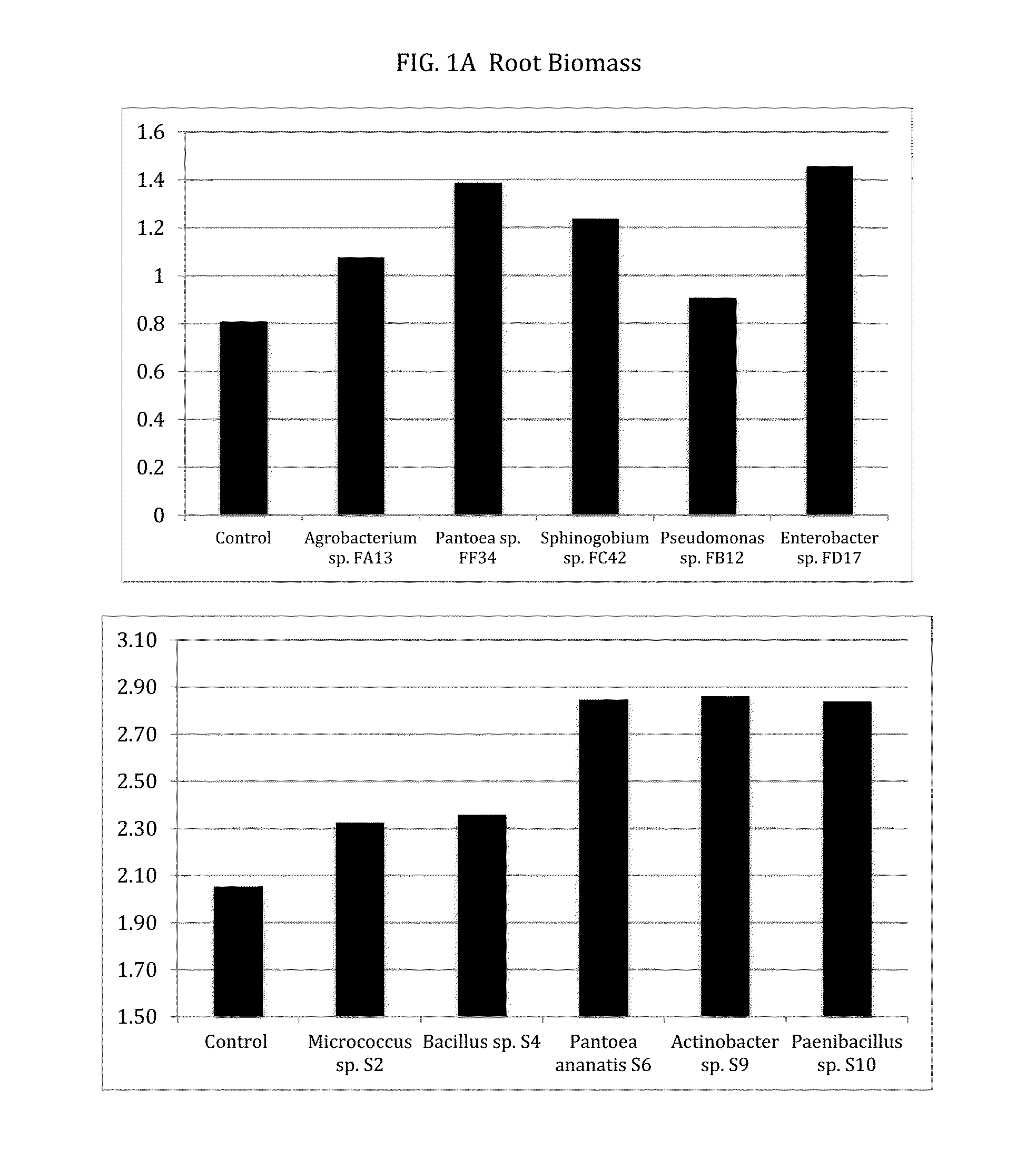
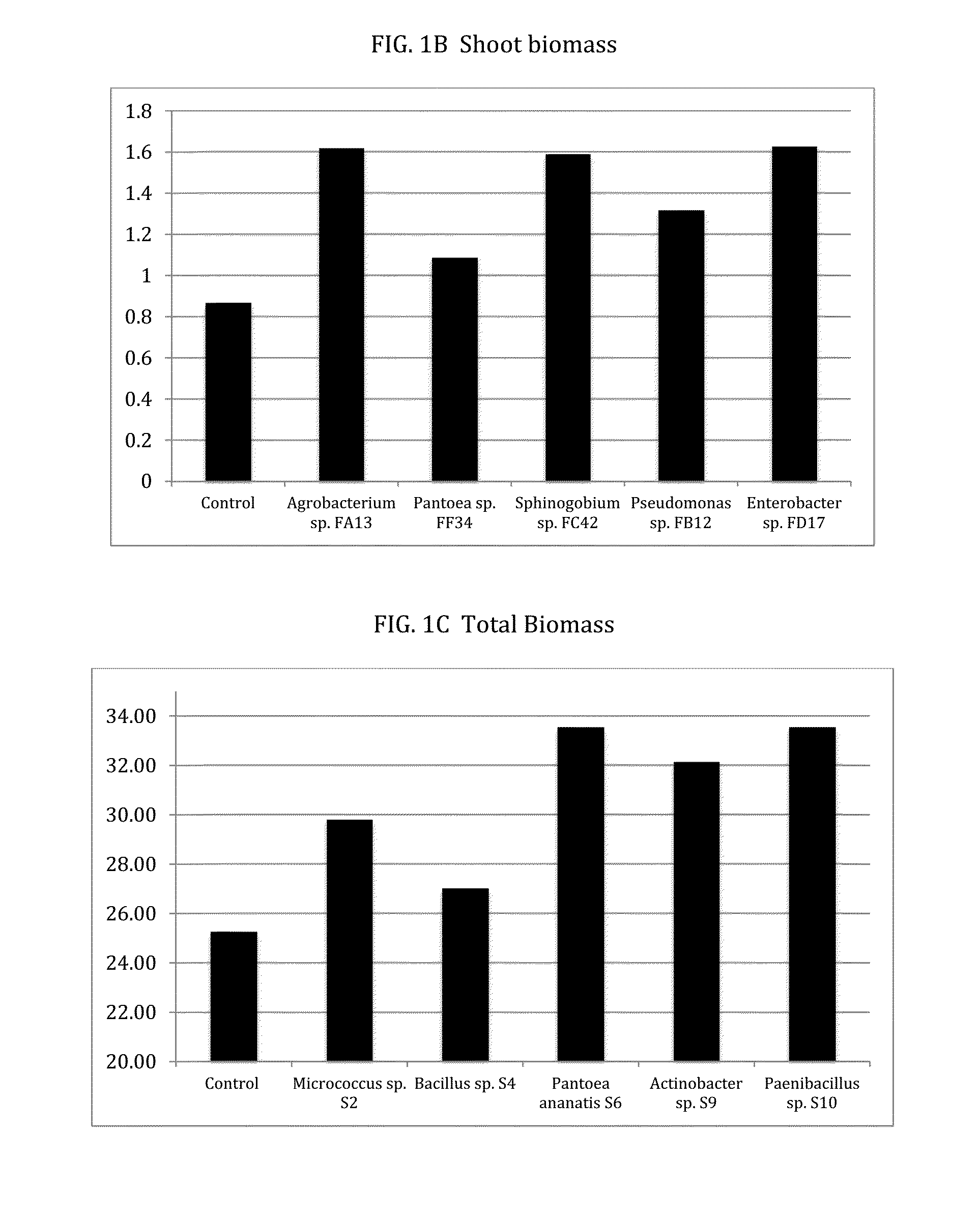
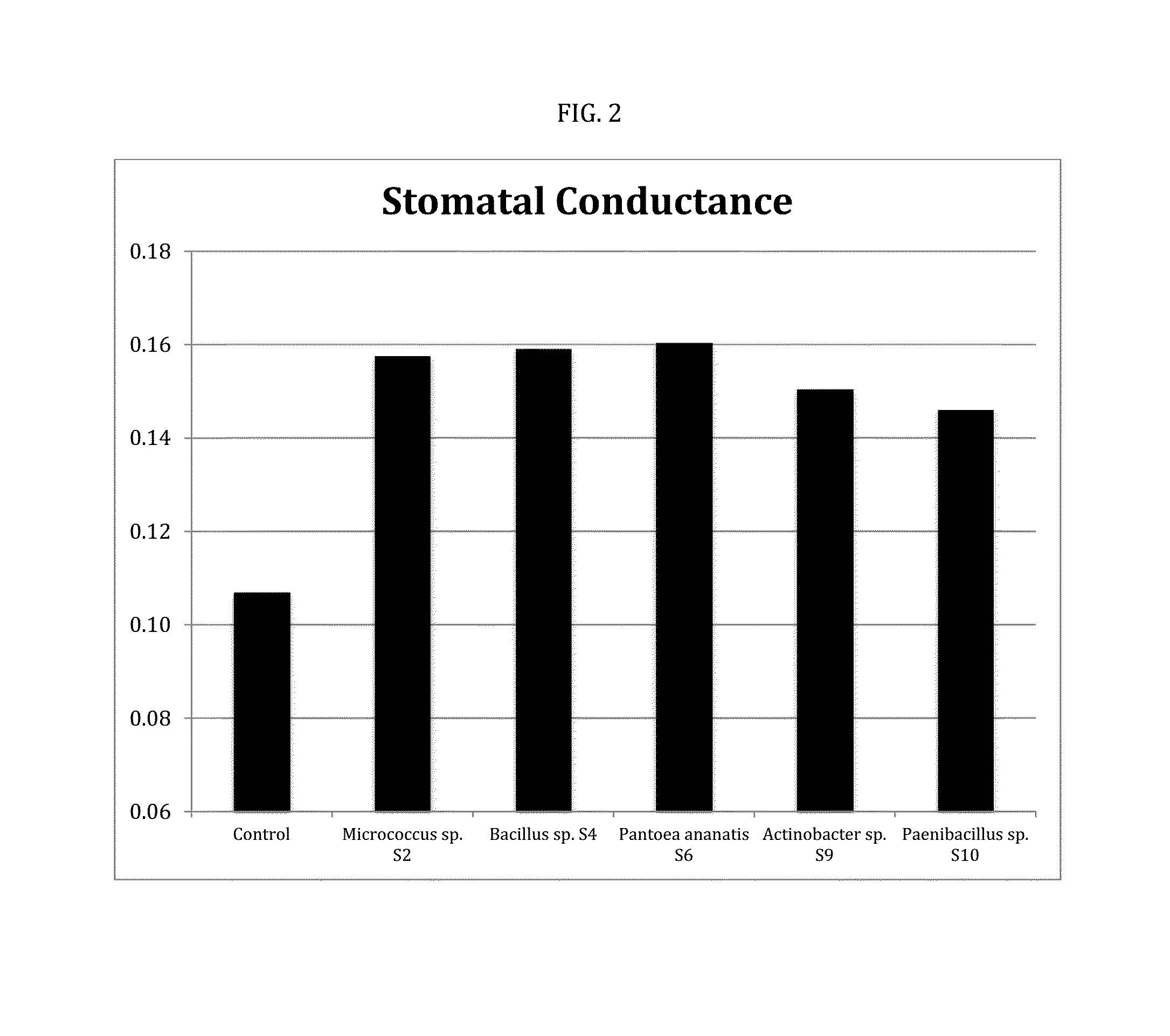
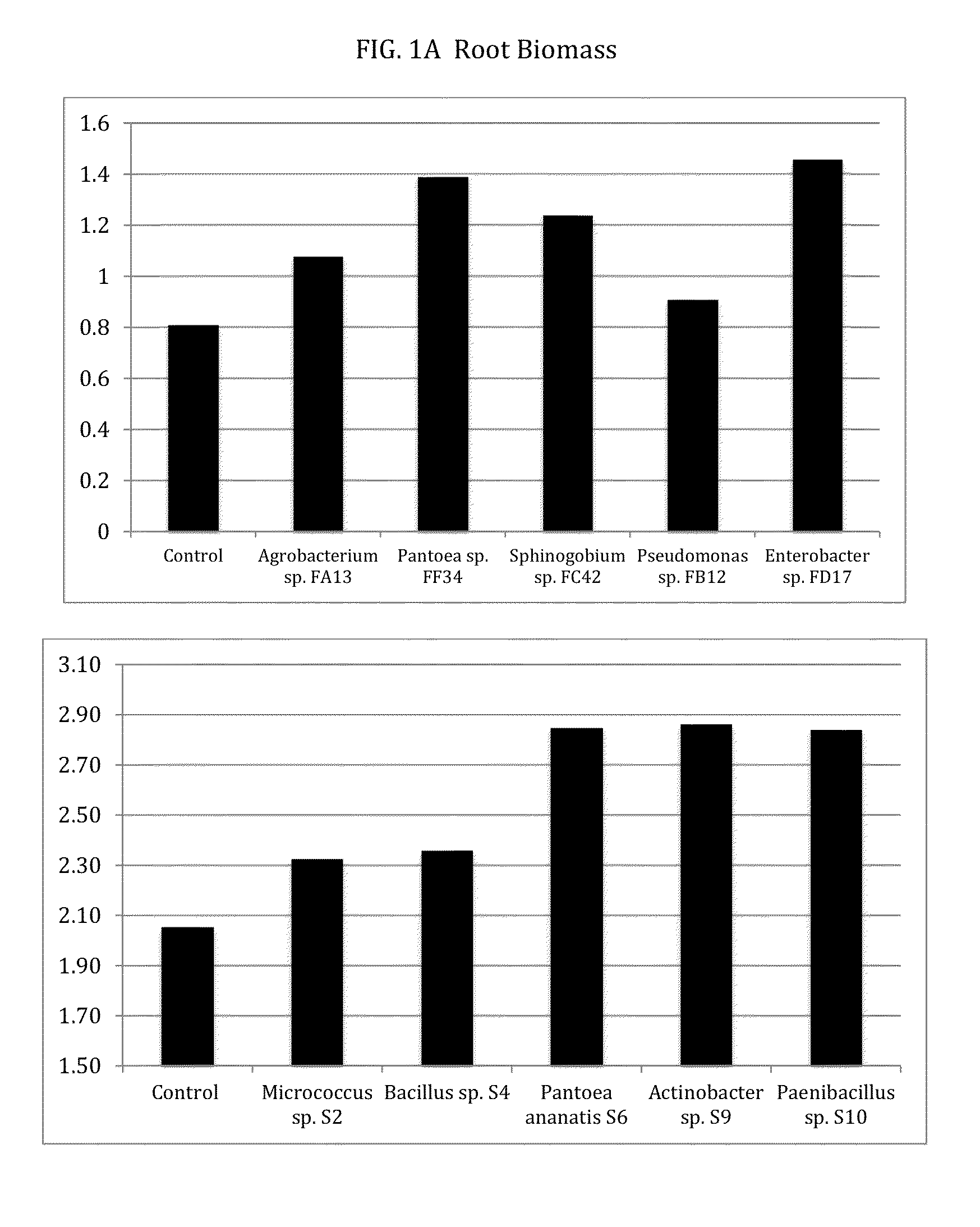
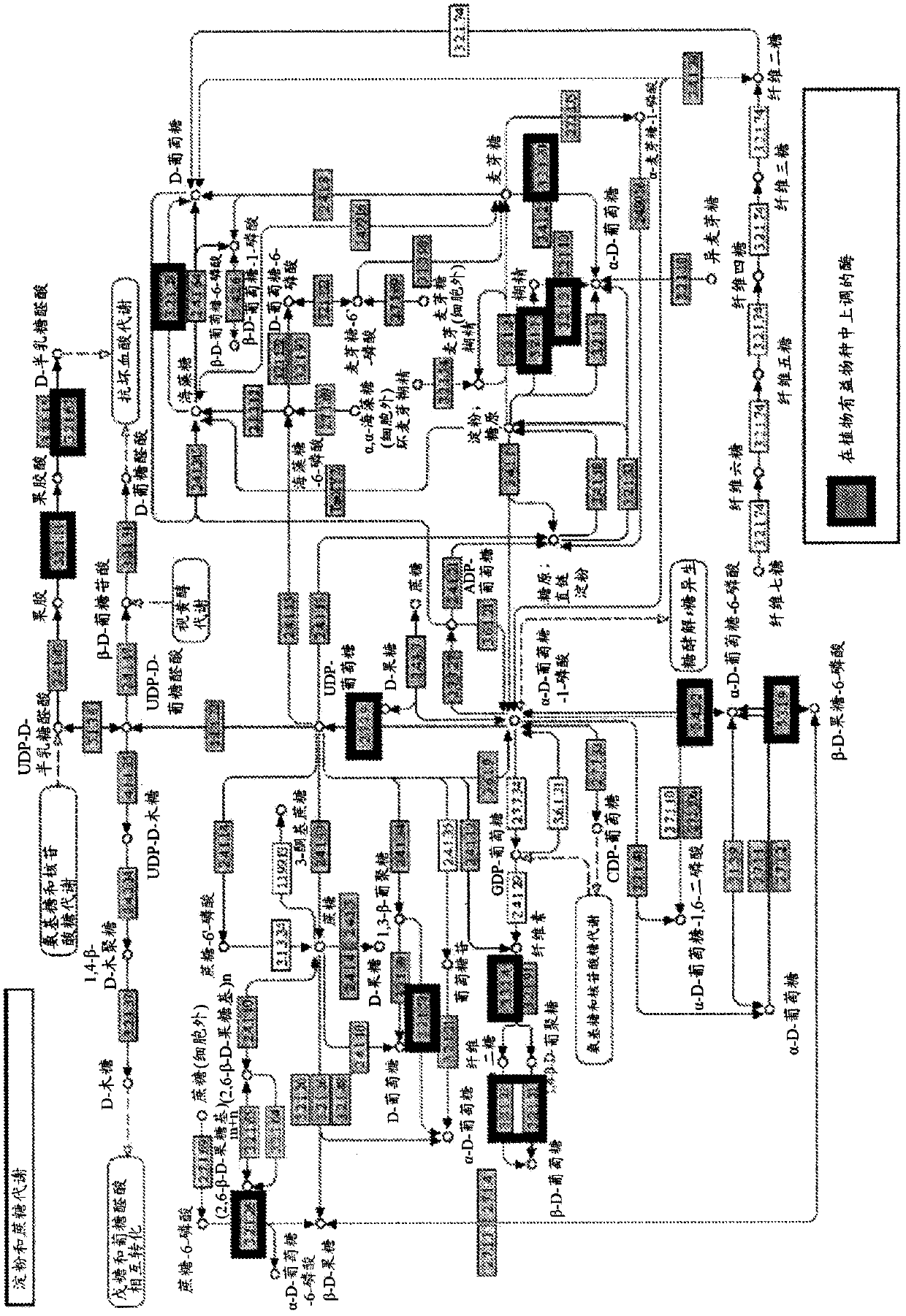
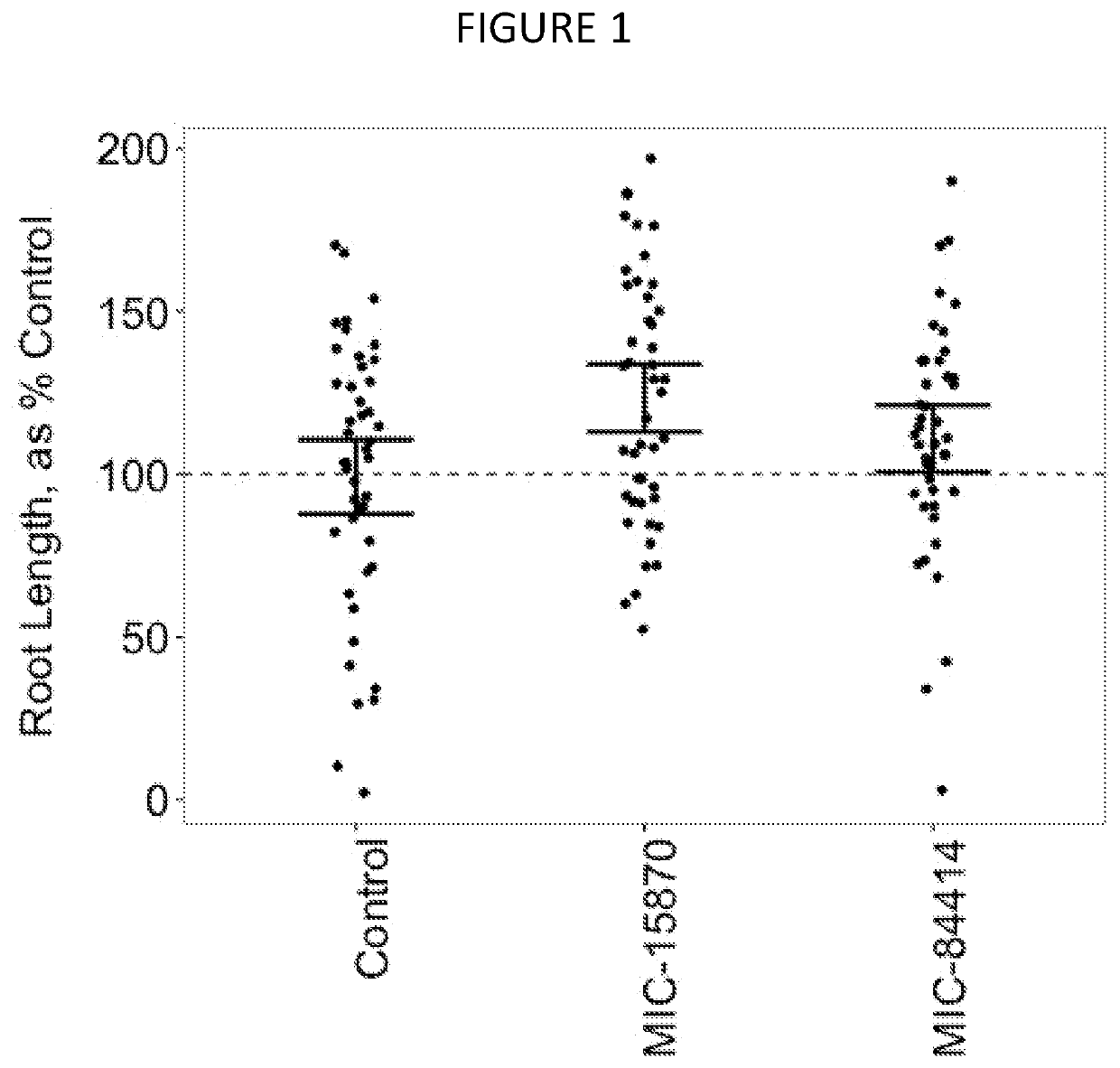
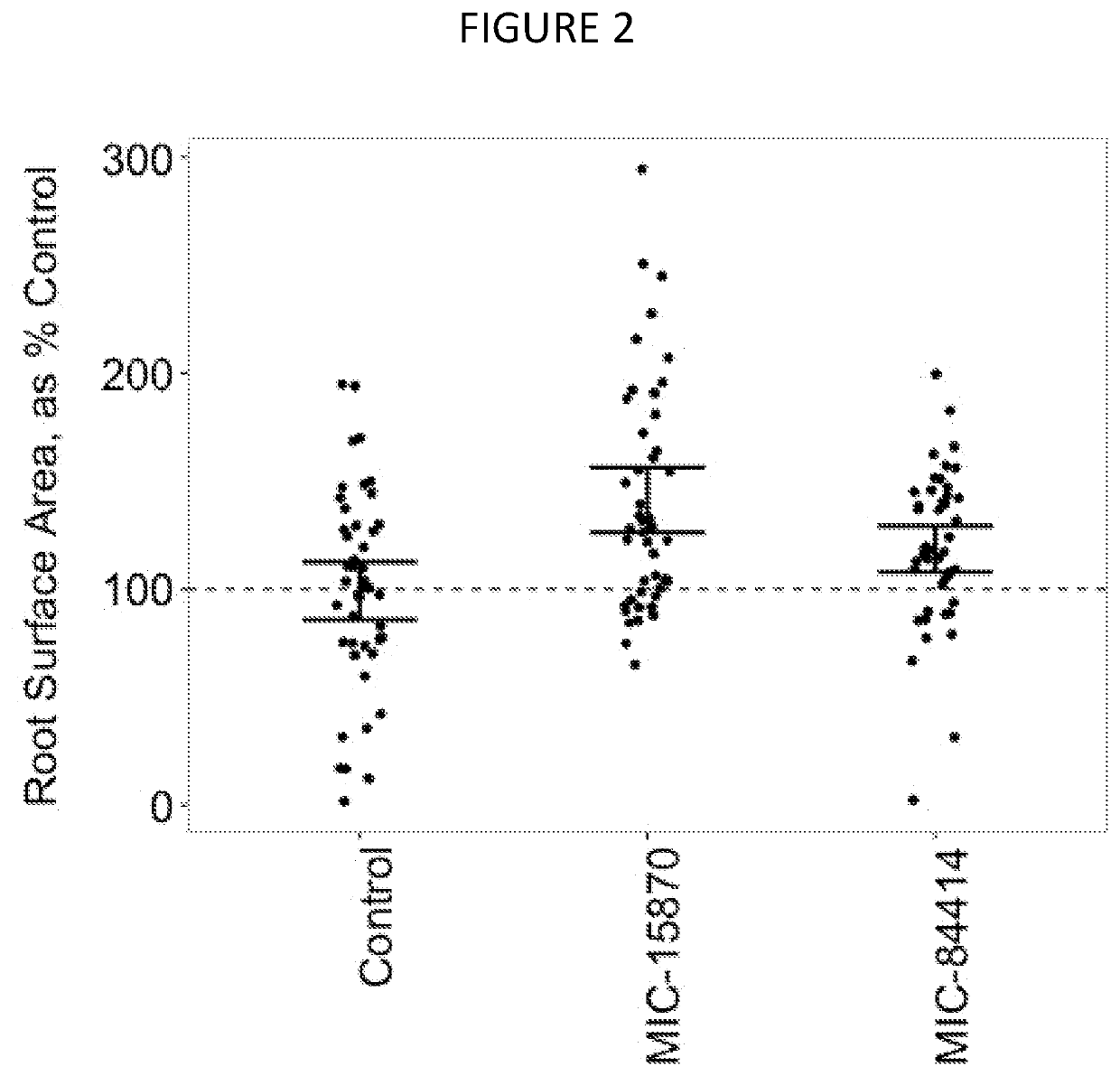
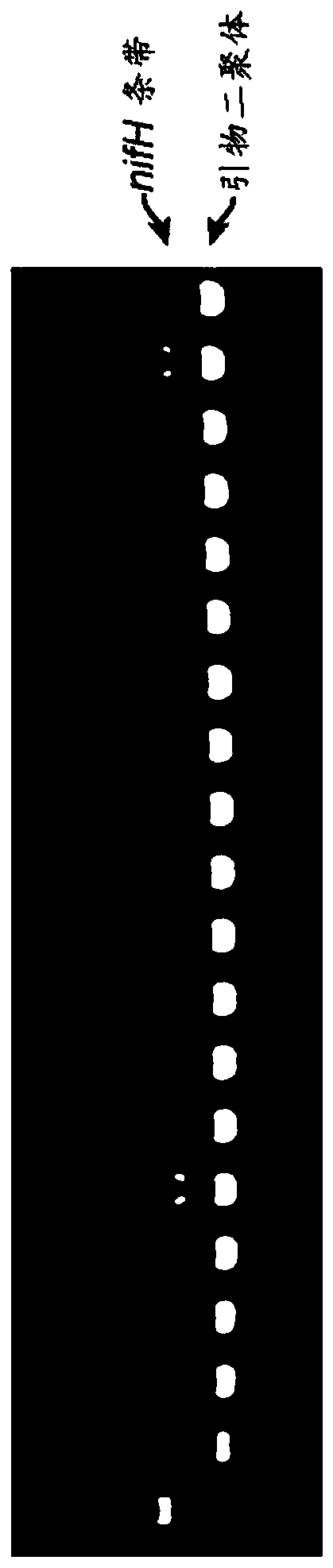
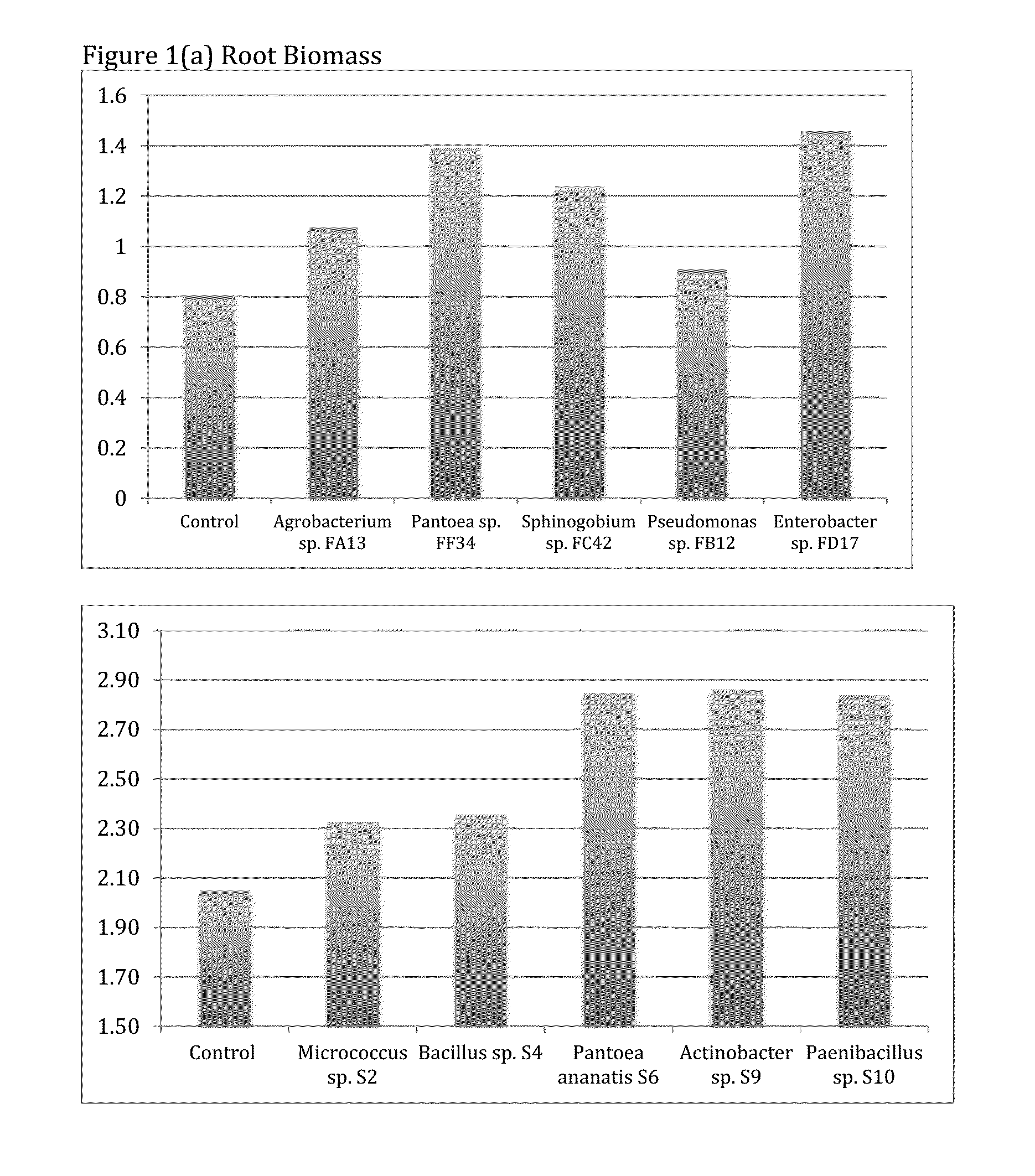
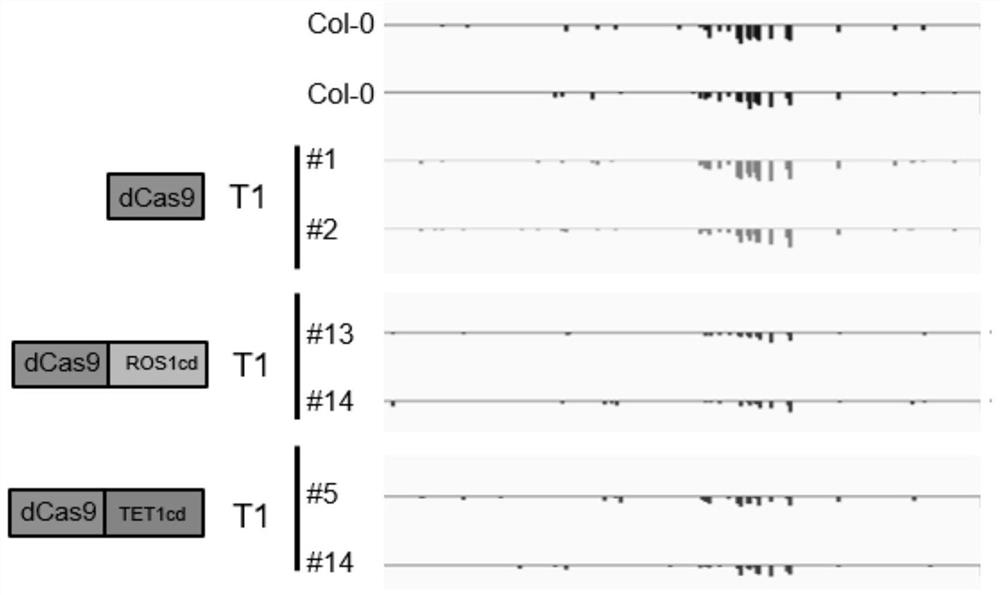
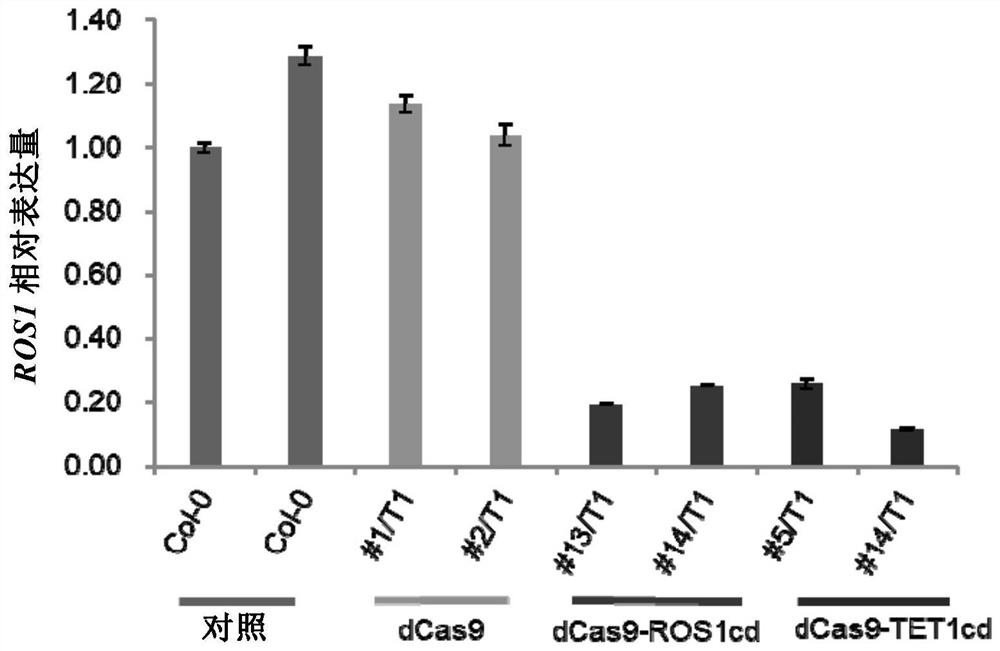
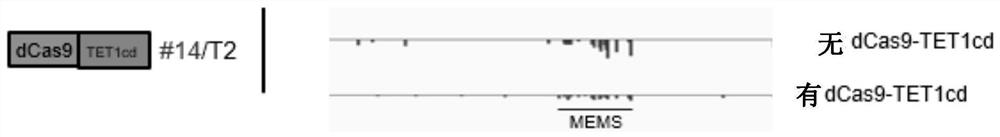
