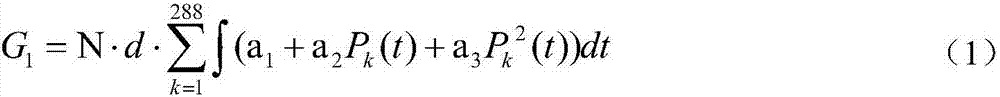Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
79 results about "Demand load" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
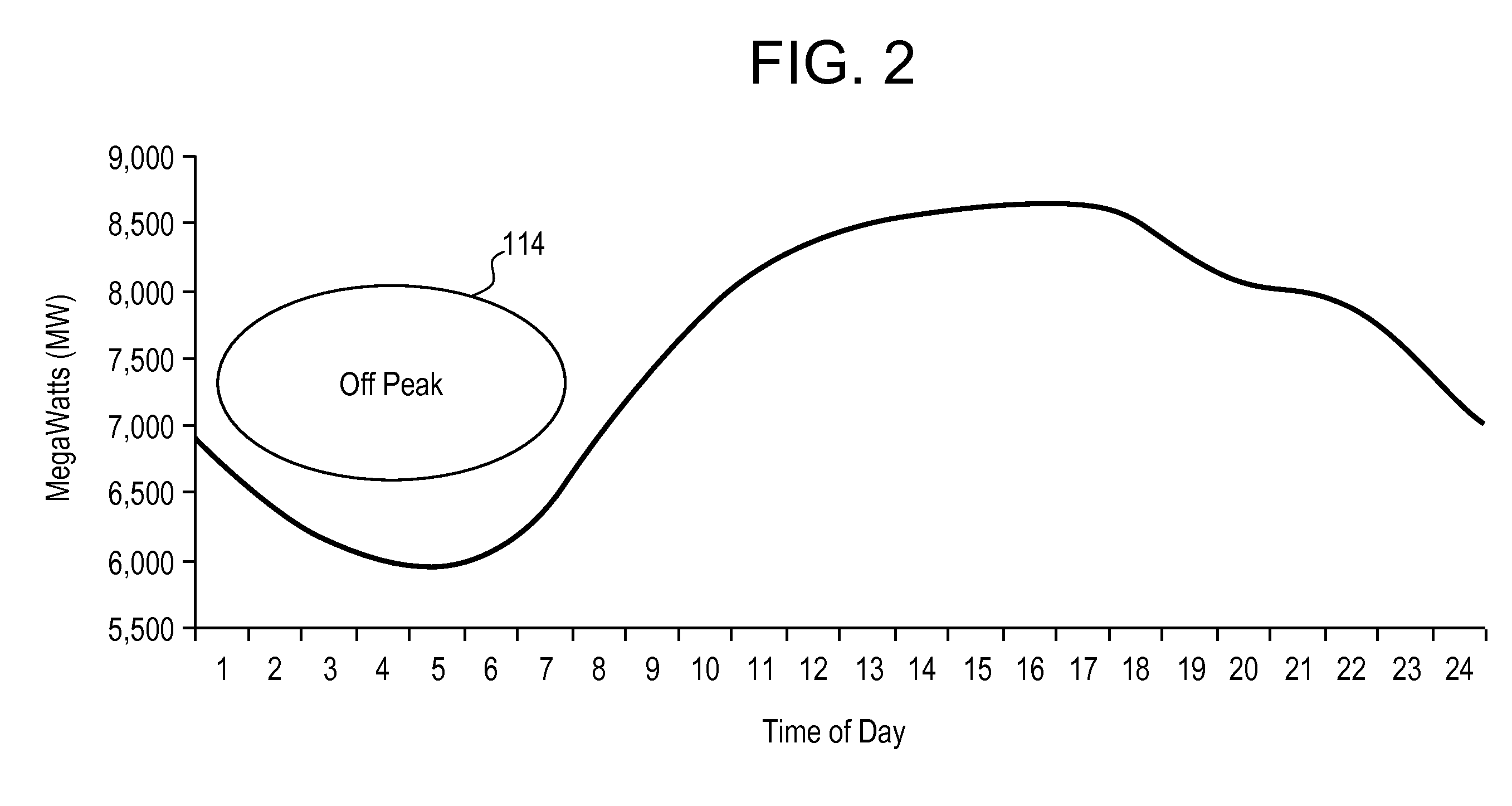
In telecommunication, the term demand load can have the following meanings: In general, the total power required by a facility. The demand load is the sum of the operational load and nonoperational demand loads. It is determined by applying the proper demand factor to each of the connected loads and a diversity factor to the sum total. At a communications center, the power required by all automatic switching, synchronous, and terminal equipment, control and keying equipment, plus lighting, ventilation, and air- conditioning equipment required to maintain full continuity of communications. The power required for ventilating equipment, shop lighting, and other support items that may be operated simultaneously with the technical load. The sum of the technical demand and nontechnical demand loads of an operating facility. At a receiver facility, the power required for all receivers and auxiliary equipment that may be operated on prime or spare antennas simultaneously, those in standby condition, multicouplers, control and keying equipment, plus lighting, ventilation, and air conditioning equipment required for full continuity of communications.
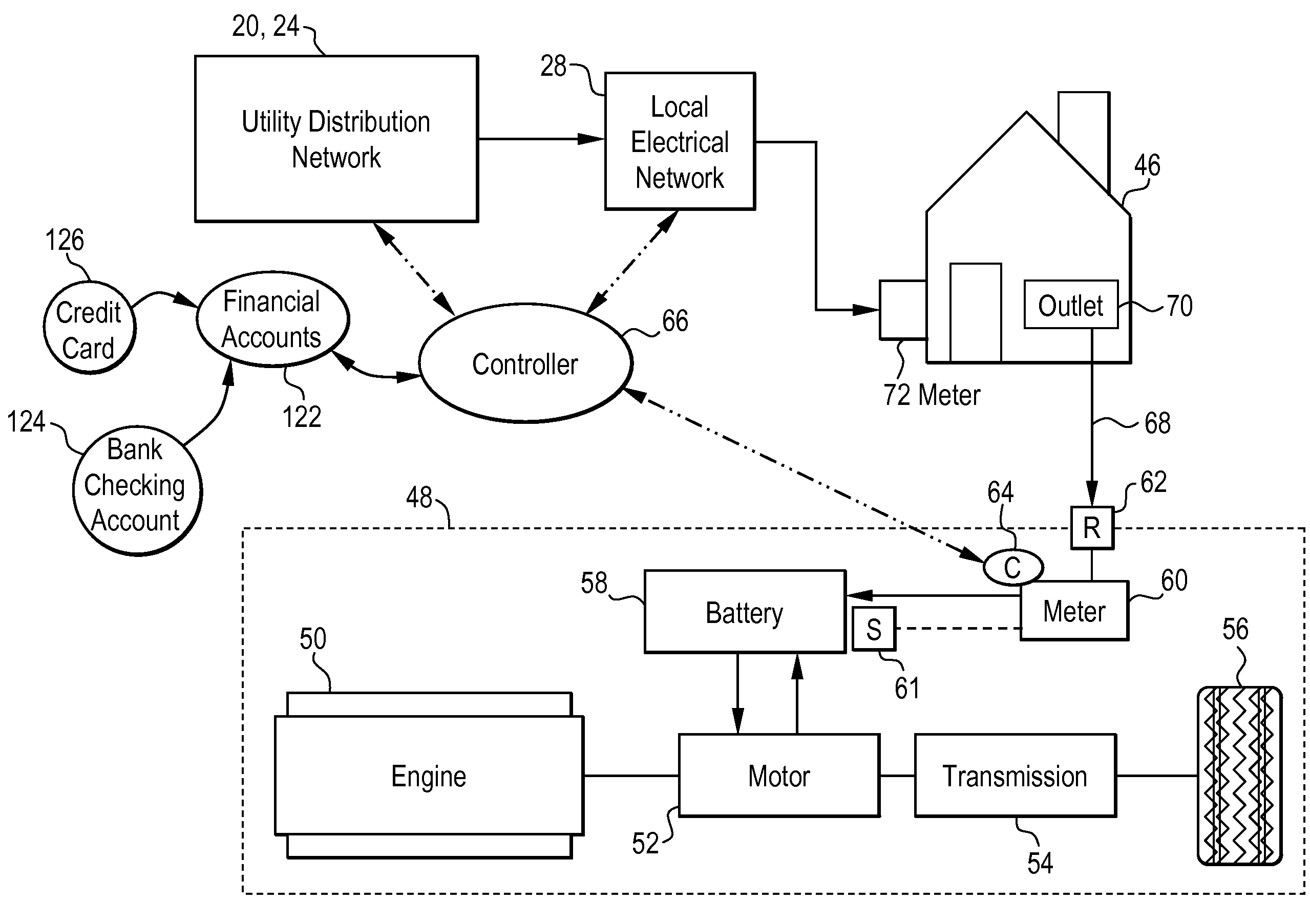
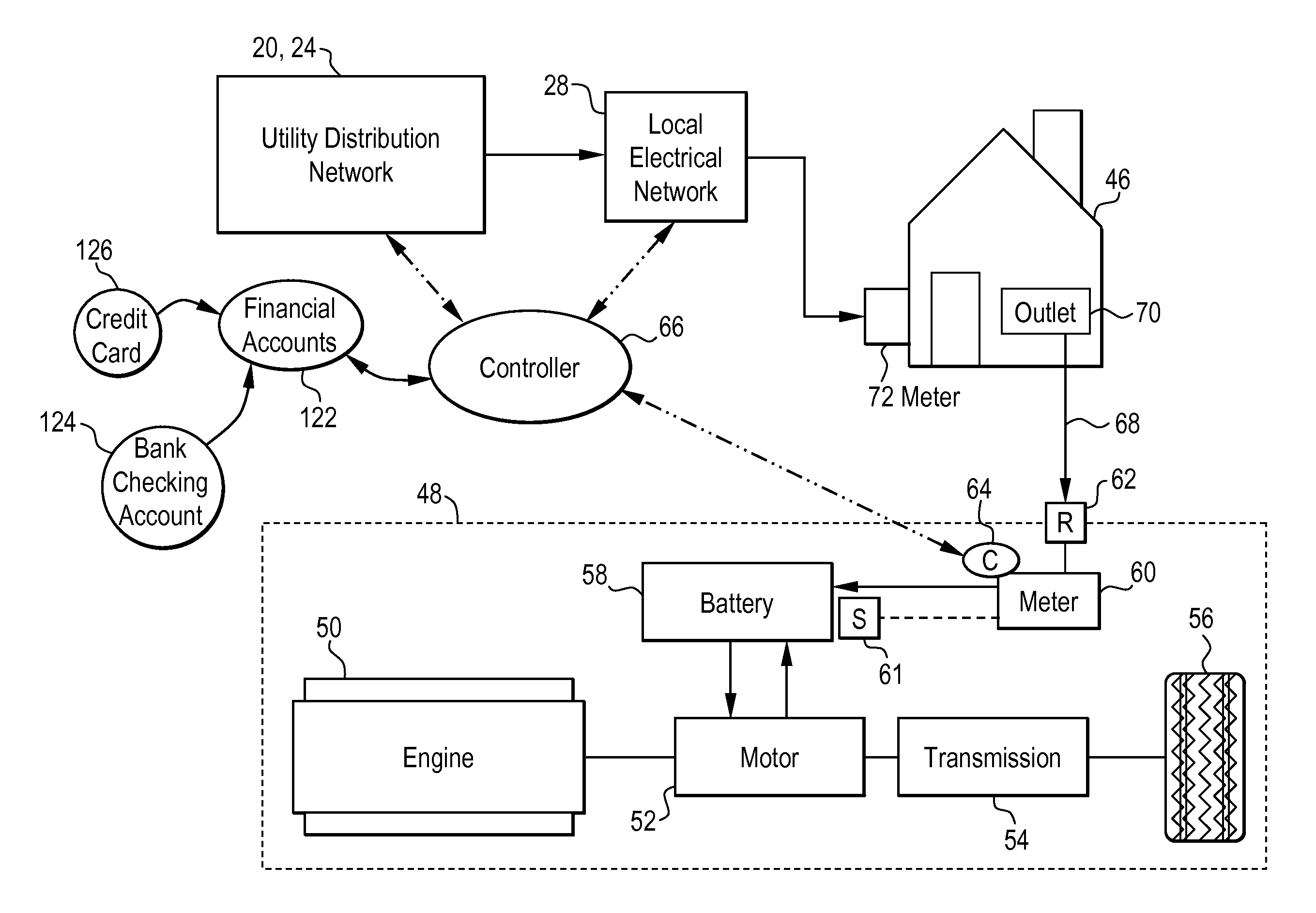
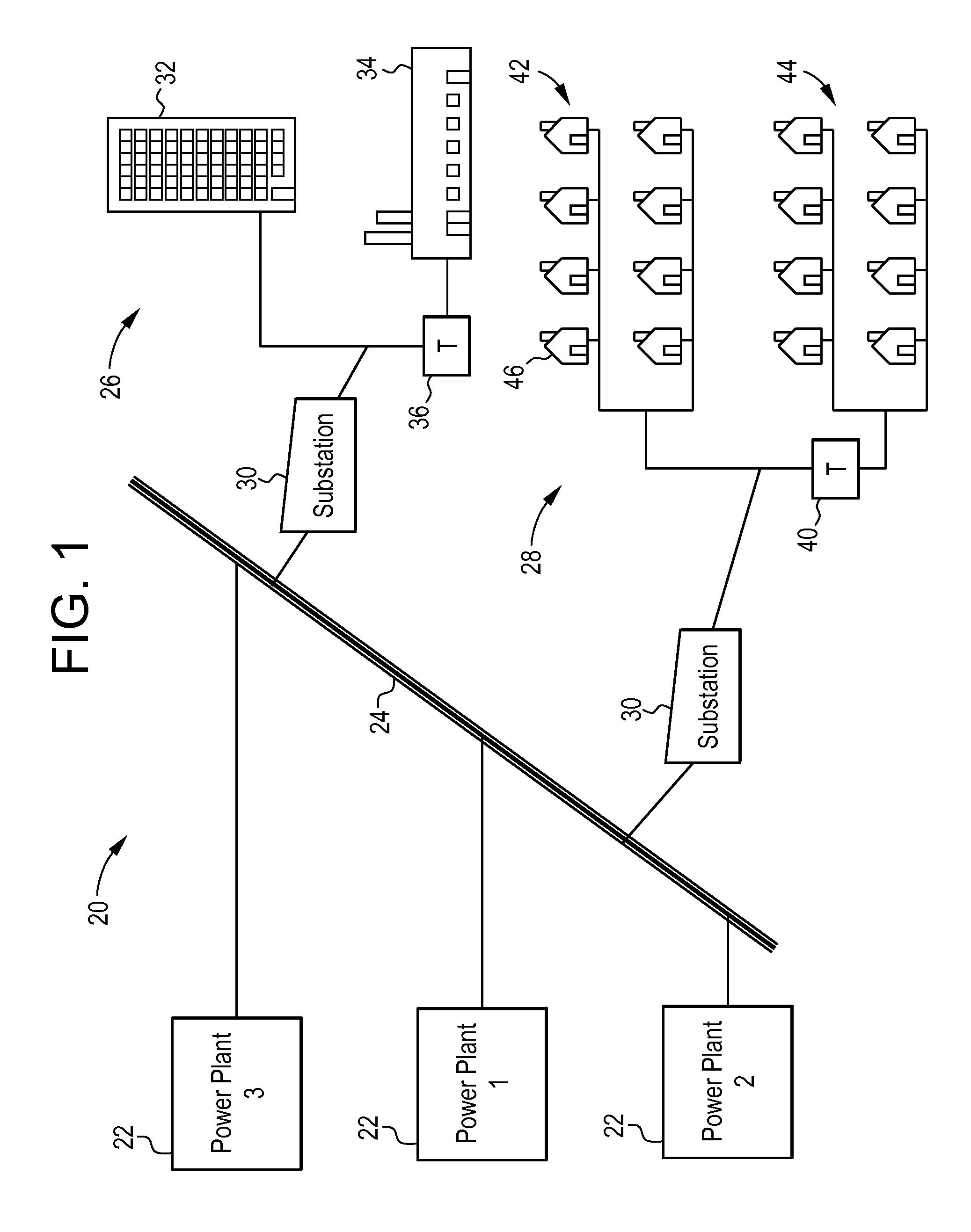
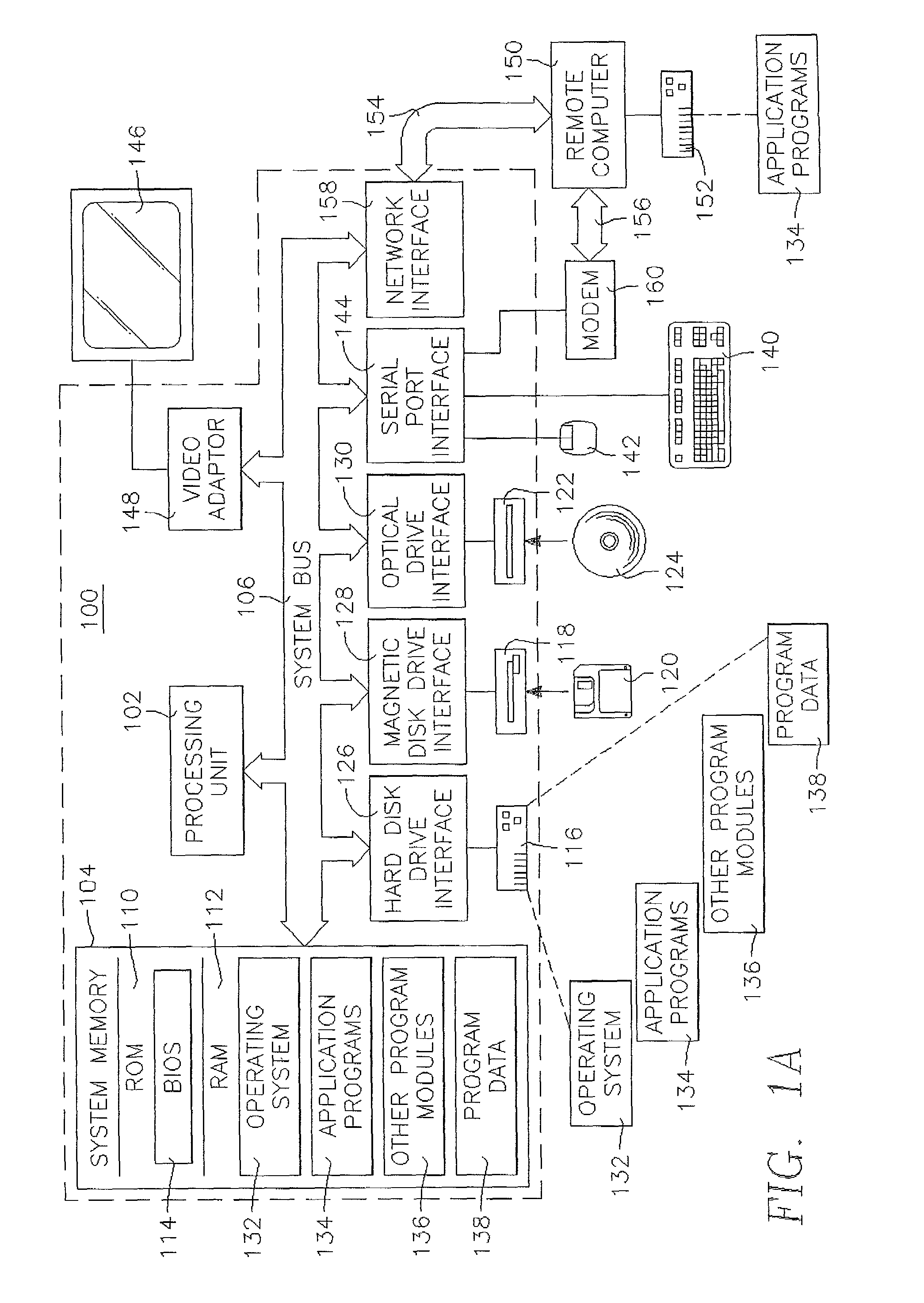
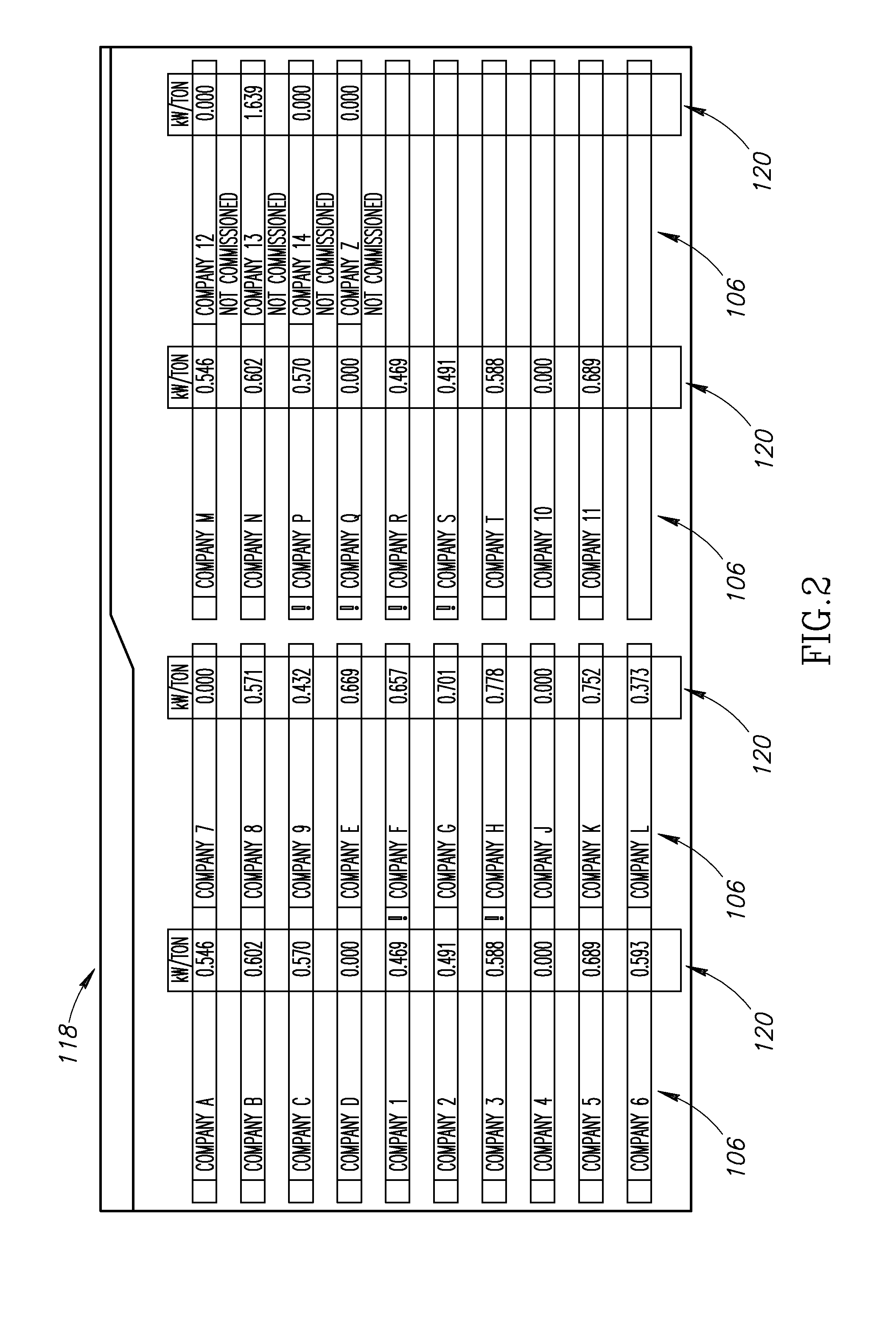
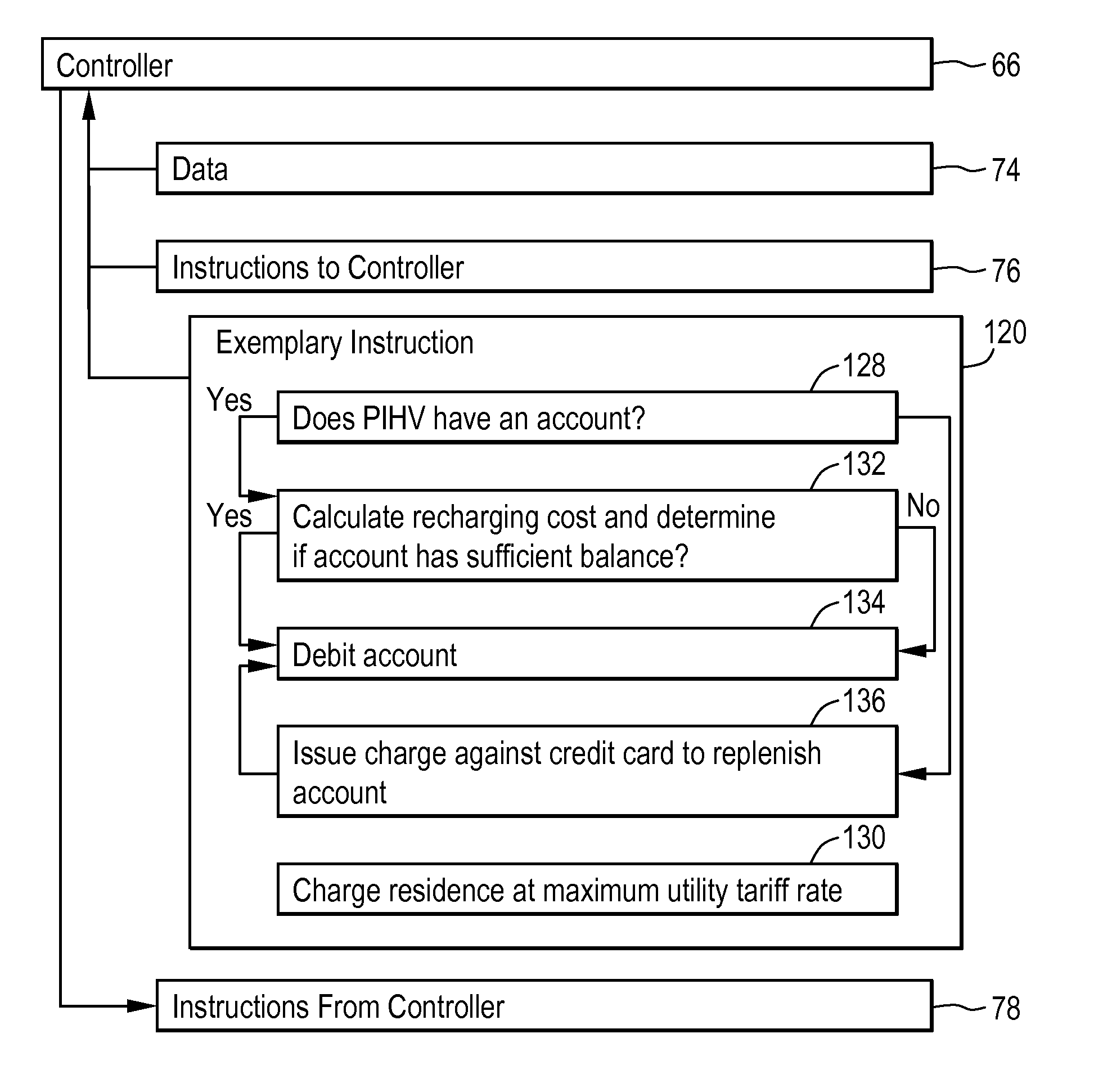
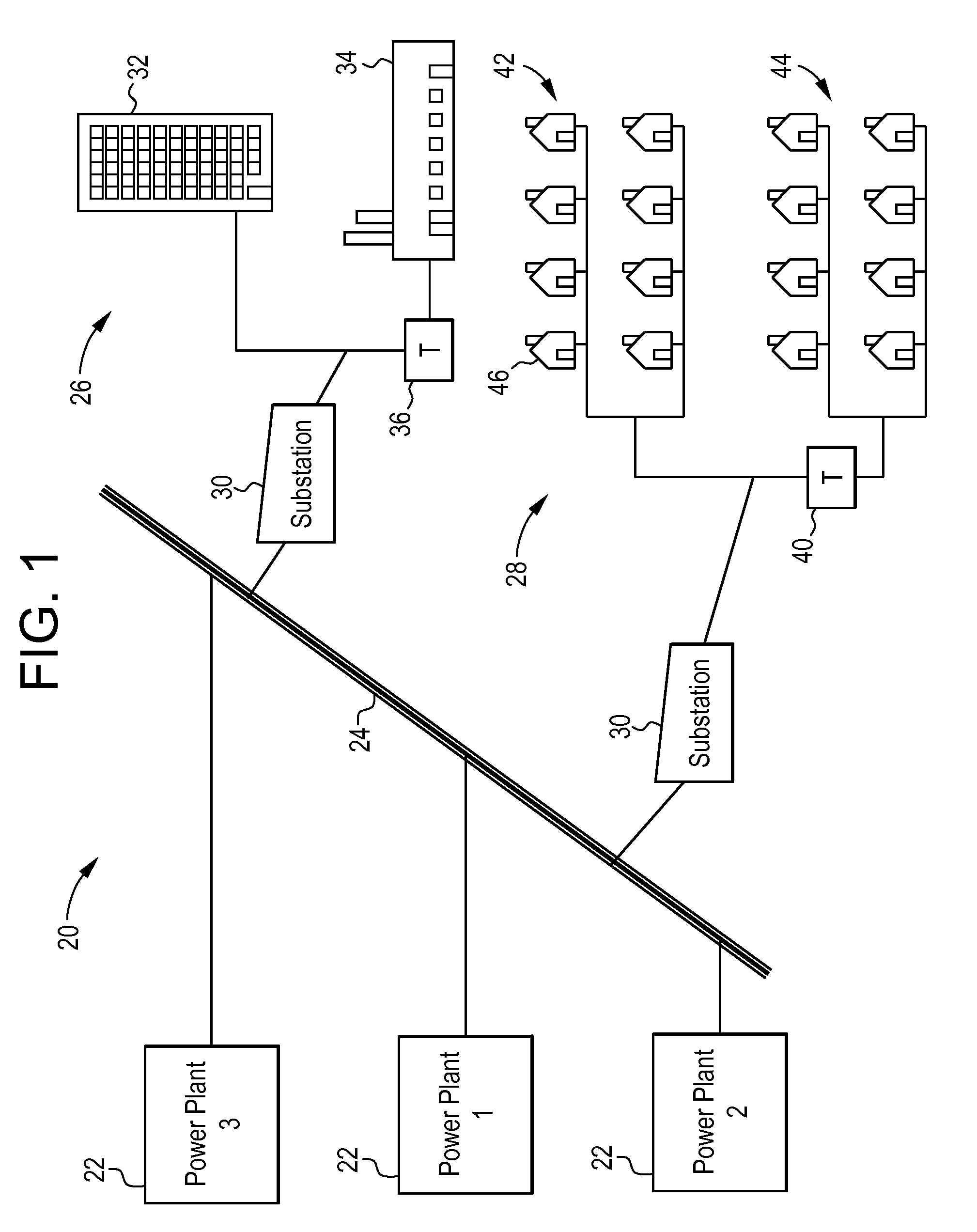
Hybrid vehicle recharging system and method of operation
A system and method for recharging a plug-in hybrid vehicle. The system includes a controller that schedules the recharging of the vehicles on local electrical distribution networks. The system arranges the schedule to minimize the demand loading on the local distribution network to more efficiently operate power plants providing electrical power to the distribution networks. A system for collecting charges associated with the recharging of plug-in hybrid vehicles is also disclosed providing for prepaid utility accounts.
