Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
212 results about "Scatterometer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
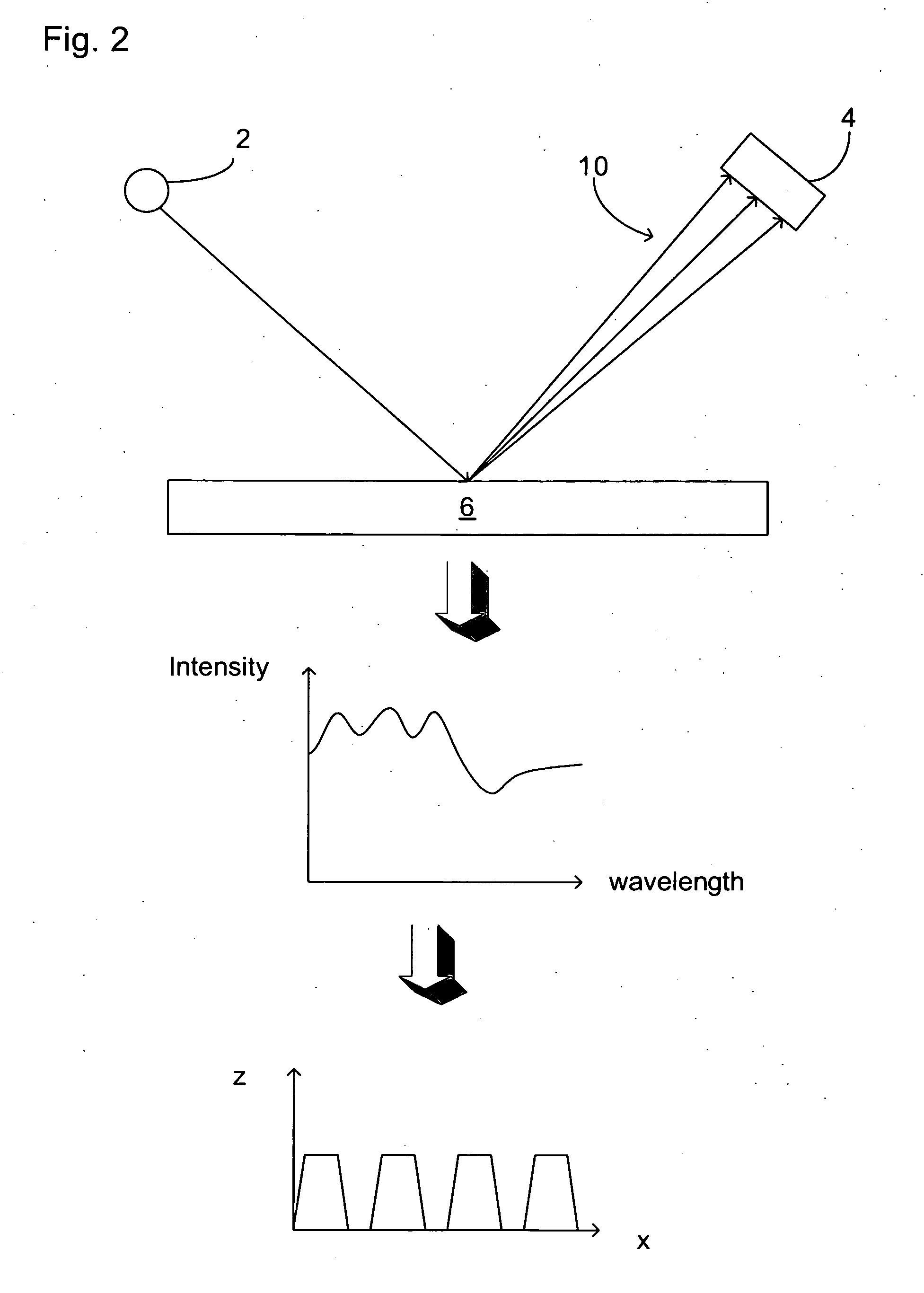
A scatterometer or diffusionmeter is a scientific instrument to measure the return of a beam of light or radar waves scattered by diffusion in a medium such as air. Diffusionmeters using visible light are found in airports or along roads to measure horizontal visibility. Radar scatterometers use radio or microwaves to determine the normalized radar cross section (σ⁰, "sigma zero" or "sigma naught") of a surface. They are often mounted on weather satellites to find wind speed and direction, and are used in industries to analyze the roughness of surfaces.
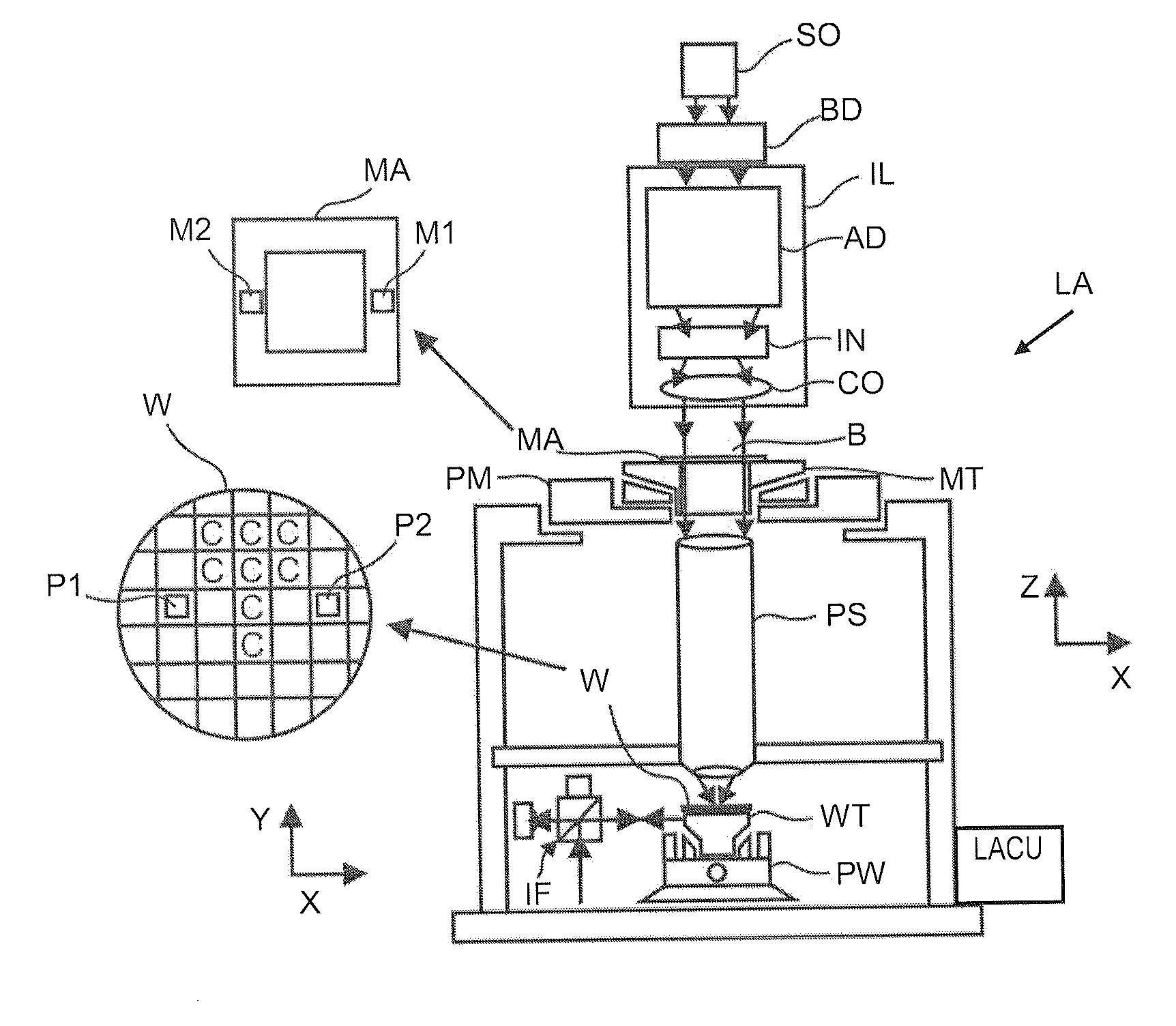
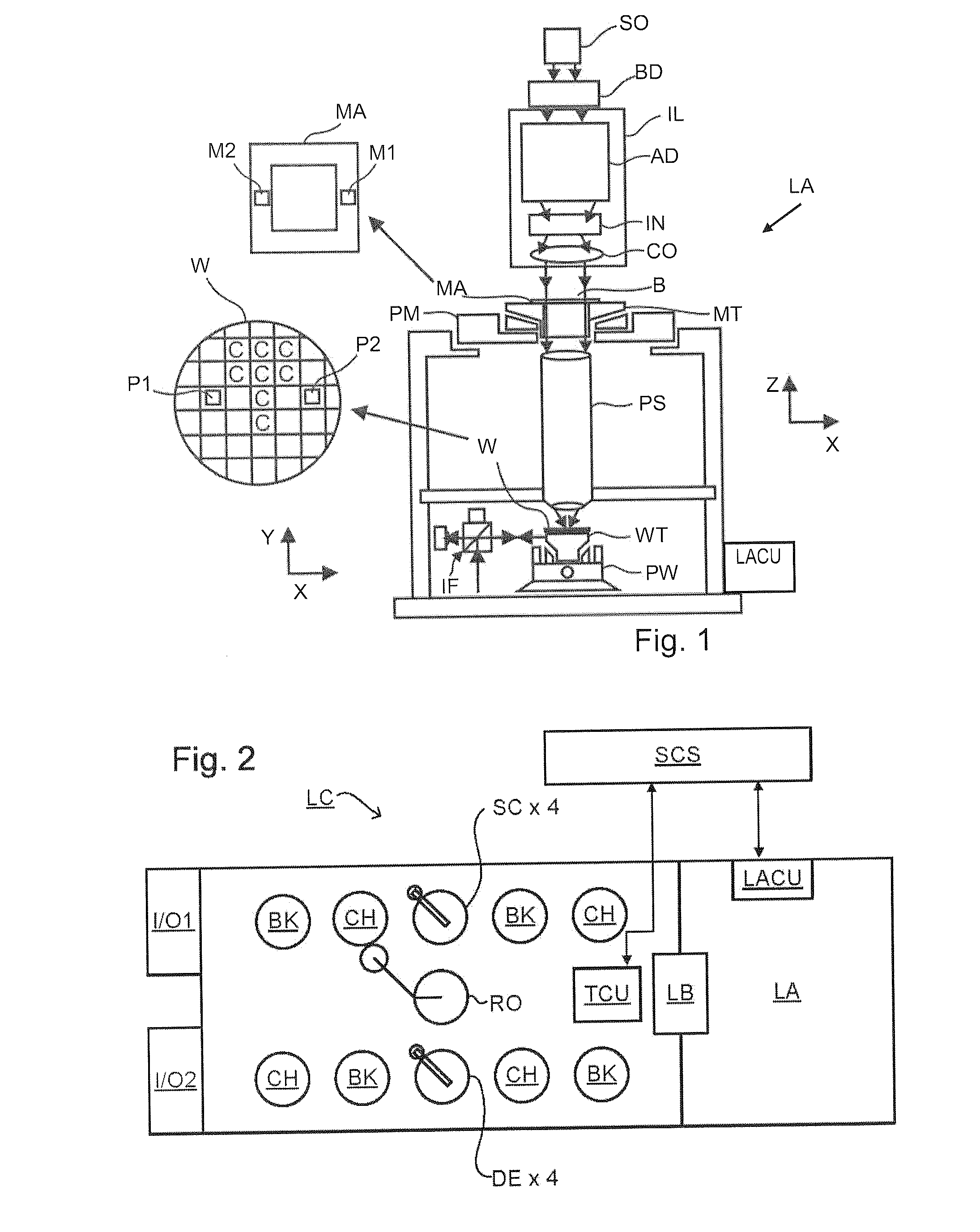
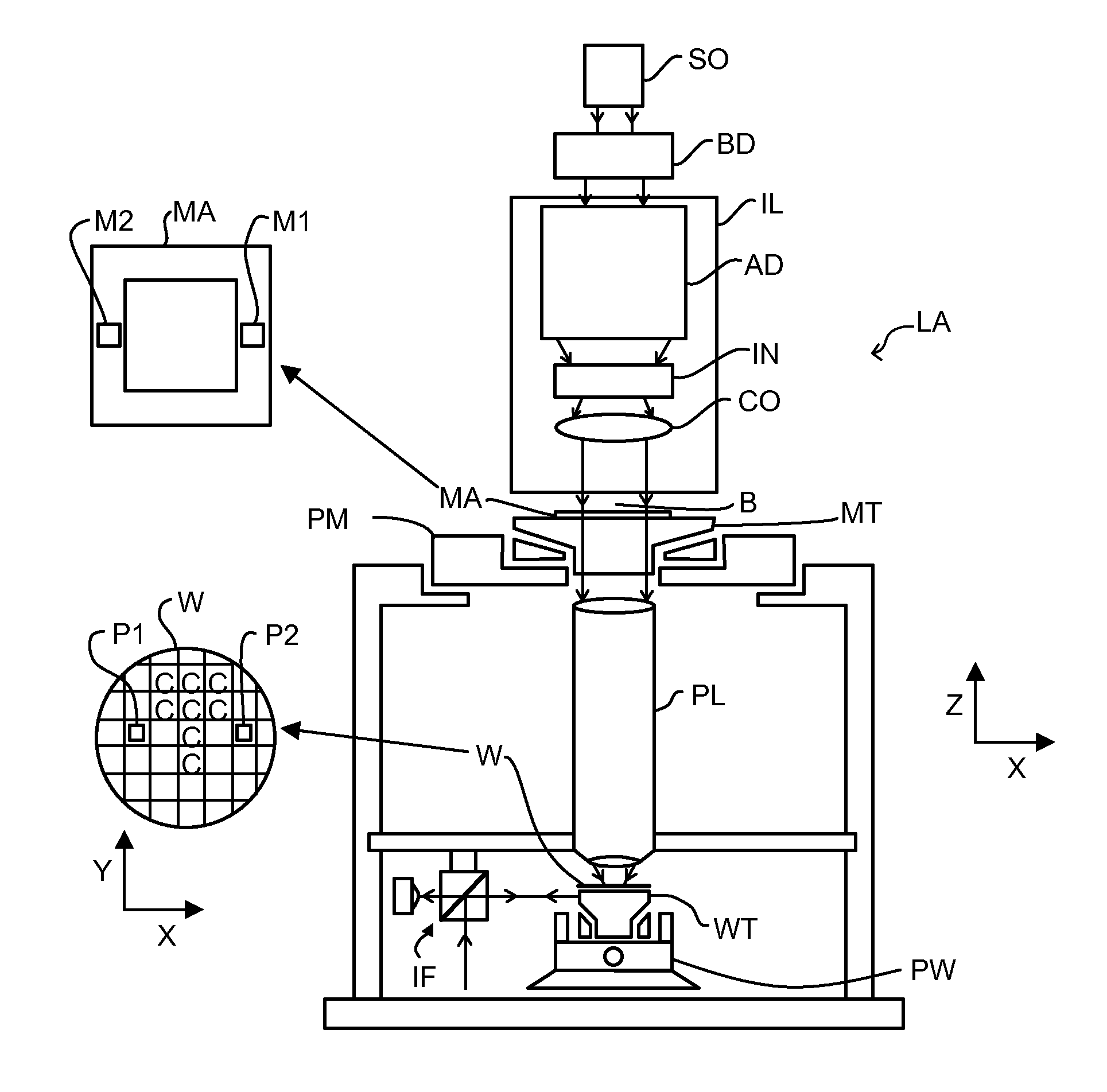
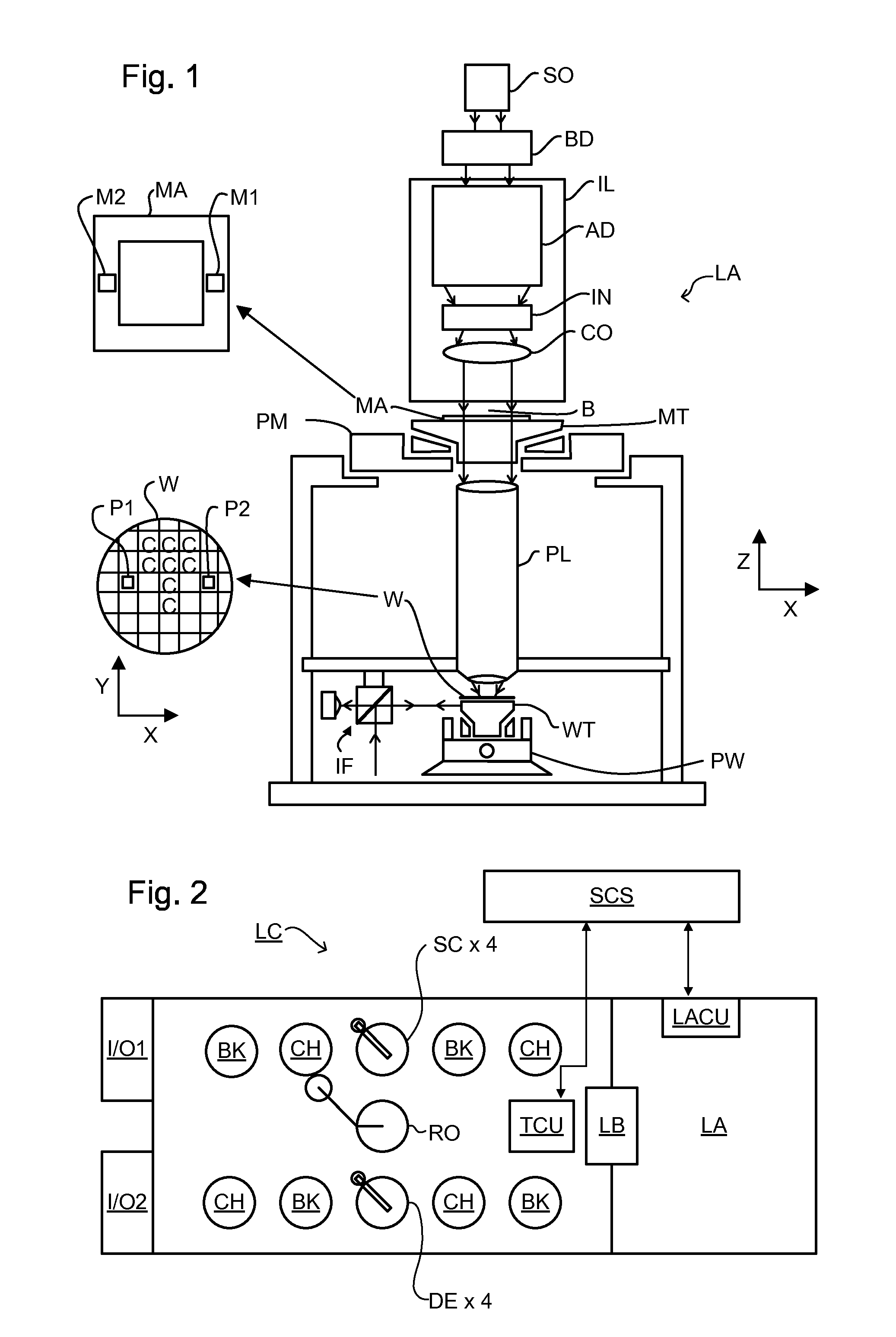
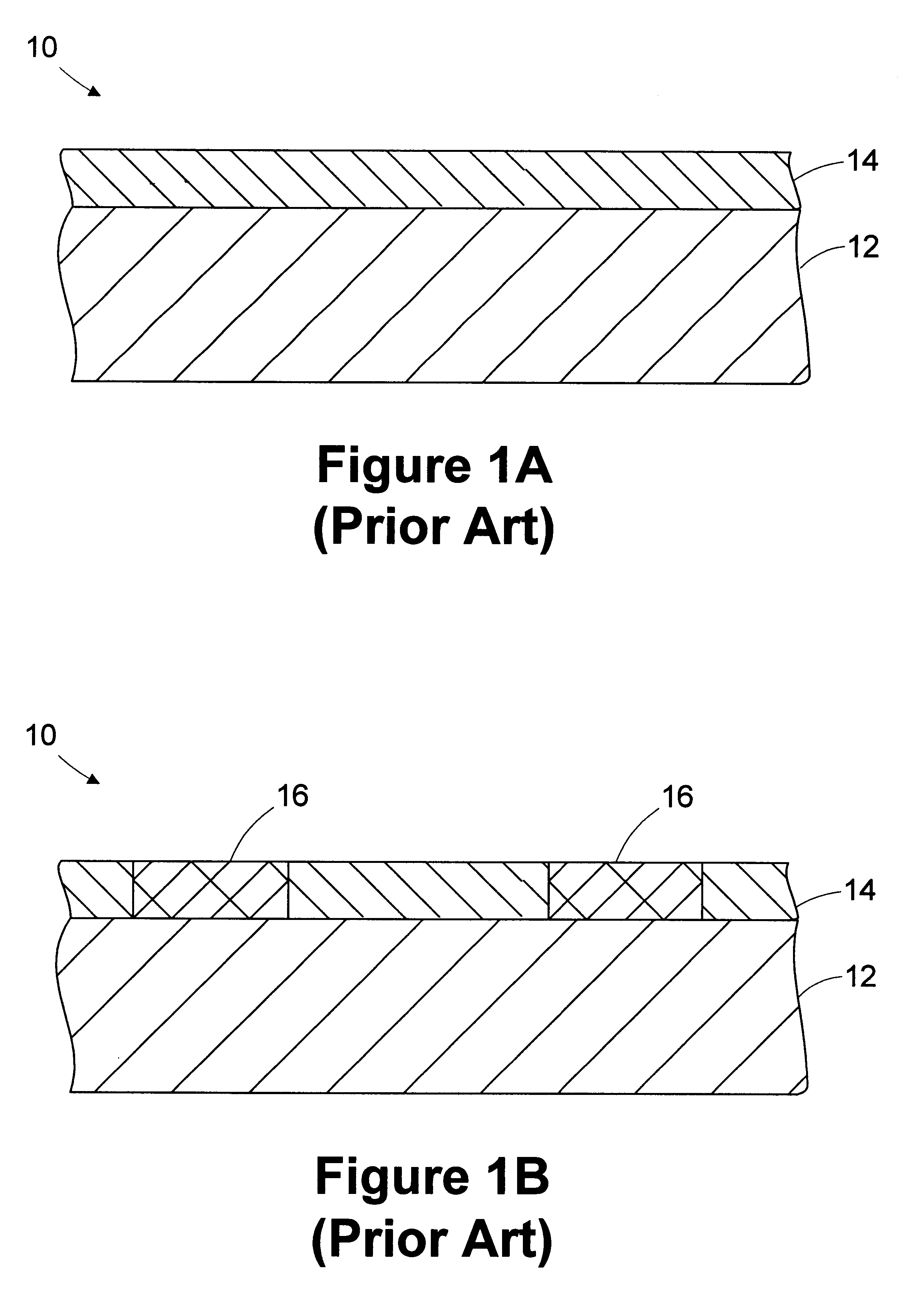
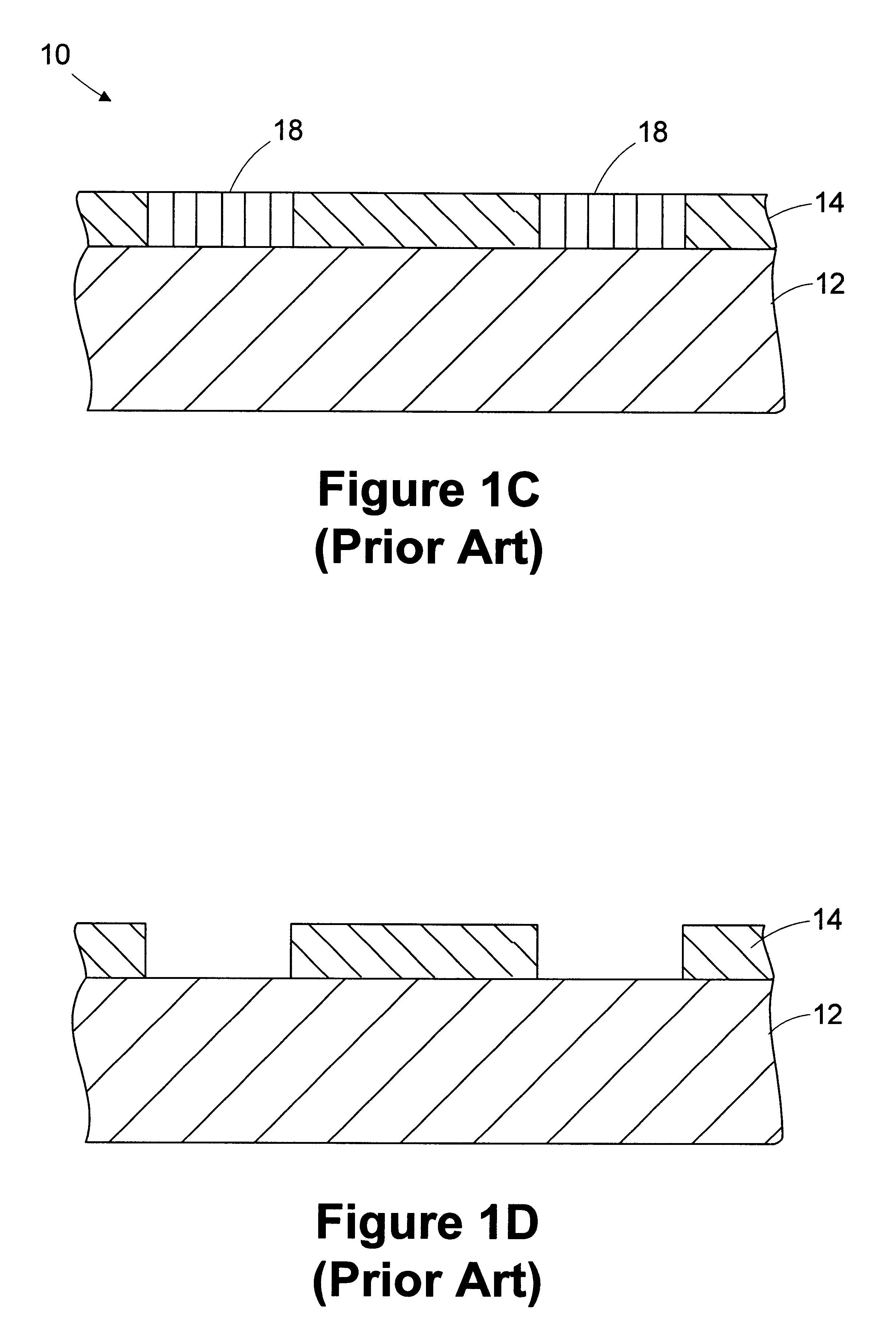
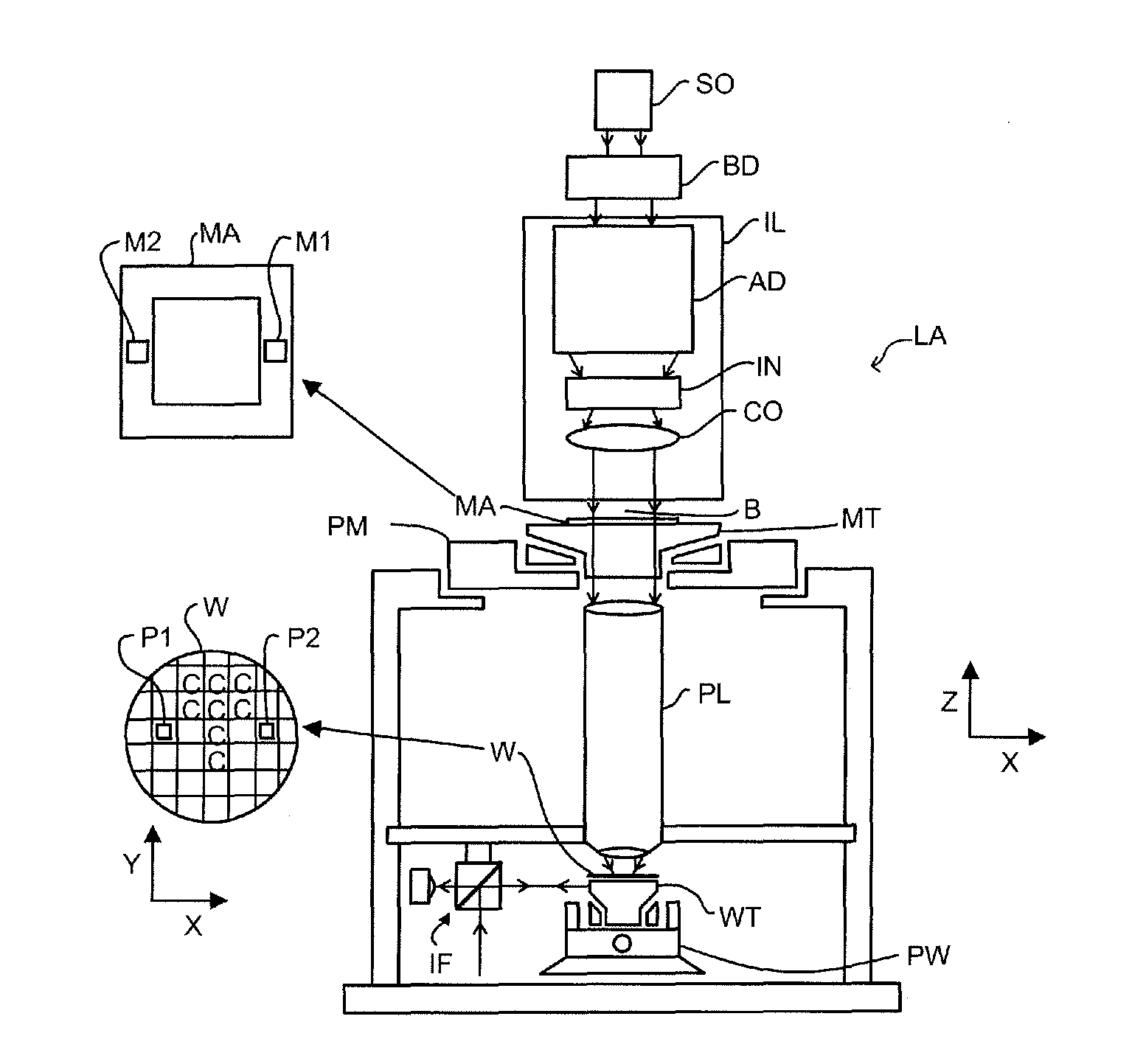
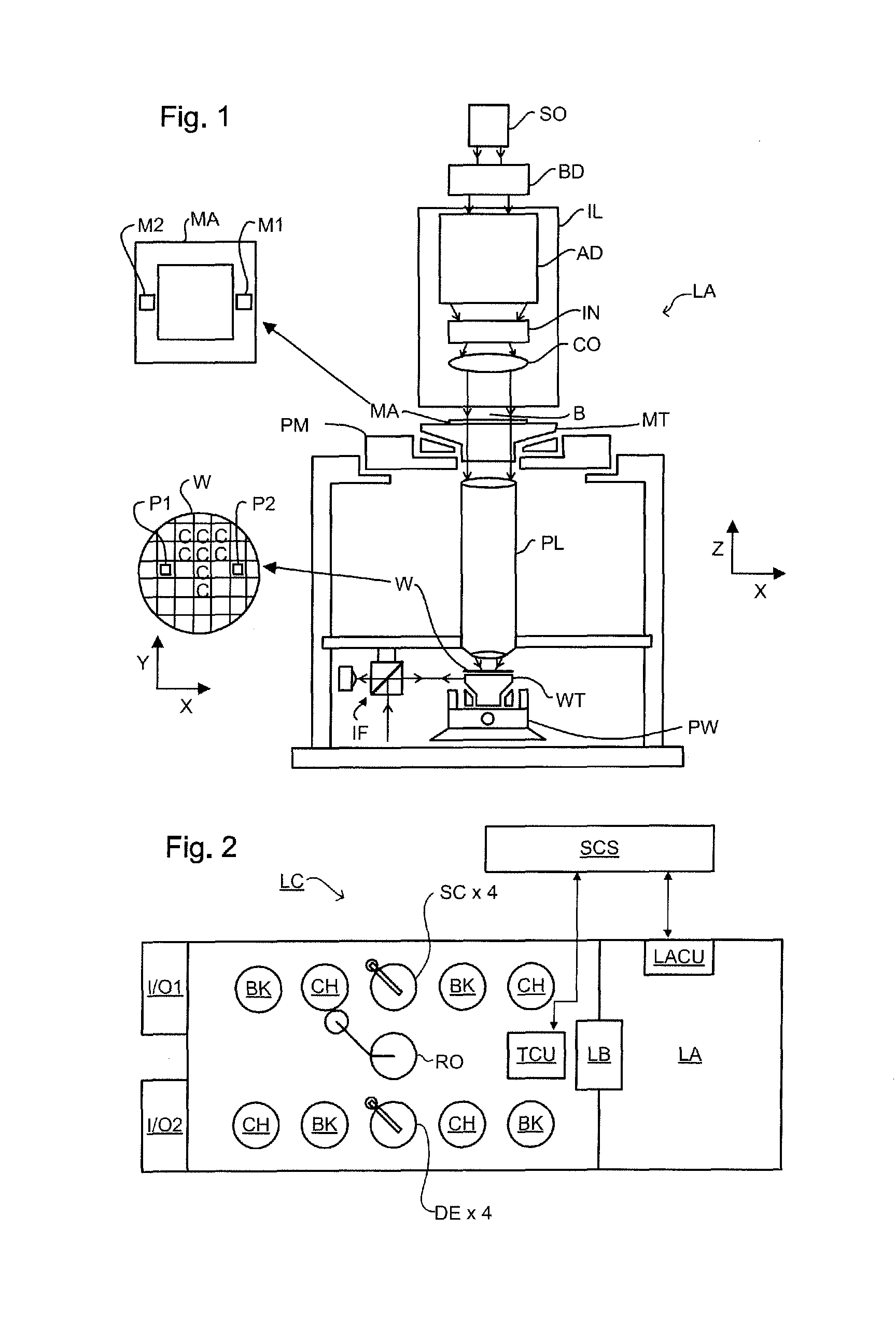
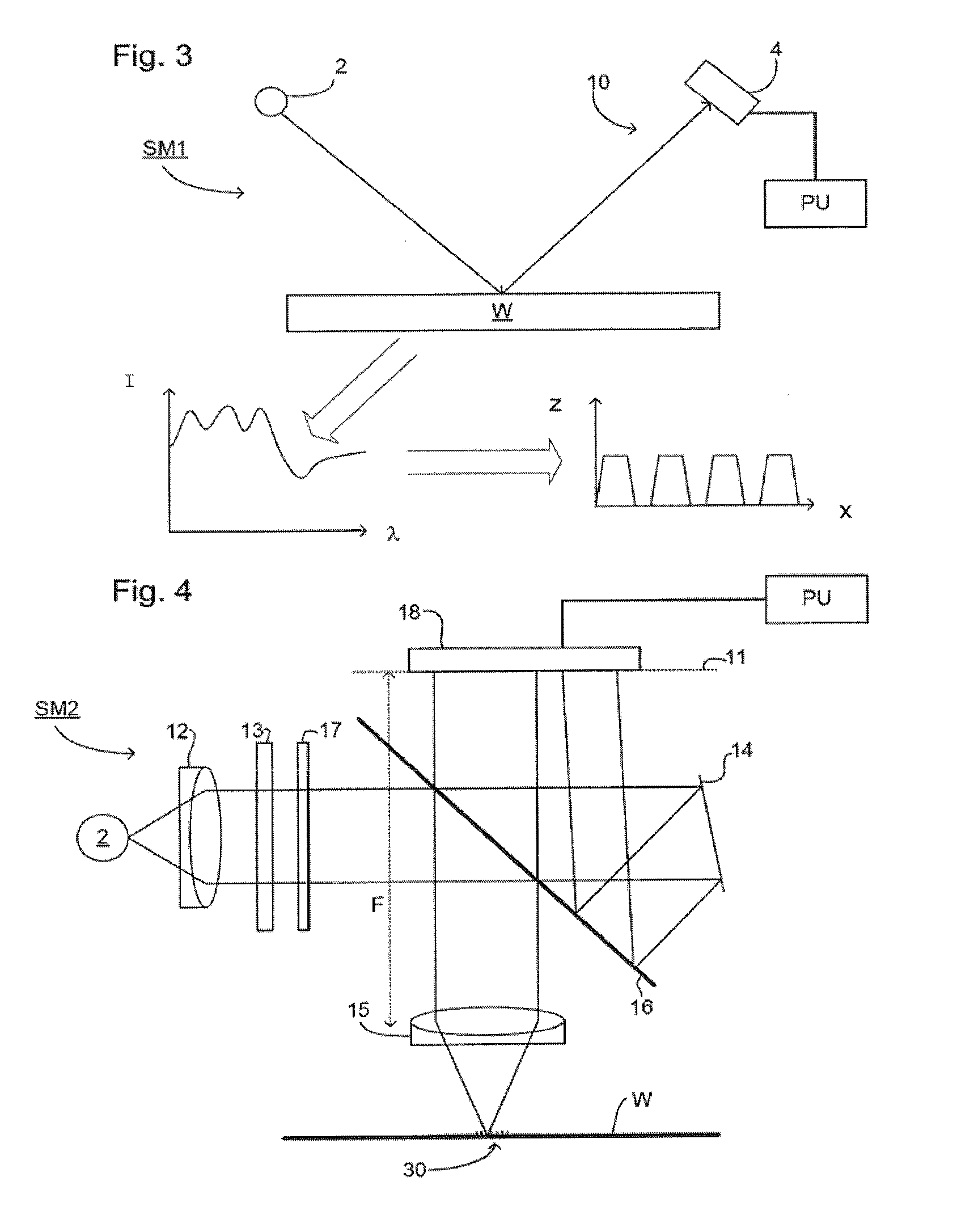
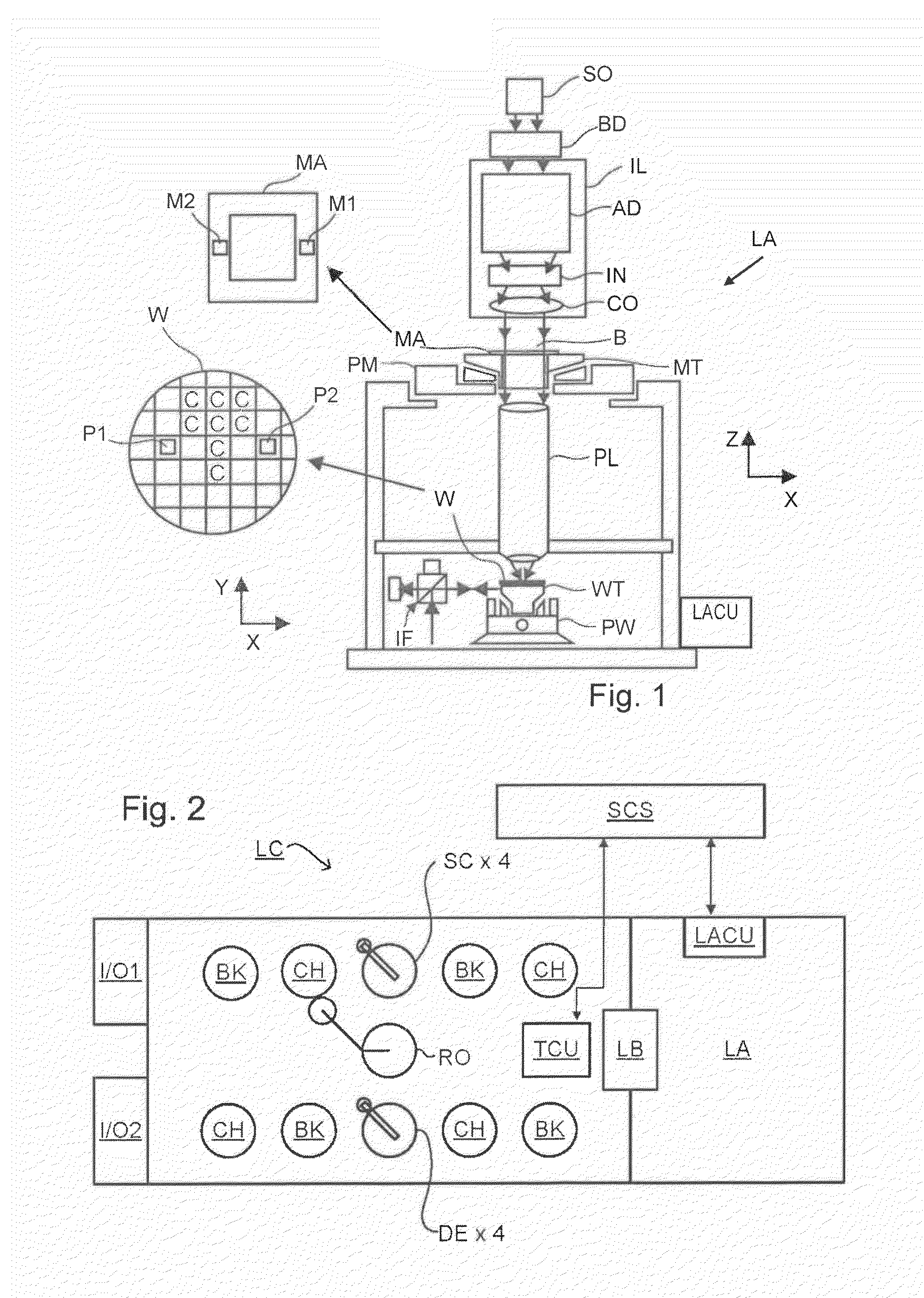
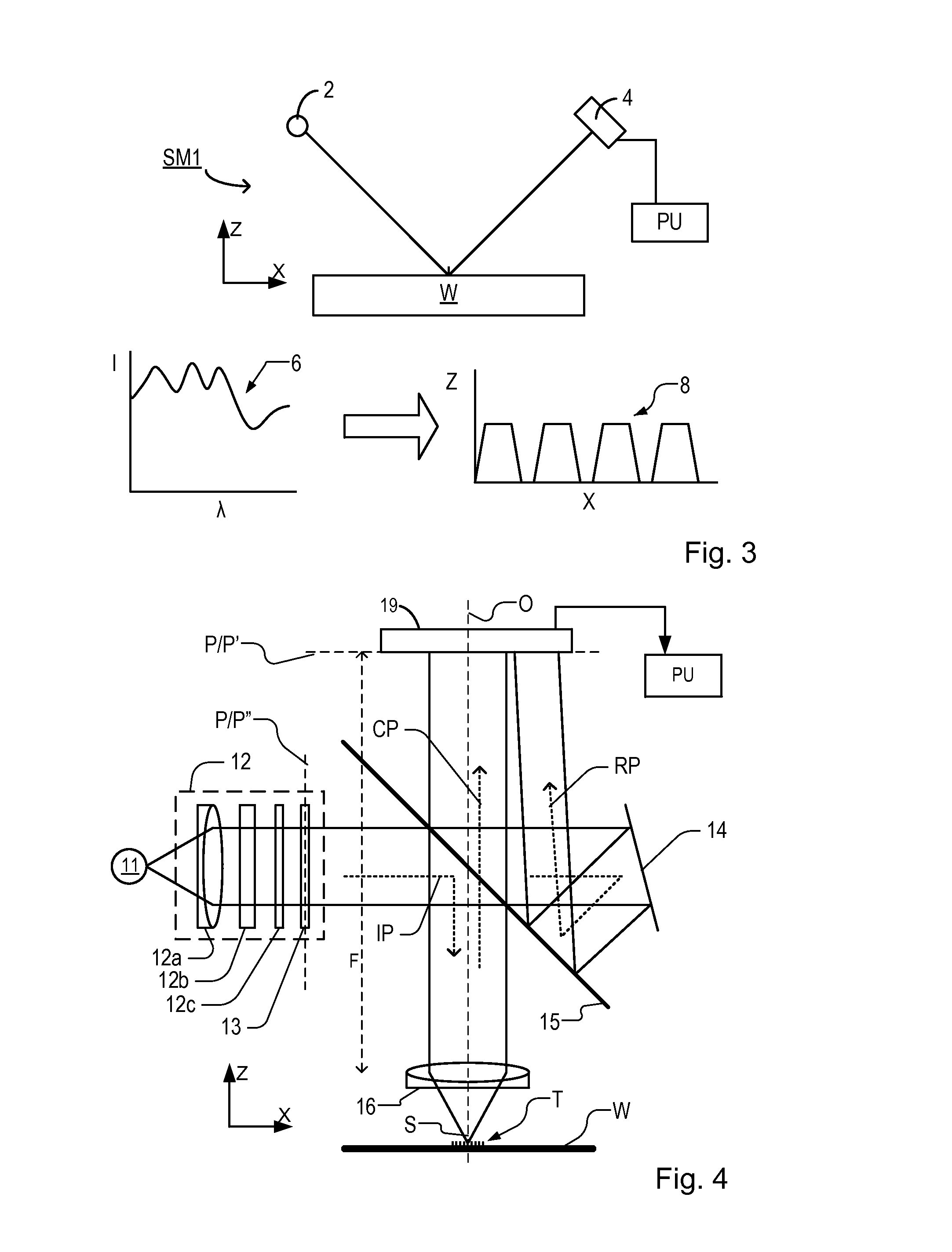
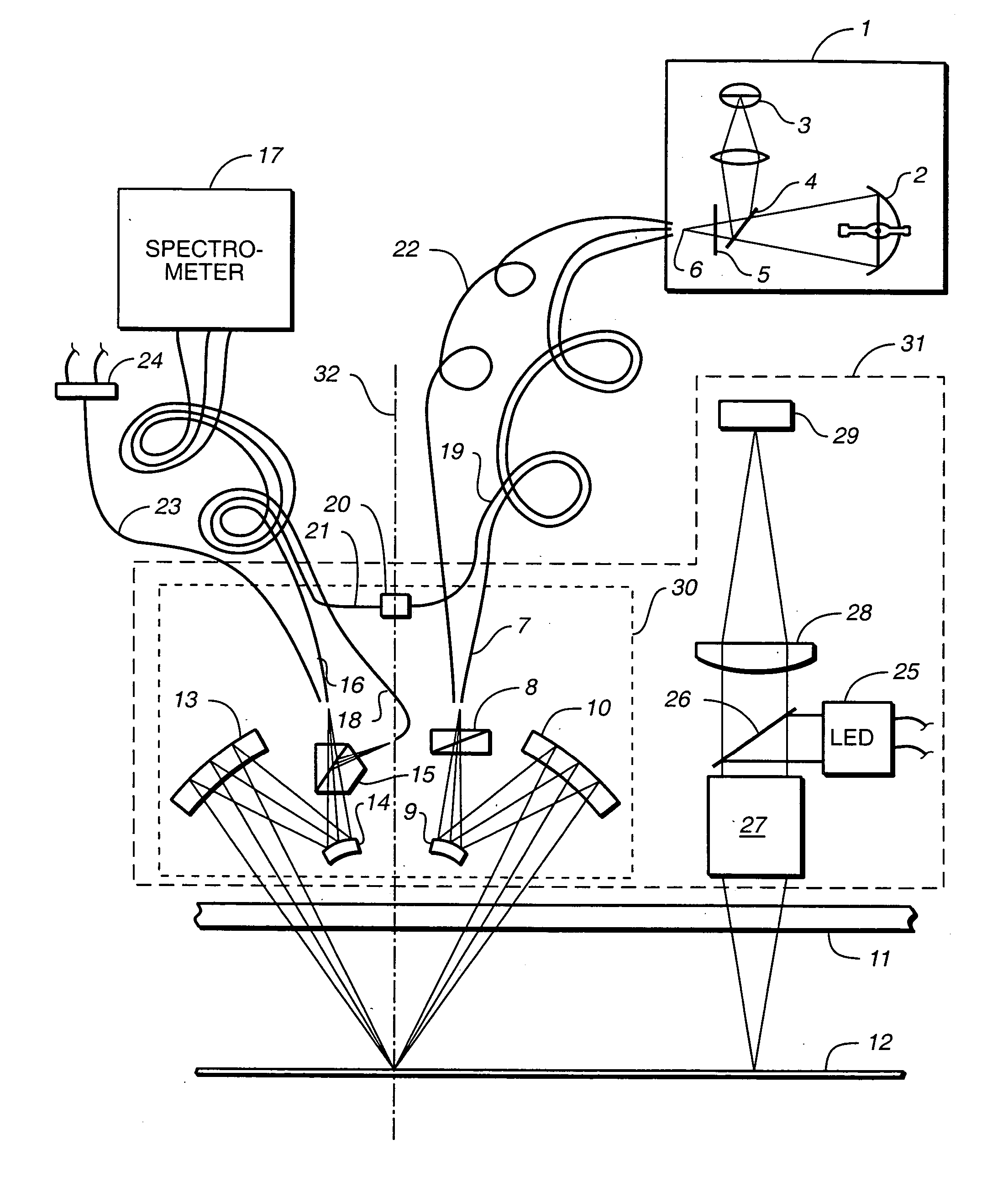
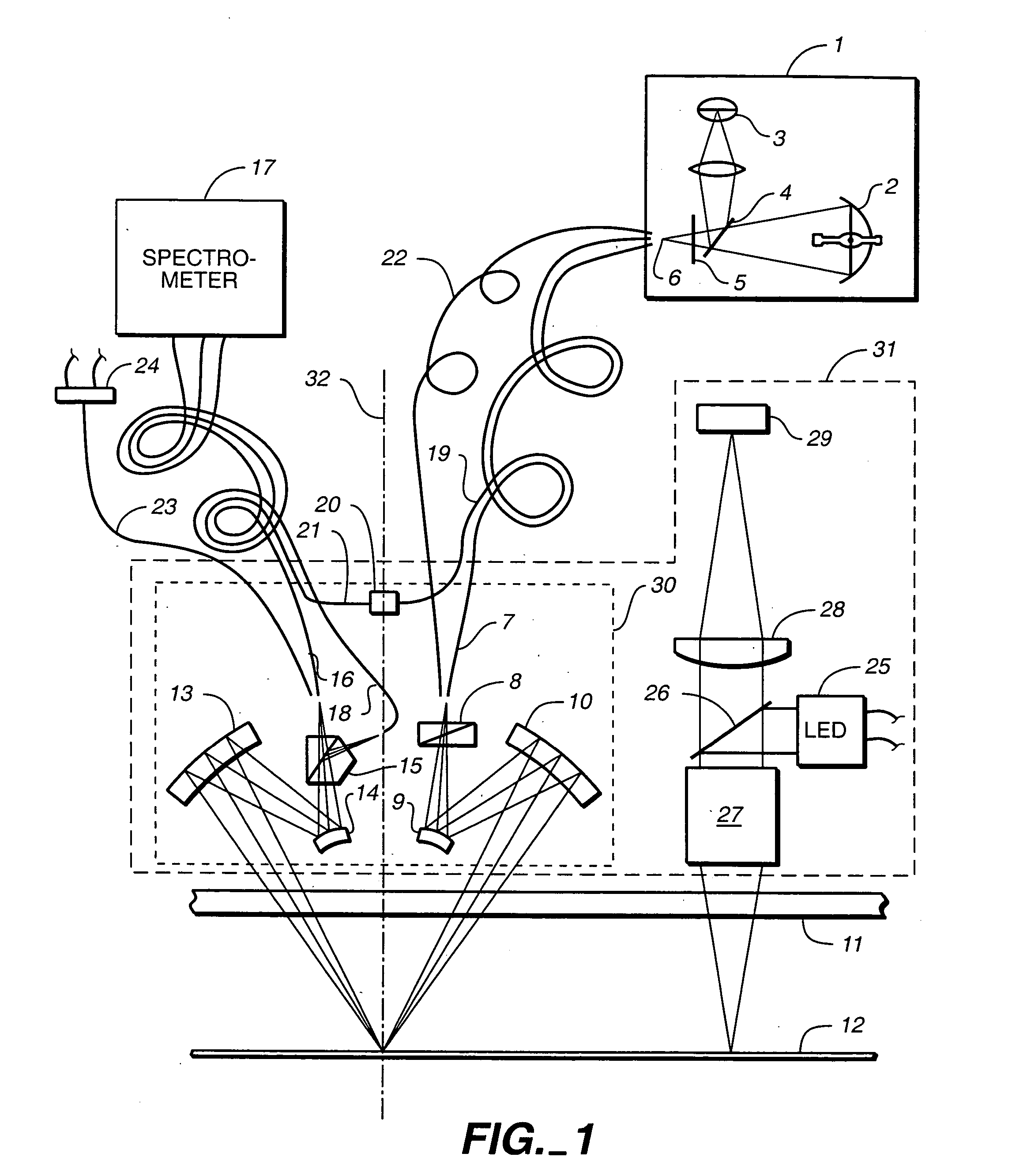
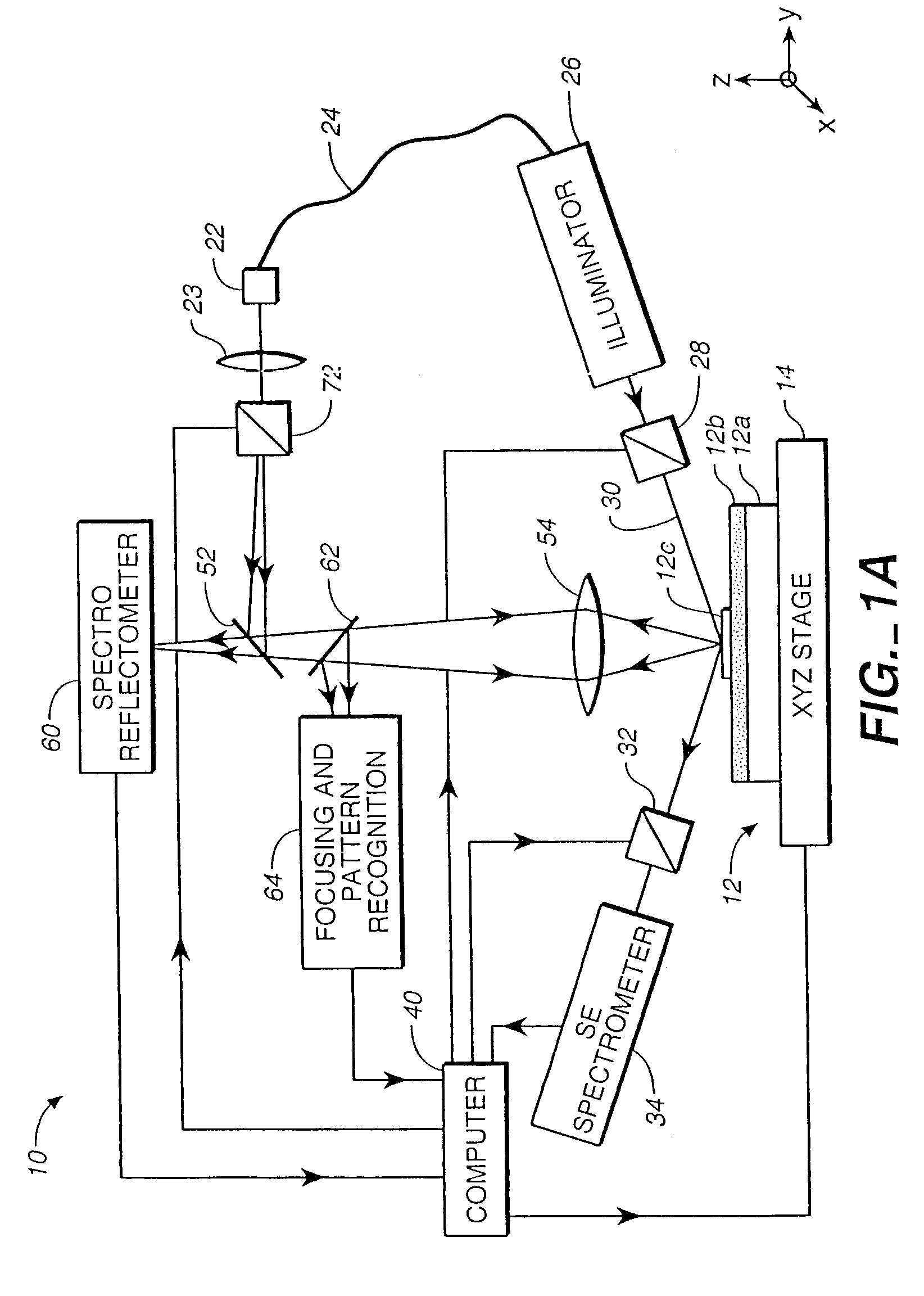
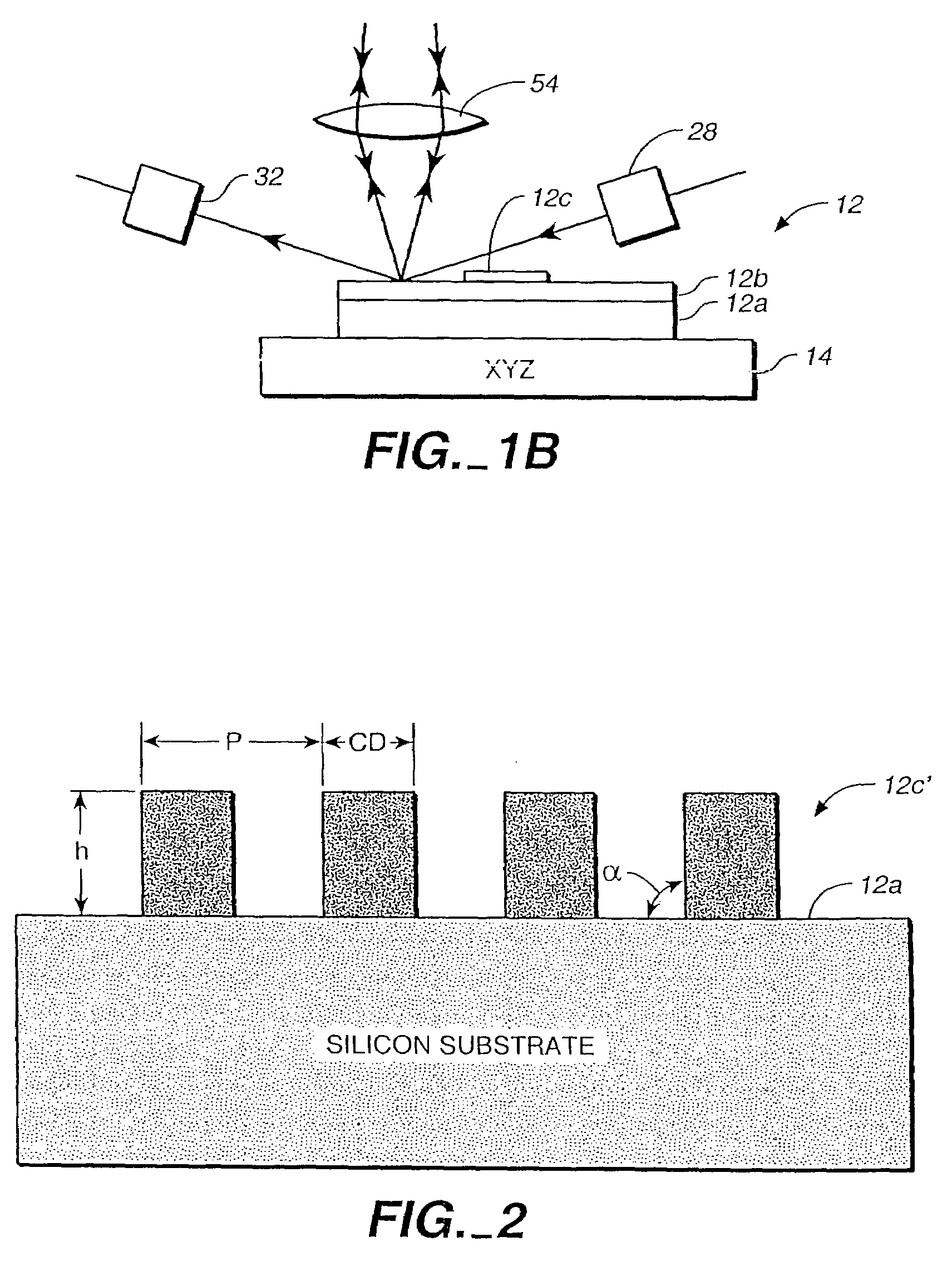
Methods and Scatterometers, Lithographic Systems, and Lithographic Processing Cells
ActiveUS20110027704A1Scattering properties measurementsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingScatterometerEngineering
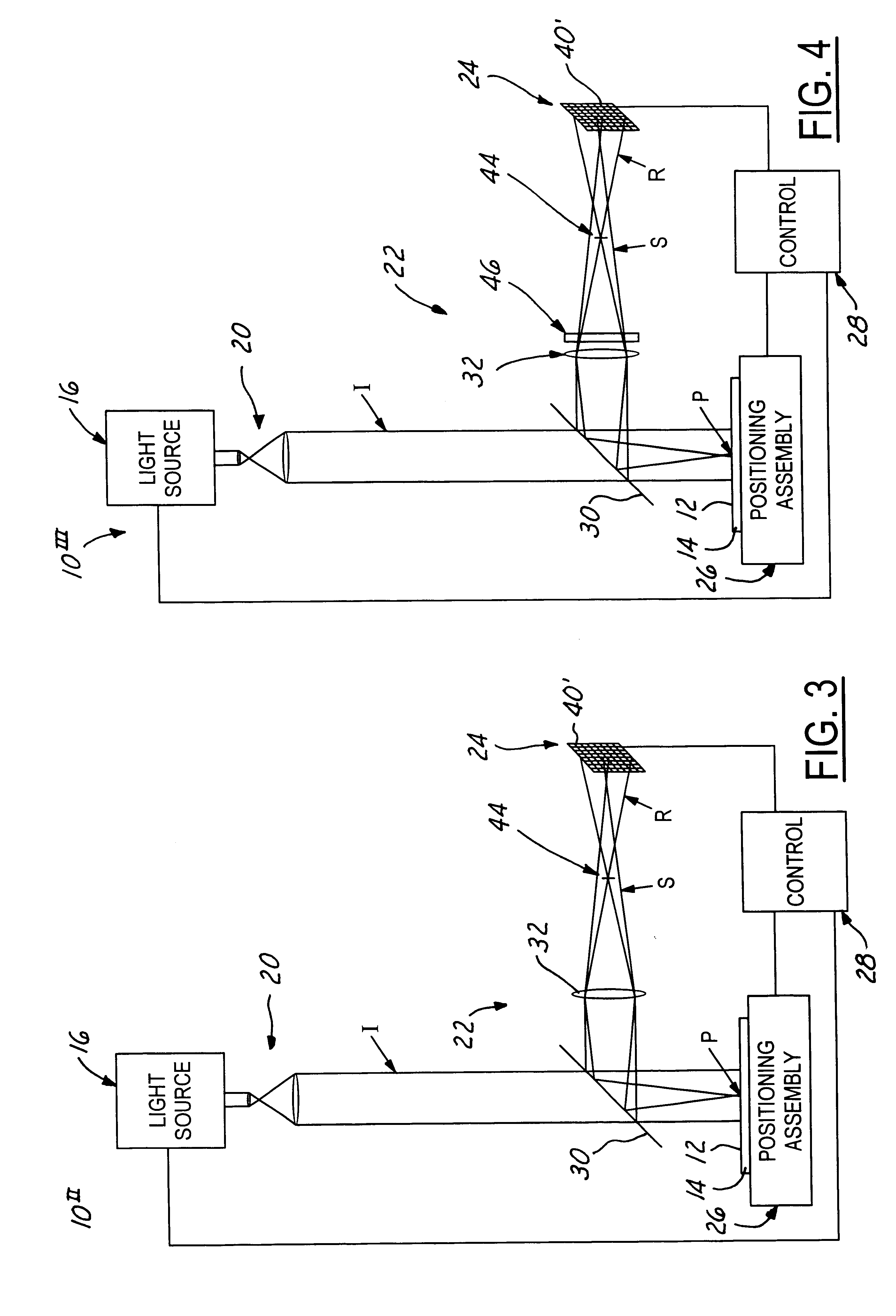
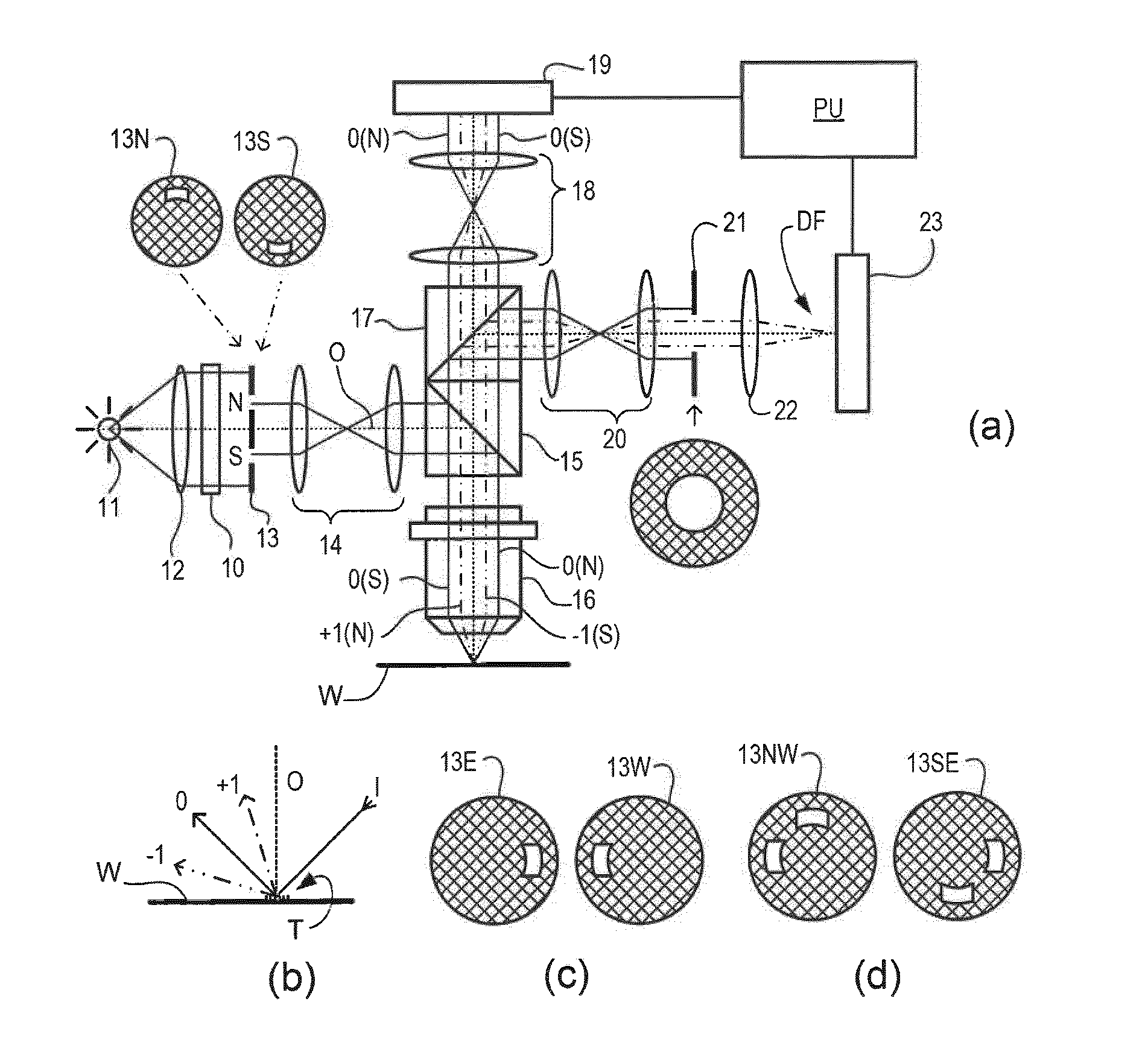
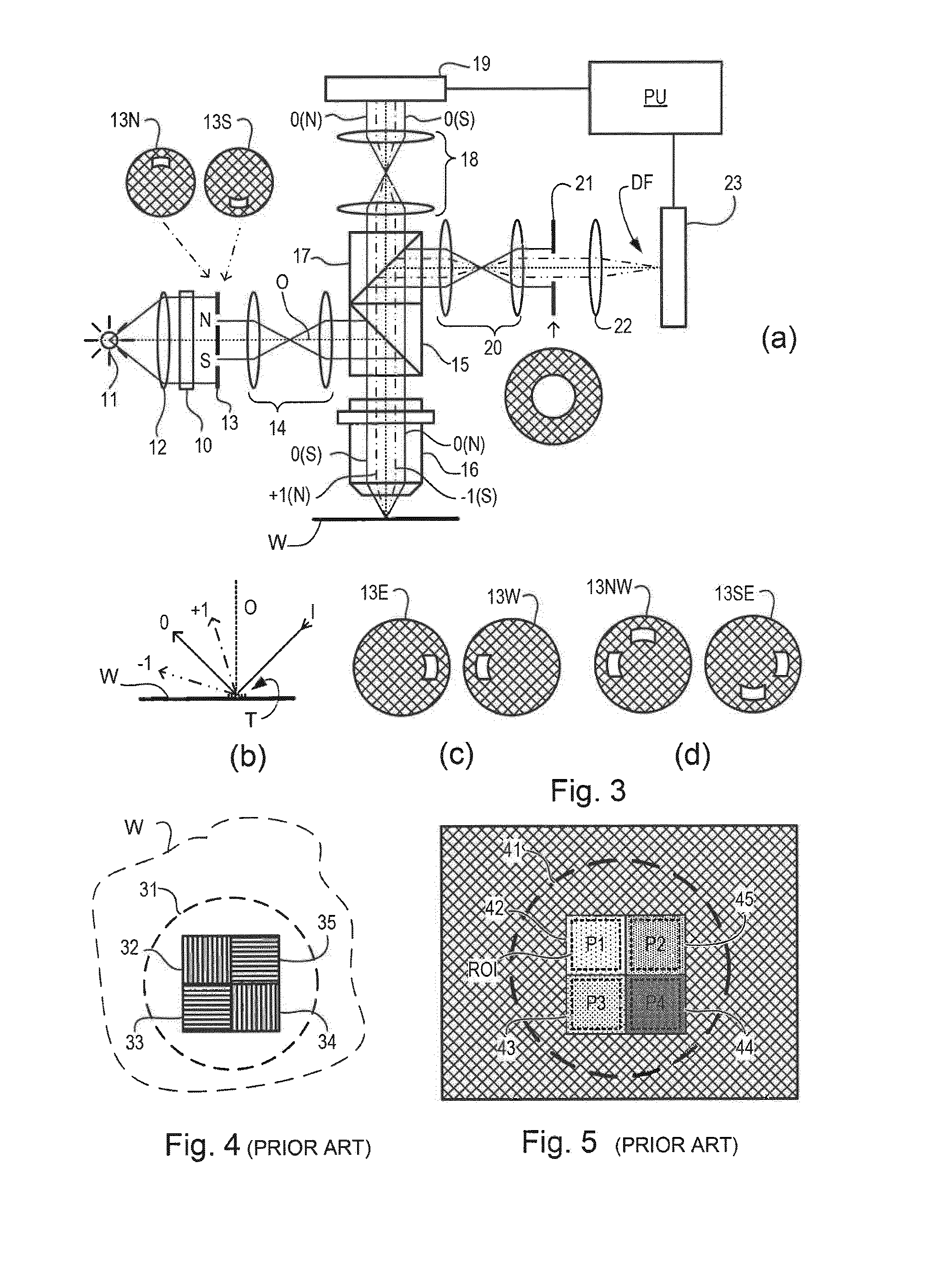
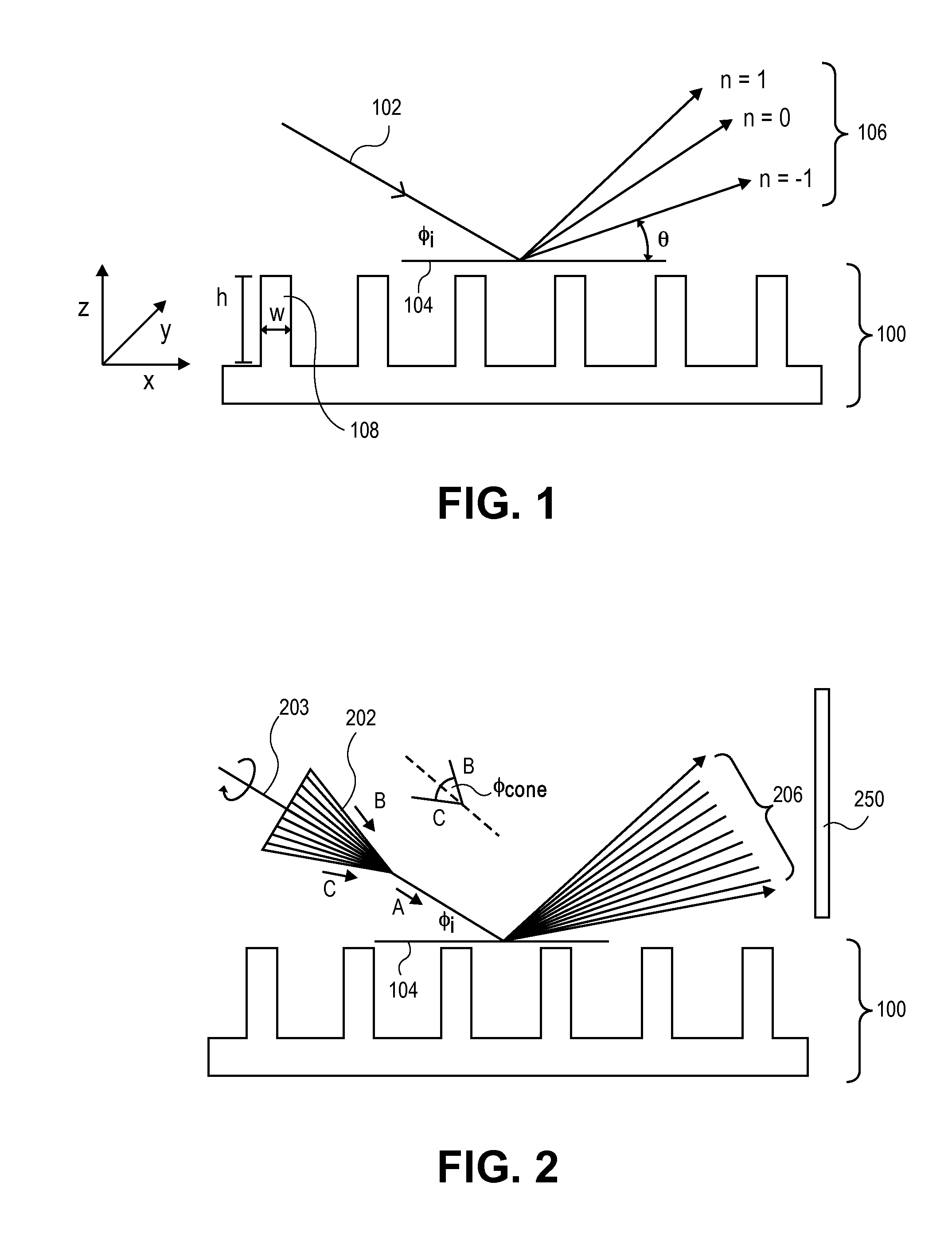
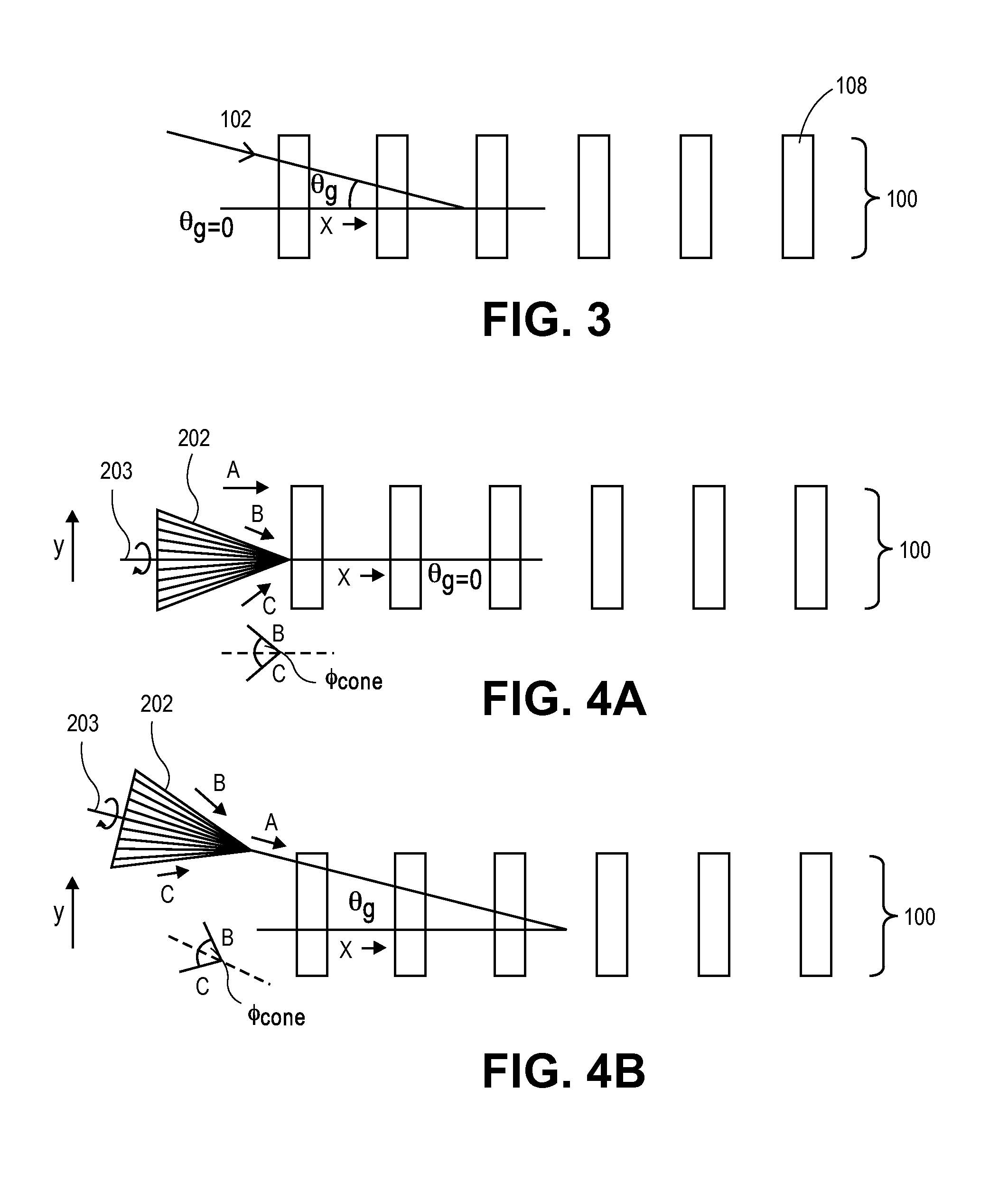
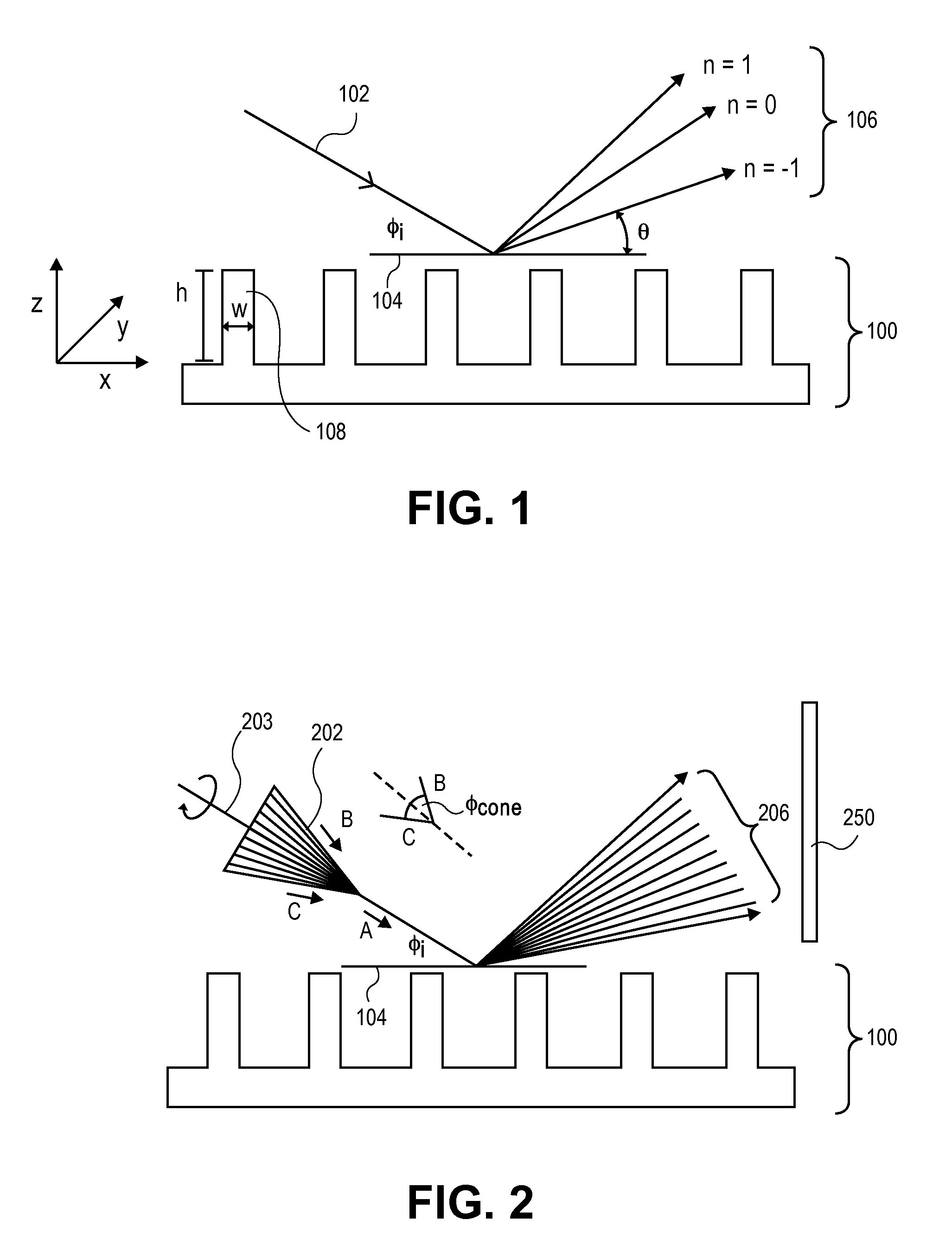
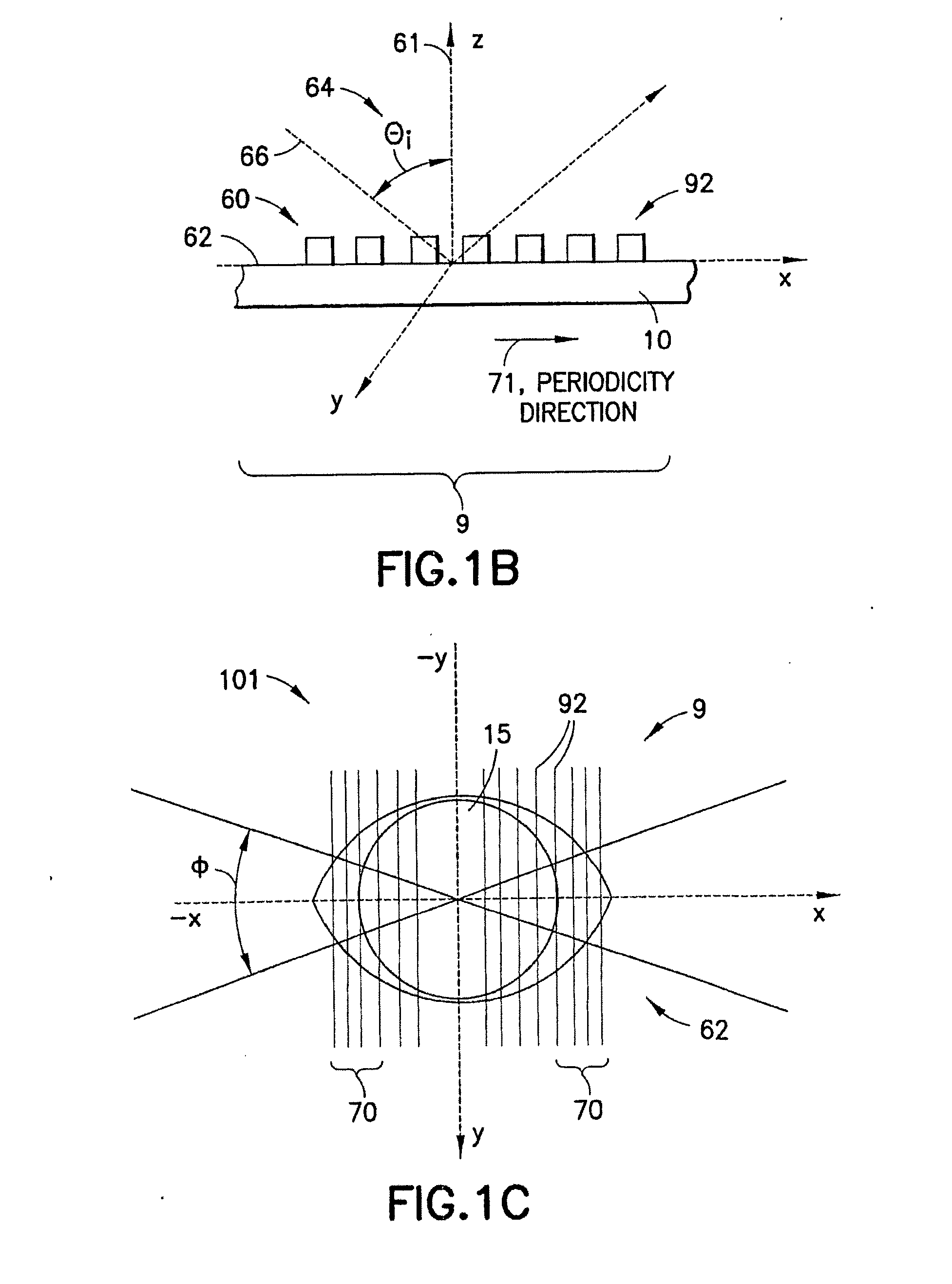
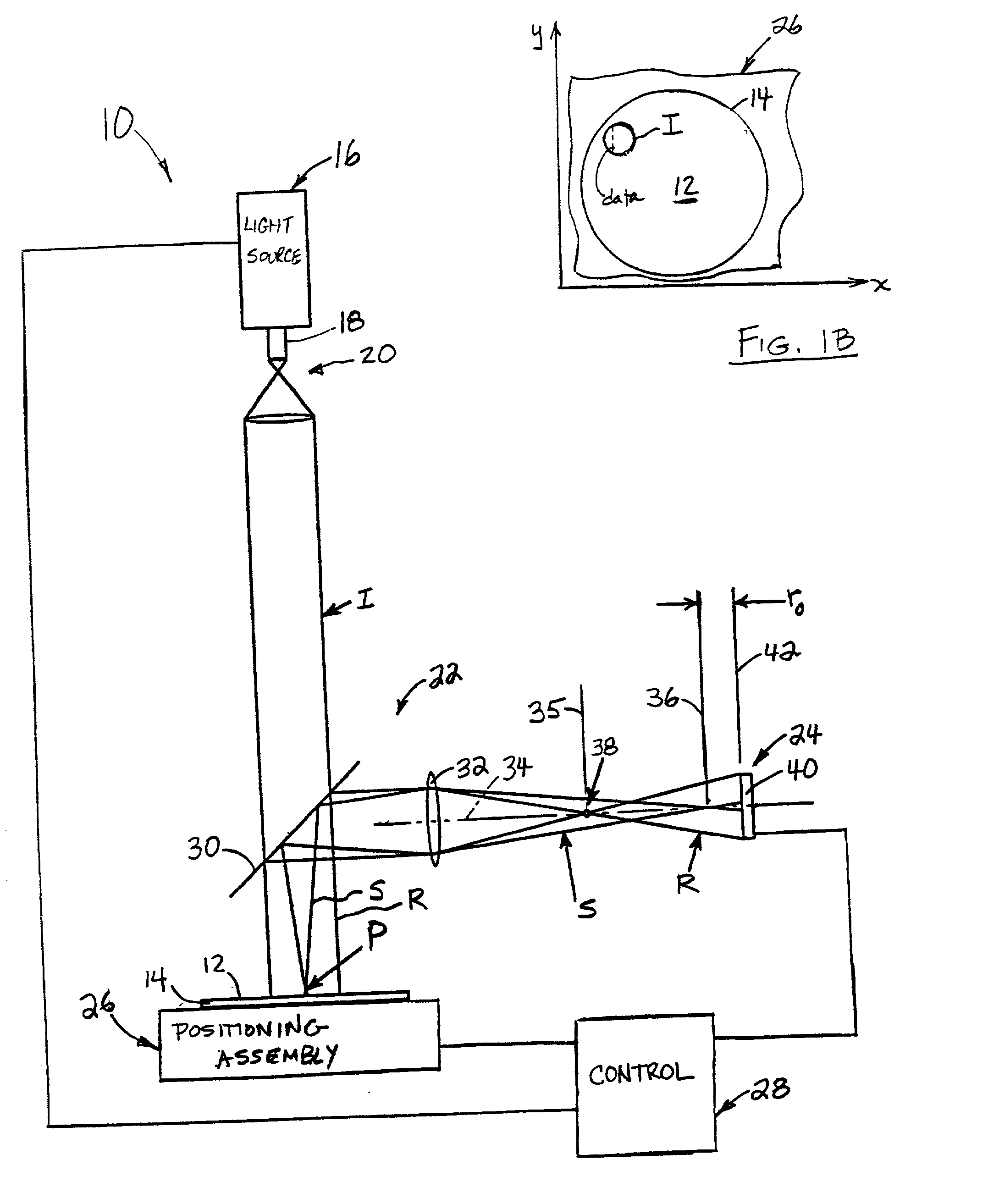
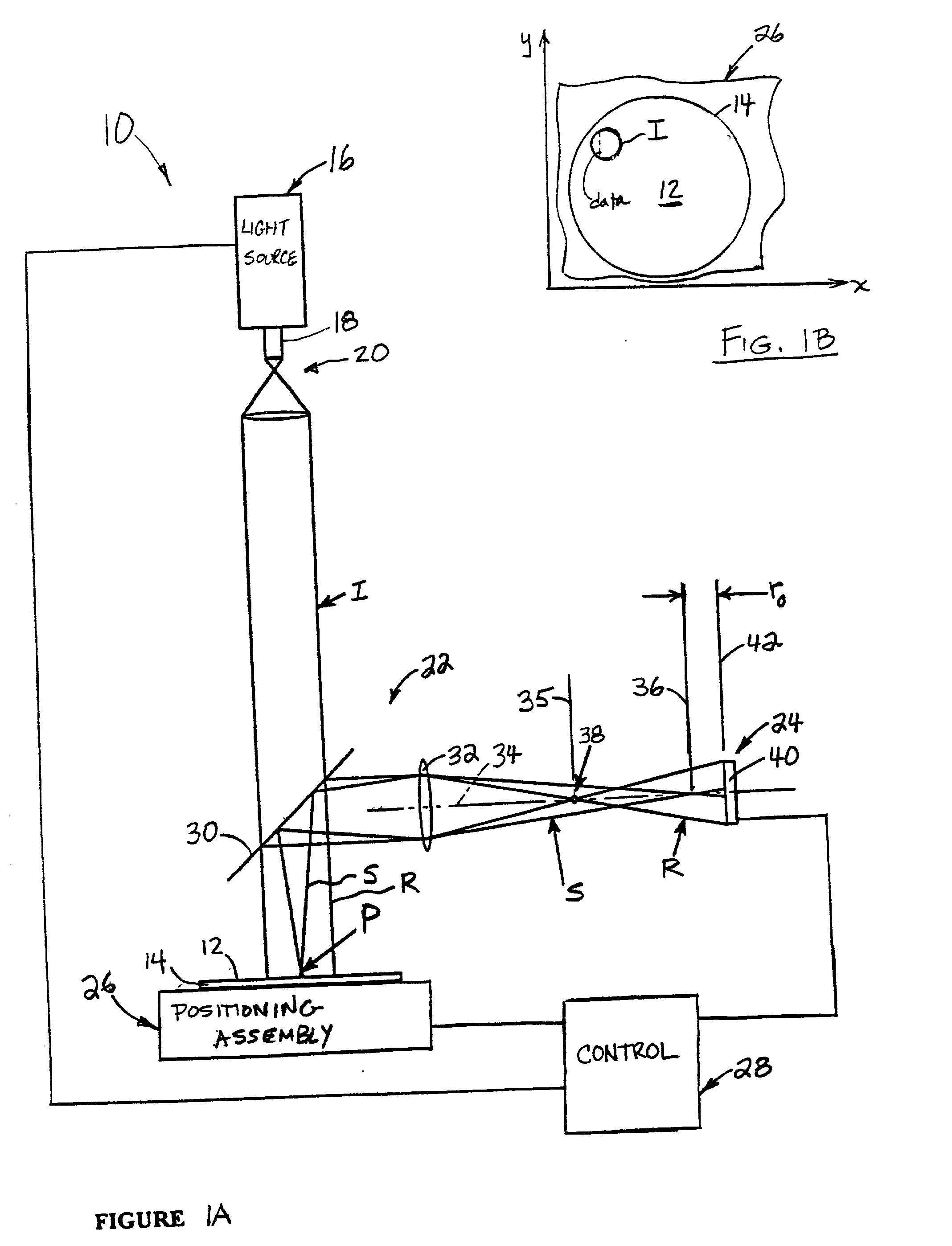
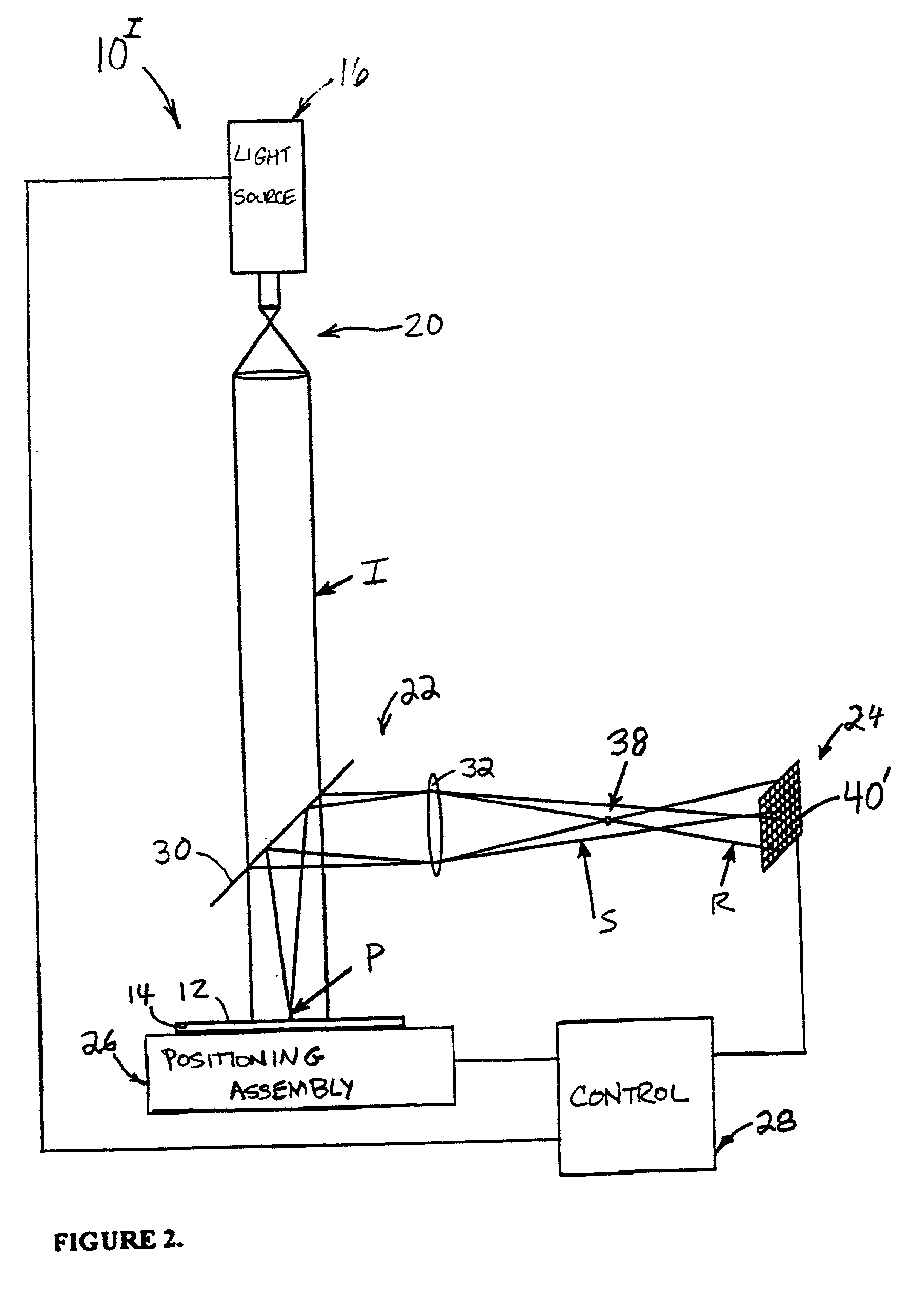