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
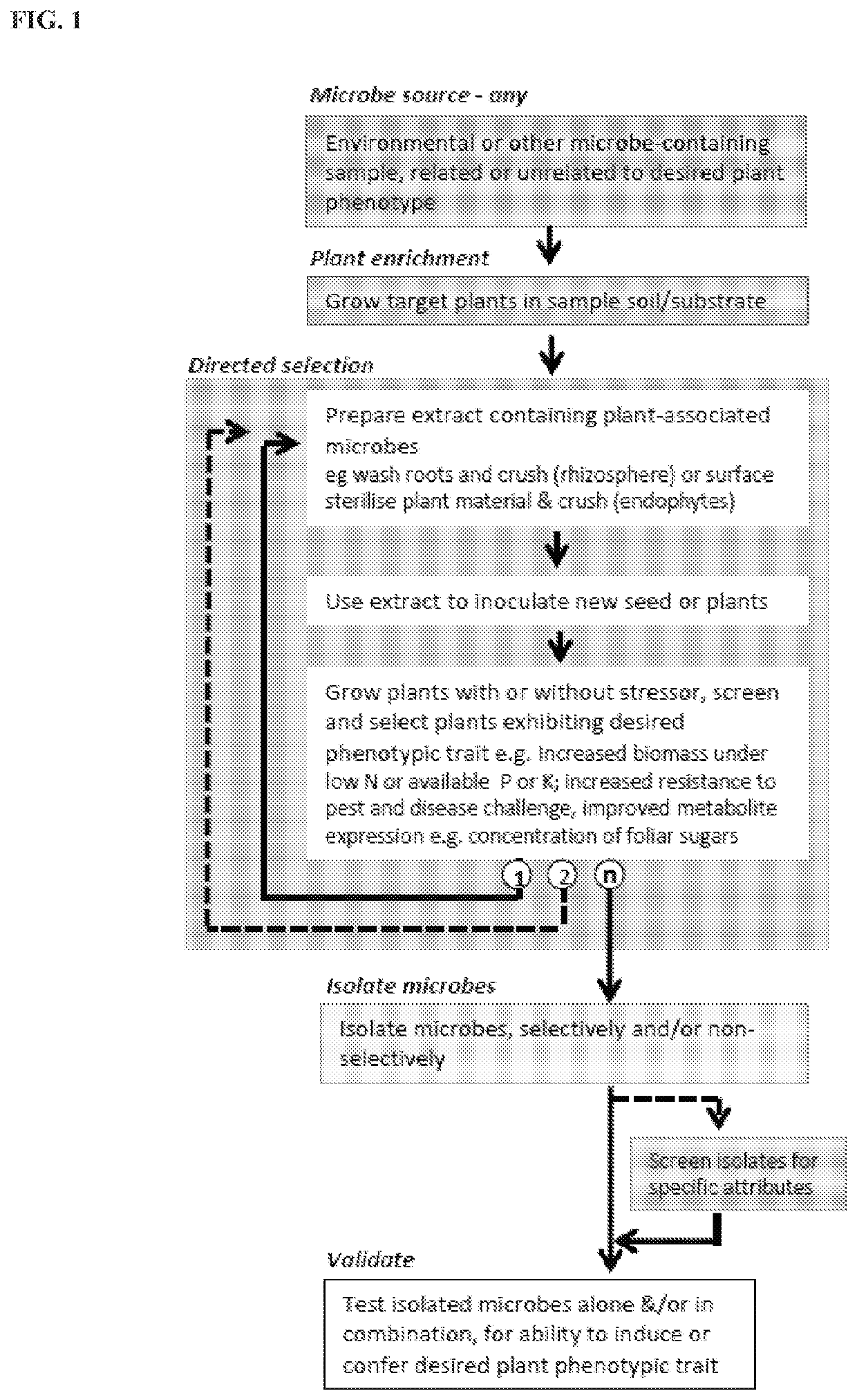
119 results about "Plant traits" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Plant-endophyte combinations and uses therefor
ActiveUS9364005B2Increase productionImprove productivityBiocideBacteriaPlant traitsProviding material
The disclosure provides materials and methods for conferring improved plant traits or benefits on plants. The materials can include a formulation comprising an exogenous endophytic bacterial population, which can be disposed on an exterior surface of a seed or seedling, typically in an amount effective to colonize the plant. The formulations can include at least one member selected from the group consisting of an agriculturally compatible carrier, a tackifier, a microbial stabilizer, a fungicide, an antibacterial agent, an herbicide, a nematicide, an insecticide, a plant growth regulator, a rodenticide, and a nutrient.
