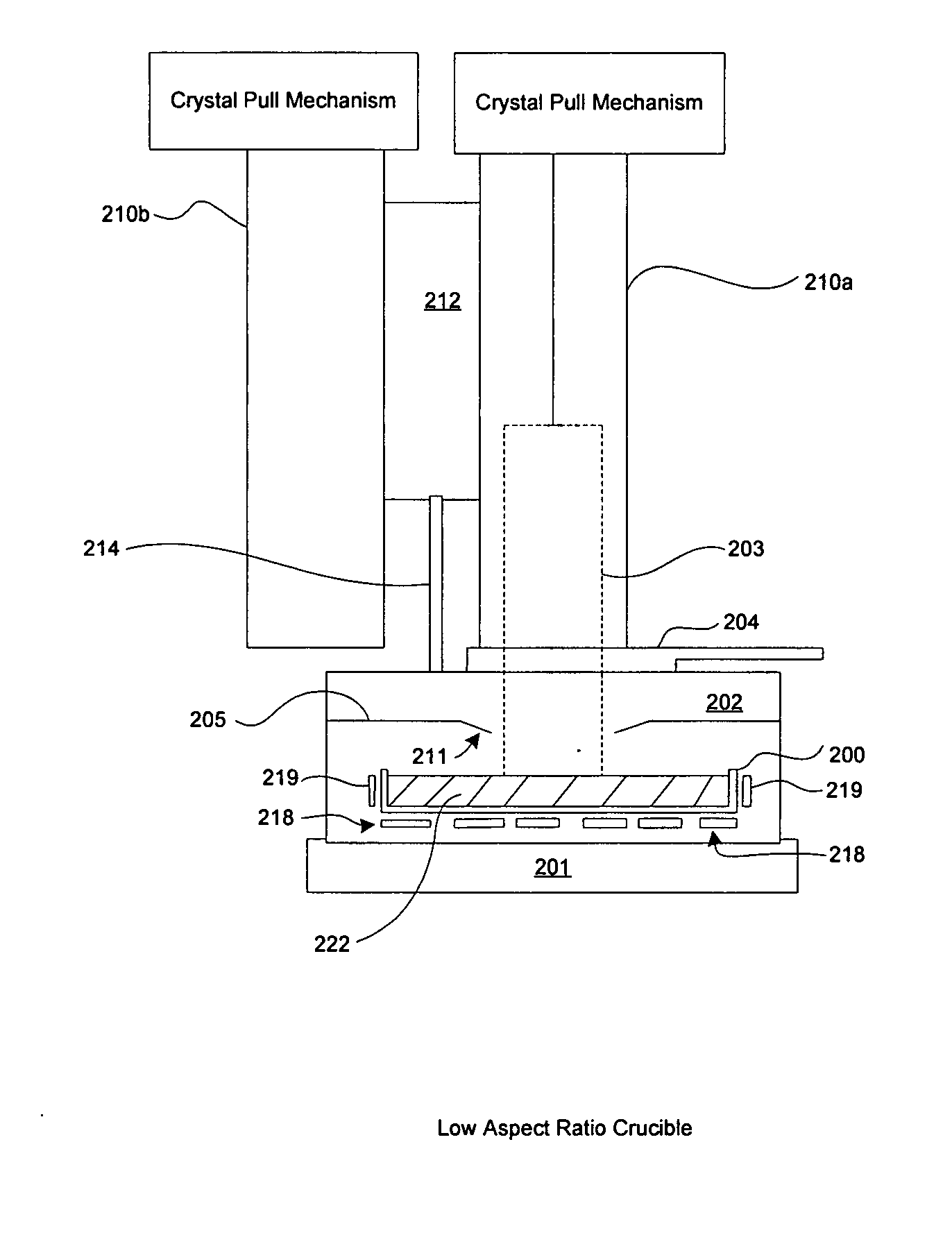
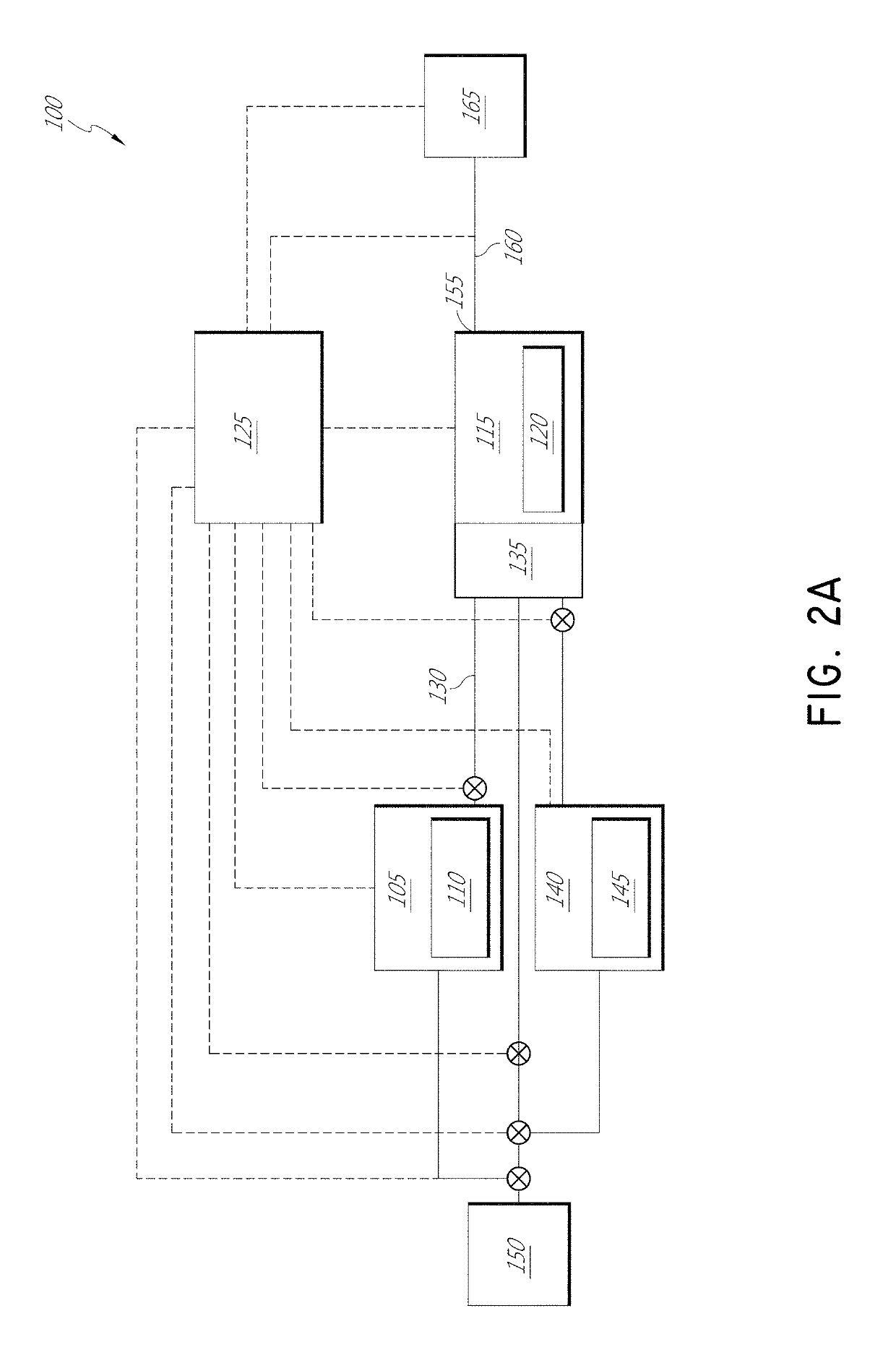
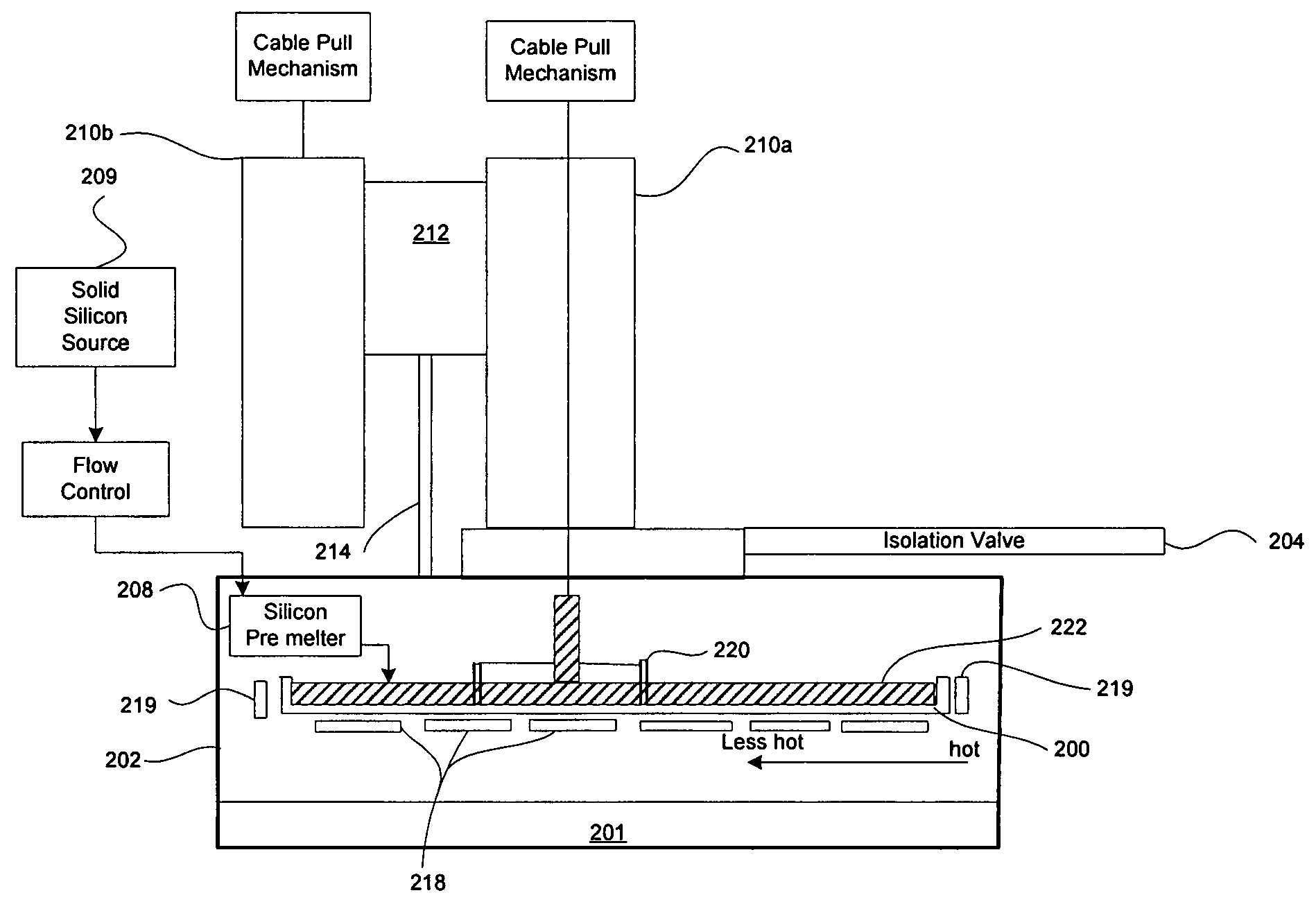
ActiveUS20050092236A1Easy temperature controlAccelerated crystal growthAfter-treatment apparatusPolycrystalline material growthHot zoneSingle crystal
An improved system based on the Czochralski process for continuous growth of a single crystal ingot comprises a low aspect ratio, large diameter, and substantially flat crucible, including an optional weir surrounding the crystal. The low aspect ratio crucible substantially eliminates convection currents and reduces oxygen content in a finished single crystal silicon ingot. A separate level controlled silicon pre-melting chamber provides a continuous source of molten silicon to the growth crucible advantageously eliminating the need for vertical travel and a crucible raising system during the crystal pulling process. A plurality of heaters beneath the crucible establish corresponding thermal zones across the melt. Thermal output of the heaters is individually controlled for providing an optimal thermal distribution across the melt and at the crystal / melt interface for improved crystal growth. Multiple crystal pulling chambers are provided for continuous processing and high throughput.
Owner:CORNER STAR LTD
Protective Layer To Enable Damage Free Gap Fill
ActiveUS20090286381A1High aspect ratioNarrow widthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingSputteringEtching
In-situ semiconductor process that can fill high aspect ratio (typically at least 6:1, for example 7:1 or higher), narrow width (typically sub 0.13 micron, for example 0.1 micron or less) gaps without damaging underlying features and little or no incidence of voids or weak spots is provided. A protective layer is deposited to protect underlying features in regions of the substrate having lower feature density so that unwanted material may be removed from regions of the substrate having higher feature density. This protective layer may deposits thicker on a low density feature than on a high density feature and may be deposited using a PECVD process or low sputter / deposition ratio HDP CVD process. This protective layer may also be a metallic oxide layer that is resistant to fluorine etching, such as zirconium oxide (ZrO2) or aluminum oxide (Al2O3).
