Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
667results about How to "Vibration minimization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
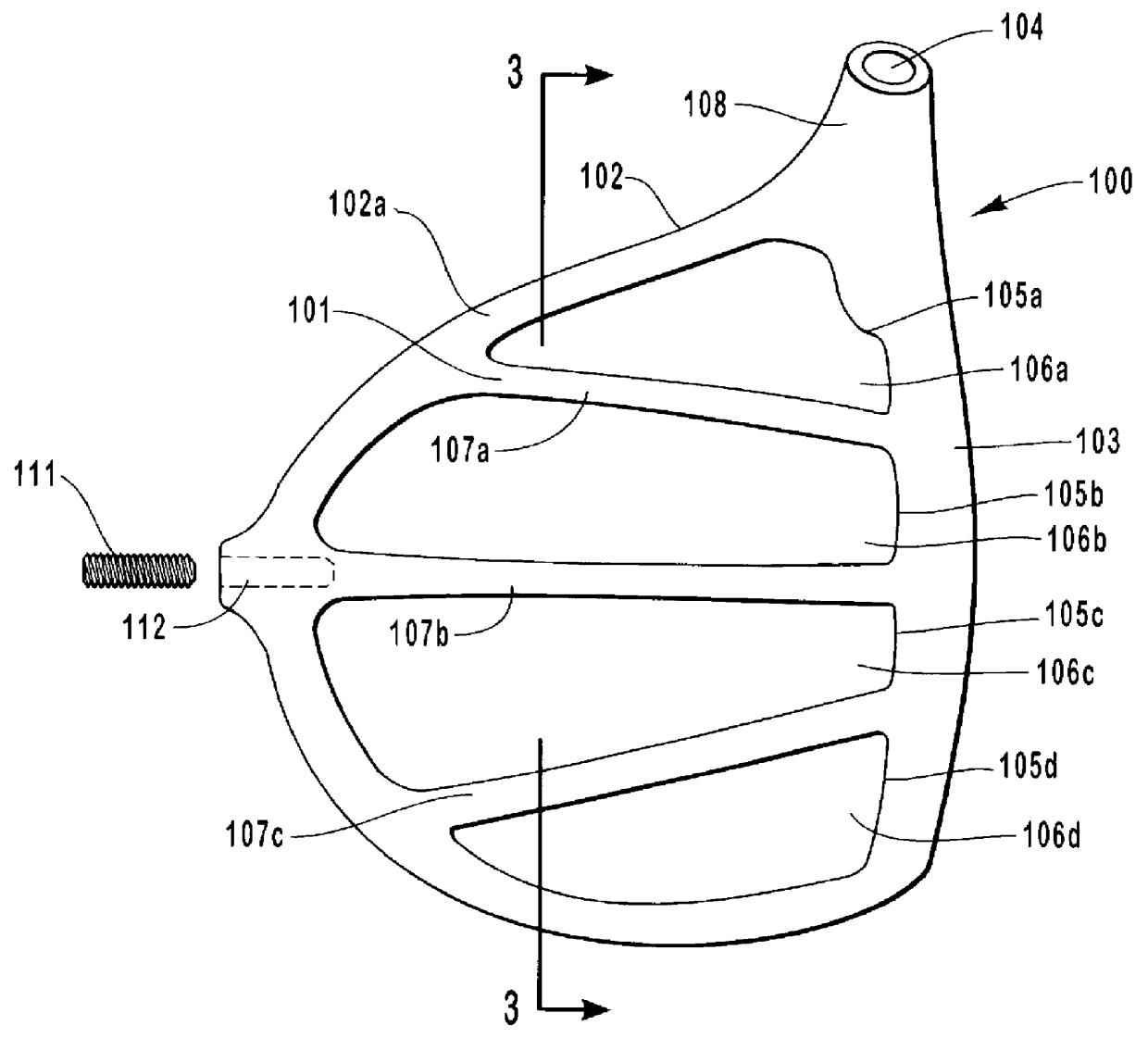
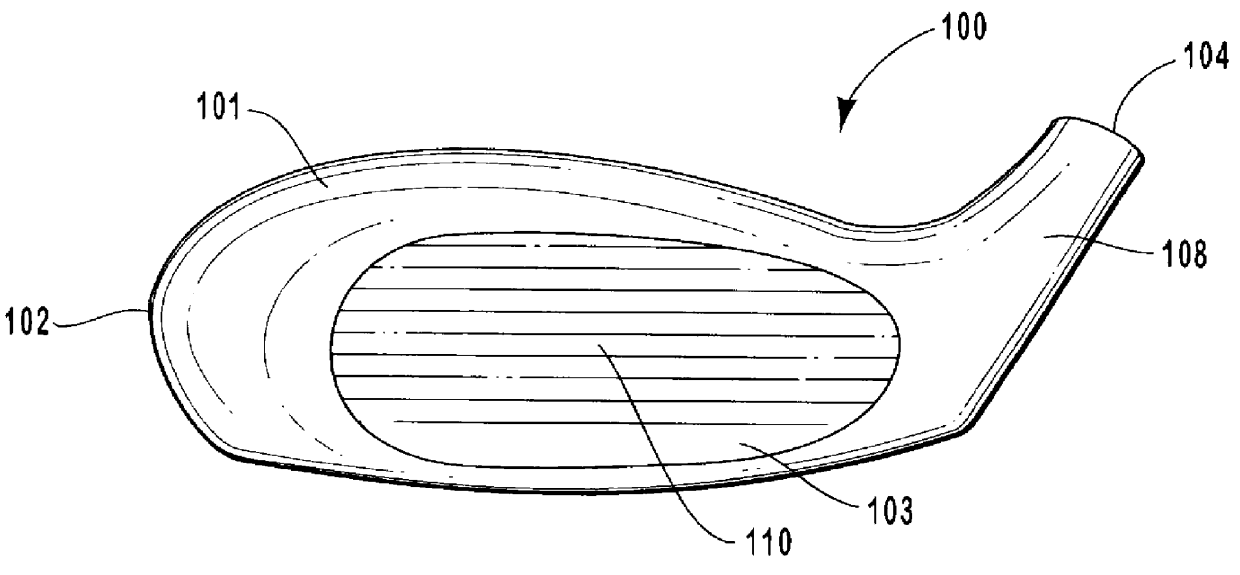
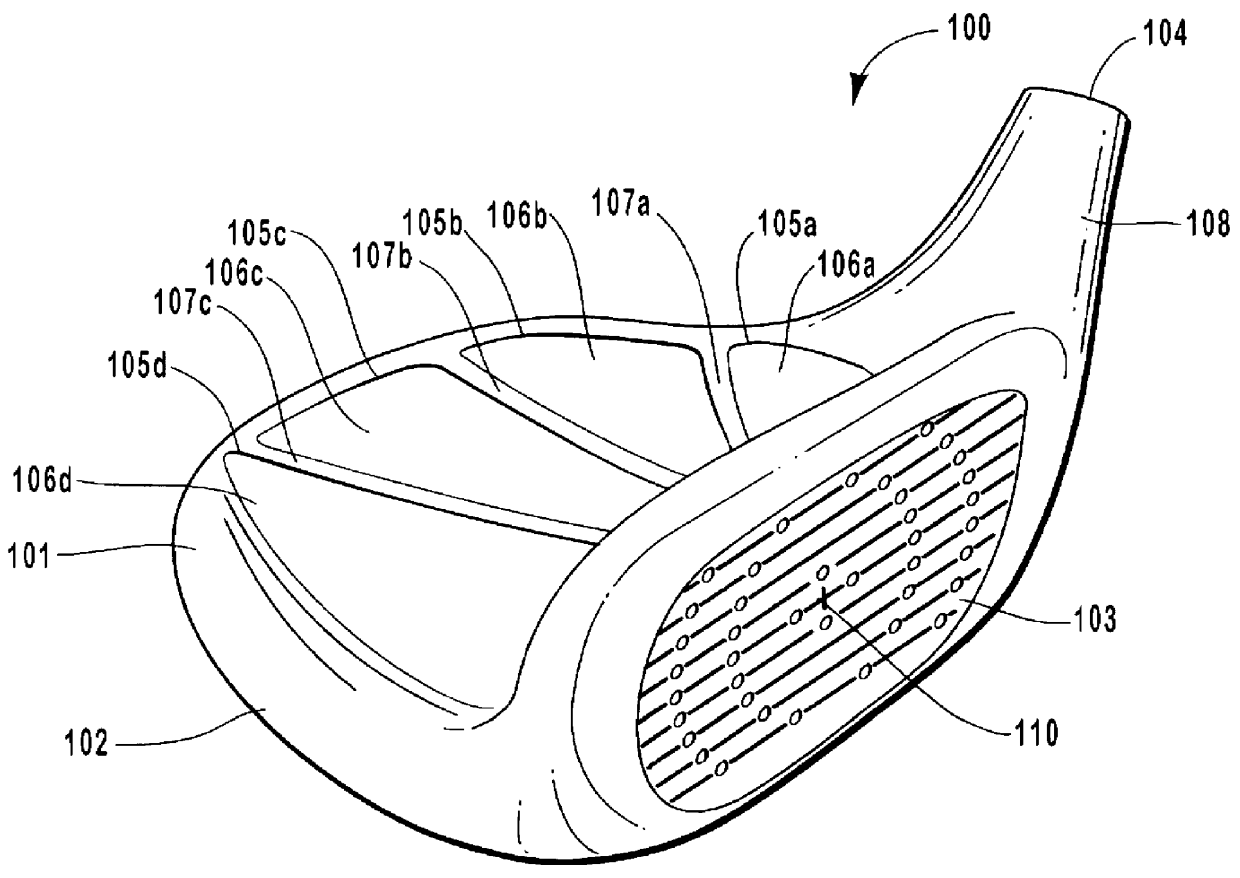
Golf club head having performance-enhancing structure
InactiveUS6059669AEconomical and labor-efficientGreat distance of ball flightGolf clubsRacket sportsFiberEngineering
A golf club that is preferably made from fiber-reinforced plastic composite by an injection molding process. The preferred golf club head includes a striking face for striking a golf ball, an outer periphery, a cavity formed between the outer periphery and the back of the striking face, a sole enclosing the bottom portion of said cavity, and at least one elongate power bar extending across the cavity from the striking face to the outer periphery. The sole is preferably integrally formed with the face plate and outer periphery. The cavity of the golf club head opens to the top of the club head. Each elongate power bar separates the cavity into receptacles. Inserts may be placed within the receptacles for aesthetic, aerodynamic, acoustic, and other purposes.
Owner:EDIZONE LC
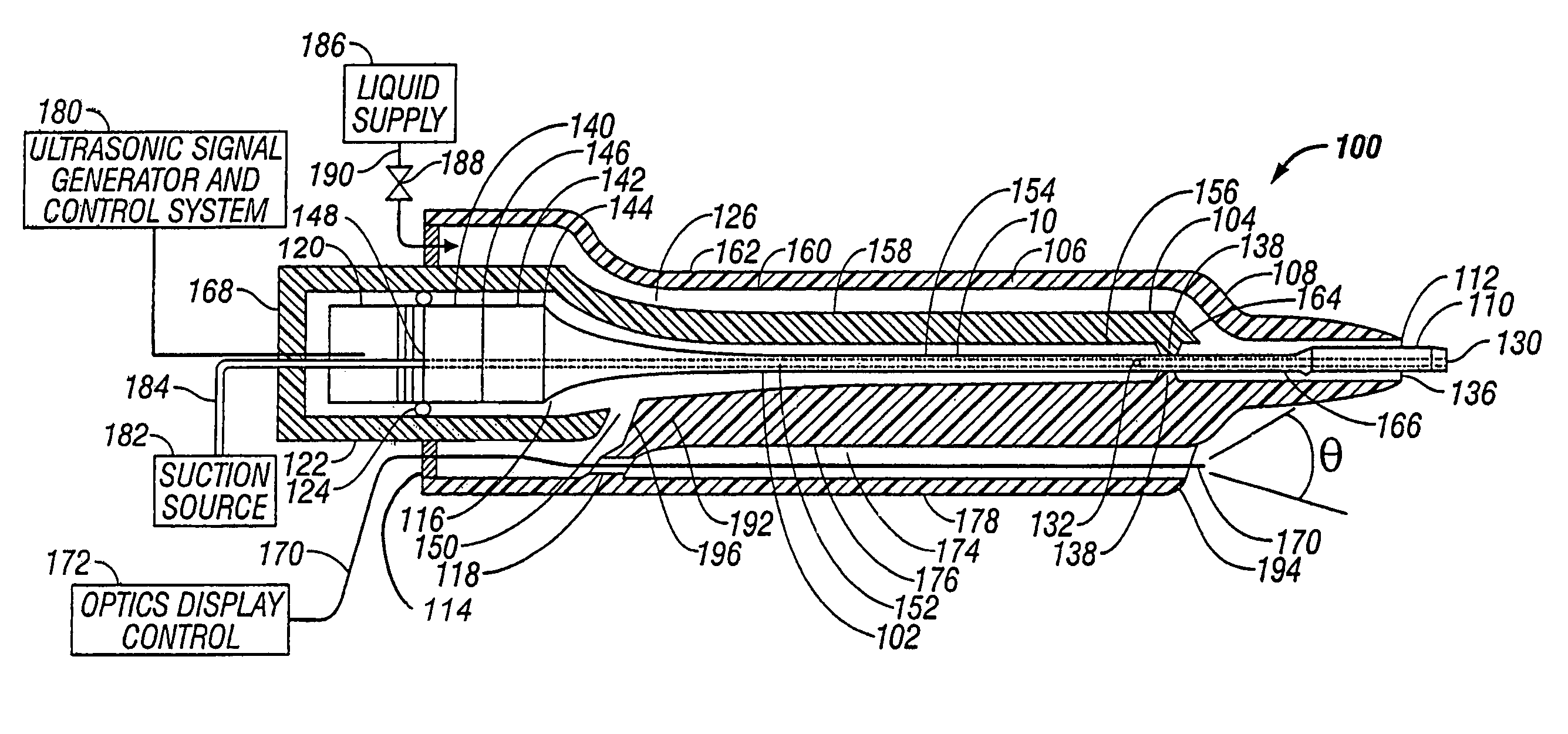
Endoscopic ultrasonic surgical aspirator for use in fluid filled cavities
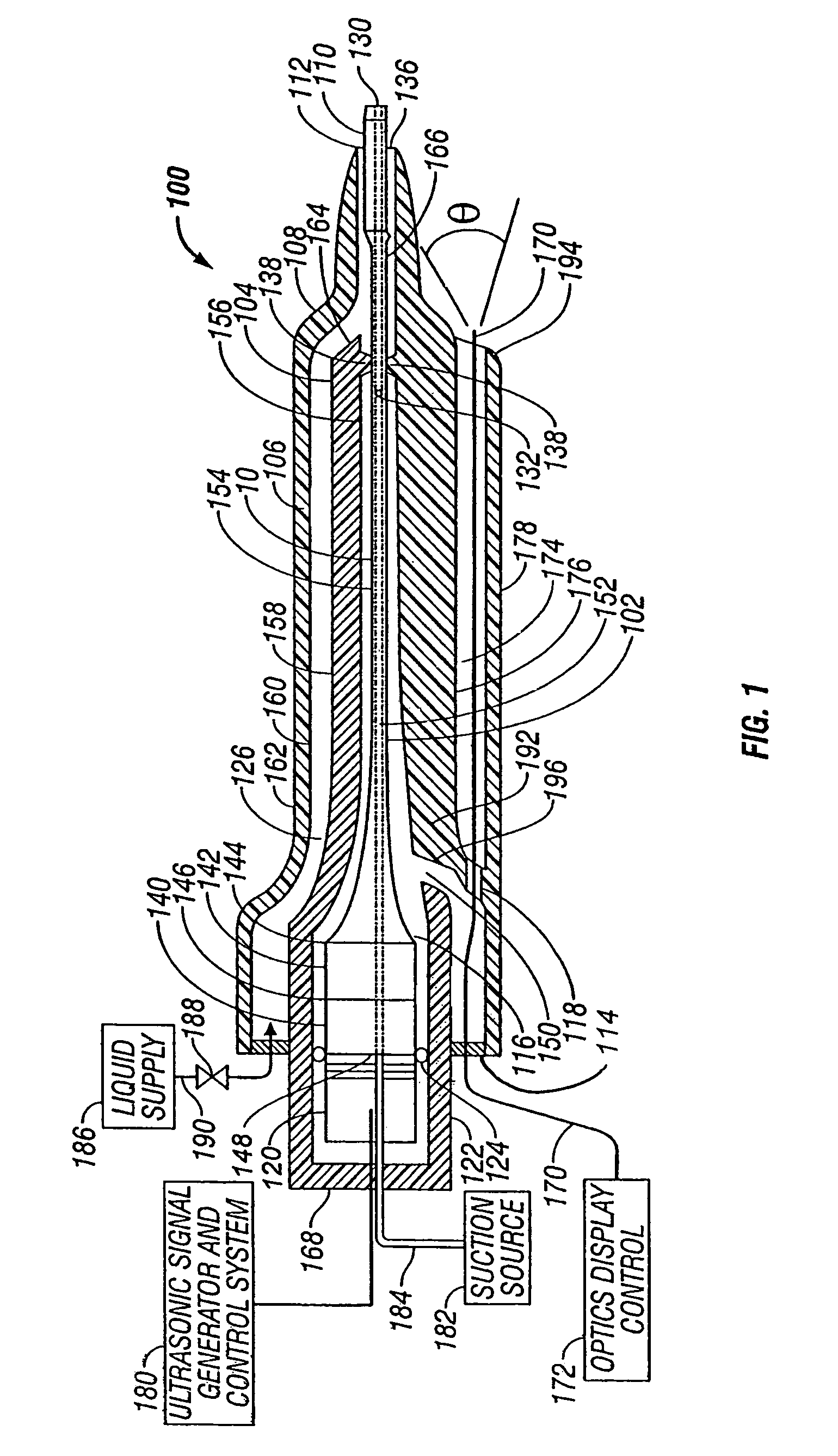
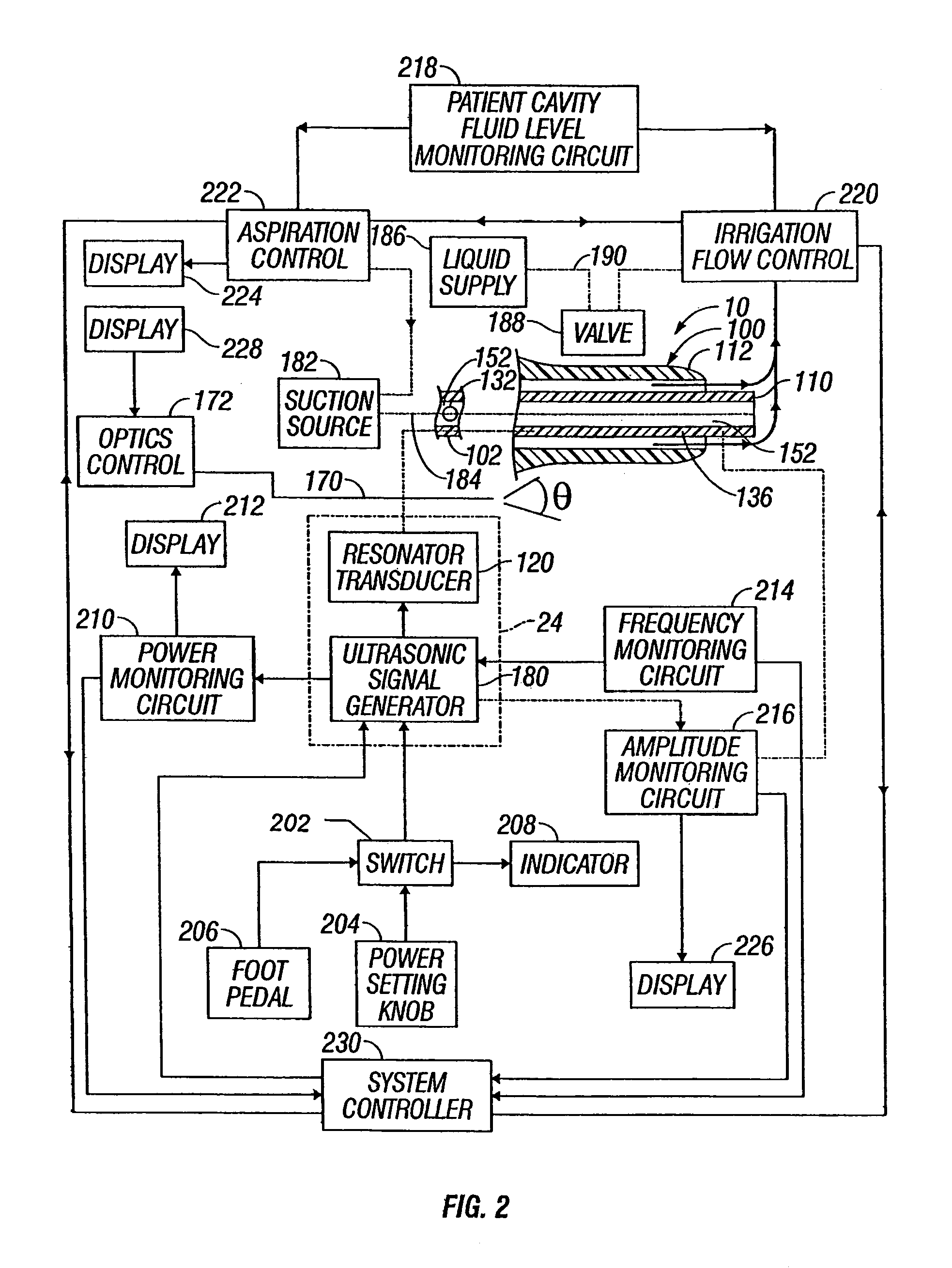
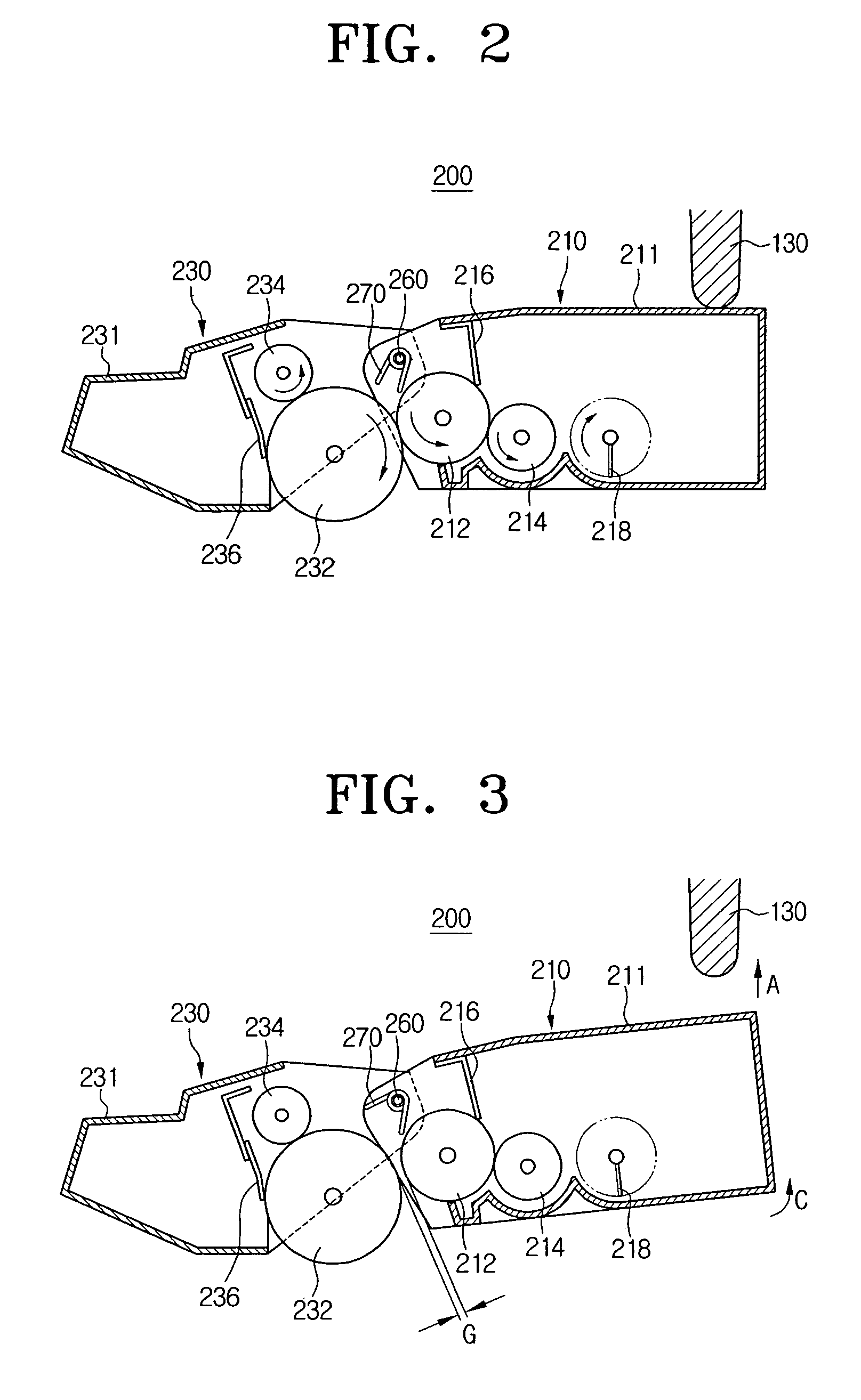
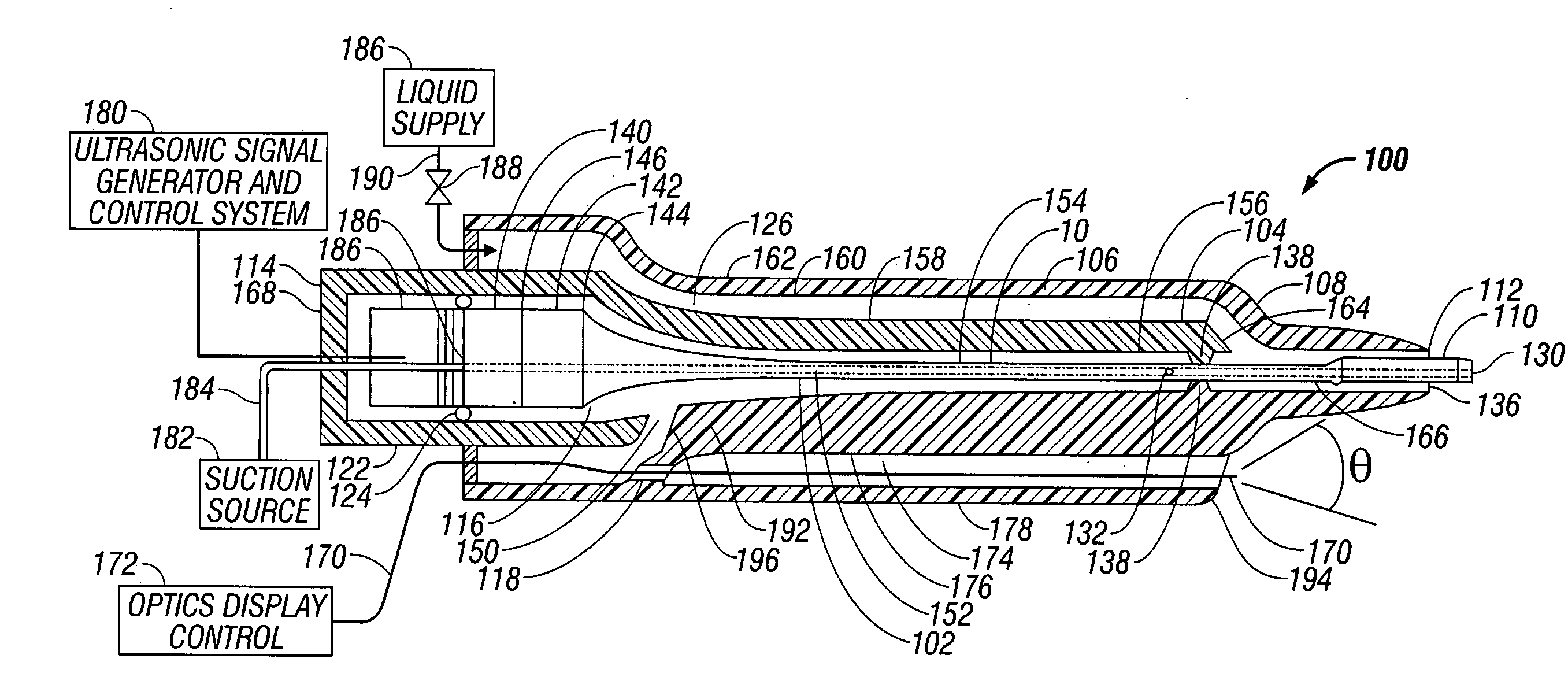
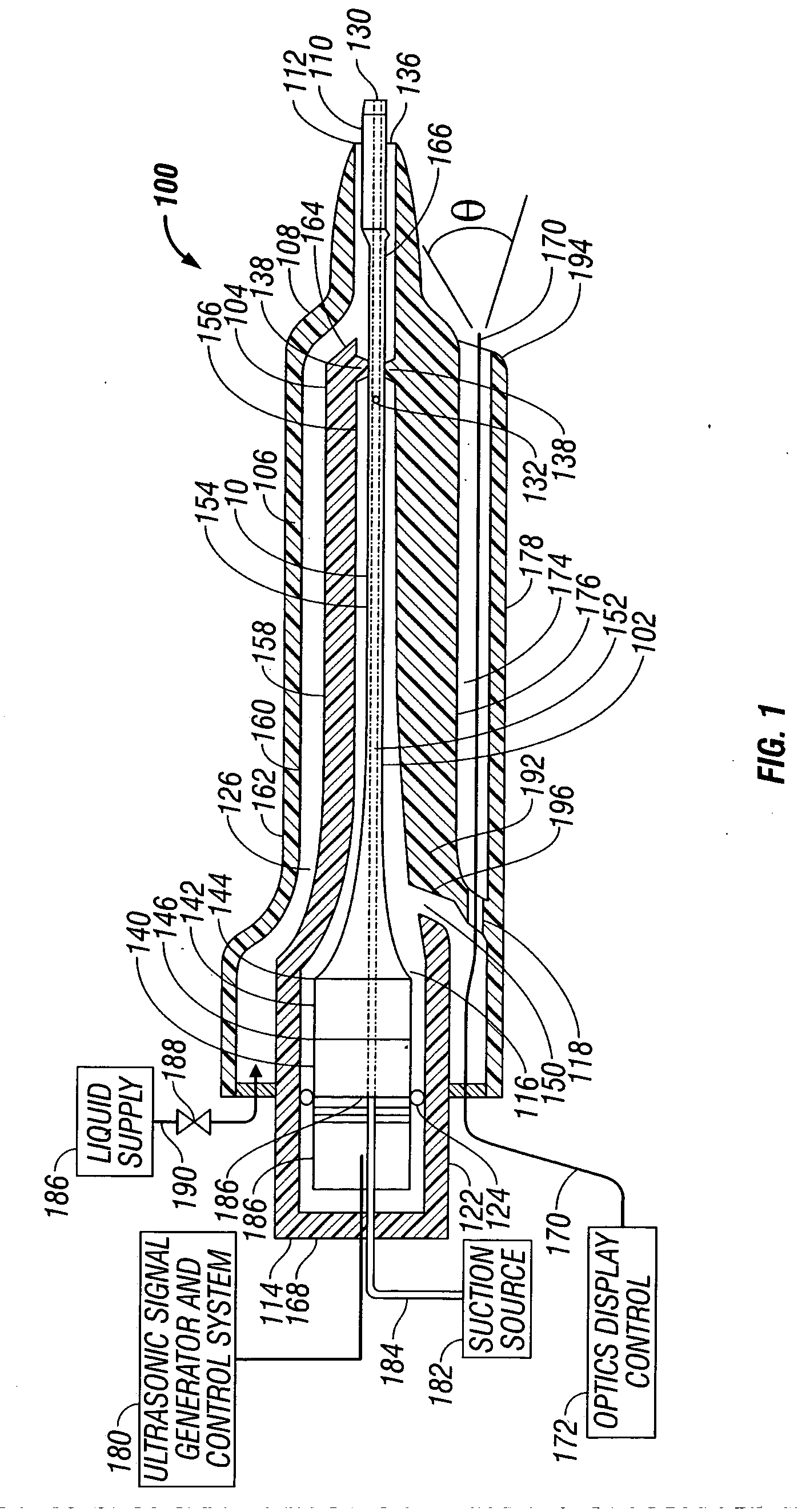
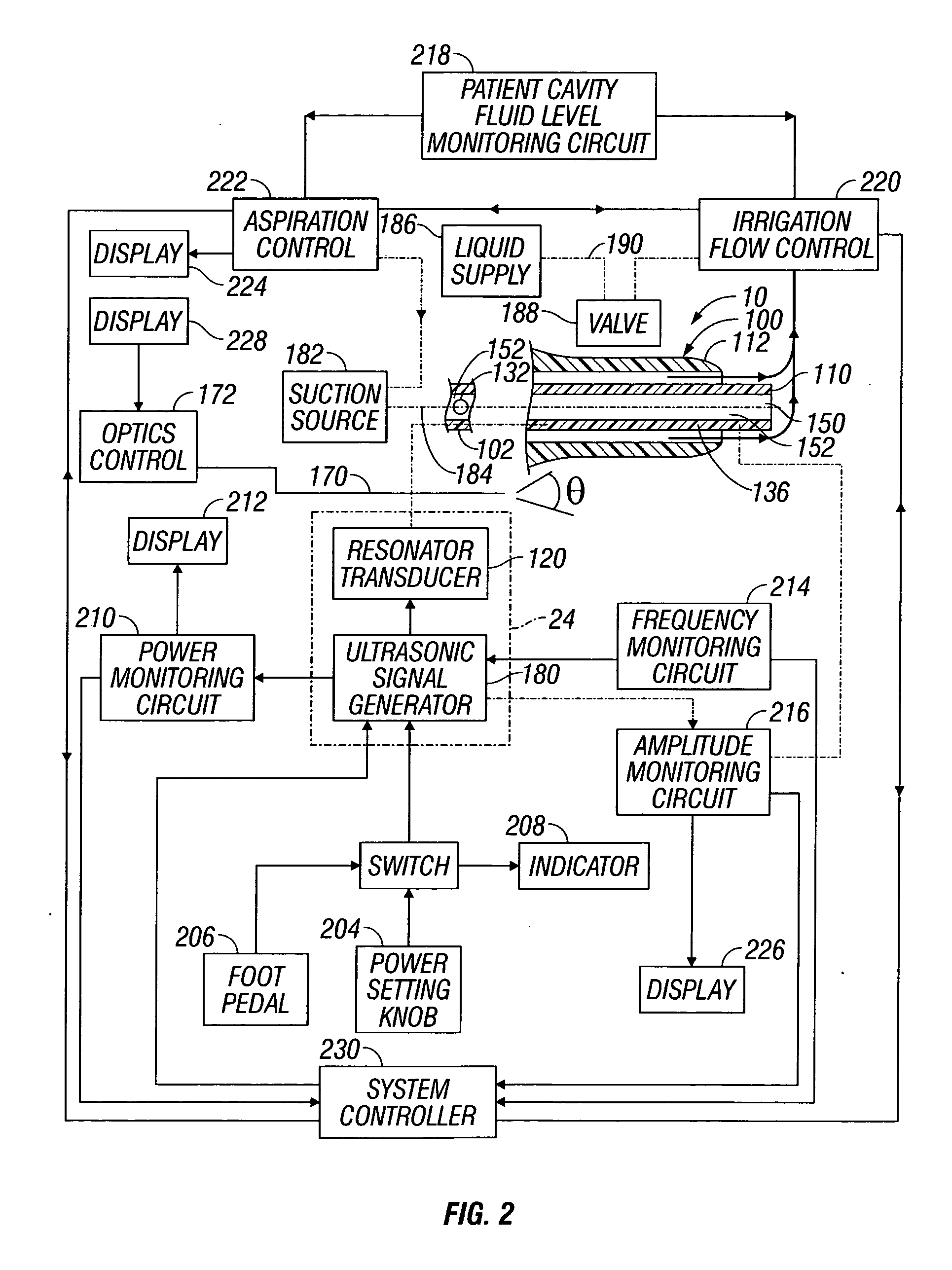
ActiveUS7871392B2Minimize damping vibrationVibration minimizationDiagnosticsSurgeryControl powerMedicine
An ultrasonic horn assembly is configured so that irrigating fluid can be supplied only to a vibrating tip portion of the ultrasonic horn and so that suction aspiration can occur through a portion of the ultrasonic horn not in contact with the irrigating fluid. Controllers supplying irrigation fluid during a surgical procedure and controlling suction aspiration via monitoring of fluid level in the patient cavity are operatively coupled one to another to coordinate control of the fluid level in the patient cavity. Circuitry controlling power, frequency and amplitude of the tip of the ultrasonic horn occurring as a result of operation of a source of ultrasonic signal generating power controls either or both the supply of irrigation fluid and the suction aspiration so as to minimize damping of vibration of the tip of the ultrasonic horn. An optical viewing element is provided to view the tip of the ultrasonic horn.
