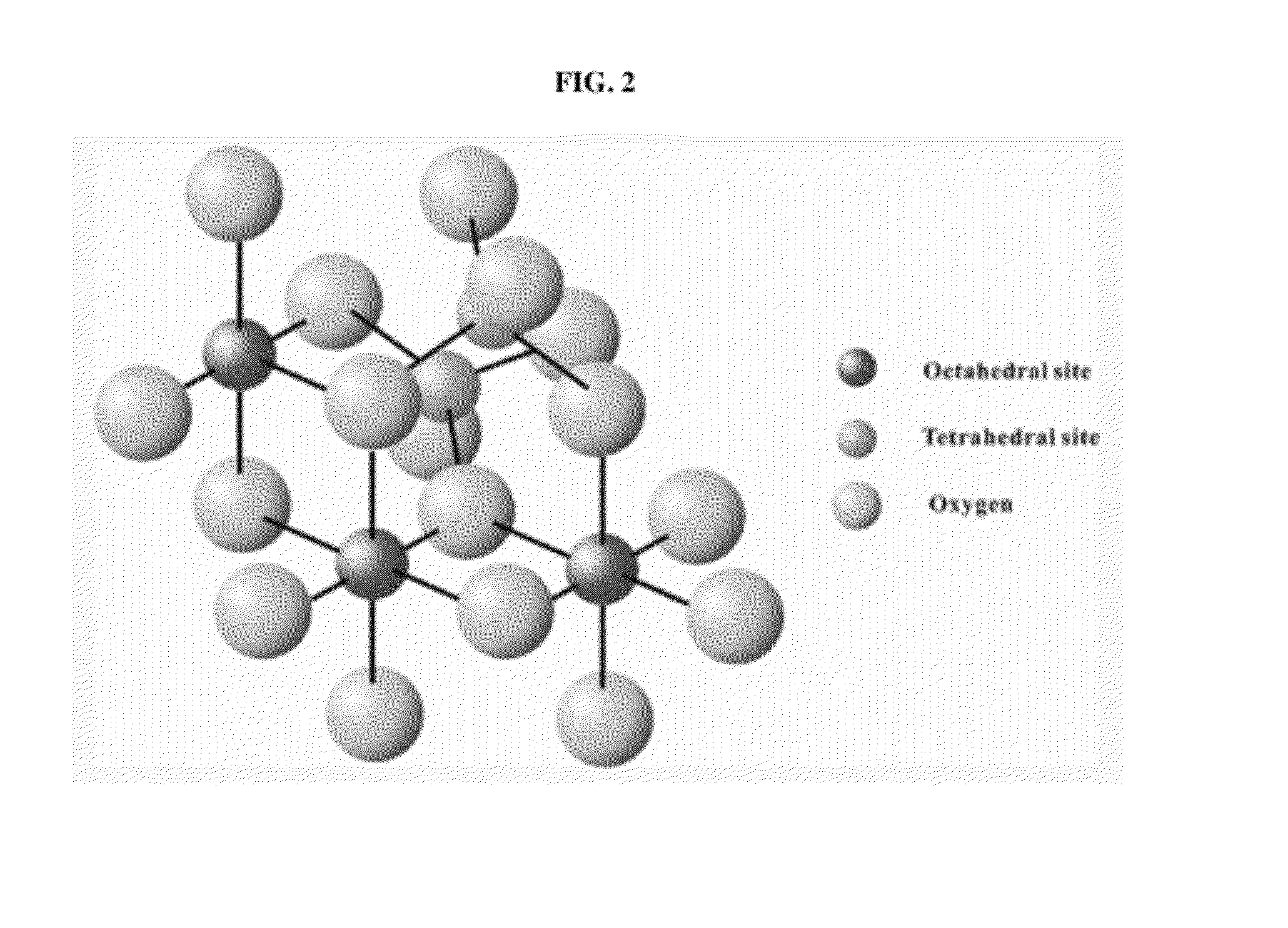
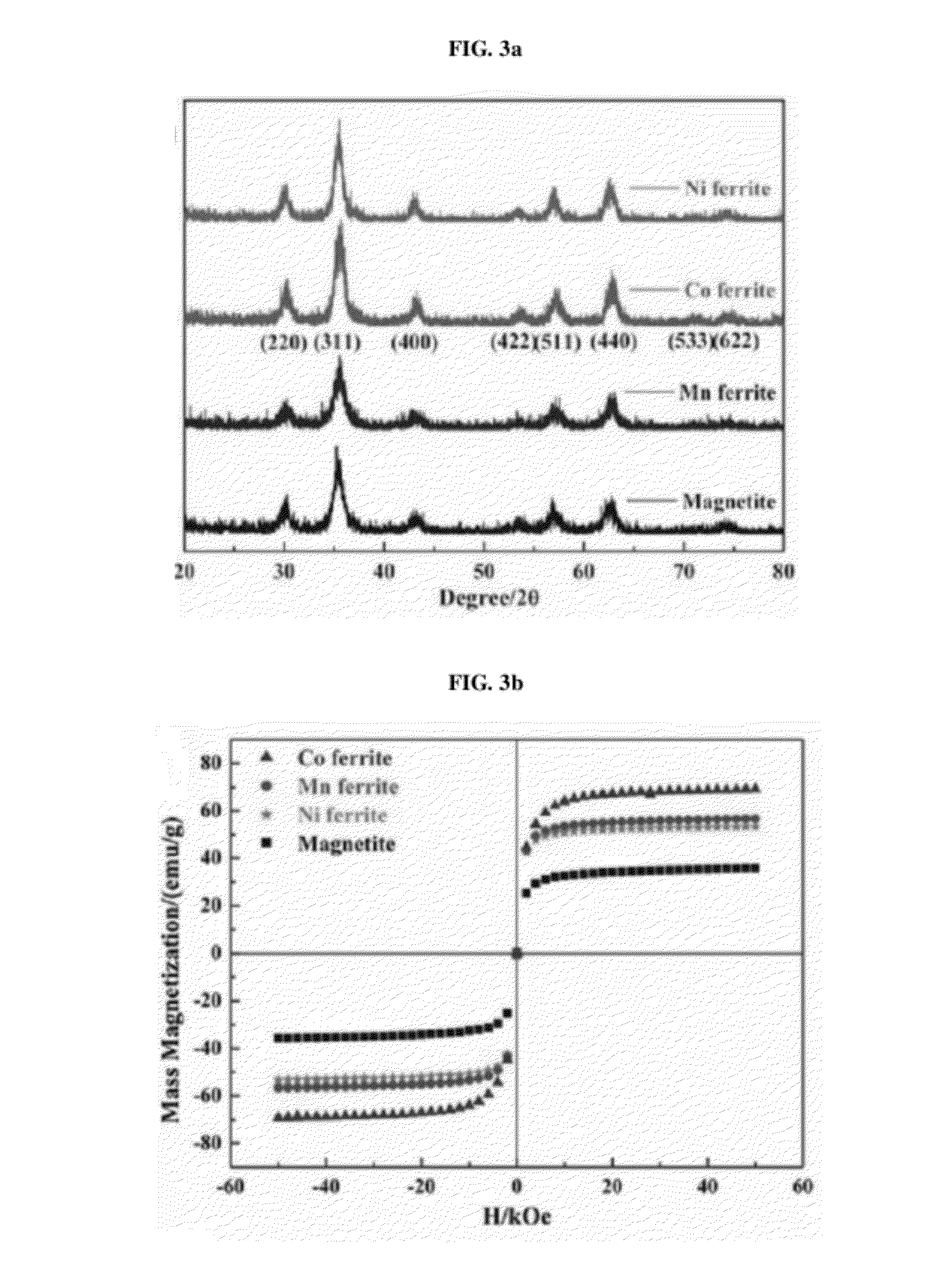
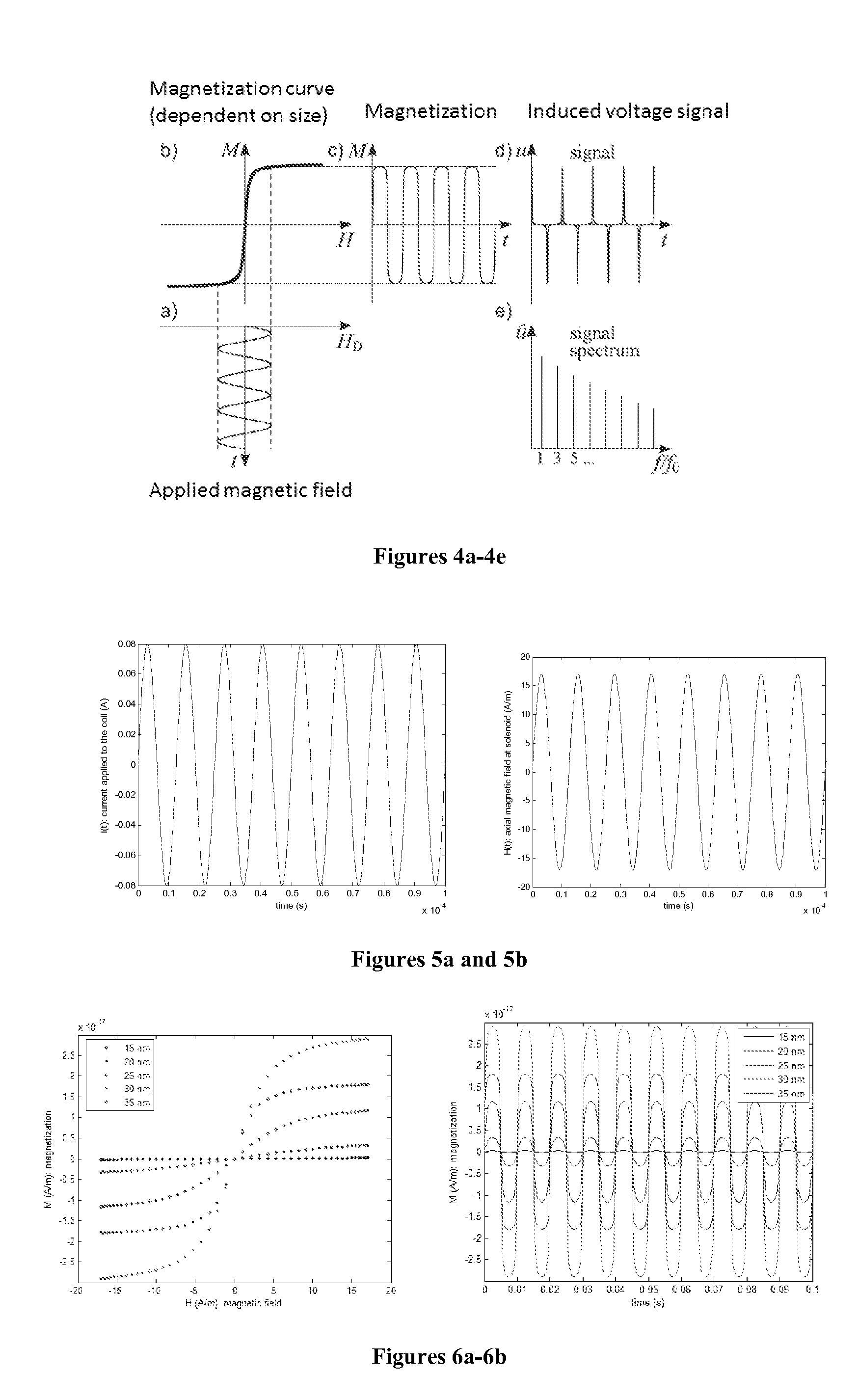
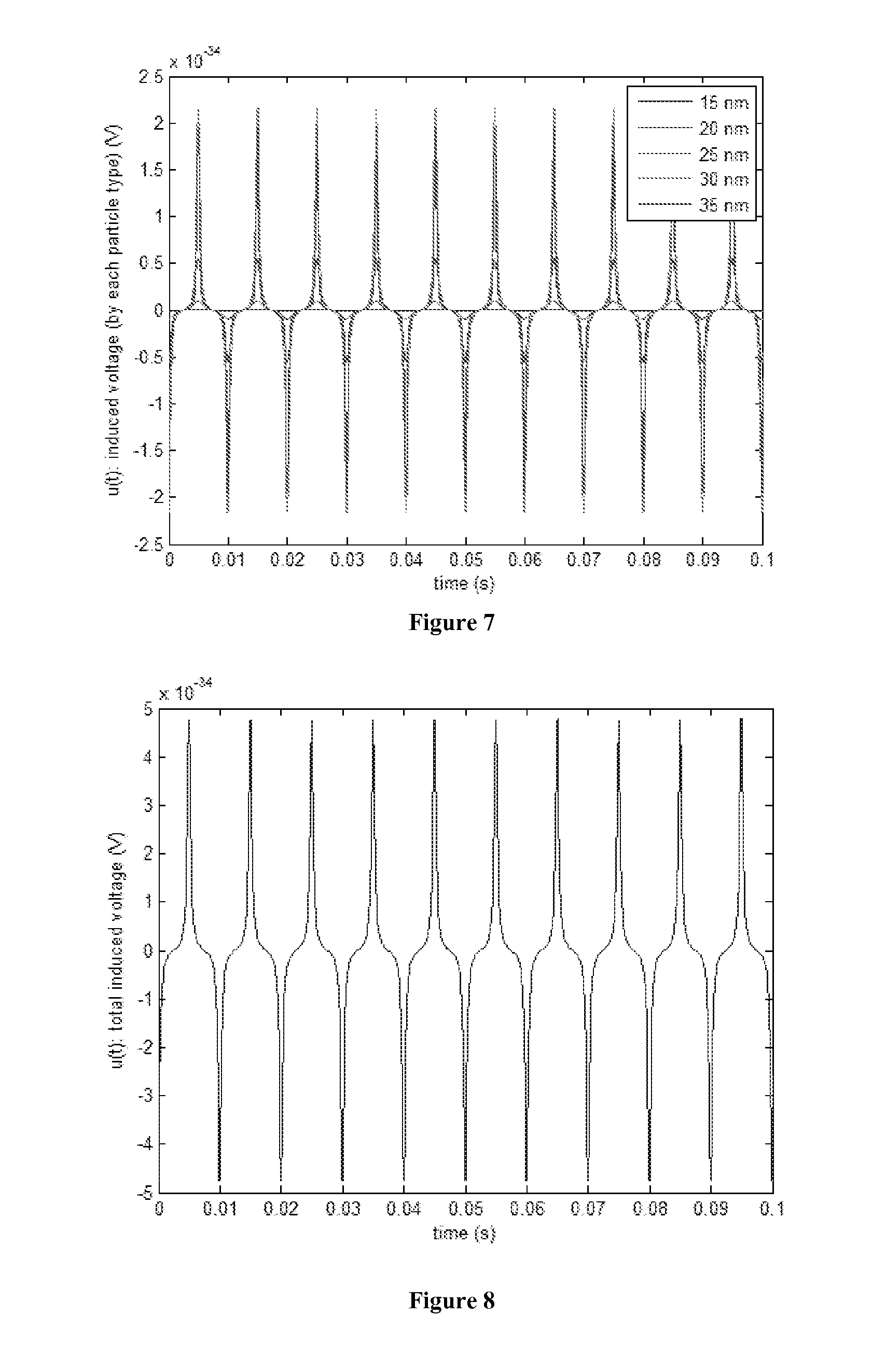
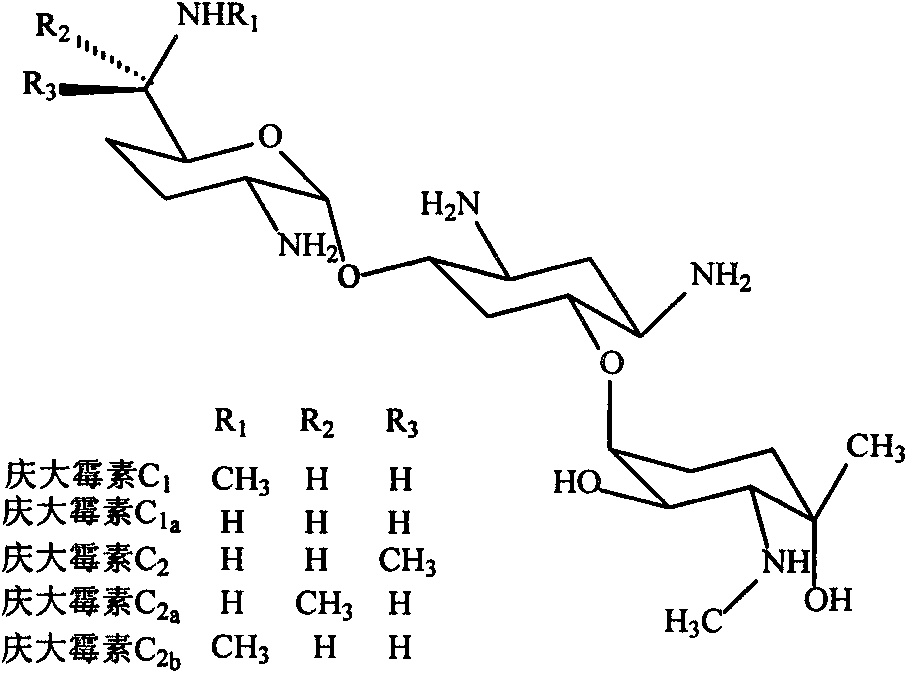
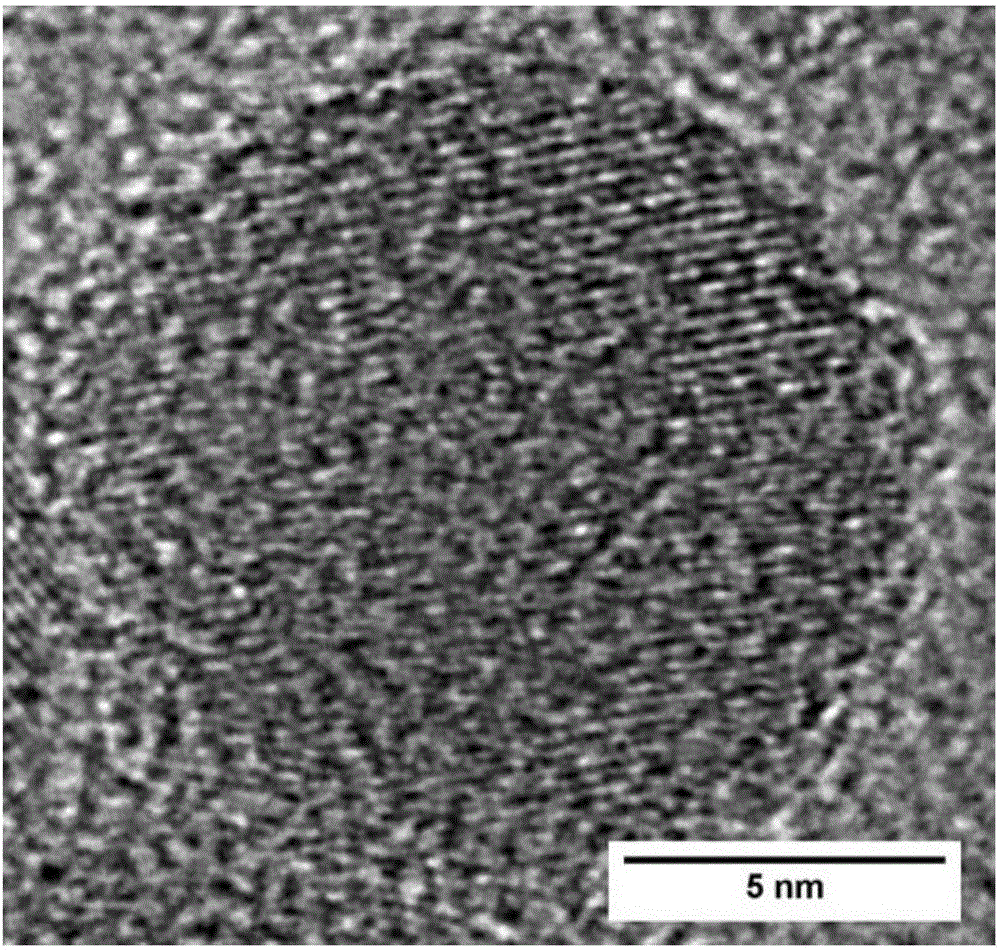
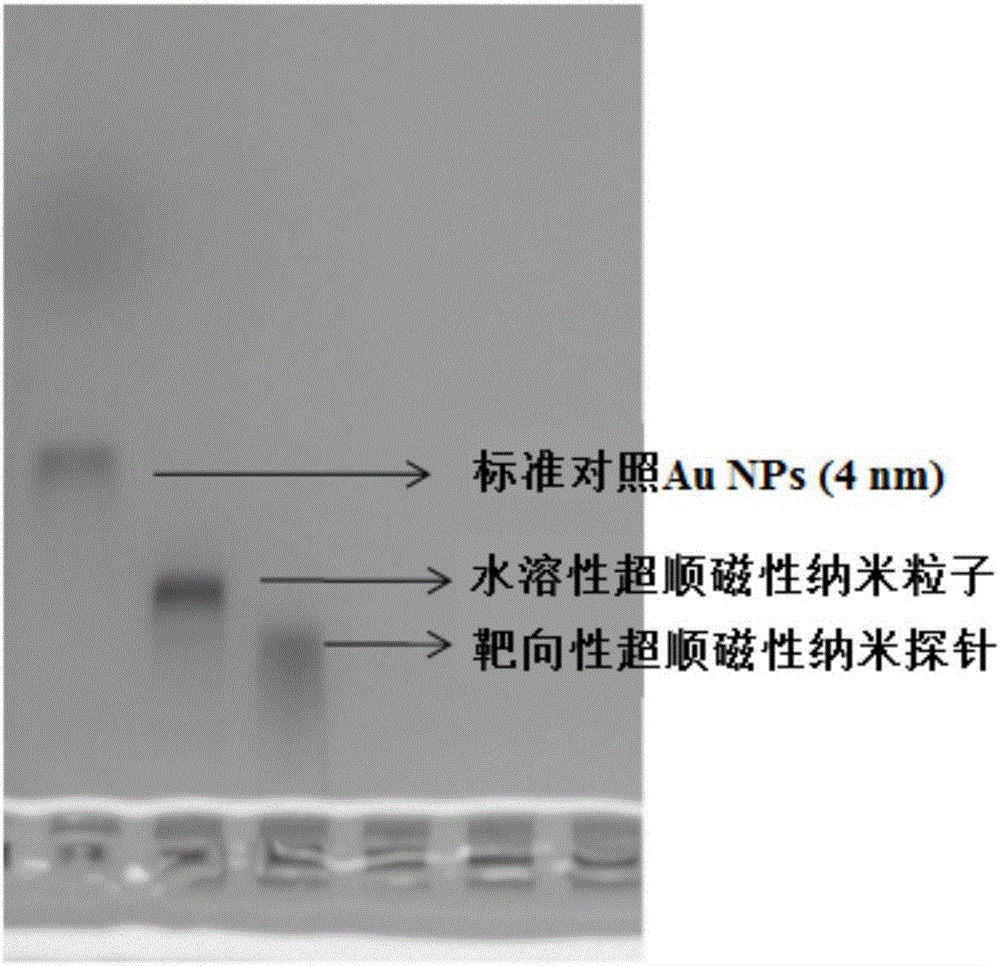
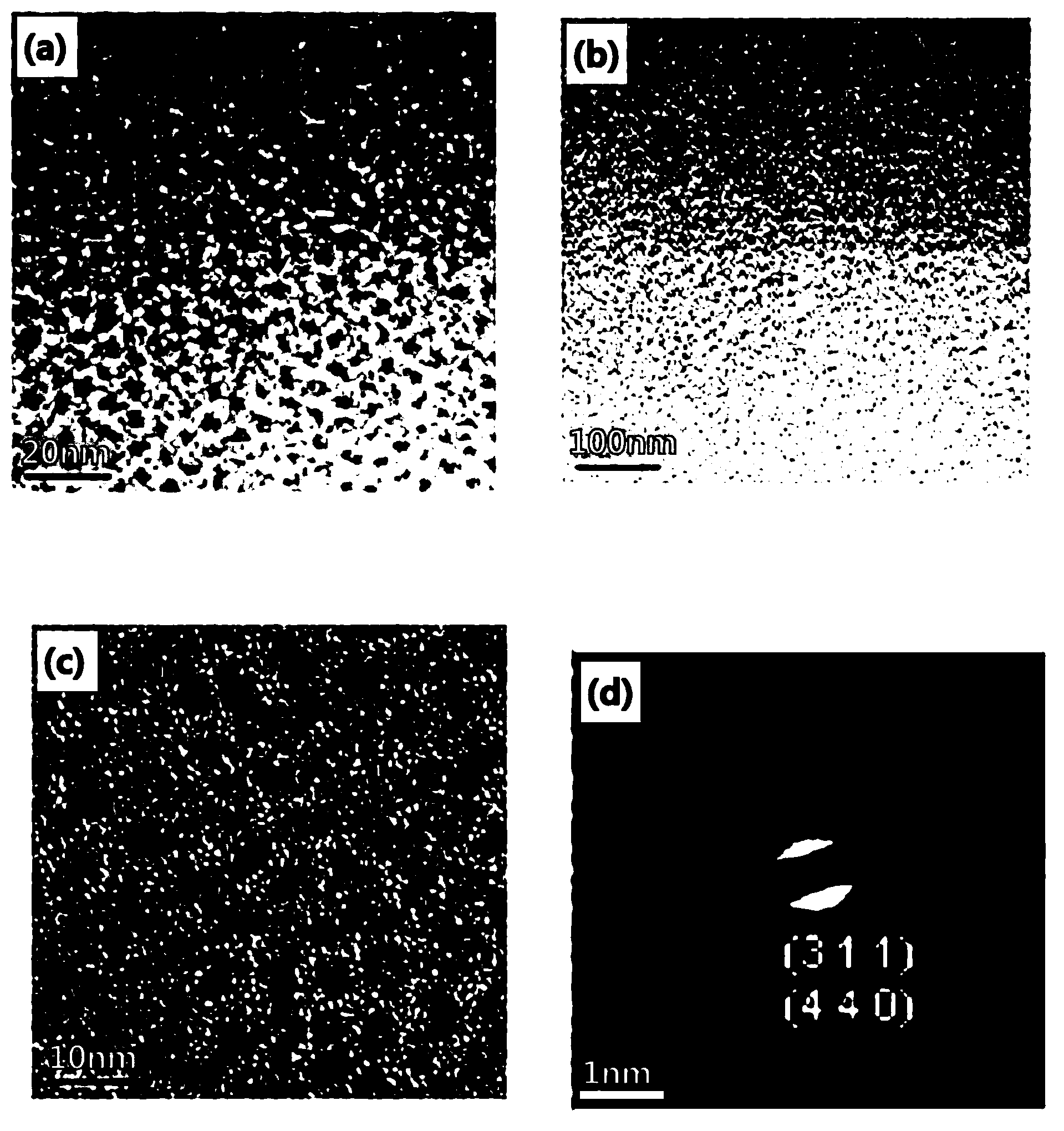
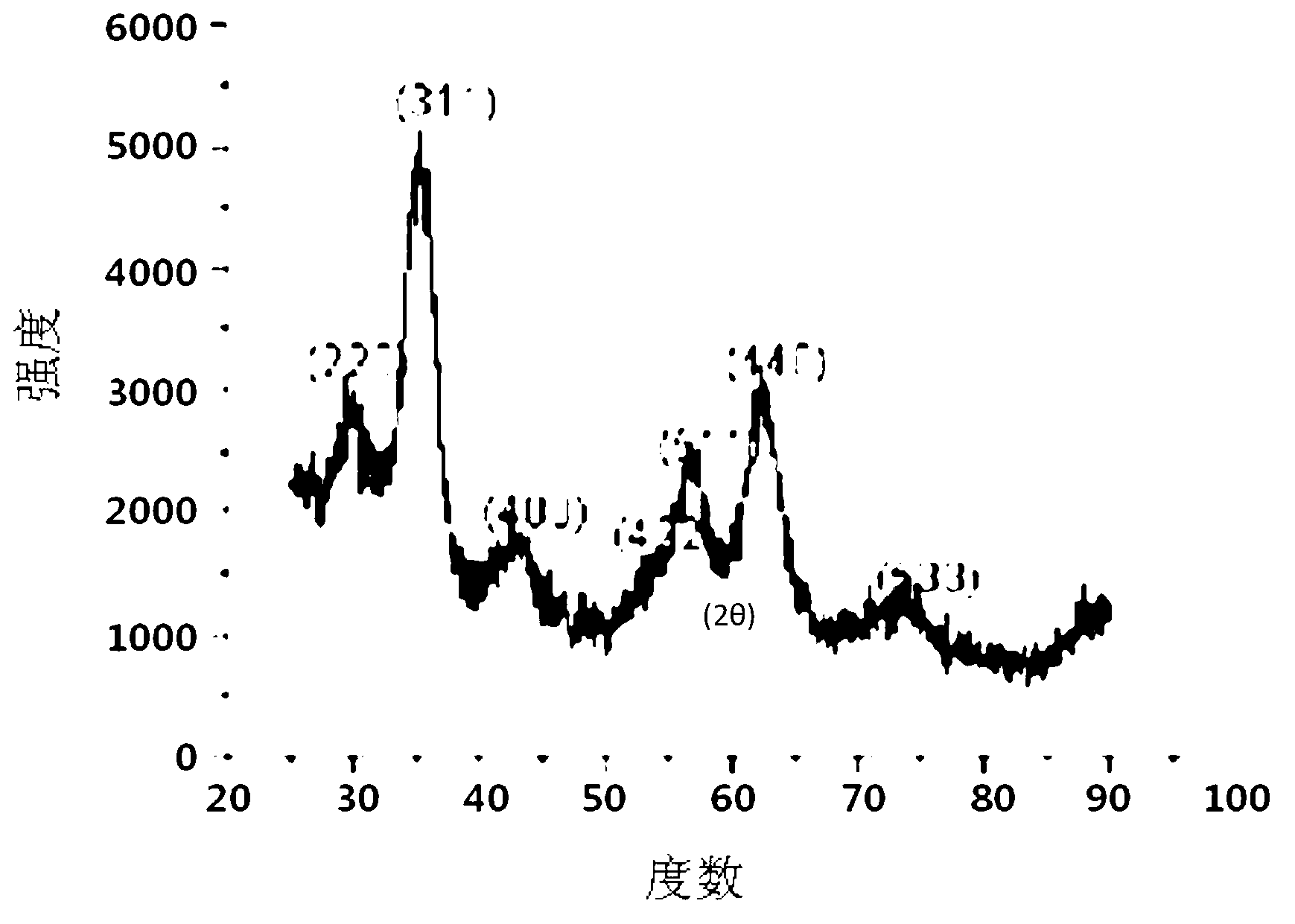
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
79 results about "Paramagnetic nanoparticles" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
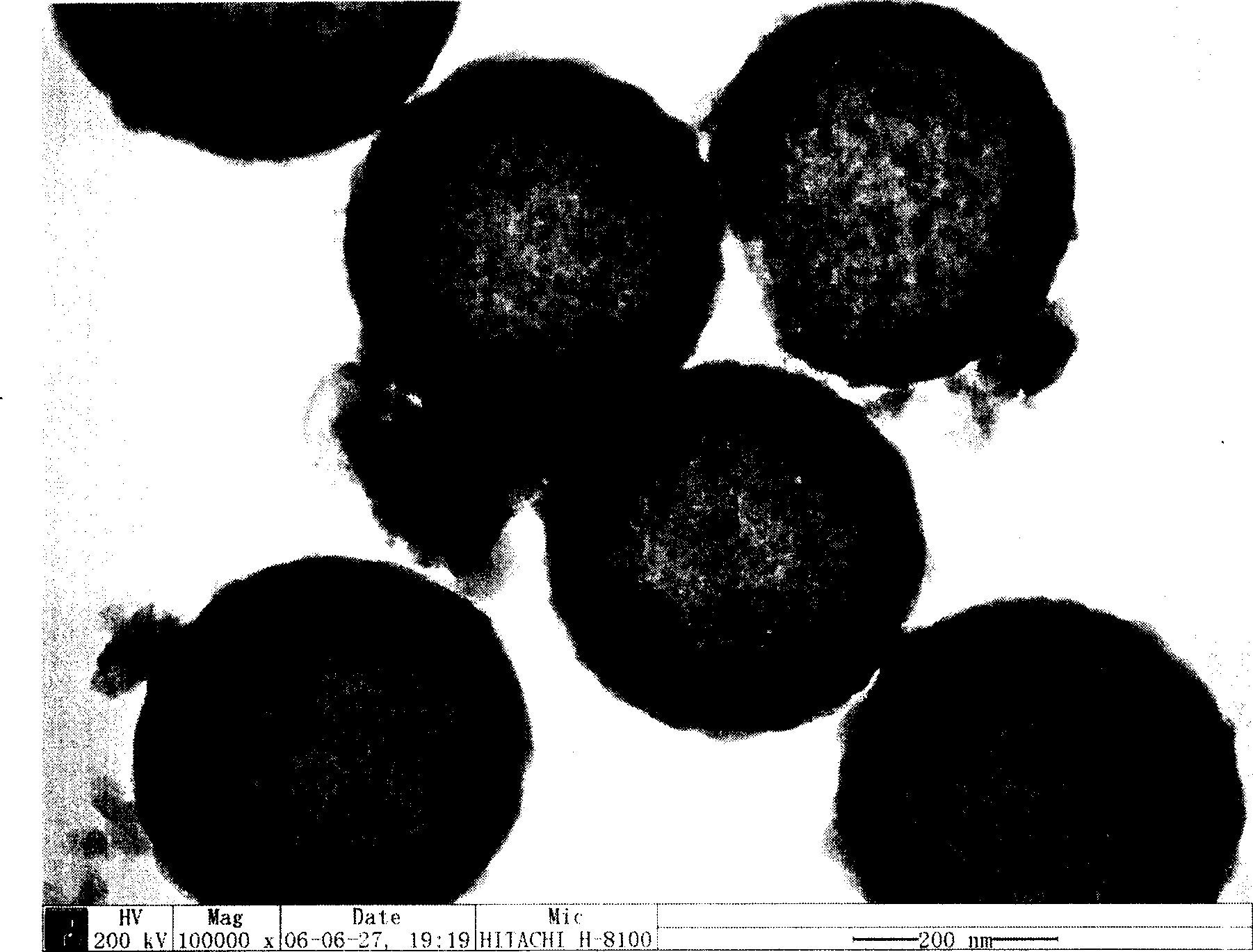
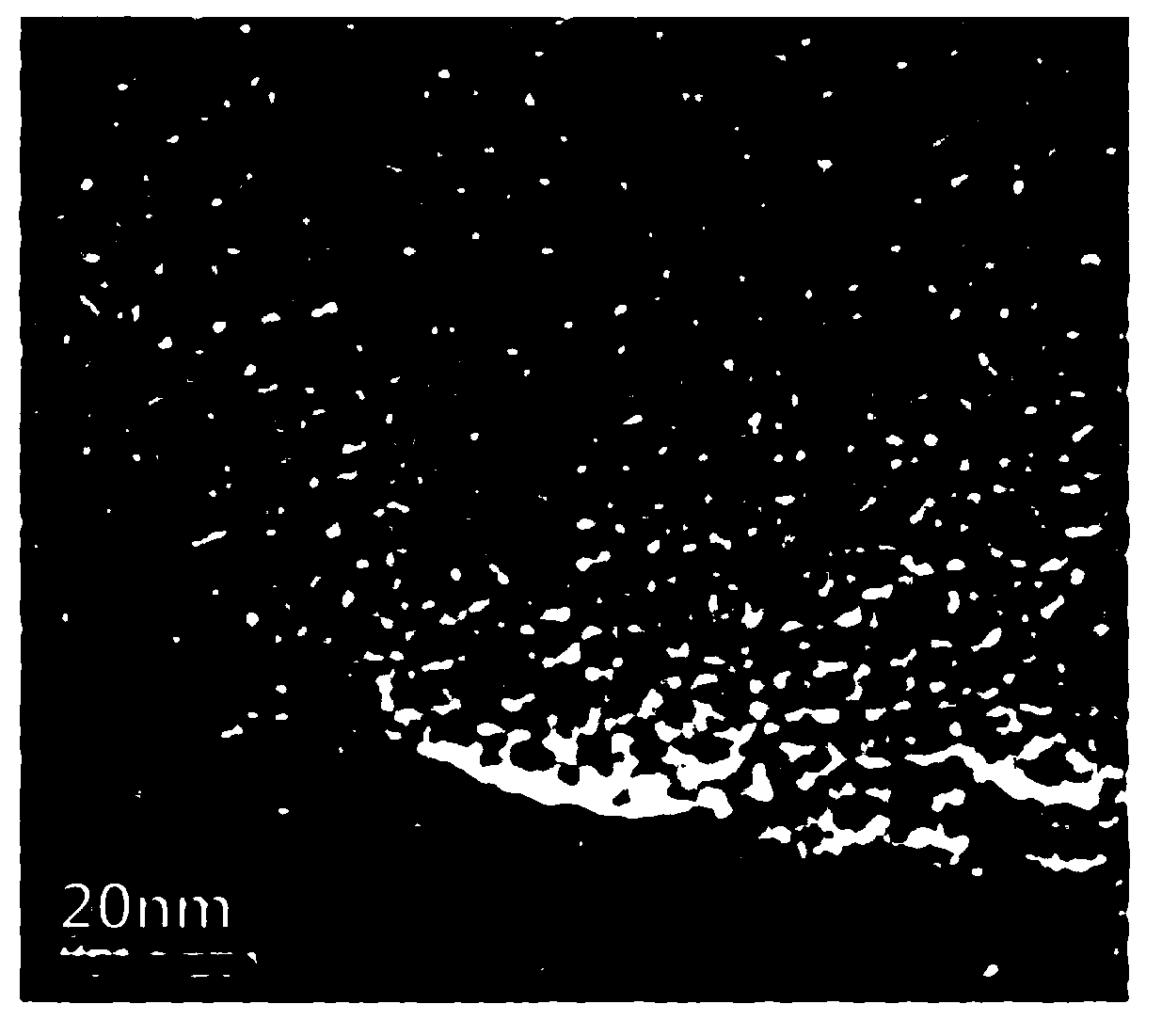
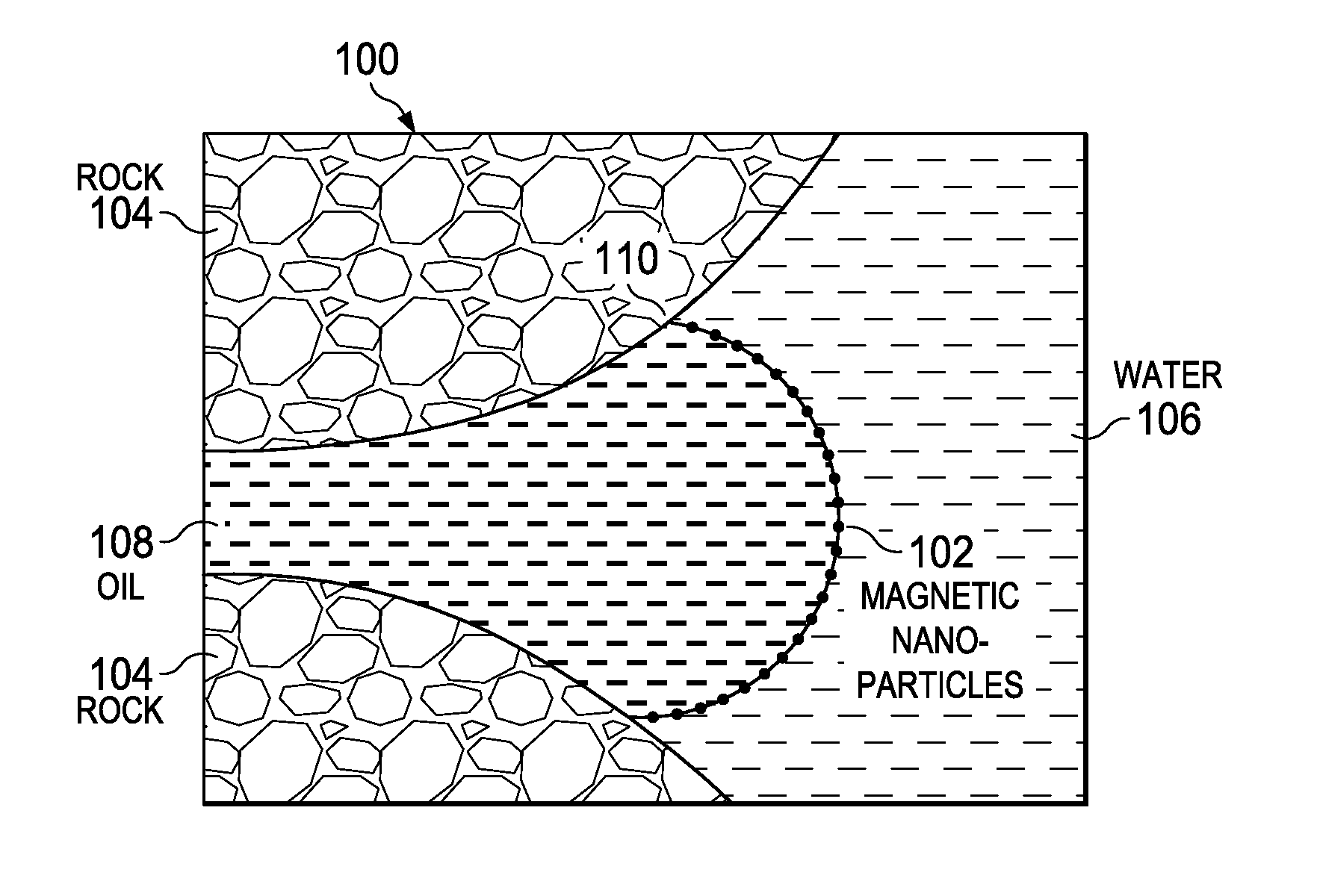
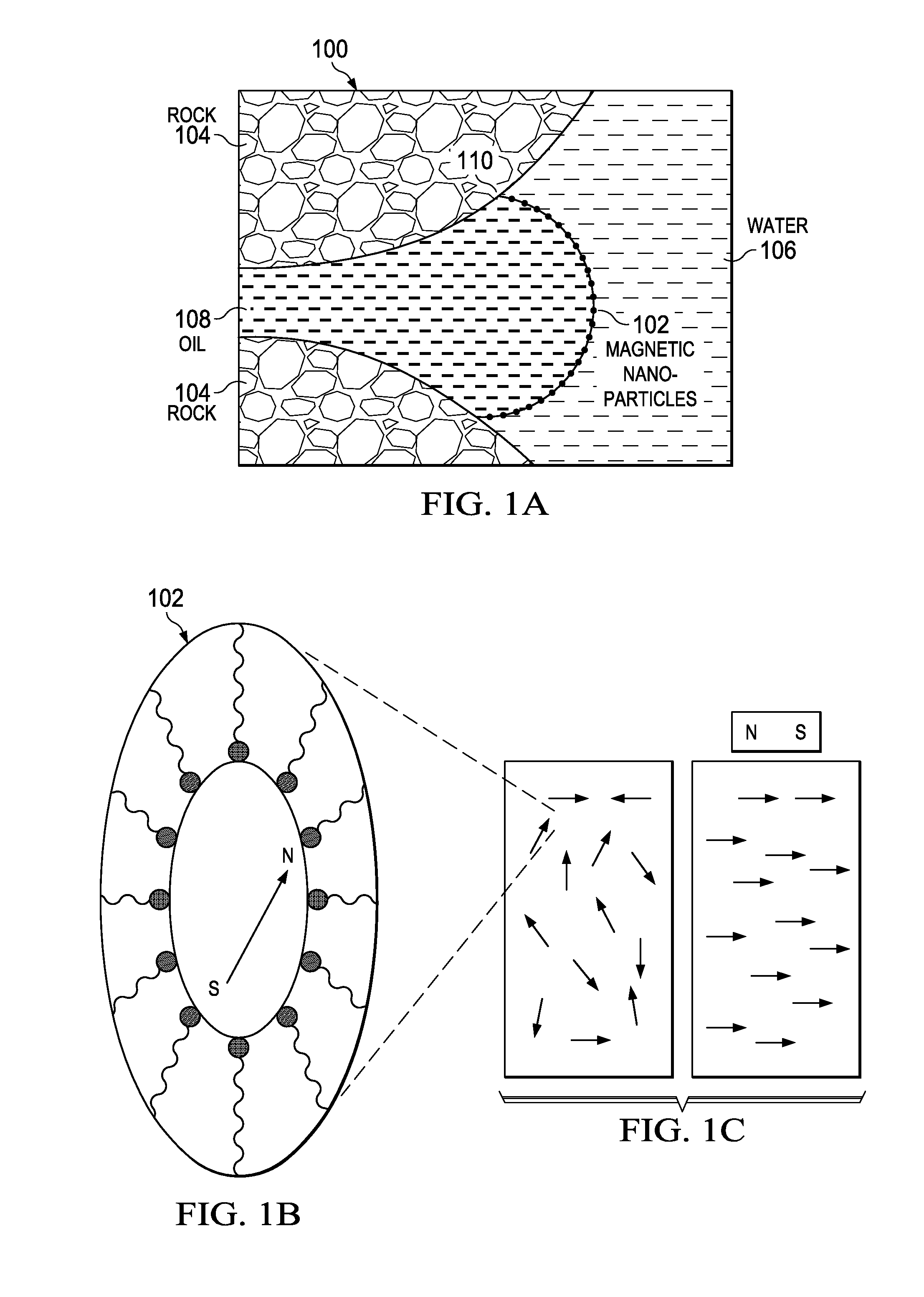
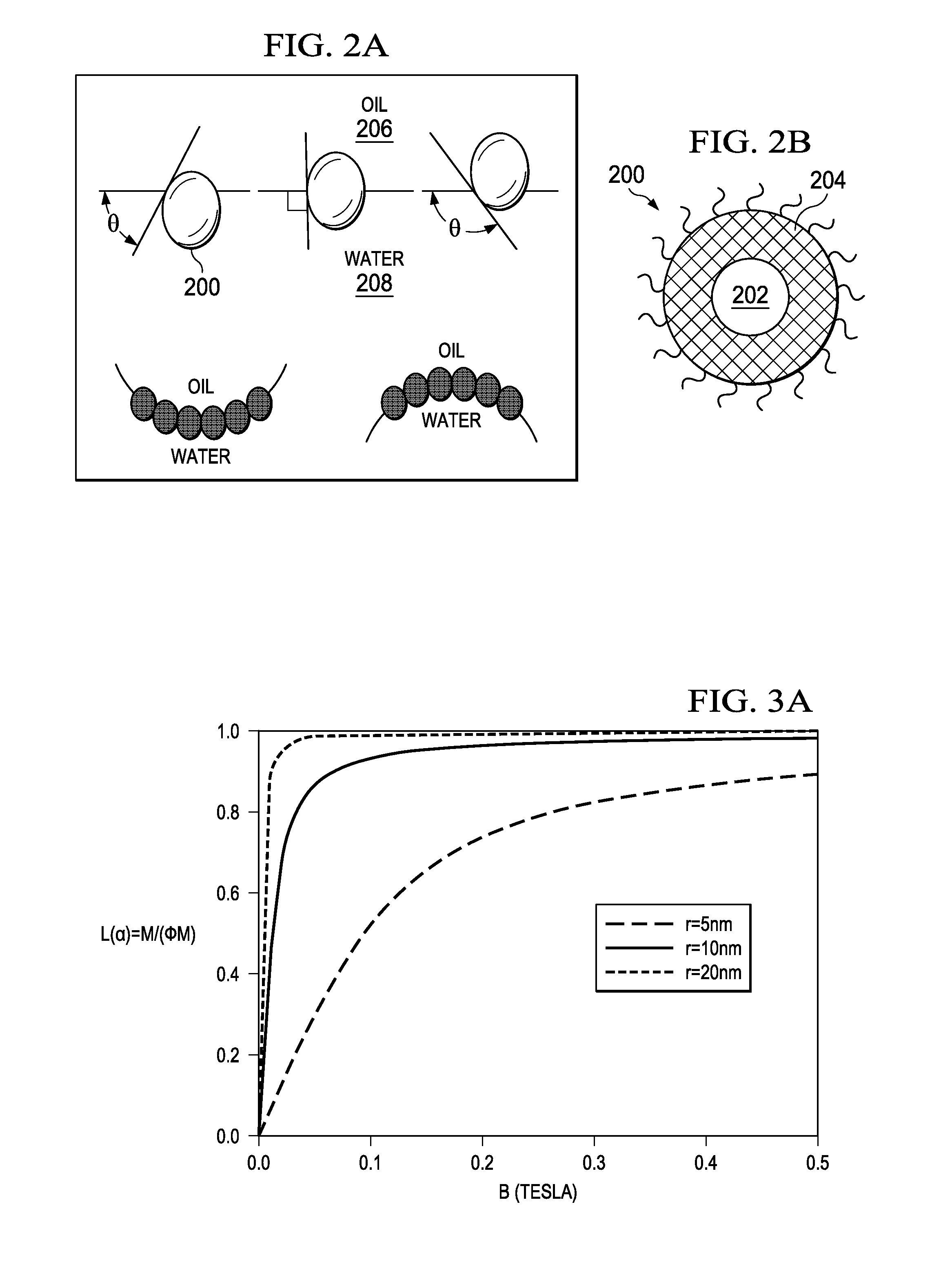
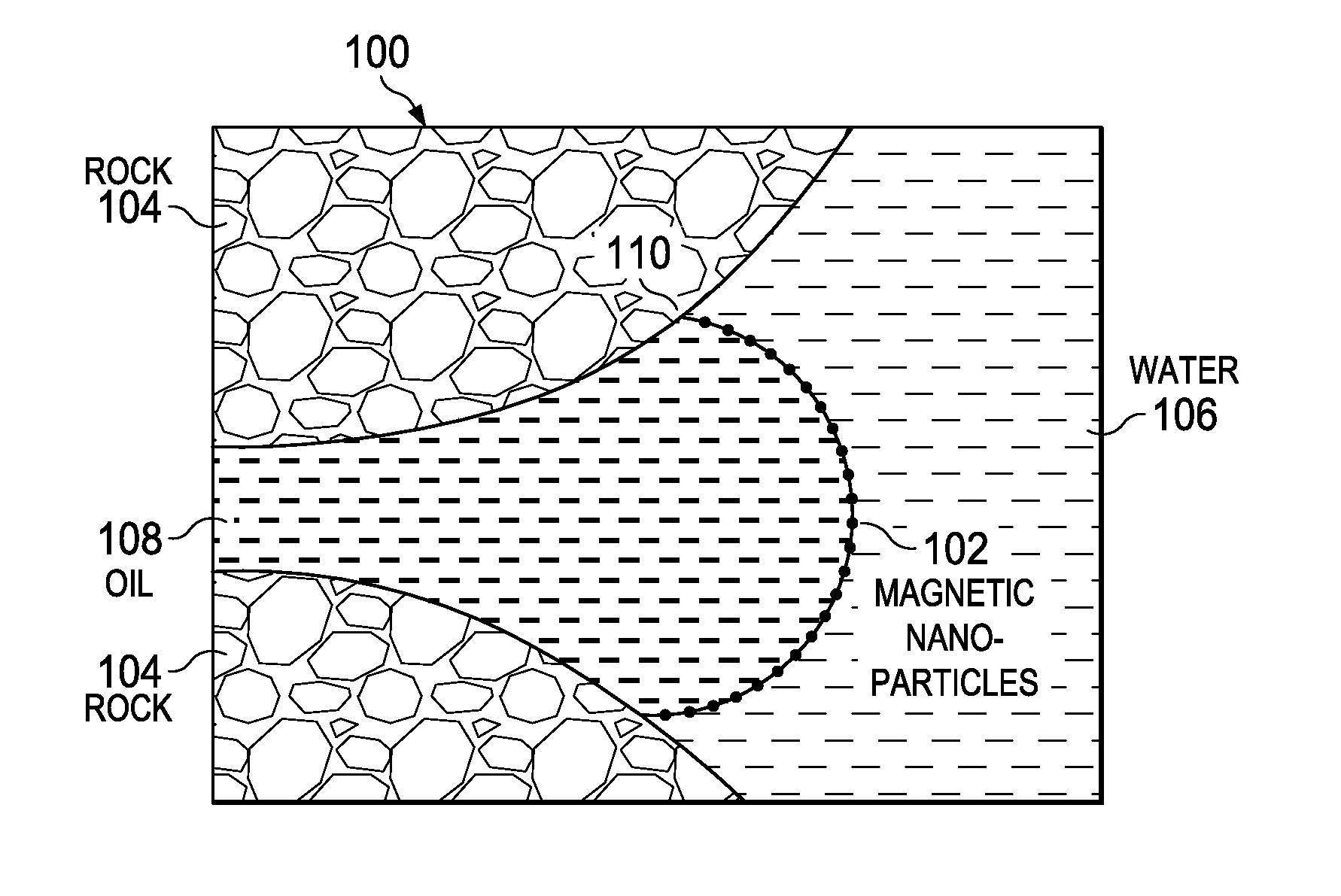
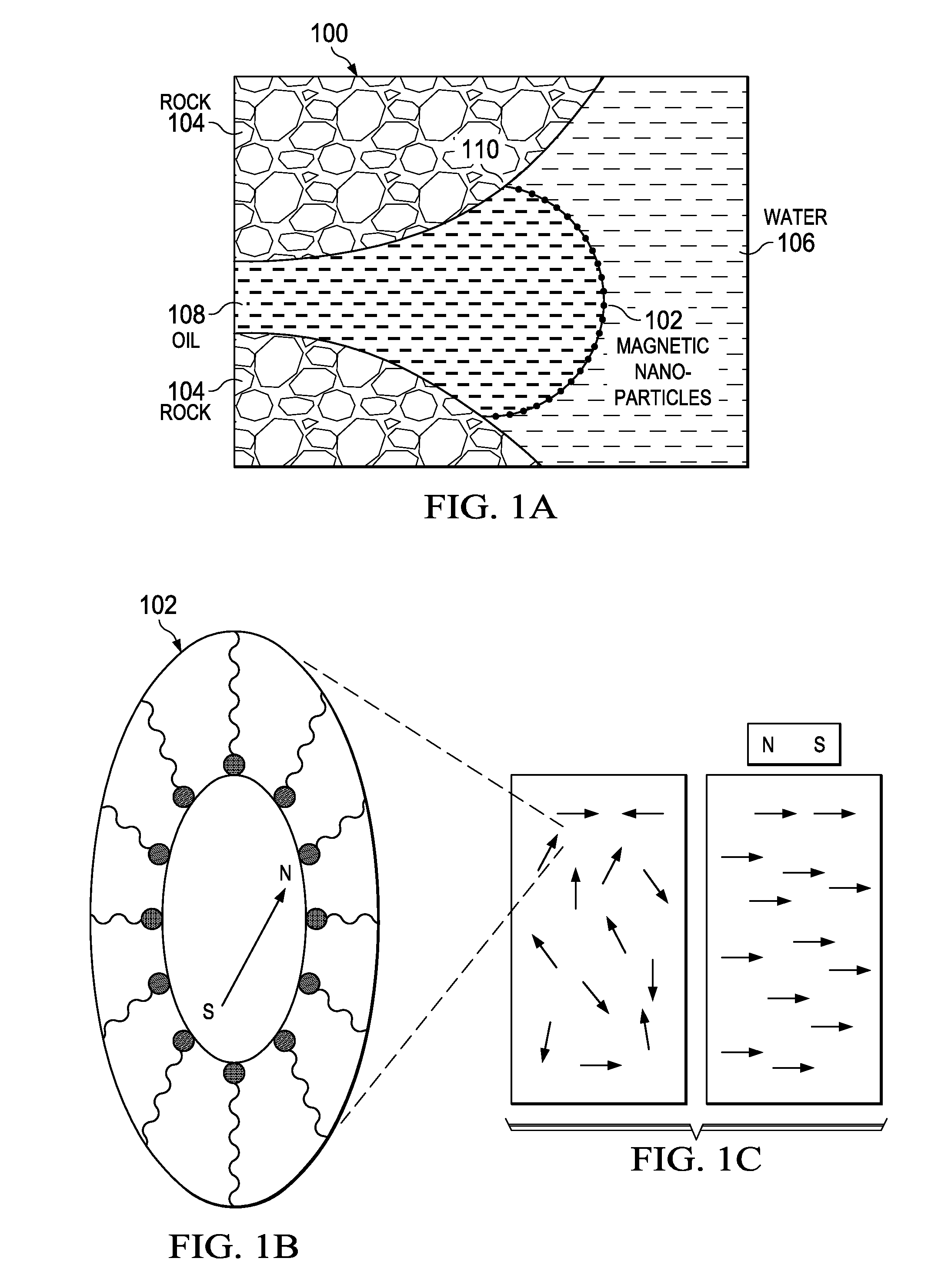
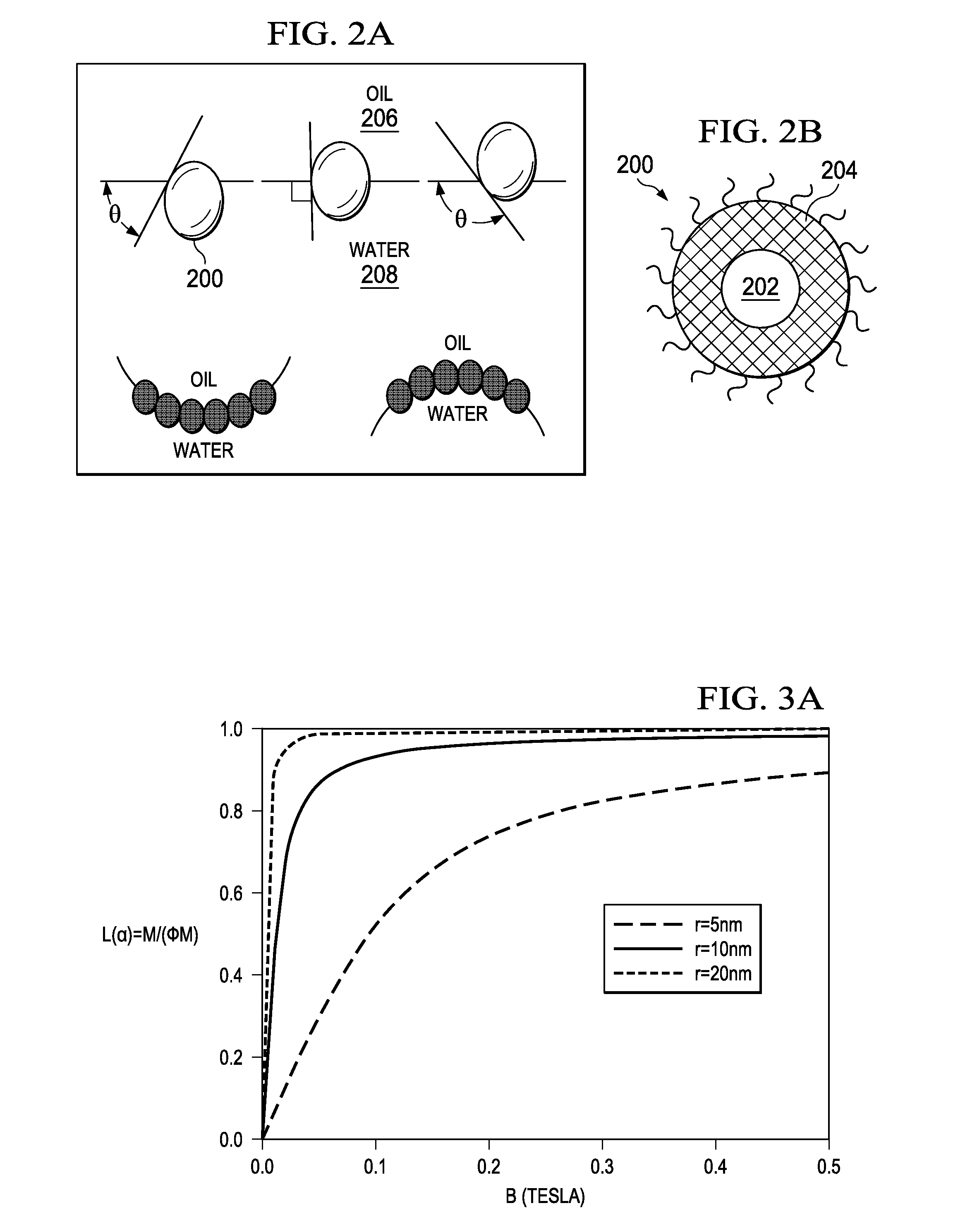
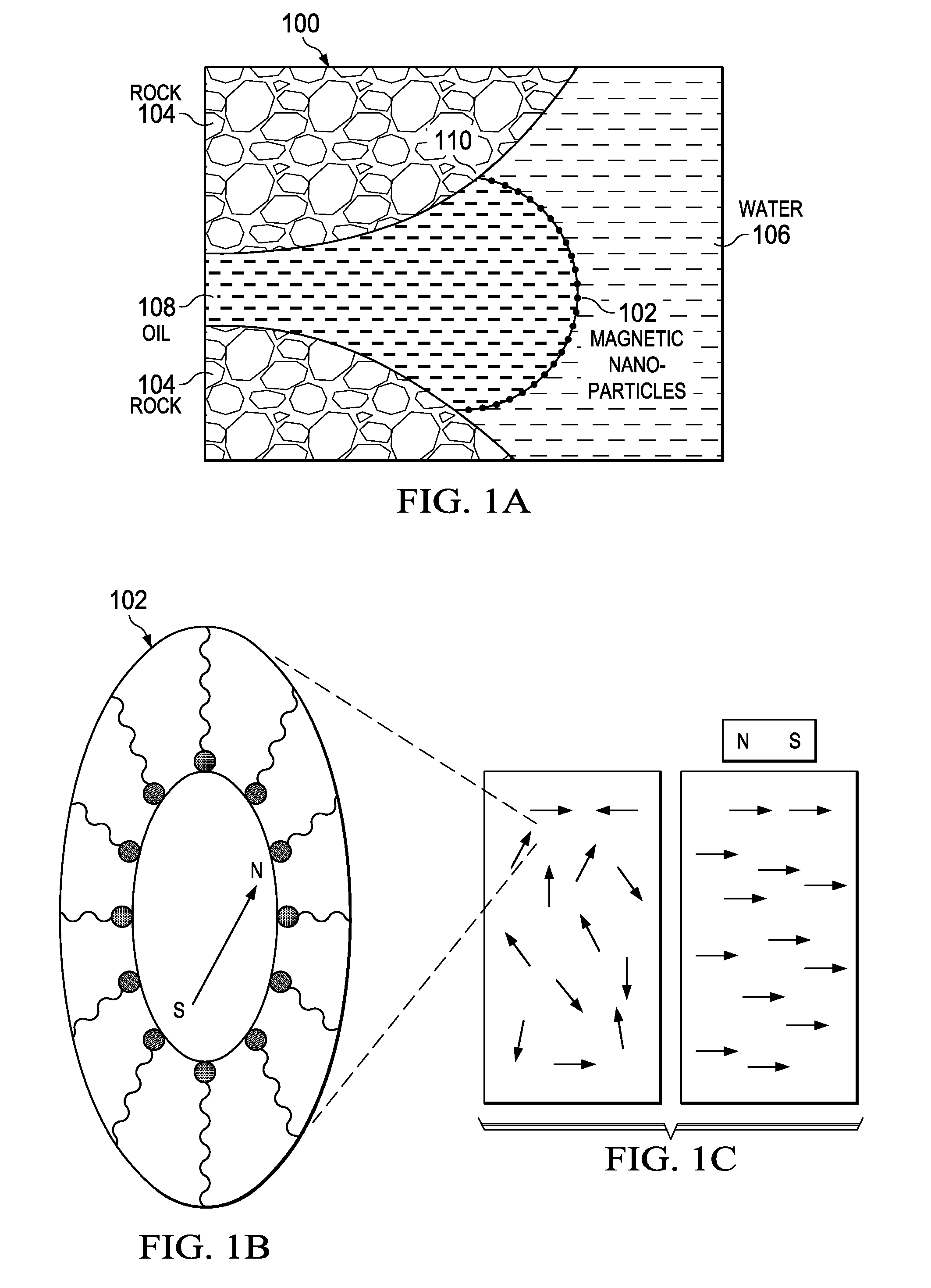
Determination of oil saturation in reservoir rock using paramagnetic nanoparticles and magnetic field
ActiveUS20130091941A1Improve salt tolerancePrevent disengagementSurveyConstructionsParamagnetic nanoparticlesAqueous dispersion
Methods for detection of the presence and distribution of oil in subsurface formation are described herein. The present invention involves injection of an aqueous dispersion of the nanoparticles into the potentially oil containing subsurface formation, followed by a remote detection of the oscillation responses of the nanoparticles in the oil / water interfaces in the reservoir rock by applying magnetic field.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
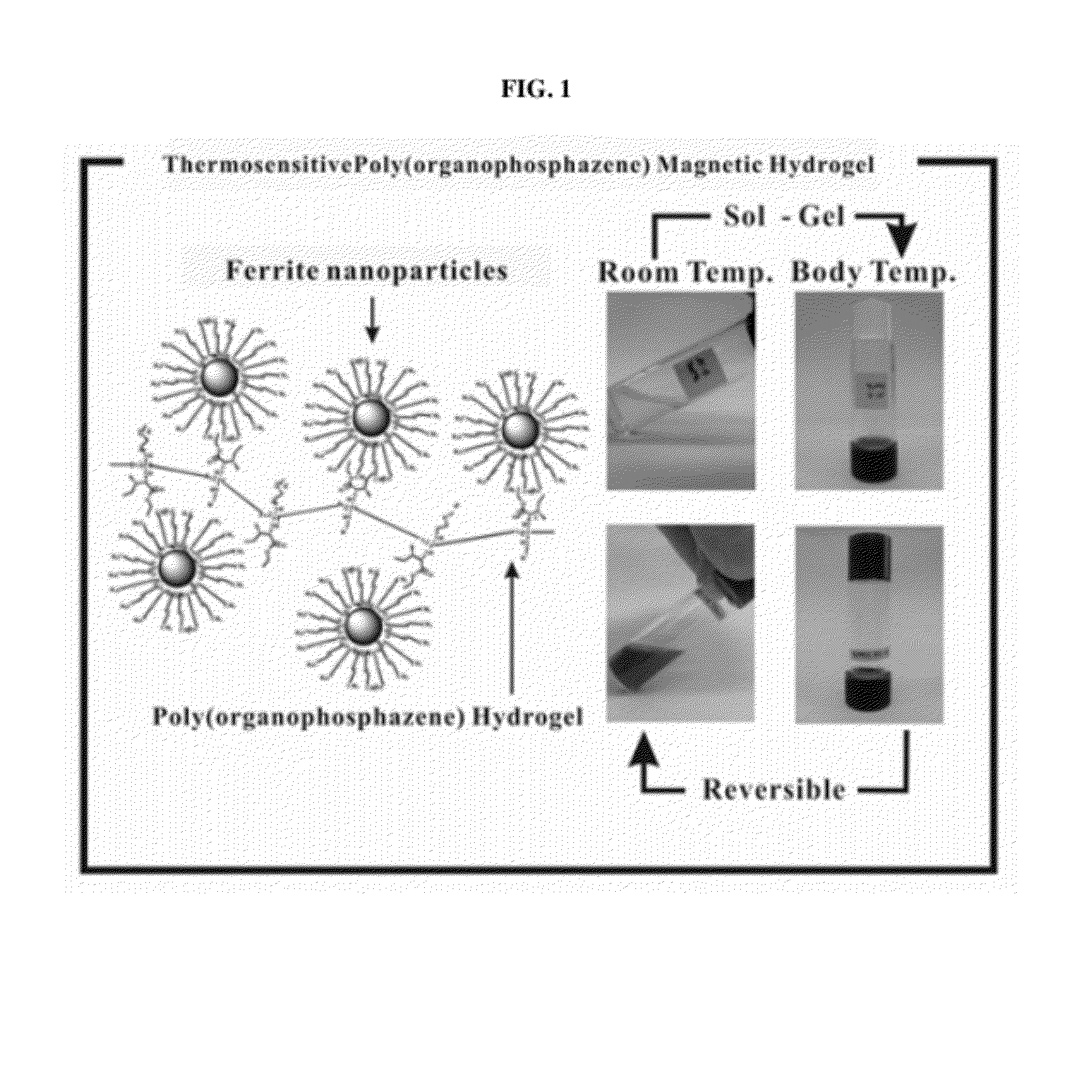
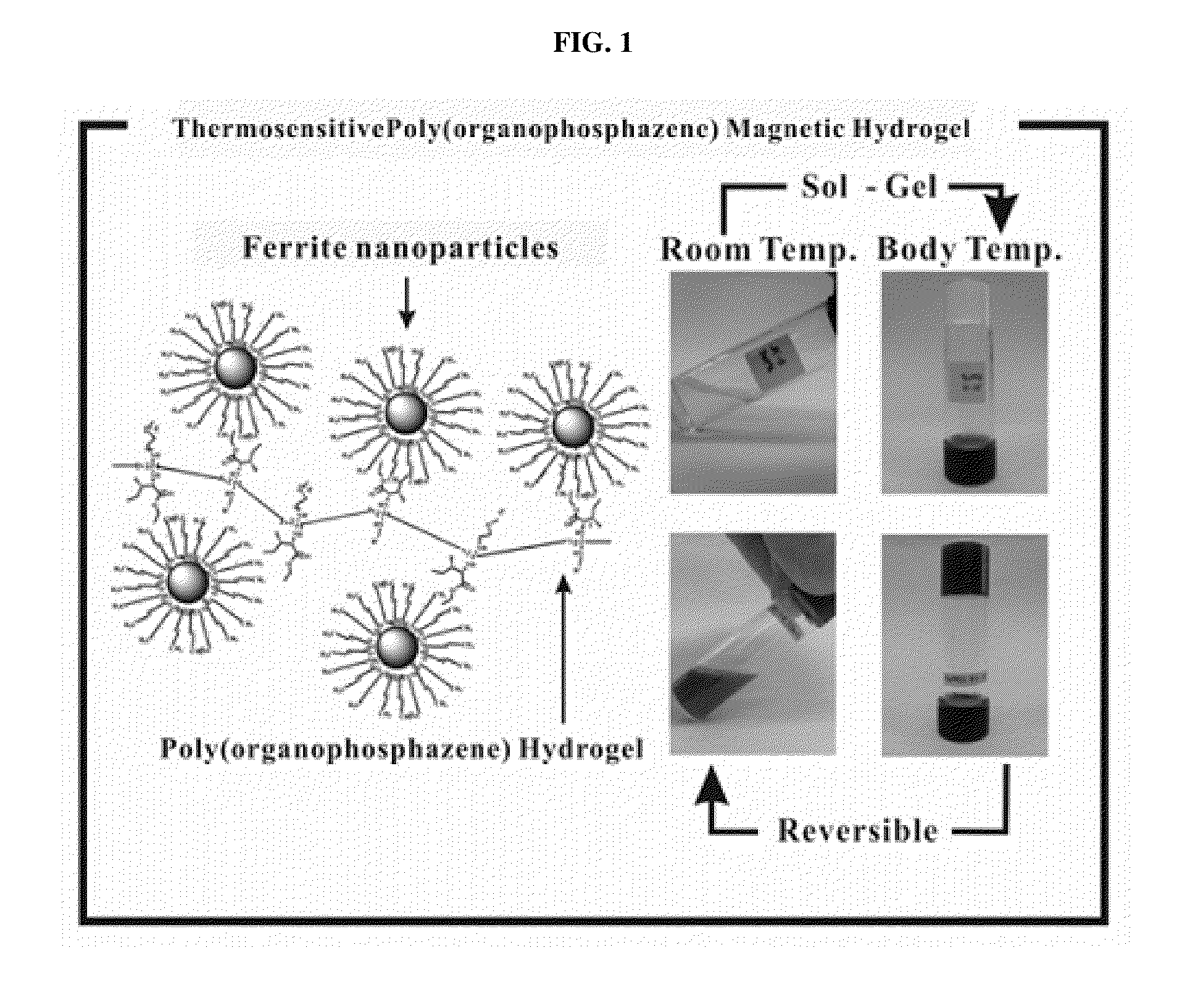
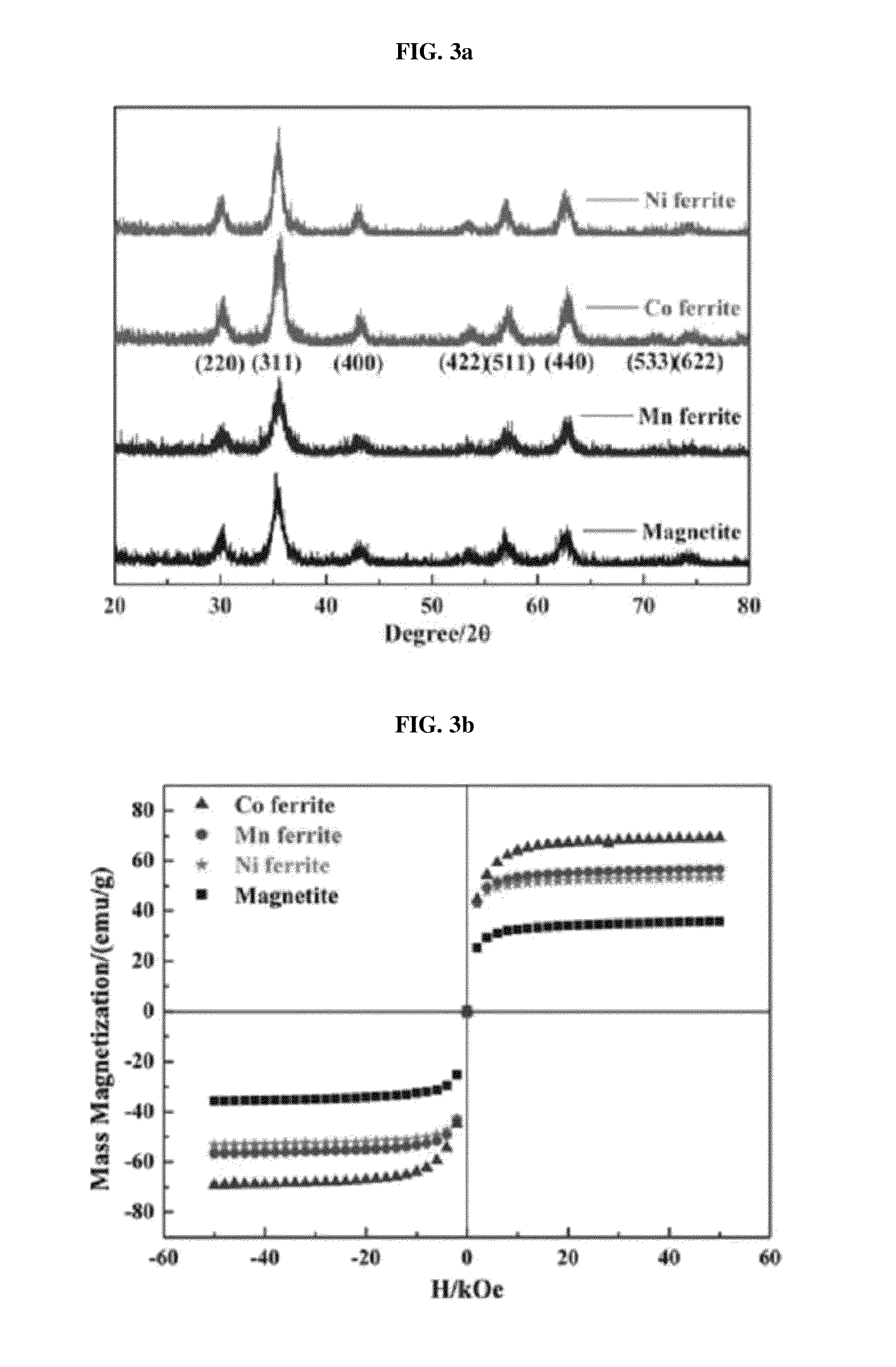
Biodegradable and thermosensitive poly(organophosphazene)-superparamagnetic nanoparticle complex, preparation method and use thereof
ActiveUS20120121517A1Facilitated releaseImprove load effectMaterial nanotechnologyBiocideMRI contrast agentFerrite nanoparticles
