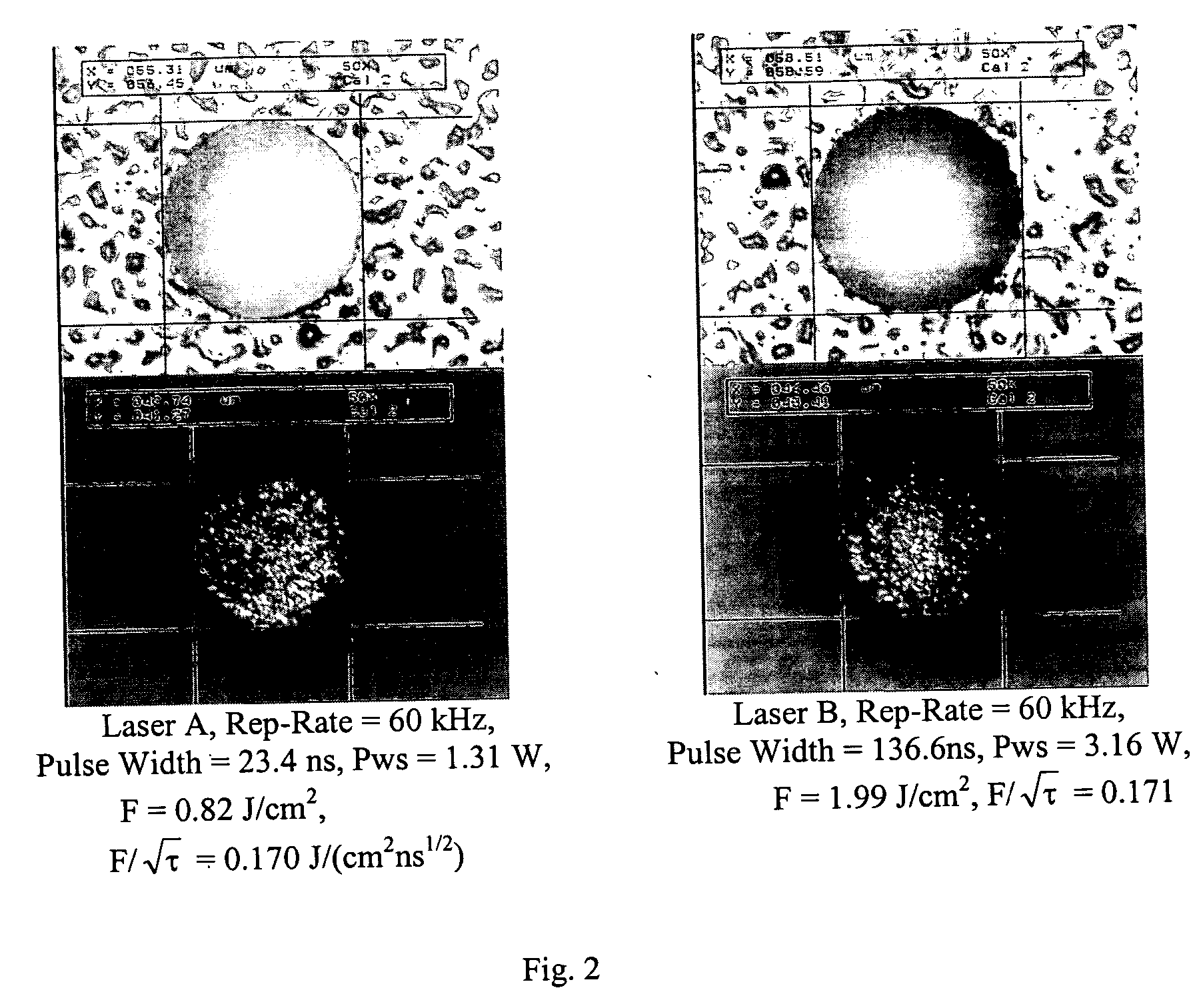
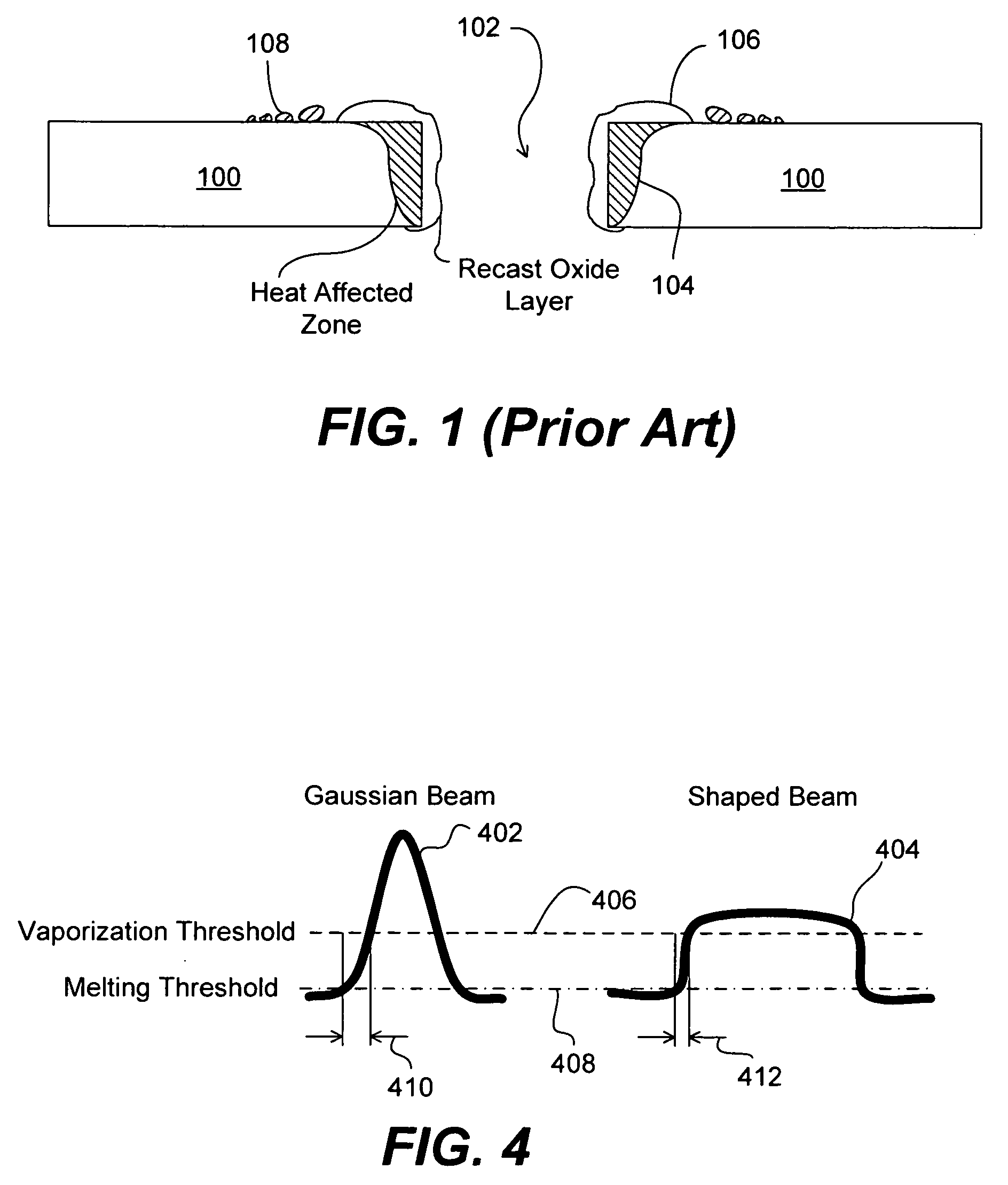
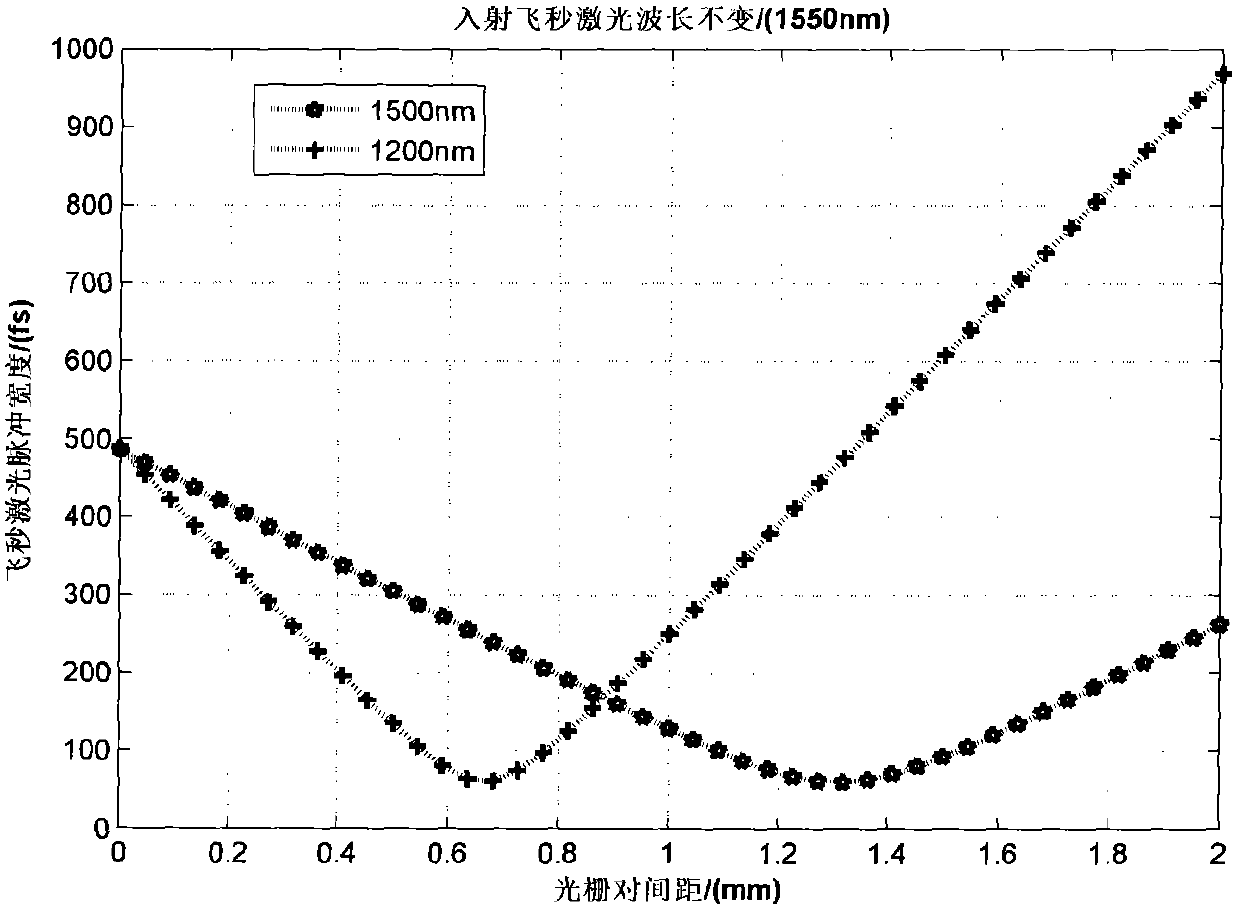
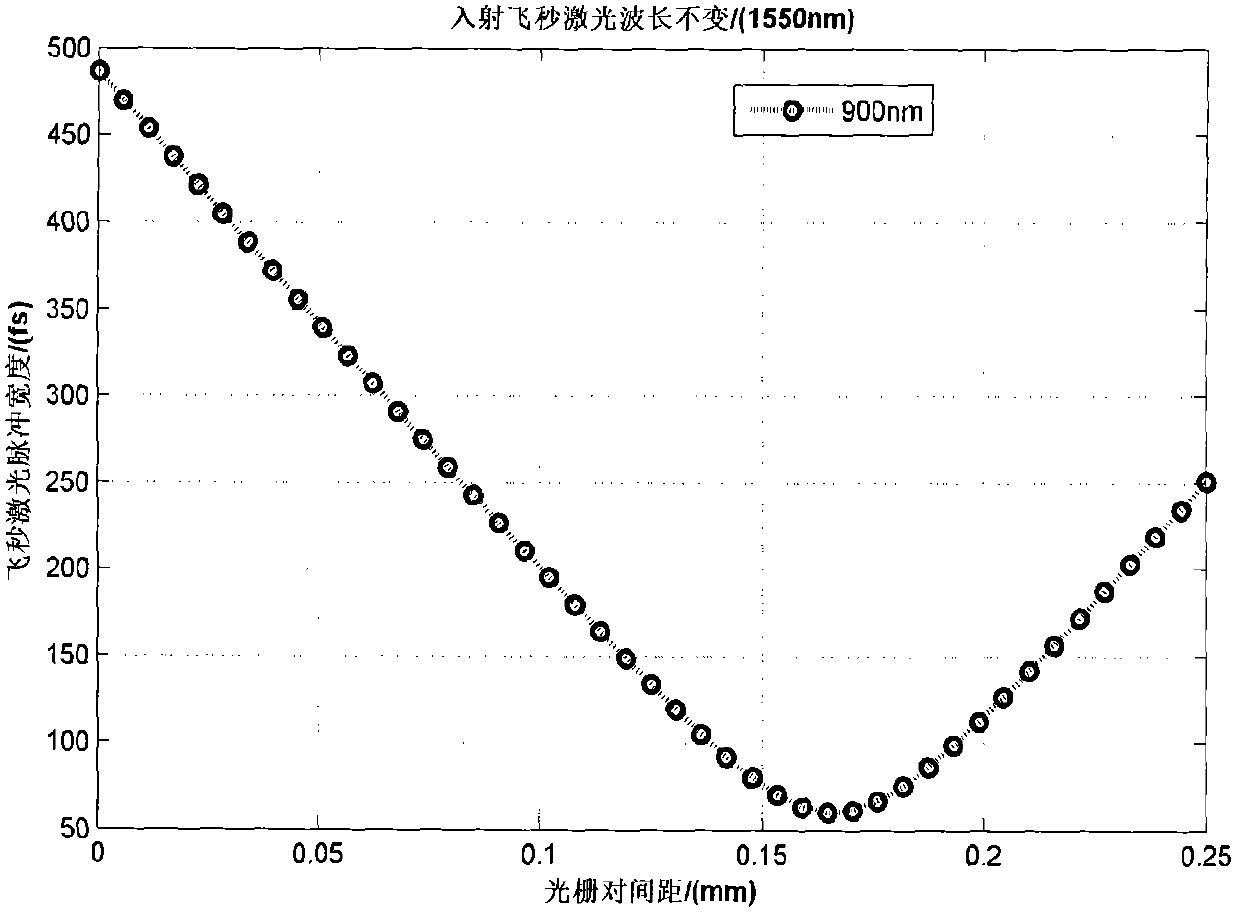
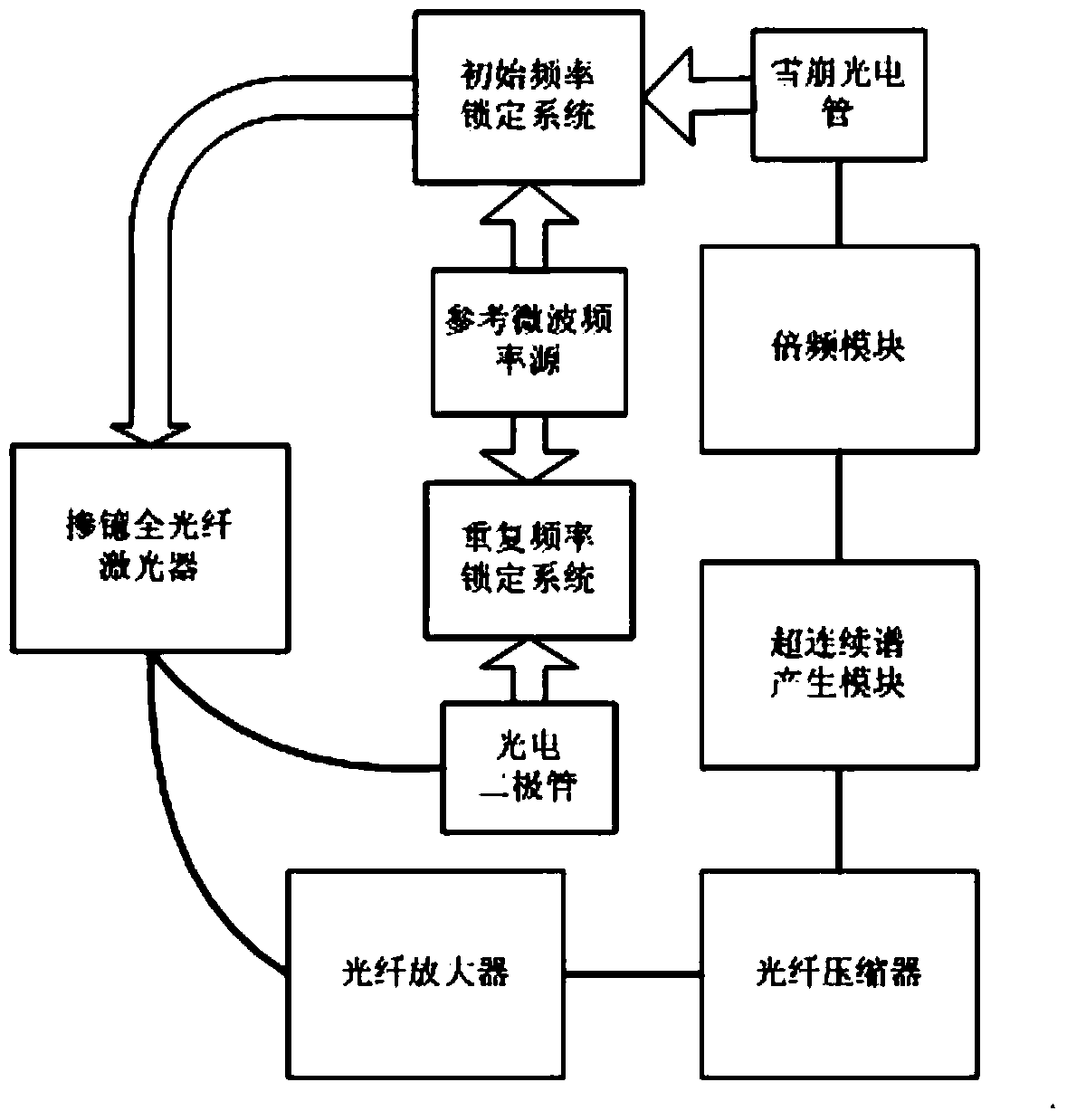
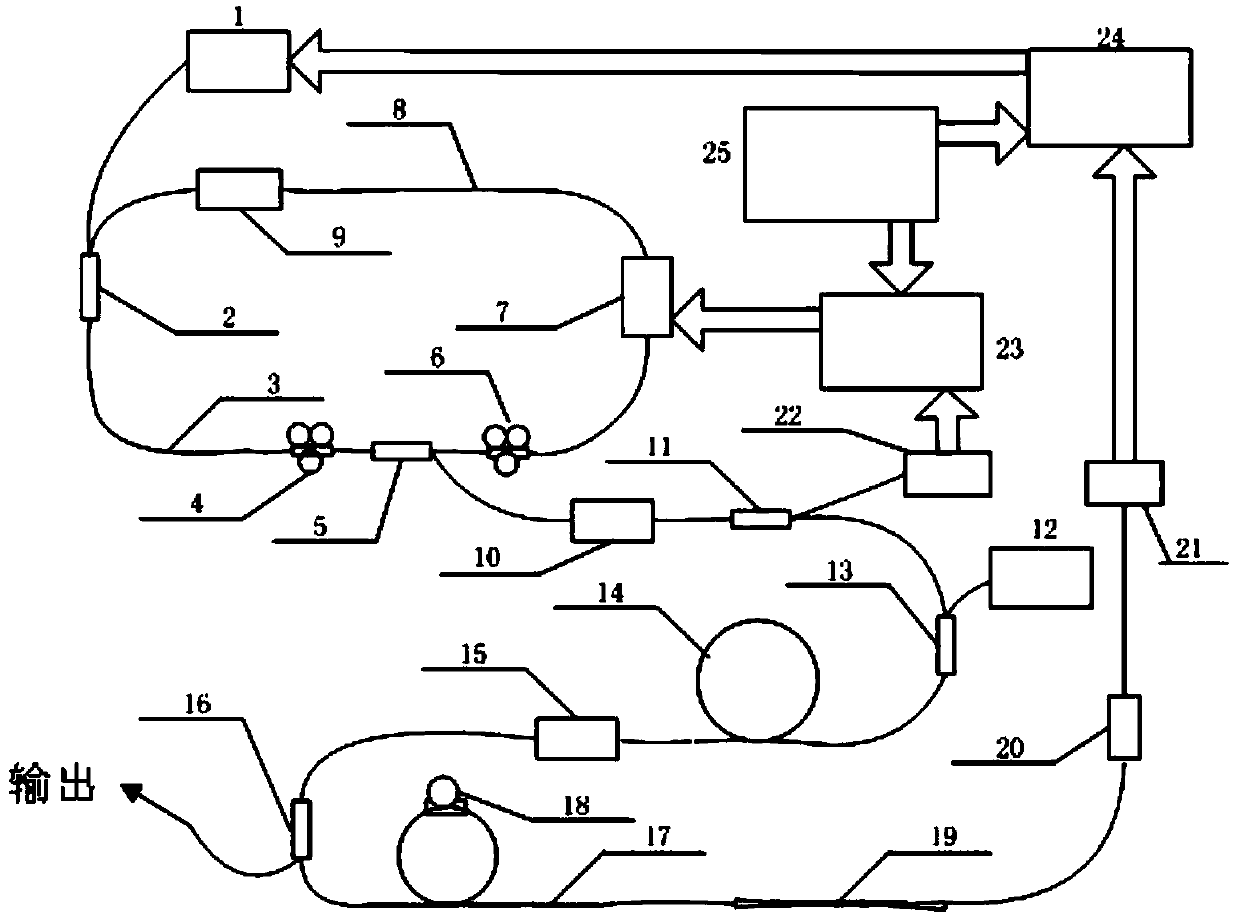
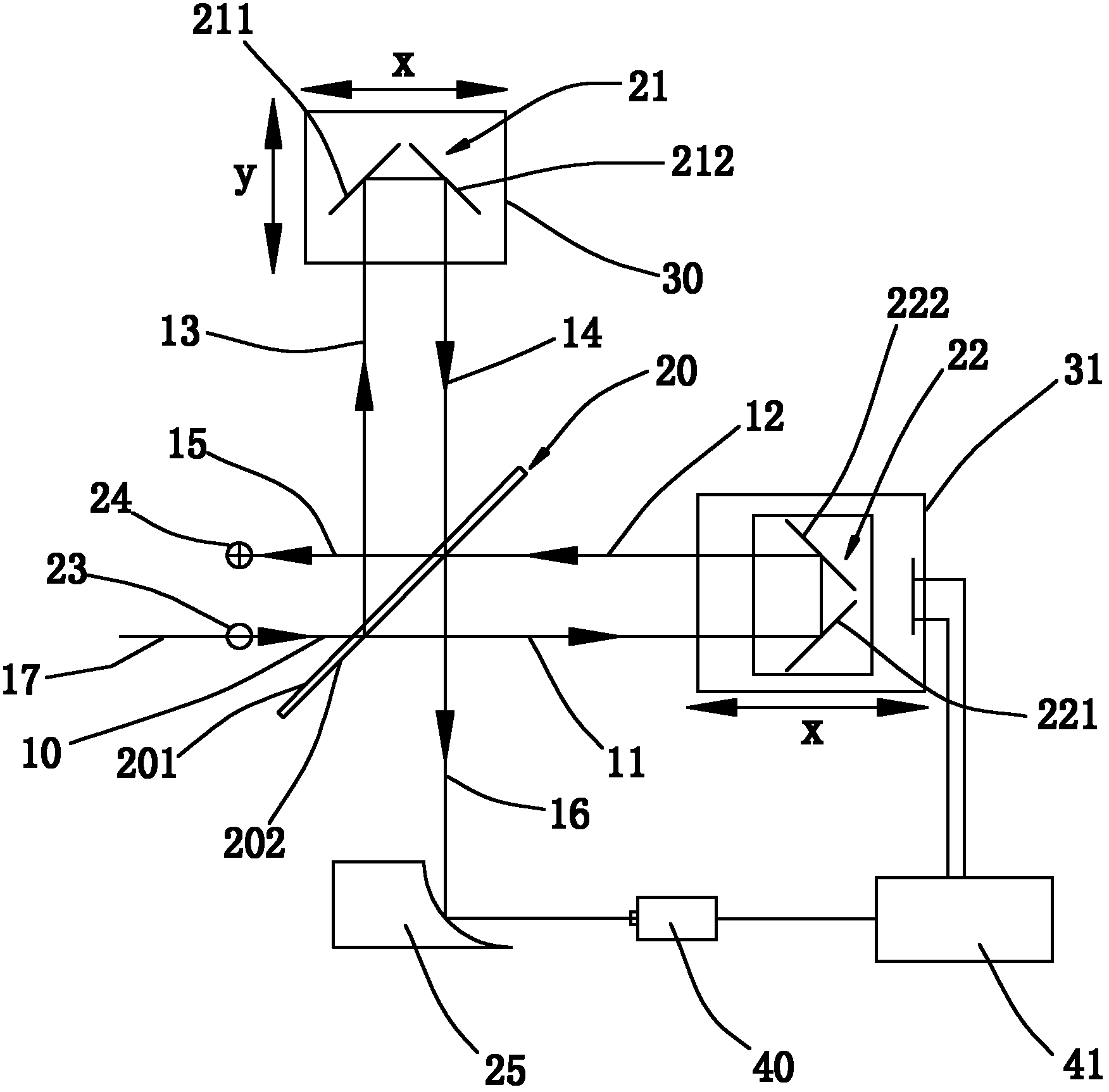
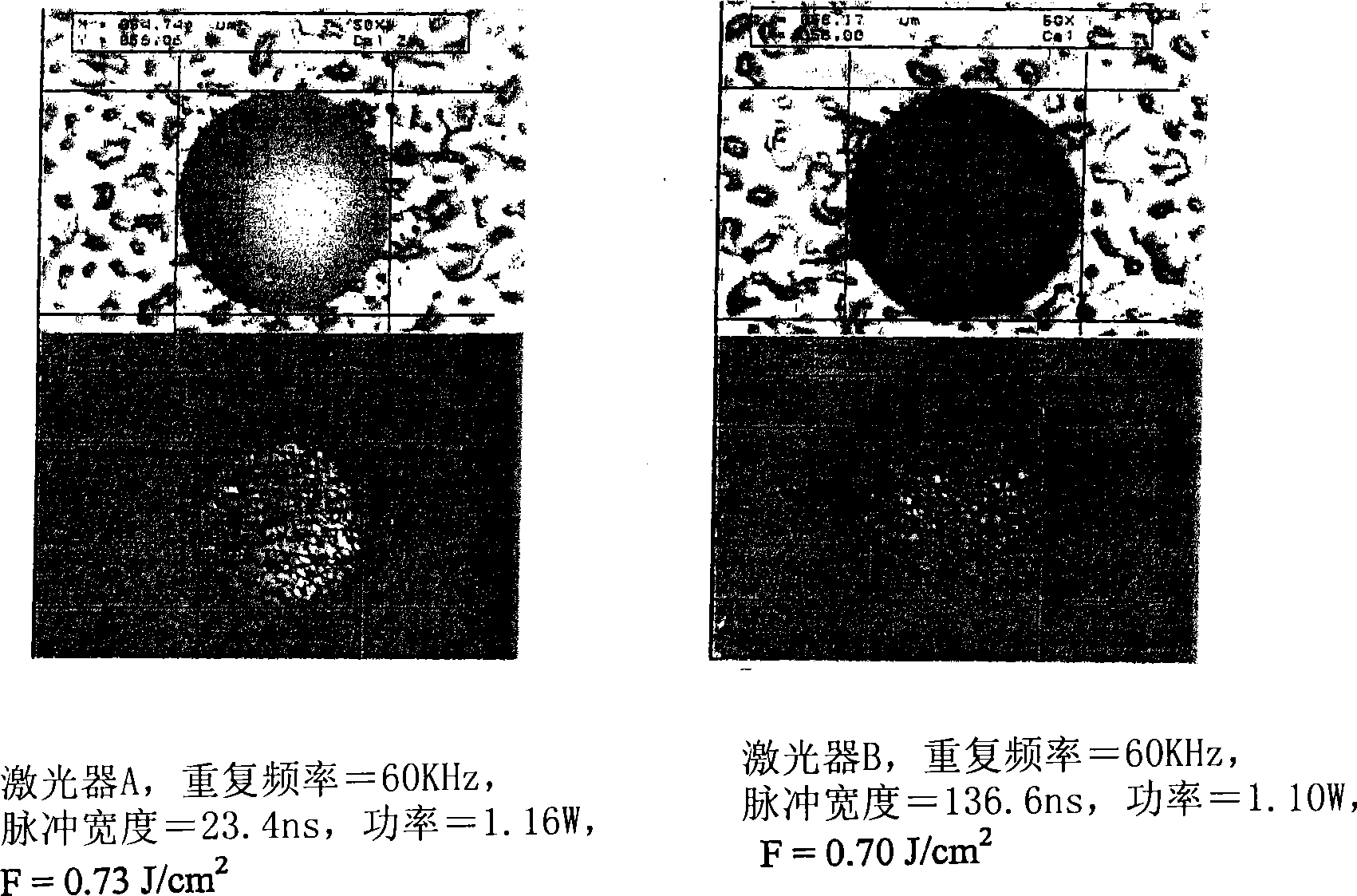
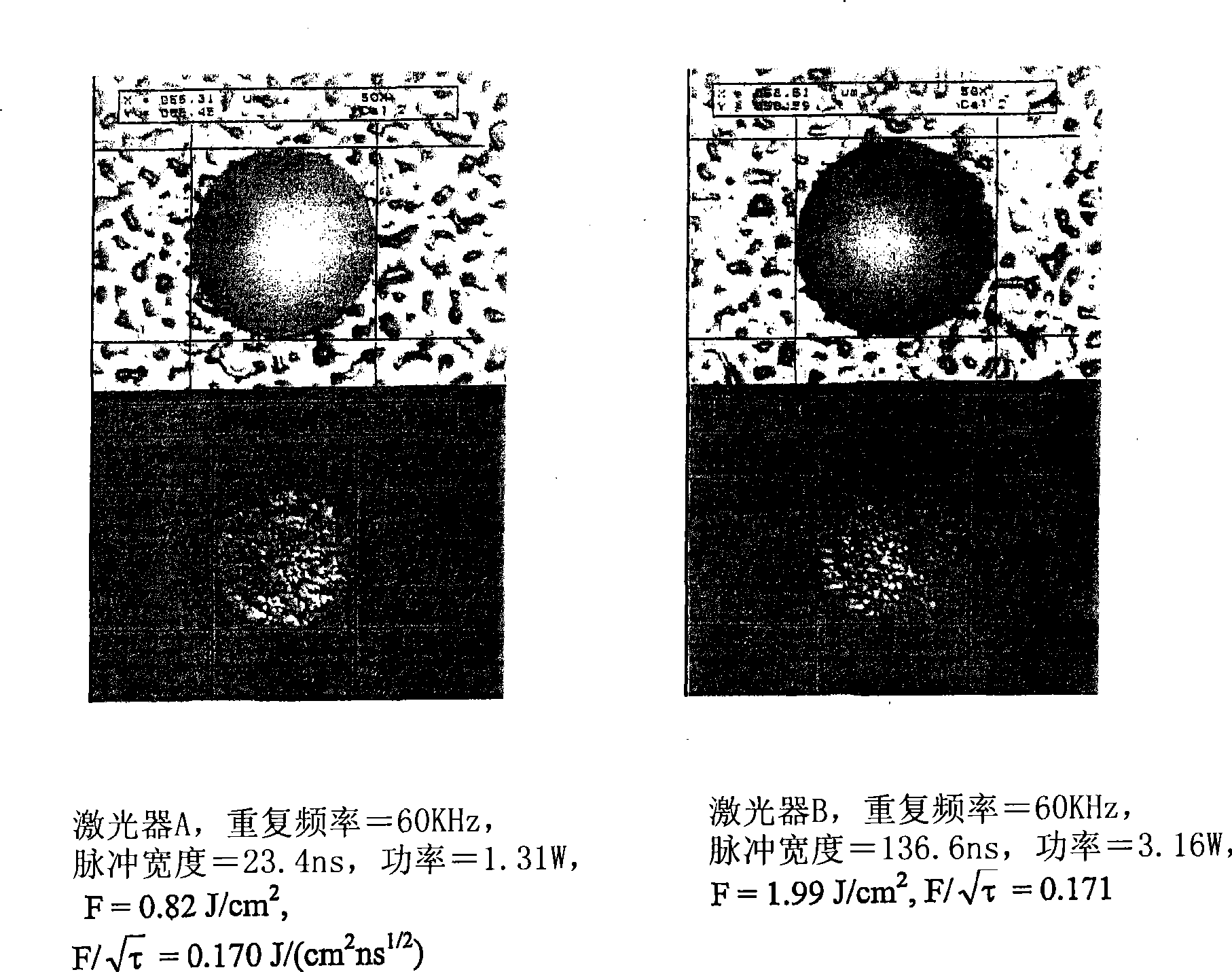
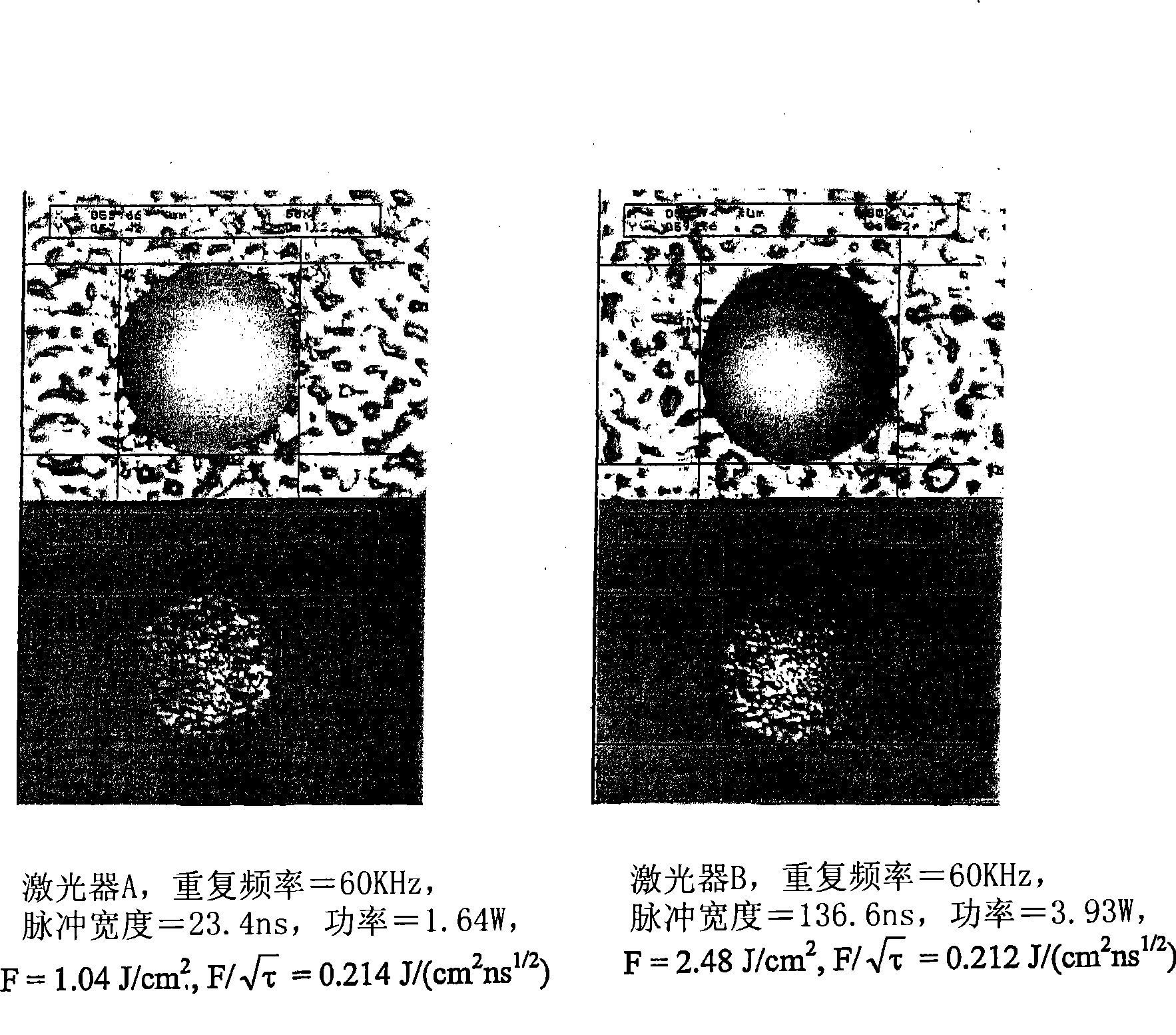
