Method for improving rice resistance to bacterial leaf blight by using leaf specific expression artificial microRNA
A leaf blight resistance and specific technology, applied in the field of plant genetic engineering, can solve the problems of pollen fertility decline and expression decline, and achieve the effect of reducing fertility decline
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Example 1 Design of amiRNA sequence and construction of amiRNA precursor
[0029] Obtain the sequence number "DQ421395" of the Xa13 gene in Genebank according to the literature published by Chu et al. According to the sequence of DQ421395, perform blastn on the TIGR Rice website (http: / / rice.plantbiology.msu.edu / LocusNameSearch.shtml) to obtain its locus identifier in TIGR Rice: Os08g42350.1. On the Web MicroRNA Designer webpage (http: / / wmd3.weigelworld.org / cgi-bin / webapp.cgi?page=Designer; project=stdwmd) input Os08g42350.1, the software returns 17 amiRNA sequences of Xa13, manually screened out Two of them were named amiA (sequence TAGACTACTAGTAGATCCGCT) and amiB (sequence TGTAGCGAGAATCTGTCGCCG) for further research.
[0030] Referring to the method published by Warthmann et al. (2008), using the plasmid pNW55 as a template (containing the precursor sequence of the rice natural miRNA Osa-miR528, donated by Prof. Detlef Weigel from the Max Planck Institute of Developmen...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Example 2 Obtaining of leaf-specific expression promoter
