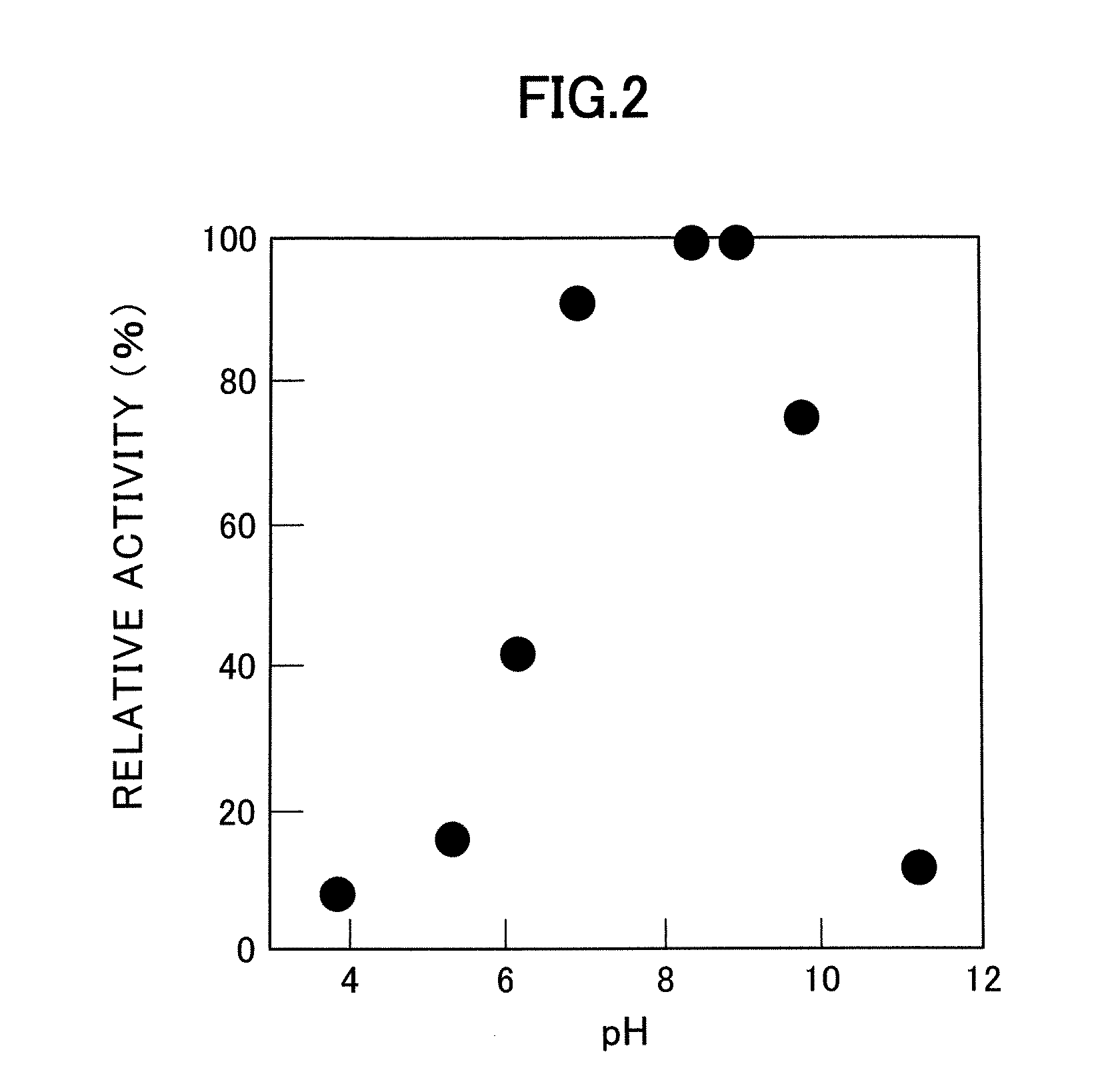
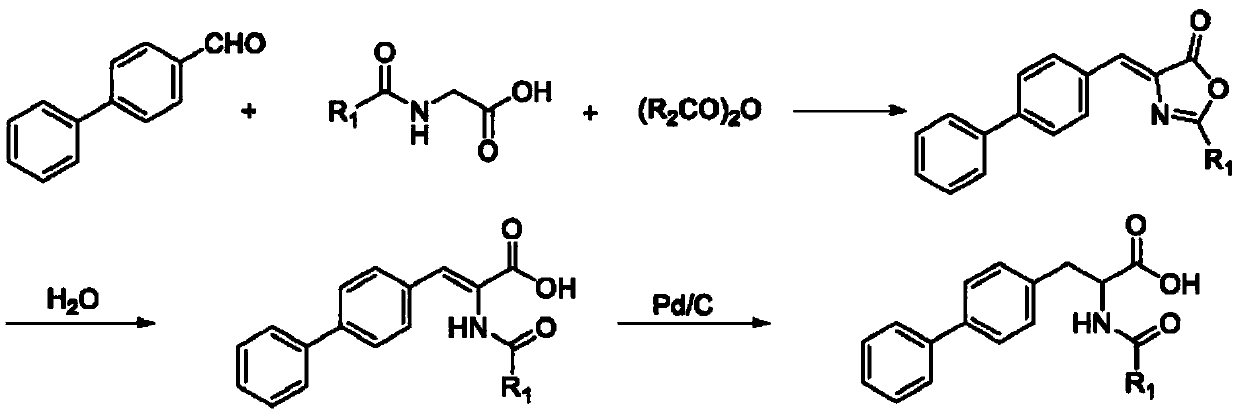
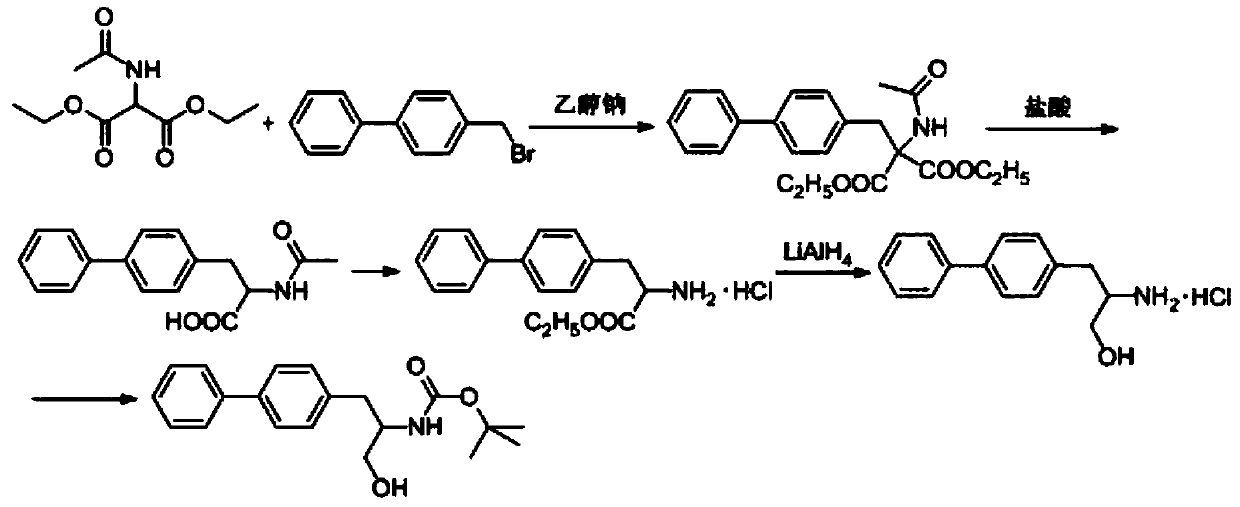
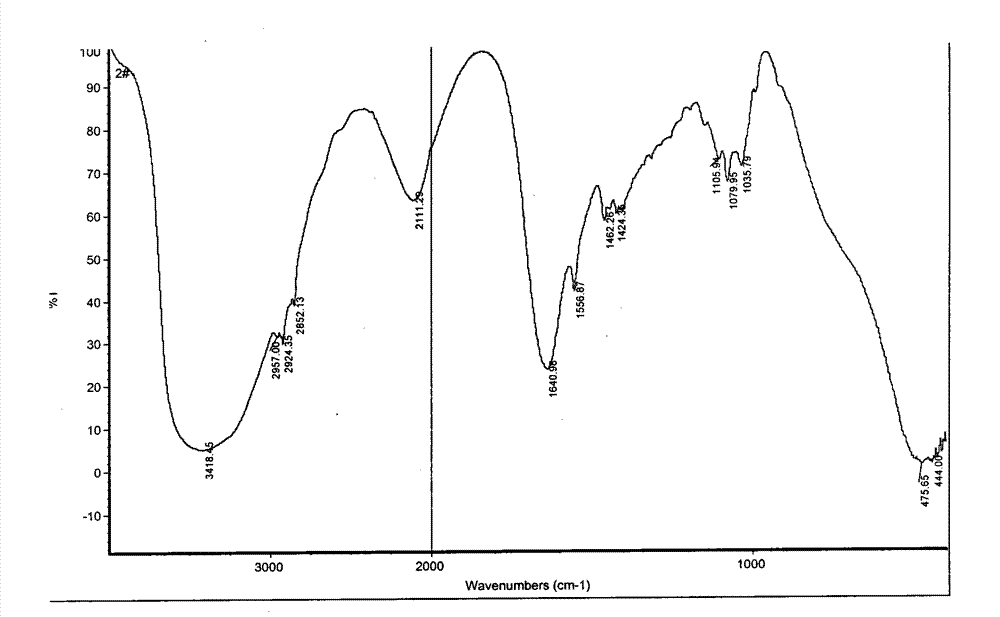
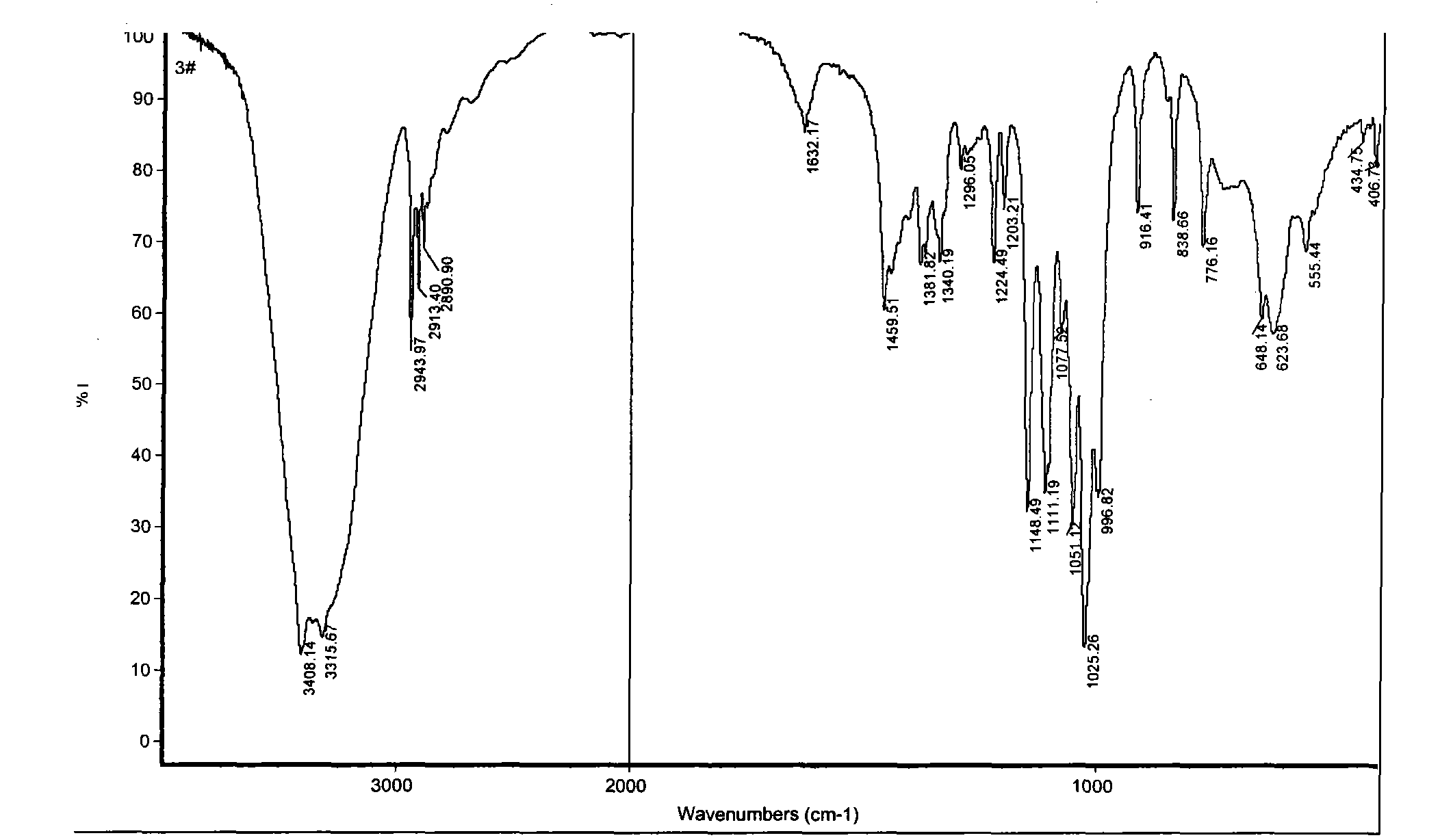
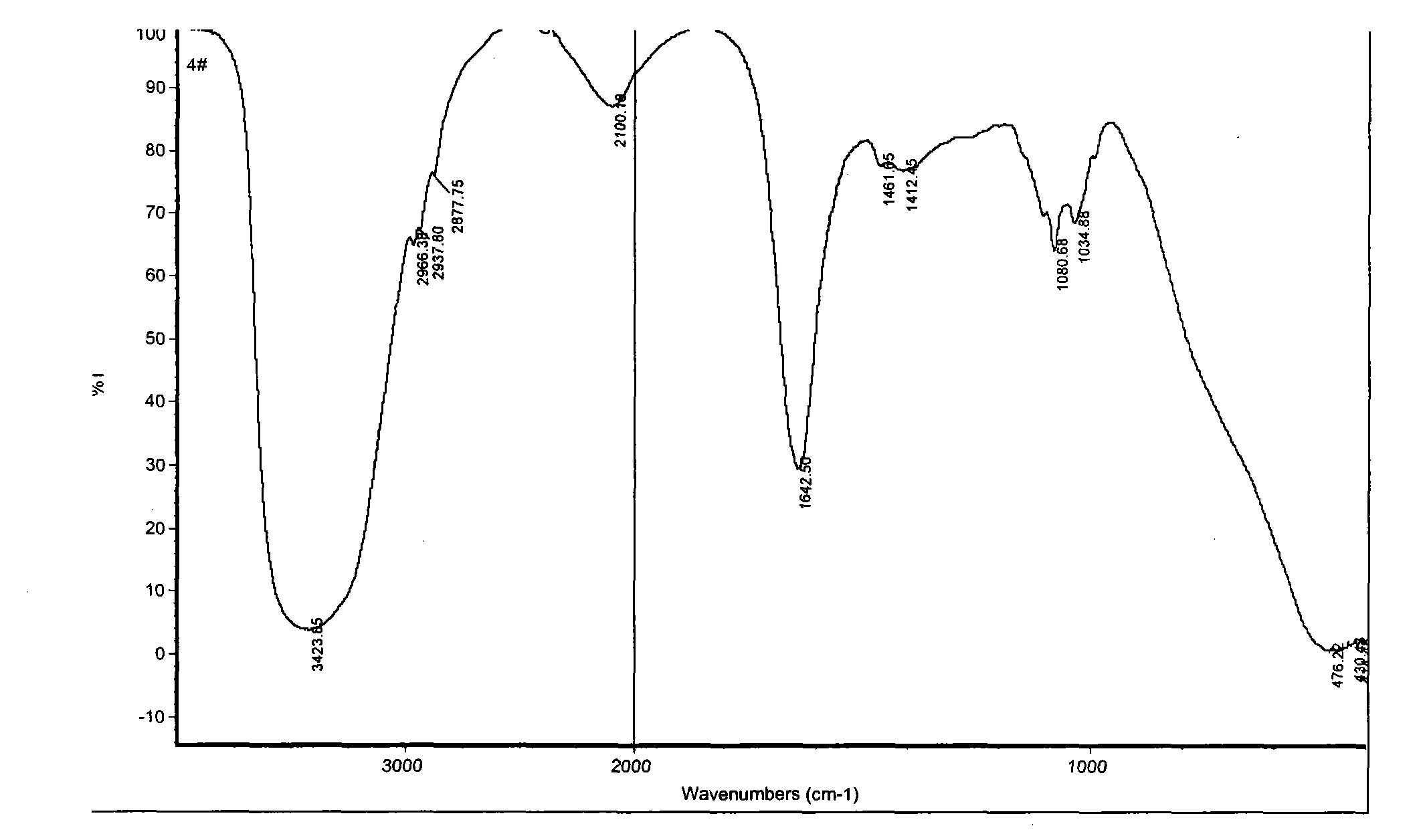
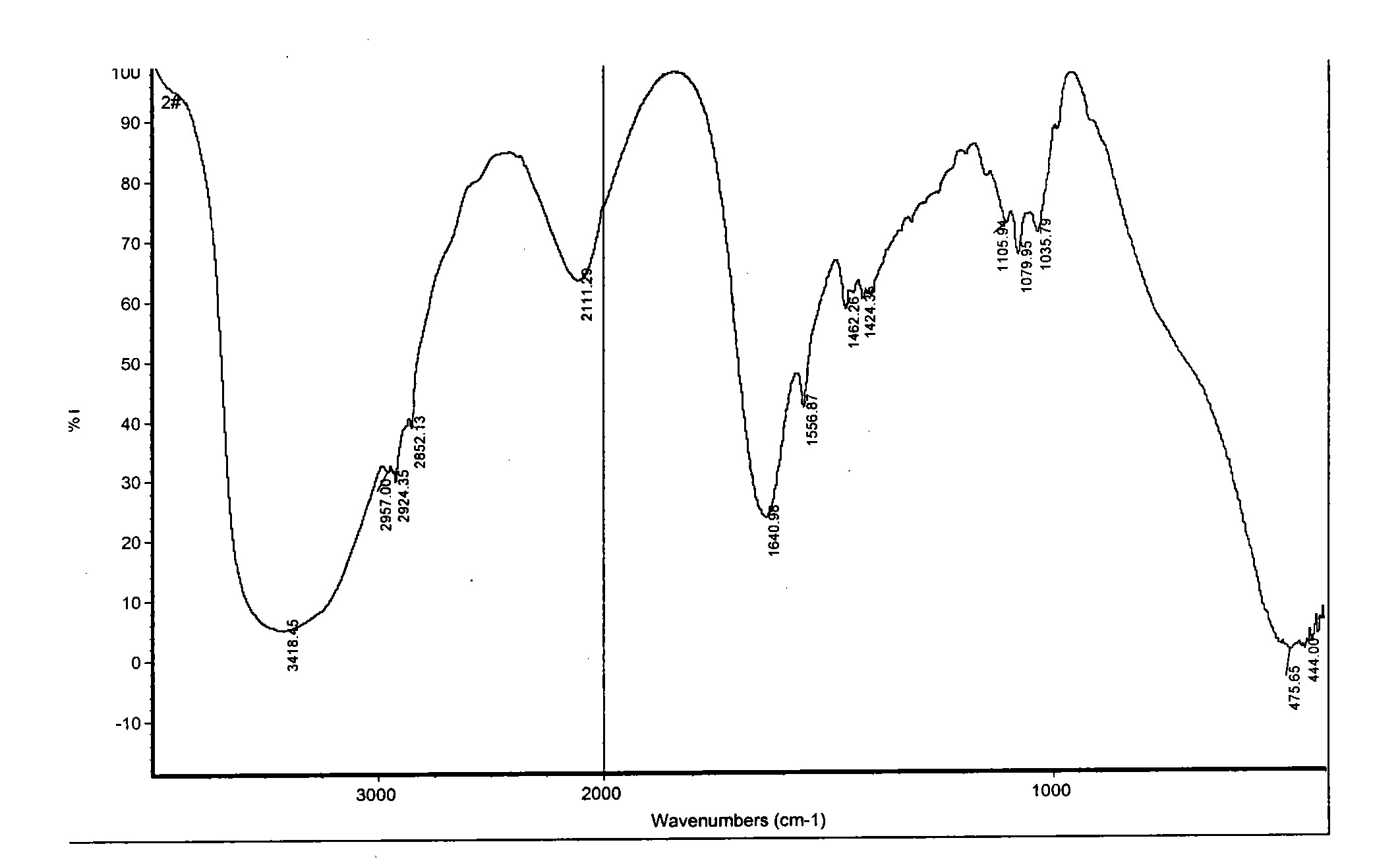
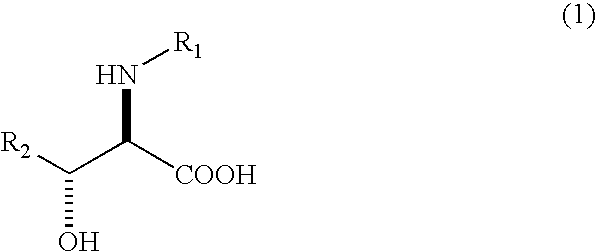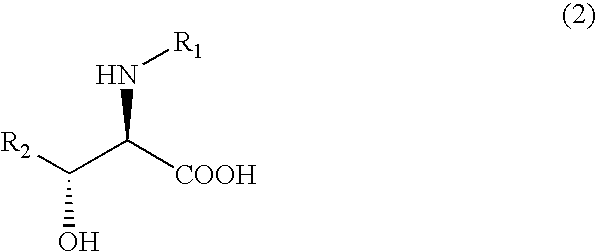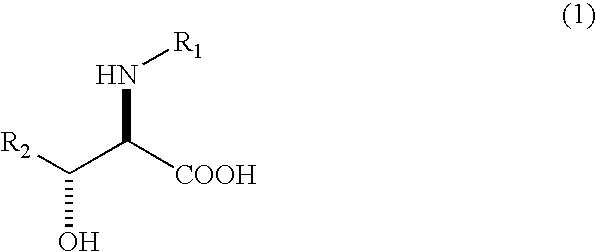Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
40 results about "Aminoacylase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In enzymology, an aminoacylase (EC 3.5.1.14) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction...
Method for synthesizing theanine
InactiveCN101597239ALow priceReduce manufacturing costOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid amides preparationL-theanineReaction speed
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing theanine, which comprises the following steps: aminating L-N-acyl glutamic acid-gamma-ester in 70-percent ethylamine aqueous solution to obtain L-N-acyltheanine; hydrolyzing the L-N-acyltheanine by adopting L-aminoacylase to remove the acyl group of the L-N-acyltheanine; and performing separation in ethanol aqueous solution to obtain high-quality L-theanine. The method combines the advantages of industrialized acyl hydrolyzation by the L-aminoacylase, uses cheap acyl group as a protective group, and uses the L-aminoacylase to hydrolyze the acyl group after reaction with the ethylamine aqueous solution to obtain the L-theanine. The method has the characteristics of low raw material price, low production cost, high selectivity, high reaction speed and high yield. The used raw materials and reagents are suitable for industrial production, the operation process is simple, and the product quality can be ensured.
Owner:TIANJIN PHARMA GROUP CORP
Novel coumarin derivative for detection of cysteine and process for the synthesis thereof
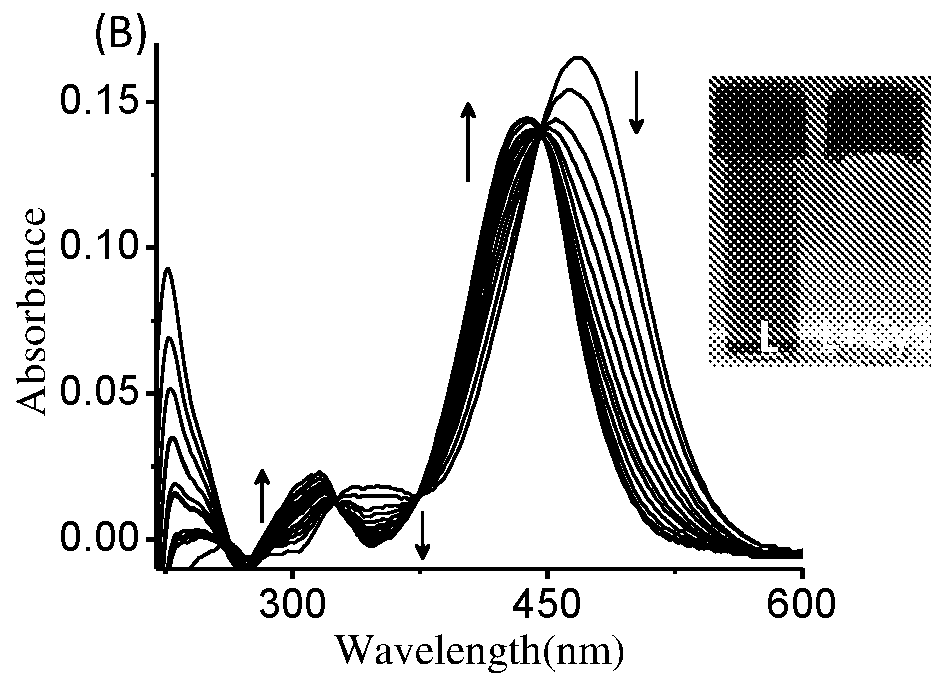
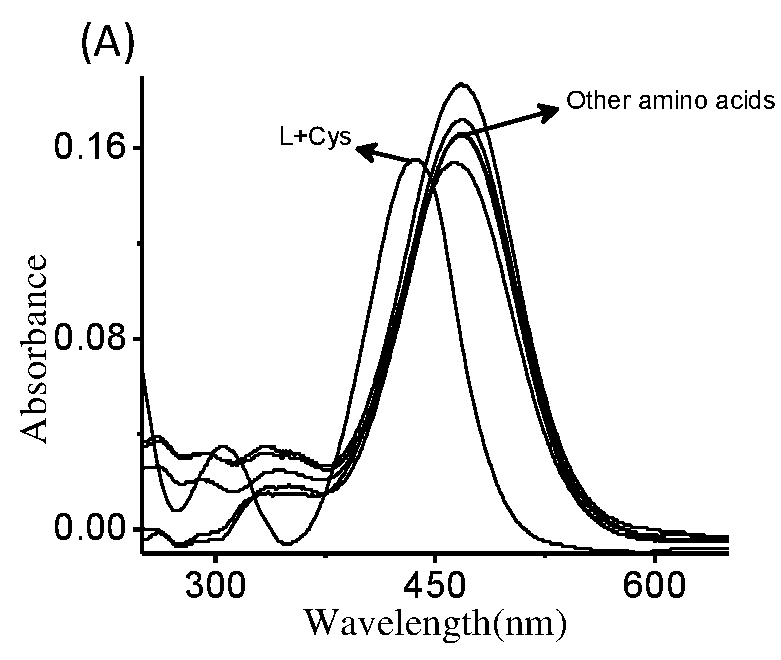
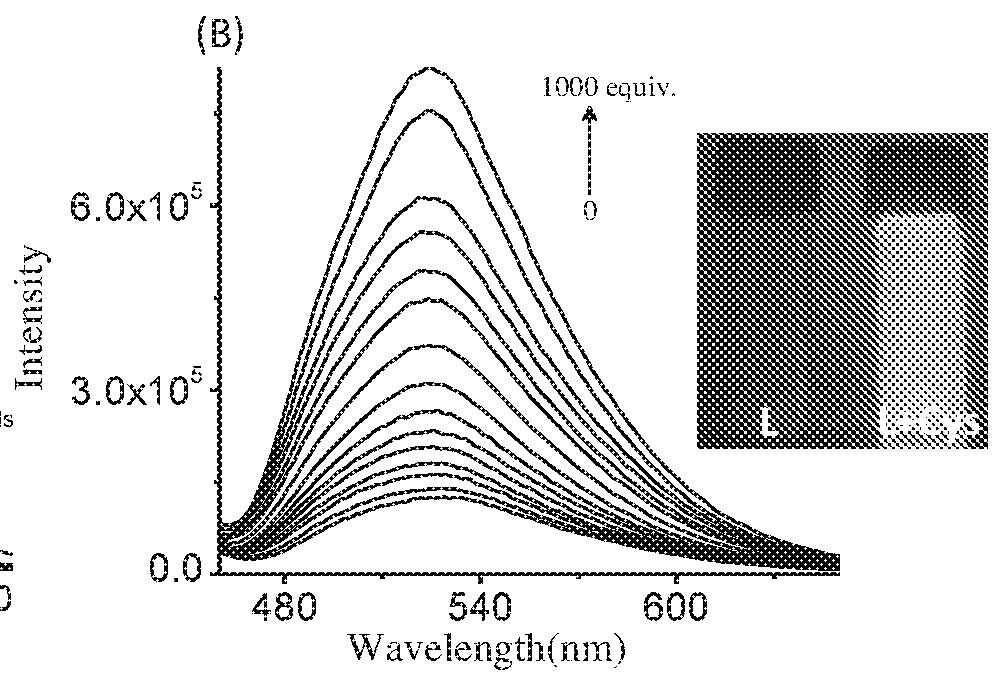
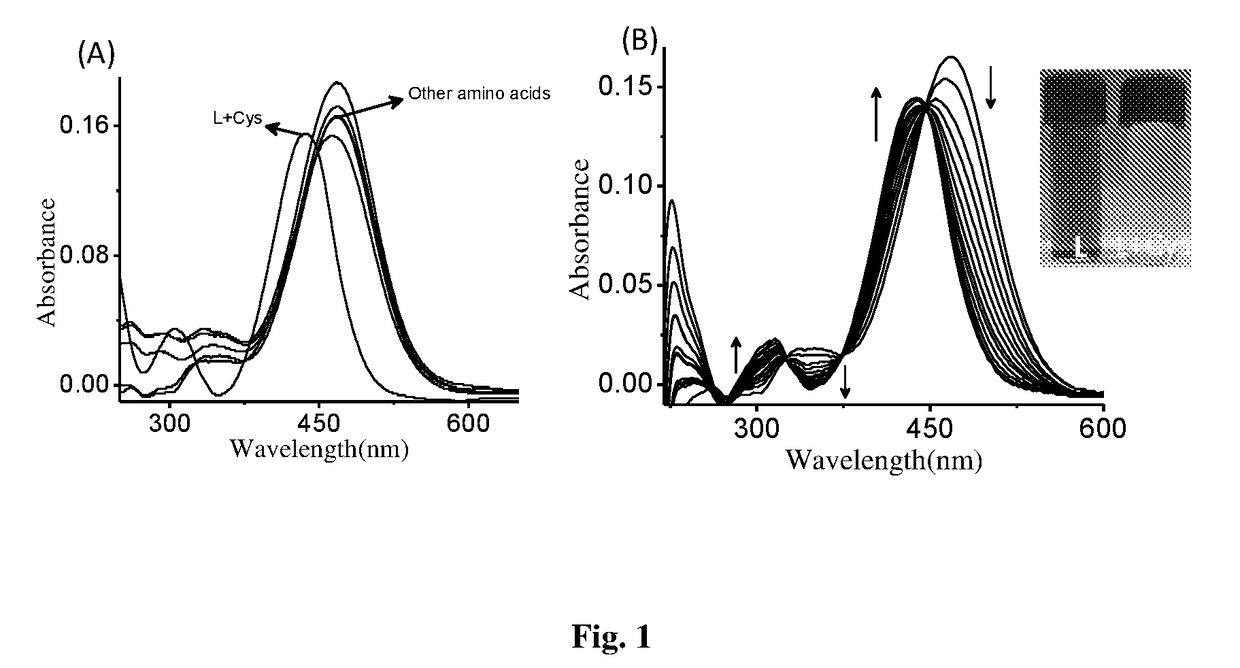
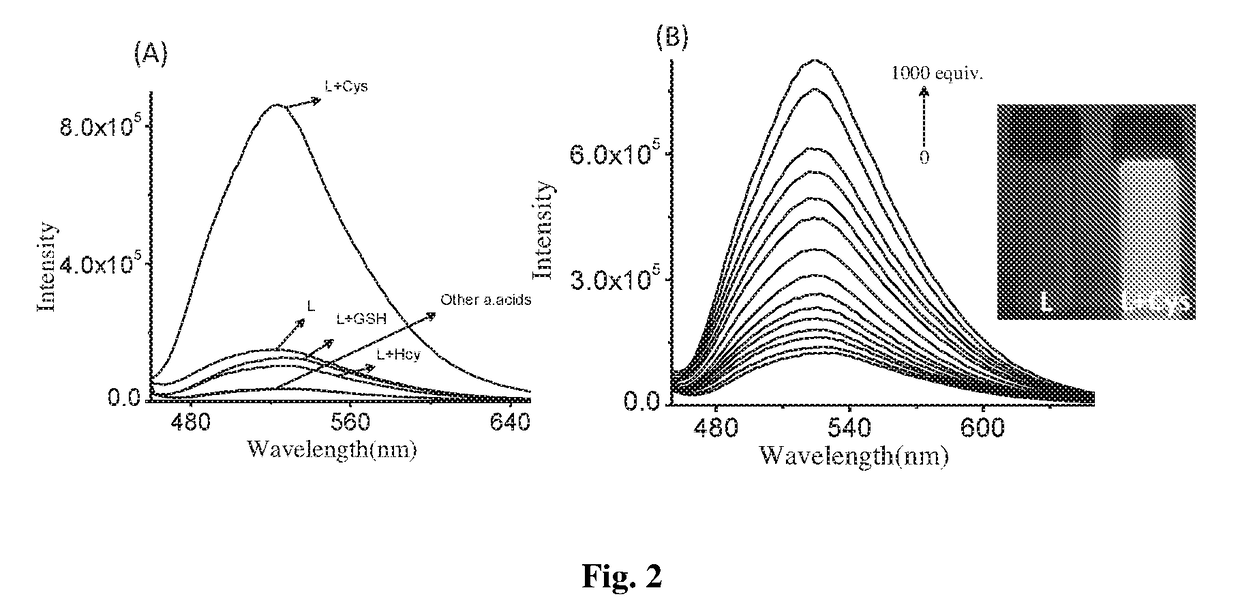
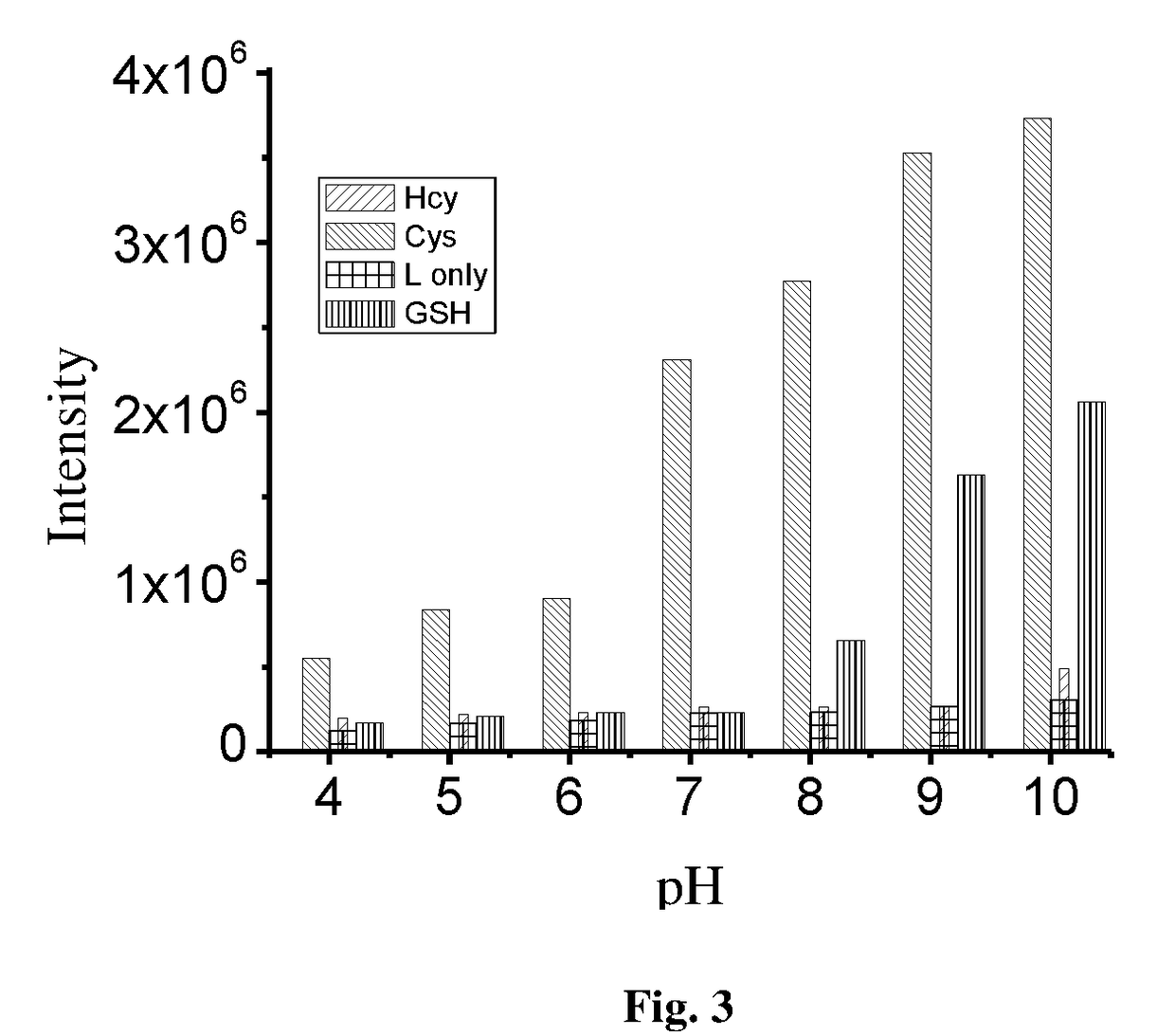
The present invention relates to a coumarin derivative of Formula (L) for detection of cysteine and process for preparation thereof. The present invention further relates to a process of detection of cysteine residues present in protein as well as the cysteine released by the enzymatic action of aminoacylase 1 by using coumarin derivative of Formula (L).