Owner:AIT AUSTRIAN INST OF TECH
Plant-endophyte combinations and uses therefor
ActiveUS20160255844A1Increase productionImprove productivityBiocideBacteriaPlant traitsProviding material
The disclosure provides materials and methods for conferring improved plant traits or benefits on plants. The materials can include a formulation comprising an exogenous endophytic bacterial population, which can be disposed on an exterior surface of a seed or seedling, typically in an amount effective to colonize the plant. The formulations can include at least one member selected from the group consisting of an agriculturally compatible carrier, a tackifier, a microbial stabilizer, a fungicide, an antibacterial agent, an herbicide, a nematicide, an insecticide, a plant growth regulator, a rodenticide, and a nutrient.
Owner:AIT AUSTRIAN INST OF TECH
Ap2 transcription factors for modifying plant traits
This invention relates to polynucleotide and polypeptide transcription factor sequences that are of use for the transformation of plants. The AP2 transcription factors include G979, polynucleotide and polypeptide SEQ ID NOs: 1 and 2, respectively, and phylogenetically-related sequences.
Owner:MENDEL BIOTECHNOLOGY INC
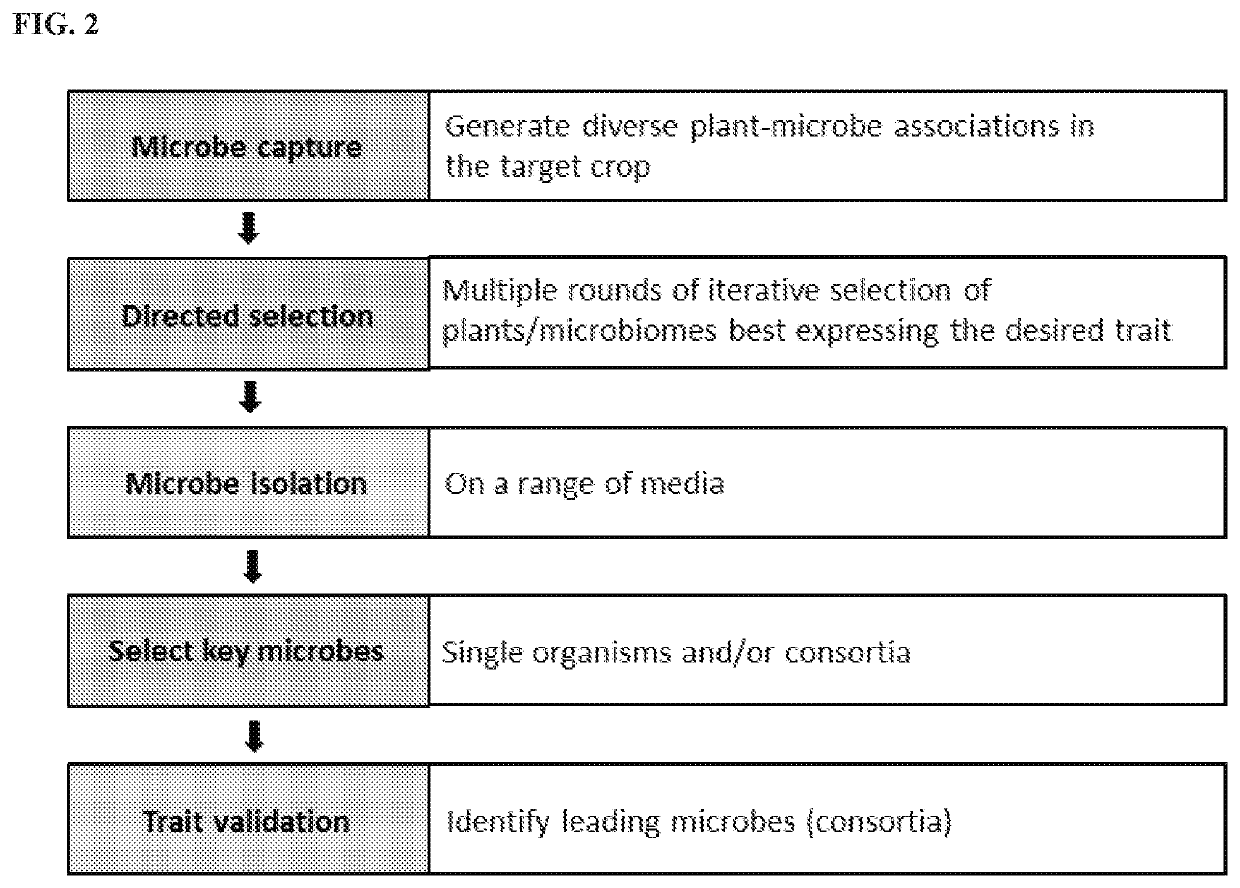
Agriculturally beneficial microbes, microbial compositions, and consortia
ActiveUS20180020671A1Improve crop performanceClosing worldwide yield gapBiocideBacteriaPlant traitsCrop species
Owner:BIOCONSORTIA
Agriculturally beneficial microbes, microbial compositions, and consortia
The disclosure relates to isolated microorganisms-including novel strains of the microorganisms-microbial consortia, and agricultural compositions comprising the same. Furthermore, the disclosure teaches methods of utilizing the described microorganisms, microbial consortia, and agricultural compositions comprising the same, in methods for imparting beneficial properties to target plant species. In particular aspects, the disclosure provides methods of increasing desirable plant traits in agronomically important crop species.
Owner:生物联盟有限公司
Methods for modifying plant cell walls and modified plants produced thereby
InactiveUS7317136B1Improve digestibilitySpeed up the processClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesPlant cellPlant traits
The present invention provides methods for modulating cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin composition and deposition in secondary cell wall layers of plants to improve plant traits that are commercially desirable (e.g., enhanced digestibility of forage crops by animals, increased post-harvest processing of wood and crops for energy production and pulping, increase mechanical strength of plants, and others). The invention also provides methods for identifying genes encoding transcription factors that regulate the formation of secondary cell walls, polynucleotide sequences that encode key components of secondary cell walls, and transgenic plants comprising these sequences.
