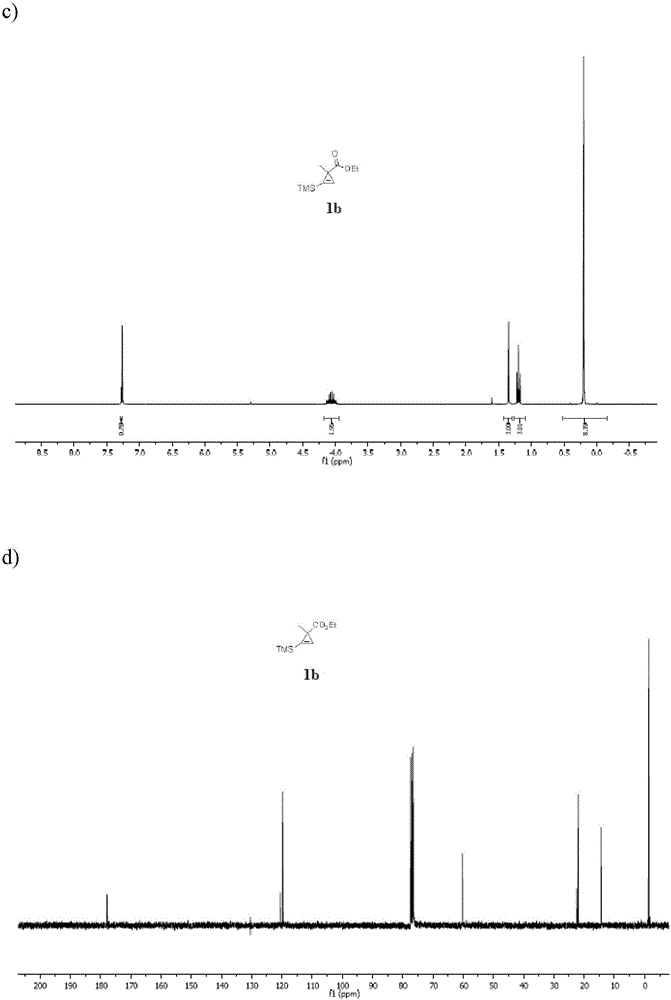
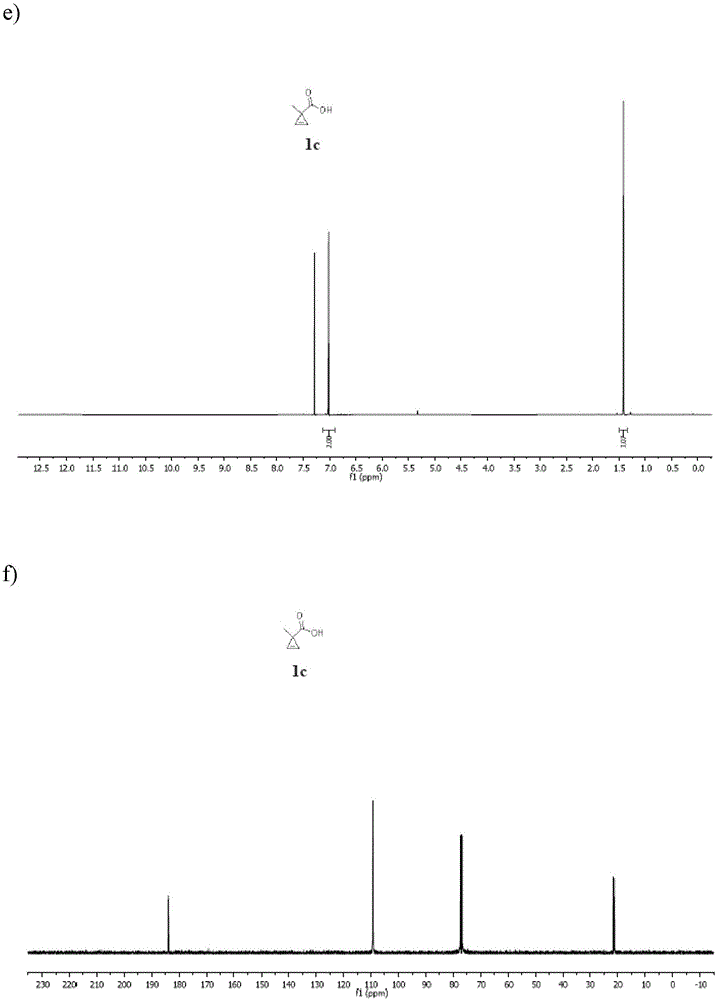
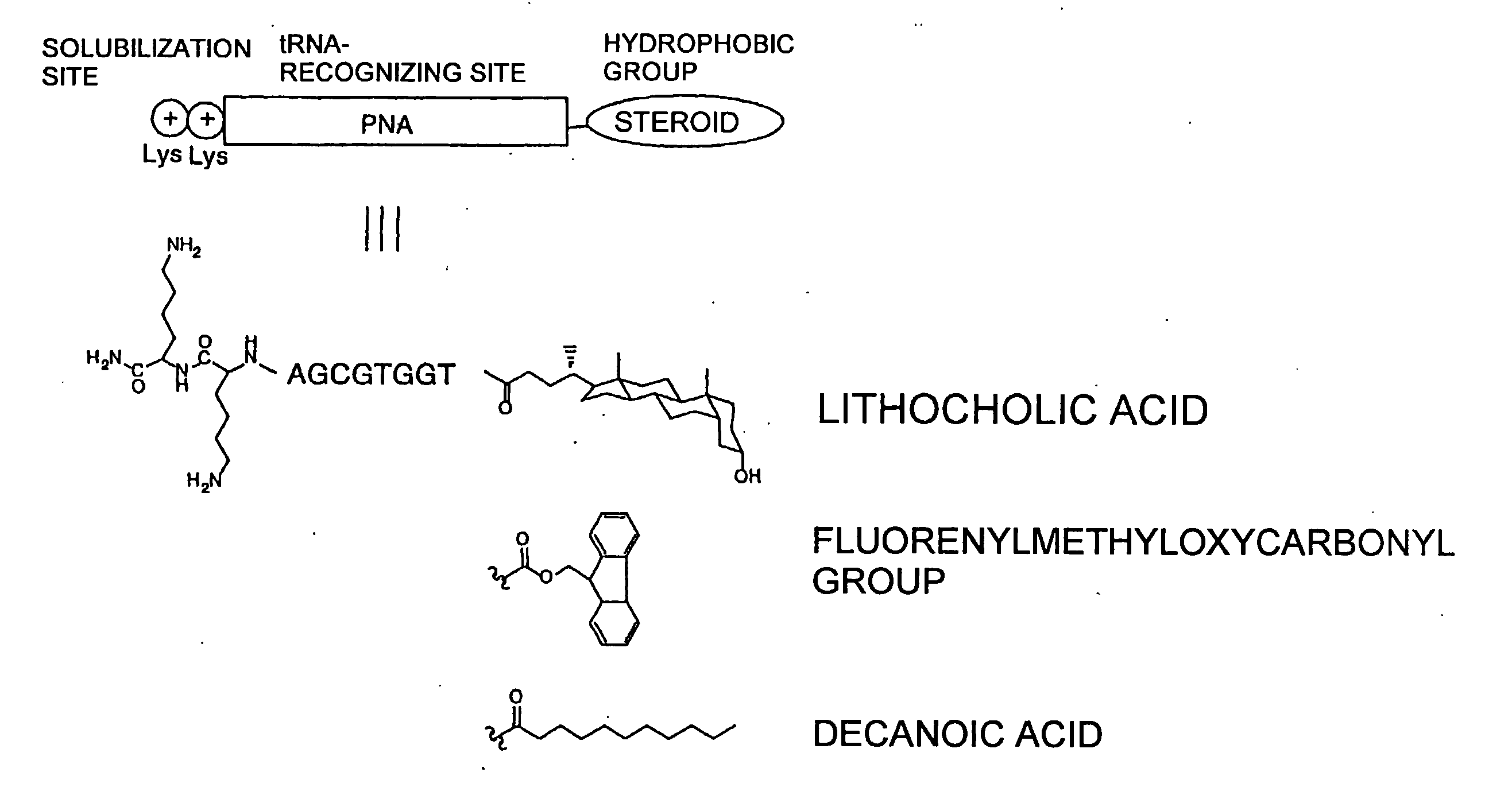
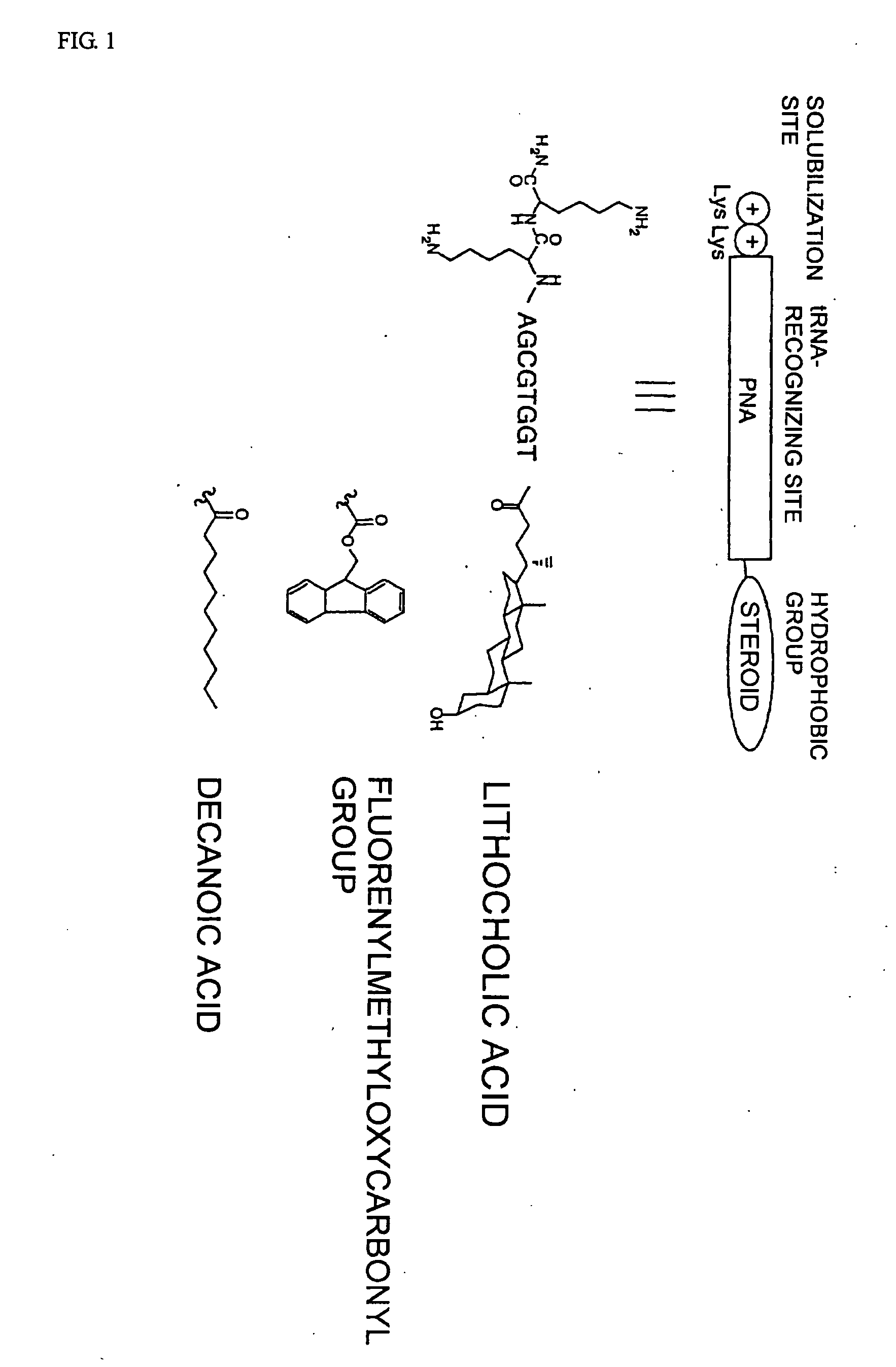
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
52 results about "Aminoacylation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Aminoacylation is the process of adding an aminoacyl group to a compound.
Method and system for rapid biomolecular recognition of amino acids and protein sequencing
InactiveUS6846638B2Low costHigh sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProtein Sequence DeterminationDigestion
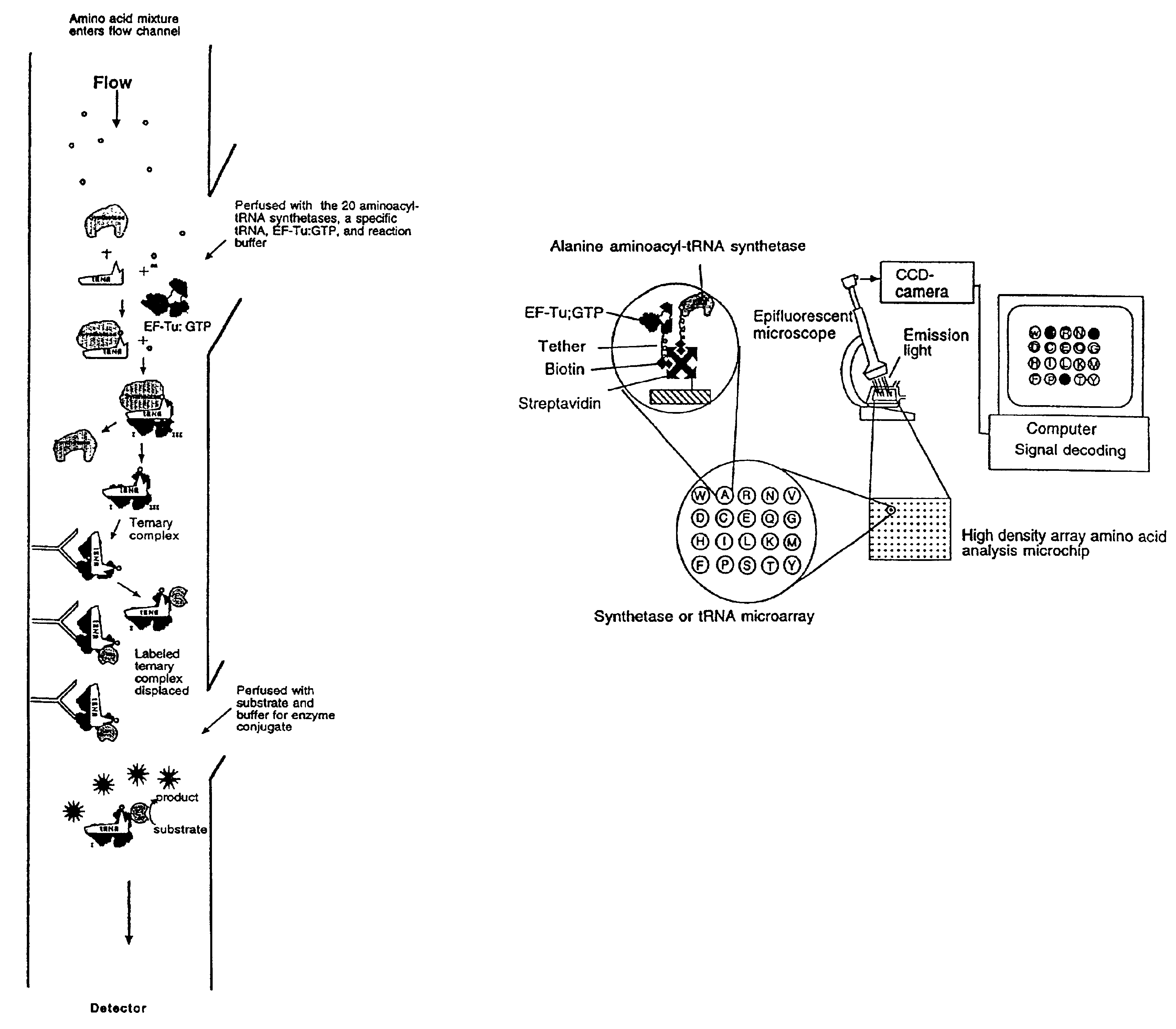
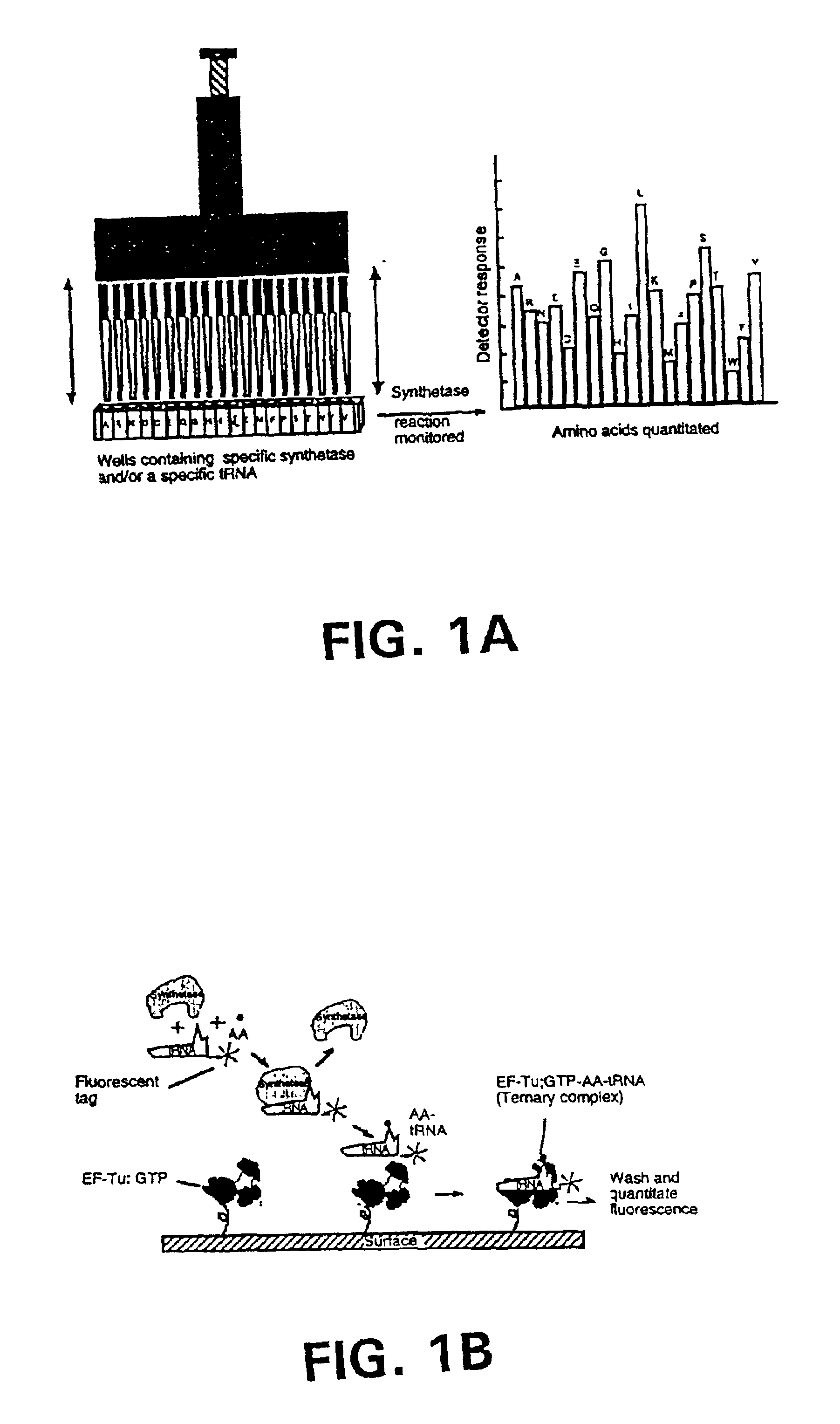
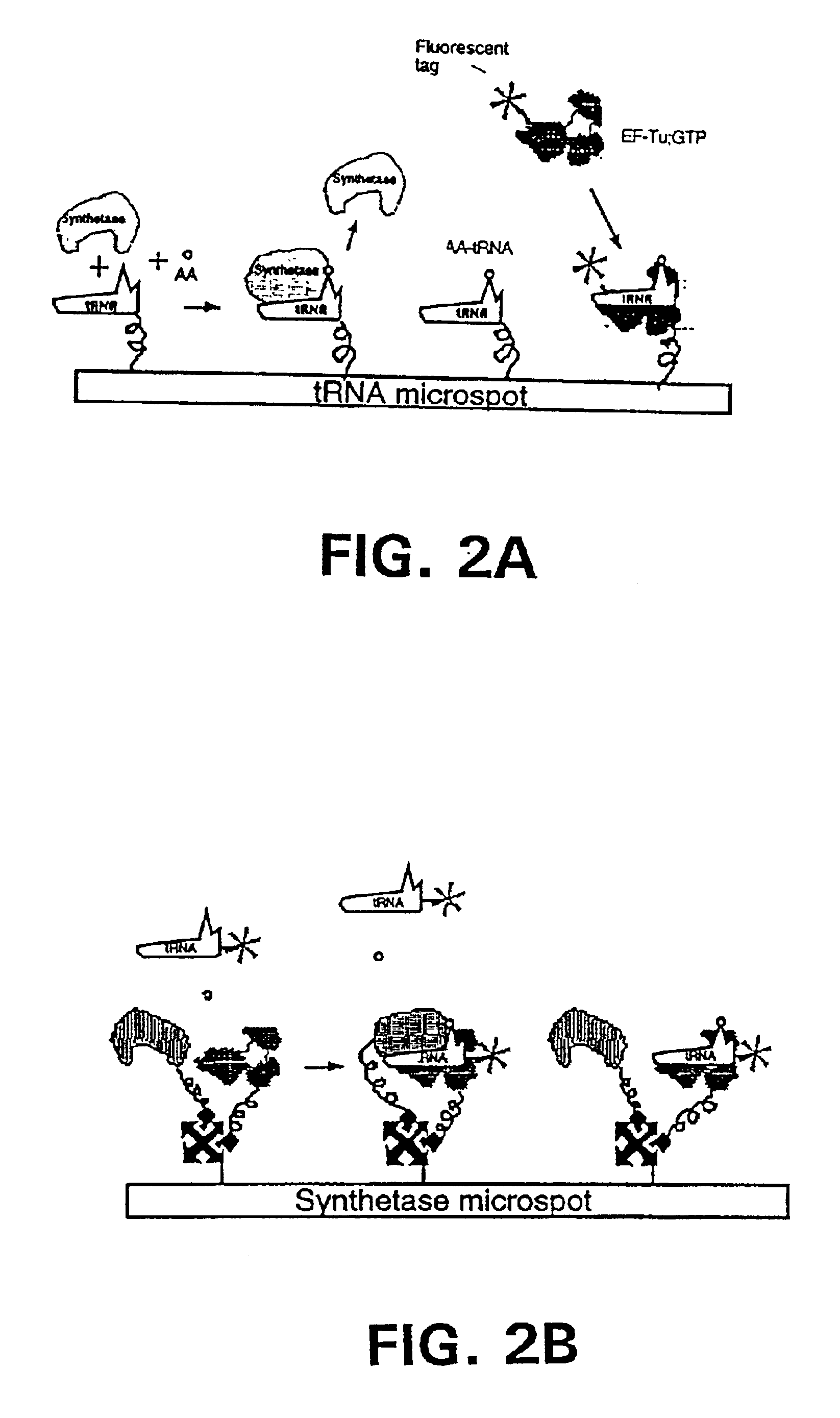
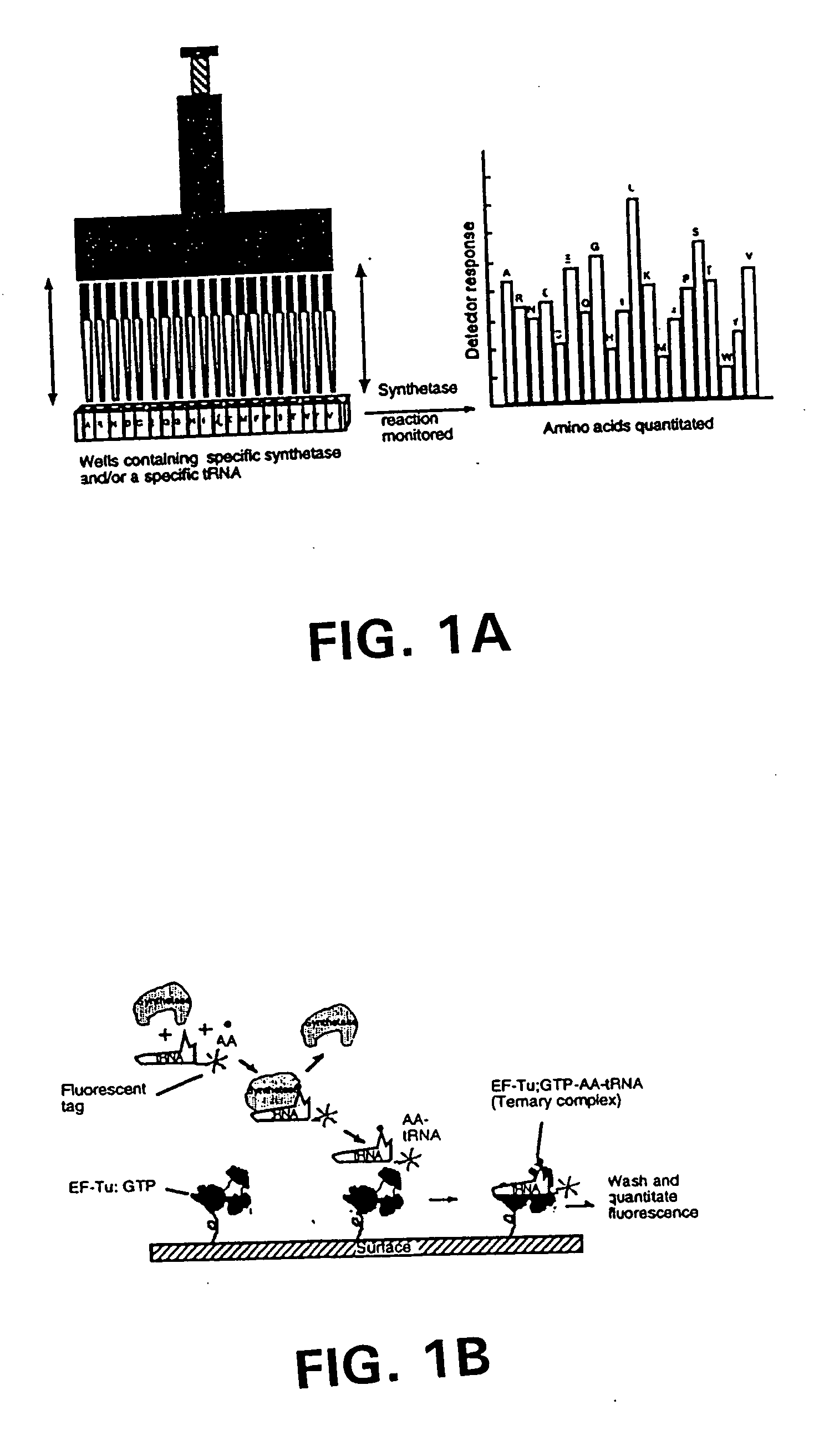
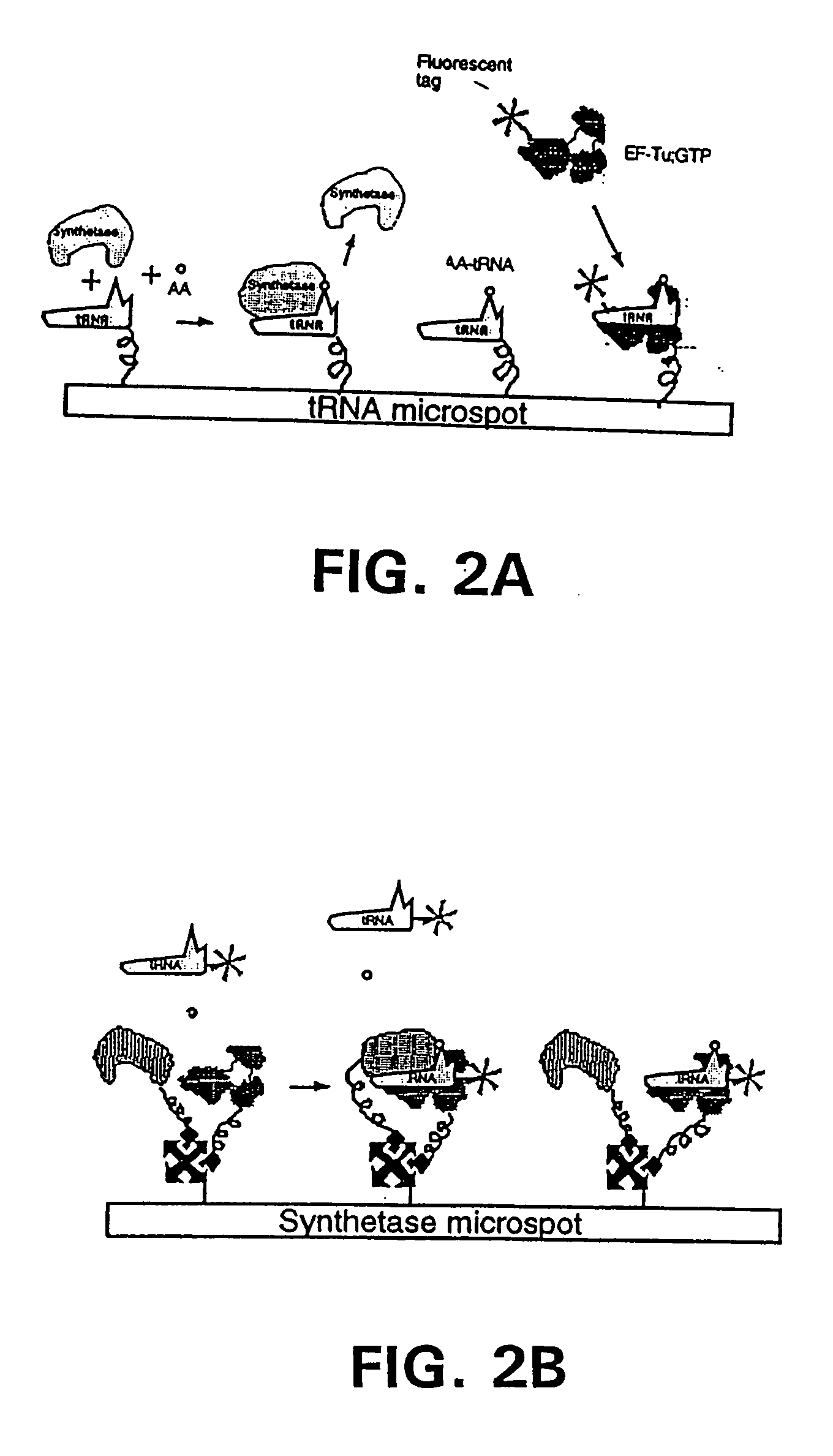
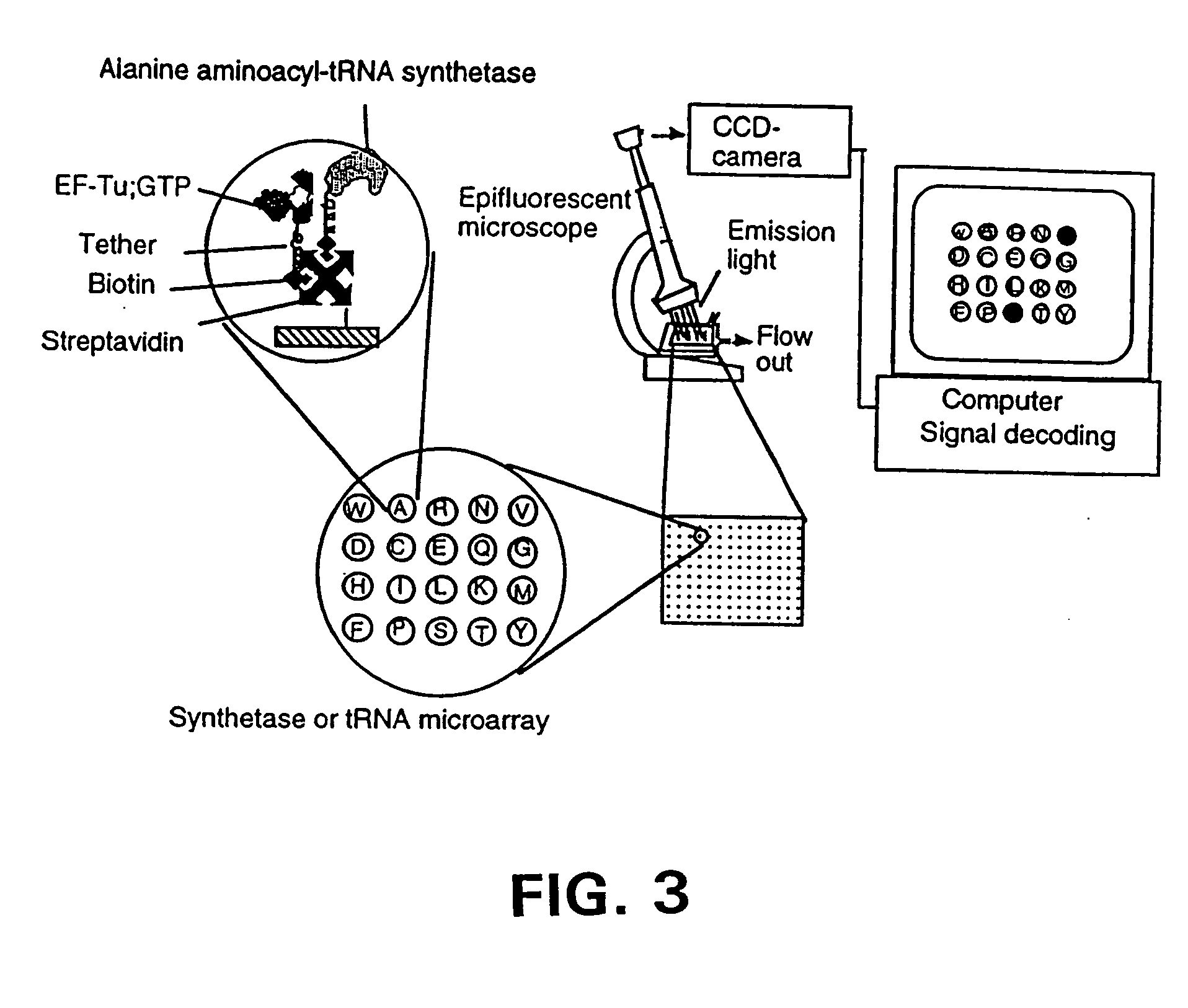
Methods, compositions, kits, and apparatus are provided wherein the aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase system is used to analyze amino acids. The method allows very small devices for quantitative or semi-quantitative analysis of the amino acids in samples or in sequential or complete proteolytic digestions. The methods can be readily applied to the detection and / or quantitation of one or more primary amino acids by using cognate aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase and cognate tRNA. The basis of the method is that each of the 20 synthetases and / or a tRNA specific for a different amino acid is separated spatially or differentially labeled. The reactions catalyzed by all 20 synthetases may be monitored simultaneously, or nearly simultaneously, or in parallel. Each separately positioned synthetase or tRNA will signal its cognate amino acid. The synthetase reactions can be monitored using continuous spectroscopic assays. Alternatively, since elongation factor Tu:GTP (EF-Tu:GTP) specifically binds all AA-tRNAs, the aminoacylation reactions catalyzed by the synthetases can be monitored using ligand assays. Microarrays and microsensors for amino acid analysis are provided. Additionally, amino acid analysis devices are integrated with protease digestions to produce miniaturized enzymatic sequenators capable of generating either N- or C-terminal sequence and composition data for a protein or peptide. The possibility of parallel processing of many samples in an automated manner is discussed.
Owner:NANOBIODYNAMICS
Method and system for rapid biomolecular recognition of amino acids and protein sequencing
InactiveUS20050164264A1Quick analysisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProtein Sequence DeterminationDigestion
Methods, compositions, kits, and apparatus are provided wherein the aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase system is used to analyze amino acids. The method allows very small devices for quantitative or semi-quantitative analysis of the amino acids in samples or in sequential or complete proteolytic digestions. The methods can be readily applied to the detection and / or quantitation of one or more primary amino acids by using cognate aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase and cognate tRNA. The basis of the method is that each of the 20 synthetases and / or a tRNA specific for a different amino acid is separated spatially or differentially labeled. The reactions catalyzed by all 20 synthetases may be monitored simultaneously, or nearly simultaneously, or in parallel. Each separately positioned synthetase or tRNA will signal its cognate amino acid. The synthetase reactions can be monitored using continuous spectroscopic assays. Alternatively, since elongation factor Tu:GTP (EF-Tu:GTP) specifically binds all AA−tRNAs, the aminoacylation reactions catalyzed by the synthetases can be monitored using ligand assays. Microarrays and microsensors for amino acid analysis are provided. Additionally, amino acid analysis devices are integrated with protease digestions to produce miniaturized enzymatic sequenators capable of generating either N- or C-terminal sequence and composition data for a protein or peptide. The possibility of parallel processing of many samples in an automated manner is discussed.
Owner:NANOBIODYNAMICS
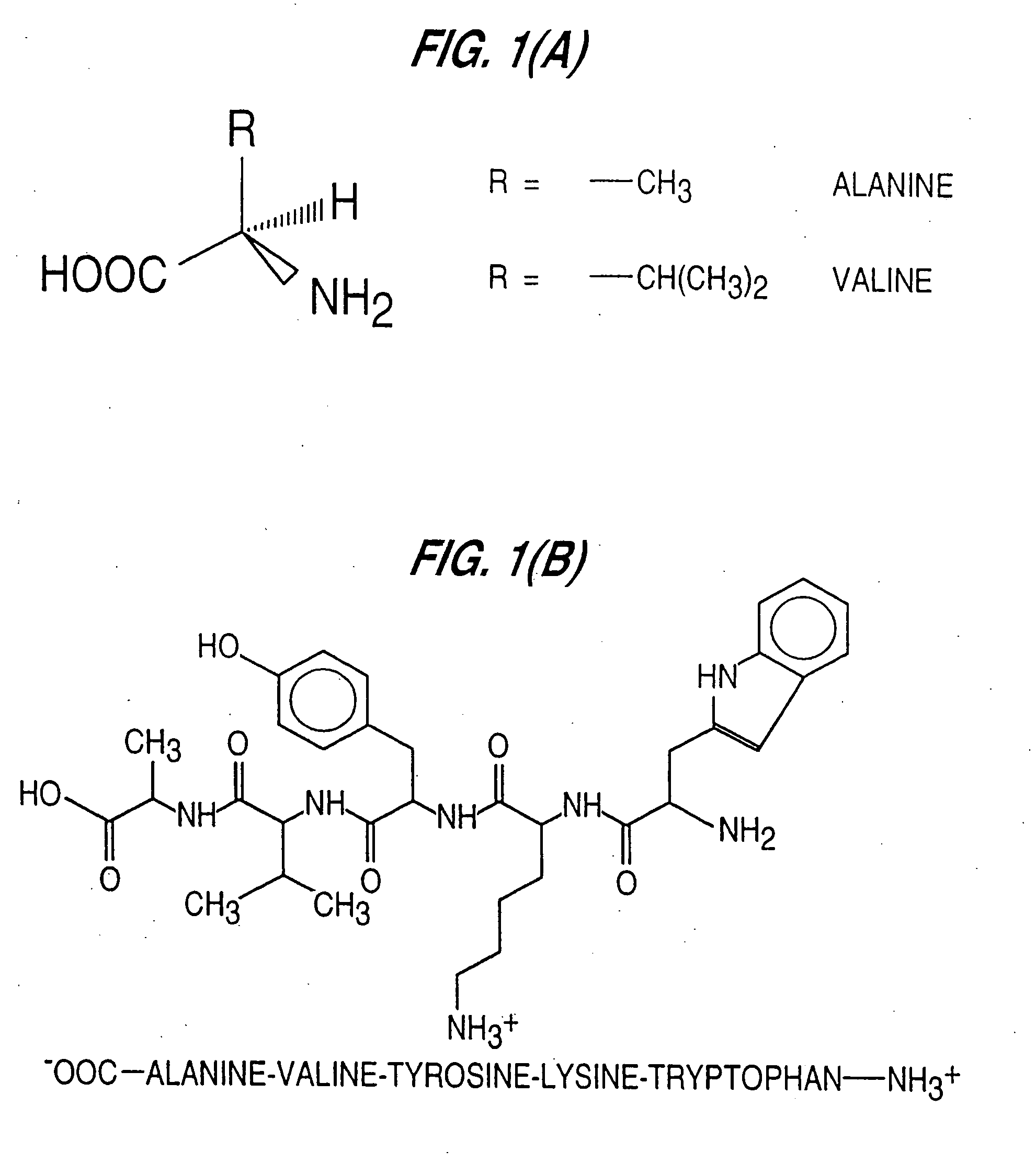
Methods for the preparation of chemically misaminoacylated tRNA via protective groups
The present invention relates to methods for the preparation of chemically aminoacylated tRNAs for the purpose of introduction of markers into nascent proteins. The present invention also relates to methods for the non-radioactive labeling, detection, quantitation and isolation of nascent proteins translated in a cellular or cell-free translation system utilizing chemically aminoacylated tRNAs. tRNA molecules are misaminoacylated with non-radioactive markers which may be non-native amino acids, amino acid analogs or derivatives. Markers may comprise cleavable moieties, detectable labels, reporter properties wherein markers incorporated into protein can be distinguished from unincorporated markers, or coupling agents which facilitate the detection and isolation of nascent protein from other components of the translation system.
