Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
40results about How to "Plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
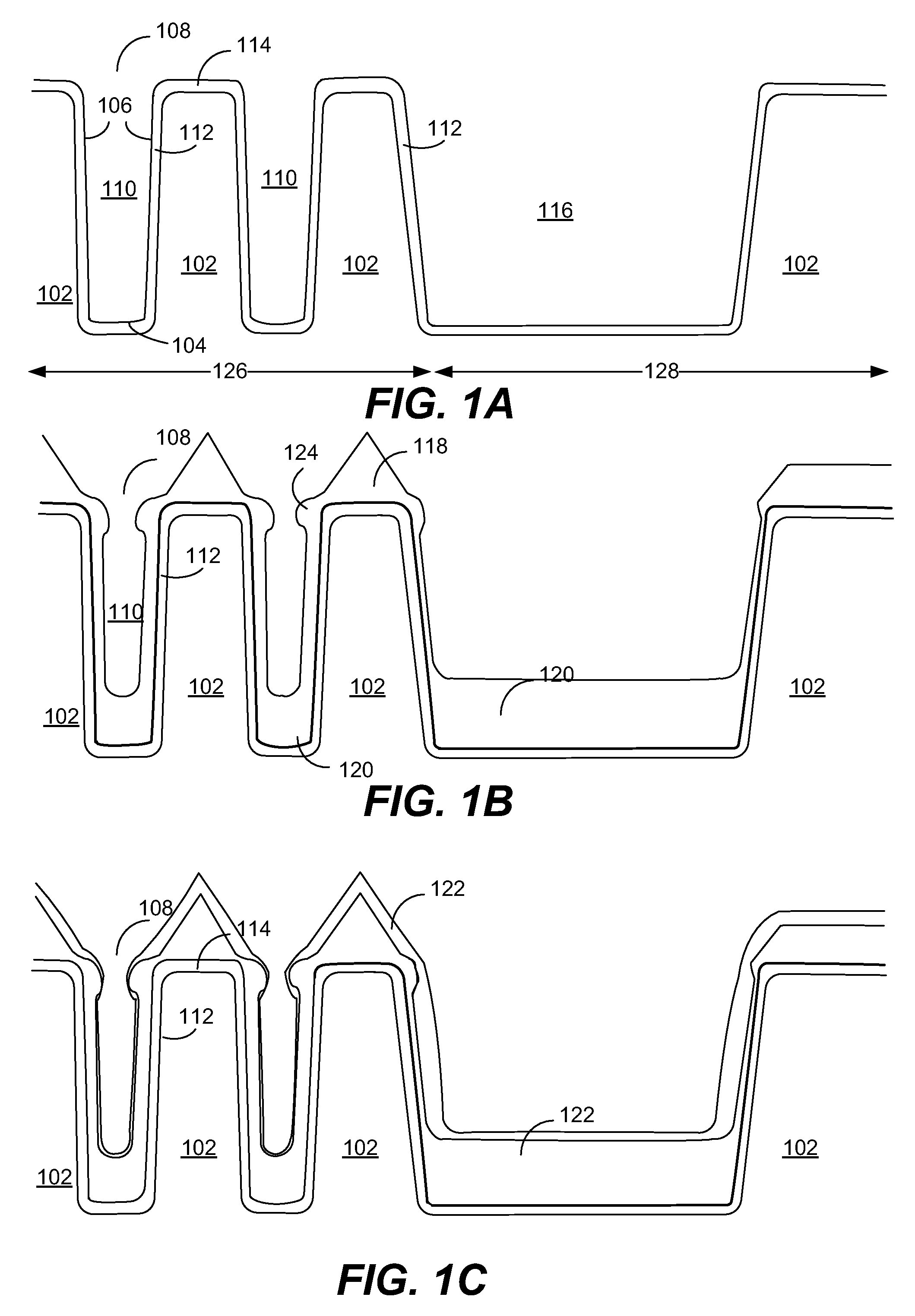
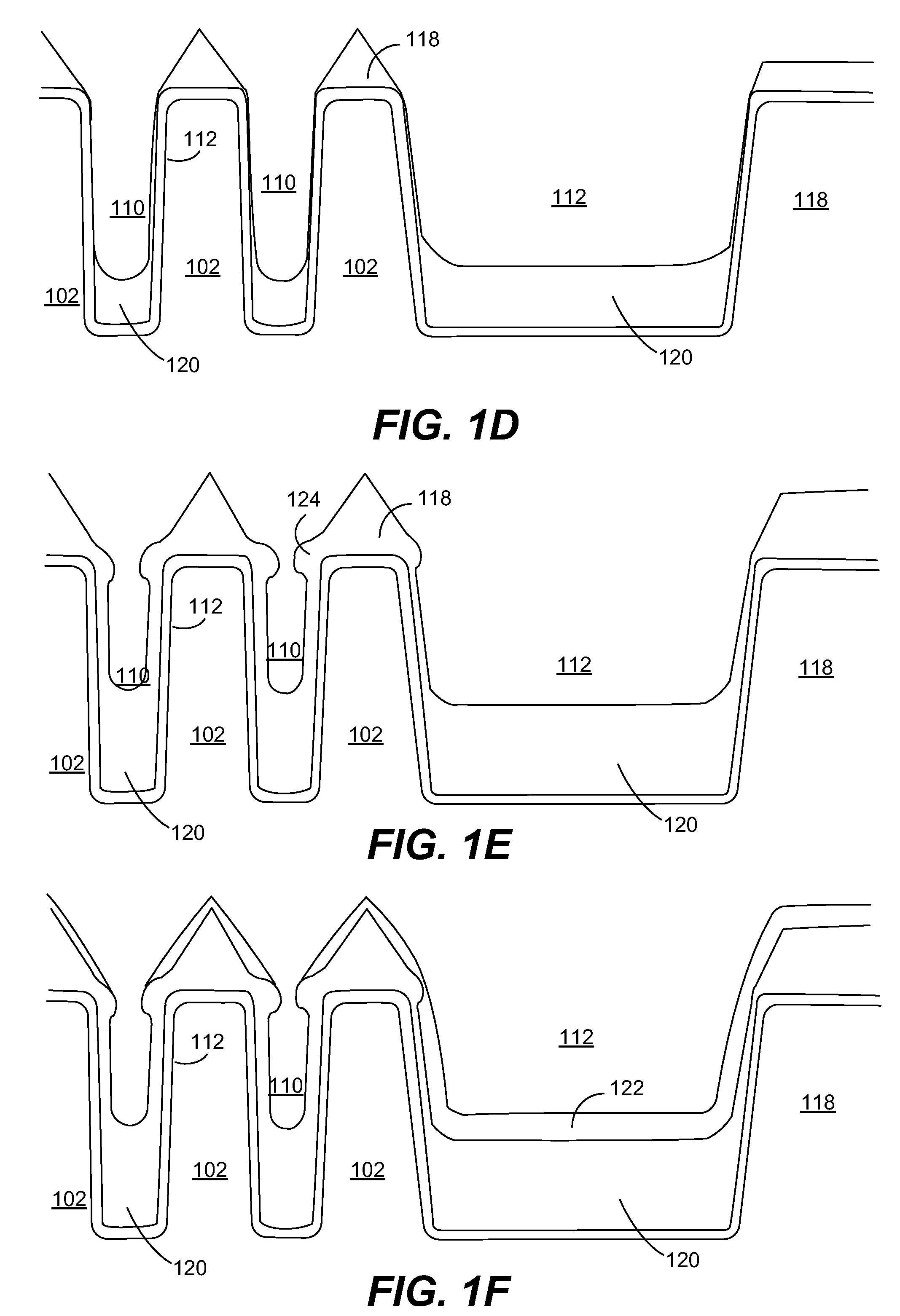
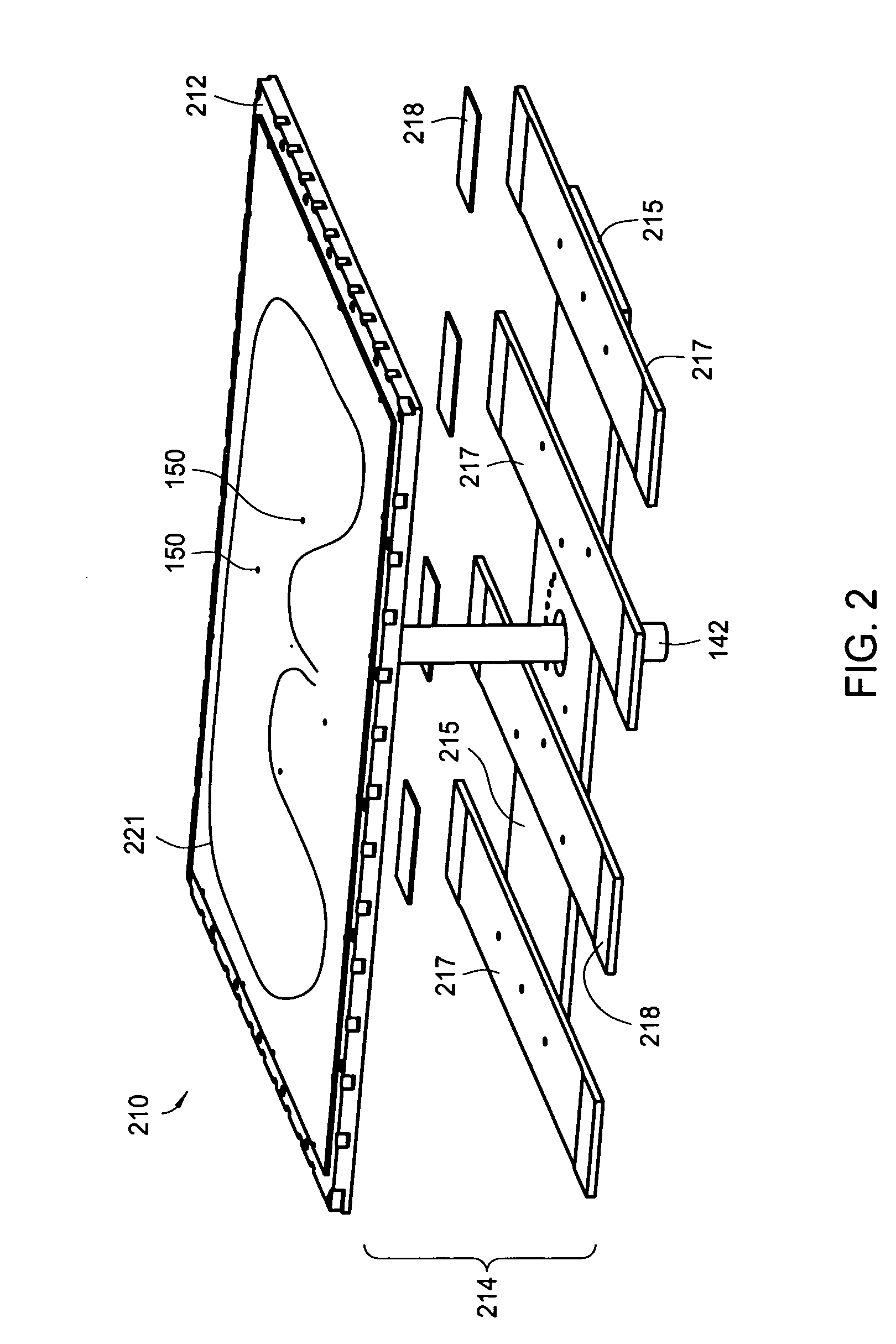
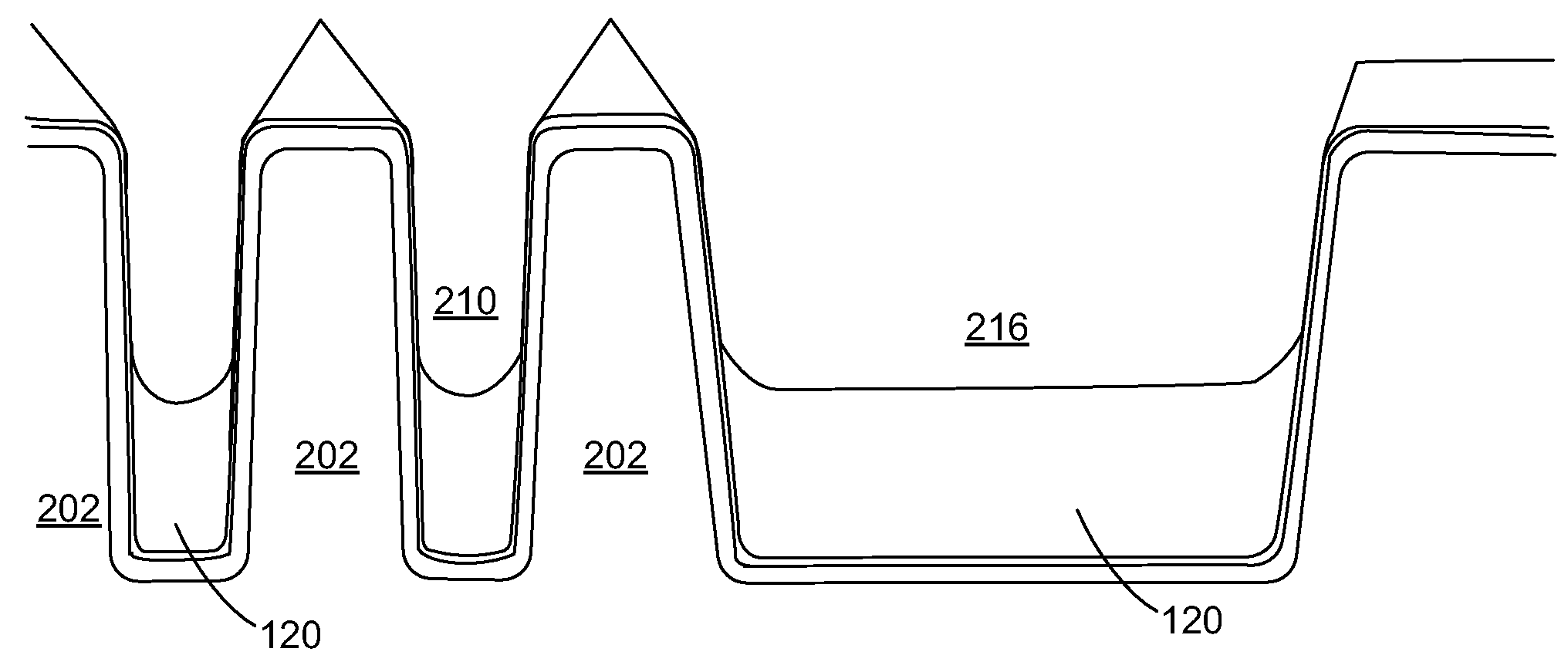
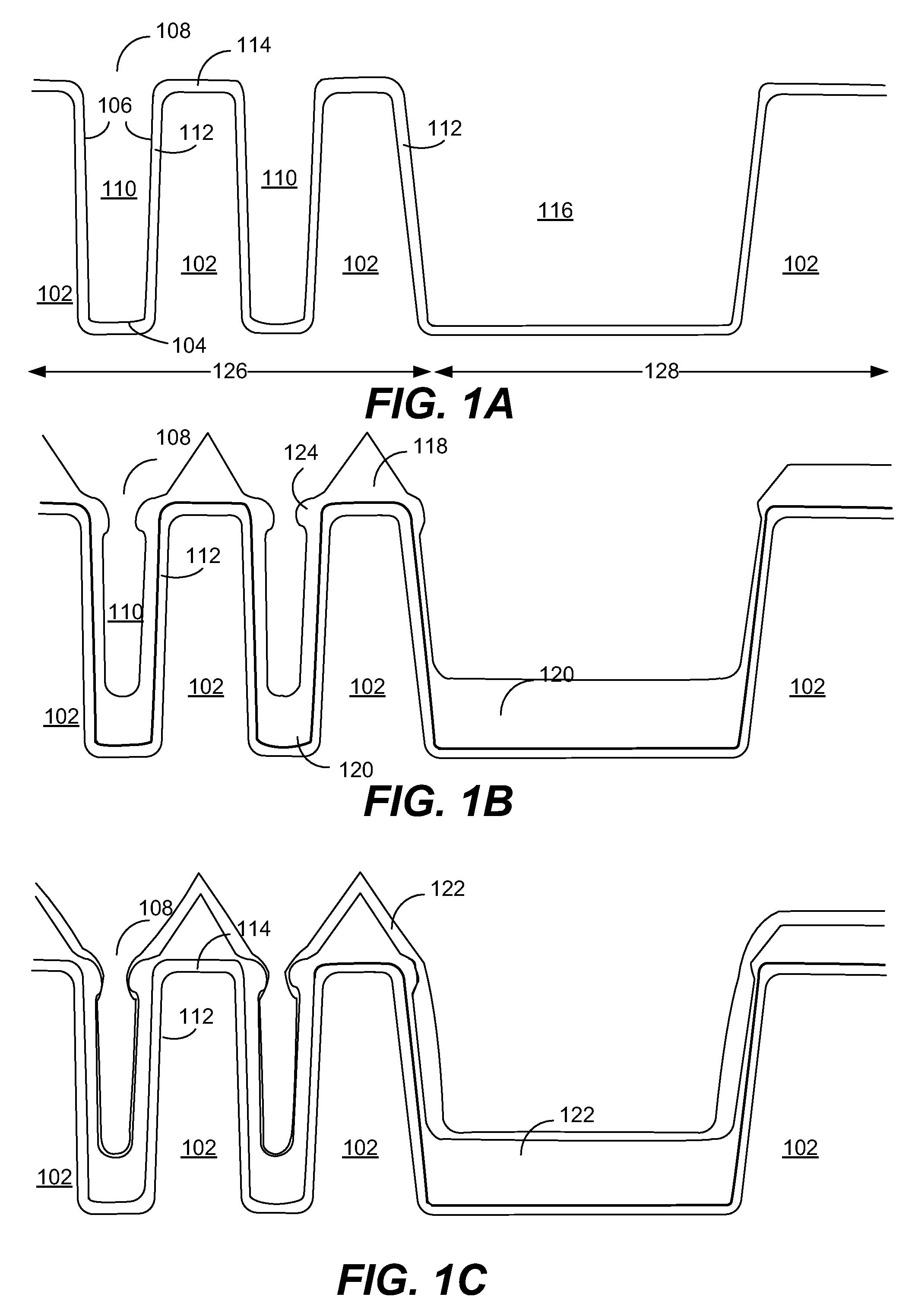
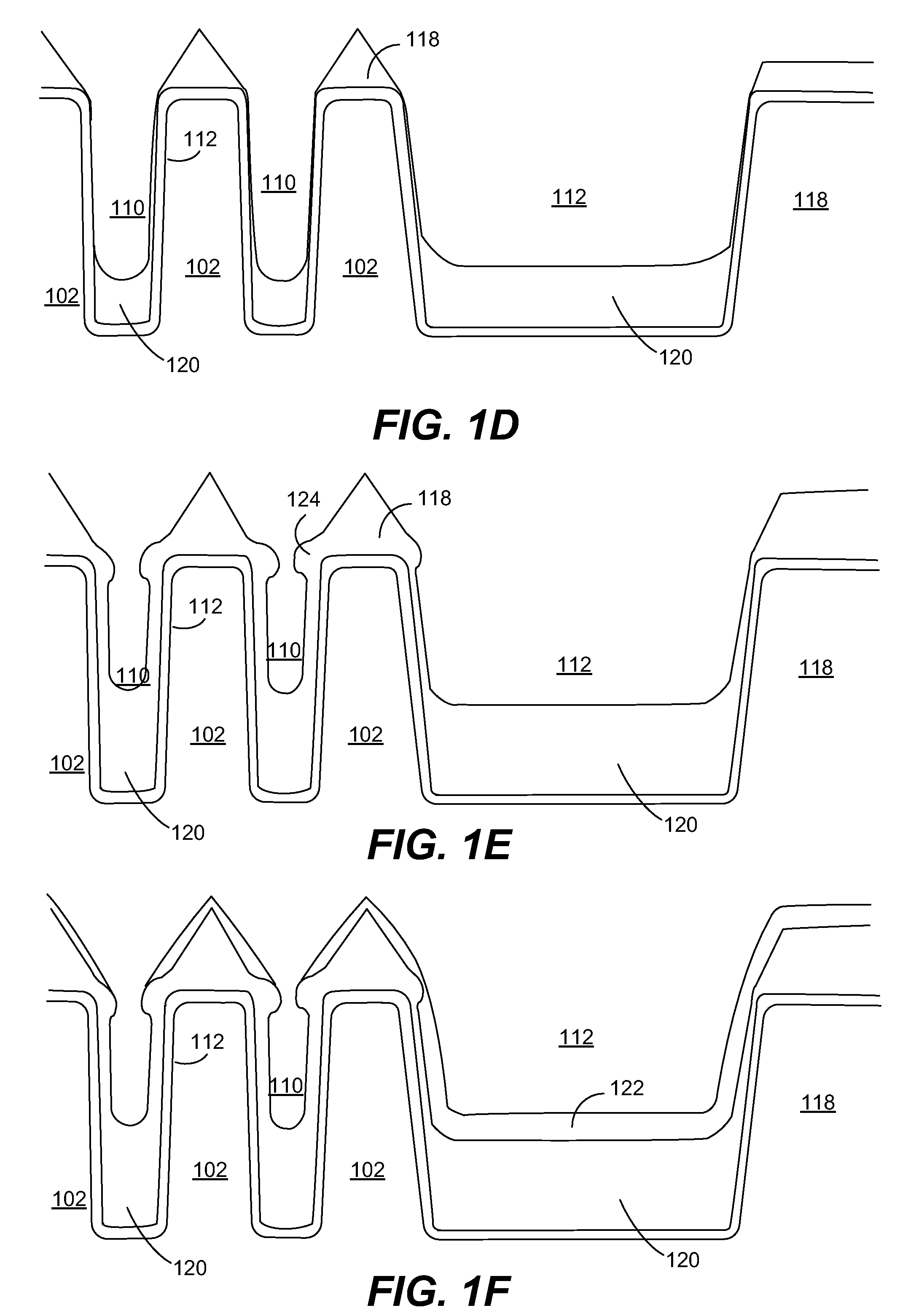
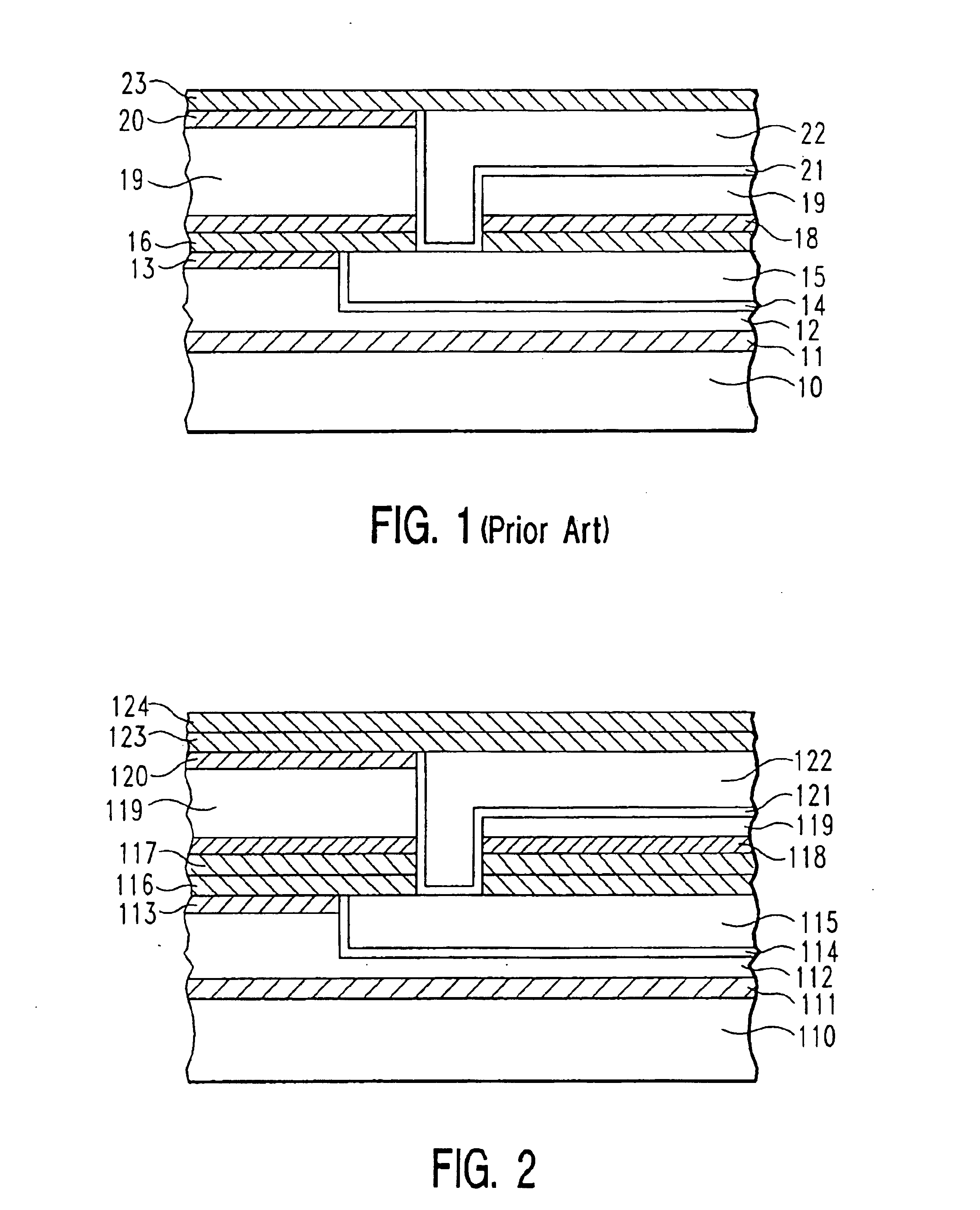
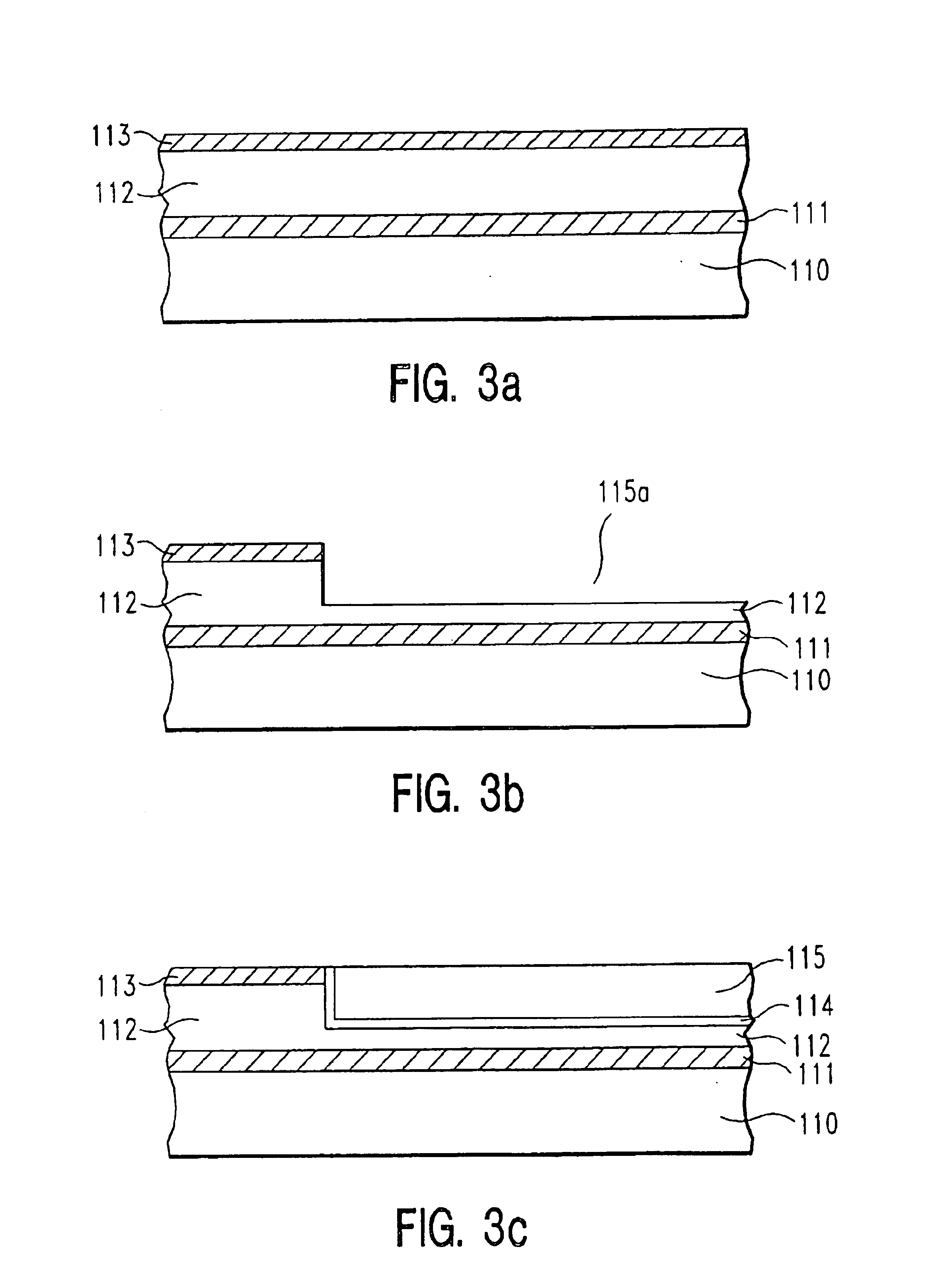
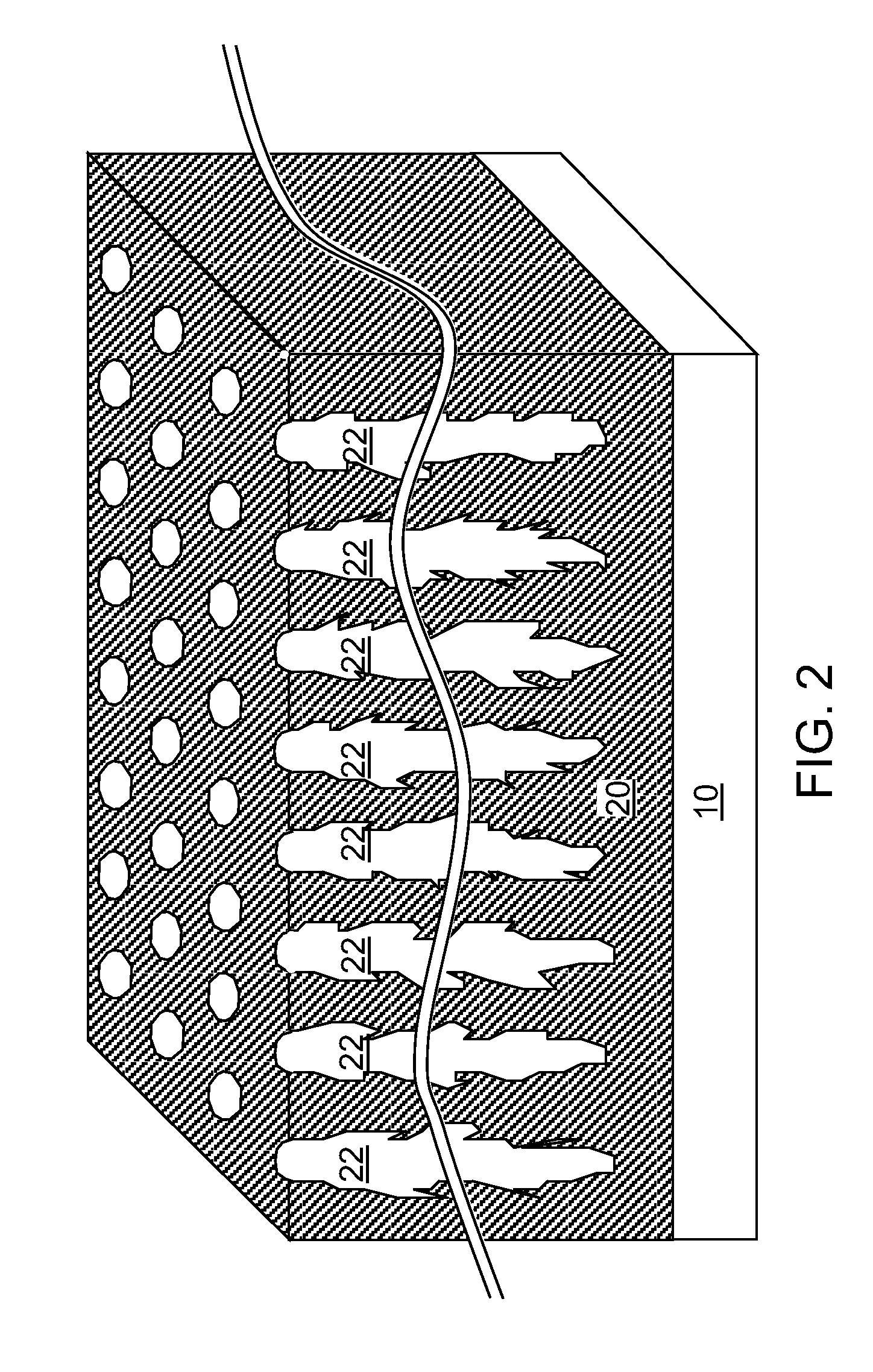
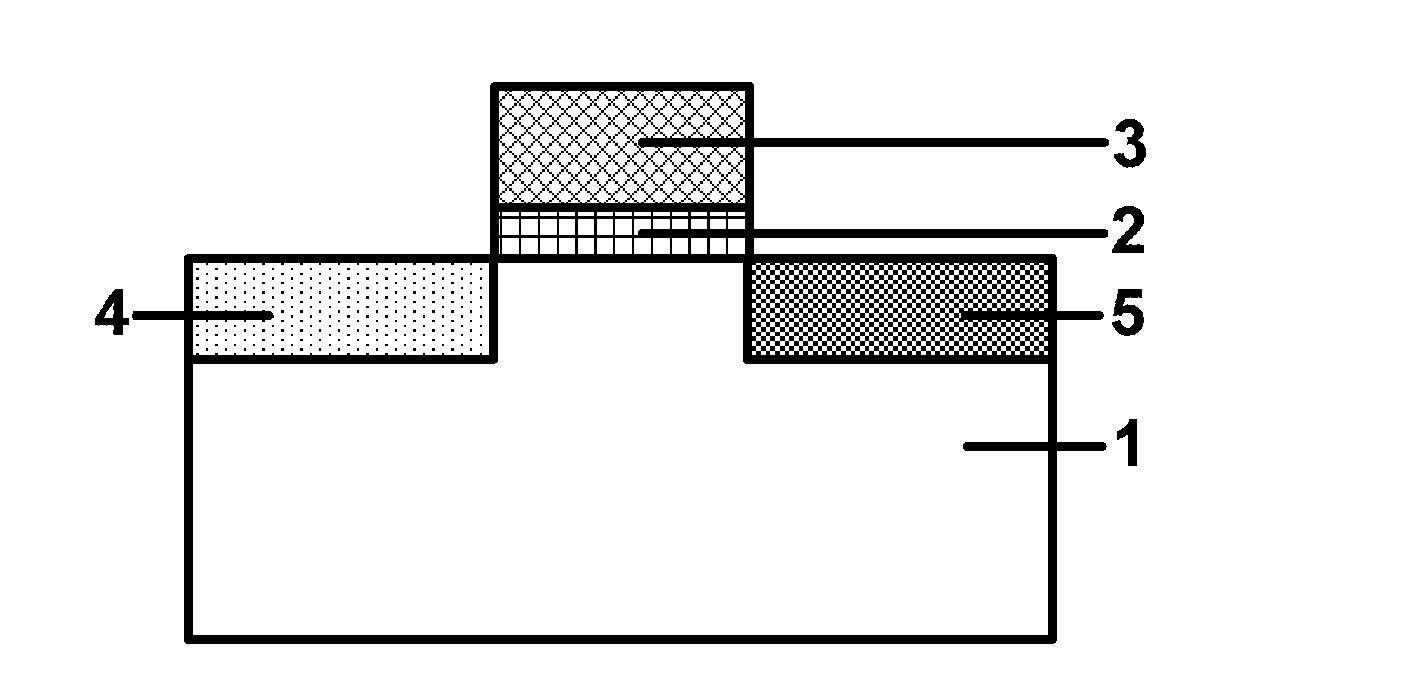
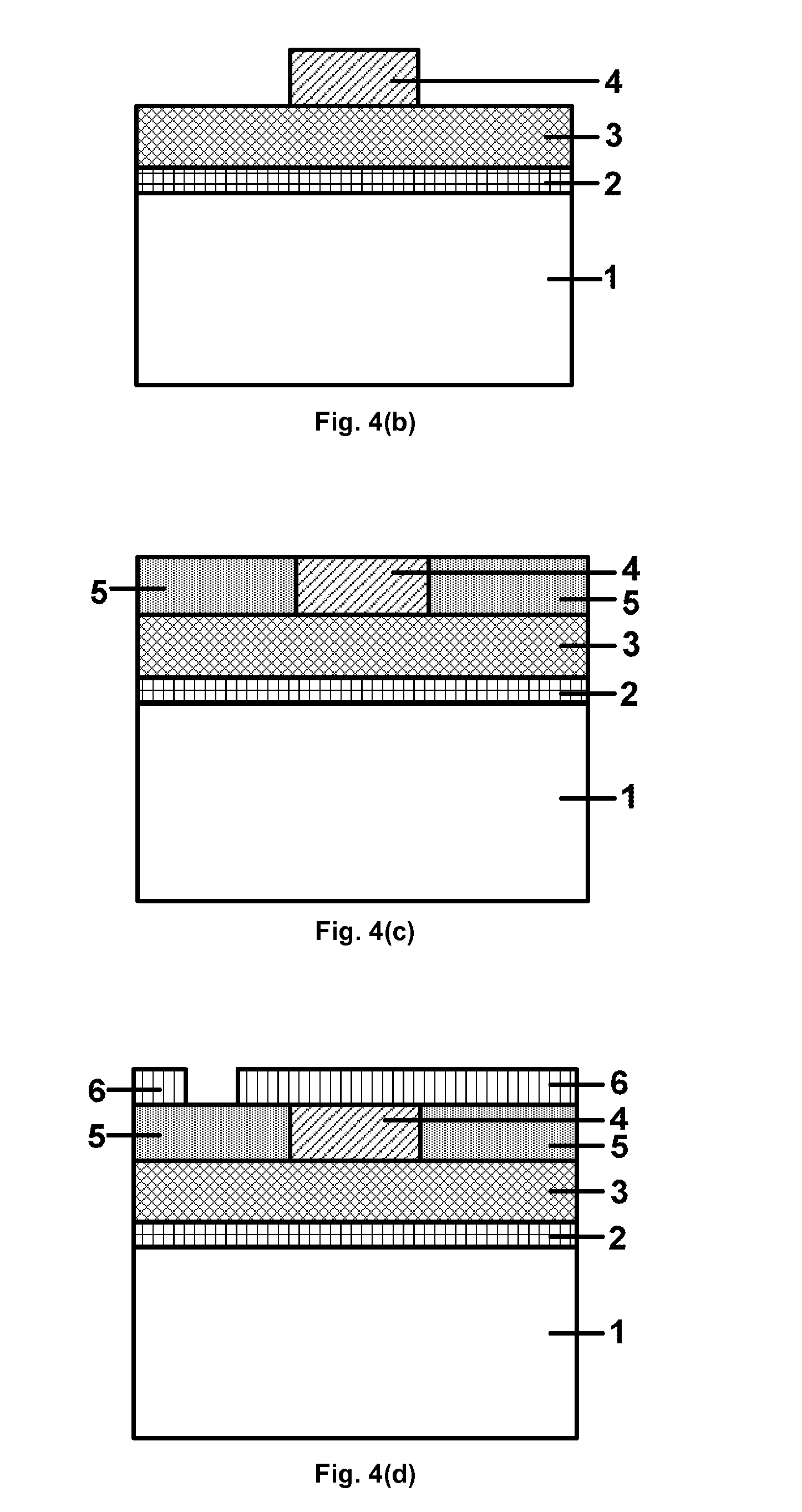
Method for forming silicon nitride film selectively on sidewalls or flat surfaces of trenches
ActiveUS20170243734A1Improve film qualityDecreasing density of filmElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEtchingChemical resistance
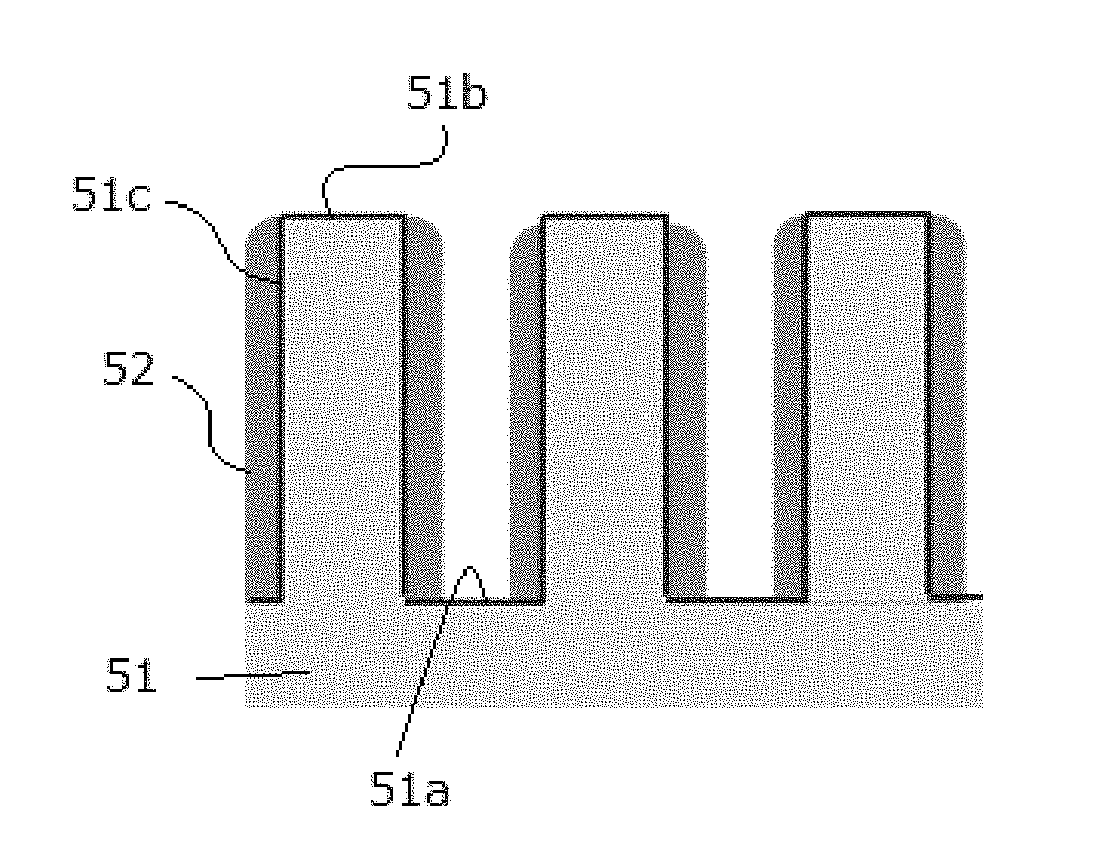
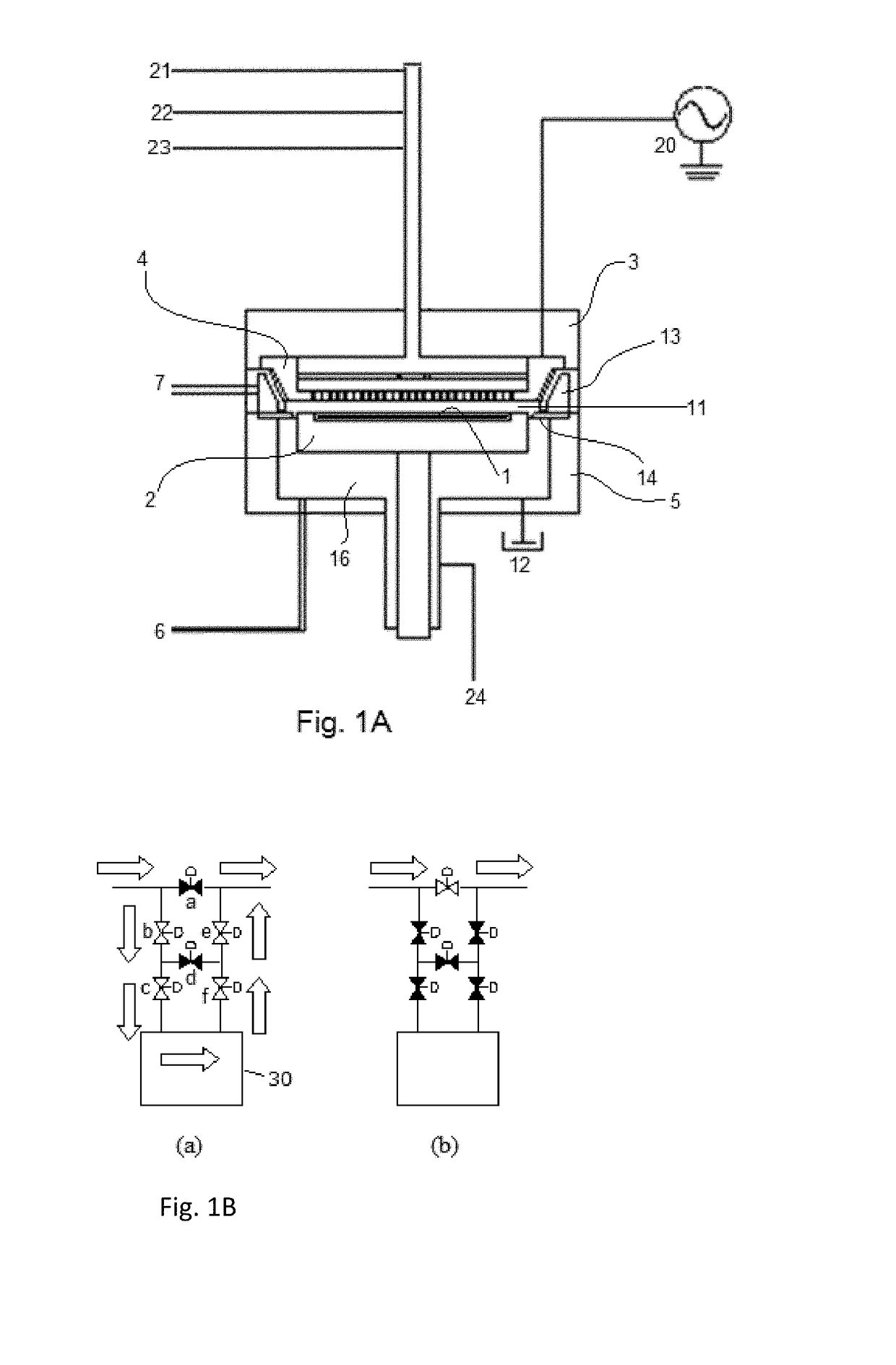
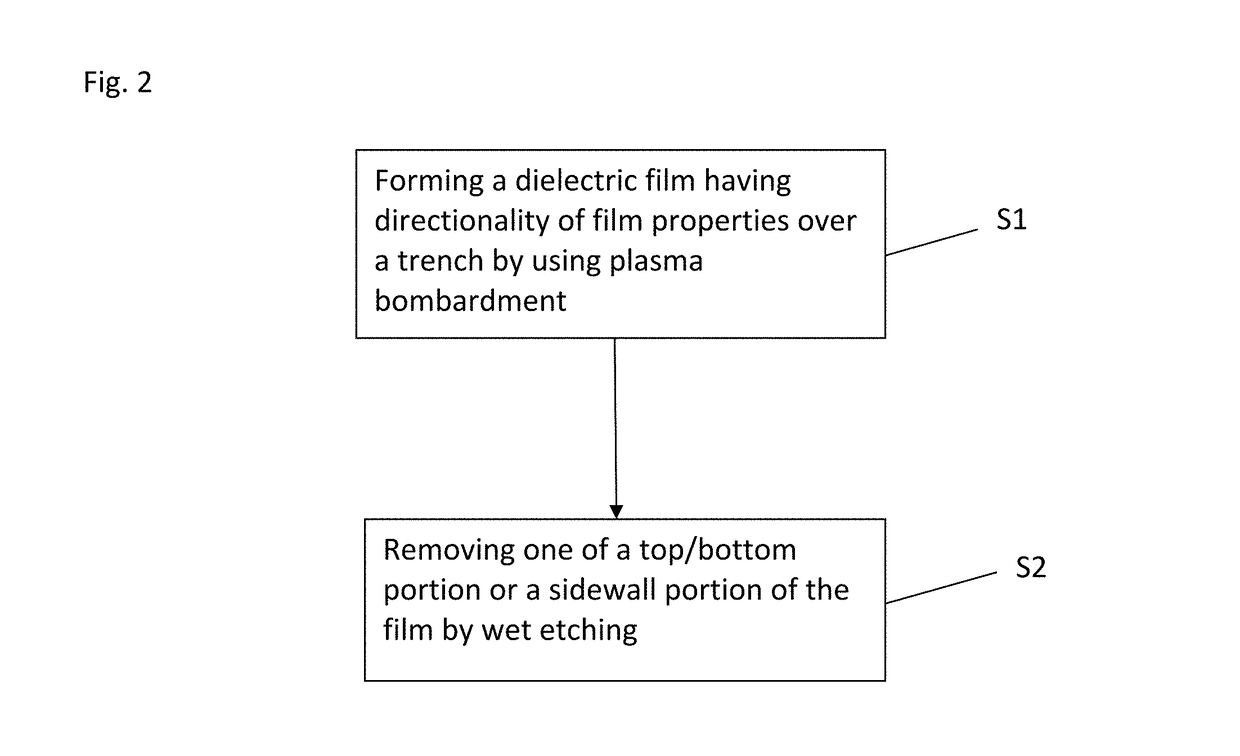
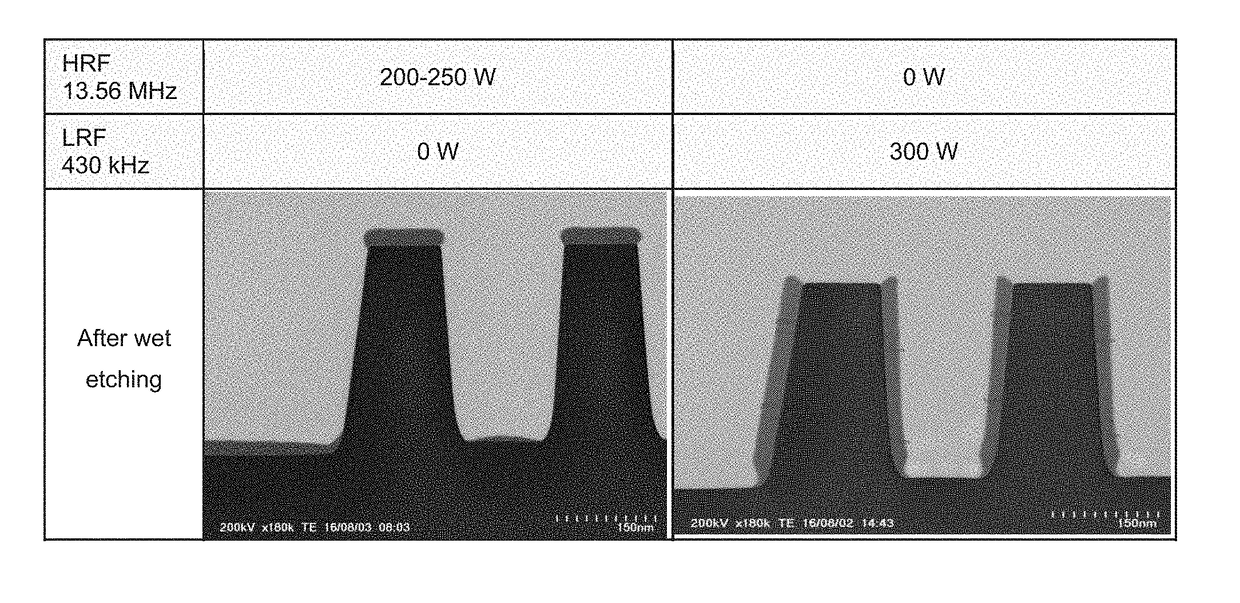
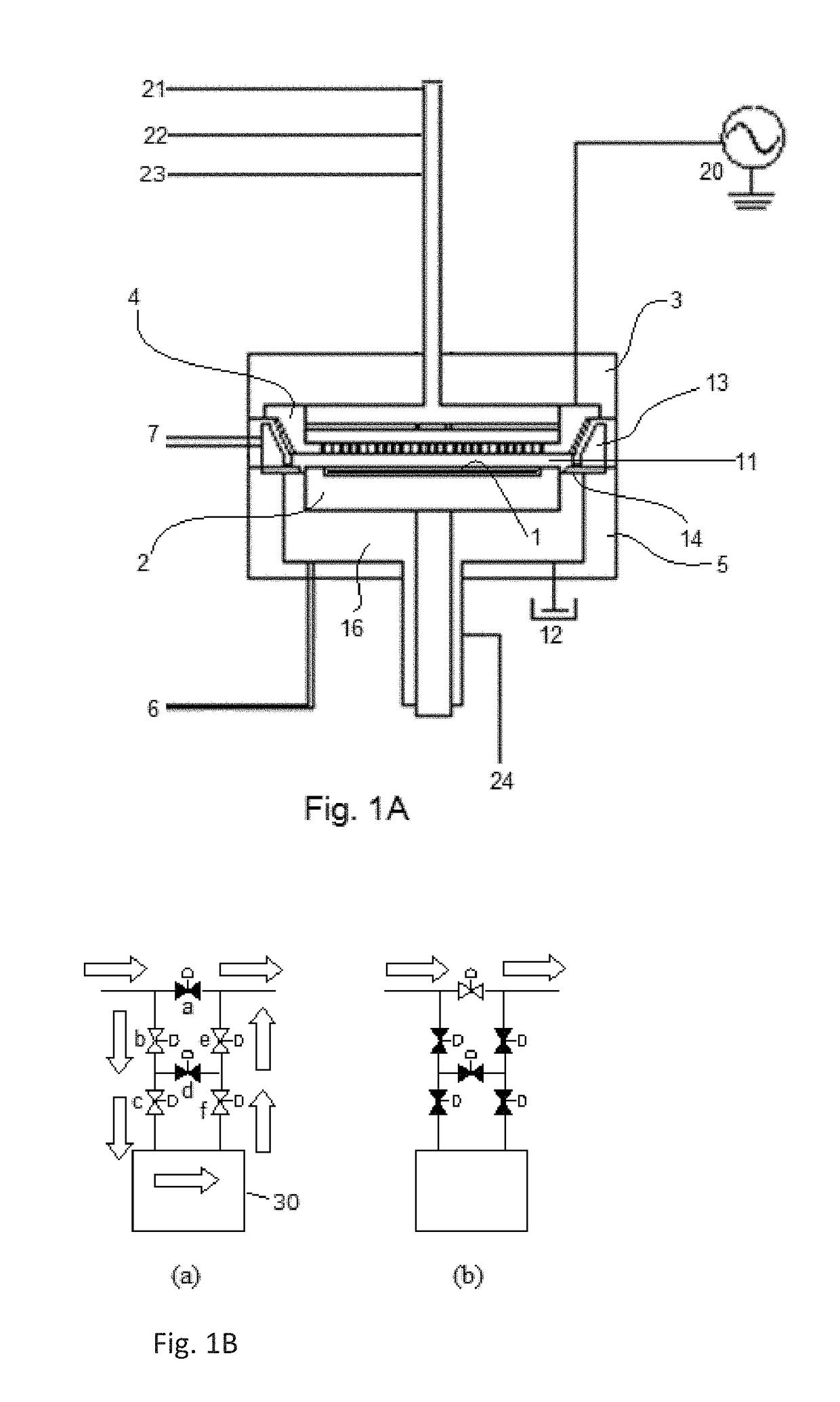
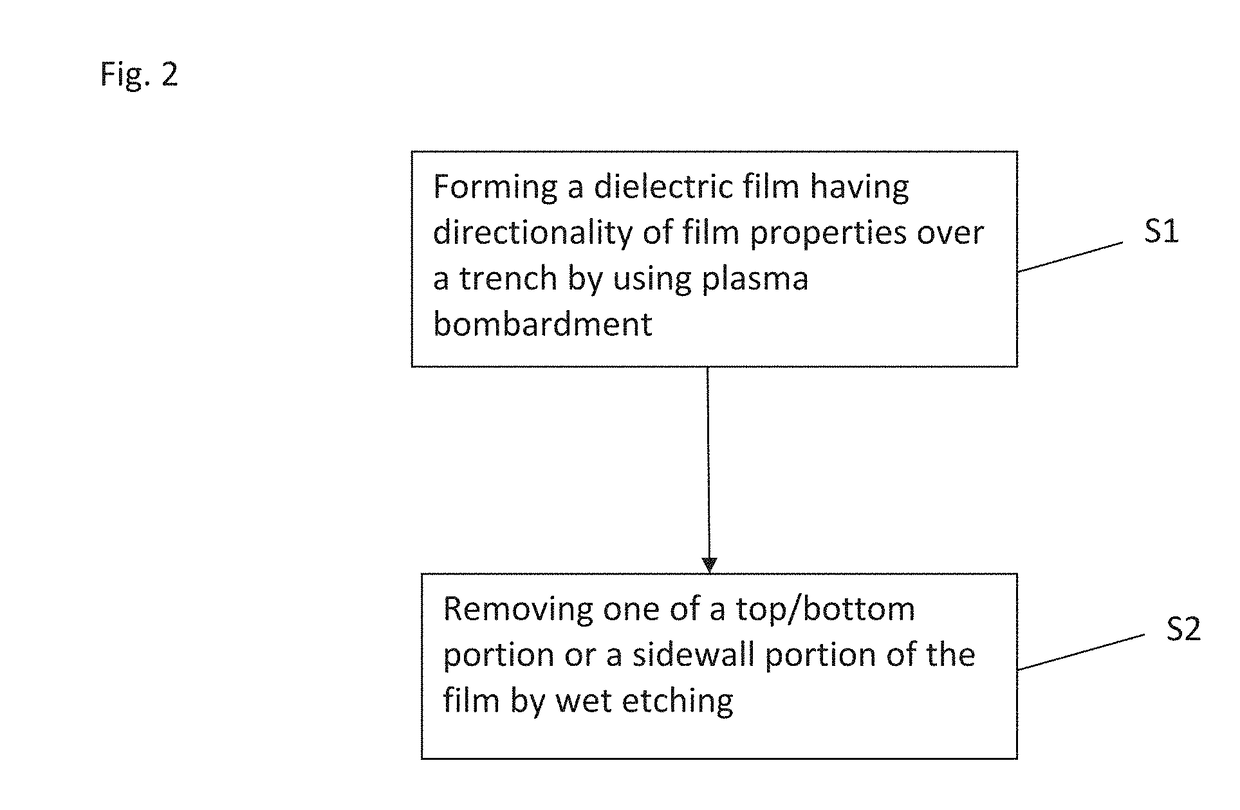
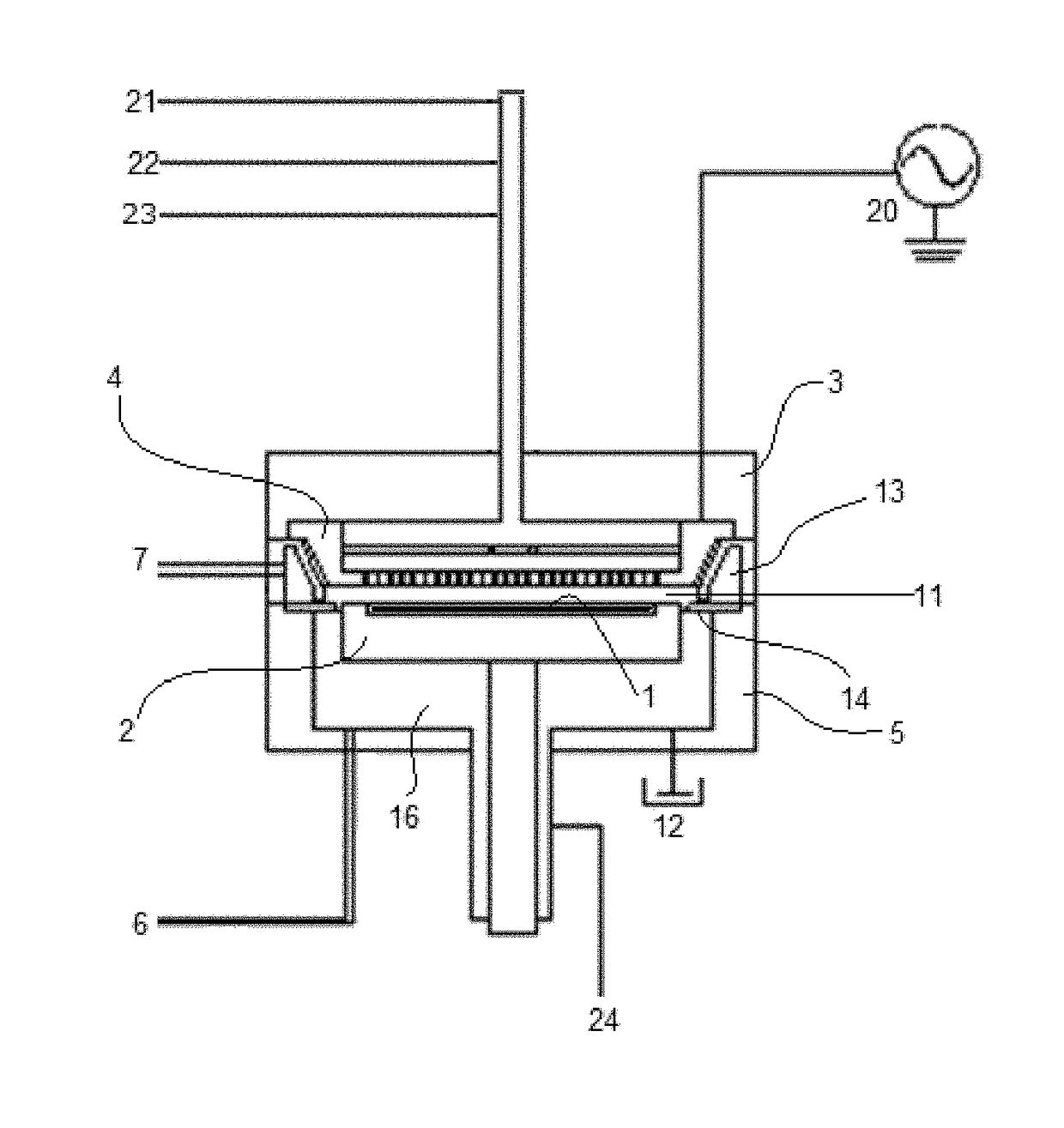
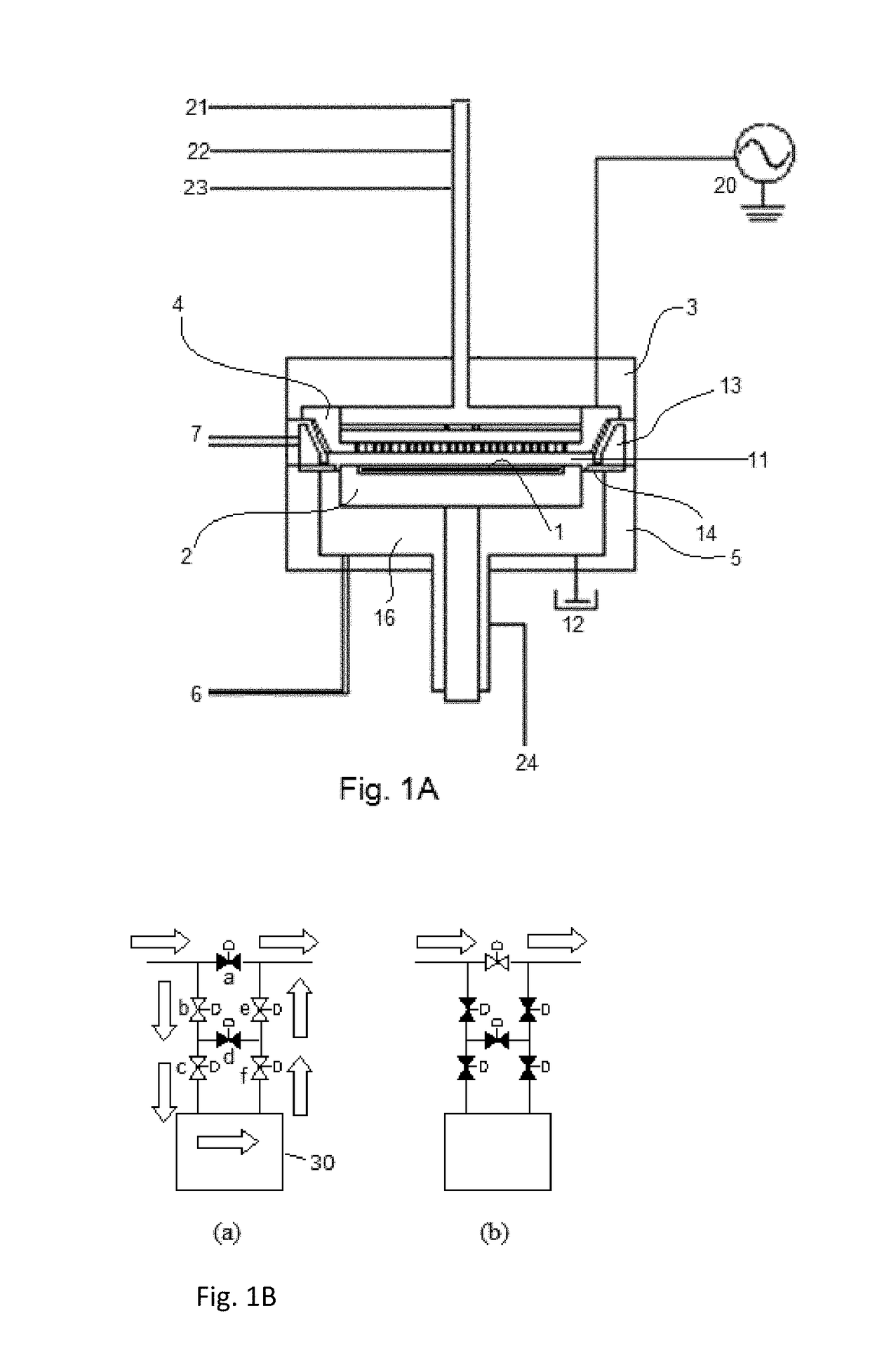
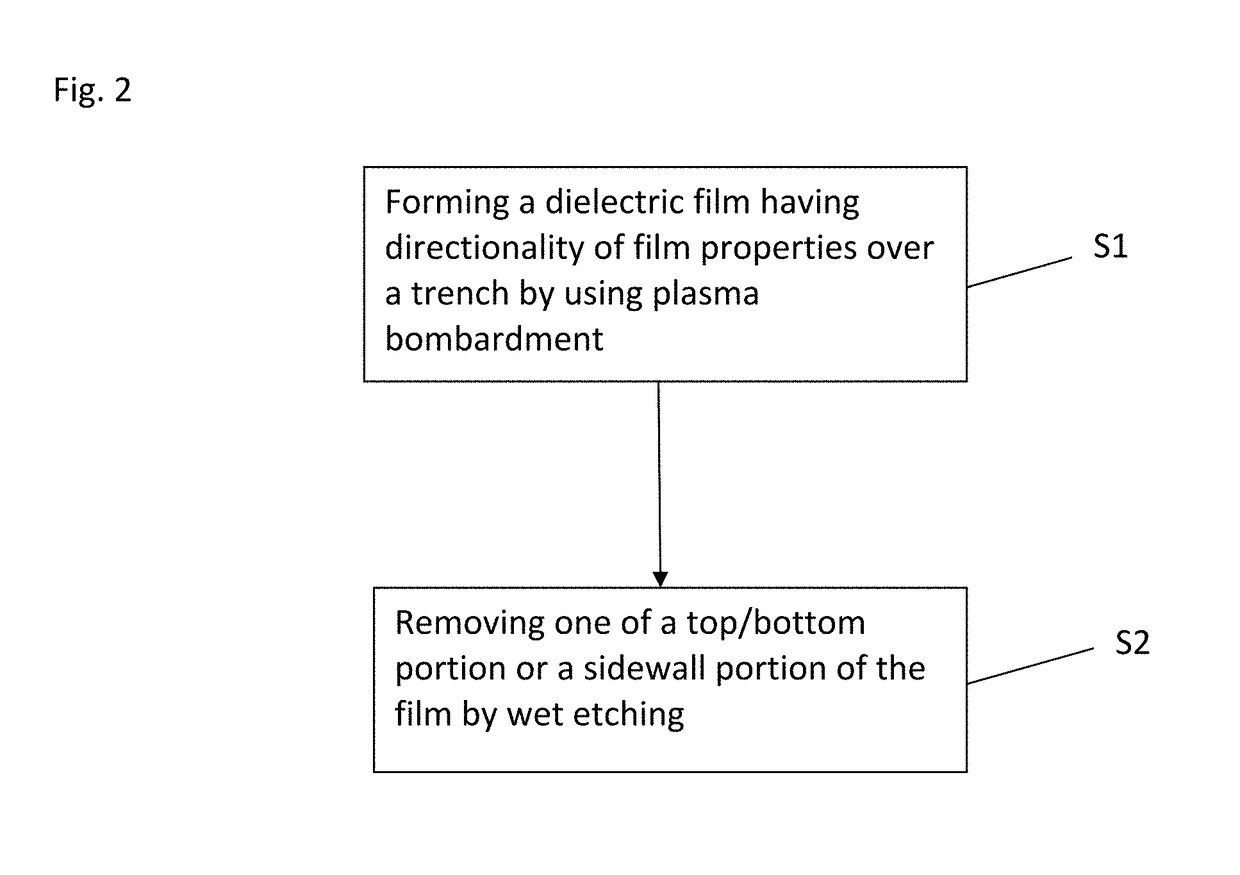
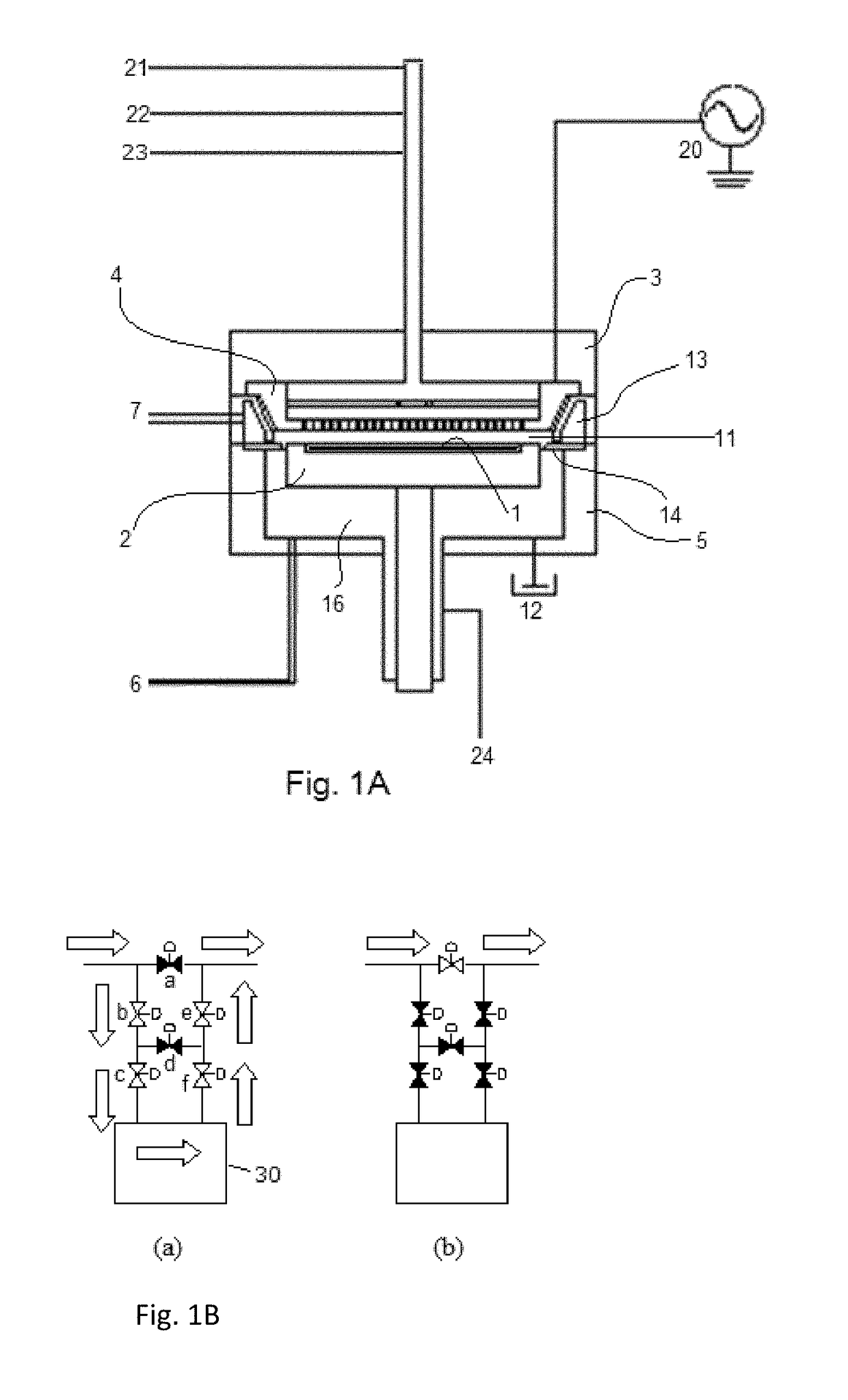
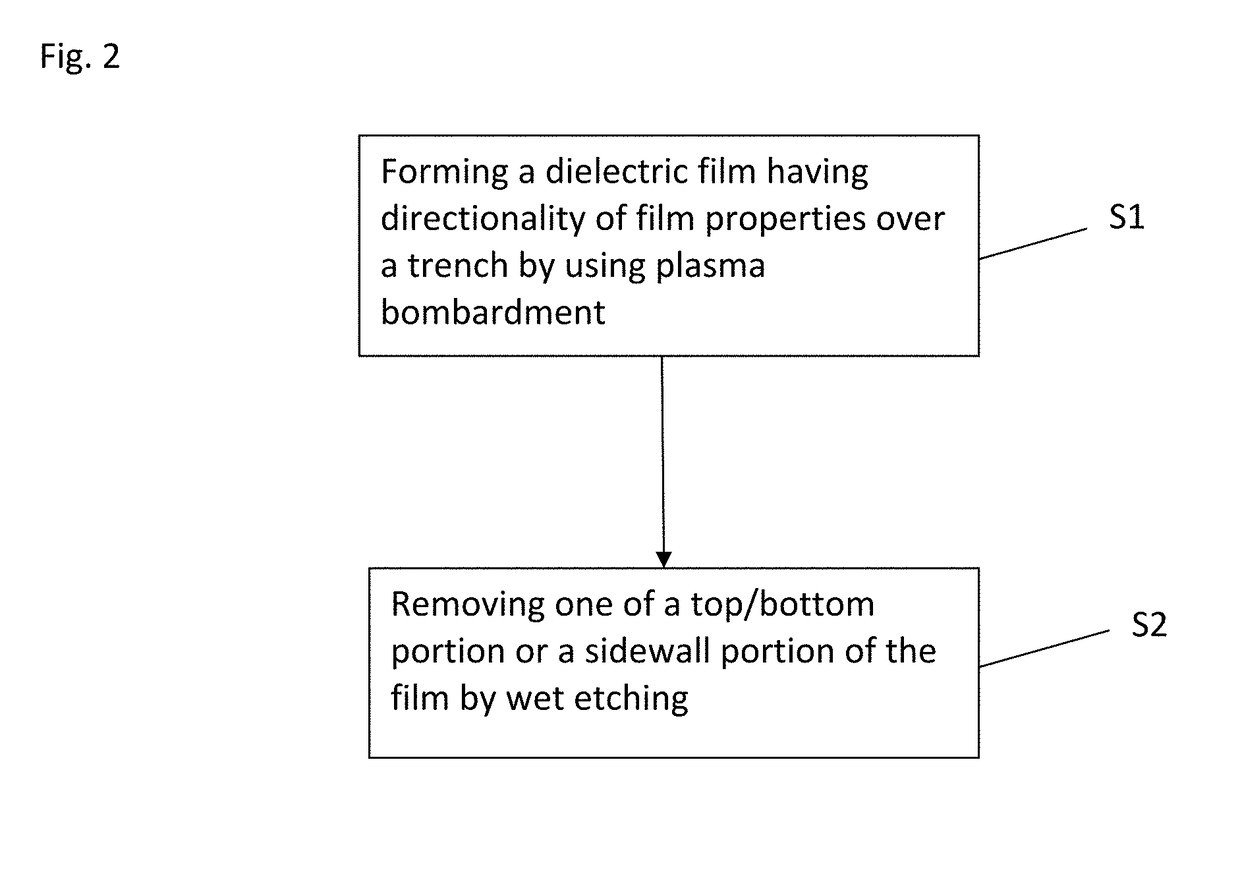
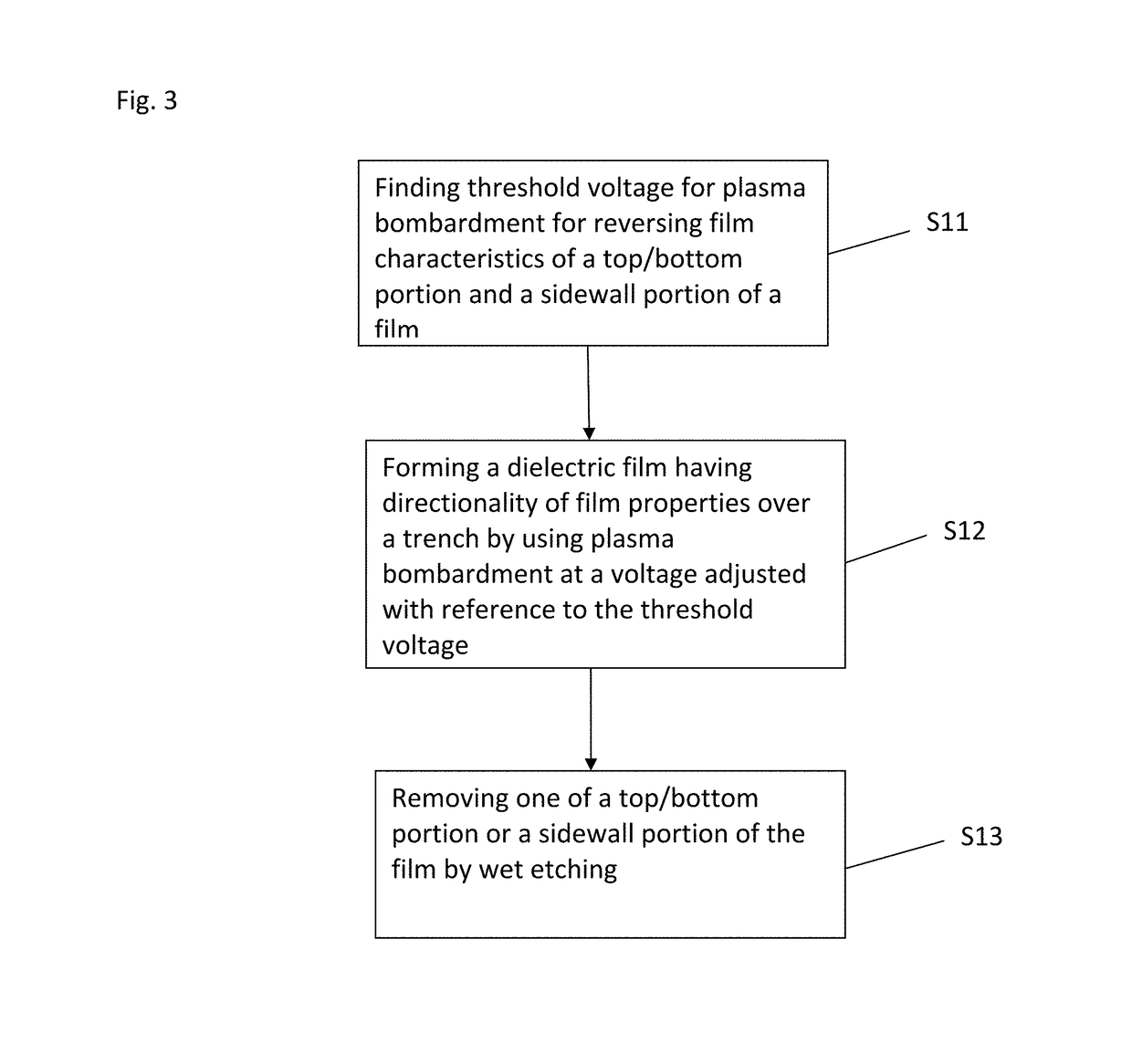
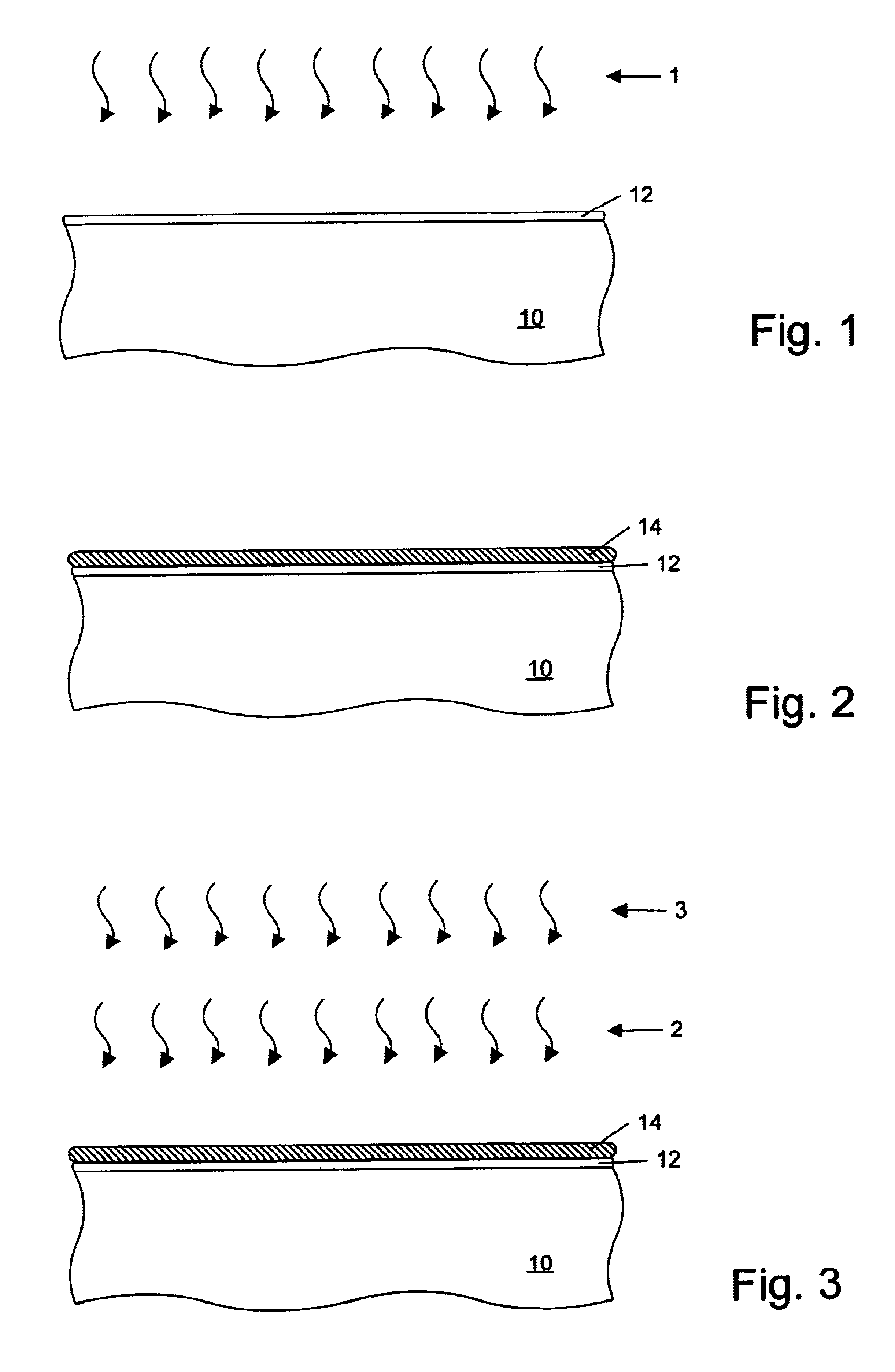
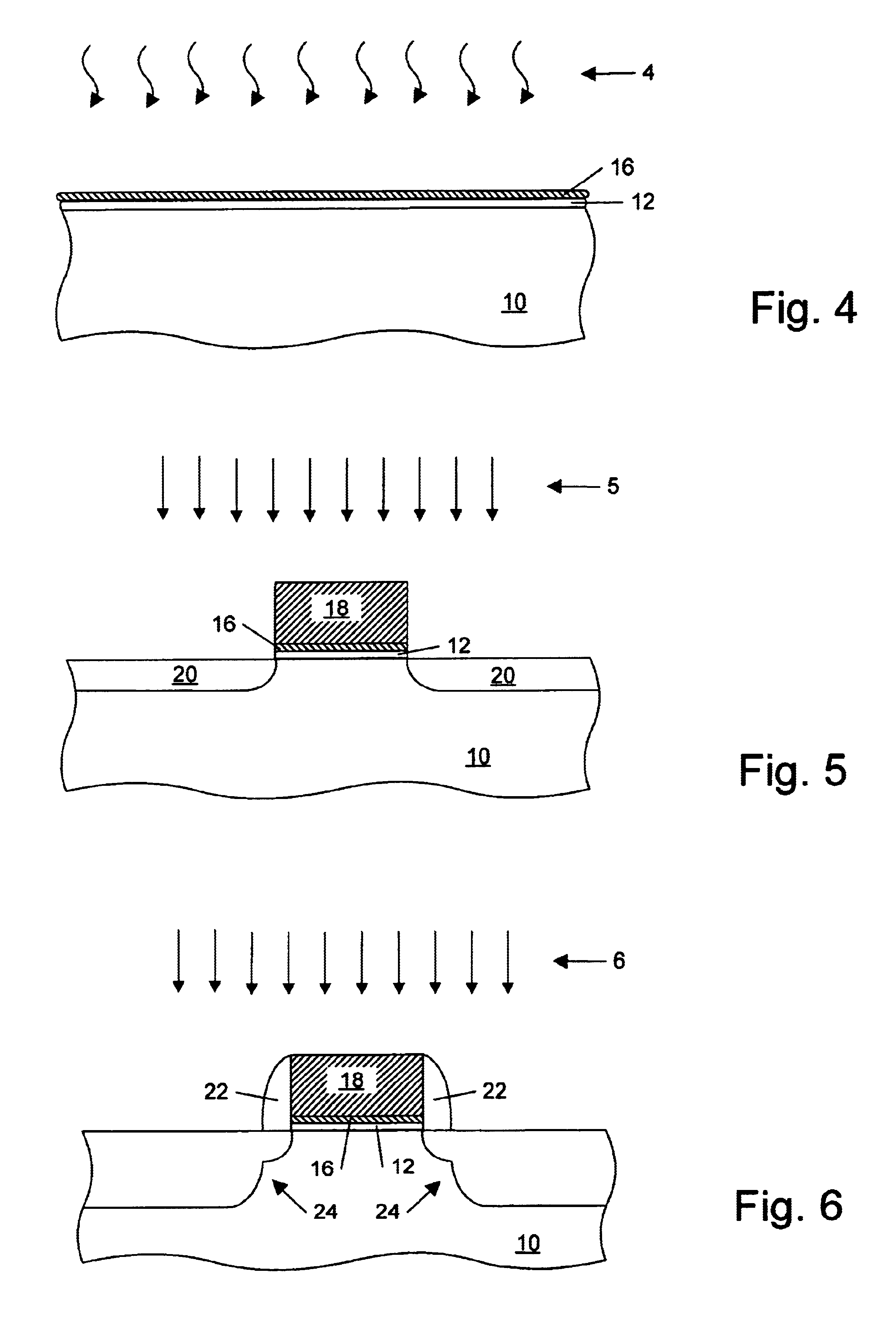
A method for fabricating a layer structure in a trench includes: simultaneously forming a dielectric film containing a Si—N bond on an upper surface, and a bottom surface and sidewalls of the trench, wherein a top / bottom portion of the film formed on the upper surface and the bottom surface and a sidewall portion of the film formed on the sidewalls are given different chemical resistance properties by bombardment of a plasma excited by applying voltage between two electrodes between which the substrate is place in parallel to the two electrodes; and substantially removing either one of but not both of the top / bottom portion and the sidewall portion of the film by wet etching which removes the one of the top / bottom portion and the sidewall portion of the film more predominantly than the other according to the different chemical resistance properties.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Method for forming silicon nitride film selectively on sidewalls or flat surfaces of trenches
ActiveUS20170250068A1Improve film qualityDecreasing density of filmElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilicon nitrideEtching