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Optical device
ActiveUS20150236201A1Improve efficiencyNarrow beam profileSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPower flowSemiconductor materials
An optical device and method for fabricating an optical device. The optical device comprising: a semiconductor material comprising an active layer configured to emit light when an electrical current is applied to the device and / or to generate an electrical current when light is incident on the active layer, wherein the semiconductor material comprises a first surface and an opposed second surface, from which light is emitted from and / or received by the device, and wherein the first surface defines a first structure comprising the active layer and configured to reflect light emitted from the active layer toward the second surface and / or to reflect light received by the device toward the active layer, and the second surface defines a second structure configured to permit light incident on the second surface at an angle outside a critical angle range to the planar normal to pass therethrough.
Owner:META PLATFORMS TECH LLC
Light-emitting diode structure and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20130292719A1Closely arrangedHigh light efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInterconnectionActive layer
A light-emitting diode (LED) structure includes an insulation substrate; LED chips each includes an epitaxial layer having a first conductivity type semiconductor layer, an active layer, and a second conductivity type semiconductor layer stacked on the insulation substrate, and comprises a mesa structure and an exposed portion of the first conductivity type semiconductor layer adjacent to each other, and a first isolation trench within the mesa structure; interconnection layers connect the LED chips; electrode pads respectively connected to exposed portions of the semiconductor layers; a reflective insulating layer covering the interconnection layers, the mesa structures and the electrode pads, and having penetration holes respectively exposing a portion of the electrode pads; and bonding pads located on a portion of the reflective insulating layer and connected to the electrode pads through the penetrating holes. A method of manufacturing the LED structure.
