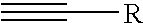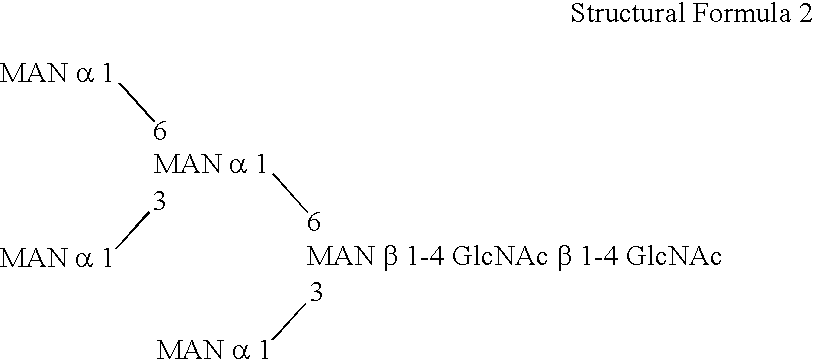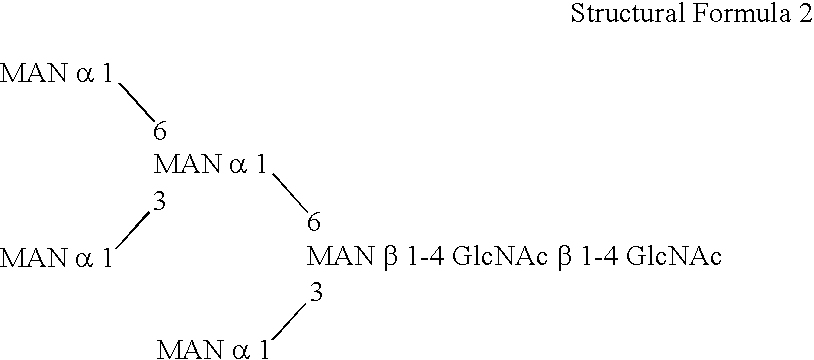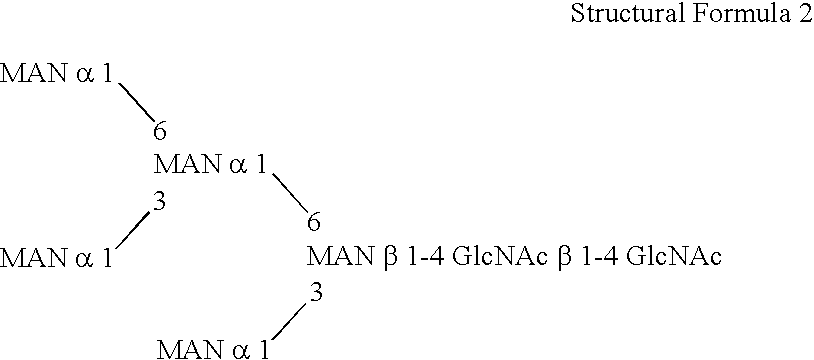Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1176 results about "Synzyme" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Synzymes are substances with catalytic capabilities. The name synzyme is derived from synthetic enzyme. Current synzymes consist mainly of organic molecules tailored in such a way that they catalyse certain kinds of reactions. Like enzymes, they bind a transition state of a substrate in an active site, and like enzymes they generally obey Michaelis-Menten kinetics.
Method and system for rapid biomolecular recognition of amino acids and protein sequencing
InactiveUS6846638B2Low costHigh sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProtein Sequence DeterminationDigestion
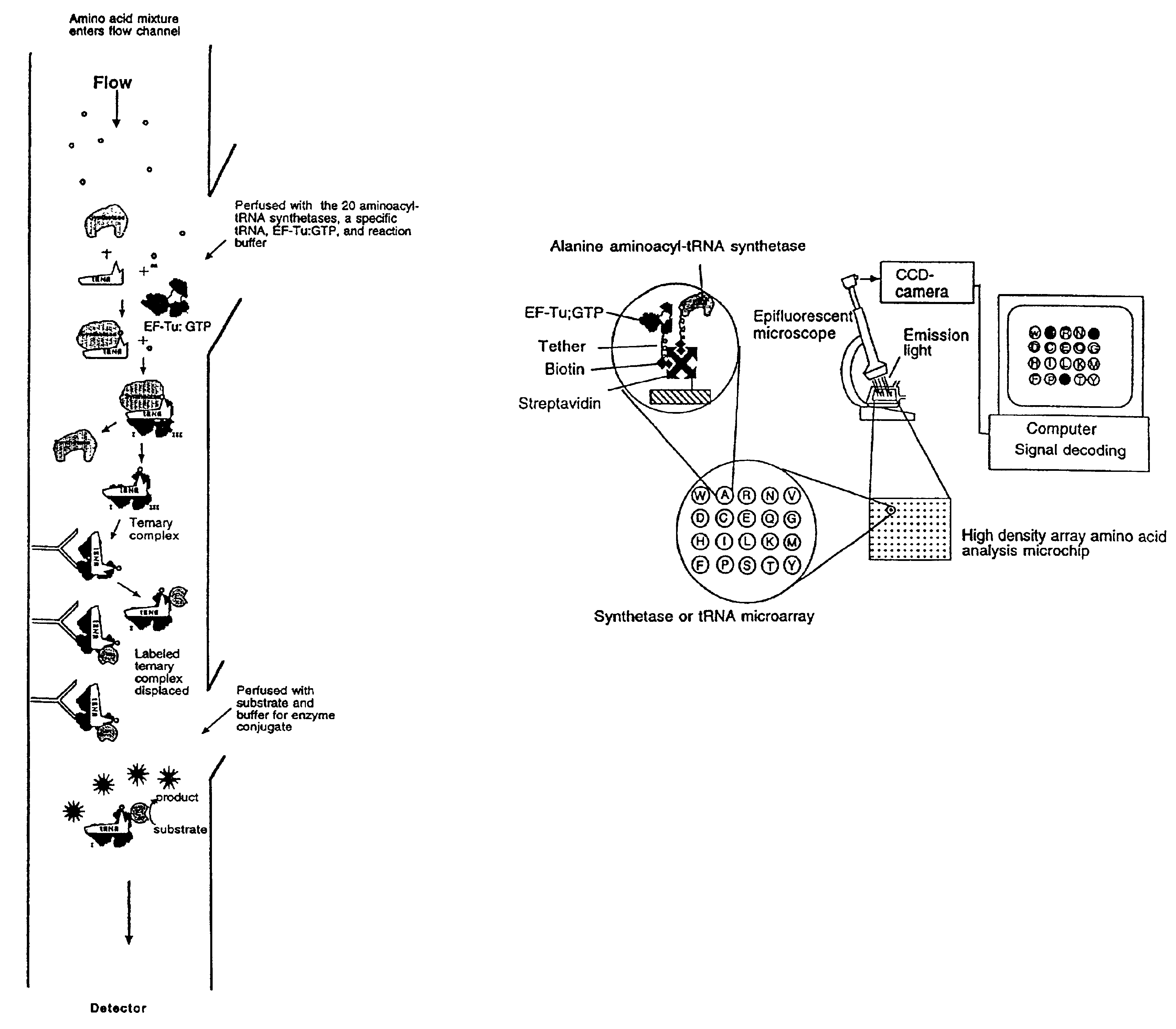
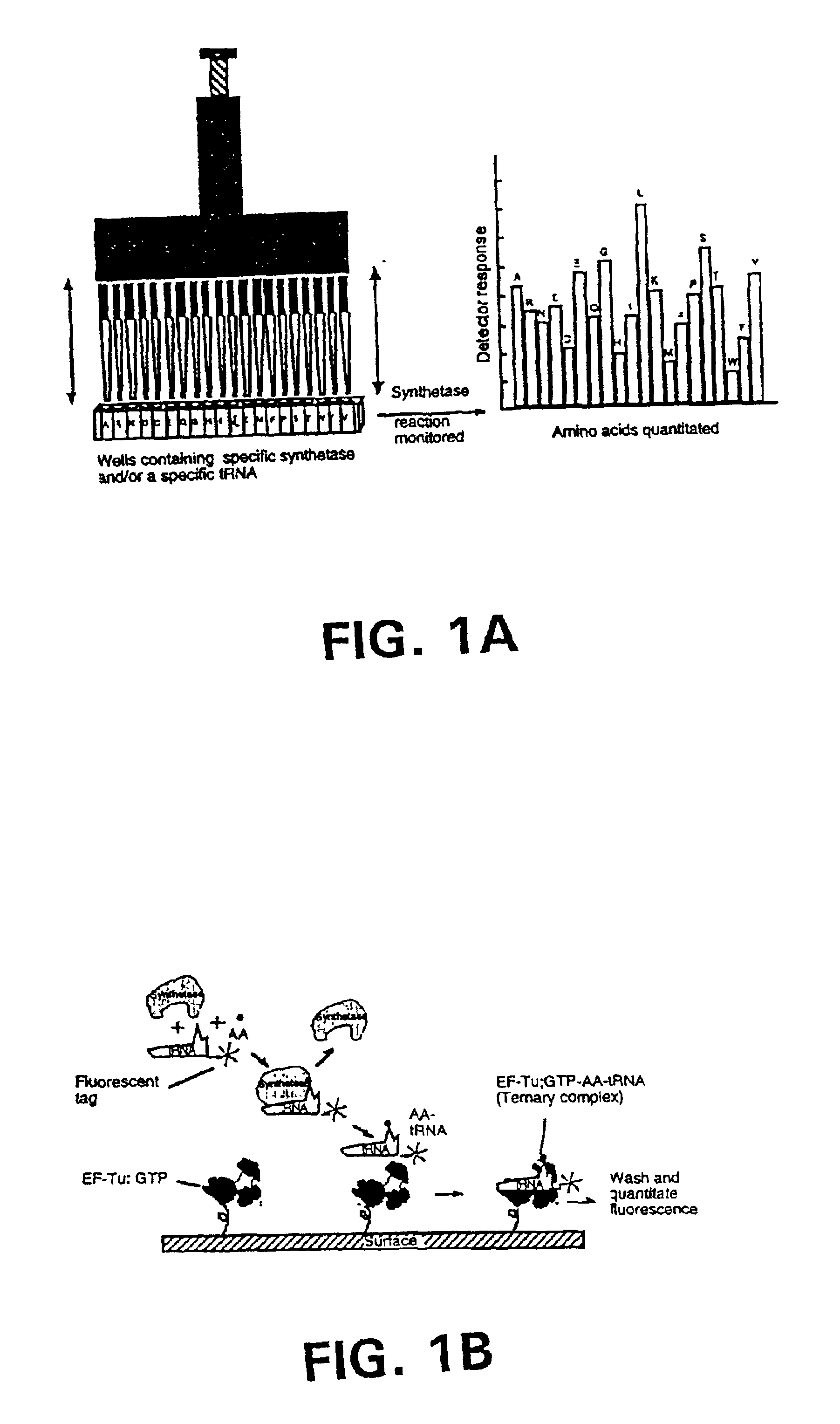
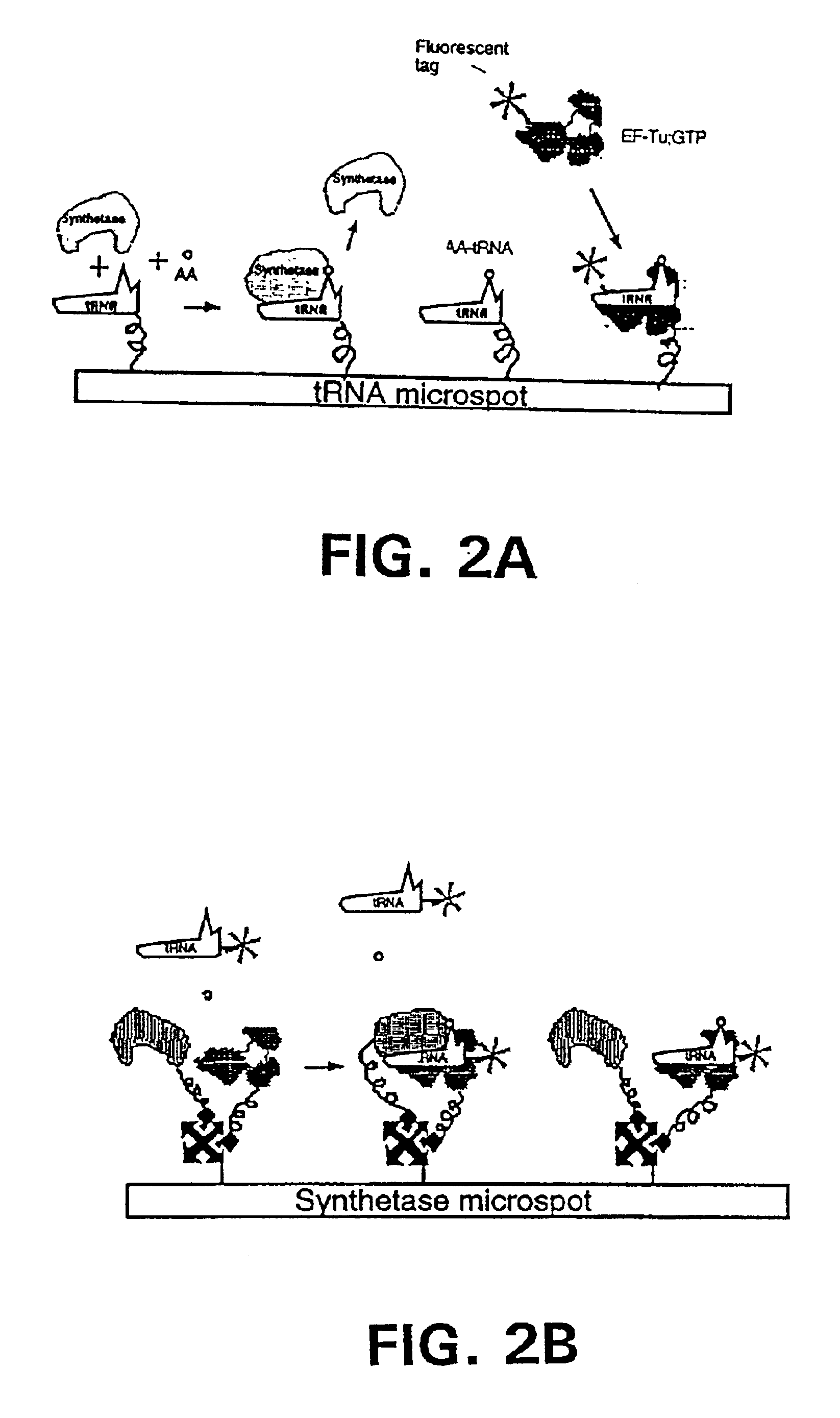
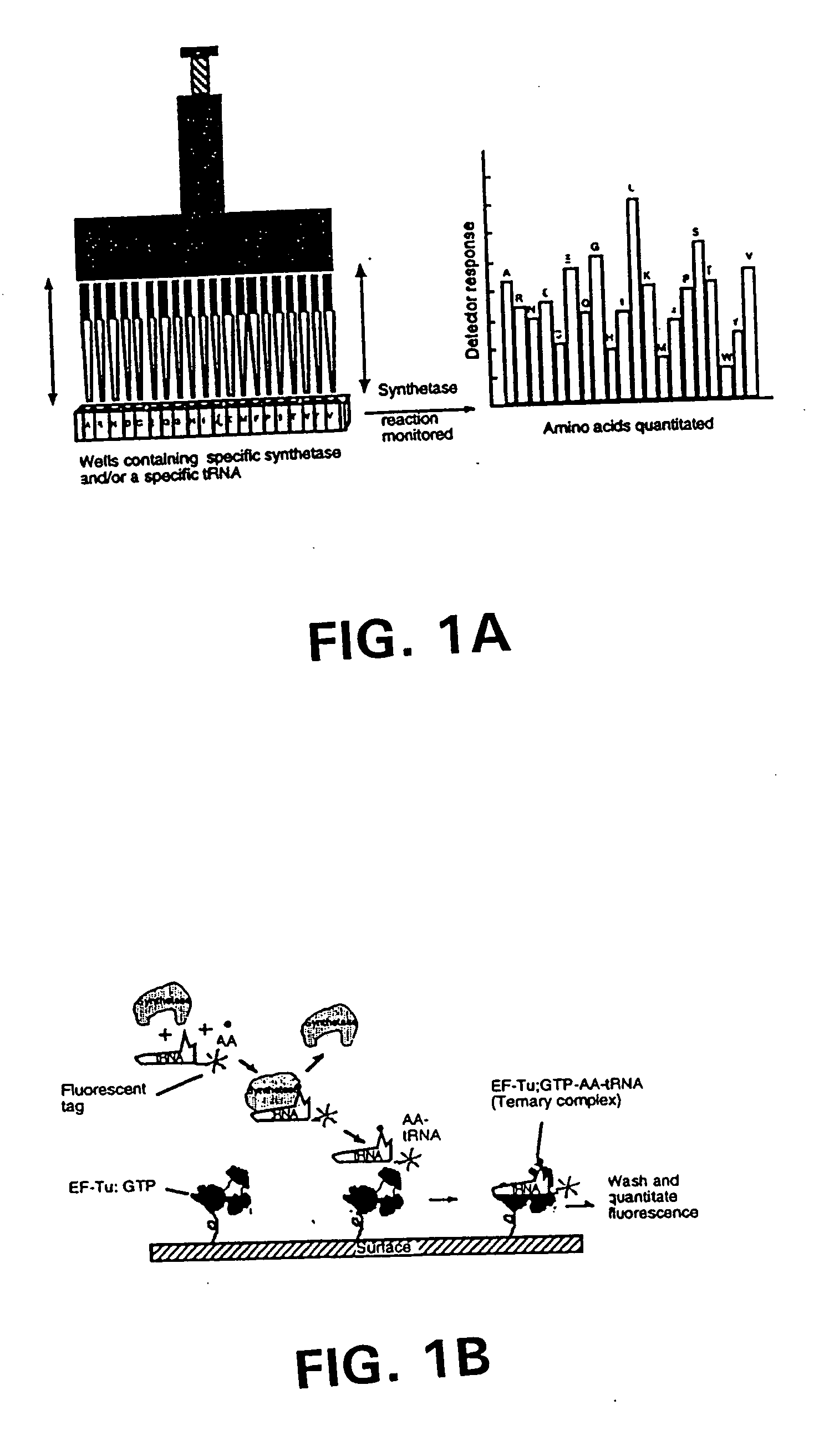
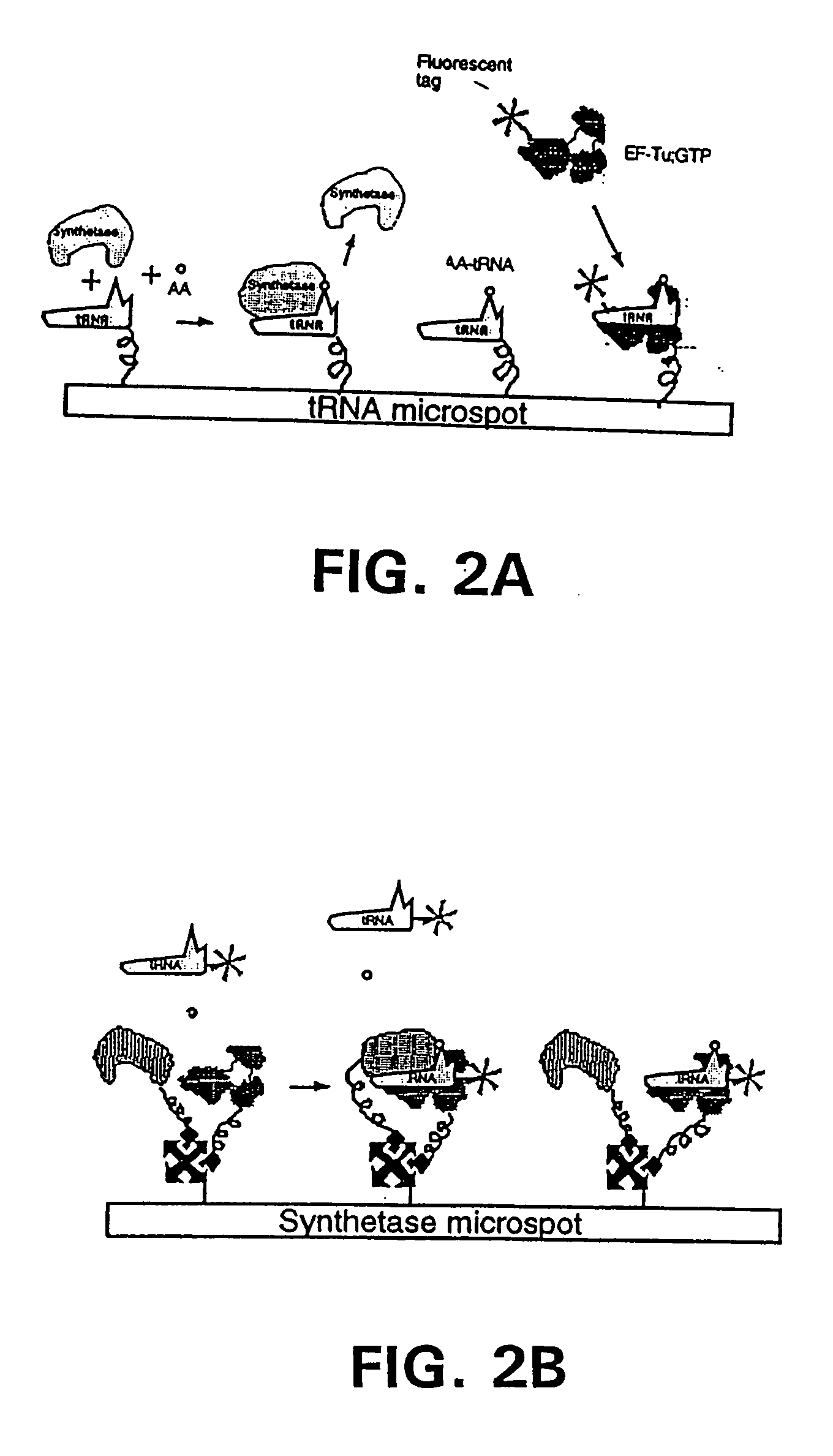
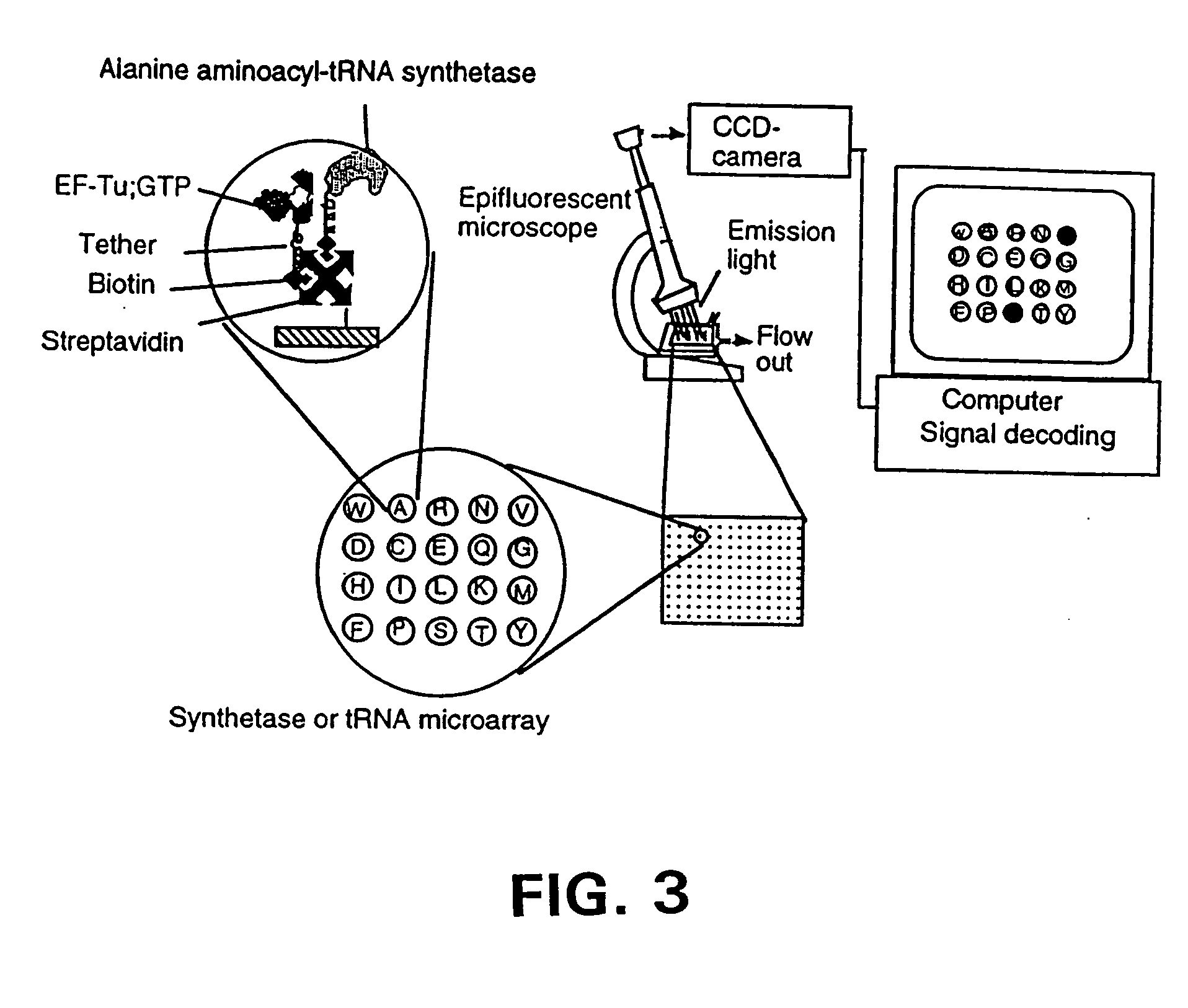
Methods, compositions, kits, and apparatus are provided wherein the aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase system is used to analyze amino acids. The method allows very small devices for quantitative or semi-quantitative analysis of the amino acids in samples or in sequential or complete proteolytic digestions. The methods can be readily applied to the detection and / or quantitation of one or more primary amino acids by using cognate aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase and cognate tRNA. The basis of the method is that each of the 20 synthetases and / or a tRNA specific for a different amino acid is separated spatially or differentially labeled. The reactions catalyzed by all 20 synthetases may be monitored simultaneously, or nearly simultaneously, or in parallel. Each separately positioned synthetase or tRNA will signal its cognate amino acid. The synthetase reactions can be monitored using continuous spectroscopic assays. Alternatively, since elongation factor Tu:GTP (EF-Tu:GTP) specifically binds all AA-tRNAs, the aminoacylation reactions catalyzed by the synthetases can be monitored using ligand assays. Microarrays and microsensors for amino acid analysis are provided. Additionally, amino acid analysis devices are integrated with protease digestions to produce miniaturized enzymatic sequenators capable of generating either N- or C-terminal sequence and composition data for a protein or peptide. The possibility of parallel processing of many samples in an automated manner is discussed.