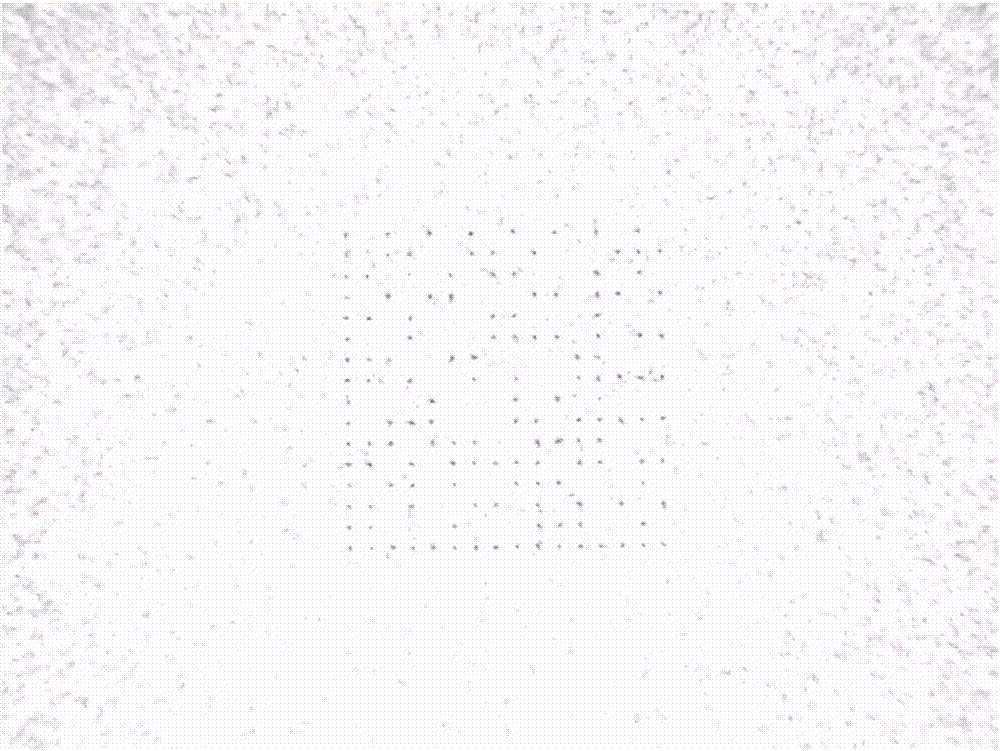Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
244 results about "Laser pulse width" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
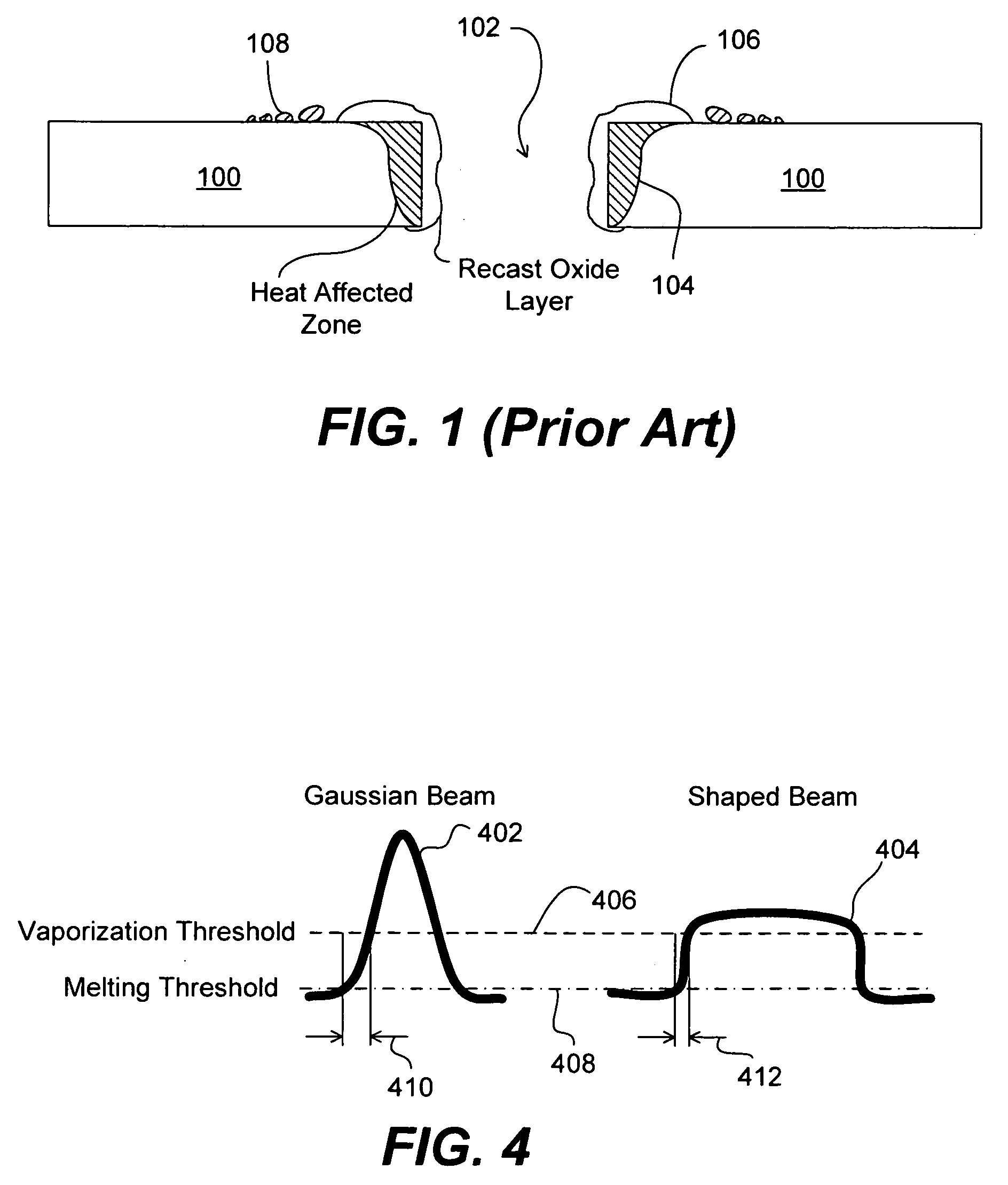
Pulse Width (Laser Welding) When the laser is in pulse mode the duration of the pulse is known as the pulse width. In many process applications pulse width is used to tune the process, as opposed to peak power which is the gross process adjustment.