Owner:CHI MEI LIGHTING TECH
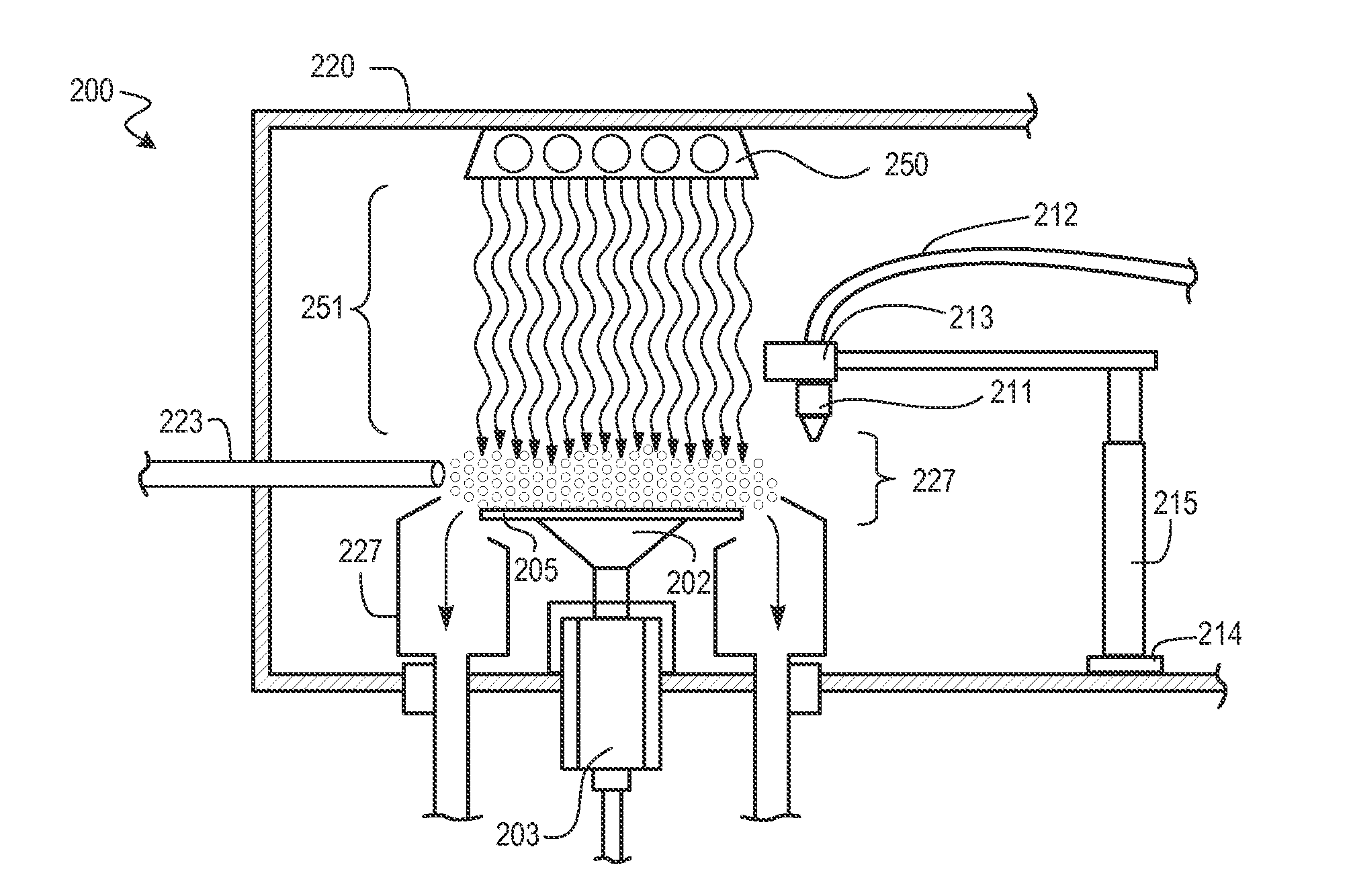
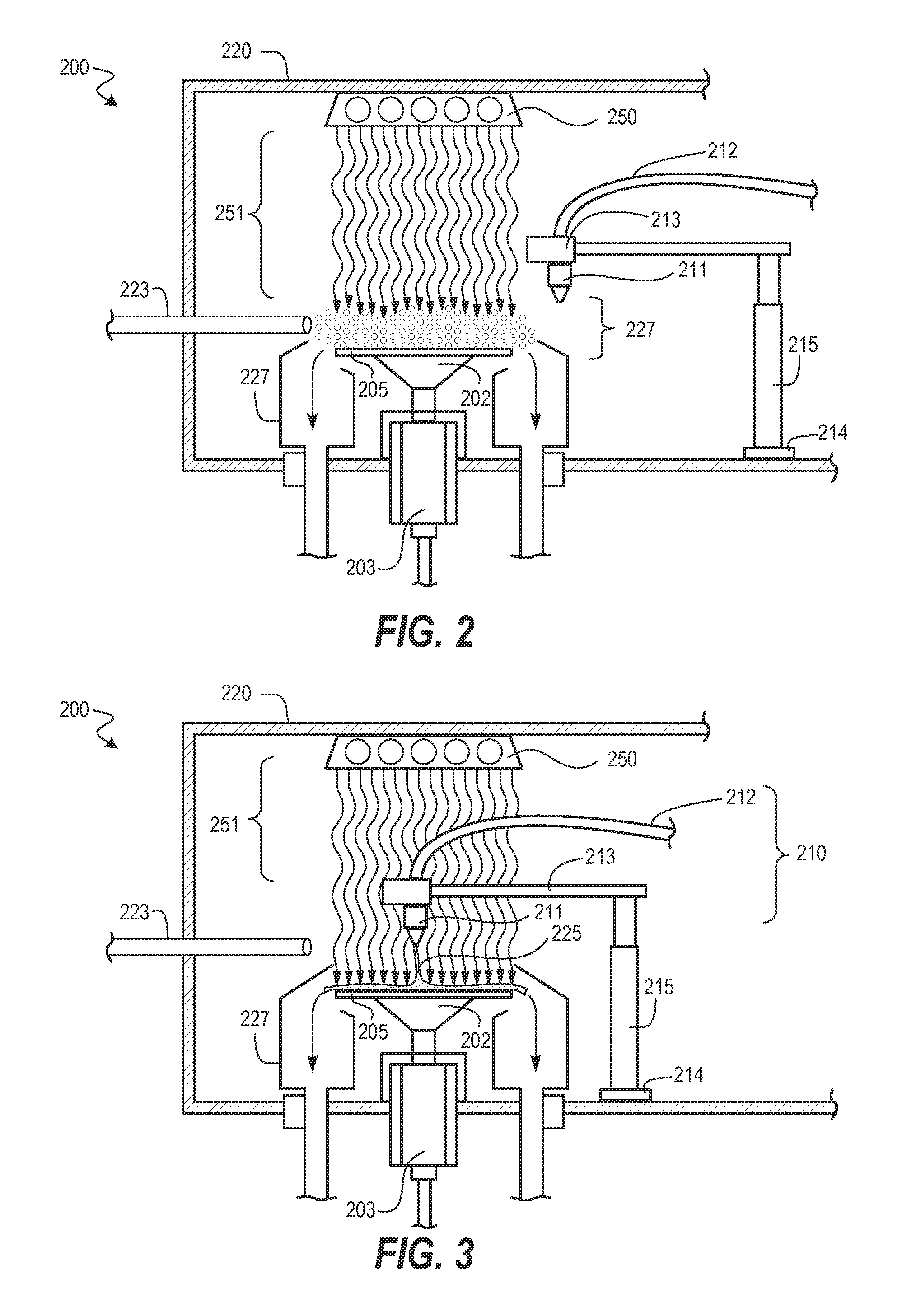
Method and Hardware for Enhanced Removal of Post Etch Polymer and Hardmask Removal
ActiveUS20150128991A1Enhanced sputteringRegulate deliveryElectrostatic cleaningSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogenUltraviolet
Methods for cleaning substrates are described including cleaning substrates having hardmask masks and polymer films, such part of semiconductor fabrication. Cleaning methods include ultraviolet (UV) light exposure of process gas mixtures and liquid cleaning chemistries. A substrate and / or process fluids are exposed to ultraviolet radiation. A process gas mixture being irradiated can include an oxidizing gas mixture (air, clean dry air, oxygen, peroxygen, etc.). Reducing gas mixtures, having hydrogen, can also be irradiated. Reactive species from irradiated gas mixtures are exposed to the substrate to chemically modify film properties, such as by facilitating a subsequent liquid cleaning step. Liquid cleaning chemistries on a substrate surface can also be irradiated. Such cleaning techniques enable shorter cleaning times, lower processing temperatures, and reduced damage to underlying or intermediate layers such as dielectric layers.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Structures including synchronously deployable frame members and methods of deploying the same
InactiveUS7211722B1Low deployment aspect ratioReduce aspect ratioPhotovoltaic supportsPV power plantsMechanical engineeringBlanket
A lightweight structure for space application is deployable from a compact bundle of interconnected struts into a plurality of tiled substantially rectangular bays. Each bay preferably comprises four or six hinged strut members having substantially rectangular cross sections, such that a solar or other suitable blanket may be compactly nested within the bundled struts. In one aspect of the invention, the blanket is attached to two opposed strut members of a six-member strut bundle, such that the blanket is unfolded during deployment of the strut bundle into a substantially rectangular bay. In another aspect of the invention, the blanket is attached to, and held against, a single strut in a strut bundle. After the strut bundle is deployed into a substantially rectangular bay, the blanket is spread across the bay via a cable mechanism or other deployment mechanism.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
CMOS devices with improved gap-filling
ActiveUS20070235823A1Reduce aspect ratioAspect ratioSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCMOSGap filling