Owner:AMBERGEN
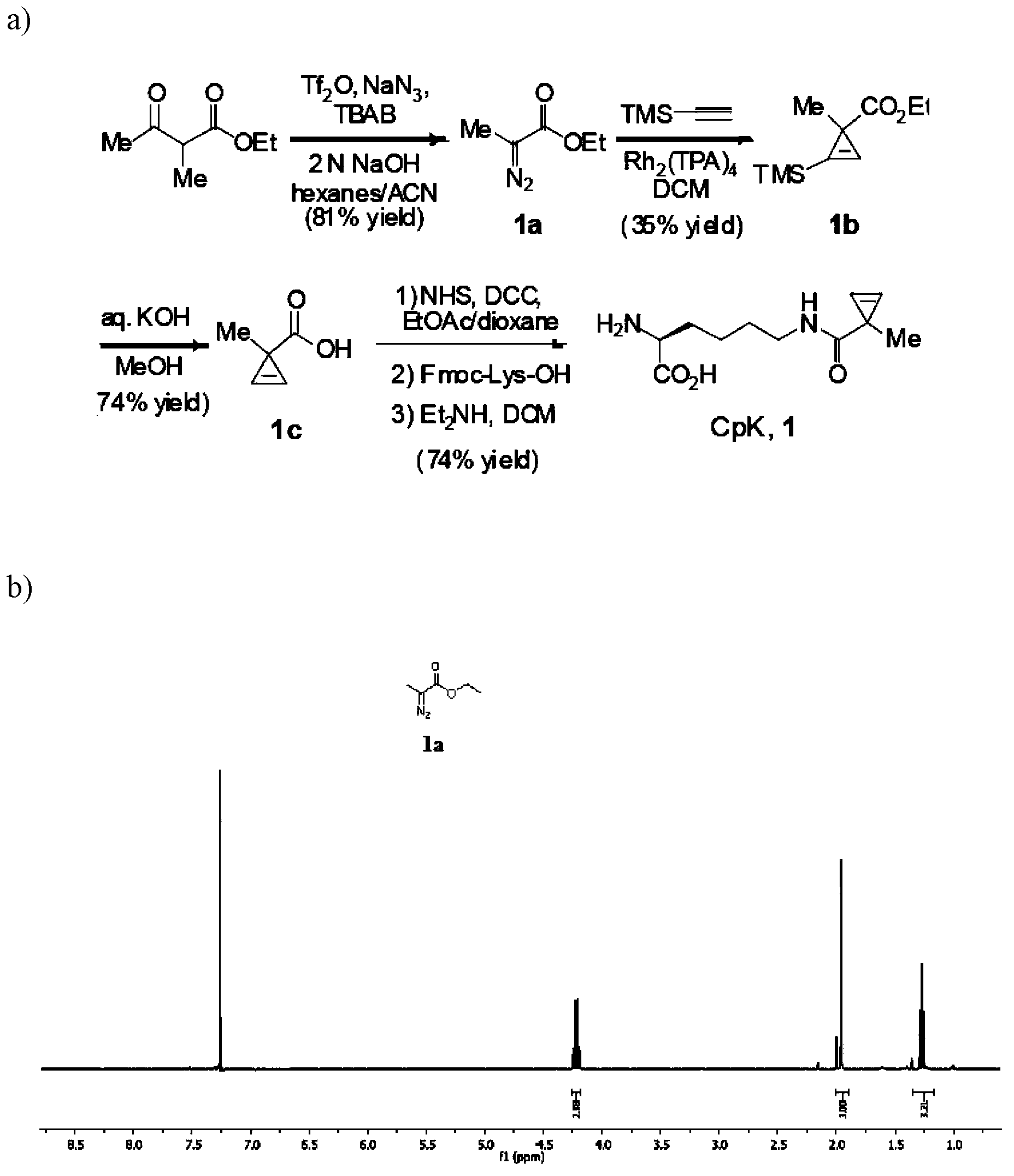
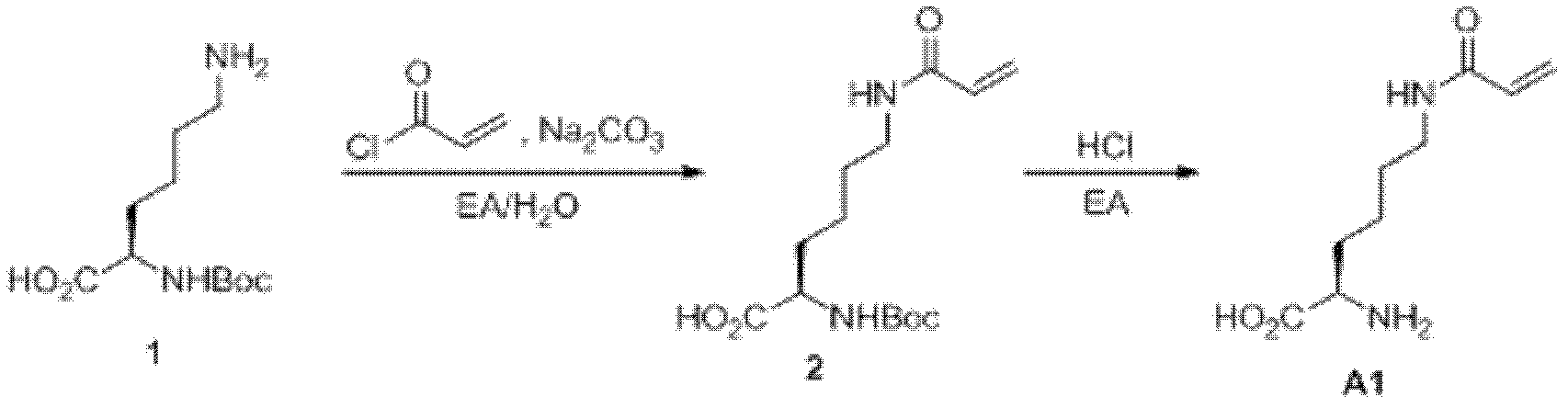
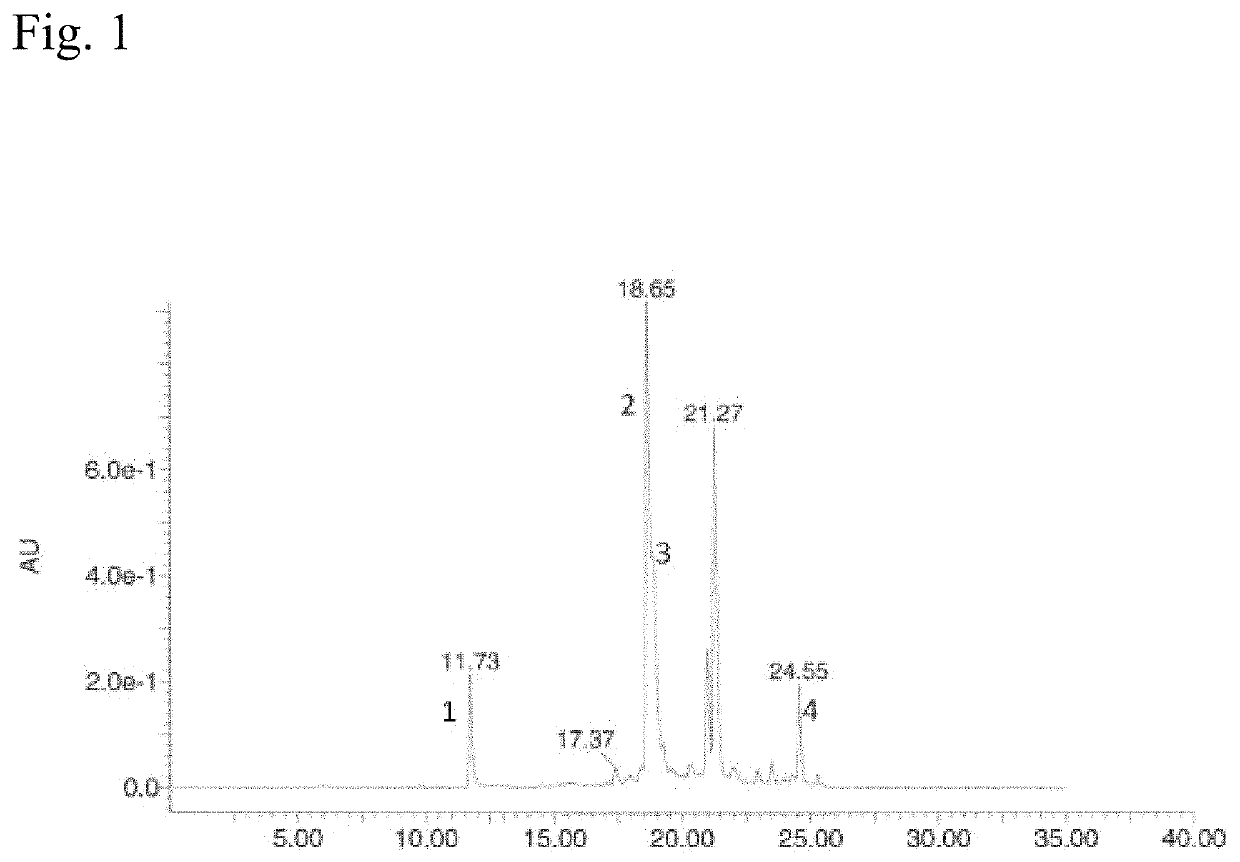
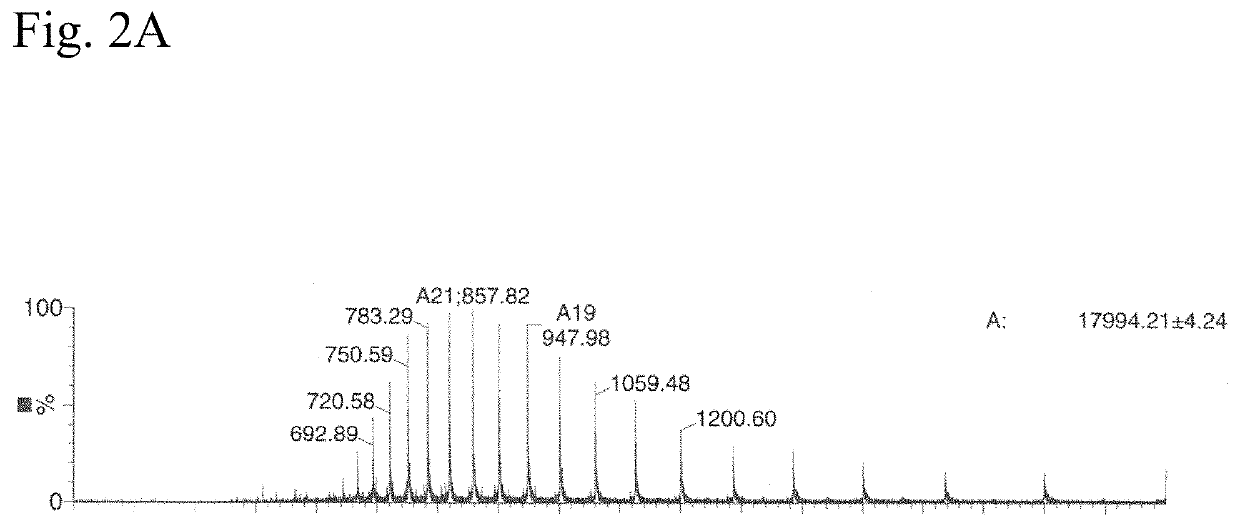
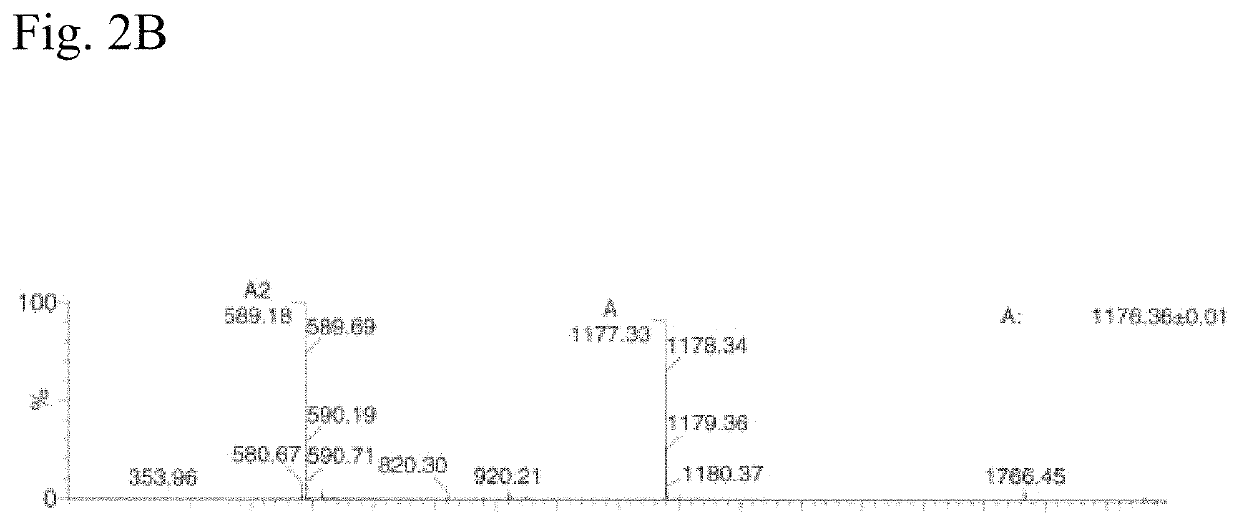
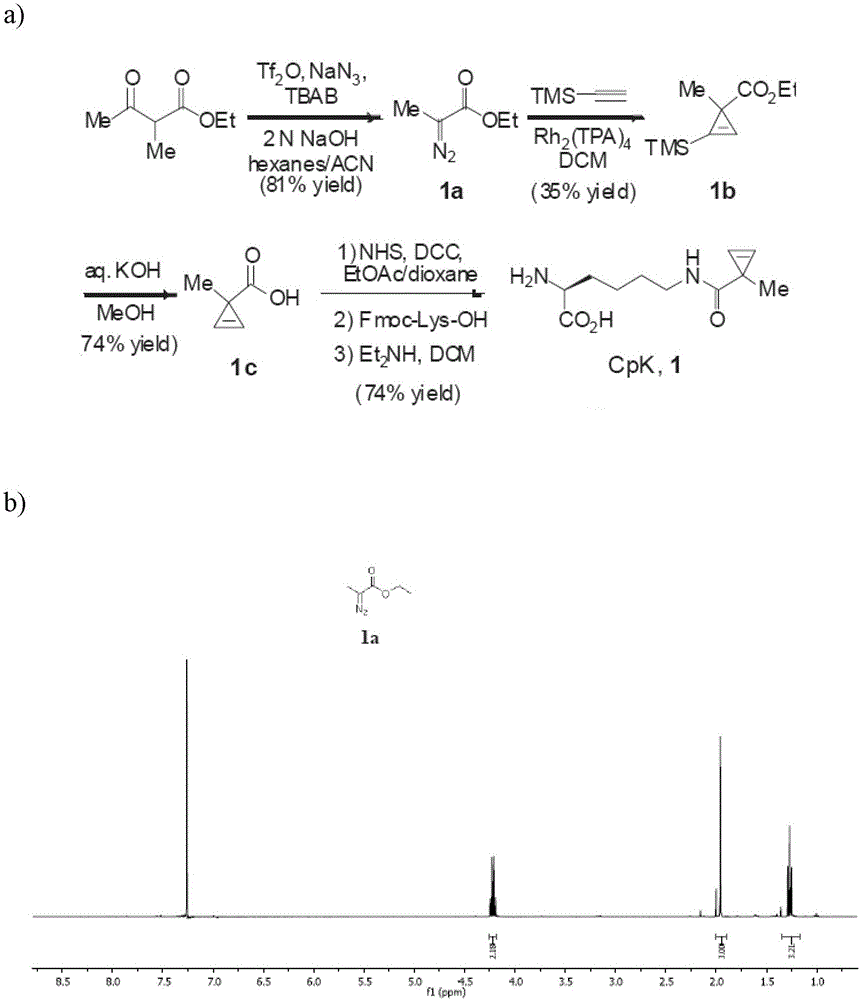
N<epsilon>-(1-methylcyclopropyl-2-acrylamide)-lysine translation system and application thereof
ActiveCN103667202AValid markEfficient expressionBacteriaHaemoglobins/myoglobinsProtein targetAminoacyl-tRNA synthetases
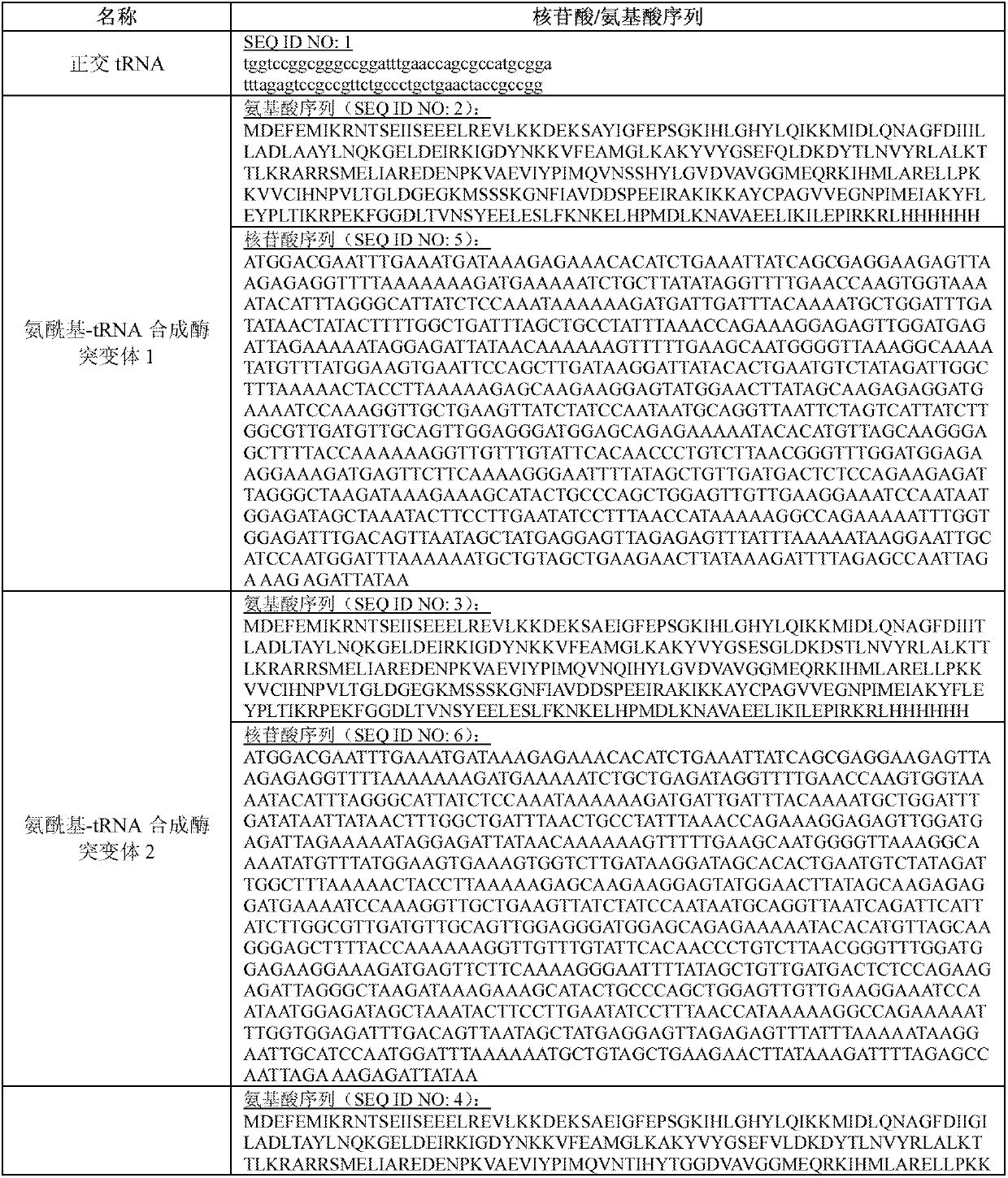
The invention relates to an aminoacyl-tRNA (transfer ribonucleic acid) synthetase mutant containing an amino acid sequence selected from groups consisting of amino acids shown by SEQ ID NO:4 and conservative variants thereof. The invention provides a CpK (short for N<epsilon>-(1-methylcyclopropyl-2-acrylamide)-lysine) translation system for fixed point specific insertion of N<epsilon>-(1-methylcyclopropyl-2-acrylamide)-lysine in a target protein through pairing of orthogonal tRNA and orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase, and a method for fixed point specific insertion of CpK in the target protein by using the translation system. The CpK translation system comprises (i) N<epsilon>-(1-methylcyclopropyl-2-acrylamide)-lysine, (ii) the orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase, (iii) the orthogonal tRNA and (iv) a nucleic acid for coding the target protein, wherein the orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase is used for realizing aminoacylation of the orthogonal tRNA preferentially by using CpK, and the nucleic acid contains at least one selective codon specifically identified by the orthogonal tRNA. The invention also relates to an application of a mutant protein for fixed point specific insertion of CpK in protein labeling through a light click reaction with a tetrazole compound.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
3-chlorinated tyrosine translation system and application thereof
The invention relates to an aminoacyl-tRNA (transfer ribonucleic acid) synthetase mutant, wherein the amino acid sequence contained therein is selected from a group composed of the amino acids shown by the SEQ ID No. 2, 3 and 4 and the conservative mutants thereof. The invention provides a 3-chlorinated tyrosine translation system doping 3-chlorinated tyrosine into the target protein by use of the orthogonal tRNA, orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase and the pairing thereof, and a method for doping the 3-chlorinated tyrosine into the target protein by use of the translation system. The 3-chlorinated tyrosine translation system comprises (i) 3-chlorinated tyrosine, (ii) orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase, (iii) orthogonal tRNA and (iv) nucleic acid coding the target protein, wherein the orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase performs aminoacylation of the orthogonal tRNA by use of the 3-chlorinated tyrosine by priority; and the nucleic acid contains at least one selection coder for specificity identification of the orthogonal tRNA.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
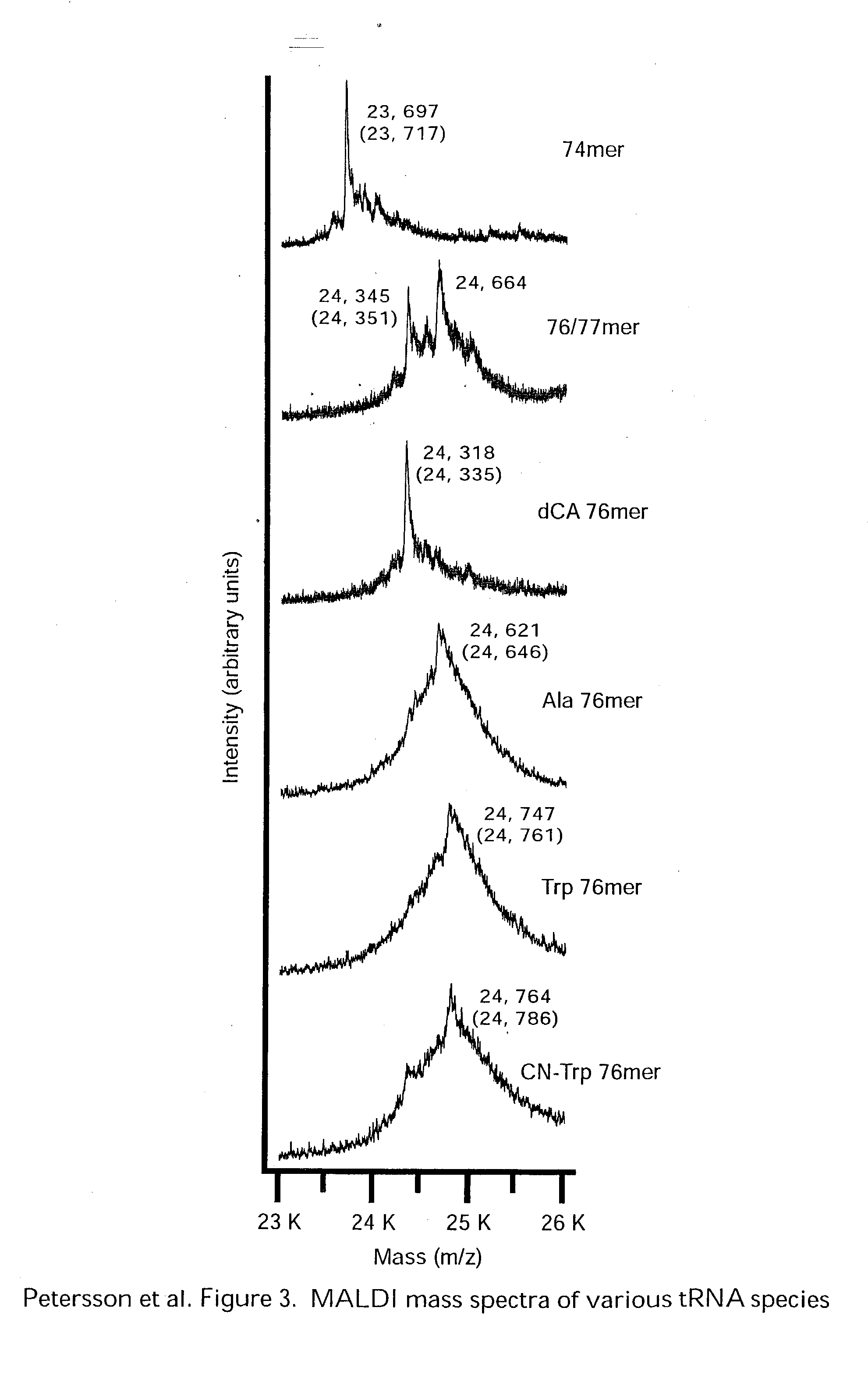
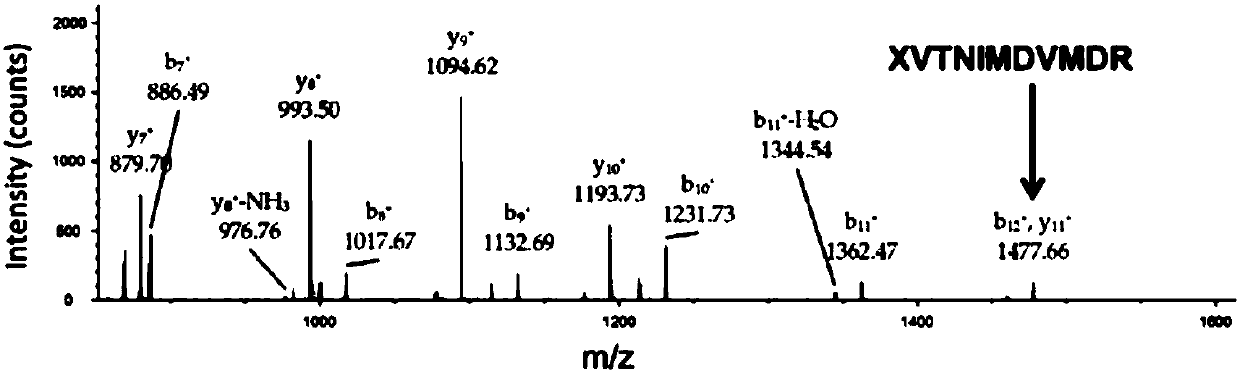
Methods for evaluation of in vitro aminoacyl tRNA production using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry
InactiveUS20050074759A1Less timeLess materialTime-of-flight spectrometersSamples introduction/extractionSide chainProtein structure
The present invention relates to a new use for matrix-assisted laser desorption / ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS). Specifically, the present invention provides a new method for evaluating the aminoacylation state of tRNAs, which are useful for site-directed mutagenesis of both sidechain and backbone protein structures. Further, the present invention useful for the generation of novel peptides, polypeptides, and proteins that may be used in drug design and screening, and in the design of small molecule agonists or antagonists for receptors, enzymes and other proteins and molecules involved in various disease states. Additionally, the present invention is useful in the field of tRNA aminoacylation, particularly in the design of synthetases.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
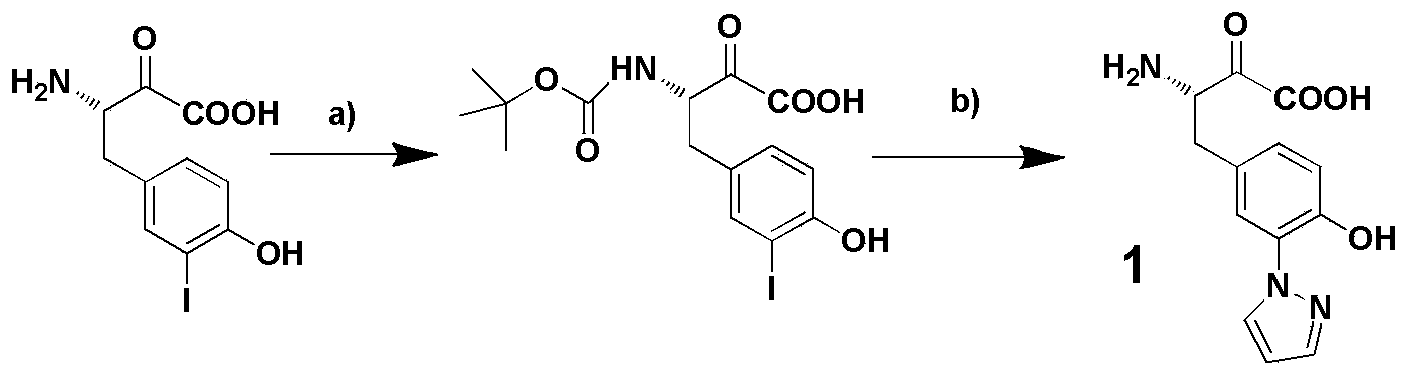
3-pyrazolyl tyrosine translation system and application thereof
