Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
38results about How to "Eliminates and greatly reduces and problem" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
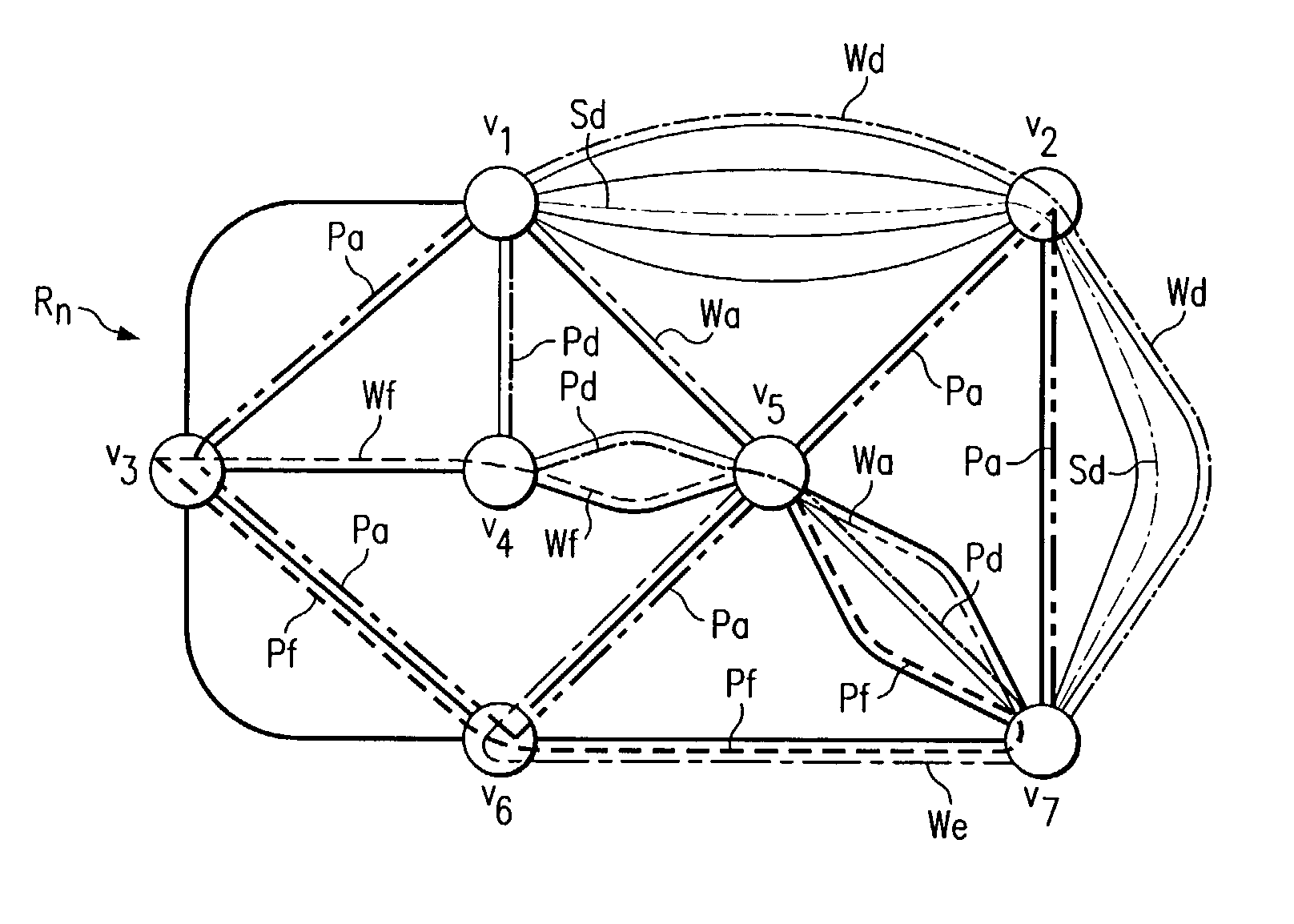
Method for allocating protection bandwidth in a telecommunications mesh network
InactiveUS7308198B1Eliminates and greatly reduces disadvantage and problemEliminates and greatly reduces disadvantageMultiplex system selection arrangementsOptical multiplexCross connectionLogical graph
A telecommunications mesh network includes a plurality of nodes each interconnected by an edge. A traffic demand is received having a working path with a link of edges interconnecting a source node with a destination node. The telecommunications mesh network has one or more pre-cross-connected trails associated therewith that are subdivided into one or more subtrails. Subtrails that do not meet pre-determined conditions are discarded. A logical graph representation of the telecommunications mesh network is created from subtrails that have not been discarded. Unused, shortcut, and rival edges are inserted into the logical graph. A shortest admissible protection path from the source node to the destination node is identified from the logical graph.
Owner:TELLABS OPERATIONS
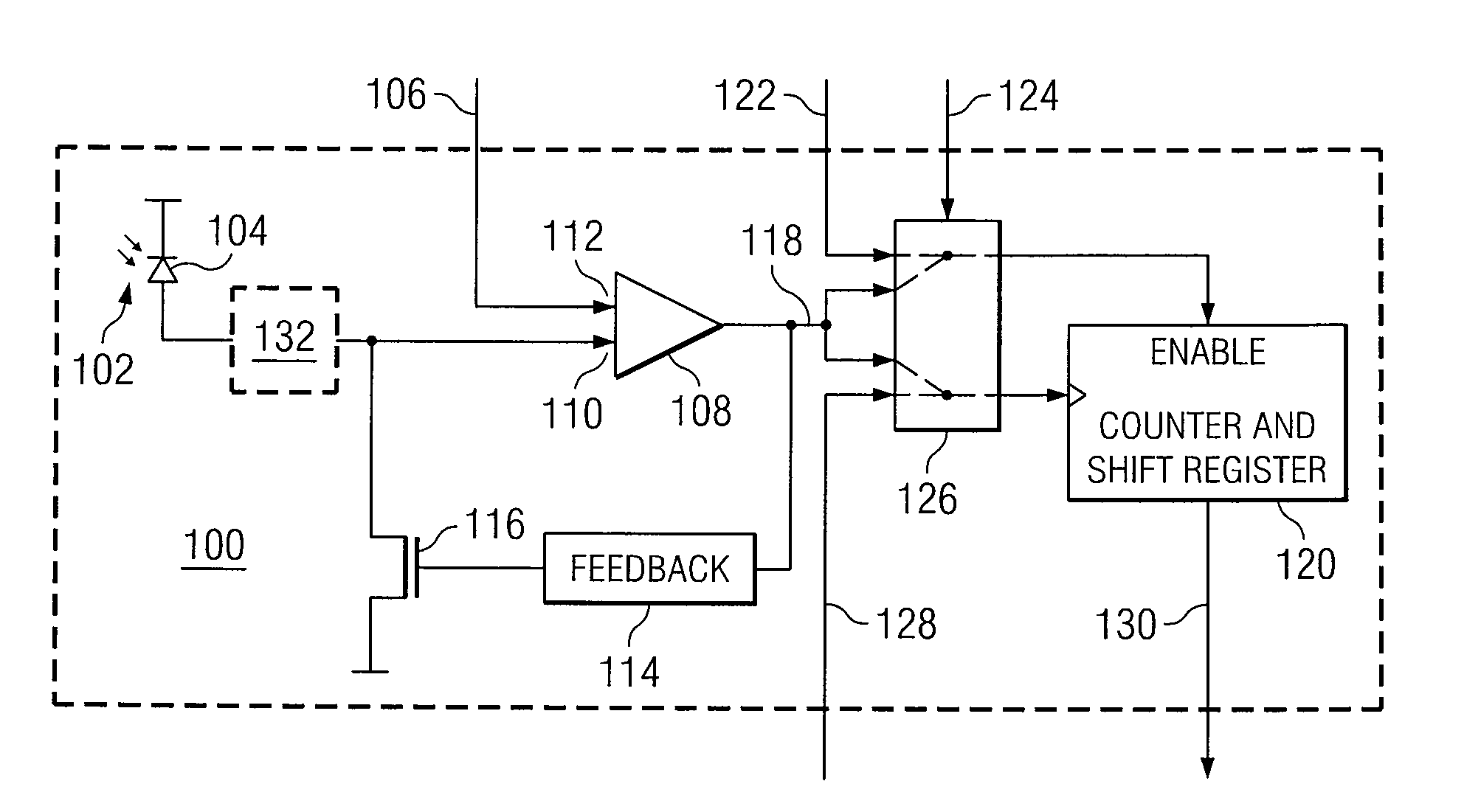
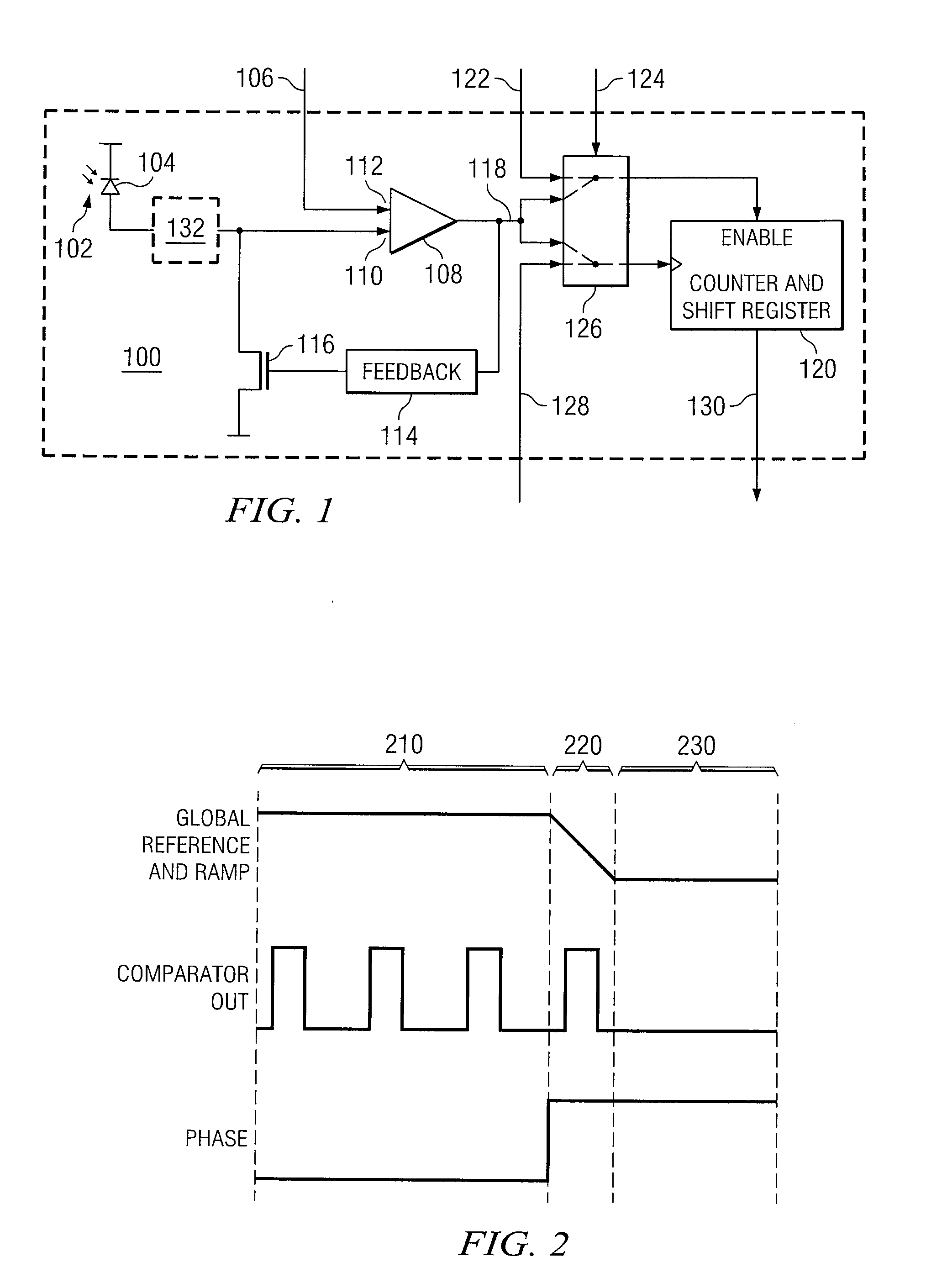
Time-frequency fusion digital pixel sensor
ActiveUS20100181464A1Eliminate disadvantagesImprove dynamic rangeTelevision system detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansFrequency conversionElectric signal
Light is converted to an electric signal by performing a light-to-frequency conversion of the light received during a first phase of operation. Following the first phase of operation, a light-to-time conversion is performed on light received during a second phase of operation. Following the second phase of operation a digital representation of the light is generated in response to the light-to-frequency conversion and the light-to-time conversion.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
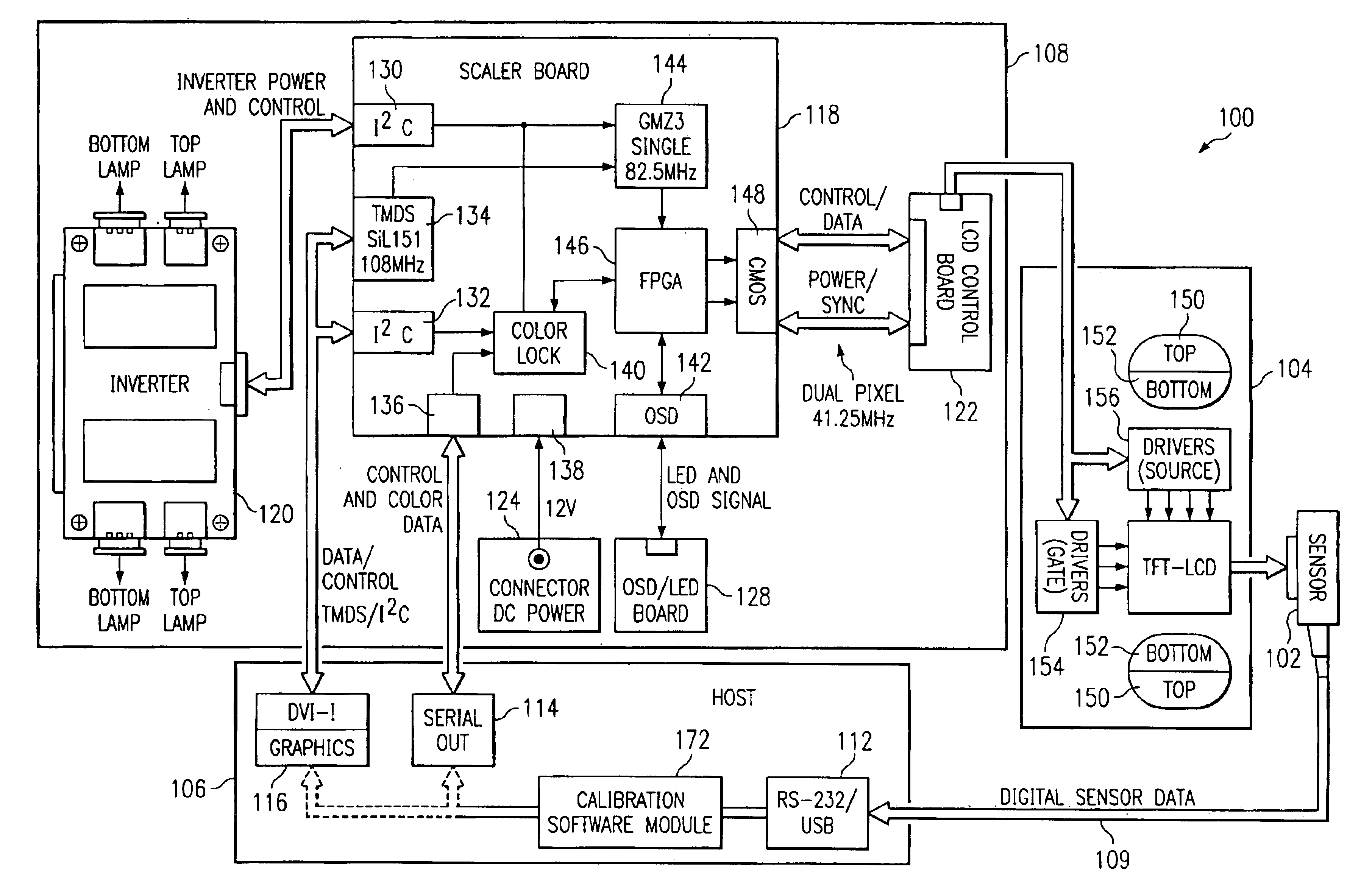
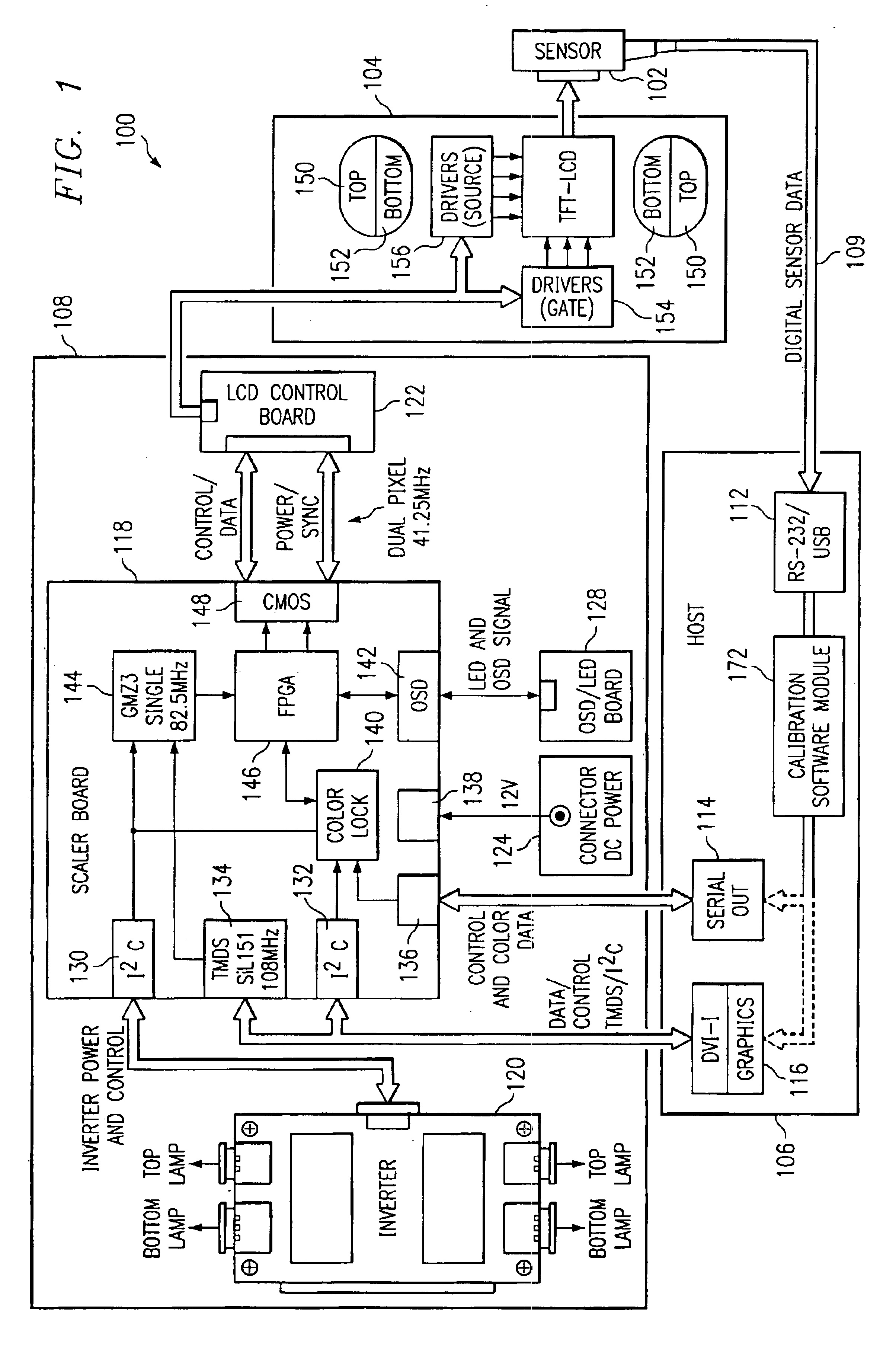
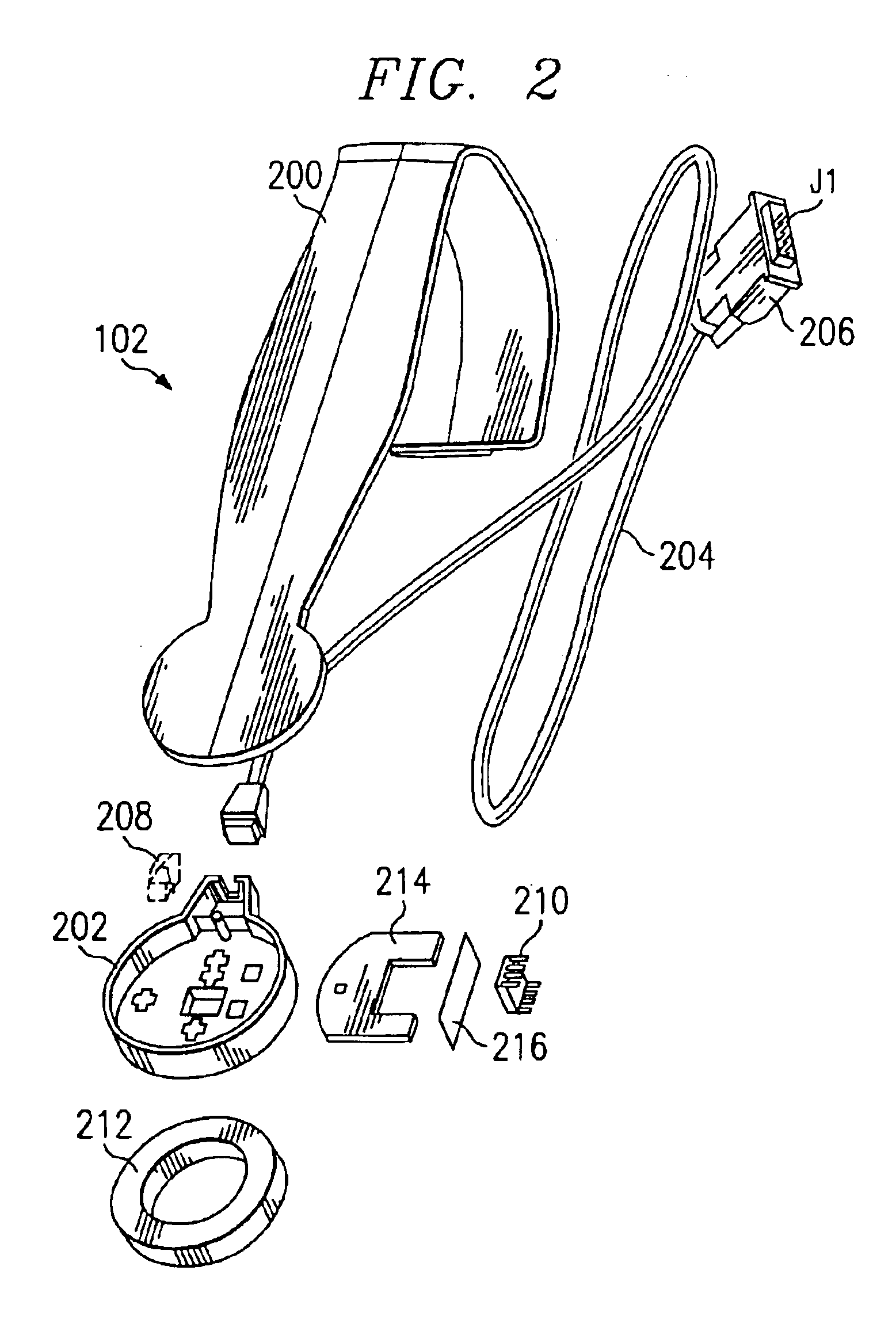
Compact flat panel color calibration system
InactiveUS6853387B2Accurately measureEliminates and greatly reduces disadvantageTelevision system detailsRadiation pyrometryPhotodetectorPhotovoltaic detectors
A compact flat panel color calibration system includes a lens prism optic able to pass a narrow, perpendicular, and uniform cone angle of incoming light to a spectrally non-selective photodetector. The calibration system also includes a microprocessor operable to determine the luminance of the display based upon the information gathered by the photodetector. A software module included in the calibration system is then operable to process the luminance information in order to adjust the flat panel display.
Owner:MORGAN STANLEY +1
Compact flat panel color calibration system
InactiveUS20050157298A1Eliminates and greatly reduces disadvantageEliminates and greatly reduces and problemTelevision system detailsRadiation pyrometryPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
A compact flat panel color calibration system includes a lens prism optic able to pass a narrow, perpendicular, and uniform cone angle of incoming light to a spectrally non-selective photodetector. The calibration system also includes a microprocessor operable to determine the luminance of the display based upon the information gathered by the photodetector. A software module included in the calibration system is then operable to process the luminance information in order to adjust the flat panel display.