The present invention relates to a poly(organophosphazene)-superparamagnetic nanoparticle complex including a biodegradable and thermosensitive poly(organophosphazene) and a iron oxide (Fe3O4, Magnetite)-series ferrite superparamagnetic nanoparticle, a preparation method, and uses of carrying a physiologically-active material, a bio-material and a biomaterial for cancer hyperthermia. The iron oxide is used as a MRI contrast agent for T-2 and T2* weighted image, and the poly(organophosphazene) shows a sol-to-gel behavior depending upon the temperature change. The complex is a bound-type where the superparamagnetic ferrite nanoparticle is bonded to phosphazene-based polymer via hydrophobic binding, and a mixed-type where the superparamagnetic ferrite nanoparticle is physically mixed with the phosphazene-based polymer.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Determination of oil saturation in reservoir rock using paramagnetic nanoparticles and magnetic field
InactiveUS9133709B2Enhance the imageImproved determinationSurveyConstructionsParamagnetic nanoparticlesRemote detection
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Methods and compositions for conformance control using temperature-triggered polymer gel with magnetic nanoparticles
InactiveUS20150159079A1Low viscosityEnhanced overall recoveryElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyProduction rateMedicine
The present disclosure provides a polymer gel and method of making and using the same for use in high-permeability layers. This precision conformance control is accomplished by using paramagnetic nanoparticles and the application of the magnetic oscillation of prescribed frequency at the wellbore. If the polymer gel were created unintentionally at a certain layer, or there is a need to remove the gel blockage at the later stage of oil production, the gel could be broken and removed to restore the productivity from the layer.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Superparamagnetic particle imaging and its applications in quantitative multiplex stationary phase diagnostic assays
ActiveUS20190317167A1Improve responseMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansLaboratory glasswaresStationary phasePoint of care
