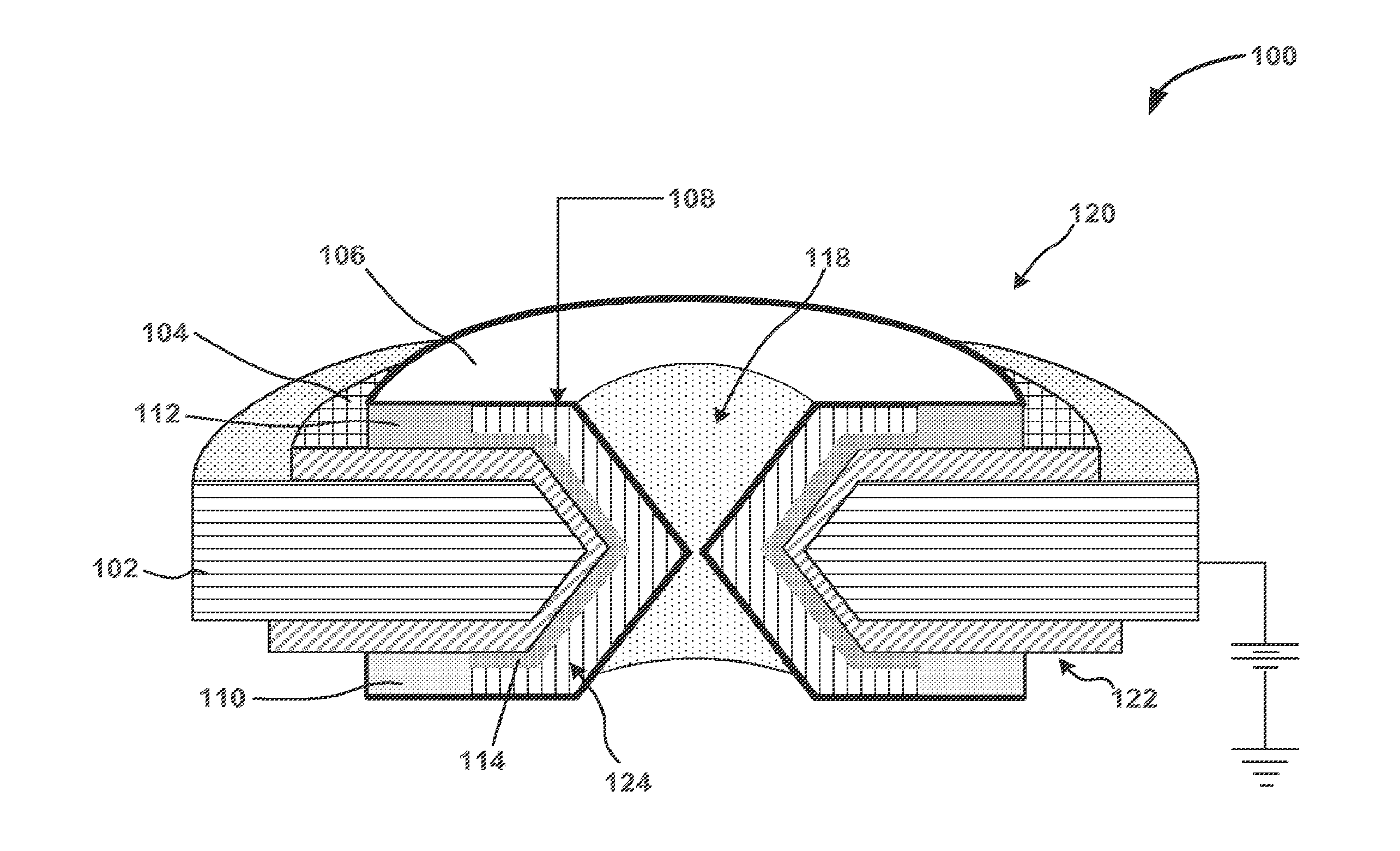
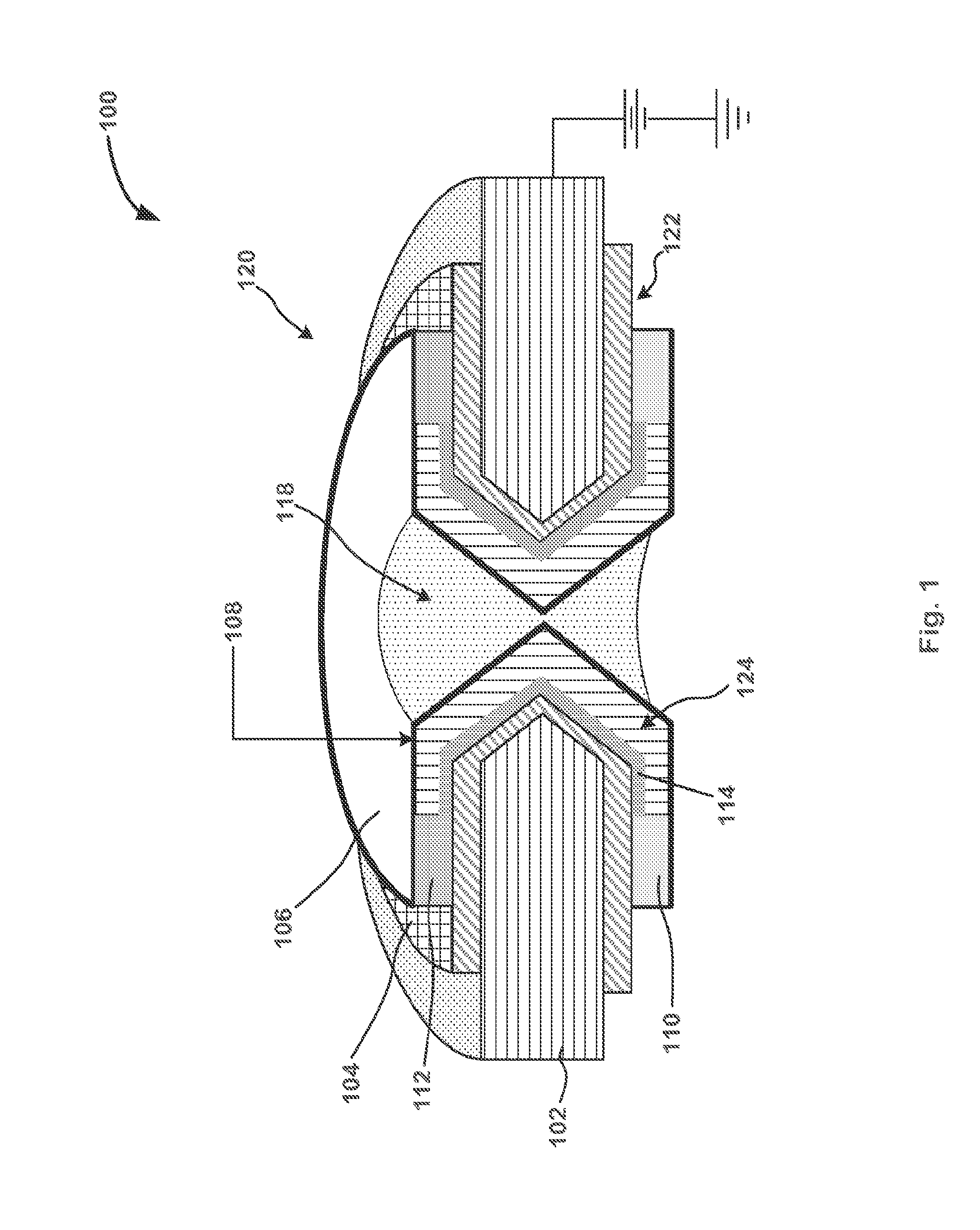
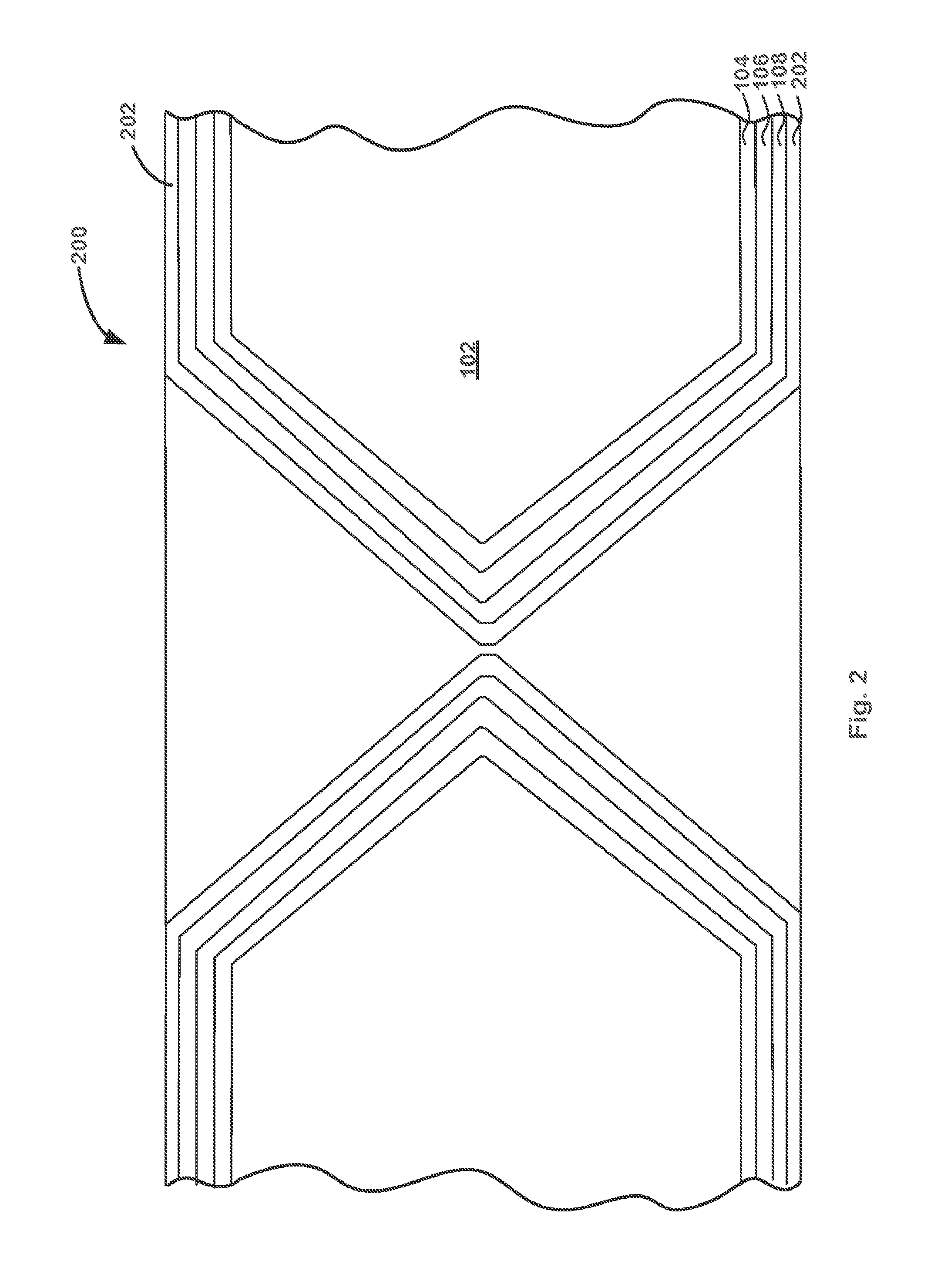
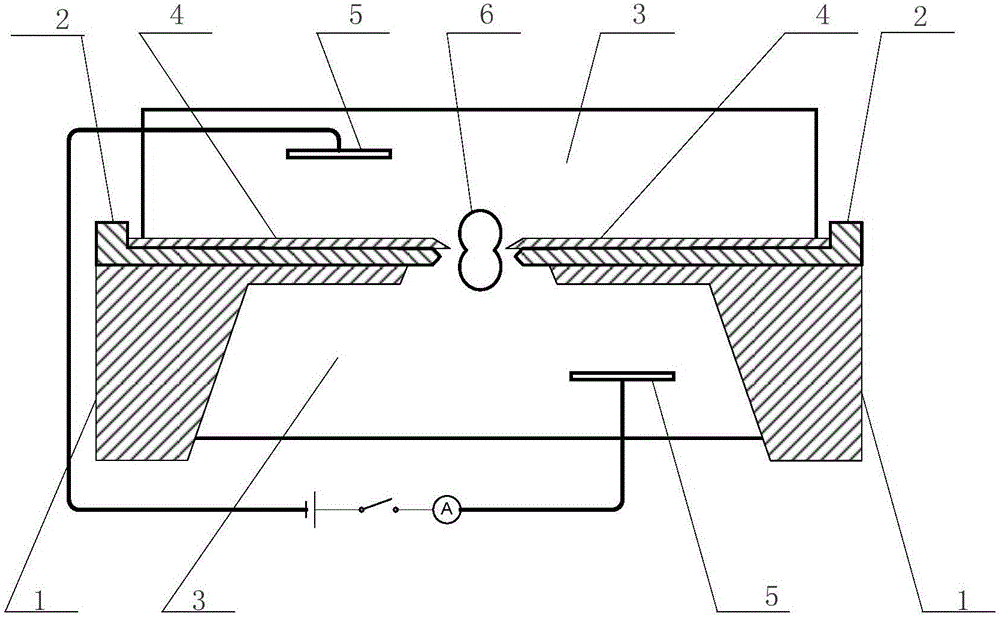
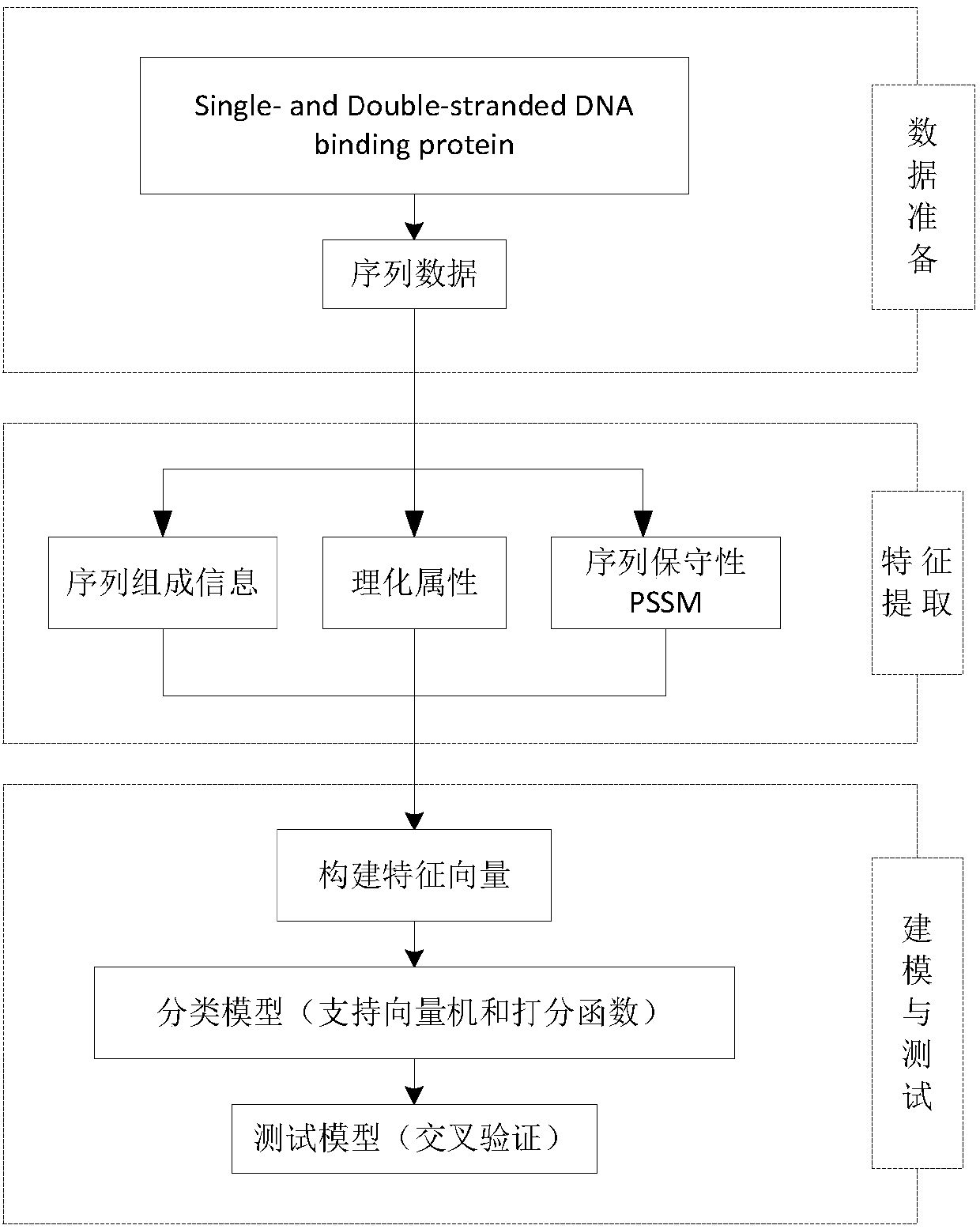
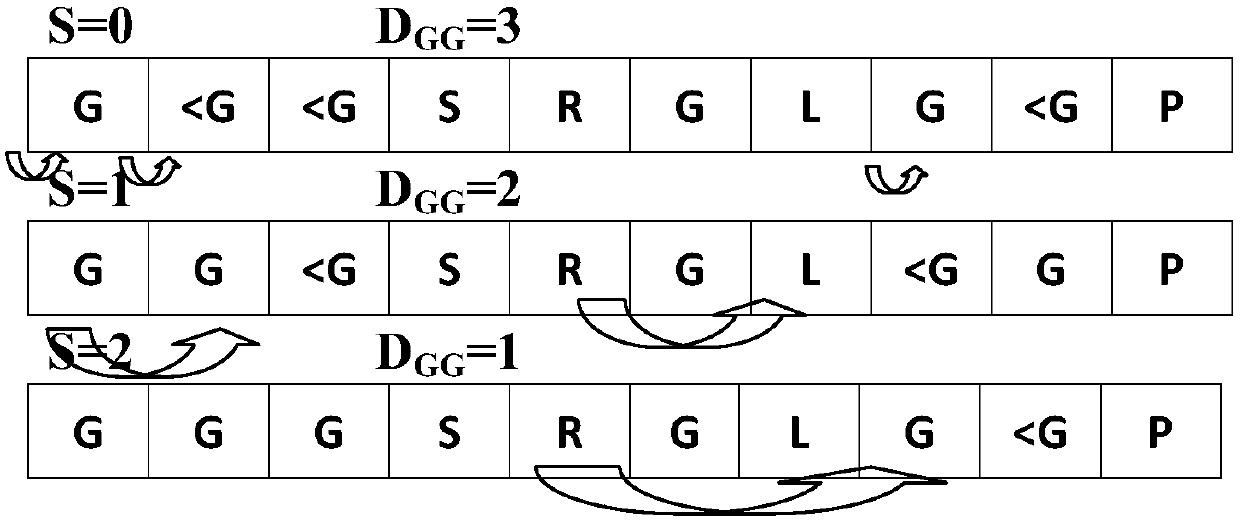
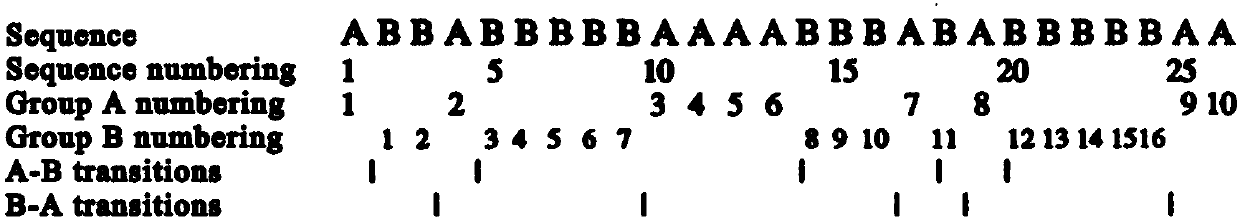
