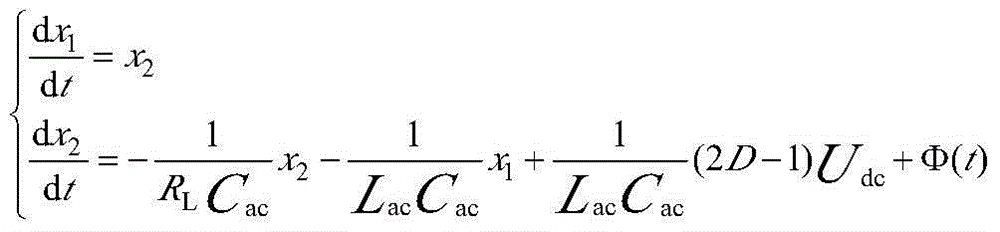Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
277 results about "Back stepping" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
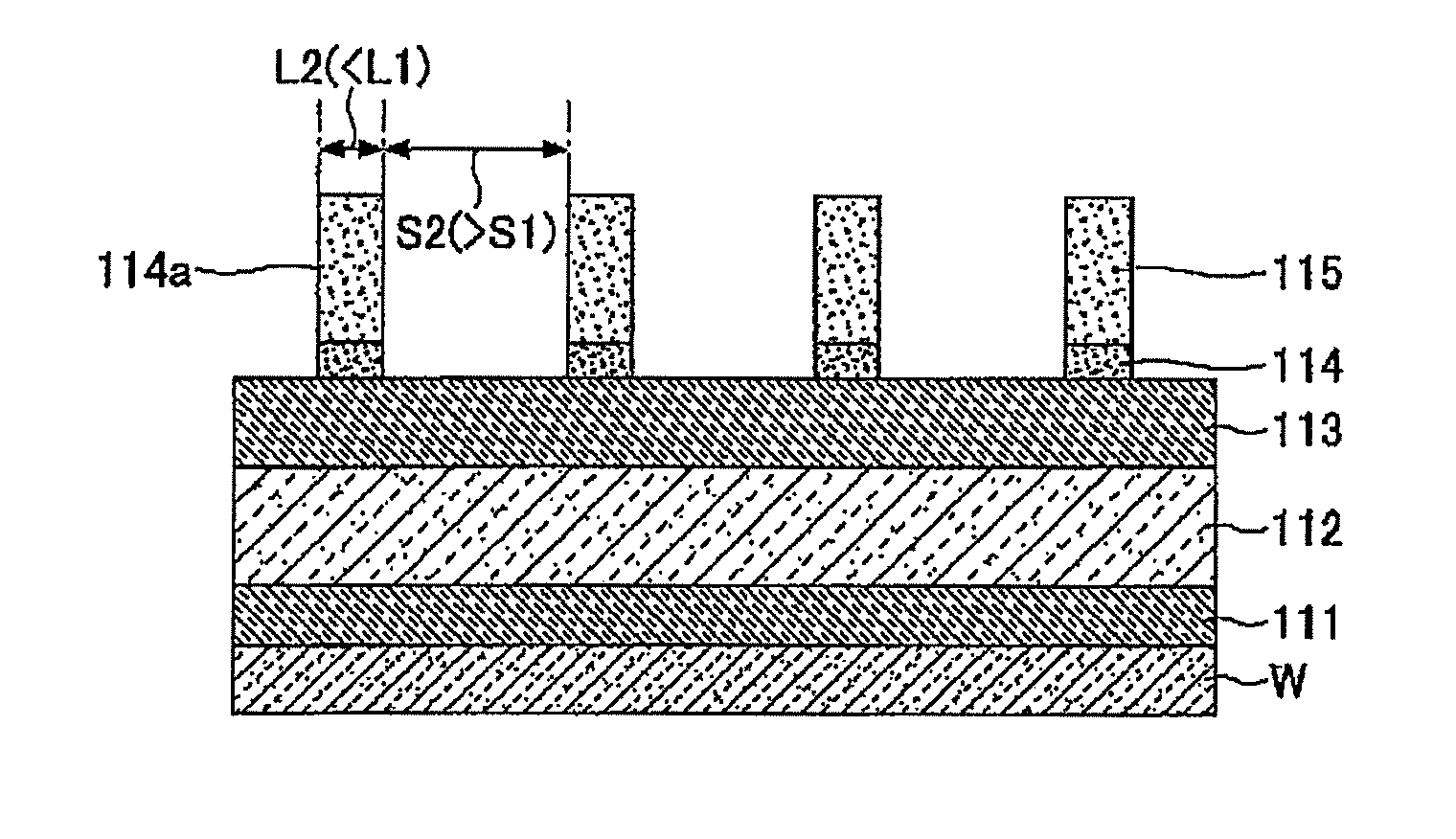
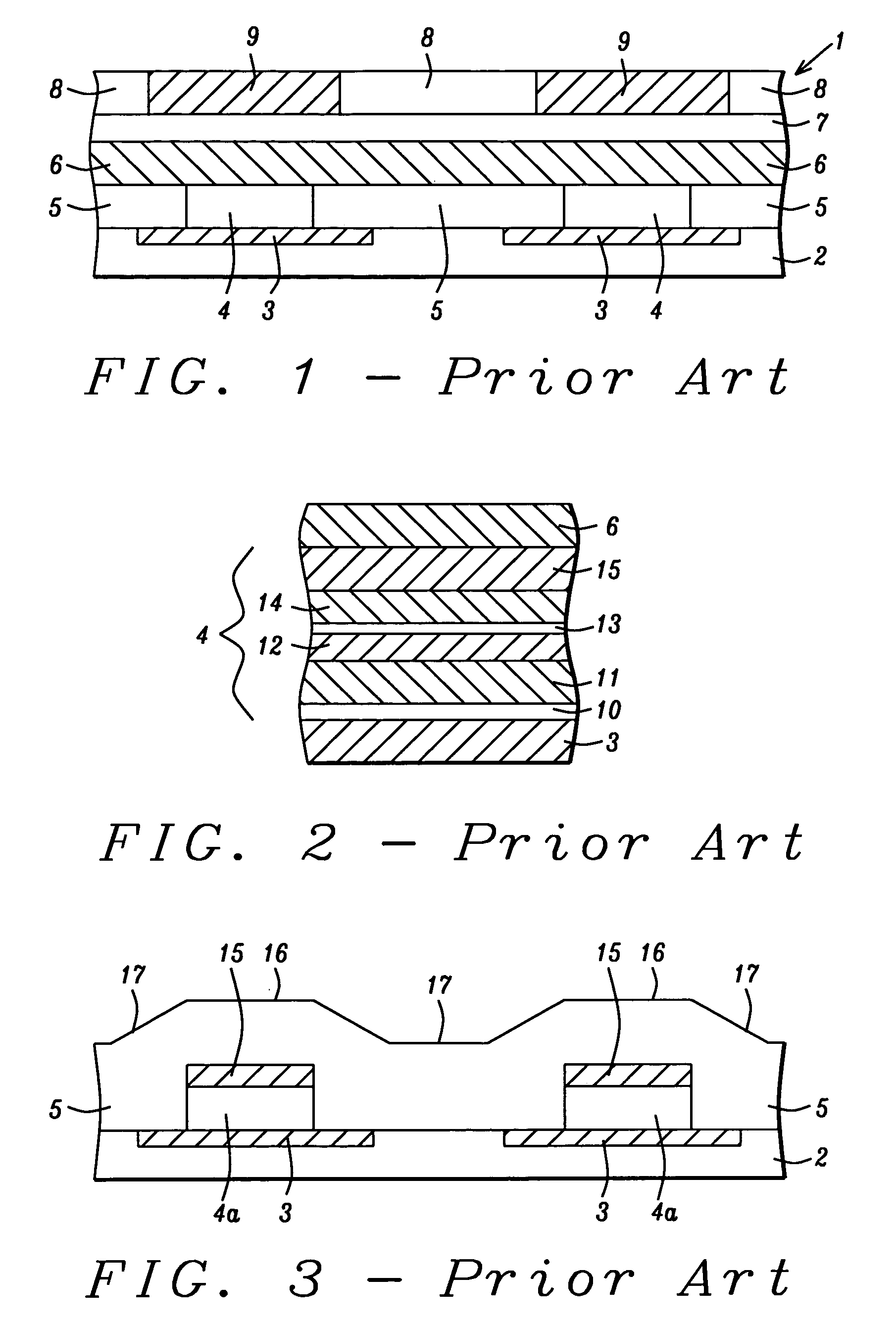
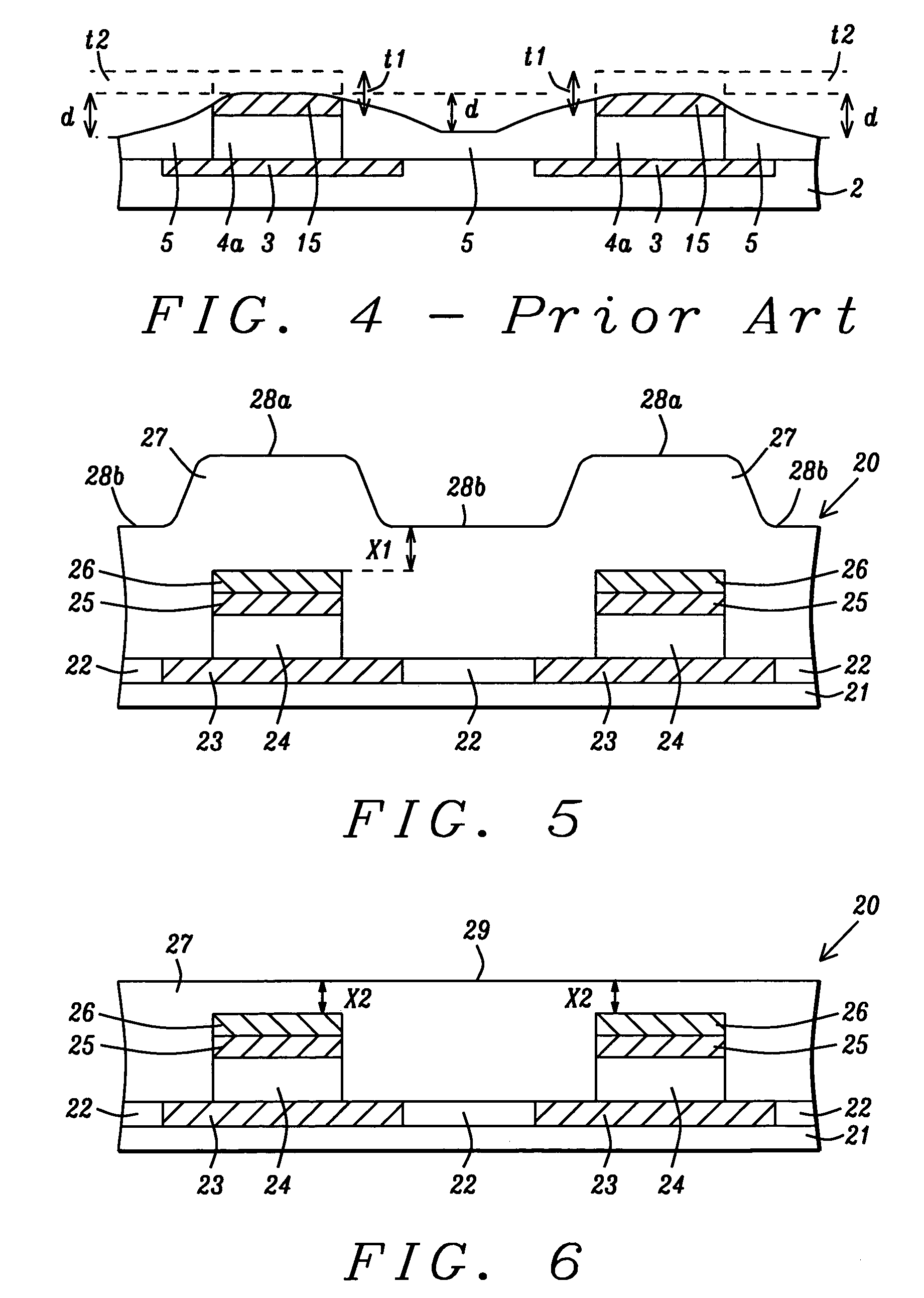
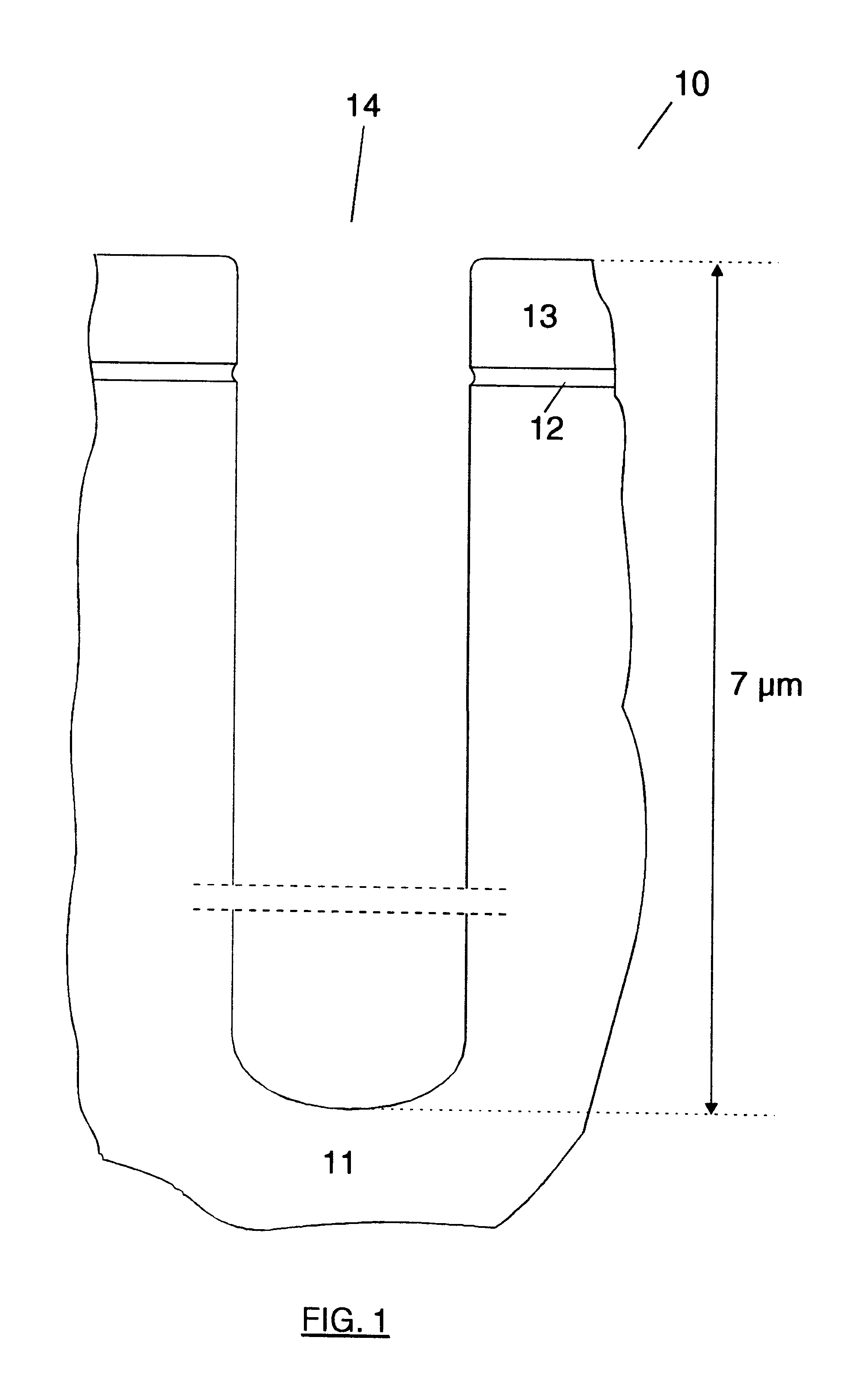
Method of forming mask pattern and method of manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS20130023120A1Avoid deformationElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResistSilicon oxide
A method of forming a mask pattern includes a first pattern forming step of etching an anti-reflection coating film by using as a mask a first line portion made up of a photo resist film formed on the anti-reflection film to form a pattern including a second line portion made up of the photo resist film and the anti-reflection film; an irradiation step of irradiating the photo resist film with electrons; a silicon oxide film forming step to cover the second line portion isotropically; and an etch back step of etching back the silicon oxide film such that the silicon oxide film is removed from the top of the second line portion as sidewalls of the second line portion. The method further includes a second pattern forming step of ashing the second line portion to form a mask pattern including a third line portion made up of the silicon oxide film and remains.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
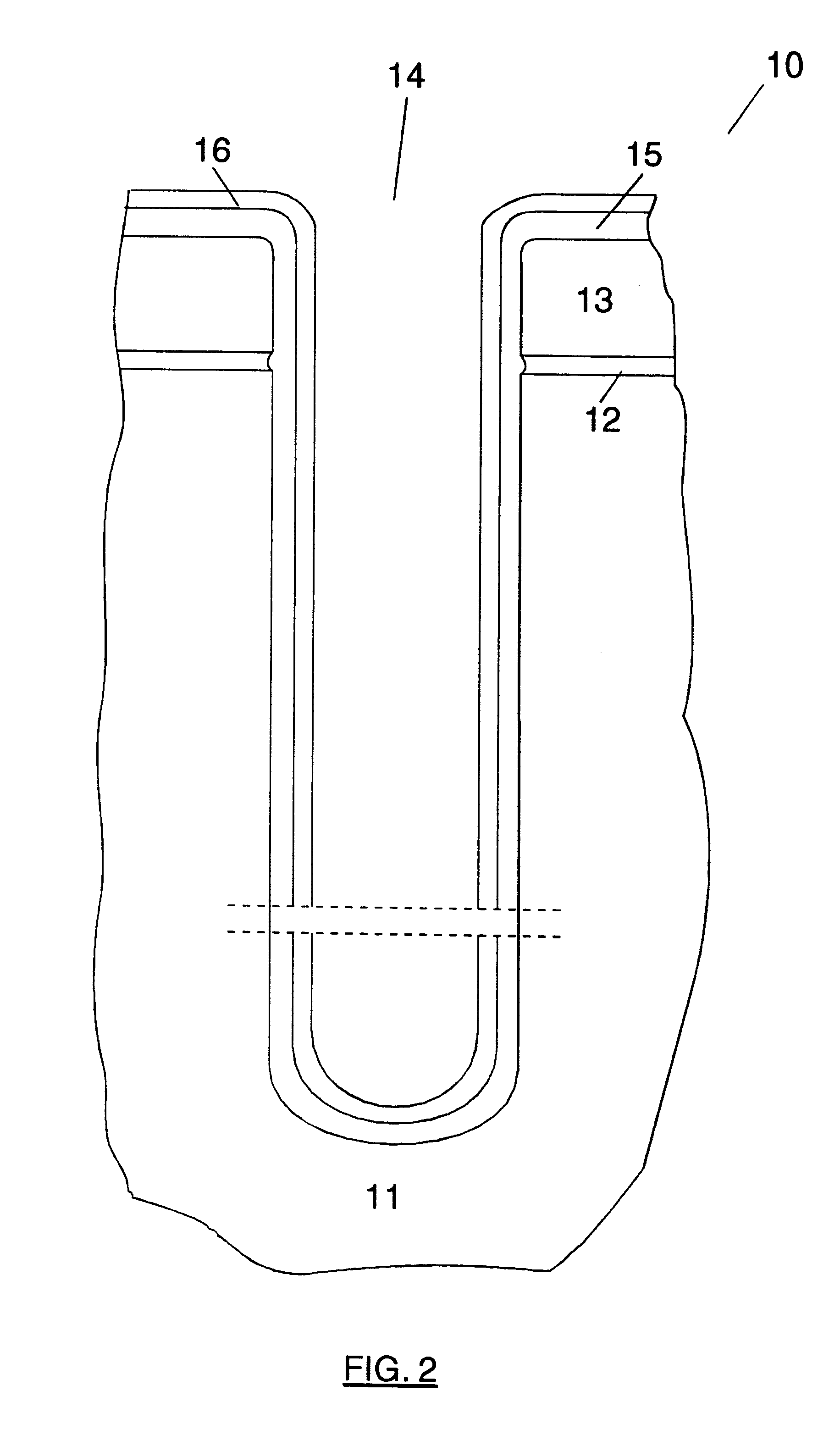
MRAM cell structure and method of fabrication
ActiveUS7045368B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBit lineInsulation layer
An MRAM structure is disclosed where the distance from a bit line or word line to an underlying free layer in an MTJ is small and well controlled. As a result, the bit line or word line switching current is reduced and tightly distributed for better device performance. A key feature in the method of forming the MRAM cell structure is a two step planarization of an insulation layer deposited on the MTJ array. A CMP step flattens the insulation layer at a distance about 60 to 200 Angstroms above the cap layer in the MTJ. Then an etch back step thins the insulation layer to a level about 50 to 190 Angstroms below the top of the cap layer. Less than 5 Angstroms of the cap layer is removed. The distance variation from the free layer to an overlying bit line or word line is within + / −5 Angstroms.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