[0047] According to the master's degree thesis of Huang Haiqun, the State Key Laboratory of Crop Genetic Improvement of Huazhong Agricultural University, the primers OsrbcS-F and OsrbcS-R of the rice rbcS promoter Osrbcsp, and the primer sequence AtrbcS- of the Arabidopsis rbcS1A promoter Atrbcsp were obtained. F and AtrbcS-R (see Table 1). The promoters Osrbcsp and Atrbcsp of rbcs genes in rice (genotype Nipponbare) and Arabidopsis (genotype Col) were amplified respectively by using these two pairs of primers. The PCR reaction system was: 5 μl of 10xPCR buffer, 5 μl of 2mM dNTPs, 2 μl of each 10 μM primer, 20 ng of large sample DNA, 0.5 μl of LA Taq (purchased from Treasure Bioengineering Dalian Co., Ltd.), and sterilized double-distilled water was added to 50 μl. Reaction conditions: 94°C for 2min; 32 cycles of 94°C for 45s, 57°C for 2min, 72°C for 45s; 72°C for 7min. Take 10 μl of the PCR product and run 1%...
Embodiment 3
[0048] The construction of embodiment 3 plant expression vectors
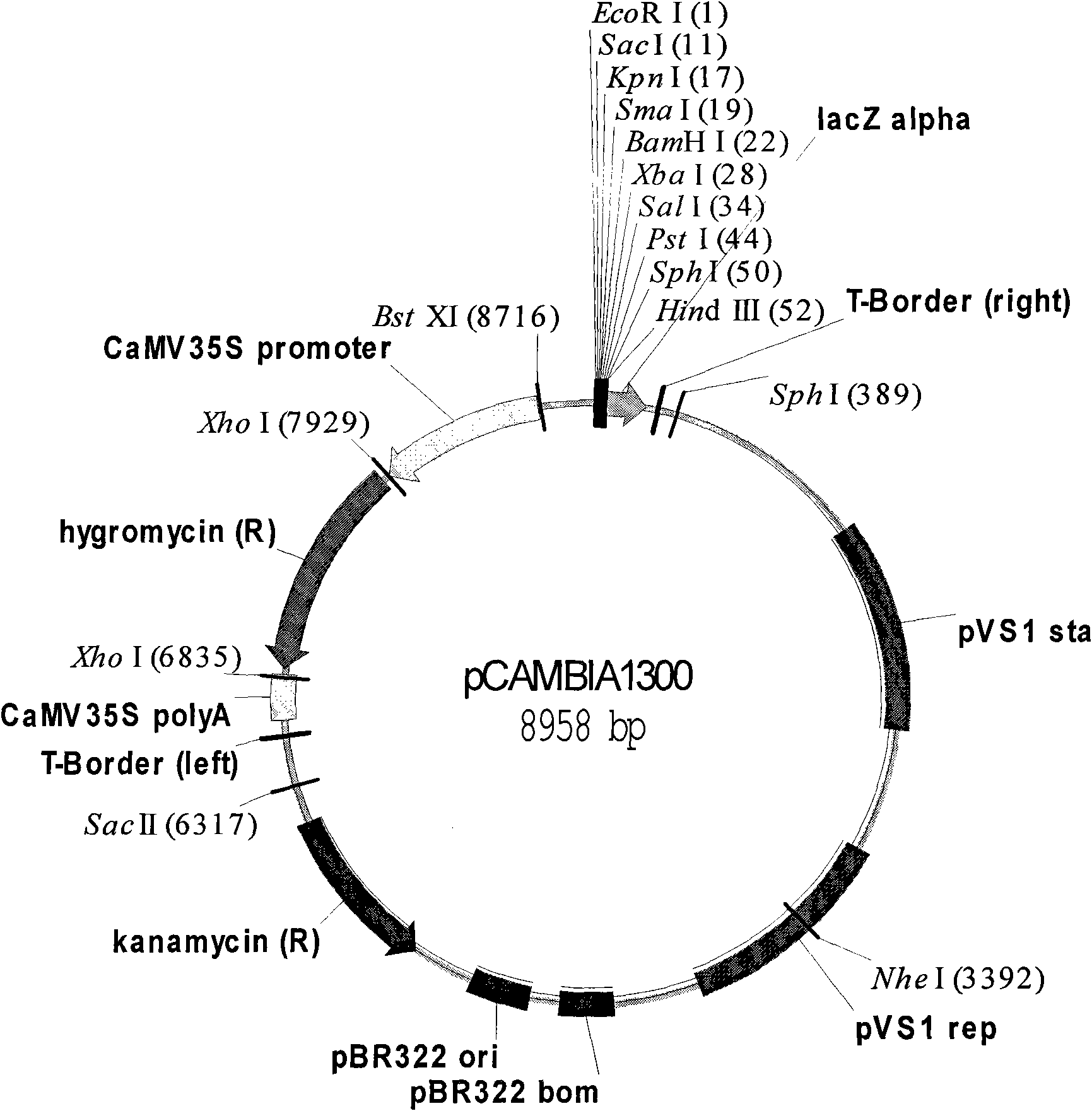
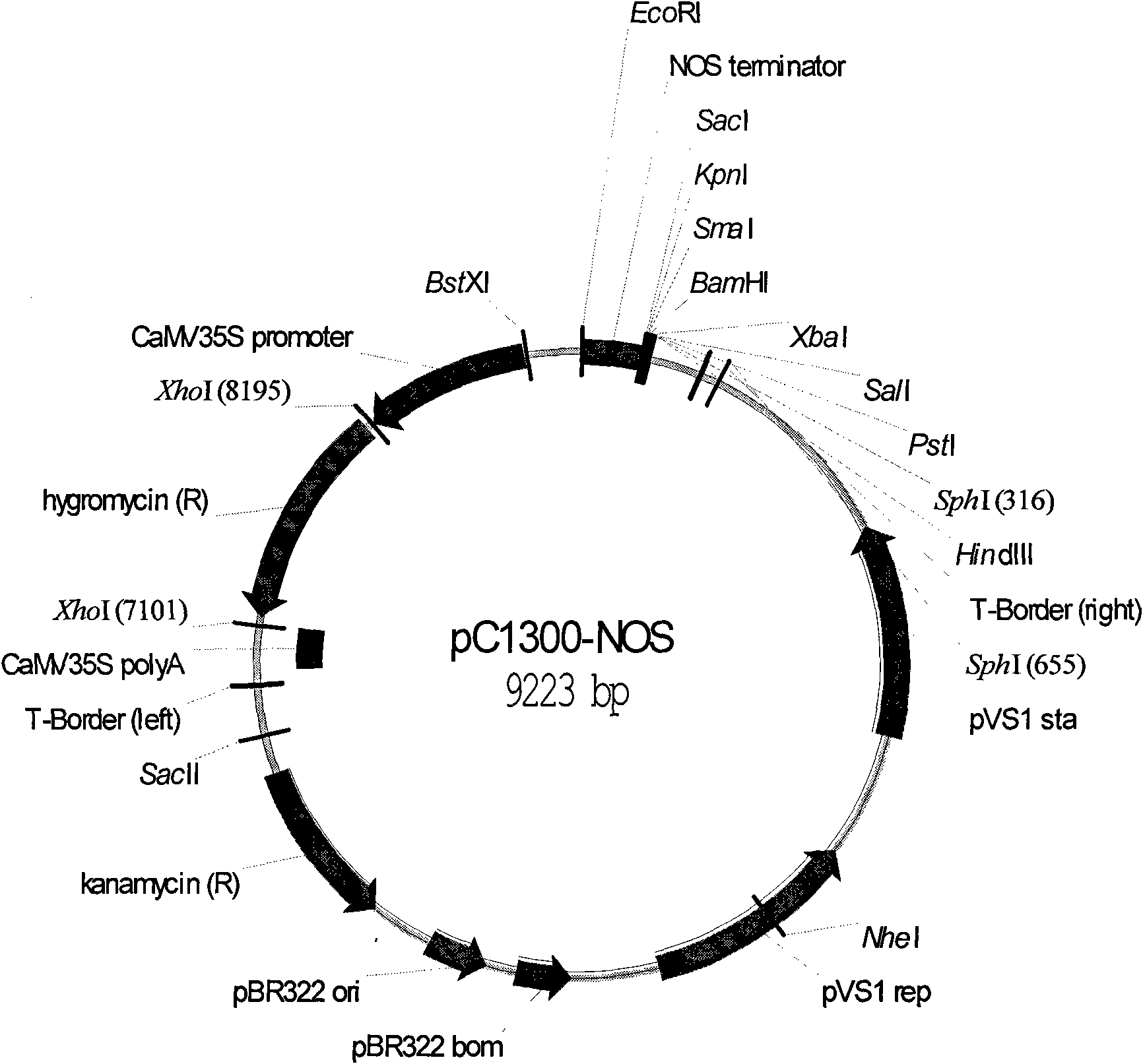
[0049] First digest the plasmid PUC-Bt (this plasmid is artificially synthesized by our laboratory and contain the NOS terminator of the nopaline synthase gene of 0.3 kb) with restriction endonucleases EcoR I and Sac I to obtain the NOS terminator of 0.3 kb, which will be recovered The NOS terminator was constructed on the pCAMBIA1300 vector which was also cut with EcoR I and Sac I ( figure 1 , the plasmid was donated by the CAMBIA laboratory in Australia) to form the intermediate vector pC1300-Nos ( figure 2 ).