The invention relates to a 3-pyrazolyl tyrosine translation system and an application thereof. The invention relates to an aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase mutant, and an amino acid sequence contained in the aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase mutant is selected from a group consisting of amino acids as shown in SEQ (sequence) ID (identity) NO: 3 and conservative variants thereof. The invention provides a 3-pyrazolyl tyrosine translation system inserting 3-pyrazolyl tyrosine (pyTyr) into target proteins in a fixed-point specific manner by utilizing the pairing of orthogonal tRNA (transfer ribonucleic acid) and orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase and a method for inserting the 3-pyrazolyl tyrosine into the target proteins in a fixed-point specific manner by utilizing the translation system. The 3-pyrazolyl tyrosine translation system contains (i) the 3-pyrazolyl tyrosine; (ii) the orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase; (iii) the orthogonal tRNA, wherein the orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase uses the 3-pyrazolyl tyrosine to perform priority aminoacylation on the orthogonal tRNA; and (iv) nucleic acid encoding the target proteins, wherein the nucleic acid contains at least one selector codon which is specifically identified by the orthogonal tRNA.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
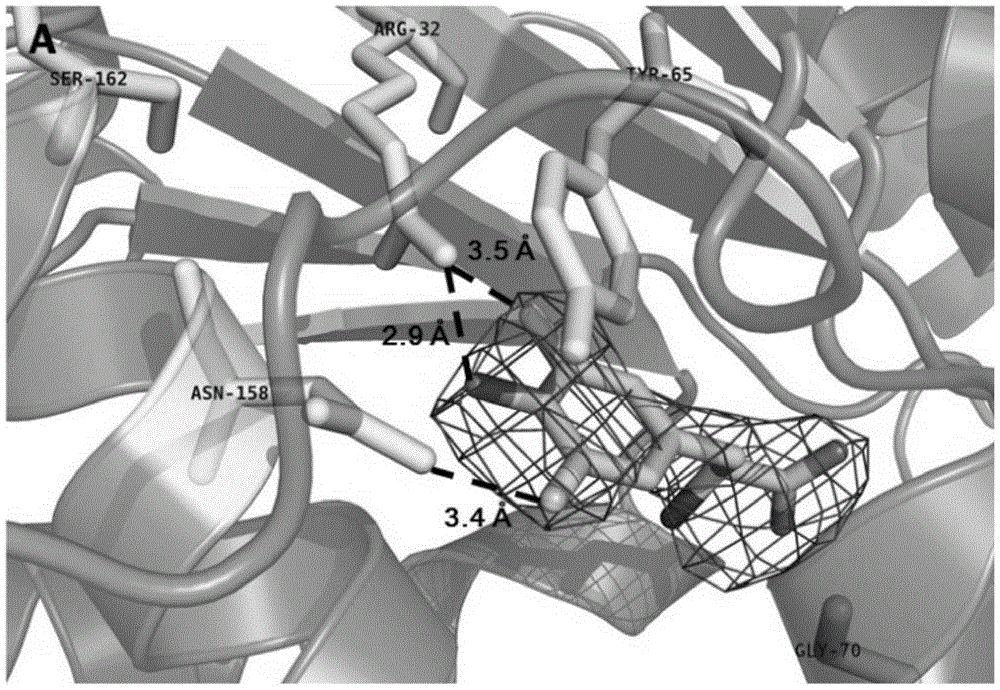
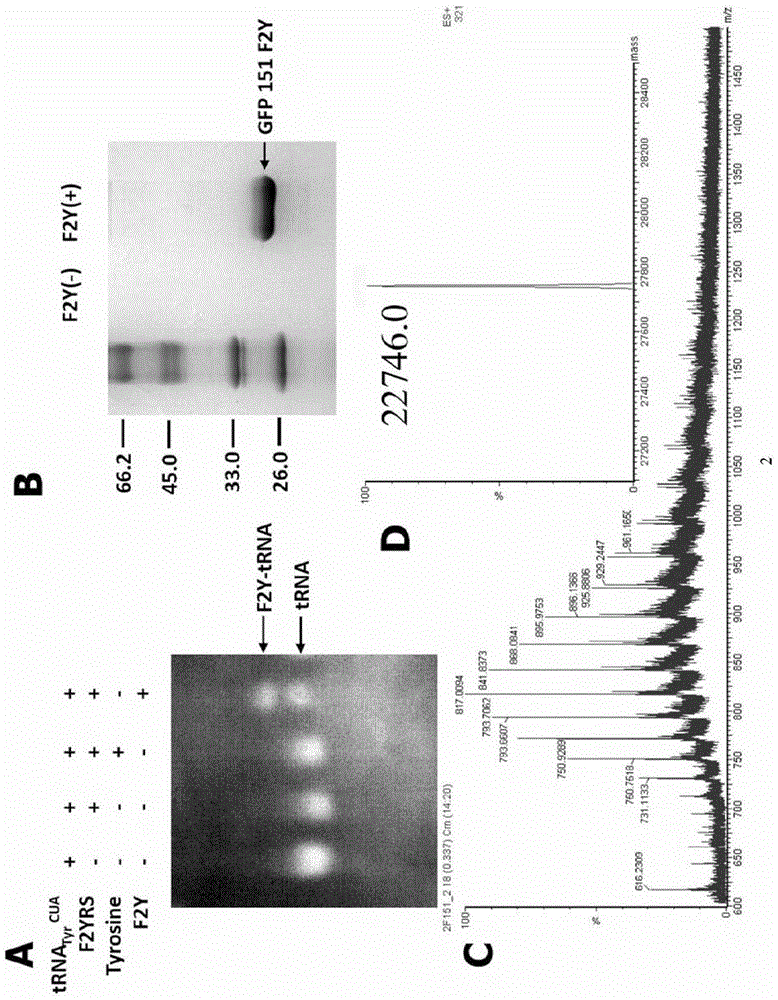
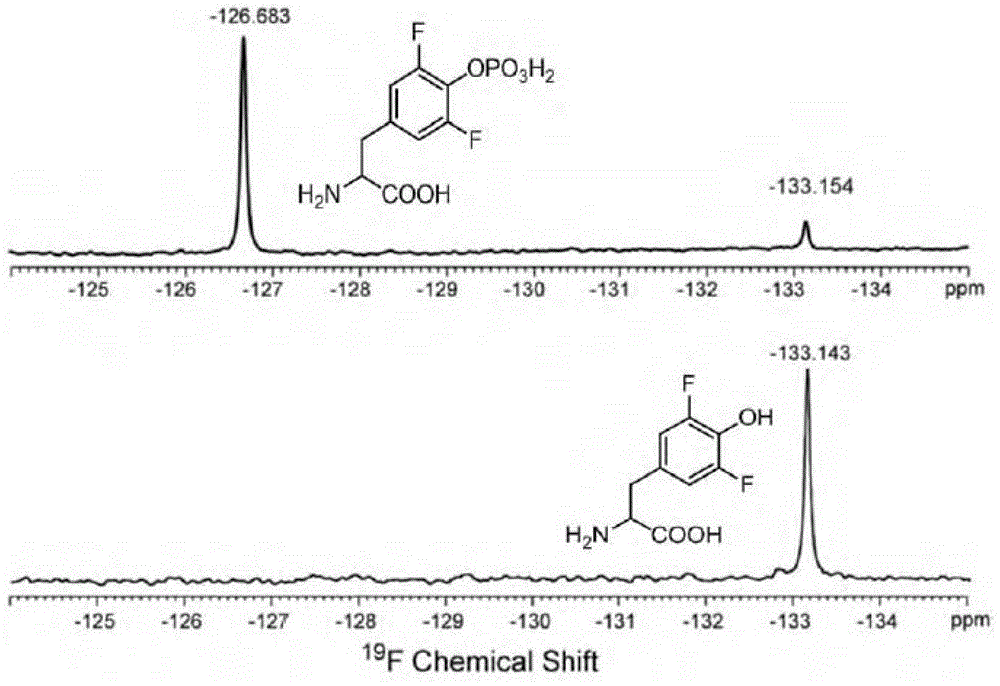
3,5-difluoro-tyrosine translation system and application thereof
ActiveCN104004723AElucidating dynamic propertiesShort manufacturing timeBacteriaTransferasesProtein targetTyrosine
The invention relates to an aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase mutant which is orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase. The amino acid sequence of the synthetase is selected from a group composed of an amino acid sequence presented in SEQ ID NO:4 and conservative variants of the amino acid sequence presented in SEQ ID NO:4, and the conservative variants have enzyme activity the same as the amino acid sequence presented in SEQ ID NO:4. The invention further provides a 3,5-difluoro-tyrosine translation system which comprises (i) 3,5-difluoro-tyrosine, (ii) the orthogonal aminoacyl-tRAN synthetase, (iii) orthogonal tRNA and (iv) nucleic acid of encoded target protein, wherein the orthogonal aminoacyl-tRAN synthetase carries out prior aminoacylation on the orthogonal tRNA through the 3,5-difluoro-tyrosine, and the nucleic acid contains at least one selective codon for specific recognition of the orthogonal tRNA.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
Prevention and treatment of neurodegenerative diseases through autophagy activity mediated by ligand or arginylated bip binding to p62 zz domain
The drug action mechanisms and core techniques of the present invention are summarized in figure 1. Specifically, the invention provides malignant denatured proteins, such as mutant Huntingtin proteinor alpha-synuclein, stick together to grow into oligomer aggregates (1, 2), fibrillar aggregates (3), and ultimately inclusion bodies (4). Young neuronal cells produce a large quantity of Nt-Arg through N-terminal arginylation (5) of endoplasmic reticulum chaperones, such as BiP, and thereafter, arginylated BiP (R-BiP) comes into the cytoplasm and binds with denatured proteins (6). Nt-Arg of R-BiP, as a ligand, binds with the ZZ domain of p62 (7) to induce the structural activation of p62 (8) while the ordinarily closed inactive form of p62 is changed with an open form thereof, and thus PB1 and LC3-binding domains are exposed. On the basis of oligomerization (9) by the PB1 domain, p62 binds with the denatured protein aggregates to be concentrated to autophagically degradable aggregates, that is, p62 bodies (10). Thereafter, p62 completes autophagy targeting (11) and lysosomal proteolysis through binding with LC3 protruding on the autophagosomal membranes. In young neuronal cells, theautophagic proteolysis occurring through steps 5-11 is strong, and thus the cytotoxic protein aggregates (1-5) do not accumulate, but in aged neuronal cells, the autophagic proteolysis occurring through steps 5-11 is weakened, and thus the protein aggregates (1-5) accumulate, resulting in a vicious cycle. The present invention attempts to effectively remove Huntingtin and alpha-synuclein protein aggregates and the like by artificially activating p62 using low-mass ligands of the p62 ZZ domain (12, 13). Specifically, p62 binding the ligands through step 12 promotes p62-R-BiP-denatured protein oligomerization (9) and autophagy aggregate formation (10). In addition, the ligand-62 conjugates step 13 act as autophagy activators (14), to promote LC3 synthesis, the conversion of LC3-I into LC3-II, and the like, thereby promoting the formation of autophagosomes (15).