Owner:NANOBIODYNAMICS
Modulating pH-sensitive binding using non-natural amino acids
InactiveUS20050260711A1Prolong half-life in vivoSame effectAnimal cellsSugar derivativesSide chainTumor antigen
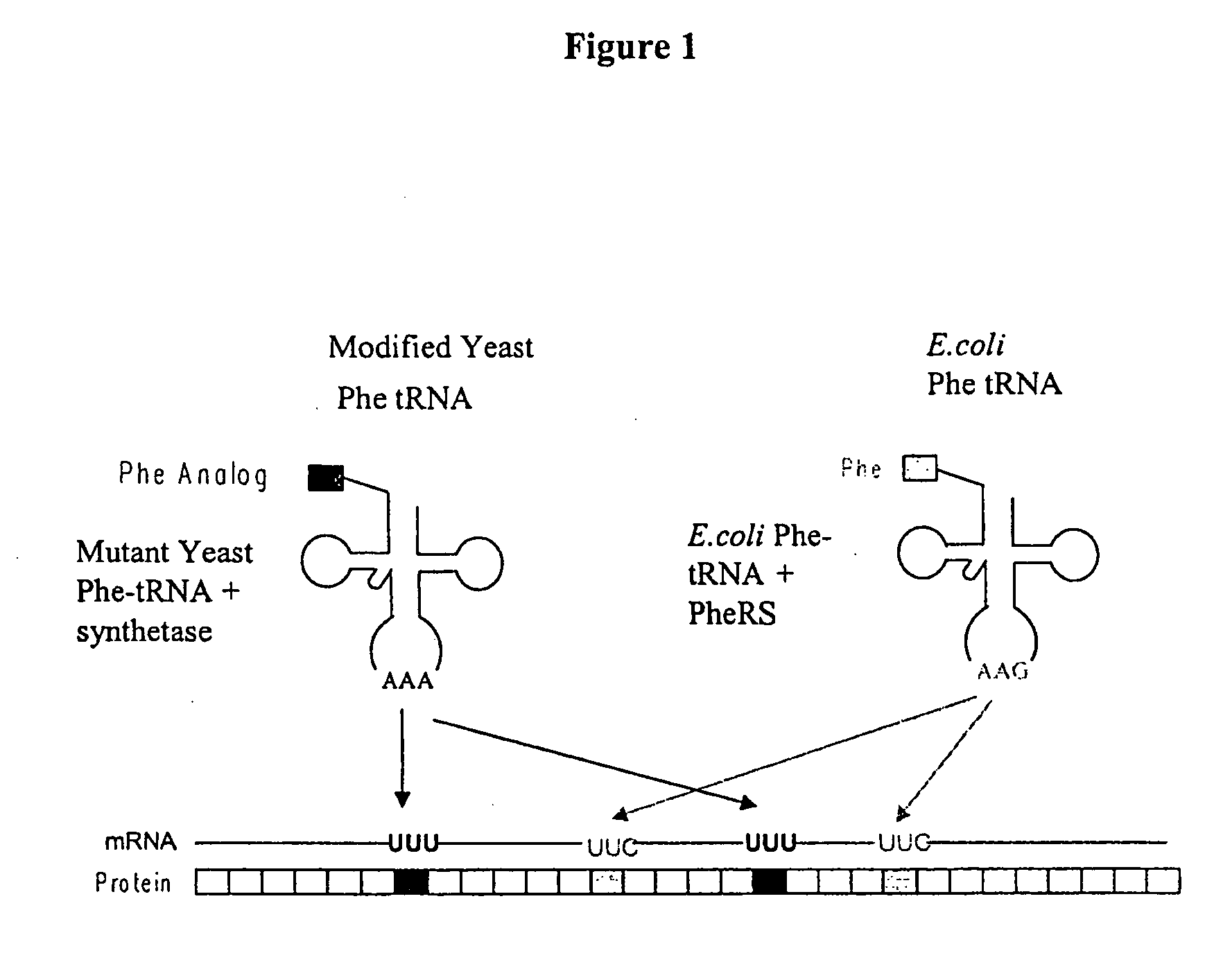
The invention provides methods, systems and reagents for regulating pH-sensitive protein interaction by incorporating non-natural amino acids into the protein (e.g. an antibody, or its functional fragment, derivative, etc.). The invention also relates to specific uses in regulating pH-sensitive binding of antibodies to tumor site, by conferring enhanced tumor-specificity / selectivity. In that embodiment, the non-natural amino acids preferably have desirable side-chain pKa's, such that at below physiological pH (e.g. about pH 6.3-6.5) the non-natural amino acid confer enhanced binding to tumor antigens in acidic environments. Such non-natural amino acids can be incorporated by any suitable means, such as by utilizing a modified aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase to charge the nonstandard amino acid to a modified tRNA, which forms strict Watson-Crick base-pairing with a codon that normally forms wobble base-pairing with natural tRNAs (e.g. the degenerate codon orthogonal system.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Methods of treating Parkinson's disease using recombinant adeno-associated virus virions
ActiveUS7588757B2Reduce deliveryIncrease in fine motor taskingBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsGene deliveryDisease
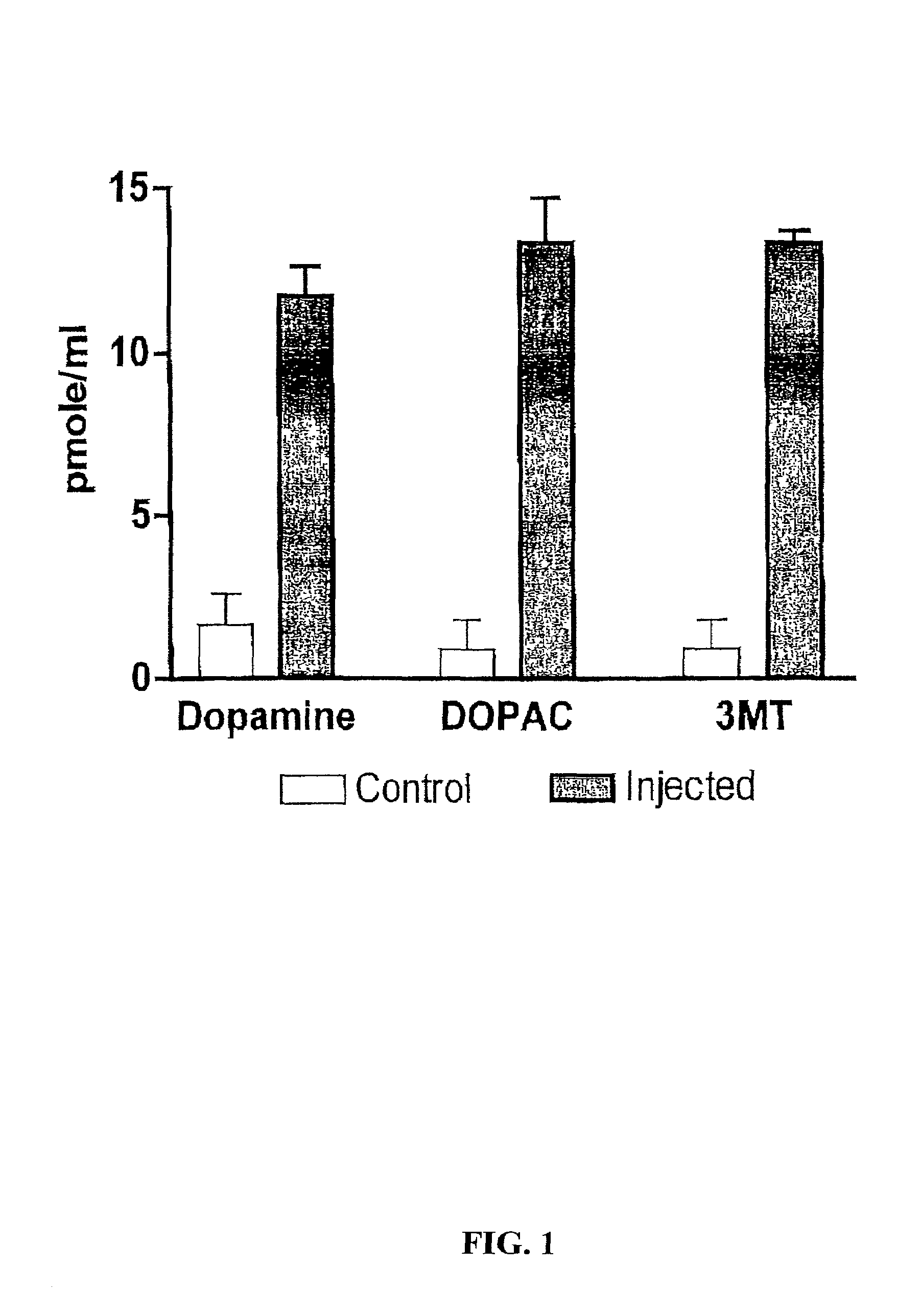
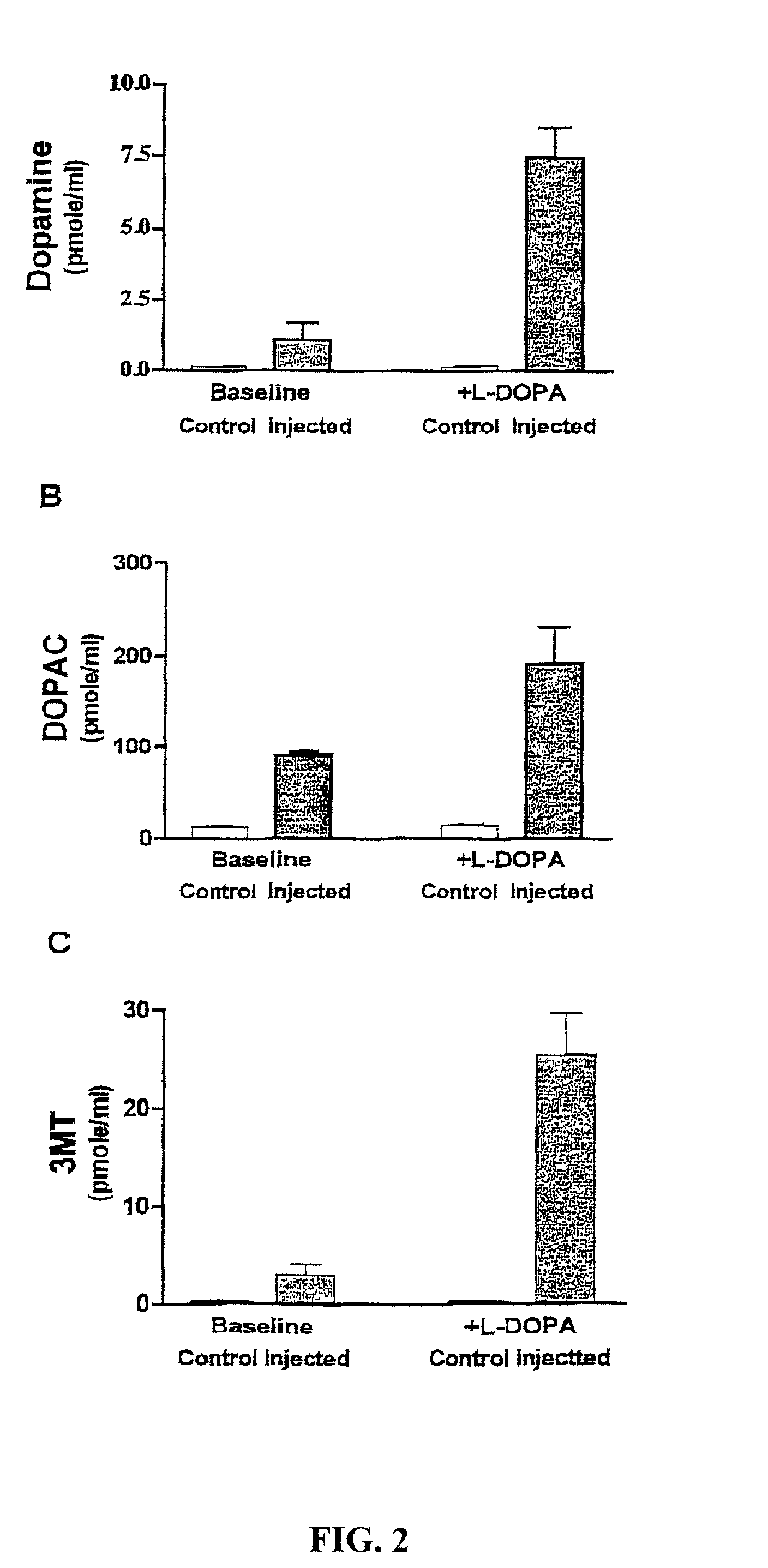
Methods for treating Parkinson's disease (PD) are provided. Recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) virions are used to deliver genes encoding dopamine-synthesizing enzymes to the central nervous system of a primate. Once delivered, the genes are expressed, which then results in dopamine synthesis and amelioration in the clinical signs and symptoms of PD. The methods of the present invention can be used to deliver the three central dopamine synthesizing enzymes: tyrosine hydroxylase, aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase, and guanosine triphosphate cyclohydrolase I thereby enhancing dopamine biosynthesis and providing for enhanced therapeutic efficacy.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Selective posttranslational modification of phage-displayed polypeptides