A method for fabricating a layer structure in a trench includes: simultaneously forming a dielectric film containing a Si—N bond on an upper surface, and a bottom surface and sidewalls of the trench, wherein a top / bottom portion of the film formed on the upper surface and the bottom surface and a sidewall portion of the film formed on the sidewalls are given different chemical resistance properties by bombardment of a plasma excited by applying voltage between two electrodes between which the substrate is place in parallel to the two electrodes; and substantially removing either one of but not both of the top / bottom portion and the sidewall portion of the film by wet etching which removes the one of the top / bottom portion and the sidewall portion of the film more predominantly than the other according to the different chemical resistance properties.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Method for forming silicon nitride film selectively on sidewalls or flat surfaces of trenches
ActiveUS9754779B1Low densityPlasma-enhanced chemical vapor depositionElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEtchingChemical resistance
A method for fabricating a layer structure in a trench includes: simultaneously forming a dielectric film containing a Si—N bond on an upper surface, and a bottom surface and sidewalls of the trench, wherein a top / bottom portion of the film formed on the upper surface and the bottom surface and a sidewall portion of the film formed on the sidewalls are given different chemical resistance properties by bombardment of a plasma excited by applying voltage between two electrodes between which the substrate is place in parallel to the two electrodes; and substantially removing either one of but not both of the top / bottom portion and the sidewall portion of the film by wet etching which removes the one of the top / bottom portion and the sidewall portion of the film more predominantly than the other according to the different chemical resistance properties.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Method for forming silicon nitride film selectively on sidewalls of trenches
ActiveUS20190057857A1Low densityPlasma-enhanced chemical vapor depositionElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEtchingChemical resistance