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Preparation method of enzymatic conversion of L-2-propalanine
ActiveCN101538596AHigh yieldLow costMicroorganism based processesFermentationAcetic anhydrideIon exchange
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, in particular relates to a preparation method of enzymatic conversion of L-2-propalanine. The preparation method takes DL-2-propalanine as a starting material; N-acetyl-DL-2-propalanine is synthesized by acetic anhydride; somatic cells containing aminoacylase or extract of aminoacylase is mixed with N-acetyl-DL-2- propalanine water solution to carry out enzymatic reaction at temperature of 30 to 60 DEG C; the converted product is separated by isoelectric point crystallization or the combination of isoelectric point crystallization and ion exchange resin to obtain high-purity L-2-propalanine; and the N-acetyl-DL-2-propalanine remained in the reaction is used for enzymatic resolution again after chemical racemization. The method has the advantages of low material price, easy operation, short conversion time, low production cost, and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
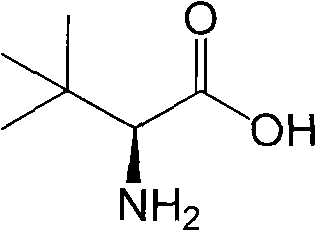
L-succinylaminoacylase and process for producing l-amino acid using it
ActiveUS20110244530A1Efficient productionSugar derivativesHydrolasesNucleic acid sequencingL-tert-leucine
The present invention provides an L-aminoacylase which is able to produce L-tert-leucine being useful as an intermediate for pharmaceuticals. A protein which is characterized in being represented by any of the following (a) to (d): (a) a protein coded by a gene consisting of a nucleic acid sequence shown in SEQ ID No: 1; (b) a protein consisting of an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID No: 2; (c) a protein coded by a polynucleotide which hybridizes under a stringent condition with a nucleic acid sequence which is complementary to the nucleic acid sequence shown in SEQ ID No: 1 and having an L-succinylaminoacylase activity; and (d) a protein which consists of an amino acid sequence where one or several amino acid (s) is / are substituted, deleted, inserted and / or added in the protein consisting of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID No: 2 and has an L-succinylaminoacylase activity.
Owner:TOYO TOYOBO CO LTD +1
Method for synthesizing theanine
InactiveCN1789237ALow priceReduce manufacturing costOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid amides preparationAlcoholL-theanine
