Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
43results about How to "Sufficient throughput" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
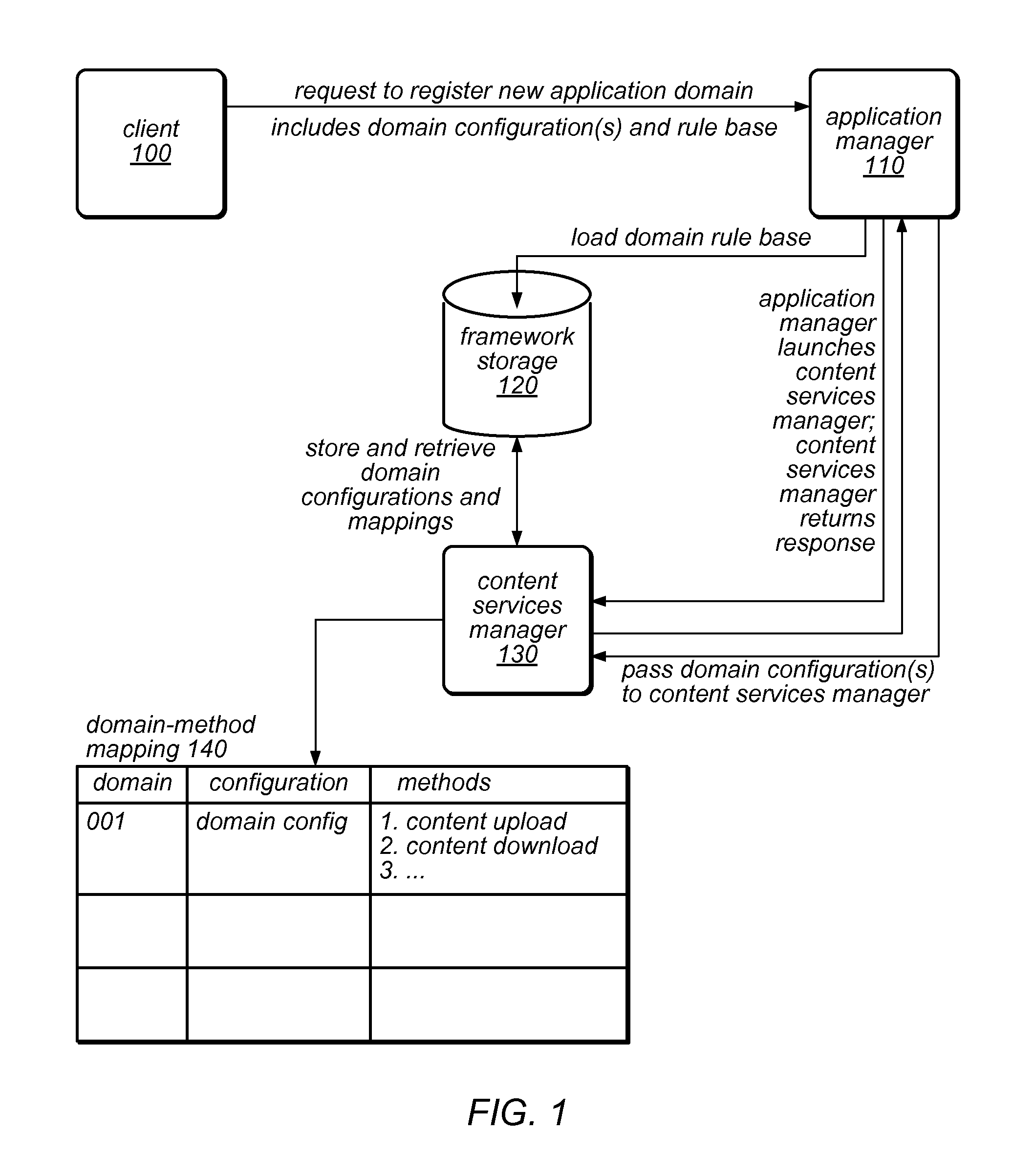
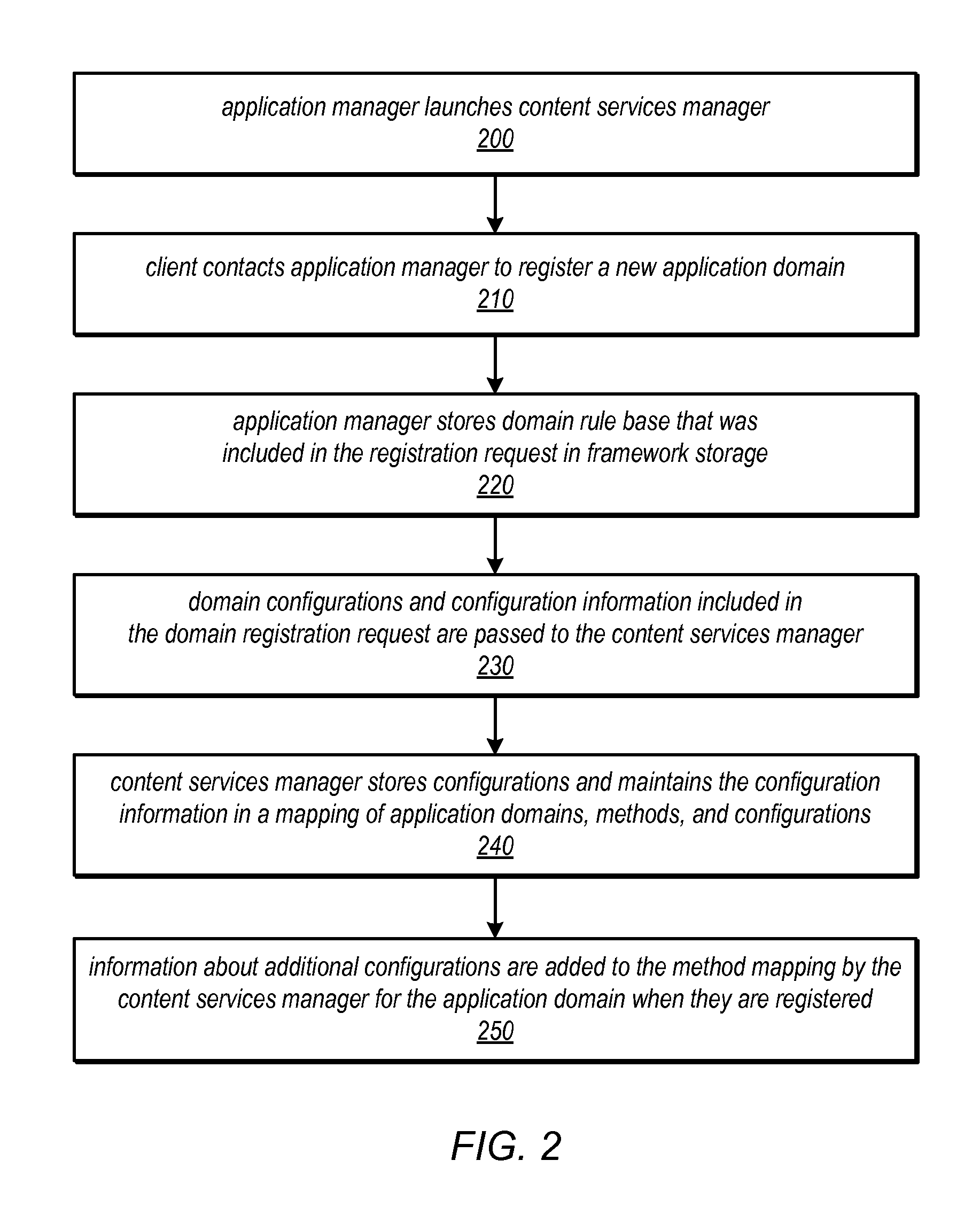
System and Method for Installation and Management of Cloud-Independent Multi-Tenant Applications
ActiveUS20120047239A1Efficient constructionSufficient throughputDigital computer detailsProgram controlApplication softwareCloud storage
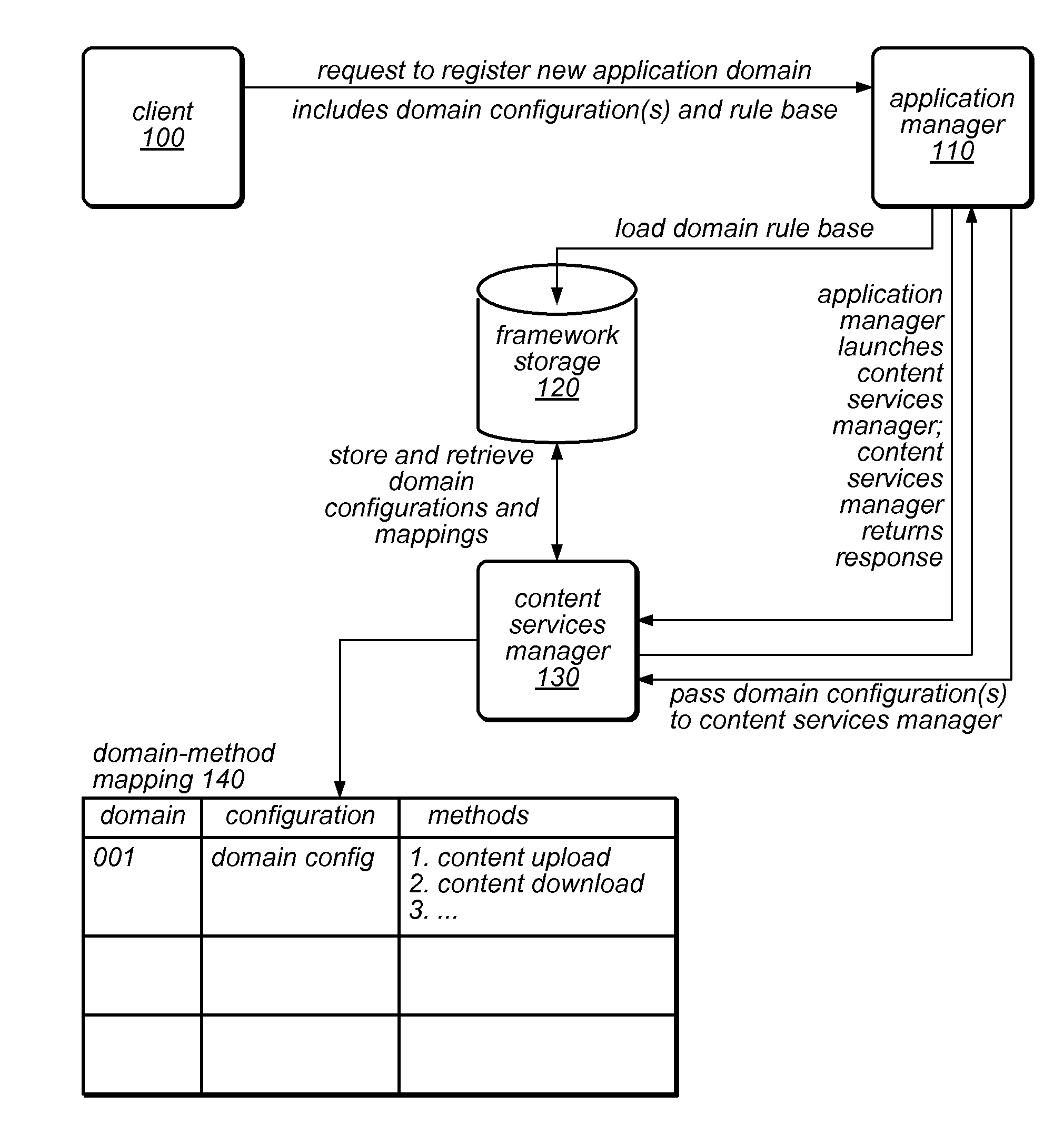
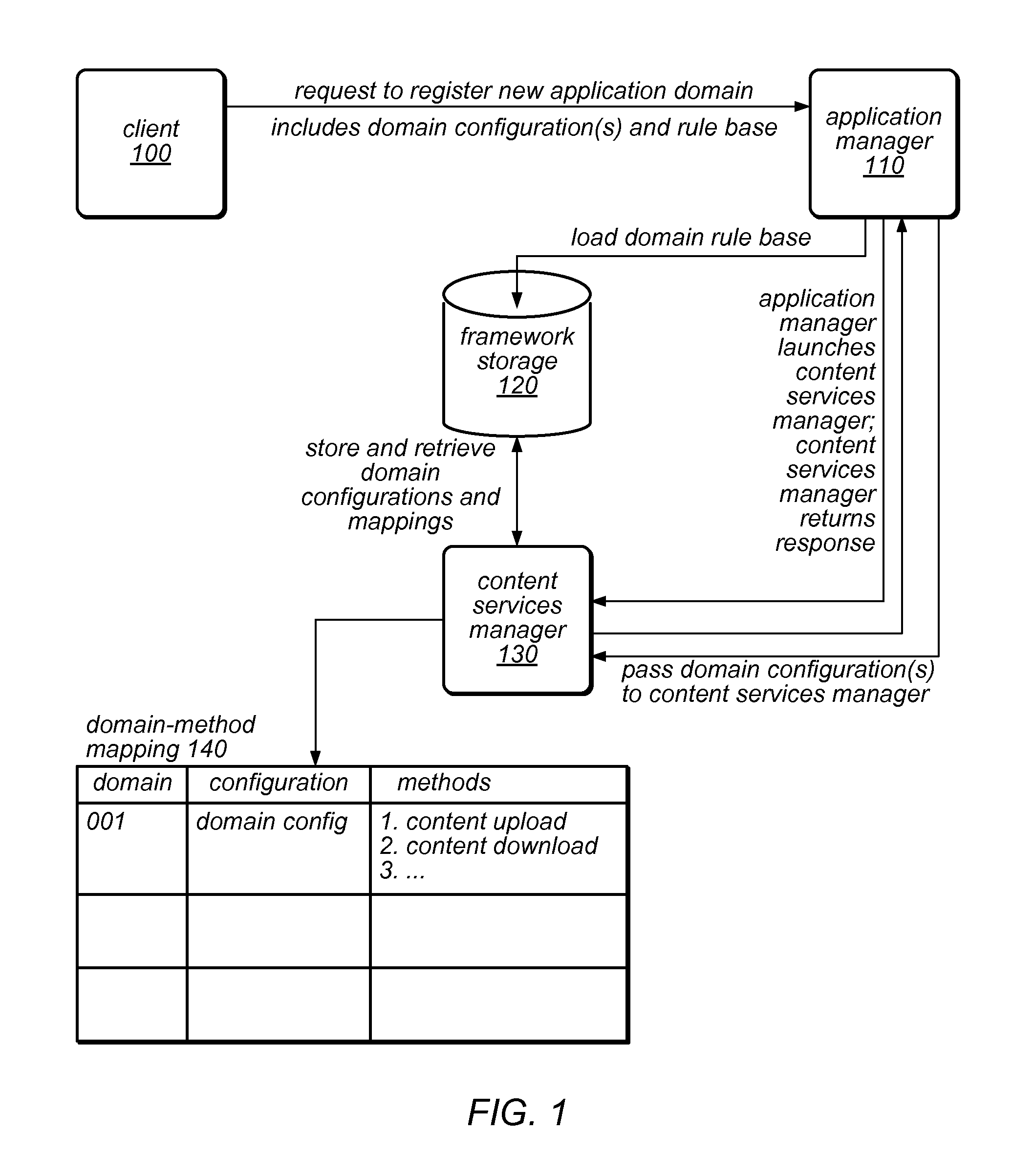
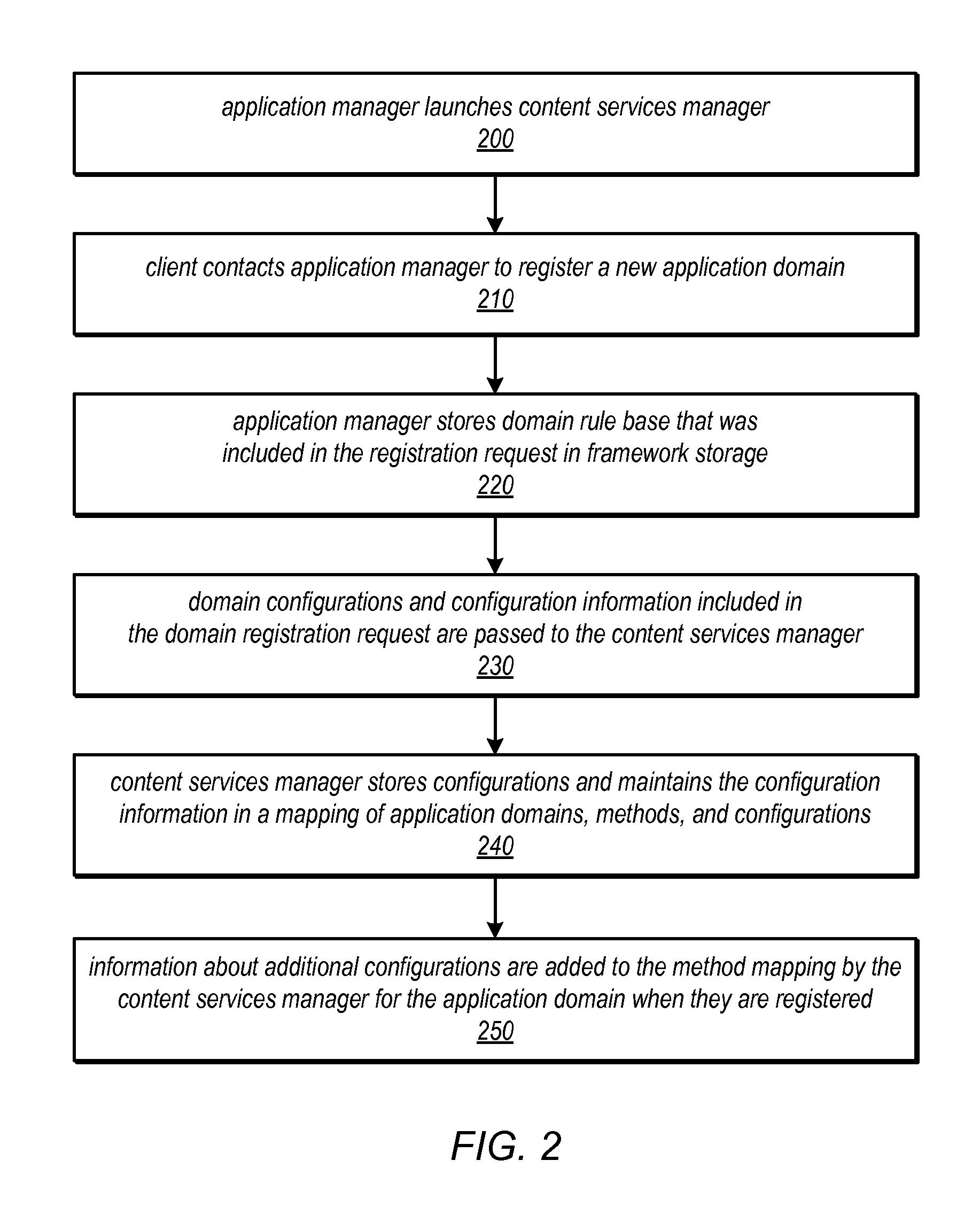
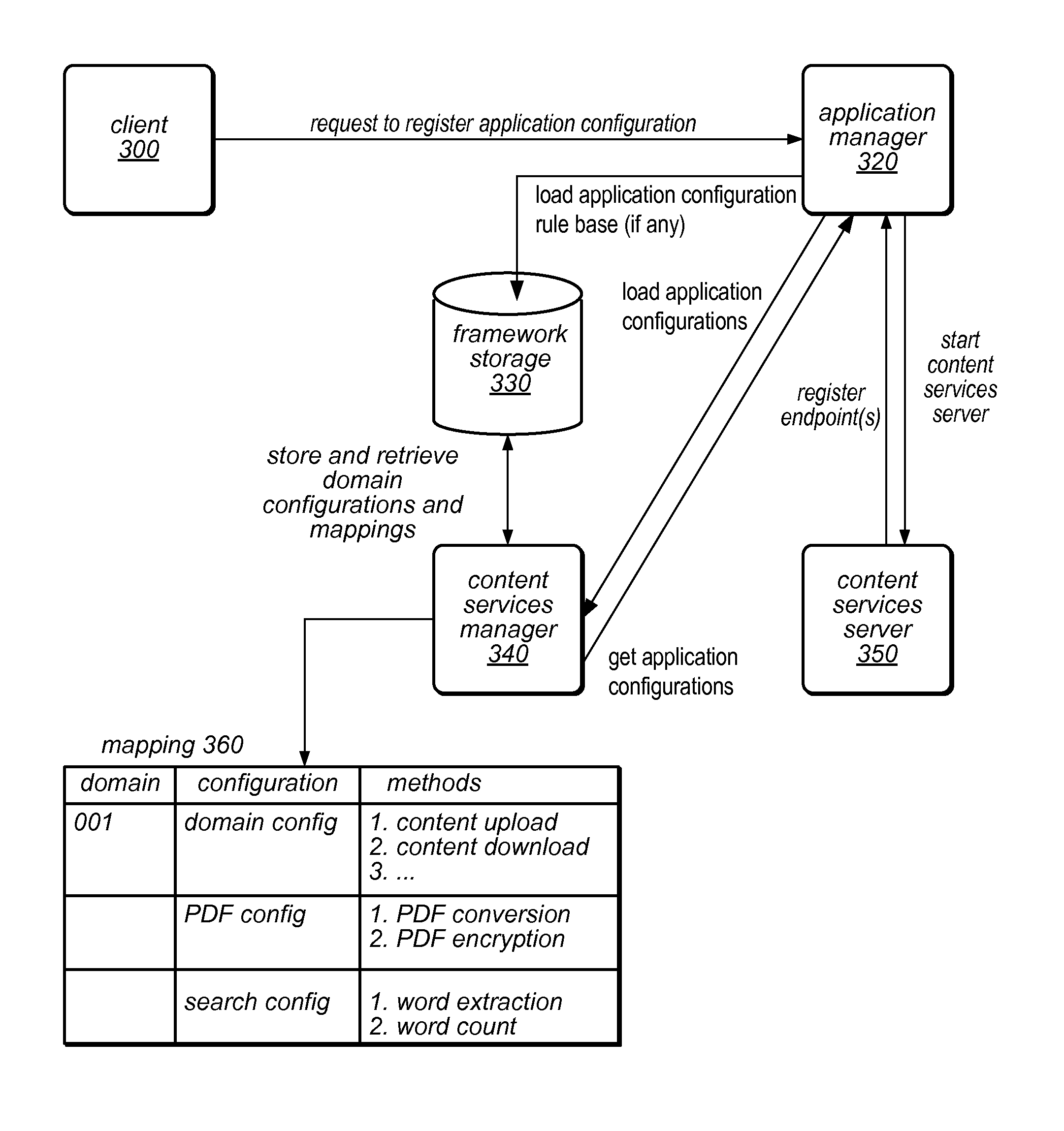
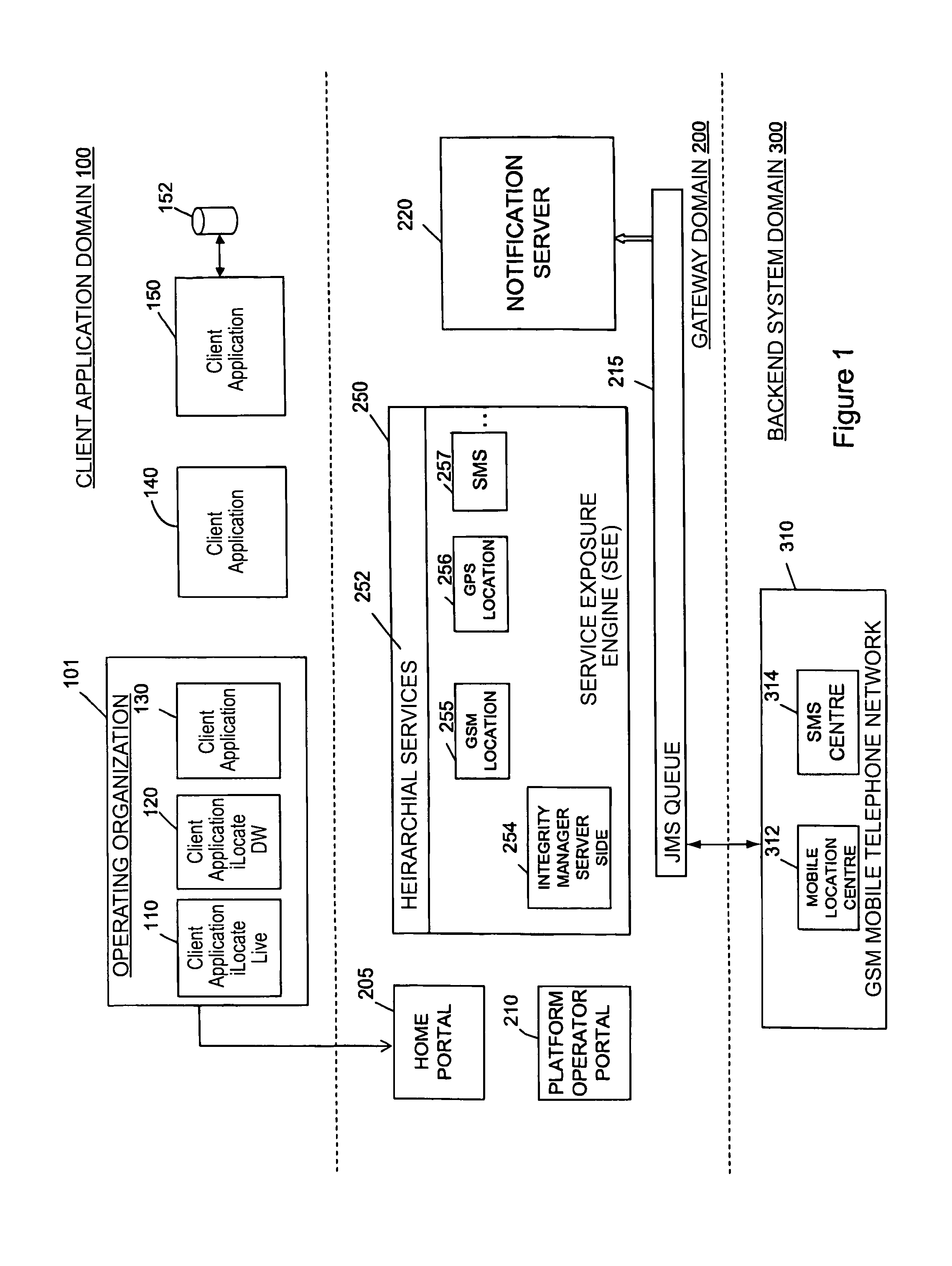
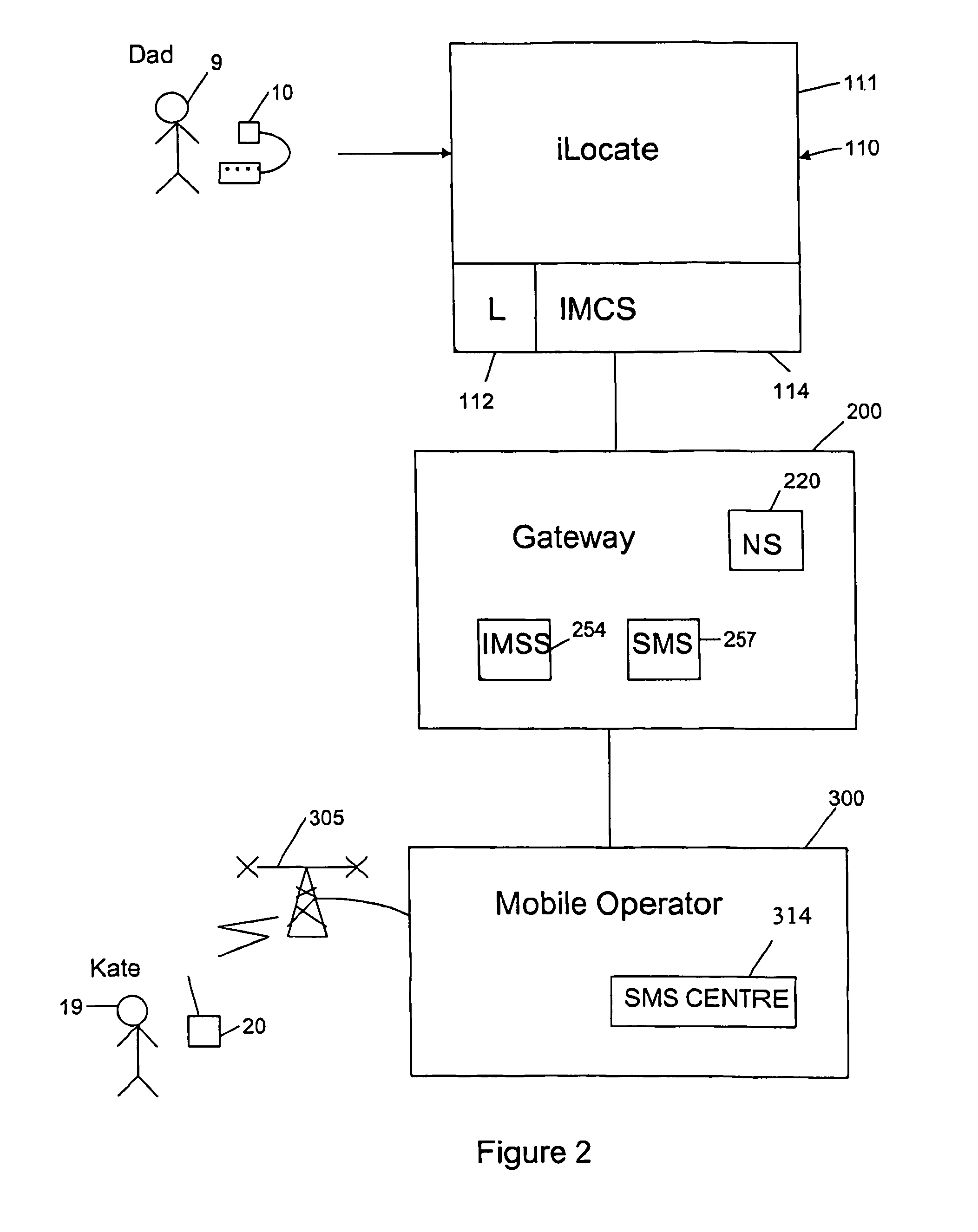
An application framework may include a cloud-independent application manager, a cloud-independent content services manager, and cloud-independent content services servers. The framework may dynamically install and manage scalable, multi-tenant applications in a cloud, and may scale the applications, as needed. The application manager may receive and handle requests to install application domains and configurations thereof, and may receive and respond to requests for information about servers on which installed methods are available. The content services servers may execute installed methods, using underlying resources of the cloud, through a cloud-specific SPI. The content services manager and application manager may work together using shared cloud storage to provide scalable content services at a very large scale. In the context of the framework described herein, an “application” may be defined by methods bundled into configurations, and by various cost-based and / or performance-based rules that specify how server instances providing those methods are to be managed.