In a method of determining the focus of a lithographic apparatus used in a lithographic process on a substrate, the lithographic process is used to form a structure on the substrate, the structure having at least one feature which has an asymmetry in the printed profile which varies as a function of the focus of the lithographic apparatus on the substrate. A first image of the periodic structure is formed and detected while illuminating the structure with a first beam of radiation. The first image is formed using a first part of non-zero order diffracted radiation. A second image of the periodic structure is foamed and detected while illuminating the structure with a second beam of radiation. The second image is formed using a second part of the non-zero order diffracted radiation which is symmetrically opposite to the first part in a diffraction spectrum. The ratio of the intensities of the measured first and second portions of the spectra is determined and used to determine the asymmetry in the profile of the periodic structure and / or to provide an indication of the focus on the substrate. In the same instrument, an intensity variation across the detected portion is determined as a measure of process-induced variation across the structure. A region of the structure with unwanted process variation can be identified and excluded from a measurement of the structure.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Lithographic Focus and Dose Measurement Using A 2-D Target
ActiveUS20110249244A1Minimize overall surface areaArea minimizationPhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRadiologyScatterometer
In order to determine whether an exposure apparatus is outputting the correct dose of radiation and its projection system is focusing the radiation correctly, a test pattern is used on a mask for printing a specific marker onto a substrate. This marker is then measured by an inspection apparatus, such as a scatterometer, to determine whether there are