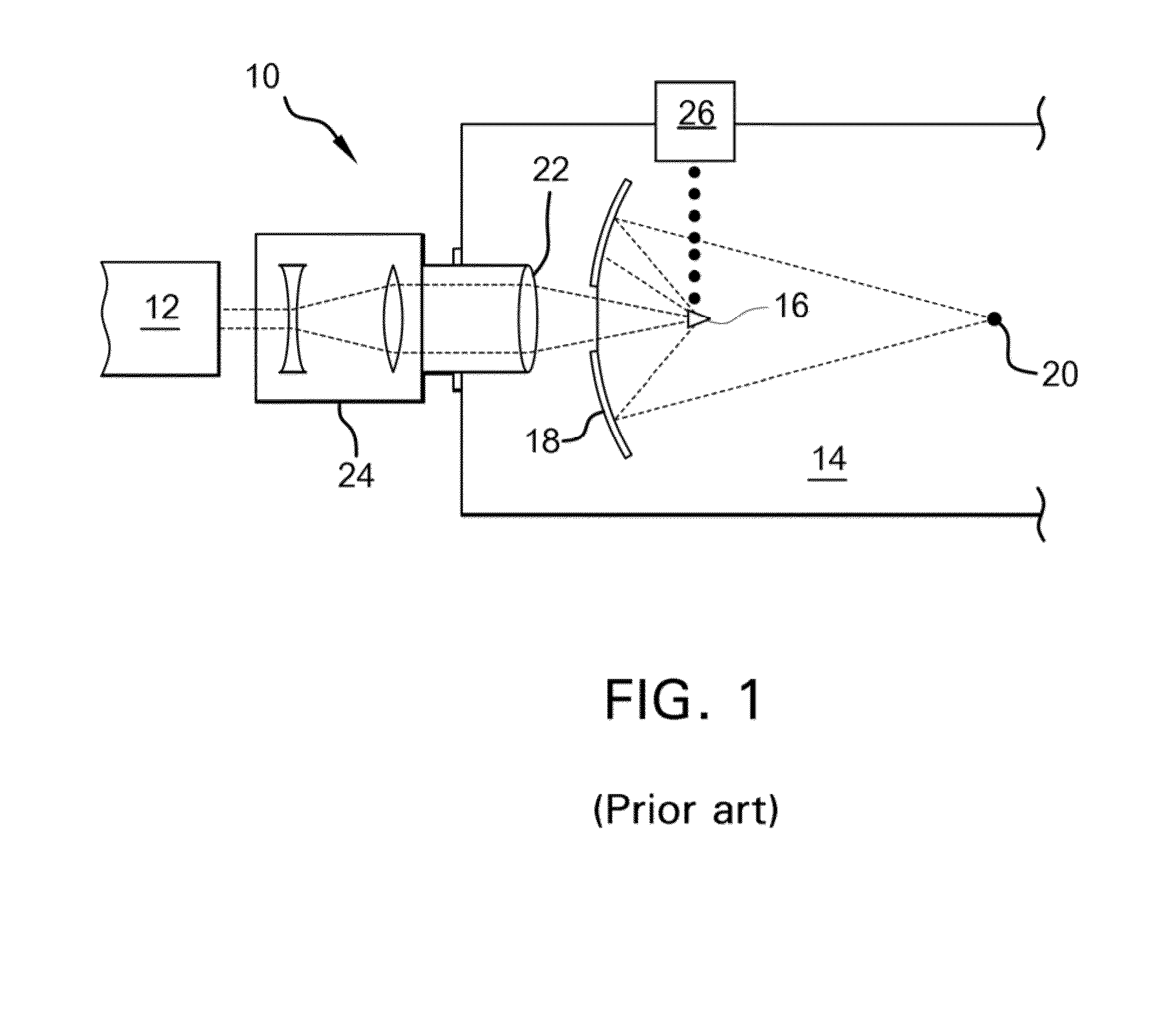
Method for controlling configuration of laser induced breakdown and ablation
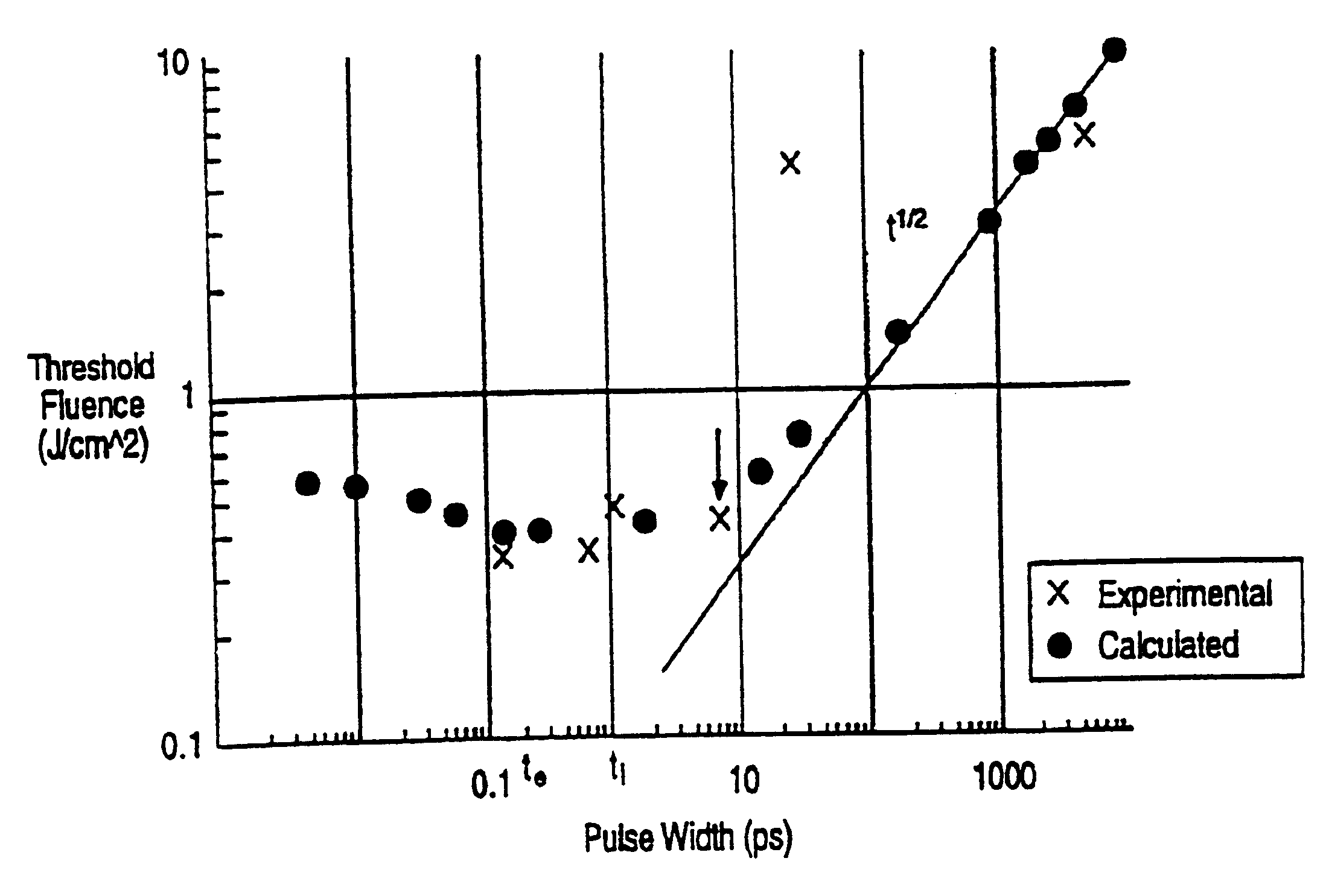
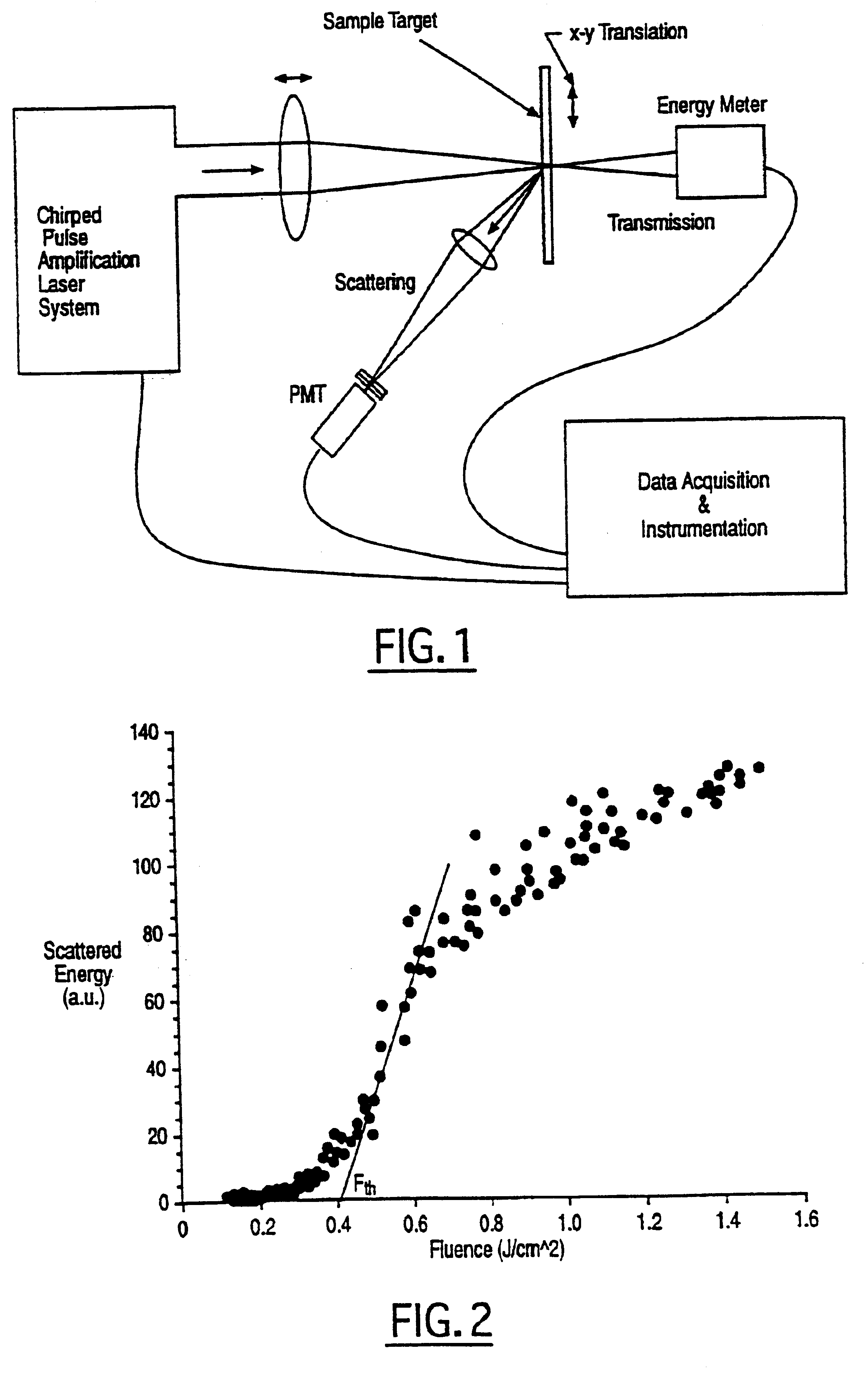
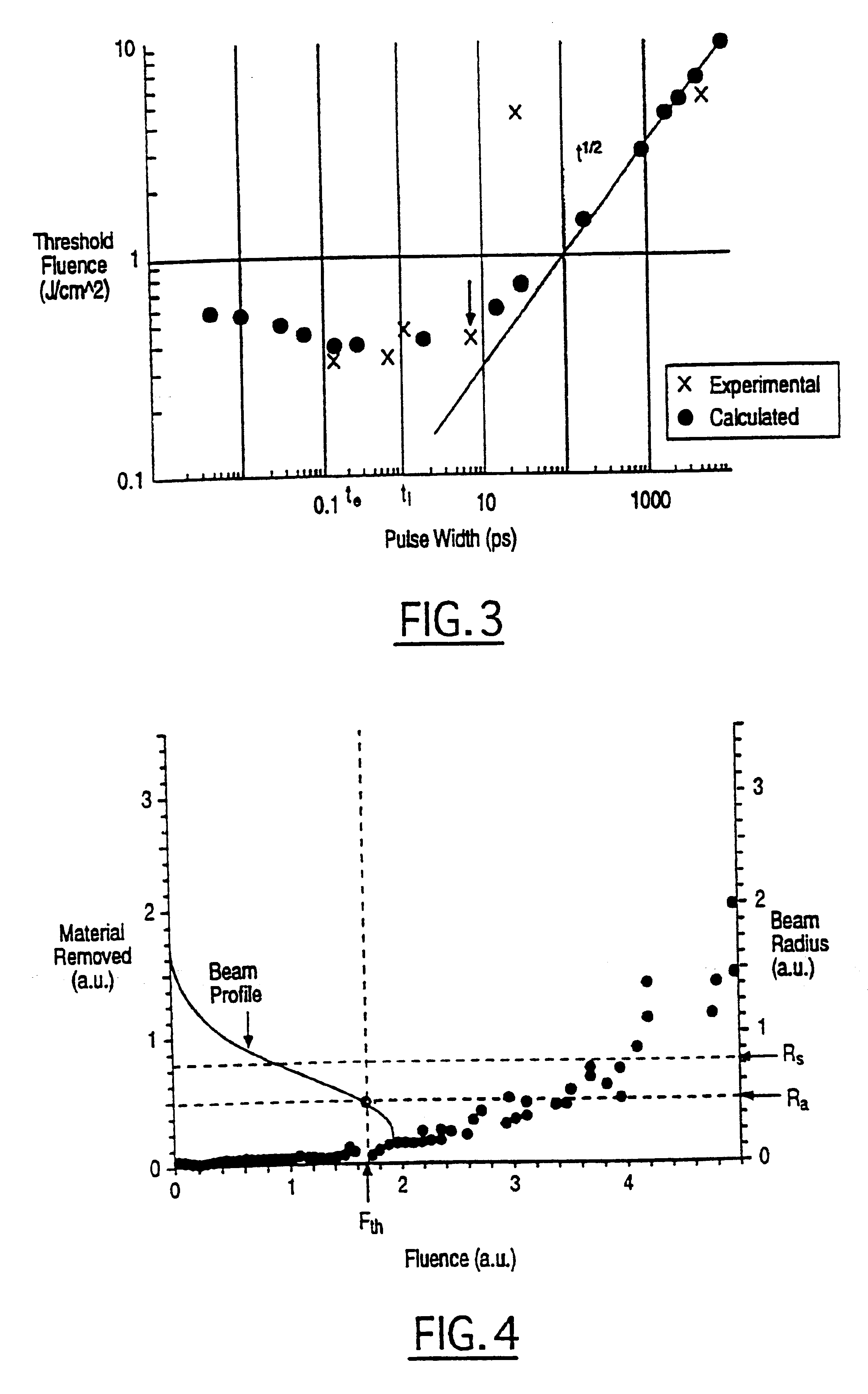
In one aspect the invention provides a method for laser induced breakdown of a material with a pulsed laser beam where the material is characterized by a relationship of fluence breakdown threshold (Fth) versus laser beam pulse width (T) that exhibits an abrupt, rapid, and distinct change or at least a clearly detectable and distinct change in slope at a predetermined laser pulse width value. The method comprises generating a beam of laser pulses in which each pulse has a pulse width equal to or less than the predetermined laser pulse width value. The beam is focused to a point at or beneath the surface of a material where laser induced breakdown is desired.The beam may be used in combination with a mask in the beam path. The beam or mask may be moved in the x, y, and Z directions to produce desired features. The technique can produce features smaller than the spot size and Rayleigh range due to enhanced damage threshold accuracy in the short pulse regime.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Ultrashort laser pulse wafer scribing
InactiveUS20070272668A1Improve mechanical stressImprove thermal stressSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWelding/soldering/cutting articlesLight beamOptoelectronics
Systems and methods are provided for scribing wafers with short laser pulses so as to reduce the ablation threshold of target material. In a stack of material layers, a minimum laser ablation threshold based on laser pulse width is determined for each of the layers. The highest of the minimum laser ablation thresholds is selected and a beam of one or more laser pulses is generated having a fluence in a range between the selected laser ablation threshold and approximately ten times the selected laser ablation threshold. In one embodiment, a laser pulse width in a range of approximately 0.1 picosecond to approximately 1000 picoseconds is used. In addition, or in other embodiments, a high pulse repetition frequency is selected to increase the scribing speed. In one embodiment, the pulse repetition frequency is in a range between approximately 100 kHz and approximately 100 MHz.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Method for minimizing sample damage during the ablation of material using a focused ultrashort pulsed laser beam
In one aspect the invention provides a method for laser induced breakdown of a material with a pulsed laser beam where the material is characterized by a relationship of fluence breakdown threshold (Fth) versus laser beam pulse width (T) that exhibits an abrupt, rapid, and distinct change or at least a clearly detectable and distinct change in slope at a predetermined laser pulse width value. The method comprises generating a beam of laser pulses in which each pulse has a pulse width equal to or less than the predetermined laser pulse width value. The beam is focused above the surface of a material where laser induced breakdown is desired. The region of least confusion (minimum beam waist or average spot size) is above the surface of the material in which laser induced breakdown is desired since the intensity of the beam falls off in the forward direction, preferably the region of the beam at or within the surface is between the region of least confusion and sufficient to remove material and the minimum intensity necessary for laser induced breakdown of the material to be removed, most preferably the region of minimum intensity is disposed at the surface of the material to be removed. The beam may be used in combination with a mask in the beam path. The beam or mask may be moved in the x, y, and Z directions to produce desired features. The technique can produce features smaller than the spot size and Rayleigh range due to enhanced damage threshold accuracy in the short pulse regime.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Ultraviolet laser ablative patterning of microstructures in semiconductors