Owner:CONSOL EDISON OF NEW YORK
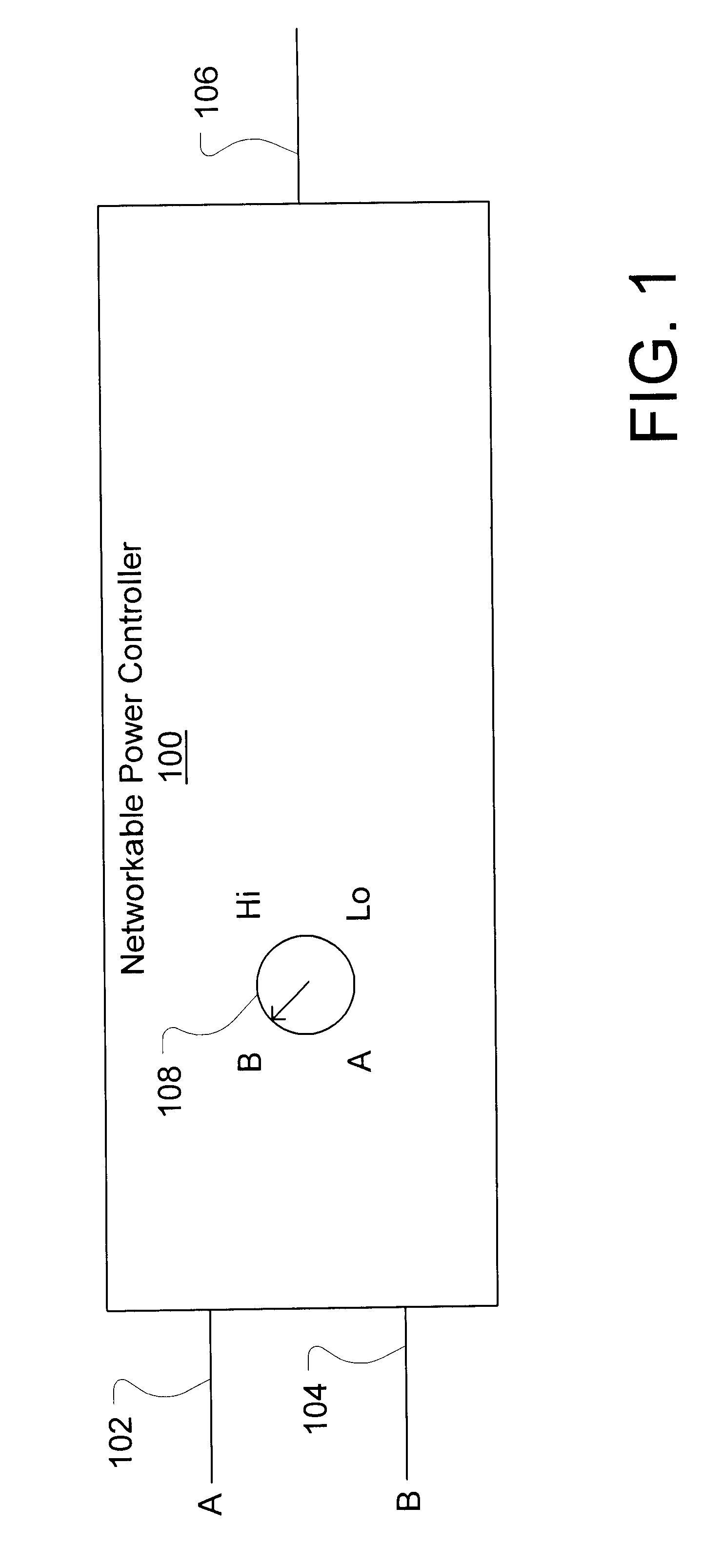
Networkable power controller
InactiveUS6400103B1Telemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsDigital controlBuilding automation
A networkable power controller includes a mode selector for selectively conducting of a plurality of input signals to an output of the networkable power controller, where the input signals and the output signals satisfy the same signaling protocol. The networkable power controller may be networked with other networkable power controllers, lighting ballasts and other building automation control devices, and user-controlled voltage selectors to provide a lighting control network. A power controller may include a mode selector that may be used in combination with other control devices or components, including a rotary dimmer control, a digital slide dimmer control, a demand load shedder component, a photometer component, and a communications interface. The communications interface allows digital control of the networkable power controller.
Owner:POWER CIRCUIT INNOVATIONS
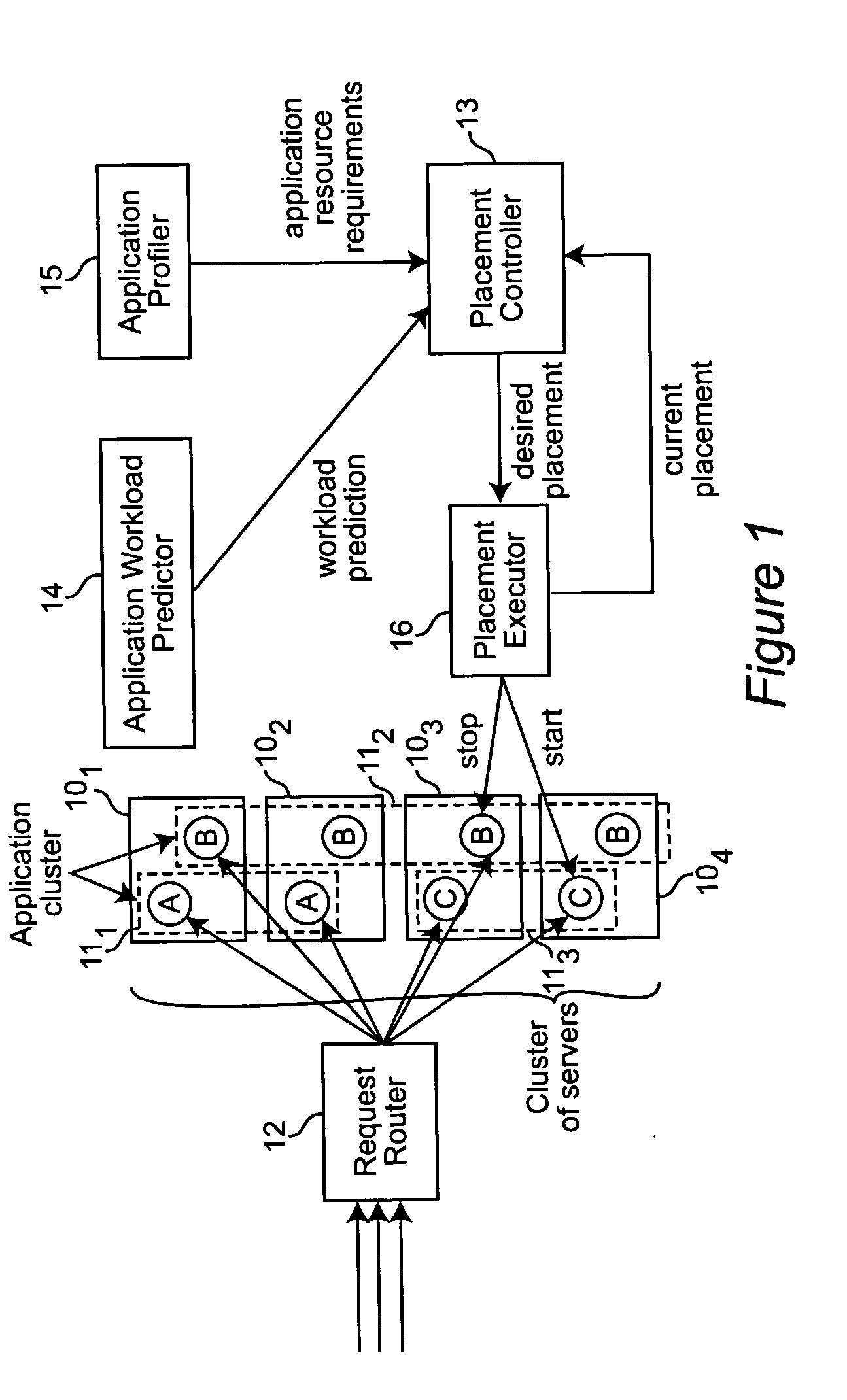
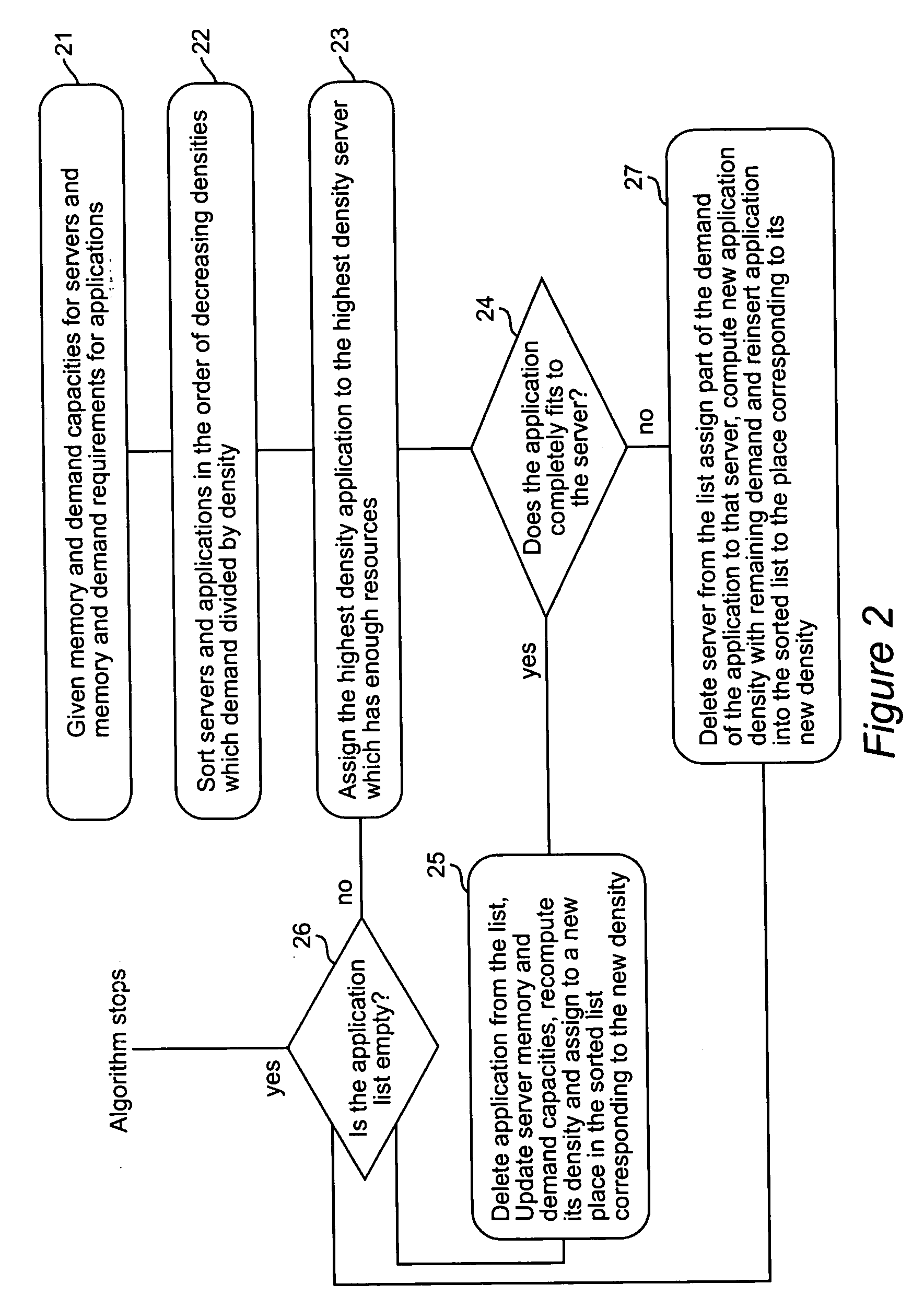
Dynamic application placement under service and memory constraints
InactiveUS20060242647A1Fine granularityIncrease capacityMultiprogramming arrangementsMemory systemsProgramming languageTerm memory
An optimization problem models the dynamic placement of applications on servers under two types of simultaneous resource requirements, those that are dependent on the loads placed on the applications and those that are independent. The demand (load) for applications changes over time and the goal is to satisfy all the demand while changing the solution (assignment of applications to servers) as little as possible.