Owner:ADOBE SYST INC
System and method for installation and management of cloud-independent multi-tenant applications
ActiveUS8812627B2Efficient constructionSufficient throughputResource allocationDigital computer detailsCloud storageApplication framework
An application framework may include a cloud-independent application manager, a cloud-independent content services manager, and cloud-independent content services servers. The framework may dynamically install and manage scalable, multi-tenant applications in a cloud, and may scale the applications, as needed. The application manager may receive and handle requests to install application domains and configurations thereof, and may receive and respond to requests for information about servers on which installed methods are available. The content services servers may execute installed methods, using underlying resources of the cloud, through a cloud-specific SPI. The content services manager and application manager may work together using shared cloud storage to provide scalable content services at a very large scale. In the context of the framework described herein, an “application” may be defined by methods bundled into configurations, and by various cost-based and / or performance-based rules that specify how server instances providing those methods are to be managed.
Owner:ADOBE SYST INC
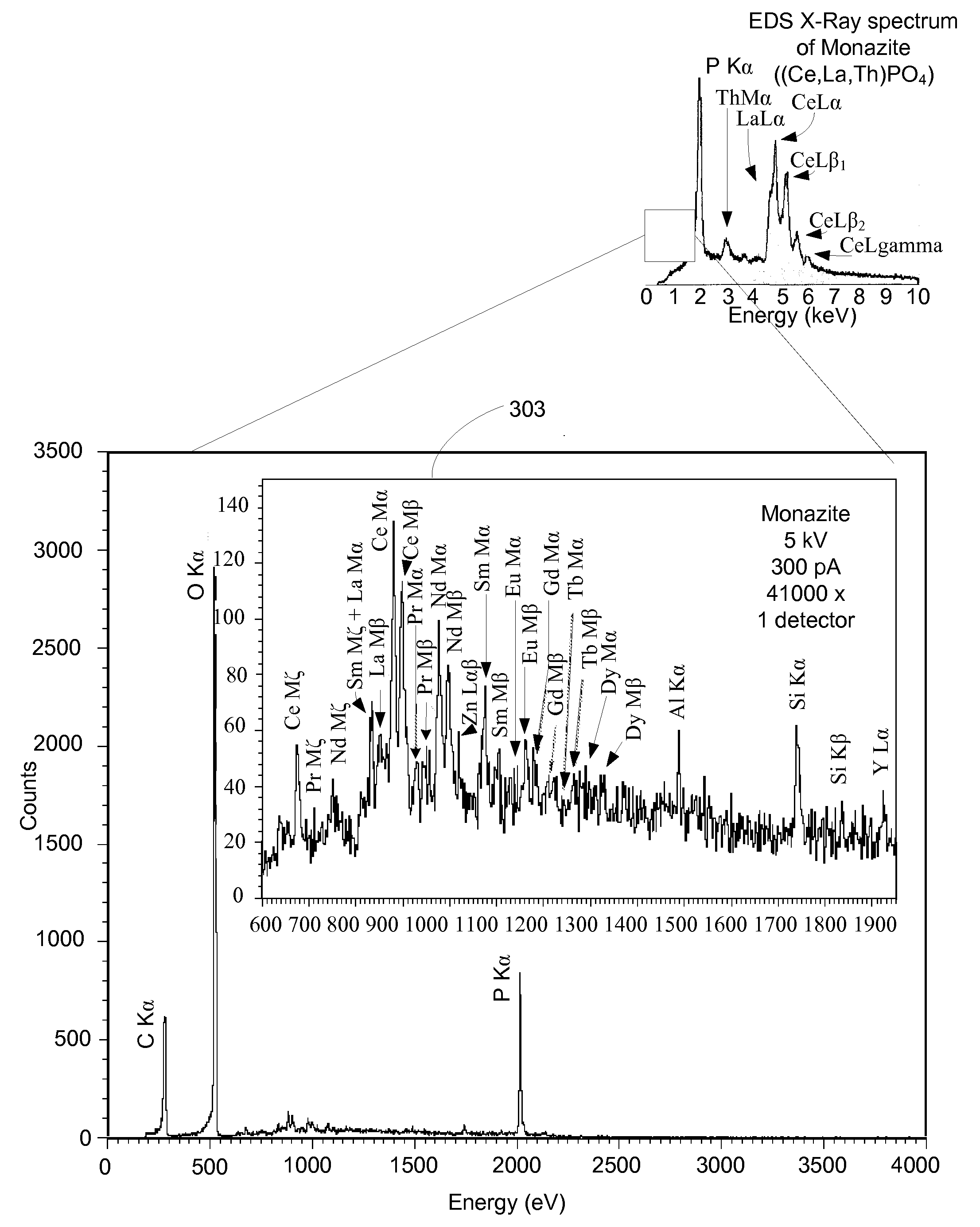
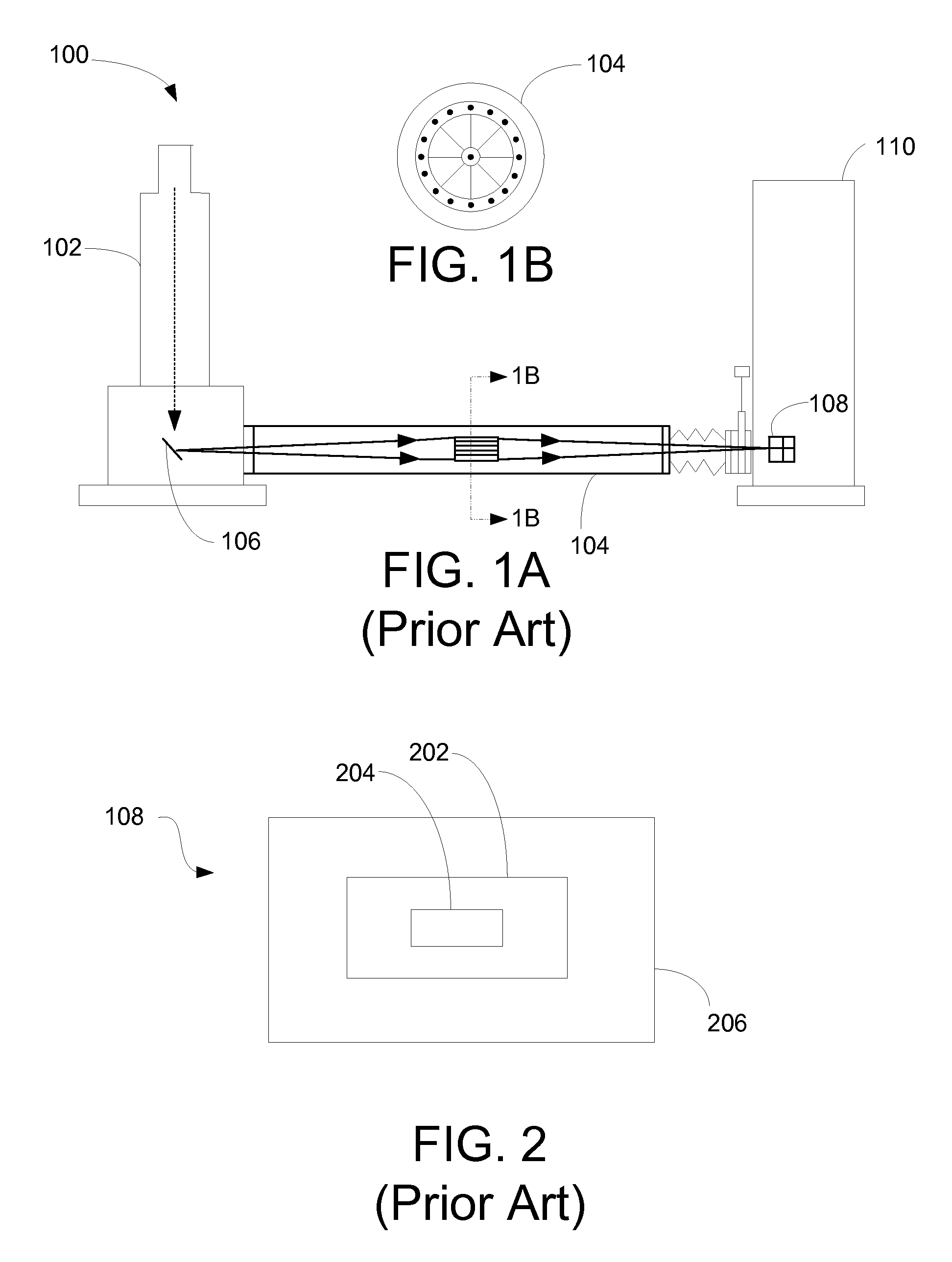
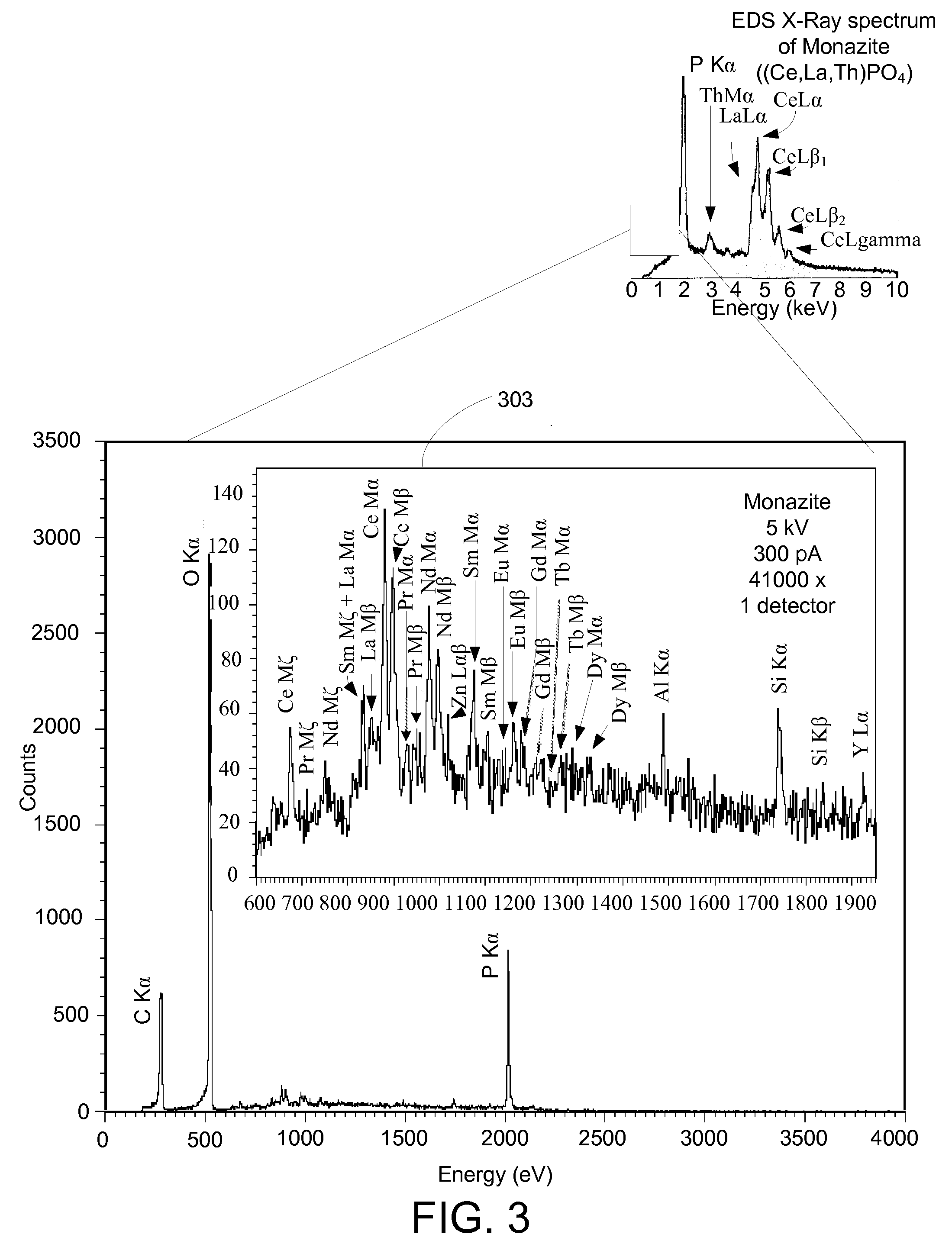
Microcalorimetry for x-ray spectroscopy
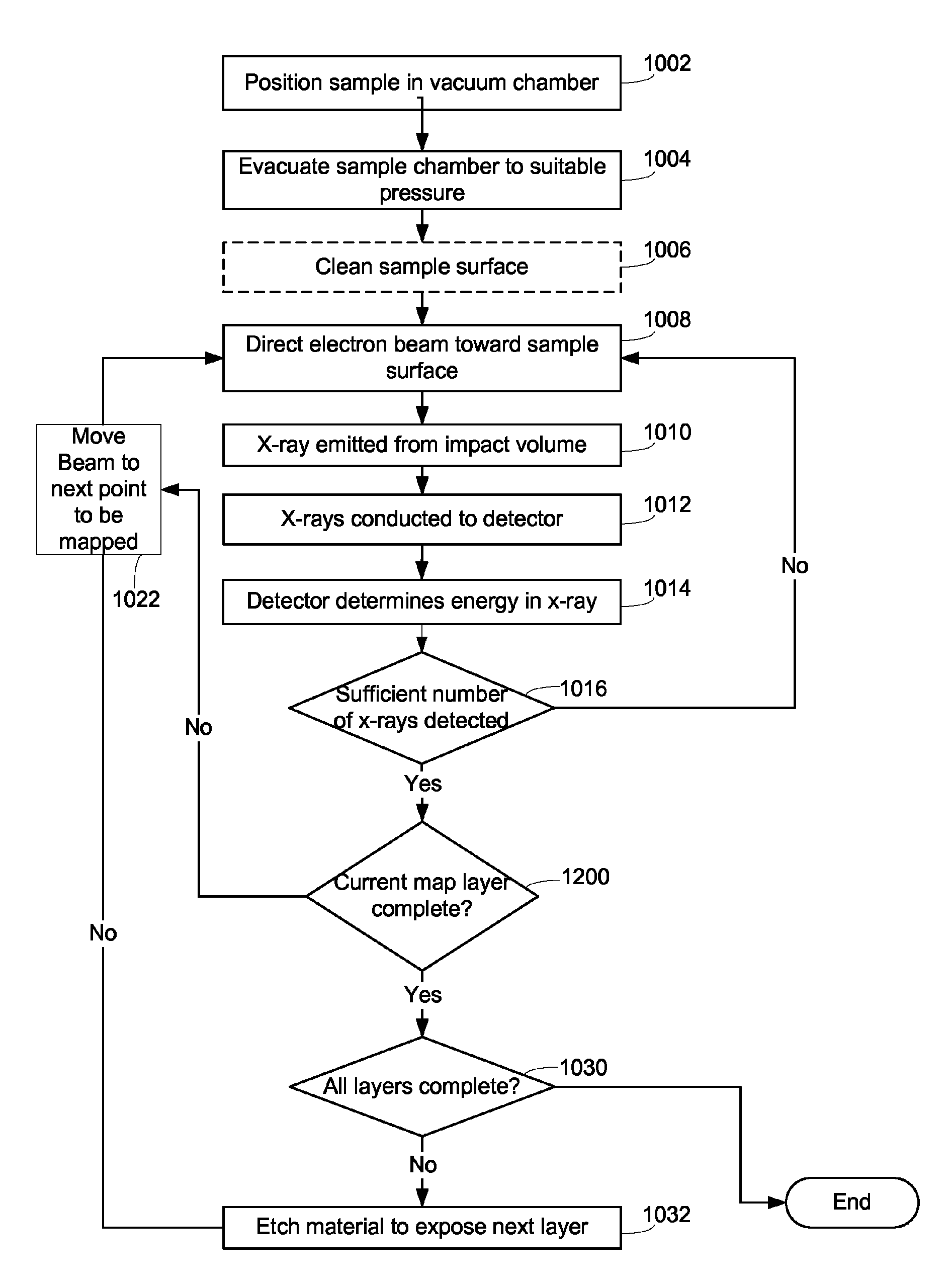
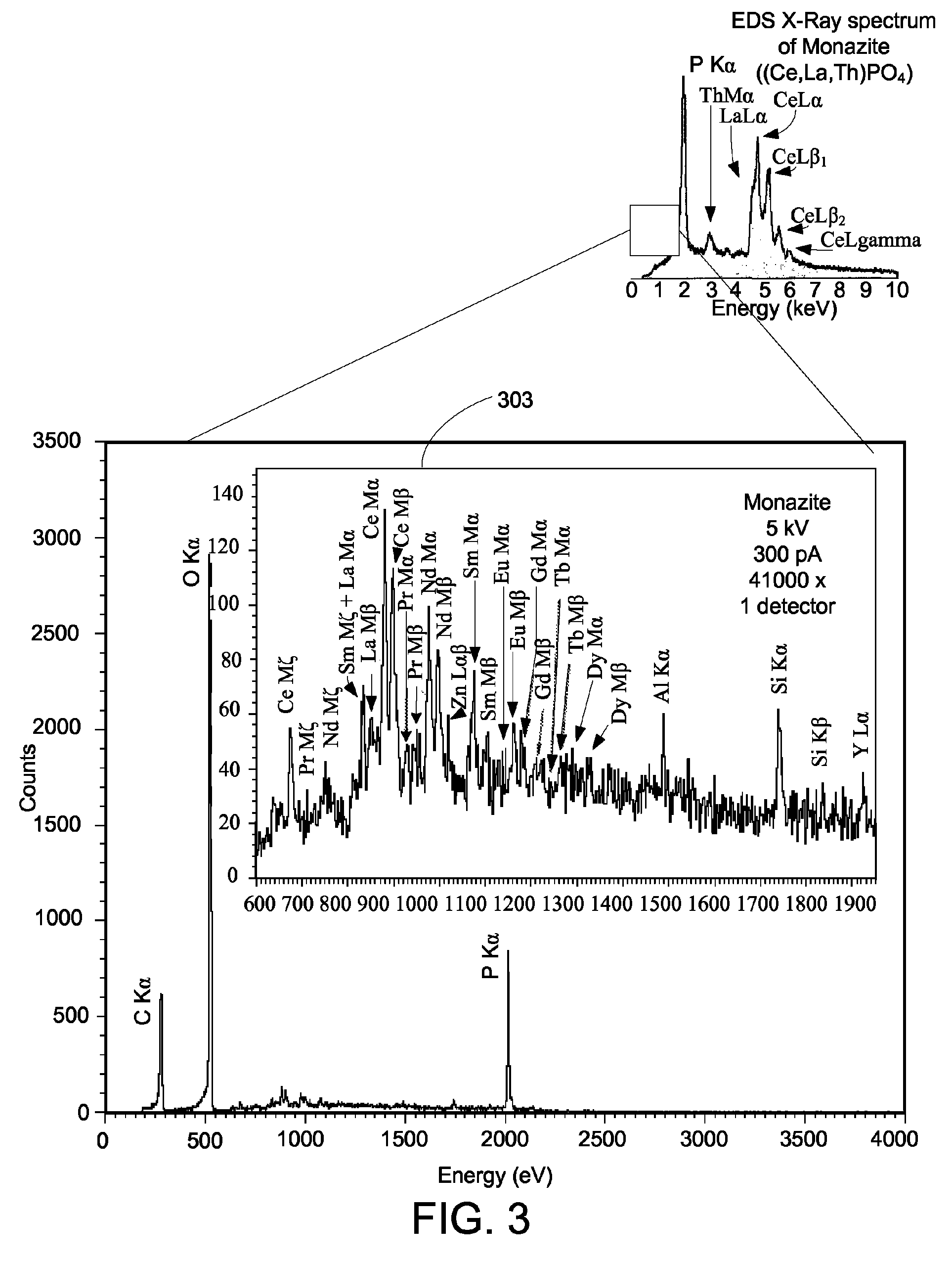
ActiveUS20110064191A1High resolution mappingSolve the lack of resolutionThermometer detailsX-ray spectral distribution measurementBeam energySpectrometer
An improved microcalorimeter-type energy dispersive x-ray spectrometer provides sufficient energy resolution and throughput for practical high spatial resolution x-ray mapping of a sample at low electron beam energies. When used with a dual beam system that provides the capability to etch a layer from the sample, the system can be used for three-dimensional x-ray mapping. A preferred system uses an x-ray optic having a wide-angle opening to increase the fraction of x-rays leaving the sample that impinge on the detector and multiple detectors to avoid pulse pile up.