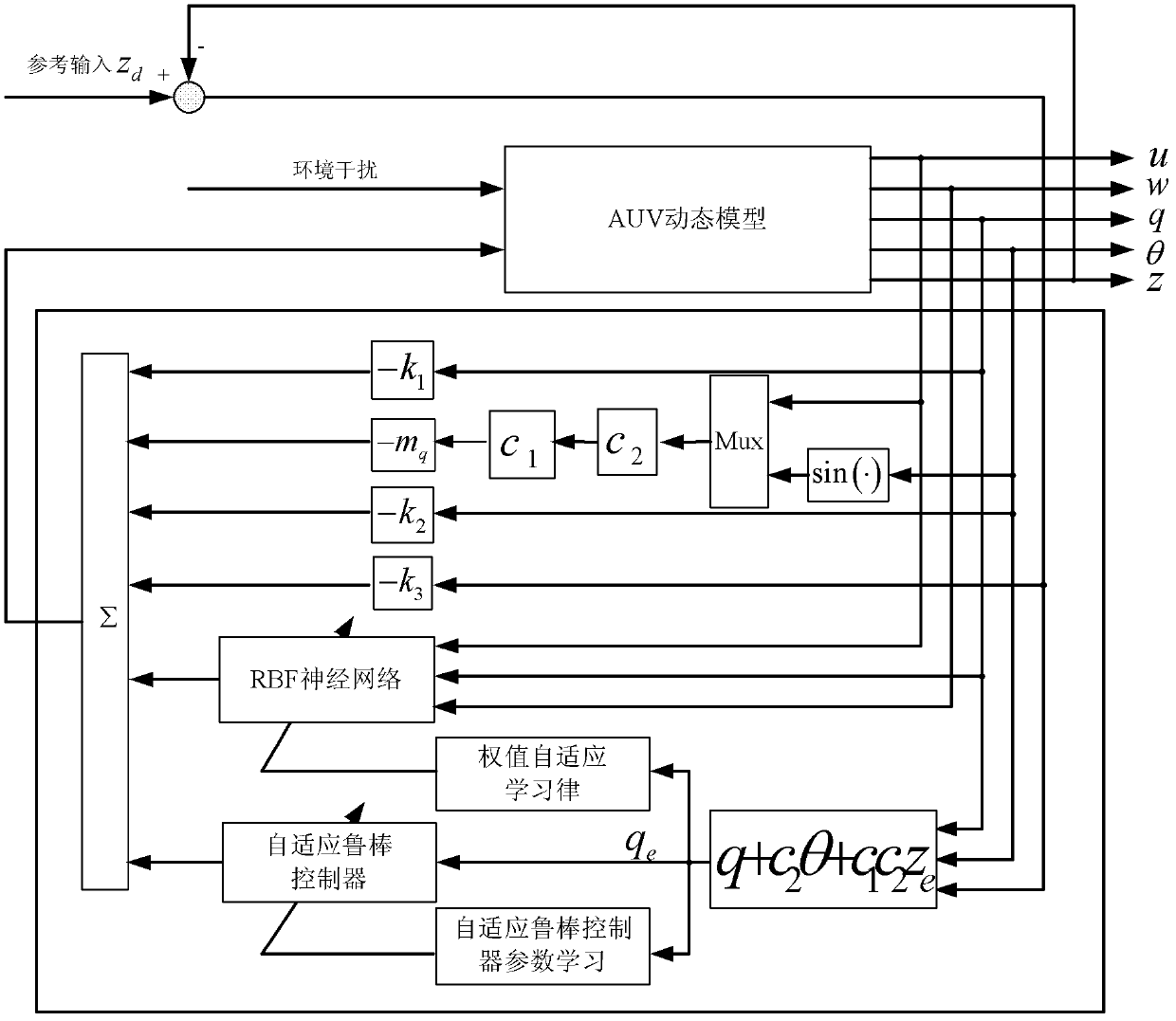
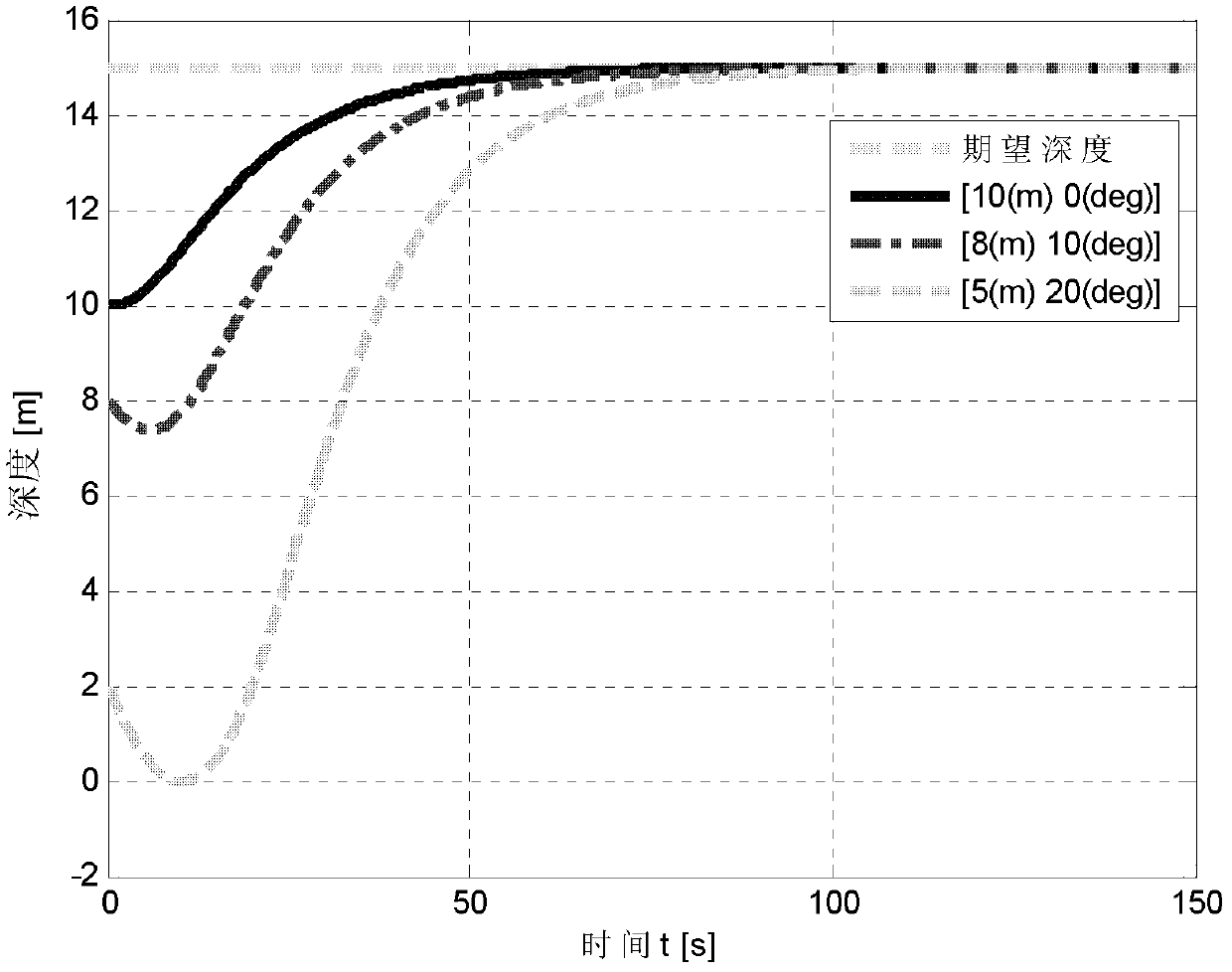
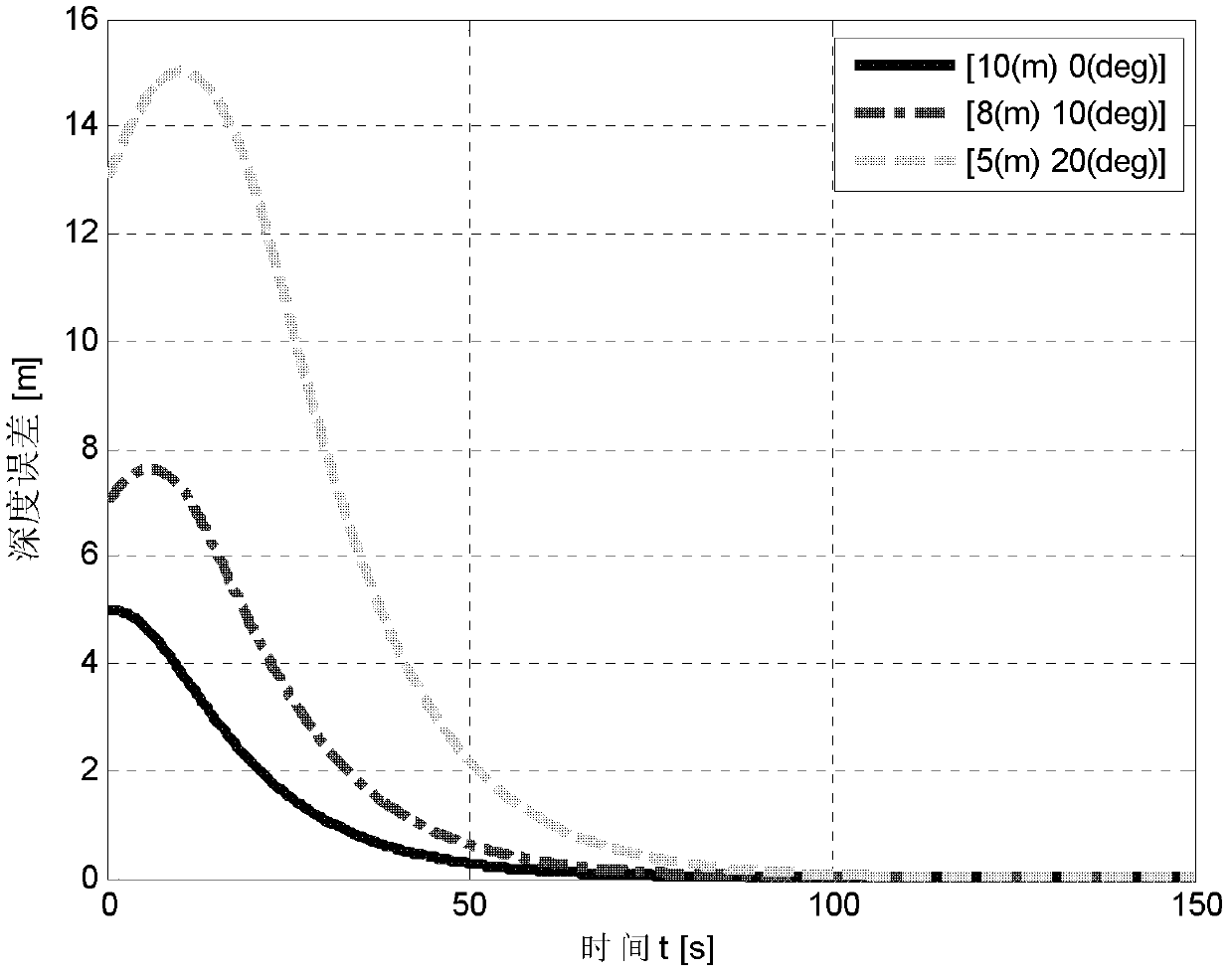
Deepening controlling method of underactuated automatic underwater vehicle based on neural network back stepping method
ActiveCN102385316AAvoid more complicated formsPromote engineering applicationAdaptive controlBack steppingMarine currents
A deepening controlling method of an underactuated automatic underwater vehicle based on a neural network back stepping method relates to the technical field of control of the underactuated automatic underwater vehicle. The deepening controlling method includes first collecting pressure information through a pressure sensor, obtaining corresponding depth of the automatic underwater vehicle (AUV) by calculation according to the pressure information, then building a mathematical model of the underactuated automatic underwater vehicle and a robust deepening controller model, building a mathematical model of the underactuated AUV according to ocean current environment and AUV water power parameter, designing the robust deepening controller model by adopting the feedback gained back stepping method, finally obtaining online learning arithmetic based on neural network weight and self-adaptive law of self-adaptive robust controller parameter, conducting online recognition and error estimation on uncertainty existing in the obtained mathematical model, compensating and optimizing final output signals of the controller, and achieving deepening control of the underactuated AUV by adopting the controller.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
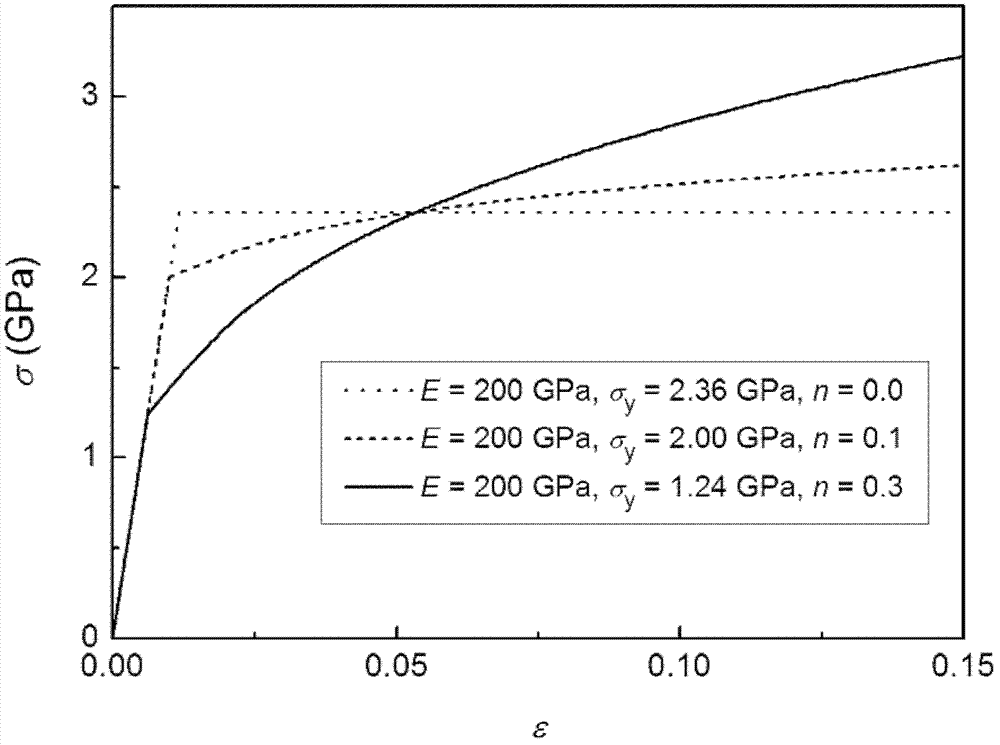
Process for characterizing elastoplasticity of metal material through indentation method
