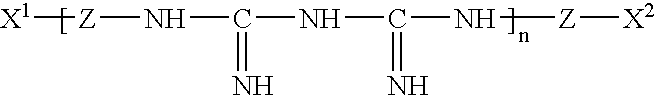
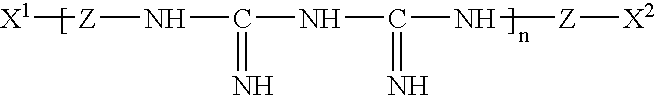
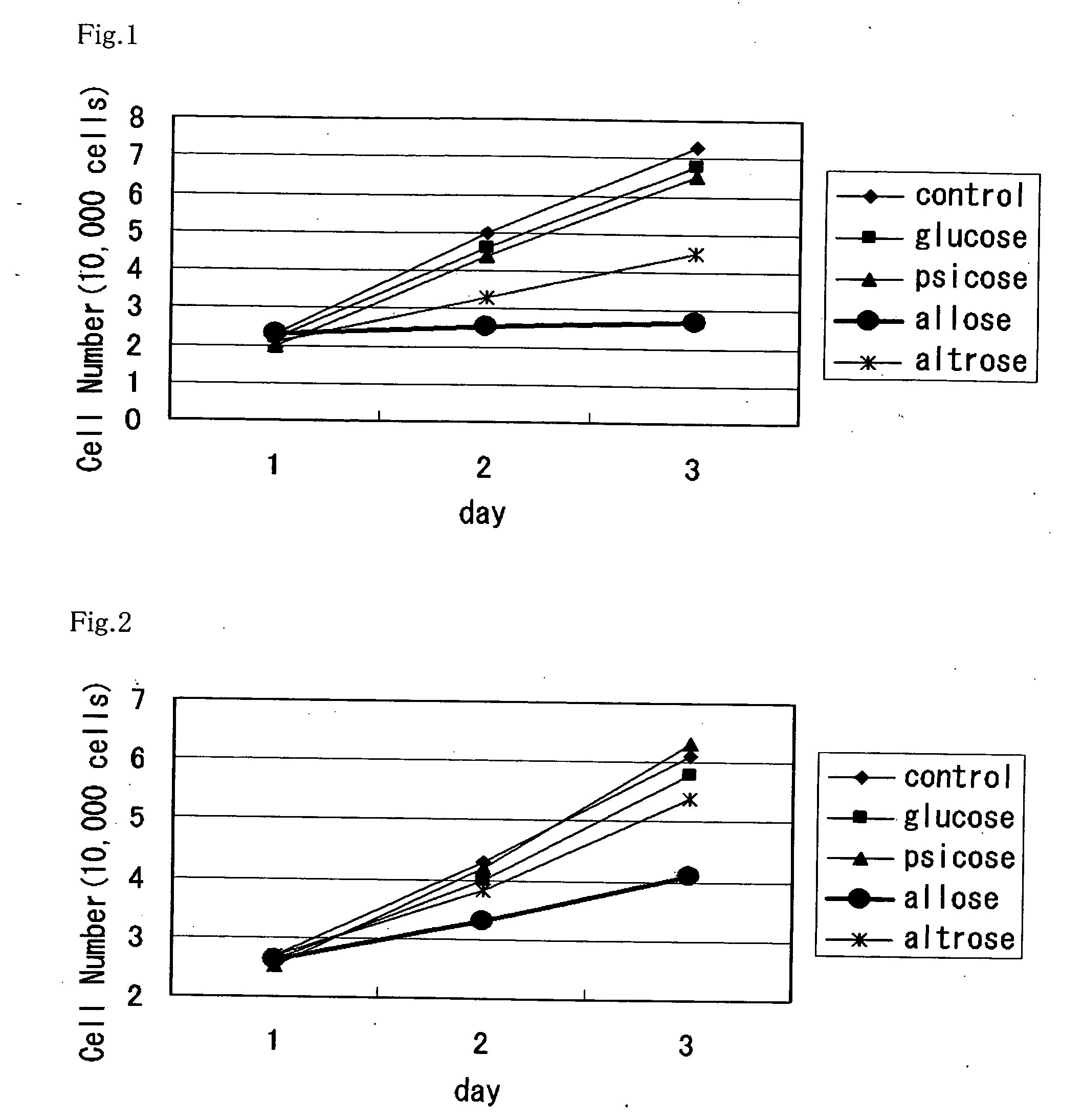
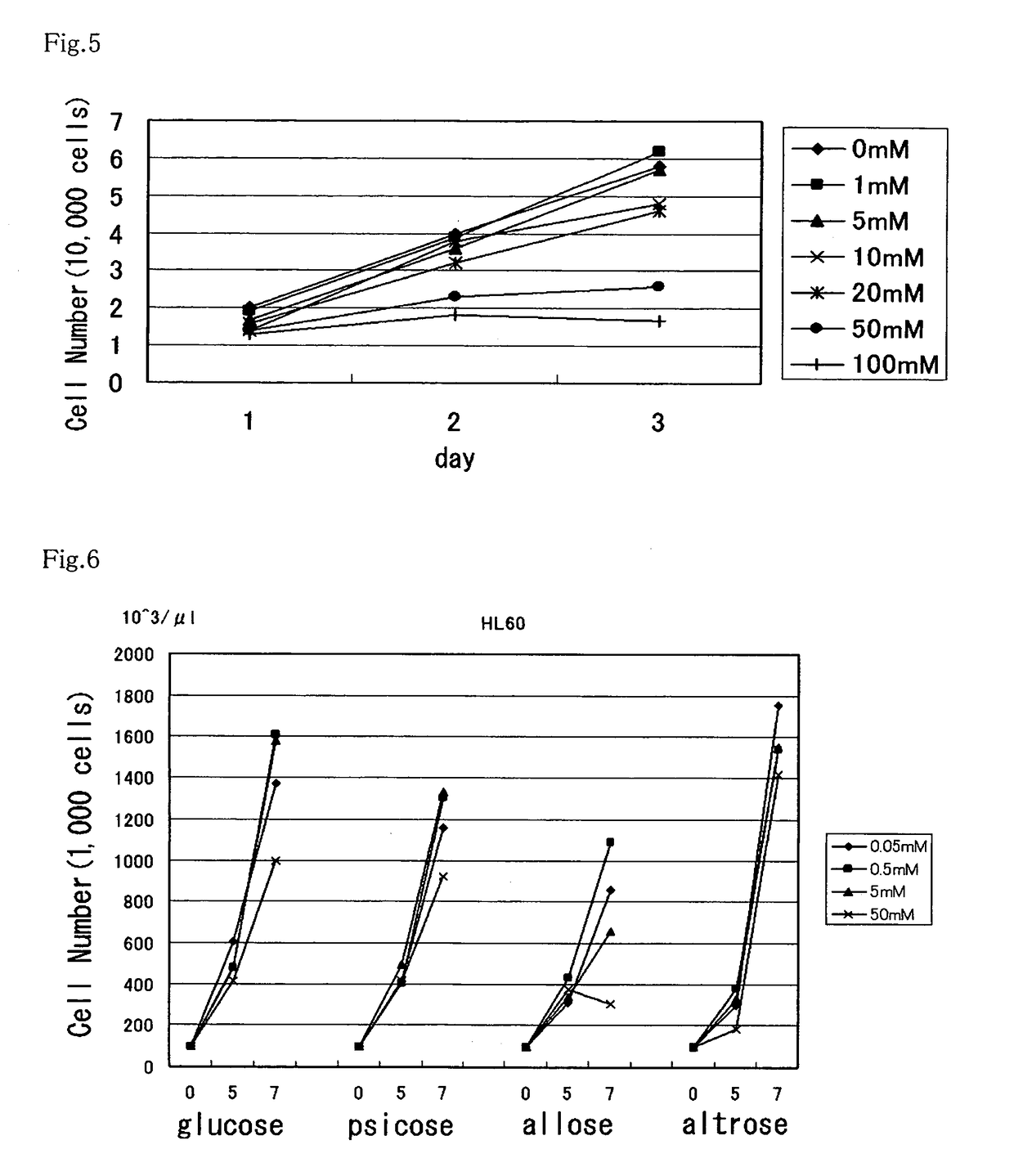
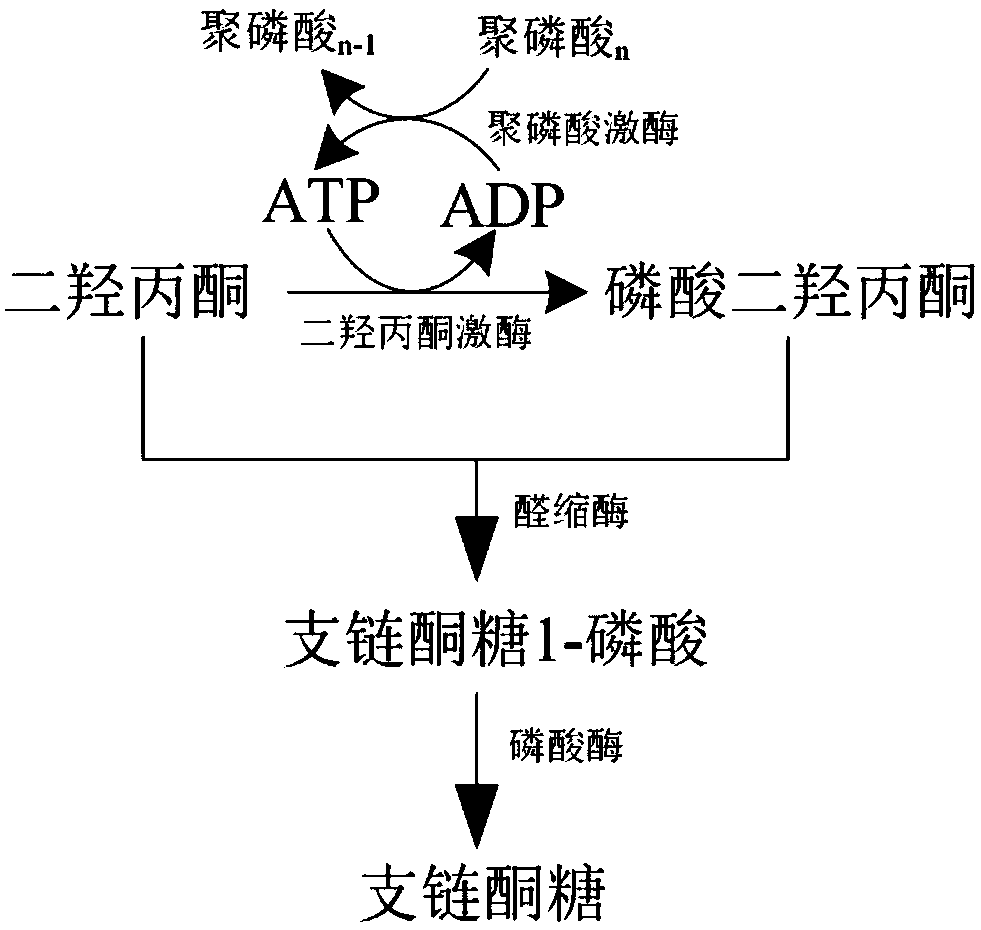
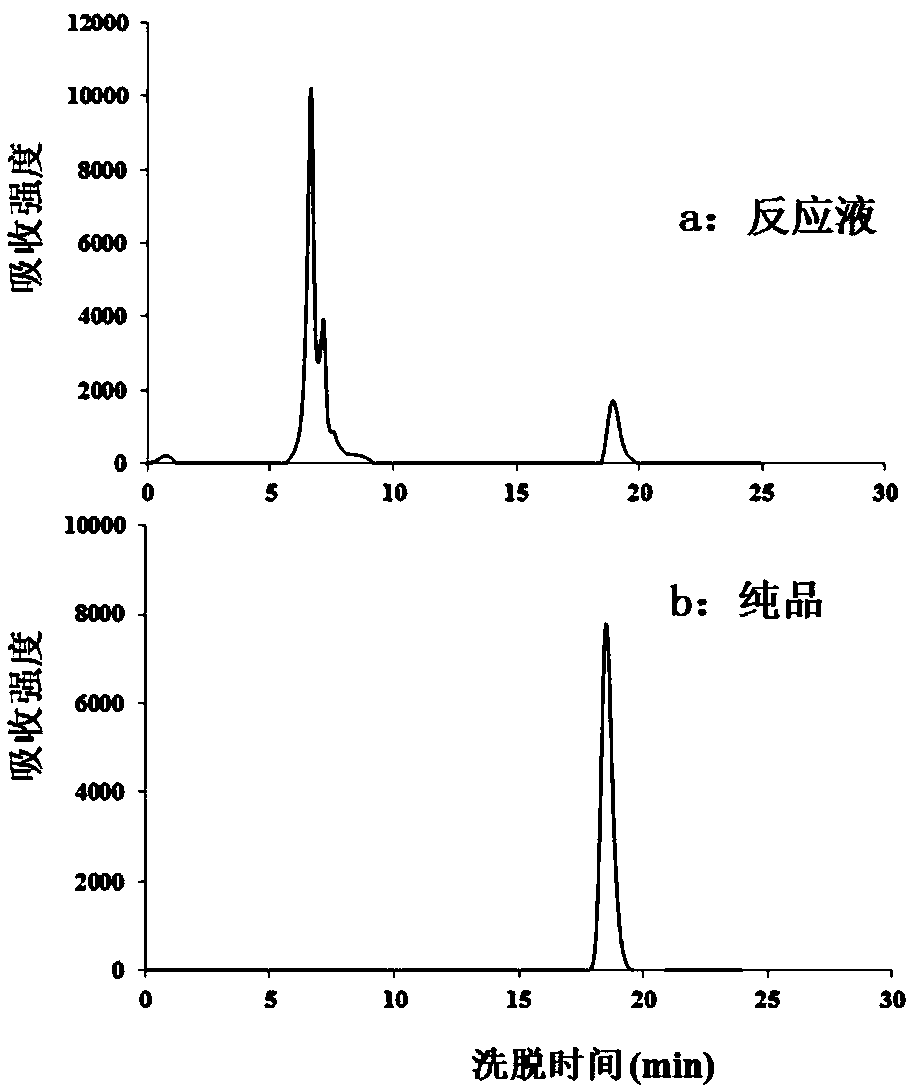
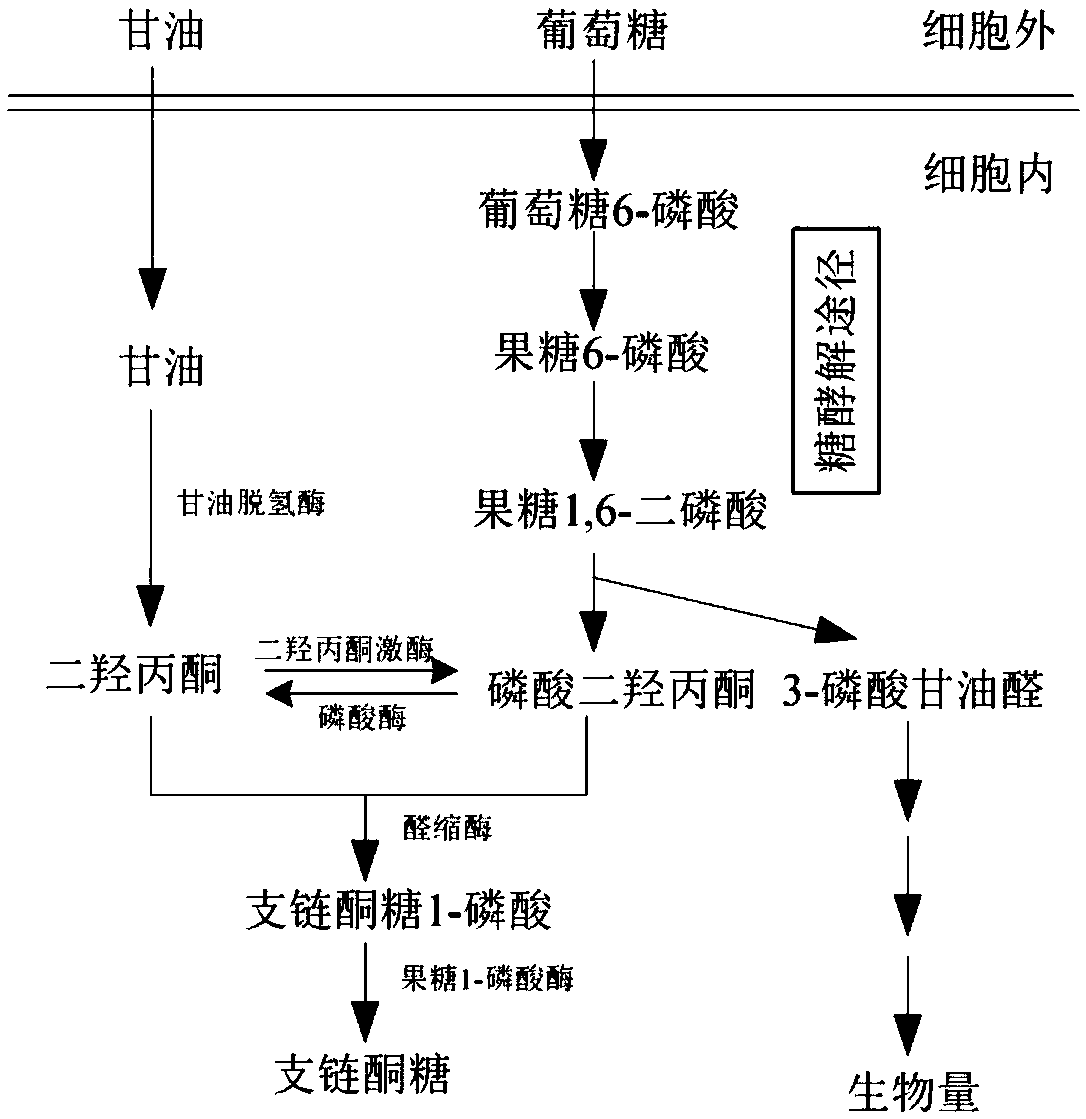
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
54 results about "Ketose" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A ketose is a monosaccharide containing one ketone group per molecule. The simplest ketose is dihydroxyacetone, which has only three carbon atoms, and it is the only one with no optical activity. All monosaccharide ketoses are reducing sugars, because they can tautomerize into aldoses via an aldol intermediate, and the resulting aldehyde group can be oxidised, for example in the Tollens' test or Benedict's test. Ketoses that are bound into glycosides, for example in the case of the fructose moiety of sucrose, are nonreducing sugars.
Process for the continuous production of ethylene glycol from carbohydrates
ActiveUS20150329449A1Organic compound preparationOxygen compounds preparation by reductionHydrogenPropylene glycol
A continuous process for converting carbohydrates to ethylene and propylene glycol. The carbohydrates are mixed with water and passed through a reactor at a temperature that hydrolyzes the carbohydrate mixture at least partially to monosaccharides. The reactor has a first