Owner:IBM CORP
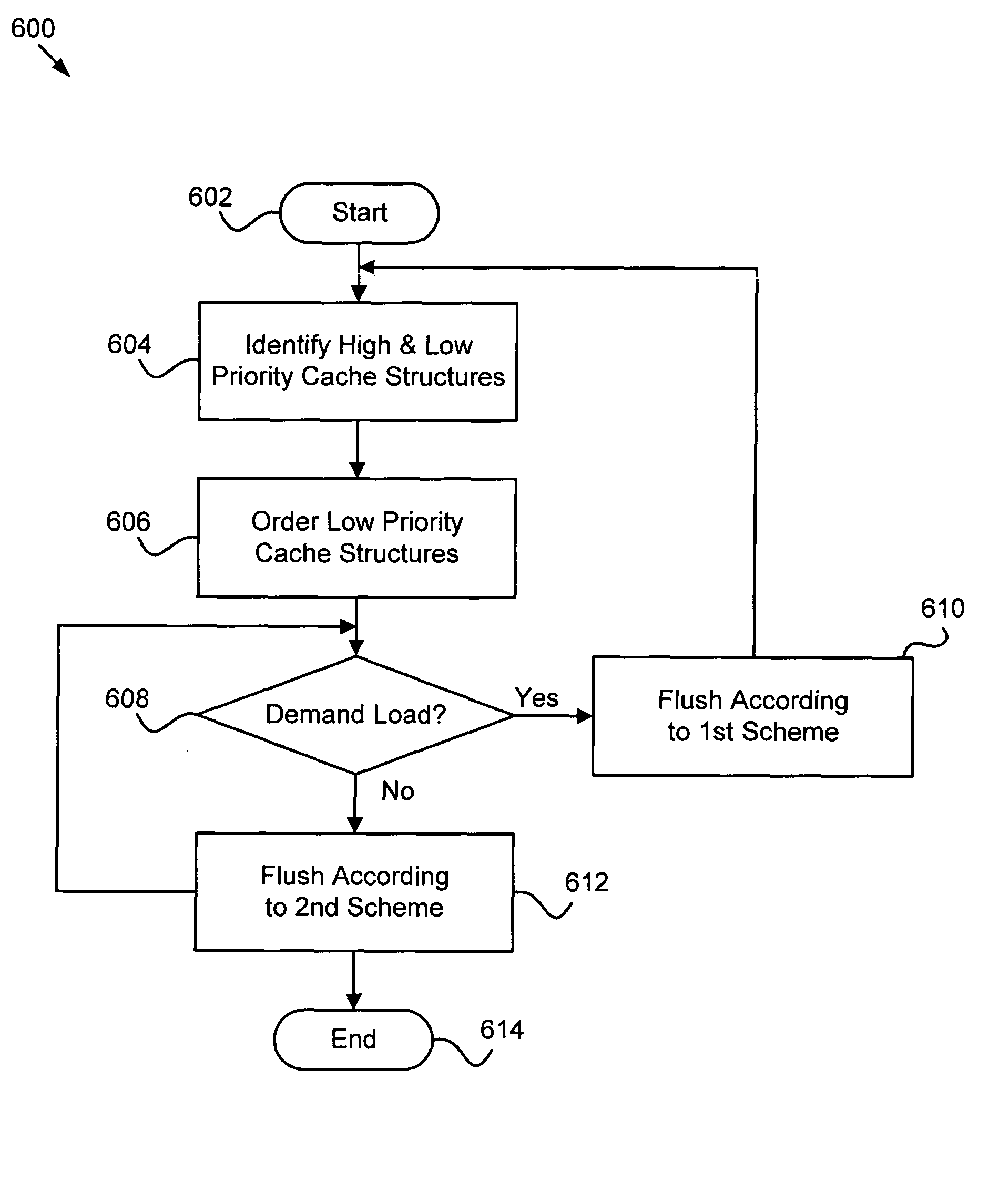
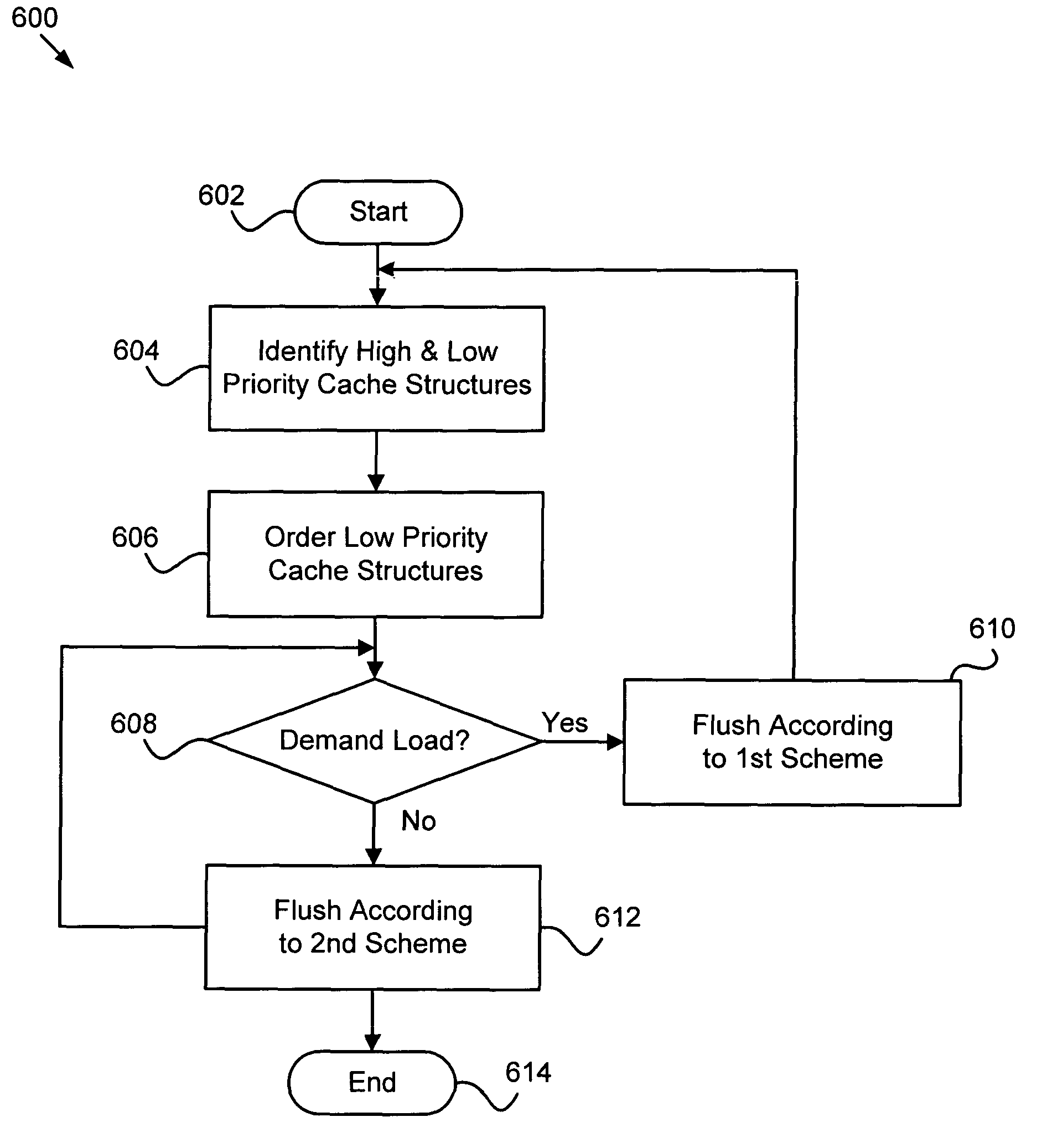
Apparatus, system, and method flushing data from a cache to secondary storage
InactiveUS20050055512A1Good choiceMemory adressing/allocation/relocationInput/output processes for data processingParallel computingAuxiliary memory
An apparatus, system, and method is provided for flushing data from a cache to secondary storage. The apparatus, system, and method identifies predefined high priority cache structures and predefined low priority cache structures. The apparatus, system, and method selectively flushes low priority cache structures according to a first scheme when the cache is under a demand load and according to a second scheme when the cache is under substantially no demand load. The first scheme is defined to flush low priority cache structures as efficiently as possible and the second scheme is defined to flush low priority cache structures in a less efficient manner.
Owner:IBM CORP
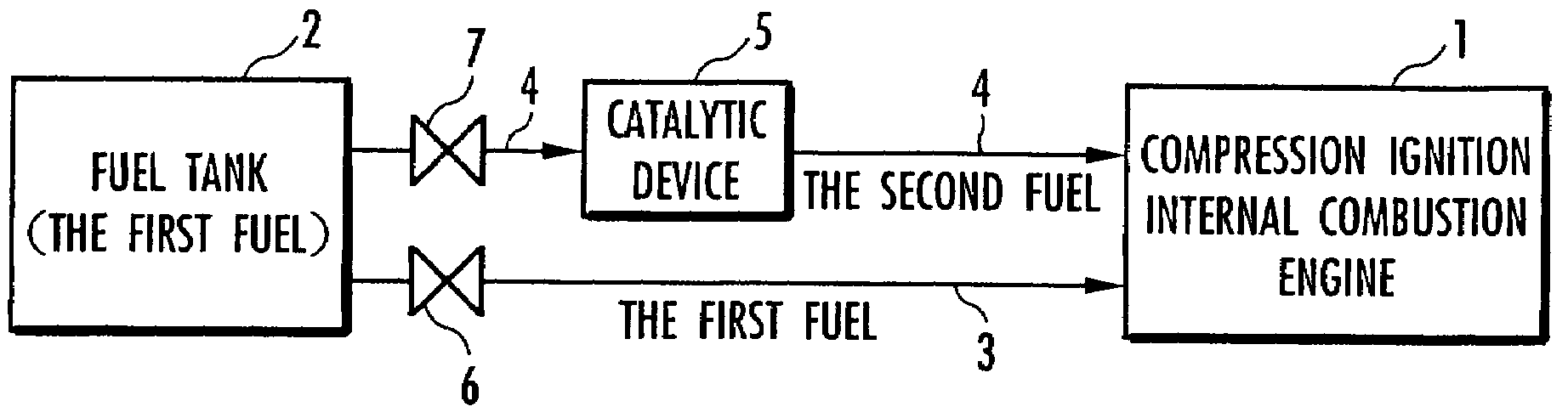
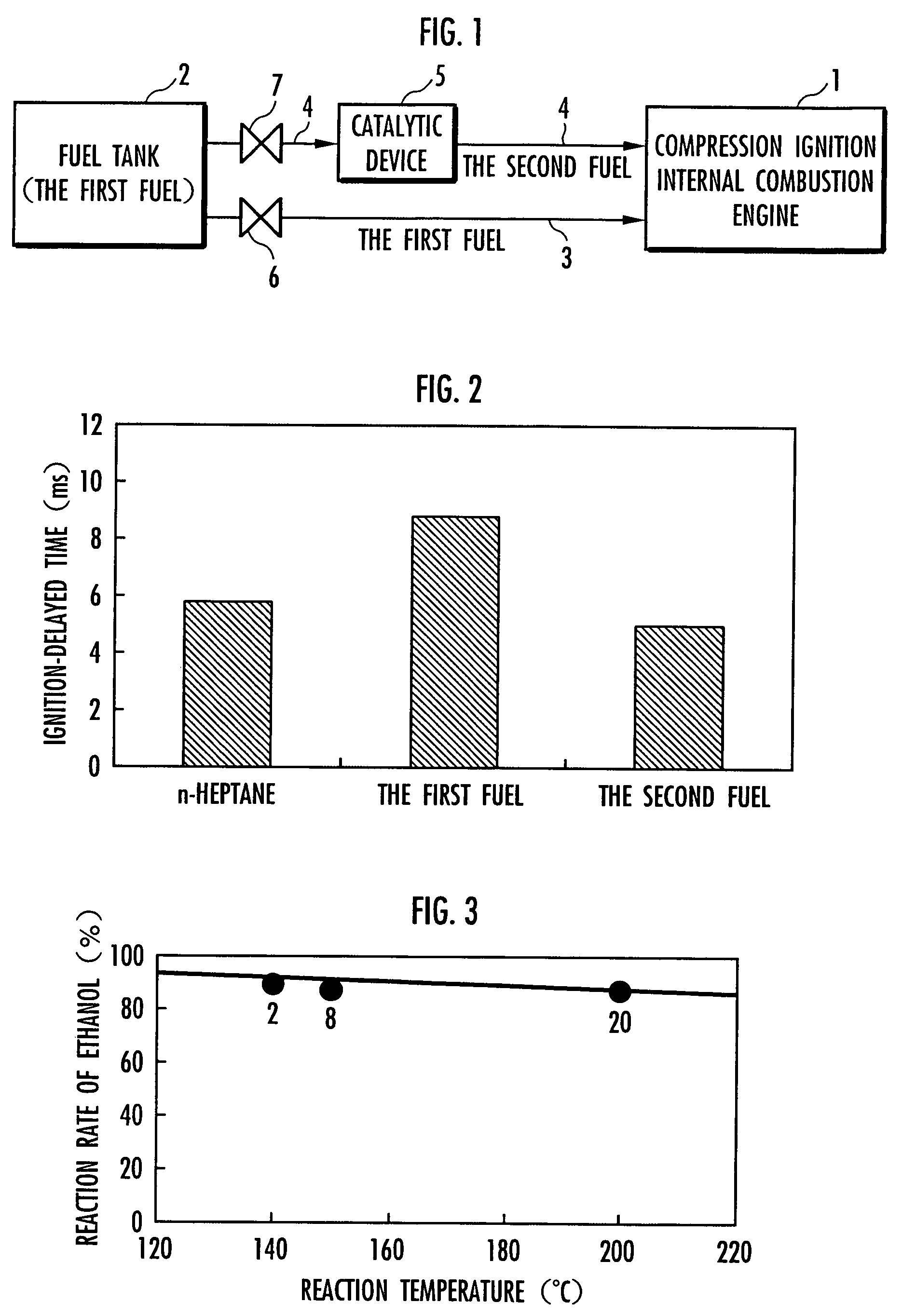
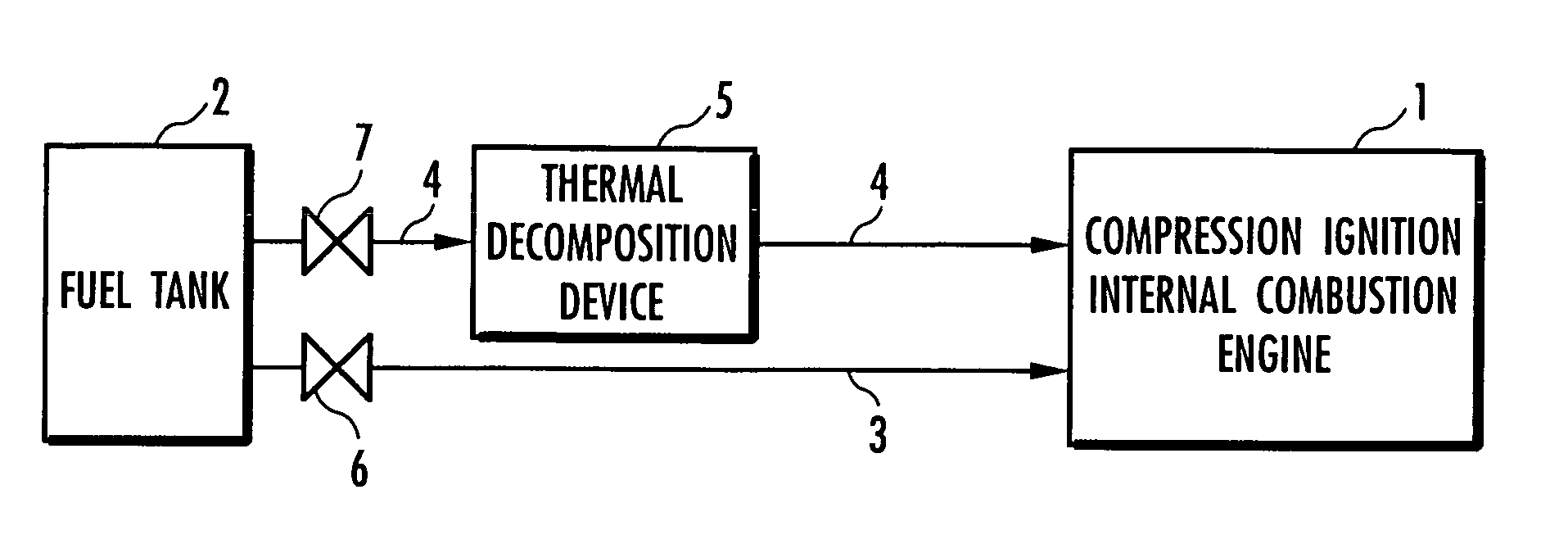
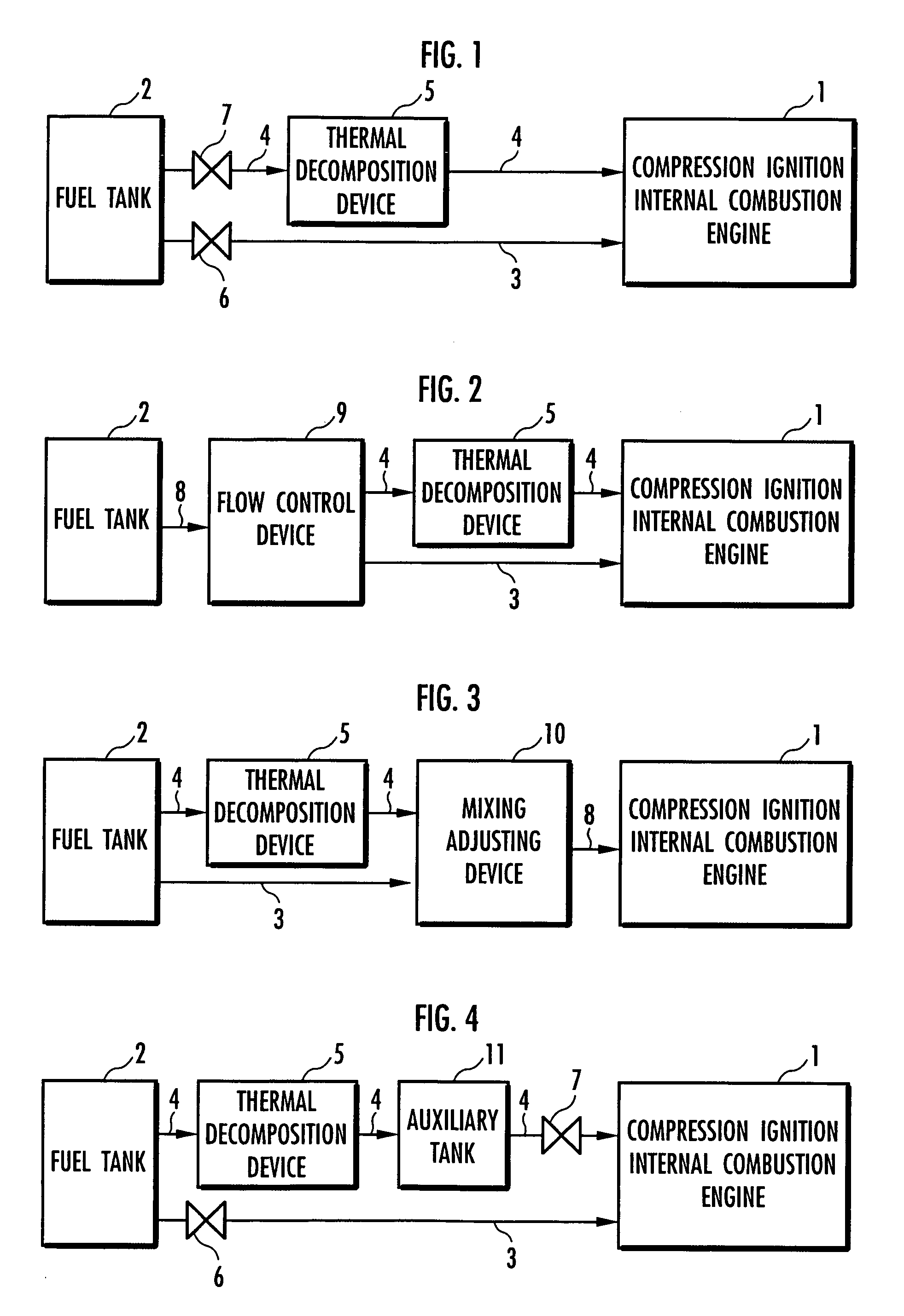
Method for controlling compression ignition internal combustion engine
InactiveUS7261065B2Improve flammabilityRaise the possibilityElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesRoom temperatureInternal combustion engine
The present invention provides a method for controlling a compression ignition internal combustion engine, which can easily cope with a wide range of demand loads. The compression ignition internal combustion engine 1 has a first fuel 2 containing ethanol, and reforming means 5 for reforming the first fuel into a second fuel having higher ignitability than the first fuel, by converting at least one part of ethanol contained in the first fuel 2 to diethyl ether, and each amount of the first fuel and the second fuel to be supplied to the compression ignition internal combustion engine is varied, in accordance with the change of a load required to the compression ignition internal combustion engine 1. Thus, the proportion of the first fuel to the total fuels supplied to the internal combustion engine 1 is increased, with the increase of the demand load, while the proportion of the second fuel to the total fuels supplied to the internal combustion engine 1 is increased, with the decrease of the demand load. The first fuel 2 contains ethanol and a hydrocarbon which is liquid at room temperature.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Networkable power controller
InactiveUS20020171379A1Telemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsEngineeringBuilding automation
A networkable power controller includes a mode selector for selectively conducting one of a plurality of input signals to an output of the networkable power controller, where the input signals and the output signals satisfy the same signaling protocol. The networkable power controller may be networked with other networkable power controllers, lighting ballasts and other building automation control devices, and user-controlled voltage selectors to provide a lighting control network. A power controller may include a mode selector that may be used in combination with other control devices or components, including a rotary dimmer control, a digital slide dimmer control, a demand load shedder component, a photometer component, and a communications interface. The communications interface allows digital control of the networkable power controller.
