Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
477 results about "Reference mirror" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
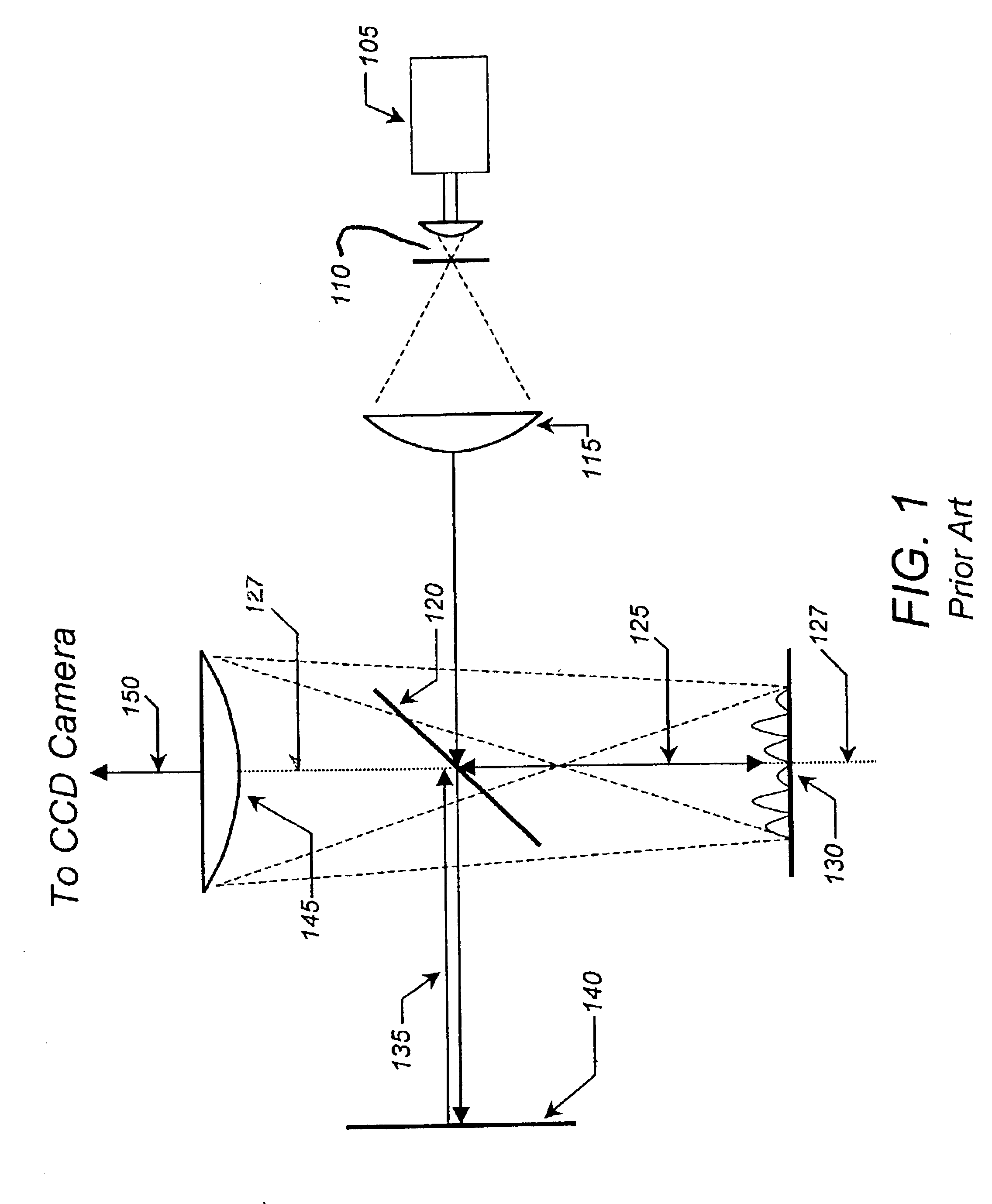
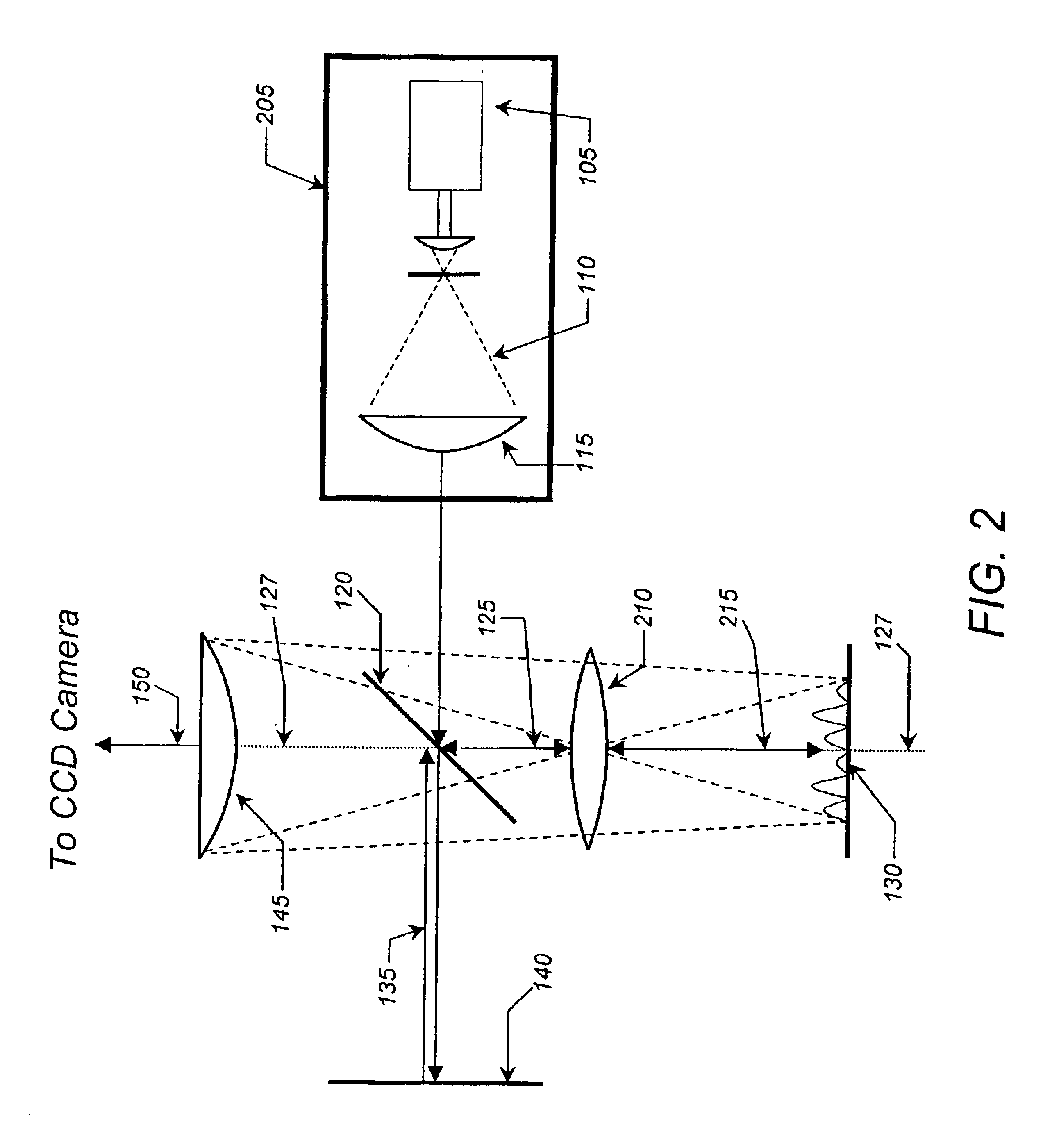
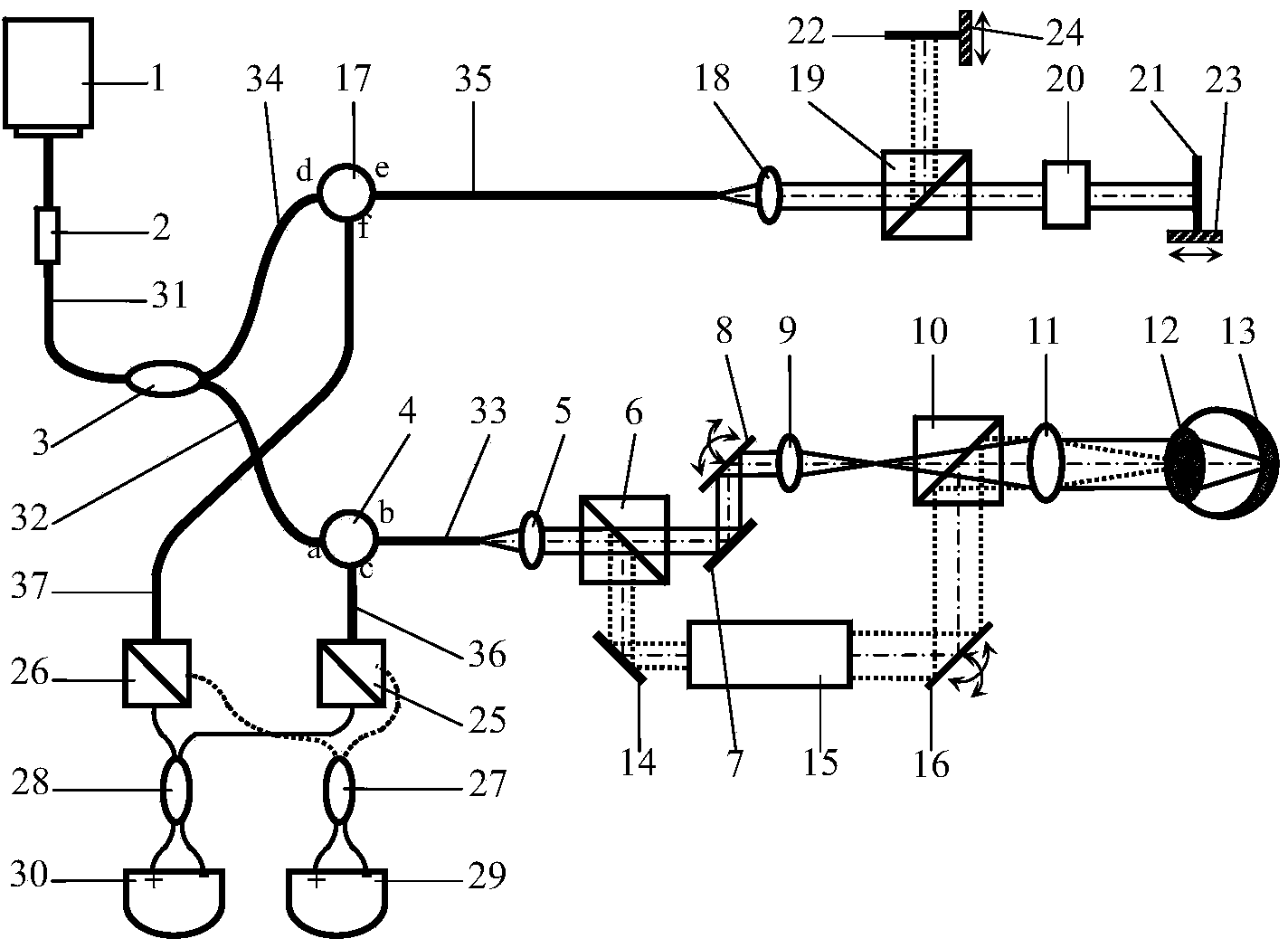
Method of characterising the transmission losses of an optical system
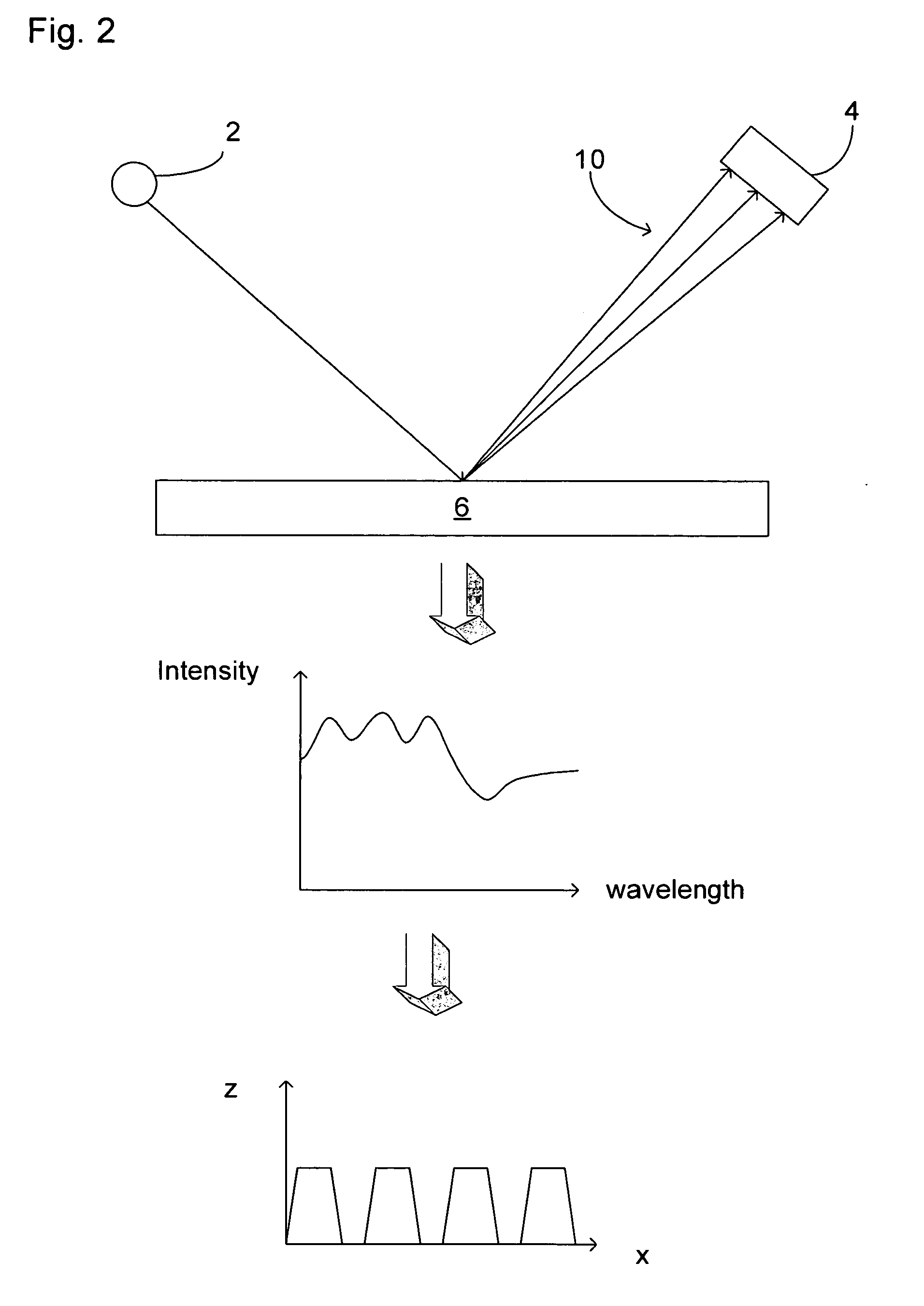
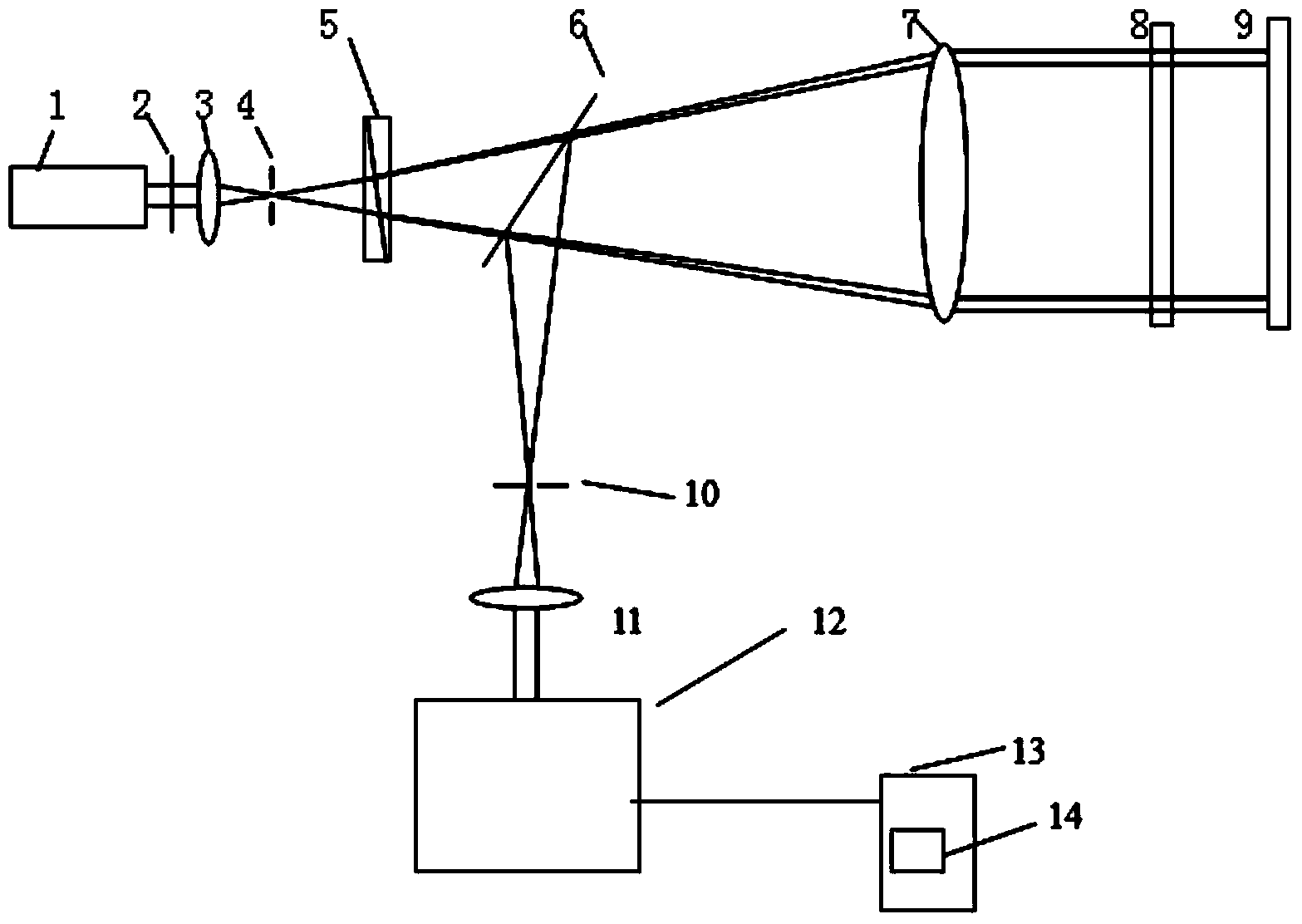
ActiveUS20070296960A1Minimize impactPhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTransmission lossOptic system
The illumination profile of a radiation beam is initially measured using a CCD detector. A reference mirror is then placed in the focal plane of the high aperture lens and the reflected radiation measured. By comparing the illumination profile and the detected radiation it is possible to determine the transmission losses for S and P polarisation which can then be used in scatterometry modeling.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Embedded interferometer for reference-mirror calibration of interferometric microscope
InactiveUS6545761B1Implemented easily and economicallyAccurately determineInterferometersUsing optical meansClosed loopOptoelectronics
A laser interferometer is embedded into an interference microscope to precisely determine the in-focus position of the microscope objective's reference mirror. A collimated laser beam is introduced into the microscope system and split into two beams directed toward a calibration reference surface and the interference objective. The light reflected from the calibration reference surface is returned to the camera. The light into the interference objective is focused onto the reference mirror and returned to the camera. For the purpose of calibration, the two beams are combined at the camera to produce interference fringes. When the reference mirror is in focus, the returned beam is collimated; if the mirror is on either side of focus, the beam is either converging or diverging. Accordingly, the interferogram produced at the camera reflects the in-focus or out-of-focus condition of the reference mirror. The curvature of the wavefront returned from the reference mirror is determined electronically by analyzing the interference fringes produced with the beam returned from the calibration reference surface. By minimizing the curvature of the reference-mirror wavefront as the mirror is translated along the optical path, the reference mirror can be focused with an accuracy greater than possible by visual observation. Furthermore, by automating the focusing system with a precise translation mechanism driven by closed-loop control, operator-to-operator variations are completely eliminated.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
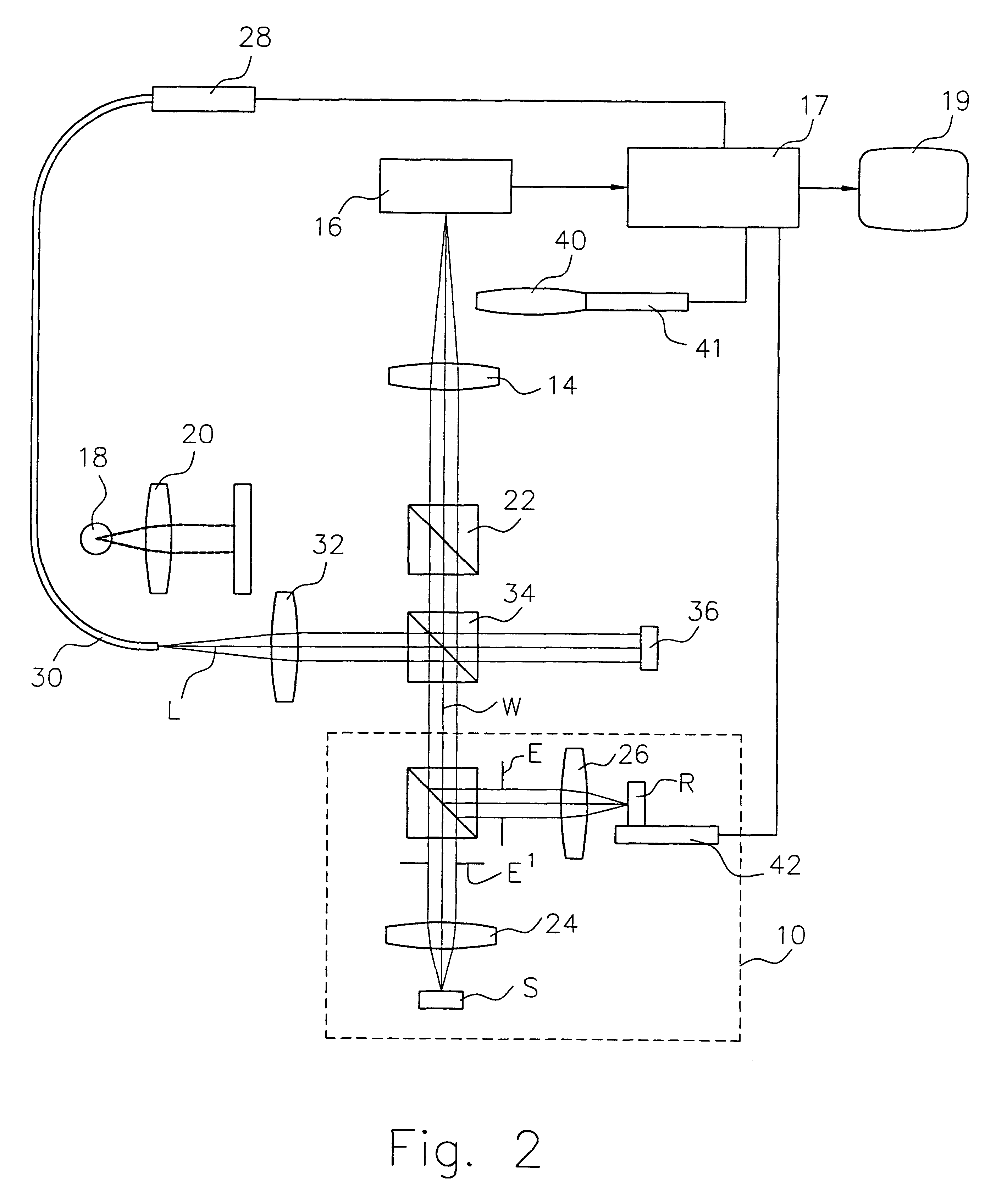
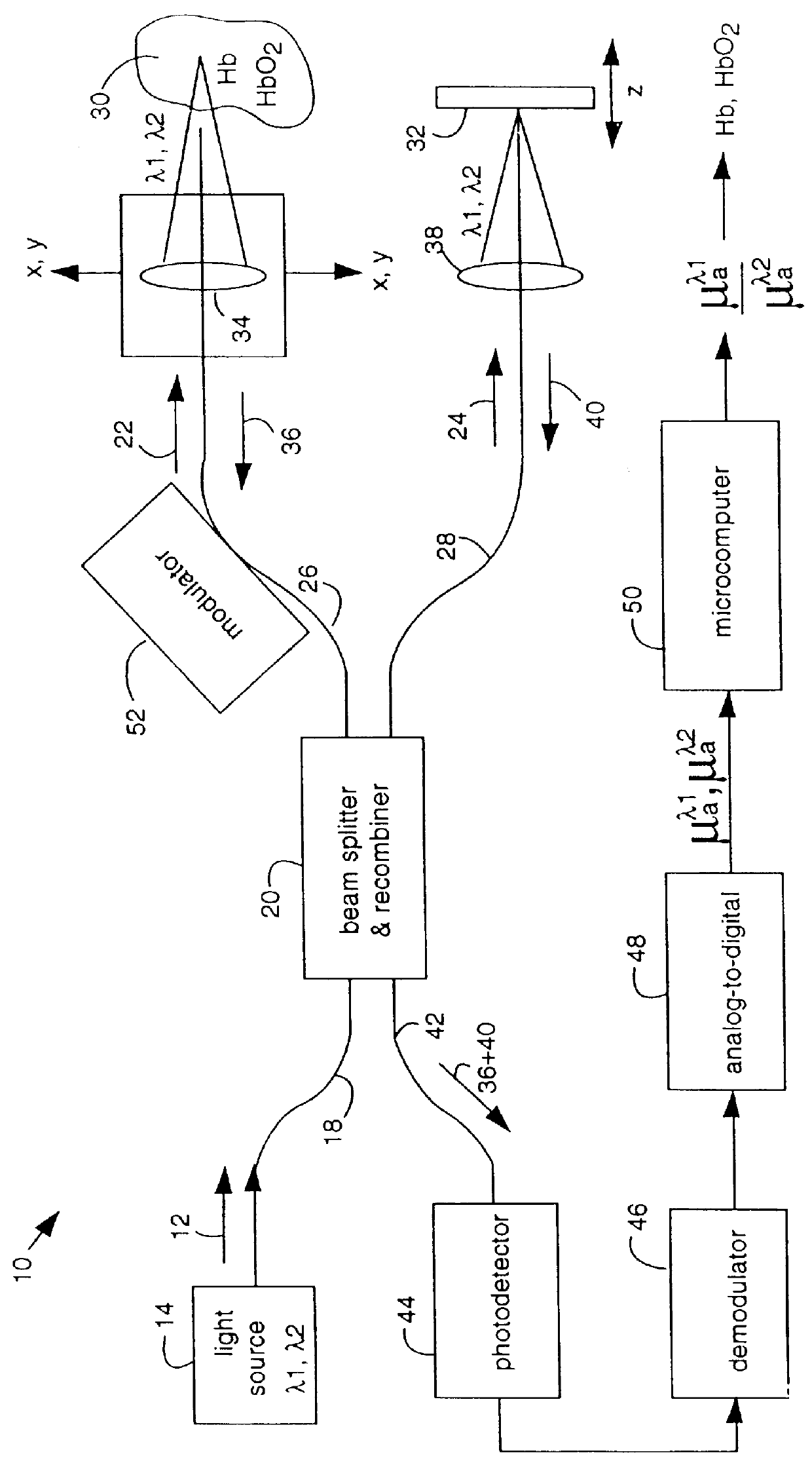
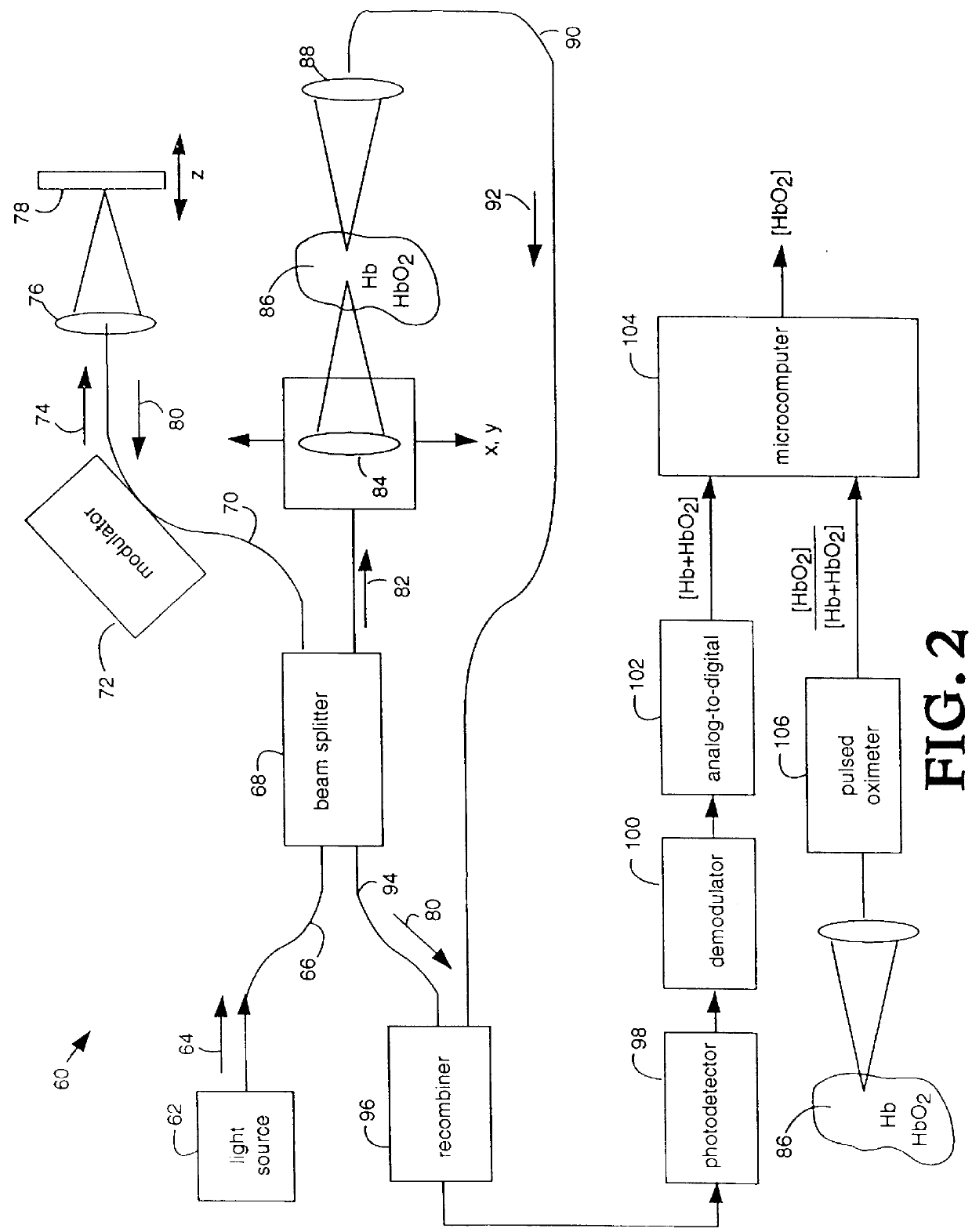
Multiple-wavelength spectroscopic quantitation of light-absorbing species in scattering media
InactiveUS6015969ASimplified determinationRadiation pyrometryPhotoelectric discharge tubesFiberMultiwavelength spectroscopy
An oxygen concentration measurement system for blood hemoglobin comprises a multiple-wavelength low-coherence optical light source that is coupled by single mode fibers through a splitter and combiner and focused on both a target tissue sample and a reference mirror. Reflections from both the reference mirror and from the depths of the target tissue sample are carried back and mixed to produce interference fringes in the splitter and combiner. The reference mirror is set such that the distance traversed in the reference path is the same as the distance traversed into and back from the target tissue sample at some depth in the sample that will provide light attenuation information that is dependent on the oxygen in blood hemoglobin in the target tissue sample. Two wavelengths of light are used to obtain concentrations. The method can be used to measure total hemoglobin concentration [Hb.sub.deoxy +Hb.sub.oxy ] or total blood volume in tissue and in conjunction with oxygen saturation measurements from pulse oximetry can be used to absolutely quantify oxyhemoglobin [HbO.sub.2 ] in tissue. The apparatus and method provide a general means for absolute quantitation of an absorber dispersed in a highly scattering medium.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
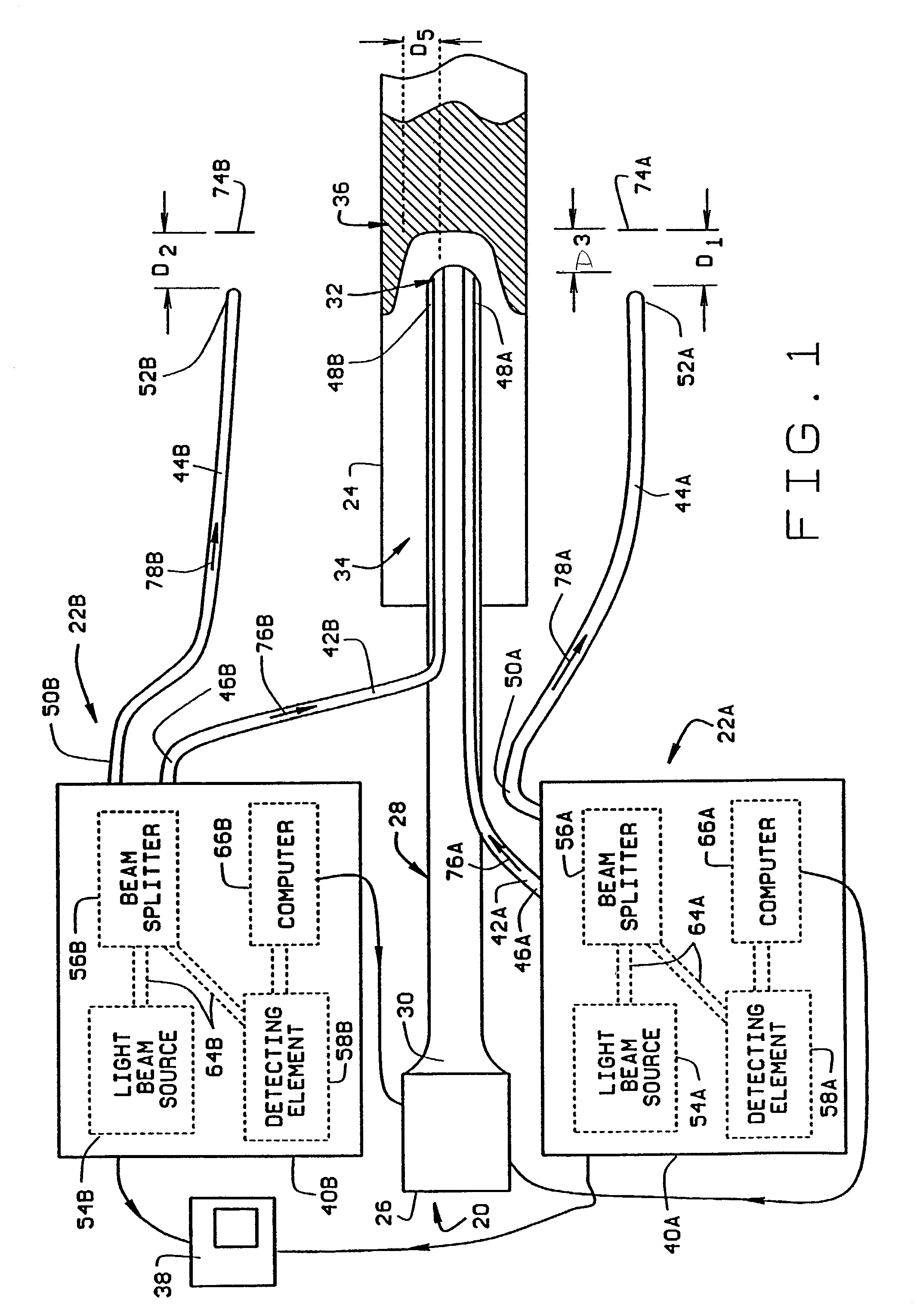
Method for guiding a medical instrument through a body
InactiveUS6970732B2Accurate imagingEasy to implementUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsEndoscopesFiberGuidance system