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing theanine, which consists of ammonifying the L-N-acyl aminoglutaric acid-ª†-ester with aminoethane solution of 70% and getting L-N-acyl theanine, hydrolyzing with L-aminoacylase, and only L-N-acyl theanine is hydrolyzed to remove the acyl, and evoluting in alcohol solution to get the L-theanine of high quality. The invention combines the dominance of already industrialized L-aminoacylase hydrolyzing acyl, employing cheap acyl as protective group and reacting with aminoethane solution, then hydrolyzing acyl with L-aminoacylase to get L-theanine. The invention is characterized by the cheap raw material, low production cost, high selectivity, fast reaction speed and high productivity. The raw material and agent is suited for industrial production, the operation process is simple and the product quality can be guaranteed.
Owner:天津金耀氨基酸有限公司
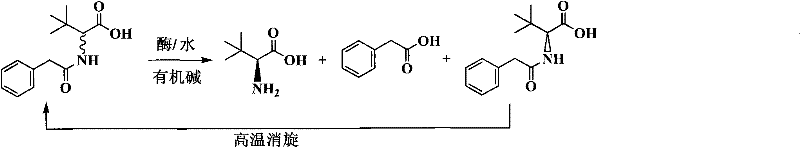
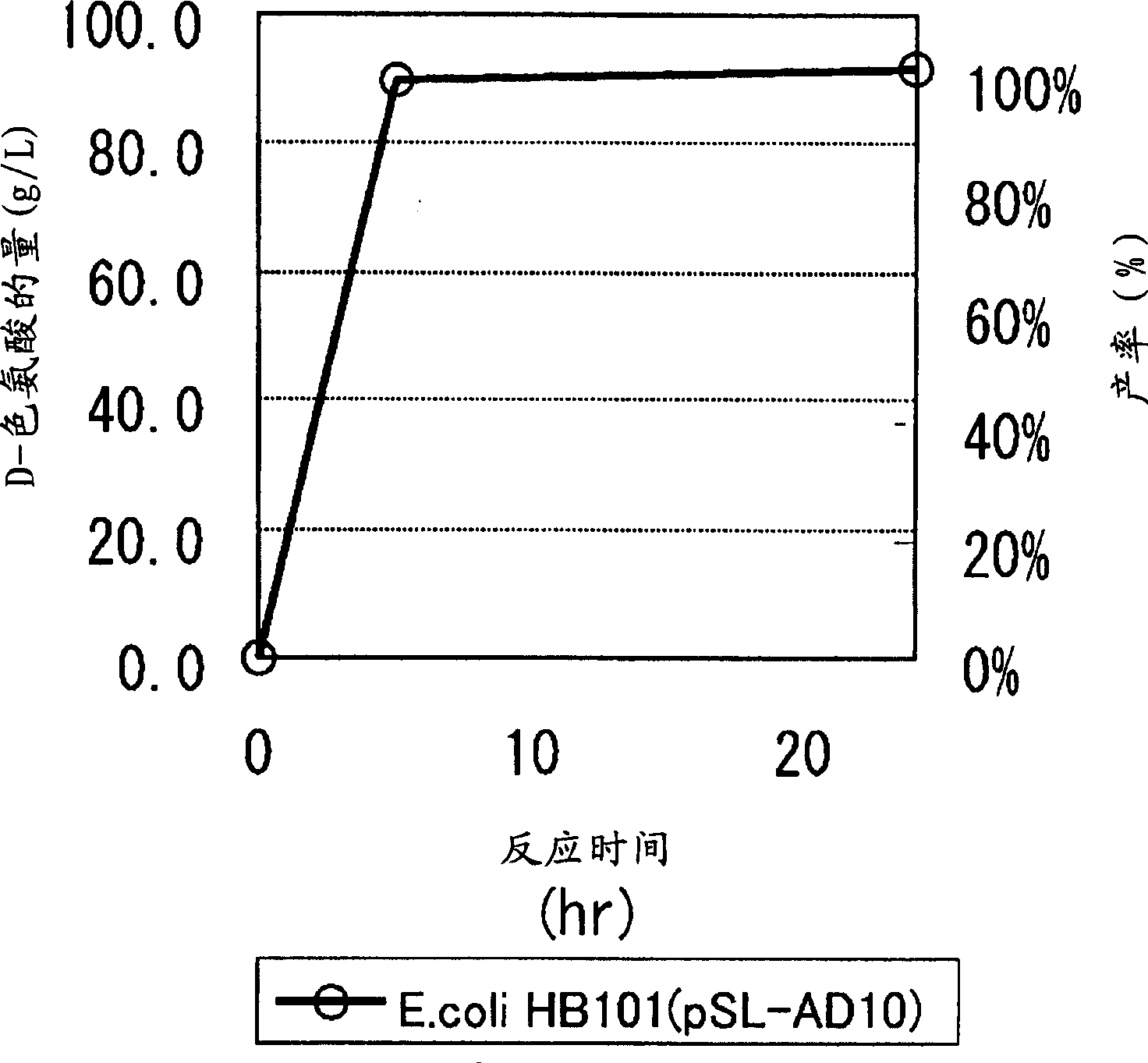
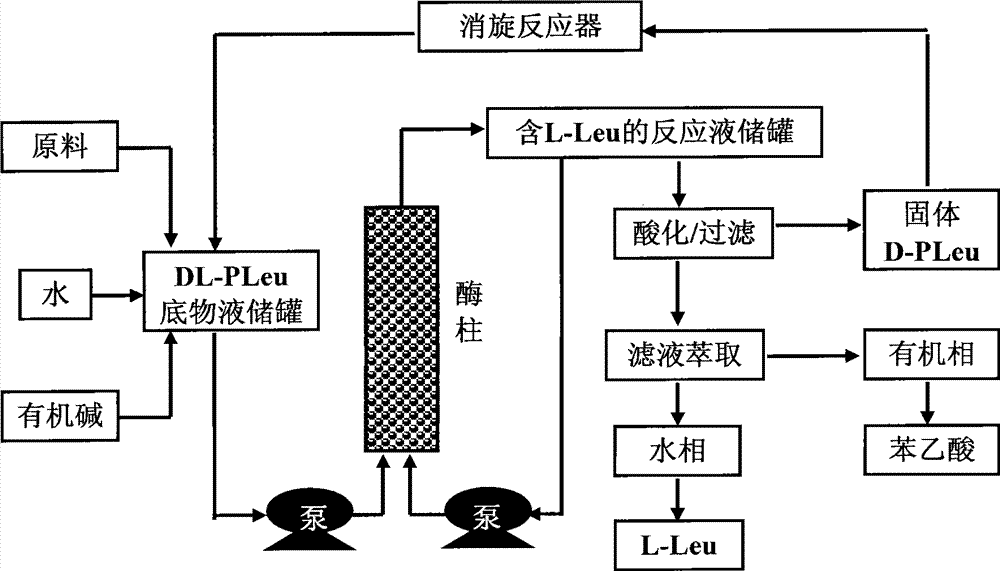
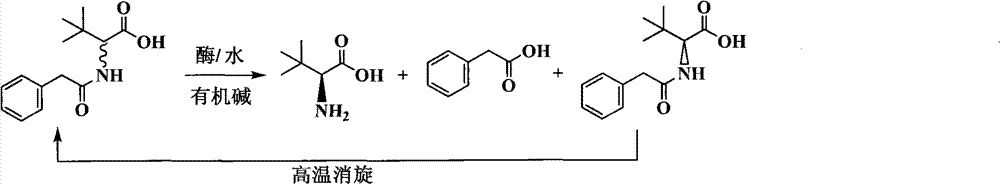
Continuous enzymatic method for producing L-tert-leucine
ActiveCN102533888AIncrease profitReduce manufacturing costFermentationSimple Organic CompoundsReflux
The invention relates to a method for preparing an optical isomer by continuously resolving a nitrogenous organic compound raceme with an enzyme, and particularly relates to a method for preparing L-tert-leucine by resolution with an aminoacylase, specifically a continuous enzymatic method for producing L-tert-leucine. The method comprises the following steps: by using N-phenylacetyl-DL-tert-leucine and an inorganic alkali as raw materials and pure water as a reaction medium, preparing a substrate solution with a certain concentration; passing the substrate solution through an aminoacylase reaction column at a certain flow rate; under the enzyme catalytic actions, selectively hydrolyzing N-phenylacetyl-L-tert-leucine to generate L-tert-leucine and phenylacetic acid; and after the reaction finishes, acidifying the reaction solution, carrying out vacuum filtration to separate out unreacted N-phenylacetyl-D-tert-leucine, and separating and extracting phenylacetic acid from the filtrate with an organic solvent, wherein the L-tert-leucine is in the water phase, and the unavailable N-phenylacetyl-D-tert-leucine is racemized by high-temperature reflux and put into the resolving reaction again.