zone comprising a retro-aldol catalyst and a second zone comprising a reducing catalyst. The aldose is converted in the first zone into glycolaldehyde by the retro-aldol catalyst and the glycolaldehyde, in the presence of hydrogen, is converted to ethylene glycol in the second zone of the reactor. The reaction products are removed from the reactor and the ethylene glycol is recovered. The selectivity to propylene glycol can be enhanced via feeding ketose as the carbohydrate.
Owner:TECH PRECESS TECH INC
Ophthalmic and contact lens solutions containing simple saccharides as preservative enhancers
InactiveUS20070098818A1Effective preservationDegree of reductionBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsTagatoseSucrose
The present invention relates to an ophthalmic solution comprising 0.00001 to 10.0 weight percent of a simple saccharide, at least 0.00001 weight percent of a preservative, and not more than about 0.2 percent by weight chloride. The simple saccharide is chosen from the group consisting of: inositol; mannitol; sorbitol; sucrose; dextrose; glycerin; propylene glycol; ribose; triose; tetrose; erythrose; threose; pentose; arabinose; ribulose; xylose; xylulose; lyxose; hexose; allose; altrose; fructose; galactose; glucose; gulose; idose; mannose; sorbose; talose; tagatose; adlose; ketose; heptose; sedoheptulose; monosaccharides; disaccharides; sugar alcohols; xylitol; and polyol.
