Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
195results about "Electrode with substrate and coating" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
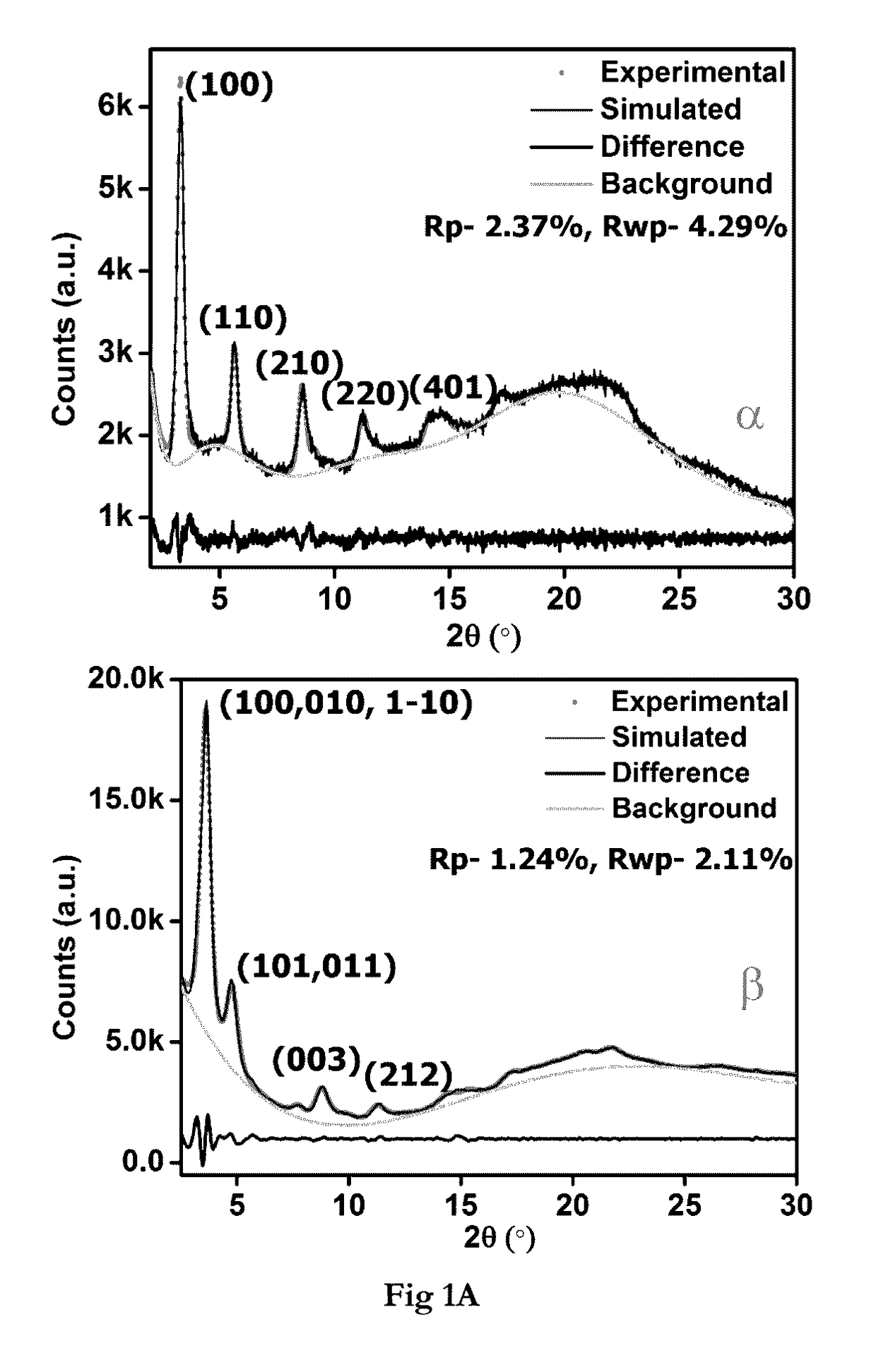
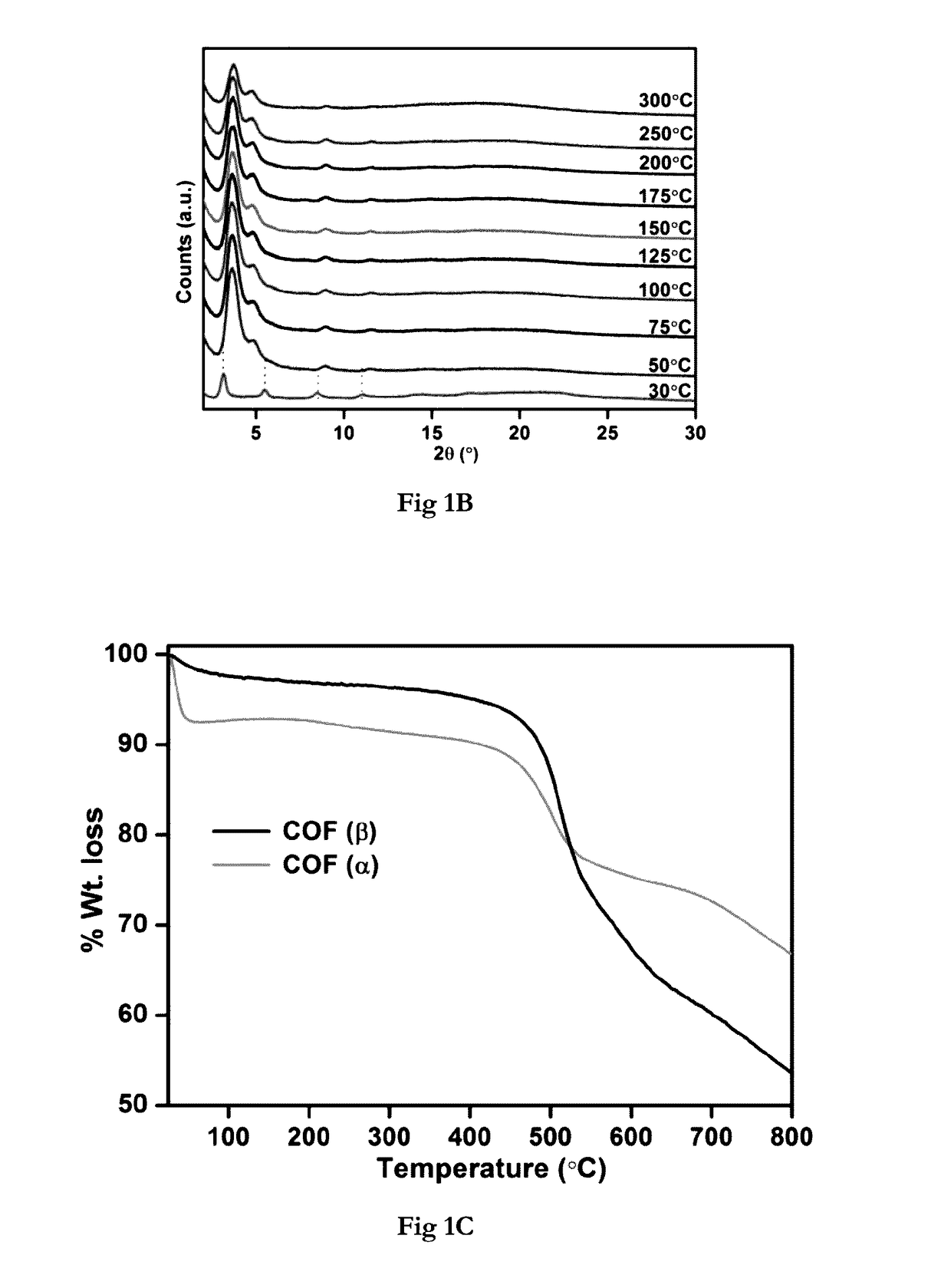
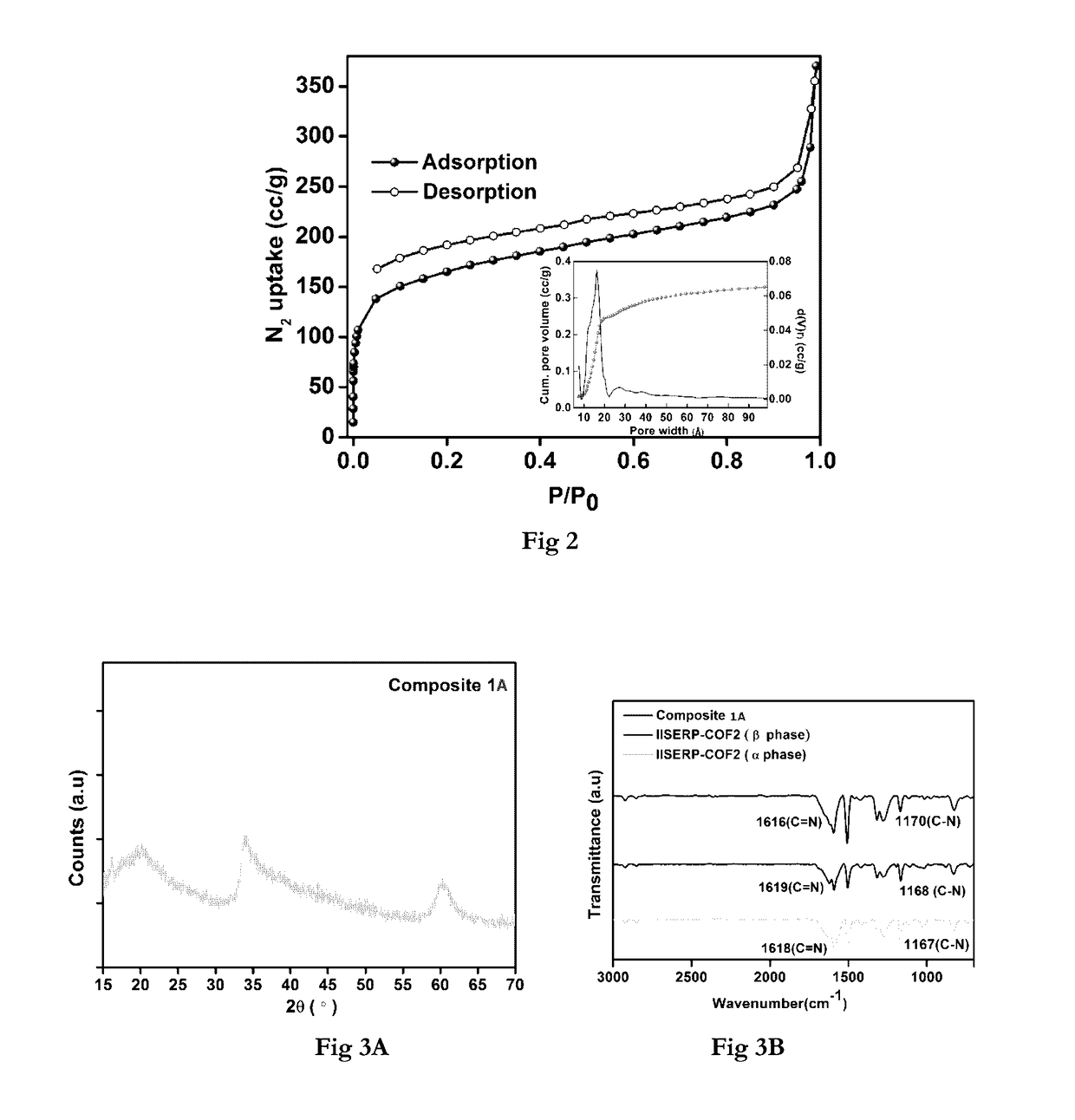
Covalent organic frameworks as porous supports for non-noble metal based water splitting electrocatalysts
ActiveUS20170130349A1Smooth connectionImprove performanceMultiple component coatingsElectrode with substrate and coatingMetal-organic frameworkManganese
The present invention discloses porous covalent organic frameworks (COF) supported noble metal-free nanoparticles which are useful as electrocatalysts for a water splitting system, and to the process for preparation of such electrocatalysts. The covalent organic frameworks (COF) supported noble metal-free nanoparticles have general formula (I):COF_AxBy(M)n (Formula I)wherein COF is selected from a Tris (4-formylphenyl)amine terephthaldehyde polymer or a benzimidazole-phloroglucinol polymer;‘A’ and ‘B’ each independently represent a transition metal selected from the group consisting of Ni, Co, Fe, Mn, Zn, and mixtures thereof; or ‘A’ and ‘B’ together represent a transition metal selected from the group consisting of Ni, Co, Fe, Mn, Zn, and mixtures thereof;‘M’ represents hydroxide or a nitride ion;‘x’ and ‘y’ represent the weight % of the metal loadings; or a ratio of x:y is between 0:1 and 1:0; and‘n’ is an integer 1 or 2 or 3.
Owner:INDIAN INST OF SCI EUDCATION & RES
Ion-conducting membranes
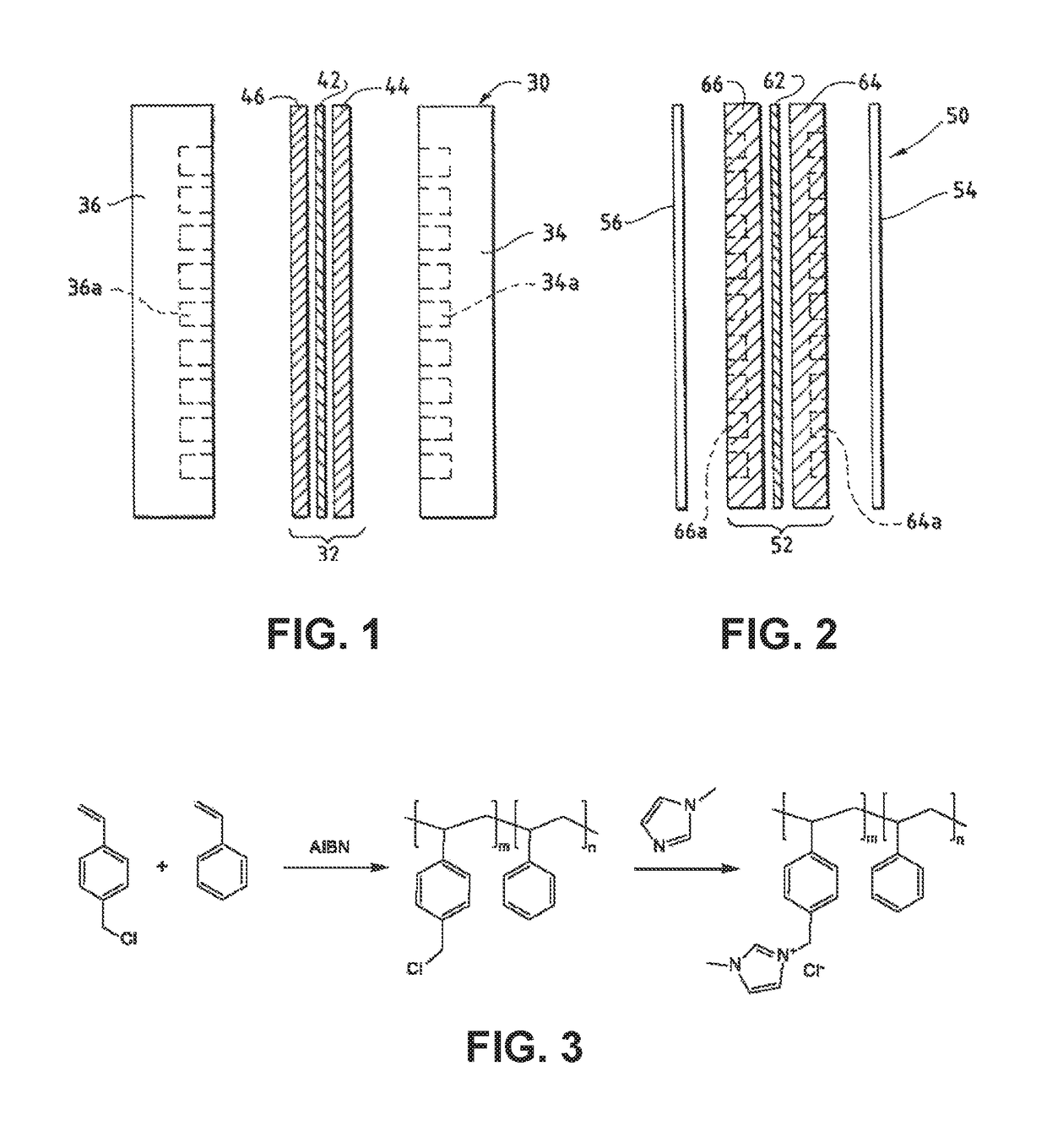
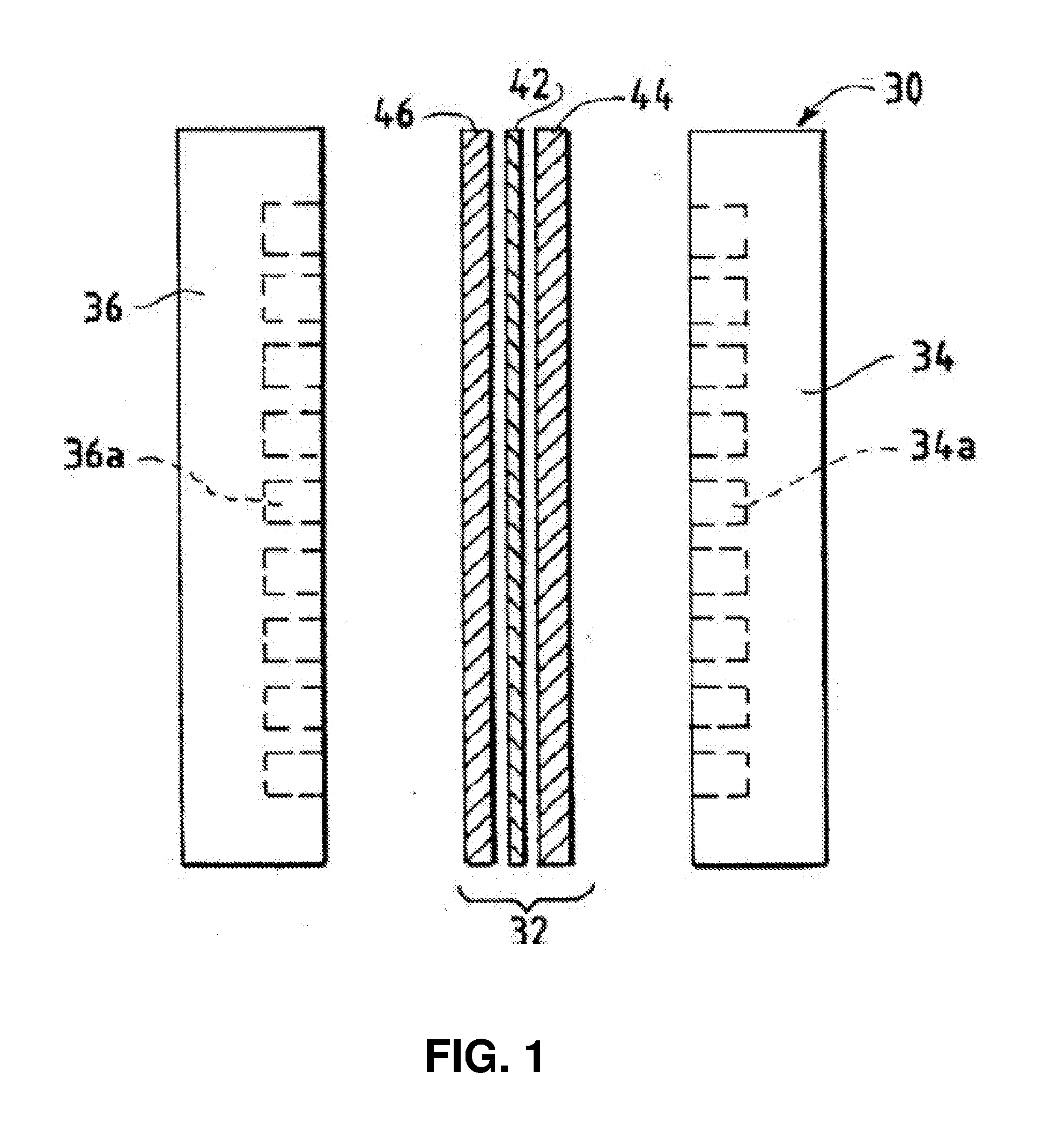
An anion-conducting polymeric membrane comprises a terpolymer of styrene, vinylbenzyl-Rs and vinylbenzyl-Rx. Rs is a positively charged cyclic amine group. Rx is at least one constituent selected from the group consisting Cl, OH and a reaction product between an OH or Cl and a species other than a simple amine or a cyclic amine. The total weight of the vinylbenzyl-Rx groups is greater than 0.3% of the total weight of the membrane. In a preferred embodiment, the membrane is a Helper Membrane that increases the faradaic efficiency of an electrochemical cell into which the membrane is incorporated, and also allows product formation at lower voltages than in cells without the Helper Membrane.