Superparamagnetic nanoparticle-based analytical method comprising providing a sample having analytes in a sample matrix, providing a point of care chip having analytical regions, each of which is a stationary phase having at least one or more sections, labeling each of the analytes with a superparamagnetic nanoparticle and immobilizing the labeled analytes in the stationary phase, providing an analytical device having a means for exciting the superparamagnetic nanoparticles in vitro and a means for sensing, receiving, and transmitting response of the excited superparamagnetic nanoparticles, placing the chip in the analytical device and exciting the superparamagnetic nanoparticles in vitro, sensing, receiving, and transmitting the response of the superparamagnetic nanoparticles, and analyzing the response and determining characteristic of the analytes, wherein the response of the superparamagnetic nanoparticles comprises harmonics. The present invention also provides the hybrid point of care chip and analyzer to be used in the analytical method.
Owner:MARS SCI LTD
Hydrophobic Paramagnetic Nanoparticles as Intelligent Crude Oil Tracers
InactiveUS20150376493A1Easy to manageElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyMagnetic susceptibilityParamagnetic nanoparticles
Hydrophobic paramagnetic nanoparticles can be injected with the enhanced oil recovery injection water by incorporating them inside of surfactant micelles to serve as an oil tracer. A variety of paramagnetic nanoparticles that show different susceptibility and magnetization responses to applied magnetic oscillation can be injected at different injectors, so that the origin of the oil from the different enhanced oil recovery patterns could be quantitatively identified. The concentrations of the nanoparticles in the produced crude oil and brine can be easily and instantly measured individually, employing the magnetic susceptibility meter without contacting the fluids directly.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Hollow structured magnetic microsphere coated with mono-dispersed silicon dioxide and its preparation method
InactiveCN1911495ASimple manufacturing methodUniform number of coresInorganic material magnetismMicroballoon preparationMicrosphereParamagnetic nanoparticles