Owner:POWER CIRCUIT INNOVATIONS
Apparatus, system, and method flushing data from a cache to secondary storage
InactiveUS7085895B2Good choiceMemory adressing/allocation/relocationInput/output processes for data processingParallel computingAuxiliary memory
An apparatus, system, and method is provided for flushing data from a cache to secondary storage. The apparatus, system, and method identifies predefined high priority cache structures and predefined low priority cache structures. The apparatus, system, and method selectively flushes low priority cache structures according to a first scheme when the cache is under a demand load and according to a second scheme when the cache is under substantially no demand load. The first scheme is defined to flush low priority cache structures as efficiently as possible and the second scheme is defined to flush low priority cache structures in a less efficient manner.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Decentralized application placement for Web application middleware
InactiveUS20070180083A1Optimizes dynamic placementReduce complexityDigital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsWeb applicationDemand load
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and system for clearing dependent speculations from a request queue
InactiveUS6487637B1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationConcurrent instruction executionMemory hierarchyBit field
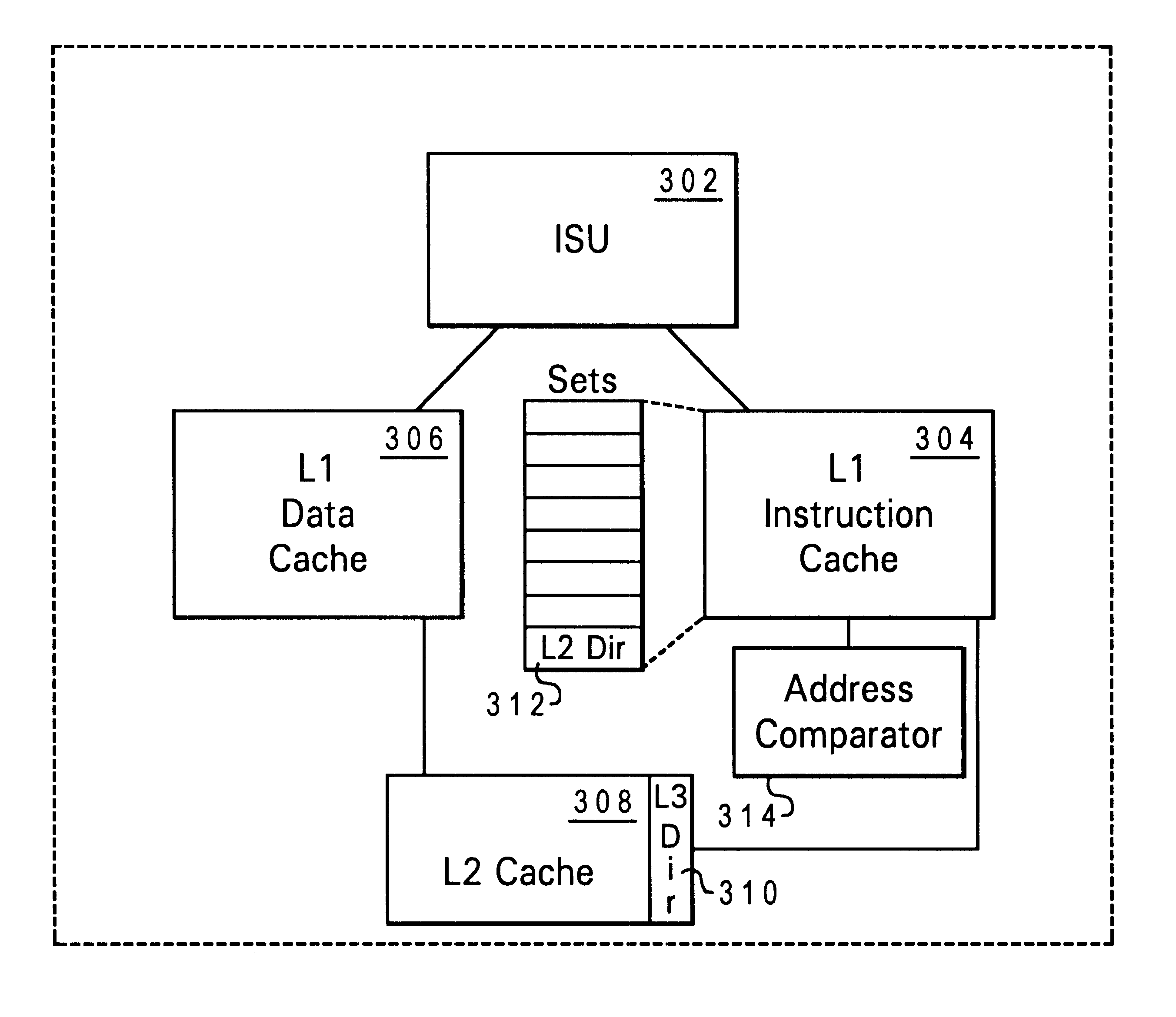
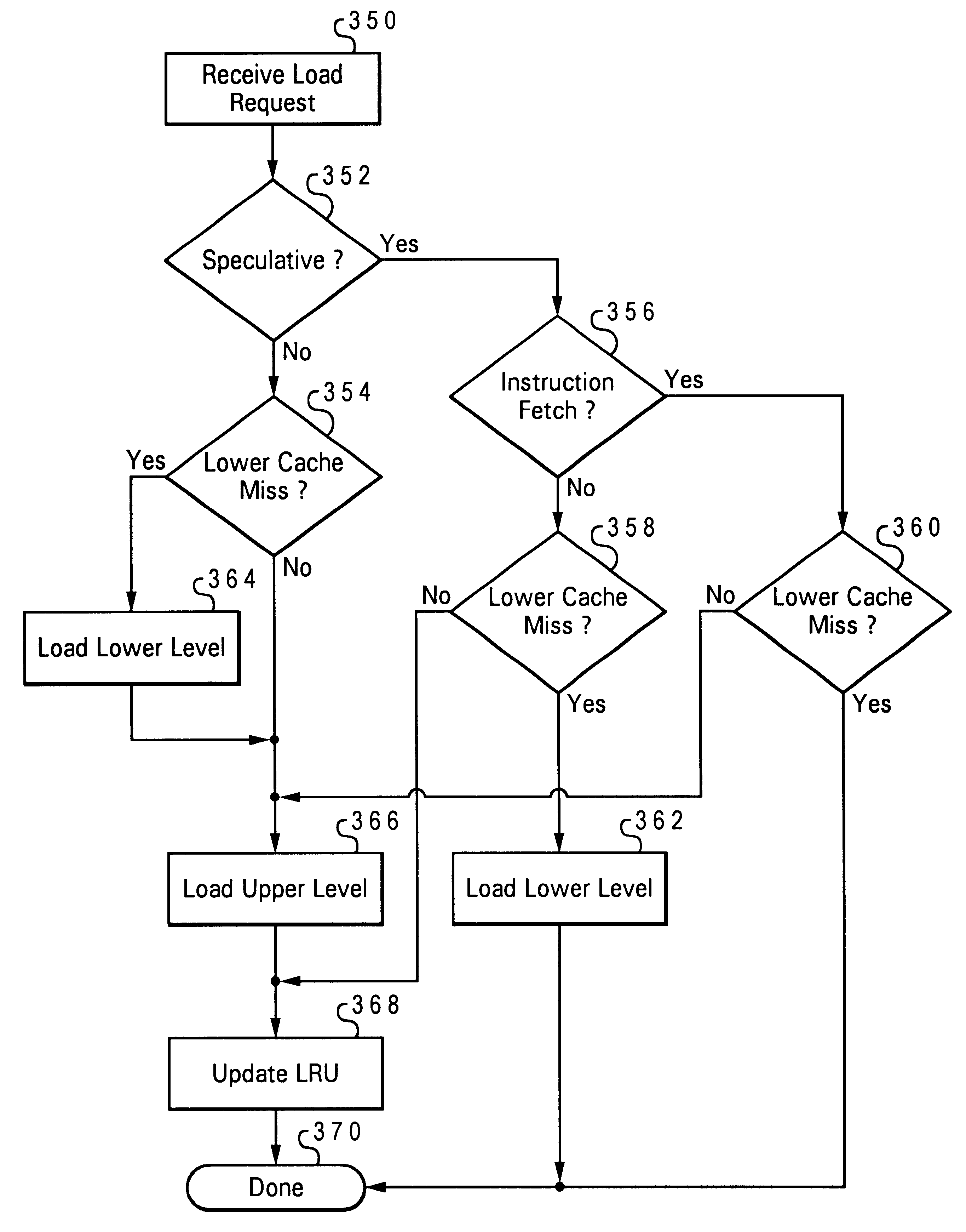
A method of operating a multi-level memory hierarchy of a computer system and apparatus embodying the method, wherein instructions issue having an explicit prefetch request directly from an instruction sequence unit to a prefetch unit of the processing unit. The invention applies to values that are either operand data or instructions. These prefetch requests can be demand load requests, where the processing unit will need the operand data or instructions, or speculative load requests, where the processing unit may or may not need the operand data or instructions, but a branch prediction or stream association predicts that they might be needed. Further branch predictions or stream associations that were made based on an earlier speculative choice are linked by using a tag pool which assigns a bit fields in the tag pool entries to the level of speculation depth. Each entry shares in common the bit field values associated with earlier branches or stream associations. When a branch or stream predicted entry is no longer needed, that entry can be cancelled and all entries that were to be loaded dependent on that entry can likewise be cancelled by walking through all entries sharing the bit fields corresponding to the speculation depth of the cancelled entry and tagging those entries as invalid.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and system for managing speculative requests in a multi-level memory hierarchy
InactiveUS6418516B1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital computer detailsProcessing InstructionMemory hierarchy
A method of operating a multi-level memory hierarchy of a computer system and apparatus embodying the method, wherein instructions issue having an explicit prefetch request directly from an instruction sequence unit to a prefetch unit of the processing unit. The invention applies to values that are either operand data or instructions and treats instructions in a different manner when they are loaded speculatively. These prefetch requests can be demand load requests, where the processing unit will need the operand data or instructions, or speculative load requests, where the processing unit may or may not need the operand data or instructions, but a branch prediction or stream association predicts that they might be needed. The load requests are sent to the lower level cache when the upper level cache does not contain the value required by the load. If a speculative request is for an instruction which is likewise not present in the lower level cache, that request is ignored, keeping both the lower level and upper level caches free of speculative values that are infrequently used. If the value is present in the lower level cache, it is loaded into the upper level cache. If a speculative request is for operand data, the value is loaded only into the lower level cache if it is not already present, keeping the upper level cache free of speculative operand data.
Owner:IBM CORP
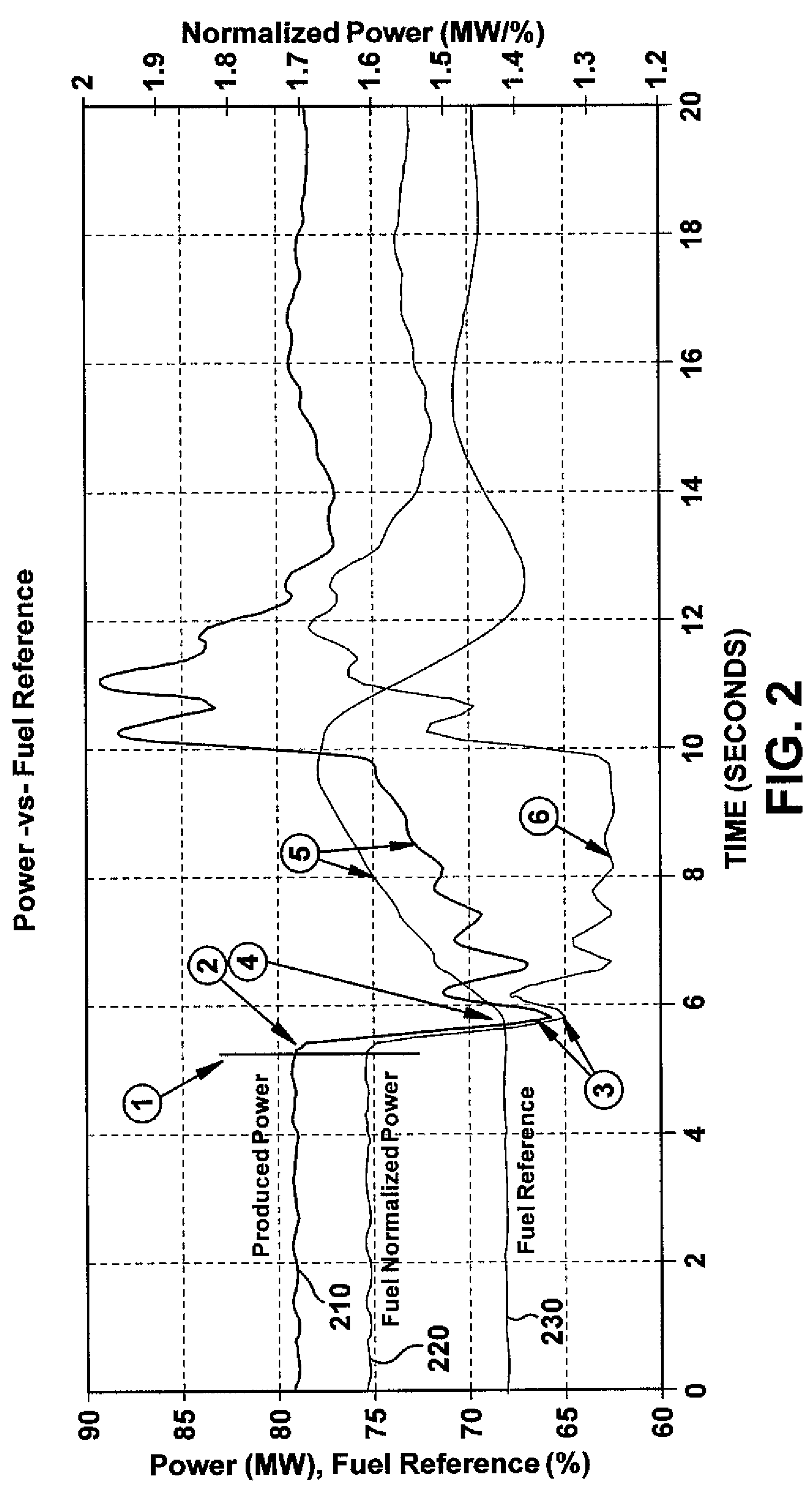
Method and system for detection of gas turbine combustion blowouts utilizing fuel normalized power response
A method and controller for identifying lean blowout conditions in a Dry Low NOx (DLN) combustor during a premix mode. An effective approach to quickly and reliably identify a blowout during operation in the premix mode is by the effect on fuel normalized power (FNP). FNP is a useful signal, in that a power reduction from a blowout may be distinguished much slower changes in power resulting from global fuel demand (changing load request). A difference between the FNP and a filtered FNP parameter may be compared against a predetermined threshold. If the difference exceeds the threshold, a lean blowout is identified and a signal may be transmitted to the turbine controller to reposition combustor operation away from blowout conditions.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Hybrid vehicle recharging system and method of operation
InactiveUS20100012406A1Hybrid vehiclesTicket-issuing apparatusPower stationElectric distribution network
A system and method for recharging a plug-in hybrid vehicle. The system includes a controller that schedules the recharging of the vehicles on local electrical distribution networks. The system arranges the schedule to minimize the demand loading on the local distribution network to more efficiently operate power plants providing electrical power to the distribution networks. A system for collecting charges associated with the recharging of plug-in hybrid vehicles is also disclosed providing for prepaid utility accounts.
Owner:CONSOL EDISON OF NEW YORK
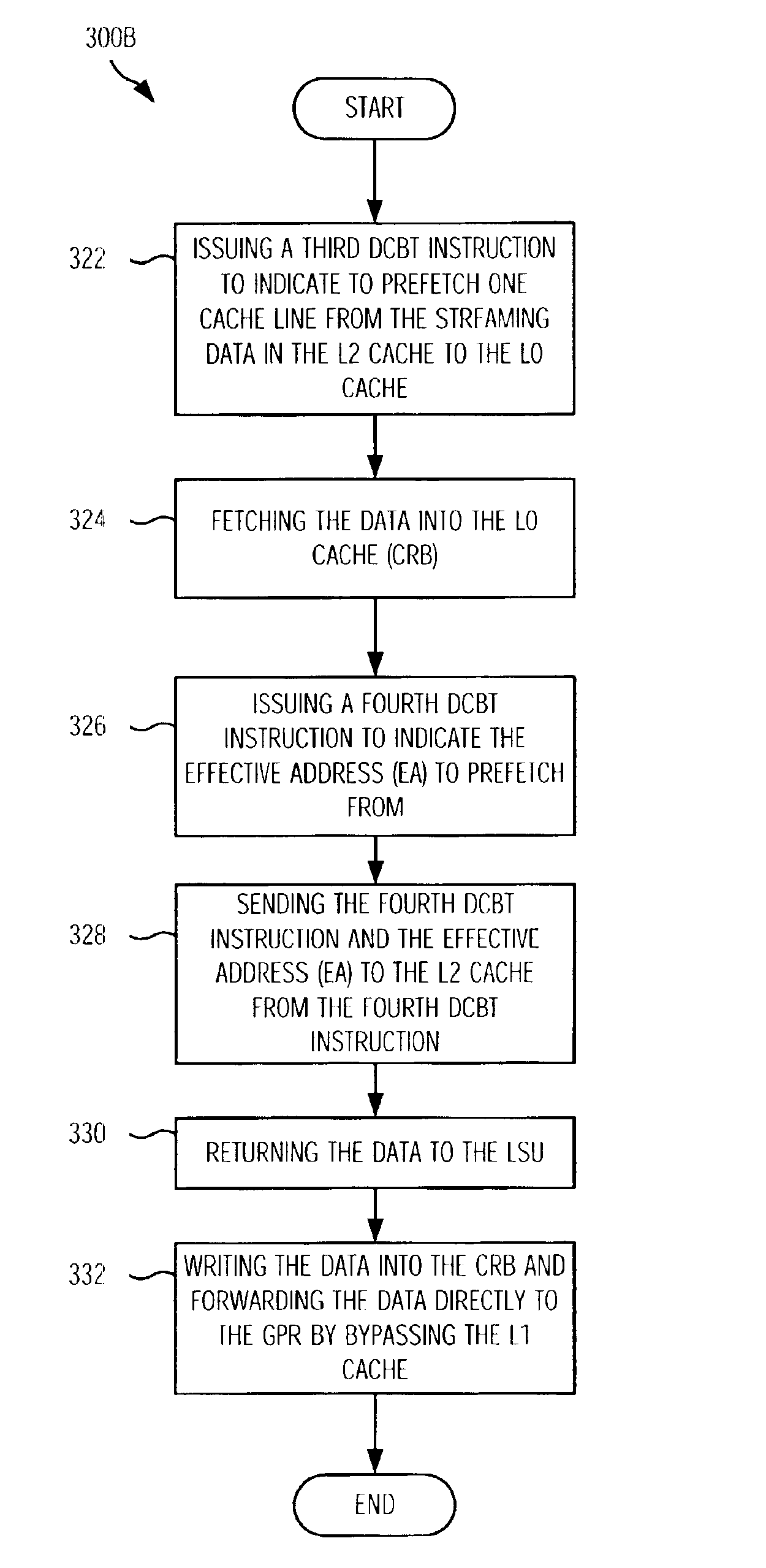
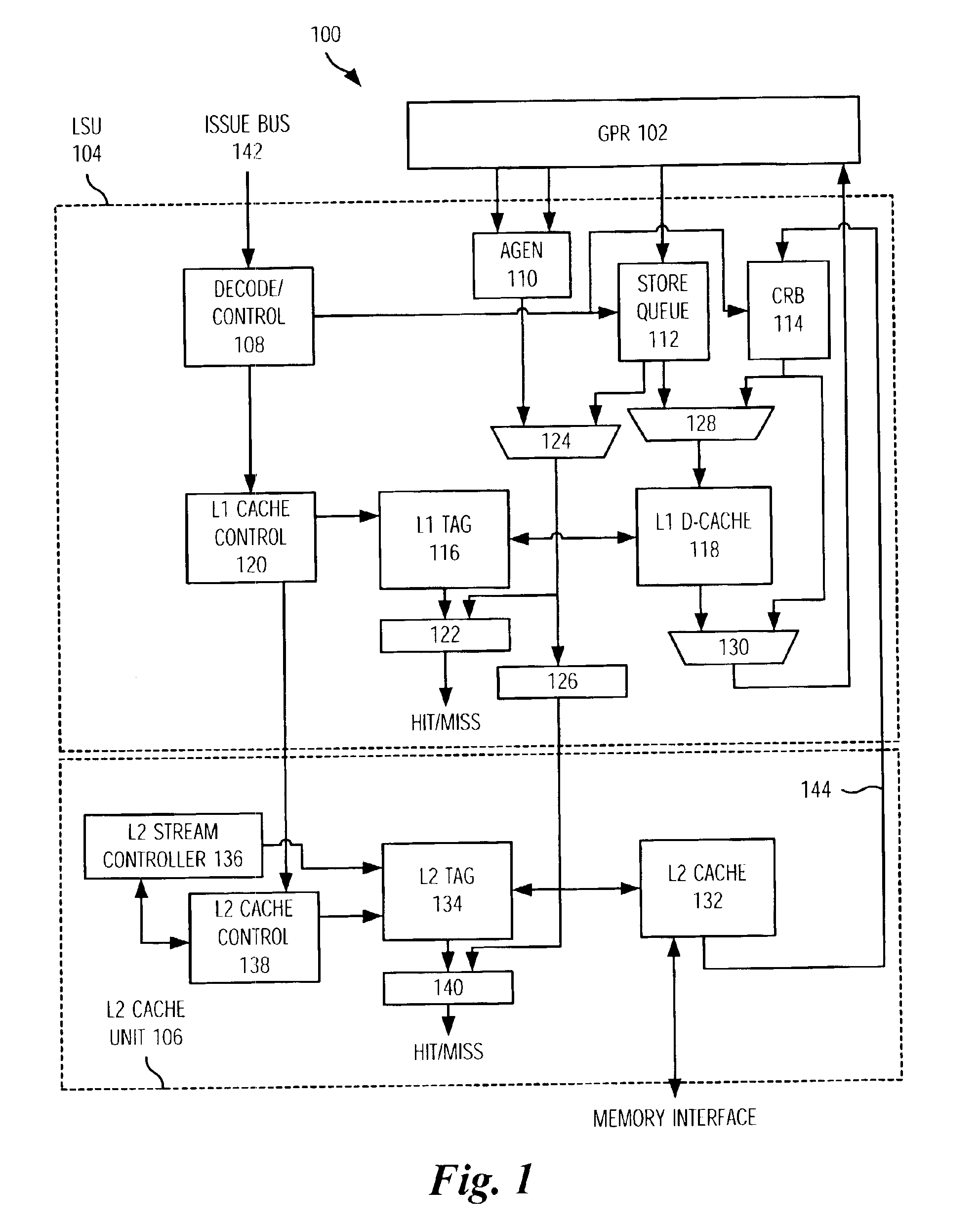
Data streaming mechanism in a microprocessor
ActiveUS6957305B2Memory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital computer detailsCache hierarchyData stream
This invention provides a dual usage cache reload buffer (CRB) to hold both demand loads as well as prefetch loads. A new form of a data cache block touch (DCBT) instruction specifies which level of the cache hierarchy to prefetch data into. A first asynchronous form of a DCBT instruction is issued to prefetch a stream of data into a L2 cache. A second synchronous form of a DCBT instruction is used to prefetch data from the L2 cache to the CRB in the main CPU, which will bypass the L1 data cache and forward data directly to the register file. This CRB has a dual usage and is used to hold both normal cache reloads as well as the aforementioned prefetched cache lines.