A method for fabricating a layer structure in a trench includes: simultaneously forming a dielectric film containing a Si—N bond on an upper surface, and a bottom surface and sidewalls of the trench, wherein a top / bottom portion of the film formed on the upper surface and the bottom surface and a sidewall portion of the film formed on the sidewalls are given different chemical resistance properties by bombardment of a plasma excited by applying voltage between two electrodes between which the substrate is place in parallel to the two electrodes; and substantially removing the sidewall portion of the film by wet etching which removes the sidewall portion of the film more predominantly than the top / bottom portion according to the different chemical resistance properties.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Gap-fill techniques
InactiveUS20050136684A1Excellent dielectric propertiesPlasma-enhanced chemical vapor depositionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingRemote plasmaHigh density
A variety of techniques may be employed, separately or in combination, to improve the gap-filling performance of a dielectric material formed by chemical vapor deposition (CVD). In one approach, a first dielectric layer is deposited using sub-atmospheric chemical vapor deposition (SACVD), followed by a second dielectric layer deposited by high density plasma chemical vapor deposition (HDP-CVD) or plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD). In another approach, a SACVD dielectric layer is deposited in the presence of reactive ionic species flowed from a remote plasma chamber into the processing chamber, which performs etching during the deposition process. In still another approach, high aspect trenches may be filled utilizing SACVD in combination with oxide layers deposited at high temperatures.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Protective layer to enable damage free gap fill
ActiveUS8133797B2Improve throughputPlasma-enhanced chemical vapor depositionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingEtchingProtection layer
In-situ semiconductor process that can fill high aspect ratio (typically at least 6:1, for example 7:1 or higher), narrow width (typically sub 0.13 micron, for example 0.1 micron or less) gaps without damaging underlying features and little or no incidence of voids or weak spots is provided. A protective layer is deposited to protect underlying features in regions of the substrate having lower feature density so that unwanted material may be removed from regions of the substrate having higher feature density. This protective layer may deposits thicker on a low density feature than on a high density feature and may be deposited using a PECVD process or low sputter / deposition ratio HDP CVD process. This protective layer may also be a metallic oxide layer that is resistant to fluorine etching, such as zirconium oxide (ZrO2) or aluminum oxide (Al2O3).
