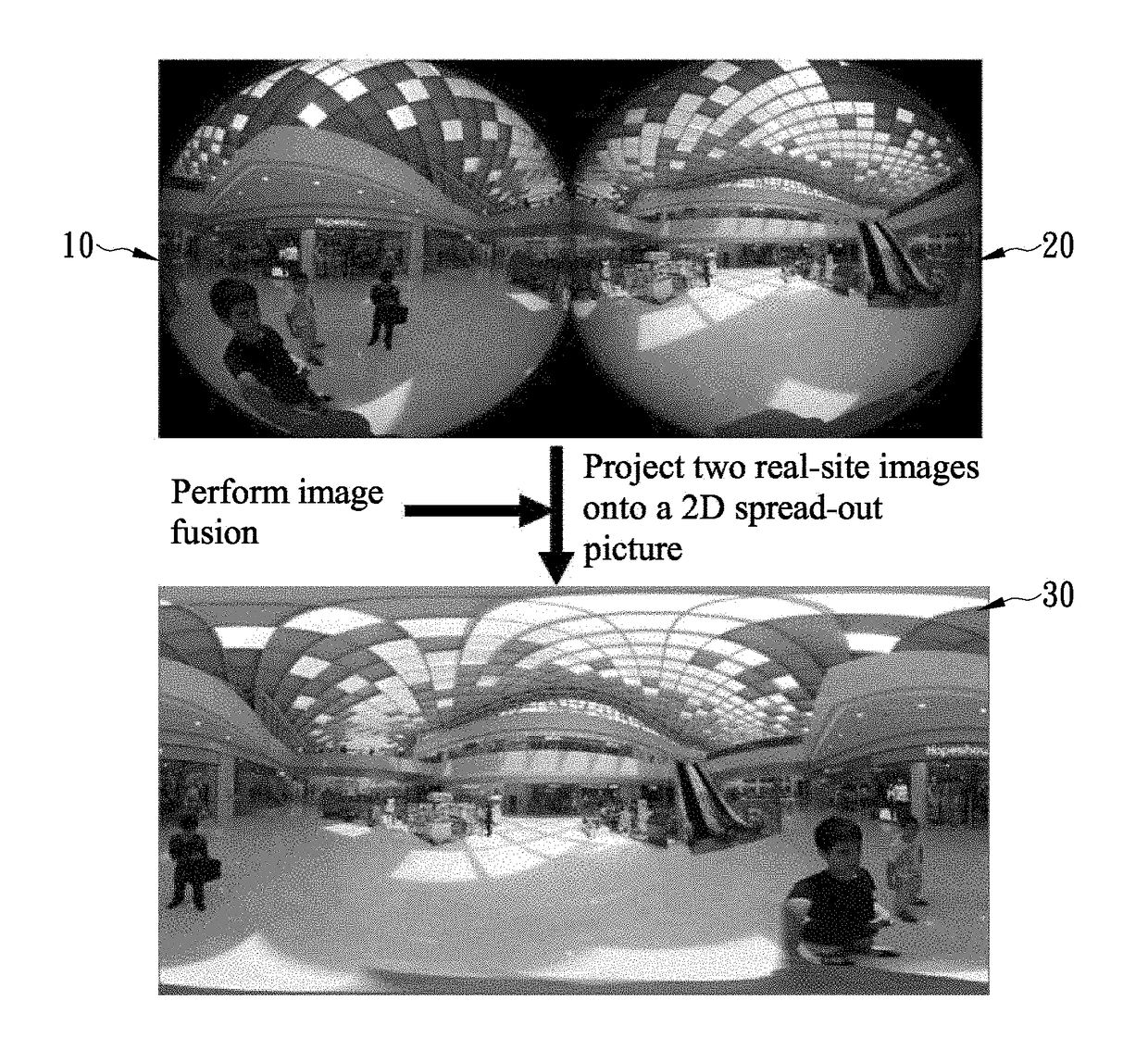
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
66 results about "Vignetting" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
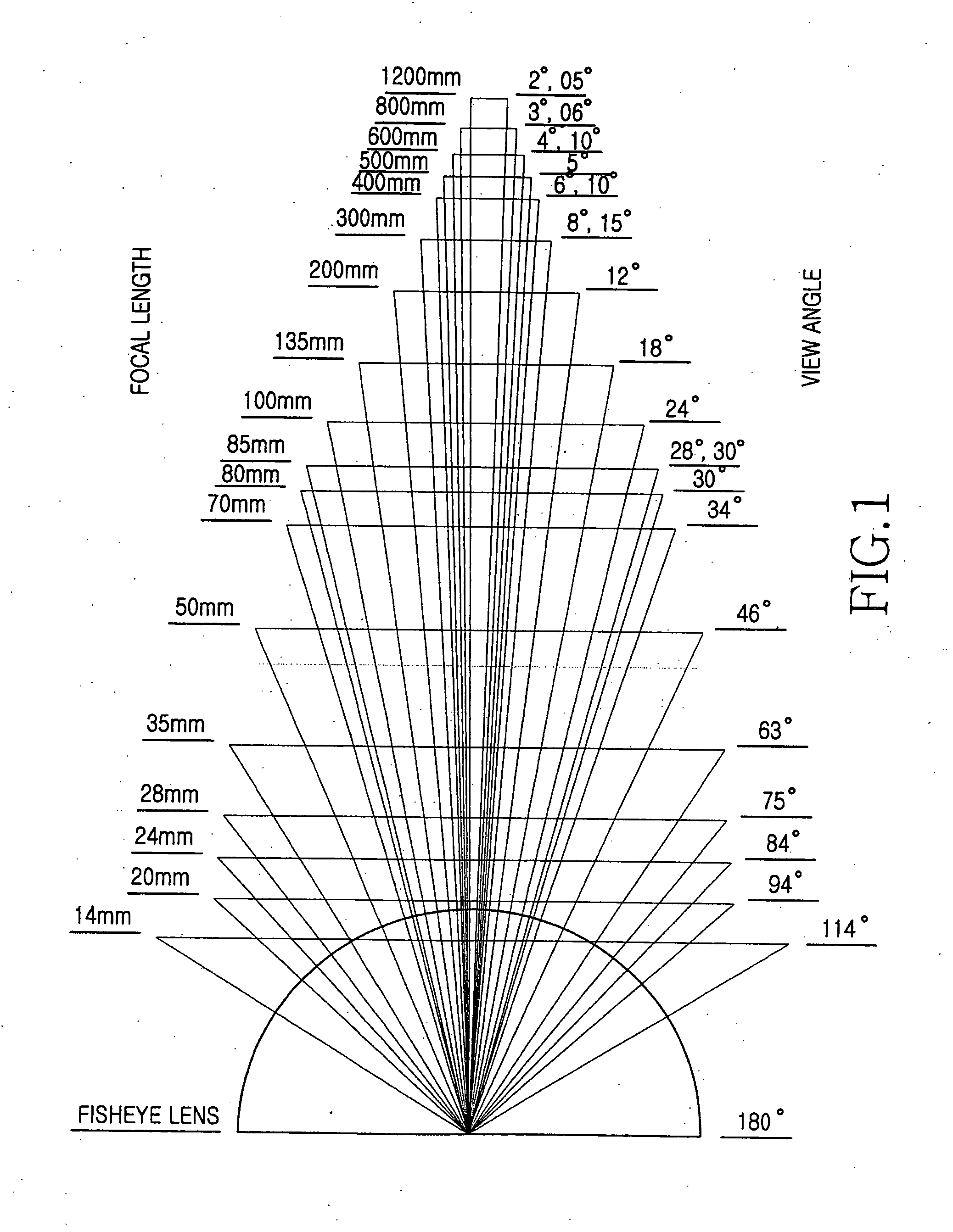
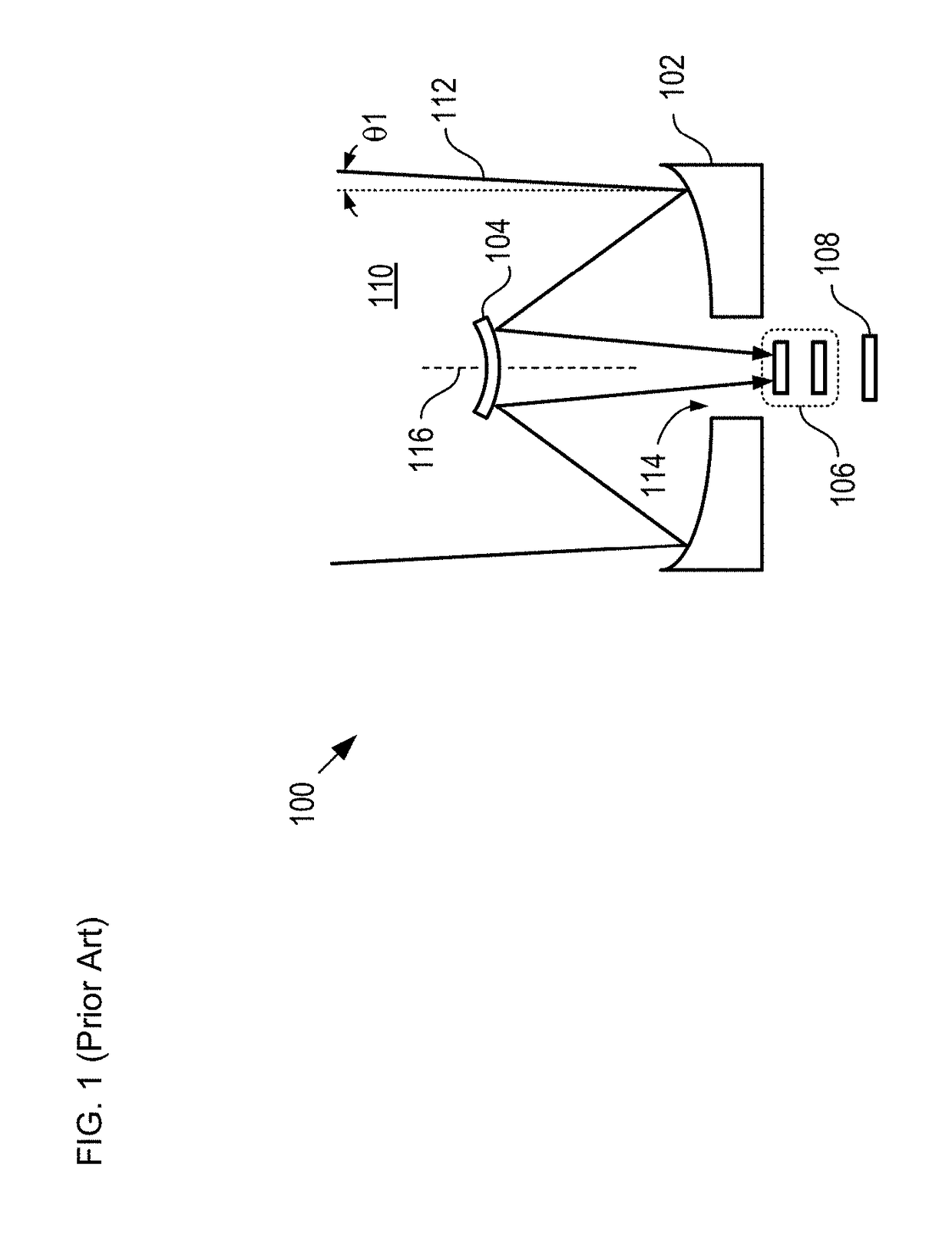
In photography and optics, vignetting (/vɪnˈjɛtɪŋ, viːnˈ-/; French: vignette) is a reduction of an image's brightness or saturation toward the periphery compared to the image center. The word vignette, from the same root as vine, originally referred to a decorative border in a book. Later, the word came to be used for a photographic portrait that is clear at the center and fades off toward the edges. A similar effect is visible in photographs of projected images or videos off a projection screen, resulting in a so-called "hotspot" effect.
Scanning laser ophthalmoscope for selective therapeutic laser
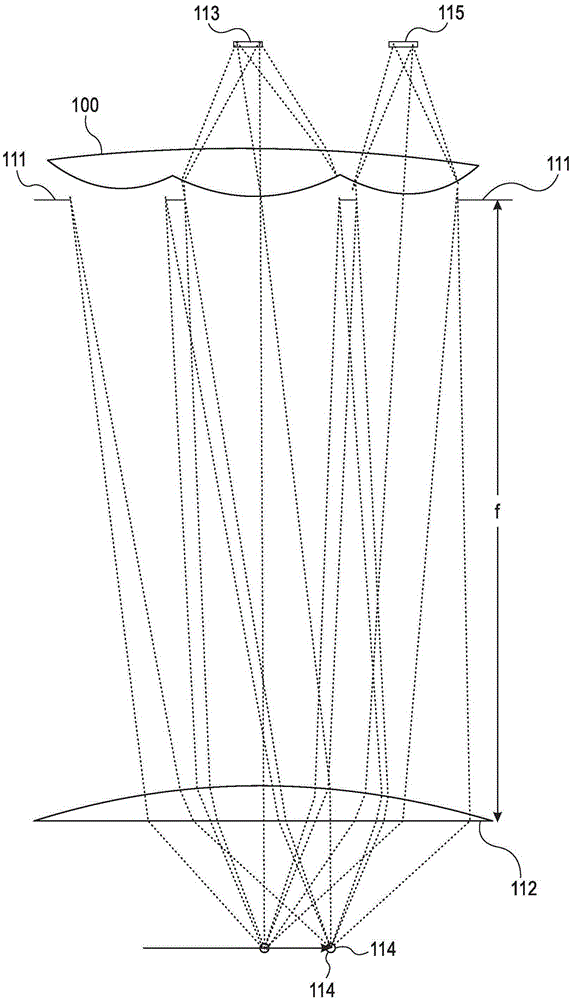
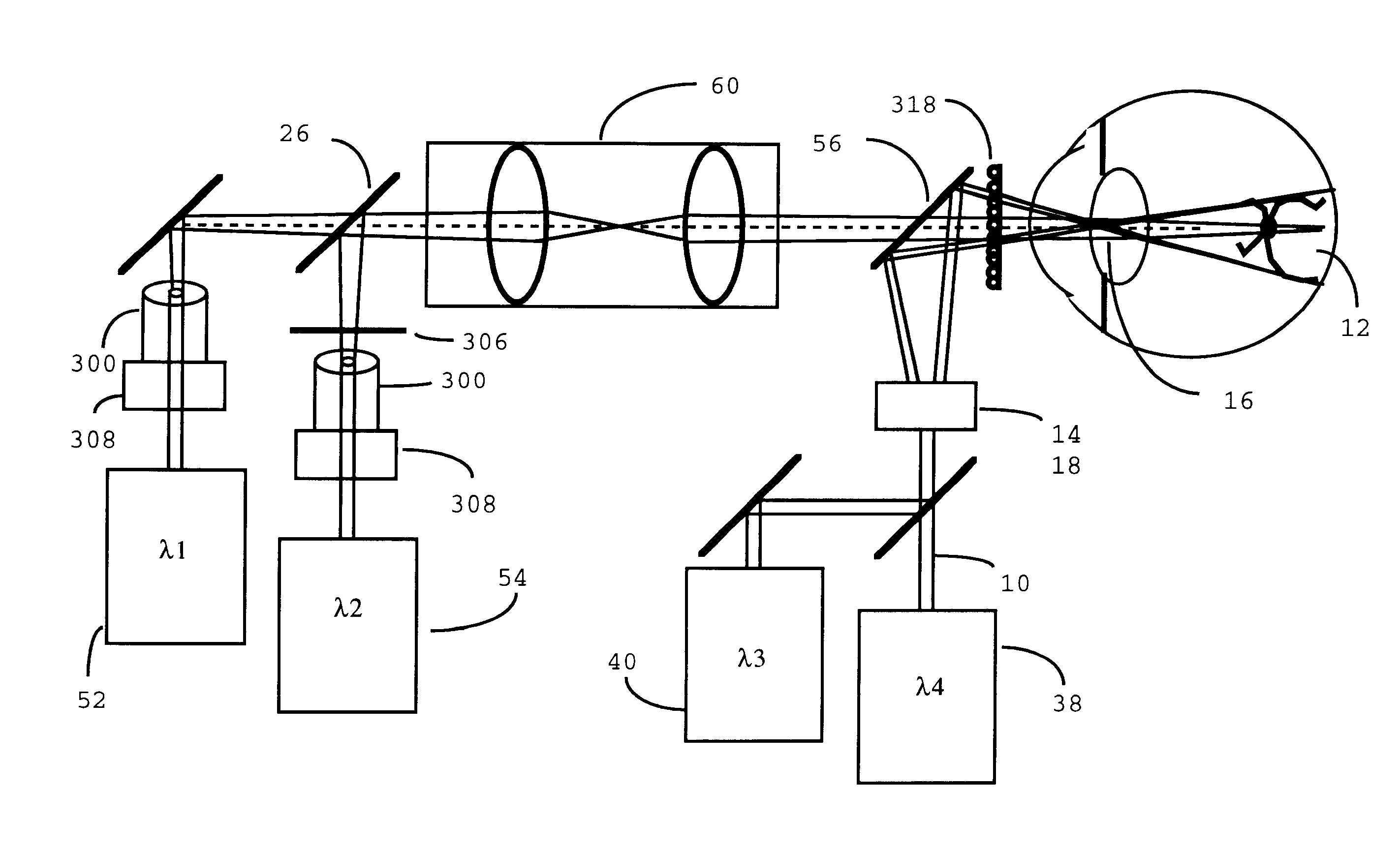
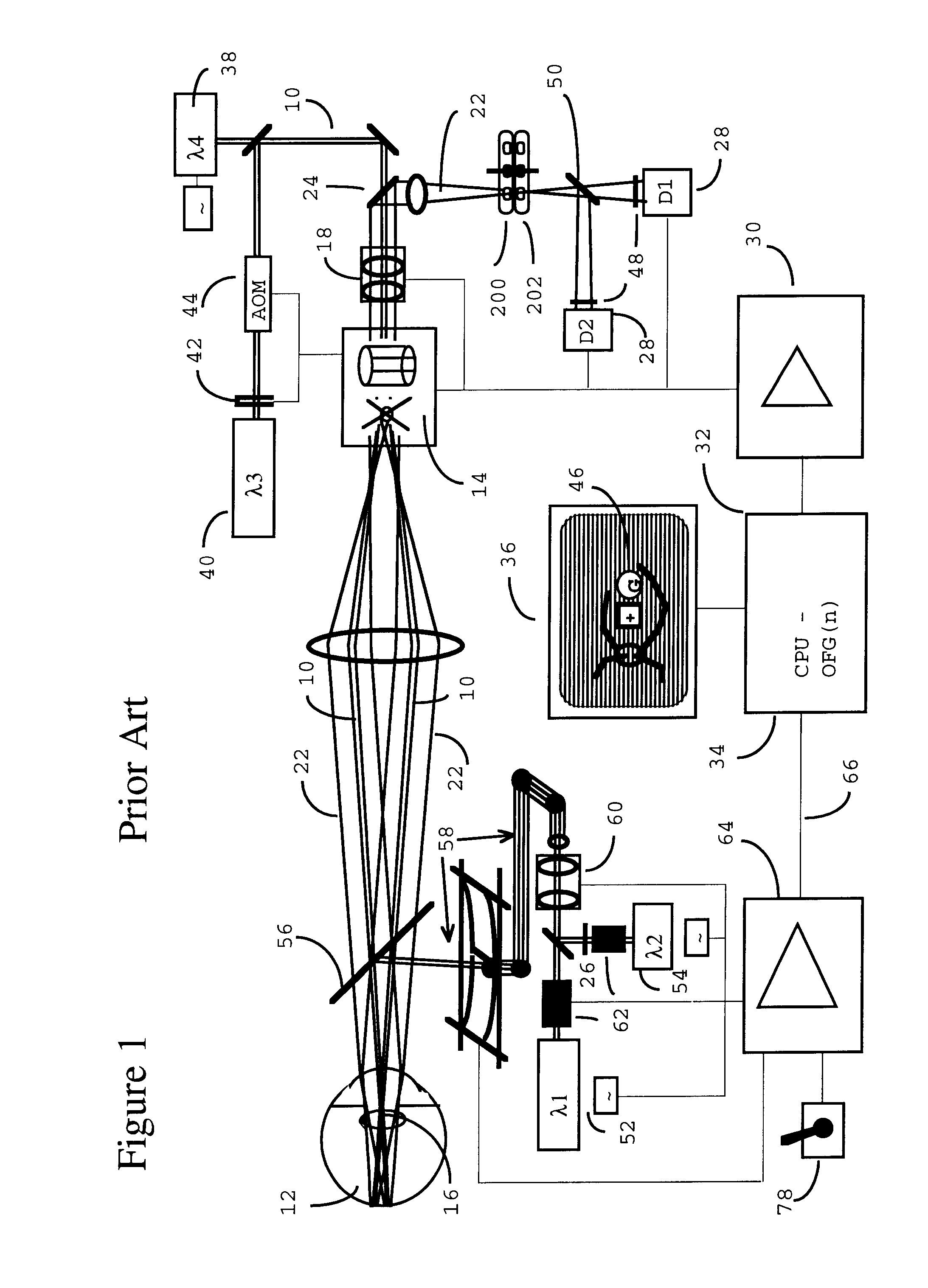
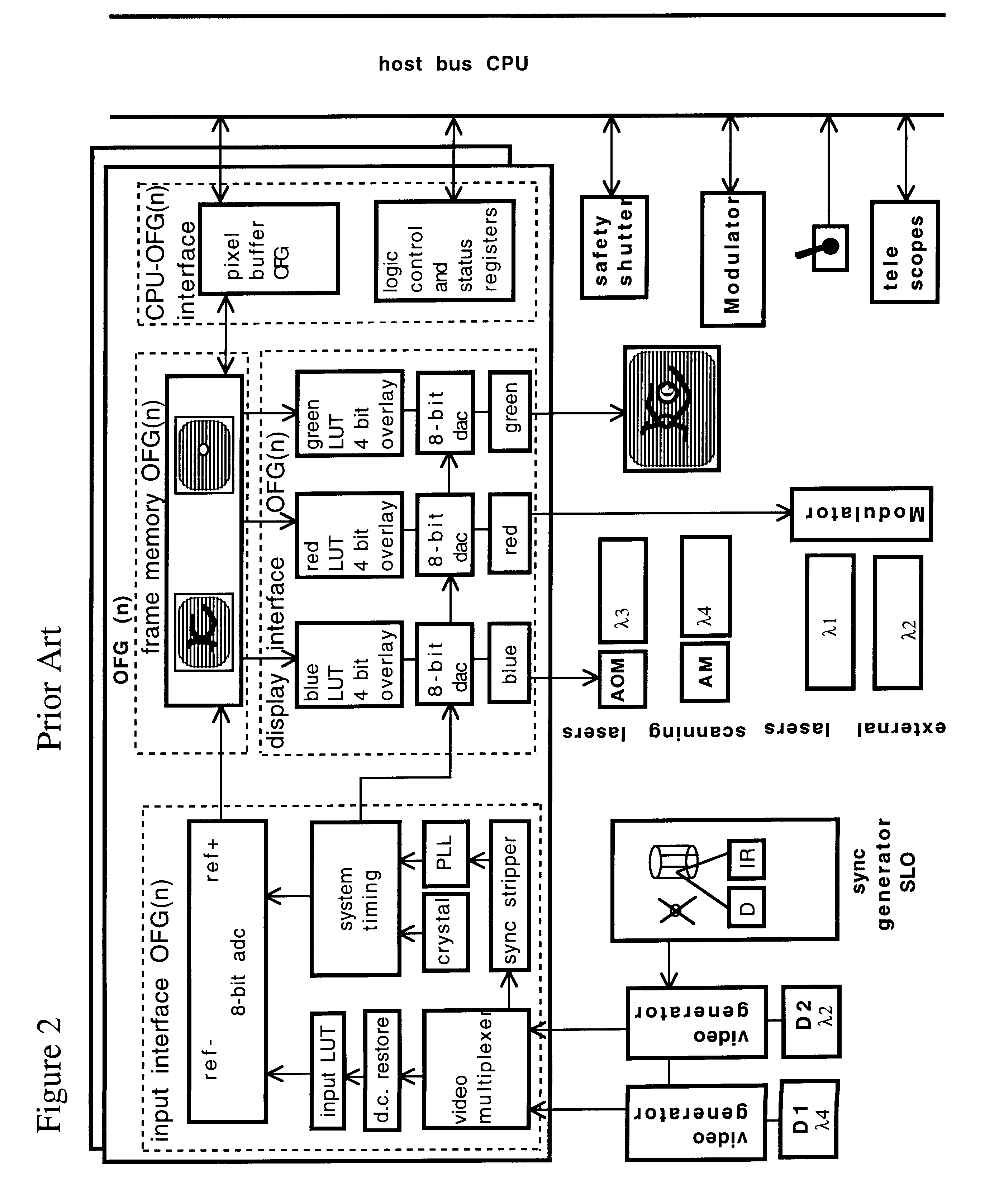
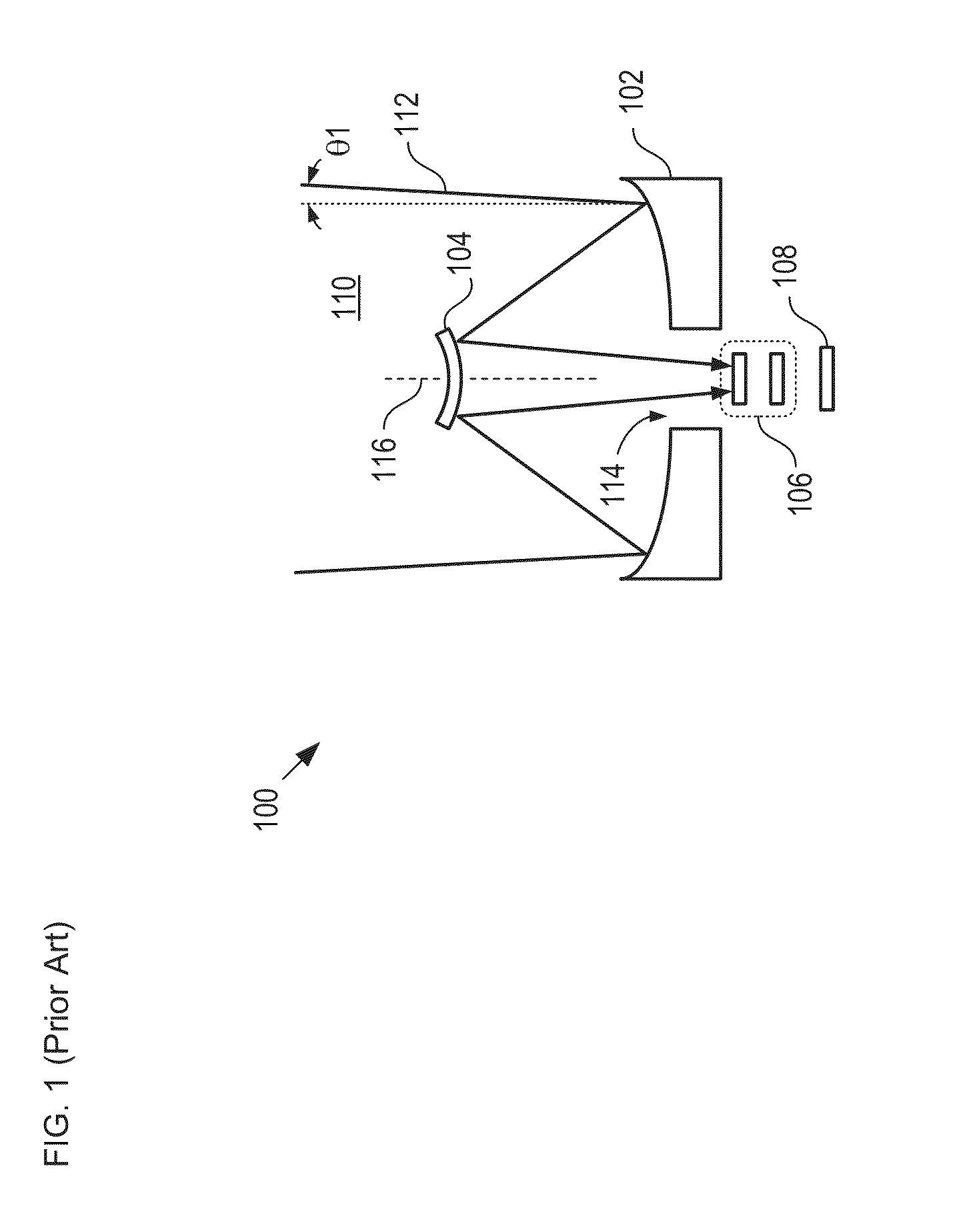
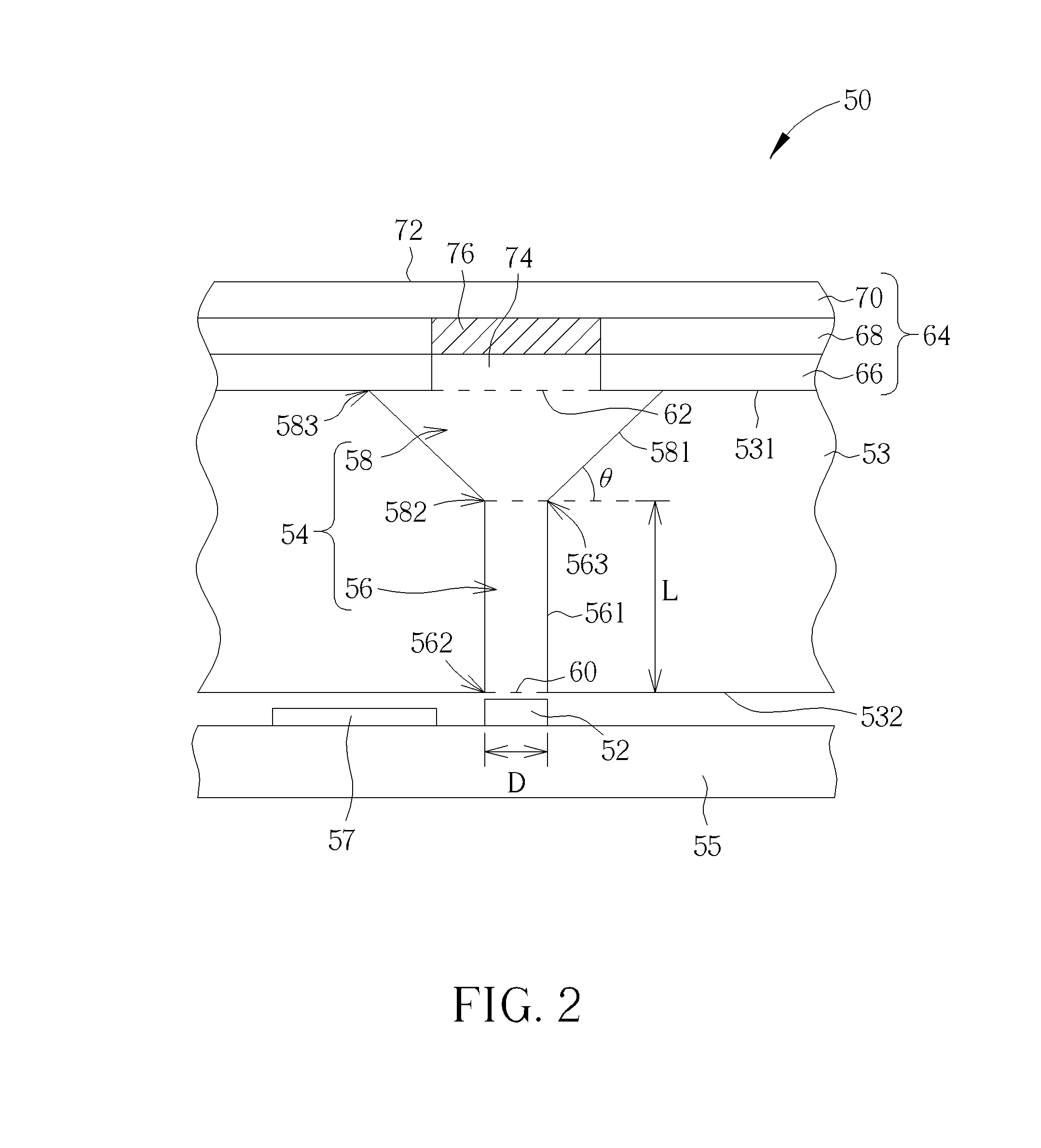
A combination of a scanning laser ophthalmoscope and external laser sources (52) is used for microphotocoagulation and photodynamic therapy, two examples of selective therapeutic laser. A linkage device incorporating a beamsplitter (56) and collimator-telescope (60) is adjusted to align the pivot point (16) of the scanning lasers (38, 40) and external laser source (52). A similar pivot point minimizes wavefront aberrations, enables precise focusing and registration of the therapeutic laser beam (52) on the retina without the risk of vignetting. One confocal detection pathway of the scanning laser ophthalmoscope images the retina. A second and synchronized detection pathway with a different barrier filter (48) is needed to draw the position and extent of the therapeutic laser spot on the retinal image, as an overlay (64). Advanced spatial modulation increases the selectivity of the therapeutic laser. In microphotocoagulation, an adaptive optics lens (318) is attached to the scanning laser ophthalmoscope, in proximity of the eye. It corrects the higher order optical aberrations of the eye optics, resulting in smaller and better focused applications. In photodynamic therapy, a spatial modulator (420) is placed within the collimator-telescope (60) of the therapeutic laser beam (52), customizing its shape as needed. A similar effect can be obtained by modulating a scanning laser source (38) of appropriate wavelength for photodynamic therapy.
Owner:VAN DE VELDE JOZEK F
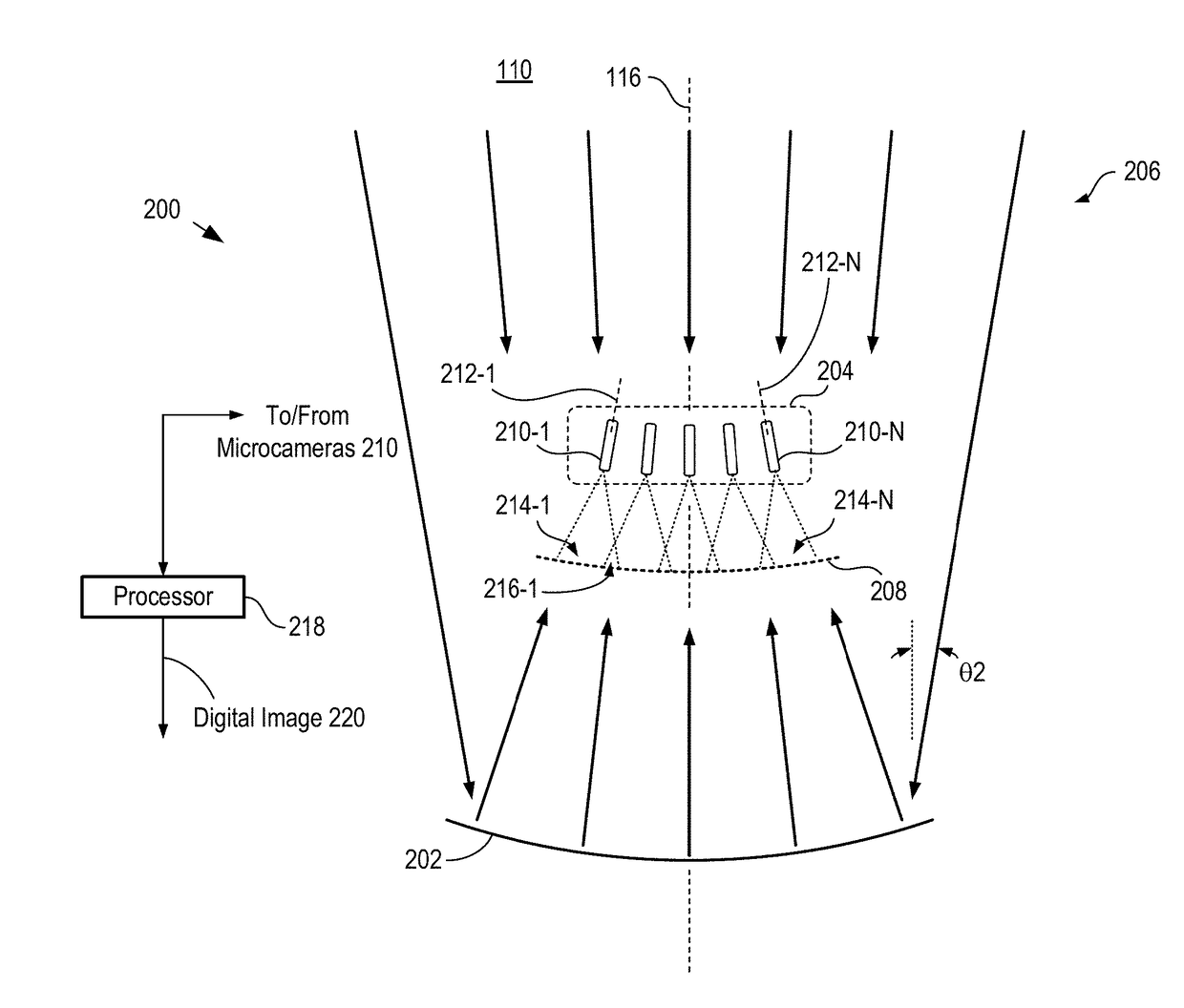
Multiscale telescopic imaging system
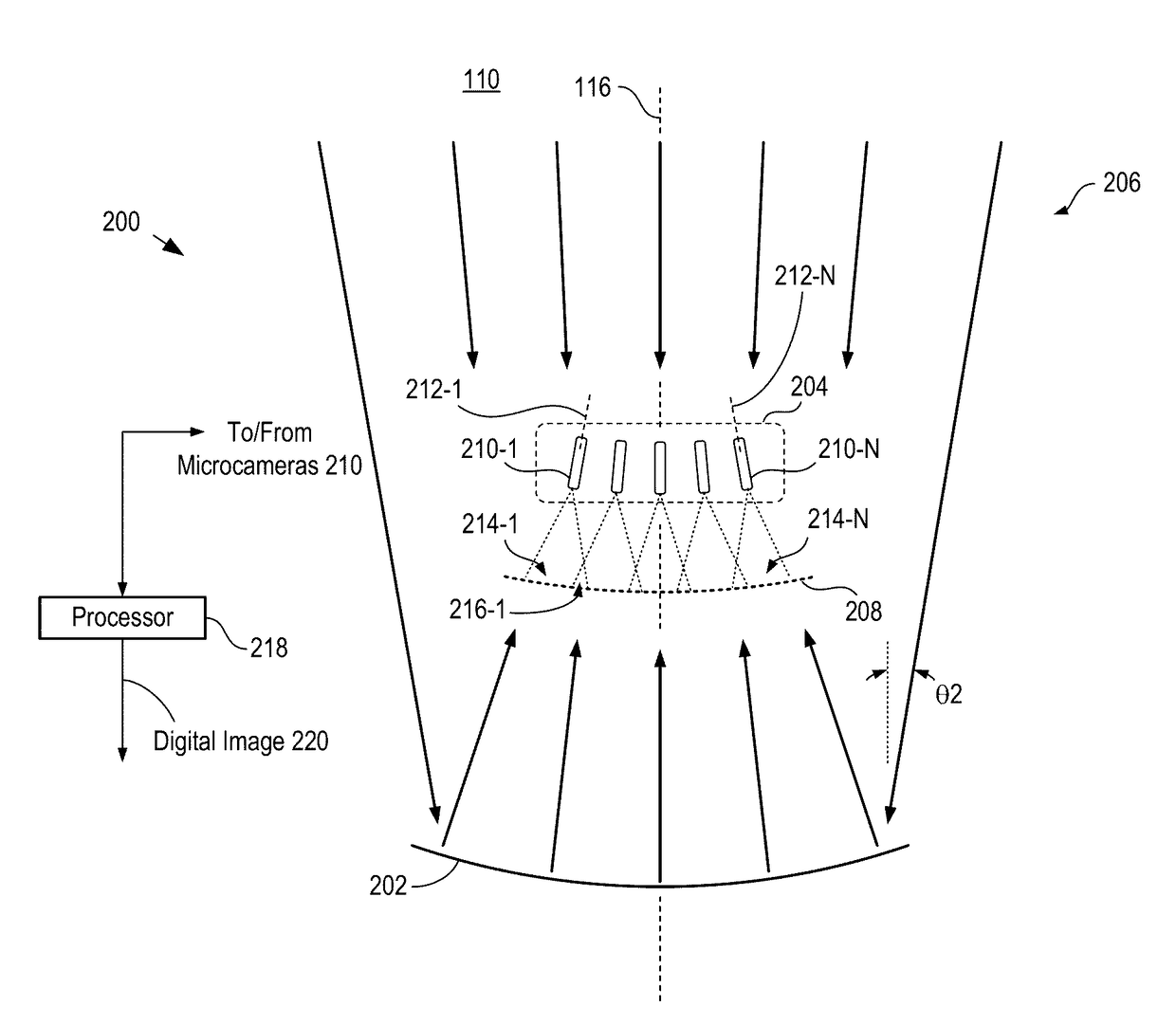
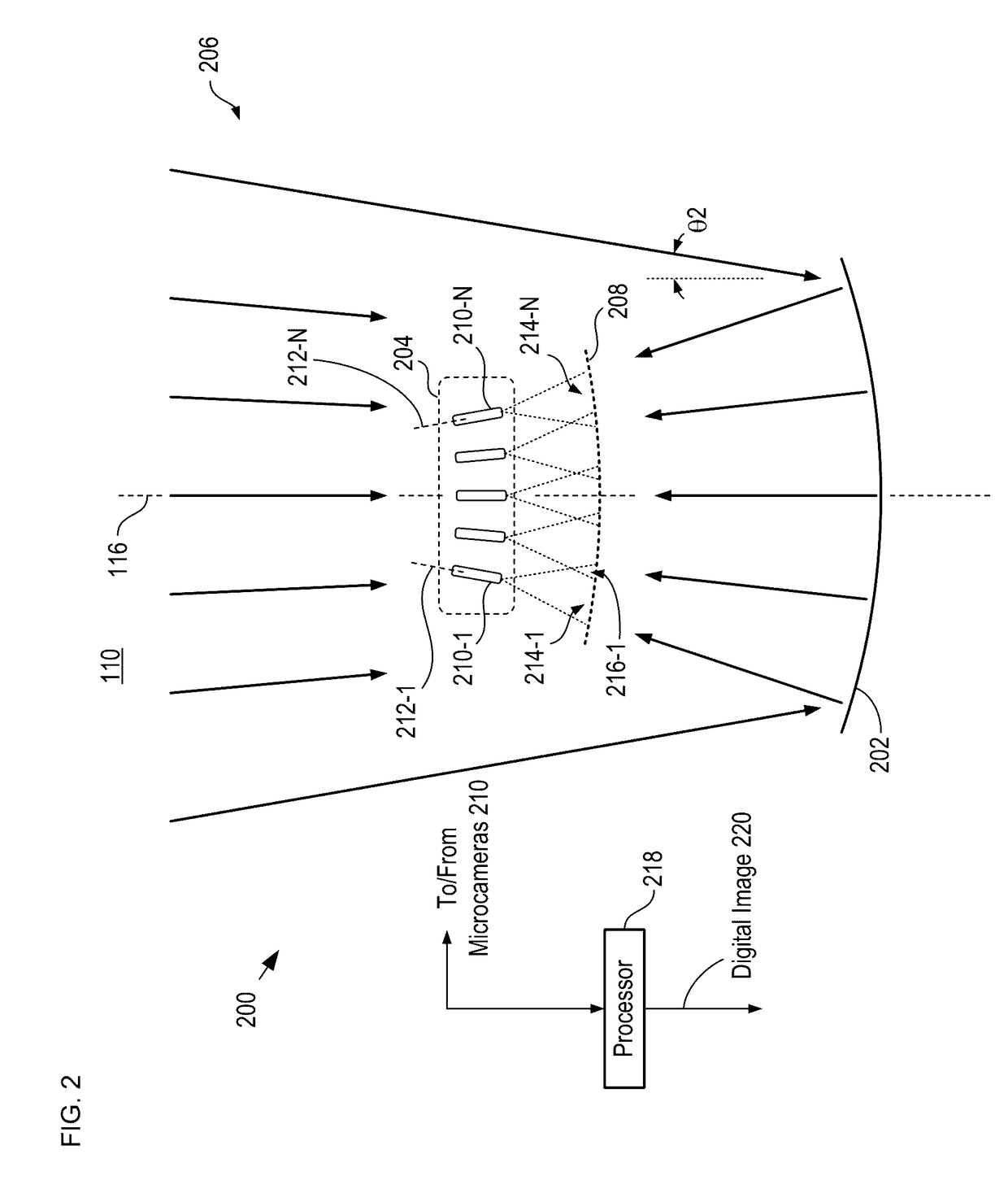
ActiveUS20140176710A1Reducing first magnitudeReduce occlusionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsIntermediate imageVignetting