Owner:IBM CORP
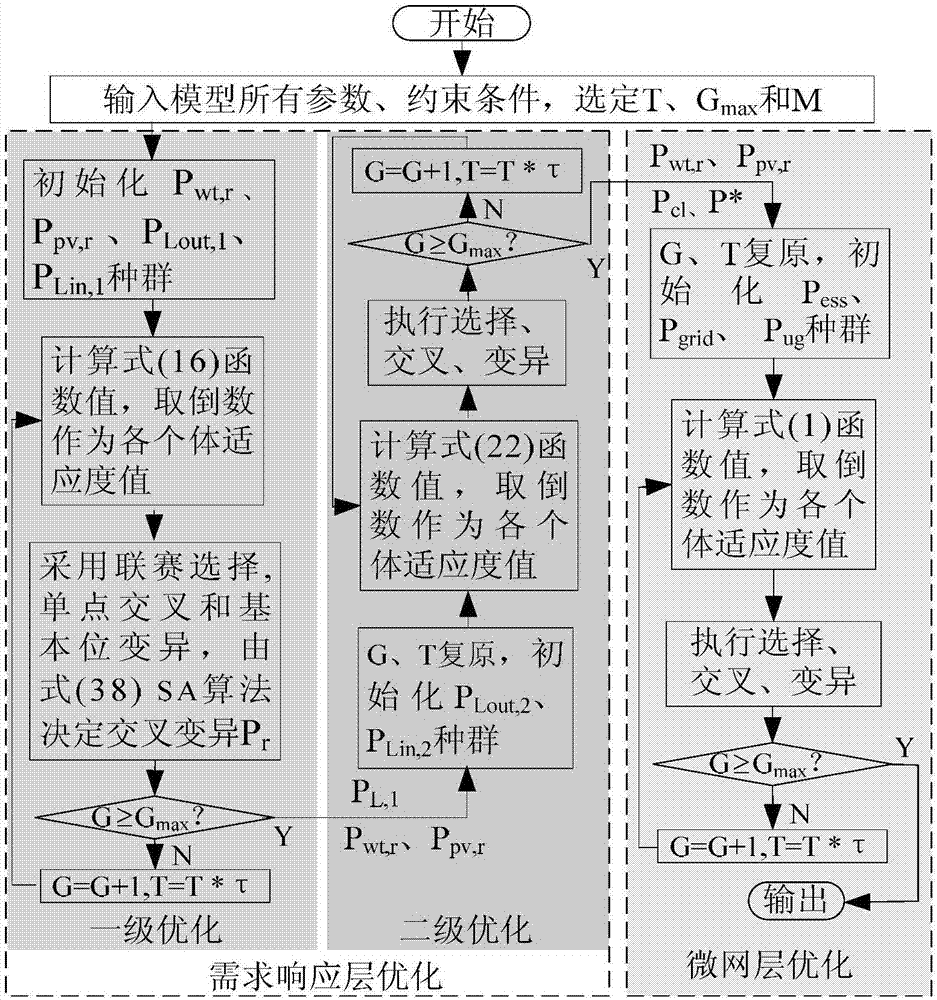
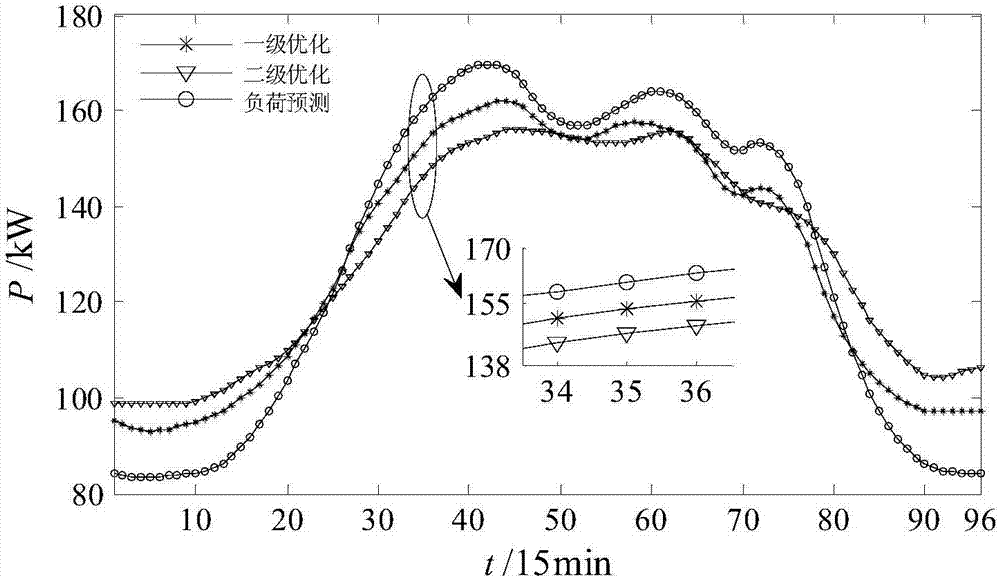
Grid-connecting micro-grid double-layer optimization method based on two-stage demand response
ActiveCN108009693AEfficient development and utilizationIncrease the proportionForecastingSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsElectricity priceEngineering
The invention relates to a grid-connecting micro-grid double-layer optimization method based on two-stage demand response. A demand response layer guides a user actively track clean energy power generation output in power consumption through one-stage optimization, thereby promoting high-efficiency development and utilization of the clean energy, and increasing ratio of the clean energy in terminal energy consumption. Through demand load adjustment by two-stage optimization, a more stable electric power load operation state is formed and output stability of a controllable micro-source is improved. A micro-grid layer minimizes comprehensive operation cost at the aspect of economic property of the micro-grid based on the method. A reasonable grid connecting micro-grid double-layer optimization model is constructed through sufficiently considering the demand-side response based on time-variable electricity price, and furthermore the model is solved by a heredity algorithm based on simulated annealing, thereby improving convergence speed and precision in model solving.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
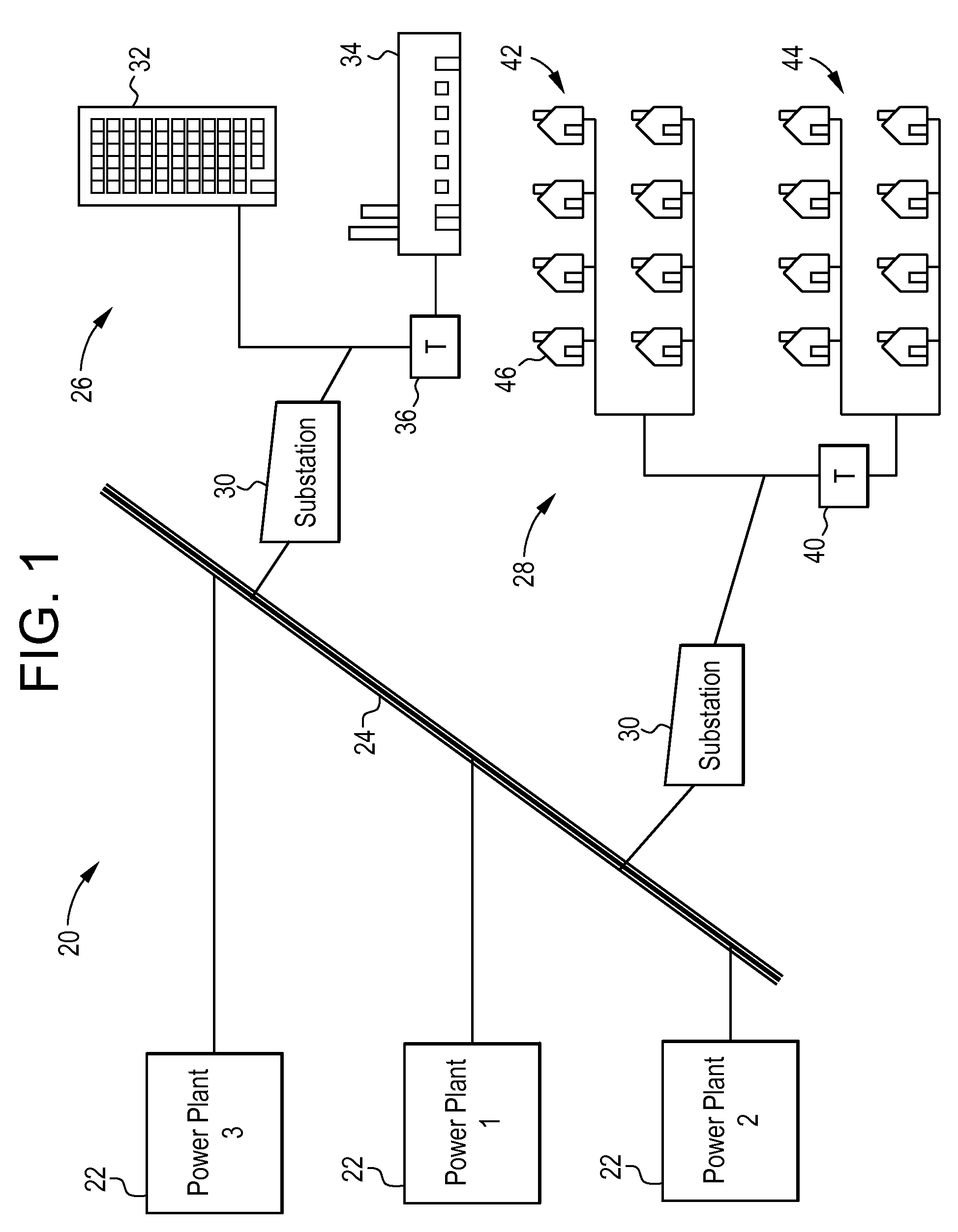
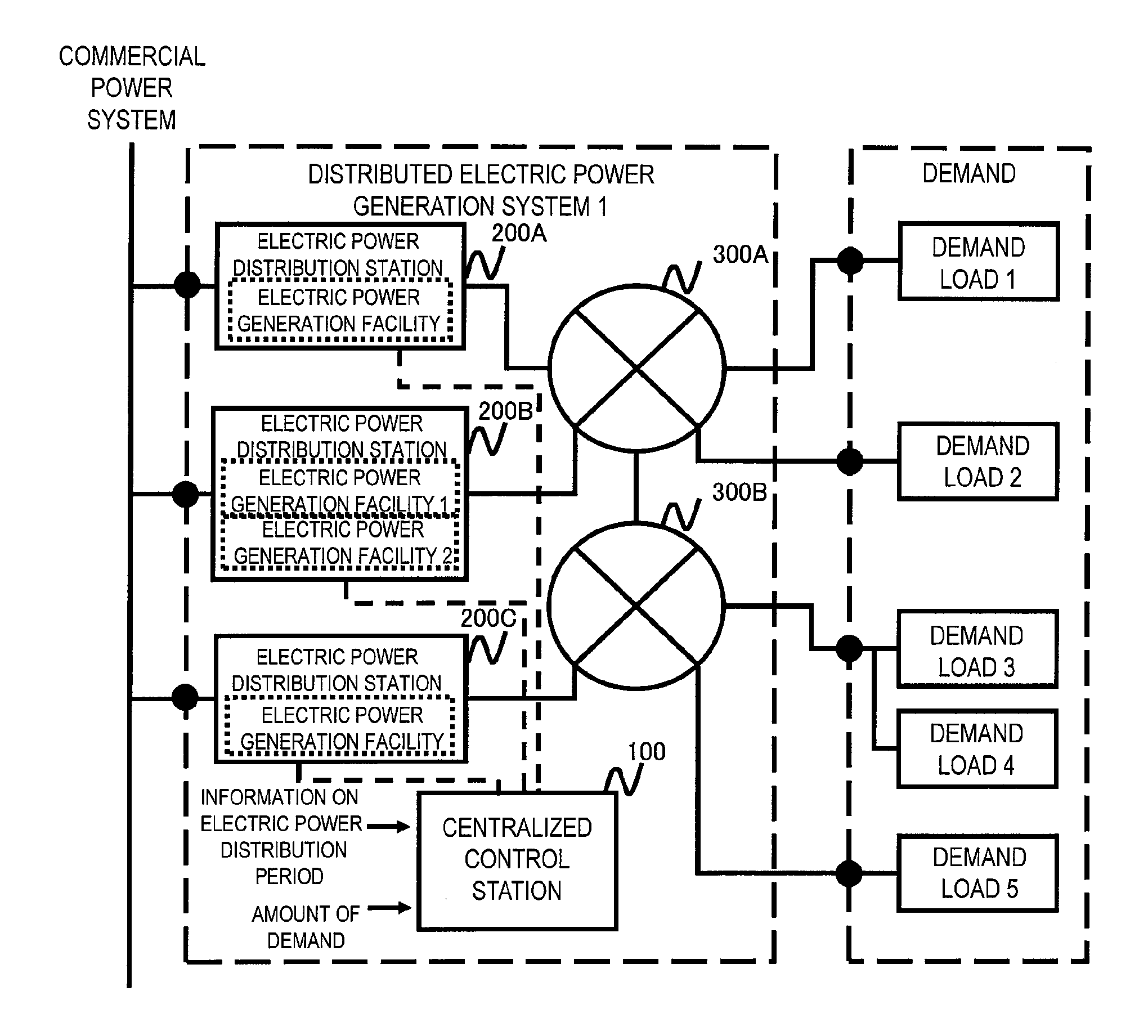
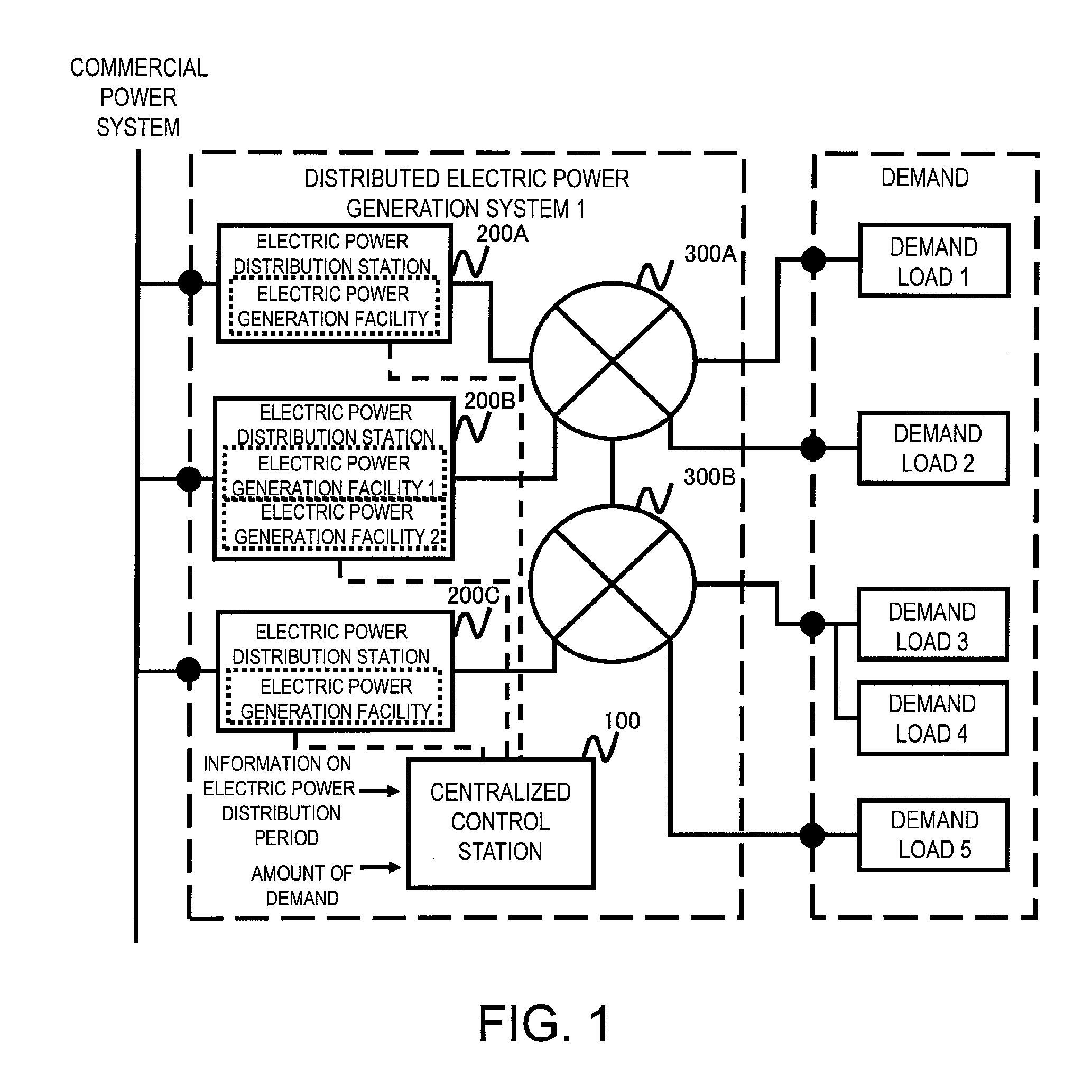
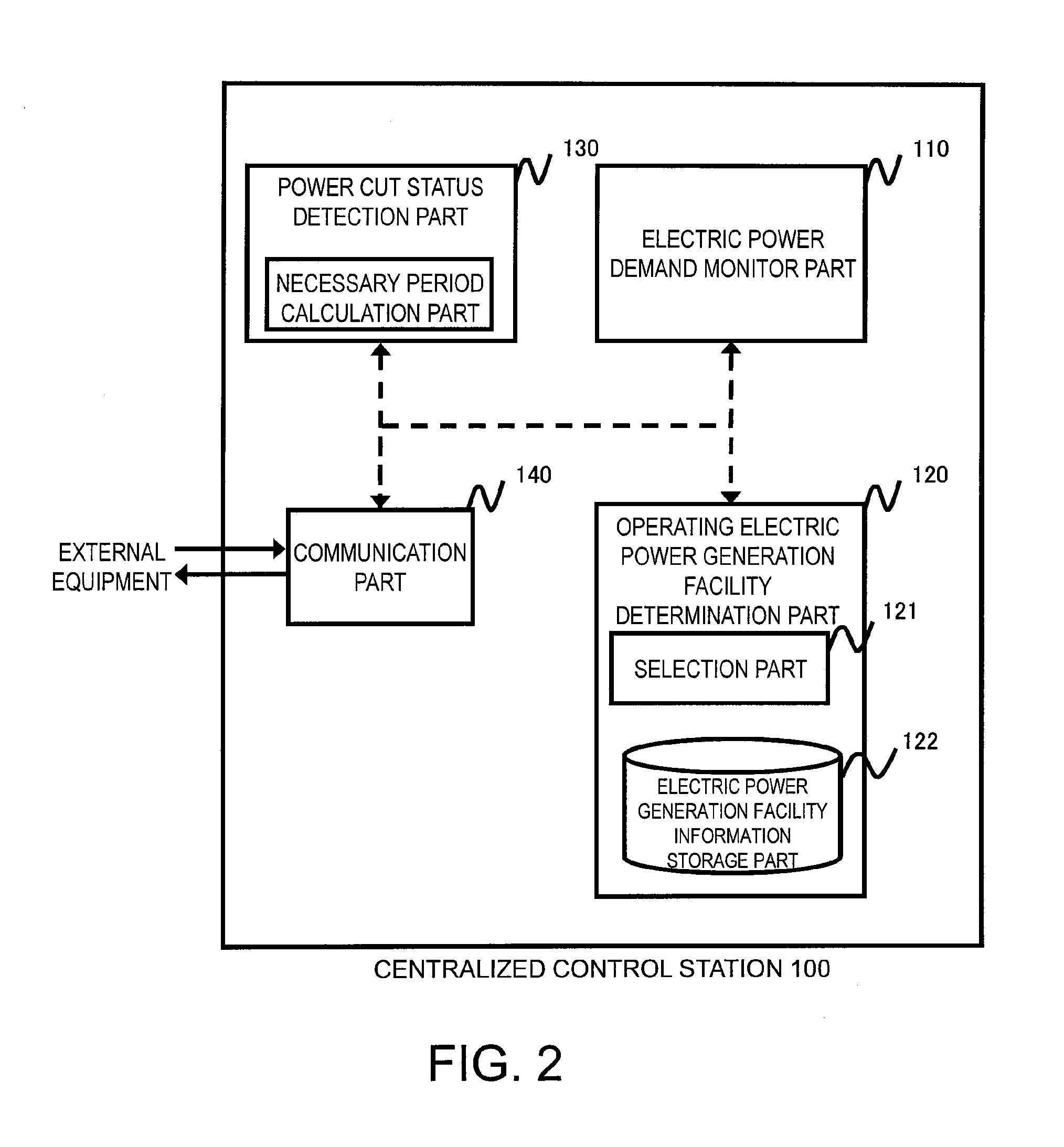
Distributed electric power generation system, control station, and method of controlling the same
ActiveUS20150318698A1Low running costImprove efficiencyMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlElectric power transmissionGrid network
A distributed electric power generation system is configured to include a plurality of electric power distribution stations operable to receive electric power from an external power source and generate electric power in a balanced manner, a power transmission grid network connected to the plurality of electric power distribution stations for supplying received electric power to a plurality of demand loads using electric power, and a control station operable to acquire information on an electric power distribution period used to calculate a period during which electric power supply is needed, acquire an amount of power supply demand to be supplied via the power transmission grid network during the period during which electric power supply is needed, the period being determined from the acquired information on the electric power distribution period, and select one or a required number of electric power generation facilities for supplying electric power to the plurality of demand loads at a low cost based upon a start and stop cost and a running cost of each of the electric power distribution stations in accordance with the calculated electric power distribution period and the amount of power supply demand.
