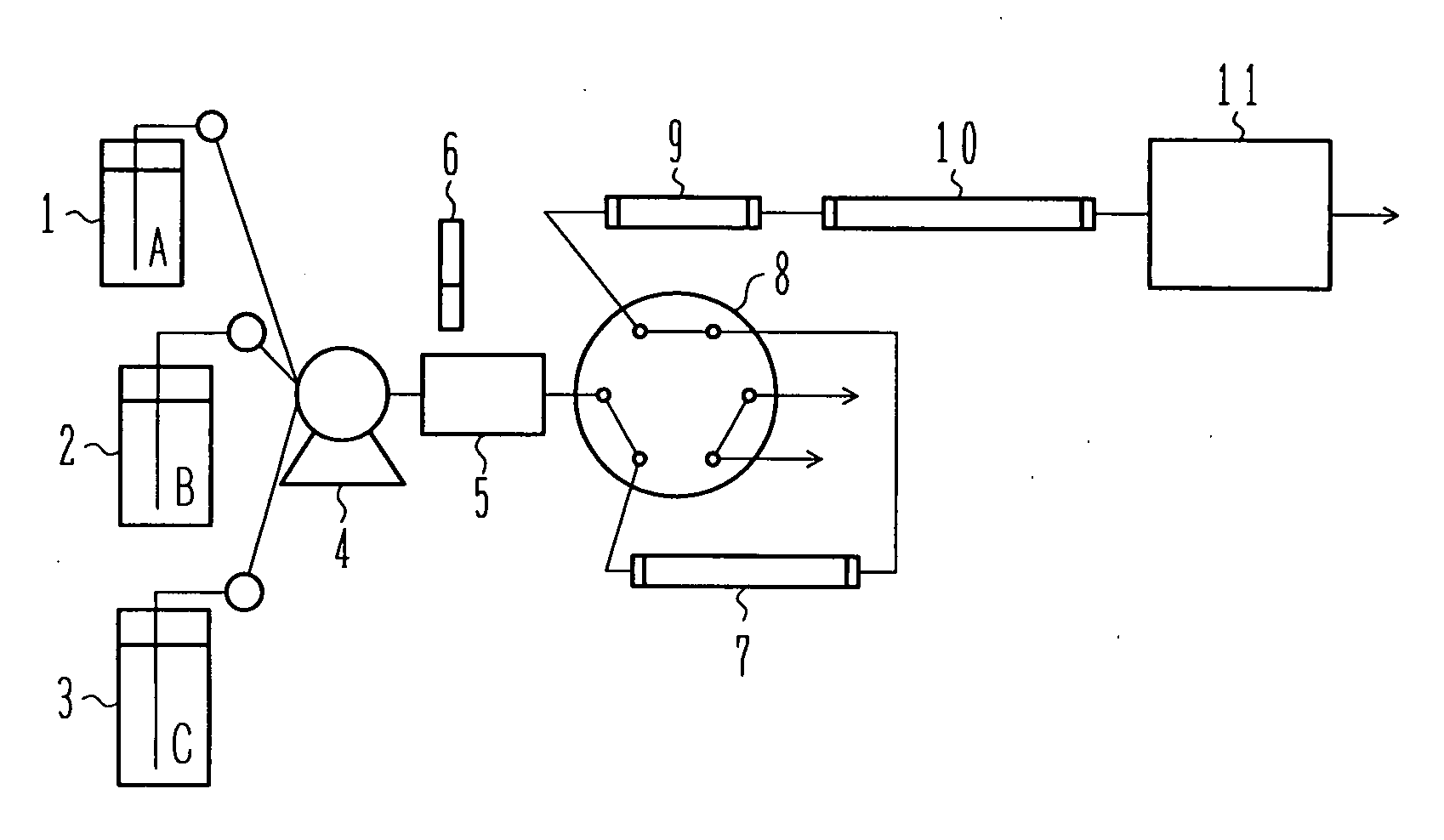
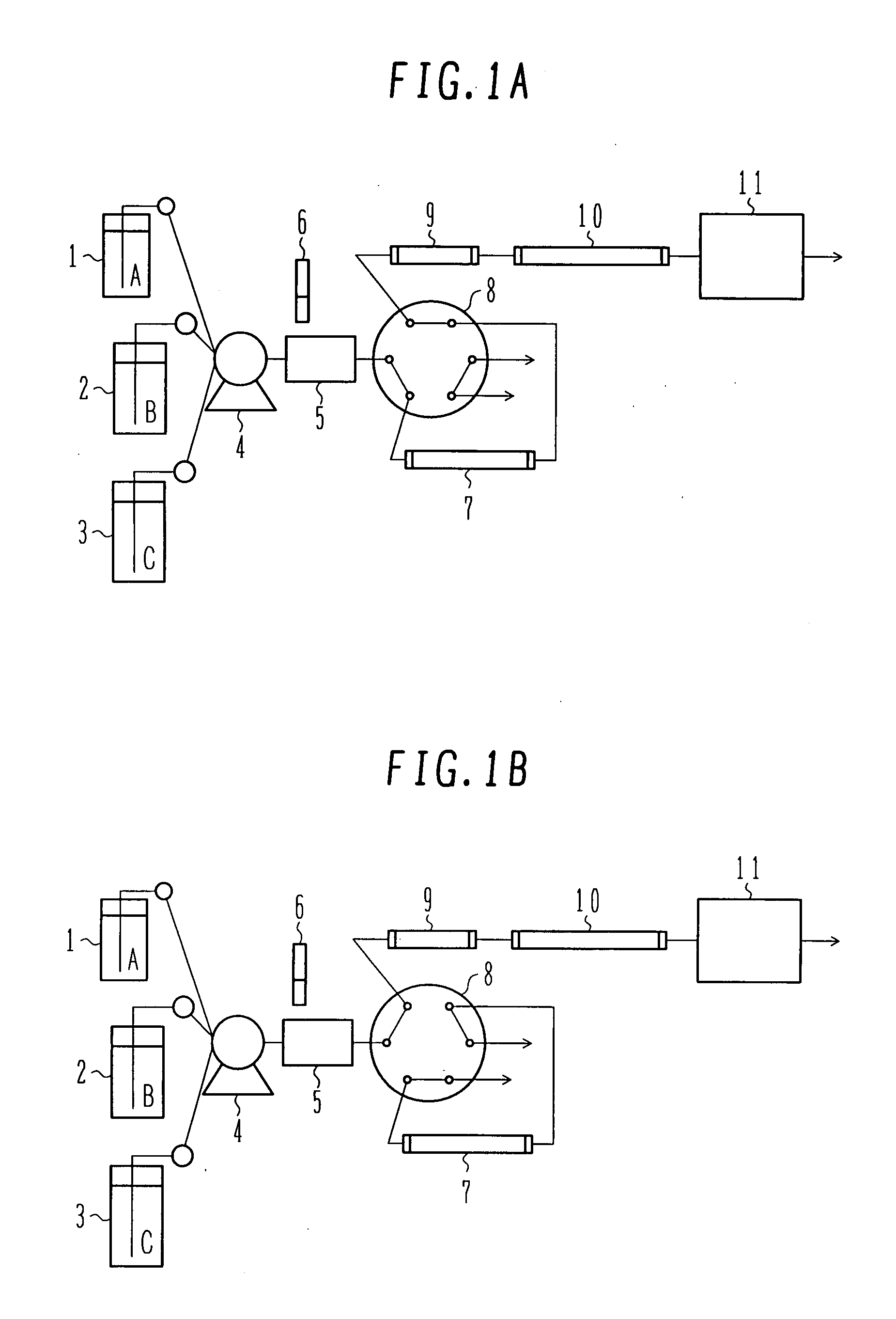
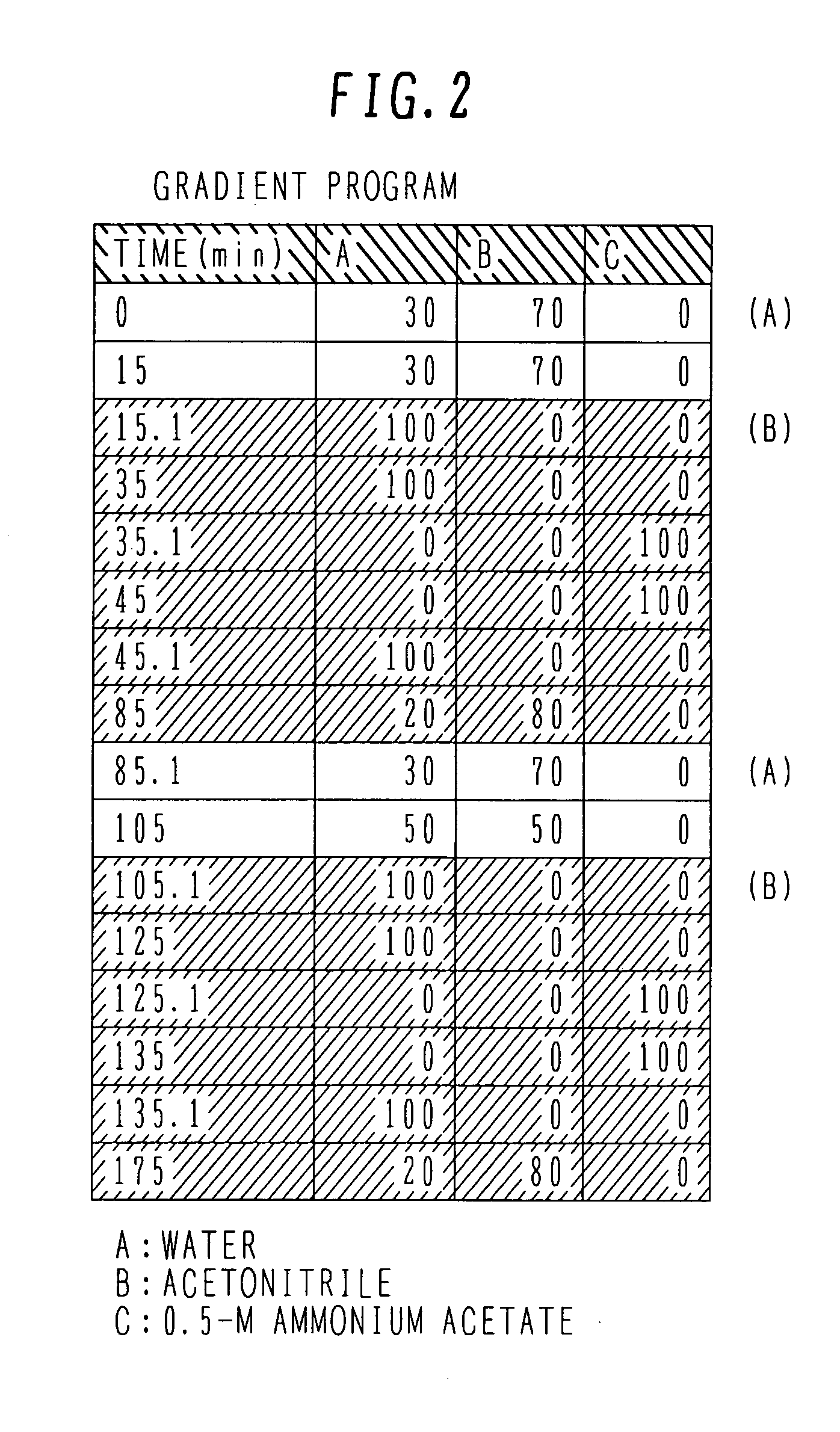
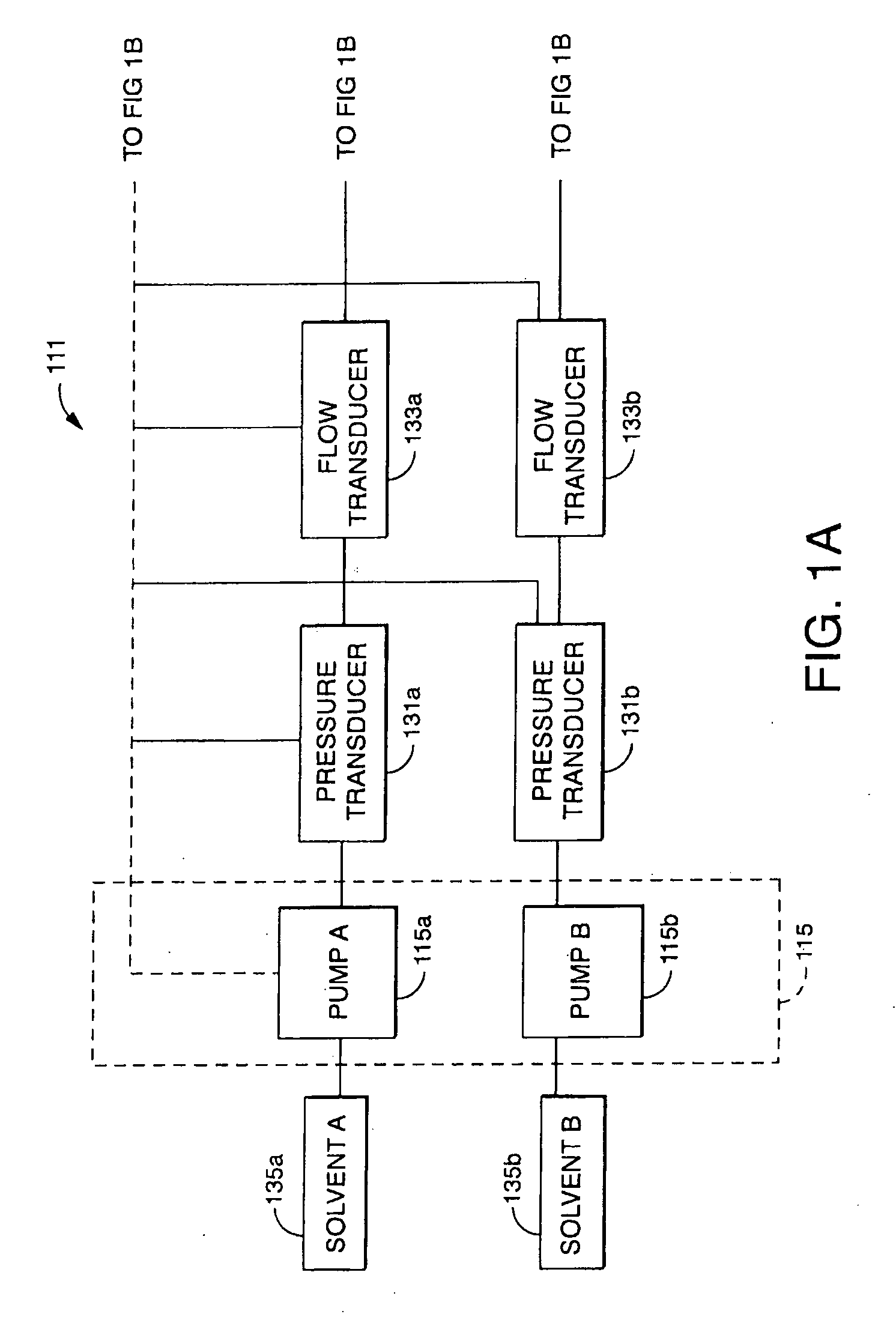
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1149 results about "Separation column" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Separation Columns. Columns are considered to be the heart of Gas Chromatography system as it physically separates compounds into separate components. This separation is based on mass transfer between stationary phase (coating on surface of column) and mobile phase (carrier gas). Our group has been active in both development...
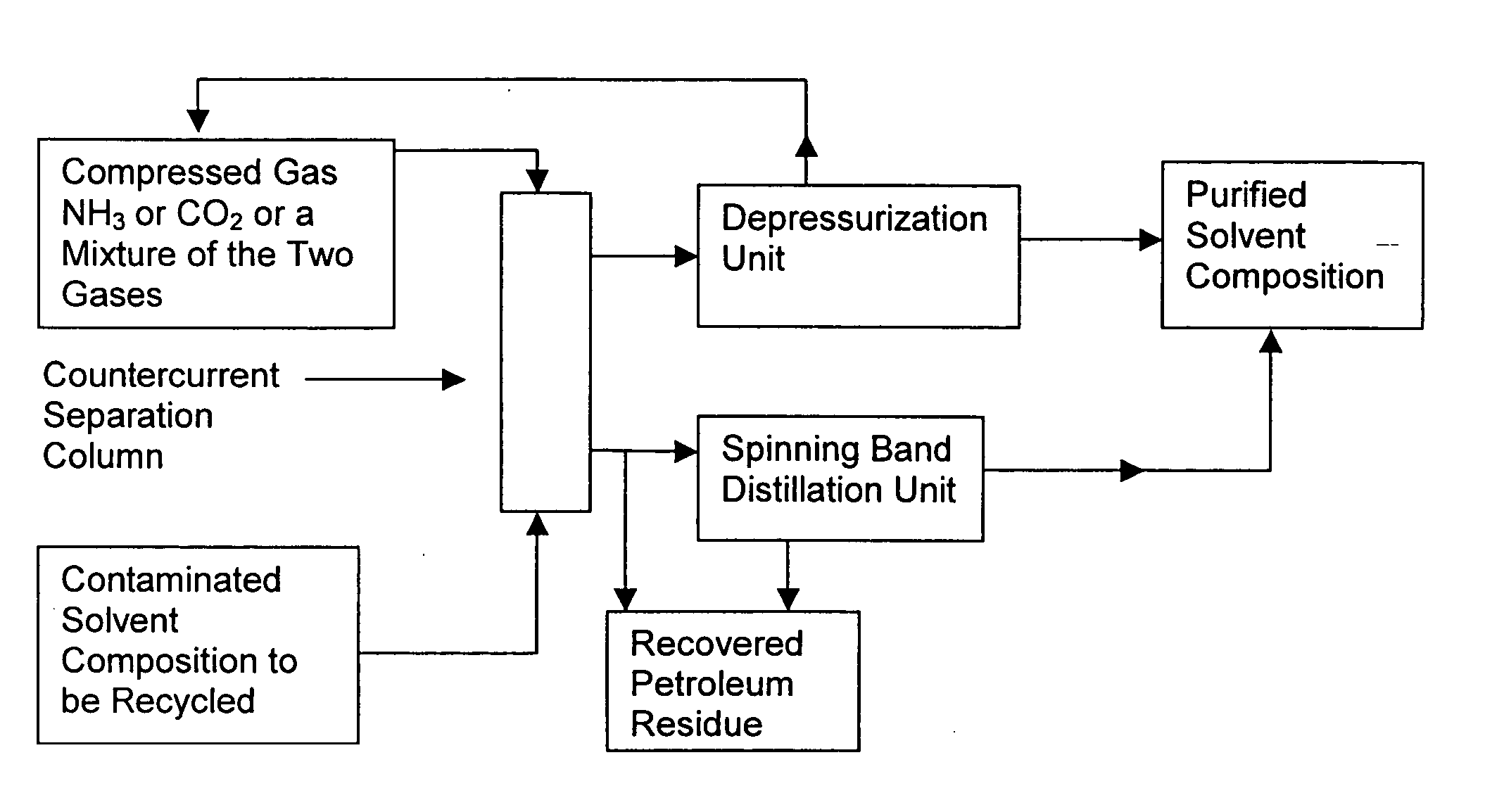
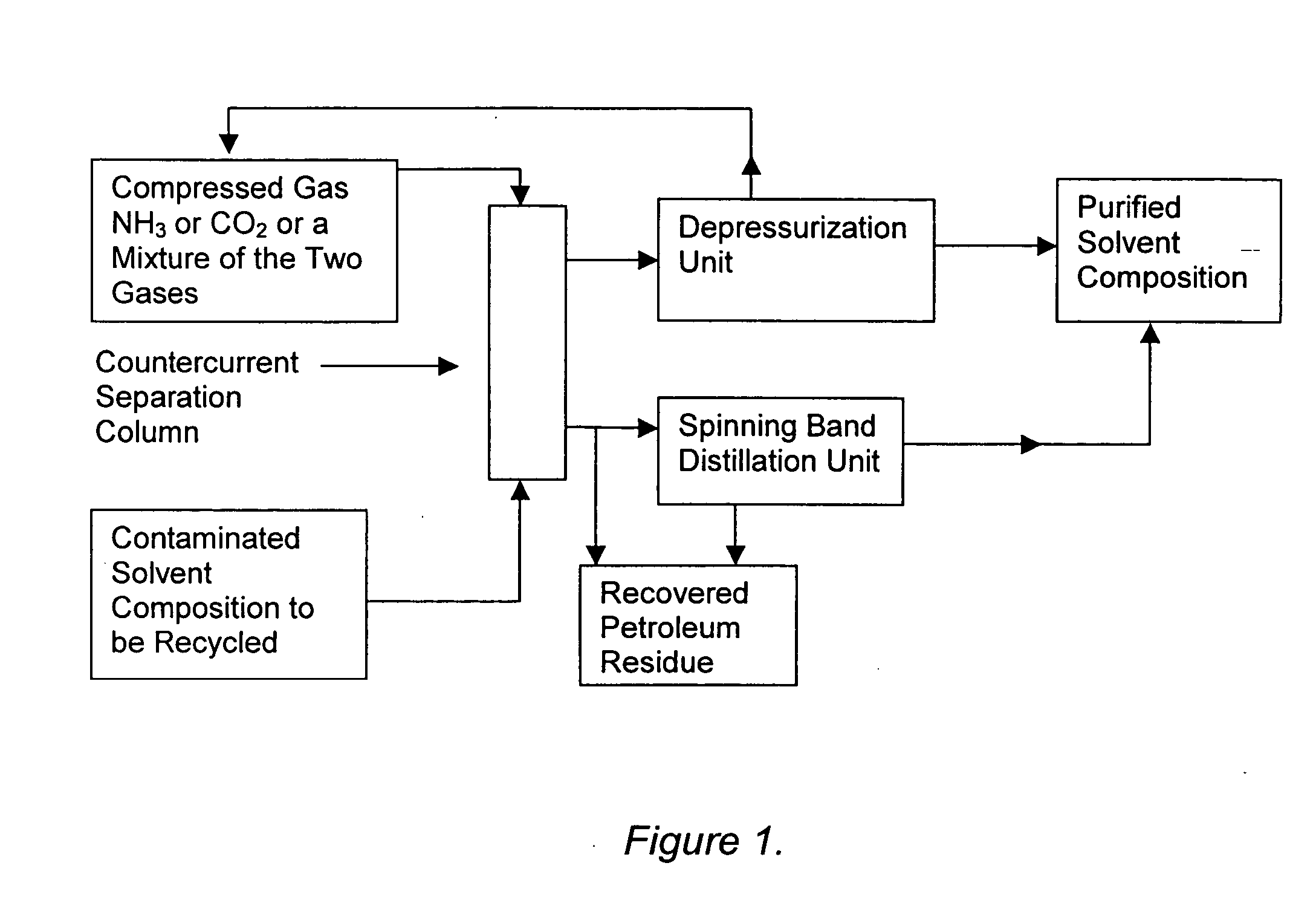
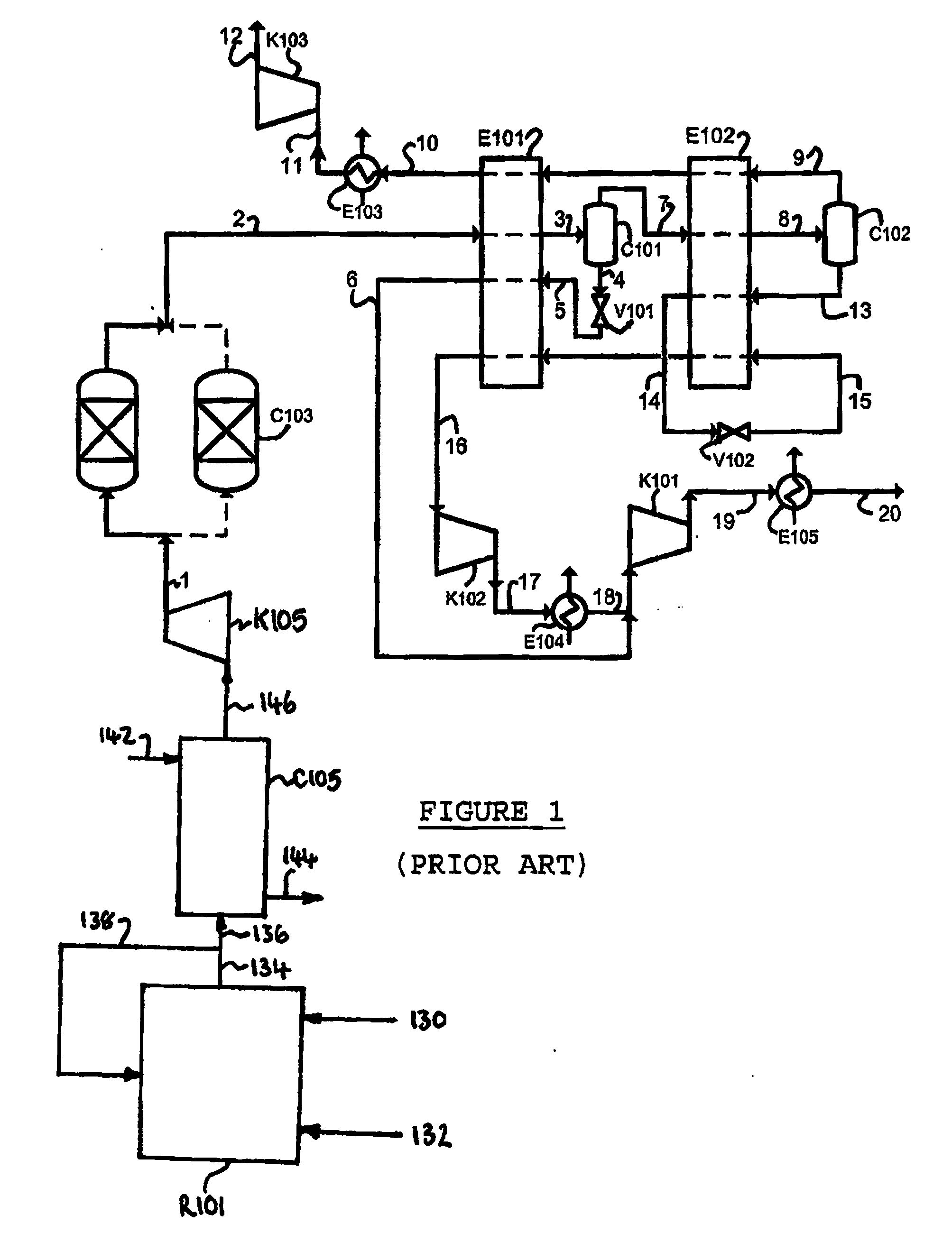
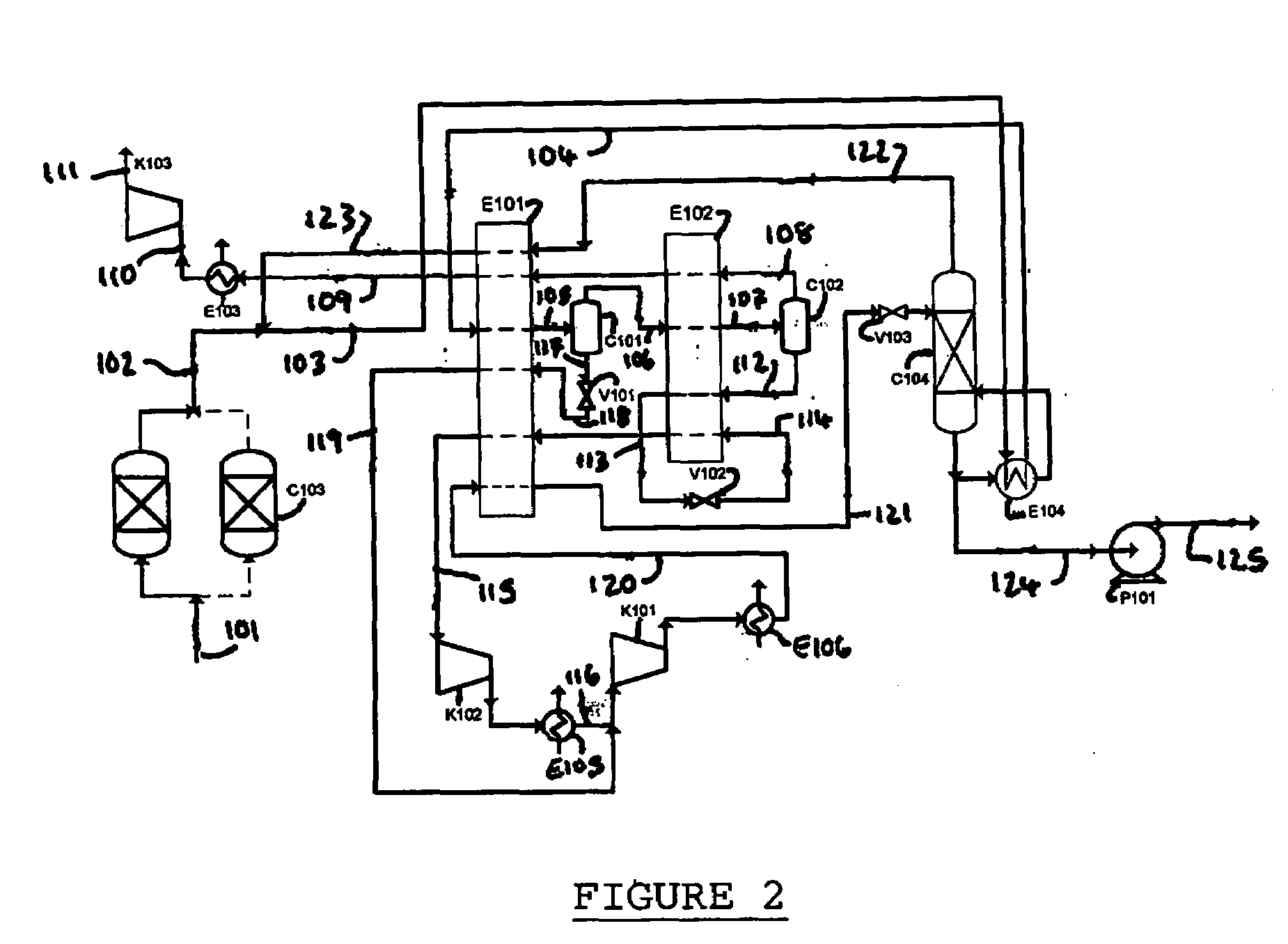
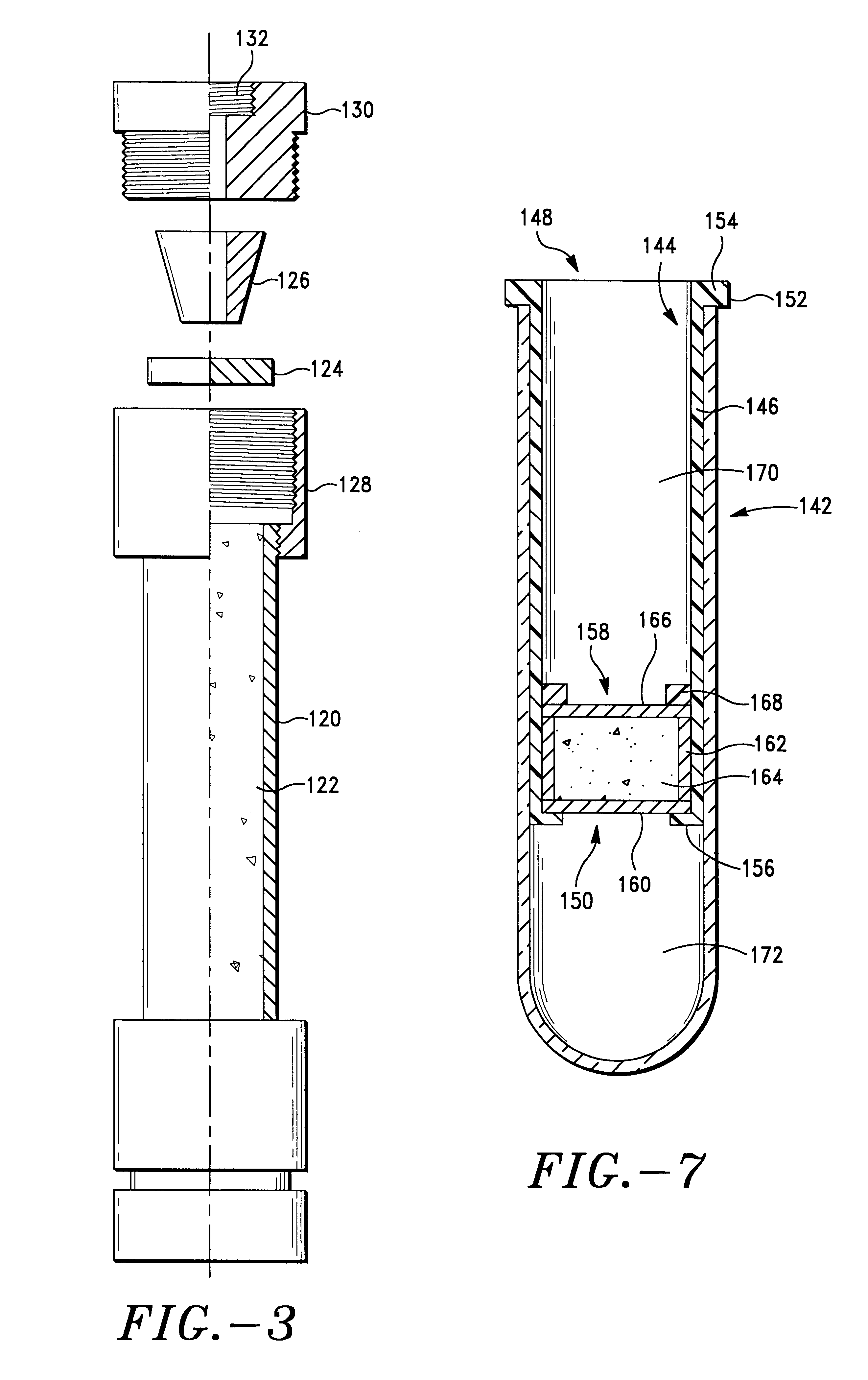
Solvent compositions for removing petroleum residue from a substrate and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20050197267A1Cationic surface-active compoundsNon-ionic surface-active compoundsSpinning band distillationPetroleum
Water-soluble solvent compositions, including from about 10% to about 60% by weight of an aromatic ester; from about 30% to about 60% by weight of an aliphatic ester; from 0% to about 15% by weight of a co-solvent; from 0% to about 20% of one of a cyclic terpene and a terpenoid; from 0% to about 1% by weight of an odor-masking agent; and from 0% to about 20% by weight of a nonionic surfactant, for removing petroleum residue from a substrate, and methods of use thereof. The composition can further comprise water. The composition also can comprise an aqueous solution. The method for removing petroleum residue from a substrate can further comprise recycling the solvent composition by using a countercurrent separation column charged with compressed ammonia and / or carbon dioxide and a spinning band distillation column to separate the solvent composition from the petroleum residue.
Owner:CRUDE SPILL CLEANING CO INC
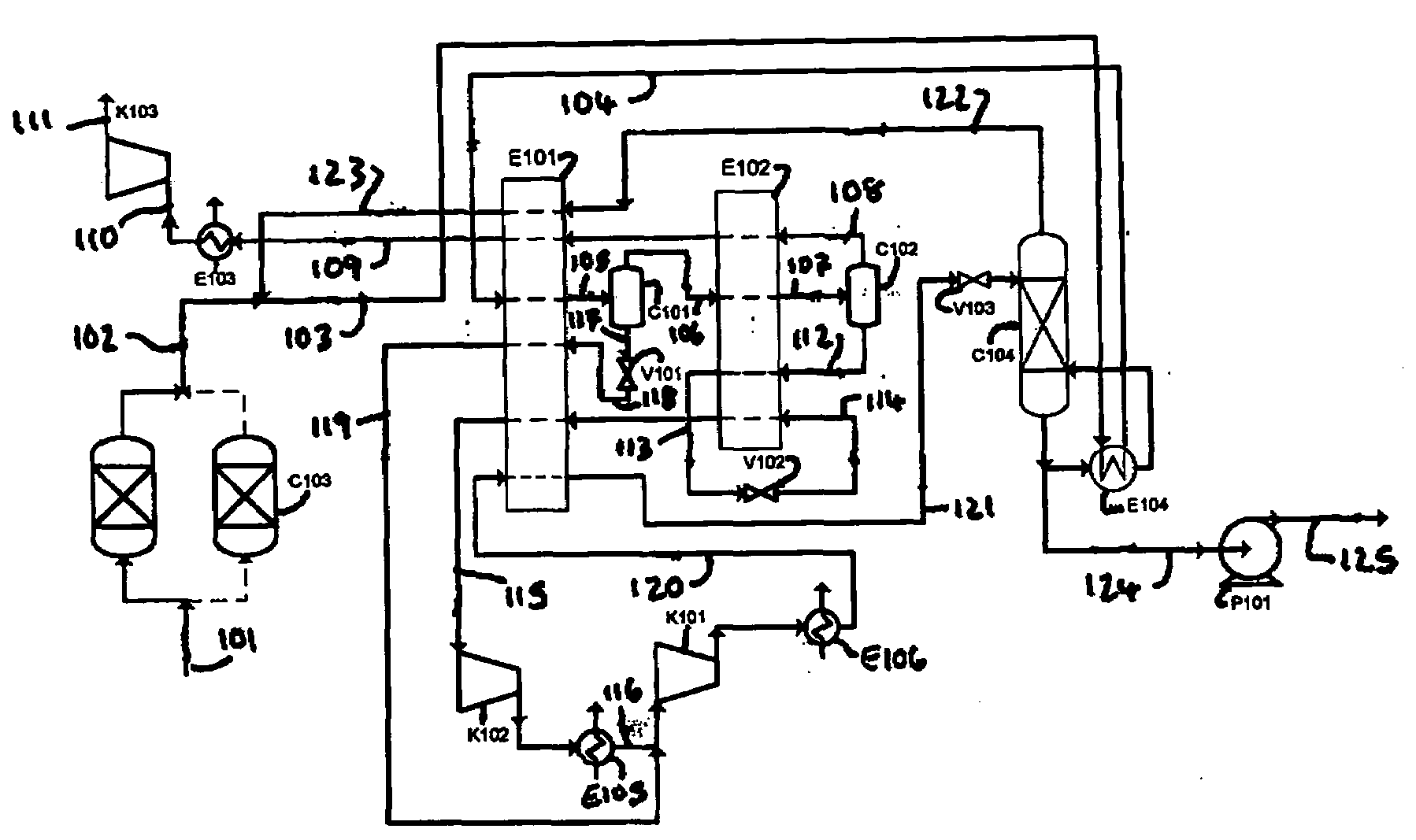
Purification of carbon dioxide
Impure carbon dioxide (“CO2”) comprising a first contaminant selected from the group consisting of oxygen (“O2”) and carbon monoxide (“CO”) is purified by separating expanded impure carbon dioxide liquid in a mass transfer separation column system. The impure carbon dioxide may be derived from, for example, flue gas from an oxyfuel combustion process or waste gas from a hydrogen (“H2”) PSA system.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