Owner:DIOXIDE MATERIALS
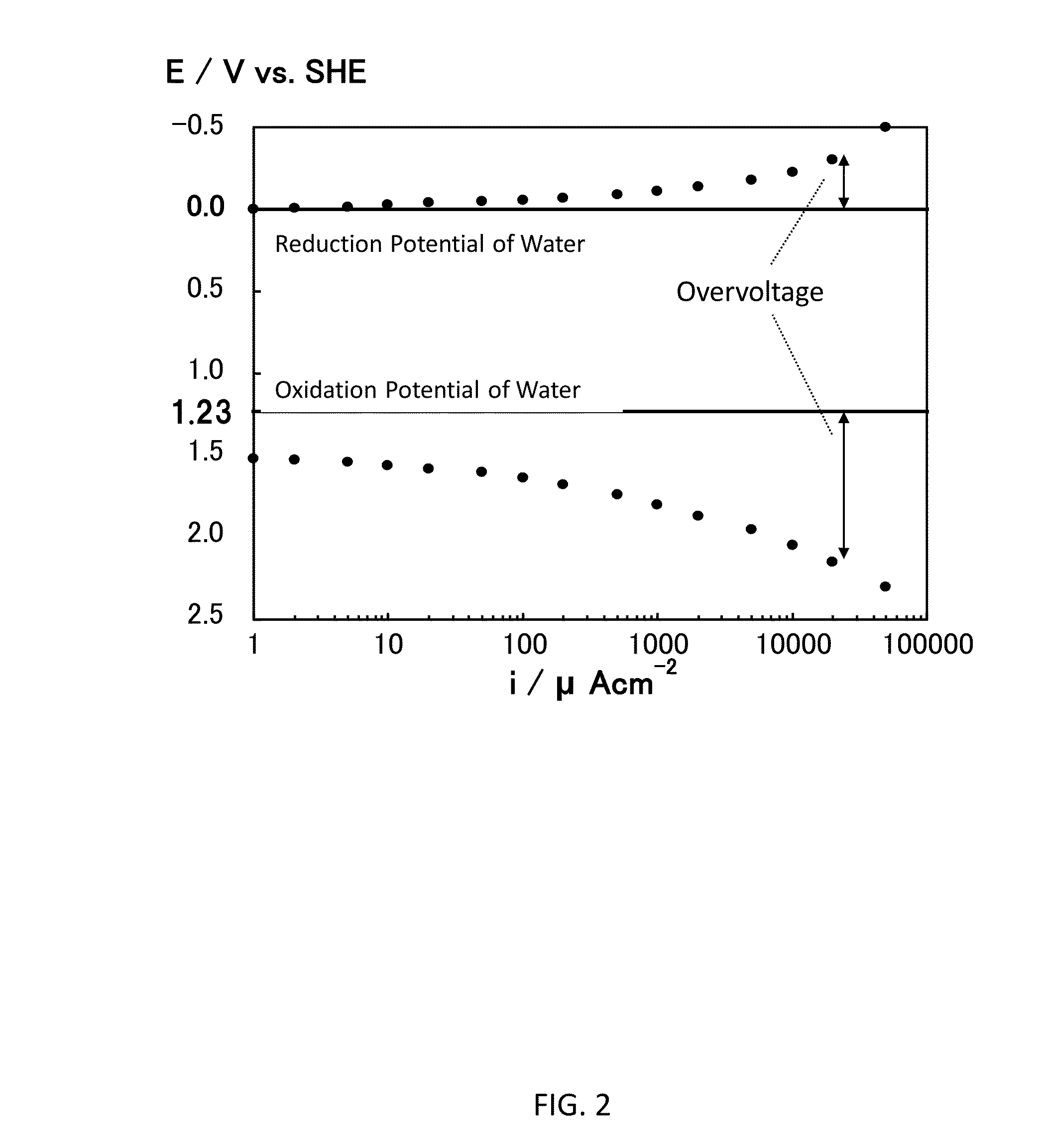
Stress-induced bandgap-shifted semiconductor photoelectrolytic/photocatalytic/photovoltaic surface and method for making same
ActiveUS7485799B2Improve efficiencyIncrease photocatalytic surface areaLight-sensitive devicesInternal combustion piston enginesStress inducedHydrogen
Titania is a semiconductor and photocatalyst that is also chemically inert. With its bandgap of 3.0, to activate the photocatalytic property of titania requires light of about 390 nm wavelength, which is in the ultra-violet (UV), where sunlight is very low in intensity. A method and devices are disclosed wherein stress is induced and managed in a thin film of titania in order to shift and lower the bandgap energy into the longer wavelengths that are more abundant in sunlight. Applications of this stress-induced bandgap-shifted titania photocatalytic surface include photoelectrolysis for production of hydrogen gas from water, photovoltaics for production of electricity, and photocatalysis for detoxification and disinfection.
Owner:NANOPTEK CORP
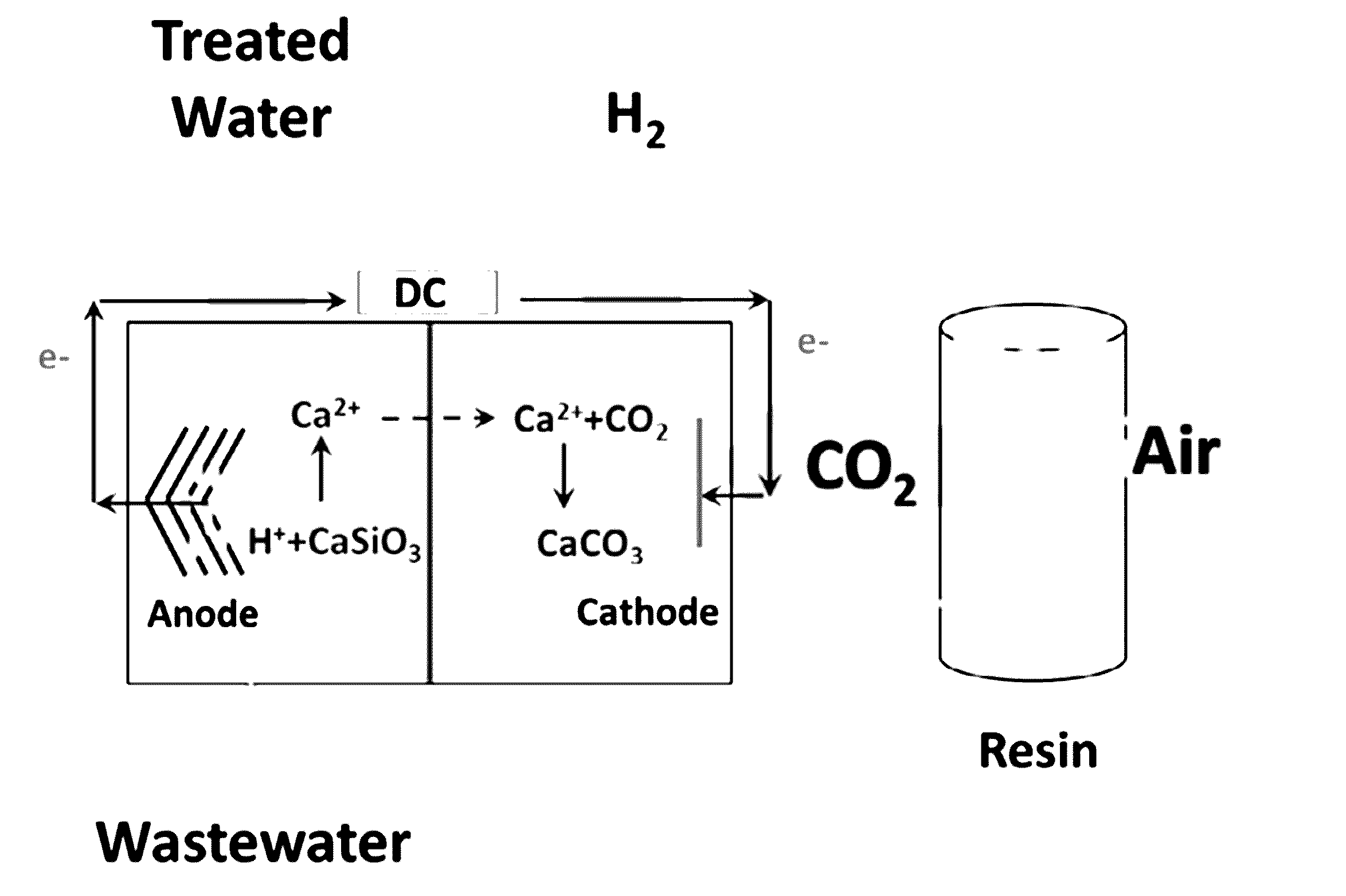
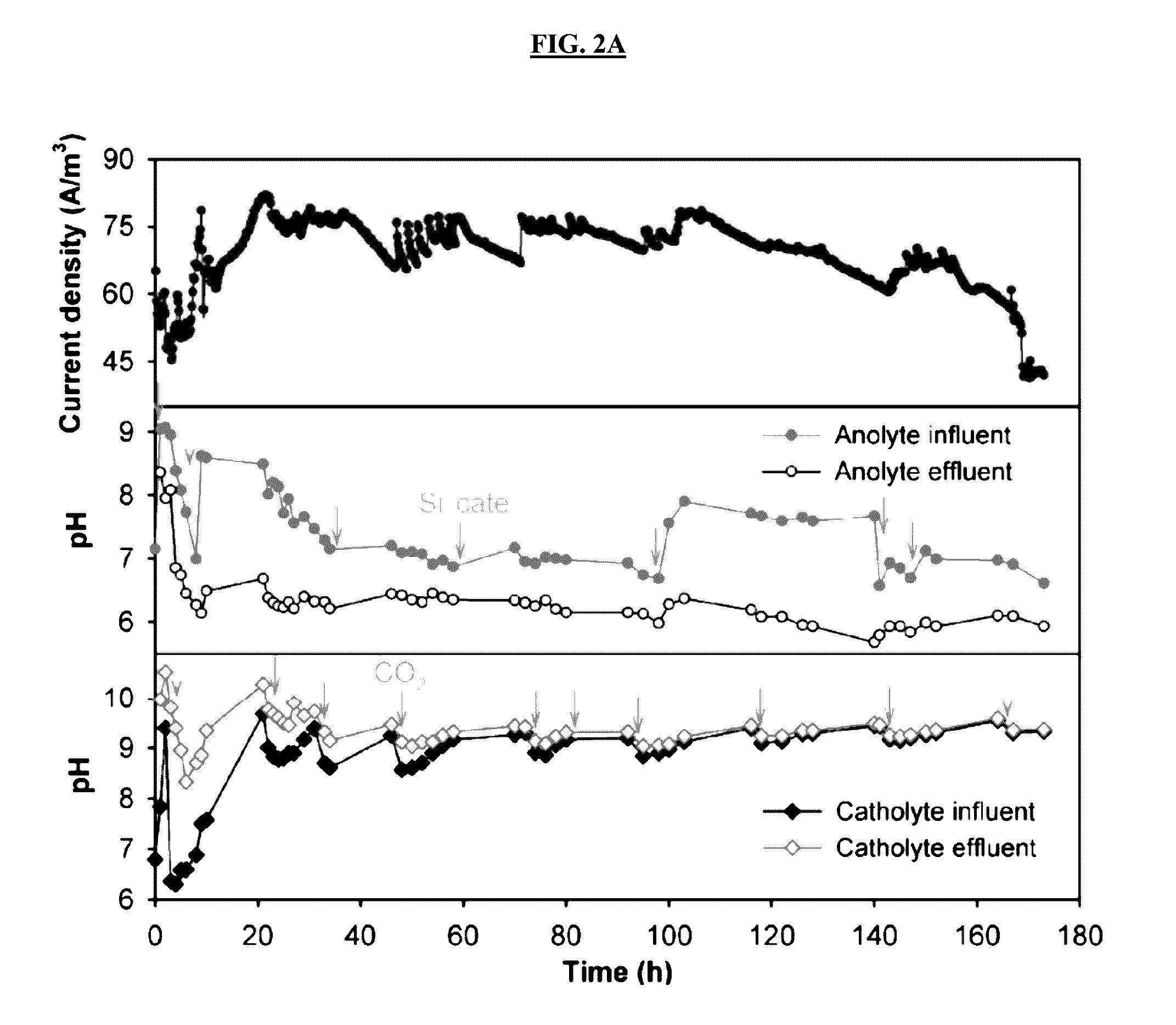
Carbon dioxide capture and storage electrolytic methods
ActiveUS20160362800A1Less solubleTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesSeawater treatmentHydrogenWastewater
The present invention relates to the unexpected discovery of systems for capturing carbon dioxide and producing hydrogen gas. In certain embodiments, the system treats wastewater. In certain embodiments, the system captures and sequesters CO2 as carbonate salts.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
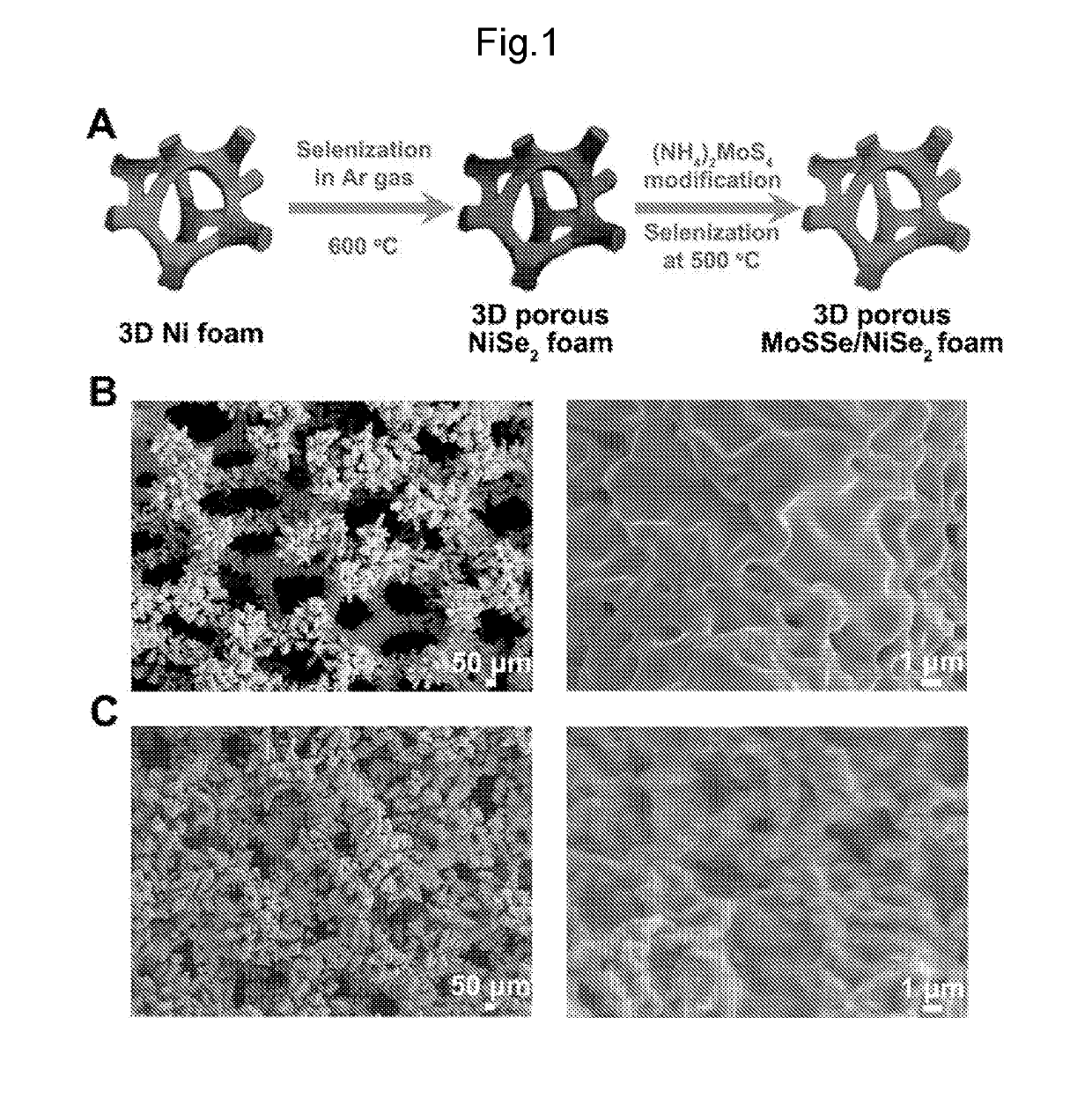
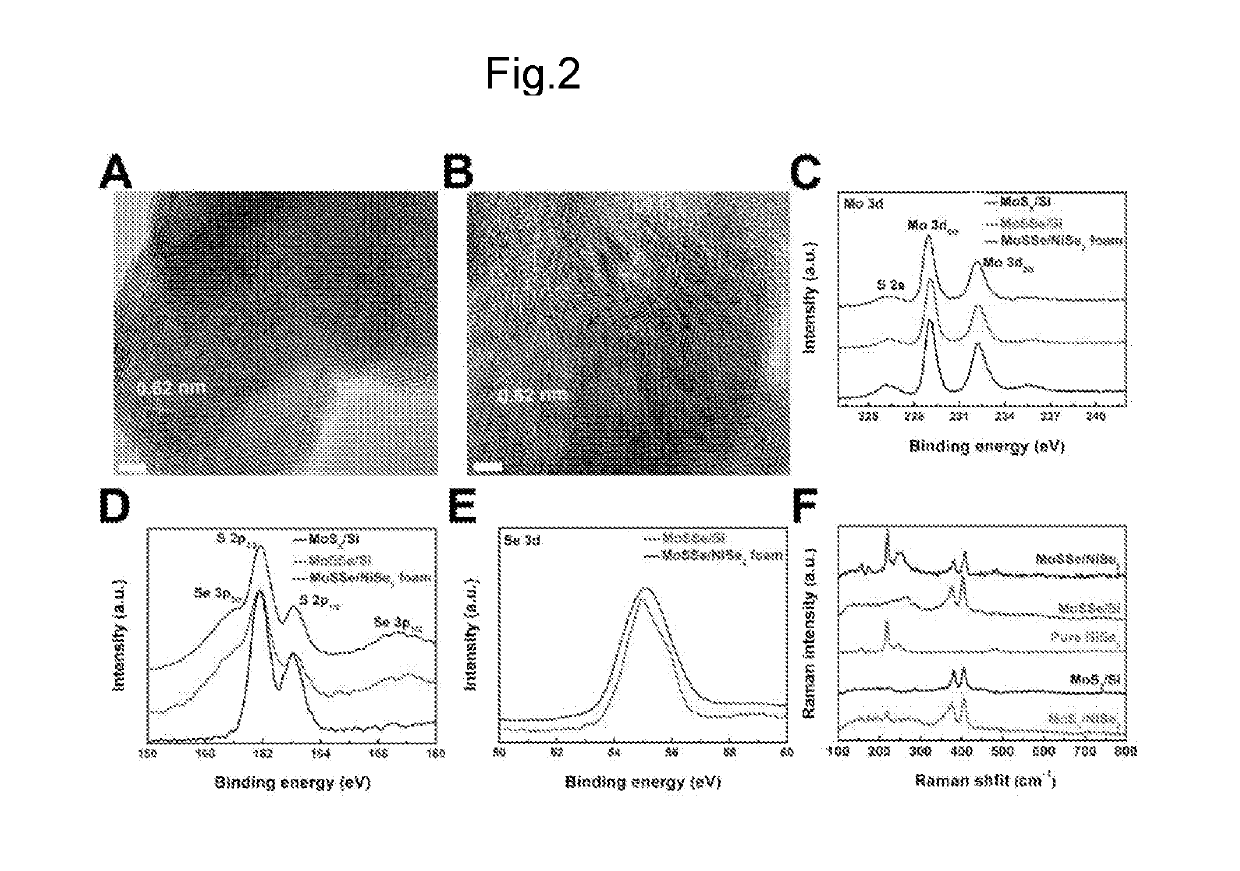
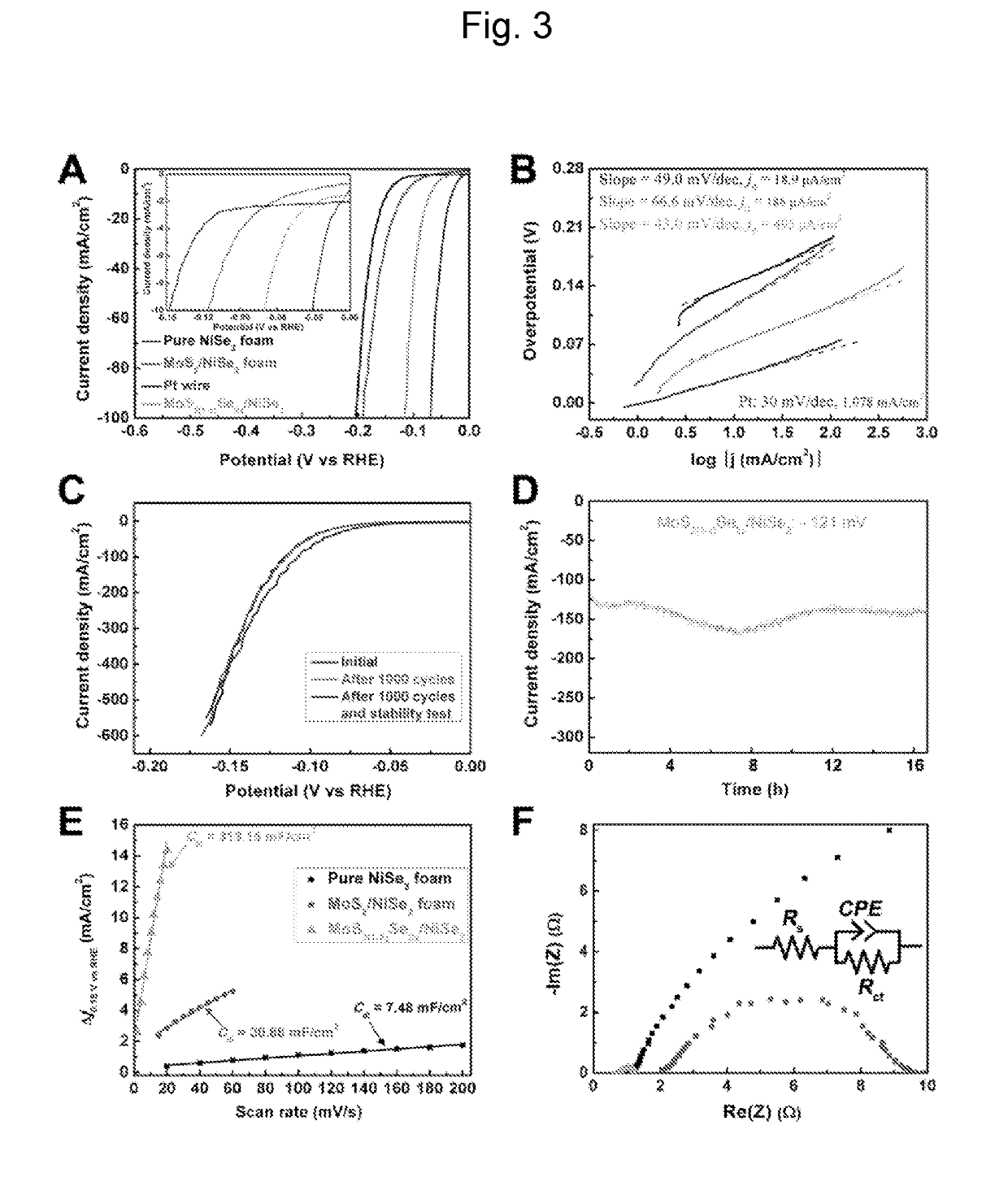
THREE-DIMENSIONAL POROUS NiSe2 FOAM-BASED HYBRID CATALYSTS FOR ULTRA-EFFICIENT HYDROGEN EVOLUTION REACTION IN WATER SPLITTING
ActiveUS20190218674A1High catalytic activityCheap and efficient and sizableCell electrodesMultiple component coatingsExchange current densityParticle position
A hybrid three dimensional (3D) hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) catalyst that is formed from a porous Ni foam support, a NiSe2 scaffold positioned on the support; and layered transition metal dichalcogenide (LTMDC) or first-row transition metal dichalcogenide particles positioned on the NiSe2 scaffold. The catalyst provides a low onset potential, large cathode current density, small Tafel slopes, and large exchange current densities, similar in catalytic power to Pt HER catalysts.
Owner:UNIV HOUSTON SYST
Non-noble metal based electro-catalyst compositions for proton exchange membrane based water electrolysis and methods of making
ActiveUS20170233879A1Shorten the timeReduced service lifeCellsMaterial nanotechnologyElectrolysisTitanium oxide
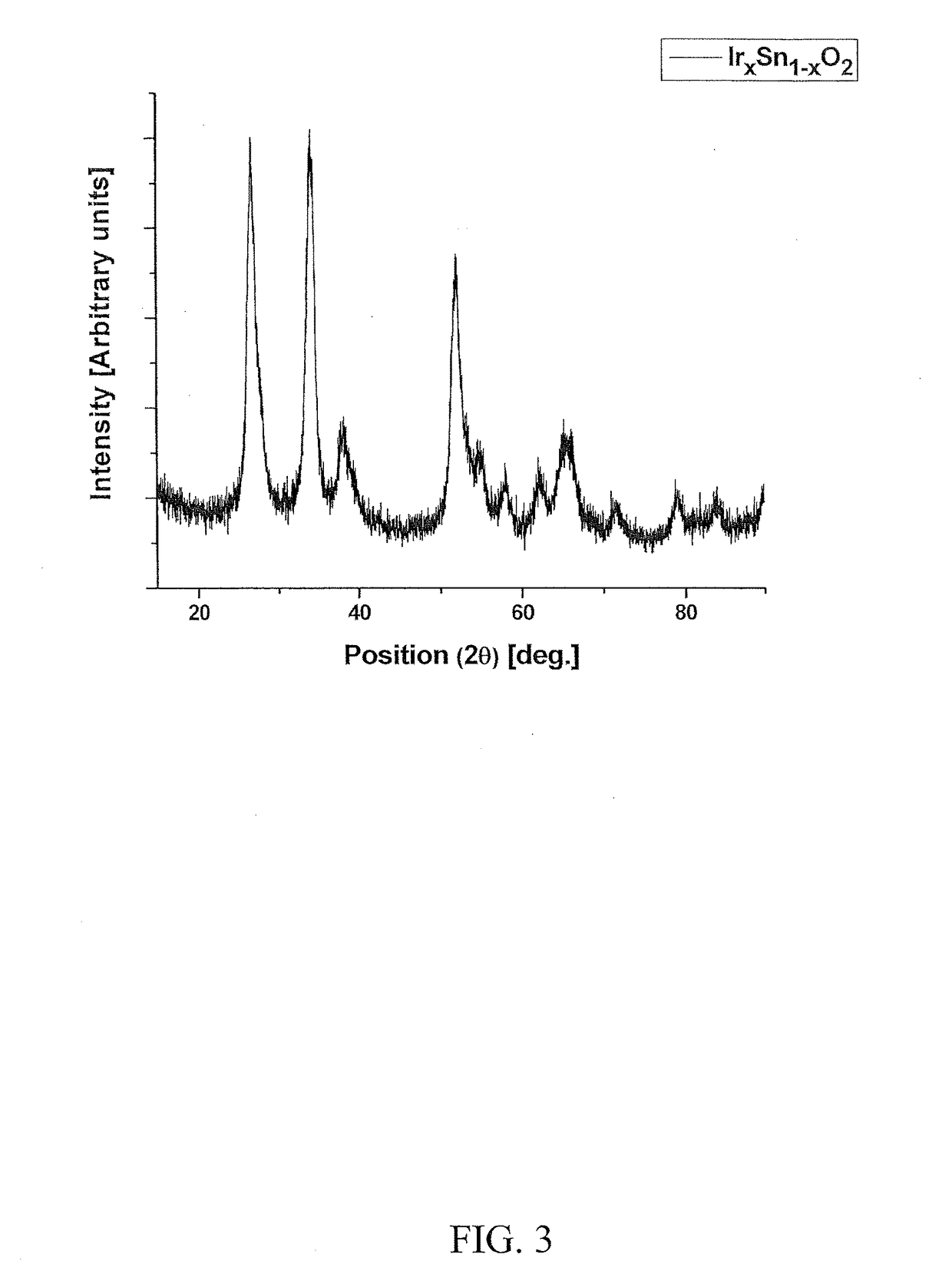
The invention provides electro-catalyst compositions for an anode electrode of an acid mediated proton exchange membrane-based water electrolysis system. The compositions include a noble metal component selected from the group consisting of iridium oxide, ruthenium oxide, rhenium oxide and mixtures thereof, and a non-noble metal component selected from the group consisting of tantalum oxide, tin oxide, niobium oxide, titanium oxide, tungsten oxide, molybdenum oxide, yttrium oxide, scandium oxide, cooper oxide, zirconium oxide, nickel oxide and mixtures thereof. Further, the non-noble metal component can include a dopant. The dopant can be at least one element selected from Groups III, V, VI and VII of the Periodic Table. The compositions can be prepared using any solution based methods involving a surfactant approach or a sol gel approach. Further, the compositions are prepared using noble metal and non-noble metal precursors. Furthermore, a thin film containing the compositions can be deposited onto a substrate to form the anode electrode.