Owner:NEC CORP
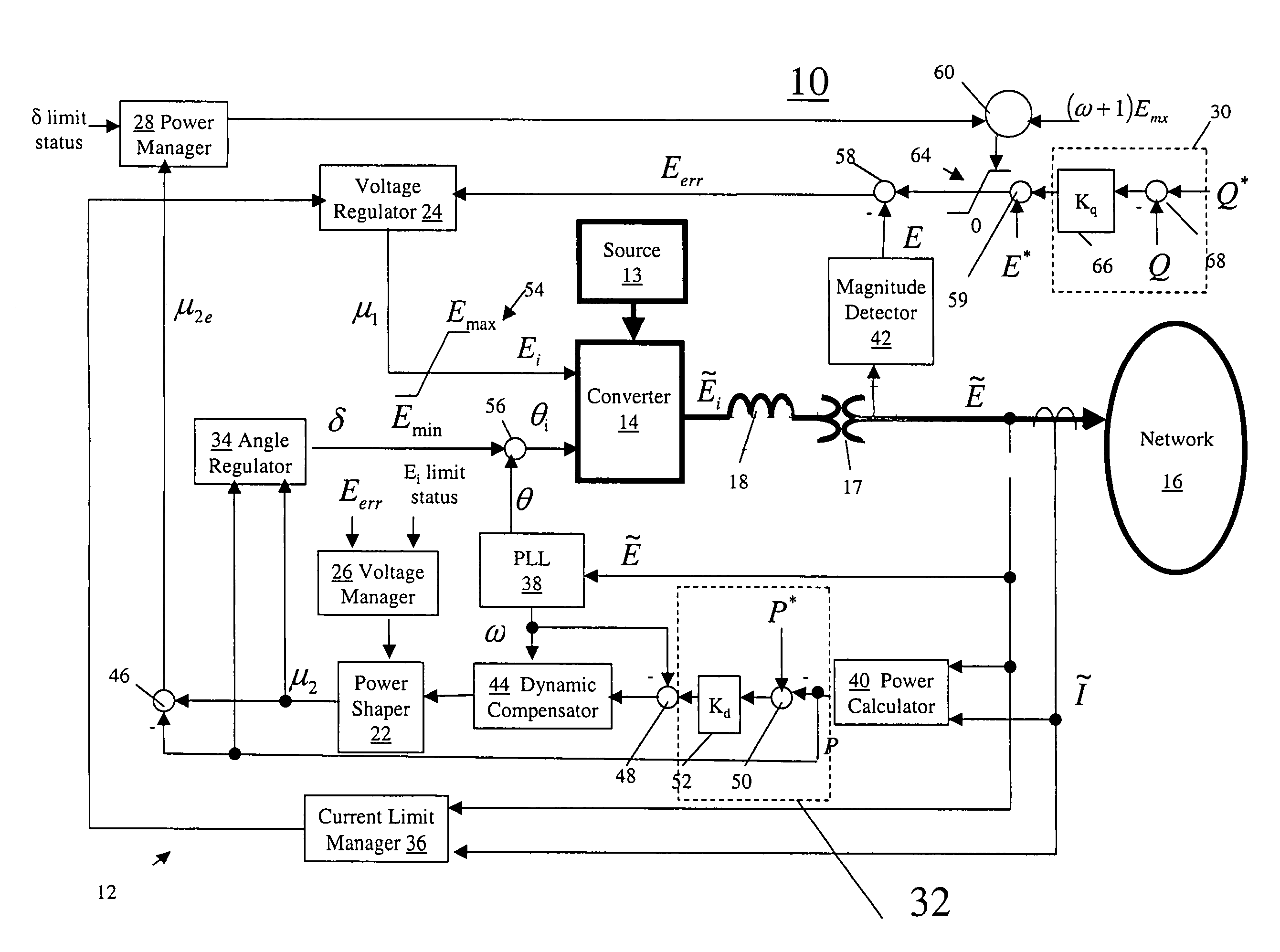
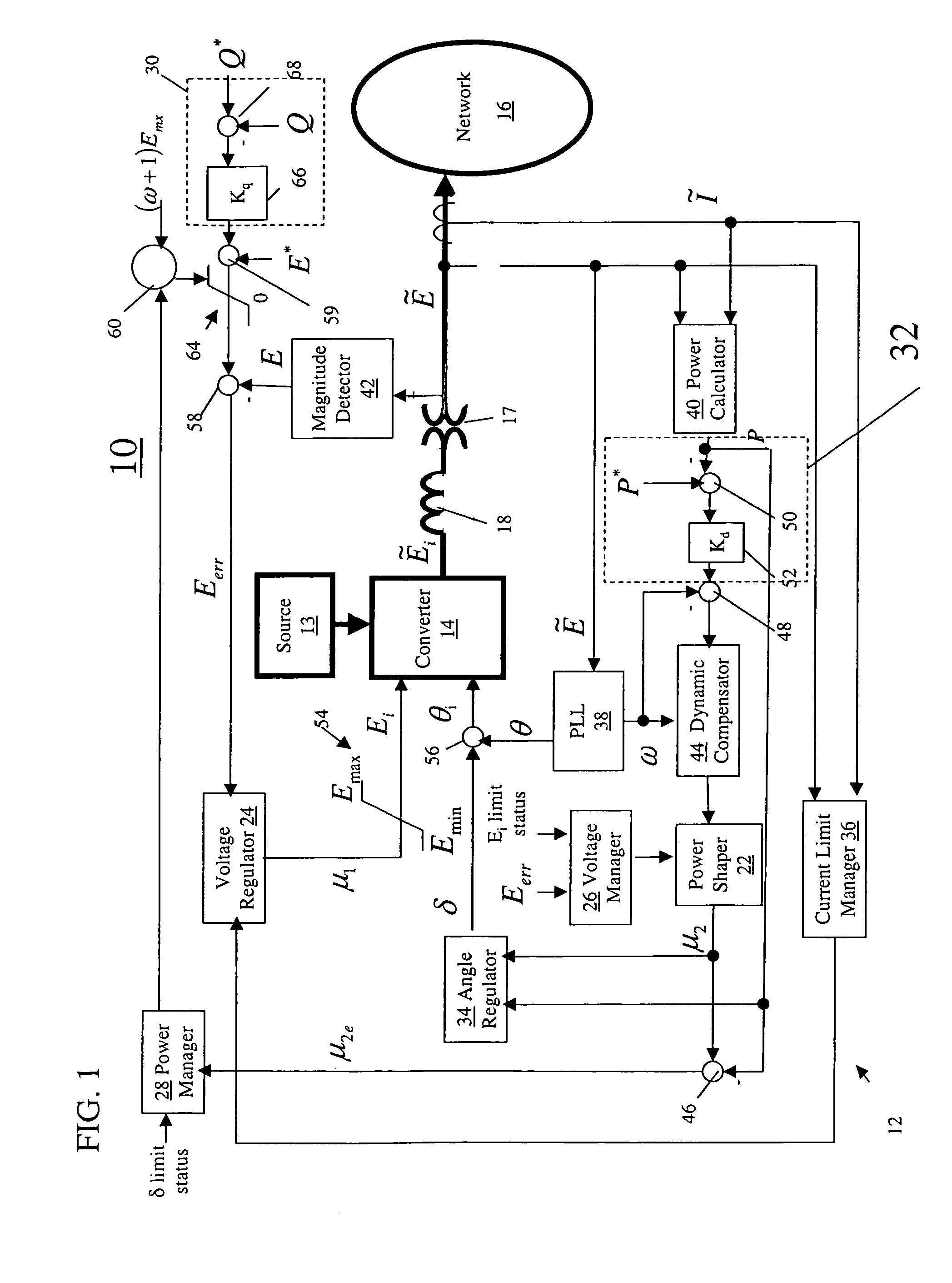
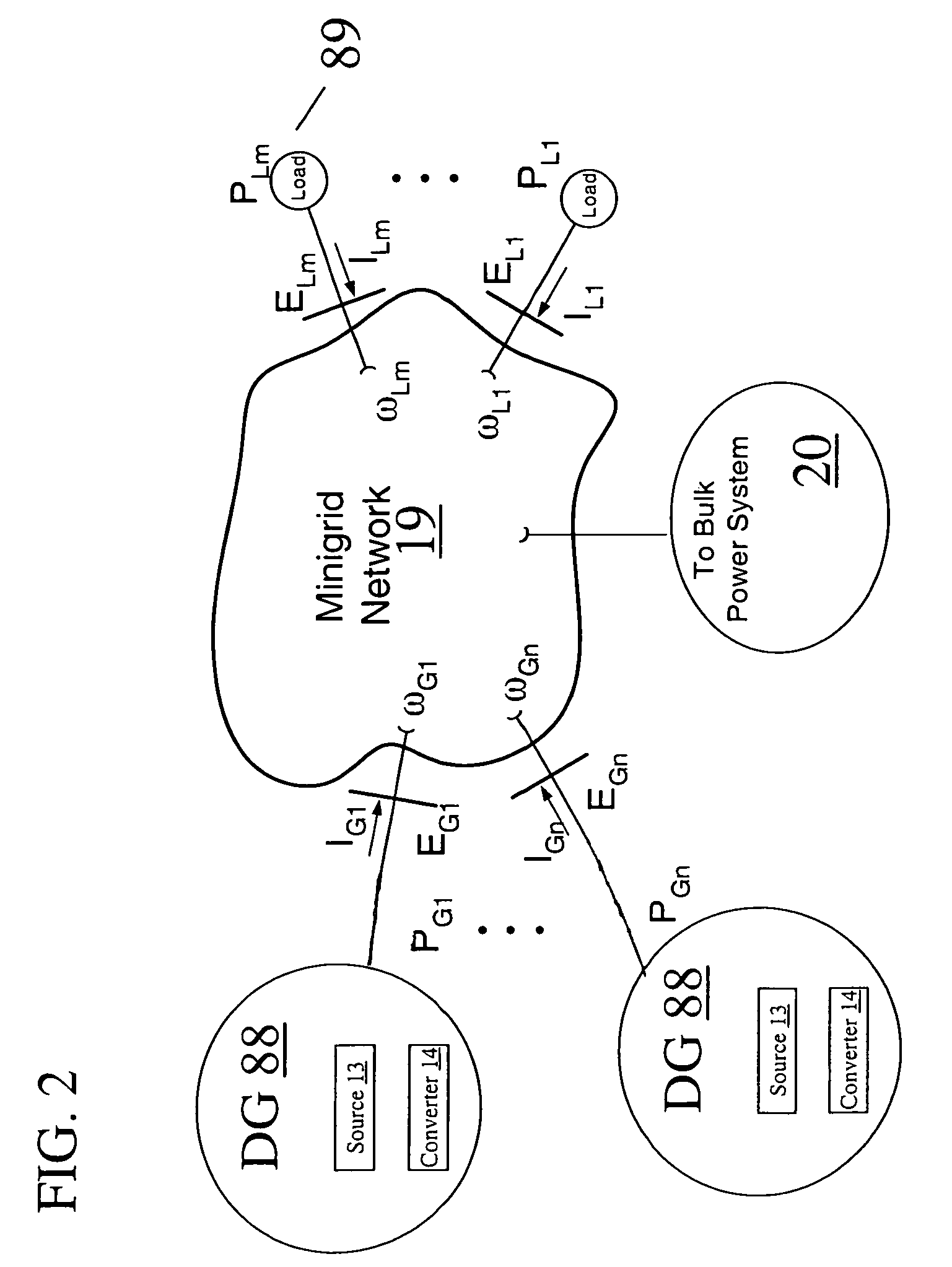
Power generation system
InactiveUS7680562B2Reduce load demandReduce electricity demandMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlControl systemEngineering
A power generation system includes a converter configured for supplying power from a constrained power or energy source to a power network and a control system configured for balancing instantaneously available power from the constrained source against demanded load from the power network by dynamically adjusting power network voltage, power network frequency, or a combination of power network voltage and power network frequency.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
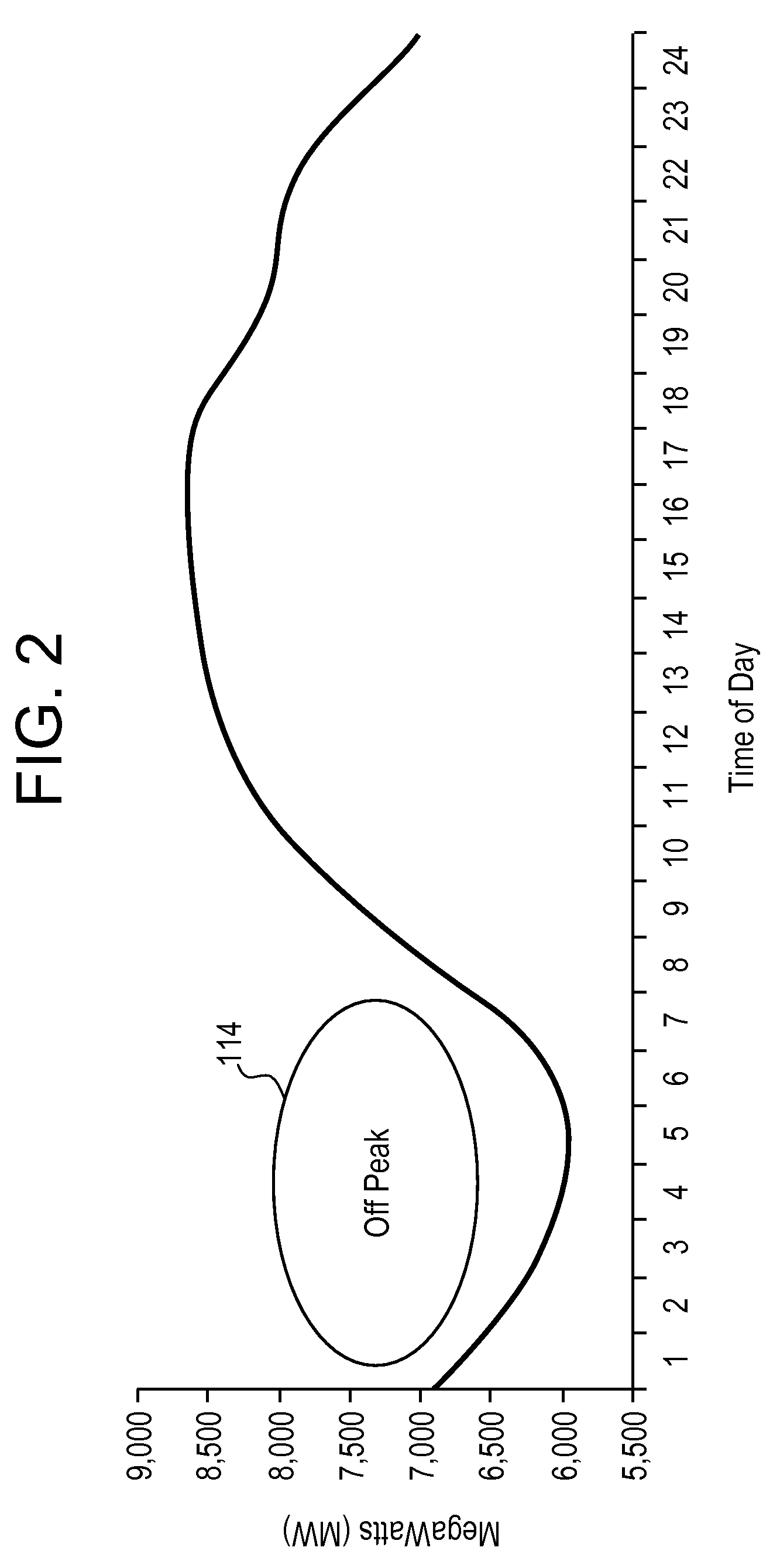
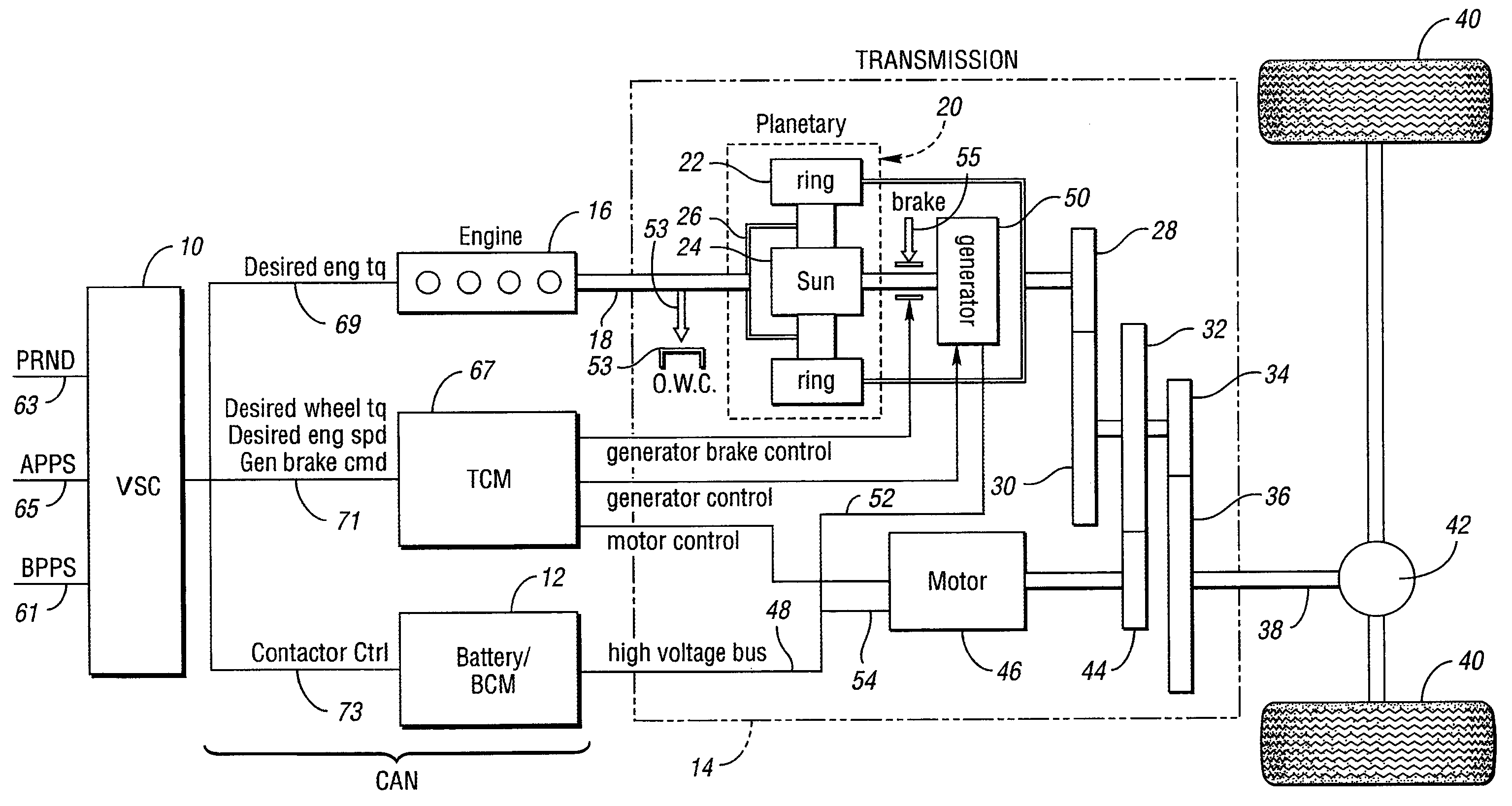
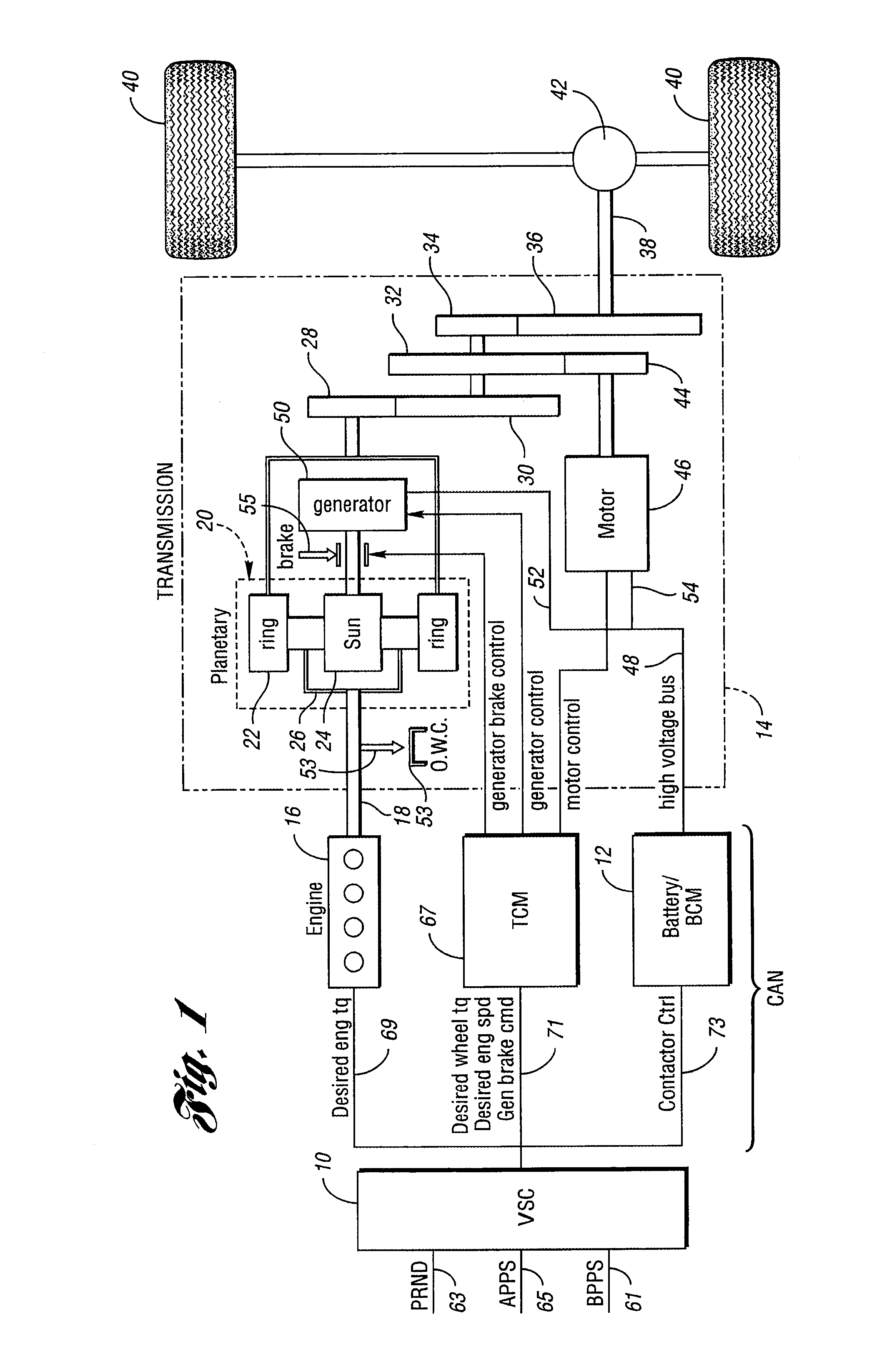
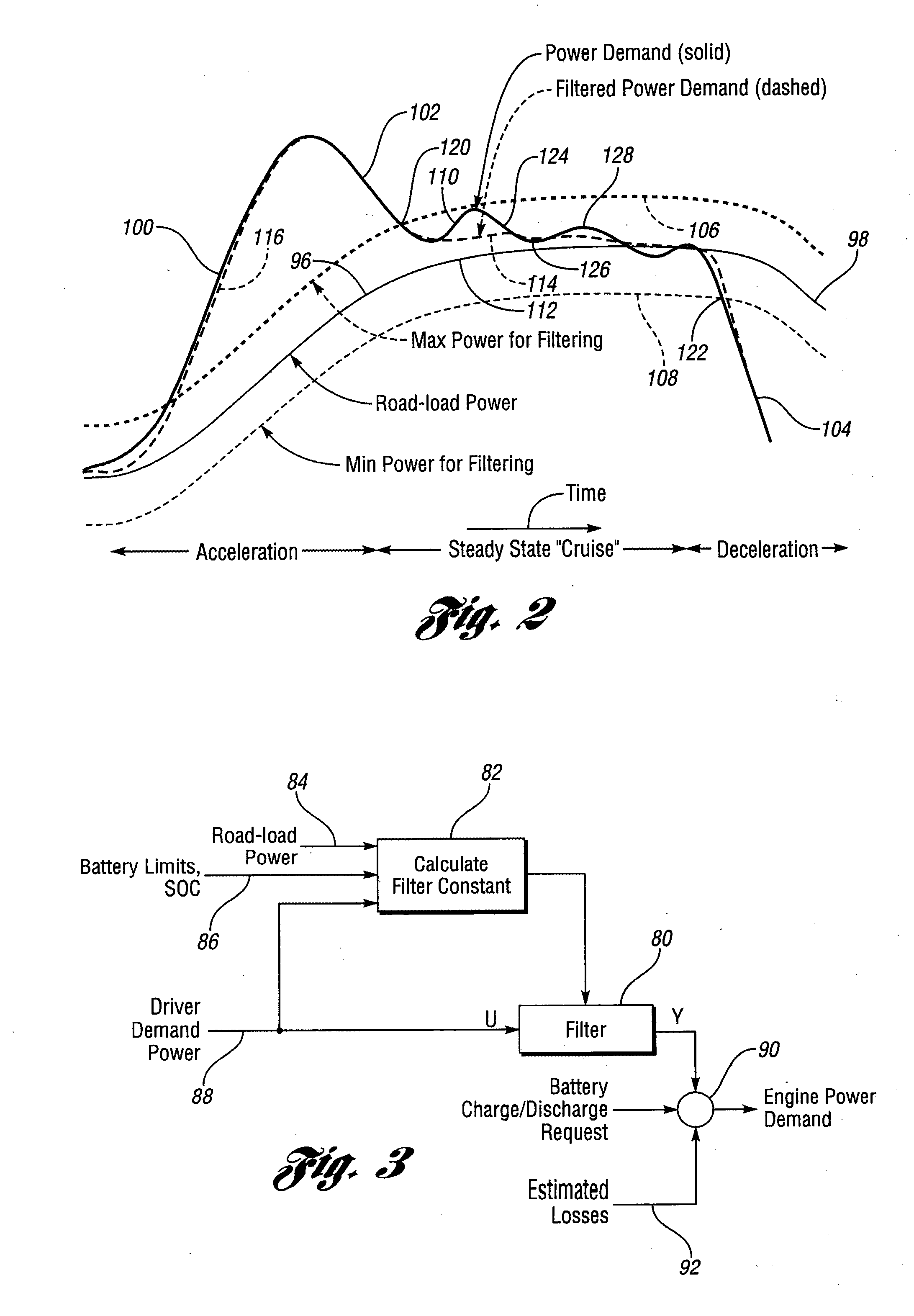
Engine Power Demand Load-Leveling for a Hybrid Electric Vehicle
InactiveUS20100017054A1Rapid responseDigital data processing detailsEmergency protective circuit arrangementsPower splitOperation mode
A method for controlling a demand for engine power in a control for an engine in a hybrid electric vehicle with power-split characteristics. Following transitions from acceleration or deceleration operating modes to a steady-state operating mode, power demand excursions from road-load power are attenuated or avoided by filtering the power demand using a filter constant that changes within battery power constraints as a function of a normalized driver demand for power at traction wheels for the vehicle.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
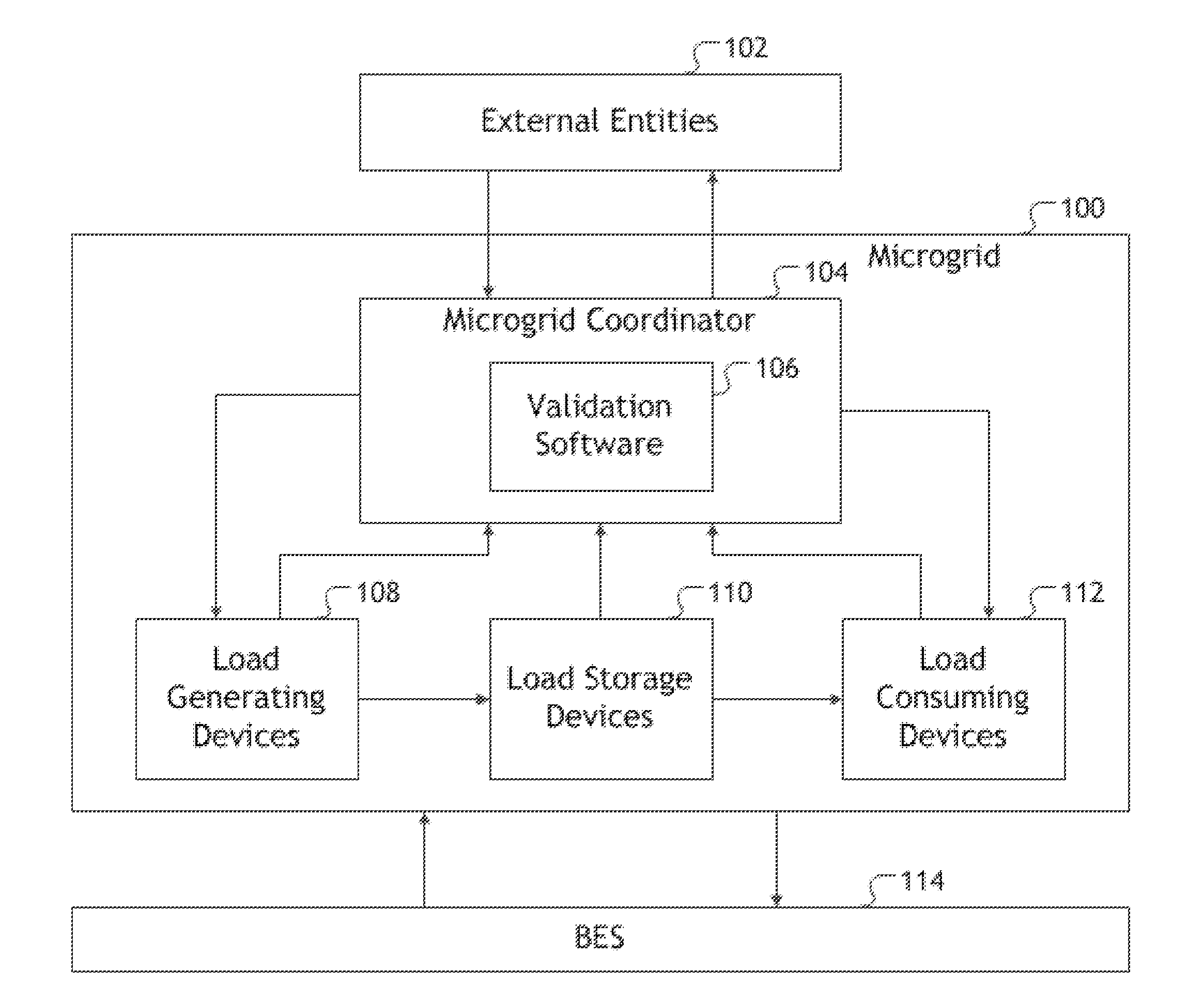
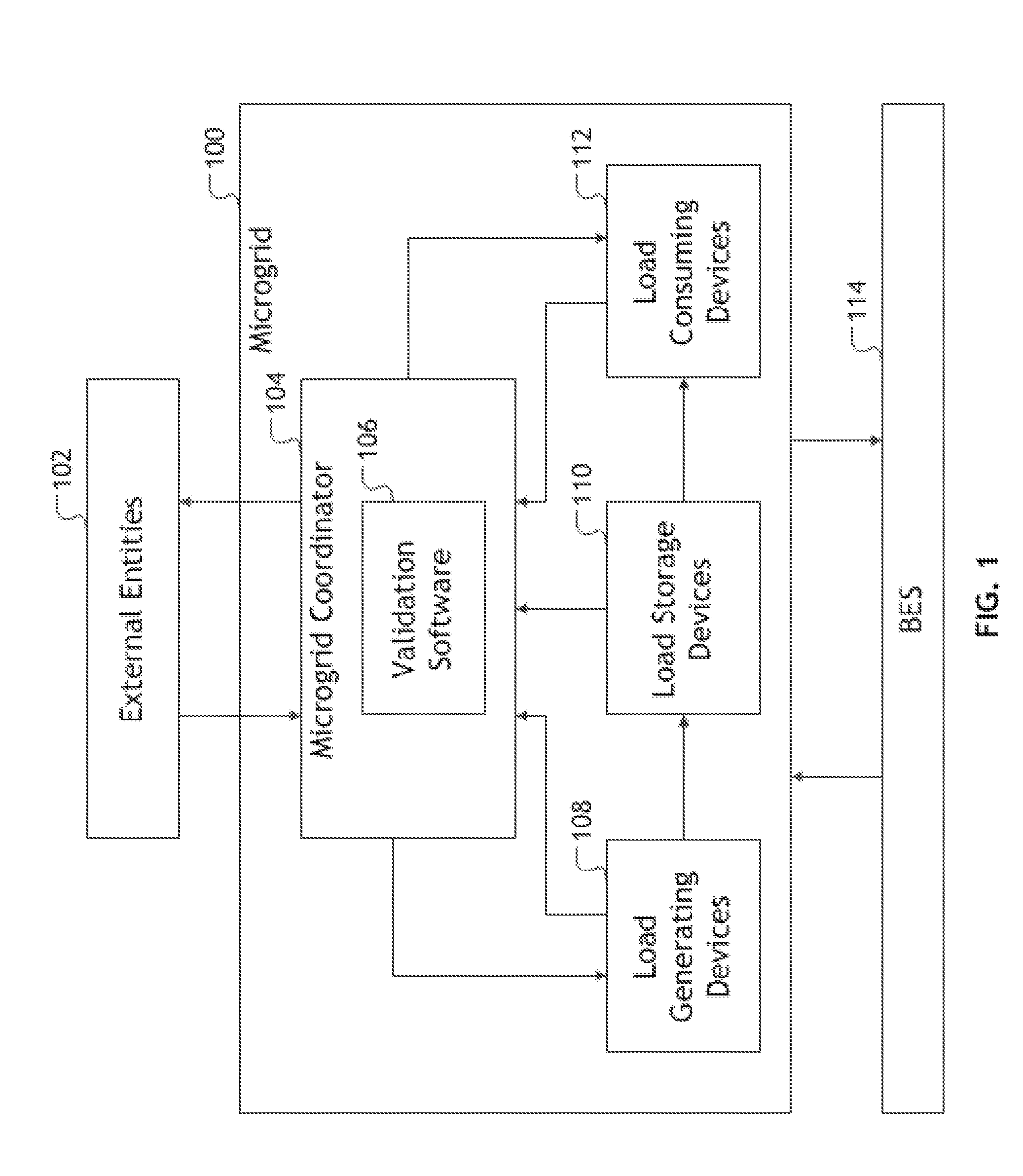
Cloud-based microgrid control
ActiveUS20150261240A1Improve Load Forecasting AccuracyConvenient sourceLevel controlLoad forecast in ac networkPower flowSmart microgrid
A method and system of optimizing microgrid operations is provided. One or more intelligent microgrid coordinators interface with the microgrid such that those microgrid coordinators are able to measure and control all microgrid asset activities. The microgrid coordinator is used to forecast the microgrid's demanded load more accurately, and assign asset commands so as to optimize microgrid consumption, generation, and storage of load. The method and system incorporate a valuation of dispatchable load in optimization functions. The microgrid coordinator is further used to protect the microgrid assets from over-current situations when the microgrid is connected to the bulk electric system and when islanded. The method and system provide a means to test the microgrid controller prior to implementation on the microgrid in order to assure proper operation.
Owner:OPEN ACCESS TECH INT
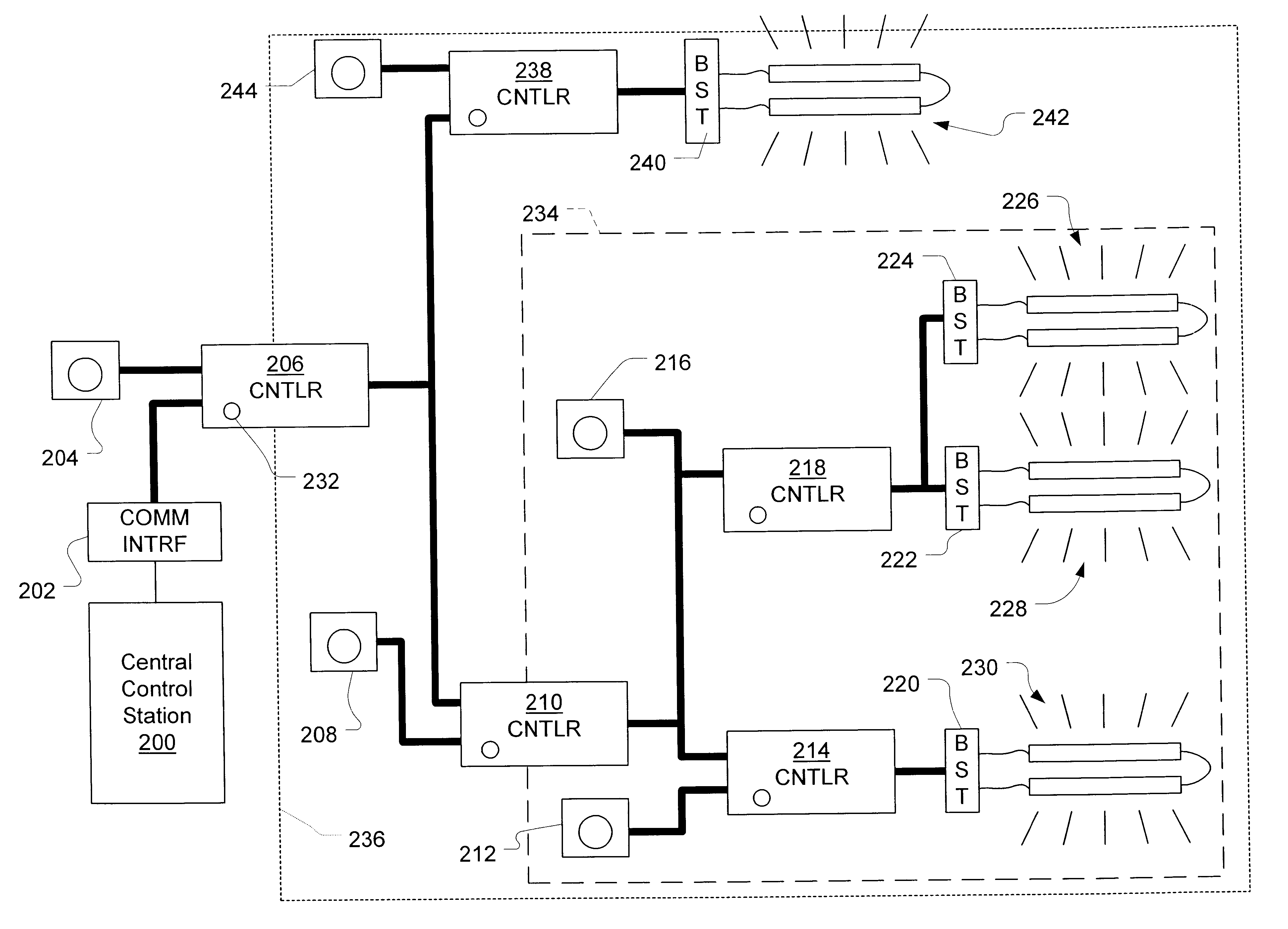
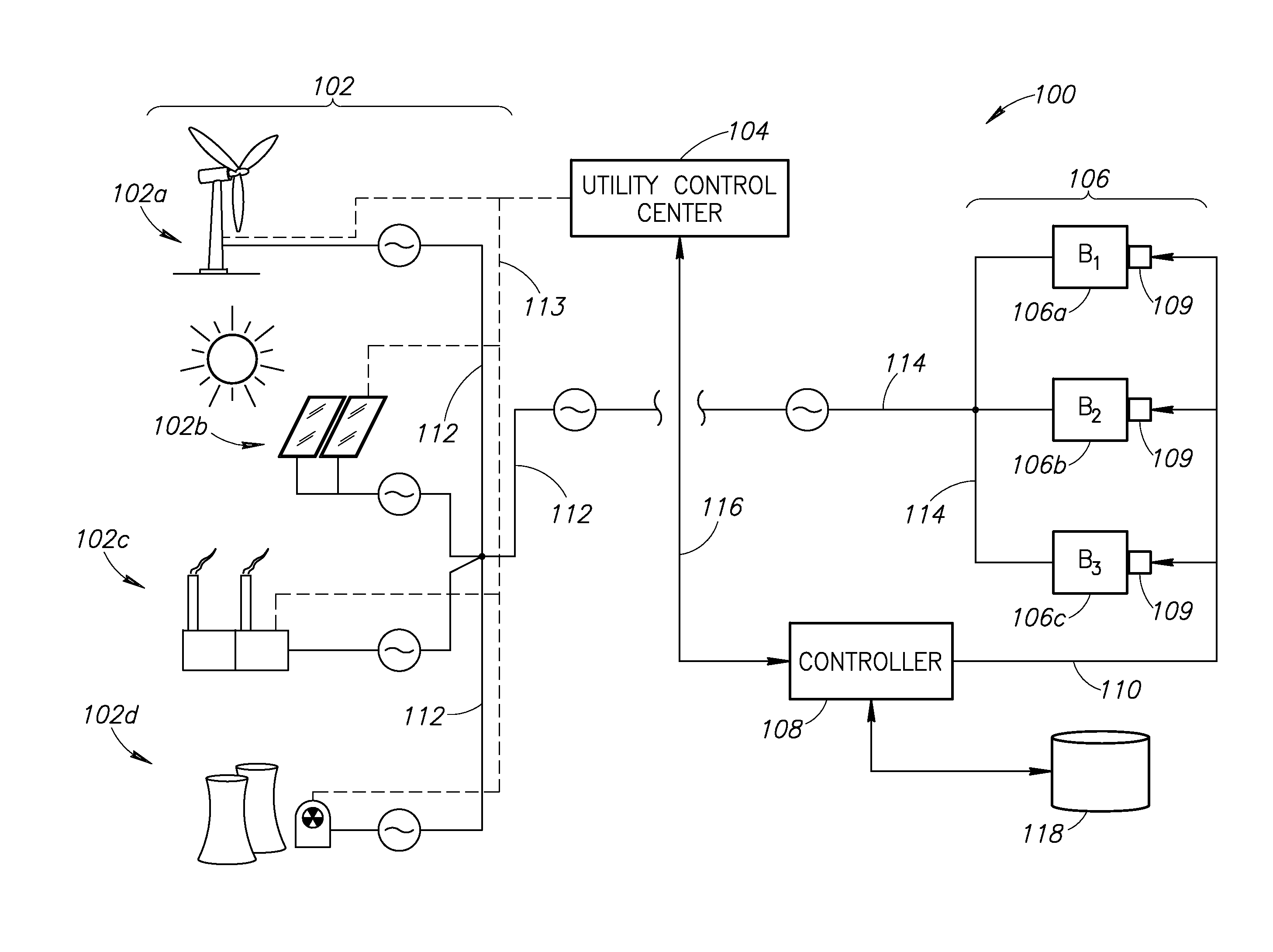
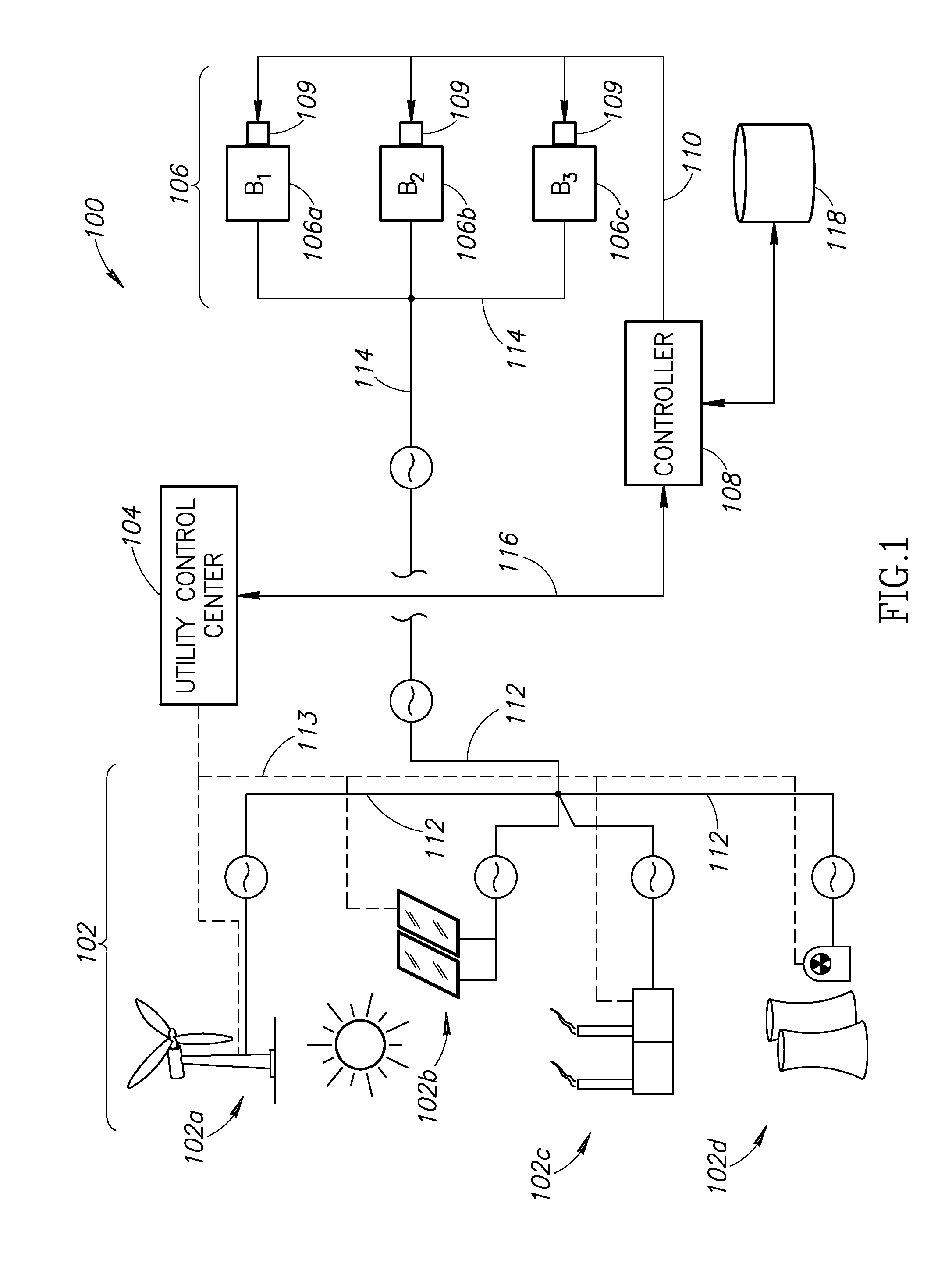
Systems and methods for balancing an electrical grid with networked buildings