Owner:RPX CORP +1
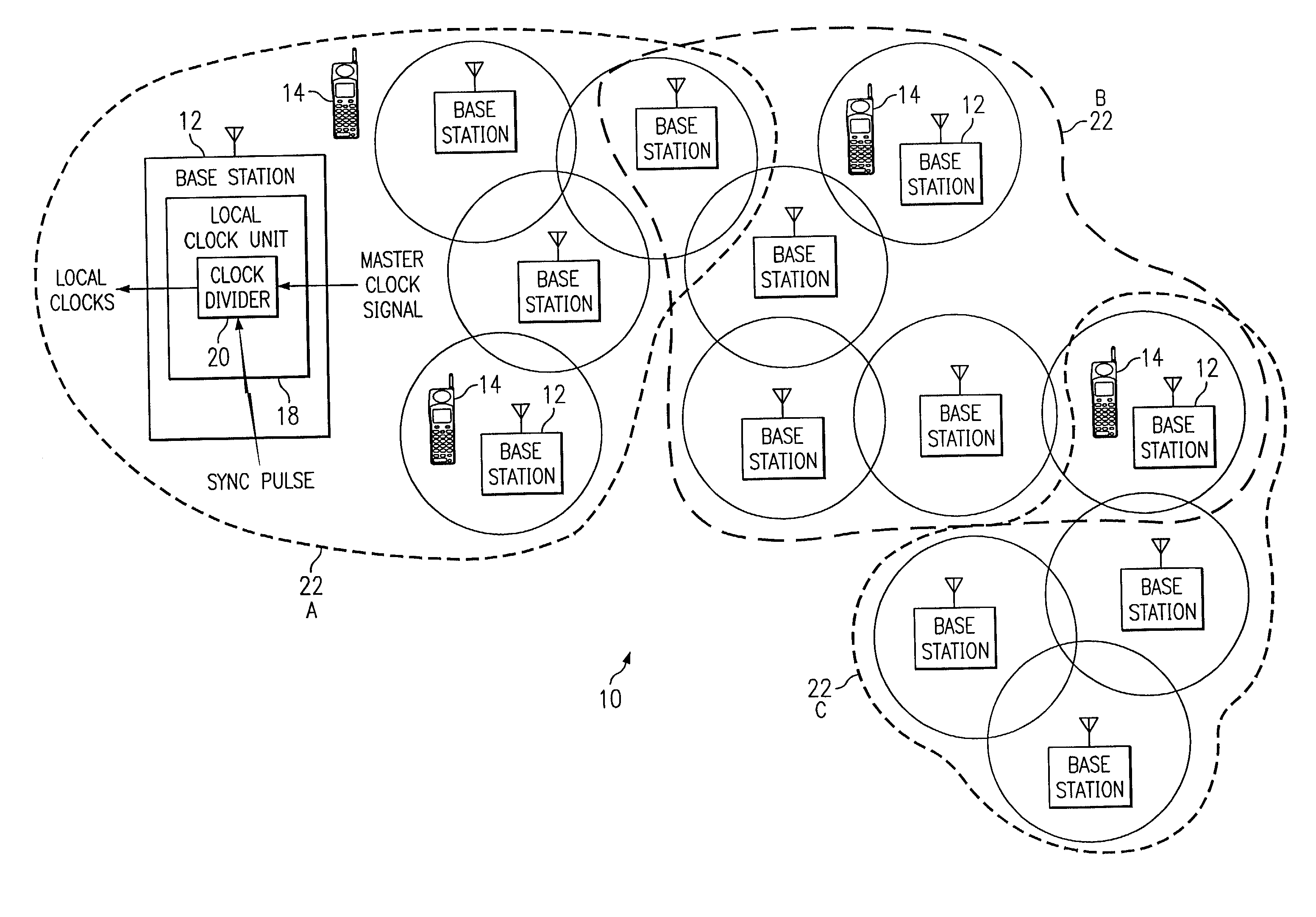
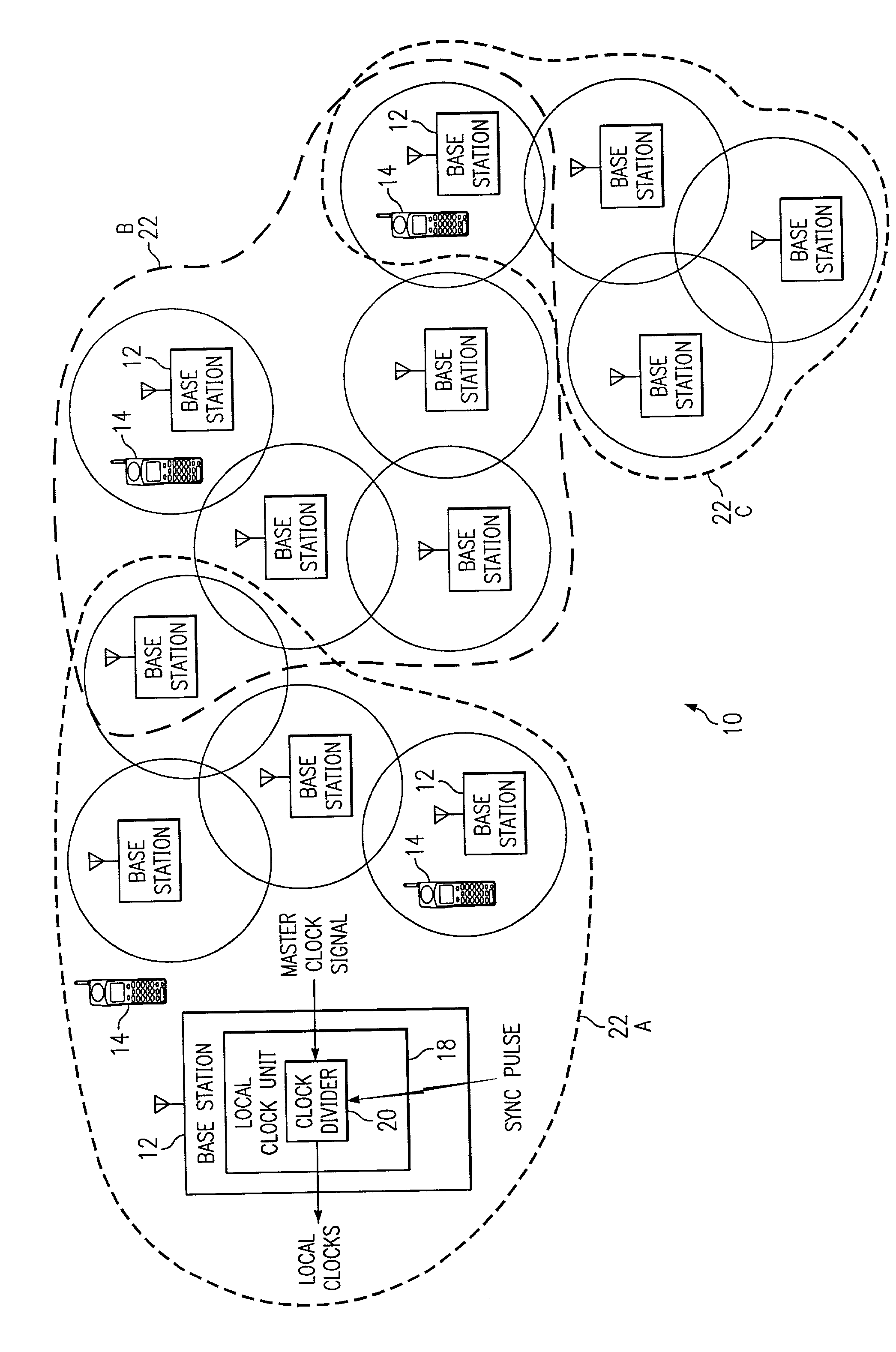
System and method for synchronizing clock dividers in a wireless network
InactiveUS6975877B1Eliminates and greatly reduces disadvantageEliminates and greatly reduces and problemTime-division multiplexRadio transmissionWireless mesh networkMobile station
A wireless network includes a plurality of base stations that provide a wireless communication capability for a plurality of mobile stations. Each base station includes a local clock unit with a clock divider that generates local clock signals from a master clock signal received from a master clock source. The base stations are partitioned into a plurality of clusters. A sync pulse is propagated to each base station of the wireless network in order to reset their respective clock dividers. resetting of the clock dividers provides synchronization of local clock signals among the base stations. The sync pulse is propagated to all bases stations within a first cluster wherein one of the base stations in the first cluster is also a member of a second cluster. The base station that is part of the first and second clusters then propagates the sync pulse to other base stations in the second cluster and so on until the sync pulse has been delivered to all base stations in the wireless network.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method for assessing information technology needs in a business
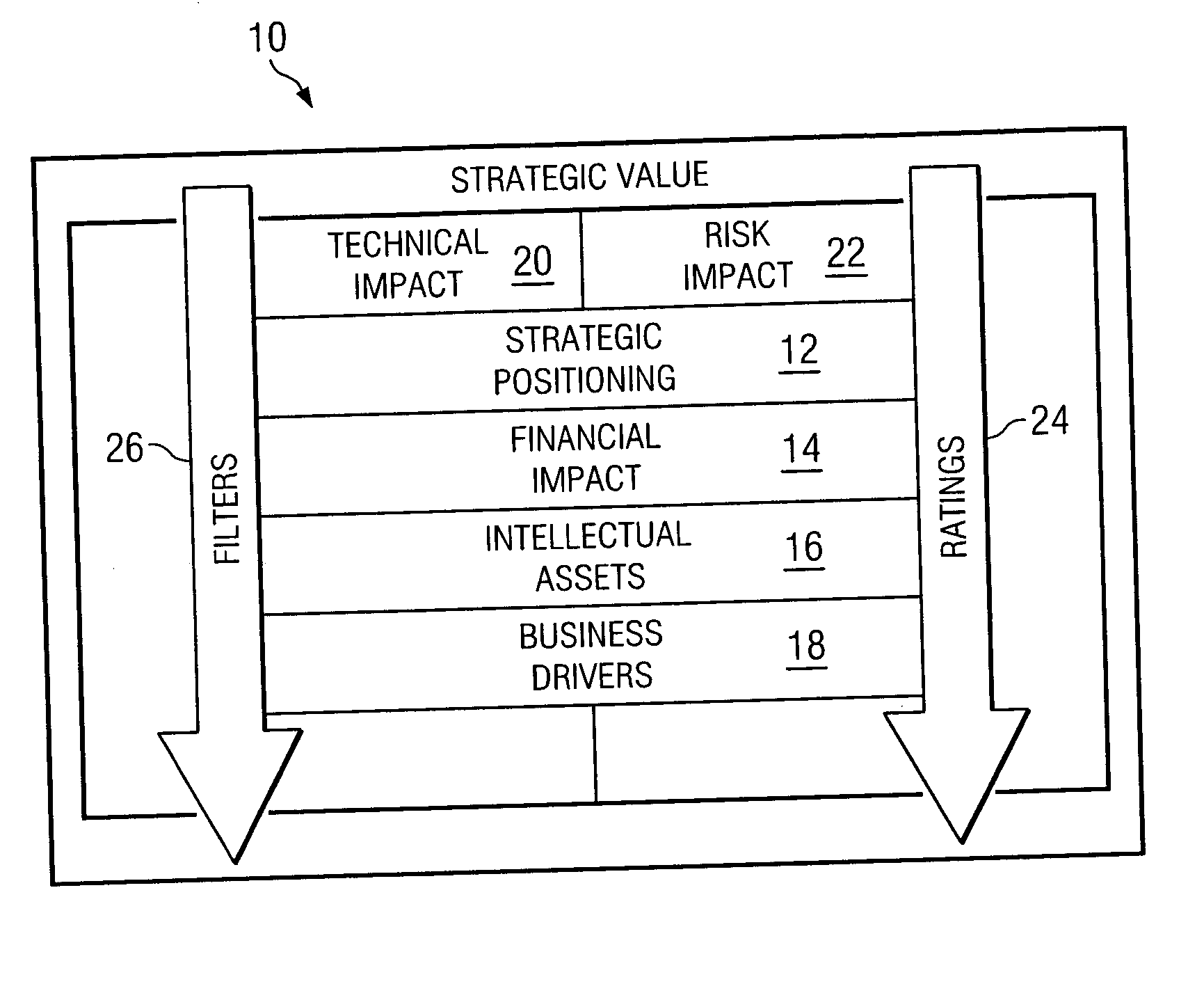
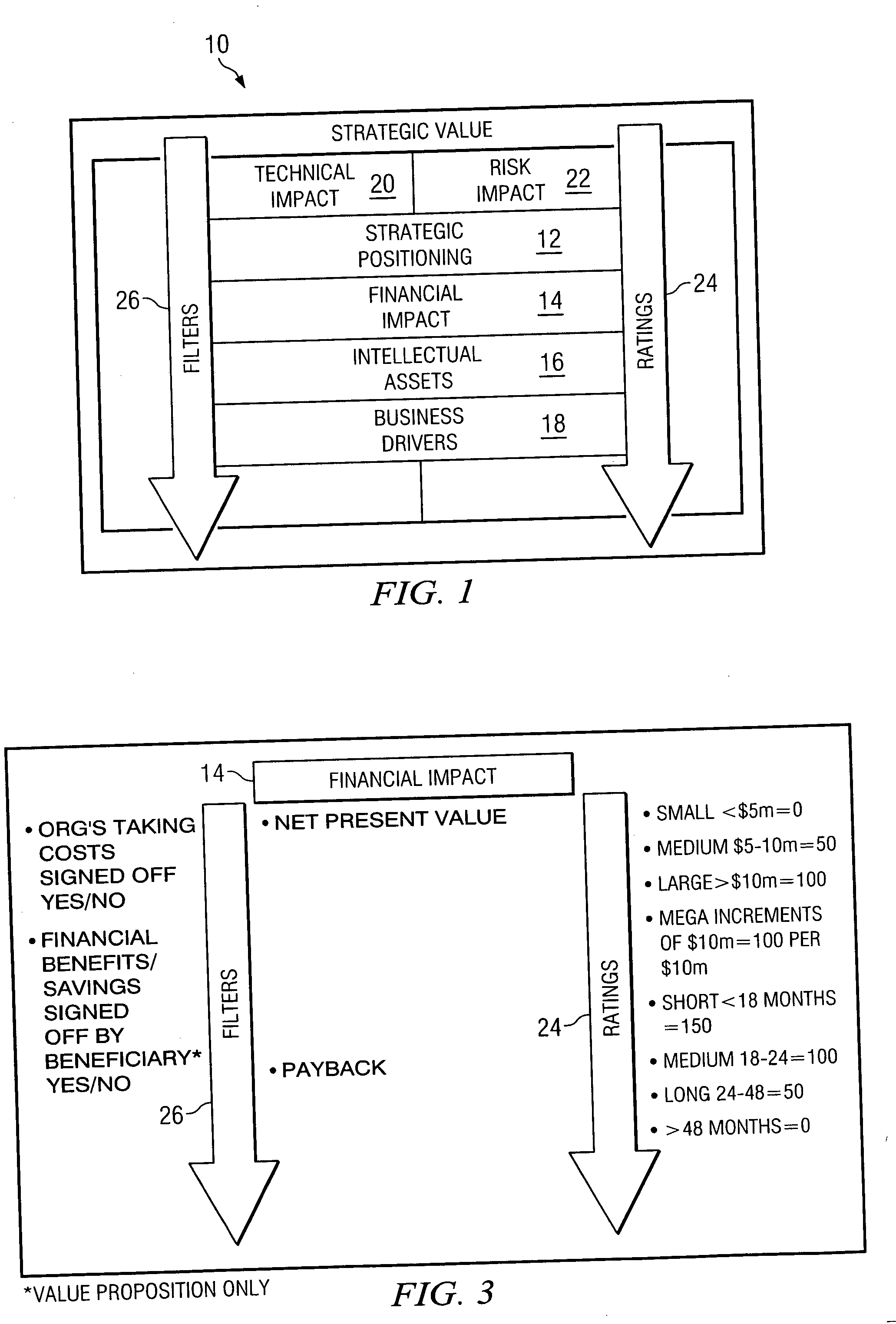
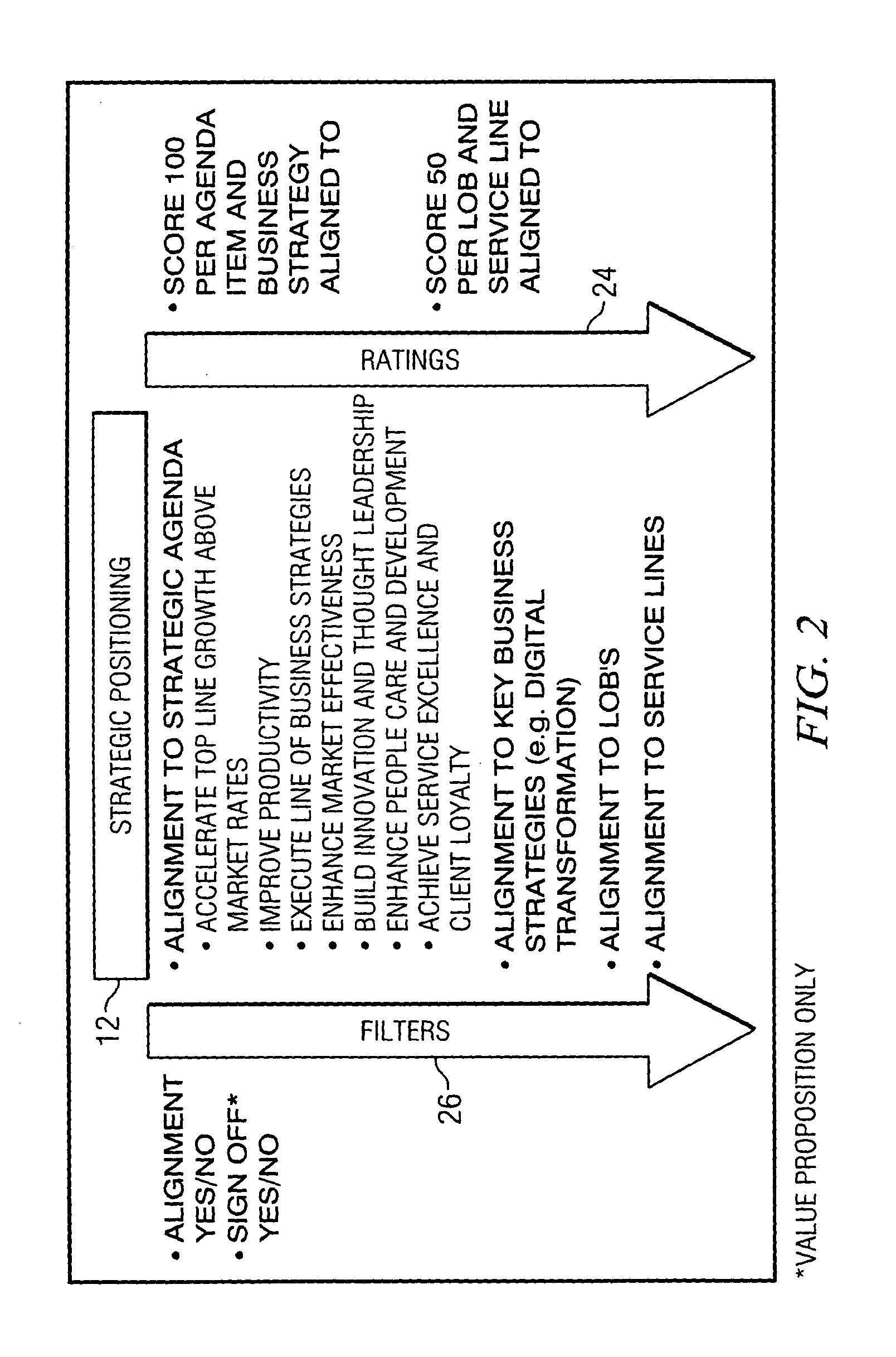
InactiveUS20050065841A1Increase valueEliminates and greatly reduces disadvantageOffice automationSpecial data processing applicationsKnowledge managementInformation technology
A strategic value model provides an ability to evaluate the feasibility of implementing an information technology initiative. The flow process begins by gathering information associated with the operation of the business in categories pertaining to the information technology initiative desired to be implemented. Strategic value ratings are applied to each criteria in the categories. The initiatives are categorized so that like initiatives are assessed against each other. A determination is made to identify which initiatives are to be funded in accordance with the applied strategic value ratings. Funding can then be established for an initiative based on this determination.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
System, device, and method for providing access in a cardiovascular environment