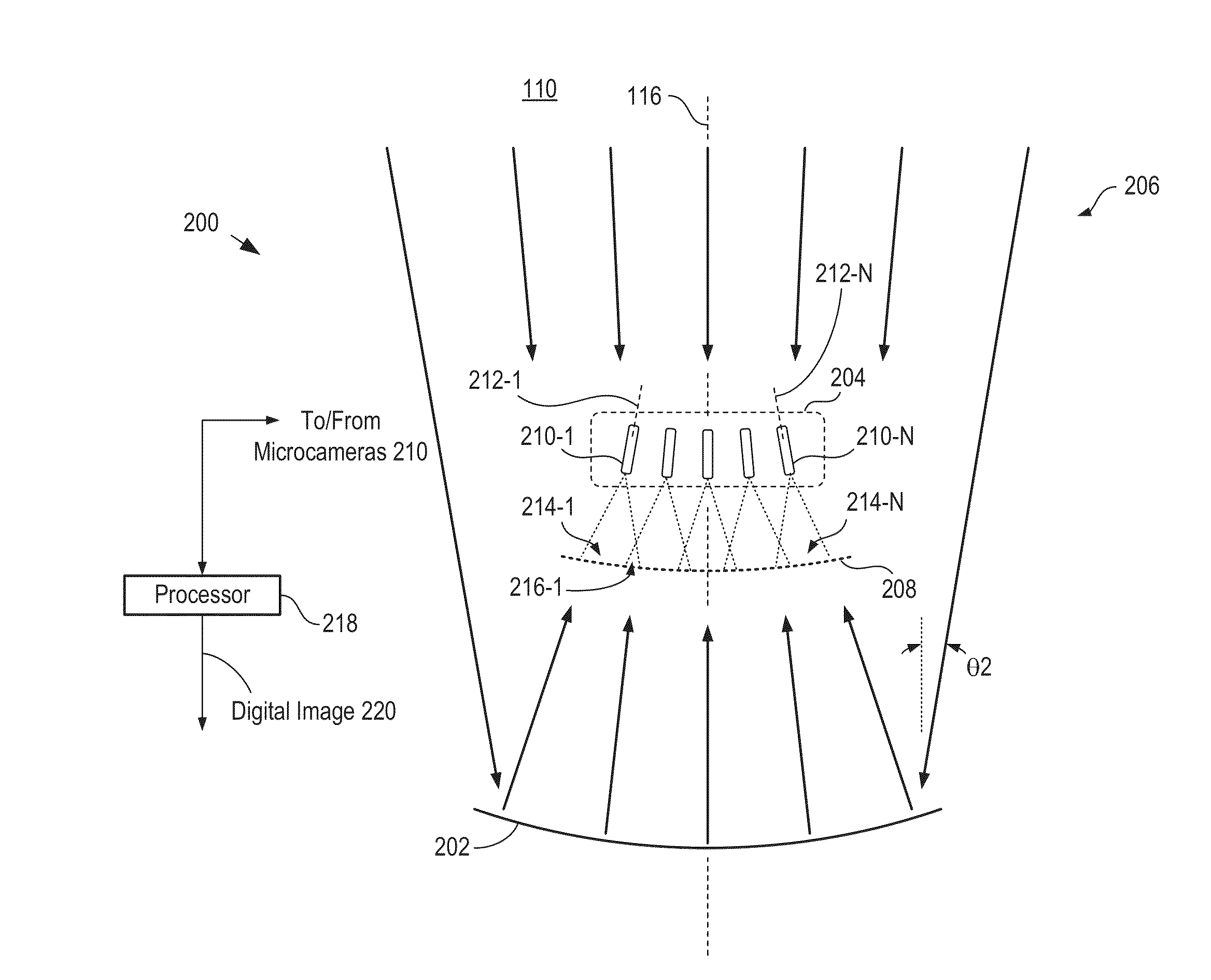
A multiscale telescopic imaging system is disclosed. The system includes an objective lens, having a wide field of view, which forms an intermediate image of a scene at a substantially spherical image surface. A plurality of microcameras in a microcamera array relay image portions of the intermediate image onto their respective focal-plane arrays, while simultaneously correcting at least one localized aberration in their respective image portions. The microcameras in the microcamera array are arranged such that the fields of view of adjacent microcameras overlap enabling field points of the intermediate image to be relayed by multiple microcameras. The microcamera array and objective lens are arranged such that light from the scene can reach the objective lens while mitigating deleterious effects such as obscuration and vignetting.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
System and method for camera color calibration and image stitching
InactiveUS7259784B2Low costImprove image qualityImage enhancementTelevision system detailsVignettingCamera auto-calibration
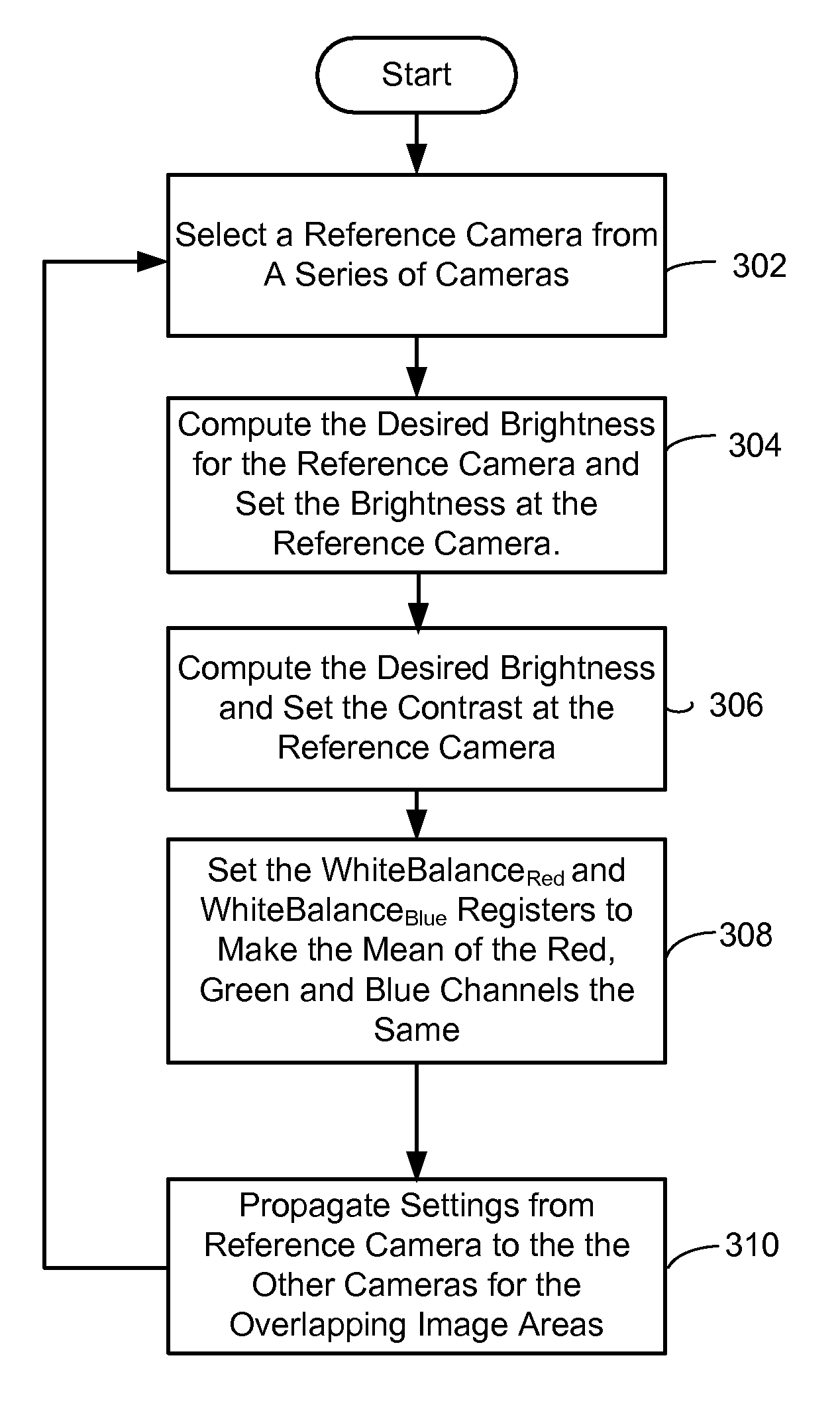
A practical, real-time calibration of digital omnidirectional cameras in the areas of de-vignetting, brightness, contrast, and white balance control. Novel solutions for the color calibration of an omnidirectional camera rig, and an efficient method for devignetting images are presented. Additionally, a context-specific method of stitching images together into a panorama or a mosaic is provided.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Lens shading algorithm
ActiveUS20050179793A1Efficient and fast calculationFast and efficient to calculateImage enhancementTelevision system detailsSensor arrayVignetting
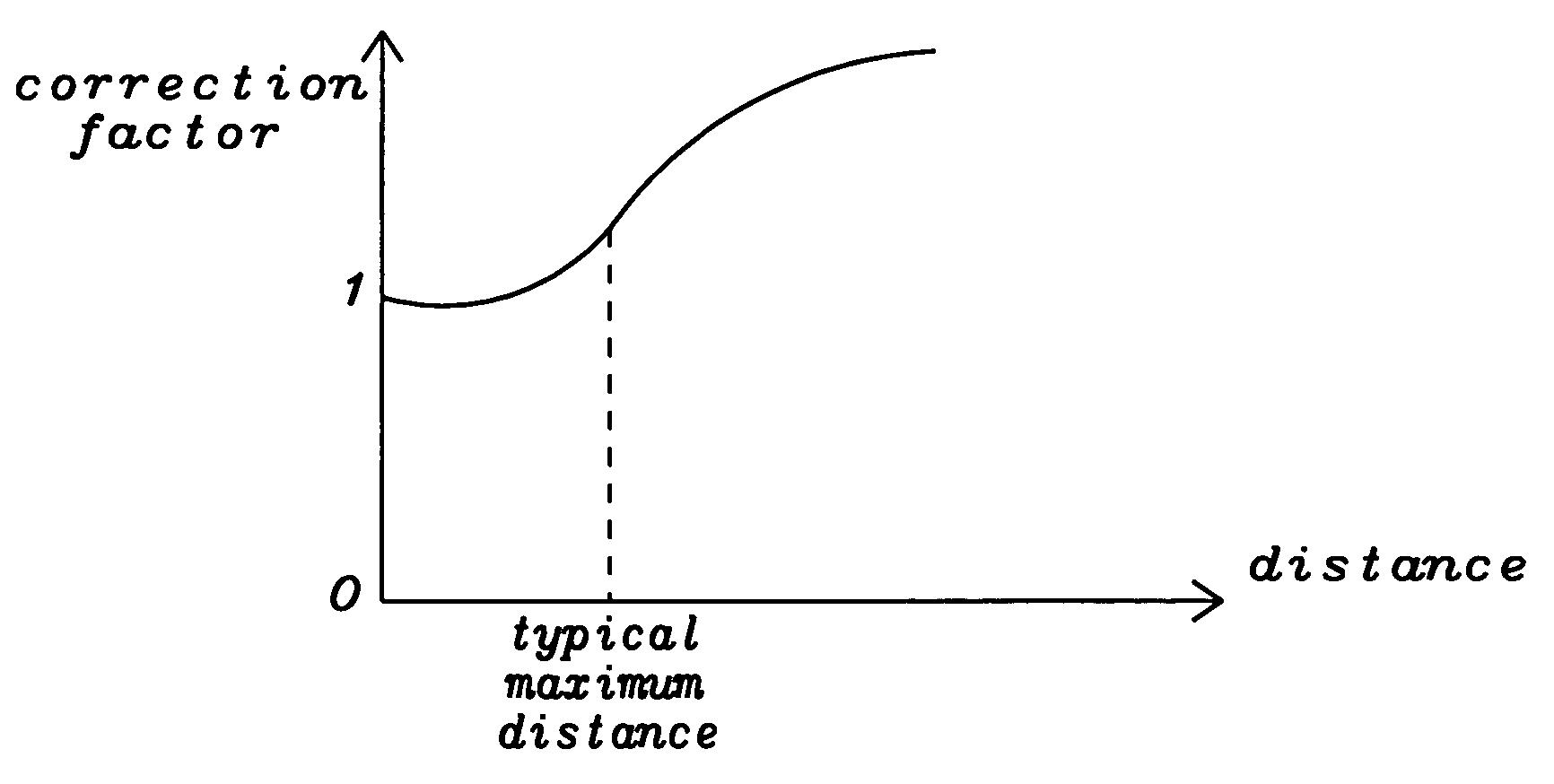
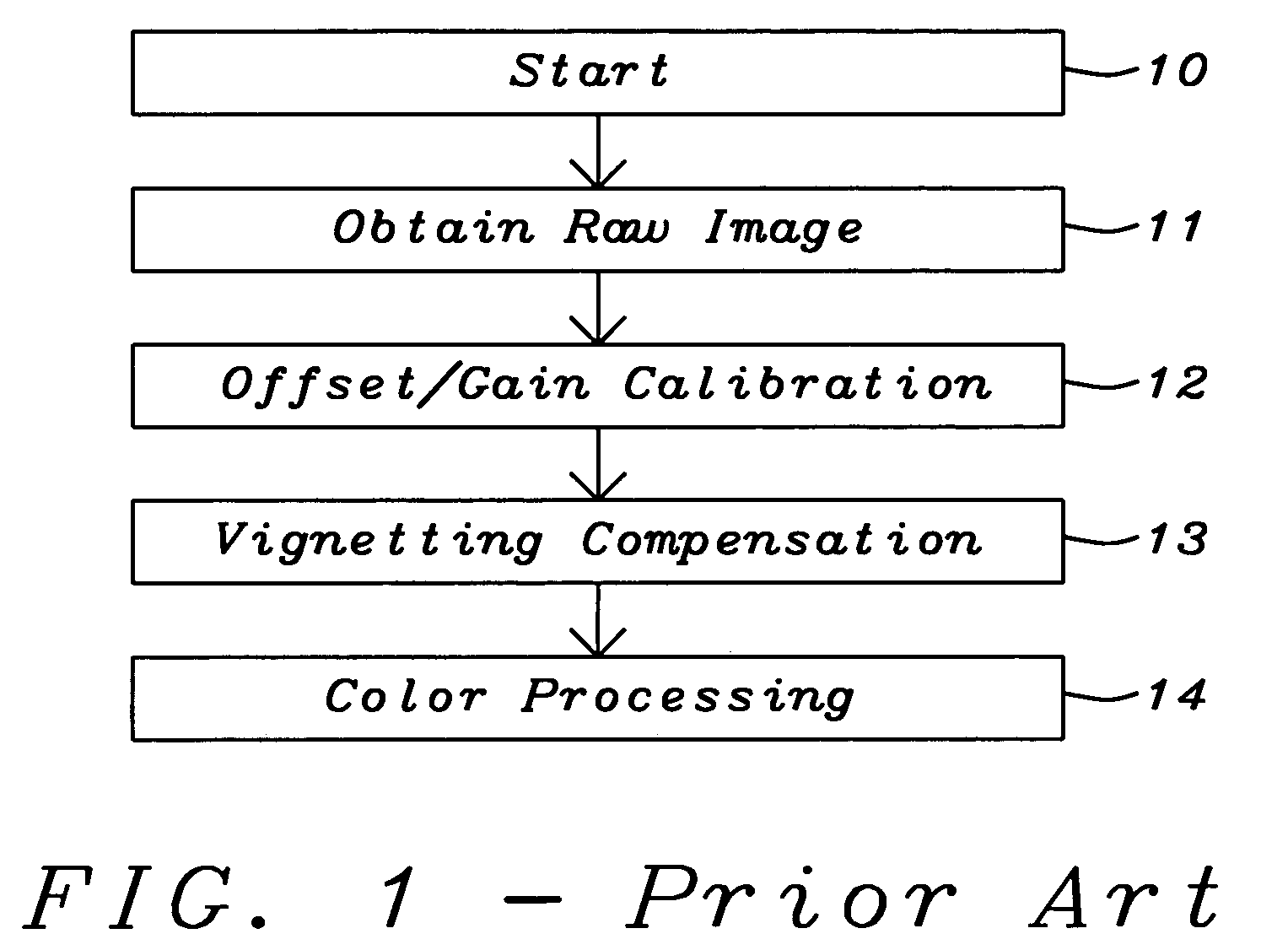
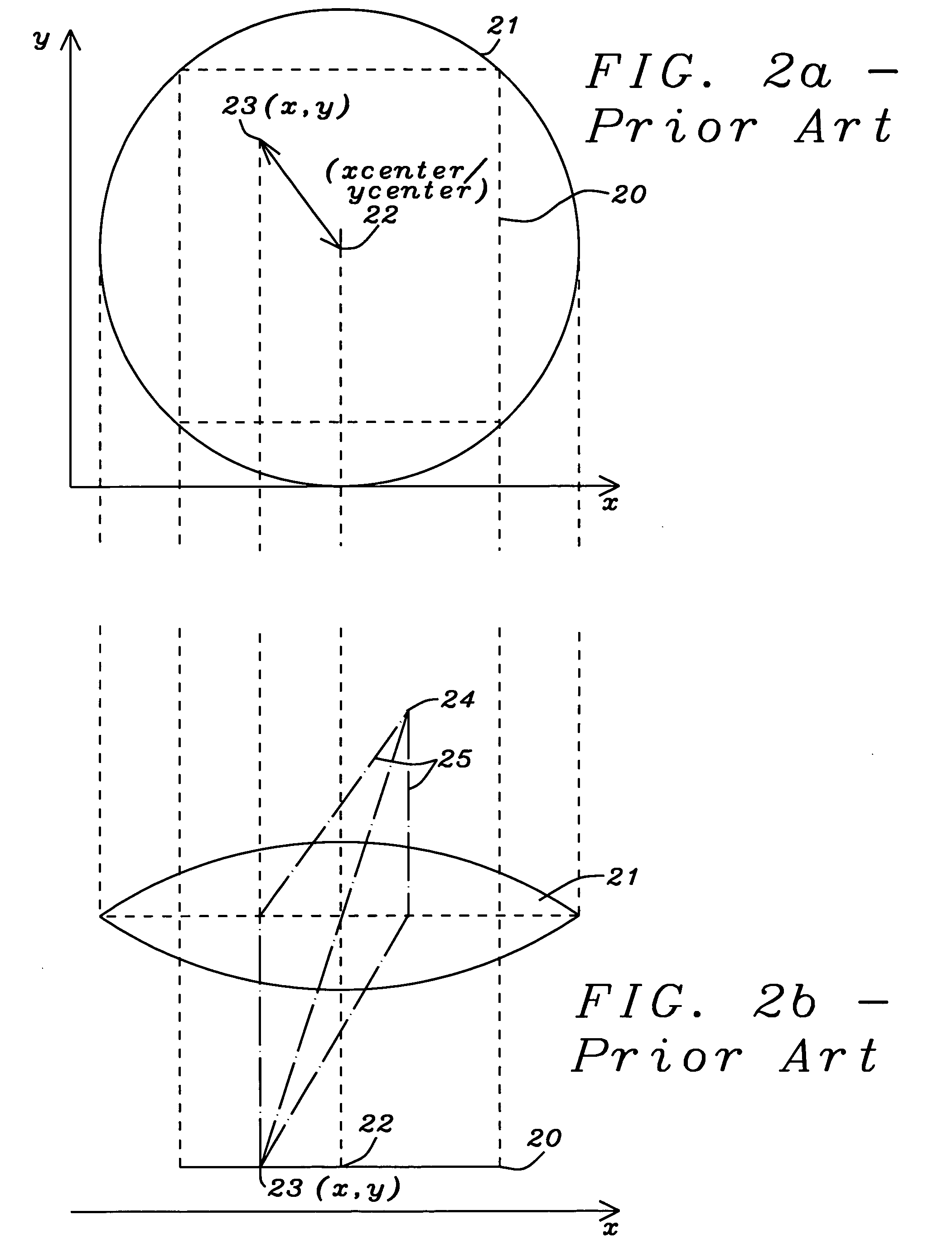
A method used for the compensation of vignetting in digital cameras has been achieved. The compensation for vignetting is performed by multiplying pixel output of the sensor array with a correction factor. In a preferred embodiment of the invention all pixels are multiplied with an adequate correction factor. Alternatively pixels, being close to the center of the sensor array, can be left unchanged. Said correction factor can be calculated in a very fast and efficient way by using two constant factors describing the specific geometry of the lens / sensor array system and by multiplying a first of said factors with the square of the distance between a pixel and the center of the sensor array and by multiplying a second of said factors with the distance between a pixel and the center of the sensor array to the power of four. The result of the second multiplication is subtracted from the result of the first multiplication and this result is added to one to get the final correction factor. Each original pixel output is multiplied with said correction factor to get output data compensated for the vignetting effects of the lens.