Owner:奧土择破利悟
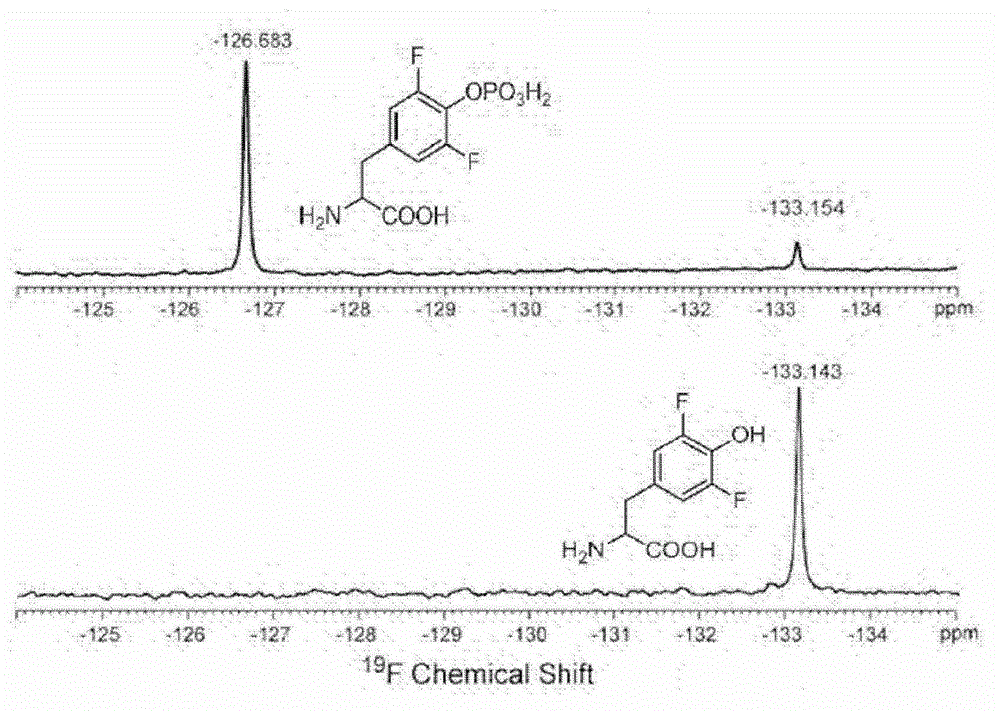
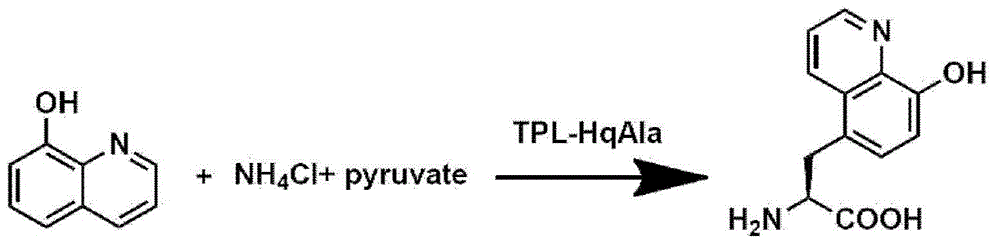
8-hydroxyquinoline alanine translation system and application thereof
ActiveCN104059891AEasy to foldHigh sensitivityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesProtein targetADAMTS Proteins
The invention relates to an aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase mutant which has an amino acid sequence selected from a group comprising an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:4 and conservative variants of the amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:4, wherein the conservative variants have the same enzymatic activity as the amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:4. The The invention also provides a translation system which comprises: (i) 8-hydroxyquinoline alanine or its structure analogs; (ii) an orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase of the invention; (iii) orthogonal tRNA, wherein the orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase realizes prior aminoacylation of the orthogonal tRNA by the 8-hydroxyquinoline alanine or its structure analogs; and (iv) nucleic acid coding target protein, wherein the nucleic acid contains at least one selection codon specifically recognized by the orthogonal tRNA. Finally, the invention provides a tyrosine phenol lyase mutant which can catalyze 8-hydroxyquinoline to generate 8-hydroxyquinoline alanine, and has an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:5.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
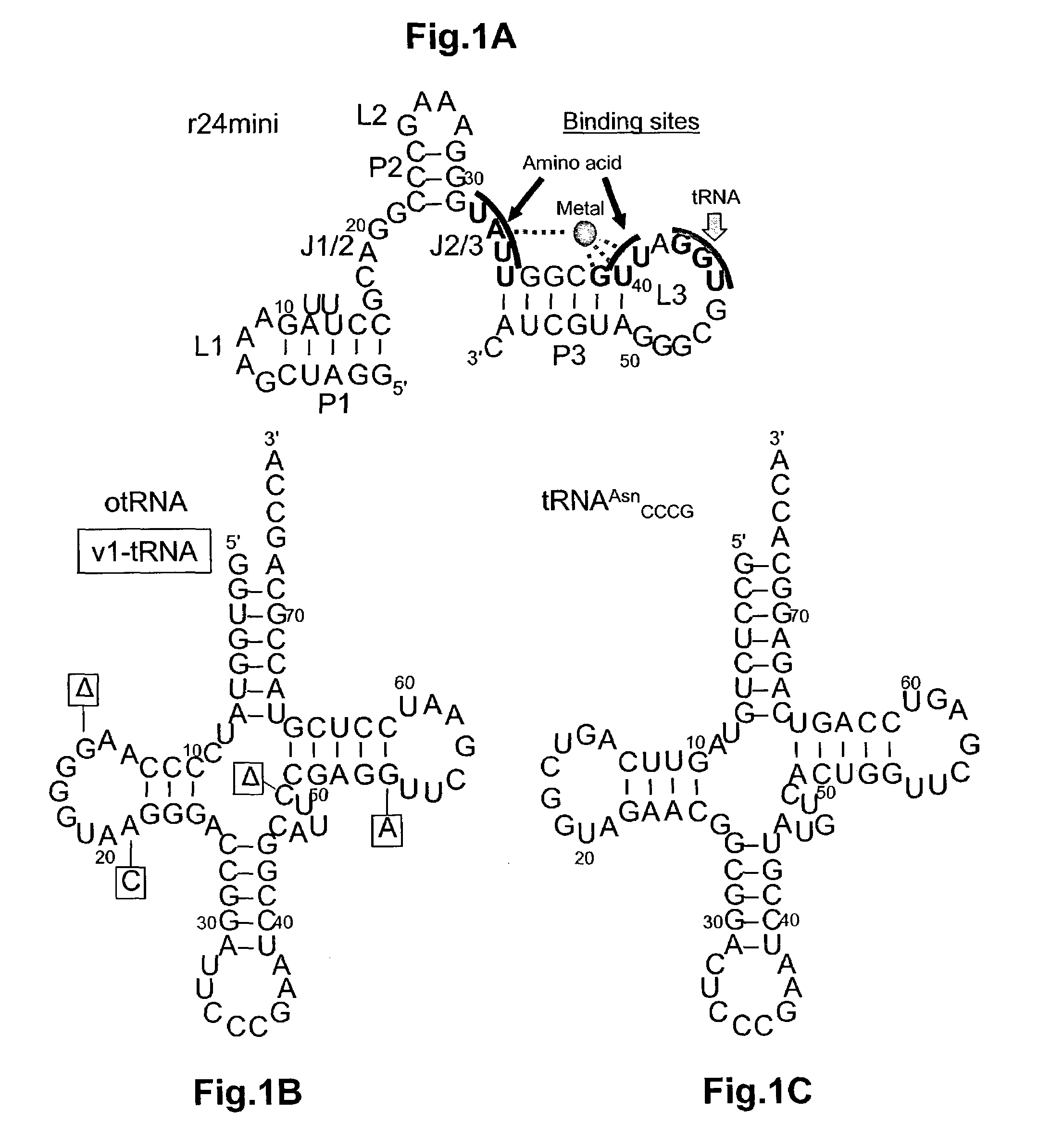
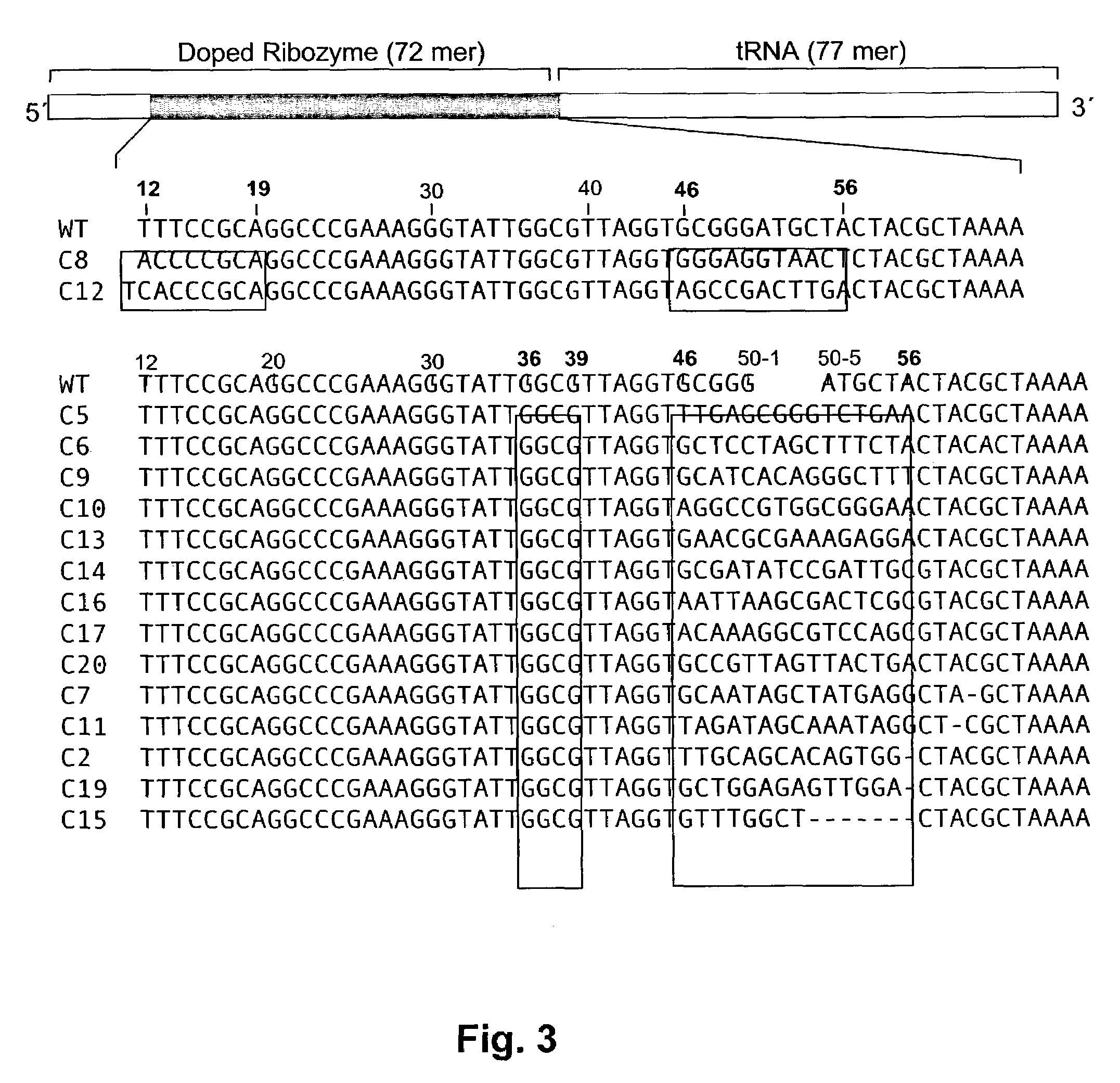
Ribozymes with broad tRNA aminoacylation activity
The present invention provides catalytic RNA molecules having cis or trans aminoacylation activity. The catalytic RNA molecules having cis aminoacylation activity comprise a catalytic domain and an aminoacylation domain. The catalytic RNA molecules having trans aminoacylation activity only have the catalytic domain. A method is provided for constructing and screening of these molecules. These molecules are suitable for aminoacylating with specific amino acids.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Acrylyl lysine translation system and application thereof
ActiveCN102925427AValid markRealize site-specific fluorescent labelingBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein targetMutated protein
The invention provides an acrylyl lysine translation system which dopes acrylyl lysine into target protein by using an orthogonal tRNA, an orthogonal acrylyl lysine aminoacyl tRNA synthetase and their combination, and also provides a method for specifically doping acrylyl lysine into target protein at a fixed point by using the translation system. The acrylyl lysine translation system comprises: (i) acrylyl lysine; (ii) the orthogonal acrylyl lysine aminoacyl tRNA synthetase; (iii) the orthogonal tRNA, wherein the orthogonal acrylyl lysine aminoacyl tRNA synthetase is used for preferential aminoacylation of the orthogonal tRNA by the acrylyl lysine; and (iv) nucleic acid coding the target protein, wherein the nucleic acid contains at least one selection codon specifically recognized by the orthogonal tRNA. The invention also relates to an application of the mutant protein doped with the acrylyl lysine.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
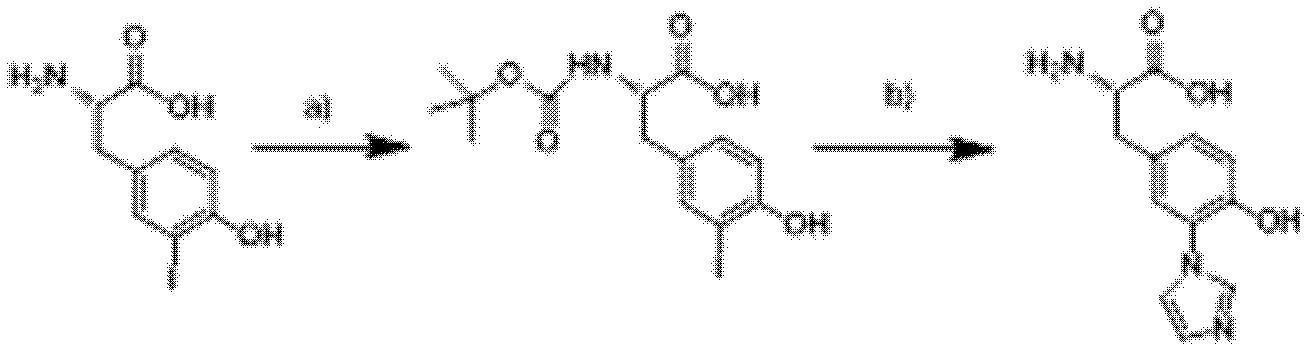
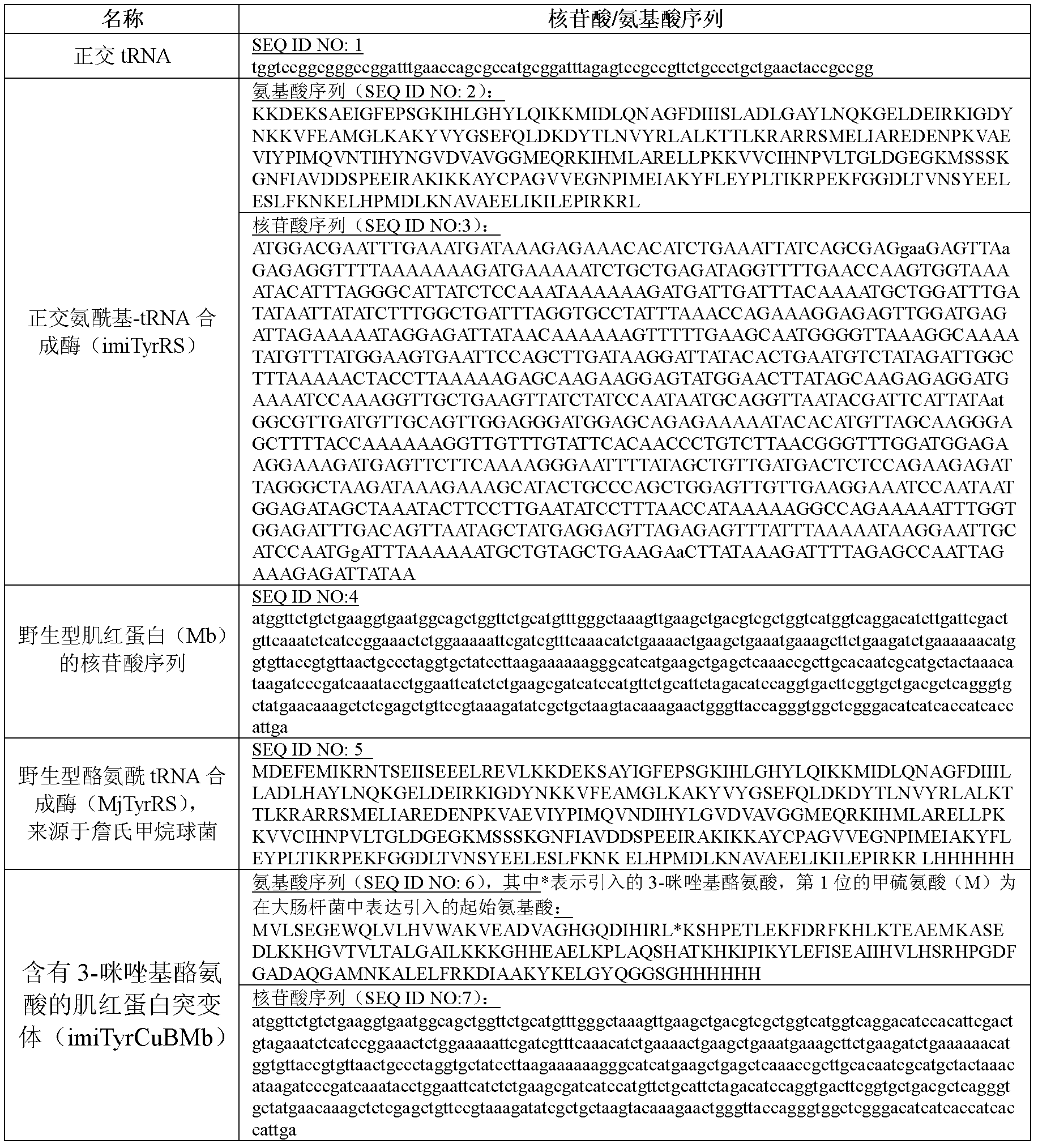
3-imidazolyl tyrosine translation system and use thereof
ActiveCN103215235ASimple structureAchieve insertionBacteriaHaemoglobins/myoglobinsProtein targetOxygenase activity