InactiveUS20060178675A1Eliminates and greatly reduces disadvantageEliminates and greatly reduces and problemEar treatmentCannulasEngineering
Owner:CASTLEWOOD MEDICAL TECH
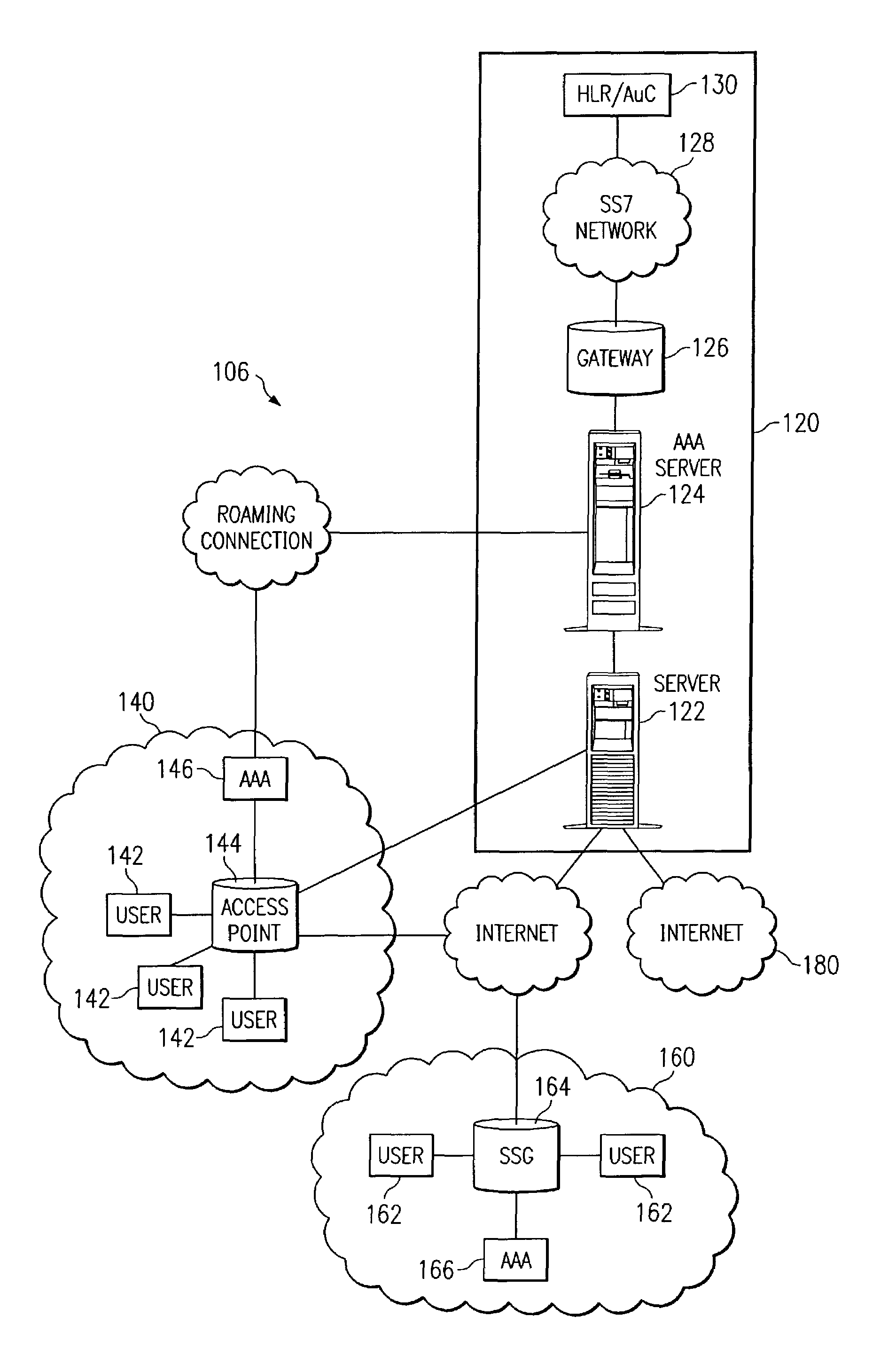
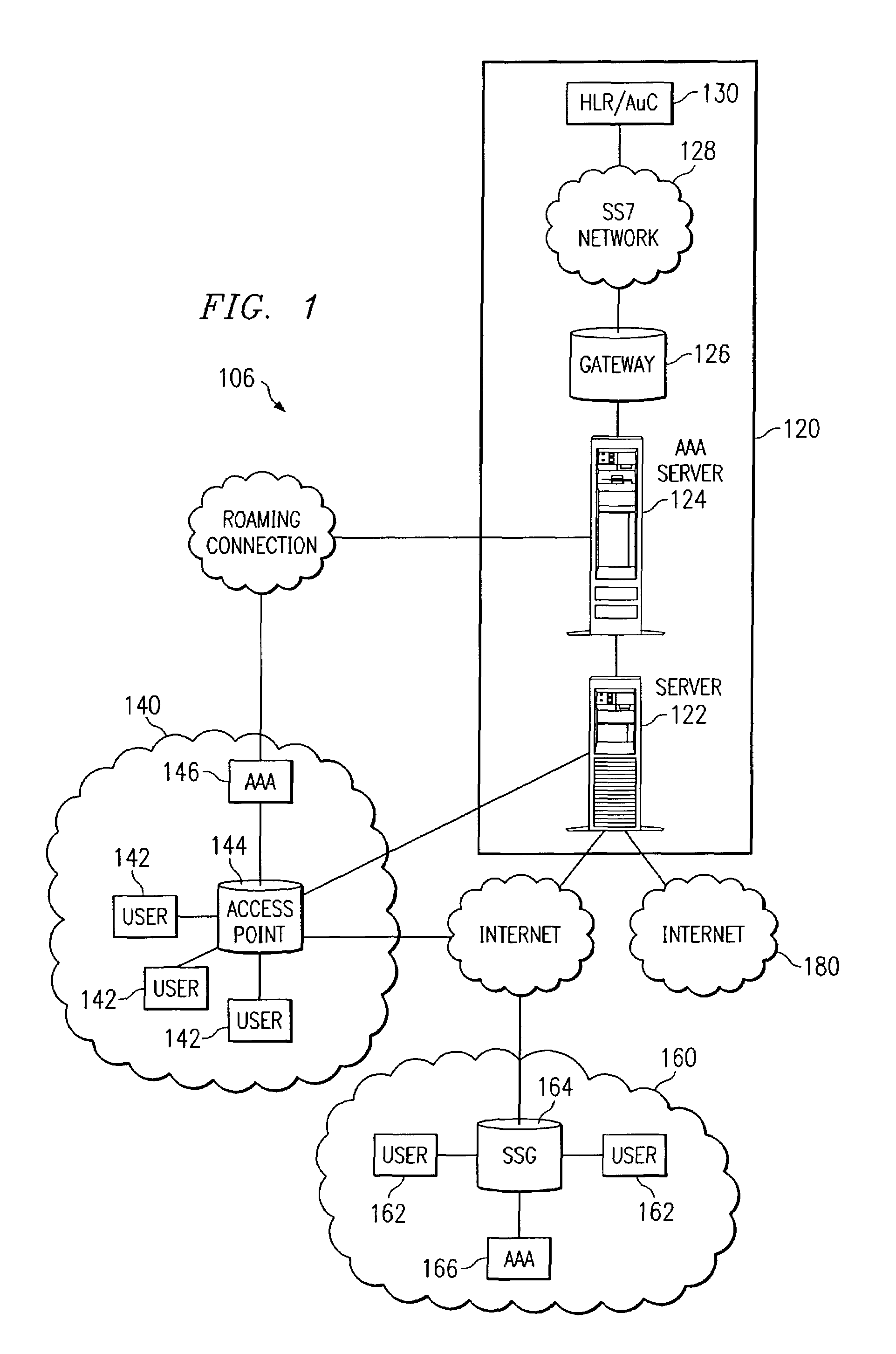
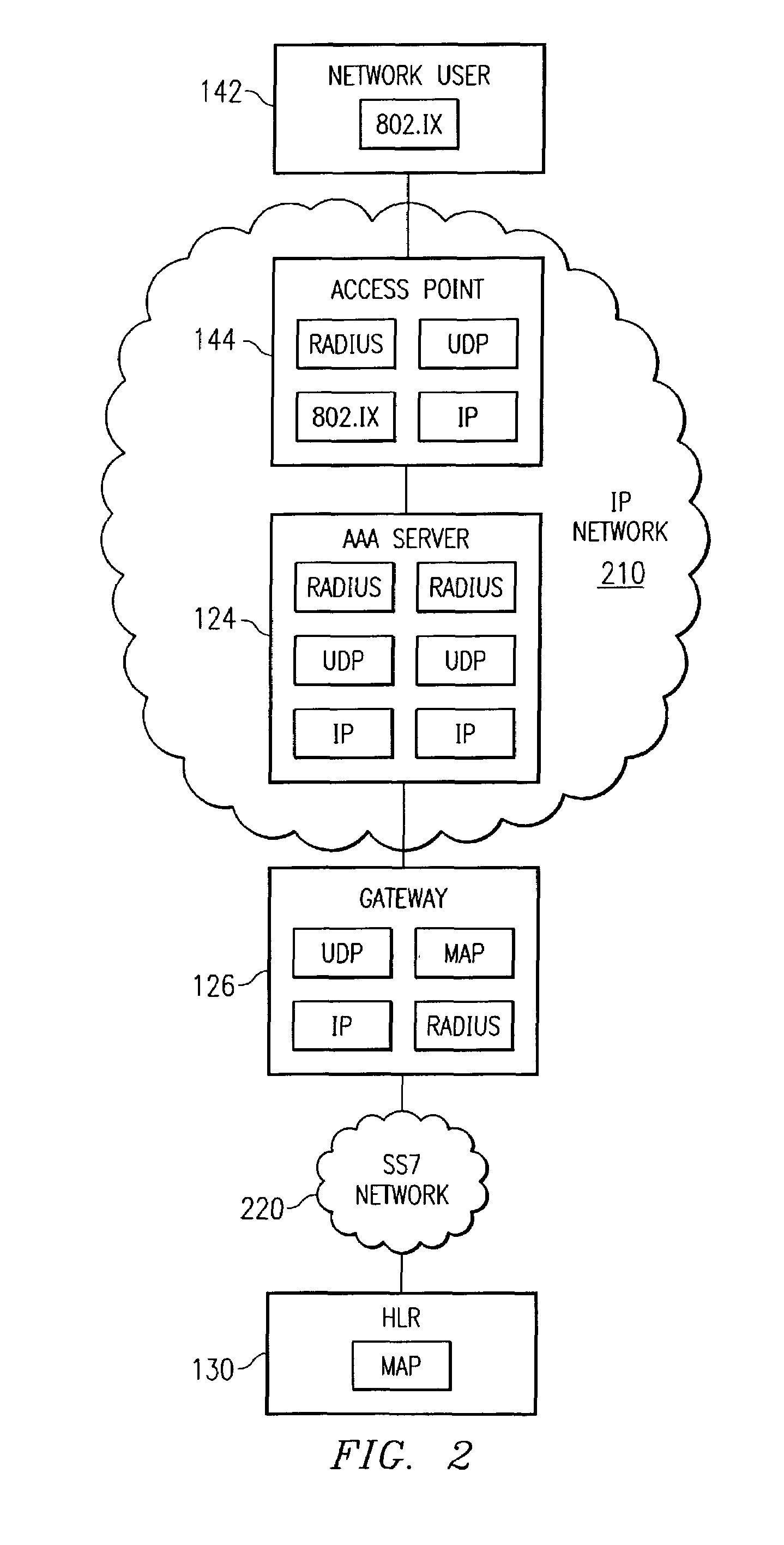
System and method for network user authentication
InactiveUS7716723B1Sure easyEliminates and greatly reduces disadvantageDigital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsComputer networkUser authentication
A system for user authentication includes a gateway operable to receive a user authentication request in an Internet Protocol format from a server. The gateway communicates the user authentication request in a Signaling System 7 protocol to a user registry. The gateway is also operable to receive a user authentication response in the Signaling System 7 protocol from the user registry. The gateway communicates the user authentication response in the Internet Protocol format to the server.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
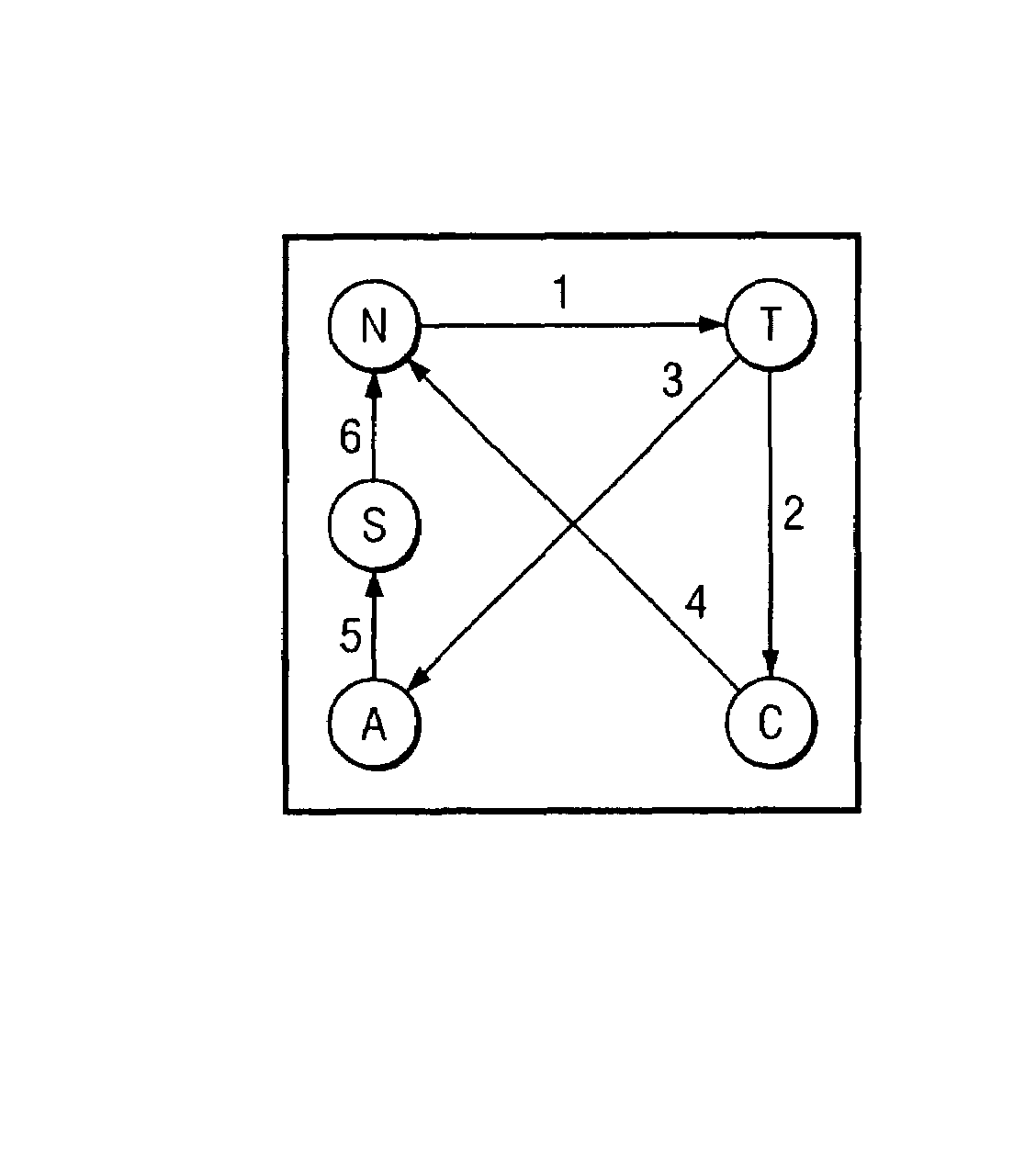
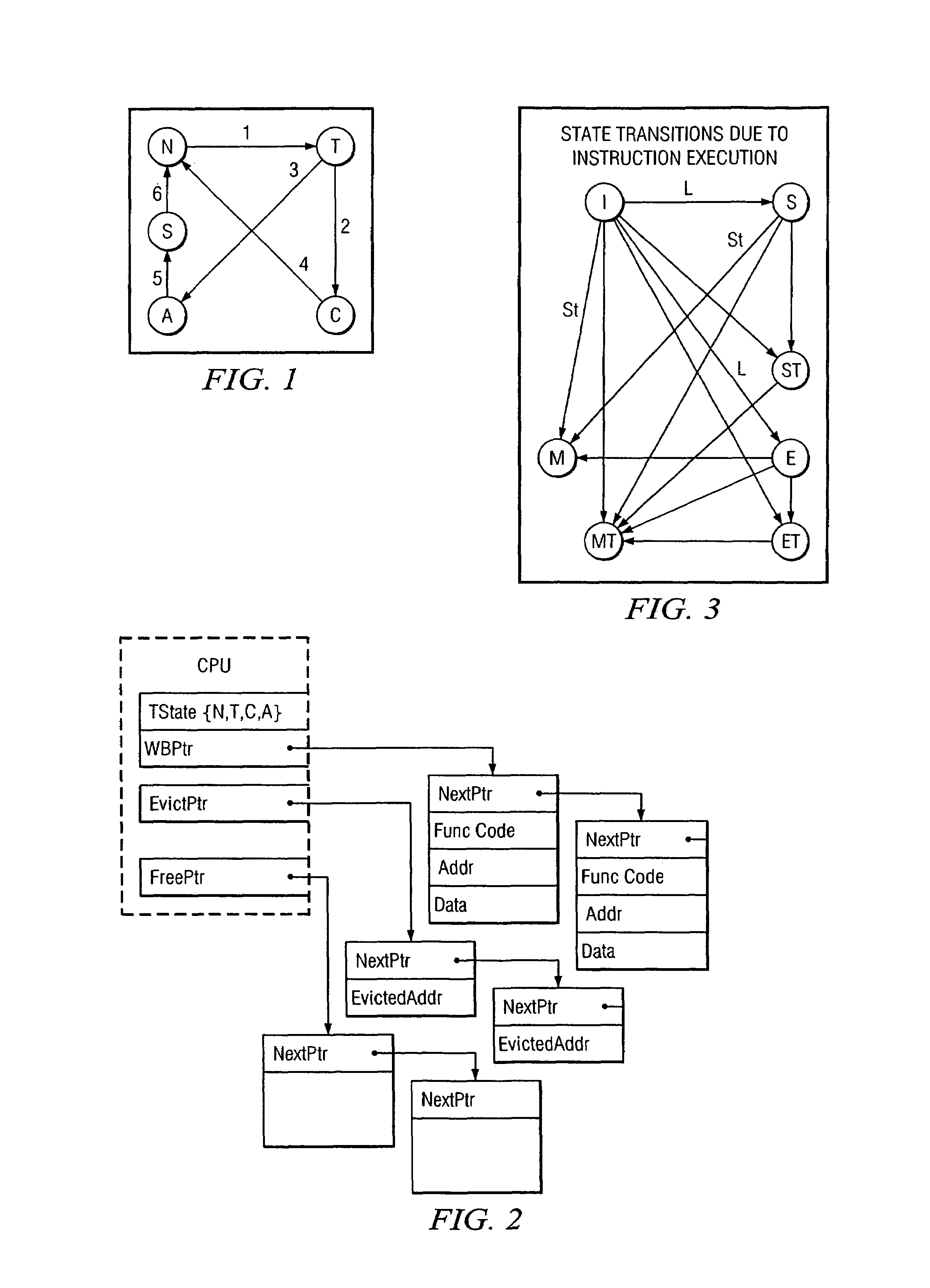
Method for performing cache coherency in a computer system
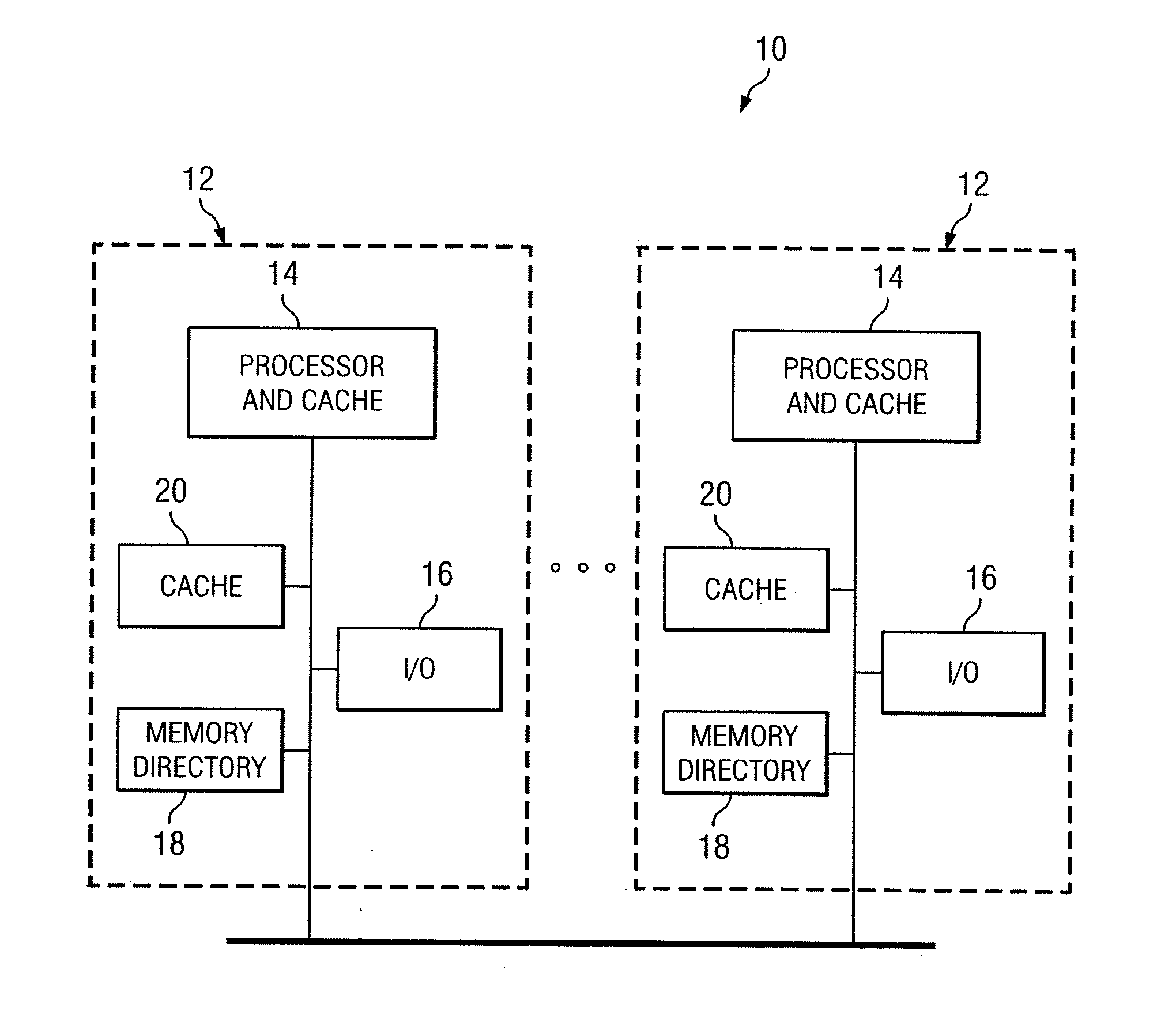
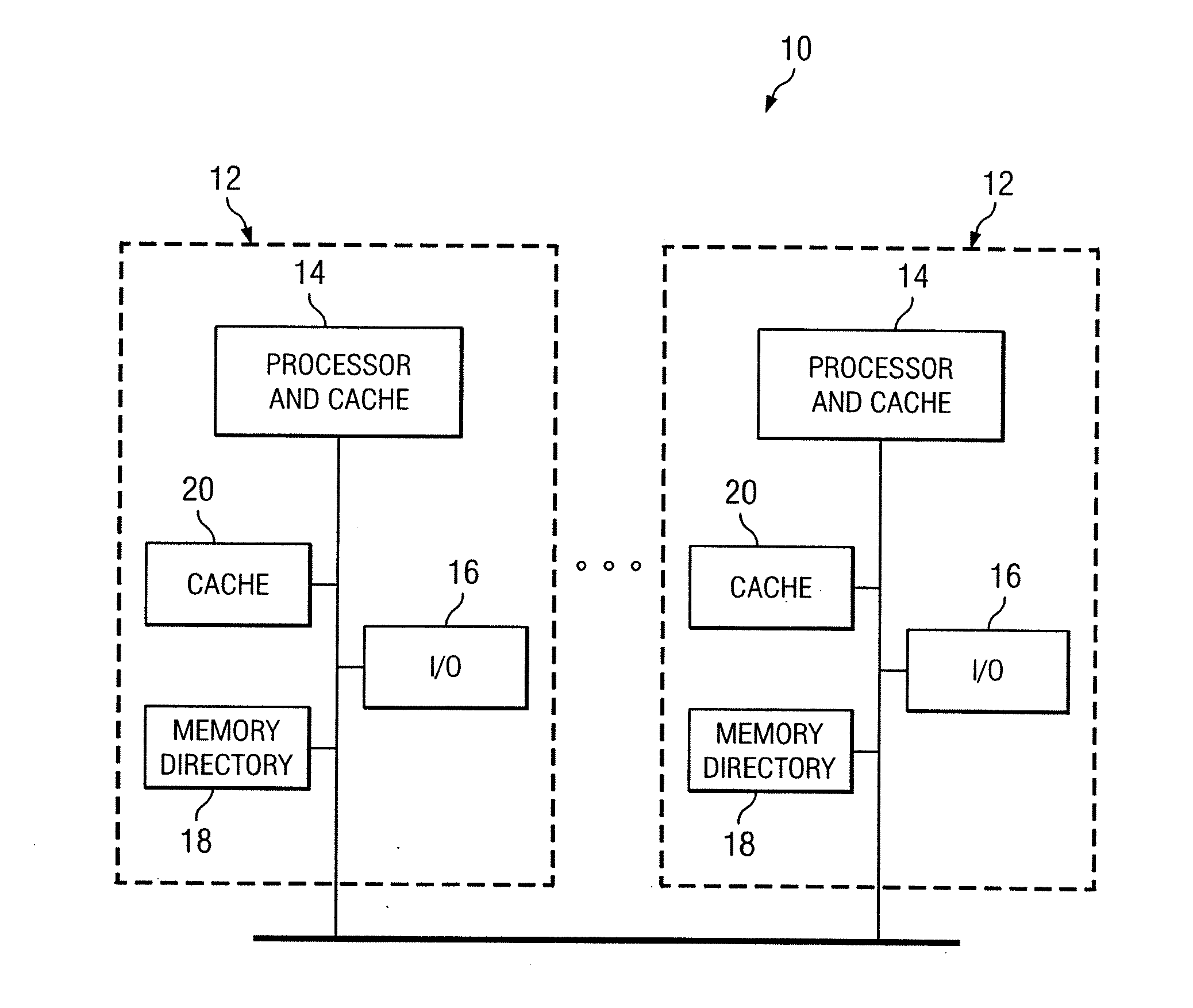
ActiveUS7802058B1Improve delivery capabilitiesSelectively usedMemory adressing/allocation/relocationComputerized systemParallel computing
In a computing system, cache coherency is performed by selecting one of a plurality of coherency protocols for a first memory transaction. Cache coherency is performed on appropriate caches in the computing system in accordance with the selected one of the plurality of coherency protocols. For a second memory transaction, another selection is made of the plurality of coherency protocols. The selected one of the coherency protocols for the second memory transaction may be the same as or different from the selected one of the plurality of coherency protocols for the first memory transaction.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
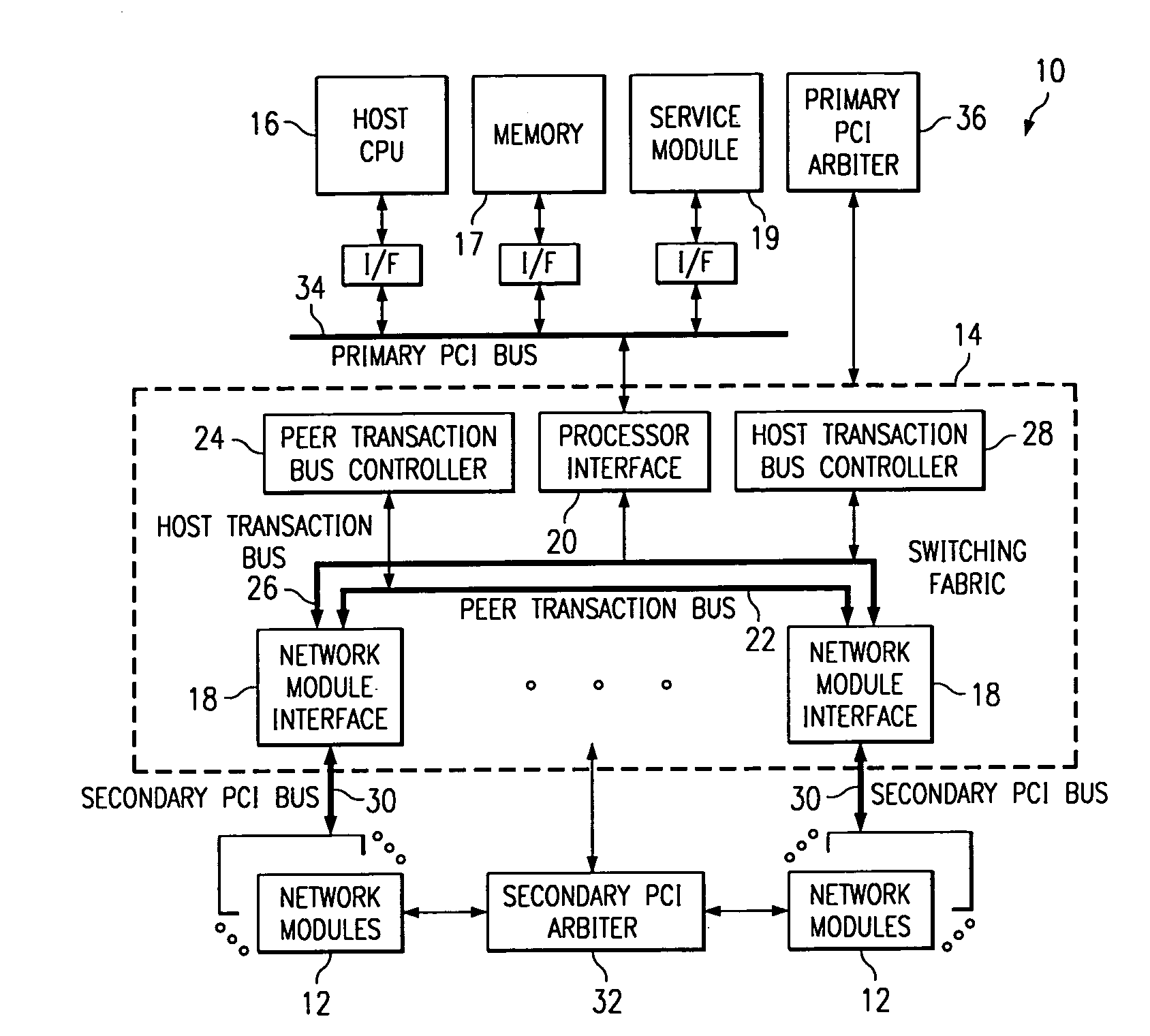
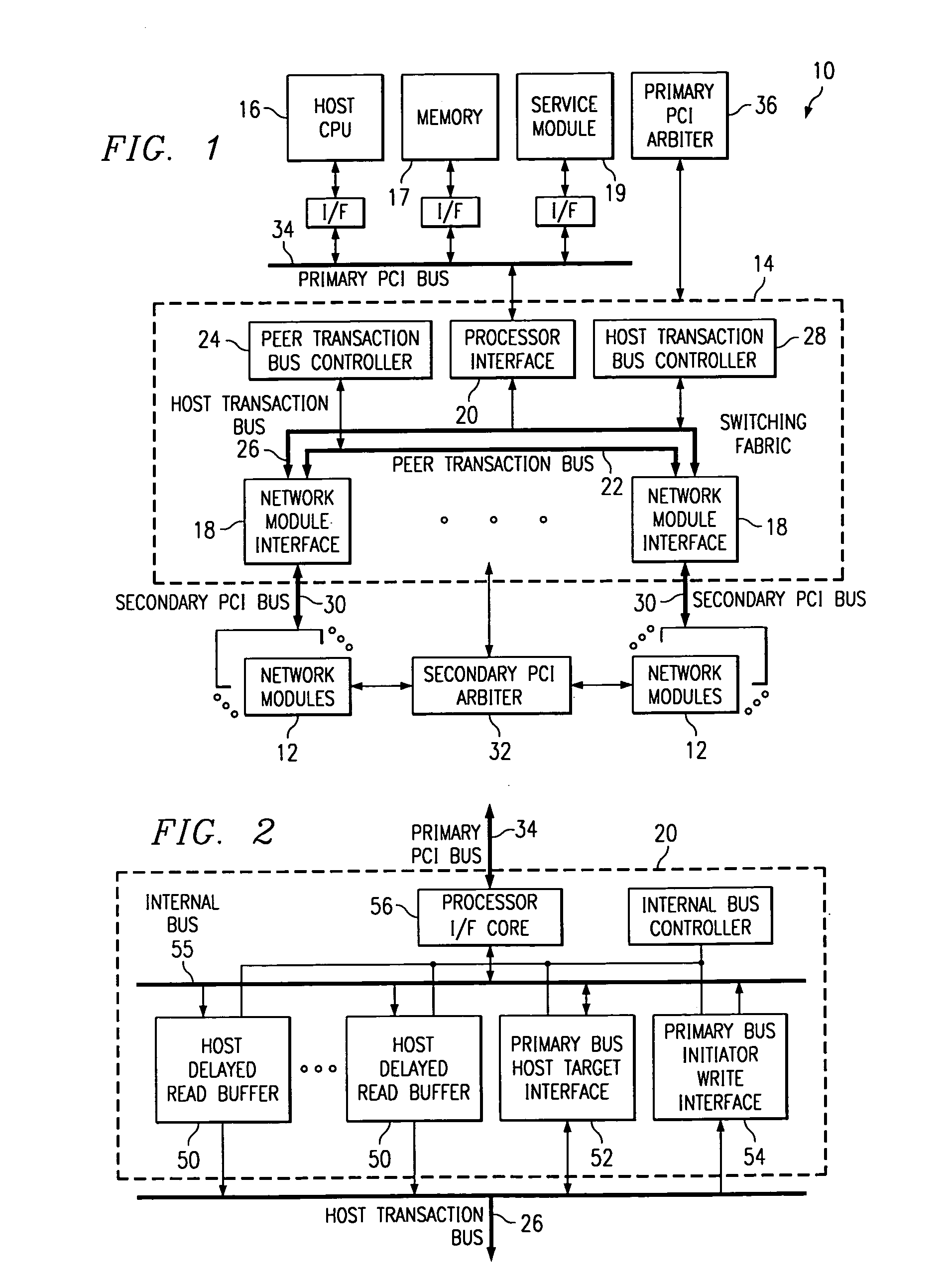
Switching fabric for interfacing a host processor and a plurality of network modules
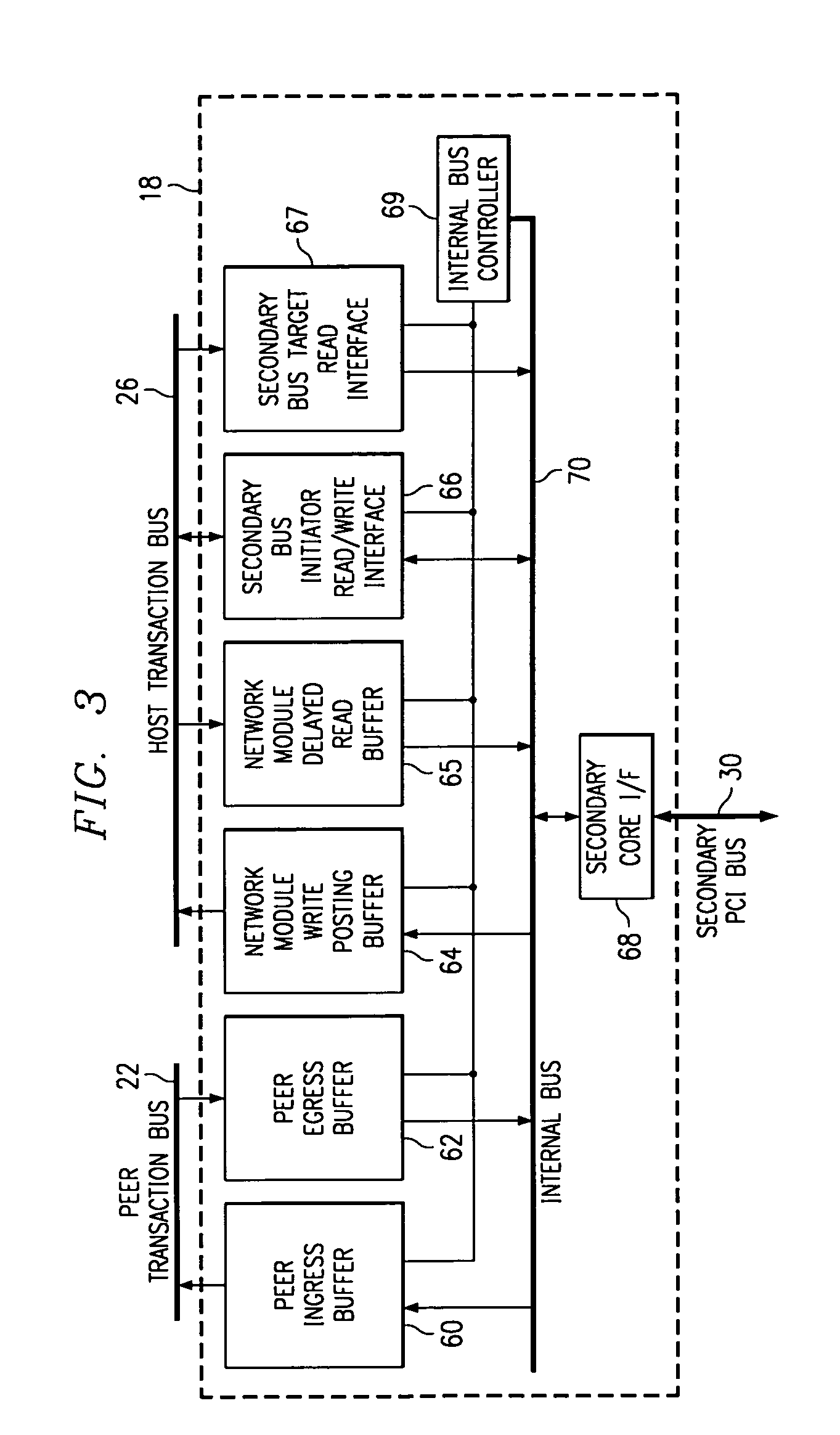
InactiveUS6973093B1Eliminates and greatly reduces disadvantageEliminates and greatly reduces and problemFrequency-division multiplexData switching by path configurationTransport systemMaster processor