Owner:GULA CONSULTING LLC
Solid state image sensors and microlens arrays
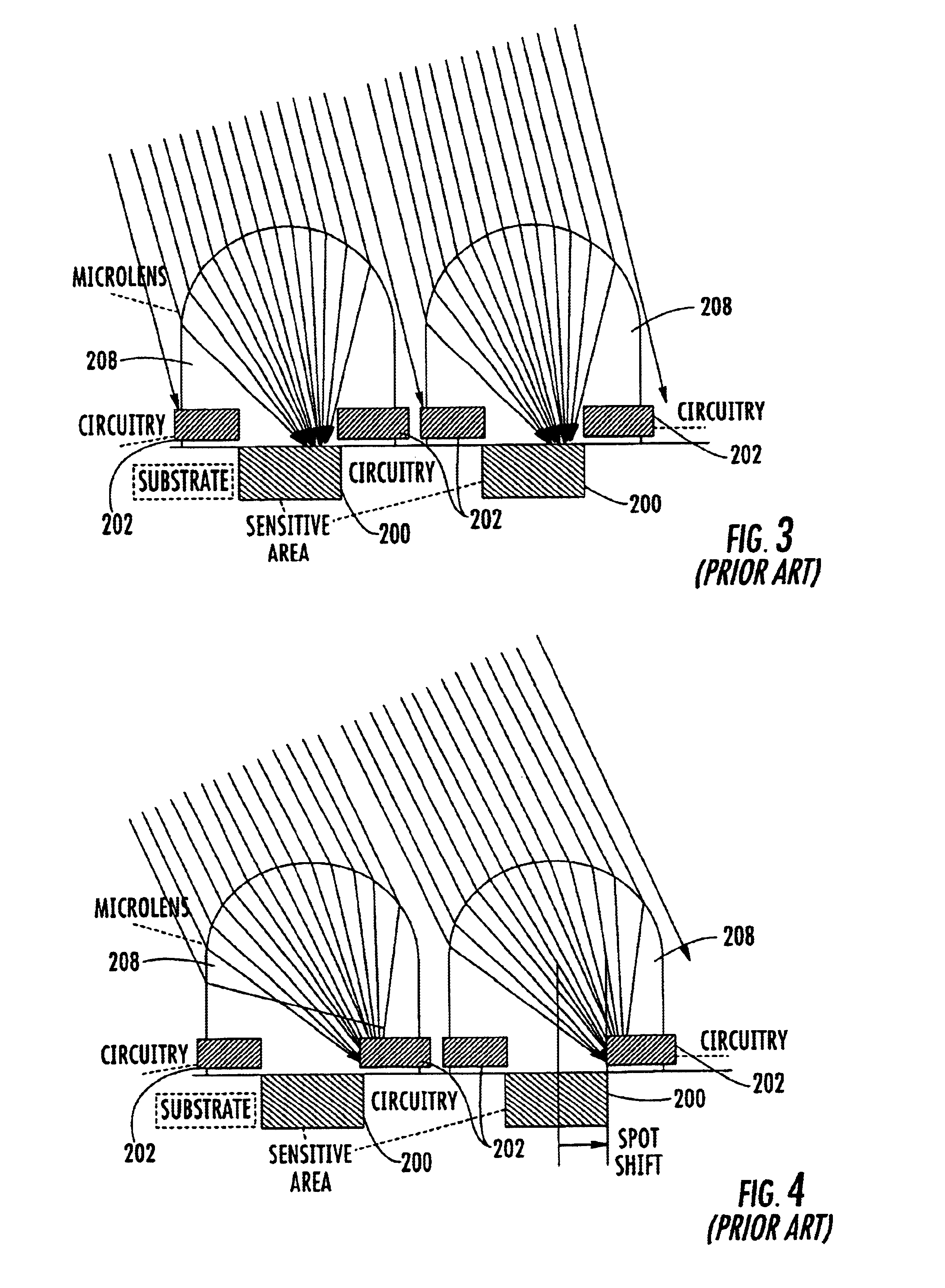
InactiveUS6884985B2Reduce vignettingMitigate aforesaid disadvantageTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsVignettingOptical axis
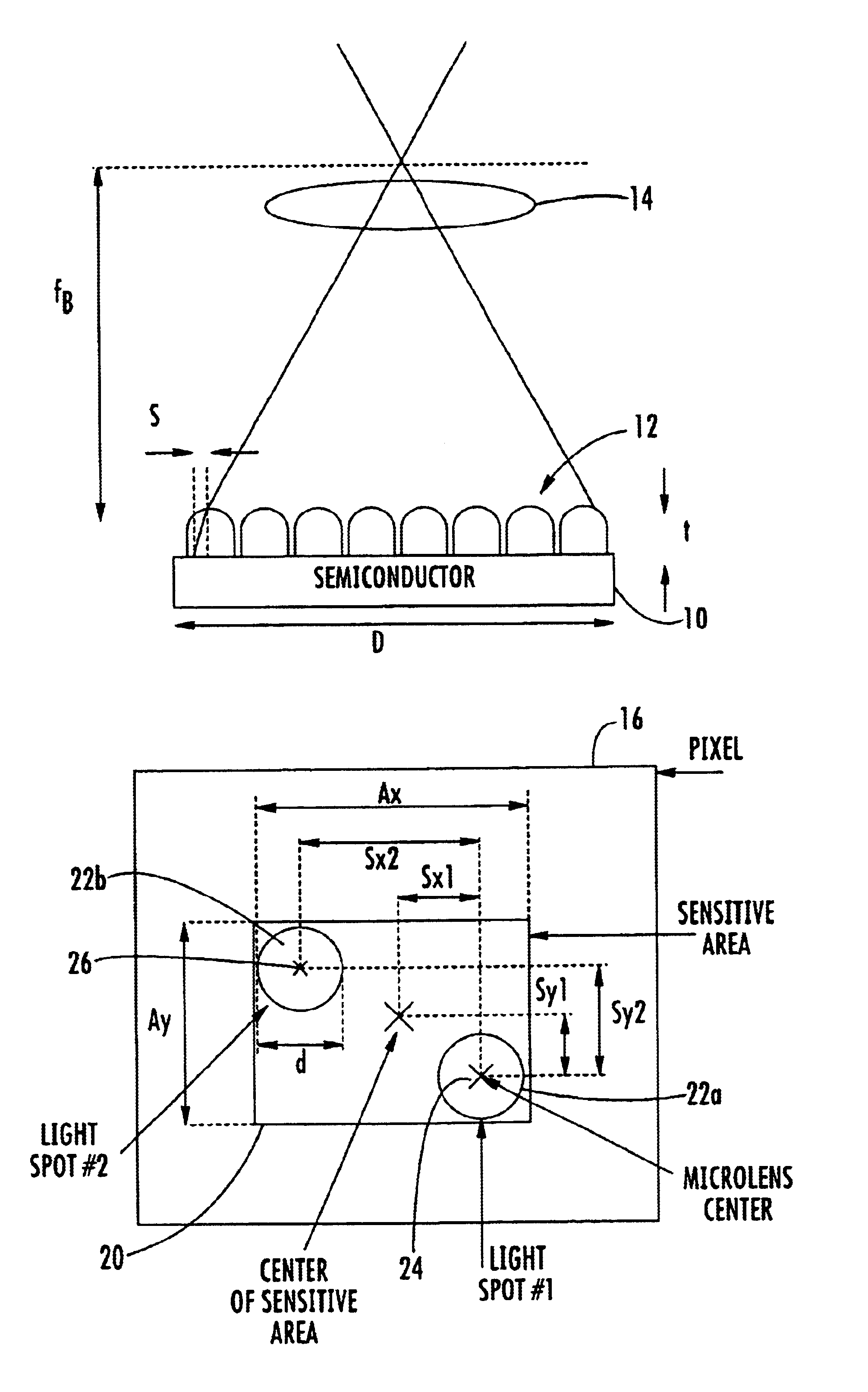
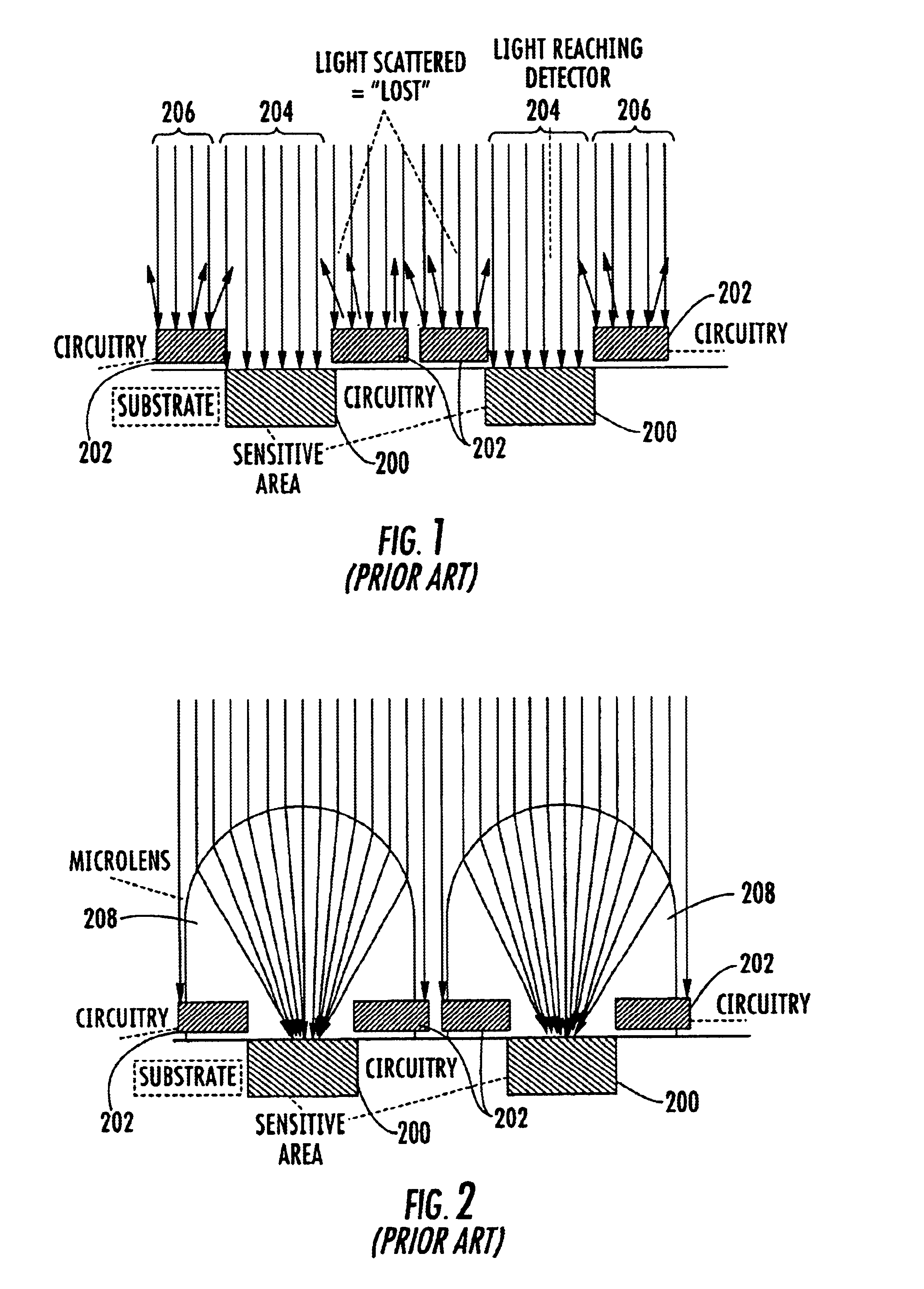
A solid state image sensor includes an array of pixels and a corresponding array of microlenses. The positions of the microlenses relative to their corresponding pixels may vary according to the distances of the pixels from a central optical axis of the image sensor to substantially eliminate vignetting of light collected by the microlenses.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS LTD
System and method for camera calibration and images stitching
InactiveUS7936374B2Low costImprove image qualityTelevision system detailsImage enhancementVignettingCamera auto-calibration
A practical, real-time calibration of digital omnidirectional cameras in the areas of de-vignetting, brightness, contrast, and white balance control. Novel solutions for the color calibration of an omnidirectional camera rig, and an efficient method for devignetting images are presented. Additionally, a context-specific method of stitching images together into a panorama or a mosaic is provided.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
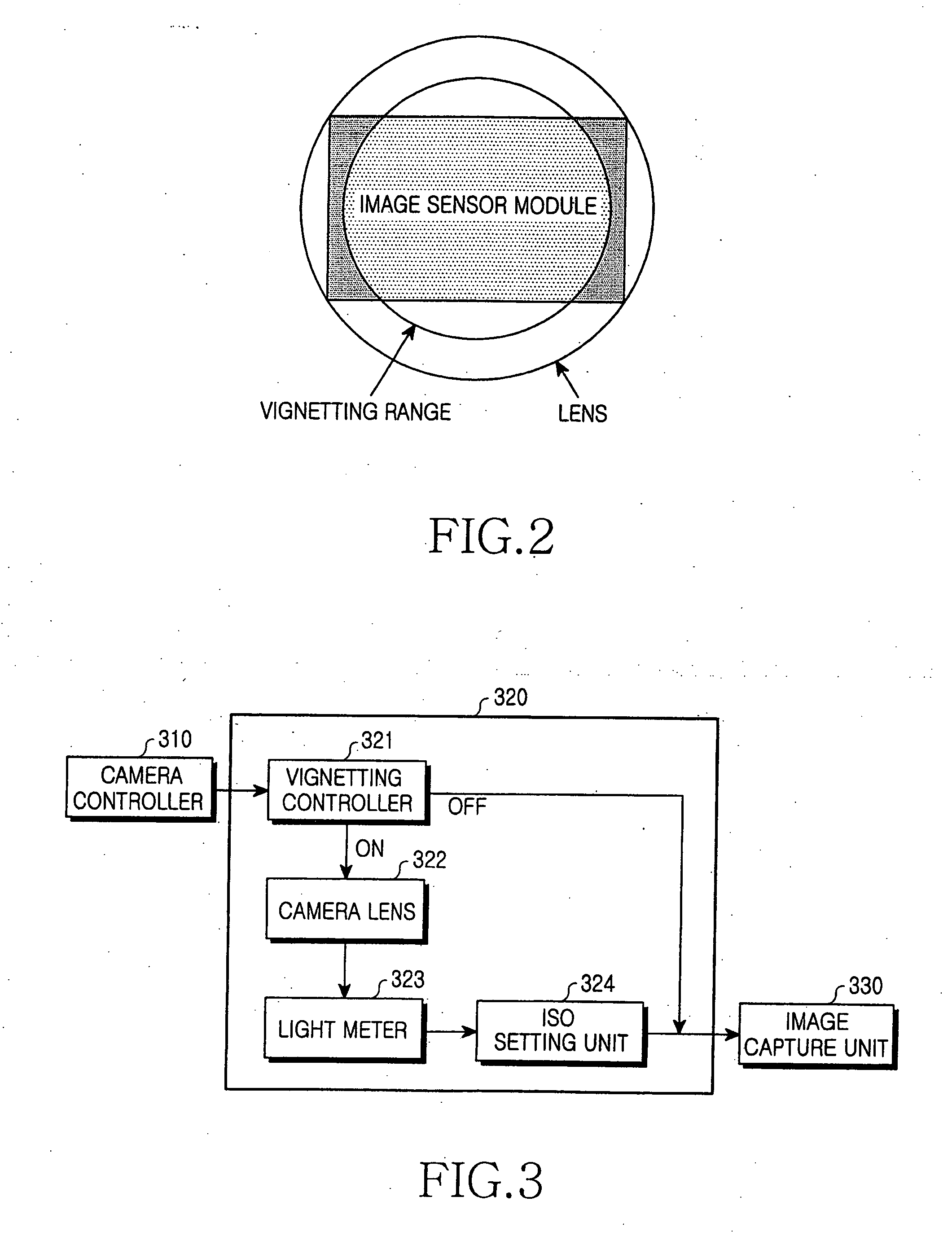
Apparatus and method for excluding vignetting in a digital camera
InactiveUS20060104627A1Eliminate vignettingTelevision system detailsExposure controlVignettingCamera module
An apparatus and method is provided for excluding vignetting occurring during wide-angle shooting using a camera. When a focal length of the camera is computed and an ISO range is set using a result of measuring an amount of light, a view angle wider than the inherent view angle of a camera module can be provided. Therefore, vignetting can be removed and an image of an area wider than the current capture range can be captured.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Plenoptic camera device and shading correction method for the camera device
InactiveUS20150130907A1The effect is accurateTelevision system detailsColor television detailsVignettingComputer science
A plenoptic camera device and a shading correction method thereof are provided. The plenoptic camera device includes a processor including a shading correction block configured to determine a four-dimensional axis with respect in a raw image, generate a four-dimensional profile by applying a polynomial fit with respect to the plurality of pixels in the raw image based on the four-dimensional axis, and calculate a gain using the four-dimensional profile and a non-volatile memory device configured to store the gain. Accordingly, the plenoptic camera device can remove a vignetting effect using the gain.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