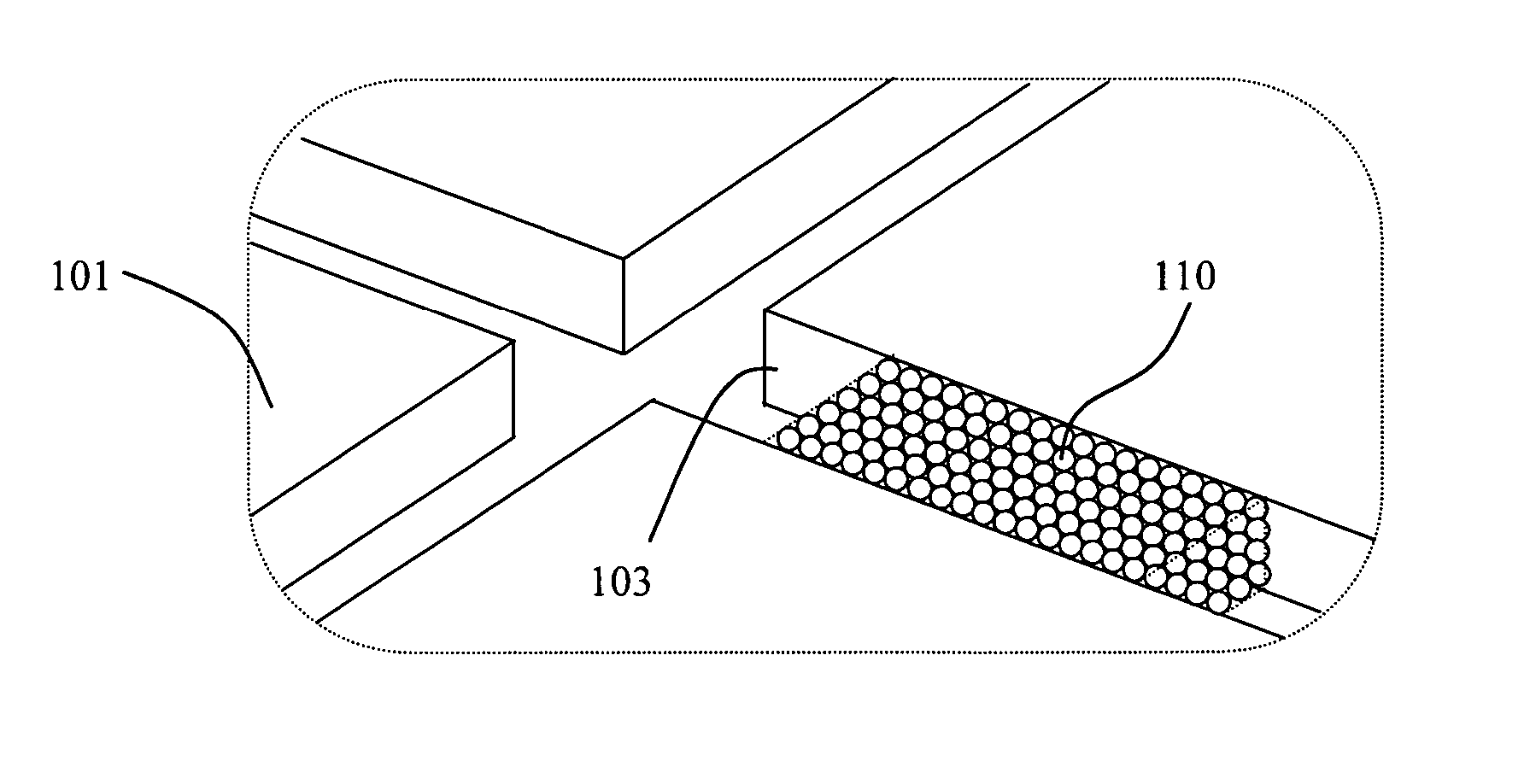
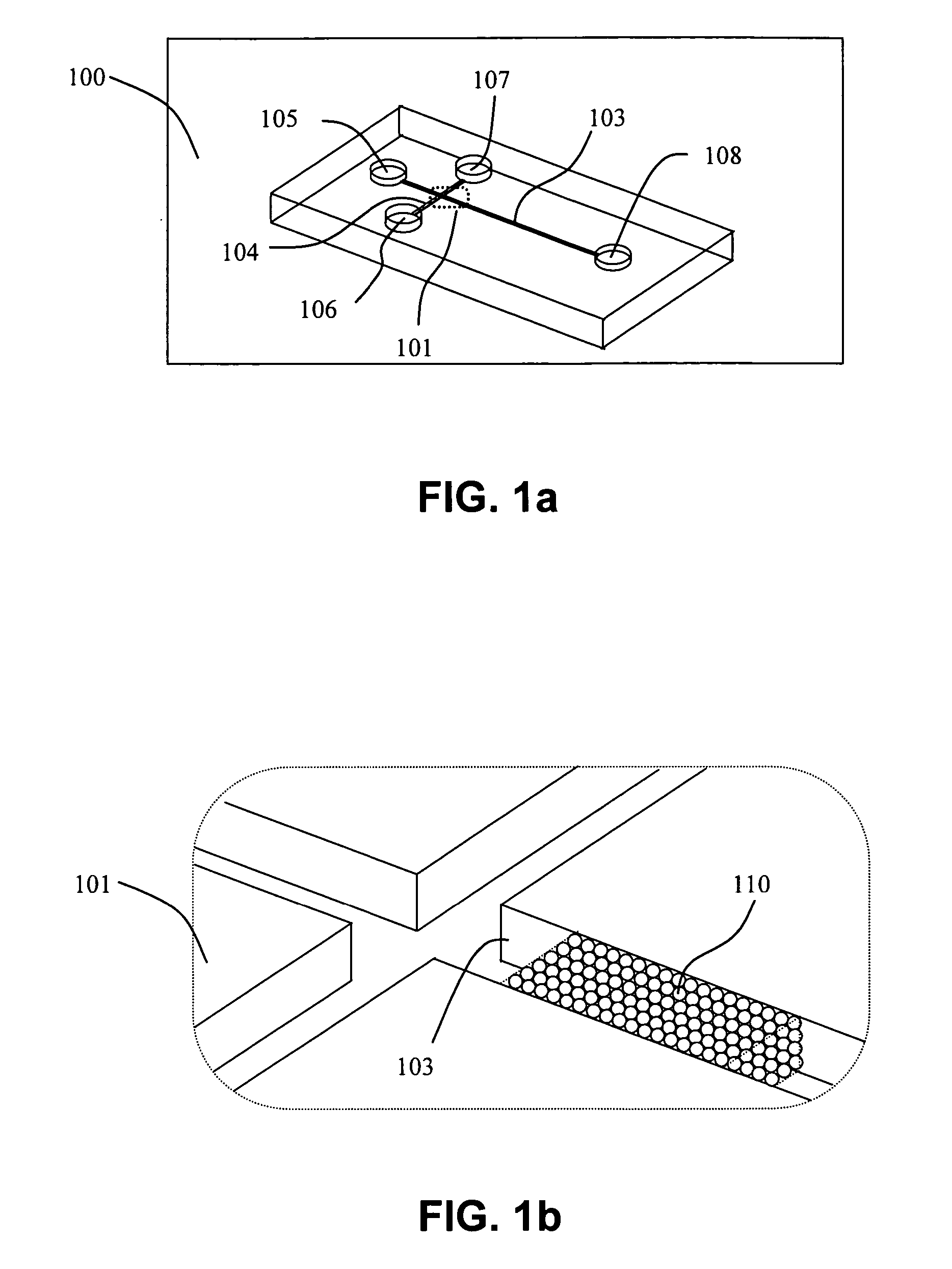
Separation column devices and fabrication methods
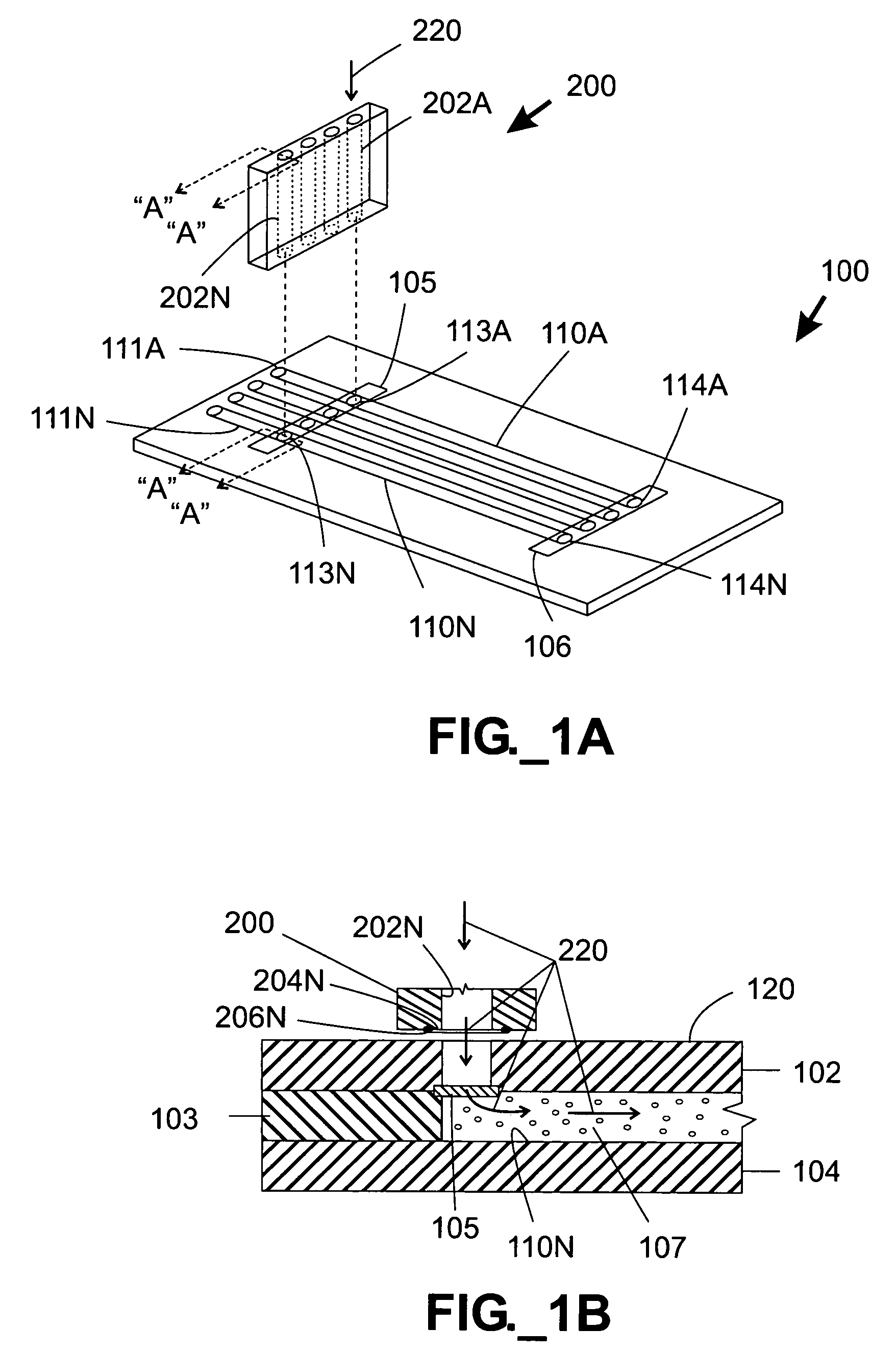
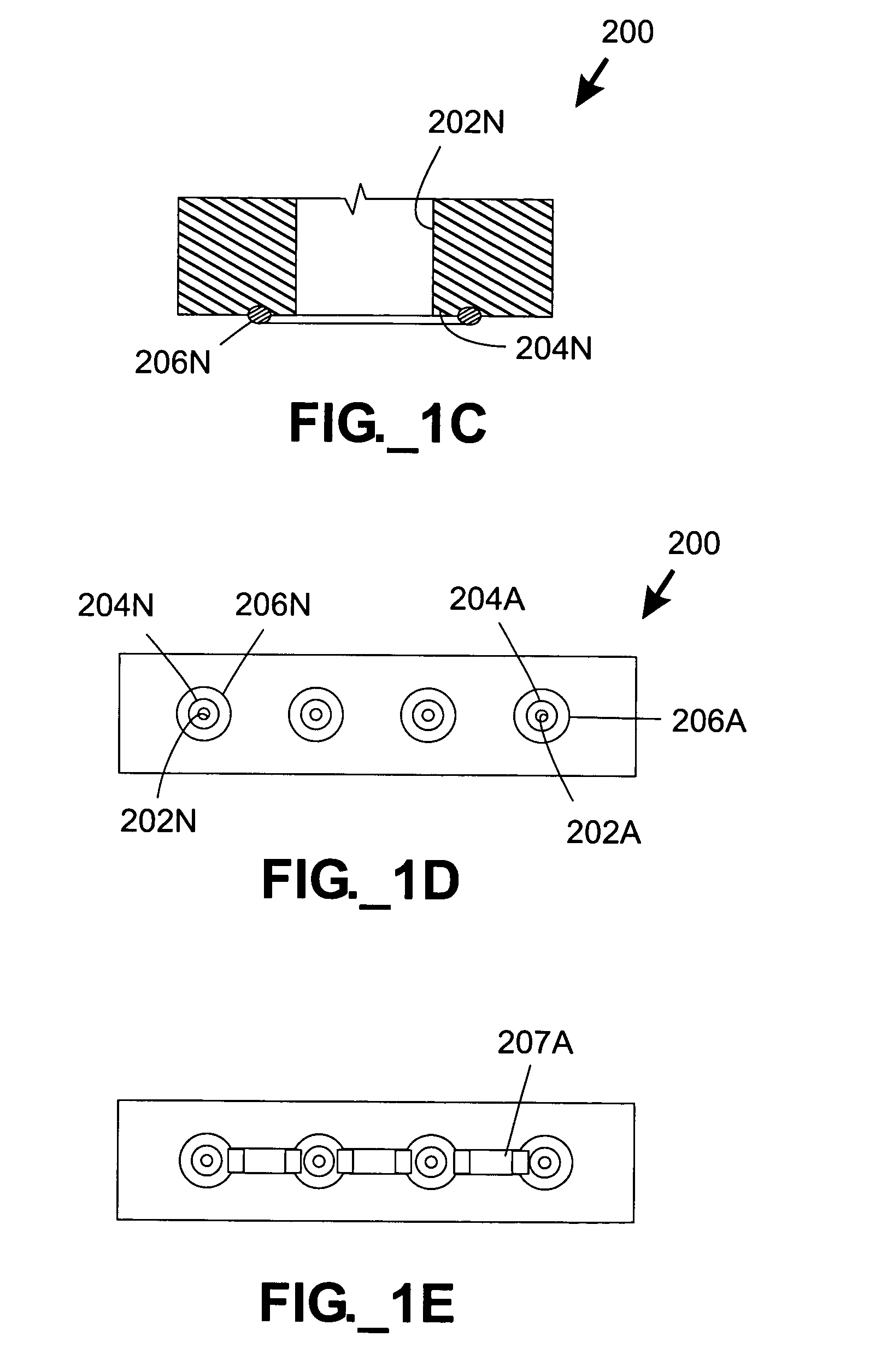
Pressure-driven microfluidic separation devices, such as may be used for performing high performance liquid chromatography, are provided. Multiple separation columns may be defined in a single device and packed with stationary phase material retained by porous frits. One or more splitters may be provided to distribute slurry and / or mobile phase among multiple separation columns. In one embodiment, separation devices are substantially planar and fabricated with multiple device layers. Systems and methods employing slurry for packing separation devices are also provided.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Pre-concentrator and sample interface
ActiveUS20090090197A1Easy constructionImprove portabilityComponent separationWithdrawing sample devicesInjection volumeDead volume
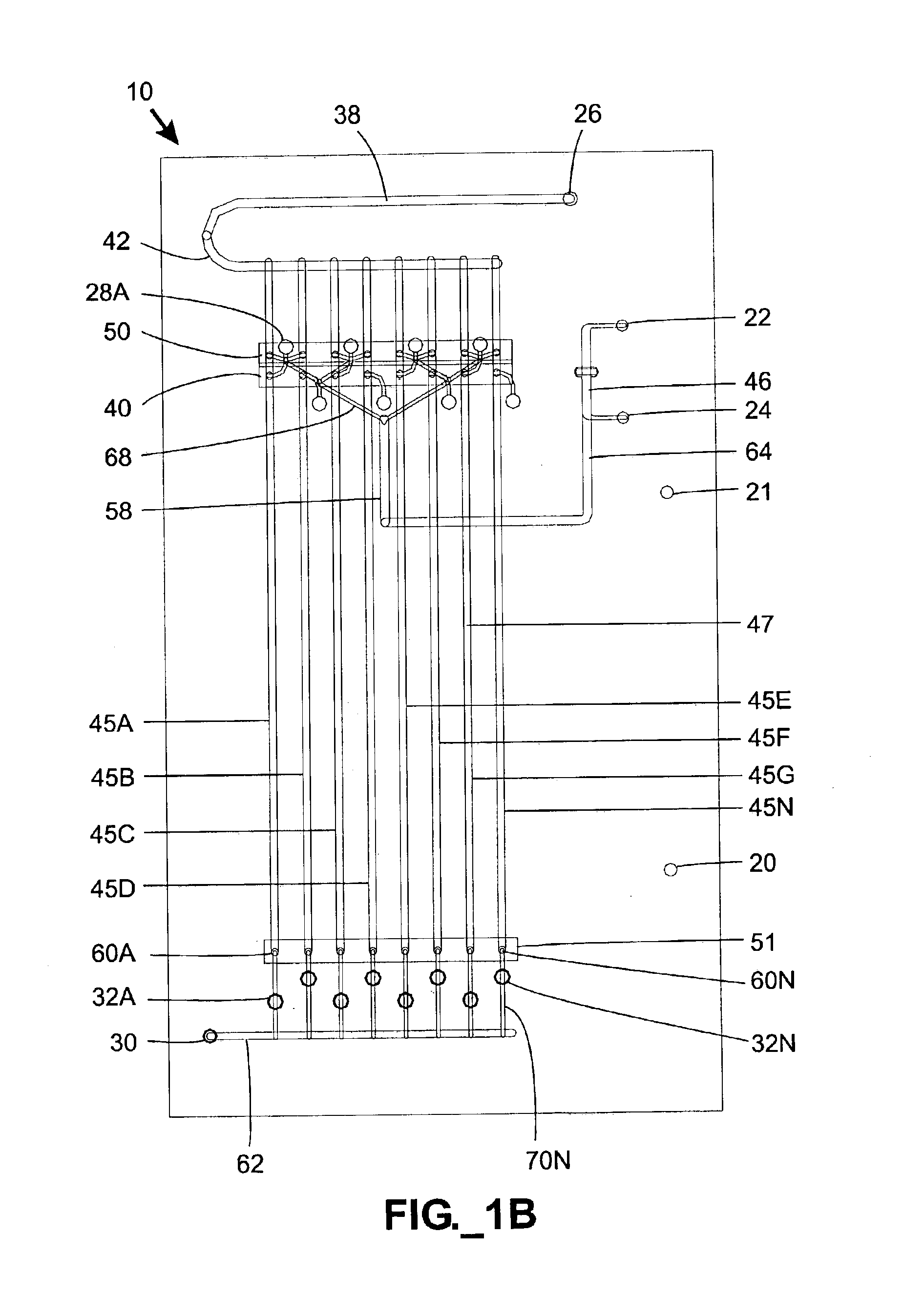
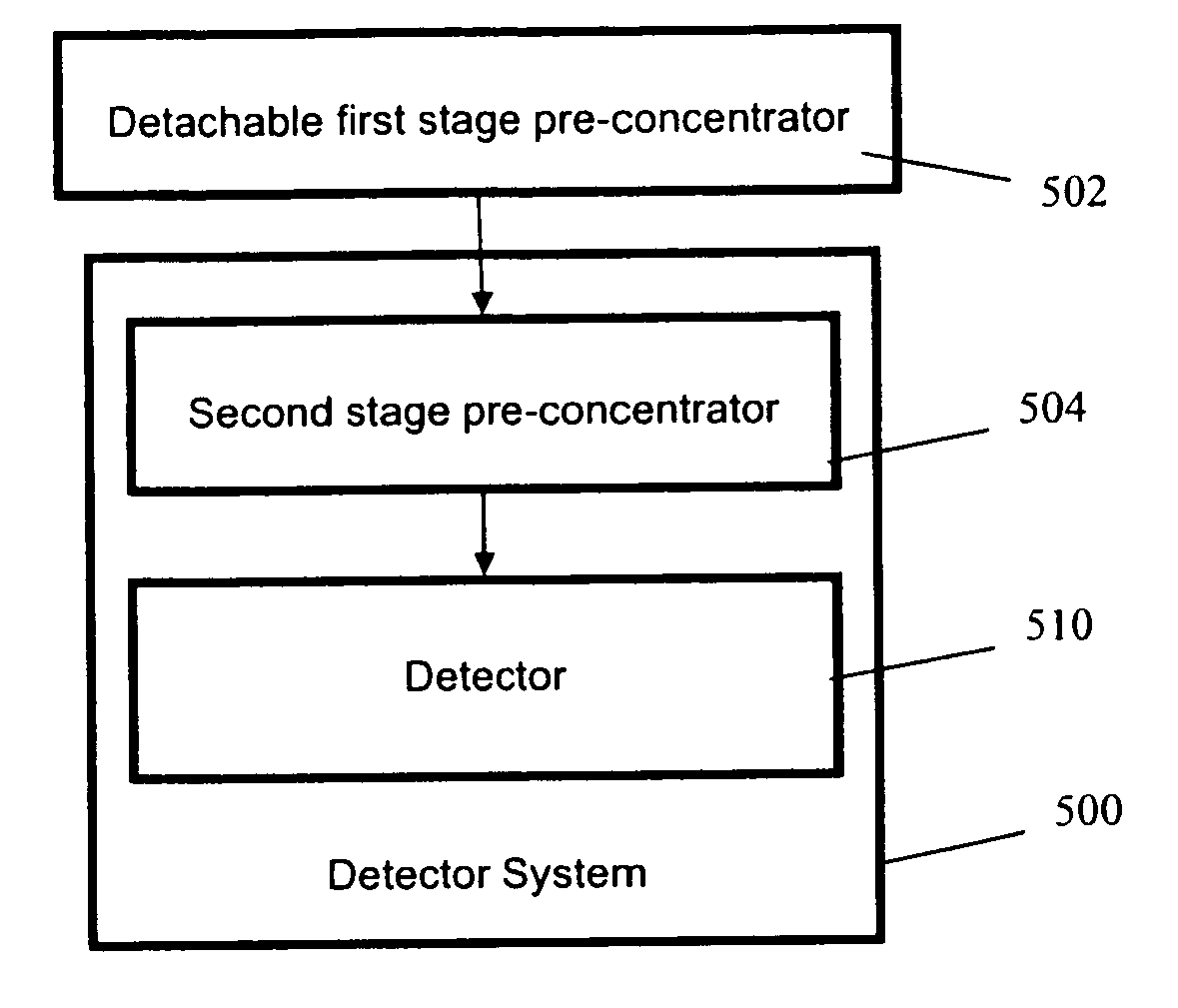
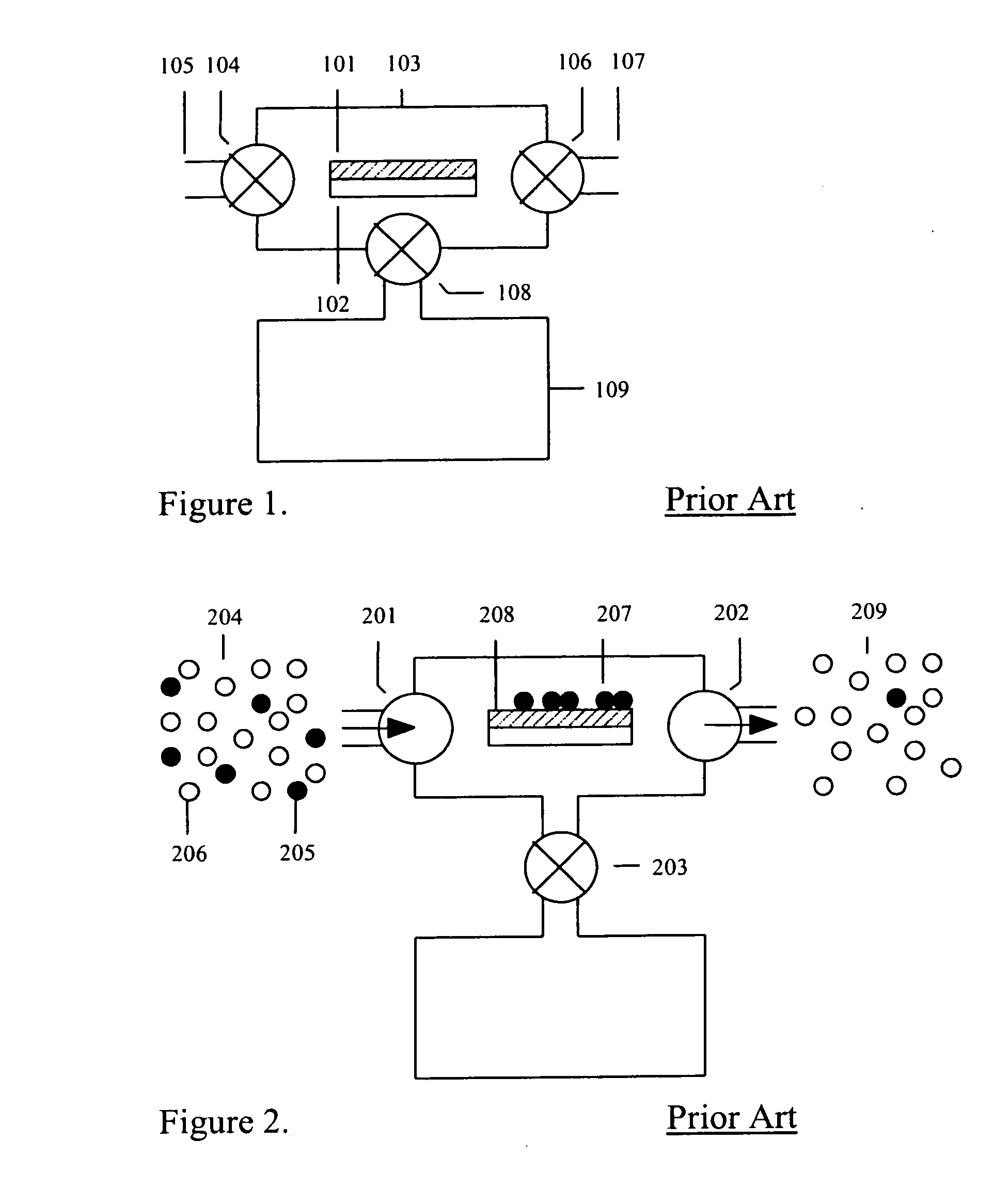
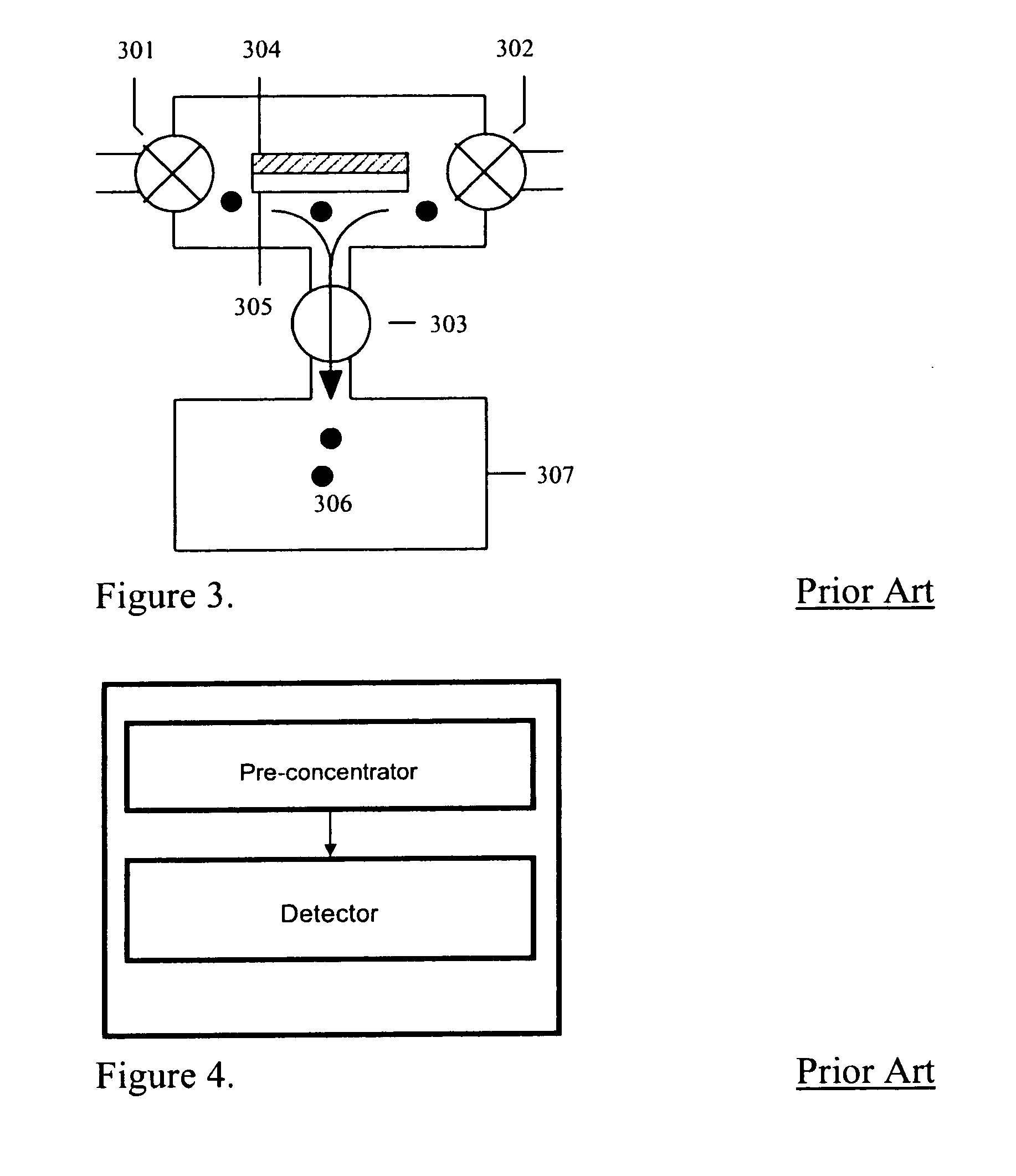
This invention describes a multi-stage pre-concentrator device for use with a detector system. One pre-concentrator stage is detachable and may be used to collect sample remotely from the detection system. The detachable pre-concentrator stage mates with the detector system and can transfer its desorbed sample to another pre-concentrator stage which also incorporates the functions of a sample loop serving as an injection volume to the separation column of an analytical instrument. In one embodiment the fixed pre-concentrator stage serves as a sample loop that preferably integrates suitable valves with sorbent materials onto the same structure to minimise dead volume, maximise sensitivity, improving column loading efficiency, reducing duty cycles and minimising detection system response time.
Owner:MICROSAIC SYST
Purification of carbon dioxide
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Bonded phase photopolymerized sol-gel column and associated methods
InactiveUS6884346B2Preparation of a fritless separation mediumSimple preparation processIon-exchange process apparatusOther chemical processesStationary phaseAnalyte