Owner:瑞博(杭州)医药科技有限公司
Preparation technology of chiral amino acid
ActiveCN102628076AEfficient removalIncrease acetylation contentFermentationAcetic anhydrideMethylamines
The invention discloses a preparation technology of chiral amino acid, comprising the following steps of: 1) performing acetylation between L-amino acid or DL-amino acid and acetic anhydride; 2) distilling the reactant obtained from the step 1), and cooling for crystallization; 3) mixing acetylated L-amino acid or acetylated DL-amino acid obtained from the step 2), toluene and a methylamine aqueous solution, an ethylamine aqueous solution or a caustic soda flake aqueous solution until the temperature reaches 80-90 DEG C, maintaining for 1.5-2.5 hours, distilling at minus 0.001-minus 0.1 MPa at 50-95 DEG C for 4-6 hours, adding water, and adjusting pH to 7-8; and 4) carrying out resolution on the substance obtained from the step 3) and D-aminoacylase or L-aminoacylase. By the preparation technology provided by the invention, impurities in the method for resolution of chiral amino acid from aminoacylase can be effectively removed, acetylation content can be raised, and the resolution effect can be obviously improved in comparison with the prior art.
Owner:滨海瀚鸿生化有限公司
Aminoacylase 1 and application for examining liver cancer by antibody of same
According to the acylized amino acid hydrolase enzyme 1 having different expression in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues and carcinoma surrounding tissues, the invention uses it for the detection of hepatocellular carcinoma protein molecular marker, and then using the antibody of acylized amino acid hydrolase enzyme 1, to prepare the solution or reagent box for the detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. The method has high detection accuracy rate, strong specificity, simple operation, and can be widely used in clinical diagnosis.
Owner:上海中科新生命生物科技有限公司
Method for the detection of renal damage
InactiveUS20120220480A1Damage causedFailure causedLibrary screeningDisease diagnosisAlpha-enolaseFetuin b
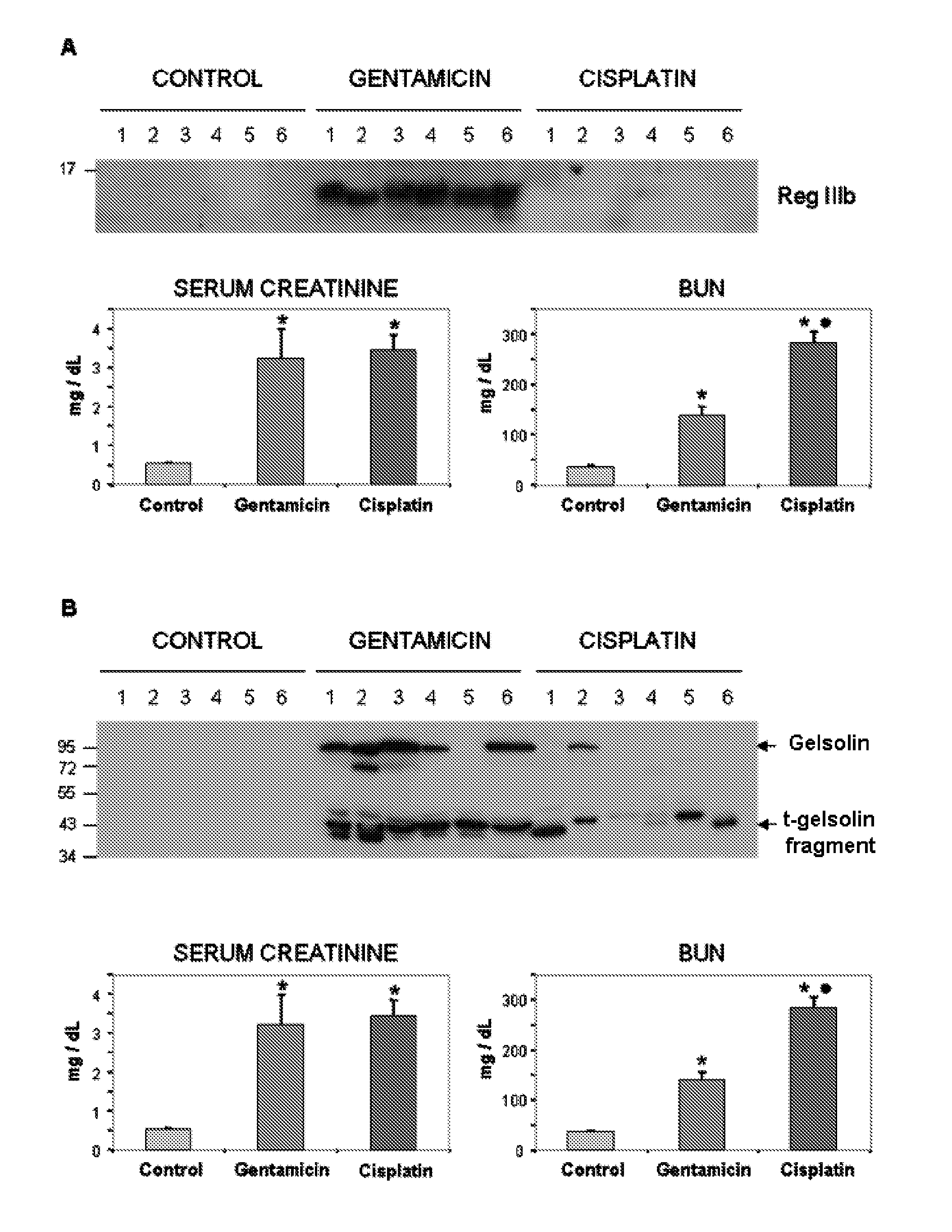
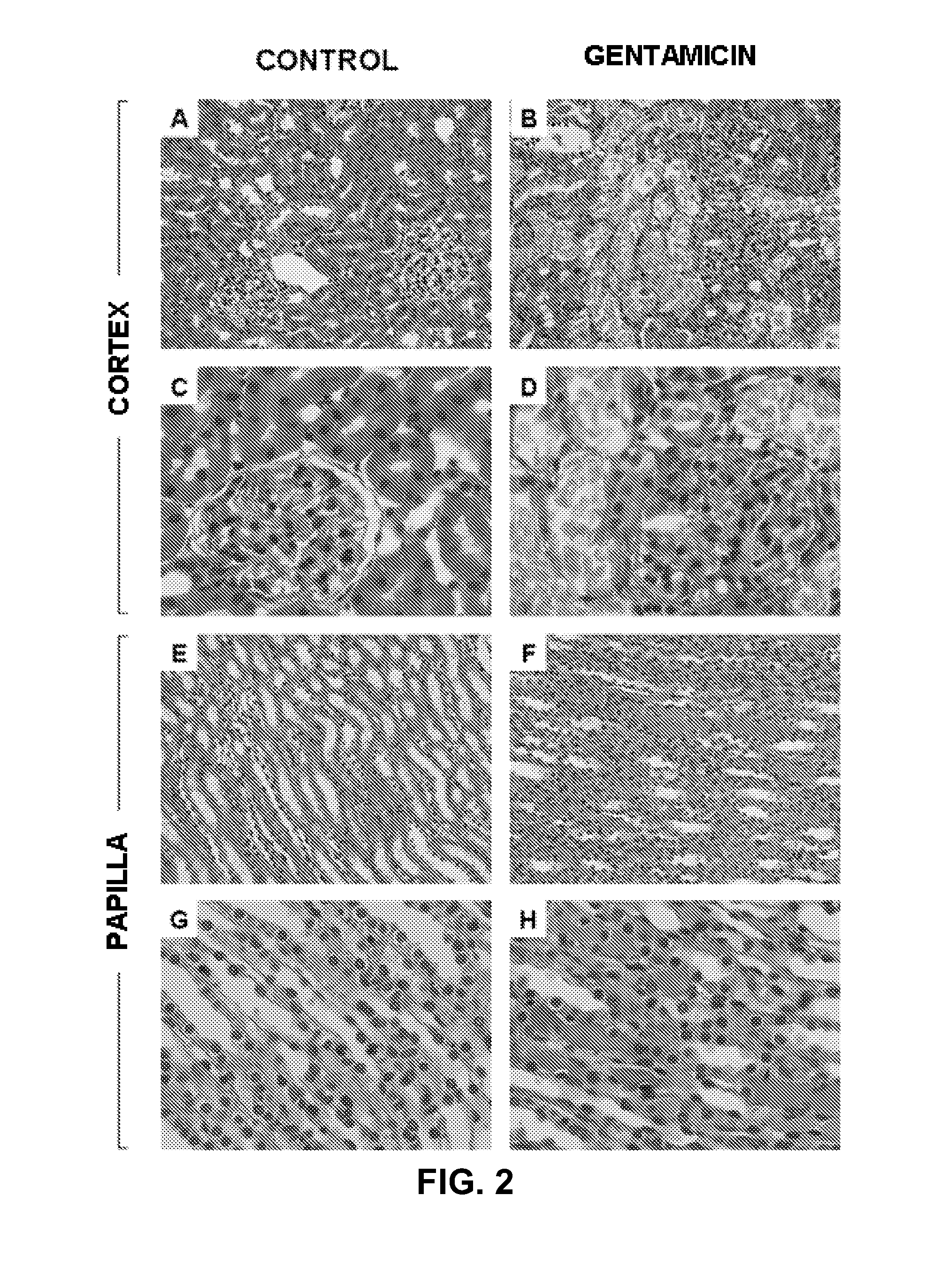
The invention relates to a method for determining the presence of renal damage in an individual and also to a method for detecting one or several proteins selected from the list comprising Reg3B, fetuin B, Ras-related GTP-binding protein A serine protease inhibitor A3L, subunit 1 of COP9, gamma subunit of ATP synthase, gelsolin, ribonuclease UK114, aminoacylase 1A, alpha-enolase, keratin 5, parvalbumin alpha, ribonuclease 4 or serine protease inhibitor A3K. The renal damage may be acute renal failure. Said renal pathologies may be caused by the administration of a nephrotoxic agent, wherein the nephrotoxic agent may be an aminoglycoside antibiotic such as gentamicin, or cisplatin. The invention also provides means to differentiate the renal damage or renal failure induced by gentamicin from that induced by cisplatin, through the biochemical analysis of the urinary level of Reg3B and / or gelsolin, or fragments thereof.