Owner:FEI CO
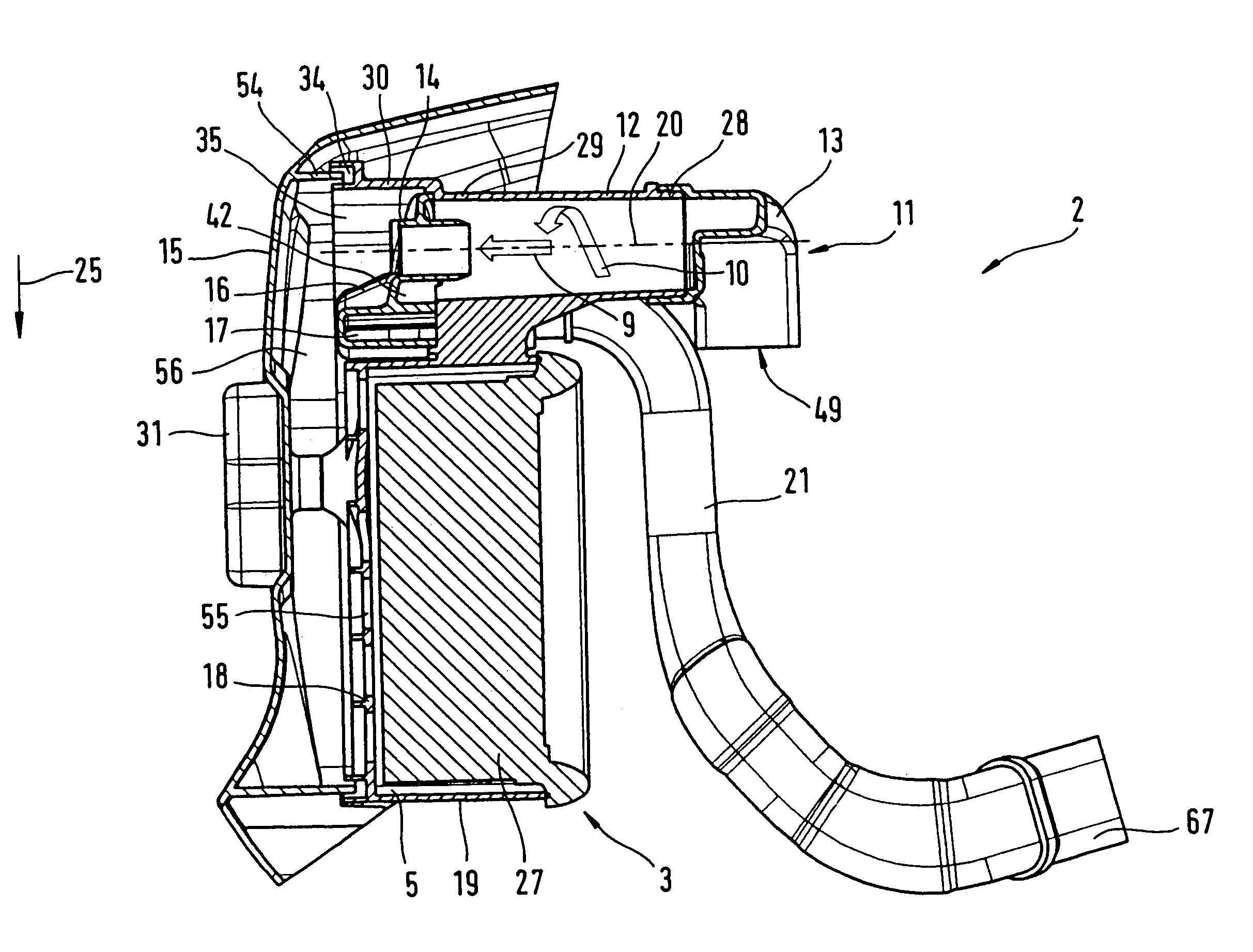
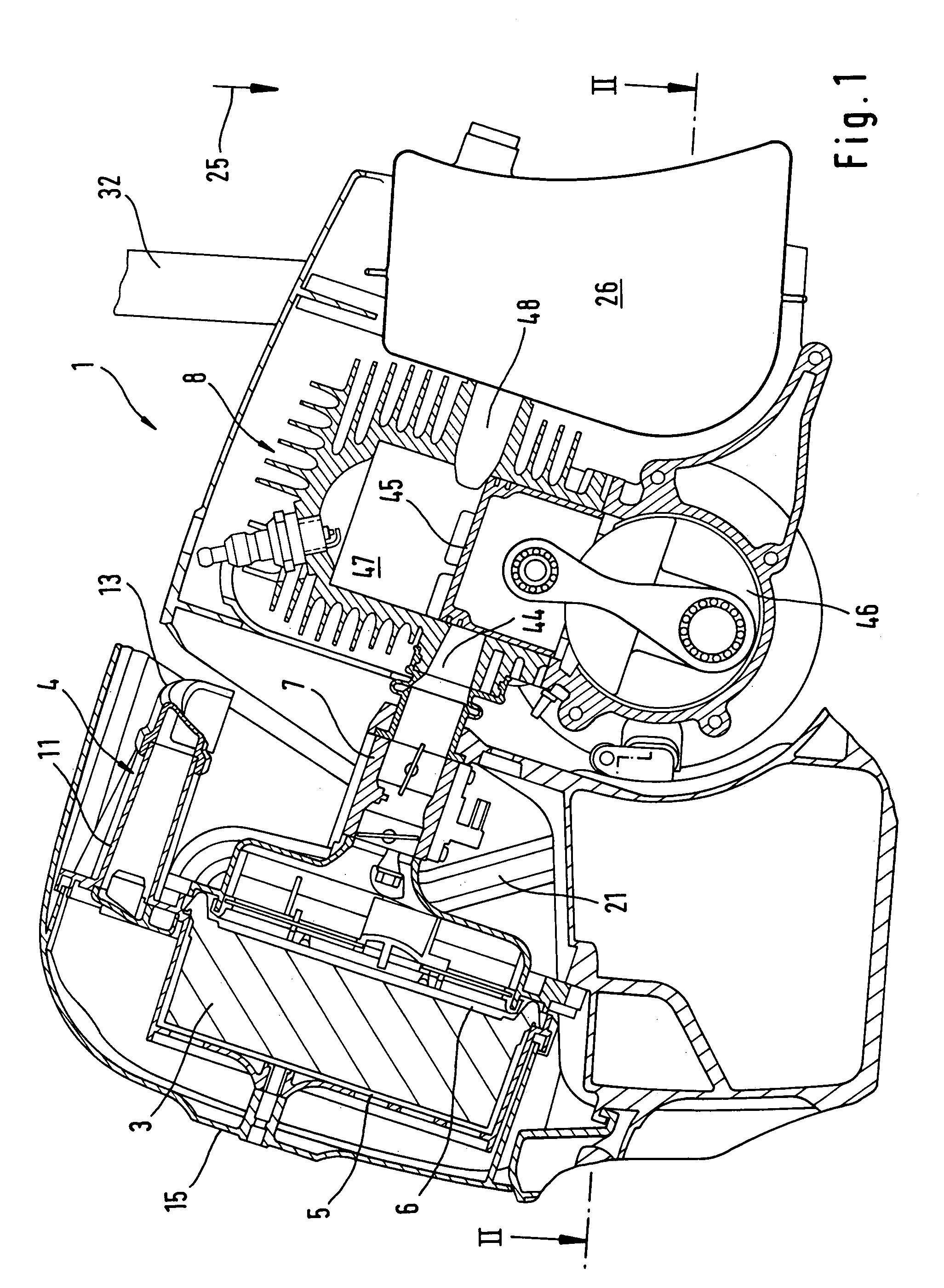
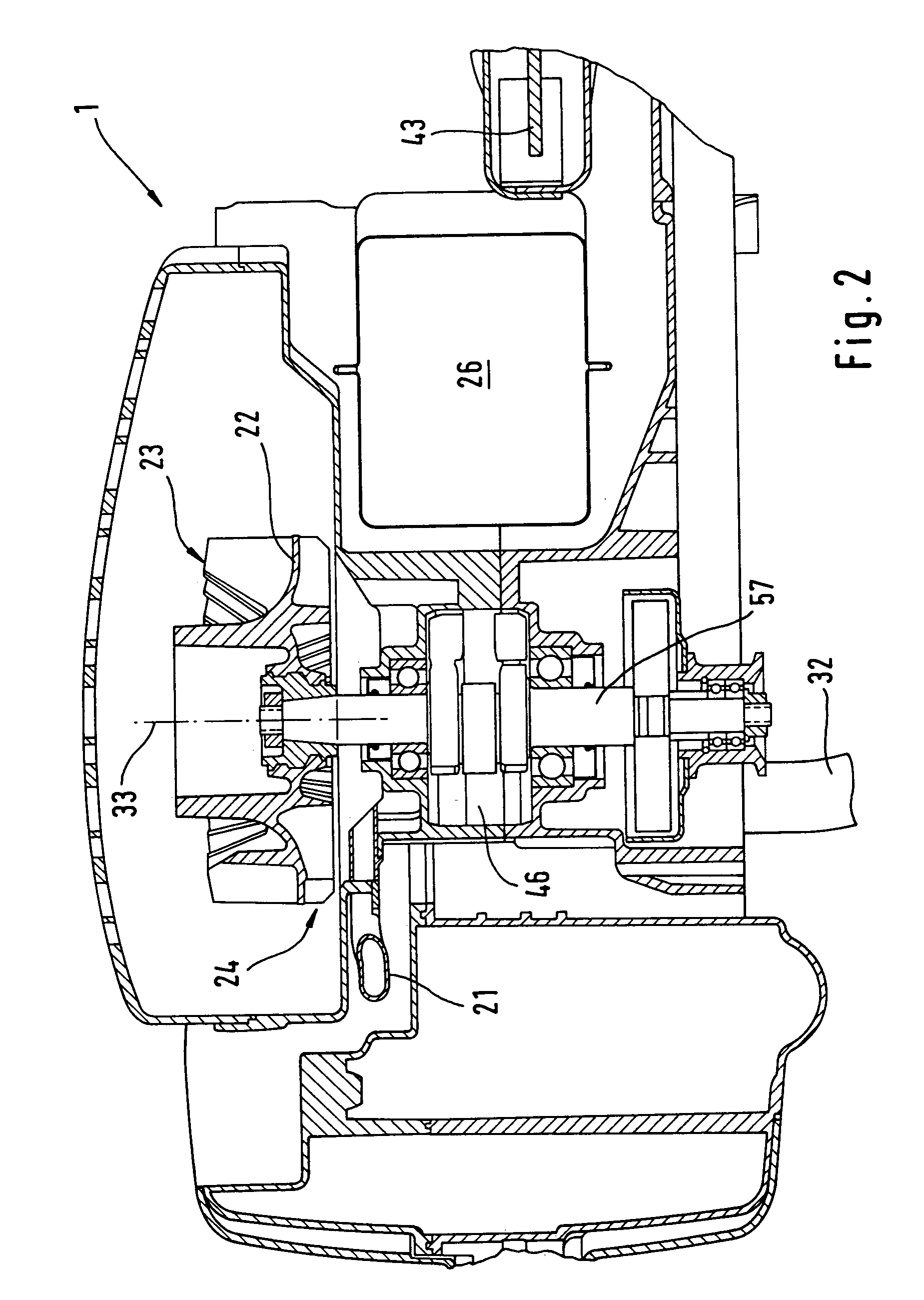
Intake system
An intake system for the combustion air of a motor of a hand held implement is provided. The system includes an air filter and a centrifugal separator. The air filter has a dirt chamber and a clean chamber that is separated therefrom by a filter medium. The clean chamber is fluidically connected with a carburetor of the motor to convey combustion air to the motor. The centrifugal separator splits the air stream into a core flow having low particle density and a peripheral flow having high particle density. The centrifugal separator includes at least two cyclones, wherein the discharged flows from the cyclones are respectively combined in pairs and open out into a common suction tube.
Owner:ANDREAS STIHL AG & CO KG
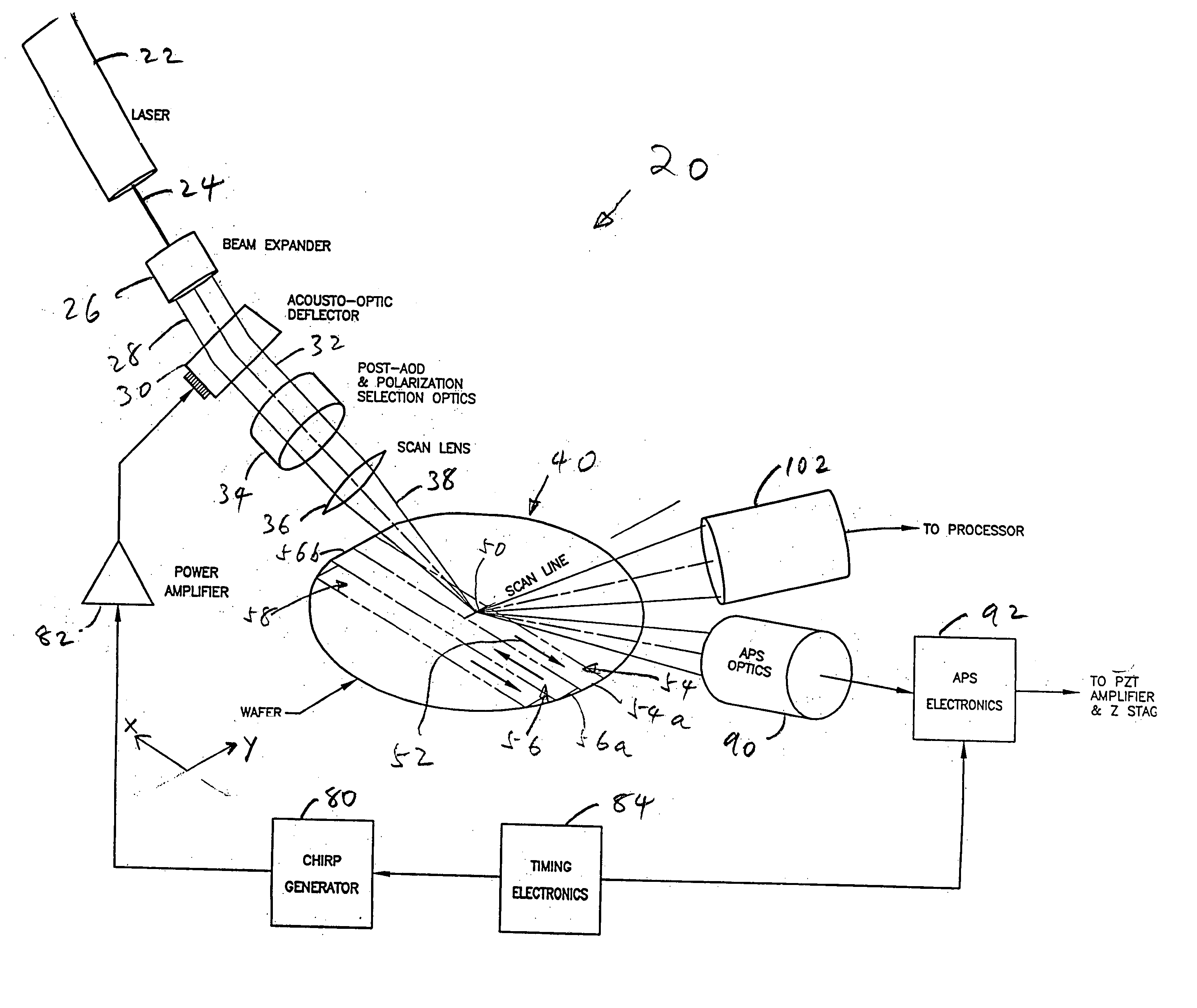
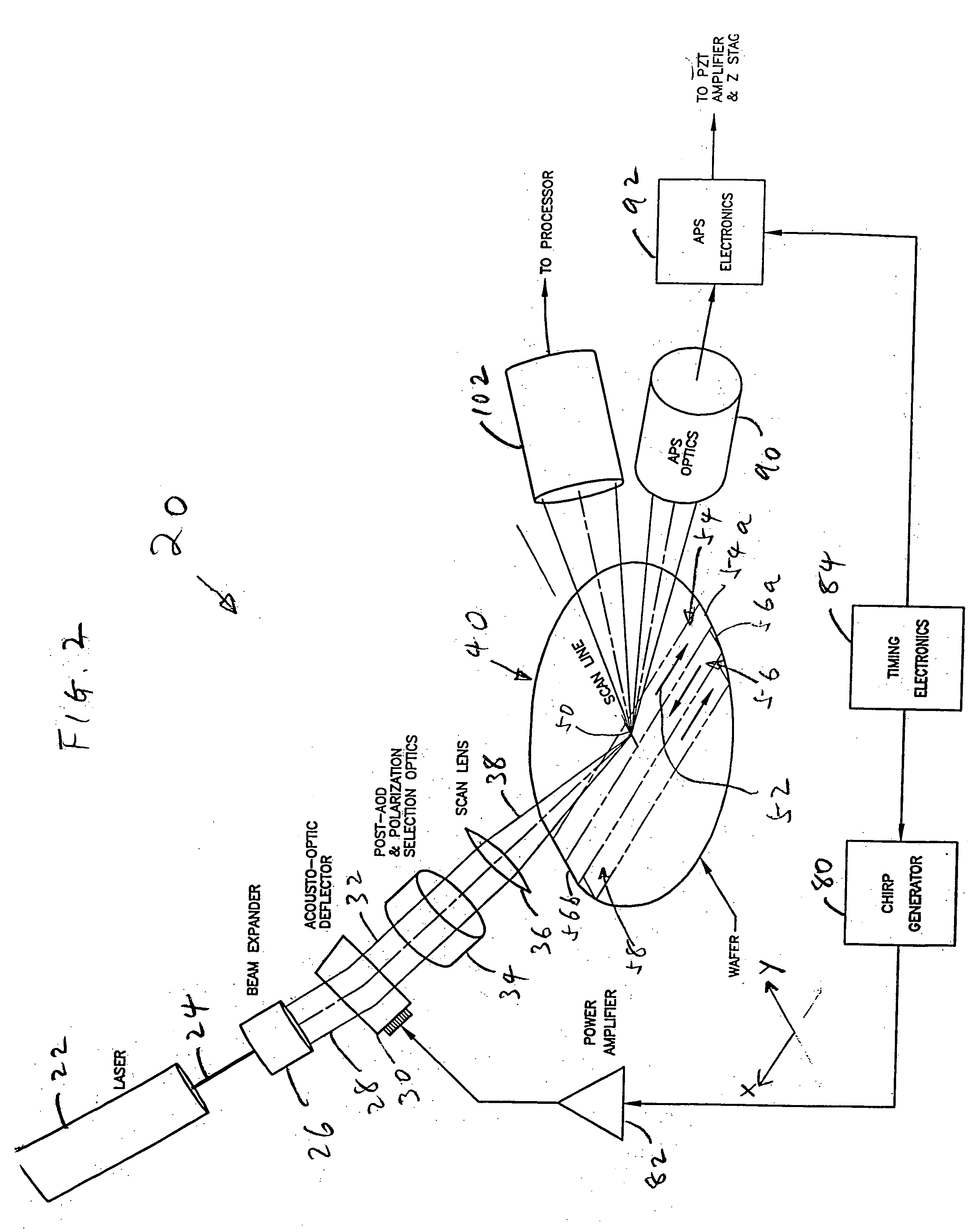
Scanning system for inspecting anamolies on surfaces
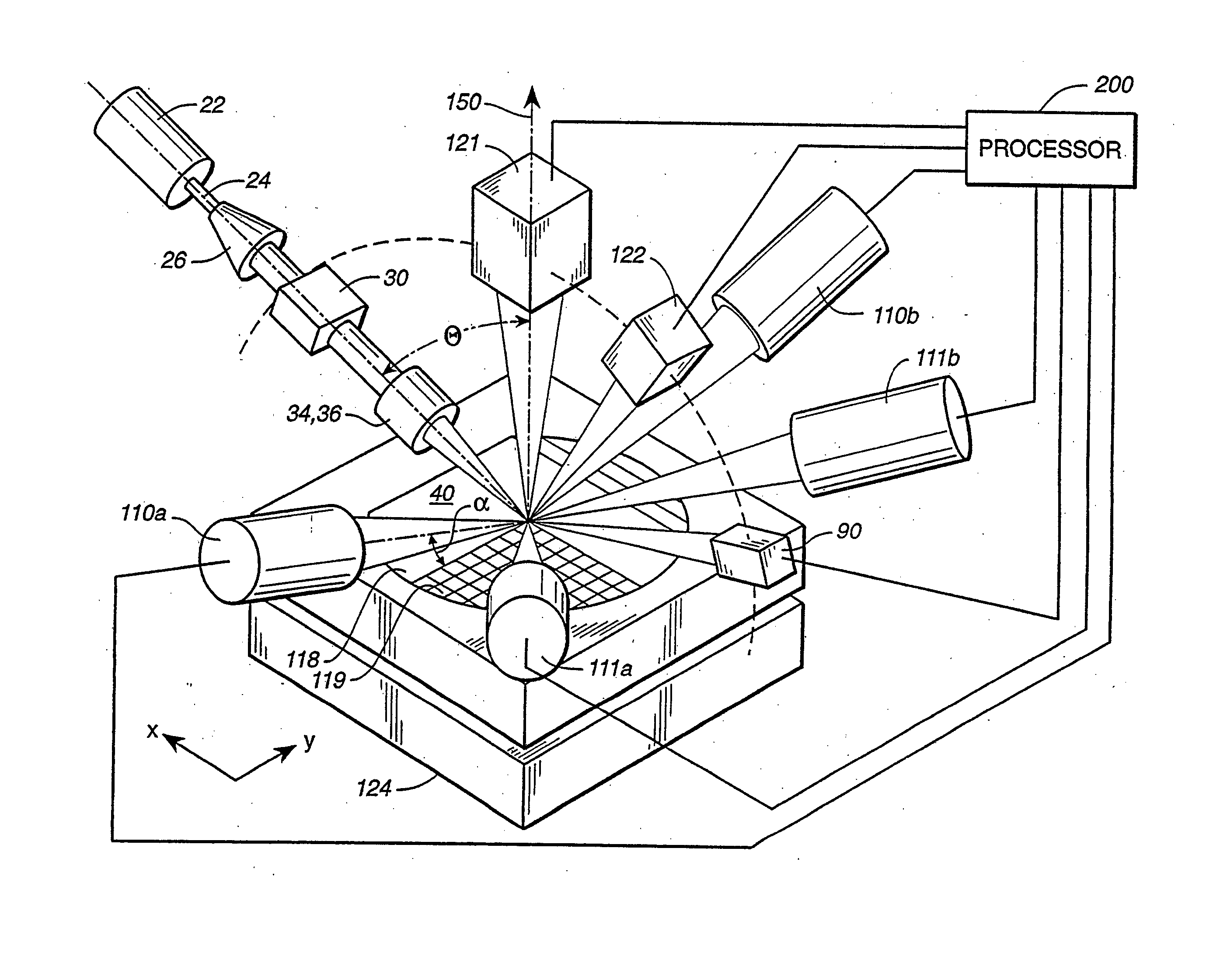
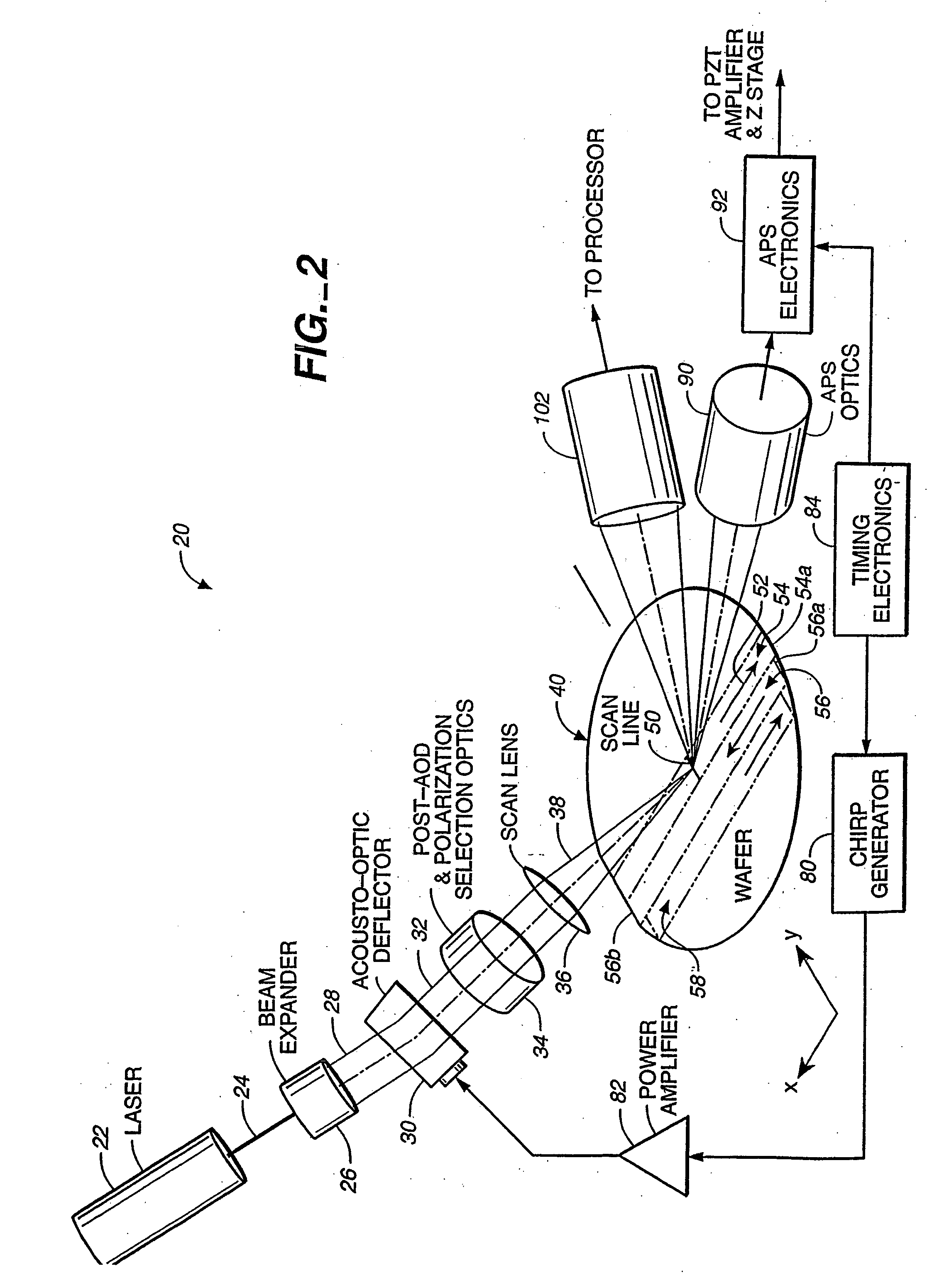
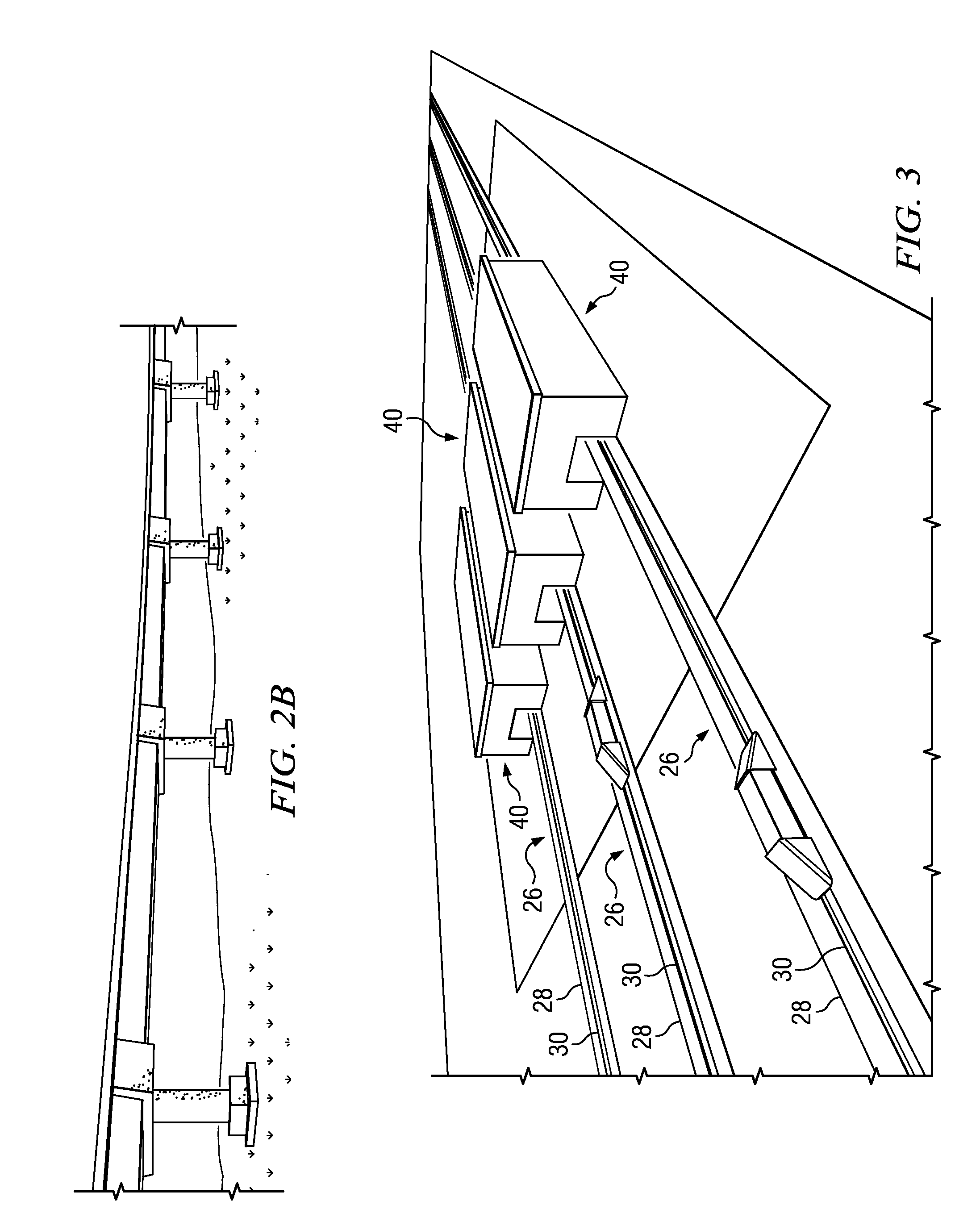
InactiveUS20050110986A1Maintain consistencyReduce areaOptically investigating flaws/contaminationParticulatesOptical scanning
An optical scanning system and method for detecting anomalies, including pattern defects and particulate contaminants, on both patterned and unpatterned surfaces, using a light beam, scanning at a grazing angle with respect to the surfaces, a plurality of detectors and an interchannel communication scheme to compare data from each detector, which facilitates characterizing anomalies. The light beam illuminates a spot on the surface which is scanned over a short scan-line. The surface is moved in a manner so that the spot is scanned over its entire area in a serpentine fashion along adjacent striped regions. The plurality of detectors include groups of collector channels disposed circumferentially around the surface, a bright field reflectivity / autoposition channel, an alignment / registration channel and an imaging channel. The collector channels in each group are symmetrically disposed, in the azimuth, on opposite sides of the center of the scan line. The position of the collector channels, as well as the polarization of the beam, facilitates distinguishing pattern defects from particulate contaminants. The bright field reflectivity / autoposition channel is positioned to receive specularly reflected light that carries information concerning local variation in reflectivity, which is used to classify detected anomalies, as well as determine variations in the height of the surface. The alignment / registration channel is positioned to detect a maximum of the light scattered from the pattern on the surface to ensure that the streets of die present on the surface are oriented so as not to be oblique with respect to the scan line. The imaging channel combines the advantages of a scanning system and an imaging system while improving signal / background ratio of the present system.
