Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
260 results about "Application domain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
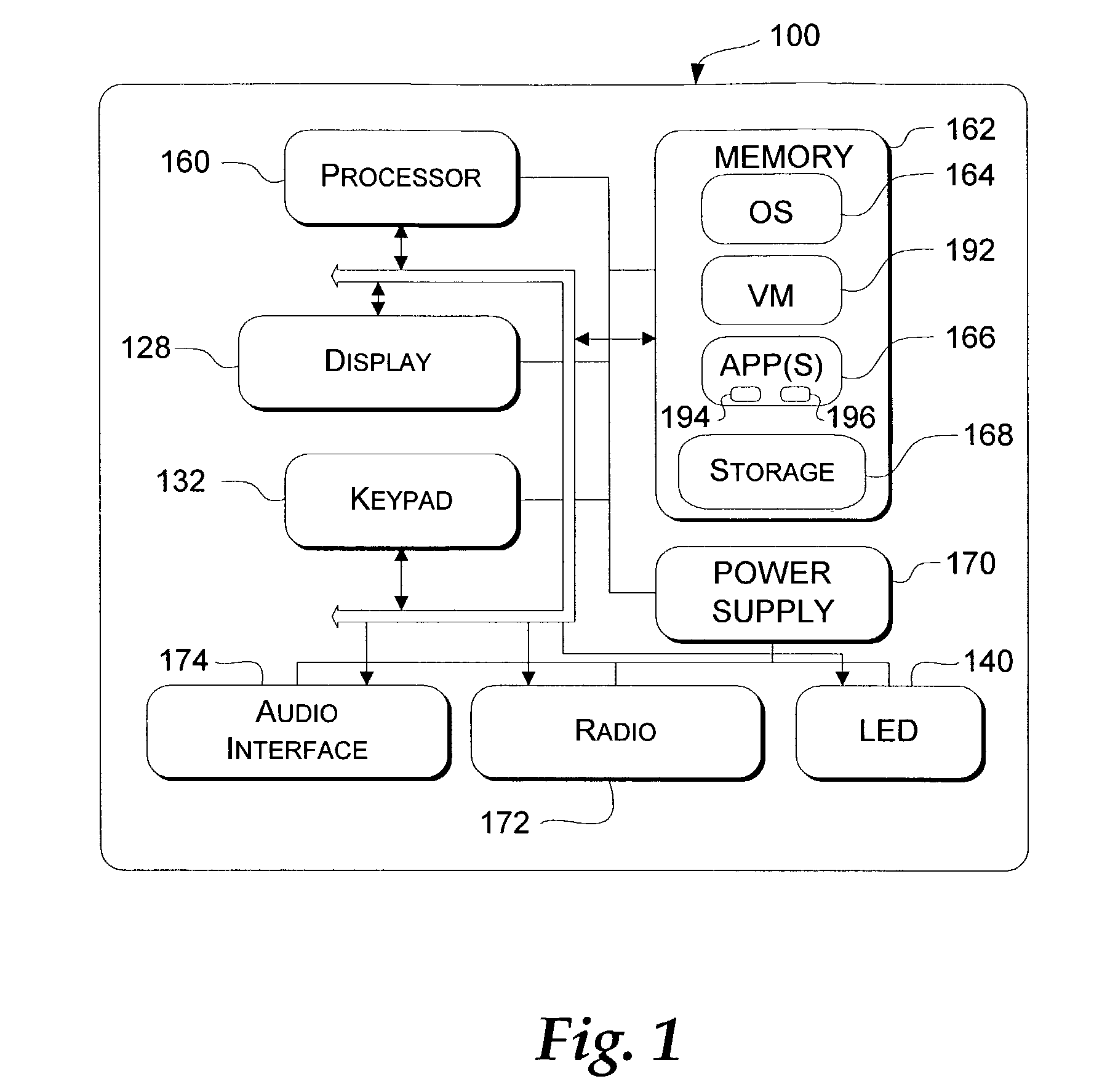
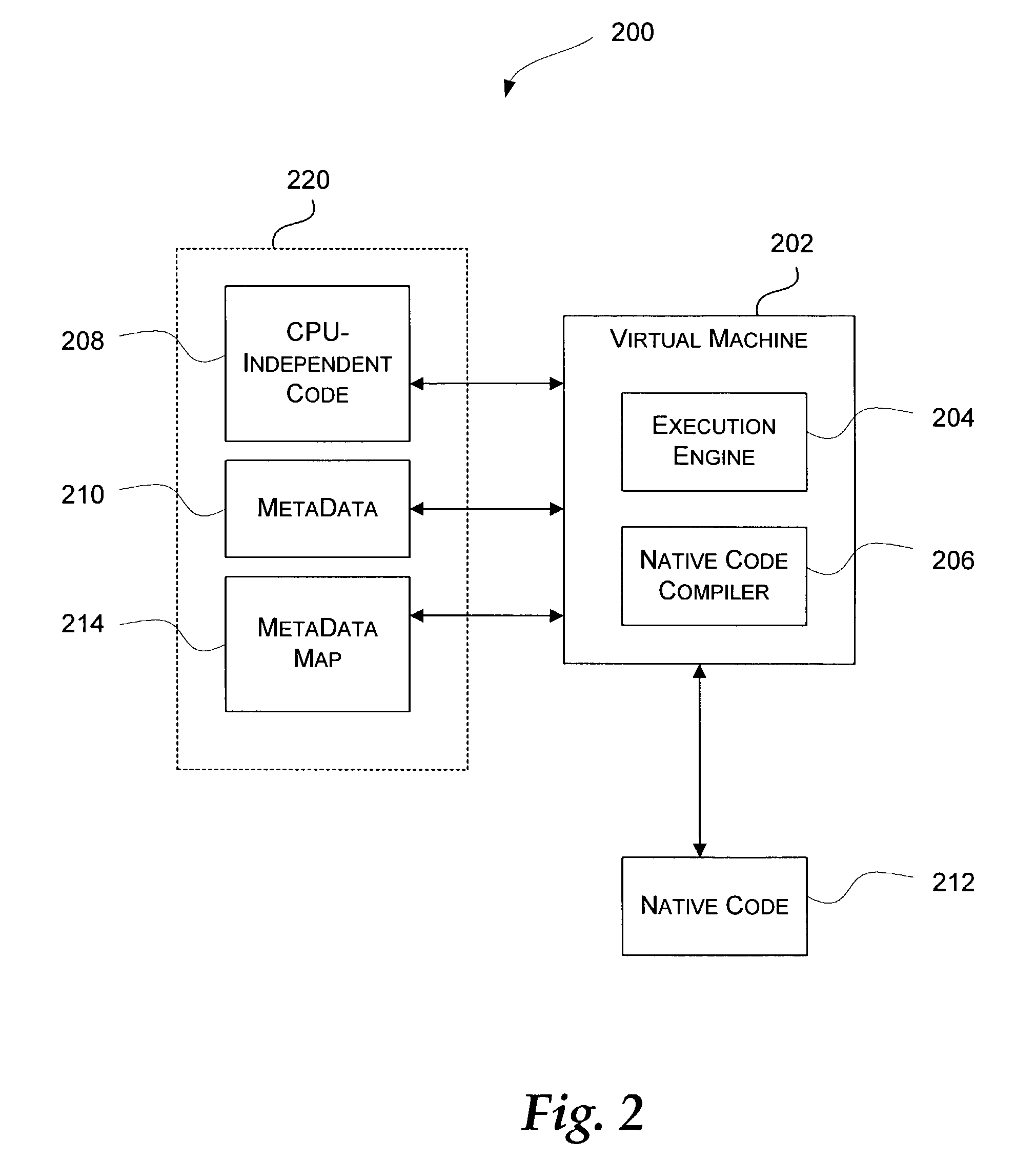
An application domain is a mechanism (similar to a process in an operating system) used within the Common Language Infrastructure (CLI) to isolate executed software applications from one another so that they do not affect each other. Each application domain has its own virtual address space which scopes the resources for the application domain using that address space.
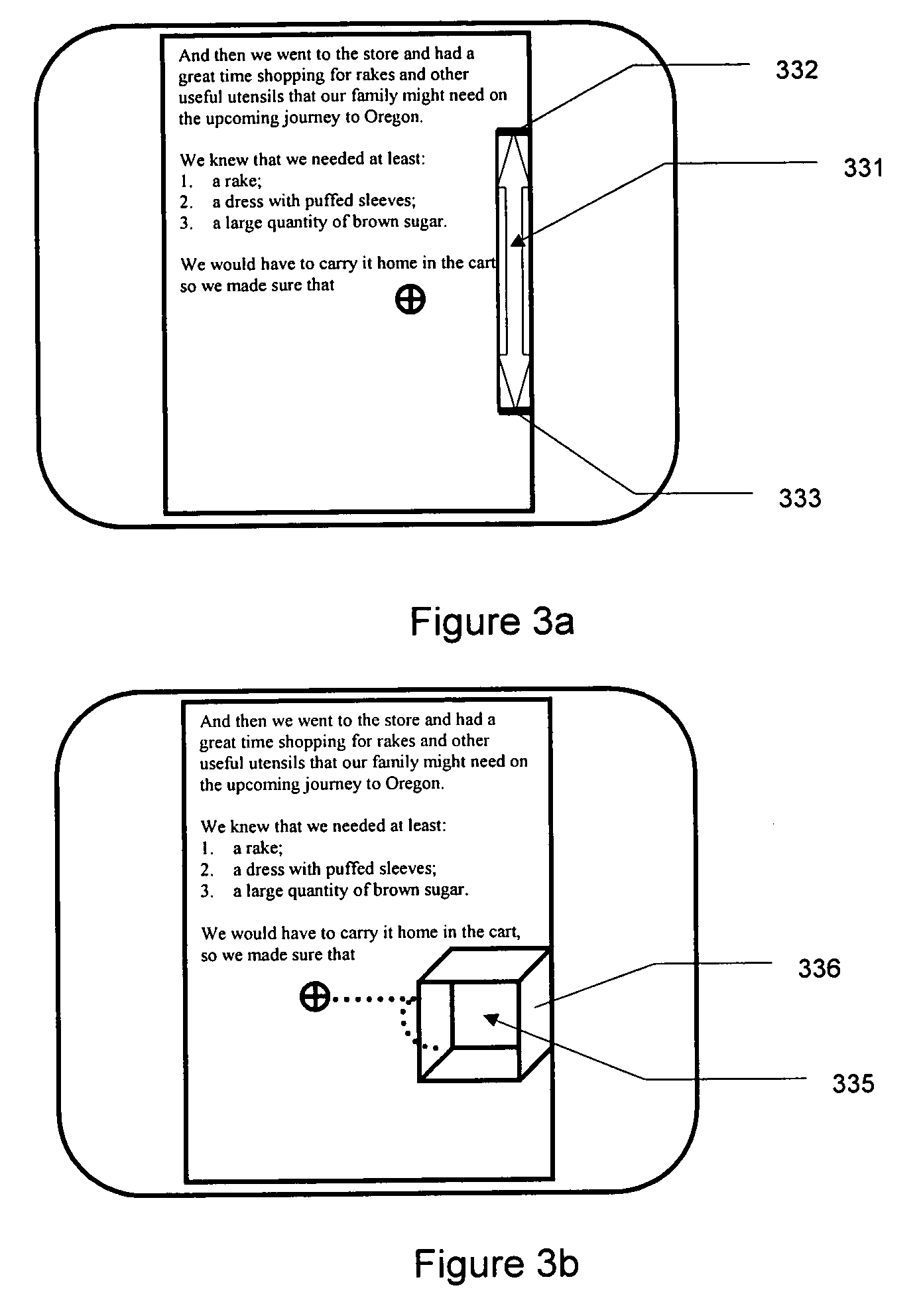
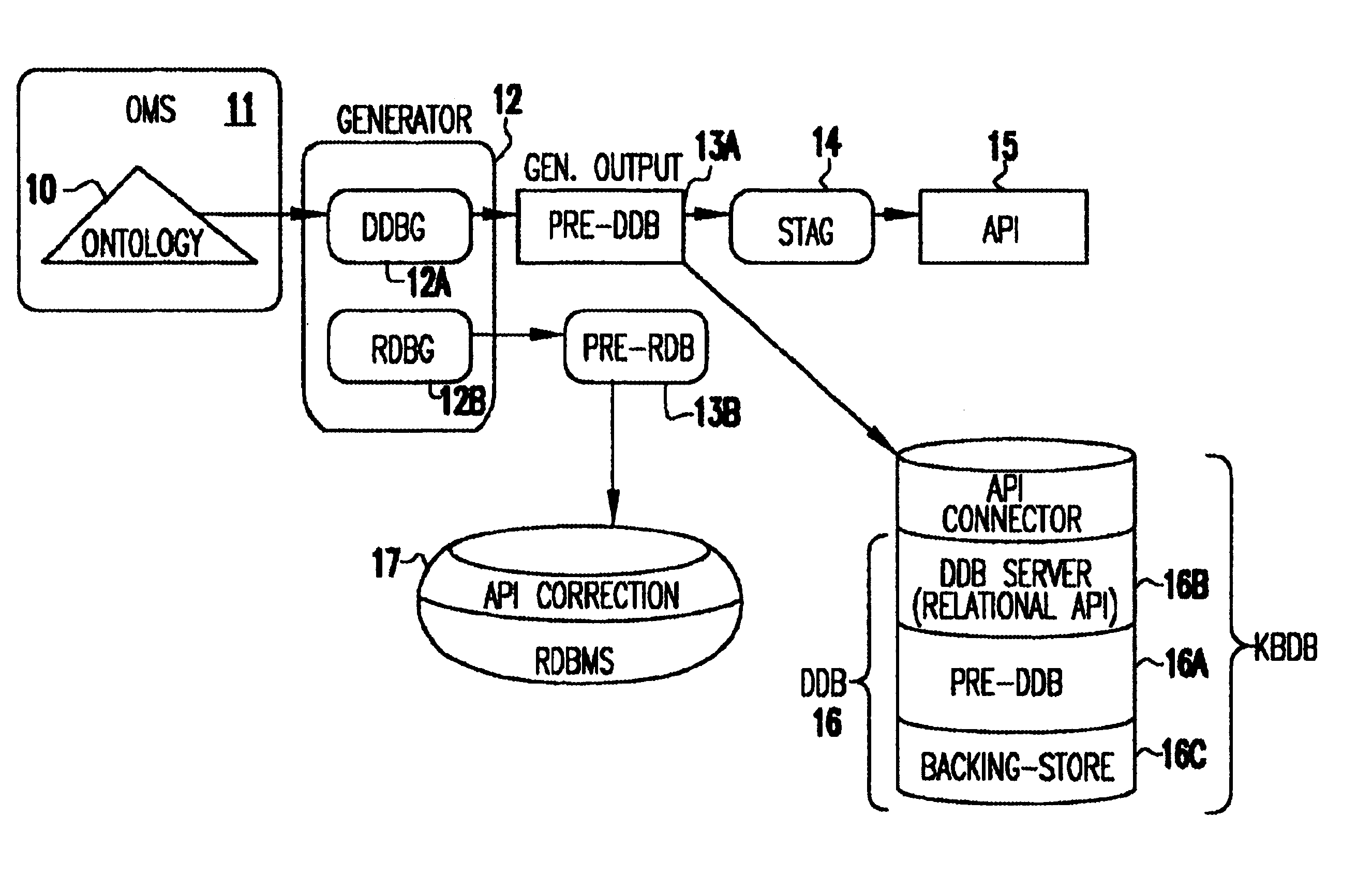
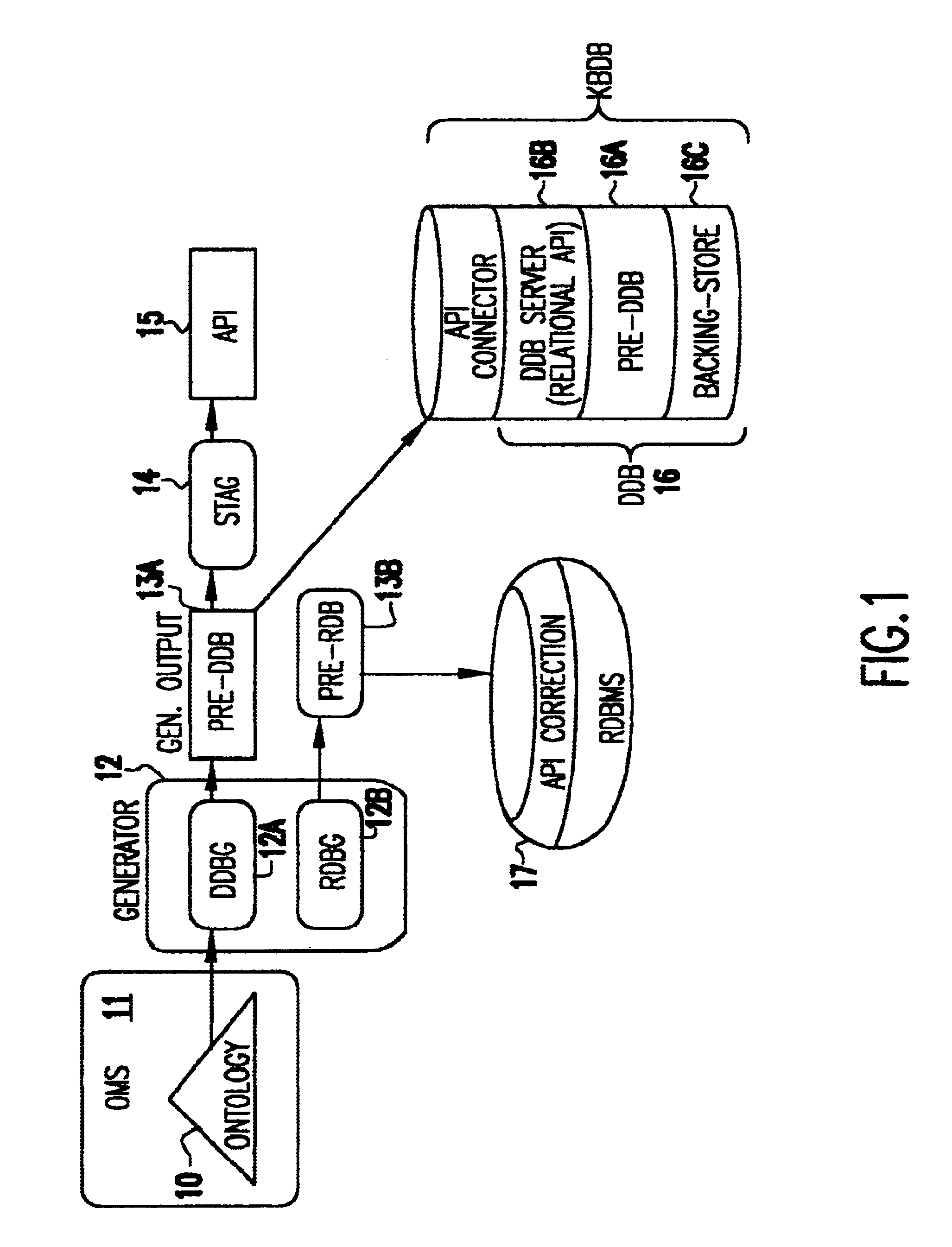
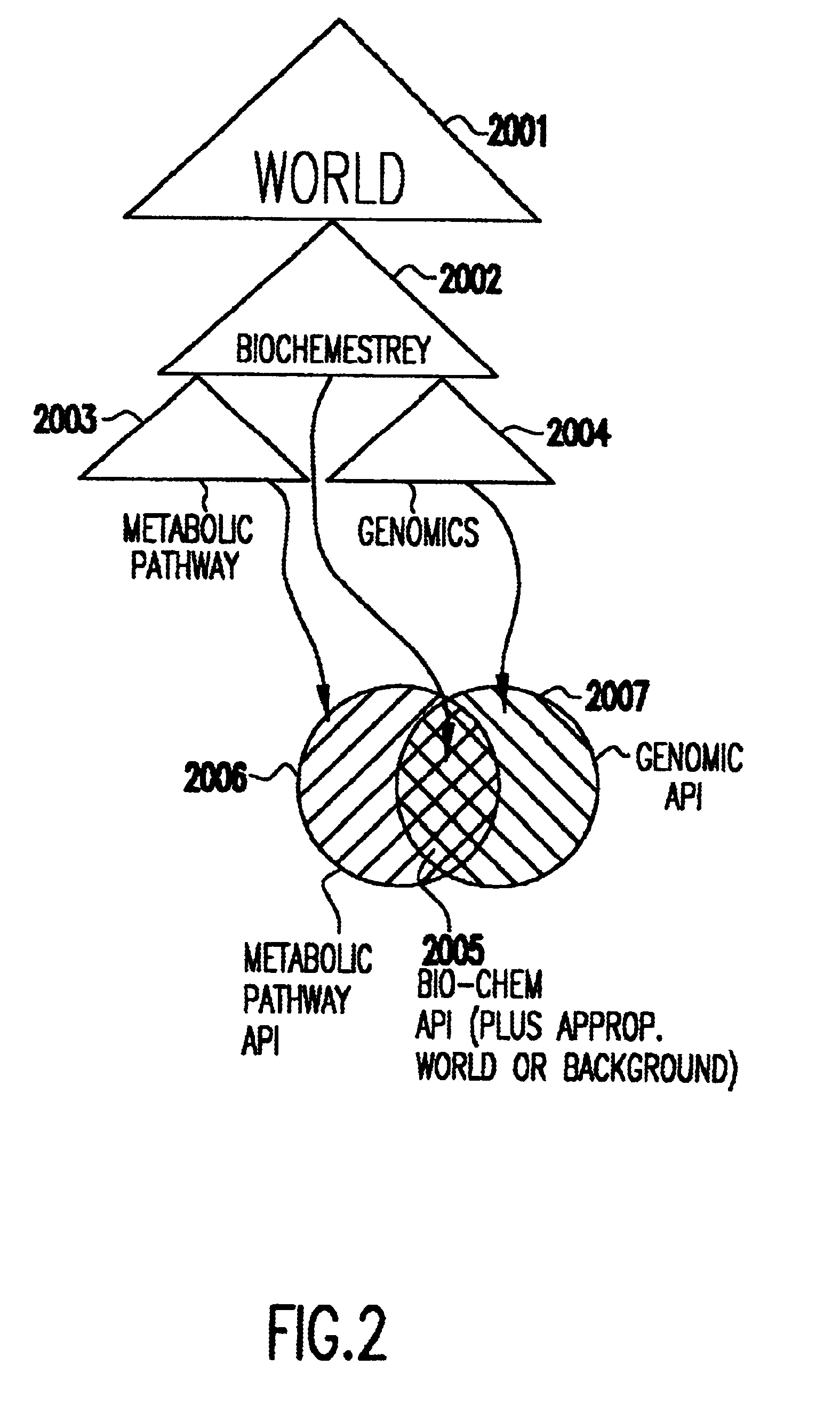
Object management system supporting the use of application domain knowledge mapped to technology domain knowledge
InactiveUS6226792B1Easy to browseThrough simpleSoftware reuseSpecific program execution arrangementsCatalogingAssociate - relationship
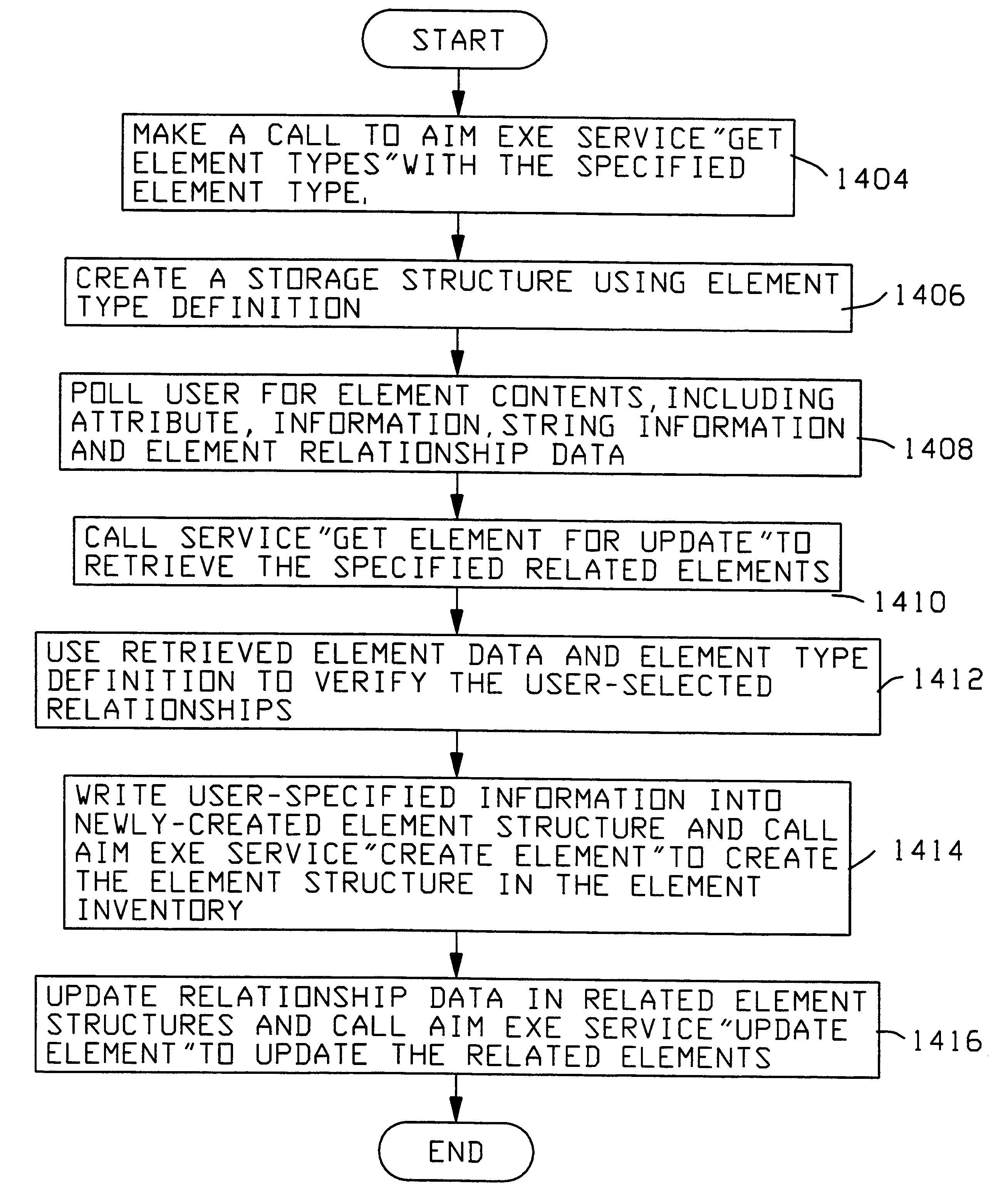
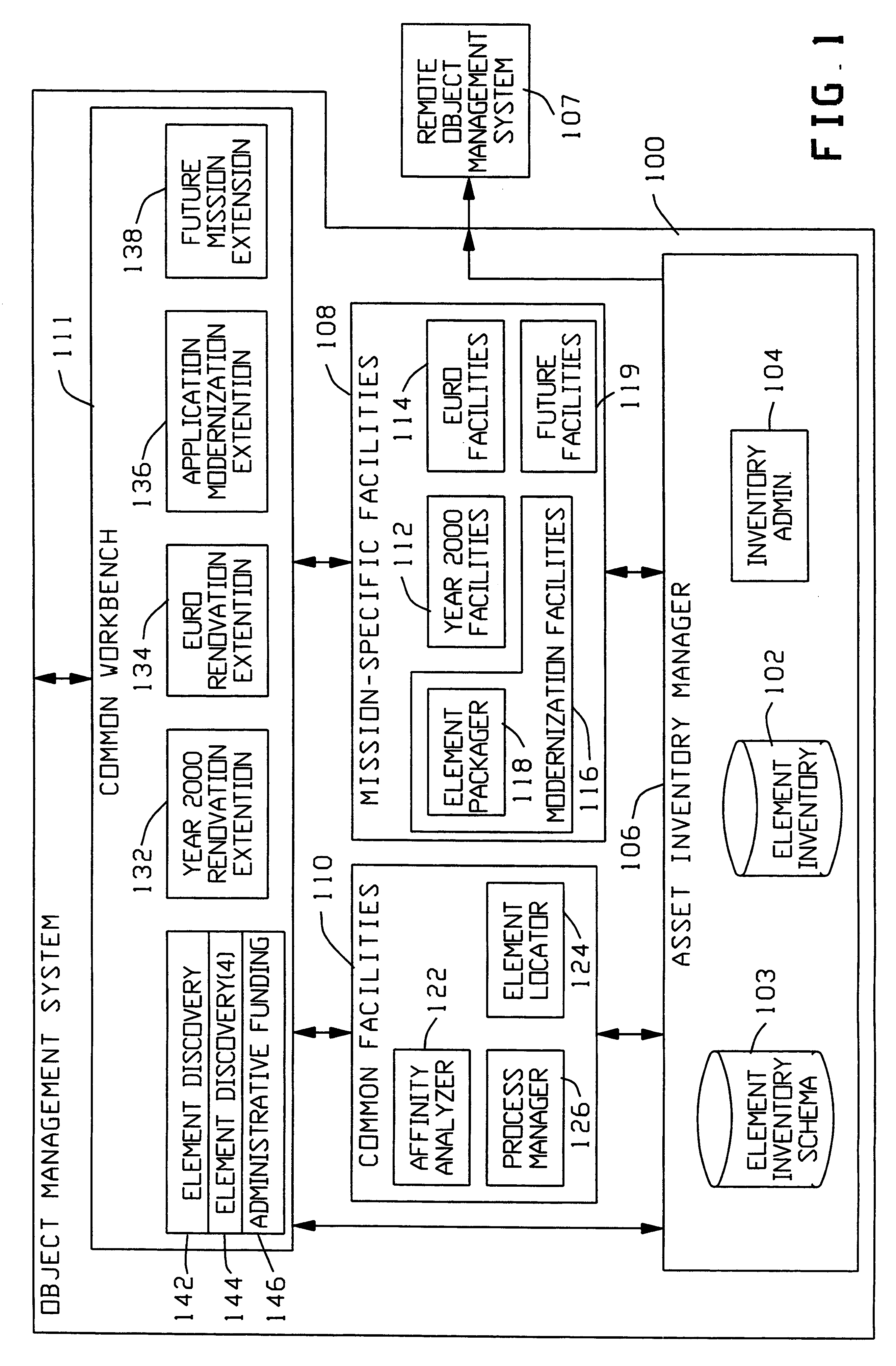
An object management system is providing for managing, cataloging, and discovering various potentially reusable code and data components that exist within an Information Technology (IT) platform, and which each have well-defined interfaces with other components. For each of these re-usable code and data components, an associated software object called an "asset element" is created that describes the associated component. Relationships are created between various asset elements to represent the relationships existing between the software components. Other software objects called "locator elements" are created that each describes an application concept or sub-concept. This application concept or sub-concept is associated with a problem solved by the code and data components within the IT platform. Relationships are created between the various locator elements to correlate the concepts and sub-concepts to software constructs represented by asset elements. The object management system further supports various object discovery tools capable of identifying locator elements associated with a particular concept. These locator elements and the associated relationships may then be efficiently traced to identify related asset elements and the associated software and code constructs. This provides an efficient concept-based search mechanism for the code constructs. Other tools are provided for creating, modifying, and deleting the elements. A model may be used to define the various types of relationships and elements that may exist within the system, thereby simplifying the various tools needed to support element creation, modification, deletion, and traversal.