Owner:UNIV DE SALAMANCA
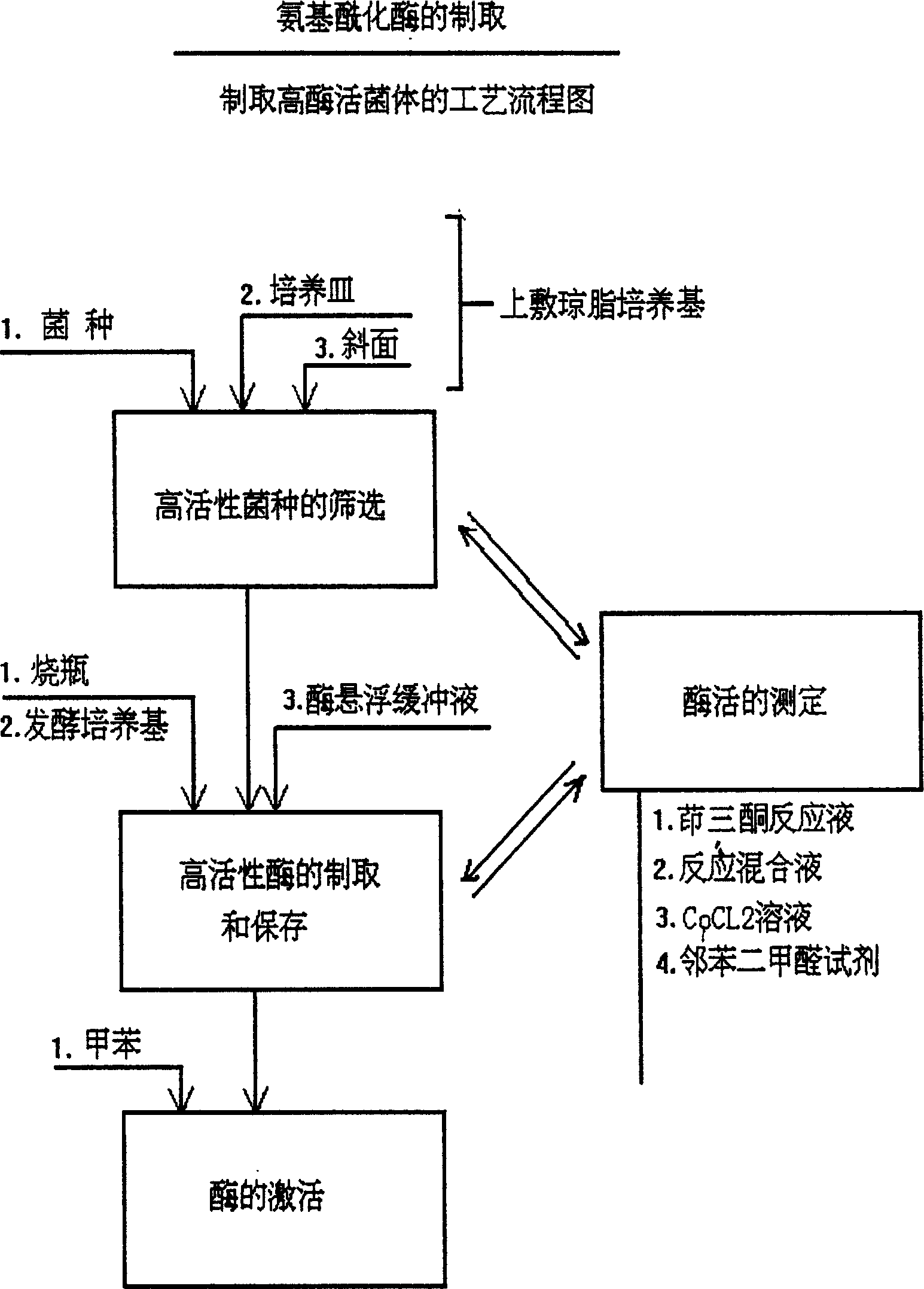
Preparation method of immobilized aminoacylase and product and application thereof
ActiveCN101671664ALow freezing pointHigh mechanical strengthChemical industryOn/in organic carrierOrganic solventCarrageenan
The invention discloses a preparation method of immobilized aminoacylase, comprising the following steps: dissolving immobilizing materials (carrageenan and gelatin) in water at 60 to 90 DEG C, cooling to 40 to 60 DEG C, adding aminoacylase, uniformly mixing, adding the mixed liquid to an organic solvent with the temperature of 20 to 35 DEG C, and stirring and filtering to obtain granules; addingthe granules to a KCL water solution for immobilization to obtain the immobilized aminoacylase, wherein the KCL water solution also contains glutaraldehyde. The invention also discloses the immobilized aminoacylase prepared by the method and the application thereof. The preparation method of the invention can effectively reduce the solidifying points of the immobilizing materials, and the preparedimmobilized aminoacylase is in a granule shape, has good fluidity, and can effectively and conveniently resolve optically active amino acid.
Owner:滨海瀚鸿生化有限公司
N-epsilon-acyl-l-lysine-specific aminoacylase
InactiveUS20070298469A1High activityImprove abilitiesBacteriaSugar derivativesCarboxylic acidGreek letter epsilon
The present invention provides an aminoacylase having superior abilities in specifically acylating and hydrolyzing e-amino group of Lys, and a method of producing Nε-acyl-L-lysine. The present invention provides Nε-acyl-L-lysine-specific aminoacylase containing the amino acid sequence of SERPXTTLLRNGDVH (X unknown) at the N-terminal, and a method of producing Nε-acyl-L-lysine comprising acting the aminoacylase on L-Lys and a carboxylic acid.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC +1
Process for preparing transformed microorganism, D-aminoacylase
A transformed microorganism prepared by inserting into a host microorganism with zinc tolerance a D-aminoacylase-producing gene which selectively produces D-aminoacylase alone between D-aminoacylase and L-aminoacylase. A process comprising culturing the transformed microorganism in a culture medium containing zinc ion and obtaining D-aminoacylase from the culture at a high efficiency.
Owner:AMANO ENZYME INC
Transformed microorganism and process for producing D-aminoacylase
A transformed microorganism prepared by inserting into a host microorganism with zinc tolerance a D-aminoacylase-producing gene which selectively produces D-aminoacylase alone between D-aminoacylase and L-aminoacylase. A process comprising culturing the transformed microorganism in a culture medium containing zinc ion and obtaining D-aminoacylase from the culture at a high efficiency.
Owner:AMANO ENZYME INC
Process for producing L-methionine, aminoacylase strain and aminoacylase
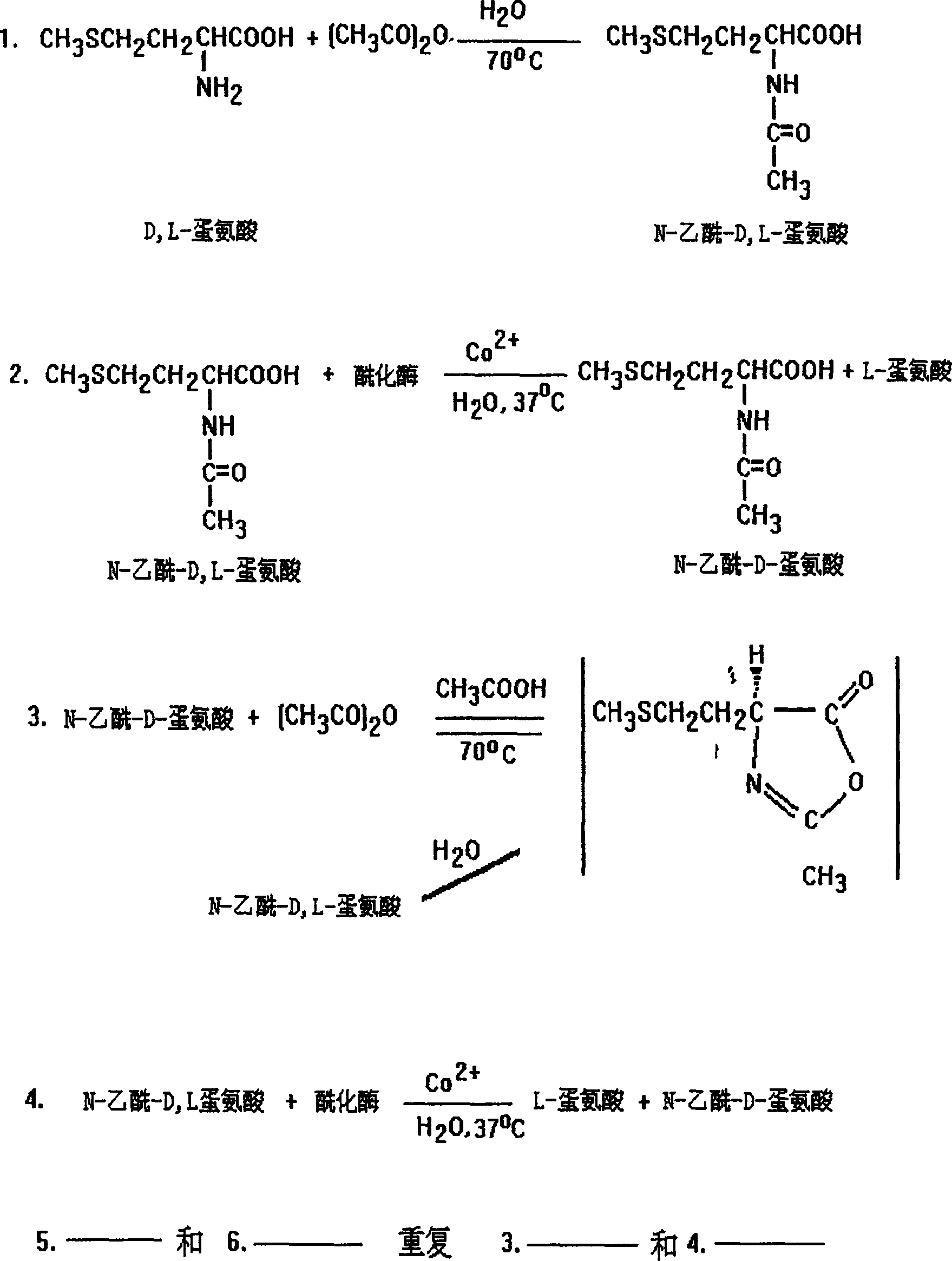
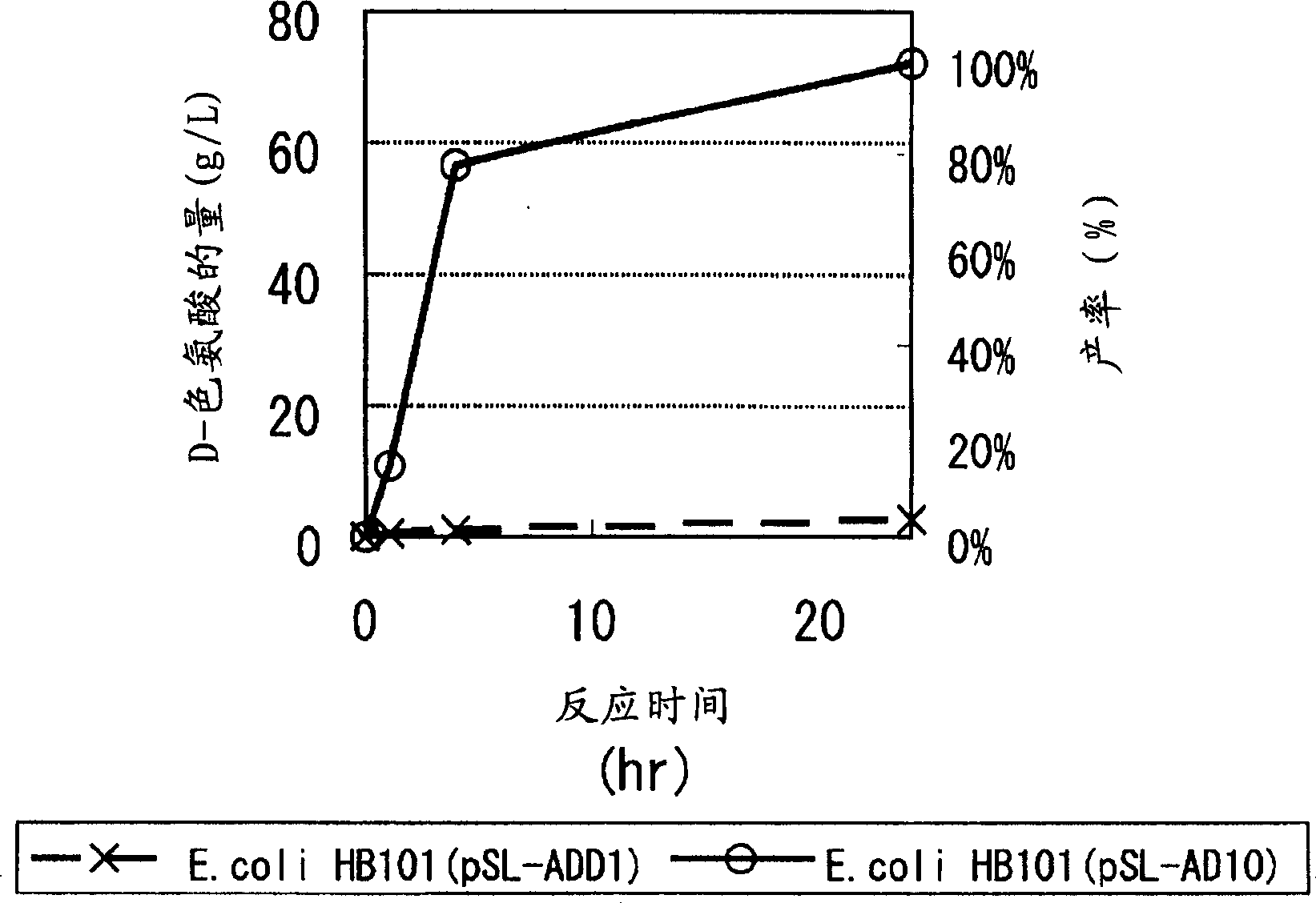
InactiveCN1279176CGenerate efficientlySave foreign exchangeBacteriaHydrolasesEscherichia coliMethionine biosynthesis
The invention relates to the process for preparing L-methionine by using escherichia coli gene engineering bacterium (storage number CGMCC No. 0368), the invention also relates to the escherichia coli aminoacylase strain and method for preparation, and aminoacylase originated from the escherichia coli genetic engineering bacterium. The process for preparing the L-methionine comprises using N-acetyl-D, L-methionine as raw material, and using the aminoacylase, cultured thalline or the thalline treatment article as enzyme source for enzymolysis reaction to produce the L-methionine.