An information transport system includes a switching fabric that transfers information between network modules and between a host processor and the network modules. The switching fabric includes network module interfaces each associated with one or more network modules. The network module interfaces communicate with each other over a peer transaction bus to allow information to be transferred from one network module to another network module. The switching fabric also includes a processor interface associated with the host processor. The processor interface communicates with the network module interfaces over a host transaction bus to allow information transfer between the host processor and each network module. The peer transaction bus and the host transaction bus separately support routed packet data and peer to peer data transactions in order to prevent one type of transaction from blocking the other and avoid performance dependencies.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method for Performing Cache Coherency in a Computer System
InactiveUS20110016277A1Significant comprehensive benefitsEliminates and greatly reduces disadvantageMemory adressing/allocation/relocationParallel computingComputerized system
In a computing system, cache coherency is performed by selecting one of a plurality of coherency protocols for a first memory transaction. Each of the plurality of coherency protocols has a unique set of cache states that may be applied to cached data for the first memory transaction. Cache coherency is performed on appropriate caches in the computing system by applying the set of cache states of the selected one of the plurality of coherency protocols.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
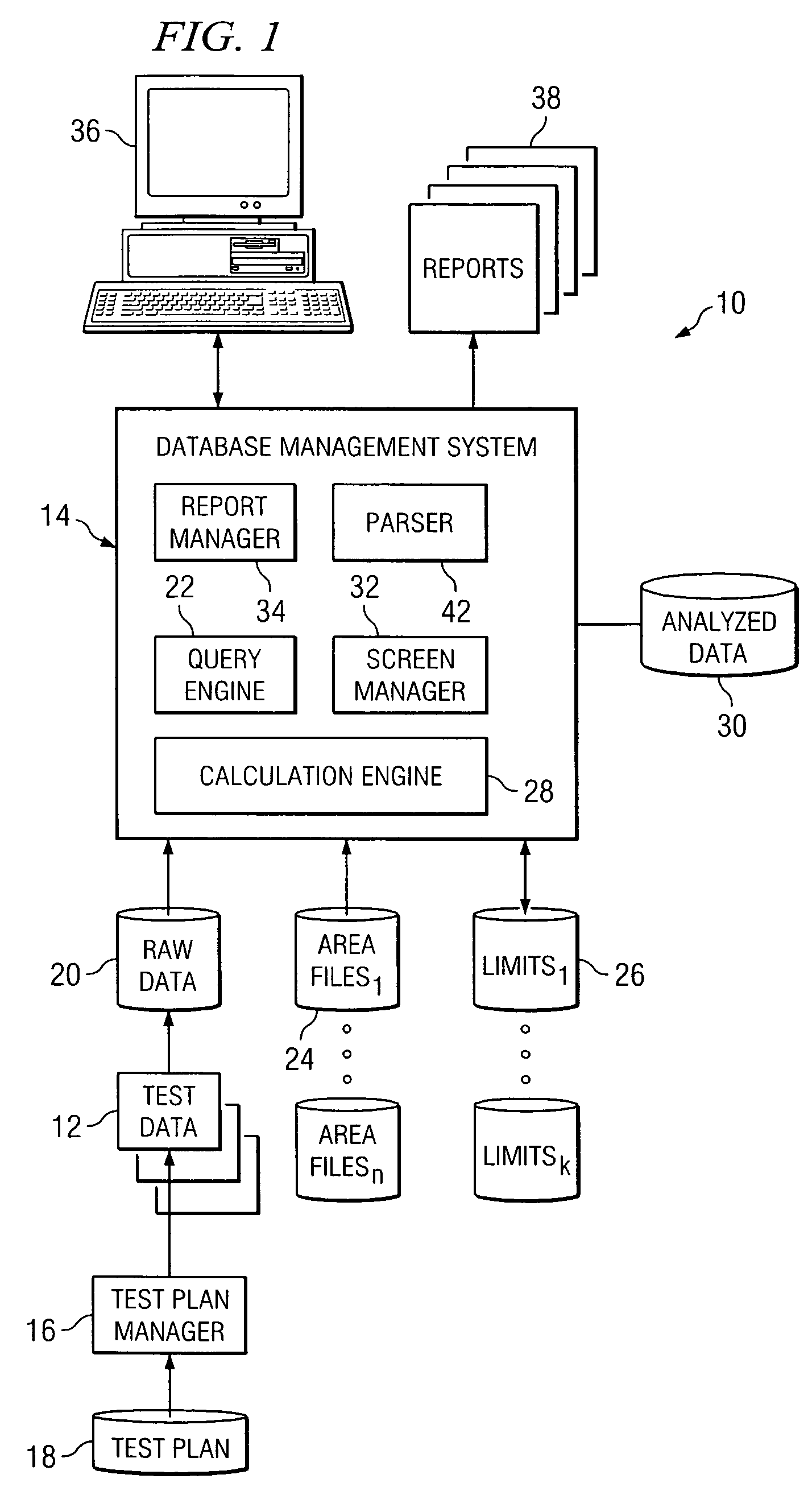
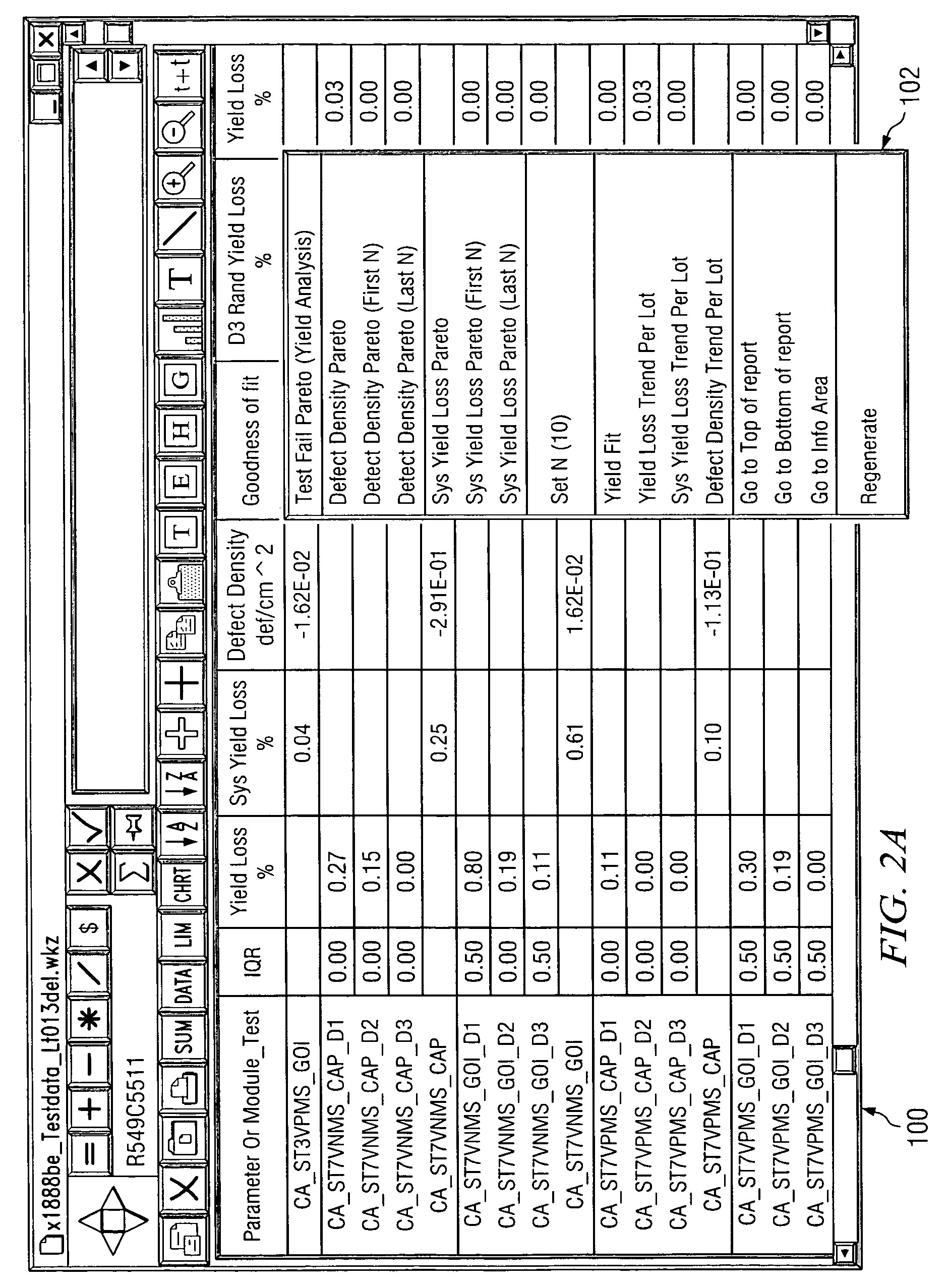
System and method for the analysis of semiconductor test data
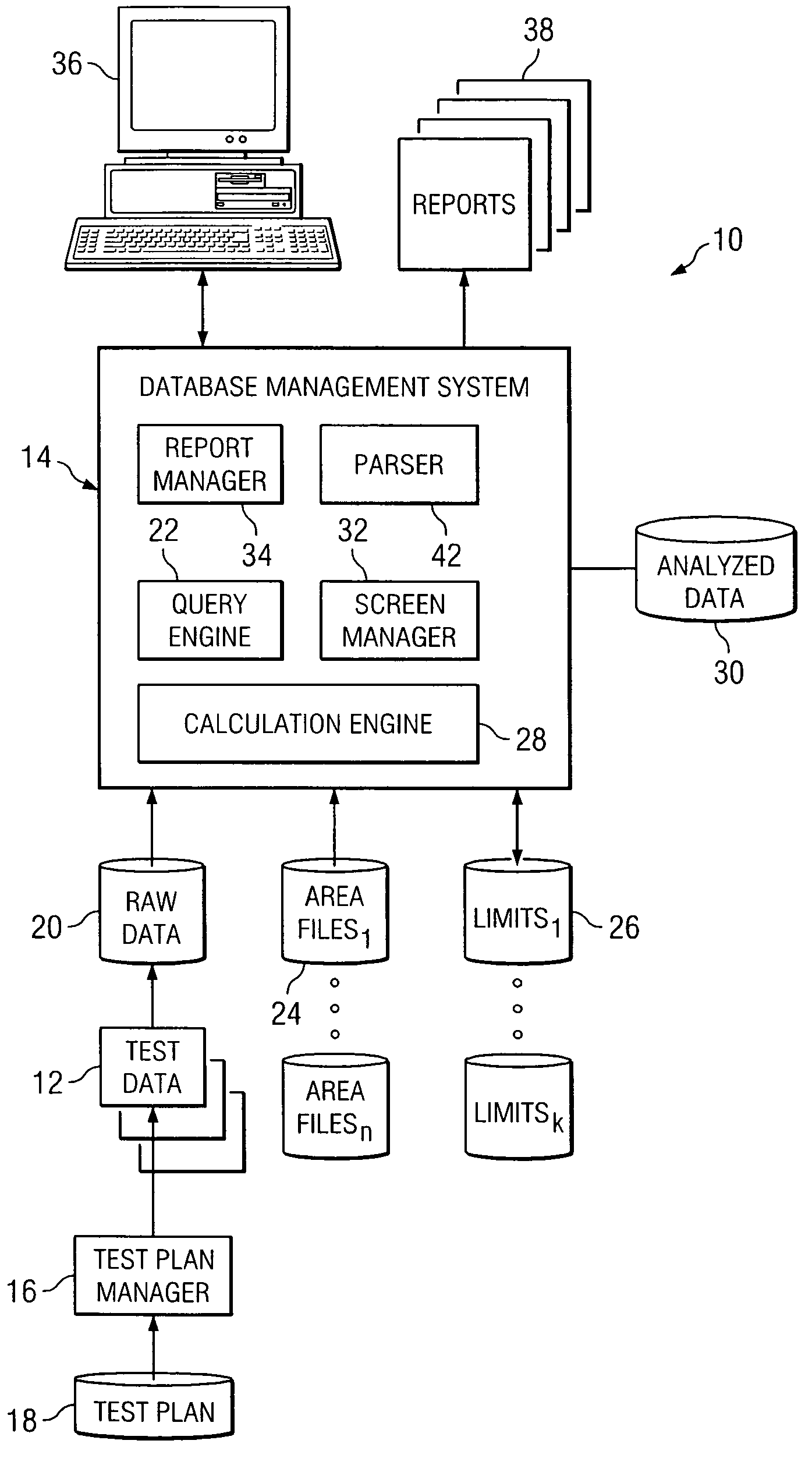
ActiveUS7171335B2Eliminates and greatly reduces disadvantageEliminates and greatly reduces and problemData processing applicationsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementReporting parametersData mining
According to one embodiment, a method of analyzing semiconductor test data includes receiving a plurality of raw data entries from a testing system. Each raw data entry is associated with a test structure of a semiconductor device, and each raw data entry is uniquely identified by a name including a plurality of parseable fields. The plurality of data entries is parsed using a selected one of the plurality of parseable fields to identify a grouping of raw data entries. At least one reportable parameter indicative of the functionality of the test structures associated with the grouping of raw data entries is calculated, and the at least one reportable parameter is provided to a user.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