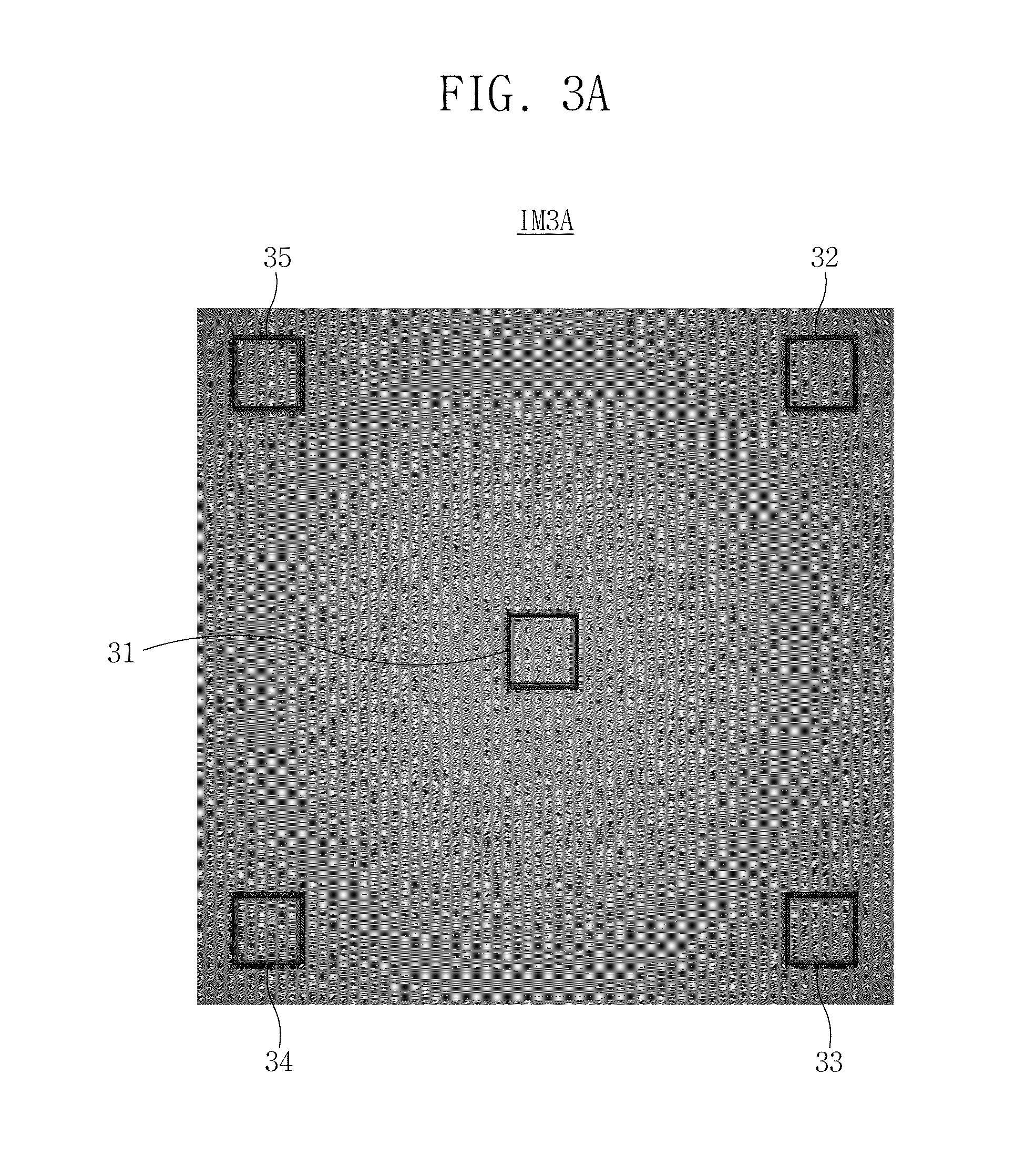
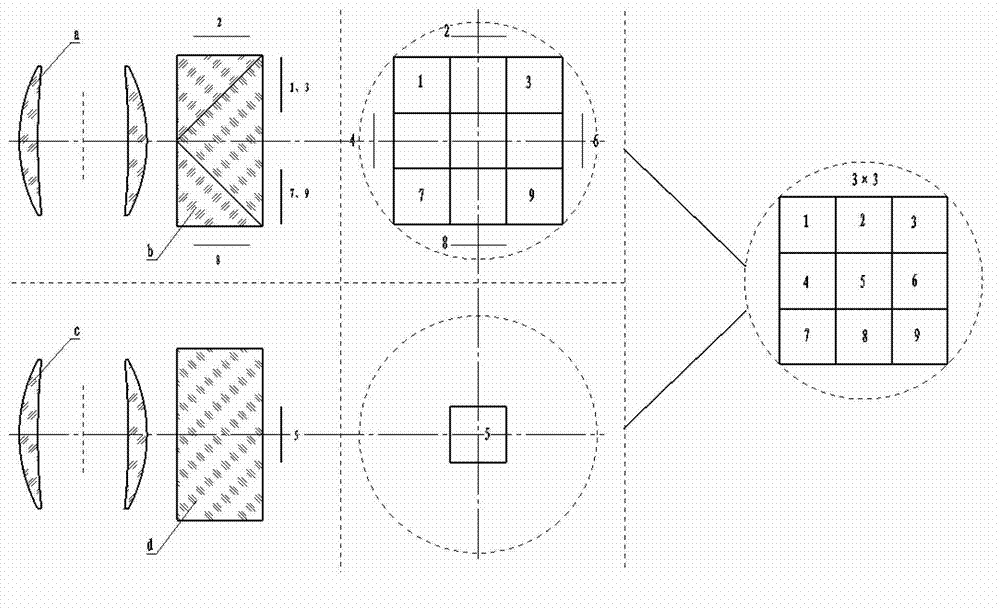
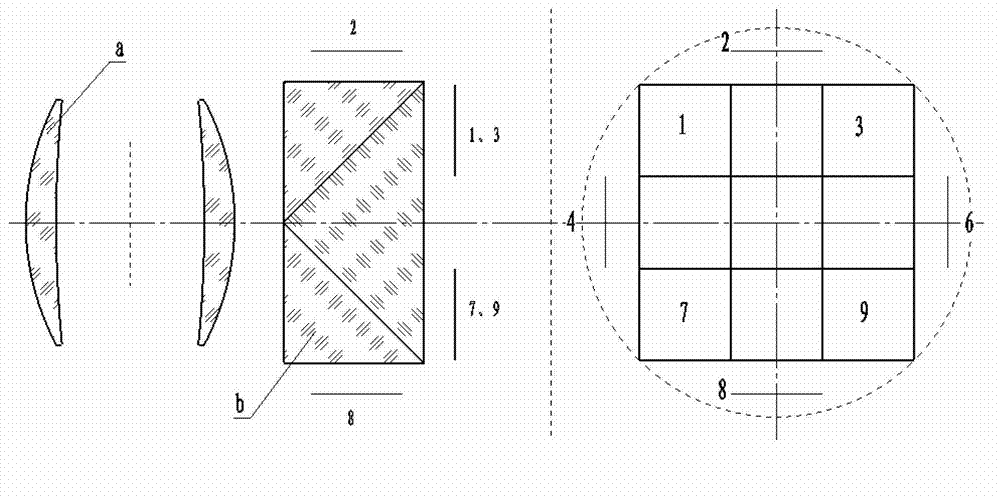
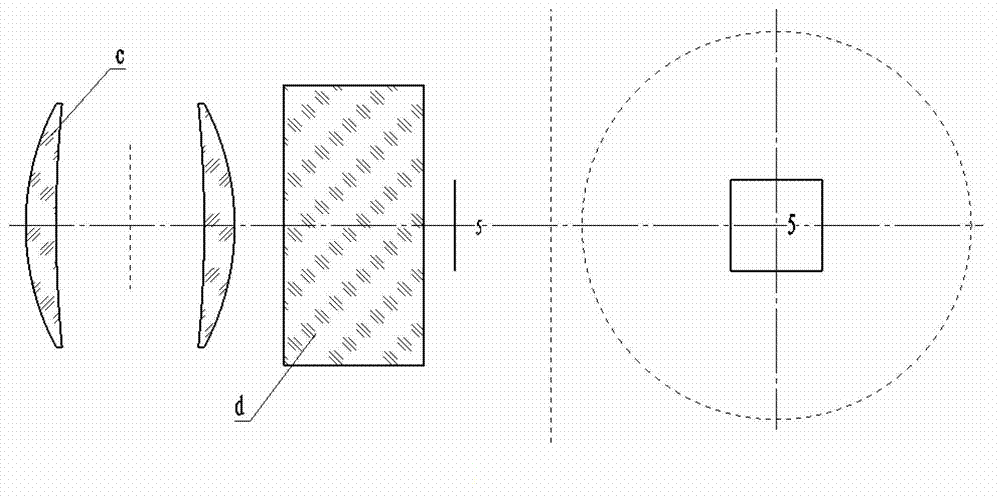
Seamless splicing imaging photoelectric system based on double lenses and nine surface array detectors
InactiveCN102905061ANo vignettingNo movement mechanismTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesCamera lensAviation
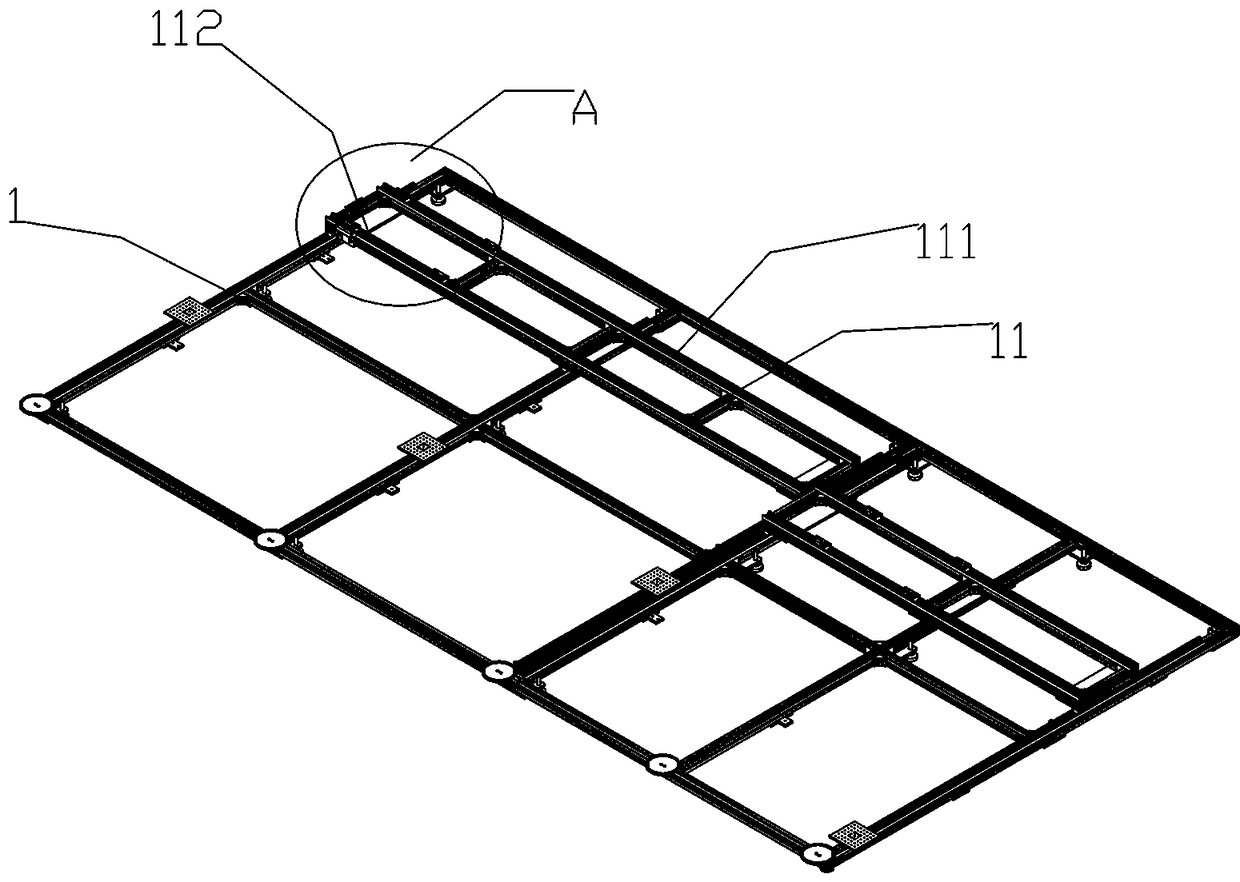
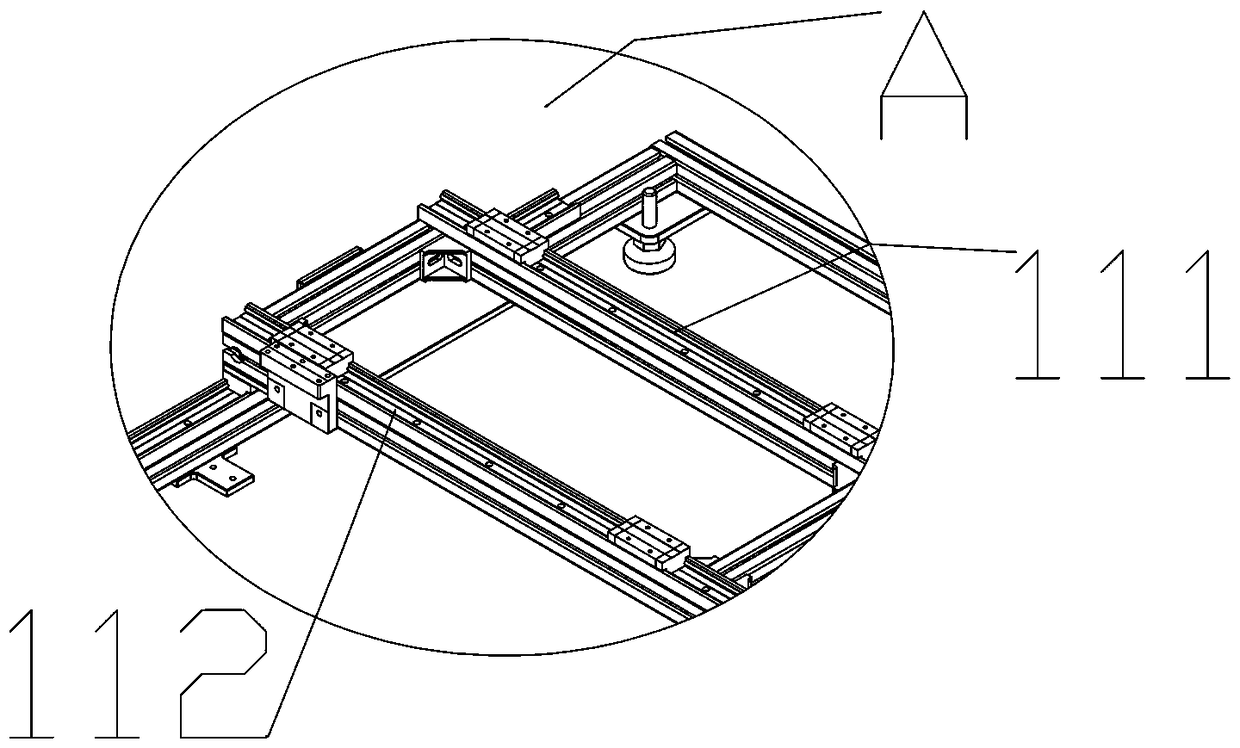
The invention discloses a seamless splicing imaging photoelectric system based on double lenses and nine surface array detectors. The seamless splicing imaging photoelectric system has two imaging system structure and adopts a prism beam splitting mode; imaging of eight surface array detectors is realized on a first lens, wherein four surface array detectors are arranged on a main image surface and four surface array detectors are arranged on four side image surfaces respectively; imaging of the last surface array detector is realized on a second lens; and the two imaging systems and the surface array detectors are combined together to realize image surface seamless splicing formed by the nine surface array detectors in a 3*3 mode. A beam splitting prism is a combination of a rectangular pyramid and four half rectangular pyramid mirrors; and a beam splitting surface realizes beam splitting in a semi-transparency and semi-reflection manner, so that equivalent beam splitting is realized, and spliced vignetting of the surface array detectors can be eliminated. The seamless splicing imaging photoelectric system can be applied to aviation and aerospace optical imaging devices and optical detectors as well as equipment, in particular to aviation and aerospace mapping cameras of large-view-field ultra-large surface array detectors.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Telecentric bright field and annular dark field seamlessly fused illumination
Described is an illumination system for an area inspection apparatus. The described illumination provides telecentric bright field and annular dark field light that are seamlessly fused together. In one or more embodiments, the illumination system incorporates a unified optical lens assembly that combines different lenses that image illuminations positioned at different planes to a single plane in a seamless way. In one or more embodiments, the different parts of the illumination system have common aperture stop, therefore no vignetting is present in the optical path resulting in high quality of the optical images acquired by the inspection system.