Owner:NIKOONAHAD MEHRDAD +3
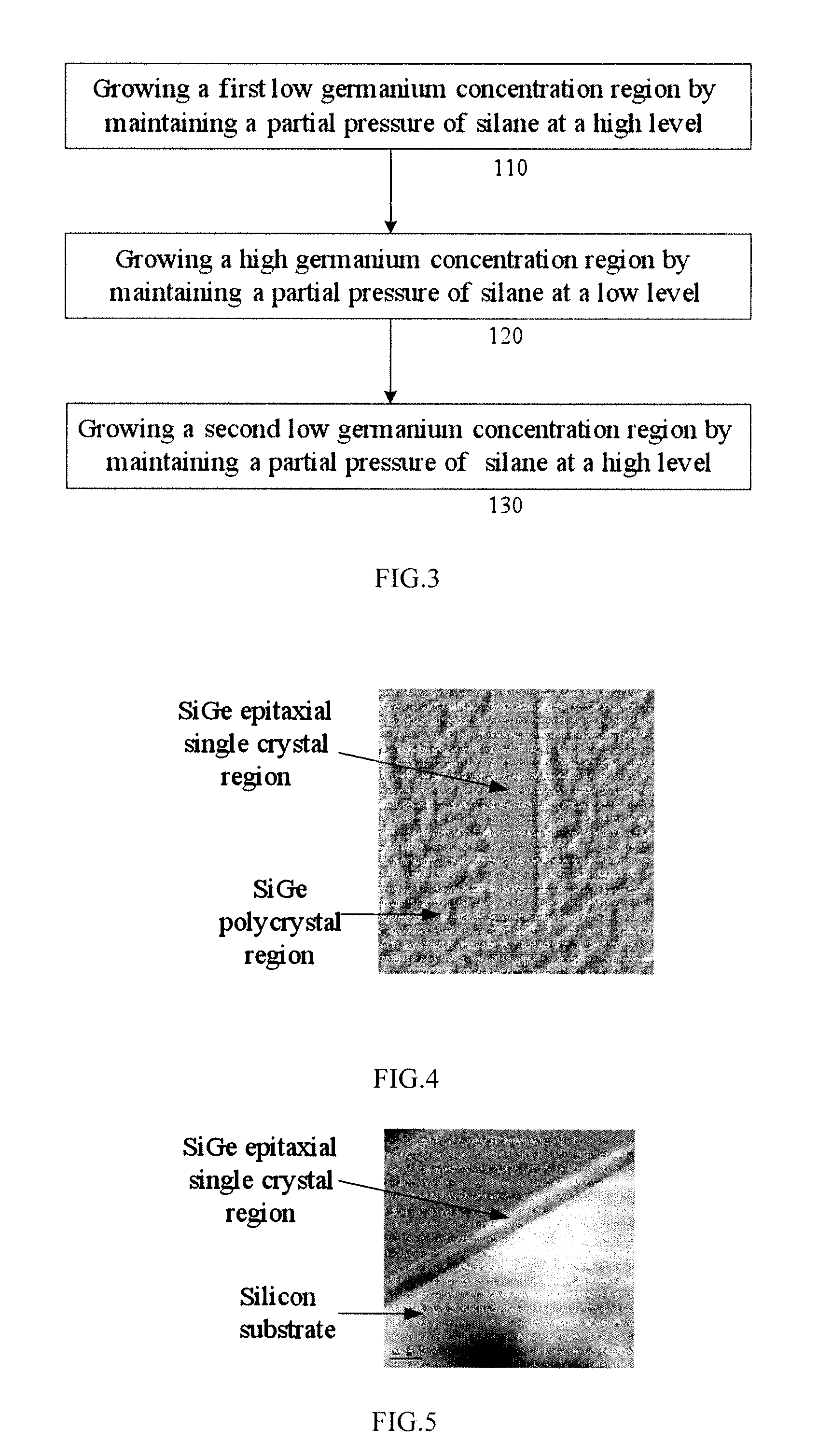
Method of sige epitaxy with high germanium concentration
InactiveUS20120115310A1High concentrationSufficient throughputPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGermananeSilanes
The present invention discloses a method of SiGe epitaxy with high germanium concentration, a germanium concentration can be increased by reducing the percentage of silane and germane during introduction silane and germane. With the same flow of germanium source, the germanium concentration is significantly increased as the germane flow is reduced, therefore a defect-free SiGe epitaxial film with a germanium atomic percentage of 25˜35% can be obtained. The present invention can balance epitaxial growth rate and germanium doping concentration by using existing equipments to obtain a high germanium concentration, and the epitaxial growth rate is only reduced a little, which can keep the SiGe epitaxial layer having no defect to meet the requirements of devices and can maintain sufficient throughput.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
Microcalorimetry for X-ray spectroscopy
ActiveUS8357894B2Solve the lack of resolutionSufficient throughputThermometer detailsStability-of-path spectrometersBeam energyElectron
An improved microcalorimeter-type energy dispersive x-ray spectrometer provides sufficient energy resolution and throughput for practical high spatial resolution x-ray mapping of a sample at low electron beam energies. When used with a dual beam system that provides the capability to etch a layer from the sample, the system can be used for three-dimensional x-ray mapping. A preferred system uses an x-ray optic having a wide-angle opening to increase the fraction of x-rays leaving the sample that impinge on the detector and multiple detectors to avoid pulse pile up.
Owner:FEI CO
System and Method for Increasing Polymer/Nanopore Interactions
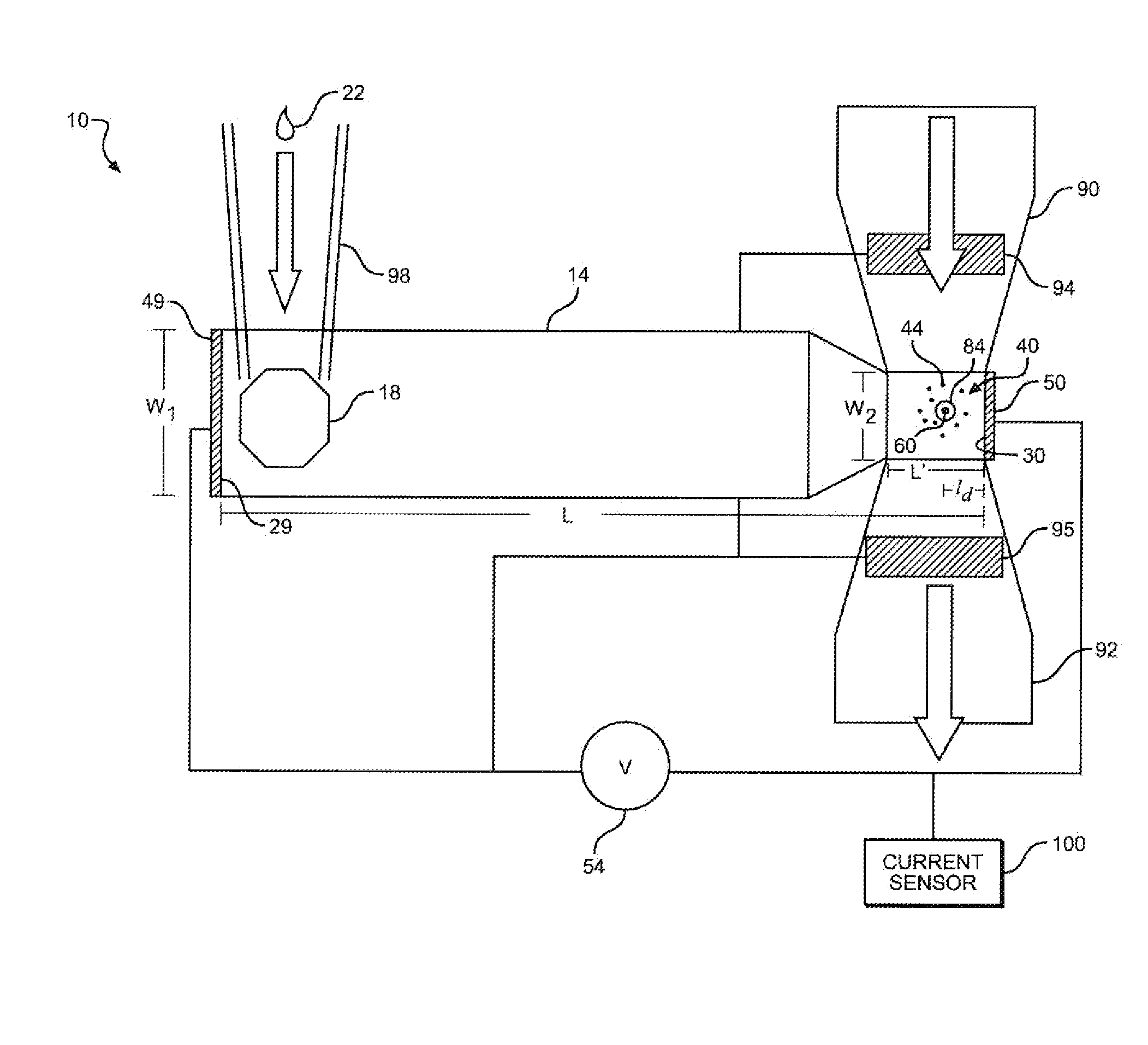
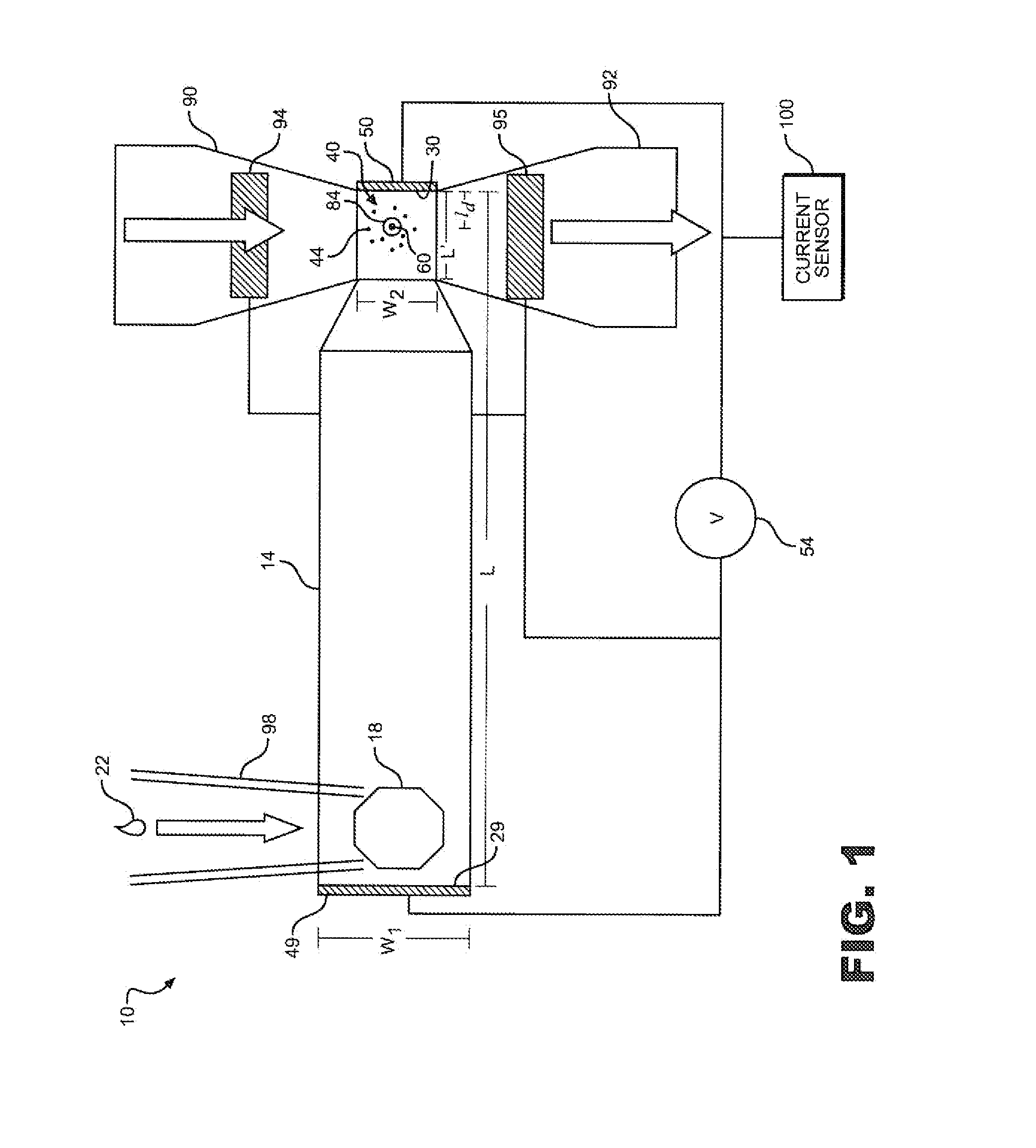
InactiveUS20110162963A1Increase the number ofSufficient throughputSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementAnalyteCurrent sensor
An electrolytic system includes an analyte chamber having an access port for introducing a sample containing a molecules of interest, such as DNA. Electrodes create an electric field along a length of the analyte chamber to drive molecules toward an interaction region containing a nanopore, thereby increasing the arrival rate of molecules at the nanopore. Additional electrodes may be utilized to create an electric field through the nanopore to drive a molecule into the nanopore. A current sensor may be utilized to count, discriminate or characterize the molecules as they interact with the nanopore. Advantageously, system can be utilized for unamplified DNA sequencing.
Owner:ELECTRONICS BIOSCI
Point of care analytical processing system
ActiveUS20160025639A1Efficient workflowIncrease turnaround timeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMultiplexingPoint of care
A point of care testing system includes a reader having an incubator disposed within a reader housing, the incubator having a rotor supported for rotation and having a plurality of circumferentially disposed slots. A drive mechanism is configured to rotate the rotor about a center axis A plurality of analytical test elements are sized for fitting in the slots of the incubator either manually or on demand. Each analytical test element commonly includes a support within a cartridge. The support retains at least one of a dry chemistry chip comprising a porous spreading layer disposed in stacked relation with at least one reagent layer or a lateral flow assay device wherein the plurality of test elements can assume a common form factor with multiplexed capability, and in which cartridges are preferably gated to enable random access processing.
Owner:ORTHO-CLINICAL DIAGNOSTICS
Lithography system and method of processing substrates in such a lithography system
ActiveUS20120175527A1High throughput operationSufficient throughputElectric discharge tubesPhotomechanical apparatusLithographic artistVacuum chamber
The invention relates to a lithography system comprising a plurality of lithography system units. Each lithography system unit comprises a lithography apparatus arranged in a vacuum chamber for patterning a substrate; a load lock system for transferring substrates into and out of the vacuum chamber; and a door for enabling entry into the vacuum chamber for servicing purposes. The load lock system and the door of each lithography system unit are provided at the same side and face a free area at a side of the lithography system, in particular the service area.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
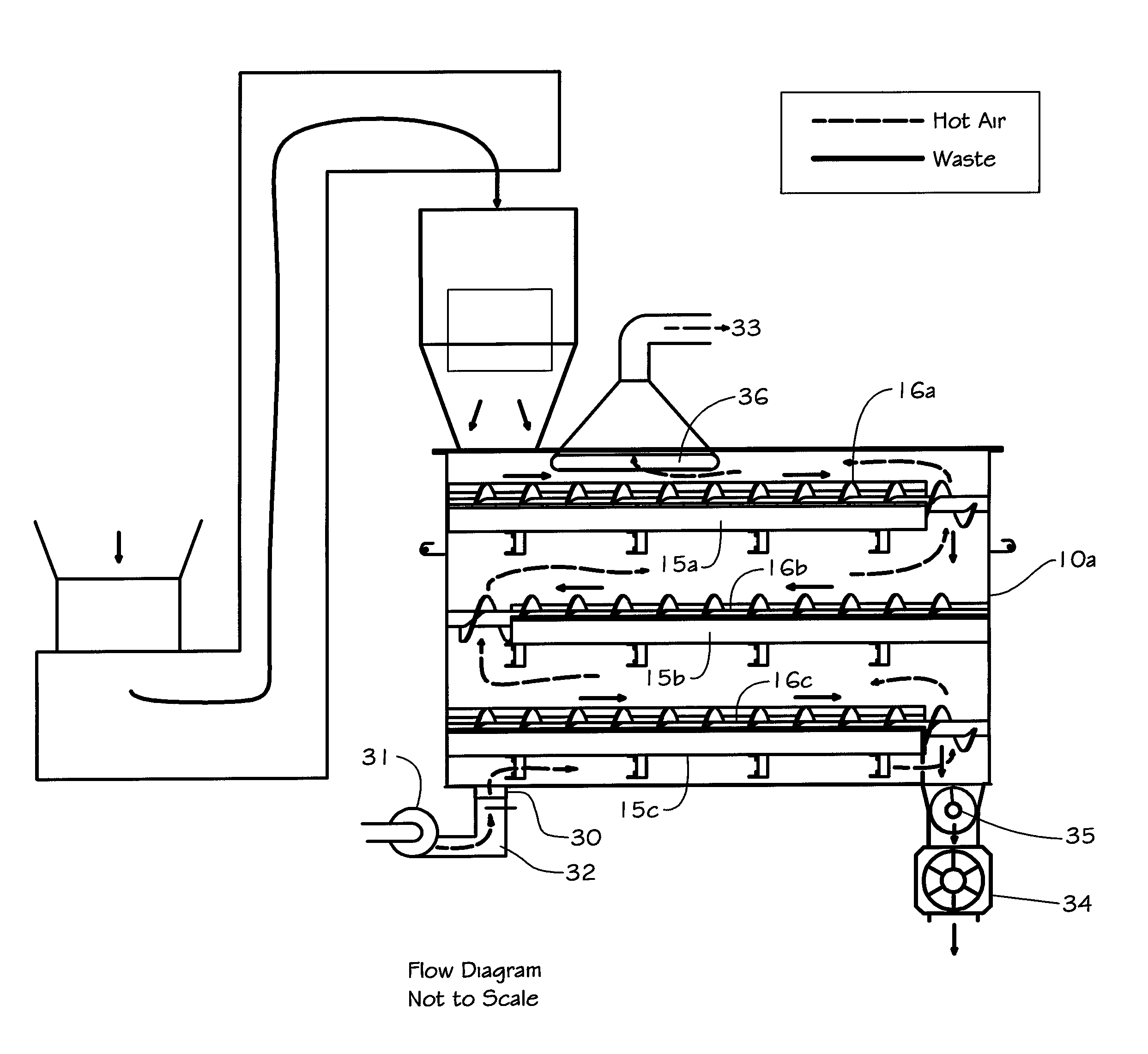
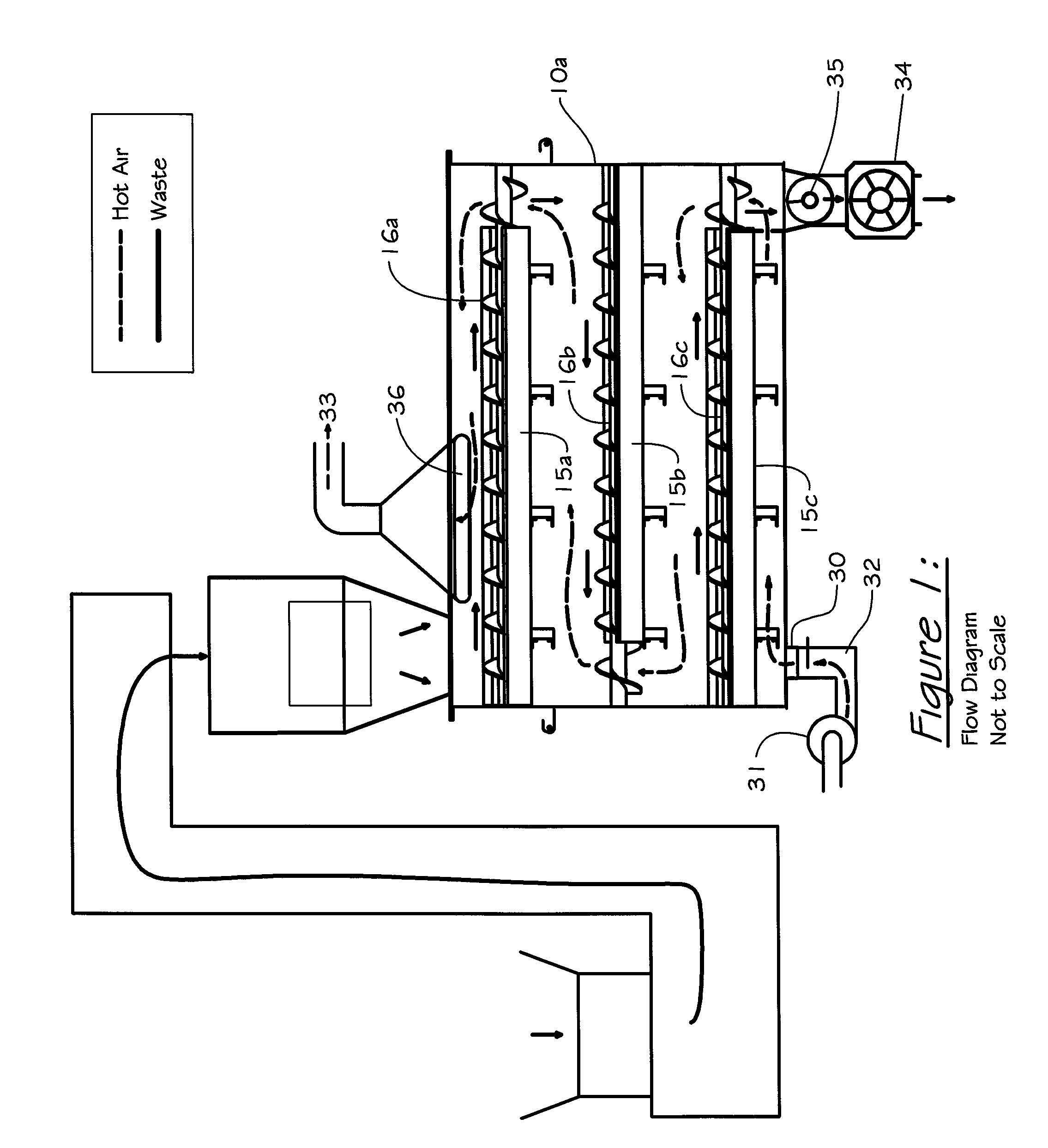
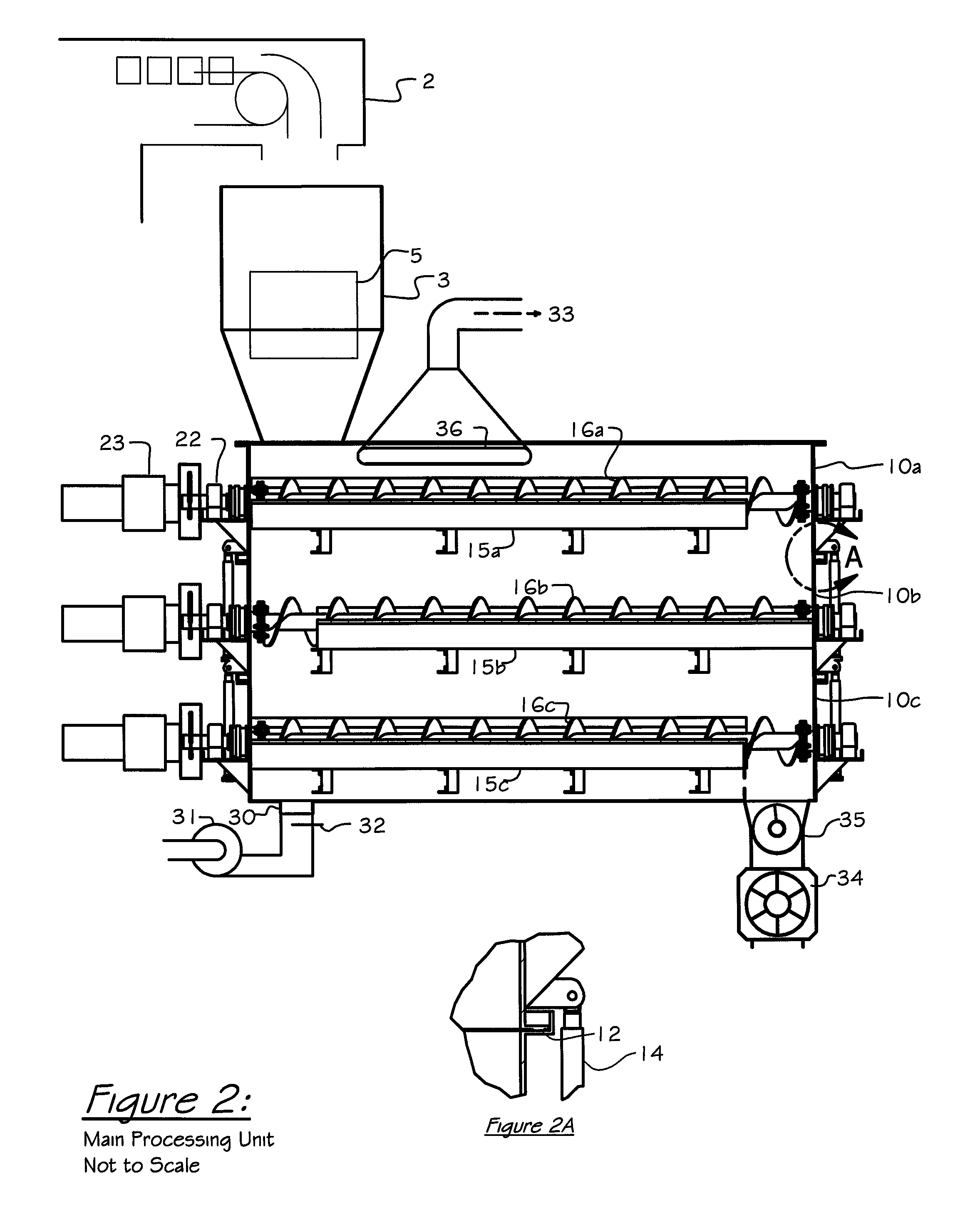
Animal waste processing
InactiveUS8147772B2Efficient dryingSave spaceManure dryingSolid waste disposalMold sporesEquine Species
A method and apparatus for eliminating mold spores, pathogens and odor from material like equine bedding. The apparatus includes two or more pairs of augers including blades to control the size of the material and to move it in a zigzag fashion through heat.