A separation column and a method of making the separation column are provided. The separation column includes a separation channel and a separation medium in the channel. The separation medium includes a porous matrix, and the porous matrix includes a support and a stationary phase. The support includes a metal organic polymer, such as a photopolymer, and the stationary phase includes a bonded phase. The separation medium can be used to separate a sample of analytes.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Apparatus and method for separating and purifying polynucleotides
InactiveUS6265168B1Rapid and efficient base-pair length size separationAvoid pollutionIon-exchange process apparatusSugar derivativesCounterionDNA fragmentation
A method for removing a target DNA fragment having a predetermined base-pair length from a mixture of DNA fragments comprises the following steps. A mixture of DNA fragments which may contain the target DNA fragments is applied to a separation column containing media having a nonpolar, nonporous surface, the mixture of DNA fragments being in a first solvent mixture containing a counterion and a DNA binding concentration of driving solvent in a cosolvent. The target DNA fragments are separated from the media by contacting it with a second solvent solution containing a counterion and a concentration of driving solvent in cosolvent which has been predetermined to remove DNA fragments having the target DNA fragment base pair length from the media. The target DNA fragments can be collected and optionally amplified. When the method is being applied to collect a putative fragment, if present, no DNA fragments having the base pair length of the target DNA could be present in the mixture. Alternatively, DNA fragments having the base pair length of the target DNA are present in the mixture. The disclosure also describes an ambient or low pressure device for separating polynucleotide fragments from a mixture of polynucleotide fragments comprises a tube having an upper solution input chamber, a lower eluant receiving chamber, and a fixed unit of separation media supported therein. The separation media has nonpolar separation surfaces which are free from multivalent cations which would react with counterion to form an insoluble polar coating on the surface of the separation media.