errors in focus and dose and other related properties. The test pattern is configured such that changes in focus and dose may be easily determined by measuring the properties of a pattern that is exposed using the mask. The test pattern may be a 2D pattern where physical or geometric properties, e.g., pitch, are different in each of the two dimensions. The test pattern may also be a one-dimensional pattern made up of an array of structures in one dimension, the structures being made up of at least one substructure, the substructures reacting differently to focus and dose and giving rise to an exposed pattern from which focus and dose may be determined.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
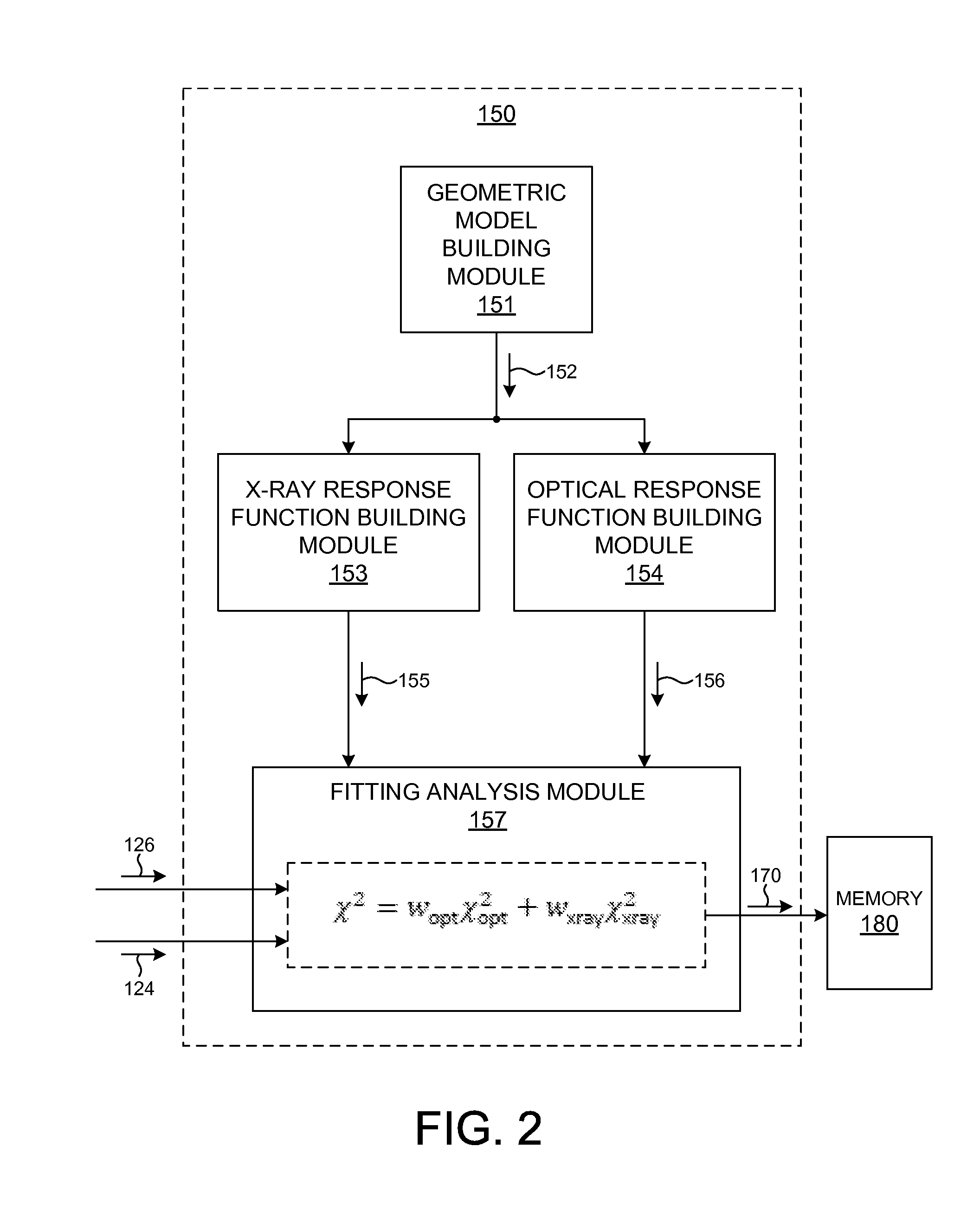
Metrology Tool With Combined X-Ray And Optical Scatterometers
ActiveUS20130304424A1Reduce correlationImprove accuracyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceData setMetrology
Methods and systems for performing simultaneous optical scattering and small angle x-ray scattering (SAXS) measurements over a desired inspection area of a specimen are presented. SAXS measurements combined with optical scatterometry measurements enables a high throughput metrology tool with increased measurement capabilities. The high energy nature of x-ray radiation penetrates optically opaque thin films, buried structures, high aspect ratio structures, and devices including many thin film layers. SAXS and optical scatterometry measurements of a particular location of a planar specimen are performed at a number of different out of plane orientations. This increases measurement sensitivity, reduces correlations among parameters, and improves measurement accuracy. In addition, specimen parameter values are resolved with greater accuracy by fitting data sets derived from both SAXS and optical scatterometry measurements based on models that share at least one geometric parameter. The fitting can be performed sequentially or in parallel.