Owner:UNISYS CORP
Algorithms for identity anonymization on graphs
InactiveUS20090303237A1Preserving individual privacy and basic structure of networkDrawing from basic elementsTransmissionGraphicsRe identification
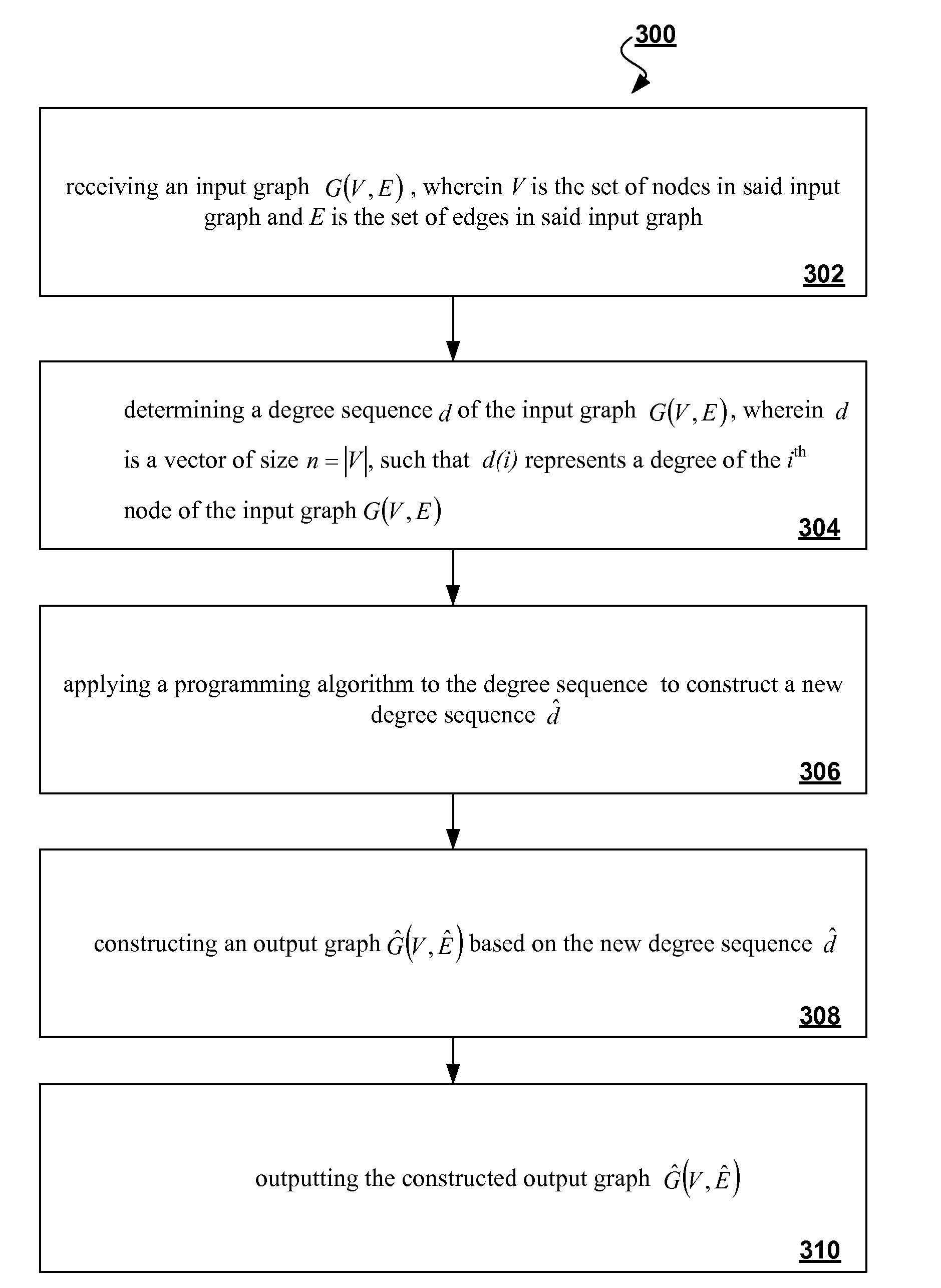
The proliferation of network data in various application domains has raised privacy concerns for the individuals involved. Recent studies show that simply removing the identities of the nodes before publishing the graph / social network data does not guarantee privacy. The structure of the graph itself, and in is basic form the degree of the nodes, can be revealing the identities of individuals. To address this issue, a specific graph-anonymization framework is proposed. A graph is called k-degree anonymous if for every node v, there exist at least k−1 other nodes in the graph with the same degree as v. This definition of anonymity prevents the re-identification of individuals by adversaries with a priori knowledge of the degree of certain nodes. Given a graph G, the proposed graph-anonymization problem asks for the k-degree anonymous graph that stems from G with the minimum number of graph-modification operations. Simple and efficient algorithms are devised for solving this problem, wherein these algorithms are based on principles related to the realizability of degree sequences.
Owner:IBM CORP
Human-computer interface including haptically controlled interactions
InactiveUS6954899B1Lower requirementEasy to controlInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsPresent methodHuman–machine interface
The present invention provides a method of human-computer interfacing that provides haptic feedback to control interface interactions such as scrolling or zooming within an application. Haptic feedback in the present method allows the user more intuitive control of the interface interactions, and allows the user's visual focus to remain on the application. The method comprises providing a control domain within which the user can control interactions. For example, a haptic boundary can be provided corresponding to scrollable or scalable portions of the application domain. The user can position a cursor near such a boundary, feeling its presence haptically (reducing the requirement for visual attention for control of scrolling of the display). The user can then apply force relative to the boundary, causing the interface to scroll the domain. The rate of scrolling can be related to the magnitude of applied force, providing the user with additional intuitive, non-visual control of scrolling.
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC
Ontology for database design and application development
InactiveUS6640231B1Improve fidelityImprove efficiencyData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsEntity typeMaintainability
A system and method lets a user create or import ontologies and create databases and related application software. These databases can be specially tuned to suit a particular need, and each comes with the same error-detection rules to keep the data clean. Such databases may be searched based on meaning, rather than on words-that-begin-with-something. And multiple databases, if generated from the same basic ontology can communicate with each other without any additional effort. Ontology management and generation tools enable enterprises to create databases that use ontologies to improve data integration, maintainability, quality, and flexibility. Only the relevant aspects of the ontology are targeted, extracting out a sub-model that has the power of the full ontology restricted to objects of interest for the application domain. To increase performance and add desired database characteristics, this sub-model is translated into a database system. Java-based object-oriented and relational application program interfaces (APIs) are then generated from this translation, providing application developers with an API that exactly reflects the entity types and relations (classes and methods) that are represented by the database. This generation approach essentially turns the ontology into a set of integrated and efficient databases.
Owner:KYNDI
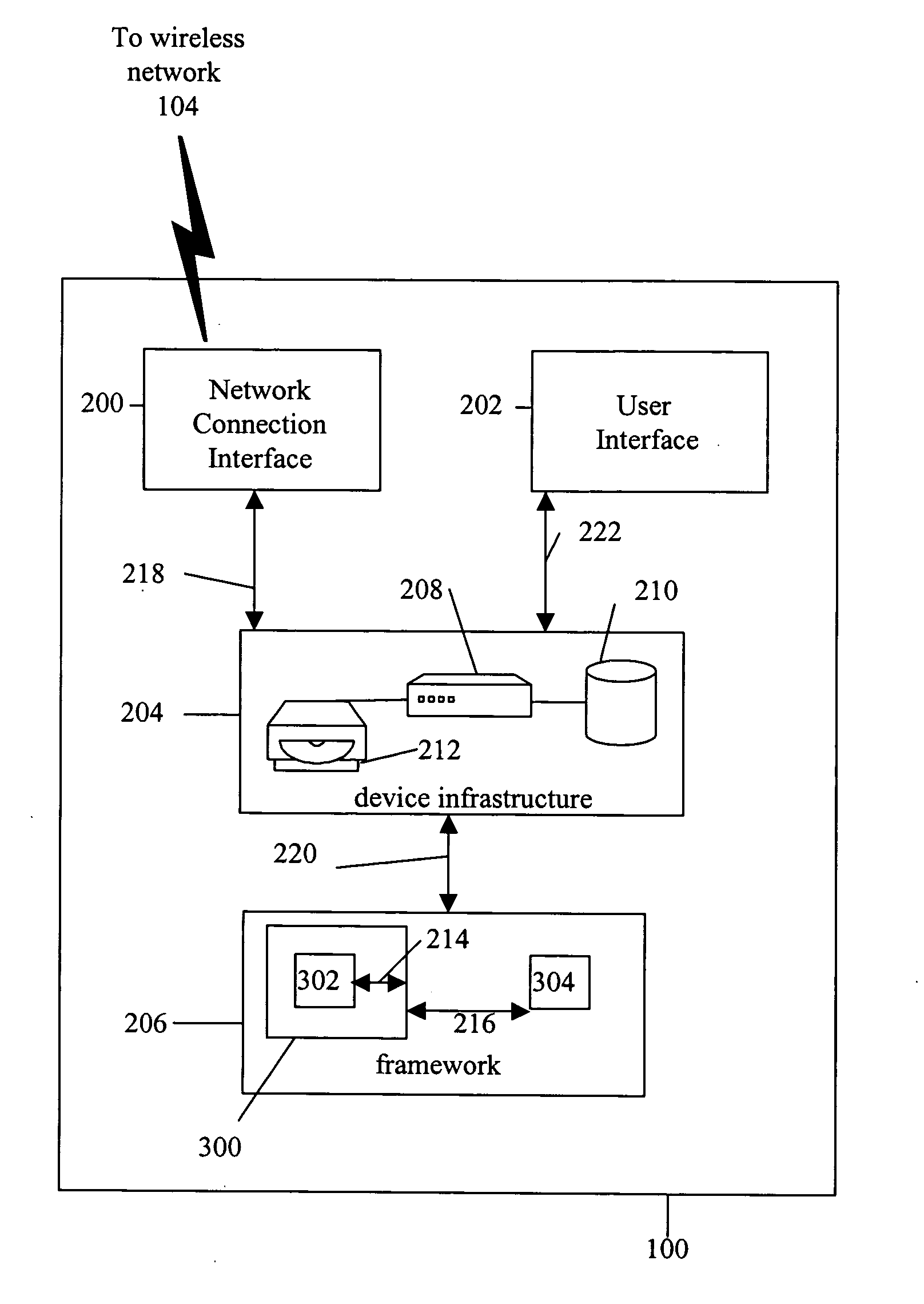
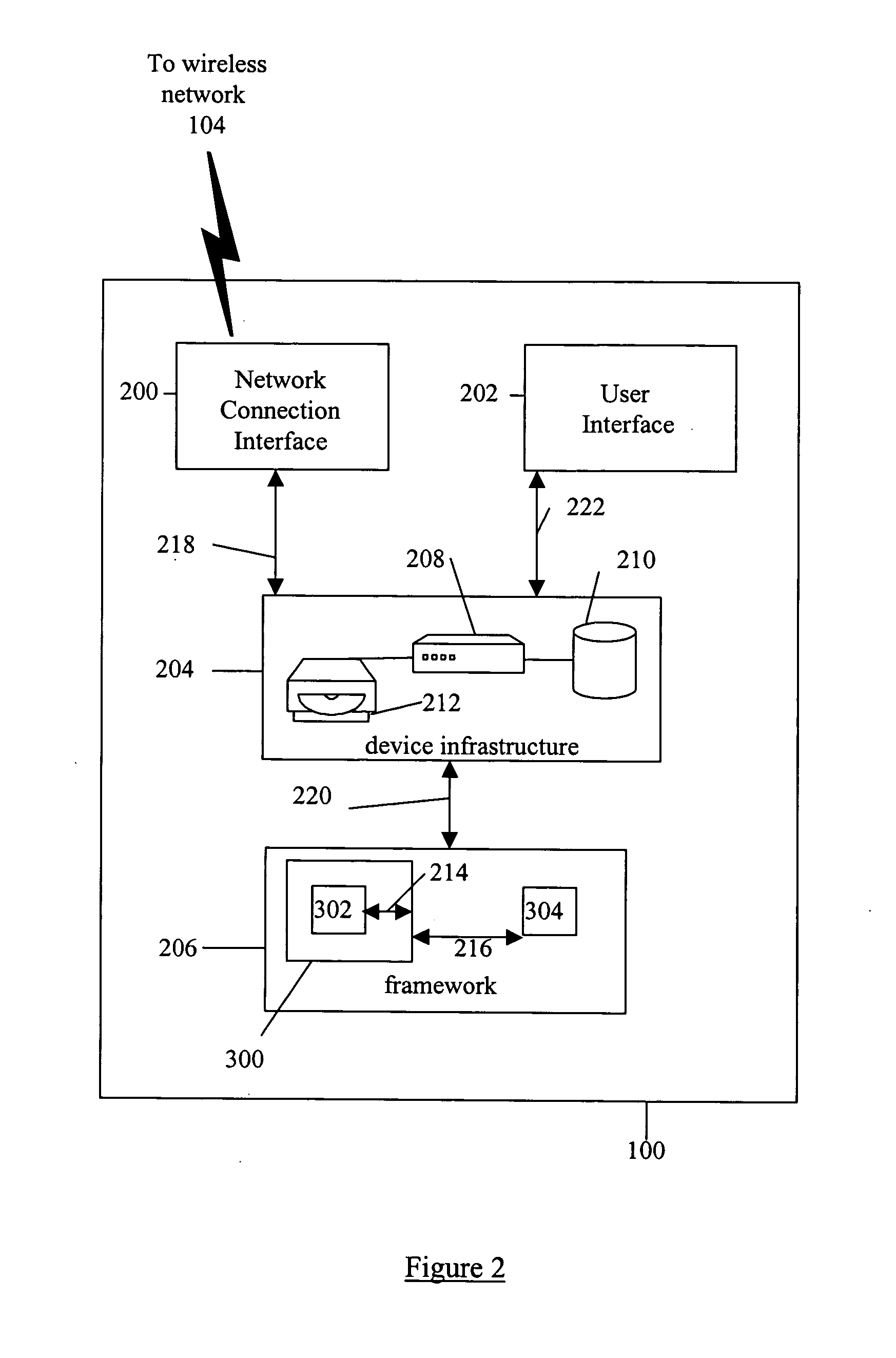
System and method for building wireless applications with intelligent mapping between user interface and data components
ActiveUS20050057560A1Reduce complexitySimplify development workDigital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsData domainBasic service