Owner:FXS VENTURES LLC
Method of utilizing physiological activity of rare saccharide and composition containing rare saccharide
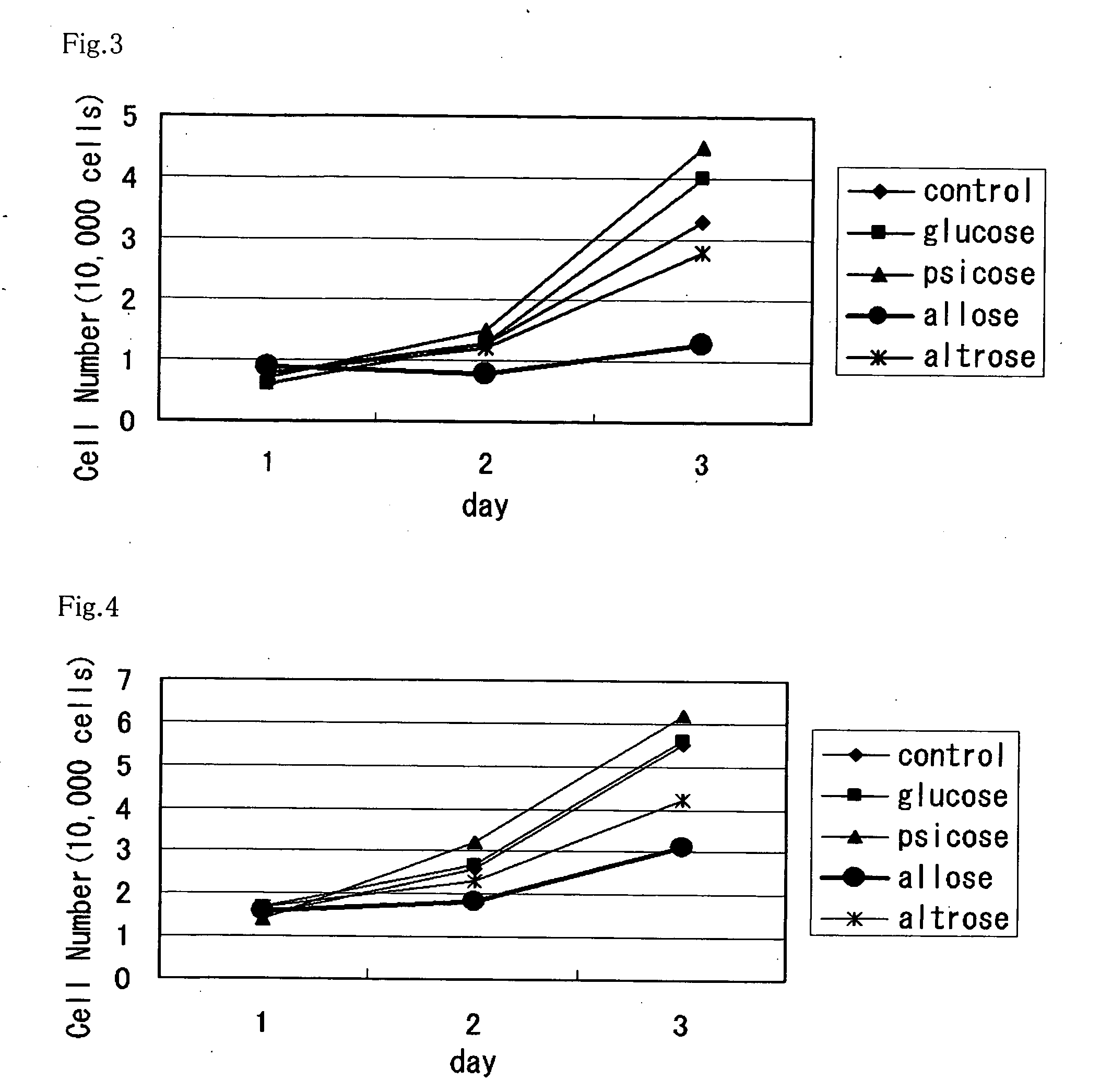
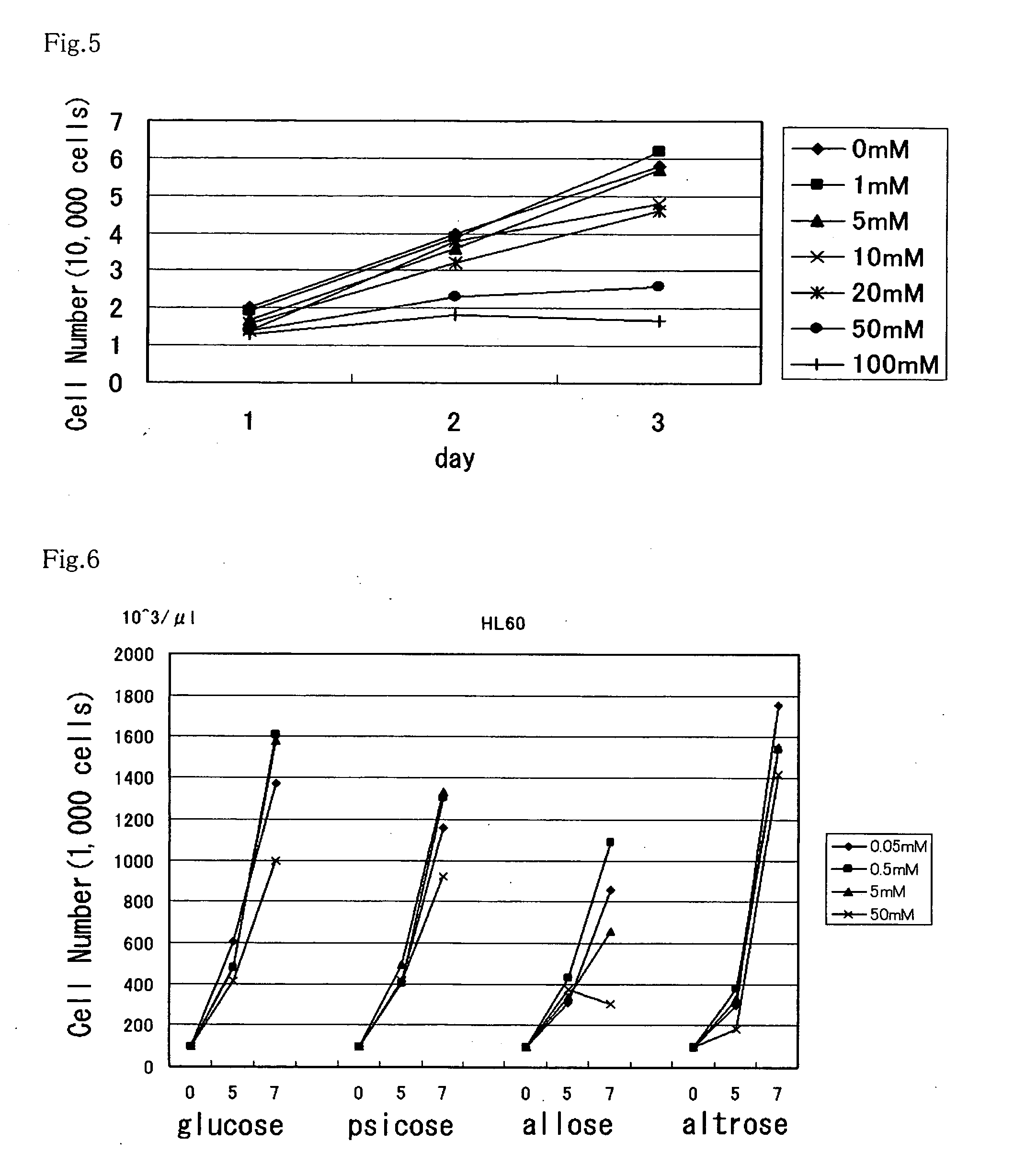
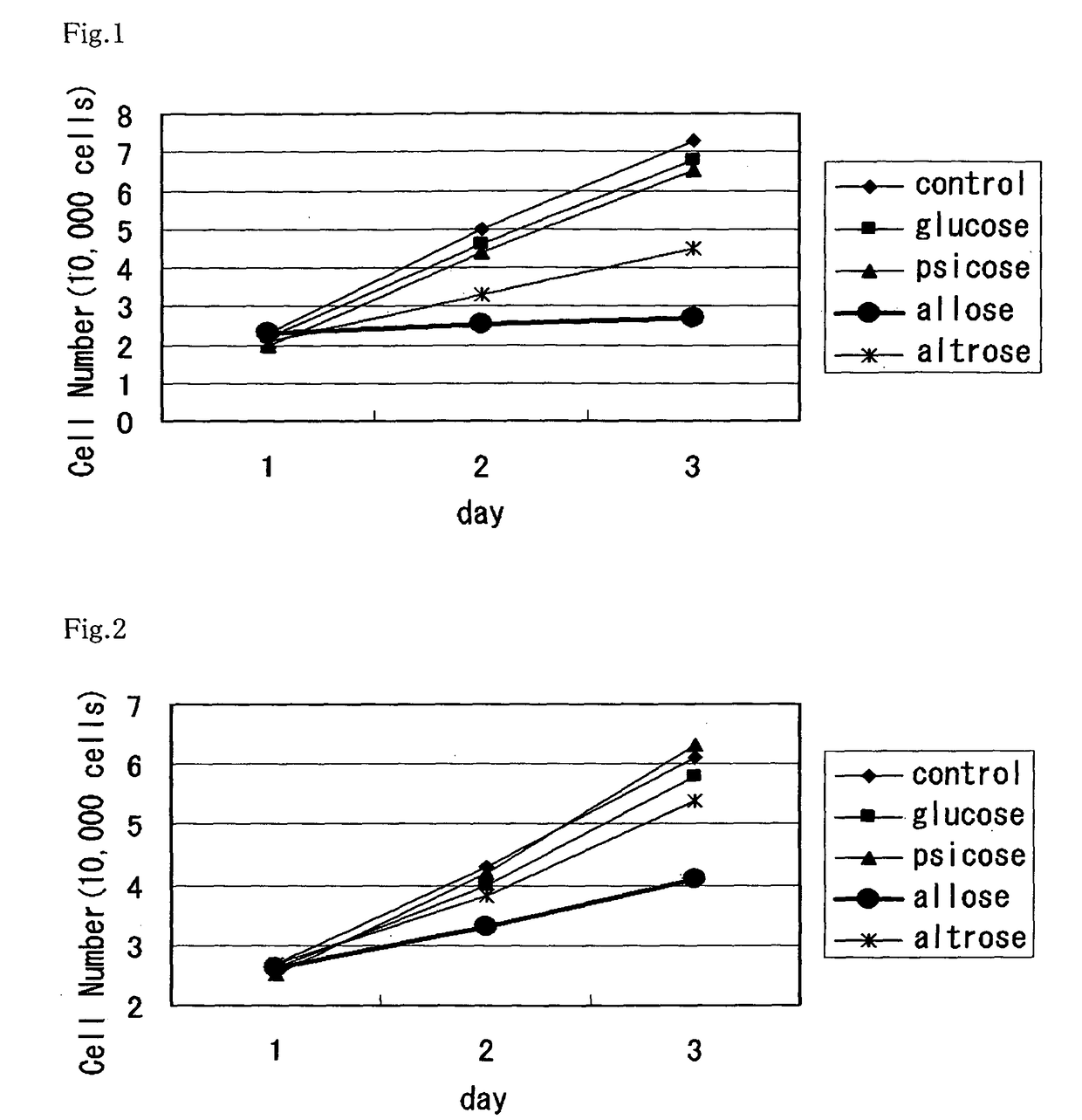
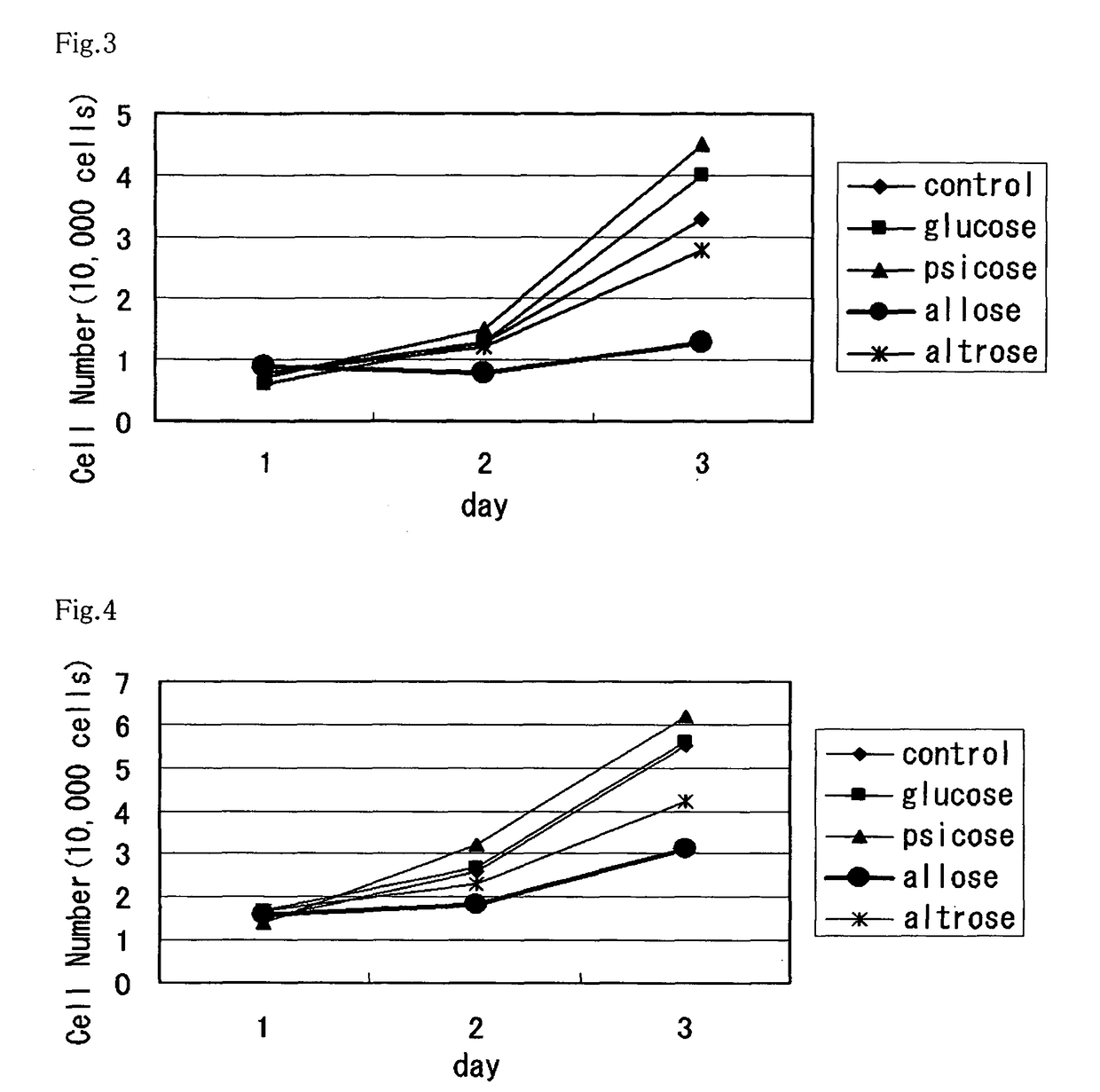
A method of utilizing the physiological activity of a rare saccharide, wherein physiological-activity sensitive cells are treated with the rare saccharide to modify the function of the cells. A composition containing, as an active ingredient, a rare saccharide which is introduced into physiological-activity sensitive cells and has an effect of modifying the function of the cells. The cells are human cells. The composition is a functional food, a drug, or a cosmetic. The rare saccharide is a rare saccharide belonging to aldose and / or ketose. The aldose is D-allose, and the cells are selected from the group consisting of cancer-cell proliferation inhibitory activity sensitive cells and active-oxygen production inhibitory activity sensitive cells. The ketose is D-psicose, and the cells are selected from the group consisting of chemokine secretion inhibitory activity sensitive cells, microglia migration inhibitory activity sensitive cells, and hypoglycemic activity sensitive cells.
Owner:MATSUTANI CHEM INDS CO LTD +2
Utilization of Rare Sugars in Plant or Microorganism
InactiveUS20080182752A1Low toxicityEasy to degradePlant growth regulatorsBiocidePlant hormoneGrowth retardant
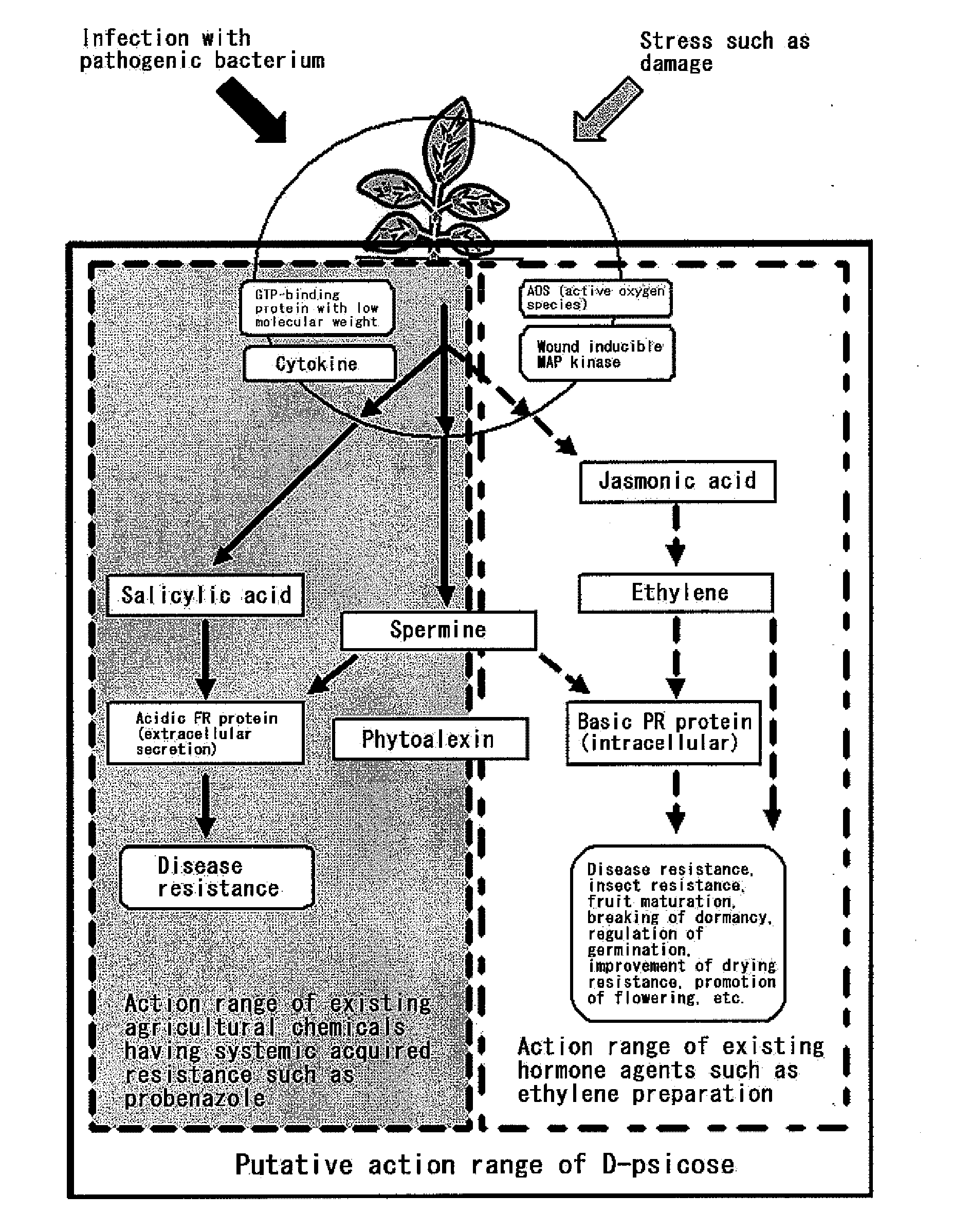
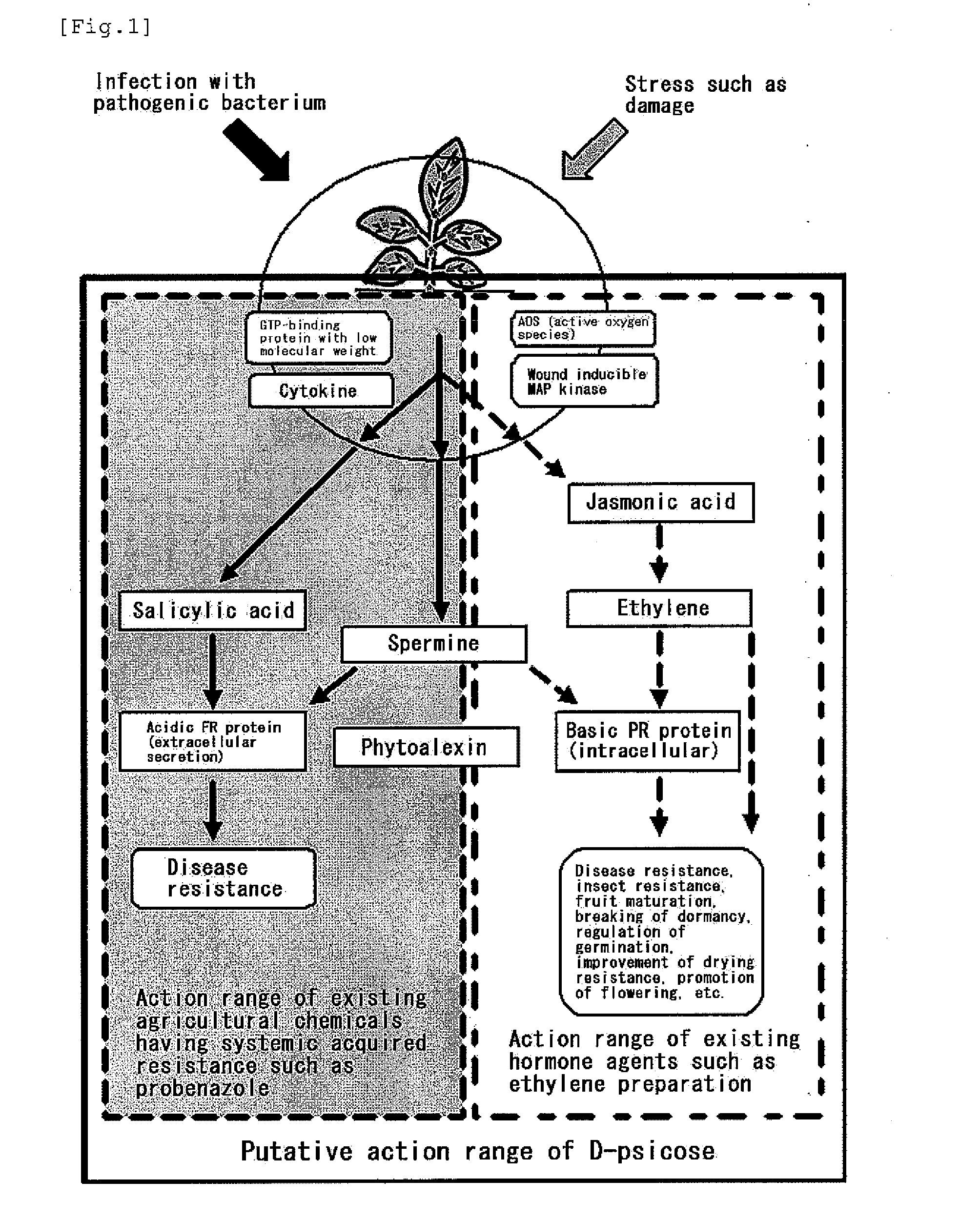
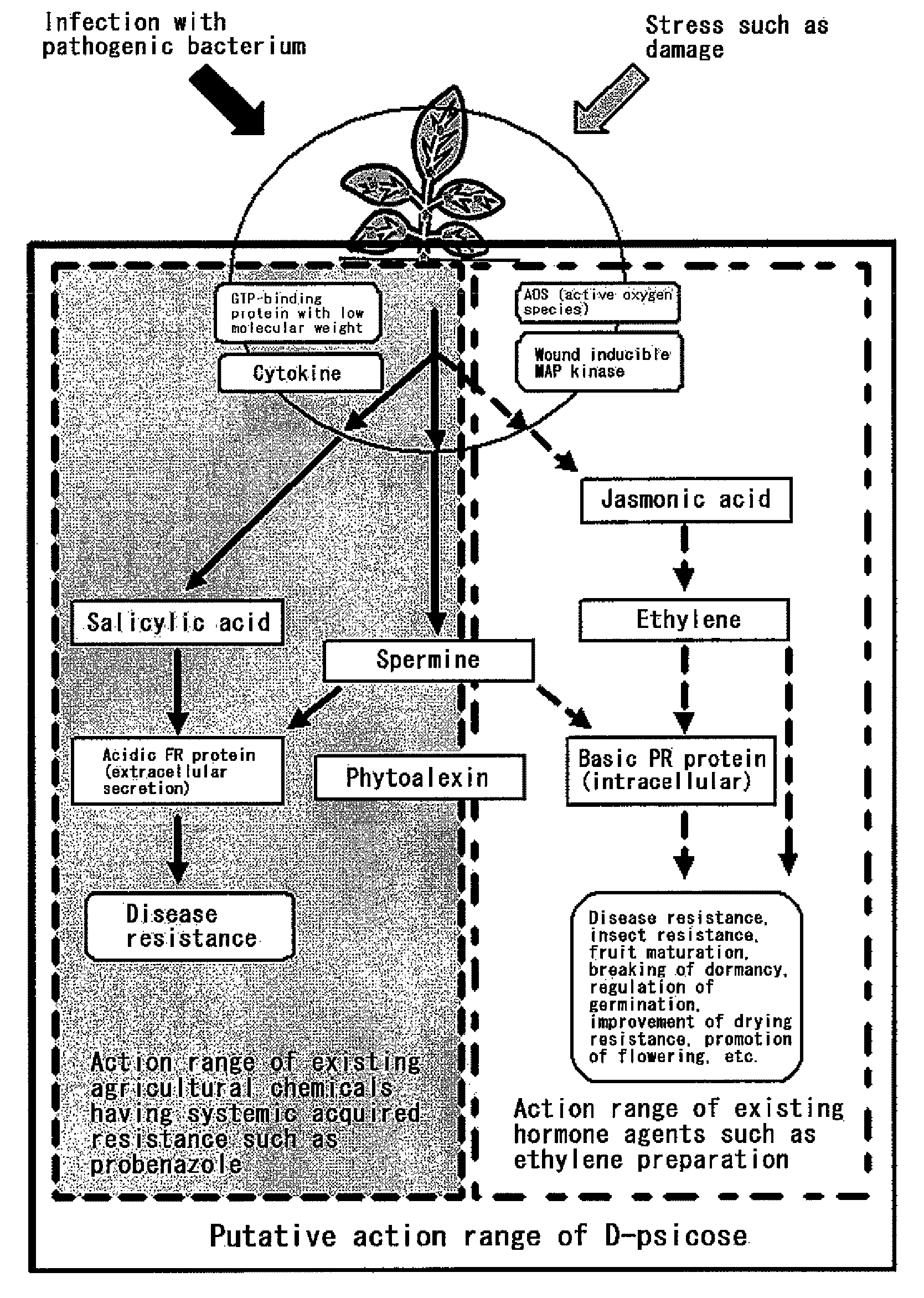
[OBJECT] To provide an agricultural chemical and the like with the use of an effect of inducing systemic acquired resistance in a plant. To provide a growth inhibitor of not only a plant pathogenic bacterium but also a harmful microorganism.