InactiveUS7157038B2High aspect ratioGreat depth of focusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWelding/soldering/cutting articlesUltravioletSingle crystal
Patterns with feature sizes of less than 50 microns are rapidly formed directly in semiconductors, particularly silicon, GaAs, indium phosphide, or single crystalline sapphire, using ultraviolet laser ablation. These patterns include very high aspect ratio cylindrical through-hole openings for integrated circuit connections; singulation of processed die contained on semiconductor wafers; and microtab cutting to separate microcircuit workpieces from a parent semiconductor wafer. Laser output pulses (32) from a diode-pumped, Q-switched frequency-tripled Nd:YAG, Nd:YVO4, or Nd:YLF is directed to the workpiece (12) with high speed precision using a compound beam positioner. The optical system produces a Gaussian spot size, or top hat beam profile, of about 10 microns. The pulse energy used for high-speed ablative processing of semiconductors using this focused spot size is greater than 200 μJ per pulse at pulse repetition frequencies greater than 5 kHz and preferably above 15 kHz. The laser pulsewidth measured at the full width half-maximum points is preferably less than 80 ns.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
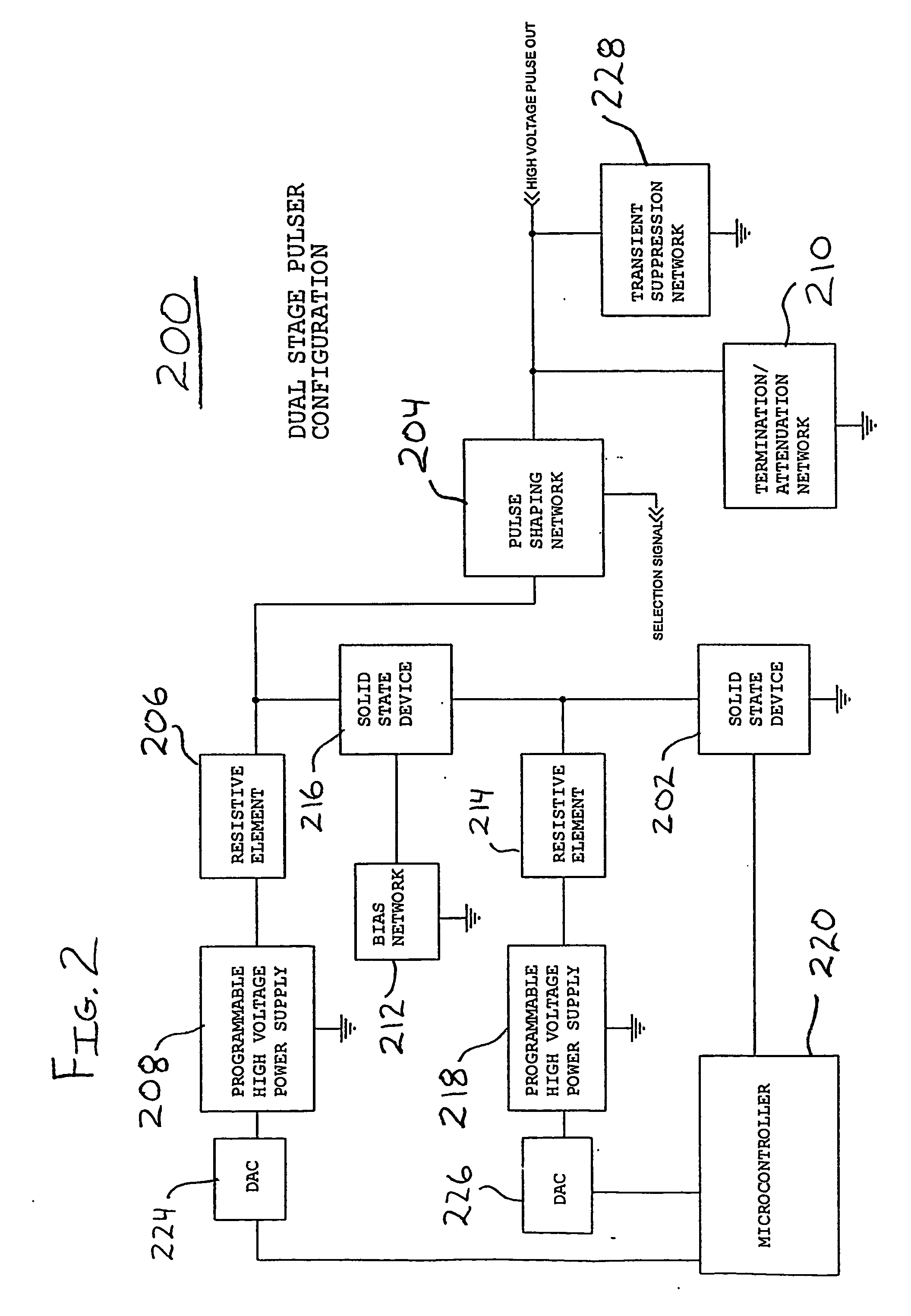
Short duration variable amplitude high voltage pulse generator
InactiveUS20070018504A1Wide range of useImprove accuracyElectric discharge tubesDigital data processing detailsMOSFETHigh voltage pulse
An improved electrical pulse generator incorporating MOSFET components, a programmable high voltage power supply, and a shaping network for generating short duration signals having narrow pulse widths and short rise times.
Owner:WIENER SCOTT ALBERT +1
Method and system for laser processing targets of different types on a workpiece
InactiveUS20080067155A1Increased process windowSimple processLaser detailsWelding/soldering/cutting articlesLaser processingPulse shaping
A method and system for laser processing targets of different types on a workpiece are provided. The method includes setting a laser pulse width of one or more laser pulses to selectively provide one or more laser output pulses having one or more set pulse widths based on a first type of target to be processed. The method further includes setting a pulse shape of the one or more output pulses to selectively provide the one or more output pulses having the set pulse shape based on the types of targets to be processed. The method still further includes delivering the one or more output pulses having the one or more set pulse widths and the set pulse shape to at least one target of the first type. The method finally includes resetting the laser pulse width of one or more laser pulses to selectively provide one or more laser output pulses having one or more reset pulse widths based on a second type of target to be processed.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
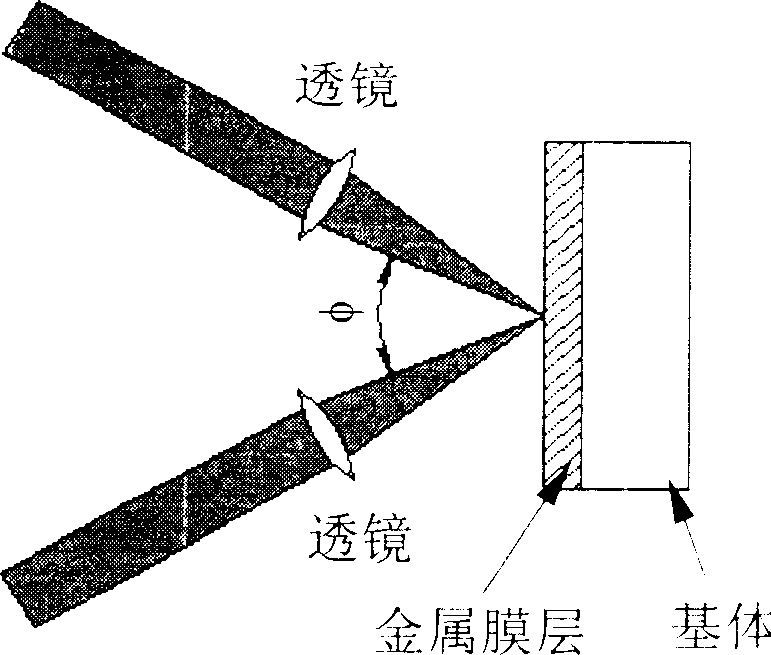
Method for preparing periodic microstructure on metallic film by femto second laser
InactiveCN1448755ASimple preparation processImprove efficiencyNon-linear opticsOptical elementsFemto second laserLaser beams
The laser beam produced by titanium jewel femto second laser is split into two beams and the two laser beams are focused by lenses to realize temporal and spatial coherent superposing before acting on metal film on quartz, common glass or silicon substrate. The laser pulse width, pulse frequency and single pulse energy are so controlled that the laser beam can burn out metal film and produce no damage of the substrate. The coherent laser beam is fixed and the sample on 3D platform is computer-controlled to move to prepare periodical microstructure of metal film.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Short burst laser cleaning method of metal surface