Owner:ARBORGEN
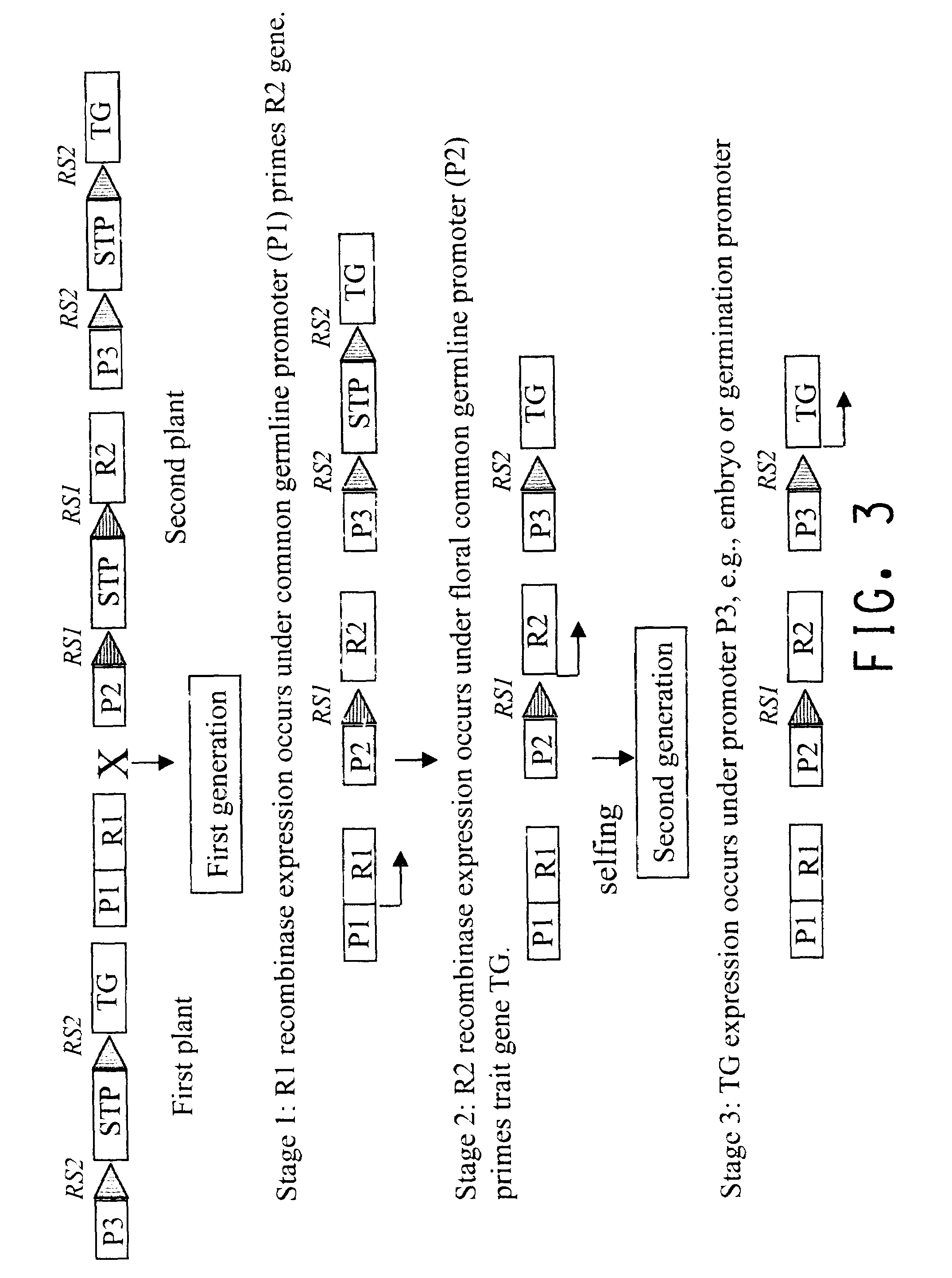
Methods for regulated expression of triats in plants using multiple site-specific recombination systems
InactiveUS7115798B1Promote reproductionProcess safety and environmental protectionSsRNA viruses positive-senseVirus peptidesDevelopmental stagePlant tissue
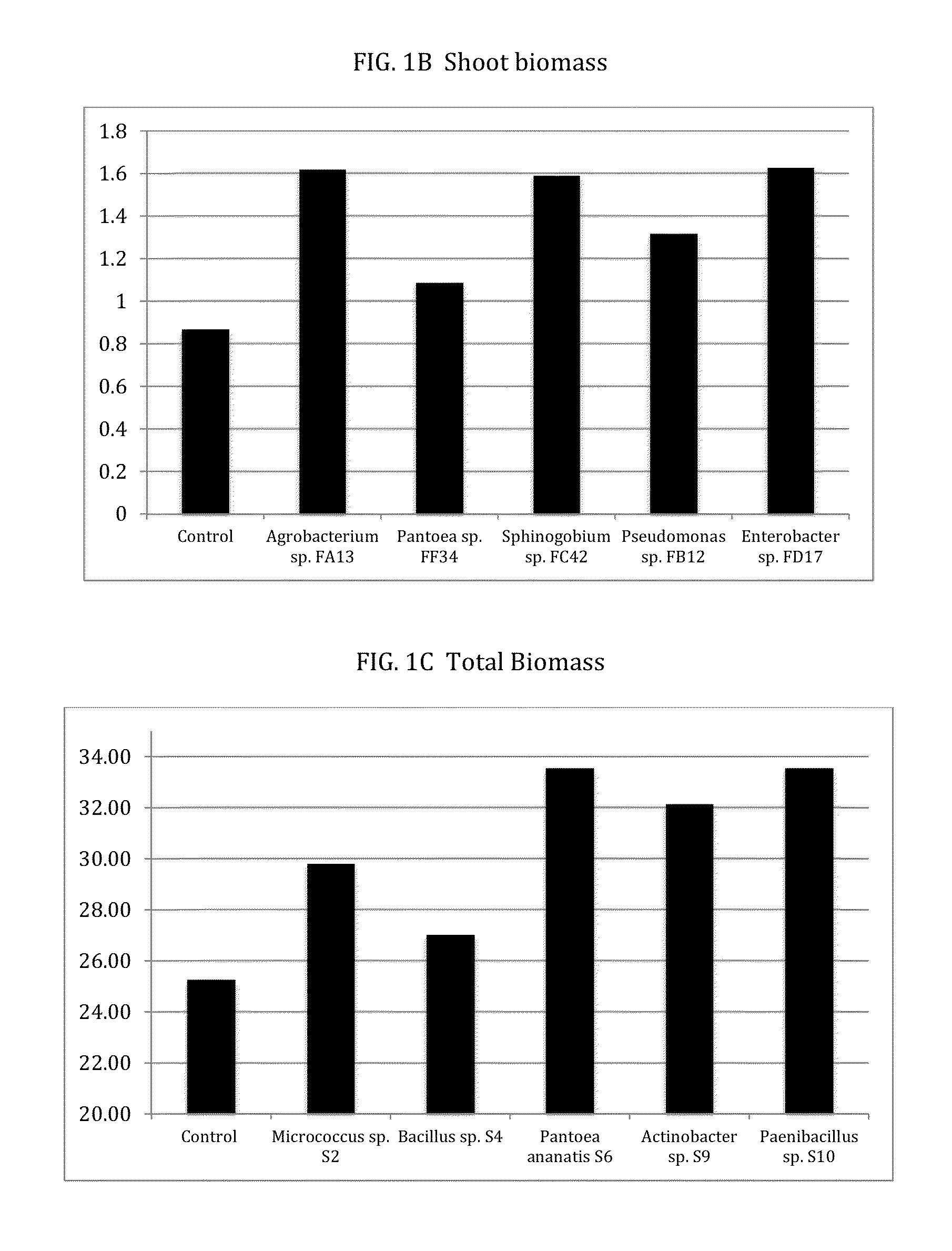
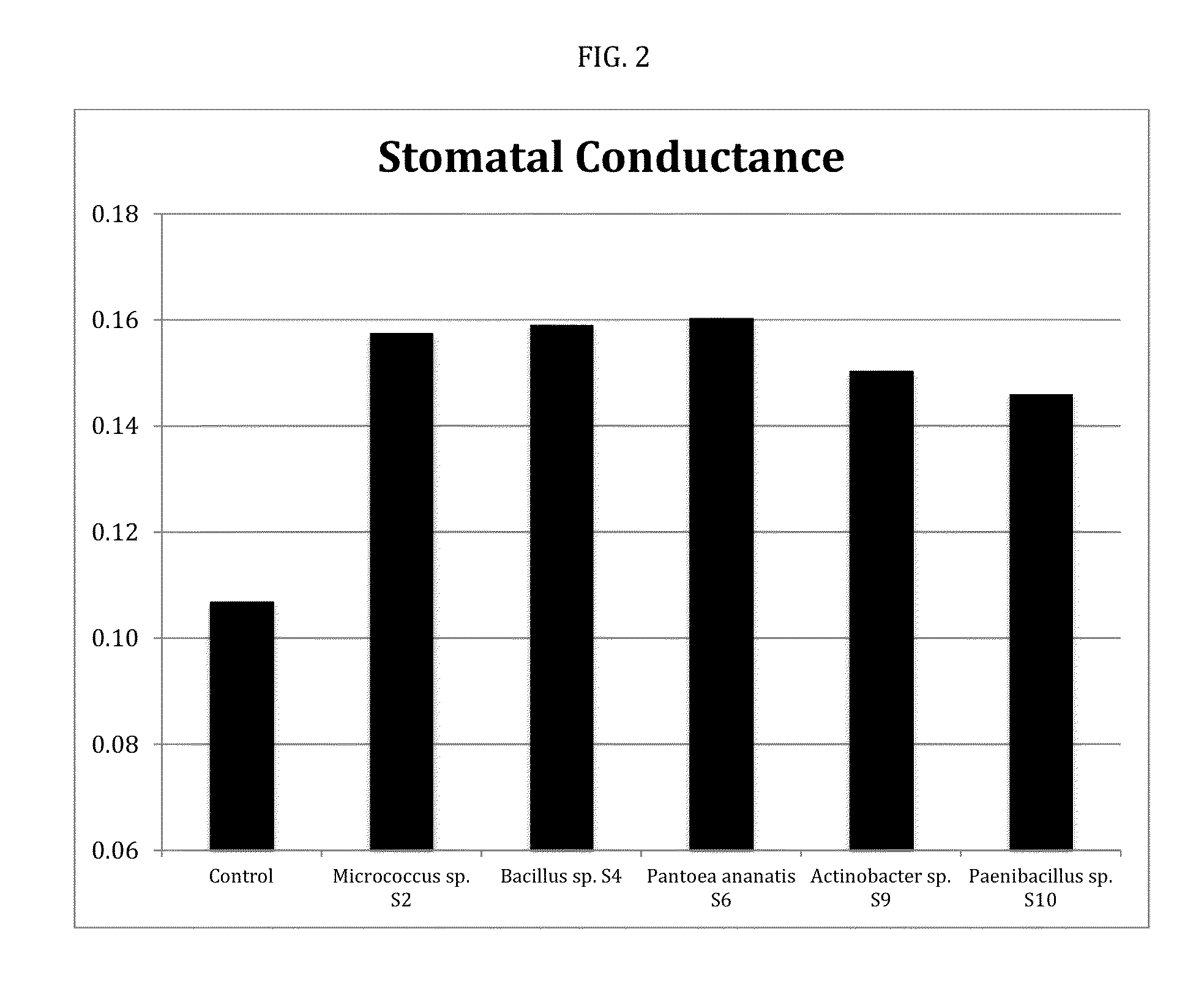
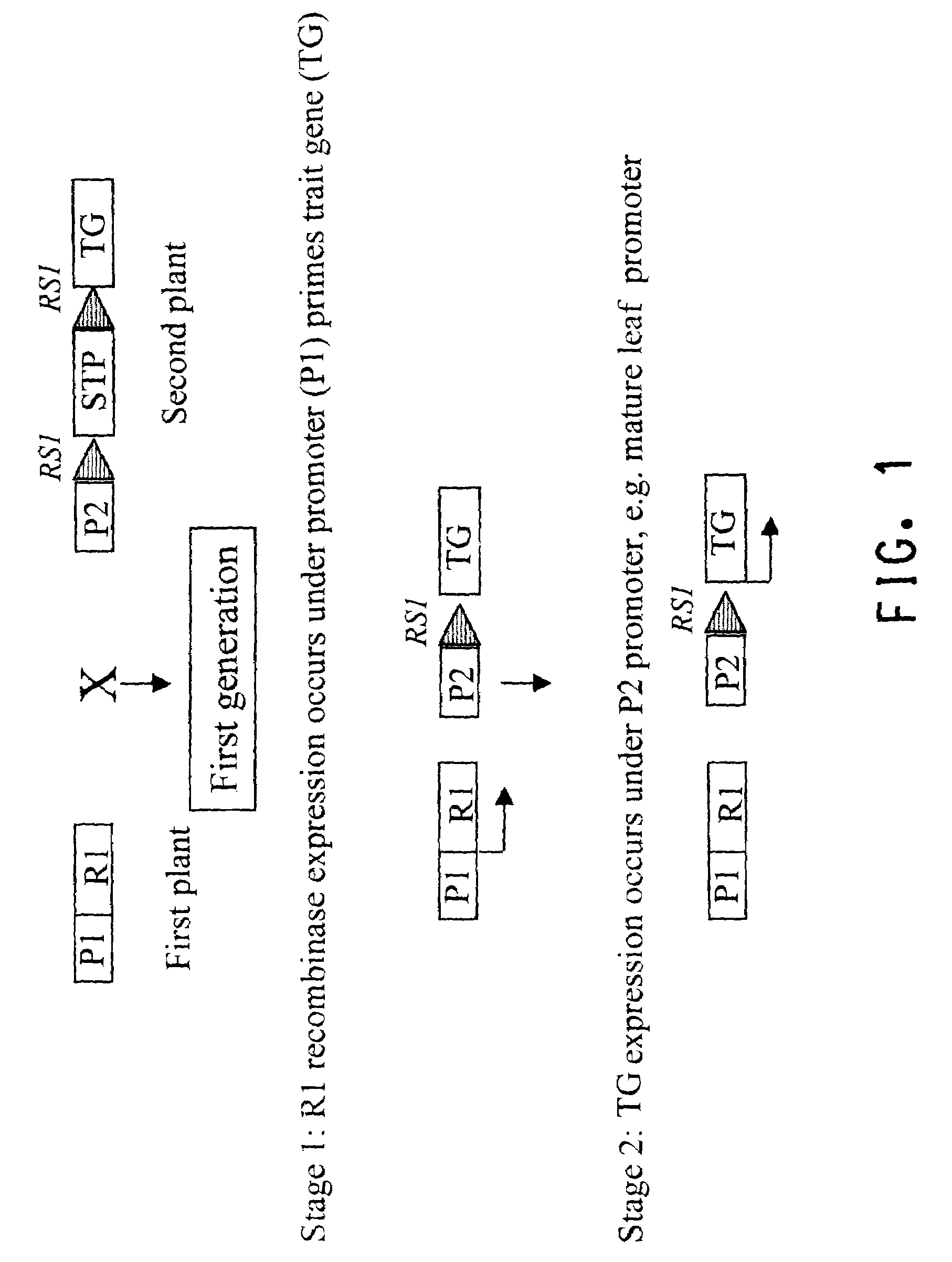
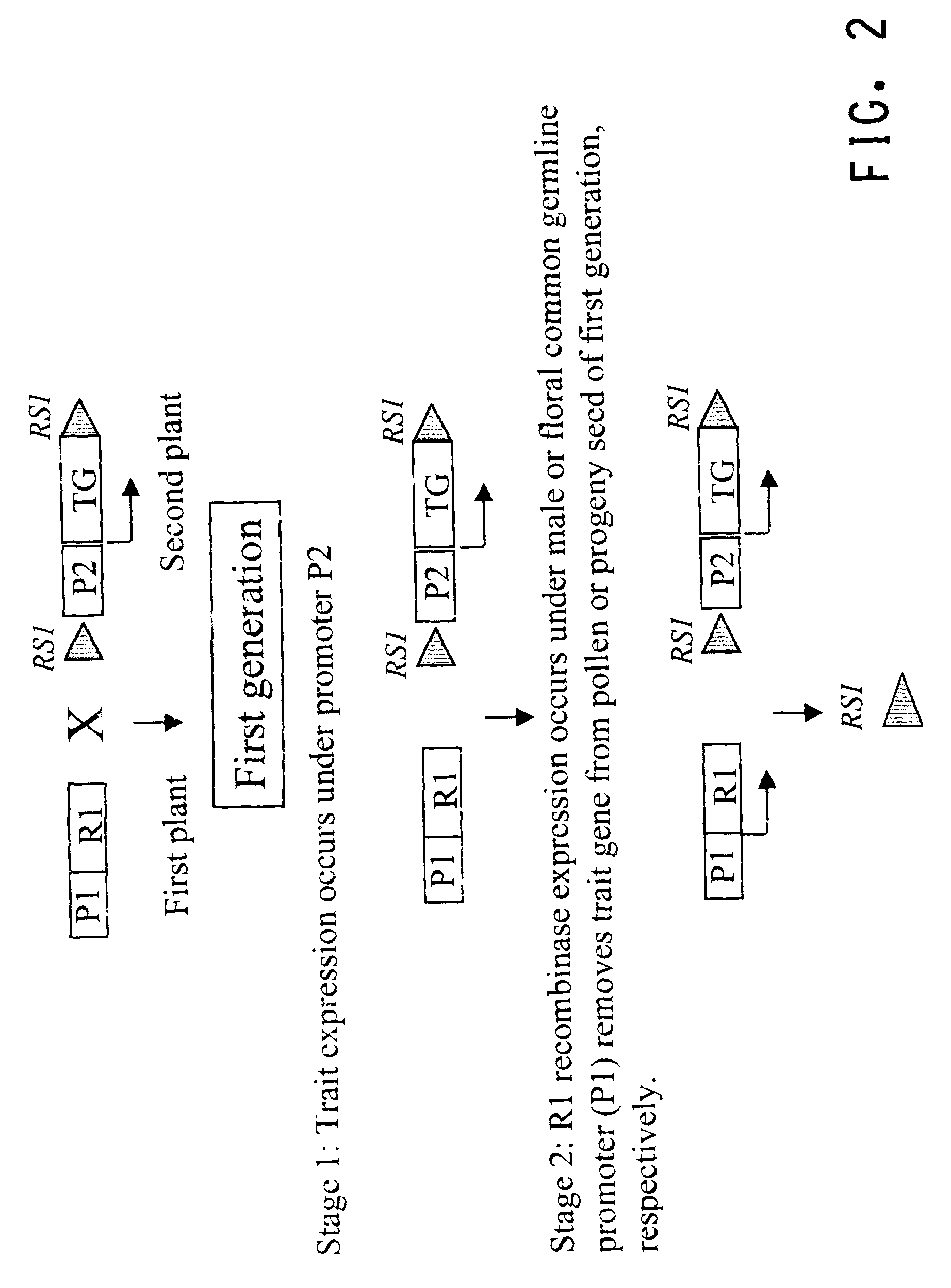
This invention relates to constructs for the conditional or regulated expression of transgenes in plants using site-specific recombinase systems. The constructs comprise a variety of constitutive, inducible, tissue specific or developmental stage-specific promoters operably linked to either a transgene or the elements of one or more site-specific recombinase system. By matching promoters, responsive to various inducers, plant tissues or plant developmental states with the recombinase systems, stop fragments and transgenes, virtually any trait may be expressed at any plant development stage or in any plant generation.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Herbicide-resistant rape directive breeding method based on acetolactate synthase (ALS) target esterase
InactiveCN103070068AImprove breeding efficiencyReduce chanceSeed and root treatmentPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyEthylmethane Sulfonate
The invention provides a herbicide-resistant rape directive breeding method based on acetolactate synthase (ALS) target esterase, which belongs to a plant trait breeding method. The method comprises the following steps of selecting materials needed by production of rape or breeding of the rape, processing seeds with ethylmethane sulfonate (EMS), mutagenizing the seeds to be isolated and propagated to a M2 generation, and directionally screening herbicide-resistant mutant characters in a large group under the selection pressure of the herbicide adopting the ALS as the target esterase. In order to increase the probability for acquiring the mutant characters, the directive screening can be continuously conducted in multiple years, or conducted in multiple places in the same year or conducted in multiple places in multiple years until the needed mutant material is screened out.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Transcription factor capable of being used to adjust plant traits
The invention relates to a transcription factor capable of being used to adjust plant traits. The plant shape, the blossom period, and the mature time and size of the harvest organs such as fruits are prominently improved through changing the expression of the transcription factor in plants. Thus the transcription factor can be used to create plants with ideal traits.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
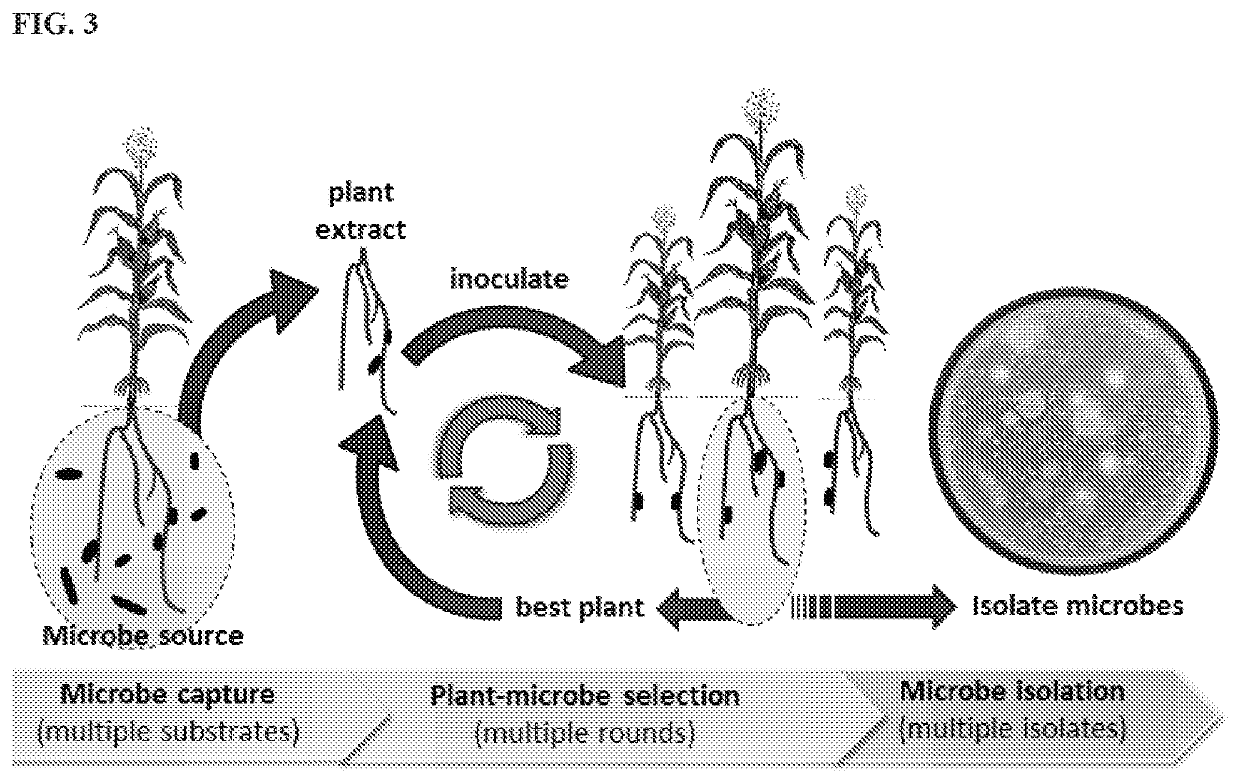
Seed endophytes across cultivars and species, associated compositions, and methods of use thereof
Owner:靛蓝股份公司
Endophyte compositions and methods for improvement of plant traits
Owner:INDIGO AG INC
Endophyte compositions and the methods for improvement of plant traits
This invention relates to methods and materials for modulating the characteristics of a plant, said plant having been heterologously disposed to an endophyte or a plurality of endophytes, or derived from a plant reproductive element heterologously disposed to an endophyte or a plurality of endophytes.