Owner:ORBOTECH LTD
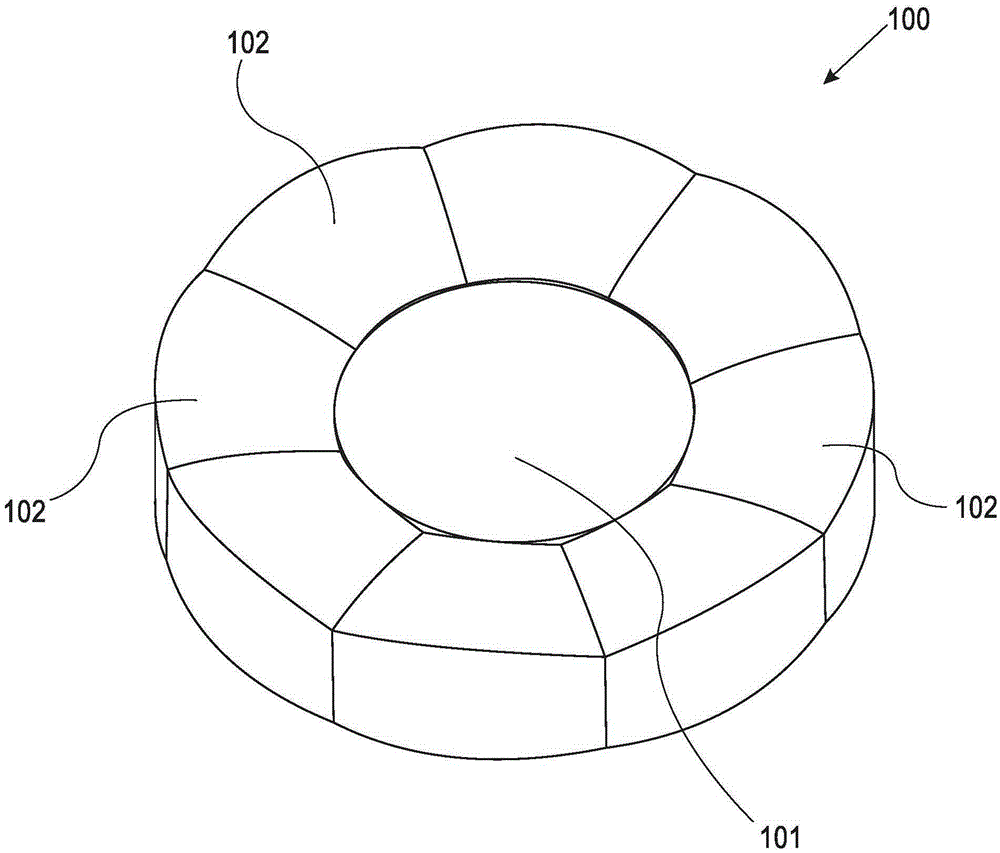
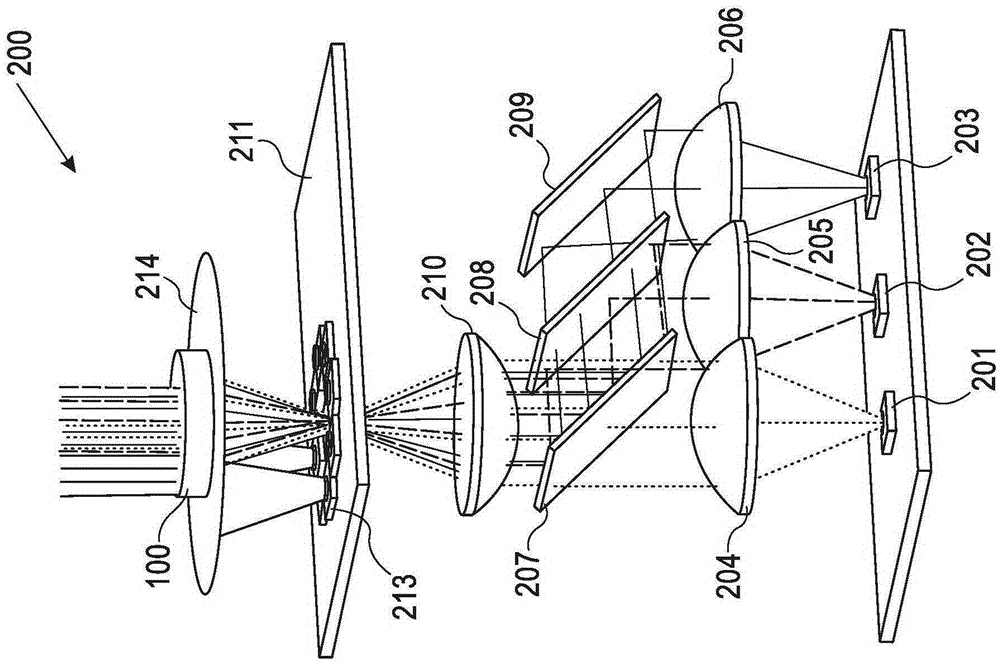
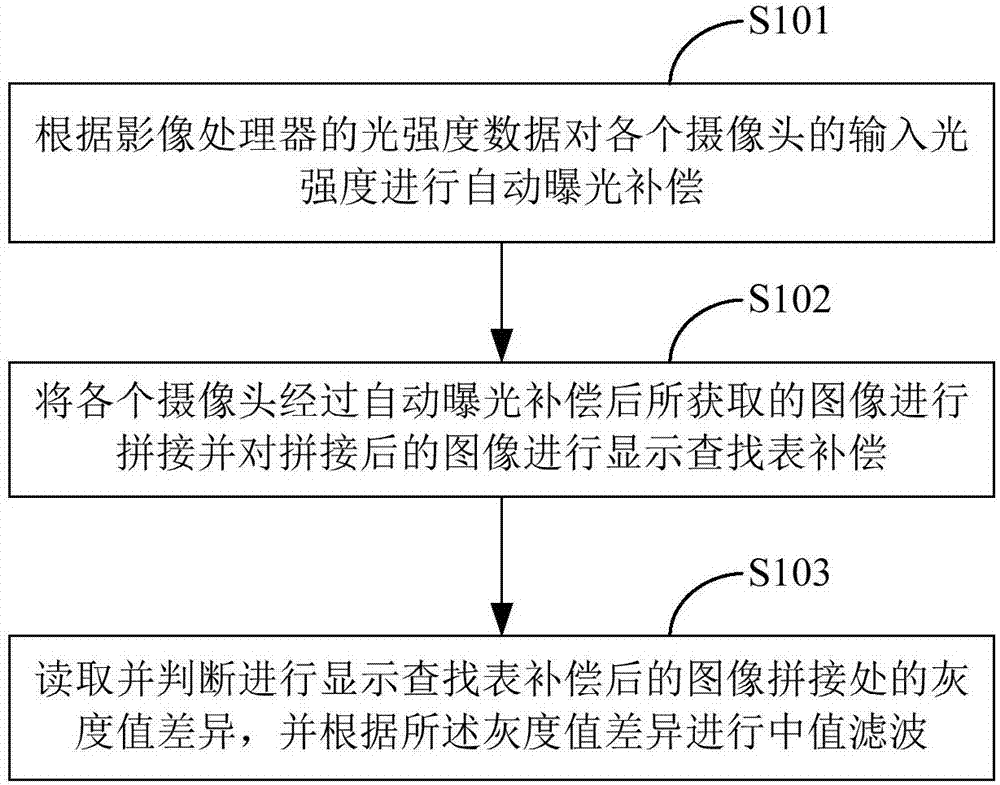
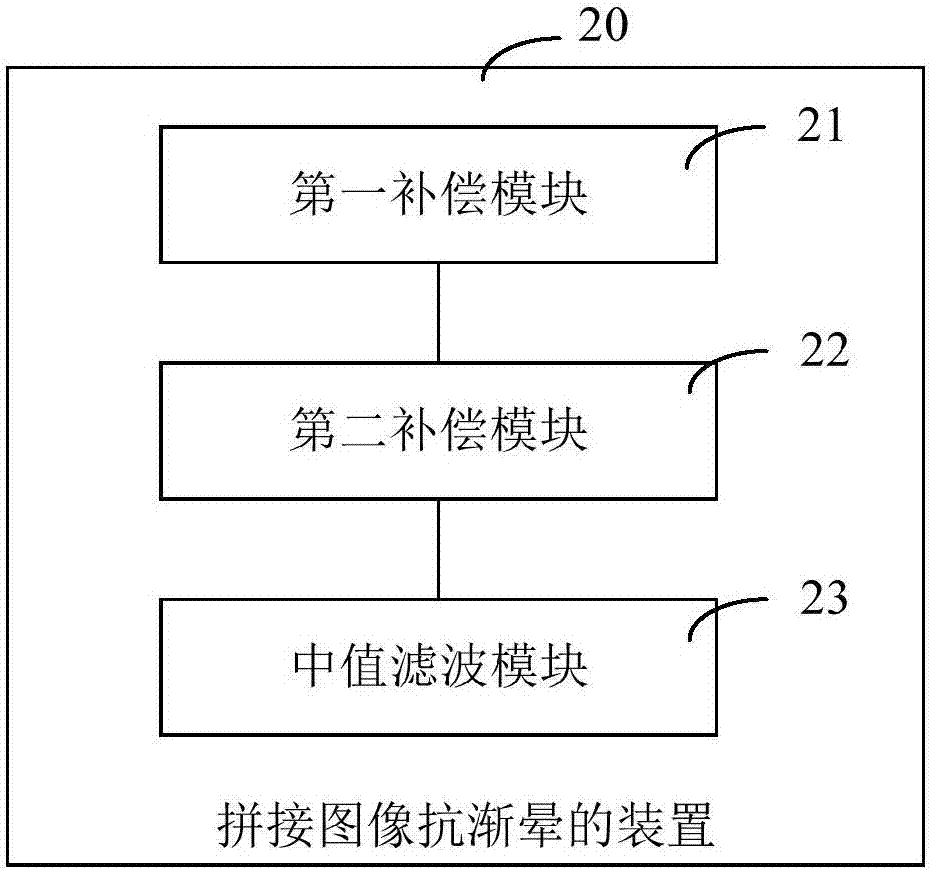
Anti-vignetting method and device for spliced image, and terminal equipment
InactiveCN107257443AEliminate vignettingImprove imaging effectTelevision system detailsColor television detailsVignettingImaging processing
The invention is applicable to the technical field of image processing, and provides an anti-vignetting method and an anti-vignetting device for a spliced image, and terminal equipment. The method comprises the steps of performing automatic exposure compensation on input light intensity of each camera according to exposure data of an image processor; splicing the images acquired by each camera after automatic exposure compensation and performing display lookup table compensation on the spliced image; and reading and judging a gray value difference at the image joint after the display lookup table compensation is performed, and performing median filtering on the gray value difference. The problem that the images acquired by the plurality of cameras are inconsistent in brightness is solved by performing automatic exposure compensation on light intensity of the image acquired by each camera, then corresponding compensation factor compensation is performed on the corresponding pixel position of the spliced image via the display lookup table, and median filtering is performed on the gray value difference at the image joint, so that the vignetting effect of the spliced image can be effectively eliminated, and the imaging effect of the spliced image is reinforced.
Owner:THUNDER SOFTWARE TECH SHENZHEN
Imaging device and imaging system
InactiveUS20090021633A1Easy to identifySure easyTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensVignetting
To provide the technology of an image-pickup device that can easily determine whether or not an image is photographed by mounting an interchangeable lens designed for an image-pickup device of an exposure-surface size different from an image-pickup element provided in a camera body. In an image-pickup system, when shooting is performed by mounting an interchangeable lens ready for an image-pickup surface of a size smaller than an image-pickup surface of an image-pickup element installed in the camera body (camera-main body), the main image (high-resolution record image) corresponding to a partial region at the center of the image-pickup surface, the partial region being free of vignetting caused by an insufficient circle, is generated, and a reduced image (e.g, a thumbnail image) is generated by reducing a whole image obtained on the entire image-pickup surface (steps ST10 and ST12). Subsequently, the vignetting can be visually identified in an image photographed in the state where an inappropriate interchangeable lens is mounted when the reduced image is displayed (when the image reproduction is performed) so that it becomes possible to easily determine that the image is photographed by mounting the inappropriate interchangeable lens.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method for stitching together images taken through fisheye lens in order to produce 360-degree spherical panorama
ActiveUS10136055B2Eliminate any noticeable seamEliminate the effects ofImage enhancementTelevision system detailsCamera lensFisheye lens
Owner:ARCSOFT MULTIMEDIA TECH LTD
Guide rail photographing device
The invention relates to a guide rail photographing device. The guide rail photographing device comprises a support. A rotating plate is connected to the support through a first sliding mechanism in aleft-right or front-back sliding mode. A case is connected to the rotating plate rotationally. An operating platform is fixedly connected to the case. A fine adjustment mechanism for mounting a camera is connected to the upper end face of the operating platform through a second sliding mechanism in a left-right or front-back sliding mode. A photographing hole is formed in the support. A combinedlight source is arranged on each of two sides of the photographing hole. The guide rail photographing device has the advantages that the regional guide rail space design is adopted, and three-dimensional accurate adjustment and positioning can be achieved through guide rail sliding during 360-degree rotation, so that accurate photographing is guaranteed, photographed pictures are not deflected anddeformed, and vignetting is avoided.
Owner:JIANGXI HOLITECH TECH
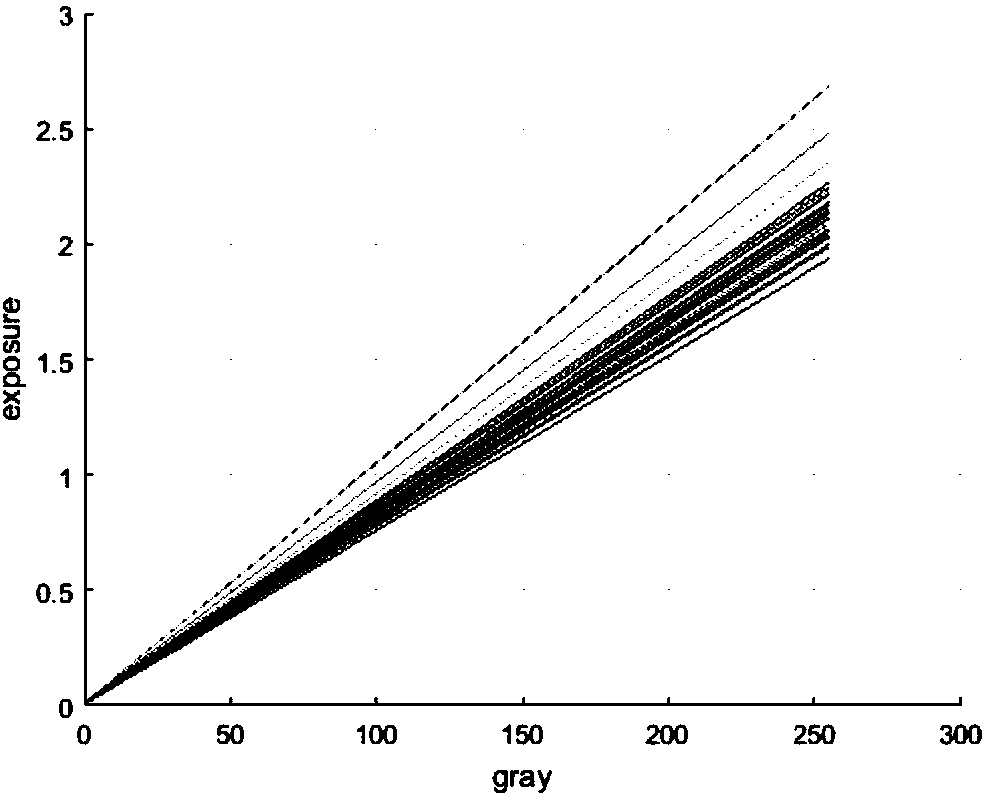
Consistent correction method and system of image sensor non-uniformity
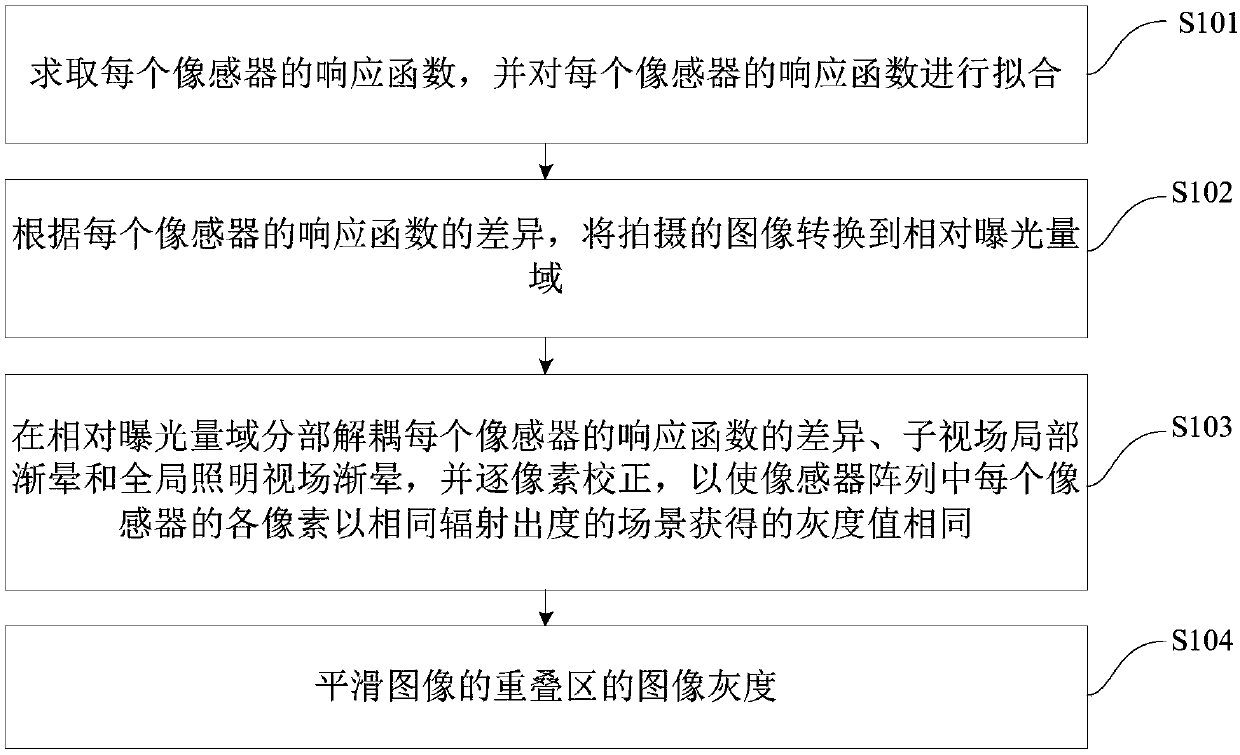
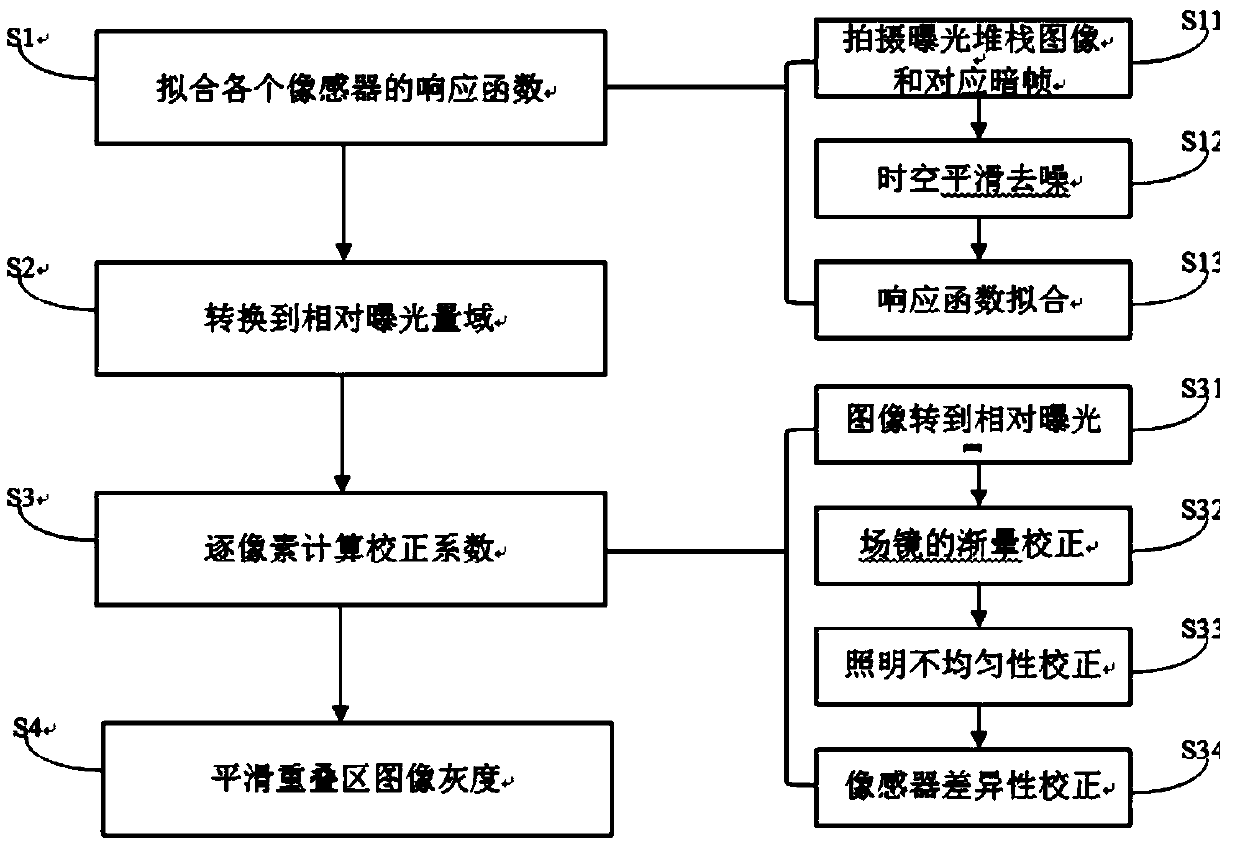
ActiveCN108055487AEffective compensationEffective handlingTelevision system detailsColor television detailsPattern recognitionVignetting
The invention discloses a consistent correction method and system of image sensor non-uniformity. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining a response function of each image sensor, and fitting the response function of each image sensor; converting a shot image to a relative exposure domain according the difference of the response function of each image sensor; decoupling the differenceof the response function of each image sensor, sub-field local vignetting and global illumination field vignetting, and correcting one pixel by one pixel, thereby enabling each pixel of each image sensor in an image sensor array to acquire the same gray value by using the same radiation out-degree scene; and smoothing the image gray of an overlapping region of the image. Through the method disclosed by the invention, the model error and universality absence caused by the traditional optical system modelling can be effectively avoided, the method does not depend on the overlapping rate betweenthe sub-fields and the representation way of the vignetting, so that the correction effect is obvious, and good universality and extensive application scene are provided.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