The invention relates to an aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase mutant. The aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase mutant has an amino acid sequence composed of amino acids shown in the formula of SEQ ID NO.2 and their conservative mutants. The invention provides a 3-imidazolyl tyrosine translation system for specific and fixed-point insertion of 3-imidazolyl tyrosine (imiTyr) into a target protein by utilization of an orthogonal tRNA, an orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase and their complex, and also provides a method for specific and fixed-point insertion of the 3-imidazolyl tyrosine into the target protein by the 3-imidazolyl tyrosine translation system. The 3-imidazolyl tyrosine translation system comprises 1), 3-imidazolyl tyrosine, 2), the orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase, 3), the orthogonal tRNA, wherein the orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase is obtained by preferential aminoacylation of the orthogonal tRNA by the 3-imidazolyl tyrosine, and 4), a nucleic acid for encoding a target protein, wherein the nucleic acid contains at least one selection codons specifically recognized by the orthogonal tRNA. The invention also relates to a method for specific and fixed-point insertion of 3-imidazolyl tyrosine in Myoglobin (Mb) so that the Myoglobin has oxidase activity, and a use of the method.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
MODIFIED AMINOACYL-tRNA SYNTHETASE AND USE THEREOF
ActiveUS20180127761A1Without complicated reactionEfficiently attachedHydrolasesLigasesThreonineTryptophan
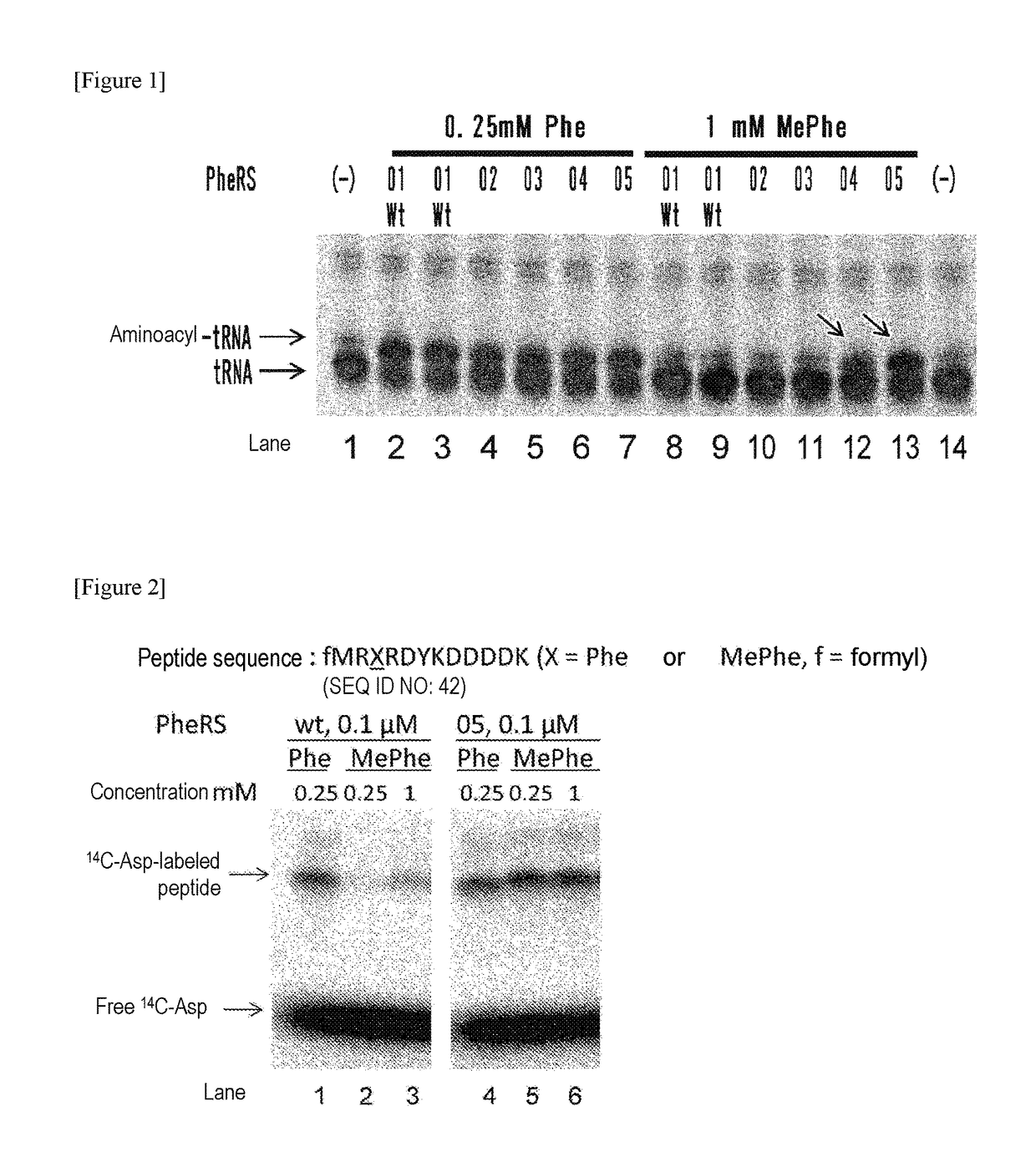
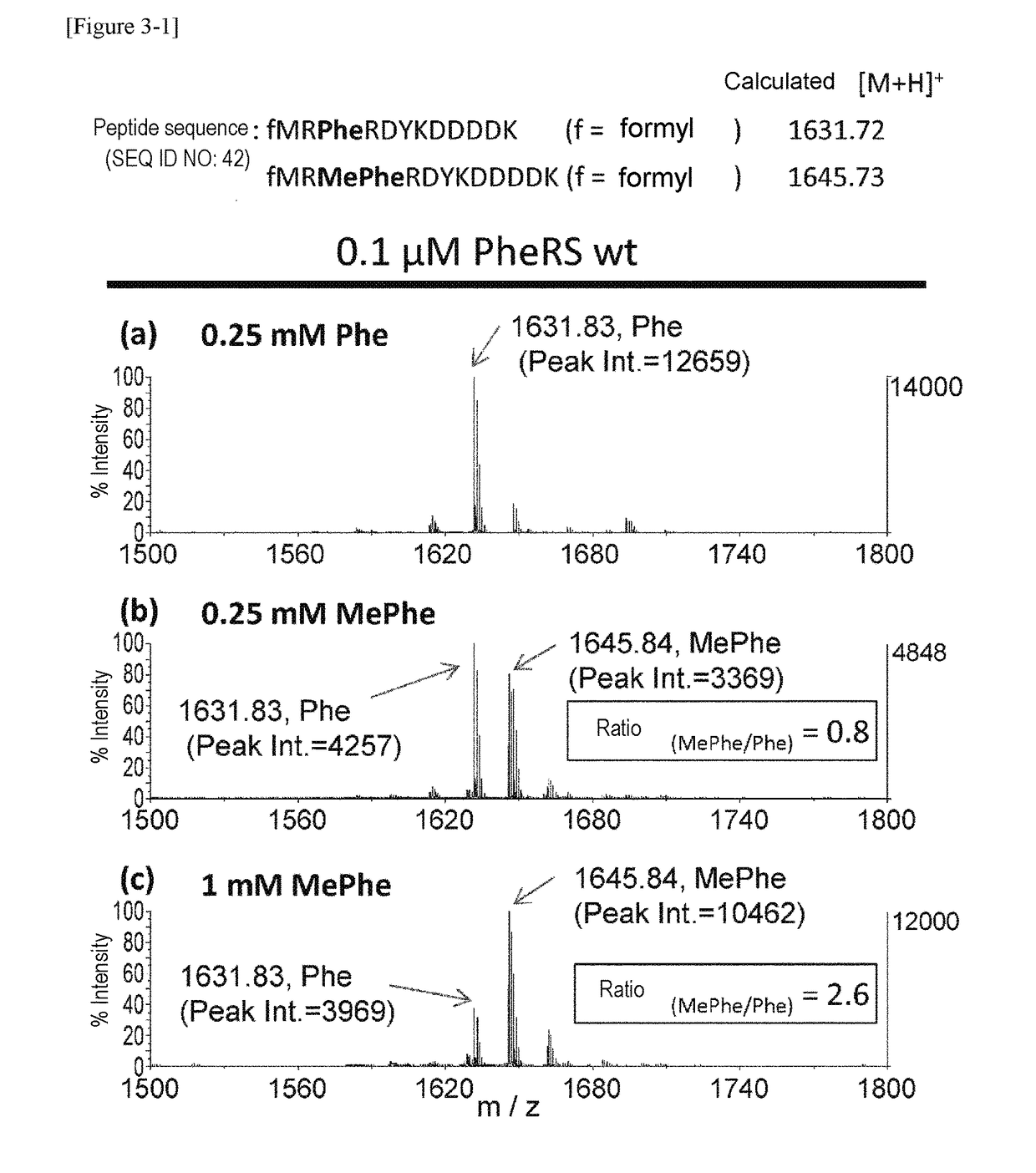
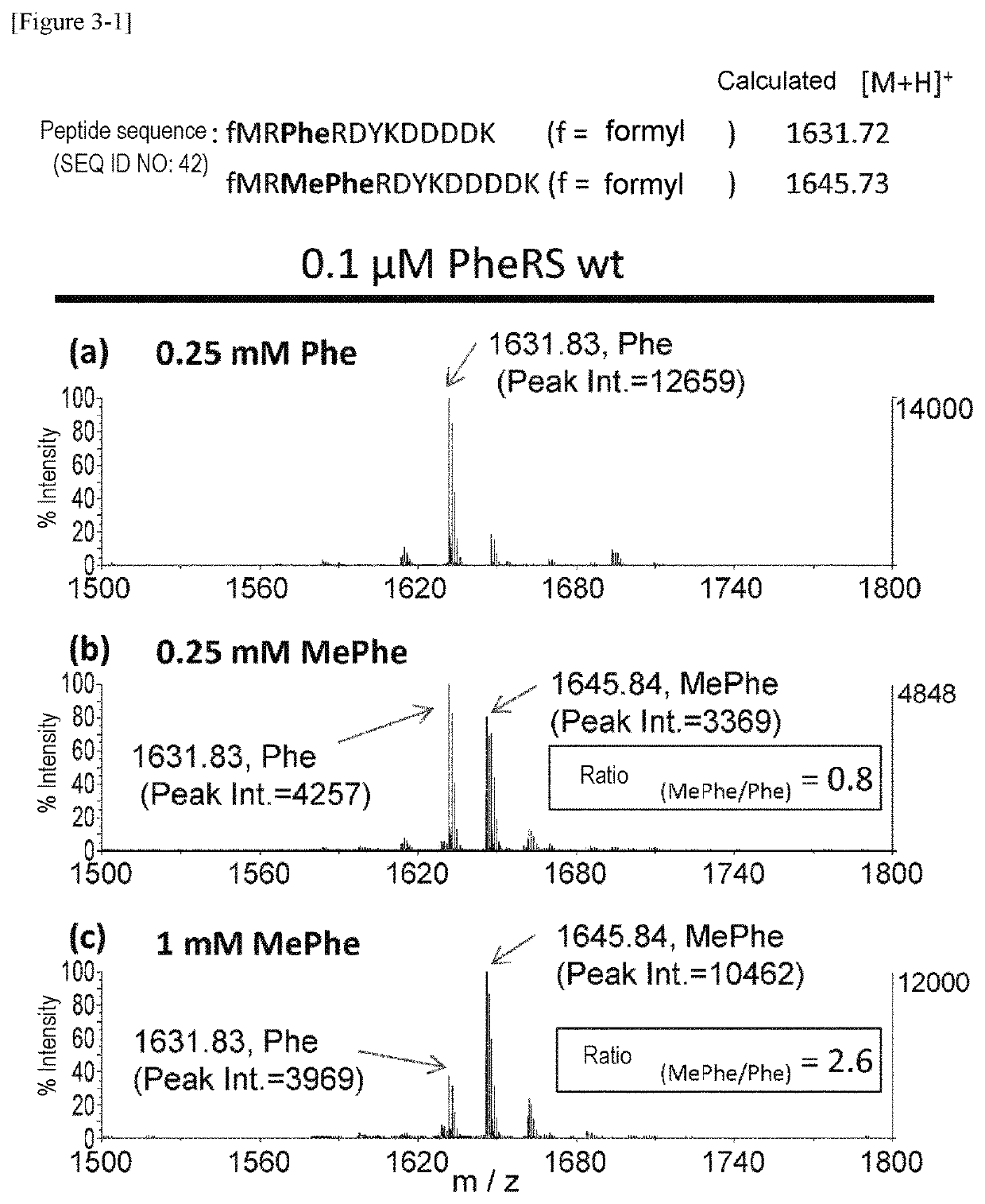
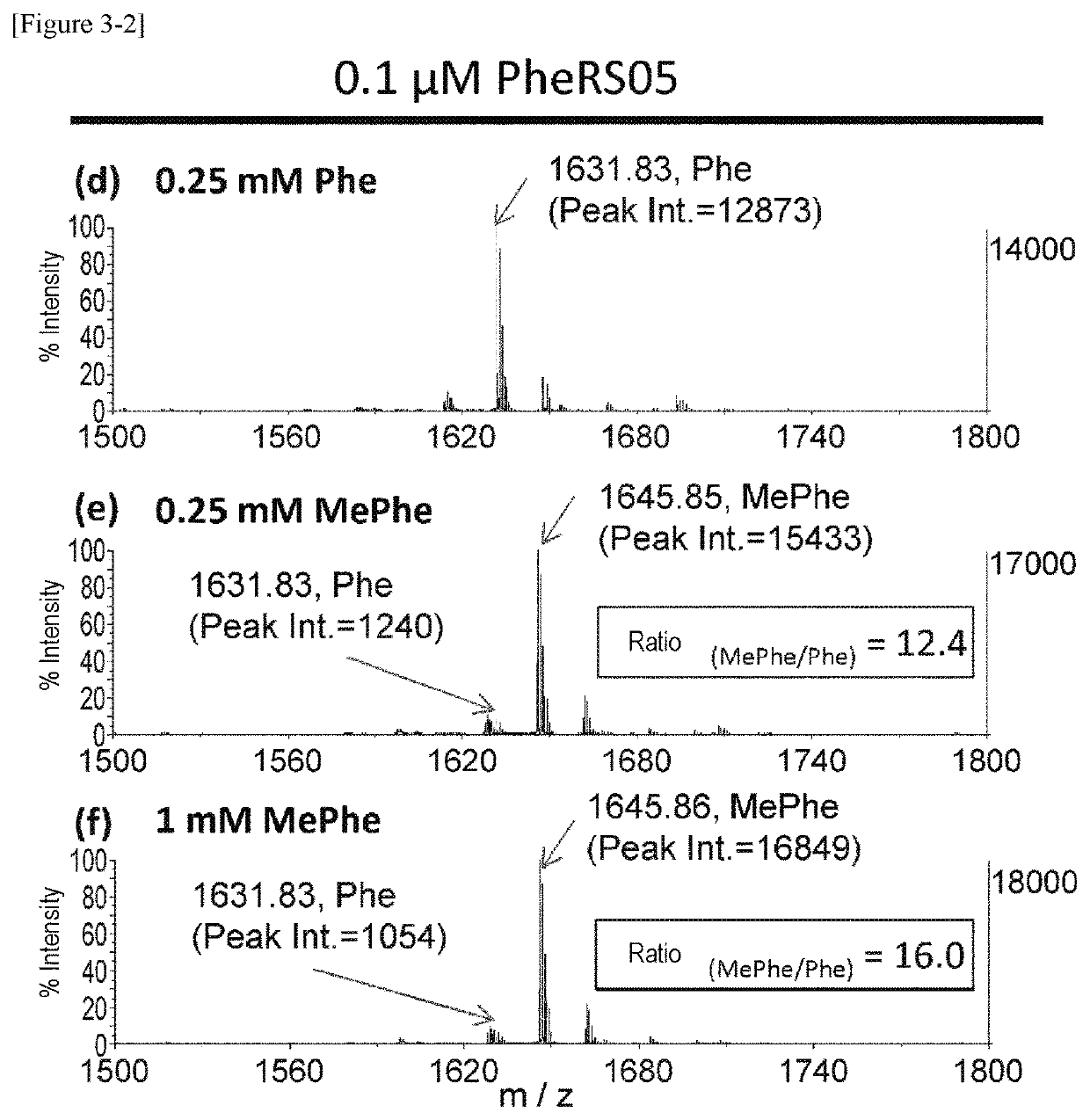
The present invention provides modified aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases (ARSs) having increased reactivity with N-methyl amino acids compared to natural aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. The modified aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases according to the present invention can aminoacylate tRNAs with their corresponding N-methyl-substituted amino acids such as N-methyl-phenylalanine, N-methyl-valine, N-methyl-serine, N-methyl-threonine, N-methyl-tryptophan, and N-methyl-leucine more efficiently than natural aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. The present invention enables a more efficient production of polypeptides containing N-methyl amino acids.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
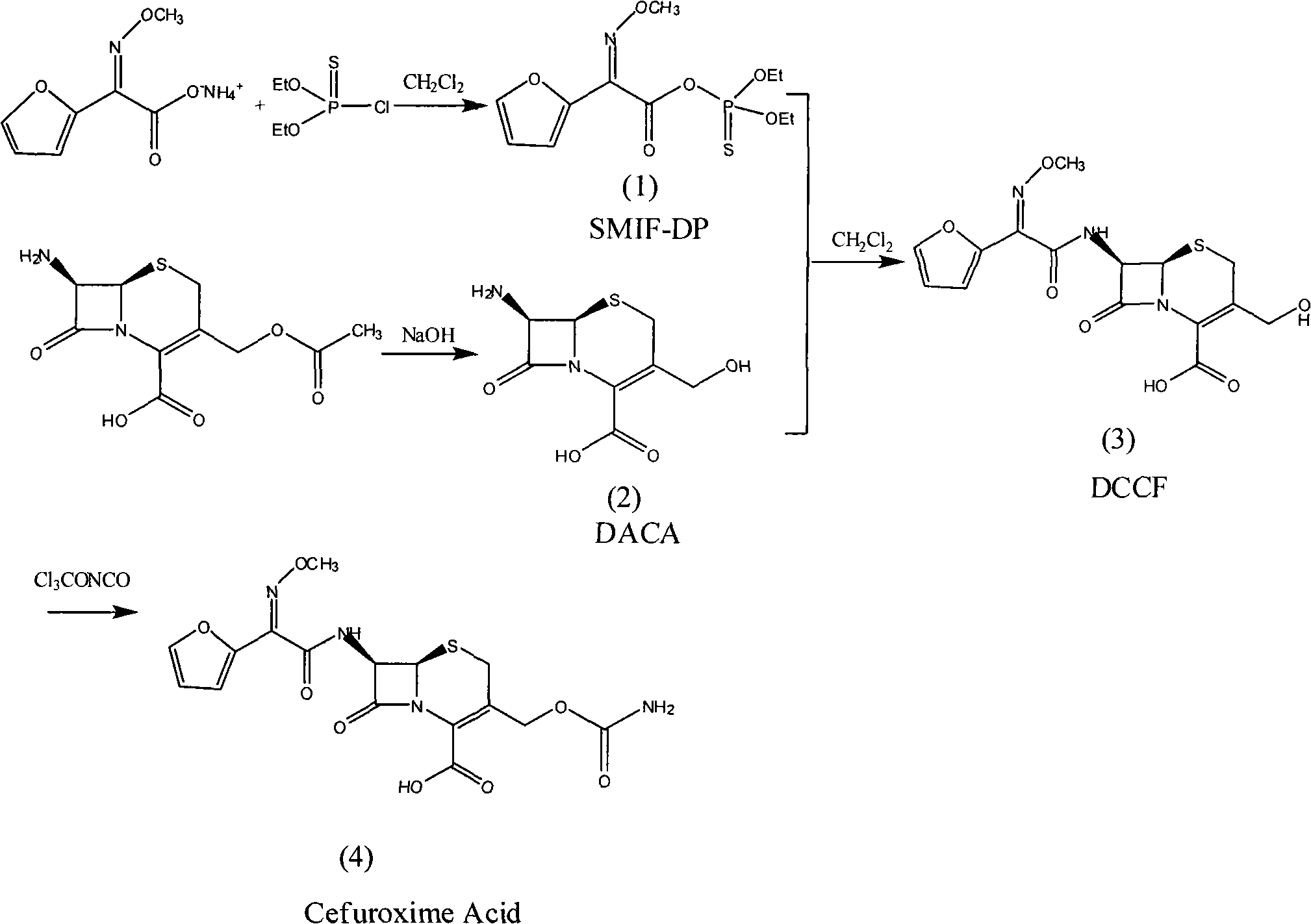
Method for synthesizing cefuroxime acid
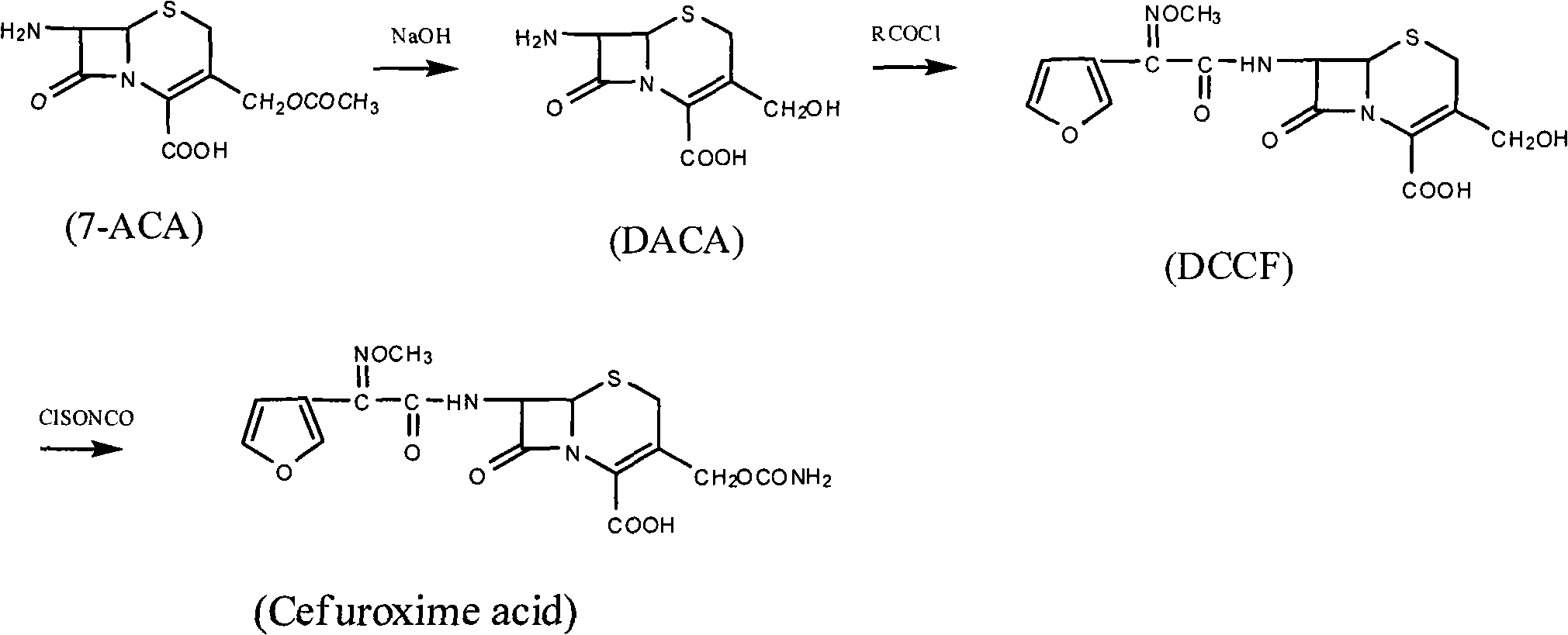
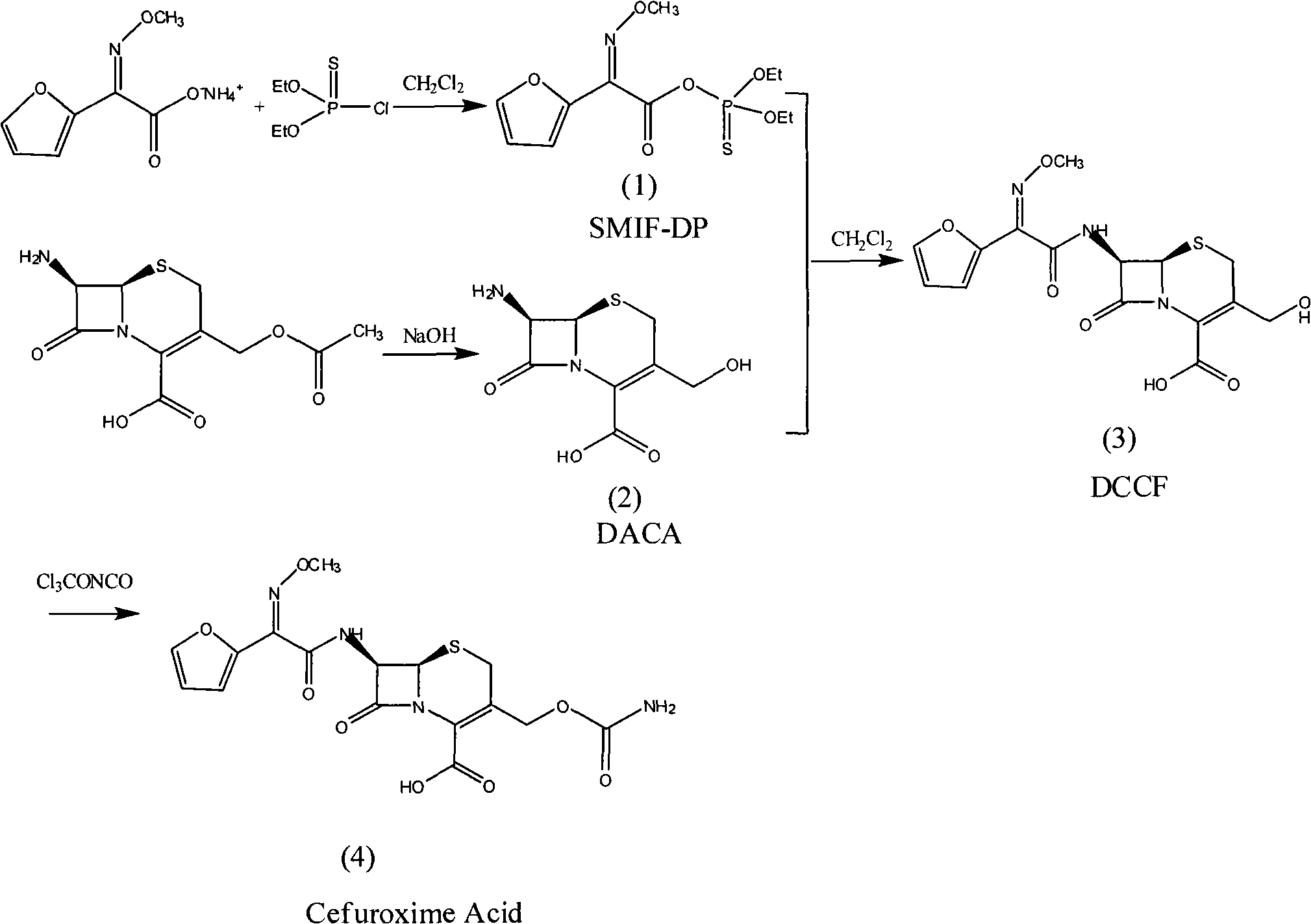
The invention provides a method for synthesizing cefuroxime acid. In the method, a phosphorus acyl active resin is subjected to hydrolysis reaction, the product of the hydrolysis reaction is subjected to aminoacylation, and a 3-decarba-moyl cefuroxime acid intermediate is synthesized by a one-pot method without separating the intermediate, the step of cefuroxime acid synthesis is saved, and the yield of the product is improved greatly.
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV +1
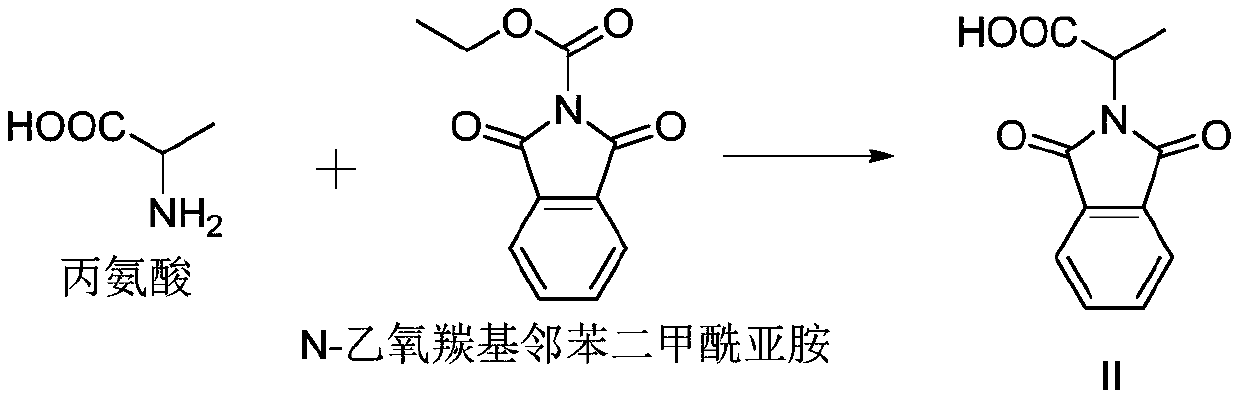
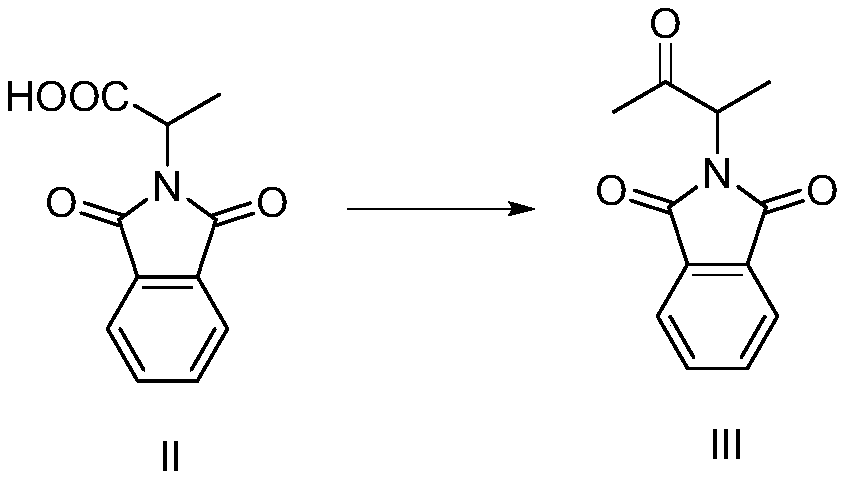
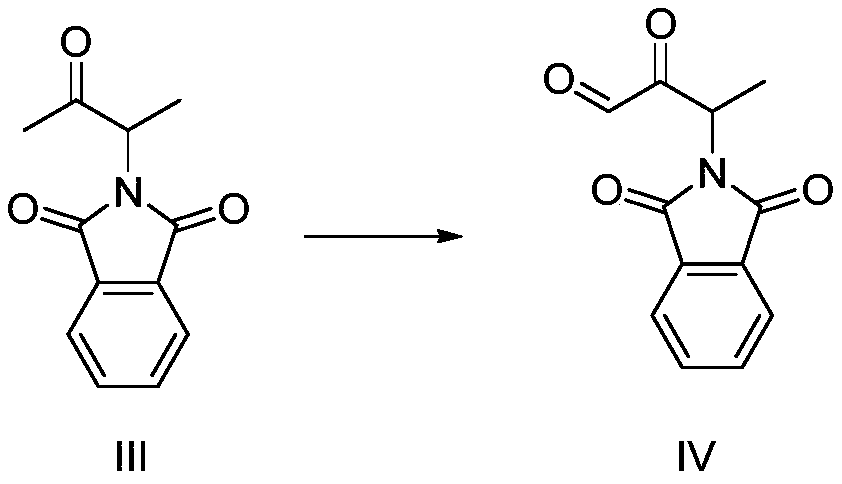
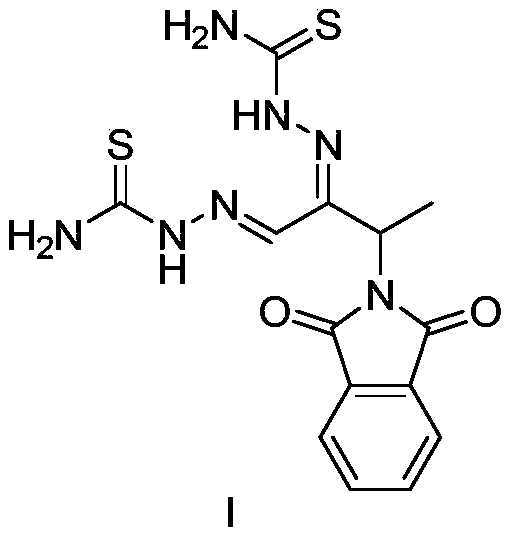
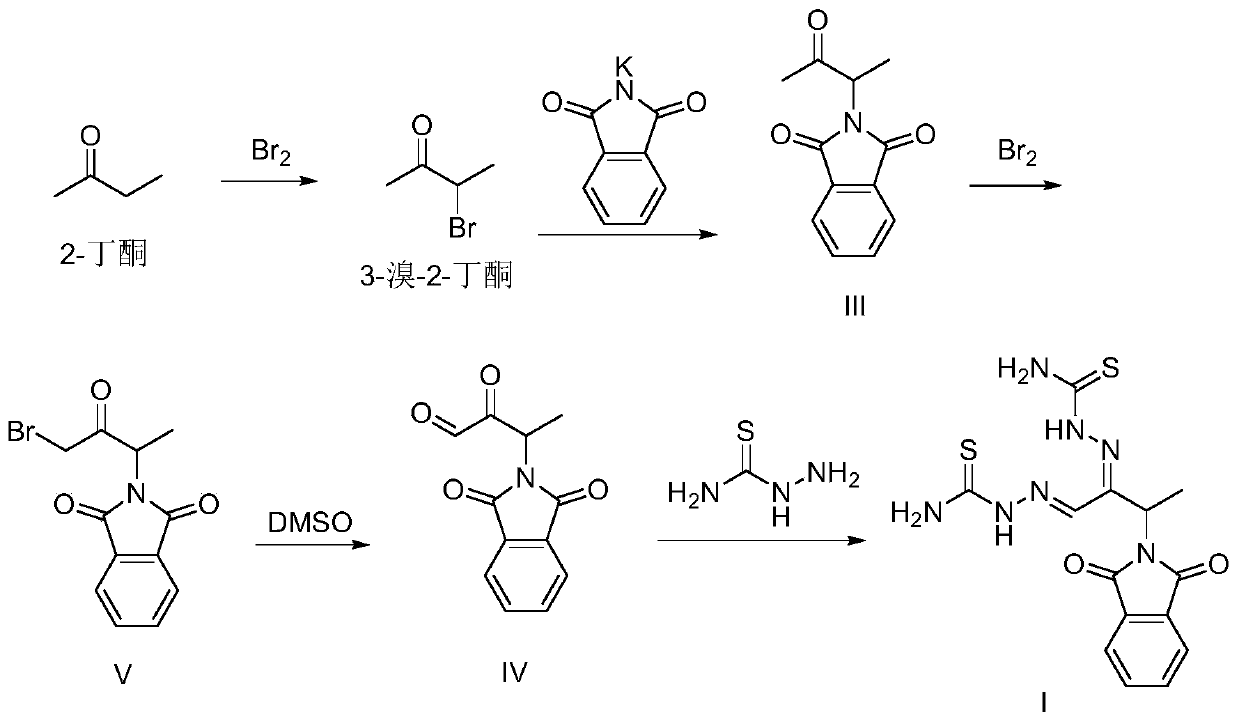
Preparation method of 3-phthalimide-2-oxy-n-butyraldehyde thiosemicarbazide
The invention relates to a preparation method of 3-phthalimide-2-oxy-n-butyraldehyde thiosemicarbazide (I). The preparation method comprises the steps: adopting alanine and N-ethoxycarbonyl phthalimide as a starting material, and performing aminoacylation, methyl-lithium addition, an oxidation reaction and a condensation reaction so as to obtain the target product 3-phthalimide-2-oxy-n-butyraldehyde thiosemicarbazide (I). The method for synthesizing 3-phthalimide-2-oxy-n-butyraldehyde thiosemicarbazide has the advantages of few reaction steps, simple operation, suitability for large-scale production and the like.