The invention discloses a process for characterizing the elastoplasticity of a metal material by introducing an extra residual area through an indentation method, belonging to the field of researches on the mechanical properties of a material. Experiment devices required by the method mainly comprise an indentor, and an atomic force microscope or a three-dimensional optical imaging system. The method mainly comprises the following steps: indenting a material to be tested through the indentor to obtain an indention load displacement curve, extracting relevant parameters from the indention load displacement curve, substituting the extracted parameters to an established model, and calculating to obtain the elastoplasticity of the material. The method mainly has the following advantages: different materials having similar indention curves can be successfully separated, and the obtained solution is only; and the solution obtained through back-stepping has a high precision. So the only high-precision elastoplasticity of the indented material can be obtained through back-stepping by utilizing the theoretic model in the invention.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
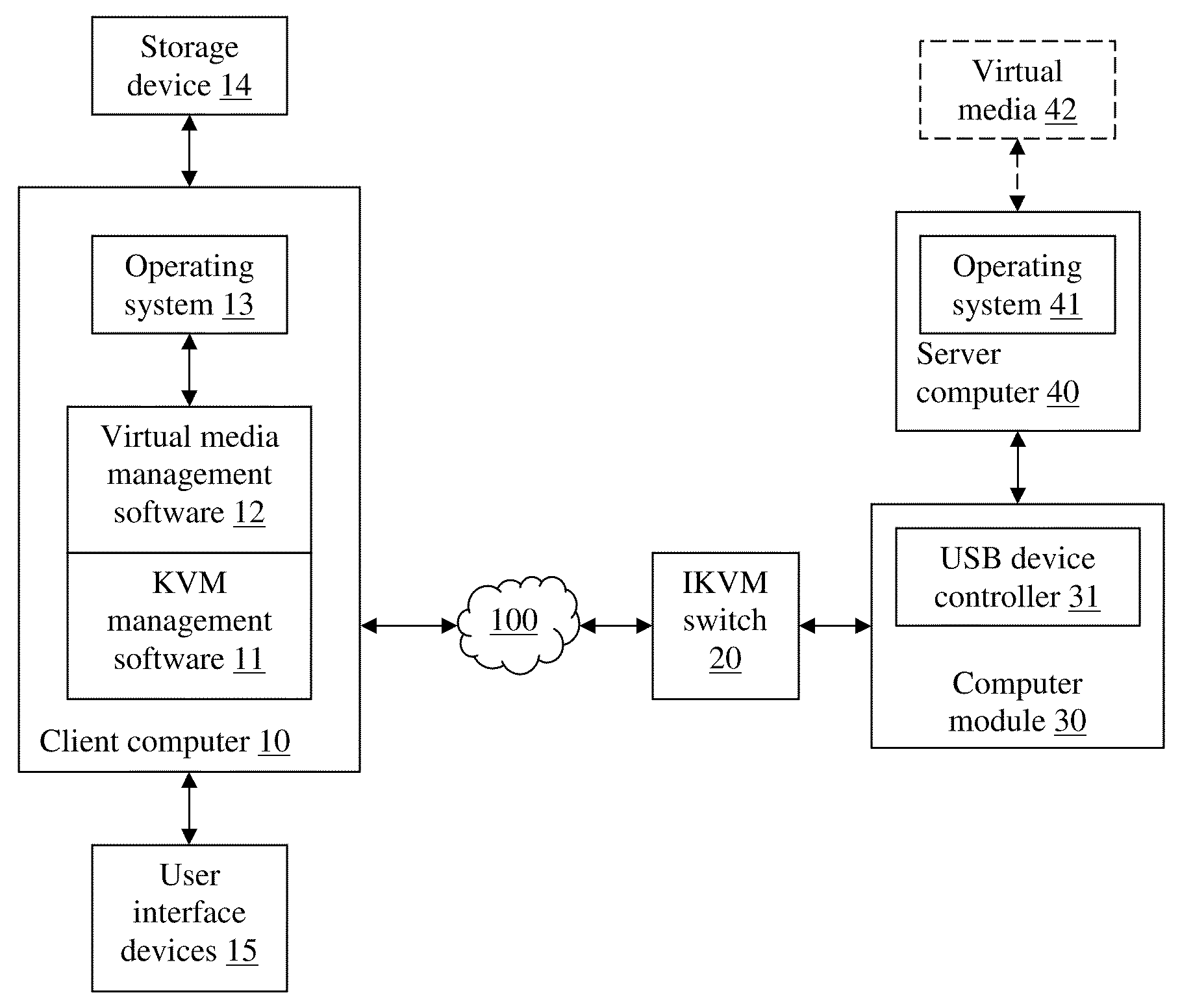
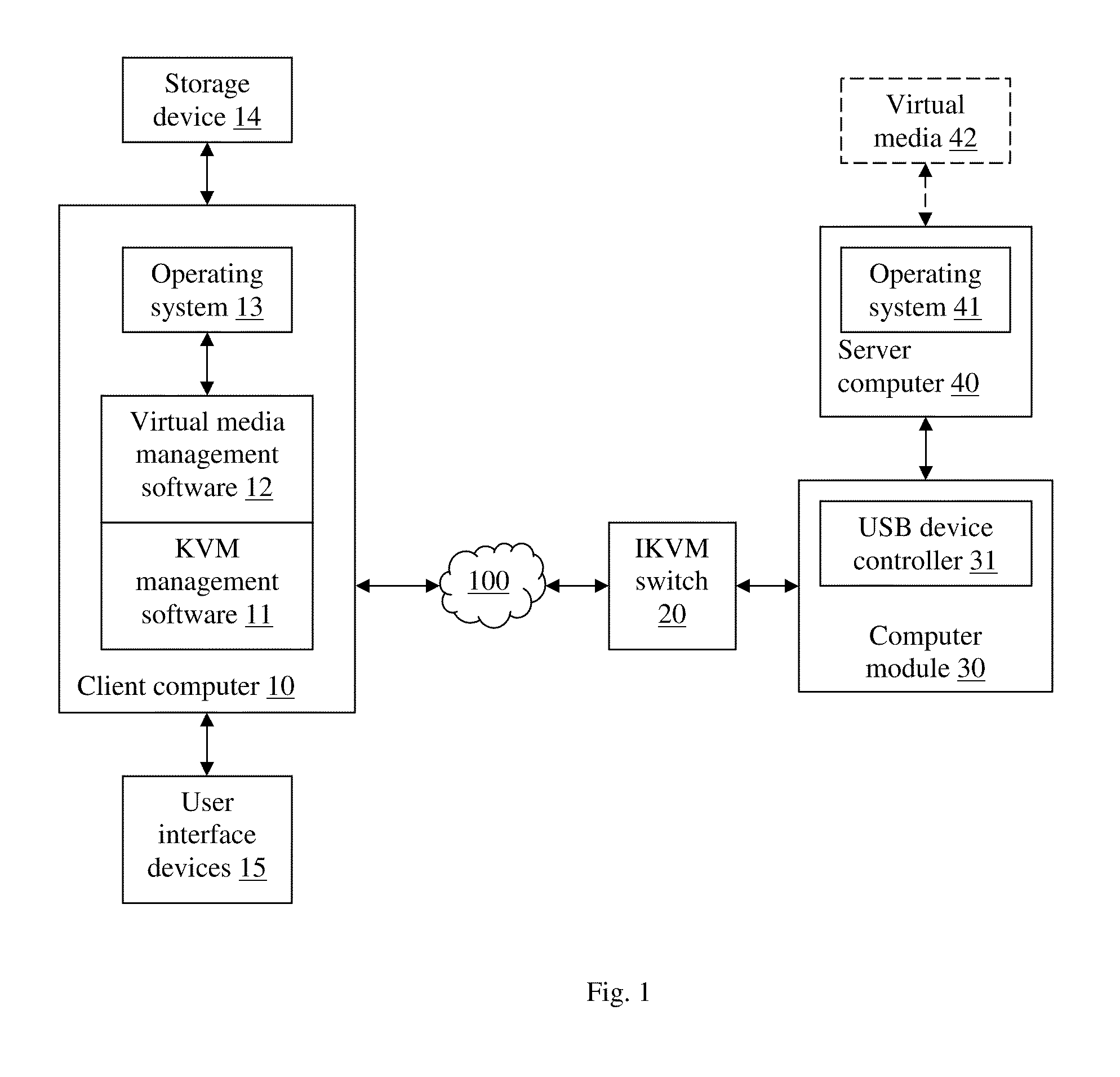
Virtual media with folder-mount function
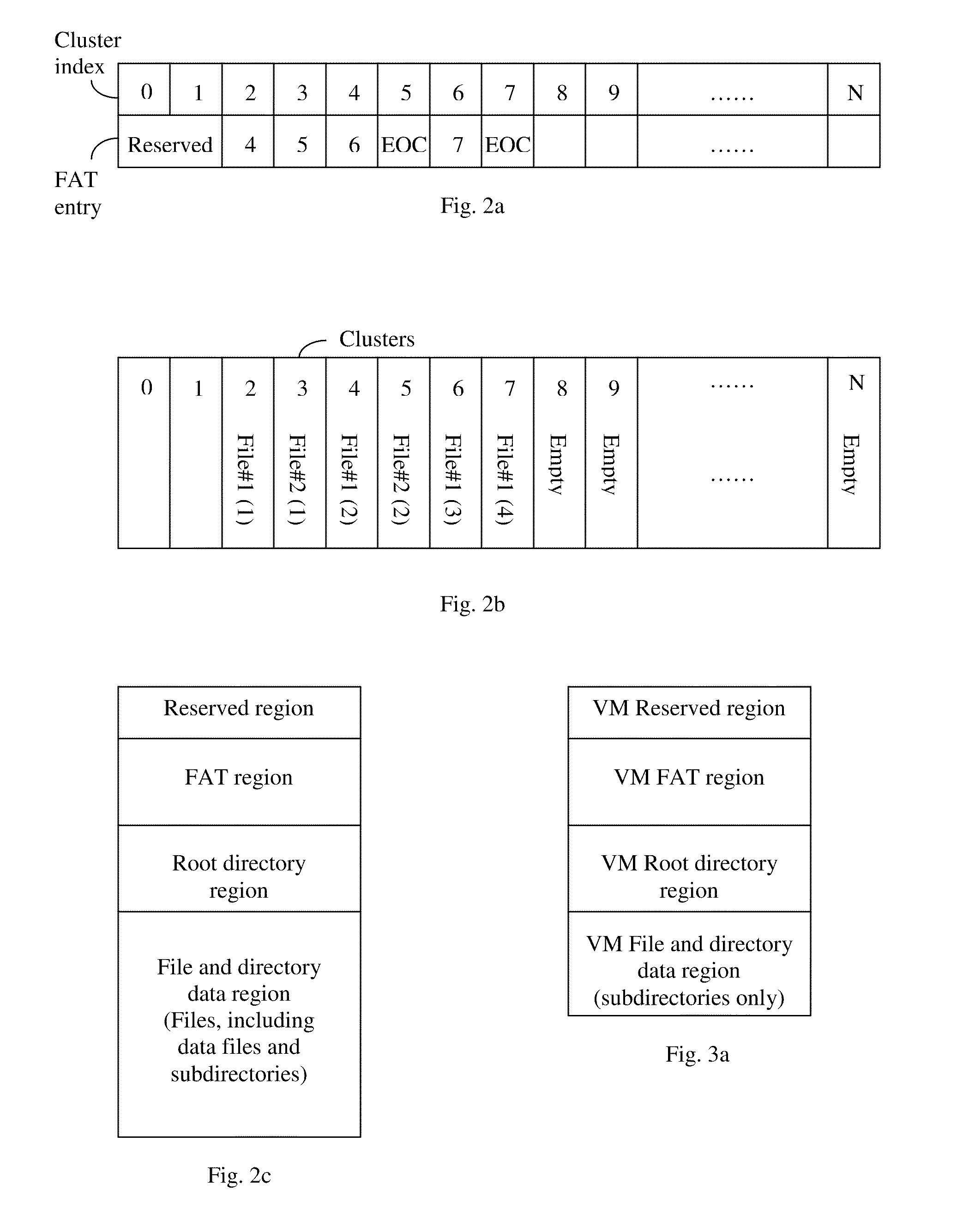
ActiveUS20110016466A1Eliminate the problemMultiple digital computer combinationsSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationFile allocationFile system
A virtual media (VM) method for mounting a folder stored in a storage device of a client for accessed by a server as a virtual drive. The client assigns virtual cluster indices to each file in the folder, and creates a file-cluster index table to store the assigned virtual cluster indices. The client also creates a VM file system complying with the FAT file system standard except that only subdirectories and no data files are stored in the VM FAT file system. The VM FAT table uses virtual cluster indices rather than actual cluster indices. Data written by the server are stored in a temporary data area without modifying the actual file system of the storage device. The virtual sectors requested to be written are “dirty”, and the dirty sector numbers and corresponding temporary sector numbers are stored in a dirty sector index table for use in a write-back step.