Guidance systems for guiding a catheter through tissue within a body are described. In one form, the system is implemented in connection with a catheter which includes a catheter body having a optic fibers extending between a first end and a second end thereof. The guidance system is coupled to the catheter body and includes a first optic fiber, a second optic fiber, and a detecting element. The first optic fiber includes a first end and a second end, and is coupled to the catheter body so that the first optic fiber second end is adjacent the catheter second end. The second optic fiber also includes a first end and a second end, and a reference mirror is positioned adjacent the second optic fiber second end. The first optic fiber first end is communicatively coupled to the detecting element and the second optic fiber first end is communicatively coupled to the detecting element. The detecting element is configured to determine interference between a light beam propagating through the first optic fiber and a light beam propagating through the second optic fiber.
Owner:SPECTRANETICS
Method and apparatus using interferometric metrology for high aspect ratio inspection
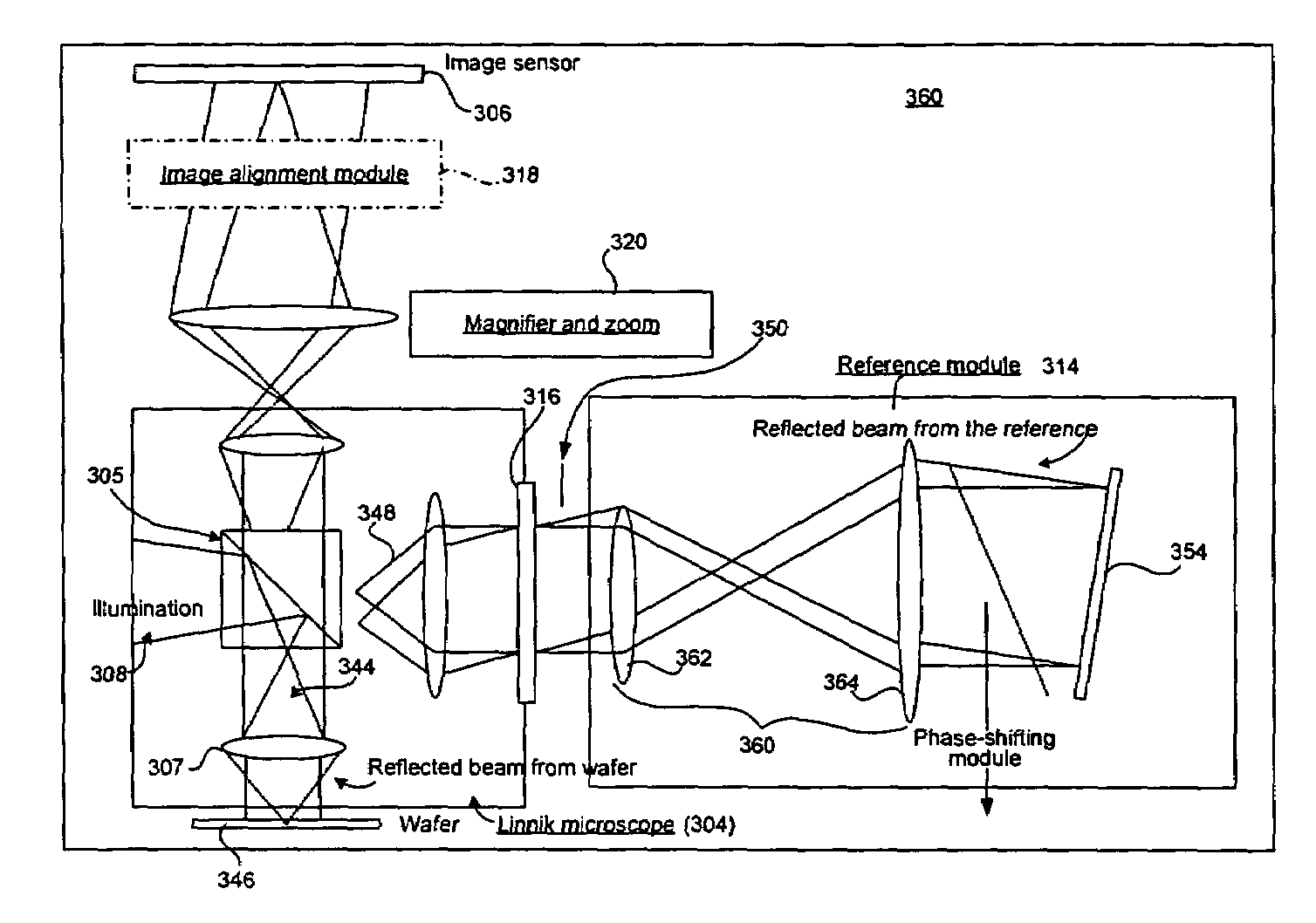
ActiveUS7061625B1Easy alignmentMaterial analysis by optical meansUsing optical meansMetrologyOptical path
In one embodiment, the present invention provides an interferometric inspection system for inspecting semiconductor samples. The system includes at least one illumination source for generating an illumination beam and an interferometric microscope module for splitting the illumination beam into a test beam directed to the semiconductor sample and a reference beam directed to a tilted reference mirror. The beams are combined to generate an interference image at an image sensor. The tilted reference mirror is tilted at a non-normal angle with respect to the reference beam that is incident on the mirror to thereby generate fringes in the interference image. The system also includes an image sensor for acquiring the interference image from the interferometric microscope module and generates an inherence signal. The system further includes a processing module configured to generate complex field information corresponding to the sample from the interference image signal and an alignment module located in the optical path between the interferometric module and the image sensor. In another embodiment, the processing module is configured to generate complex field information from either spatial fringe analysis or temporal fringe analysis performed on the interference image signal.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
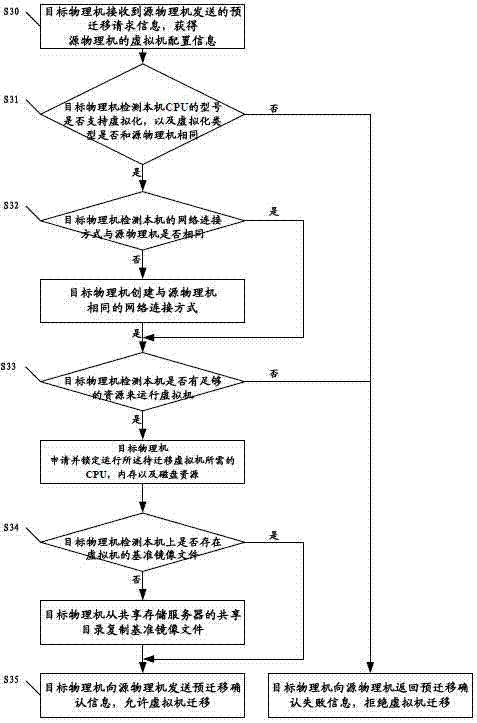
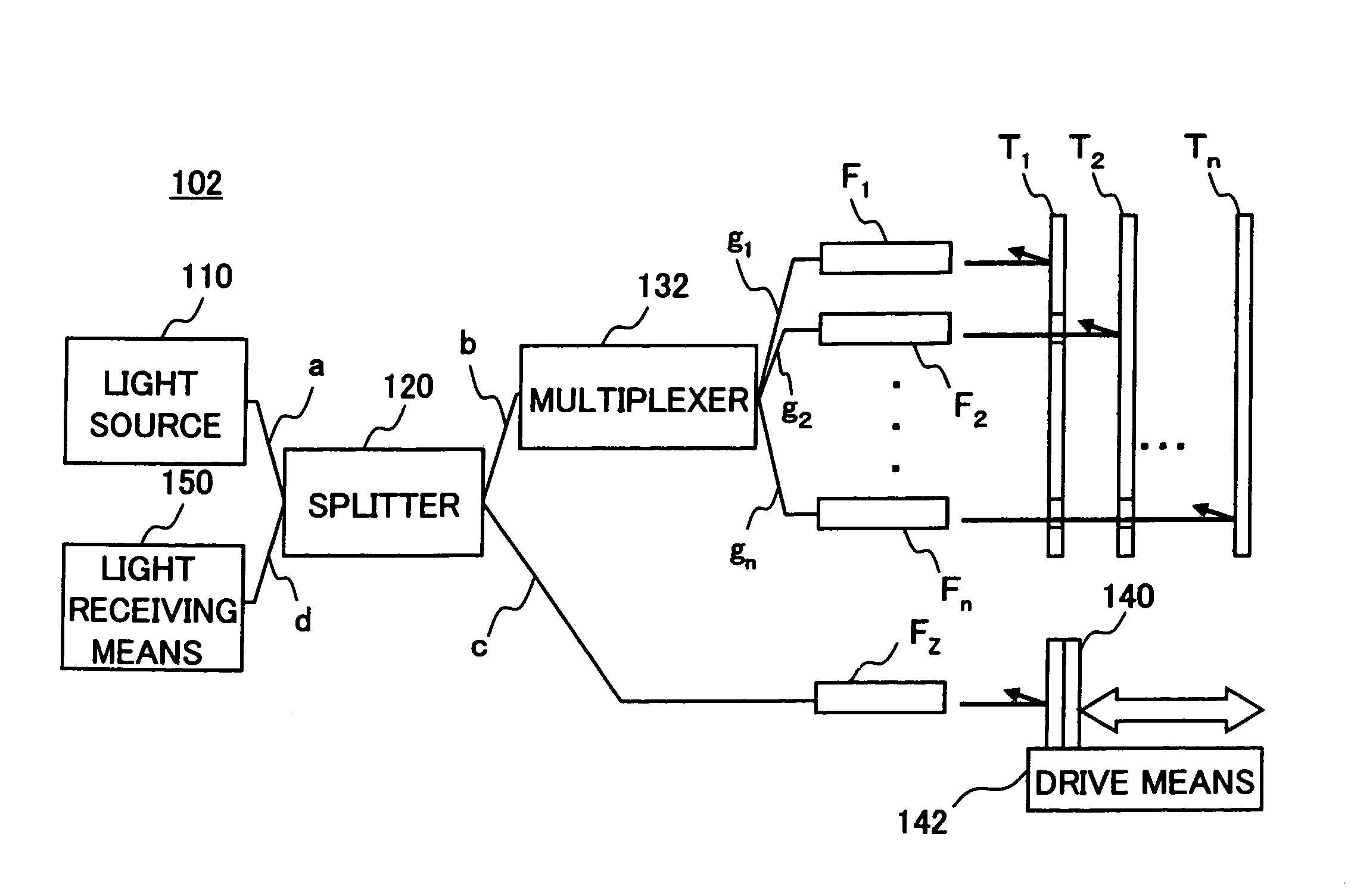
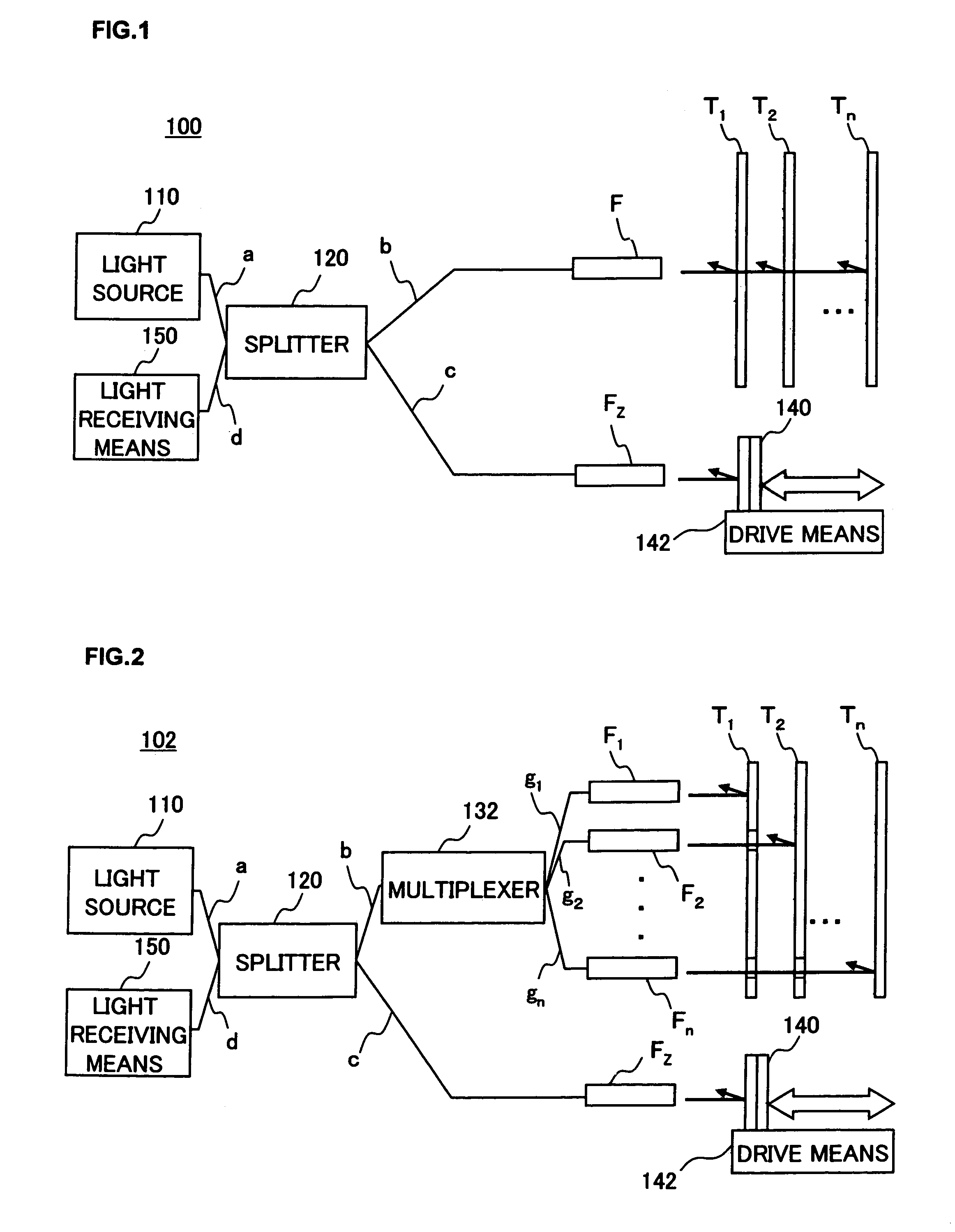
Method and cloud system for realizing virtual machine migration
ActiveCN102821158AUse will not affectIncrease success rateTransmissionSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationInternal memoryMirror image
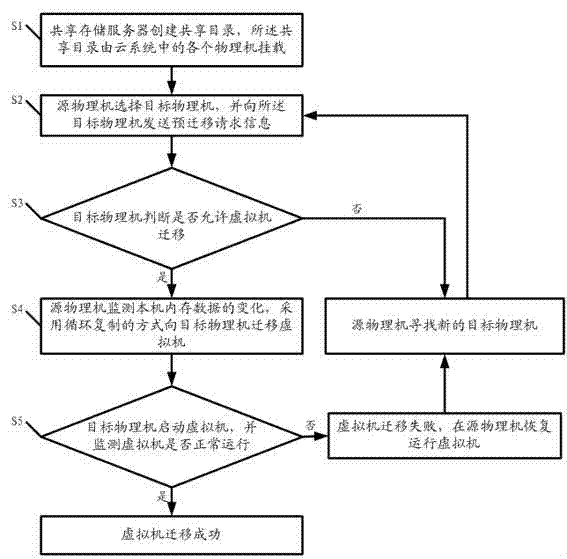
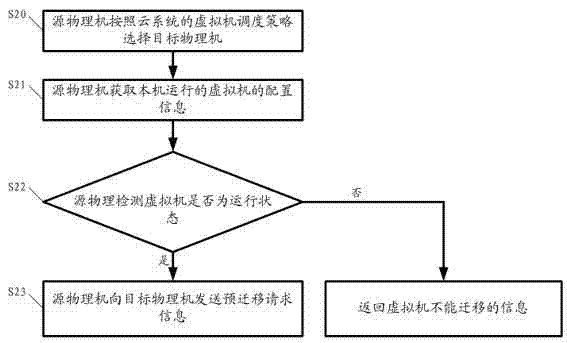
The invention discloses a method and a cloud system for realizing virtual machine migration. The method comprises the following steps that a sharing storage server creates a sharing content for storing a reference mirror image and an increment mirror image, a physical machine is adopted for mounting, and the physical machine copies the reference mirror image of a virtual machine to be migrated from the sharing content during the migration of the virtual machine; a source physical machine selects a target physical machine and sends pre-migration request information to the target physical machine; the target physical machine judges whether the virtual machine migration is allowed or not; when the target physical machine allows the virtual machine migration, the source physical machine monitors local internal memory data change, and a circulation copying mode is adopted for migrating the virtual machine to the target physical machine; the target physical machine starts the virtual machine and monitors whether the virtual machine normally operates or not; when the virtual machine normally operates, the virtual machine migration is successful, otherwise, the virtual machine migration is failed, and the operation of the virtual machine is recovered at the source physical machine. The embodiment of the invention has the advantages that the virtual machine migration process can be fast completed on the premise of not influencing the use of users, and in addition, the migration success rate is high.