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
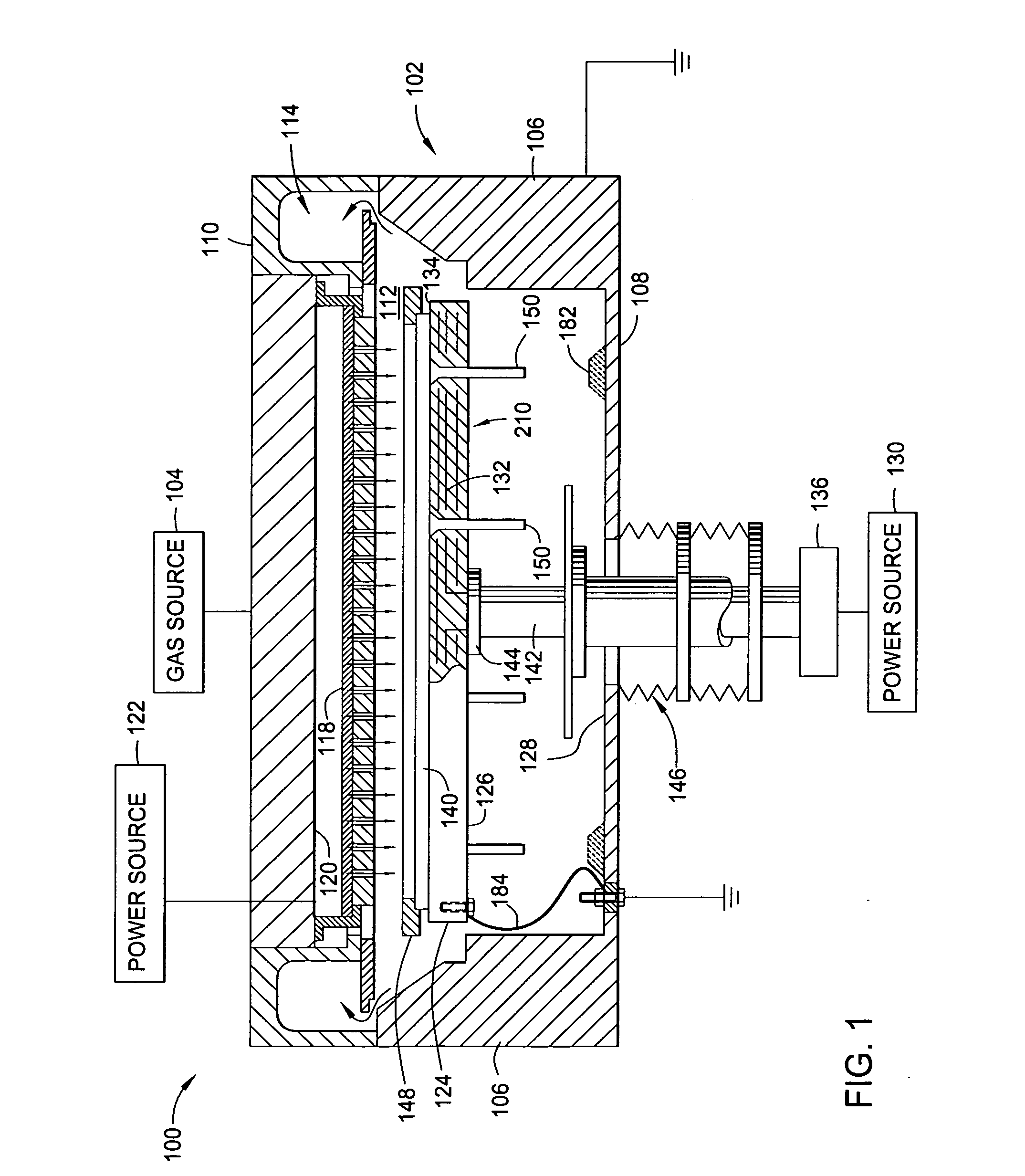
Apparatus and method of shaping profiles of large-area PECVD electrodes
InactiveUS20060005771A1Plasma-enhanced chemical vapor depositionHigh strengthElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringOperating temperature
An apparatus and method for shaping profiles of a large-area PECVD electrode is provided. A plasma-enhanced CVD chamber for processing a large-area substrate is first provided. The chamber includes a lower electrode that supports a large area substrate. The lower electrode is shaped to selectively conform the supported substrate in a selected orientation under operating conditions. The orientation may be either planar or nonplanar. The substrate complies with the shape of the electrode so the substrate is substantially parallel to an upper electrode in the chamber, and / or to a gas diffusion plate in the chamber. The lower electrode comprises a substrate support fabricated from a material of insufficient strength to support itself at operating temperatures and pressure in the chamber. The shape of the substrate support is adjusted by modifying the dimensions and / or planarity of a supporting base structure, and / or by appropriately varying the thickness of the substrate support.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Protective Layer To Enable Damage Free Gap Fill
ActiveUS20090286381A1High aspect ratioNarrow widthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingSputteringEtching
In-situ semiconductor process that can fill high aspect ratio (typically at least 6:1, for example 7:1 or higher), narrow width (typically sub 0.13 micron, for example 0.1 micron or less) gaps without damaging underlying features and little or no incidence of voids or weak spots is provided. A protective layer is deposited to protect underlying features in regions of the substrate having lower feature density so that unwanted material may be removed from regions of the substrate having higher feature density. This protective layer may deposits thicker on a low density feature than on a high density feature and may be deposited using a PECVD process or low sputter / deposition ratio HDP CVD process. This protective layer may also be a metallic oxide layer that is resistant to fluorine etching, such as zirconium oxide (ZrO2) or aluminum oxide (Al2O3).