ActiveUS20070178448A1Easy to detectEasy to quantifyAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsVirus peptidesArylCycloaddition
The invention relates to posttranslational modification of phage-displayed polypeptides. These displayed polypeptides comprise at least one unnatural amino acid, e.g., an aryl-azide amino acid such as p-azido-L-phenylalanine, or an alkynyl-amino acid such as para-propargyloxyphenylalanine, which are incorporated into the phage-displayed fusion polypeptide at a selected position by using an in vivo orthogonal translation system comprising a suitable orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase and a suitable orthogonal tRNA species. These unnatural amino acids advantageously provide targets for posttranslational modifications such as azide-alkyne [3+2] cycloaddition reactions and Staudinger modifications.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
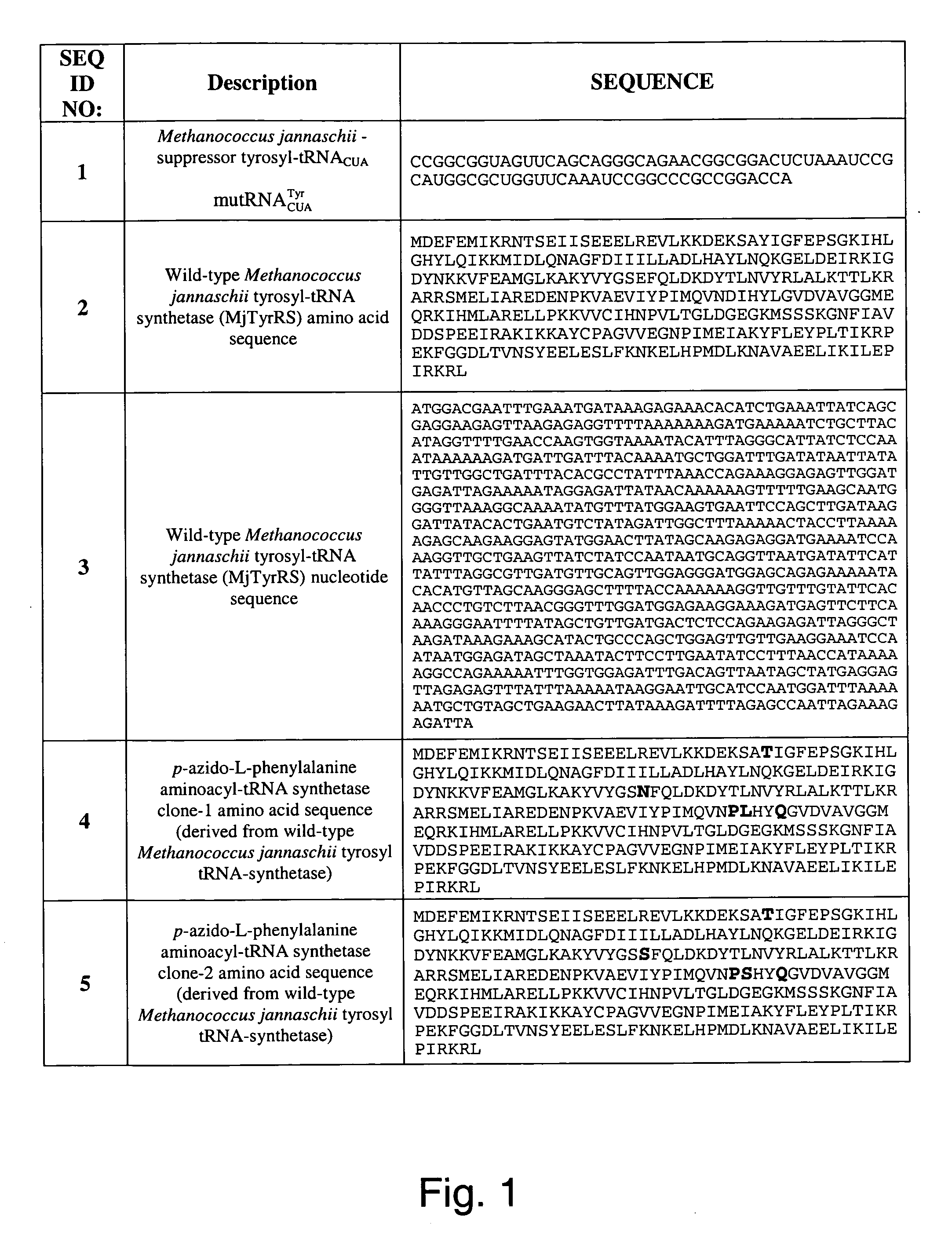
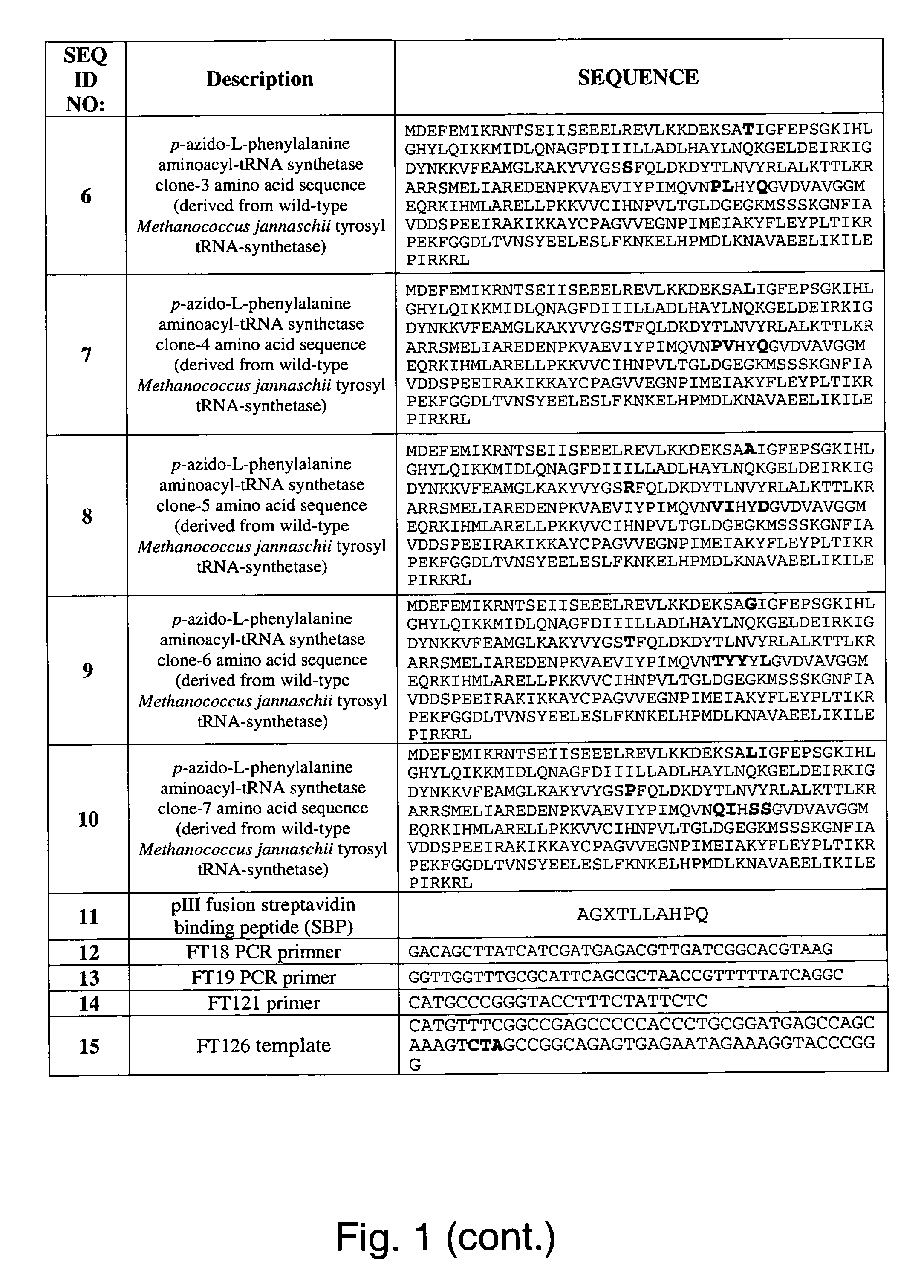
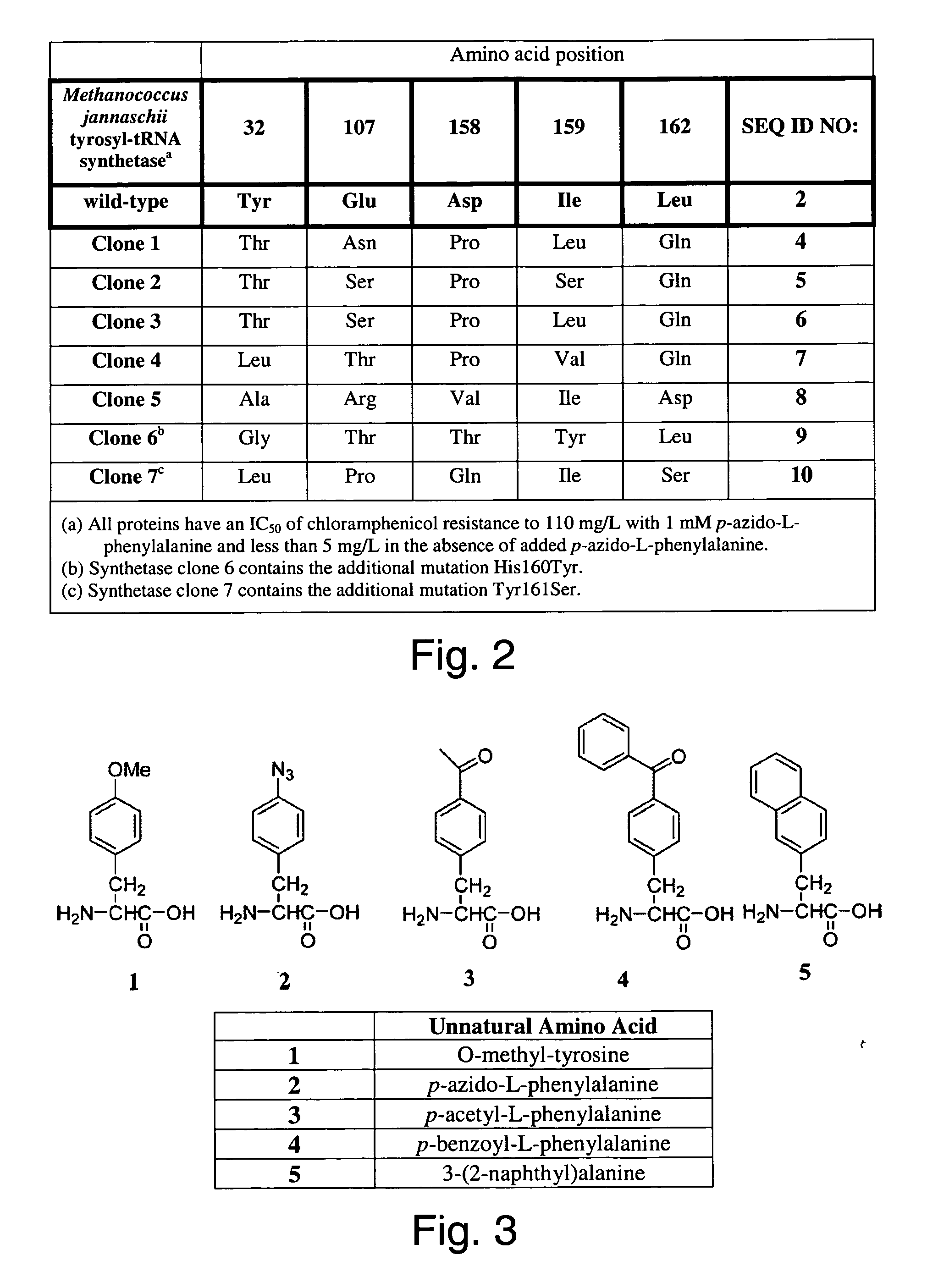
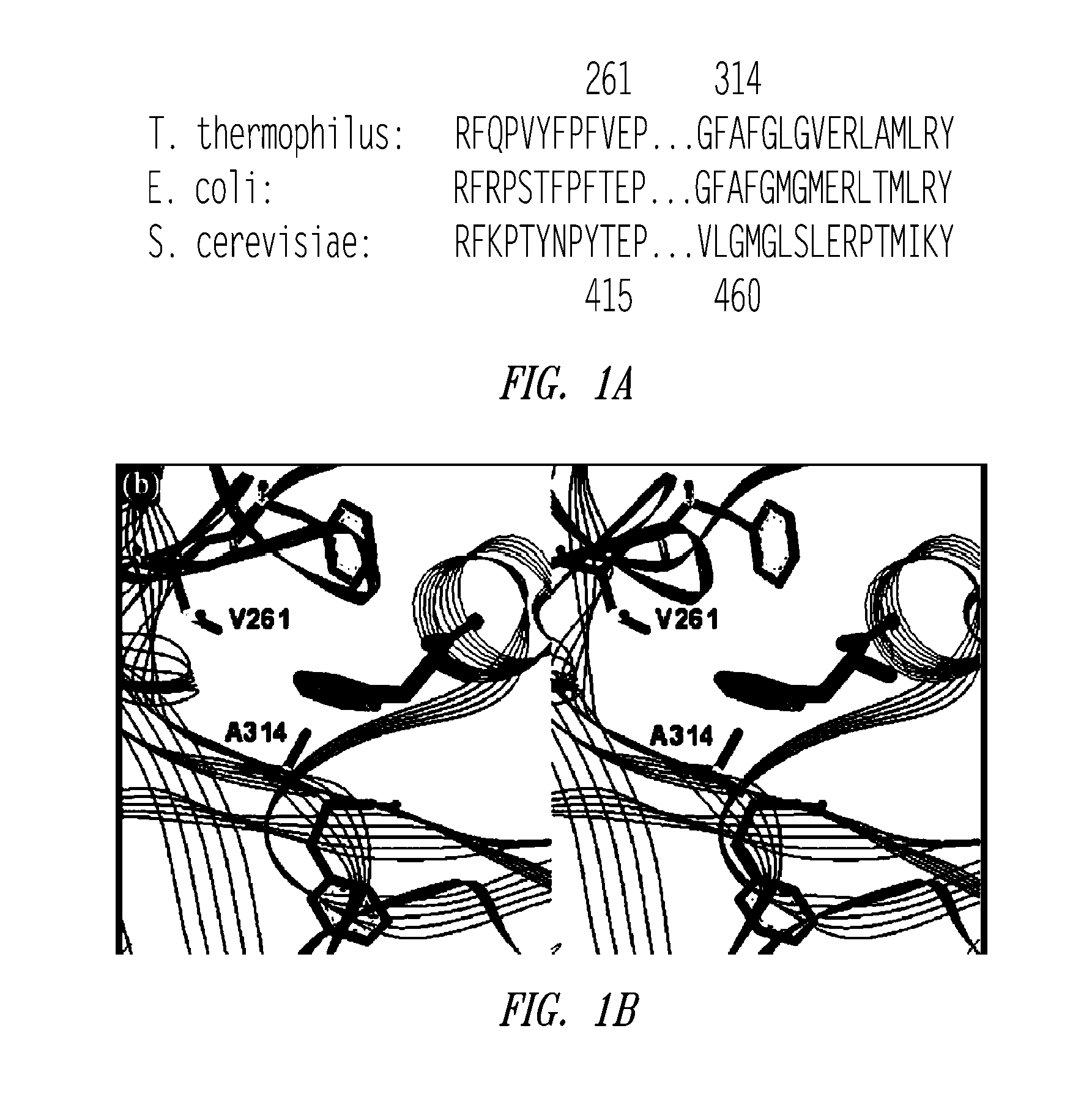
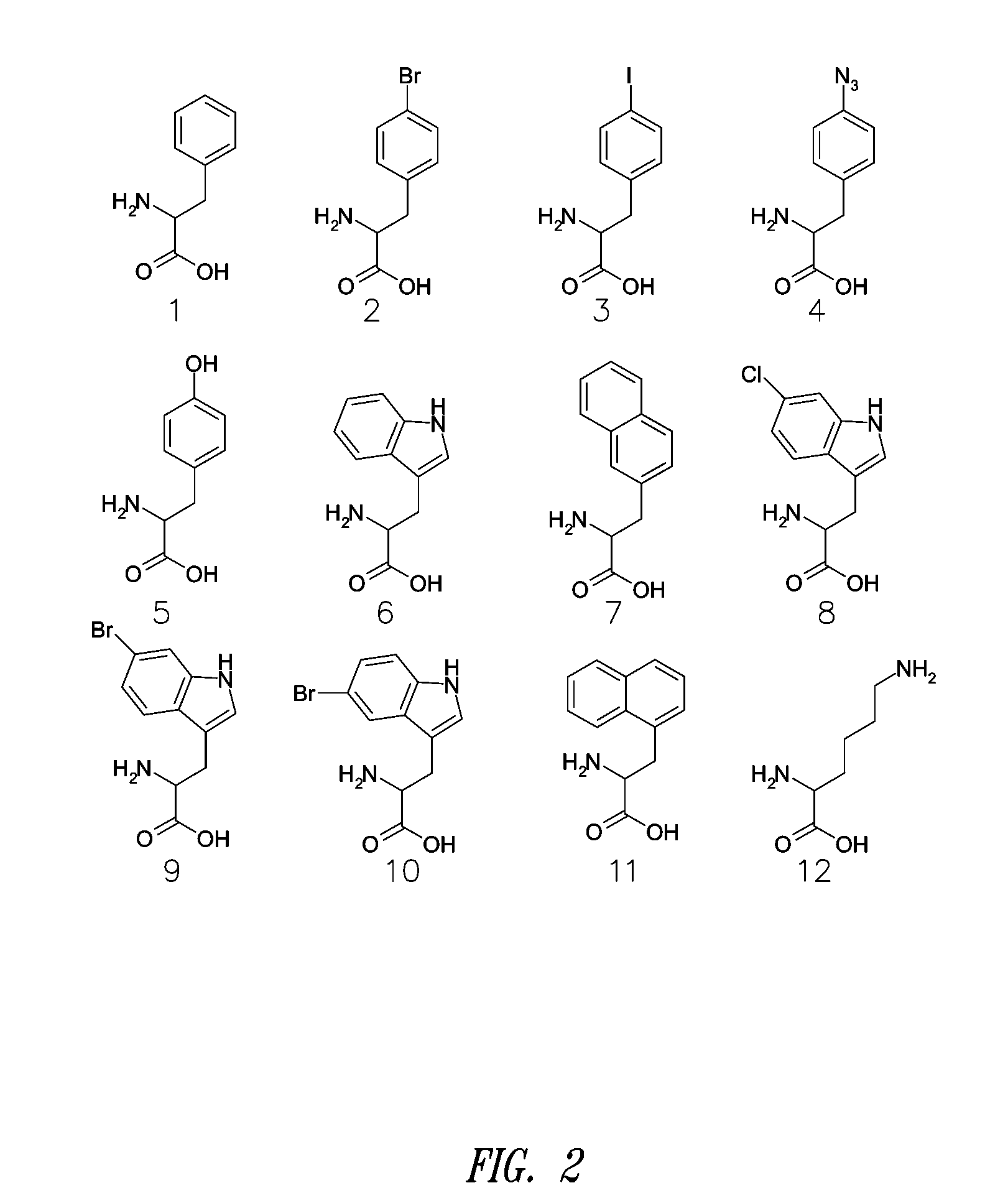
Site-specific incorporation of amino acids into molecules
The invention provides certain embodiments relating to methods and compositions for incorporating non-natural amino acids into a polypeptide or protein by utilizing a mutant or modified aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase to charge the non-natural amino acid to a the corresponding tRNA. In certain embodiments, the tRNA is also modified such that the complex forms strict Watson-Crick base-pairing with a codon that normally forms wobble base-pairing with unmodified tRNA / aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase pairs.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Thrombopoietic activity of tyrosyl-trna synthetase polypeptides
InactiveUS20100092434A1Reduce lung inflammationReduce inflammationBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsTyrosyl-tRNA SynthetaseIncreased Thrombopoiesis
Thrombopoietic compositions are provided comprising tyrosyl tRNA synthetase polypeptides, including truncations and / or variants thereof. Also provided are methods of using such compositions in the treatment of conditions that benefit from increased thrombopoiesis, such as thrombocytopenia.