Owner:GCI SCI & TECH
Fourier-Domain Oct Ray-Tracing On The Eye
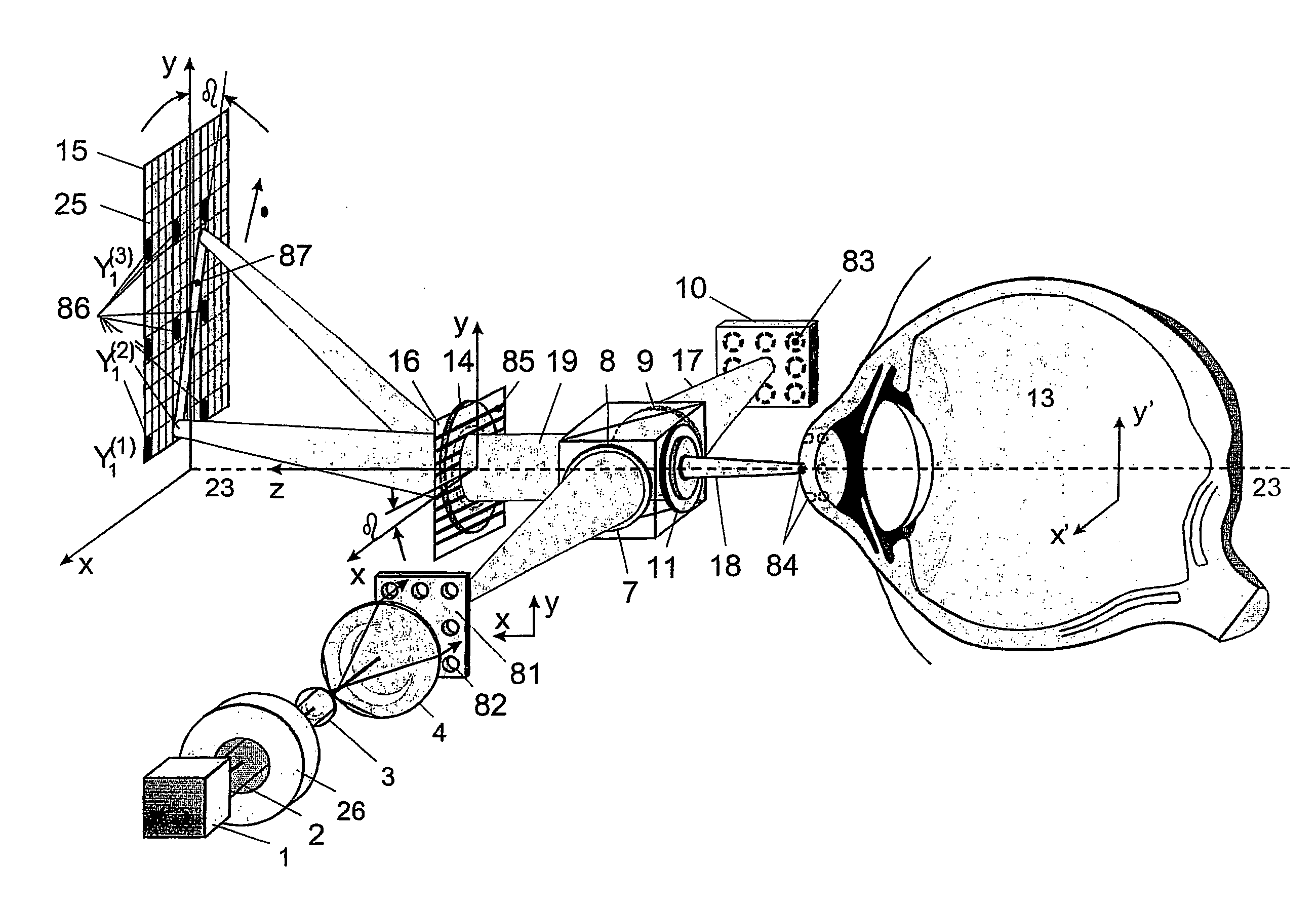
The present invention is directed to an ophthalmologic measurement method which can depict three-dimensional structures of the interfaces of an eye by short-coherence interferometry based on reference points. For this purpose, the pupil is illuminated at a plurality of points by a short-coherence illumination source. The measurement beam reflected at these points by the interfaces and surfaces of the eye is superimposed with a reference beam. The measurement data which are generated in this way are spectrally split by a diffraction grating, imaged on a two-dimensional detector array and conveyed to a control unit which determines a three-dimensional structure of all intraocular interfaces and surfaces of the eye. In the suggested Fourier domain OCT method, the depiction of three-dimensional structures is preferably carried out by spline surfaces or polygon surfaces. In doing so, it is possible to determine the depth positions of the measurement beams in many points of the pupil with a single recording of the array camera in that the pupils are illuminated by a diaphragm grid and the reference mirror contains a periodic phase grid.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Optical image measuring device, optical image measuring program, fundus observation device, and fundus observation program
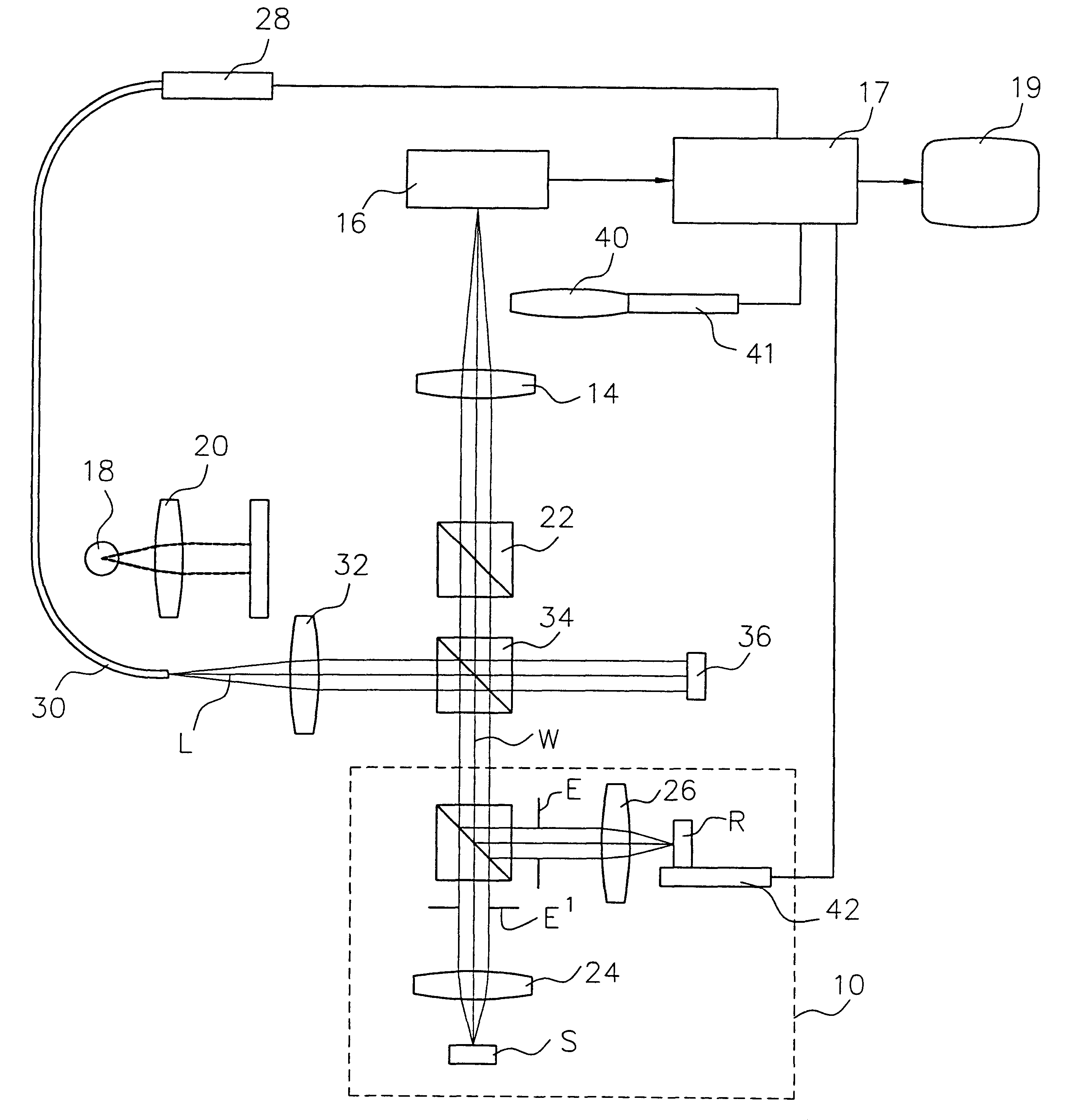
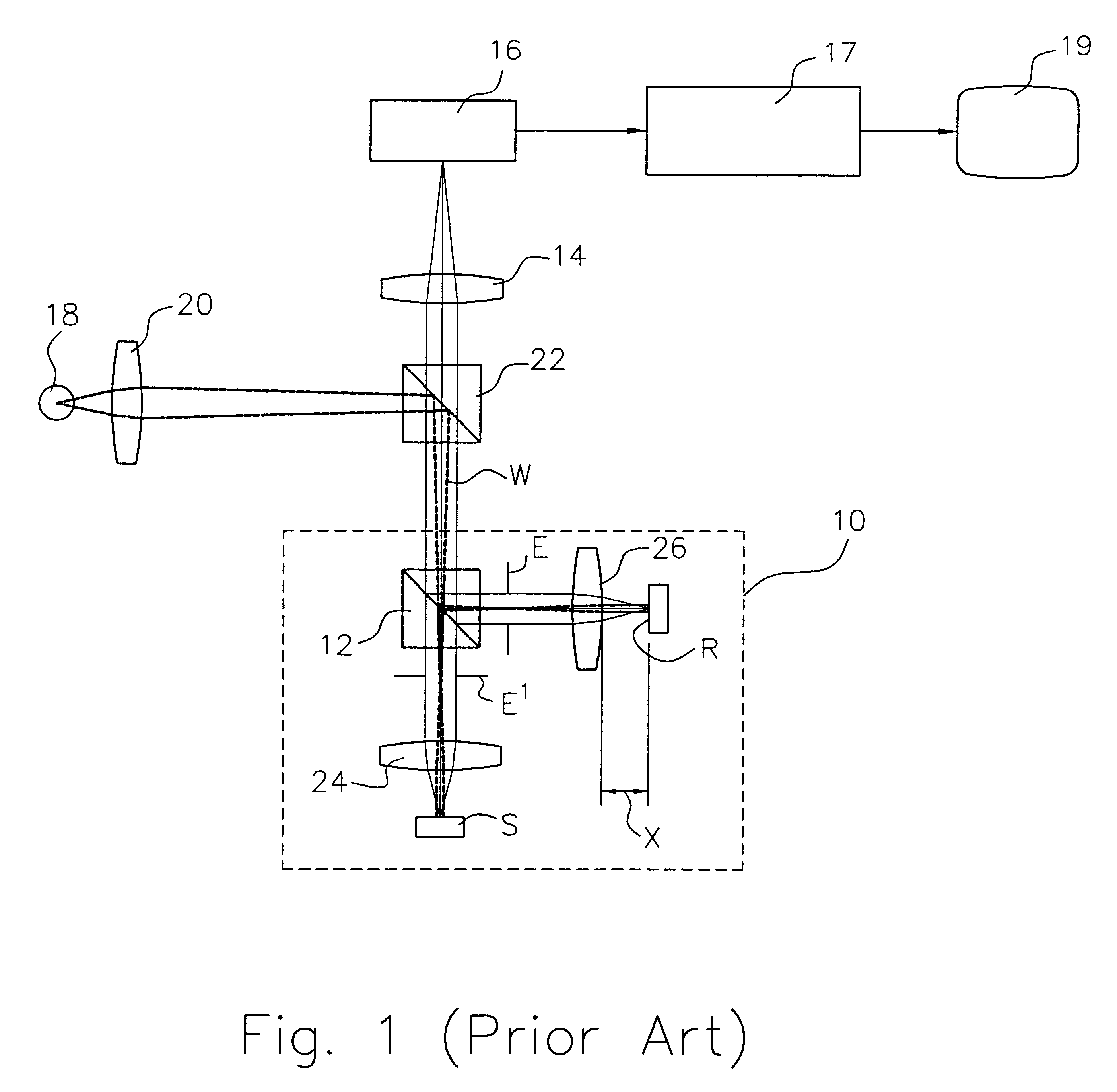
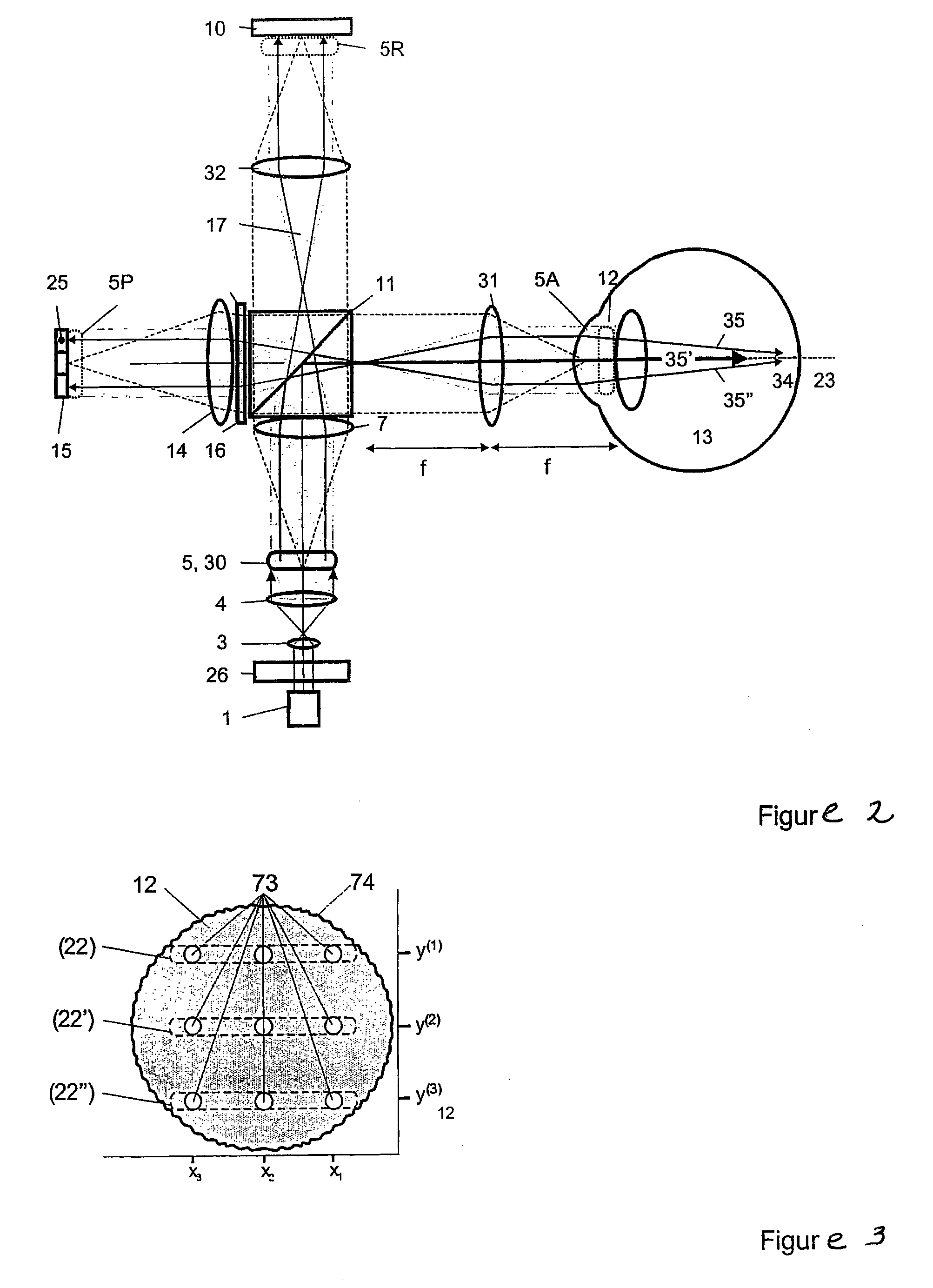
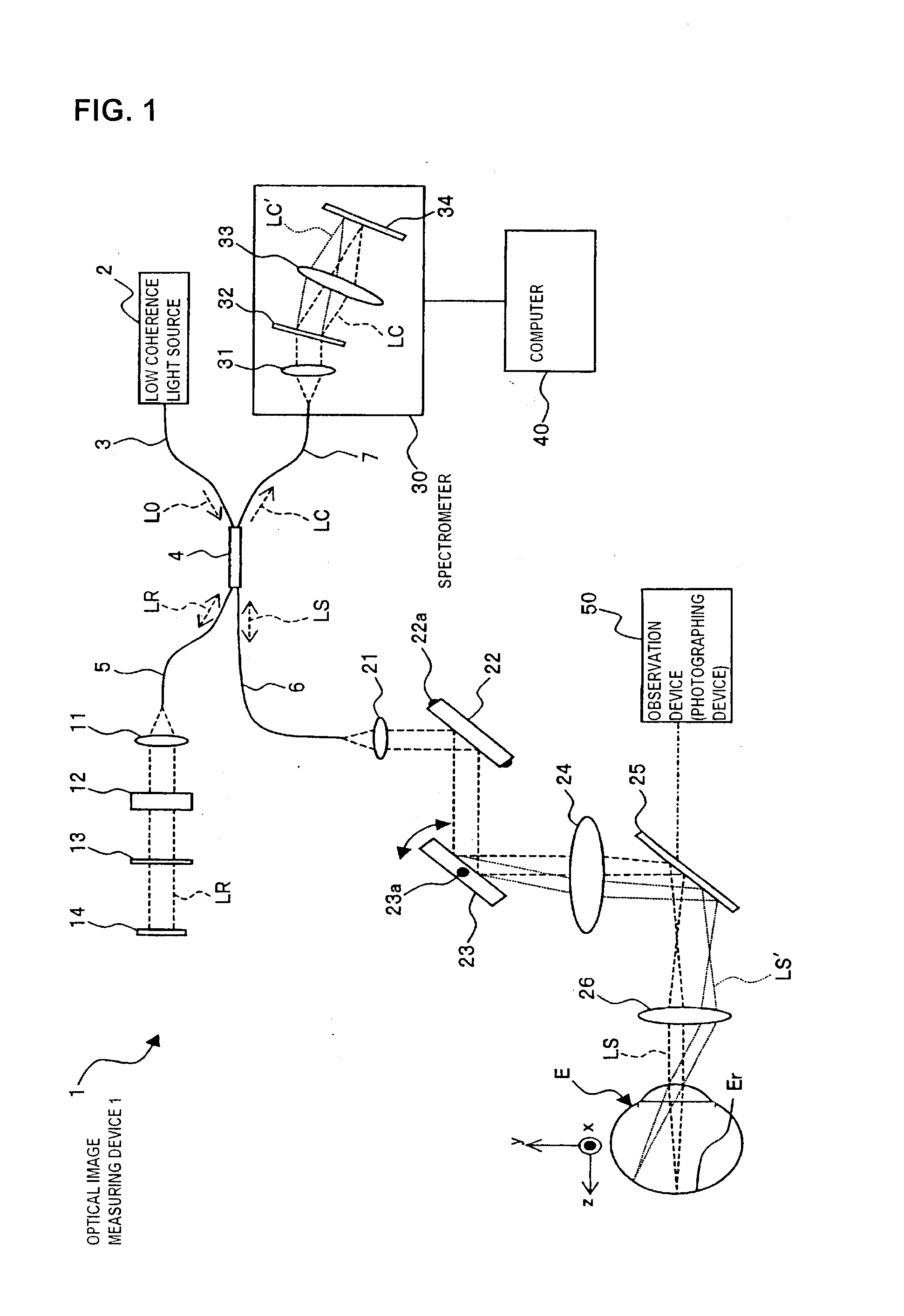
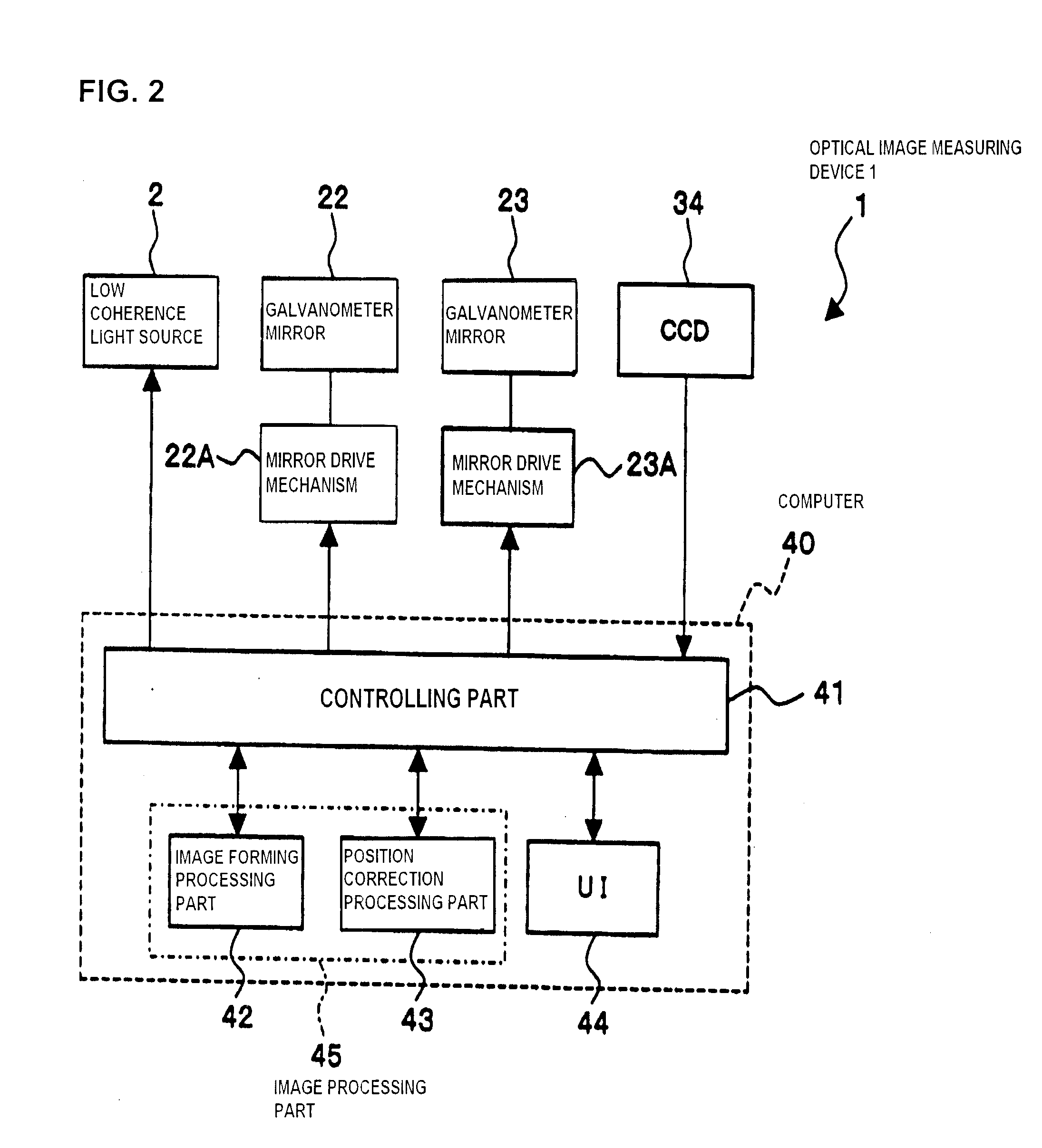
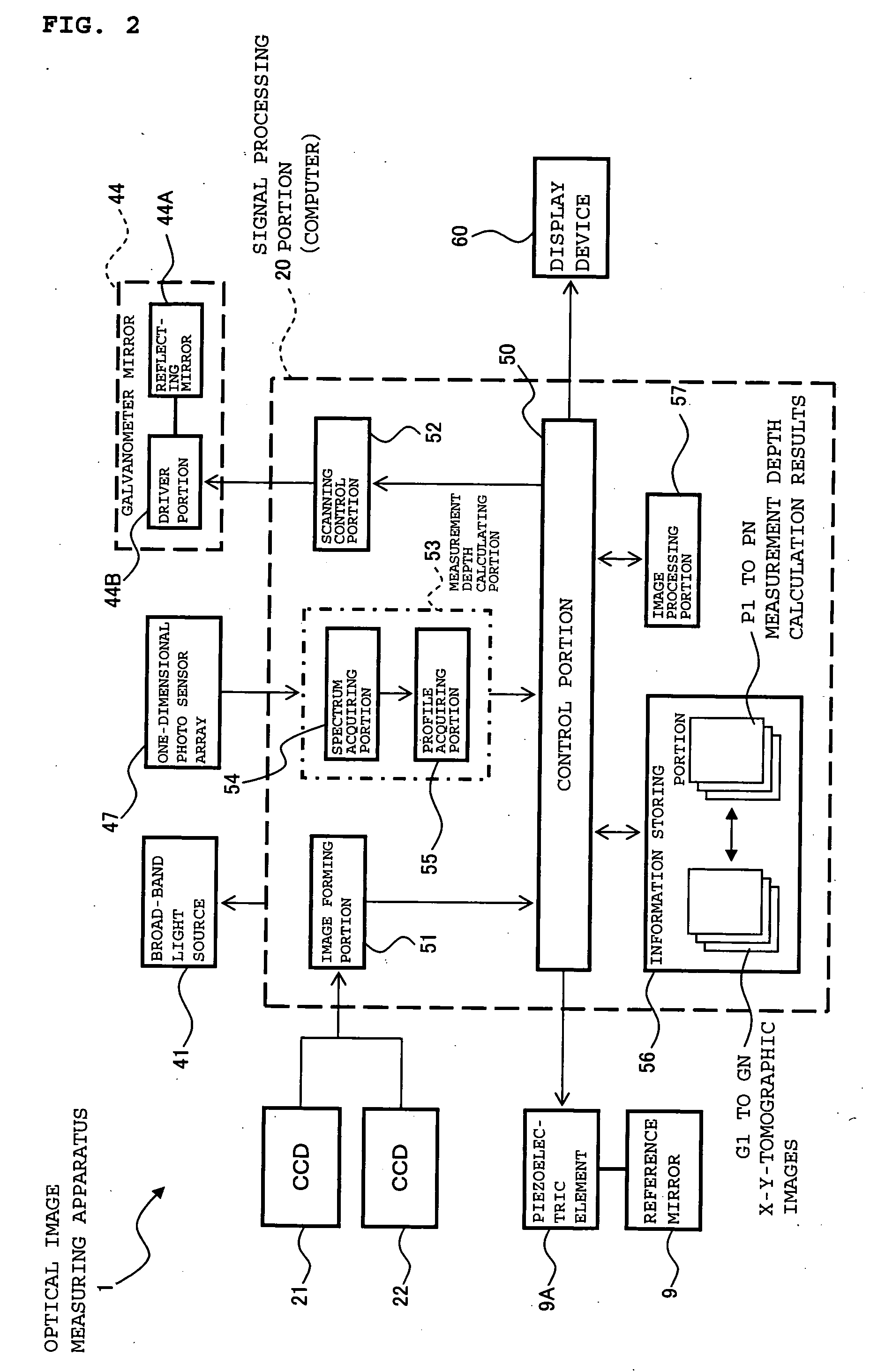
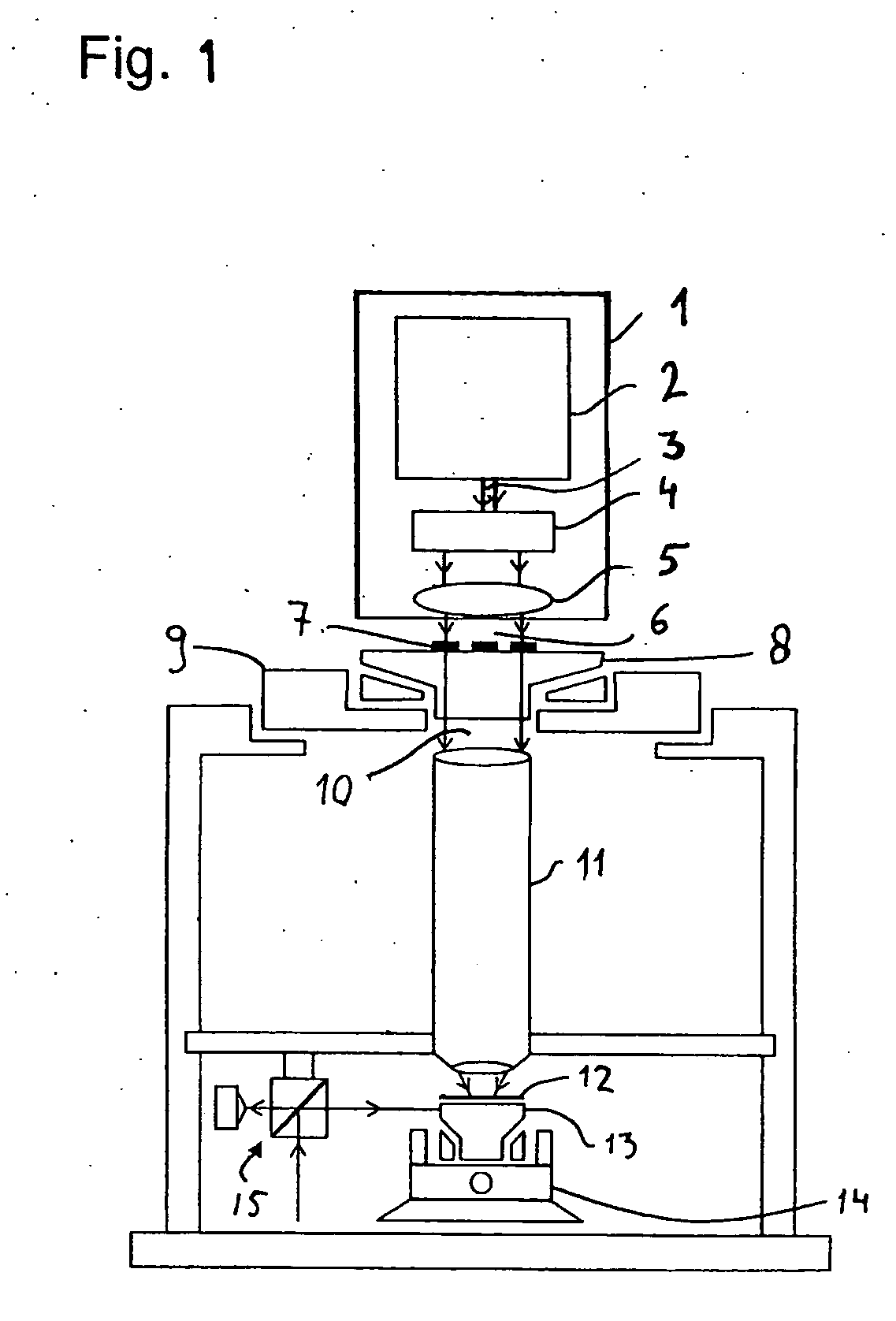
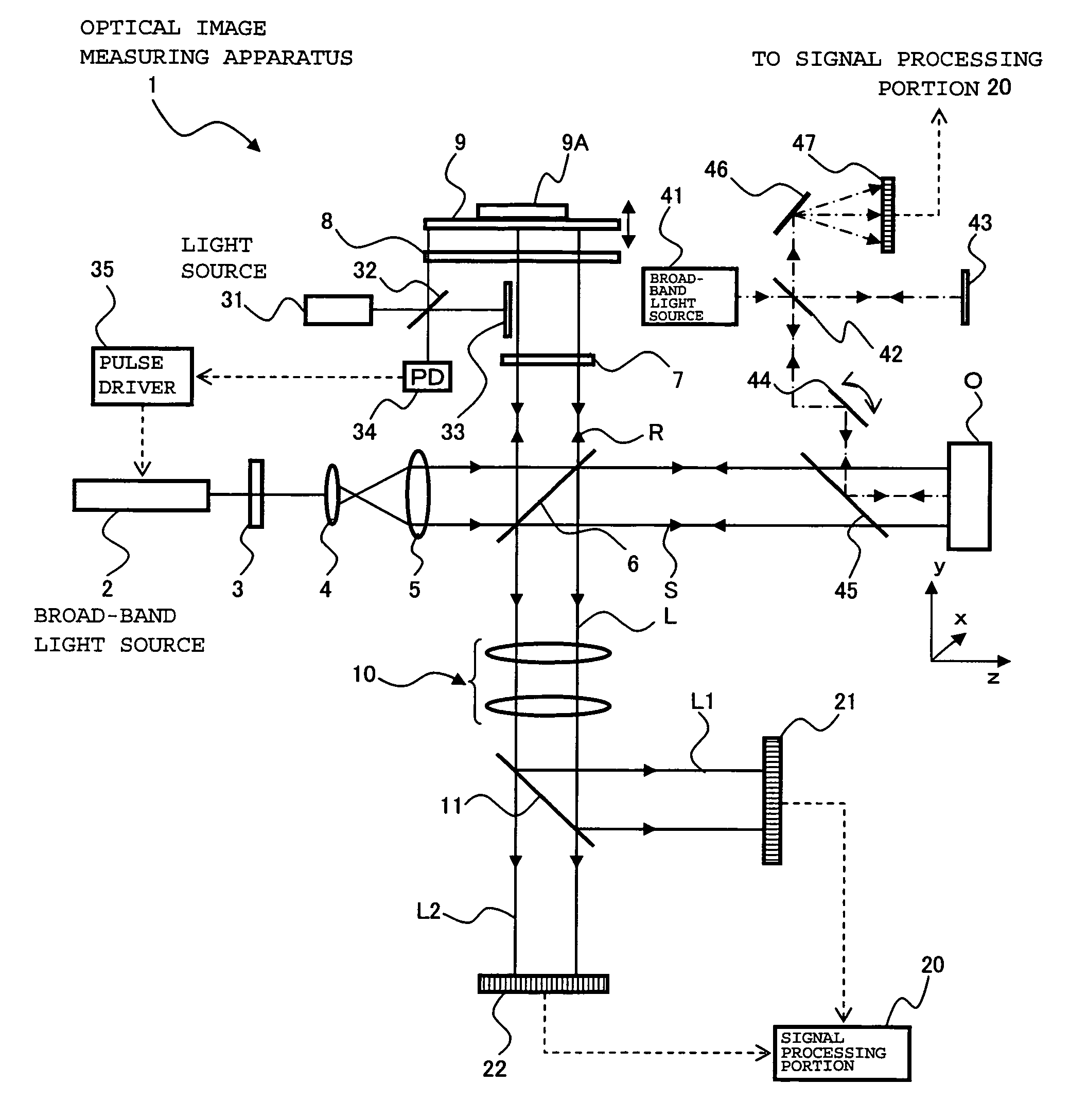
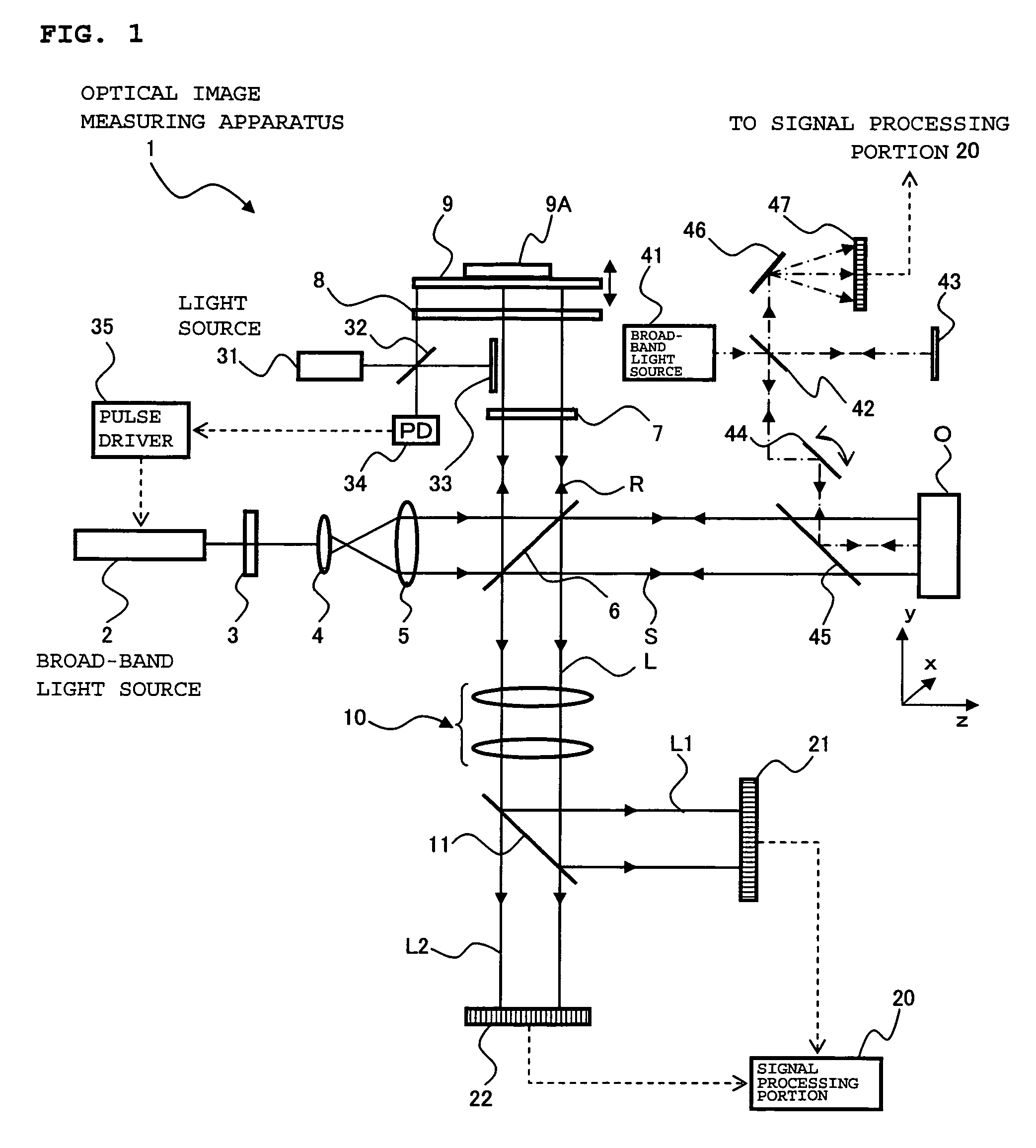
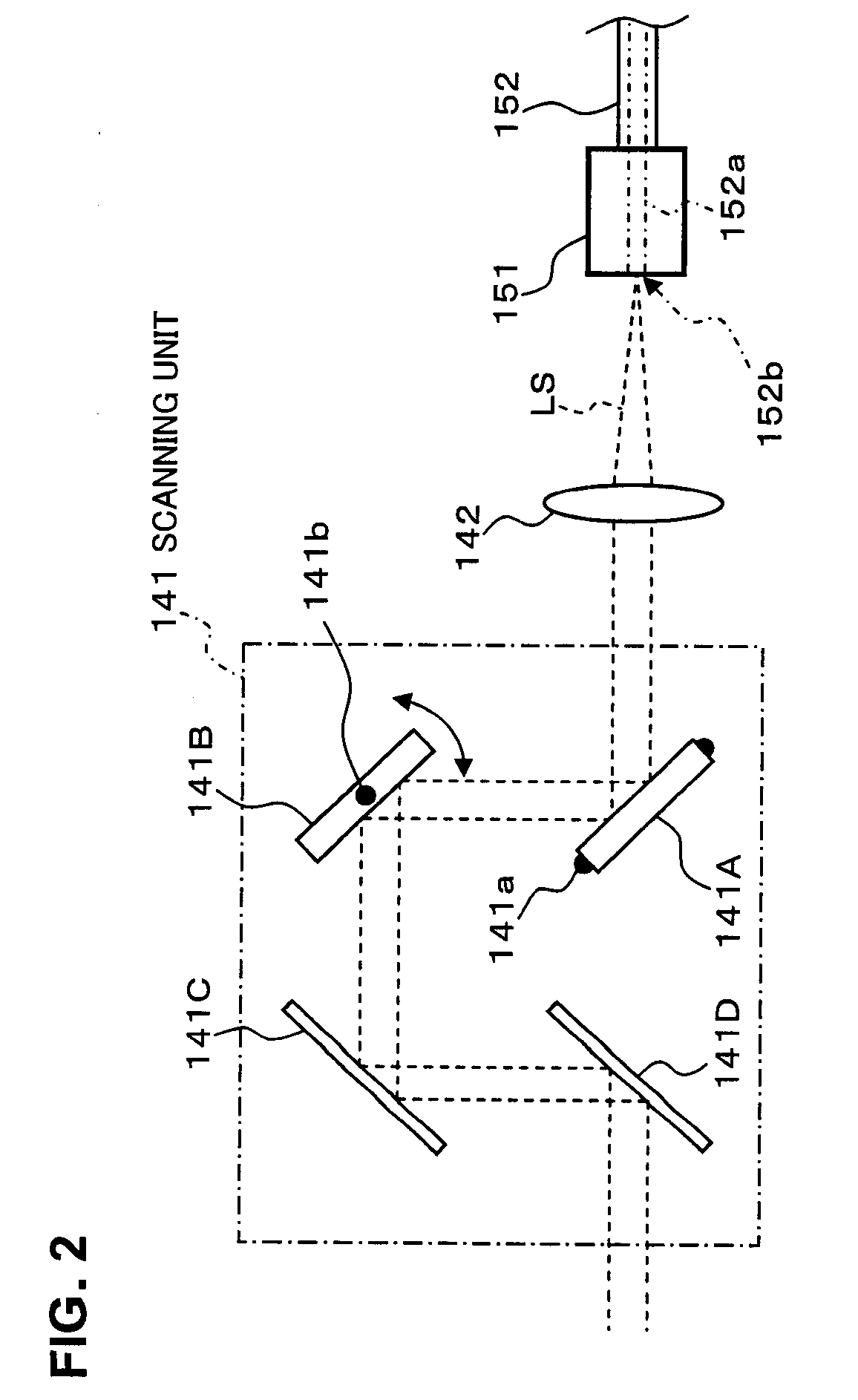
ActiveUS20100142780A1Accurate imagingAccurate displacementMaterial analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionGalvanometerSignal light
An optical image measuring device which can form a highly reliable image even if an object moves during scanning of a signal light is provided. An optical image forming device 1 comprises: an interferometer that splits a low coherence light L0 into a signal light LS and a reference light LR and generates an interference light LC by overlaying the signal light LS reflected by a fundus oculi with the reference light LR reflected by a reference mirror 14; a CCD 34 which receives the interference light LC and outputs a detection signal; Galvanometer mirrors 22 and 23 to scan the signal light LS in a main scanning direction and a sub-scanning direction; and a computer 40 forming tomographic images G1 to Gm along the main scanning direction at different positions of the sub-scanning direction. The Galvanometer mirrors 22 and 23 scan the signal light LS in a given direction crossing the main scanning direction, and the computer 40 forms a tomographic image for correction GR along the given direction to correct displacement of each topographic image Gi based on the tomographic image for correction GR.
Owner:KK TOPCON
Optical image measuring apparatus and optical image measuring method