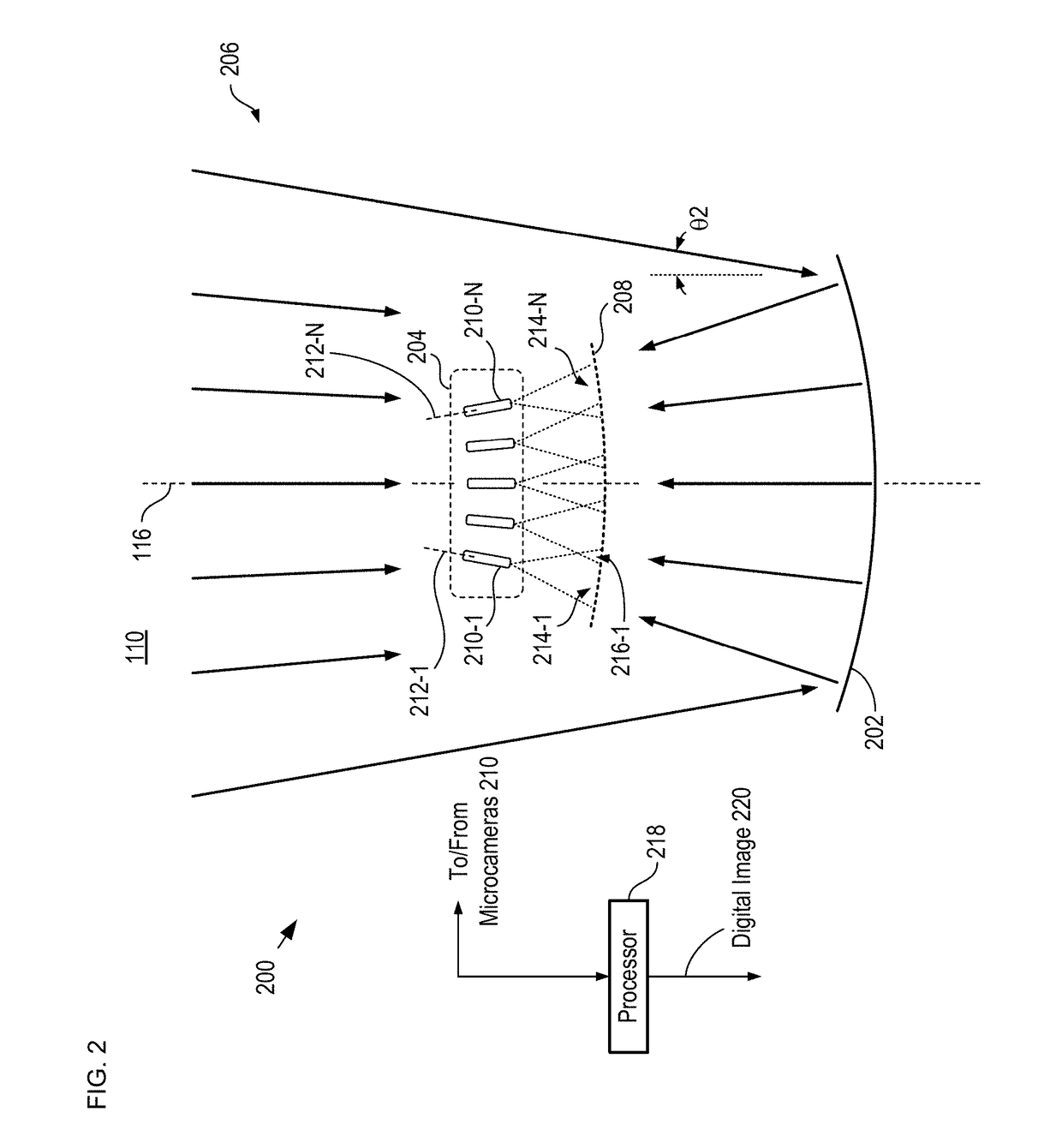
Multiscale telescopic imaging system
ActiveUS20170254999A1Reduce occlusionReduced magnitudeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsIntermediate imageVignetting
A multiscale telescopic imaging system is disclosed. The system includes an objective lens, having a wide field of view, which forms an intermediate image of a scene at a substantially spherical image surface. A plurality of microcameras in a microcamera array relay image portions of the intermediate image onto their respective focal-plane arrays, while simultaneously correcting at least one localized aberration in their respective image portions. The microcameras in the microcamera array are arranged such that the fields of view of adjacent microcameras overlap enabling field points of the intermediate image to be relayed by multiple microcameras. The microcamera array and objective lens are arranged such that light from the scene can reach the objective lens while mitigating deleterious effects such as obscuration and vignetting.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
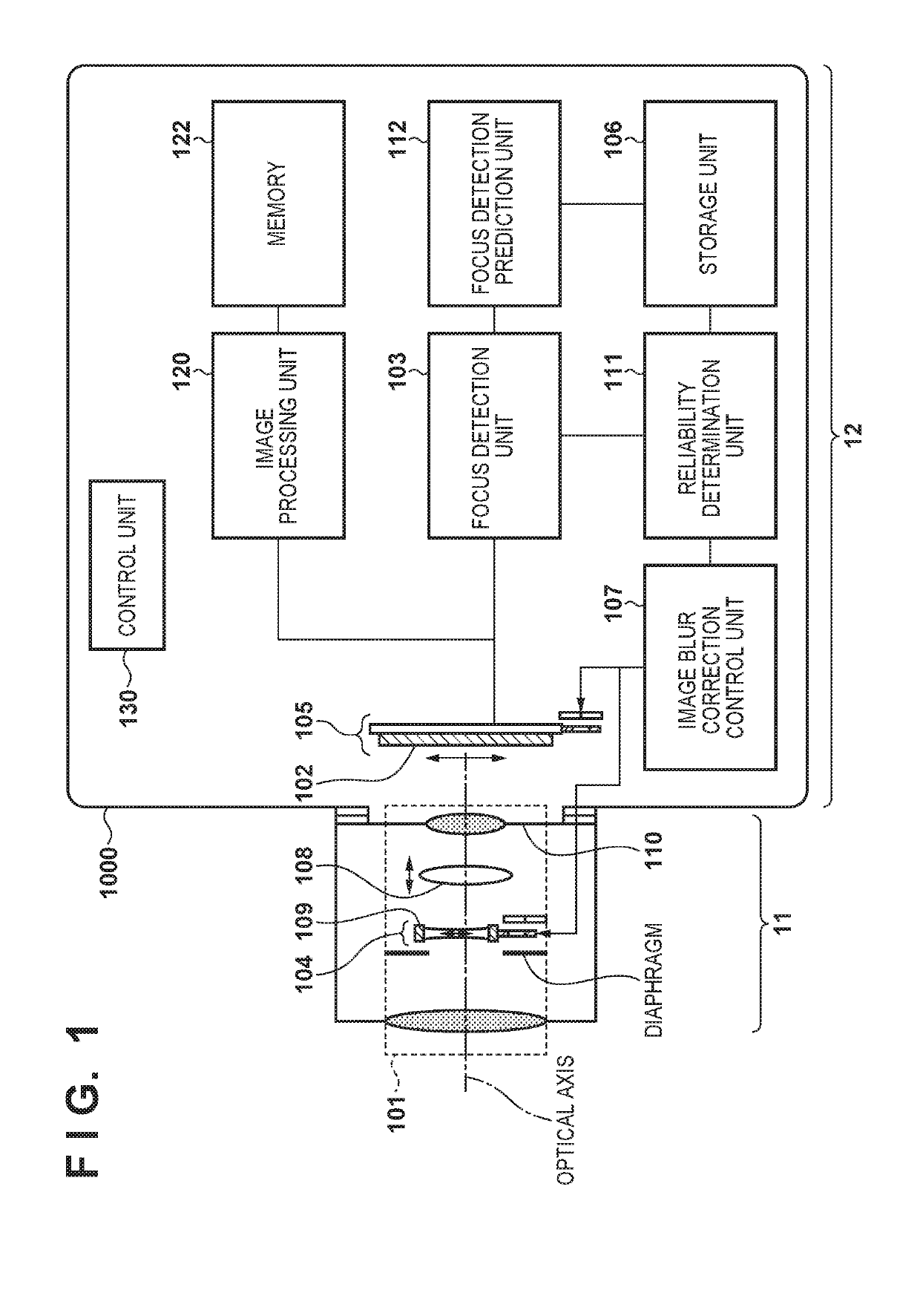
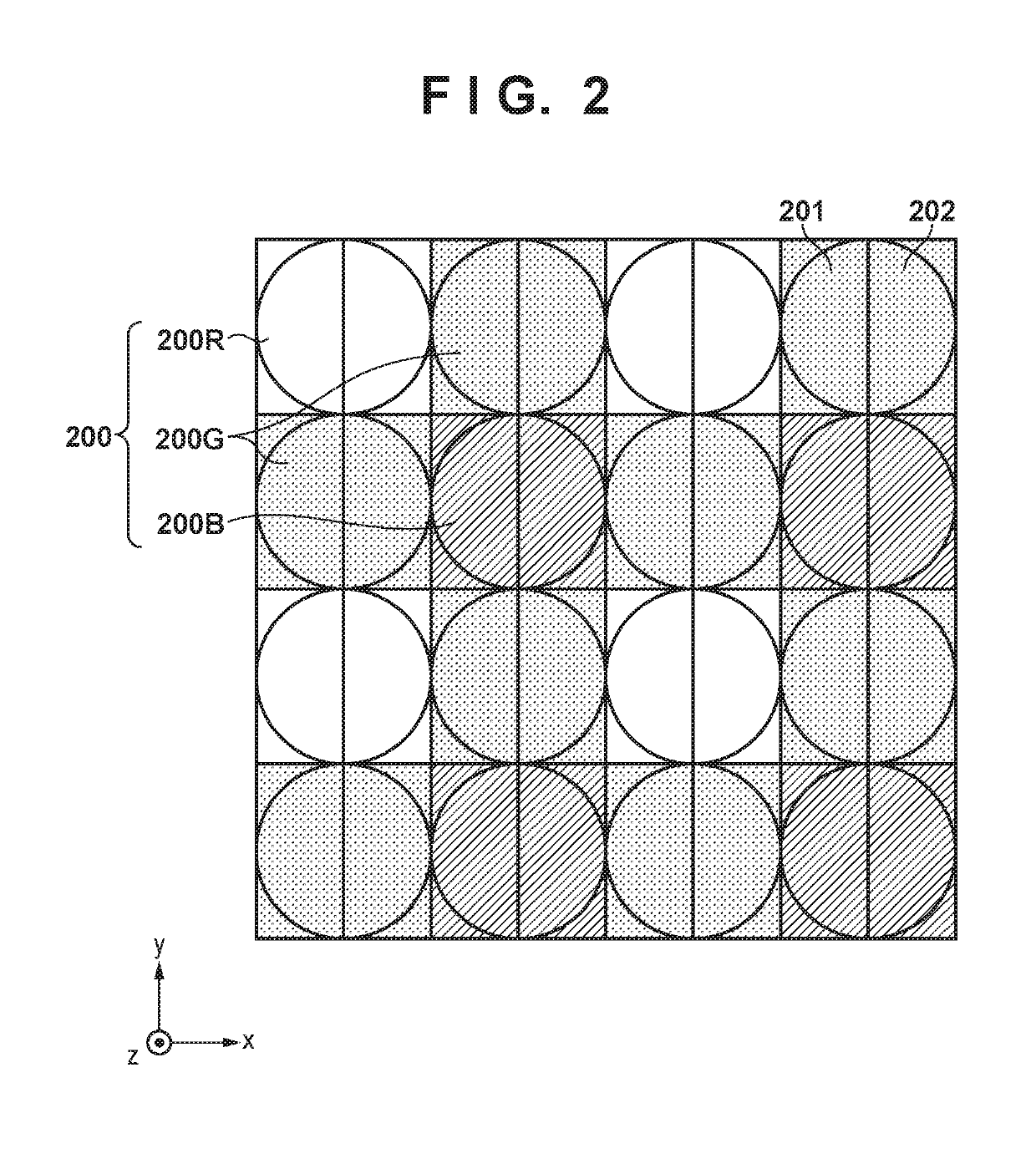
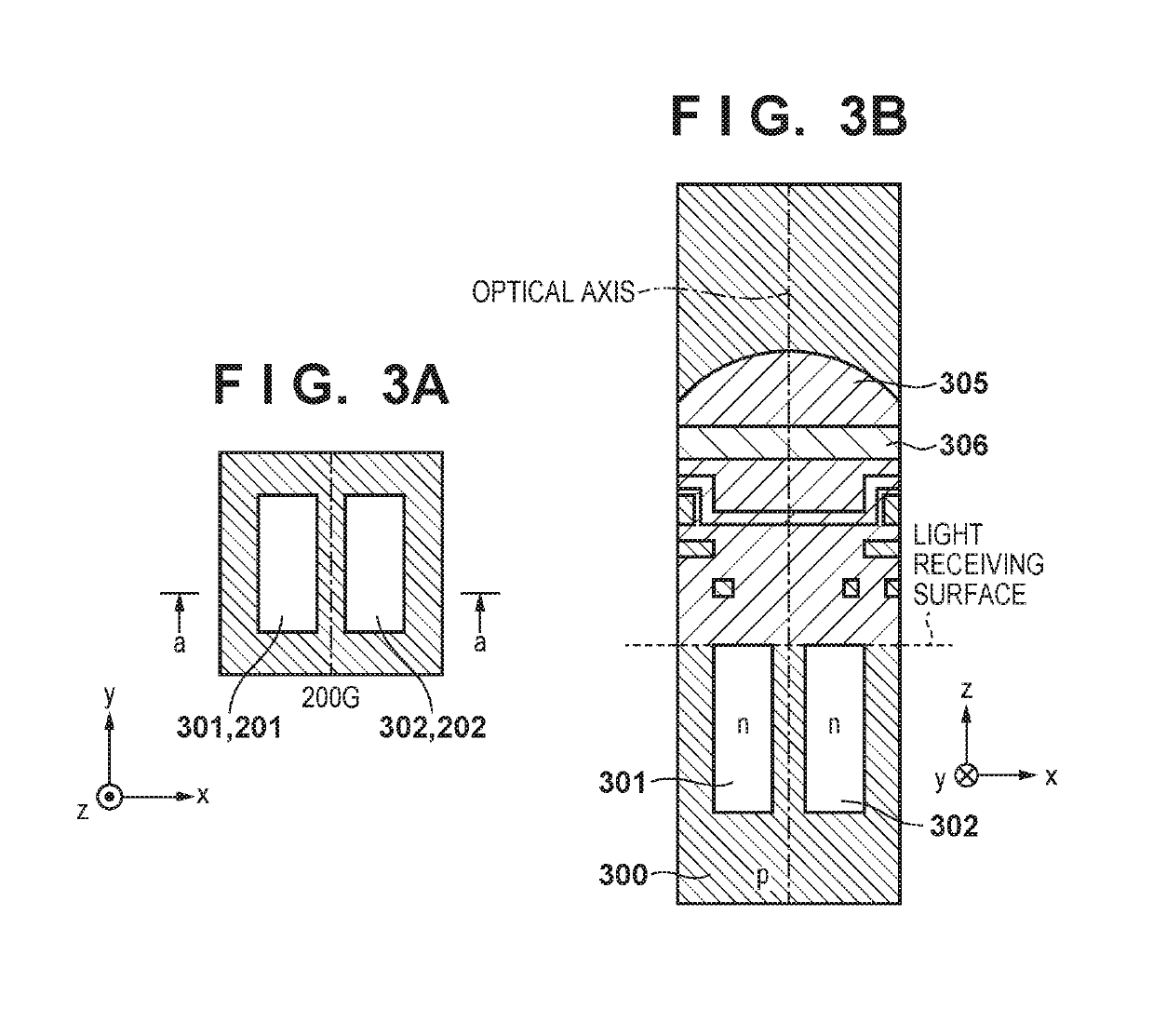
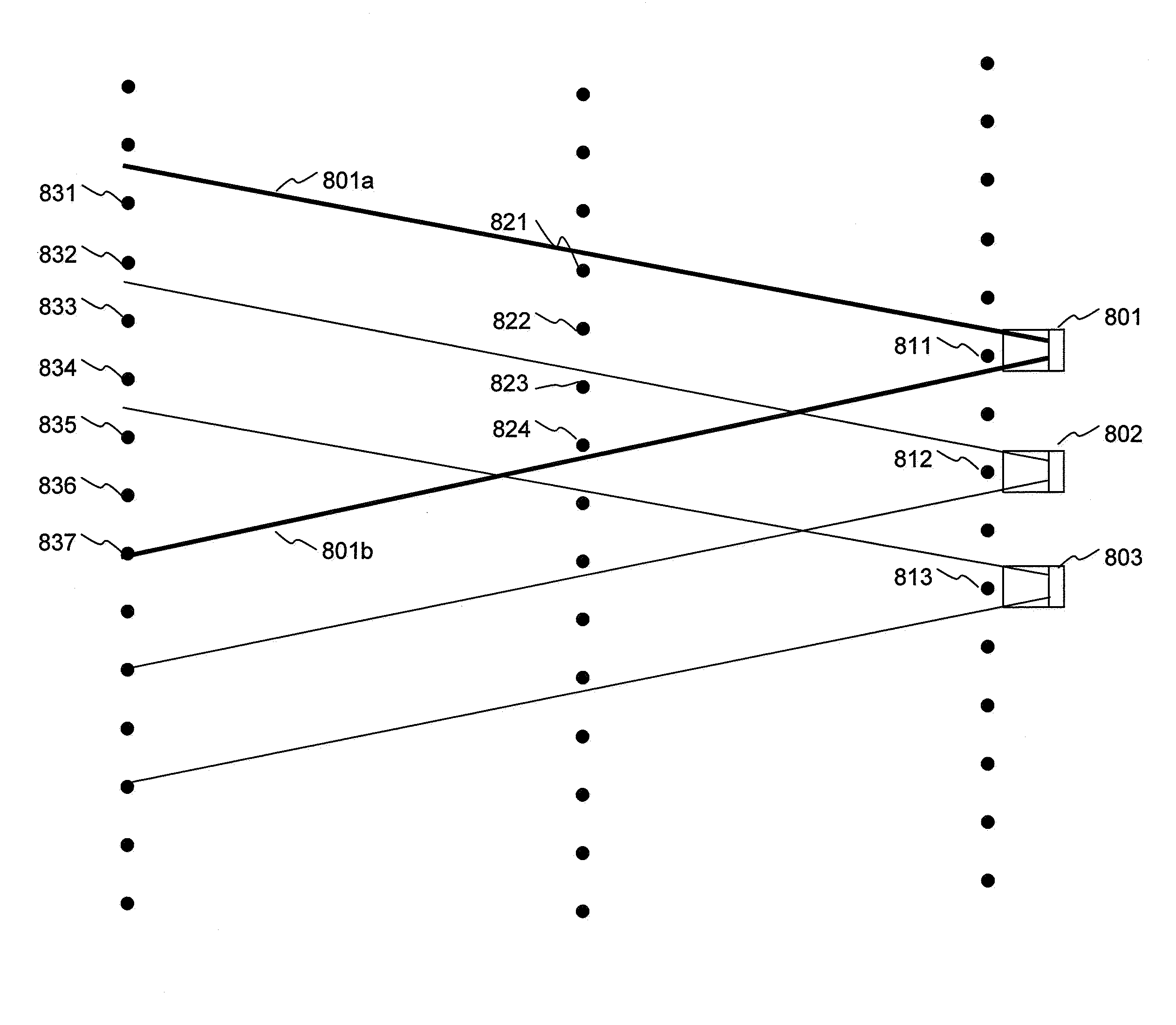
Image capturing apparatus, control method of controlling the same, and storage medium
ActiveUS20190158744A1Television system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionVignettingPhase difference
An image capturing apparatus includes: a focus detection unit configured to perform focus detection based on a phase difference between a plurality of image signals obtained by photo-electrically converting light beams that respectively pass through different partial pupil regions of an imaging optical system; an image blur correction unit configured to correct image blur of an object image by driving an optical member for image blur correction; and a determination unit configured to determine reliability of a focus detection result detected by the focus detection unit based on information regarding a focus detection area with respect to which the focus detection unit performs focus detection, and information regarding vignetting that occurs in light beams that pass through the imaging optical system as a result of the image blur correction unit correcting the image blur.
Owner:CANON KK
Synthetic image formation via signal processing for vignetted optoelectroinc arrays, lensless cameras, and integrated camera-displays
InactiveUS20110025864A1Many contactsMore experienceTelevision system detailsColor television detailsColor imageSensor array
Algorithms and methods for performing electronic image formation and refinement from overlapping measurement vignettes captured by an array of image sensors and associated micro-optics are presented. The invention is directed to a new type of image formation system that combines readily-fabricated micro-optical structures, a two-dimensional image sensor array with electronic or digital image processing to actually construct the image. Image formation is performed without a conventional large shared lens and associated separation distance between lens and image sensor, resulting in a “lensless camera.”In an application, a readily fabricatable LED array is used as a light-field sensor. In an application, the LED array further serves as a color “lensless camera.” In an application, the LED array also serves as an image display. In an application, the LED array further serves as a color image display. In an embodiment, one or more synergistic features of an integrated camera / display surface are realized.
Owner:NRI R&D PATENT LICENSING LLC
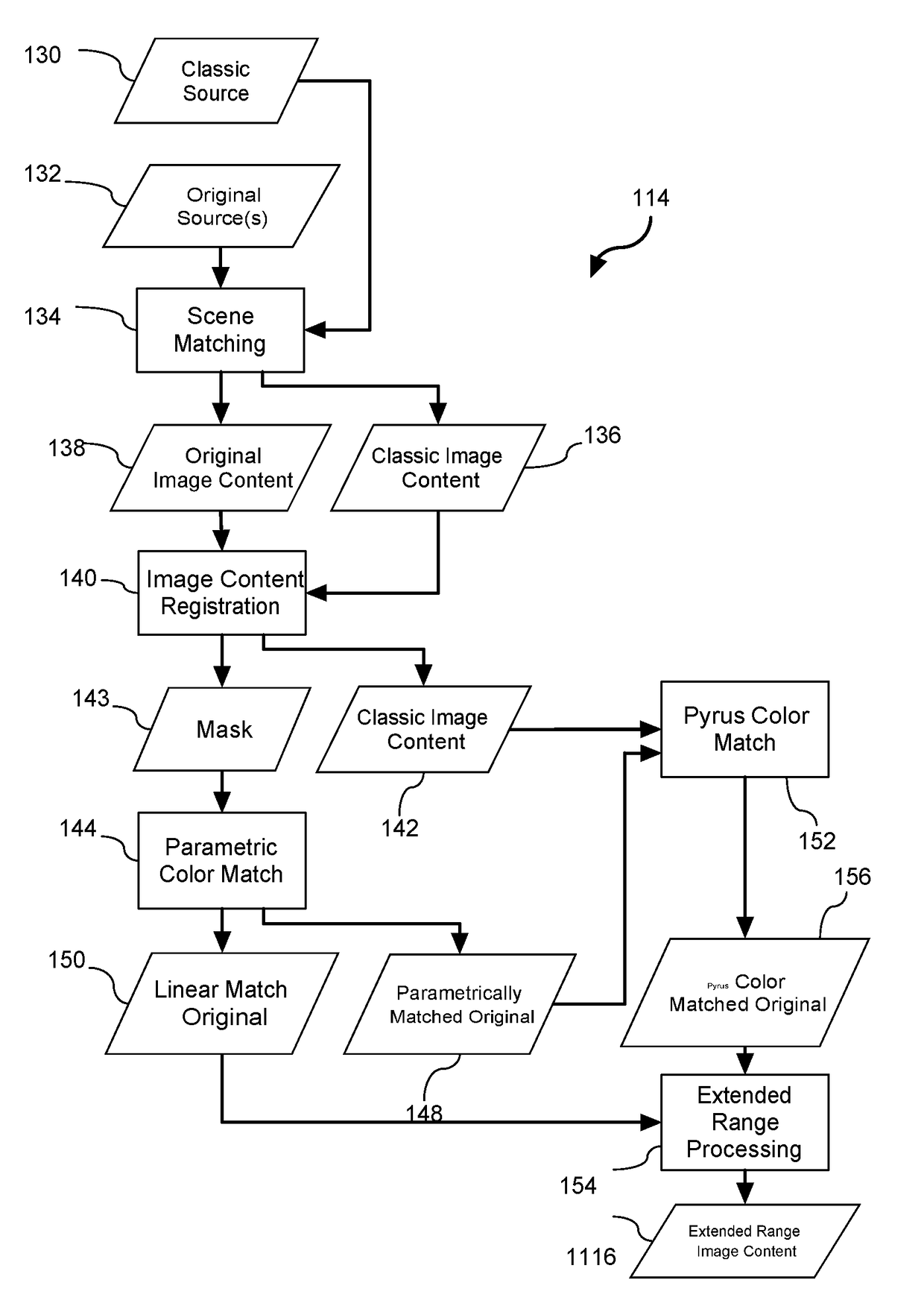
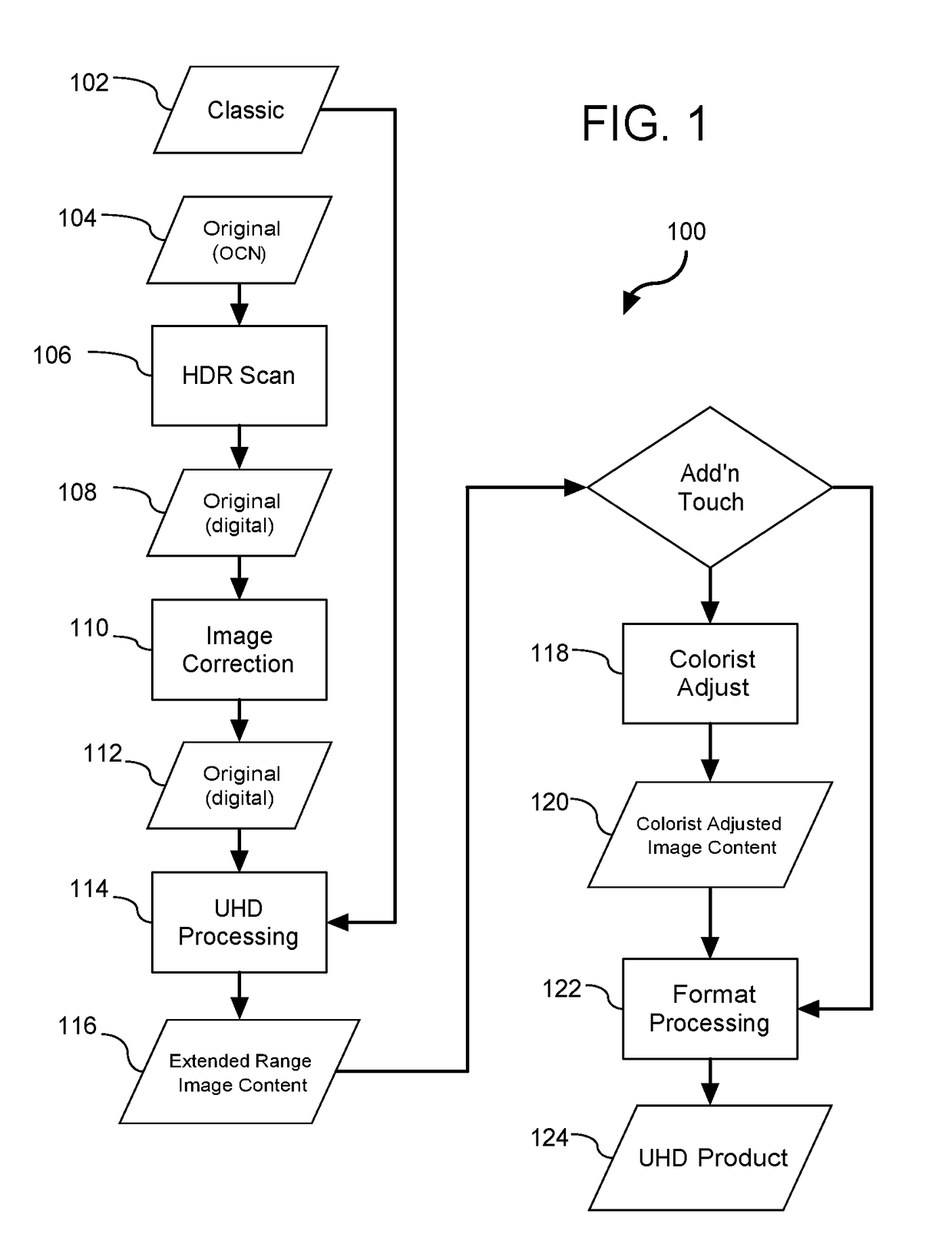
Method and system for processing image content for enabling high dynamic range (UHD) output thereof and computer-readable medium comprising UHD content created using same
Implementations disclosed herein (e.g., systems, methods, and computer-readable program products) provide a high definition range “UHD” compatible version of classic image content (e.g., as-released motion pictures) that was created in an era of limited dynamic range and that maintains aesthetic characterization defined by “Director's Intent” of the classic image content. Such implementations advantageously use clues to the Director's Intent found in the classic image content to make intelligent estimations as to what a Director (or other image content editing professional) was attempting to achieve in the classic image content relative to a corresponding original image content (e.g., as-shot image content). The original image content holds original imagery details that have been altered or omitted during creation of corresponding classic image content. The classic image content exhibits attributes that reflect the Director's Intent such as, for example color, contrast, vignetting, saturation, and the like.