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Stress-induced bandgap-shifted semiconductor photoelectrolytic/photocatalytic/photovoltaic surface and method for making same
InactiveUS20090110591A1Avoid delaminationImprove matchLight-sensitive devicesInternal combustion piston enginesStress inducedUltraviolet
Owner:NANOPTEK CORP
Compositions and methods for synthesis of hydrogen fuel
The invention provides new methods and compositions for synthesizing hydrogen fuel using simple and inexpensive materials.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Non-precious metal based water electrolysis catalyst for oxygen evolution at anode and hydrogen evolution at cathode and preparation method of the same
ActiveUS20160199821A1Excellent oxygen evolution reaction activityHigh oxidation numberMaterial nanotechnologyCatalyst activation/preparationHydrogenElectrolysis
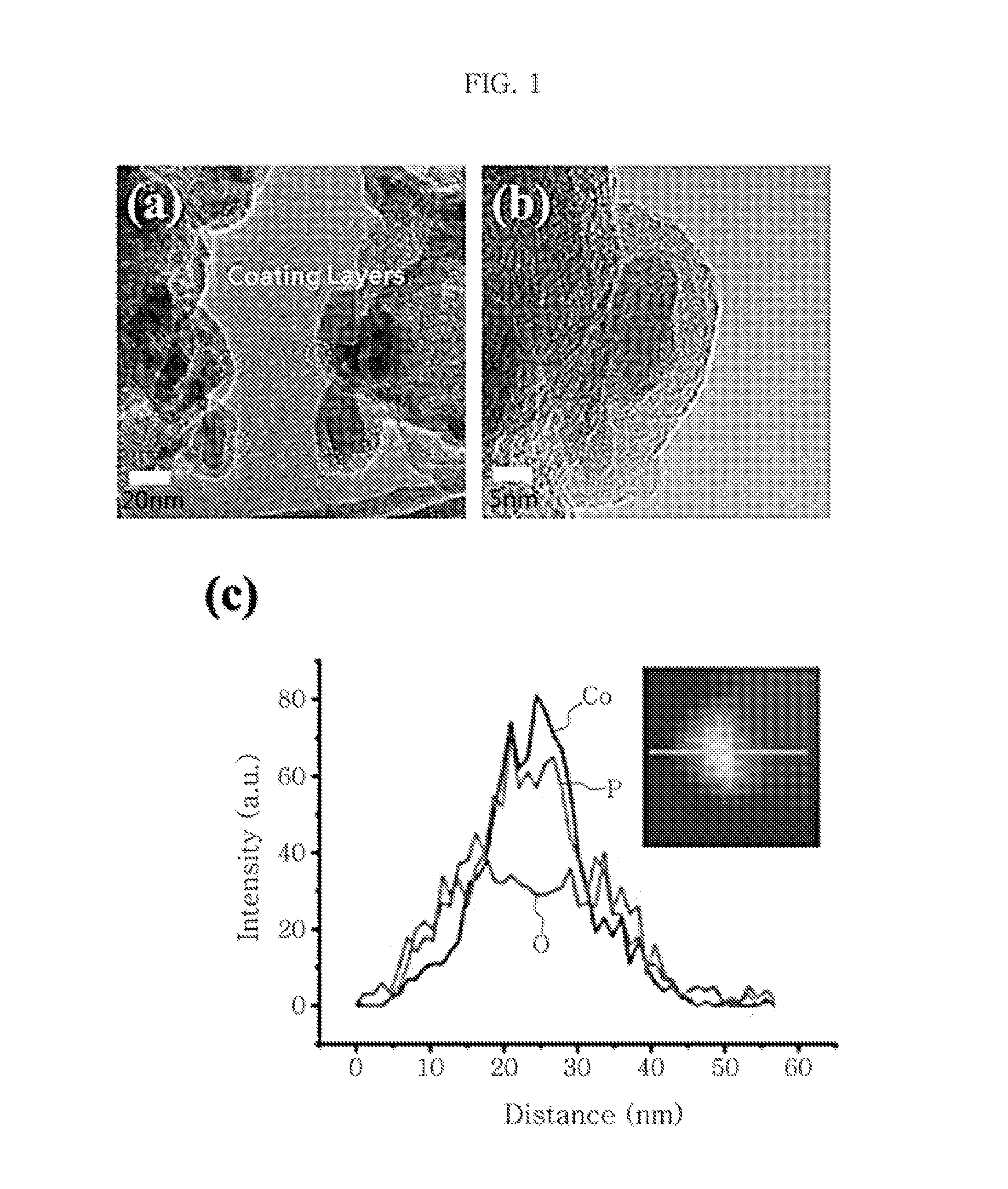
Disclosed is a non-precious metal based water electrolysis catalyst represented by CoX / C (X is at least one selected from the group consisting of P, O, B, S and N) for evolution of hydrogen and oxygen at a cathode and anode, respectively, at the same time, the catalyst including a cobalt-containing compound fixed to a carbon carrier.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Electrolytic water splitting using a carbon-supported mnox-composite
InactiveUS20150068917A1High activityInexpensive and scalable techniqueMachining electrodesMaterial nanotechnologyWater useElectrolysis
The present invention relates to the electrolytic splitting of water using a carbon-supported manganese oxide (MnOx) composite. Specifically, the present electrolytic splitting of water is carried under neutral electrolyte conditions with a high electrolytic activity, while using an oxygen evolution reaction (OER)-electrode comprising the present carbon-supported MnOx composite. Next, the present invention relates to a process for producing such a carbon-supported MnOx composite as well as to a composite obtainable by the present process for producing the same and to an OER-electrode comprising the carbon-supported MnOx composite obtainable by the present process.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
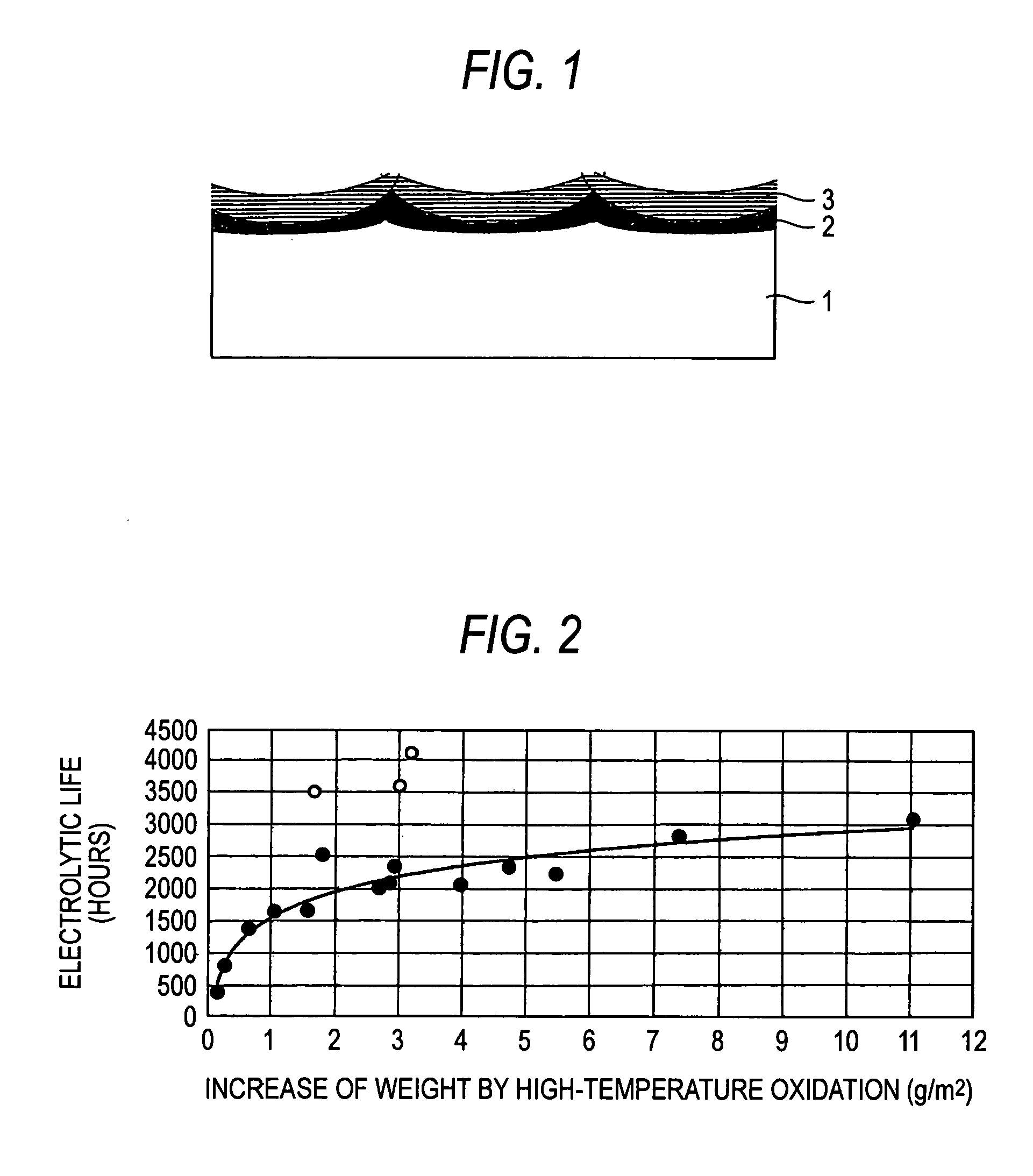
Electrolytic electrode and process of producing the same
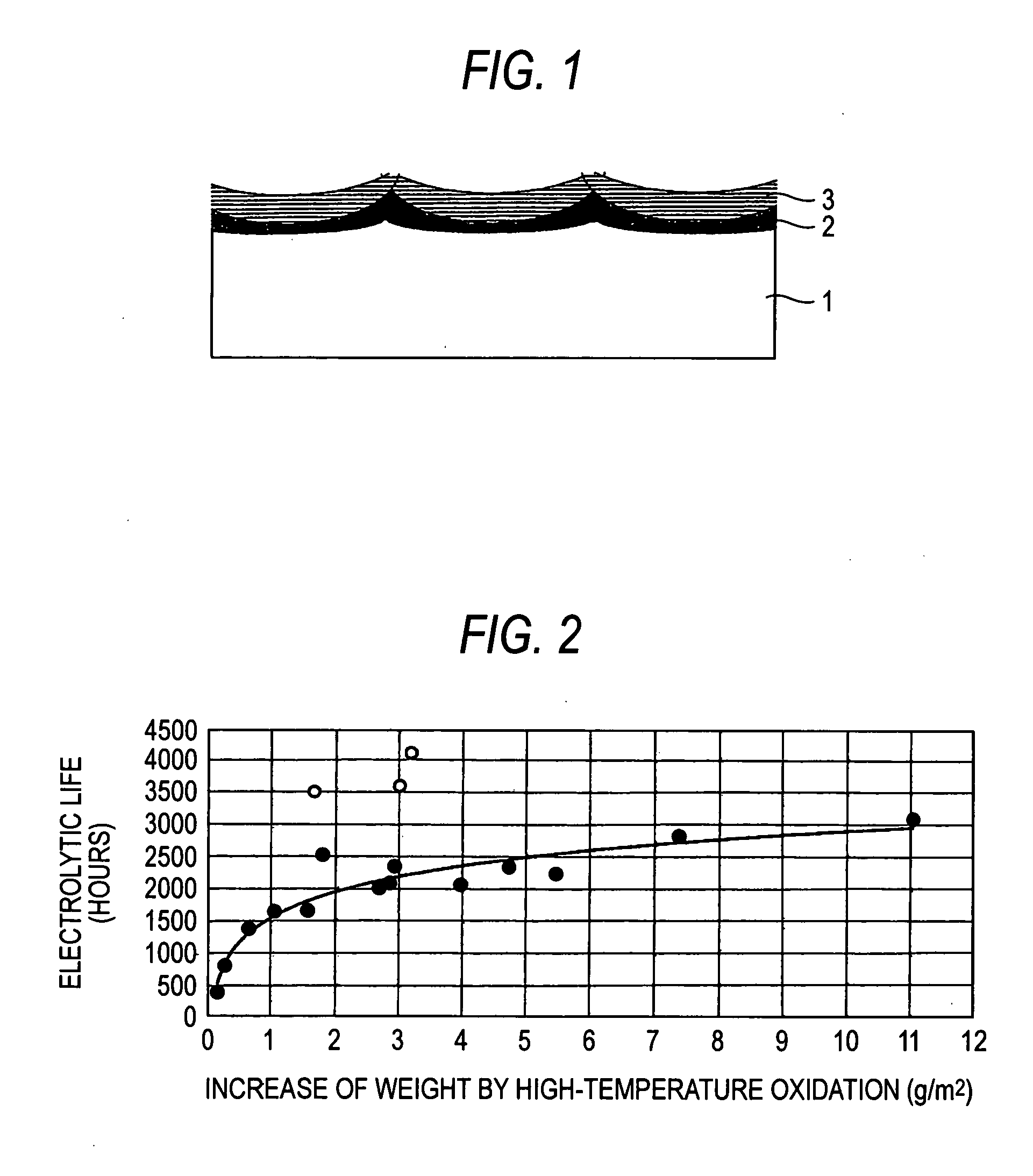
An electrolytic electrode having an interlayer having more excellent peeling resistance and corrosion resistance and longer electrolytic life than conventional electrolytic electrodes and capable of flowing a large amount of current at the industrial level and a process of producing the same are provided. The electrolytic electrode includes a valve metal or valve metal alloy electrode substrate on the surface of which is formed a high-temperature oxidation film by oxidation, and which is coated with an electrode catalyst. The high-temperature oxidation film is integrated with the electrode substrate, whereby peeling resistance is enhanced. Further, by heating the high-temperature oxidation film together with the electrode catalyst, non-electron conductivity of the interlayer is modified, thereby making it possible to flow a large amount of current.