Owner:ATEN INT CO
Tail angle restraining guidance method based on sliding mode control
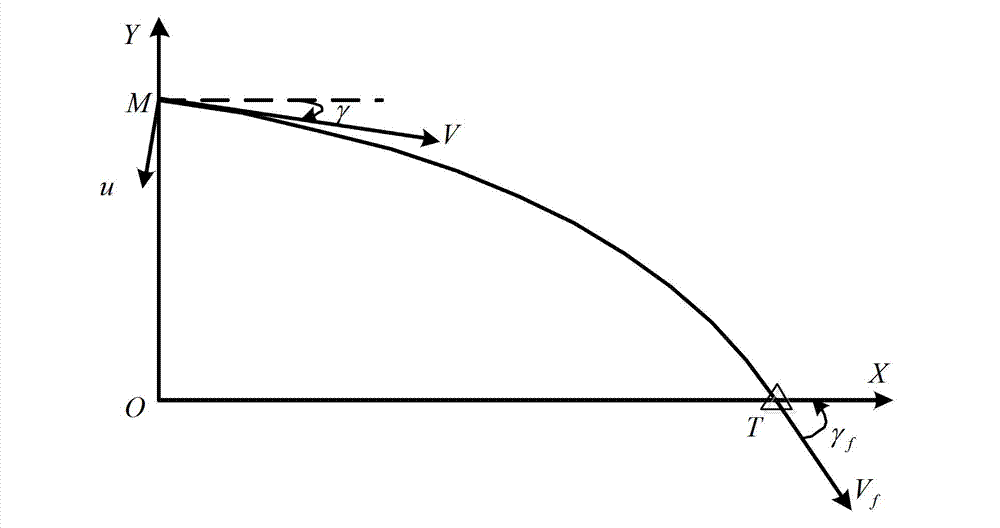
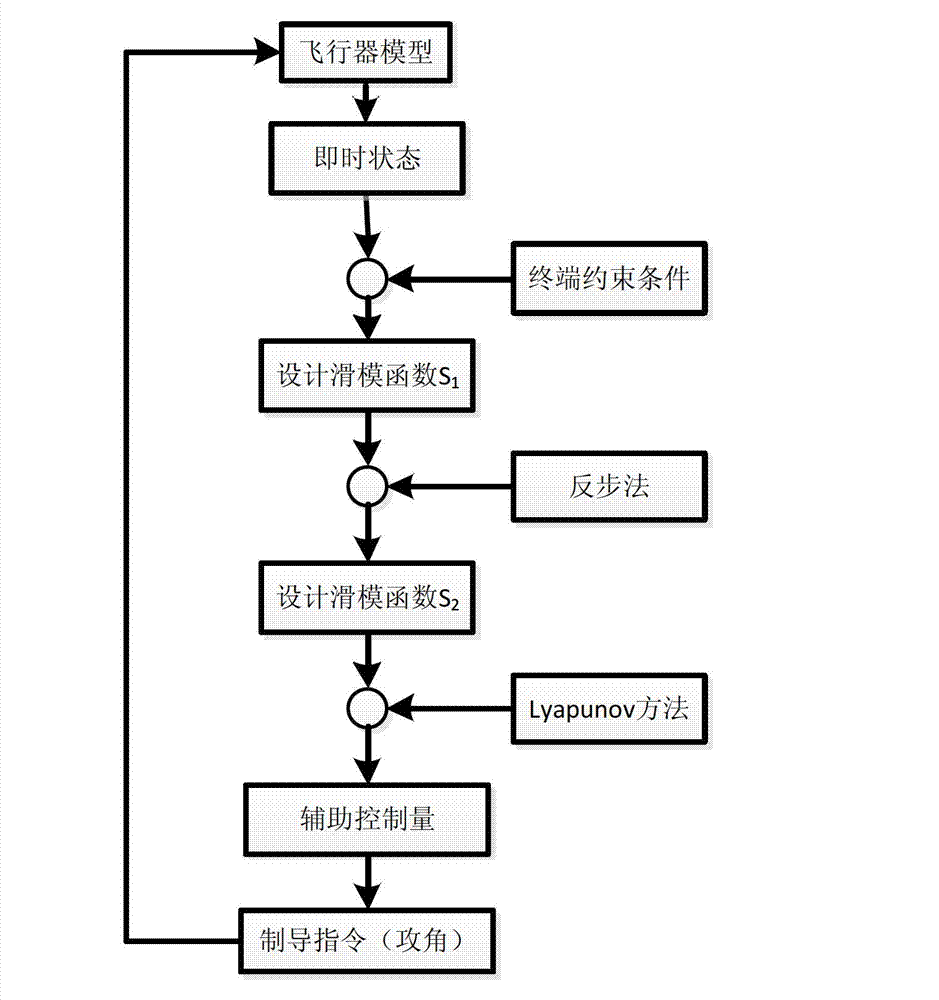
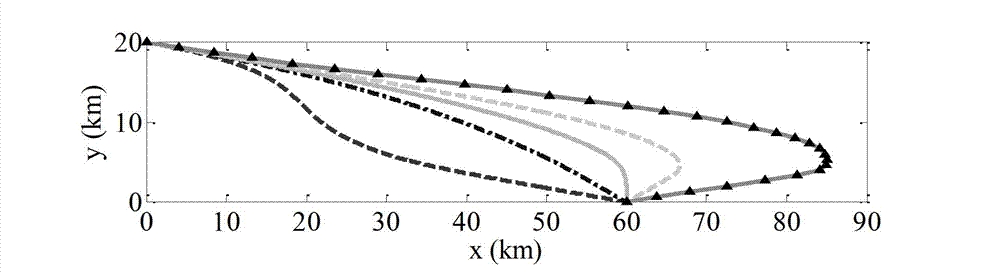
InactiveCN103090728AEasy to trackLess information requiredAiming meansDifferential coefficientKinematics
The invention relates to a tail angle restraining guidance method based on sliding mode control, and belongs to the technical field of guidance. Firstly, a novel aircraft kinematics and dynamics model is built, then tail time is guided, distance between aircraft position coordinates and target position coordinates (xf, yf) is minimum, an expected tail end trajectory dip angle gamma f is a designed target, according to a back stepping method, a virtual control volume is designed to enable a sliding mode function and a differential coefficient to be simultaneously up to 0 in the tail time of flying, and according to Lyapunov method, trajectory dip angle change rate gamma' of an auxiliary control volume is obtained in a solving mode. The trajectory dip angle change rate is converted into an attack angle alpha, an aircraft novel model which is initially built is inputted, a track of the aircraft is adjusted in a real-time mode so as to meet an expected terminal condition, and therefore tail guidance is achieved. The method considers effect of aerodynamic characteristics of the aircraft on a guidance process, is more close to an actual condition, needs little information volume, and is wide in obtained trajectory dip angle tail value range, and smooth in obtained control volume change, and an attitude control system is easy to track.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Nonlinear robust controller design method based on back-stepping and sliding mode control technologies and aimed at nonlinear model of quad-rotor unmanned plane
InactiveCN105676641AAvoid negative effectsAvoid restrictionsAttitude controlAdaptive controlSystems designNonlinear model
The invention discloses a nonlinear robust controller design method based on back-stepping and sliding mode control technologies and aimed at a nonlinear model of a quad-rotor unmanned plane. A sliding mode controller of a speed-constant reaching law is designed to an attitude angle system of the quad-rotor unmanned plane, and rapid tracking for the attitude angle is ensured. To realize track tracking for the spatial position of the quad-rotor unmanned plane, a sliding mode surface and a virtual control quantity are constructed according to a stepping back control idea to realize nonlinear control law design and system stability design from the kernel to the external layer of a system. After an equation of the related virtual control quantity is obtained, an expected track value of the attitude angle is obtained by solving the equation via arithmetic inverse operation, and a design method of the speed-constant reaching law is used to determine a final input control law of the quad-rotor unmanned plane system. According to the method of the invention, the characteristic that sliding mode control is uncertain for the model and insensitive to external interference is utilized, robust trace tracking for the nonlinear quad-rotor unmanned plane can be controlled under interference.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Ship self-adaptive robust course tracking control method based on back stepping method
InactiveCN103324195AReduce complexityFast convergencePosition/course control in two dimensionsMathematical modelLow-pass filter
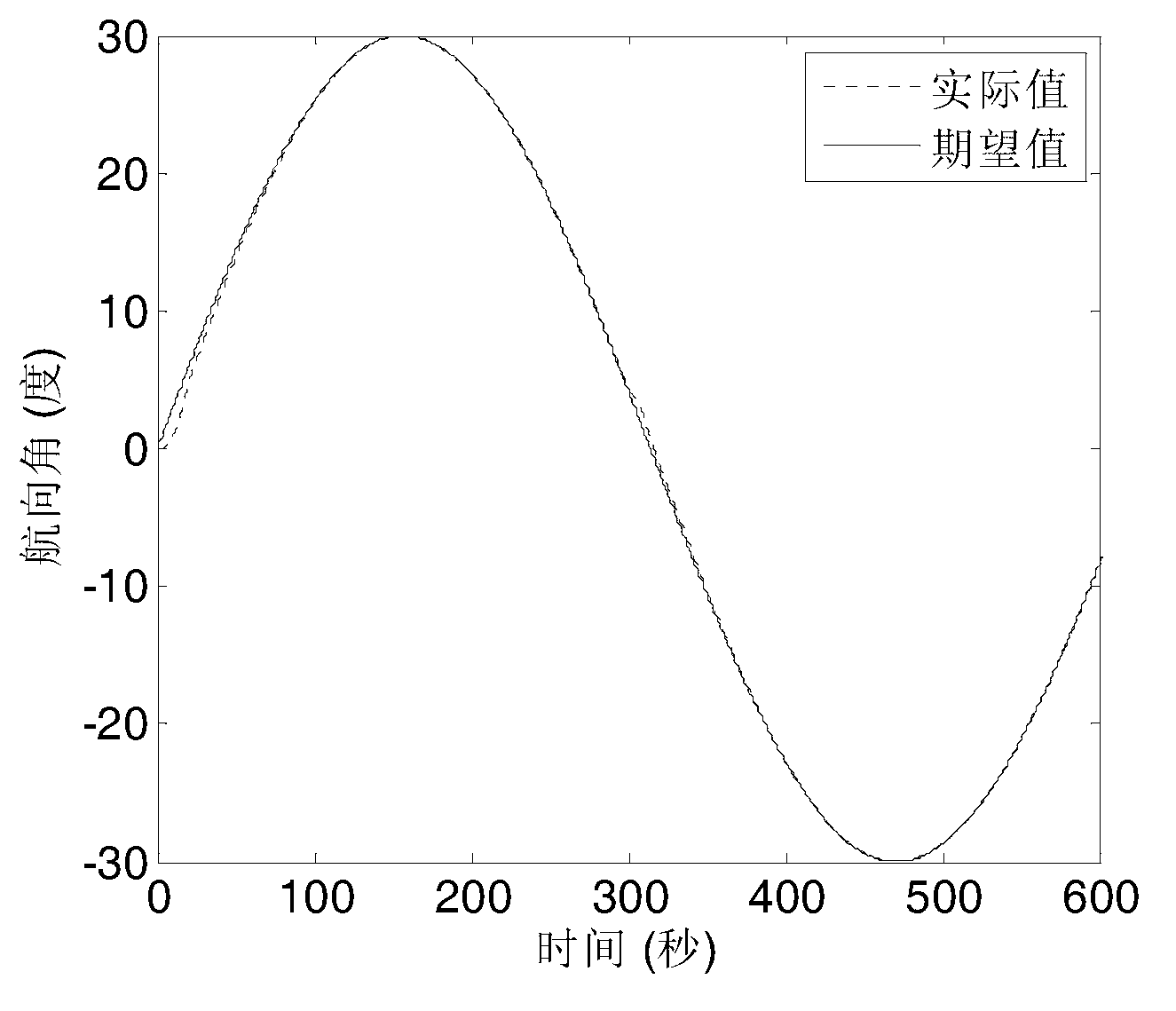
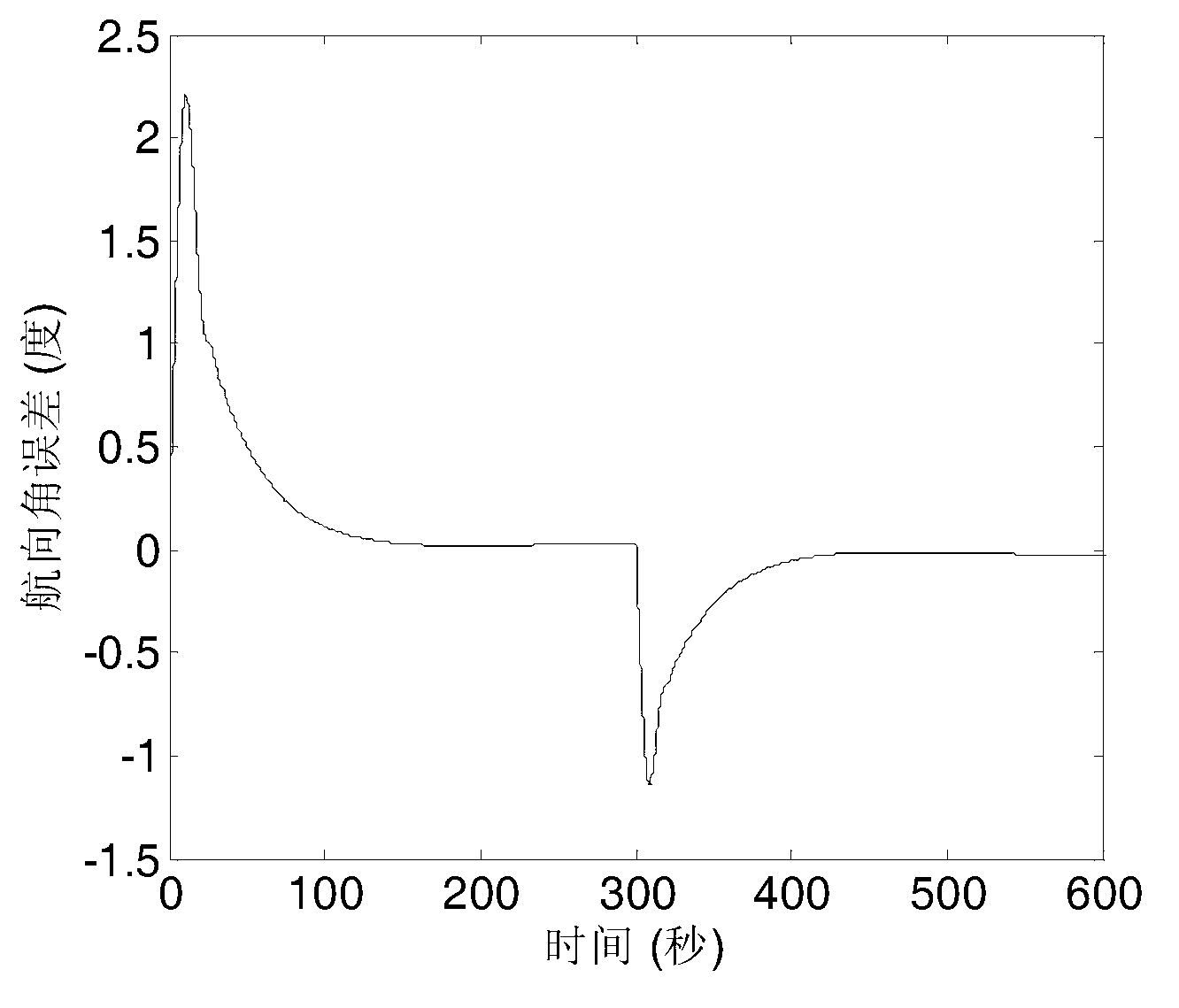
The invention provides a ship self-adaptive robust course tracking control method based on a back stepping method. A sensor collects the actual course and a rudder angle of a ship, the actual course and an expected course are combined to generate a course tracking error equation, a new state variable is obtained through differentiable homeomorphism conversion, the new state variable is transmitted to an angle virtual controller and a terminal sliding mode controller, the new state variable, estimated model uncertainties, external disturbance and known nonlinear terms of a system are transmitted to an angular speed expectation virtual controller, an angular speed expectation virtual control law is solved through a first-order low-pass filter to obtain an angular speed virtual control law, the angular speed virtual control law is transmitted to a controller to generate a control command rudder angle, and a drive steering engine enables the ship to track the expected course. The ship course can track the expected course stably without accurately obtaining a ship mathematic model; a closed-loop control system is made to have the self-adaptive robust function on an uncertain model and unknown disturbance; the complexity of the controller is reduced.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Dynamic traffic simulation platform and simulation method thereof
ActiveCN103412975ASolve the problem of quickly matching to the road segmentSolve congestionSpecial data processing applicationsSimulationTraffic simulation
The invention relates to a dynamic traffic simulation platform which comprises a perception layer, a fusion layer, an application layer and a presentation layer. The perception layer is connected with a dynamic traffic data collecting device, multivariate heterogeneous traffic flow data are obtained and transmitted to the fusion layer in real time, and the fusion layer is connected with the application layer. The multivariate heterogeneous traffic flow data and GIS data are received for processing, the application layer obtains road network dynamic traffic flow data, and a traffic simulation model is formed. Through the traffic simulation model and a traffic OD matrix, dynamic traffic simulation is performed, and the presentation layer receives the traffic simulation result of the dynamic traffic simulation in the application layer, and provides service application and presentation to a terminal client. The problem that in the prior art, a large number of real-time dynamic traffic data can not be rapidly matched with a road section well is solved. Therefore, the multifunctional dynamic traffic simulation platform is capable of performing OD back stepping and real-time dynamic traffic early warning on dynamic traffic flows on the basis of a GIS grid rapid matching technology.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for buried plate formation in deep trench capacitors
InactiveUS6281068B1Manufacturing process flow simplificationBig advantageSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringPolymer
An improved method of forming the buried plate regions in deep trench capacitors used in DRAM memory semiconductor circuits in which the polymer used in the deep trench is etched down to the desired depth in a reactive ion etch tool using an O2 / CF4 chemistry. Since optical / interferometric etch end-point detection system can be used to monitor the etch back step in its totality, the quantity of the polymer remaining in deep trenches can be very accurately controlled, which in turn will produce a well controlled buried plate region during the out-diffusion step of the arsenic dopant contained in the arsenic doped silicon glass layer.