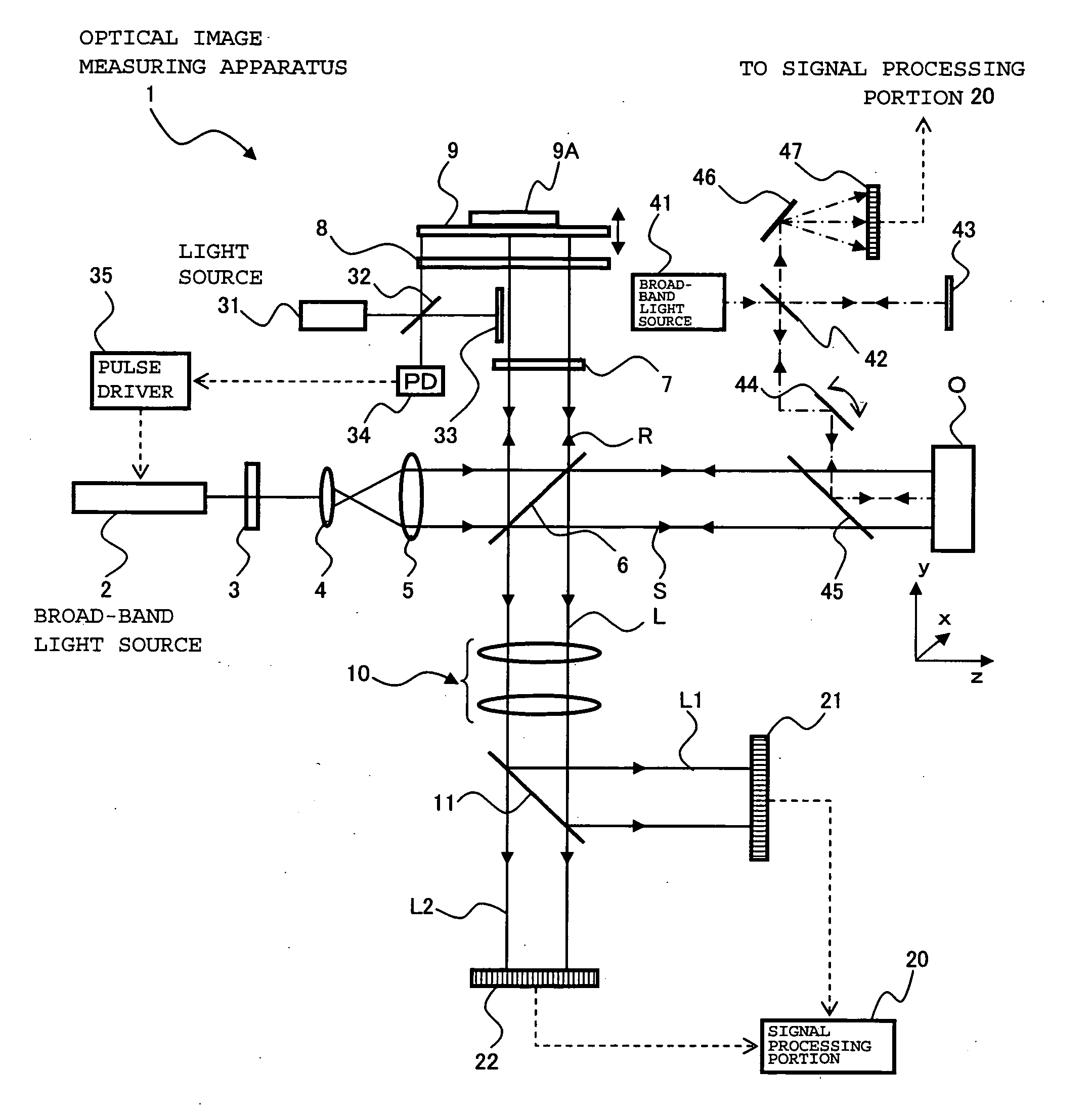
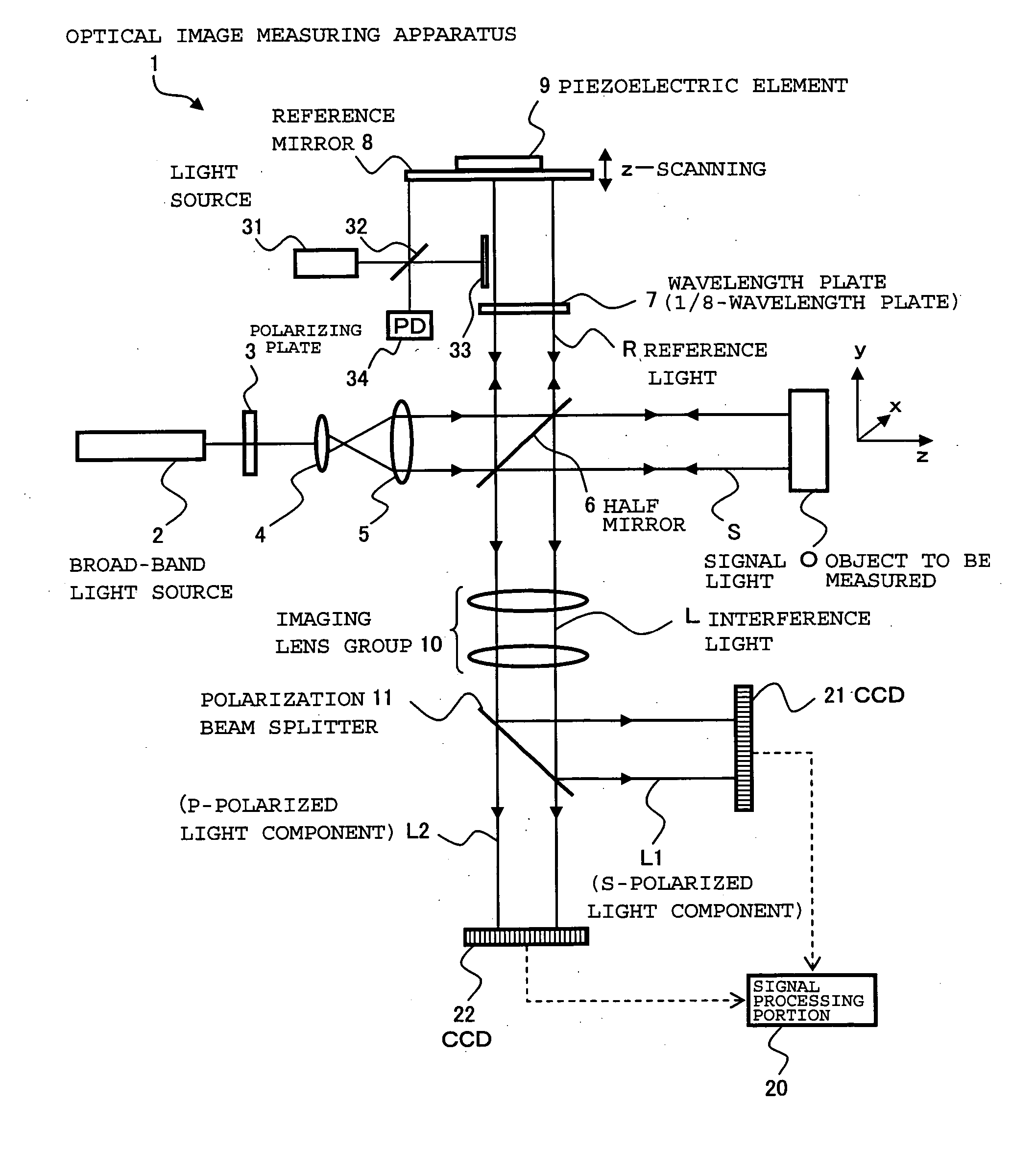
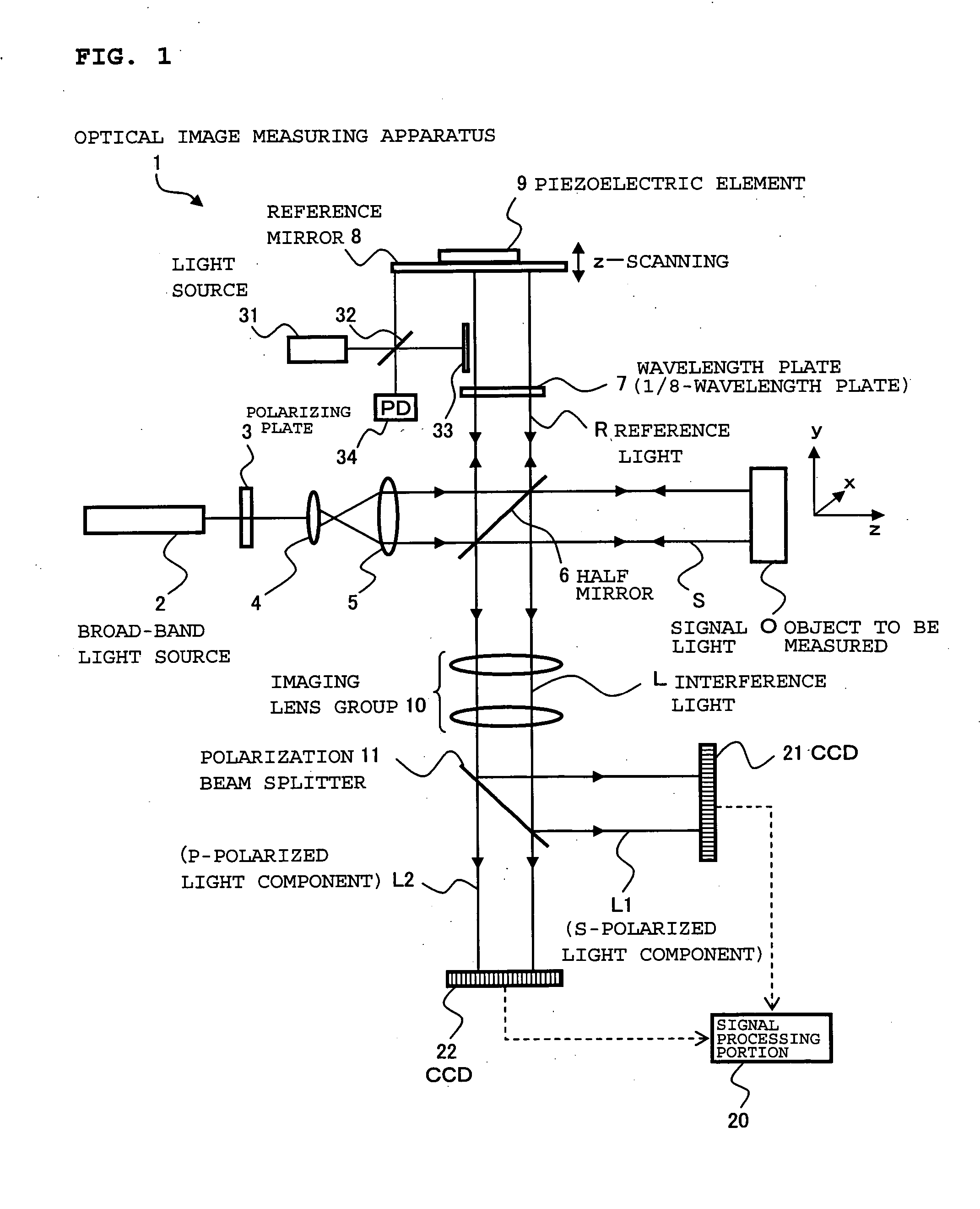
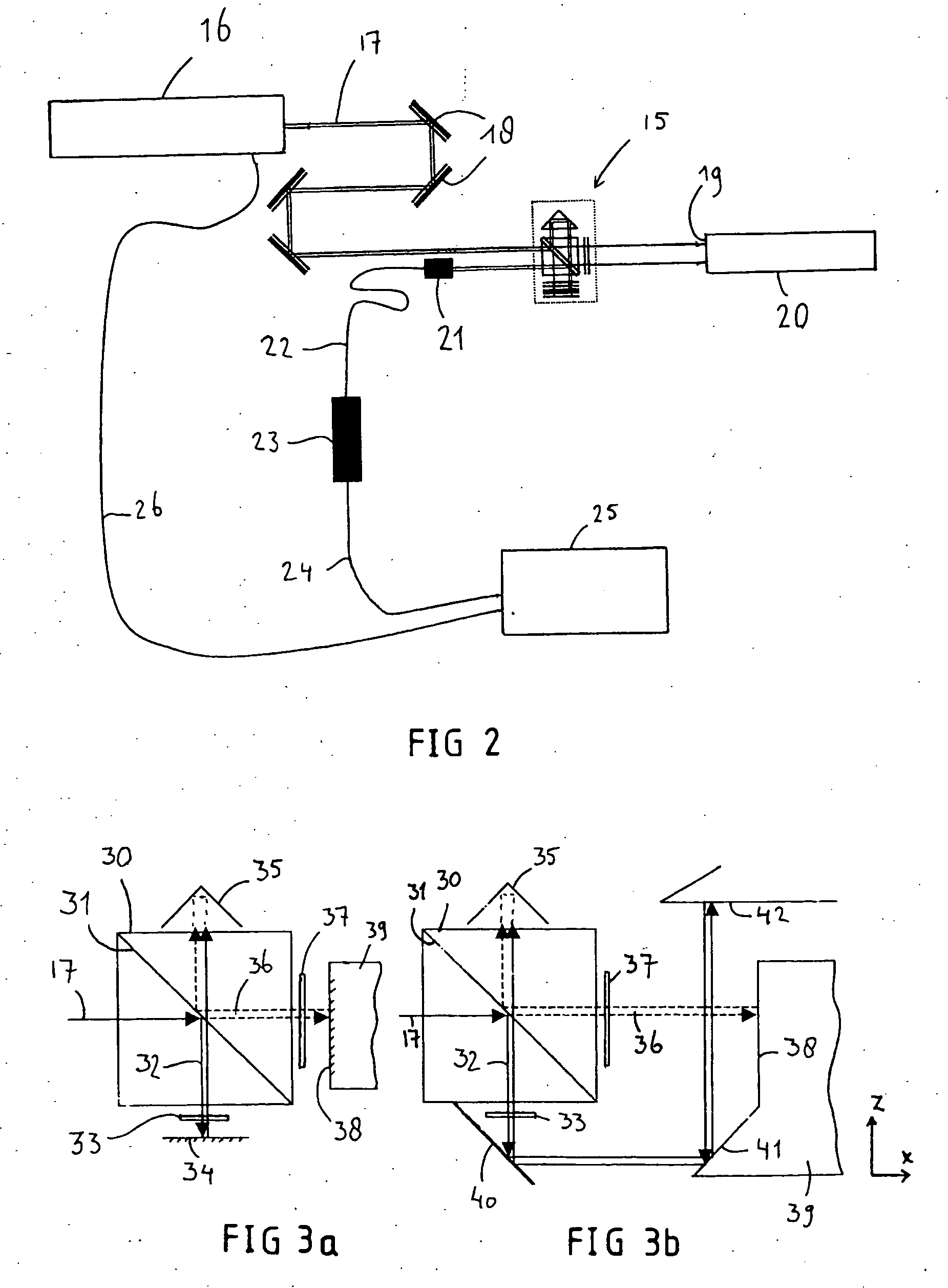
InactiveUS20060077395A1Improve accuracyHigh precision formingInterferometersUsing optical meansOptoelectronicsSignal light
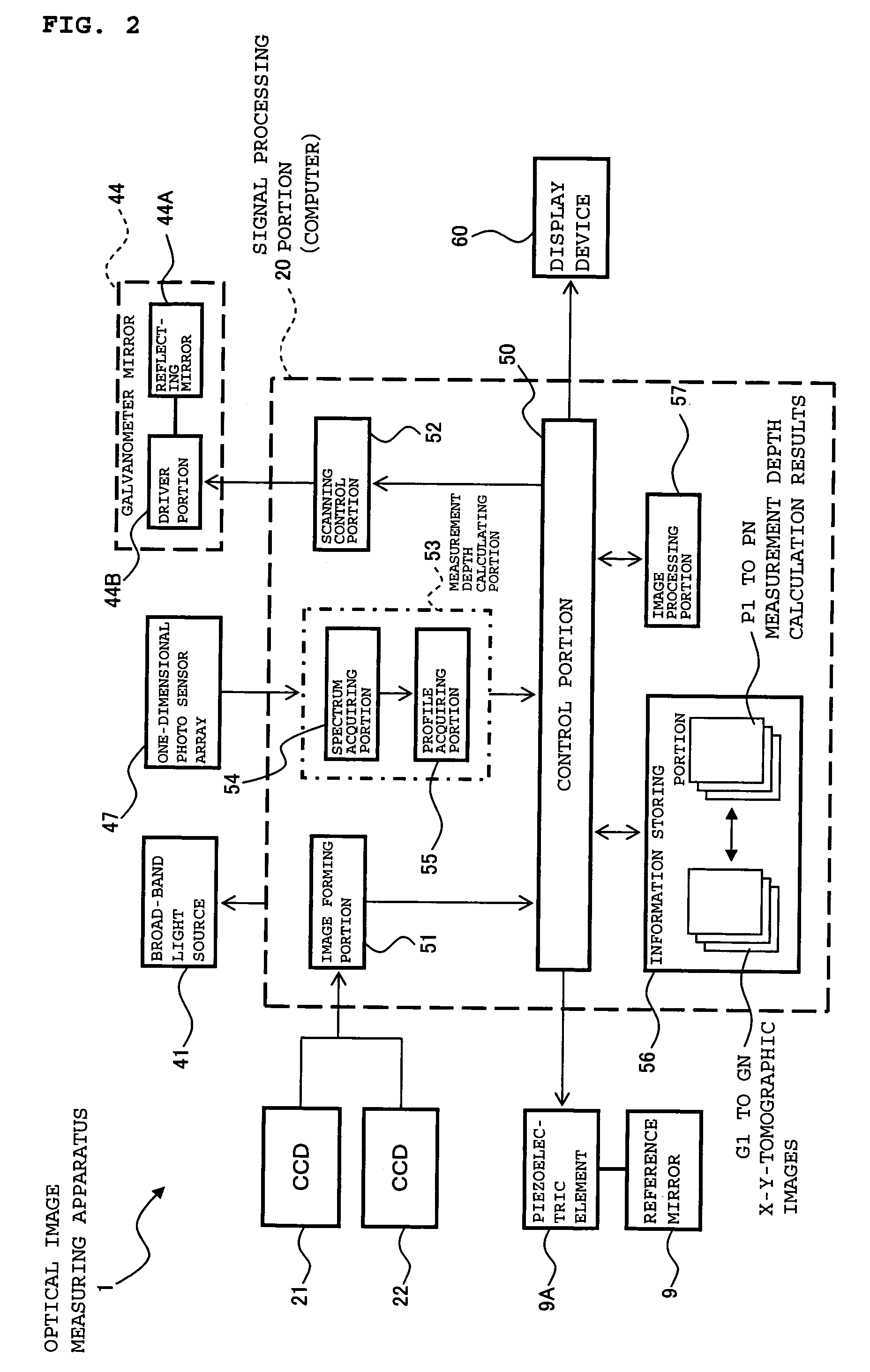
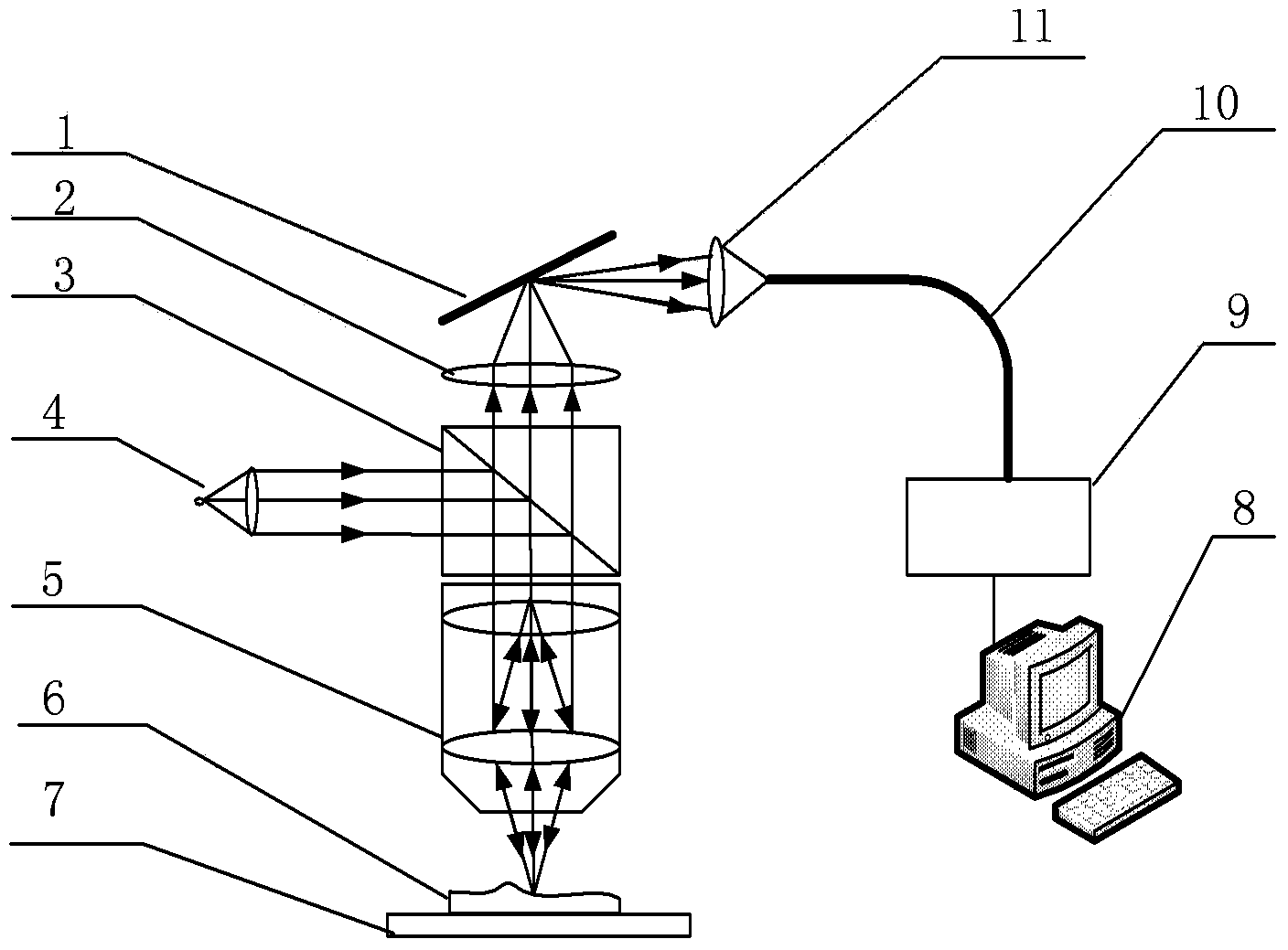
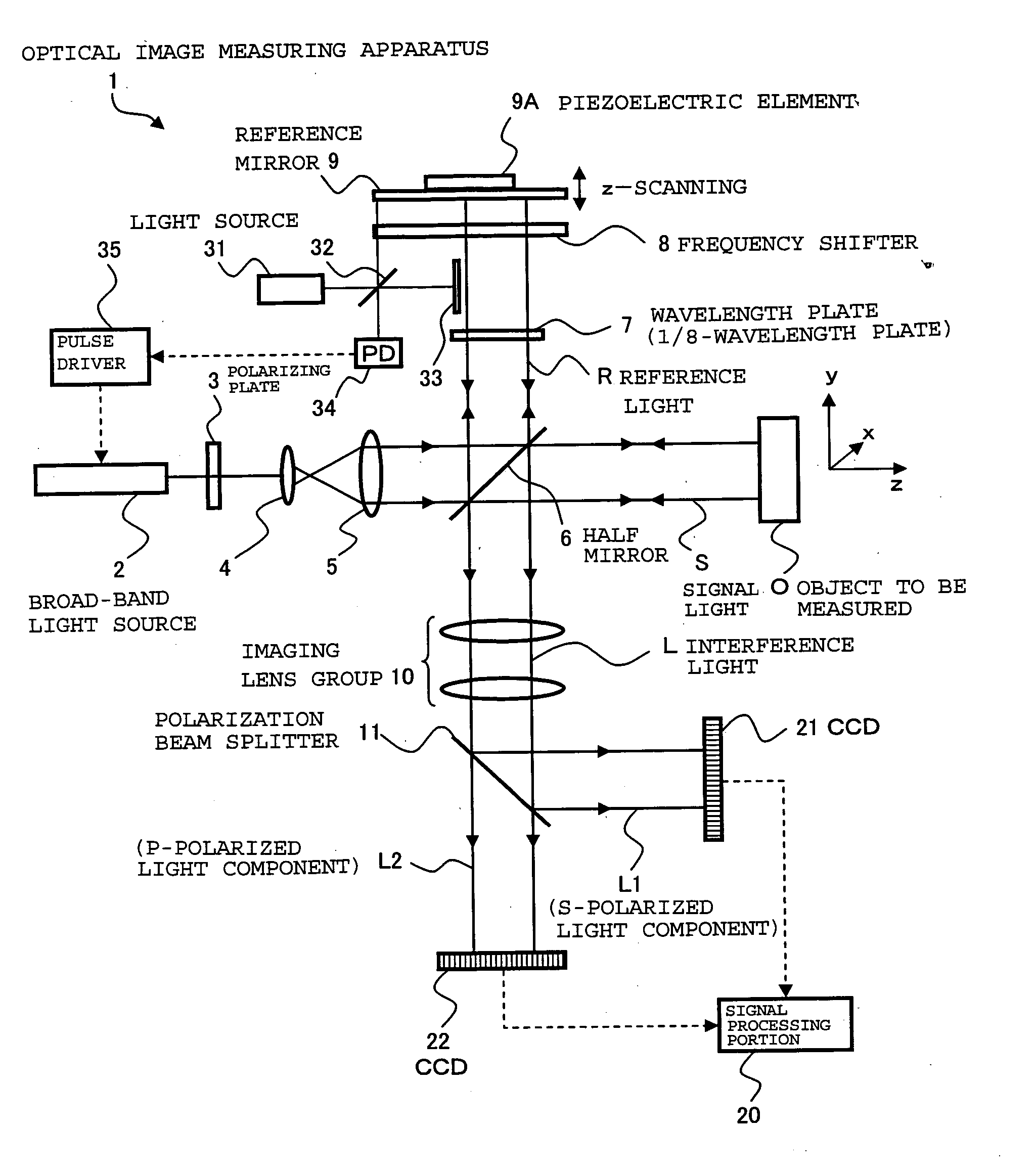
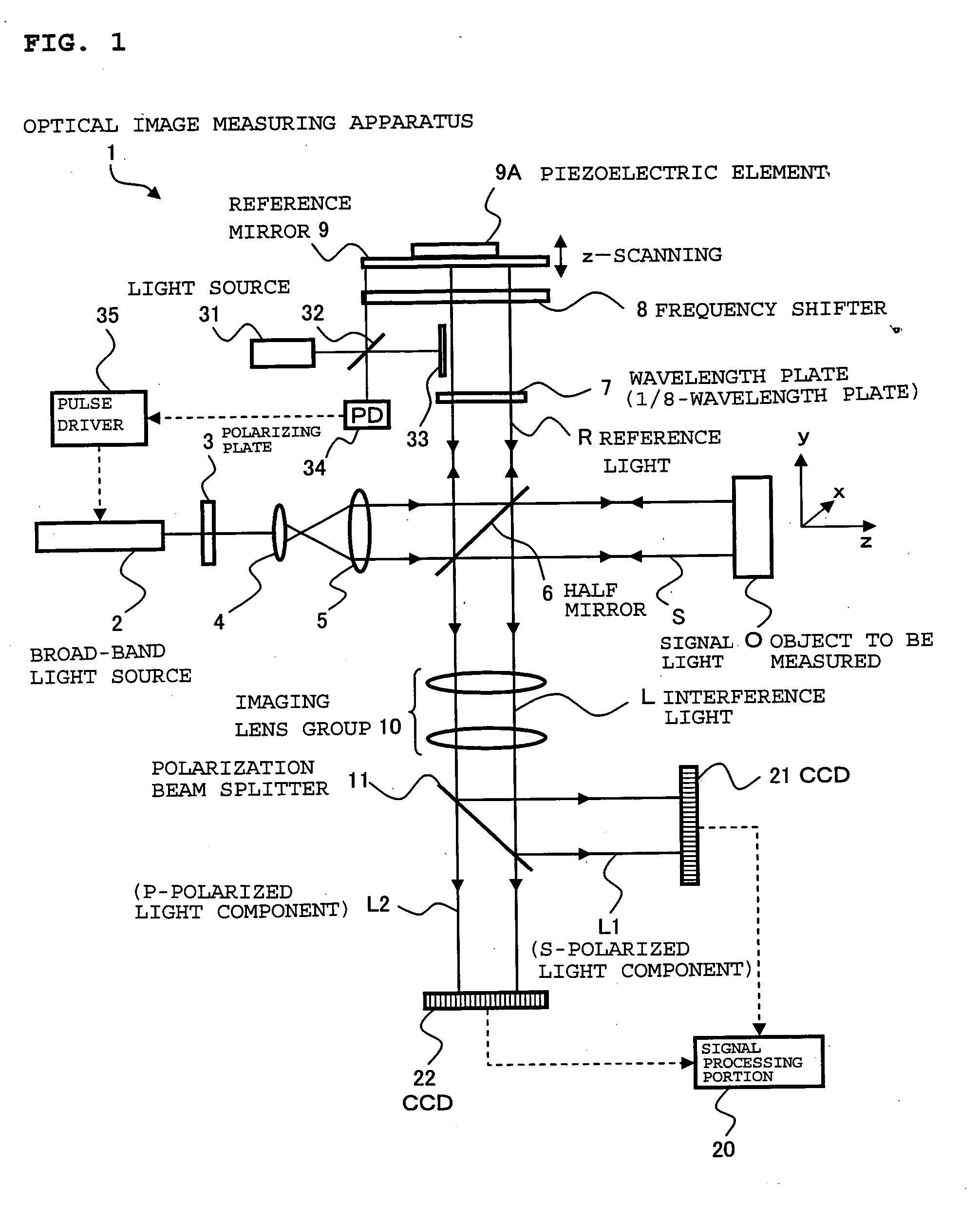
Provided is an optical image measuring apparatus forming a three-dimensional image based on tomographic images of an object, acquired at various depths even when the object moves during measurement. Including a half mirror (6) for dividing a light beam signal light (S) and reference light (R), a frequency shifter (8), a reference mirror (9) and a piezoelectric element (9A) used to change an optical path length of the reference light (R), CCDs (21, 22) for receiving interference light beams (L) resulting from interference light produced by superimposing the signal light (S) and the reference light (R) on each other by the half mirror (6) and outputting detection signals, an image forming portion for forming tomographic images based on the detection signals, a measurement depth calculating means (53), and an image processing portion (57). Forming a three-dimensional image or the like based on the arranged tomographic images.
Owner:KK TOPCON
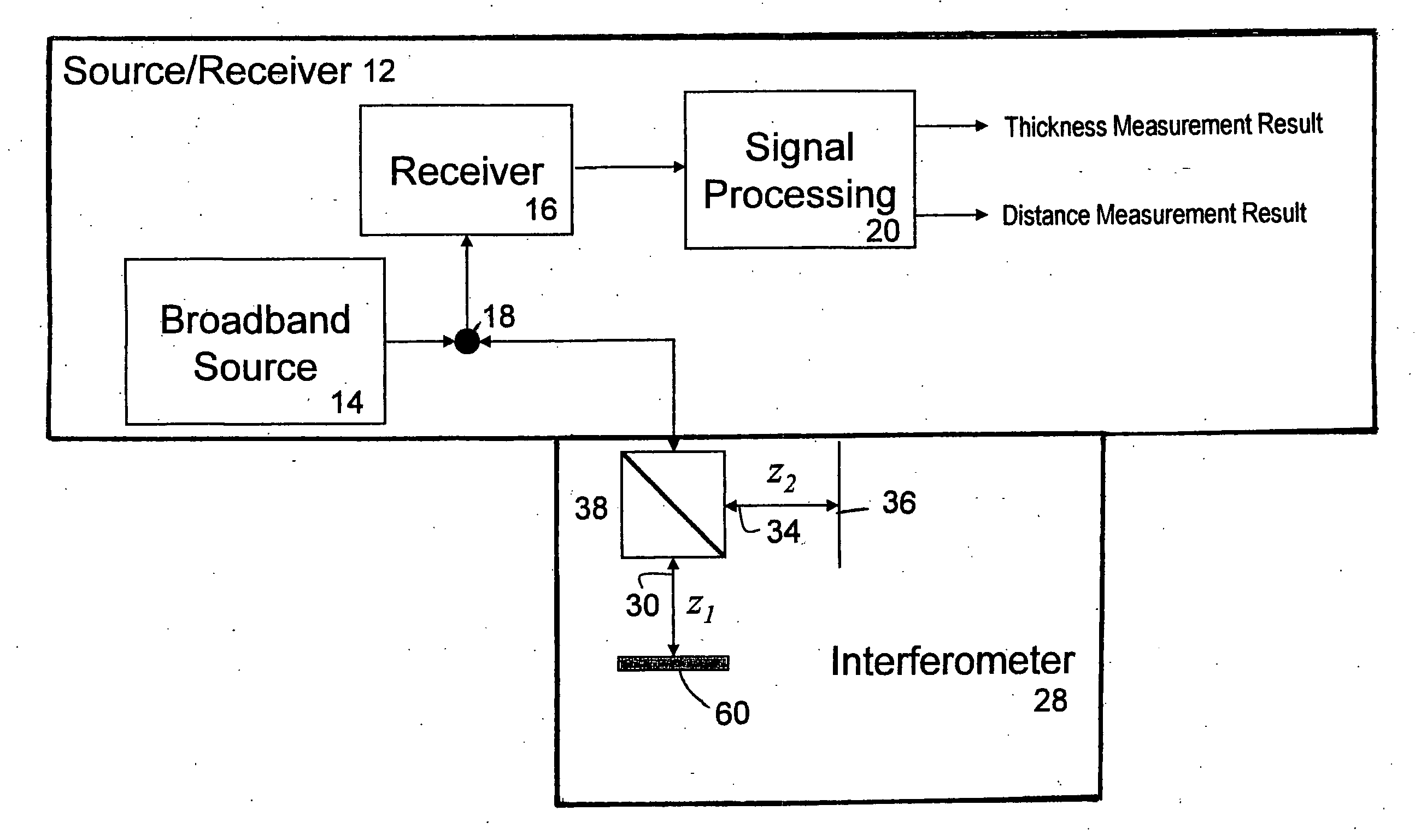
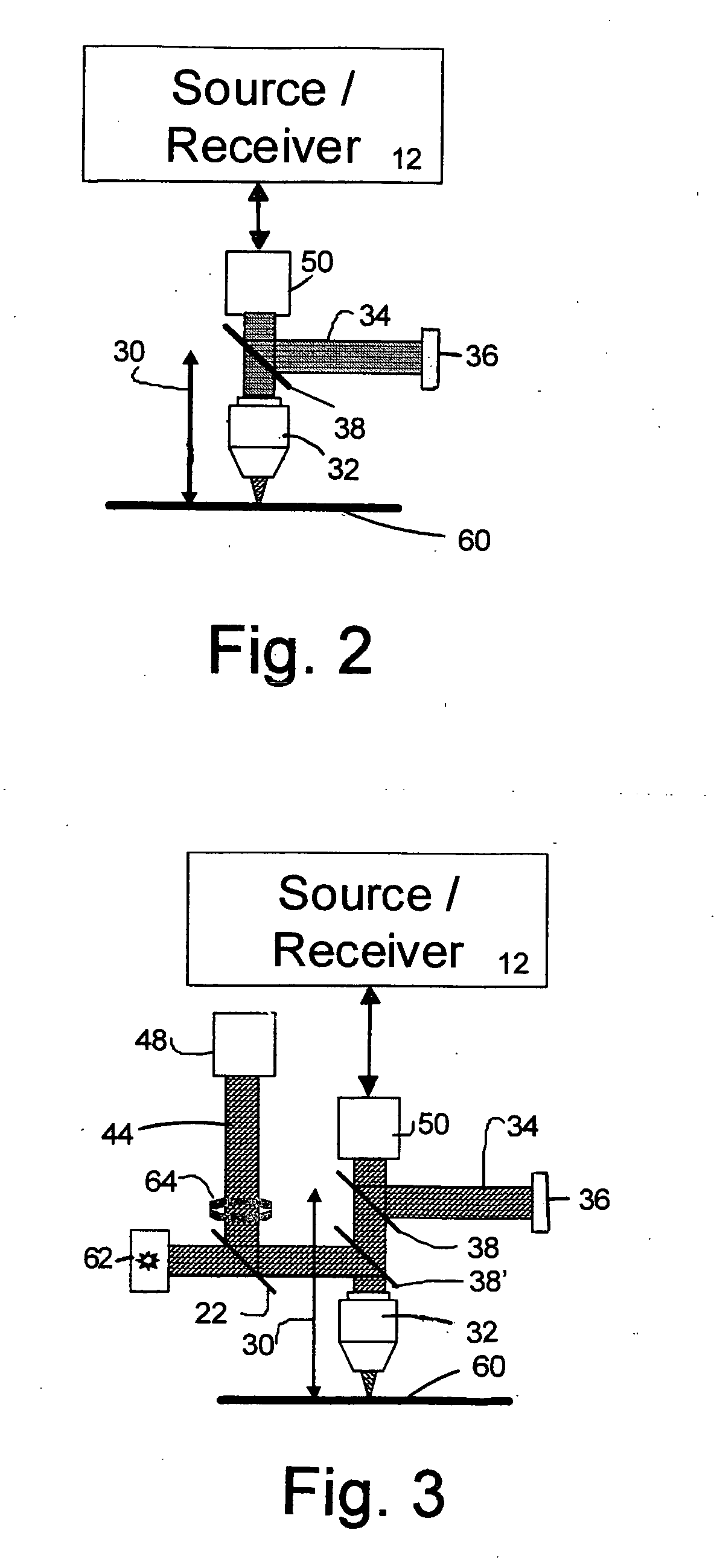
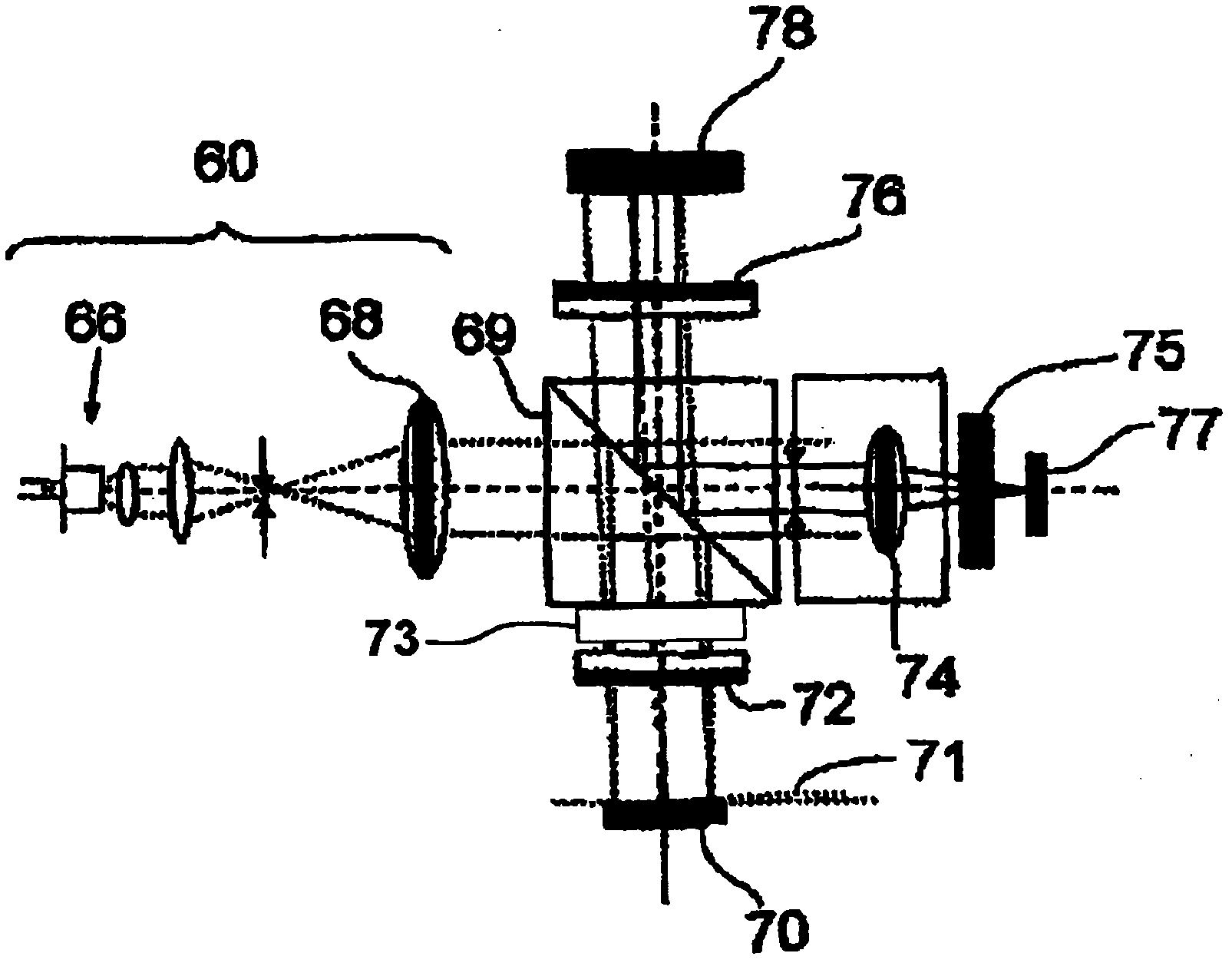
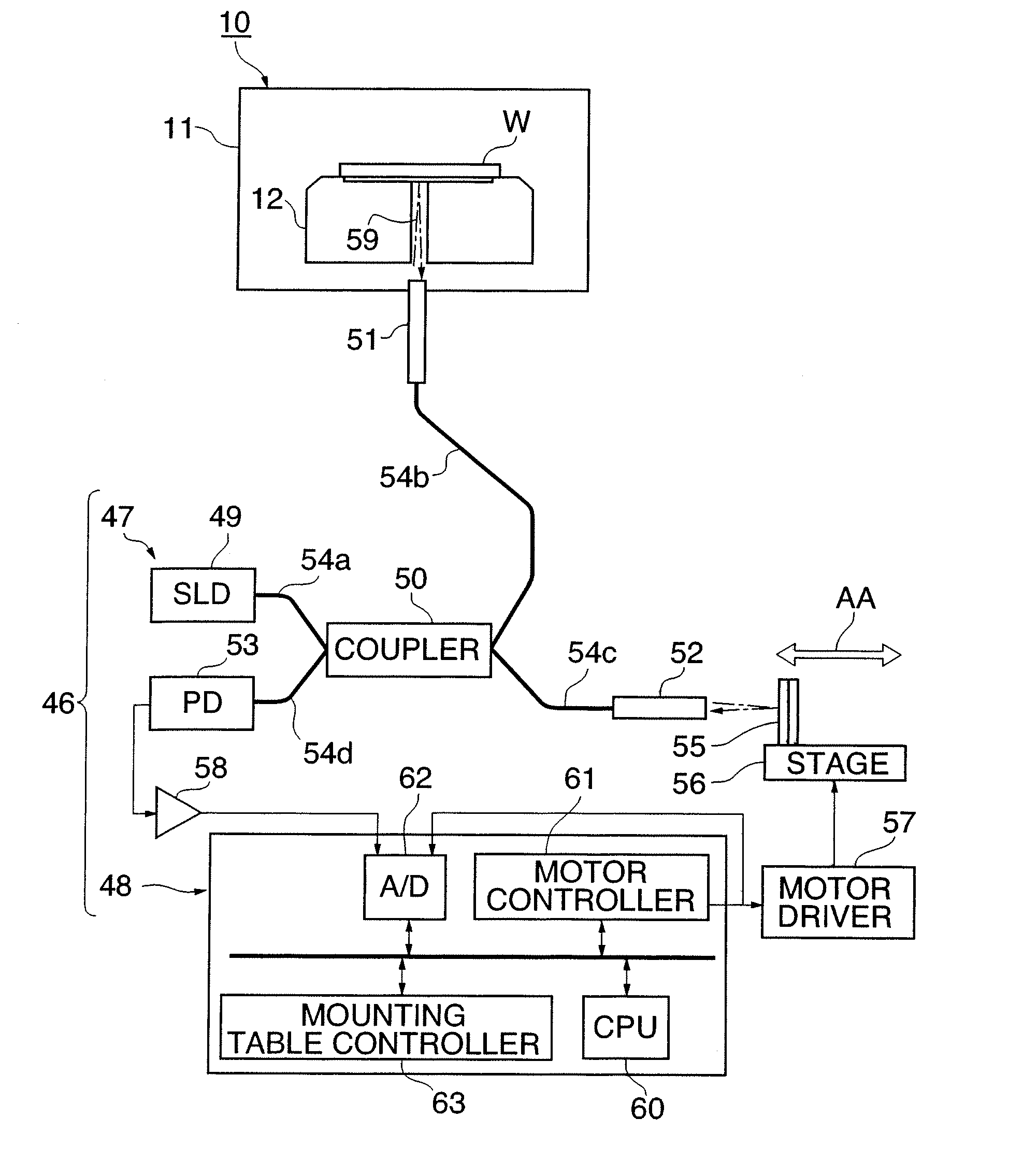
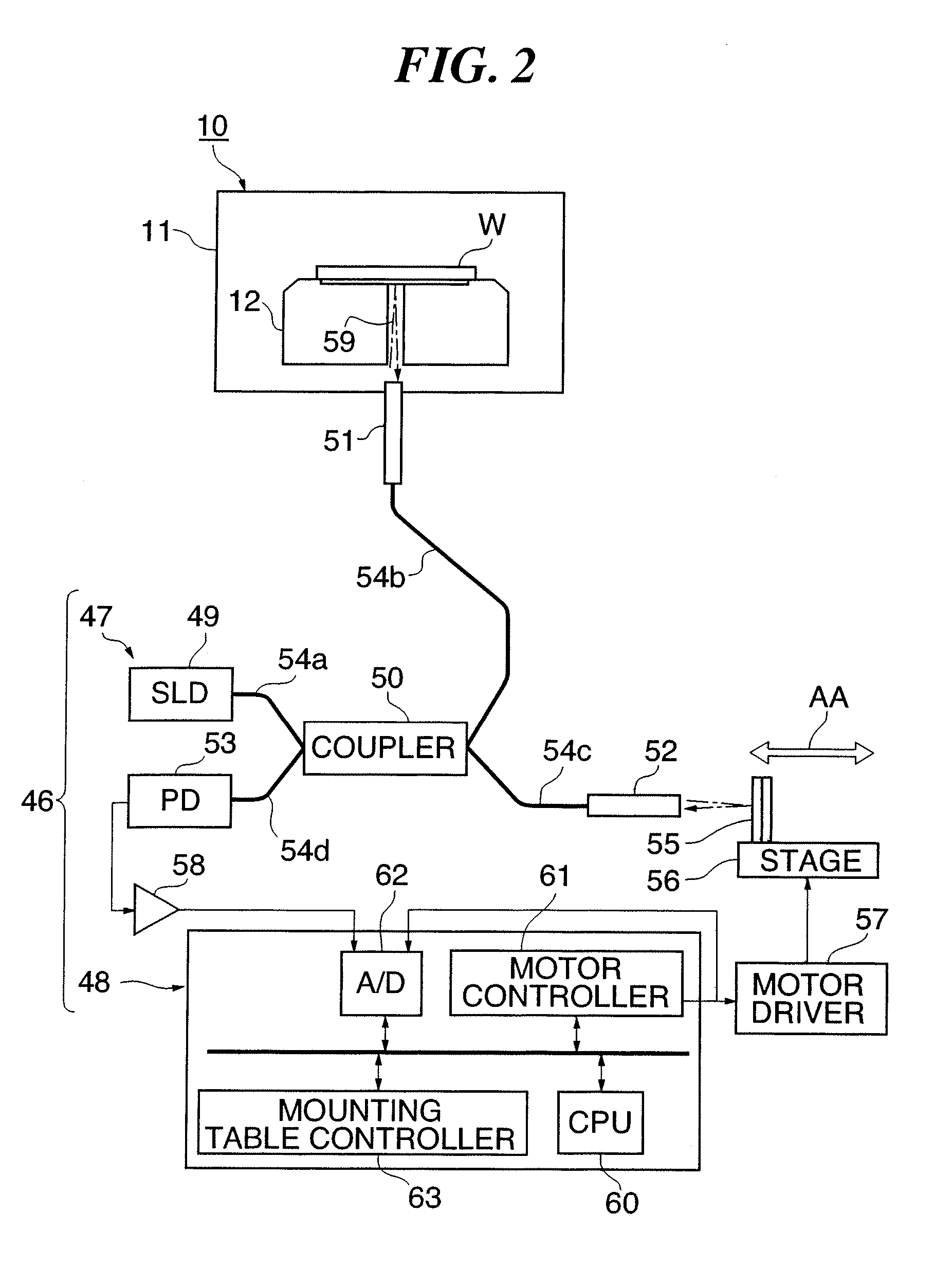
Wafer shape thickness and trench measurement
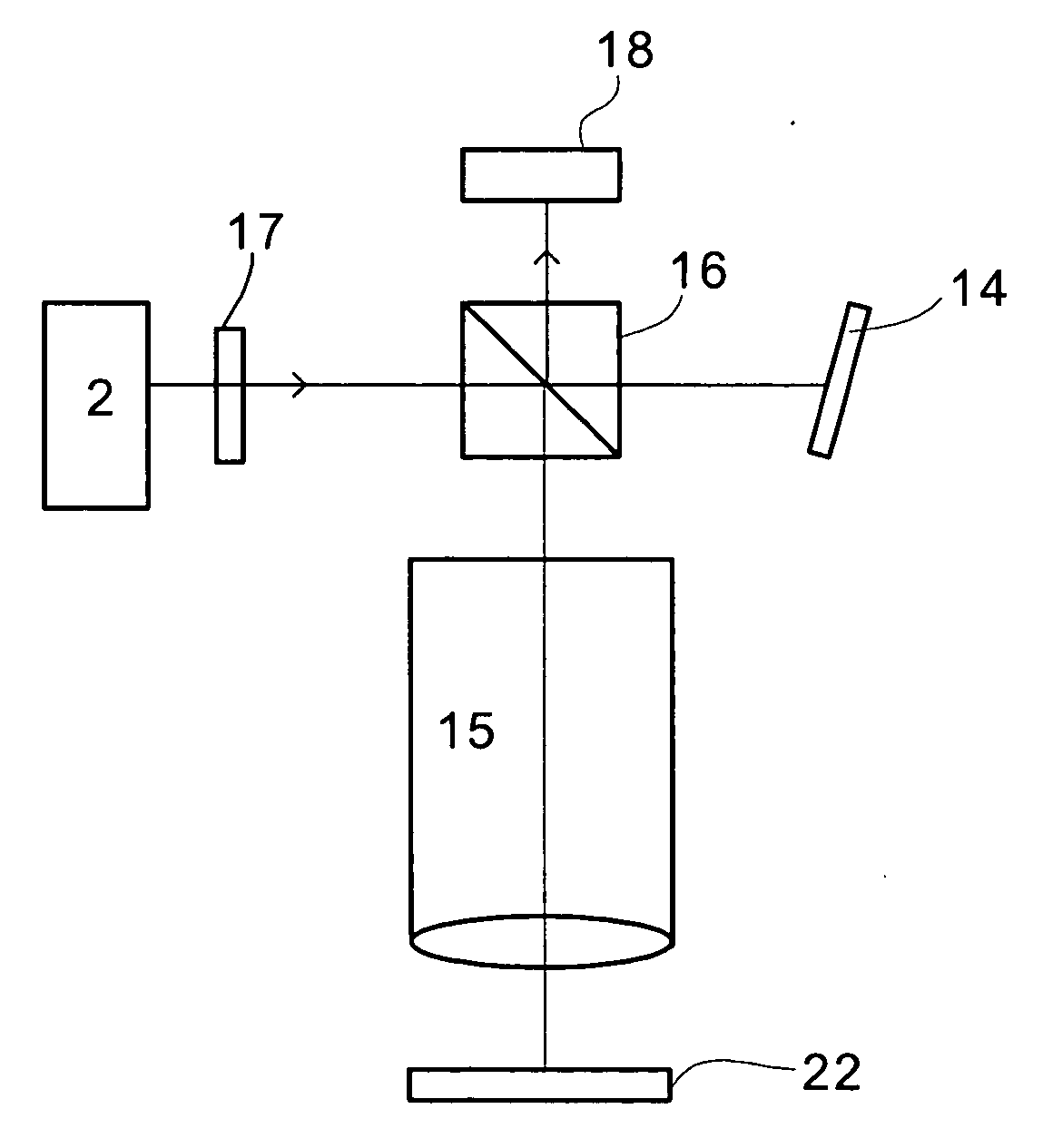
A device (10) and methods for simultaneously measuring the thickness of individual wafer layers, the depth of etched features on a wafer, and the three-dimensional profile of a wafer. The structure of the device (10) is comprised of a source / receiver section (12) having a broadband source (14), a receiver (16) and a signal processing section (20). An interferometer (28) separates or combines measurement and reference light and has a measurement leg (30) and a reference leg (34), and a reference mirror (36). The device (10) analyzes a received spectrum which is comprised of a measurement of intensity versus wavelength. There are two measurement methods disclosed: the first method is utilized for taking a single measurement and the second method is utilized for multiple measurements.
Owner:ONTO INNOVATION INC
Precise assembling and adjusting device and method for detector chip of imaging system
ActiveCN104406541AEasy to readAccurate displacement and recordingUsing optical meansAccessory structureControl system
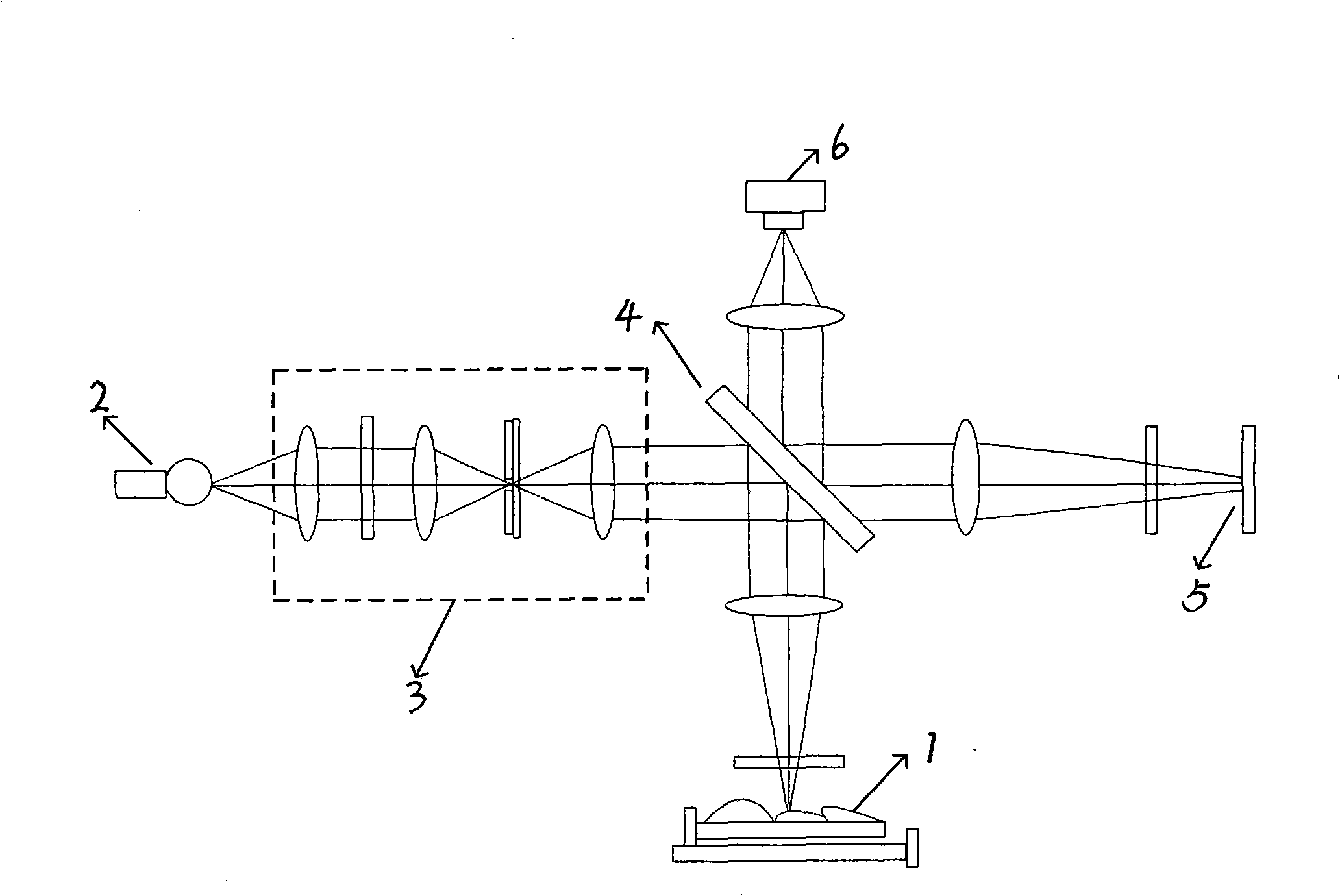