Owner:ATYR PHARM INC
In vivo incorporation of alkynyl amino acids into proteins in eubacteria
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Inhibitors of the Human Aldosterone Sythase CYP11B2
ActiveUS20110112067A1Promote degradationImprove survival rateBiocideOrganic chemistryDiseaseAldosterone Synthase Deficiency
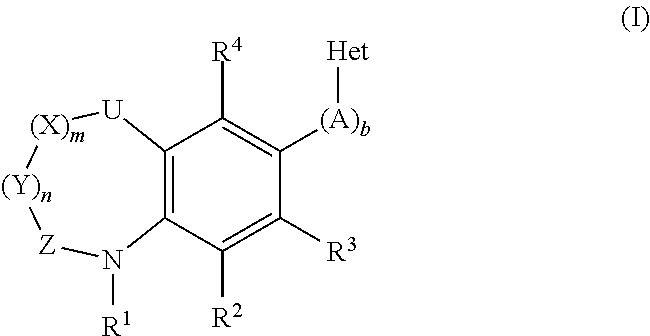
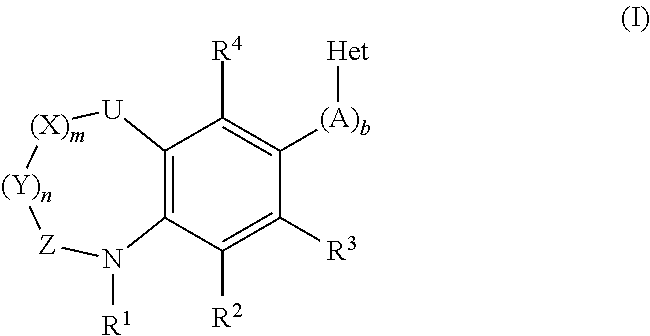
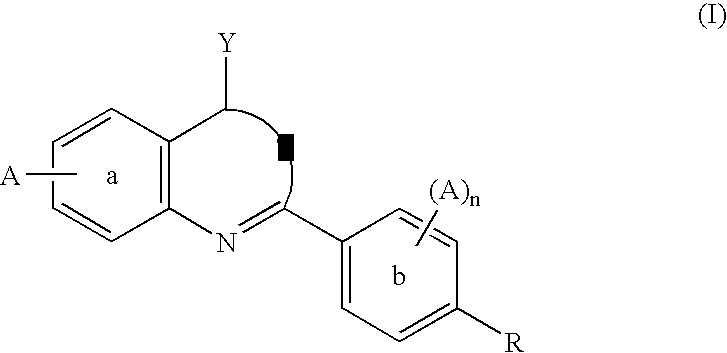
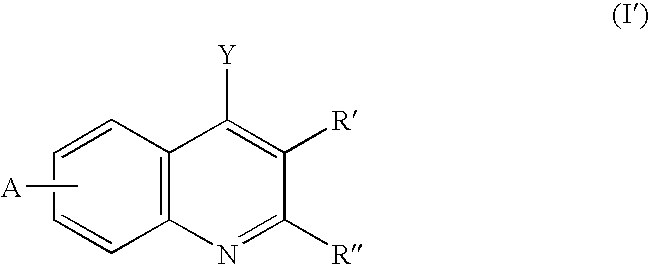
The invention provides compounds of the general formula (I)which are inhibitors of the human aldosterone synthase, and also pharmaceutical compositions containing these compounds, and a method of treating of hyperaldosteronism and / or disorders or diseases that are mediated by 11β-hydroxylase (CYP11B1) with these compounds.
Owner:ELEXOPHARM
Polypeptide having activity of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase and use thereof
A polypeptide according to the present invention includes: an altered polypeptide obtained by altering an ArgRS, a CysRS, a MetRS, a GlnRS, a GluRS, a LysRS, a TyrRS, or a TrpRS so that an unnatural amino acid is recognized; and an editing polypeptide derived from a PheRS, a LeuRS, an IleRS, a ValRS, an AlaRS, a ProRS, or a ThrRS, the editing polypeptide having been either inserted between a Rossman-fold N domain and a Rossman-fold C domain that exist in the altered polypeptide, or bound to an N terminal of the altered polypeptide. Thus provided are a new aaRS that exhibits high substrate specificity to an unnatural amino acid and a technique that involves the use of such an aaRS.
Owner:RIKEN
Method for producing L-methionine by fermentation
InactiveUS7611873B1High activityIncrease productivityBacteriaSugar derivativesSerine dehydrogenaseThreonine
L-Methionine is produced by culturing a microorganism which is deficient in repressor of L-methionine biosynthesis system and / or enhanced intracellular homoserine transsuccinylase activity is cultured in a medium so that L-methionine should be produced and accumulated in the medium, and collecting the L-methionine from the medium. The microorganism preferably further exhibits reduced intracellular S-adenosylmethionine synthetase activity, L-threonine auxotrophy, enhanced intracellular cystathionine γ-synthase activity and enhanced intracellular aspartokinase-homoserine dehydrogenase II activity. The present invention enables breeding of L-methionine-producing bacteria, and L-methionine production by fermentation.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
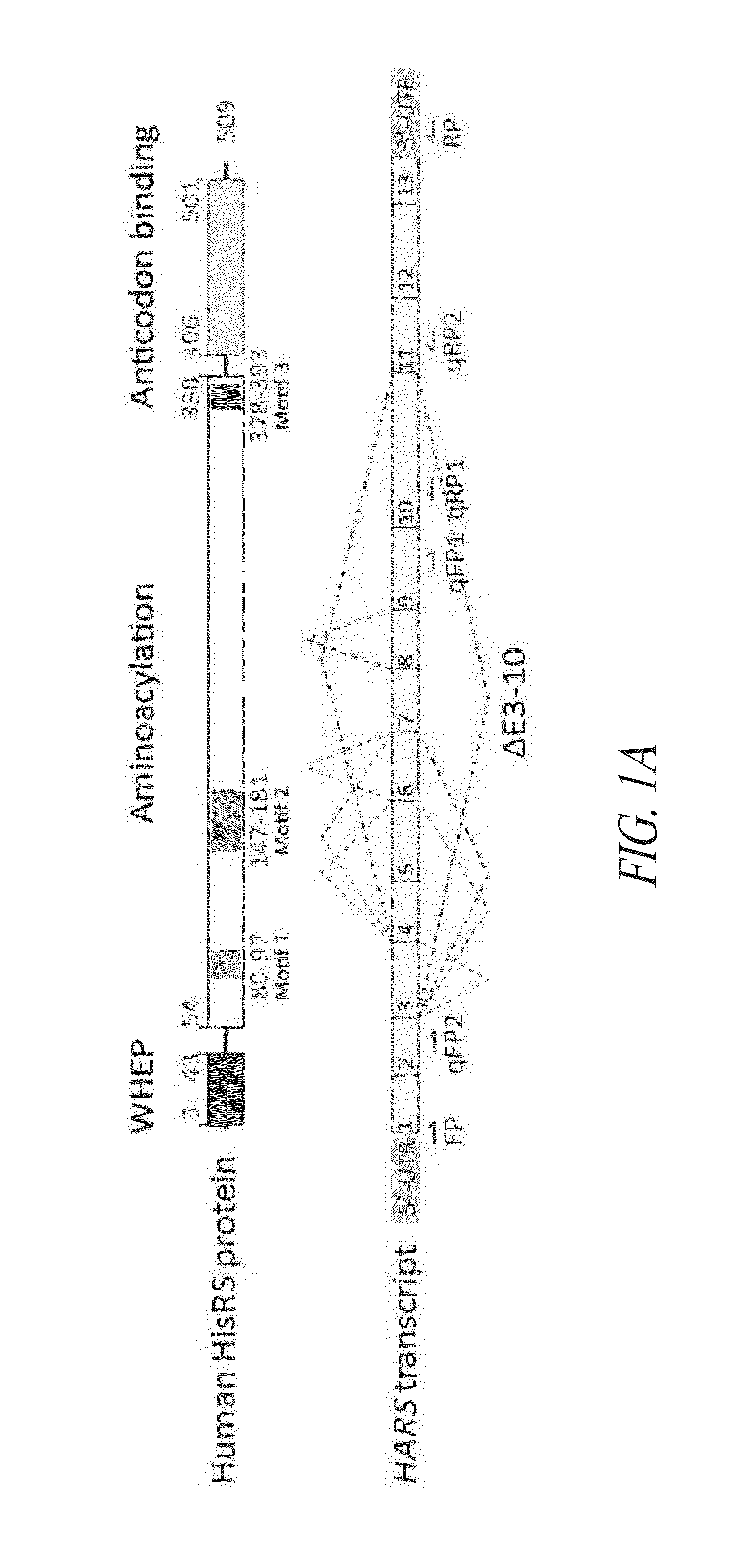
Structures of human histidyl-trna synthetase and methods of use
InactiveUS20140066321A1Improve homogeneityLibrary screeningAnalogue computers for chemical processesMedicineX-ray
Provided are histidyl-tRNA synthetase variant polypeptides, X-ray crystallographic and NMR spectroscopy structures of HRS polypeptides, and related compositions and methods for therapy and drug discovery.
Owner:ATYR PHARM INC +1
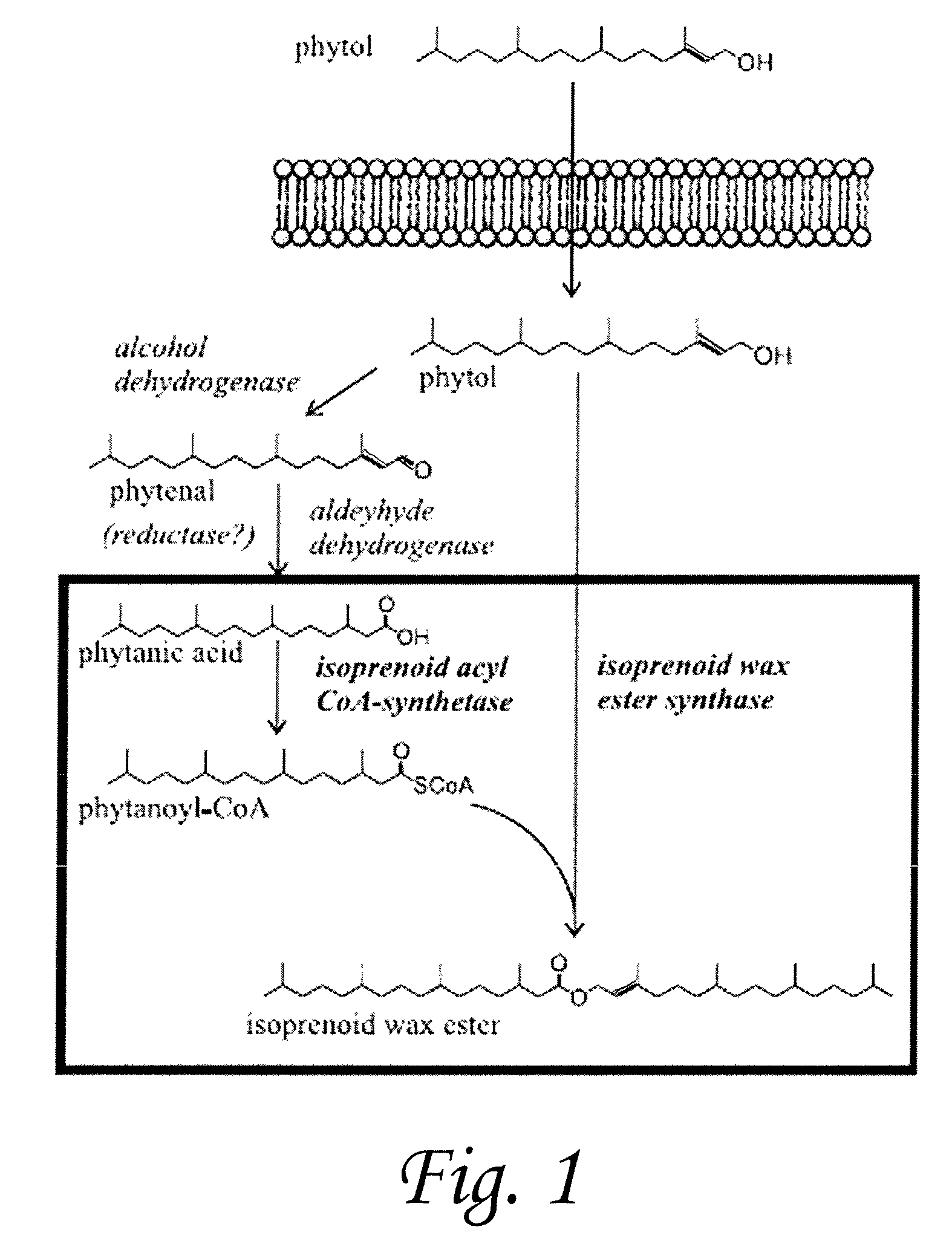
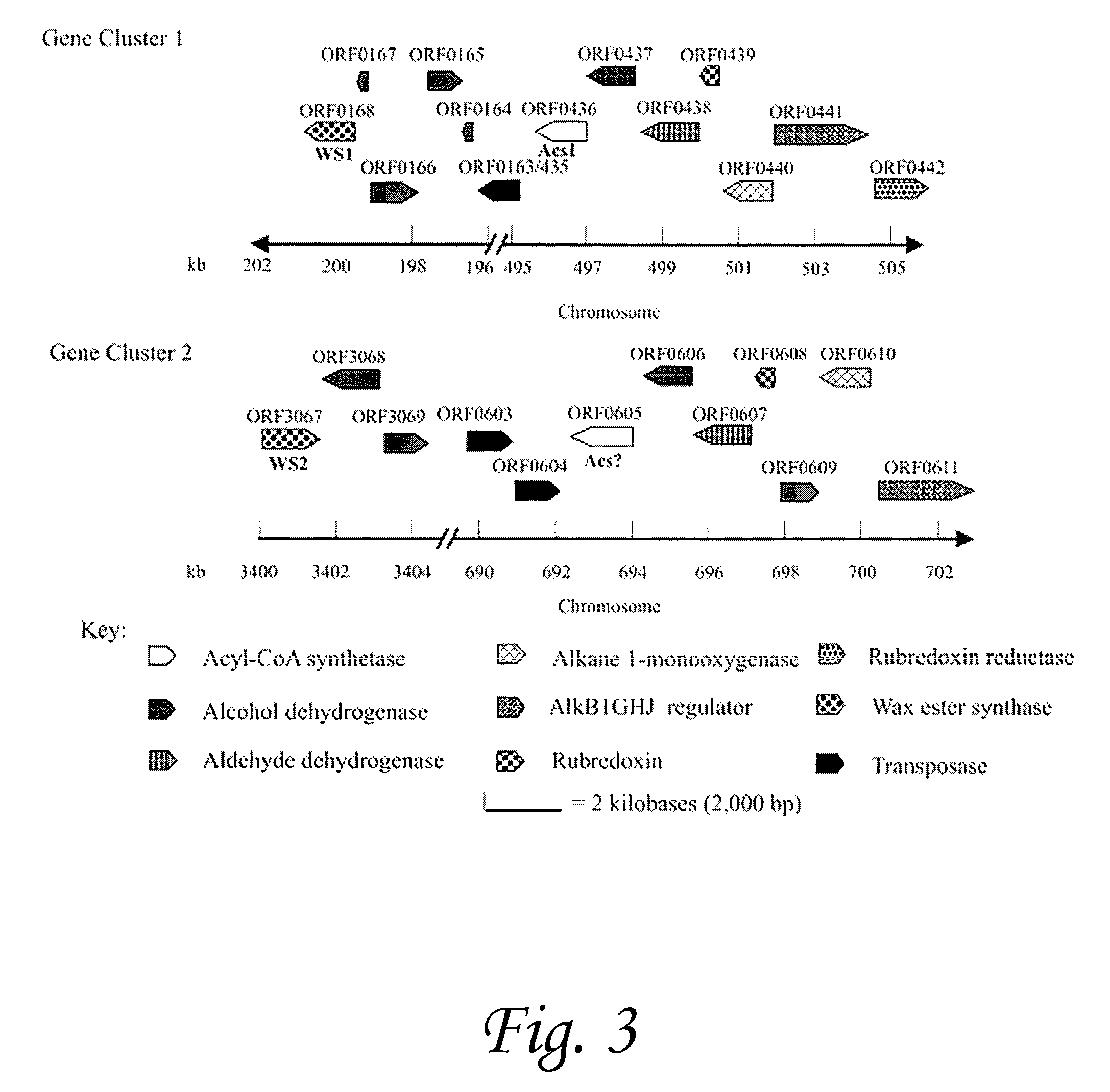
Isoprenoid wax ester synthases, isoprenoid acyl coa-synthetases, and uses thereof
The present invention provides isolated polynucleotides and isolated polypeptides. The polypeptides of the present invention have isoprenoid wax ester synthase activity or isoprenoid acyl CoA-synthetase activity. The present invention also includes methods of using the polynucleotides and polypeptides of the present invention. For instance, the methods include producing biodiesel and producing wax esters.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
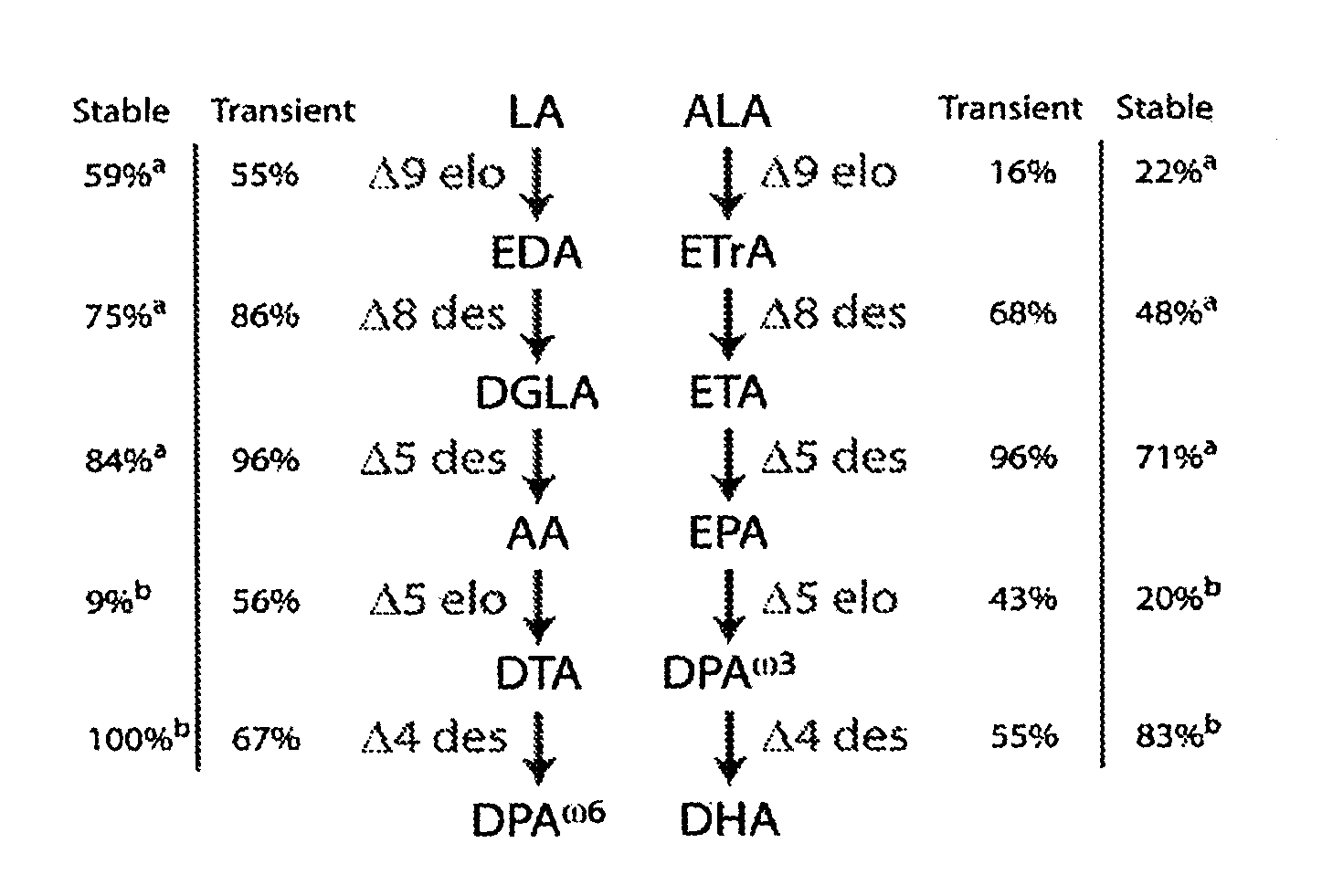
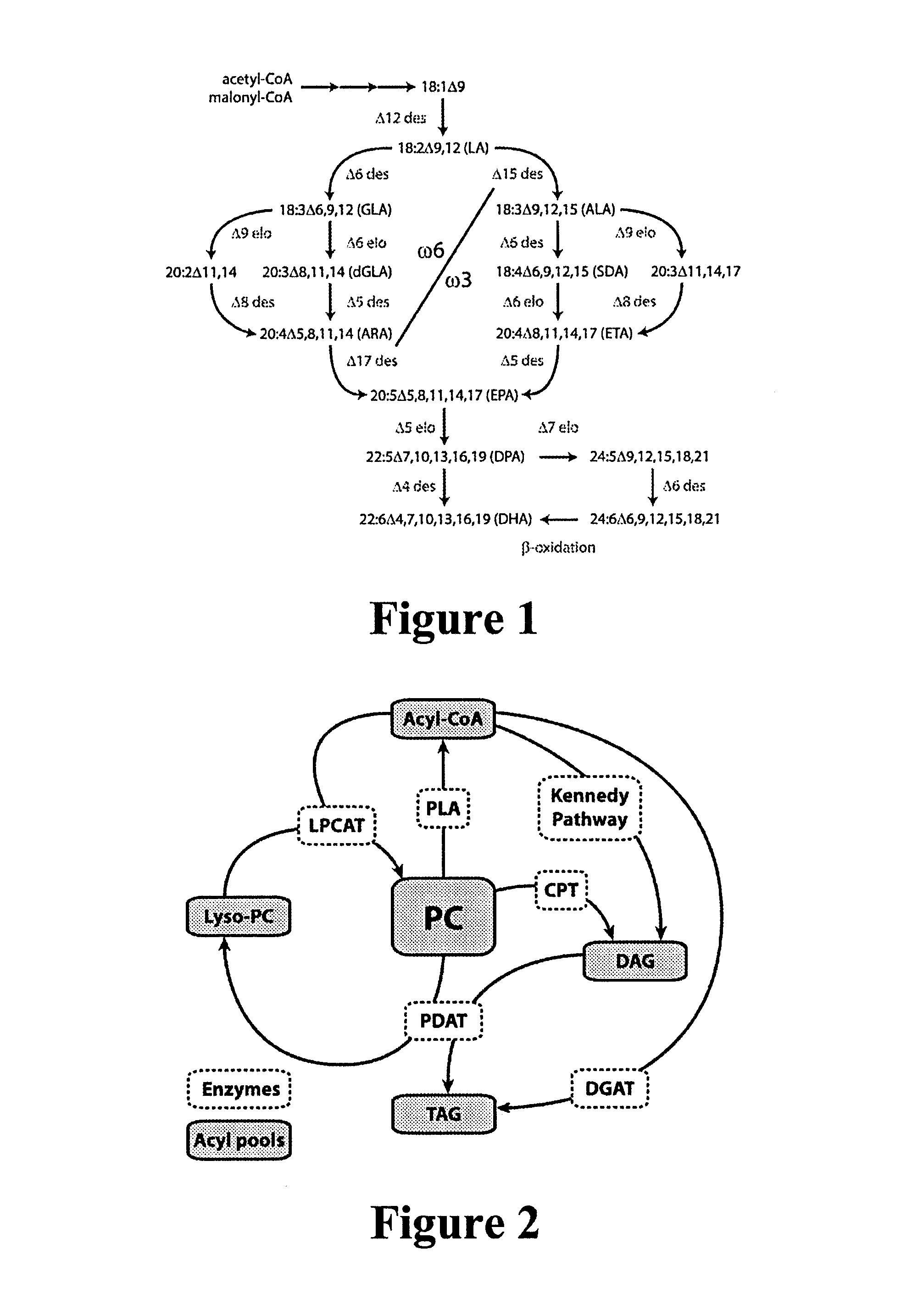
Enzymes and methods for producing omega-3 fatty acids
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG +1
Method and system for rapid biomolecular recognition of amino acids and protein sequencing
InactiveUS20050164264A1Quick analysisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProtein Sequence DeterminationDigestion
Methods, compositions, kits, and apparatus are provided wherein the aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase system is used to analyze amino acids. The method allows very small devices for quantitative or semi-quantitative analysis of the amino acids in samples or in sequential or complete proteolytic digestions. The methods can be readily applied to the detection and / or quantitation of one or more primary amino acids by using cognate aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase and cognate tRNA. The basis of the method is that each of the 20 synthetases and / or a tRNA specific for a different amino acid is separated spatially or differentially labeled. The reactions catalyzed by all 20 synthetases may be monitored simultaneously, or nearly simultaneously, or in parallel. Each separately positioned synthetase or tRNA will signal its cognate amino acid. The synthetase reactions can be monitored using continuous spectroscopic assays. Alternatively, since elongation factor Tu:GTP (EF-Tu:GTP) specifically binds all AA−tRNAs, the aminoacylation reactions catalyzed by the synthetases can be monitored using ligand assays. Microarrays and microsensors for amino acid analysis are provided. Additionally, amino acid analysis devices are integrated with protease digestions to produce miniaturized enzymatic sequenators capable of generating either N- or C-terminal sequence and composition data for a protein or peptide. The possibility of parallel processing of many samples in an automated manner is discussed.