Owner:ADS BIOTEC INC
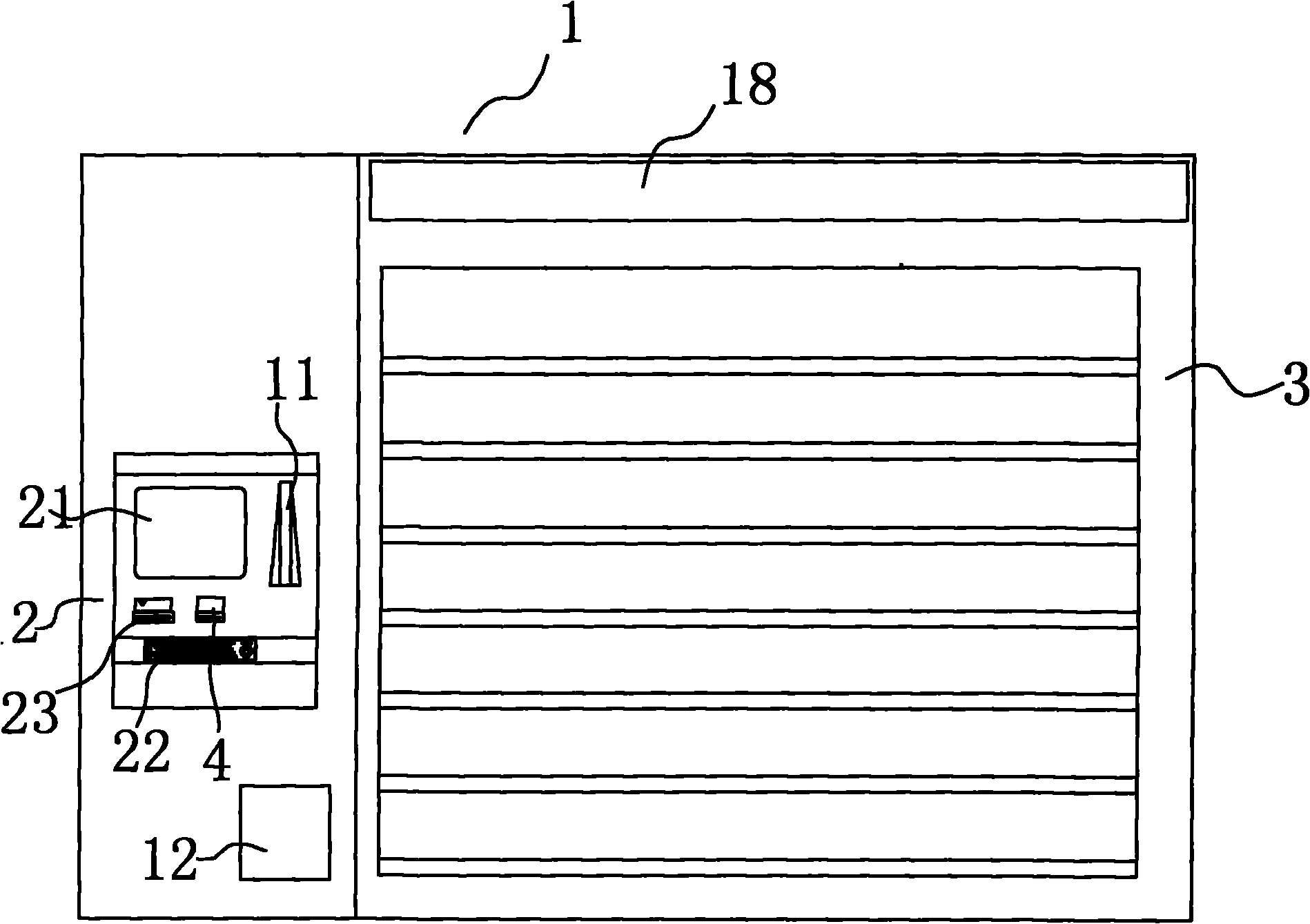
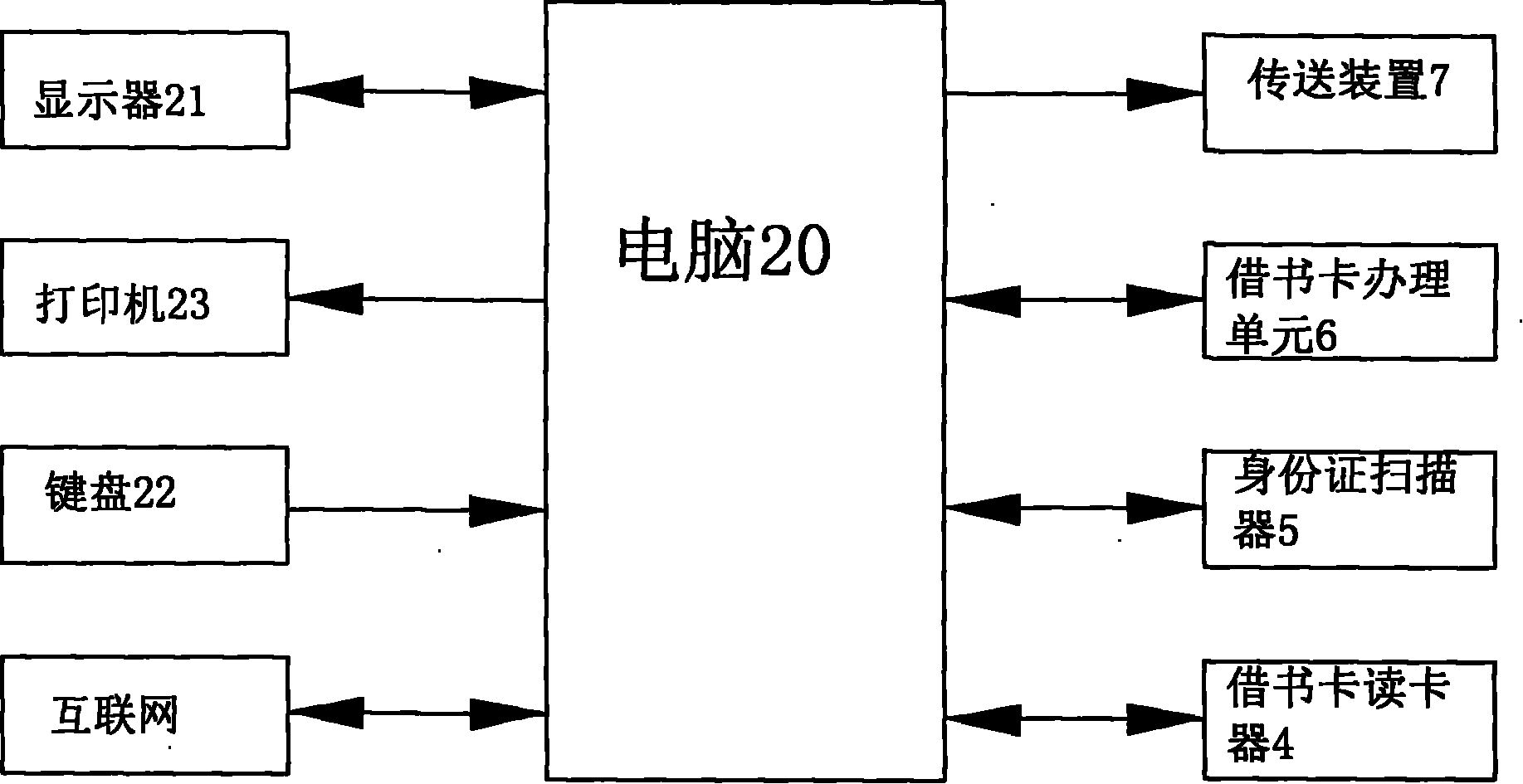
Full-automatic library service station and operation method thereof
InactiveCN101908251AUnderstand the status of the collectionAnti-smashGripping headsCash registersLibrary cardLibrary services
The invention provides a full-automatic library service station and an operation method thereof. The service station comprises a computer, a displayer, a printer, a keyboard, a library card reader, an identification card scanner, a library card transaction unit and a mechanical conveying device, wherein the computer serves as a main control unit; the displayer and the printer serve as information output units; the keyboard serves as an information input unit; the library card reader and the identification card scanner serve as information input equipment; the library card transaction unit is connected with the computer; the mechanical conveying device is controlled by the computer; the service station main body is a sealed cabinet body which comprises an operation platform and book shelves; the displayer, the keyboard, the printer, the library card reader, the identification card scanner and the library card transaction unit are positioned on the operation platform which is also provided with a book inlet and a book outlet; book separation columns are formed on the book shelves by clapboards; each book separation column corresponds to a piece of position information; under the control of the computer, the conveying device conveys books between the book inlet, the book outlet and the shelves by manipulators arranged per se.
Owner:东莞市树煜智能图书设备科技有限公司
Parallel detection chromatography systems
High throughput liquid chromatography systems include multiple separation columns and multiple flow-through detection regions in sensory communication with a common radiation source and a multi-channel detector. Preferred detector types include a multi-anode photomultiplier tube, a charge-coupled device detector, a diode array, and a photodiode array. In certain embodiments, separation columns are microfluidic and integrated into a unitary microfluidic device. The optical path through a detection region is preferably coaxial with the path of eluate flow along a flow axis through a detection region. On-board or off-board detection regions may be provided.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
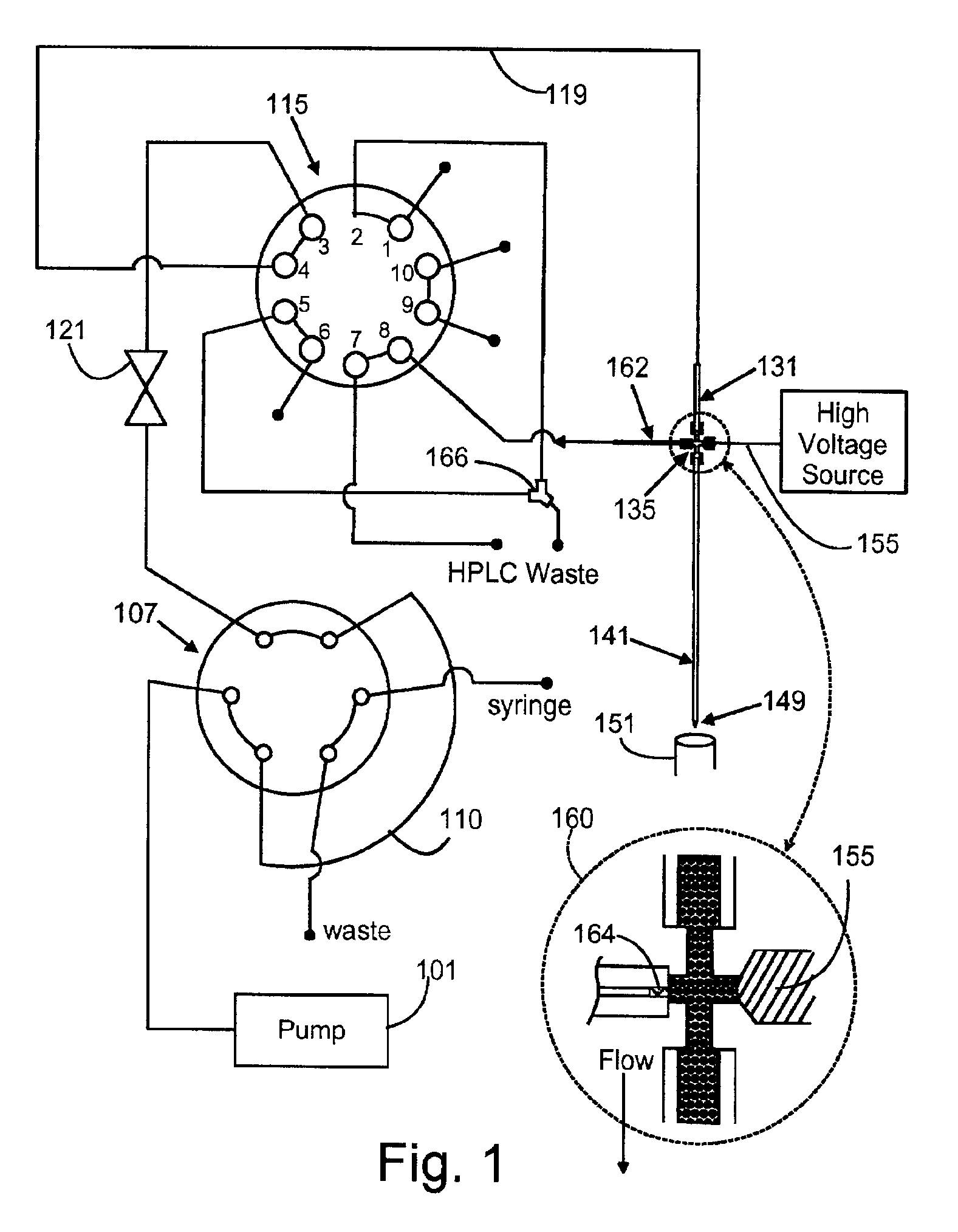
HPLC schematic with integrated sample cleaning system
InactiveUS20100258487A1Extended service lifeImprove protectionIon-exchange process apparatusComponent separationEngineeringContamination
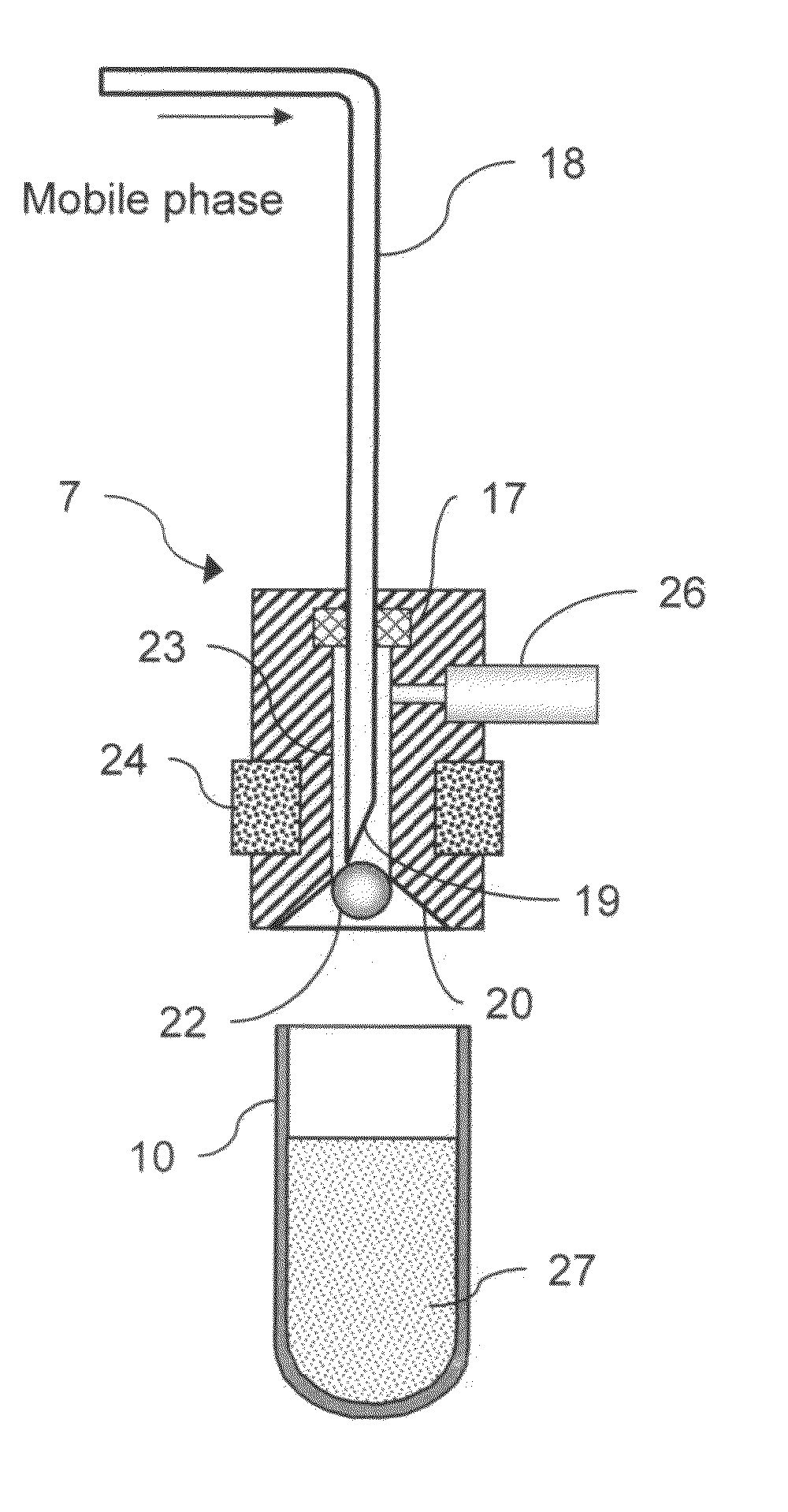
The disclosed HPLC flow schematic back-flushes the guard column with mobile phase once every operating cycle, the regular cleaning maintaining its effectiveness and useful life. This mobile phase flow reversal is accomplished by imposing a two position multiple port switching valve between the guard and separation columns. In one valve position, the mobile phase is pumped in one flow direction through both the separation and guard columns, but the switched valve maintains the same flow direction only through the separation column and reverses the mobile phase flow direction through the guard column, for effectively cleaning the guard column. Moreover, the mobile phase back flow is directed over the emptied sample drawing needle for cleaning it to reduce possible sample cross contamination. The improved flow circuits use basically only the typical HPLC system components, except for some insignificant modifications from existing injector designs.
Owner:SIELC TECH
Method of controlling the rate of oxygen produced by an oxygen concentrator
A method of providing concentrated oxygen product gas to a patient. The method comprises producing product gas by a vacuum swing adsorption (VSA) process with an oxygen concentrator comprising a plurality of separation columns connected to a vacuum source driven by a motor. Separated product gas is then pumped to a product reservoir. The pressure of the reservoir is monitored and used to adjust the speed of the motor based on the reservoir pressure. The separated gas is then delivered to the patient.