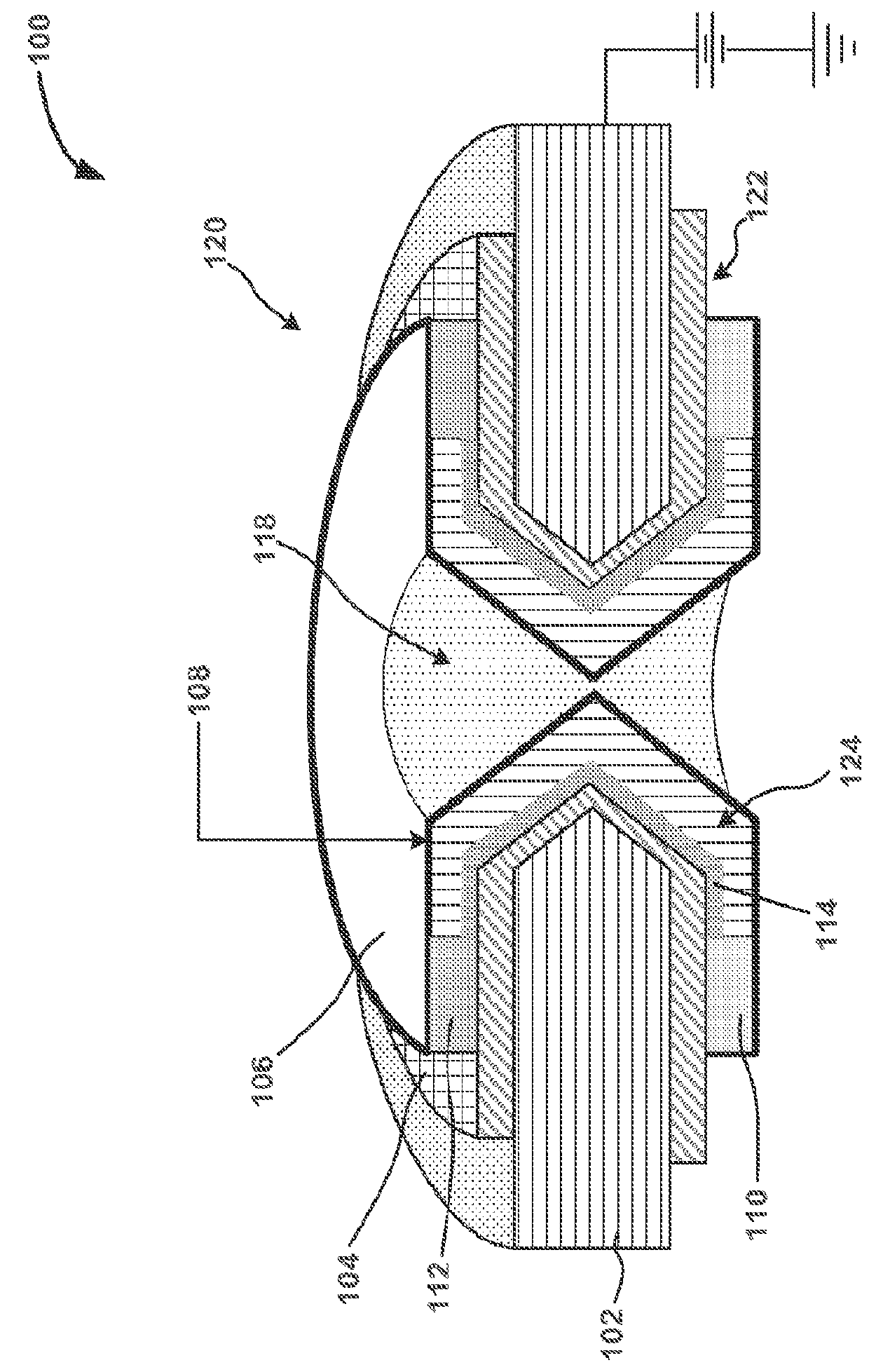
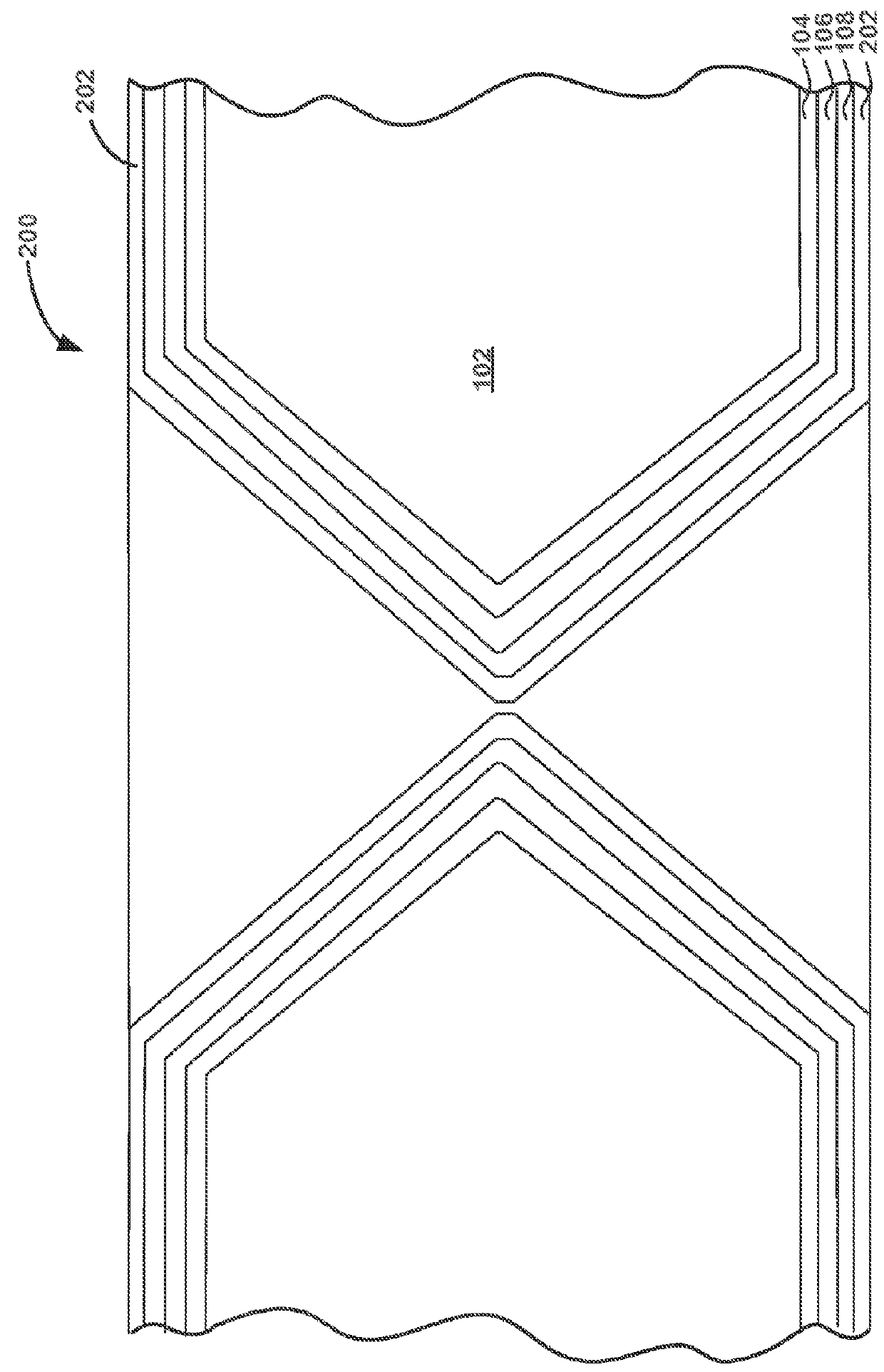
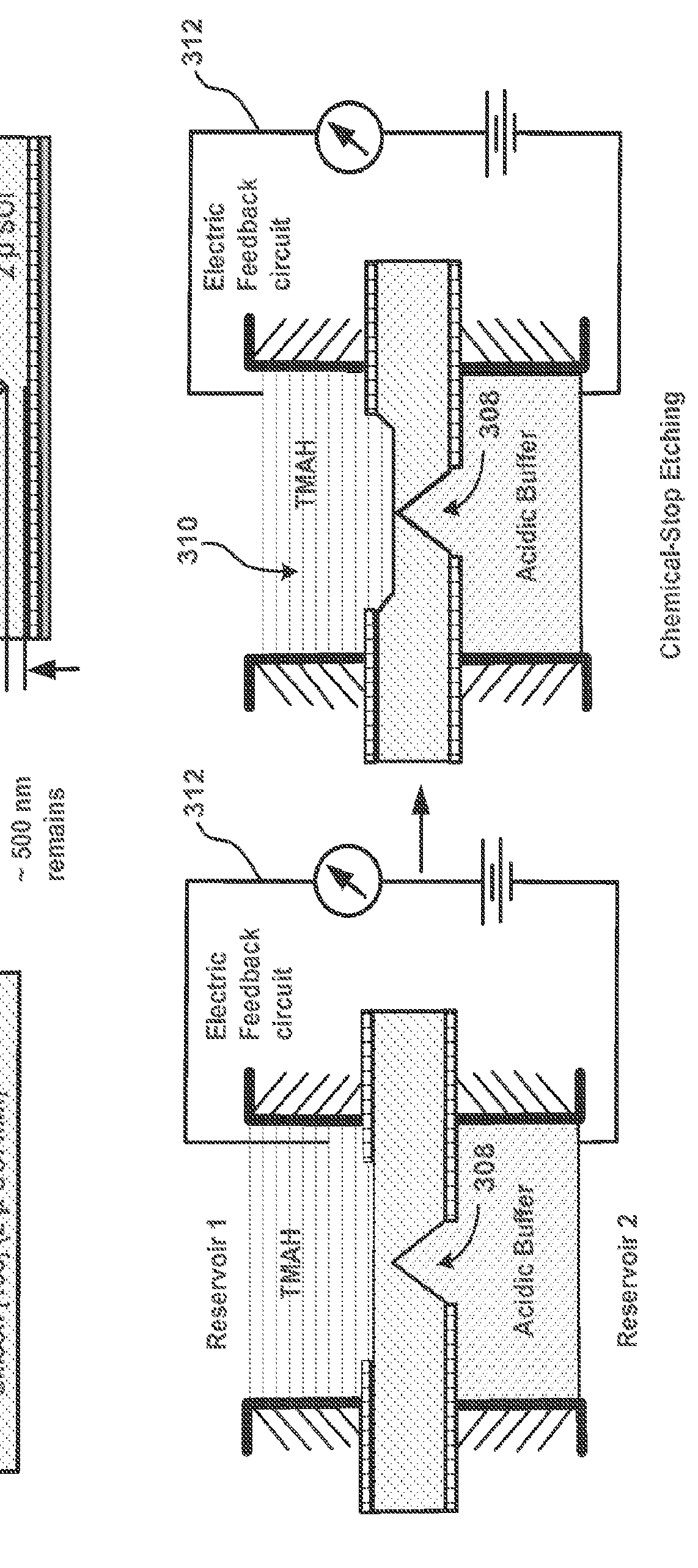
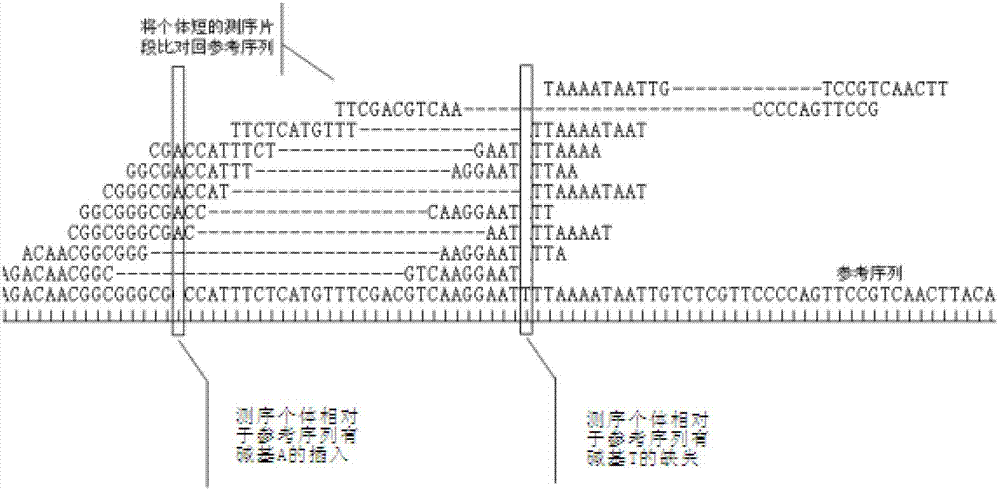
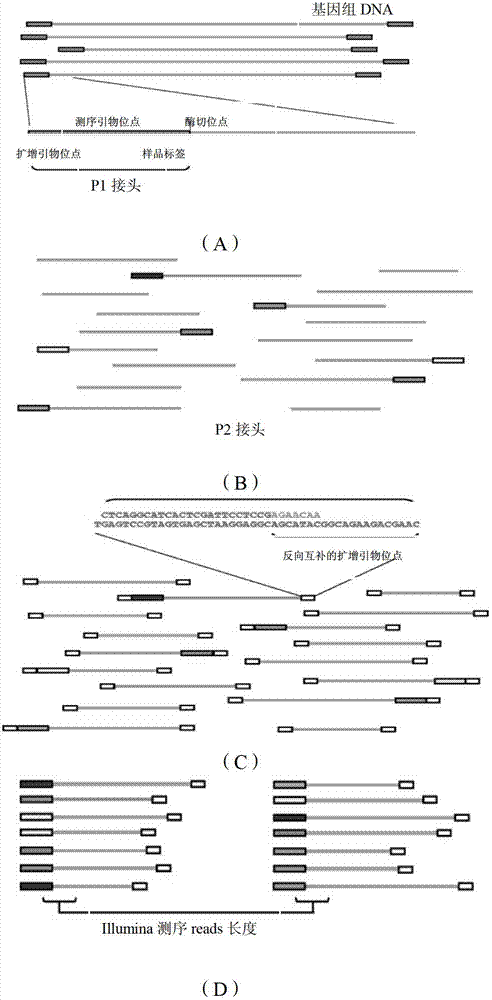
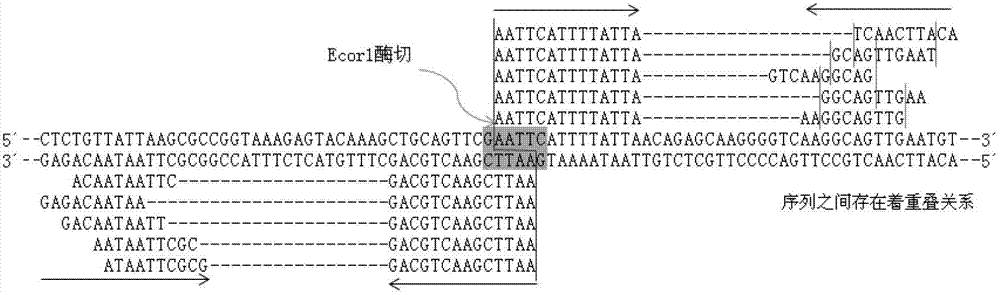
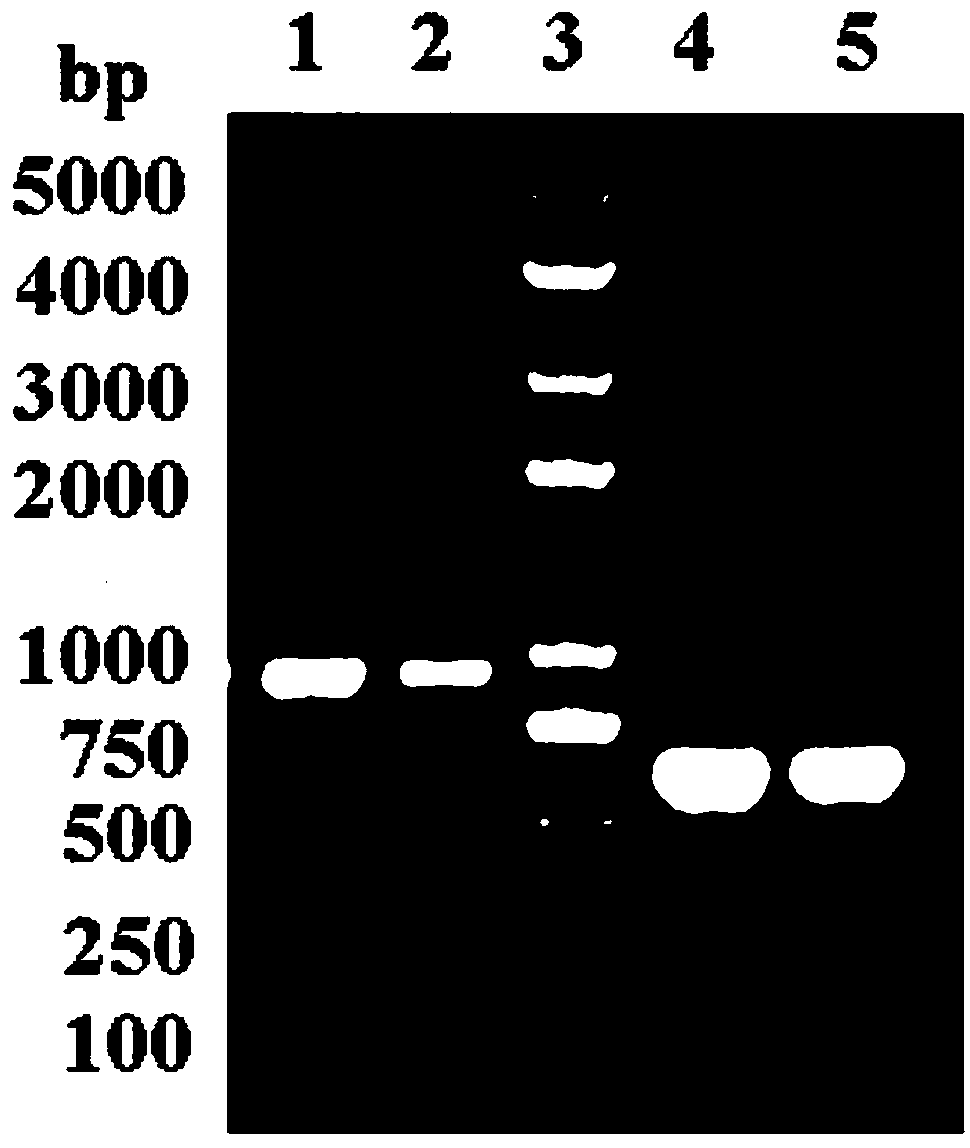
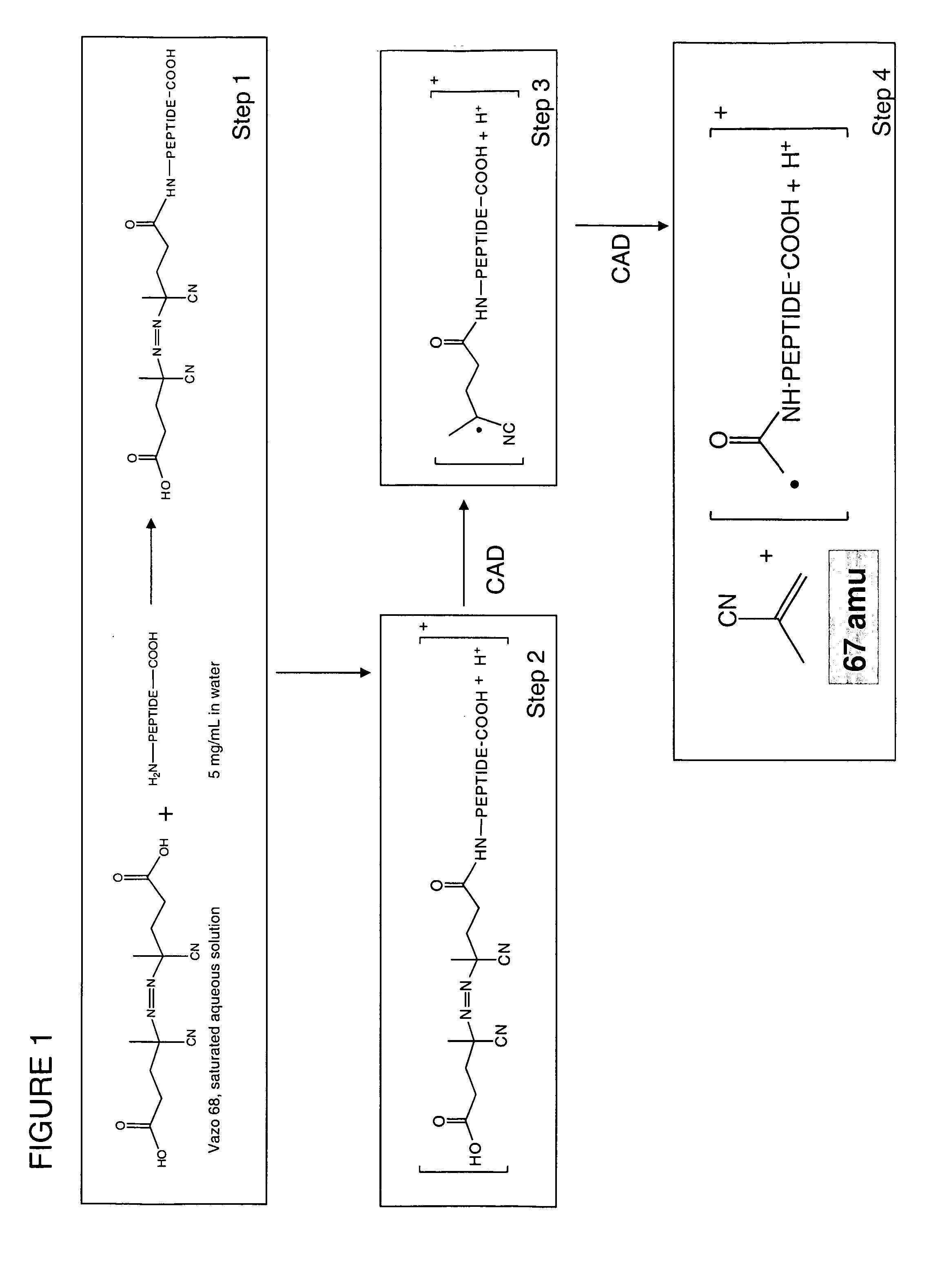
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
64 results about "Protein sequencing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Protein sequencing is the practical process of determining the amino acid sequence of all or part of a protein or peptide. This may serve to identify the protein or characterize its post-translational modifications. Typically, partial sequencing of a protein provides sufficient information (one or more sequence tags) to identify it with reference to databases of protein sequences derived from the conceptual translation of genes.