Owner:ASTRAL IMA
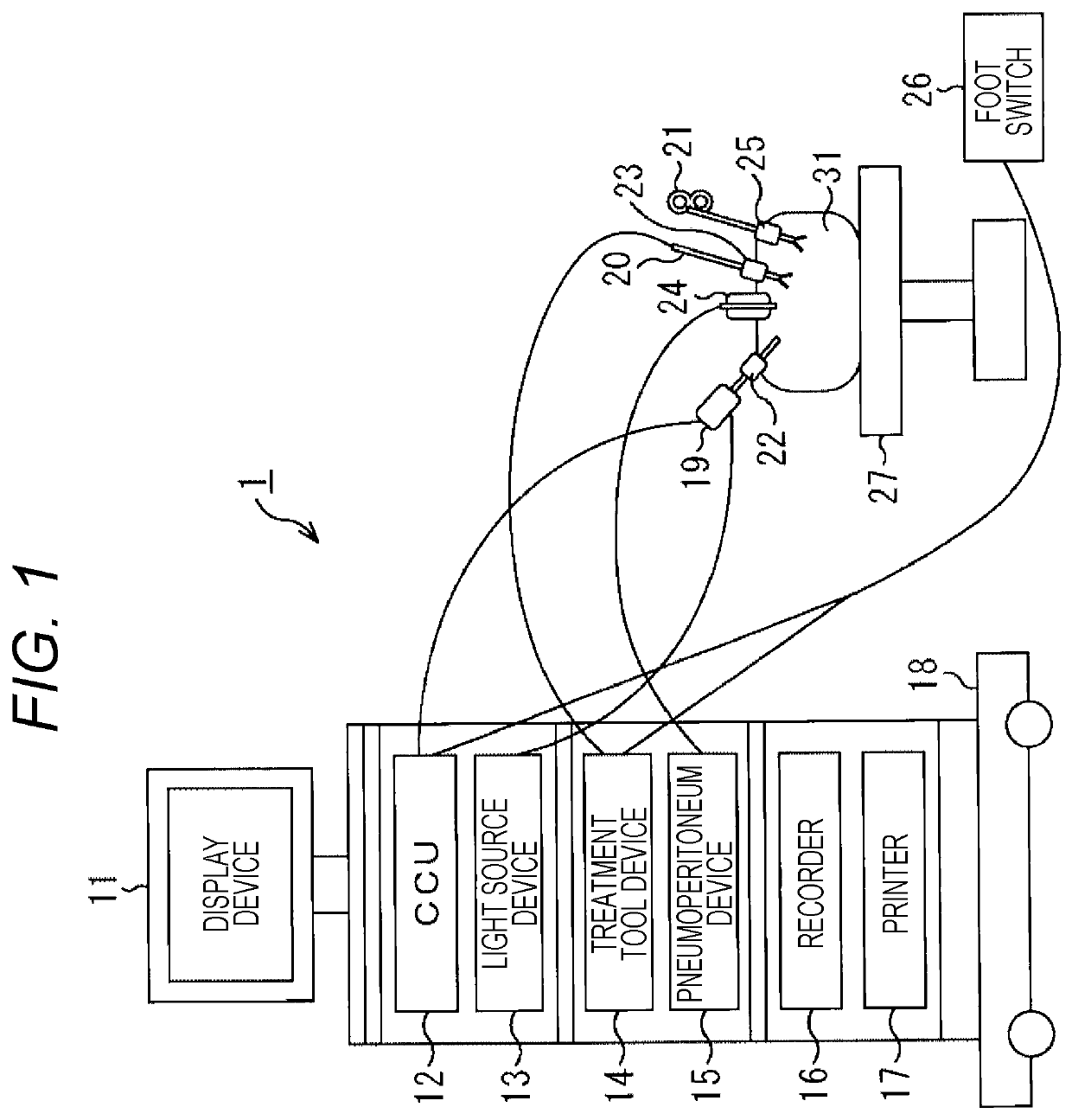
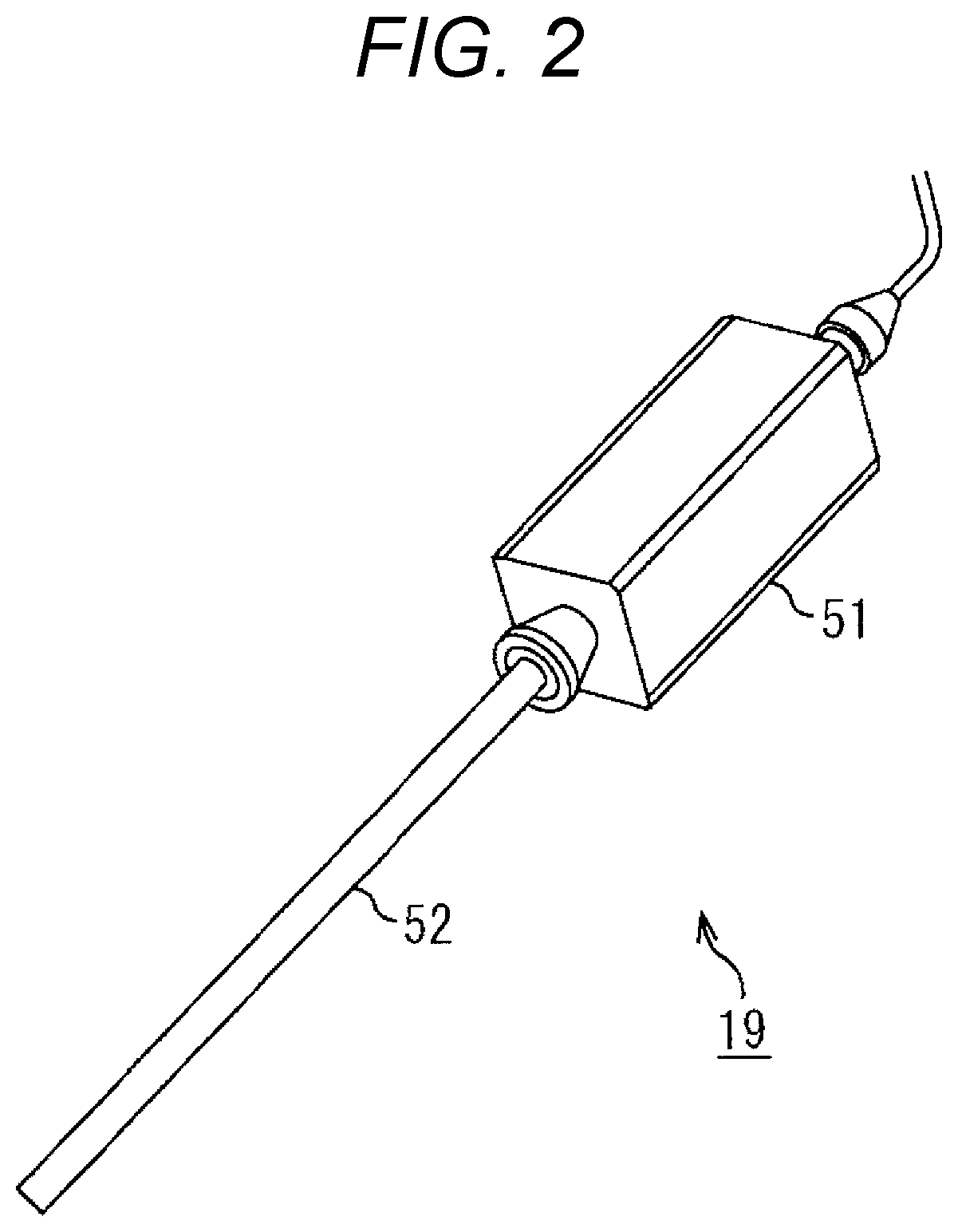
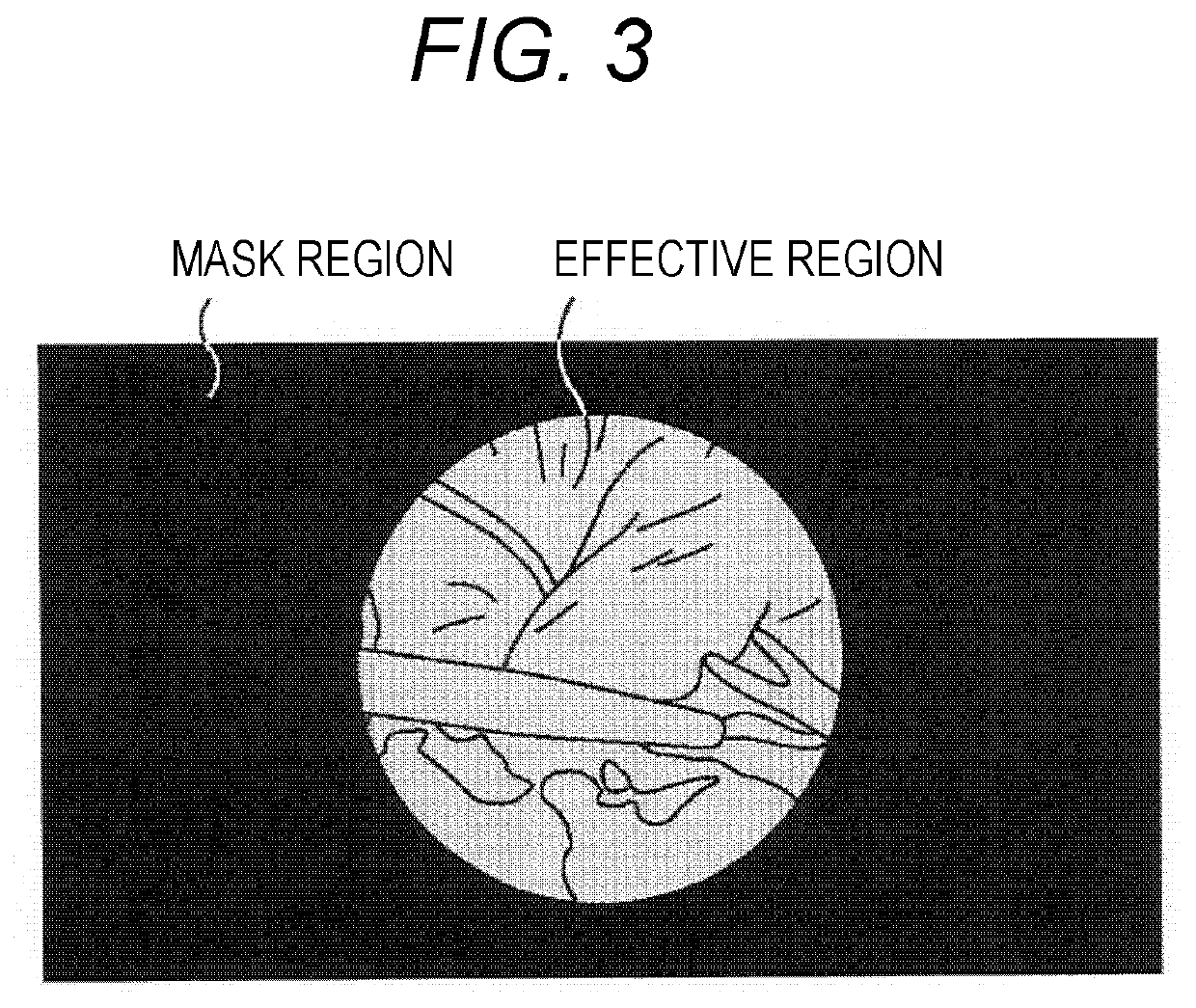
System with endoscope and image sensor and method for processing medical images
ActiveUS20210019884A1FocusAdvantageous white balance processingTelevision system detailsImage enhancementVignettingAutofocus
A system includes an endoscope including a scope and an image sensor. The image sensor is configured to capture medical image data that includes effective image portion data and a mechanical vignetting portion data, the mechanical vignetting portion data of the medical image data being generated due to mechanical vignetting caused by a difference in the image sensor which generates the medical image data and the scope. There is also circuitry configured to determine evaluation information from image data which is from the effective image portion data, and execute a control process to at least partially control at least one of an autofocus processing, and an auto white balance processing on the endoscope on the basis of the evaluation information.
Owner:SONY CORP
Night vision system and control method thereof
InactiveUS7045759B2Appropriate displayDegree of halationTelevision system detailsPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementVignettingTime signal
A second circuit separately extracts a synchronization signal and brightness signal from an image signal output from a camera for capturing an image of a subject. A gamma amplifier produces a gamma correction signal based on a brightness ratio characteristic in which a display brightness increases as the signal level of the brightness signal increases and the display brightness is set using a display brightness correction ratio which is preferably 70 to 90% of an equi-proportional display brightness correction ratio when the signal level of the brightness signal falls in a high-brightness range. A liquid crystal display receives the gamma correction signal and displays an image captured by the camera with the display brightness set in accordance with the brightness ratio characteristic while synchronizing with a drive timing signal output from a first circuit. Thus, the difference in display brightness between different high-brightness regions or subjects is made large, whereby halation which may otherwise occur between those regions or subjects can be prevented.
Owner:DENSO CORP +1
Bionic optical imaging system
PendingCN108259723AAvoid interferenceImprove uniformity of illuminationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsVignettingHigh resolution imaging
The invention relates to the field of large-field-of-view and high-resolution imaging technology, in particular to a bionic optical imaging system. The imaging system comprises at least two subsystems, each subsystem comprises a concentric spherical objective lens and at least two sub-aperture cameras, and the optical axis of each sub-aperture camera of each subsystem passes through the center ofthe concentric spherical objective lens of the corresponding subsystem. Field angles are set at intervals for images captured by the sub-aperture cameras, and the vacant parts of the field angles setat intervals are complemented by image overlapping of the subsystems and are continuous within the set field of view, so that the adjacent sub-aperture cameras are spaced a certain angle, the interference between the sub-apertures is effectively prevented, vignetting of the imaging system is reduced, the imaging system has good illumination uniformity in the field of view, and the problems of lowimaging quality, difficult stitching and the like caused by structural interference and vignetting of the edge field of view of the acquired image in the existing large-field-of-view and high-resolution optical imaging system are solved.
Owner:LUOYANG INST OF ELECTRO OPTICAL EQUIP OF AVIC
Vignetting correction system and method
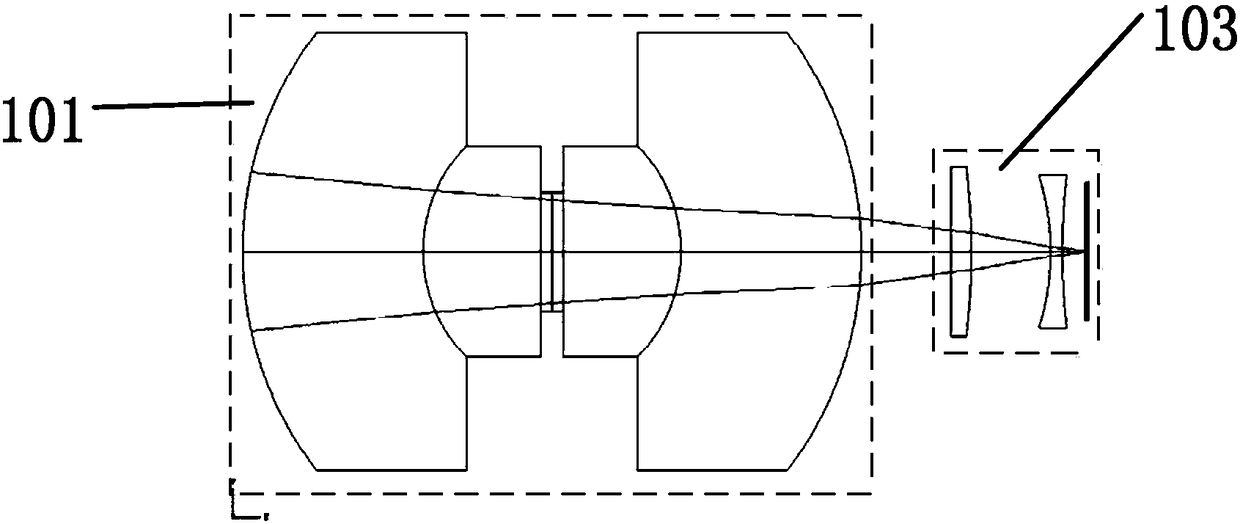
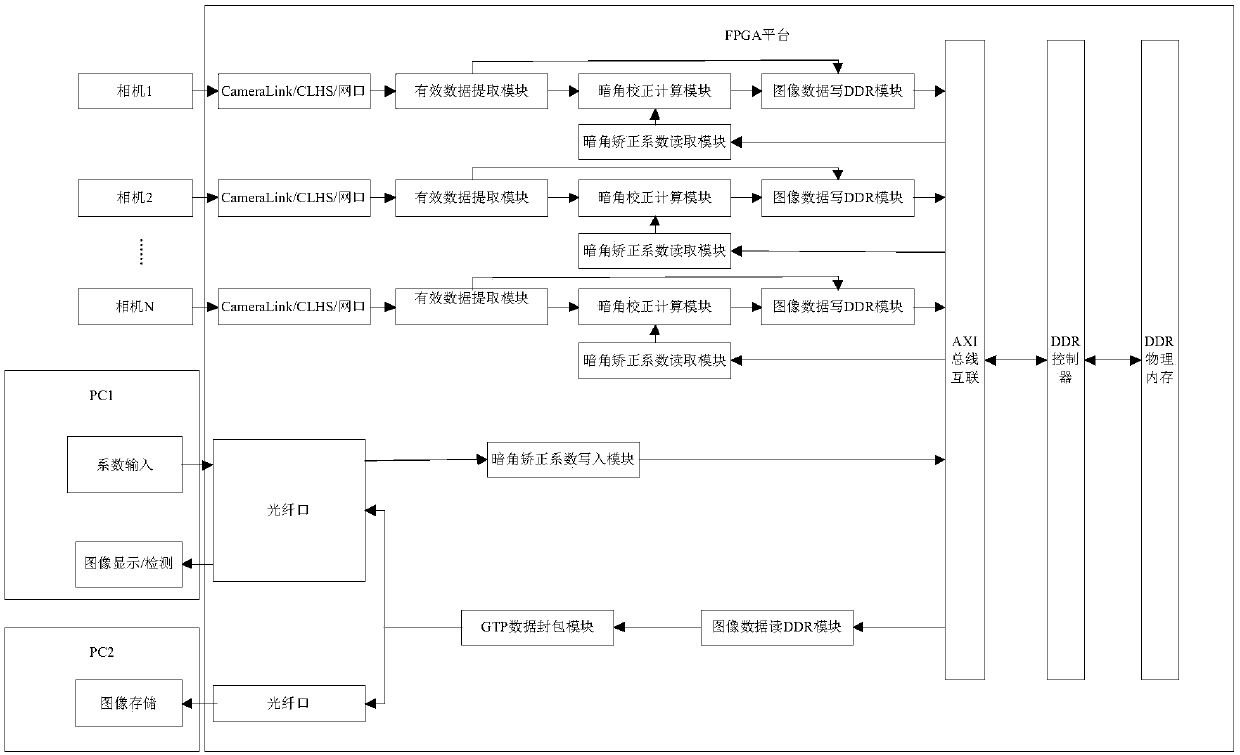
ActiveCN108111777AReduce loadGood vignetting correctionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImaging processingVignetting
The invention belongs to the technical field of image processing, and discloses a vignetting correction system and method. The method includes: obtaining a vignetting correction coefficient accordingto a plurality of images; obtaining a test image and obtaining image pixel data through analysis; and performing vignetting correction on the image pixel data according to the vignetting correction coefficient, and obtaining, packaging and outputting vignetting correction image data. The system comprises a first PC terminal, cameras and a FPGA platform; the cameras are used for shooting and obtaining test images; the FPGA platform is used for analyzing the test images, obtaining image pixel data, performing vignetting correction on the image pixel data according to the vignetting correction coefficient, and obtaining, packaging and outputting the vignetting correction image data; and the first PC terminal is used for obtaining the vignetting correction coefficient and displaying and / or detecting the vignetting correction image data according to a plurality of images. According to the system and method, the problem that in the prior art, the vignetting is misjudged as the defect or missed detection defects are caused by adjustment of the algorithm to avoid misjudgment in automated optical inspection is solved.
Owner:WUHAN JINGLI ELECTRONICS TECH
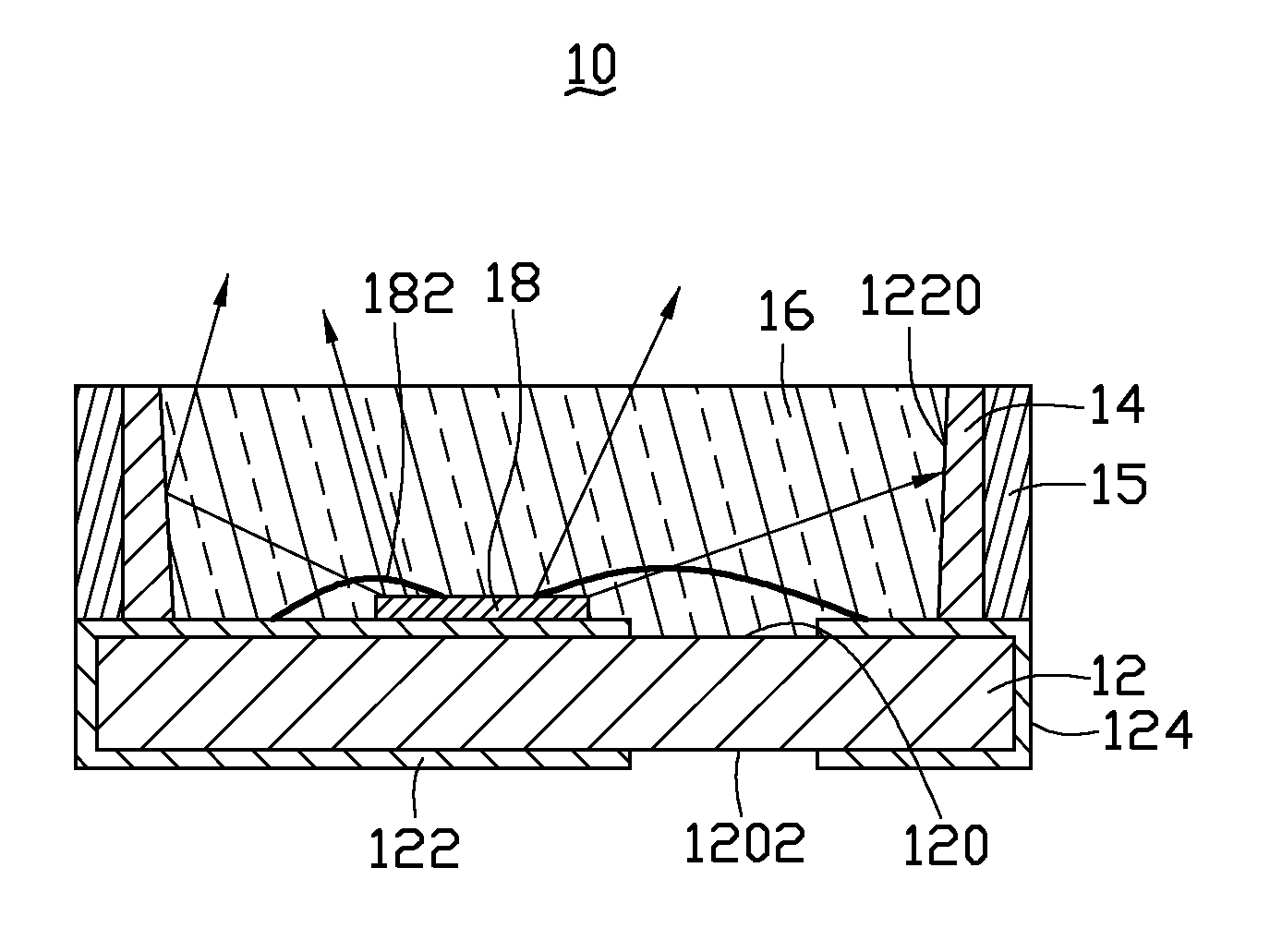
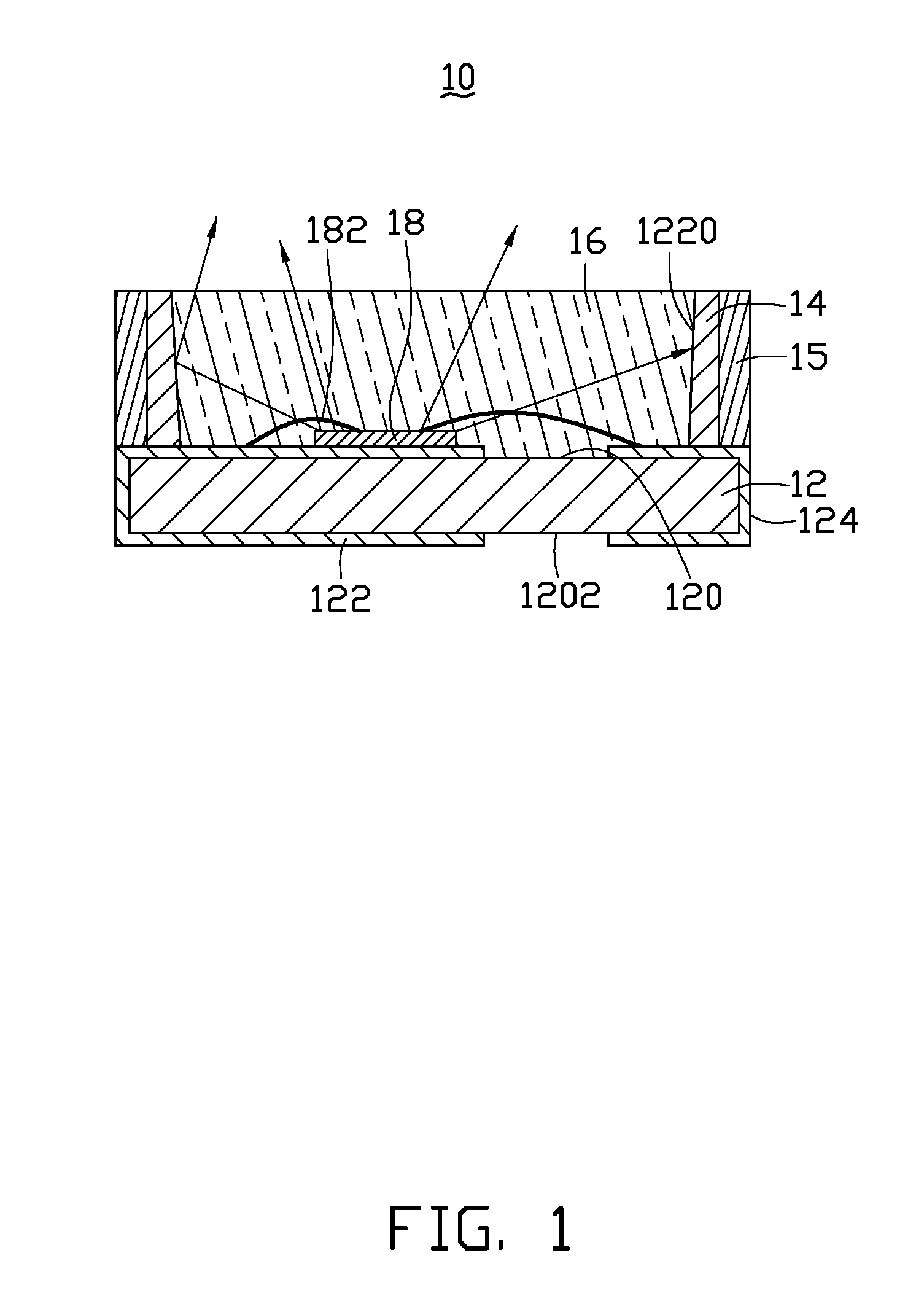
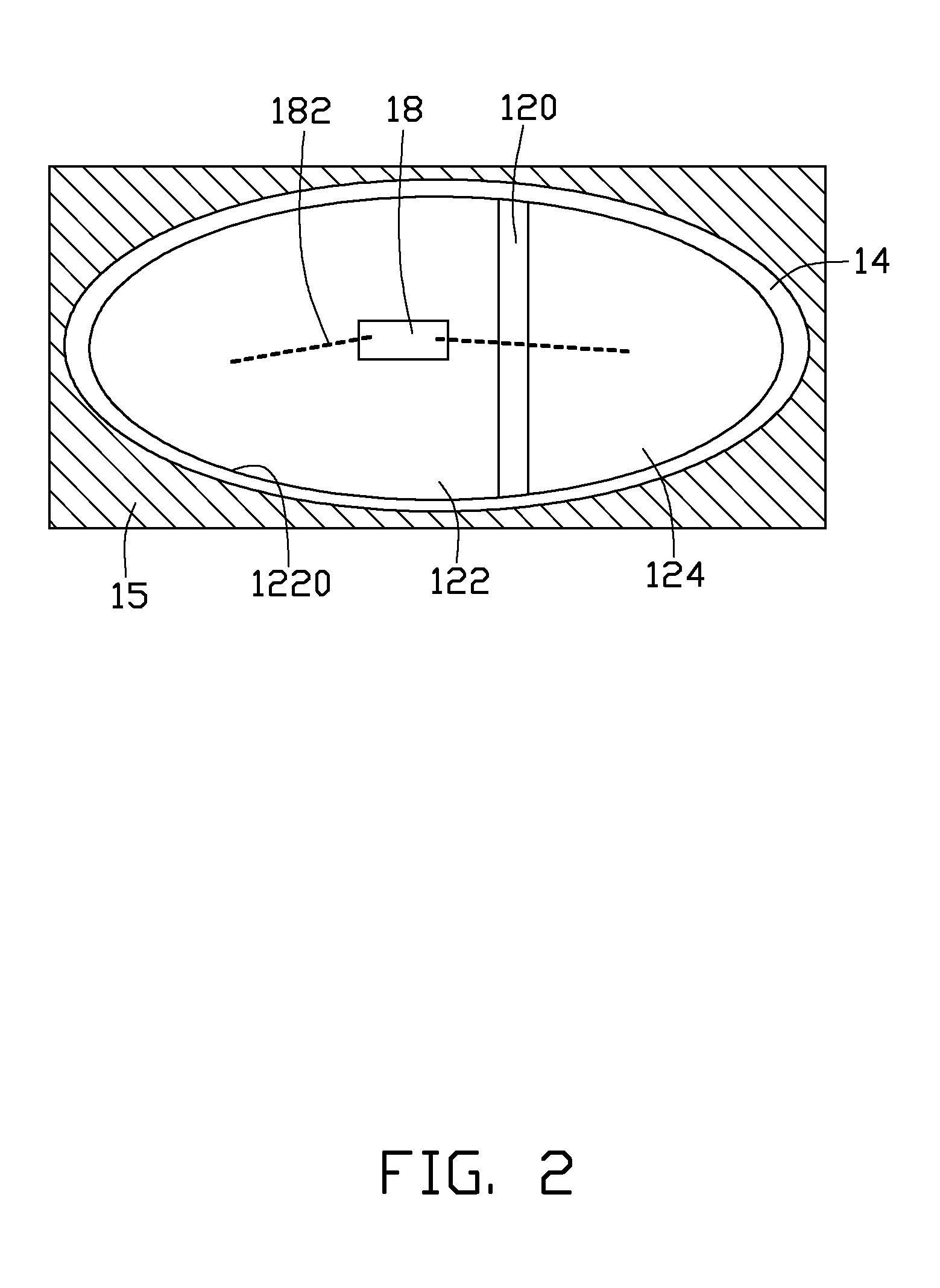
Light-emitting device with vignetting effect
ActiveUS8974103B2Reduce brightnessBeautiful appearanceTelevision system detailsDigital data processing detailsVignettingLight guide
A light-emitting device includes a light source, a panel and a light guiding structure. The light guiding structure includes a first light guiding tunnel and a second light guiding tunnel. The first light guiding tunnel includes a first end and a second end. A first opening is formed at the first end and close to the light source. The second light guiding tunnel includes a first end and a second end. The first end of the second light guiding tunnel communicates with the second end of the first light guiding tunnel. A diameter of the second end of the second light guiding tunnel is greater than a diameter of the first end of the second light guiding tunnel. A second opening is formed at the second end of the second light guiding tunnel. A diameter of the second opening is greater than a diameter of the first opening.