[MEANS FOR RESOLUTION] Utilization of a rare sugar for inducing systemic acquired resistance in a plant or inhibiting the growth of a microorganism. Utilization thereof as an agricultural chemical with the use of the effect of inducing systemic acquired resistance in a plant, a plant disease inhibitor, an inducer of a plant growth regulatory factor (i.e., an inducer of plant hormone-like actions consisting of disease resistance, insect resistance, fruit maturation, breaking of dormancy, regulation of germination, drying resistance, and other than this, resistance to environmental stresses such as low temperature resistance, high temperature resistance, salt resistance and heavy metal resistance and promotion of flowering) and a microorganism growth inhibitor. The rare sugar is an aldose (D-allose, D-altrose or L-galactose) or a ketose (D-psicose or a mixture of D-psicose and D-fructose).
Owner:KAGAWA UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of temperature regulating fiber
ActiveCN104831388APhase change performance is maintained for a long timeNot easy to loseArtificial filaments from viscoseHeat-exchange elementsFiltrationKetone
The invention discloses a preparation method of a temperature regulating fiber. The method comprises the following steps: 1, carrying out two-stage dipping, squeezing, crushing, ageing, yellowing reaction, filtration, deaeration and maturation on cellulose pulp to obtain a spinning solution; 2, packaging phase change paraffin in the honeycomb micropores of a packaging material honeycomb silica to prepare phase change particles, adding an osmotic agent, an emulsifier and a ketose cross-linking agent, and uniformly mixing to prepare a phase change emulsion; 3, fully mixing the phase change emulsion with the spinning solution to prepare a phase change spinning solution, wherein the addition amount of the phase change particles is 5-25wt% of alpha-cellulose in the spinning solution; and 4, carrying out spinning formation on the phase change spinning solution, and post-processing to obtain the temperature regulating fiber. The phase change fiber prepared in the invention has the advantages of stable phase change temperature, good phase change performance, long service life and high physical and mechanical performances.