The invention discloses precise assembling and adjusting device and method for a detector chip of an imaging system. The assembling and adjusting device comprises a movement control system, a detection system, an accessory structure and a computer; the movement control system is composed of a translation stage, a revolving stage and a tilting table and used for adjusting the spatial positions of a device to be detected and the detection system; the detection system is composed of an autocollimation and a telecentric digital microimaging system and used for measuring the angle and positional deviation of the device to be detected; and the compute is able to control the movement of the translation stage and record the position coordinates and can also be used for acquiring an image of the device to be detected from the telecentric digital microimaging system and analyzing and calculating. The assembling and adjusting method includes the assembling and adjusting of a reference mirror, the transmission of the angle and position of the detector chip, and the assembling and adjusting of the detector chip; the measurement precision of the angle and position respectively reaches second level and micro dimension during the assembling and adjusting; and the deviation of angle and position of the detector chip can be respectively less than 1 and 0.02mm after the assembling and adjusting.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Optical image measuring apparatus
InactiveUS20060055939A1Easy to sampleImprove accuracyInterferometersUsing optical meansSignal lightAlternating current
Provided is an optical image measuring apparatus capable of effectively receiving interference light, particularly an alternating current component thereof using a smaller number of photo sensors. The optical image measuring apparatus includes a polarizing plate for converting a light beam from a broad-band light source to linearly polarized light, a half mirror for dividing the light beam into signal light and reference light, a piezoelectric element for vibrating a reference mirror, a wavelength plate for converting the reference light to circularly polarized light, a polarization beam splitter for extracting two different polarized light components from interference light produced from the signal light and the reference light which are superimposed on each other by the half mirror, CCDs for detecting the two different polarized light components, and a signal processing portion for producing an image of an object to be measured based on the detected polarized light components. A frequency for intensity modulation of the light beam is synchronized with a beat frequency of the interference light. A frequency of vibration of the reference mirror is synchronized with the beat frequency of the interference light and an amplitude of vibration thereof is set to be equal to or smaller than a wavelength of the interference light.
Owner:KK TOPCON
Device and method for measuring synchronous phase shifting interference of Fizeau quasi-common optical path structure
ActiveCN104034257AReduce vibration effectsHigh measurement accuracyUsing optical meansImaging lensCcd camera