Owner:KLA CORP
Line profile asymmetry measurement using scatterometry
InactiveUS6856408B2Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingScatterometerLength wave
A method of and apparatus for measuring line profile asymmetries in microelectronic devices comprising directing light at an array of microelectronic features of a microelectronic device, detecting light scattered back from the array comprising either or both of one or more angles of reflection and one or more wavelengths, and comparing one or more characteristics of the back-scattered light by examining data from complementary angles of reflection or performing a model comparison.
Owner:ONTO INNOVATION INC
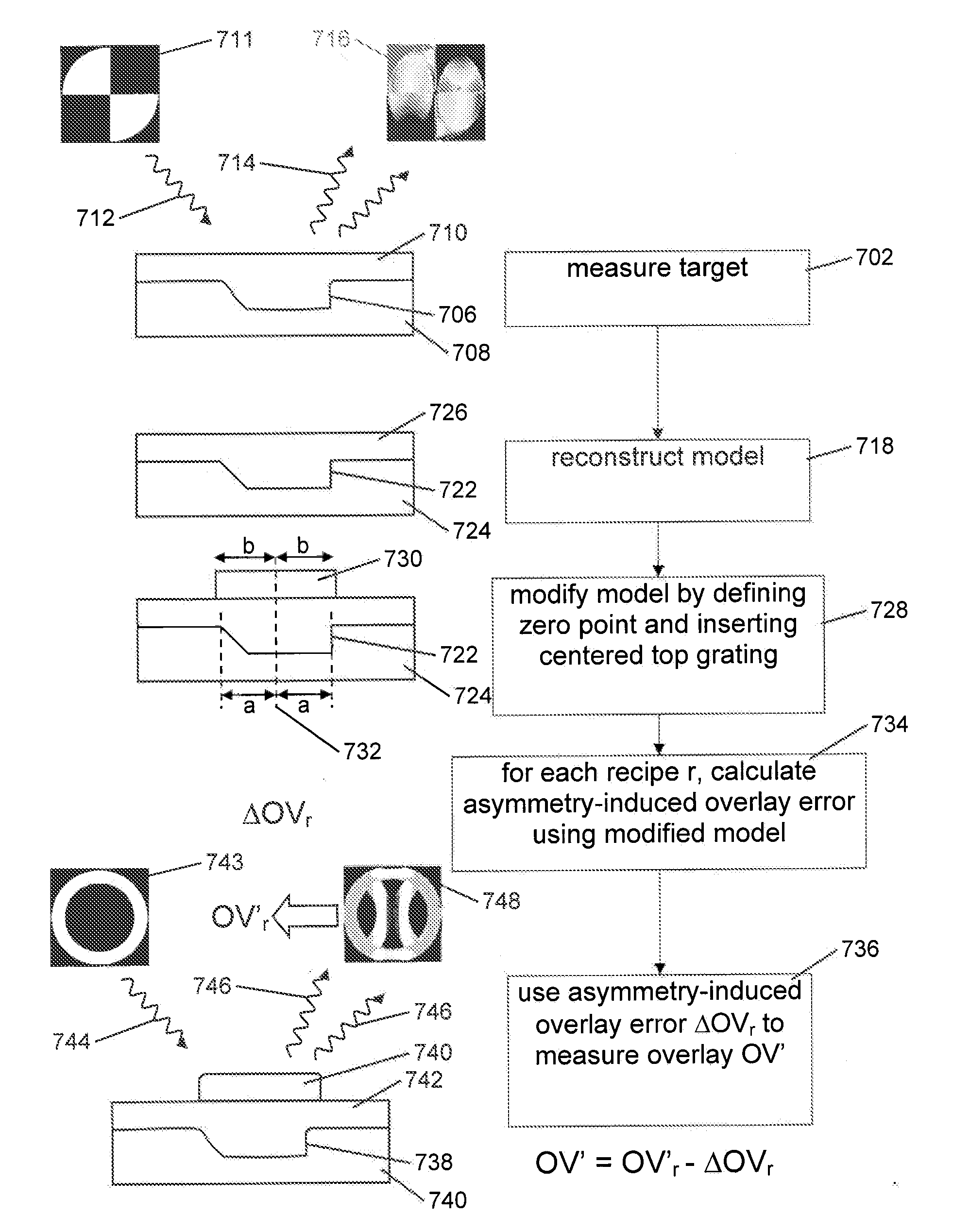
Method and Apparatus for Determining an Overlay Error
ActiveUS20120013881A1Scattering properties measurementsPhotomechanical apparatusAsymmetric inductionScatterometer
A method of determining an overlay error. Measuring an overlay target having process-induced asymmetry. Constructing a model of the target. Modifying the model, e.g., by moving one of the structures to compensate for the asymmetry. Calculating an asymmetry-induced overlay error using the modified model. Determining an overlay error in a production target by subtracting the asymmetry-induced overlay error from a measured overlay error. In one example, the model is modified by varying asymmetry p(n′), p(n″) and the calculating an asymmetry-induced overlay error is repeated for a plurality of scatterometer measurement recipes and the step of determining an overlay error in a production target uses the calculated asymmetry-induced overlay errors to select an optimum scatterometer measurement recipe used to measure the production target.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Method and apparatus for controlling photolithography parameters based on photoresist images
InactiveUS6259521B1Material analysis by optical meansPhotomechanical exposure apparatusScatterometerPhotoresist
A method for controlling uniformity in a wafer is provided. A wafer is provided. A layer of photoresist is formed on the wafer, and the photoresist layer is patterned. A portion of the patterned photoresist layer is illuminated in at least first and second positions. Light reflected at the two positions is measured to generate first and second measurements. A recipe of a stepper is adjusted in response to the first measurement differing from the second measurement. A wafer processing system includes a stepper, a scatterometer, and a process controller. The stepper is adapted to expose a layer of photoresist in accordance with a recipe to generate an exposed layer of photoresist. The scatterometer is adapted to take first and second measurements in at least first and second positions on the exposed layer of photoresist. The process controller is adapted to compare the first and second measurements and adjust the recipe based on the first and second measurements.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Automated overlay metrology system
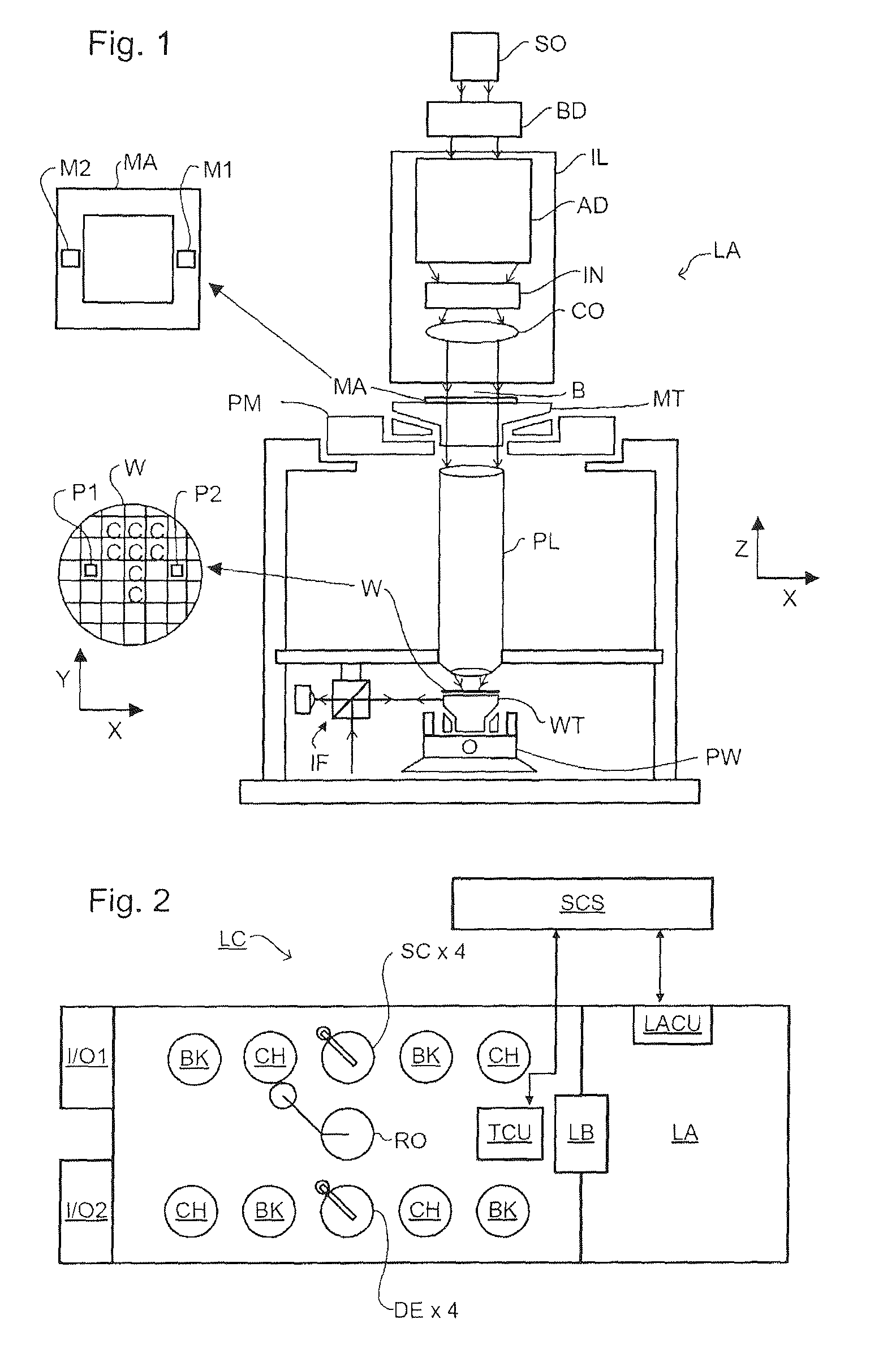
InactiveUS20020192577A1Reduced expense and complexityHigh resolutionSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSpectral curveSpectral response
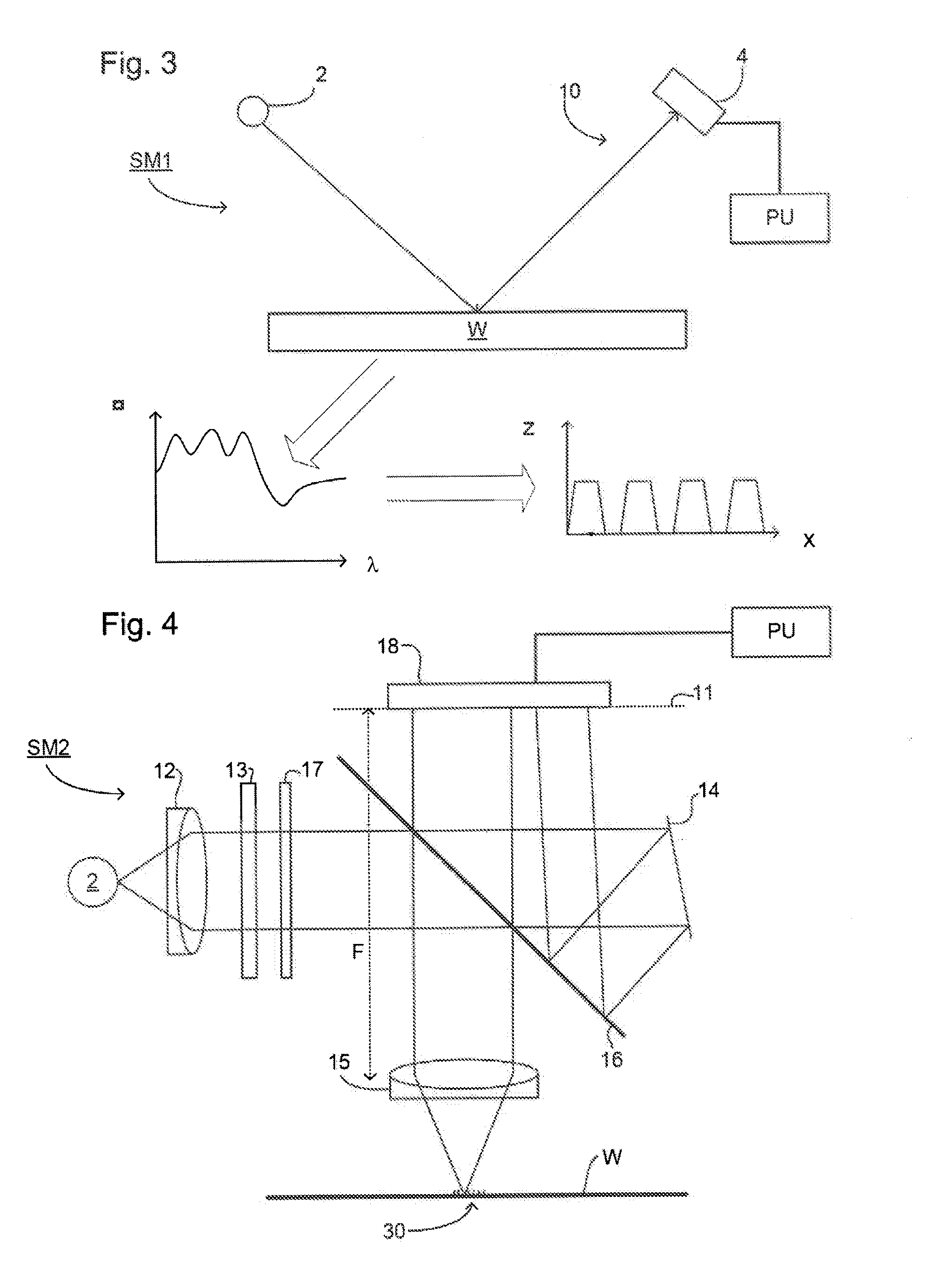
Non-imaging measurement is made of misalignment of lithographic exposures by illuminating periodic features of a mark formed by two lithographic exposures with broadband light and detecting an interference pattern at different wavelengths using a specular spectroscopic scatterometer including a wavelength dispersive detector. Misalignment can be discriminated by inspection of a spectral response curve and by comparison with stored spectral response curves that may be empirical data or derived by simulation. Determination of best fit to a stored spectral curve, preferably using an optimization technique can be used to quantify the detected misalignment. Such a measurement may be made on-line or in-line in a short time while avoiding tool induced shift, contact with the mark or use of a tool requiring high vacuum.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Metrology Method and Apparatus, and Device Manufacturing Method
ActiveUS20130100427A1Reduce the impactReduce impactScattering properties measurementsPhotomechanical apparatusMetrologyScatterometer
An approach is used to estimate and correct the overlay variation as function of offset for each measurement. A target formed on a substrate includes periodic gratings. The substrate is illuminated with a circular spot on the substrate with a size larger than each grating. Radiation scattered by each grating is detected in a dark-field scatterometer to obtain measurement signals. The measurement signals are used to calculate overlay. The dependence (slope) of the overlay as a function of position in the illumination spot is determined. An estimated value of the overlay at a nominal position such as the illumination spot's center can be calculated, correcting for variation in the overlay as a function of the target's position in the illumination spot. This compensates for the effect of the position error in the wafer stage movement, and the resulting non-centered position of the target in the illumination spot.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Inspection Method and Apparatus, Lithographic Apparatus, Lithographic Processing Cell and Device Manufacturing Method
In order to determine whether an exposure apparatus is outputting the correct dose of radiation and a projection system of the exposure apparatus is focusing the radiation correctly, a test pattern is used on a mask for printing a specific marker onto a substrate. This marker may be measured by an inspection apparatus, such as, for example, a scatterometer to determine whether errors in focus, dose, and other related properties are present. The test pattern is arranged such that changes in focus and dose may be easily determined by measuring properties of a pattern that is exposed using the mask. The test pattern of the mask is arranged so that it gives rise to a marker pattern on the substrate surface. The marker pattern contains structures that have at least two measurable side wall angles. Asymmetry between side wall angles of a structure is related to focus (or defocus) of the exposure radiation from the exposure apparatus. The extent of defocus may thereby be determined by measuring an asymmetry in side wall angle of the printed marker pattern structures.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Differential numerical aperture methods and device
InactiveUS20020039184A1Small footprintRadiation pyrometryPolarisation-affecting propertiesMetrologyAngle of incidence
Devices and methods for differential numerical aperture analysis of samples, utilizing angle-of-incidence measurements resulting from variable illumination or observation numerical apertures, or both. Metrology applications are provided, and more particularly including scatterometer, ellipsometer and similar analysis methods, including bi-directional reflectance or transmission distribution function measurement. The provided devices and methods enable analysis of critical dimensions of samples utilizing a minimum of moving parts, with the range of striking or scattering angles varied by means of a variable numerical aperture or apertures.
Owner:ONTO INNOVATION INC
Method of Overlay Measurement, Lithographic Apparatus, Inspection Apparatus, Processing Apparatus and Lithographic Processing Cell
In order to improve overlay measurement, product marker gratings on a substrate are measured in a lithographic apparatus by an alignment sensor using scatterometry. Then information relating to the transverse profile of the product marker grating, such as its asymmetry, is determined from the measurement. After printing an overlay marker grating on a resist film, the lateral overlay of the overlay marker grating with respect to the product marker grating is measured by scatterometry and using the determined asymmetry information in combination with a suitable process model. The alignment sensor data may be used to first reconstruct the product grating and this information is fed forward to the scatterometer that measures the stack of product and resist grating and light scattered by the stack is used for reconstruction of a model of the stack to calculate overlay. The overlay may then, optionally, be fed back to the lithographic apparatus for correction of overlay errors.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Differential numerical aperture methods and device
InactiveUS6750968B2Small footprintMinimum of moving partRadiation pyrometryPolarisation-affecting propertiesAngle of incidenceMetrology
Devices and methods for differential numerical aperture analysis of samples, utilizing angle-of-incidence measurements resulting from variable illumination or observation numerical apertures, or both. Metrology applications are provided, and more particularly including scatterometer, ellipsometer and similar analysis methods, including bi-directional reflectance or transmission distribution function measurement. The provided devices and methods enable analysis of critical dimensions of samples utilizing a minimum of moving parts, with the range of striking or scattering angles varied by a variable numerical aperture or apertures.
Owner:ONTO INNOVATION INC
Methods and Scatterometers, Lithographic Systems, and Lithographic Processing Cells
ActiveUS20140139814A1Scattering properties measurementsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingScatterometerEngineering
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
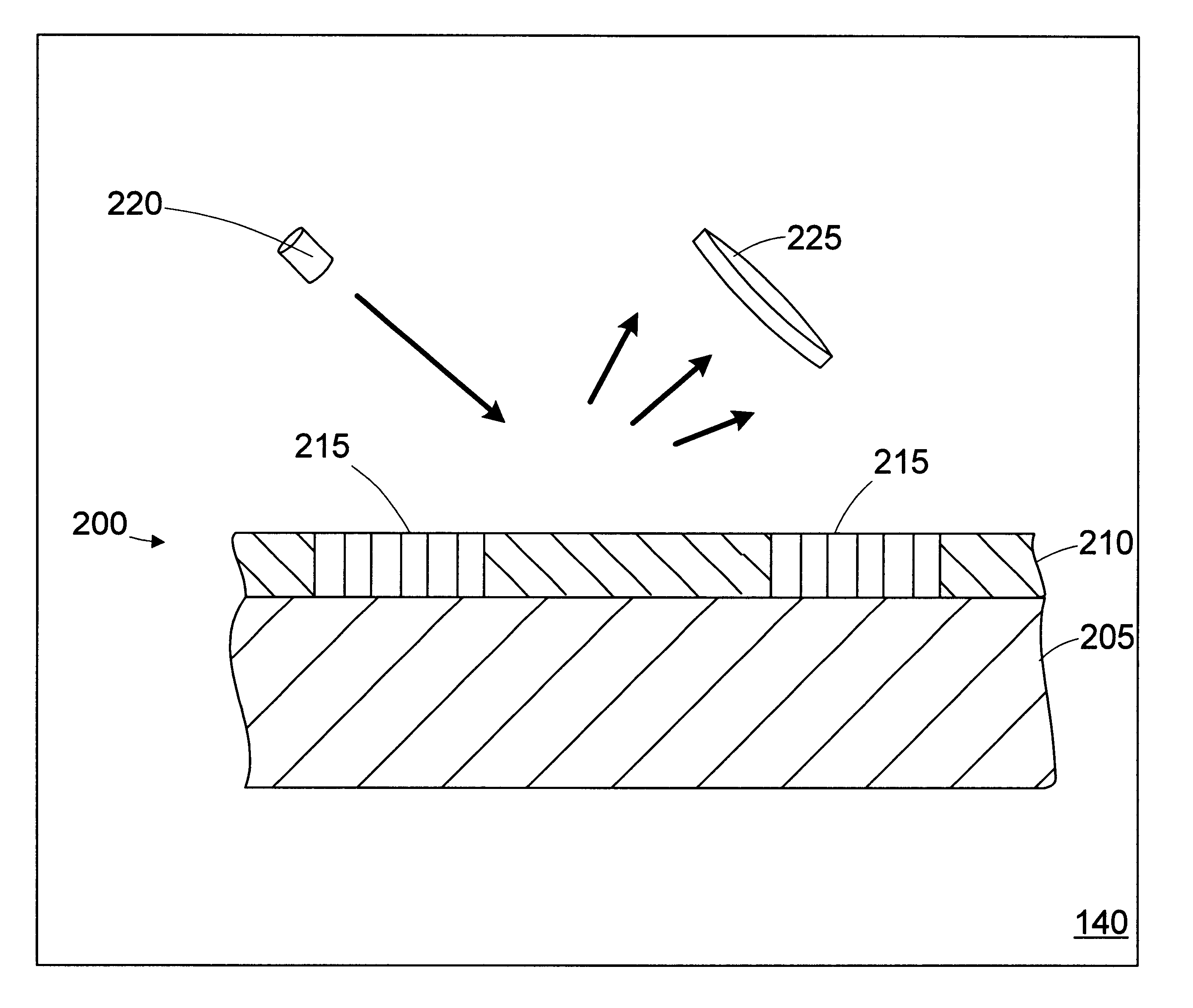
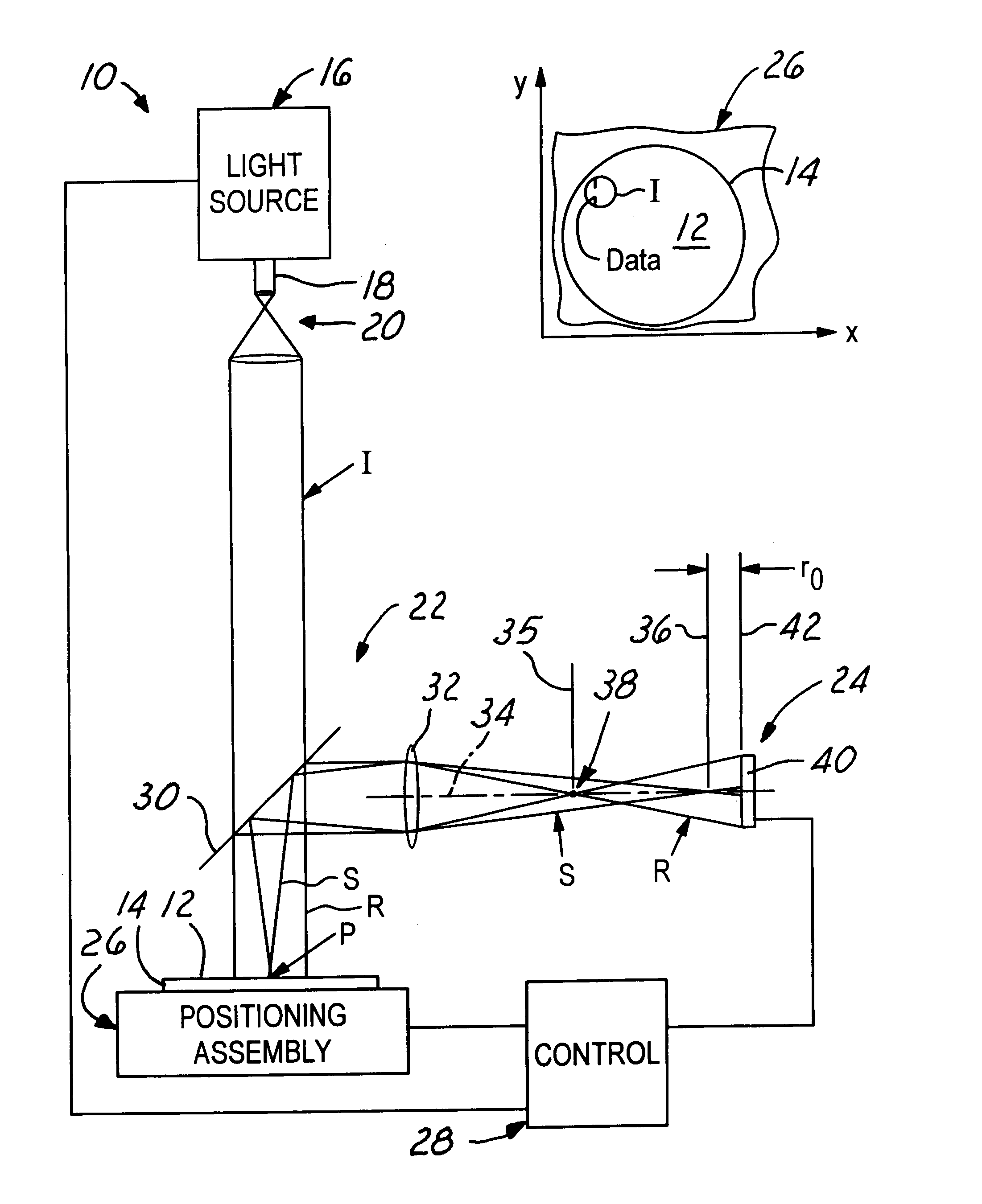
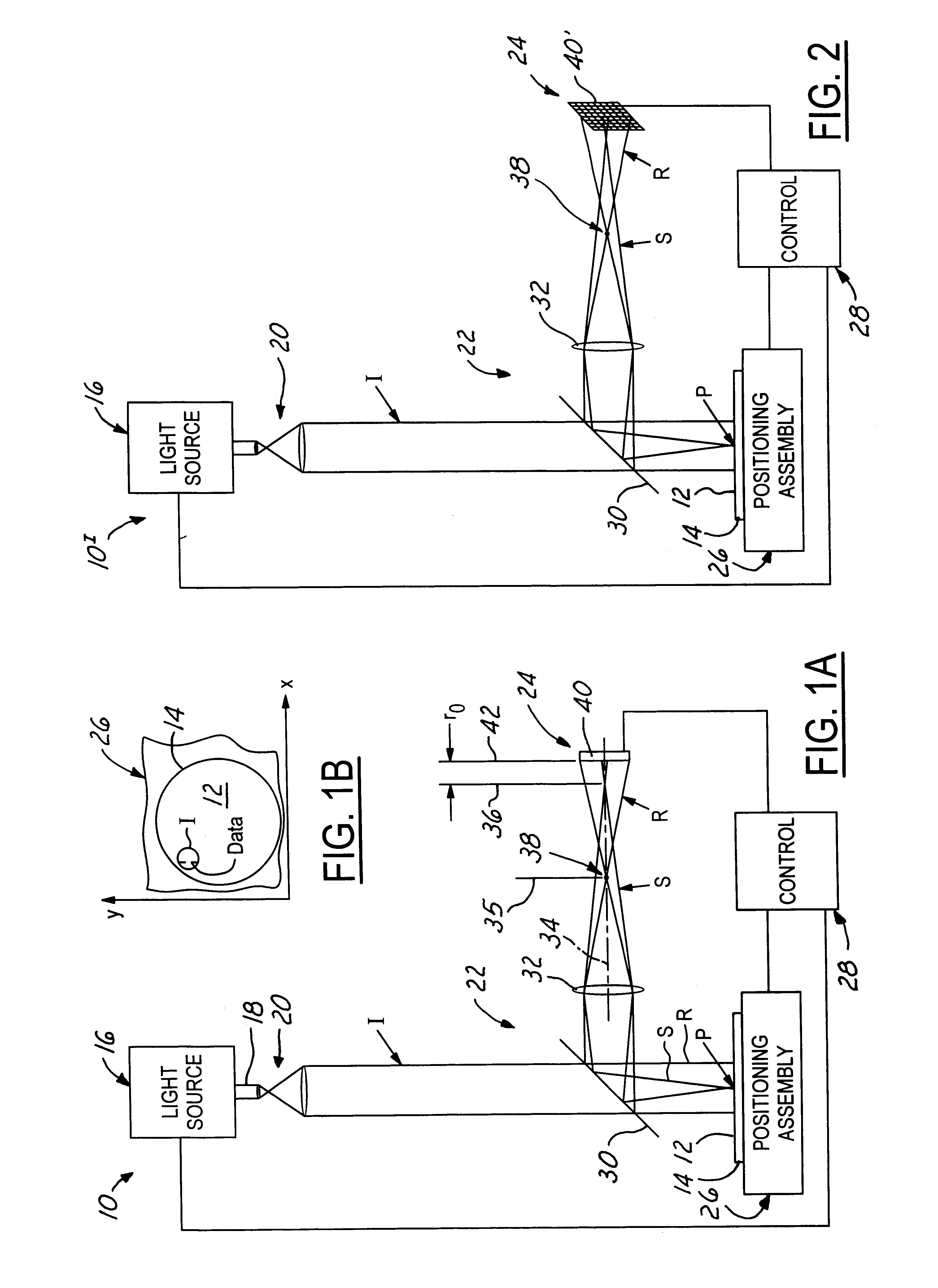
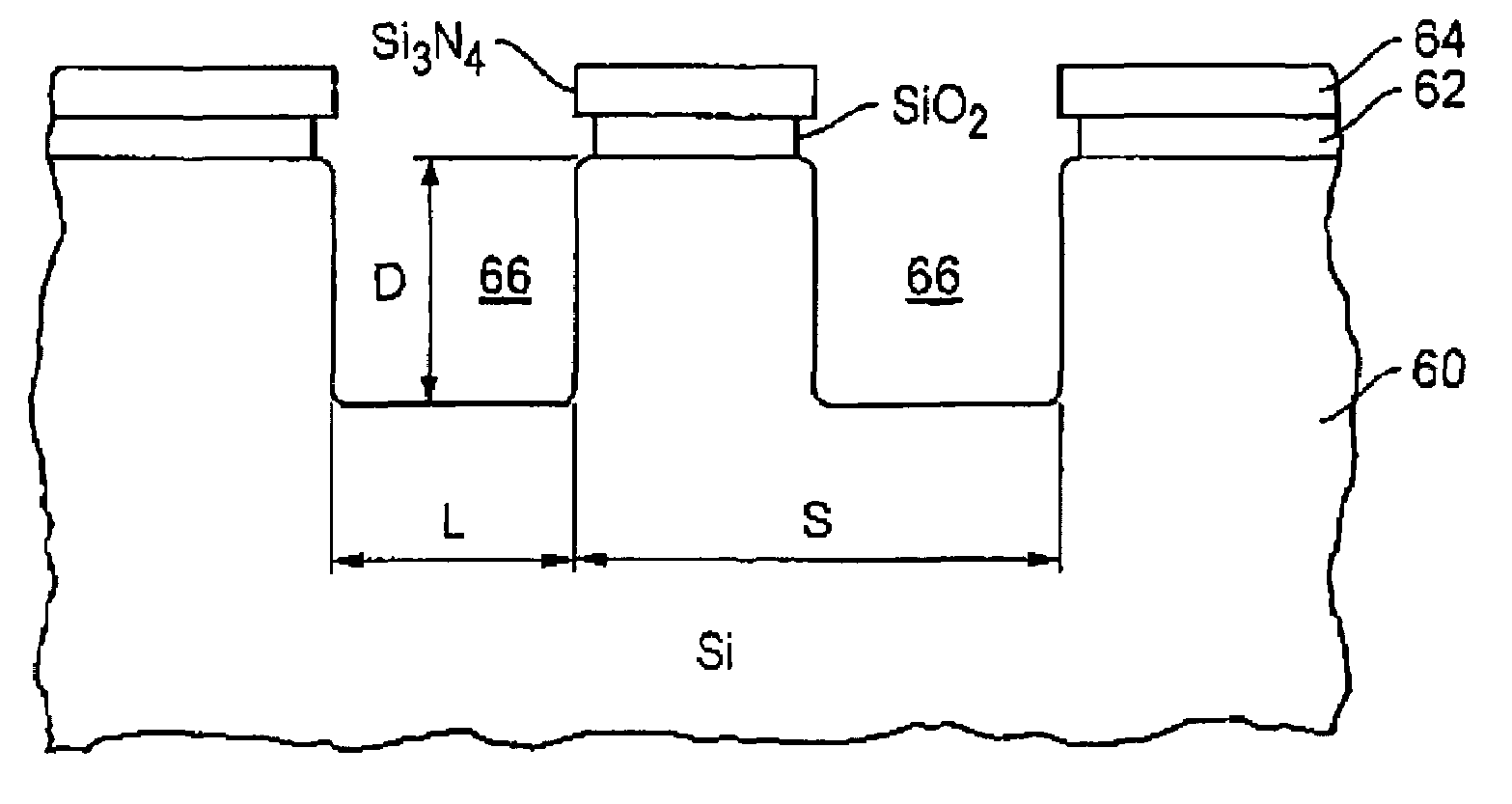
Holographic scatterometer for detection and analysis of wafer surface deposits
InactiveUS6597446B2Prevent false detectionErroneous detectionInvestigating moving sheetsOptically investigating flaws/contaminationChemical compositionScatterometer
A holographic scatterometer with continuous readout can rapidly identify the presence of deposits (particles or other defects) on an unpatterned wafer surface and determine the volume density (size) and location. The scatterometer can also determine chemical composition of the detected deposits. The range of the deposit (particle) size to be measured is below 80 nm, which currently existing scatterometer type instruments cannot readily detect. The inspection can be achieved as an in-line stage during the processing of wafers or in situ in combination with another processing tool or as a separate off-line analysis device.