Owner:INTEGRA LIFESCI IRELAND
Image forming apparatus
InactiveUS20060034637A1Noise minimizationVibration minimizationElectrographic process apparatusImage formationEngineering
Owner:S PRINTING SOLUTION CO LTD
Endoscopic ultrasonic surgical aspirator for use in fluid filled cavities
ActiveUS20070162050A1Minimize damping vibrationVibration minimizationDiagnosticsSurgeryControl powerMedicine
An ultrasonic horn assembly is configured so that irrigating fluid can be supplied only to a vibrating tip portion of the ultrasonic horn and so that suction aspiration can occur through a portion of the ultrasonic horn not in contact with the irrigating fluid. Controllers supplying irrigation fluid during a surgical procedure and controlling suction aspiration via monitoring of fluid level in the patient cavity are operatively coupled one to another to coordinate control of the fluid level in the patient cavity. Circuitry controlling power, frequency and amplitude of the tip of the ultrasonic horn occurring as a result of operation of a source of ultrasonic signal generating power controls either or both the supply of irrigation fluid and the suction aspiration so as to minimize damping of vibration of the tip of the ultrasonic horn. An optical viewing element is provided to view the tip of the ultrasonic horn.
Owner:INTEGRA LIFESCI IRELAND
Device and method for mounting a turbine engine
InactiveUS20090064685A1Reduce vibrationVibration minimizationPortable framesPump componentsTurbineGas turbines
A device and a method for mounting a turbine engine, e.g., a gas turbine system, are described, in which a rotor unit is mounted to rotate inside a stationary external housing, having at least two supports for taking up the weight of the turbine engine, these supports being arranged at a spacing from one another in an axial longitudinal direction in relation to the external housing and at one side being articulated directly or indirectly on the external housing and at the other being supported directly or indirectly on a base frame. At least one support provides at least one support face which is supported exclusively in partial regions on at least two support plate elements. The at least one support face of the support is in operational engagement with the base frame by way of the support plate elements.