InactiveUS20140379139A1Lower Level RequirementsLevel controlContigency dealing ac circuit arrangementsControl systemPower grid
An electrical power grid includes multiple, networked buildings that receive electrical power from one or more power generation sources. A networking control system communicates with a utility control center to obtain information regarding the amount of power being supplied by the power generation sources. The networking control system further obtains information from one or more building automation controllers that are controllably associated with a plurality of networked buildings. The networking control system determines whether the total amount of power being supplied exceeds a total demand load for the plurality of buildings. And if so, the networking control system commands one or more of the building automation controllers to operate one or more of the buildings a reduced energy efficiency level, which may take the form of an optimization curve.
Owner:OPTIMUM ENERGY
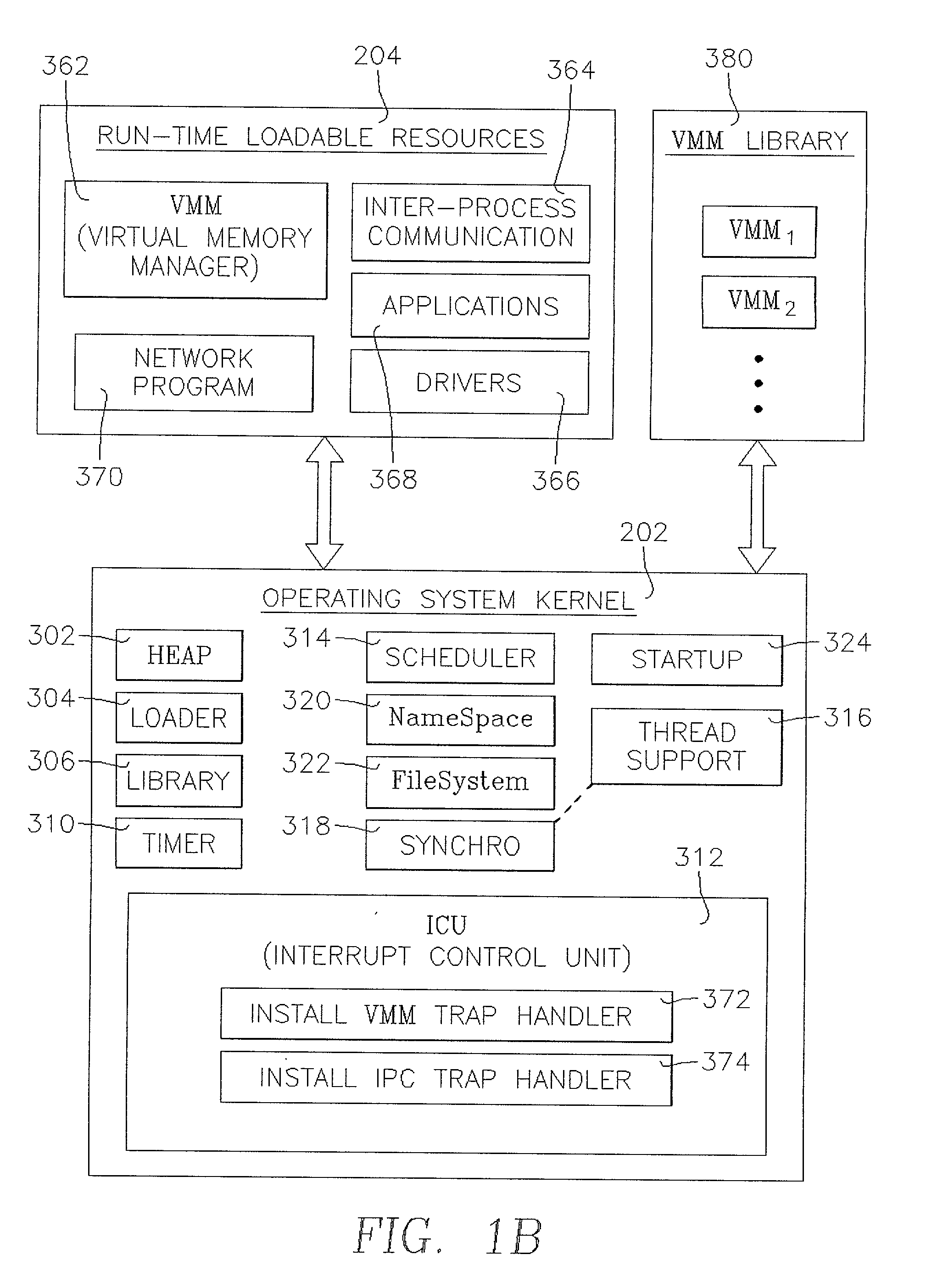
Highly componentized system architecture with a demand-loading namespace and programming model
InactiveUS7143421B2Severely restrictedInterprogram communicationDigital computer detailsEntry pointParallel computing
The invention is embodied in software executable on a computer having a working memory with demand-loadable components initially stored outside of the working memory, each component having an entry point including a constructor for an object. Preferably, the demand-loadable components are initially provided in a memory within the computer or a location external of the computer. A Namespace in the working memory provides access in the working memory to the components as they become needed by applications running in the computer. The Namespace provides the access by managing demand-loading and unloading of the components in the working memory.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Systems and methods for balancing an electrical grid with networked buildings
InactiveUS20140012429A1Weaken energyLower Level RequirementsLevel controlContigency dealing ac circuit arrangementsControl systemPower grid
An electrical power grid includes multiple, networked buildings that receive electrical power from one or more power generation sources. A networking control system communicates with a utility control center to obtain information regarding the amount of power being supplied by the power generation sources. The networking control system further obtains information from one or more building automation controllers that are controllably associated with a plurality of networked buildings. The networking control system determines whether the total amount of power being supplied exceeds a total demand load for the plurality of buildings. And if so, the networking control system commands one or more of the building automation controllers to operate one ore more of the buildings a reduced energy efficiency level, which may take the form of an optimization curve.