Owner:NANOBIODYNAMICS
Bacterial glutamine synthetases and methods of use
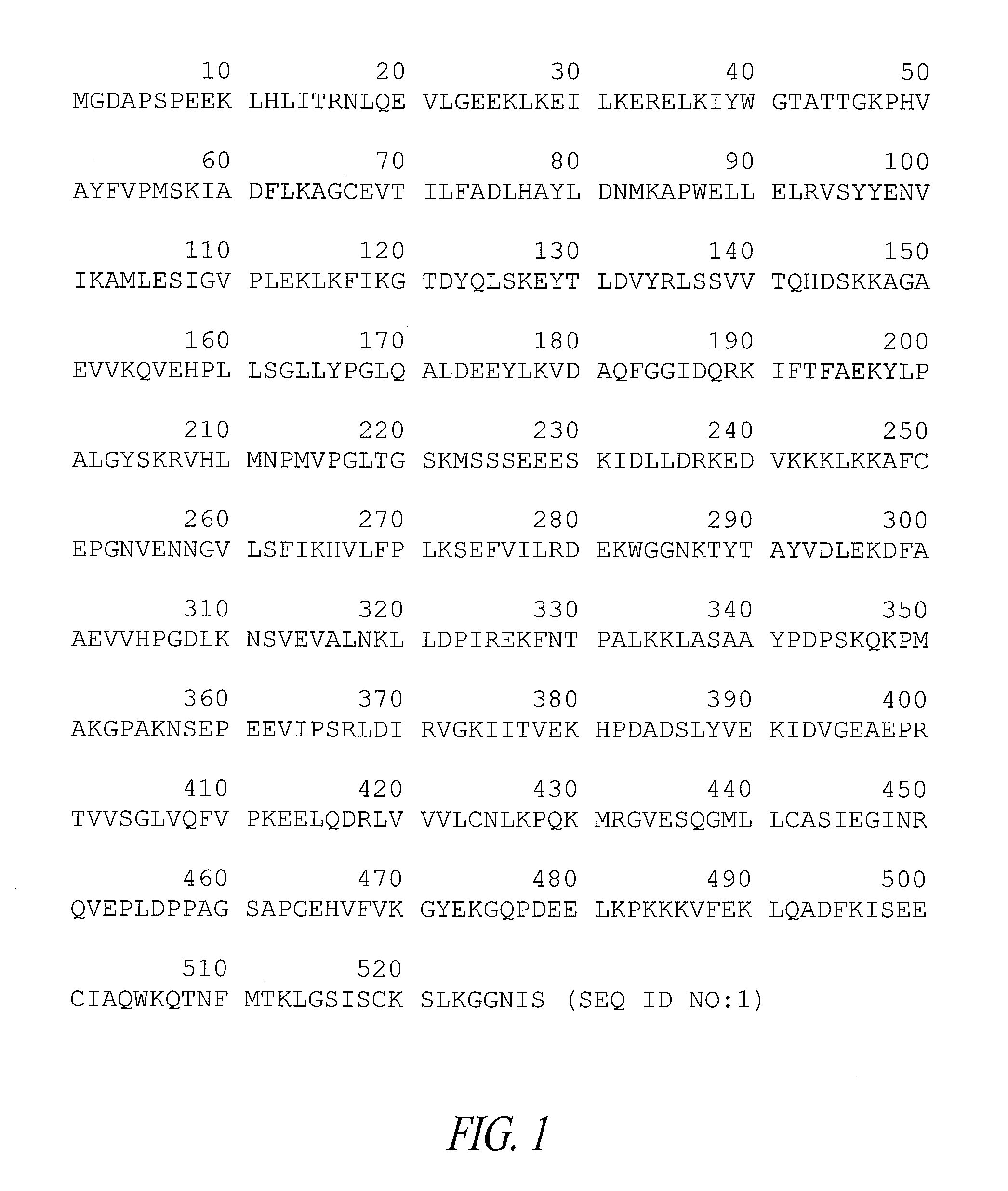
Compositions and methods for conferring herbicide resistance to and improving nitrogen utilization of bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions comprising a coding sequence for a polypeptide that confers resistance or tolerance to herbicidal glutamine synthetase inhibitors are provided. The coding sequences can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and expression in plants. Compositions also comprise transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In particular, isolated polynucleotides corresponding to herbicidal glutamine synthetase inhibitor-resistant polynucleotides are provided. Additionally, polypeptides corresponding to the polynucleotides are encompassed. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated polynucleotides comprising a variant of SEQ ID NO:1, wherein the variant polynucleotide encodes a polypeptide that is resistant to inhibition by herbicidal glutamine synthetase inhibitor.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Methods and materials for identifying polymorphic variants, diagnosing susceptibilities, and treating disease
InactiveUS20080213775A1Increased susceptibilitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseCarbon metabolism
The invention is directed to materials and methods associated with polymorphic variants in two enzymes involved in folate-dependent and one-carbon metabolic pathways: MTHFD1 (5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase, 5,10-methenyltetrahydrofolate cyclohydrolase, 10-formyltetrahydrofolate synthetase) and methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase (NADP+dependent) 1-like (MTHFD1L). Diagnostic and therapeutic methods are provided involving the correlation of polymorphic variants in MTBFD1, MTHFD1, and other genes with relative susceptibility for various pregnancy-related and other complications.
Owner:GOVERNMENT OF THE US REPRESENTED BY THE SEC +2
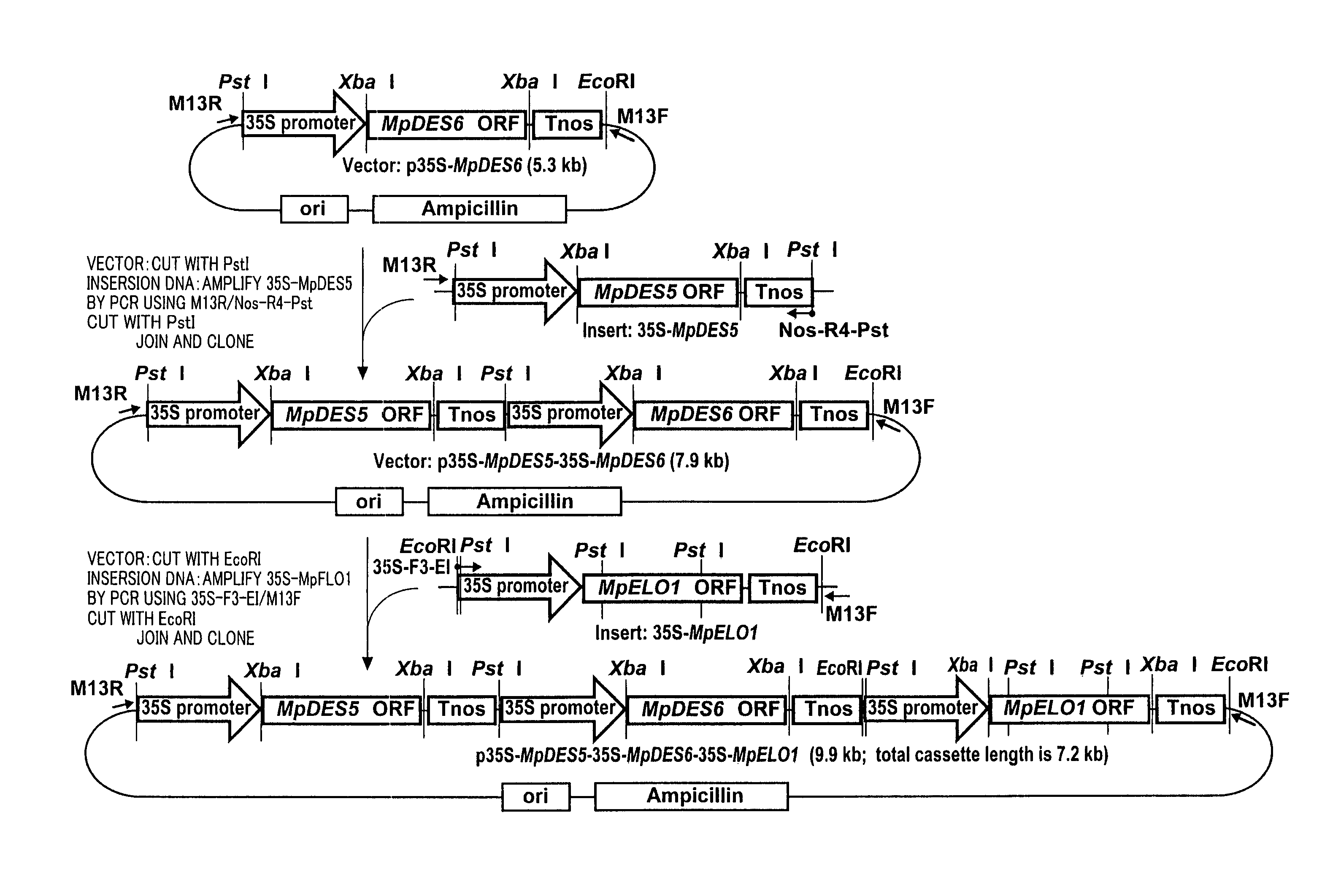
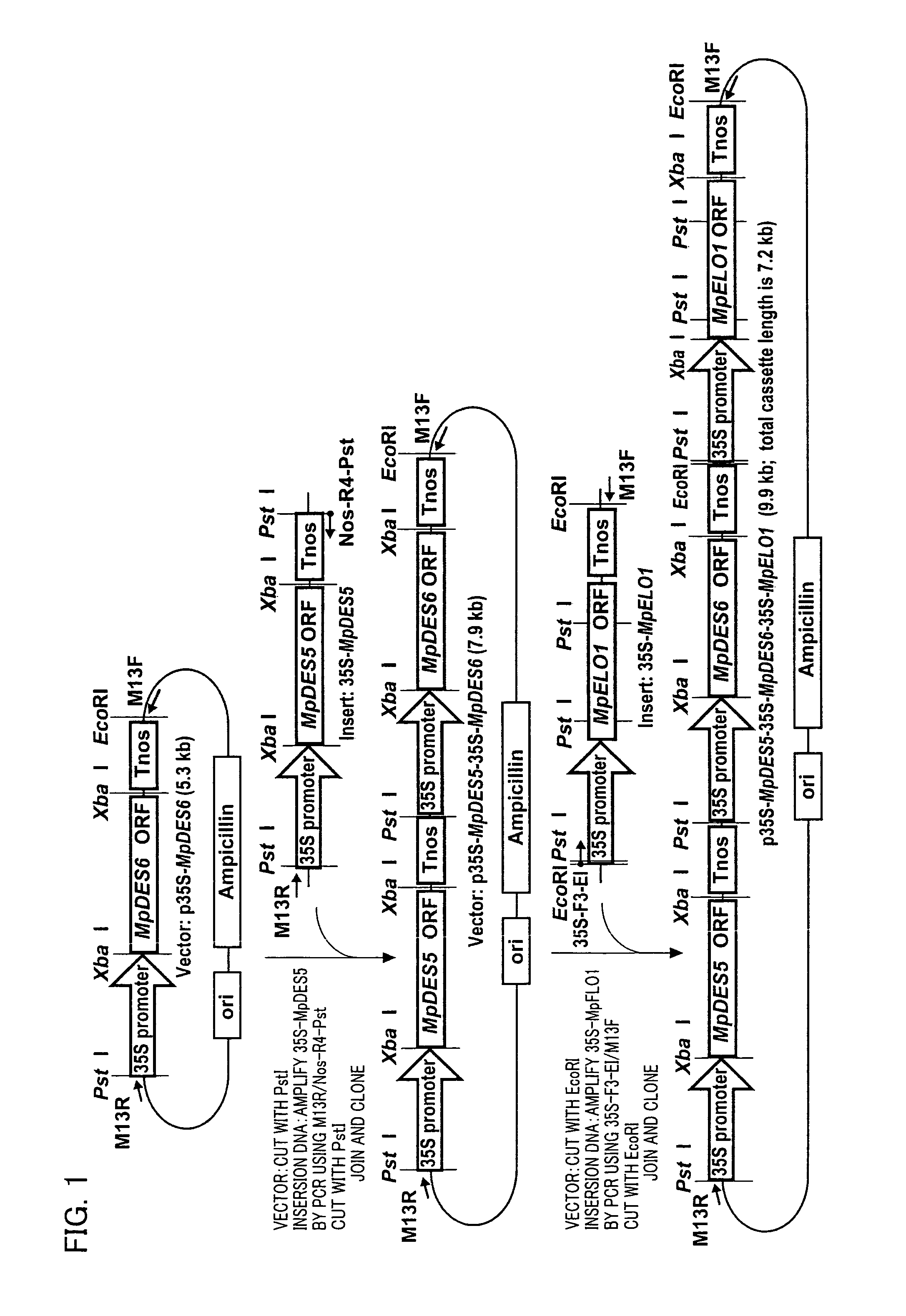
Marchantiales-Derived Unsaturated Fatty Acid Synthetase Genes And Use Of The Same
InactiveUS20080057495A1ImmunoglobulinsOxidoreductasesUnsaturated fatty acid synthesisEicosapentaenoic acid
A Δ5 fatty acid desaturase gene, a Δ6 fatty acid desaturase gene, and a Δ6 fatty-acid-chain elongase gene are isolated from a single species of Marchantiales. By introducing these genes into higher plants, transformed plants which can produce arachidonic acid and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) are obtained.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
Organisms for the production of cyclohexanone
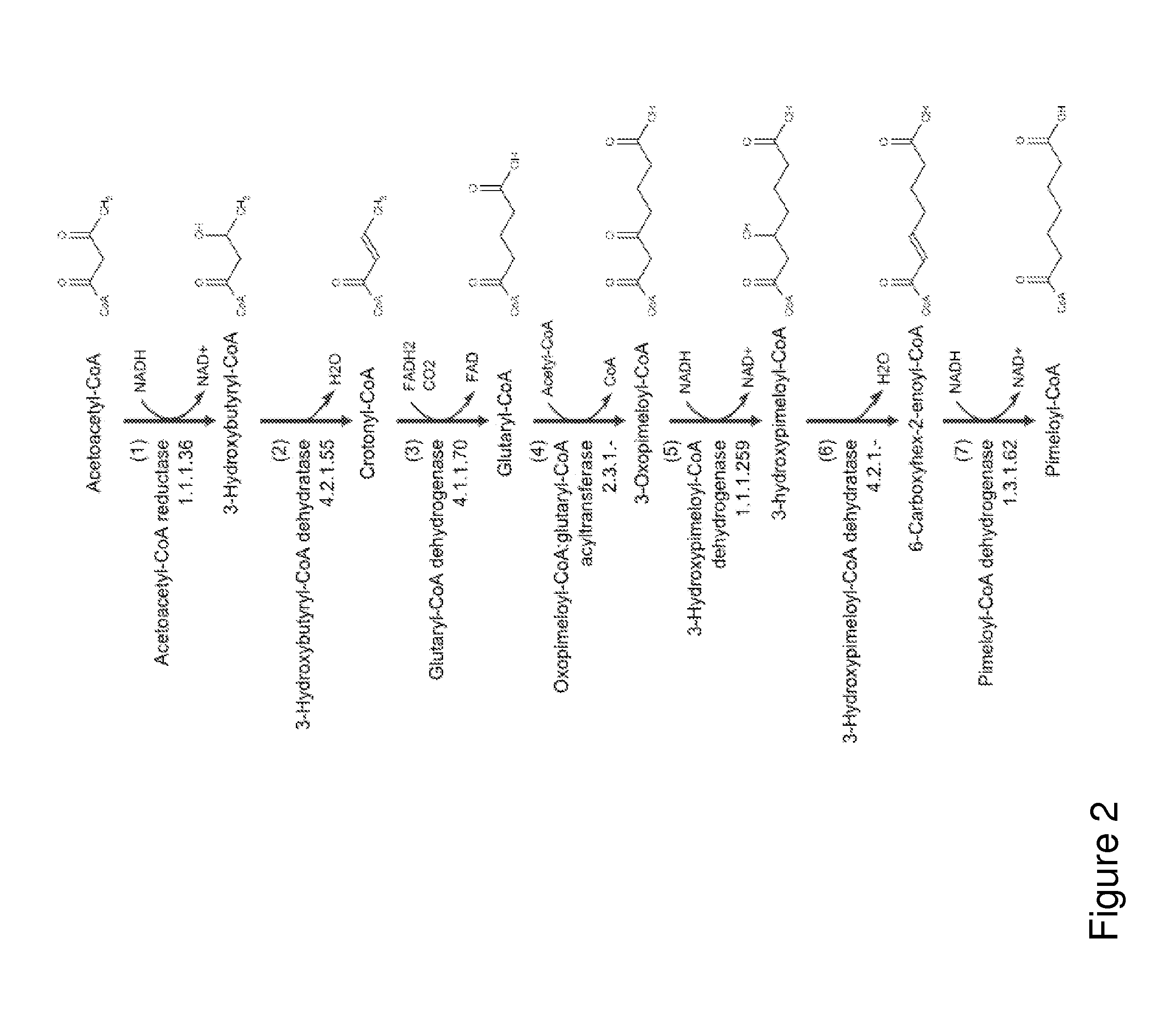
A non-naturally occurring microbial organism has cyclohexanone pathways that include at least one exogenous nucleic acid encoding a cyclohexanone pathway enzyme. A pathway includes a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxyl-CoA hydrolase (acting on C—C bond), a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxylate decarboxylase and an enzyme selected from a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxyl-CoA hydrolase (acting on thioester), a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxyl-CoA transferase, and a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxyl-CoA synthetase. A pathway includes an enzyme selected from a 6-ketocyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxyl-CoA hydrolase (acting on C—C bond), a 6-ketocyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxyl-CoA synthetase, a 6-ketocyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxyl-CoA hydrolase (acting on thioester), a 6-ketocyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxyl-CoA transferase, a 6-ketocyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxyl-CoA reductase, a 6-ketocyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxylate decarboxylase, a 6-ketocyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxylate reductase, a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxyl-CoA synthetase, a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxyl-CoA transferase, a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxyl-CoA hydrolase (acting on thioester), a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxylate decarboxylase, and a cyclohexanone dehydrogenase. A pathway includes an adipate semialdehyde dehydratase, a cyclohexane-1,2-diol dehydrogenase, and a cyclohexane-1,2-diol dehydratase. A pathway includes a 3-oxopimelate decarboxylase, a 4-acetylbutyrate dehydratase, a 3-hydroxycyclohexanone dehydrogenase, a 2-cyclohexenone hydratase, a cyclohexanone dehydrogenase and an enzyme selected from a 3-oxopimeloyl-CoA synthetase, a 3-oxopimeloyl-CoA hydrolase (acting on thioester), and a 3-oxopimeloyl-coA transferase. Each these pathways can include a PEP carboxykinase. A method for producing cyclohexanone includes culturing these non-naturally occurring microbial organisms.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