A system and method is described for effective management of a User Interface (UI) of a wireless device by implementing direct mapping between the application data domain and UI screens and controls. The device has an intelligent wireless device runtime environment (Device Runtime) that provides a set of basic services to manage the wireless application, including a series of linked screen and data component definitions, and their interactions can simplify the development effort and reduce resource allocation. The data domain for this category of applications is defined using the atomic data component definitions. The communication between a device user interface and data components is defined using atomic screen component definitions. Both screen and data component definitions are described in metadata using a structured definition language such as XML. The relationships between the screen and data component definitions are embedded in the XML definitions in the form of screen / data mappings. Typically, rendered screens for display are derived from some underlying data component and screens controls affected by user events impact the current state (or data representation) of the application Changes to the application domain data are automatically synchronized with the user interface, and user-entered data is automatically reflected in the application domain data. The primary mechanism behind this synchronization is the mapping of screens and data. This mechanism enables creation of dynamic and interactive screens. All changes to the data component can be immediately reflected on the screen and vice versa. This model allows building effective wireless applications based on server-to-device notifications. The data updates asynchronously pushed from the server are instantaneously reflected at the UI screen.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
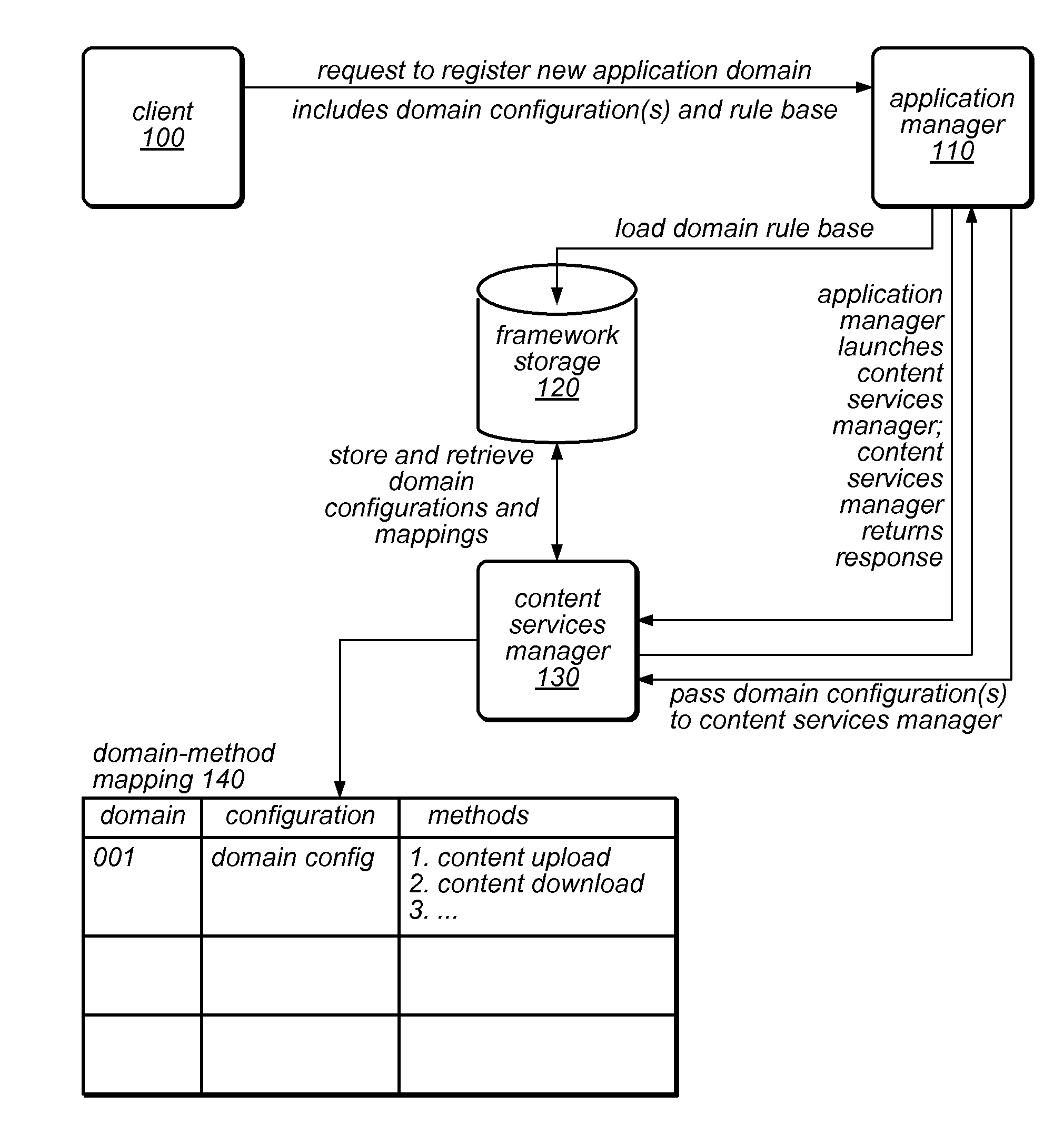
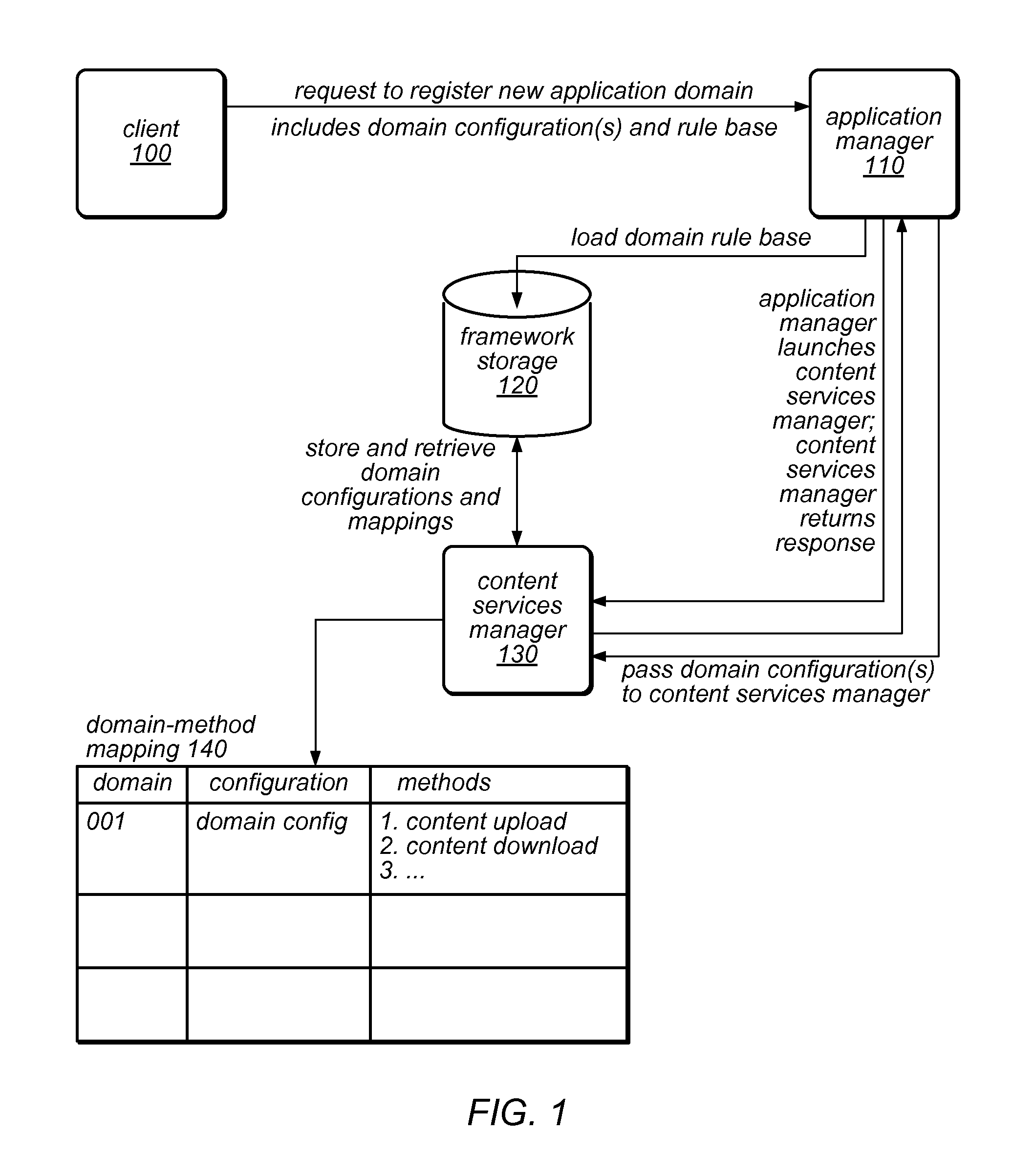
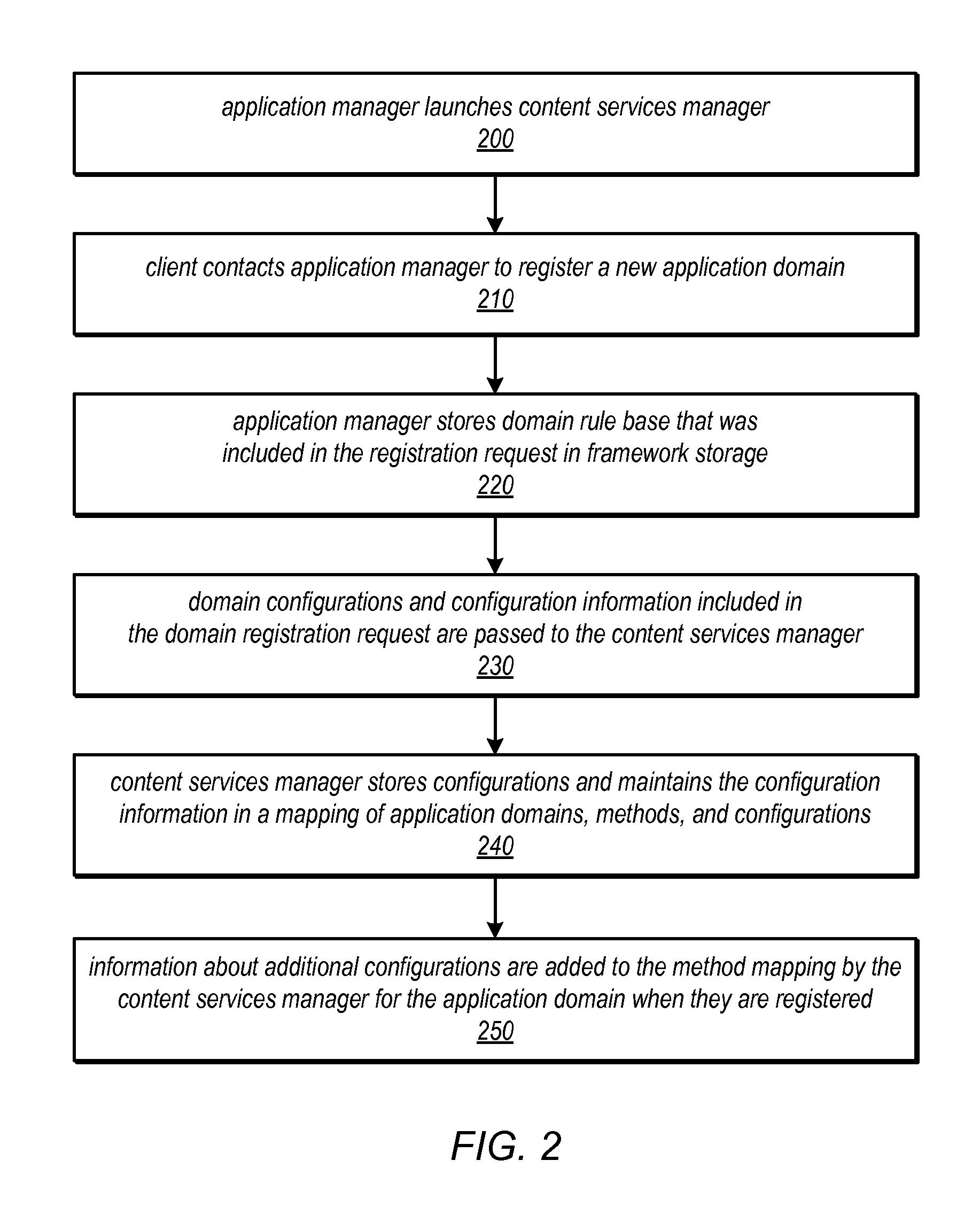
System and Method for Installation and Management of Cloud-Independent Multi-Tenant Applications
ActiveUS20120047239A1Efficient constructionSufficient throughputDigital computer detailsProgram controlApplication softwareCloud storage
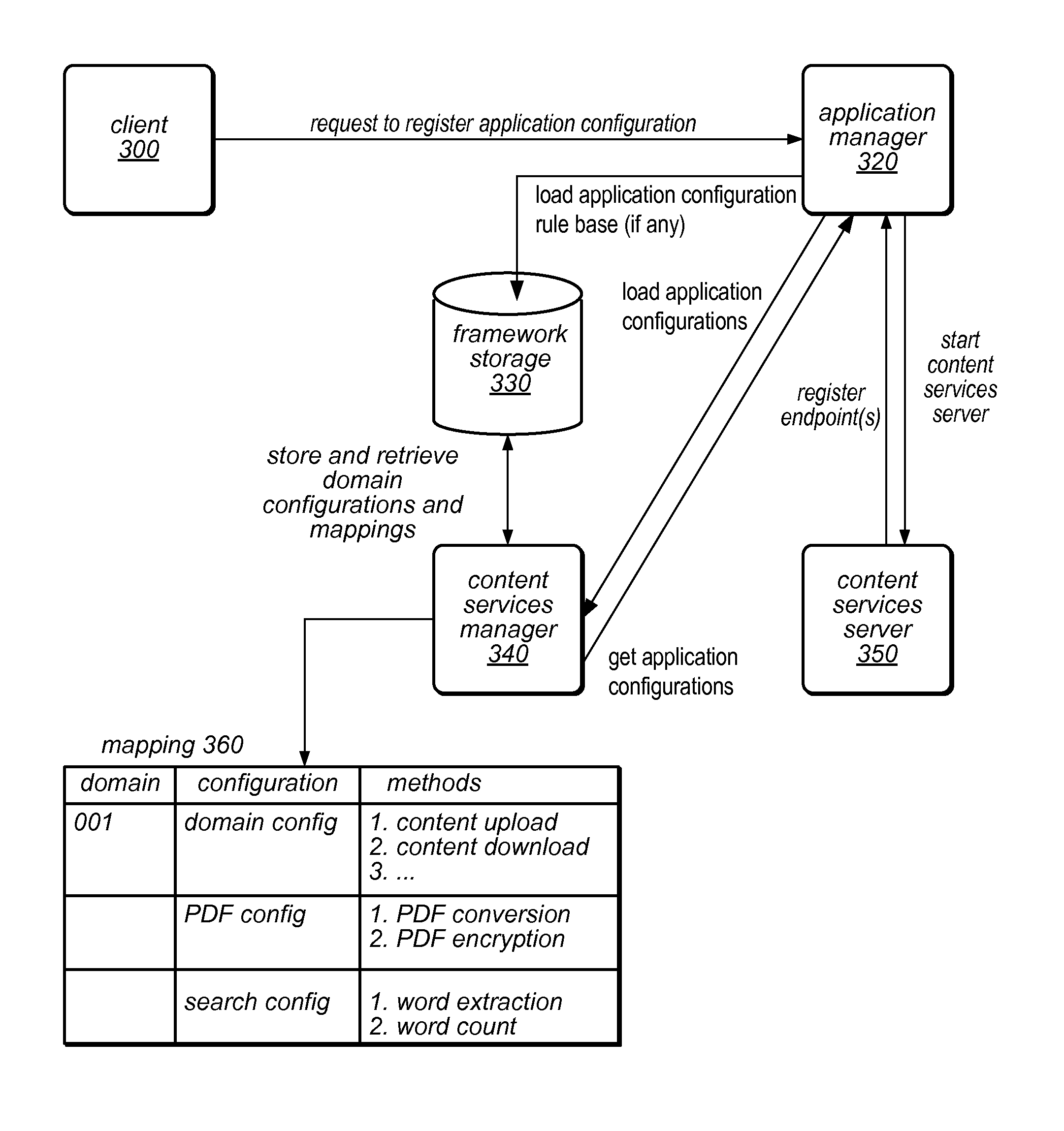
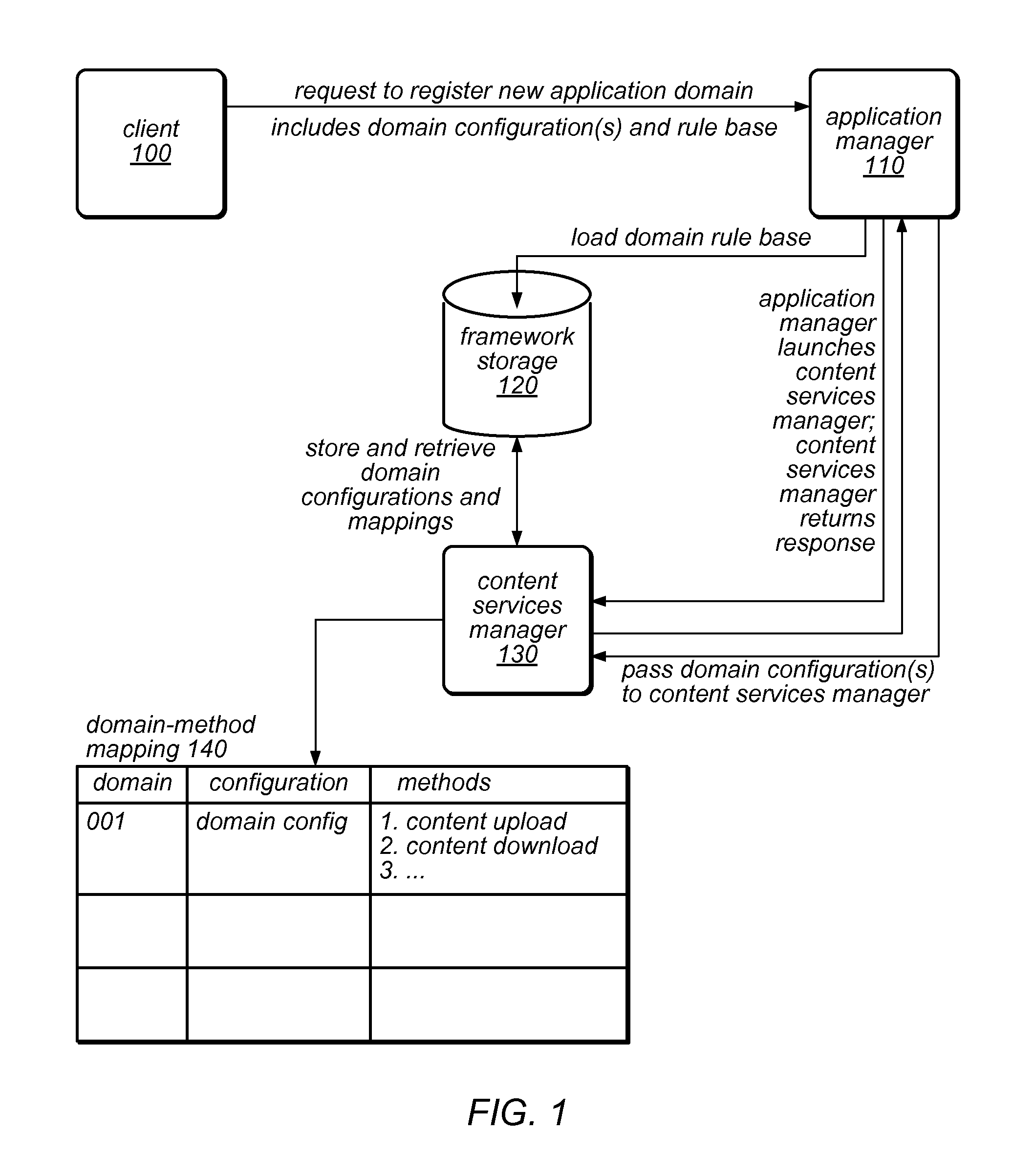
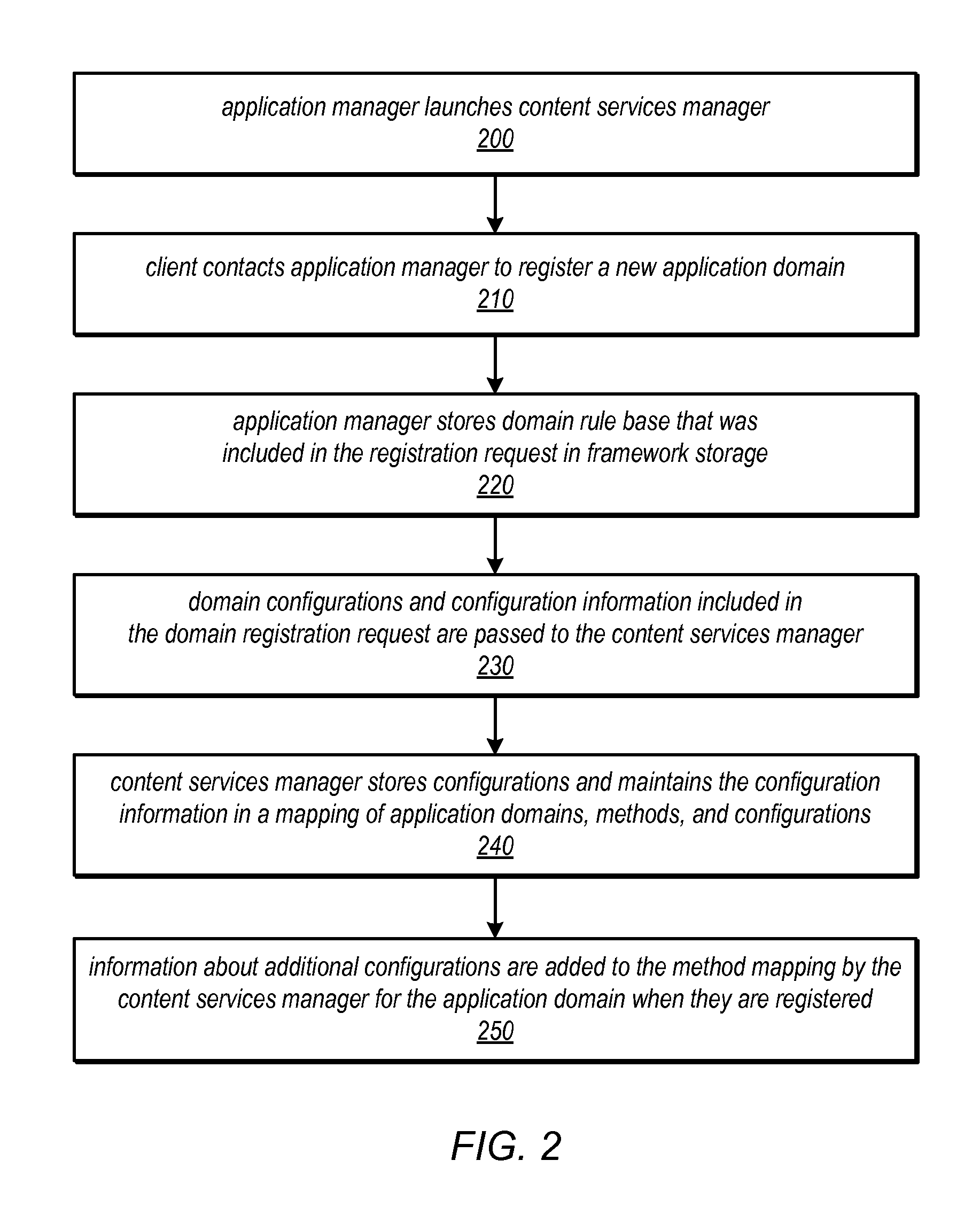
An application framework may include a cloud-independent application manager, a cloud-independent content services manager, and cloud-independent content services servers. The framework may dynamically install and manage scalable, multi-tenant applications in a cloud, and may scale the applications, as needed. The application manager may receive and handle requests to install application domains and configurations thereof, and may receive and respond to requests for information about servers on which installed methods are available. The content services servers may execute installed methods, using underlying resources of the cloud, through a cloud-specific SPI. The content services manager and application manager may work together using shared cloud storage to provide scalable content services at a very large scale. In the context of the framework described herein, an “application” may be defined by methods bundled into configurations, and by various cost-based and / or performance-based rules that specify how server instances providing those methods are to be managed.
Owner:ADOBE SYST INC
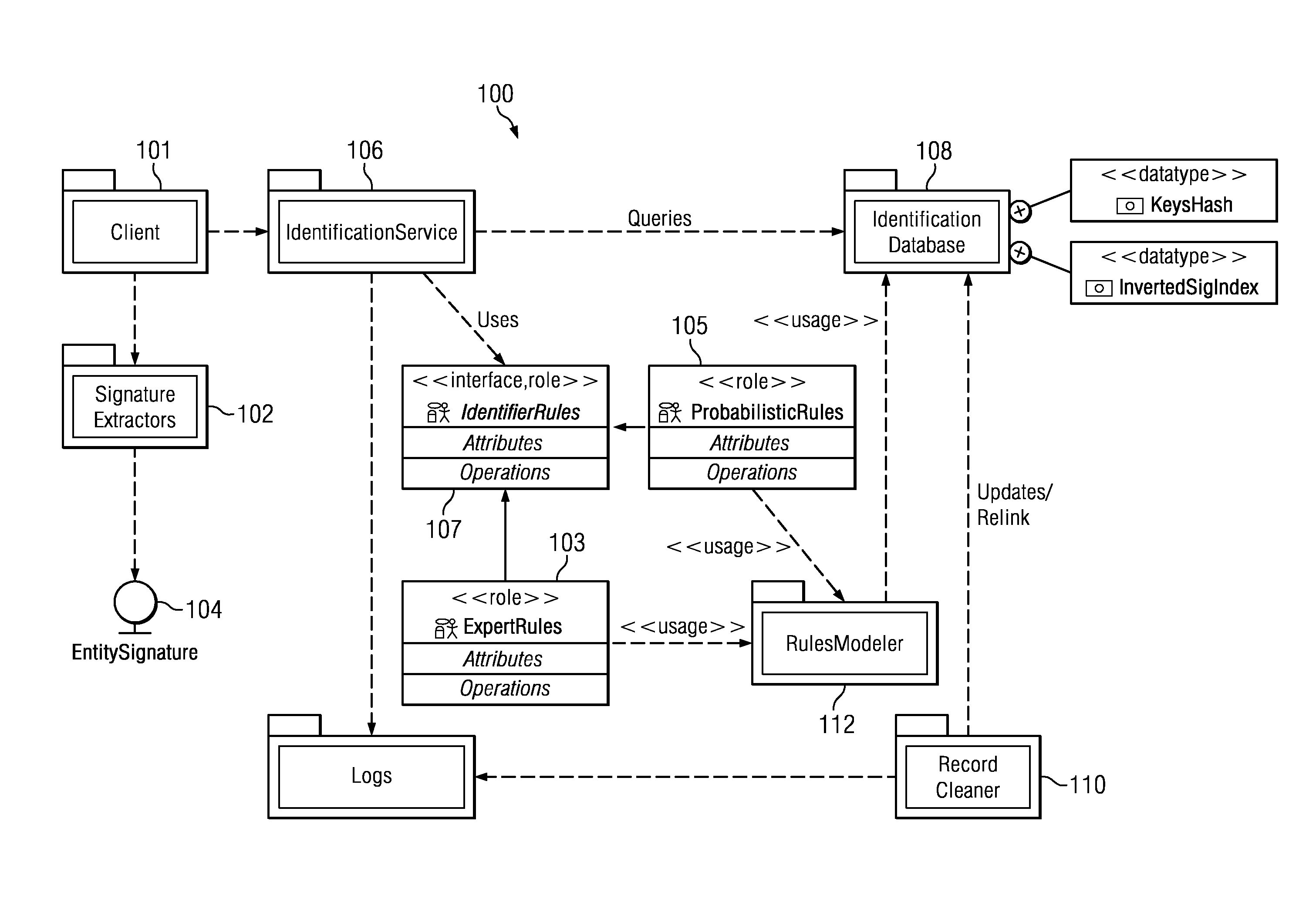
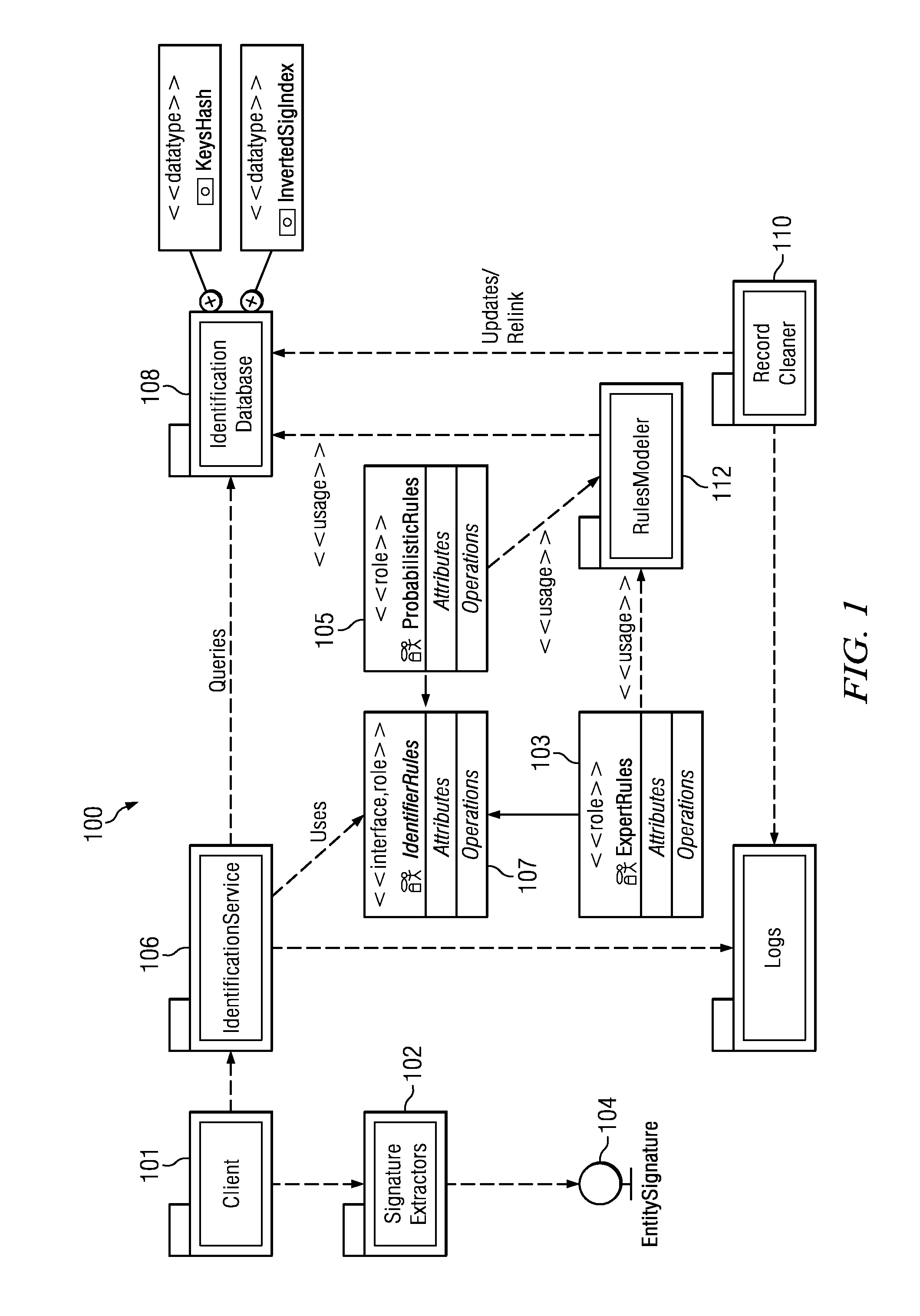
Uniquely identifying a network-connected entity
ActiveUS8438184B1Digital data processing detailsTransmissionNetwork connectionDeterministic algorithm
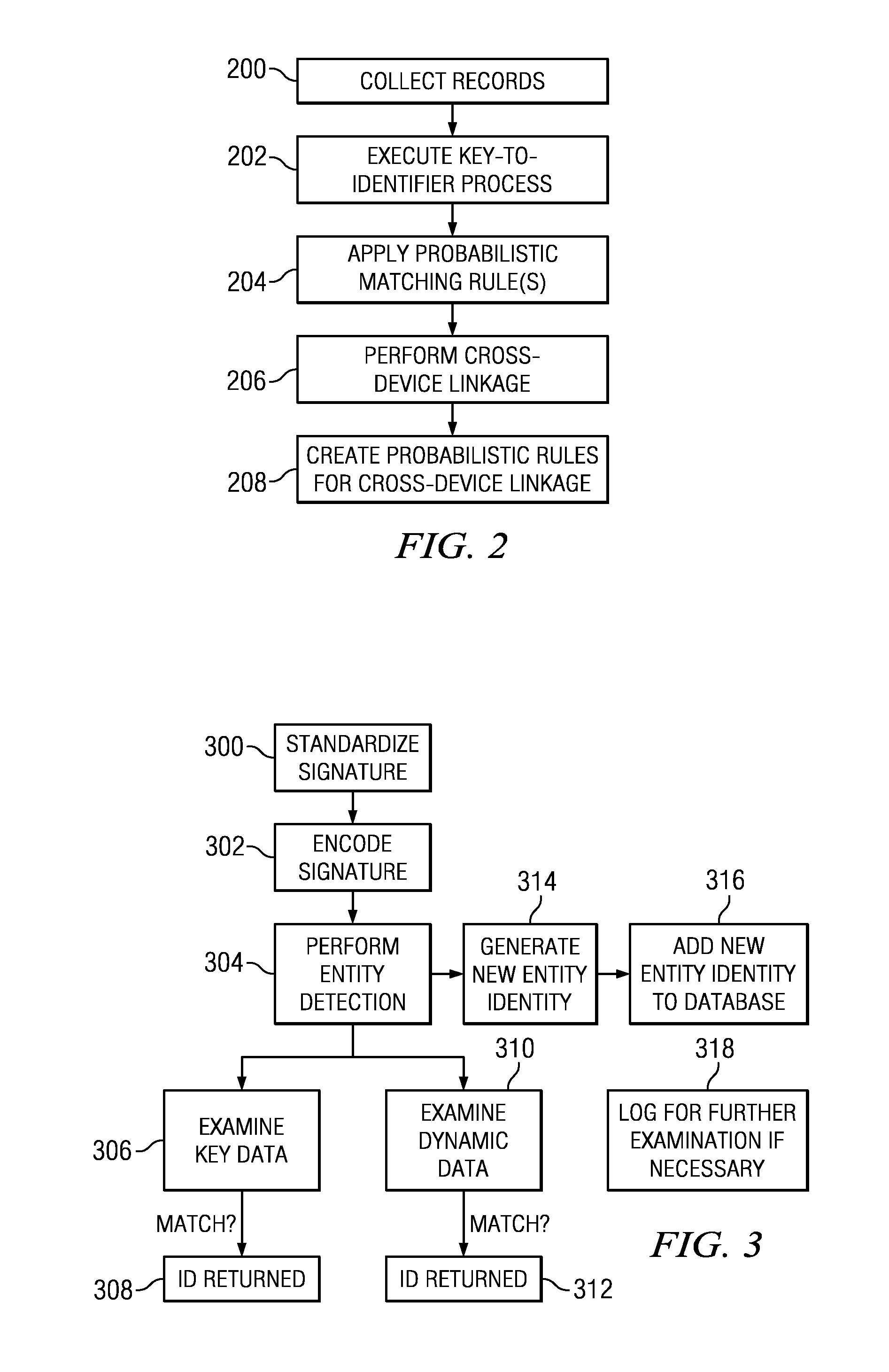
An entity (a device, a user of a device or set of devices, a user of one or more applications on a device, a group of users of the device or set of devices, or the like) is identified across multiple device, usage, and application domains. The entity is assigned a unique entity identity that is generated from a set of feature data that model the entity. The feature data typically includes deterministic data, device and system-specific feature data, and usage feature data. The identity is generated by applying to the feature data one or more rules that identify which of the feature data to use to generate the entity identity. The rules include at least one deterministic rule, and at least one probabilistic rule. Periodically, an identity is merged into one or more entity identities that are found, by applying a rule, to represent a same entity.