Owner:新疆威仕达实业(集团)股份有限公司
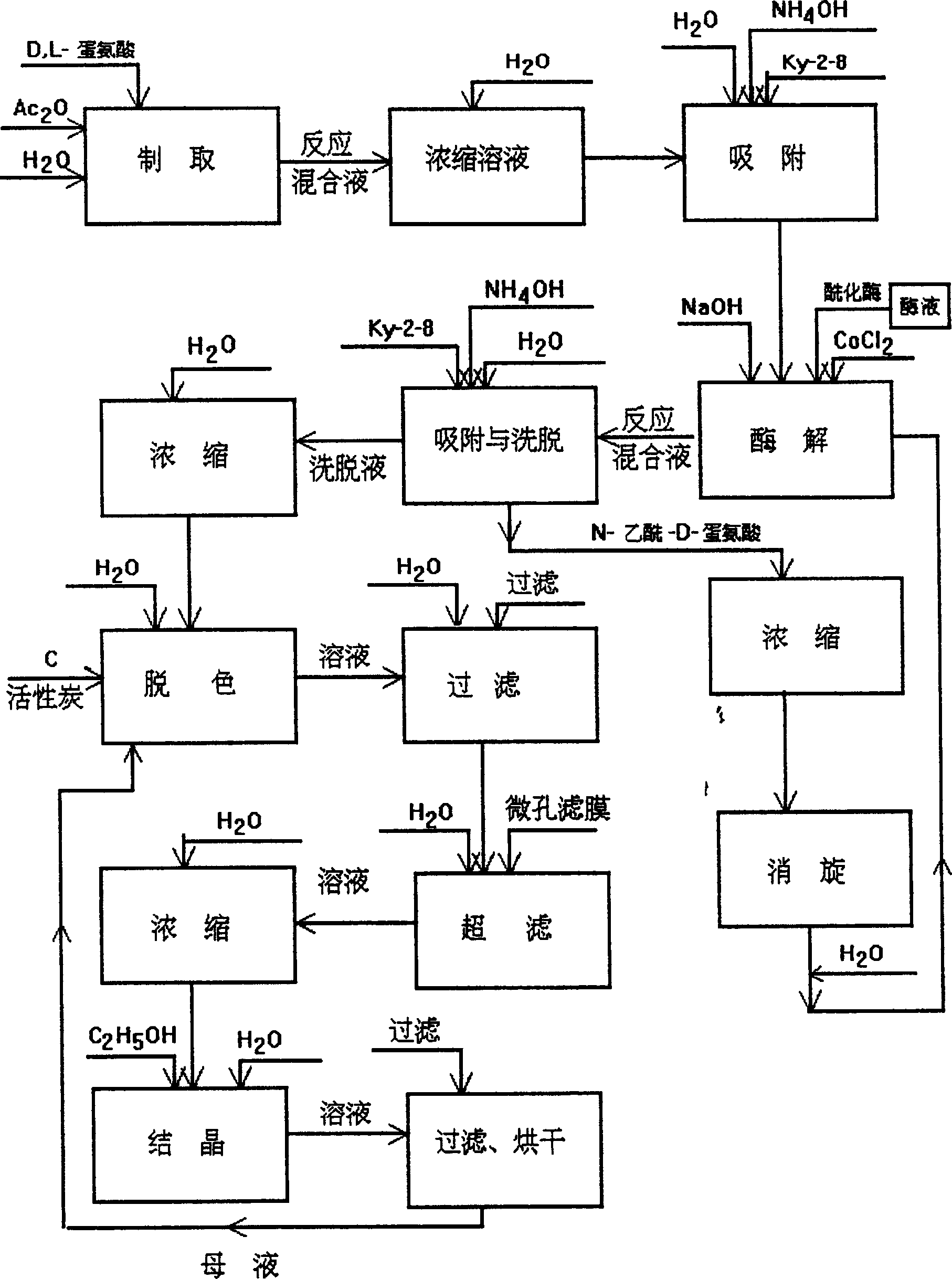
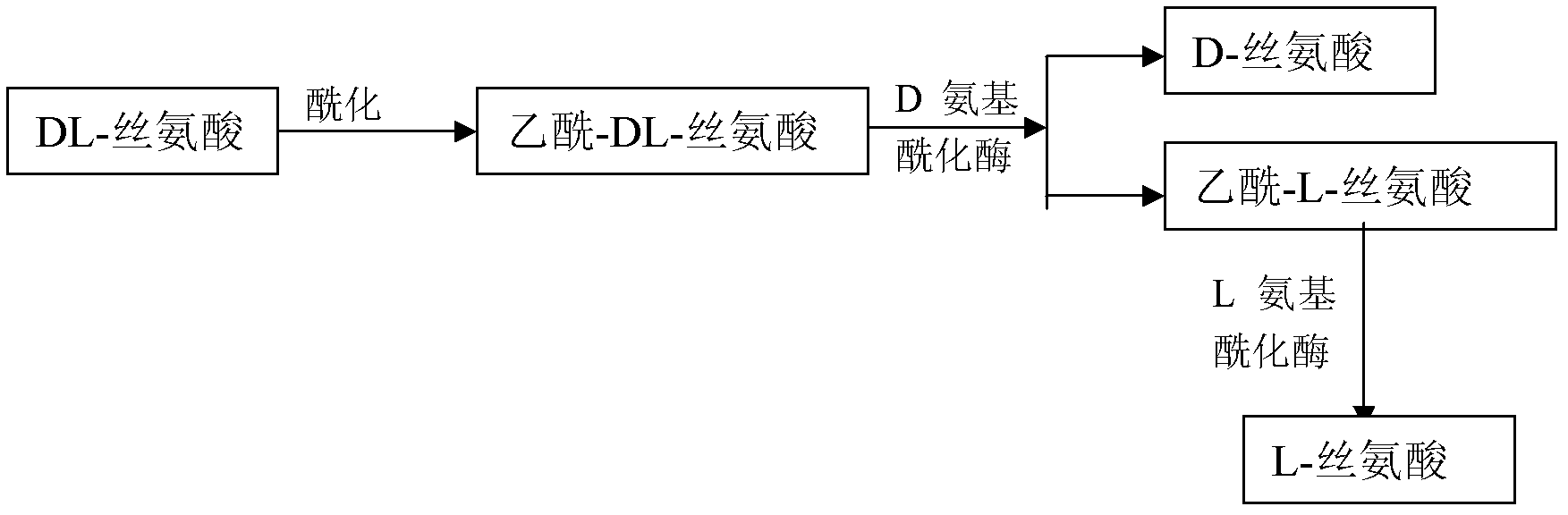
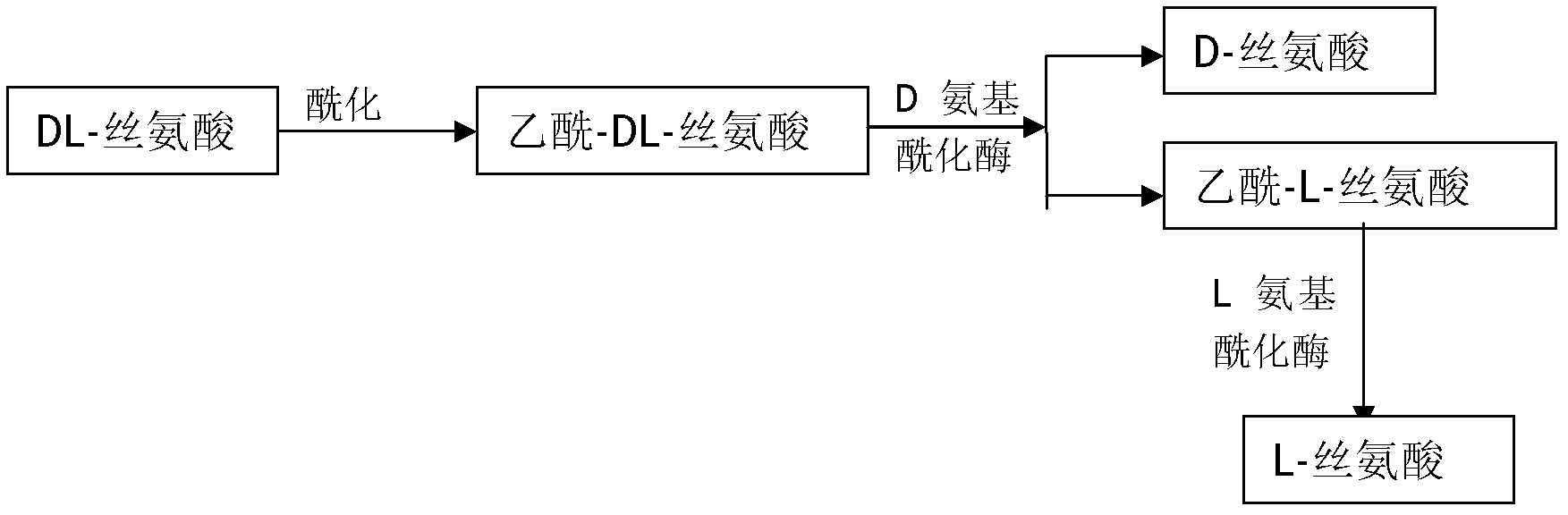
Method for preparing D-serine and L-serine with DL-serine as raw material
The invention relates to a method for preparing D-serine and L-serine with DL-serine as a raw material. The method comprises the following steps: 1) performing acylation on the DL-serine to prepare N-acetyl-DL-serine in an alkaline solution; 2) hydrolyzing the N-acetyl-D-serine in the step 1) by using D-aminoacylase; 3) extracting D-serine in the step 2) by using a strong acidic cationic resin; 4) splitting unhydrolyzed acetyl-DL-serine in the step 3) by using the L-aminoacylase; 5) separating acetyl-L-serine from the un-split acetyl-DL-serine in the step 5) by using a cationic resin column; and 6) adding the un-split acetyl-DL-serine in the step 5) into the hydrolysis solution in the step 2) for recycle. Through the combination of the steps, preparation methods of the D-serine and the L-serine can be implanted in an industrial level; the high yield and the lower waste rate of the raw material can be obtained; the steps are simplified: the utilization rate of the raw material and the product yield are increased; and the cost is reduced. Therefore, the method for preparing the D-serine and the L-serine with the DL-serine as the raw material is superior to the method in the prior art.
Owner:闫博
Enzyme method for detaching and preparing L-methionine-15N and D-methionine-15N
InactiveCN1884566AAchieve separationSimple methodMicroorganism based processesFermentationAspergillus oryzaeMethionine biosynthesis
This invention is associated with the method of preparation of L- Methionine -15N and D- Methionine -15N with enzymatic resolution. This method uses dissociate aspergillus oryzae mycelium cell or directly split DL- Methionine -15N with aminoacylase. It uses racemic acetyl- Methionine -15N (N-AC-DL-Met-15N) as raw material, and uses aminoacylase (EC.3,5,14) in dissociate aspergillus oryzae mycelium cell or aminoacylase powder as hydrolysis catalyst. The L- Methionine -15N and D- Methionine -15N obtained by this method have high output. It also has high chemical purity and optical purity.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES INST OF CHEM IND
Process for producing optically active erythro 3-cyclohexylserines
InactiveUS20060166337A1Improve efficiencyGood optical performanceHydrolasesOrganic compound preparationPhenyl groupAnti-hiv drugs
The present invention relates to a process in which N-acyl form of DL-erythro 3-substituted serines represented by the following general formula (1): (wherein, R1 means an alkanoyl group having 1-10 carbons, a benzoyl group, a halogen-substituted alkanoyl group having 1-5 carbons or a halogen-substituted benzoyl group, and R2 means a phenyl group or a cyclohexyl group) is subjected to asymmetrical hydrolysis with L-aminoacylaseorD-aminoacylase, there by giving unreacted N-acyl-D-erythro3-substituted serine in the case of L-aminoacylase or hydrolyzed D-erythro 3-substituted serine in the case of D-aminoacylase. The D-erythro forms are useful as an intermediate for medicines, for example, known to be useful as an anti-HIV drug (WO 01 / 40227).
Owner:NIPPON KAYAKU CO LTD
Method of preparing L-methionine by recycling acetyl-DL-methionine
The invention relates to a method of preparing L-methionine by recycling acetyl-DL-methionine. The method comprises the following steps: dissolving aminoacylase in an acetyl-DL-methionine aqueous solution, and carrying out resolution reaction to obtain L-methionine crystals and a mother liquor containing acetyl-DL-methionine; adding a NaOH aqueous solution into the obtained mother liquor, and carrying out racemization reaction to obtain a racemization liquor; cooling the racemization liquor, and regulating a pH value of a solution by using acetic acid to obtain sodium acetate trihydrate crystals and a concentrated solution; adding acetic anhydride into the obtained concentrated solution, and carrying out acylation to obtain the sodium acetate trihydrate crystals and a mother liquor containing acetyl-DL-methionine, wherein the mother liquor, serving as the acetyl-DL-methionine aqueous solution, is used for preparing L-methionine. According to the method disclosed by the invention, acetyl-DL-methionine is recycled, waste liquors and waste solids are reduced in the process of preparing L-methionine, and green production is realized.
Owner:BENGBU BBCA MEDICINE SCI DEV
Nε-acyl-L-lysine-specific aminoacylase
The present invention provides an aminoacylase having superior abilities in specifically acylating and hydrolyzing e-amino group of Lys, and a method of producing Nε-acyl-L-lysine. The present invention provides Nε-acyl-L-lysine-specific aminoacylase containing the amino acid sequence of SERPXTTLLRNGDVH (X unknown) at the N-terminal, and a method of producing Nε-acyl-L-lysine comprising acting the aminoacylase on L-Lys and a carboxylic acid.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC +1
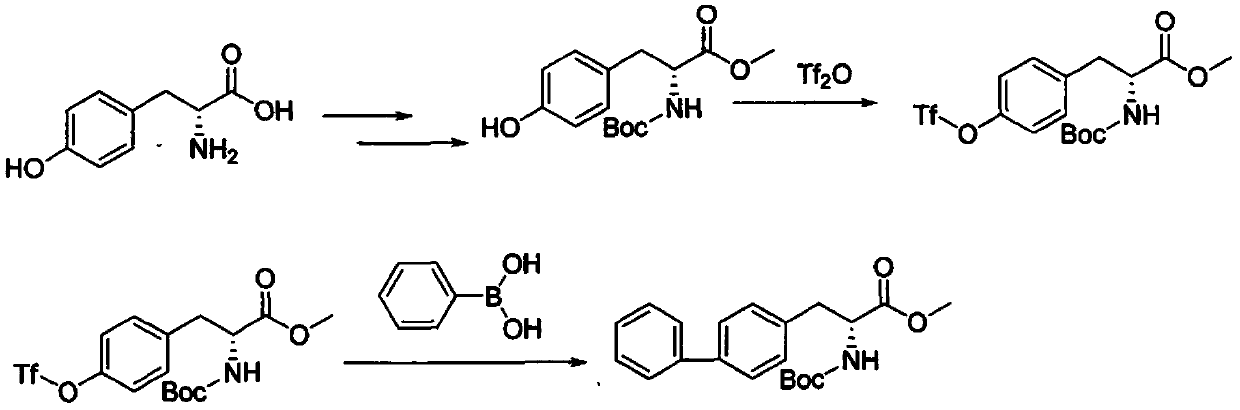
Method for synthesizing D-biphenyl alanine
The invention provides a method for synthesizing D-biphenyl alanine. The method comprises the following steps: 1) adding a solvent to a reaction kettle; during stirring, sequentially adding diethyl acetamidomalonate, metallic sodium and 4-bromomethyl biphenyl; after conducting a reaction, reacting a condensation product, which is obtained through cooling crystallization, and hydrochloric acid while conducting stirring, and conducting cooling crystallization so as to obtain N-acetyl-DL-biphenyl alanine; and 2) dissolving the N-acetyl-DL-biphenyl alanine in water; adjusting pH to 6.5-8.0 by virtue of ammonia water; adding catalyzing enzymes; and after a reaction, conducting centrifuging, rinsing with water and drying so as to obtain the D-biphenyl alanine, wherein the added catalyzing enzymes include L-aminoacylase and L-alanine racemase, and the total addition of the catalyzing enzymes is 0.1-0.15% of the mass of the N-acetyl-DL-biphenyl alanine. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that the method has fewer steps, and the method is mild in reaction, free from high temperature and high pressure, highly environment-friendly, high in yield and the like.