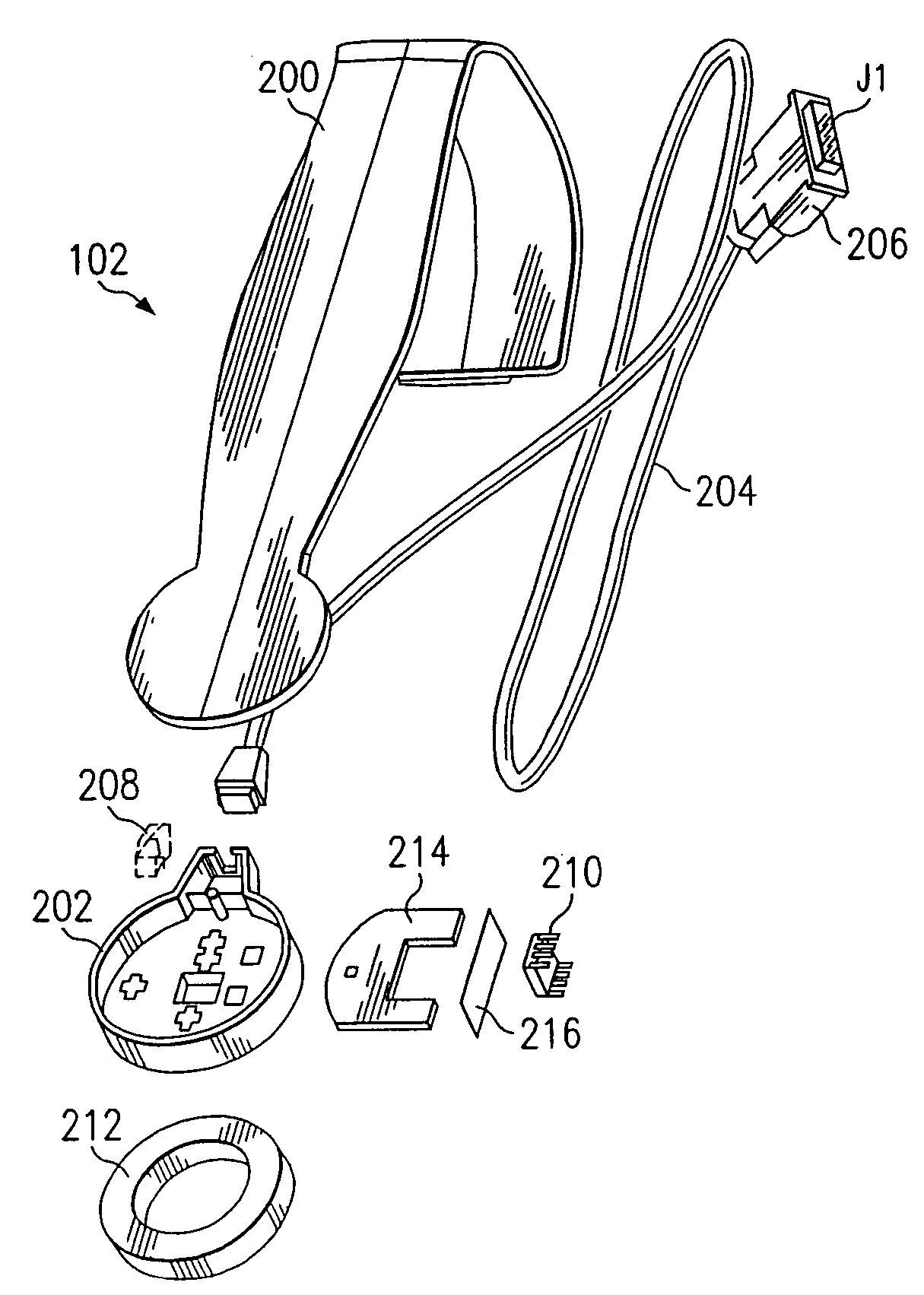
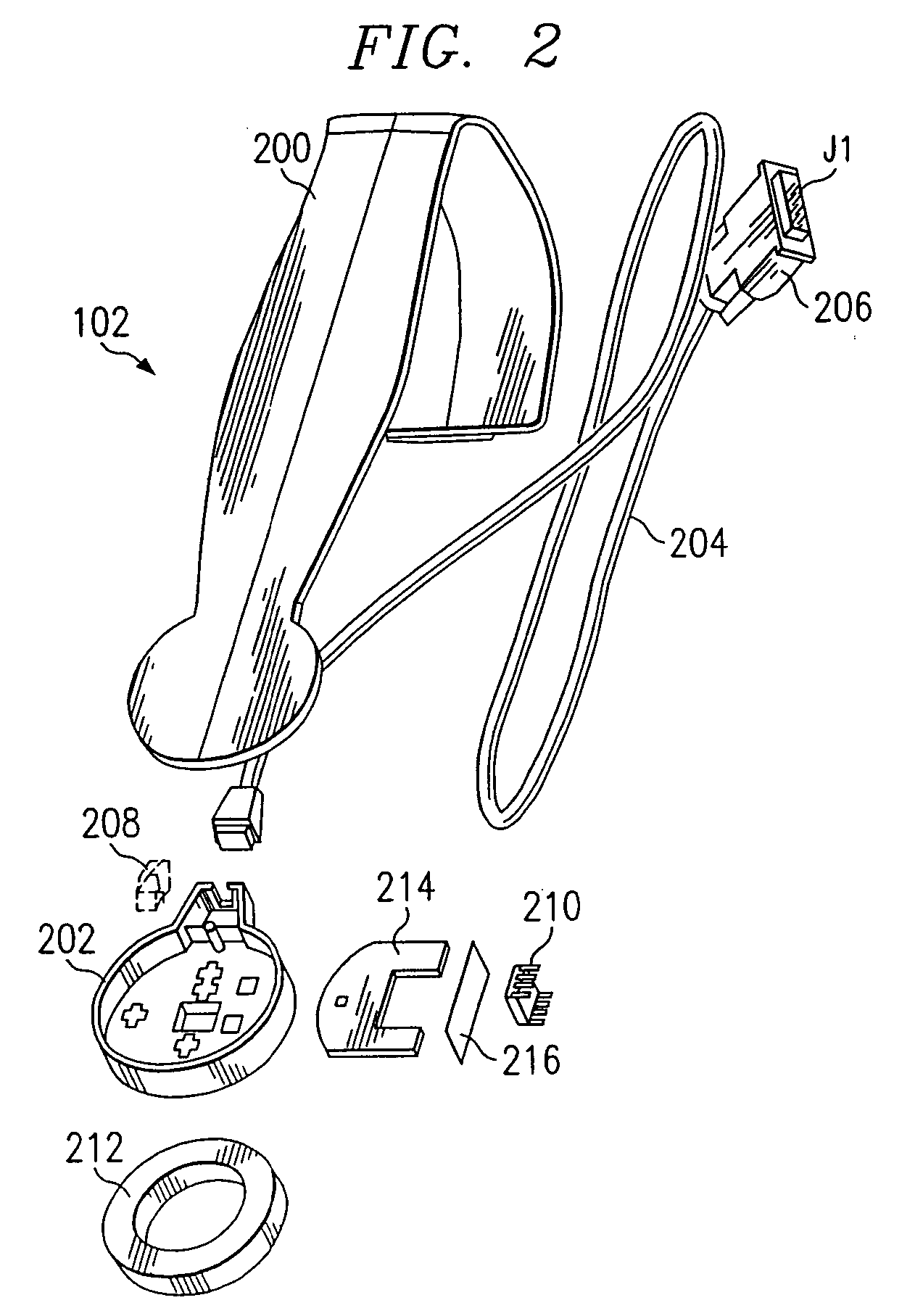
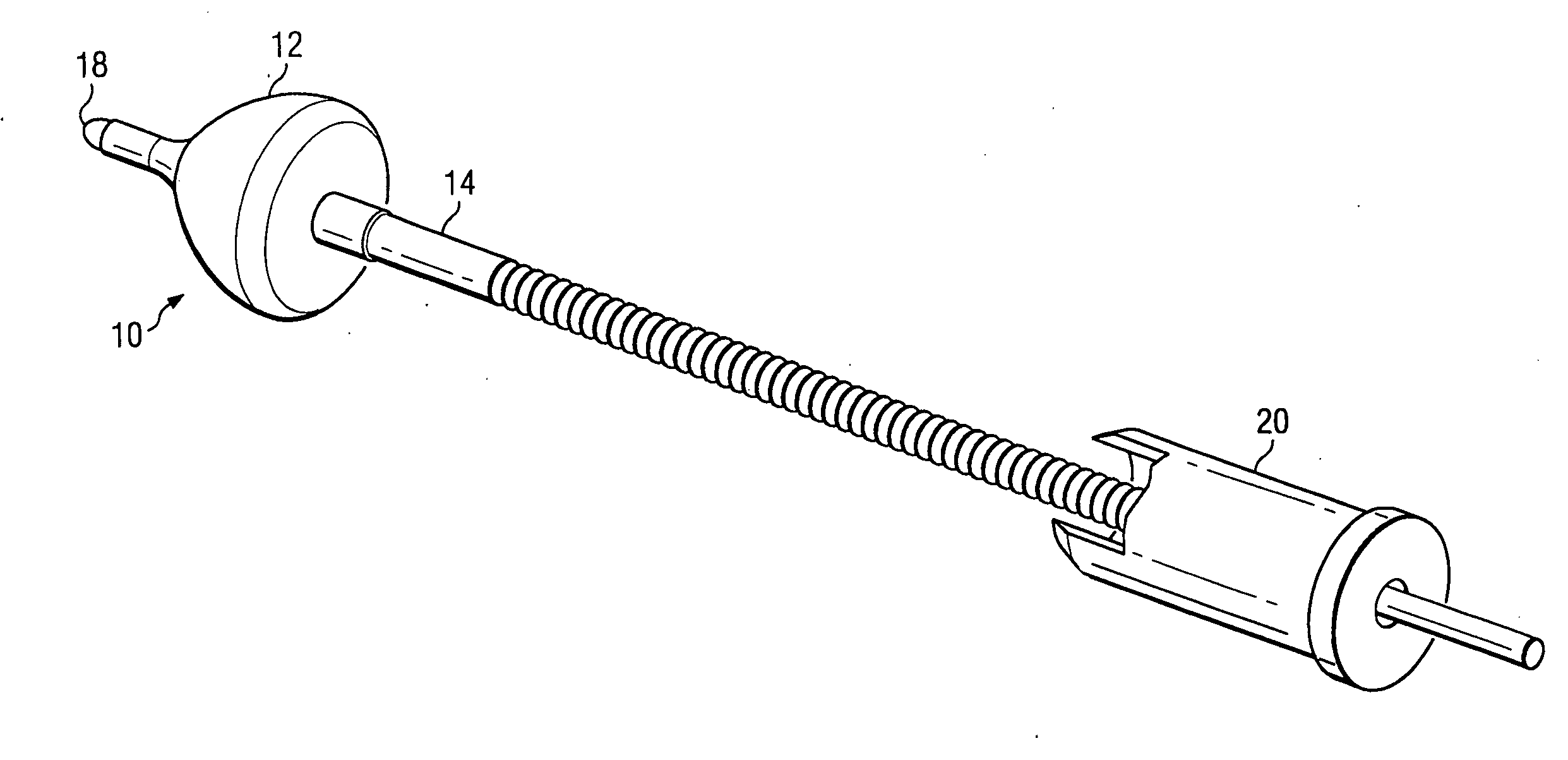
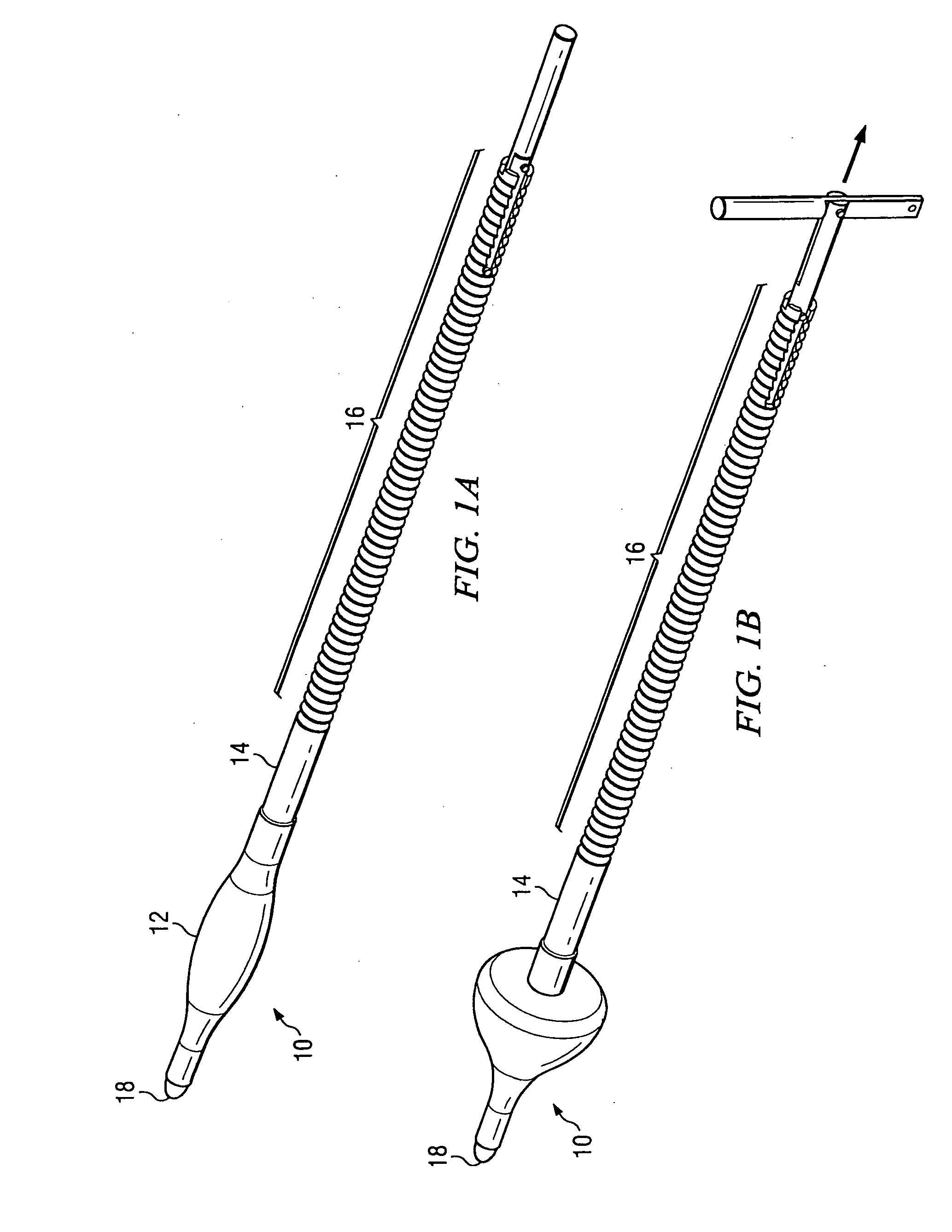
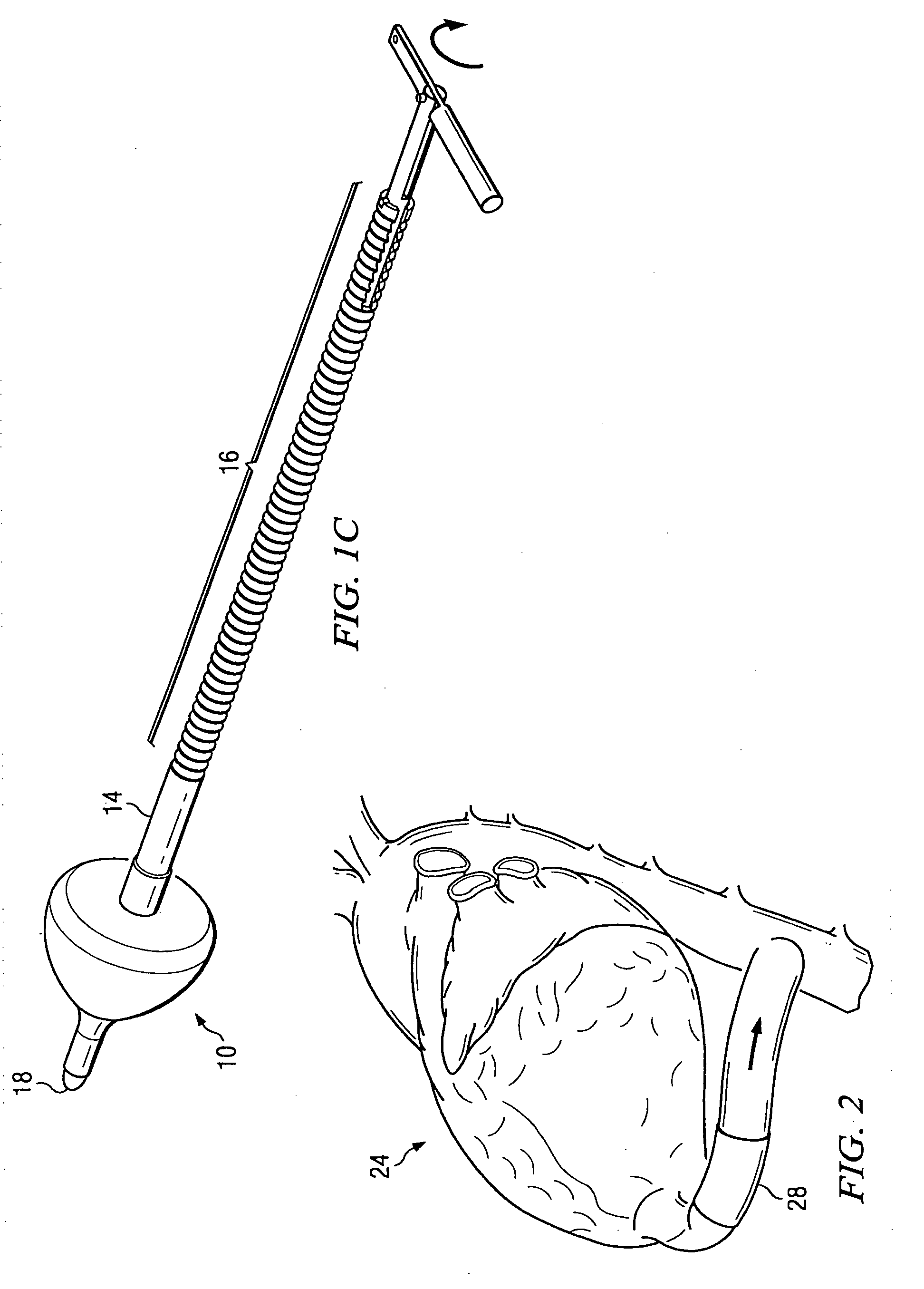
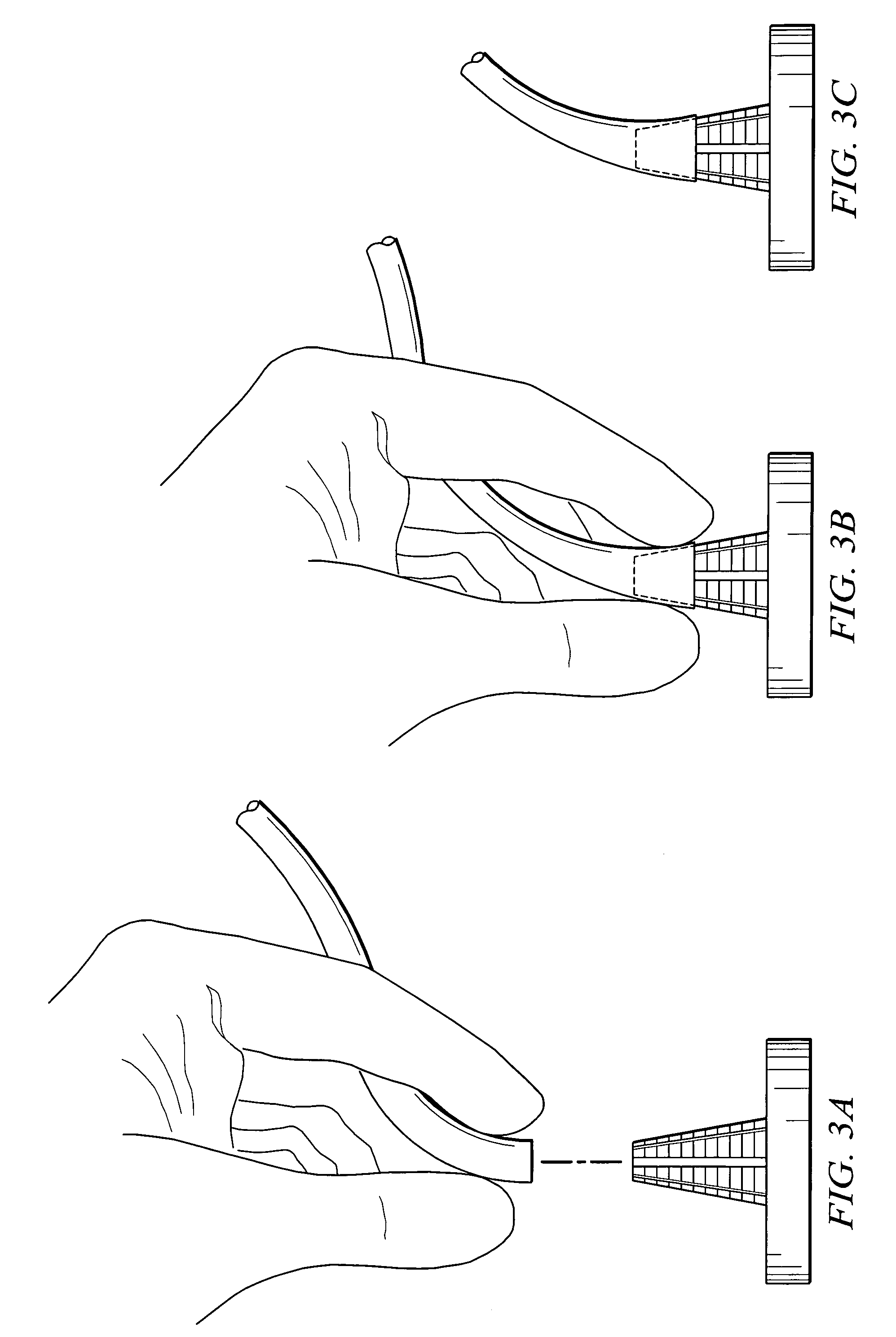
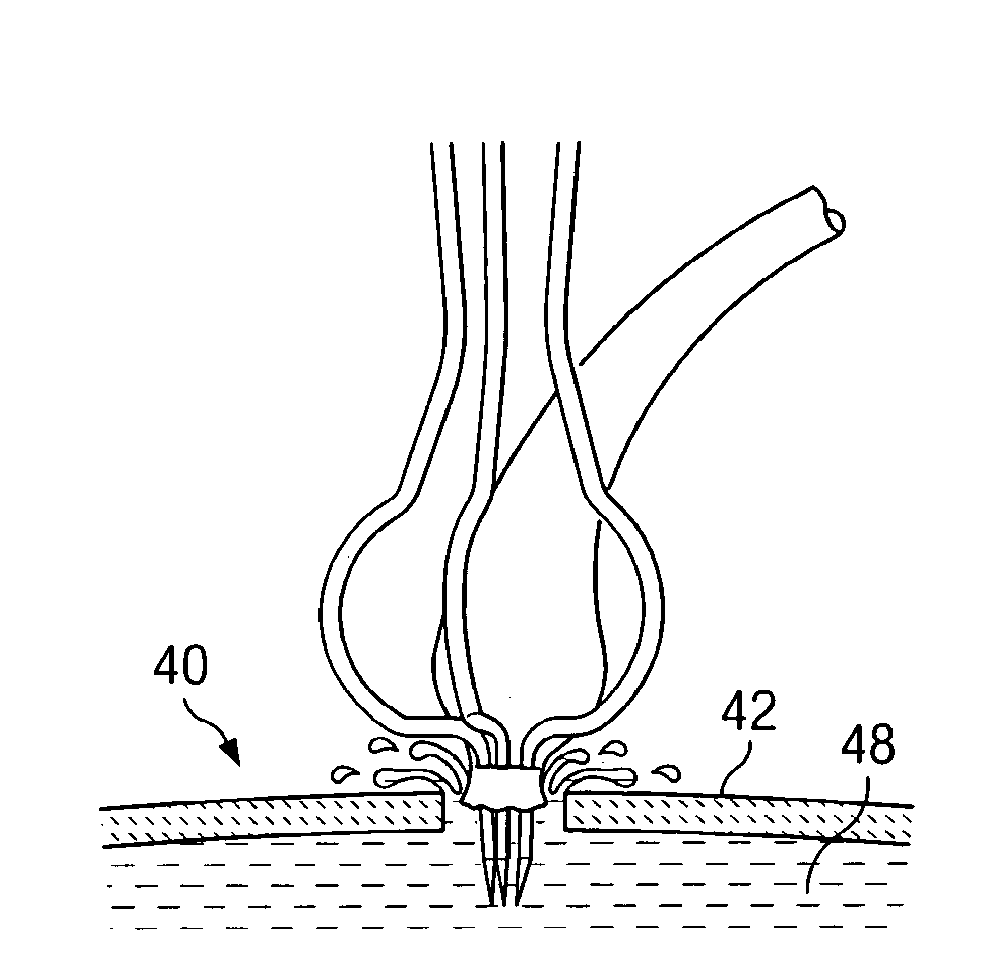
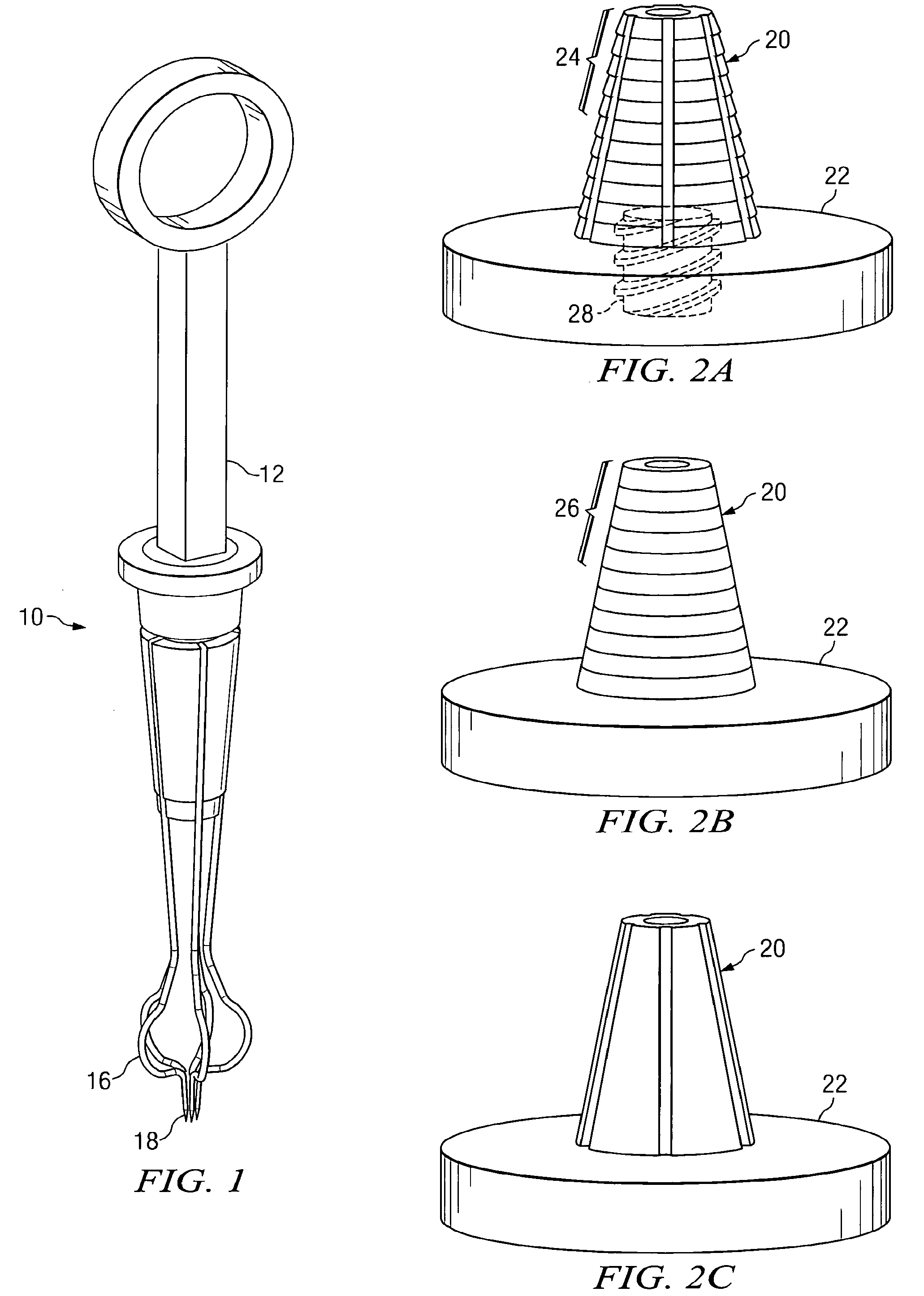
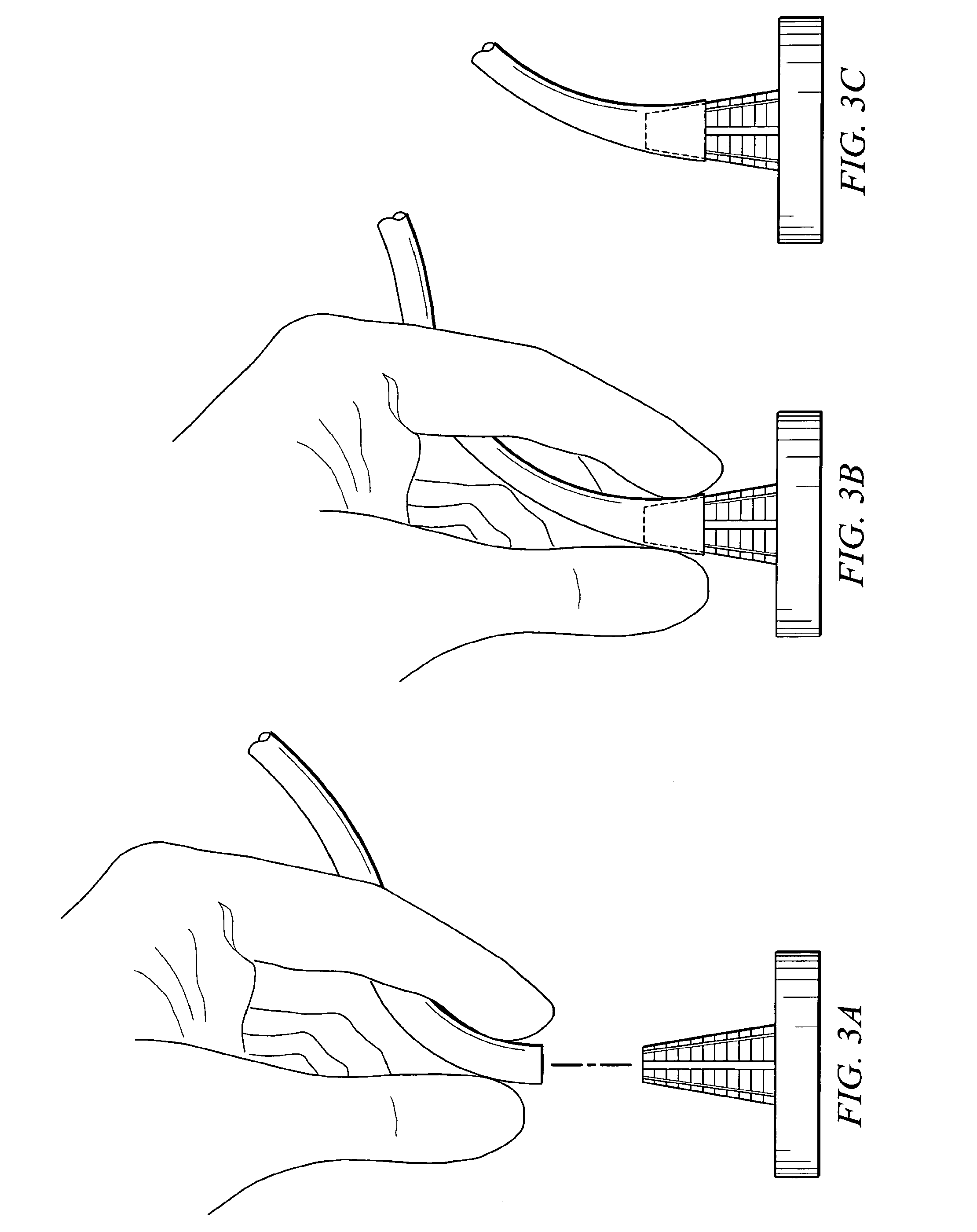
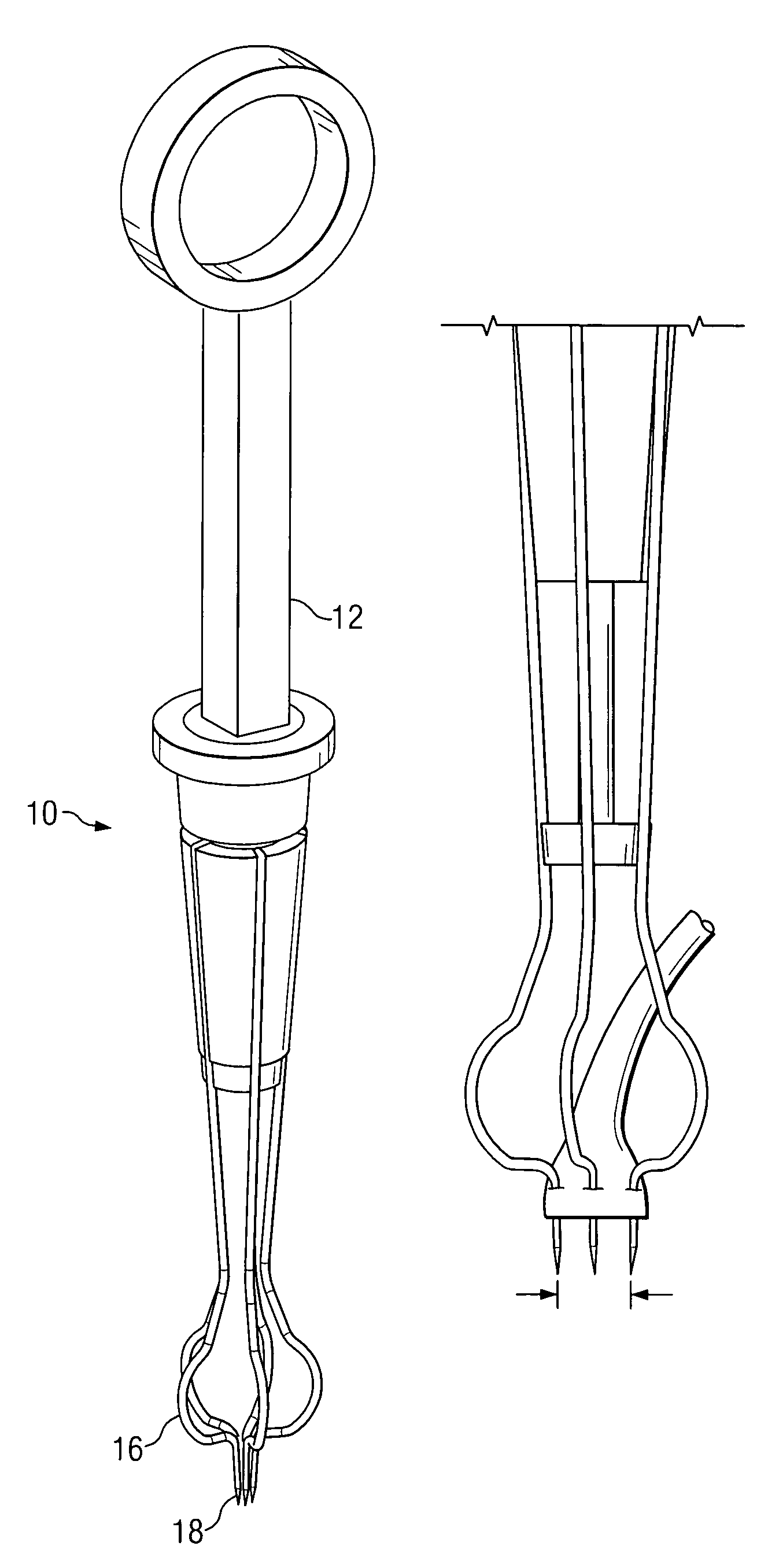
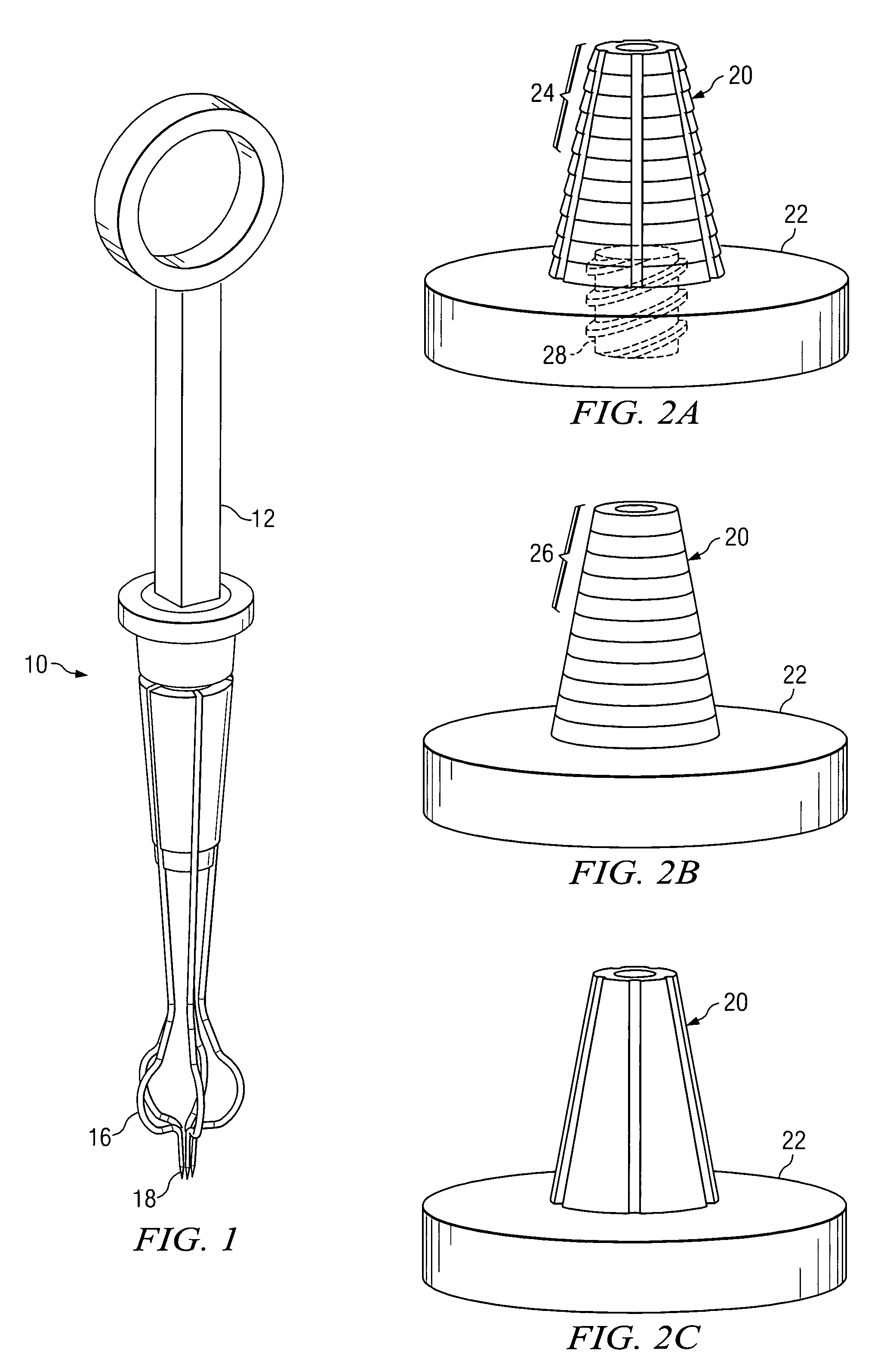
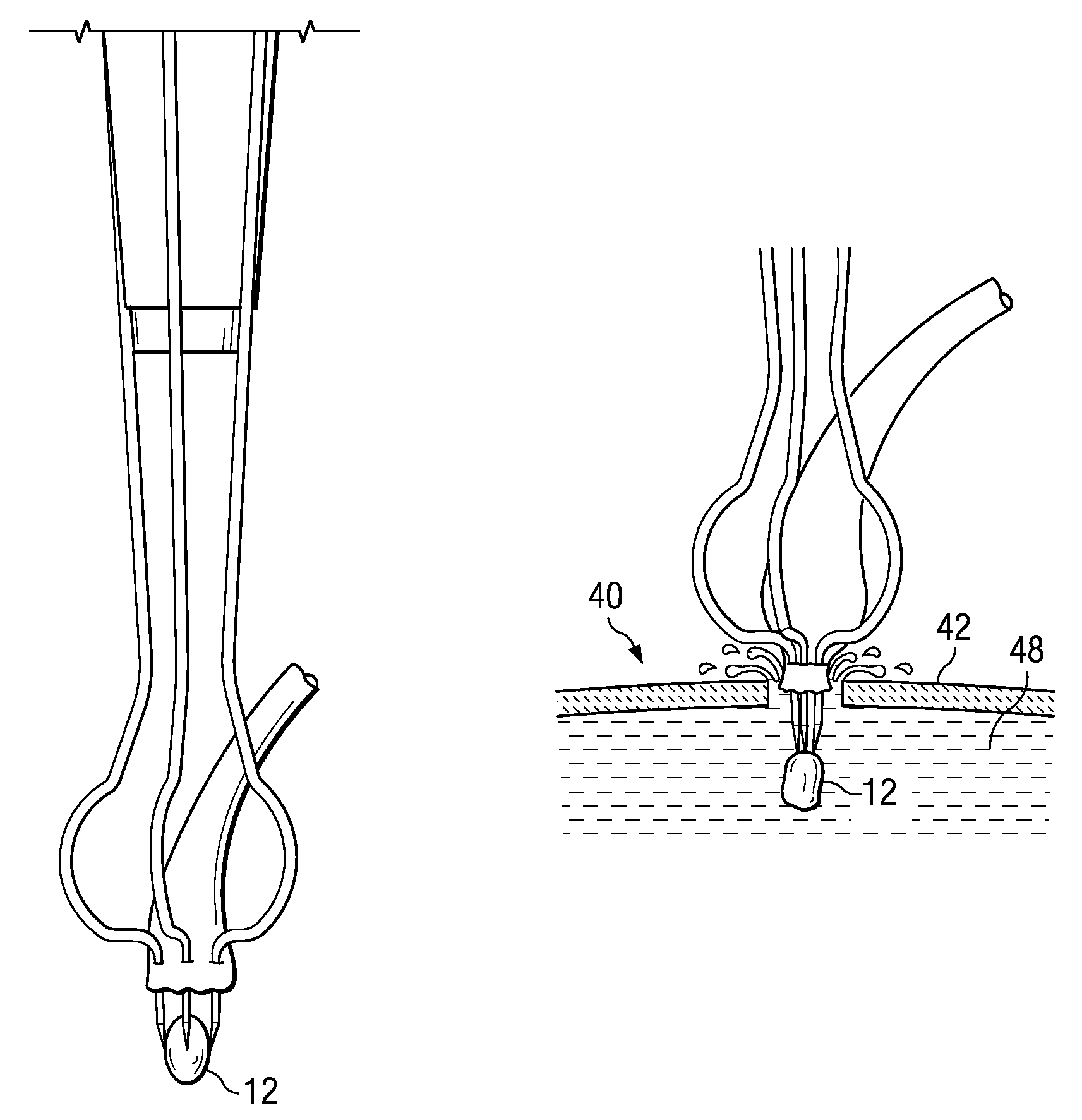
System and method for attaching a vein, an artery, or a tube in a vascular environment
InactiveUS20060212066A1Eliminates and greatly reduces disadvantageEliminates and greatly reduces and problemSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesVeinCatheter
A device for assisting in a vascular procedure is provided that includes a handle and one or more legs that are operable to move in response to a force being applied to the handle. The legs are operable to extend and to contract in order to manipulate a conduit. In a more particular embodiment, the device can be used in conjunction with a stand operable to receive the conduit such that the conduit can be removed from the stand by the device. The stand may include one or more graduations that indicate the size of the conduit once it is positioned on the stand.
Owner:CASTLEWOOD SURGICAL
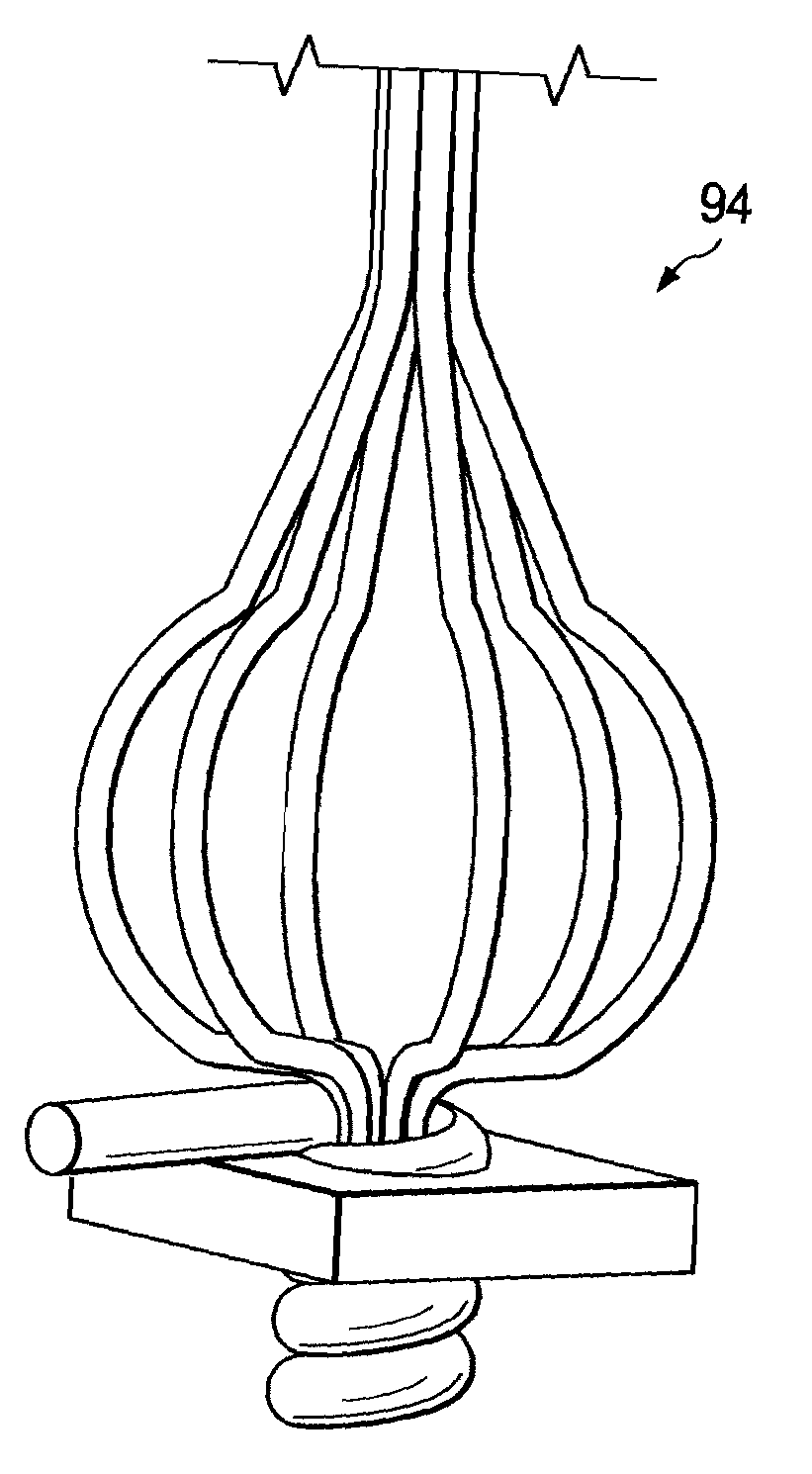
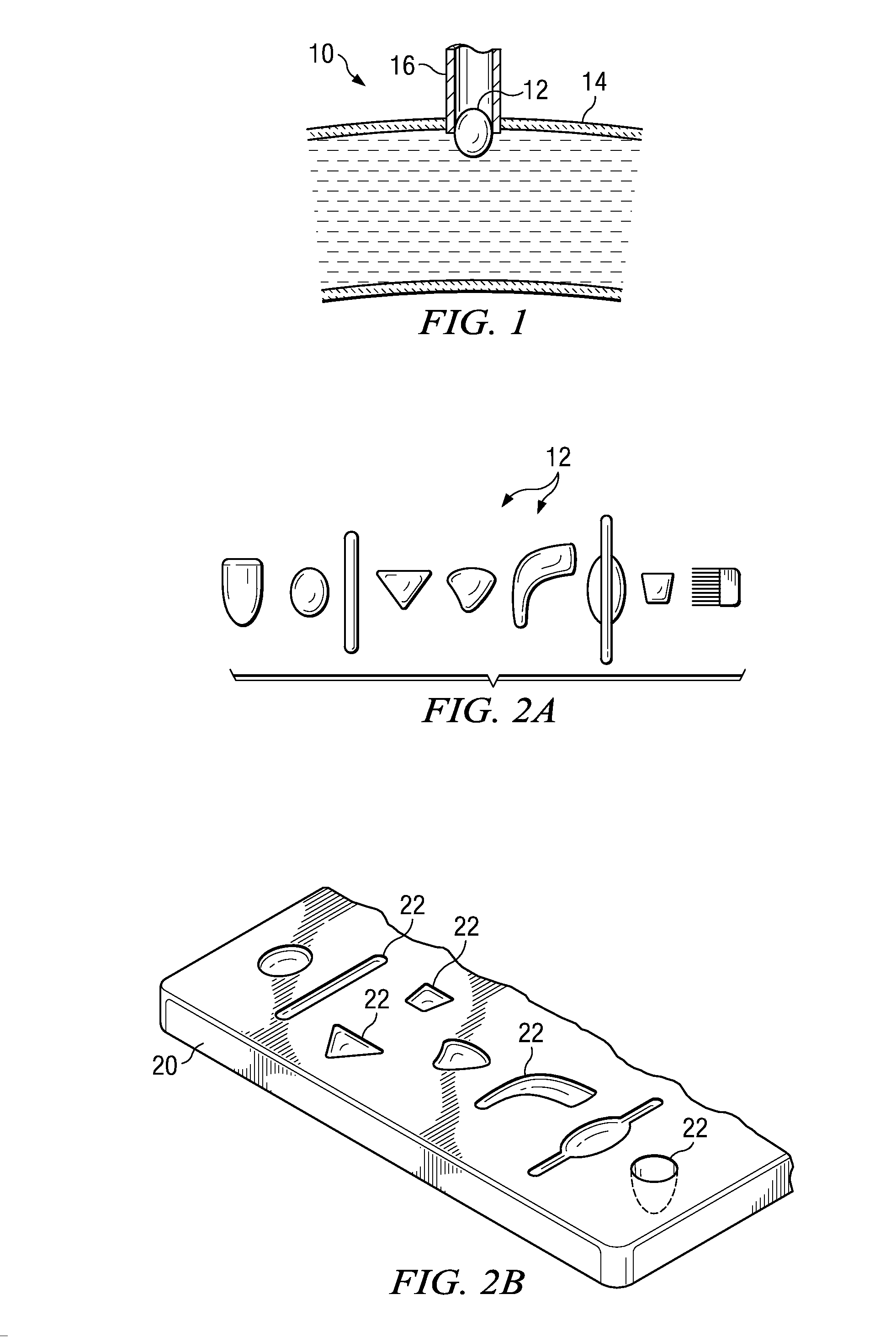
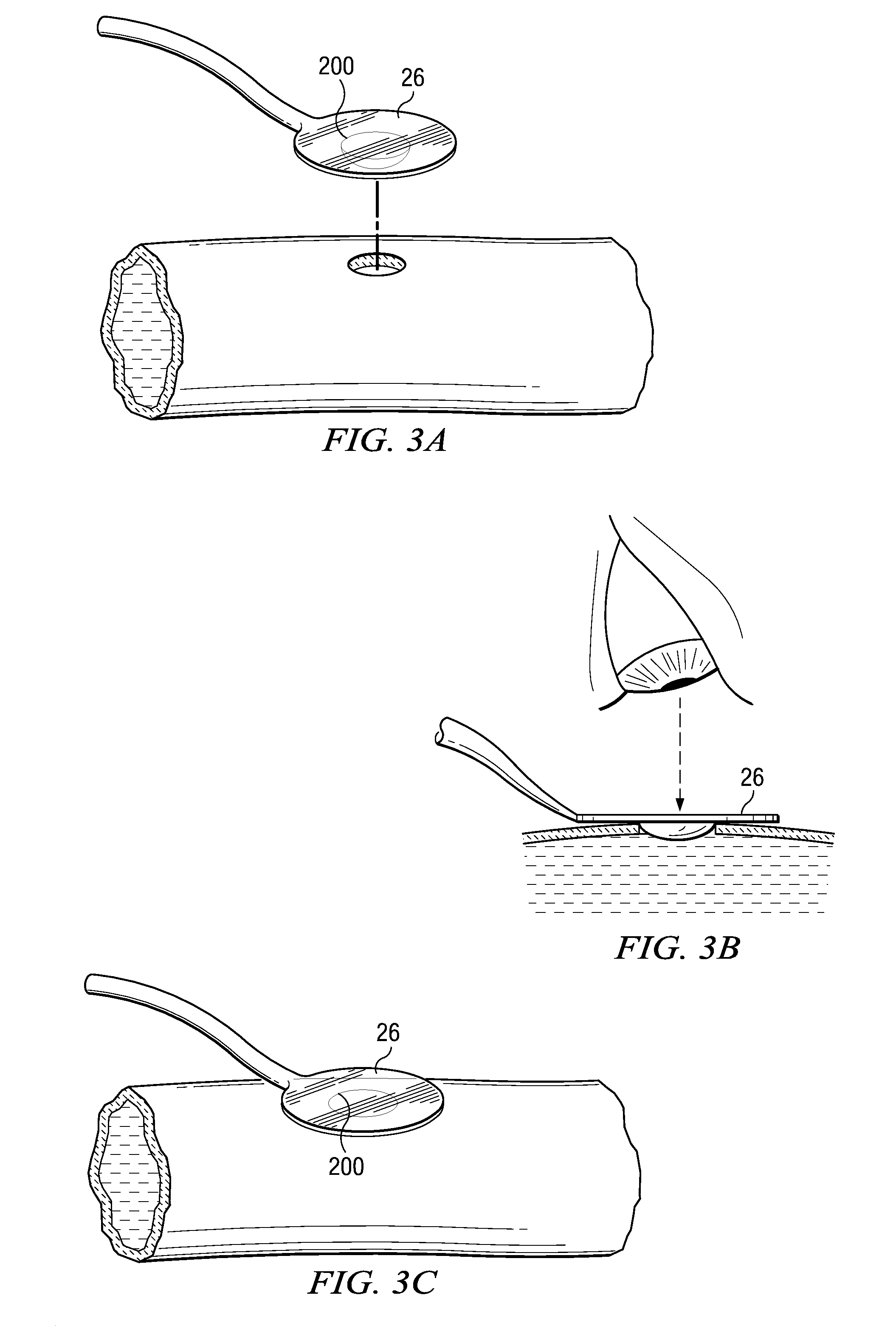
System and Method for Providing a Coil Element in a Vascular Environment
InactiveUS20090093825A1Eliminates and greatly reduces disadvantageEliminates and greatly reduces and problemSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsBlood vesselTissue surface
An apparatus is provided in one example and includes a coil that receives one or more tips of an instrument. An interior of the coil interfaces with the tips and the coil and the tips can be positioned together in a hole cut in a surface of tissue. The coil operable to be unwound such that a portion of the tips is revealed as the coil is unwound. In more specific embodiments, the instrument is a vein-holding apparatus, and the tips hold a vein to be sutured at the hole. In still other embodiments, the coil is helically shaped and includes a tail element that is pulled to unwind the coil incrementally. The tail element can be pulled until the tips are exposed from the coil.