The invention relates to a device and a method for measuring synchronous phase shifting interference of a Fizeau quasi-common optical path structure. The device comprises a laser, a half wave plate, a focusing lens, a spatial filter, a circularly polarized light beam splitter (an optically active crystal), a spectroscope, a collimating lens, a reference mirror, a pin-hole diaphragm, an imaging lens, a light splitting and phase shifting system, a computer control system and a CCD camera. According to the device and the method disclosed by the invention, a synchronous phase shifting technology is combined with a Fizeau interference method, so that technical difficulties of a conventional interferometer in poor stability and disability of realizing dynamic measurement are solved; the device and the method are characterized by utilizing an optical rotation effect of the crystal and adding the circularly polarized light beam splitter with a very small splitting angle in the Fizeau interfering structure, so as to realize orthogonally polarized separation of reference lights and test lights in a common optical path. The device and the method disclosed by the invention avoid utilization of a high-quality quarter wave plate in a synchronous phase-shifting interference system, and also greatly decrease a phase measurement error caused by a stress birefrigent effect which exists in an optical element of the system.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Lithographic interferometer system
ActiveUS20050111005A1Increase flexibilityReduce complexityInterferometersSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPlane mirrorLight beam
An improved lithographic interferometer system, is presented herein. The lithographic interferometer system comprises a beam generating mechanism, mirrors which reflect those beams, and detection devices for detecting an interference pattern of overlapping reflected beams. The beam generating mechanism comprises a beam-splitter, which splits the beams into reference beams and measuring beams, a reference mirror that provides a plane mirror interferometer, and a reflective surface that emits at least one reference beam used in a differential plane mirror interferometer.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Optical image measuring apparatus
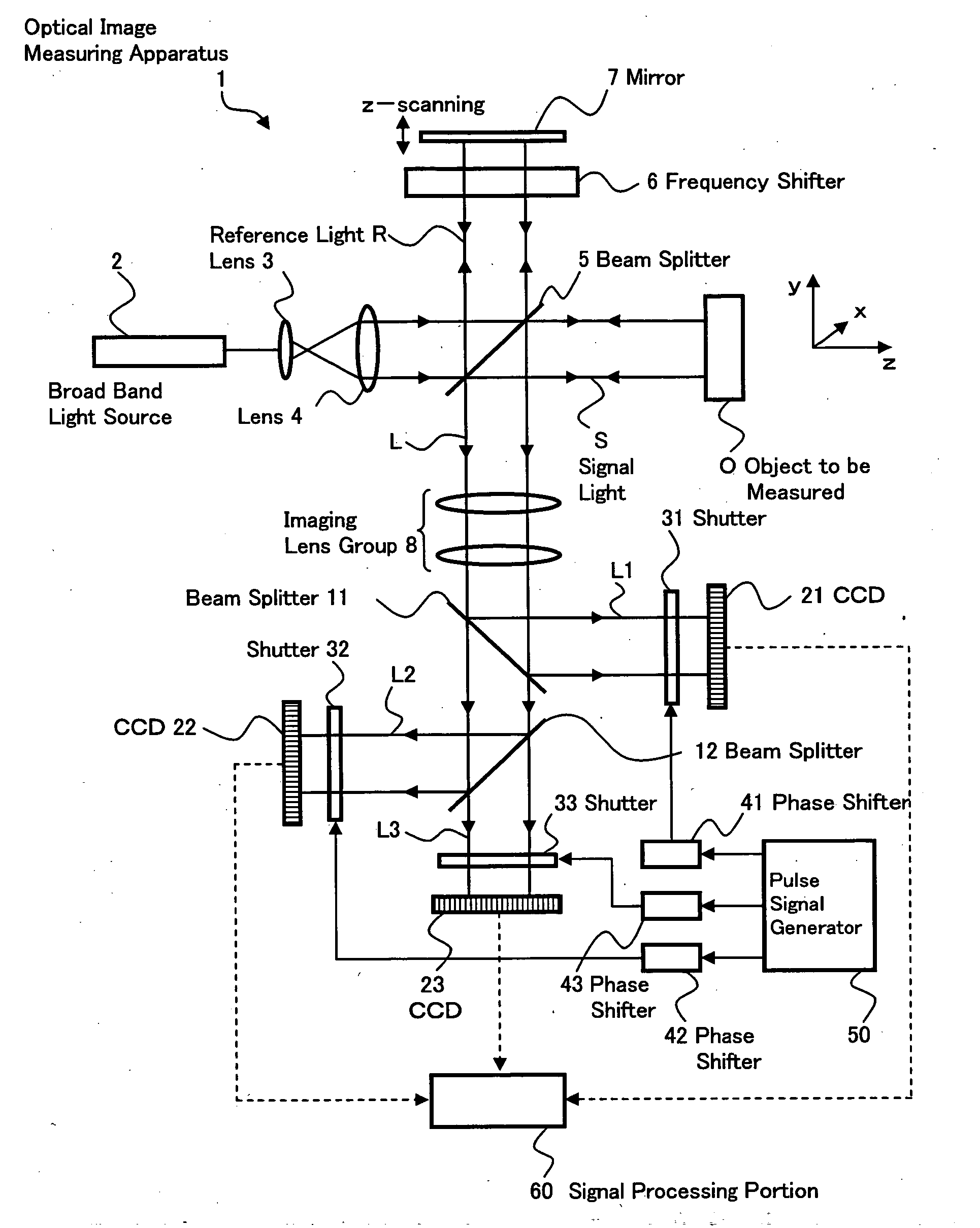
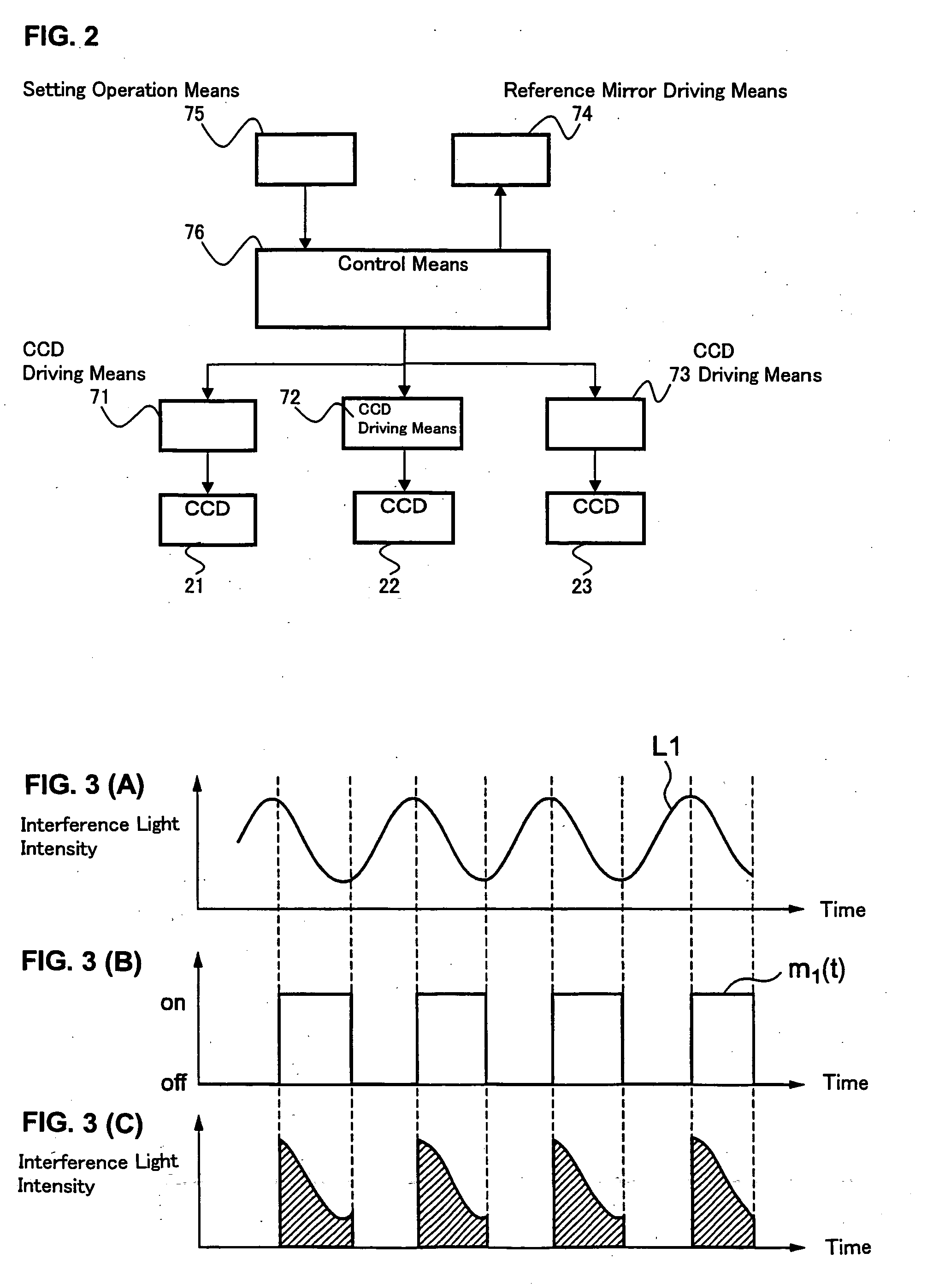
InactiveUS20050219545A1Improve accuracyEasy to changeInterferometersScattering properties measurementsWindow shutterSignal light
Provided is an optical image measuring apparatus capable of easily changing a scanning interval of an object to be measured in a depth direction with high precision. The apparatus includes an interference optical system for superimposing signal light propagating through the object to be measured on reference light subjected to frequency shift to produce interference light, a reference mirror driving unit for driving a mirror to scan the object to be measured in the depth direction, shutters for sampling interference light beams, CCDs for storing charges for only a predetermined storage time and outputting electrical signals, a control unit for changing the storage time of the CCDs, a signal processing portion for calculating intensities and phases of interference light beams corresponding to each depth of the object to be measured which are successively detected by the CCDs during scanning based on the electrical signals successively outputted from the CCDs every changed storage time, and a setting operation unit for setting the storage time of the CCDs by an operator.