Owner:ANSALDO ENERGIA IP UK LTD
Cuvette for flow-type particle analyzer
ActiveUS8233146B2Easy to replaceVibration minimizationWithdrawing sample devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansCuvettePhysics
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
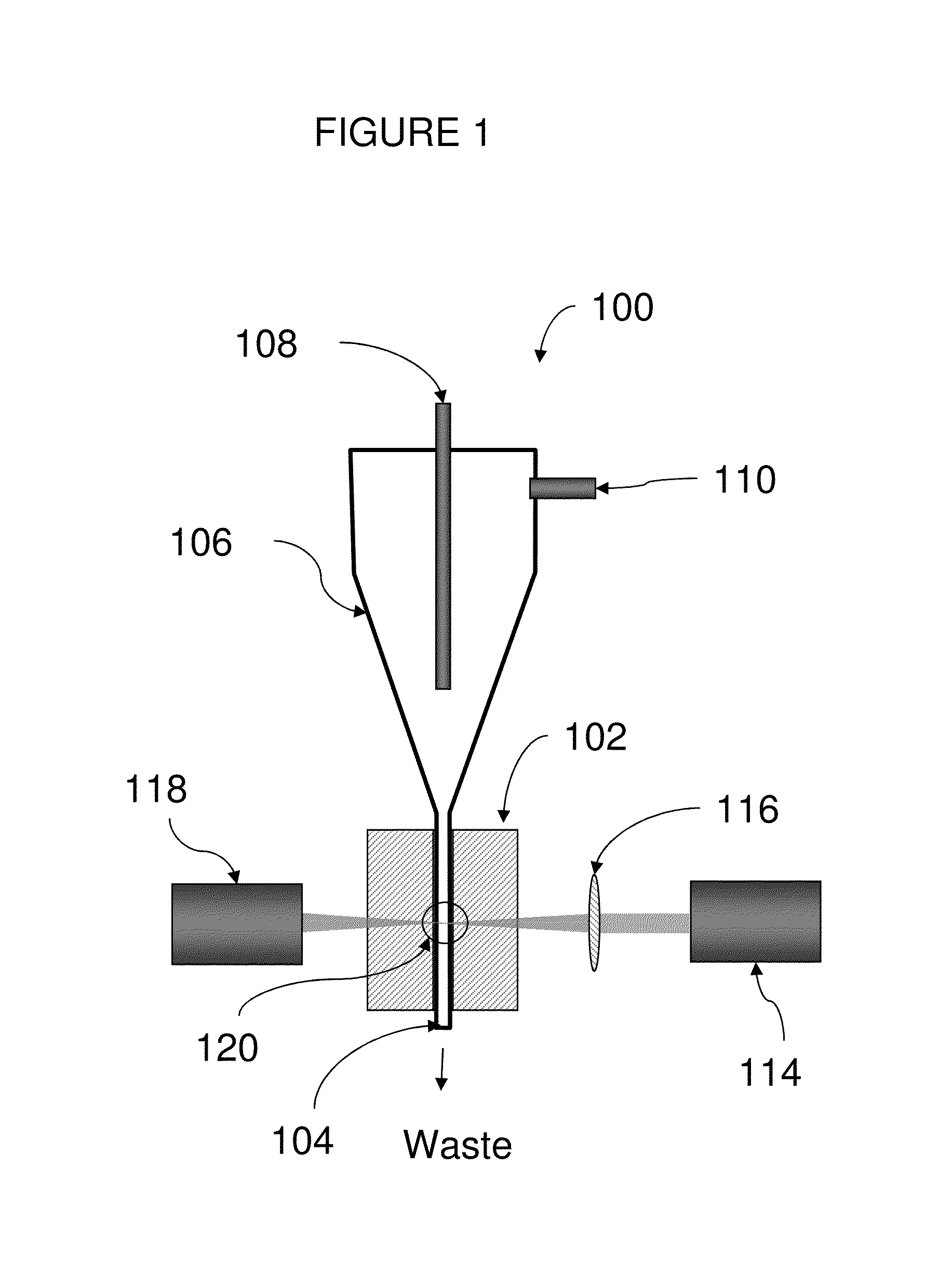
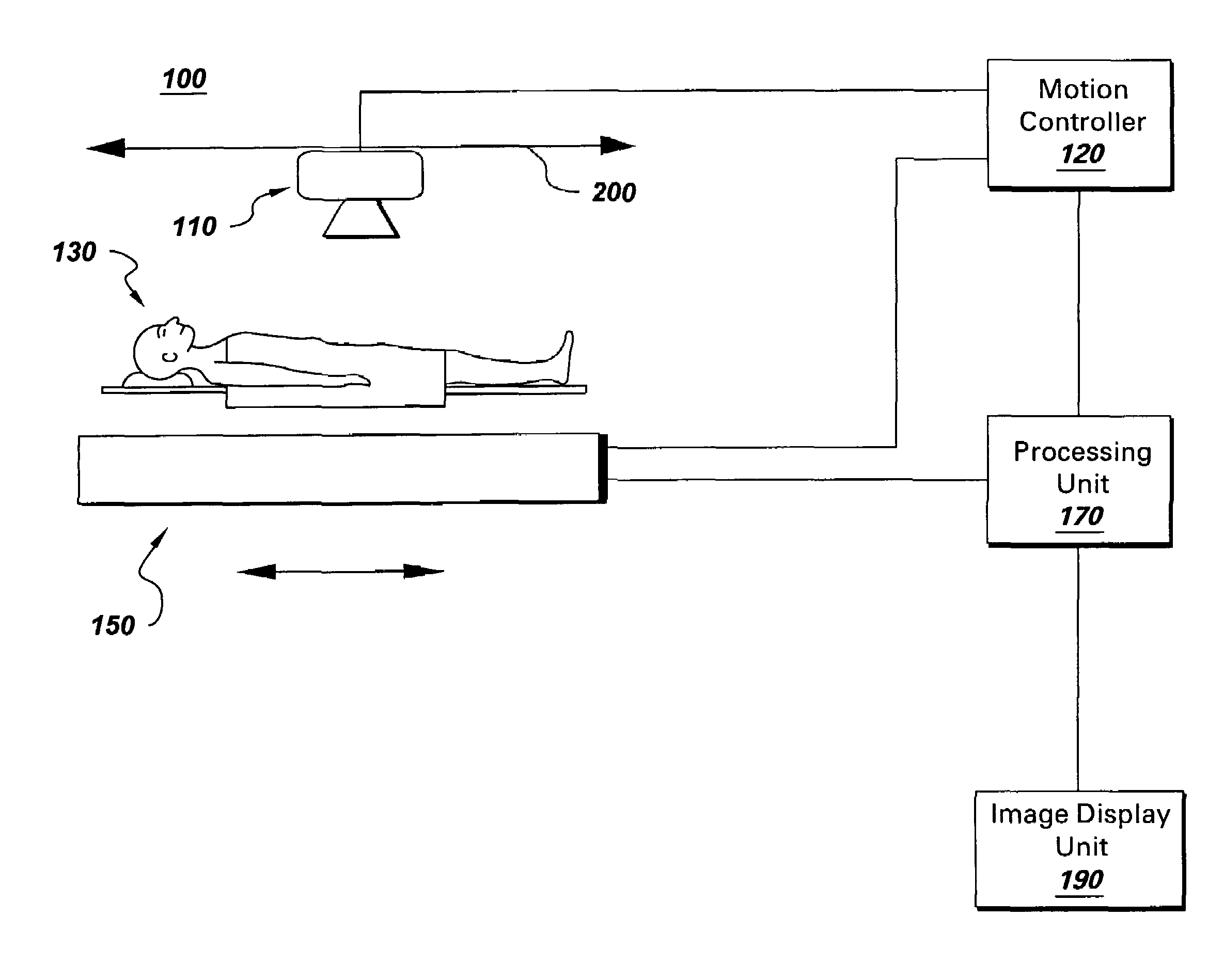
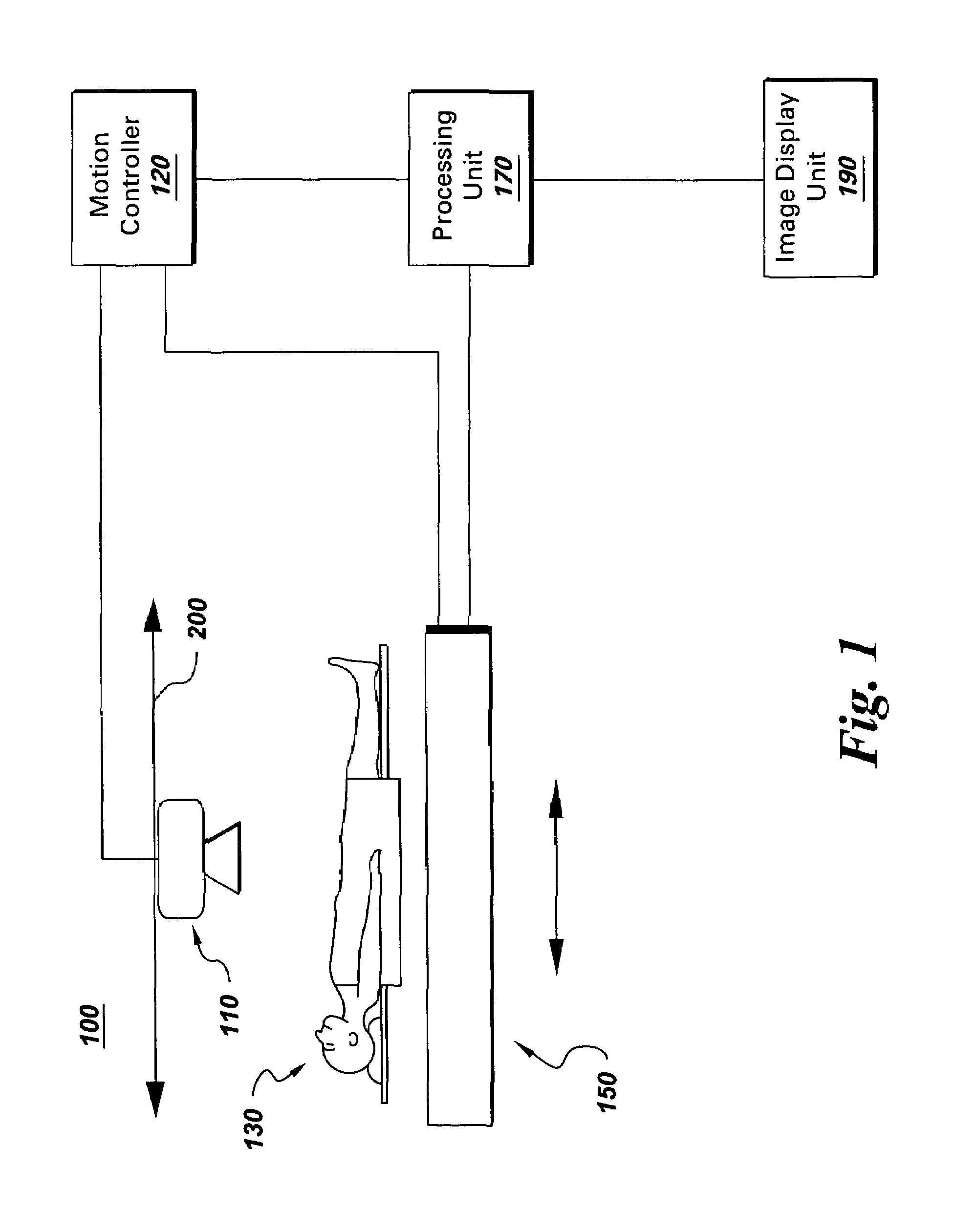
Continuous scan RAD tomosynthesis system and method
InactiveUS6970531B2Vibration minimizationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingSoft x rayTomosynthesis
An imaging system for performing tomosynthesis on a region of an object comprises an x-ray source, motion controller, an x-ray detector and a processing unit. The x-ray source is positioned at a predetermined distance from the object and continuously moves along a linear path relative to the object. The x-ray source transmits x-ray radiation through the region of the object at a plurality of predetermined locations. The motion controller is coupled to the x-ray source and continuously moves the x-ray source along the path relative to the object. The x-ray source minimizes vibration in the imaging system due to continuous movement. The x-ray detector is positioned at a predetermined distance from the x-ray source and detects the x-ray radiation transmitted through the region of the object, thus acquiring x-ray image data representative of the region of the object. The processing unit is coupled to the x-ray detector for processing the x-ray image data into at least one tomosynthesis image of the region of the object.
Owner:DUKE UNIV +1
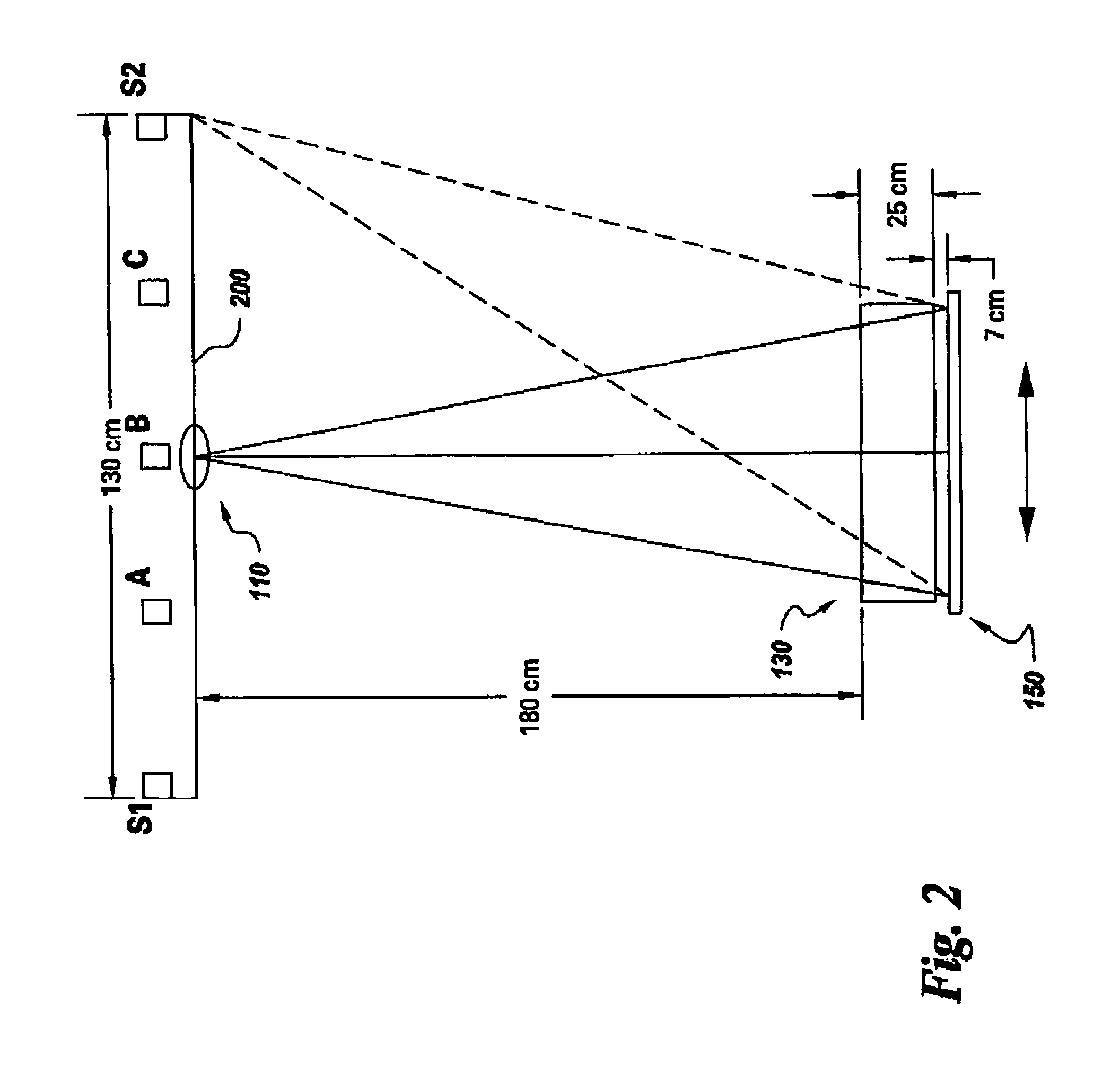
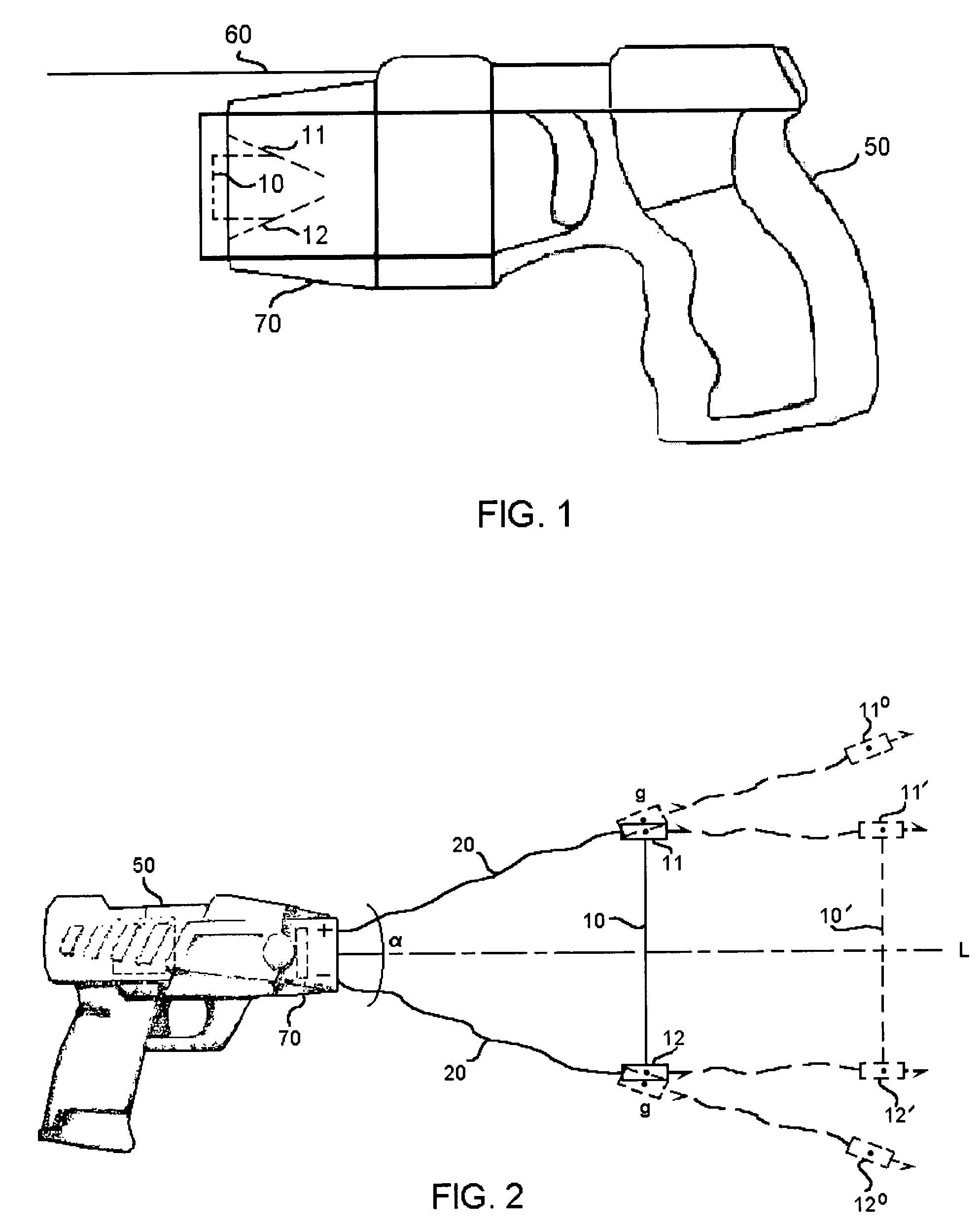
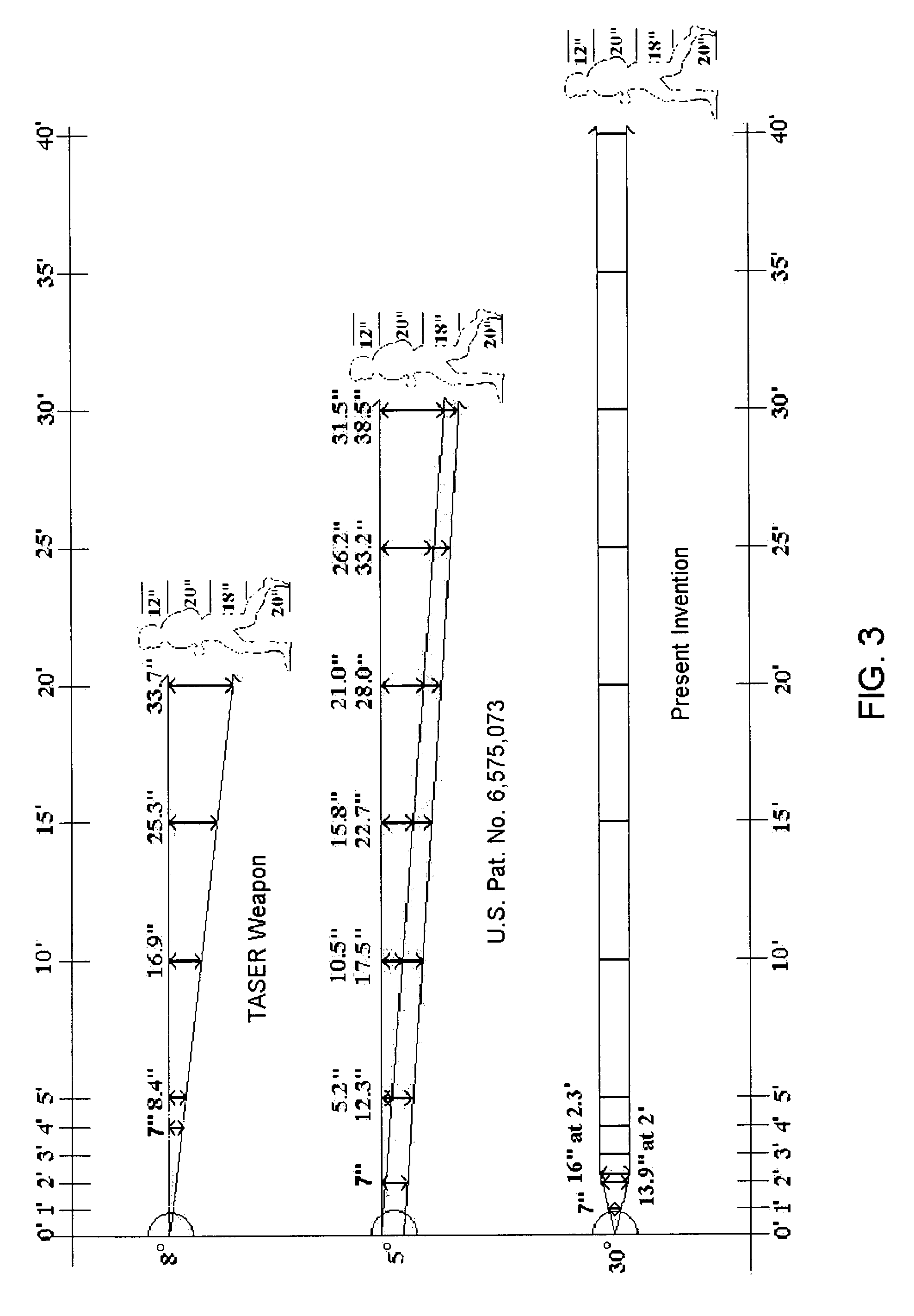
Apparatus and method for electrical immobilization weapon
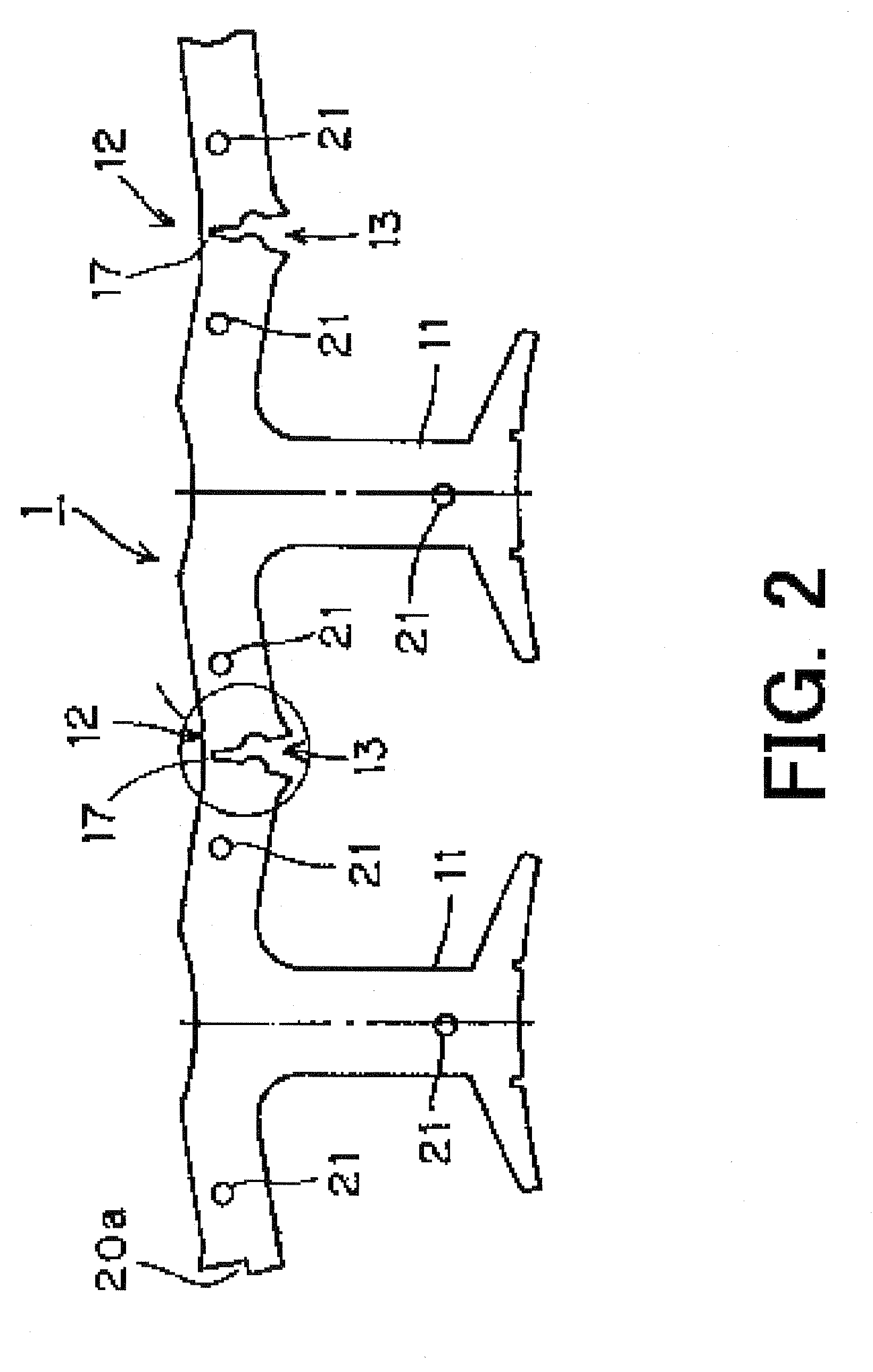
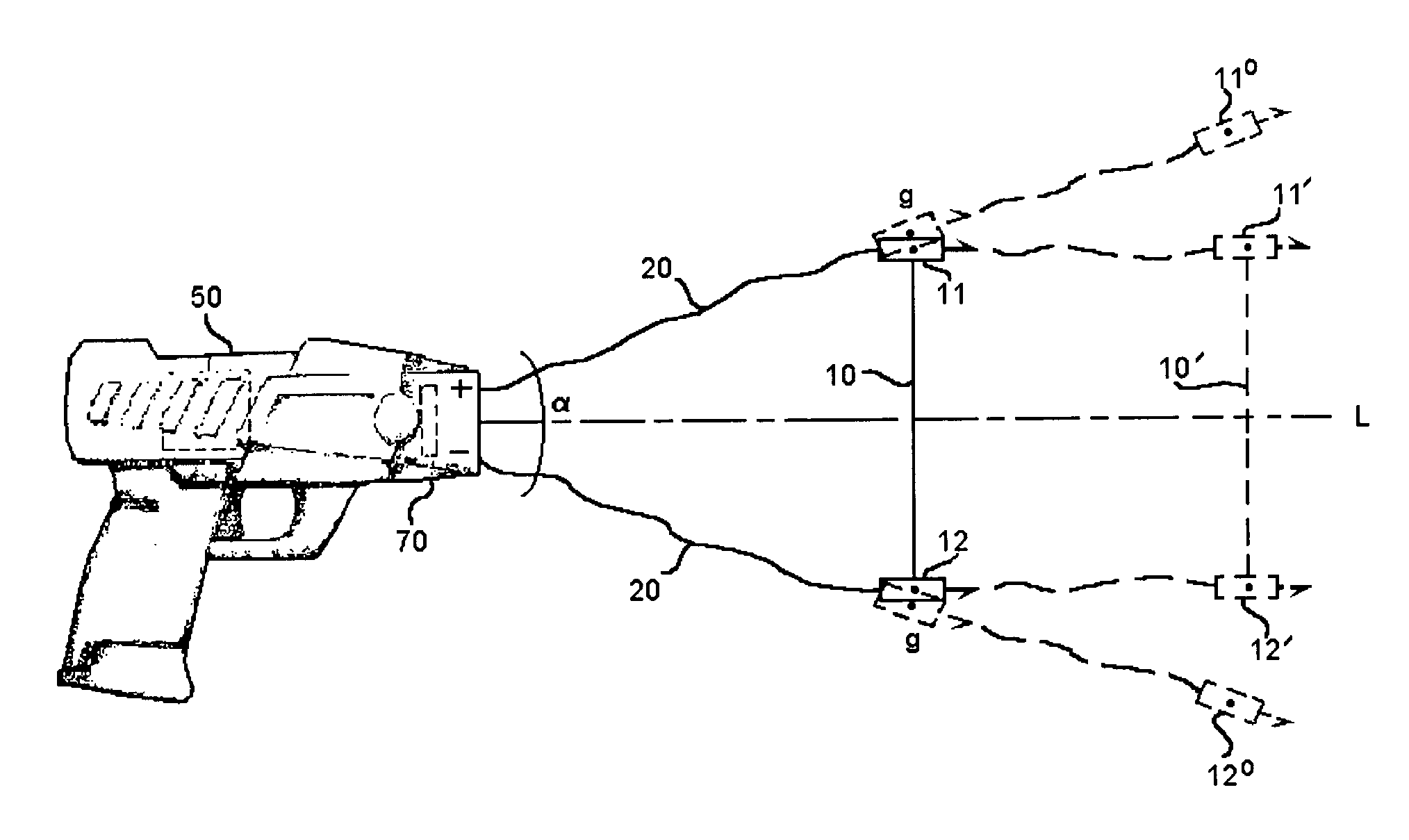
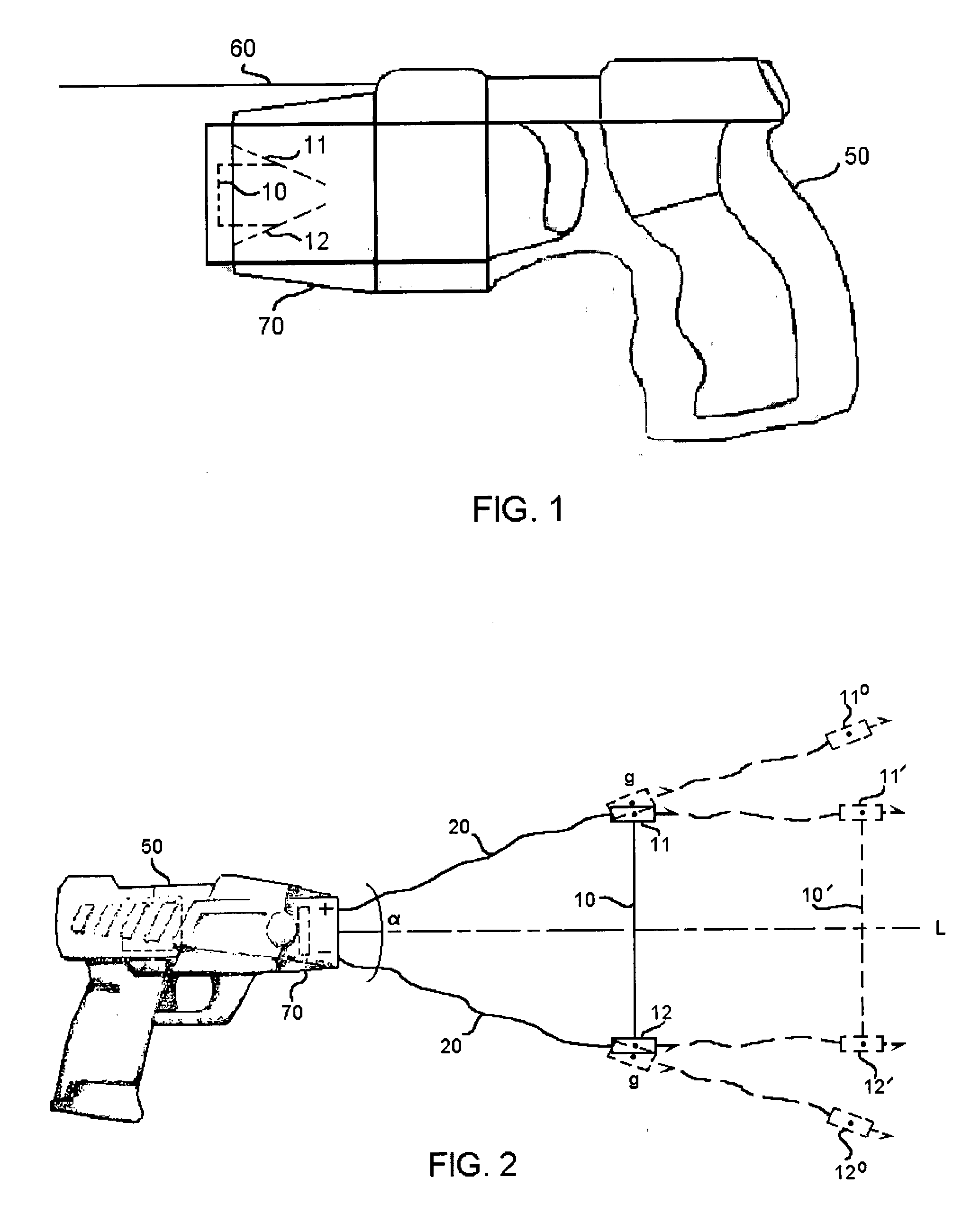
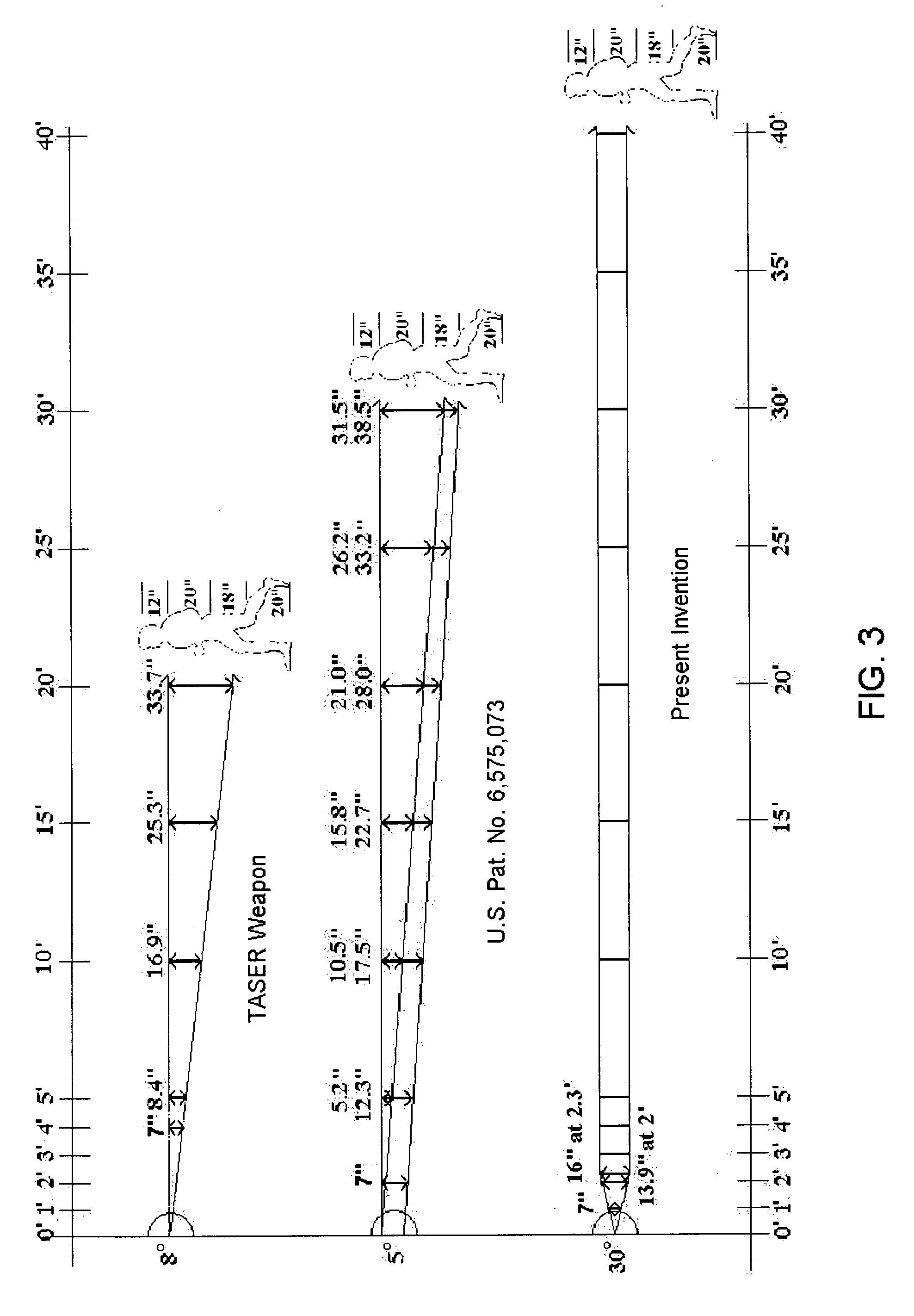
ActiveUS7314007B2Suitable for useEffective shooting rangeAmmunition projectilesElectric shock equipmentsInvolved musclesTaser
An electrical immobilization weapon having a prolonged range of effectiveness and improved accuracy compared to conventional Taser weapons, while being compact in structure and lightweight. The weapon having a replaceable cartridge which, when employed, can space a pair of electrodes to a specific critical area on a remote target, so the electrical energy carried by the electrodes can induce the involuntary contraction of the involved muscles through the critical area within a significant range of length between the electrodes for effective immobilization. The electrical energy generated by a power source of the weapon completes an electrical circuit through a minimum path being a length of at least 5 inches between the two points on the target.