Owner:WILFORD PHILIP GRAHAM
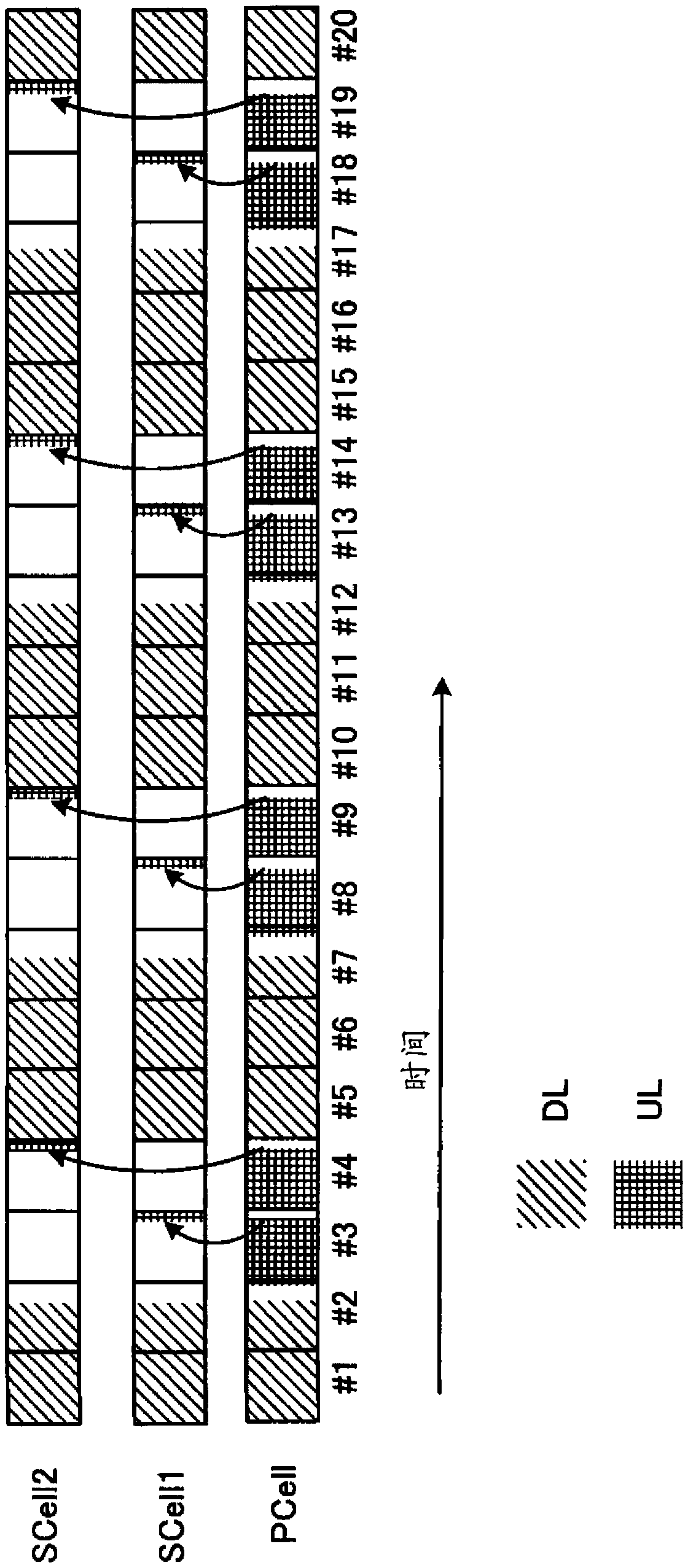
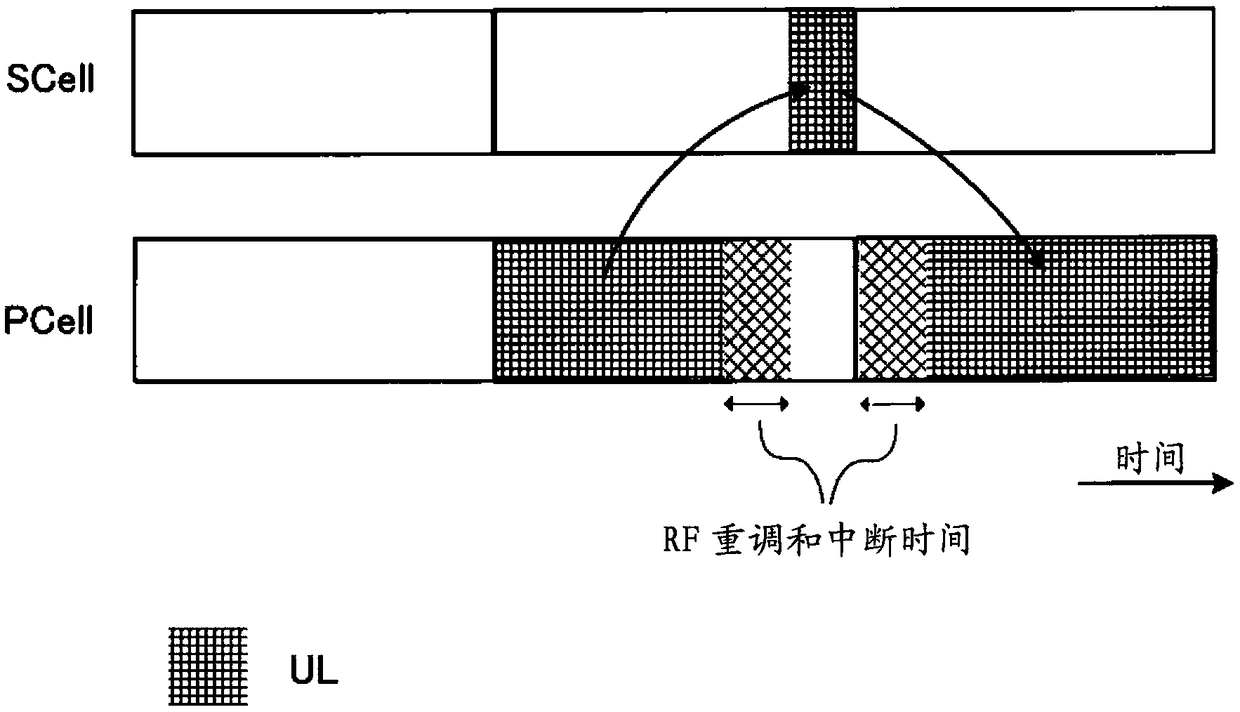
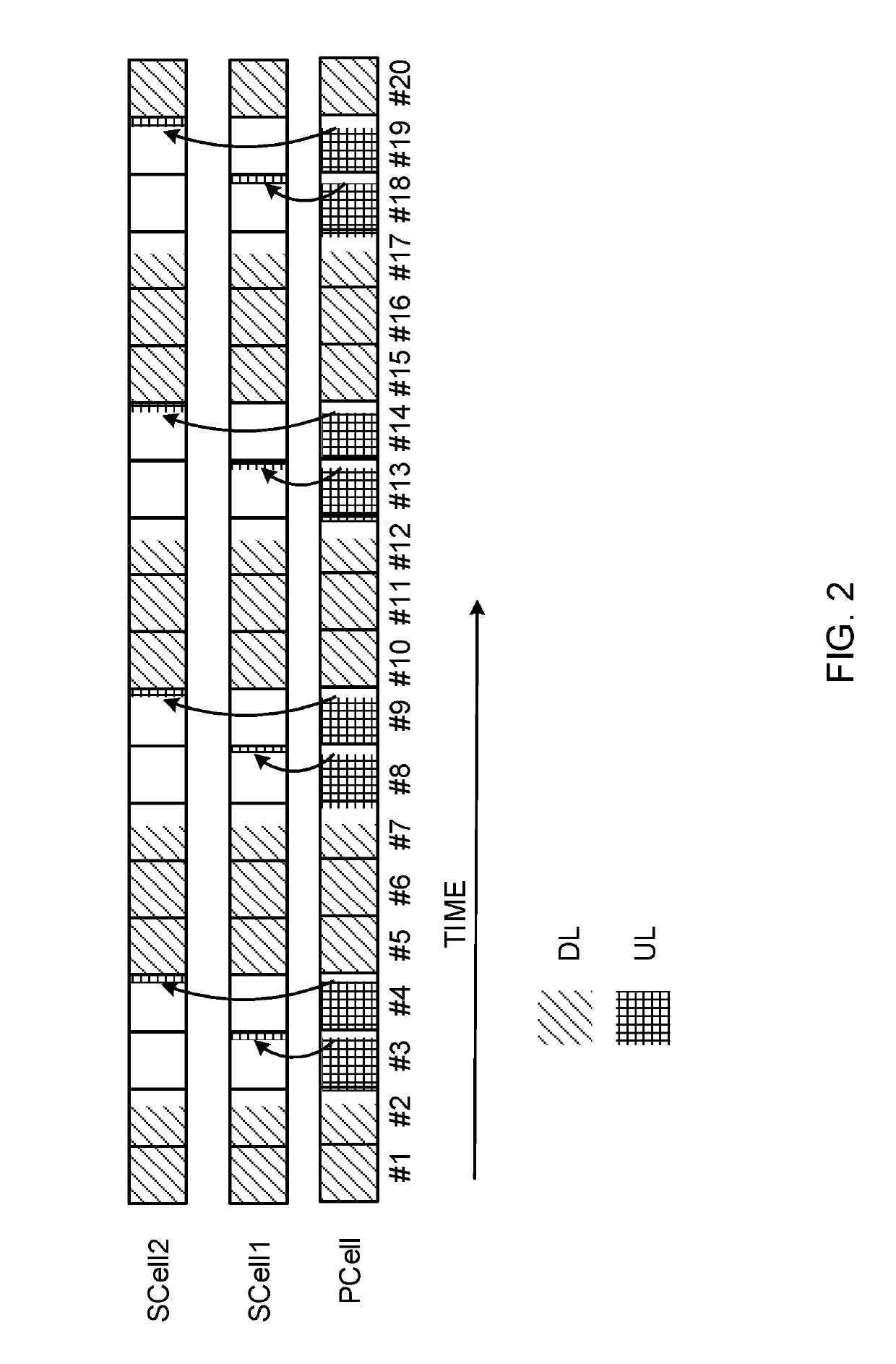
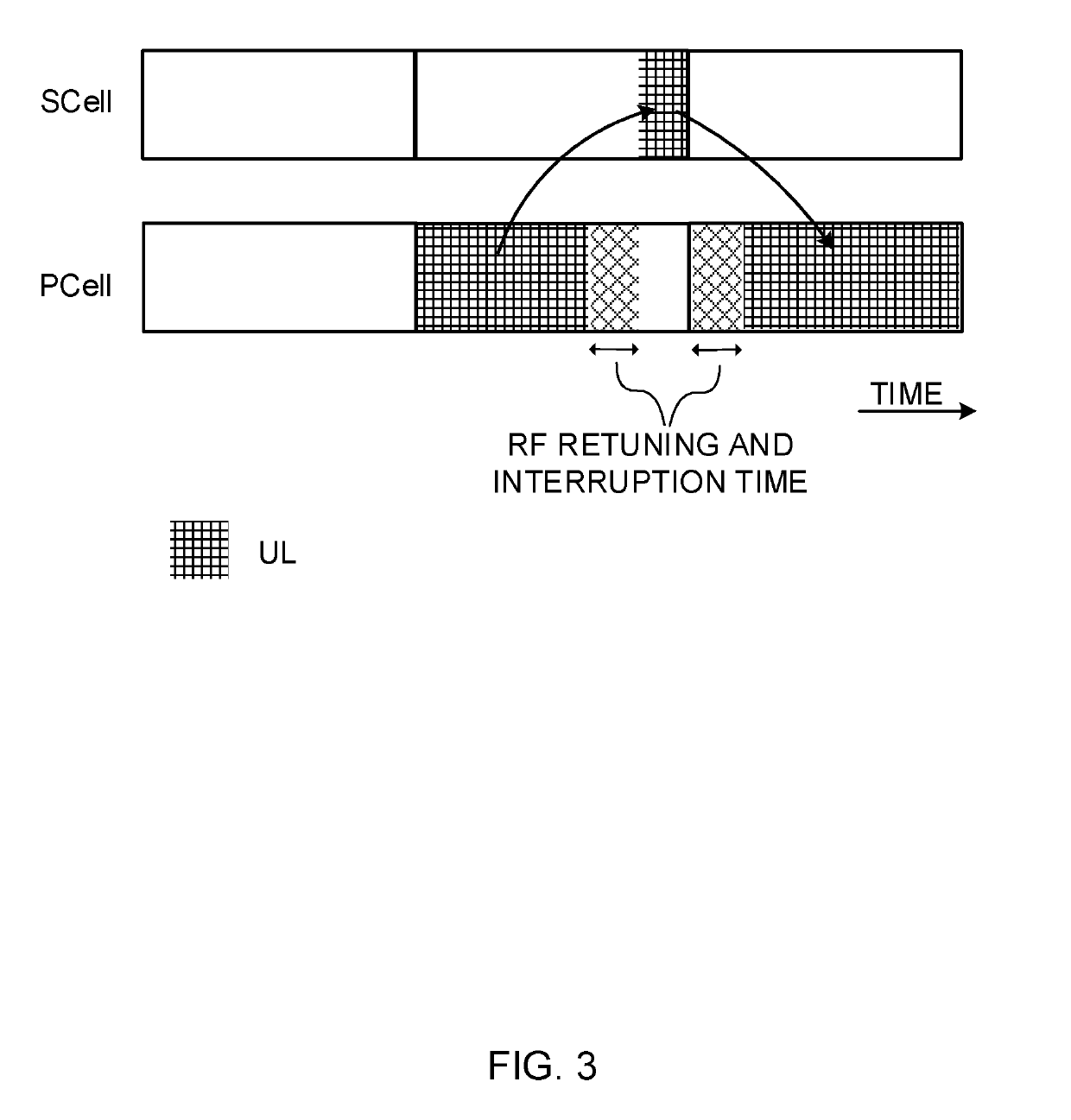
User terminal, wireless base station, and wireless communication method
ActiveCN109076334ASufficient throughputTransmission path divisionPilot signal allocationControl cellElectrical and Electronics engineering
The present invention achieves sufficient throughput even when a provisional frequency-switching technology is used in TDD. A user terminal that comprises: a transmission / reception unit that performsuplink transmission and / or downlink reception via a first cell; and a control unit that controls the transmission / reception unit such that the transmission / reception unit transmits capability information related to UL reference signal switching that is for switching from the first cell to a second cell that is different from the first cell and transmitting a UL reference signal.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
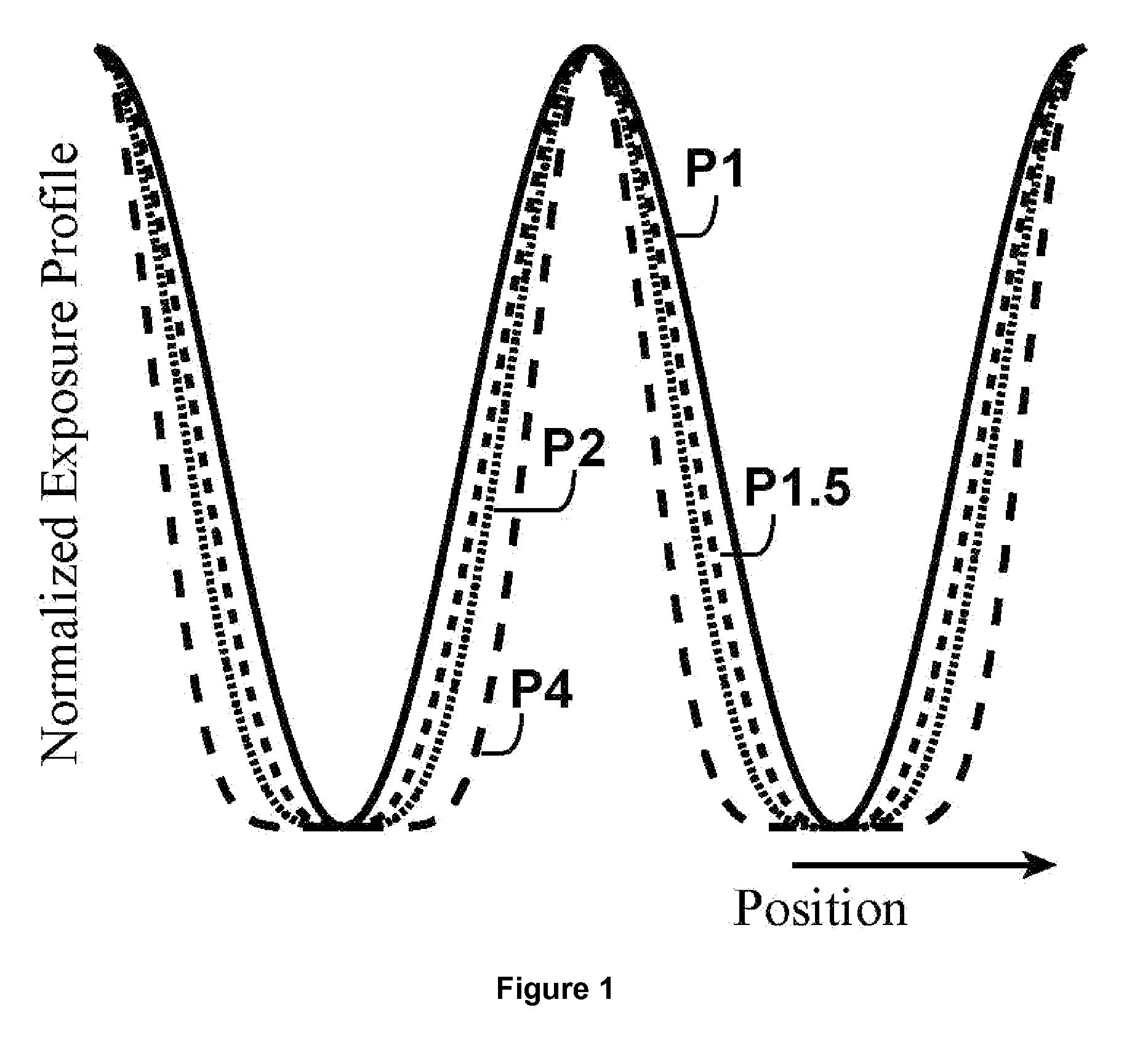
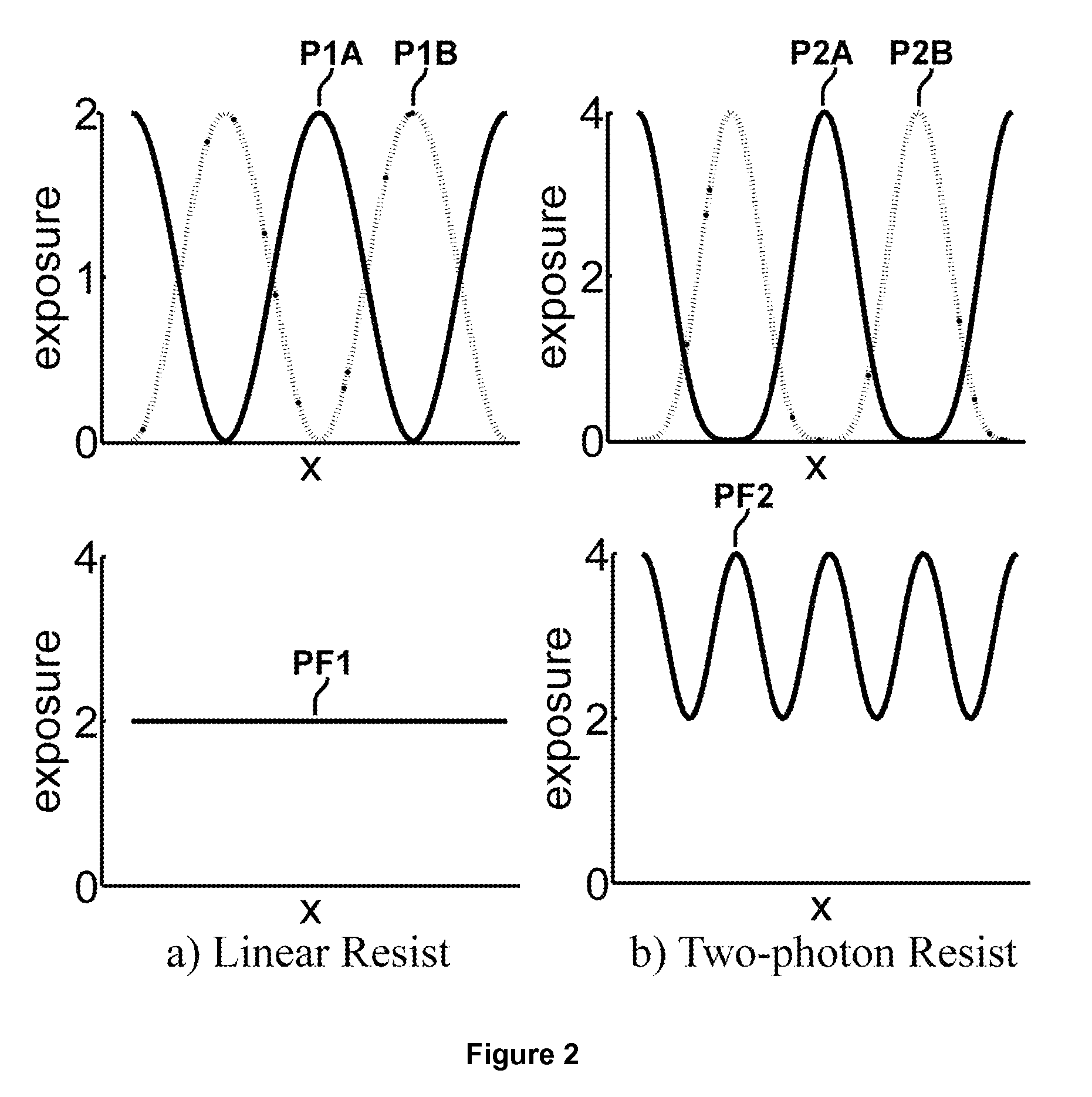
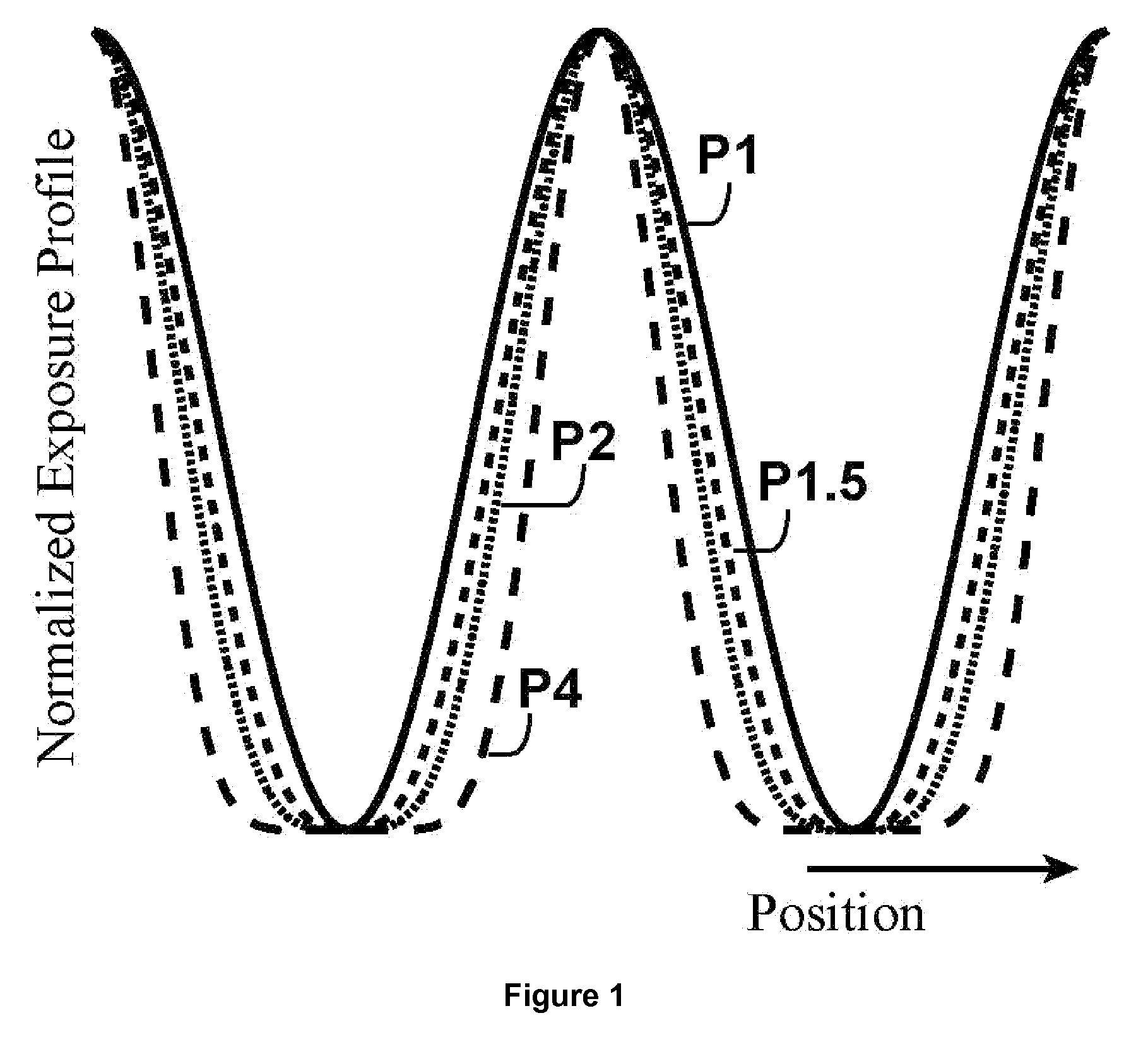
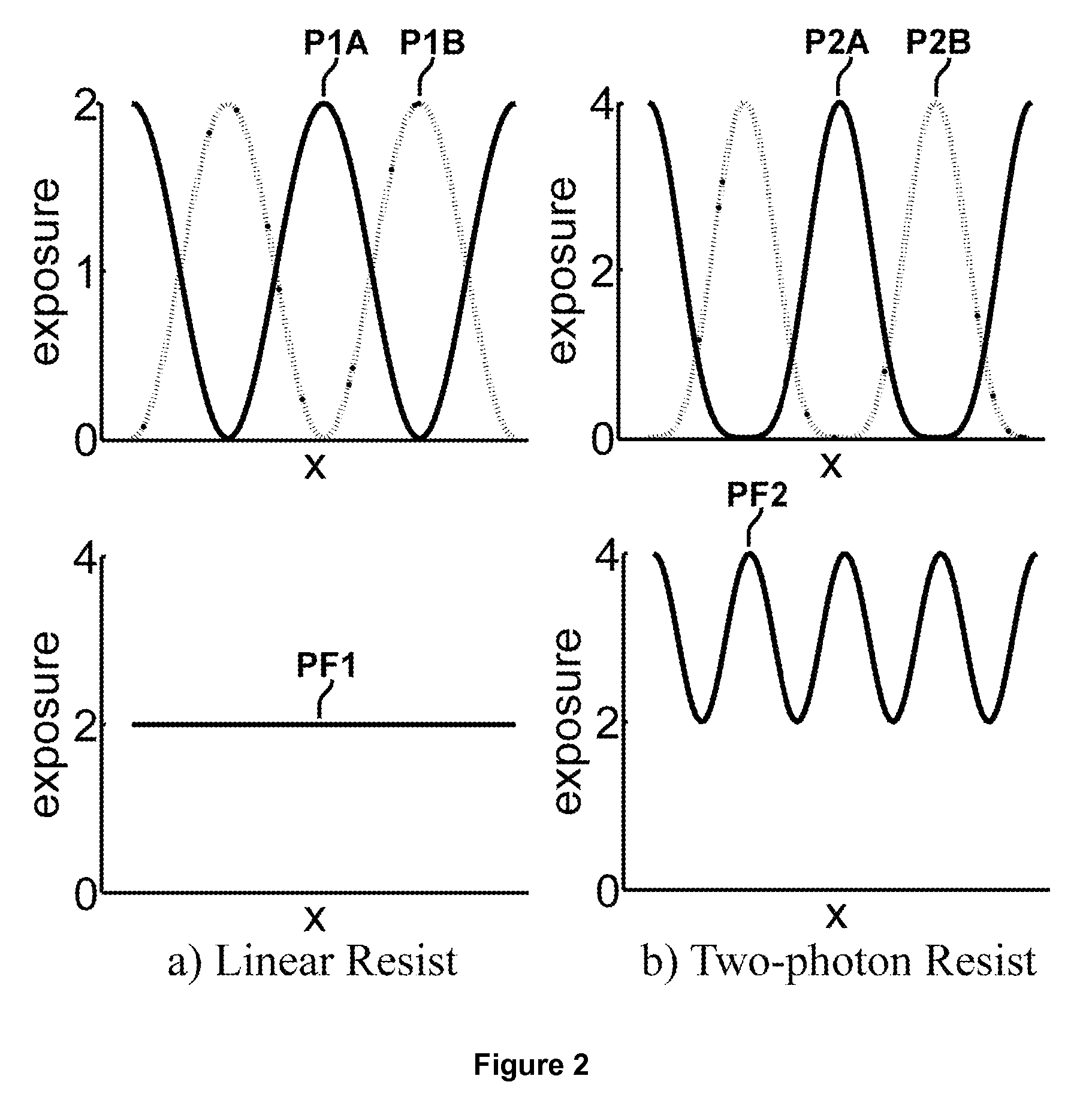
Resists for lithography
InactiveUS20080176166A1Promote growthImprove performanceNanostructure manufacturePhotosensitive materialsResistLithographic artist
New routes involving multi-step reversible photo-chemical reactions using two-step techniques to provide non-linear resist for lithography are described in this disclosure. They may provide exposure quadratically dependant on the intensity of the light. Several specific examples, including but not limited to using nanocrystals, are also described. Combined with double patterning, these approaches may create sub-diffraction limit feature density.
Owner:PIXELLIGENT TECH LLC
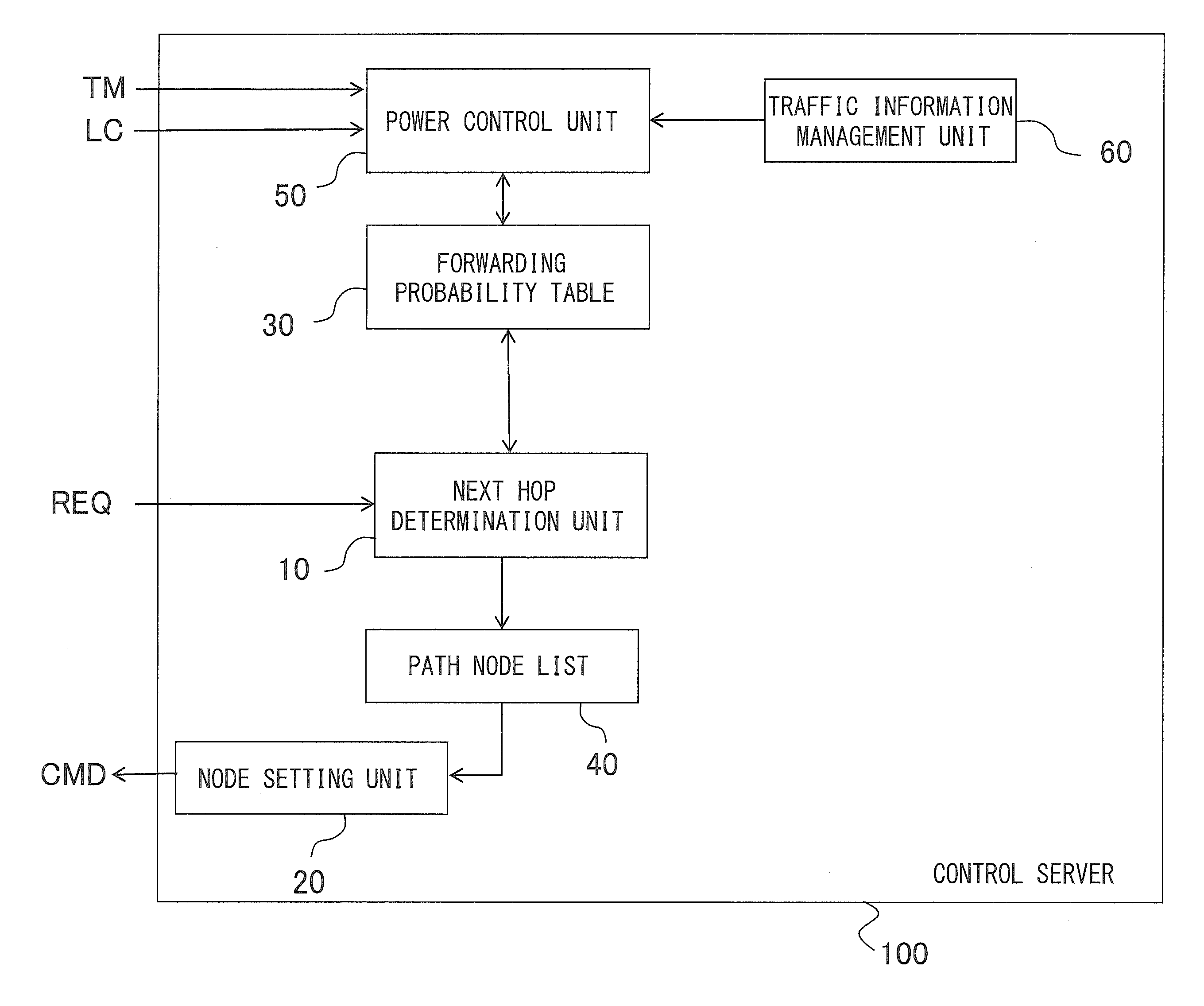
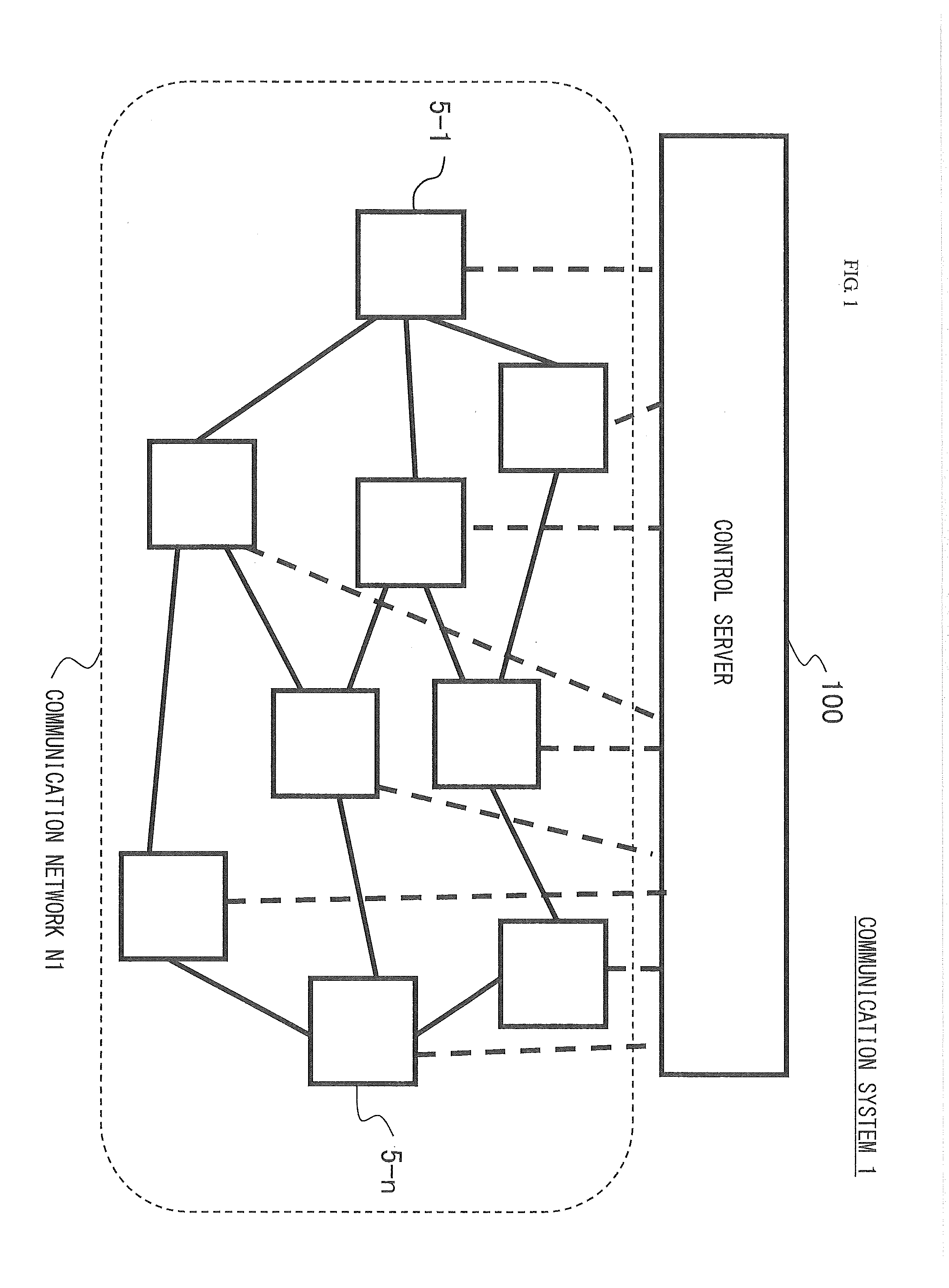
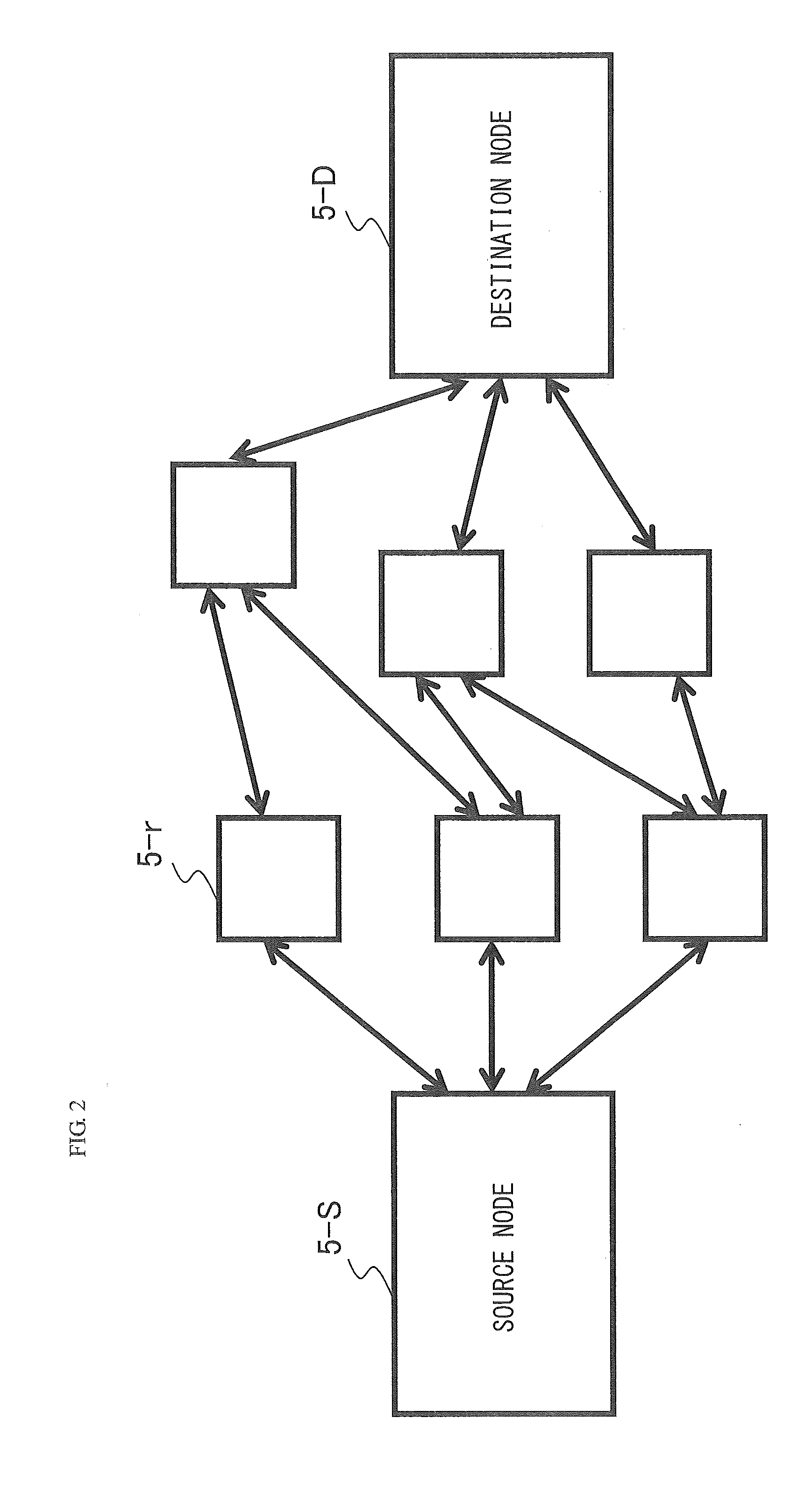
Control server, network control method, and program
InactiveUS20140025970A1Reduce power consumptionSufficient throughputVolume/mass flow measurementHybrid transportNetwork controlBroadcast communication network
A control server selects part of nodes included in a first communication network, generates a second communication network from the selected nodes, determines a forwarding probability of a packet between a node and its next hop node in the second communication network to calculate a communication volume between at least one pair of nodes included in the second communication network with respect to a prescribed traffic