Owner:KK TOPCON
Optical image measuring apparatus and optical image measuring method
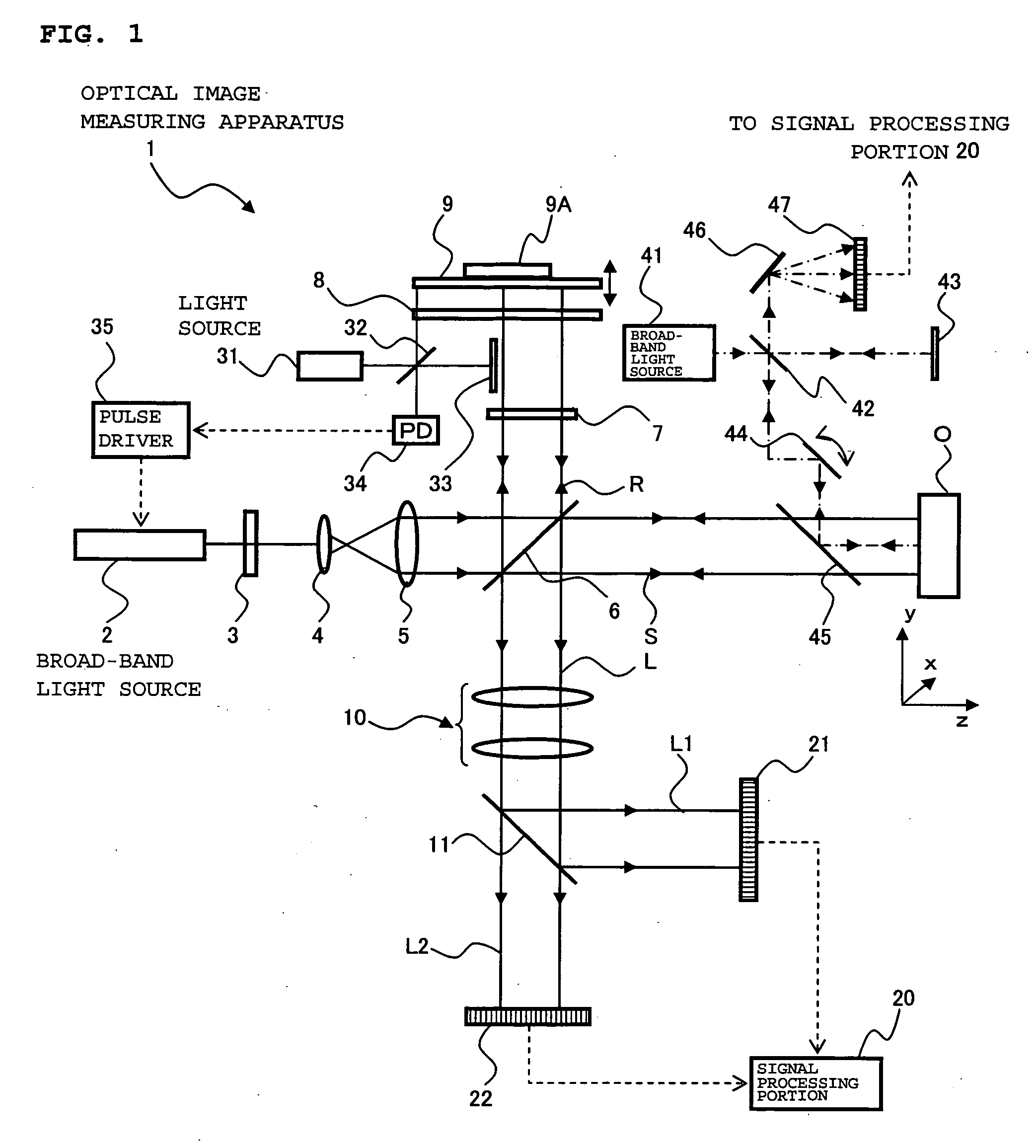
InactiveUS7492466B2Improve accuracyHigh precision formingInterferometersUsing optical meansObject basedSignal light
Provided is an optical image measuring apparatus forming a three-dimensional image based on tomographic images of an object, acquired at various depths even when the object moves during measurement. Including a half mirror (6) for dividing a light beam signal light (S) and reference light (R), a frequency shifter (8), a reference mirror (9) and a piezoelectric element (9A) used to change an optical path length of the reference light (R), CCDs (21, 22) for receiving interference light beams (L) resulting from interference light produced by superimposing the signal light (S) and the reference light (R) on each other by the half mirror (6) and outputting detection signals, an image forming portion for forming tomographic images based on the detection signals, a measurement depth calculating means (53), and an image processing portion (57). Forming a three-dimensional image or the like based on the arranged tomographic images.
Owner:KK TOPCON
Off-axis illumination direct-to-digital holography
InactiveUS6747771B2Cost effectiveImprove imaging resolutionUsing optical meansOptical axisFourier transform on finite groups
Systems and methods are described for off-axis illumination direct-to-digital holography. A method of recording an off-axis illuminated spatially heterodyne hologram including spatially heterodyne fringes for Fourier analysis, includes: reflecting a reference beam from a reference mirror at a non-normal angle; reflecting an object beam from an object at an angle with respect to an optical axis defined by a focusing lens; focusing the reference beam and the object beam at a focal plane of a digital recorder to form the off-axis illuminated spatially heterodyne hologram including spatially heterodyne fringes for Fourier analysis; digitally recording the off-axis illuminated spatially heterodyne hologram including spatially heterodyne fringes for Fourier analysis; Fourier analyzing the recorded off-axis illuminated spatially heterodyne hologram including spatially heterodyne fringes by transforming axes of the recorded off-axis illuminated spatially heterodyne hologram including spatially heterodyne fringes in Fourier space to sit on top of a heterodyne carrier frequency defined as an angle between the reference beam and the object beam; applying a digital filter to cut off signals around an original origin; and then performing an inverse Fourier transform.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
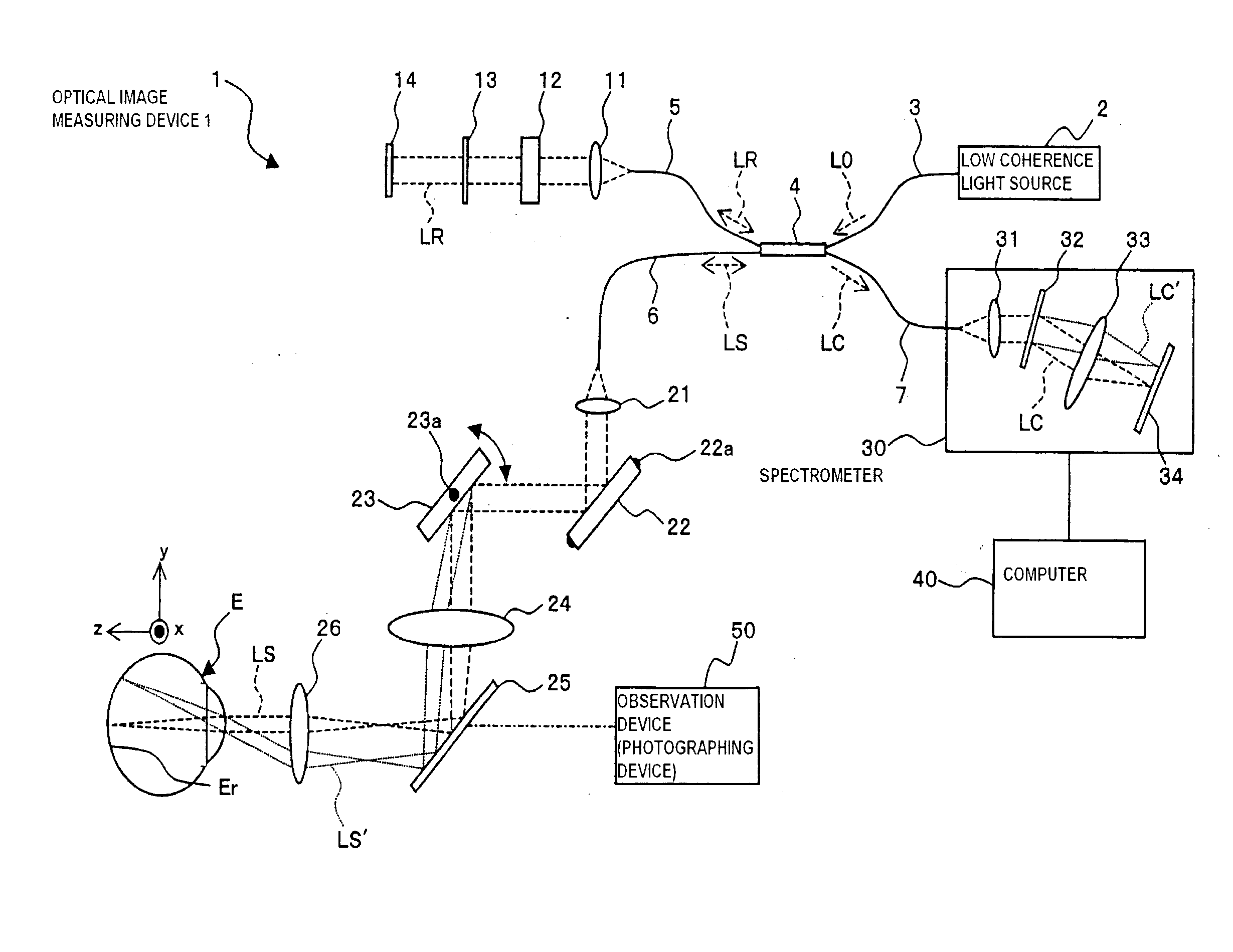
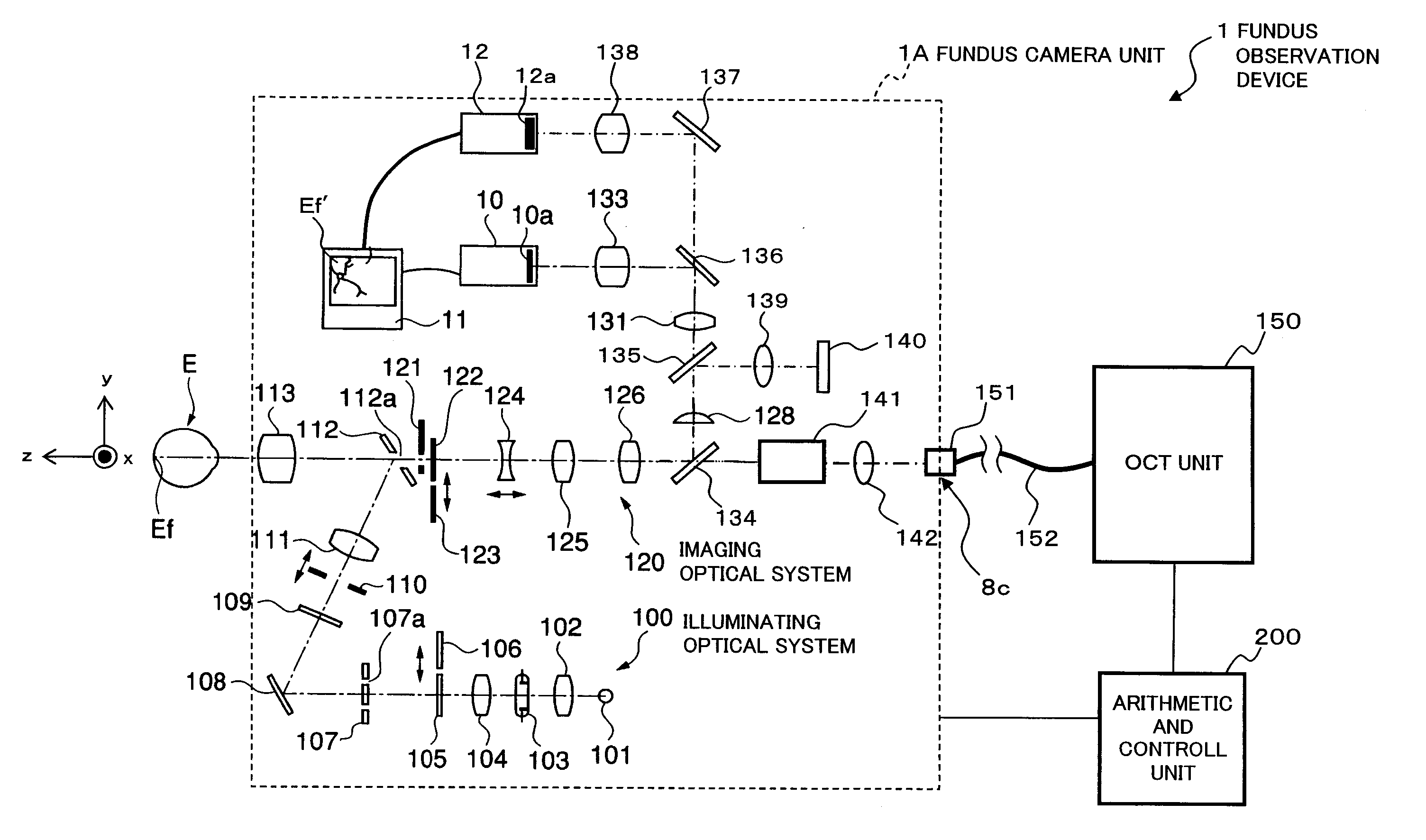
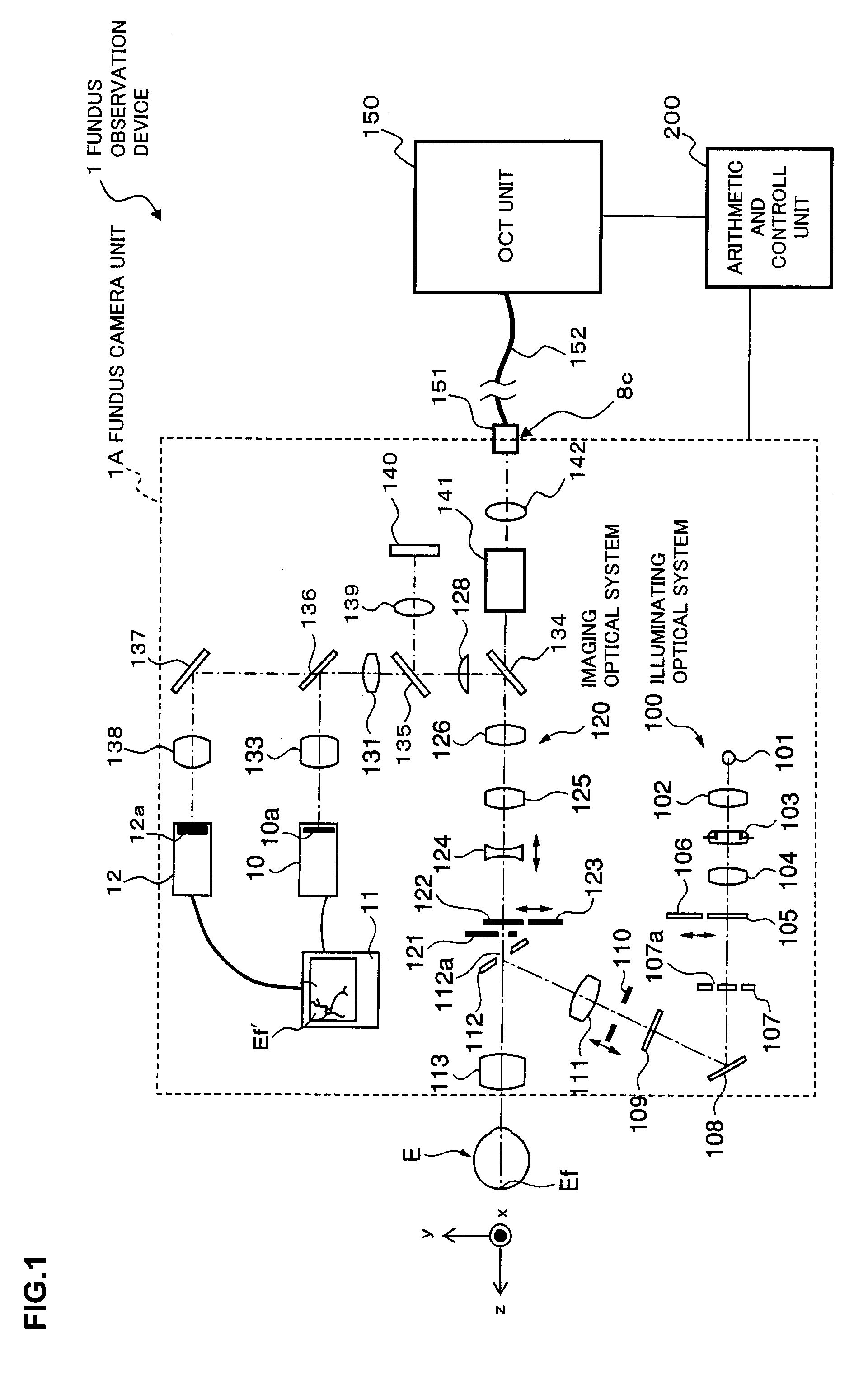
Fundus Observation Device
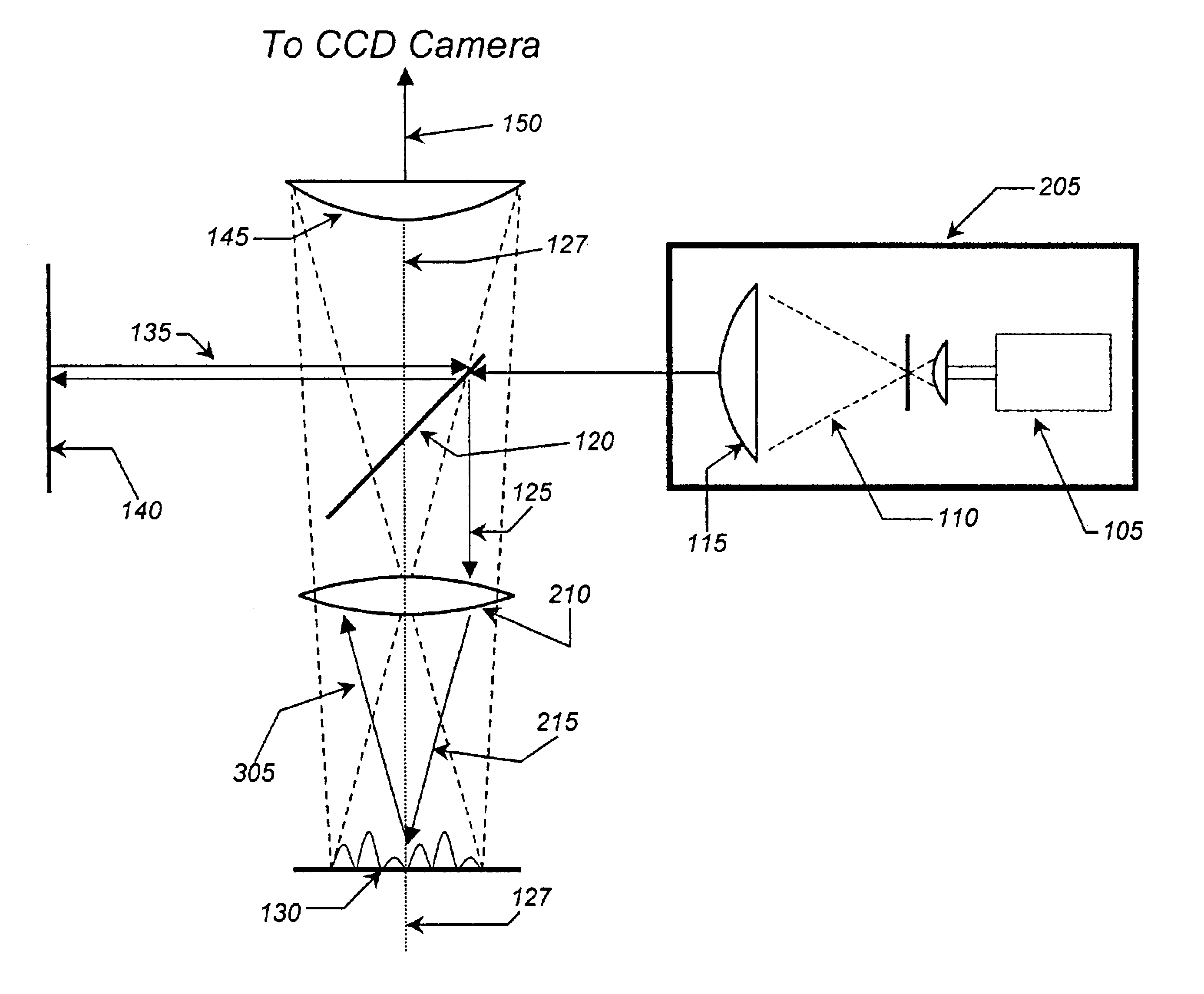
ActiveUS20070159595A1Interference can be controlledHigh interference efficiencyOthalmoscopesFundus cameraOphthalmology
A fundus observation device which can simultaneously capture both surface images and tomographic images of the fundus oculi is provided. The fundus observation device 1 has a fundus camera unit 1A, an OCT unit 150, and an arithmetic and control unit 200. The fundus camera unit 1A has an illuminating optical system 100 and an imaging optical system 120. The arithmetic and control unit 200 forms the surface image of fundus oculi Ef based on signals from fundus camera unit 1A. The OCT unit 150 divides low coherence light LO into the signal light LS and the reference light LR, and detects the interference light LC that can be obtained from the signal light LS passing through fundus oculi Ef and the reference light LR passing through reference mirror 174. The arithmetic and control unit 200 forms tomographic images of fundus oculi Ef based on these detecting results. A Dichroic mirror 134 combines the optical path of the signal light LS toward fundus oculi Ef into the optical path for imaging of the imaging optical system 120, and separates the optical path of the signal light LS towards fundus oculi Ef from the optical path for imaging.