Owner:NANJING REDWOOD FINE CHEM CO LTD
Enzyme method for detaching and preparing L-methionine-15N and D-methionine-15N
InactiveCN100392090CAchieve separationSimple methodMicroorganism based processesFermentationDL-methionineAspergillus oryzae
This invention is associated with the method of preparation of L- Methionine -15N and D- Methionine -15N with enzymatic resolution. This method uses dissociate aspergillus oryzae mycelium cell or directly split DL- Methionine -15N with aminoacylase. It uses racemic acetyl- Methionine -15N (N-AC-DL-Met-15N) as raw material, and uses aminoacylase (EC.3,5,14) in dissociate aspergillus oryzae mycelium cell or aminoacylase powder as hydrolysis catalyst. The L- Methionine -15N and D- Methionine -15N obtained by this method have high output. It also has high chemical purity and optical purity.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES INST OF CHEM IND
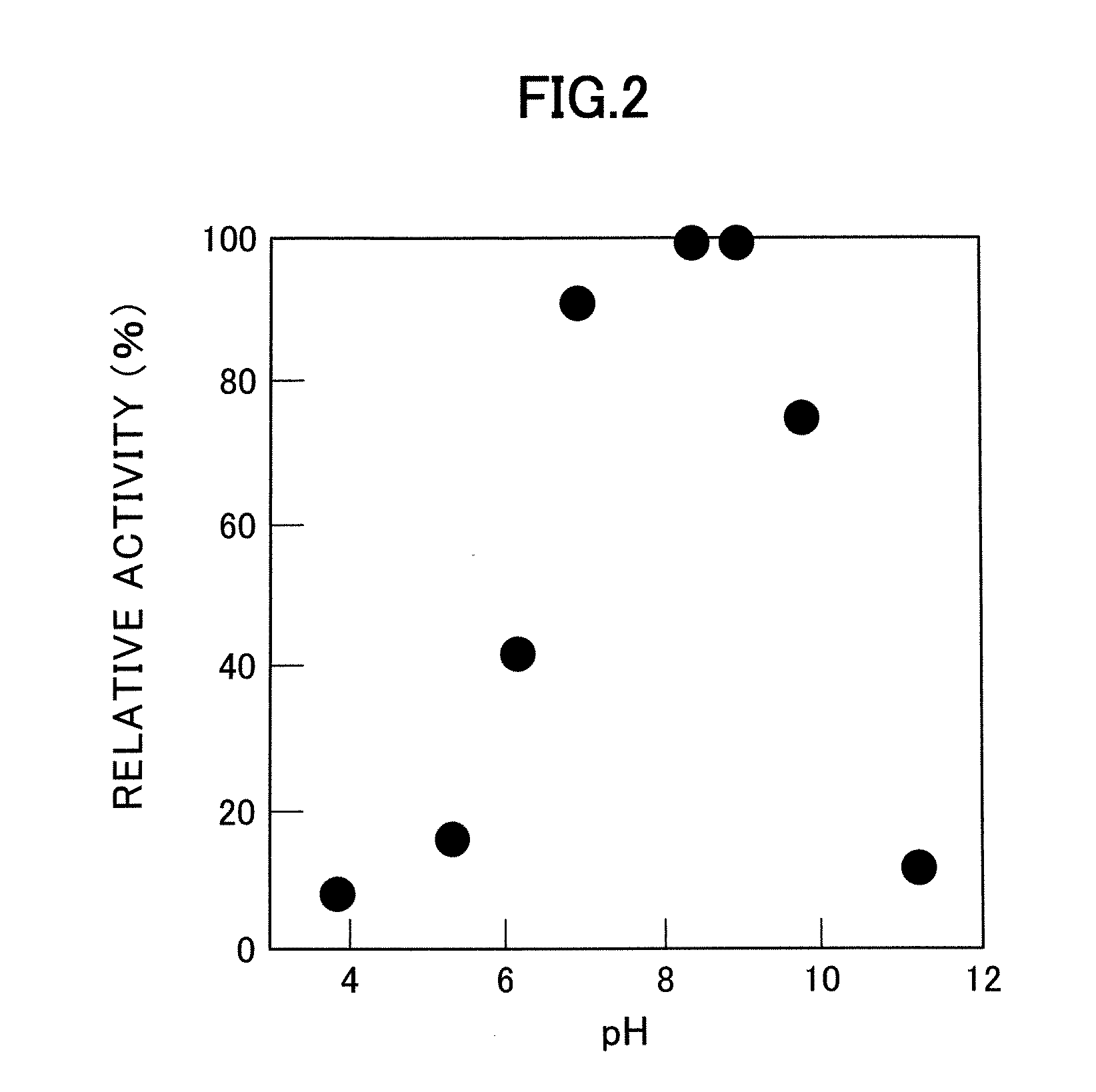
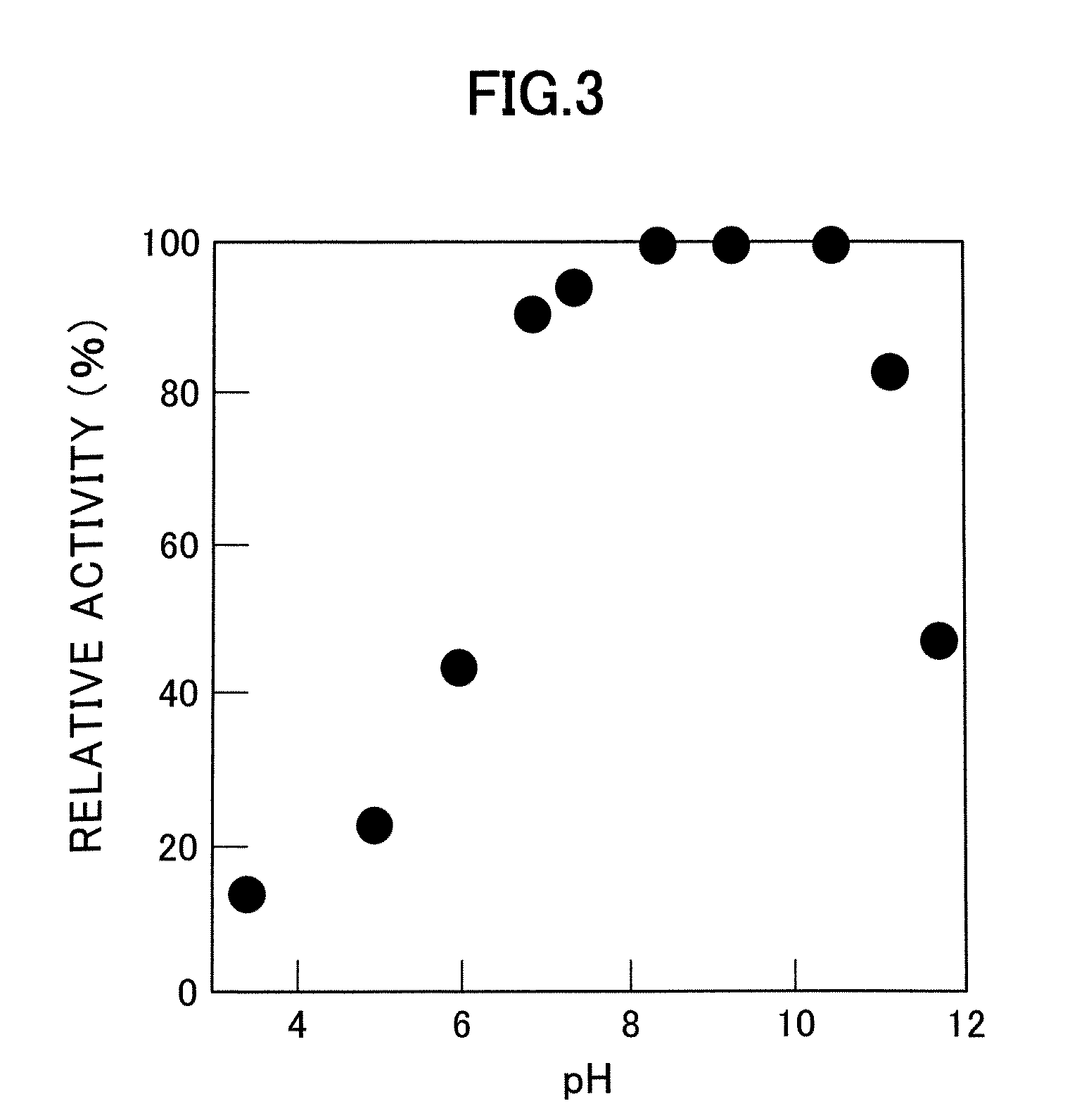
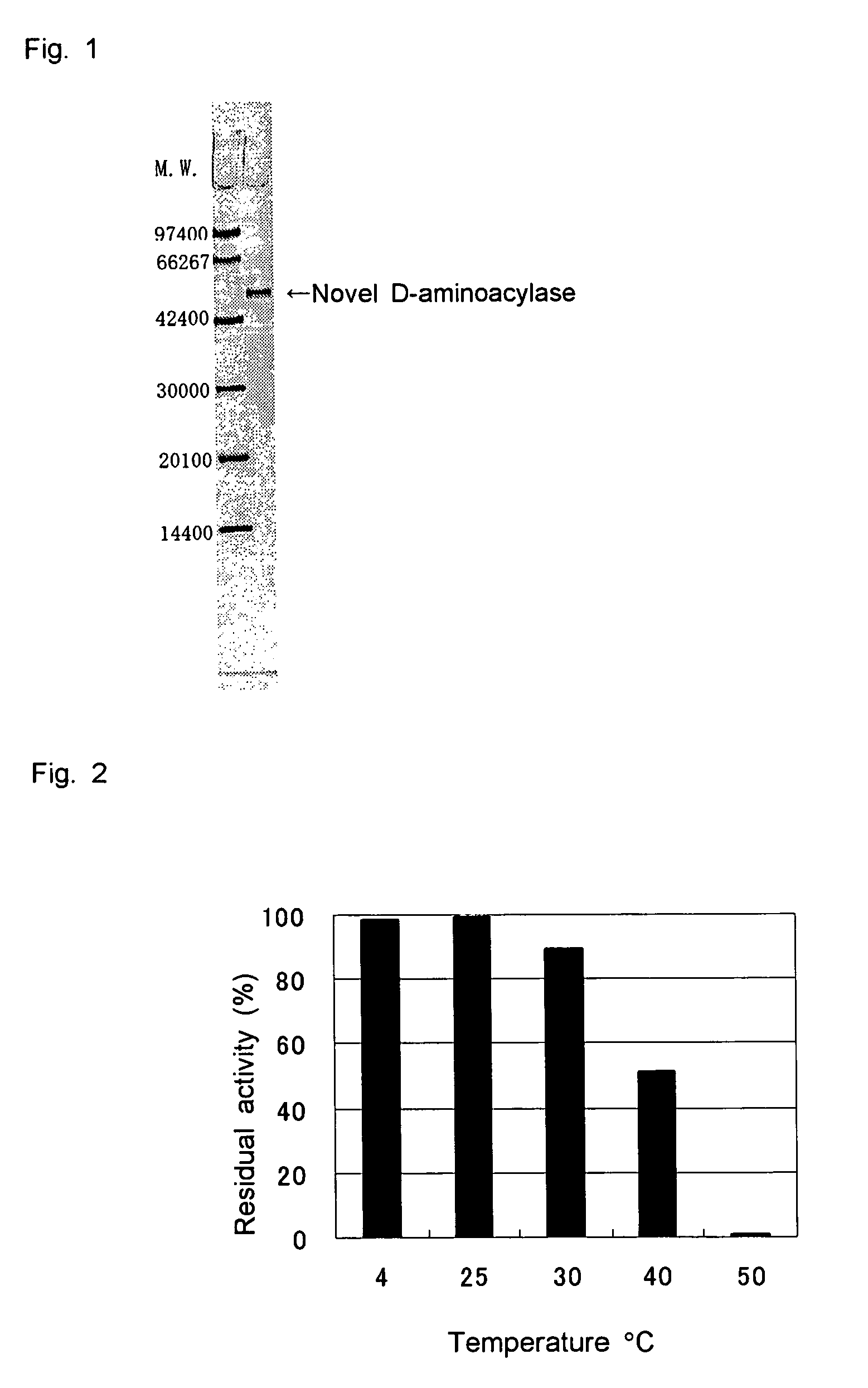
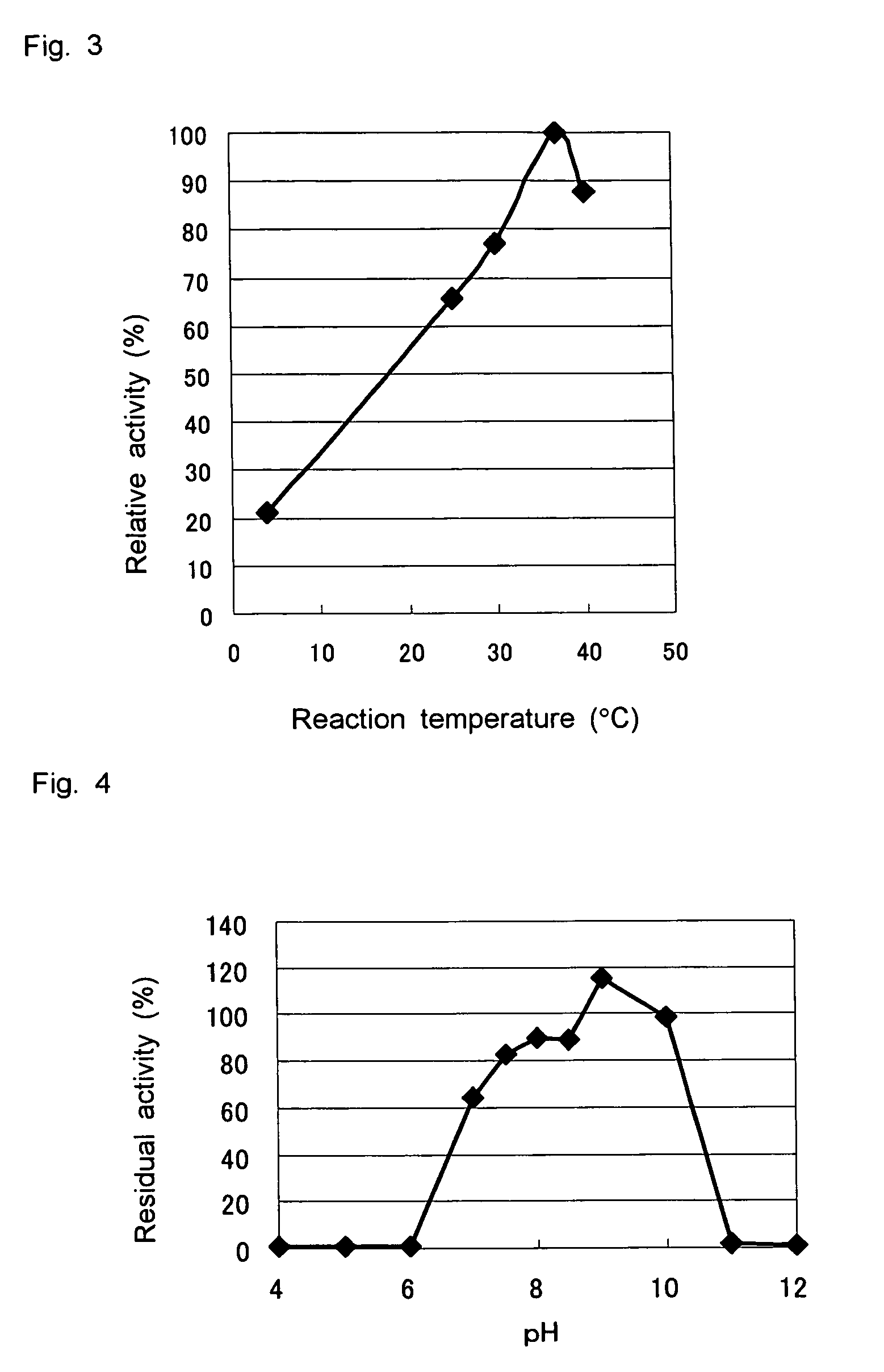
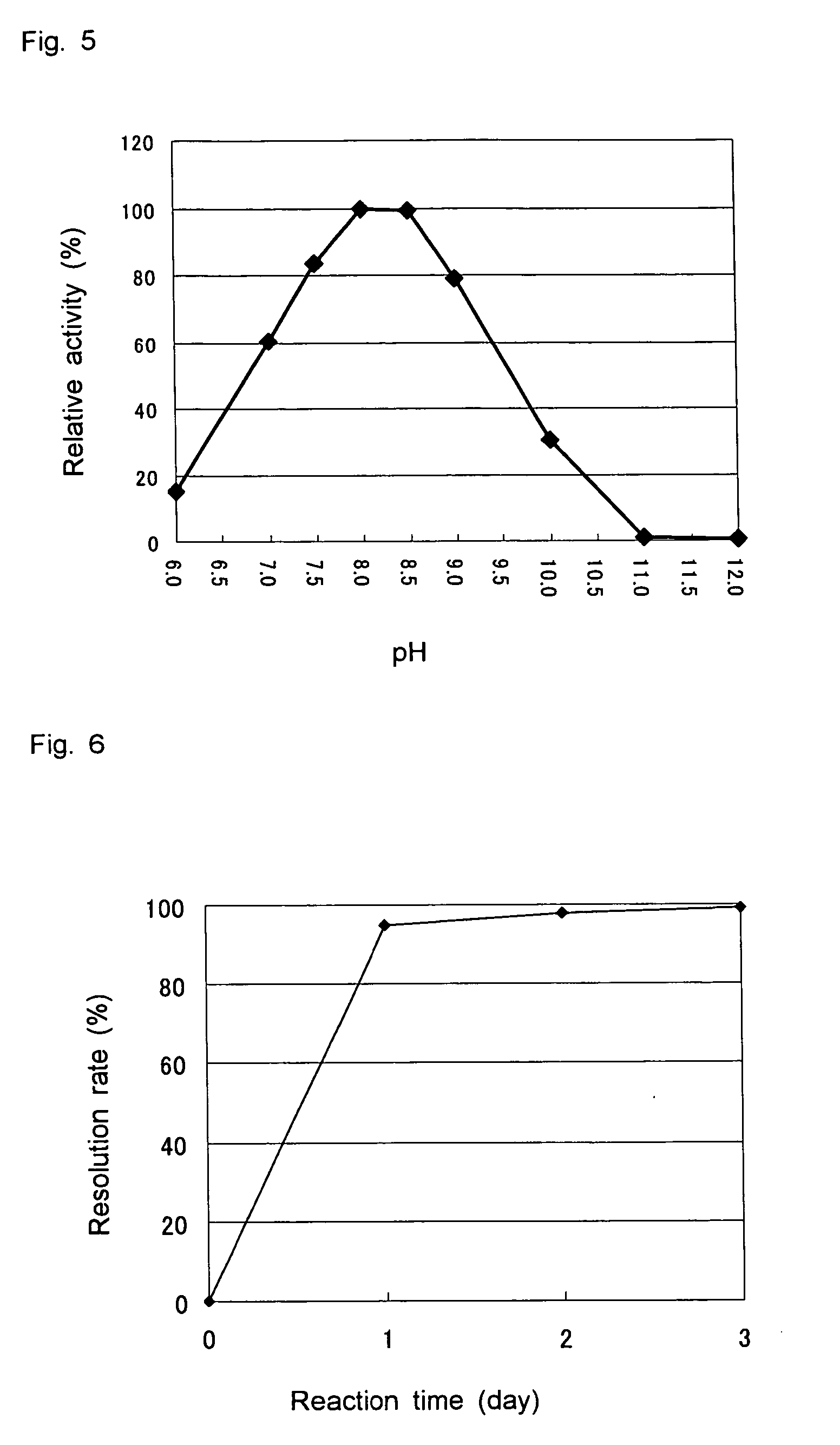
D-aminoacylase
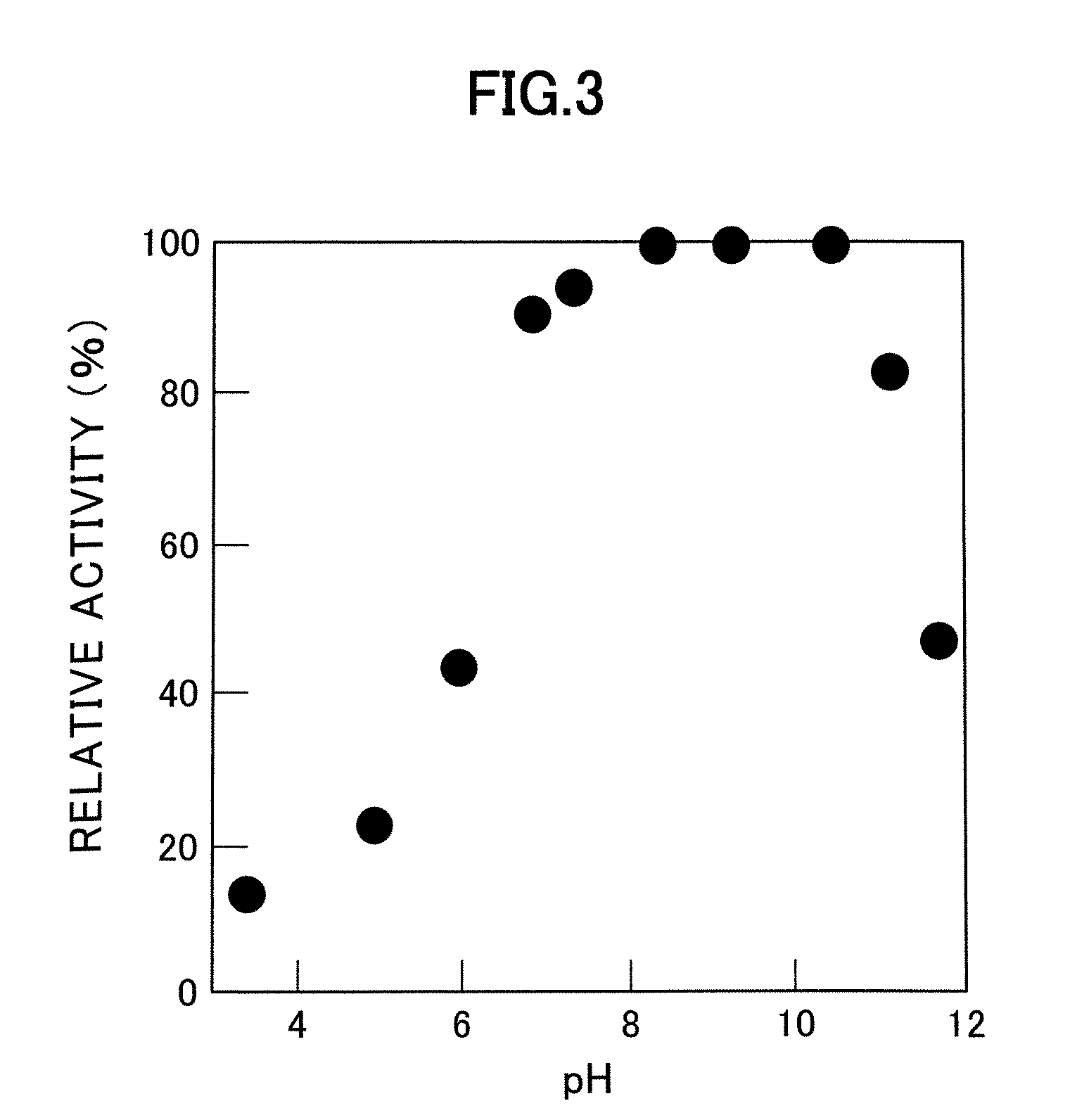
A D-aminoacylase having a high substrate specificity is provided. This D-aminoacylase can produce D-amino acids from N-acetyl-D,L-amino acids conveniently and efficiently at a low cost. A D-aminoacylase produced by a microorganism of genus Defluvibacter; which acts on a N-acetyl-D-amino acid; which has a molecular weight (as determined by electrophoresis) of about 55,000 daltons, and an isoelectric point (as determined by two-dimensional electrophoresis for denatured system) of 5.3; which acts on N-acetyl-D-valine, N-acetyl-D-leucine, and the like, but not on N-acetyl-L-valine, N-acetyl-L-leucine, and the like; which has an optimal temperature of 37° C. (pH 8) and an optimal pH value of 8 to 8.5 at 37° C.; and whose activity is inhibited by Mn2+, Co2+, Ni2+, and Zn2+ each at 1 mmol / L, and by dithiothreitol, 2-mercaptoethanol, o-phenanthroline, and L-cysteine each at 5 mmol / L.
Owner:SEKISUI MEDICAL CO LTD +1
The method for synthesizing d-biphenylalanine
The invention provides a method for synthesizing D-biphenyl alanine. The method comprises the following steps: 1) adding a solvent to a reaction kettle; during stirring, sequentially adding diethyl acetamidomalonate, metallic sodium and 4-bromomethyl biphenyl; after conducting a reaction, reacting a condensation product, which is obtained through cooling crystallization, and hydrochloric acid while conducting stirring, and conducting cooling crystallization so as to obtain N-acetyl-DL-biphenyl alanine; and 2) dissolving the N-acetyl-DL-biphenyl alanine in water; adjusting pH to 6.5-8.0 by virtue of ammonia water; adding catalyzing enzymes; and after a reaction, conducting centrifuging, rinsing with water and drying so as to obtain the D-biphenyl alanine, wherein the added catalyzing enzymes include L-aminoacylase and L-alanine racemase, and the total addition of the catalyzing enzymes is 0.1-0.15% of the mass of the N-acetyl-DL-biphenyl alanine. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that the method has fewer steps, and the method is mild in reaction, free from high temperature and high pressure, highly environment-friendly, high in yield and the like.
Owner:NANJING REDWOOD FINE CHEM CO LTD
Synthesis method of starch-based N-butyl glucose lauramide used as surfactant
The invention discloses a synthesis method of starch-based N-butyl glucose lauramide used as a surfactant, which comprises the following steps of: adding water to starch to prepare starch milk, regulating the pH value, adding calcium chloride and amylase, heating in a water bath to enable the starch to be subjected to liquefaction reaction, inactivating enzymes at high temperature after complete liquefaction, regulating the pH value, adding saccharifying enzymes, heating in the water bath, carrying out saccharification, inactivating enzymes at high temperature, cooling and filtering to obtaina hydrolyzed glucose solution; adding the hydrolyzed glucose solution and n-butylamine by the amino-sugar ratio, adding water, a color resisting agent and a polymer rhodium catalyst simultaneously, heating while stirring, controlling the pH value of the system, and carrying out amination to prepare N-butyl glucosamine; and adding aminate and lauric acid, adding aminoacylase simultaneously, heating while stirring, controlling the pH value of the system, and carrying out acidylation to prepare the N-butyl glucose lauramide. The invention has the advantages of simple process, low cost and high utilization ratio of raw materials and the product has low surface tension, excellent foaming performance, no toxicity and no stimulation and can be biologically degraded easily.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Method for preparing l-selenomethionine by enzymatic resolution
The invention discloses a method for preparing L-selenomethionine by using an enzyme resolution method, which comprises the following steps: 1. Crushing and separating fresh animal viscera with phosphate buffer solution; Dilute salt solution to make aminoacylase for later use; 2. Take NaOH and Na2CO3 and add water to make buffer solution, stir and add DL-selenomethionine to dissolve it, add acetic anhydride dropwise to adjust to negative, and use concentrated HCl to adjust the pH of the solution to 1-2 , sealed and placed to precipitate pale yellow crystals, filtered with suction, washed with deionized water, washed with ether until neutral, and dried to obtain the finished product of N-acetyl-DL-selenomethionine; 3. Use N-acetyl-DL-selenomethionine Dilute with deionized water, adjust with NaOH, add CoCl2 solution and aminoacylase, neutralize with acetic acid, decolorize with activated carbon, evaporate the filtrate to dryness, extract with ethyl acetate to obtain crude L-selenomethionine, and obtain L- Selenomethionine boutique.