A semiconductor structure includes a substrate, and a first MOS device on the first region of the substrate wherein the first MOS device includes a first spacer liner. The semiconductor structure further includes a second MOS device on the second region wherein the second MOS device includes a second spacer liner. A first stressed film having a first thickness is formed over the first MOS device and directly on the first spacer liner. A second stressed film having a second thickness is formed over the second MOS device and directly on the second spacer liner. The first and the second stressed films may be formed of a same material.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
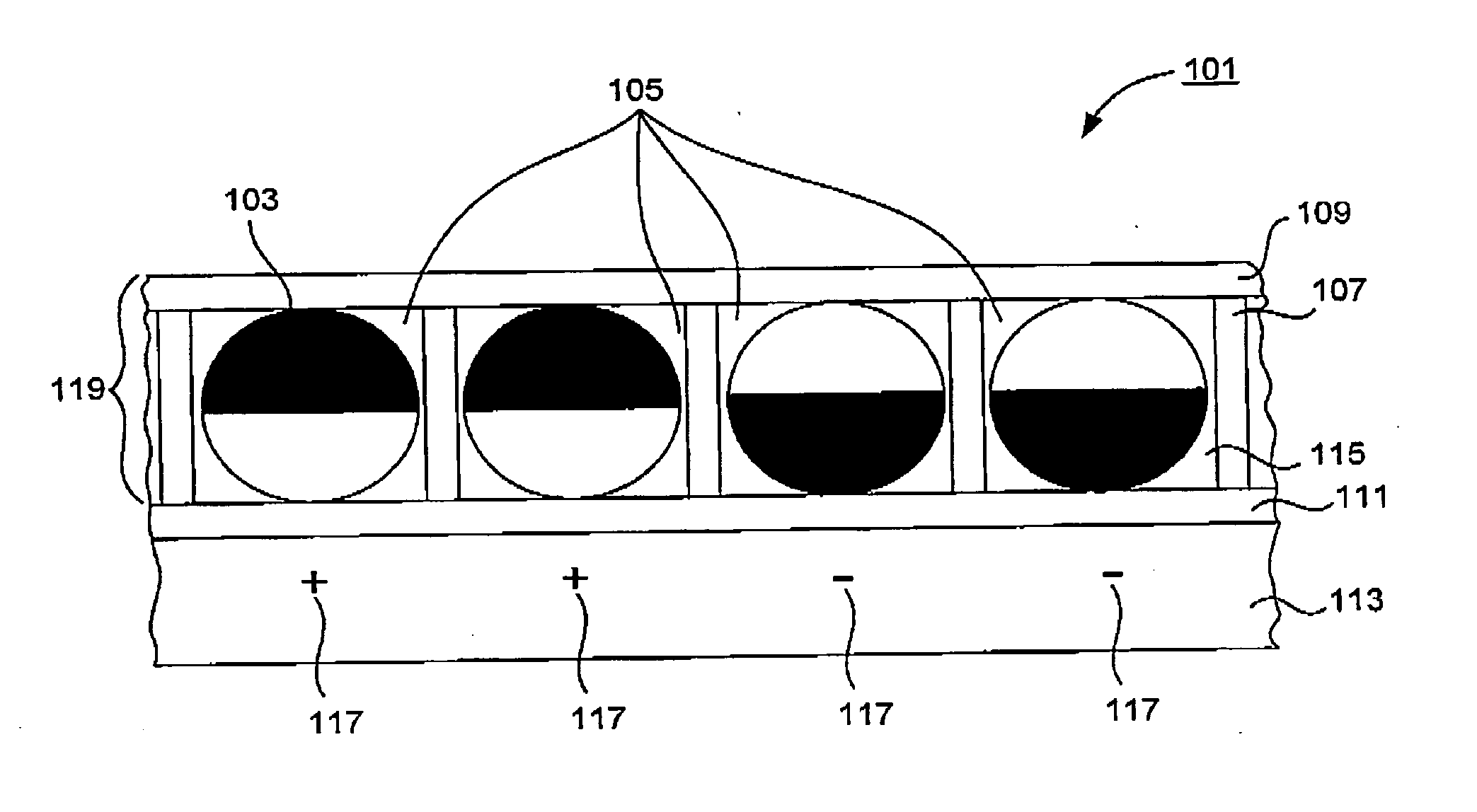
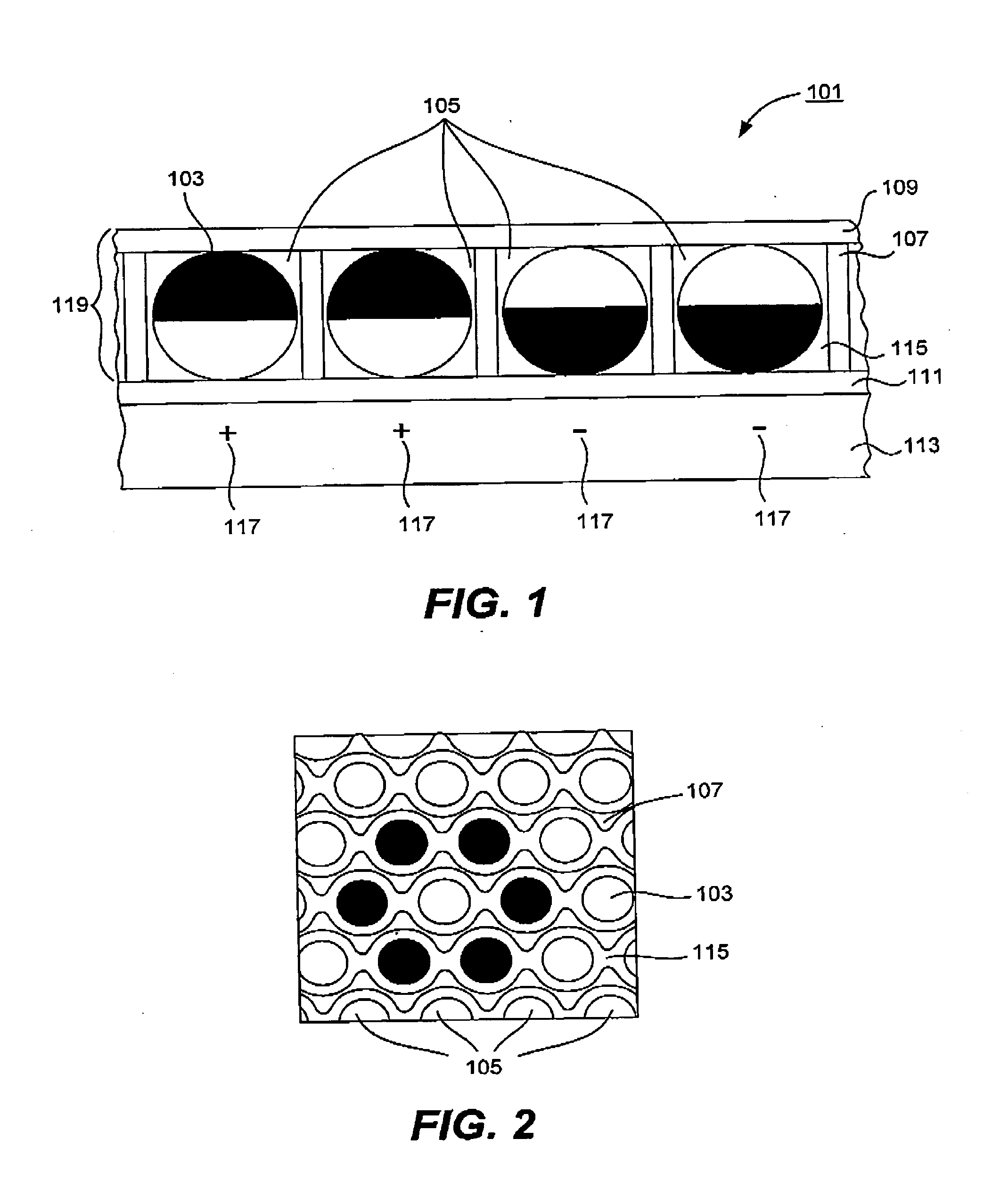
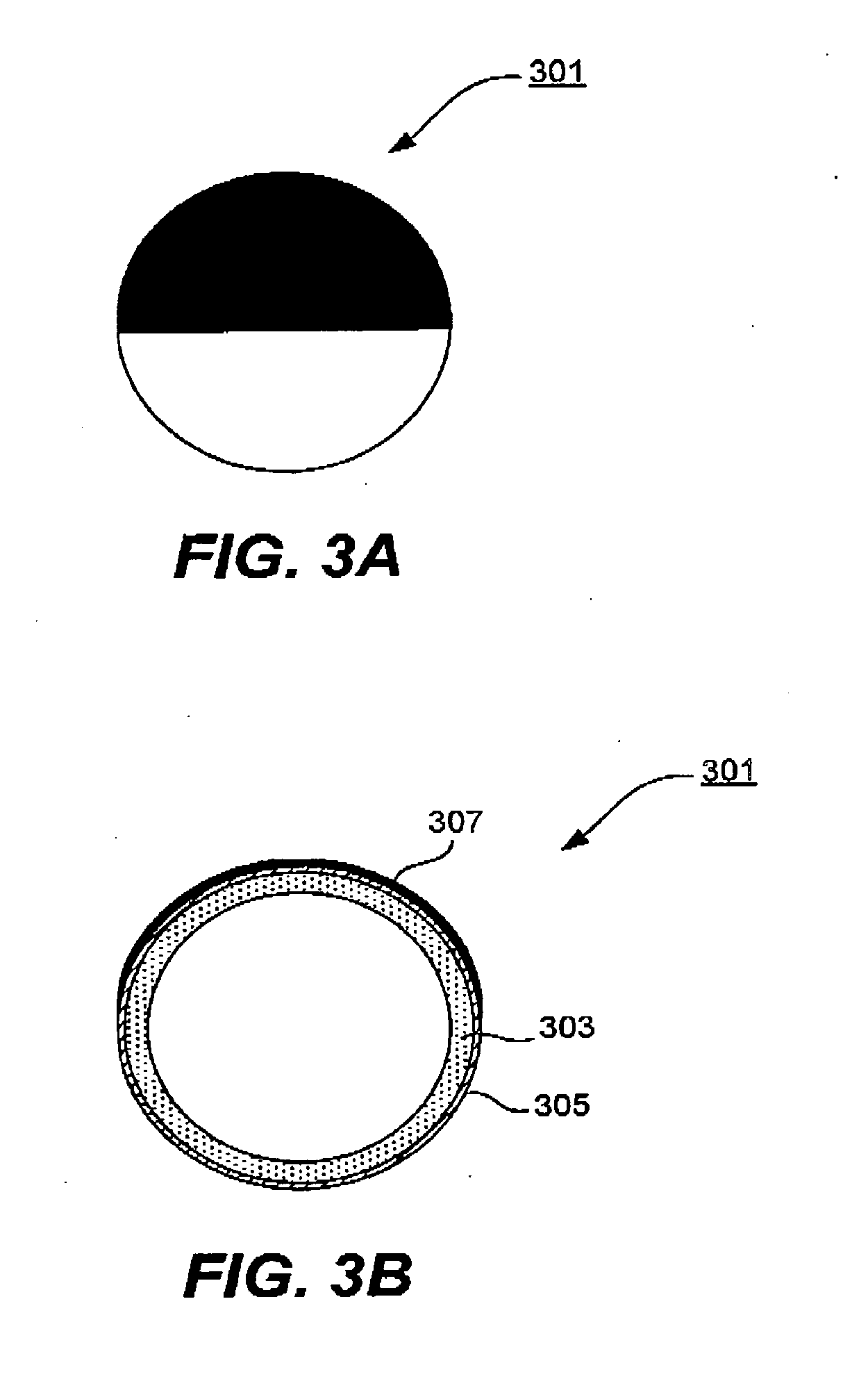
Electro-optic display
InactiveUS20080100907A1Improve reflectivityFacilitate inter-cell fluid transportLamination ancillary operationsLaminationElectricityFluid transport
An electro-optic display includes a “matrix” for confining moving elements of the display (e.g., rotating or twisting elements). The matrix (or at least the viewable portions thereof) may have a high reflectivity, comparable to that of white paper. This results in an overall “whiter” or brighter display. The matrix may include channels to facilitate inter-cell fluid transport and high-density element packing. In some cases, the matrix elements provide a hexagonal arrangement of cells for holding the rotating elements. The rotating elements of the display may be electrically and optically anisotropic hemispherically coated spheres. The hemispherical coating typically provides the necessary charge to create electrical anisotropy.
Owner:FANTASY SHINE LTD +1
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20080303968A1Lower resistanceReduce the overall diameterTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDevice materialEngineering
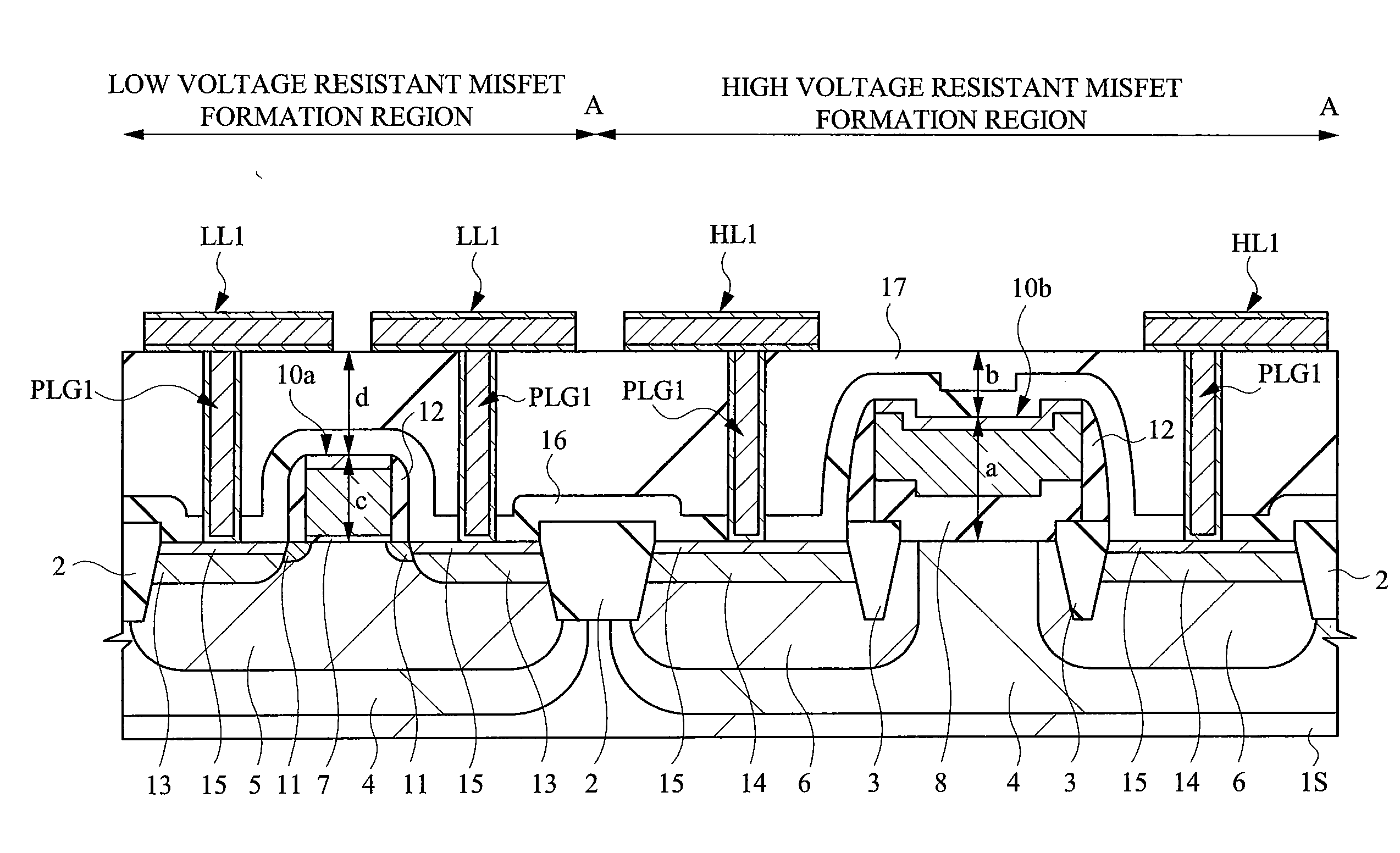
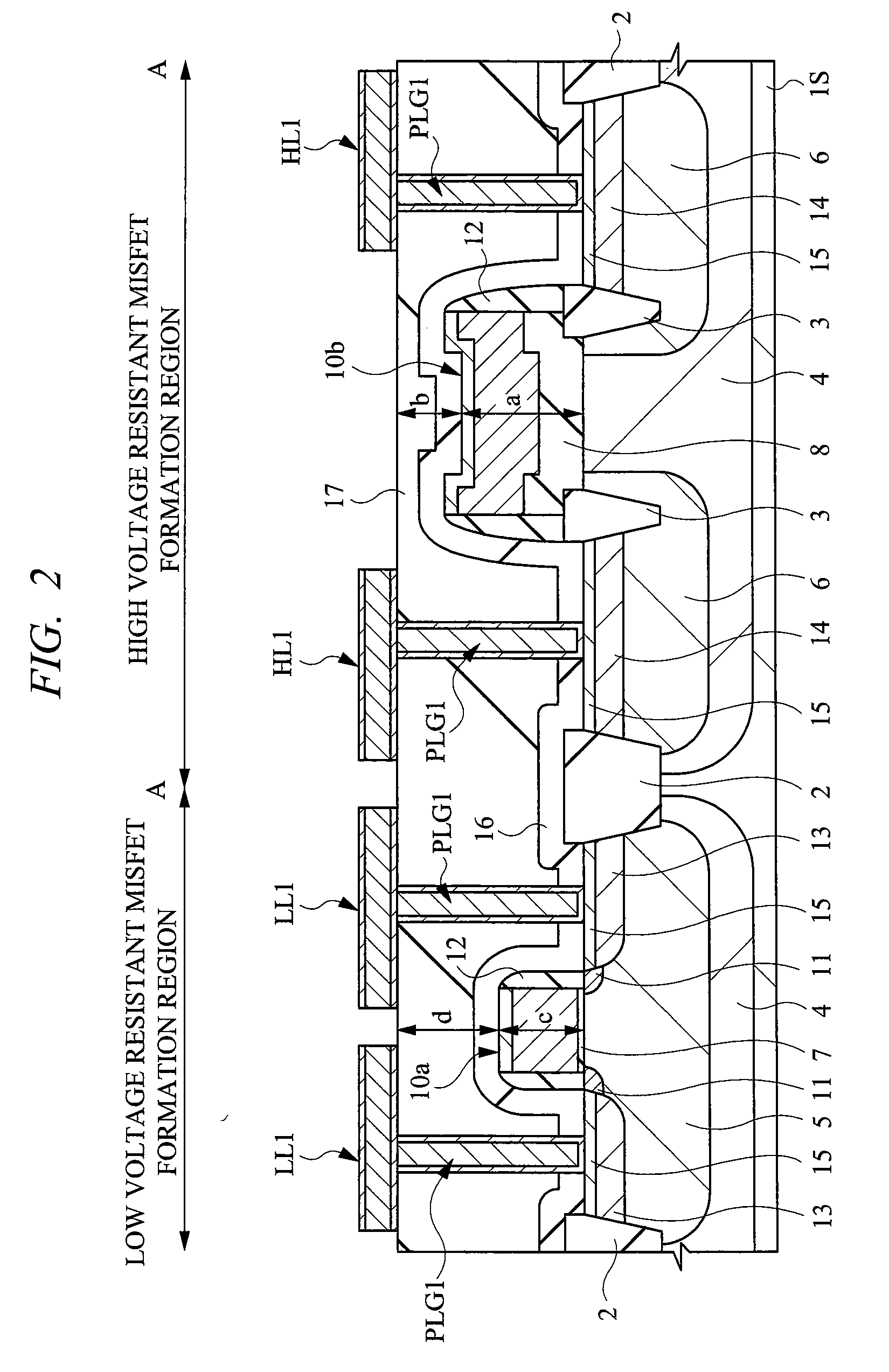
In an LCD driver, in a high voltage resistant MISFET, end portions of a gate electrode run onto electric field relaxing insulation regions. Wires to become source wires or drain wires are formed on an interlayer insulation film of the first layer over the high voltage resistant MISFET. At this moment, when a distance from an interface between a semiconductor substrate and a gate insulation film to an upper portion of the gate electrode is defined as “a”, and a distance from the upper portion of the gate electrode to an upper portion of the interlayer insulation film on which the wires are formed is defined as “b”, a relation of a>b is established. In such a high voltage resistant MISFET structured in this manner, the wires are arranged so as not to be overlapped planarly with the gate electrode of the high voltage resistant MISFET.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