Owner:CASTLEWOOD SURGICAL
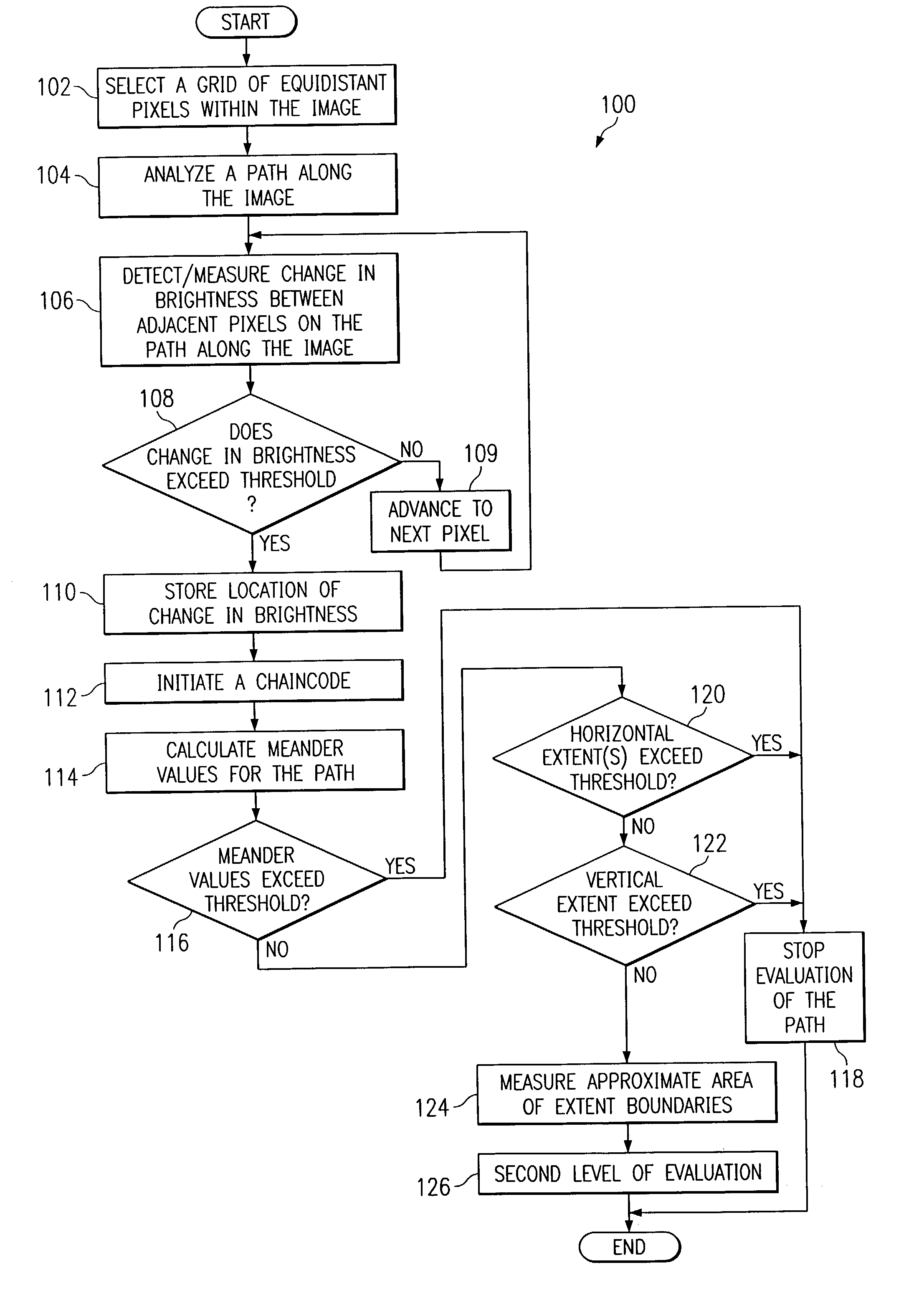
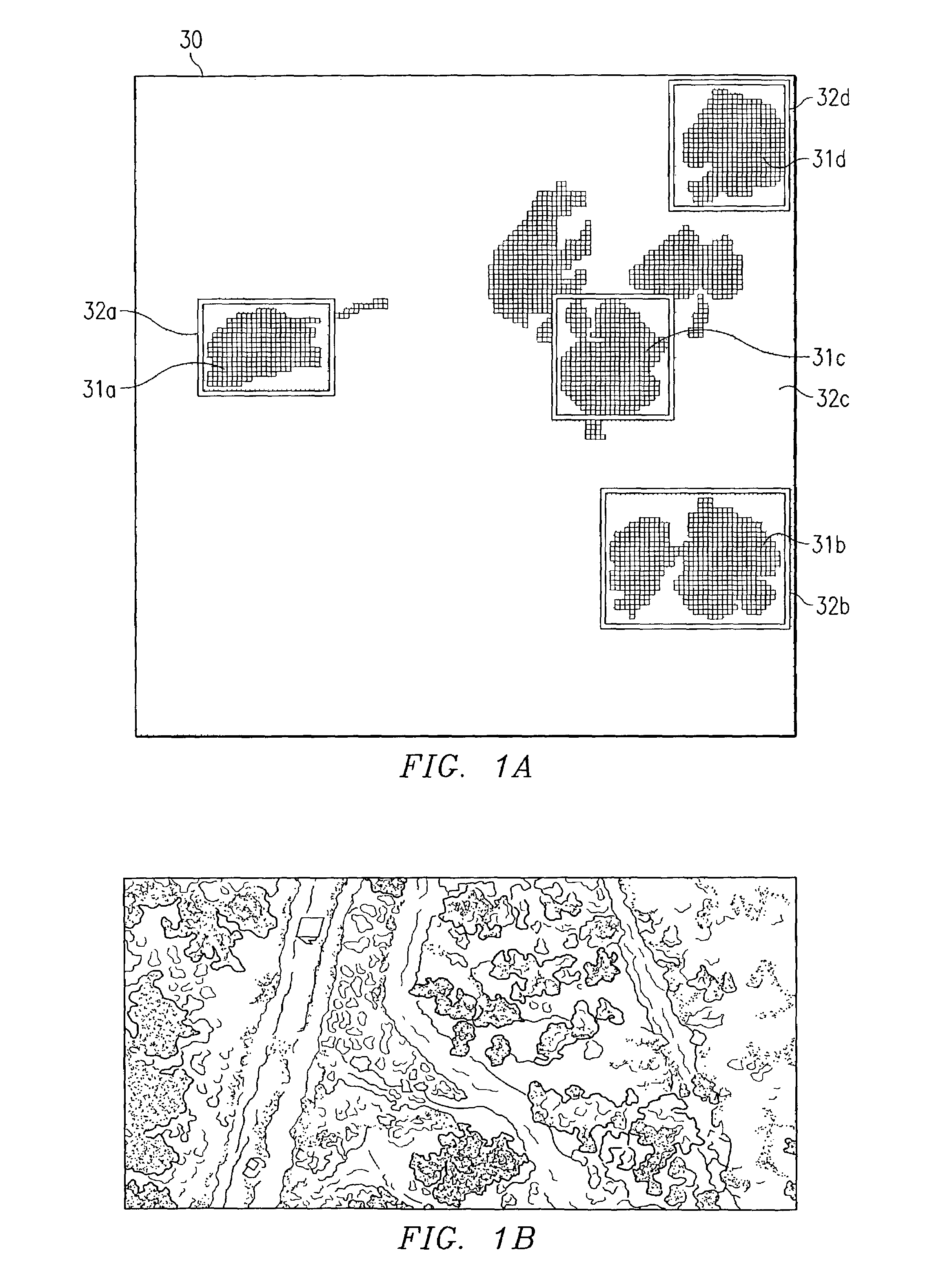
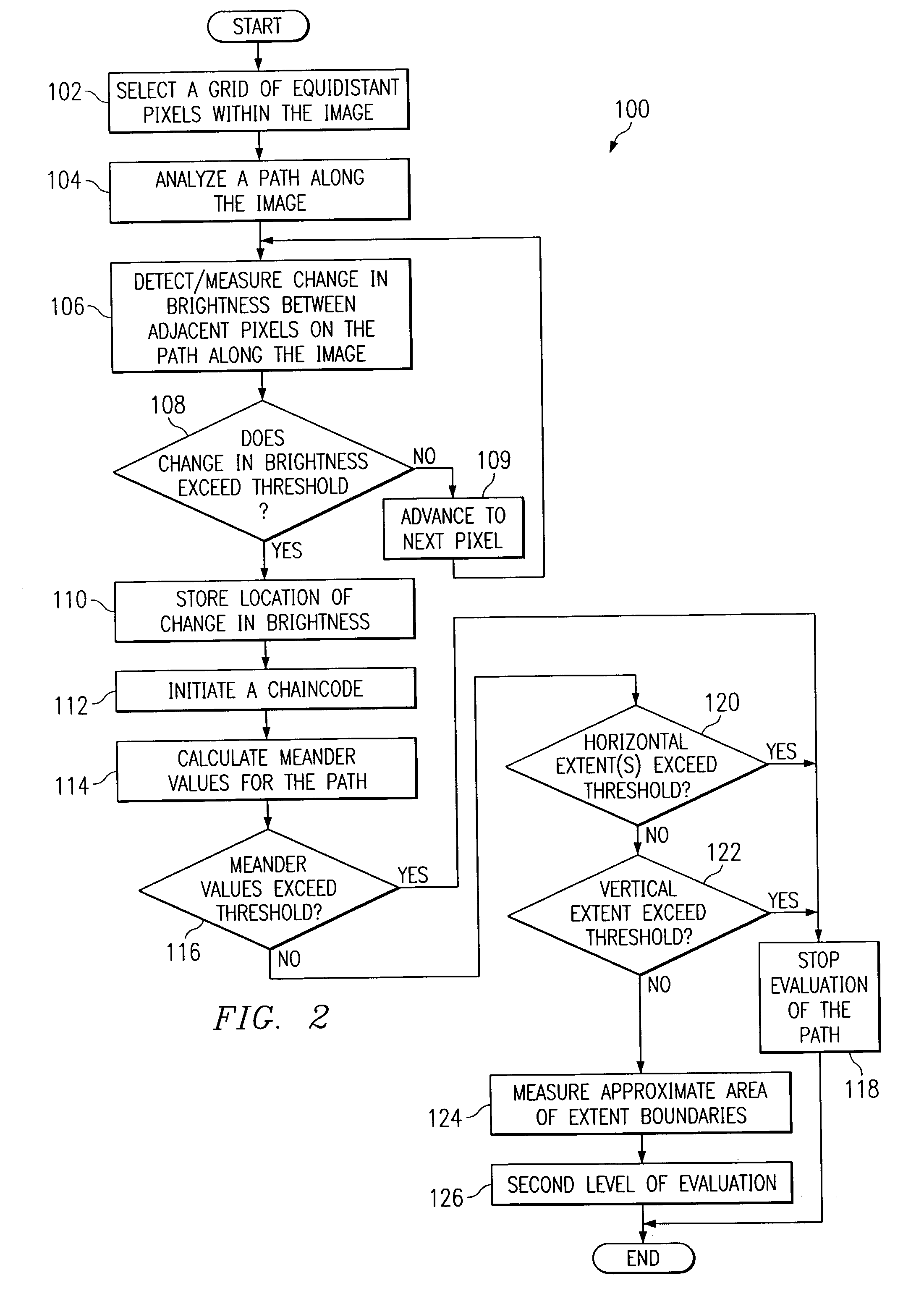
System and method for image analysis using a chaincode
ActiveUS7146057B2Eliminates and greatly reduces disadvantageEliminates and greatly reduces and problemImage enhancementImage analysisImaging analysisStraight segment
The present invention includes a method for analyzing an image to screen for target candidates wherein an edge-follower detects straight segments within a plurality of longer edges and detects also from the longer edges, contours that go around areas that are the right size. The invention also contemplates starting the edge-follower from seeds on the image and terminating the edge-following process if the edge meanders too much to ever become an acceptable contour. In accordance with another embodiment, the straight segments can be further screened by measuring the gradient direction and then noting the deviation from the mean of those direction values. The highly straight edges thus found, in confluence with each other, or near a correct size contour define likely candidates.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
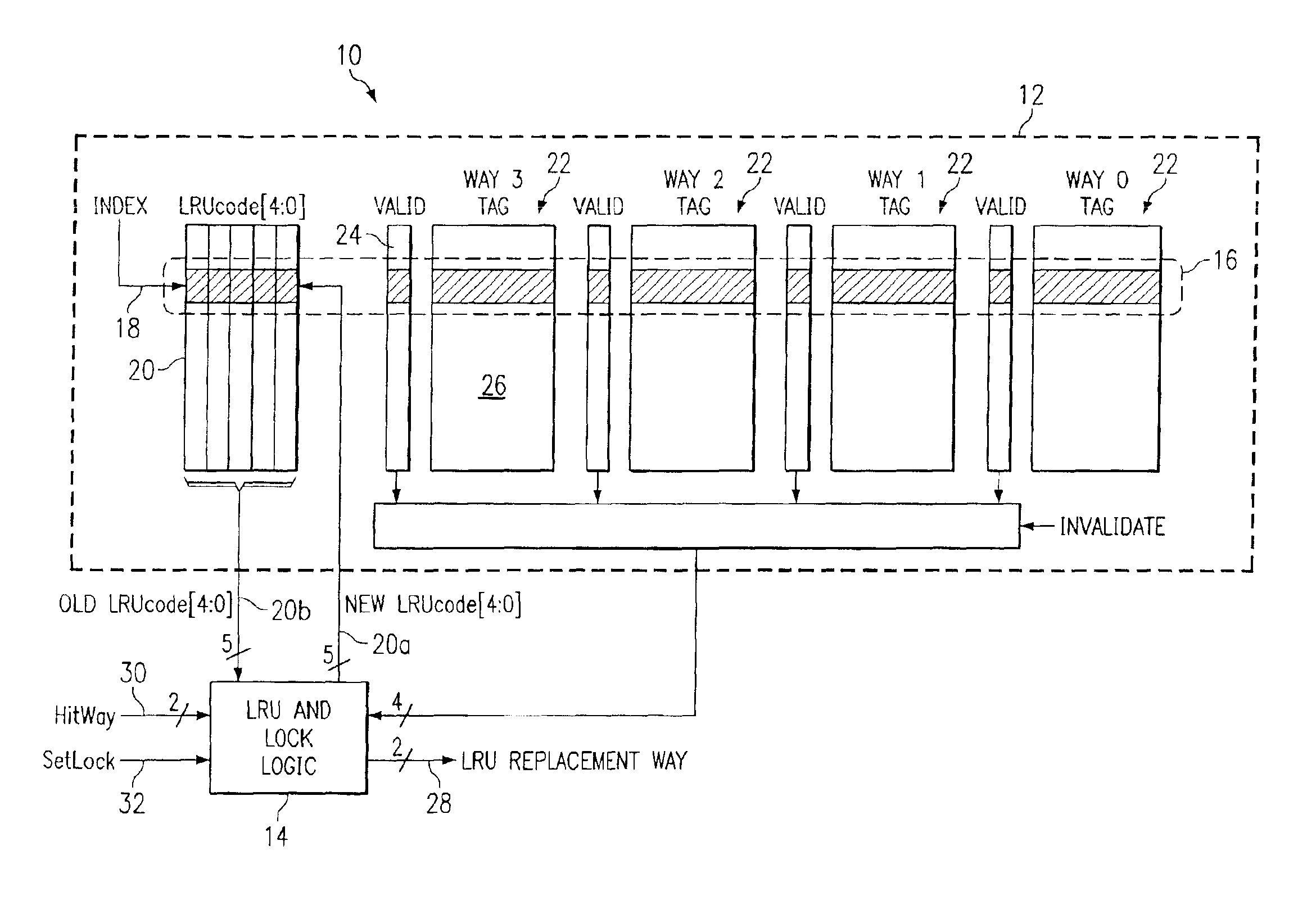
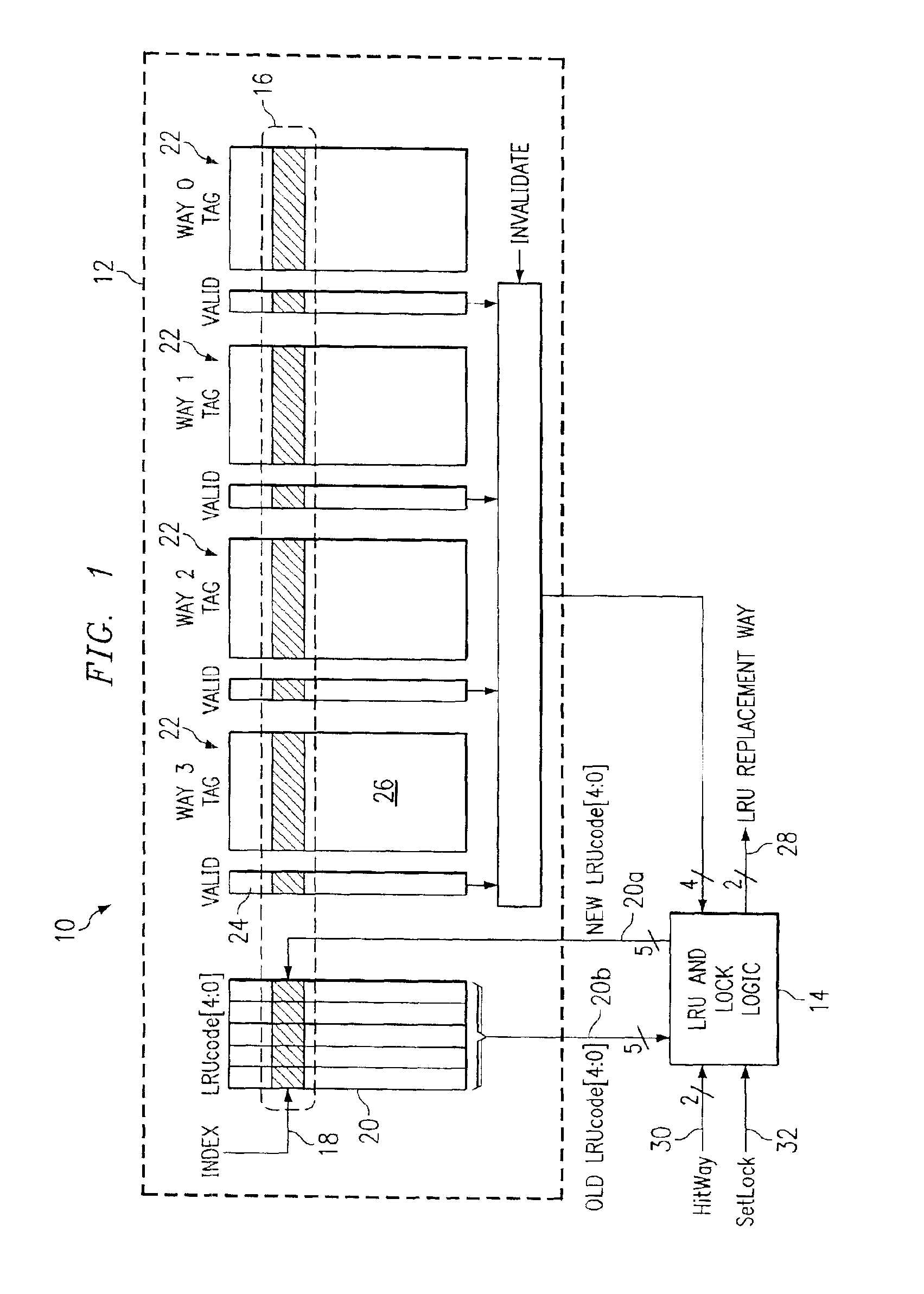
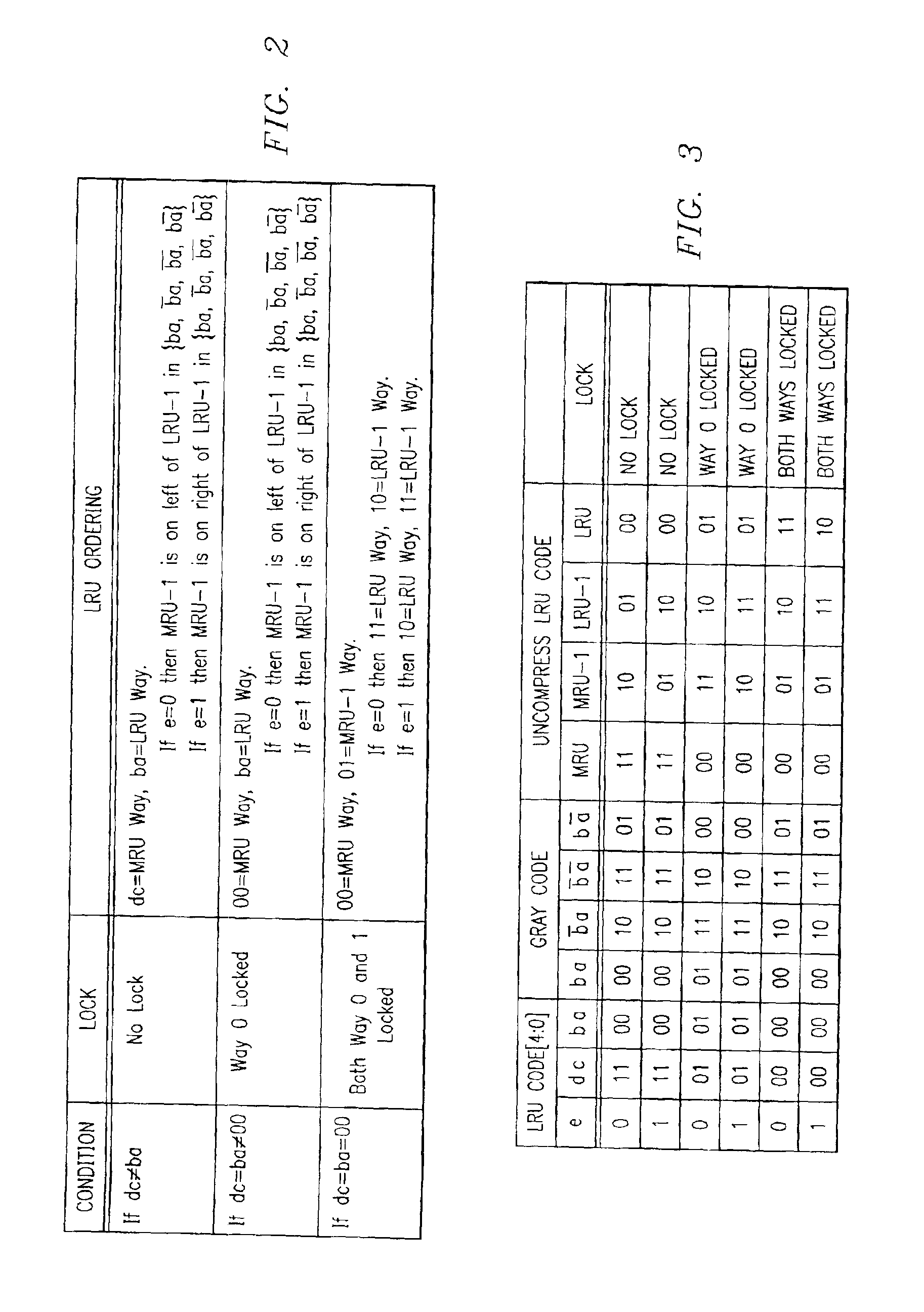
Cache memory for identifying locked and least recently used storage locations
InactiveUS6904501B1Eliminates and greatly reduces disadvantageEliminates and greatly reduces and problemMemory adressing/allocation/relocationParallel computingData memory
A cache memory includes a plurality of data memory blocks and a code memory block. Each data memory block has a plurality of storage locations and has a particular storage location identified by a same index value. The code memory block has a plurality of code values with a particular code value being associated with the same index value. The particular code value is operable to identify which ones of the particular storage locations associated with the same index value are locked to prevent alteration of contents therein. The particular code value is also operable to identify which particular storage location has been most recently used and which particular storage location has been least recently used of the particular storage locations associated with the same index value.
Owner:RPX CORP +1
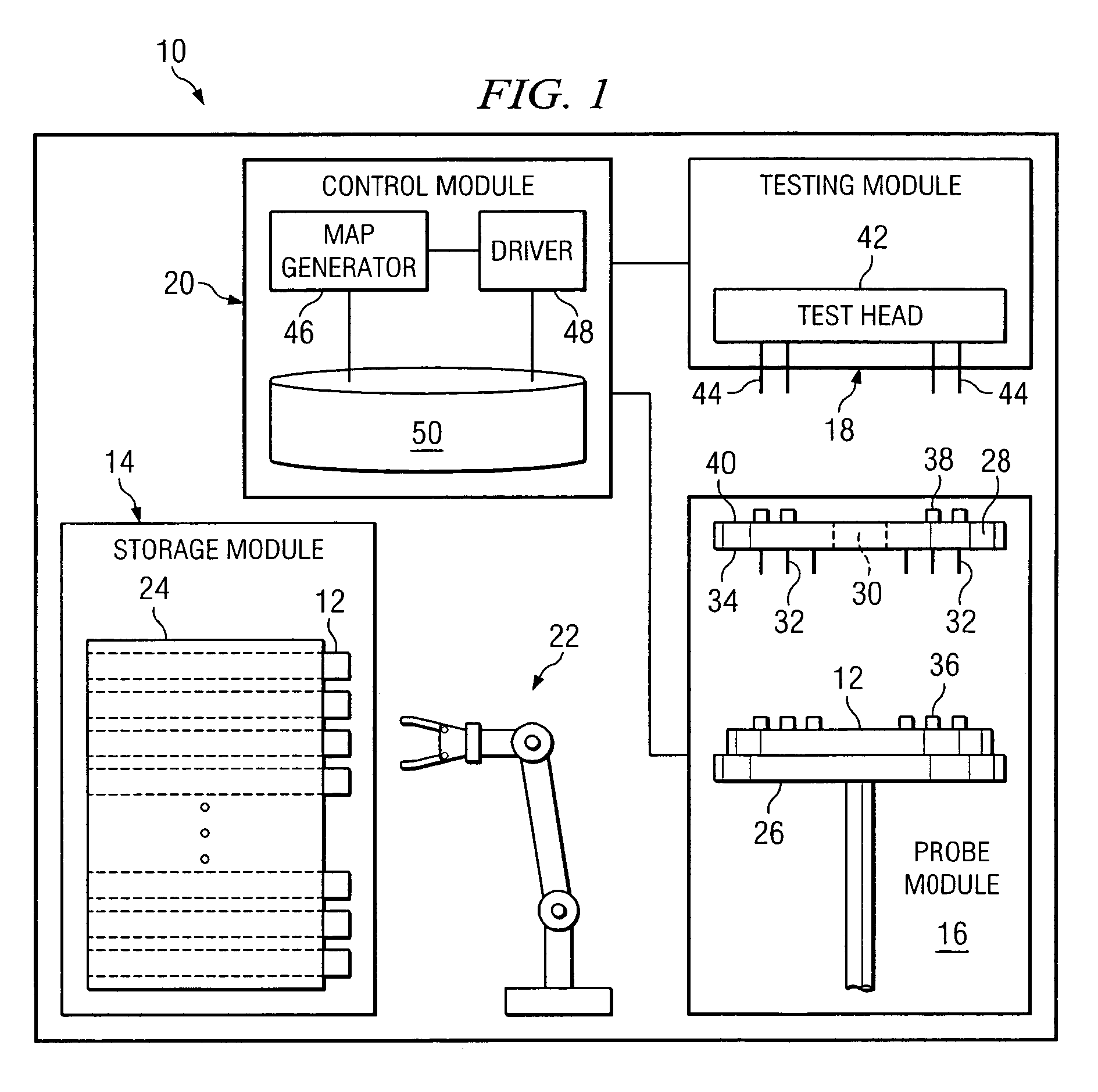
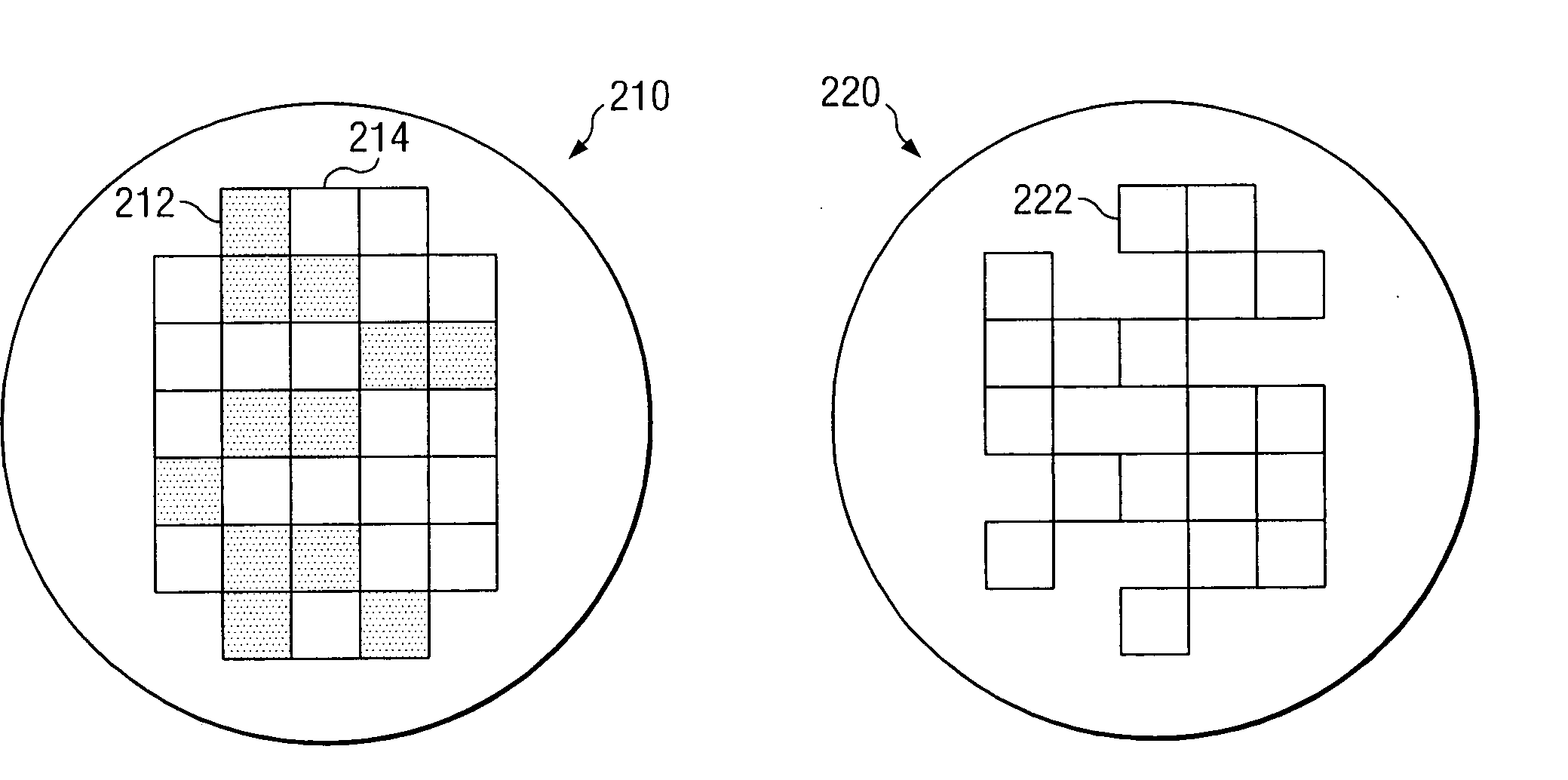
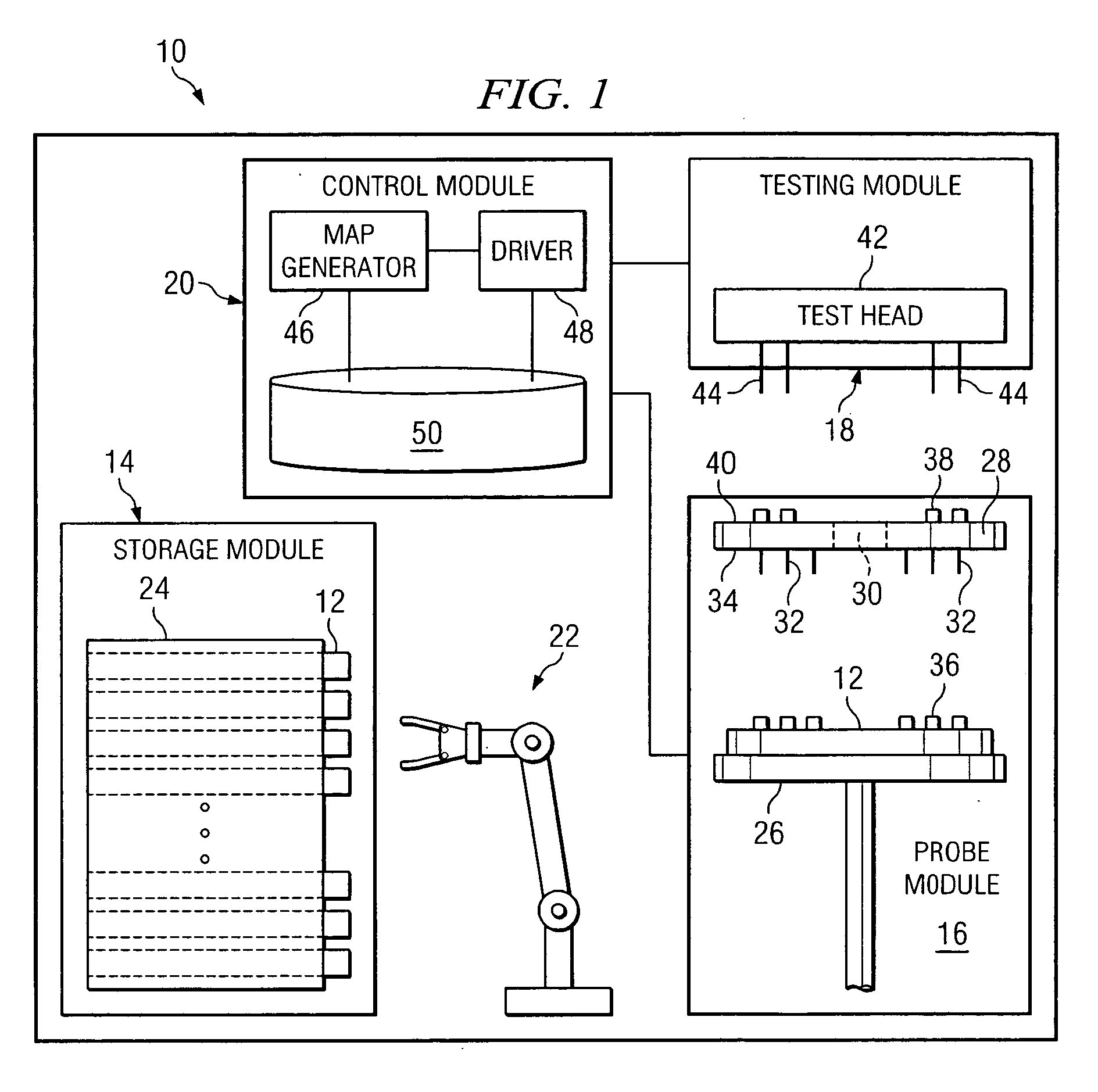
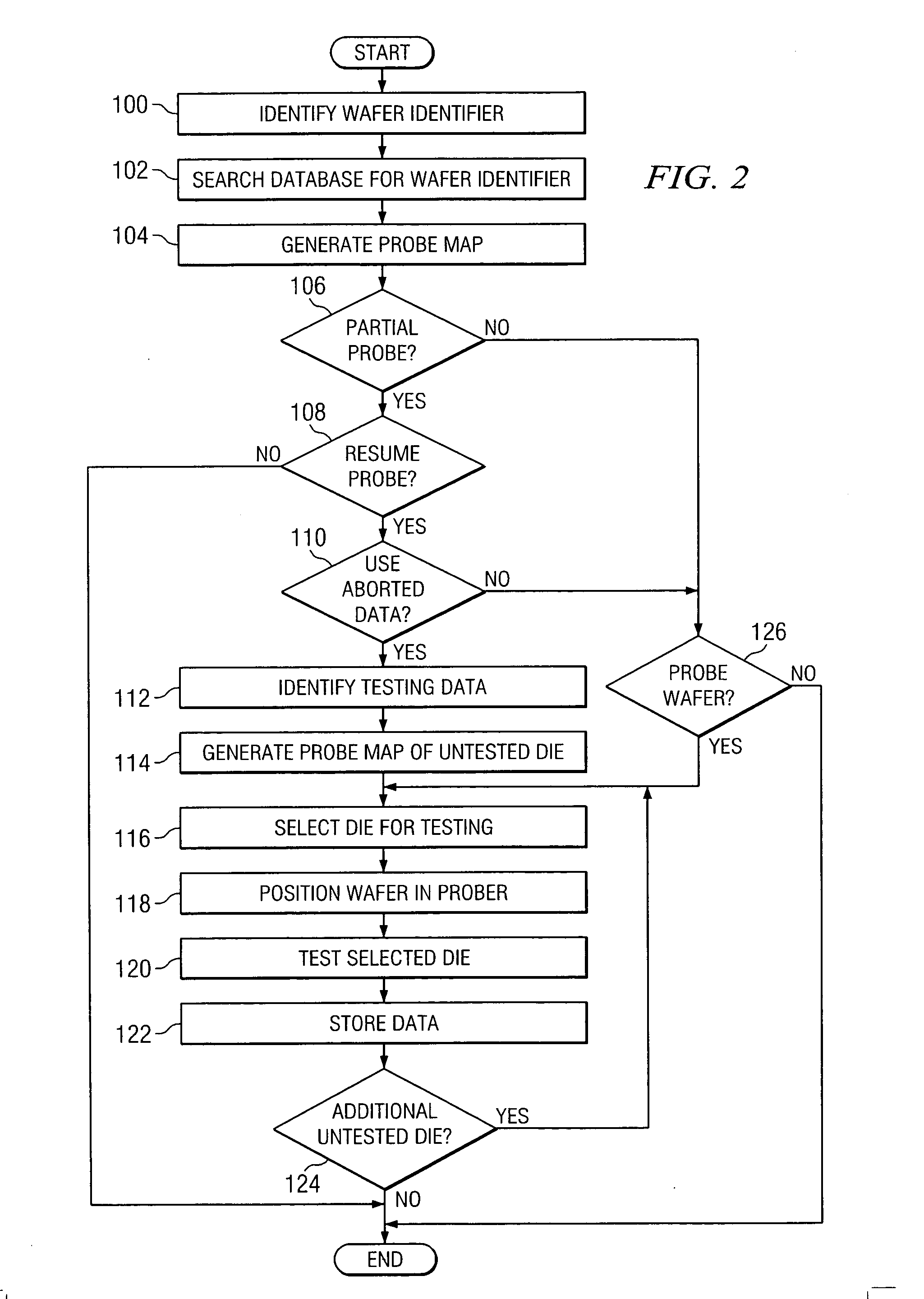
System and method for the probing of a wafer
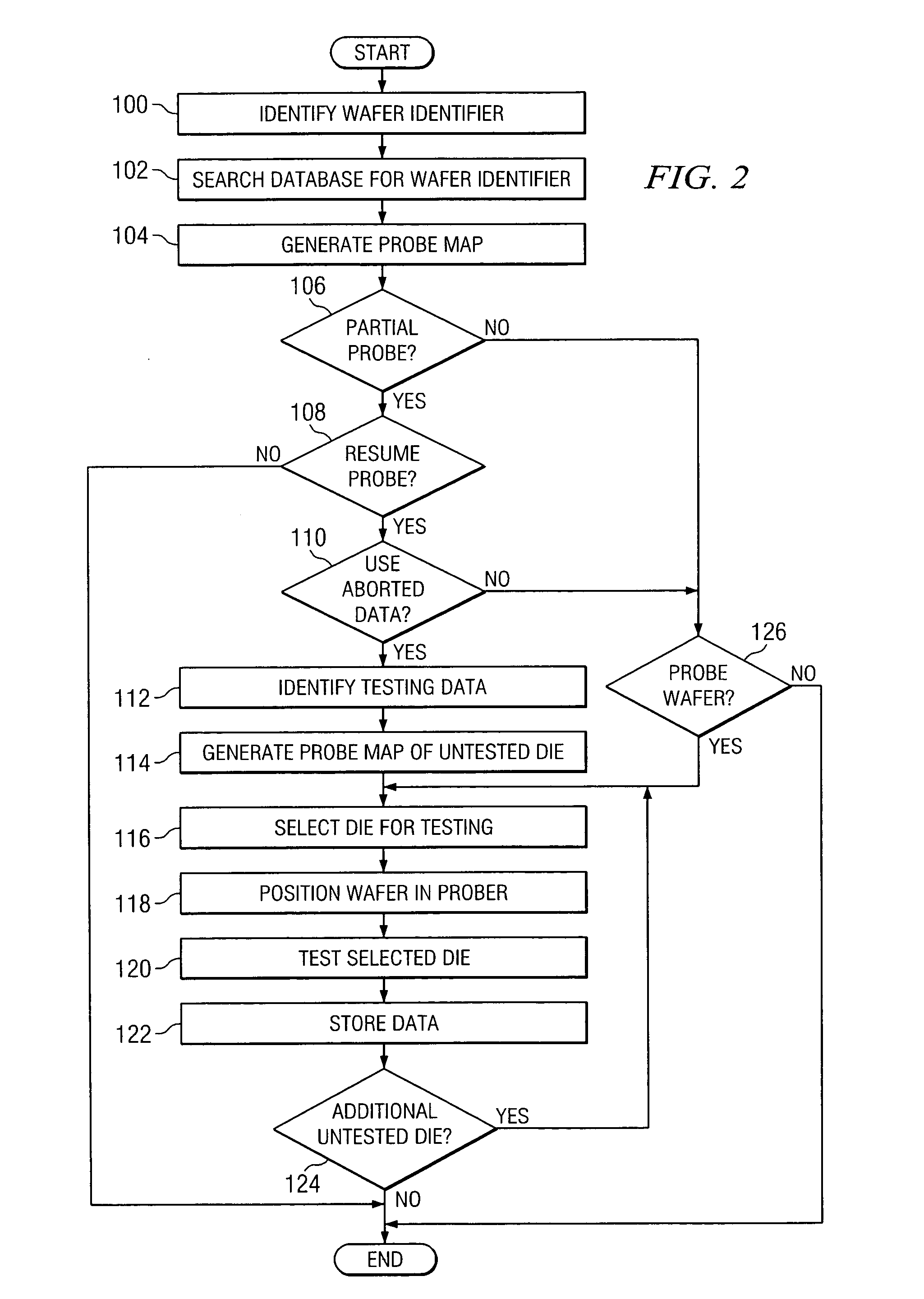
ActiveUS7148716B2Eliminates and greatly reduces disadvantageEliminates and greatly reduces and problemAutomated test systemsIndividual semiconductor device testingData setComputer science
According to one embodiment of the invention, a method for resuming the probing of a wafer includes identifying a data set associated with a wafer. The data set identifies at least one unprobed die supported on the surface of the wafer. The method also includes determining that the data set associated with the wafer is useable and generating a probe map of the wafer from the data set. The probe map identifies a physical position associated with each unprobed die supported on the surface of the wafer. The probe map and one or more probe commands are communicated to a probe module to drive the probe module in resuming the probe of the wafer.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
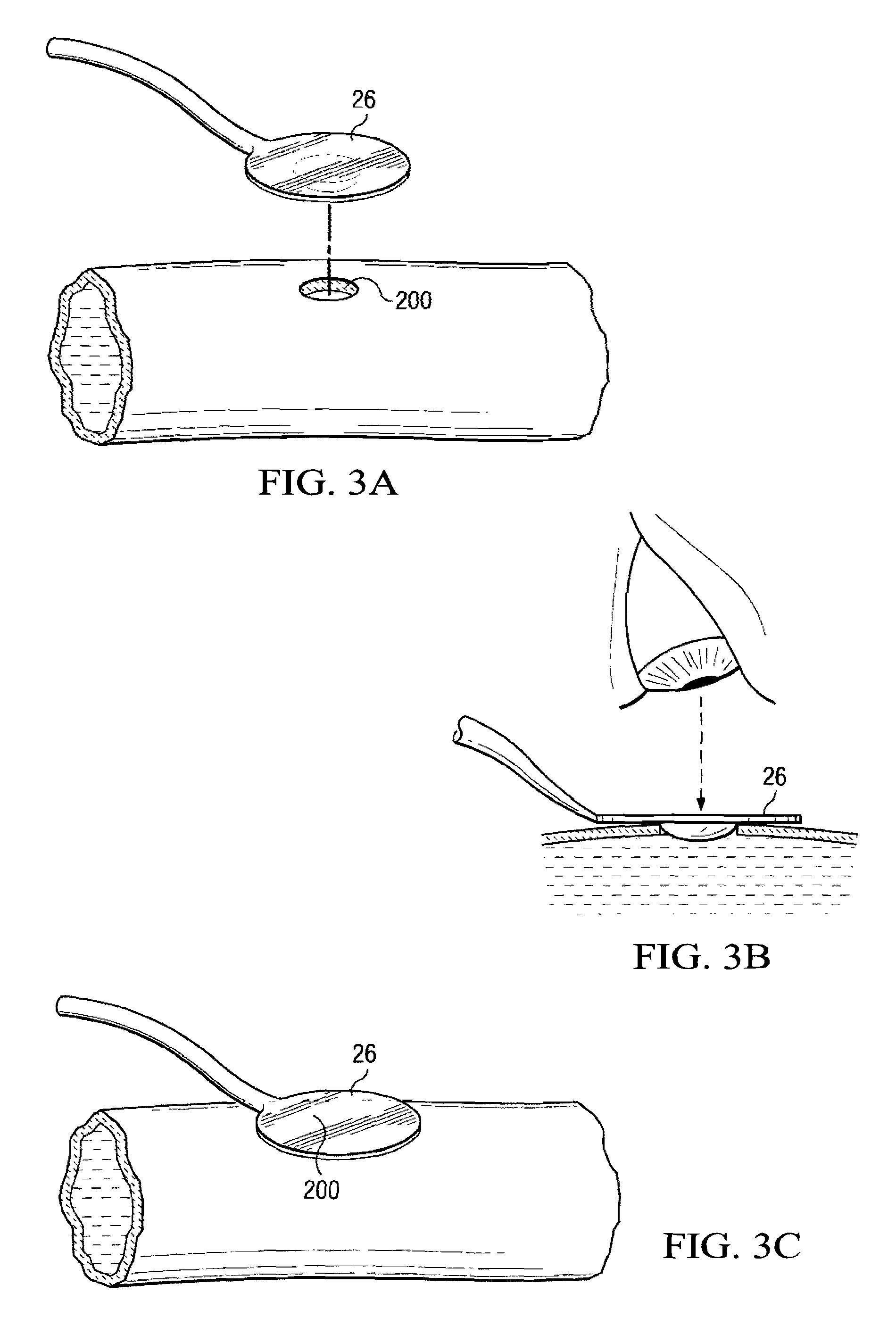
System and Method for Providing an Obturator for Enhanced Directional Capabilities in a Vascular Environment
InactiveUS20090054841A1Eliminates and greatly reduces disadvantageEliminates and greatly reduces and problemDiagnosticsInfusion syringesDry iceCombined use
An apparatus for assisting in a vascular procedure includes an obturator operable to be mounted on a medical device to guide the medical device into a targeted region, whereby the obturator is substantially blunt such that it exhibits a snag-resistant property. In alternative embodiments, the apparatus includes an interface element operable to be used in conjunction with the obturator and to engage an interface of the targeted region such that pressure is maintained within the targeted region. The interface element includes a convex portion that operates to seat the interface element at a selected location. The interface element is substantially transparent and includes a magnification element that magnifies materials underlying the interface element. In other embodiments, the apparatus includes a tray operable to provide a mold for forming the obturator, which may comprise a gas, water, sugar, clotted blood, a gelatinous material, a protein, a saline solution, or dry-ice.