using the determined forwarding probability, and calculates a link cost for at least one pair of nodes included in the second communication network based on the determined forwarding probability and the calculated communication volume, adds at least one node included in the first communication network to the second communication network so that the calculated link cost satisfies a prescribed condition, and puts nodes not included in the second communication network in a low power consumption mode.
Owner:NEC CORP
Resists for lithography
InactiveUS8383316B2Sufficient throughputNanostructure manufacturePhotosensitive materialsResistChemical reaction
New routes involving multi-step reversible photo-chemical reactions using two-step techniques to provide non-linear resist for lithography are described in this disclosure. They may provide exposure quadratically dependant on the intensity of the light. Several specific examples, including but not limited to using nanocrystals, are also described. Combined with double patterning, these approaches may create sub-diffraction limit feature density.
Owner:PIXELLIGENT TECH LLC
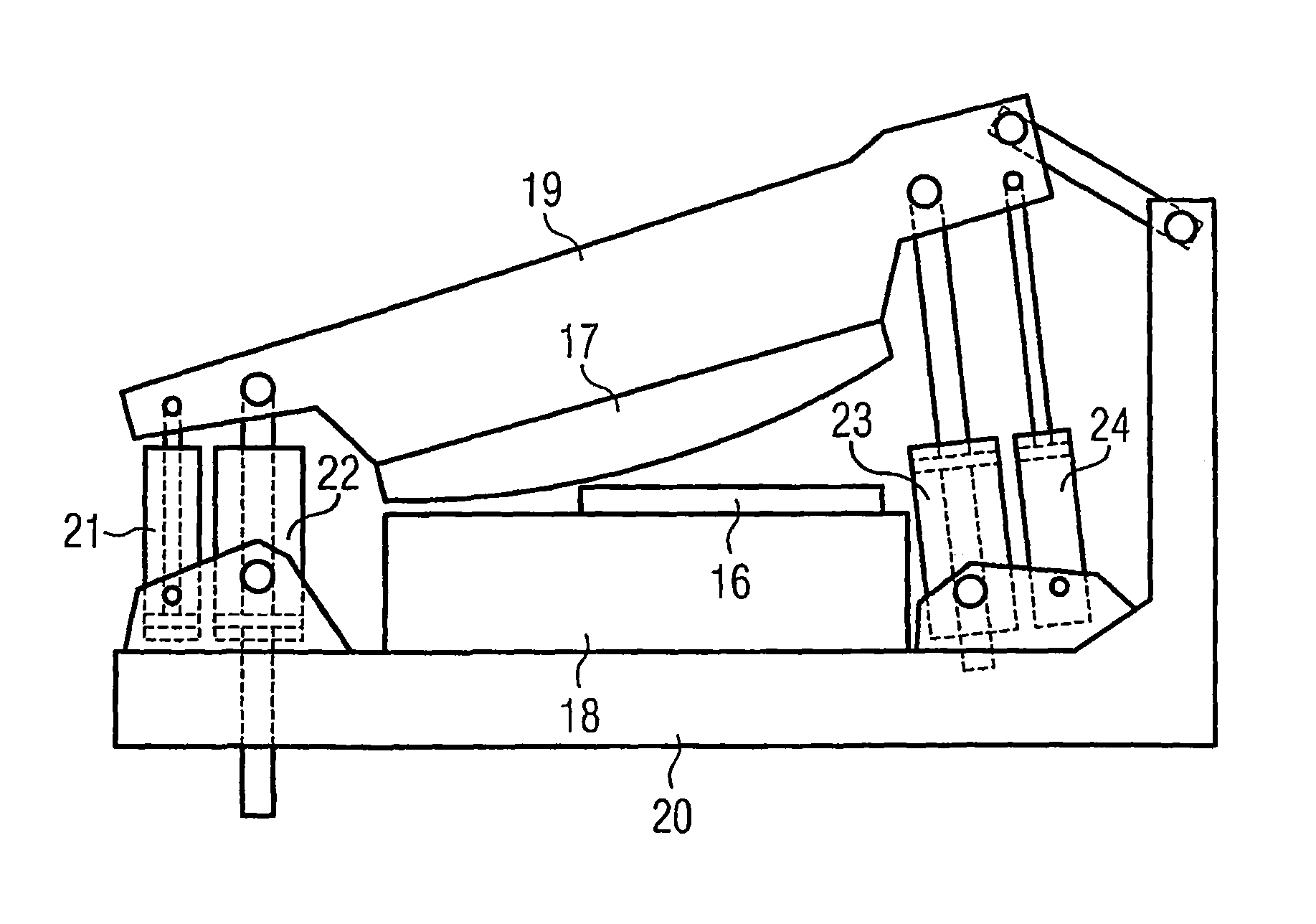
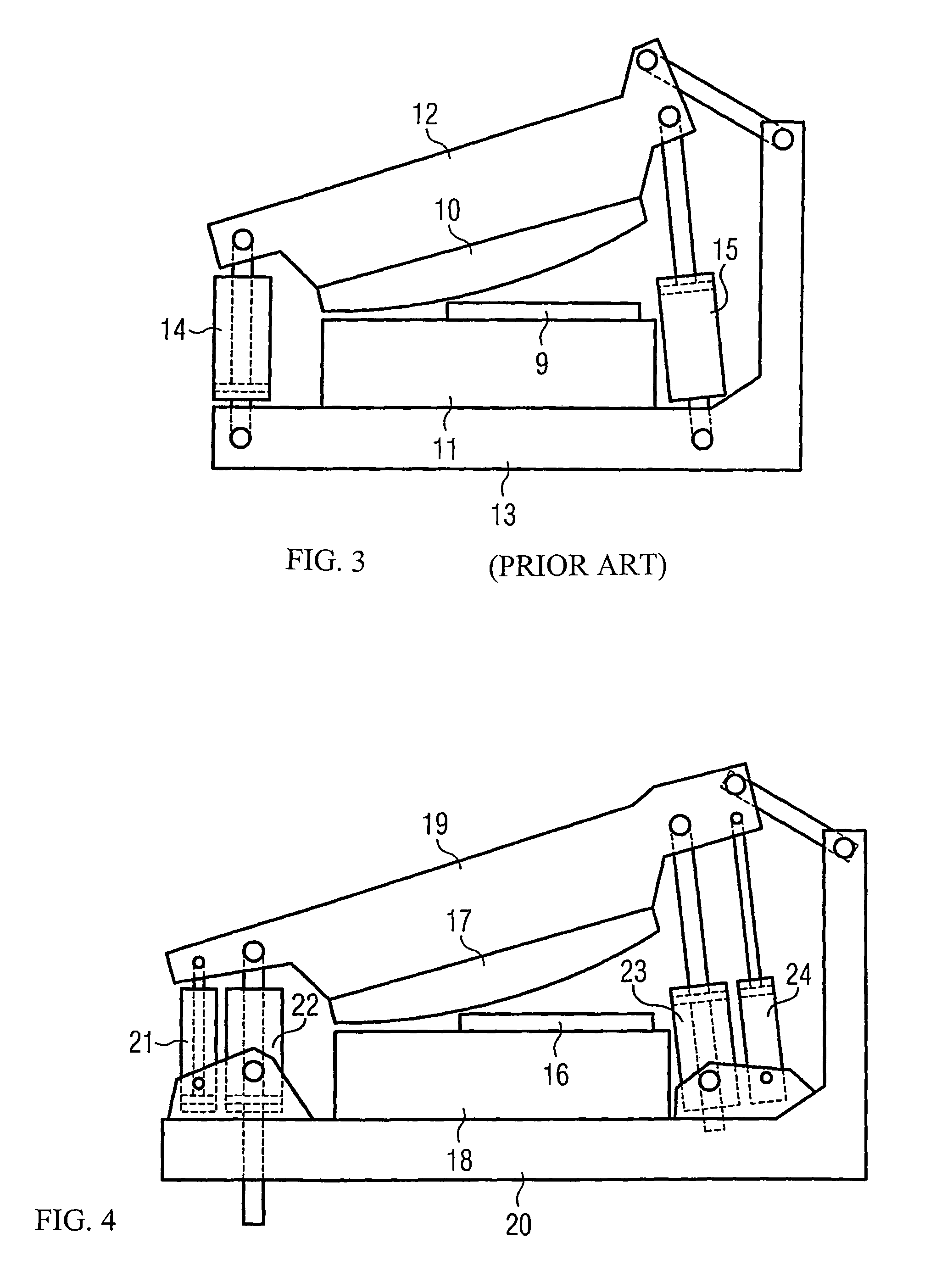
Multiple actuating-force shearing machine
InactiveUS20100229705A1Sufficient throughputSize of pump reducedShearing machinesMetal working apparatusHydraulic cylinderTime function
A method, and an apparatus, for operating a hydraulic shearing machine. For cutting a shearing-movement of at least one shear blade which is curved, starting from a starting-position under application of an overall actuating-force and for resetting of the shear blades which were moved for cutting to their starting-position after accomplishment of the shearing-movement, a reset-movement under application of an overall reset-force. The shearing-movement and the reset-movement are accomplished by a hydraulic actuating-mechanism comprising hydraulic cylinders, wherein the overall actuating-force and the overall reset-force being applied to the moved shear blades by at least one hydraulic cylinder of the actuating-mechanism. The magnitude of the overall actuating-force is adjustable by switching one or several hydraulic cylinders of the actuating-mechanism in and out of operation-mode. The method proposes that the positions of the curved shear blade are controlled by a control system by regulating the flow of hydraulic fluid to the hydraulic cylinders according to setpoints for a shear blade position versus time function and the overall actuating-force and overall reset-force requirements.