Owner:HUAIBEI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
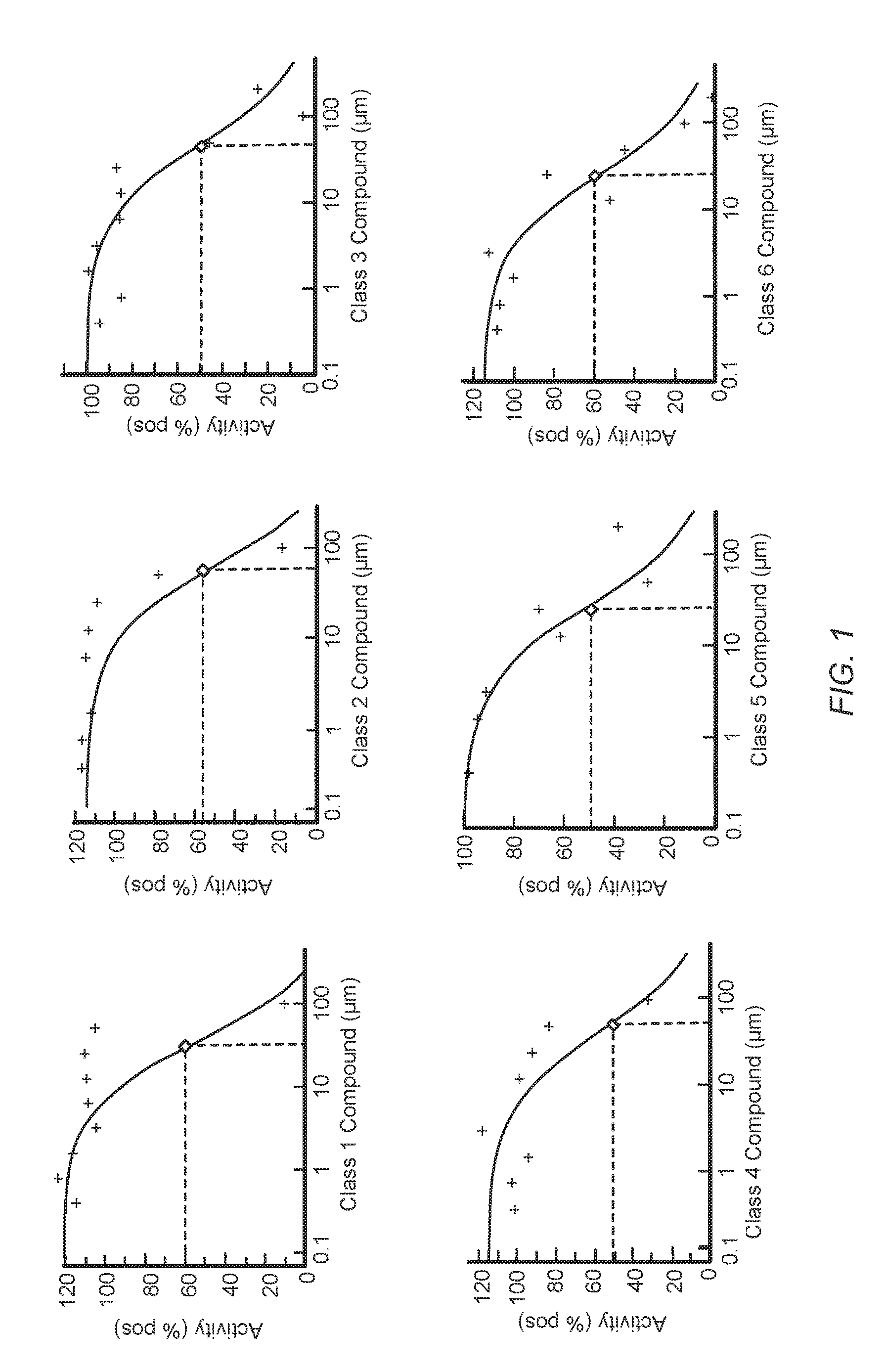
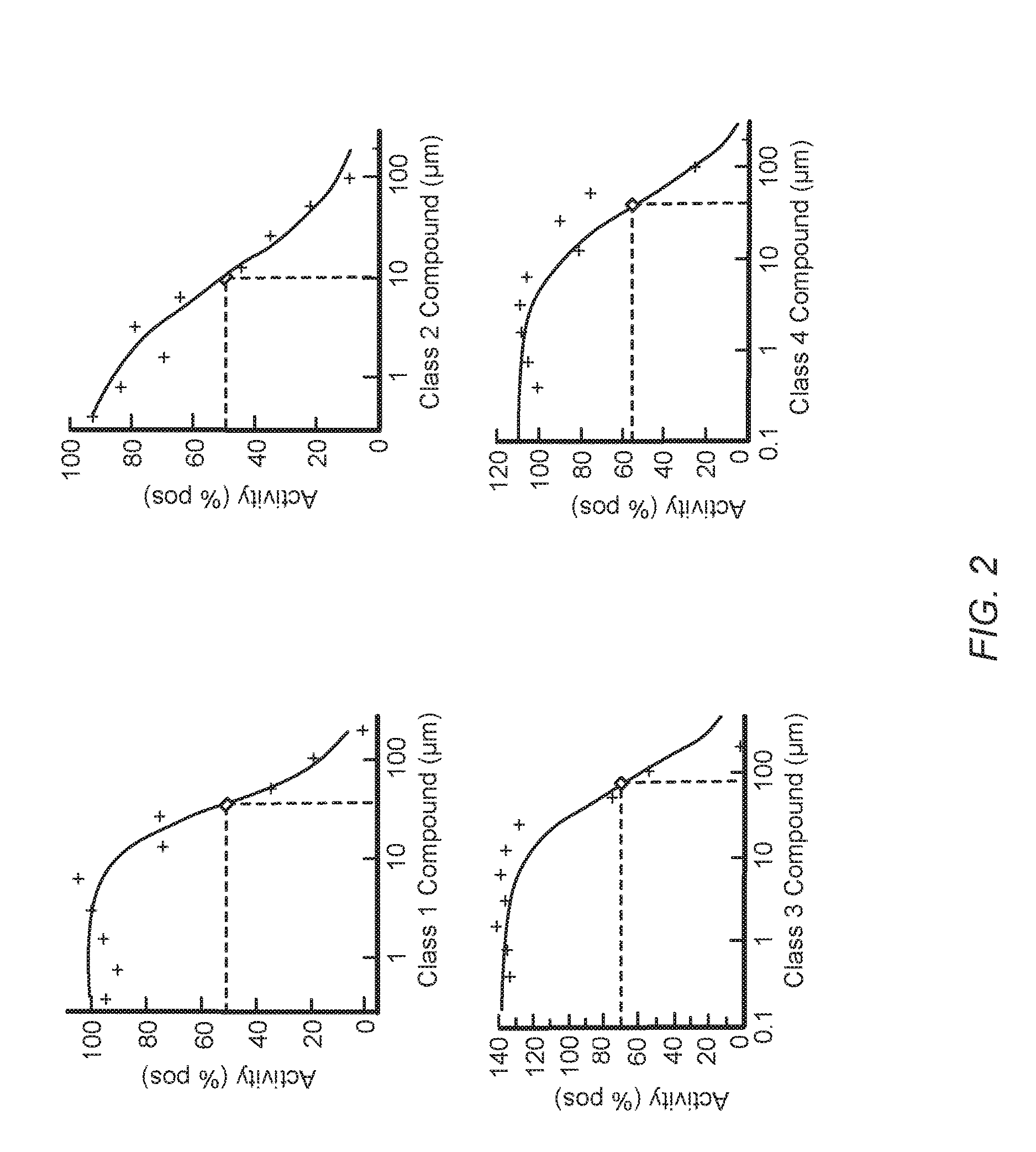
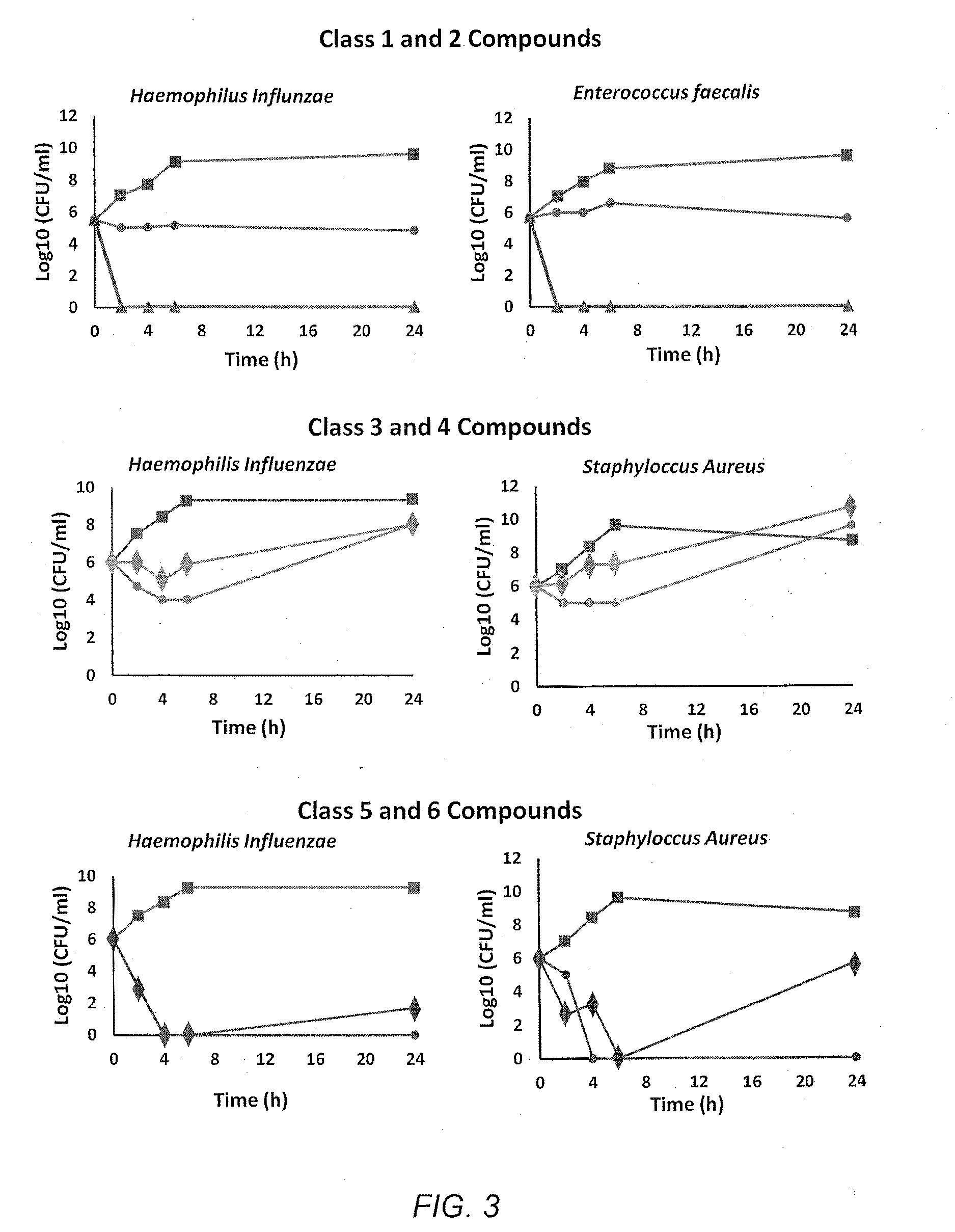
Antibiotic compounds that inhibit bacterial protein synthesis
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Modified aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase and use thereof
ActiveUS10815489B2Without complicated reactionImprove efficiencyHydrolasesLigasesThreonineTryptophan
The present invention provides modified aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases (ARSs) having increased reactivity with N-methyl amino acids compared to natural aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. The modified aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases according to the present invention can aminoacylate tRNAs with their corresponding N-methyl-substituted amino acids such as N-methyl-phenylalanine, N-methyl-valine, N-methyl-serine, N-methyl-threonine, N-methyl-tryptophan, and N-methyl-leucine more efficiently than natural aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. The present invention enables a more efficient production of polypeptides containing N-methyl amino acids.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
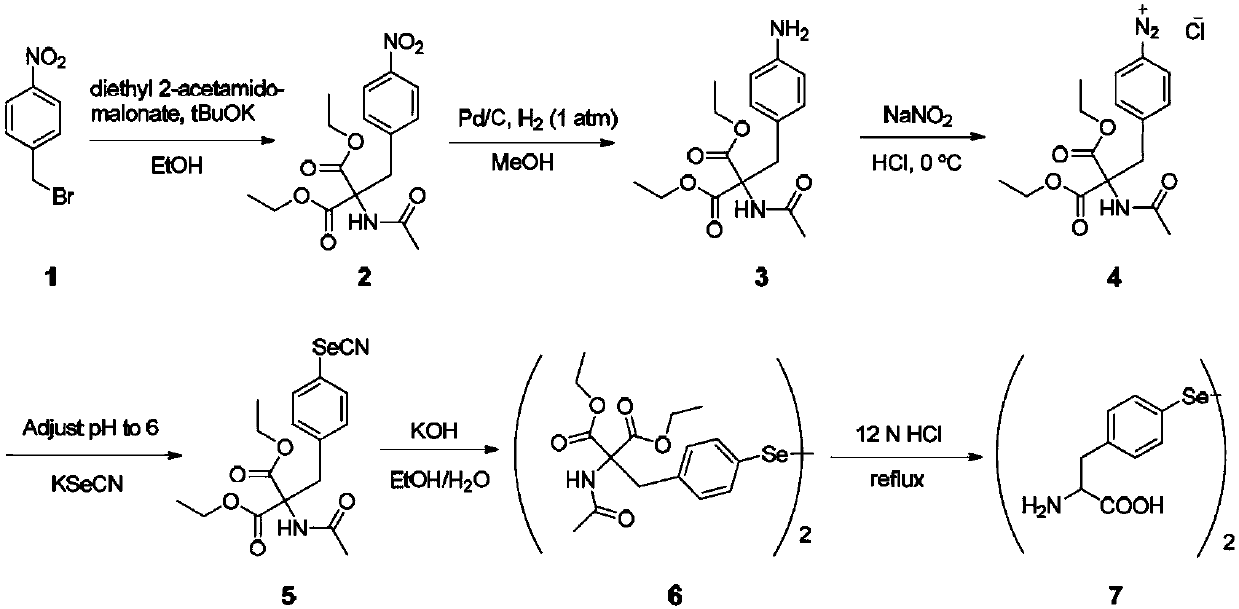
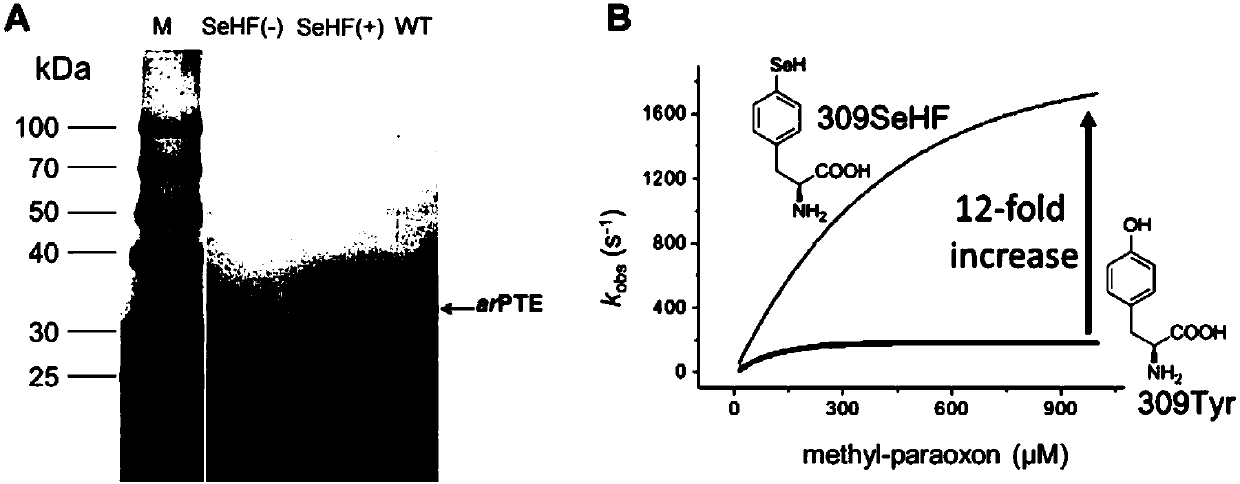
Selenotyrosine translation system and application thereof
ActiveCN110117580AIncrease enzyme activityHigh activityHydrolasesLigasesSystems designProtein target
The invention relates to an aminoacyl-tRNA synthase mutant, which is an orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthase. The amino acid sequence contained in the mutant is selected from the amino acid sequence shown in SEQIDNO:4 or its conservative variants or homologues with the same enzyme activity. The invention further provides a selenotyrosine translation system, which comprises (i) selenotyrosine, (ii) the orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase, (iii) orthogonal tRNA and (iv) nucleic acid for encoding target protein, wherein the orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase adopts the selenotyrosine for aminoacylation of the orthogonal tRNA preferentially, and the nucleic acid contains at least one selection codon for specifically recognizing the orthogonal tRNA. Moreover, the invention provides a method for modifying protease by utilizing the design of the selenotyrosine translation system and protease produced by encoding through the method.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
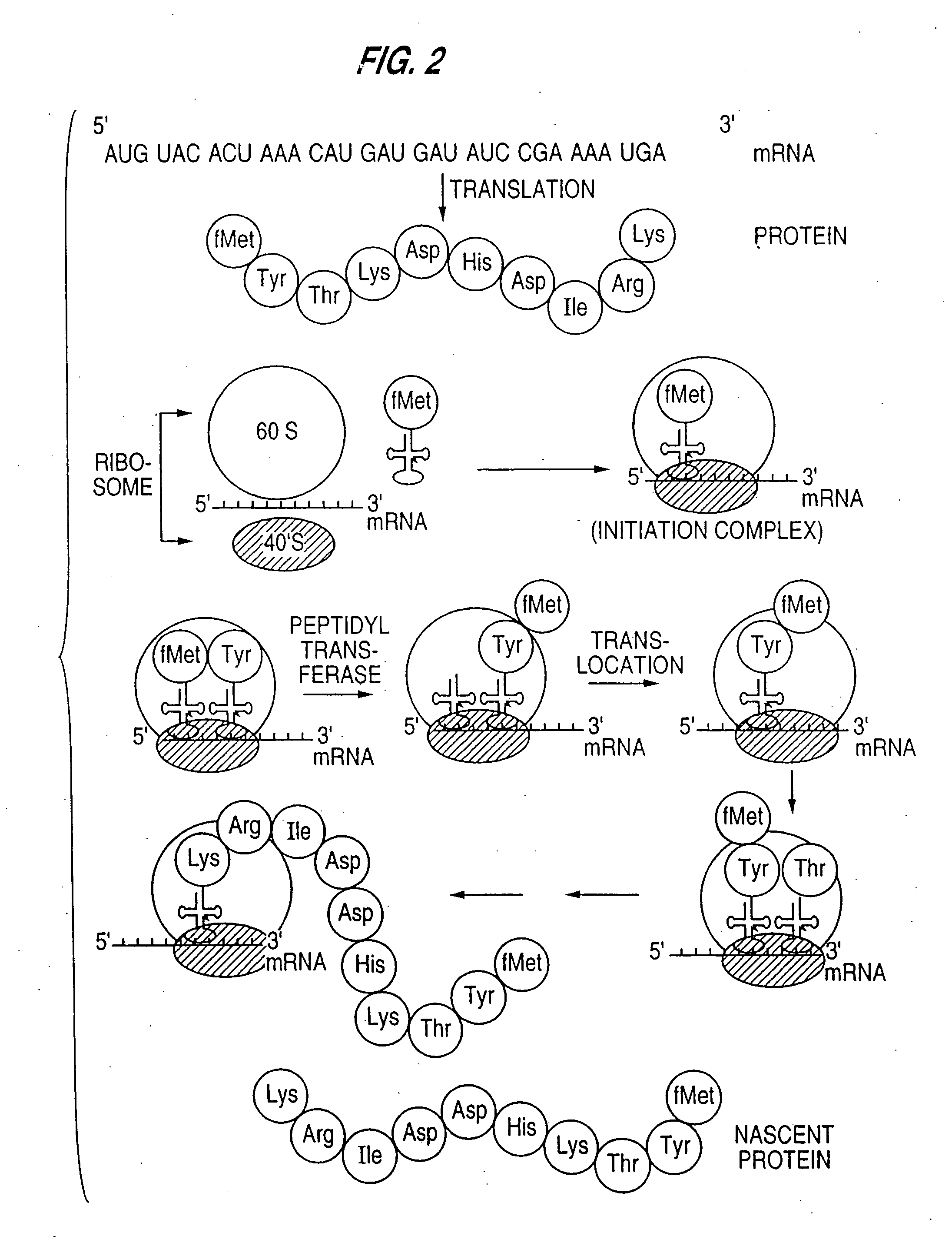
Detection of markers in nascent proteins
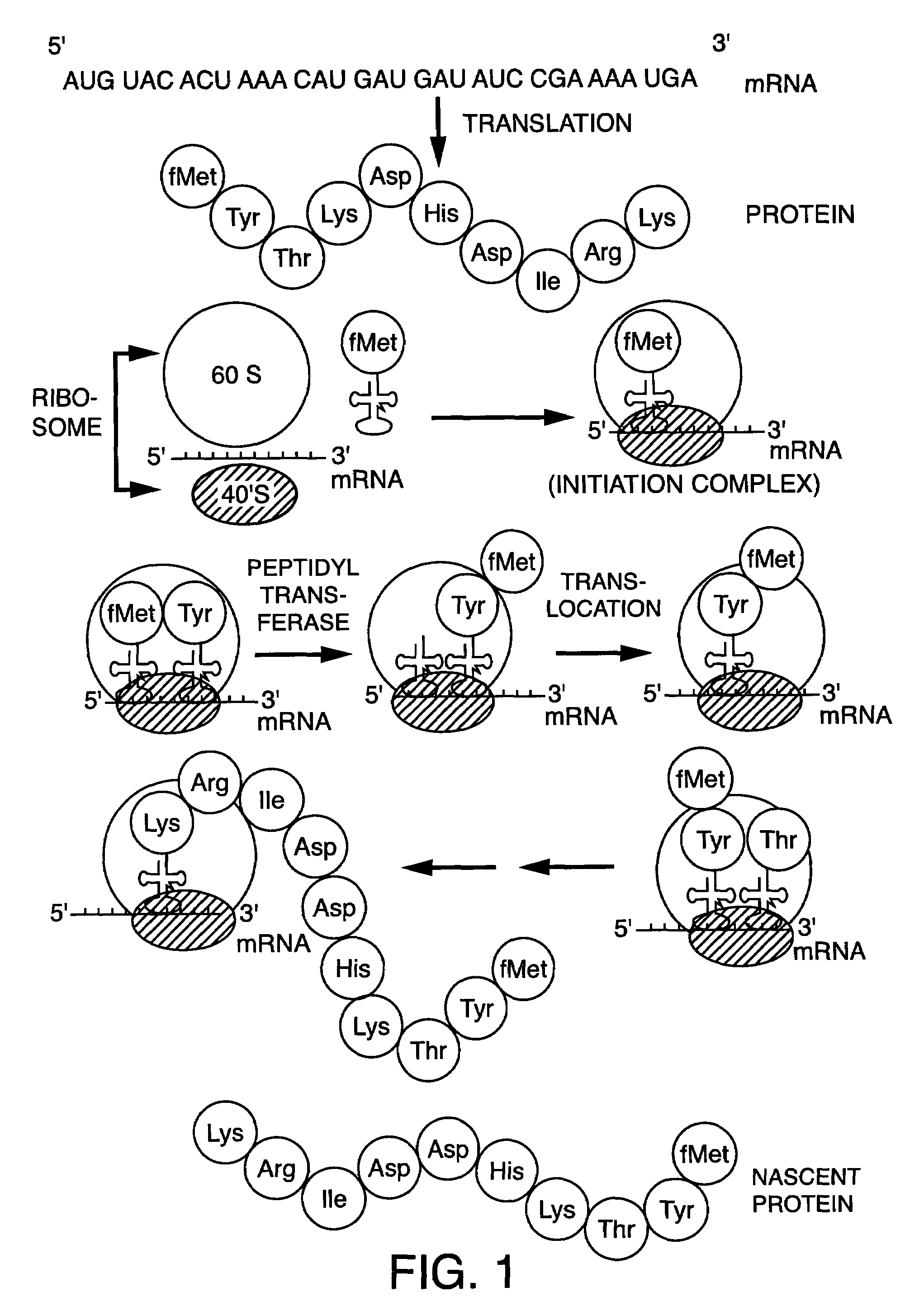
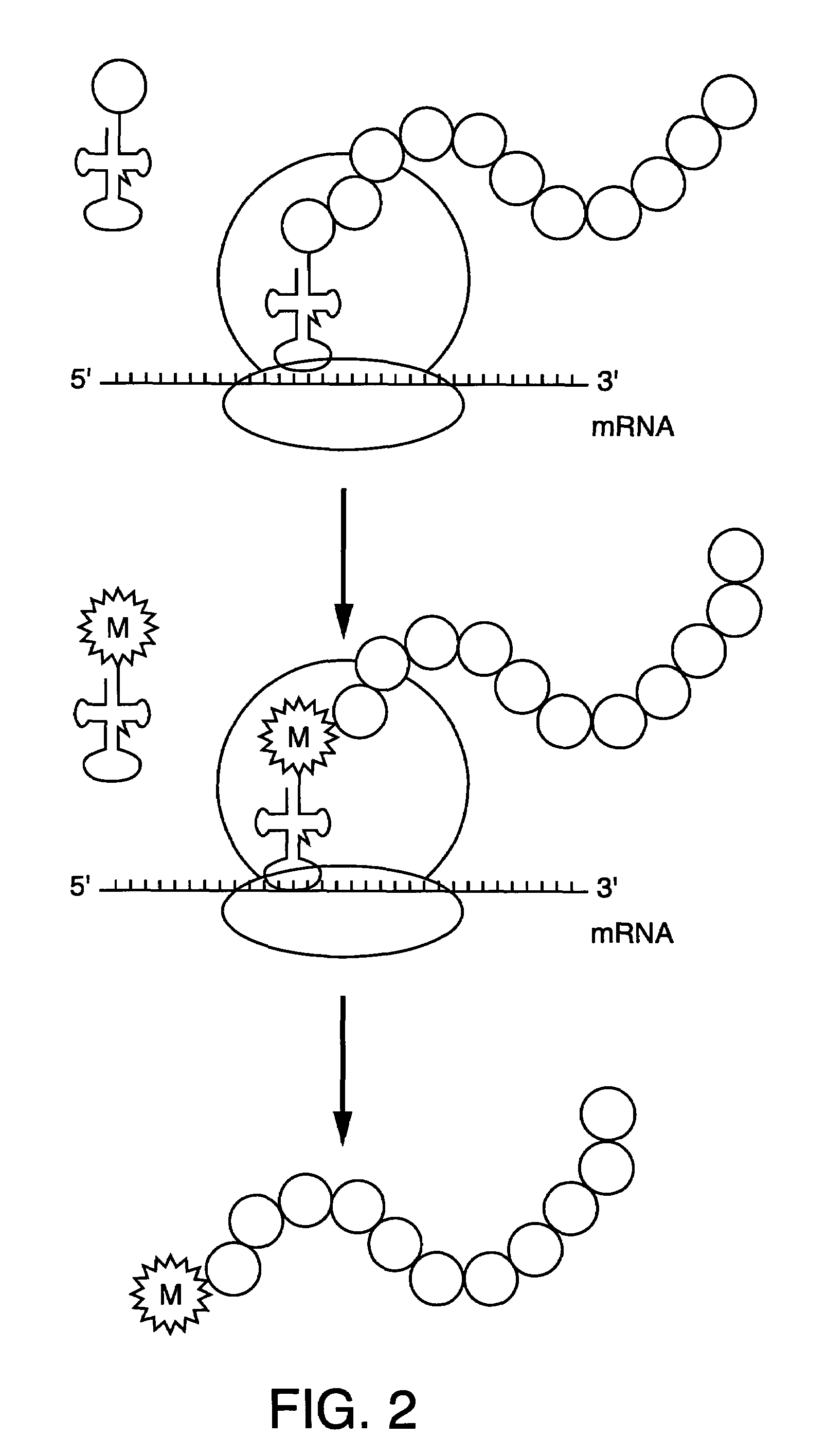
The invention is directed to methods for the non-radioactive labeling, detection, quantitation and isolation of nascent proteins translated in a cellular or cell-free translation system. tRNA molecules are misaminoacylated with non-radioactive markers which may be non-native amino acids, amino acid analogs or derivatives, or substances recognized by the protein synthesizing machinery. Markers may comprise cleavable moieties, detectable labels, reporter properties wherein markers incorporated into protein can be distinguished from unincorporated markers, or coupling agents which facilitate the detection and isolation of nascent protein from other components of the translation system. The invention also comprises proteins prepared using misaminoacylated tRNAs which can be utilized in pharmaceutical compositions for the treatment of diseases and disorders in humans and other mammals, and kits which may be used for the detection of diseases and disorders.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
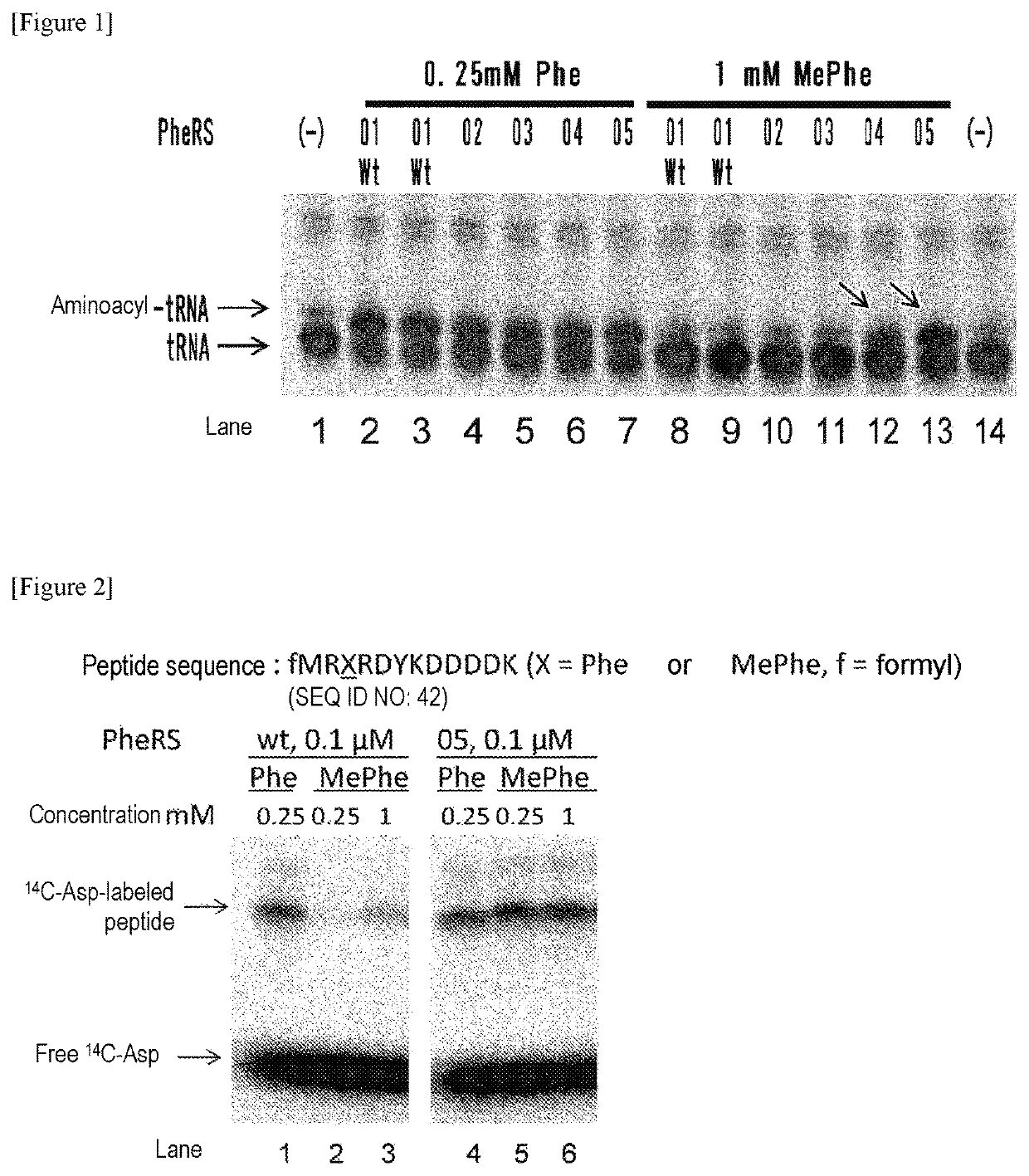
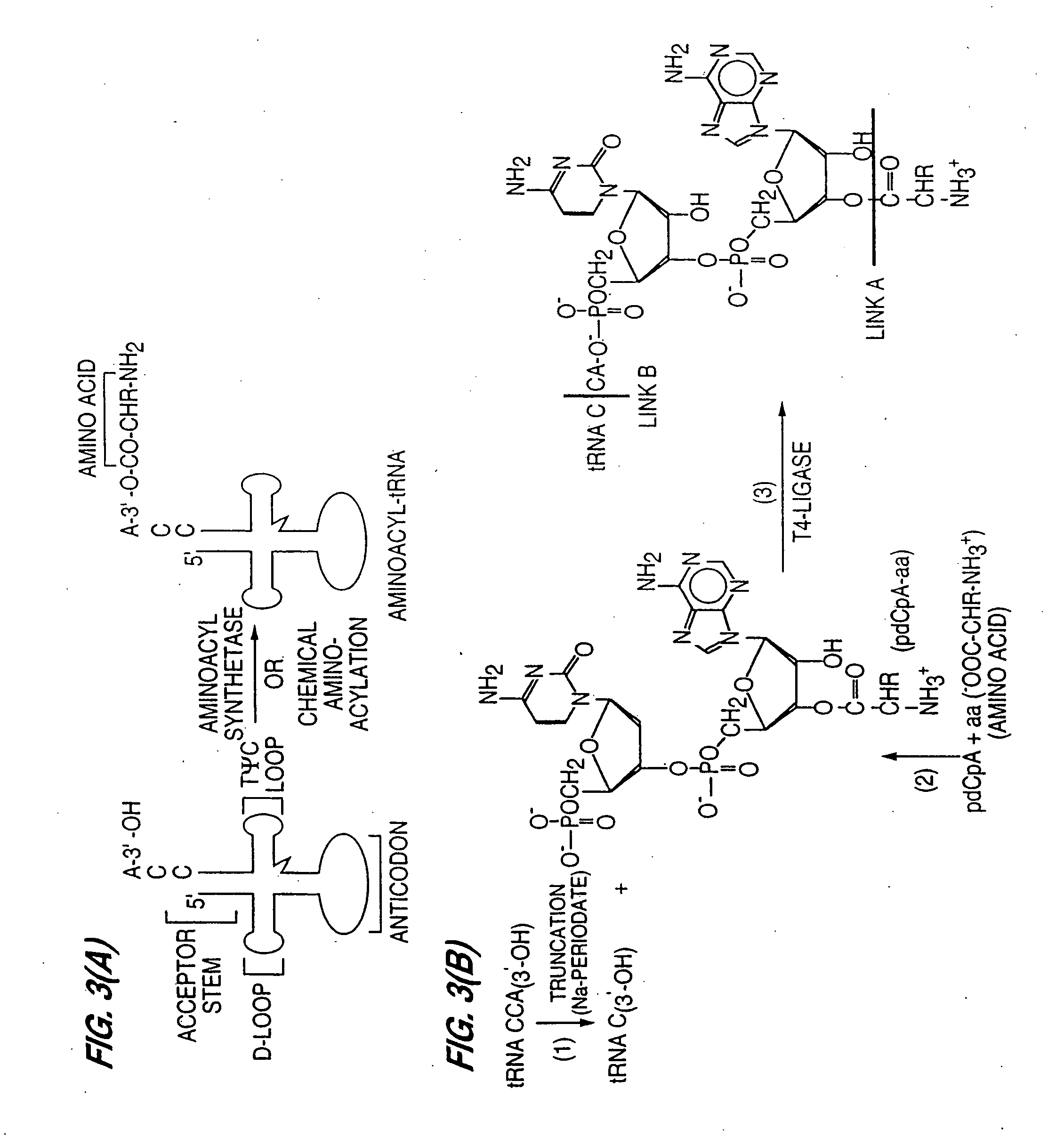
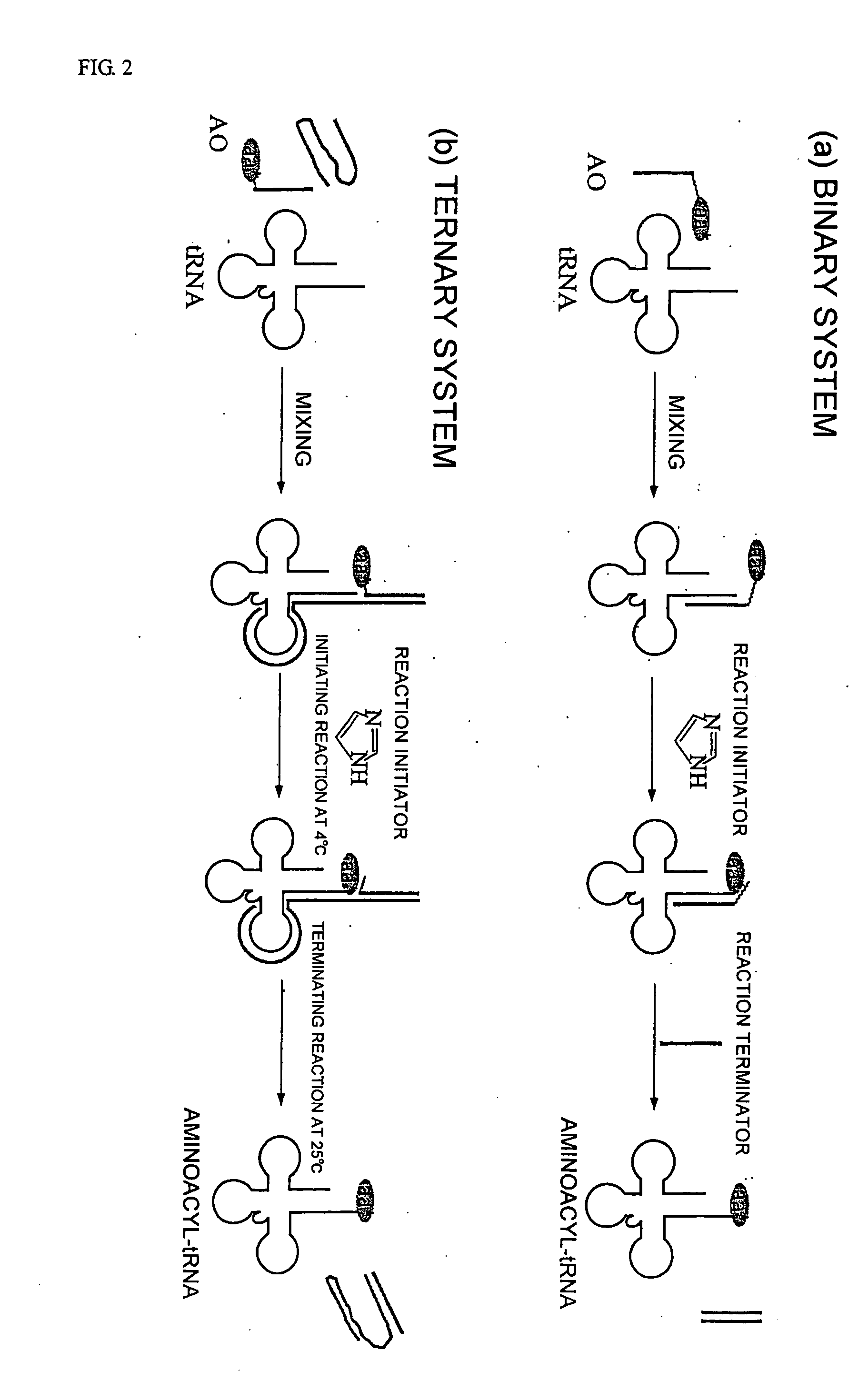
Method of aminoacylating trna
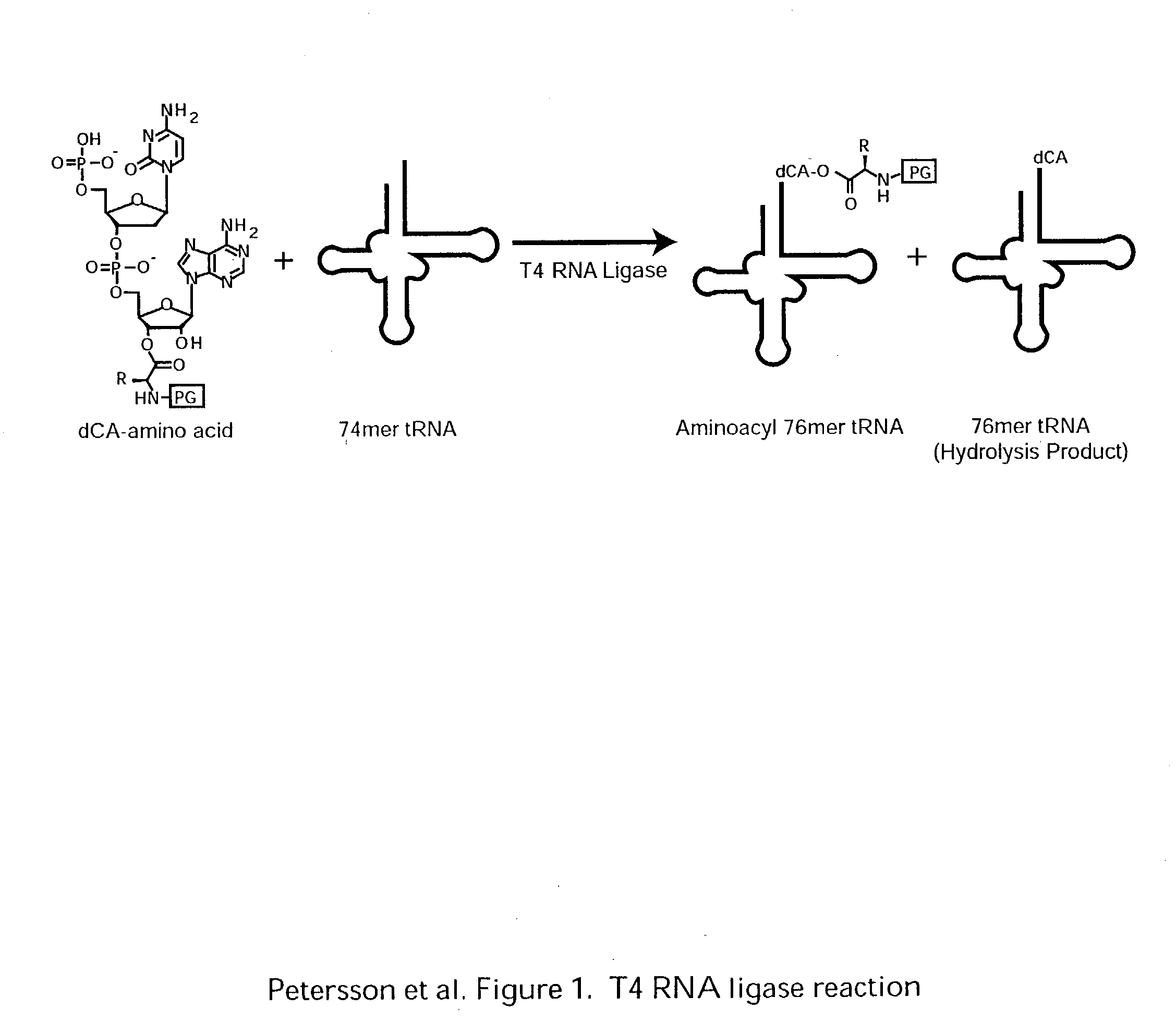
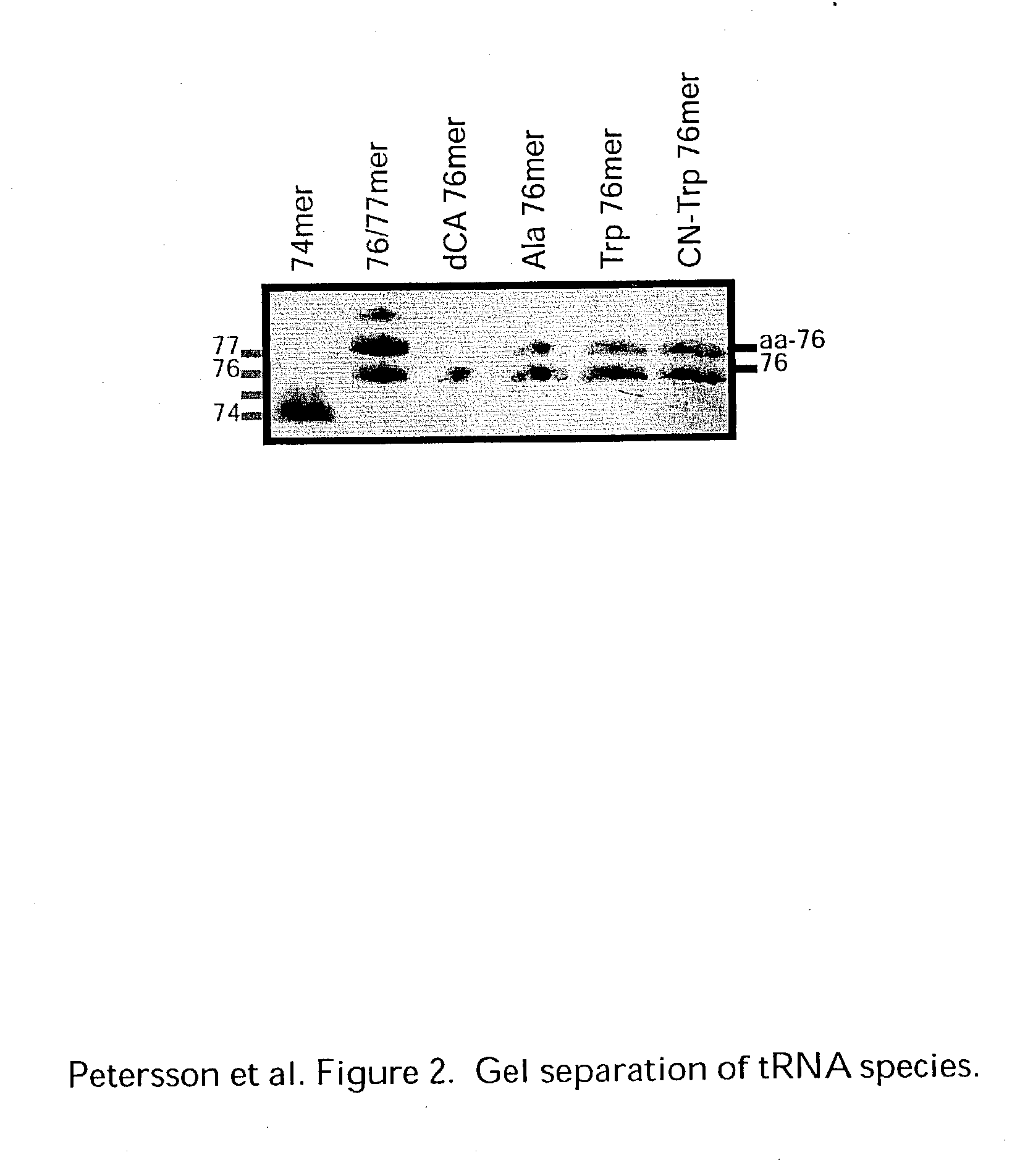
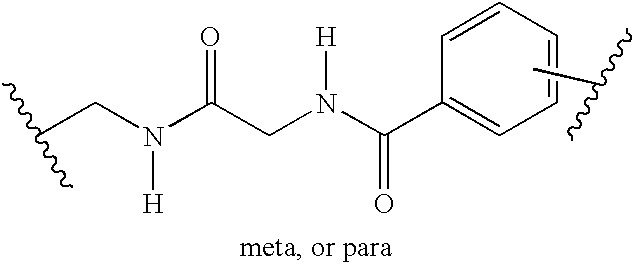
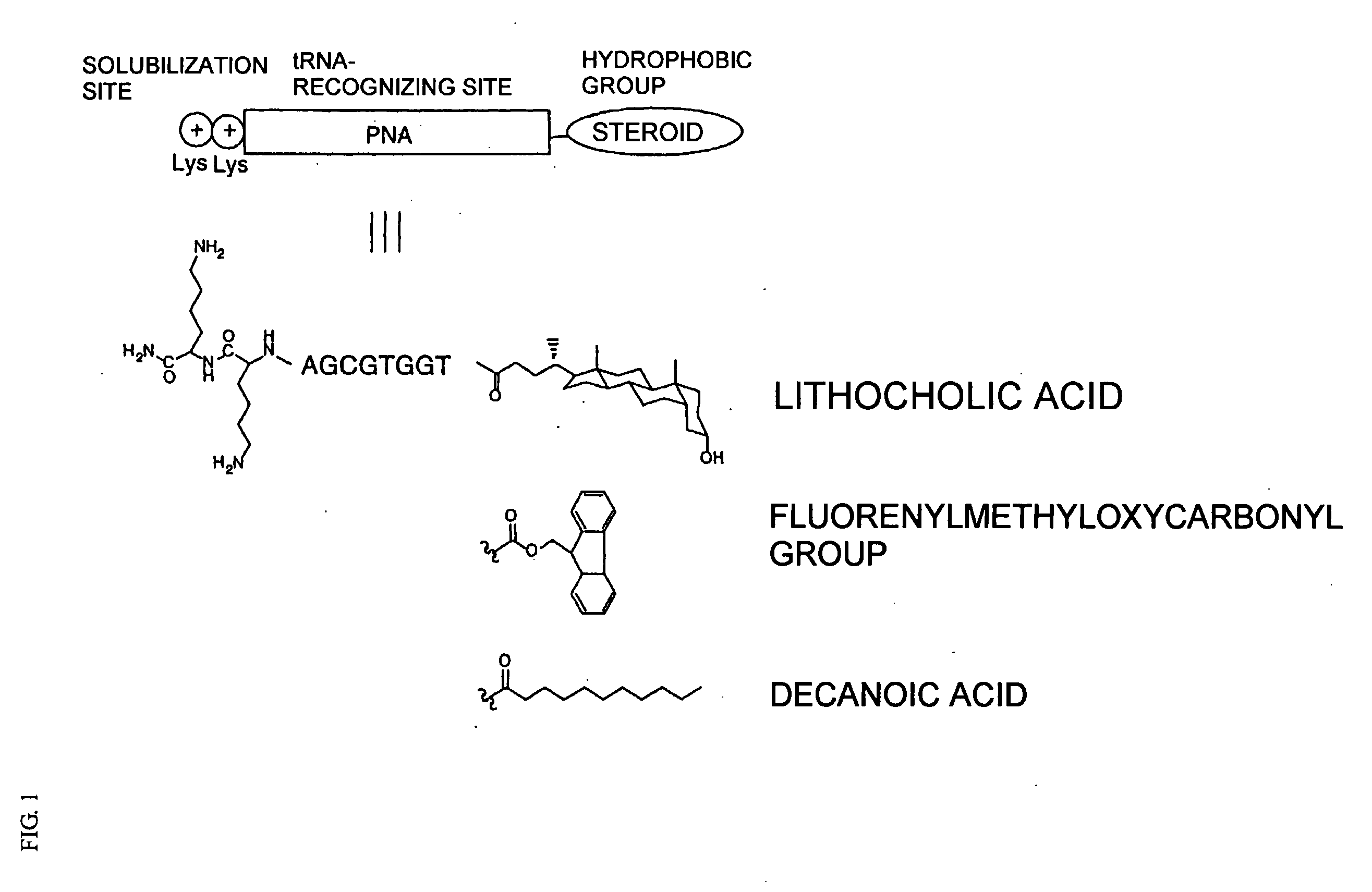
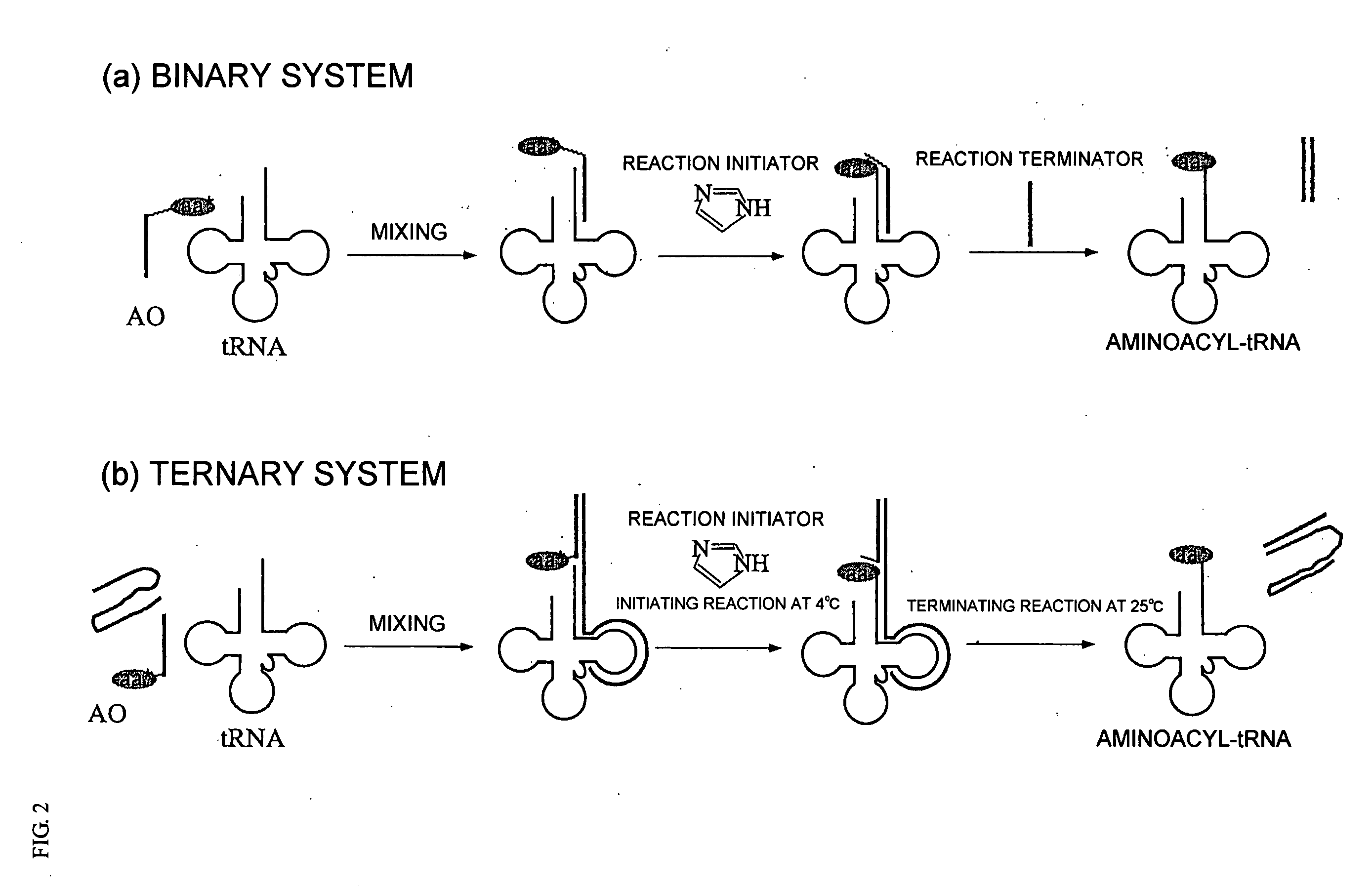