Owner:DE NORA PERMELEC LTD
Catalyst Layers And Electrolyzers
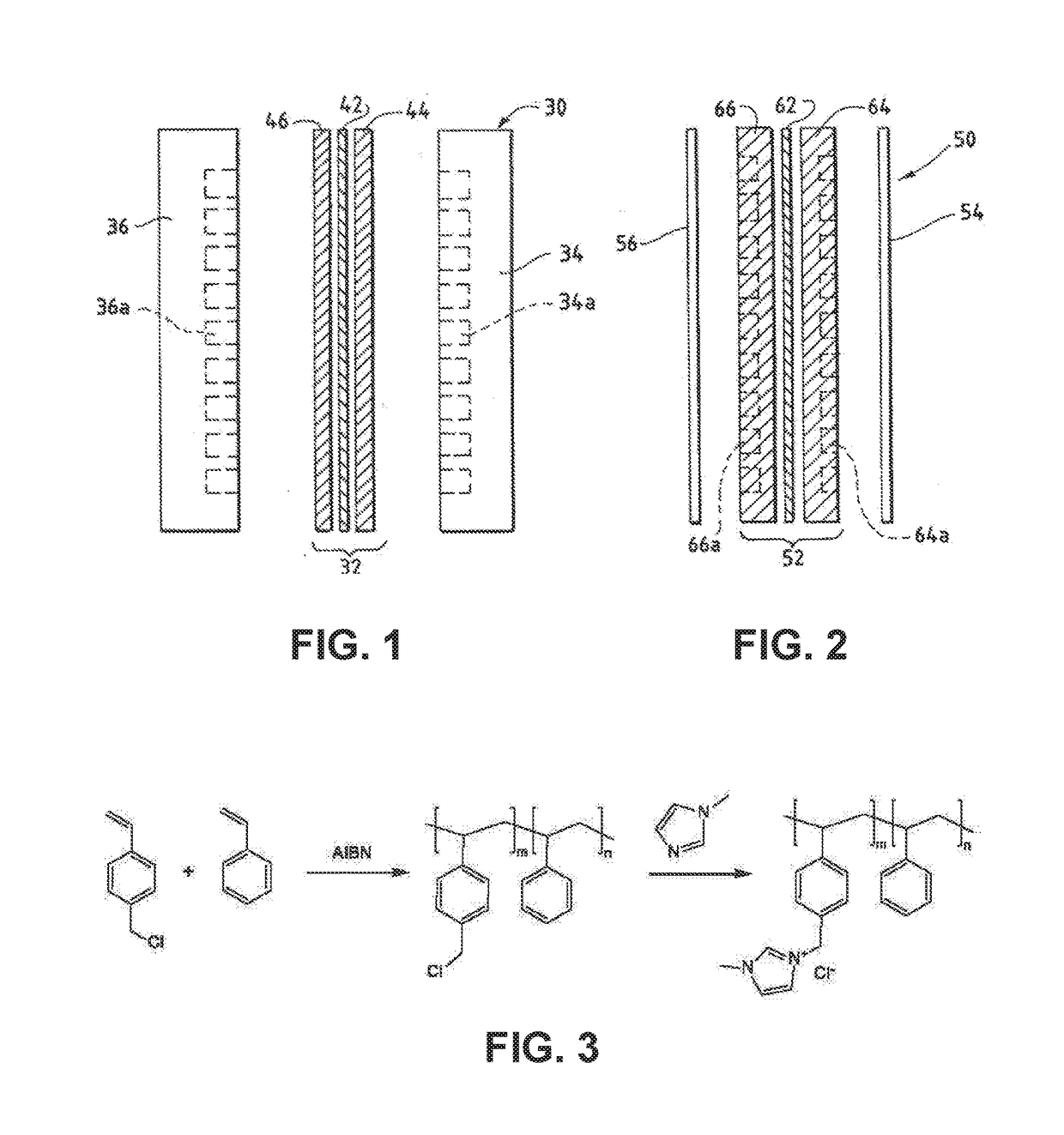
A catalyst layer for an electrochemical device comprises a catalytically active element and an ion conducting polymer. The ion conducting polymer comprises positively charged cyclic amine groups. The ion conducting polymer comprises at least one of an imidazolium, a pyridinium, a pyrazolium, a pyrrolidinium, a pyrrolium, a pyrimidium, a piperidinium, an indolium, a triazinium, and polymers thereof. The catalytically active element comprises at least one of V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Sn, Zr, Nb, Mo, Ru, Rh, Pd, Ag, Cd, Hf, Ta, W, Re, Ir, Pt, Au, Hg, Al, Si, In, Tl, Pb, Bi, Sb, Te, U, Sm, Tb, La, Ce and Nd. In an electrolyzer comprising the present catalyst layer, the feed to the electrolyzer comprises at least one of CO2 and H2O.
Owner:DIOXIDE MATERIALS
Electrode for electrochlorination
InactiveUS20130087450A1Promote achievementReduce loadMachining electrodesCellsHypochloriteElectrical polarity
The invention relates to an electrode for electrochemical generation of hypochlorite. The electrode comprises a valve metal substrate coated with a catalytic system consisting of two super-imposed layers of distinct composition and having a different activity towards hypochlorite anodic generation from chloride solutions. The electrode has a high duration in cathodic operation conditions, imparting self-cleaning characteristics thereto when used in combination with an equivalent one with periodic polarity reversal. Moreover, the deactivation of the electrode at the end of its life cycle occurs in two subsequent steps, allowing to schedule the substitution thereof with a significant notice period.
Owner:IND DE NORA SPA
Ion-Conducting Membranes
An anion-conducting polymeric membrane comprises a terpolymer of styrene, vinylbenzyl-Rs and vinylbenzyl-Rx. Rs is a positively charged cyclic amine group. Rx is at least one constituent selected from the group consisting Cl, OH and a reaction product between an OH or Cl and a species other than a simple amine or a cyclic amine. The total weight of the vinylbenzyl-Rx groups is greater than 0.3% of the total weight of the membrane. In a preferred embodiment, the membrane is a Helper Membrane that increases the faradaic efficiency of an electrochemical cell into which the membrane is incorporated, and also allows product formation at lower voltages than in cells without the Helper Membrane.
Owner:DIOXIDE MATERIALS
Electrode for electrochlorination
ActiveCN102918184ASpecific water treatment objectivesMultiple component coatingsElectrolysisHypochlorite
The invention relates to an electrode for electrochemical generation of hypochlorite. The electrode comprises a valve metal substrate coated with a catalytic system consisting of two super-imposed layers of distinct composition and having a different activity towards hypochlorite anodic generation from chloride solutions. The electrode has a high duration in cathodic operation conditions, imparting self-cleaning characteristics thereto when used in combination with an equivalent one with periodic polarity reversal. Moreover, the deactivation of the electrode at the end of its life cycle occurs in two subsequent steps, allowing to schedule the substitution thereof with a significant notice period.