Owner:IBM CORP
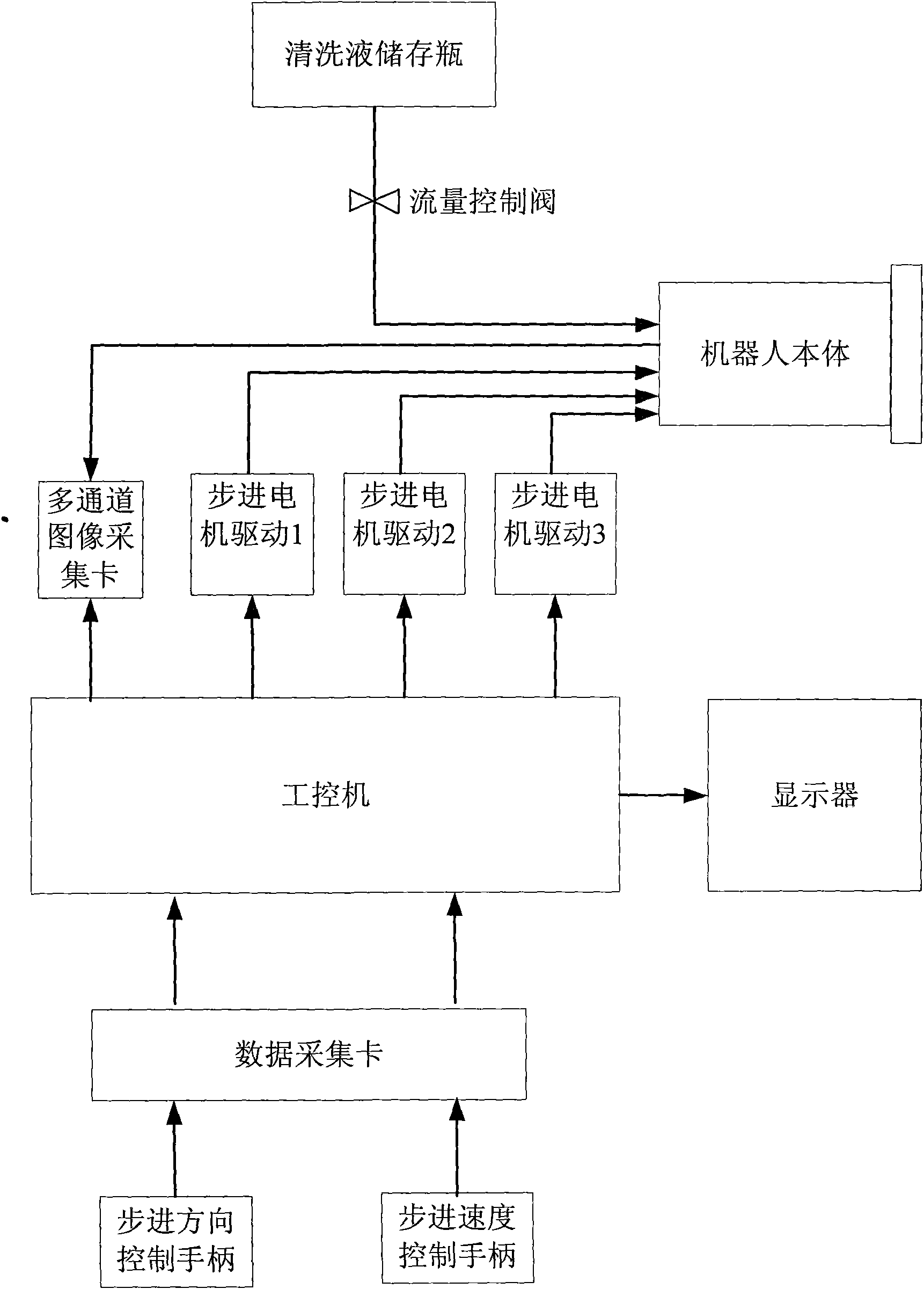
Robot for cleaning inner wall of barrel
InactiveCN101776418ARealize automatic scrubbingImplement positional scrubbingHollow article cleaningWeapon cleaningComputer moduleEngineering
The invention discloses a robot for cleaning the inner wall of a barrel, which comprises a cleaning module and a driving module which realize relative telescopic movement through a thread transmission mechanism. The cleaning module comprises a front outer shell, a sliding plate, a front stepping motor, a front combined driving mechanism and a cleaning brush, wherein the cleaning brush is arrangedon an output shaft of the front combined driving mechanism; the front combined driving mechanism is connected with the sliding plate, in which central inner threads are processed, by the front outer shell; and the front stepping motor is arranged in the front outer shell and is used for driving the front combined driving mechanism. A back combined driving mechanism in the driving module is connected with a motor fixing plate by a back outer shell; a back stepping motor and a mobile stepping motor are arranged in the back outer shell; the back stepping motor is fixed on the back combined driving mechanism and drives the back combined driving mechanism to move; the mobile stepping motor is fixed on the motor fixing plate; an output screw shaft is fit with the central inner threads of the sliding plate in the cleaning module. The robot has simple structure, small volume, light weight and convenient installation.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Specified performance back-stepping control method of mechanical arm servo system
ActiveCN104698846AAvoid dead zone with additional compensationAvoid buffetingAdaptive controlDynamic modelsTime-variant system
The invention provides a specified performance back-stepping control method of a mechanical arm servo system. The method comprises the steps of constructing a dynamic model of the mechanical arm servo system; initializing the system state, sampling time and control parameters; linearly approximating a nonlinear input dead area of the system as a simple time varying system according to the differential mean value theorem; deviating a mechanical arm servo system model with the unknown dead area; calculating the tracking error of the control system, FC (funnel control) error variation and differential. With the adoption of the method, the problem of control buffeting of a sliding die can be reduced, the system of the dead area input on the system can be effectively avoided, and the specified performance control of the mechanical arm control system can be achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Intelligent electric vehicle adaptive cruise control system and method
ActiveCN108437991ASolving Nonlinear Problems of Speed ControlSolve nonlinear problemsExternal condition input parametersMode controlCruise control
The invention provides an intelligent electric vehicle adaptive cruise control system and method, and relates to vehicle safety driving assistance control. The system includes an information acquisition module, an operation mode selection module, a control action switching module, a desired torque calculation module, a converter module and an actuator module. A safety distance control strategy anda driving / brake switching strategy are proposed. The neural-fuzzy-based back-stepping sliding-mode adaptive cruise tracking mode control method is adopted, and the nonlinear problem of speed controlof the electric vehicle adaptive cruise control system and the high coupling performance of the system state are solved. The ability of the vehicle tracking a preceding vehicle during adaptive cruisedriving is ensured, the utilization of traffic roads is improved, and the safety and comfort of vehicle driving is improved.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
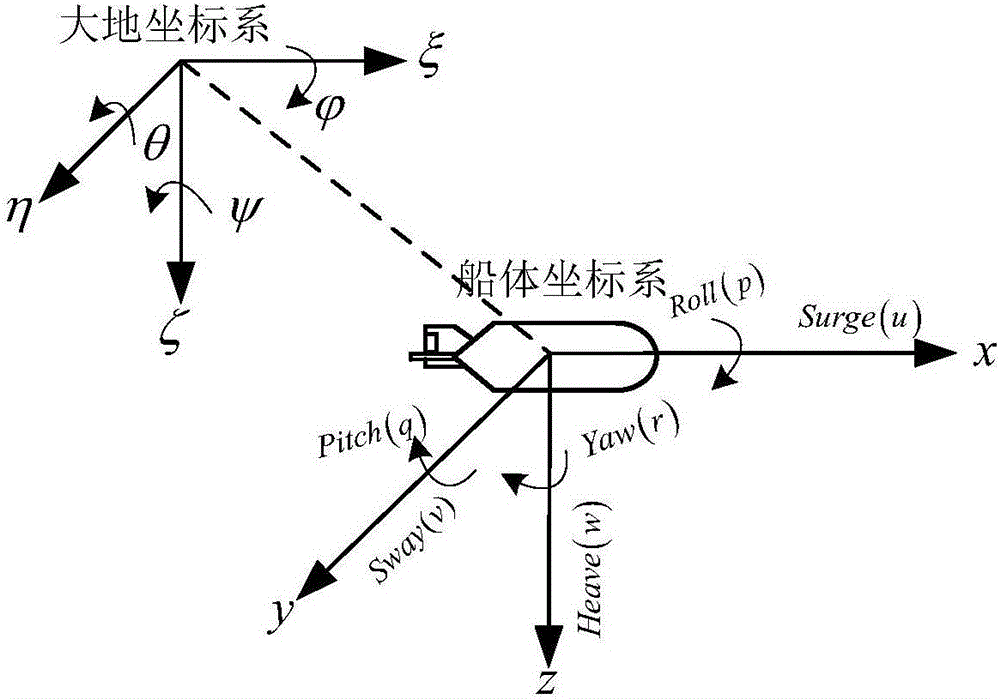
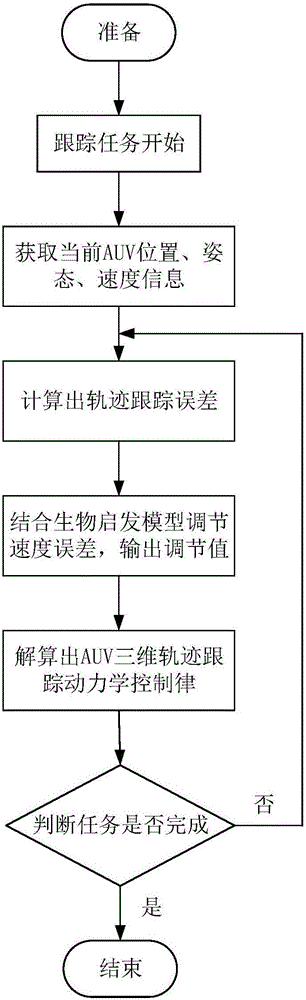
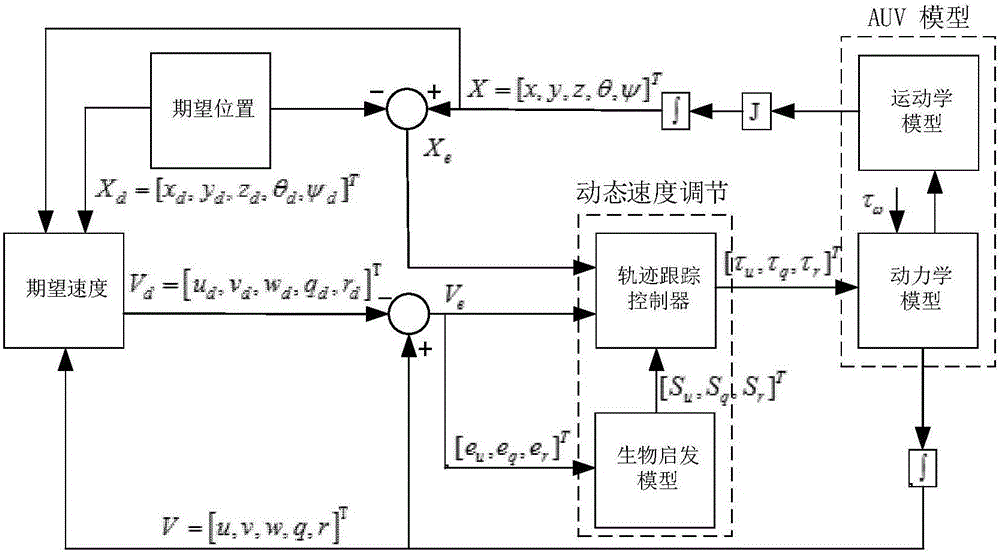
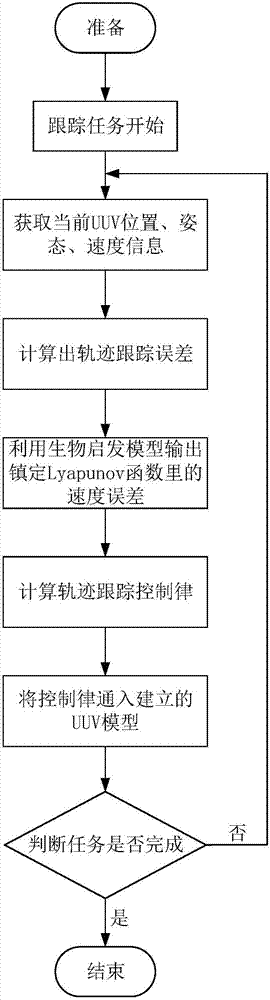
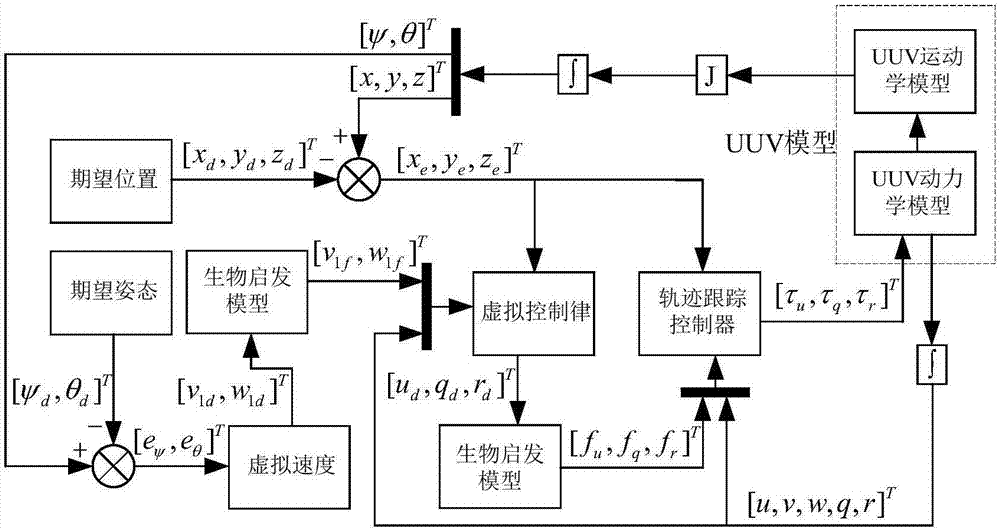
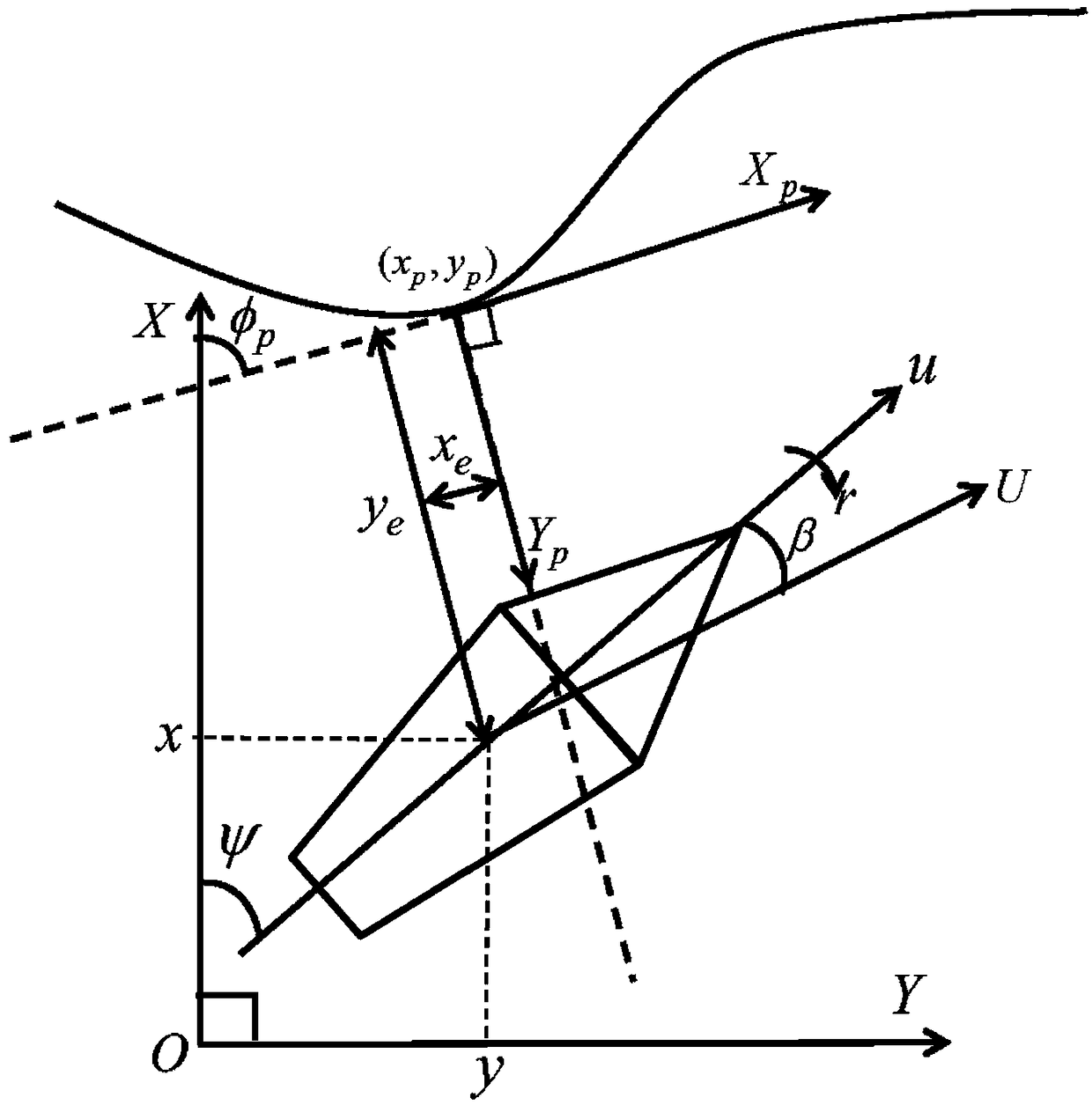
Under-actuated AUV (autonomous underwater vehicle) three-dimensional trajectory tracking control method based on biological speed regulation
ActiveCN106444806AAchieve precise tracking controlImprove performanceAttitude controlMathematical modelVirtual control
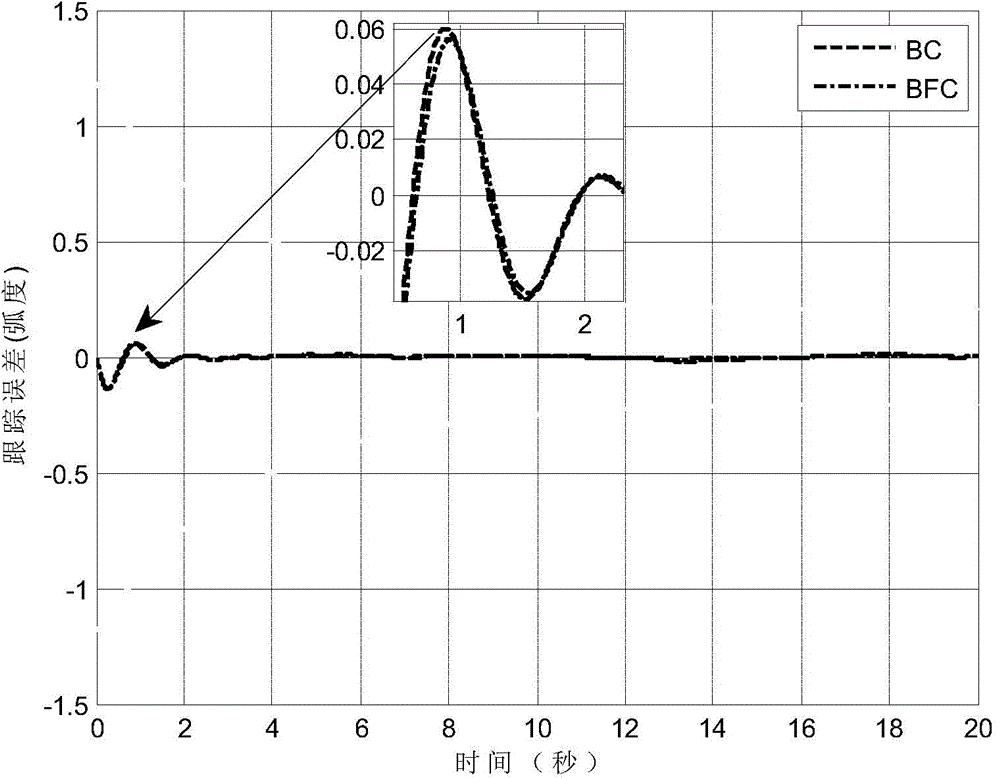
The invention provides an under-actuated AUV (autonomous underwater vehicle) three-dimensional trajectory tracking control method based on biological speed regulation. The method comprises the following steps: (1) giving expected trajectory position information by an AUV according to the current task, and obtaining current position and attitude information; (2) obtaining position and attitude error variables by use of the mathematical model of an under-actuated UUV (unmanned underwater vehicle); (3) calculating a virtual control law by a method of defining a virtual speed error variable; (4) finishing dynamic regulation of the speed error through a biological inspiration model; and (5) deducing a dynamic speed regulation controller. In the method provided by the invention, the speed error of the under-actuated AUV can be dynamically regulated, the performance of the controller is improved while the singular value of the traditional back-stepping method occurring when the heading angle error is 90 degrees is avoided, and accurate tracking of a time-varying three-dimensional trajectory is realized under external constant disturbance.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Finite time fault-tolerant control method for approaching and tracking space non-cooperative target
ActiveCN105159304AAchieve attitude controlHigh precisionAttitude controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsKinematics equationsAttitude control
A finite time fault-tolerant control method for approaching and tracking a space non-cooperative target belongs to the field of orbit control and attitude control, and aims to solve the problem of low tracking supervision precision caused by big tracking control error of an existing tracking spacecraft which performs line-of-sight tracking for a non-cooperative target. The finite time fault-tolerant control method is characterized in that dynamical and kinematical equations are established under a line-of-sight coordinate system, the situations such as nondeterminacy of a system, partially unknown motion parameters of the non-cooperative target, control input saturation and dead zone are taken into consideration, self-adaptive estimation and compensation can be performed through adoption of an RBF neural network, and a back-stepping thought is adopted to design a controller so that the tracking spacecraft can converge to an expected attitude and orbit within finite time and can keep the attitude and the orbit. The finite time fault-tolerant control method of the present invention has the advantages of quick control convergence, good robustness and high tracking control precision.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Binary chop tracking method of shortest paths in network map
InactiveCN101788999AHigh speedOvercoming reverse order search and trace thinkingSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmStep number