Owner:VBOX
System and method for performing multiple parallel chromatographic separations
ActiveUS6936167B2Ion-exchange process apparatusComponent separationChromatographic separationAnalyte
Systems and methods for performing multiple parallel chromatographic separations are provided. Microfluidic cartridges containing multiple separation columns allow multiple separations to be performed in a limited space by a single instrument containing high-pressure pumps and analyte detectors. The use of pressure fit interfaces allows the microfluidic cartridges to easily be removed and replaced within the instrument, either manually or robotically.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
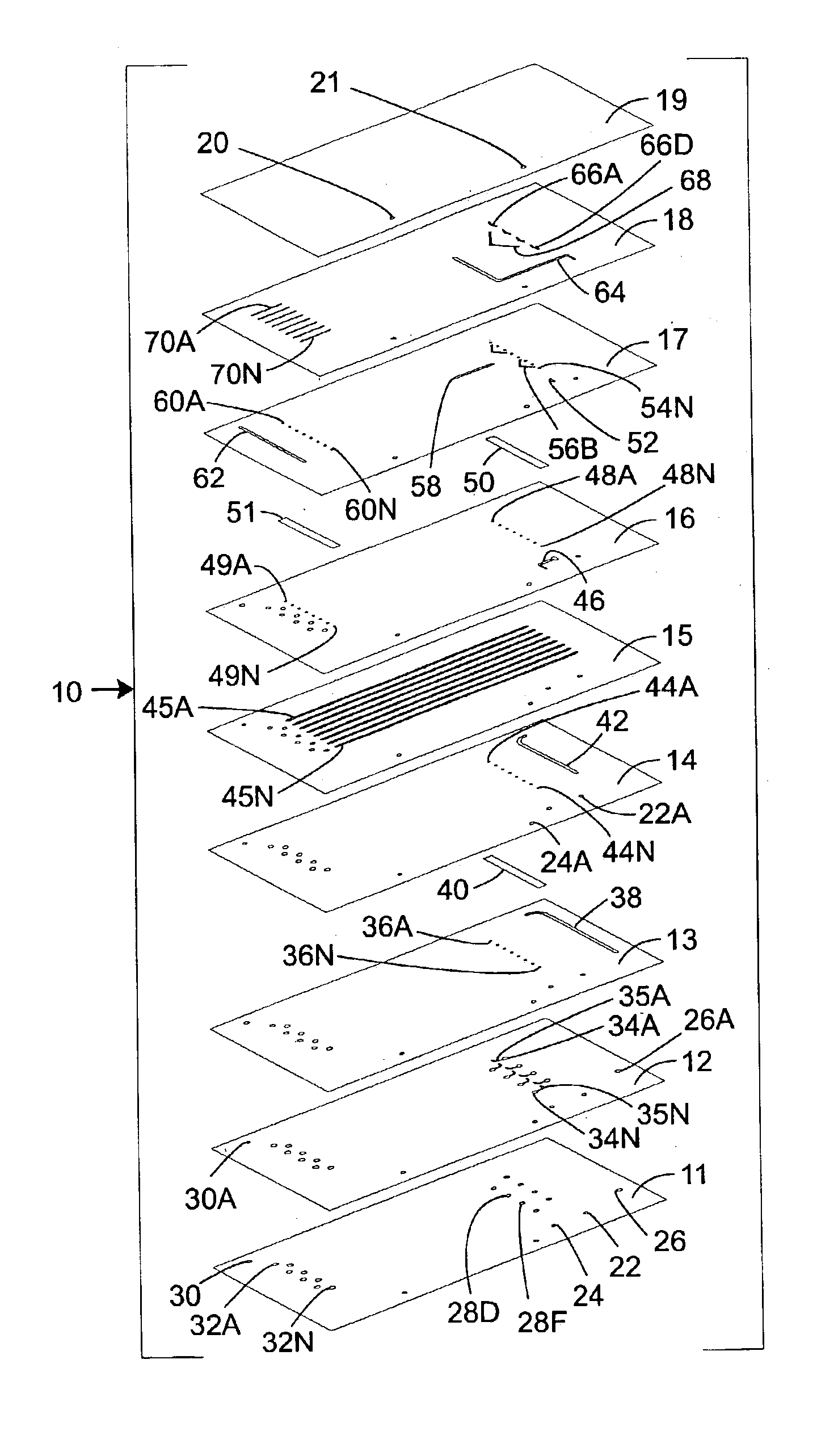
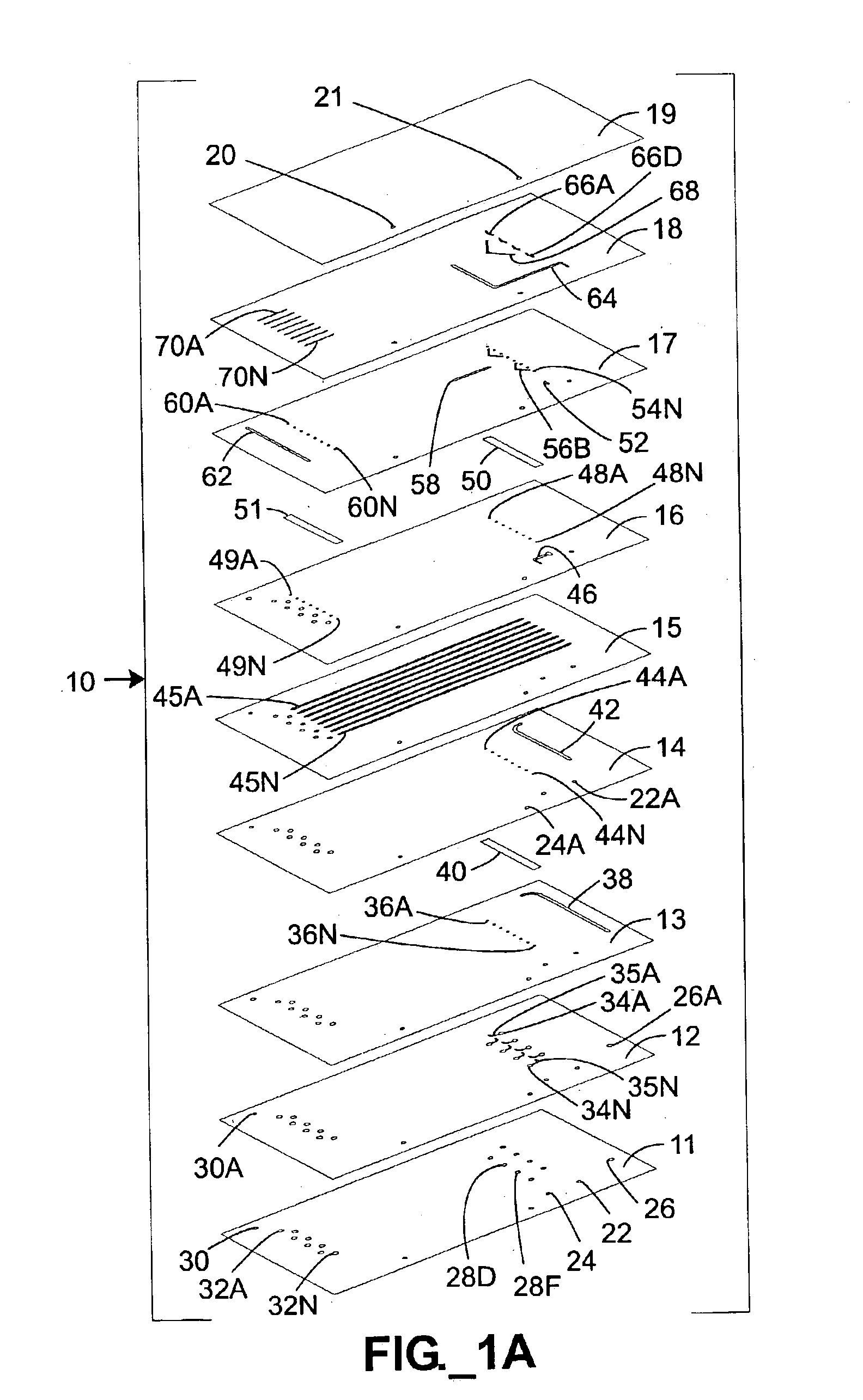
Sample processing system and methods
ActiveUS8727132B2High magnetic separationImprove efficiencyOther blood circulation devicesElectrostatic separationEngineeringCentrifugal force
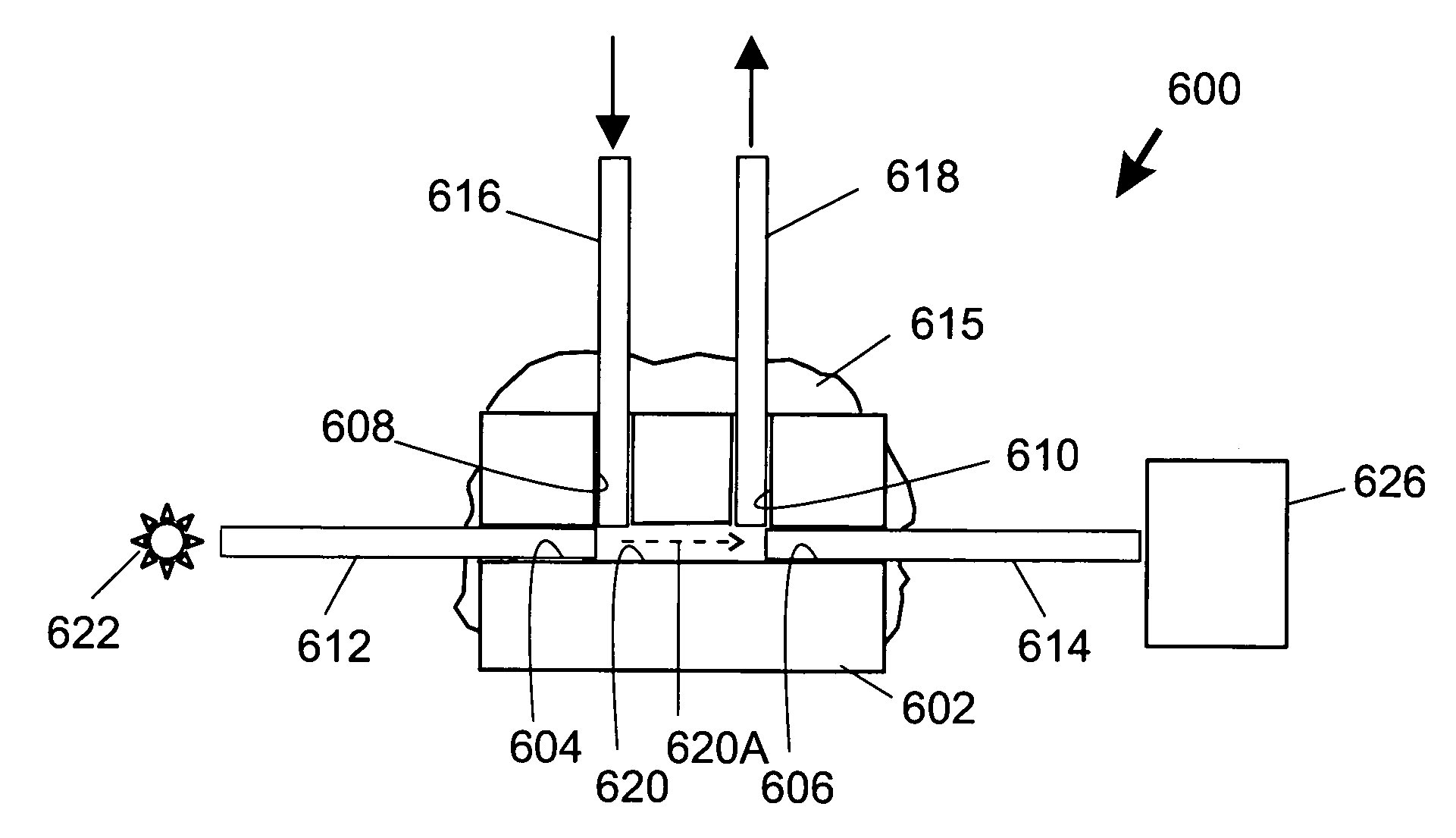
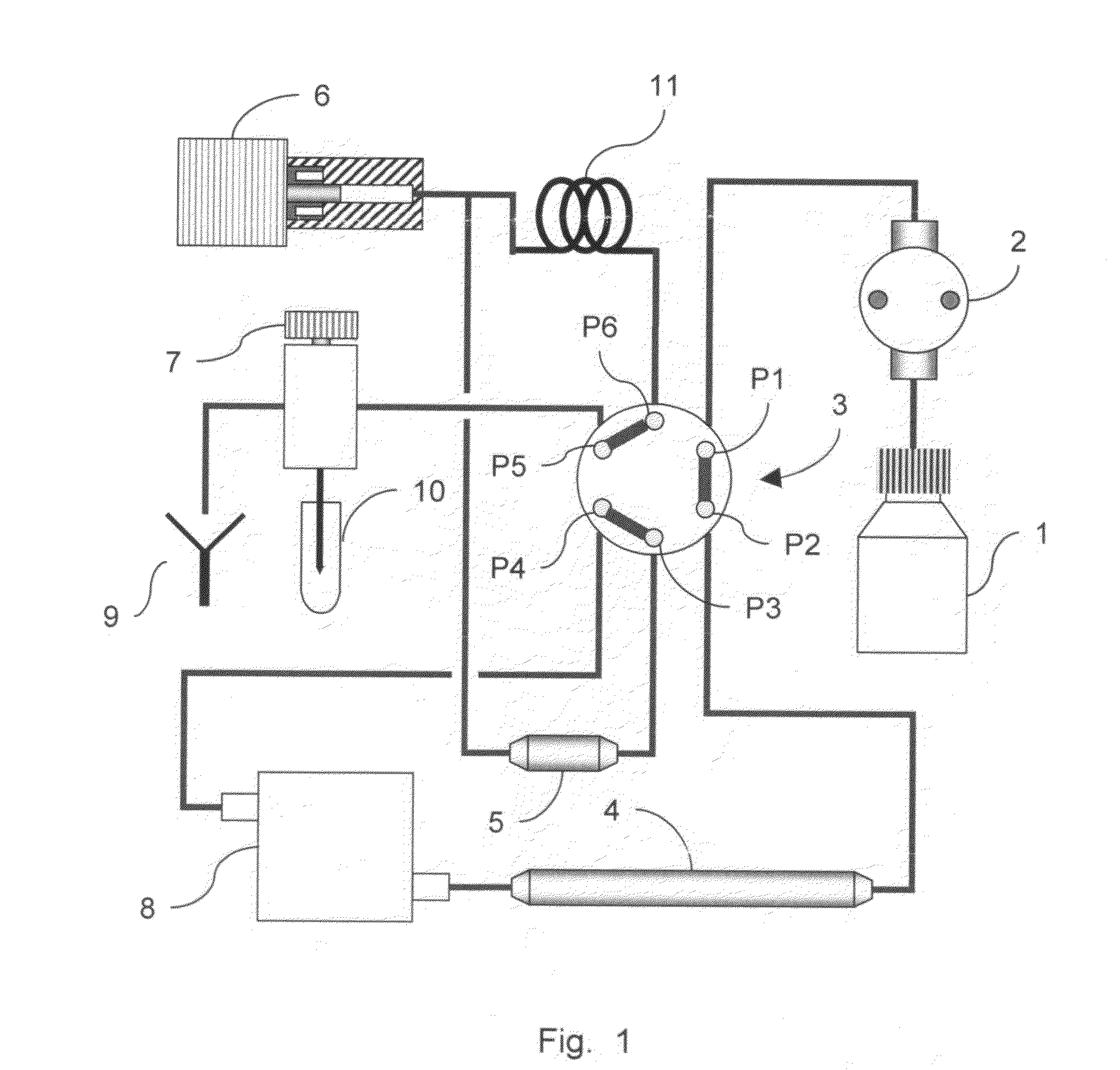
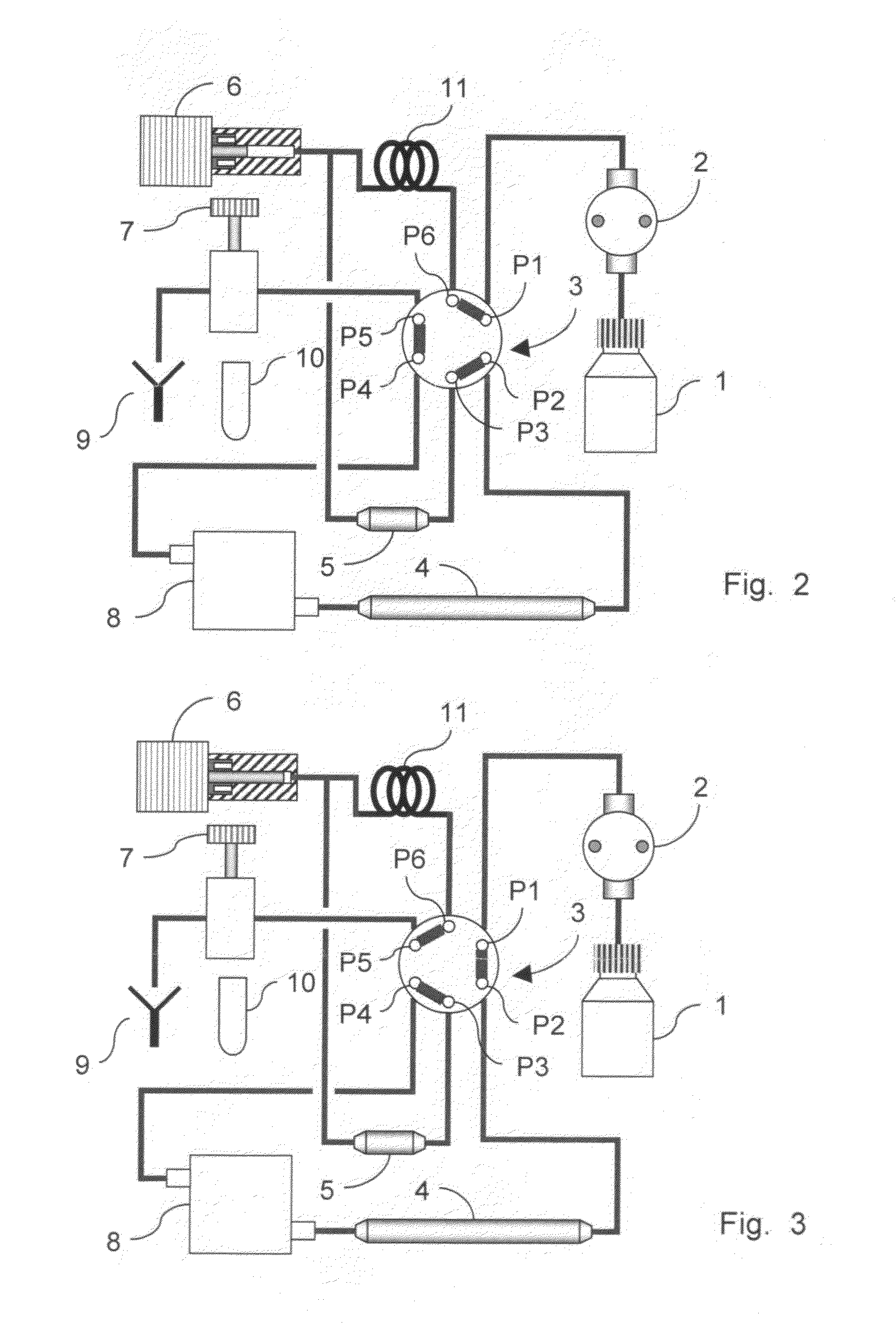
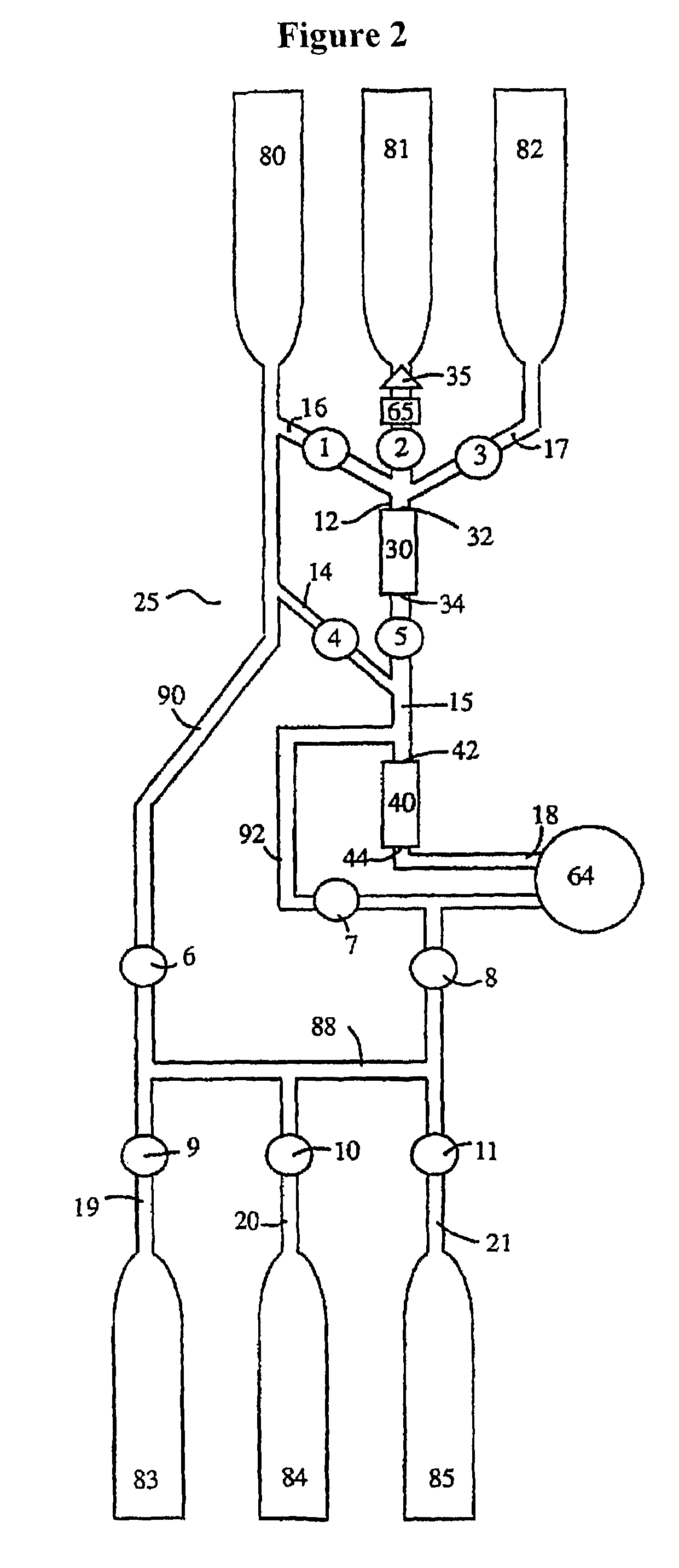
The invention relates to a system, comprising: a) a sample processing unit, comprising an input port and an output port coupled to a rotating container having at least one sample chamber, the sample processing unit configured provide a first processing step to a sample or to rotate the container so as to apply a centrifugal force to a sample deposited in the chamber and separate at least a first component and a second component of the deposited sample; and b) a sample separation unit coupled to the output port of the sample processing unit, the cell separation unit comprising separation column holder (42), a pump (64) and a plurality of valves (1-11) configured to at least partially control fluid flow through a fluid circuitry and a separation column (40) positioned in the holder, the separation column configured to separate labeled and unlabeled components of sample flowed through the column.
Owner:MILTENYI BIOTEC B V & CO KG
Three-dimensional liquid chromatography
InactiveUS20070199874A1Easy to separateIon-exchange process apparatusAnalysis using chemical indicatorsIntermediate stageMixed states
In a liquid chromatography apparatus, a separation column of intermediate stage is additionally connected between a separation column of first stage and a separation column of second stage. Preferably, a switching unit and a liquid feed unit for mixing and feeding a plurality of solutions are added to improve a separation capability. A three-dimensional liquid chromatography apparatus capable of avoiding the “solution interference” can be realized. Even a complex sample containing a hydrophilic component and a hydrophobic component in a mixed state can be separated and analyzed satisfactorily on-line.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Solvent delivery system for liquid chromatography that maintains fluid integrity and pre-forms gradients
ActiveUS20090205409A1Prevent backAvoid feedback instabilitySamplingComponent separationHigh pressureSolvent
A solvent delivery subsystem for a chromatography device performs relatively low pressure, high flow mixing of solvents to form a gradient and subsequent high pressure, low flow delivery of the gradient to the separation column. The mixing of the gradient is independent and does not interfere with the gradient delivery. To form the gradient, the outputs of an aqueous pump and an organic pump are mixed to fill a storage capillary while a downstream point from the storage capillary is vented to atmosphere. After gradient formation, the vent to atmosphere is closed, the solvent delivery system rises to high pressure, and only the aqueous pump runs for gradient delivery. To maintain integrity of the fluid stream, the solvent delivery system uses feed forward compensation and controls at least one parameter selected from the group consisting of pressure and flow in the conduit means to follow a gradual ramp.