Owner:VOLGER INT AB
Method and apparatus for monitoring load size and load imbalance in washing machine
InactiveUS20060242768A1Vibration minimizationOther washing machinesControl devices for washing apparatusHorizontal axisEngineering
A method of determining static and dynamic imbalance conditions in a horizontal axis washing machine is disclosed. The method utilizes a number of algorithms to automatically determine the total load size, the magnitude of any static load imbalance, and the magnitude of any dynamic load imbalance for any given load in a given washing machine based on power measurements from the washing machine motor. Methods of obtaining the algorithms for the given washing machine are disclosed.
Owner:WHIRLPOOL CORP
Centrifuge assembly
InactiveUS20070004577A1Minimizes detrimental forceExtend motor lifeCentrifugesAir managementMotor drive
A centrifuge system includes a drive motor mounted independently relative to a sample carrier to eliminate detrimental forces born by a motor drive shaft. The rotatable sample carrier or tray includes a rotating center operably connected to the drive motor. The drive motor cooperates with a resilient mounting system enabling self-centering, force and vibration compensation, and improving motor life. The rotatable sample tray and a sample tube holder have respective operably cooperative contoured surfaces enabling relative smooth pivoting motion in the sample tube holder during rotation, while minimizing sample vibration, and improving the desired sample separation while minimizing sample remixing. An air management system enables effective motor cooling and minimizes sample heating.
Owner:CENTURION LLC
Control Modes for Extendable Rotor Blades
InactiveUS20100158687A1Maximize incomeReduce paymentPropellersRotary propellersAccelerometerEngineering
A wind turbine may be controlled in a variety of manners to optimize operating parameters. In one arrangement, for example, the length or the pitch of a wind turbine rotor blade may be adjusted to avoid harmonic resonance frequencies. In another example, the length of a rotor blade may be modified to reduce noise or to optimize profits or both. The controls may be based on data from various types of sensors including accelerometers, sound meters, strain gauges and the like. Actuation of extendable rotor blades can rotate wind turbine rotors without wind or generator pulsing affording multiple advantages. A battery test control may also be used to determine the operational readiness of a battery useful for a variety of purposes in a turbine.