Owner:PRIMETALS TECH
User terminal, radio base station and radio communication method
InactiveUS20190165908A1Sufficient throughputTransmission path divisionPilot signal allocationUplink transmissionComputer terminal
Even when a temporary frequency switching technique is used by TDD, a sufficient throughput is achieved. A user terminal includes: a transmission / reception section that performs uplink transmission and / or downlink reception via a first cell; and a control section that controls the transmission / reception section to transmit capability information related to UL reference signal switching for switching the first cell to a second cell different from the first cell and transmitting a UL reference signal.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Animal waste processing
InactiveUS20110091362A1Reduce any lumpEliminate foul odorManure dryingSolid waste disposalEngineeringMold spores
A method and apparatus for eliminating mold spores, pathogens and odor from material like equine bedding. The apparatus includes two or more pairs of augers including blades to control the size of the material and to move it in a zigzag fashion through heat.
Owner:WILFORD PHILIP GRAHAM
Liquid feeding device for the generation of droplets
ActiveUS20170219283A1Avoid disadvantagesEasy to receivePowder deliveryDrying solid materials without heatFreeze-dryingSpray nozzle
The present invention provides, inter alia, for a liquid feeding device for the generation of droplets, in particular for the use in a process line for the production of freeze-dried particles, with a droplet ejection section for ejecting liquid droplets in an ejection direction, the droplet ejection section comprising at least one inlet port for receiving a liquid to be ejected, a liquid chamber for retaining the liquid, and a nozzle for ejecting the liquid from the liquid chamber to form droplets, wherein the liquid chamber is restricted by a membrane on one side thereof, the membrane being vibratable by an excitation unit, wherein the longitudinal axis of the liquid chamber is tilted relative to the longitudinal axis of the nozzle, and / or the liquid feeding device further comprises a deflection section for separating the droplets from each other by means of at least one gas jet, wherein the deflection section gas jet intersects perpendicular with an ejection path of the liquid ejected from the liquid chamber.
Owner:SANOFI PASTEUR SA
Point of care analytical processing system
ActiveUS10031085B2Efficient workflowQuick turnaround timeMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorLaboratory glasswaresMultiplexingPoint of care
A point of care testing system includes a reader having an incubator disposed within a reader housing, the incubator having a rotor supported for rotation and having a plurality of circumferentially disposed slots. A drive mechanism is configured to rotate the rotor about a center axis A plurality of analytical test elements are sized for fitting in the slots of the incubator either manually or on demand. Each analytical test element commonly includes a support within a cartridge. The support retains at least one of a dry chemistry chip comprising a porous spreading layer disposed in stacked relation with at least one reagent layer or a lateral flow assay device wherein the plurality of test elements can assume a common form factor with multiplexed capability, and in which cartridges are preferably gated to enable random access processing.
Owner:ORTHO-CLINICAL DIAGNOSTICS
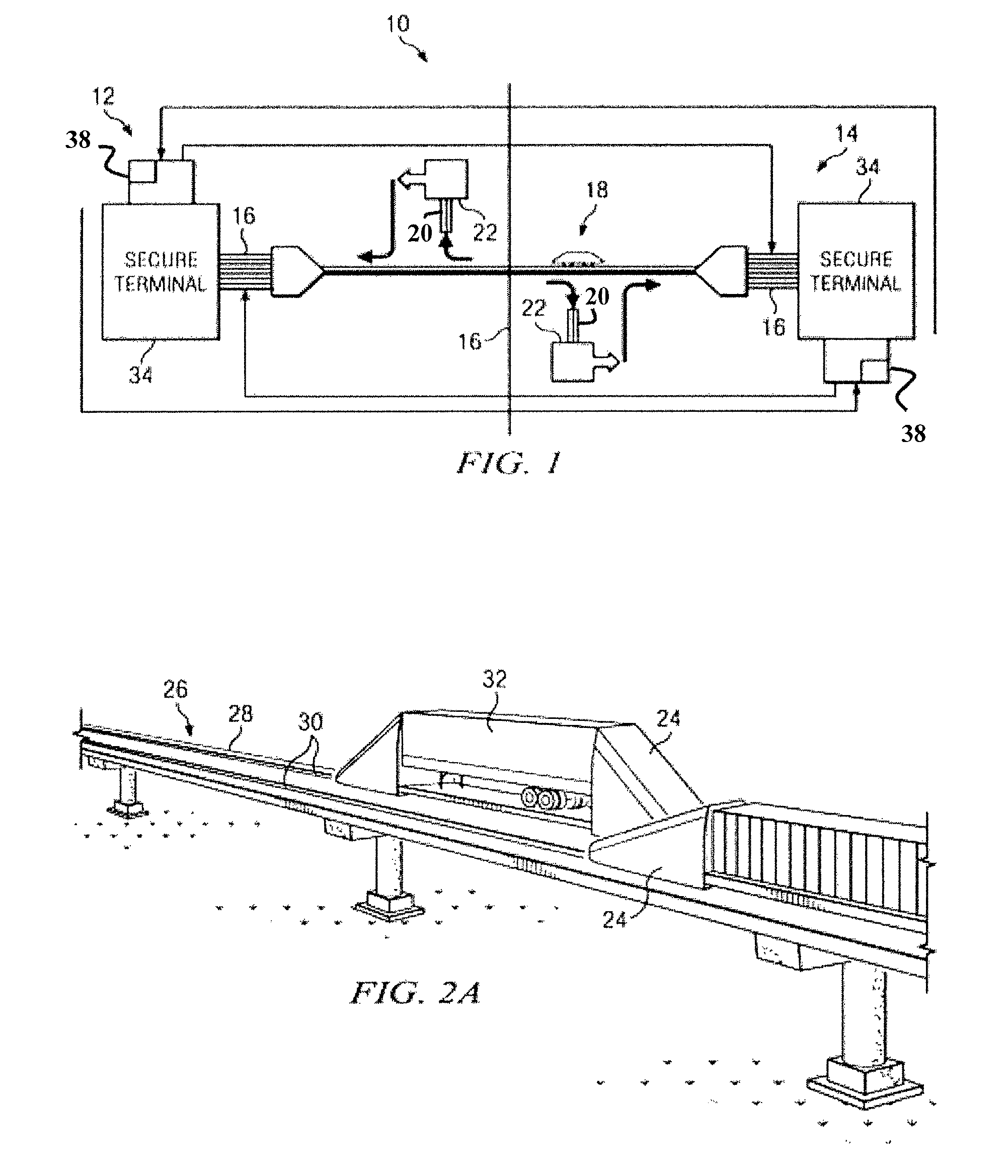
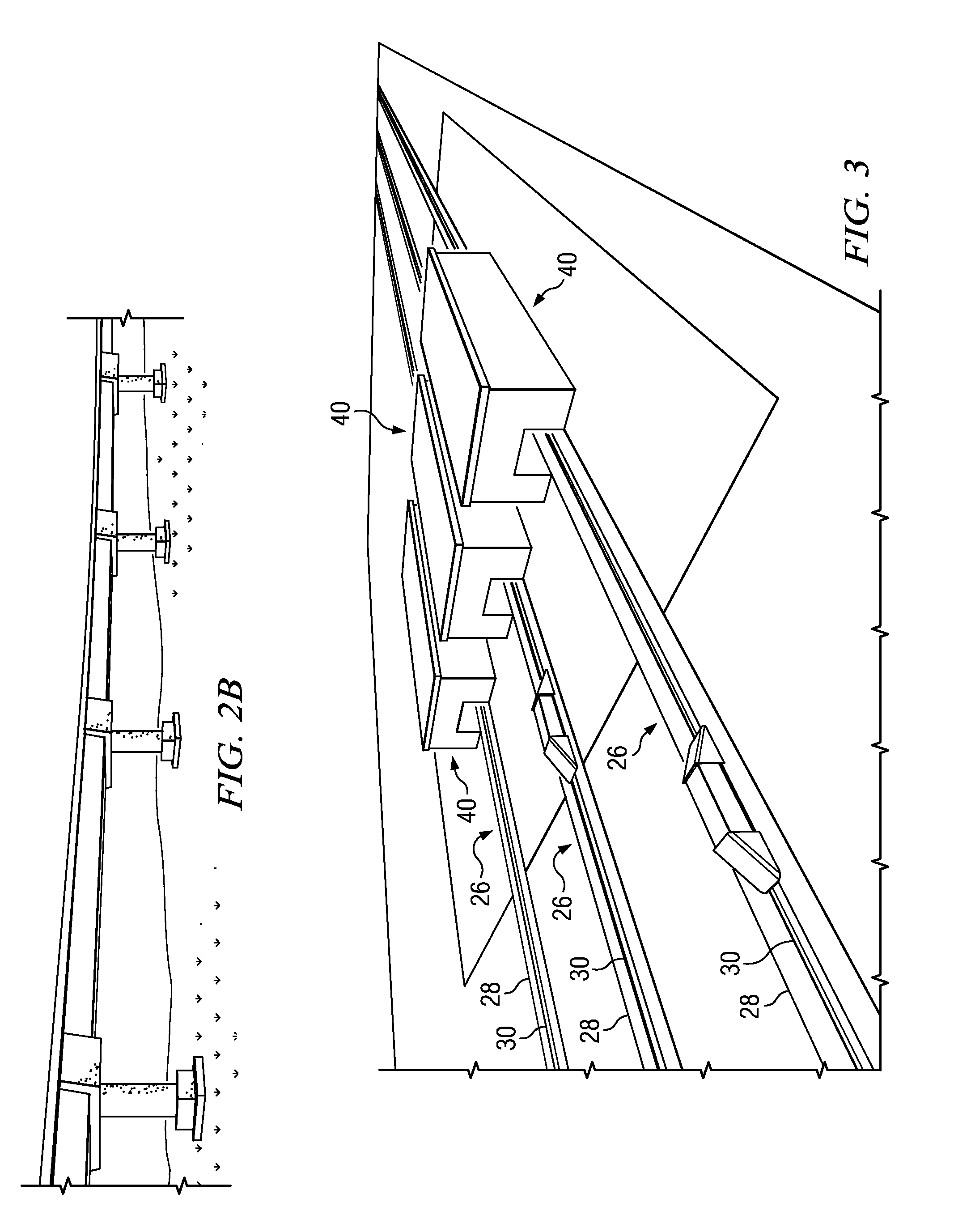
Cargo inspection system
ActiveUS9176076B2Improve integrityImprove securityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMonorailsEngineeringInspection method
According to one embodiment, a cargo inspection method includes transporting a first guideway vehicle over a guideway from a first inspection station to a second inspection station. A first non-intrusive scanning mechanism associated with the first inspection station is used to acquire a first set of data associated with cargo stored in the first guideway vehicle. The first set of data acquired by the first non-intrusive scanning mechanism associated with the first inspection station is analyzed to determine the identity of the cargo stored on the first guideway vehicle. The first set of data acquired by the first non-intrusive scanning mechanism is compared with a first manifest that describes the cargo that is declared to be stored on the first guideway vehicle. It is determined that the first guideway vehicle contains contraband cargo if the identity of the cargo does not match the first manifest.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
Multiple actuating-force shearing machine
InactiveUS8505426B2Sufficient throughputSmall sizeShearing machinesMetal working apparatusHydraulic cylinderTime function
A method, and an apparatus, for operating a hydraulic shearing machine. For cutting a shearing-movement of at least one shear blade which is curved, starting from a starting-position under application of an overall actuating-force and for resetting of the shear blades which were moved for cutting to their starting-position after accomplishment of the shearing-movement, a reset-movement under application of an overall reset-force. The shearing-movement and the reset-movement are accomplished by a hydraulic actuating-mechanism comprising hydraulic cylinders, wherein the overall actuating-force and the overall reset-force being applied to the moved shear blades by at least one hydraulic cylinder of the actuating-mechanism. The magnitude of the overall actuating-force is adjustable by switching one or several hydraulic cylinders of the actuating-mechanism in and out of operation-mode. The method proposes that the positions of the curved shear blade are controlled by a control system by regulating the flow of hydraulic fluid to the hydraulic cylinders according to setpoints for a shear blade position versus time function and the overall actuating-force and overall reset-force requirements.
Owner:PRIMETALS TECH
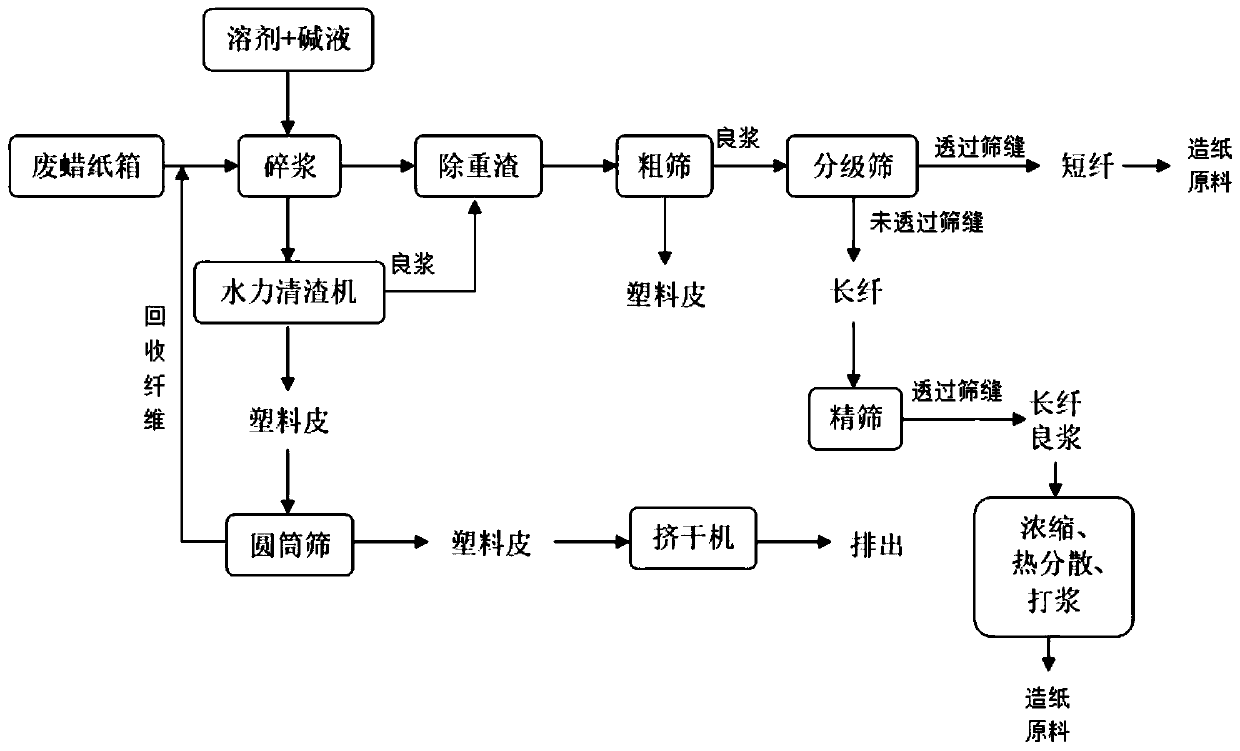
Wax and paper separation process for waste wax cartons and application of wax and paper separation process
InactiveCN110552221AGood disintegrationEasy to separatePulp beating methodsPaper recyclingPulp and paper industryCompressive strength
The invention discloses a wax and paper separation process for waste wax cartons and application of the wax and paper separation process, and belongs to the technical field of paper making. The wax and paper separation process includes the following steps: (1) the waste wax cartons are collected into a pulper; (2) pulping is conducted, specifically, a solvent and lye are added, and meanwhile, an intermittent pulping mode is adopted; (3) heavy slag is removed; (4) coarse sieving is conducted; (5) grading sieving is conducted; (6) fine sieving is conducted; and (7) secondary treatment of good long fiber pulp is conducted. The pulper is a hydraulic pulper, and the rotating speed of the pulper is 300-500 r / min; the solvent is water or pulping white water or a mixture of the water and the pulping white water, the temperature of the solvent is 45-55 DEG C, and the additive amount of the solvent enables the concentration of wax paper to be 8-12%; and the lye includes but is not limited to a caustic soda or potassium hydroxide solution. According to the wax and paper separation process, wax and paper on the wax cartons can be effectively separated, paper fiber after separation of the wax can serve as a raw material for manufacturing the cartons, the obtained cartons have good compressive strength, and the industry use standard is met.