Method and system for rapid biomolecular recognition of amino acids and protein sequencing
InactiveUS6846638B2Low costHigh sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProtein Sequence DeterminationDigestion
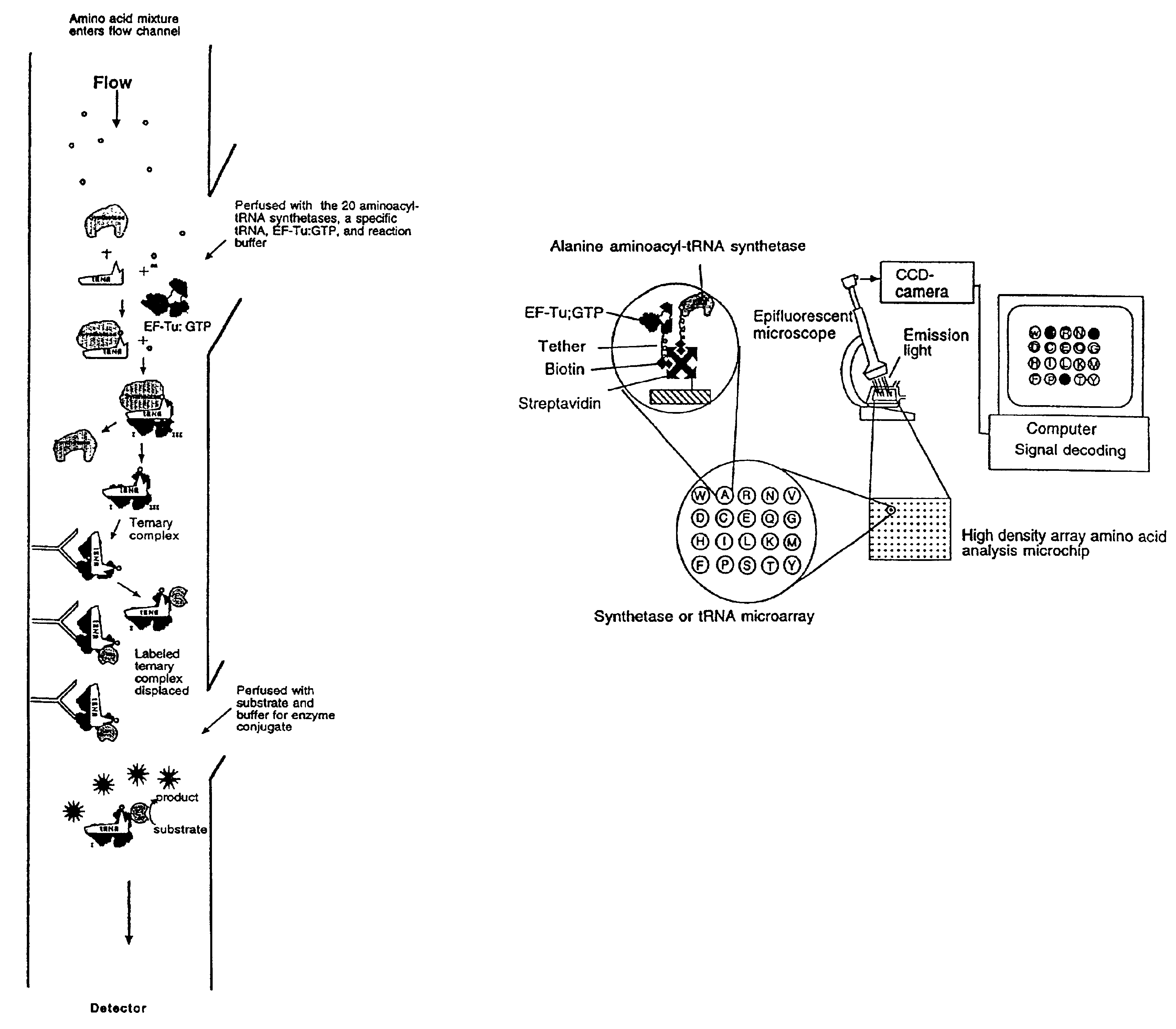
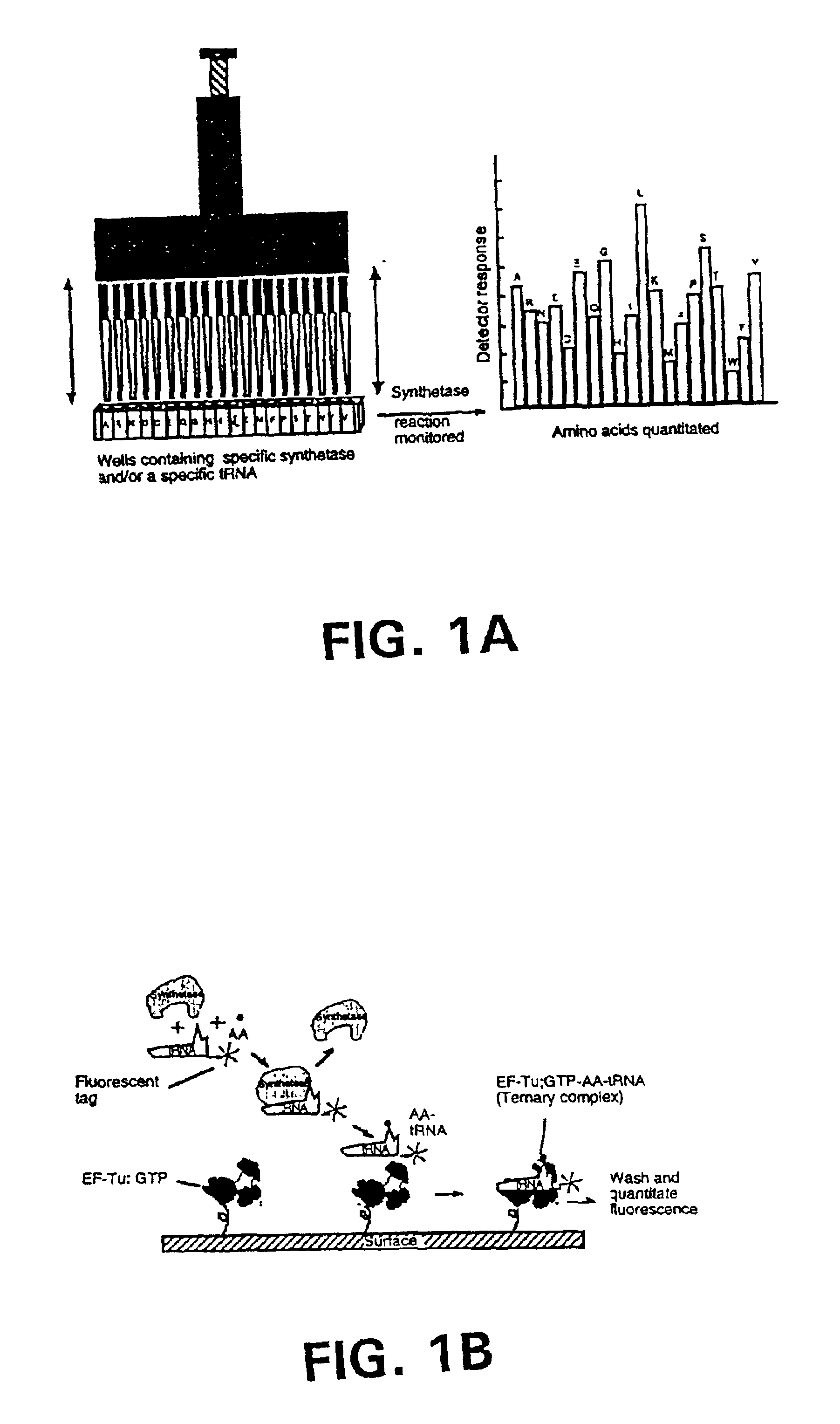
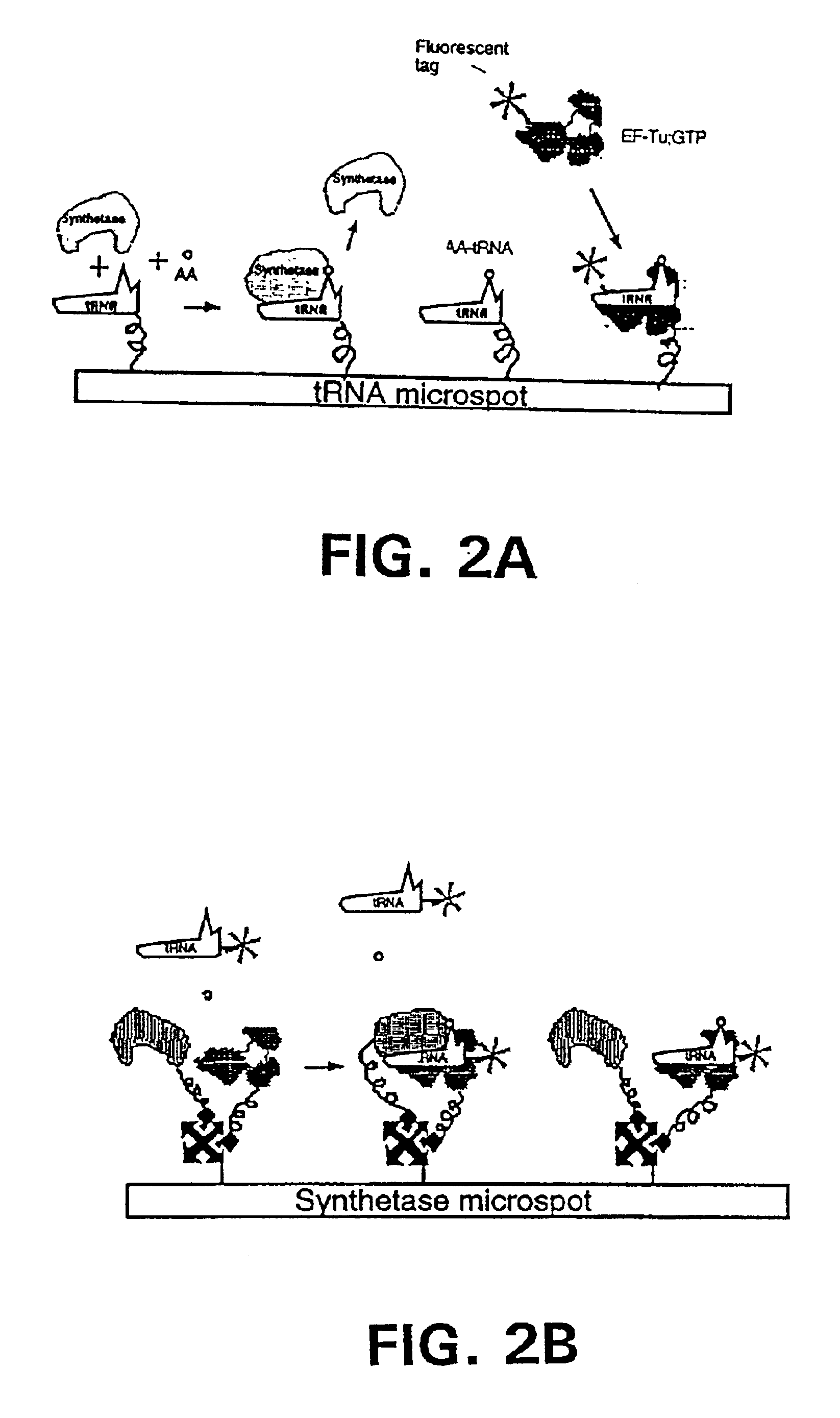
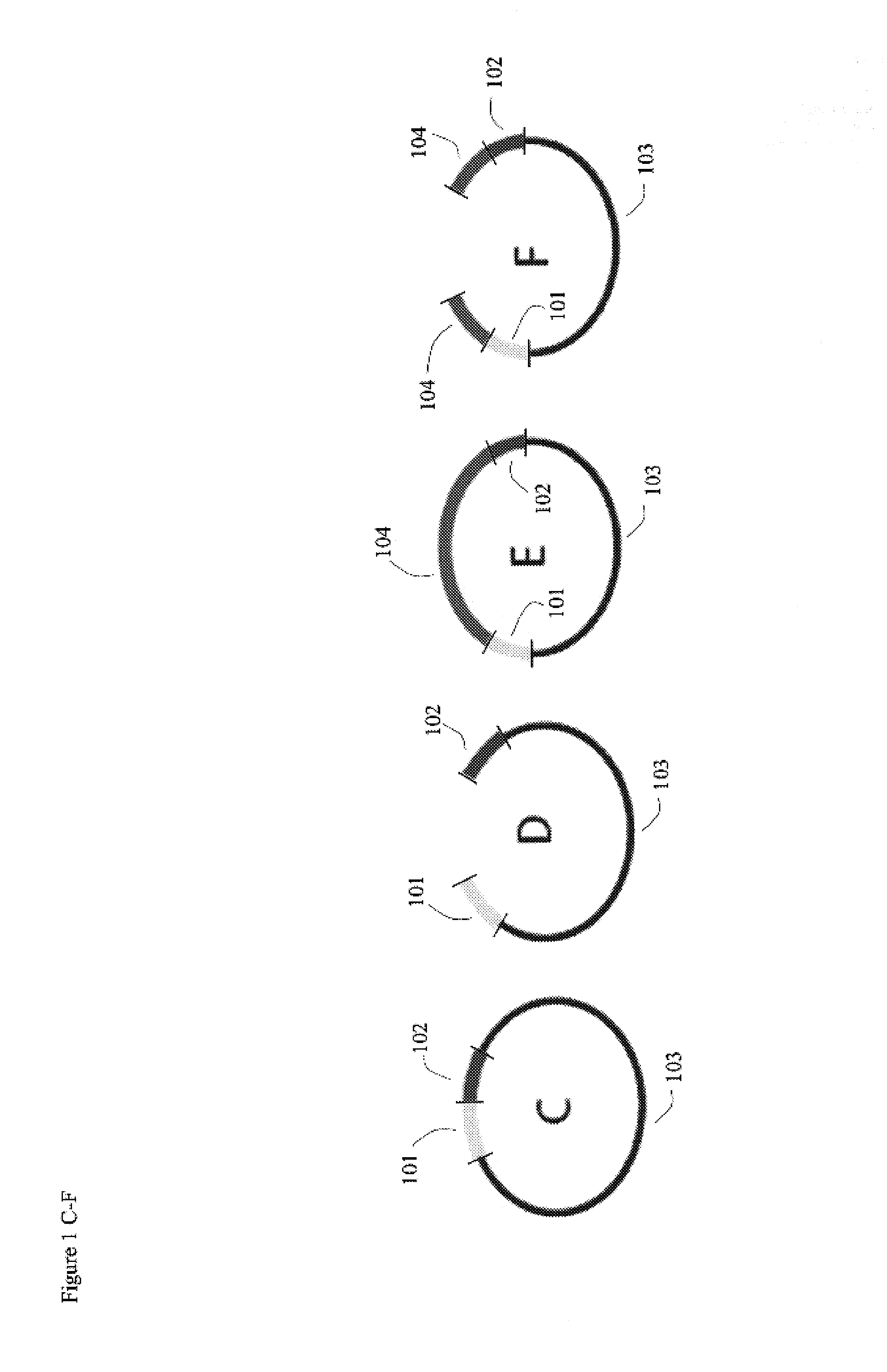
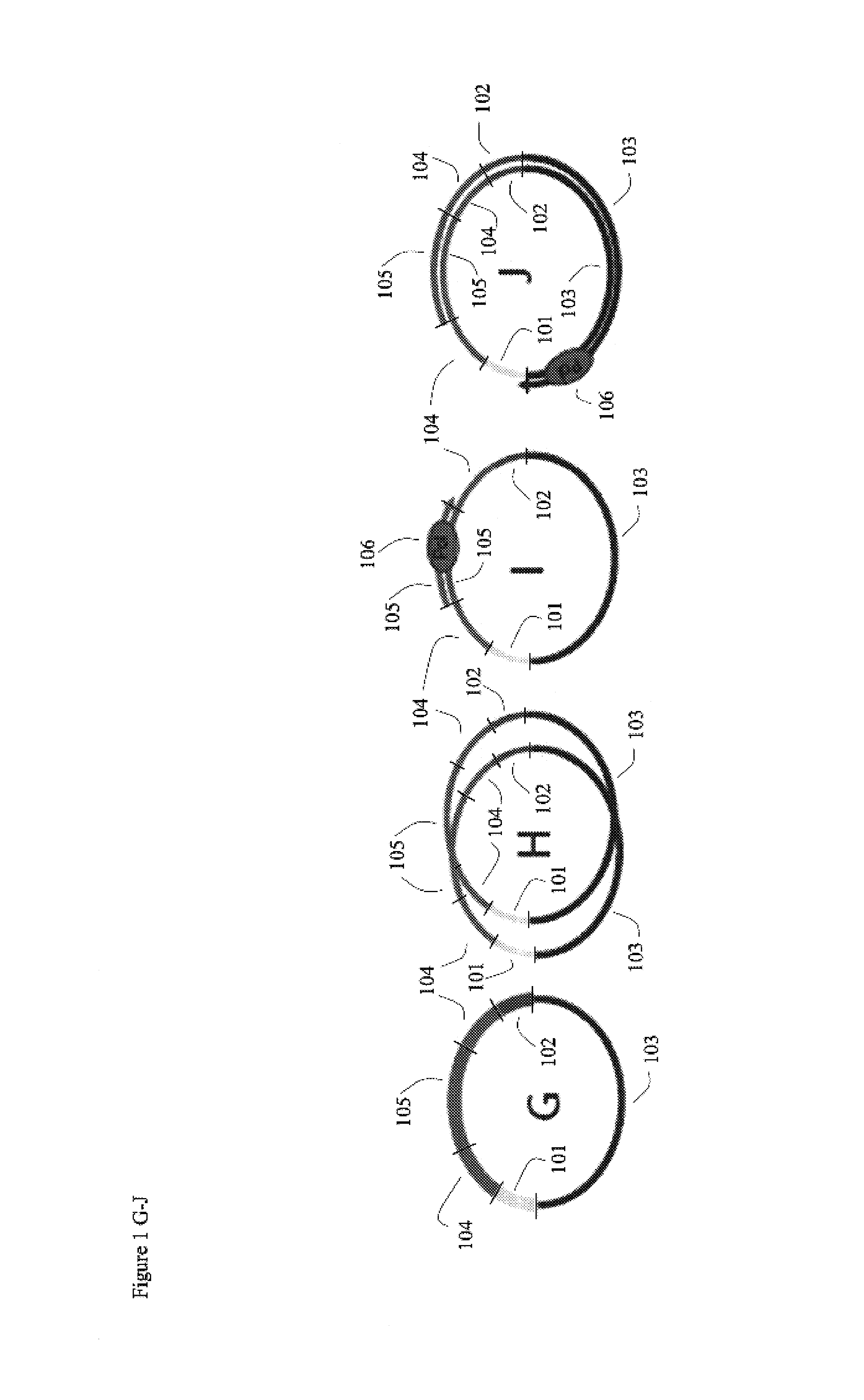
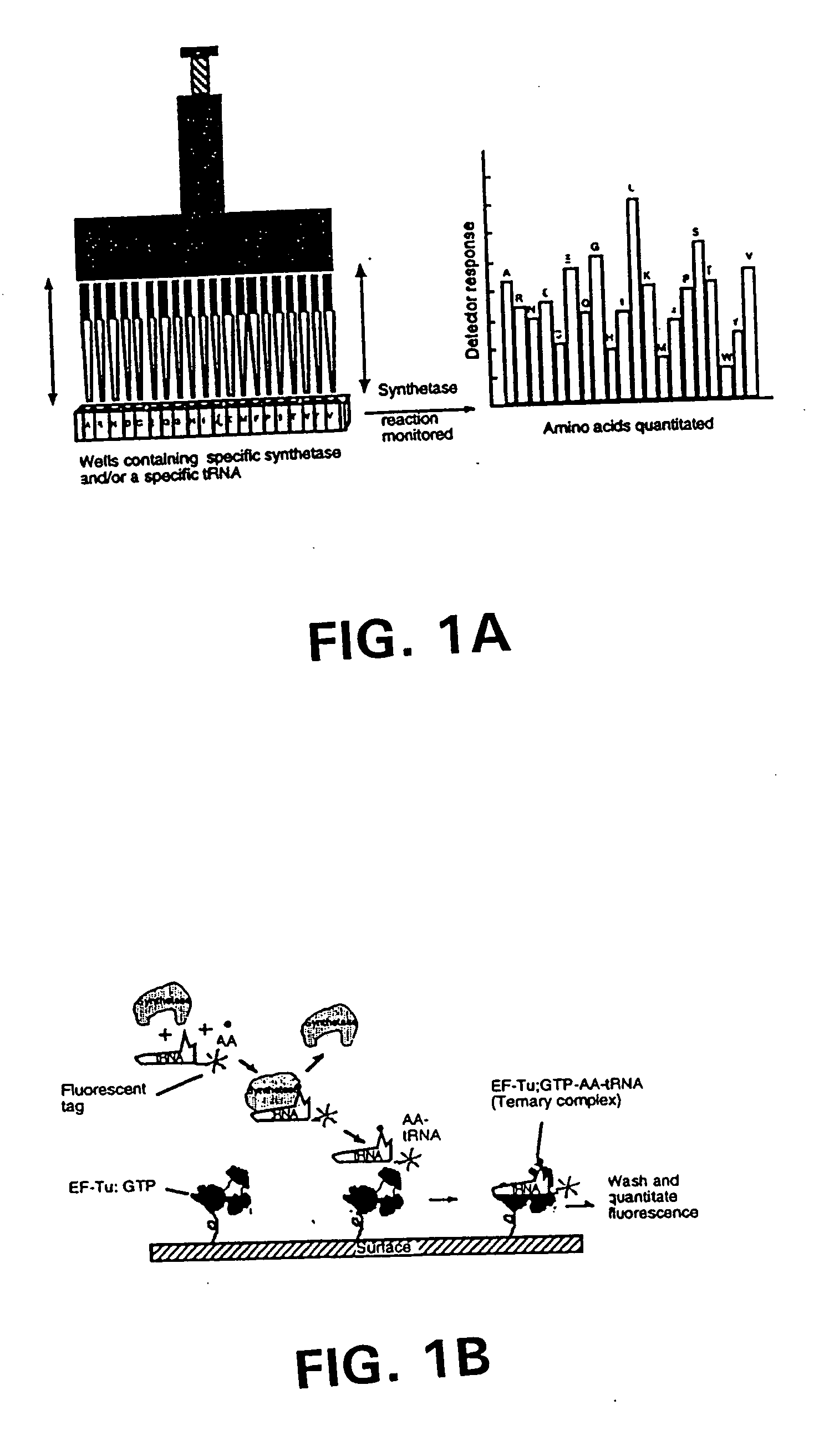
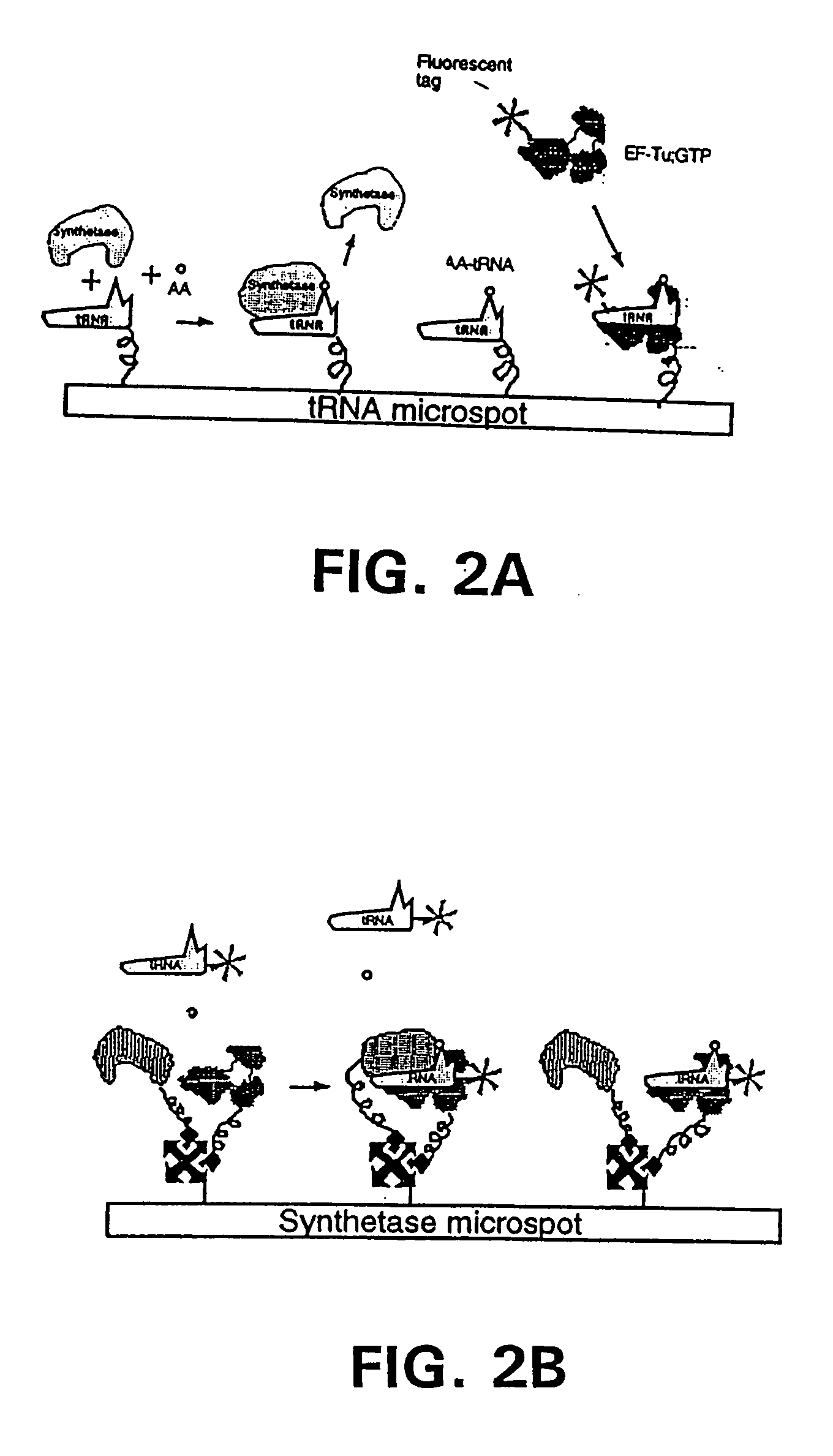
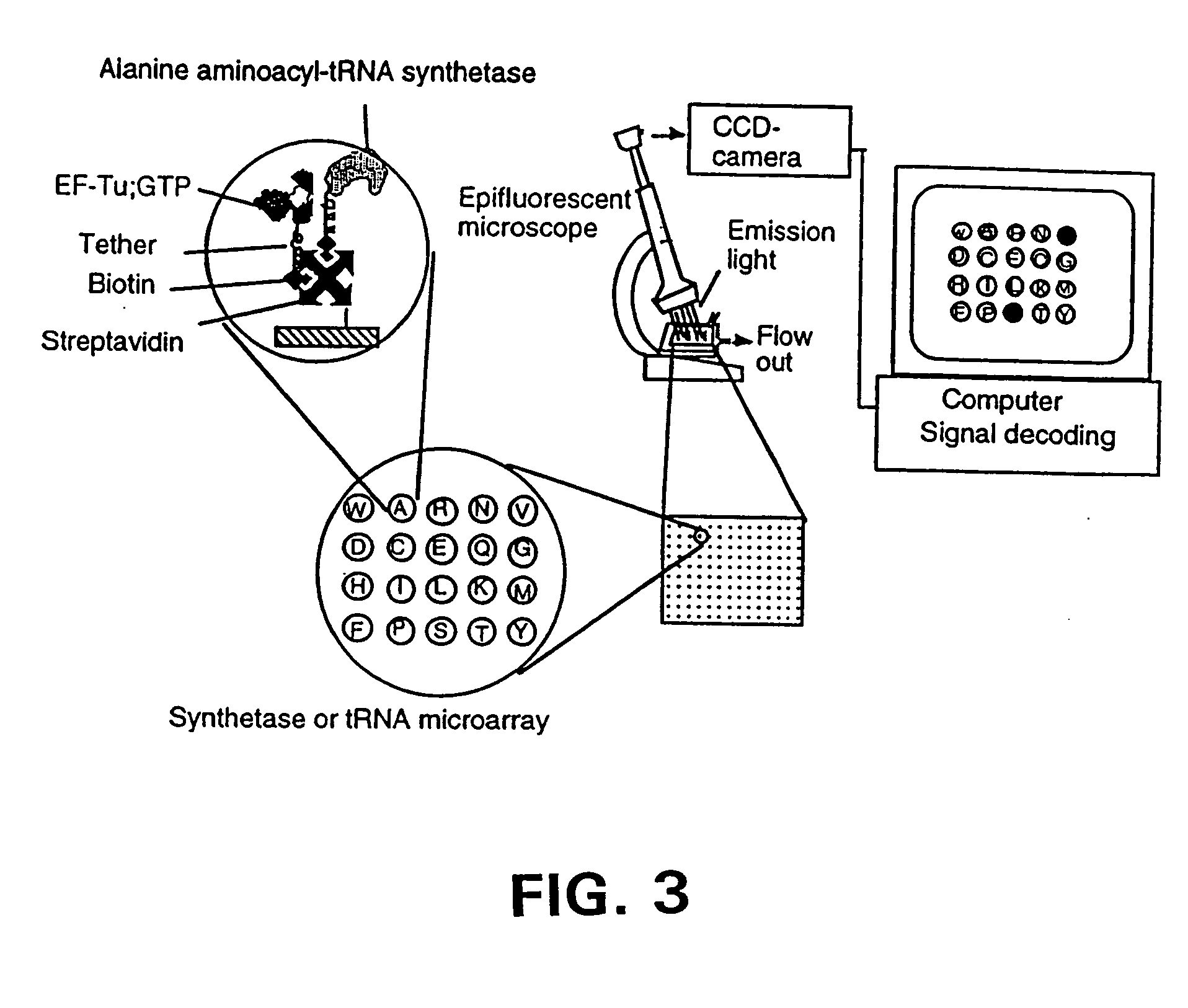
Methods, compositions, kits, and apparatus are provided wherein the aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase system is used to analyze amino acids. The method allows very small devices for quantitative or semi-quantitative analysis of the amino acids in samples or in sequential or complete proteolytic digestions. The methods can be readily applied to the detection and / or quantitation of one or more primary amino acids by using cognate aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase and cognate tRNA. The basis of the method is that each of the 20 synthetases and / or