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Method of patterning MTJ cell without sidewall damage
ActiveUS9362490B1Increased reluctanceImprove device performanceMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic device detailsIonMagnetoresistance
A method of removing a damaged magnetic layer at the sidewall of MTJ edge is provided to form damage-free MRAM cell. In this method, the MTJ film stack outside the Ta hard mask protected area is first etched by high-power magnetic reactive ion etch (RIE) using methanol (CH3OH) or Co & NH3 as etchant gases. Then a very mild chemical vapor trimming (CVT) process is used to remove a damaged layer (by the high power RIE) from the MTJ sidewall followed by an in-situ edge passivation with Si nitride (SiN) layer formed by PECVD. The MRAM cell formed by such method will have higher magnetoresistance with good device performance and better reliability.
Owner:XIAO RONGFU
Bilayer HDP CVD/PE CVD cap in advance BEOL interconnect structures and method thereof
InactiveUS6887783B2Plasma-enhanced chemical vapor depositionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorInter layer
An advanced back-end-of-line (BEOL) metallization structure is disclosed. The structure includes a bilayer diffusion barrier or cap, where the first cap layer is formed of a dielectric material preferably deposited by a high density plasma chemical vapor deposition (HDP CVD) process, and the second cap layer is formed of a dielectric material preferably deposited by a plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PE CVD) process. A method for forming the BEOL metallization structure is also disclosed. The invention is particularly useful in interconnect structures comprising low-k dielectric material for the inter-layer dielectric (ILD) and copper for the conductors.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Ultrathin high-K gate dielectric with favorable interface properties for improved semiconductor device performance
InactiveUS6911707B2High dielectric constantImprove the immunitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDielectricCapacitance
An ultrathin gate dielectric having a graded dielectric constant and a method for forming the same are provided. The gate dielectric is believed to allow enhanced performance of semiconductor devices including transistors and dual-gate memory cells. A thin nitrogen-containing oxide, preferably having a thickness of less than about 10 angstroms, is formed on a semiconductor substrate. A silicon nitride layer having a thickness of less than about 30 angstroms may be formed over the nitrogen-containing oxide. The oxide and nitride layers are annealed in ammonia and nitrous oxide ambients, and the nitride layer thickness is reduced using a flowing-gas etch process. The resulting two-layer gate dielectric is believed to provide increased capacitance as compared to a silicon dioxide dielectric while maintaining favorable interface properties with the underlying substrate. In an alternative embodiment, a different high dielectric constant material is substituted for the silicon nitride. Alternatively, both nitride and a different high dielectric constant material may be used so that a three-layer dielectric is formed.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
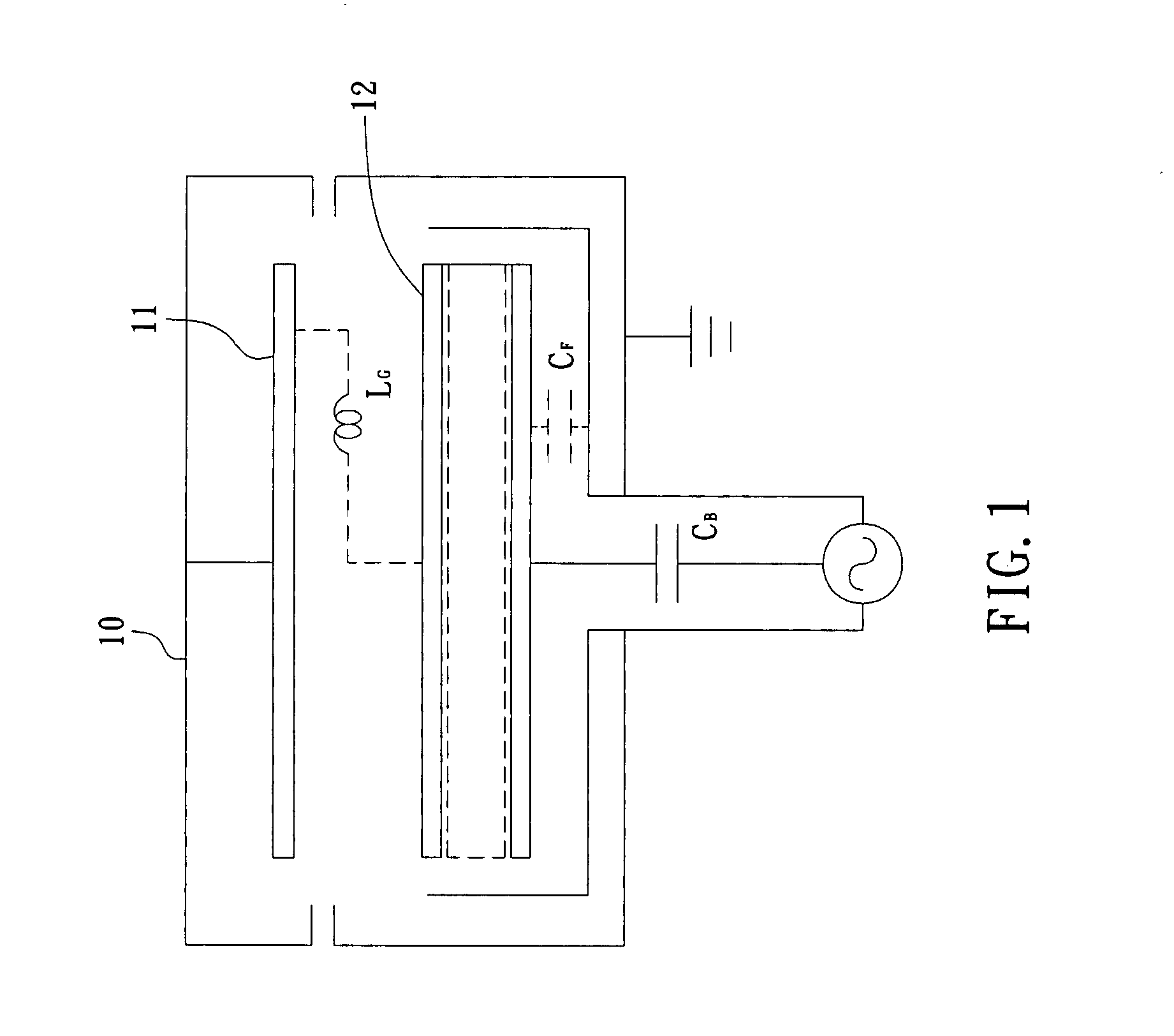
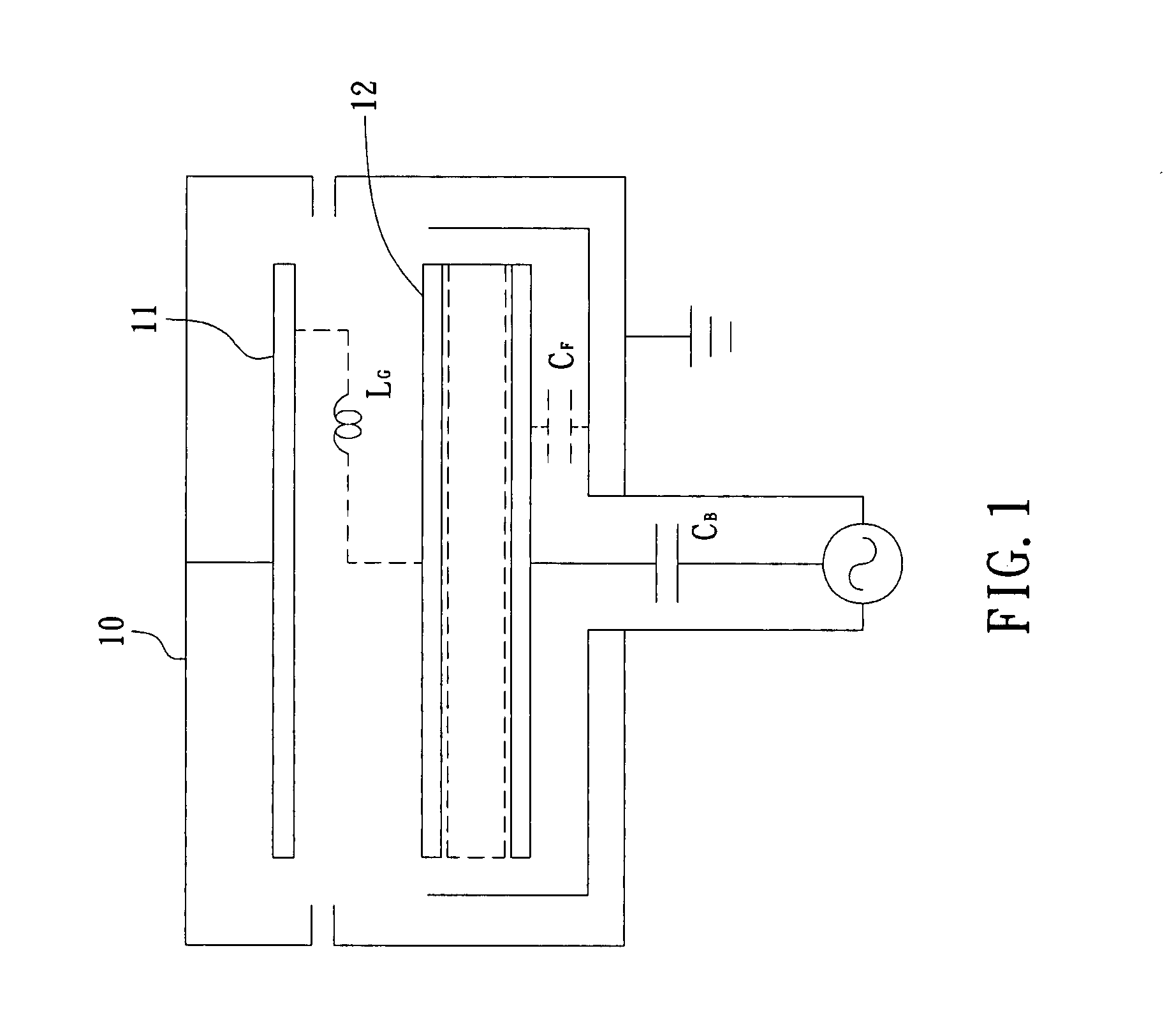
Capacitively coupled plasma equipment with uniform plasma density
InactiveUS20140138030A1Plasma-enhanced chemical vapor depositionAvoid defectsElectric discharge tubesVacuum evaporation coatingCapacitancePlasma density
Techniques disclosed herein include apparatus and processes for generating plasma having a uniform electron density across an electrode used to generate the plasma. An upper electrode of a capacitively coupled plasma system can include structural features configured to assist in generating the uniform plasma. Such structural features define a surface shape, on a surface that faces the plasma. Such structural features can include a set of concentric rings having an approximately rectangular cross section, and protruding from the surface of the upper electrode. Such structural features can also include nested elongated protrusions having a cross-sectional size and shape, with spacing of the protrusions selected to result in a system that generates uniform density plasma. A dielectric member or sheet can be positioned on the structural features to prevent or inhibit erosion from plasma while still maintaining plasma uniformity.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
RF Hollow Cathode Plasma Generator
InactiveUS20110192348A1High densityAdvantageously uniform distributionElectric arc lampsSolid cathode detailsPlasma generatorEngineering