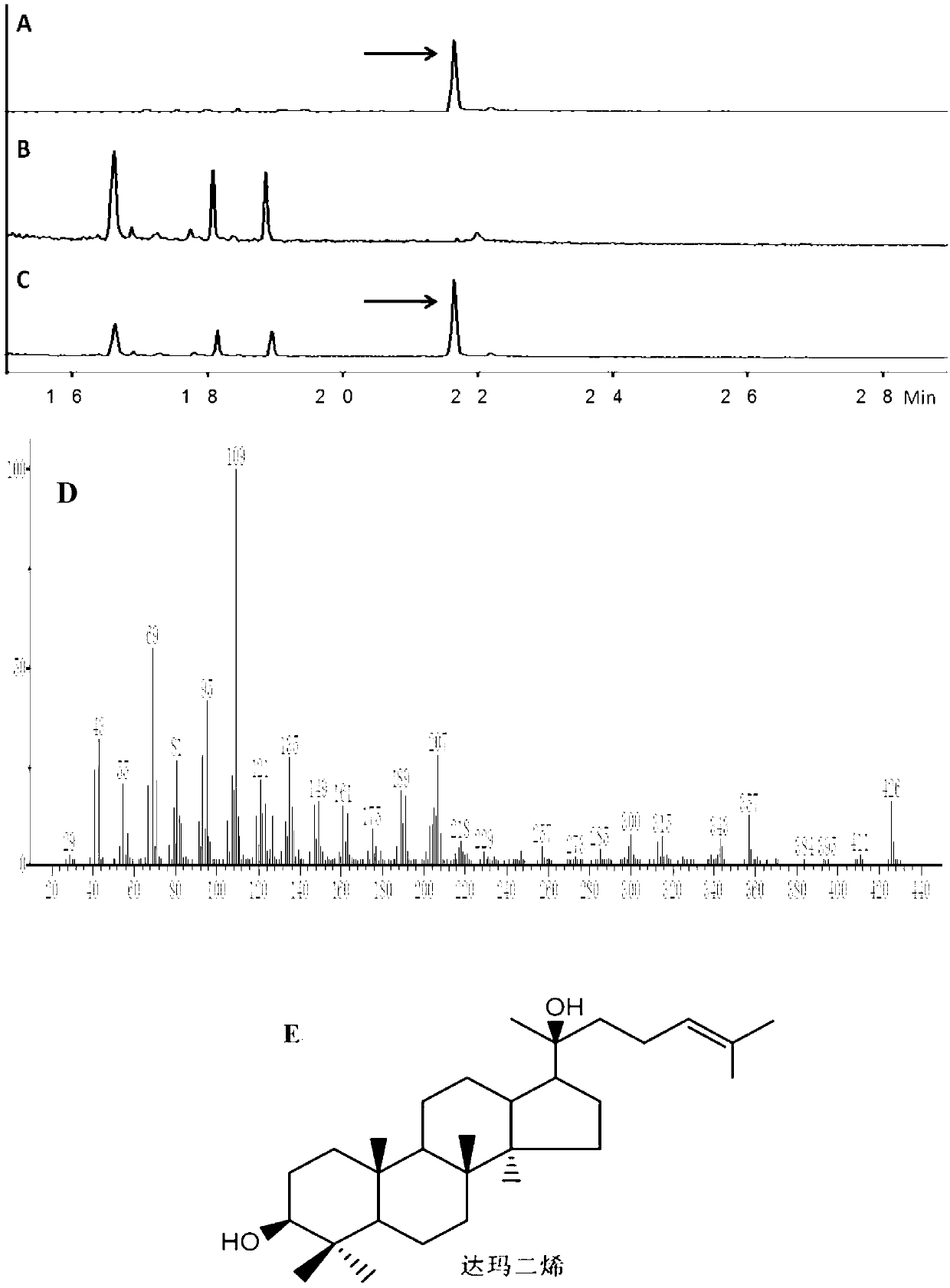
Recombinant microorganism for preparing dharma diene and protopanoxadiol and construction method thereof
ActiveCN102925376AHigh activityIncrease productionFungiMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismCytochrome P450 reductase
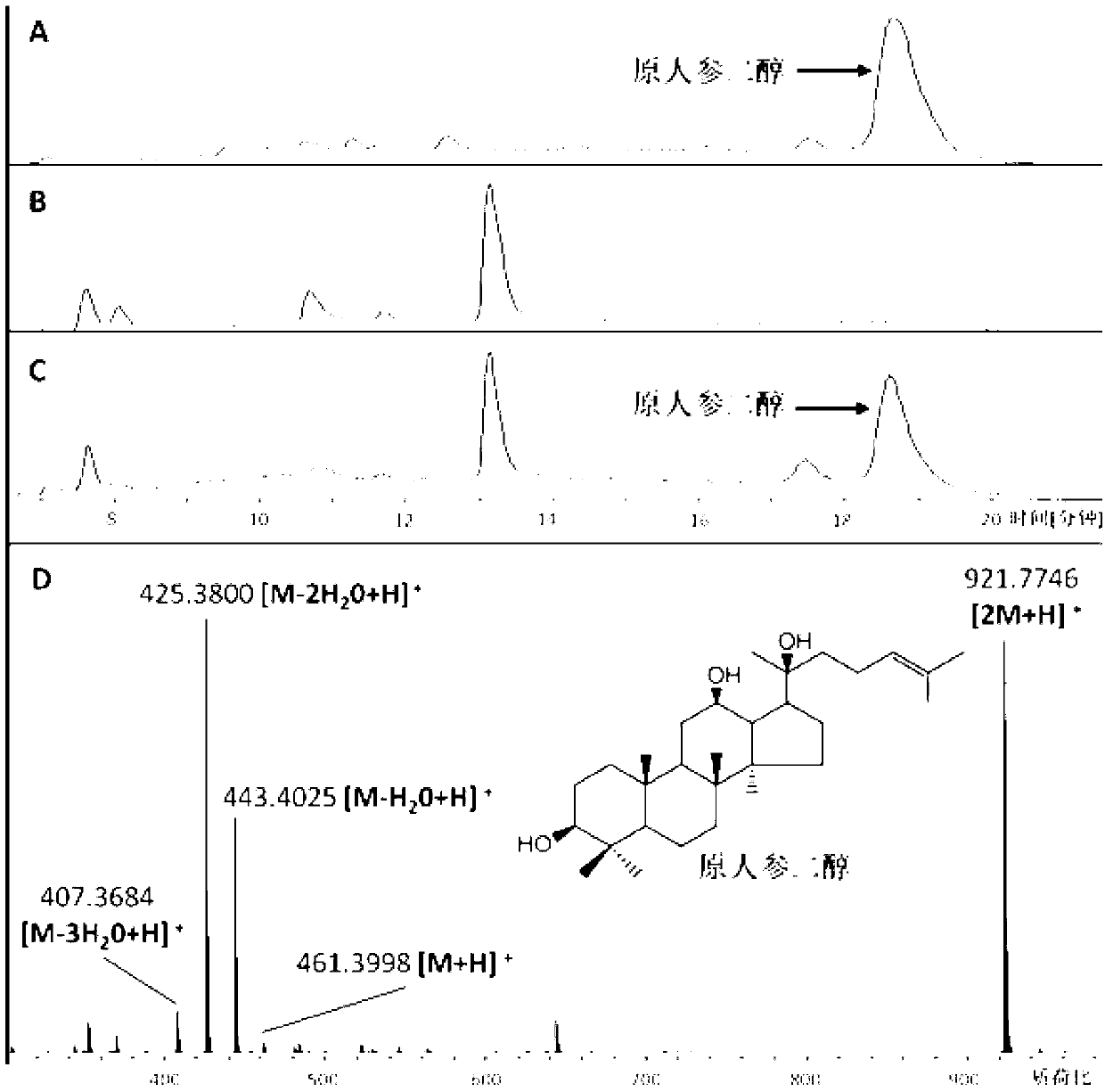
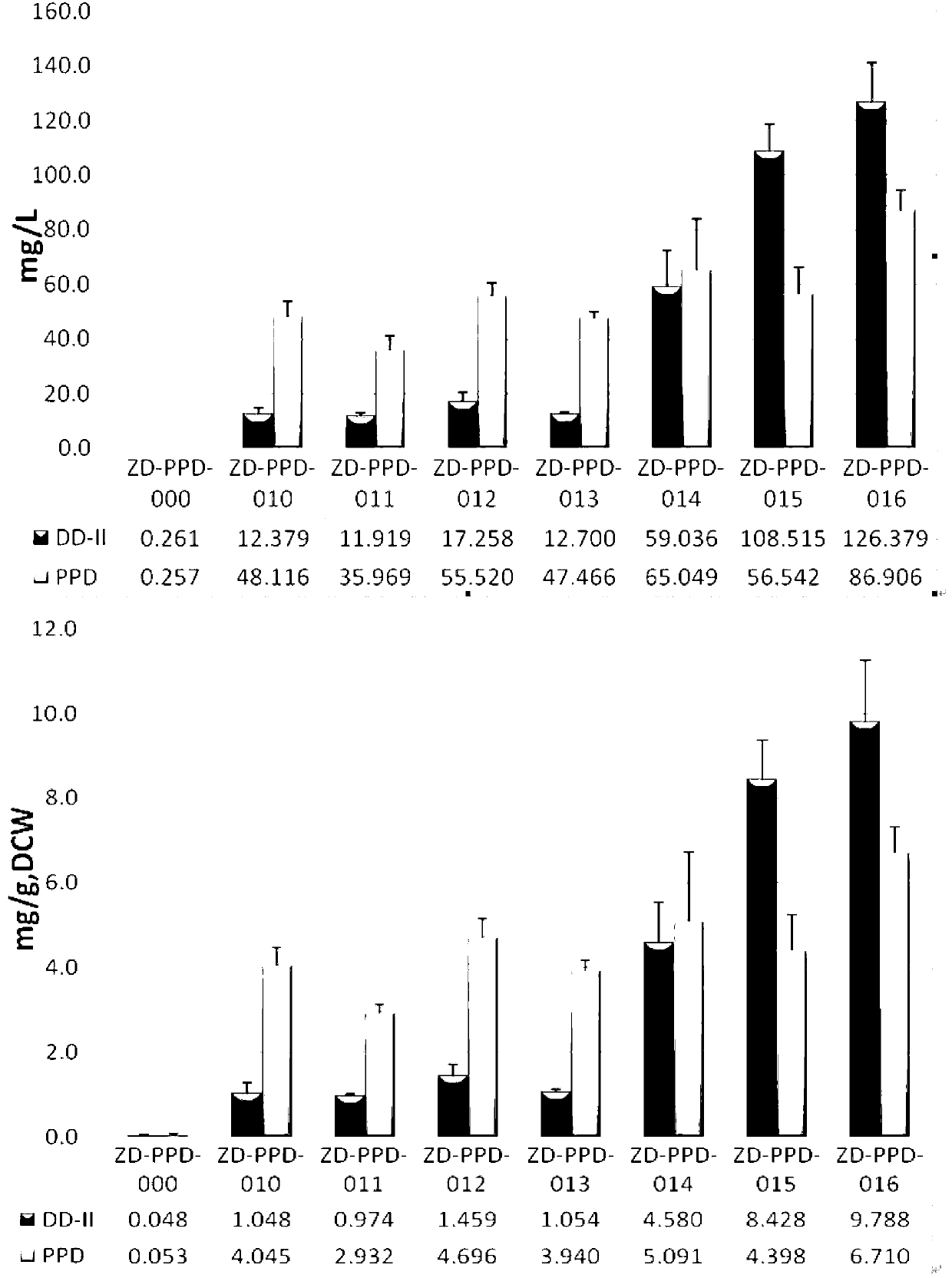
The invention discloses a recombinant microorganism for preparing dharma diene and protopanoxadiol and a construction method of the recombinant microorganism. The construction method of the recombinant bacteria comprises a step of adding dharma diene synthase, protopanoxadiol synthase and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate - cytochrome P450 reductase encoding gene into saccharomyces cerevisiae to obtain recombinant bacteria I. According to the recombinant microorganism for preparing the dharma diene and the protopanoxadiol and the construction method of the recombinant microorganism, by means of homologous recombination, the dharma diene synthase, the protopanoxadiol synthase and the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate - the cytochrome P450 reductase encoding gene are all added into the saccharomyces cerevisiae to obtain the initial recombinant bacteria, and the effect that the initial recombinant bacteria can produce trace amount of the dharma diene and trace amount of the protopanoxadiol is discovered; tHMG1 activity of the initial recombinant bacteria is further improved, and therefore intermediate recombinant bacteria are obtained, and by means of the intermediate recombinant bacteria, the yield of the dharma diene and the yield of the protopanoxadiol are significantly increased; the activity of one or two or three of ERG1, ERG9 and ERG20 are improved on the basis of the intermediate recombinant bacteria, and the effect that the recombinant bacteria which can be used to increase the yield of the dharma diene and the yield of the protopanoxadiol are constructed is also discovered. By means of the recombinant microorganism for preparing the dharma diene and the protopanoxadiol and the construction method of the recombinant microorganism, the foundation is laid for artificially synthesizing the dammar diene and the protopanoxadiol.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
Enzymatic antioxidant of allene oxide for lipid peroxidation in biological systems
InactiveUS6132711ABeneficial antioxidativeExtend effective lifeSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsLipid formationFatty acid
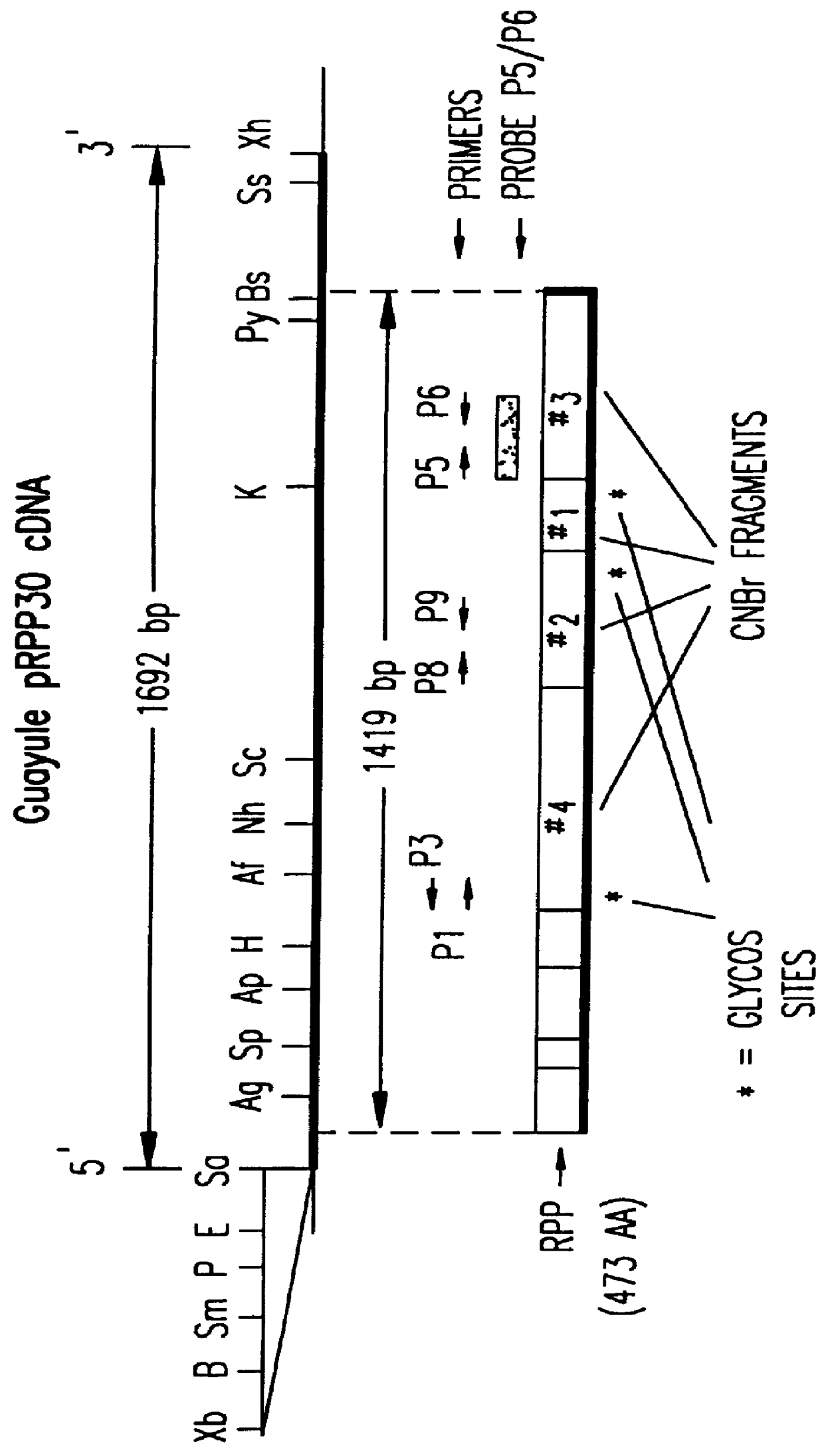
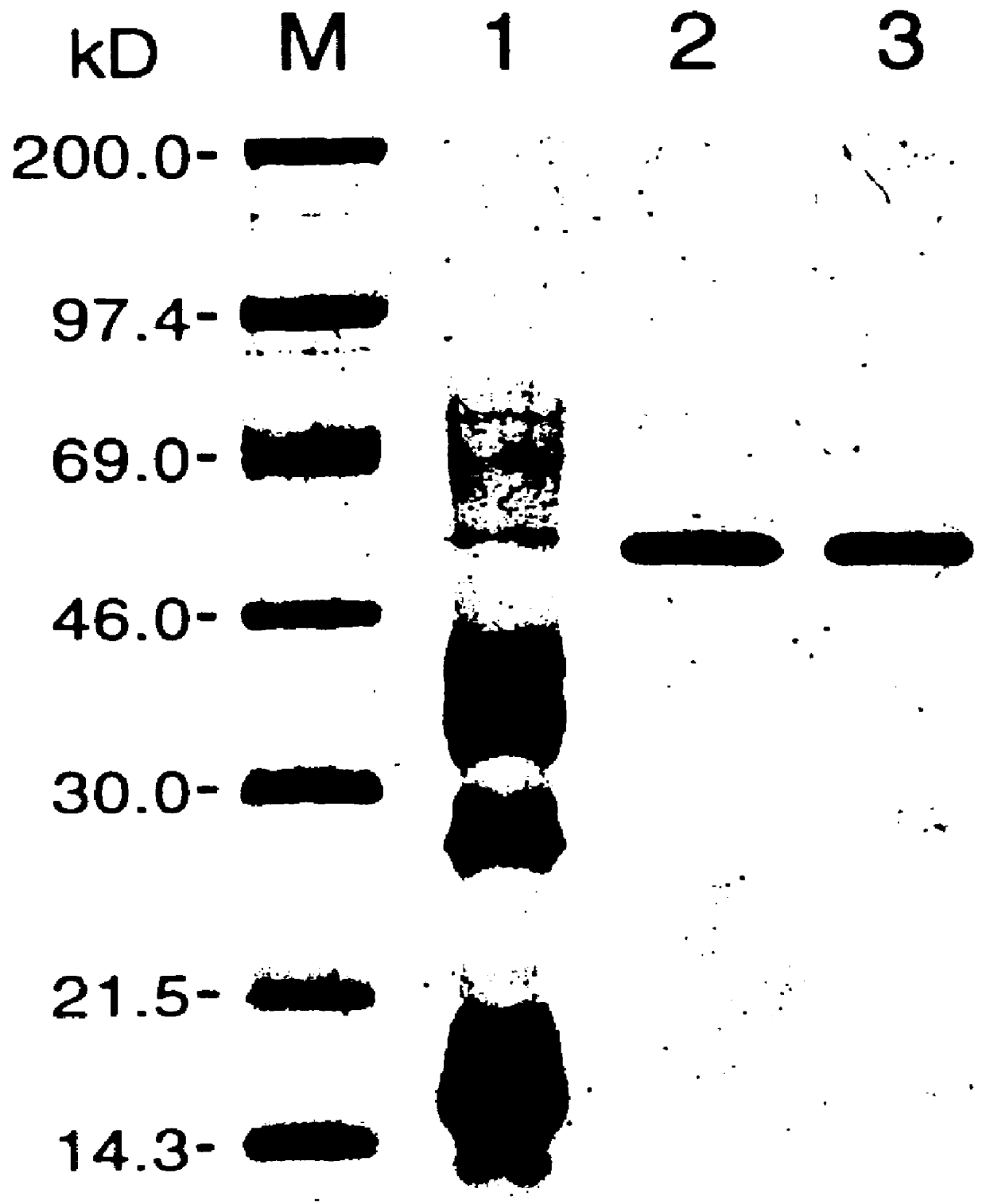
The present invention relates to the isolation and use of an allene oxide synthase enzyme as an antioxidant of lipid peroxides in biological systems. It is based, at least in part, on the discovery that antioxidation is accomplished enzymatically by RPP, a species of allene oxide synthase, in guayule, and on the discovery that the allene oxide synthase RPP disrupts the chain reaction and propagation steps of lipid peroxidation. The present further invention relates to the use of an allene oxide synthase to result in a time-dependent disappearance of conjugated dienes (i.e. lipid hydroperoxides). The allene oxide synthase rapidly converts free or esterified fatty acid peroxides or hydroperoxides into their corresponding epoxides, which, in turn are converted to ketols. The lipid peroxide and hydroperoxide substrates for this enzyme are known to be toxic to biological organisms and can generate additional peroxides by chain propagation reactions. In the presence of an allene oxide synthase these compounds are rapidly and effectively converted to allene oxides (the epoxide), thus breaking the chain reaction.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Methylotroph producing mammalian type sugar chain
ActiveUS20060148039A1FungiImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsBiotechnologyHeterologous
This invention is to provide a process for producing a glycoprotein comprising a mammalian type sugar chain, characterized in that the process comprises introducing an α-1,2-mannosidase gene into a methylotrophic yeast having a mutation of a sugar chain biosynthesizing enzyme gene, so that the α-1,2-mannosidase gene is expressed under the control of a potent promoter in the yeast; culturing in a medium the methylotrophic yeast cells with a heterologous gene transferred thereinto; and obtaining the glycoprotein comprising a mammalian type sugar chain from the culture. Using the newly created methylotrophic yeast having a sugar chain mutation, a neutral sugar chain identical with a high mannose type sugar chain produced by mammalian cells such as human cells, or a glycoprotein comprising such a neutral sugar chain, can be produced in a large amount at a high purity. By introducing a mammalian type sugar chain biosynthesizing gene into the above-described mutant, a mammalian type sugar chain, such as a hybrid or complex, or a protein comprising a mammalian type sugar chain can be efficiently produced.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH +1
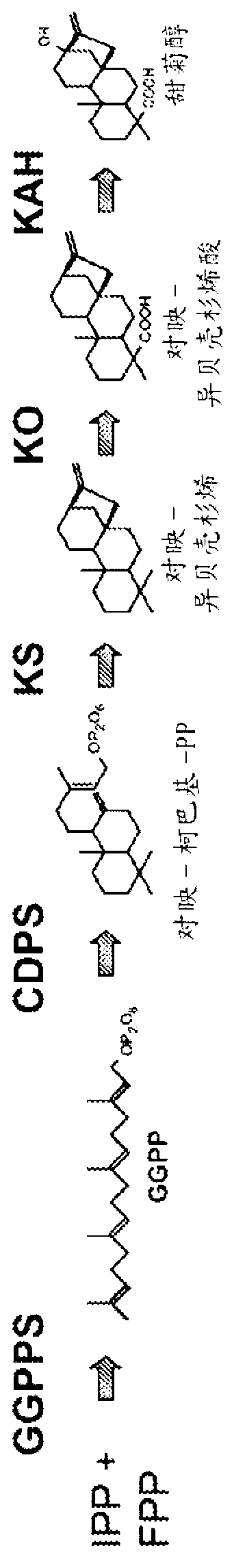
Recombinant production of steviol glycosides
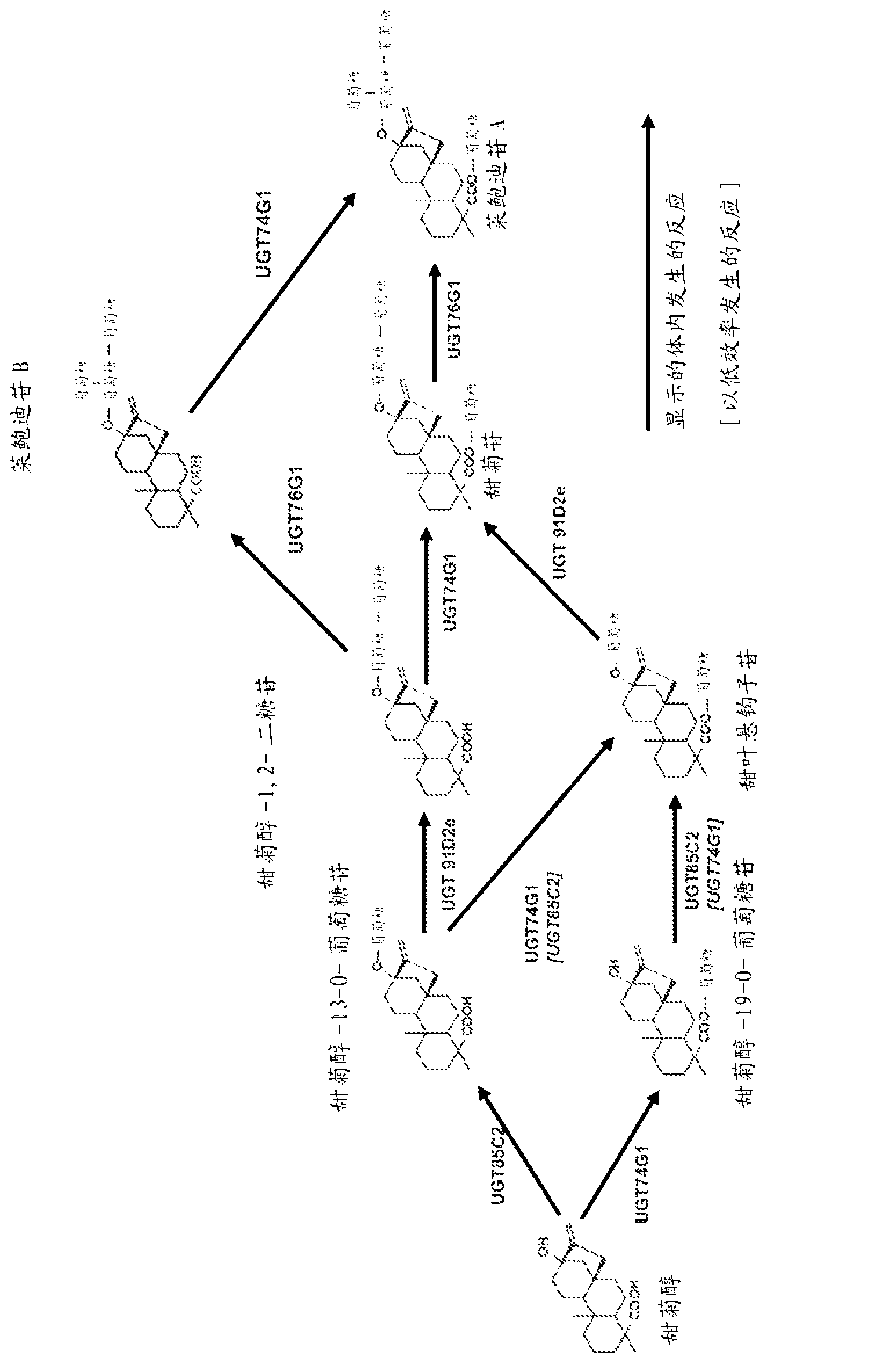
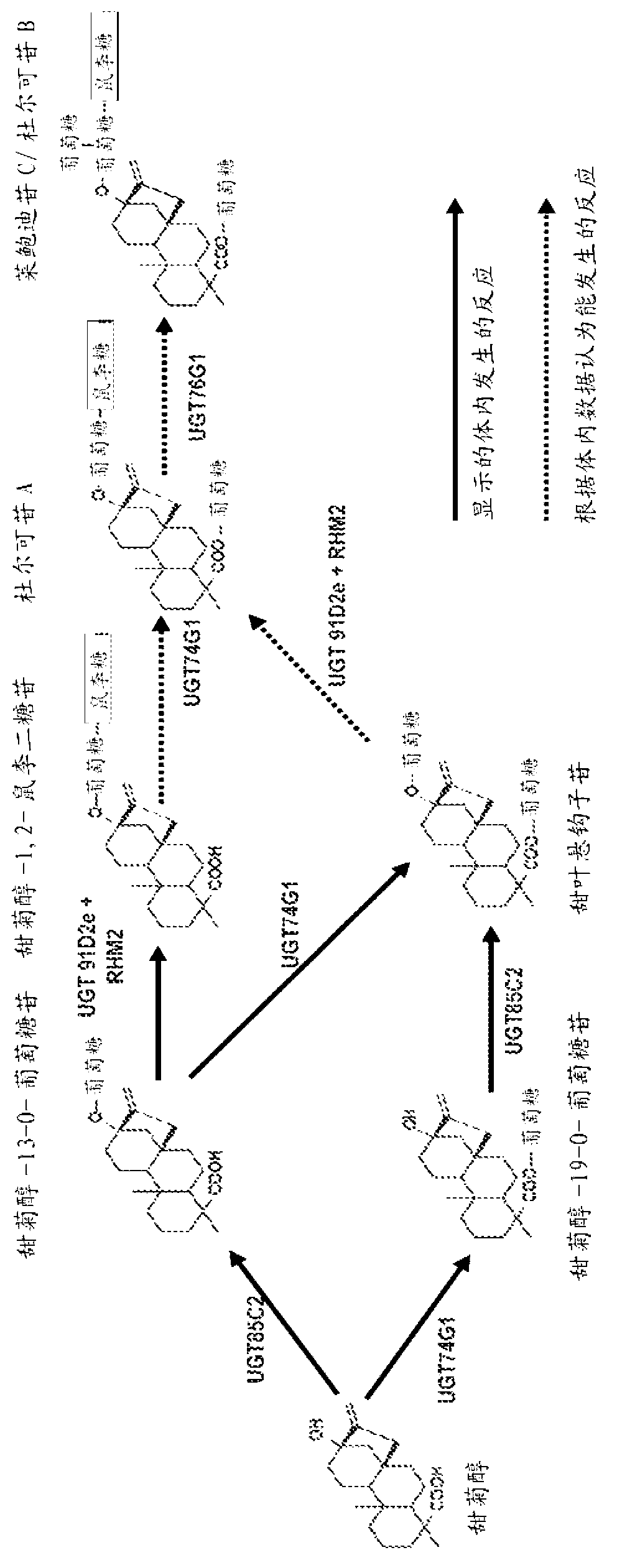
Recombinant microorganisms, plants, and plant cells are disclosed that have been engineered to express novel recombinant genes encoding steviol biosynthetic enzymes and UDP-glycosyltransferases (UGTs). Such microorganisms, plants, or plant cells can produce steviol or steviol glycosides, e.g., rubusoside or Rebaudioside A, which can be used as natural sweeteners in food products and dietary supplements.
Owner:沃维公司
Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase inhibitors for the treatment of viral-mediated diseases
InactiveUS6841561B1Potent activityBiocideOrganic chemistryDiseaseDihydroorotate Dehydrogenase Inhibitor
Flavivirus, rhabdovirus and paramyxovirus infections may be treated by administering an inhibitor of the enzyme dihydroorotate dehydrogenase such as 6-fluoro-2-(2′-fluoro-1,1′-biphenyl-4-yl)-3-methyl-4-quinolinearcarboxylic acid sodium salt (Brequinar). A synergistic effect can be obtained if an interferon such as interferon α2, interferon α8 or interferon β, or an inhibitor of a second enzyme selected from inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase, guanosine monophosphate synthetase, cytidine triphosphate synthetase and S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase, is also administered.
Owner:INST OF MOLECULAR & CELL BIOLOGY
Materials and methods for prevention and treatment of RNA viral diseases
InactiveUS20040009152A1Preventing and decreasing severity of symptomBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseMononuclear cell infiltration
The subject invention concerns a method of inhibiting an RNA virus infection within a patient by increasing the amount of 2-5 oligoadenylate synthetase (2-5 AS) activity within the patient. Preferably, the preventative and therapeutic methods of the present invention involve administering a nucleotide encoding 2-5 AS, or at least one catalytically active fragment thereof, such as the p40, p69, p100 subunits, to a patient in need thereof. The present inventors have determined that overexpression of 2-5AS causes a reduction in epithelial cell damage, reduction in infiltration of mononuclear cells in the peribronchiolar and perivascular regions, and reduction in thickening of the septa in the lungs. Levels of chemokines, such as MIP1-alpha, are also reduced upon overexpression of 2-5AS. The subject invention also pertains to pharmaceutical compositions containing a nucleotide sequence encoding 2-5 AS and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, as well as vectors for delivery of the 2-5 AS nucleotide sequence.
Owner:IB SECURITYHOLDERS +1
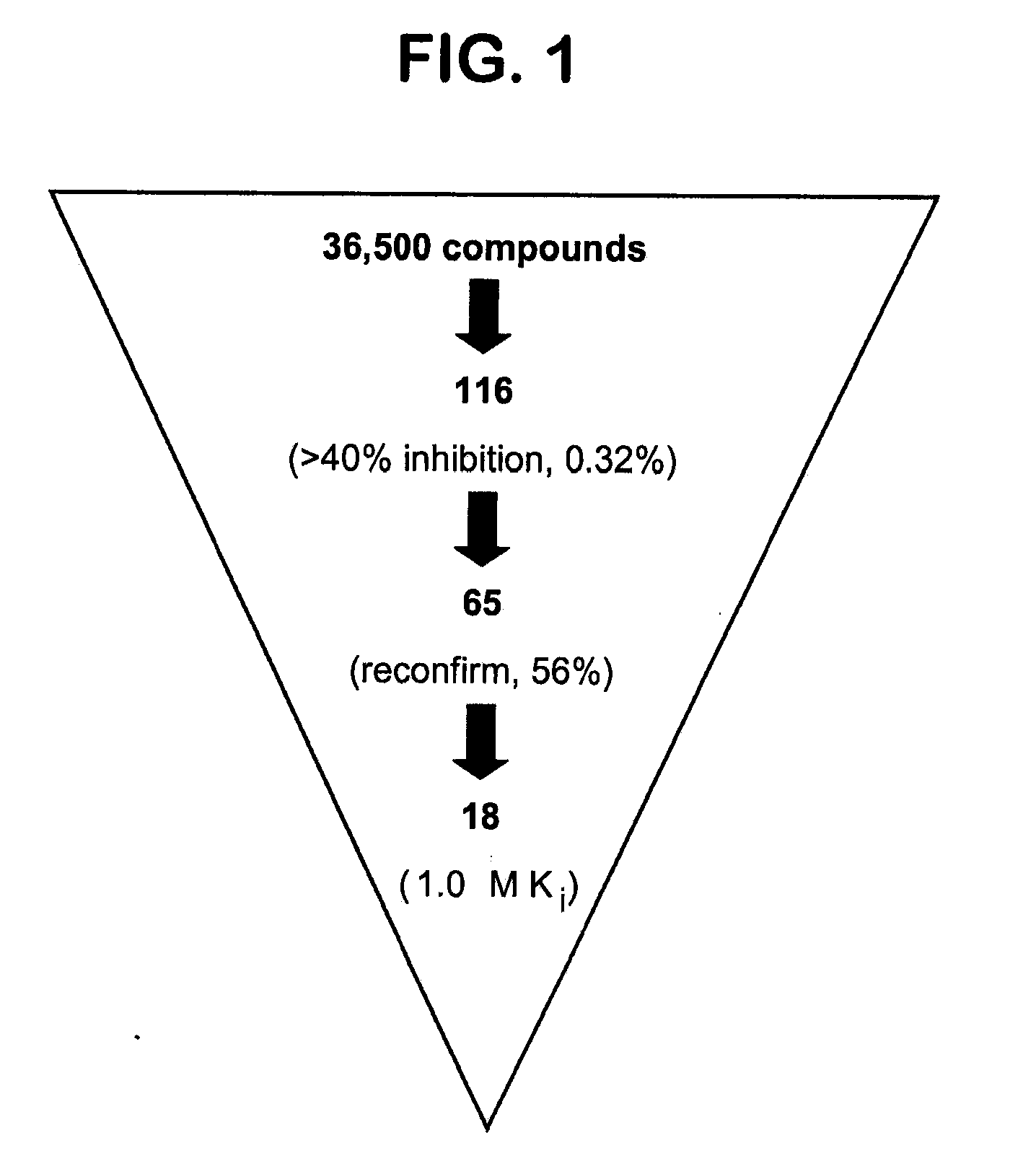
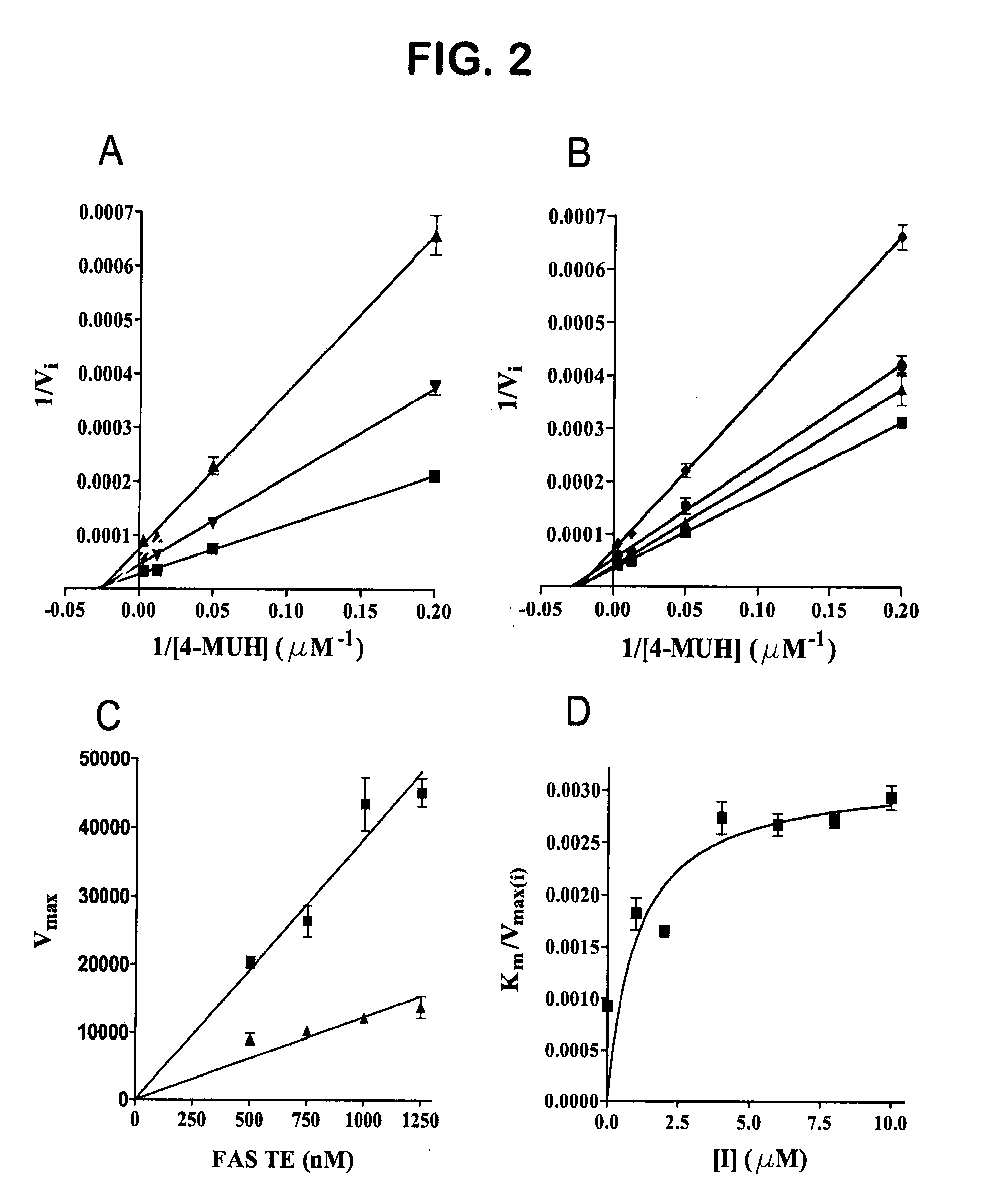
Novel antagonists of the human fatty acid synthase thioesterase
Owner:BURNHAM INST FOR MEDICAL RES
Genetically engineered bacteria for efficiently producing N-acetylglucosamine
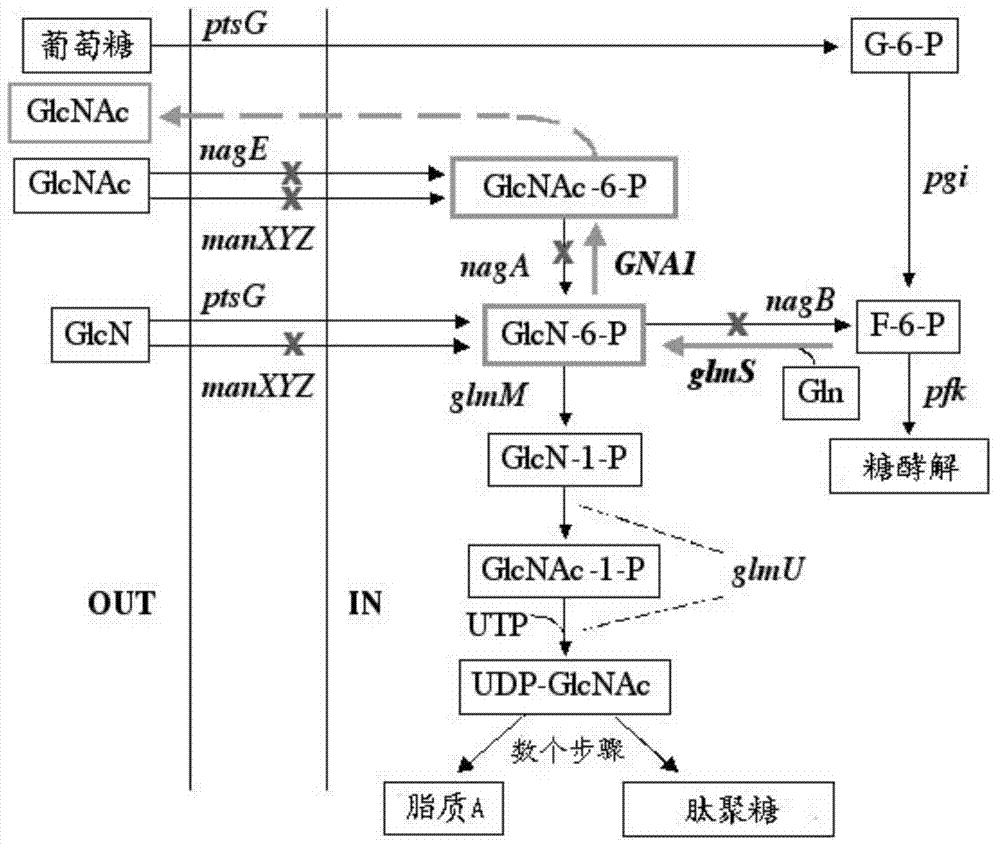
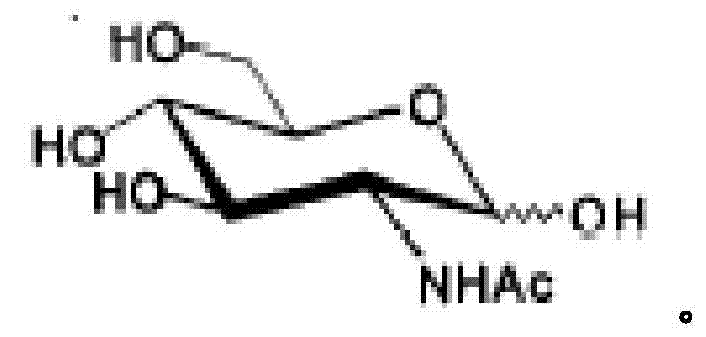
InactiveCN104293724AImprove fermentation yieldImprove stabilityBacteriaHydrolasesEscherichia coliBiotechnology