Owner:SENTEC CORP
HY-2 satellite scatterometer sea surface wind field retrieval method and device
InactiveCN103698750AAccurate removalImprove accuracyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionAmbiguityScatterometer
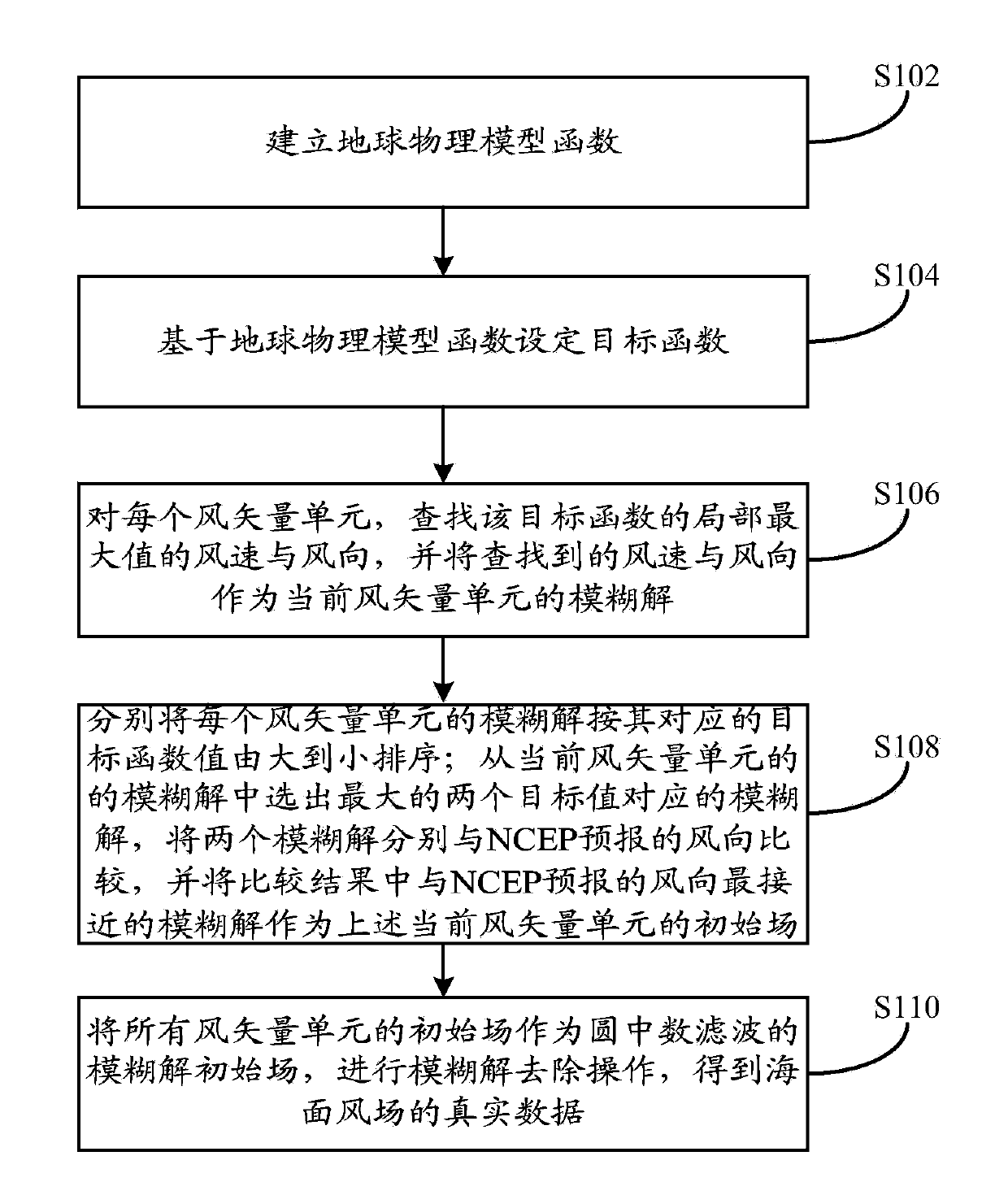
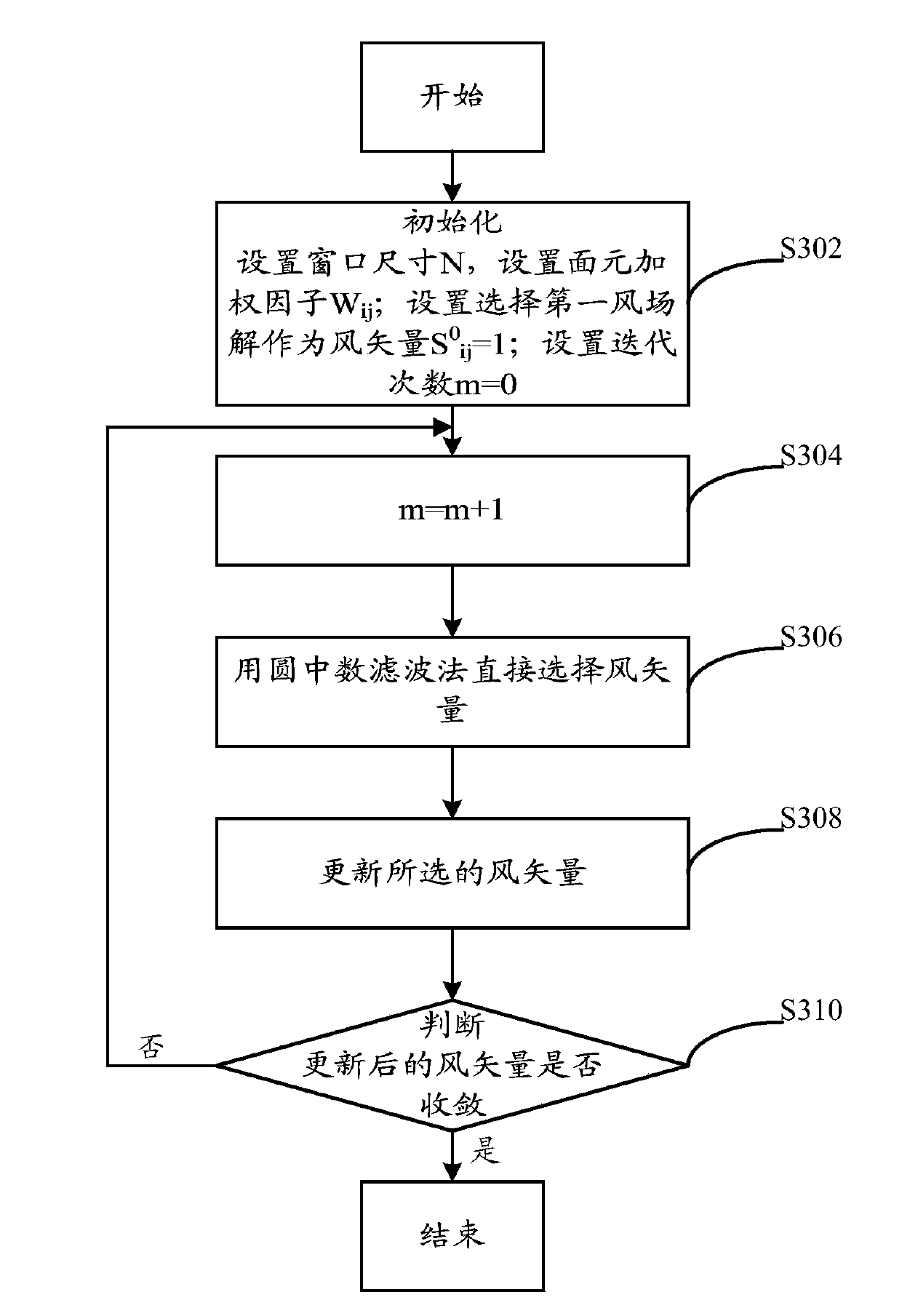
The invention provides an HY-2 satellite scatterometer sea surface wind field retrieval method and device. The method comprises the steps of building a physical geography module function; setting a target function based on the physical geography module function; searching for the local maximal wind speed and wind direction of the target function for each wind vector unit, and taking the obtained wind speed and wind direction as ambiguity solutions of the current wind vector unit; selecting ambiguity solutions corresponding to two maximal target values from the ambiguity solutions of the current wind vector unit, respectively comparing the two ambiguity solutions with an NCEP (National Centers for Environmental Prediction) forecast wind direction, and taking the ambiguity solution which is closest to the NCEP forecast wind direction as the initial field of the current wind vector unit in the comparative results; taking initial fields of all wind vector units as an ambiguity solution initial field of circle median filter, and performing ambiguity solution removal operation to obtain real data of a sea surface wind field. The HY-2 satellite scatterometer sea surface wind field retrieval method and device are adaptive to the requirements of ambiguity solution removal needed by the scatterometer wind field inversion under various complex environmental conditions, and the forecast accuracy is improved.
Owner:NAT SATELLITE OCEAN APPL SERVICE
Method of Determining Dose and Focus, Inspection Apparatus, Patterning Device, Substrate and Device Manufacturing Method
ActiveUS20150293458A1Improve accuracyPhotometry using reference valueScattering properties measurementsLithography processScatterometer
A method of determining exposure dose of a lithographic apparatus used in a lithographic process on a substrate. Using the lithographic process to produce a first structure on the substrate, the first structure having a dose-sensitive feature which has a form that depends on exposure dose of the lithographic apparatus on the substrate. Using the lithographic process to produce a second structure on the substrate, the second structure having a dose-sensitive feature which has a form that depends on the exposure dose of the lithographic apparatus but which has a different sensitivity to the exposure dose than the first structure. Detecting scattered radiation while illuminating the first and second structures with radiation to obtain first and second scatterometer signals. Using the first and second scatterometer signals to determine an exposure dose value used to produce at least one of the first and second structures.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Methods and systems for measuring periodic structures using multi-angle x-ray reflectance scatterometry (XRS)
ActiveUS20150204802A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementX-rayScatterometer
Methods and systems for measuring periodic structures using multi-angle X-ray reflectance scatterometry (XRS) are disclosed. For example, a method of measuring a sample by X-ray reflectance scatterometry involves impinging an incident X-ray beam on a sample having a periodic structure to generate a scattered X-ray beam, the incident X-ray beam simultaneously providing a plurality of incident angles and a plurality of azimuthal angles. The method also involves collecting at least a portion of the scattered X-ray beam.
Owner:NOVA MEASURING INSTRUMENTS INC
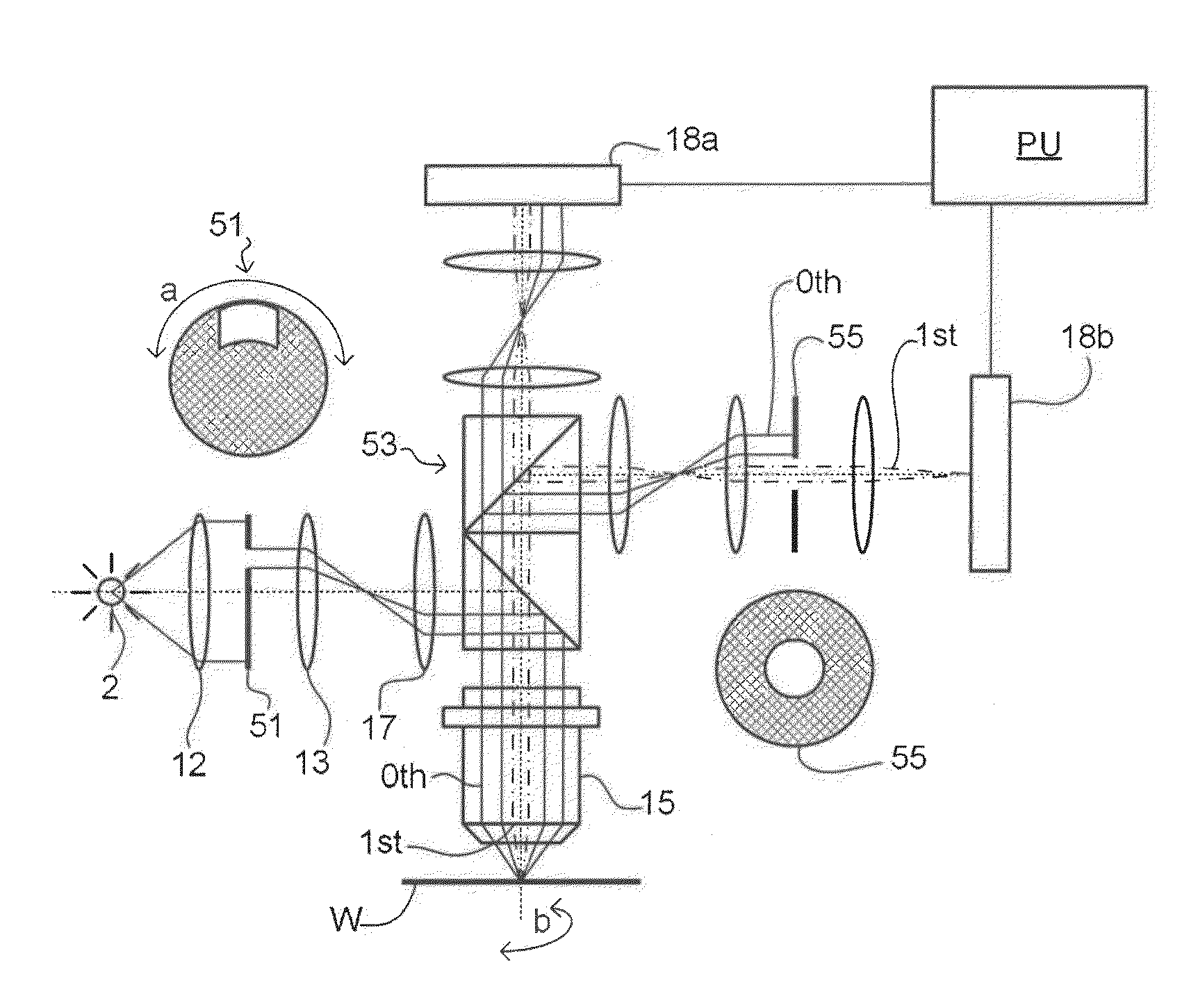
Illumination System, Inspection Apparatus Including Such an Illumination System, Inspection Method and Manufacturing Method
ActiveUS20160025992A1Great freedomEffective positioningBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsPhotometrySpatial light modulatorBeam splitter
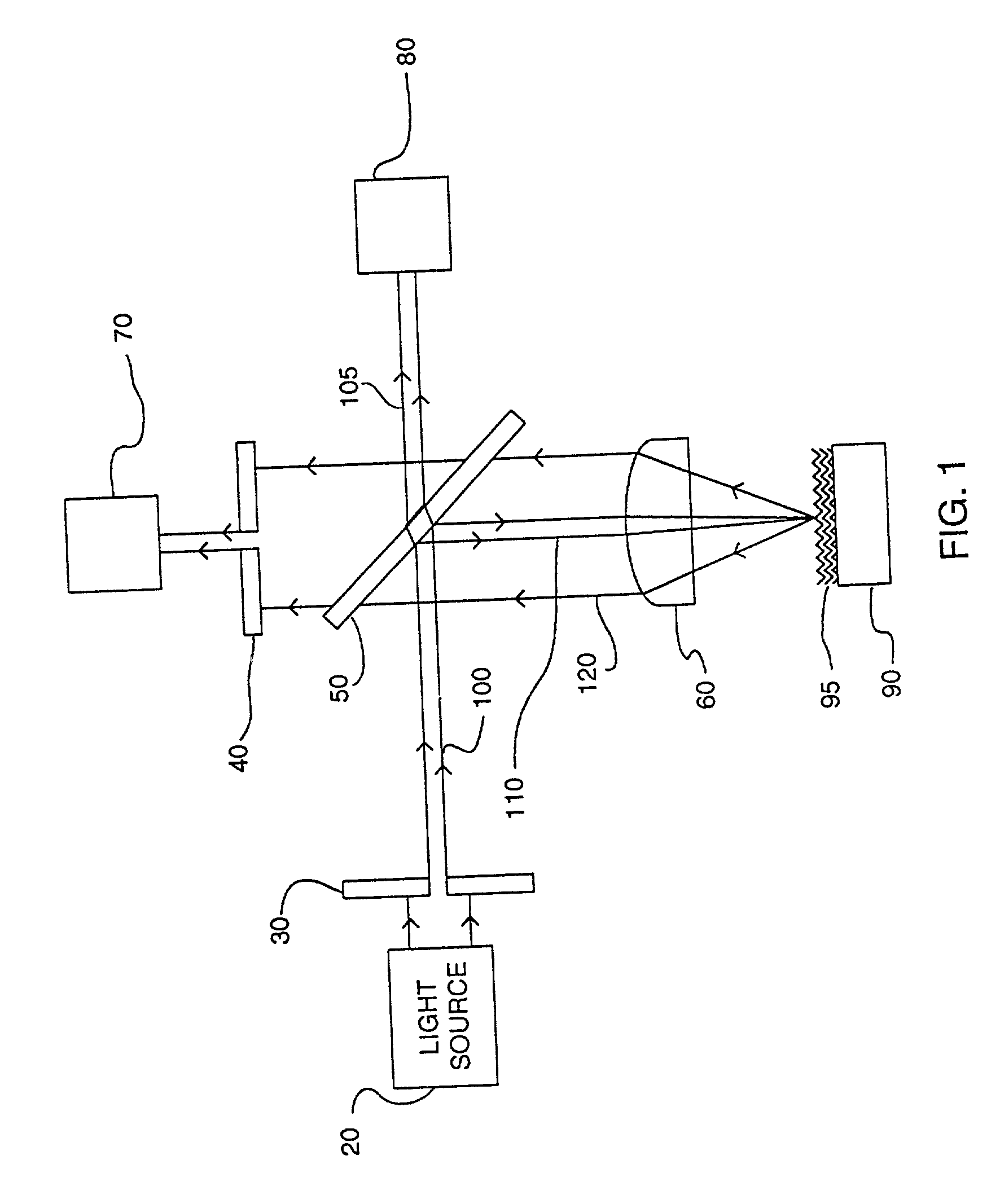
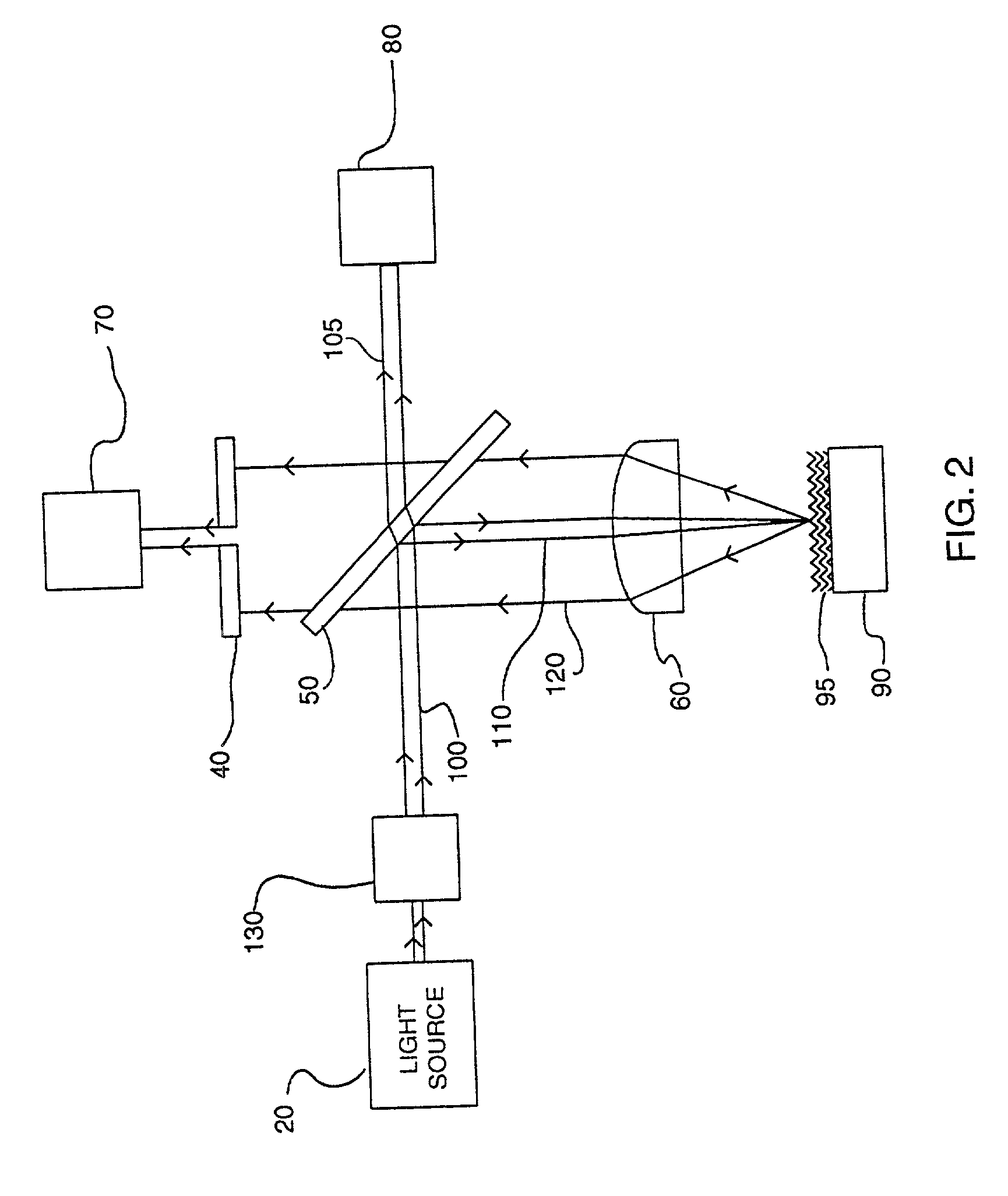