Owner:IND DE NORA SPA
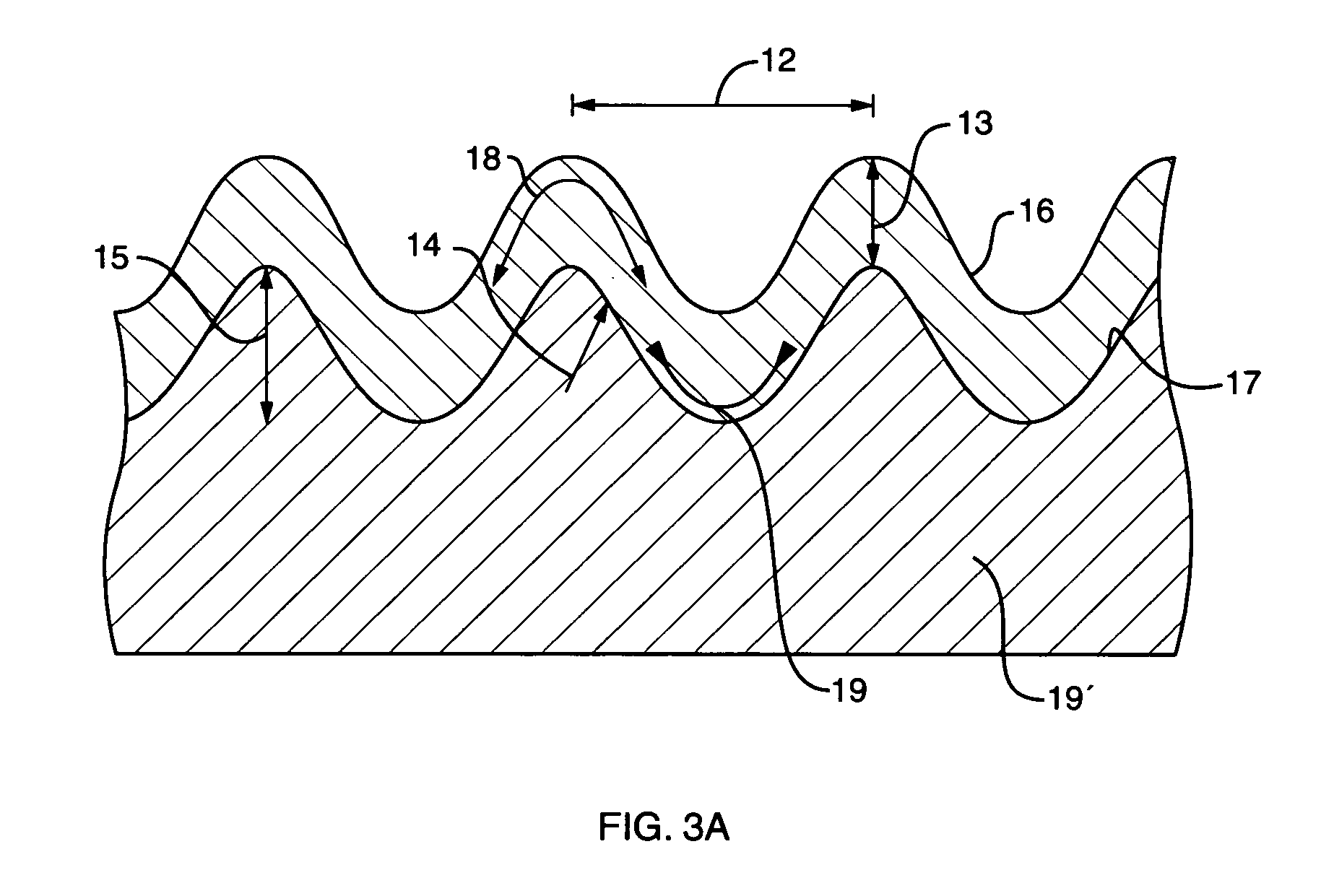
Electrode for electrolysis and method of manufacturing electrode for electrolysis
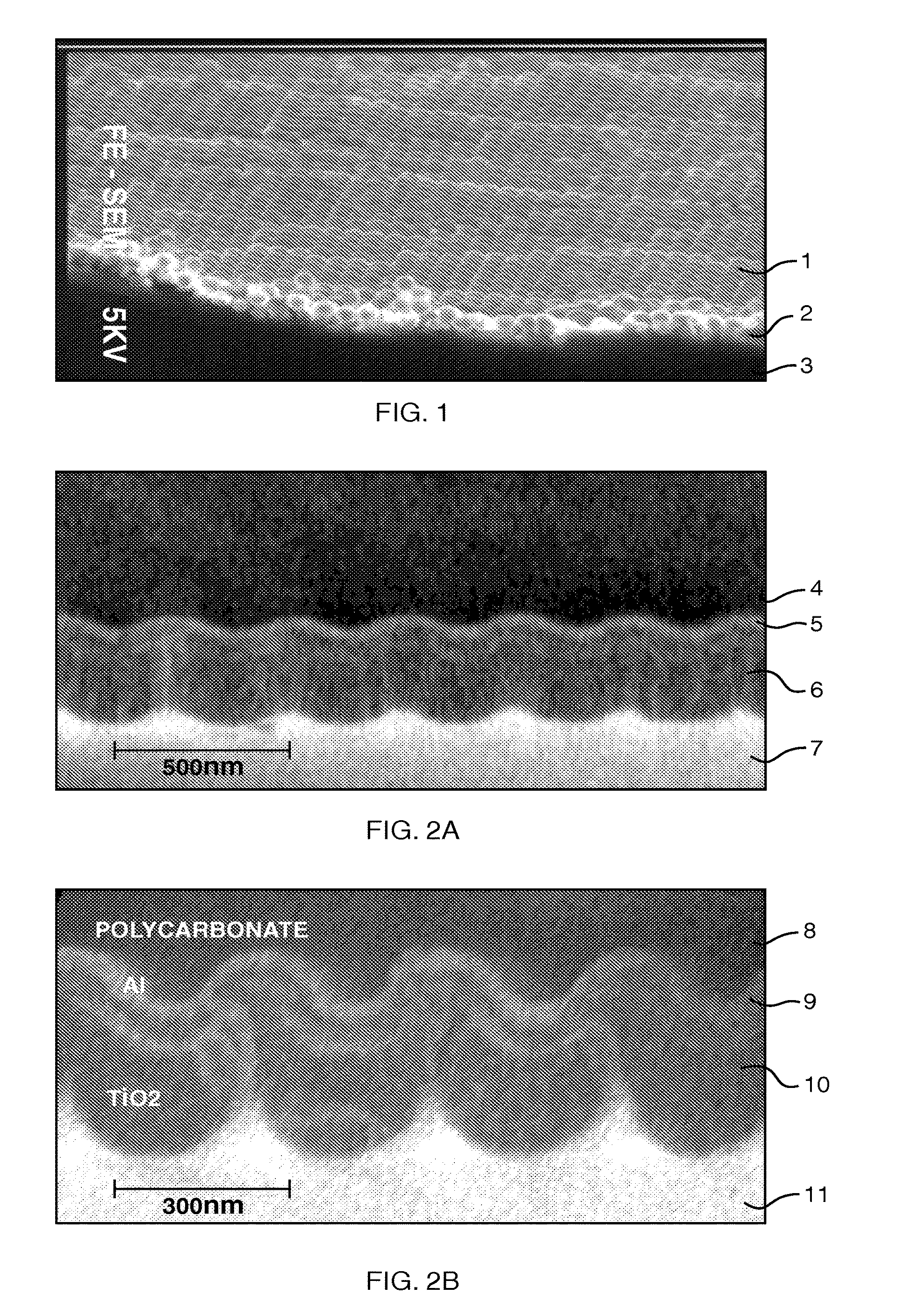
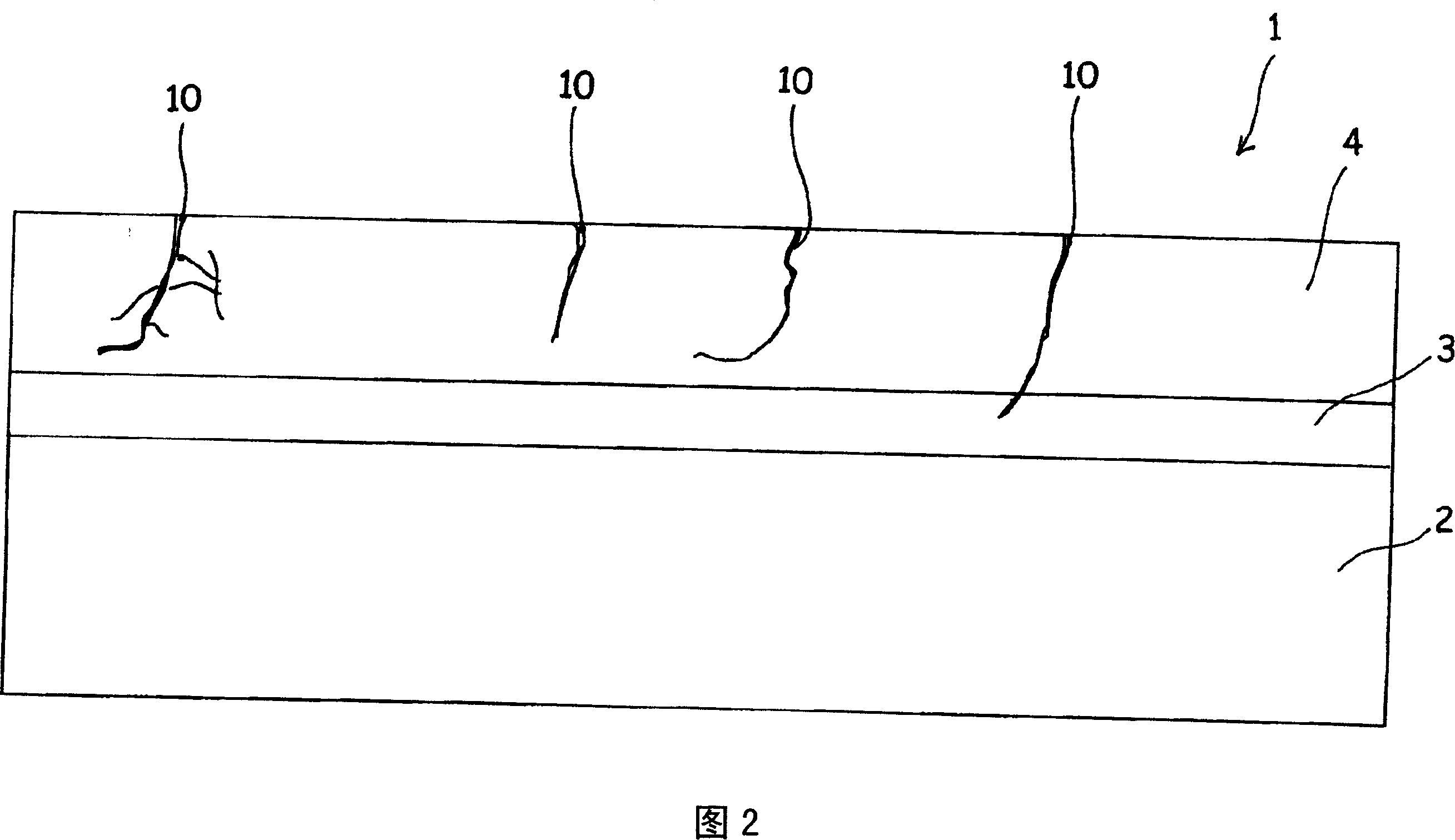
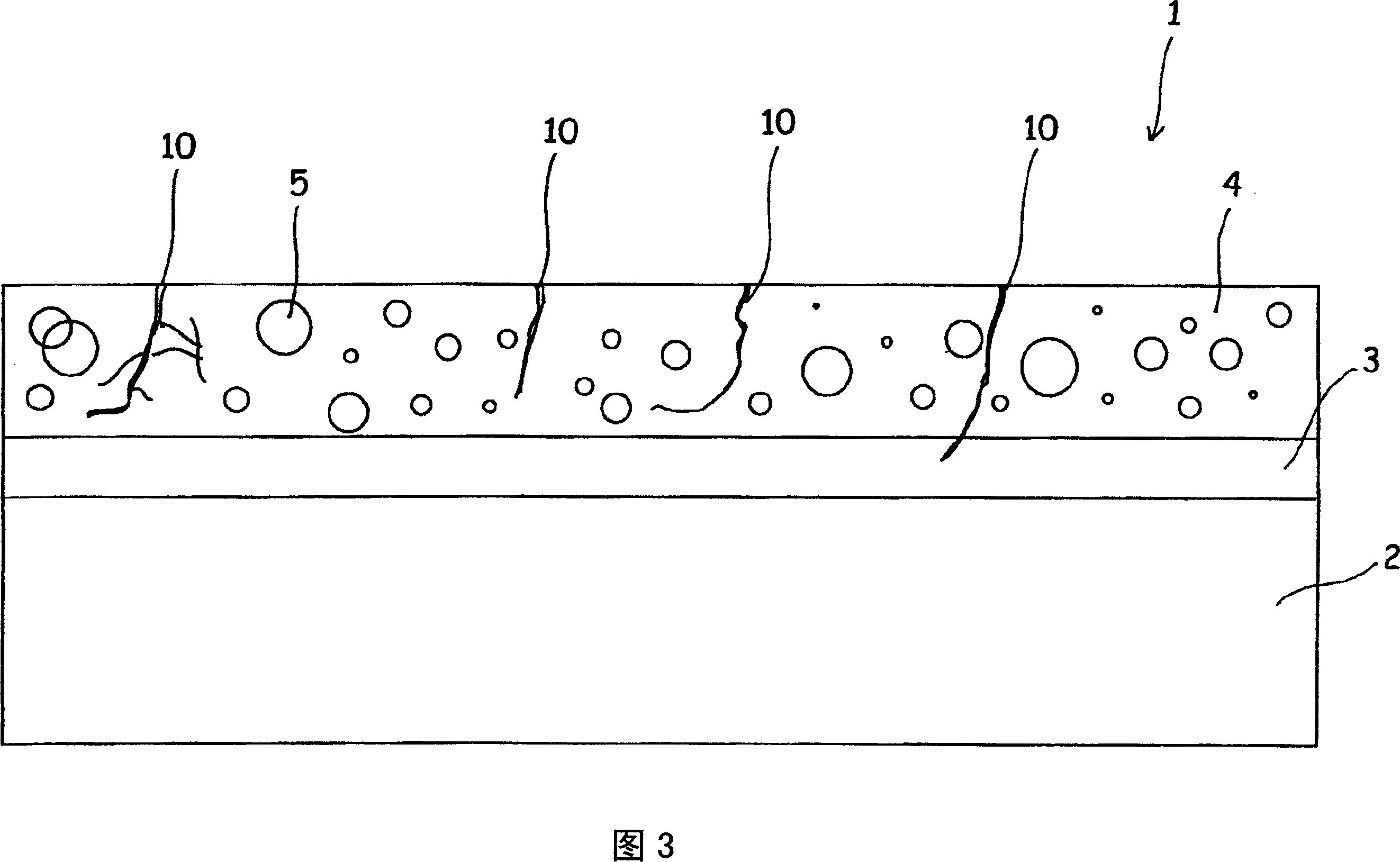
InactiveUS20070034505A1Generate efficientlyIncrease energy levelPretreated surfacesWater/sewage treatmentSurface layerVolumetric Mass Density
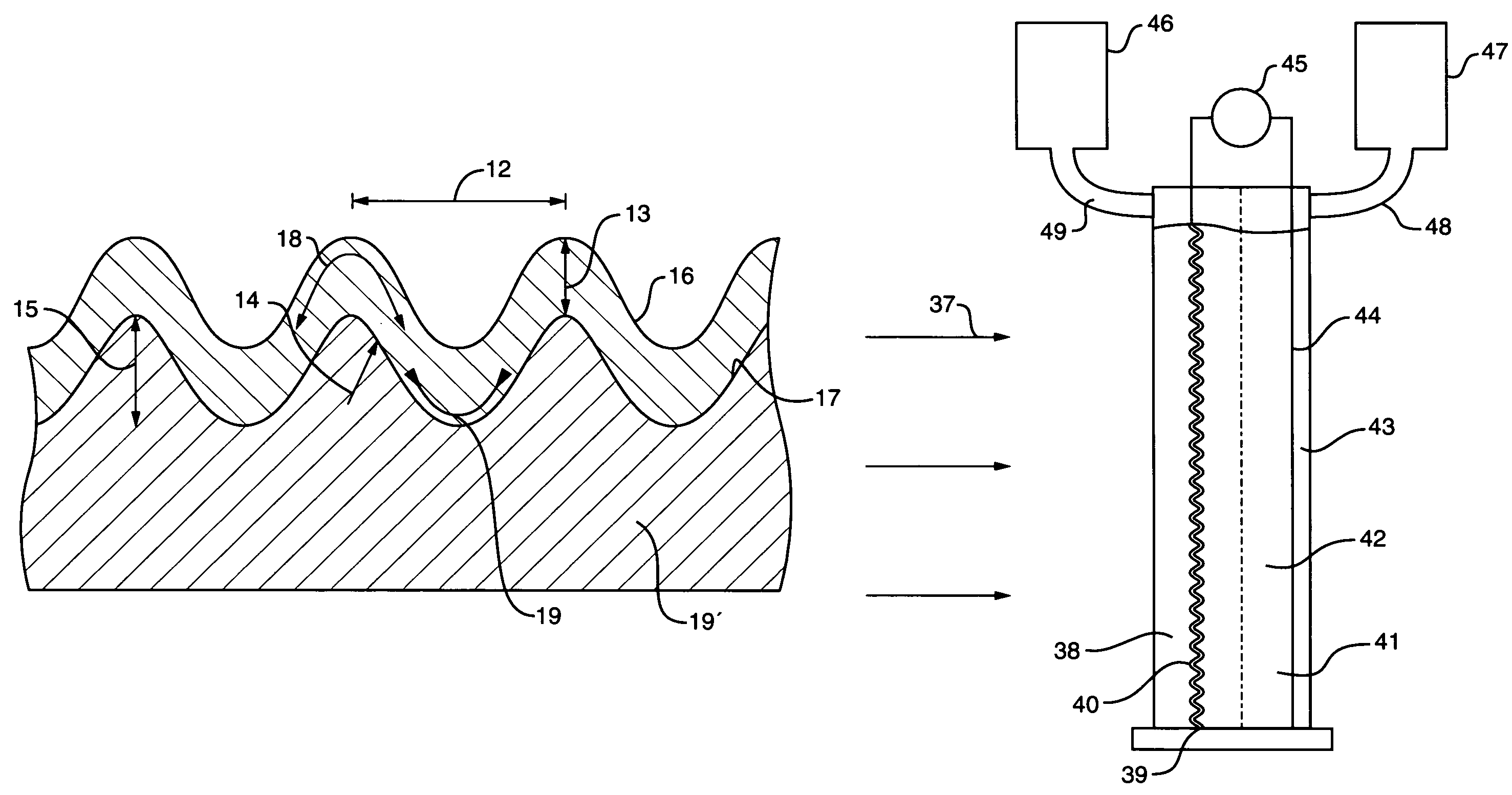
An object is to provide an electrode for electrolysis capable of generating ozone water with a high efficiency by electrolysis of water at a low current density. An ozone generating electrode includes: a substrate; and a surface layer formed on the surface of the substrate and including a dielectric material, the surface layer includes holes which inwardly continuously extend from the surface of the surface layer, and a distance from the hole closest to the surface of the substrate to the surface of the substrate is more than 0 and 2000 nm or less.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Method for operating an soec-type stack reactor for producing methane in the absence of available electricity
ActiveUS20160355932A1Speed up the processImproved thermal managementCellsGaseous fuelsElectricitySyngas
A method for the operation of an SOEC stack reactor (Solid Oxide Electrolyser Cell), according to which, in the absence of electricity, synthesis gas H2+CO or a mixture H2+CO2 is injected at the cathode inlet of the reactor in such a way as to produce methane inside the reactor. Since the catalytic methanation reaction is exothermic, the stack reactor can therefore be held at temperature, without loss of fuel. The fuel used for the methanation (synthesis gas or hydrogen) can advantageously be that which has been previously produced during the operating phases with available electricity.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
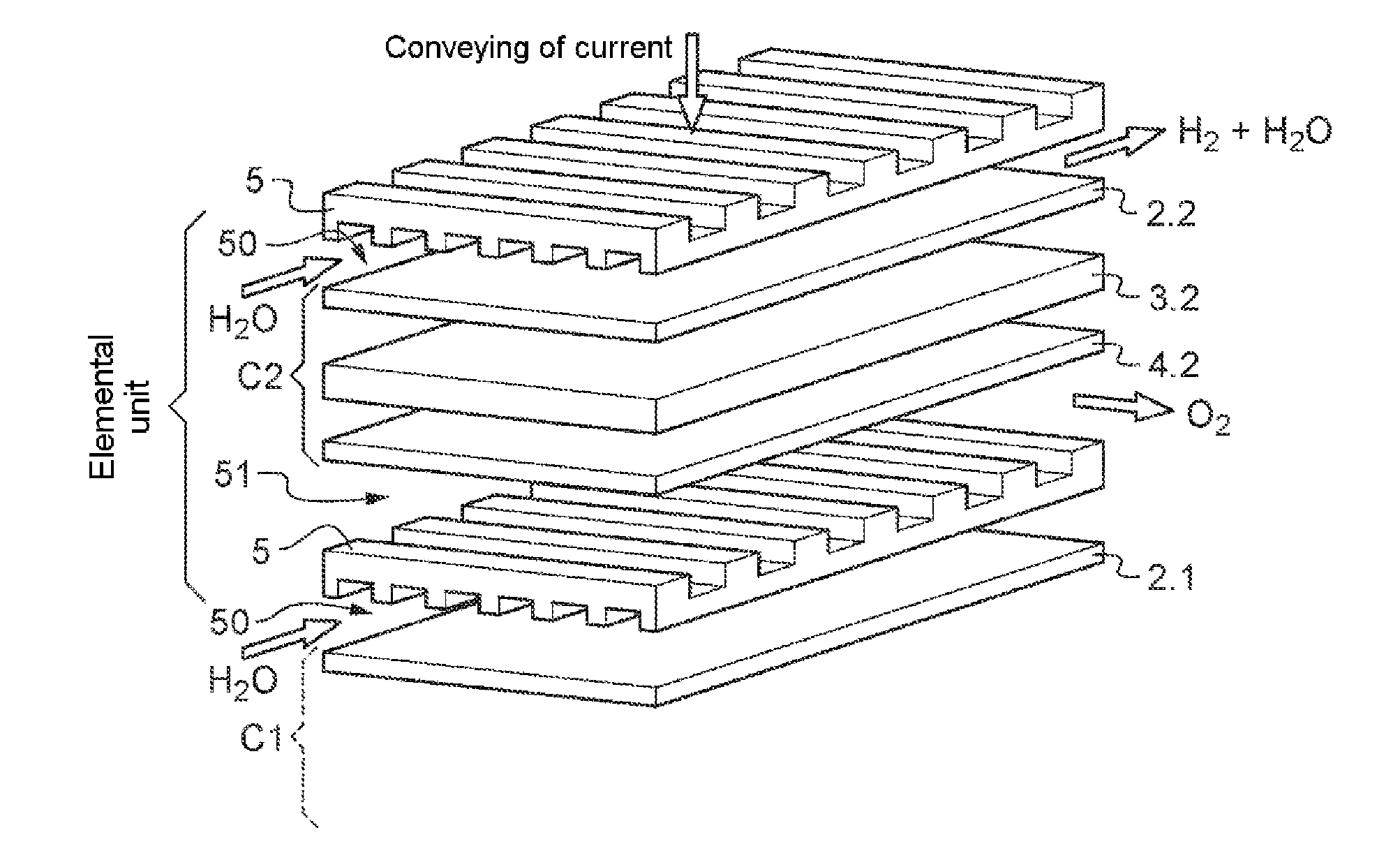
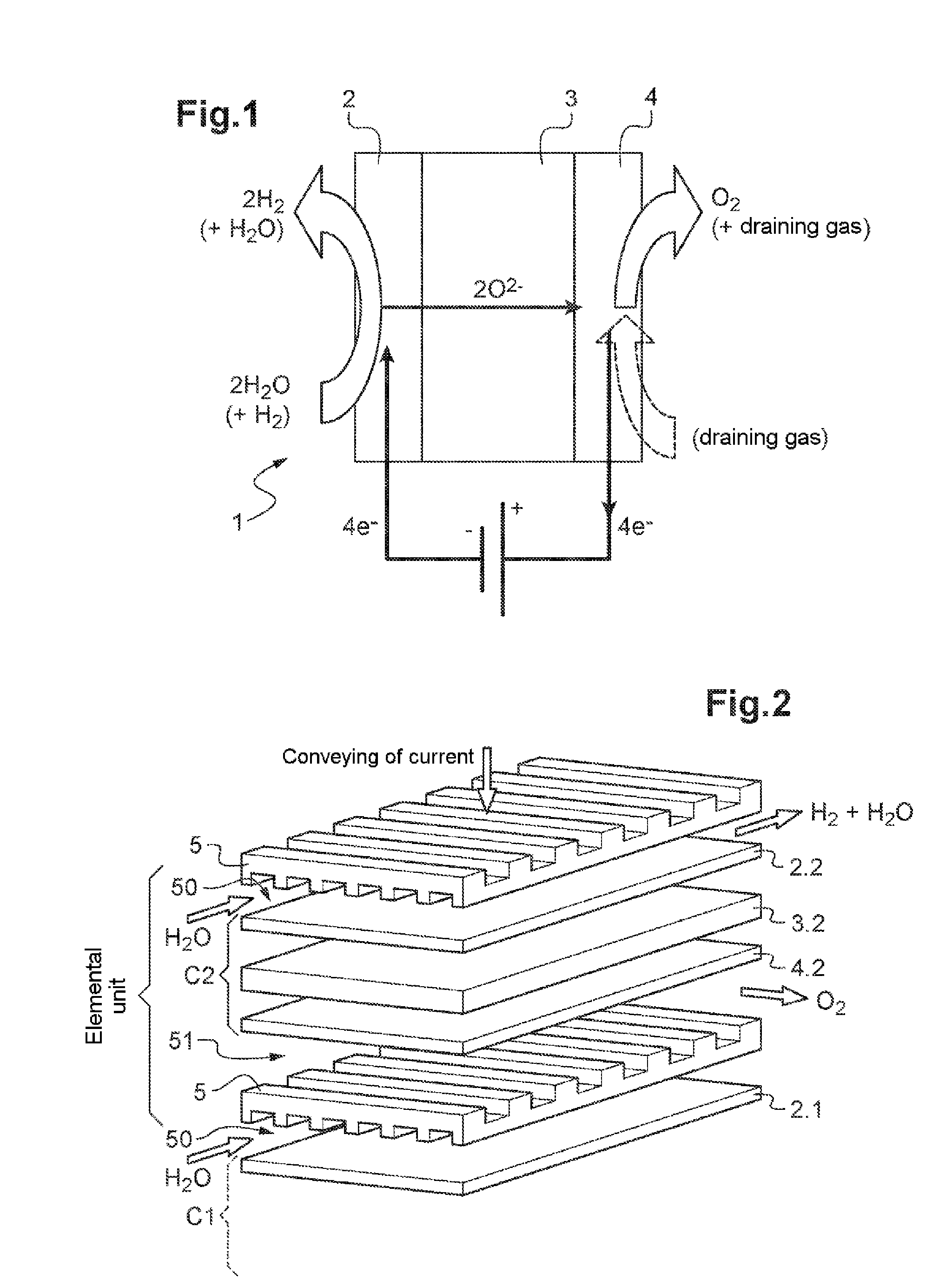
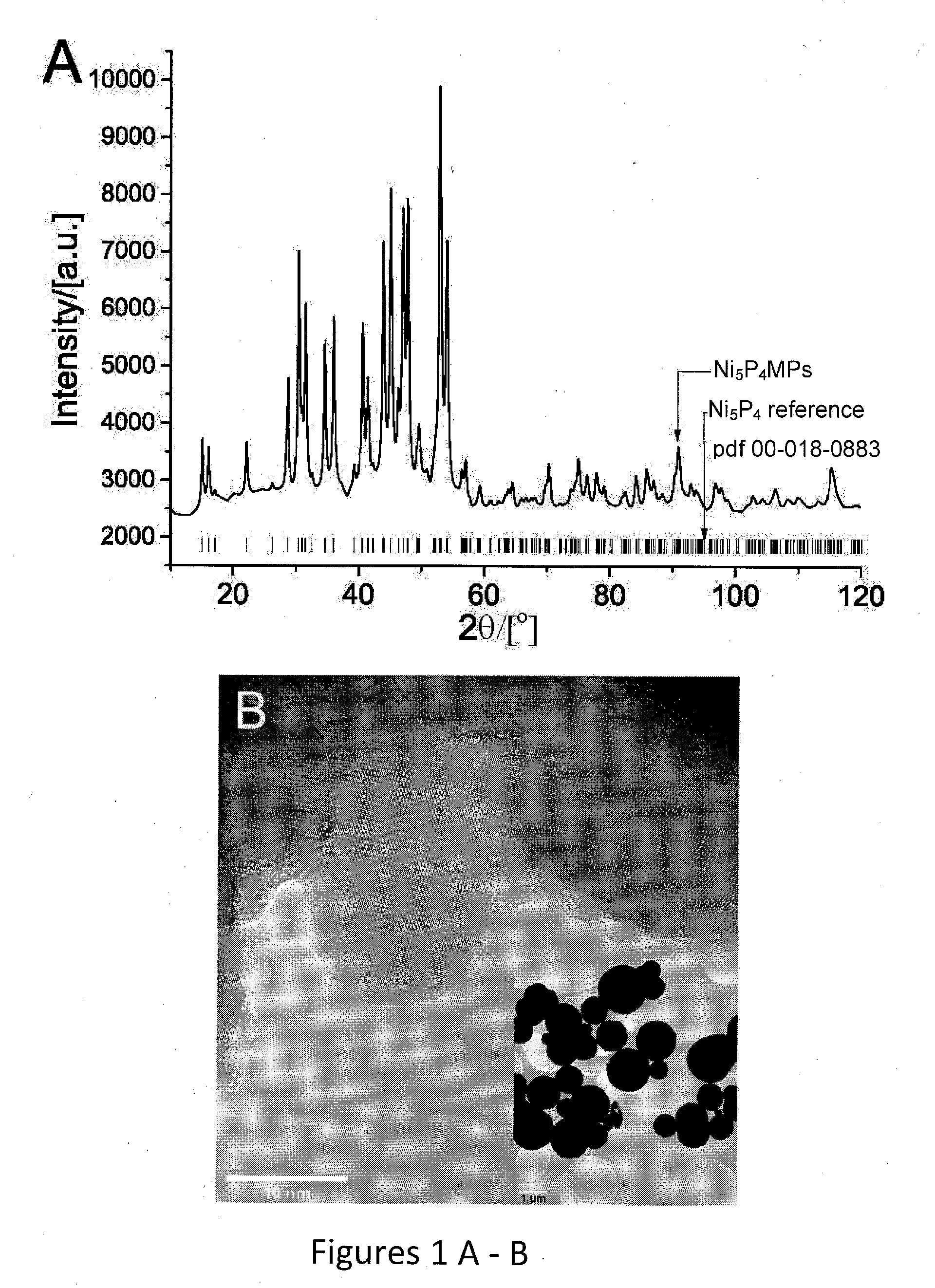
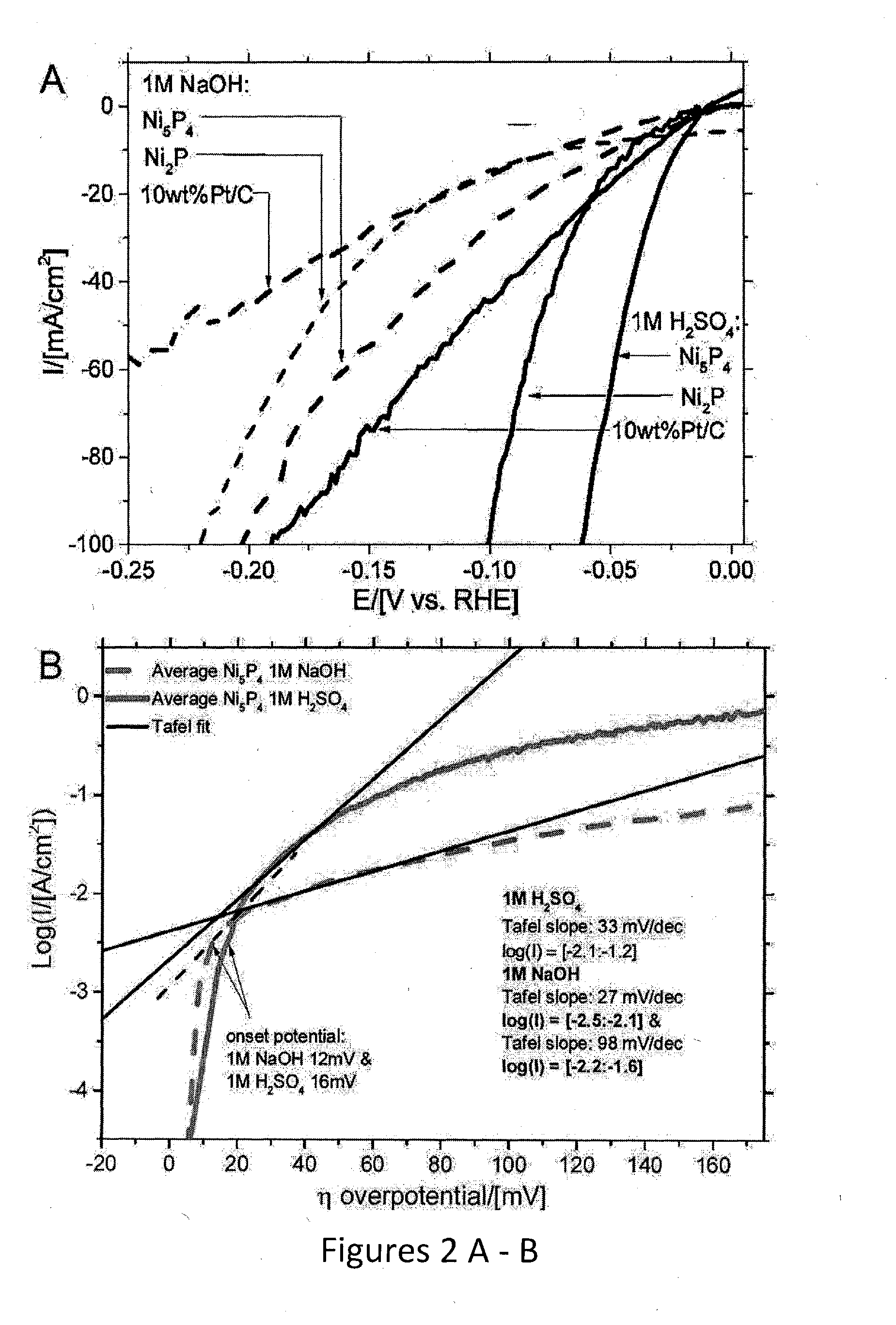
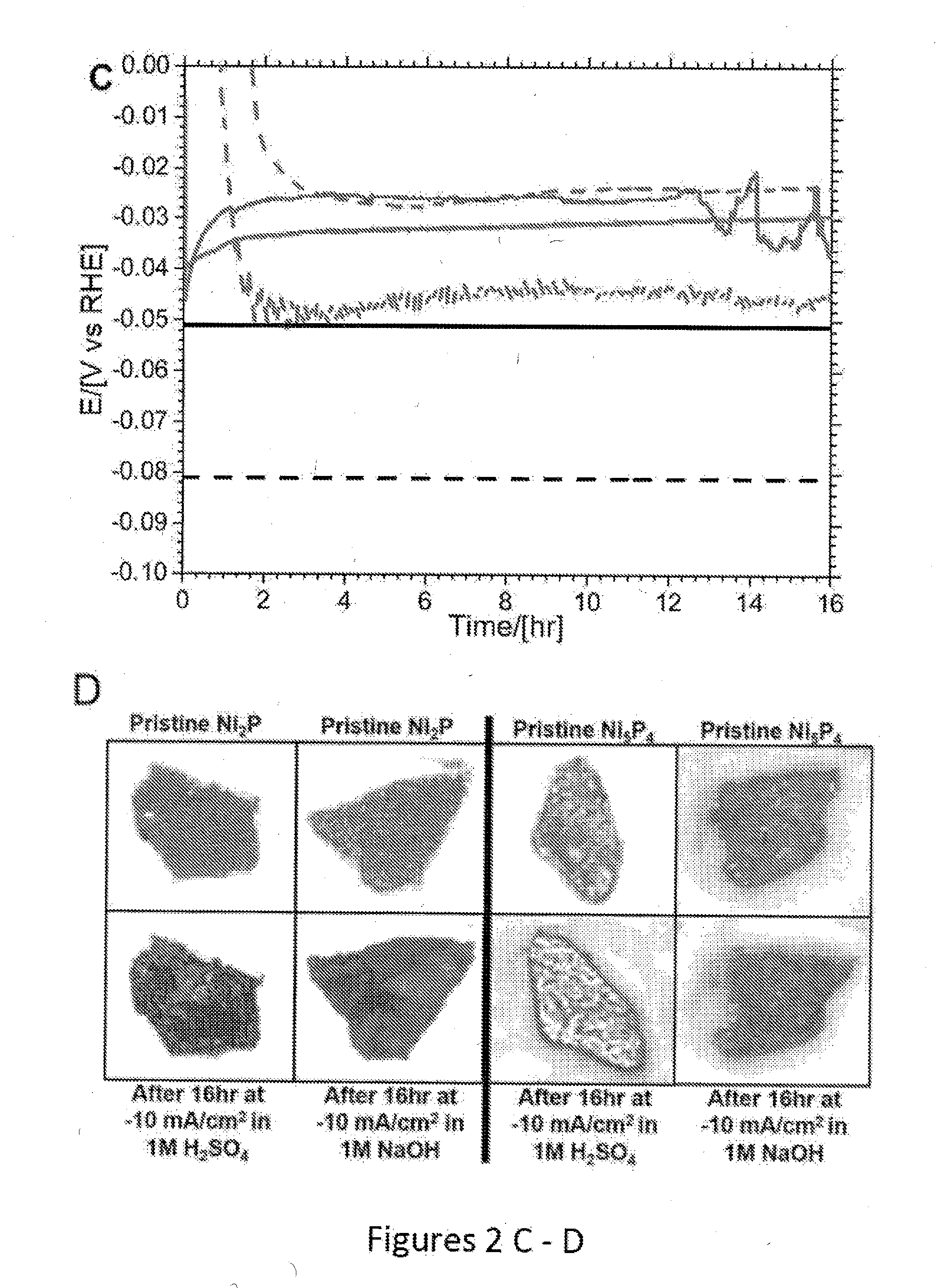
Nickel phosphides electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution and oxidation reactions
ActiveUS20160355936A1CellsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsElectricityElectrolysis
Disclosed are cathodes comprising a conductive support substrate having a catalyst coating including Ni5P4 nanocrystals. The conductive support substrate is capable of incorporating a material to be reduced, such as water or hydrogen cations. Also disclosed are methods for generating hydrogen gas from water via an electrolysis reaction or from the reduction of hydrogen cations, wherein the catalyst is part of a conductive support within a cathode, including (a) placing an anode and the inventive cathode in an electrolyte, (b) placing the anode and cathode in conductive contact with an external source of electricity, (c) providing a source of water to the cathode, and (d) using the external source of electricity to drive an electrolysis reaction at the cathode, whereby the hydrogen gas is generated from water. In certain embodiments, the reaction uses a free catalyst, wherein the catalyst is placed in proximity to the cathode.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Semiconductor photoelectrode and method for splitting water photoelectrochemically using photoelectrochemical cell comprising the same
InactiveUS20150083605A1Improve quantum efficiencyImprove power generation efficiencyCellsPhysical/chemical process catalystsPhotoelectrochemical cellSemiconductor
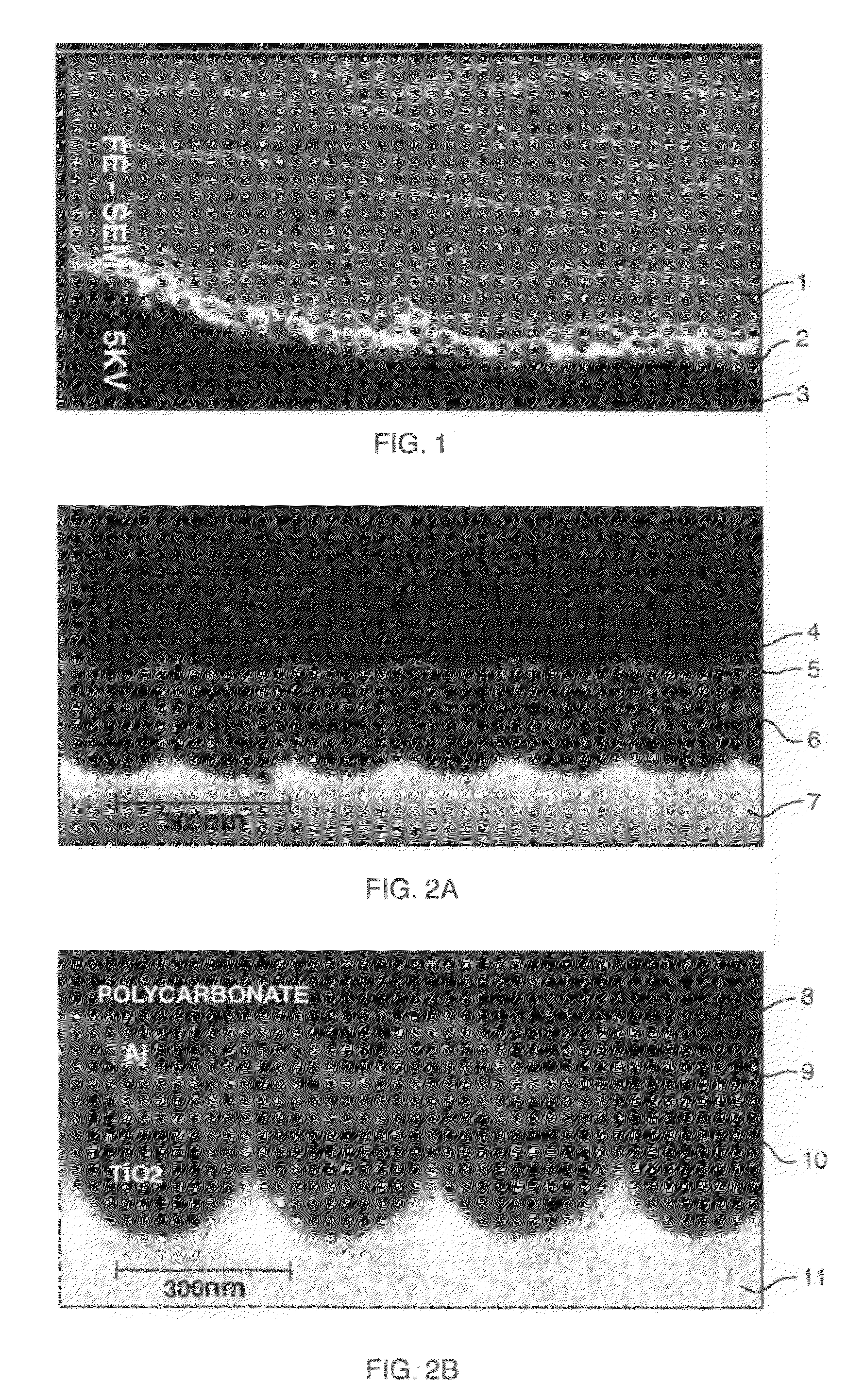
Provided is a semiconductor photoelectrode comprising a conductive substrate; a first semiconductor photocatalyst layer provided on a surface of the conductive substrate; a second semiconductor photocatalyst layer provided on a surface of the first semiconductor photocatalyst layer. The semiconductor photoelectrode has a plurality of pillar protrusions on the surface thereof. A surface of each of the pillar protrusions is formed of the second semiconductor photocatalyst layer.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Anode catalyst suitable for use in an electrolyzer
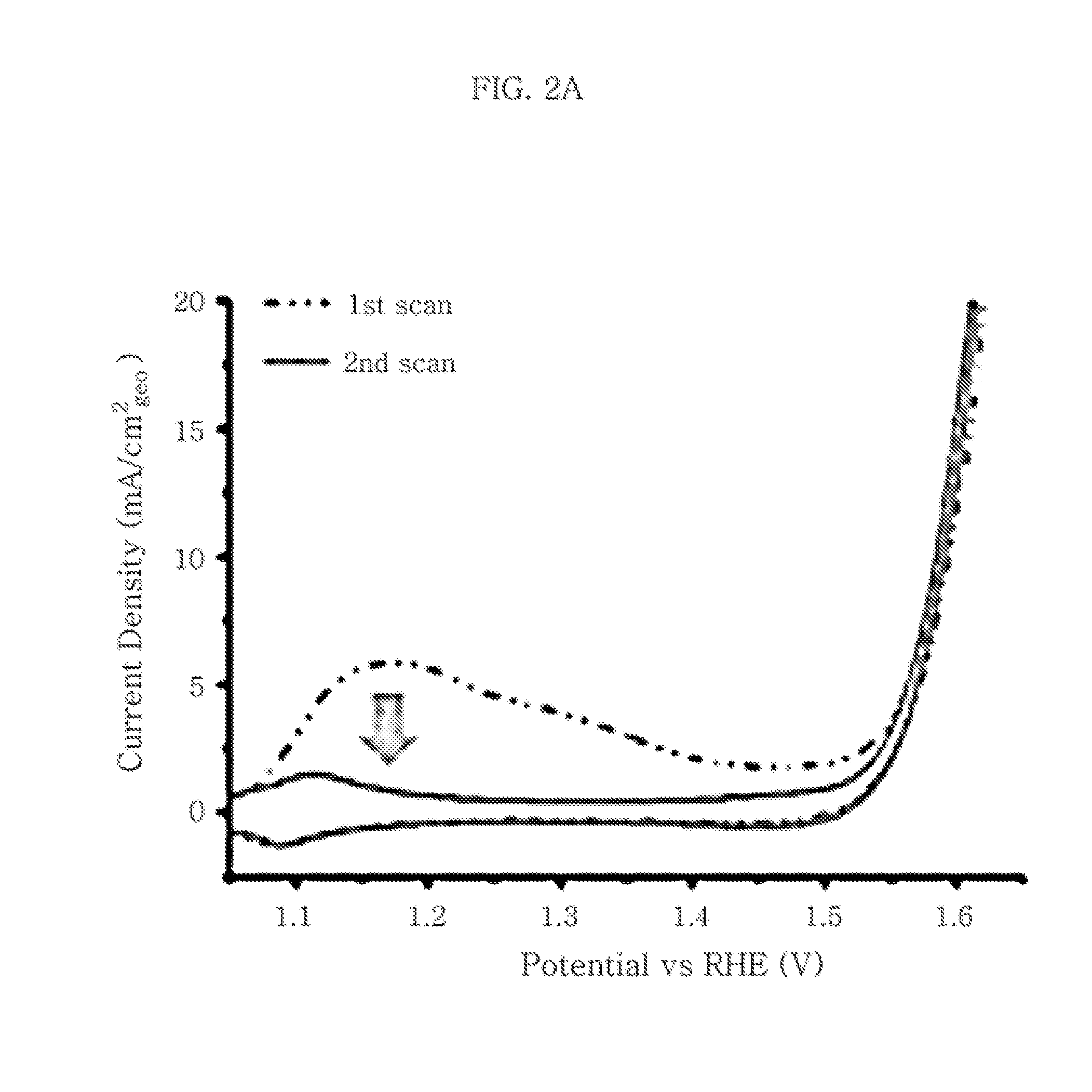
An anode catalyst suitable for use in an electrolyzer. The anode catalyst includes a support and a plurality of catalyst particles disposed on the support. The support may include a plurality of metal oxide or doped metal oxide particles. The catalyst particles, which may be iridium, iridium oxide, ruthenium, ruthenium oxide, platinum, and / or platinum black particles, may be arranged to form one or more aggregations of catalyst particles on the support. Each of the aggregations of catalyst particles may include at least 10 particles, wherein each of the at least 10 particles is in physical contact with at least one other particle. The support particles and their associated catalyst particles may be dispersed in a binder.
Owner:PLUG POWER