Owner:ADELPHIC LLC
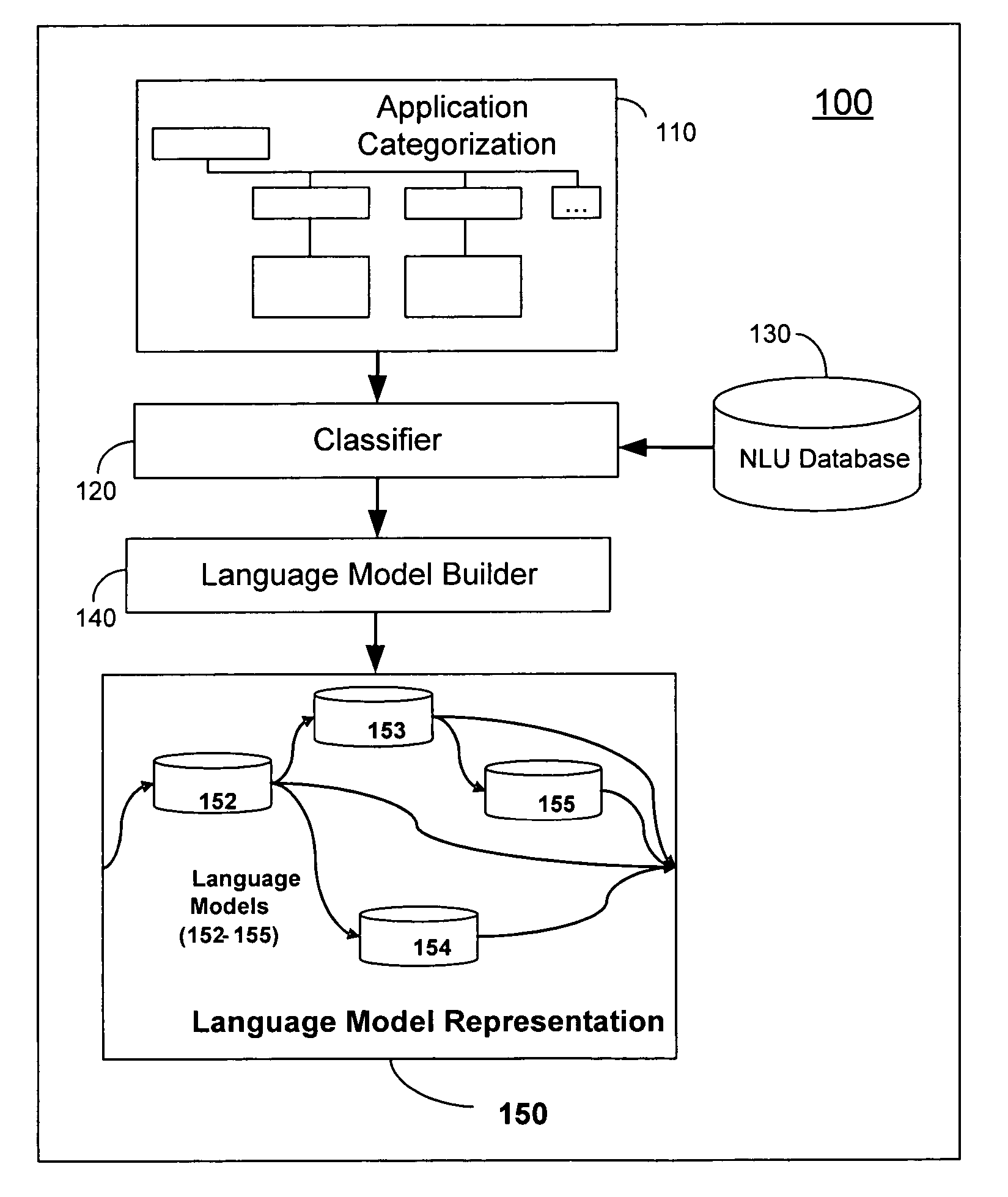
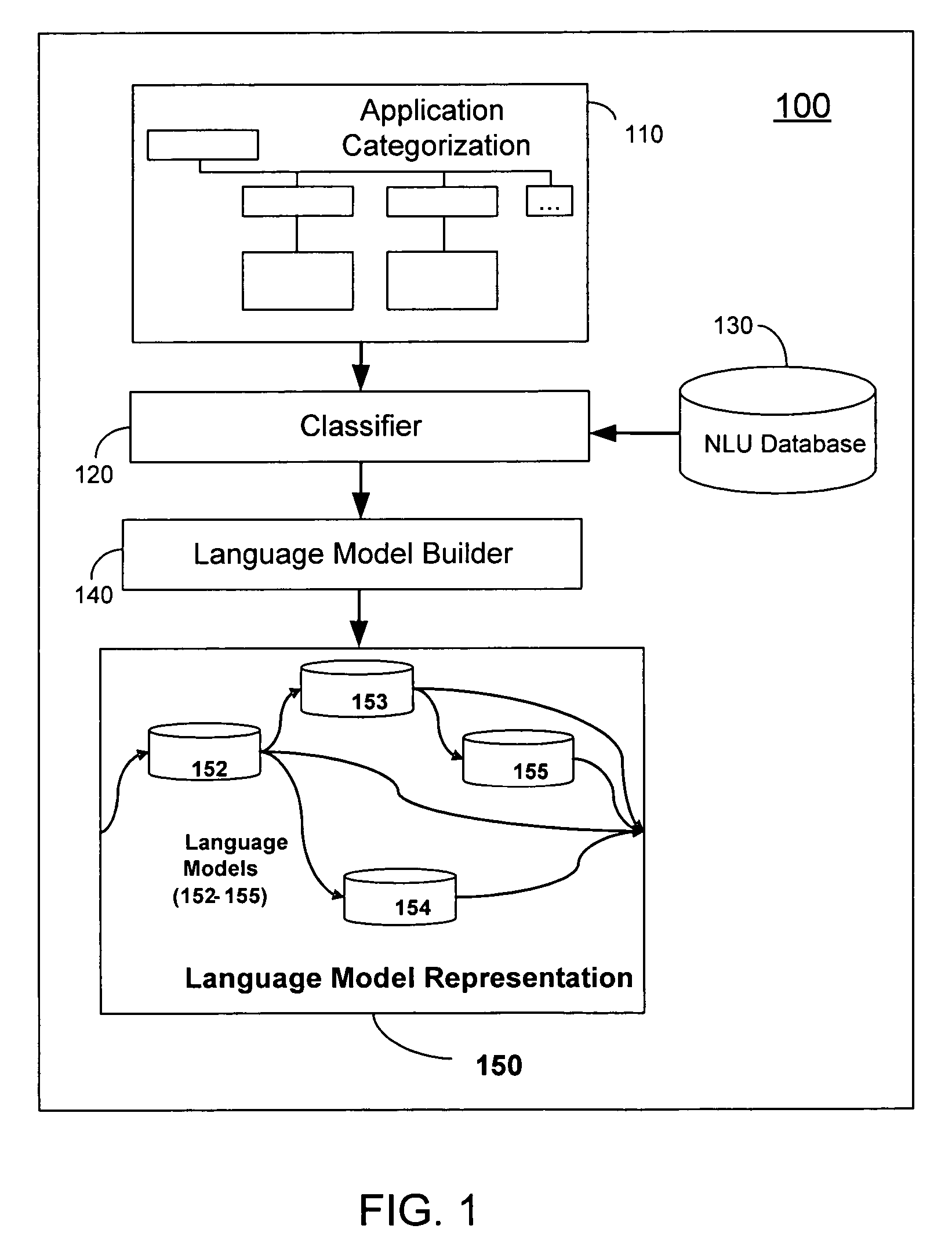
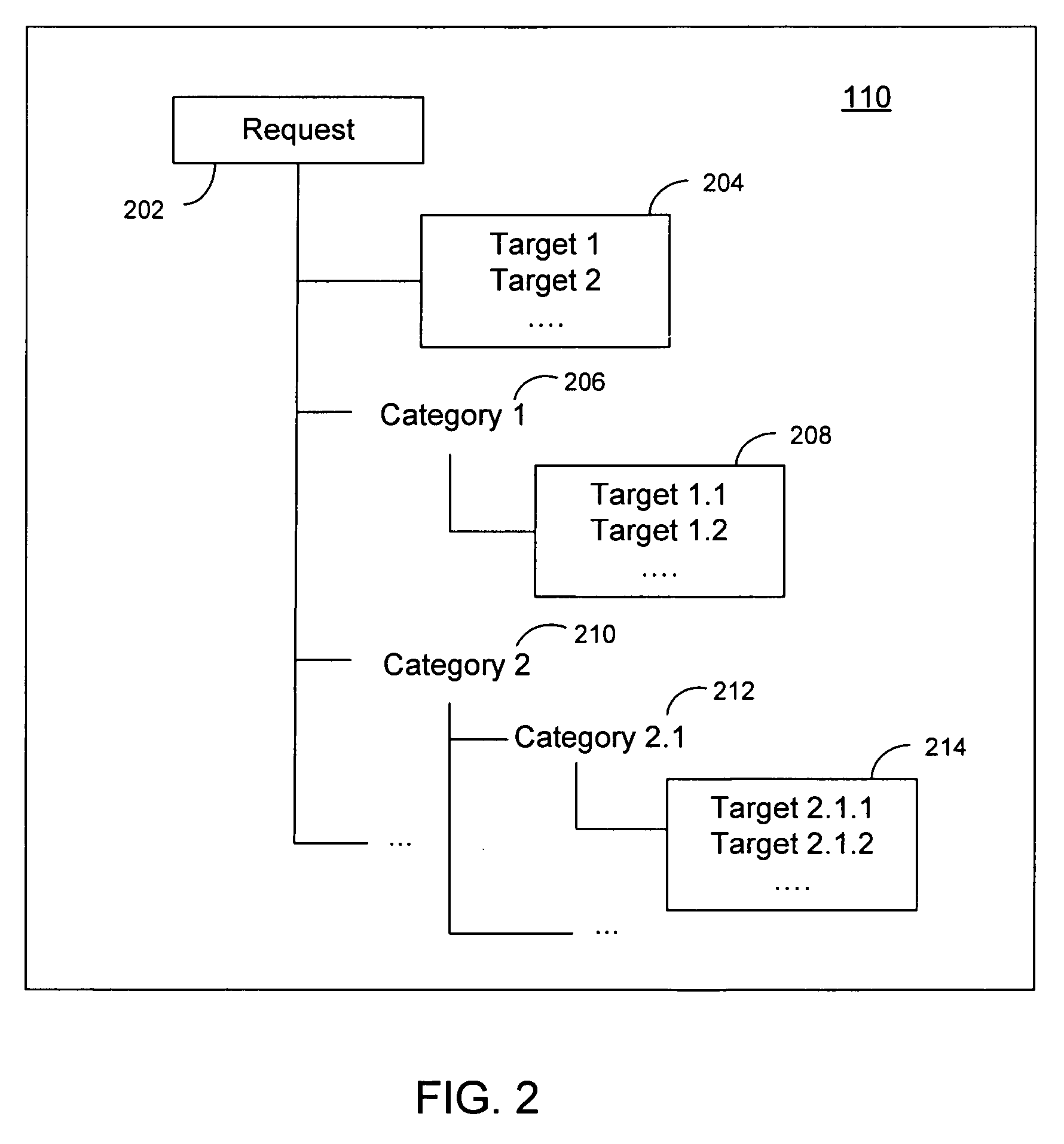
Method and system for automatically building natural language understanding models
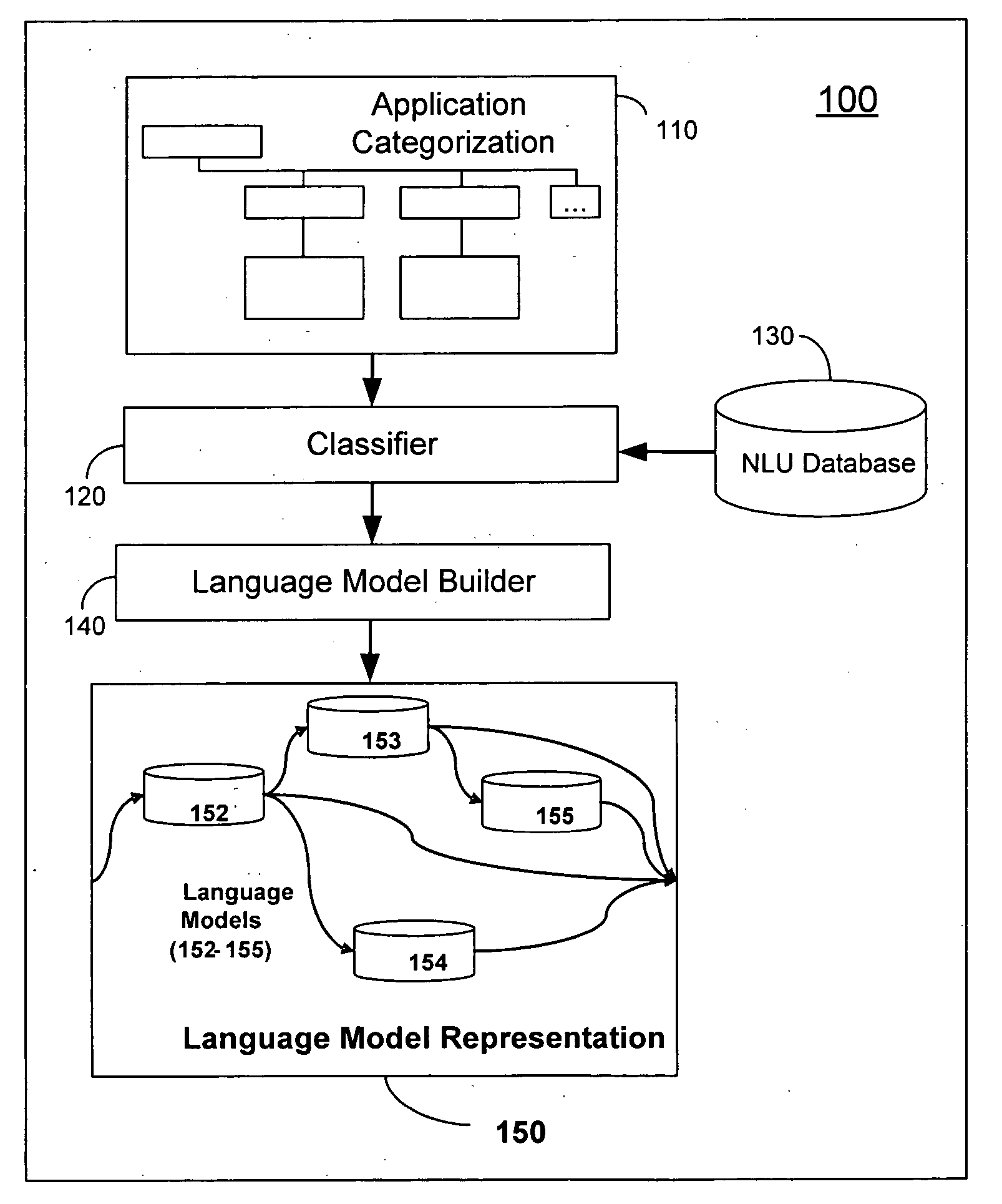
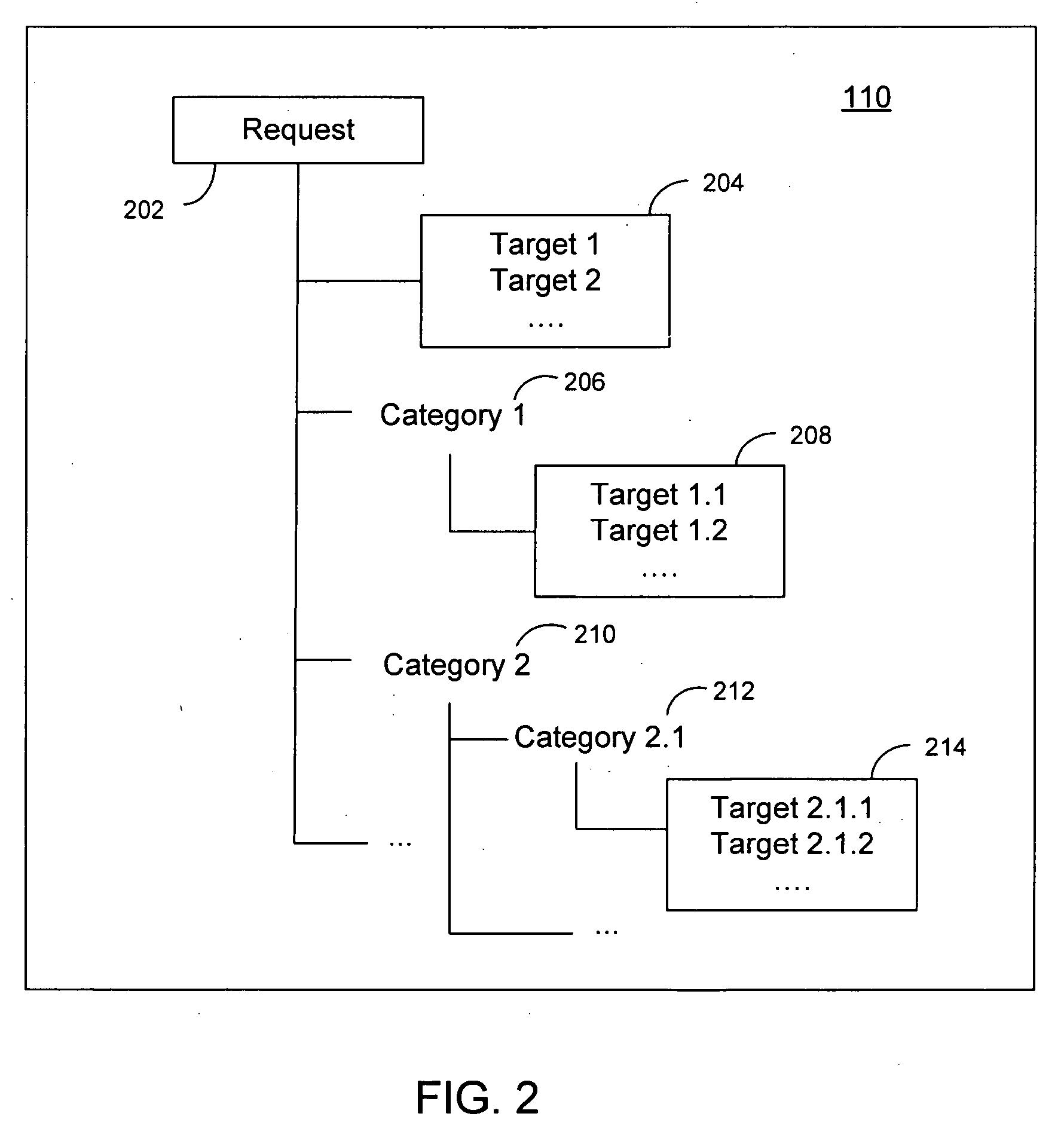
ActiveUS20070156392A1Maximize interpretationPerformance maximizationNatural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsNatural language understandingDATR
The invention disclosed herein concerns a system (100) and method (600) for building a language model representation of an NLU application. The method 500 can include categorizing an NLU application domain (602), classifying a corpus in view of the categorization (604), and training at least one language model in view of the classification (606). The categorization produces a hierarchical tree of categories, sub-categories and end targets across one or more features for interpreting one or more natural language input requests. During development of an NLU application, a developer assigns sentences of the NLU application to categories, sub-categories or end targets across one or more features for associating each sentence with desire interpretations. A language model builder (140) iteratively builds multiple language models for this sentence data, and iteratively evaluating them against a test corpus, partitioning the data based on the categorization and rebuilding models, so as to produce an optimal configuration of language models to interpret and respond to language input requests for the NLU application.
Owner:NUANCE COMM INC
Method and apparatus for non-disruptive embedding of specialized elements
InactiveUS20090288064A1Efficient conversionSimple processData processing applicationsDigital computer detailsAuto-configurationStatistical analysis
Techniques for non-disruptive embedding of specialized elements are disclosed. In one aspect of the techniques, ontology is defined to specify an application domain. A program interface (API) is also provided for creating raw features by a developer. Thus a module is provided for at least one form of statistical analysis within the ontology. The module is configured automatically in a computing device with the API in response to a system consistent with the ontology, wherein the system has no substantial requirement for specialized knowledge of that form of statistical analysis, and the module has no substantial requirement for specialized knowledge of particular functions provided by the system.
Owner:YEN WEI
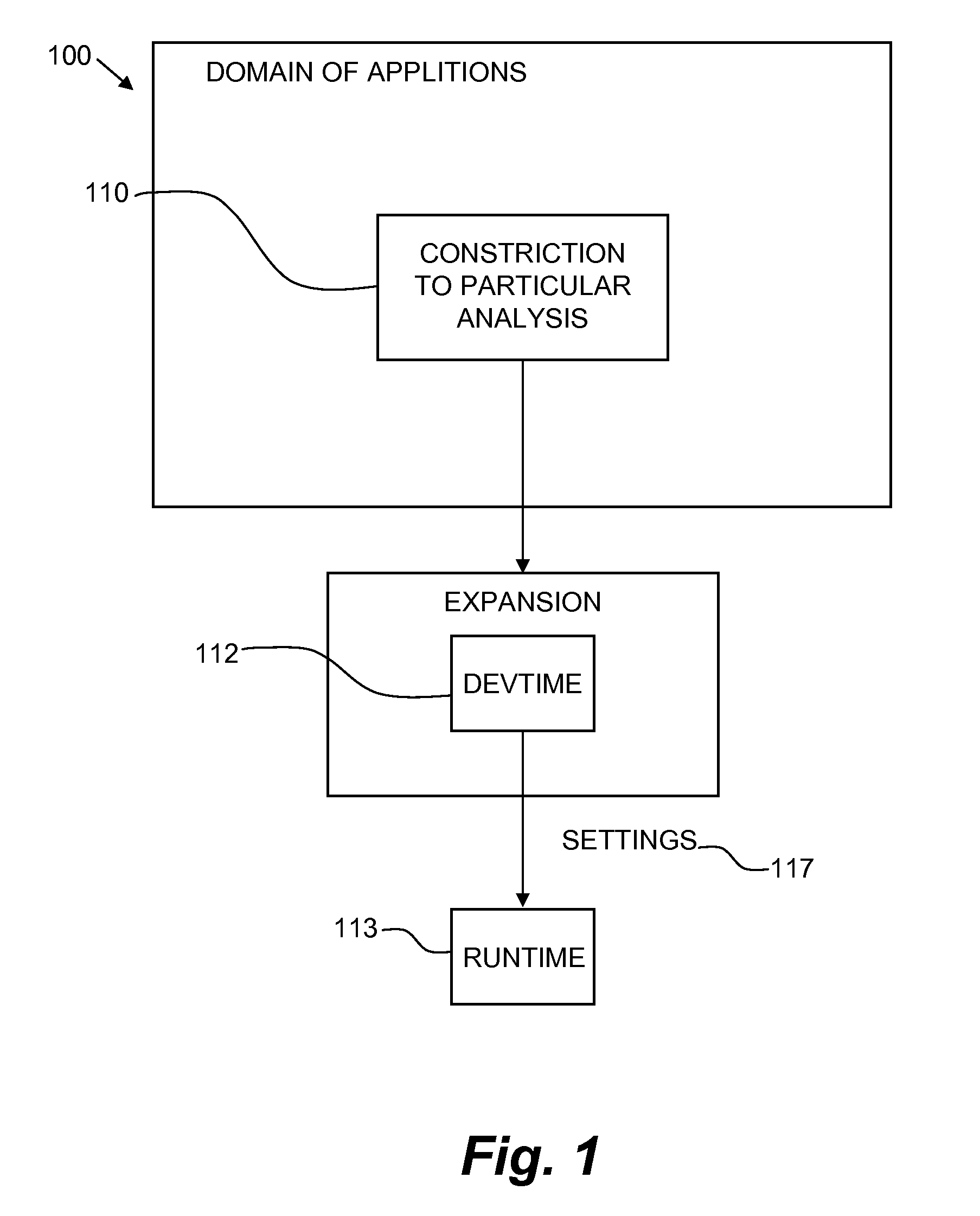
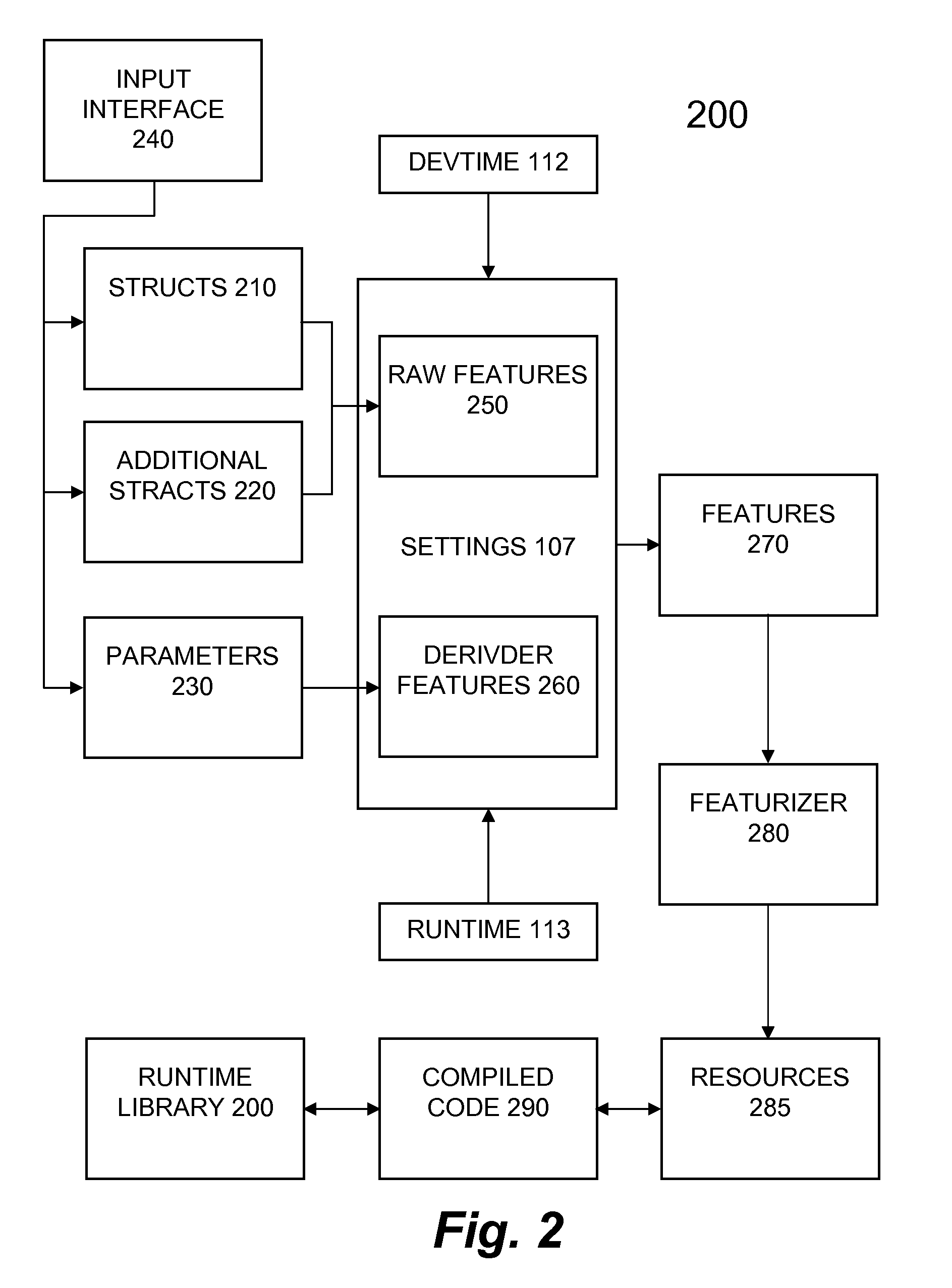
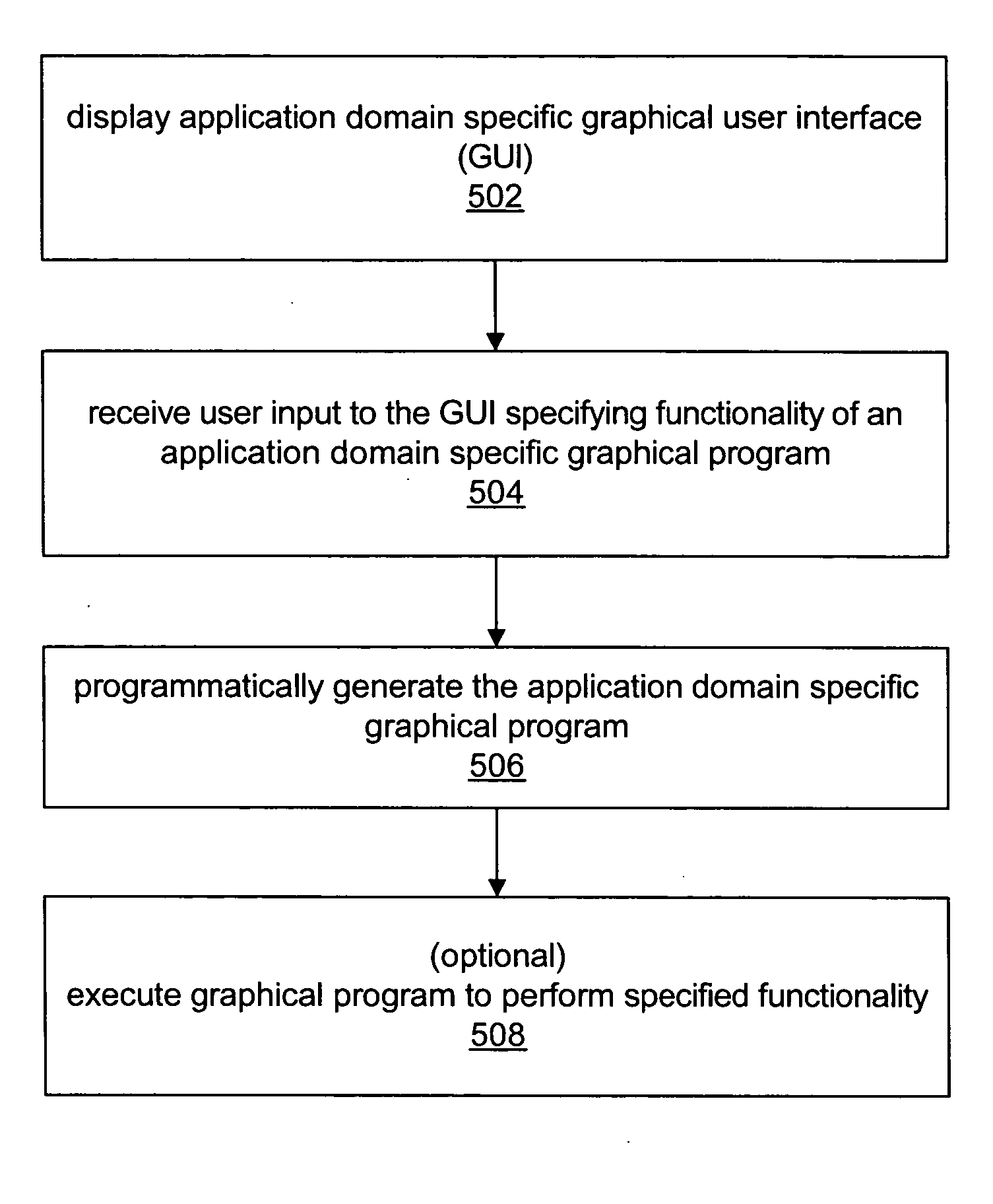
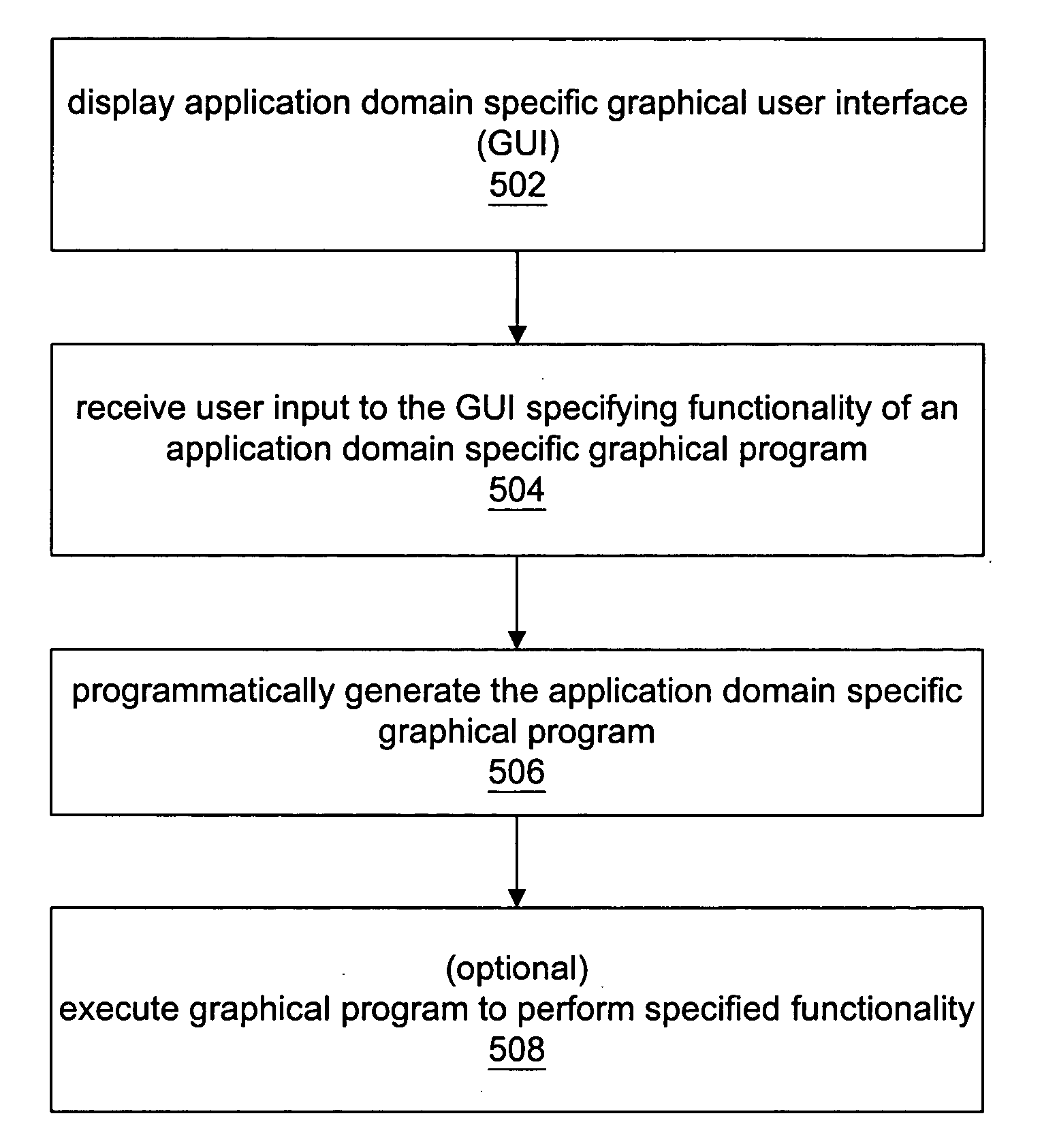
Automatic generation of application domain specific graphical programs
InactiveUS20060225034A1Easy to completeError detection/correctionDigital computer detailsGraphicsGraphical user interface
System and method for generating an application domain specific graphical program. A graphical user interface (GUI) for specifying functionality of a graphical program in an application domain is displayed, where the GUI corresponds specifically to the application domain. User input to the GUI specifying the functionality of the graphical program is received, and the graphical program generated in response, where the graphical program is executable to perform the specified functionality, and comprises multiple interconnected graphical program nodes that visually represent the graphical program functionality. The GUI includes graphical interface elements operable to indicate and / or specify, e.g., via user input, respective attributes of the graphical program such as timing, triggering, analog and / or digital input / output (I / O), resource allocation, processing option, inclusion of one or more external files, and one or more target devices, among others, and may determine the graphical interface elements based on the specified one or more target devices.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
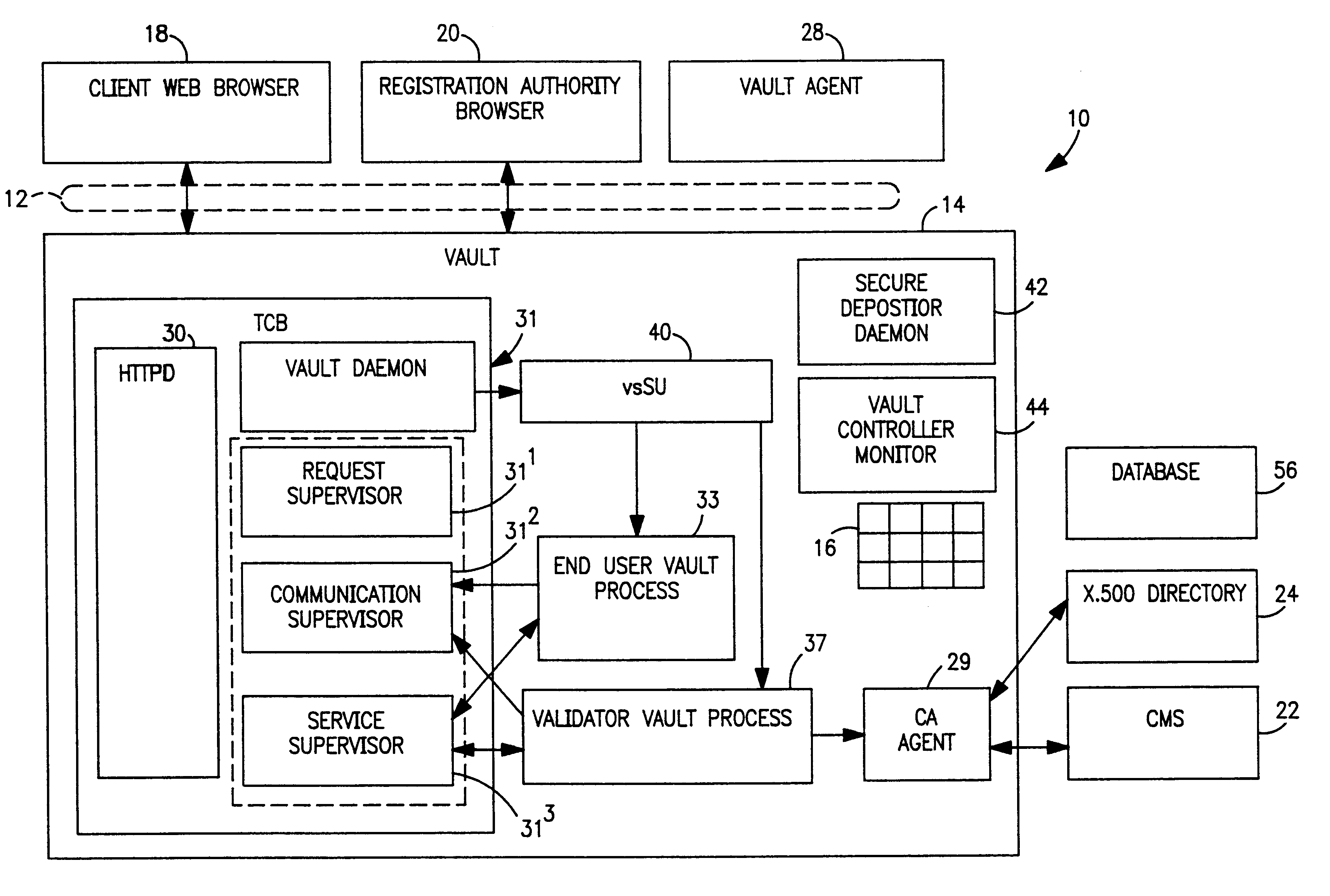
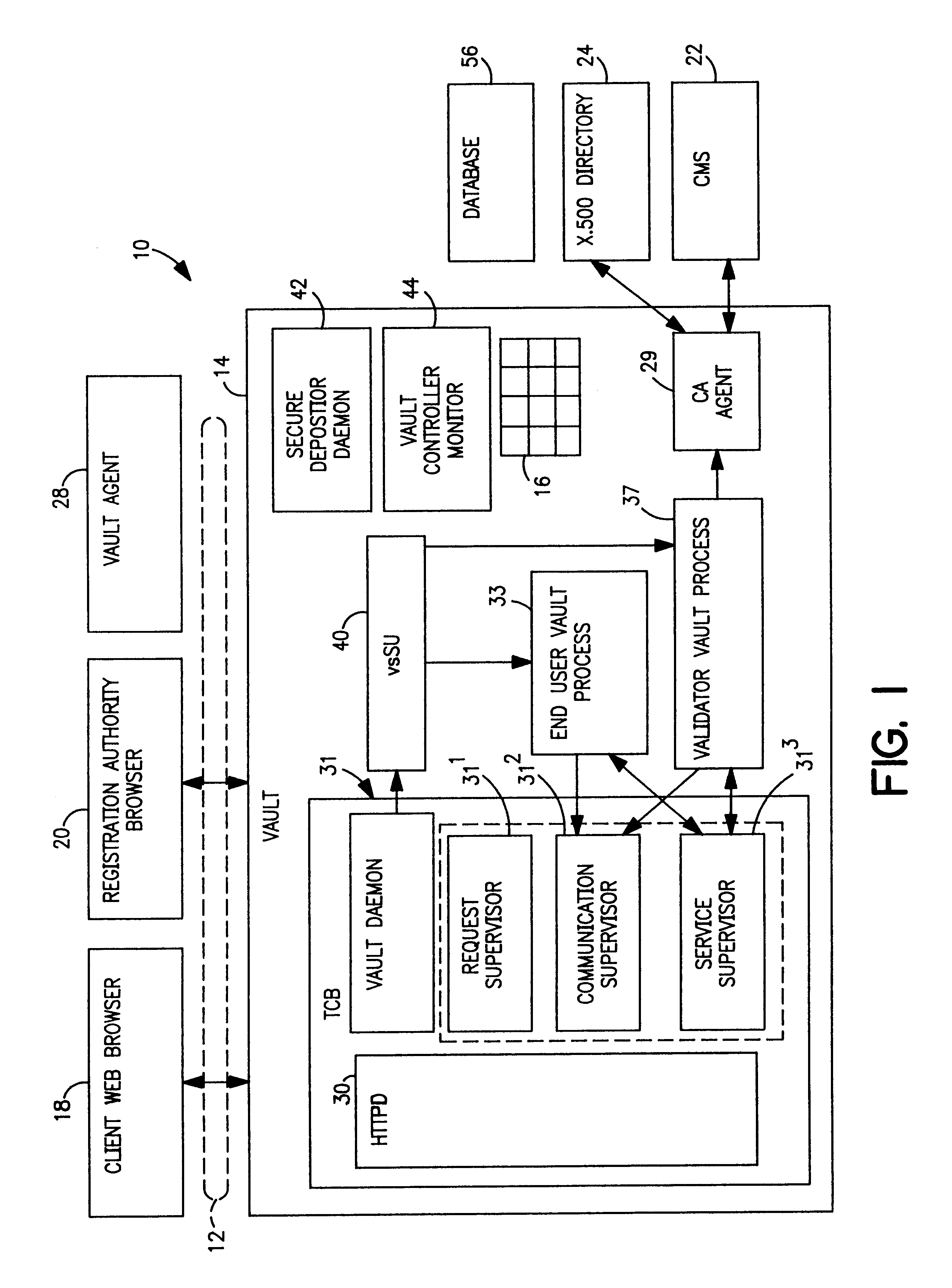
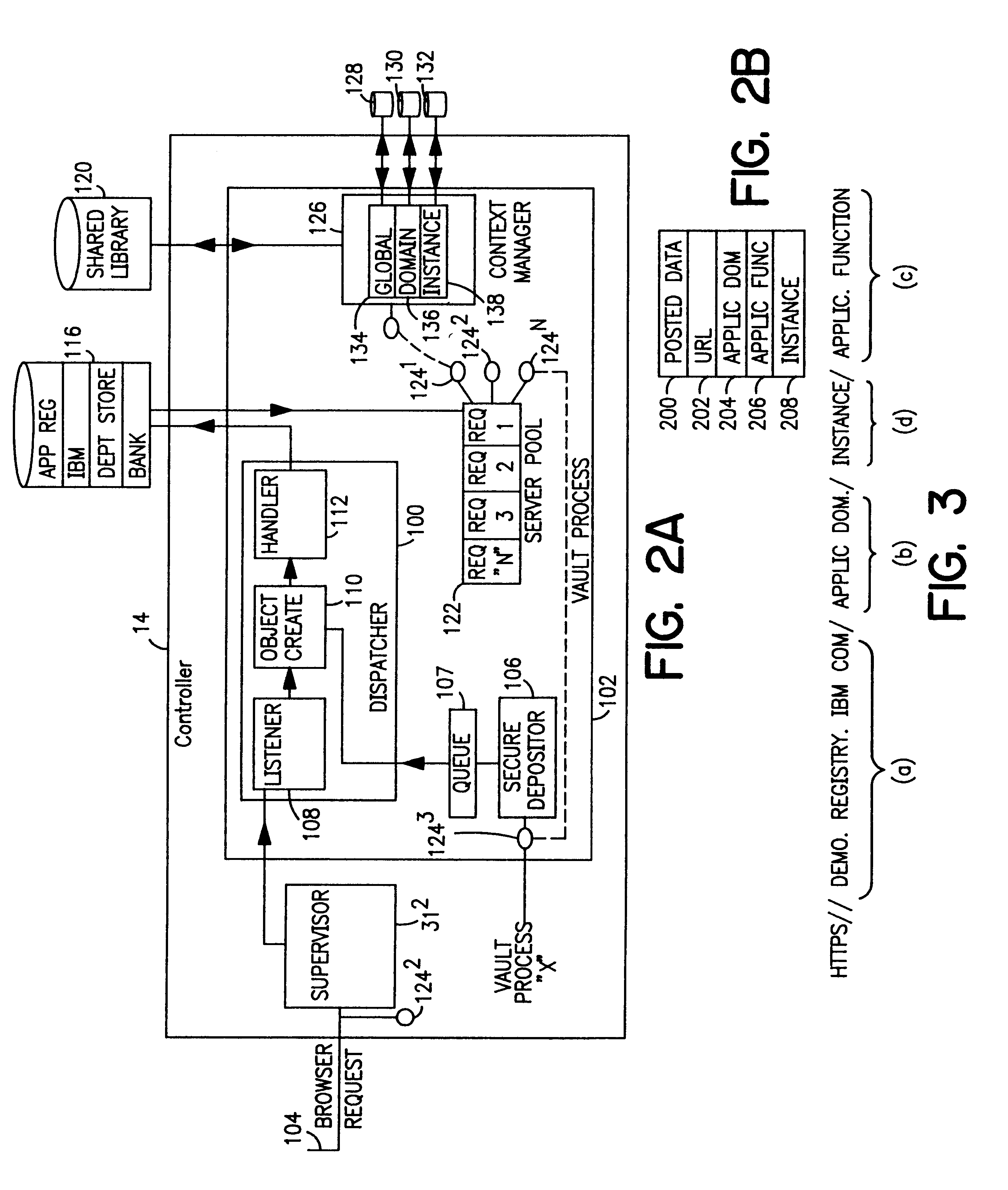
Vault controller dispatcher and methods of operation for handling interaction between browser sessions and vault processes in electronic business systems
InactiveUS6202159B1Digital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionExternal storageContext manager
A vault controller in an electronic business system includes a dispatcher for servicing browser requests initiated by a user for conducting business with an enterprise or organization using a vault process. The dispatcher further responds to a secure depositor receiving requests from other vault processes running in the controller. The request is in the form a URL containing an application domain / local context and application name. The request is detected and processed by event creator which forms an event object definitive of the request in the URL. An event handler parses the event object and enters a vault system application registry to locate the application in a shared memory. The location of the application is passed to a server pool, which assign a processing thread to handle the request. The thread engages a context manager which decrypts and imports application domain, application function and local context information from external storage to process the request. The application is located in the shared memory and the request implemented. The context manager encrypts and exports the processed information to external storage and provides a return code in the response to the user. The return code is used to locate the context information in a subsequent request by the user. The requests received from other vault processes through the secure depositor are handled in like manner to the user request. After execution of a user request, the vault process loops for some defined time during which other requests are received from the user. The absence of requests causes the vault process to shut down and store the variables for the next user request which retraces the steps of the original request.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and method for installation and management of cloud-independent multi-tenant applications
ActiveUS8812627B2Efficient constructionSufficient throughputResource allocationDigital computer detailsCloud storageApplication framework
An application framework may include a cloud-independent application manager, a cloud-independent content services manager, and cloud-independent content services servers. The framework may dynamically install and manage scalable, multi-tenant applications in a cloud, and may scale the applications, as needed. The application manager may receive and handle requests to install application domains and configurations thereof, and may receive and respond to requests for information about servers on which installed methods are available. The content services servers may execute installed methods, using underlying resources of the cloud, through a cloud-specific SPI. The content services manager and application manager may work together using shared cloud storage to provide scalable content services at a very large scale. In the context of the framework described herein, an “application” may be defined by methods bundled into configurations, and by various cost-based and / or performance-based rules that specify how server instances providing those methods are to be managed.