Owner:湖州珠力纳米材料科技开发有限公司
Method of culturing microorganism
In cultivating a microorganism having nitrile hydratase production ability, by allowing at least one of a ketose, such as fructose, and a sugar alcohol, such as mannitol, to be present, growth inhibition by cobalt ion is prevented, thereby achieving cultivation at a high concentration and with a high activity.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Ketose 3-epimerase, its preparation and uses
An object of the present invention is to provide a novel ketose 3-epimerase, a process for producing the same, a DNA encoding the enzyme, a recombinant DNA and transformant comprising the DNA, and a process for producing a ketose by using the enzyme. The present invention solves the above objects by providing a ketose 3-epimerase which is obtainable from a microorganism of the genus Rhizobium, a process for producing the same, a DNA encoding the enzyme, a recombinant DNA and transformant comprising the DNA, and a process for converting D- or L-ketohexose into corresponding D- or L-ketohexose by epimerizing the hydroxyl group at the C-3 position of the D- or L-ketohexose; and D- or L-ketopentose into corresponding D- or L-ketopentose by epimerizing the hydroxyl group at the C-3 position of the D- or L-ketopentose; by using the enzyme.
Owner:HAYASHIBARA BIOCHEMICAL LAB INC
Enzyme produced by arthrobacter globiformis
Task: There are provided a highly safe epimerase usable in food industry, and a method for producing a ketose. Resolution: The epimerase is a ketose 3-epimerase obtainable from a microorganism of the genus Arthrobacter, and having (1) substrate specificity whereby a D- or L-ketose is epimerized at position 3 to produce a corresponding D- or L-ketose, and (2) the highest substrate specificity for D-fructose and D-psicose among D- and L-ketoses.