Owner:WATERS TECH CORP
Fully packed capillary electrophoretic separation microchips with self-assembled silica colloidal particles in microchannels and their preparation methods
InactiveUS20060147344A1Rapid and improved separationEnhanced interactionComponent separationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCapillary electrophoresisElectrophoresis
A novel CEC column preparation method for various forms of CEC separation using selectively or fully packed microchannels with self-assembled silica colloidal particles is disclosed. The method relies on the three dimensional uniform silica colloidal packing through selective regions or whole channels resulting in uniform EOF and reproducibility. The fully packed capillary electrophoretic separation microchip is inherently suited for a handheld system since it exploits uniquely fully packed separation channels to achieve better separation efficiency and stability. The fully packed capillary electrophoretic separation microchip can be easily fabricated using low-cost, rapid manufacturing techniques, and can provide high performance for CEC separation with various chromatographic stationary support packing, functionalized surface of packed beads. The fully packed microchannels with self-assembled silica colloidal particles can be applied for preparation of a built-in submicron filter. Embodiments of the present invention address a significant challenge in the development of disposable CEC microchips, specifically, providing a reliable solution for preparation of the CEC separation column in a device that may be immediately applied for a variety of CEC applications.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CINCINNATI
Automated capillary liquid chromatography small volume analysis system
InactiveUS6989129B2Reduce flow rateImprove performanceSamplingComponent separationChromatographic separationAutosampler
A system for automatically performing liquid chromatography analysis of low volume liquid chemical samples at nanosecond flow rates using an analysis column that integrates a pre-concentration trapping column and a chromatography separation column terminating at an electrospray nozzle of an online mass spectrometer. The analysis column consists of a capillary having an inside diameter of between 75 and 125 microns packed throughout with a porous bed of micron particles. A branch outlet positioned 10 to 16 centimeters upstream from the nozzle divides the analysis column into an upstream pre-concentration trap and a downstream separation column. An autosampler delivers low volume liquid samples to the upstream inlet via a two-position valve. Feed connections couple the autosampler to upstream inlet when the valve is open to inject a liquid sample into the pre-concentration trap at a maximum loading flow rate in the range from 0.5 to 50 microliters / minute. Thereafter, when the valve closes, it terminates the further injection the sample, and a concentrated portion of the sample then passes though the chromatography separation column at a much slower flow rate between 10 and 1,000 nanoliters per minute. Throughput can be doubled by coupling two such analysis columns to a single autosampler using a ten-port, two position valve. A single column can be supplied through a six port two-position valve.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
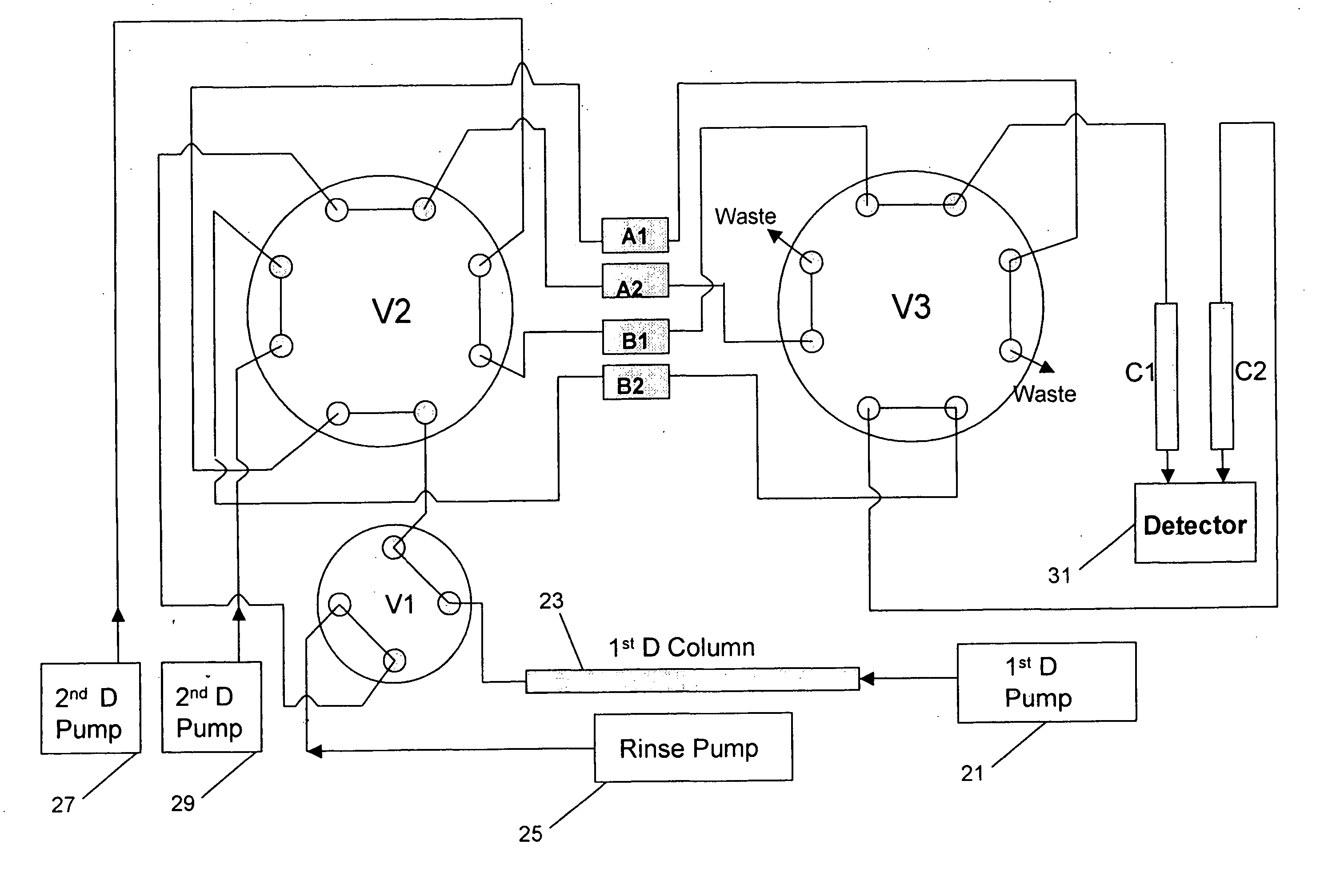
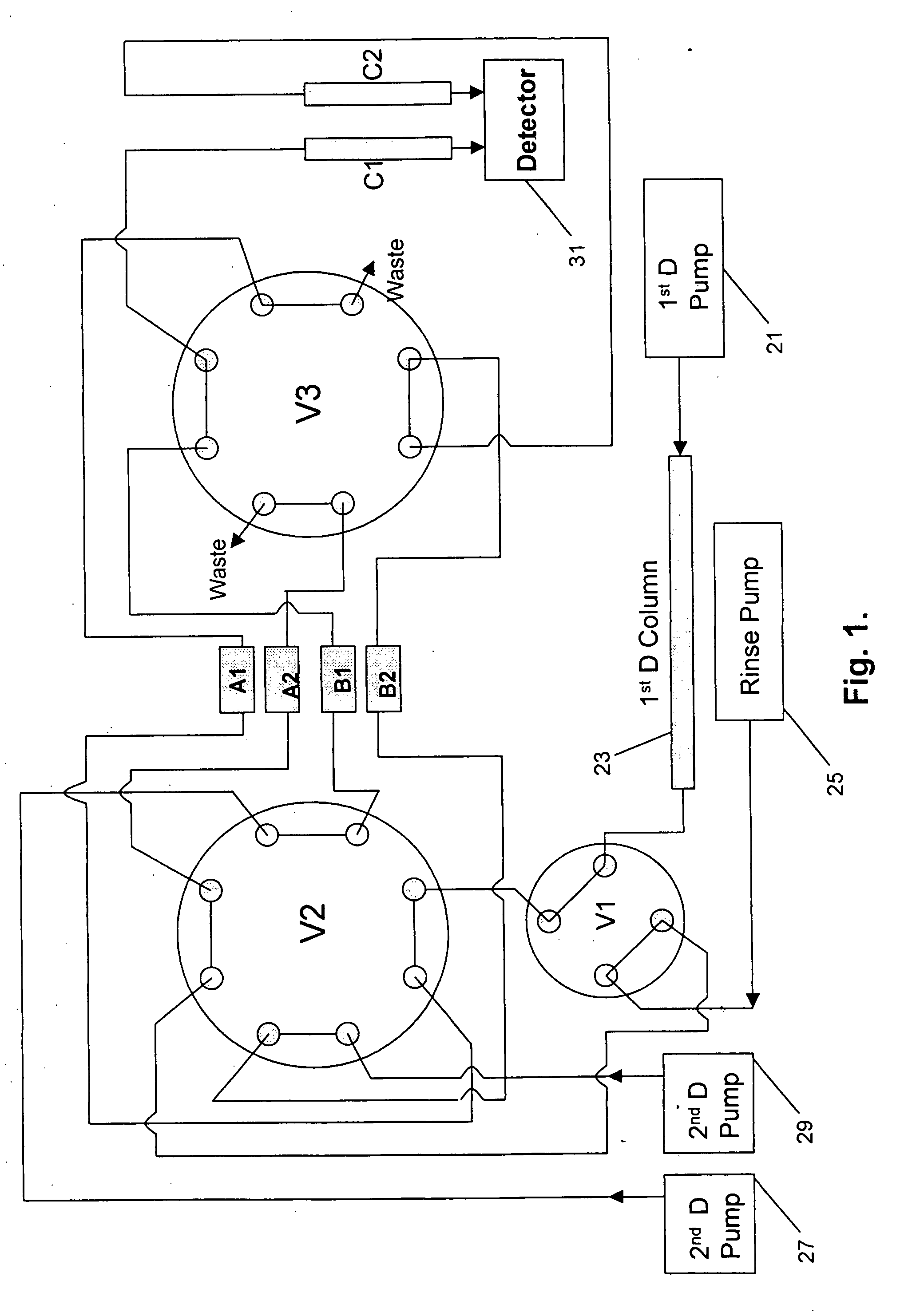
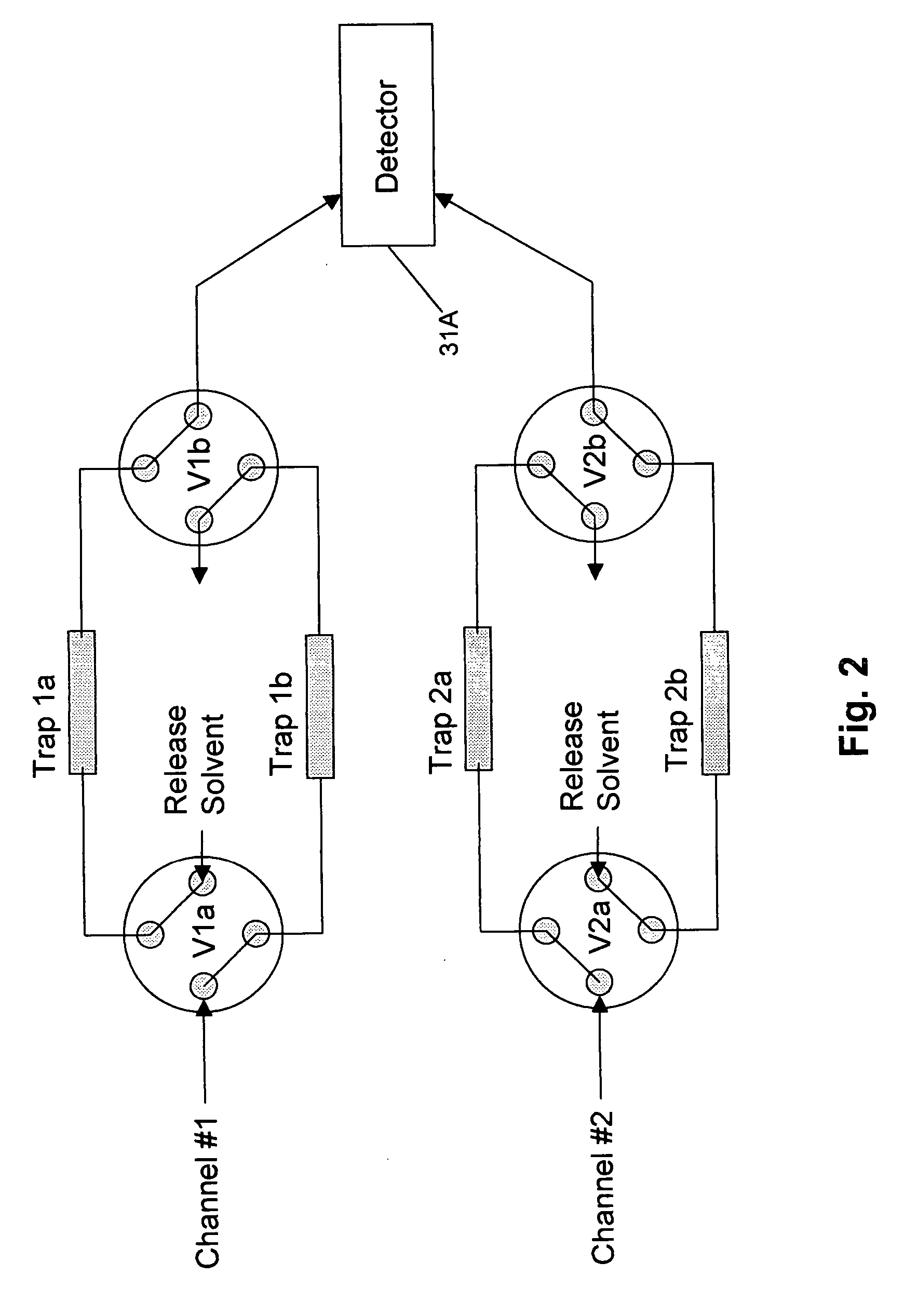
Multi-dimensional liquid chromatography separation system and method
InactiveUS20060156792A1Improve throughputIncrease separation speedComponent separationInternal standardStream flow
A multi-dimensional separation system having parallel traps for effluent from prior separation dimension and parallel latter separation columns, the latter columns being coupled to the traps. At least one trap enriches components of effluent while at least one other trap is releasing trapped components to a detector, which may be a mass spectrometer. Internal standards may be provided, as in a release solvent, for the calibration of one of the chromatographic columns and the detection system. The system may comprise a multiple channel selector for multiple streams, wherein all of the streams flow at the same time.
Owner:CERNO BIOSCI
Process for separating propane and propylene using a distillation column and a membrane separation column
InactiveUS20110049051A1Distillation purification/separationSolid sorbent liquid separationDistillationPropane
Process for separating propane and propylene using a distillation column and at least one membrane separation unit constituted by one or more modules operating in series, said membrane separation unit being placed either upstream, or downstream, or upstream and downstream of the distillation column.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
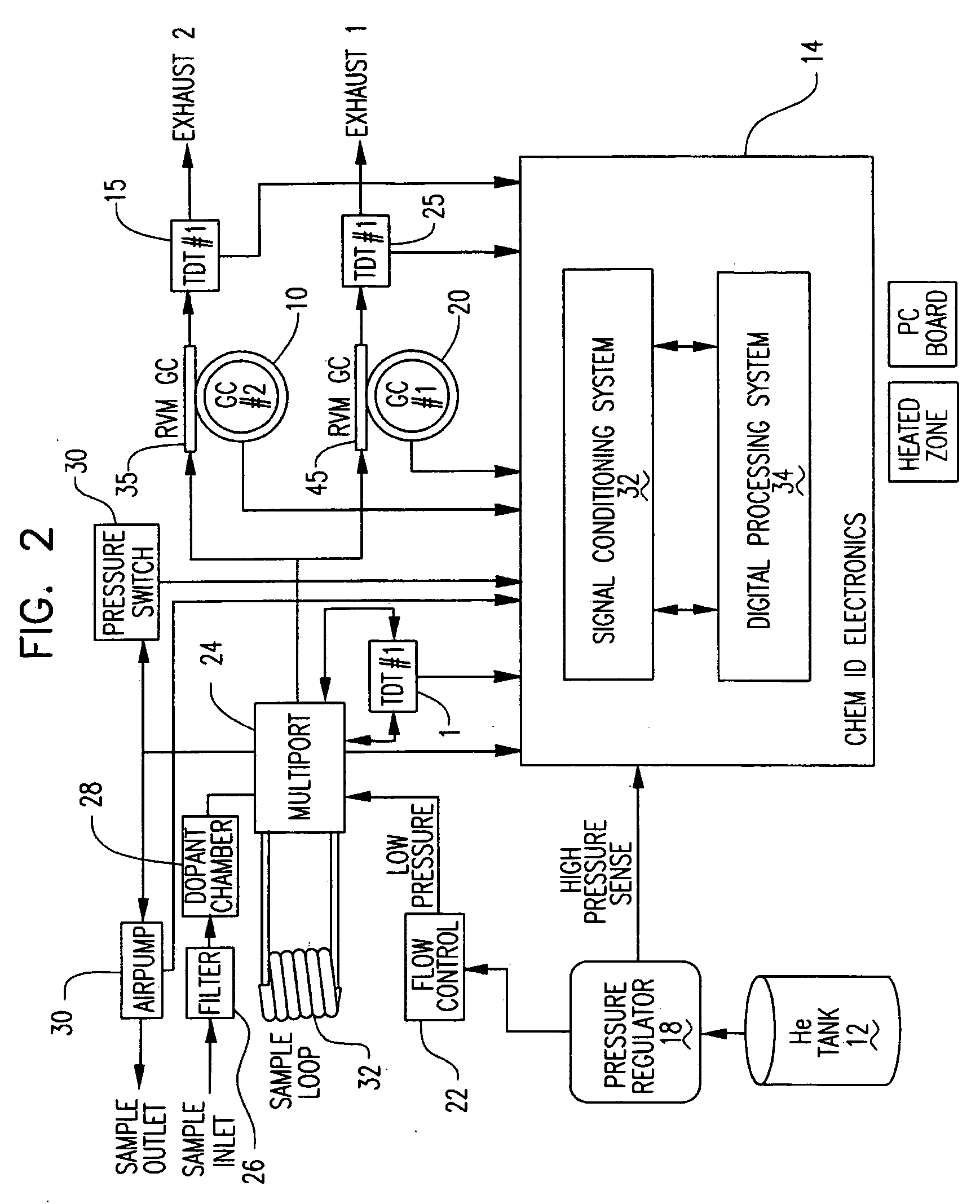
Multi-dimensional portable gas chromatograph system
ActiveUS20070266858A1Reduce pressureAssist in operationSamplingComponent separationGas liquid chromatographicEngineering
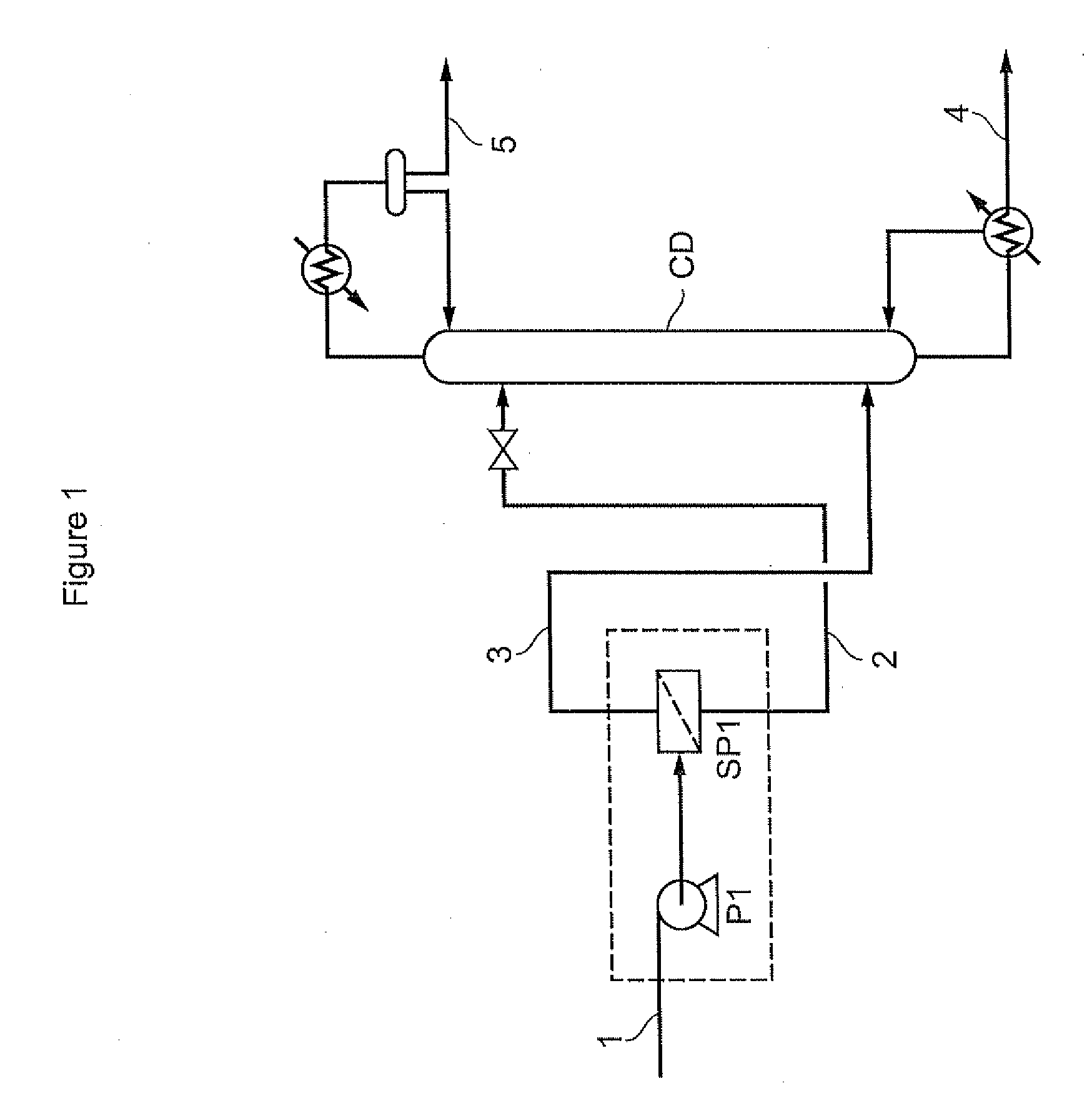
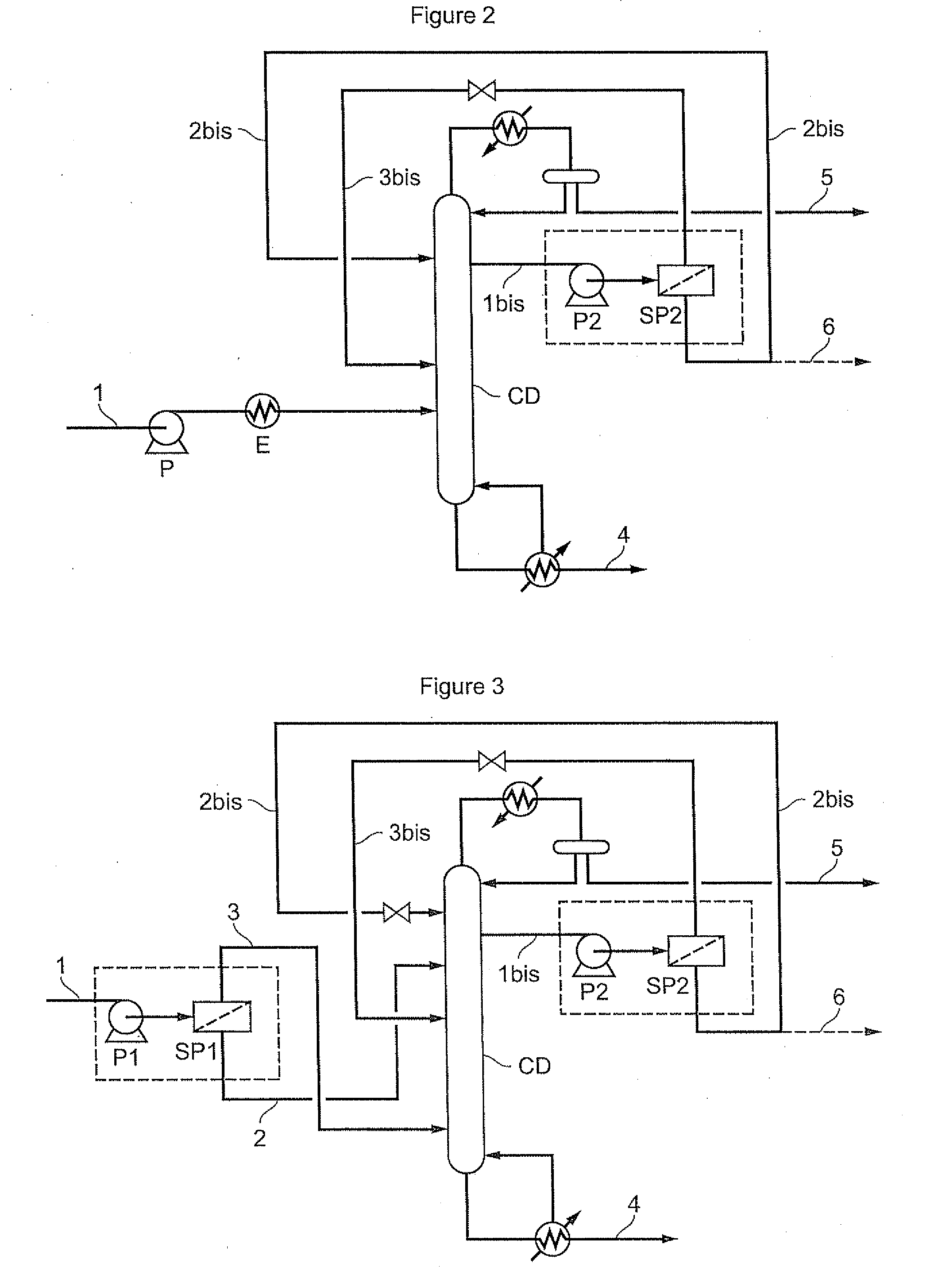
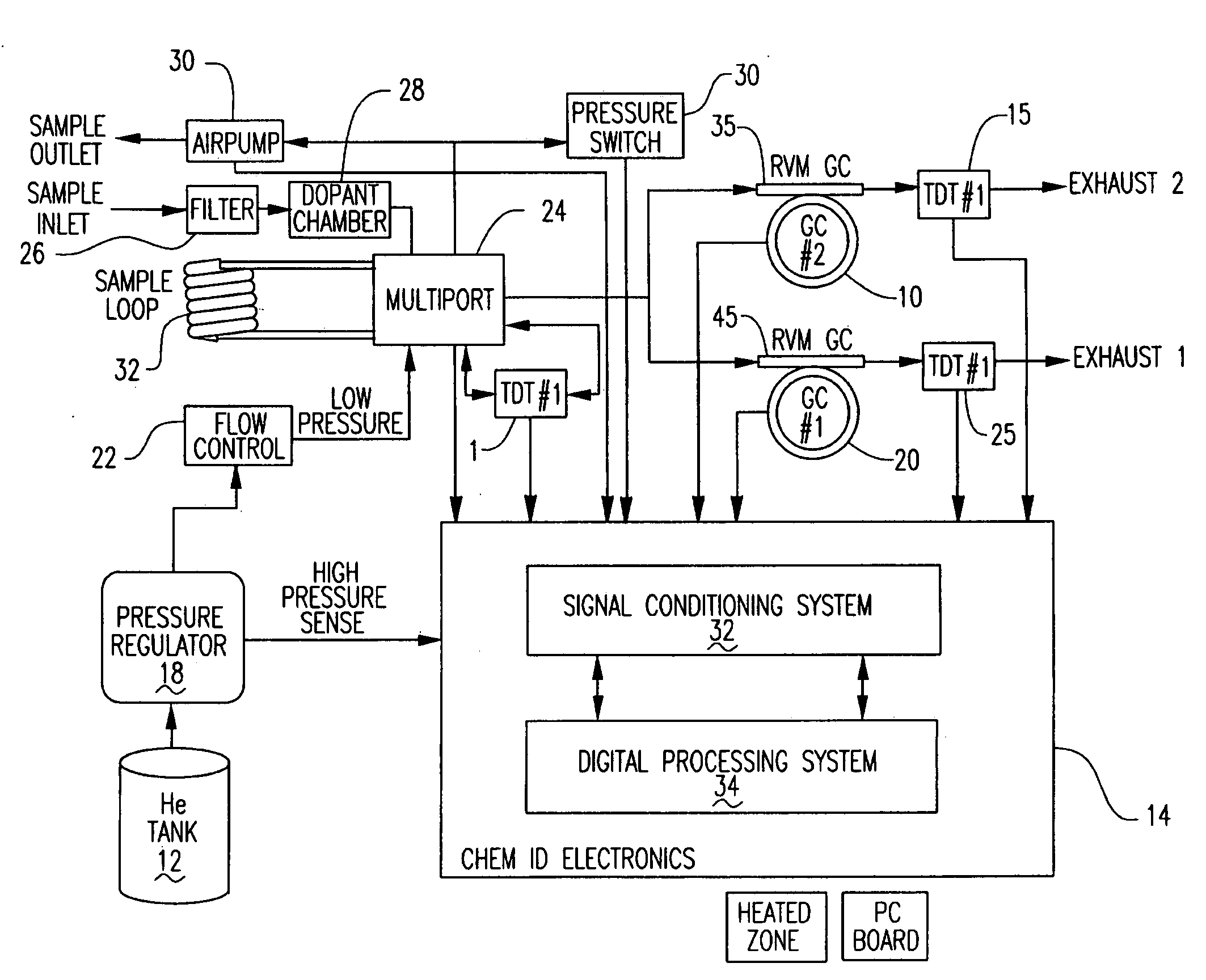
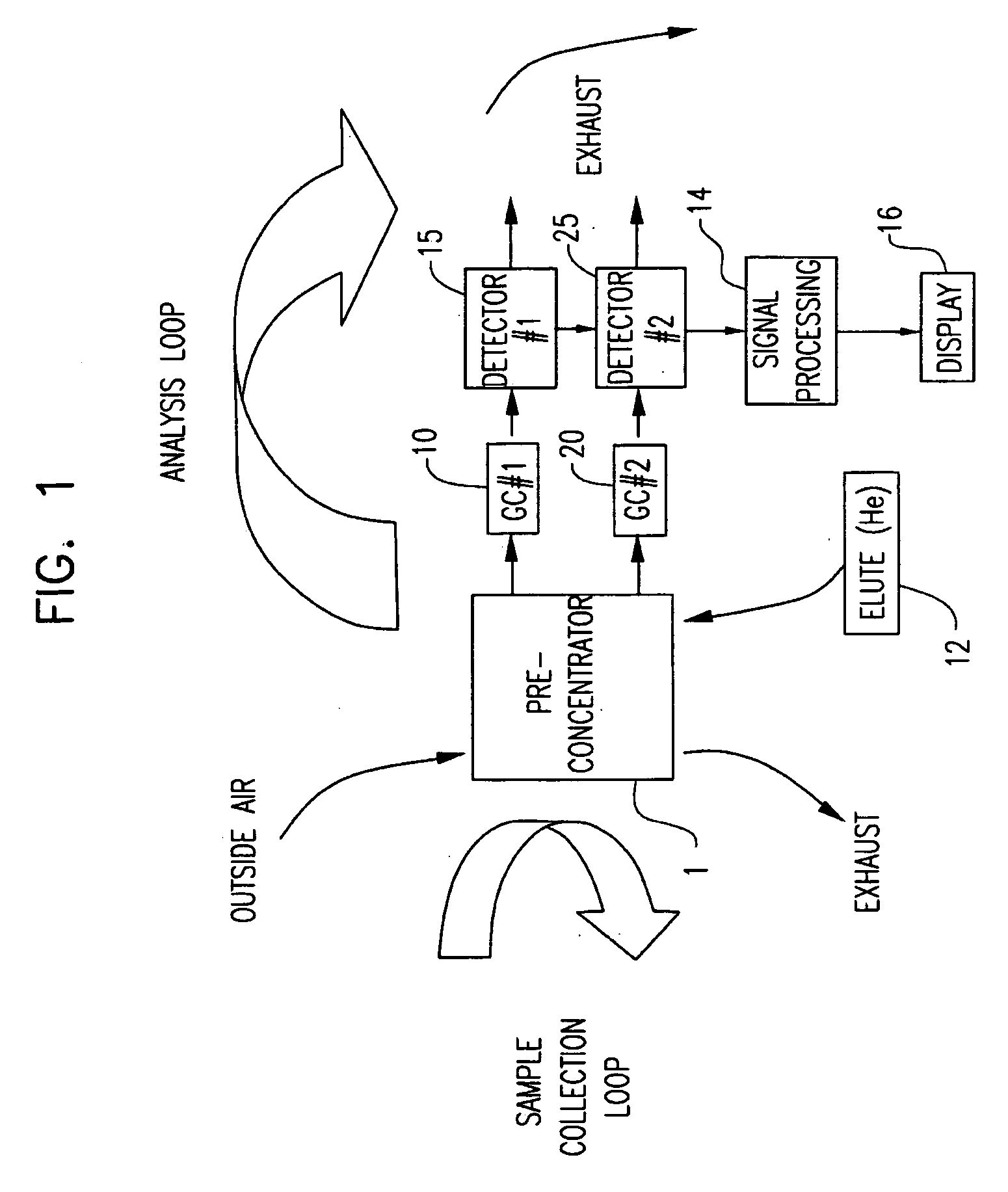
A portable multi-dimensional gas chromatograph, the gas chromatograph including a carrier gas container, a regulator fluidly connected to the carrier gas container, a dopant chamber containing a reference chemical, at least one pre-concentrator which is fluidly connected to the regulator and the dopant chamber, a first separation column fluidly connected to the at least one pre-concentrator, a second separation column fluidly connected to the at least one pre-concentrator, a first detector fluidly connected to the first separation column, and a second detector fluidly connected to the second separation column.