NAND-type flash memory devices and methods of fabricating the same
InactiveUS20050023600A1Low resistanceMinimize aspect ratioTransistorSolid-state devicesCross overCommon source line
NAND-type flash memory devices and methods of fabricating the same are provided. The NAND-type flash memory device includes a plurality of isolation layers running parallel with each other, which are formed at predetermined regions of a semiconductor substrate. This device also includes a string selection line pattern, a plurality of word line patterns and a ground selection line pattern which cross over the isolation layers and active regions between the isolation layers. Source regions are formed in the active regions adjacent to the ground selection line patterns and opposite the string selection line pattern. The source regions and the isolation layers between the source regions are covered with a common source line running parallel with the ground selection line pattern.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Vapor phase deposition of organic films
ActiveUS10343186B2Reduce aspect ratioPretreated surfacesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOrganic filmGas phase
Methods and apparatus for vapor deposition of an organic film are configured to vaporize an organic reactant at a first temperature, transport the vapor to a reaction chamber housing a substrate, and maintain the substrate at a lower temperature than the vaporization temperature. Alternating contact of the substrate with the organic reactant and a second reactant in a sequential deposition sequence can result in bottom-up filling of voids and trenches with organic film in a manner otherwise difficult to achieve. Deposition reactors conducive to depositing organic films are provided.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
System for continuous growing of monocrystalline silicon
ActiveUS7635414B2Low oxygenEliminate downtimeAfter-treatment apparatusPolycrystalline material growthHot zoneSingle crystal
An improved system based on the Czochralski process for continuous growth of a single crystal ingot comprises a low aspect ratio, large diameter, and substantially flat crucible, including an optional weir surrounding the crystal. The low aspect ratio crucible substantially eliminates convection currents and reduces oxygen content in a finished single crystal silicon ingot. A separate level controlled silicon pre-melting chamber provides a