Owner:CASTLEWOOD SURGICAL
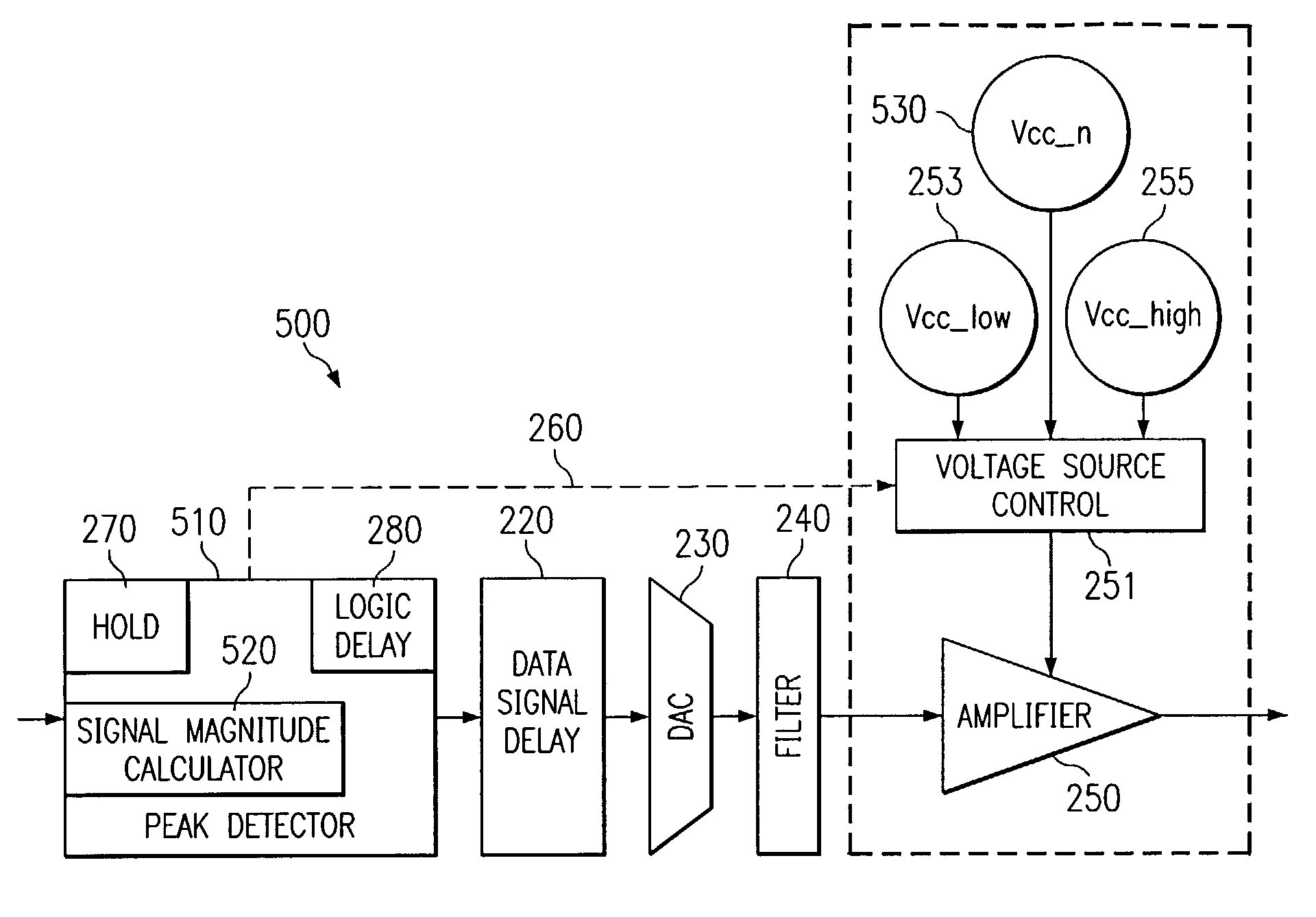
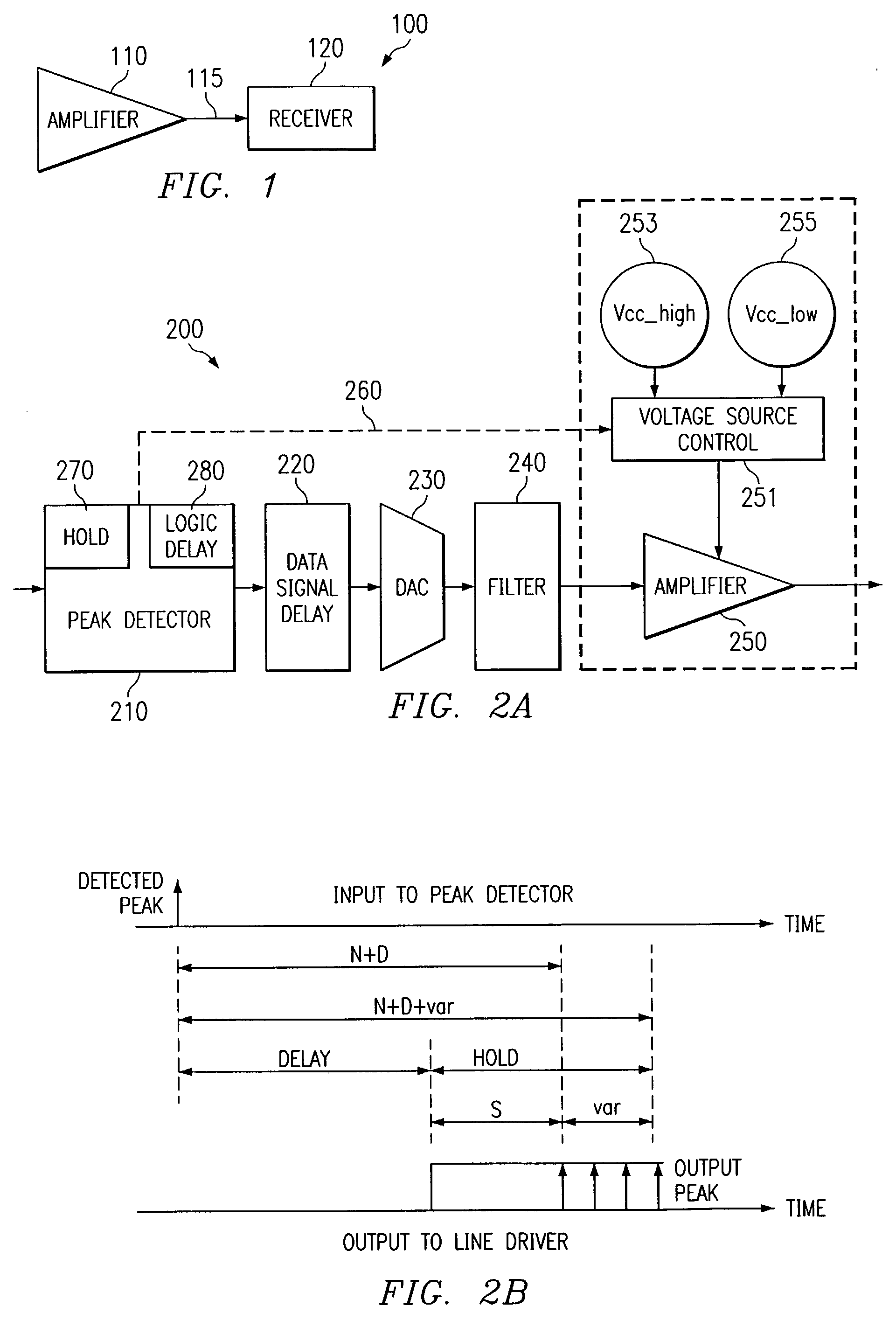
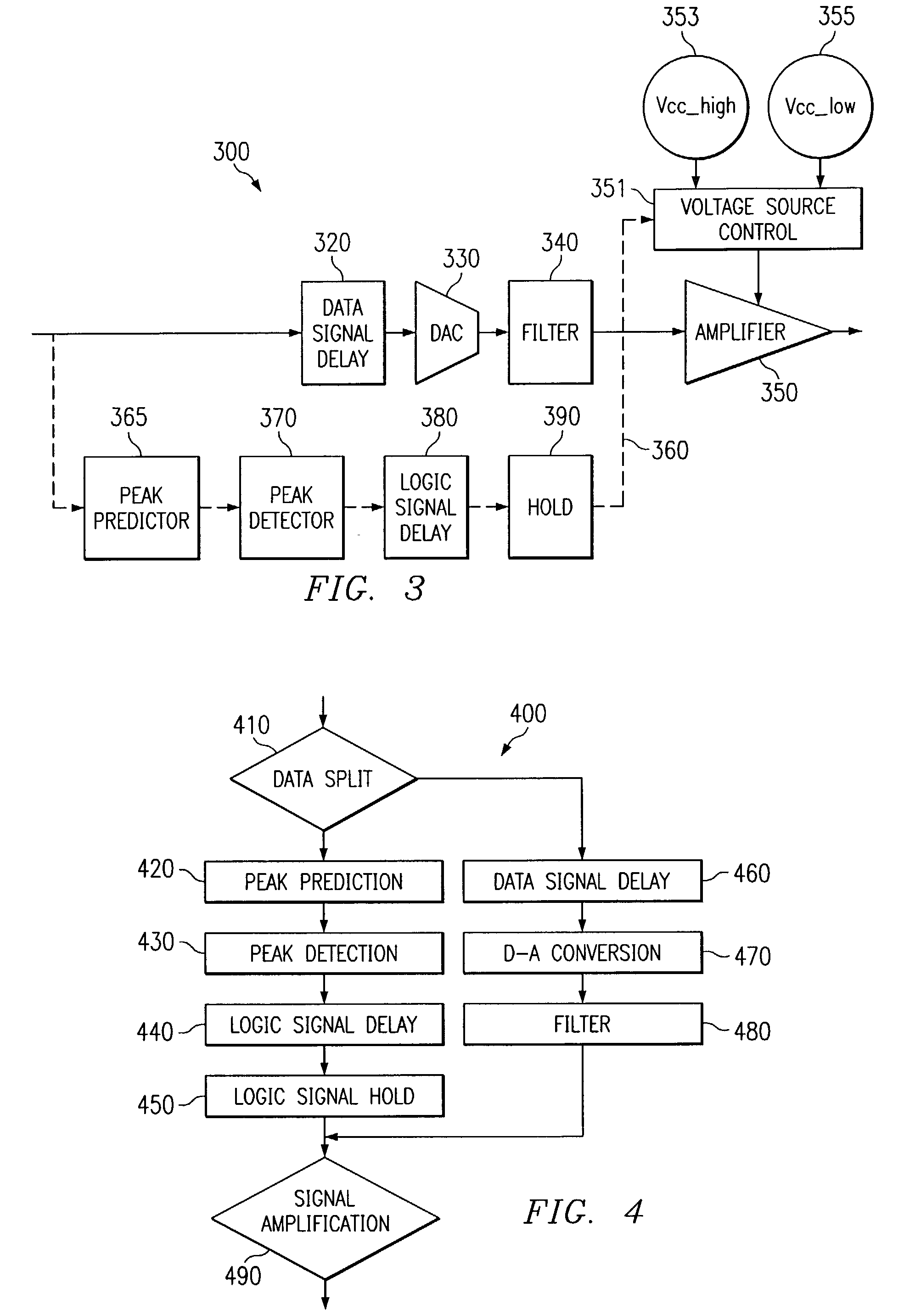
Line Driver apparatus
ActiveUS7130415B2Preventing signal clippingEliminates and greatly reduces disadvantageInterconnection arrangementsGain controlAudio power amplifierTime delays
A line driver apparatus includes a peak detector operable to receive a data signal and output a first logic signal when the data signal is below a threshold value and output one of a plurality of alternate logic signals when the data signal exceeds the threshold value. The peak detector includes a signal magnitude calculator operable to calculate an amount by which the data signal exceeds the threshold value. The line driver apparatus also includes an amplifier operable to receive a filtered analog data signal and one of a time-delayed first logic signal and one of a time-delayed alternate logic signal, wherein the amplifier operates at a first voltage level upon receiving the time-delayed first logic signal, and the amplifier operates at a voltage level that is increasing toward one of an alternate voltage level upon receiving the time-delayed second logic signal.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
System and method for attaching a vein, an artery, or a tube in a vascular environment
InactiveUS20090018555A1Eliminates and greatly reduces disadvantageEliminates and greatly reduces and problemSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesVeinEngineering
Owner:CASTLEWOOD SURGICAL
System and method for attaching a vein, an artery, or a tube in a vascular environment
InactiveUS7763037B2Eliminates and greatly reduces disadvantageEliminates and greatly reduces and problemSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesVeinCatheter
Owner:CASTLEWOOD SURGICAL
Method for device addressing using SNMP community string-based routing
ActiveUS7167473B1Sure easyEliminates and greatly reduces disadvantageTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationComputer network
A method of addressing a data packet includes receiving the data packet and creating a packet header for the data packet. The method also includes providing routing information in a community string format in the packet header and communicating the packet header and data packet to a gateway, wherein the gateway is operable to forward the data packet to a destination uniquely defined by the routing information.
Owner:GENBAND US LLC
System and method for the probing of a wafer
ActiveUS20050275421A1Eliminates and greatly reduces disadvantageEliminates and greatly reduces and problemAutomated test systemsIndividual semiconductor device testingData setComputer science
According to one embodiment of the invention, a method for resuming the probing of a wafer includes identifying a data set associated with a wafer. The data set identifies at least one unprobed die supported on the surface of the wafer. The method also includes determining that the data set associated with the wafer is useable and generating a probe map of the wafer from the data set. The probe map identifies a physical position associated with each unprobed die supported on the surface of the wafer. The probe map and one or more probe commands are communicated to a probe module to drive the probe module in resuming the probe of the wafer.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
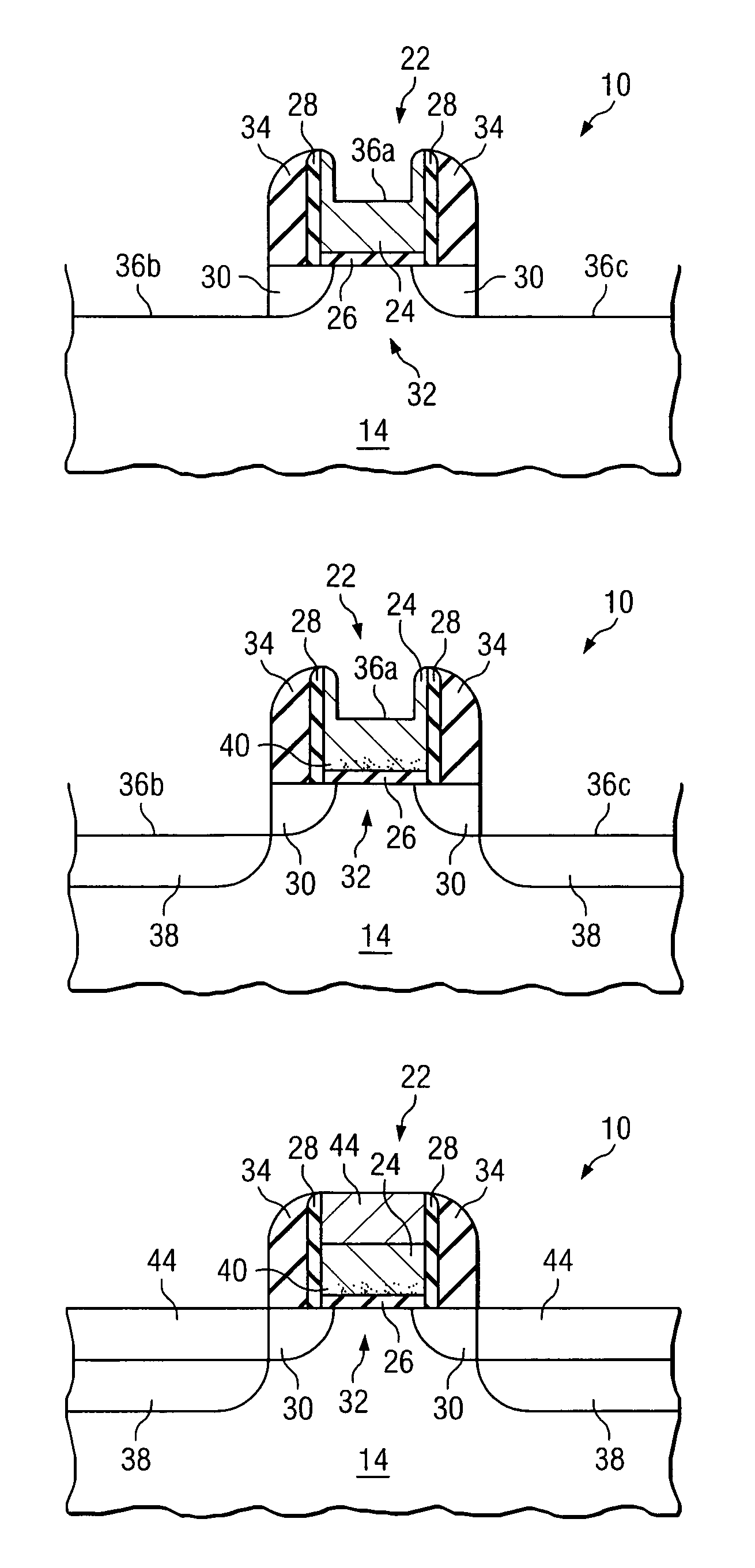
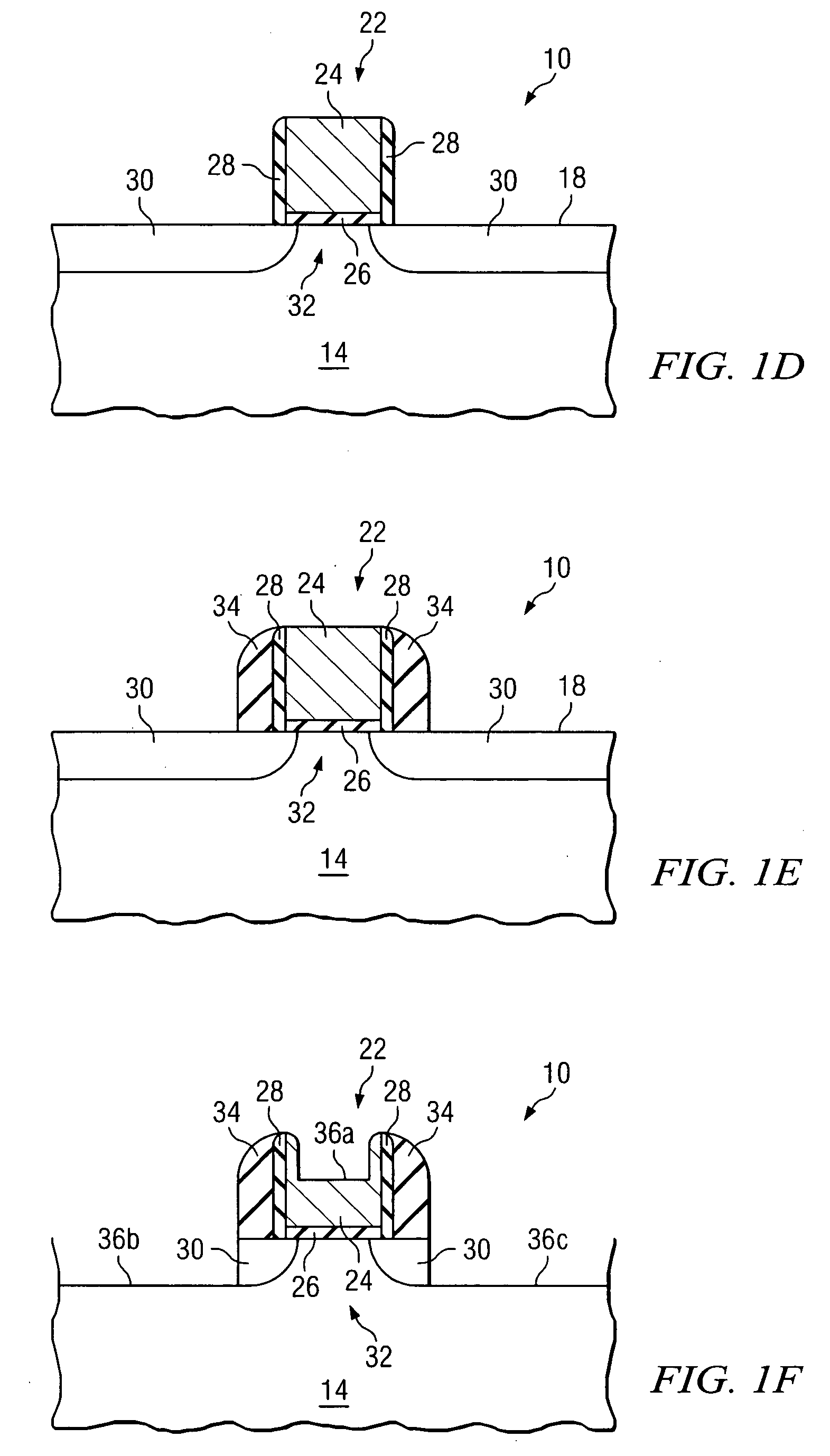
System and method for improved dopant profiles in CMOS transistors
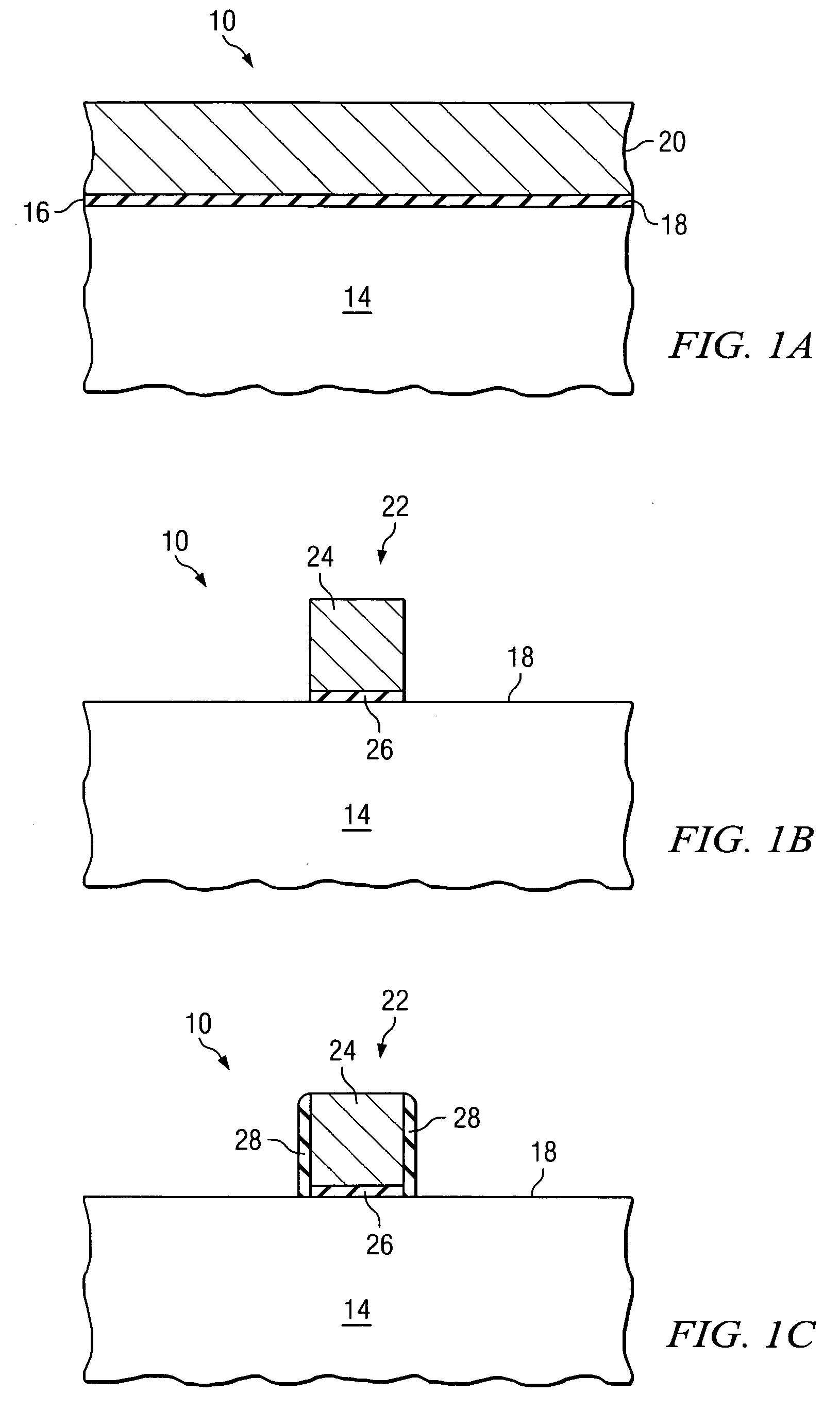
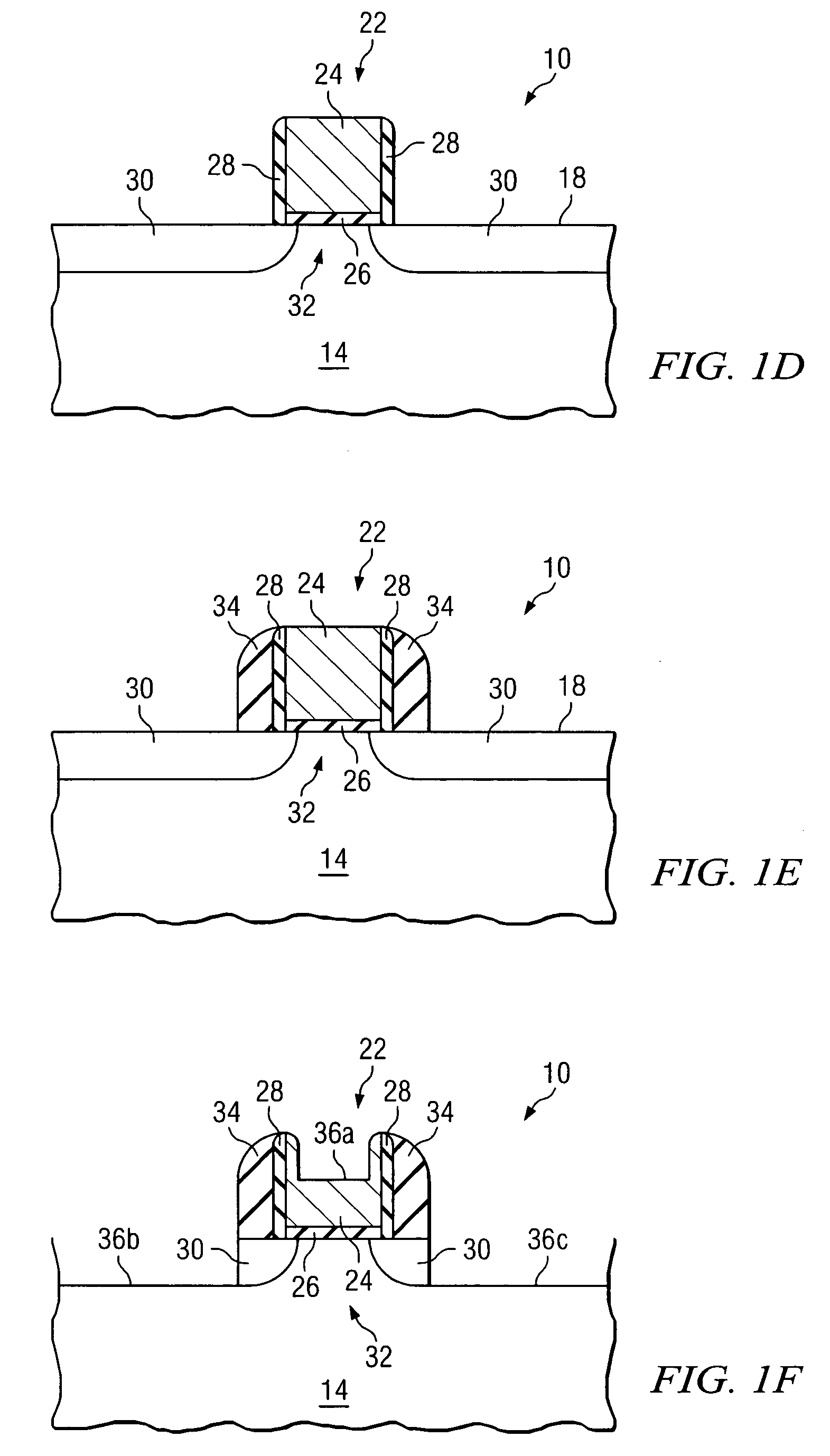
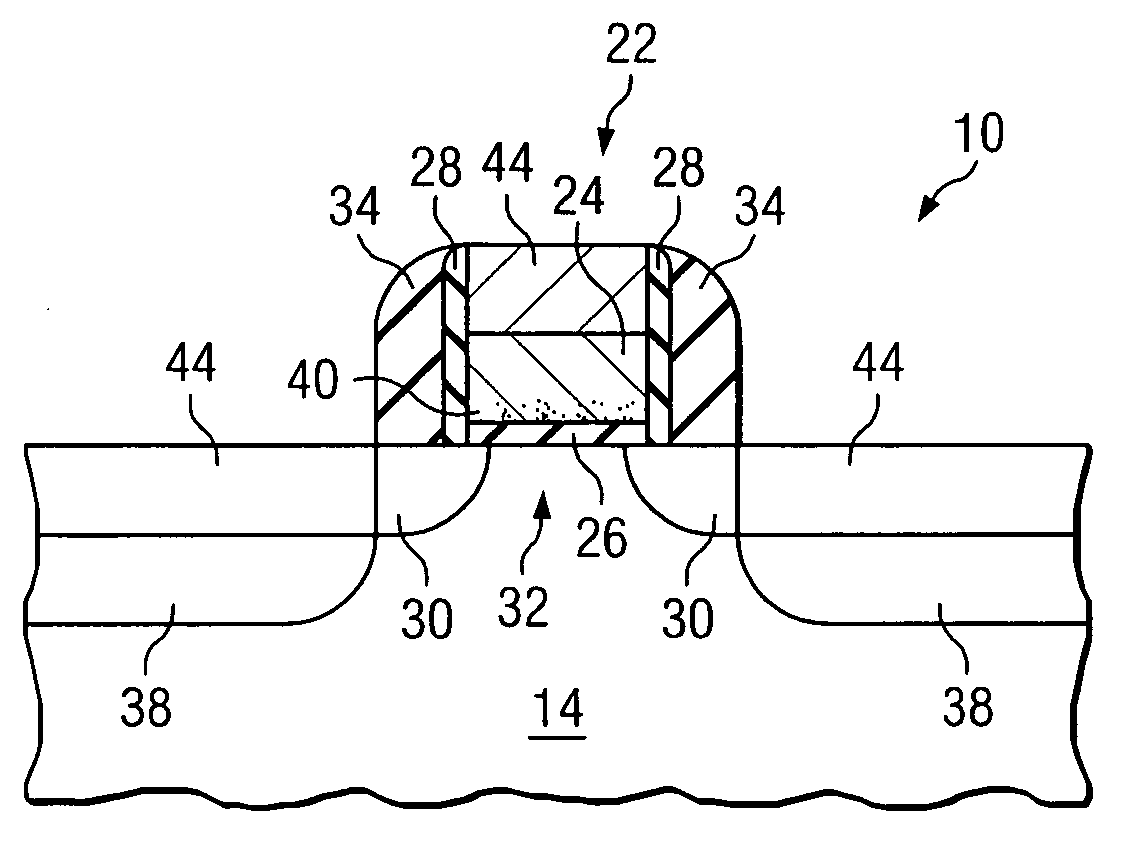
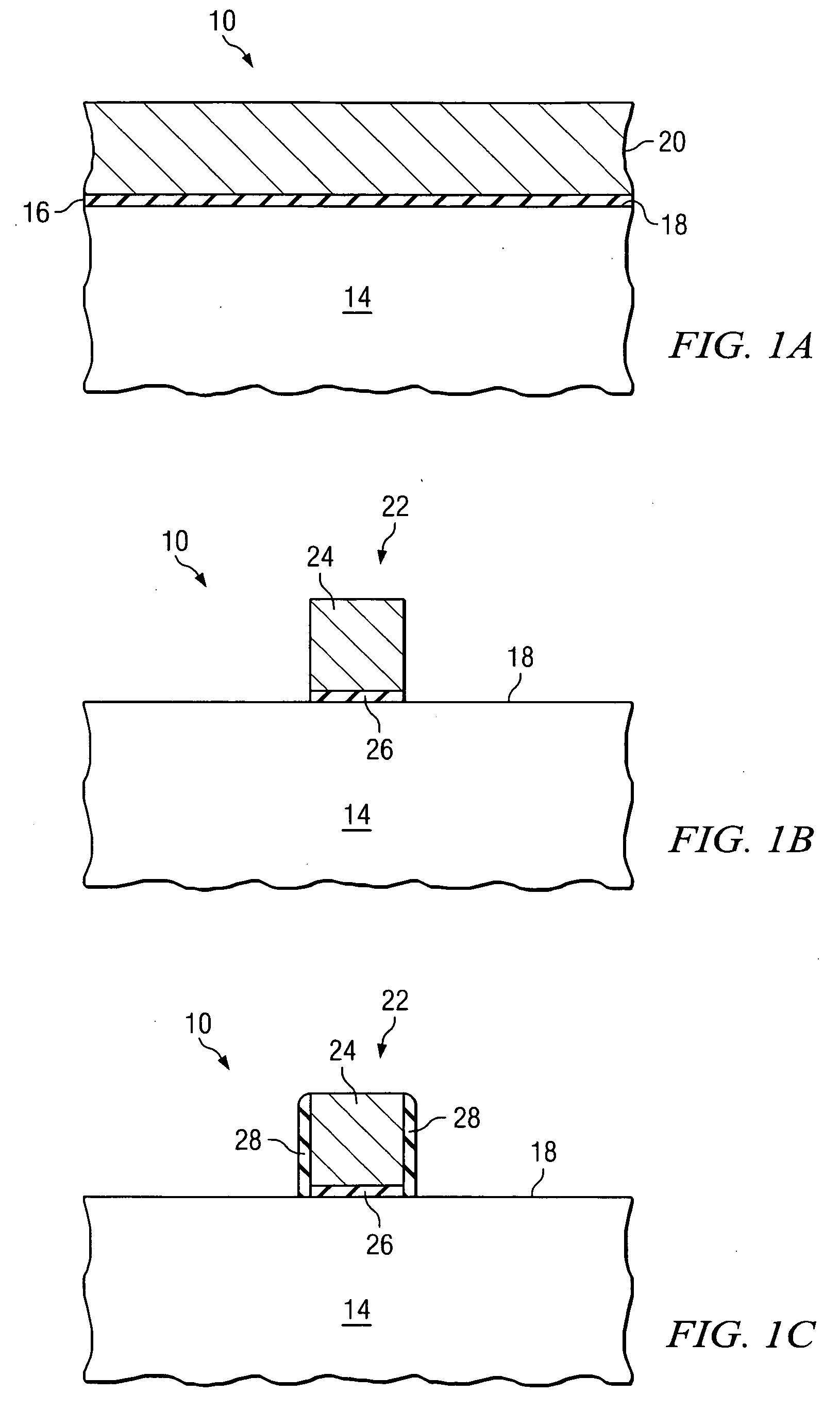
ActiveUS7118977B2Eliminates and greatly reduces disadvantageEliminates and greatly reduces and problemTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantCMOS
According to one embodiment of the present invention, a method of forming a semiconductor device includes forming a gate stack on an outer surface of a semiconductor body. First and second sidewall bodies are formed on opposing sides of the gate stack. A first recess is formed in an outer surface of the gate stack, and a first dopant is implanted into the gate stack after the first recess is formed. The first dopant diffuses inwardly from the outer surface of the gate stack that defines the first recess. The first dopant diffuses toward an interface between the gate stack and the semiconductor body. The first recess increases the concentration of the first dopant at the interface.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
System and method for improved dopant profiles in CMOS transistors
ActiveUS20060099744A1Eliminates and greatly reduces disadvantageEliminates and greatly reduces and problemTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantCMOS
According to one embodiment of the present invention, a method of forming a semiconductor device includes forming a gate stack on an outer surface of a semiconductor body. First and second sidewall bodies are formed on opposing sides of the gate stack. A first recess is formed in an outer surface of the gate stack, and a first dopant is implanted into the gate stack after the first recess is formed. The first dopant diffuses inwardly from the outer surface of the gate stack that defines the first recess. The first dopant diffuses toward an interface between the gate stack and the semiconductor body. The first recess increases the concentration of the first dopant at the interface.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