InactiveUS20060020111A1Efficient and highly practicalSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsChemical synthesisAminoacyl-tRNA
It is intended to provide a method of chemically synthesizing an aminoacyl tRNA which is completely different from the existing methods, namely, a highly efficient and practically usable method for synthesizing an aminoacyl tRNA whereby any nonnatural amino acid can be conveniently aminoacylated without a need for genetic engineering techniques and detected without resort to a radioactive isotope. The above-described aminoacylation method comprises enclosing a tRNA and an amino acid in the vicinity of the micelle-water interface and bringing them close to each other to thereby react the same, or providing between them a peptide nucleic acid specifically binding to the tRNA as an antisense molecule and bringing them close to each other to thereby react the same.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
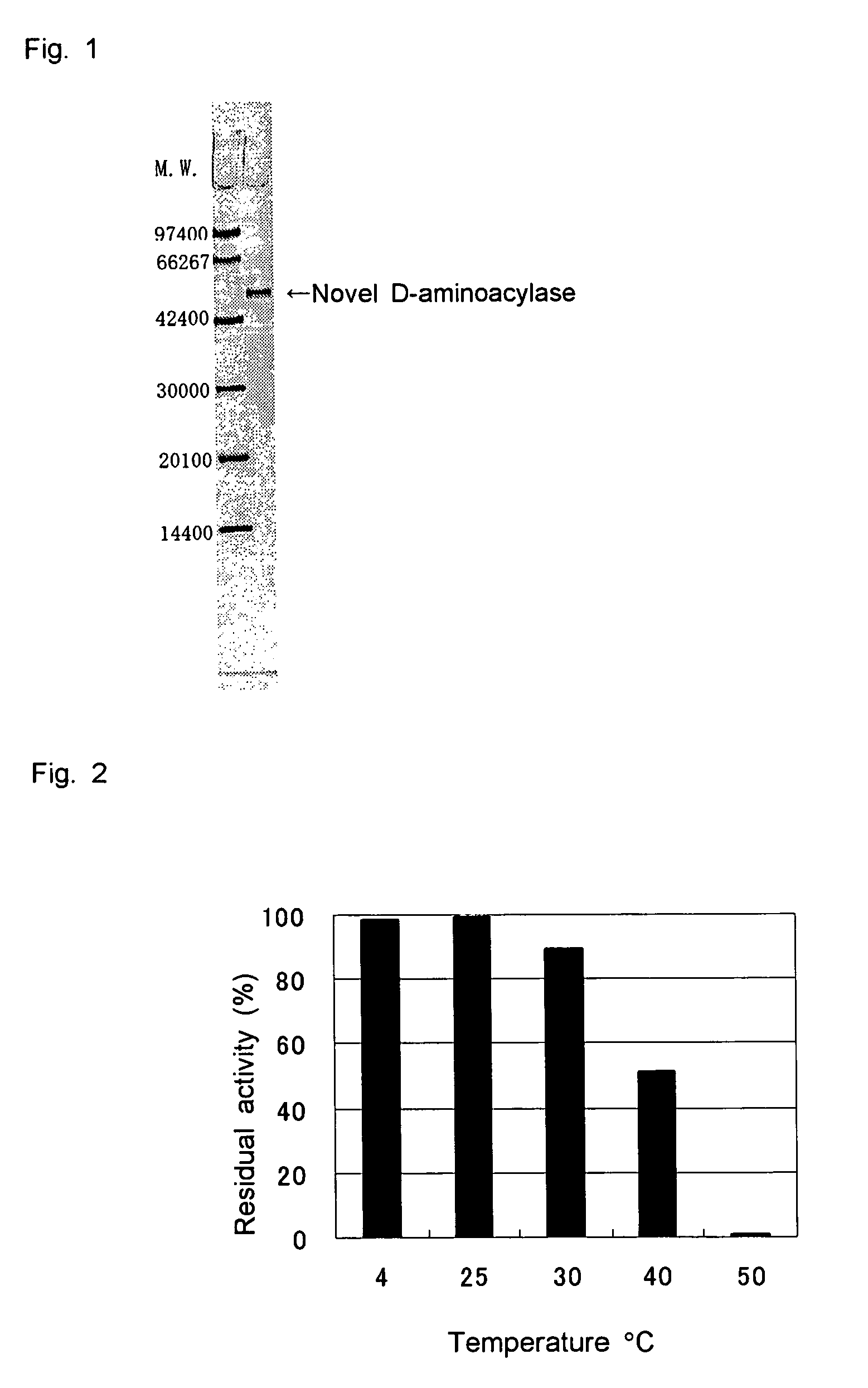
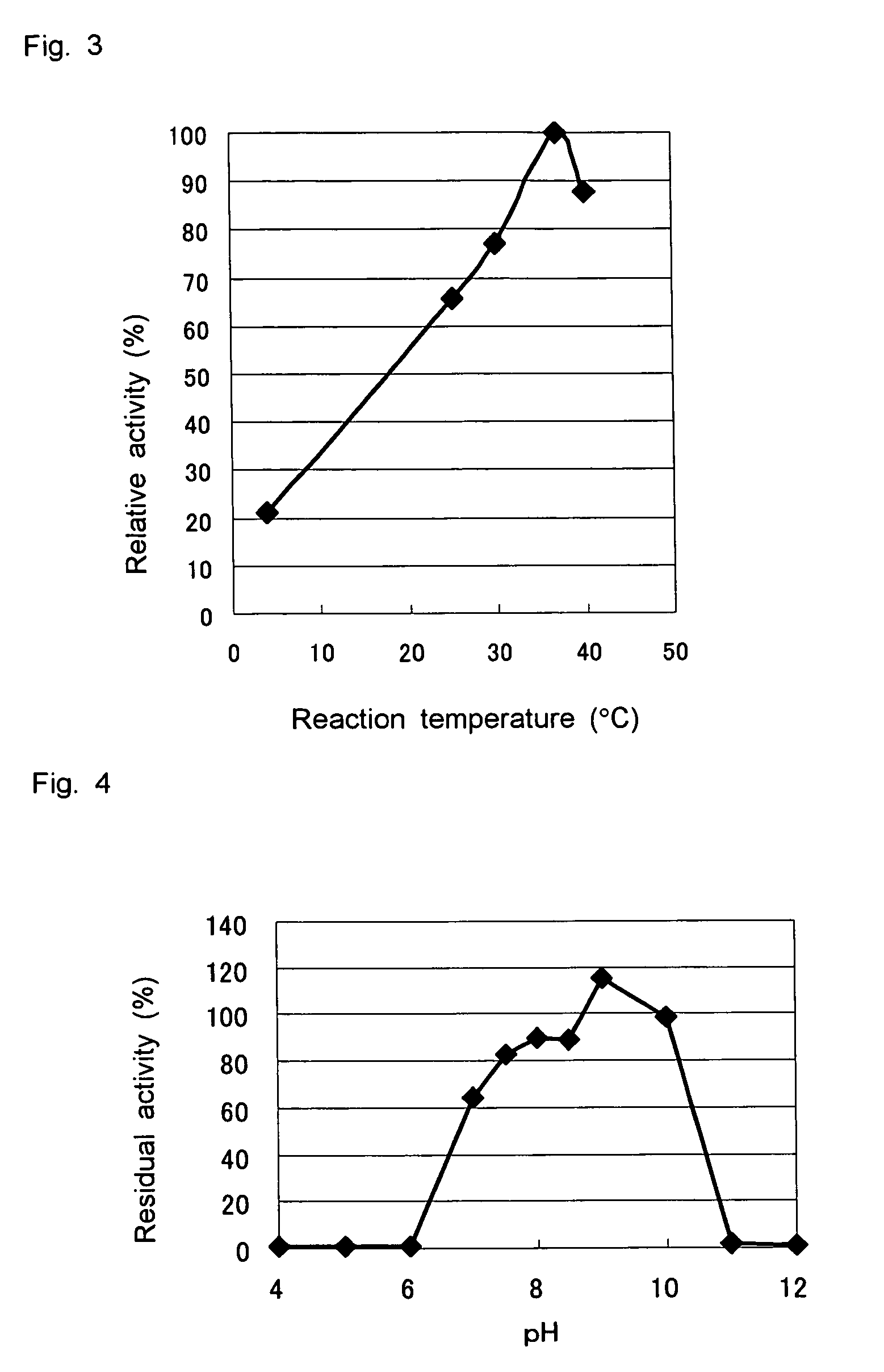
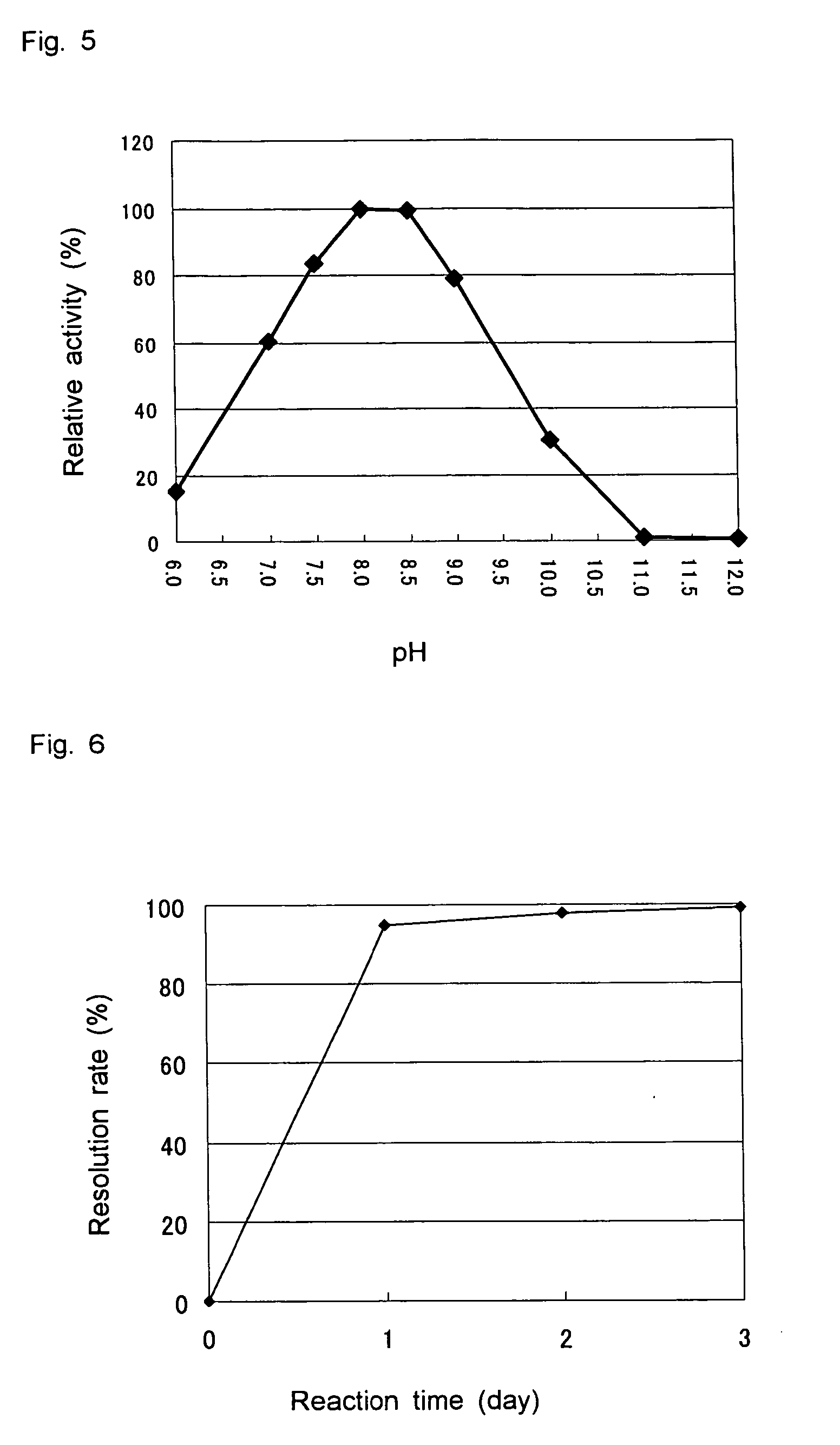
D-aminoacylase
A D-aminoacylase having a high substrate specificity is provided. This D-aminoacylase can produce D-amino acids from N-acetyl-D,L-amino acids conveniently and efficiently at a low cost. A D-aminoacylase produced by a microorganism of genus Defluvibacter; which acts on a N-acetyl-D-amino acid; which has a molecular weight (as determined by electrophoresis) of about 55,000 daltons, and an isoelectric point (as determined by two-dimensional electrophoresis for denatured system) of 5.3; which acts on N-acetyl-D-valine, N-acetyl-D-leucine, and the like, but not on N-acetyl-L-valine, N-acetyl-L-leucine, and the like; which has an optimal temperature of 37° C. (pH 8) and an optimal pH value of 8 to 8.5 at 37° C.; and whose activity is inhibited by Mn2+, Co2+, Ni2+, and Zn2+ each at 1 mmol / L, and by dithiothreitol, 2-mercaptoethanol, o-phenanthroline, and L-cysteine each at 5 mmol / L.
Owner:SEKISUI MEDICAL CO LTD +1
Ribozyme with tRNA synthetase activity and methods of manufacturing and using the same
Ribozymes exhibiting tRNA synthetase activity and substrate specificity, as well as methods for engineering and producing the same, are disclosed. The ribozymes of the present disclosure comprise a T-box RNA module fused with a flexizyme module. The flexizyme module provides high promiscuity with respect to amino acid substrates and the T-box module provides tRNA substrate specificity. Systems are also described for aminoacylation of suppressor tRNAs with unnatural amino acids (uAAs), such systems comprising the ribozyme previously mentioned, suppressor tRNA, and the desired uAAs. Methods for incorporating a uAA into a growing polypeptide chain using the ribozyme hereof are also provided.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC +1
3,5-Difluorotyrosine translation system and its application
ActiveCN104004723BElucidating dynamic propertiesShort manufacturing timeBacteriaTransferasesProtein targetTyrosine
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
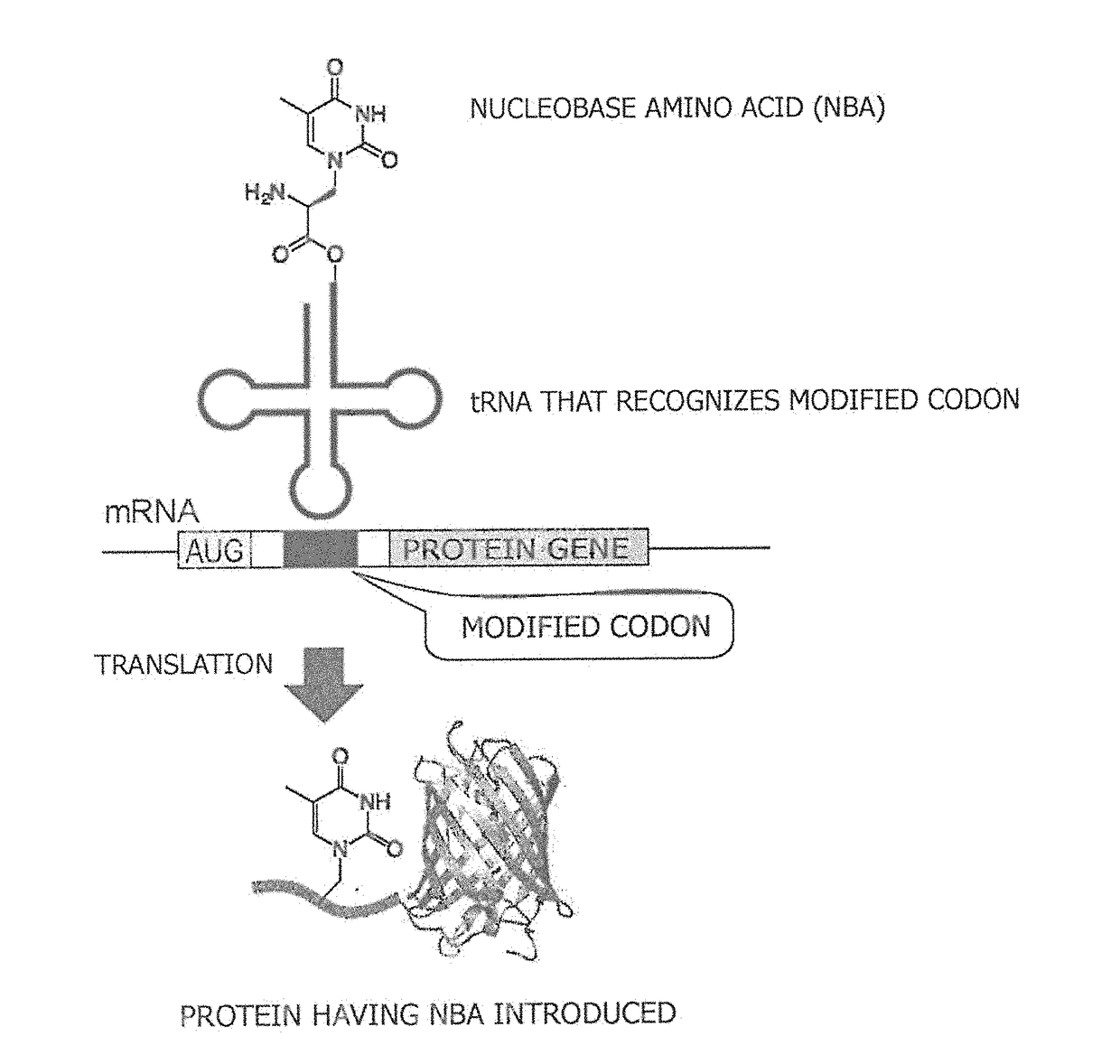
Amino acid-modified nucleic acid and utilization thereof
ActiveUS20180251759A1Improve efficiencyImprove purification efficiencyEnzymesFusion with protease siteBase JStart codon
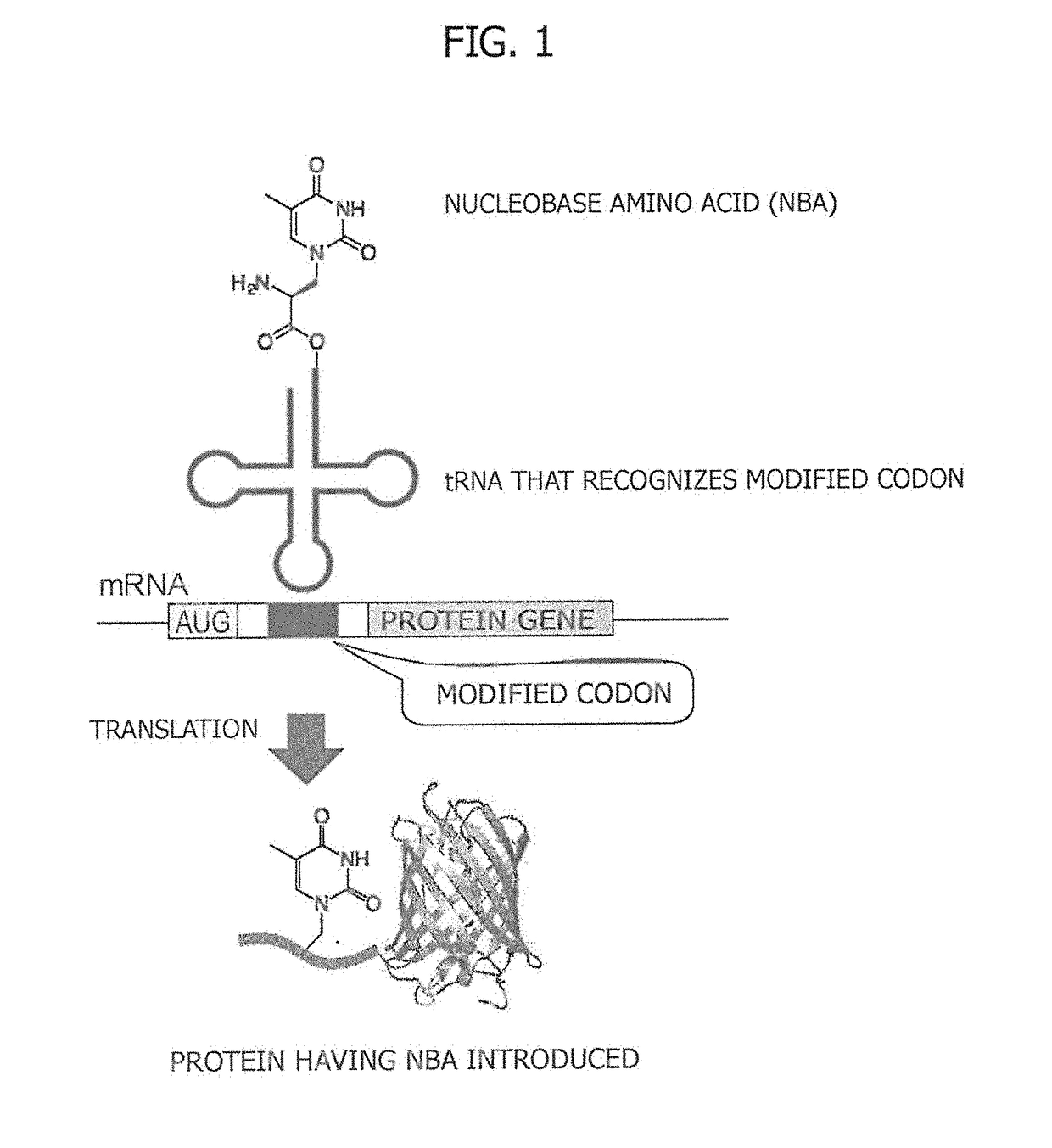
Provided is a method for synthesizing a protein, into which a nucleobase amino acid (NBA) is introduced at a desired position, that comprises: a step for preparing mRNA into which a modified codon is inserted at a desired position downstream of an initiation codon; and a step for translating the aforesaid mRNA into a protein in the presence of tRNA, said tRNA recognizing the modified codon and being acylated with the NBA. Also provided is a ribozyme that catalyzes the aminoacylation of tRNA and comprises two RNA molecules.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
A kind of preparation method of 3-phthalimide-2-oxygen-n-butyraldehyde bisthiosemicarbazide