Owner:FRONTIER WIND LLC
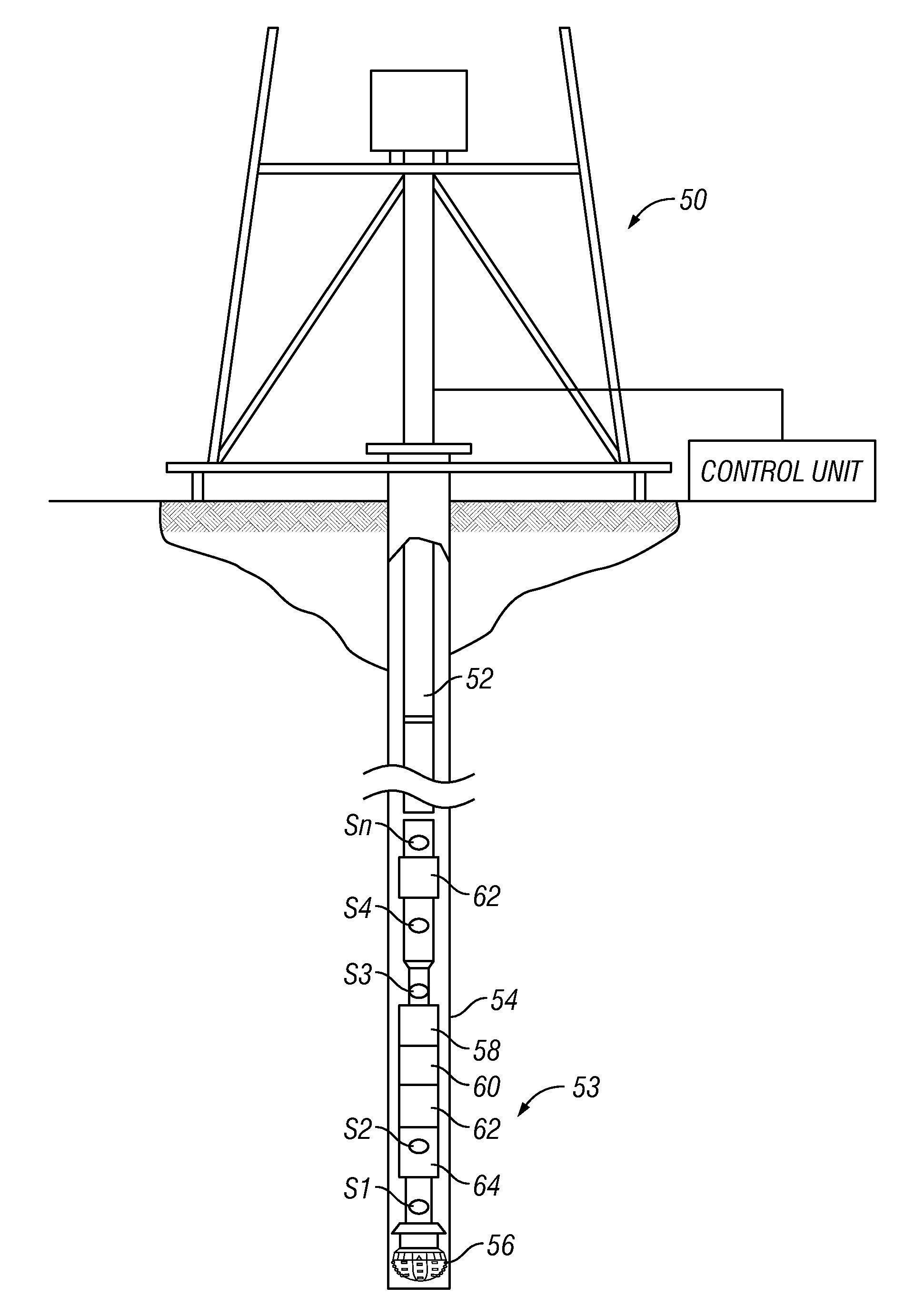
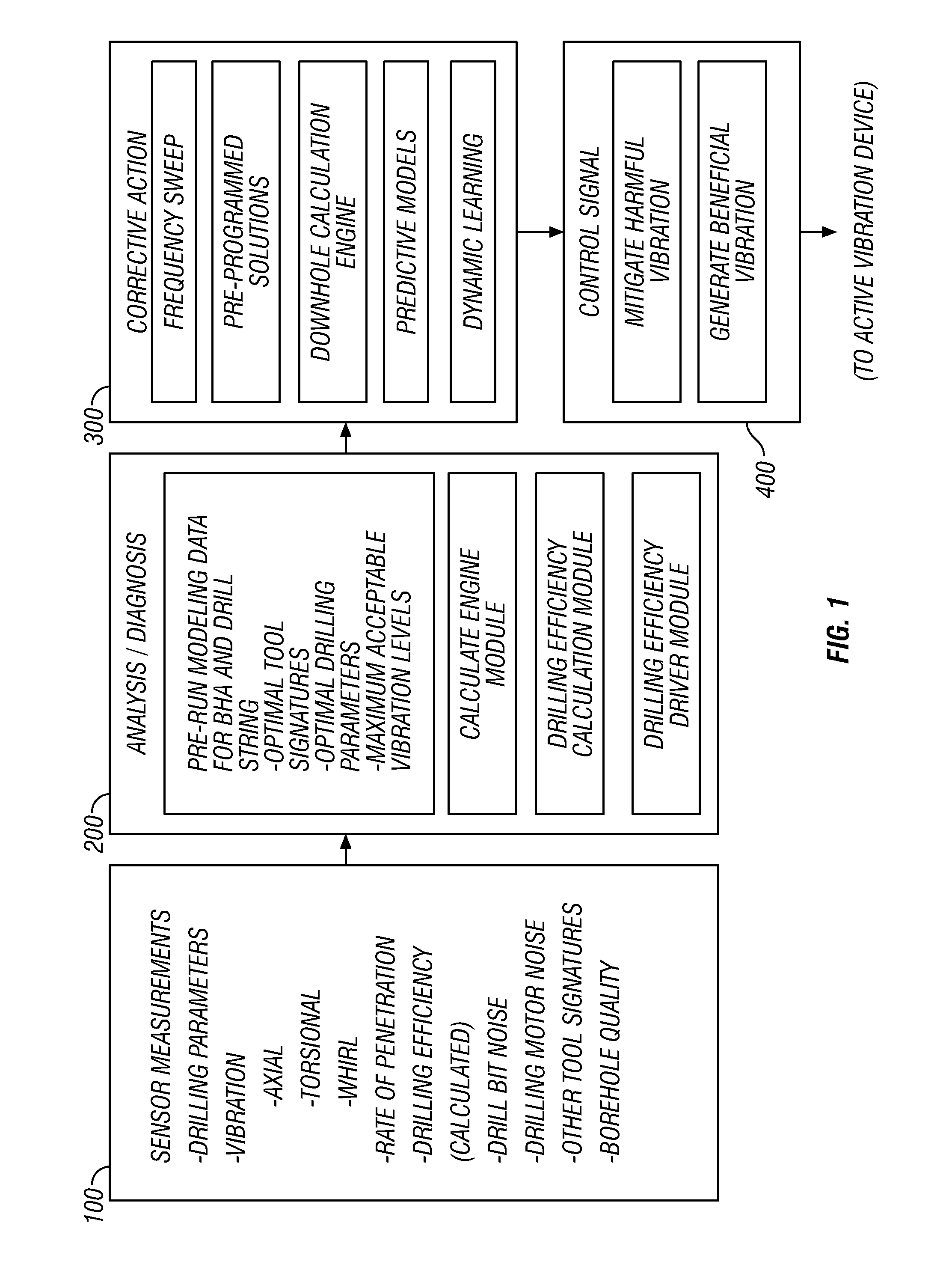
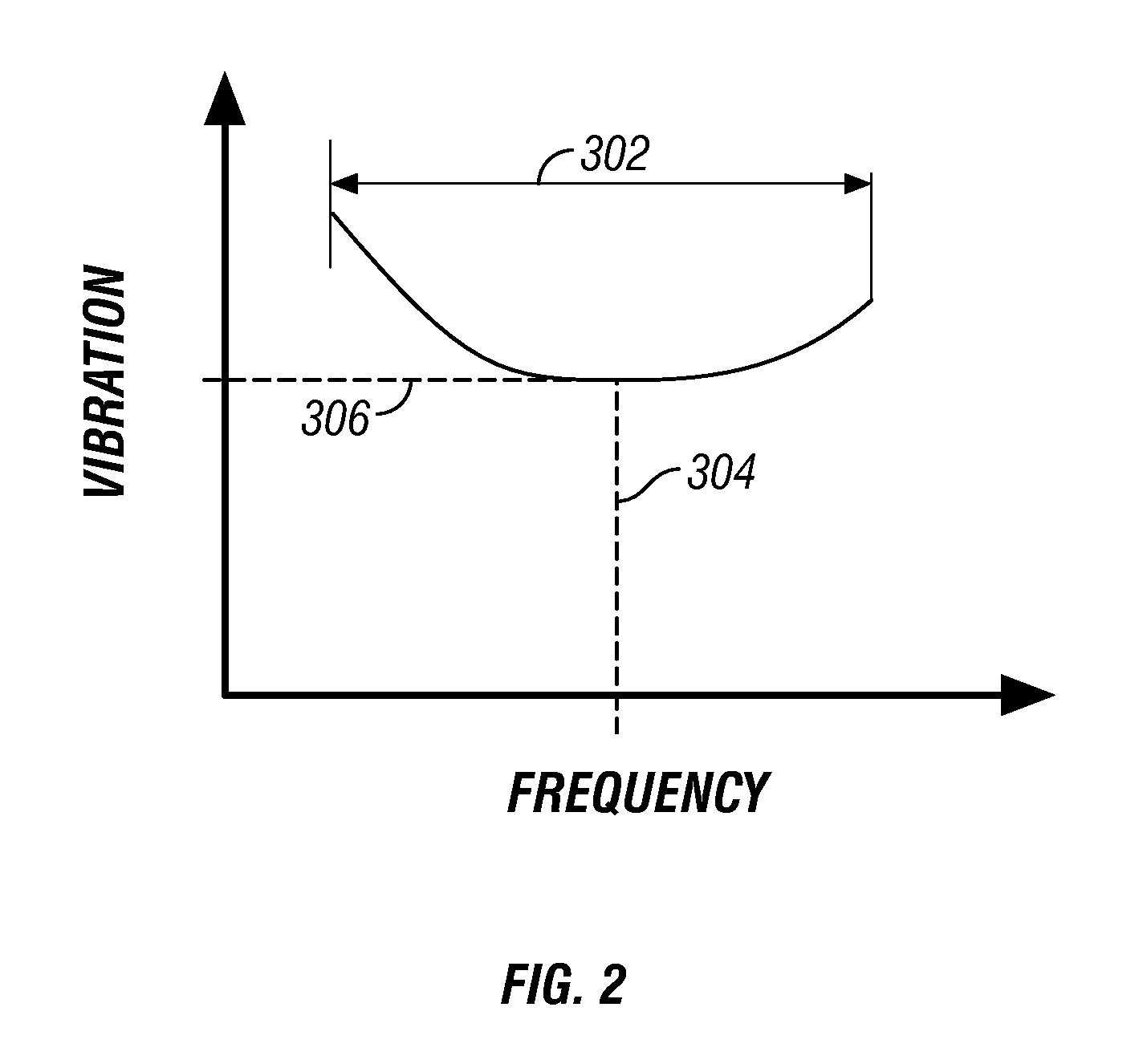
Active Vibration Control for Subterranean Drilling Operations
InactiveUS20100139977A1Prevent and minimize occurrenceImproves one and more aspectDirectional drillingVibration devicesControl signalWell drilling
An active vibration control device improves drilling by actively applying a dampening profile and / or a controlled vibration to a drill string and / or bottomhole assembly (BHA). Embodiments of the present invention control the behavior of a drill string and / or BHA in order to prevent or minimize the occurrence of harmful drill string / BHA motion and / or to apply a vibration to the drill string / BHA that improves one or more aspects of the drilling process. Measurements of one or more selected parameters of interest are processed to determine whether the undesirable vibration or motion is present in the drill string or BHA and / or whether the drill string and / or BHA operation can be improved by the application of a controlled vibration. If either or both conditions are detected, corrective action is formulated and appropriate control signals are transmitted to one or more devices in the drill string and / or BHA.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
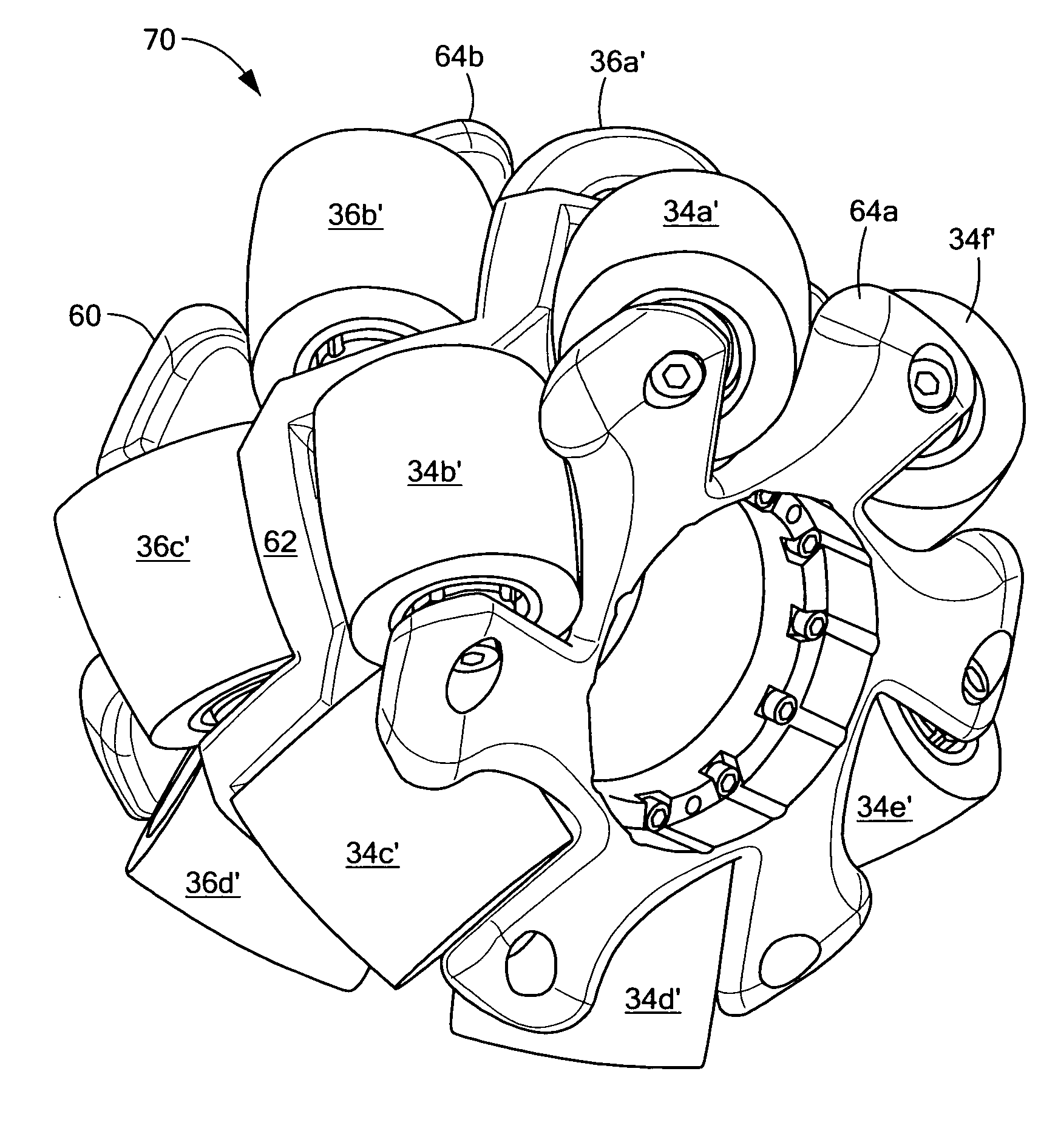
Omni-directional wheel
ActiveUS20100187779A1Vibration minimizationAvoid swingingVehicle body stabilisationHubsEngineeringOmni directional
Owner:FOSTER-MILLER
Marine payload handling craft and system
InactiveUS20060191457A1Easy to carryMinimizing motionsTowing/pushing equipmentCargo handling apparatusMarine engineeringOrbit
A marine handling craft and system is intended for use in deploying, inspecting and receiving vessels and payloads to and from locations on, under, over or near water and wet soils in potentially turbulent aquatic or atmospheric conditions. The marine handling craft may operate as a robot, or deployed from a crane or boom on a mother ship or other platform or helicopter so that it can transport and mate and dock at various locations, such as supply ships or autonomous marine vessels, at a stand off distance to limit potential harm to valuable assets. A sliding fastener and track are included on the marine handling craft so that it can be tethered and lifted by a single line or cable, and so can be manipulated by a single crane or helicopter. The utility of the handling craft is not limited to the transport of payloads and it may function as a stand-alone vessel for various remote sensing purposes. Smart communication between the marine handling craft and other vessels or other nodes in a distributed computer network facilitates simultaneous, hierarchical and multi-tasking control of the craft and permits verification and inspection of payloads, which might otherwise cause damage when proximate to more valuable assets.
Owner:ADVANCED MARITIME SUPPORT TECH
Stator core, an electric motor in which it is utilized, and method of manufacturing a stator core
ActiveUS20050067912A1Low production costExtended service lifeMagnetic circuit stationary partsCentering/balancing rotorsEngineeringOblique line
In a stator core is formed by laminated strip-shaped straight cores including a plurality of teeth portions, bent portions being provided with V-shaped notches, which define V-shaped gaps opened to one direction and interposing between each of the teeth portions, the straight cores being formed into an annular configuration by bending the bent portions in a direction so as to close the V-shaped notches and circular holes being provided at the bent portions so as to form a series of gaps between each of the teeth portions. The straight cores further include deformation preventing portions formed on the bent portions by cutting off a part of a pair of oblique lines defining the V-shaped notches toward the circular holes so as to expand the gaps of the V-shaped notches and the circular holes for preventing the bent portions from deforming by stress of bending process.
Owner:NIDEC SHIBAURA CORP
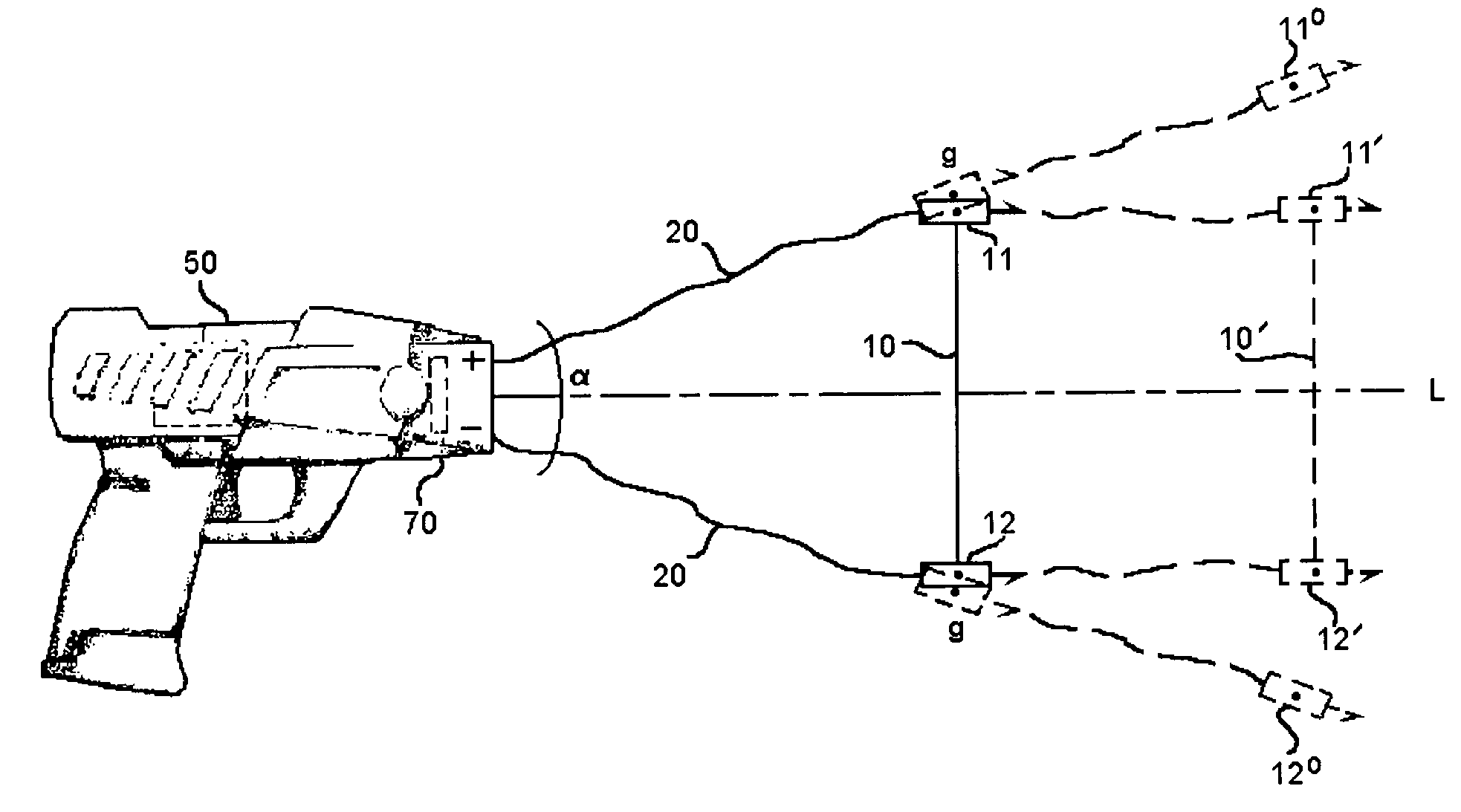
Electrical immobilization weapon
ActiveUS20060187610A1Vibration minimizationImprove efficiencyAmmunition projectilesElectrical apparatusEngineeringProjectile
A cartridge for an electrical immobilization weapon for optimized effectiveness and accuracy, comprising: a housing means for accommodating first and second projectiles adapted for being spaced within a targeted portion, having a length of at least from 5 inches to 25 inches, of a human body and for transmitting the electrical energy to the target; connecting means having at least one such length for interconnecting the first and second projectiles and available outside the housing means for retaining the projectiles within the said length in between thereof; means including the housing means for separating the first and second projectiles for immediately achieving a said length in between after leaving the housing means; means secured to the housing means for propelling the projectiles from the housing means for reaching the targeted portion; and means for coupling the projectiles to the electrical energy of the weapon's power supply.