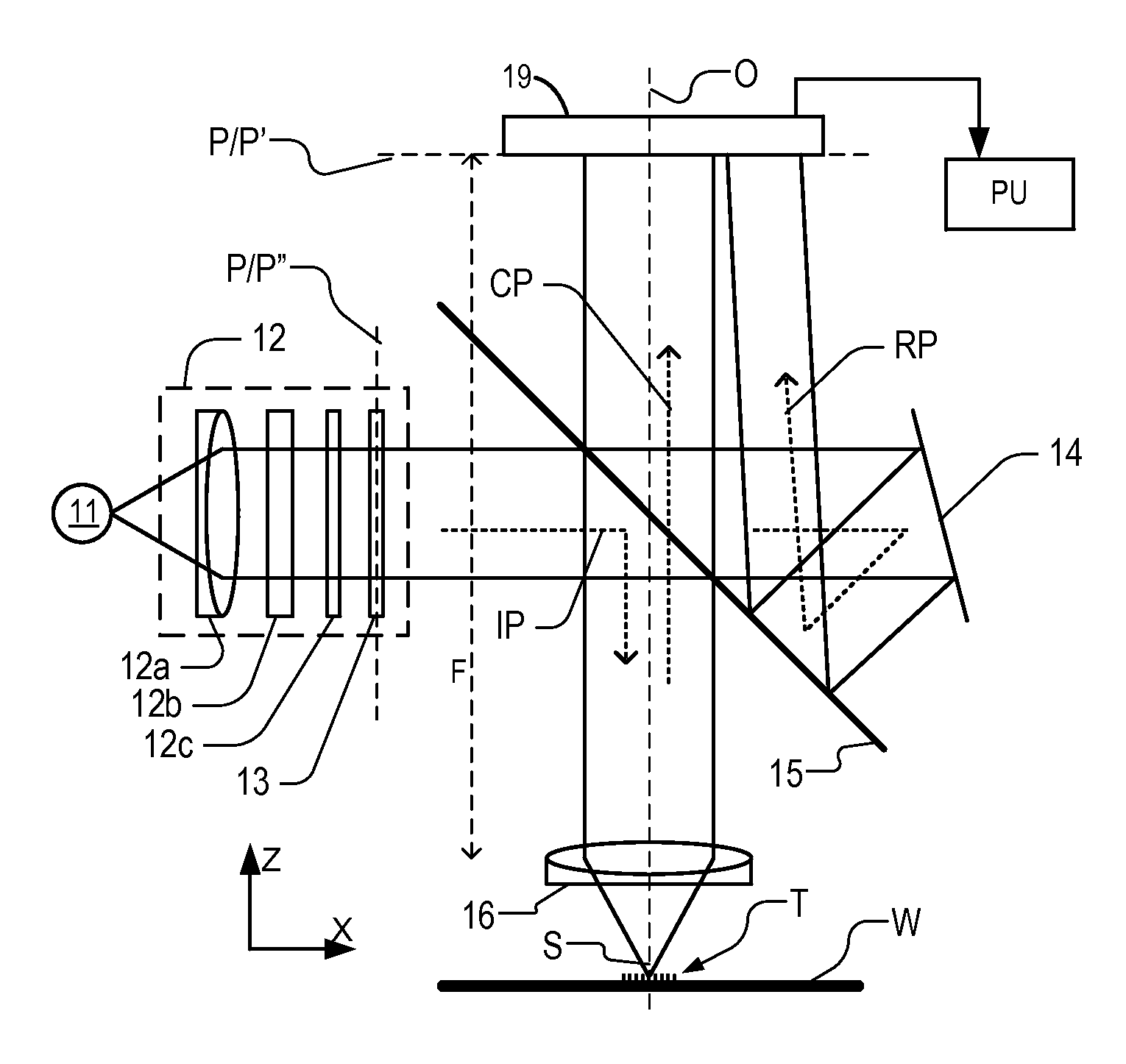
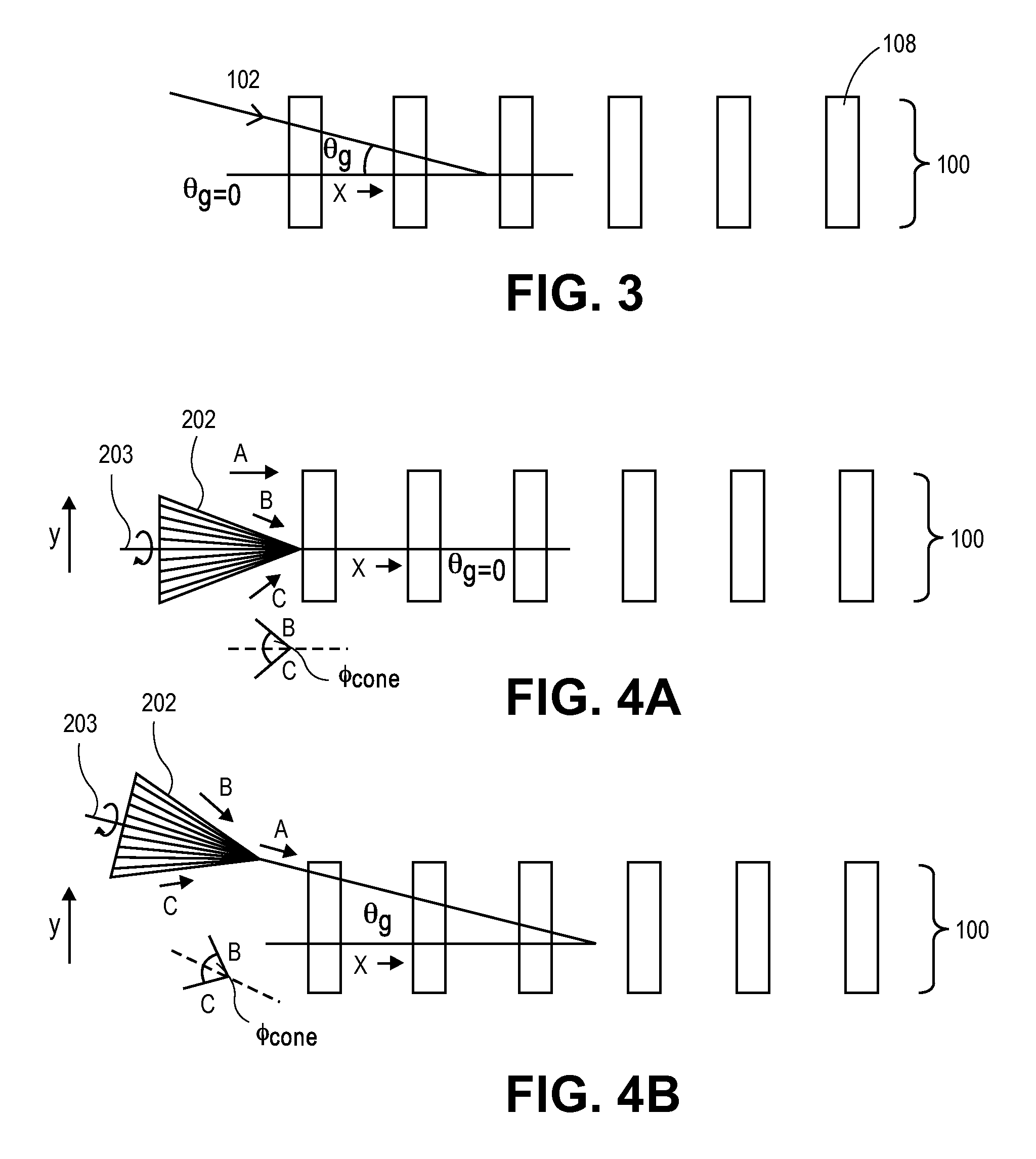
In an illumination system (12, 13) for a scatterometer, first and second spatial light modulators lie in a common plane and are formed by different portions of a single liquid crystal cell (260). Pre-polarizers (250) apply polarization to first and second radiation prior to the spatial light modulators. A first spatial light modulator (236-S) varies a polarization state of the first radiation in accordance with a first programmable pattern. Second spatial light modulator (236-P) varies a polarization state of the second radiation accordance with a second programmable pattern. A polarizing beam splitter (234) selectively transmits each of the spatially modulated first and second radiation to a common output path, depending on the polarization state of the radiation. In an embodiment, functions of pre-polarizers are performed by the polarizing beam splitter.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
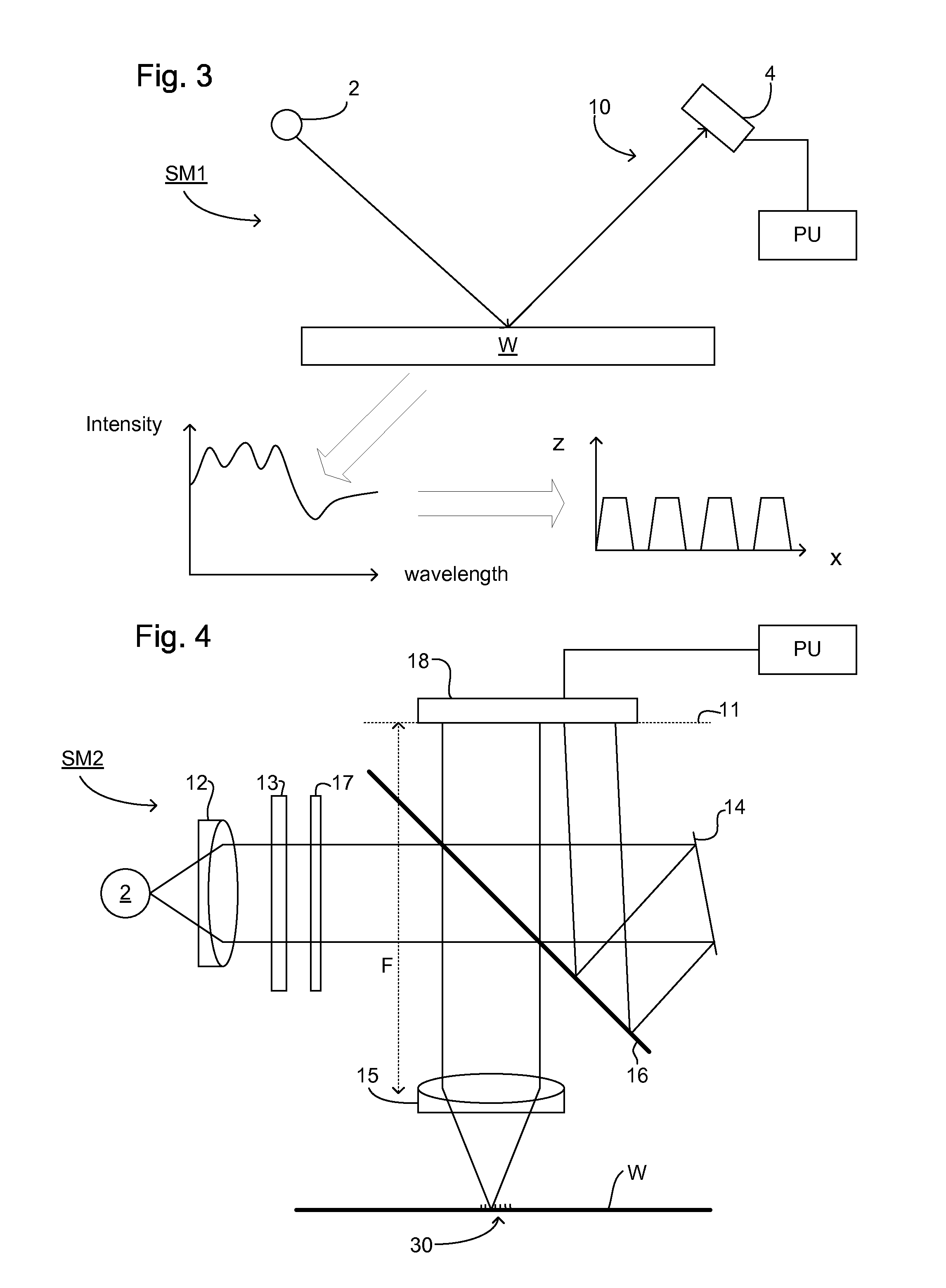
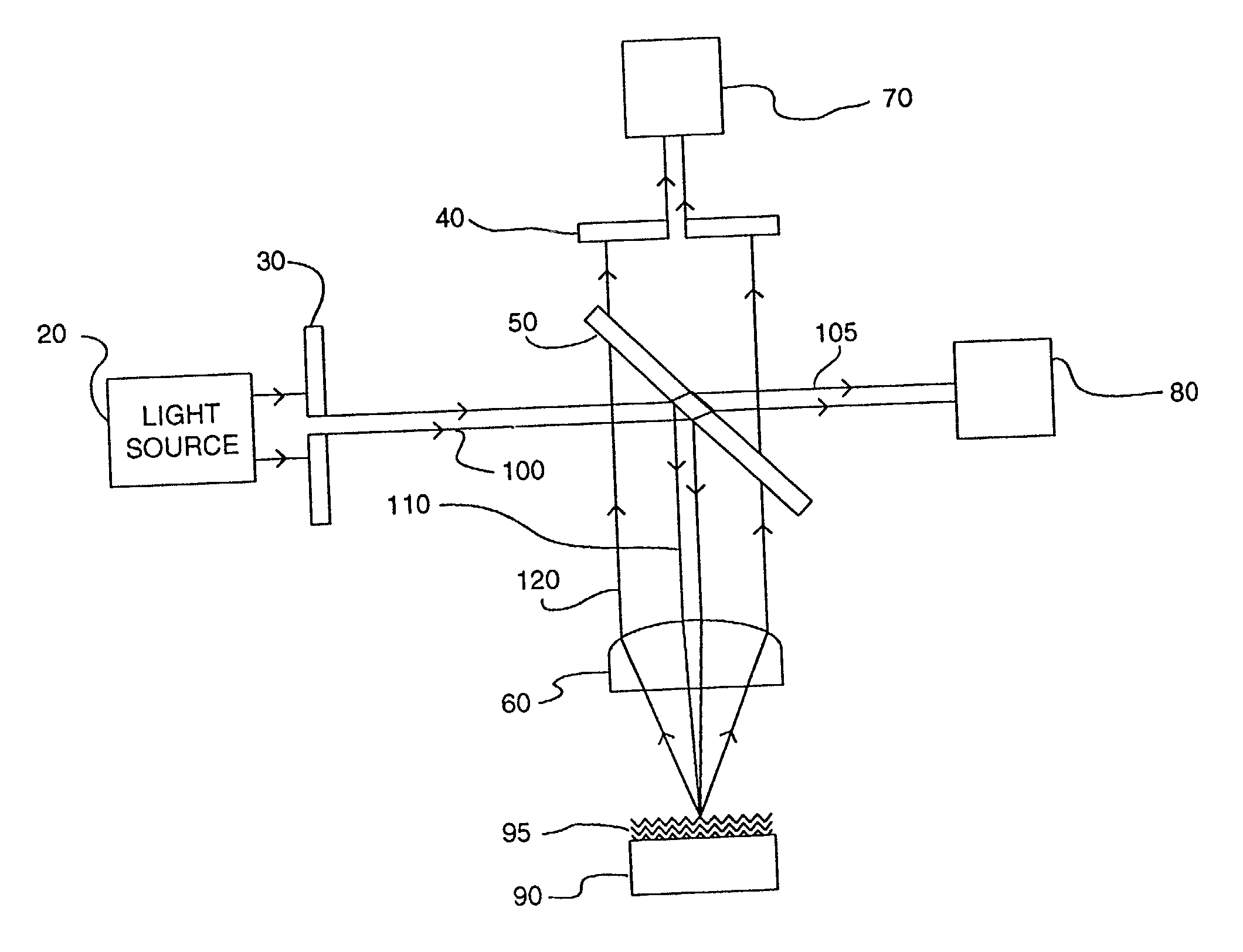
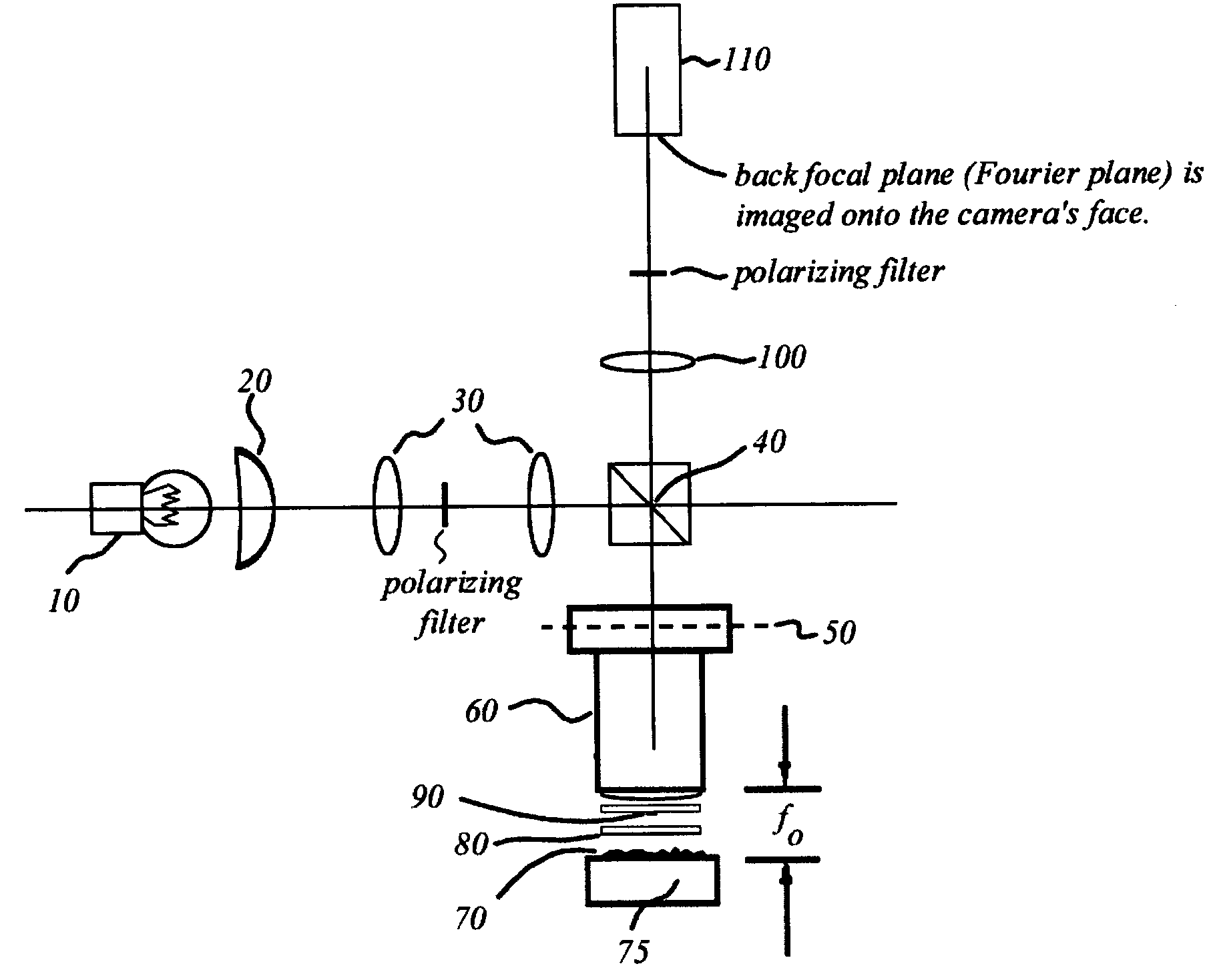
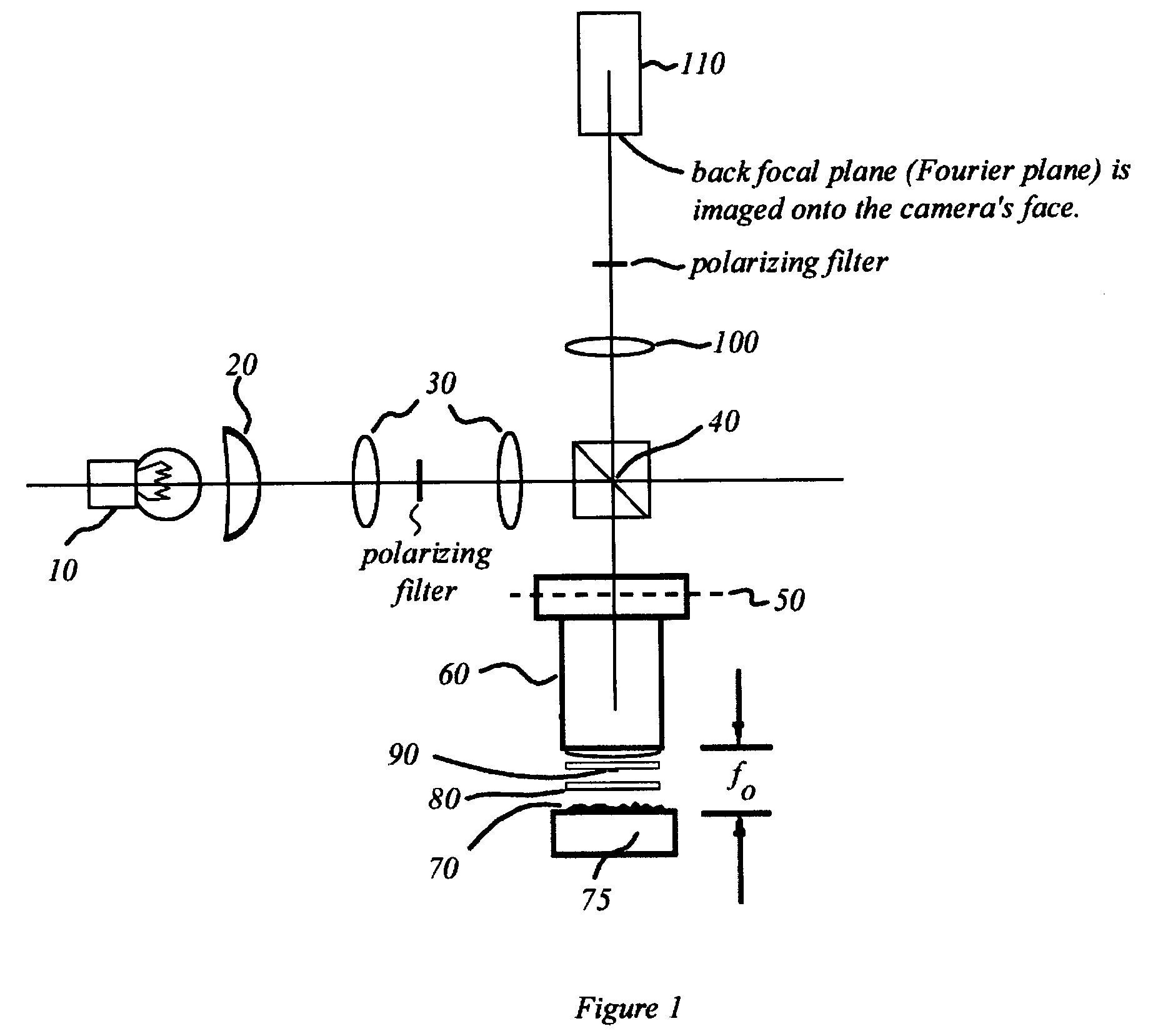
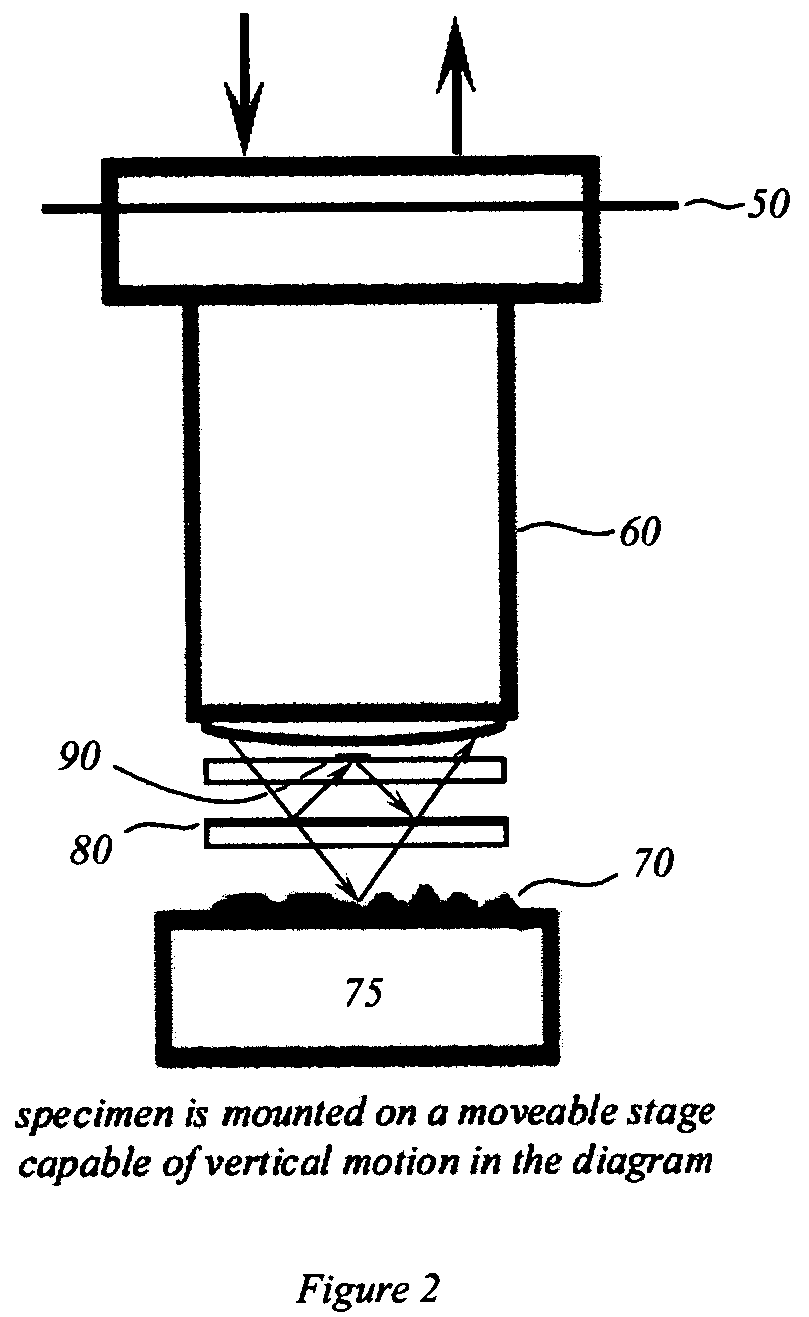
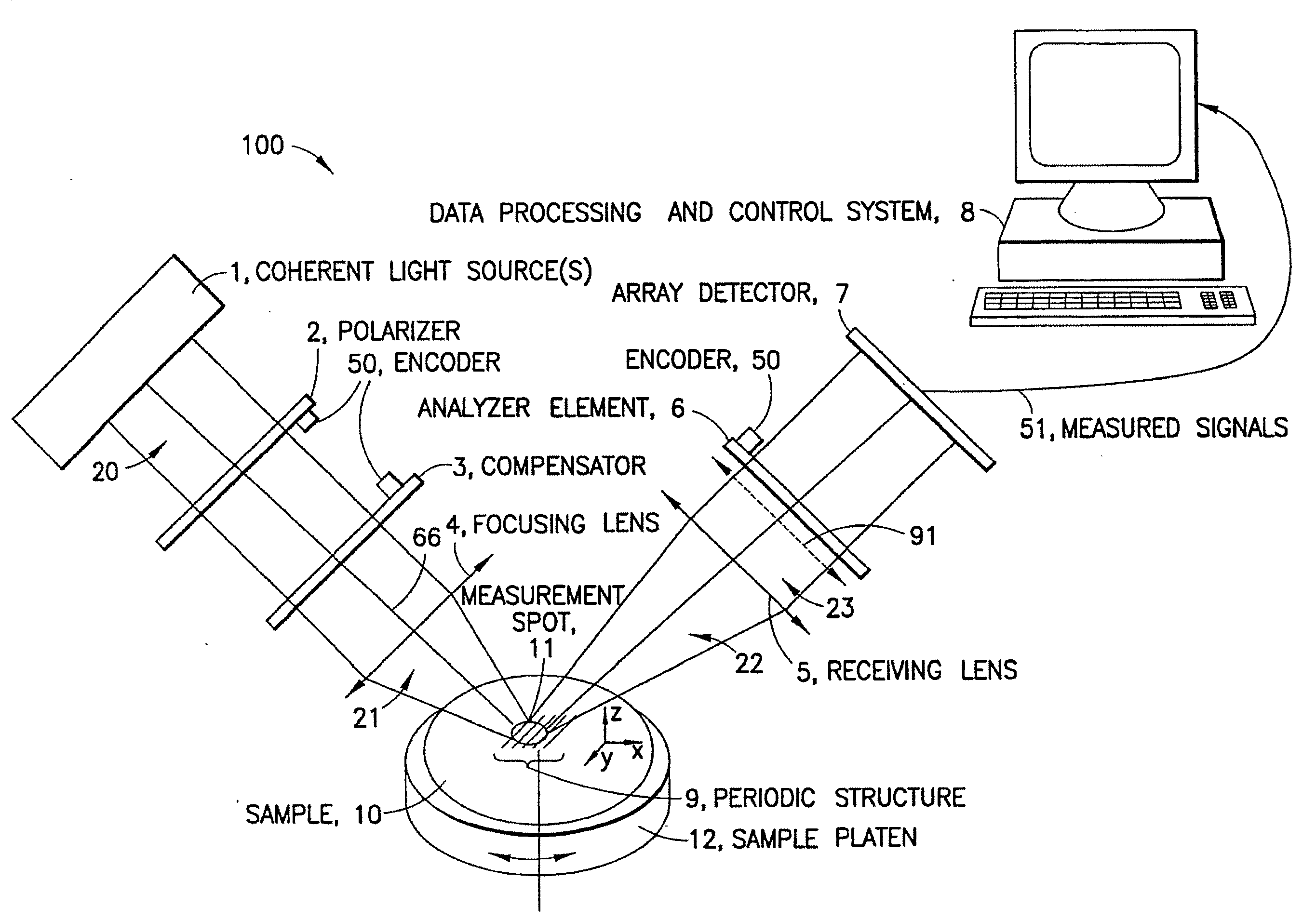
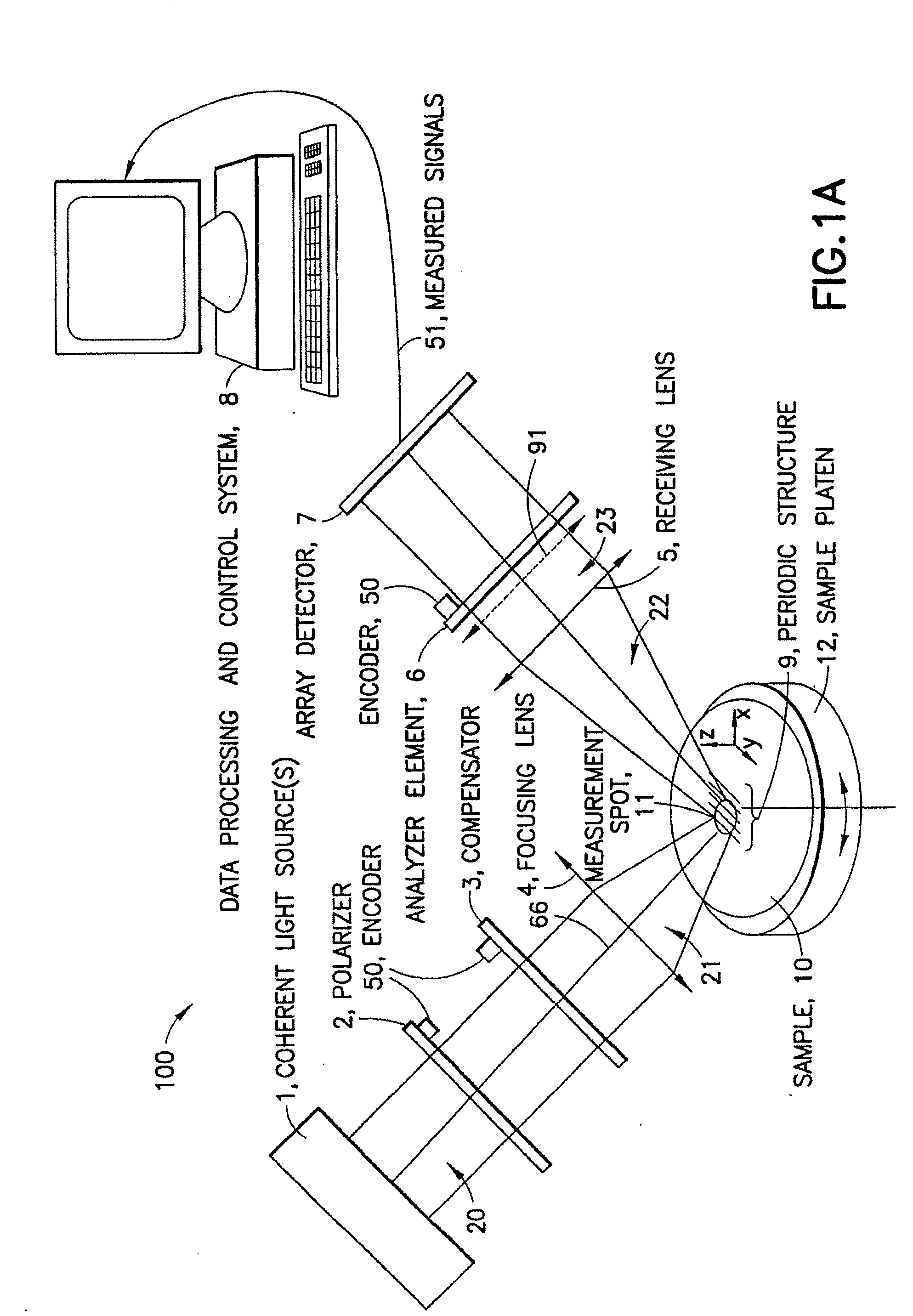
Interference scatterometer
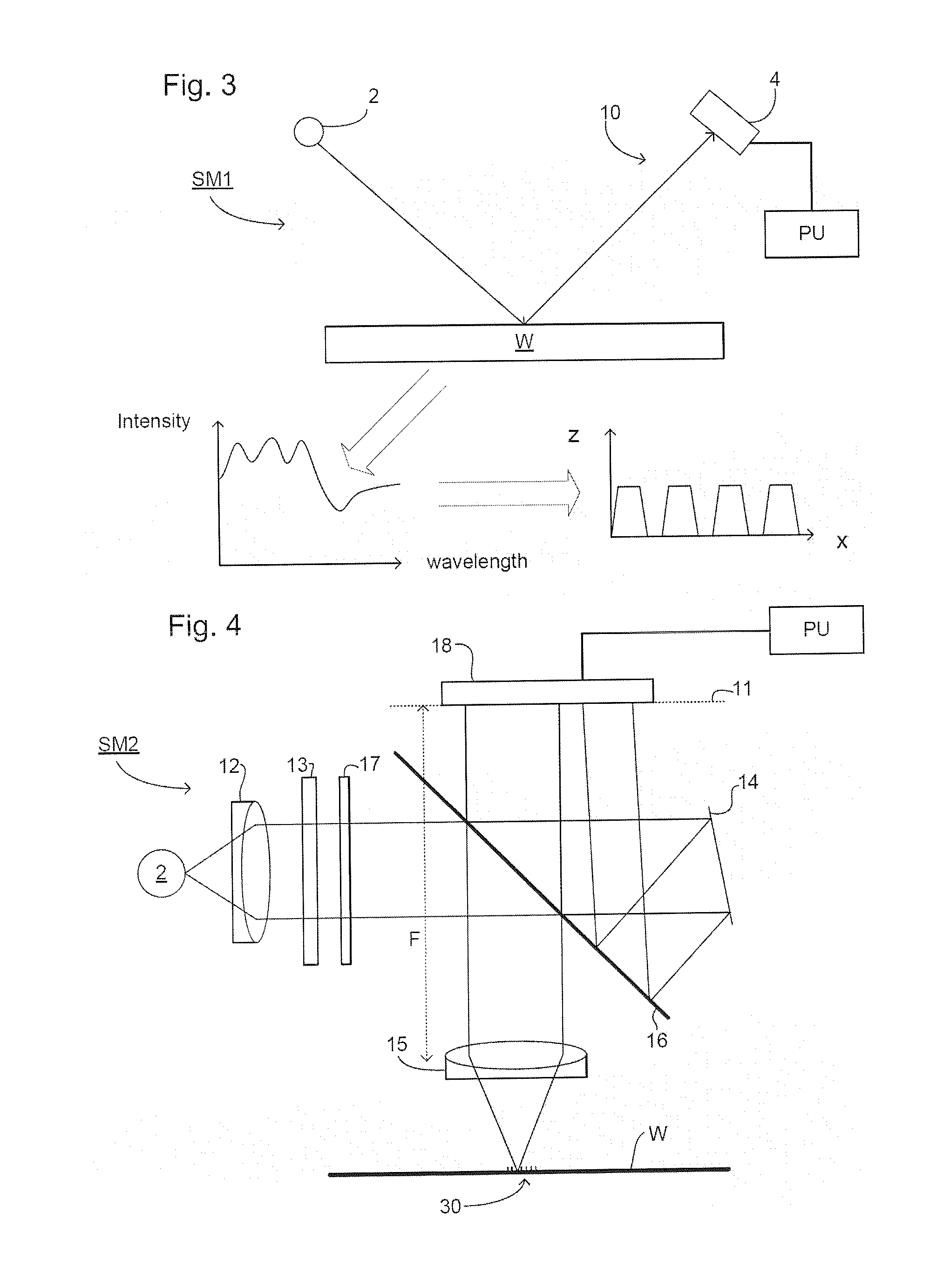
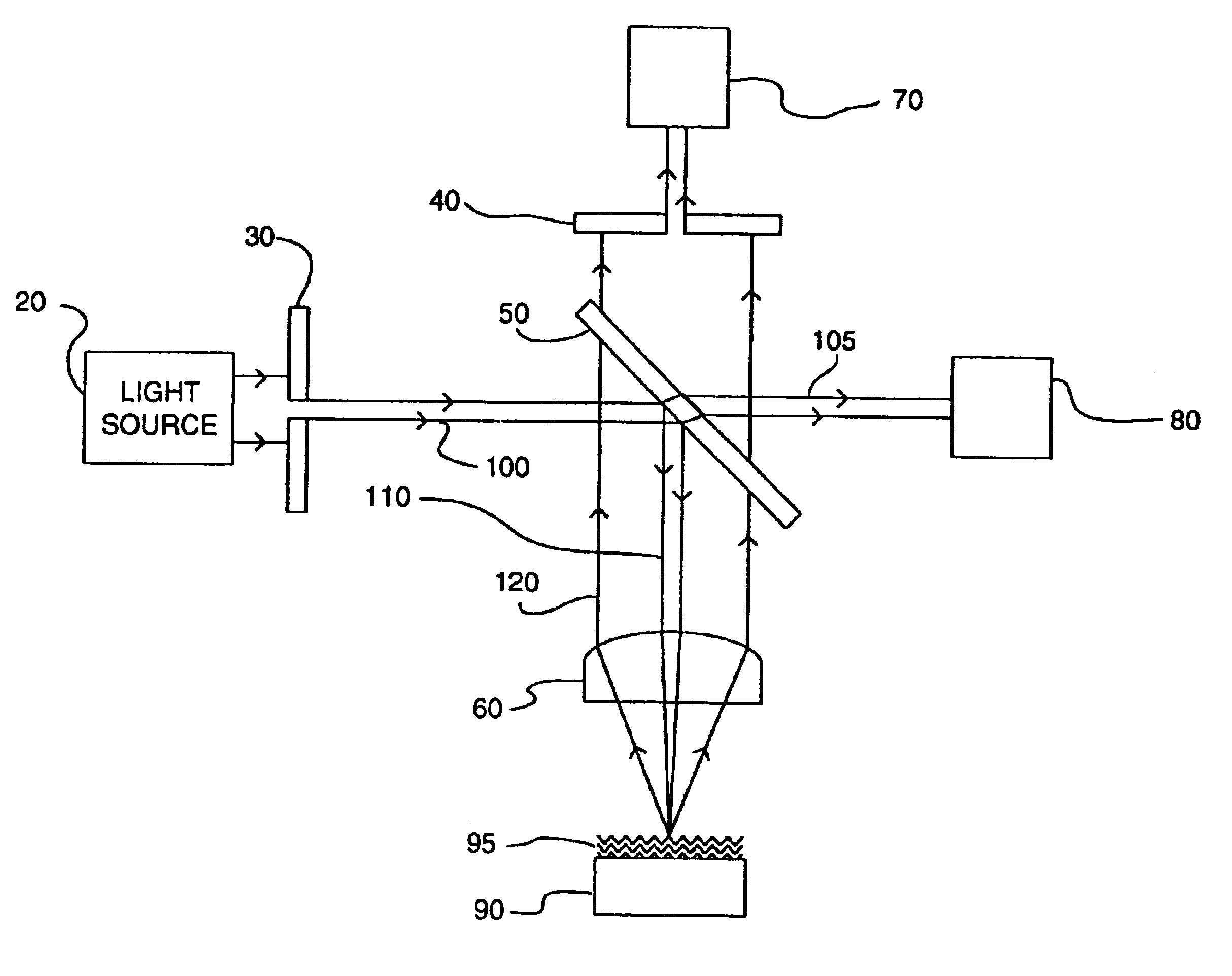
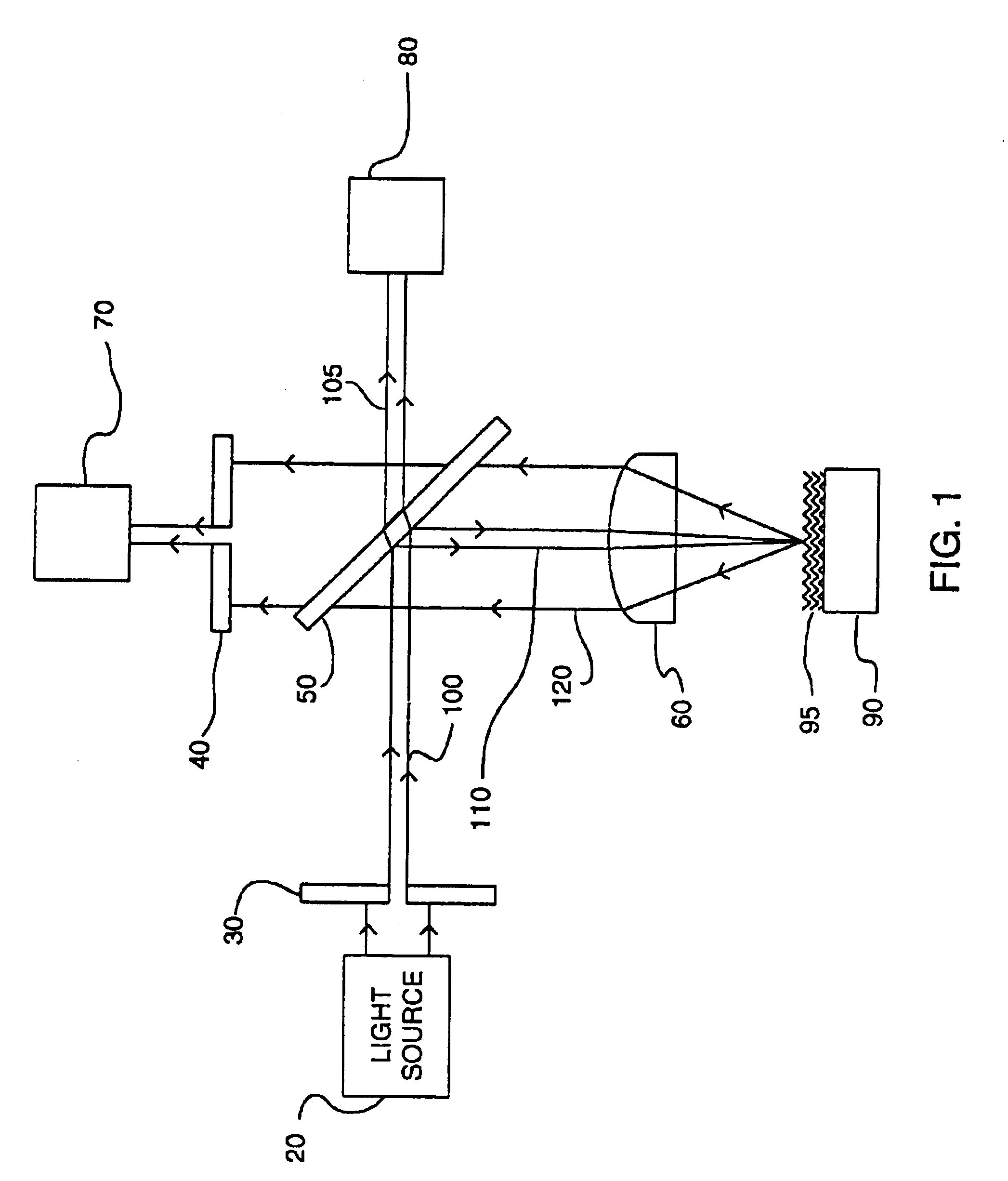
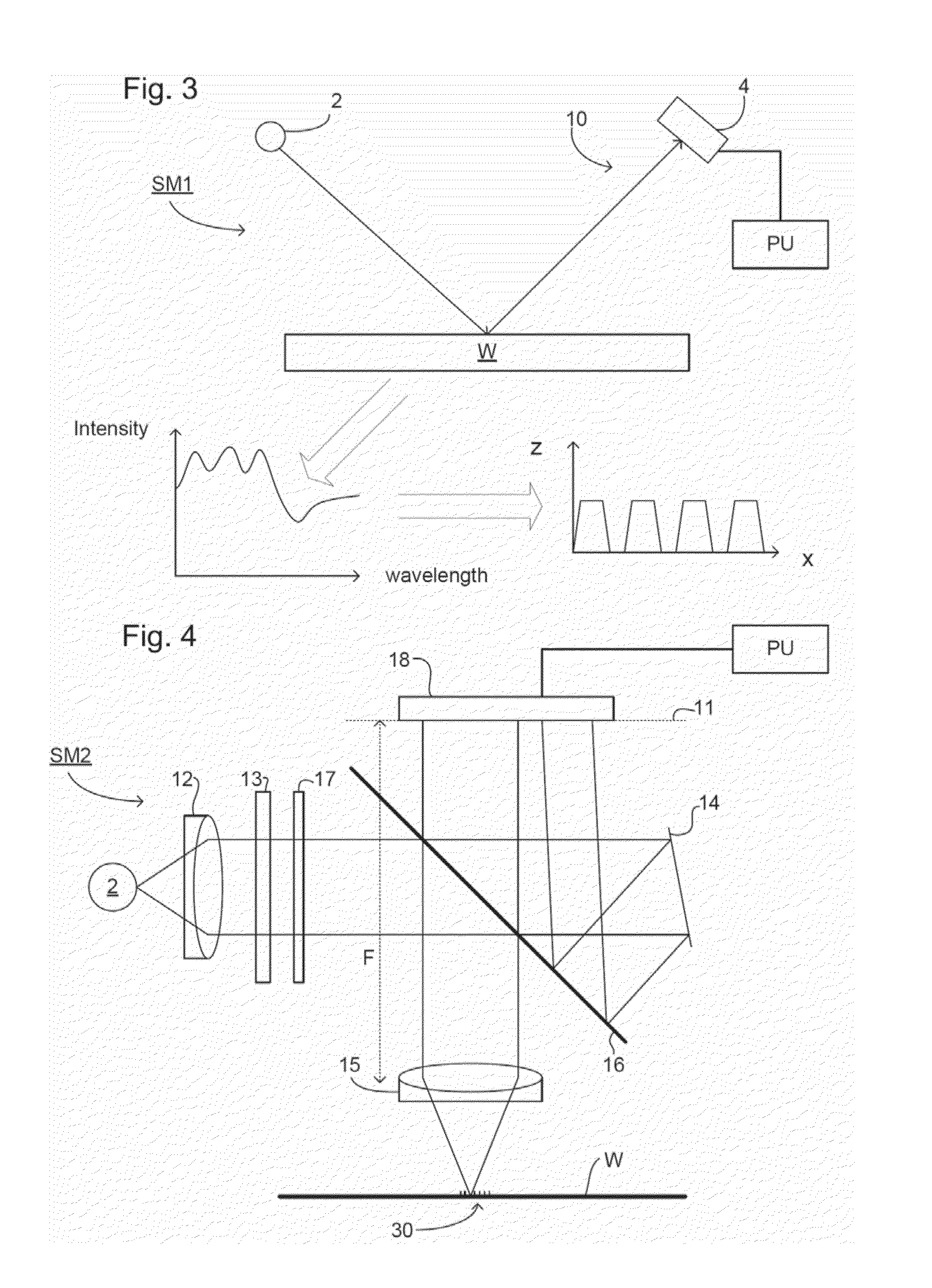
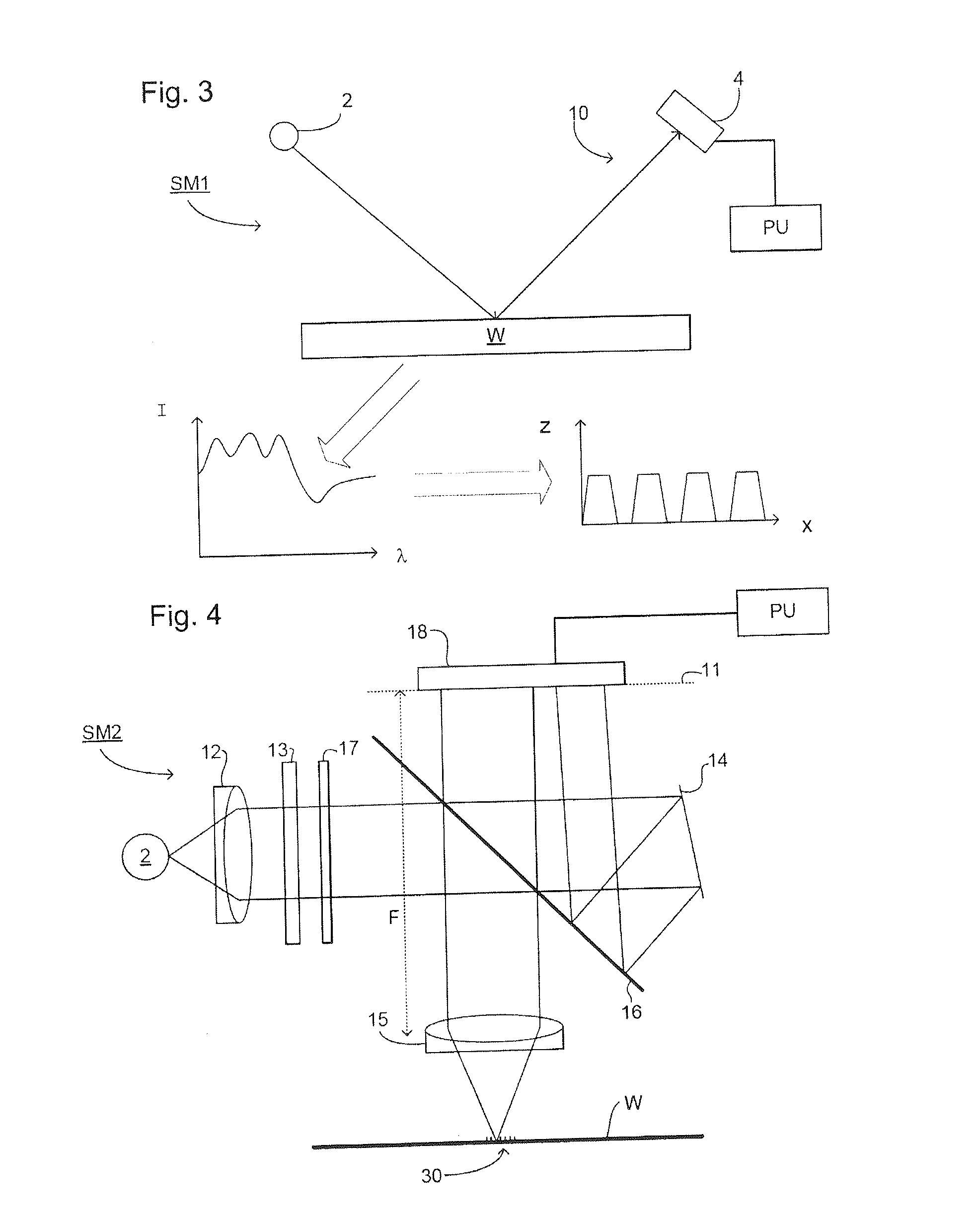
An interference spectroscopy instrument provides simultaneous measurement of specular scattering over multiple wavelengths and angles. The spectroscopy instrument includes an interference microscope illuminated by Koehler illumination and a video camera located to image the back focal plane of the microscope's objective lens while the path-length difference is varied between the reference and object paths. Multichannel Fourier analysis transforms the resultant intensity information into specular reflectivity data as a function of wavelength. This multitude of measured data provides a more sensitive scatterometry tool having superior performance in the measurement of small patterns on semiconductor devices and in measuring overlay on such devices.
Owner:ZYGO CORPORATION
Polarimetric scatterometry methods for critical dimension measurements of periodic structures
InactiveUS20050174575A1Polarisation-affecting propertiesScattering properties measurementsMotor driveOptical property
An optical measurement system for evaluating a sample has a motor-driven rotating mechanism coupled to an azimuthally rotatable measurement head, allowing the optics to rotate with respect to the sample. A polarimetric scatterometer, having optics directing a polarized illumination beam at non-normal incidence onto a periodic structure on a sample, can measure optical properties of the periodic structure. An E-O modulator in the illumination path can modulate the polarization. The head optics collect light reflected from the periodic structure and feed that light to a spectrometer for measurement. A beamsplitter in the collection path can ensure both S and P polarization from the sample are separately measured. The measurement head can be mounted for rotation of the plane of incidence to different azimuthal directions relative to the periodic structures. The instrument can be integrated within a wafer process tool in which wafers may be provided at arbitrary orientation.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Estimating overlay error and optical aberrations
Aberration marks, which may be used in conjunction with lenses in optical photolithography systems, may assist in estimating overlay errors and optical aberrations. Aberration marks may include an inner polygon pattern and an outer polygon pattern, wherein each of the inner and outer polygon patterns include a center, and two sets of lines and spaces having a different feature size and pitch that surround the outer polygon pattern. In some embodiments, the marks can be used with scatterometry or scanning electron microscope devices.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Method and Apparatus for Measuring Line End Shortening, Substrate and Patterning Device