The present invention is monodisperse silica coated hollow magnetic microsphere and its preparation process and belongs to the field of nanometer magnetic material technology. Superparamagnetic nanometer ferrite particle is first prepared in coprecipitatin method and monodisperse polymer microsphere with surface functional radical is synthesized in emulsion polymerization; the superparamagnetic nanometer ferrite particle and the monodisperse polymer microsphere is then compounded by means of coordination effect, and the compound is coated with silica; and the composition particle is finally calcined at 500-700 deg.c for 5-12 hr to produce the silica coated hollow magnetic microsphere. The present invention has simple preparation process and controllability of the granularity and cavity size of the magnetic microsphere, and the magnetic microsphere has high chemical and colloid stability and may be used in biological detection and other fields.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
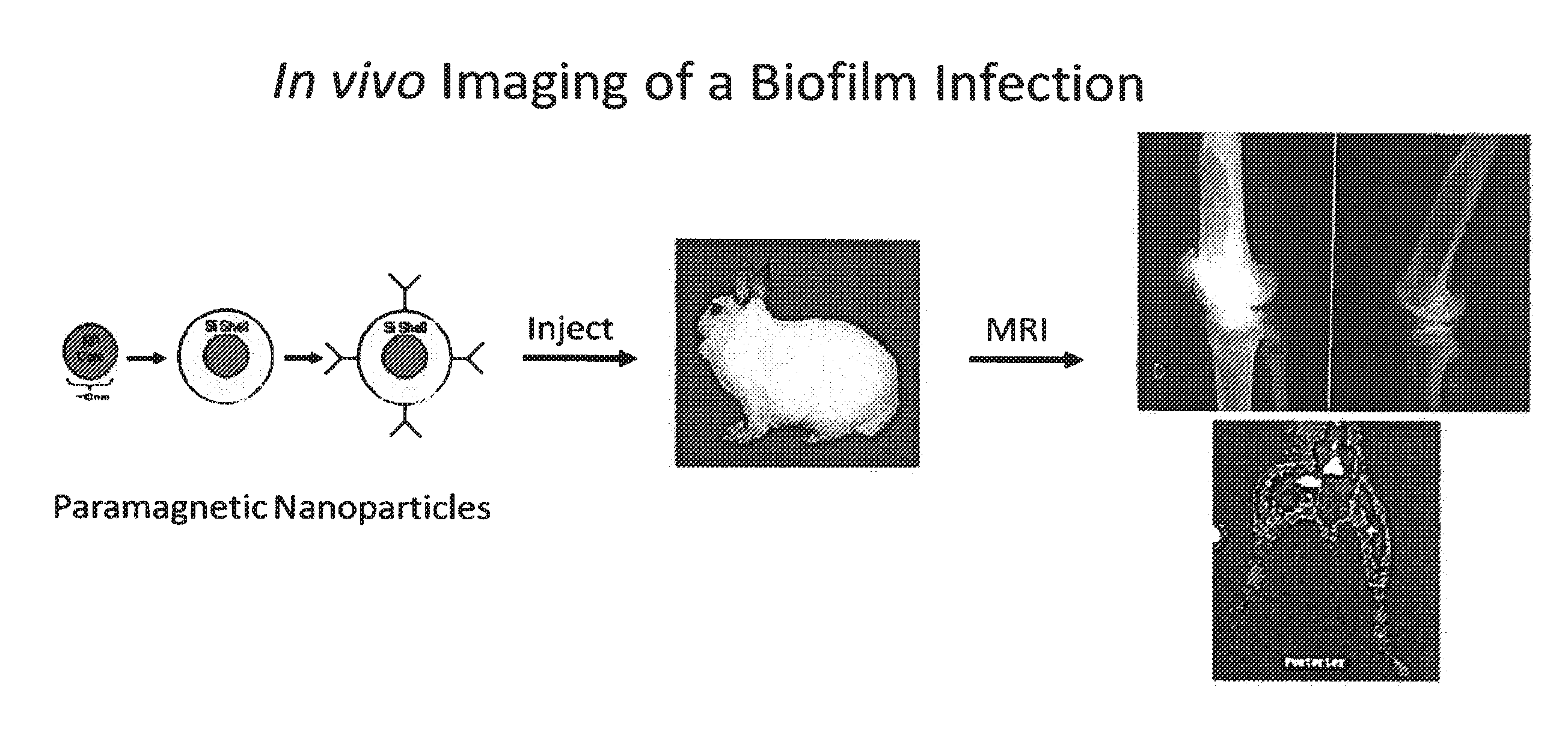
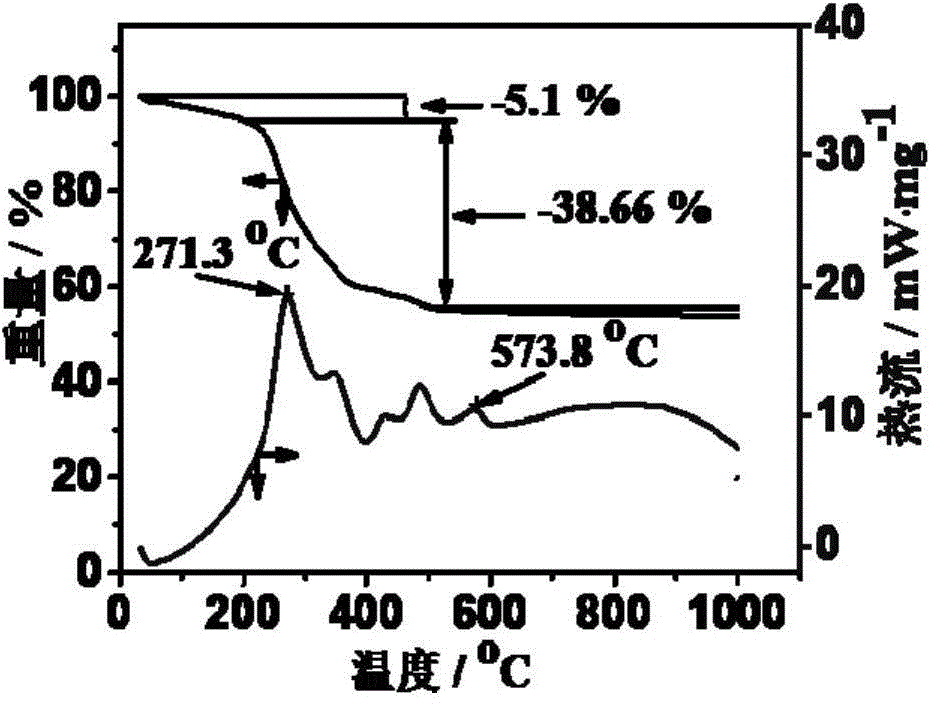
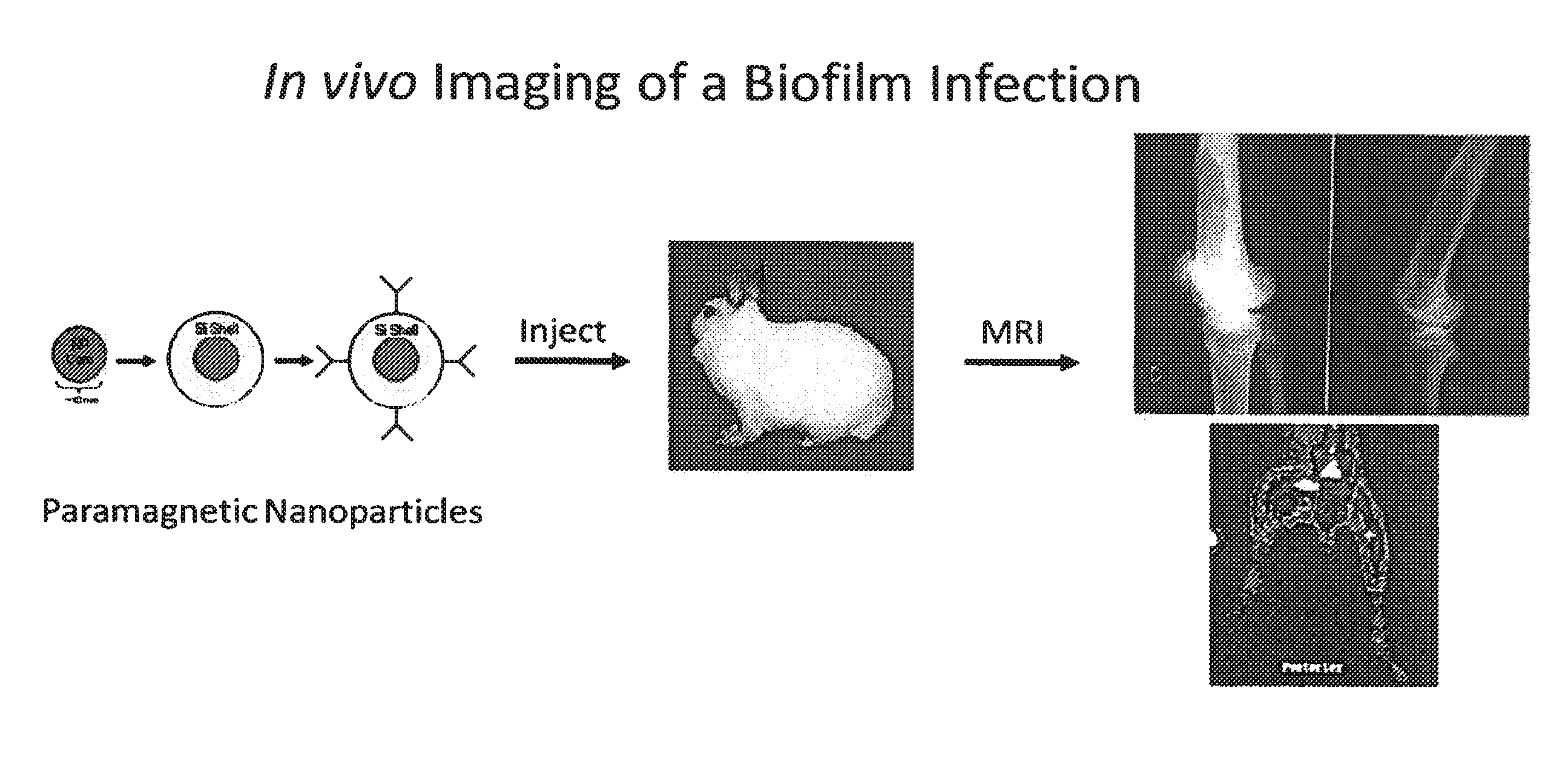
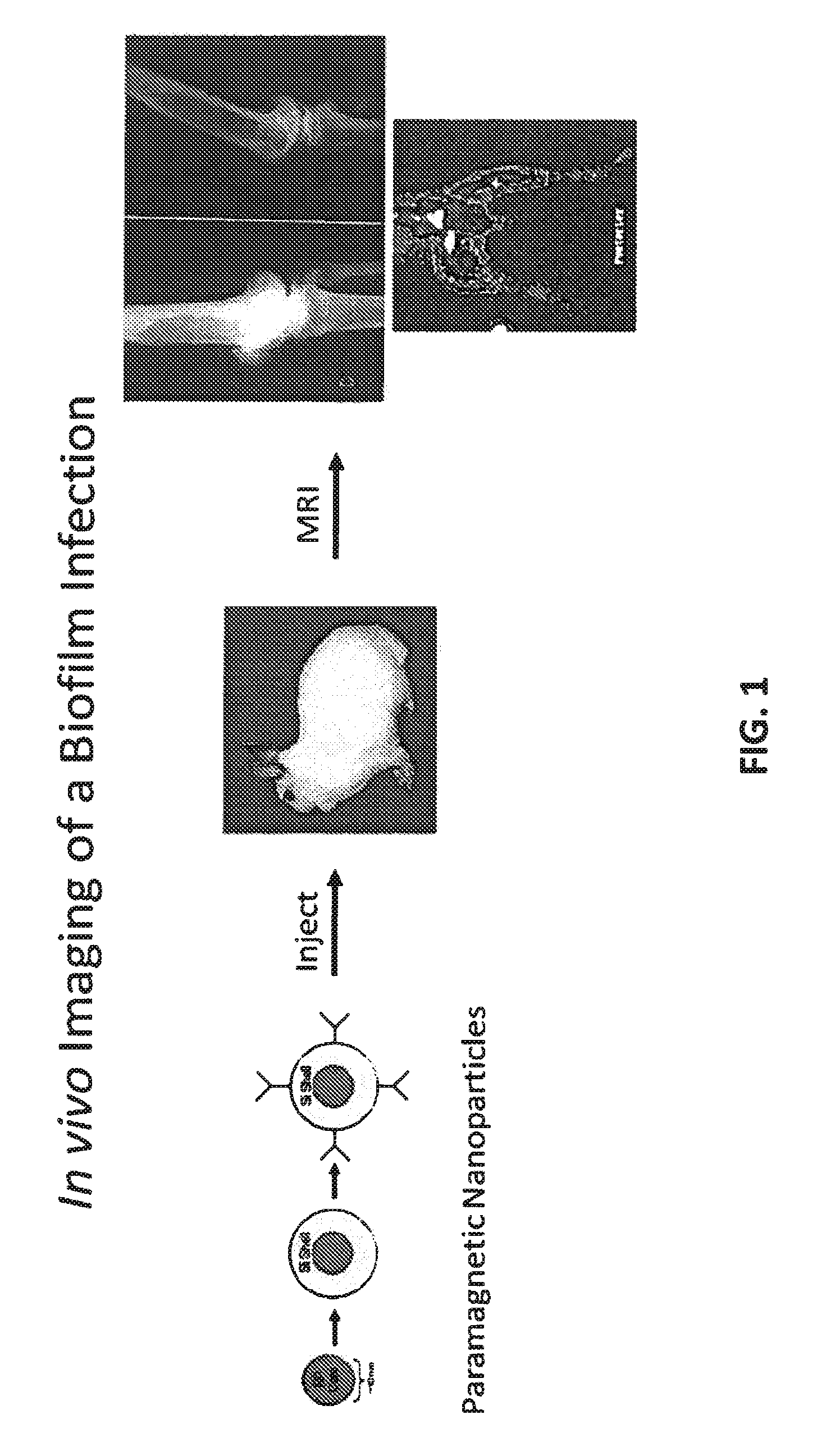
In Vivo Biofilm Infection Diagnosis and Treatment
InactiveUS20110171123A1Convenient to subjectNon-invasiveOvalbuminNanomedicineBiofilmInfection diagnosis
The present invention relates to a method for in vivo detection of a biofilm infection residing in a mammal, the method comprising (i) administering to the mammal a diagnostic-effective amount of a biofilm-specific probe, wherein the probe comprises a bio film-targeting moiety and a paramagnetic nanoparticle core; and (ii) imaging the mammal to detect the presence of the biofilm infection by observing the mammal using a magnetic resonance diagnostic technique after the biofilm-specific probe has been provided sufficient time to selectively bind to the bio film infection that may be present in the mammal. The invention also relates to methods of treatment of a bio film infection, and compositions and kits useful in the detection and / or treatment of bio film infections.