Owner:ADOBE SYST INC
System and method for jointly managing dynamically generated code and data
ActiveUS7127709B2Clear dataData processing applicationsResource allocationLimited resourcesWaste collection
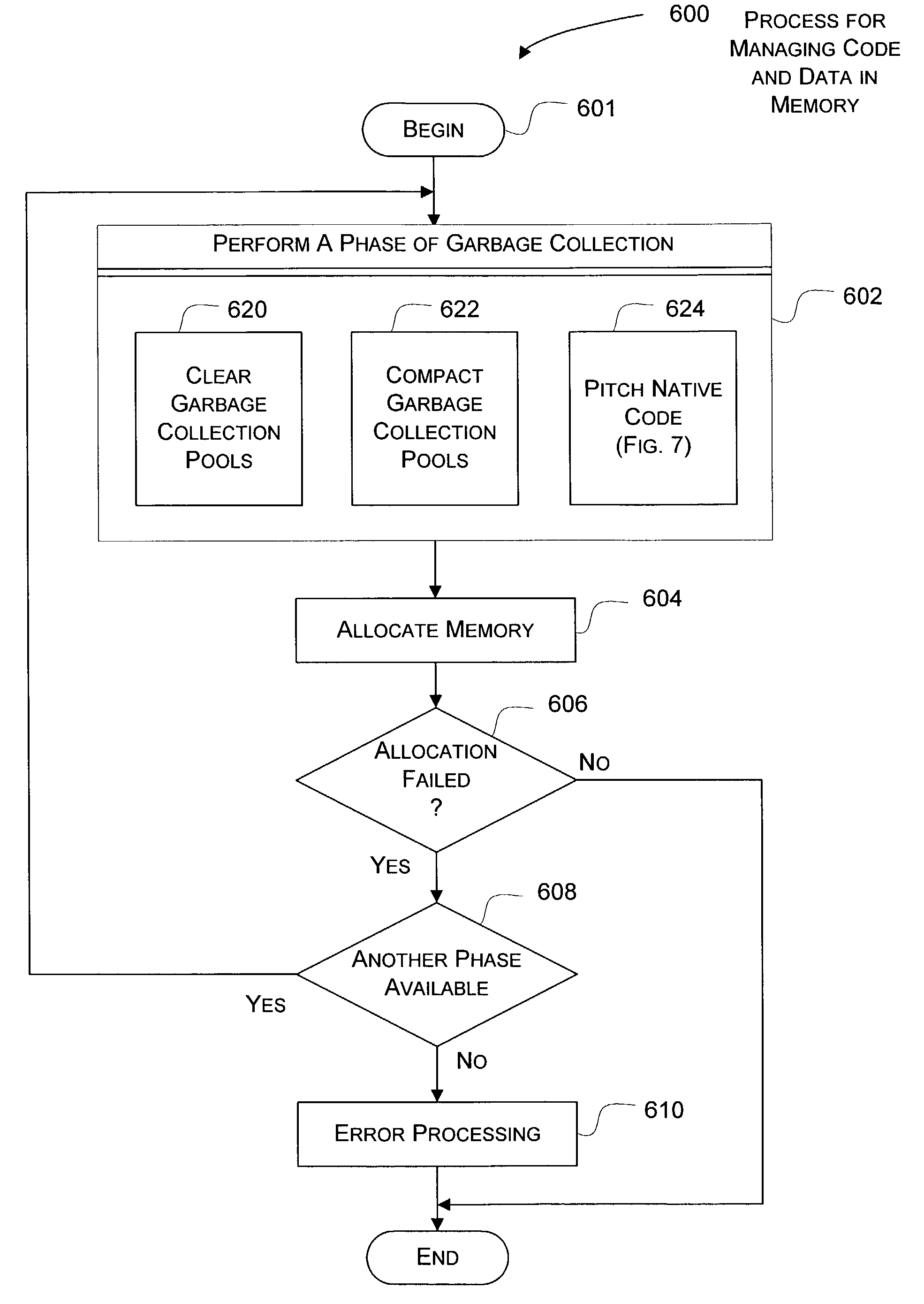
The present invention is directed at a virtual machine environment operating on portable devices with limited resources. The virtual machine environment includes a method for managing dynamically generated code and data together in order to shift memory usage to / from generated code or data as needed. Each application domain manages several code pools and several garbage collection pools that are allocated from a system memory heap. When additional memory is not available for allocation from the system memory heap, garbage collection is performed until sufficient memory becomes available. During garbage collection, unreachable data in each garbage collection pool is cleared. The garbage collection process may further compact the garbage collection pools in order to empty one or more of the garbage collection pools. Still further, code pools may be released back to the system memory heap if the generated code is not associated with a current application domain, is executed infrequently, or is not associated with an instruction on a stack. Thus, memory may flow from data to code or vice versa as needed and among application domains.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Local Causal and Markov Blanket Induction Method for Causal Discovery and Feature Selection from Data
In many areas, recent developments have generated very large datasets from which it is desired to extract meaningful relationships between the dataset elements. However, to date, the finding of such relationships using prior art methods has proved extremely difficult especially in the biomedical arts. Methods for local causal learning and Markov blanket discovery are important recent developments in pattern recognition and applied statistics, primarily because they offer a principled solution to the variable / feature selection problem and give insight about local causal structure. The present invention provides a generative method for learning local causal structure around target variables of interest in the form of direct causes / effects and Markov blankets applicable to very large datasets and relatively small samples. The method is readily applicable to real-world data, and the selected feature sets can be used for causal discovery and classification. The generative method GLL-PC can be instantiated in many ways, giving rise to novel method variants. In general, the inventive method transforms a dataset with many variables into either a minimal reduced dataset where all variables are needed for optimal prediction of the response variable or a dataset where all variables are direct causes and direct effects of the response variable. The power of the invention and significant advantages over the prior art were empirically demonstrated with datasets from a diversity of application domains (biology, medicine, economics, ecology, digit recognition, text categorization, and computational biology) and data generated by Bayesian networks.
Owner:ALIFERIS KONSTANTINOS CONSTANTIN F +1
Programmatic generation of application domain specific graphical programs
InactiveUS20050251789A1Easy to completeMeasurement arrangements for variableDigital computer detailsGraphicsGraphical user interface
System and method for generating an application domain specific graphical program. A graphical user interface (GUI) for specifying functionality of a graphical program in an application domain is displayed, where the GUI corresponds specifically to the application domain. User input to the GUI specifying the functionality of the graphical program is received, and the graphical program generated in response, where the graphical program is executable to perform the specified functionality, and comprises multiple interconnected graphical program nodes that visually represent the graphical program functionality. The GUI includes graphical interface elements operable to indicate and / or specify, e.g., via user input, respective attributes of the graphical program such as timing, triggering, analog and / or digital input / output (I / O), resource allocation, processing option, inclusion of one or more external files, and one or more target devices, among others, and may determine the graphical interface elements based on the specified one or more target devices.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
Network global expectation model for multi-tier networks
InactiveUS20050197993A1Quick costRapidly needWavelength-division multiplex systemsFuzzy logic based systemsSensitivity analysisNetwork cost
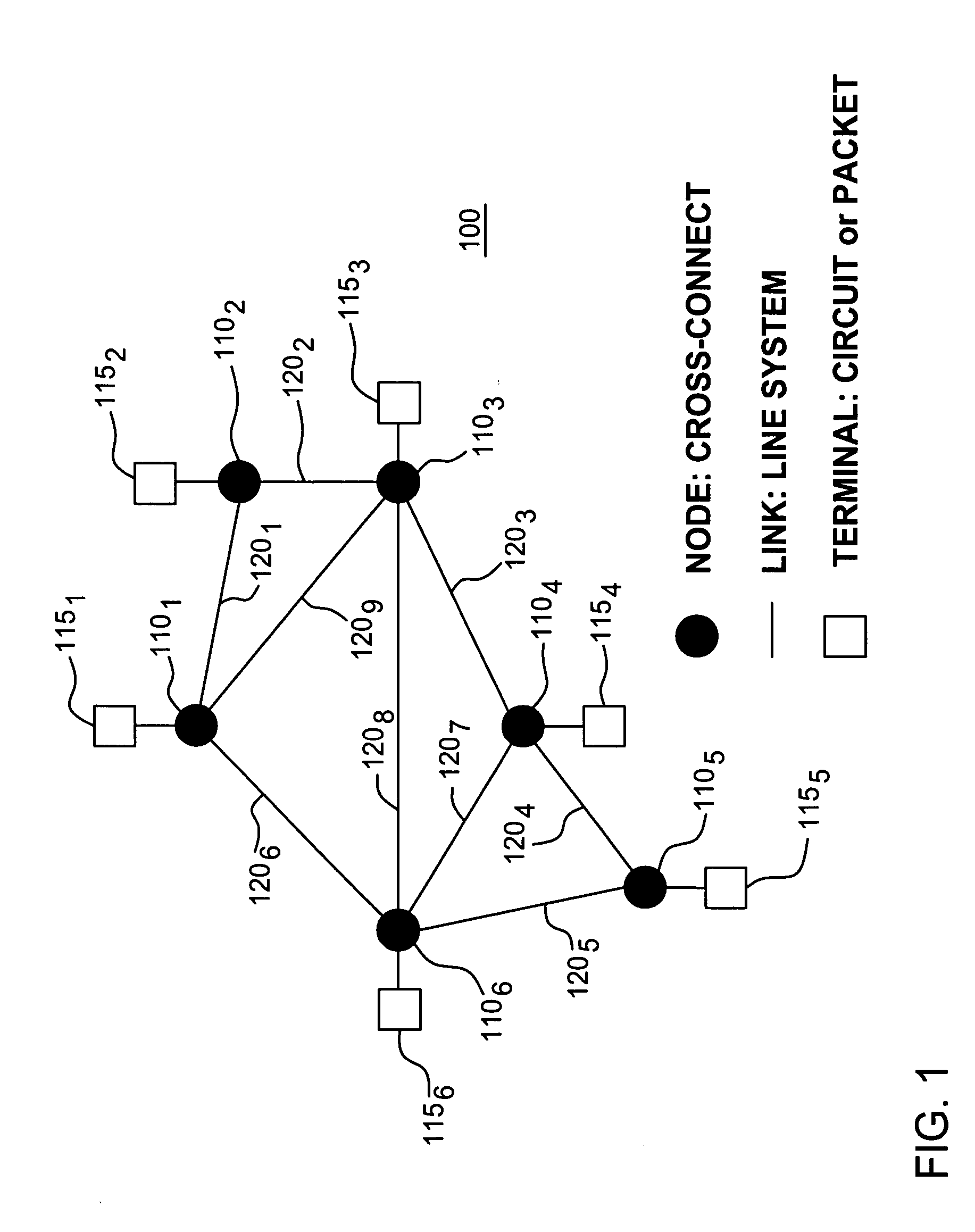
In the Network Global Expectation Model, expectation values evaluated over the entire network are used as a multi-moment description of the required quantities of key network and network element (NE) resources and commensurate network costs. The Network Global Expectation Model naturally and analytically connects the global (network) and local (network element) views of the communication system, and thereby may be used as a tool to gain insight and very quickly provide approximate results for the preliminary evaluation and design of dynamic networks. Further, the Network Global Expectation Model may serve as a valuable guide in the areas of network element feature requirements, costs, sensitivity analyses, scaling performance, comparisons, product definition and application domains, and product and technology roadmapping. The network is arranged as a multiple tier network of nodes in order to apply the analysis methods of the Network Global Expectation Model. The analytical method is developed to include non-uniform demands on the network.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
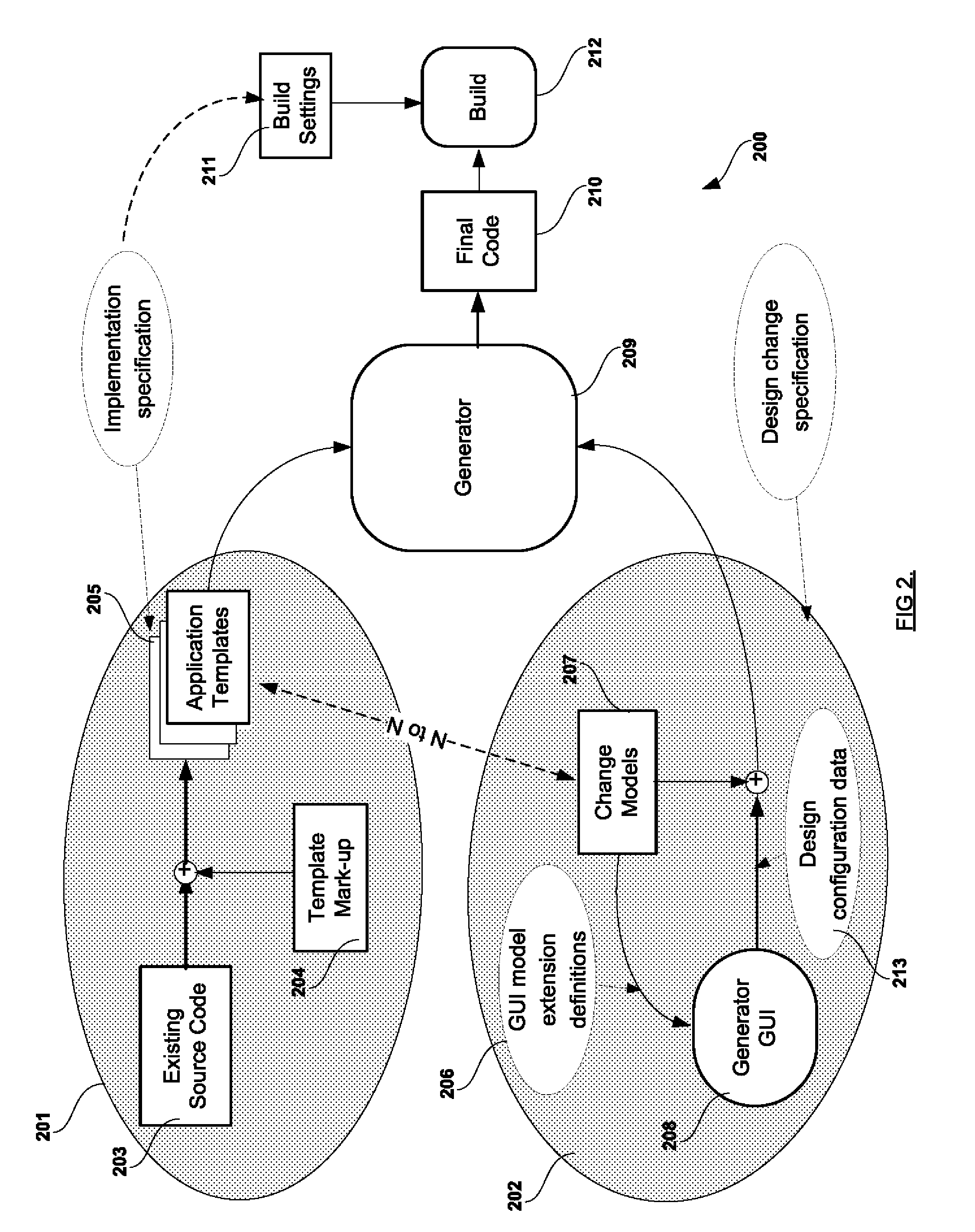
System and Method for Generating Modified Source Code Based on Change-Models
ActiveUS20090125878A1Avoid introducingOpenSpecific program execution arrangementsMemory systemsApplication softwareSource code
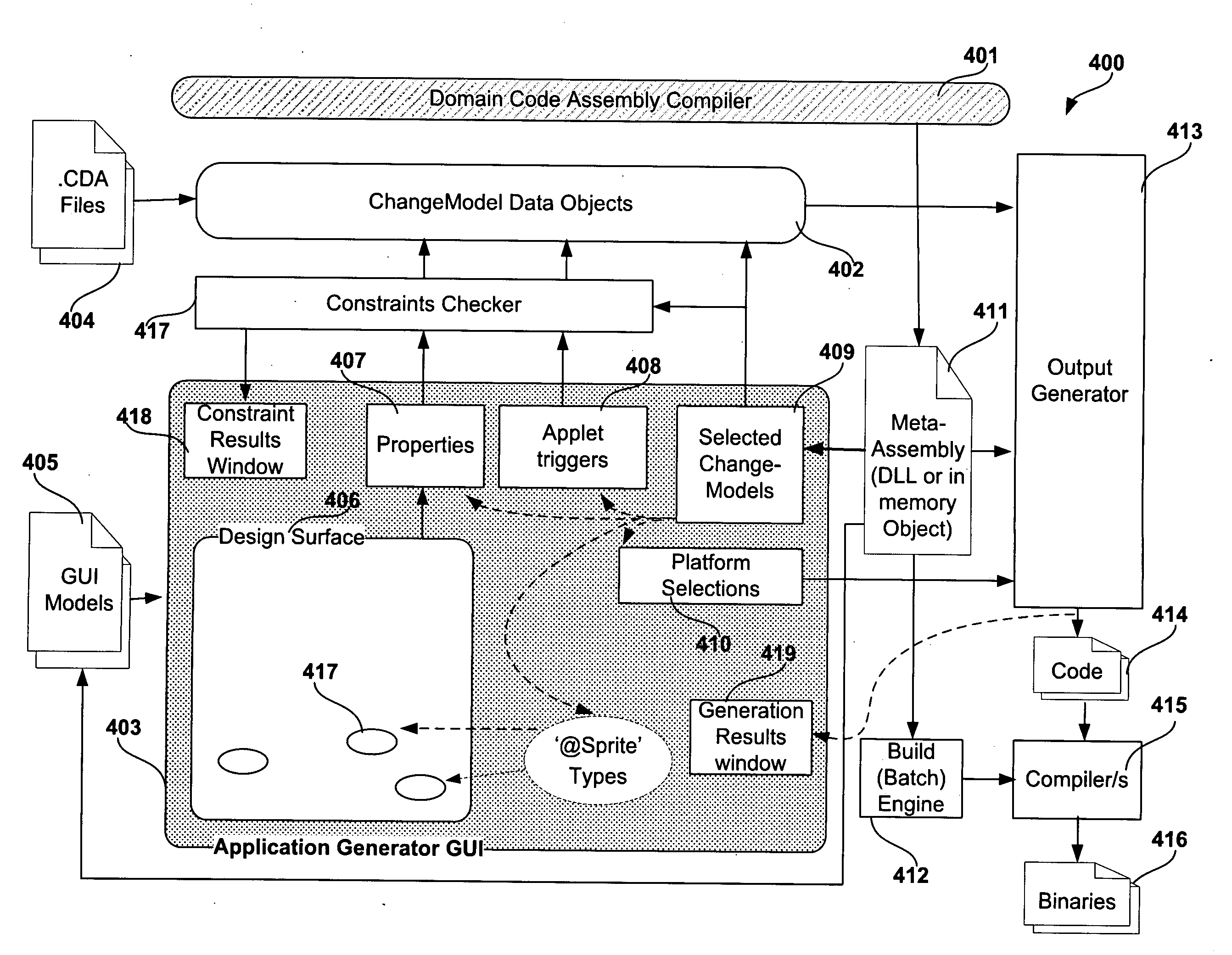
A computer implemented method for automatically generating domain specific applications based on model driven changes of the source code base for existing applications. Abstracted declarative design change-models, separate from detailed implementation source coding, are used to define the possible set of changes for specific application domains. Generalized implementations of the design changes, mapped to the defined Change-Model abstracted representations but separate from the representations themselves, are implemented via Application-Templates consisting of existing source code plus mark-up. The application domain is thus defined by the change-model linked to allied application-templates. Meta generation facilities are implicitly provided as the code generator for a specific application domain is defined by the Change-Model plus related set of Application-Templates. Additionally, the generator GUI is automatically modified or generated from the Change-Model with optional GUI model extensions definitions to tailor the generator GUI for each specific application domain.