Owner:OPTIMUM ENERGY
Optimization of abstract rule processing
InactiveUS20090125500A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsDemand loadData mining
Embodiments of the invention provide techniques for optimizing the processing of abstract rules. In general, the results of executing an abstract query may be used as data inputs for processing an abstract rule. In one embodiment, query results may be sorted according to input field values required for processing a deterministic abstract rule. If a record of the sorted query results includes the same input values as a preceding record, then the rule output of the preceding record may be reused, rather than processing the abstract rule again. Accordingly, the demand load placed on a rule engine may be reduced.
Owner:IBM CORP
Hybrid vehicle recharging system and method of operation
InactiveUS20100017043A1Level controlVolume/mass flow measurementPower stationElectric distribution network
A system and method for recharging a plug-in hybrid vehicle. The system includes a controller that schedules the recharging of the vehicles on local electrical distribution networks. The system arranges the schedule to minimize the demand loading on the local distribution network to more efficiently operate power plants providing electrical power to the distribution networks. A system for collecting charges associated with the recharging of plug-in hybrid vehicles is also disclosed providing for prepaid utility accounts.
Owner:CONSOL EDISON OF NEW YORK
Optimization of abstract rule processing
InactiveUS7917501B2Digital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsDemand loadData mining
Embodiments of the invention provide techniques for optimizing the processing of abstract rules. In general, the results of executing an abstract query may be used as data inputs for processing an abstract rule. In one embodiment, query results may be sorted according to input field values required for processing a deterministic abstract rule. If a record of the sorted query results includes the same input values as a preceding record, then the rule output of the preceding record may be reused, rather than processing the abstract rule again. Accordingly, the demand load placed on a rule engine may be reduced.
Owner:IBM CORP
Air conditioner control method and device as well as computer readable storage media
ActiveCN110686382AImprove accuracyReduce consumptionMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsStart timeControl engineering
The invention discloses an air conditioner control method. The air conditioner control method comprises the following steps that whether a time interval between a current moment and a preset on-duty moment is less than or equal to a maximum early start time is determined; if the time interval is less than or equal to the maximum early start time, a preliminary demand load corresponding to a central air conditioner is acquired and a startup combined load corresponding to the central air conditioner is acquired; and the starting time of a to-be-started main machine is determined based on the startup combined load and the preliminary demand load; the invention further discloses an air conditioner control device and a computer readable storage media. According to the air conditioner control method and device as well as the computer readable storage media, the starting moment of the main machine in the central air conditioner can be determined according to the preliminary demand load, and then the central air conditioner can be started in advance advantageously in later stage according to the starting moment, so that the comfort degree of a room corresponding to the on-duty moment is guaranteed while energy consumption is reduced, and the pre-cooling or preheating accuracy of the central air conditioner is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI MEICON INTELLIGENT CONSTR CO LTD +1
Method for controlling compression ignition internal combustion engine
InactiveUS7165512B2Wide loadGuaranteed uptimeInternal combustion piston enginesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelNitriteDi-tert-butyl peroxide
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
System and method for power station and compressed air combination energy storage power generation
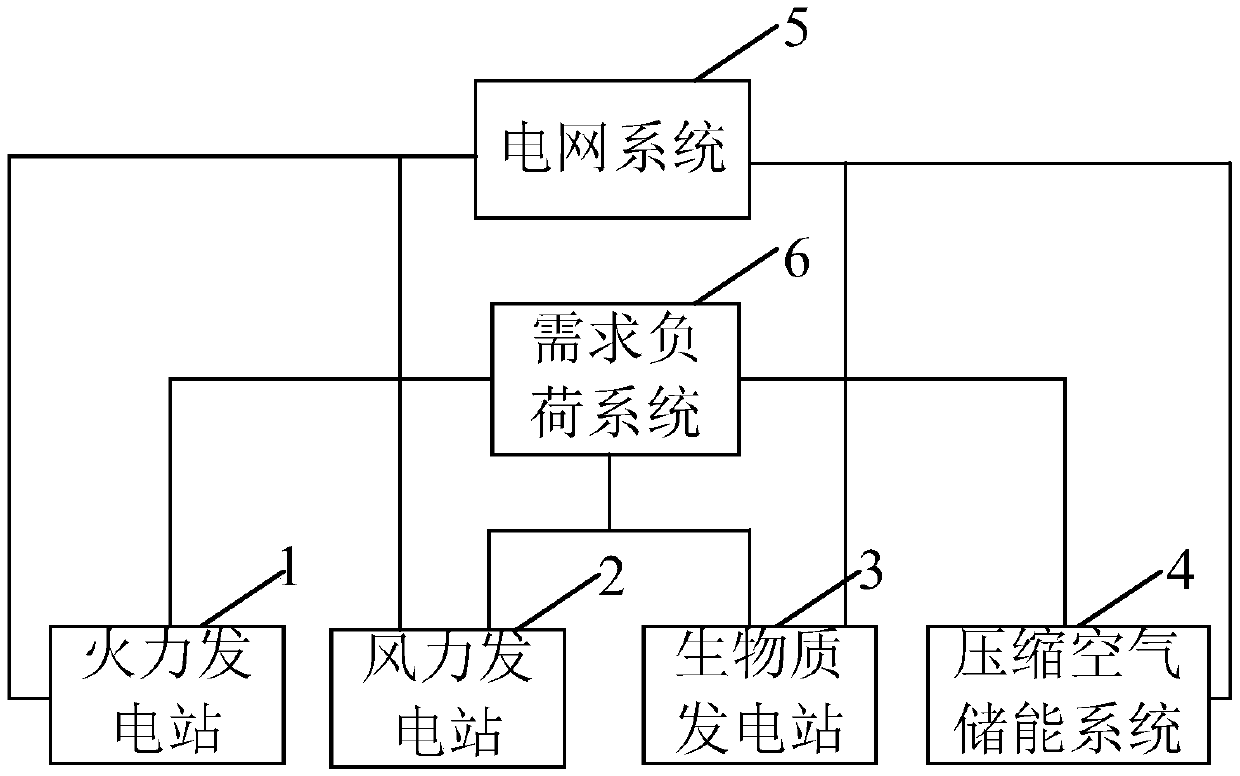
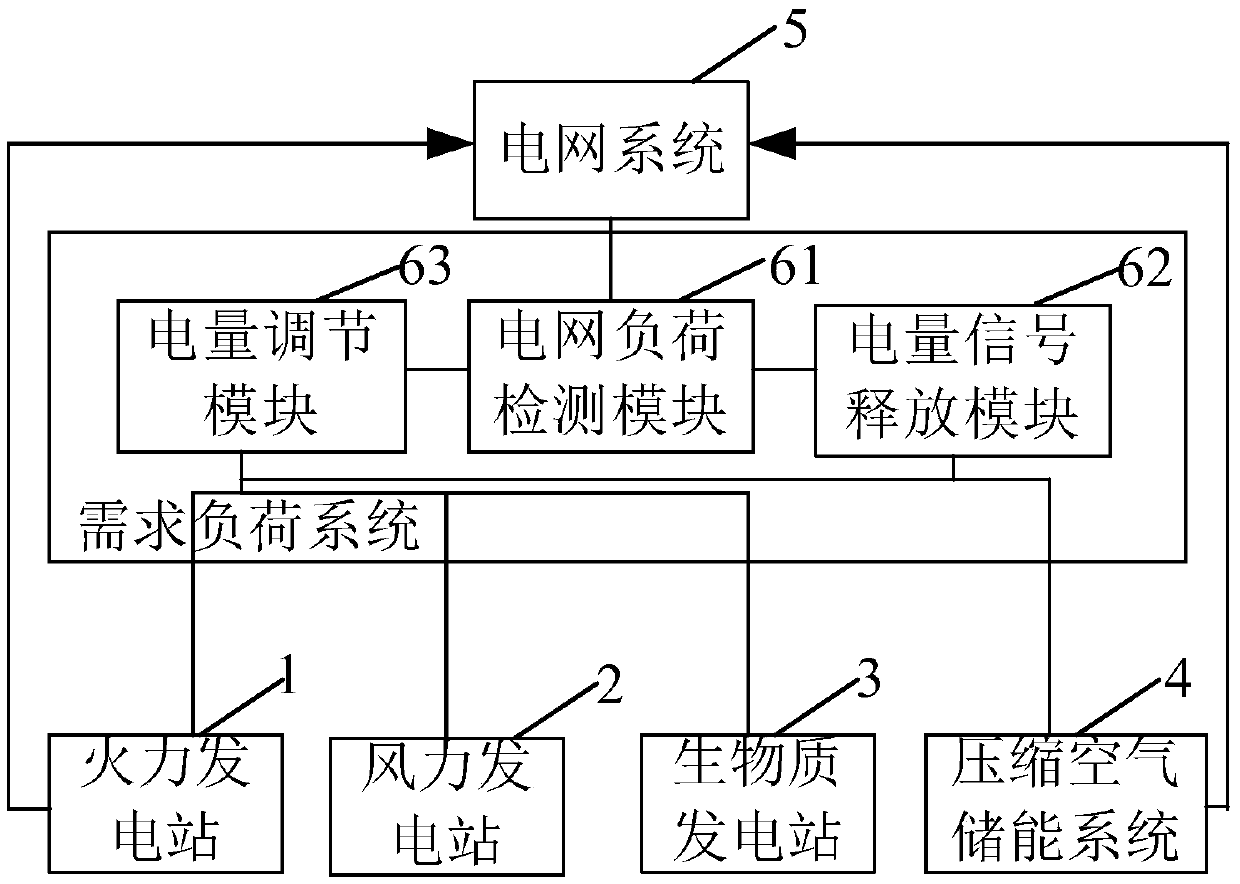
InactiveCN105515028AElectricity peak shavingReduce wasteWind energy with garvitational potential energyEnergy industryEngineeringClean energy
The invention provides a system and method for power station and compressed air combination energy storage power generation. The system for power station and compressed air combination energy storage power generation comprises a heat power station, a wind power station, a biomass power station, a compressed air energy storage system, a power grid system and a demand load system. The heat power station, the wind power station and the biomass power station are connected with the compressed air energy storage system, and the compressed air energy storage system is connected with the power grid system. The demand load system is connected with the heat power station, the wind power station, the biomass power station, the power grid system and the compressed air energy storage system. According to the technical scheme, on the conditions of not affecting power grid peak regulation performance, clean energy is introduced, and the clean energy utilization rate is improved.
Owner:YUNNAN POWER GRID CO LTD ELECTRIC POWER RES INST
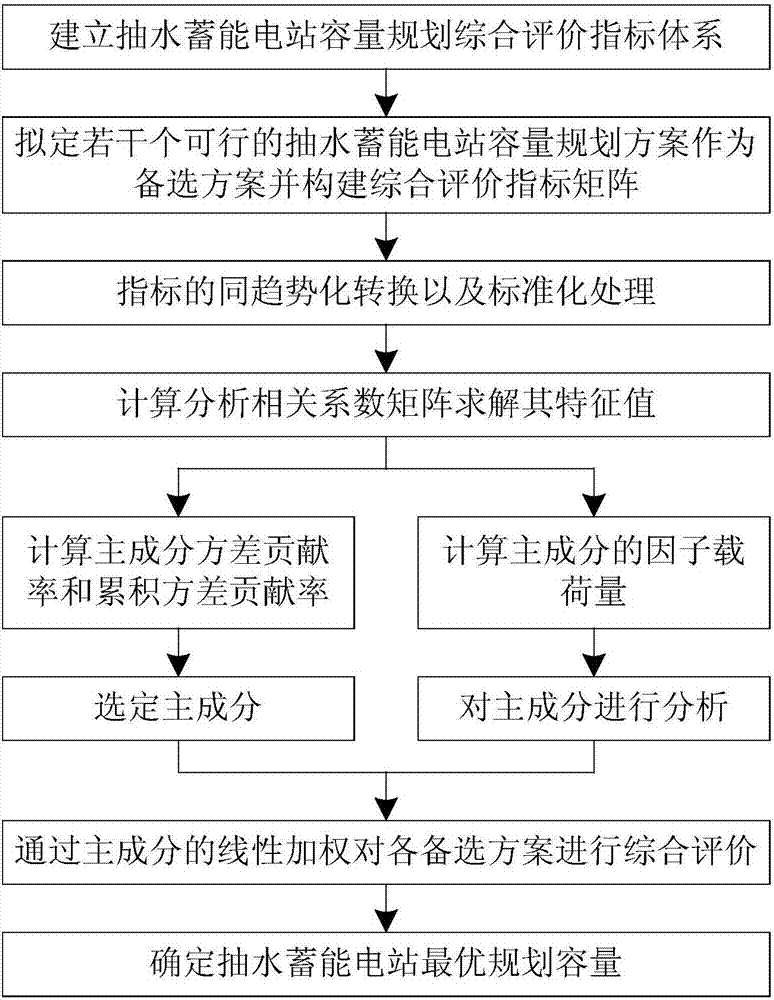
Principal component analysis-based pumped storage power station capacity optimal planning method
The invention is a principal component analysis based capacity optimization planning method for a pumped storage power station, which is characterized in that it includes: establishing a comprehensive evaluation index system for the capacity planning of a pumped storage power station, generating a capacity planning scheme for a pumped storage power station, and constructing a comprehensive evaluation Index matrix, convert the comprehensive evaluation index matrix to the same trend, perform standardized transformation on X′, calculate the correlation coefficient matrix for the comprehensive evaluation index matrix after the standardized transformation, calculate the variance contribution rate and cumulative variance contribution rate of the principal components and select Principal components, calculation of the selected w principal components, calculation of factor loads, comprehensive evaluation of each alternative, and determination of the optimal planning capacity of the pumped storage power station. It has the advantages of scientific and reasonable method, simple and practical, fast calculation speed and higher precision.
Owner:NORTHEAST DIANLI UNIVERSITY
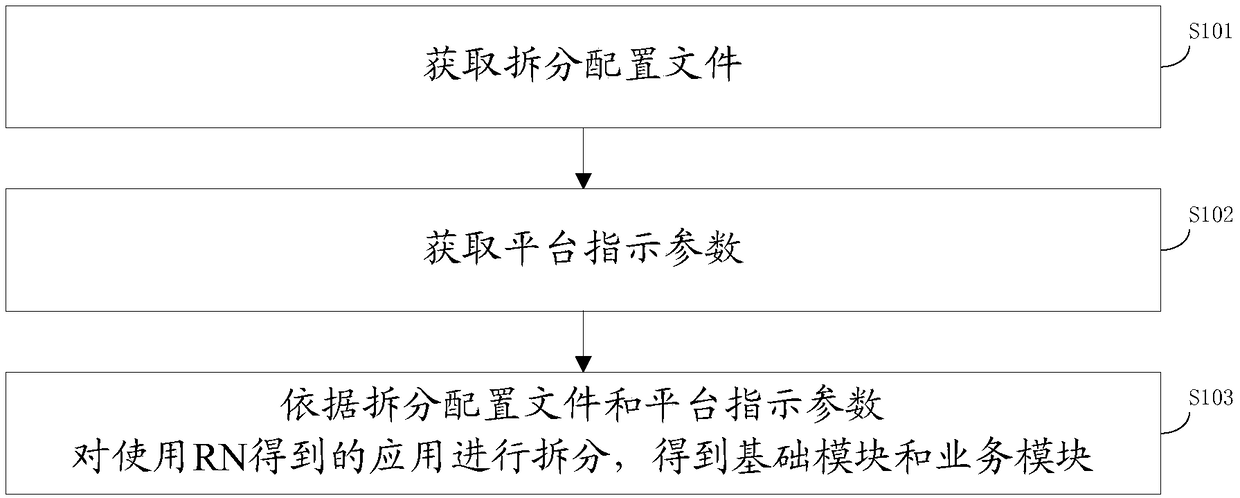
A method and apparatus for apply splitting and on-demand load
InactiveCN109298900AImplement on-demand loadingShorten the timeProgram loading/initiatingDemand loadService module
A method for apply splitting and on-demand load is provided, The device splits the application obtained by using the RN according to the splitting configuration file and the platform indication parameter to obtain the basic module and the service module. When the application is started, the basic module and the service module clicked by the user are loaded, so that the service module can be loadedon demand, thereby saving time and resources.
Owner:AGRICULTURAL BANK OF CHINA
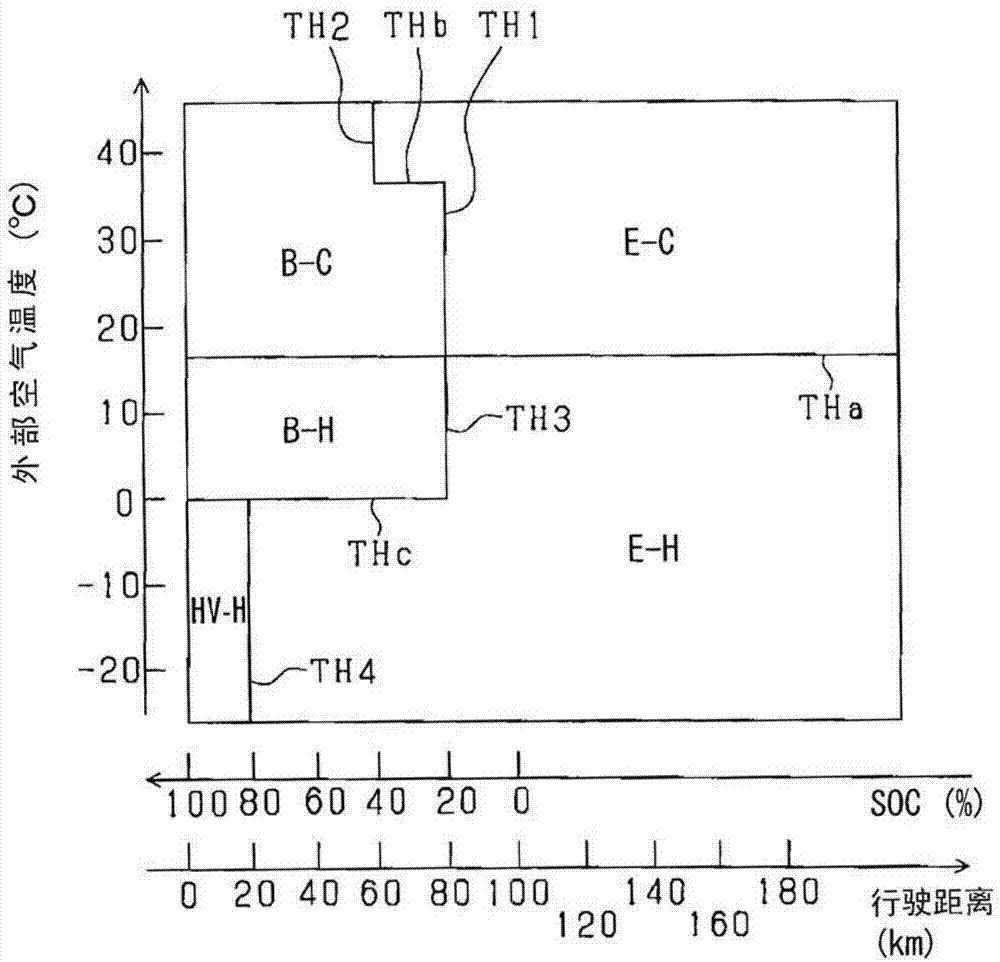
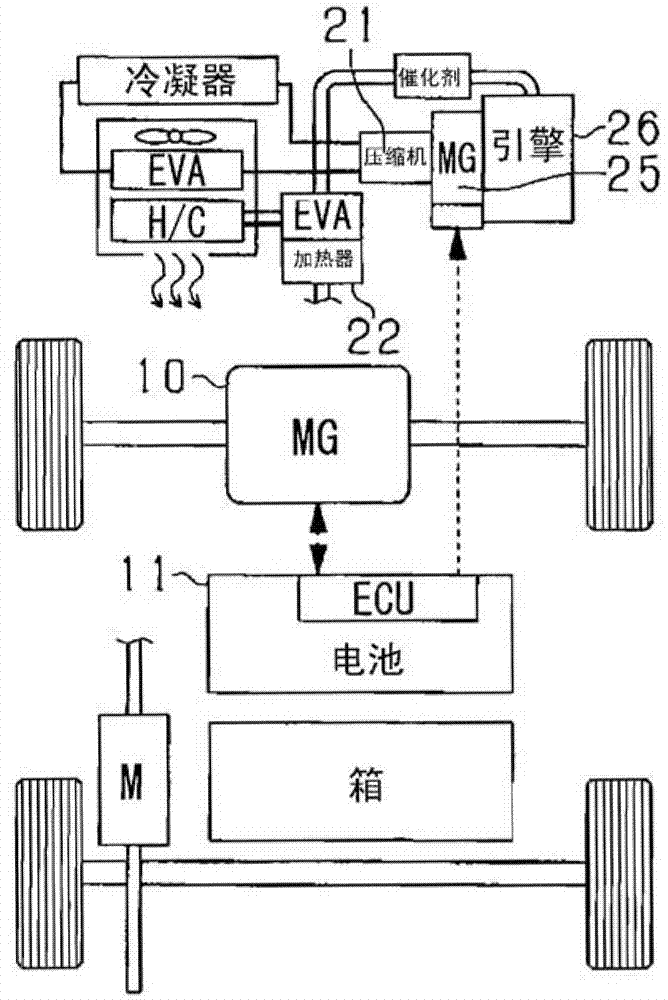
Air-conditioning control device for electric vehicle
InactiveCN102774251AIncrease distanceAir-treating devicesPropulsion using engine-driven generatorsCombustionElectrical battery
A detector (30) detects a remaining power of a battery (11). A calculator (31b) calculates a demand load of air-conditioning based on at least one of a preset temperature set for air in a passenger compartment of an electric vehicle and an outside temperature of air outside of the electric vehicle. A switching portion (31c) switches a mode of air-conditioning between a battery mode and an engine mode based on the calculated demand load and the detected remaining power of the battery. The battery mode causes the battery to supply electric power for air-conditioning, and the engine mode causes an engine (26) of the electric vehicle to supply combustion energy for air-conditioning.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com