Owner:ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS A BODY OF THE STATE OF ARIZONA ACTING FOR & ON BEHALF OF NORTHERN ARIZONA UNIV +1
Biodegradable and thermosensitive poly(organophosphazene)-superparamagnetic nanoparticle complex, preparation method and use thereof
ActiveUS9017726B2Facilitated releaseImprove load effectPowder deliveryNanomedicineHybrid typeMRI contrast agent
Owner:NEXGEL BIOTECH CO LTD
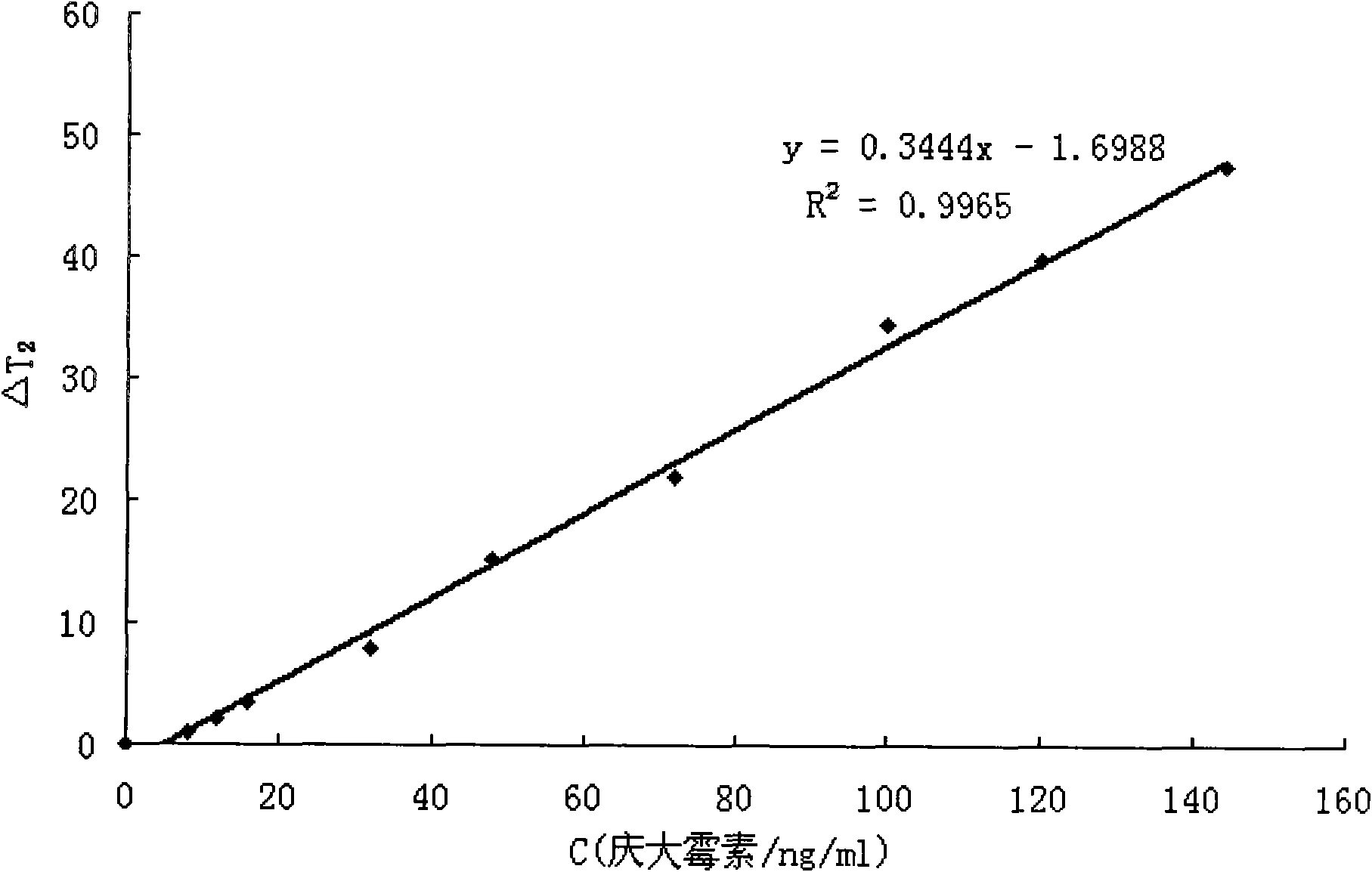
Method for detecting gentamicin through clinical magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveCN101566592ASimple and fast operationGood water solubilityWater resource assessmentAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceParamagnetic nanoparticlesSolubility
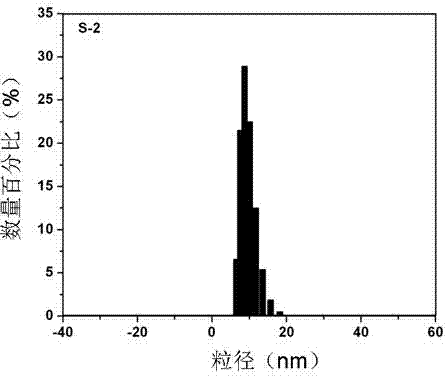
The invention relates to a method for detecting gentamicin through clinical magnetic resonance imaging, and belongs to the technical field of immunodetection. The method is to add standard gentamicin supernatant or gentamicin supernatant to be measured, gentamicin antibodies and goat-anti and rabbit-anti antibodies into gentamicin modified magnetic nano particles, and use the antibodies and the gentamicin modified magnetic nano particles to form immune polymers so as to generate magnetic resonance signals and perform magnetic resonance detection. The magnetic resonance signal detection method utilizes the antibodies and the gentamicin modified magnetic nano particles to form the immune polymers, and effectively shortens the transverse relaxation time T2 value of protons in water so as to generate signals. In general, when the concentration of the gentamicin in a sample is larger, the quantity of the gentamicin caught by the antibodies is more, the quantity of the antibodies which are combined with the gentamicin on the surface of the magnetic nano particles is fewer, and the measured T2 value is larger. The method does not need complex sample pretreatment, is simple and convenient to operate, only needs to add the sample to be measured for incubation and directly measure the T2 value, and can complete the process by one step. Moreover, the particle diameter of superparamagnetic nano particles for marking is approximately 10 nanometers, so that the water solubility is high and the dispersity and the stability are good.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Detection, measurement, and imaging of cells such as cancer and other biologic substances using targeted nanoparticles and magnetic properties thereof
ActiveUS20120035458A1Useful propertyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSubstance useParamagnetic nanoparticles
The present invention can provide a method of determining the presence, location, quantity, or a combination thereof, of a biological substance, comprising: (a) exposing a sample to a plurality of targeted nanoparticles, where each targeted nanoparticle comprises a paramagnetic nanoparticle conjugated with one or more targeting agents that preferentially bind with the biological substance, under conditions that facilitate binding of the targeting agent to at least one of the one or more biological substances; (b) subjecting the sample to a magnetic field of sufficient strength to induce magnetization of the nanoparticles; (c) measuring a magnetic field of the sample after decreasing the magnetic field applied in step b below a threshold; (d) determining the presence, location, quantity, or a combination thereof, of the one or more biologic substances from the magnetic field measured in step (c).
Owner:IMAGION BIOSYST INC
Method for rapidly detecting and screening Enterobacter sakazakii
InactiveCN101865919ALower requirementEasy to operateBiological testingQuantum dotParamagnetic nanoparticles
The invention discloses a method for rapidly detecting and screening Enterobacter sakazakii, which comprises the following steps: adding immunized super-paramagnetic nanoparticles in a sample to be detected to enable the immunized super-paramagnetic nanoparticles to be specifically combined with Enterobacter sakazakii; collecting the immunized super-paramagnetic nanoparticles, and after washing the immunized super-paramagnetic nanoparticles, adding immunized luminescent quantum dots to enable the immunized luminescent quantum dots to be specifically combined with Enterobacter sakazakii carried by the immunized super-paramagnetic nanoparticles; and using an applied magnetic field to adsorb and collect Enterobacter sakazakii and immunized luminescent quantum dot combinations carried by the immunized super-paramagnetic nanoparticles, and after washing the combinations, conducting qualitative or quantitative fluorescence detection. By adopting the method, the target bacteria can be rapidly separated from all kinds of samples and can be efficiently enriched, the operation is convenient and simple, the reliability is high and the requirement on the supporting equipment is low.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Polymer-brush-modified magnetic composite microsphere as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention provides a polymer-brush-modified magnetic composite microsphere as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The polymer-brush-modified magnetic composite microsphere comprises a polymer core, a super-paramagnetic nanoparticle shell and a polymer brush in sequence from inside to outside, wherein the polymer brush is directly grafted onto the super-paramagnetic nanoparticle shell through atom transfer radical polymerization by using a carboxyl-containing water-soluble unsaturated monomer. By grafting the polymer brush onto a magnetic nanoparticle surface, the specific surface area and the protein binding site of the microsphere can be increased greatly, and the probability of the contact of a protein with a material is increased. Moreover, a specific functional group can be further grafted onto the polymer brush conveniently, so that the specific binding ability of the microsphere with a separation object is improved, and the aim of finer separation is fulfilled. The preparation method is simple, and is convenient to promote and apply; and the stability, operability and environmental friendliness of a reaction system are improved.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Determination of oil saturation in reservoir rock using paramagnetic nanoparticles and magnetic field
InactiveUS20160002523A1Enhance the imageImproved determinationSurveyConstructionsParamagnetic nanoparticlesRemote detection
Methods for detection of the presence and distribution of oil in subsurface formation are described herein. The present invention involves injection of an aqueous dispersion of the nanoparticles into the potentially oil containing subsurface formation, followed by a remote detection of the oscillation responses of the nanoparticles in the oil / water interfaces in the reservoir rock by applying magnetic field.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Mn element and Zn element-doped super-paramagnetic ferrite nanoparticles and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102786299AControlling Saturation MagnetizationRegular shapeMaterial nanotechnologyHexadecaneActive agent
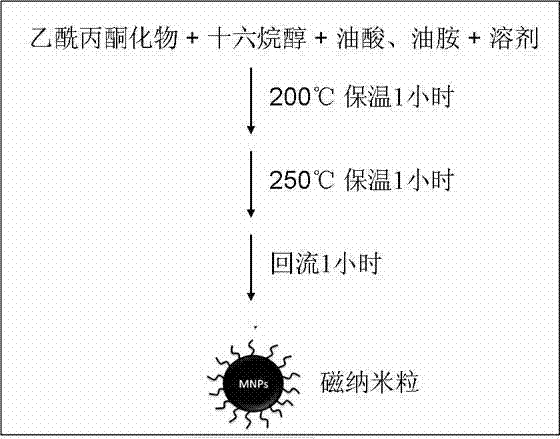
The invention discloses Mn element and Zn element-doped super-paramagnetic ferrite nanoparticles and a preparation method thereof. Manganese element is added or manganese element and zinc element are simultaneously added into a face-centered cubic crystal structure of ferriferrous oxide nanoparticles by using a method of decomposing metal precursor compound at a high temperature; the magnetic performance of the prepared super-paramagnetic nanoparticles is improved by changing the doping amount and the distribution of the metal element; and primarily, the saturation magnetization is improved. The preparation method specifically comprises the following steps of: mixing acetylacetones of Fe and Mn as well as Zn with 1,2-hexadecanol; performing high-temperature decomposition in high-boiling-point solvent by taking oleic acid and oleylamine as surfactants; or performing high-temperature decomposition on composite oleate of Fe, Mn and Zn by taking the oleic acid as the surfactant; heating and preserving heat in stages in argon or nitrogen protective atmosphere to guarantee growth of nanoparticle nuclear; and cooling to room temperature after reaction is finished and settling and centrifuging to finally obtain the super-paramagnetic ferrite nanoparticles which are uniformly dispersed in normal hexane solution.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Paramagnetic nanoparticle
InactiveUS20040156784A1Narrow size distributionBiocideDispersion deliveryContrast levelOrganic synthesis
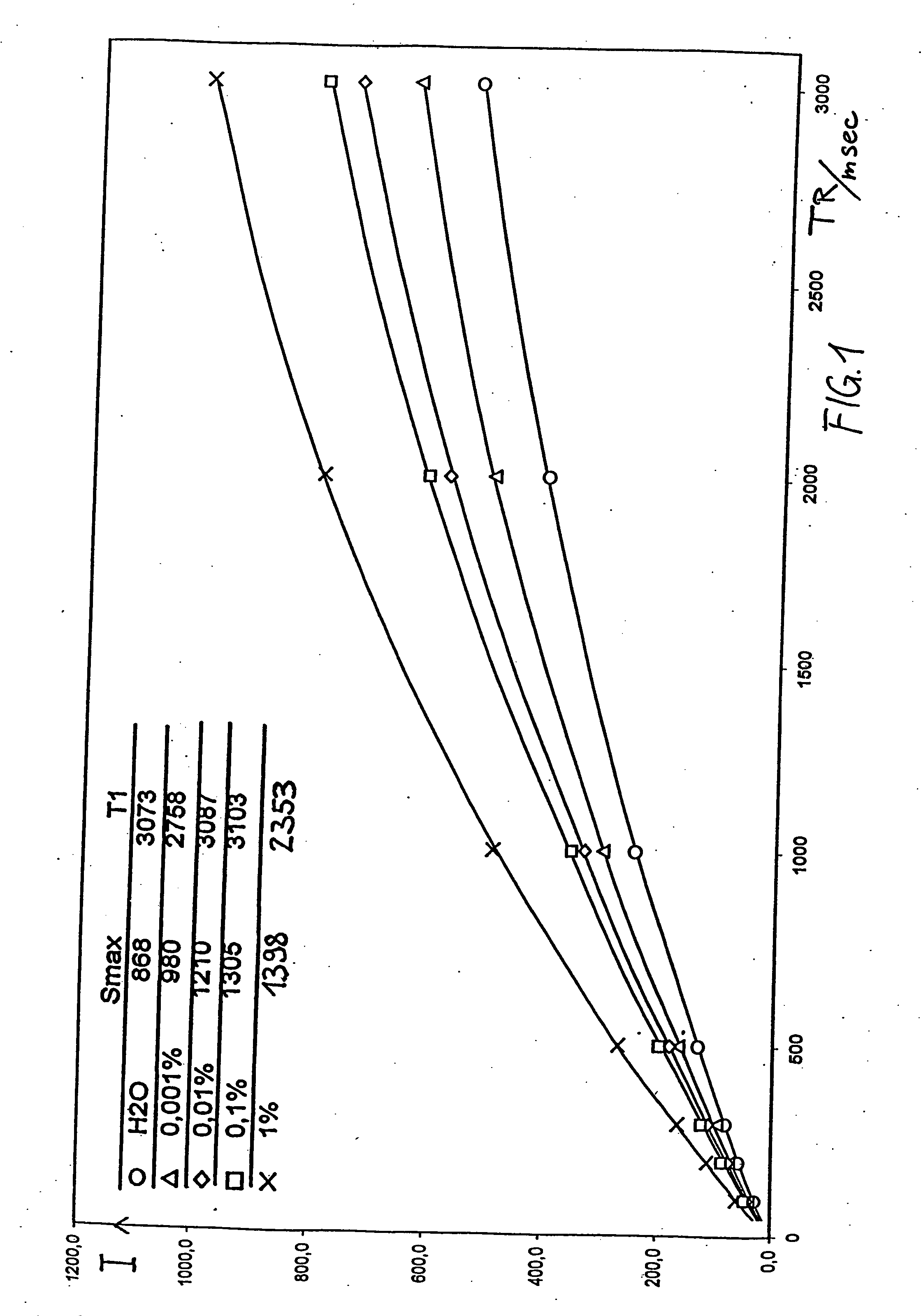
The present invention relates to the preparation and use of nanoparticles, in particular paramagnetic nanoparticles, and their use as contrast enhancers for NMR-based methods of examination. A significant increase in contrast (e.g. from 100 to 200%) takes place according to the invention. An aqueous or organic synthesis leads to small nanoparticles which have a narrow size distribution and can also be advantageously used for many other industrial applications.