The invention discloses a binary chop tracking method of shortest paths in a network map, which is characterized in that the method comprises the following steps: extracting the step number of the shortest paths from a source node to a gathered node according to a shortest path step number matrix; reducing and separating the step number by half into the front step number and the back step number; searching nodes with the step number equal to the front step number in a source node row vector of the shortest path step number matrix, using the nodes as a front step number node set, searching nodes with the step number equal to the back step number in a gathered node column vector of the shortest path step number matrix, using the nodes as a back step number node set; taking an intersection set of the front step number node set and the back step number node set as middle nodes; using each node in the intersection as the reference; using the method for solving the middle node of the source node and the node, and the middle node of the node and the gathered node until the shortest path step number between the solved nodes is 1; and sequentially inserting the middle nodes into corresponding positions to obtain all shortest paths from the source node to the gathered node. The method of the invention is used for finding all shortest paths between two points, and the invention can provide various schemes for the preferential path selection of the network map abstracted from actual data.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Mechanical arm system saturation compensation control method based on back-stepping sliding mode control
The invention provides a mechanical arm system saturation compensation control method based on back-stepping sliding mode control. The method comprises the following steps of building a dynamic model of a mechanical arm servo system, and initializing the system state, the sampling time and the control parameter; carrying out saturation linearization processing on the nonlinear input in a system according to the differential mean value theorem, and deriving a mechanical arm servo system model with unknown saturation; calculating the control system tracking error, the sliding mode surface and the differentiation. The invention provides the back-stepping sliding mode control method capable of effectively avoiding the influence of unknown saturation input on the system position tracking control performance and using the saturation compensation control method based on back-stepping sliding mode control and the stable and fast tracking of the system is realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Bidirectional direct-current converter feedback linearized back-stepping sliding-mode control mode
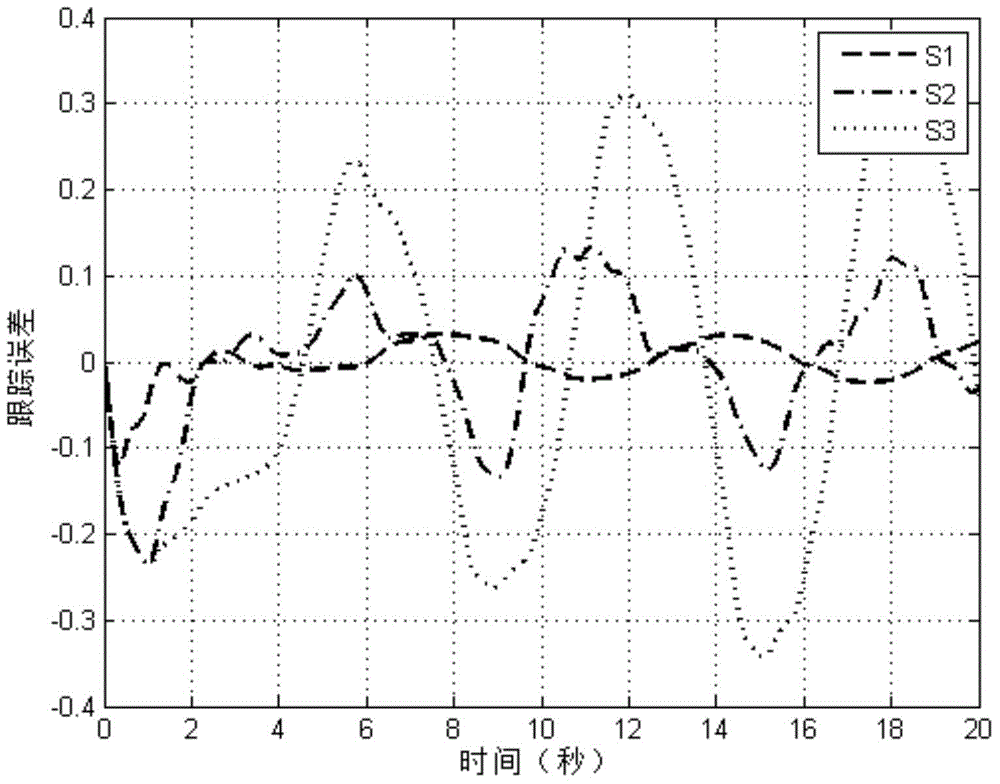
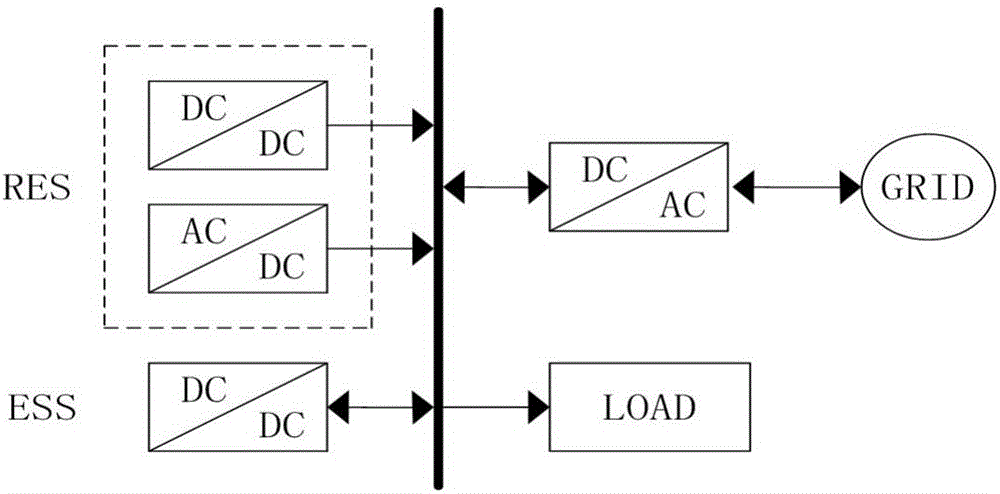
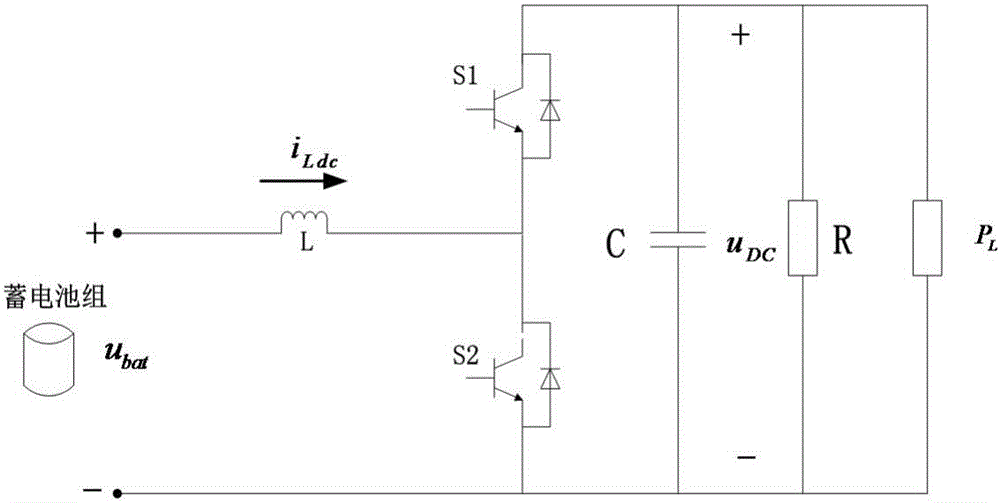
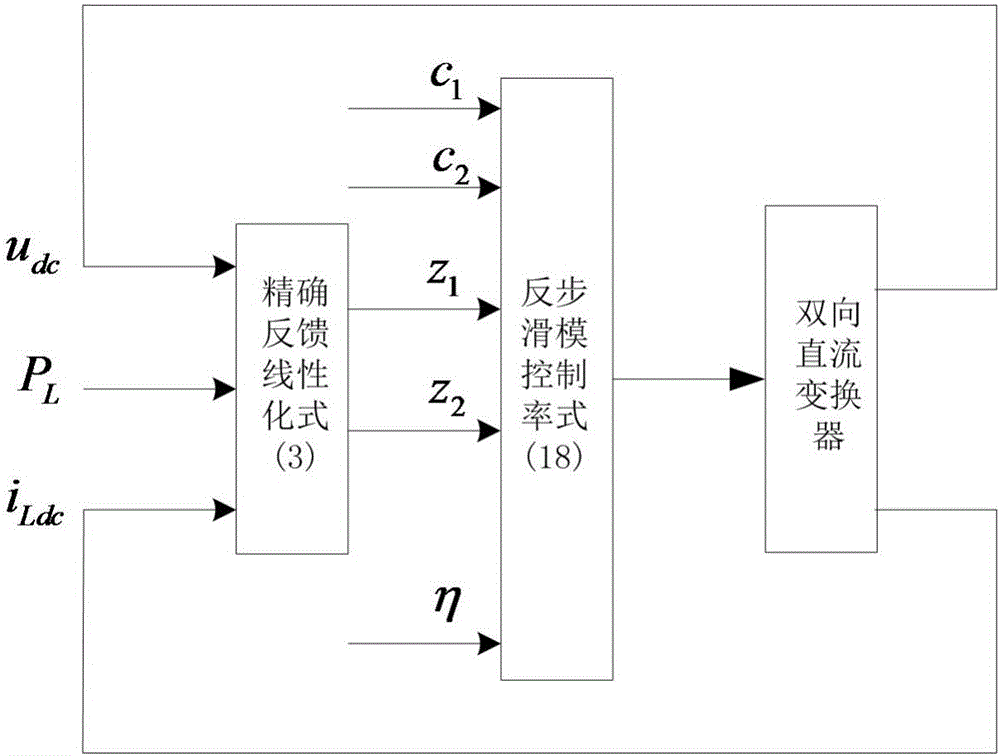
ActiveCN106230257AWaveform distortion is smallReduce dependencyDc network circuit arrangementsDc-dc conversionMathematical modelFeedback control
The invention discloses a bidirectional direct-current converter feedback linearized back-stepping sliding-mode control mode. The bidirectional direct-current converter feedback linearized back-stepping sliding-mode control method comprises steps of using a filtering capacitance voltage and inductive current as control variables to establish a mathematic model of a bidirectional direct-current converter, performing feedback linearization on an original state variable to form a new linearized state equation, tracking an error with a new state variable as an input of a controller, combining a back-stepping method with a sliding-mode variable structure and designing a feedback control rule of a converter system, wherein the feedback control rule of the inverter system is performed on pulse width modulation and controls the bidirectional direct-current converter. The bidirectional direct-current converter feedback linearized back-stepping sliding-mode control mode combines the feedback linearization with the back-stepping sliding mode control to apply to the bidirectional direct-current converter, solves a non-minimum phase characteristic and a variable structure characteristic of the converter, greatly reduces fluctuation of bus voltage, expands a stable area of a system and has a good engineering application prospect.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
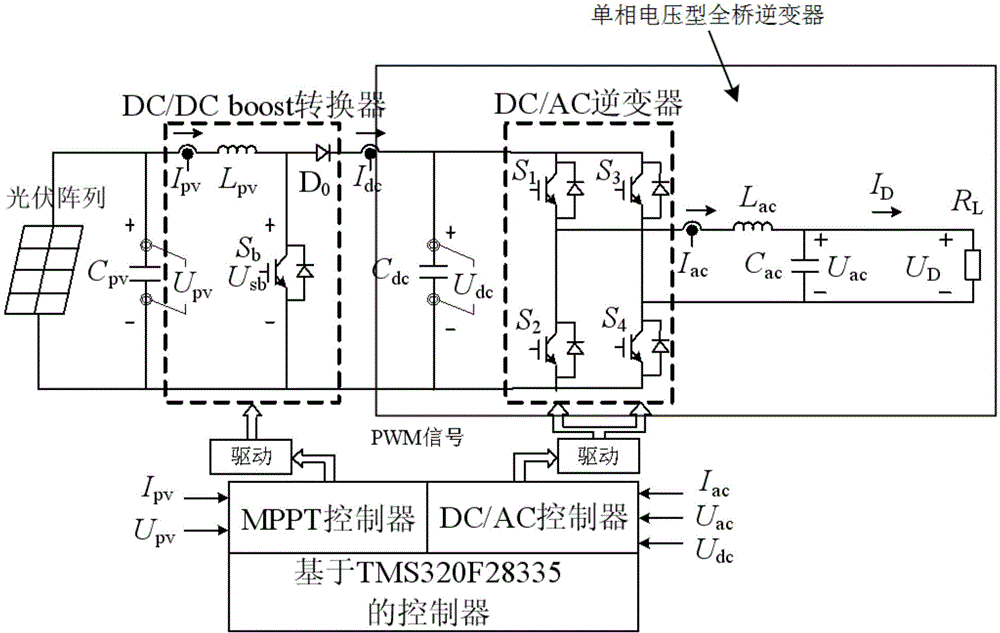
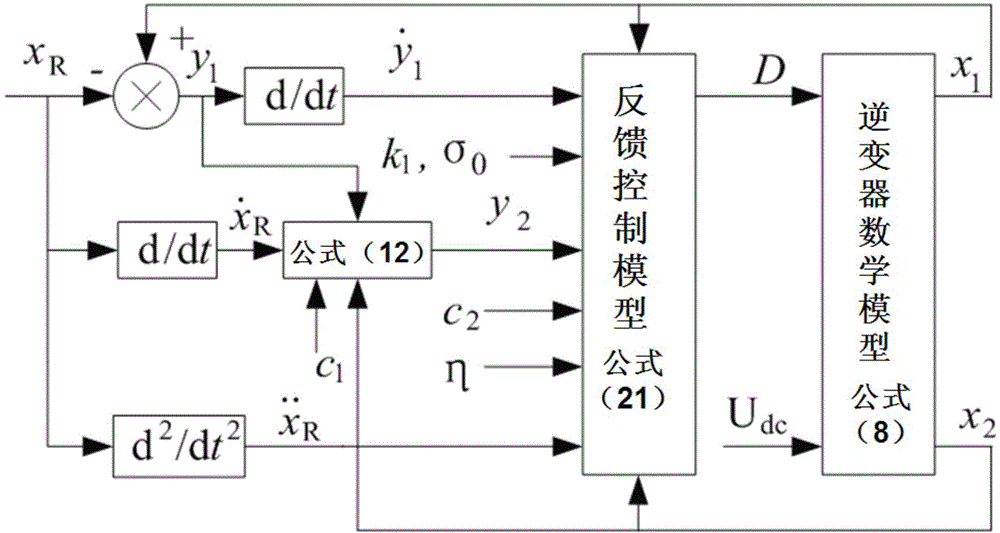
Control method for photovoltaic grid-connected inverter on basis of back-stepping sliding-mode control
InactiveCN103916039AImprove robustnessImprove homeostasisAc-dc conversionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsSystems designMathematical model
The invention relates to a control method for a photovoltaic grid-connected inverter on the basis of back-stepping sliding-mode control. The control method is technically characterized in that direct current voltage Udc of a photovoltaic side bus is collected, a mathematical model of a photovoltaic grid-connected single-phase voltage full-bridge inverter is set up, a tracking error of a control variable uac is set, a back-stepping sliding-mode control model of the photovoltaic grid-connected single-phase voltage full-bridge inverter is set up, and the single-phase photovoltaic grid-connected inverter is controlled according to the mathematical model and the back-stepping sliding-mode control model of the photovoltaic grid-connected single-phase voltage full-bridge inverter. The control method is reasonable in design, a back-stepping method and a sliding-mode control method are combined, the stable state and the dynamic property are good, and the control method is suitable for linear and non-linear loads and adapts to engineering application reality, provides a new thought for the inverter control system design and has the good engineering application prospect.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
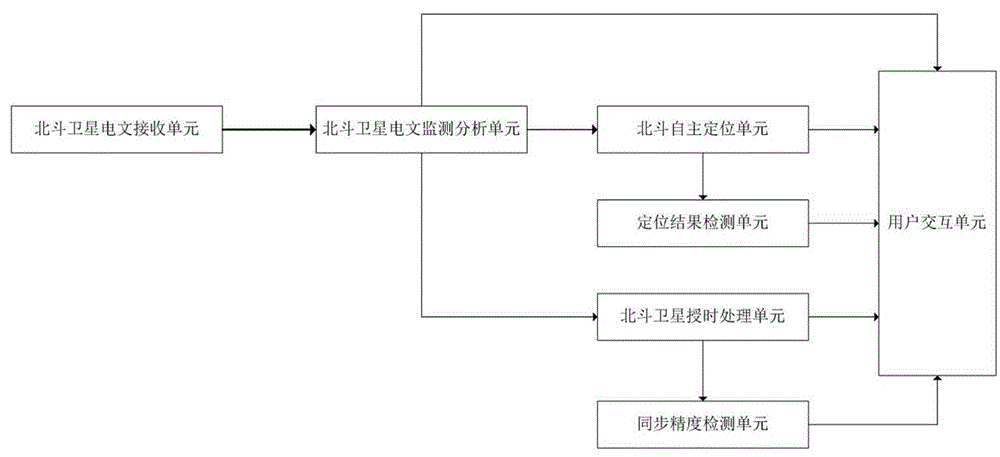
Beidou satellite navigation system performance monitoring device and monitoring method thereof
InactiveCN105527629AAvoid damageImprove performanceSatellite radio beaconingMonitoring methodsBack stepping
The invention relates to a Beidou satellite navigation system performance monitoring device. The Beidou satellite navigation system performance monitoring device comprises a Beidou satellite text reception unit, a Beidou text monitoring analysis unit, a Beidou satellite autonomous positioning unit, a Beidou satellite time service unit, a positioning result detection unit, a synchronization precision detection unit, a user interaction unit and a power supply unit. The invention further provides a monitoring method for the Beidou satellite navigation system performance monitoring device. Abnormal text and data are timely identified and indicated in a satellite text monitoring process, corresponding measures can be conveniently adopted, reduction of damage caused by the abnormal text data is facilitated; accuracy of each type of text data can be identified, which satellite has abnormal parameters can be acquired through back stepping according to the positioning and time service result, abnormality reasons can be rapidly positioned on the condition of positioning and time service, and solution efficiency is improved. Beidou positioning and time service are carried out in real time, mastering performance of Beidou systems can be facilitated, reasonable positioning and time service algorithms can be selected, and development of high-performance Beidou application products is facilitated.