Titanium base material, method for producing titanium base material, electrode for water electrolysis, and water electrolysis device
PendingUS20200407858A1Improve conductivityImprove corrosion resistanceCell electrodesMultiple component coatingsElectrolysisTitanium
This titanium base material has a base material body formed of titanium or a titanium alloy, in which a Magneli phase titanium oxide film formed of a Magneli phase titanium oxide represented by a chemical formula TinO2n-1 (4≤n≤10) is formed on a surface of the base material body. Here, the Magneli phase titanium oxide film preferably contains at least one or both of Ti4O7 and Ti5O9.
Owner:MITSUBISHI MATERIALS CORP
Anode for alkaline water electrolysis
InactiveUS20160237578A1Maintain crystal structureCorrosion resistanceMultiple component coatingsEnergy inputLithiumAlloy
An anode for alkaline water electrolysis includes a conductive substrate having at least a surface made of nickel or a nickel-base alloy and a lithium-containing nickel oxide catalytic layer formed on a surface of the substrate. The molar ratio (Li / Ni) of lithium and nickel in the catalytic layer is in the range of 0.005 to 0.15.
Owner:NAT UNIV CORP YOKOHAMA NAT UNIV +2
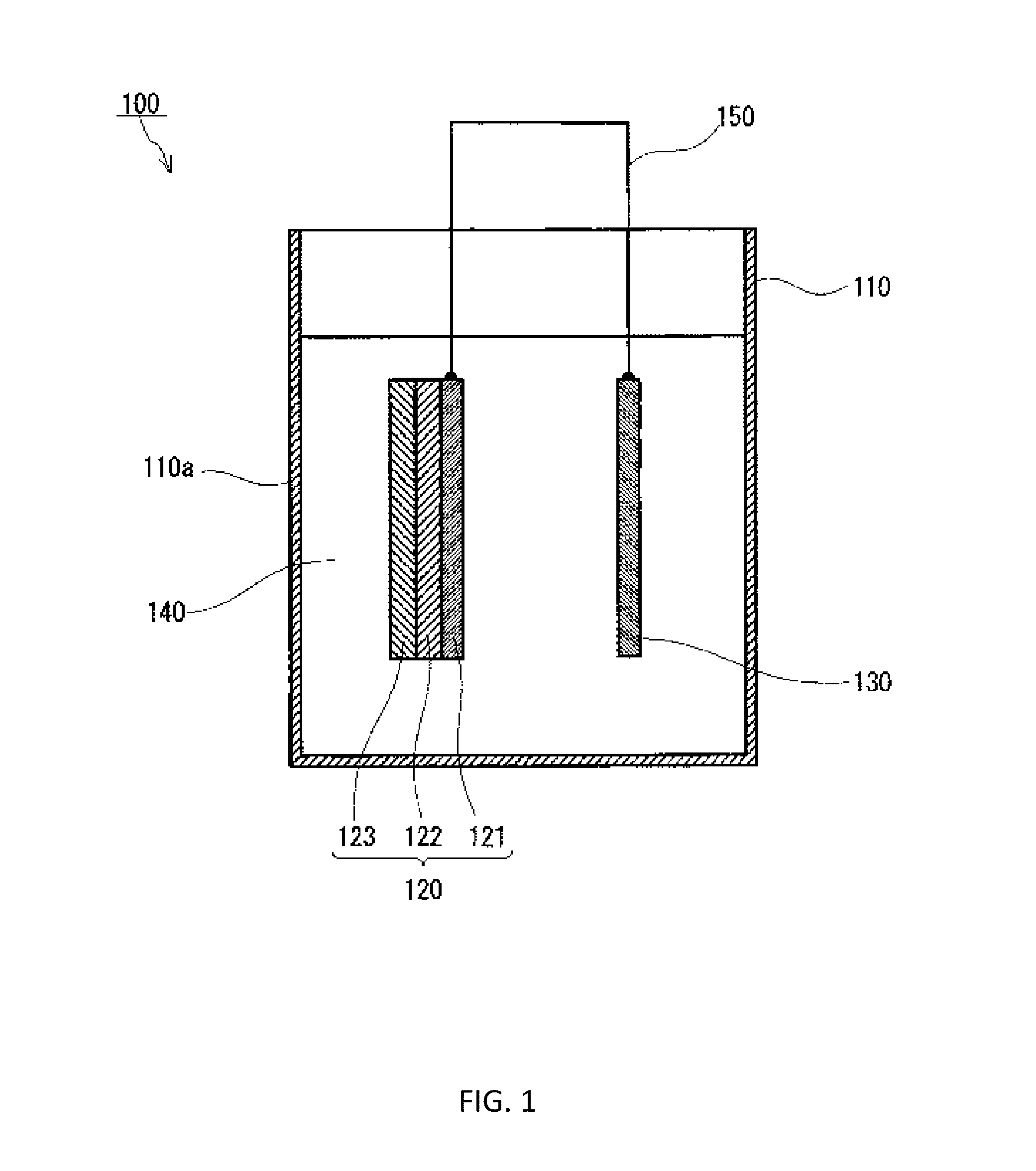
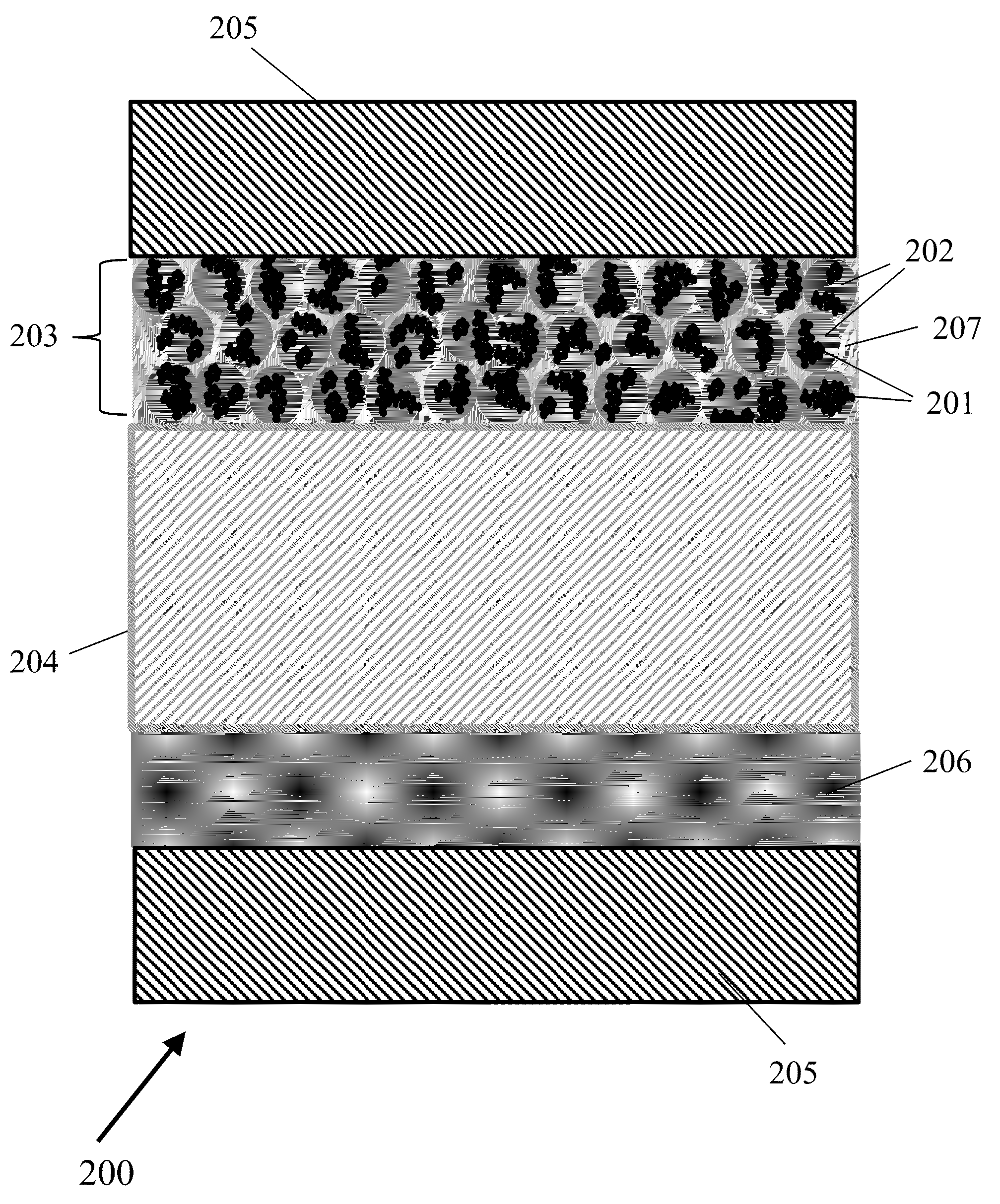
Electrochemical Device Comprising Thin Porous Metal Sheet
ActiveUS20190376193A1Improve electronic conductivityElectrolytic capacitorsCell electrodesCeramic coatingElectrochemistry
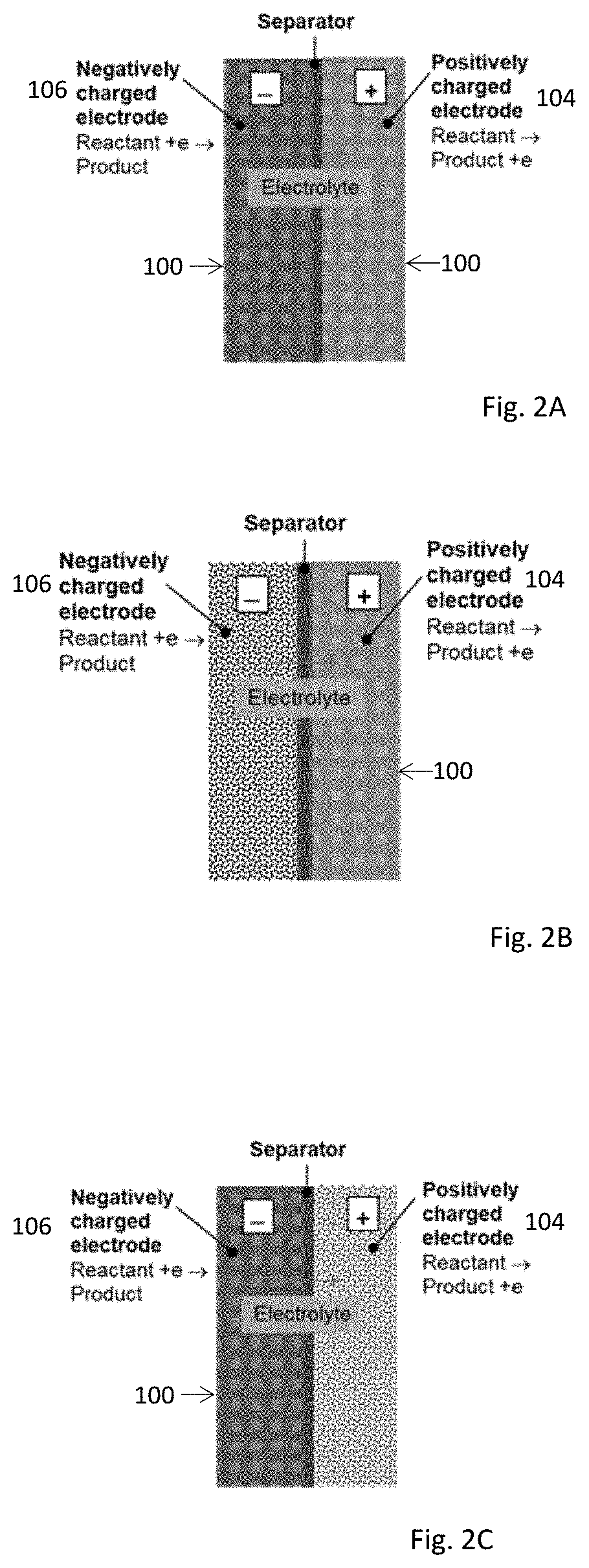
Electrochemical device using thin micro-porous metal sheets. The porous metal sheet may have a thickness less than 200 μm, provides three-dimensional networked pore structures of pore sizes in the range of 2.0 nm to 5.0 μm, and is electrically conductive. The micro-porous metal sheet is used for positively and / or negatively-charged electrodes by providing large specific contact surface area of reactants / electron. Nano-sized catalyst or features can be added inside pores of the porous metal sheet of pore sizes at sub- and micrometer scale to enhance the reaction activity and capacity. Micro-porous ceramic materials may be coated on the porous metal sheet at a thickness of less than 40 μm to enhance the functionality of the porous metal sheet. The ceramic coating layer of non-electrical conductivity can function as a membrane separator. The electrochemical device may be used for decomposing molecules and for synthesis of molecules such as synthesis of ammonia from water and nitrogen molecules.