An RF hollow cathode plasma source consists of a vacuum chamber, a pipe, a hollow cathode, at least two compartments, a conduit and input electrodes. The pipe is inserted into the chamber for introducing working gas into the chamber. The hollow cathode is disposed in the chamber and formed with a large number of apertures. At least two compartments are located below the hollow cathode. Each of the compartments includes small apertures for uniformly spreading the working gas into the apertures of the hollow cathode. The conduit is disposed along two sides of the hollow cathode to circulate cooling water around the hollow cathode. The plural input power leads are arranged near the hollow cathode. The input power leads, the pipe and the conduits are connected to the hollow cathode though the electrically-insulated walls of the grounded vacuum chamber.
Owner:INST NUCLEAR ENERGY RES ROCAEC
Chemical sensors containing carbon nanotubes, method for making same, and uses therof
InactiveUS20110244585A1Well formedSensitive highMaterial nanotechnologyElectrolysis componentsChemical compoundChemistry
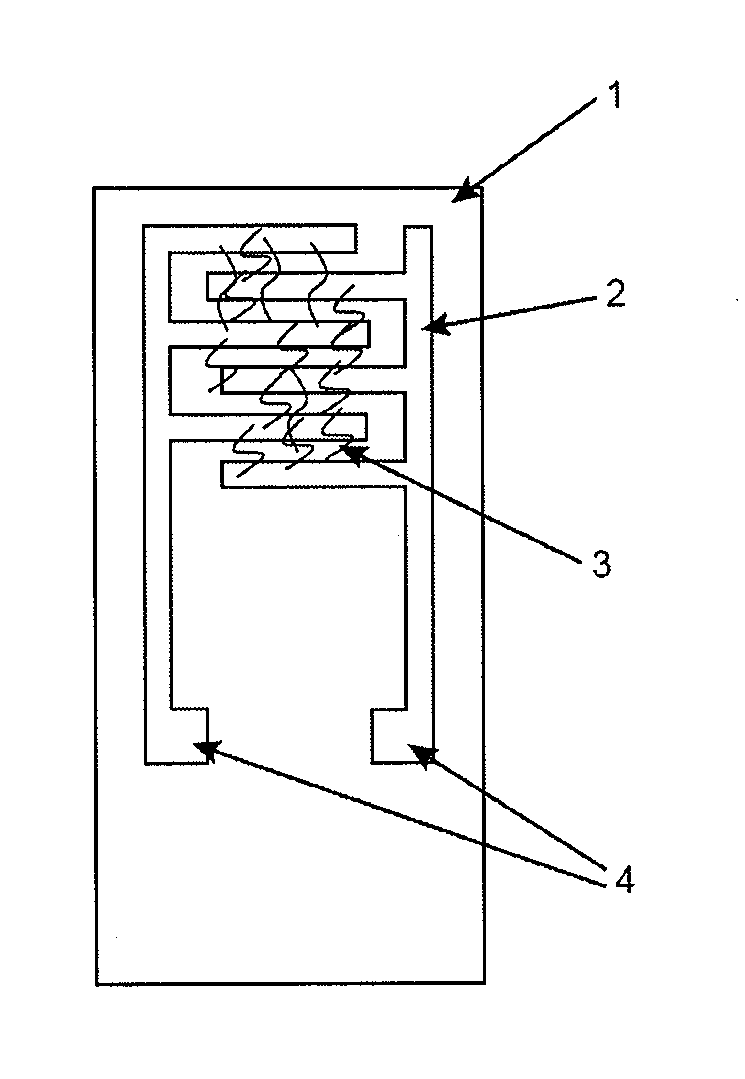
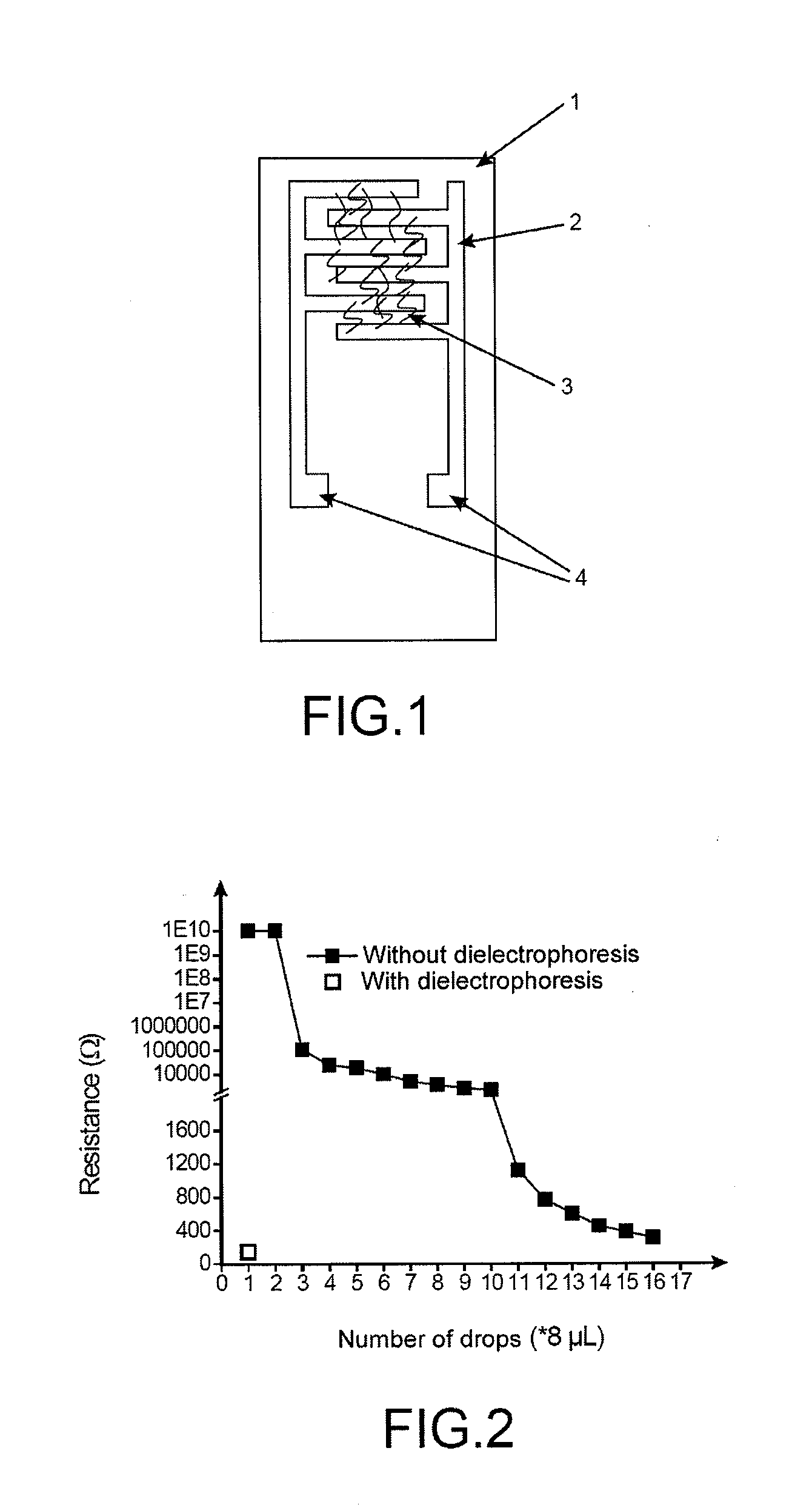
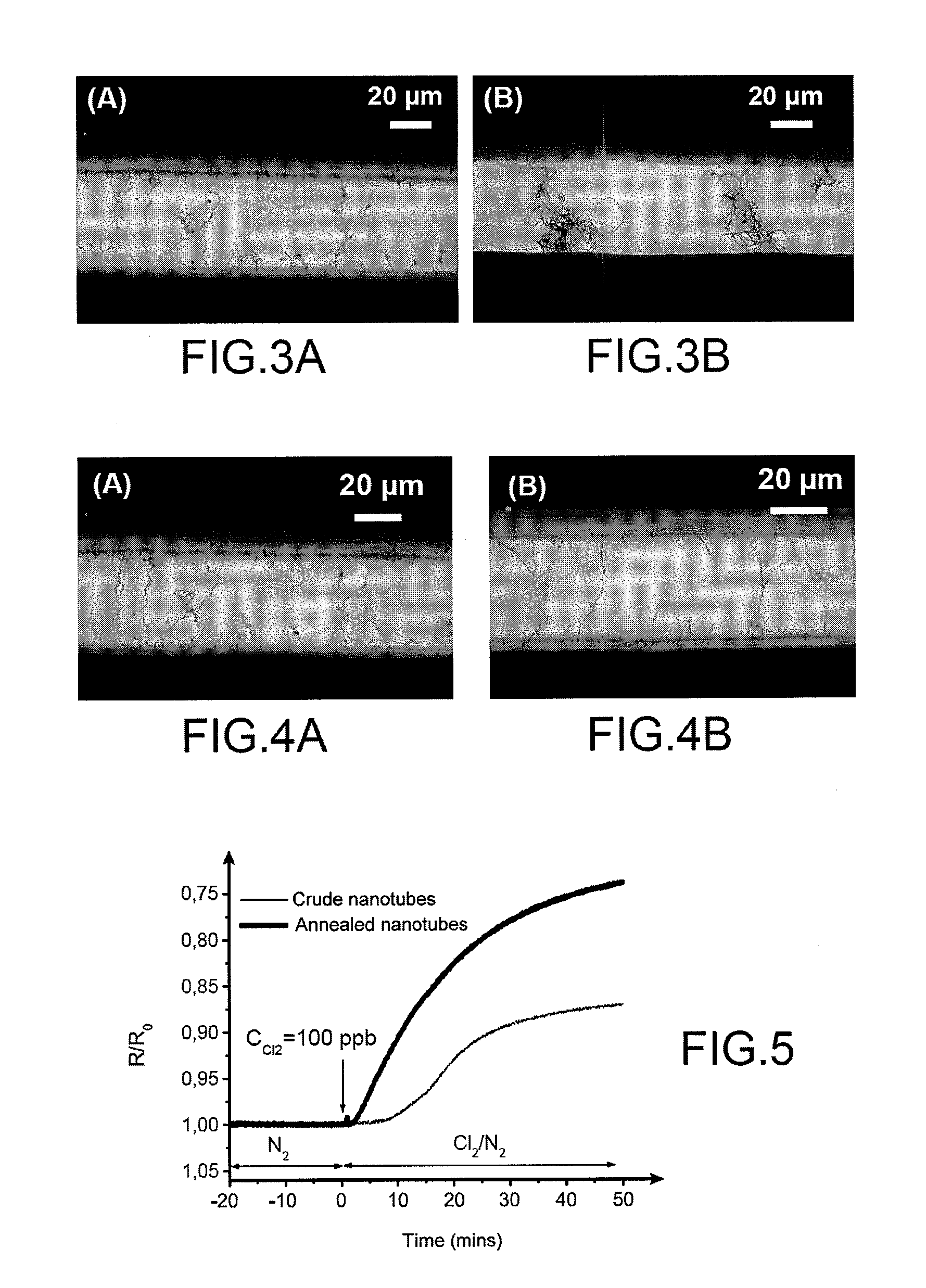
A device is disclosed for detecting at least one chemical compound comprising at least one carbon nanotube with several graphene layers, on which is grafted at least one molecule bearing group G1 capable of reacting with the chemical compound or a precursor of such a group G1. The uses and the method of making such a device is also disclosed.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
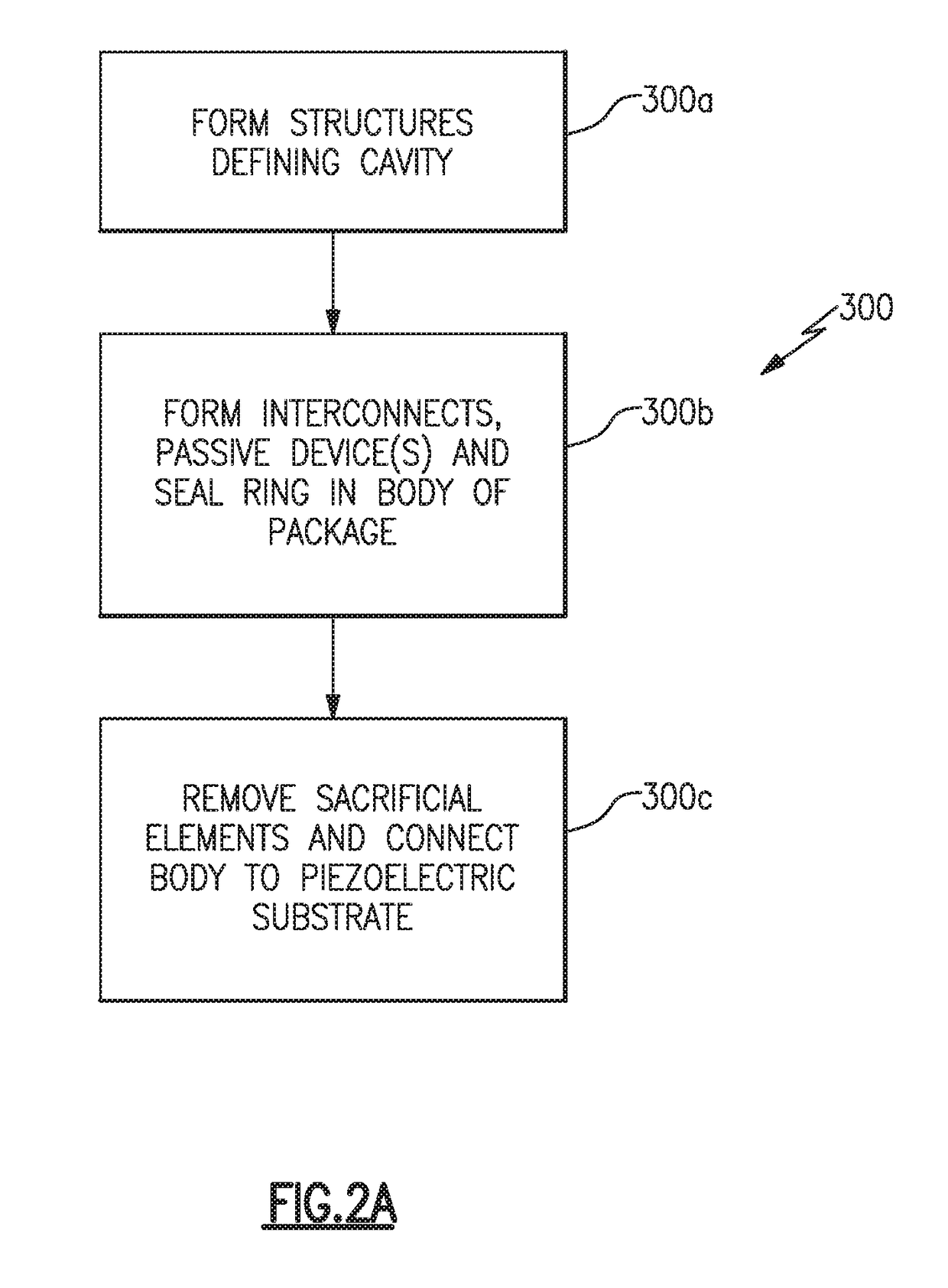
Method of providing protective cavity and integrated passive components in wafer level chip scale package using a carrier wafer
ActiveUS20170163243A1Eliminate bowingPlasma-enhanced chemical vapor depositionImpedence networksSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectrical connectionChip-scale package
A wafer-level chip-scale package includes a body, a conductive via passing through the body, a contact bump formed at a lower portion of the body and in electrical connection with a lower end of the conductive via, a piezoelectric substrate directly bonded to an upper end of the conductive via, and a cavity defined between a portion of the body and the piezoelectric substrate.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
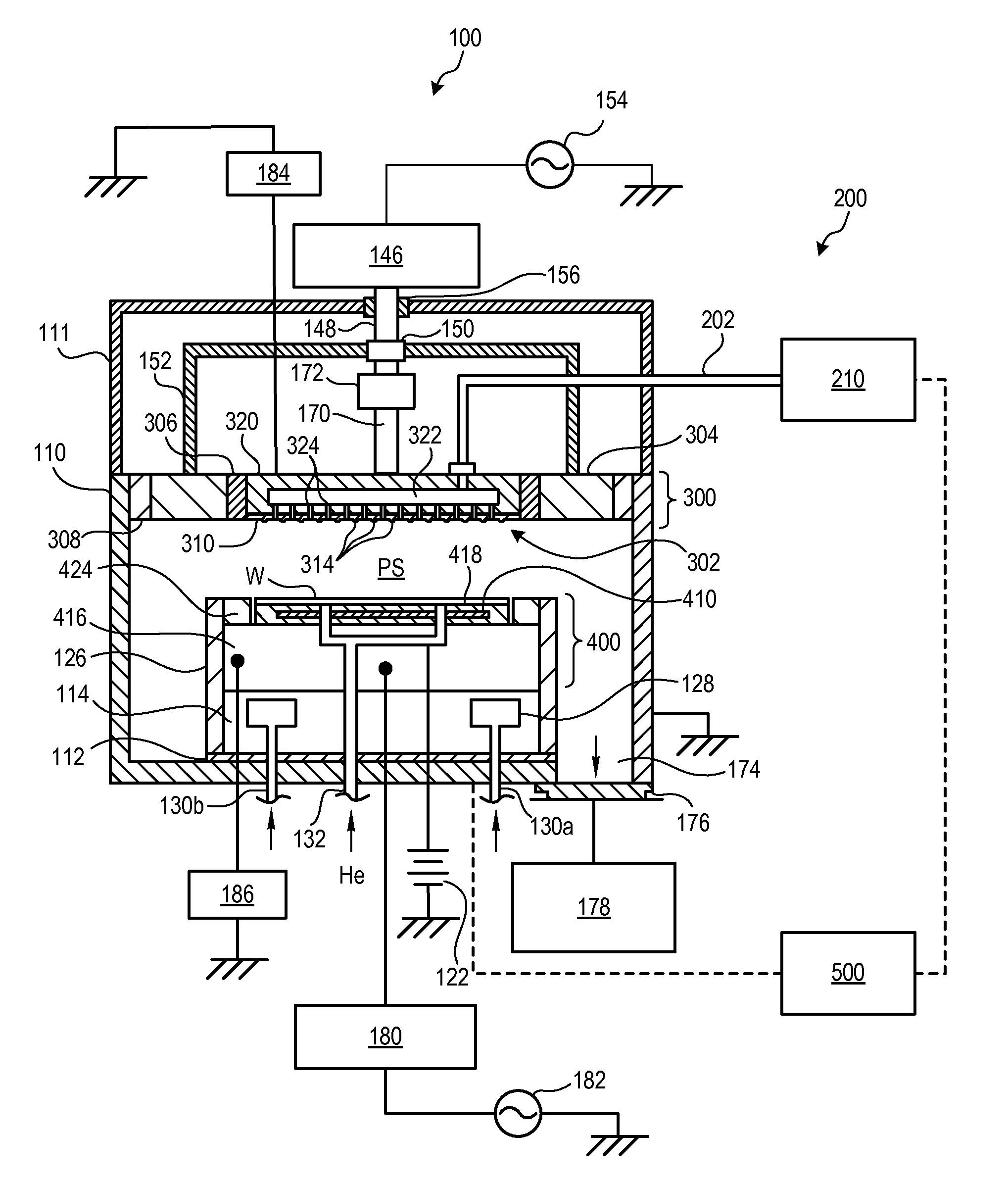
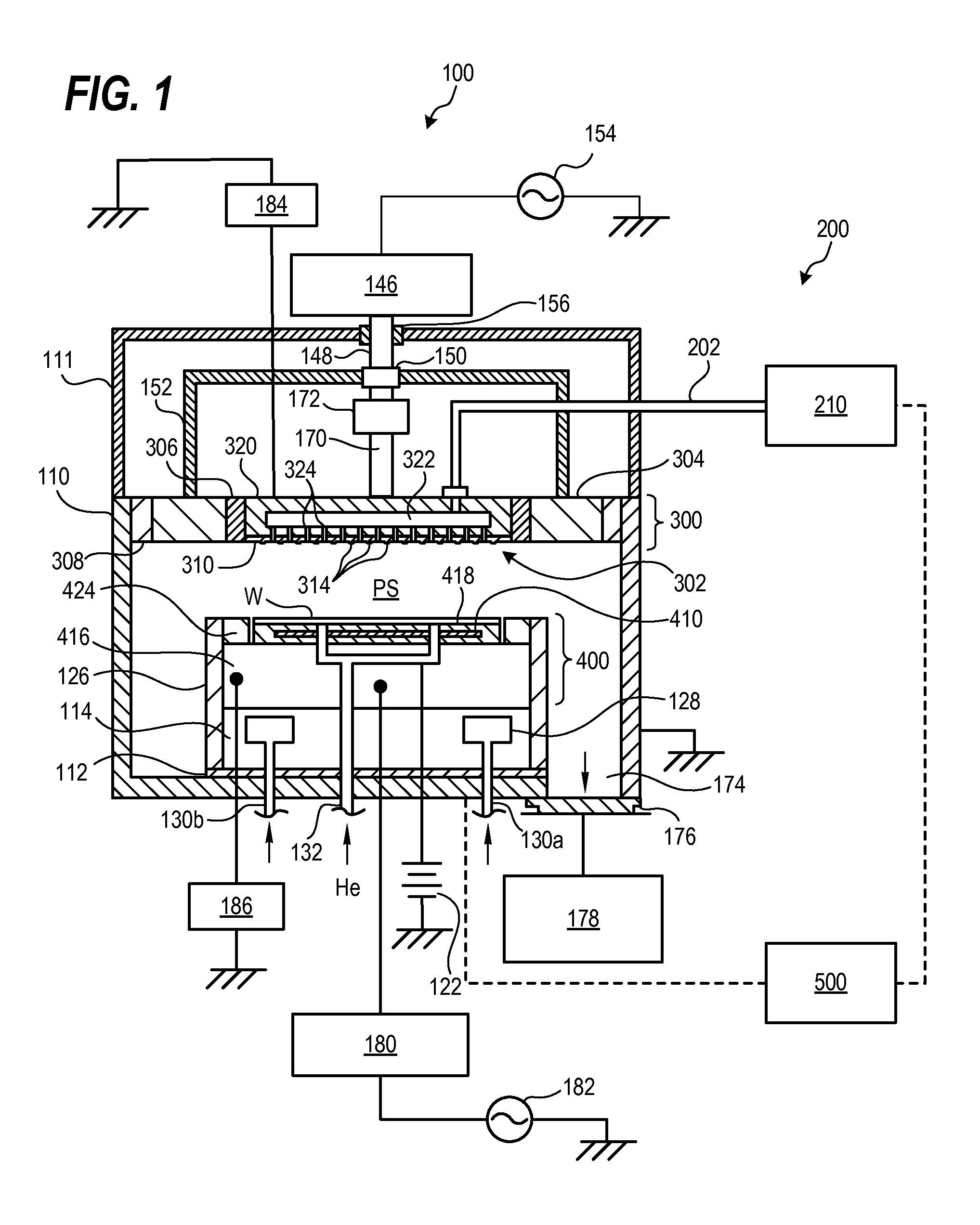
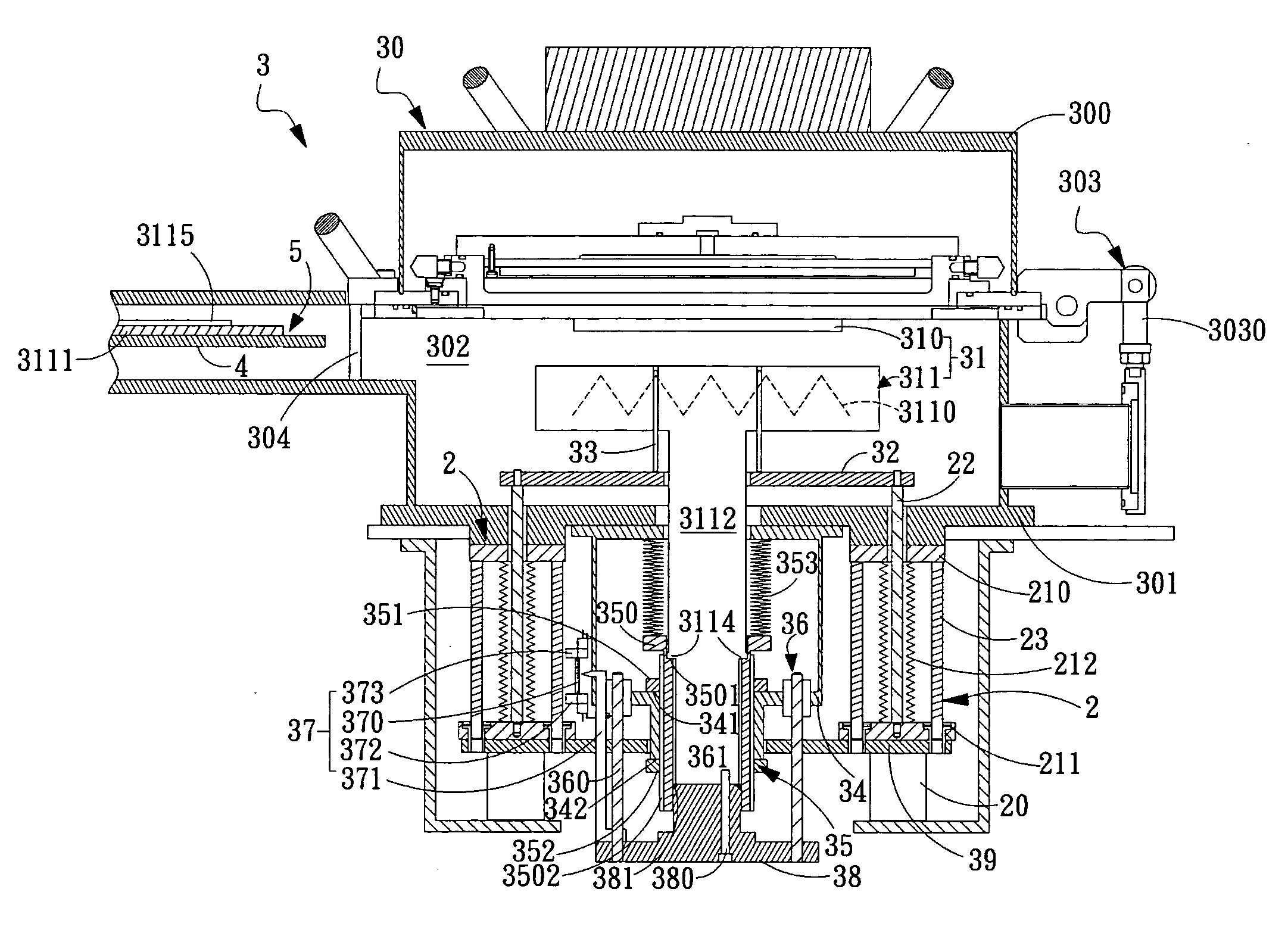
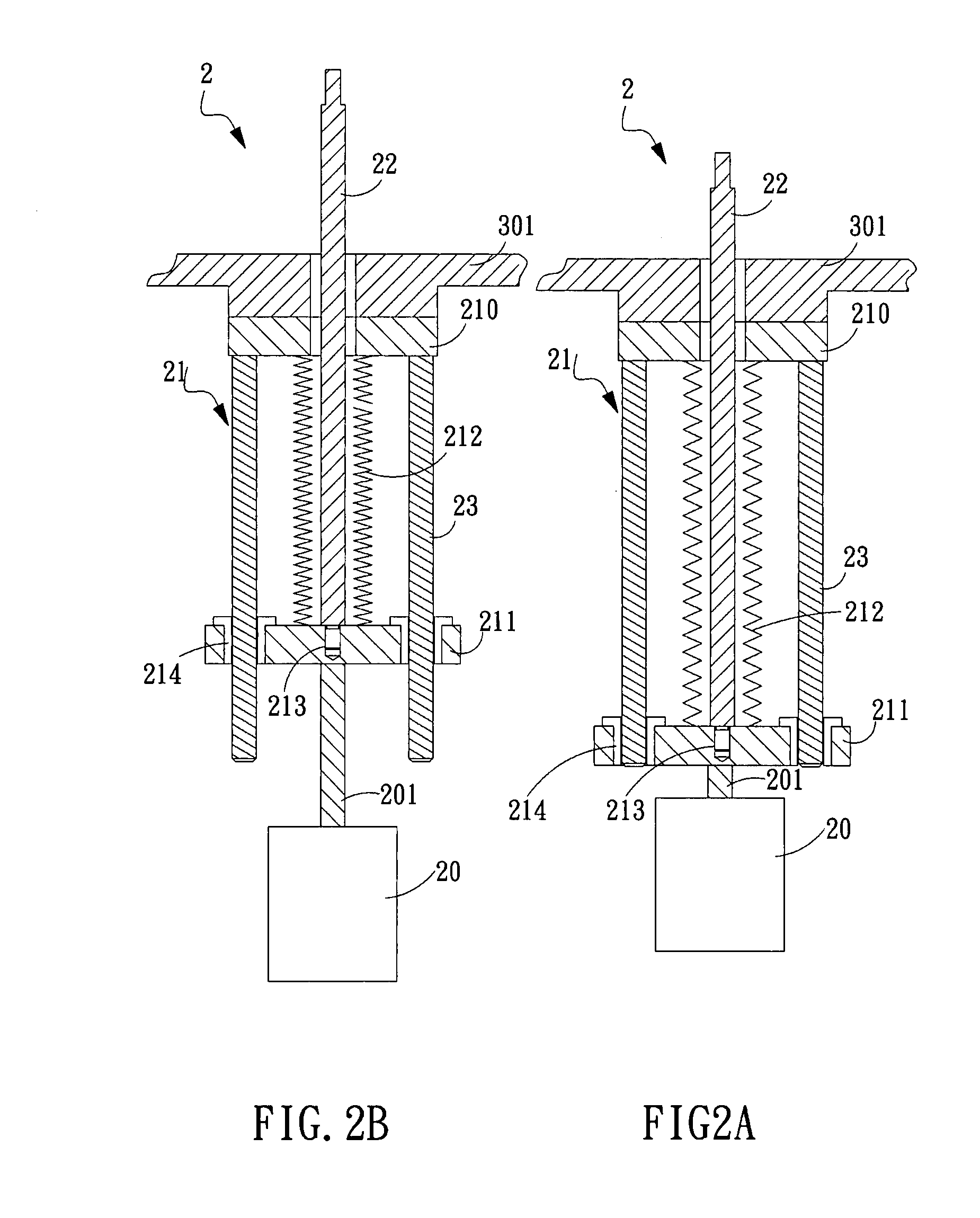
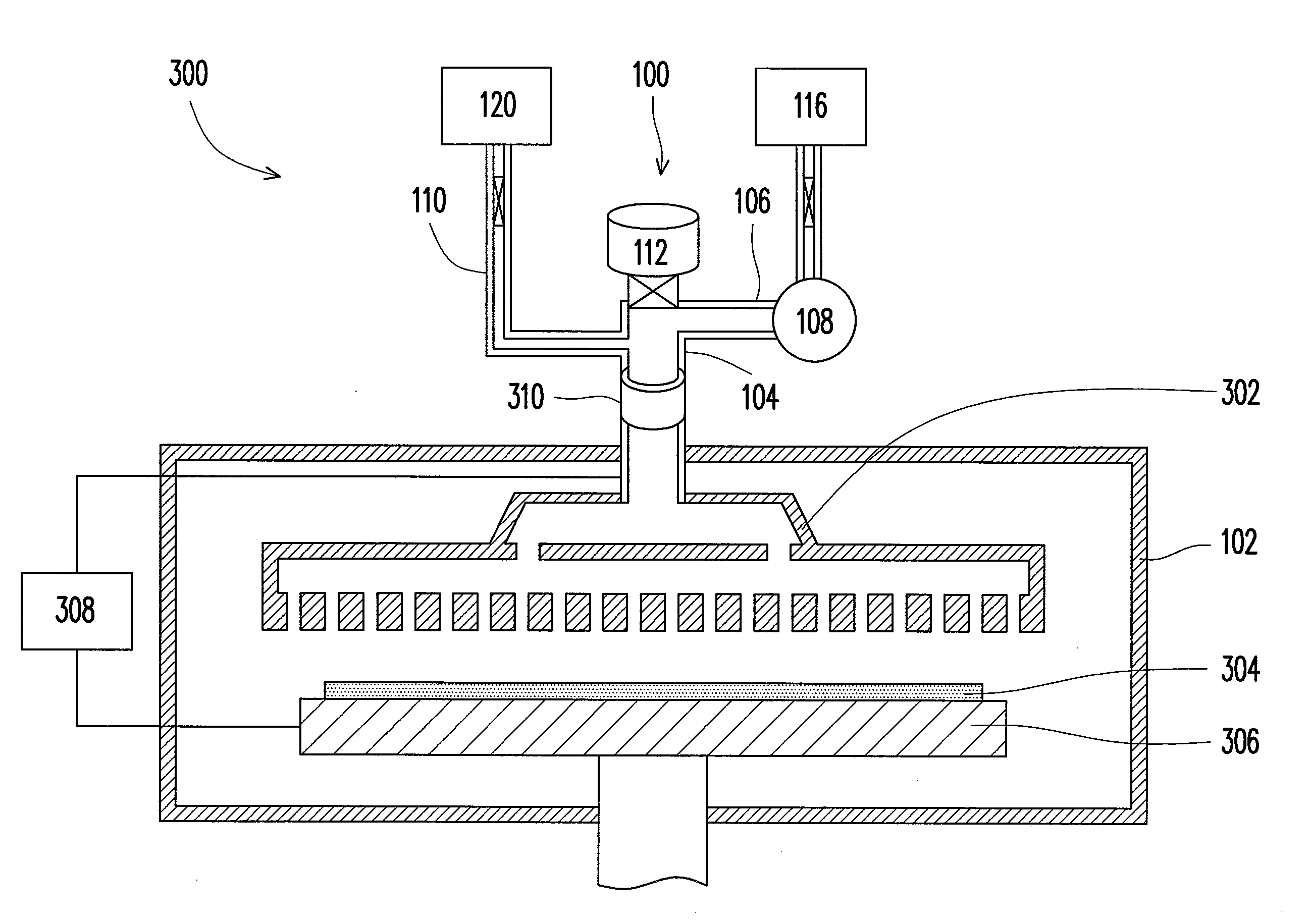
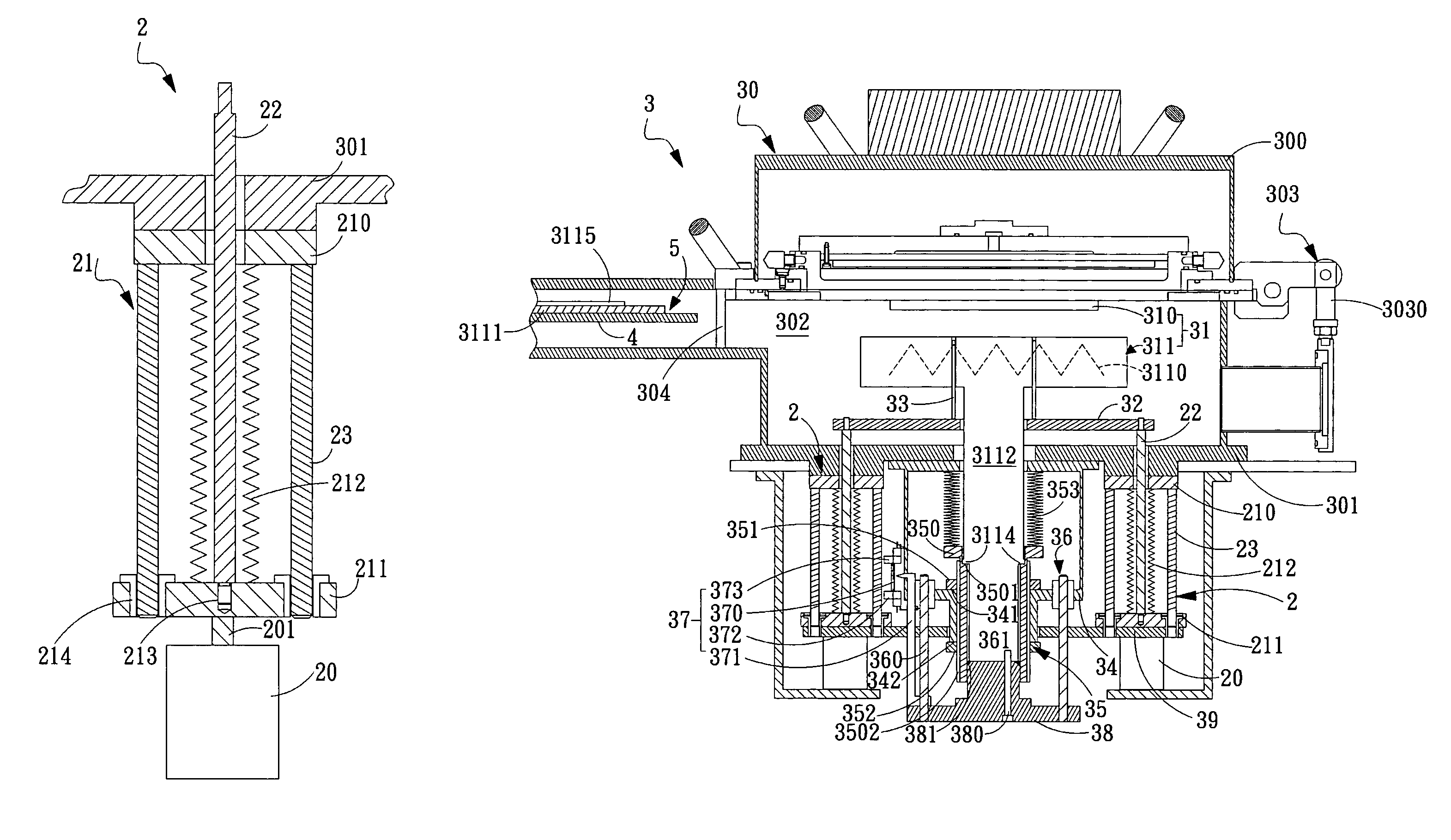
Power-delivery mechanism and apparatus of plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition using the same
InactiveUS20080295771A1Improve automationReduce chanceLiquid surface applicatorsElectric discharge tubesGas phaseEngineering
A power-delivery mechanism is provided in the present invention, which utilizes an element with airtight and flexible characteristics coupled to a power-generating unit so as to generate a motion in a specific direction. Besides, an apparatus of plasma -enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) is also provided in the present invention, which comprises the power-delivery mechanism to load / unload a workpiece onto a stage for processing automatically. Meanwhile, the present invention also provides a height-adjusting unit and a position-indicating unit allowing the operator to adjust the distance between an upper electrode and a lower electrode of the PECVD so that the operator is capable of monitoring and adjusting the distance easily between the upper electrode and the lower electrode outside the chamber of the PECVD.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition apparatus and method of manufacturing display apparatus using the same
ActiveUS20150024147A1Increase temperatureInhibition formationElectric discharge tubesChemical vapor deposition coatingSusceptorEngineering
A plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (“PECVD”) apparatus includes: an ejecting unit which is configured to eject a gas toward a substrate onto which the gas is deposited; a lift which is configured to support and selectively raise or lower a mask unit in which is defined a pattern through which the gas ejected from the ejecting unit passes towards the substrate; and a susceptor into which a portion of the lift is inserted, and which is configured to linearly move the substrate. A temperature of the lift is variable.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
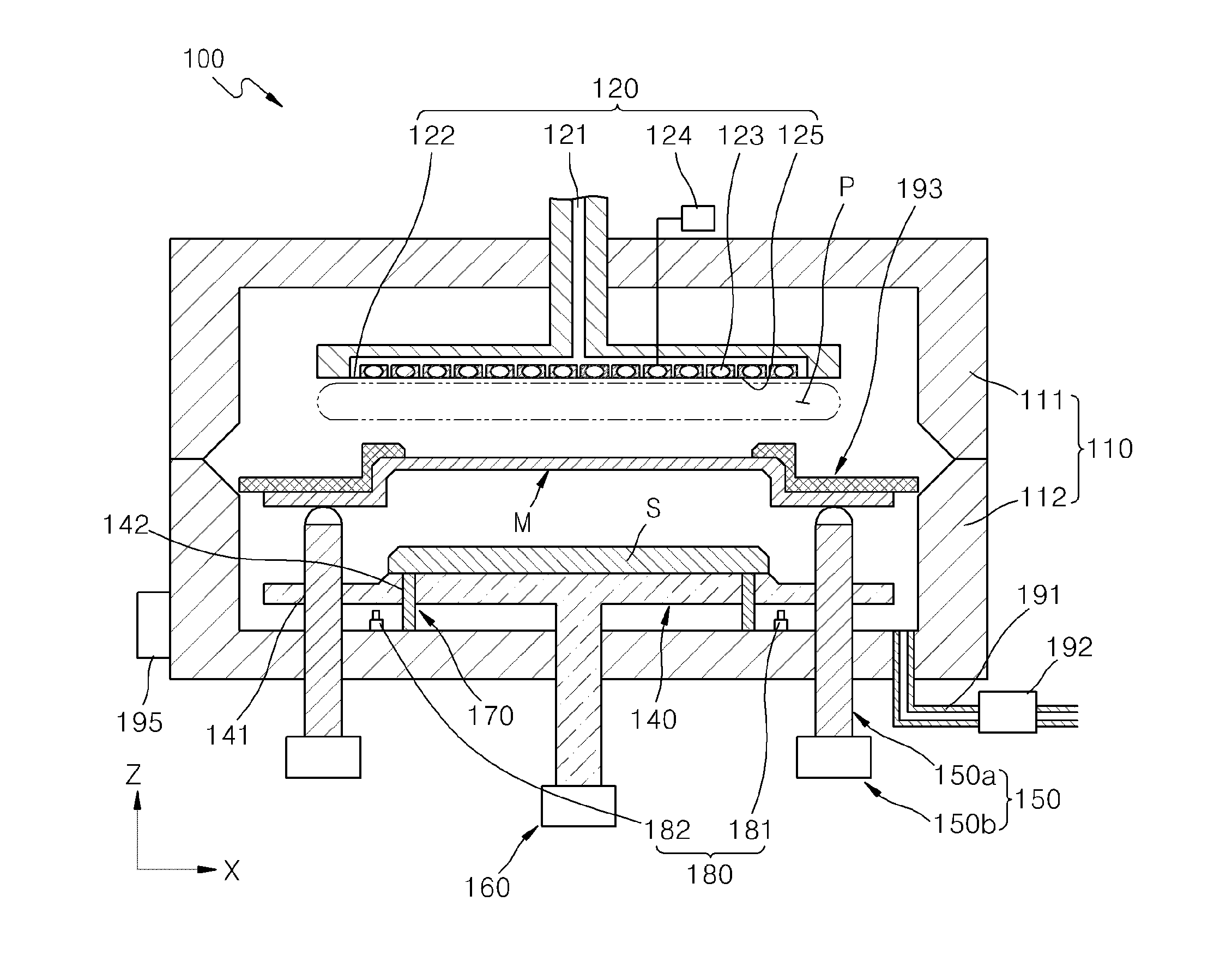
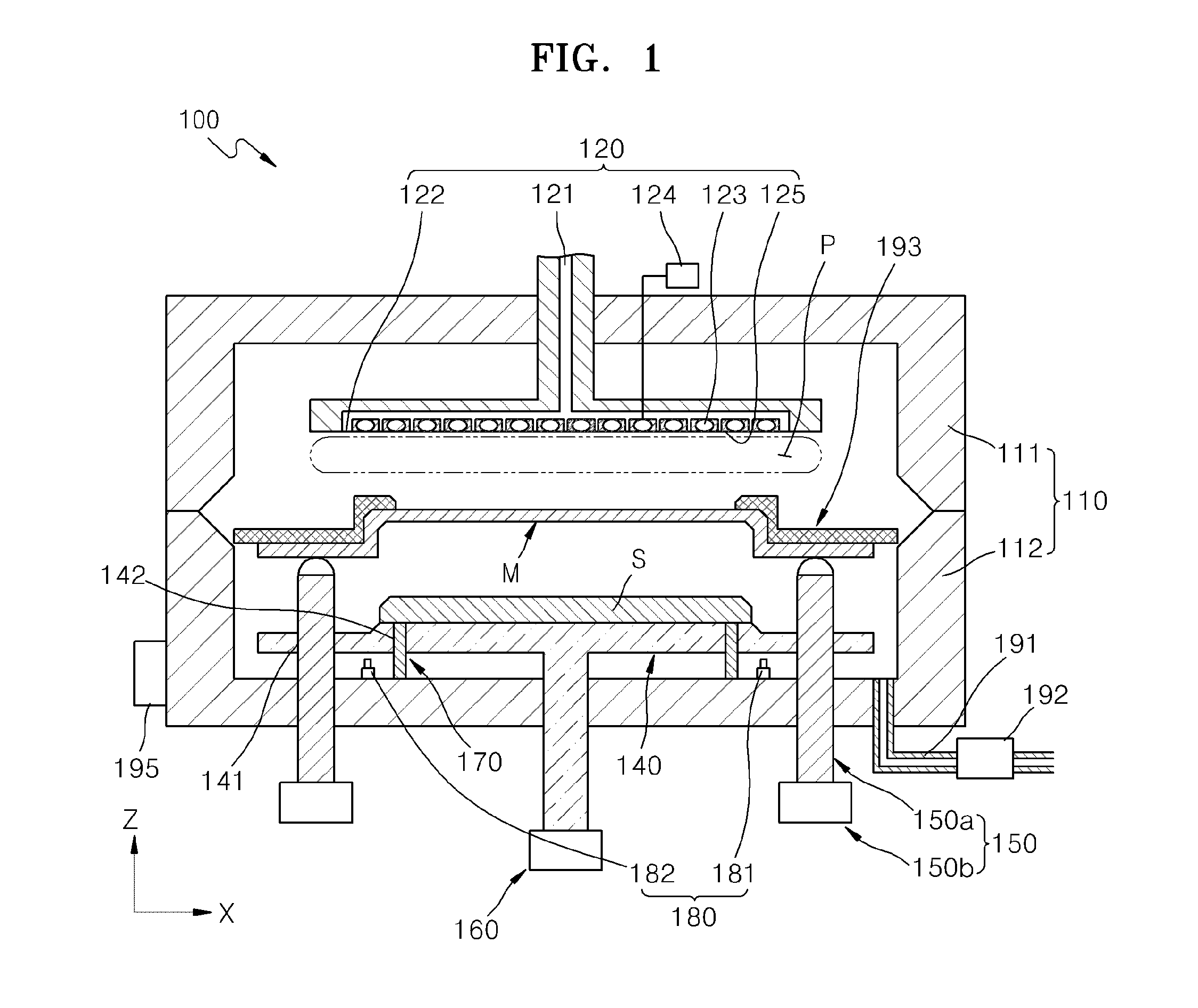
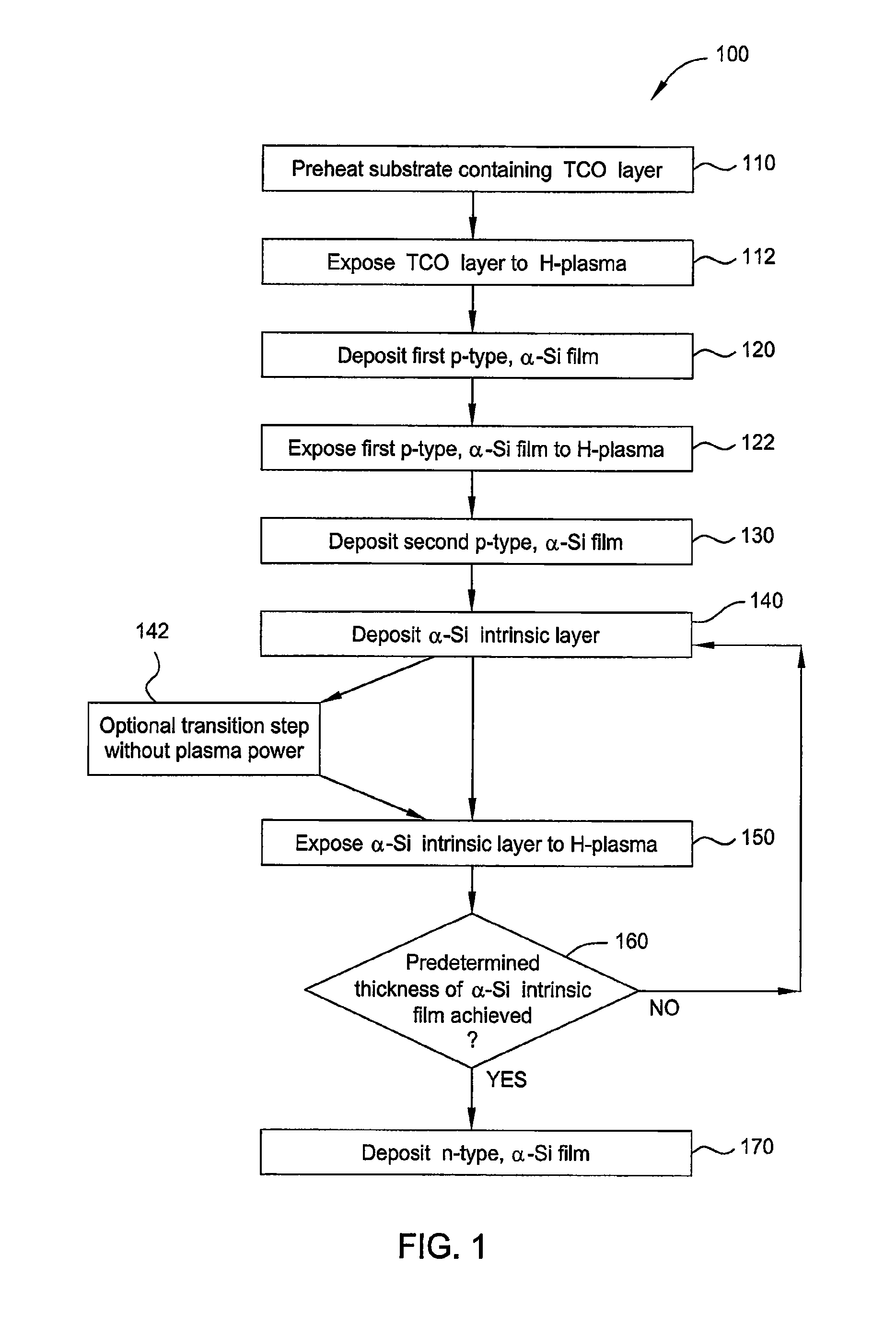
In-situ hydrogen plasma treatment of amorphous silicon intrinsic layers
InactiveUS20120202315A1Less premature failureLess impurityFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPlasma treatmentConductive oxide