Owner:MATSUTANI CHEM INDS CO LTD +1
Extraction and separation method for sand starfish mucopolysaccharide
The invention applies alkaline extraction method combined with enzymatic hydrolysis to extract acidic mucopolysaccharide from sand starfish, and sample powder has good solubility. The acidic mucopolysaccharide can be effectively discolored through hydrogen peroxide, and the binding proteins contained therein can be effectively removed through secondary enzymolysis process; and sand starfish acidic mucopolysaccharide I, II can be obtained after ethanol precipitation, wherein the total content of the mucopolysaccharides are up to 75% and 82% respectively, and protein contents thereof are 1.57% and 1.46% respectively. After further study on the mucopolysaccharide II, the mucopolysaccharide II further is found to be an acidic mucopolysaccharide containing sulfate and aldose residues without ketose and is composed of one major ingredient, the average molecular weight of the mucopolysaccharide II is about 12kD, and the charge distribution is uniform.
Owner:NANTONG XINYING DESIGN SERVICE
Catalytic conversion method of aldose into ketose
ActiveCN106032386ARich varietyHigh isomerization rateSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationKetoneNanotube
The invention provides a method for simultaneous isomerism of aldose into corresponding ketose and epimer aldose. The method uses the aldose as a substrate, and selects oxidation modified carbon nanotube supported with iron, aluminum, calcium, magnesium, molybdenum, chromium, and manganese elements of carbon nanotubes, or graphene as a catalyst. When the catalyst is mixed with the substrate aldose to not only catalyze aldehyde ketone isomerism to obtain corresponding ketose but also catalyze isomerism of C2 to obtain a corresponding C2 isomerism aldose catalyst, so as to realize simultaneous isomerism by one catalyst to obtain two rare functional sugars. The method has the advantages of high isomerism efficiency, simple operation conditions, reutilization of catalyst, small energy consumption, green, low cost, and potential in industrial mass production.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method of utilizing physiological activity of rare saccharide and composition containing rare saccharide
A method of utilizing the physiological activity of a rare saccharide, wherein physiological-activity sensitive cells are treated with the rare saccharide to modify the function of the cells. A composition containing, as an active ingredient, a rare saccharide which is introduced into physiological-activity sensitive cells and has an effect of modifying the function of the cells. The cells are human cells. The composition is a functional food, a drug, or a cosmetic. The rare saccharide is a rare saccharide belonging to aldose and / or ketose. The aldose is D-allose, and the cells are selected from the group consisting of cancer-cell proliferation inhibitory activity sensitive cells and active-oxygen production inhibitory activity sensitive cells. The ketose is D-psicose, and the cells are selected from the group consisting of chemokine secretion inhibitory activity sensitive cells, microglia migration inhibitory activity sensitive cells, and hypoglycemic activity sensitive cells.
Owner:MATSUTANI CHEM INDS CO LTD +2
Method for measuring carbohydrates in water by using fluorescence spectrum
The invention provides a method for measuring carbohydrates in water by using a fluorescence spectrum. The method comprises the following steps: adding concentrated sulfuric acid into a to-be-tested sample and heating to obtain a reacted to-be-tested sample; carrying out fluorescent spectroscopy detection on the reacted to-be-tested sample to obtain fluorescence intensity; obtaining the content ofthe ketose and the aldose in the to-be-tested sample according to a fluorescence intensity standard model of ketose and aldose, wherein the heating time is greater than or equal to 0 minute. Comparedwith the prior art, the method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that by adding the concentrated sulfuric acid into the to-be-tested sample, the carbohydrates which have no fluorescent signals are dehydrated to generate fluorescent hydroxymethyl furfural and other fluorescent by-products; by measuring the fluorescence signals of products, quantitative analysis of the carbohydrates inthe water can be realized; in addition, different fluorescence data can be identified by utilizing different ways of generating hydroxymethyl furfural by the aldose and the ketose and fluorescence differences of reaction by-products , thereby realizing quantitative analysis of the contents of the aldose and the ketose in the to-be-tested sample at the same time.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Saccharide-alkyleneoxy derivative and ink
InactiveUS7888406B2Improve permeabilityPrintableSugar derivativesDuplicating/marking methodsAlcohol sugarsOrganic chemistry
A saccharide-alkyleneoxy derivative comprising a compound represented by the following formula (1):A-(EP)n-OH (1)wherein A represents a skeleton of a saccharide selected from the group consisting of C3 to C12 aldoses, ketoses and sugar alcohols; EP represents an ethyleneoxy group and / or a propyleneoxy group; and n represents an average number of the repeating units. Also disclosed are a method for producing the saccharide alkyleneoxy derivative, and an ink containing the saccharide-alkyleneoxy derivative.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Biological synthesis method of branched ketose
The invention discloses a branched ketose method. According to the invention, the new function of known aldolase is provided, wherein the aldolase can catalyze an aldol condensation reaction between dihydroxyacetone phosphate and dihydroxyacetone to synthesize branched ketose, so that the invention discloses a method for synthesizing branched ketose by constructing an in-vitro multi-enzyme cascadereaction system to catalyze dihydroxyacetone on the basis, and the conversion rate is 90%; the invention also discloses a construction method of a corynebacterium glutamicum recombinant strain for producing branched ketose, wherein the branched ketose is synthesized by fermenting a cheap substrate glucose or glycerol with the obtained recombinant strain, and the yield reaches 36.3 g / L; and compared with the existing chemical method for synthesizing branched ketose, the branched ketose synthesis method provided by the invention has the advantages of cheap substrate, environmental friendliness,high product synthesis efficiency, single product and convenience in separation, has industrial application potential, and provides a basis for synthesis of 4-hydroxymethylfurfural.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
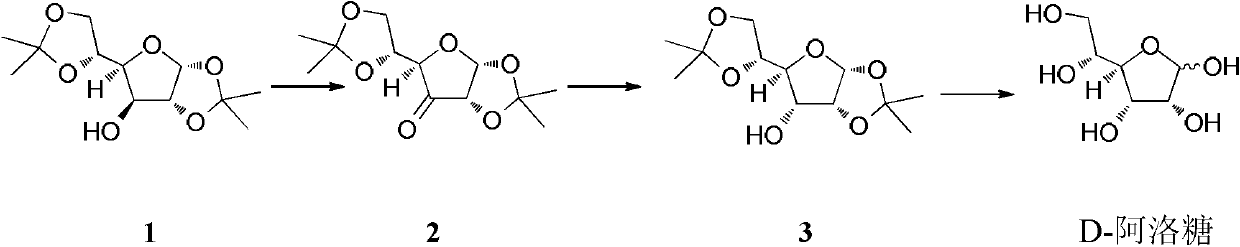
A method for preparing d-allose by reducing ketose by catalytic hydrogenation
ActiveCN102268048AHigh stereoselectivityEasy post-processingSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationAlloseHydrogen
The invention discloses a method for preparing D-allose by reducing ketose by a catalytic hydrogenation process, which comprises the following steps: 1) subjecting the compound of formula (II) to reduction reaction in the presence of a transitional metal catalyst and hydrogen to obtain a compound of a formula III, wherein R1 and R2 are dihydroxyl protective groups; and 2) removing the R1 and R2 protective groups from the compound of the formula III to obtain D-allose. The method has the advantages of high stereoselectivity, high cleanness, convenience for post treatment and the like and is a preparation method suitable for industrial production.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Utilization of rare sugars in plant or microorganism
To provide an agricultural chemical and the like with the use of an effect of inducing systemic acquired resistance in a plant. To provide a growth inhibitor of not only a plant pathogenic bacterium but also a harmful microorganism.Utilization of a rare sugar for inducing systemic acquired resistance in a plant or inhibiting the growth of a microorganism. Utilization thereof as an agricultural chemical with the use of the effect of inducing systemic acquired resistance in a plant, a plant disease inhibitor, an inducer of a plant growth regulatory factor (i.e., an inducer of plant hormone-like actions consisting of disease resistance, insect resistance, fruit maturation, breaking of dormancy, regulation of germination, drying resistance, and other than this, resistance to environmental stresses such as low temperature resistance, high temperature resistance, salt resistance and heavy metal resistance and promotion of flowering) and a microorganism growth inhibitor. The rare sugar is an aldose (D-allose, D-altrose or L-galactose) or a ketose (D-psicose or a mixture of D-psicose and D-fructose).
Owner:KAGAWA UNIVERSITY
Method for determining content of saccharide components in ixeri sonhifolia injection
ActiveCN104316630AOvercoming Hard-to-Detect ShortcomingsAccurate detectionComponent separationVapor phase chromatographyPhysical chemistry
The invention relates to an identification method for a traditional Chinese injection, and particularly relates to a method for determining the content of saccharide components in an ixeri sonhifolia injection by using GC-MS. The method comprises the following steps of (a) preparation of a sample, comprising a pretreatment method of the sample; (b) preparation of a standard substance, comprising a derivatization method of aldose components and a derivatization method of ketose components; (c) chromatographic conditions: a GC-MS analyzer employs a GC-MS-QP2010SE and capillary column is shown in the description; and (d) determination: taking the standard substance and the sample precisely, injecting into a gas chromatograph, determining by gas chromatography, and making a fingerprint spectrum of the saccharide components in the ixeri sonhifolia injection. With the method, the difficultly detectable saccharide components in an ixeri sonhifolia can be detected accurately by adopting the derivatization method.
Owner:TONGHUA HUAXIA PHARMA
Sorbitol dehydrogenase gene from pseudomonas syringae and application of sorbitol dehydrogenase gene
ActiveCN105154457AImprove conversion rateEfficient catalytic conversionFungiBacteriaEscherichia coliIsomerase
The invention discloses a sorbitol dehydrogenase gene from pseudomonas syringae and application of the sorbitol dehydrogenase gene. The gene nucleic acid sequenc is shown as SEQ ID NO:1, a recombinant vector is built, cloning and expression are conducted in escherichia coli, and the sorbitol dehydrogenase amino acid sequence of the gene coding is shown as SEQ ID NO:2. The sorbitol dehydrogenase can effectively catalyze conversion of various important polyhydric alcohols and ketose corresponding to the polyhydric alcohols, the conversion rate to substrate of the sorbitol dehydrogenase is larger than 99%, compared with a traditional production method depending on isomerase, the later-period separation and decoloration costs are greatly lowered, and the sorbitol dehydrogenase gene has important industrial application value.