continuous source of molten silicon to the growth crucible advantageously eliminating the need for vertical travel and a crucible raising system during the crystal pulling process. A plurality of heaters beneath the crucible establish corresponding thermal zones across the melt. Thermal output of the heaters is individually controlled for providing an optimal thermal distribution across the melt and at the crystal / melt interface for improved crystal growth. Multiple crystal pulling chambers are provided for continuous processing and high throughput.
Owner:CORNER STAR LTD
Laminated RF device with vertical resonators
InactiveUS20100265015A1To offer comfortCompact structureMultiple-port networksResonatorsElectrical connectionConductive materials
The present invention relates to a resonator device having a stacked arrangement of laminated layers including a plurality of dielectric layers, and at least one resonator comprising a short-circuit electrode, a first capacitor electrode and a second capacitor electrode. Each electrode comprises at least a portion of a layer of electrically conductive material provided on a surface of one of the dielectric layers. The second capacitor electrode is disposed spaced, in the stacking direction, from the short-circuit electrode and the first capacitor electrode. The short-circuit electrode and the second capacitor electrode are electrically interconnected by a first electrical connection comprising at least one via hole penetrating one or more of the dielectric layers.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
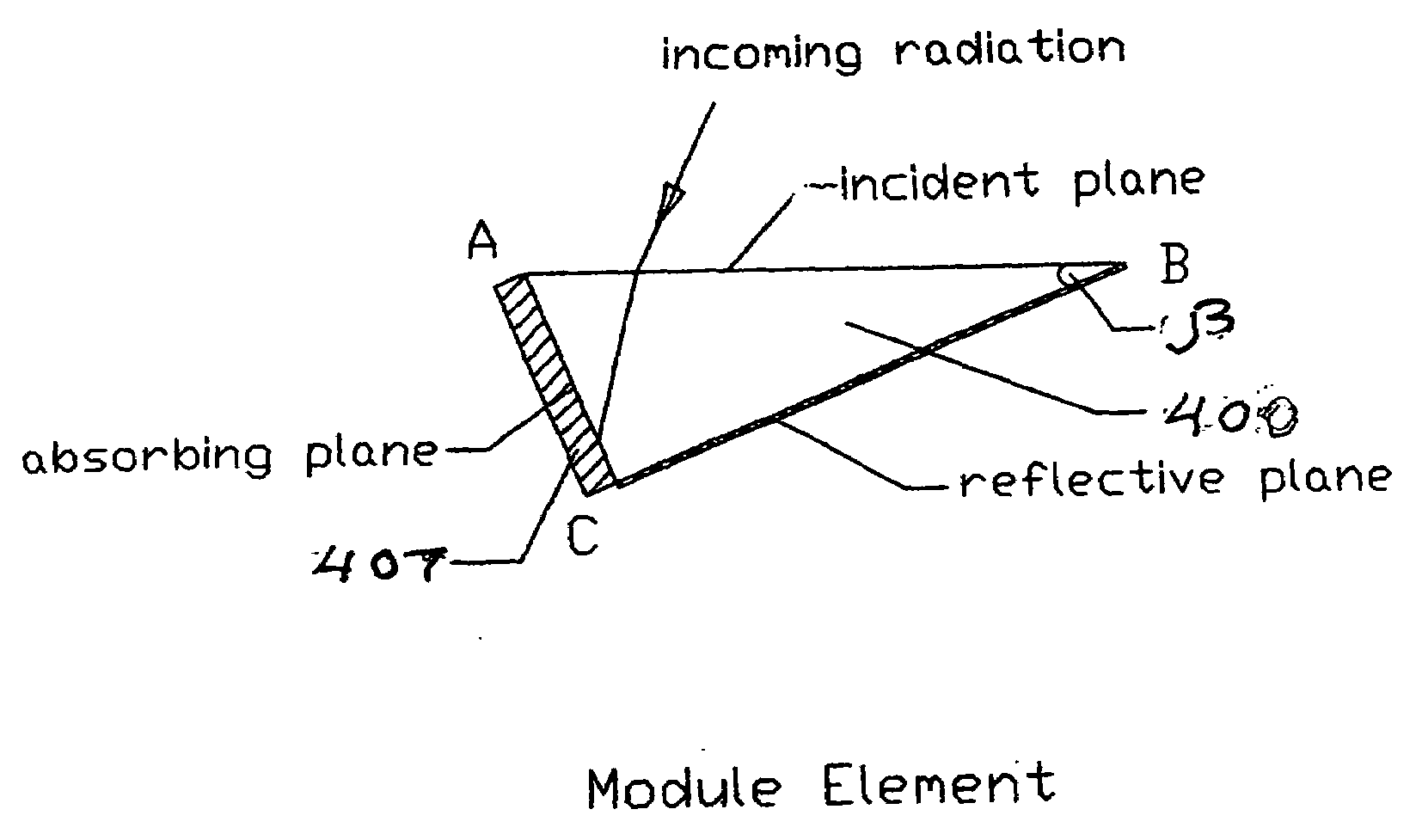
Low aspect ratio concentrator photovoltaic module with improved light transmission and reflective properties
InactiveUS20070227582A1Low aspect ratioImproved surface characteristicSolar heating energySolar heat devicesAspect ratioPrism
A low aspect ratio concentrator photovoltaic module has blazed grating surfaces on the light incident and / or reflective light planes that direct optimal wavelengths of light energy to a photo receptor enabling a total internal reflection condition to be achieved with a significantly smaller apex angle. Apex angles can be achieved that are 10° or less depending on the blazed grating angle and groove density, thereby providing a low aspect ratio prism that achieves a dramatic savings in silicon; using only 15 to 20 per cent of the silicon used in a conventional solar module without loss of photovoltaic efficiency. This achieves a significant reduction in the overall material and weight of the prism, making possible a low cost, lightweight, and highly efficient PV module suitable for widespread implementation.