Owner:VOLGER INT AB
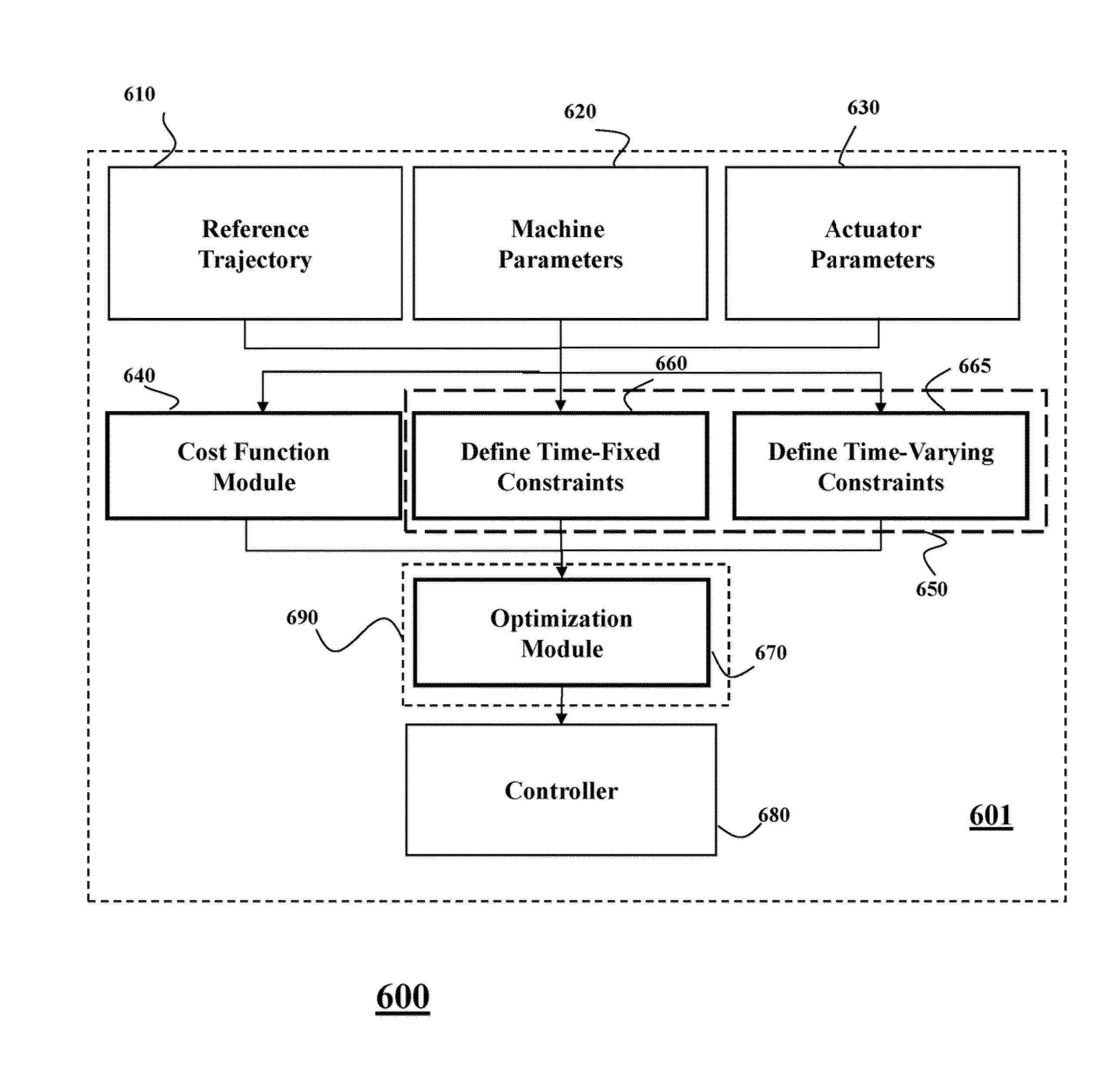
System and Method for Controlling Redundant Actuators of a Machine
ActiveUS20130190898A1Accurately traversedVibration minimizationElectric controllersIgnition automatic controlSequence controlActuator
A method controls redundant actuators of a machine based on a reference trajectory. The method determines a cost function representing operations of the redundant actuators and minimizes the cost function subject to constraints to produce a sequence of commands for each actuator. The redundant actuators are controlled according to the sequences of commands.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Structure of air-packing device
InactiveUS7165677B2Vibration minimizationPrevent reverse flow of airBagsSacksInterior spaceEngineering
An air-packing device has an improved shock absorbing capability to protect a product in a container box. The air-packing device is configured by first and second plastic films which are bonded at predetermined portions thereby creating a plurality of air containers, each of the air containers having a plurality of series connected air cells; a plurality of check valves established at inputs of the corresponding air containers for allowing compressed air to flow only in a forward direction; and an air input commonly connected to the plurality of check valves. Through a post heat-seal treatments, predetermined edge portions are bonded, thereby creating an inner space for packing a product therein and an opening for loading the product therethrough.
Owner:AIR PAQ
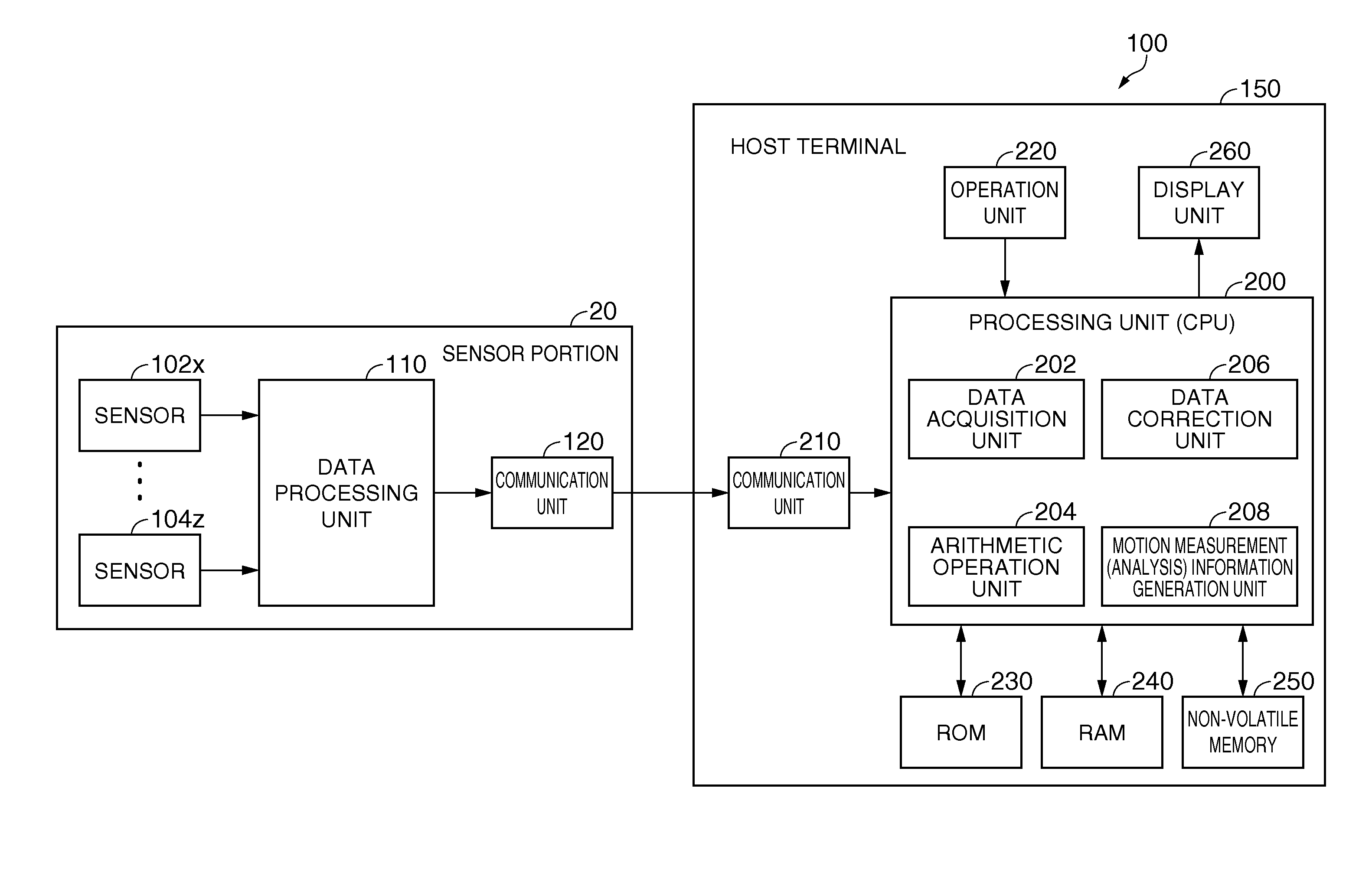
Sensor unit and motion measurement system using the same
InactiveUS20130319113A1Reduce transmissionTransmission can be minimizedAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsEngineeringMotion measurement
The first buffer portion provides a first base portion and a first outer wall provided on a peripheral edge of the first base portion. The second buffer portion provides a second base portion which provides a mounting surface outside to a measurement target, and a second outer wall provided on a peripheral edge of the second base portion. The buffer body provides the first base portion and a top surface of the second outer wall abutting against each other. A housing portion for the sensor portion is provided inside. A holding portion which holds the sensor portion is provided at least at a part of the top surface of at least one of the first buffer portion and the second buffer portion. The sensor portion is held by the holding portion.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Crash energy absorption assembly for a motor vehicle
InactiveUS6893065B2Vibration minimizationImproves overall driving and handling characteristicVehicle seatsUnderstructuresMobile vehicleEnergy absorption
The modular front end forms the front portion of a motor vehicle. The modular front end includes a bulkhead defining a plurality of integrally formed attachment mounts. A drive train assembly carrying at least an engine of the motor vehicle is attached to the bulkhead at the attachment mounts. A crash energy absorption assembly is attached to the attachment mounts on the bulkhead and generally extends around the drive train assembly. An apron assembly is attached to the bulkhead at the attachment mounts and is generally positioned above the drive train assembly and crash energy absorption assembly.
Owner:ARCONIC TECH LLC
Rim-driven propulsion pod arrangement
InactiveUS6837757B2Vibration minimizationMinimize wearRotary propellersPropulsion power plantsThrust bearingWater flow
In the embodiments described in the specification, a rim-driven propulsion pod arrangement has a cylindrical housing with a duct providing a flow path for water and a rotor assembly supported from a central shaft and containing a rotating blade row and driven by a rim drive permanent magnet motor recessed in the housing. An array of vanes downstream from the rotating blade row is arranged to straighten the flow of water emerging from the rotating blade row. Radial bearing members on the rotor have a hardness less than that of the shaft on which the rotor is supported and relatively soft protrusions are provided in the space between the rotor and the housing to limit excursion of the rotor. A thrust bearing has wedges arranged to form a water wedge between facing surfaces of the rotor and the rotor support during rotation of the rotor.
Owner:ELECTRIC BOAT CORP
Structure of air-packing device
InactiveUS7533772B2Vibration minimizationMinimize shock and vibrationBagsSacksEngineeringCheck valve
Owner:AIR PAQ
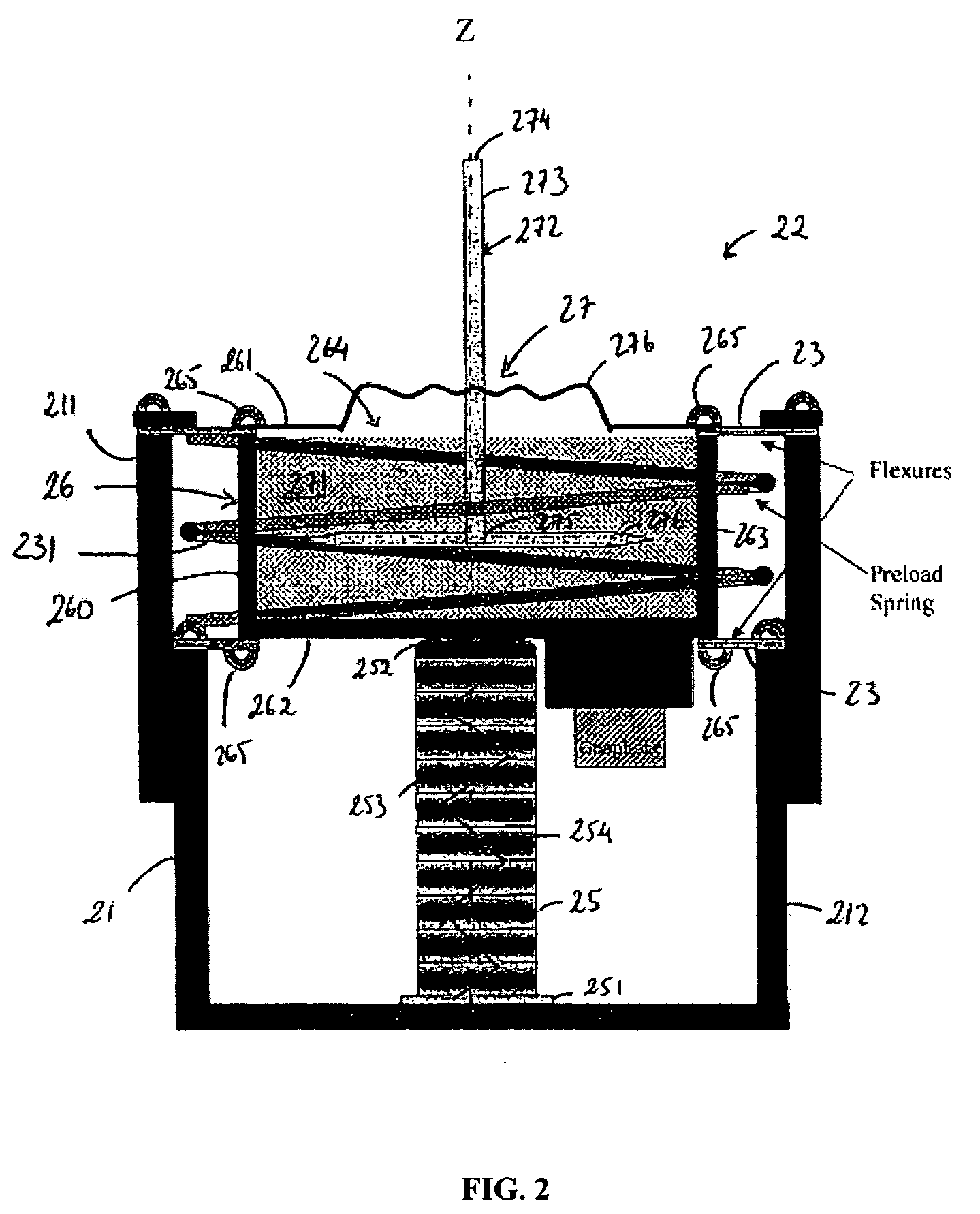
Rotational PZT micro-actuator, head gimbal assembly, and disk drive unit with the same
InactiveUS7379274B2Precise positioningImprove featuresArm with actuatorsRecord information storageMicro actuatorControl theory
A head gimbal assembly (HGA) for a disk drive unit that includes a micro-actuator, a slider and a suspension to load the slider and the micro-actuator. The micro-actuator includes a pair of actuator side arms, a PZT element extending between and connecting the actuator side arms; a rotatable plate positioned between the actuator side arms, wherein the slider is mounted on the rotatable plate; and a pair of connection elements that connect the rotatable plate to the actuator side arms, respectively. The rotatable plate rotates in a first direction when the PZT element contracts and a second direction when the PZT element expands.