The invention provides a method for cleaning a metal surface by short pulsed laser. The method cleans the area to be cleaned on the metal surface in a manner of round lapping irradiated by defocusing facula of laser and is characterized in that: (1) the short pulsed laser is adopted to clean the surface, wherein, the laser pulse width is less than 100ns, and the peak power density is more than 100MW / cm<2>; (2) when processed, the end face, as well as the upper surface and the lower surface near the end face, need to be cleaned, and the laser irradiates the upper surface of a sheet metal at an inclined angle of 45 - 60 degrees, with part of the laser facula being projected on the end face and the other part of the laser facula being projected on the upper surface; mainly aiming at meeting the requirements for cleaning a thin layer of oxide film on the surface of titanium alloy, aluminum alloy and the like before welding, the method can obtain higher surface cleaning quality than the conventional laser cleaning method and faster process flow than acid cleaning method, is suitable for rapid treatment of laser processing, and has good reference value for the fast flow of processing production line and wide applicability.
Owner:BEIJING AVIATION MFG ENG INST CHINA AVIATION NO 1 GRP
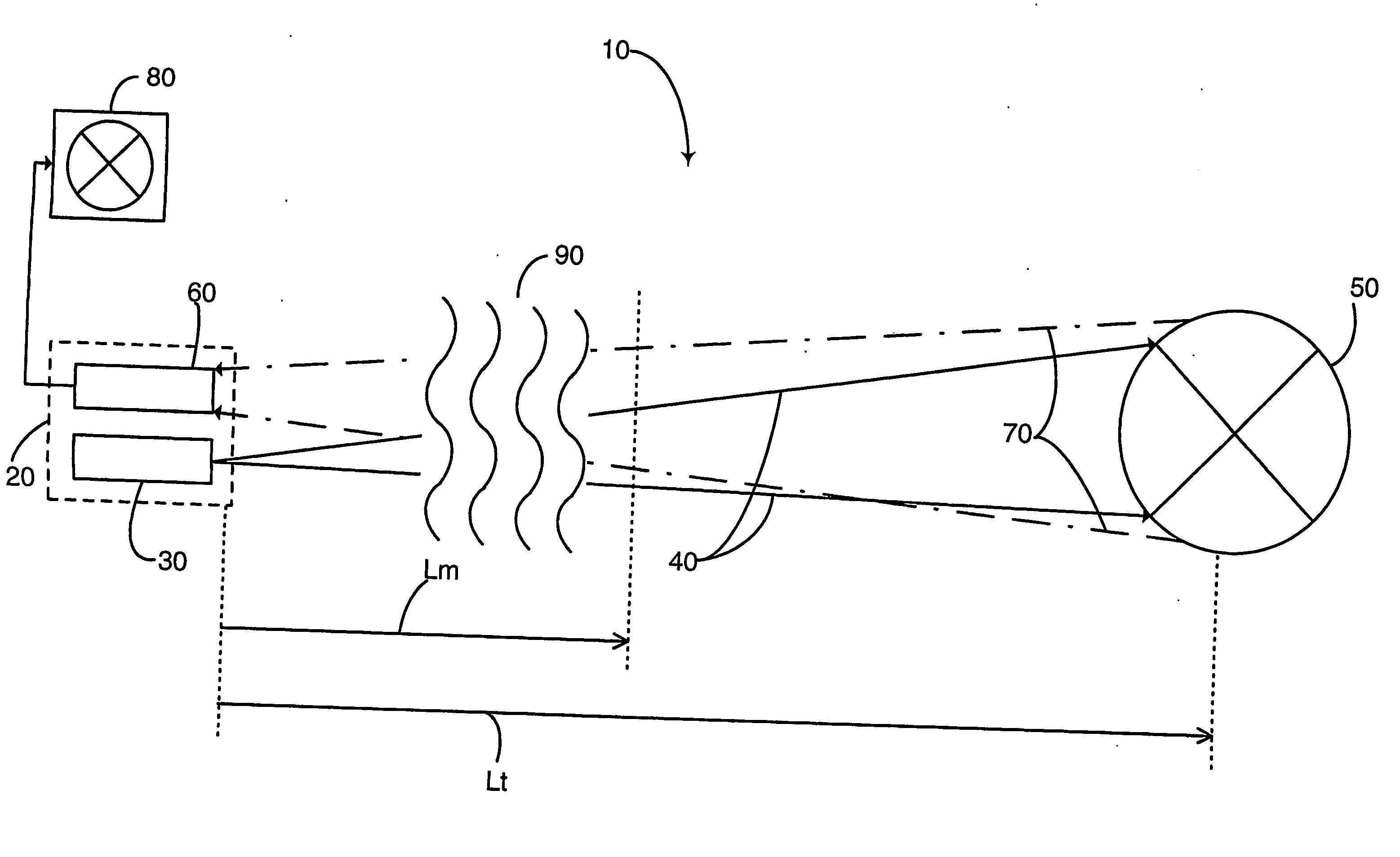
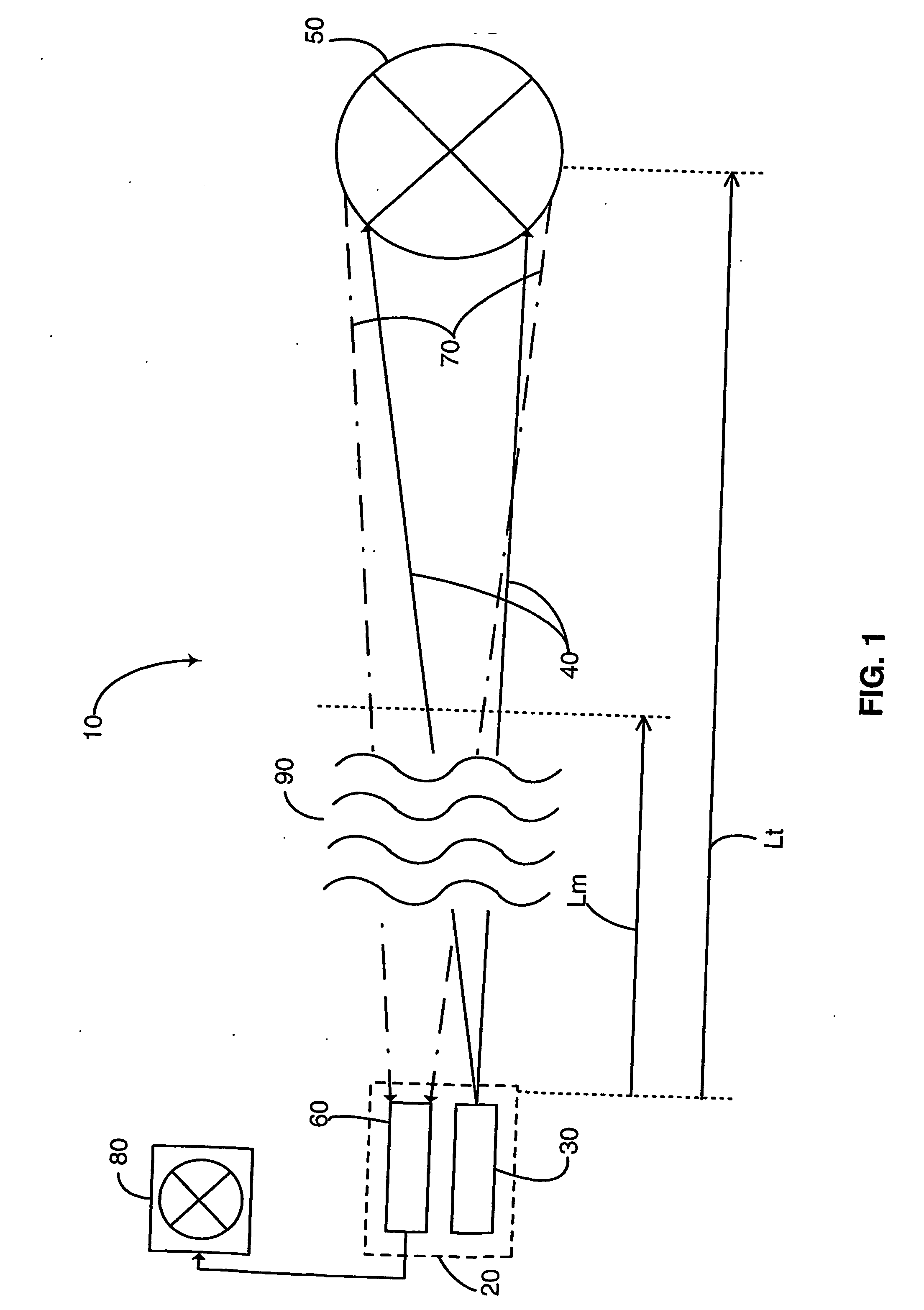
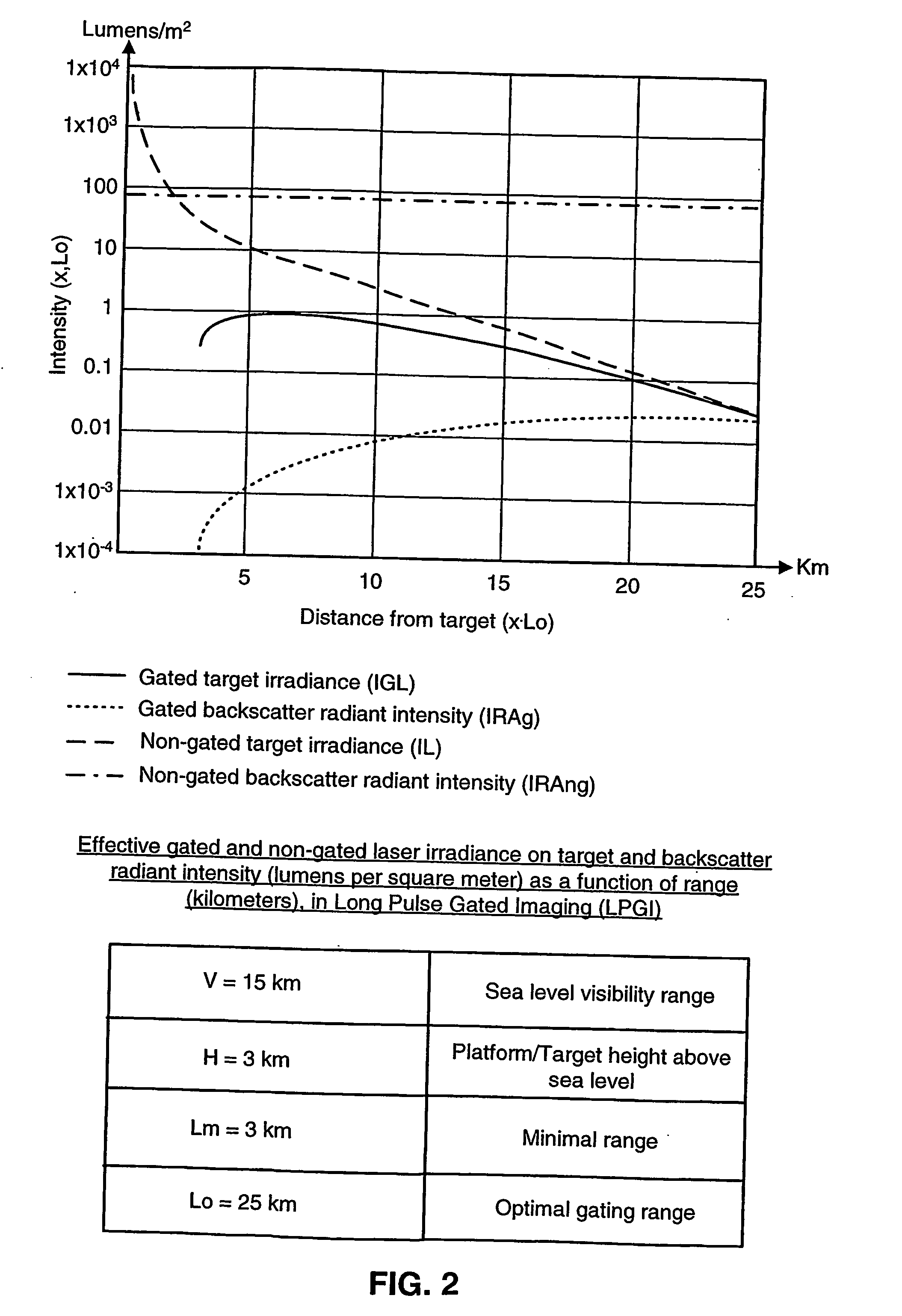
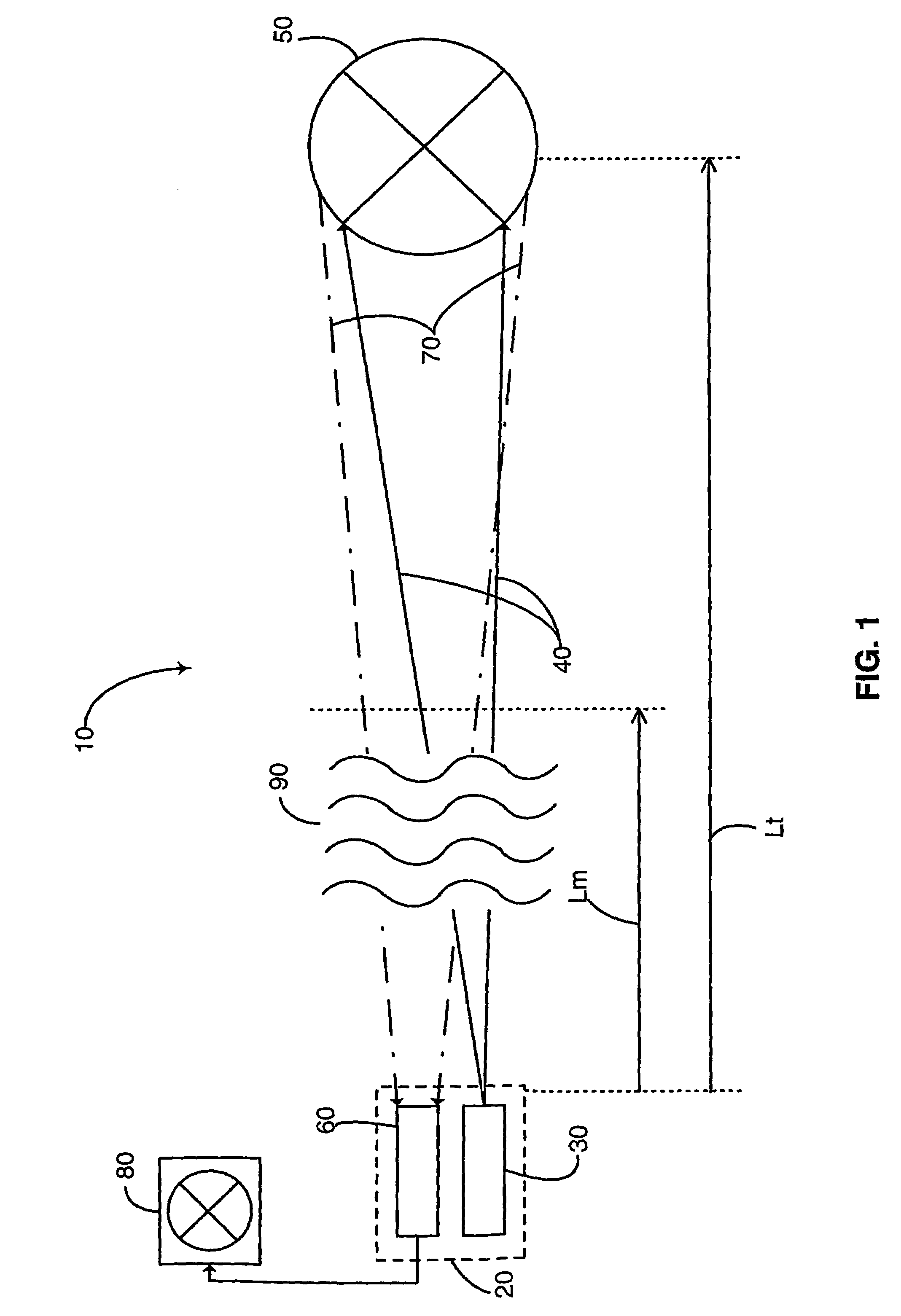
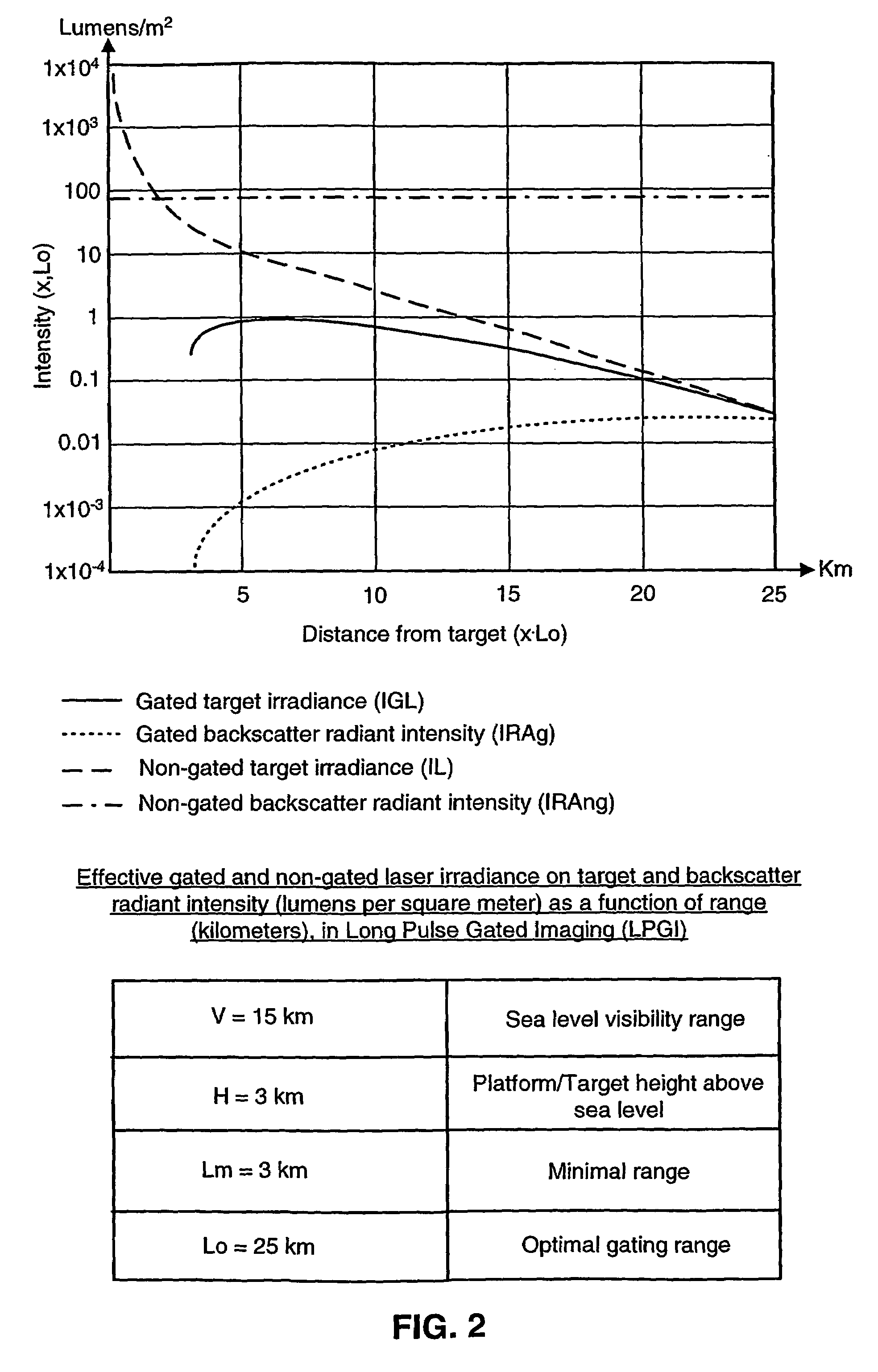
Laser gated camera imaging system and method
A gated camera imaging system and method, utilizing a laser device for generating a beam of long duration laser pulses toward a target. A camera receives the energy of light reflexes of the pulses reflected from the target. The camera gating is synchronized to be set OFF for at least the duration of time it takes the laser device to produce a laser pulse in its substantial entirety, including an end of the laser pulse, in addition to the time it takes the laser pulse to complete traversing a zone proximate to the system and back to the camera, and set ON for an ON time duration thereafter until the laser pulse reflects back from the target and is received in the camera. The laser pulse width substantially corresponds to at least the ON time duration. Preferably, the laser device includes a Diode Laser Array (DLA).
Owner:ELBIT SYST LTD
Fast, High Resolution 3-D Flash LADAR Imager
InactiveUS20130107243A1Optical rangefindersAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influencePhotovoltaic detectorsImage resolution
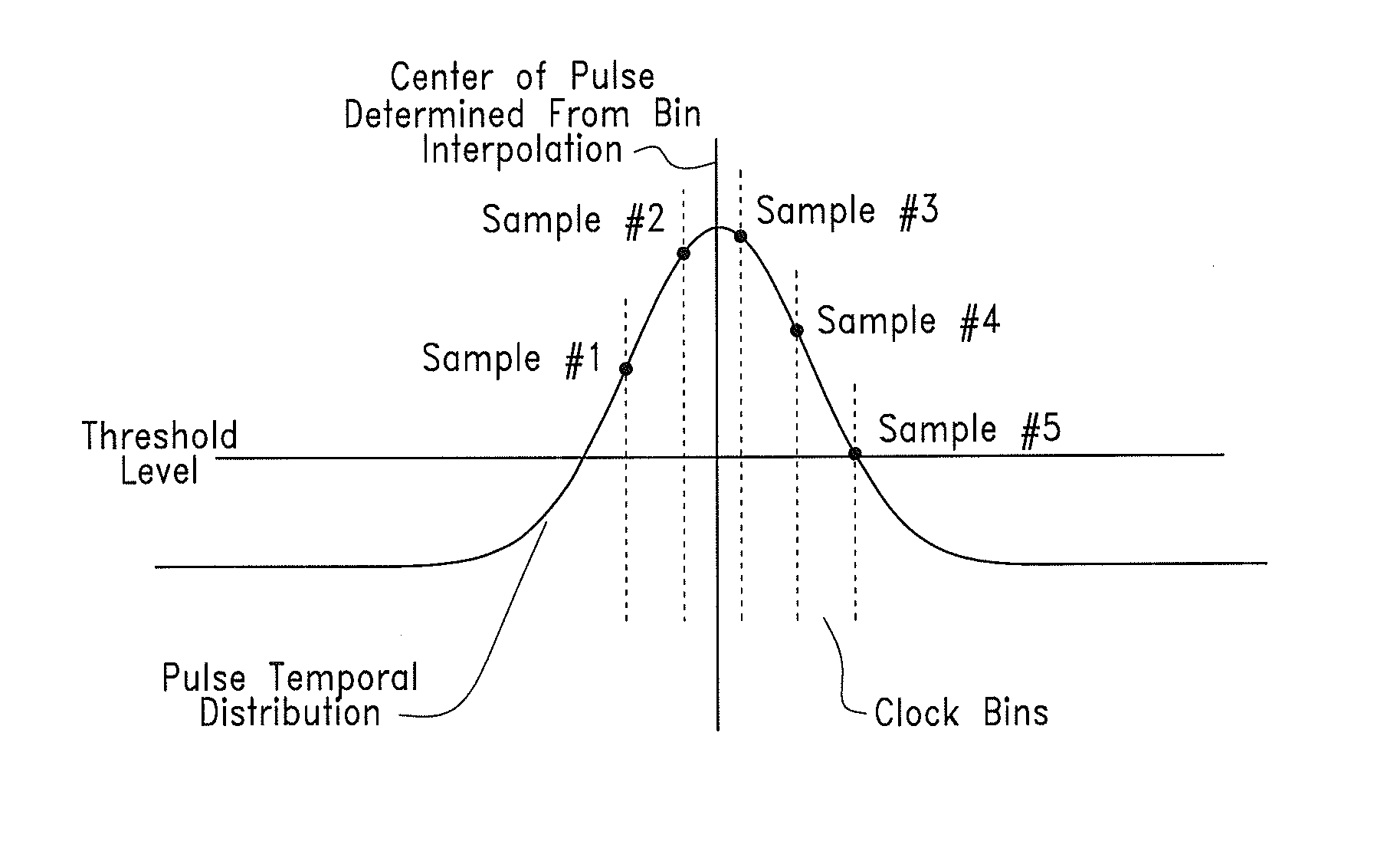
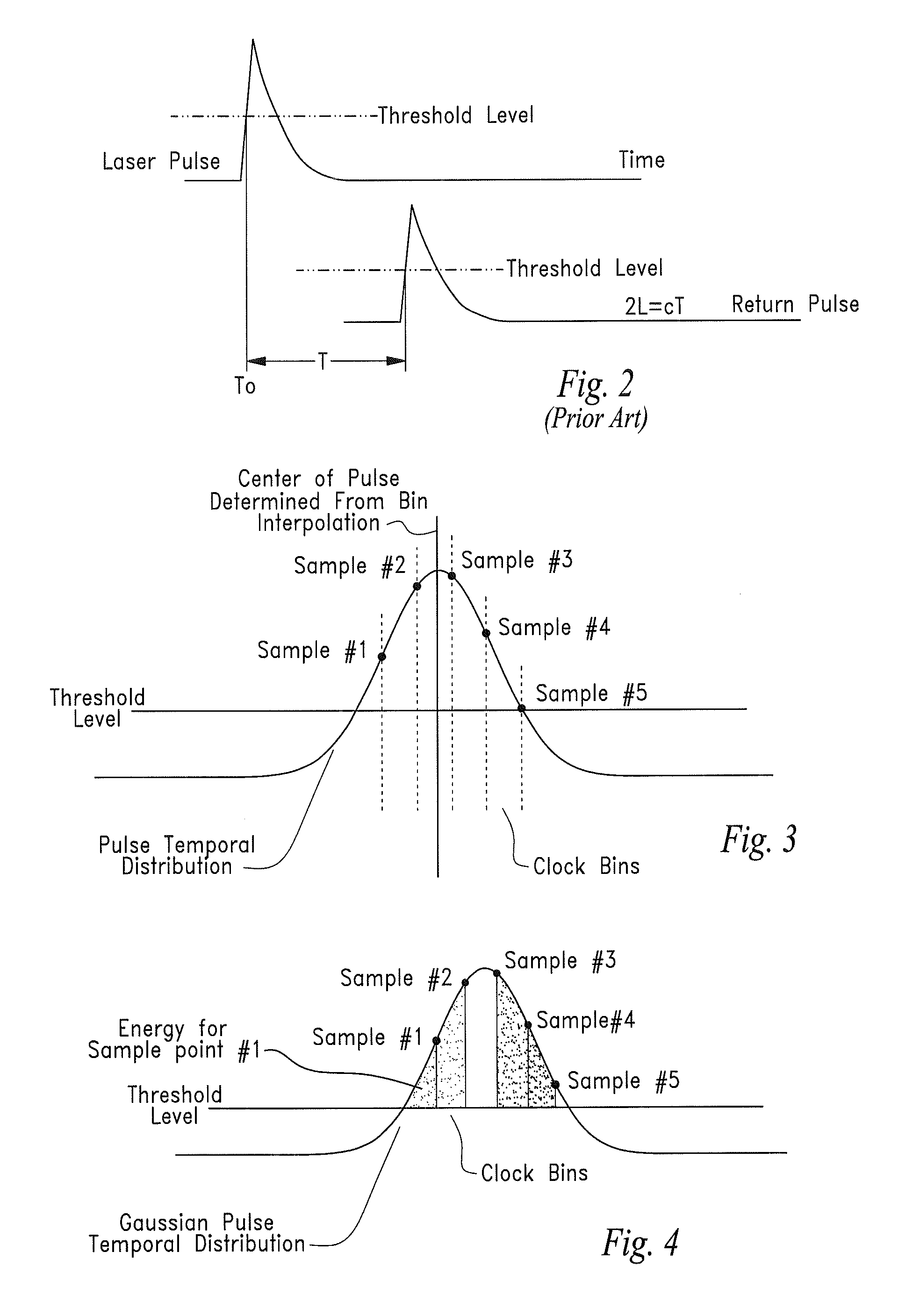
A device and method for LADAR ranging using relatively long laser pulse widths and slower system clock speeds is provided. The center points of the sent and received laser signal such as Gaussian laser pulses are identified by time sampling the sent and received laser signal waveforms at predetermined time positions.The signal energy within each time sample of the respective sent and received laser signals defines a clock “bin”. The received laser signal generates an output from a photodetector cell on a focal plane array that is converted into voltage. The signal energy is integrated using a capacitor array for each of the clock bins and is representative of the signal energy in each time sample.The output of the capacitor array is collected in buffer and digitized. Signal processing means extracts the center of the transmitted and received pulses and the time-of-flight calculated as the time between the transmitted and returned centers of the laser signal pulses.