a tRNA specific for a different amino acid is separated spatially or differentially labeled. The reactions catalyzed by all 20 synthetases may be monitored simultaneously, or nearly simultaneously, or in parallel. Each separately positioned synthetase or tRNA will signal its cognate amino acid. The synthetase reactions can be monitored using continuous spectroscopic assays. Alternatively, since elongation factor Tu:GTP (EF-Tu:GTP) specifically binds all AA-tRNAs, the aminoacylation reactions catalyzed by the synthetases can be monitored using ligand assays. Microarrays and microsensors for amino acid analysis are provided. Additionally, amino acid analysis devices are integrated with protease digestions to produce miniaturized enzymatic sequenators capable of generating either N- or C-terminal sequence and composition data for a protein or peptide. The possibility of parallel processing of many samples in an automated manner is discussed.
Owner:NANOBIODYNAMICS
Paired end sequencing
The present invention provides for a method of preparing a target nucleic acid fragments to produce a smaller nucleic acid which comprises the two ends of the target nucleic acid. Specifically, the invention provides cloning and DNA manipulation strategies to isolate the two ends of a large target nucleic acid into a single small DNA construct for rapid cloning, sequencing, or amplification.
Owner:454 LIFE SCIENCES CORP
Method and system for rapid biomolecular recognition of amino acids and protein sequencing
InactiveUS20050164264A1Quick analysisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProtein Sequence DeterminationDigestion
Methods, compositions, kits, and apparatus are provided wherein the aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase system is used to analyze amino acids. The method allows very small devices for quantitative or semi-quantitative analysis of the amino acids in samples or in sequential or complete proteolytic digestions. The methods can be readily applied to the detection and / or quantitation of one or more primary amino acids by using cognate aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase and cognate tRNA. The basis of the method is that each of the 20 synthetases and / or a tRNA specific for a different amino acid is separated