Owner:SHANYING INT HLDG CO LTD
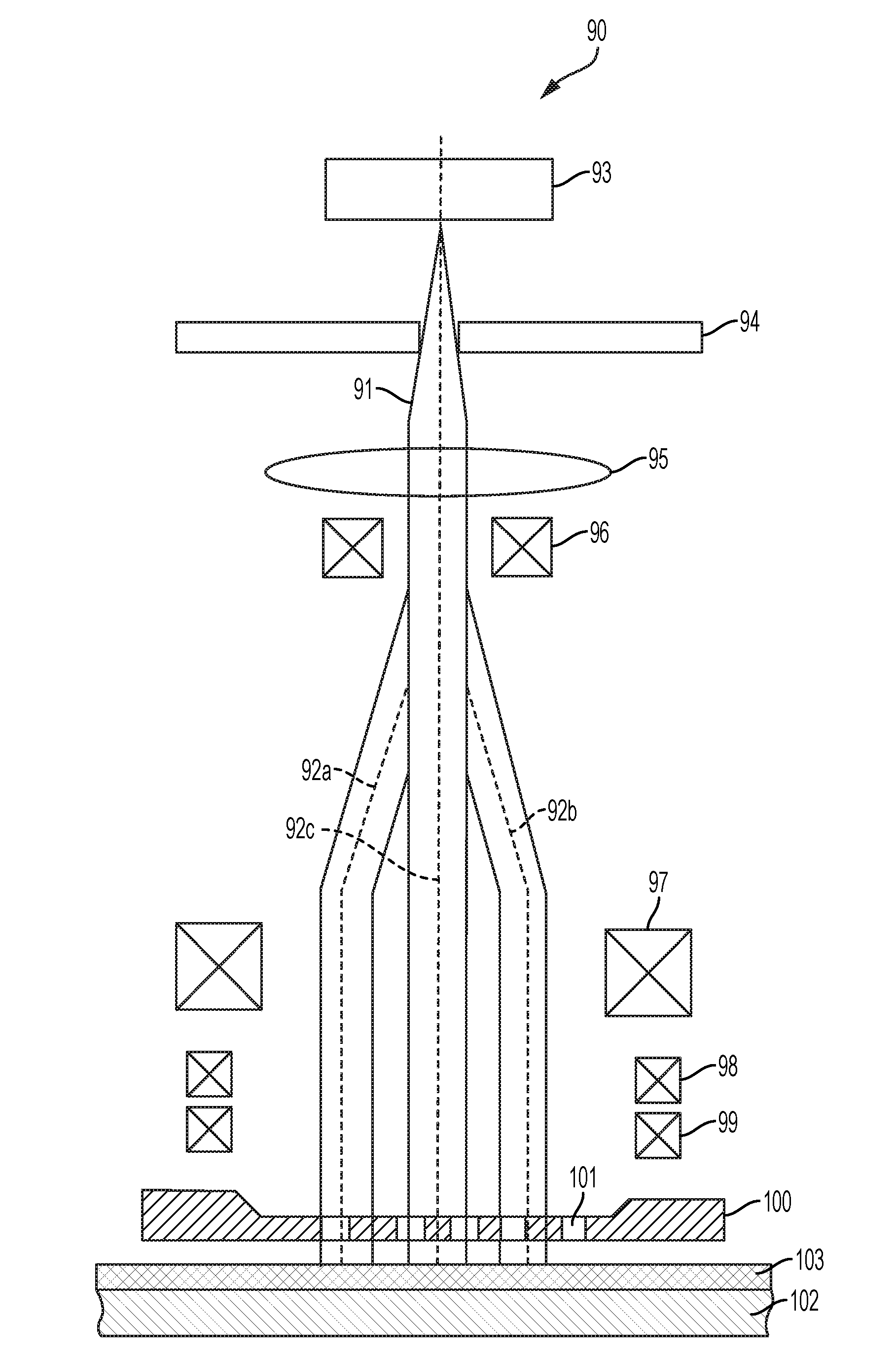
Low energy electron beam lithography
InactiveUS20160274474A1Minimize placement errorCompensate for misalignmentElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResistElectron-beam lithography
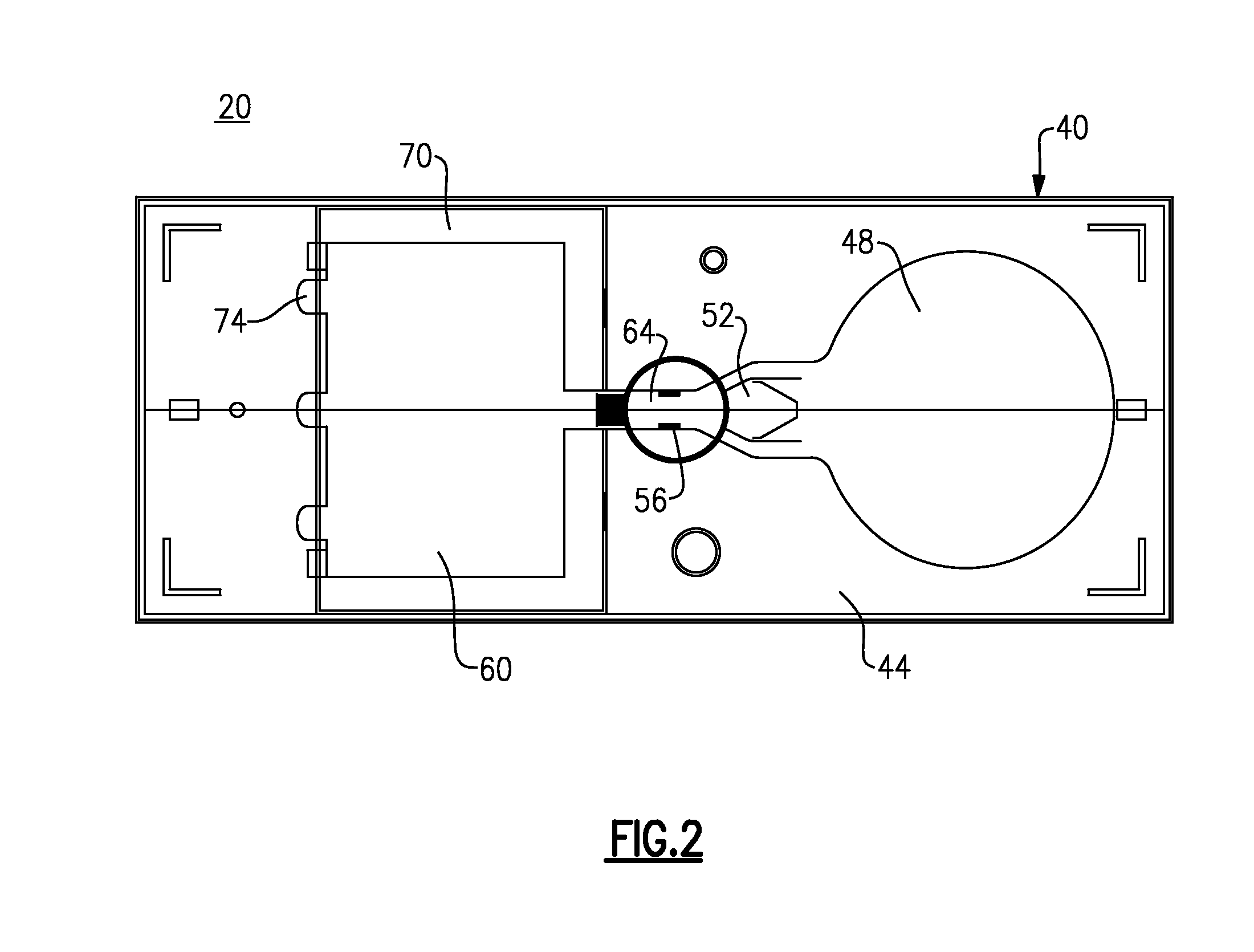
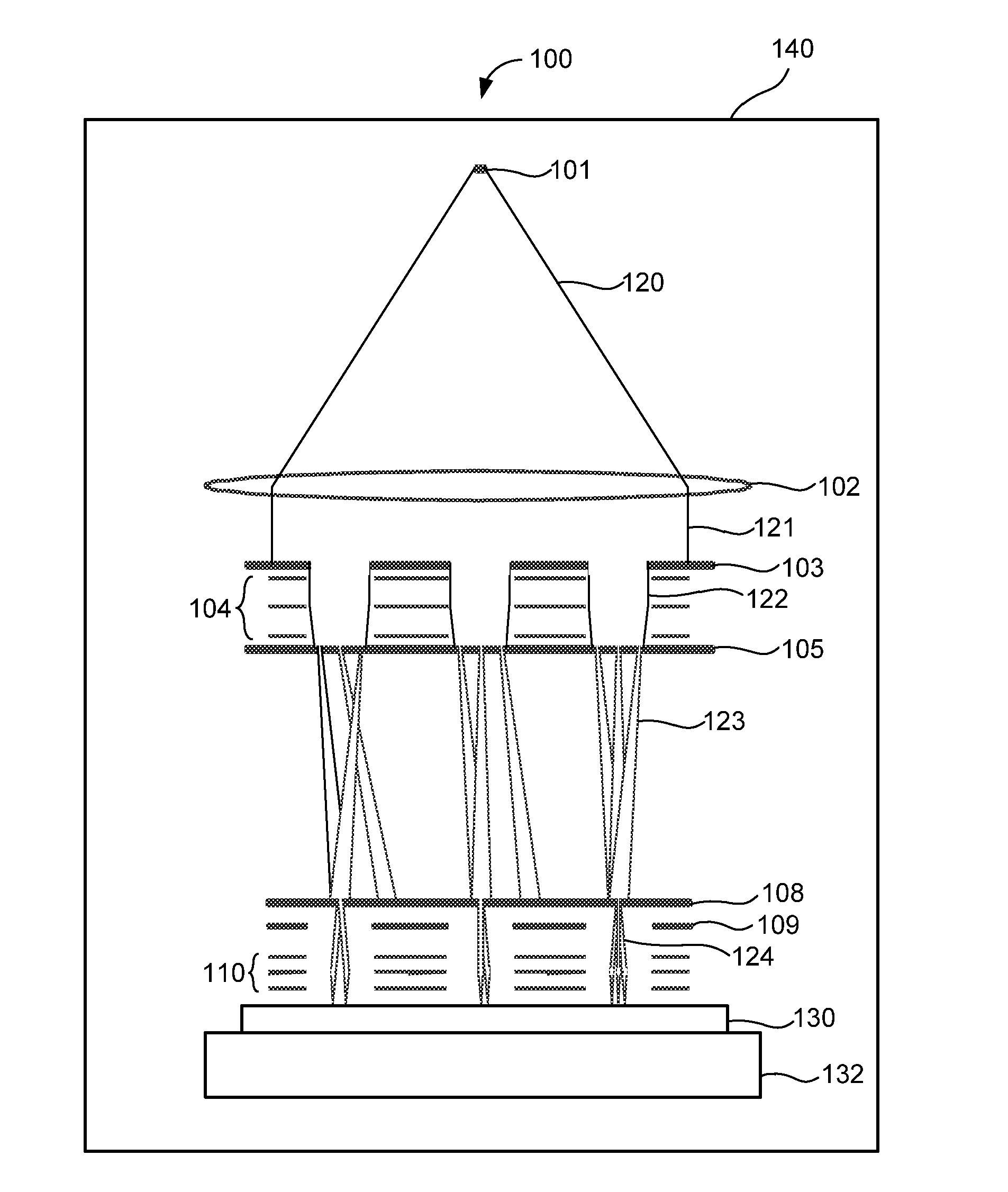
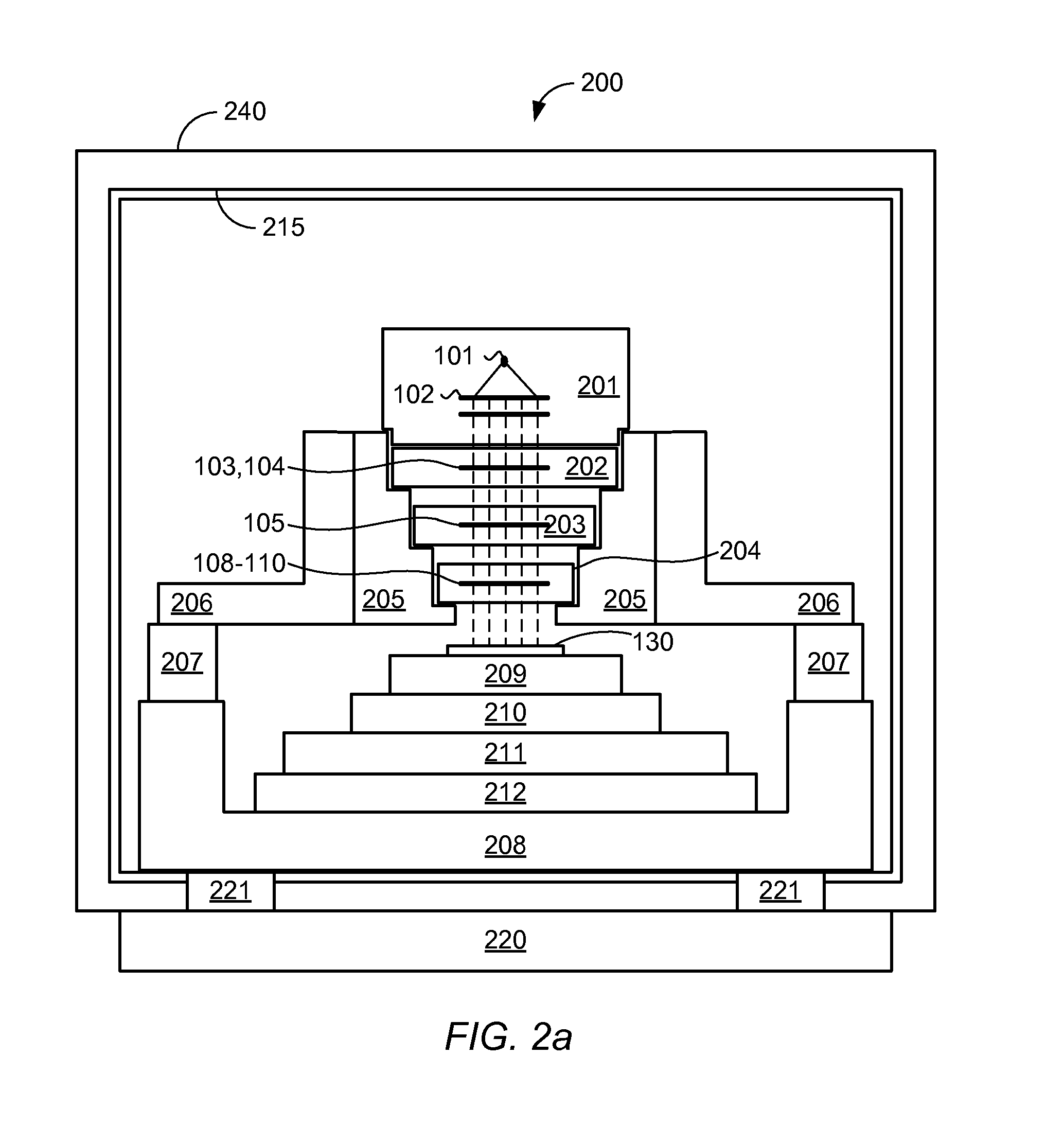
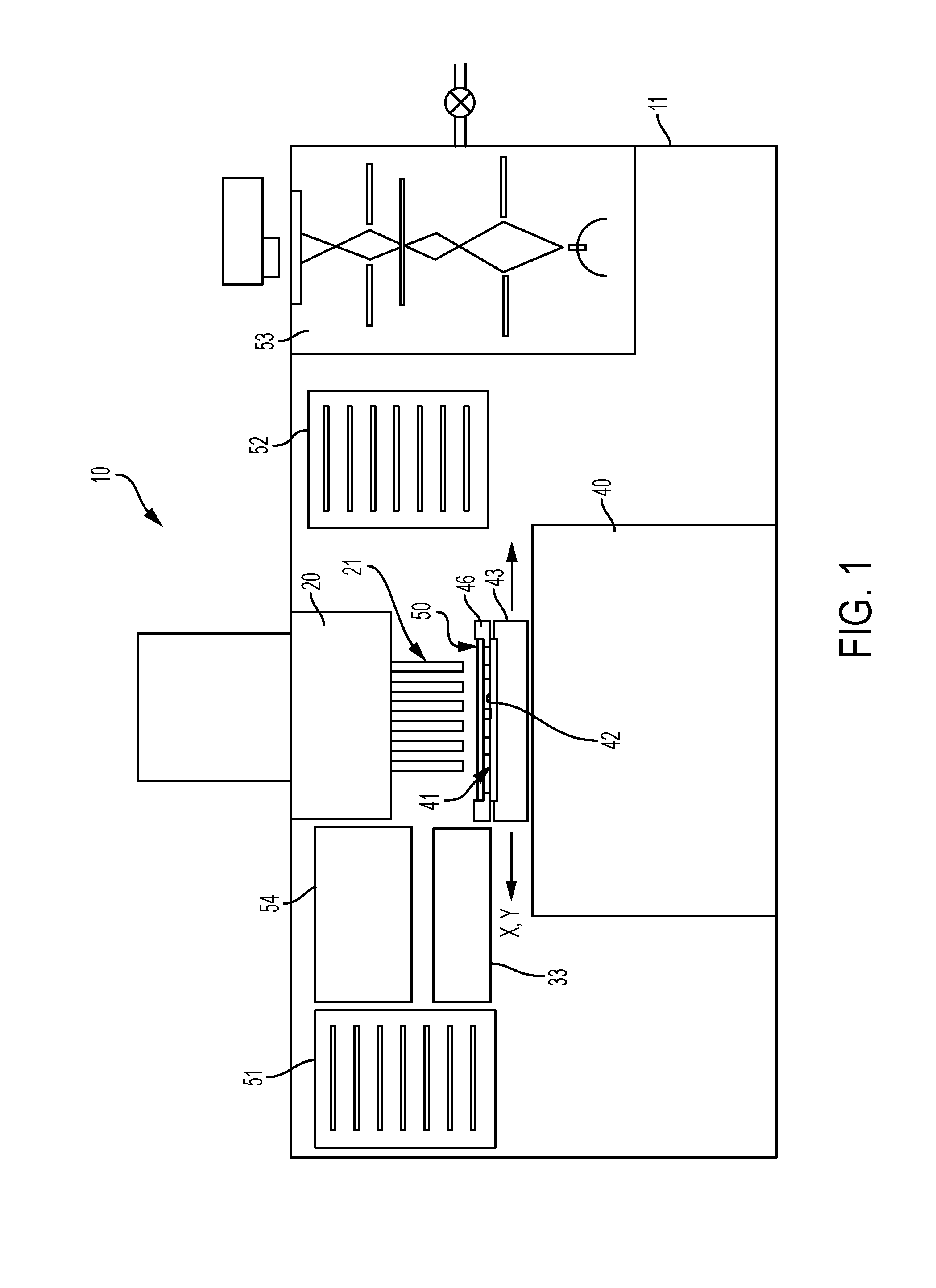
The system for drawing a pattern on a resist layer covering a semiconductor wafer, comprising an electron gun housing unit provided with a plurality of small-sized electron guns (wherein the housing unit has a hollow column section for releasing an electron beam, and a micro deflection unit is disposed inside for adjusting the inclination of the electron beam), a movable stage capable of moving in the X-Y directions, a wafer stage disposed on the movable stage to support a semiconductor wafer, a mask wafer having struts on its rear side for supporting membranes on which a pattern to be transferred is formed, a mask stage for holding the mask wafer, a matching detection unit for detecting a misalignment between the mask wafer and the semiconductor wafer, and an inclination means connected to the micro deflection unit and the matching detection unit for inclining the electron beam.
Owner:UTSUMI TAKAO
Virtual carrier sense networking communication method based on half-duplex channel
InactiveCN104320411AIncrease profitSufficient throughputPower distribution line transmissionConnection managementTelecommunicationsNetworking protocol
The invention discloses an application layer networking communication method based on a half-duplex channel and provides a virtual carrier sense networking communication method based on the half-duplex channel, wherein a virtual carrier sense networking algorithm and a virtual carrier sense networking protocol are included. According to the virtual carrier sense networking algorithm, network nodes of sharing the half-duplex channel are logically divided into master nodes and slave nodes, the master nodes periodically send virtual carrier sense messages to the slave nodes through a drip timer, and the slave nodes match destination addresses of the received virtual carrier sense messages with networking node addresses of the slave nodes. According to the virtual carrier sense networking protocol, an interplate interface adopted for transmitting a protocol message is determined; the format of the protocol message is defined, and constituent elements of an interface message between an application layer and a link layer are stipulated; the message type of a networking control protocol is defined; the drip timer is realized. The virtual carrier sense networking communication method is applied to networking control software in a synchronous data voice transmission network, can increase the utilization rate of the half-duplex channel, provides enough handling capacity for application of synchronous data voice transmission, and achieves the reliable synchronous data voice transmission function in a network environment.
Owner:BEIFANG LIANCHUANG COMM
High Magnetic Hardening Assembly and Method
ActiveUS20140261913A1Improve material performanceImprove power densityFurnace typesIncreasing energy efficiencyHeat treatedMetal
The present invention relates to an apparatus, system and method for heat treating metal parts that are stacked together and moved through an induction heating system and quench system. The present invention is specifically directed to an Induction Thermo Magnetic Processing (ITMP) apparatus, method and system which uses a magnetic field processing with induction high-frequency heat treatment to process metal components so as to inductively hardening materials.
Owner:AJAX MAGNETHERMIC CORP
Scanning system for inspecting anamolies on surfaces
InactiveUS20050036137A1High detection sensitivitySmall spot sizeOptically investigating flaws/contaminationLight beamRelative motion
A high sensitivity and high throughput surface inspection system directs a focused beam of light at a grazing angle towards the surface, to be inspected. Relative motion is caused between the beam and the surface so that the beam scans a scan path covering substantially the entire surface and light scattered along the path is collected for detecting anamolies. The scan path comprises a plurality of arrays of straight scan path segments. The focused beam of light illuminates an area of the surface between 5-15 microns in width and this system is capable of inspecting in excess of about 40 wafers per hour for 150 millimeter diameter wafers (6-inch wafers), in excess of about 20 wafers per hour for 200 millimeter diameter wafers (8-inch wafers) and in excess of about 10 wafers per hour for 300 millimeter diameter wafers (12-inch wafers).
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Cargo Inspection System
ActiveUS20120219389A1Improve integrityImprove securityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMonorailsEngineeringInspection method
According to one embodiment, a cargo inspection method includes transporting a first guideway vehicle over a guideway from a first inspection station to a second inspection station. A first non-intrusive scanning mechanism associated with the first inspection station is used to acquire a first set of data associated with cargo stored in the first guideway vehicle. The first set of data acquired by the first non-intrusive scanning mechanism associated with the first inspection station is analyzed to determine the identity of the cargo stored on the first guideway vehicle. The first set of data acquired by the first non-intrusive scanning mechanism is compared with a first manifest that describes the cargo that is declared to be stored on the first guideway vehicle. It is determined that the first guideway vehicle contains contraband cargo if the identity of the cargo does not match the first manifest.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
Method and apparatus for communicating data between computer devices
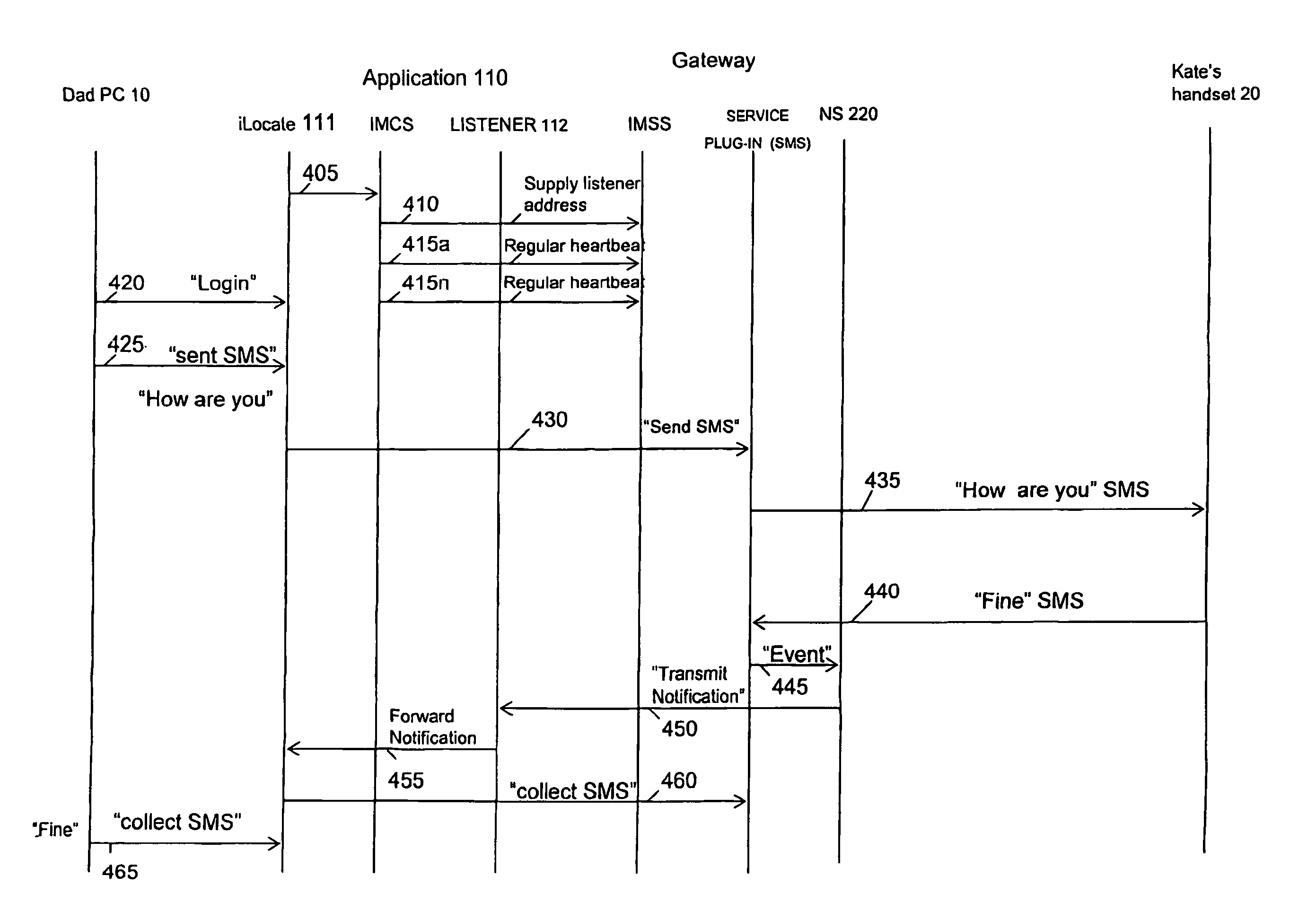
ActiveUS8666940B2Easy to useLaunched cost-effectivelyDigital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsEngineeringClient server systems
A client server system uses a client subsystem, a server subsystem and an interconnecting data network. The client subsystem client application initiates a secure connection over the network with the server subsystem which includes a server application cooperating with the client application to complete a secure connection with the client application and which transmits output data over such a connection in response to requests for service by the client application. The server subsystem additionally generates a notification, in response to detecting an event in the absence of a secure connection between the server and the client, and transmits the notification to the notification server which forwards the notification over the interconnecting network to the client application.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
Low energy electron beam lithography
InactiveUS9557658B2Sufficient accuracySufficient throughputElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResistElectron-beam lithography
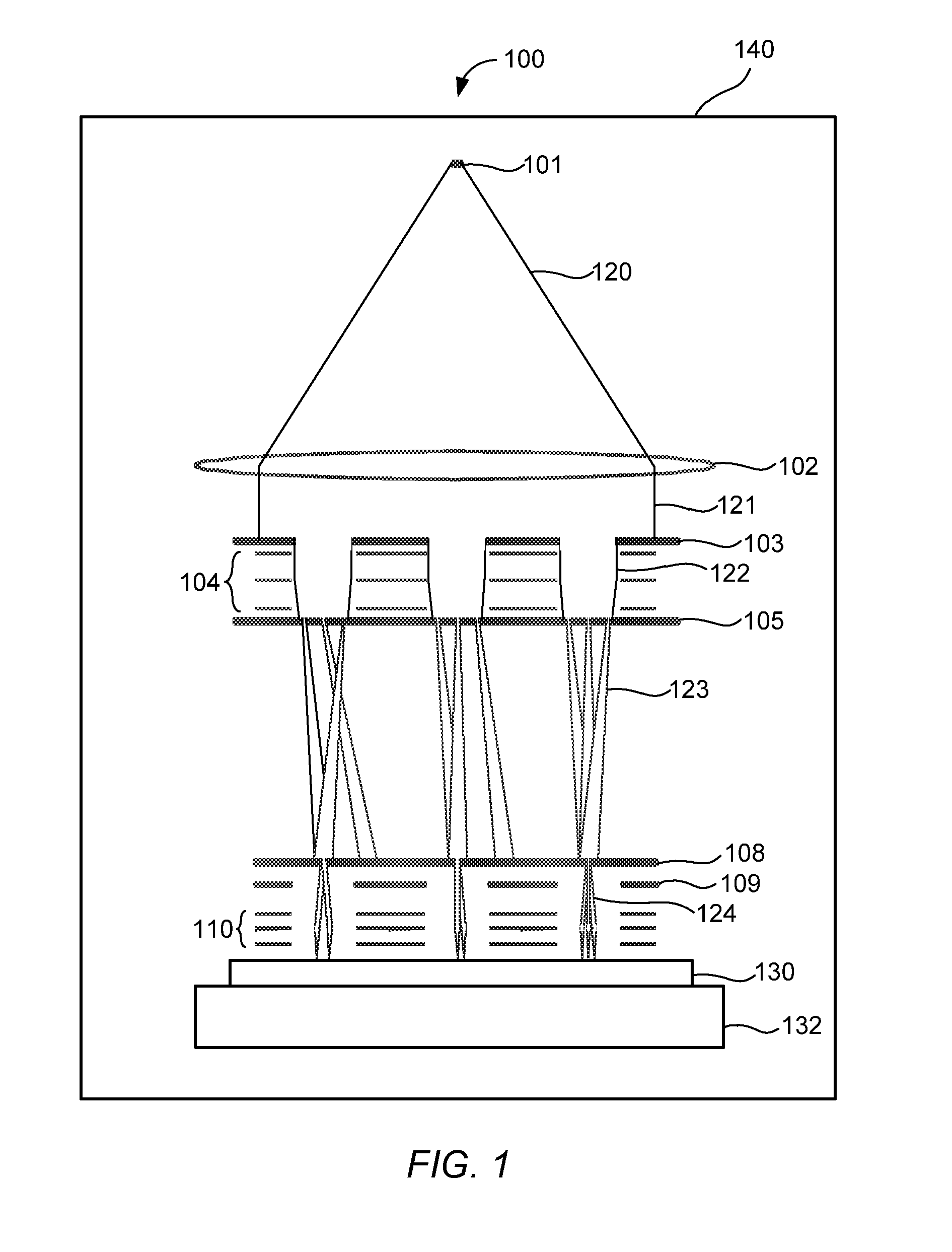
The system for drawing a pattern on a resist layer covering a semiconductor wafer, comprising an electron gun housing unit provided with a plurality of small-sized electron guns (wherein the housing unit has a hollow column section for releasing an electron beam, and a micro deflection unit is disposed inside for adjusting the inclination of the electron beam), a movable stage capable of moving in the X-Y directions, a wafer stage disposed on the movable stage to support a semiconductor wafer, a mask wafer having struts on its rear side for supporting membranes on which a pattern to be transferred is formed, a mask stage for holding the mask wafer, a matching detection unit for detecting a misalignment between the mask wafer and the semiconductor wafer, and an inclination means connected to the micro deflection unit and the matching detection unit for inclining the electron beam.
Owner:UTSUMI TAKAO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com