Owner:META GAMES UNIVERSAL LTD
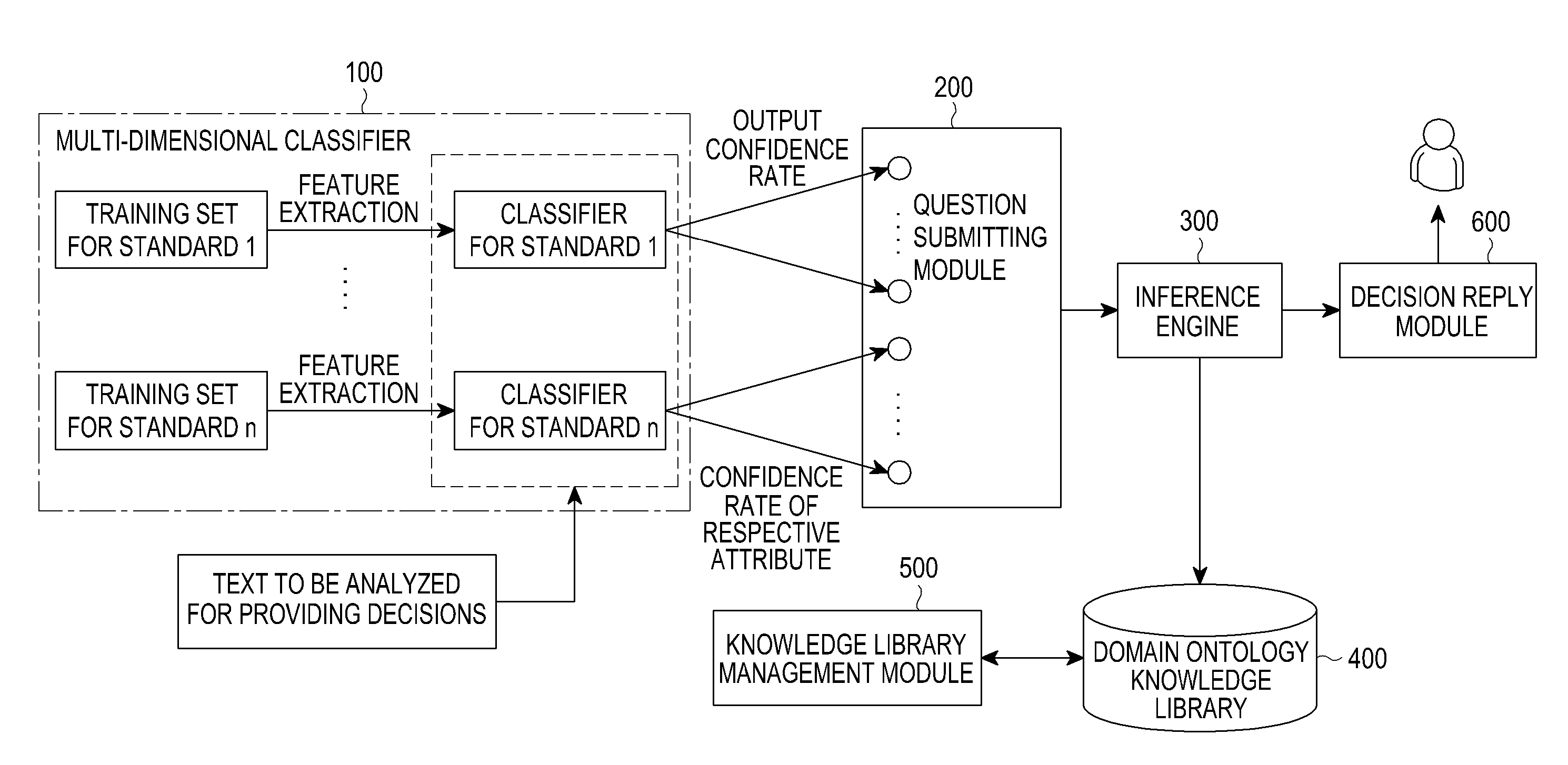
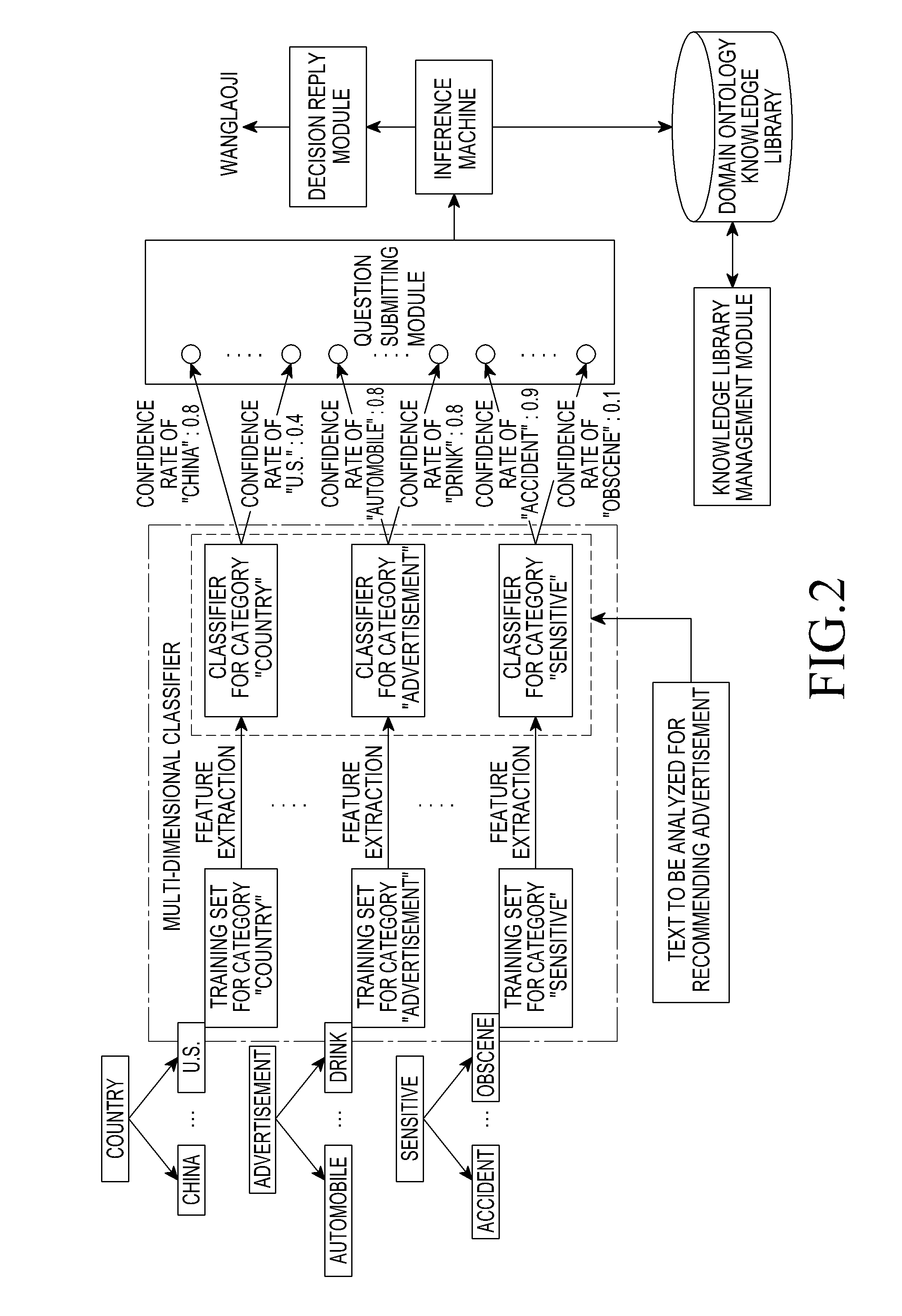
Intelligent decision supporting system and method for making intelligent decision
ActiveUS20110191270A1Intelligent decisionSemantic analysisDigital computer detailsSupporting systemA domain
An intelligent decision supporting system and a method for making an intelligent decision are provided. The intelligent decision supporting system includes a multi-dimensional classifier comprising a plurality of classifiers that define different semantic standards and are trained based on the different semantic standards, for classifying a text by the semantic standards and for outputting a plurality of attributes of the text and a confidence rate of each of the plurality of attributes, a question submitting module for receiving the output of the multi-dimensional classifier, for forming a question based on the plurality of attributes of the text and the confidence rate of each attribute, and for submitting the question to an inference machine, the inference machine for receiving the question submitted by the question submitting module, for inquiring of a domain ontology knowledge library based on the question, and for providing an answer for the question to an decision reply module, a domain ontology knowledge library module for storing a domain ontology knowledge library related to an application domain of the intelligent decision supporting system, wherein the domain ontology knowledge library records description of rules for deriving decisions corresponding to the semantic standards of the multi-dimensional classifier, and the decision reply module for providing the answer for the question provided by the inference machine to the user.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
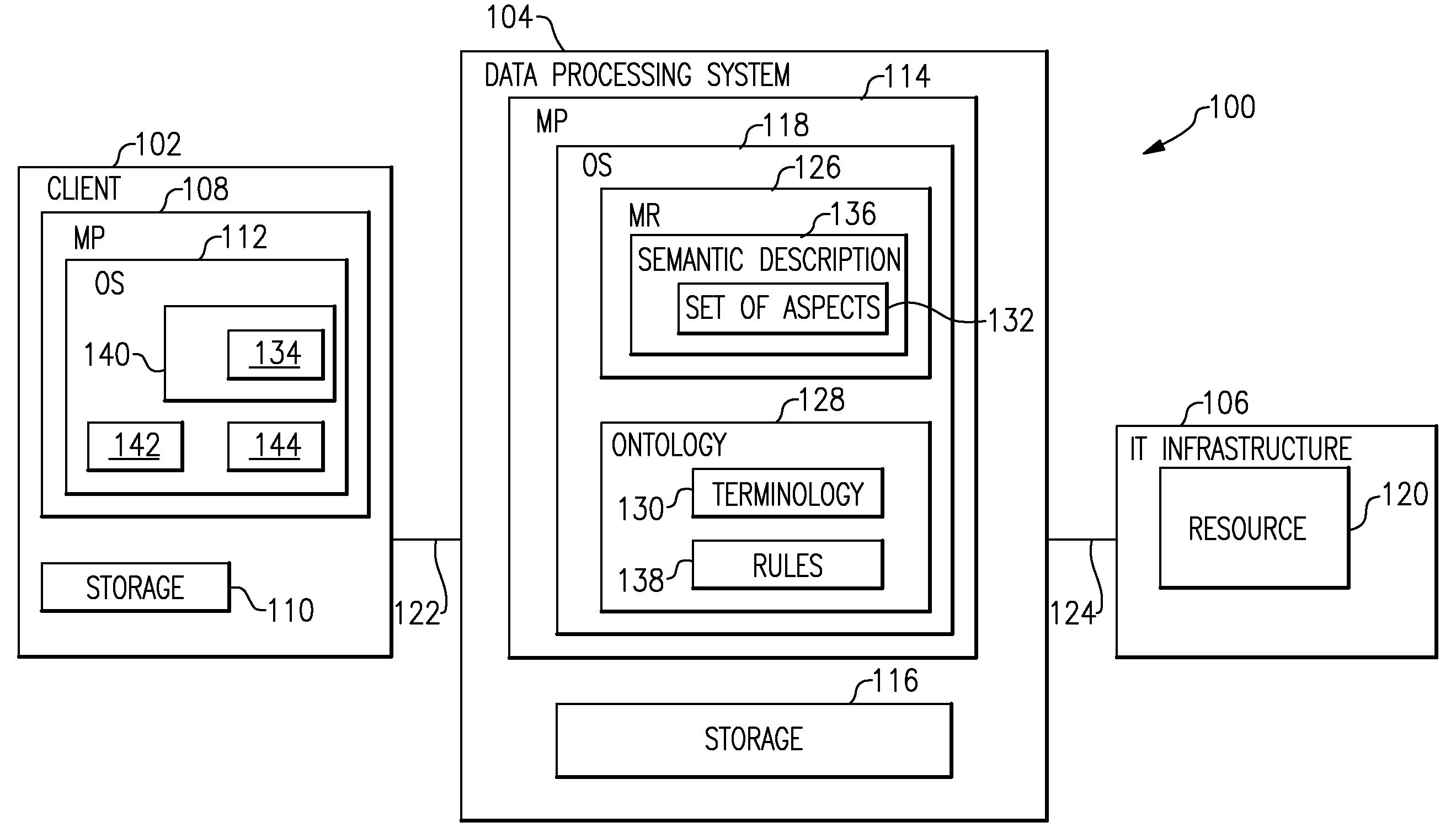
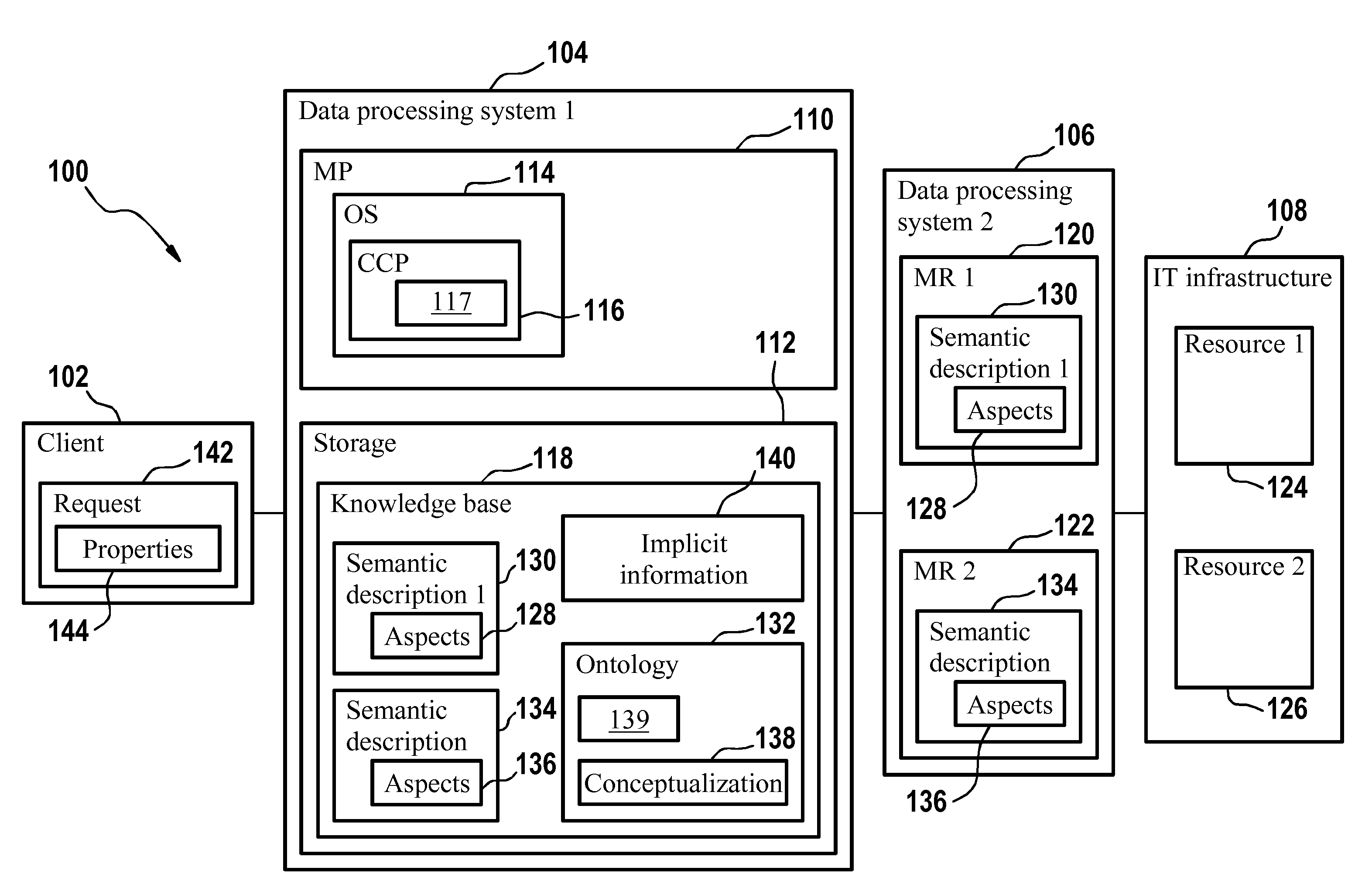
Machine-Processable Semantic Description For Resource Management
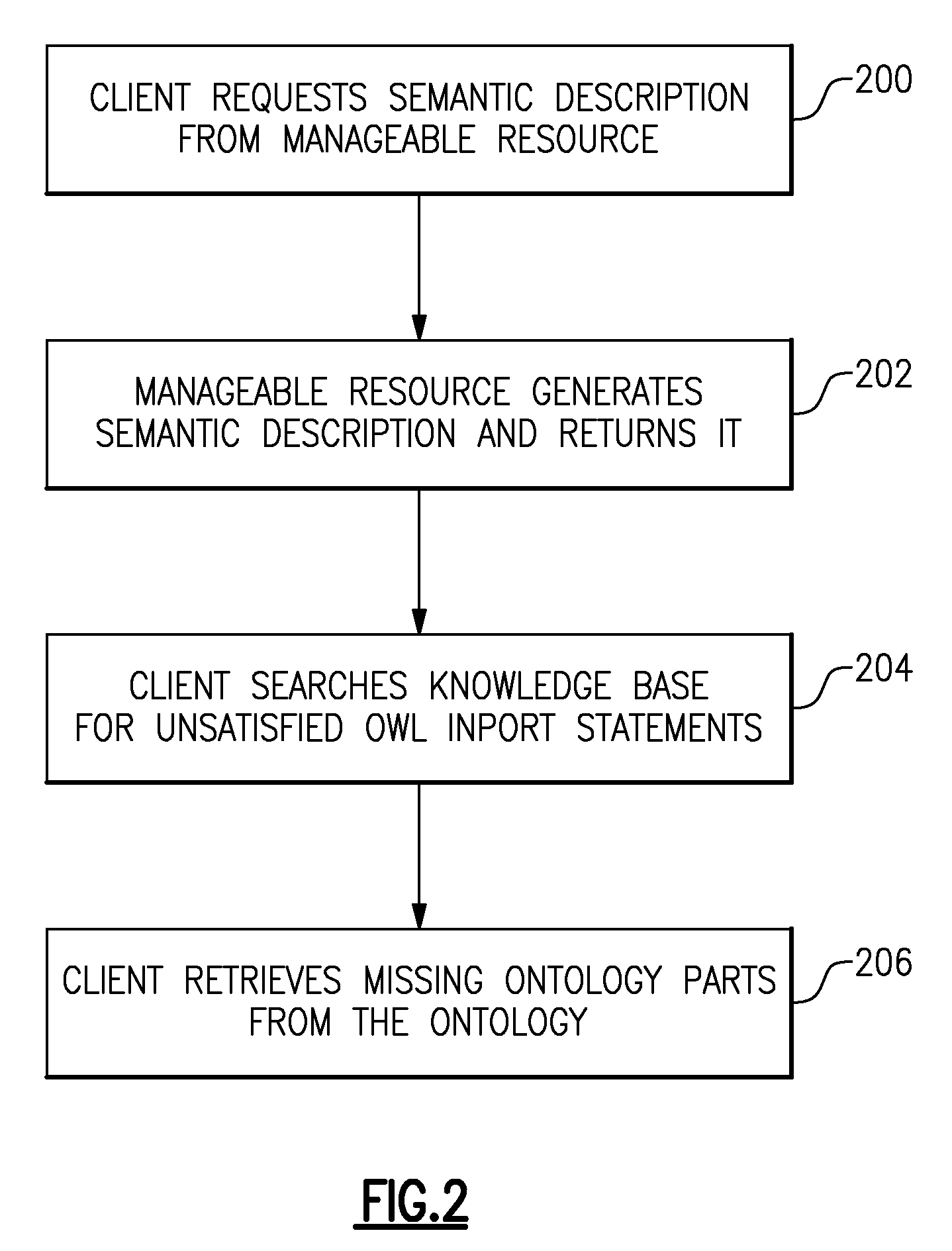
ActiveUS20090177777A1Digital data information retrievalDigital computer detailsResource managementApplication software
A method and associated apparatus is provided for generating a machine-processable semantic description of a first manageable resource of an application domain. In accordance with an embodiment of the invention, the first manageable resource is characterized by a set of aspects. Accordingly, an ontology is provided for the application domain that provides a terminology and rules for describing the set of aspects of the first manageable resources of the application domain in a semantic way. The semantic description of the first manageable resource is then generated compliant to the terminology and the rules of the ontology to describe semantically the set of aspects.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and system for automatically building natural language understanding models
ActiveUS7835911B2Maximize interpretationPerformance maximizationNatural language data processingSpeech recognitionNatural language understandingAlgorithm
The invention disclosed herein concerns a system (100) and method (600) for building a language model representation of an NLU application. The method 500 can include categorizing an NLU application domain (602), classifying a corpus in view of the categorization (604), and training at least one language model in view of the classification (606). The categorization produces a hierarchical tree of categories, sub-categories and end targets across one or more features for interpreting one or more natural language input requests. During development of an NLU application, a developer assigns sentences of the NLU application to categories, sub-categories or end targets across one or more features for associating each sentence with desire interpretations. A language model builder (140) iteratively builds multiple language models for this sentence data, and iteratively evaluating them against a test corpus, partitioning the data based on the categorization and rebuilding models, so as to produce an optimal configuration of language models to interpret and respond to language input requests for the NLU application.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
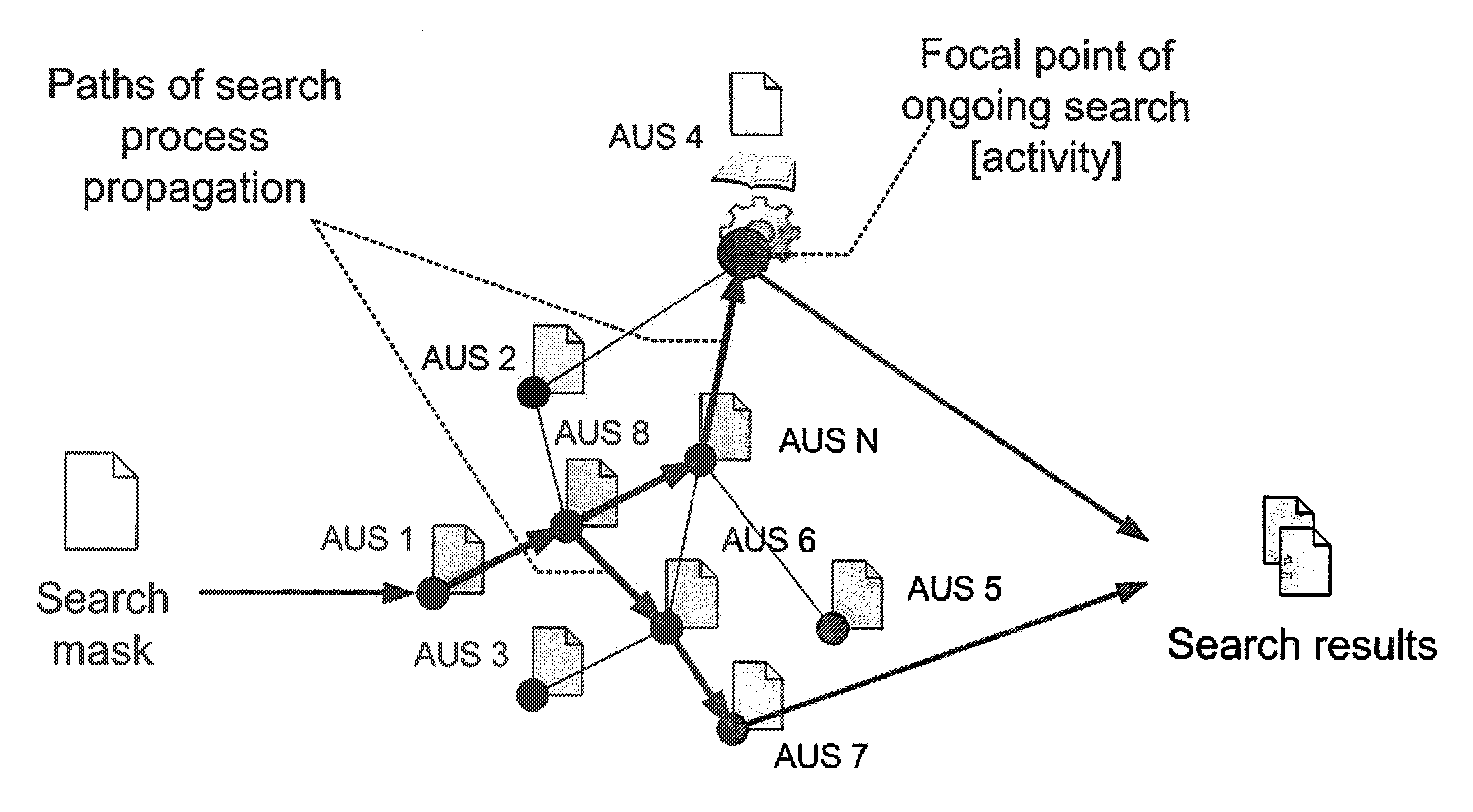
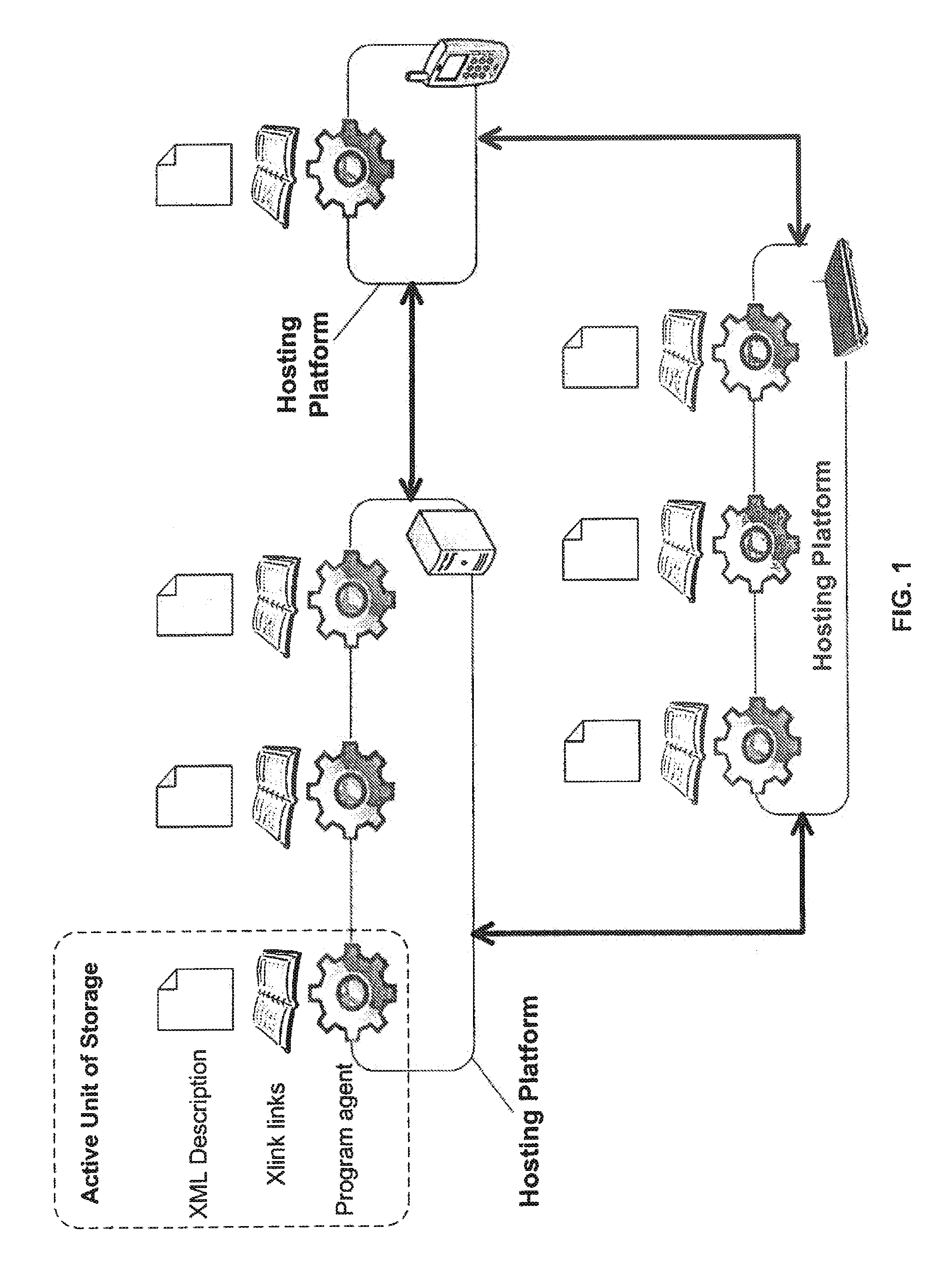
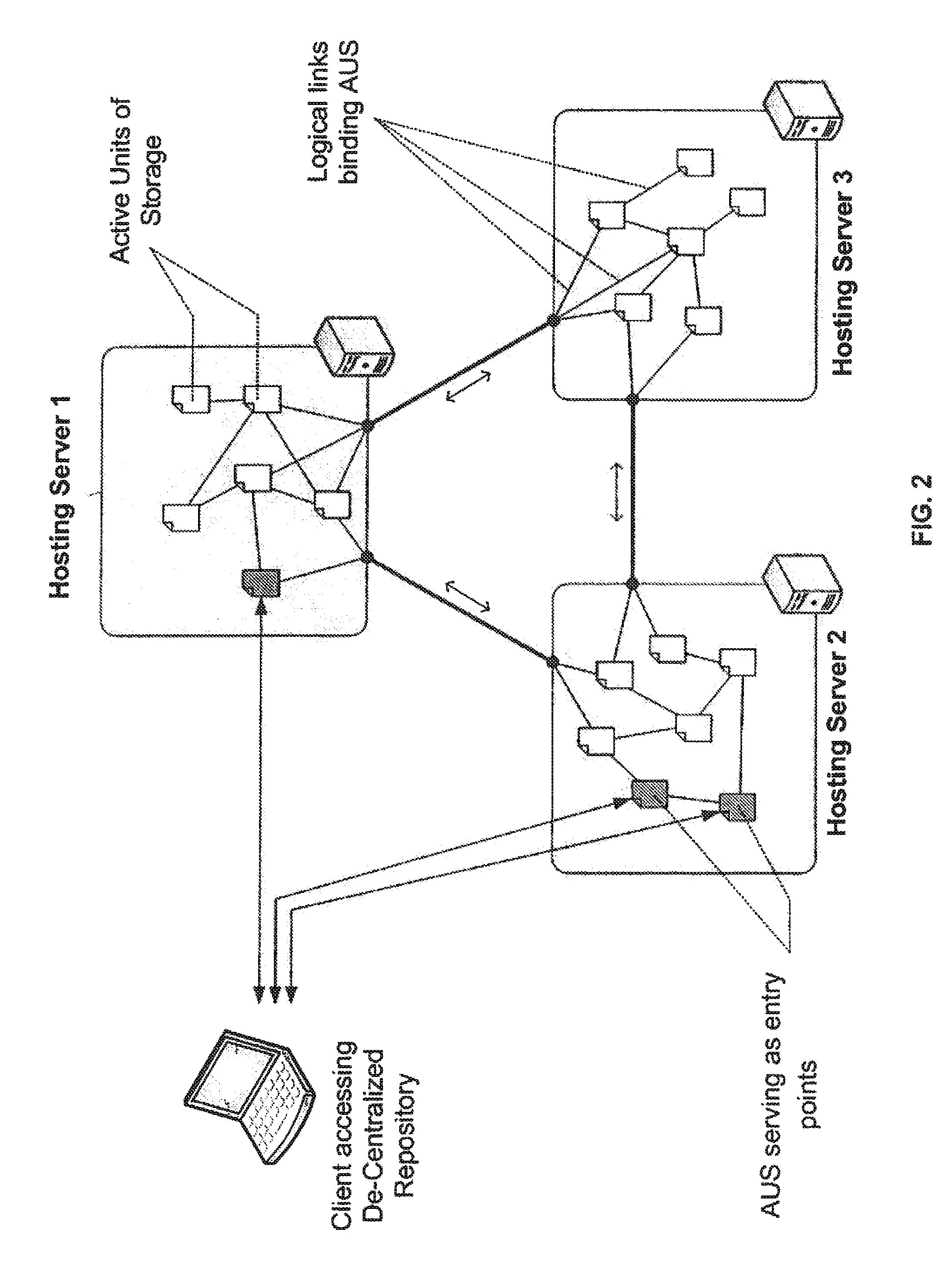
Method and system for storing, searching and retrieving information based on semistructured and de-centralized data sets
InactiveUS20100223262A1High similarityDigital data processing detailsSpecial data processing applicationsData setInformation object
A system for storage and methods for search and retrieval of information presentable as a plurality of tree-structured information objects of an arbitrary application domain are disclosed. The system comprises a distributed computer system consisting of computing devices, interconnected with each other by physical communication lines, and a connected logical storage network, every node of which is an active unit of storage (AUS), incorporating an information object, a program agent and a list of links of said AUS to a plurality of other AUS on the network, wherein the links form connections among the nodes of the logical storage network. Links of an AUS pointing at a plurality of other AUS are created based on a metric calculated taking into account the intrinsic structure of stored and retrieved information objects, and enabling determination and use of the degree of relevance between search information attributes and respective attributes of a search query. Methods for storing and retrieving information in the disclosed system are provided. The system and methods enable efficient storage, searching and retrieving information.