Owner:CENT FUR ANGEWANDTE NANOTECH
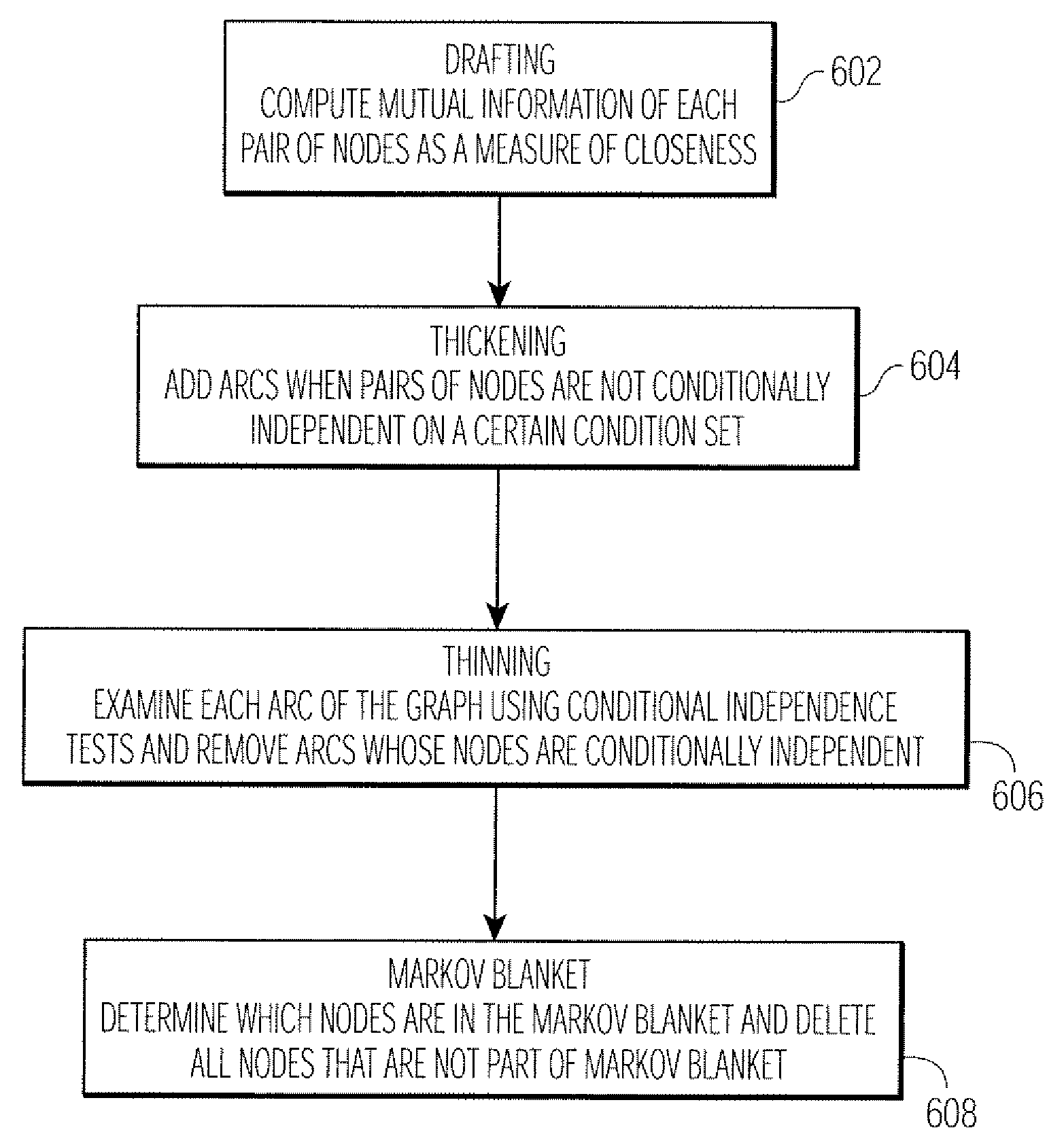
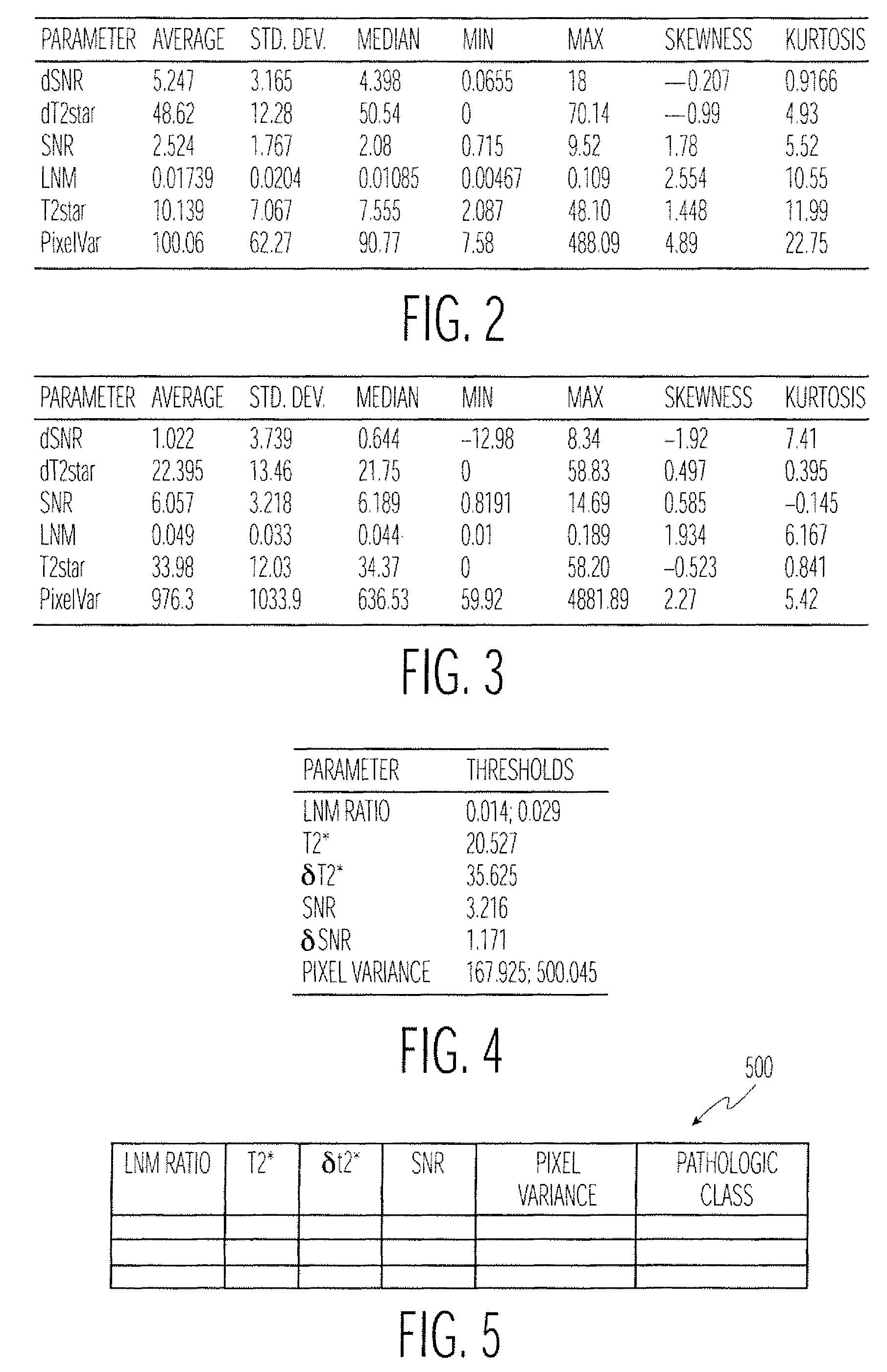
Method and apparatus for classifying tissue using image data
Disclosed is a technique for classifying tissue based on image data. A plurality of tissue parameters are extracted from image data (e.g., magnetic resonance image data) to be classified. The parameters are preprocessed, and the tissue is classified using a classification algorithm and the preprocessed parameters. In one embodiment, the parameters are preprocessed by discretization of the parameters. The classification algorithm may use a decision model for the classification of the tissue, and the decision model may be generated by performing a machine learning algorithm using preprocessed tissue parameters in a training set of data. In one embodiment, the machine learning algorithm generates a Bayesian network. The image data used may be magnetic resonance image data that was obtained before and after the intravenous administration of lymphotropic superparamagnetic nanoparticles.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
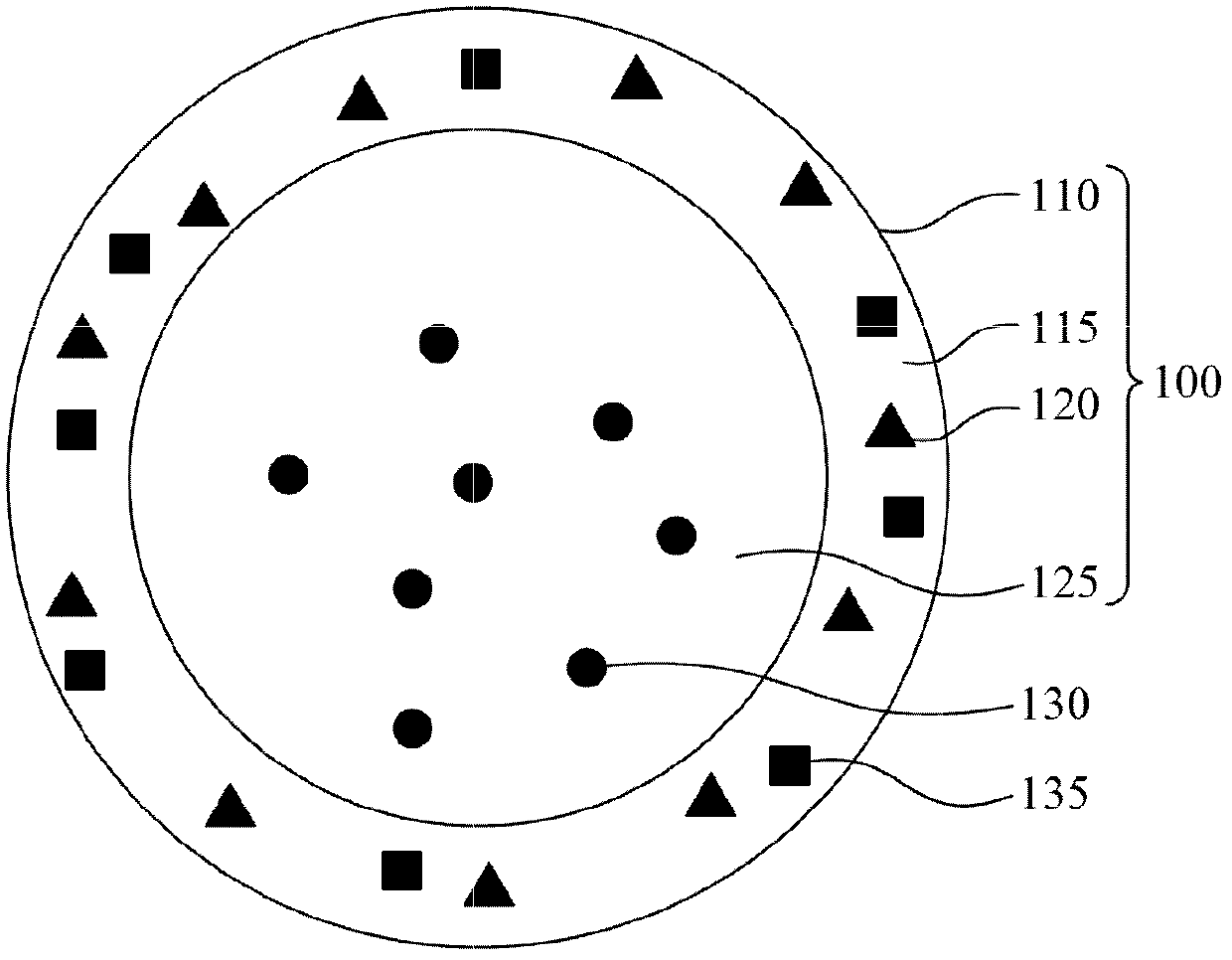
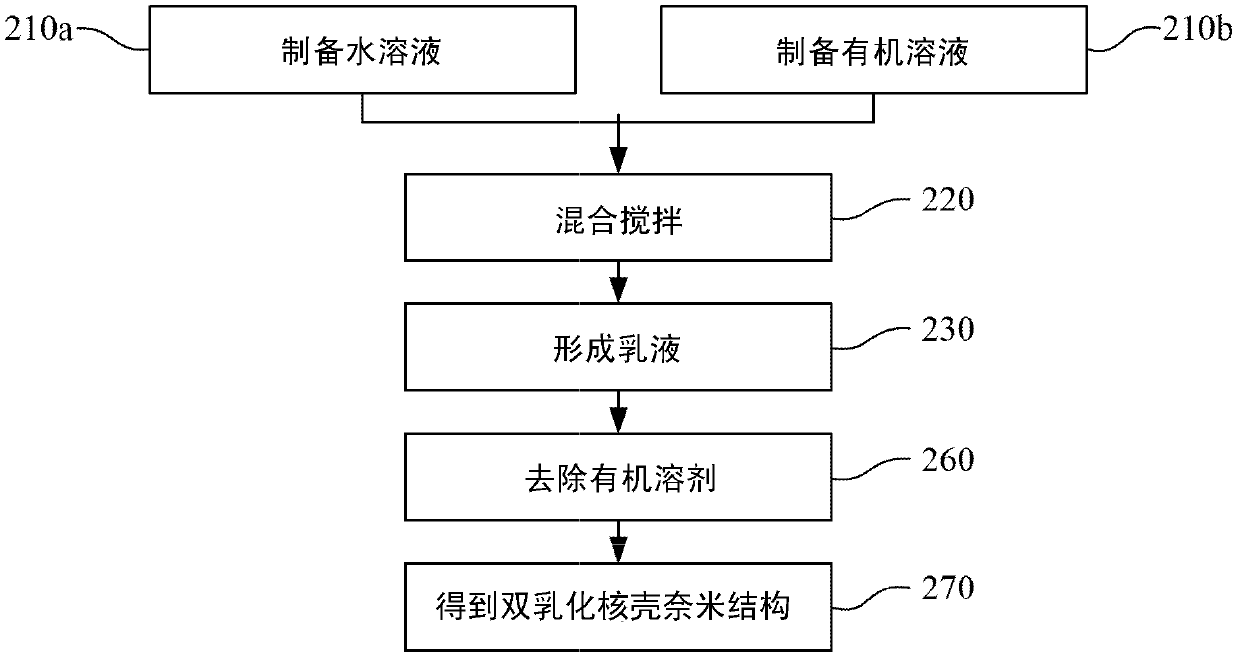
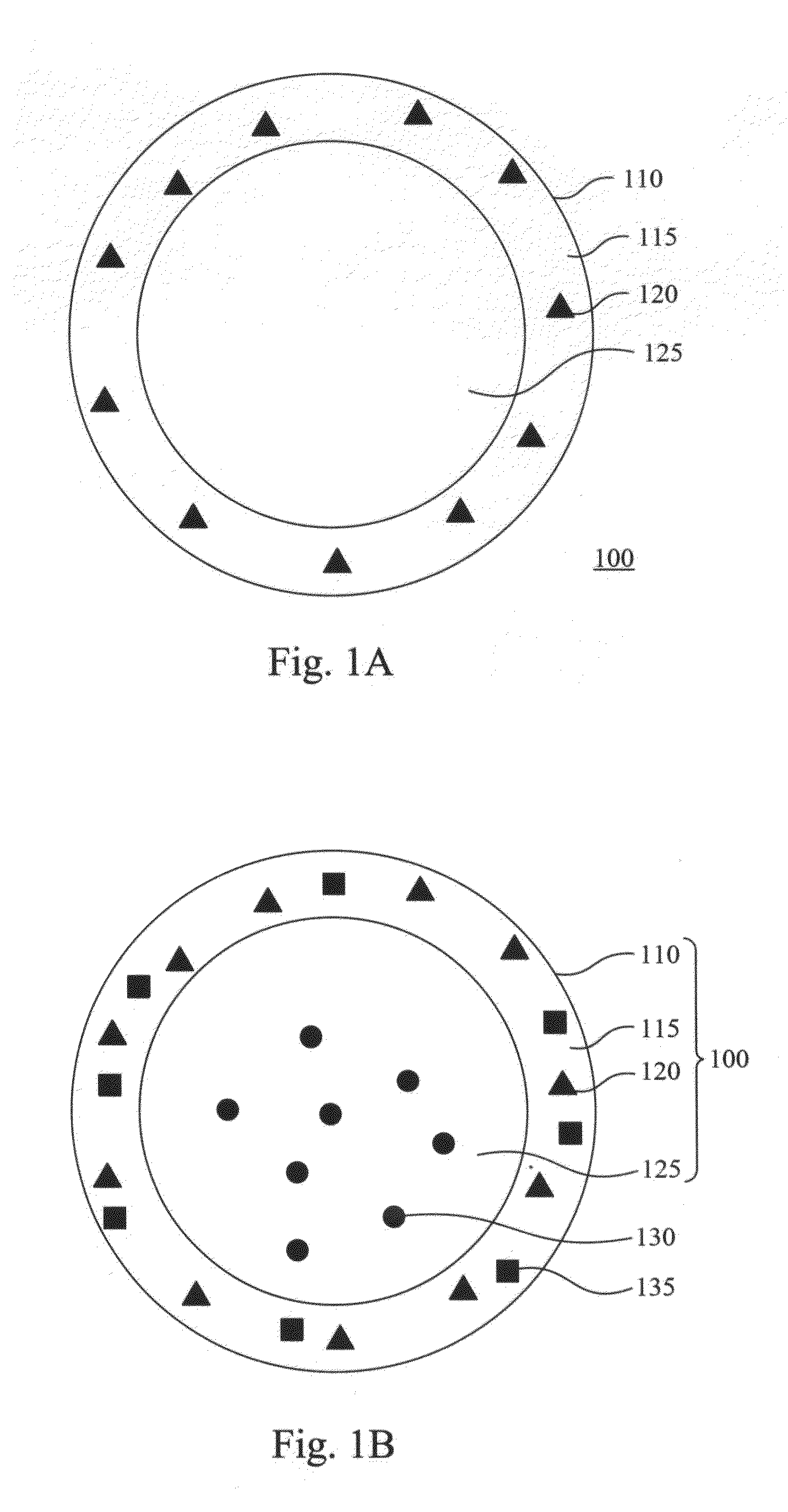
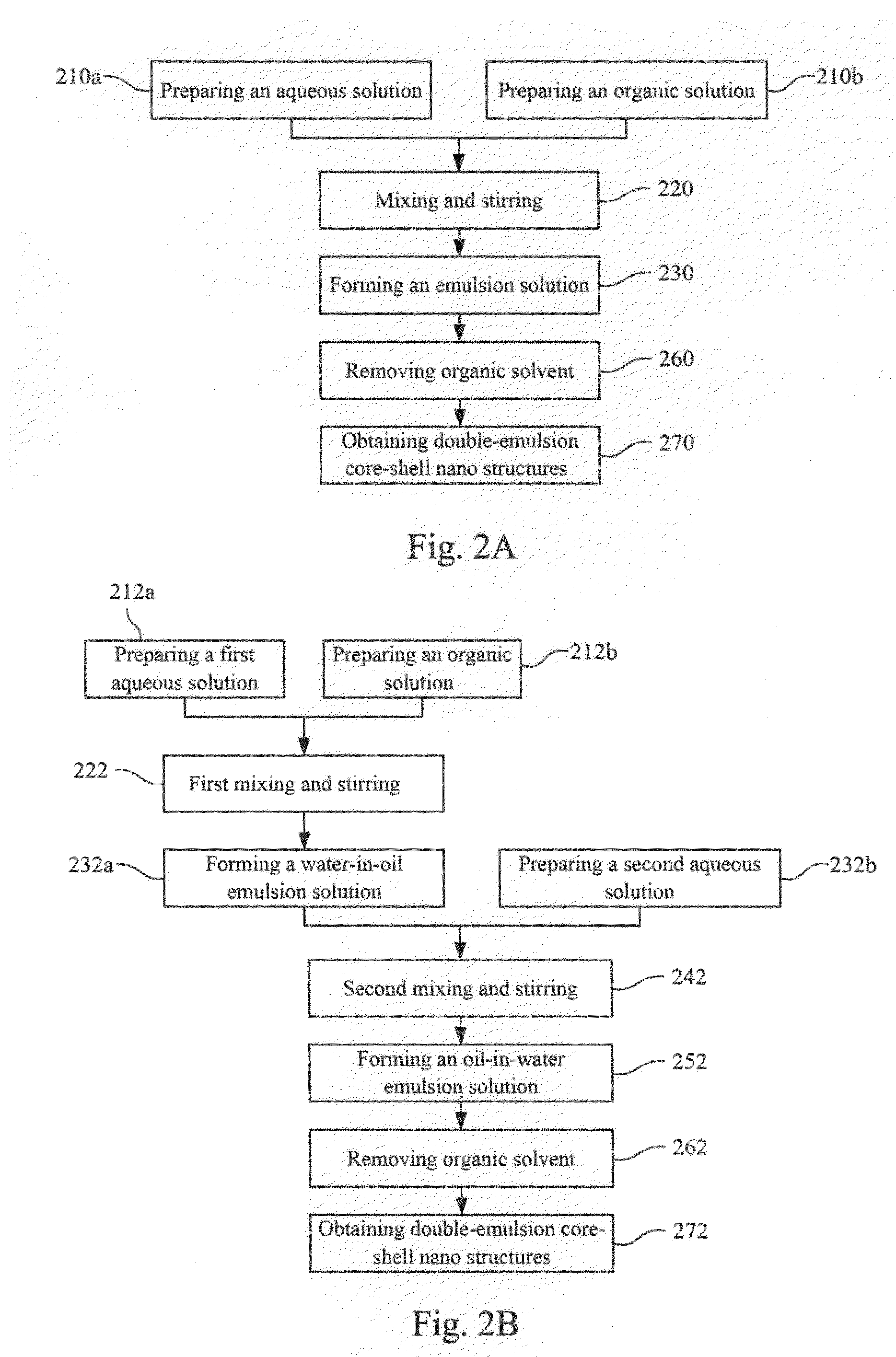
Double emulsion core-shell nano-structure and preparation methods thereof
InactiveCN103126985AEasy Mixing Stirring StepsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsEmulsion deliveryPolymer scienceNano structuring
A double-emulsion core-shell nano-structure and preparation methods thereof are provided. The double-emulsion core-shell nano-structure is a structure of an oil shell enclosing a water core. The double-emulsion core-shell nano-structure can be prepared by simply mixing and stirring to emulsify an aqueous solution of a water soluble polymer and an organic solution of hydrophobic paramagnetic nanoparticles
Owner:SPRING FOUND OF NCTU
Double emulsion core-shell nano-structure and preparation methods thereof
InactiveUS20130137917A1Simple emulsifying methodSuitable for usePowder deliveryElectrotherapyPolymer scienceNano structuring
A double-emulsion core-shell nano-structure and preparation methods thereof is provided. The double-emulsion core-shell nano-structure is a structure of an oil shell enclosing a water core. The double-emulsion core-shell nano-structure can be prepared by simply mixing and stirring to emulsify an aqueous solution of a water soluble polymer and an organic solution of hydrophobic paramagnetic nanoparticles.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
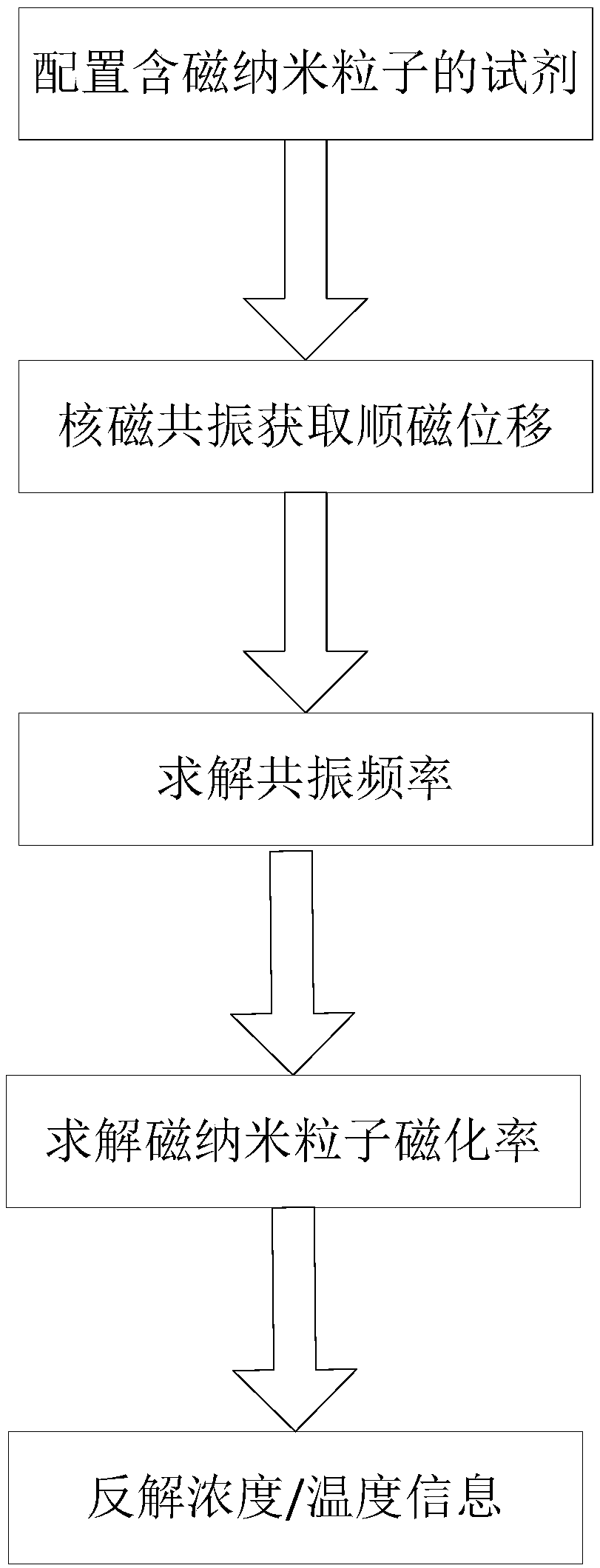
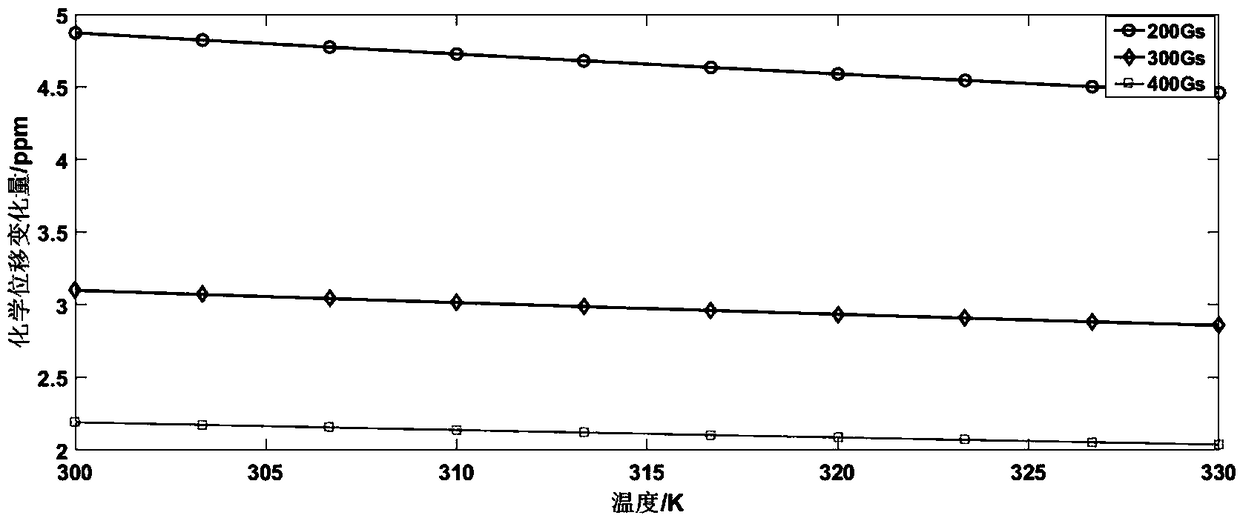
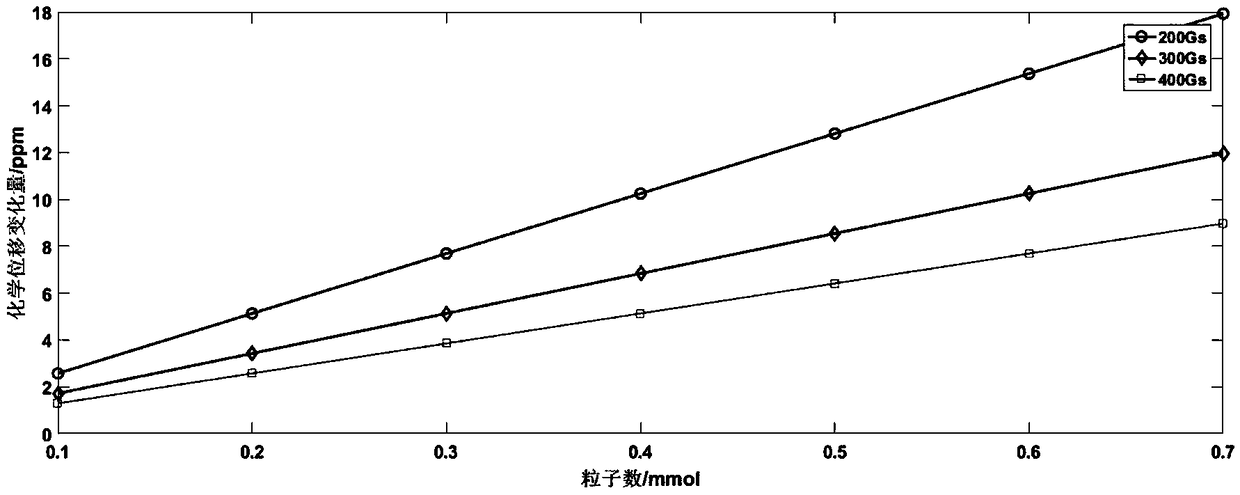
Magnetic nanoparticle concentration and temperature measurement method based on paramagnetic shift
ActiveCN108663391AIncrease concentrationHigh measurement accuracyNanotechMagnetic measurementsMagnetic susceptibilityParamagnetic nanoparticles
The invention discloses a magnetic nanoparticle concentration and temperature measurement method based on paramagnetic shift. NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance) equipment is utilized for measuring chemical shift of a liquid sample containing paramagnetic particles so as to measure concentration and temperature of magnetic nanoparticles, and concentration and temperature measurement with high measurement accuracy is realized effectively. The paramagnetic nanoparticles are added to an NMR sample reagent, and the paramagnetic shift of the sample is obtained through NMR. Resonance frequency is acquired through the paramagnetic shift, magnetic susceptibility is acquired according to the relation between the resonance frequency and magnetic susceptibility of the magnetic nanoparticles, and concentration information and temperature information of the sample are further inversely solved according to the relation of the magnetic susceptibility of the magnetic nanoparticles with the concentrationand the temperature. According to simulation data, concentration measurement and high-accuracy temperature measurement of the magnetic nanoparticle sample can be effectively realized on the basis of the paramagnetic shift information.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Preparation method and application method of targeted superparamagnetic nano-probe
InactiveCN106399226AUniform particle size distributionImprove stabilityArtificial cell constructsVertebrate cellsParamagnetic nanoparticlesOil phase
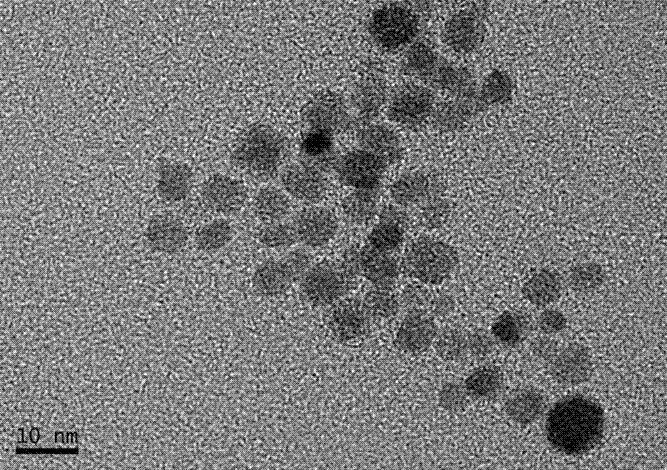
The invention provides a preparation method of a targeted superparamagnetic nano-probe. The method includes the steps of: 1. preparing ferroferric oxide nano-particles with a particle size of 10-20nm in an oil phase by high temperature thermal decomposition; 2. synthesizing an amphiphilic polymer; 3. conducting aqueous phase transformation of the ferroferric oxide nano-particles obtained by step 1 through the amphiphilic polymer obtained by step 2 so as to obtain water-soluble superparamagnetic nano-particles; and 4. under the coupling effect of EDC / NHS, subjecting the water-soluble superparamagnetic nano-particles obtained by step 3 to covalent coupling with a target molecule, thus obtaining the targeted superparamagnetic nano-probe. The invention also provides an application method of the probe. Under the action of a separation column and an applied magnetic field, the probe can specifically and effectively capture and separate target cells. Compared with the prior art, the probe prepared by the method provided by the invention has the advantages of uniform particle size, high T2 relaxation rate, good stability, high pH value, high salt tolerance, and good target cell separation effect.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Preparation of extremely small and uniform sized, iron oxide-based paramagnetic or pseudo-paramagnetic nanoparticles and mri t1 contrast agents using the same
InactiveCN103153348AEasy to manufactureControllable sizeInorganic non-active ingredientsNanomedicineT1 contrastPhysical chemistry
Provided are a preparation method of iron oxide-based paramagnetic or pseudo-paramagnetic nanoparticles, iron oxide-based nanoparticles prepared by the same, and a T1 contrast agent including the same. More particularly, the disclosure describes a method for preparation of iron oxide nanoparticles having a extremely small and uniform size of 4nm or less based on thermal decomposition of iron oleate complex, iron oxide-based paramagnetic or pseudo-paramagnetic nanoparticles prepared by the same, and a Tl contrast agent including iron oxide-based paramagnetic or pseudo-paramagnetic nanoparticles.