Owner:PFG IP +1
Distributed optical fiber Raman temperature sensor coding and decoding by adopting sequential pulse
InactiveCN101819073AAvoid nonlinear effectsHigh strengthThermometers using physical/chemical changesSignal onPeak value
The invention discloses a distributed optical fiber Raman temperature sensor coding and decoding by adopting sequential pulses, which is a distributed optical fiber temperature measuring system coding and decoding a signal on the basis of S-matrix transformation and carrying out optical fiber on-line positioning temperature measurement by utilizing the effect of optical fiber Raman light intensity modulated by temperature and an optical time domain reflection principle. The distributed optical fiber Raman temperature sensor can obtain better signal-to-noise radio under the condition of spending same measuring time by using a sequential multidigit laser pulse coding and decoding technology, increase the number of emitted photons, enhance the space resolution by narrowing the thicknesses of laser pulses and also effectively prevent the nonlinear effect of optical fibers by lowering the requirements on the peak value power of a single laser pulse; and in addition, the invention effectively solves the contradiction of space resolution enhancement-signal-to-noise radio reduction and signal-to-noise radio enhancement-space resolution reduction or measuring time increase of the traditional optical fiber distribution temperature sensor, enhances the temperature measuring precision, can be used for a distributed optical fiber temperature sensor which has ultra long range and high space resolution.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
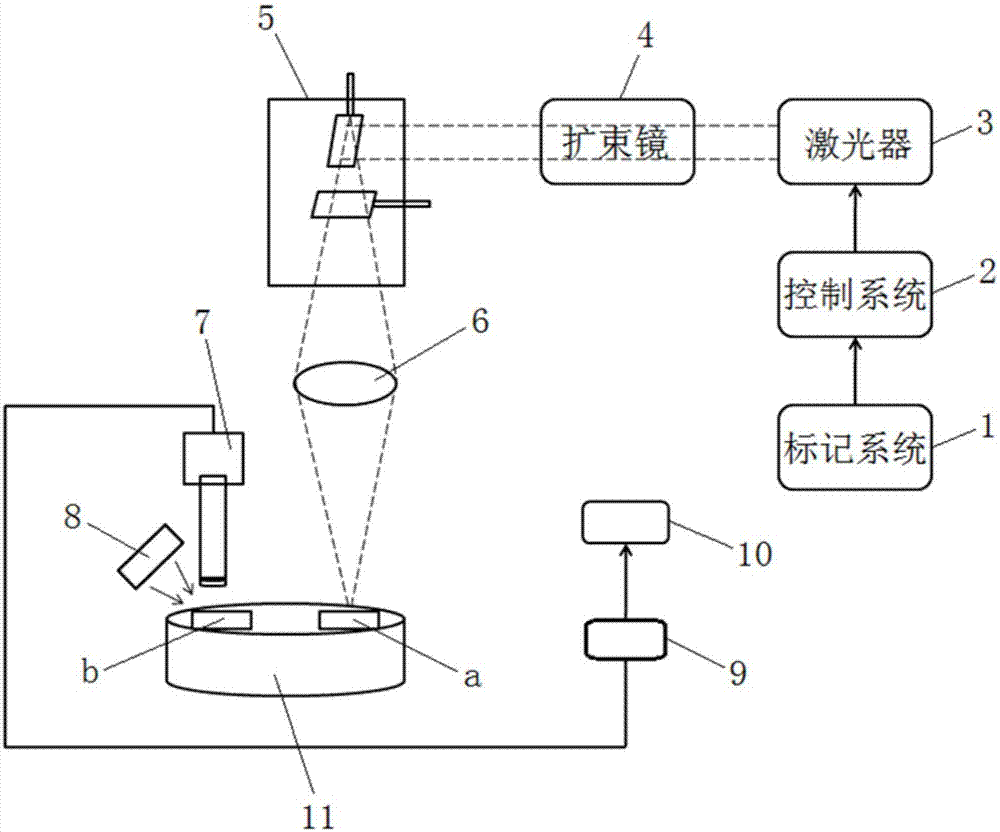
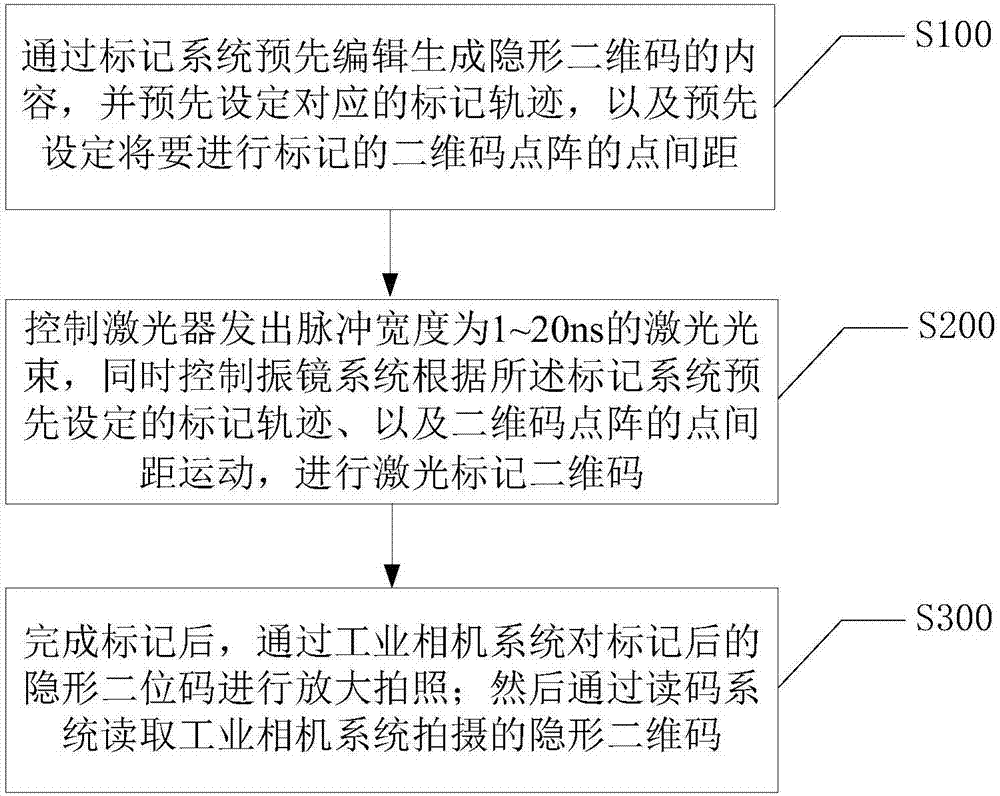
Method and device marking invisible two-dimensional code on surface of metal material through laser
ActiveCN107081970AWon't breakRealize the function of invisible anti-counterfeitingPattern printingTypewritersCamera lensDot matrix
The invention discloses a method and device marking an invisible two-dimensional code on the surface of a metal material through a laser. The device comprises a marking system, a laser device, a control system, a beam expander, a galvanometer system, an f-theta lens, an industrial camera system and a code reading system. The laser pulse width of the laser device is 1-100 ns. The nominal focal length of a camera lens of the f-theta lens is no larger than 160 nm. According to the laser marking device based on innovation, by controlling the pulse width of the laser and the dot diameter and the dot distances of a two-dimensional code dot matrix, the invisible two-dimensional code which cannot be seen by human eyes is marked on the metal material, photographing and reading of the invisible two-dimensional code are achieved through the industrial camera system and the code reading system, and therefore the invisible anti-fake function is achieved. The marking method cannot damage the surface of the material, the invisible two-dimensional code has no hand feeling and does not affect the appearance, permanent marking can be achieved, the processing process is free of pollution, no chemical needs to be used, and cost is low.
Owner:HANS LASER TECH IND GRP CO LTD
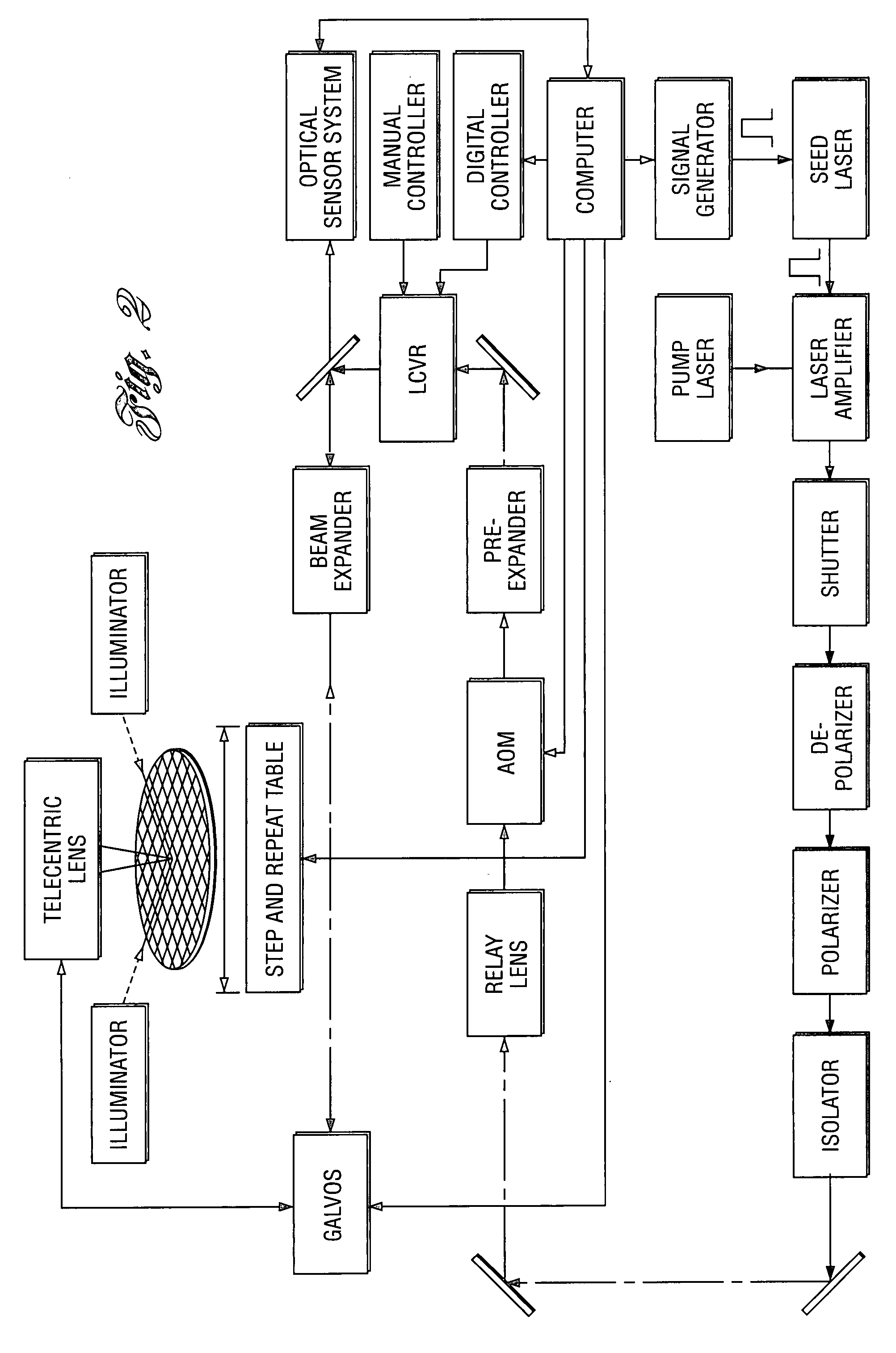
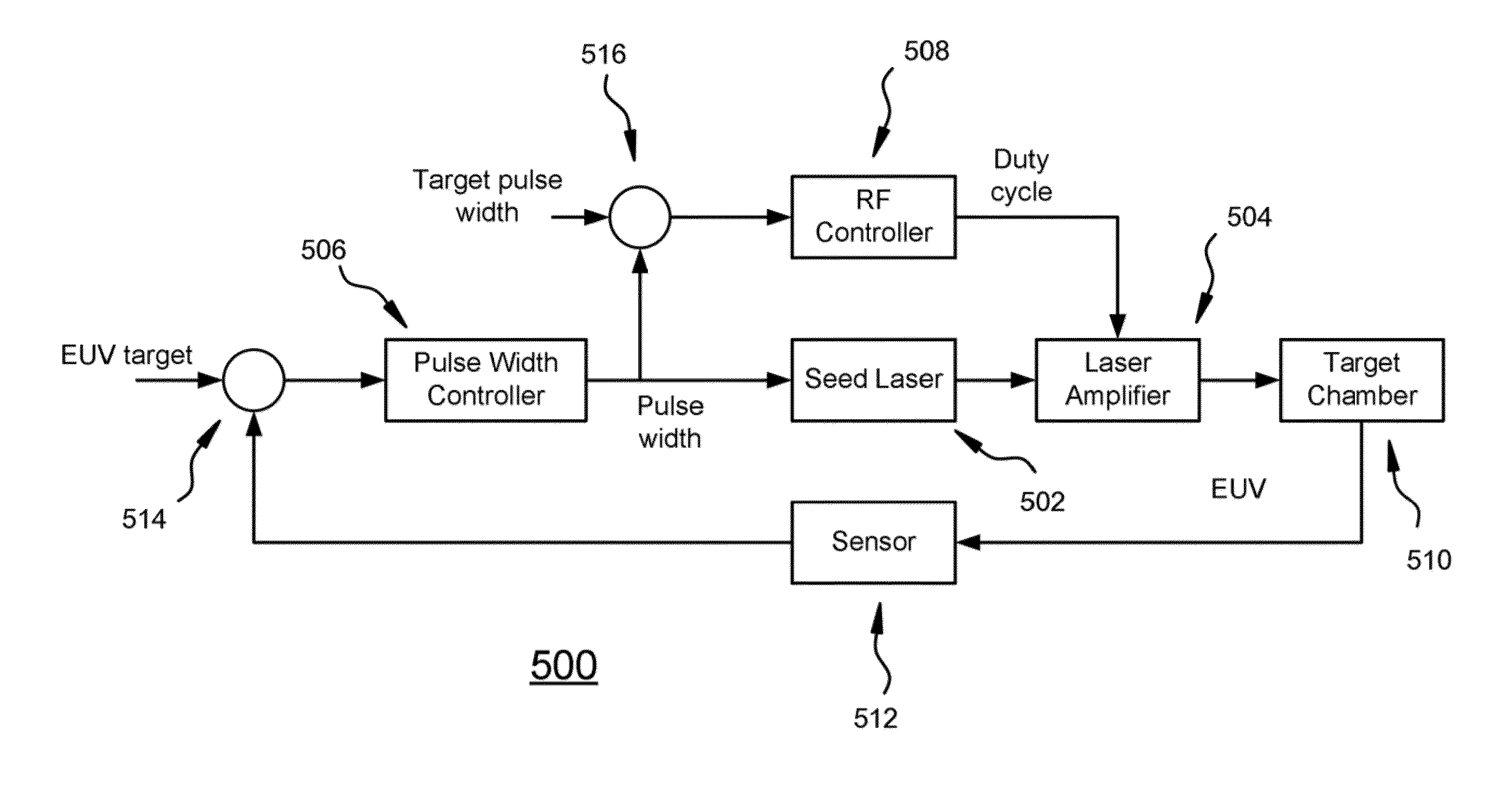
System and Method for Adjusting Seed Laser Pulse Width to Control EUV Output Energy
InactiveUS20140233005A1Photomechanical apparatusX-ray tube with very high currentAudio power amplifierLighting system
A method and apparatus for controlling the seed laser in a laser produced plasma (LPP) extreme ultraviolet (EUV) light system are disclosed. In one embodiment, a seed laser generates both pre-pulses and main pulses which are amplified and irradiate a target material. The widths of the main pulses are adjusted, for example by the use of an EOM or other optical switch, without adjusting the widths of the pre-pulses, to keep the EUV output energy at a desired level. Only if the main pulse widths are longer or shorter than a desired range is the duty cycle of the laser amplifier adjusted, to keep the main pulse widths in the desired range. Adjusting the main pulse widths in this way before adjusting the pump RF duty cycle allows for less adjustment of the duty cycle, thus causing less adjustment to the pre-pulses.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
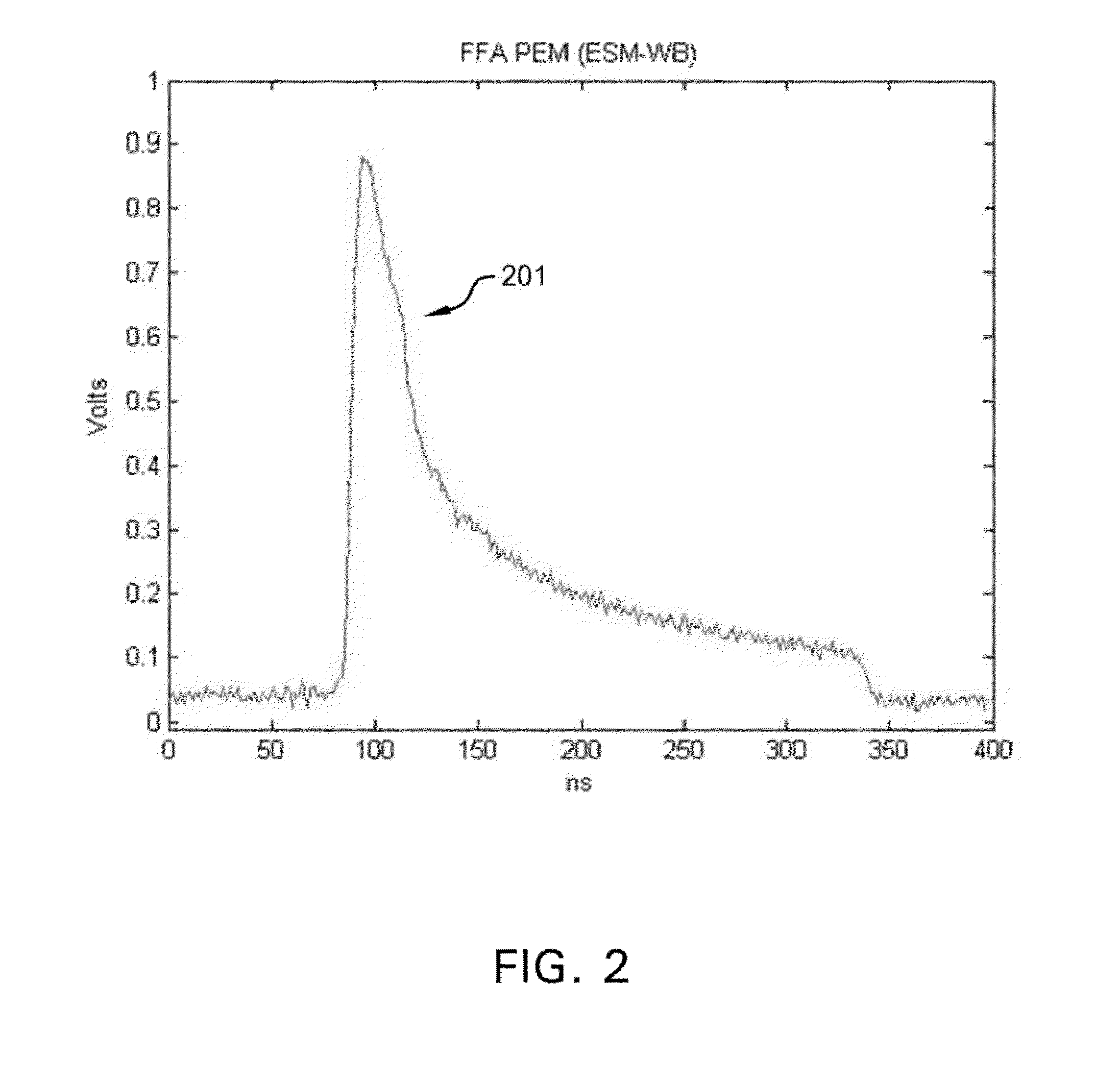
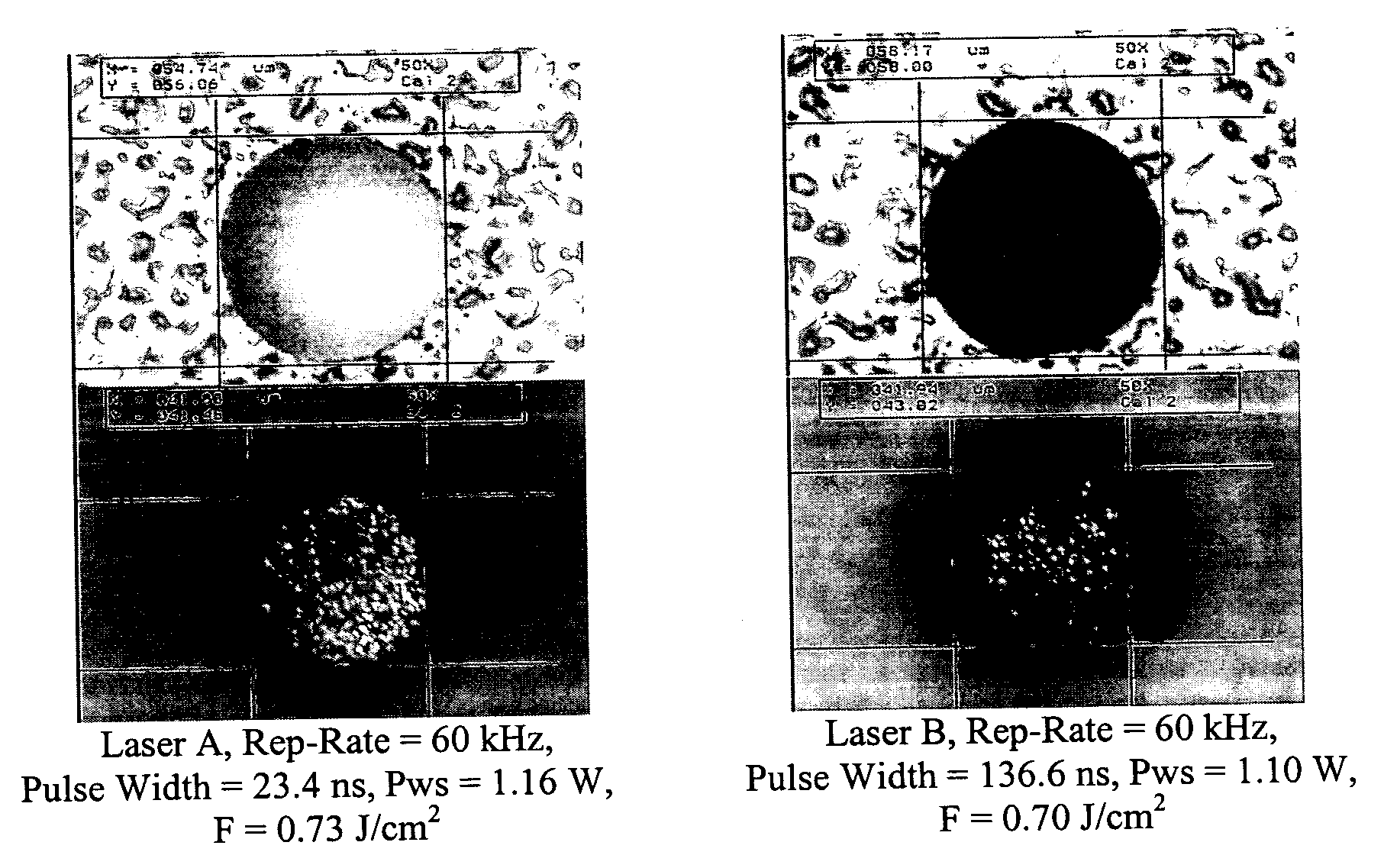
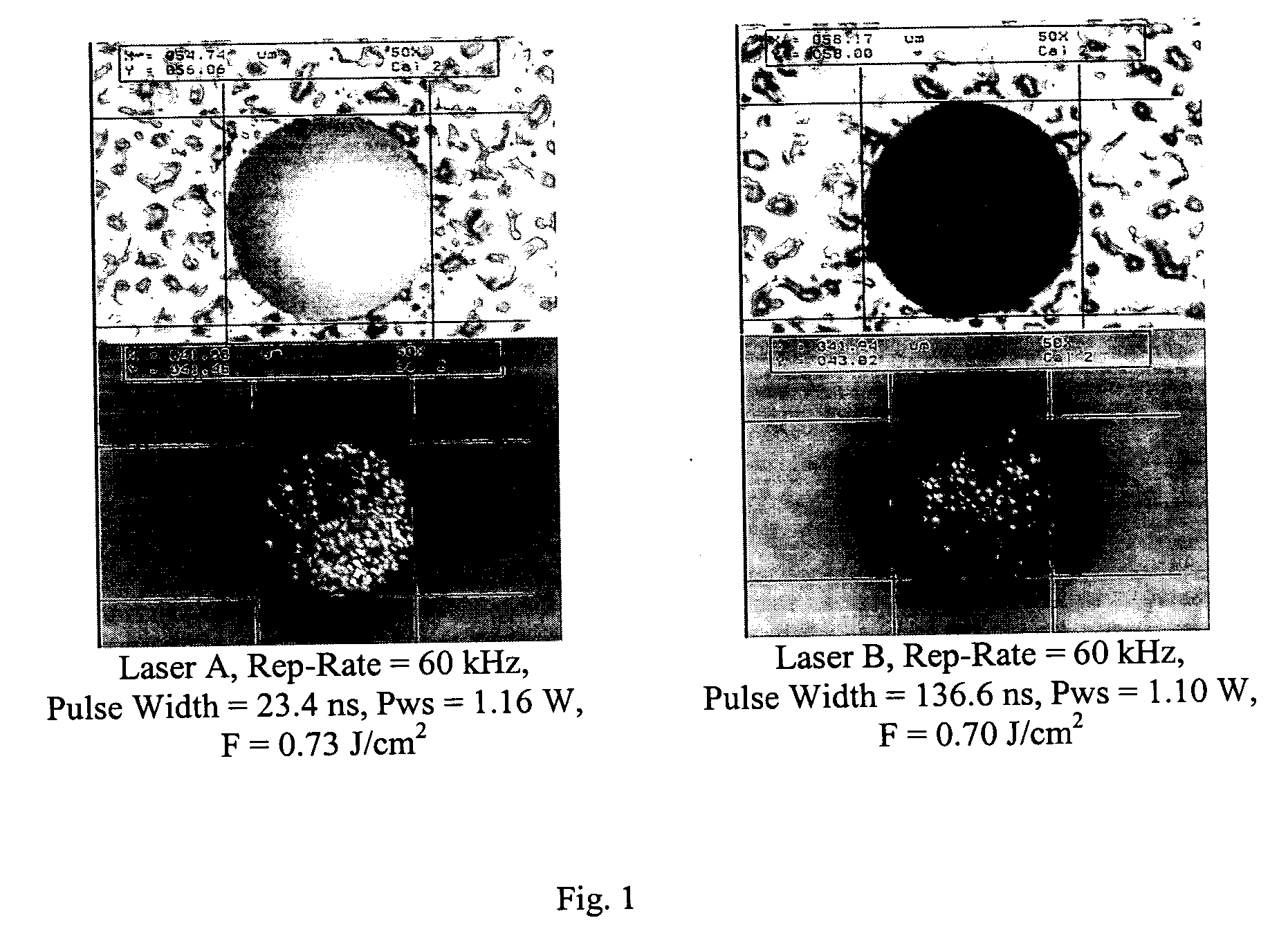
Method of providing consistent quality of target material removal by lasers having different output performance characteristics
Laser pulse energy adjustments are motivated by an understanding of the effect of laser pulse width variations among different lasers on satisfying a quality metric associated with a laser-processed target. In a preferred embodiment, the adjustments normalize this effect among different lasers drilling vias in a target specimen. The number of pulses delivered to the target specimen to form each via can be modified, based on the pulse energy applied to the via location, to control different via quality metrics.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Single-mode and all-fiber coherent Doppler wind speed measurement laser radar emission source
InactiveCN103792385AMeet the needs of wind speed measurementImprove small signal amplification capabilityFluid speed measurementBeam splitterLine width
A single-mode and all-fiber coherent Doppler wind speed measurement laser radar emission source is characterized by being formed by sequentially connecting an all-fiber seed source, a seed isolator, a seed beam splitter, an acousto-optic modulation device, a pre-amplifier stage, a chopper and a main amplifier stage in a cascading mode. The single-mode and all-fiber coherent Doppler wind speed measurement laser radar emission source has the advantages that the all-fiber property is achieved, the human eyes are protected, the line width reaches megahertz, linear polarization is achieved, the pulse contrast is high, and single-mode polarization-maintaining lasers are output; repeated frequency, laser pulse width and laser waveform can be adjusted within the wide range, and the laser radar wind speed measurement requirements for different detection distances, different distance resolution ratios and different wind speed update rates from laser radars can be met.