Owner:INDIGO AG INC
Methods and compositions for improving plant traits
Owner:PIVOT BIO
Plant-endophyte combinations and uses therefor
ActiveUS20150373992A1Improve germination rateIncrease biomassBiocideBacteriaPlant traitsProviding material
The disclosure provides materials and methods for conferring improved plant traits or benefits on plants. The materials can include a formulation comprising an exogenous endophytic bacterial population, which can be disposed on an exterior surface of a seed or seedling, typically in an amount effective to colonize the plant. The formulations can include at least one member selected from the group consisting of an agriculturally compatible carrier, a tackifier, a microbial stabilizer, a fungicide, an antibacterial agent, an herbicide, a nematicide, an insecticide, a plant growth regulator, a rodenticide, and a nutrient.
Owner:AIT AUSTRIAN INST OF TECH
Fusion protein and application thereof
PendingCN113307878APolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifFusion with DNA-binding domainNucleotideEpigenetics
The invention provides a fusion protein and an application thereof. Specifically, the invention provides a fusion protein, which comprises or consists of the following components: (1) a positioning functional element D1 with functions of targeting and combining DNA; and (2) a demethylated functional element D2 having a function of converting methylated nucleotides into non-methylated nucleotides. The demethylation method provided by the invention has accurate and efficient demethylation modification efficiency in plants, and has important scientific values for researching plant epigenetics and regulating plant traits through demethylation.
Owner:SHANDONG SHUNFENG BIOTECH CO LTD
Method for improving plant traits
The invention relates to a method for improving plant traits, wherein the subfamily gene 714 of the family of the exogenous cytochrome P450 is transferred in plants. The method can be well applied to improving the plant varieties and provides highly valuable gene resources for culturing new varieties of plants by virtue of molecular breeding techniques such as transgenosis.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Capture of ground truthed labels of plant traits method and system
ActiveUS20190200535A1Investigation of vegetal materialUnmanned aerial vehiclesPlant traitsPhenotypic trait
In embodiments, acquiring sensor data associated with a plant growing in a field, and analyzing the sensor data to extract, while in the field, one or more phenotypic traits associated with the plant from the sensor data. Indexing, while in the field, the one or more phenotypic traits to one or both of an identifier of the plant or a virtual representation of a part of the plant, and determining one or more plant insights based on the one or more phenotypic traits, wherein the one or more plant insights includes information about one or more of a health, a yield, a planting, a growth, a harvest, a management, a performance, and a state of the plant. One or more of the health, yield, planting, growth, harvest, management, performance, and the state of the plant are included in a plant insights report that is generated.