Owner:HANWHA CHEMICAL CORPORATION
Magnetic resonance contrast agent constructed by amphipathic polysaccharide-wrapped super-paramagnetic nanoparticles and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102380109AAchieve multi-functionalityEasy to operateEmulsion deliveryIn-vivo testing preparationsParamagnetic nanoparticlesSolvent
The invention discloses a magnetic resonance contrast agent constructed by amphipathic polysaccharide-wrapped super-paramagnetic nanoparticles and a preparation method thereof, and the magnetic resonance contrast agent is characterized in that amphipathic polysaccharides take glucosans as main chain grafted hydrophobic chain segment molecules (such as fatty acids), self-assembly is performed in aselective solvent for forming micelles, and hydrophobic super-paramagnetic nanoparticles (such as ferroferric oxide nano-crystals) can be loaded so as to get a water-soluble nano compound. The nano compound has good biological compatibility, and the loaded nanoparticles can keep the original advantages of physical properties. The nano-compound can be used as the magnetic resonance contrast agent,thereby having extensive application prospects in magnetic resonance enhanced imaging, early diagnosis of cancers, image tracking efficacy evaluation and other biomedical fields.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Preparation of super paramagnetic nano particles dispersible in water
InactiveCN1583575AImprove stabilityGood dispersionIron oxides/hydroxidesInorganic material magnetismParamagnetic nanoparticlesSuperparamagnetism
A process for preparing the super-paramagnetic nanoparticles dispersed in water easily includes such steps as mixing the polymer chelating agent with Fe ions, dripping alkali while reacting to generate inn oxide and continuously dripping alkali until pH=9-10.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Detection, measurement, and imaging of cells such as cancer and other biologic substances using targeted nanoparticles and magnetic properties thereof
The present invention can provide a method of determining the presence, location, quantity, or a combination thereof, of a biological substance, comprising: (a) exposing a sample to a plurality of targeted nanoparticles, where each targeted nanoparticle comprises a paramagnetic nanoparticle conjugated with one or more targeting agents that preferentially bind with the biological substance, under conditions that facilitate binding of the targeting agent to at least one of the one or more biological substances; (b) subjecting the sample to a magnetic field of sufficient strength to induce magnetization of the nanoparticles; (c) measuring a magnetic field of the sample after decreasing the magnetic field applied in step b below a threshold; (d) determining the presence, location, quantity, or a combination thereof, of the one or more biologic substances from the magnetic field measured in step (c).
Owner:IMAGION BIOSYST INC
Flexible photon nanometer chain with adjustable photonic band gap and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104629232AAdjustable bandgapShorten the diffusion distanceInorganic material magnetismParamagnetic nanoparticlesPhotonics
The invention relates to a flexible photon nanometer chain with an adjustable photonic band gap and a preparation method and application thereof. The flexible photon nanometer chain can serve as a sensor to sense the outside physical and chemical stimulation and has a single-chain one-dimensional nanometer structure formed by arranging monodisperse super-paramagnetic nanoparticles at equal particle distance in a responsive polymer matrix. The method for preparing the flexible photon nanometer chain with the adjustable photonic band gap comprises the following steps: fully dispersing the monodisperse super-paramagnetic nanoparticles in a solution containing a responsive polymer monomer, carrying out an ultraviolet or thermal induced polymerization under the action of an external magnetic field, thereby obtaining the product. Compared with the prior art, the flexible photon nanometer chain disclosed by the invention has the following main advantages that 1, the flexible photon chain is fixed in the responsive polymer; 2, the prepared flexible photon nanometer chain has the adjustable photonic band gap, the outside physical and chemical stimulation can be responsed by virtue of movement of a reflection peak, and the flexible photon nanometer chain can serve as a sensor; and 3, the diffusion distance of a detected object in a gel layer is greatly shortened and the response speed is improved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
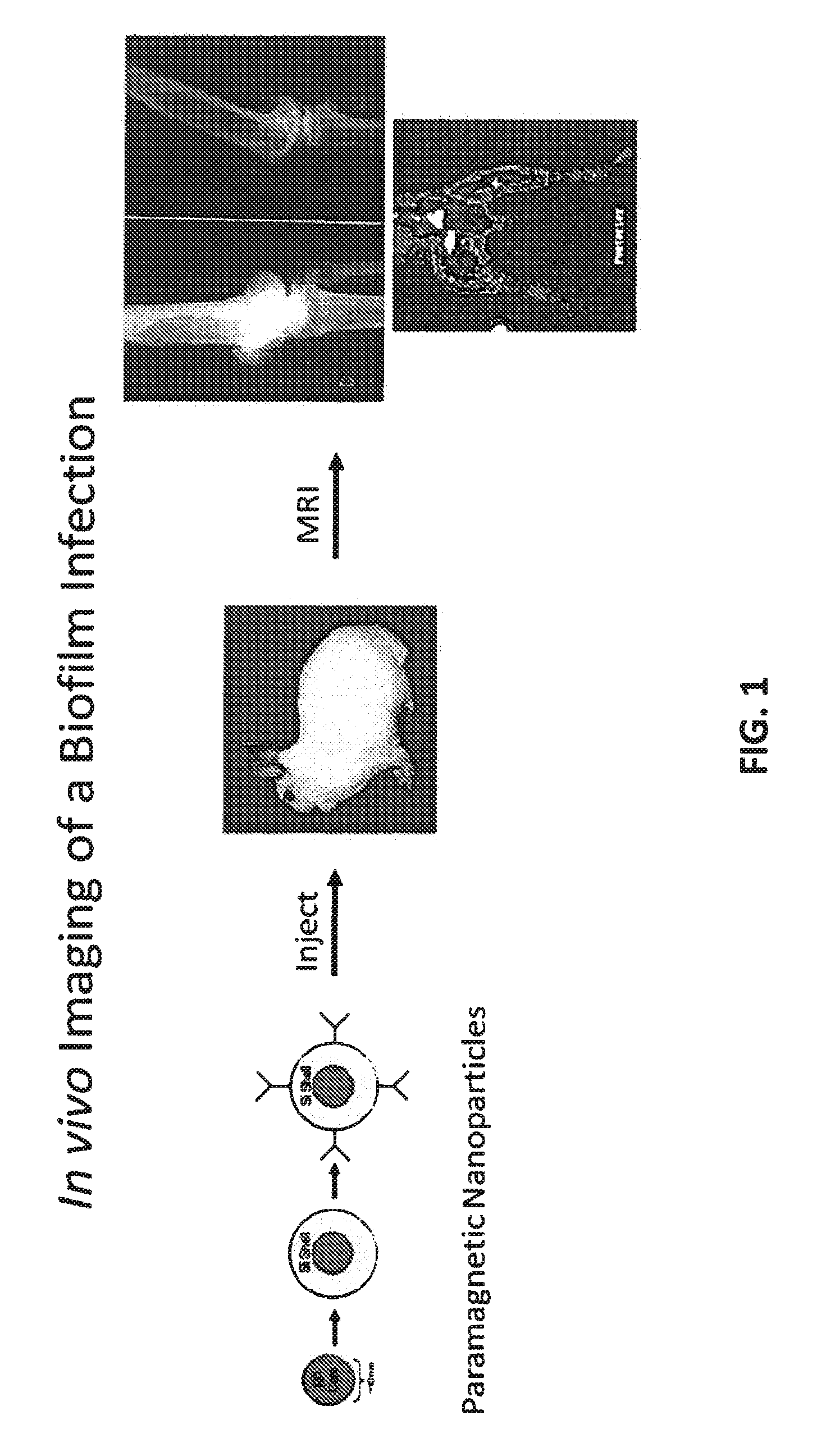
In vivo biofilm infection diagnosis and treatment
InactiveUS8697375B2Non-invasiveNon-toxicImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiofilmInfection diagnosis
The present invention relates to a method for in vivo detection of a biofilm infection residing in a mammal, the method comprising (i) administering to the mammal a diagnostic-effective amount of a biofilm-specific probe, wherein the probe comprises a bio film-targeting moiety and a paramagnetic nanoparticle core; and (ii) imaging the mammal to detect the presence of the biofilm infection by observing the mammal using a magnetic resonance diagnostic technique after the biofilm-specific probe has been provided sufficient time to selectively bind to the bio film infection that may be present in the mammal. The invention also relates to methods of treatment of a bio film infection, and compositions and kits useful in the detection and / or treatment of bio film infections.
Owner:ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS A BODY OF THE STATE OF ARIZONA ACTING FOR & ON BEHALF OF NORTHERN ARIZONA UNIV +1
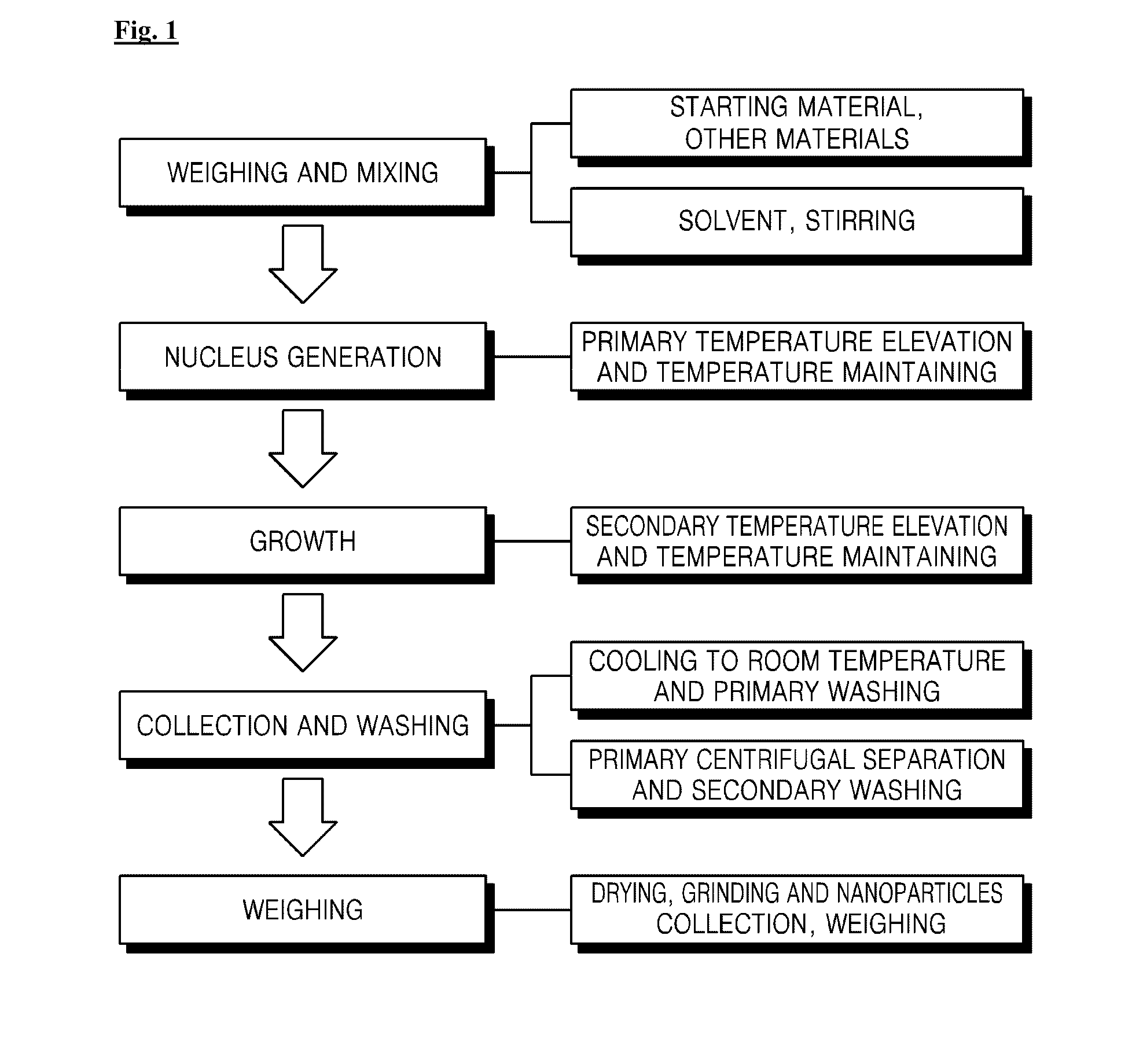
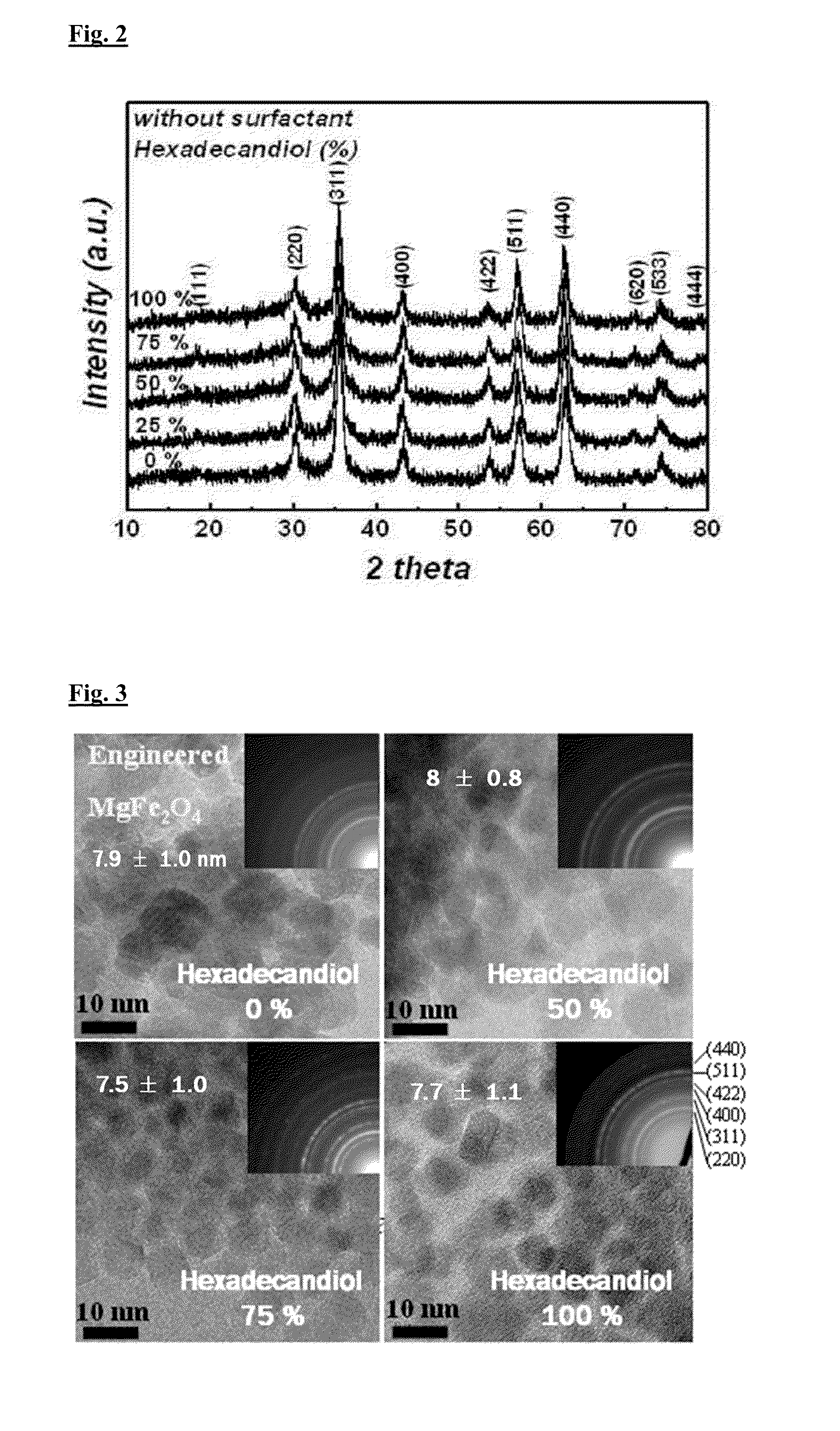
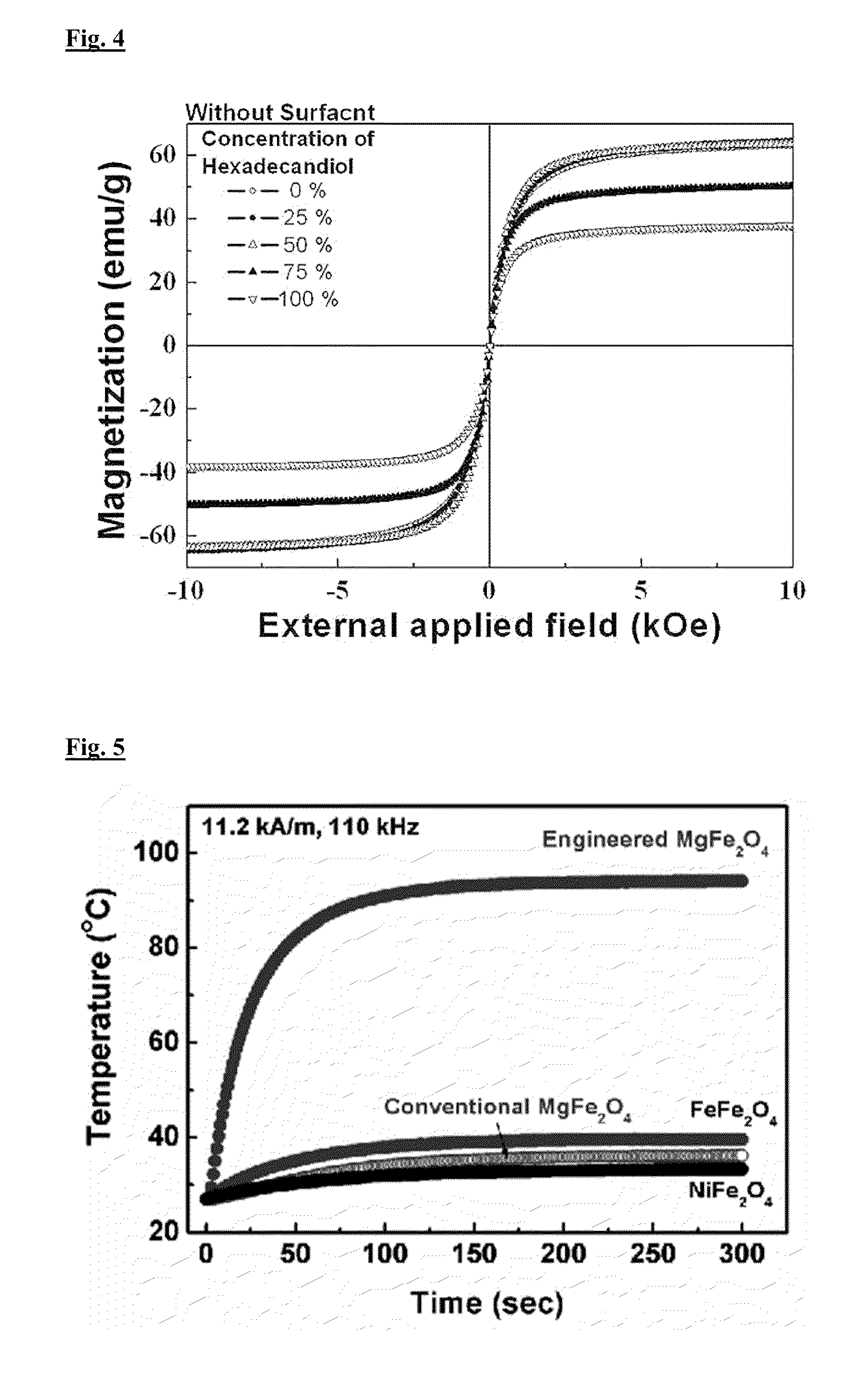
Method for preparing engineered mg doped ferrite superparamagnetic NANO particle exhibiting ac magnetic induction heating at high temperature and mg doped ferrite superparamagnetic NANO particles engineered by the method
InactiveUS20110256066A1Good biocompatibilityImproving graphical detection techniquePowder deliveryMaterial nanotechnologyMagnesium dopingCancer cell
The present invention relates to a method for preparing a ferrite superparamagnetic nano particle engineered by magnesium doping, and a technique for applying it to hyperthermia cancer cell treatment and the heat shock protein (HSP) self-defense mechanism.