Owner:MOLECULE WORKS INC
Electrode for electrolysis and method of manufacturing electrode for electrolysis
InactiveCN1920101AEfficient formationGenerate efficientlyWater/sewage treatmentElectrode with substrate and coatingSurface layerElectrolysis of water
The present invention provides an electrode for electrolysis capable of efficiently producing ozone water by electrolysis of water at a low current density. The electrode (1) for electrolysis of the present invention is composed of a substrate (2), a surface layer (4) formed on the surface of the substrate (2) and containing a dielectric, and in the surface layer (4), formed from the surface layer The surface of (4) extends continuously to the inner hole (10), and the distance from the hole (10) to the closest part of the surface of the substrate (2) is set to be greater than 0 and not more than 2000 nm.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
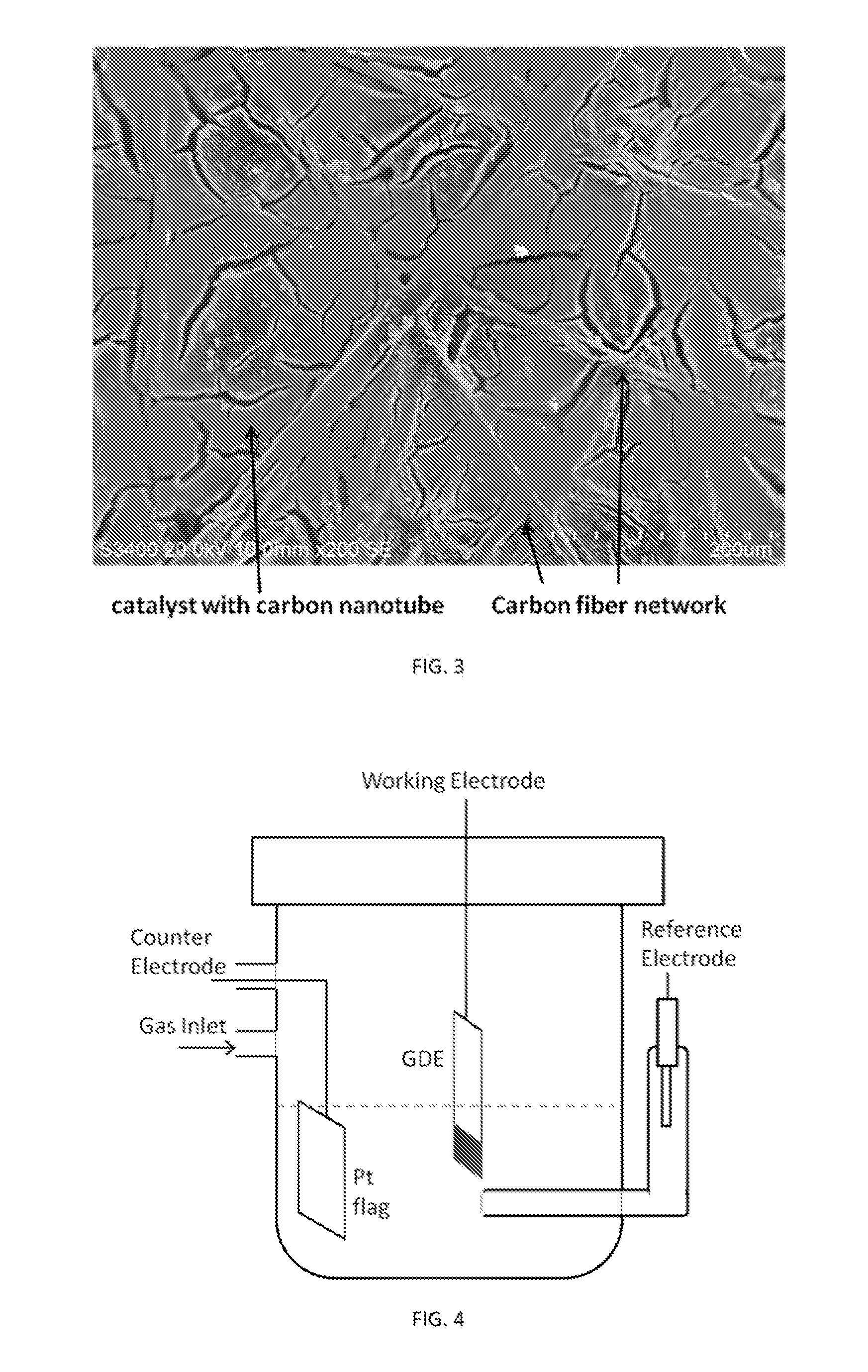
Gas Diffusion Electrodes and Methods for Fabricating and Testing Same
InactiveUS20150376803A1Improve performanceLow costCellsMachining electrodesDiffusion resistanceCurrent range
Highly effective, standalone gas-diffusion electrodes (GDEs) and the methods for their manufacture and test are disclosed, Nanocataiysis are directly bonded on a gas diffusion layer, so that the integrity of the catalyst layer holds without polymer electrolyte membrane, facilitating minimization of electronic, prottmtc, and diffusion resistances in the catalyst layer. The devised embodiments provide examples showing a facile hanging-strip method for testing the standalone GDEs in a solution electrochemical cell, which removes the mA-cm−2-scale mass transport limited currents on rotating disk electrodes to allow studies of reaction kinetics on single electrode over sufficiently wide current ranges (up to A cm−2) without mass transport limitation. Ultralow-Pi-content GDEs are fabricated as the cathode for hydrogen evolution in water eiectrolyzers and as the anode for hydrogen oxidation in hydrogen fuel cells. High performance GDEs with low loadings of platinum group metals are being developed for oxygen evolution reaction at the anode of water electrolyzers and for the oxygen reduction reaction at the cathode of fuel cells.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
Electrolytic electrode and process of producing the same
An electrolytic electrode having an interlayer having more excellent peeling resistance and corrosion resistance and longer electrolytic life than conventional electrolytic electrodes and capable of flowing a large amount of current at the industrial level and a process of producing the same are provided. The electrolytic electrode includes a valve metal or valve metal alloy electrode substrate on the surface of which is formed a high-temperature oxidation film by oxidation, and which is coated with an electrode catalyst. The high-temperature oxidation film is integrated with the electrode substrate, whereby peeling resistance is enhanced. Further, by heating the high-temperature oxidation film together with the electrode catalyst, non-electron conductivity of the interlayer is modified, thereby making it possible to flow a large amount of current.
Owner:DE NORA PERMELEC LTD
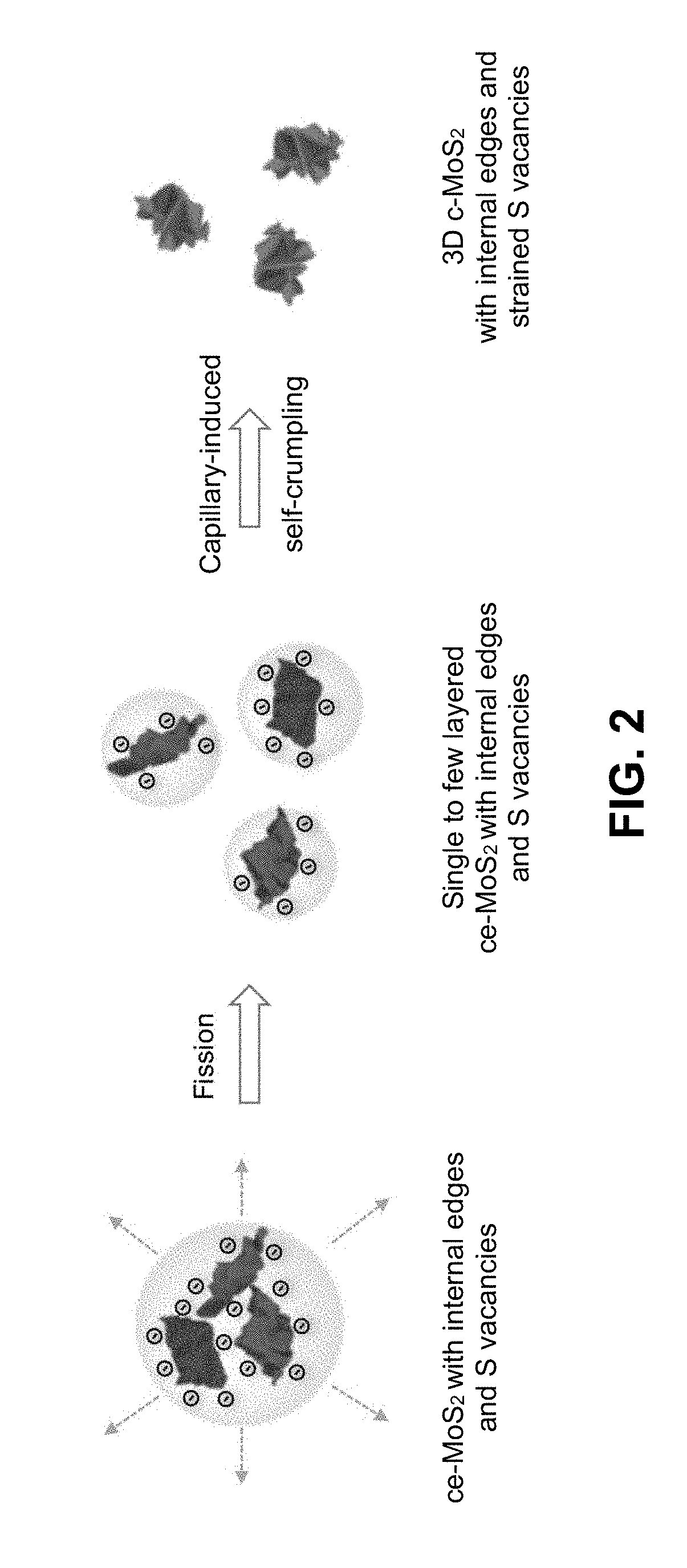
Crumpled Transition Metal Dichalcogenide Sheets
InactiveUS20190003064A1Improve throughputEfficient integrationElectrode with substrate and coatingElectrode coatingsVolumetric shrinkageEngineering
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Fuels for Fuel Cells
A hydrogen generation system comprising a solid fuel that reacts with an aqueous liquid to generate hydrogen is disclosed. The solid fuel comprises first metallic particles coated by smaller second metallic particles, such that multiple galvanic cells are formed on a surface of the first metallic particles between the metals in the first metallic particles and the second metallic particles. The first metallic particles can be further covered by smaller third particles. An example of the solid fuel is hybrid particles formed by larger magnesium particles coated by smaller iron and silicon particles. The solid fuel may also include salt such as sodium chloride and / or a fire retardant such as potassium chloride. The salt may be added to the aqueous liquid instead. The solid fuel can be formed into fuel pellets, or can be suspended in a suspension agent to form slurries or gels.
Owner:INTELLIGENT ENERGY LTD
Apparatus and method for manufacturing vitreous silica crucible
ActiveUS20120131954A1Good inner surface propertyImprove removal efficiencyPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltCrucibleMaterials science
There are provided an apparatus and a method for manufacturing a vitreous silica crucible which can prevent the deterioration of the inner surface property in the manufacturing process of a vitreous silica crucible. The apparatus includes a mold defining an outer shape of a vitreous silica crucible, and an arc discharge unit having electrodes and a power-supply unit, wherein each of the electrodes includes a tip end directed to the mold, the other end opposite to the tip end, and a bent portion provided between the tip end and the other end.
Owner:SUMCO CORP
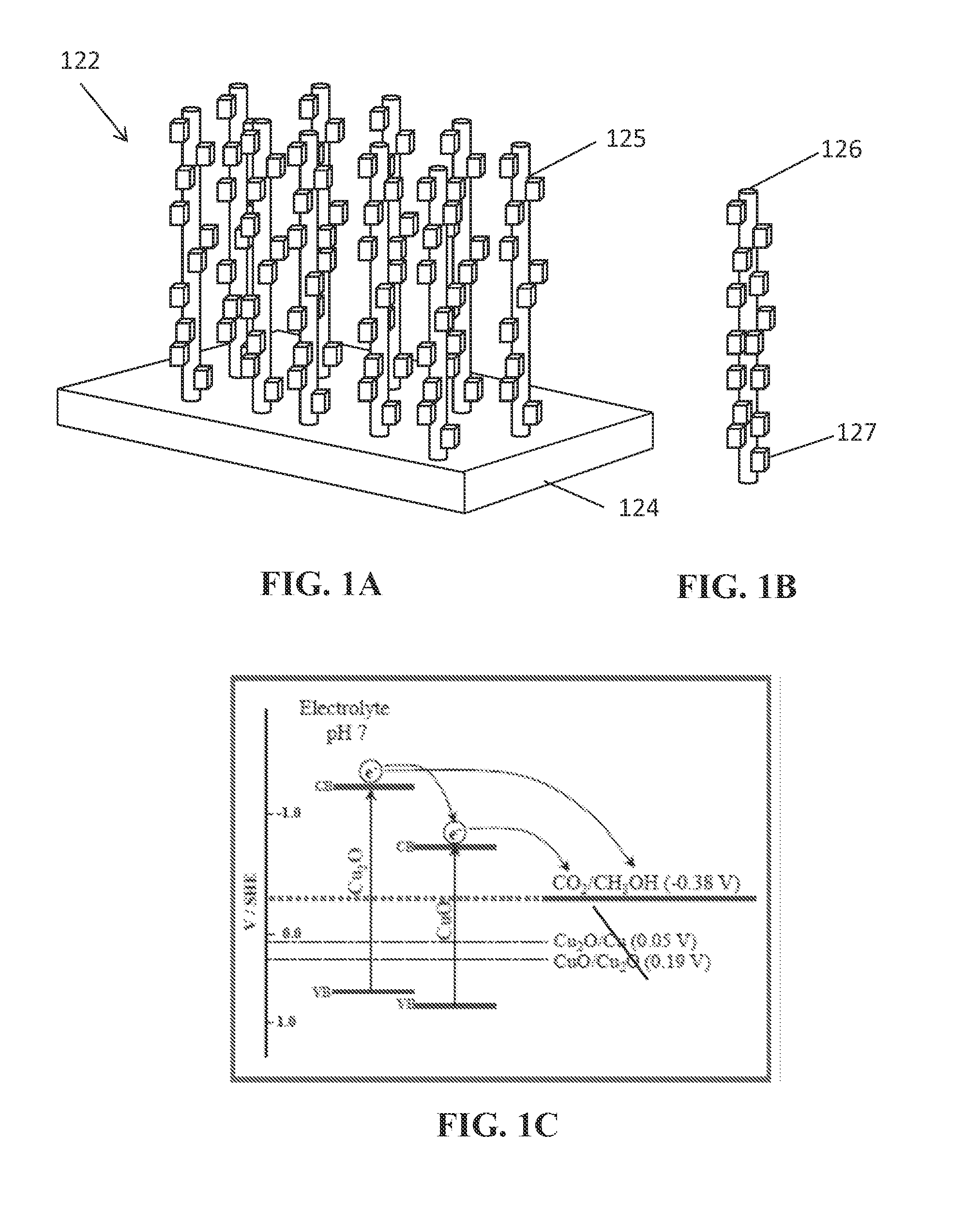
Photoelectrochemical devices, methods, and systems with a cupric oxide/cuprous oxide coated electrode
The present disclosure relates to nanocomposites of CuO / Cu2O and continuous flow solar reactors. The nanocomposites can be utilized as a photocatalyst and can be incorporated into photoelectrochemical devices. The described devices, systems, and methods can be used for converting CO2 into one or more alcohols and other small organics with the use of solar energy and electricity. Other embodiments are described.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com