Owner:KK TOPCON
Method and apparatus using microscopic and interferometric based detection
ActiveUS7095507B1Less sensitive to process noiseMaterial analysis by optical meansUsing optical meansMicroscopic examTest beam
An integrated interferometric and intensity based microscopic inspection system inspects semiconductor samples. A switchable illumination module provides illumination switchable between interferometric inspection and intensity based microscopic inspection modes. Complex field information is generated from interference image signals received at a sensor. Intensity based signals are used to perform the microscopic inspection. The system includes at least one illumination source for generating an illumination beam and an integrated interferometric microscope module for splitting the illumination beam into a test beam directed to the semiconductor sample and a reference beam directed to a tilted reference mirror. The beams are combined to generate an interference image at an image sensor. The tilted reference mirror is tilted with respect to the reference beam that is incident on the mirror to thereby generate fringes in the interference image. The system also includes an image sensor for acquiring the interference image from the inteferometric microscope module and intensity signals from the microscopic inspection image.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Microstructure appearance test method based on infrared white light interference technique
InactiveCN101266139ABreak through the shortcomings of not being able to measure deep trench structuresUsing optical meansLight sourceMicrostructure
The invention relates to the micro appearance test of a micro electro-mechanical MEMS component, concretely a microstructure appearance test method based on a white infrared light interference technology, which solves the problem existing in the prior art that the sidewall appearance of the deep trench structure of the MEMS component is unable to be surveyed, realized by the following steps: 1) the lossless processing of the impediment infrared transmission for the testing sidewall surface is carried out; 2) the infrared source is taken as the survey photo source, the infrared light is adjusted to be the parallel light when passing through a lenses group, is divided into a reference beam and a examination light beam by a dispersion component, the examination light beam transmits the sidewall of the deep trench structure, after reflected by the interface of the sidewall and the lossless processing, is carried on coherent superposition with the reference beam reflected by a reference mirror, forms a interference fringe pattern; 3) the interference fringe pattern is transmitted to the computer after passing through an optical lens, the CCD image sensor, so that the three dimensional appearance chart of the sidewall measured is obtained by analyzing and processing. The invention overcomes the shortcoming existing in the prior art that the deep trench structure surveying is unable to be realized and the application domain is wild.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
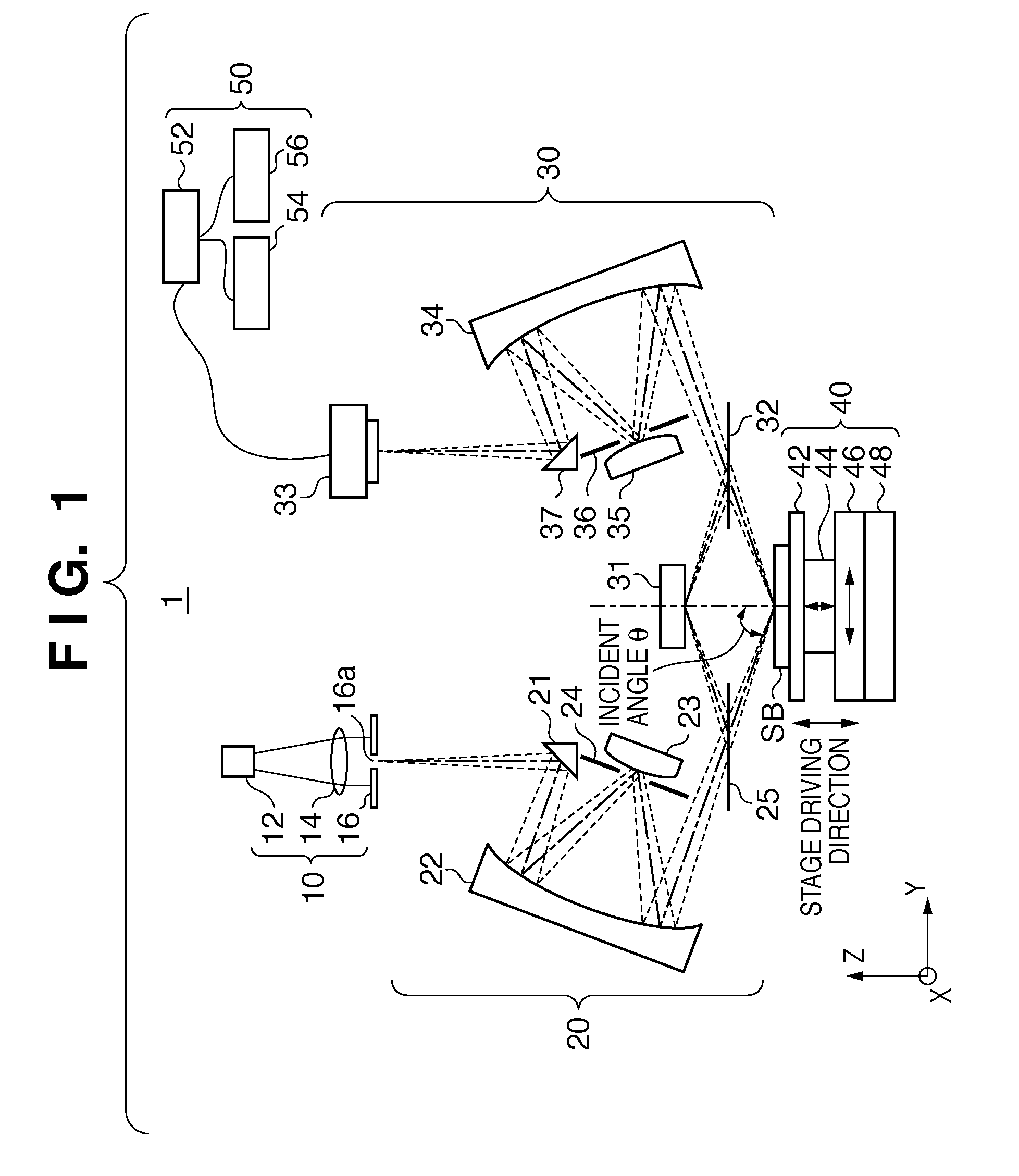
System, apparatus, and method for determining temperature/thickness of an object using light interference measurements
A measuring apparatus including a light source that emits light with a wavelength that allows the light to be transmitted through and reflected at each measurement target, a splitter that splits the light from the light source into measurement light and reference light, a reference mirror at which the reference light from the splitter is reflected, a mechanism for driving the reference mirror to adjust the optical path length of the reference light reflected from the reference mirror and a mechanism for measuring the interference of the reference light reflected from the reference mirror as the reference light from the splitter is radiated toward the reference mirror and measurement beams reflected from a plurality of measurement targets as the measurement light from the splitter is radiated toward the measurement targets so as to be transmitted through the measurement targets.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Characterization of transmission losses in an optical system
ActiveUS7791724B2Minimize impactPhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptoelectronicsTransmission loss
The illumination profile of a radiation beam is initially measured using a CCD detector. A reference mirror is then placed in the focal plane of the high aperture lens and the reflected radiation measured. By comparing the illumination profile and the detected radiation it is possible to determine the transmission losses for S and P polarisation which can then be used in scatterometry modeling.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Calibration Method and Apparatus
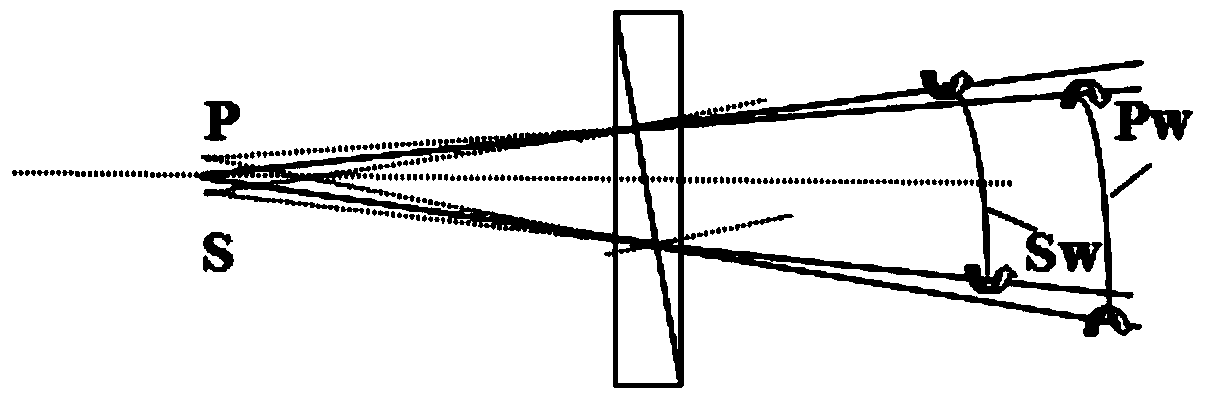
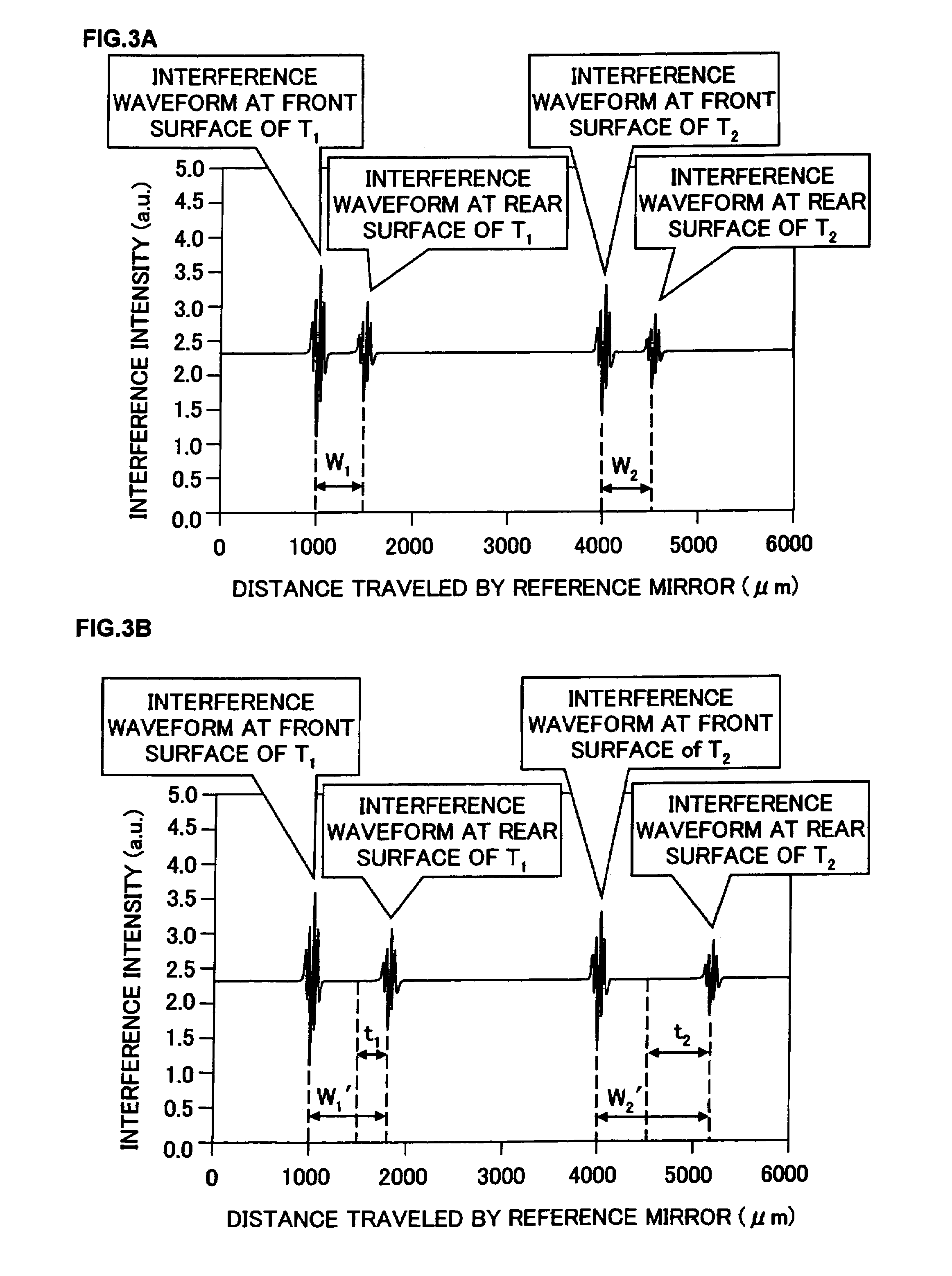
ActiveUS20110178785A1Optically investigating flaws/contaminationComputation using non-denominational number representationScatterometerMueller calculus
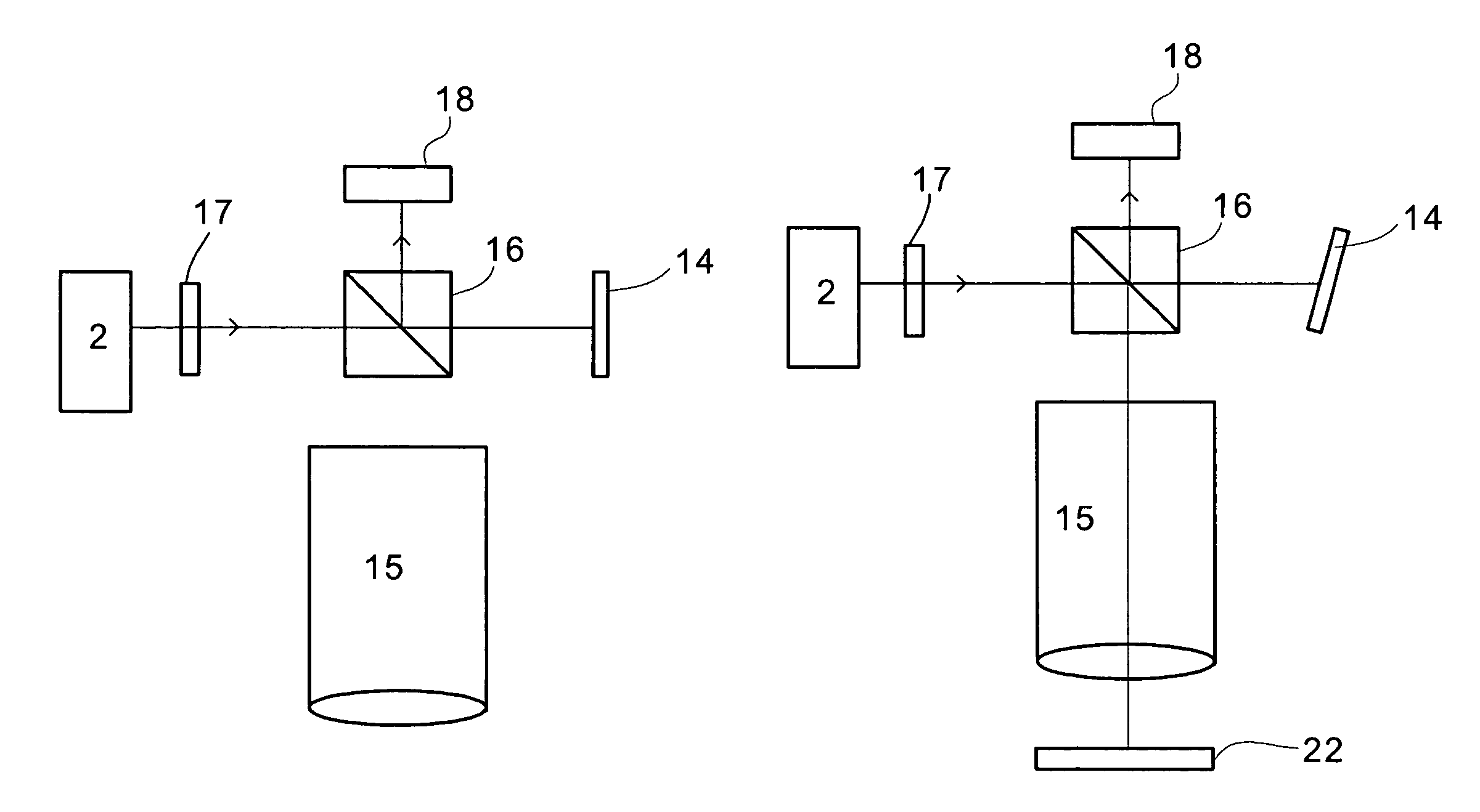
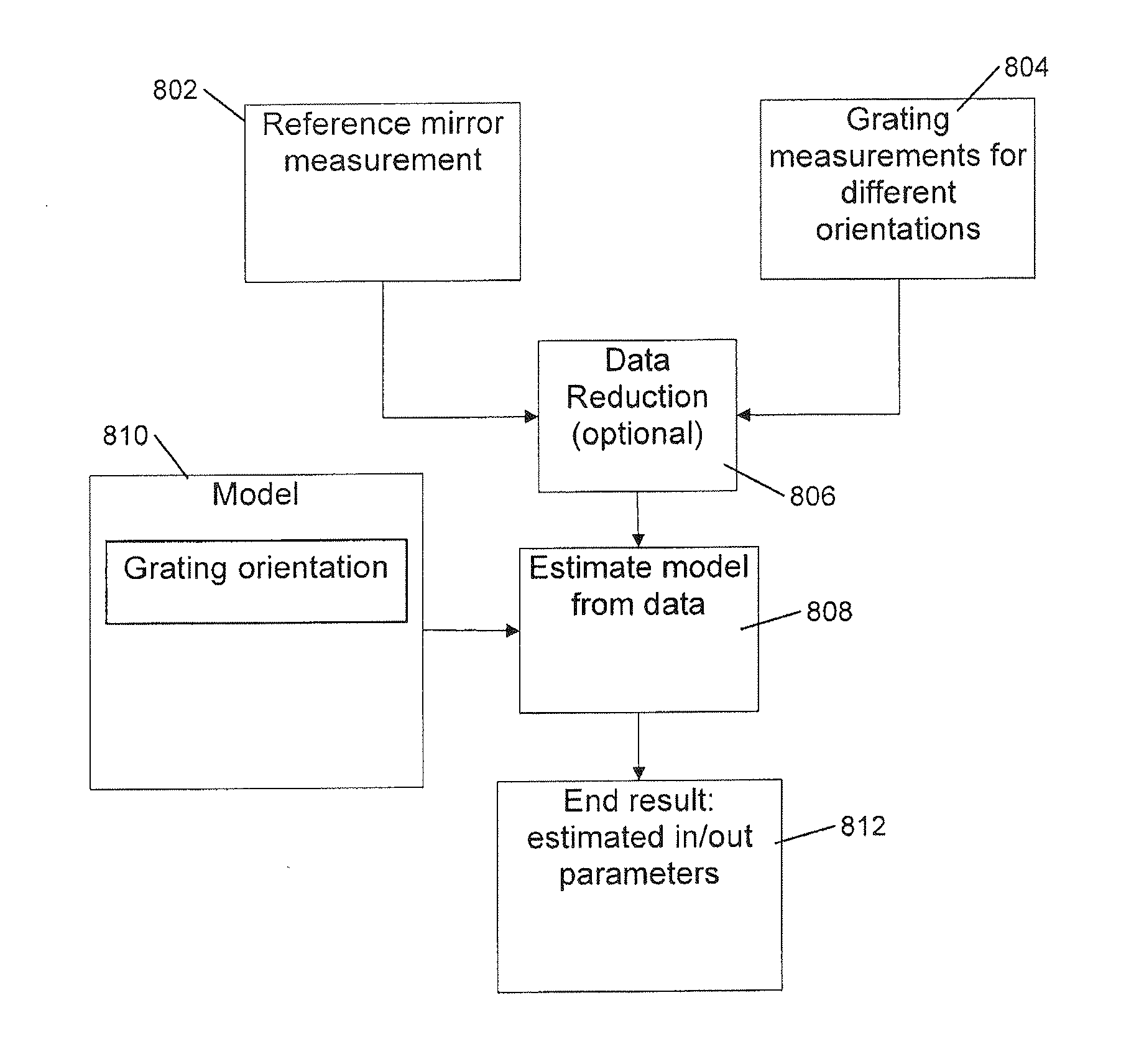
Calibration of an angularly resolved scatterometer is performed by measuring a target in two or more different arrangements. The different arrangements cause radiation being measured in an outgoing direction to be different combinations of radiation illuminating the target from ingoing directions. A reference mirror measurement may also be performed. The measurements and modeling of the difference between the first and second arrangements is used to estimate separately properties of the ingoing and outgoing optical systems. The modeling may account for symmetry of the respective periodic target. The modeling typically accounts for polarizing effects of the ingoing optical elements, the outgoing optical elements and the respective periodic target. The polarizing effects may be described in the modeling by Jones calculus or Mueller calculus. The modeling may include a parameterization in terms of basis functions such as Zernike polynomials.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
High precision split joint sub lens relative tilt error photo-electric detection system
InactiveCN101276056AHigh-quality imaging facilitatesImprove detection accuracyTelescopesTesting optical propertiesBeam splittingPrism
A high-precision splitting sub-mirror relative inclining error photoelectric detection system comprises the following components: a HE-NE laser, a spatial filter, a collimator objective, a cubic beam splitting prism, a detected splitting sub-mirror set, a reference mirror, a light path beam-contracting system, a CCD planar array photoelectric detector and a data processing system. The HE-NE laser, the spatial filter and the collimator objective form a light source arm part of the detection system together. The detected splitting sub-mirror set forms a measuring arm part of the detection system. The reference reflecting mirror forms a reference arm part of the detection system. The relative inclining error information which is detected by the detecting arm and is between the splitting sub-mirrors is detected by the CCD planar array photoelectric detector. The detected interference image information is processed by a data processing system for real-time detecting the inclining error between the splitting sub-mirrors. The invention can execute a real-time high-precision detection. The effect of the relative inclining error between the sub-mirrors to the imagining quality of the telescope can be reduced with a large scale and the invention has the advantage of simple structure.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Full-eye optical coherence tomography imager
ActiveCN103815868ARealize 3D high-resolution imagingHigh sweep rateOthalmoscopesImaging qualityData acquisition
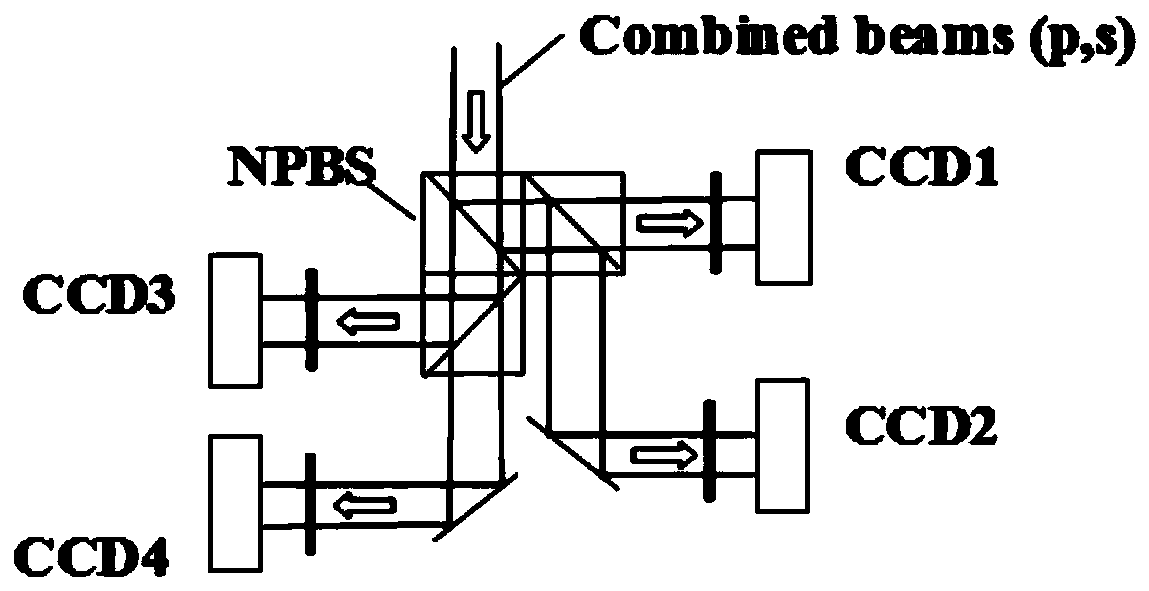
A full-eye optical coherence tomography imager comprises a frequency sweeping light source, an optical fiber polarizer, a first optical circulator, a second optical circulator, a first broadband polarization splitting prism, a second broadband polarization splitting prism, an ocular anterior segment scanning imaging light path, an eye ground scanning imaging light path, a third broadband polarization splitting prism, two reference mirrors, a fourth broadband polarization splitting prism, a fifth broadband polarization splitting prism, a second polarized light protecting coupler, a third polarized light protecting coupler, a first balance detector, a second balance detector, a function generation card, a data acquisition card, a computer and the like, wherein the first broadband polarization splitting prism, the second broadband polarization splitting prism, the ocular anterior segment scanning imaging light path and the eye ground scanning imaging light path are arranged in a sample arm; the third broadband polarization splitting prism and the two reference mirrors are arranged in a reference arm; the fourth broadband polarization splitting prism, the fifth broadband polarization splitting prism, the second polarized light protecting coupler, the third polarized light protecting coupler, the first balance detector and the second balance detector are arranged at a detecting end. The imager is based on a frequency sweeping optical coherence tomography technology, a component p and a component s of a polarized beam are used for conducting imaging on an eye ground and an ocular anterior segment respectively, and thus three-dimensional high resolution real-time imaging can be conducted on an full eye structure at the same time on the same system without any device for conversion. By means of the full-eye optical coherence tomography imager, optical path length and dispersion matching and scan setting can respectively be carried out on ocular anterior segment imaging and eye ground imaging, and thus the optimal imaging quality and the view field size of ocular anterior segment imaging and eye ground imaging can be obtained at the same time.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
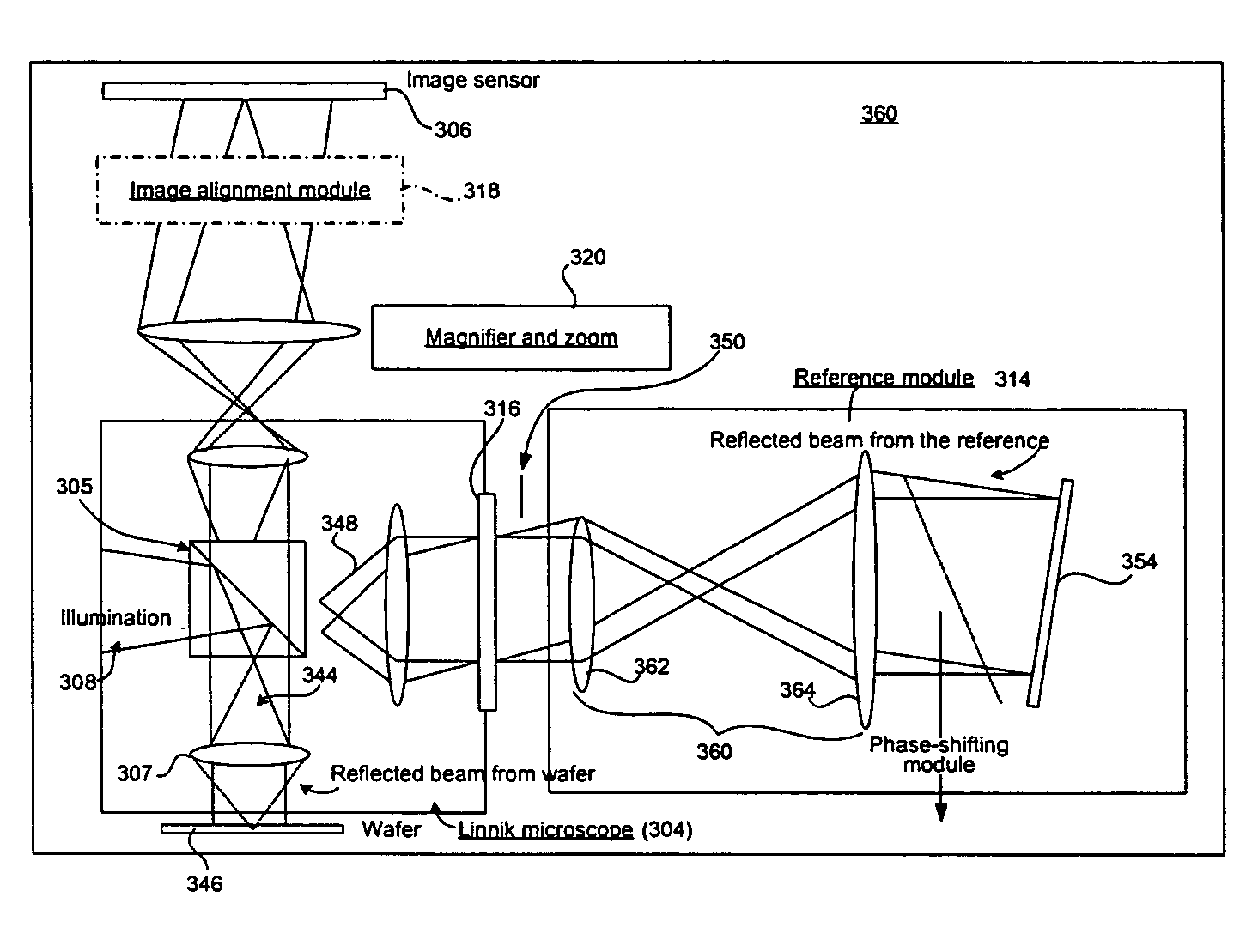
Interference microscope and measuring apparatus
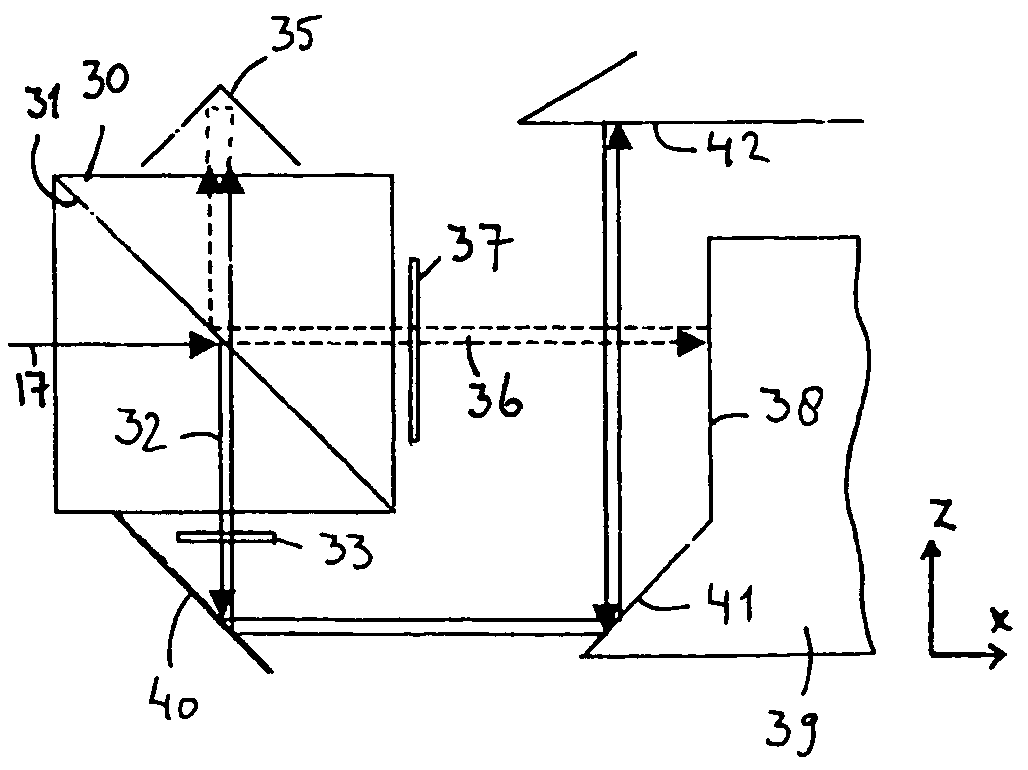
InactiveCN102472608AImprove work efficiencyInterferometersMaterial analysis by optical meansPole pieceOptoelectronics
Provided are an interference microscope wherein samples, such as a wafer, are irradiated with a laser beam, and the inside of the sample surface is observed and inspected by using an interferometer, and a measuring apparatus. A reference light path for guiding light to between a beam splitter and a reference mirror is arranged, and a measuring light path for guiding light to between the beam splitter and the sample is also arranged, thus, an optical light path difference is provided between the reference light path and the measuring light path. Furthermore, interference fringes are formed in a detecting means by slightly tilting the reference mirror. With such simple constitution, the surface shapes of the samples (subjects to be measured), such as the wafer, are measured only by slightly tilting the reference mirror, and accurate coordinate positions of dusts, pole piece and the like can be specified.
Owner:KK TOPCON
Measuring apparatus, exposure apparatus, and device fabrication method
InactiveUS20090091723A1Reduce the impactImprove accuracyNanoinformaticsPhotomechanical apparatusObject basedMeasurement device
Owner:CANON KK
Method for measuring physical quantity of measurement object in substrate processing apparatus and storage medium storing program for implementing the method
ActiveUS20070127034A1Accurate measurementRadiation pyrometryThermometers using material expansion/contactionFiberOptical pathlength
A method capable of accurately measuring a physical quantity of a measurement object in a substrate processing apparatus. In a temperature measurement apparatus for implementing the method, two interference positions are measured at different timings when a reference mirror is caused to move in the direction away from a collimator fiber, and a difference between the two interference positions is calculated. When the reference mirror remote from the collimator fiber is caused to move toward the collimator fiber, two interference positions are measured at different timings, and a difference between the two interference positions is calculated. An average value of the interference position differences is calculated, an optical path length difference is determined from the average value, and a wafer temperature is calculated from the optical path length difference.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Micro-nano structure and morphology measurement device and method based on digital scanning and white light interference
ActiveCN103900493AEliminate the effects ofImprove anti-interference abilityUsing optical meansMicro nanoMeasurement device
The invention provides a micro-nano structure and morphology measurement device and method based on digital scanning and white light interference. The method includes the steps of projecting white light processed through beam expanding and collimation to the surface of an object to the measured and the surface of a reference mirror inside an interference microscope through semi-transparent and semi-reflective mirrors by means of a device composed of a digital micro mirror array, an imaging unit, the semi-transparent and semi-reflective mirrors, a white light source, an interference microscope objective, the object to be measured, a working table, a control unit, a spectrograph, optical fibers and an optical fiber coupling unit, enabling the white light to interfere with reflected light, obtaining the interference light intensities through the semi-transparent and semi-reflective mirrors, obtaining the surface of the digital micro mirror array through the imaging unit, controlling the micro mirror defection angles corresponding to pixels of the digital micro mirror array one by one so that the light intensities corresponding to different pixels can enter the optical fiber coupling unit one by one, transmitting spectral information obtained by a spectrograph and corresponding to the interference light intensities to the control unit, and conducting phase analysis on distribution of the spectrums corresponding to the interference light intensities to obtain the relative height of the surface of the object to be measured. The micro-nano structure and morphology measurement device and method have the advantages that the structure is simplified, the measurement accuracy is high, and the anti-interference capacity is high.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Optical image measuring apparatus and optical image measuring method
InactiveUS20060028652A1High detection sensitivityImprove accuracyInterferometersUsing optical meansSignal lightPolarizer
Provided is an optical image measuring apparatus capable of effectively obtaining a signal intensity of interference light and phase information thereof by improving detection sensitivity. The optical image measuring apparatus includes a broad-band light source for outputting a light beam whose intensity is periodically modulated, a polarizing plate for converting the light beam to linearly polarized light, a half mirror for dividing the light beam into signal light and reference light and superimposing the signal light and the reference light on each other to produce interference light, a wavelength plate for converting the reference light to circularly polarized light, a frequency shifter for shifting a frequency of the reference light, a reference mirror which is moved by a piezoelectric element, a polarization beam splitter for extracting an S-polarized light component and a P-polarized light component from the interference light, CCDs for detecting the respective polarized light components and outputting detection signals, and a signal processing portion for calculating a signal intensity of the interference light and a phase thereof based on the detection signals. An image of an object to be measured is formed based on a result obtained by calculation.
Owner:KK TOPCON
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com