Owner:NURI VISTA
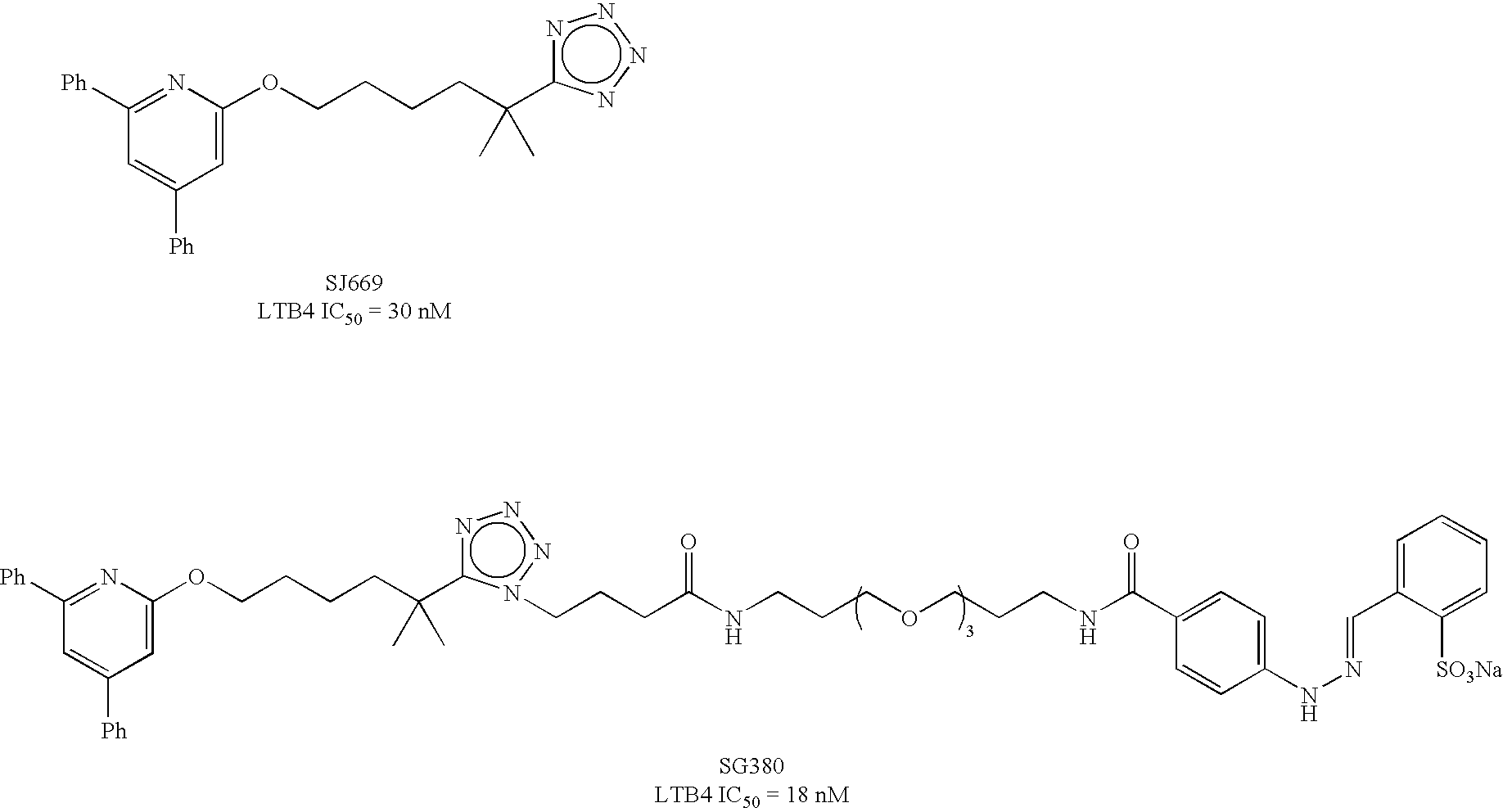
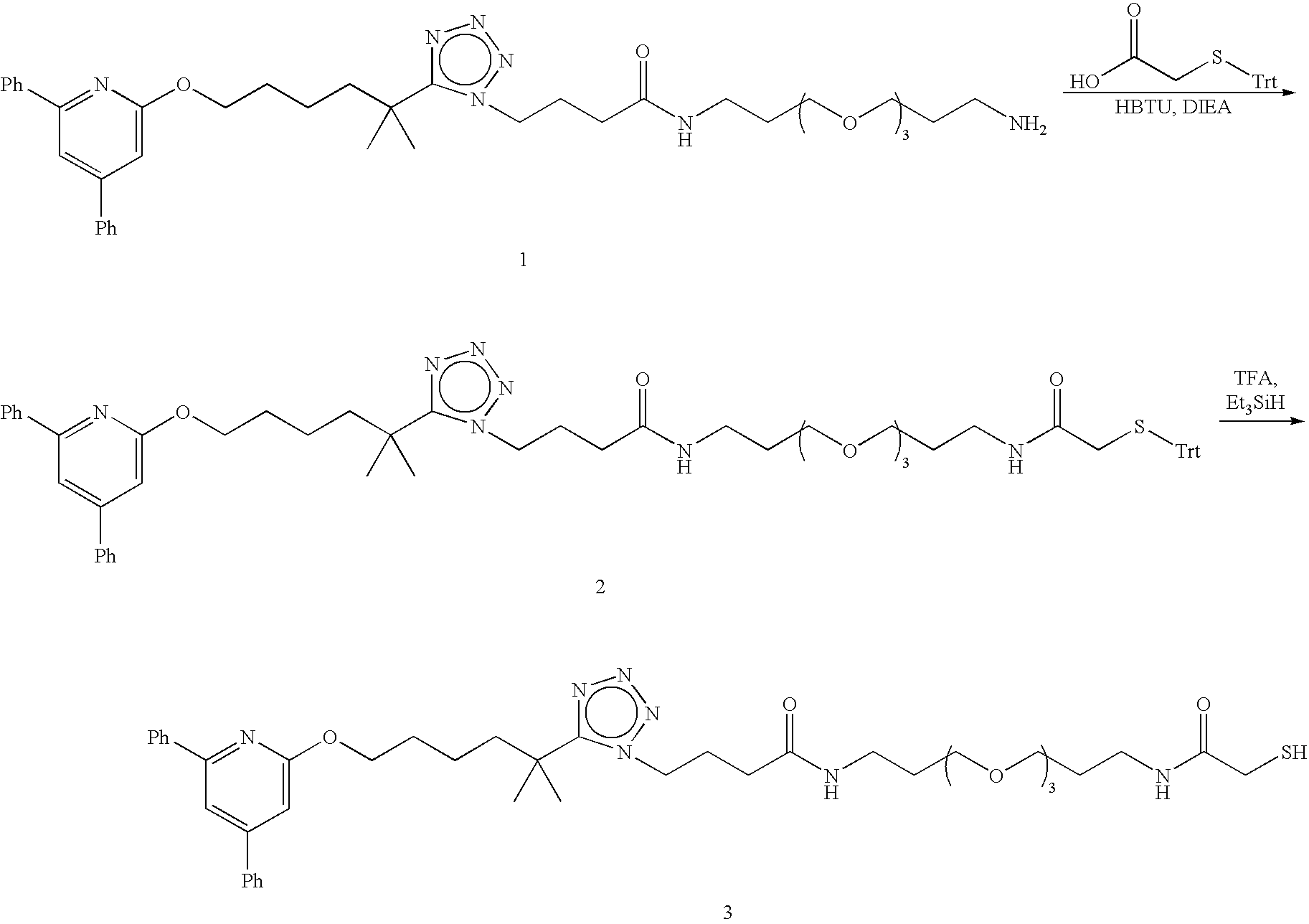
Preparation of Paramagnetic Nanoparticles Conjugated to Leukotriene B4 (LTB4) Receptor Antagonists, and Their Use as MRI Contrast Agents for the Detection of Infection and Inflammation
InactiveUS20080213181A1Improve image qualityOrganic chemistryDispersion deliveryEmulsionMRI contrast agent
Nanoparticle-based compositions and emulsions that are specifically targeted to leukotriene B4 (LTB4) receptors, and employing LTB4 receptor antagonist targeting agents, are set forth. In addition, there is provided the use of non-antibody based compositions for such targeting. The compositions of the invention are useful as imaging agents in diagnostic and therapeutic applications.
Owner:LANTHEUS MEDICAL IMAGING INC
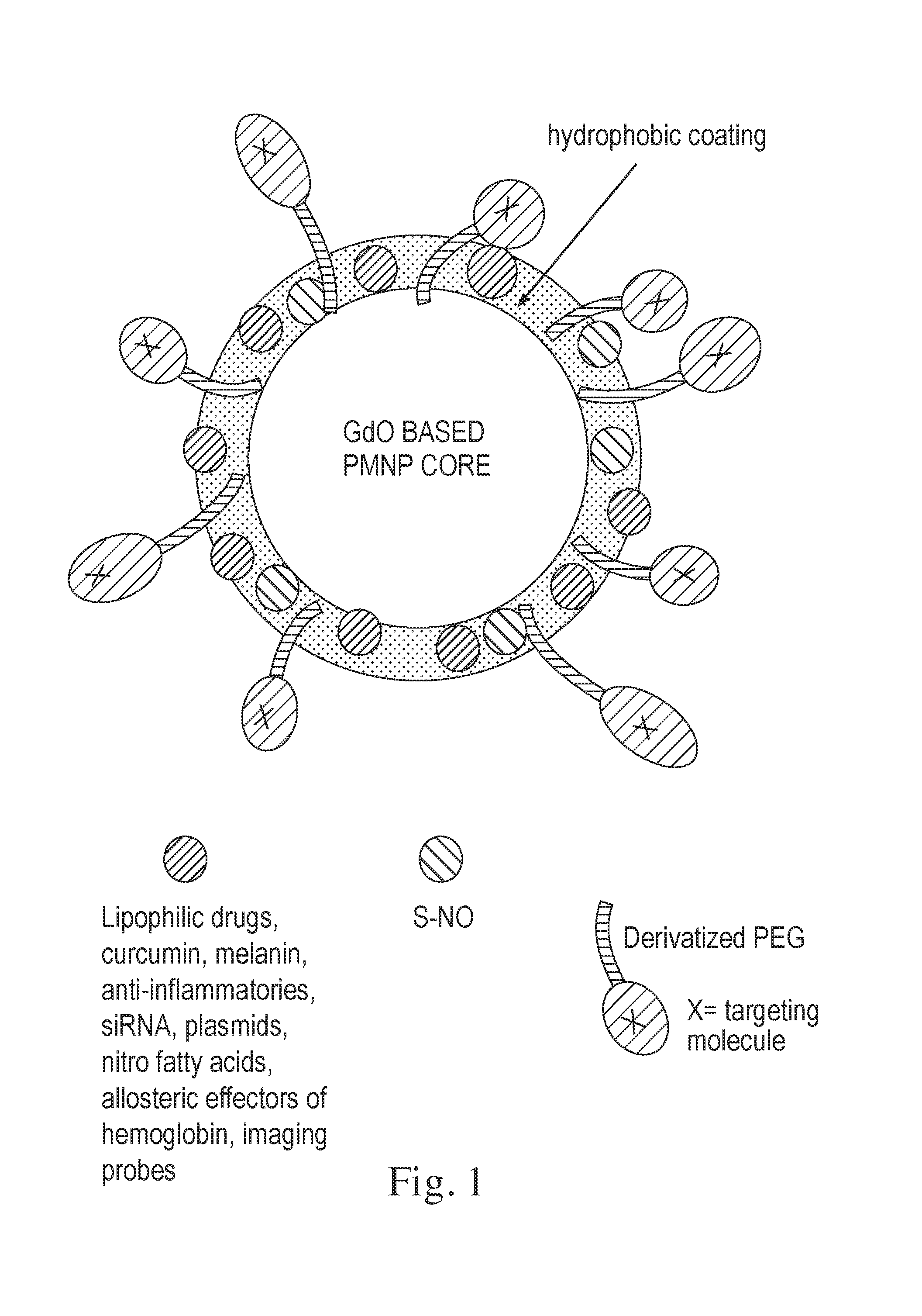
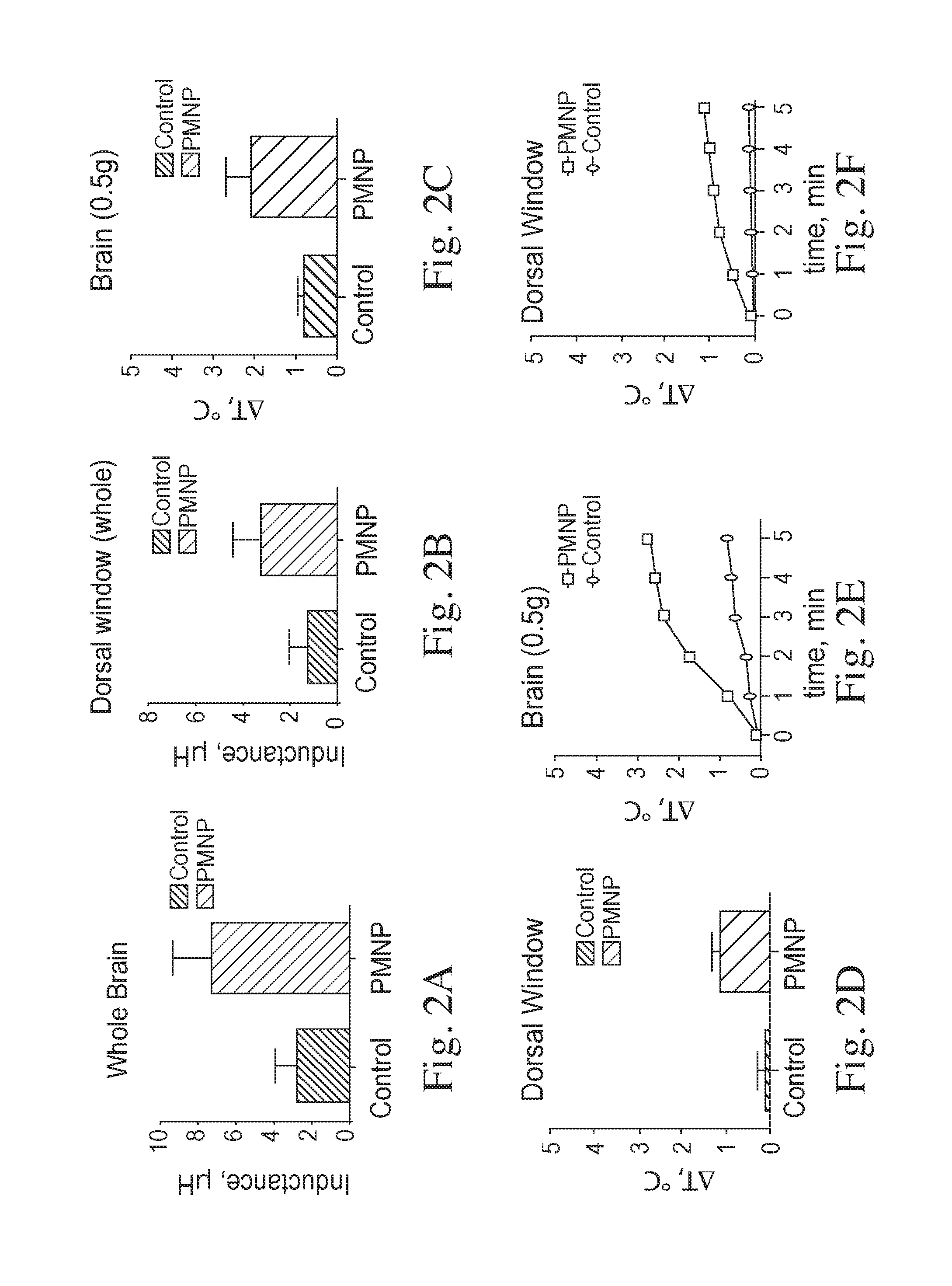
Modified paramagnetic nanoparticles for targeted delivery of therapeutics and methods thereof
InactiveUS20160346389A1High capacitive loadIncrease loopHeavy metal active ingredientsPowder deliveryDiseaseParamagnetic nanoparticles
Described herein is a method of making modified paramagnetic nanoparticles with improved therapeutic loading efficiency and enhanced circulation properties. The method comprises coating a paramagnetic nanoparticle (PMNP) with a hydrophobic coating comprising lipophilic drug and a polymer. Also described herein is a PMNP, and a composition comprising PMNP. In certain embodiment, the PMNP have improved permeability through the blood brain barrier. Also described herein is a method of using the PMNP for the treatment of diseases. In certain embodiments, the method of treatment is a combination therapy. Described herein are imaging of therapeutic delivery of PMNP and diagnostic methods using the PMNP. Also described herein is a diagnostic kit that comprises the PMNP. The invention provides compositions comprising a paramagnetic nanoparticle having an external coating comprising a small organic molecule, a polymer, a blood protein, oleic acid, a lipophilic pharmaceutical or an allosteric effector of hemoglobin, as well as methods of making thereof, and use thereof in treatment and imaging.
Owner:ALBERT EINSTEIN COLLEGE OF MEDICINE OF YESHIVA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com