Owner:SAE MAGNETICS (HK) LTD
Balanced positioning system for use in lithographic apparatus
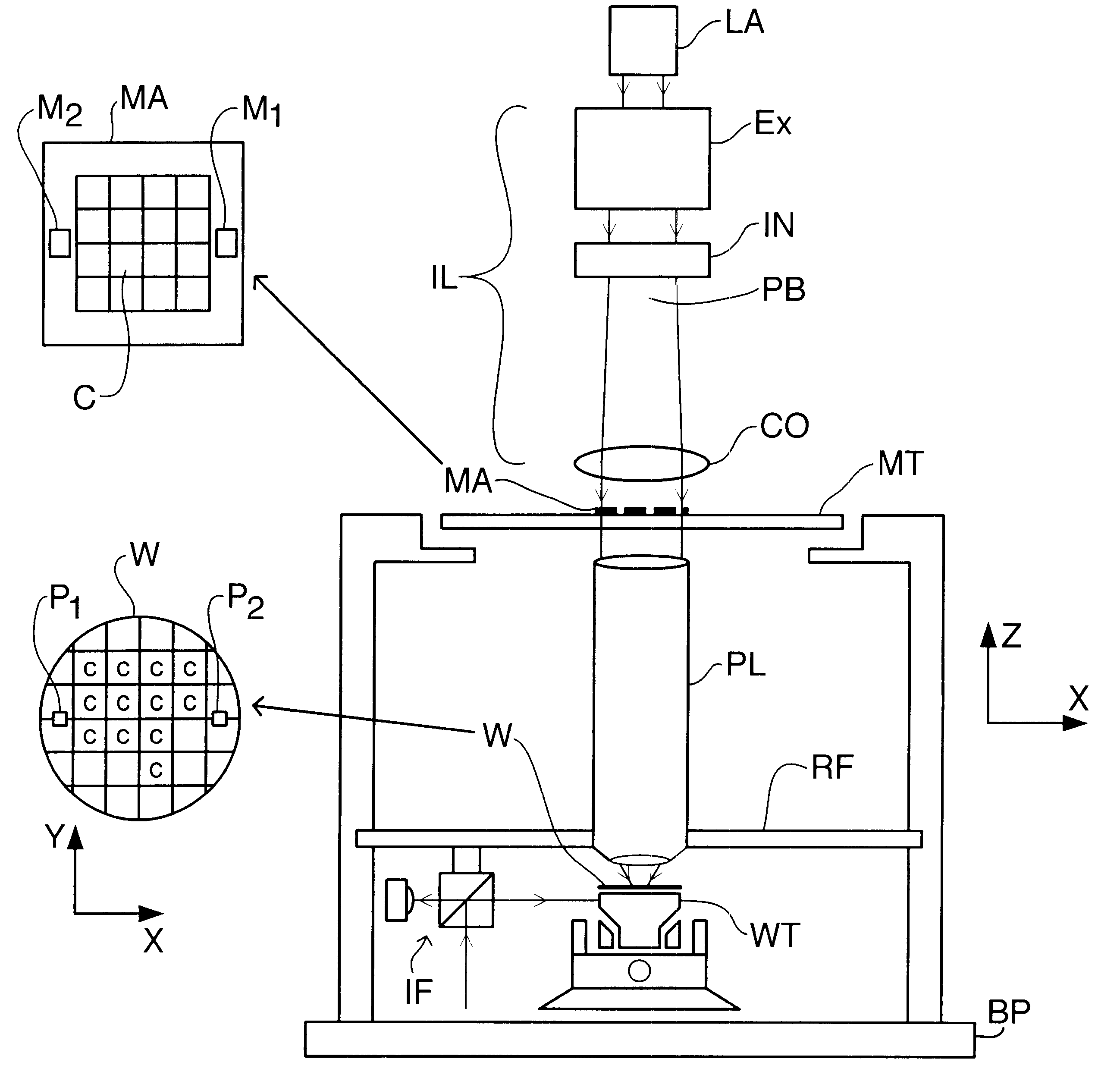
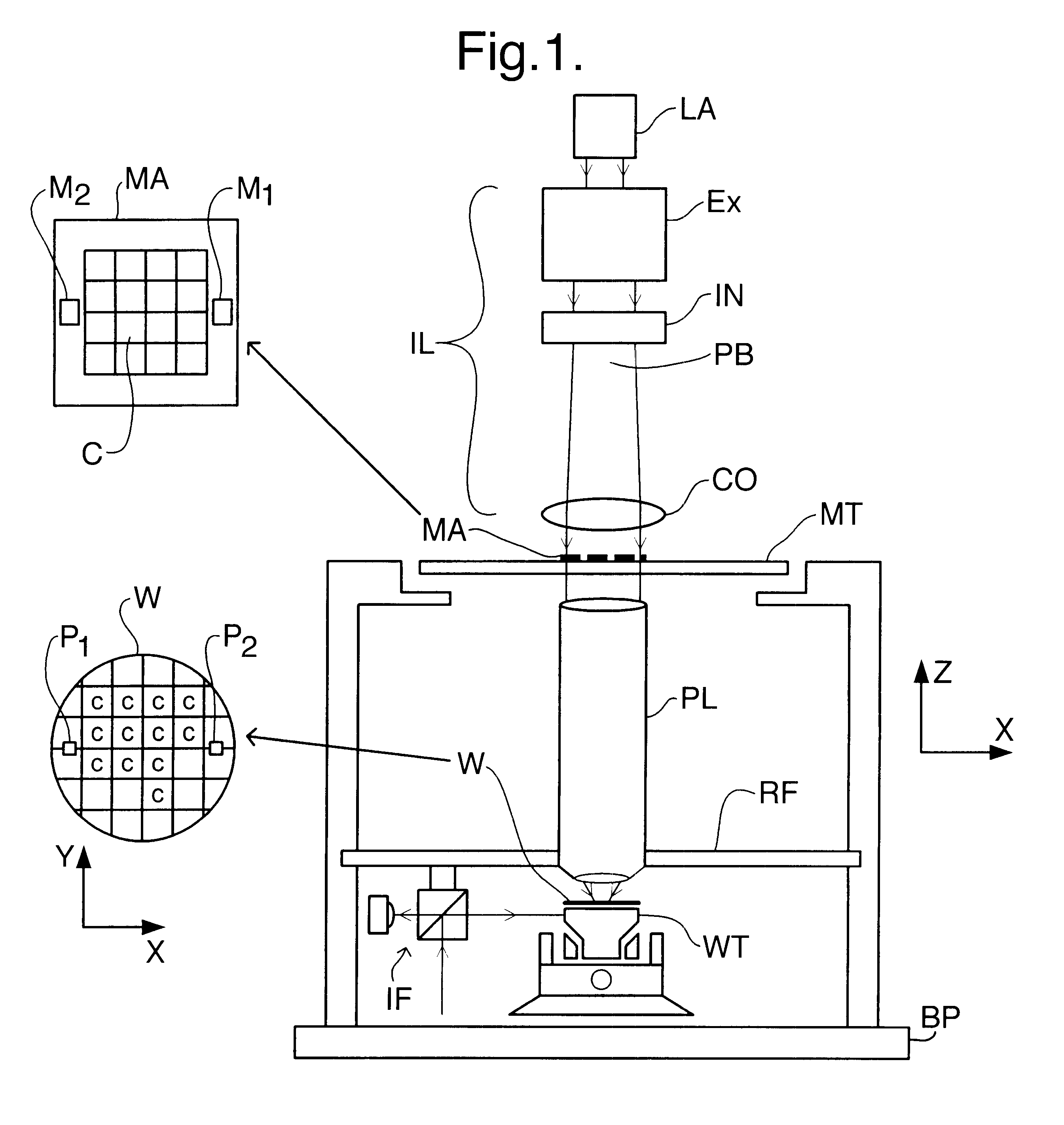
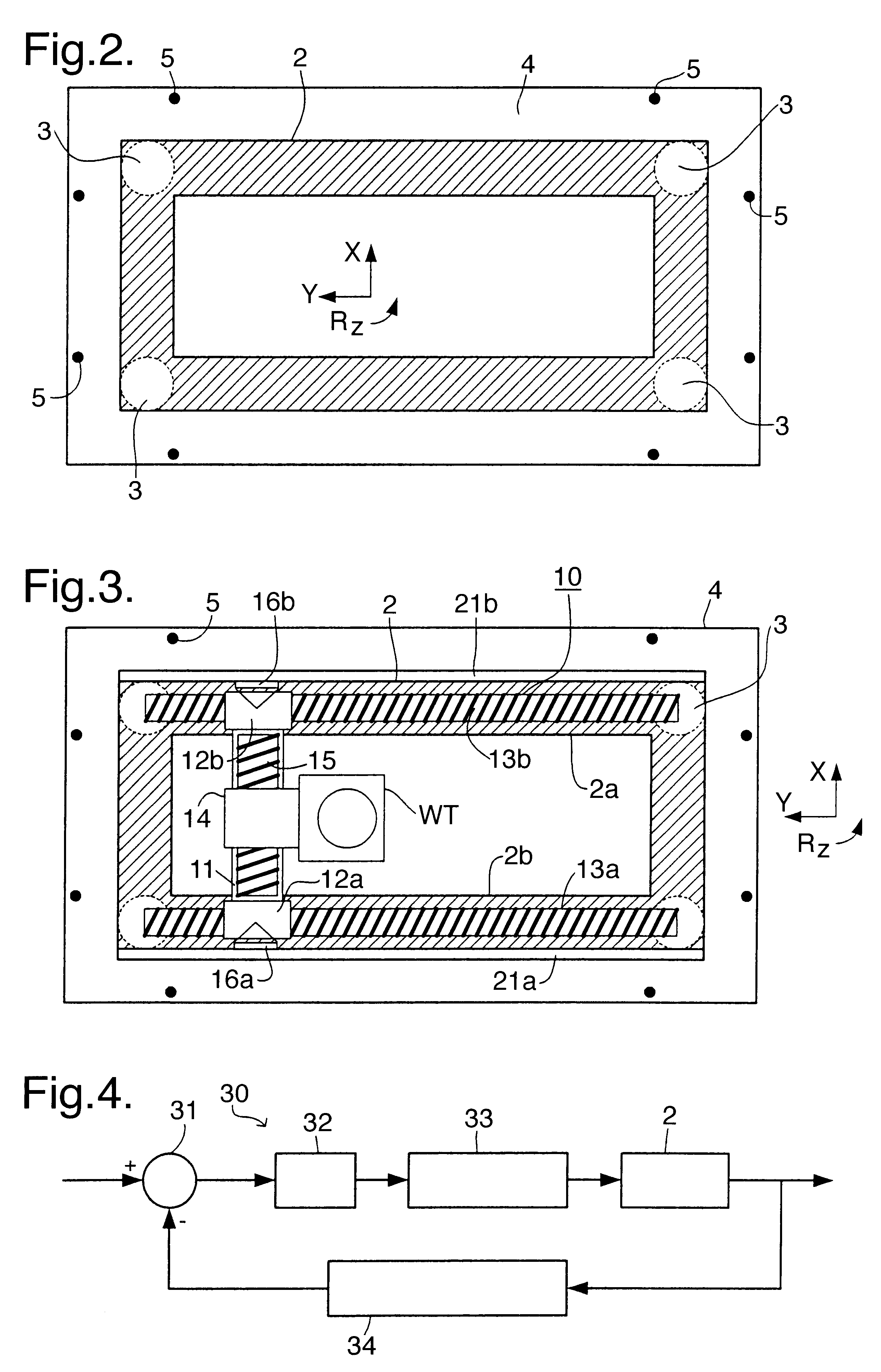
InactiveUS6525803B2Increase heightVibration minimizationPhoto-taking processesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThree degrees of freedomEngineering
A balanced positioning apparatus comprises a balance mass which is supported so as to be moveable in the three degrees of freedom, such as X and Y translations and rotation about the Z-axis. Drive forces in these degrees of freedom act directly between the positioning body and the balance mass. Reaction forces arising from positioning movements result in corresponding movement of the balance mass and all reaction forces are kept within the balanced positioning system. The balance mass may be a rectangular balance frame having the stators of two linear motors forming the uprights of an H-drive mounted on opposite sides. The cross-piece of the H-drive spans the frame and the positioned object is positioned within the central opening of the frame.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Structure of air-packing device having improved shock absorbing capability
An air-packing device has an improved shock absorbing capability to protect a product in a container box. The air-packing device is configured by first and second plastic films which are bonded at predetermined portions thereby creating a plurality of air containers, each of the air containers having a plurality of series connected air cells; a plurality of check valves established at inputs of the corresponding air containers for allowing compressed air to flow in a forward direction; an air input commonly connected to the plurality of check valves; and heat-seal flanges formed on side edges of the air-packing device. Through a post heat-seal treatment, predetermined points on the air containers and the heat-seal flanges are bonded, thereby creating a container portion having an opening for packing a product therein and a cushion portion for supporting the container portion when the air-packing device is inflated by the compressed air.
Owner:AIR PAQ
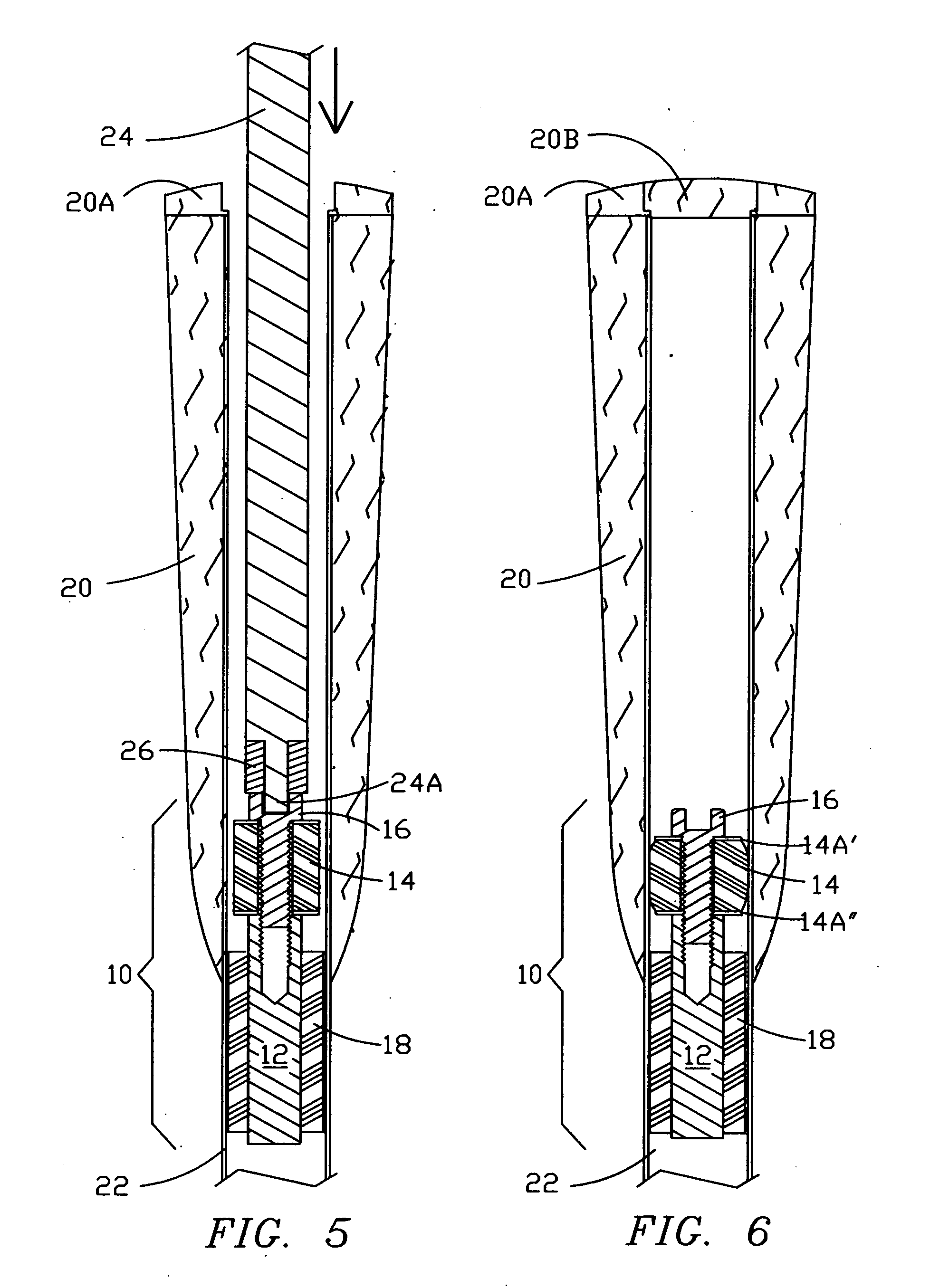
Versatile vibration-damped golf swing-weight system
ActiveUS20100105498A1Reliably securedConveniently releasedMetal working apparatusGolf clubsAxial pressureEngineering
A highly versatile damper-weight system enables the installation of adjustable swing-weight in a vibration-damped manner inside a golf club shaft. A plug assembly of selectable weight is inserted through a circular opening in the golf grip cap with a special tool, moved to any desired location within the shaft and securely fastened in place in a vibration-damped manner by radial expandable of a cylindrical resilient expandable element. A weight rod, made available in different materials, lengths and weights, is spaced from the shaft by one or more resilient damper sleeves to minimize shaft vibration. The expandable element is secured by a machine screw threaded into the upper end of the weight rod, and is dimensioned (unexpanded) to enable easy insertion and location adjustment of said plug assembly. The tool provides dual functions: as a screw head driver to expand / contract the expandable element radially by axial pressure / release as required, and as a removable coupler capable of pulling the plug assembly (with the expandable element unexpanded) upwardly, as well as pressing it downwardly within the shaft for adjustment to any desired location.