Owner:苏州科宁多元醇有限公司
A kind of acid-catalyzed method for preparing saponin by directly reacting aldose or ketose with aglycon
ActiveCN105263945BEasy to operateStrategies are simpleSugar derivativesGlycoside steroidsOrganic solventOrganic synthesis
The present invention belongs to the field of organic synthesis, relates to a method for synthesizing a saponin, and in particular, to a method for constructing a glycosidic bond in a saponin, and comprises the following steps: directly reacting an excessive amount of aldose or ketose with aglycone in a suitable organic solvent at 30 °C to a reflux temperature and with the presence of an acid catalyst, to obtain a target product saponin.
Owner:于跃
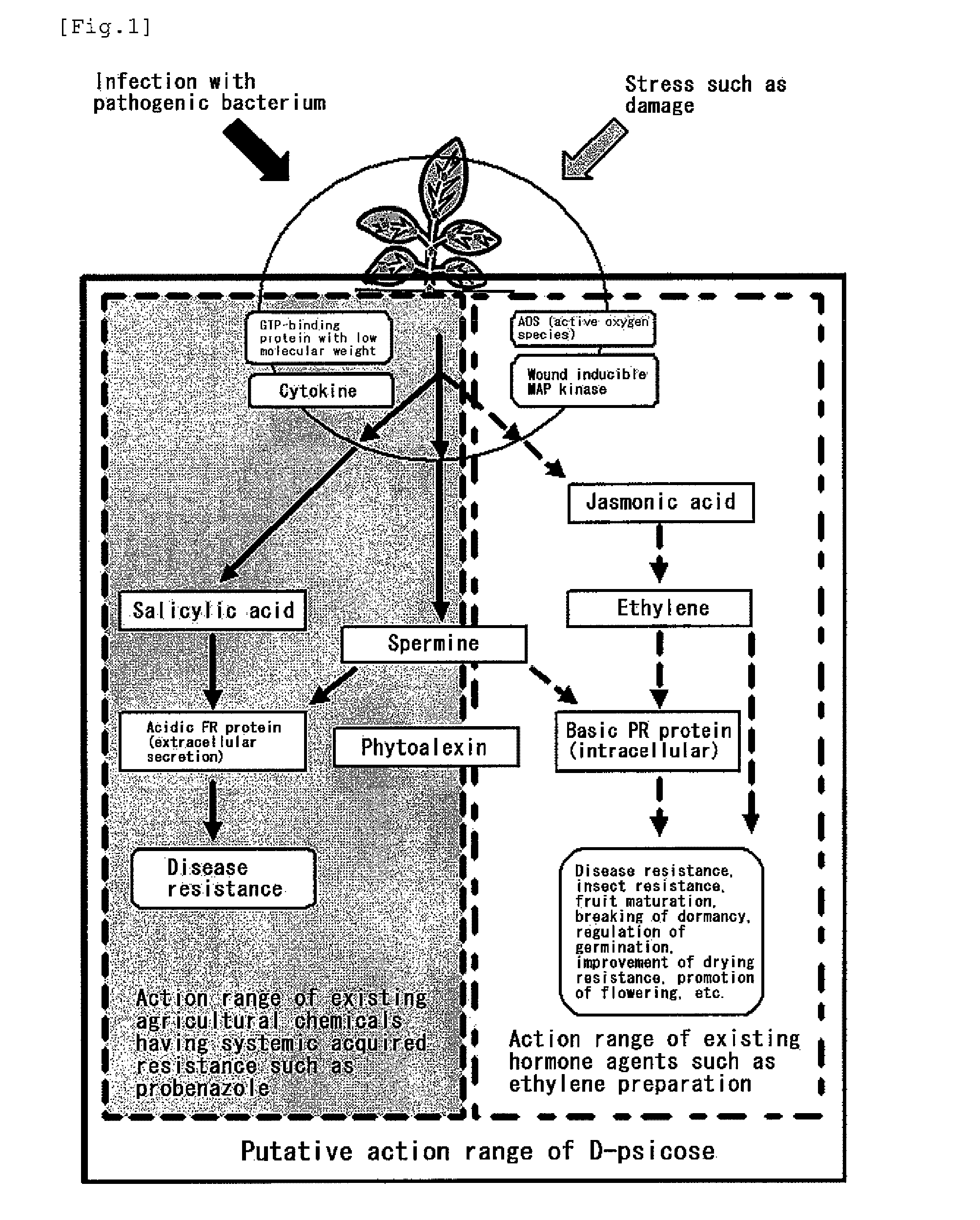
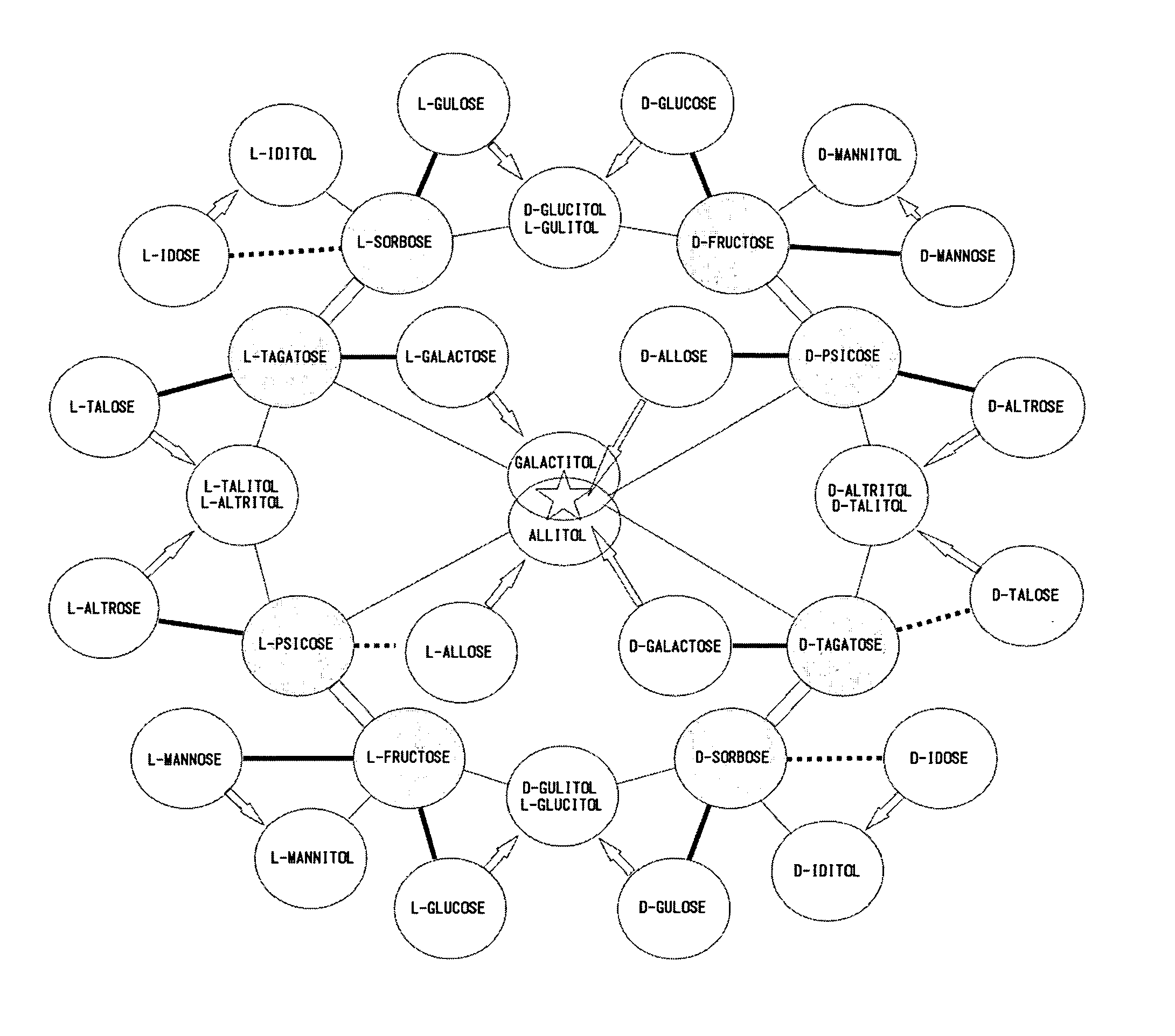
Gene sequence of l-rhamnose isomerase having new catalytic function and use thereof
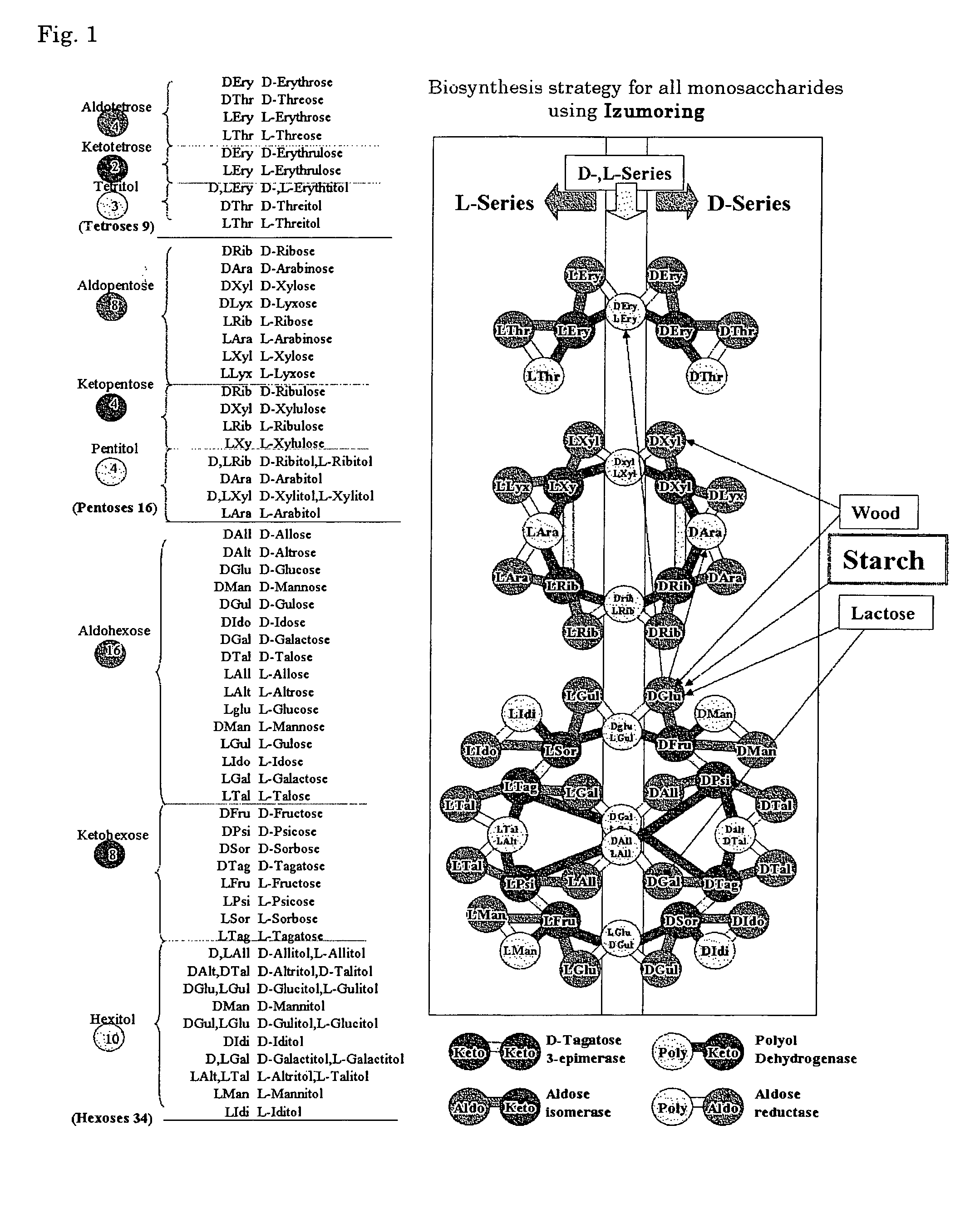
In the rare sugar strategy of Izumoring (FIG. 1), it is intended to establish a reaction system of producing rare sugars of many types by acquiring an isomerase which acts on various rare aldoses and, therefore, is most efficient in producing various rare ketoses. A DNA encoding the following protein (a) or (b). The above-mentioned DNA which is L-rhamnose isomerase derived from Pseudomonas stutzerii. A protein comprising the amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO:2. A process for producing a recombinant protein characterized by culturing a host cell containing an expression system that can express the above-mentioned protein in a medium and collecting a recombinant protein having an L-rhamnose isomerase activity from the thus obtained culture. A method of applying FIG. 1 to the production of a rare sugar characterized in that the location of a target rare sugar in the overall picture of monosaccharides is understood and thus the optimum production pathway on which the above protein is allowed to act is designed.