Embodiments of the invention generally provide methods for forming amorphous silicon-based photovoltaic devices, such as solar cells, by utilizing deposition and plasma treatment steps during a plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PE-CVD) process. In one embodiments, the method includes exposing a transparent conductive oxide (TCO) layer disposed on a substrate to hydrogen plasma during pretreatment, forming a p-type α-Si film on the TCO layer, forming an α-Si intrinsic film on the p-type α-Si film during a PE-CVD process, and forming an n-type α-Si film on the α-Si intrinsic film. In some examples, the PE-CVD process includes depositing an α-Si intrinsic layer during a deposition step, treating the α-Si intrinsic layer to form a treated α-Si intrinsic layer during a plasma treatment step, and sequentially repeating the deposition step and the plasma treatment step until obtaining a desired thickness of the α-Si intrinsic film containing a plurality of treated α-Si intrinsic layers.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Bilayer HDP CVD/PE CVD cap in advanced BEOL interconnect structures and method thereof
InactiveUS6914320B2Plasma-enhanced chemical vapor depositionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorInter layer
An advanced back-end-of-line (BEOL) metallization structure is disclosed. The structure includes a bilayer diffusion barrier or cap, where the first cap layer is formed of a dielectric material preferably deposited by a high density plasma chemical vapor deposition (HDP CVD) process, and the second cap layer is formed of a dielectric material preferably deposited by a plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PE CVD) process. A method for forming the BEOL metallization structure is also disclosed. The invention is particularly useful in interconnect structure comprising low-k dielectric material for the inter-layer dielectric (ILD) and copper for the conductors.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Multijunction hybrid solar cell incorporating vertically-aligned silicon nanowires with thin films
InactiveUS20130081679A1Improve efficiencyReduce contact resistanceMaterial nanotechnologyFinal product manufactureAbsorptanceSemiconductor materials
A low-cost method is provided for forming a photovoltaic device, which is a high-performance nanostructured multijunction cell. The multiple P-N junctions or P-I-N junctions are contiguously joined to form a single contiguous P-N junction or a single contiguous P-I-N junction. The photovoltaic device integrates vertically-aligned semiconductor nanowires including a doped semiconductor material with a thin silicon layer having an opposite type of doping. This novel hybrid cell can provide a higher efficiency than conventional photovoltaic devices through the combination of the enhanced photon absorptance, reduced contact resistance, and short carrier transport paths in the nanowires. Room temperature processes or low temperature processes such as plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) and electrochemical processes can be employed for fabrication of this photovoltaic device in a low-cost, scalable, and energy-efficient manner.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
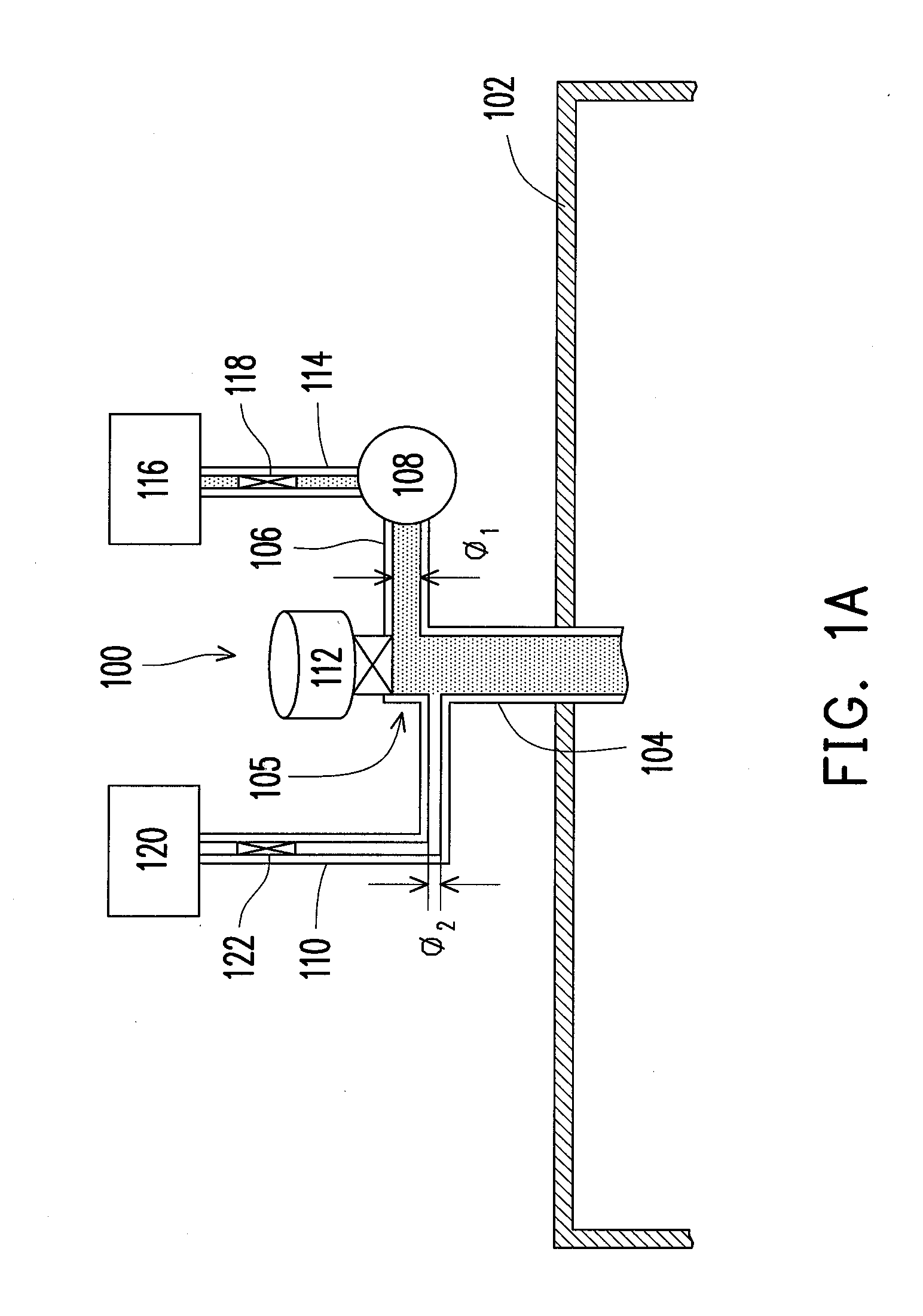
Gas supply apparatus
InactiveUS20110126764A1Extended service lifeAvoid exceptionChemical vapor deposition coatingRemote plasmaProcess engineering
A gas supply apparatus for introducing gases to a process chamber of a PECVD system is provided. The gas supply apparatus includes a gas inlet tube, a process gas pipe, a cleaning gas pipe, a remote plasma source (RPS) and a variable valve. The RPS is connected with a cleaning gas source, and the cleaning gas pipe is connected between the gas inlet tube and the RPS for introducing a cleaning gas from the RPS to the gas inlet tube. The process gas pipe is connected between the gas inlet tube and a process gas source for introducing a process gas to the gas inlet tube. The variable valve is installed in the gas inlet tube for closing a passage between the cleaning gas pipe and the gas inlet tube to prevent the process gas entering the cleaning gas pipe when the process gas is introduced to the process chamber.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
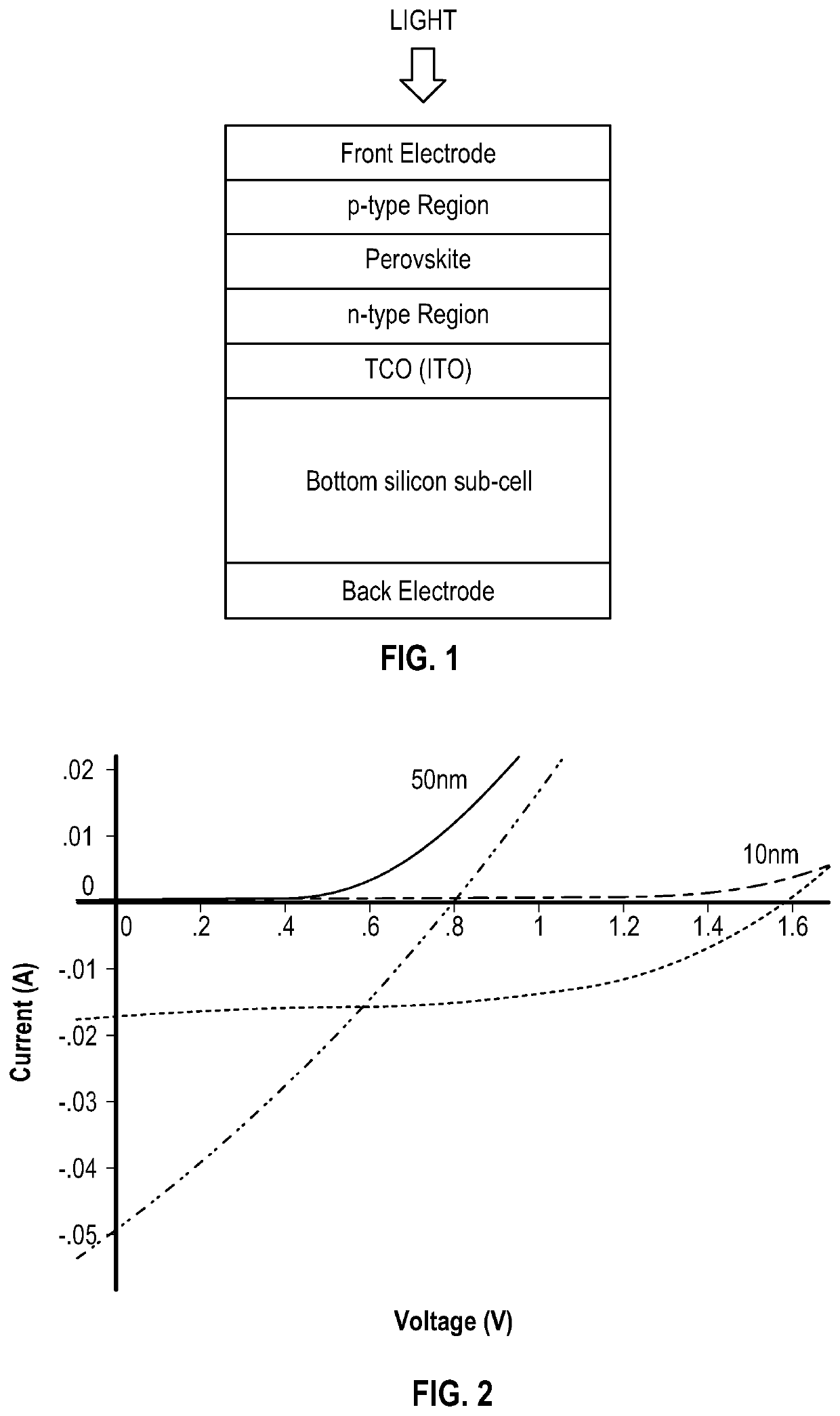
Multijunction photovoltaic device
ActiveUS20200058819A1Reduce reflection lossOvercome lack of conductivitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilicon matrixSilicon nanocrystals
There is provided a multi junction photovoltaic device comprising a first sub-cell comprising a photoactive region comprising a layer of perovskite material, a second sub-cell comprising a photoactive silicon absorber. and an intermediate region disposed between and connecting the first sub-cell and the second sub-cell. The intermediate region comprises an interconnect layer, the interconnect layer comprising a two-phase material comprising elongate (i.e. filament like) silicon nanocrystals embedded in a silicon oxide matrix.