Owner:LUDLUM MEASUREMENTS
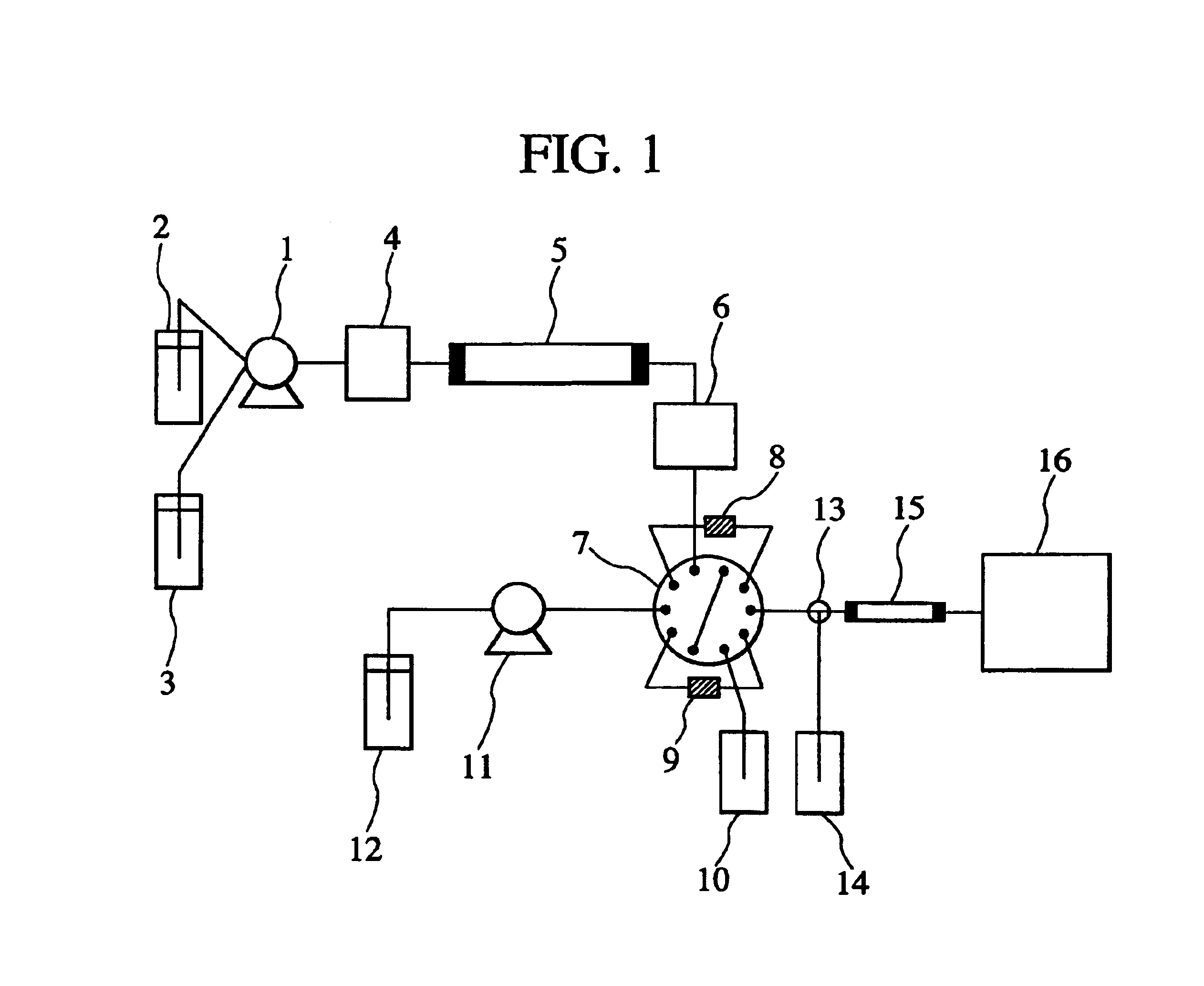
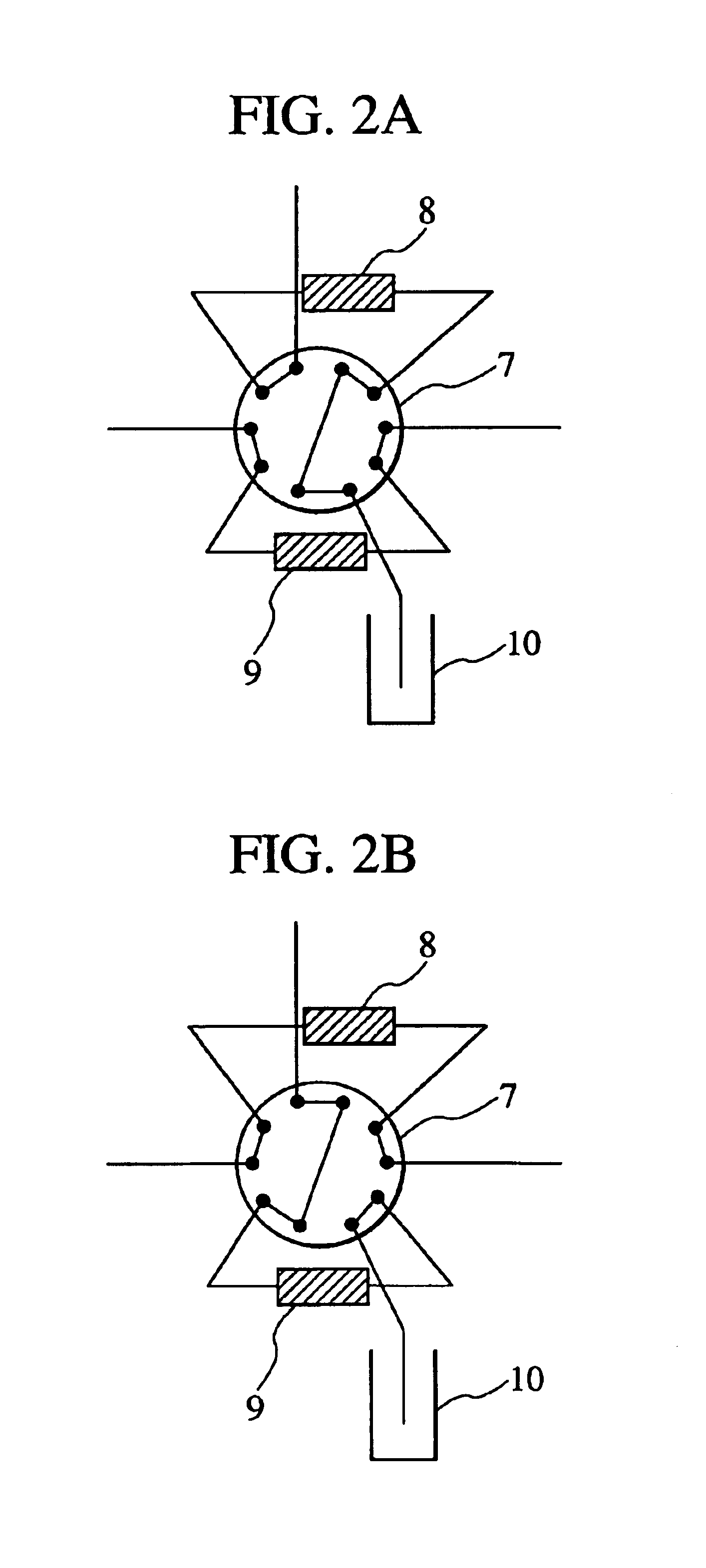
Liquid chromatograph mass spectrometer
InactiveUS6942793B2Quick detectionQuick of sensitivityIon-exchange process apparatusComponent separationSpectrometerSeparation column
A liquid chromatograph mass spectrometer comprises: a pump; a sample injector; a plurality of separation columns, including a first separation column and a second separation column; and mass spectrometer. The liquid chromatograph mass spectrometer further comprises: a plurality of trap columns for retaining a sample component separated by the first separation column; a first switching valve for switching between one of the plurality of trap columns and another one of the plurality of trap columns at regular time intervals in such a way that when the one of the plurality of trap columns is connected to the first separation column, the another one of the plurality of trap columns is connected to the pump, and vice versa; and a second switching valve for, when a trap column is connected to the pump, further connecting the trap column to the second separation column after connecting the trap column to solution discharging means during a predetermined initial time period, the second separation column being connected to the mass spectrometer and capable of separating the sample component in a shorter time than the first separation column.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
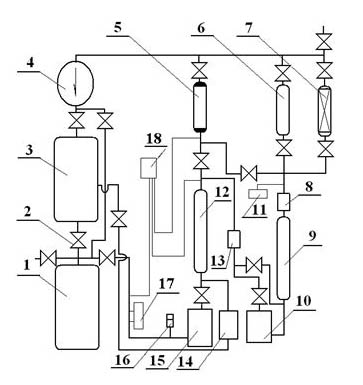
Low-temperature displacement chromatography hydrogen isotope separation device and method
ActiveCN101850215AAchieving Self-Displacement ChromatographyOvercome the disadvantage of low separation coefficientCation exchanger materialsOrganic anion exchangersSeparation factorGas release
The invention provides a low-temperature displacement chromatography hydrogen isotope separation device and a method. The invention makes the mixed gas of hydrogen isotope gas and helium after being cooled sequentially pass through a cooled main separation column and a cooled product gas collecting column which are filled with granulate palladium-loaded aluminum trioxide (Al2O3 / Pd) to obtain the product gas rich in heavy isotope components of deuterium and tritium; a hot helium flow passes through and heats the main separation column so as to make the released gas sequentially pass through the cooled secondary separation column and the product gas collecting column which are filled with granulate palladium-loaded aluminum trioxide (Al2O3 / Pd) to obtain the product gas rich in heavy isotopecomponents of deuterium and tritium; after the product gas is collected, middle rich gas flowing out from the secondary separation column is directly fed back into a raw material gas tank; and after the middle rich gas feedback process is accomplished, the main separation column and the secondary separation column are heated, and the gas released by heating is collected via a tail gas collecting column. The separation device has simple structure, reasonable separation process, and low cost for the construction and operation of the device. The invention has higher separation factor for hydrogen isotope separation.
Owner:SICHUAN INST OF MATERIALS & TECH
Liquid chromatography and column packing material
InactiveUS6360589B1Accurate analysisAvoid problemsIon-exchange process apparatusChromatographic cation exchangersFilling materialsSolvent
A liquid chromatograph and a column packing material effectively condensing cationic specimen and exhibiting a high resolution. The liquid chromatograph includes a pre-focusing column (30, 40) having a volume of less than 2.0 milliliters and packed with a column packing material, in which a porous support is coated by a silicone polymer having a Si-R-X (R is a spacer part, X is a sulfonic group) bond and a Si-R' (R' is a hydrophilic group) bond, wherein the specimen to be analyzed is supplied to the pre-focusing column in the state dispersed in a solvent for condensation. The condensed specimen is then separated in a separation column (16, 43) used for separating the specimen dispersed in the solvent, and the separated specimen is analyzed by a detector (17, 41).
Owner:SHISEIDO CO LTD
Capillary column and method of making
InactiveUS20070172960A1Simple and rapid methodQuick and easy to manufactureComponent separationDispersed particle separationStationary phaseAnalyte
The present invention concerns a new and useful structure for forming a capillary tube, e.g. for gas chromatography, and methods for forming the capillary tube are described. The capillary tube comprises a tube structure, and a deactivated surface-bonded sol-gel coating on a surface of the tube structure to form a stationary phase coating on that surface of the tube structure. According to the present invention the deactivated stationary phase sol-gel coating enables separation of analytes while minimizing adsorption of analytes on the separation column structure.
Owner:MALIK ABDUL +1
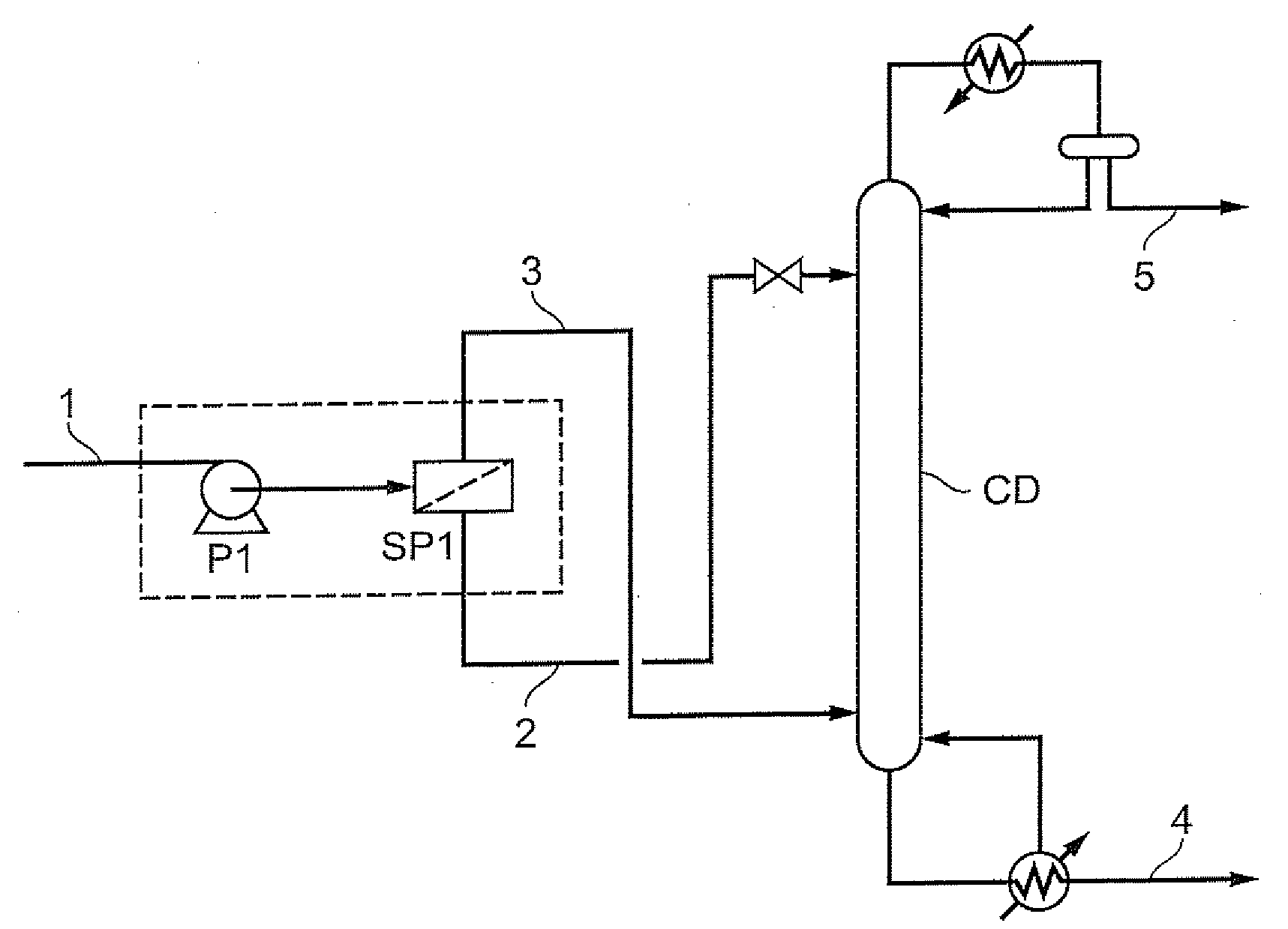
Dividing wall separation in light olefin hydrocarbon processing
ActiveUS20080081937A1Speed up the processIncrease volumeThermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingNaphthaCell separation
Processing schemes and arrangements for application of a dividing wall separation column in the processing of an effluent resulting from FCC processing modified for increased light olefin production. The dividing wall separation column desirably splits a naphtha feedstock produced or resulting from such modified FCC processing to produce or form a light fraction containing C5-C6 compounds, an intermediate fraction containing C7-C8 compounds and a heavy fraction containing C9+ compounds.