The invention relates to a preparation method of 3-phthalimide-2-oxy-n-butyraldehyde thiosemicarbazide (I). The preparation method comprises the steps: adopting alanine and N-ethoxycarbonyl phthalimide as a starting material, and performing aminoacylation, methyl-lithium addition, an oxidation reaction and a condensation reaction so as to obtain the target product 3-phthalimide-2-oxy-n-butyraldehyde thiosemicarbazide (I). The method for synthesizing 3-phthalimide-2-oxy-n-butyraldehyde thiosemicarbazide has the advantages of few reaction steps, simple operation, suitability for large-scale production and the like.
Owner:HUAIBEI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
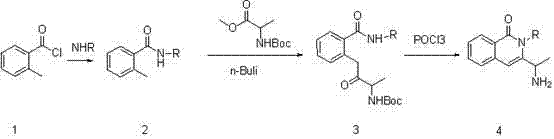
Synthesis of 3-(1-aminoethyl)-2-cyclobutyl-2-hydro-isoquinolin-1-one compound
In the prior, the conventional 3-(1-aminoethyl)-2-cyclobutyl-2-hydro-isoquinolin-1-one compound synthesis method has disadvantages of low yield, harsh conditions, and difficult purification. Based on the disadvantages in the prior art, the present invention provides a synthesis route for synthesizing a 3-(1-aminoethyl)-2-cyclobutyl-2-hydro-isoquinolin-1-one compound, wherein o-toluoyl chloride is adopted as a starting raw material, and is subjected to different aminoacylation, butyl lithium is adopted to carry out dehydrogenation on hydrogen on the methyl group, the resulting material is substituted with a protected amino acid ester, and finally a phosphorusoxychloride one-pot cooking method is adopted to obtain the final product, such that the whole process is easy to operate, the product is easy to purify, the method is suitable for industry, and raw material cost is substantially reduced.
Owner:CGENETECH (SUZHOU CHINA) CO LTD
Transamidation reaction in deep eutectic solvents
Herein is reported a method for the enzymatic production of a polypeptide comprising the step of incubating i) a first polypeptide comprising the amino acid sequence LPXTG (SEQ ID NO: 01, wherein X can be any amino acid residue) or LPXTA (SEQ ID NO: 41, wherein X can be any amino acid residue), ii) a second polypeptide that has i) a glycinyl, an alaninyl, or a cysteinyl compound at its N-terminus, or ii) an oligoglycine, or oligoalanine, or a cysteine amino acid residue followed by one to three glycine or alanine amino acid residues at its N-terminus, or iii) a lysine amino acid residue within its 5 N-terminal amino acid residues, and iii) a third polypeptide with sortase A activity, in a deep eutectic solvent and thereby producing a polypeptide.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE INC
nε-(1-methylcycloprop-2-enamide)-lysine translation system and its application
ActiveCN103667202BValid markEfficient expressionBacteriaHaemoglobins/myoglobinsMutated proteinProtein target
The invention relates to an aminoacyl-tRNA (transfer ribonucleic acid) synthetase mutant containing an amino acid sequence selected from groups consisting of amino acids shown by SEQ ID NO:4 and conservative variants thereof. The invention provides a CpK (short for N<epsilon>-(1-methylcyclopropyl-2-acrylamide)-lysine) translation system for fixed point specific insertion of N<epsilon>-(1-methylcyclopropyl-2-acrylamide)-lysine in a target protein through pairing of orthogonal tRNA and orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase, and a method for fixed point specific insertion of CpK in the target protein by using the translation system. The CpK translation system comprises (i) N<epsilon>-(1-methylcyclopropyl-2-acrylamide)-lysine, (ii) the orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase, (iii) the orthogonal tRNA and (iv) a nucleic acid for coding the target protein, wherein the orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase is used for realizing aminoacylation of the orthogonal tRNA preferentially by using CpK, and the nucleic acid contains at least one selective codon specifically identified by the orthogonal tRNA. The invention also relates to an application of a mutant protein for fixed point specific insertion of CpK in protein labeling through a light click reaction with a tetrazole compound.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
Method of aminoacylating tRNA
InactiveUS20080096259A1Efficient and highly practicalSugar derivativesFermentationChemical synthesisAminoacyl-tRNA
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com