Owner:NANJING MOVELASER TECH CO LTD
Ultrashort laser pulse wafer scribing
InactiveUS8624157B2Improve stress conditionReduced or no debrisSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWelding/soldering/cutting articlesLight beamPicosecond
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Method for continuously regulating central frequency and spectrum width of THz (terahertz) wave
ActiveCN102879971AAdjust the center frequencyAdjustable widthNon-linear opticsFrequency spectrumBirefringent crystal
The invention relates to a method for continuously regulating central frequency and spectrum width of THz (terahertz) wave. A bundle of ultrafast laser pulse passes through a movable birefringence crystal oblique split pair and a zero-order quarter wave plate to generate a novel specially-polarized light field by a polarizing gate method. The novel light field passes through a polarizer to obtain laser pulse with width of narrow pulse with linear polarization. Laser pulses different in width are obtained by controlling inserting quantity of the birefringence crystal oblique split pair, and accordingly the function of regulating central frequency and spectrum width of the THz wave is achieved. A device is simple and easy to operate, the width of the novel laser pulse can be changed only two crystals of the birefringence crystal oblique split pair simultaneously move oppositely at equal distance, and accordingly the central frequency and the spectrum width are adjusted. The method is suitable for light sources of various pulse widths and wavelengths.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Femtosecond laser ranging device and method for active dispersion compensation
ActiveCN102944218ARealize quantitative measurementReduce volumeOptical rangefindersLaser rangingData acquisition
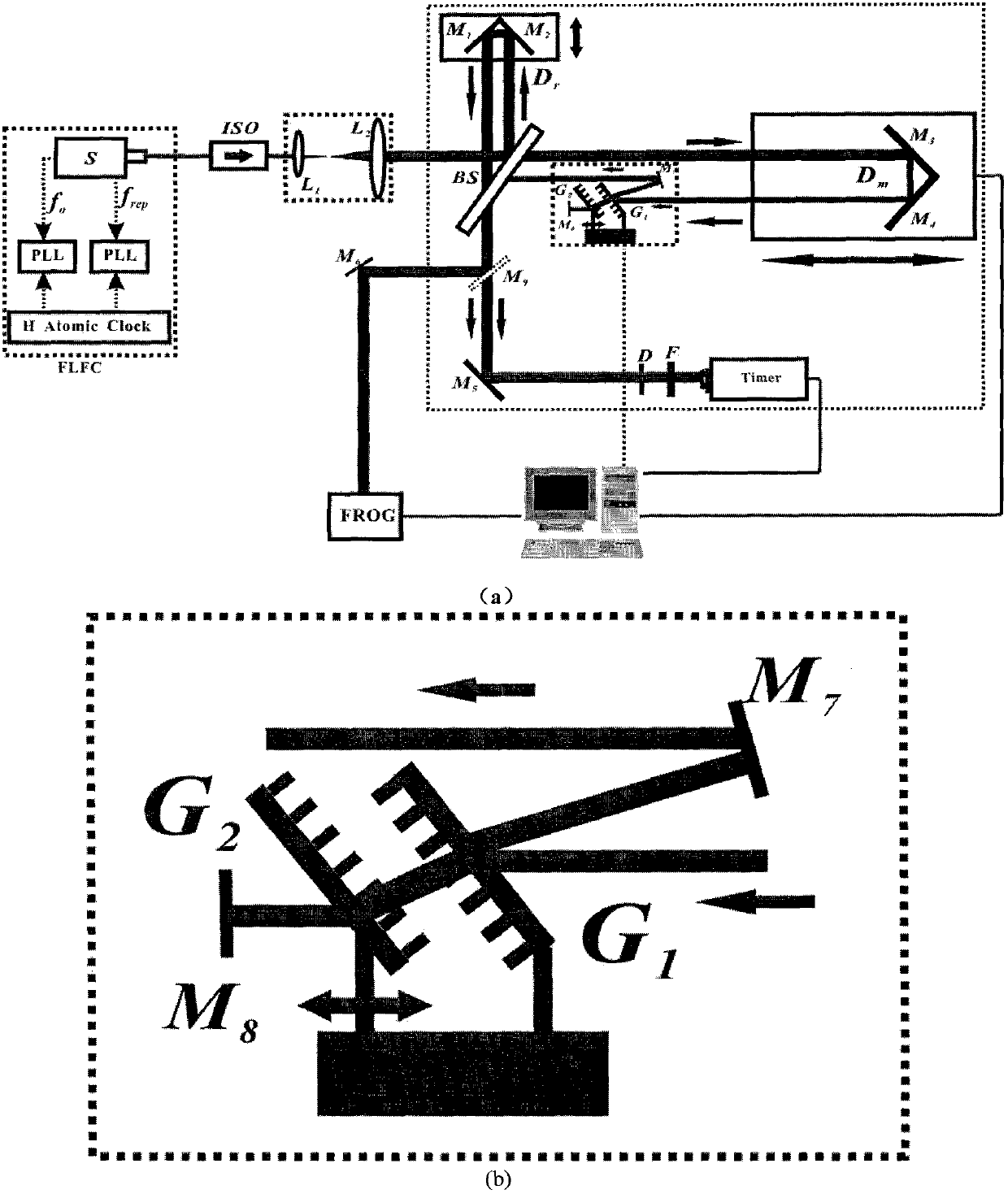
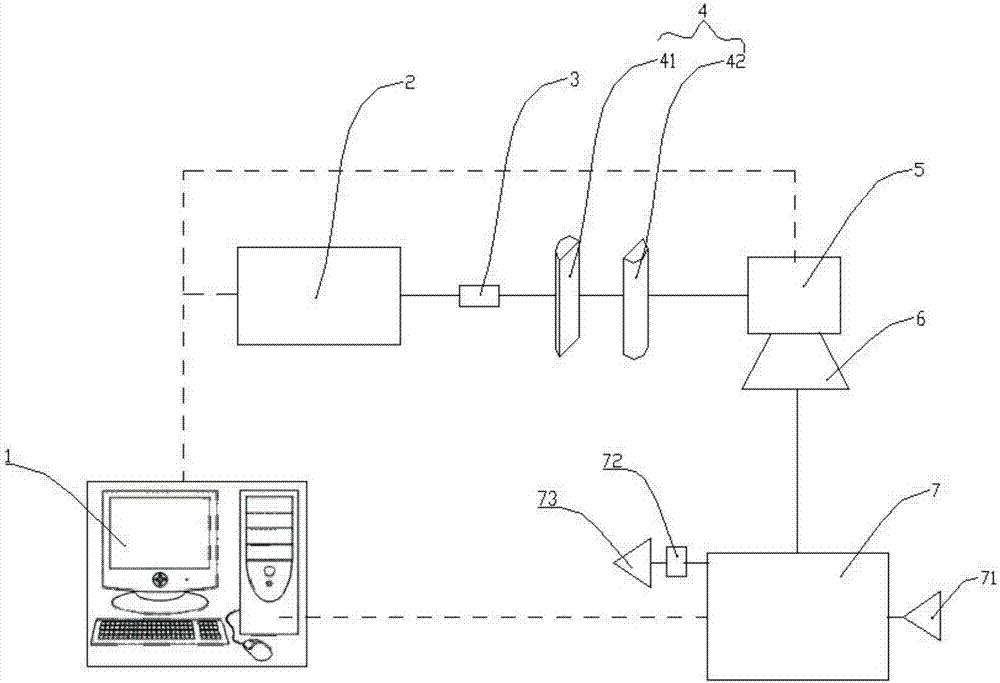
The invention relates to the field of femtosecond laser ranging, in particular to a femtosecond laser ranging device and a femtosecond laser ranging method for active dispersion compensation. The device comprises a femtosecond laser frequency comb (FLFC), a laser isolation part ISO, a femtosecond laser beam-expanding collimation part, a Michelson ranging device part, a femtosecond laser pulse width and phase measurement part (FROG) and a data acquiring and processing part. The device is small in size and flexible to operate and has wide engineering application prospects.
Owner:BEIJING CHANGCHENG INST OF METROLOGY & MEASUREMENT AVIATION IND CORP OF CHINA
Ytterbium-doped full-optical-fiber optical frequency comb system
ActiveCN103995413AImprove stabilityImprove portabilityLaser detailsNon-linear opticsOctaveFrequency comb
The invention discloses an ytterbium-doped full-optical-fiber optical frequency comb system and relates to the technical field of frequency comb measurement. The system utilizes an ytterbium-doped full-optical-fiber annular cavity mode-locked laser to achieve mode-locked laser pulse output under the non-linear polarization rotation condition, achieves control chromatic dispersion in a cavity through a first band gap photonic crystal fiber and accordingly reduces in-cavity noise. An ytterbium-doped double-clad optical fiber amplifier is utilized to perform mode-locked laser pulse amplification, and a second first band gap photonic crystal fiber is utilized to achieve compression of mode-locked laser pulse width. Compressed mode-locked laser pulses pass through a tapering photonic crystal fiber welded with an optical fiber compressor to achieve output of an octave super-continuous spectrum. The full-optical-fiber performance of the whole ytterbium-doped full-optical-fiber optical frequency comb system achieves is achieved, repetition frequency and original frequency of an optical frequency comb can be locked, and the stability and portability of the ytterbium-doped optical frequency comb with a full-optical-fiber structure are improved.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Formation of colored stero pattern inside color-less transparent glass
InactiveCN1383998AThree-dimensional effectsSpecial ornamental structuresPhotonic crystalUltraviolet lights
The present invention is method of forming colored stereo pattern inside color-less transparent glass. Laser beam with femtosecond to nanosecond pulse width and focal spot powder density greater than1 MW / sq cm is focused into Ag, Au and Cu ion doped glass with polished surface. The glass after being laser irradiated is heat treated, so that nanometer metal grains are separated from the laser irradiation area and different colors may be produced. When irradiated with ultraviolet light, the glass may glow with various color lights depending on the previous laser irradiation and heat treatment,Capable of forming colored stereo pattern, the present invention may be used in ultrahigh density 3D light memory and 3D photon crystal.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
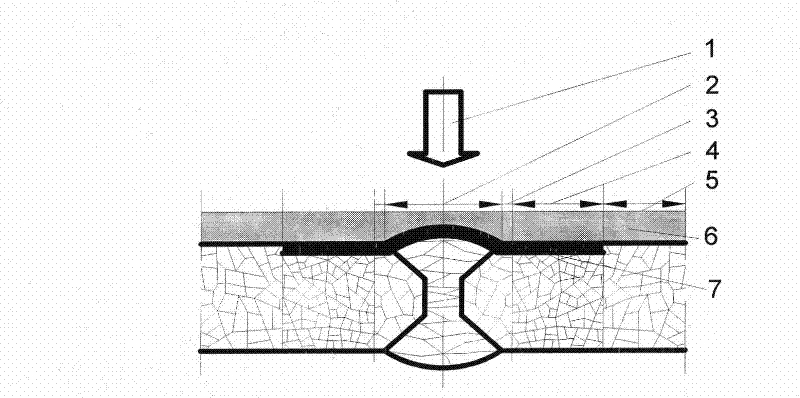
Laser-impact strengthening treatment method for steel welded joint of X70 pipeline
InactiveCN102127630AImprove anti-H <sub>2<</sub> Accelerated corrosionFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesRadiation pulseLaser pulse width
The invention relates to a laser-impact strengthening treatment method for a steel welded joint of an X70 pipeline, wherein an energy absorption layer and a restraint layer are arranged on the surface of the steel welded joint of the X70 pipeline in sequence. The laser-impact strengthening treatment method is characterized in that during laser-impact strengthening treatment, the laser pulse width is 22ns-23ns, the wavelength is 1.054mu m, the amplification spontaneous radiation pulse width is 1mu s, a focusing system with the focal length of 2m for outputting laser is used for focusing, the focusing spot diameter is 5mm-8mm, the laser pulse power is about 2.0*109W, and the spot overlapping area on the surface of the welded joint is greater than 60%. After laser-impact strengthening, the surface of the steel joint of the pipeline generates plastic deformation, grain refinement and residual compressive stress, thus effectively improving the H2S stress corrosion resistance and hydrogen induced cracking resistance of the steel welded joint of the pipeline.