Owner:郑州威科姆科技股份有限公司
Isotope dilution mass spectrometry method for determining content of uranium in uranium niobium alloy
InactiveCN104597174AEasy to measureOvercoming Disadvantages of Susceptibility to InterferenceComponent separationElement analysisDecomposition
The invention discloses an isotope dilution mass spectrometry method for determining the content of uranium in a uranium niobium alloy. A formula for calculating the content of uranium in the uranium niobium alloy is derived according to an isotope dilution mass spectrometry principle. A decomposition process of the uranium niobium alloy is researched, the sampling quantity and the amount of a diluent are optimized, and the influences of mass spectrum line interference and alloy element interference on a measurement result are discussed. The method comprises the following steps: adding nitric acid and hydrofluoric acid to quantitatively dissolve the uranium niobium alloy, adding a quantitative amount of a uranium isotope diluent to directly prepare a mixed sample solution, determining the mixed solution and the uranium isotope proportion in the uranium niobium alloy sample through mass spectrometry, and calculating the content of uranium in the uranium niobium alloy. Quantitative separation of uranium is not needed by the determined method. An XRF technique, an ICP-AES technique and an element analysis technique are used to measure the content of niobium and the total content of impurity elements in the uranium niobium alloy, and back stepping is carried out to obtain the corresponding uranium content order in order to verify the accuracy of the analytical result, and the obtained result is consistent with a result obtained through the experiment method. When the method disclosed in the invention is used to analyze the uranium niobium alloy sample, the relative standard uncertainty of determination results is 0.2% (6 determinations), and the expanded uncertainty is 0.5% (95% confidence level).
Owner:青岛齐力铸钢有限公司
Ship motion control system with control input restraints considered
ActiveCN103760900AHigh control precisionWell formedPosition/course control in two dimensionsData processing systemInformation transmission
The invention provides a ship motion control system with control input restraints considered. The ship motion control system comprises a guide system, a control system, a sensor system, a differential homeomorphism convertor and a data processing system and further comprises an input compensation system. The guide system calculates the expected pose and the expected speed of a ship at each moment according to the input expected value and the initial position of the ship; a sensor collects actual pose information and actual speed information of the ship; the data processing system obtains low-frequency pose information and the low-frequency speed of the ship; the differential homeomorphism convertor obtains new state variables; the control system conducts corresponding solution according to the new state variables to obtain corresponding control instruction information; the control instruction information is transmitted to the input compensation system to be compensated, and a final control instruction is obtained and sent to an execution mechanism of the ship. According to the ship motion control system, a model has an unknown non-linear function, the control input restraints are considered, and the ship motion control system is designed on the basis of self-adaption neural network estimation and through the filtering back-stepping method.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Traction pad for personal water board
InactiveUS7316597B2Less abrasiveCut skinWater sport boardsSnowboardsElastomerThermoplastic elastomer
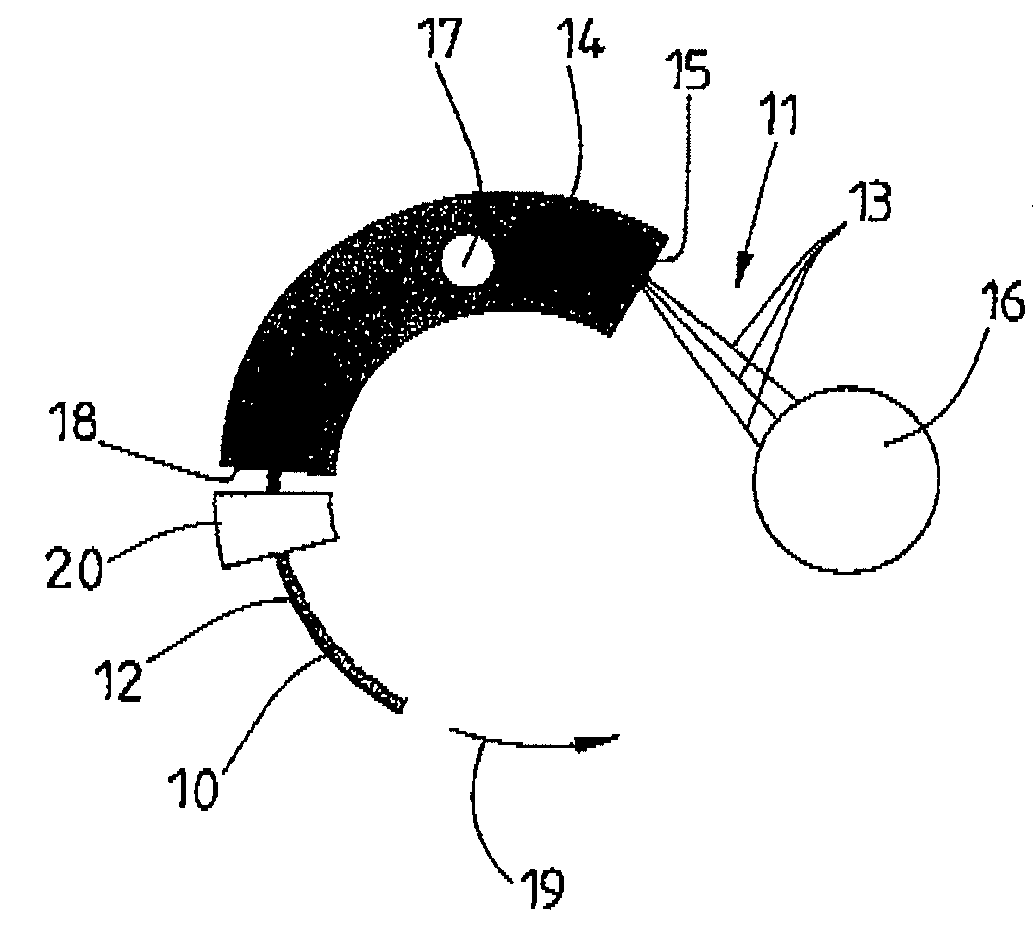
A traction surface for a water board has been developed comprising: a traction pad formed of a molded clear thermo plastic elastomer (TPE) material, and an upper surface of the pad having a roughened texture. The upper surface of the pad may include a center ridge extending a length of the pad and substantially parallel to a centerline of the board. Further, the upper surface may include a back step at a rear of the pad and a plurality of interlaced ribs and grooves extending substantially parallel to a centerline of the board. The grooves may be spaced apart at substantially the spacing of the toes of a foot of an adult male. In addition, the pad may include a bottom surface having a lip extending around a perimeter of the bottom surface. Moreover, injection molding may form the pad.
Owner:SURFCO HAWAII
UUV trajectory tracking control method for preventing differential explosion
ActiveCN107024863ASimple calculationAvoid iterative derivationAdaptive controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsMathematical modelPropeller
The invention provides a UUV trajectory tracking control method for preventing the differential explosion based on the differential output characteristics of a biological instructive model. The method comprises the following steps of 1, conducting the initialization; 2, obtaining position and attitude error variables based on an under-actuated UUV mathematical model; 3, calculating a virtual control law, and replacing a virtual expectancy control law with the output value of the biological instructive model; 4, constructing a Lyapunov function, and transferring the ballast of a position error to the ballast of a speed error, avoiding the differential explosion phenomenon through the real-time derivation of replacing a virtual control variable with the output of the biological instructive model, and realizing the ballast of the speed error; and 5, designing a trajectory tracking controller. According to the technical scheme of the invention, the differential explosion phenomenon caused by the repeated derivation of the traditional back-stepping method can be avoided, and the complexity of the controller is simplified. Meanwhile, in combination with the controller of the biological instructive model, the time constraint requirements of the thrust constraints and the under-actuated UUV trajectory tracking of a propeller on position, speed and attitude can be met.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
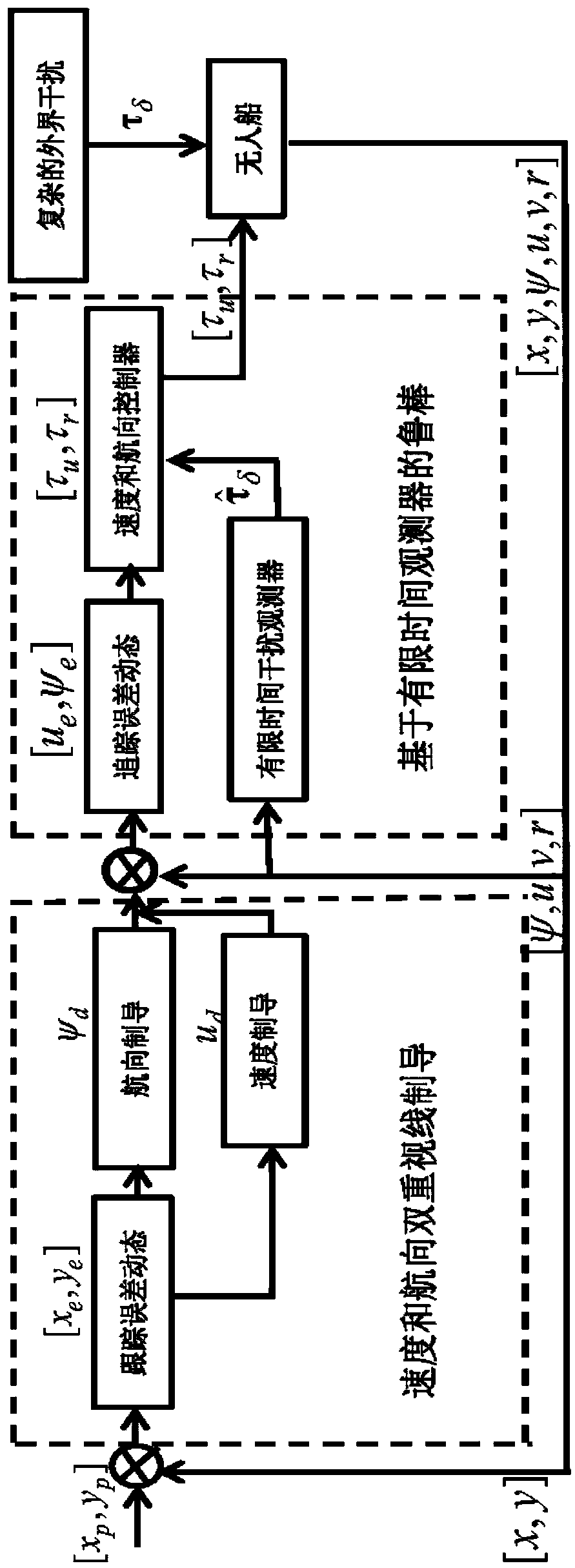
Accurate control method for path tracking of unmanned ship based on dual guidance of speed and heading
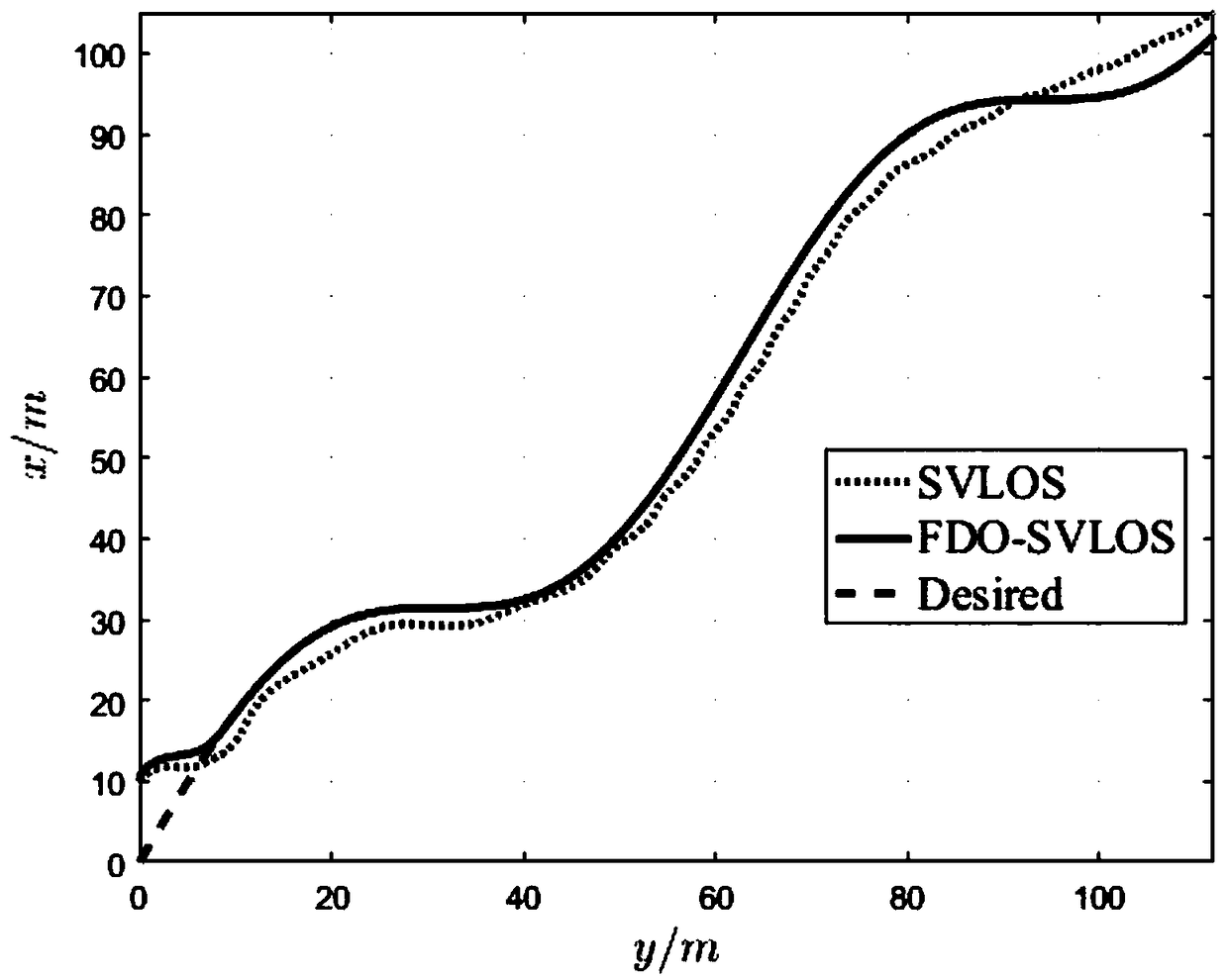
The invention discloses an accurate control method for a path tracking of an unmanned ship based on a dual guidance of the speed and the heading. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a kinematics model and a dynamics model of the unmanned ship; constructing an error dynamics of the path tracking; designing a dual guidance law of the speed and the heading; and designing a finite-time interference observer. According to the accurate control method for the path tracking of the unmanned ship based on the dual guidance of the speed and the heading, the dual guidance law of thespeed and the heading provided by the control method can simultaneously guide the speed and the heading angle according to the path tracking errors, and improves the stability and flexibility of the path tracking control system. The finite-time interference observer constructed by the control method can accurately observe the complex external disturbances; ensures that the observation error is zero for a finite time; and can avoid the limitations of bounded observations and asymptotic observations. The control method designs a speed and heading tracking controller combining the design of a finite time observer and the back stepping control technology, so that the guidance signal can be accurately tracked in the presence of a complex interference, thereby achieving the accurate control forthe path tracking of the unmanned ship.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Method and device for the production of a plastic profile
In the production of elongate plastic profiles (10), which usually takes place by the pultrusion process, the cured plastic profile (10) emerging from a die (14) is pulled through the stationary die (14) by a take-off device. This process only makes it possible to produce straight plastic profiles (10). The invention envisages producing curved plastic profiles (10) by using a die (14) corresponding to the curvature of the plastic profile (10). For moving the cured part of the plastic profile (10) out of the die (14), it is provided that the die (14) is moved back step by step in relation to the stationary plastic profile (10) counter to the direction of production (19). In order that the plastic profile (10) remains stationary in relation to the die (14) as this takes place, it is securely held outside the die (14) by a holding means (20) during the moving back of the die (14).