Owner:LIMITED LIABILITY COMPANY MERA NN
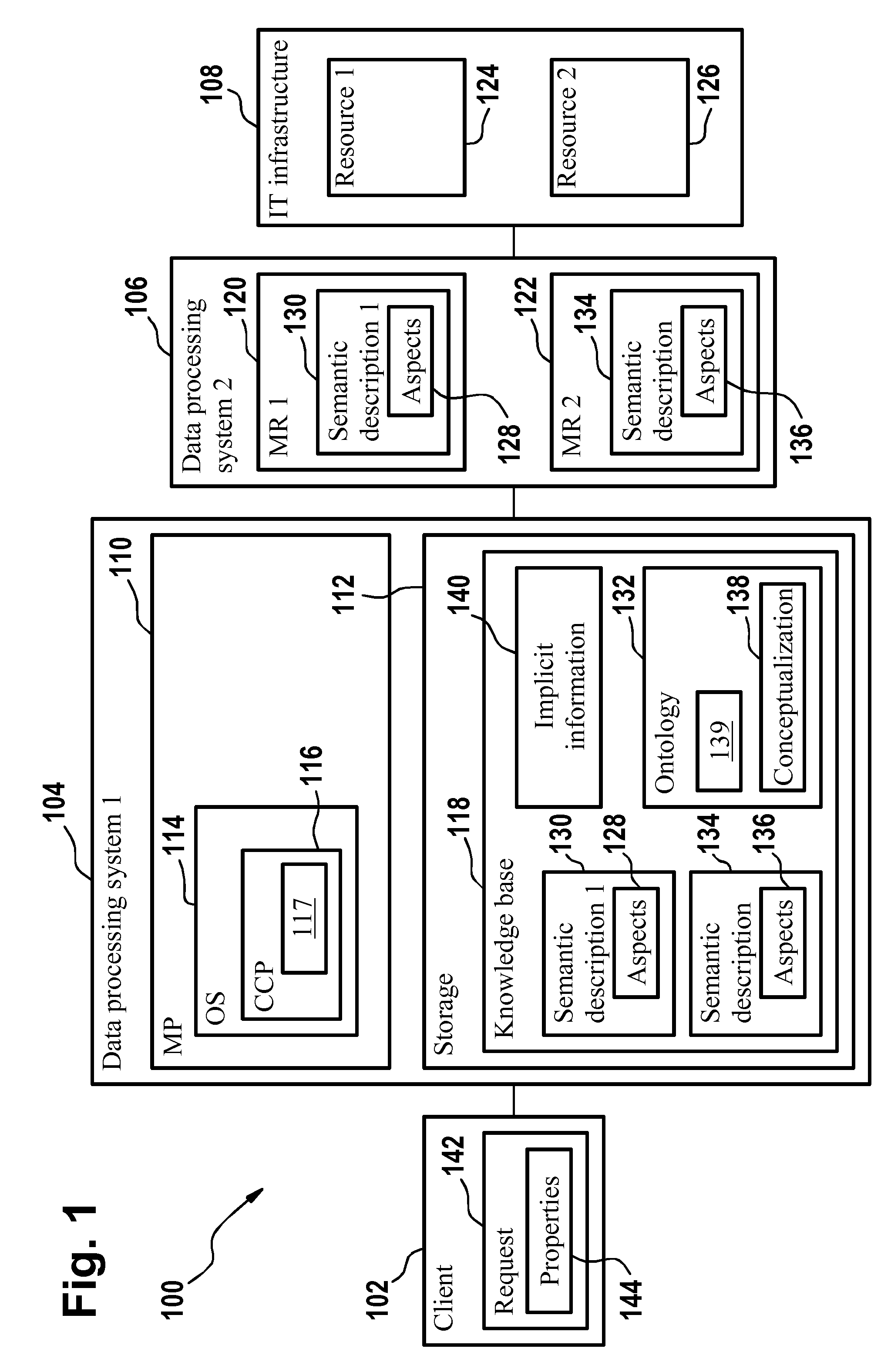
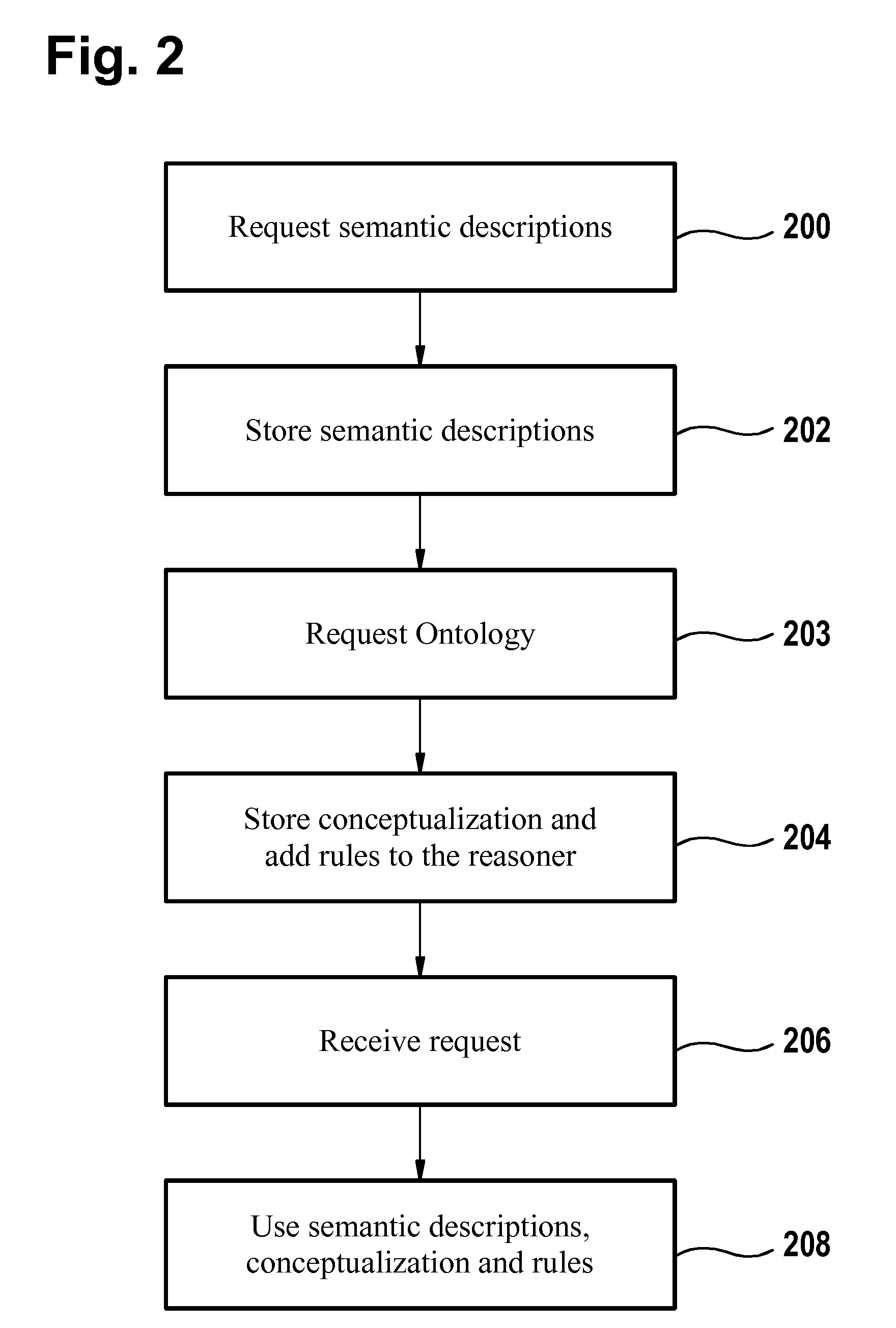
Method and System for an Application Domain
InactiveUS20090177634A1Improve developmentEasy maintenanceDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsClient-sideApplication software
Data processing comprising requesting a semantic description from each manageable resource of a plurality of manageable resources. An application domain comprises the plurality of manageable resources. The semantic description of a manageable resource comprises semantic information about a plurality of aspects of a manageable resource. The semantic information is specified by use of an ontology. The semantic descriptions and a conceptualization of the application domain is stored in a knowledge base. The conceptualization of the application domain is provided by the ontology. The conceptualization comprises semantic information about the application domain. A request from a client of the application domain to provide a manageable resource with specific properties is received. The specific properties are specified in the request. The semantic information of the conceptualization and the semantic descriptions is used for selecting the manageable resource with the specific properties from the plurality of manageable resources.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and apparatus for the processing of heterogeneous units of work
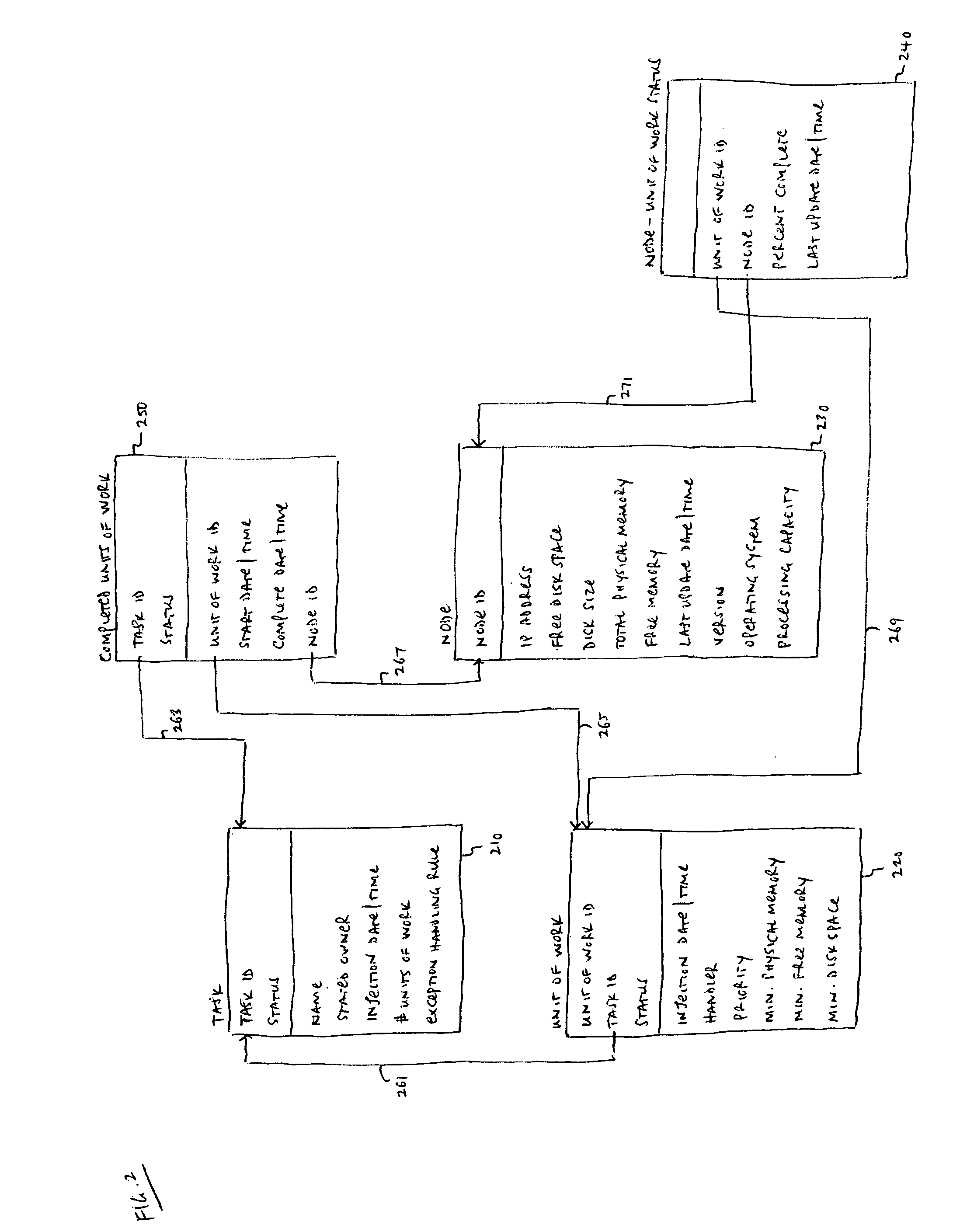
InactiveUS20070094270A1Improve abilitiesResource allocationSpeech recognitionParallel computingWork unit
Methods and apparatus are provided which may be employed to perform speech recognition processing on a grid computing system. In some embodiments, the grid computing system includes a server system which receives processing tasks from one or more client applications, divides the processing tasks into units of work, and assigns the units of work to one or more of the nodes. Dividing a processing task into units of work may involve dividing audio input data into segments defined by natural speech boundaries. A mathematical representation may be created for each segment prior to its distribution on the grid to minimize network traffic. A node in the system may perform heterogeneous units of work concurrently, such as by isolating the execution of each unit of work in an application domain.
Owner:CALLMINER INC
Method and apparatus for federated understanding
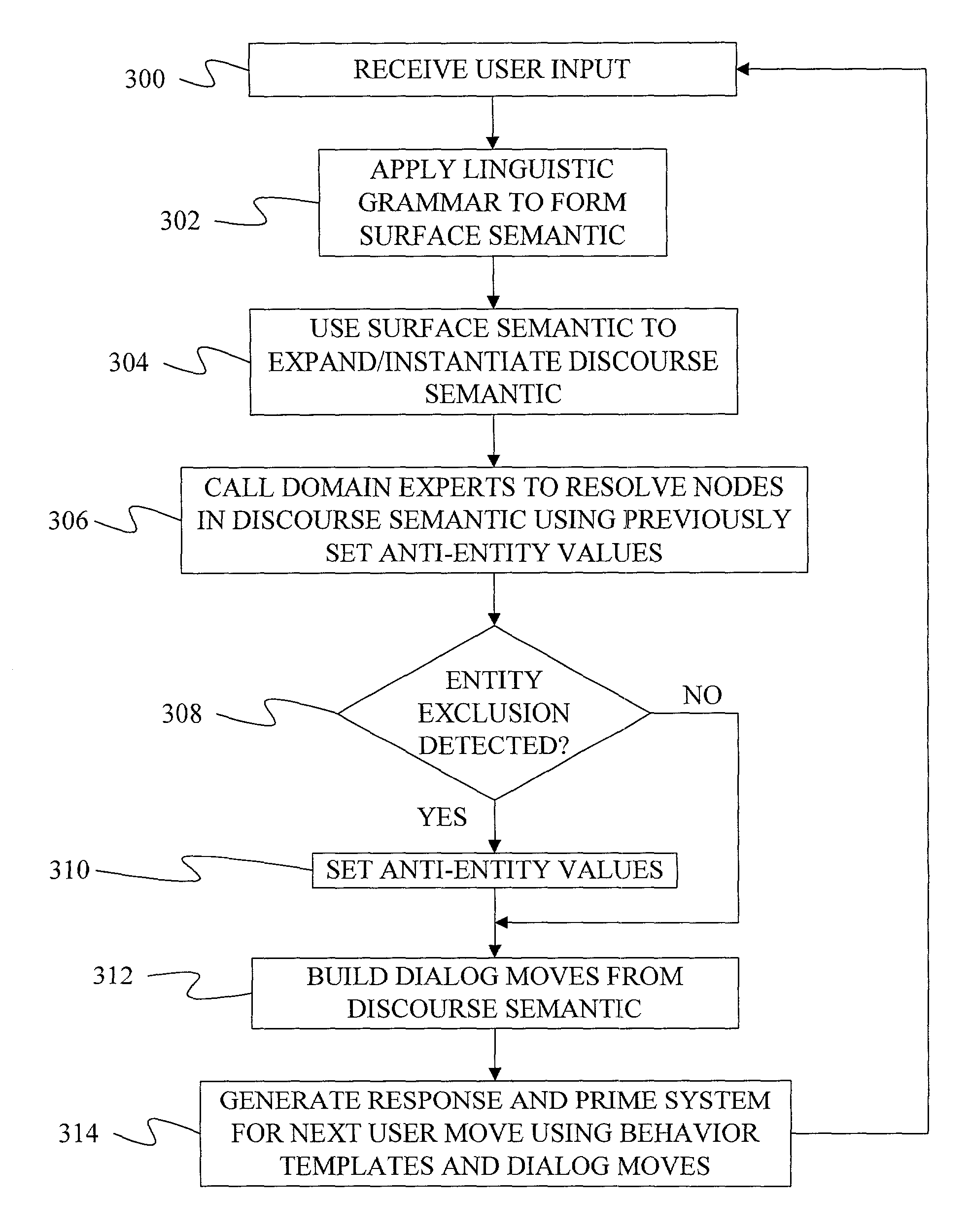
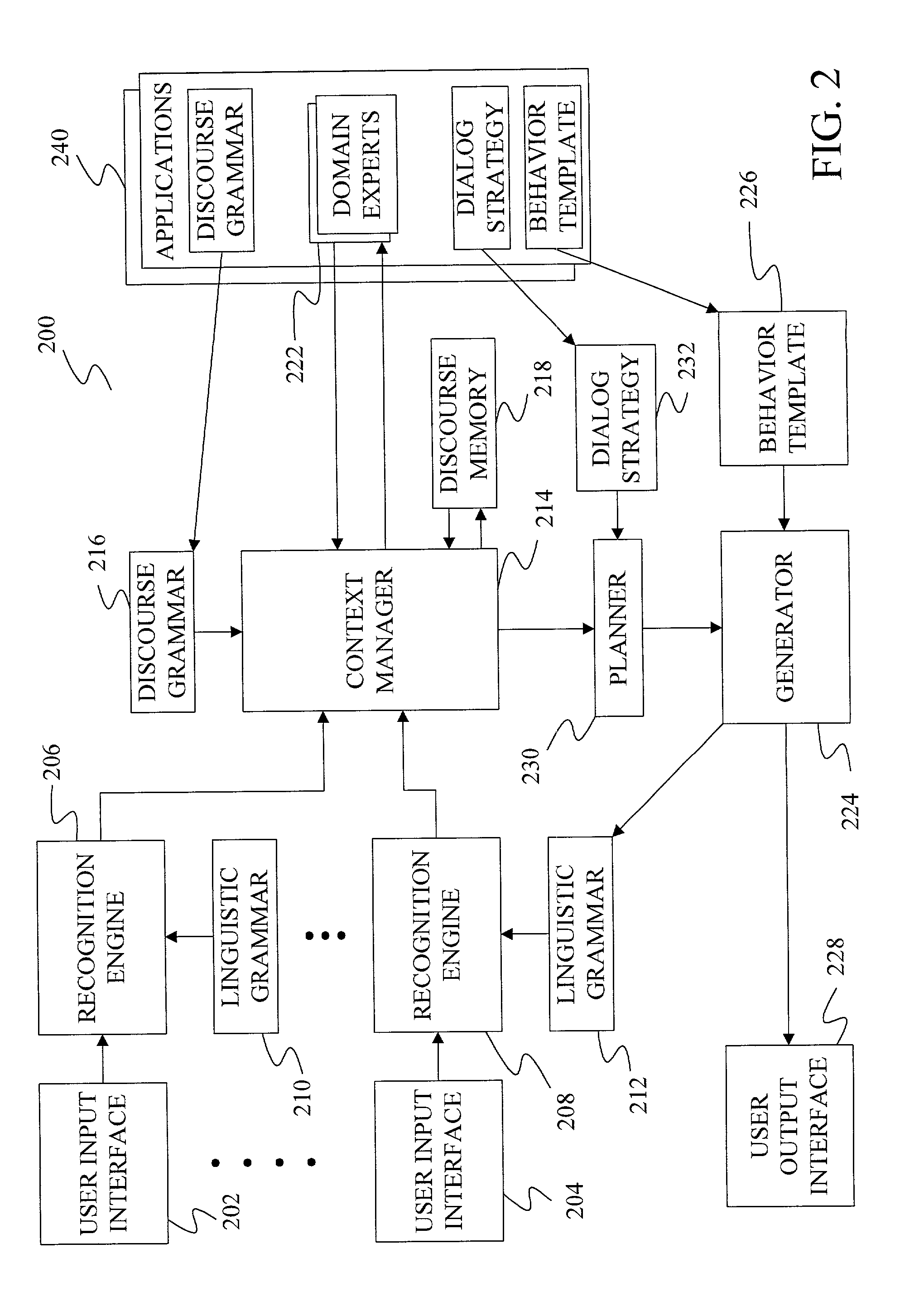
ActiveUS7502730B2Data processing applicationsNatural language data processingNatural language processingUser input
A method and apparatus are provided for resolving user input that crosses different application domains to identify a discourse item such as a command or entity. To resolve the input, a discourse item definition is selected based on the user input. The discourse item definition is associated with a first application and comprises at least one defining entity that is to be used to identify a discourse item. An entity definition associated with a second application is selected based on the user input, wherein the entity defined by the definition can fulfill the role of the defining entity in the discourse item definition. An entity is then identified using the entity definition and the user input. The discourse item is identified based on the identified entity, the discourse item definition and the user input.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
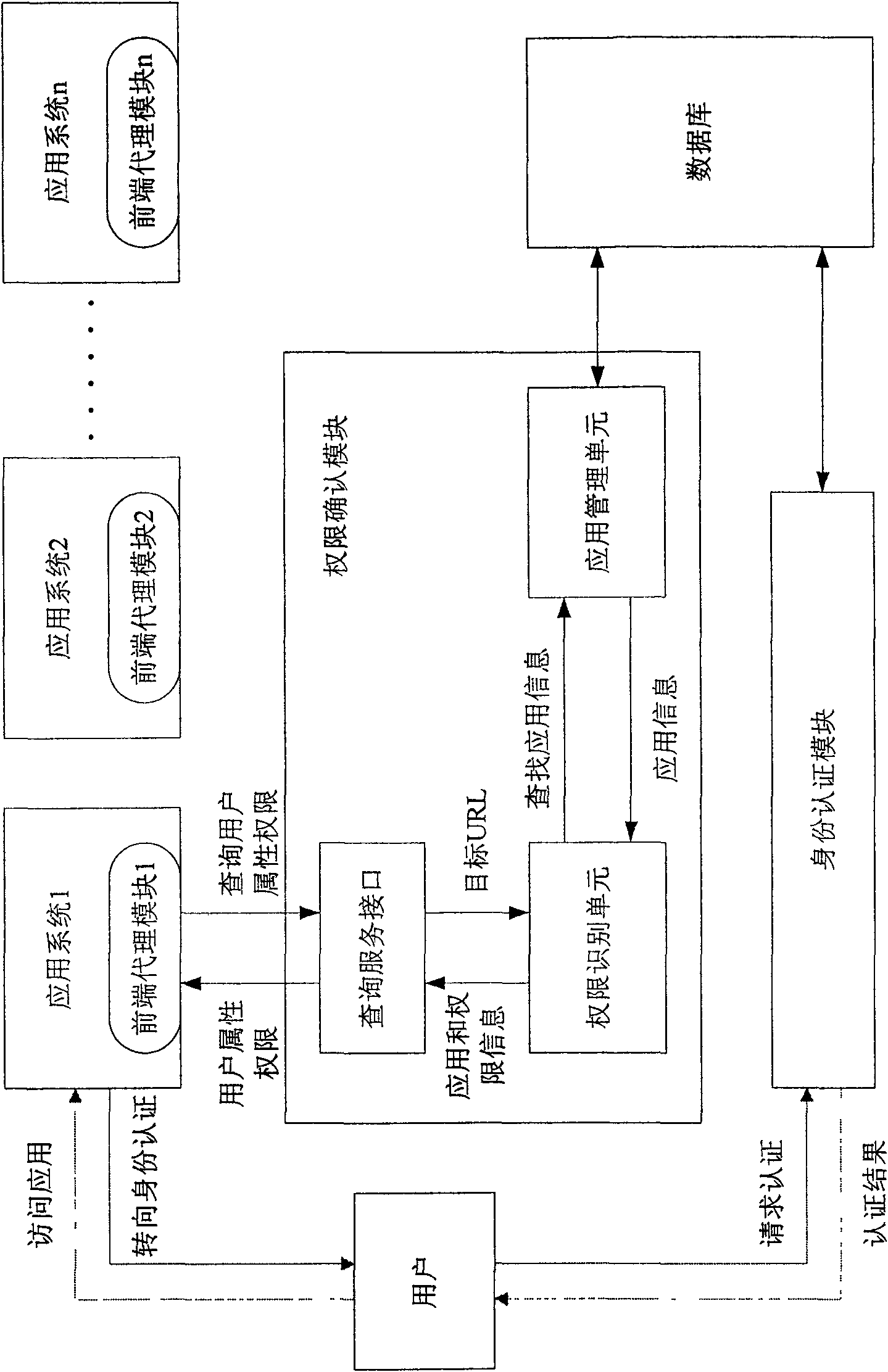
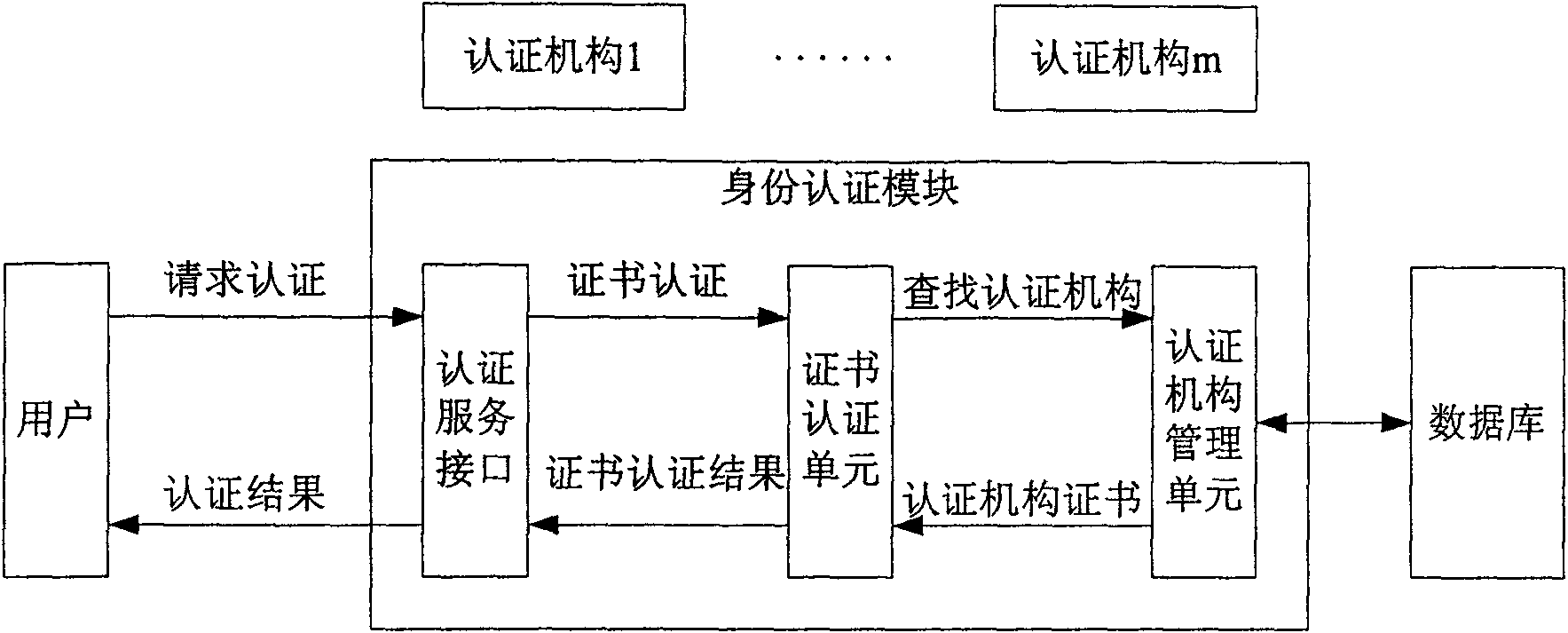
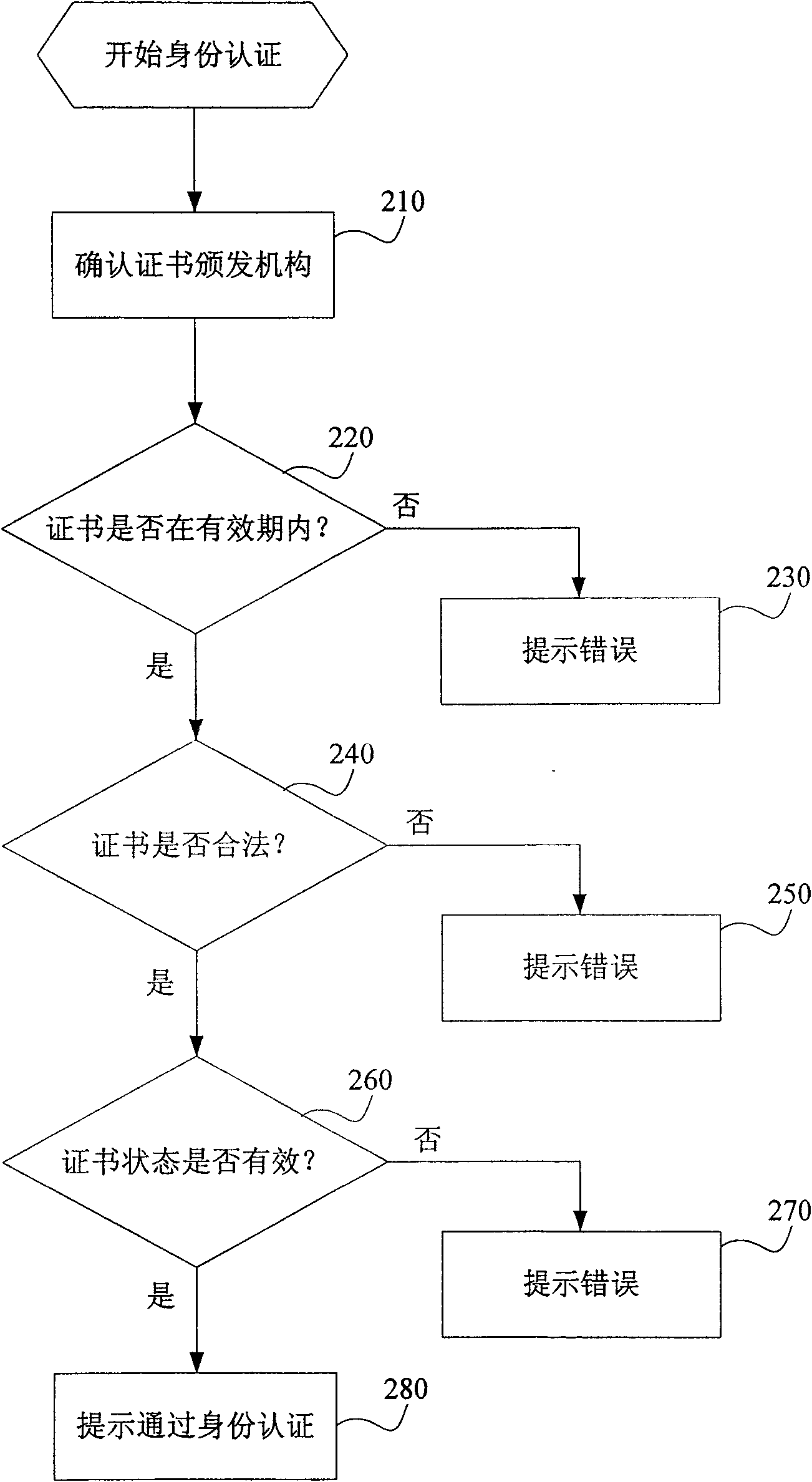
Cross-domain rights management system and method
InactiveCN101645900AImplement rights managementEnsure safetyUser identity/authority verificationRights managementData transmission
The invention discloses a cross-domain rights management system, comprising a front-end acting module, an identity authentication module, a rights confirmation module and a database; the front-end acting module is used for constructing data transmission channels between users and application systems, between application systems and the identity authentication module, and between the application systems and the rights confirmation module; the identity authentication module supports identity certificates awarded by multiple certification authorities to carry out identity authentication on usersaccessing in the application systems; the rights confirmation module is oriented to all the application systems of the whole cross-domain rights management system and is used for confirming the accessrights of users to the application systems and transmitting the confirmed access rights to the front-end acting module; the database is used for storing data related to users, multiple certificationauthorities and multiple application systems. In addition, the invention also discloses a cross-domain rights management method. The system and the method provided by the invention can realize rightsmanagement of cross trust domain and application domain, enables application systems therein to have enough adaptability and expansibility, and improves access efficiency for users simultaneously.