Owner:JIANGSU POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Laser gated camera imaging system and method
A gated camera imaging system and method, utilizing a laser device for generating a beam of long duration laser pulses toward a target. A camera receives the energy of light reflexes of the pulses reflected from the target. The camera gating is synchronized to be set OFF for at least the duration of time it takes the laser device to produce a laser pulse in its substantial entirety, including an end of the laser pulse, in addition to the time it takes the laser pulse to complete traversing a zone proximate to the system and back to the camera, and set ON for an ON time duration thereafter until the laser pulse reflects back from the target and is received in the camera. The laser pulse width substantially corresponds to at least the ON time duration. Preferably, the laser device includes a Diode Laser Array (DLA).
Owner:ELBIT SYST LTD
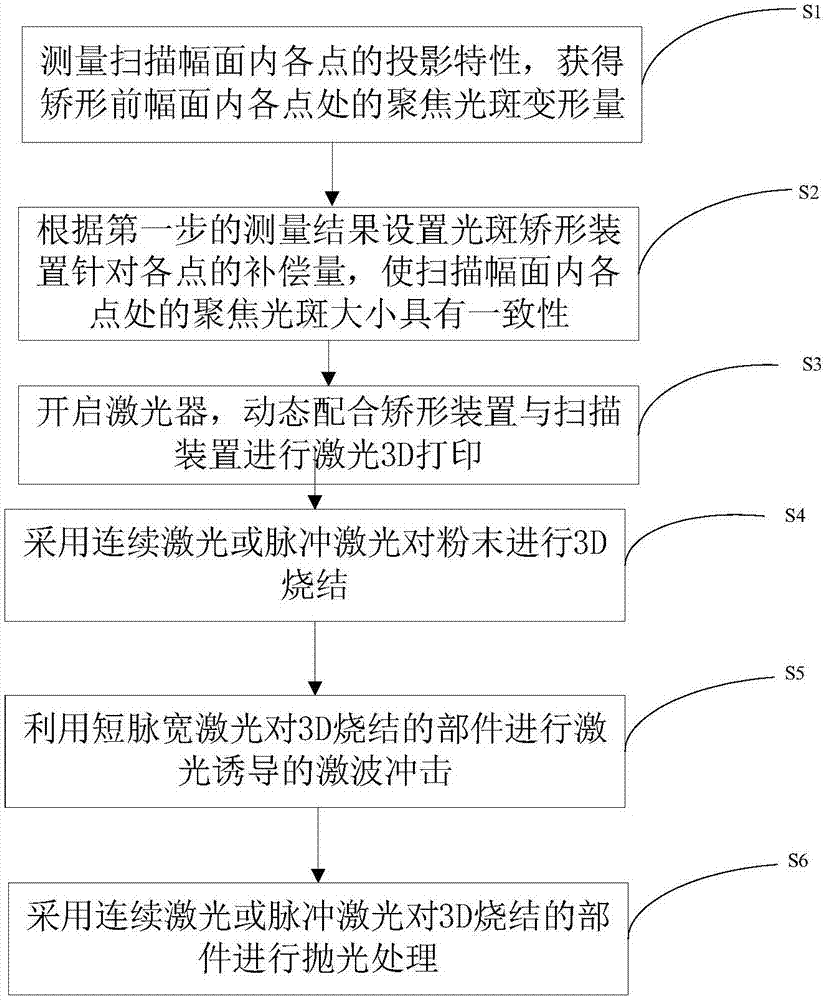
Laser 3D printing method for metal workpiece and system thereof
PendingCN107252893AHigh densityAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyPhysical chemistryPulse energy
The invention discloses a laser 3D printing method for a metal workpiece and a system thereof. The laser 3D printing method for the metal workpiece comprises the following steps that first, 3D sintering is conducted on metal powder through continuous laser or pulsed laser; second, laser-induced shock wave impact is conducted on the 3D sintered workpiece through short-pulse-width laser; and third, polishing treatment is conducted on the 3D sintered workpiece through continuous laser or pulsed laser. When the printed object contains different types of material powder, appropriate parameters such as the laser wave length, the pulse width and the pulse energy are chosen according to the optical characteristics of the material powder, and 3D printing of functionally-graded objects is realized through the three steps. Compared with the prior art, according to the laser 3D printing system, the laser sintering degree is controlled by changing the laser pulse width in the process of printing the metal workpiece, and the situations of porosity, over burning and spheroidization of the metal workpiece in the printing process are relieved, so that the compactness of the metal workpiece is improved.
Owner:INNO LASER TECH CORP LTD +1
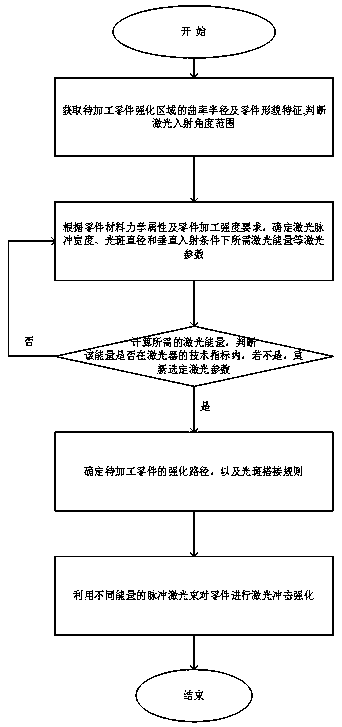
Energy compensation constant power density laser oblique impact method
ActiveCN108517400AImprove distribution uniformityReduce roughnessLaser beam welding apparatusConstant powerLaser power density
The invention relates to the technical field of material surface strengthening treatment, and concretely relates to an energy compensation constant power density laser oblique impact method. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining the curvature radius of the strengthening area of a part to be processed, and judging the incident angle range of laser; determining the pulse width, the light spot diameter, laser energy required by a vertical incidence condition, and other parameters of the laser; calculating the required laser energy at a minimum incidence angle, and judging whether the energy is within the technical indexes of a laser device or not; and performing laser impact strengthening on the part by using pulsed laser beams of different energies. The laser power or energy iscompensated according to the change of the incident angle and the curvature radius of the part to be processed to avoid the uneven strengthening effect caused by the change of the shape and the areaof the projection surface, of the laser beam, on the surface of the part, so constant strength enhancement is achieved, the constant value of the laser power density in the same area or on the same track is ensured, the uniformity of the impact effect is improved, and the roughness of the laser impact treated surface is reduced.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Autocorrelator
InactiveCN103134600ASimple structureReduce the difficulty of adjustmentInstrumentsBeam splittingOptoelectronics
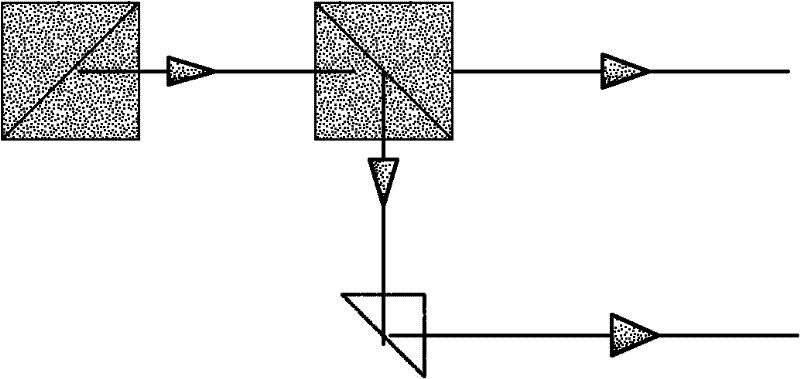
The invention discloses an autocorrelator for measuring the width of ultra-short laser pulses. The autocorrelator comprises an incidence reference hole, a wedge-shaped spectroscope, a first right-angle reflector, a second right-angle reflector, a scanning device platform, a paraboloidal mirror, a detector and a control device, wherein the incidence reference hole is used for passing to-be-detected lasers which enter horizontally and straightly at equal heights to form an incidence light path; and the wedge-shaped spectroscope is positioned on the incidence light path, and the included angle of the wedge-shaped spectroscope and the incidence light path is 45 degrees. According to the autocorrelator, the wedge-shaped spectroscope is adopted to replace two beam splitting slices in the prior art, and the two sides of each beam slitting slice are parallel to each other, so that a light path structure of the autocorrelator is simple, and interference field signals formed by multiple reflections of two surfaces of the wedge-shaped spectroscope cannot coincide with an emergent light path any more, so that the detector can detect neat autocorrelation signals.
Owner:北京量子光通科技有限公司
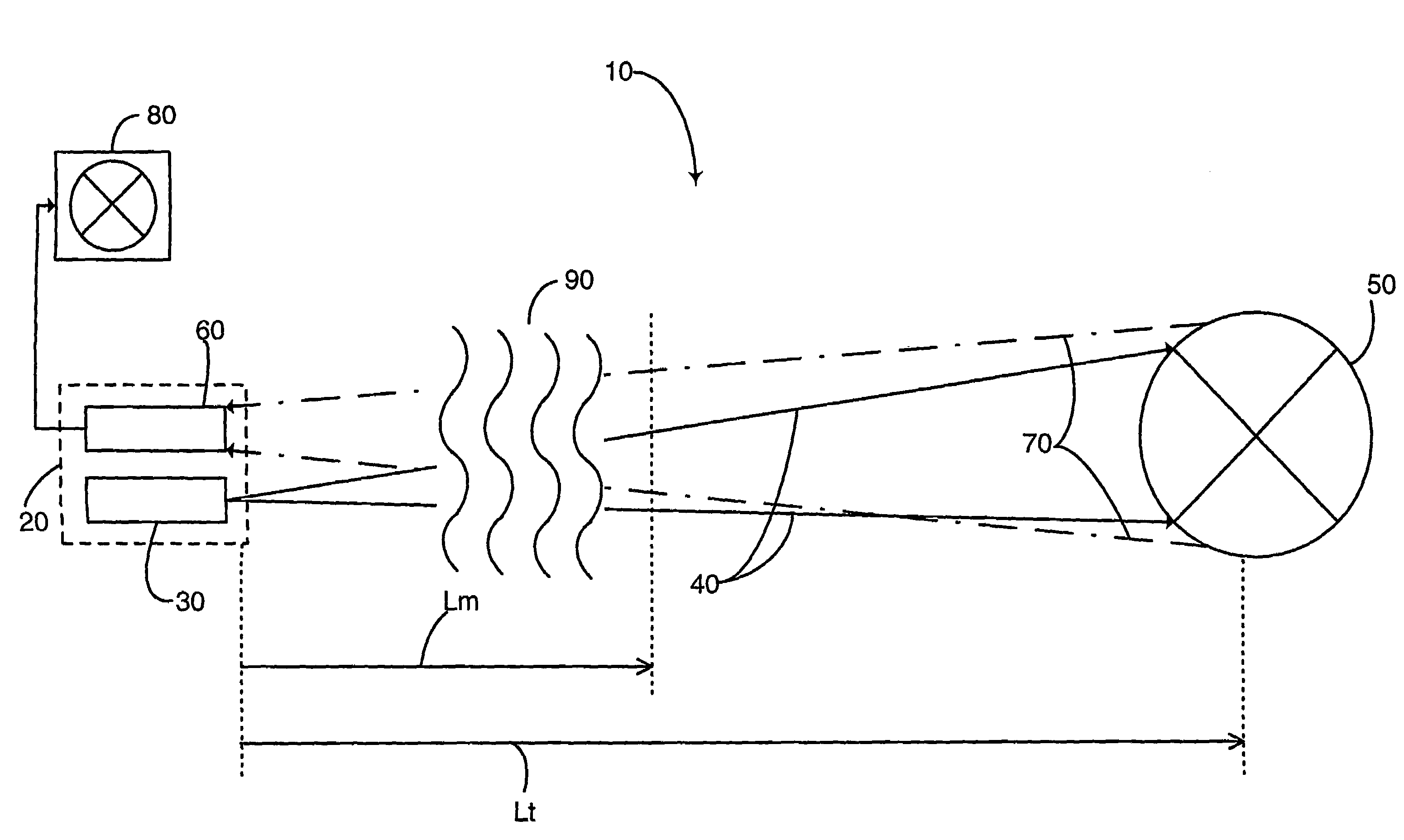
Compact ultra short pulse laser remote ranging system and ranging method thereof
InactiveCN104865576AAvoid different delay timesImprove accuracyElectromagnetic wave reradiationSystems designBeam splitter
The invention discloses a compact ultra short pulse laser remote ranging system and a ranging method thereof. The system comprises a laser source, a first beam expanding module, a second beam expanding module, a beam splitter, a transmitting and receiving module, a reflector, a filter module, a focusing lens, and a photodetector, wherein the laser source is an ultra short pulse laser transmitting laser beams, and the width of the outputted laser pulse is picosecond to subpicosecond. The system whose transmitting light path and receiving light path are coaxial is adopted, one reflector is adopted to complete sampling of main wave pulse signals; through changing coating reflectivity of the reflector, the size of an incident main wave signal is adjusted, and over strong main wave pulse signals can be prevented from damaging the photodetector; and the laser ranging system is long in ranging, high in ranging precision, simple and compact in structure, and low in cost.
Owner:LASER FUSION RES CENT CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Method and device for measuring laser pulse width and relative phase by simultaneous phase-shifting interferometry
The invention discloses a method and a device for measuring a laser pulse width and a relative phase by a simultaneous phase-shifting interferometry, which can measure a femtosecond pulse and an attosecond pulse of which the pulse width is very narrow. In the technology, a component prism is used for splitting light beams, and simultaneously, a plurality of simultaneous phase-shifting interference fringe patterns are obtained once in a spatial domain through a polarization interference method. By computational analysis on interference fields of a plurality of paths, the pulse width and the phase of an ultra-short pulse can be directly measured. The method provided by the invention is simple, clear in principles and excellent in shock resistance of the measuring result, and can implement on-site dynamic measurement and monitoring on the pulse width and the relative phase of the ultra-short pulse in an ultra-fast process. The measuring process is simple and convenient.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
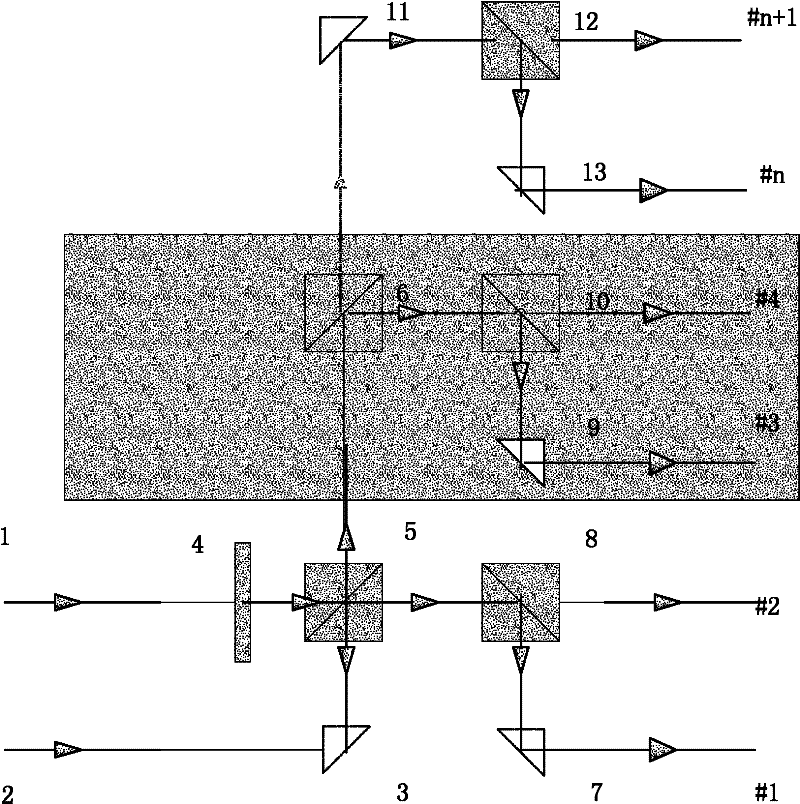
Laser 3D printing method and system with shape correction function
InactiveCN107336440AEnsure consistencyQuality improvementAdditive manufacturing apparatus3D object support structuresOptoelectronicsLaser pulse width
The invention discloses a laser 3D printing method with a shape correction function. The method comprises the following steps that (1), projection characteristics of all points in scanning breadth are measured, and the focusing light spot deformation amount of all the points in the scanning breadth before shape correction is obtained; (2), the compensation dosage of a light spot shape correction device to all the points is set according to the measurement result in the first step, and the sizes of focusing light spots at all the points in the scanning breadth can have consistency; (3), a laser is stated, and the laser is dynamically matched with the shape correction device and a scanning device for laser 3D printing. According to the laser 3D printing method and system with the shape correction function, the laser sintering degree is controlled by changing the laser pulse width in the 3D printing process, the situation that holes, superburning and nodulizing are generated in the printing process is improved, and density is improved; and besides, the shape correction device is added, it can be guaranteed that the sizes of the focusing light spots in the scanning breadth have consistency by precisely controlling the compensation amount of the light spot shape correction device, and thus 3D printing quality is guaranteed.
Owner:INNO LASER TECH CORP LTD +1
Method of providing consistent quality of target material removal by lasers having different output performance characteristics
Laser pulse energy adjustments are motivated by an understanding of the effect of laser pulse width variations among different lasers on satisfying a quality metric associated with a laser-processed target. In a preferred embodiment, the adjustments normalize this effect among different lasers drilling vias in a target specimen. The number of pulses delivered to the target specimen to form each via can be modified, based on the pulse energy applied to the via location, to control different via quality metrics.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Device and method for hoop tensile test based on laser impact biaxial loading
InactiveCN102128755AControl strain rateRealize the loadStrength propertiesDynamic stretchingTensile testing
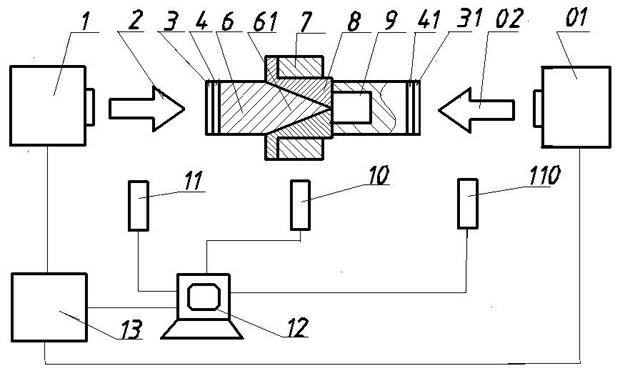
The invention relates to a material dynamic tensile mechanical property test and belongs to the technical field of a material dynamic tensile mechanical property test. By using an intense laser pulse-induced impact wave as a loading condition, the material achieves a high strain rate; and different strain rates can be loaded by changing the laser pulse width and laser energy. A device comprises ahigh-power pulse laser (13), a laser head A (1), a laser head B (01), a restraining layer A (3), a restraining layer B (31), an absorbing layer A (4), an absorbing layer B (41), a loading rod A (6), a loading rod B (9), a cylindrical driving ring (8), a laser interferometer (10), a trigger A (11), a trigger B (110) and a computer (12). The device provided by the invention can be used for researching the dynamic tensile property of the material under the condition of different strain rates. The loading process is simple, the influencing factors are few, the calculation process is simple and the test cost is low.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com