Owner:UOP LLC
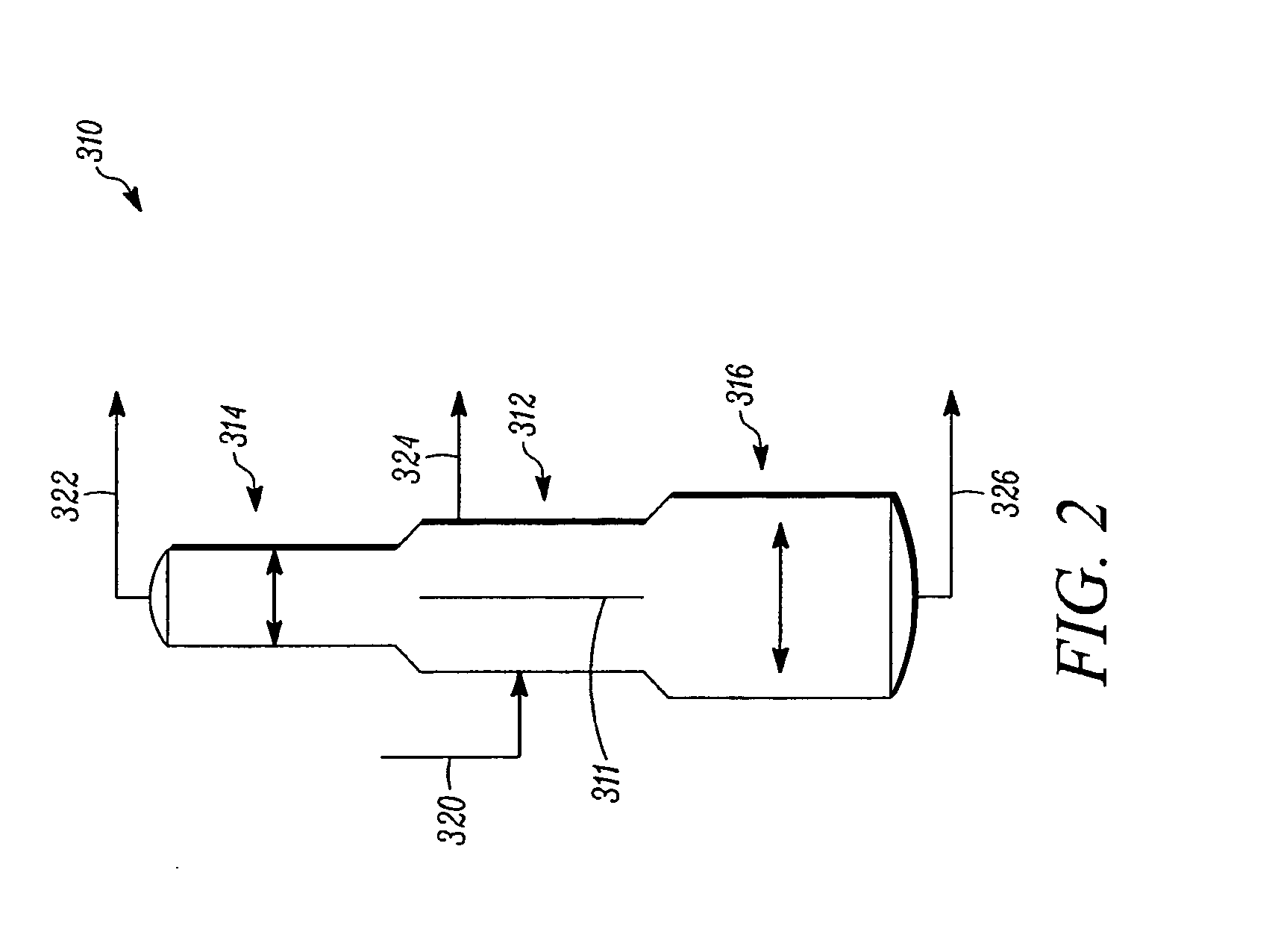
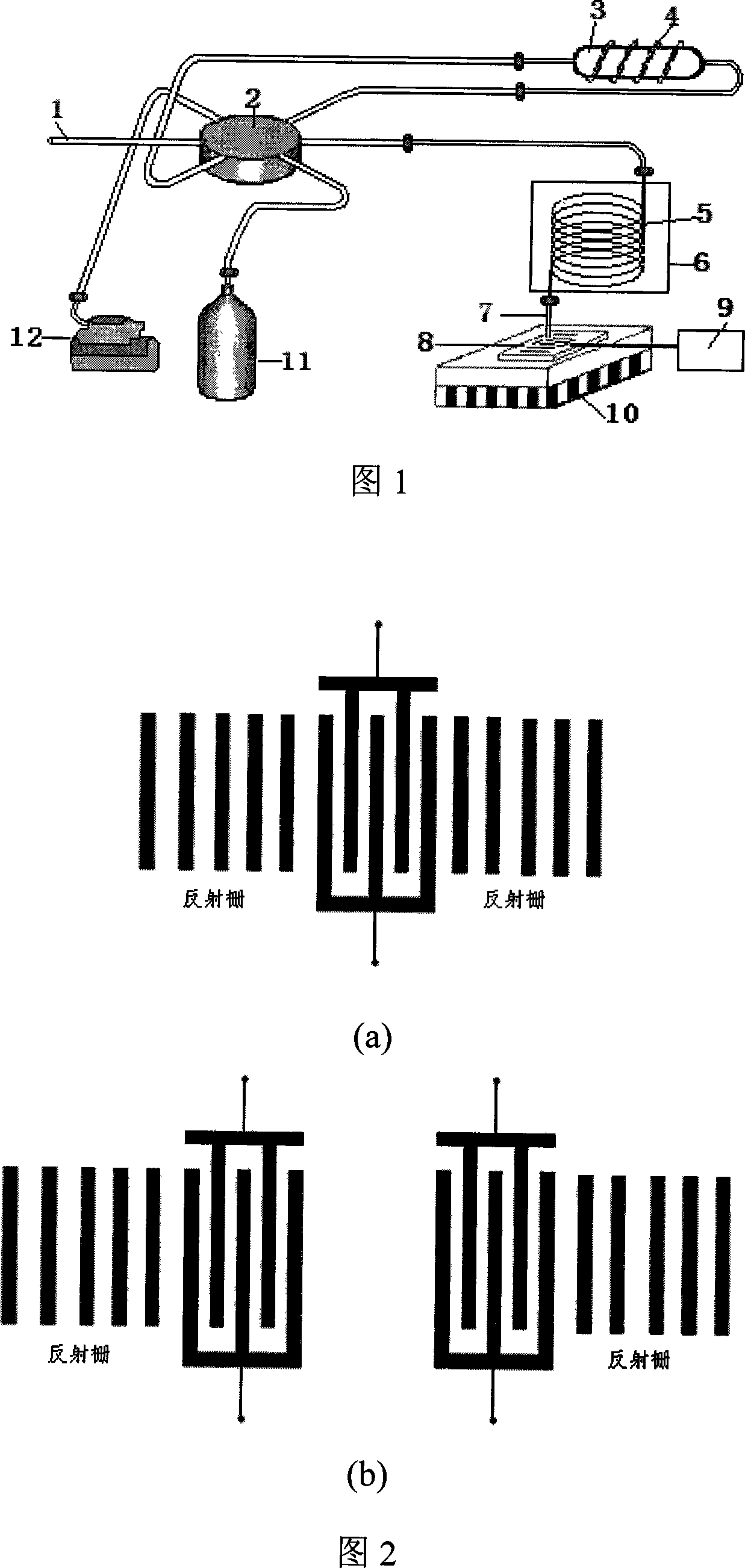
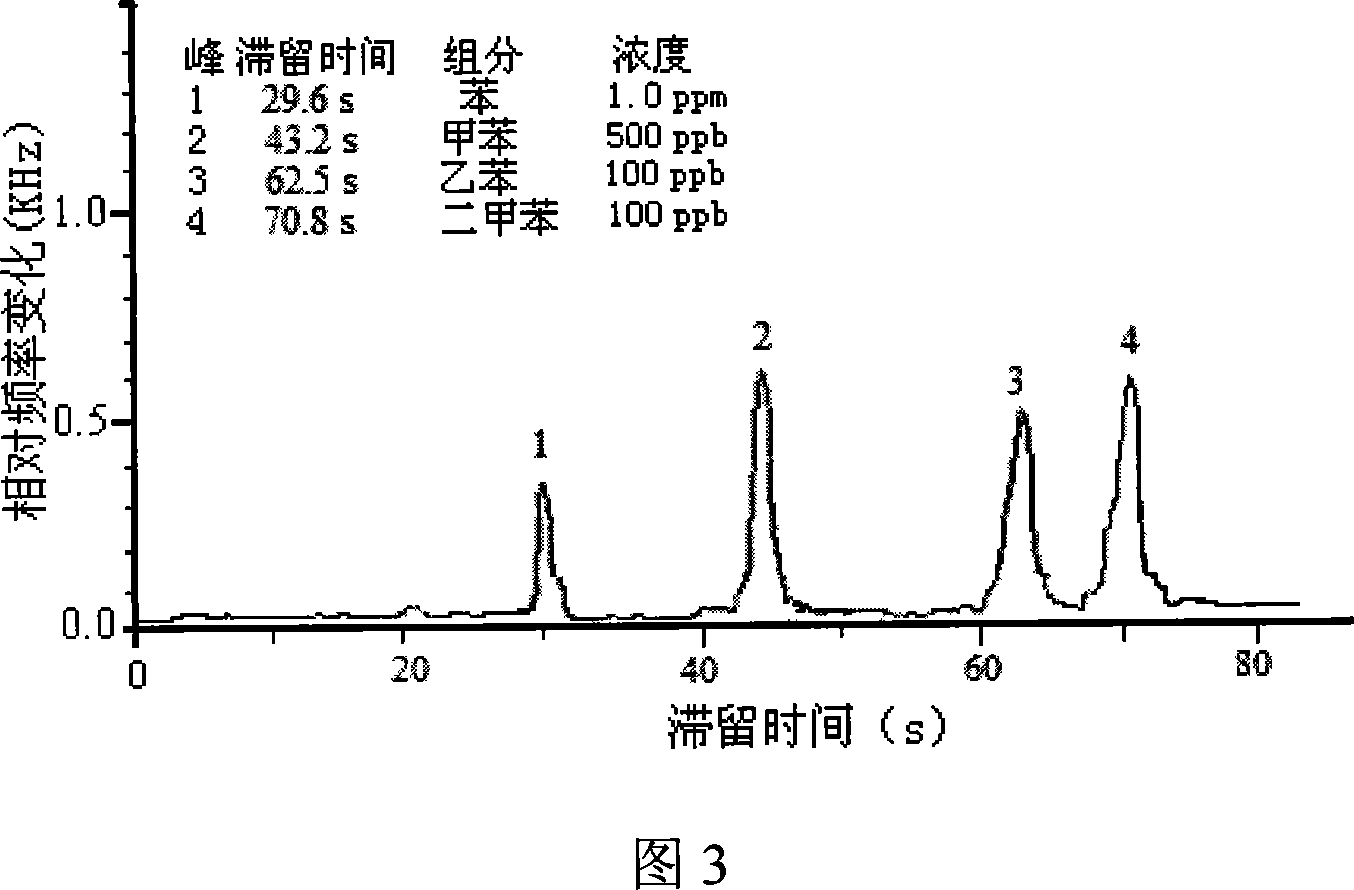
Electronic nose of using sensor of acoustic surface wave and partitioning column of gas chromatography jointly, and detection method
An electronic nose applying both sound surface wave transducer and gas-phase chromatograph separation column is prepared for connecting six-way valve separately to sample feeding-in opening, absorption tube, gas-phase chromatograph separation column, gas-carrying bottle and air pump; connecting said separation column to micro-nozzle; setting sound surface wave transducer under micro-nozzle; arranging said transducer on semiconductor refrigeration plate and connecting said transducer to frequency detector. Its detecting method is also disclosed.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Full online detection multi-dimensional liquid chromatogram separation system based on same detector
PendingCN108037233AThe separation process is measurable and controllableHigh-resolutionComponent separationFraction CollectorChromatographic separation
The invention provides a full online detection multi-dimensional liquid chromatogram separation system based on a same detector. The full online detection multi-dimensional liquid chromatogram separation system comprises a high performance liquid chromatography gradient pump A, a high performance liquid chromatography gradient pump B, a high performance liquid diluent pump, a gradient mixer A, a gradient mixer B, an injection valve, an enriching column array A, an enriching column array B, a fraction collector, a liquid chromatography separation column array, a detector, a two-position ten-wayvalve and a connecting pipeline; the conversion of the previous-dimension separation state and the current-dimension separation state is realized through the switching of the two-position ten-way valve, so that three dimensions or more than three dimensions of chromatographic separation is realized. Each dimension of chromatographic separation column is selected through the liquid chromatographyseparation column array, full online monitoring and control for multi-dimensional chromatographic separation are realized based on the same gradient elute system and the same detector, and cleanlinessdegree controllability for enriching columns and separation columns is realized. Each dimension of separation is connected through the enriching columns, and the enrichment or gathering of compoundsis assisted by using the diluent pump. According to the system, efficient separation for complex system samples with high separation difficulty is realized by selecting the combinations of different chromatographic stationary phases and moving phases.
Owner:DALIAN BOMAI TECH DEV
Method and apparatus for chromatographic purification
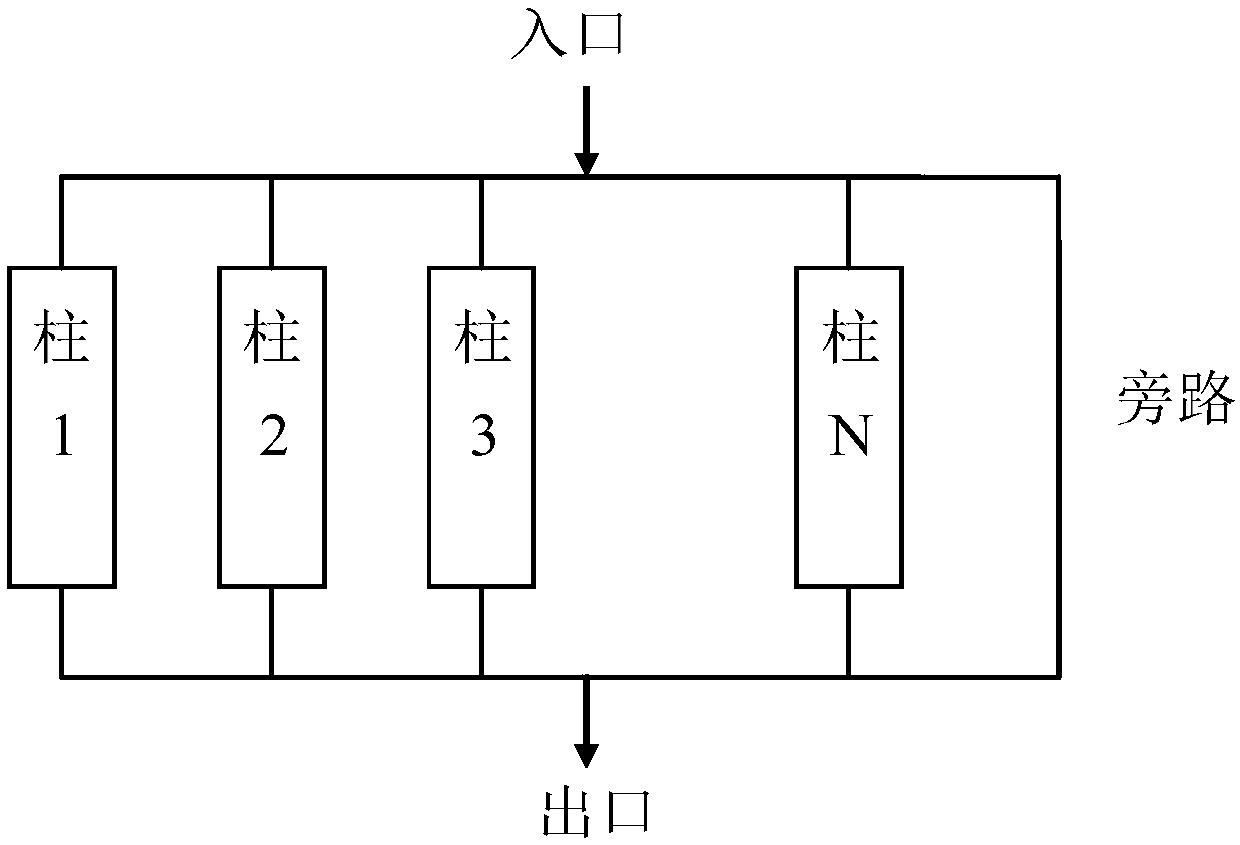
InactiveUS20140251911A1Cation exchanger materialsComponent separationChromatographic separationTwo step
The present invention relates to a method and an apparatus suitable for a continuous chromatography process which only needs three separation columns. The process is a two step procedure comprising two chromatographic steps. The first chromatographic step (capture) is performed alternating and sequentially on two separation columns, the second chromatographic step (polishing) is performed, also sequentially, on the third column.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
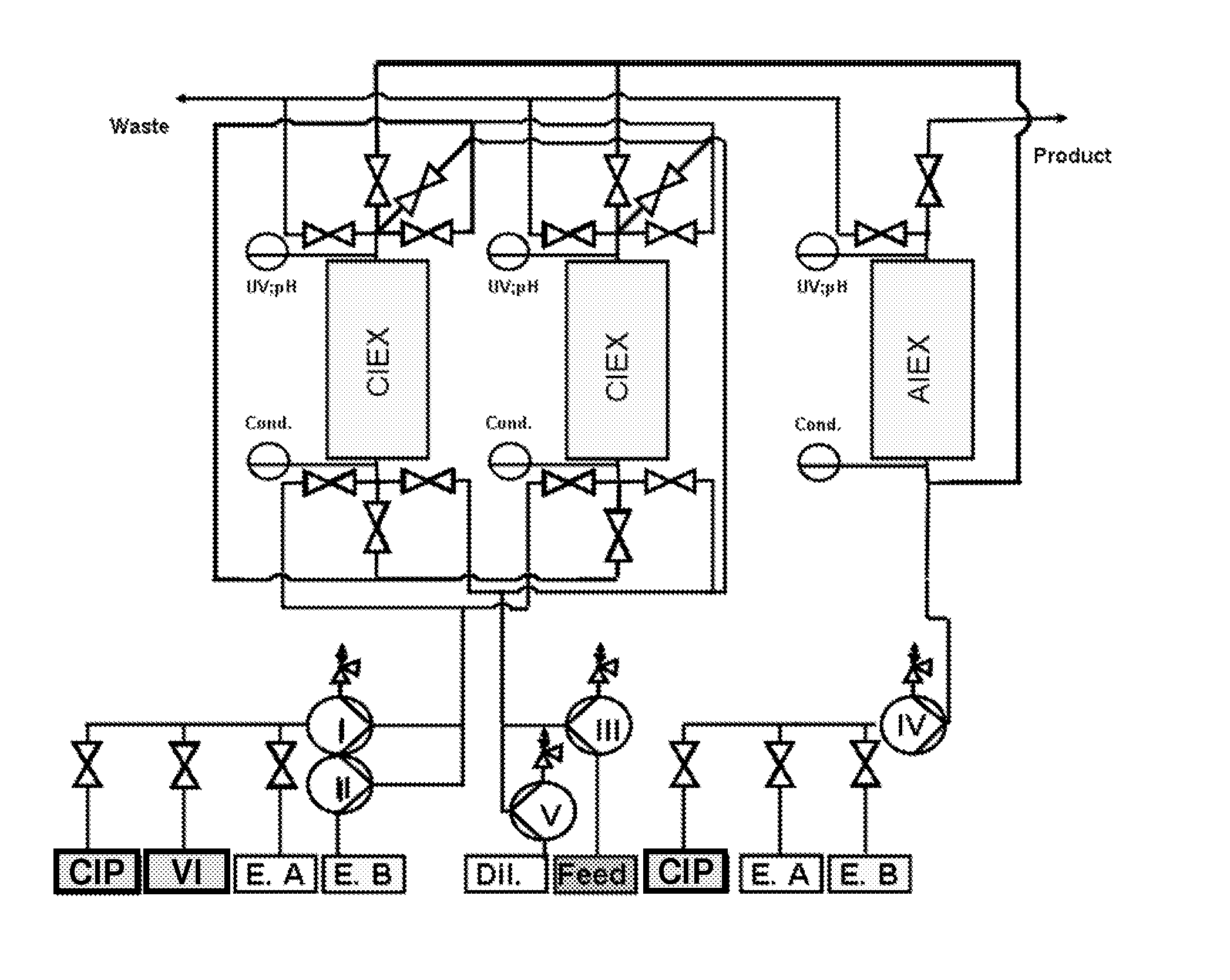
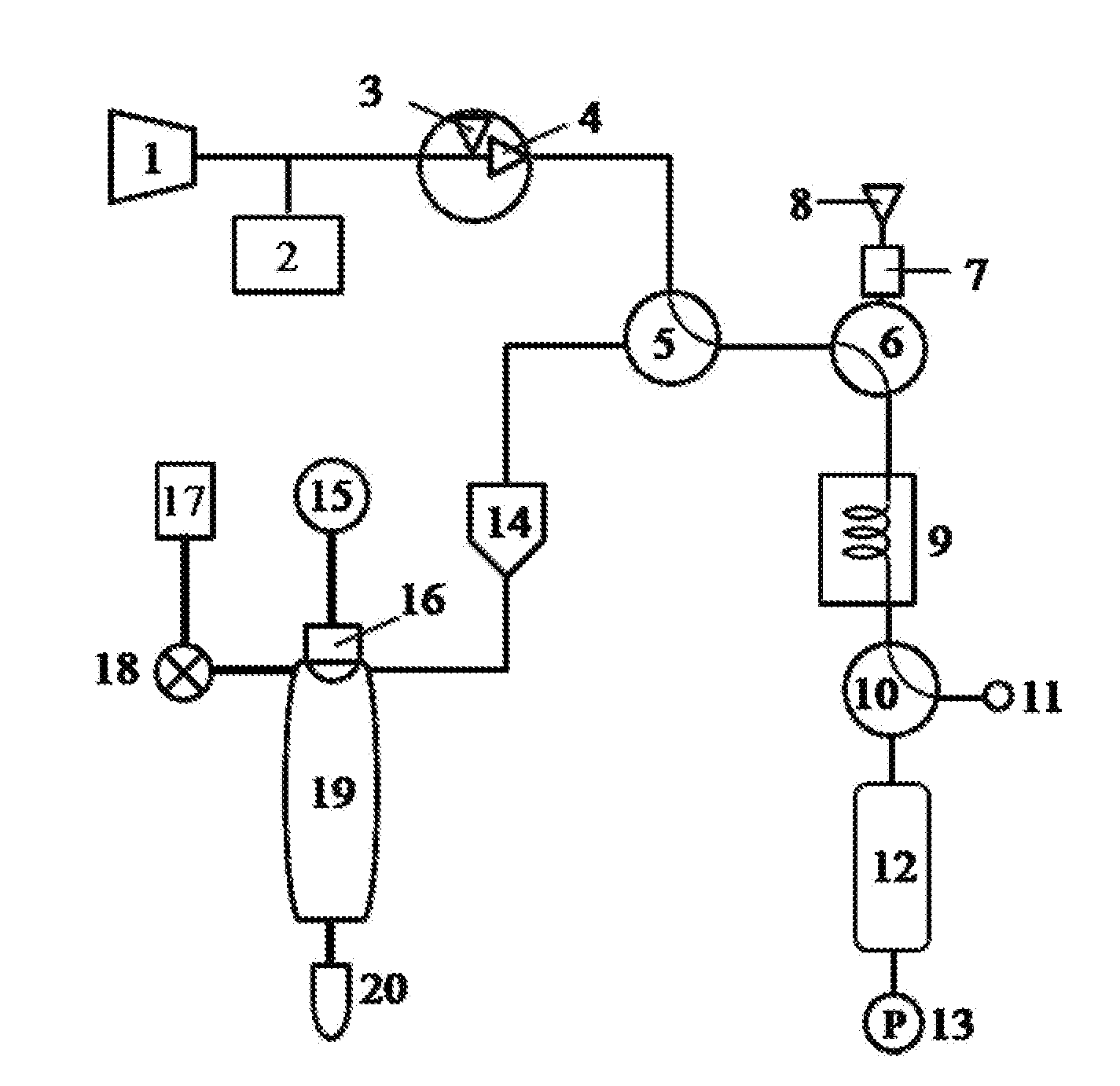
Integrated analysis device for simultaneously detecting ebcs and vocs in human exhaled breath
The present invention discloses an integrated analysis device for simultaneously detecting exhaled breath condensates (EBCs) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in human exhaled breath. The device comprises a module for sampling, separating and enriching a detected object, an EBCs detection module and a combined VOCs detection module. The module for sampling, separating and enriching a detected object is connected with the EBCs detection module via a syringe pump for sample injection. The module for sampling, separating and enriching a detected object is connected with the combined VOCs detection module by a capillary separation column. In the present invention, it is achieved that EBCs and VOCs in human exhaled breath are simultaneously sampled, separated and condensed; the heavy metal ions, cell factors, etc. in the collected EBCs are detected with a light addressable potentiometric sensor (LAPS); the condensed VOCs can be quantitatively detected by the combined VOCs detection module with a high sensitivity; and a heating rod and a platinum resistor can be conveniently replaced because a separated outlet heating piece is designed in the combined VOCs detection module.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
High pressure and high temperature chromatography
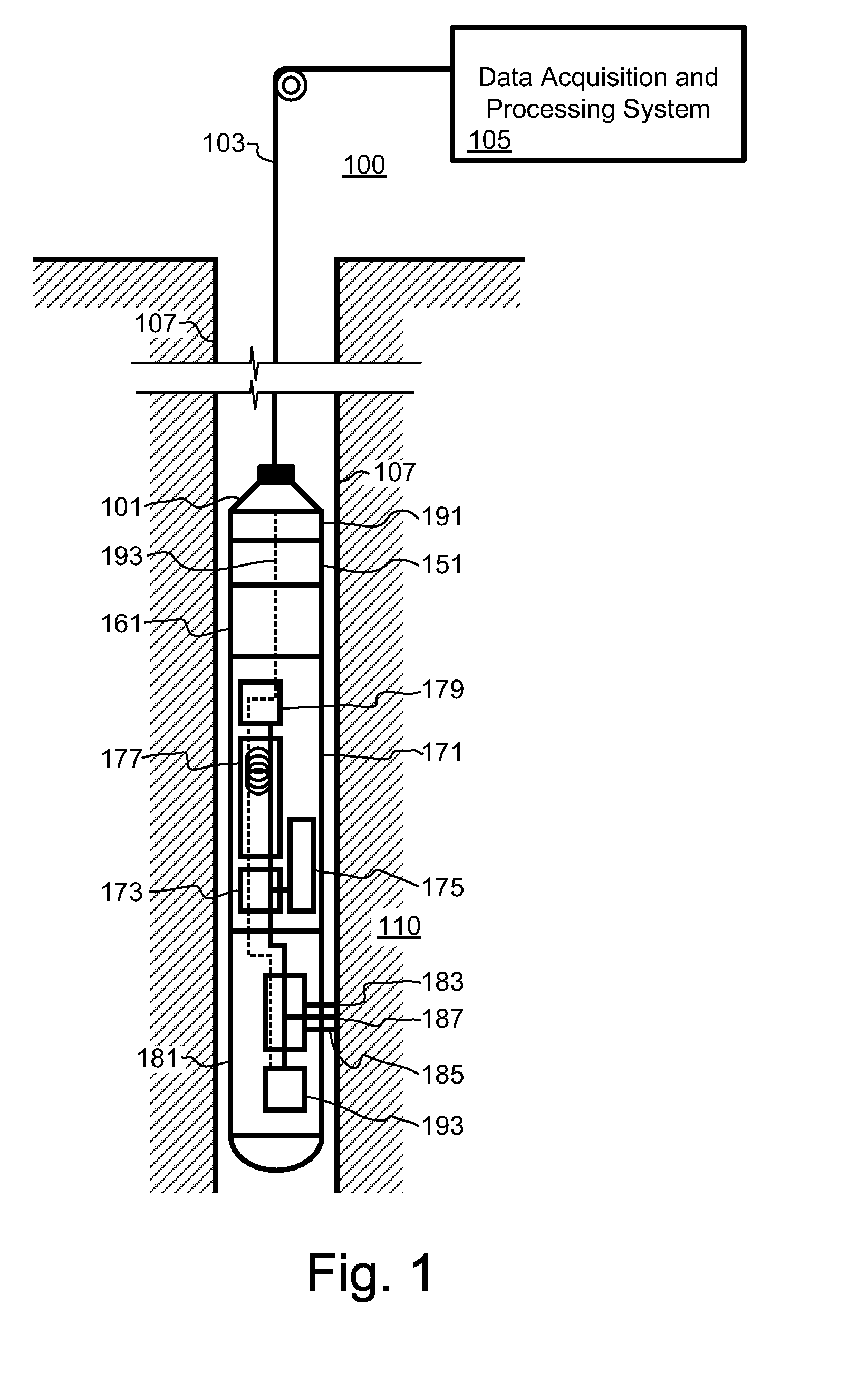
Methods and related systems are described for high pressure chromatographic analysis. The described system includes a flowpath adapted to flow a mobile phase and the sample at high pressures, an injector adapted to inject the fluid sample into a flowpath, a separation column adapted to operate at high pressures for separating various components, a detector and a processor that calculates the amount of at least one component of the fluid sample. The system can operate a pressures above 20 atm or even 100 atm, and temperatures above about 100 degrees Celsius. The system can deployed in a wellbore in a subterranean rock formation, and include fluid collection system for obtaining the fluid sample downhole. The system can also be located close to a wellhead and includes a tap in fluid communication with a surface flowline carrying produced fluids and the injector.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com