Owner:OXFORD PHOTOVOLTAICS
Power-delivery mechanism and apparatus of plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition using the same
InactiveUS7927425B2Improve automationReduce chanceLiquid surface applicatorsElectric discharge tubesGas phaseEngineering
A power-delivery mechanism is provided in the present invention, which utilizes an element with airtight and flexible characteristics coupled to a power-generating unit so as to generate a motion in a specific direction. Besides, an apparatus of plasma -enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) is also provided in the present invention, which comprises the power-delivery mechanism to load / unload a workpiece onto a stage for processing automatically. Meanwhile, the present invention also provides a height-adjusting unit and a position-indicating unit allowing the operator to adjust the distance between an upper electrode and a lower electrode of the PECVD so that the operator is capable of monitoring and adjusting the distance easily between the upper electrode and the lower electrode outside the chamber of the PECVD.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
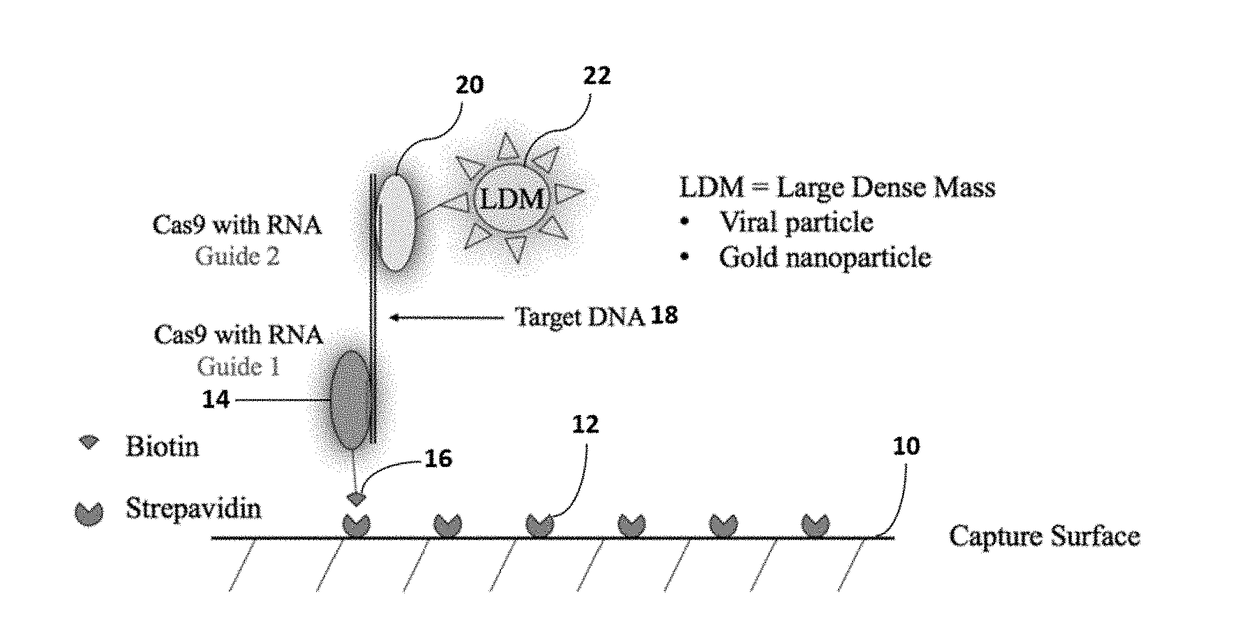
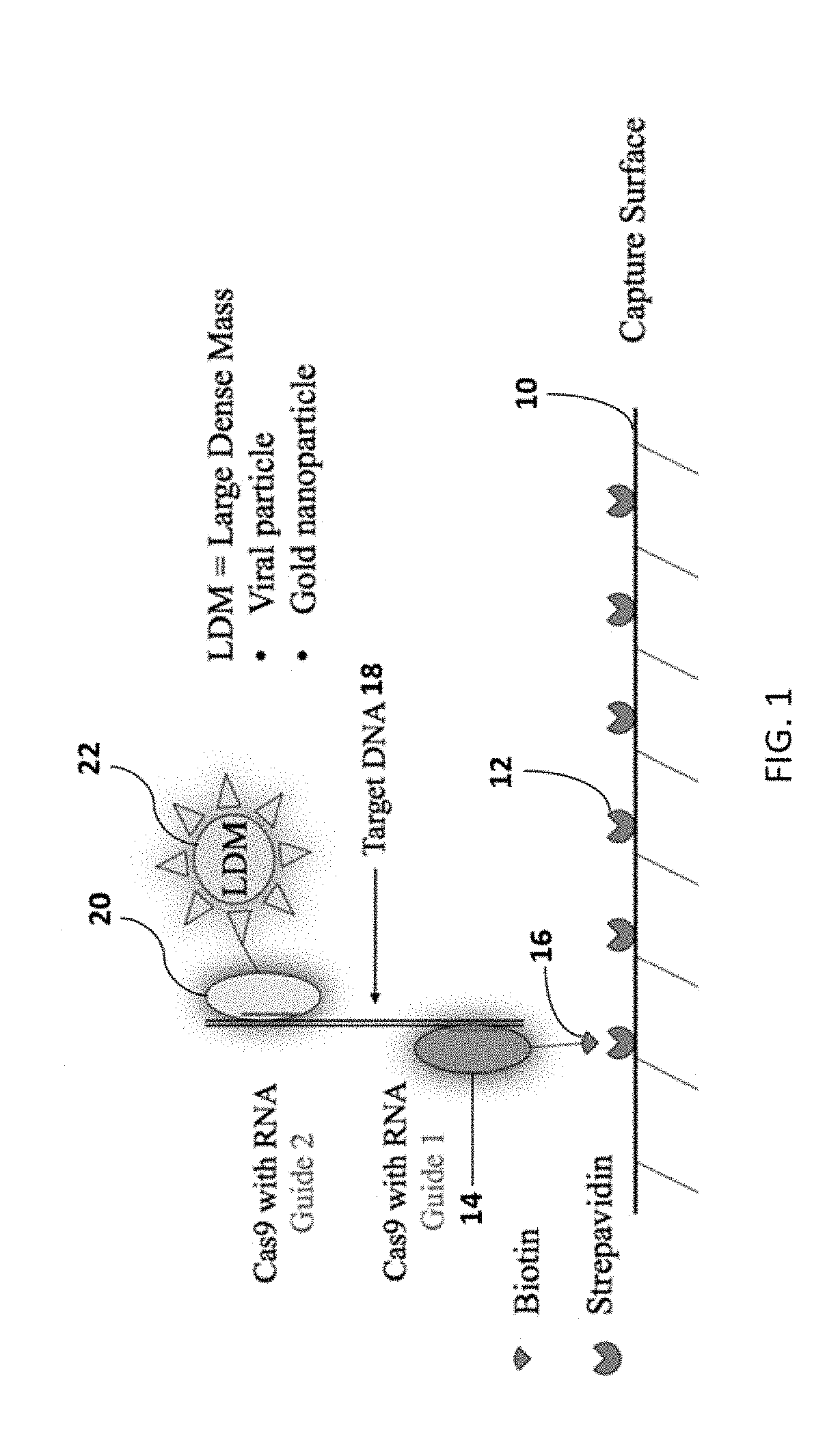
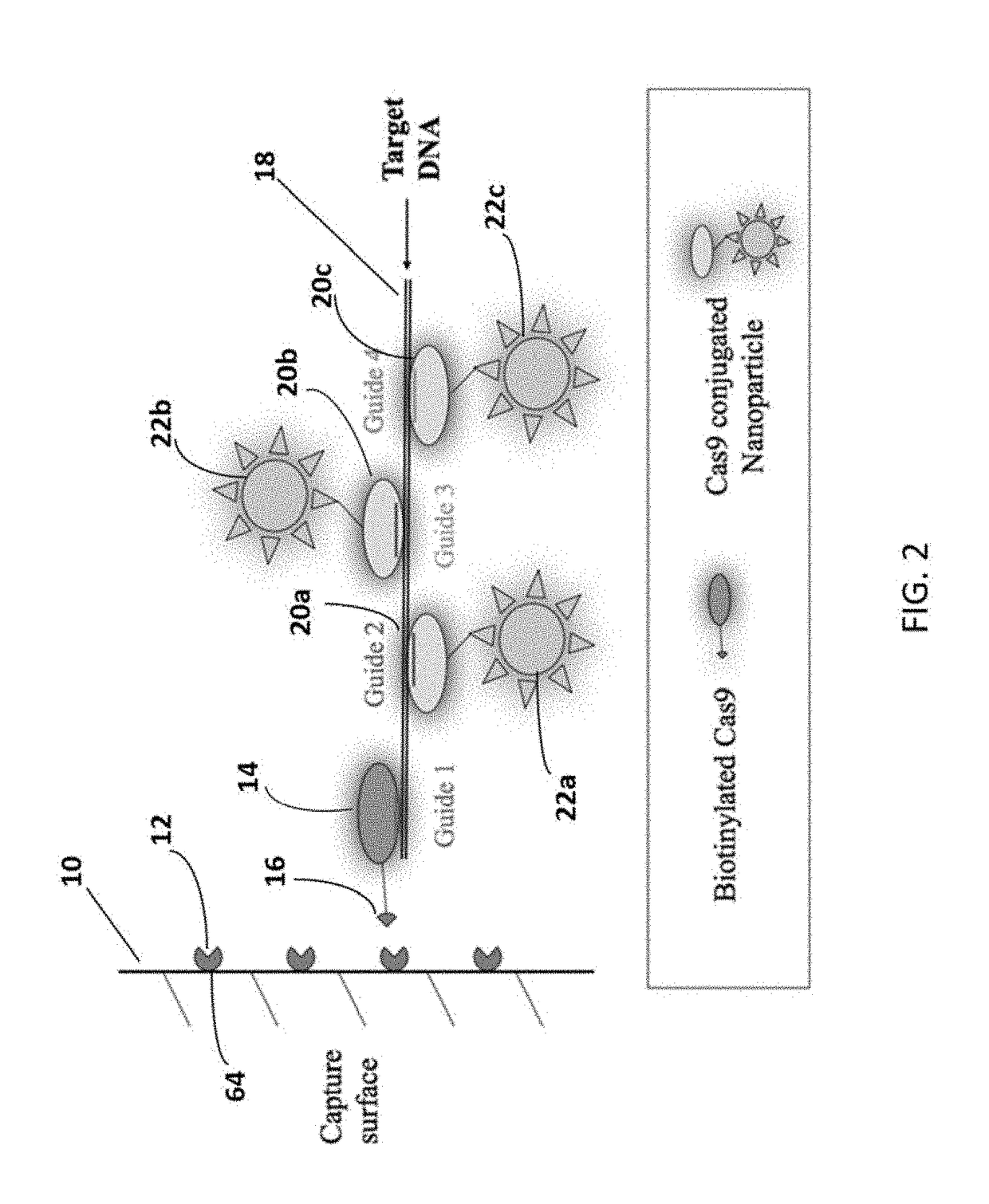
Method for isothermal DNA detection using a modified crispr/cas system and the apparatus for detection by surface acoustic waves for gene editing
InactiveUS20180334697A1Improve LODQuality improvementMicrobiological testing/measurementPharmaceutical delivery mechanismSingle electronAnalyte
A method of reducing the limit of detection in a surface acoustic wave sensor (SAW) includes the steps of: attaching a plurality of DNA segments to a detection surface of a SAW; performing a CRISPR / Cas9 preparation of the DNA segments to cut and splice a selected protein into at least one of a plurality of the DNA segments; conjugating a nanoparticle to the selected protein; and measuring the number of DNA segments with conjugated nanoparticles using a surface acoustic wave sensor (SAW). The nanoparticle may be modified to form a single electron transistor (SET) which generates a detectable signal in response to RF or ultrasonic excitation which is indicative of binding of the corresponding nanoparticle to a selected target analyte.
Owner:SENSOR KINESIS
Remote plasma generator of remote plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) system
InactiveUS20180073147A1Plasma-enhanced chemical vapor depositionEasy to useElectric discharge tubesChemical vapor deposition coatingDirect-current dischargeRemote plasma
A remote plasma generator of a remote plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) system is revealed. A direct current (DC) discharge unit, a radiofrequency (RF) discharge unit and a microwave discharge unit are arranged at the remote plasma generator separately. Source materials or process gas introduced into the remote plasma generator are / is excited by synchronous discharging of the DC discharge unit, the RF discharge unit and the microwave discharge unit to generate a plasma source required. The efficiency in use and the efficiency in manufacturing process of the remote PECVD are improved.
Owner:CHANG YU SHUN
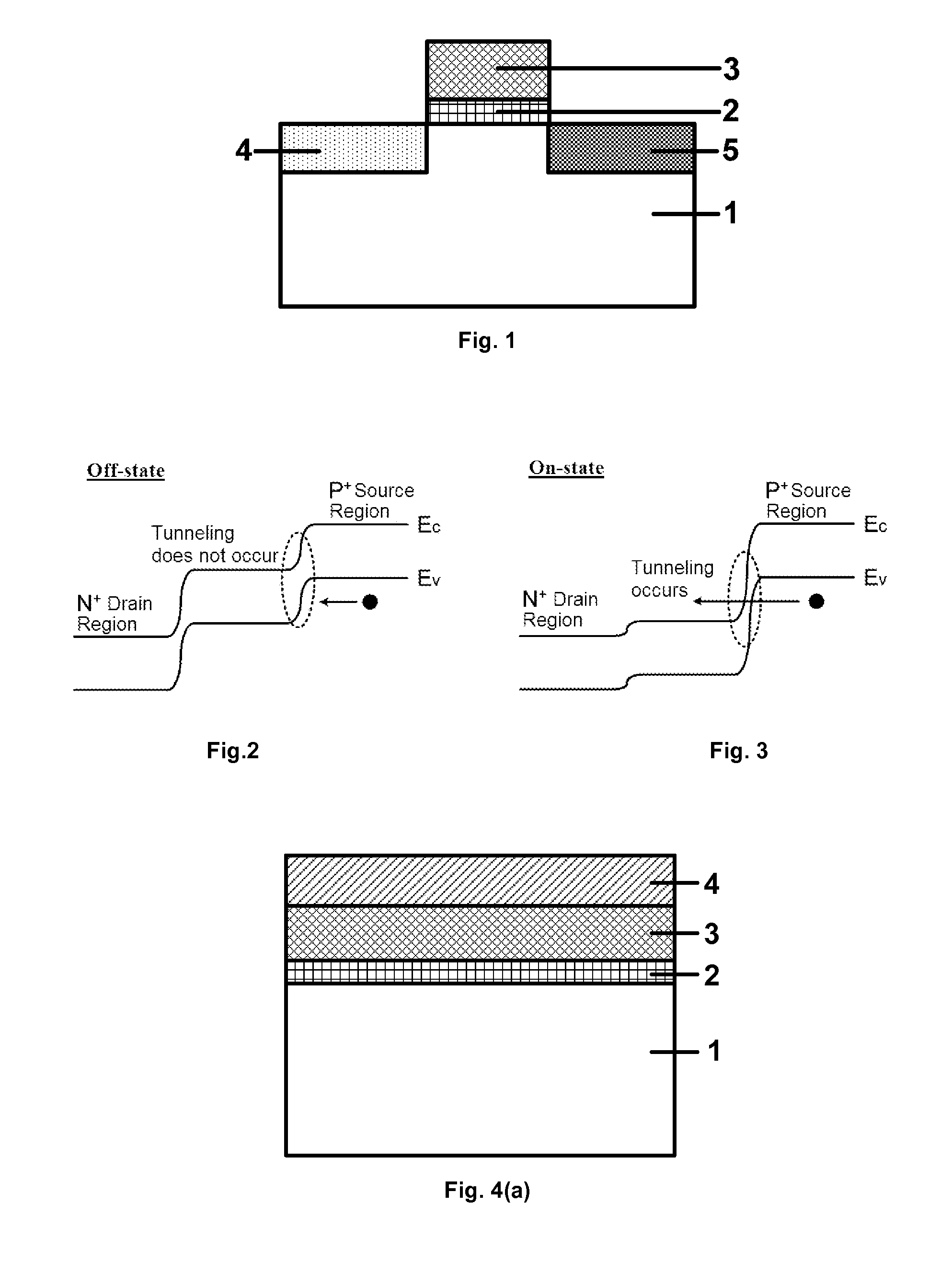
Method for fabricating a tunneling field-effect transistor
ActiveUS8288238B2Reduce diffuseRequirements on the photolithography processes for fabricating a planar TFET may be loweredSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiodePhotolithographyTunnel field-effect transistor
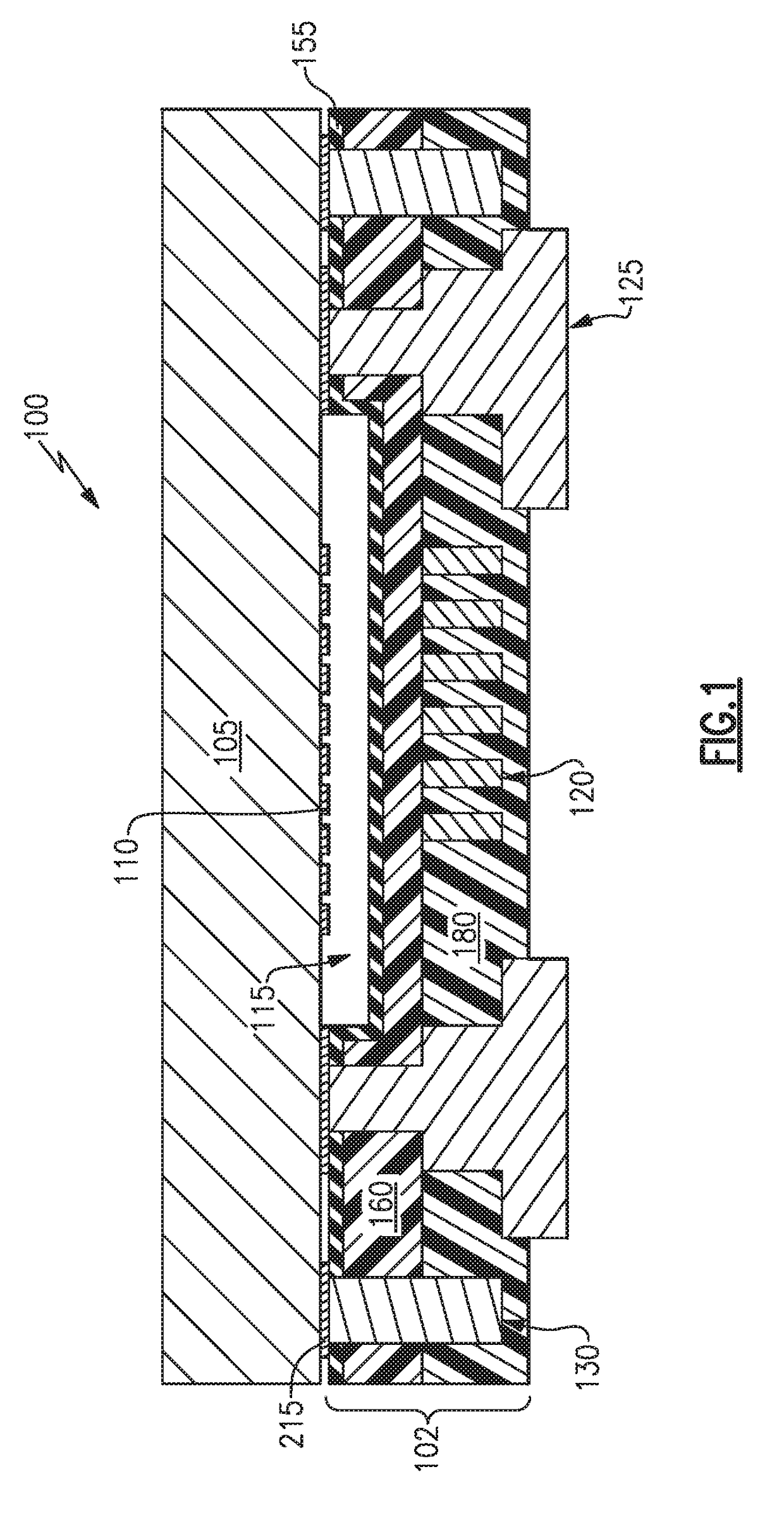
The present invention discloses a method for self-alignedly fabricating tunneling field-effect transistor (TFET) based on planar process, thereby lowering requirements on a photolithography process for fabricating the planar TFET. In the method, the source region and the drain region of the TFET are not directly defined by photolithography; rather, they are defined by another dielectric film which locates over an active region and on both sides of the gate and which is different from the dielectric film that defines the channel region. The influence due to the alignment deviation among three times of photolithography process for defining the channel region, the source and the drain regions may be eliminated by selectively removing the dielectric film over the source and drain regions by wet etching. Therefore, a planar TFET may be fabricated self-alignedly based on this process, thereby the rigid requirements on the alignment deviation of the photolithography during the fabrication procedure of a planar TFET is alleviated, which facilitates to fabricate a planar TFET device with stable and reliable characteristics.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP +1
Thin film solar cell and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20110155246A1Increase the open circuit voltageAvoid damageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationInter layerNitrogen
The present invention relates to a thin film solar cell and manufacturing method thereof. The thin film solar cell comprises a substrate, a front electrode layer, an absorber layer and a rear electrode layer stacked in such sequence, wherein the front electrode layer is formed by doping group III element into a zinc oxide. The thin-film solar cell further comprise an interlayer disposed between the front electrode layer and the absorber layer wherein the interlayer has p-type holes formed by introducing nitrogen-based gas having Argon (Ar) as a carrier gas interacted with the group III element by using PECVD or thermal treatment, implementation and diffusion on the front electrode layer surface so that the concentration of nitrogen atoms in the interlayer is greater than 1015 / cm3.
Owner:NEXPOWER TECH
Encoder for a movable shaft, a device including such an encoder, and a method of fabricating such an encoder
InactiveUS20060226830A1Minimize impactSatisfactory bondingBearing assemblyDevices using electric/magnetic meansThin layerEngineering
An encoder comprising a sleeve for holding on a shaft and an encoder element secured to the sleeve. The encoder element presents an encoding zone that is protected by protection means. The protection means comprise a thin layer of material deposited by plasma directly on the encoder element and secured thereto, the thin layer covering at least the encoding zone. A device including the encoder and a method of fabricating the encoder are described.
Owner:HUTCHINSON SA
Method of producing a magnetic structure
ActiveUS20180053523A1High magnetic flux densityImprove magnetic propertiesNanostructure applicationChemical vapor deposition applicationAtomic physicsCoating
A device and to a method of producing a device, wherein the method includes, inter alia, providing a substrate and generating at least two mutually spaced-apart cavities within the substrate. In accordance with the invention, each cavity has a depth of at least 50 μm. The cavities are filled up with magnetic particles, wherein the magnetic particles enter into contact with one another at points of contact, and wherein cavities are formed between the points of contact. At least some of the magnetic particles are connected to one another at their points of contact, specifically by coating the magnetic particles, wherein the cavities are at least partly penetrated by the layer produced in the coating process, so that the connected magnetic particles form a magnetic porous structure.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Method for fabricating a tunneling field-effect transistor
ActiveUS20120115297A1Requirement on photolithography process is very strictLower requirementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiodePhotolithographyTunneling field effect transistor
The present invention discloses a method for self-alignedly fabricating tunneling field-effect transistor (TFET) based on planar process, thereby lowering requirements on a photolithography process for fabricating the planar TFET. In the method, the source region and the drain region of the TFET are not directly defined by photolithography; rather, they are defined by another dielectric film which locates over an active region and on both sides of the gate and which is different from the dielectric film that defines the channel region. The influence due to the alignment deviation among three times of photolithography process for defining the channel region, the source and the drain regions may be eliminated by selectively removing the dielectric film over the source and drain regions by wet etching. Therefore, a planar TFET may be fabricated self-alignedly based on this process, thereby the rigid requirements on the alignment deviation of the photolithography during the fabrication procedure of a planar TFET is alleviated, which facilitates to fabricate a planar TFET device with stable and reliable characteristics.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com