Owner:MINERAL EARTH SCI LLC
Method for improving plant traits
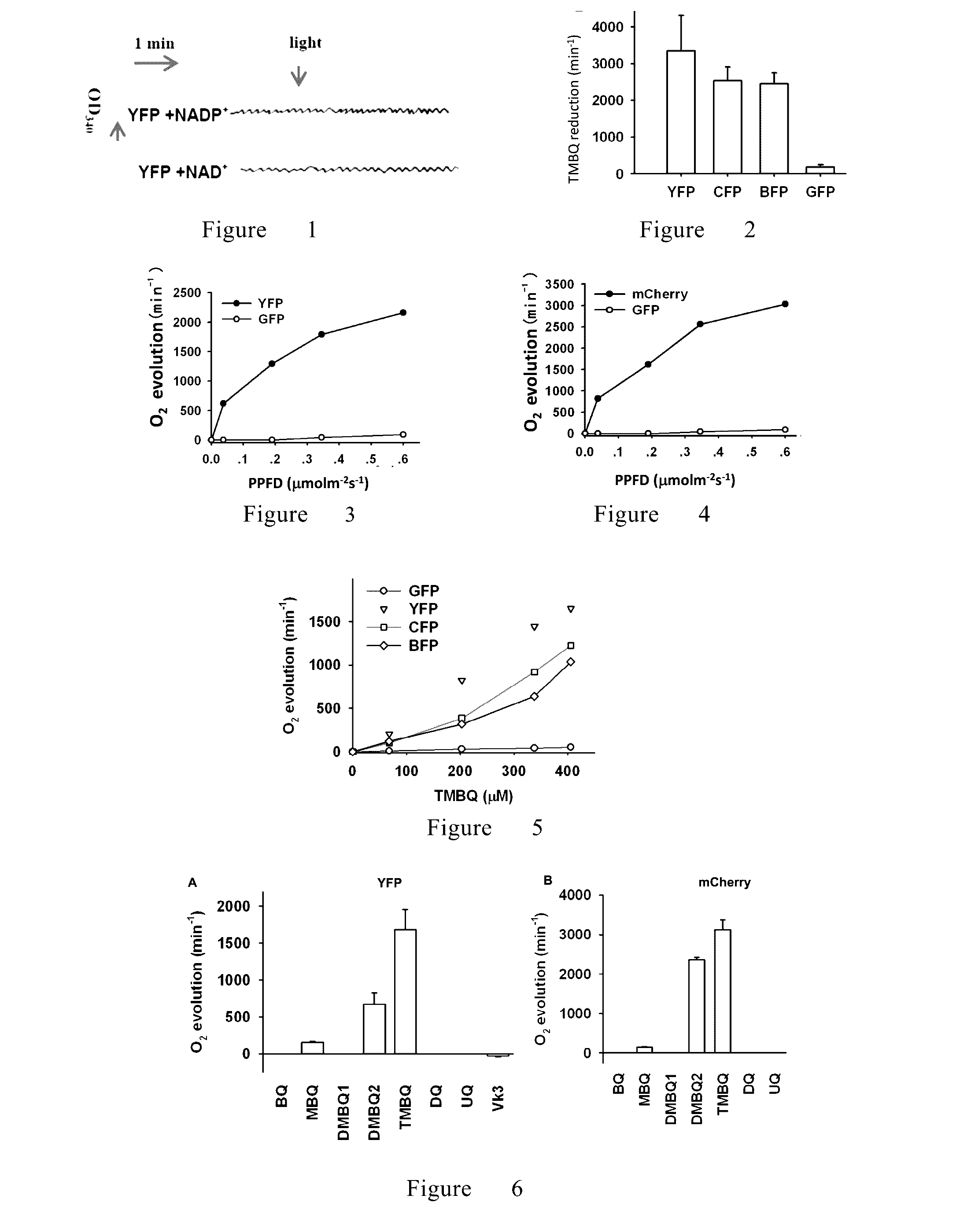
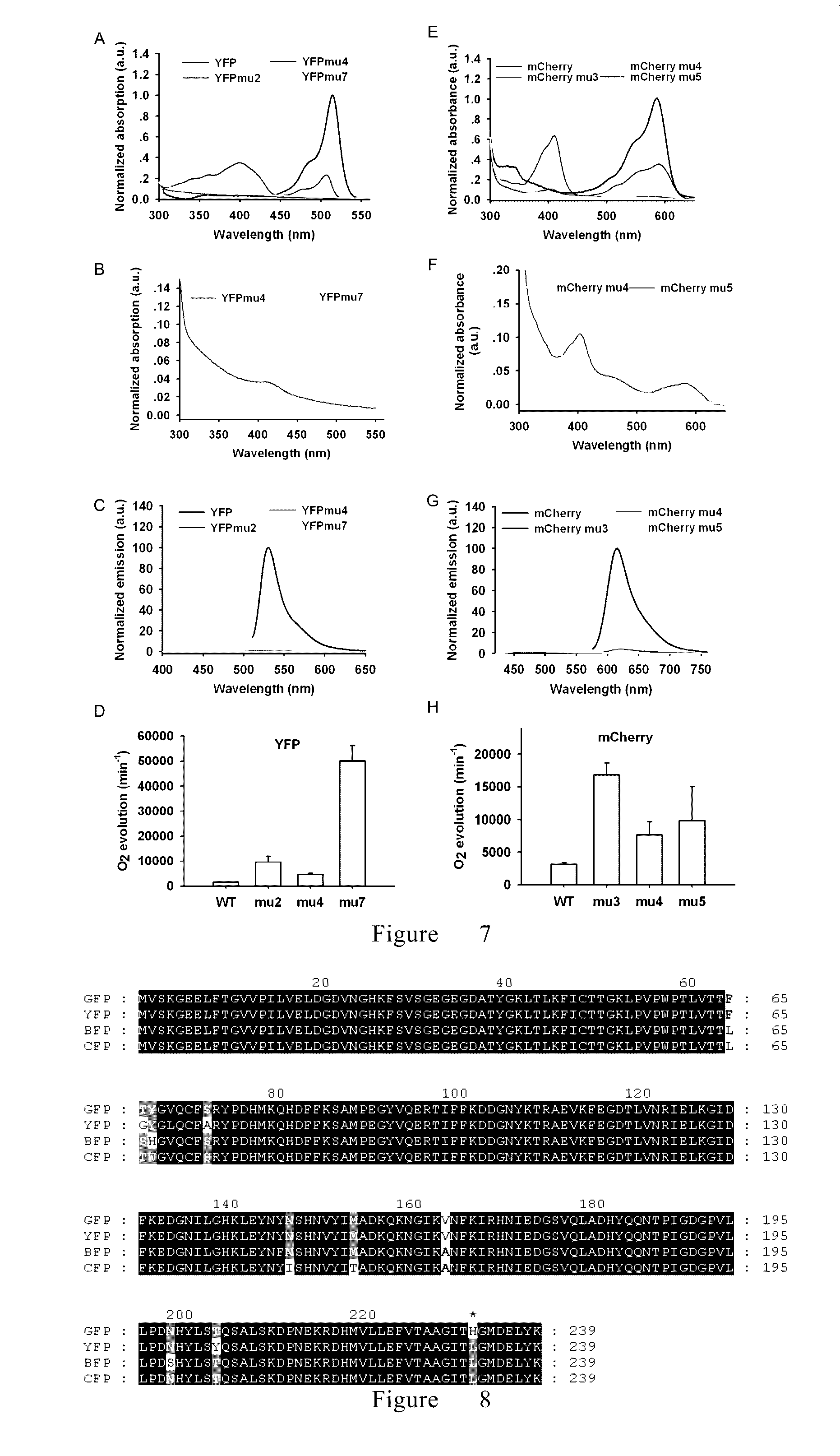
The invention relates to a method for improving plant traits and discloses for the first time a novel plant improving method with improvement of light use efficiency of a plant as a purpose. According to the method, a light energy absorption and transduction protein (LEAT protein) is expressed in a plant, absorbed light energy interacts with related methylquinone derivatives, e.g., plastoquinone, in the plant to catalyze cracking of water and release oxygen, so light use efficiency of the plant is improved. The method provided by the invention can effectively expand use of light energy by the plant and increase photosynthetic efficiency and yield.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
Transgenic plants with increased seed yield, biomass and harvest index
The present invention provides methods for producing seeds and plants with increased biomass production. More specifically, the present invention provides methods for producing plants having increased yield for a number of plant traits, including seed number, seed weight, number of seed heads, flag leaf weight, and total plant weight. The present invention also provides methods for improving the harvest index of a plant. In a preferred embodiment, the method of the present invention comprises introducing into a plant a nucleic acid selected from the group consisting of a nucleic acid comprising SEQ ID NO: 3, which hybridizes to SEQ ID NO: 3 under high stringency conditions and encodes and retains SH2 - Nucleic acid of a polypeptide with biological activity of REV6-HS, fragment of SEQ ID NO: 3 encoding a peptide retaining biological activity of SH2-REV6-HS, encoding a polypeptide comprising SEQ ID NO: 4 or its SH2-REV6-SH organism Nucleic acids of fragments of biological activity, and nucleic acids encoding SH2HS or SH2RTS polypeptides. The present invention also relates to plants obtained by the methods provided herein.
Owner:RES & DEV INST
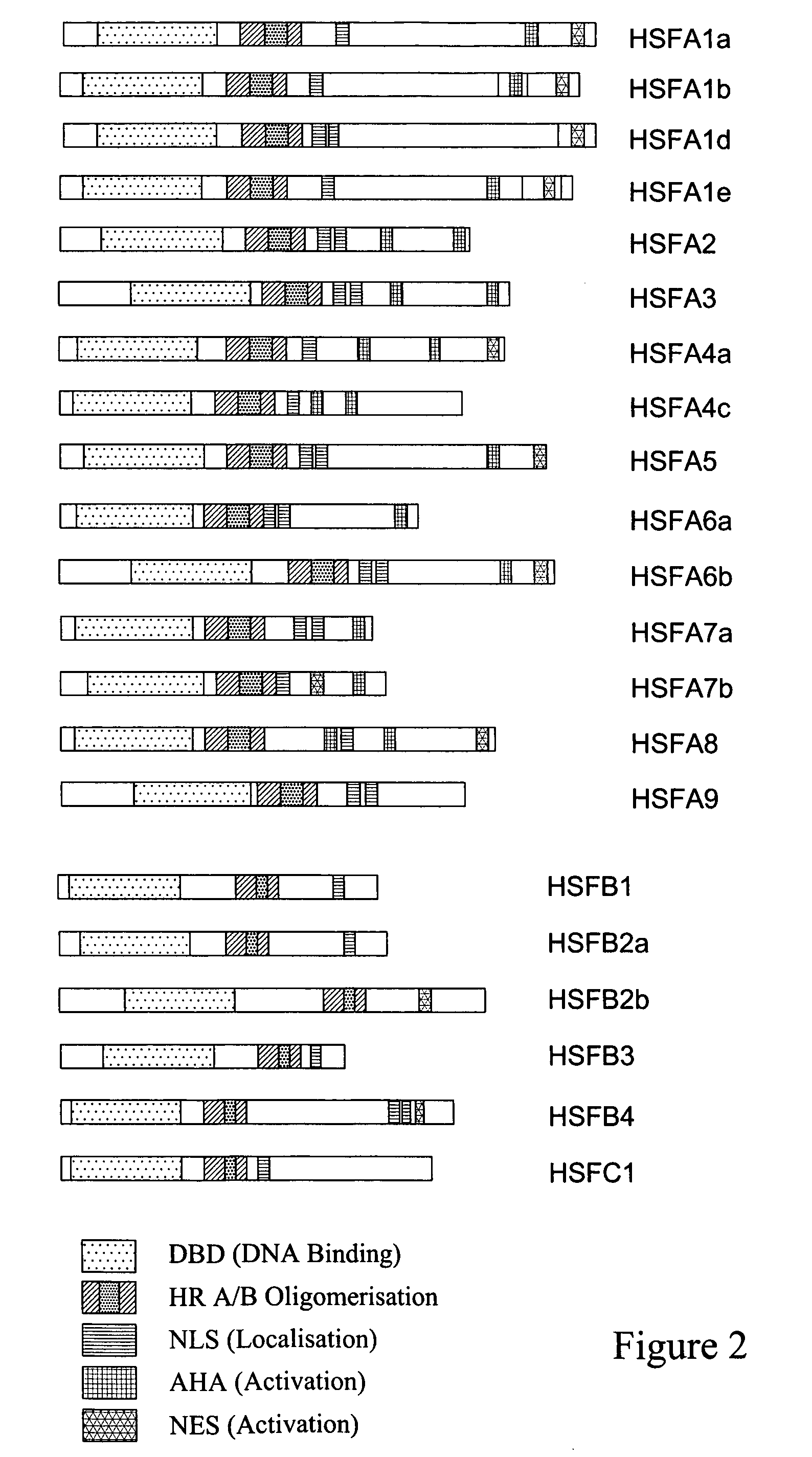
Plant Responses
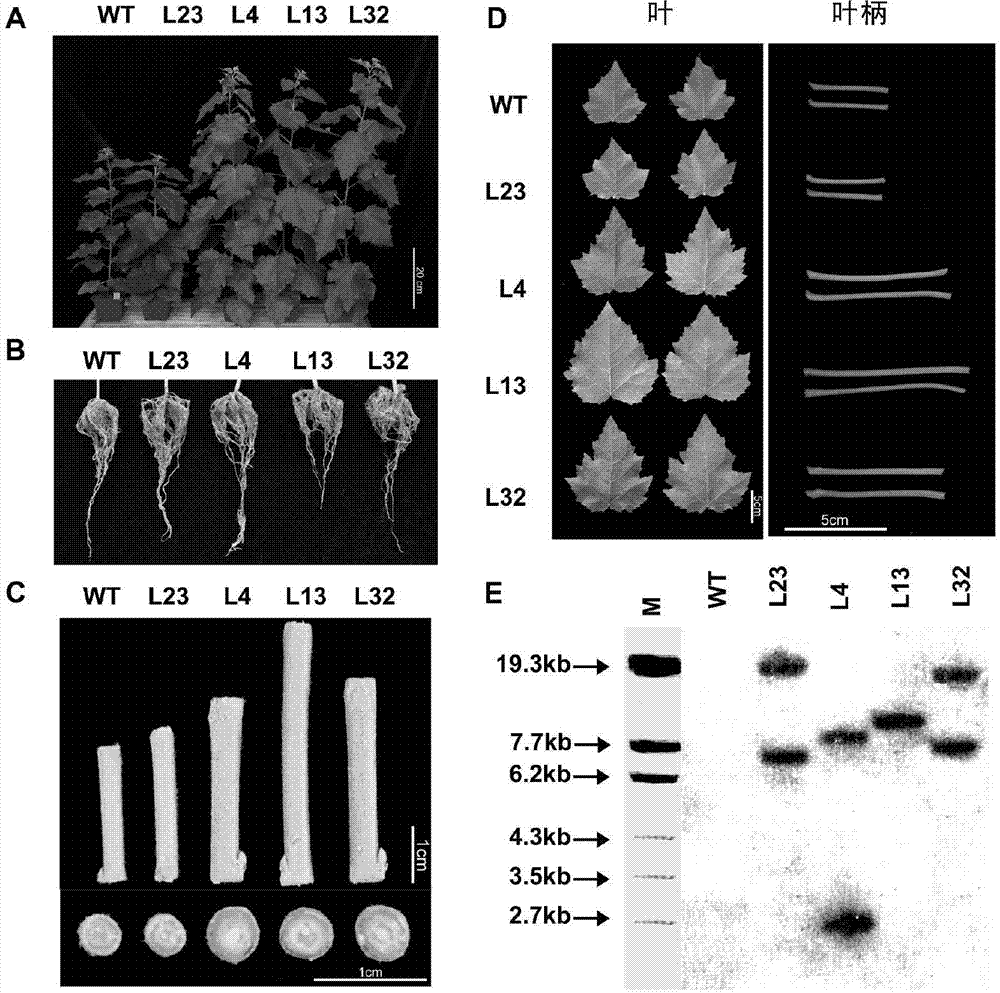
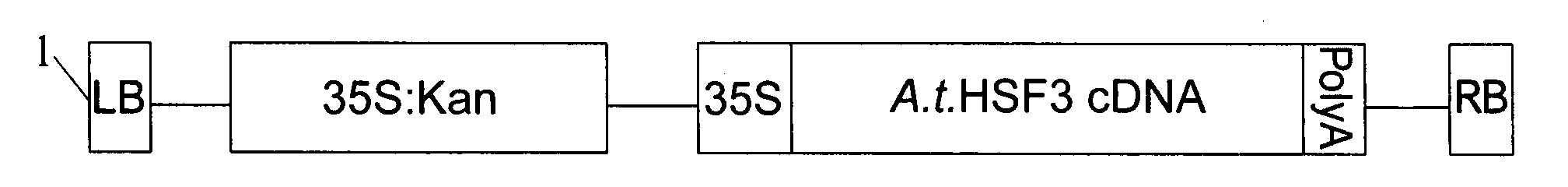
ActiveUS20100138958A1Improve toleranceImprove traitsSugar derivativesClimate change adaptationWater-use efficiencyPlant traits
The present invention relates to methods and uses for improving traits in plants which are important in the field of agriculture. In particular, the methods and uses of the invention use a plant Hsf to increase plant productivity, water use efficiency, drought or pathogen resistance.