Owner:3B LUX SARL
Multi-target control method of automobile driving suspension system
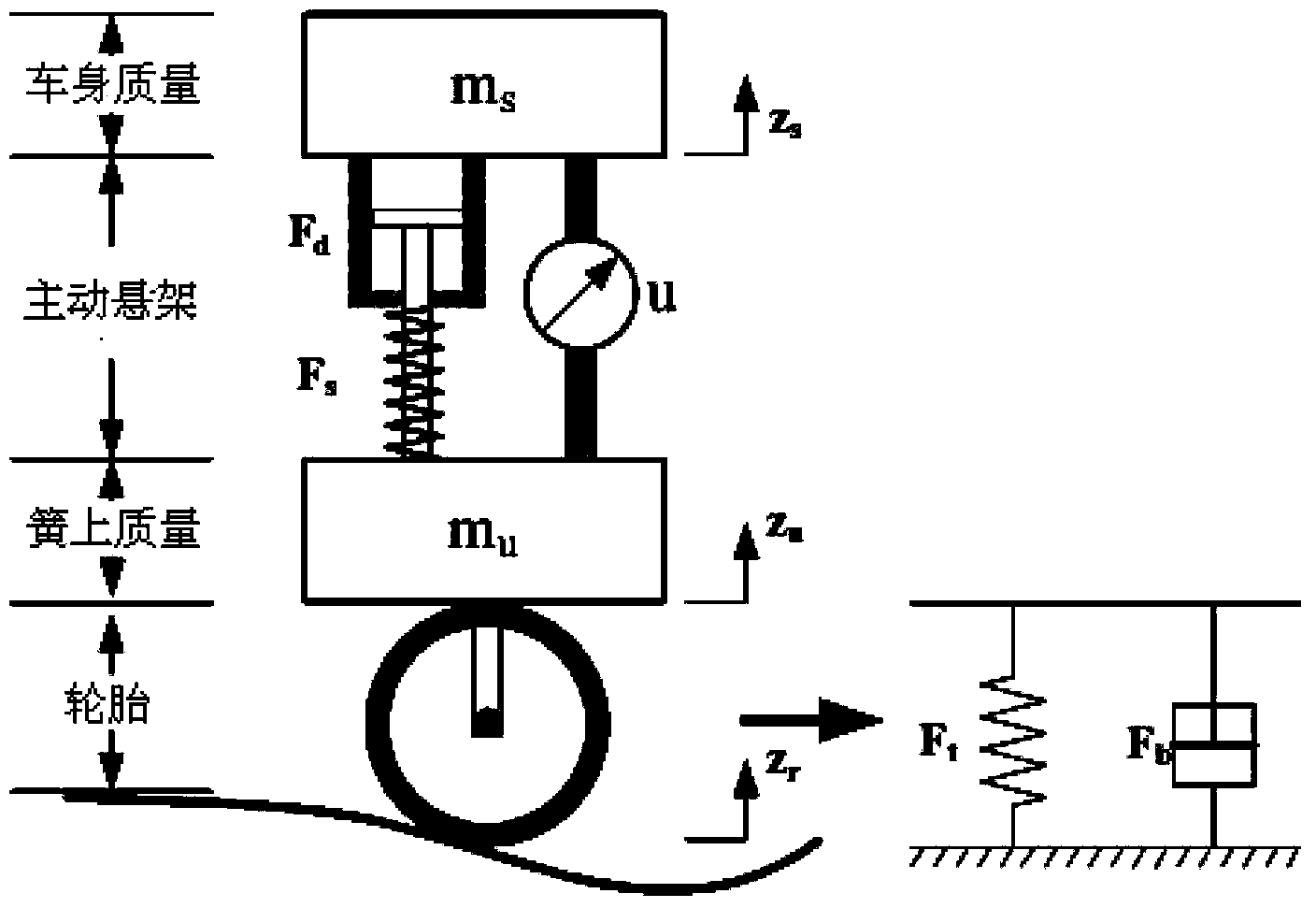
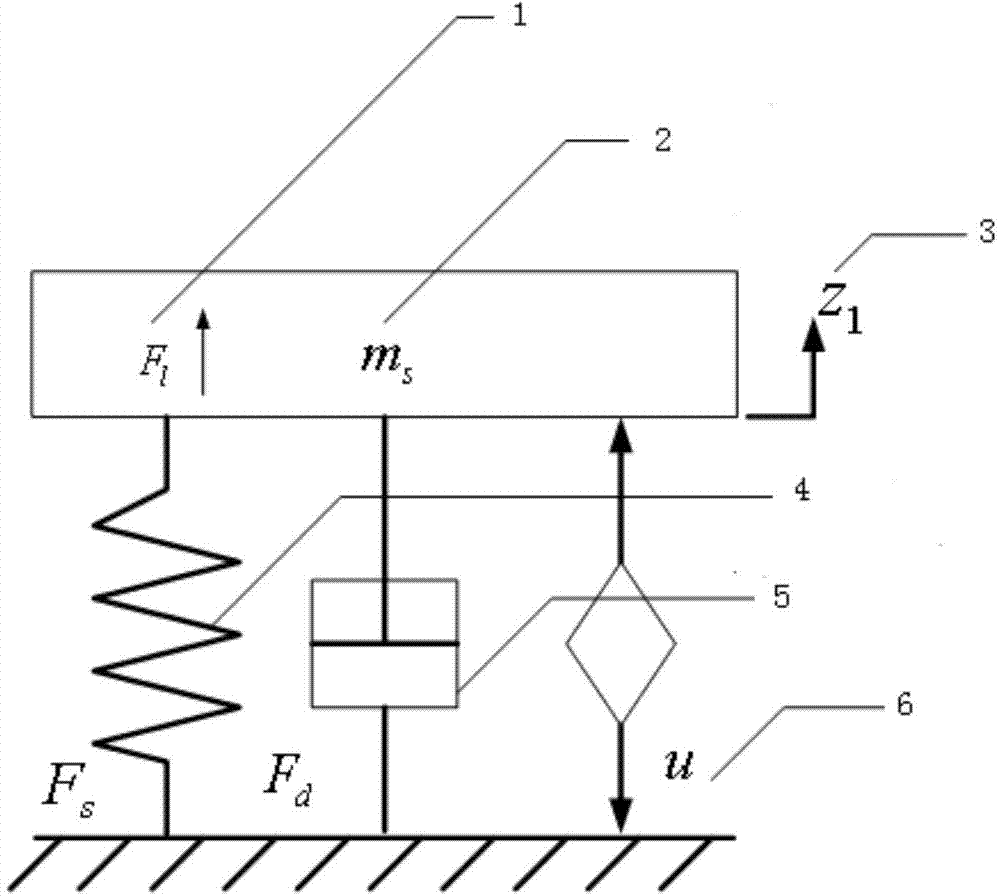
ActiveCN103434359AGuaranteed performance constraintsSolving the stabilization problem of vertical dynamicsResilient suspensionsCar drivingSelf adaptive
The invention discloses a multi-target control method of an automobile driving suspension system, relates to a control method, and particularly relates to the a multi-target control method of an the automobile driving suspension system, which aims. In order to solve the problems that the a design model in the existing suspension control technology is simpler, and can not meet the multi-target control performance of the a suspension system and can not eliminate the influence of external uncertain parameters on the control performance of the system, the invention provides a multi-target control method of the automobile driving suspension system. The multi-target control method is implemented by the following steps of: (1) establishing a quarter of non-linear uncertain driving suspension system model; (2) deducing a self-adaptive back-stepping recursive controller; and (3) adjusting a control gain parameter of the self-adaptive back-stepping recursive controller. The multi-target control method disclosed by the invention is applied to in the field of automobile driving suspension control.
Owner:哈尔滨工业大学人工智能研究院有限公司
Executor input saturation control method of automobile active suspension system
ActiveCN103522863ASolving the stabilization problem of vertical dynamicsImprove comfortResilient suspensionsActuator saturationSelf adaptive
An executor input saturation control method of an automobile active suspension system relates o executor input saturation control methods. The executor input saturation control method of the automobile active suspension system mainly solves the problems that existing design models are too simple to meet the requirements of executor saturation control of automobile suspension systems or cope with the influence of uncertain parameters and comprises the steps such as, firstly, establishing a nonlinear uncertain time-delay active suspension system model; secondly, deducting a self-adaption back stepping recurrence controller based on an instruction filter; thirdly, adjusting control gain parameters of the self-adaption back stepping recurrence controller. The executor input saturation control method of the automobile active suspension system is applicable to the field of automobile active suspension control.
Owner:哈尔滨工业大学高新技术开发总公司
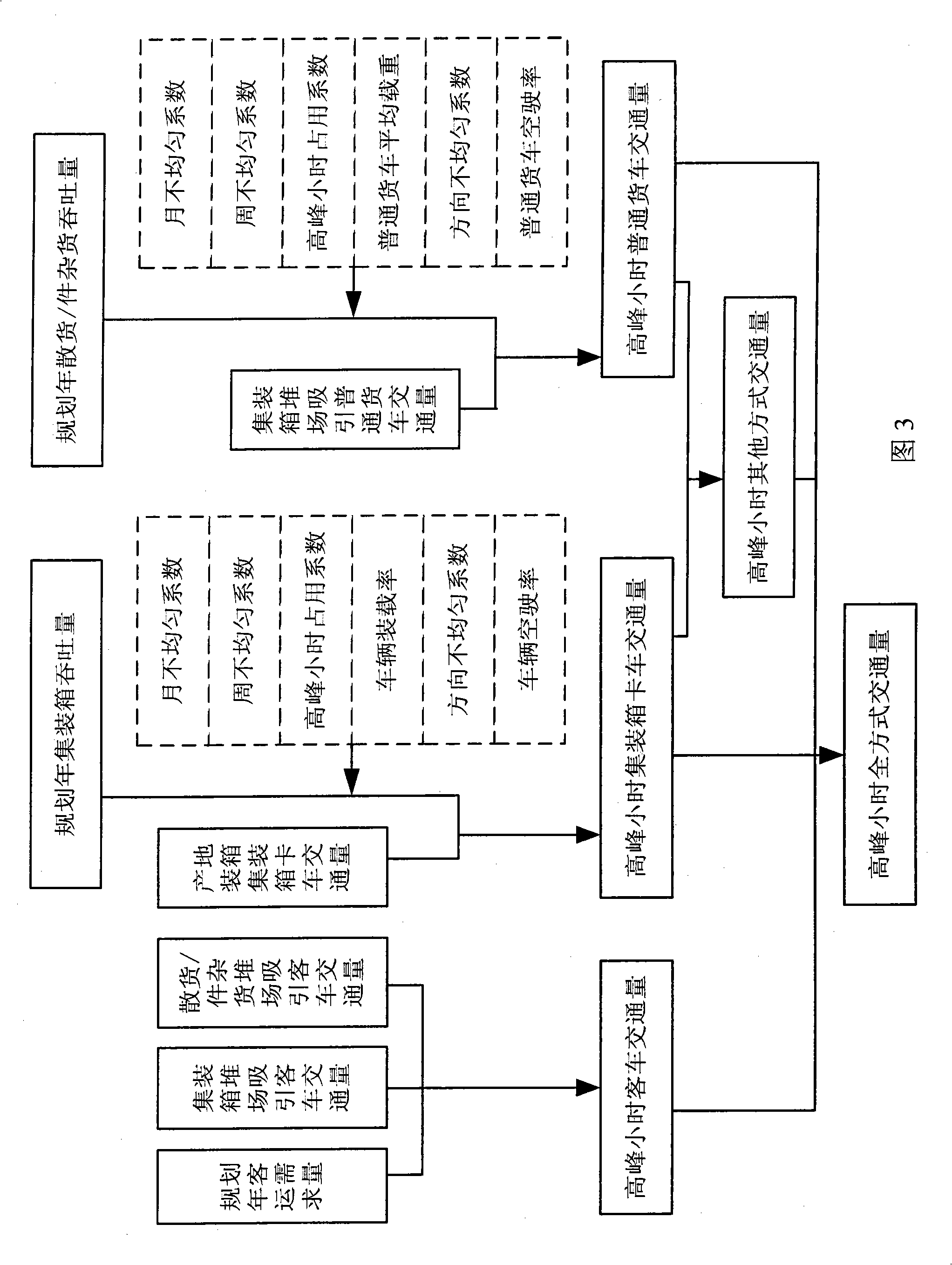
System for estimating seaport planning year traffic generative amount based on inverse calculation of goods series
ActiveCN101350138ALow costDetection of traffic movementGenetic modelsTraffic characteristicRelational graph
The invention discloses a traffic generation amount prediction system in a seaport planning year based on cargo back stepping, the technical scheme comprises the following steps: 1, a relational graph of a traffic generation amount and various traffic characteristic parameters and a traffic amount flow chart which is led by various cargo throughput are built, and current situation traffic characteristic parameters which are needed are collected. 2, the current situation traffic generation amount of a container truck, a common freight car and a bus is predicted. 3, the predicted current situation traffic generation amount is compared with the traffic generation amount which is obtained based on a current situation traffic investigation. 4, above related parameters are calibrated to obtain a group of best parameter values through a genetic algorithm. 5, prospect factors are comprehensively considered, the current situation traffic characteristic parameters of various cargo are amended, thereby obtaining the traffic characteristic parameters in a planning year. 6, various cargo public road transportation volume, the traffic characteristic parameters in the planning year and the current situation in the planning year of a building area are considered, and the prediction of the traffic generation amount in the planning year is completed based on cargo back stepping traffic amount.
Owner:TIANJIN MUNICIPAL ENG DESIGN & RES INST
Virtual media with folder-mount function
ActiveUS20140108471A1Eliminate the problemTransmissionFile/folder operationsFile allocationFile system
A virtual media (VM) method for mounting one or more folders in one or more storage devices of a client for accessed by a server as a virtual drive. The client assigns virtual cluster indices to each file, and creates a file-cluster index table to store the assigned virtual cluster indices. The client also creates a VM file system complying with the FAT file system standard except that only subdirectories and no data files are stored in the VM FAT file system. The VM FAT table uses virtual cluster indices rather than actual cluster indices. Data written by the server are stored in a temporary data area without modifying the actual file systems of the storage devices. The virtual sectors requested to be written are “dirty”, and the dirty sector numbers and corresponding temporary sector numbers are stored in a dirty sector index table for use in a write-back step.
Owner:ATEN INT CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com