Owner:MATSUTANI CHEM INDS CO LTD
Method for synthesizing rare ketohexose and ketoheptose from sugar acid lactone
InactiveCN101817851AOvercoming difficult preparationsVersatilitySugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationKetoneCarbon chain
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing rare ketohexose and ketoheptose from a raw material of sugar acid lactone, which comprises the following steps of: firstly, reacting the hydroxyl-protected sugar acid lactone with diiodomethane under the action of n-butyl lithium to prolong a carbon chain so as to obtain 1-deoxy iodo-ketose; secondly, in an alkaline environment, performing a hydrolysis reaction to ensure that hydroxyl radicals substitute iodine atoms so as to obtain a ketose intermediate; and finally, performing de-protection on the intermediate to obtain the needed rare ketoses. The method provides a new technical support for preparing the rare ketoses, has easily-available raw materials and simple and convenient operation and processing, is easy to be performed in a laboratory, is expected to realize industrialization, and has a comparatively simple and short process route and a low production cost.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Methods for High Yield Production of Furans from Biomass Sugars at Mild Operating Conditions
Facile methods for high-yield furfural and HMF production from biomass sugars are described. The methods generally involve converting the biomass sugars in high yield to their ketose isomers, resulting in furan production under low temperature and pressure conditions with efficient recycling of the process streams.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TOLEDO
Preparation method of dihydroxyacetone by transforming glycerol
ActiveCN102492732ANo biological safety hazardsLow culture conditionsMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicroorganismDihydroxyacetone
A preparation method of dihydroxyacetone by transforming glycerol relates to a polyhydroxy ketose. Flavobacterium halmsphilum ch20-1 is inoculated into seed culture medium for cultivation. Then seed liquid is added into fermentation medium containing glycerol to perform aerobic fermentation. After NaOH solution feeding and fermentation, dihydroxyacetone is obtained. According to the invention, transforming of cheap material waste glycerol into biobased platform chemical dihydroxyacetone of high added value is accomplished by the use of microorganism and an outlet of effective utilization of waste glycerol is found. The method provided by the invention uses a strain with no hidden danger of biological safety. At the same time, it has a short fermentation time, high productivity, low bacterial culture condition and low production cost.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Saccharide-alkyleneoxy derivative and ink
InactiveUS20080163791A1Improve permeabilityGenerates cloggingCosmetic preparationsLiquid surface applicatorsAlcohol sugarsSugar alcohol
A saccharide-alkyleneoxy derivative comprising a compound represented by the following formula (1):A−(EP)n−OH (1)wherein A represents a skeleton of a saccharide selected from the group consisting of C3 to C32 aldoses, ketoses and sugar alcohols; EP represents an ethyleneoxy group and / or a propyleneoxy group; and n represents an average number of the repeating units. Also disclosed are a method for producing the saccharide alkyleneoxy derivative, and an ink containing the saccharide-alkyleneoxy derivative.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Thermostable L-ribose isomerase and method for producing same and use of same
Object: To provide a thermostable L-ribose isomerase.Means for Resolution: The thermostable L-ribose isomerase with MW. 32,000 (by SDS-PAGE), optimal temperature of 45° C., optimal pH of pH 9.0 (glycine-NaOH buffer), and stable physicochemical properties such as temperature stability up to 45° C. during thermal treatment at pH 9.0 for 10 minutes, and with an action to isomerize L-ribose to generate L-ribulose or of inversely to isomerize L-ribulose to generate L-ribose. A conversion method between an aldose and a ketose comprising allowing the thermostable L-ribose isomerase as an enzyme derived from (1) Raoultella ornithinolytica strain MB426 (NITE BP-277) to interact with an aldose selected from L-ribose, D-lyxose, D-tallose, D-mannose, L-allose and L-gulose to isomerize the aldose to generate a ketose selected from the individually corresponding L-ribulose, D-xylulose, D-tagatose, D-fructose, L-psicose and L-sorbose or to interact with a ketose selected from L-ribulose, D-xylulose, D-tagatose, D-fructose, L-psicose and L-sorbose to isomerize the ketose to generate an aldose selected from the individually corresponding L-ribose, D-lyxose, D-tallose, D-mannose, L-allose and L-gulose.
Owner:KAGAWA UNIVERSITY +1
A kind of sorbitol dehydrogenase gene derived from Pseudomonas syringae and its application
ActiveCN105154457BImprove conversion rateEfficient catalytic conversionFungiBacteriaEscherichia coliIsomerase
The invention discloses a sorbitol dehydrogenase gene from pseudomonas syringae and application of the sorbitol dehydrogenase gene. The gene nucleic acid sequenc is shown as SEQ ID NO:1, a recombinant vector is built, cloning and expression are conducted in escherichia coli, and the sorbitol dehydrogenase amino acid sequence of the gene coding is shown as SEQ ID NO:2. The sorbitol dehydrogenase can effectively catalyze conversion of various important polyhydric alcohols and ketose corresponding to the polyhydric alcohols, the conversion rate to substrate of the sorbitol dehydrogenase is larger than 99%, compared with a traditional production method depending on isomerase, the later-period separation and decoloration costs are greatly lowered, and the sorbitol dehydrogenase gene has important industrial application value.
Owner:苏州科宁多元醇有限公司
Method for purifying seaweed ketose
InactiveCN102925515ASimple processImprove separation efficiencyMicroorganism based processesFermentationPurification methodsTrehalose synthase
The invention relates to a method for purifying seaweed ketose. The method comprises the following steps of: transforming 20% of sucrose solution by utilizing trehalose synthase to generate mixed syrup containing 80% of seaweed ketose; then assimilating sucrose which is not reacted in the mixed syrup, as well as byproducts, namely fructose and glucose by utilizing saccharomyces cerevisiae cells, wherein trehalose is very difficult to be degraded and assimilated by yeast; and further removing the saccharomyces cerevisiae cells in the syrup by utilizing centrifugation to get a seaweed ketose solution with single sugar component. According to the purification method, the recovery rate of the seaweed ketose can achieve 95%; and as for the seaweed ketose with the single sugar component, the syrup can be further concentrated, desalted and refined to produce the high-purity seaweed ketose.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Enzyme produced by Arthrobacter globiformis
There are provided a highly safe epimerase usable in food industry, and a method for producing a ketose. Resolution: The epimerase is a ketose 3-epimerase obtainable from a microorganism of the genus Arthrobacter, and having (1) substrate specificity whereby a D- or L-ketose is epimerized at position 3 to produce a corresponding D- or L-ketose, and (2) the highest substrate specificity for D-fructose and D-psicose among D- and L-ketoses.
Owner:MATSUTANI CHEM INDS CO LTD +1
Preparation method of high-oil-loading microcapsule powder without adding synthetic emulsifier
ActiveCN114304689AImprove hydrophilicityImprove lipophilicityFood shapingMicroballoon preparationMaillard reactionSpray dried
The invention discloses a preparation method of high-oil-loading microcapsule powder without adding a synthetic emulsifier. Vegetable protein or animal protein is used as a protein raw material, a protein dispersion solution is prepared, after protein denaturation is promoted through primary heat treatment, ketose or aldose is added, wet-method Maillard reaction is promoted through secondary heat treatment, and a pre-prepared wall material solution is generated. Grease is added, and the balance is supplemented with the micromolecular filler. And carrying out vacuum degassing, high-speed homogenization, high-pressure homogenization, UHT sterilization, spray drying and other processes to produce the high-oil-loading microcapsule powder. The microcapsule powder is high in oil carrying rate, high in embedding rate and good in dispersity, and no synthetic emulsifier is added in the microcapsule preparation process.
Owner:宝得瑞(湖北)健康产业有限公司 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com