Owner:国家信息中心
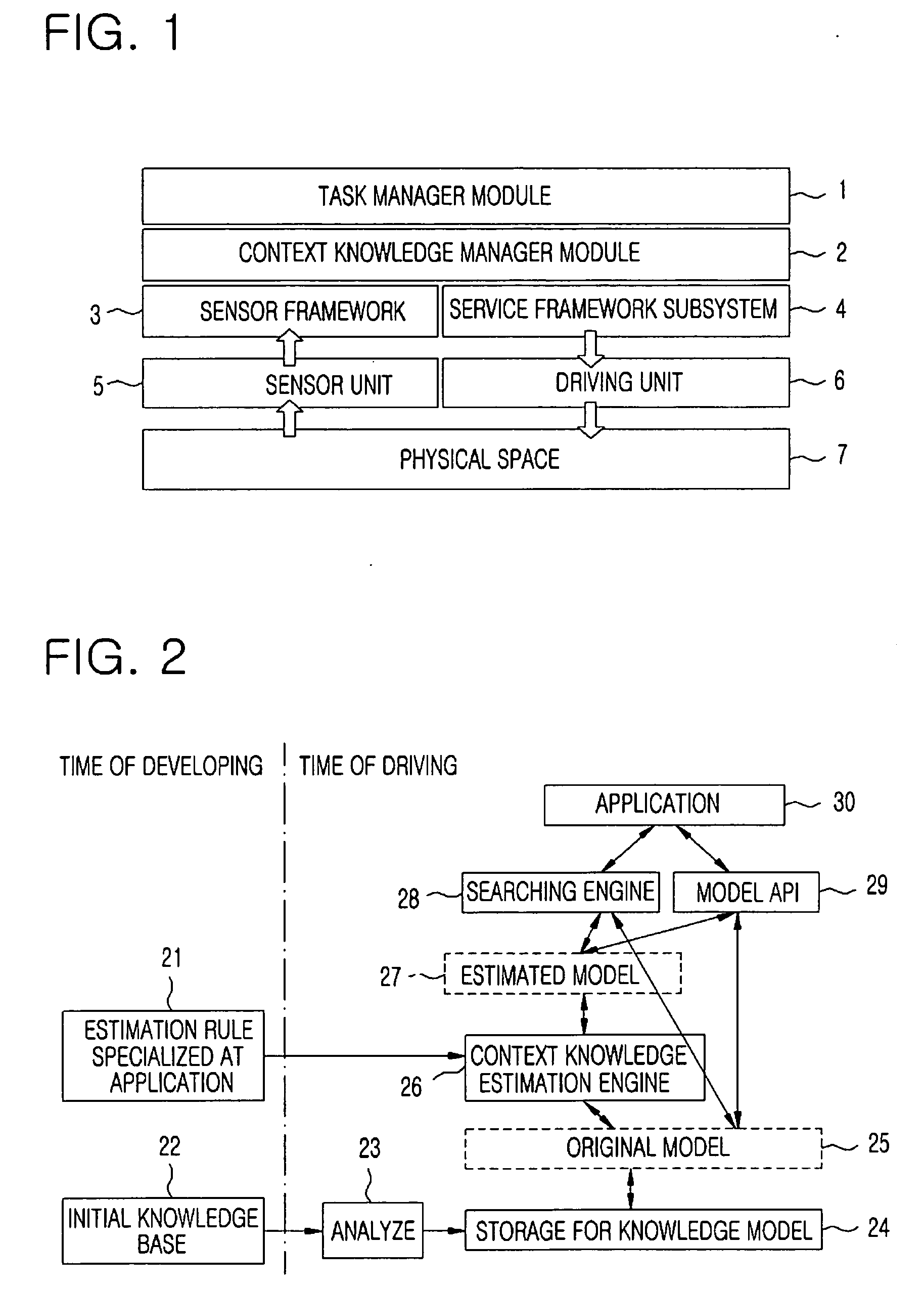
Context knowledge modeling method for sharing and reusing context knowledge in context-aware system
InactiveUS20070038438A1Easy to shareEasy to reuseDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsKnowledge applicationPerceptual system
A context knowledge modeling method is provided. The context knowledge modeling method includes the steps of: a) defining a context knowledge space as a two-dimensional space based on an abstract level and an application domain of knowledge; b) locating a share ontology as a highest level of the abstract level for defining a common ontology concept at a plurality of applications and services performed in various environment and domains; c) locating at least one of domain ontologies as a lower abstract level than the share ontology by taking over the ontology concept defined at the share ontology and defining a class and an attribute specialized at a corresponding domain and a developing application; and d) locating one or more instance bases expressing knowledge about real objects to have a lower abstract level than the domain ontologies.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
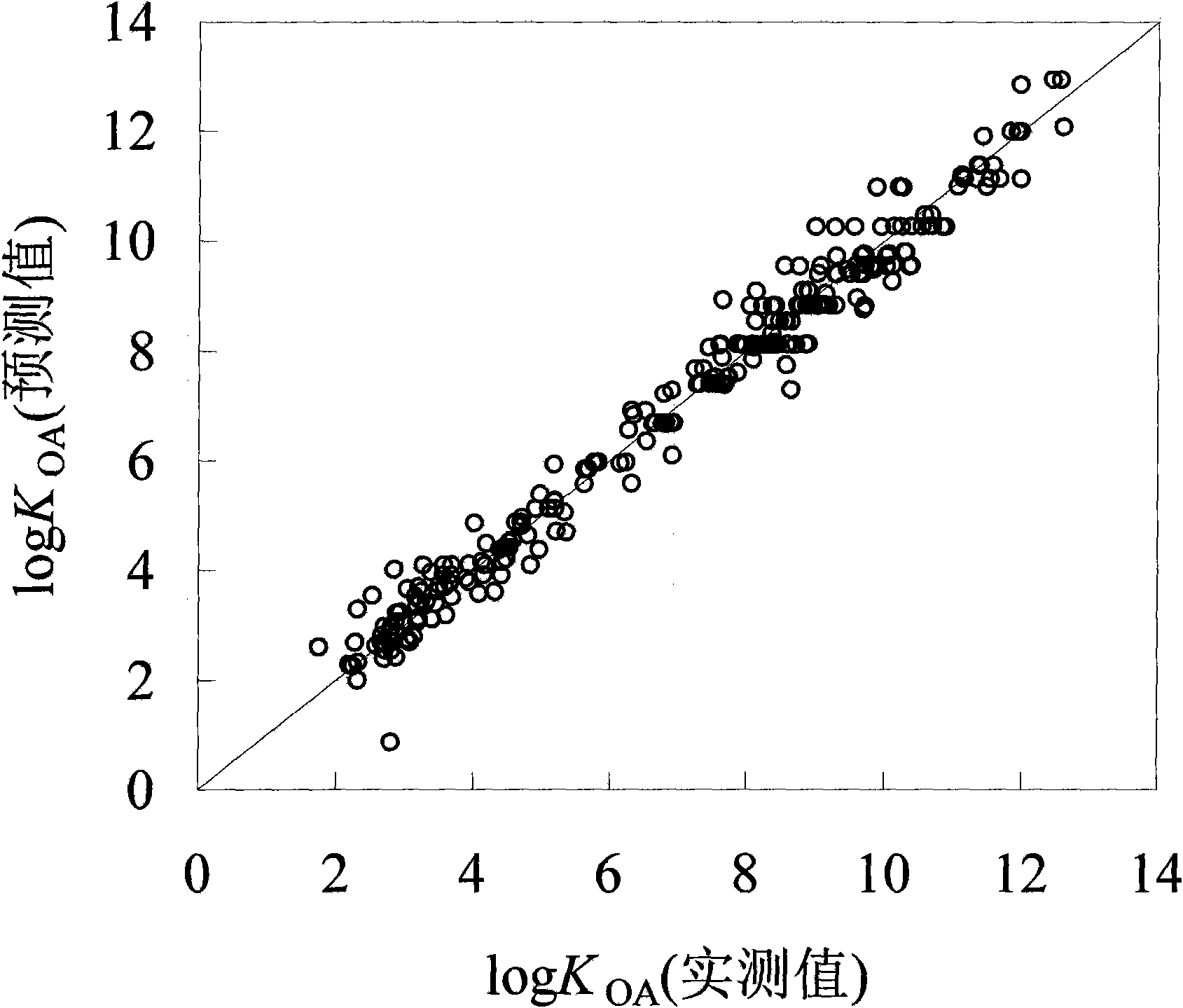
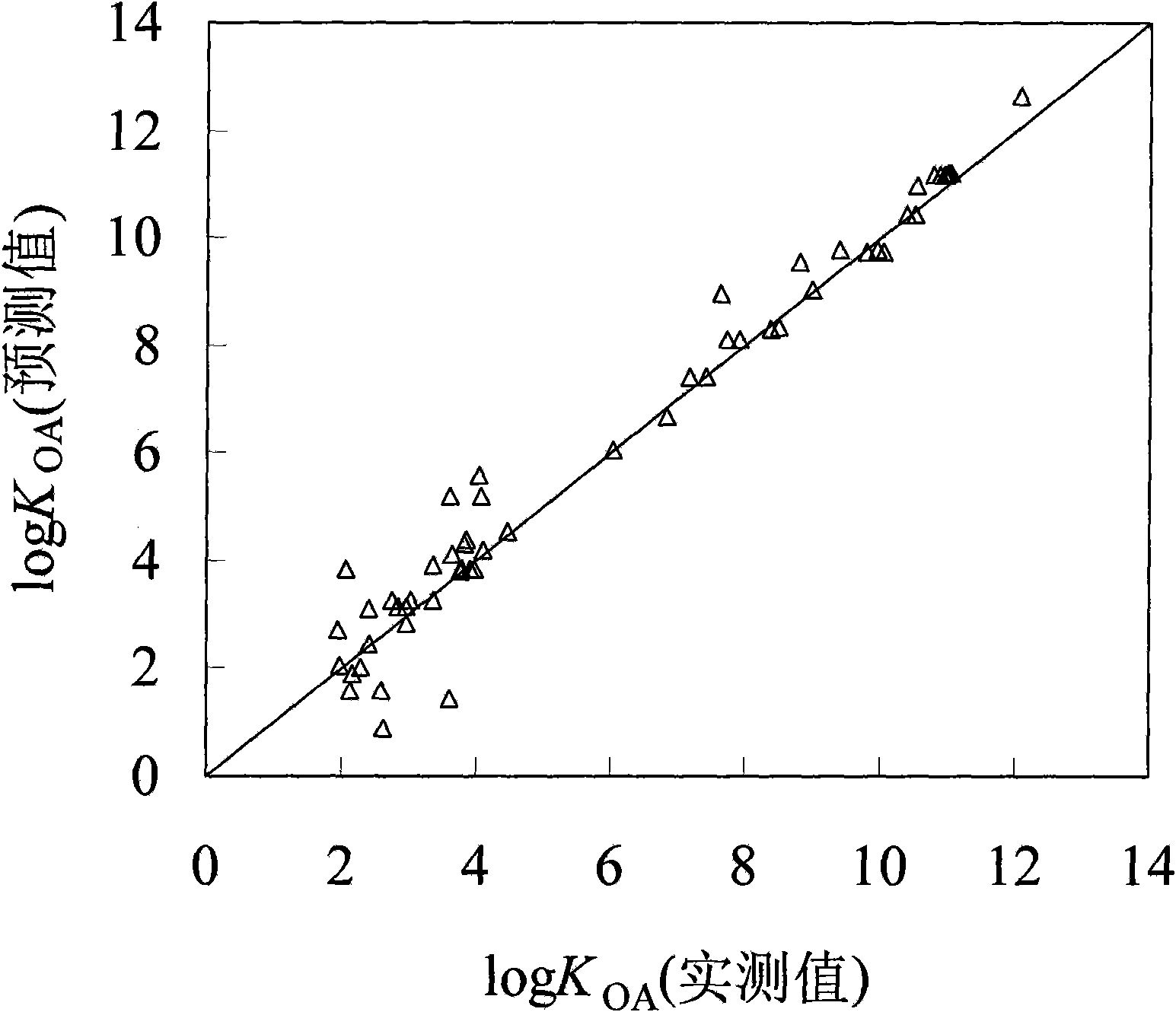
Method for fast predicting organic pollutant n-caprylic alcohol/air distribution coefficient based on molecular structure
InactiveCN101673321AEasy to divideQuick divisionSpecial data processing applicationsPredictive methodsExternal validation
The invention discloses a method for fast predicting organic pollutant n-caprylic alcohol / air distribution coefficient based on molecular structure, belonging to the technical field of quantifying structure / active relationship (QSAR) facing to the environmental risk evaluation. The method is characterized of comprising the steps of: adopting the molecular structure of atomic center fragment characterization compound; and screening the atomic center fragment combination by means of stepwise regression and partial least-squares regression, to build a group contribution model for predicting KOA.The internal authentication and the external authentication improves that the built KOA group contribution model has stability and predicting capability, and a range and distance method and a probability density method express the application domain of the group contribution model, thereby defining the application range of the model and guaranteeing the predict accuracy. The method has the effectsand benefits of being capable of fast predicting the KOA of the high flux compound, obtaining the KOA with low cost, being helpful for obtaining the high flux KOA data, and having a significant meaning for the environment supervision and the risk evaluation of chemicals.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
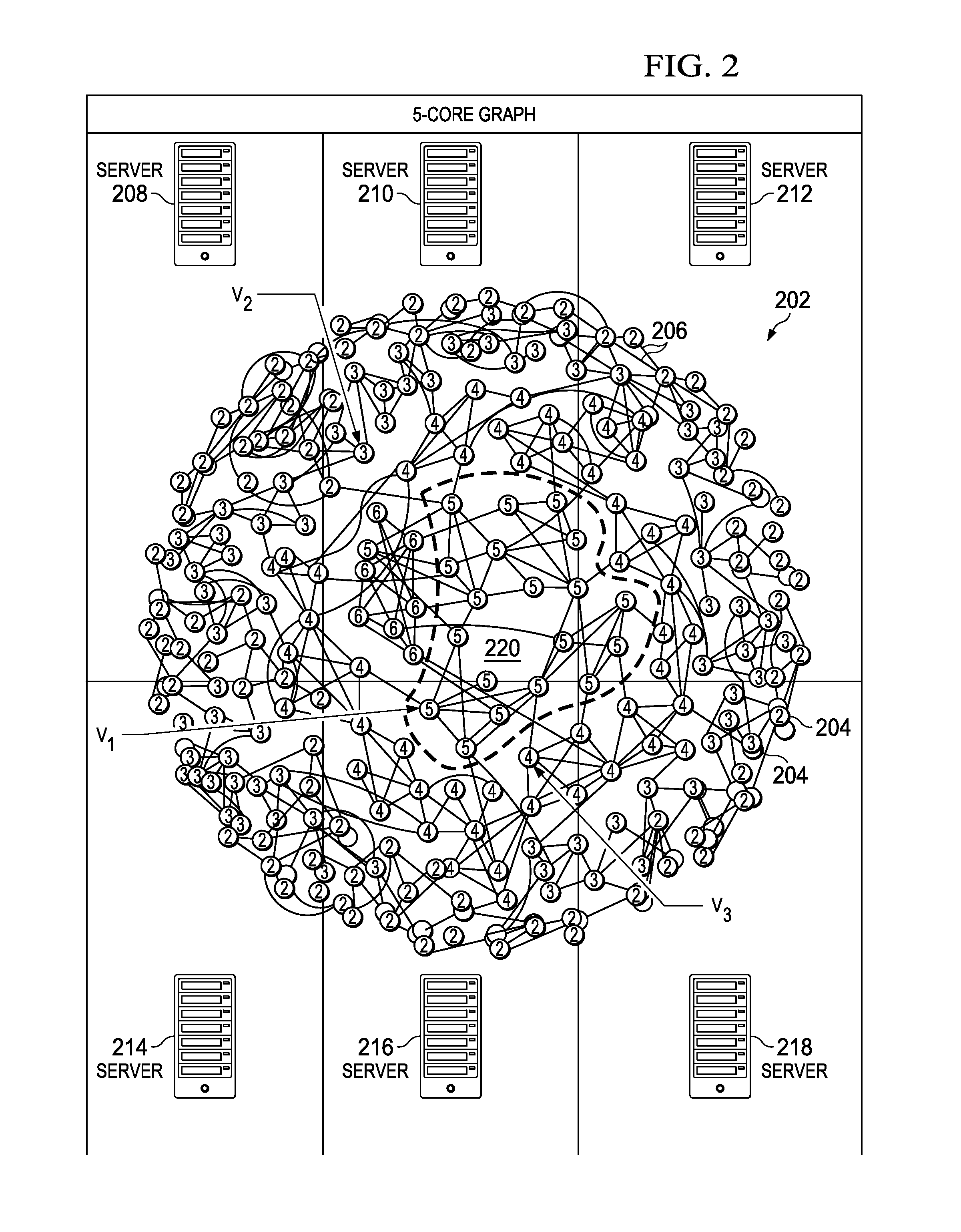
Distributed k-core view materialization and maintenance for graphs
InactiveUS20140354649A1Drawing from basic elementsData processing applicationsGraphicsApplication software
Large graph data in many application domains dynamically changes with vertices and edges inserted and deleted over time. The problem of identifying and maintaining densely connected regions in the graph thus becomes a challenge. Embodiments of the invention describe a method using a k-core measure as a metric of dense connectivity over large, partitioned graph data stored in multiple computing servers in a cluster. The method describes steps to identify a k-core subgraph in parallel and to maintain a k-core subgraph when a new edge is inserted or an existing edge is deleted. The embodiments thus enable practitioners to identify and monitor large scale graph data, such as exemplified by multiple topical communities in a social network, in a scalable and efficient manner.
Owner:IBM CORP
Microstructure appearance test method based on infrared white light interference technique
InactiveCN101266139ABreak through the shortcomings of not being able to measure deep trench structuresUsing optical meansLight sourceMicrostructure
The invention relates to the micro appearance test of a micro electro-mechanical MEMS component, concretely a microstructure appearance test method based on a white infrared light interference technology, which solves the problem existing in the prior art that the sidewall appearance of the deep trench structure of the MEMS component is unable to be surveyed, realized by the following steps: 1) the lossless processing of the impediment infrared transmission for the testing sidewall surface is carried out; 2) the infrared source is taken as the survey photo source, the infrared light is adjusted to be the parallel light when passing through a lenses group, is divided into a reference beam and a examination light beam by a dispersion component, the examination light beam transmits the sidewall of the deep trench structure, after reflected by the interface of the sidewall and the lossless processing, is carried on coherent superposition with the reference beam reflected by a reference mirror, forms a interference fringe pattern; 3) the interference fringe pattern is transmitted to the computer after passing through an optical lens, the CCD image sensor, so that the three dimensional appearance chart of the sidewall measured is obtained by analyzing and processing. The invention overcomes the shortcoming existing in the prior art that the deep trench structure surveying is unable to be realized and the application domain is wild.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
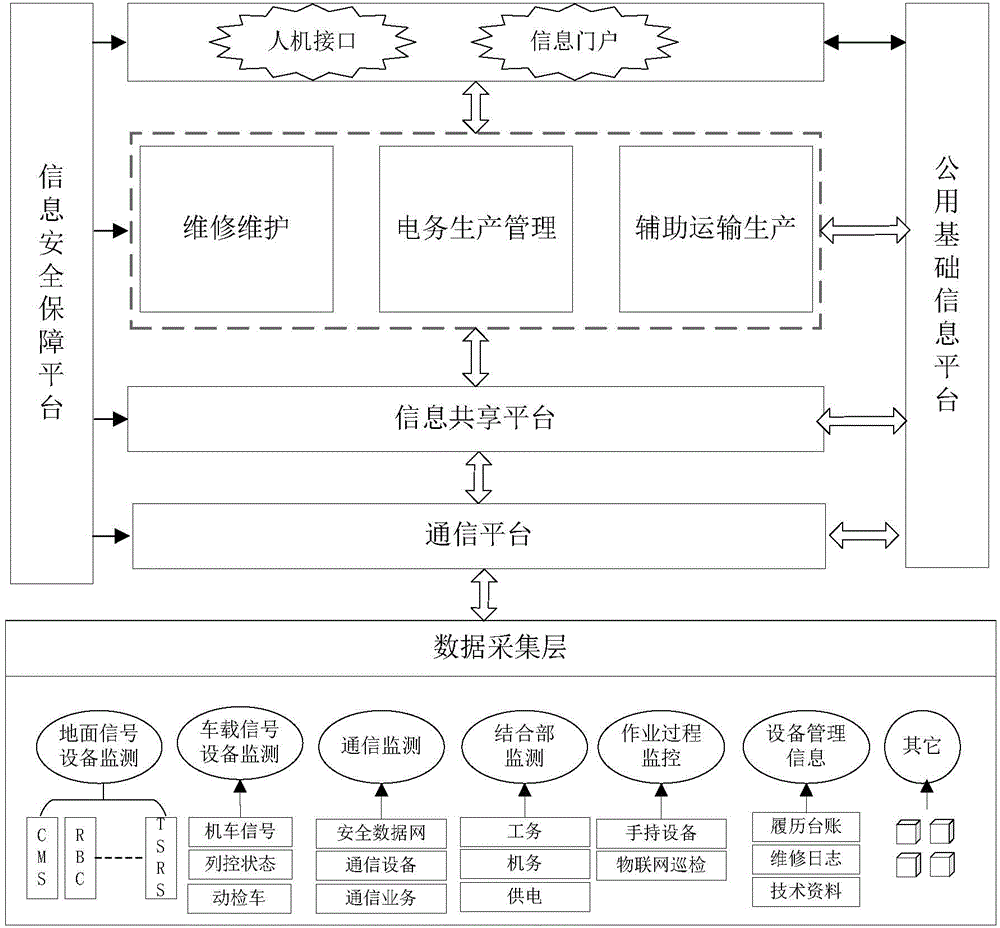
Integrated electricity monitoring and maintaining system
The invention discloses an integrated electricity monitoring and maintaining system, and relates to the field of the monitoring and maintenance of railway electricity. The integrated electricity monitoring and maintaining system sufficiently plays the roles of various monitoring systems on the aspects of the monitoring and the maintenance of railway electricity on the basis of centralized signaling monitoring systems, communication monitoring systems, vehicle-mounted equipment monitoring systems and other monitoring systems, and realizes the real-time monitoring of equipment states, real-time alarm of equipment exception, data intelligence and comprehensive analysis. The system consists of a basic data platform and a business application layer, wherein the part outside a dotted frame is the basic data platform of the integrated electricity monitoring and maintaining system, and the basic data platform provides basic environment for the business application layer; the part in the dotted frame is the business application layer, and is the realization layer of the application domains of the integrated electricity monitoring and maintaining system, and each application domain includes a plurality of application systems and software supports.
Owner:CHINA RAILWAYS CORPORATION +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com