Owner:王小松 +1
Synthesis method of starch-based N-butyl glucose lauramide used as surfactant
The invention discloses a synthesis method of starch-based N-butyl glucose lauramide used as a surfactant, which comprises the following steps of: adding water to starch to prepare starch milk, regulating the pH value, adding calcium chloride and amylase, heating in a water bath to enable the starch to be subjected to liquefaction reaction, inactivating enzymes at high temperature after complete liquefaction, regulating the pH value, adding saccharifying enzymes, heating in the water bath, carrying out saccharification, inactivating enzymes at high temperature, cooling and filtering to obtain a hydrolyzed glucose solution; adding the hydrolyzed glucose solution and n-butylamine by the amino-sugar ratio, adding water, a color resisting agent and a polymer rhodium catalyst simultaneously, heating while stirring, controlling the pH value of the system, and carrying out amination to prepare N-butyl glucosamine; and adding aminate and lauric acid, adding aminoacylase simultaneously, heating while stirring, controlling the pH value of the system, and carrying out acidylation to prepare the N-butyl glucose lauramide. The invention has the advantages of simple process, low cost and high utilization ratio of raw materials and the product has low surface tension, excellent foaming performance, no toxicity and no stimulation and can be biologically degraded easily.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Coumarin derivative for detection of cysteine and process for the synthesis thereof
The present invention relates to a coumarin derivative of Formula (L) for detection of cysteine and process for preparation thereof. The present invention further relates to a process of detection of cysteine residues present in protein as well as the cysteine released by the enzymatic action of aminoacylase 1 by using coumarin derivative of Formula (L).
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
D-aminoacylase mutants
The present invention provides mutant D-aminoacylases and use thereof. The mutant D-aminoacylases are hard to be inhibited by the substrate and, comprise the amino acid sequences of the D-aminoacylase derived from Alcaligenes denitrificans subsp. xylosoxydans MI-4 strain, wherein amino acid residues at specific sites have been modified. The mutants of the present invention have high reaction specificity as well as resistance to inhibition by the substrate. The present invention enables high-yield production of D-amino acids using higher concentrations of N-acyl-DL-amino acid as the substrate.The mutants of the present invention are useful in producing D-tryptophan in particular.
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD
Preparation technology of chiral amino acid
ActiveCN102628076BEfficient removalIncrease acetylation contentFermentationAcetic anhydrideAcetylation
The invention discloses a preparation technology of chiral amino acid, comprising the following steps of: 1) performing acetylation between L-amino acid or DL-amino acid and acetic anhydride; 2) distilling the reactant obtained from the step 1), and cooling for crystallization; 3) mixing acetylated L-amino acid or acetylated DL-amino acid obtained from the step 2), toluene and a methylamine aqueous solution, an ethylamine aqueous solution or a caustic soda flake aqueous solution until the temperature reaches 80-90 DEG C, maintaining for 1.5-2.5 hours, distilling at minus 0.001-minus 0.1 MPa at 50-95 DEG C for 4-6 hours, adding water, and adjusting pH to 7-8; and 4) carrying out resolution on the substance obtained from the step 3) and D-aminoacylase or L-aminoacylase. By the preparation technology provided by the invention, impurities in the method for resolution of chiral amino acid from aminoacylase can be effectively removed, acetylation content can be raised, and the resolution effect can be obviously improved in comparison with the prior art.
Owner:滨海瀚鸿生化有限公司
Continuous enzymatic method for producing L-tert-leucine
ActiveCN102533888BIncrease profitReduce manufacturing costFermentationSimple Organic CompoundsReflux
The invention relates to a method for preparing an optical isomer by continuously resolving a nitrogenous organic compound raceme with an enzyme, and particularly relates to a method for preparing L-tert-leucine by resolution with an aminoacylase, specifically a continuous enzymatic method for producing L-tert-leucine. The method comprises the following steps: by using N-phenylacetyl-DL-tert-leucine and an inorganic alkali as raw materials and pure water as a reaction medium, preparing a substrate solution with a certain concentration; passing the substrate solution through an aminoacylase reaction column at a certain flow rate; under the enzyme catalytic actions, selectively hydrolyzing N-phenylacetyl-L-tert-leucine to generate L-tert-leucine and phenylacetic acid; and after the reaction finishes, acidifying the reaction solution, carrying out vacuum filtration to separate out unreacted N-phenylacetyl-D-tert-leucine, and separating and extracting phenylacetic acid from the filtrate with an organic solvent, wherein the L-tert-leucine is in the water phase, and the unavailable N-phenylacetyl-D-tert-leucine is racemized by high-temperature reflux and put into the resolving reaction again.
Owner:瑞博(杭州)医药科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com