System and method for providing an obturator for enhanced directional capabilities in a vascular environment
InactiveUS8486094B2Eliminates and greatly reduces disadvantageEliminates and greatly reduces and problemDiagnosticsSurgical veterinaryCombined useDry ice
An apparatus for assisting in a vascular procedure includes an obturator operable to be mounted on a medical device to guide the medical device into a targeted region, whereby the obturator is substantially blunt such that it exhibits a snag-resistant property. In alternative embodiments, the apparatus includes an interface element operable to be used in conjunction with the obturator and to engage an interface of the targeted region such that pressure is maintained within the targeted region. The interface element includes a convex portion that operates to seat the interface element at a selected location. The interface element is substantially transparent and includes a magnification element that magnifies materials underlying the interface element. In other embodiments, the apparatus includes a tray operable to provide a mold for forming the obturator, which may include a gas, water, sugar, clotted blood, a gelatinous material, a protein, a saline solution, or dry-ice.
Owner:CASTLEWOOD SURGICAL
Reduced inductance interconnect for enhanced microwave and millimeter-wave systems
ActiveUS20090085823A1Eliminates and greatly reduces disadvantageEliminates and greatly reduces and problemAntenna arraysSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMicrowaveDielectric layer
According to one embodiment of the present invention, a microwave or millimeter wave module includes a dielectric layer having a pocket formed substantially through the dielectric layer. The dielectric is attached to a metal substrate. The pocket has substantially vertical sidewalls. An integrated circuit is disposed in the pocket. Opposing sides of the integrated circuit are substantially parallel to the sidewalls of the pocket. An interconnect electrically couples the integrated circuit to a bond pad disposed on the outer surface of the dielectric layer. The interconnect has a length that is minimized to result in reduced inductance of the semiconductor device.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
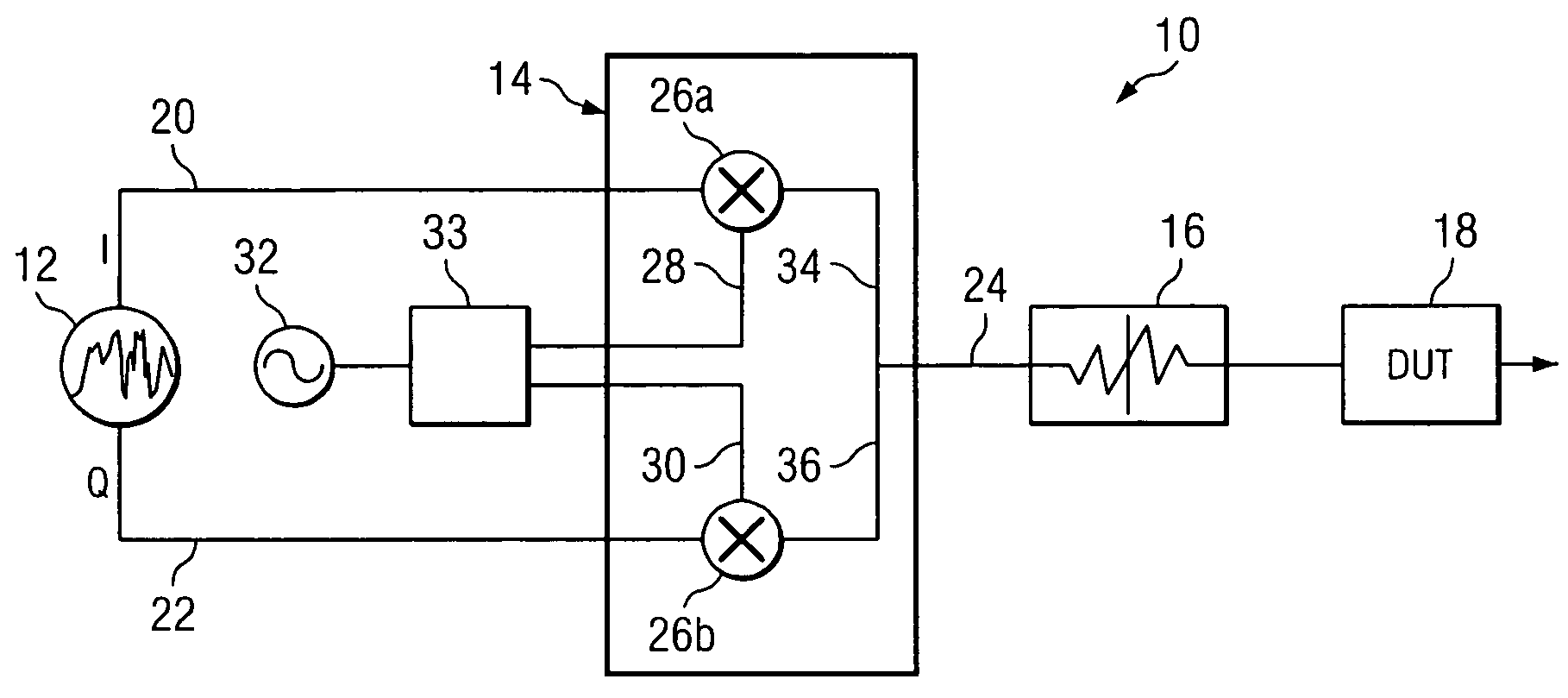
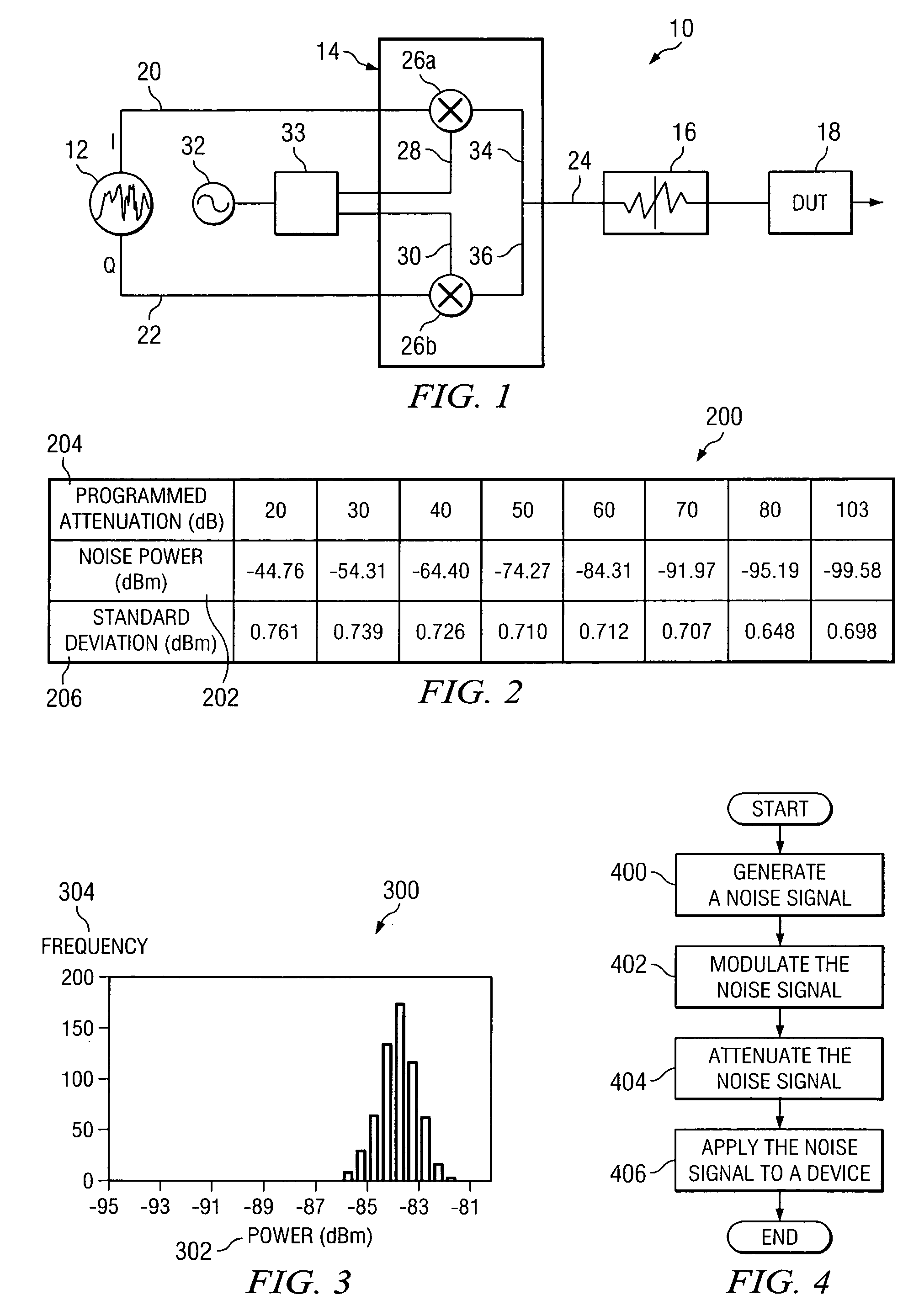
System and method for generating and measuring noise parameters
ActiveUS7177772B2Accurate measurementEliminates and greatly reduces disadvantageDigital variable displayNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementCarrier signalDevice under test
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
System and method for performing memory operations in a computing system
ActiveUS7398359B1Eliminates and greatly reduces disadvantageEliminates and greatly reduces and problemSpecific program execution arrangementsMemory systemsPosition dependentOperating system
A processor may operate in one of a plurality of operating states. In a Normal operating state, the processor is not involved with a memory transaction. Upon receipt of a transaction instruction to access a memory location, the processor transitions to a Transaction operating state. In the Transaction operating state, the processor performs changes to a cache line and data associated with the memory location. While in the Transaction operating state, any changes to the data and the cache line is not visible to other processors in the computing system. These changes become visible upon the processor entering a Commit operating state in response to receipt of a commit instruction. After changes become visible, the processor returns to the Normal operating state. If an abort event occurs prior to receipt of the commit instruction, the processor transitions to an Abort operating state where any changes to the data and cache line are discarded.
Owner:MORGAN STANLEY +1
Device for interworking asynchronous transfer mode cells
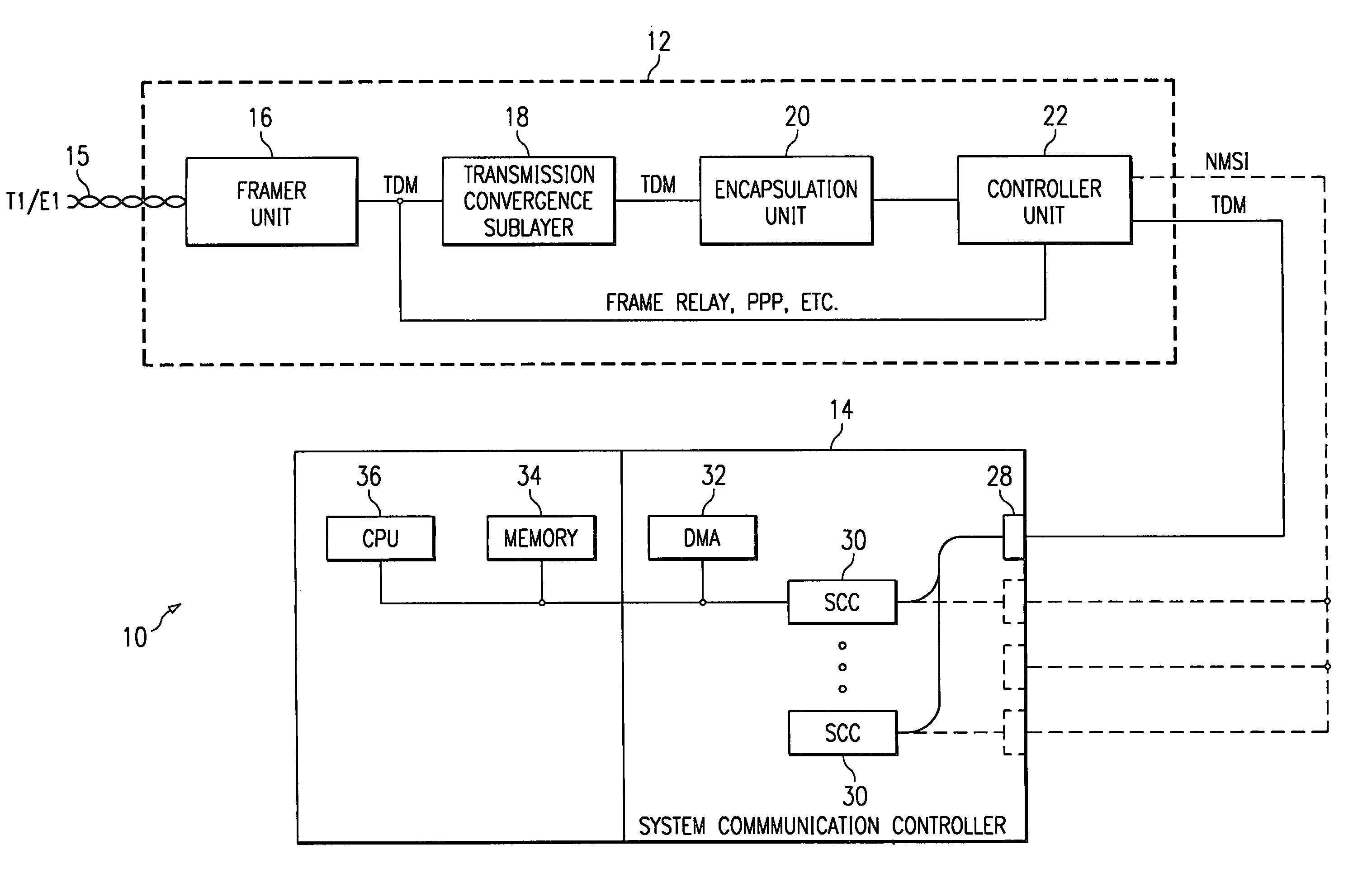
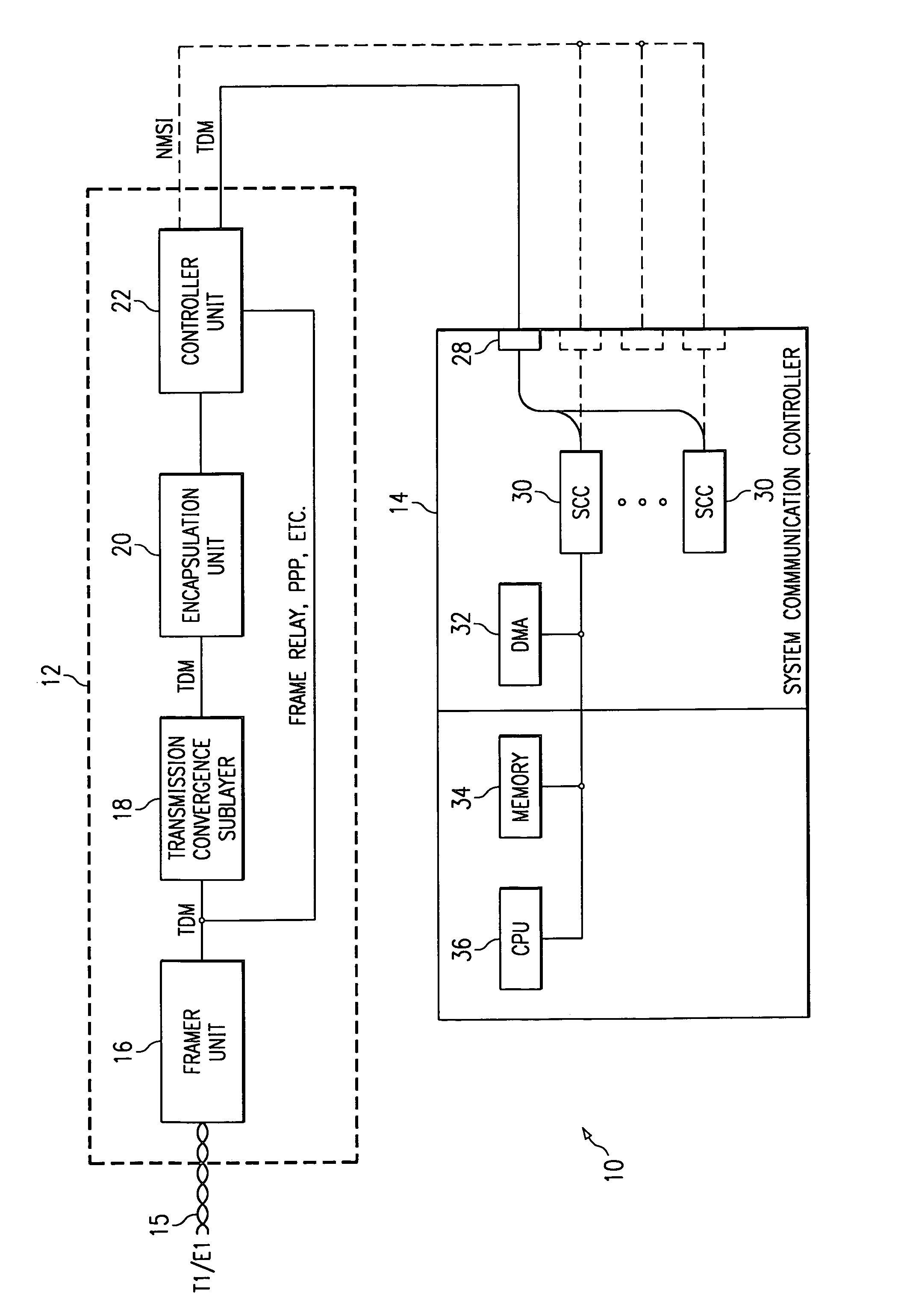
InactiveUS6963569B1Sure easyEliminates and greatly reduces disadvantageTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationTransmission convergenceSerial communication
A telecommunication environment includes an interface card and a system communication controller. The interface card provides an asynchronous transfer mode interworking capability that is compatible with a serial communications controller within the system communication controller. A transmission convergence sublayer within the interface card identifies valid asynchronous transfer mode cells carried over a T1 / E1 trunk link. The valid asynchronous transfer mode cells are transferred to an encapsulation unit within the interface card. The encapsulation unit generates encapsulated frames in a protocol format understood by the serial communications controller. The encapsulated frames carry asynchronous transfer mode cells for processing by the system communication controller. A processor within the system communication controller performs segmentation and reassembly processes on payload extracted by the serial communications controller.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com