Owner:JOHNSON JOHN
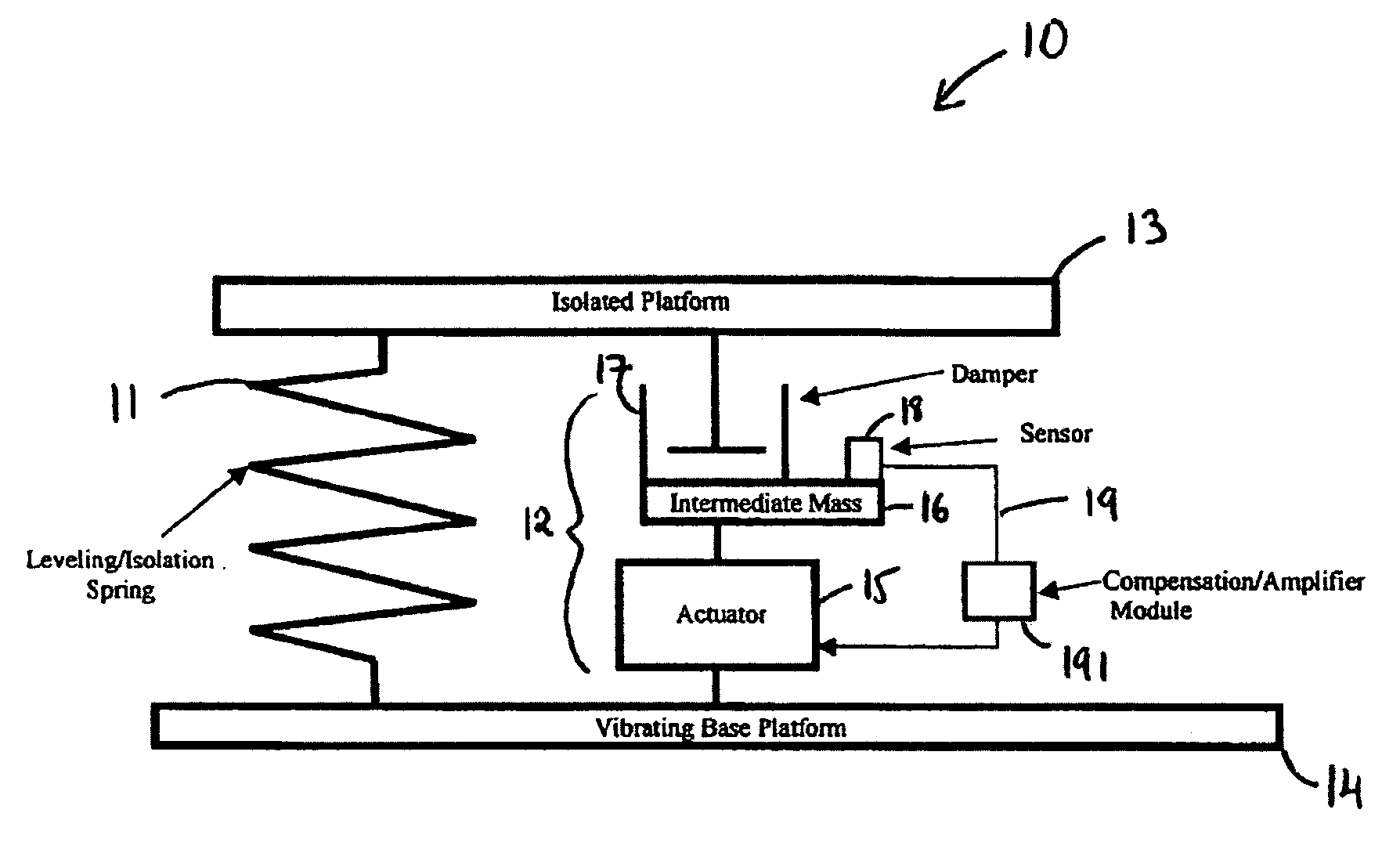
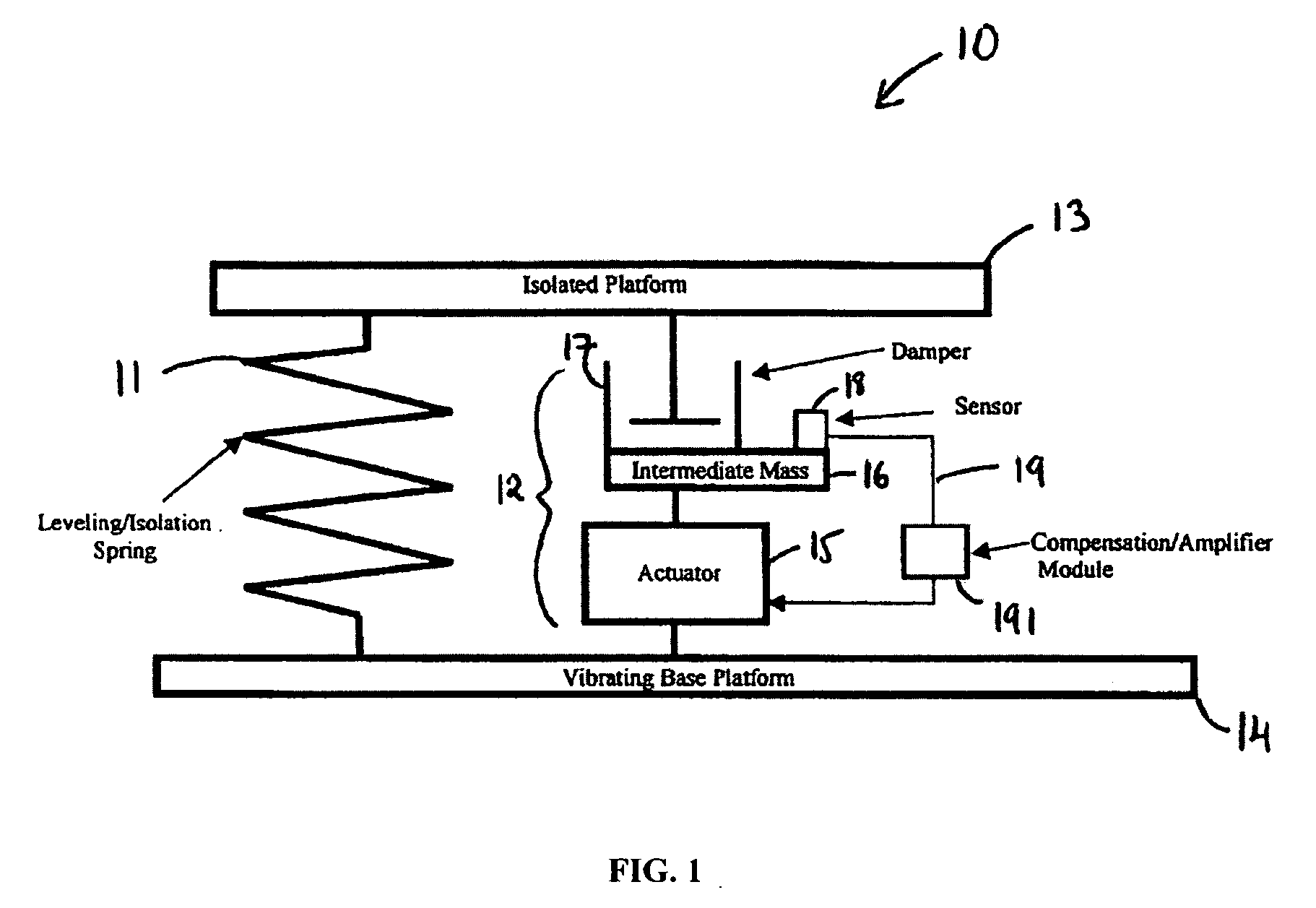
Systems and methods for active vibration damping
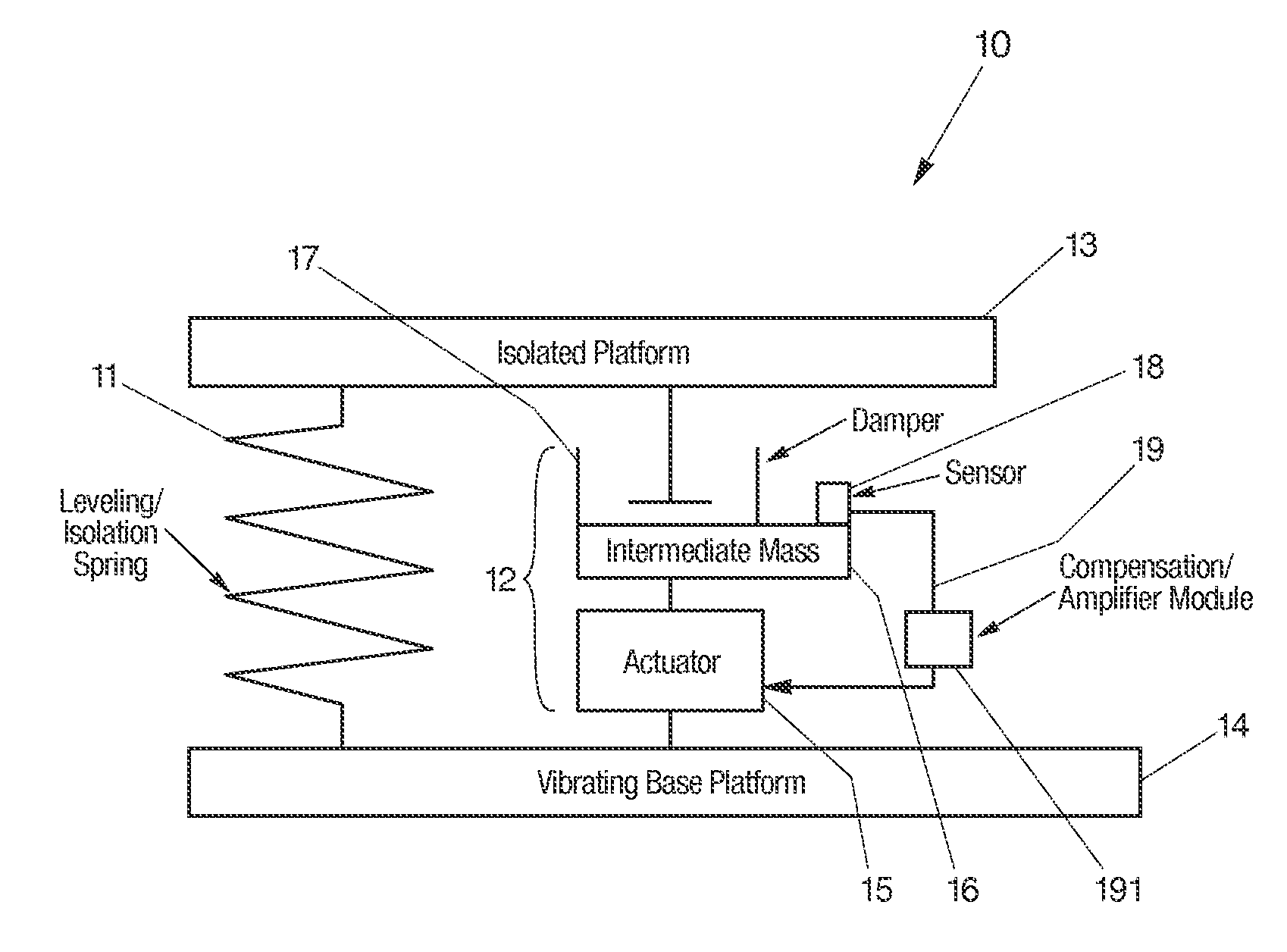
InactiveUS20060272910A1Improve isolationIncrease stiffnessSuspensionsPortable framesAudio power amplifierActuator
An active vibration damping system having a supporting spring for addressing a static force from a payload, and an independent actively isolated damper positioned in parallel between a payload and a source of vibration for damping dynamic force from the payload to an actively isolated point. The actively isolated damper includes a small intermediate mass, distinct and decoupled from the payload mass, and a passive isolator element for dynamic coupling of the isolated platform to the small intermediate mass. The small intermediate mass provides a point to which dynamic forces from the payload may be dampened. The active damper also includes at least one actuator coupled at one surface to the small intermediate mass and coupled at a second surface to the vibrating base platform. A motion sensor may also be provided on the small intermediate mass so as to generate a feedback signal as a function of the movement of the small intermediate mass. The motion sensor together with a compensation / amplifier module and the actuator act as part of a feedback compensation loop for minimizing vibration.
Owner:TECHN MFG
Systems and methods for active vibration damping
InactiveUS7726452B2Improve isolationIncrease stiffnessSuspensionsPortable framesAudio power amplifierEngineering
An active vibration damping system having a supporting spring for addressing a static force from a payload, and an independent actively isolated damper positioned in parallel between a payload and a source of vibration for damping dynamic force from the payload to an actively isolated point. The actively isolated damper includes a small intermediate mass, distinct and decoupled from the payload mass, and a passive isolator element for dynamic coupling of the isolated platform to the small intermediate mass. The small intermediate mass provides a point to which dynamic forces from the payload may be dampened. The active damper also includes at least one actuator coupled at one surface to the small intermediate mass and coupled at a second surface to the vibrating base platform. A motion sensor may also be provided on the small intermediate mass so as to generate a feedback signal as a function of the movement of the small intermediate mass. The motion sensor together with a compensation / amplifier module and the actuator act as part of a feedback compensation loop for minimizing vibration.
Owner:TECHN MFG
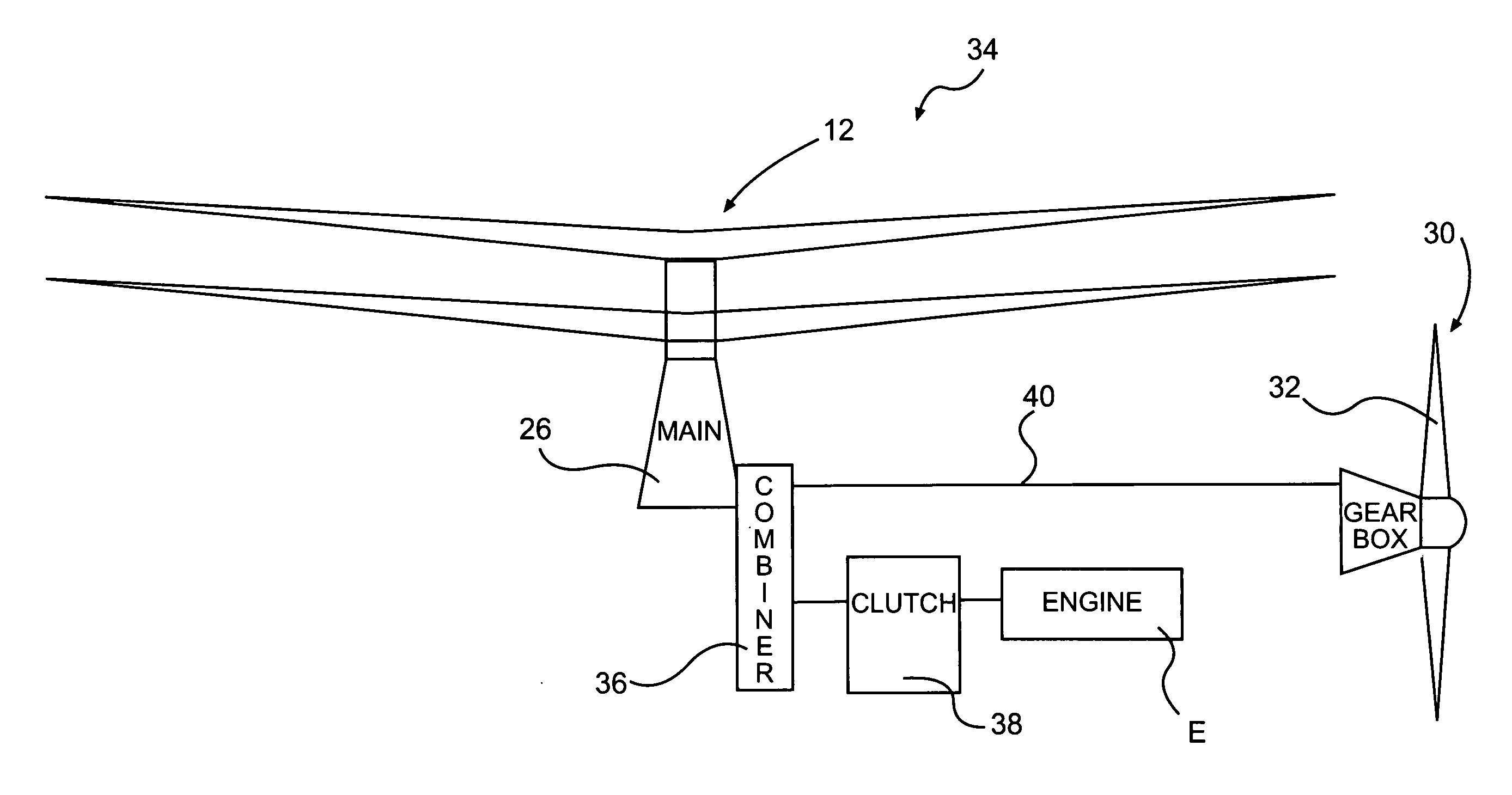
Rotor drive and control system for a high speed rotary wing aircraft
InactiveUS7967239B2Negative liftUpward liftAircraft power transmissionRotocraftControl systemRotary wing
A drive system for a high speed rotary-wing aircraft includes a combiner gearbox in meshing engagement with a main gearbox. The combiner gearbox is driven by one or more engines such that a main rotor system and a translational thrust system are driven thereby. The engine drives the combiner gearbox and thus the main gearbox through an overrunning clutch. The drive system permits the main rotor system RPM to be controlled by offloading power to the translational thrust system during a high speed flight profile.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
Resonant stator balancing of free piston machine coupled to linear motor or alternator
ActiveUS20090039655A1Vibration is reduced and minimized and eliminatedEliminate needSafety/regulatory devicesMechanical energy handlingEngineeringOperating frequency
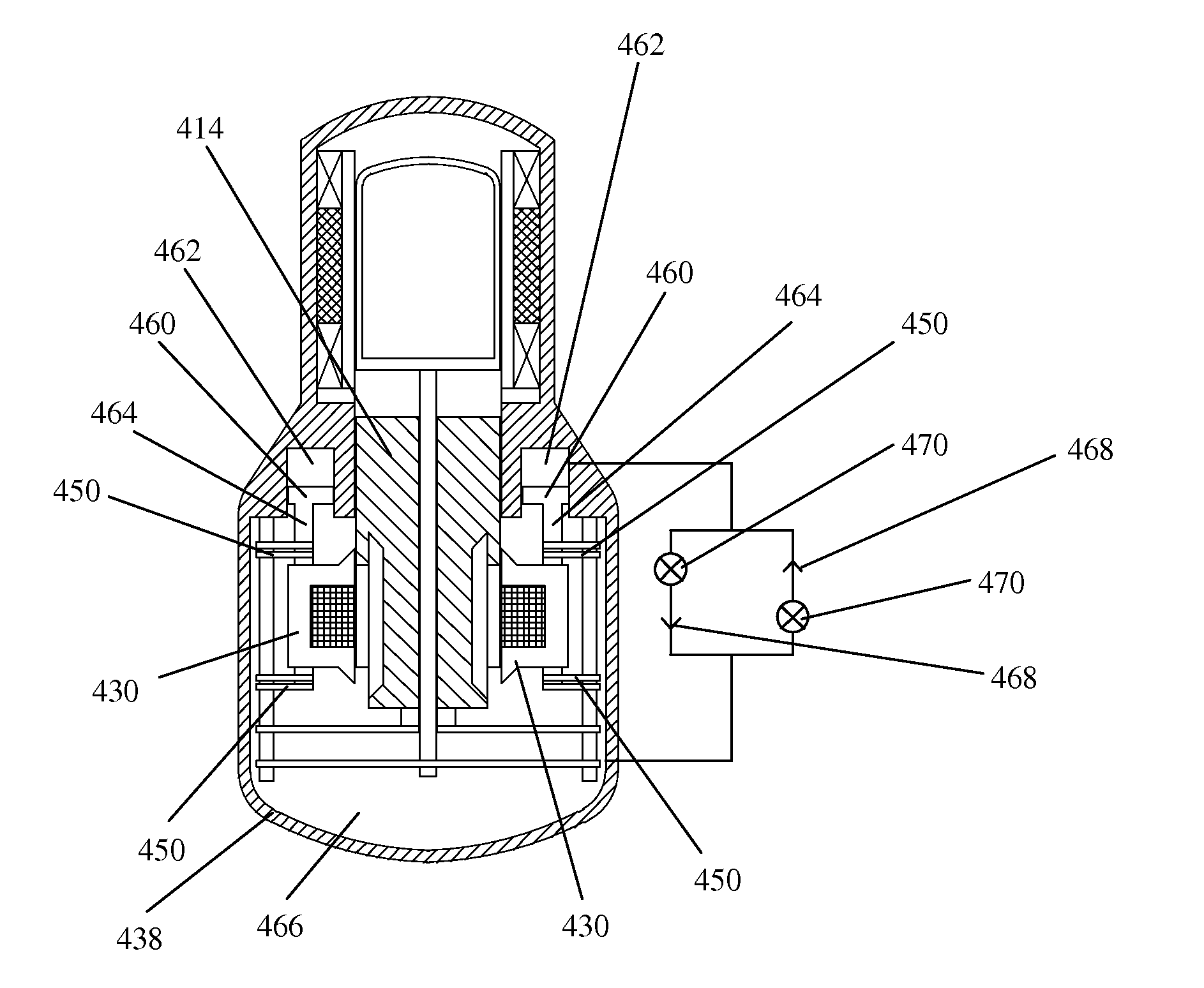
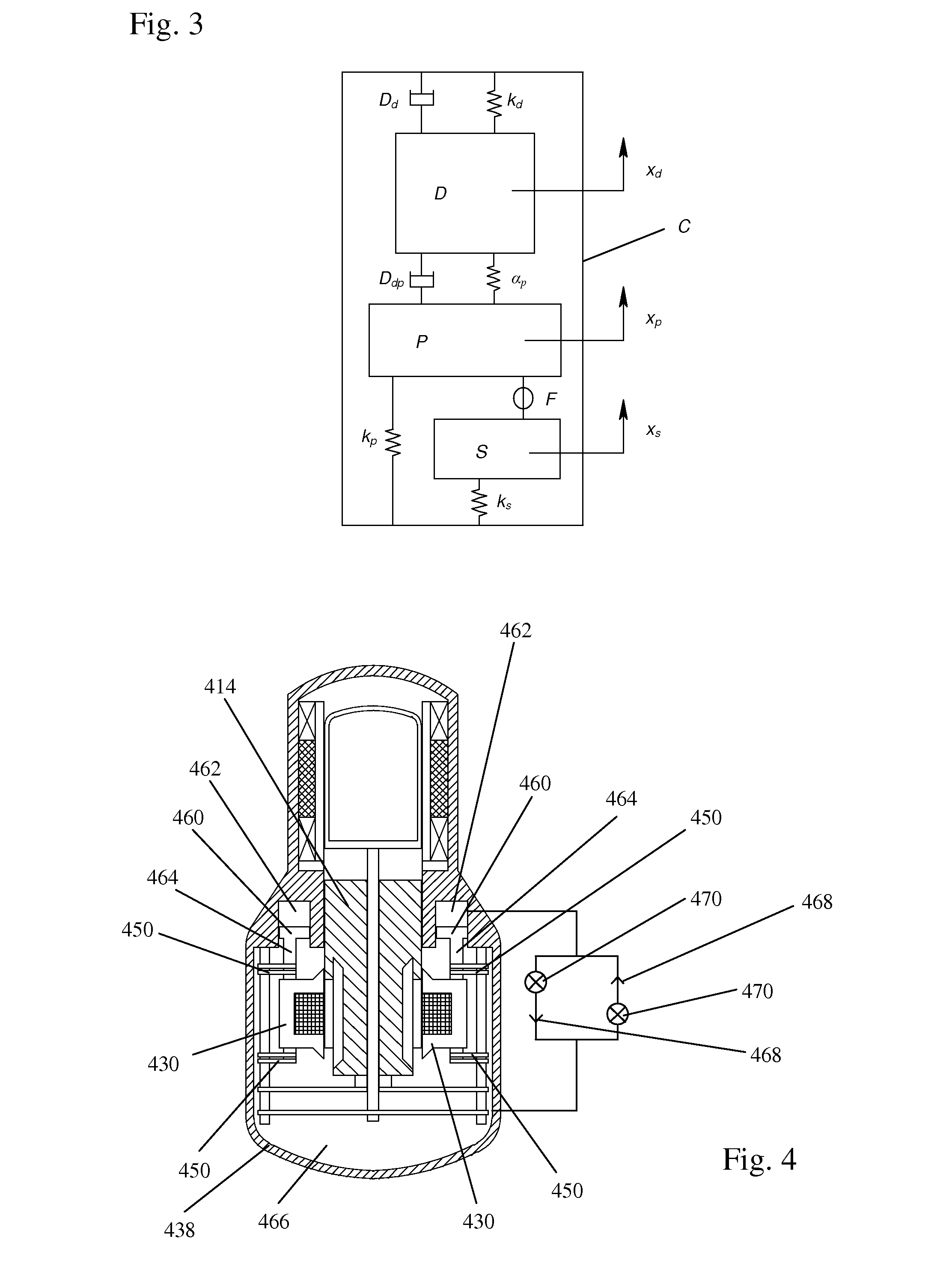
A beta-type free-piston Stirling cycle engine or cooler is drivingly coupled to a linear alternator or linear motor and has an improved balancing system to minimize vibration without the need for a separate vibration balancing unit. The stator of the linear motor or alternator is mounted to the interior of the casing through an interposed spring to provide an oscillating system permitting the stator to reciprocate and flex the spring during operation of the Stirling machine and coupled transducer. The natural frequency of oscillation, ωs, of the stator is maintained essentially equal to ωpωp1-αpkpand the natural frequency of oscillation of the piston, ∩p, is maintained essentially equal to the operating frequency, ωo of the coupled Stirling machine and alternator or motor. For applications in which variations of the average temperature and / or the average pressure of the working gas cause more than insubstantial variations of the piston resonant frequency ωp, various alternative means for compensating for those changes in order to maintain vibration balancing are also disclosed.
Owner:GLOBAL COOLING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com