ActiveUS20110109888A1Quick and inexpensive and simple to performPhotomechanical apparatusScattering properties measurementsFluenceScatterometer
End of line effect can occur during manufacture of components using a lithographic apparatus. These end of line effects can result in line end shortening of the features being manufactured. Such line end shortening may have an adverse impact on the component being manufactured. It is therefore desirable to predict and / or monitor the line end shortening. A test pattern is provided that has two separate areas such that, as designed, when the two areas are illuminated with radiation (for example from an angle-resolved scatterometer) they result in diffused radiation with asymmetry that is equal in sign to each other, but opposite in magnitude. When the test pattern is actually manufactured, line end shortening occurs, and so the asymmetry of the two areas are not equal and opposite. From the measured asymmetry of the manufactured test pattern, the amount of line end shortening that has occurred can be estimated.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Calibration Method and Apparatus
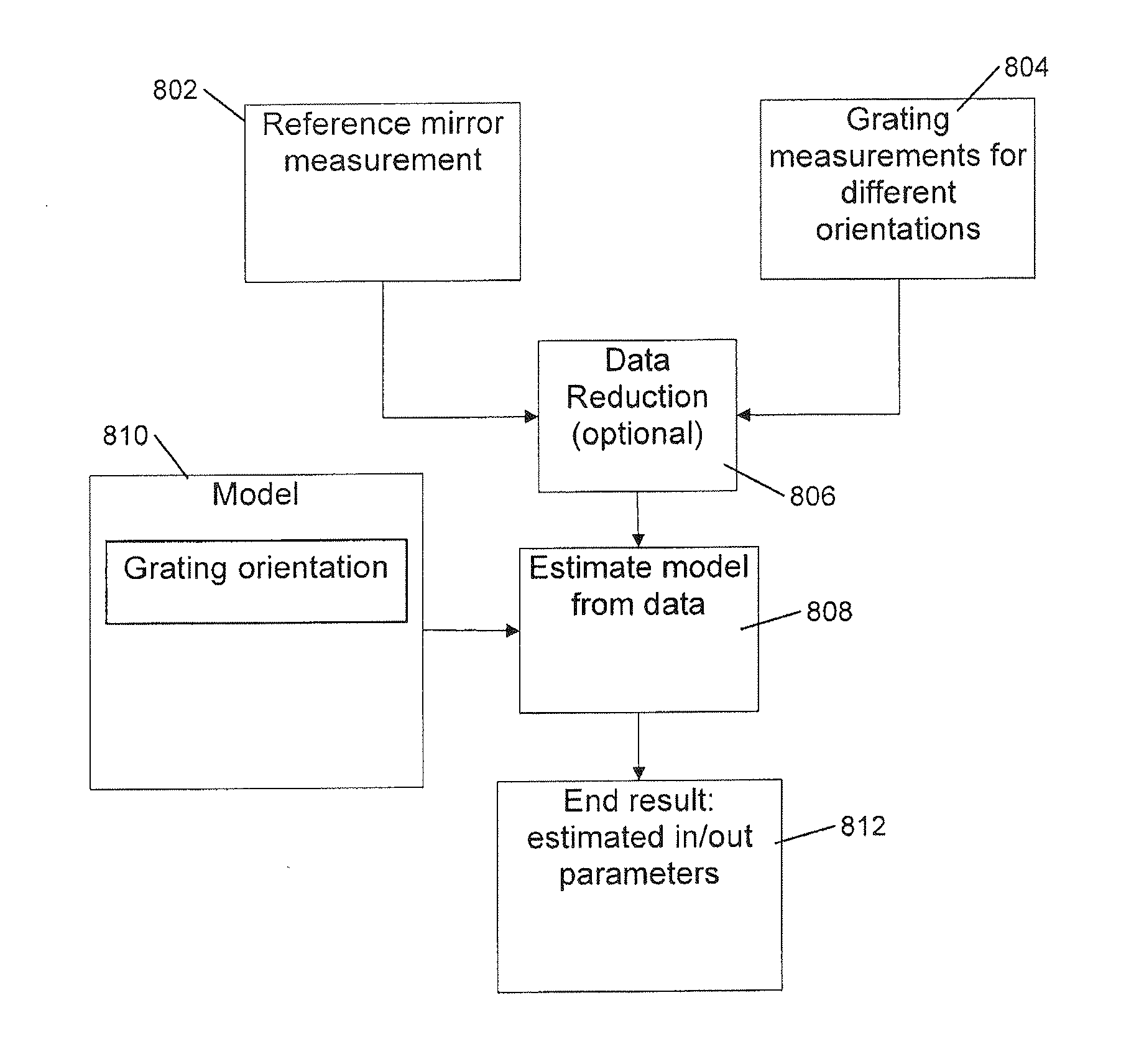
ActiveUS20110178785A1Optically investigating flaws/contaminationComputation using non-denominational number representationScatterometerMueller calculus
Calibration of an angularly resolved scatterometer is performed by measuring a target in two or more different arrangements. The different arrangements cause radiation being measured in an outgoing direction to be different combinations of radiation illuminating the target from ingoing directions. A reference mirror measurement may also be performed. The measurements and modeling of the difference between the first and second arrangements is used to estimate separately properties of the ingoing and outgoing optical systems. The modeling may account for symmetry of the respective periodic target. The modeling typically accounts for polarizing effects of the ingoing optical elements, the outgoing optical elements and the respective periodic target. The polarizing effects may be described in the modeling by Jones calculus or Mueller calculus. The modeling may include a parameterization in terms of basis functions such as Zernike polynomials.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Methods and systems for measuring periodic structures using multi-angle X-ray reflectance scatterometry (XRS)
ActiveUS9588066B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementX-rayScatterometer
Owner:NOVA MEASURING INSTRUMENTS INC
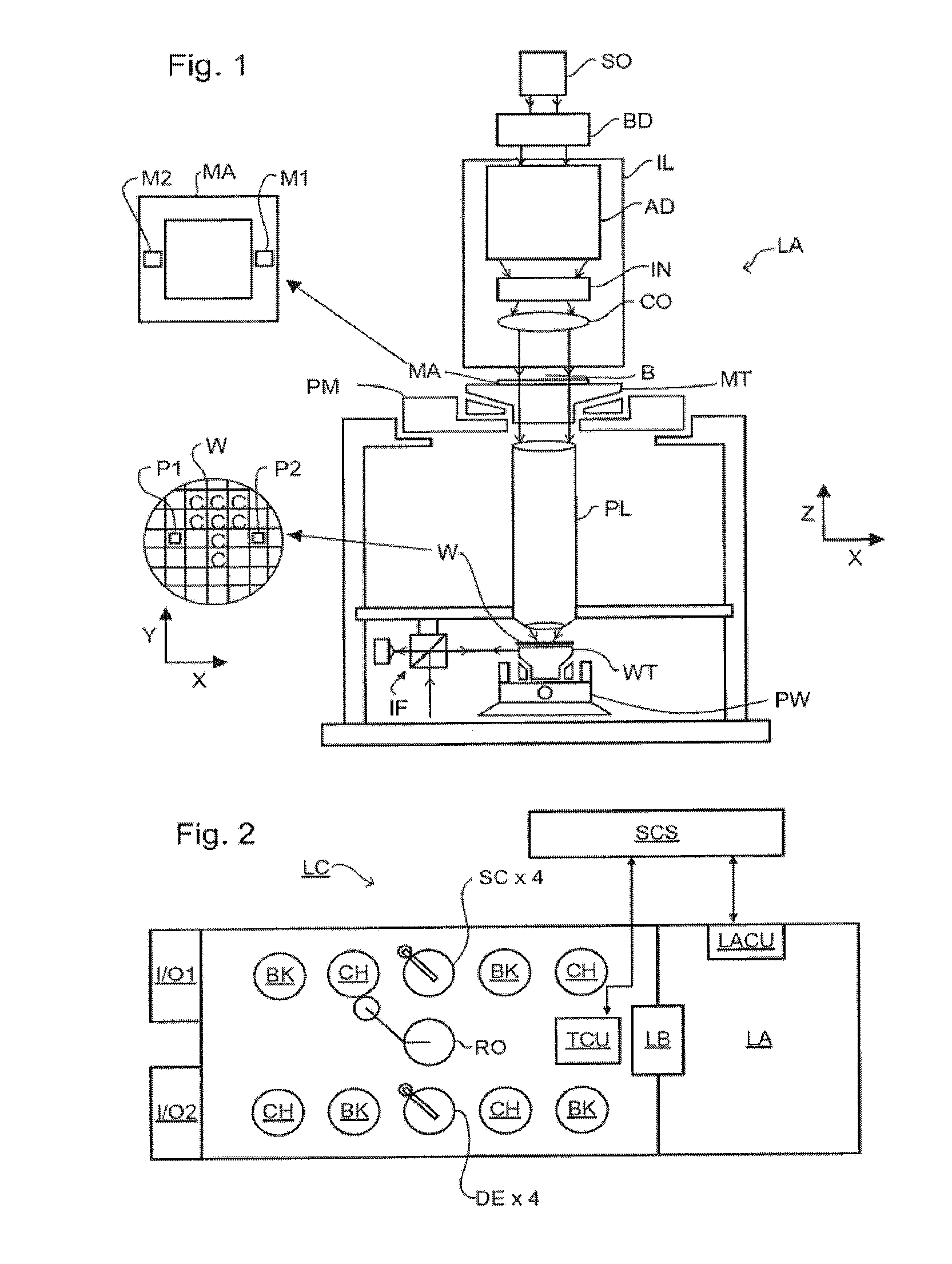
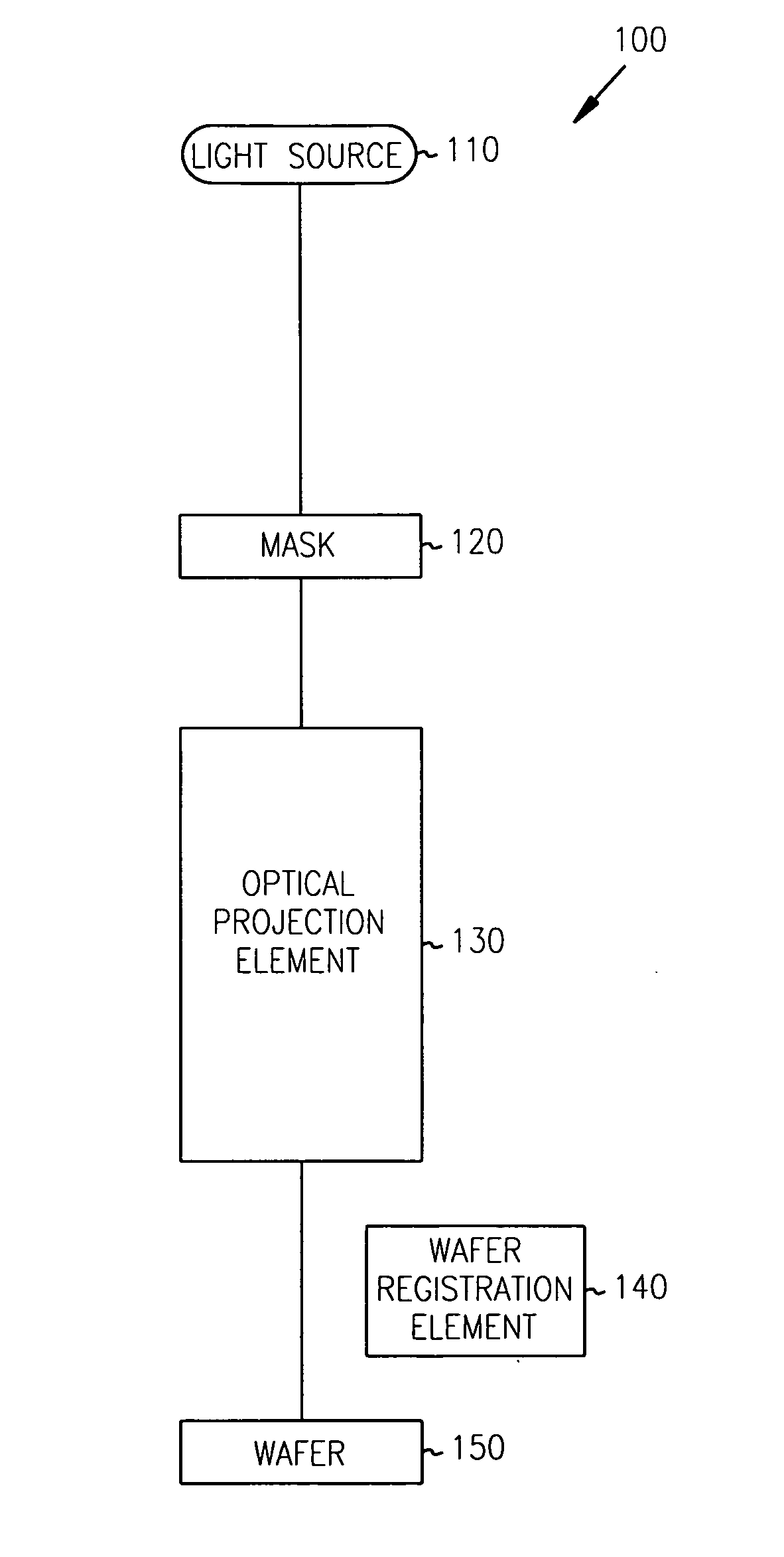
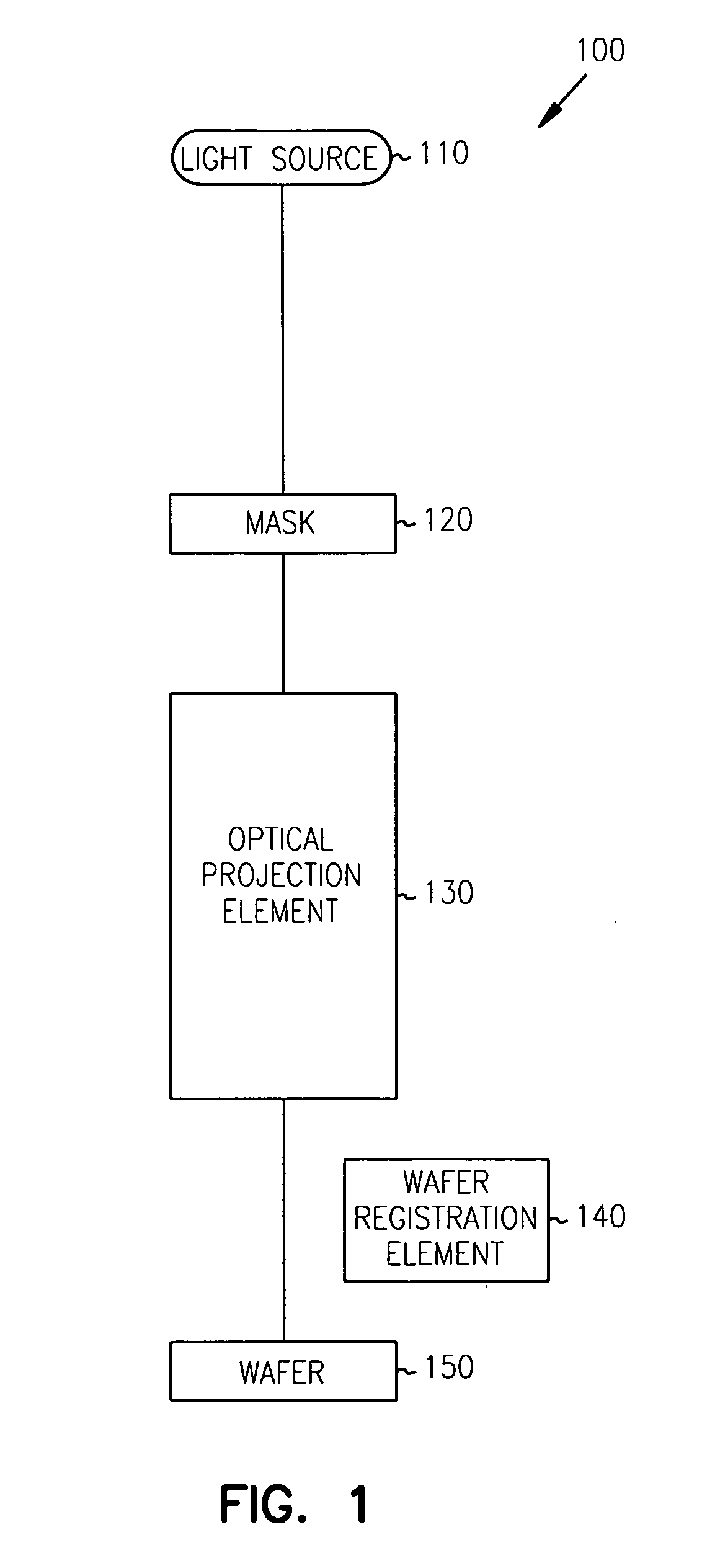
Inspection apparatus, an apparatus for projecting an image and a method of measuring a property of a substrate
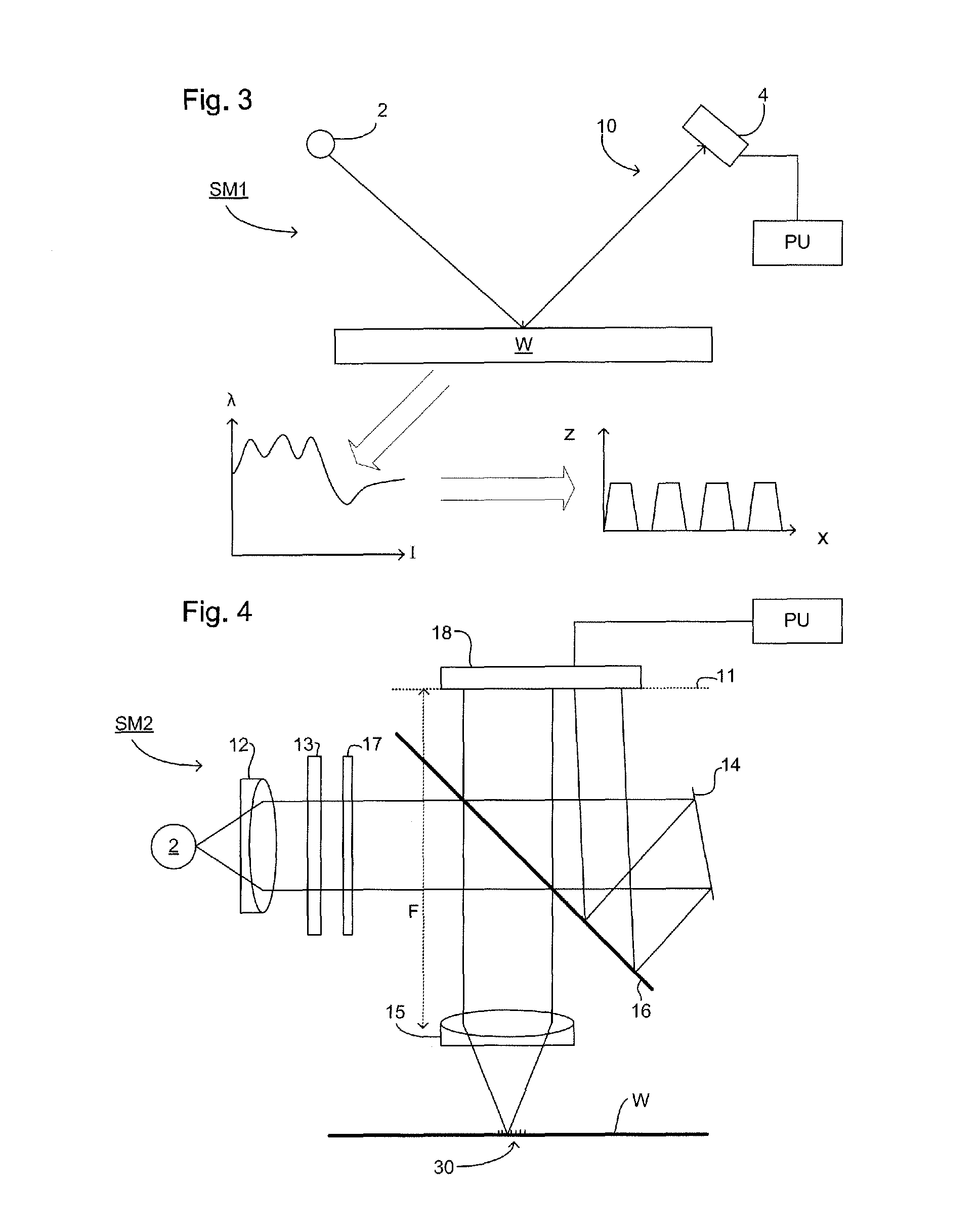
InactiveUS20080068609A1Improve image qualityScattering properties measurementsPhotomechanical apparatusHigh numerical apertureScatterometer
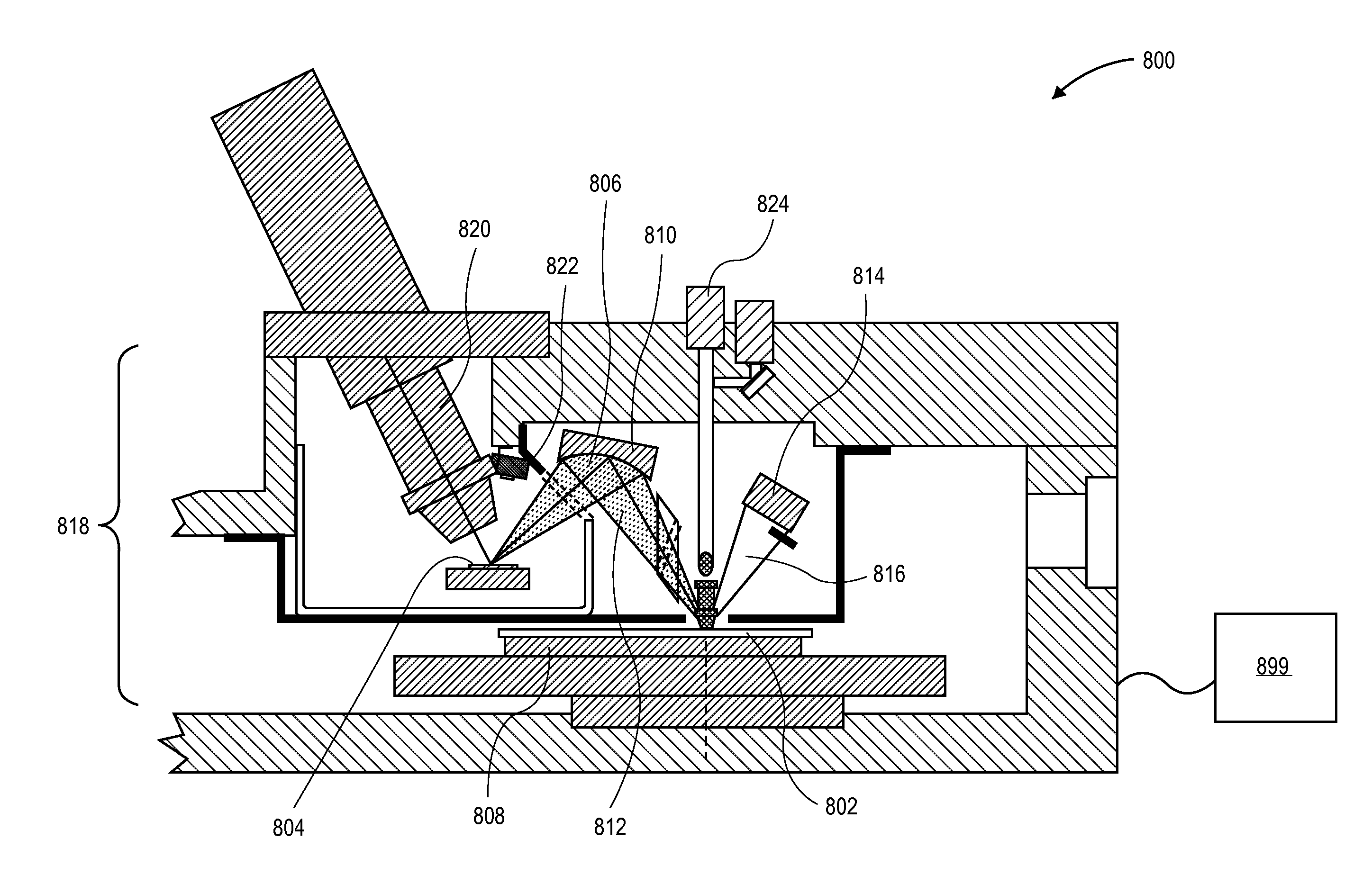
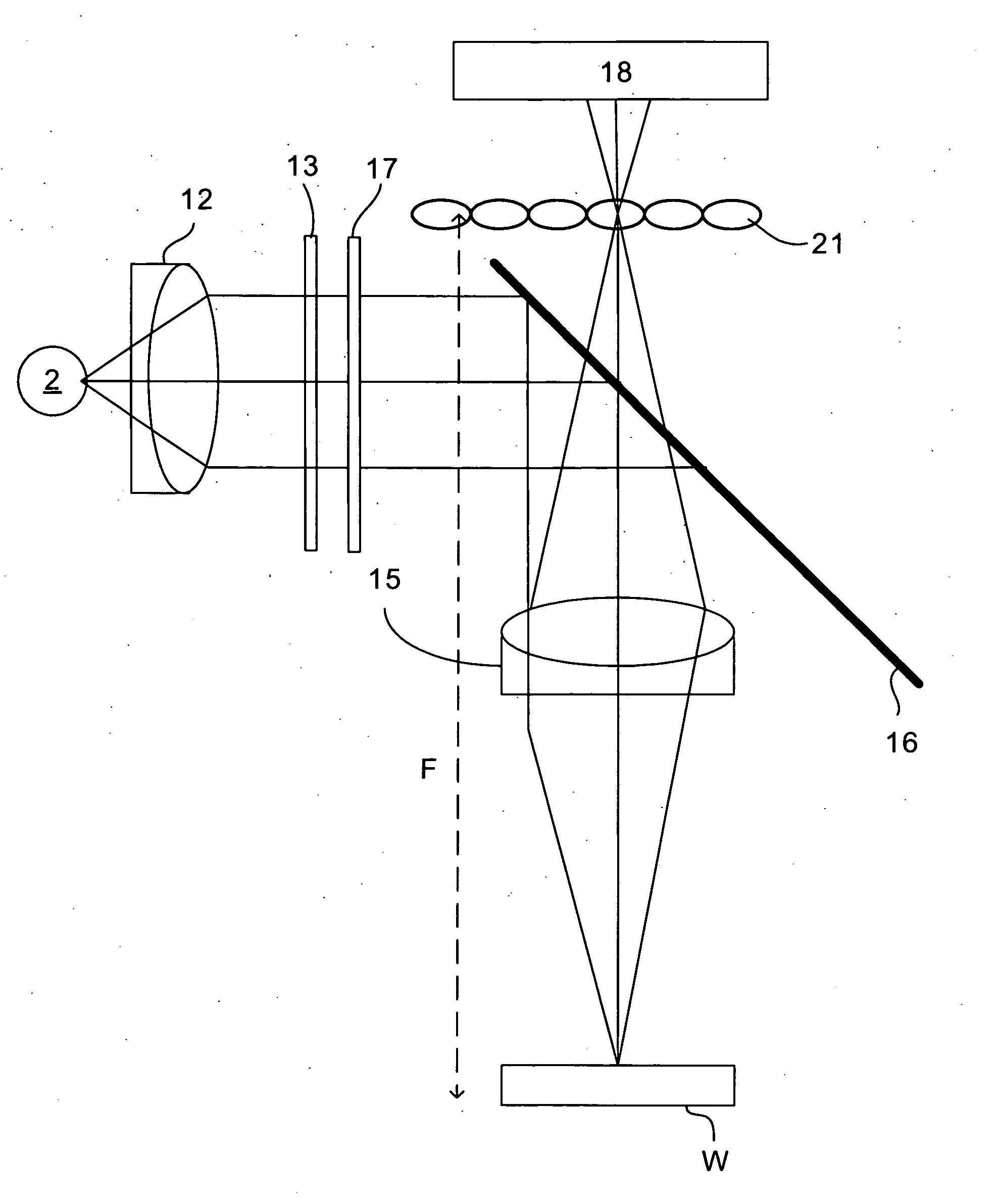
When using a scatterometer different portions of a target area may be at different focal depths. When the whole area is measured this results in part of it being out of focus. To compensate for this an array of lenses is placed in the back focal plane of the high numerical aperture lens.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Method and Apparatus for Controlling a Lithographic Apparatus
ActiveUS20110205510A1Improved off-line parameterization modelingPhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingScatterometerModel parameters
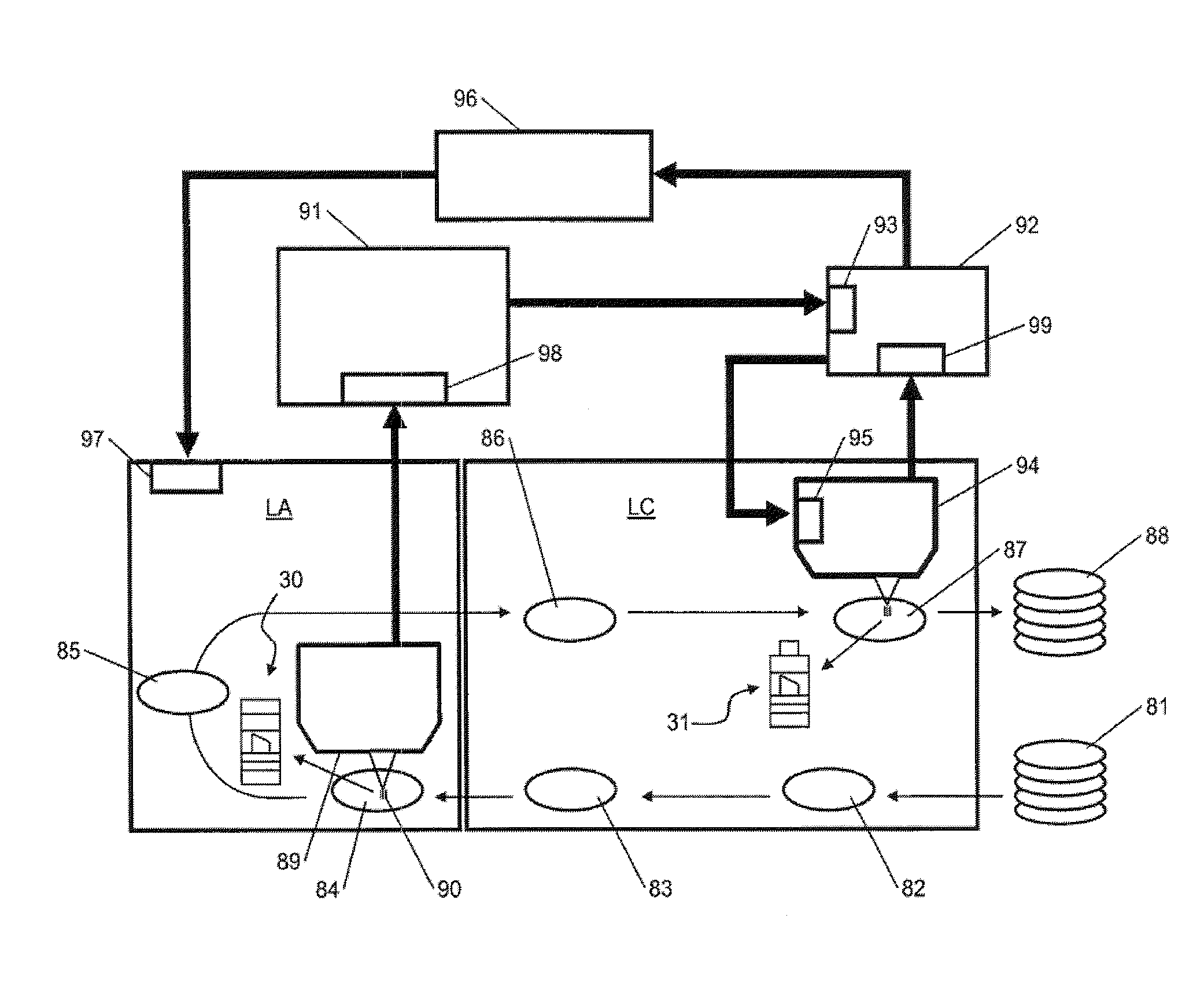
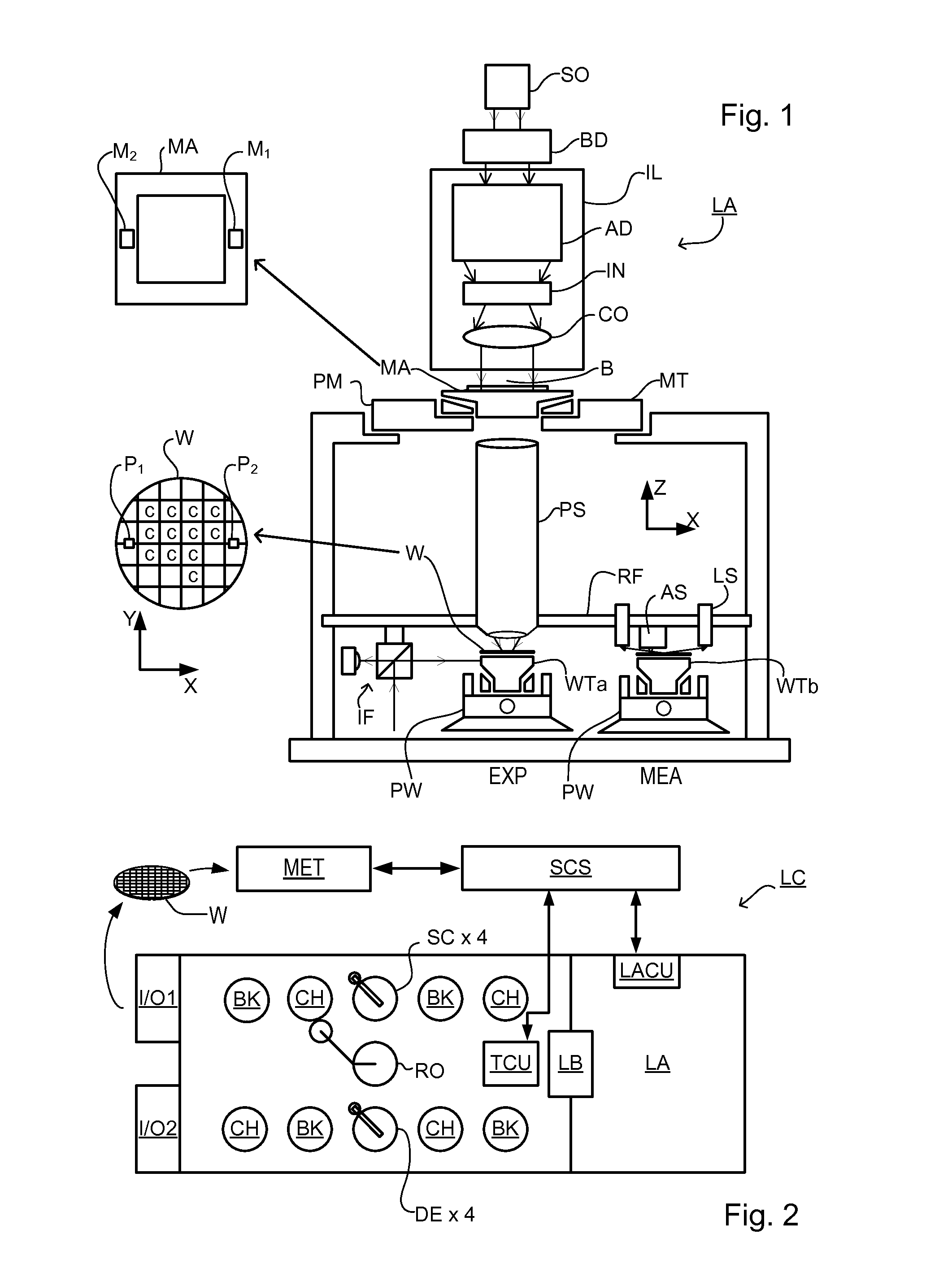
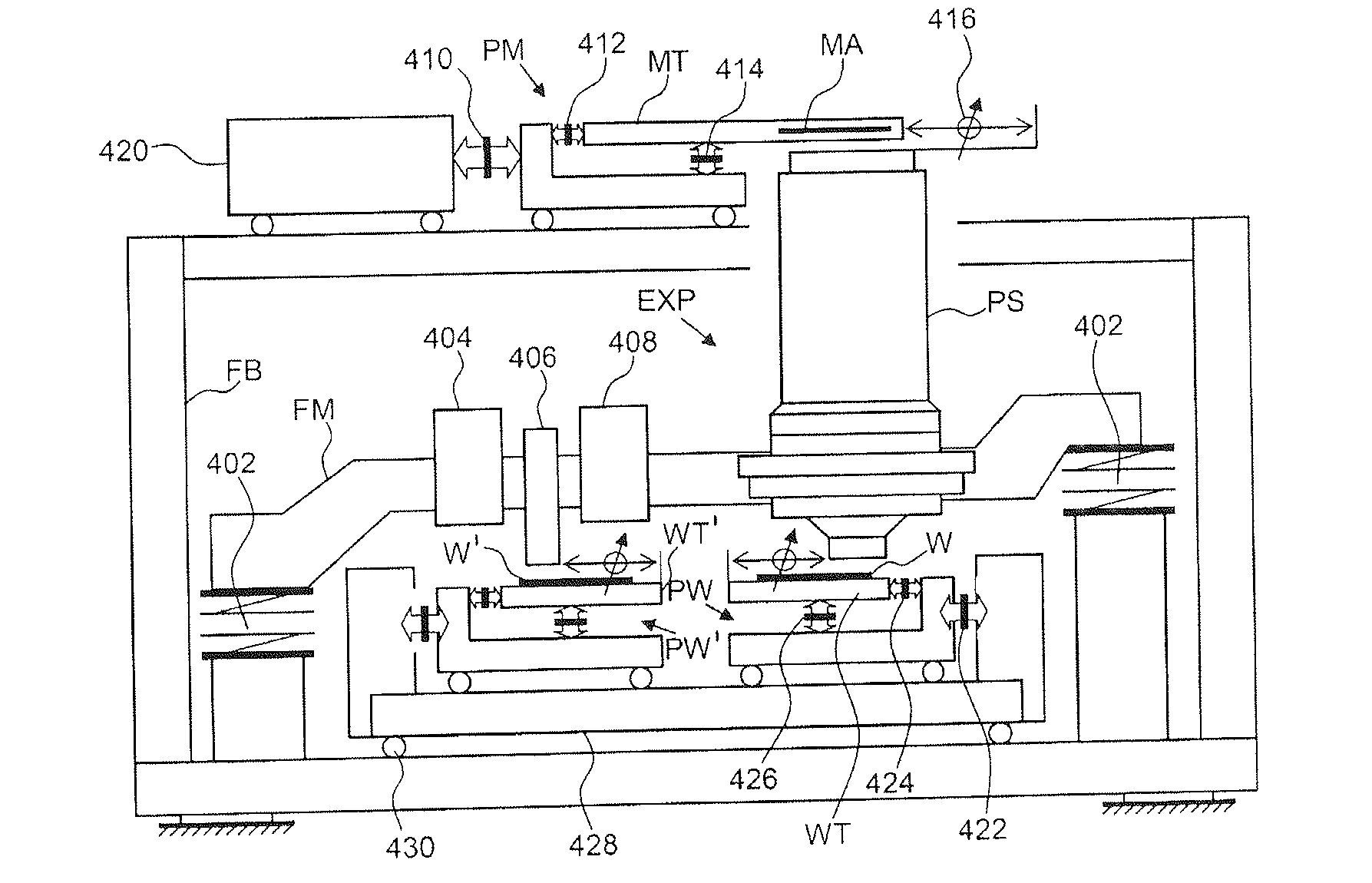