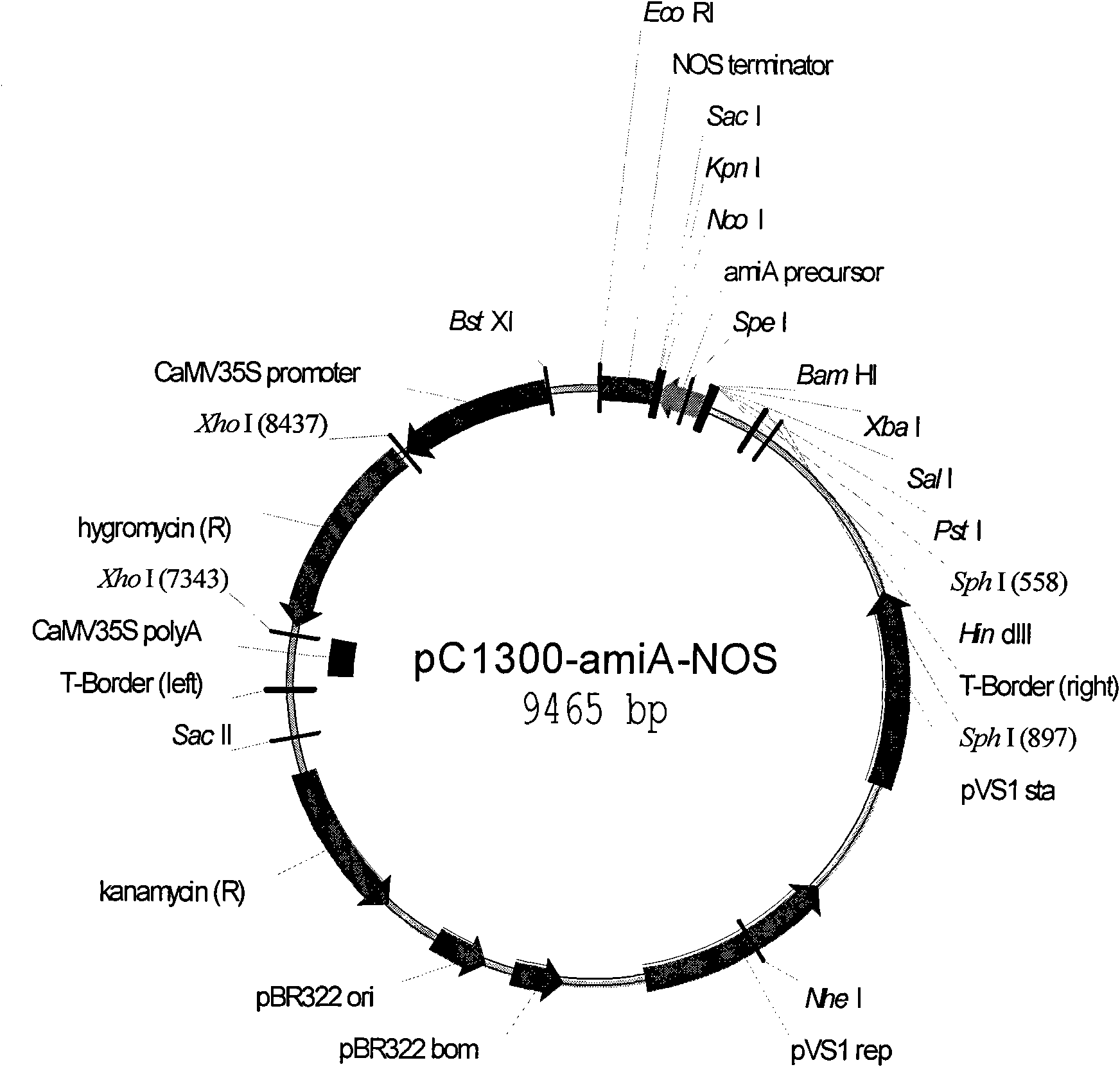
[0050] Utilize Kpn I and BamHI double enzymes to digest the T-easy vector containing the amiA and amiB precursor sequences, and construct the vector pC1300-amiA-Nos ( image 3 ) and pC1300-amiB-Nos ( Figure 4 ).
[0051] The promoter Osrbcsp cloned on the T-vector was excised with Pst I and Hind III, and constructed on the intermediate vectors pC1300-amiA-Nos and pC1300-amiB-Nos cut with the sam...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com