Owner:WISTRON CORP
LED package with light-absorbing layer
ActiveUS8569781B2Increase light intensityReduce impactSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingVignettingComputer science
An LED package comprises a substrate, a reflector, a light-absorbing layer, an encapsulation layer and an LED chip. The light-absorbing layer is located around the reflector and is able to absorb any light which penetrates through the reflector. Therefore, any vignetting or halation of light from the LED package is prevented. Moreover, the LED package can be constructed on a very small scale with no reduction in its color rendering properties.
Owner:ADVANCED OPTOELECTRONIC TECH INC
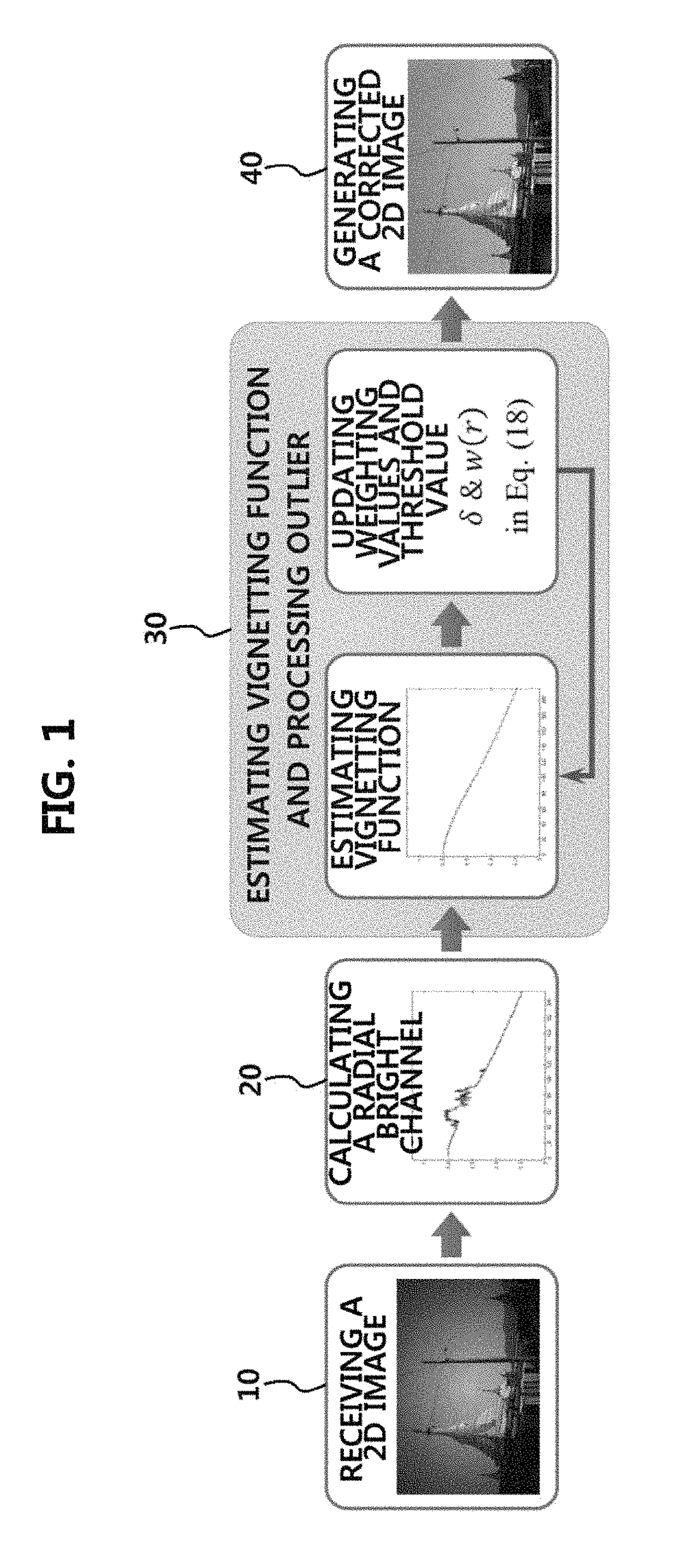
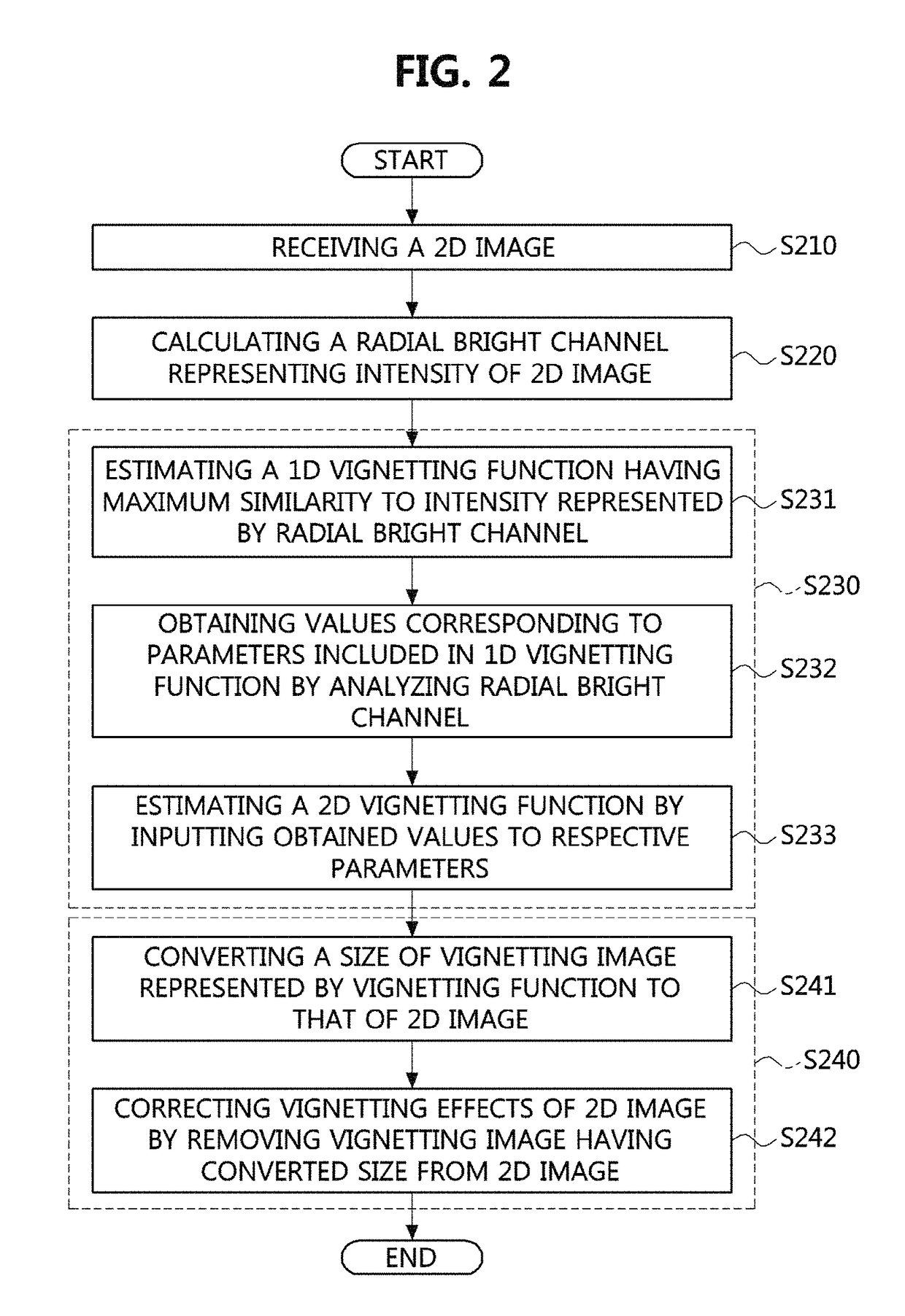
Method for vignetting correction of image and apparatus therefor
ActiveUS9740958B2The effect is accurateImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionCamera lensVignetting
Method and apparatuses for correcting vignetting effects of an image are disclosed. A method for vignetting correction of an image according to an exemplary embodiment of the present disclosure may comprise receiving a two-dimensional image; calculating a radial bright channel representing intensity of the two-dimensional image; estimating a vignetting function of the two-dimensional image having similarity to the calculated radial bright channel; and correcting the vignetting effects of the two-dimensional image by using the estimated vignetting function. The vignetting correction methods and apparatuses according to the present disclosure can rapidly correct vignetting effects of an image by using a smaller memory, and correct vignetting effects of an arbitrary single image without being affected by a camera setting and camera lenses used for the image.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND
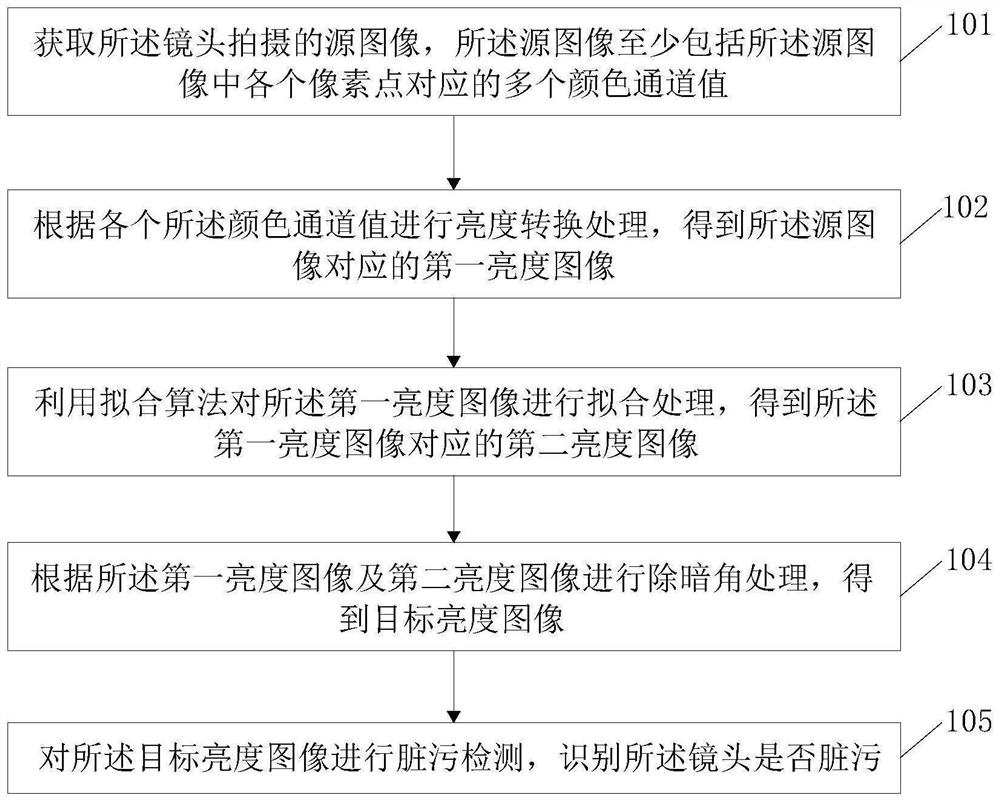
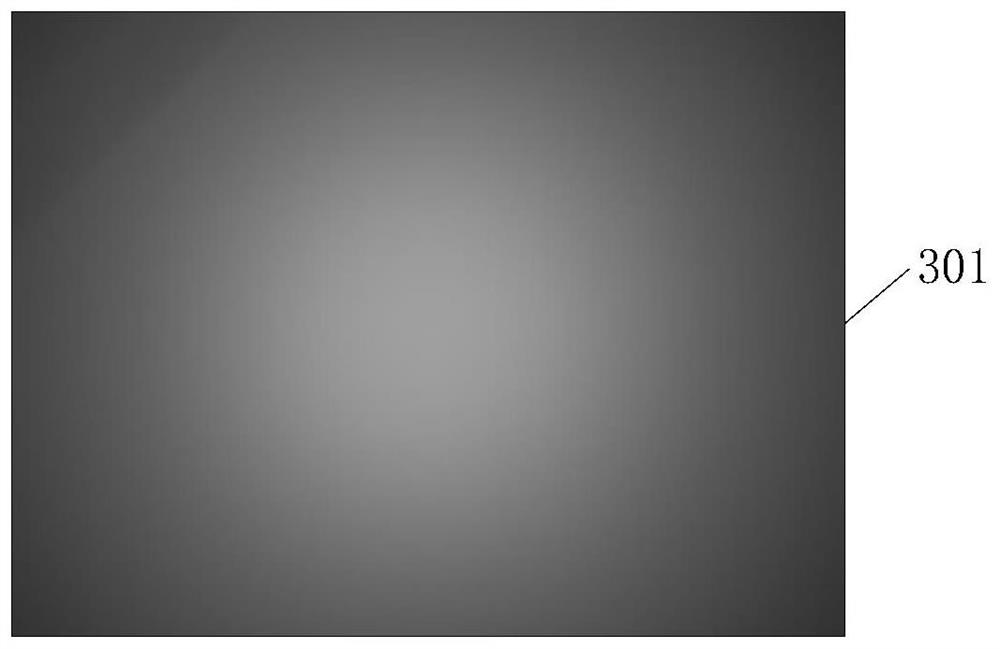
Lens dirt identification method and device, computer equipment and storage medium
PendingCN114359414AThe result is accurate and effectiveImage enhancementImage analysisVignettingRadiology
The embodiment of the invention discloses a lens smudginess identification method and device, computer equipment and a storage medium, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining a source image shot by a lens, the source image at least comprising a plurality of color channel values corresponding to each pixel point in the source image; performing brightness conversion processing according to each color channel value to obtain a first brightness image corresponding to the source image; performing fitting processing on the first brightness image by using a fitting algorithm to obtain a second brightness image corresponding to the first brightness image; performing dark corner removal processing according to the first brightness image and the second brightness image to obtain a target brightness image; and carrying out smudginess detection on the target brightness image, and identifying whether the lens is smudginess. According to the method, the target brightness image without the vignetting is obtained by using the first brightness image subjected to brightness conversion and the second brightness image subjected to fitting, and whether the lens is dirty or not is identified on the premise of removing the vignetting, so that the result is more accurate and effective.
Owner:AAC OPTICS(NANNING)TECH LTD
Multiscale telescopic imaging system
ActiveUS9635253B2Reduce occlusionReduced magnitudeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsIntermediate imageVignetting
A multiscale telescopic imaging system is disclosed. The system includes an objective lens, having a wide field of view, which forms an intermediate image of a scene at a substantially spherical image surface. A plurality of microcameras in a microcamera array relay image portions of the intermediate image onto their respective focal-plane arrays, while simultaneously correcting at least one localized aberration in their respective image portions. The microcameras in the microcamera array are arranged such that the fields of view of adjacent microcameras overlap enabling field points of the intermediate image to be relayed by multiple microcameras. The microcamera array and objective lens are arranged such that light from the scene can reach the objective lens while mitigating deleterious effects such as obscuration and vignetting.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Projection illumination system with tunnel integrator and field lens
InactiveUS20050140940A1Maximize amount of lightUniform brightnessProjectorsPicture reproducers using projection devicesIntegratorVignetting
A projector illumination system includes a tunnel integrator incorporated with a field lens at its output end. One advantage of using the field lens is to form an image of the entrance end of the tunnel integrator at the secondary stop of the illumination system when combined with other relay and / or imager field lenses in the illumination system. This reduces vignetting, resulting in an increased uniformity of illumination, and increased light throughput.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
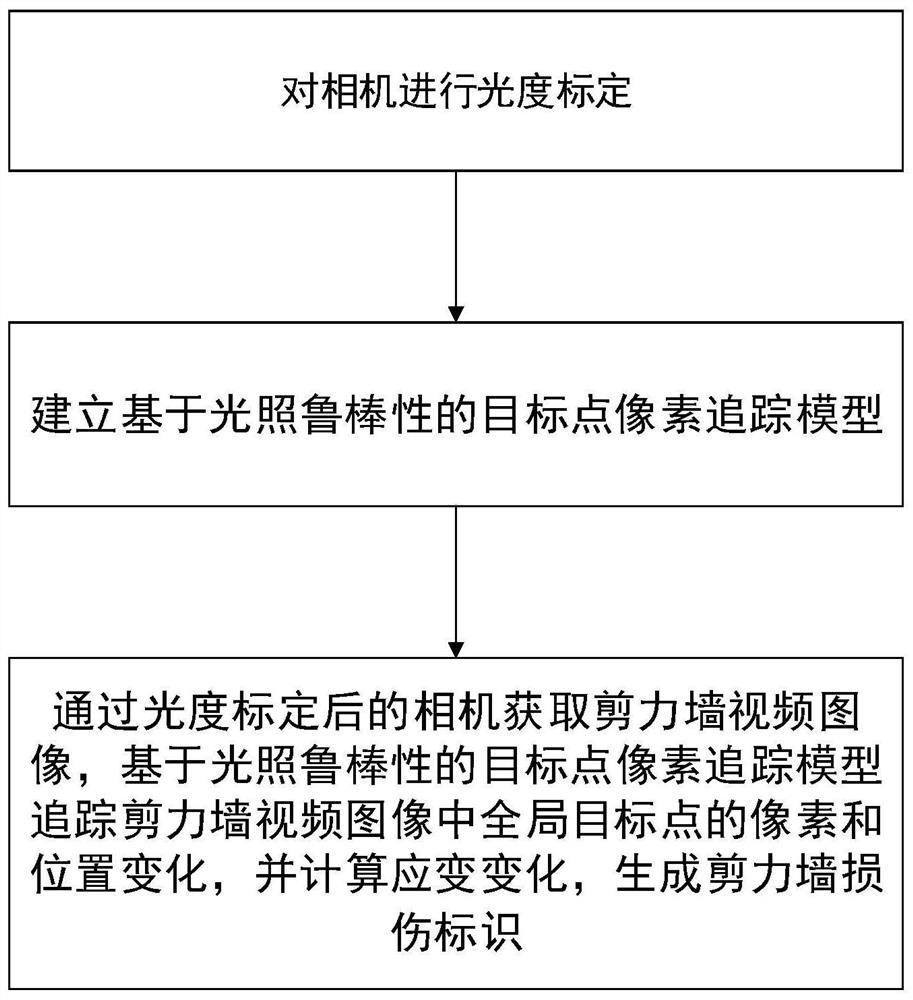
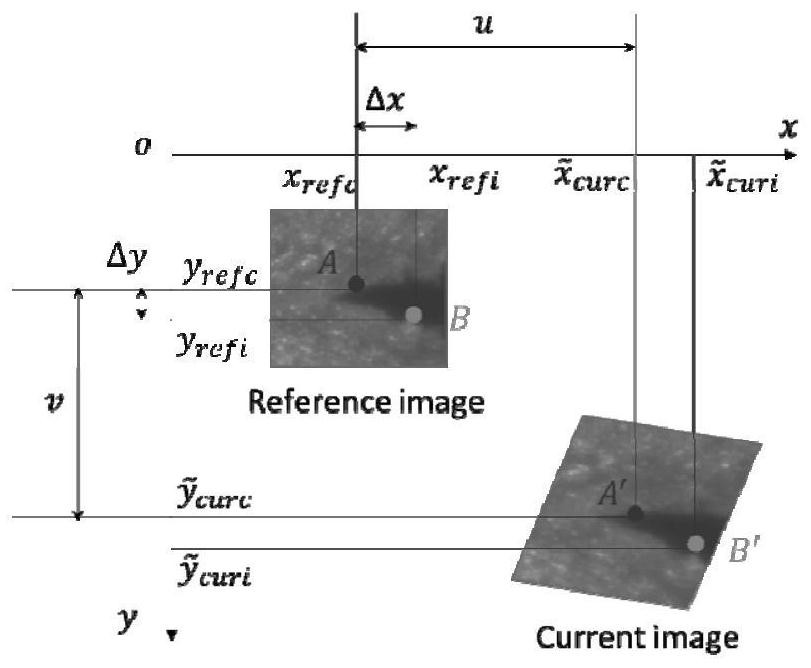
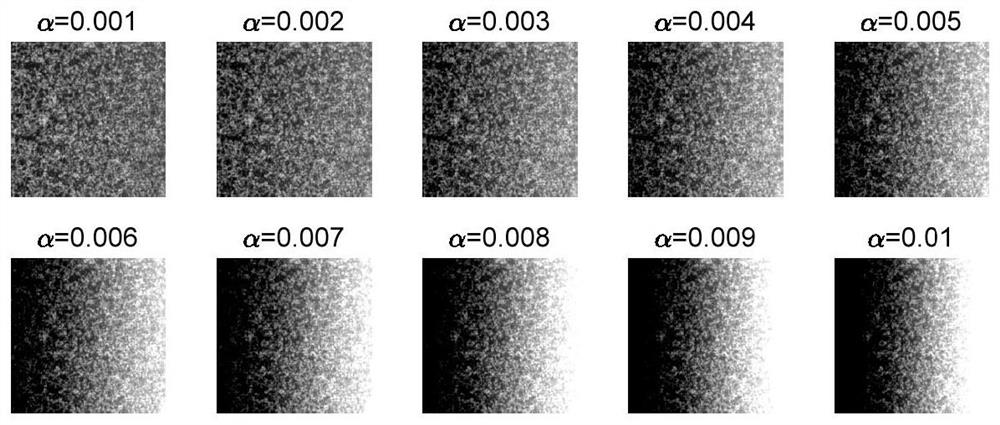
Method and equipment for measuring damage of shear wall based on digital image and medium
InactiveCN113295701AHas uneven lightingSuppress light effectsOptically investigating flaws/contaminationPattern recognitionVignetting
The invention relates to a method for measuring the damage of a shear wall based on a digital image, and the method comprises the following steps: setting a camera for collecting the image of the shear wall, and calibrating the response and vignetting of the camera based on the response function and vignetting function of the camera; obtaining a DIC digital image correlation model used for calculating a correlation function of position change of any point from a reference image of a previous frame to a current image of a next frame and pixel change of a target point based on illumination influence; collecting a video of the shear wall through a camera for photometric calibration, obtaining a front frame image and a rear frame image from the video, setting the size of an image capture window, capturing pixel change and position change of a global target point of the shear wall through a DIC digital image correlation model and a correlation function of target point pixel change based on illumination influence, and calculating the strain change of the global target point according to the pixel change and the position change of the global target point; and generating a real-time damage identifier of the shear wall according to the strain change of the global target point.
Owner:FUJIAN JIANGXIA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com