Owner:SV SOLAR INC
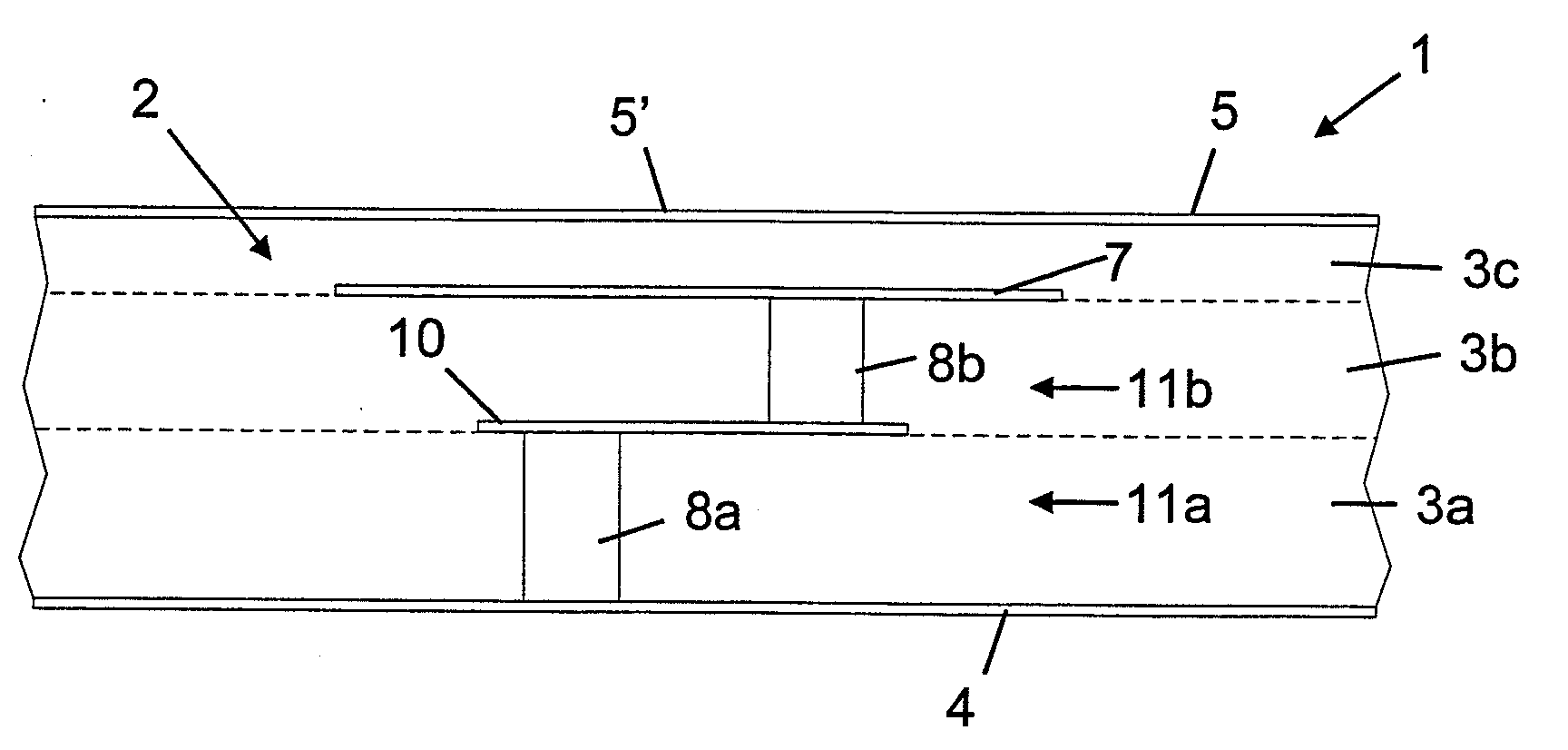
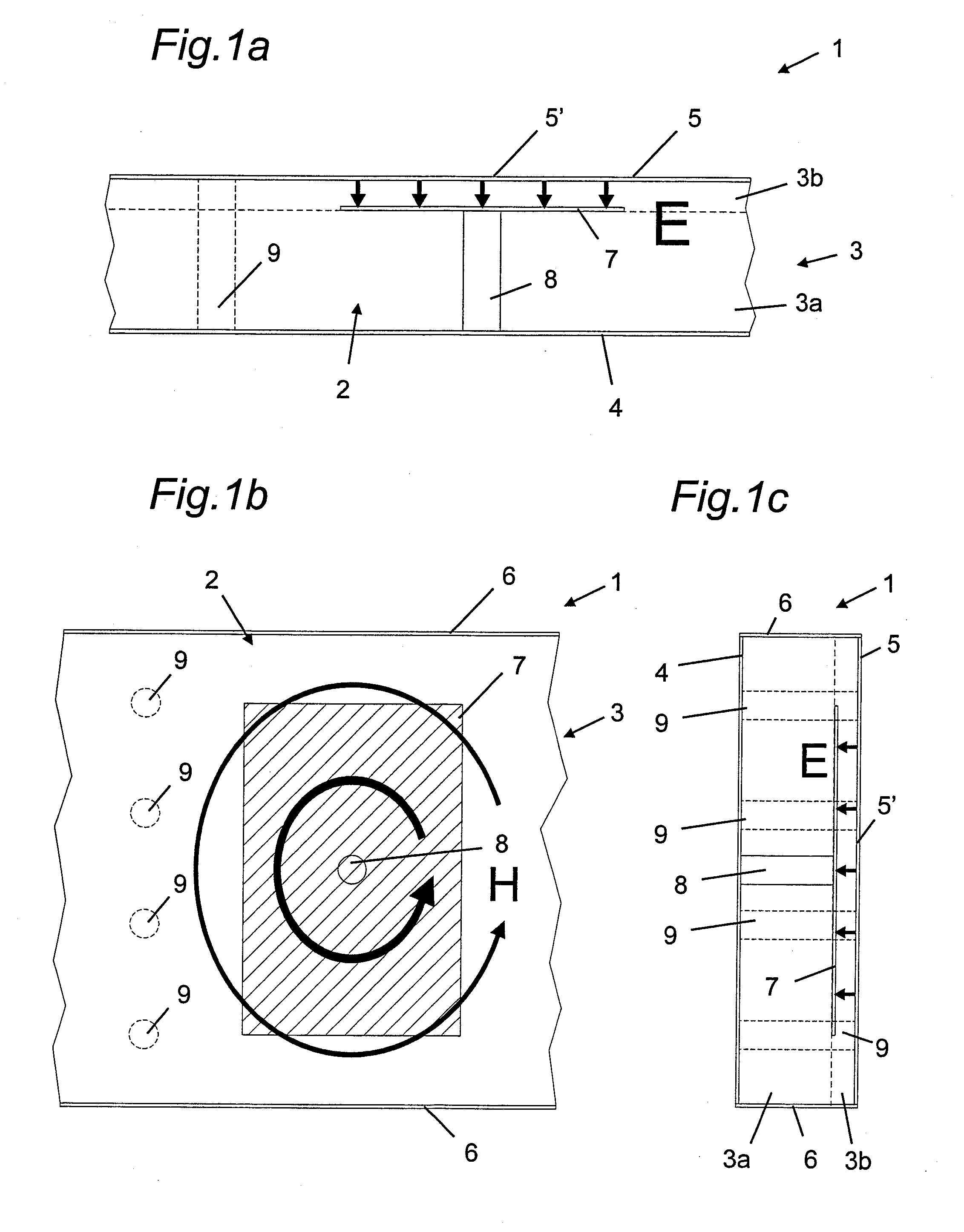
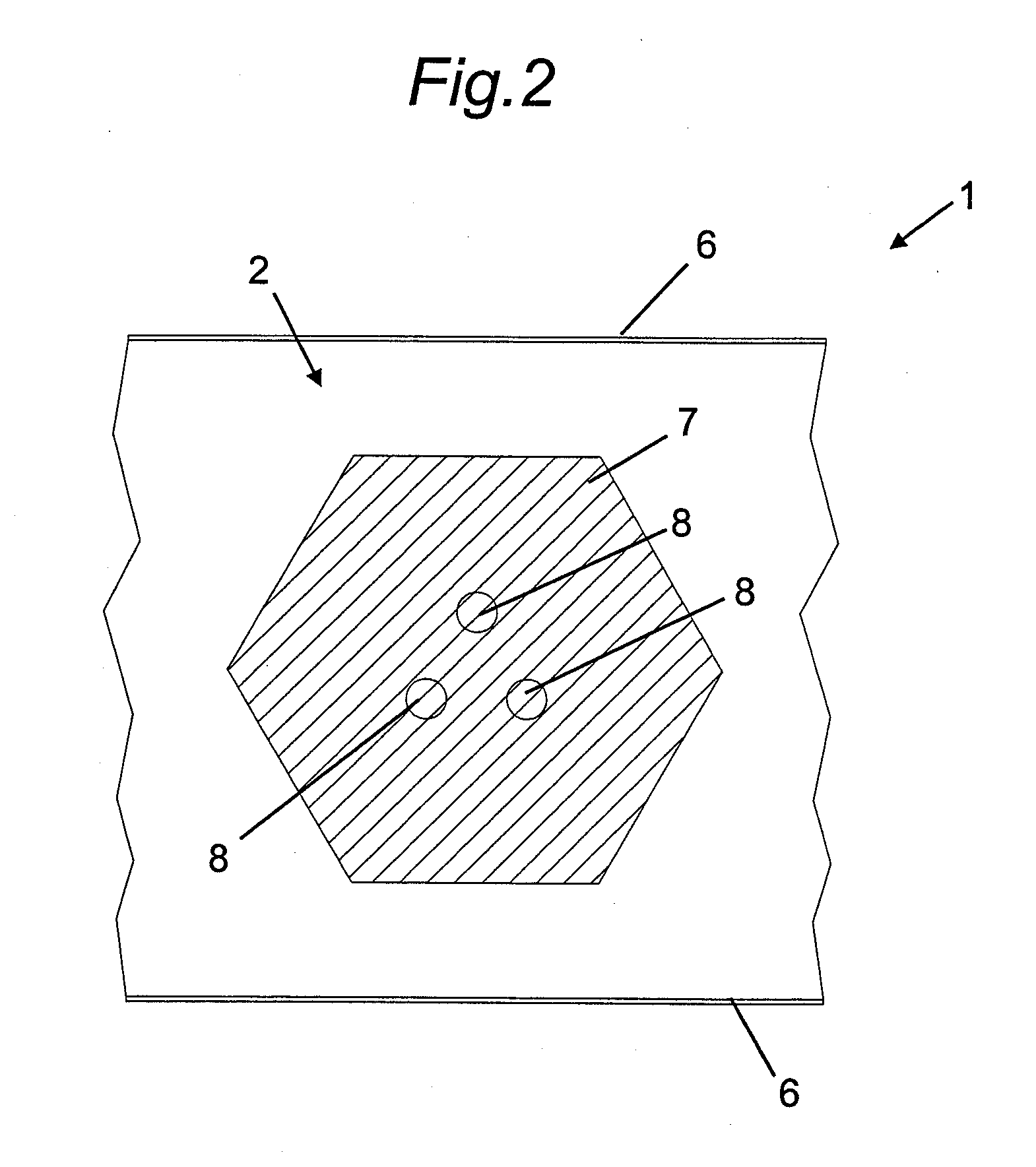
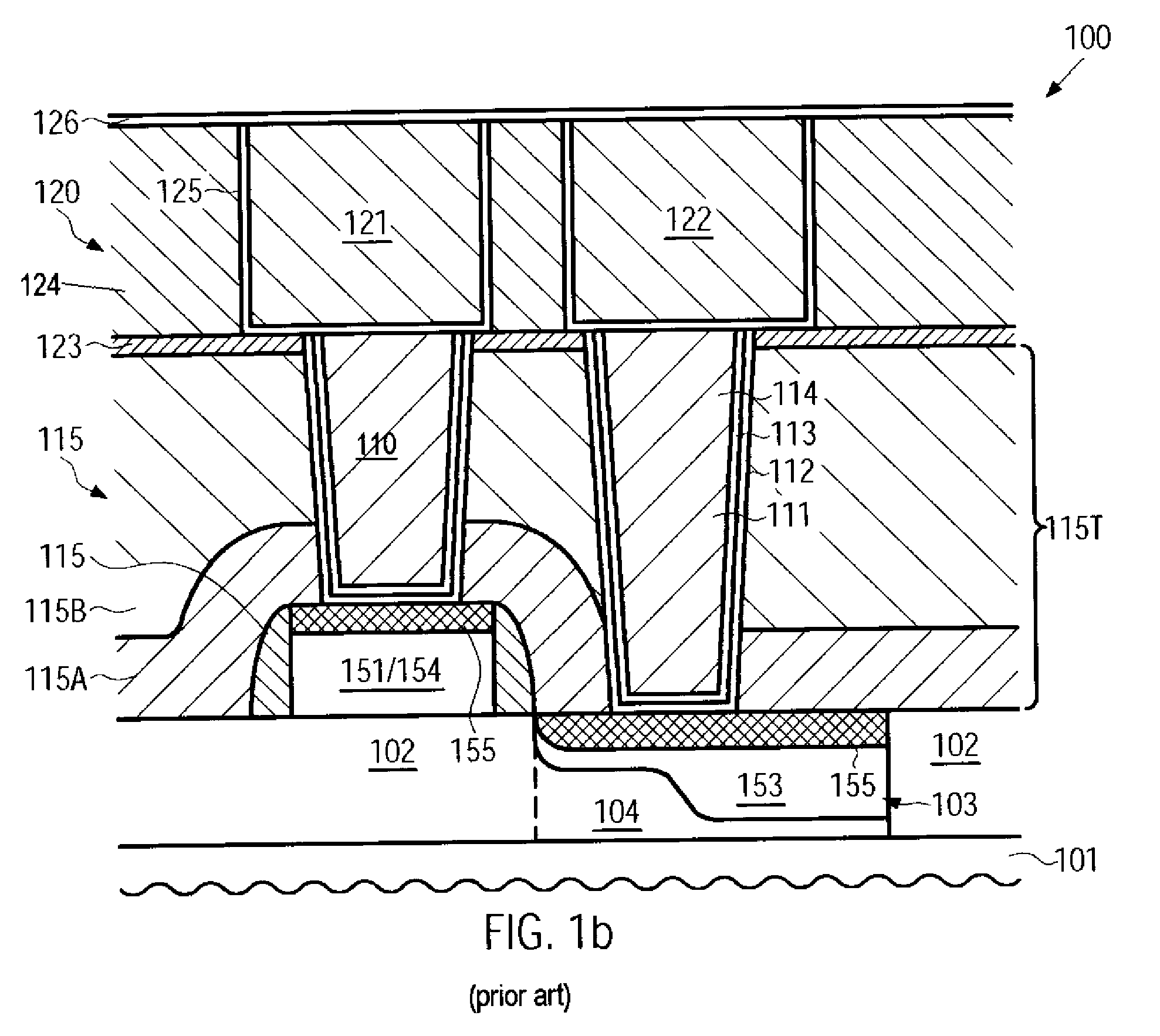
Hybrid contact structure with low aspect ratio contacts in a semiconductor device
ActiveUS20090140431A1Improved contact structureReduce aspect ratioSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical performanceEngineering
By forming the first metallization layer of a semiconductor device as a dual damascene structure, the contact elements may be formed on the basis of a significantly reduced aspect ratio, thereby enhancing process robustness and also improving electrical performance of the contact structure.
Owner:INNOVATIVE FOUNDRY TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com