The invention provides genetically engineered bacteria for efficiently producing N-acetylglucosamine. The genetically engineered bacteria are prepared by the following steps: integrating chromosome deficiency nag DCABE gene clusters of Escherichia coli, respectively connecting 6-glucosamine phosphate synthetase mutant genes and N-acetylglucosamine transferase genes which are respectively mediated by a T7 promoter and a Trc promoter with a gene expression cassette in series, wherein the 6-glucosamine phosphate synthetase mutant genes are obtained by mutating wild 6-glucosamine phosphate synthetase genes from an Escherichia coli W3110 strain source into A38T / R249C / G471S mutants. The genetically engineered bacteria constructed by the invention have the advantages of high N-acetylglucosamine fermentation yield and high strain stability and have wide industrial application prospects.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES & DEV CENT OF INDAL BIOTECH +1
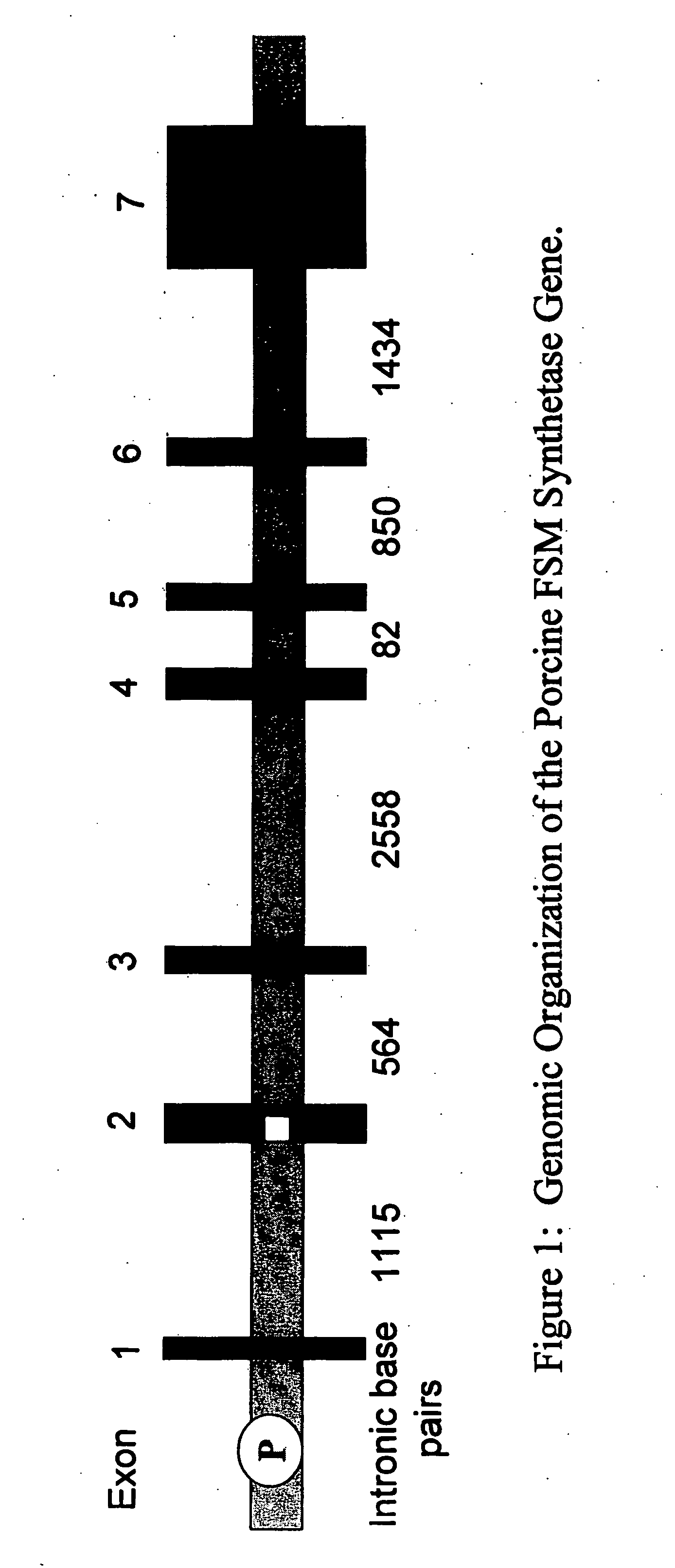
Porcine forssman synthetase protein, cDNA, genomic organization, and regulatory region
InactiveUS20060068479A1Low immunogenicityReduce expressionSugar derivativesTissue cultureN-AcetylgalactosaminyltransferasesGenomic DNA
The present invention provides porcine Forssman synthetase (FSM synthase) (Globoside α-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase) protein, cDNA, and genomic DNA sequence. Furthermore, the present invention includes porcine animals, tissue and organs as well as cells and cell lines derived from such animals, tissue and organs, which lack expression of functional FSM synthetase. Such animals, tissues, organs and cells can be used in research and in medical therapy, including in xenotransplantation. In addition, methods are provided to prepare organs, tissues, and cells lacking the porcine FSM synthetase gene for use in xenotransplantation.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Isoprenoid wax ester synthases, isoprenoid acyl CoA-synthetases, and uses thereof
The present invention provides isolated polynucleotides and isolated polypeptides. The polypeptides of the present invention have isoprenoid wax ester synthase activity or isoprenoid acyl CoA-synthetase activity. The present invention also includes methods of using the polynucleotides and polypeptides of the present invention. For instance, the methods include producing biodiesel and producing wax esters.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
Site specific incorporation of heavy atom-containing unnatural amino acids into proteins for structure determination
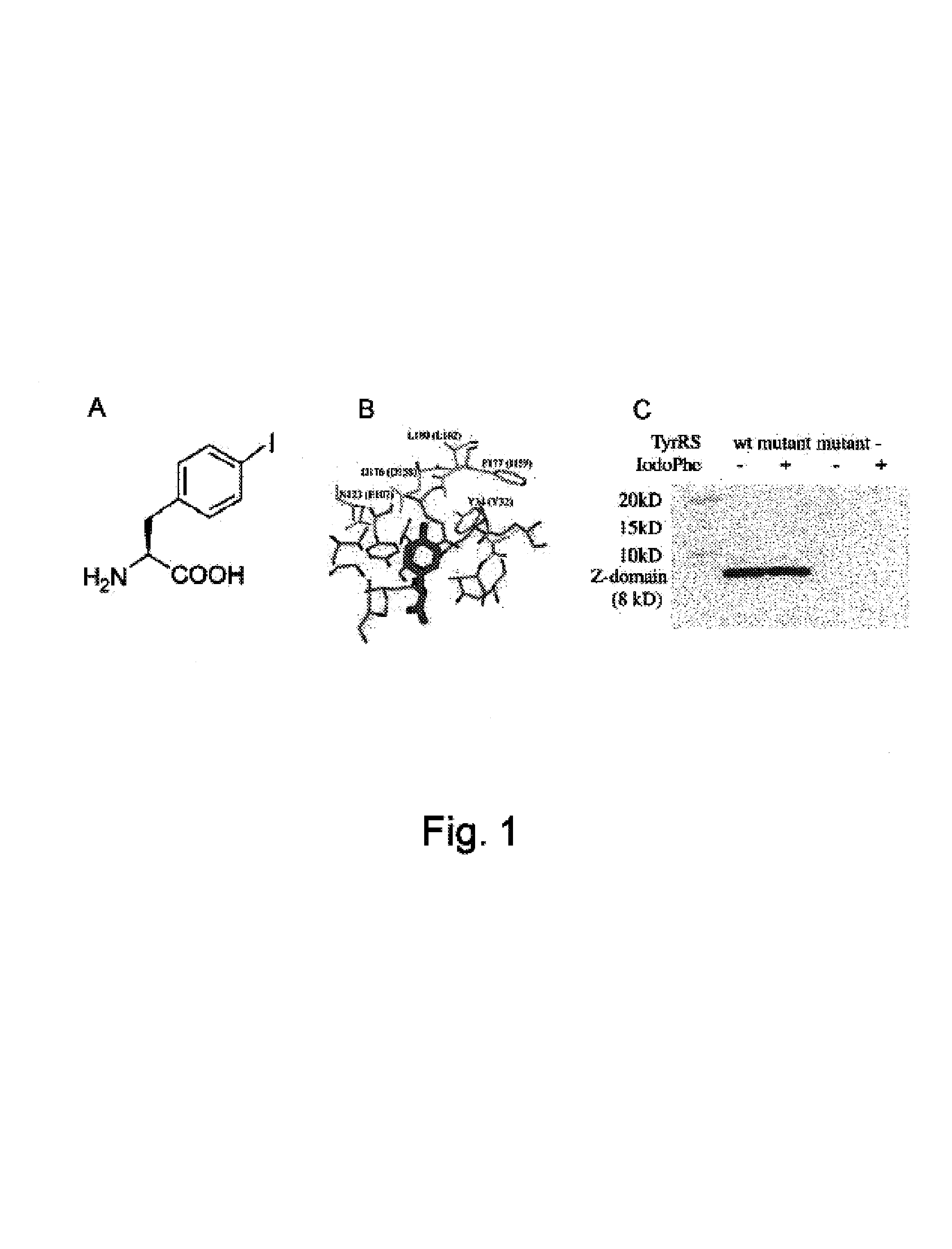
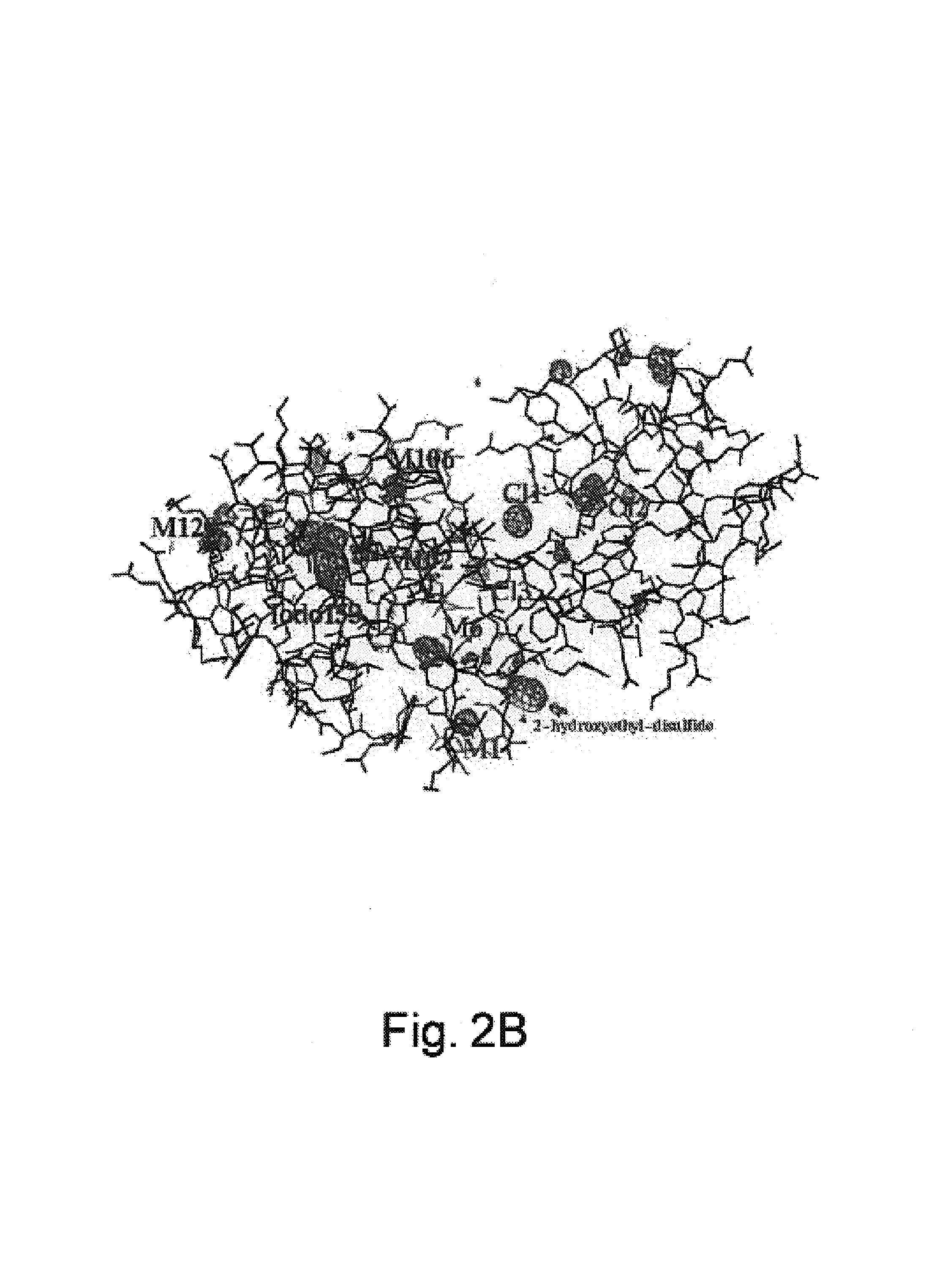
Translation systems and other compositions including orthogonal aminoacyl tRNA-synthetases that preferentially charge an orthogonal tRNA with an iodinated or brominated amino acid are provided. Nucleic acids encoding such synthetases are also described, as are methods and kits for producing proteins including heavy atom-containing amino acids, e.g., brominated or iodinated amino acids. Methods of determining the structure of a protein, e.g., a protein into which a heavy atom has been site-specifically incorporated through use of an orthogonal tRNA / aminoacyl tRNA-synthetase pair, are also described.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST +1
Novel application of malt oligosaccharide based mycose synthetase and malt oligosaccharide based mycose hydrolase in mycose production
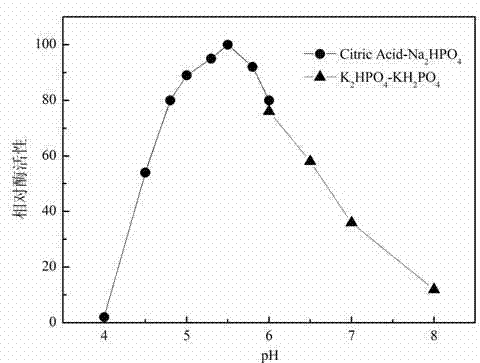
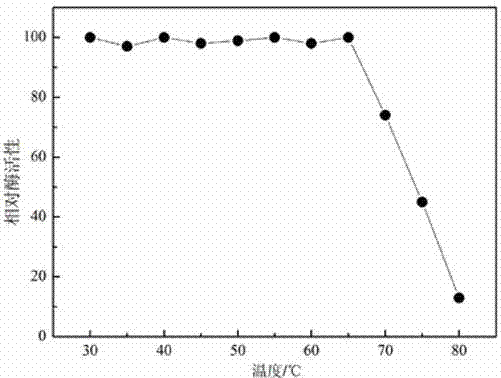
The invention discloses a novel application of malt oligosaccharide based mycose synthetase and malt oligosaccharide based mycose hydrolase in mycose production. The malt oligosaccharide based mycose synthetase has an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:1; and the malt oligosaccharide based mycose hydrolase has the amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:3. The malt oligosaccharide based mycose synthetase and malt oligosaccharide based mycose hydrolase disclosed in the invention also have higher most-suitable reaction temperature and thermal stabilities, and lower most-suitable pH values, so that contamination risks are lowered, production stability is improved, the mycose production efficiency by acting reducing glucidtemns through the malt oligosaccharide based mycose synthetase and malt oligosaccharide based mycose hydrolase and pullulanase in a combined manner is improved and the mycose cost is lowered, therefore, a solid foundation is laid up for the extensive application of the mycose in medicines, foods and cosmetics.
Owner:SHANDONG TIANLI PHARMA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com