A lithographic exposure process is performed on a substrate using a scanner. The scanner comprises several subsystems. There are errors in the overlay arising from the subsystems during the exposure. The overlay errors are measured using a scatterometer to obtain overlay measurements. Modeling is performed to separately determine from the overlay measurements different subsets of estimated model parameters, for example field distortion model parameters, scan / step direction model parameters and position / deformation model parameters. Each subset is related to overlay errors arising from a corresponding specific subsystem of the lithographic apparatus. Finally, the exposure is controlled in the scanner by controlling a specific subsystem of the scanner using its corresponding subset of estimated model parameters. This results in a product wafer being exposed with a well controlled overlay.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Integrated measuring instrument
InactiveUS6986280B2Improve accuracyImprove efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementScattering properties measurementsFast measurementMeasuring instrument
A surface analyzing system including in one system both an integrating optical instrument, such as a scatterometer, and individual-feature-measuring instrument, such as a scanning probe microscope or a beam imaging system, for example, a scanning electron microscope. In a preferred embodiment, the two instruments are capable of characterizing a wafer held on a common stage. The stage may be movable a predetermined displacement to allow the same area of the wafer to be characterized by a scatterometer at one position of the stage and to be characterized by the scanning probe microscope or beam imaging system. The scatterometer can rapidly measure wafers to indicate whether a problem exists, and the scanning probe microscope can perform detailed measurements on wafers flagged by the scatterometer.
Owner:FEI CO
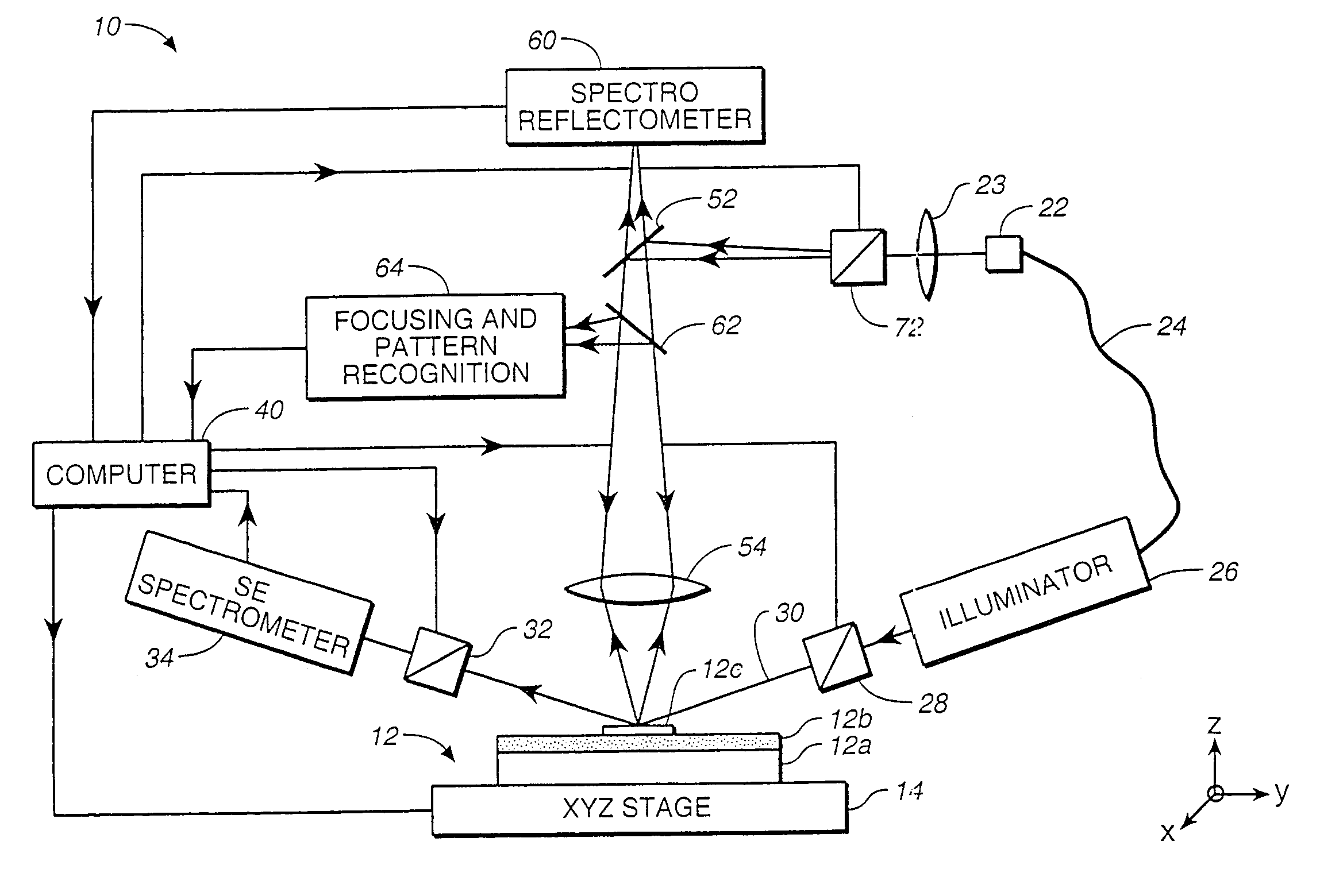
Spectroscopic scatterometer system
InactiveUS7173699B2Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementPolarisation-affecting propertiesGratingRefractive index
Before the diffraction from a diffracting structure on a semiconductor wafer is measured, where necessary, the film thickness and index of refraction of the films underneath the structure are first measured using spectroscopic reflectometry or spectroscopic ellipsometry. A rigorous model is then used to calculate intensity or ellipsometric signatures of the diffracting structure. The diffracting structure is then measured using a spectroscopic scatterometer using polarized and broadband radiation to obtain an intensity or ellipsometric signature of the diffracting structure. Such signature is then matched with the signatures in the database to determine the grating shape parameters of the structure.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
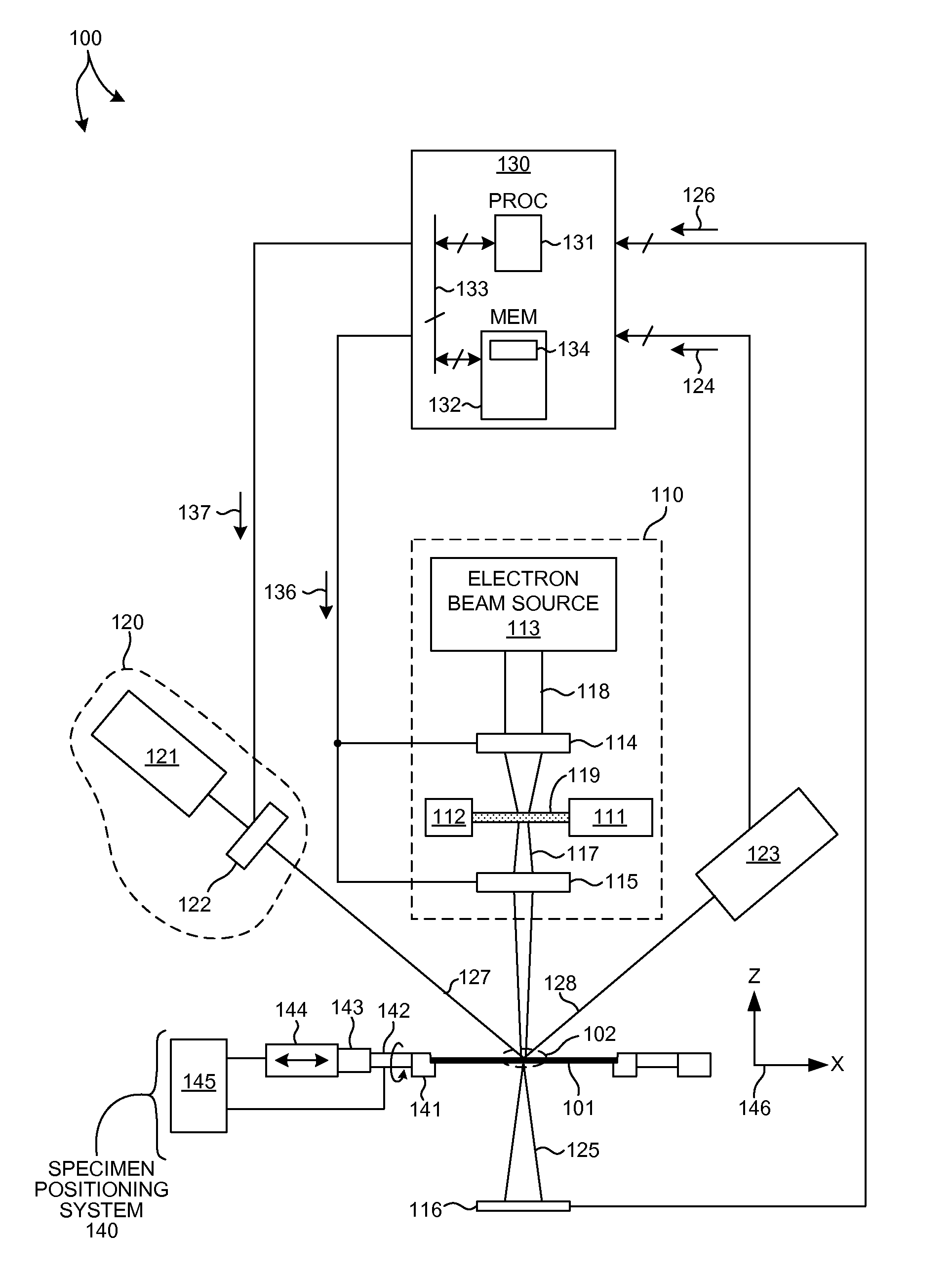
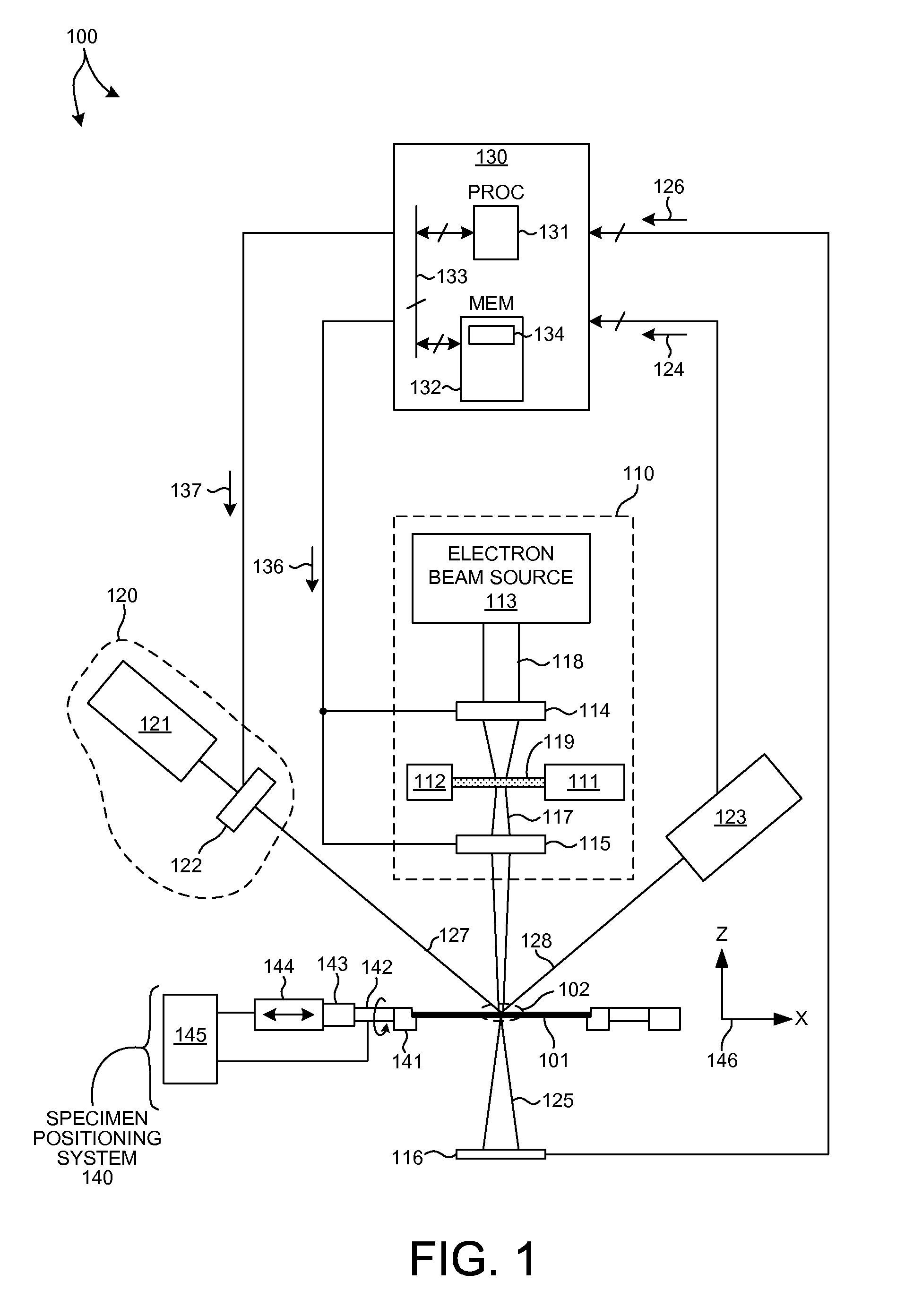
Multiple measurement techniques including focused beam scatterometry for characterization of samples
A system for monitoring thin-film fabrication processes is herein disclosed. Diffraction of incident light is measured and the results are compared to a predictive model based on at least one idealized or nominal structure. The model and / or the measurement of diffracted incident light may be modified using the output of one or more additional metrology systems.
Owner:ONTO INNOVATION INC
Holographic scatterometer for detection and analysis of wafer surface deposits
InactiveUS20020159052A1Prevent false detectionErroneous detectionInvestigating moving sheetsOptically investigating flaws/contaminationChemical compositionScatterometer
A holographic scatterometer with continuous readout can rapidly identify the presence of deposits (particles or other defects) on an unpatterned wafer surface and determine the volume density (size) and location. The scatterometer can also determine chemical composition of the detected deposits. The range of the deposit (particle) size to be measured is below 80 nm, which currently existing scatterometer type instruments cannot readily detect. The inspection can be achieved as an in-line stage during the processing of wafers or in situ in combination with another processing tool or as a separate off-line analysis device.
Owner:SENTEC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com