Owner:UNIV OF ESSEX ENTERPRISES
Method for screening transgenic plant and its used bivalent plant expression vector
InactiveCN1412323AEasy to filterMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionGlyphosatePlant traits
The present invention provides a method for screening plant transformant and its used plant bivalent expression vector. Said method uses glyphosate resistance gene instead of antibiotic resistance gene as marker gene for screening transgenic plant line. The plant bivalent expression vector used in said invented method contains glyphosate resistance gene and plant character gene to be screened. Said glyphosate resistance gene not only can be used as marker gene for screening plant, but also can be used as anti-herbicide gene, and can be linked with other inportant object character gene for transforming plant, so that it can be conveniently used for screening transformed plant and screening pure line breeding variety.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Application of Plant Poly-adp Ribose Polymerase Inhibitors in Improving Plant Traits
The invention belongs to the technical field of botany and agriculture, and particularly relates to the application of a plant poly ADP ribose polymerase inhibitor in improving plant traits. The poly ADP ribose polymerase inhibitor comprises 3-AB, BA and the like, and the improvements of plant traits refer to promotion of plant root growth, improvement of tolerance of plants to dry adverse situations and the like. The roots of the plants are developed after the inhibitor is applied for the plants, showing as increase in root and fresh weight increase at a seedling stage. Moreover, the plants also have stronger drought-tolerant capability. The invention can be used for promoting the growth of plant roots and enhancing the drought-tolerant capability of the plants.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Cyanobacterial nucleic acid fragments encoding proteins useful for controlling plant traits via nuclear or plastome transformation
InactiveUS7285701B2Improve methodEasy to identifySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPhylum CyanobacteriaBiotechnology
This invention provides cyanobacteria as an alternative source of ahas and pds genes for plant transformations and for selectable markers. In particular, it provides for cyanobacteria, for example, Synechocystis, as a source of genes encoding herbicide insensitive proteins, and elements of genes for control of expression in plastids. Nucleic acid fragments, both the acetolactate synthase (ahas) large subunit and the ahas small subunit, were found to provide herbicide resistance. Also, the present invention provides novel Synechocystis mutant phytoene desaturase (PDS) gene conferring resistance to 4′-fluoro-6[(alpha,alpha,alpha,-trifluoro-m-tolyl)oxy]-picolinamide, a bleaching herbicide. The present invention provides improvements to method involving cyanobacteria for the screening of compounds, including a new high-through-put protocol that is a rapid and cost effective way to identify target site genes.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Genetic transformation process of Chinese white poplar
InactiveCN101307323ARaise mediation frequencyHigh conversion frequencyVector-based foreign material introductionPlant genotype modificationPlant traitsHygromycin phosphotransferase
The invention provides a method for carrying out genetic transformation of agrobacterium-mediated Chinese white poplar. The method is characterized in that: an agrobacterium-mediated method is adopted to carry out genetic transformation of Chinese white poplar twice so as to introduce two exogenous genes, wherein the primary transformation adopts a plant binary expression vector containing neomycin phosphotransferase gene NptII and beta-glucuronic acid carbohydrase gene, and takes kalamycin as antibiotic; and the secondary transformation adopts a plant binary expression vector containing hygromycin phosphotransferase gene, and takes hygromycin as antibiotic. The method can effectively introduce the two exogenous genes into Chinese white poplar so as to improve plant characters better.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Method for improving plant trait
InactiveUS20170037425A1Increase planting yieldPromote plant growthPlant peptidesIsomerasesPlastoquinoneQuinone
Provided is a method for plant improvement with the aim of increasing the light use efficiency of a plant. By expressing a light energy absorption and transduction (LEAT) protein in the plant, and by utilizing light energy absorbed to interact with a related methyl-quinone derivative in the plant body, such as plastoquinone, to catalyze water splitting and to release oxygen, the present invention increases the light use efficiency of the plant. The method effectively extends the utilization of light energy by the plant, thus increasing photosynthesis efficiency and yield.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Agriculturally beneficial microbes, microbial compositions, and consortia
ActiveUS20190382714A1Improve crop performanceClosing worldwide yield gapBiocideBacteriaPlant traitsMicrobiology
The disclosure relates to isolated microorganisms—including novel strains of the microorganisms-microbial consortia, and agricultural compositions comprising the same. Furthermore, the disclosure teaches methods of utilizing the described microorganisms, microbial consortia, and agricultural compositions comprising the same, in methods for imparting beneficial properties to target plant species. In particular aspects, the disclosure provides methods of increasing desirable plant traits in agronomically important crop species.
Owner:BIOCONSORTIA
Agriculturally beneficial microbes, microbial compositions, and consortia
The disclosure relates to isolated microorganisms-including novel strains of the microorganisms-microbial consortia, and agricultural compositions comprising the same. Furthermore, the disclosure teaches methods of utilizing the described microorganisms, microbial consortia, and agricultural compositions comprising the same, in methods for imparting beneficial properties to target plant species. In particular aspects, the disclosure provides methods of increasing desirable plant traits in agronomically important crop species.
Owner:BIOCONSORTIA
Methods for trait mapping in plants
InactiveUS20130040826A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationBiotechnologyPlant traits
The present invention provides methods for identifying the nucleic acid sequences responsible for phenotypic traits in plants.
Owner:BRAUN III CARL J +3
Plant responses
ActiveUS8445747B2Improve productivitySugar derivativesClimate change adaptationWater-use efficiencyPlant productivity
Owner:UNIV OF ESSEX ENTERPRISES
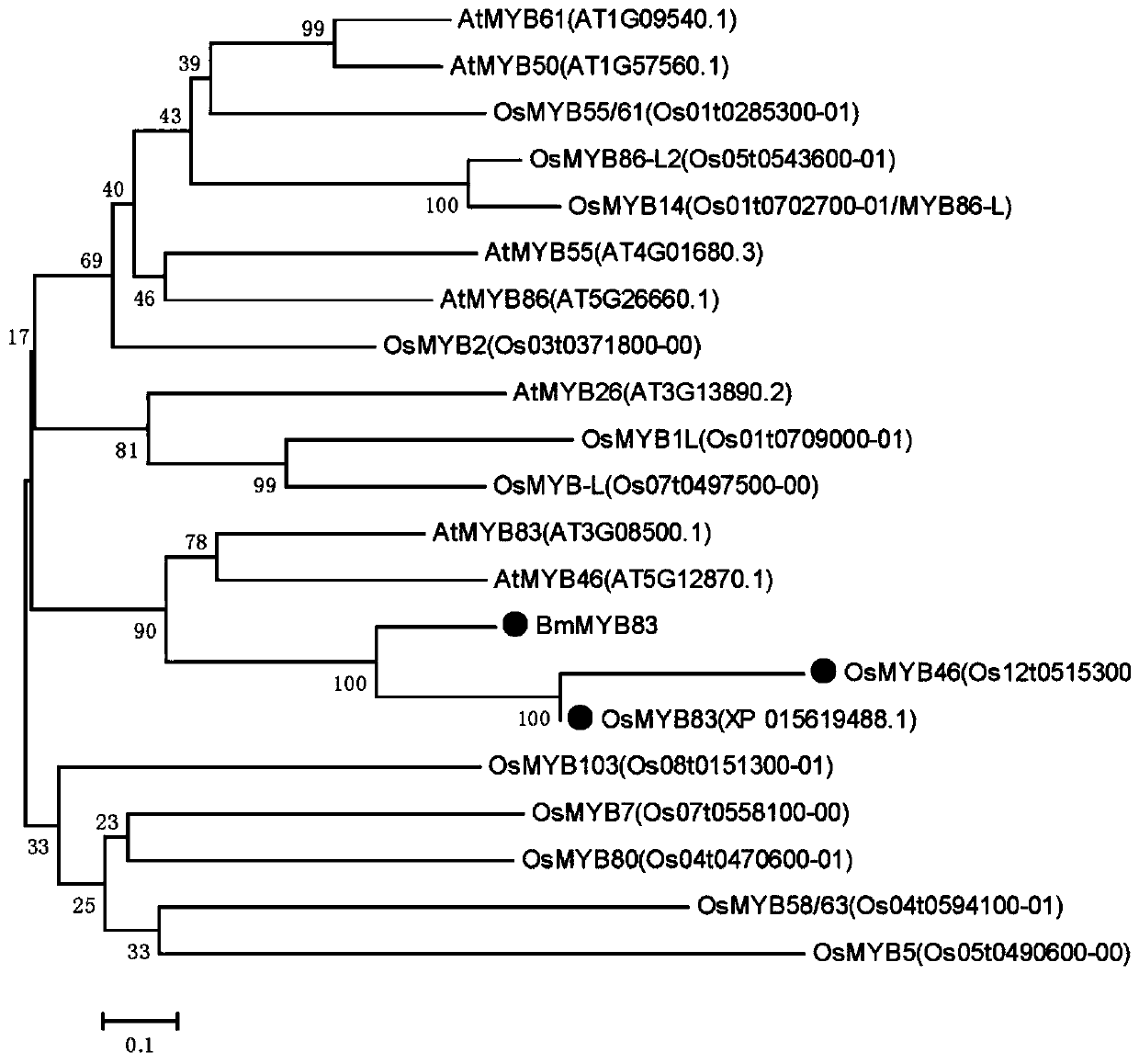
Bambusa multiplex transcription factor BmMYB83 gene and application thereof
The invention discloses a bambusa multiplex transcription factor BmMYB83 gene and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of plant gene engineering. The transcription factor BmMYB83 disclosed by the invention belongs to an MYB transcription factor family, is derived from bambusa multiplex and has a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1, and the amino acid sequence of a protein encoded by the gene is shown in SEQ ID NO.2. Through gene cloning expression and comparison analysis, the evolutionary status of an encoding gene system of the bambusa multiplex transcription factor BmMYB83 is revealed, a method for using the gene is also provided, plant type variation, such as planting dwarfing, leaf curling and number increase of scapes, of arabidopsis plants caused through over expression of the gene, and root lengths of rice can be also reduced. The gene disclosed by the invention plays a significant role in plant property improvement.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com