spatially or differentially labeled. The reactions catalyzed by all 20 synthetases may be monitored simultaneously, or nearly simultaneously, or in parallel. Each separately positioned synthetase or tRNA will signal its cognate amino acid. The synthetase reactions can be monitored using continuous spectroscopic assays. Alternatively, since elongation factor Tu:GTP (EF-Tu:GTP) specifically binds all AA−tRNAs, the aminoacylation reactions catalyzed by the synthetases can be monitored using ligand assays. Microarrays and microsensors for amino acid analysis are provided. Additionally, amino acid analysis devices are integrated with protease digestions to produce miniaturized enzymatic sequenators capable of generating either N- or C-terminal sequence and composition data for a protein or peptide. The possibility of parallel processing of many samples in an automated manner is discussed.
Owner:NANOBIODYNAMICS
Control system and apparatus for use with laser excitation or ionization
InactiveUS7105811B2Way fastMaximize sensitivityLaser detailsIon sources/gunsPhotodynamic therapyControl system
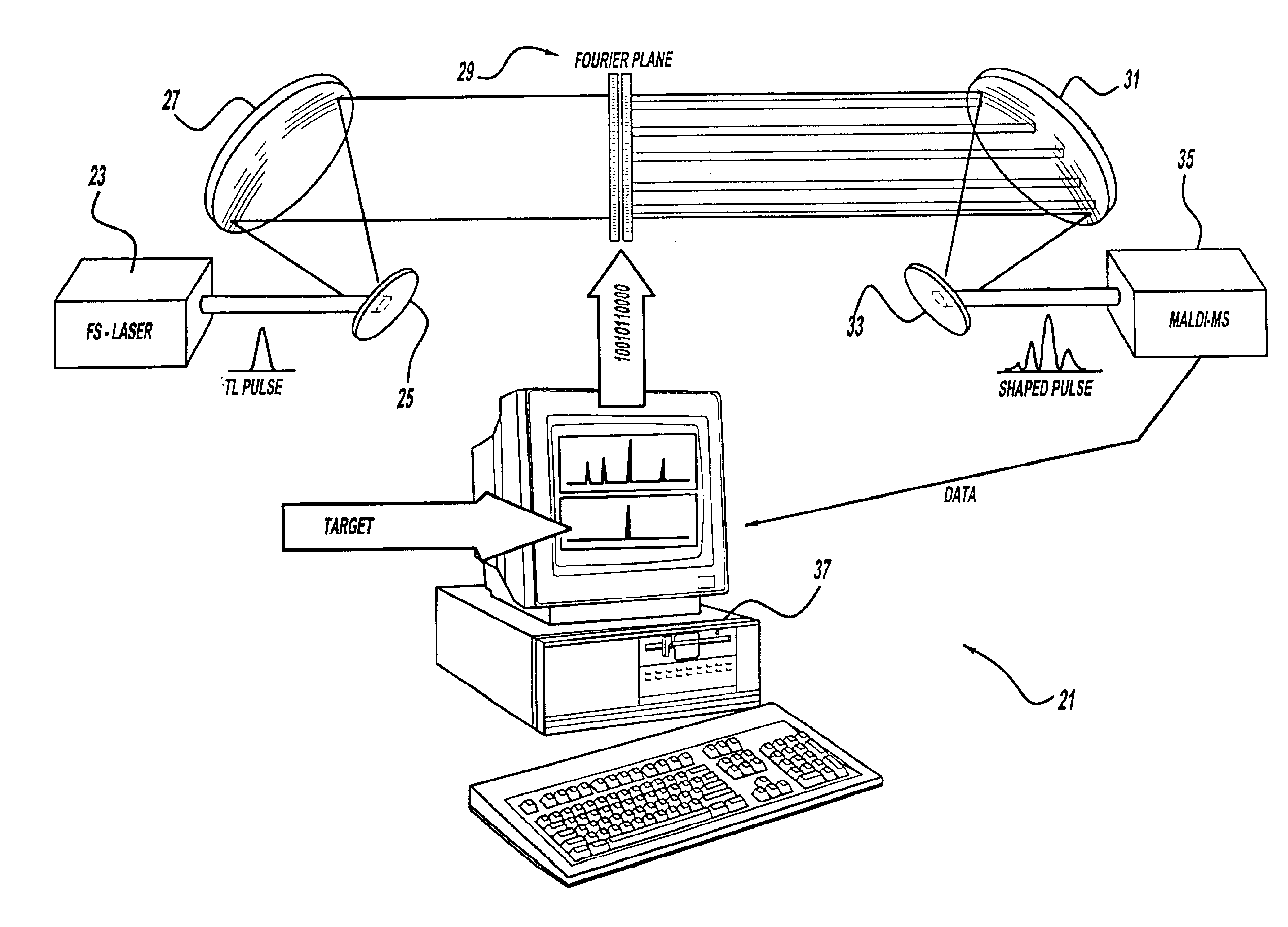
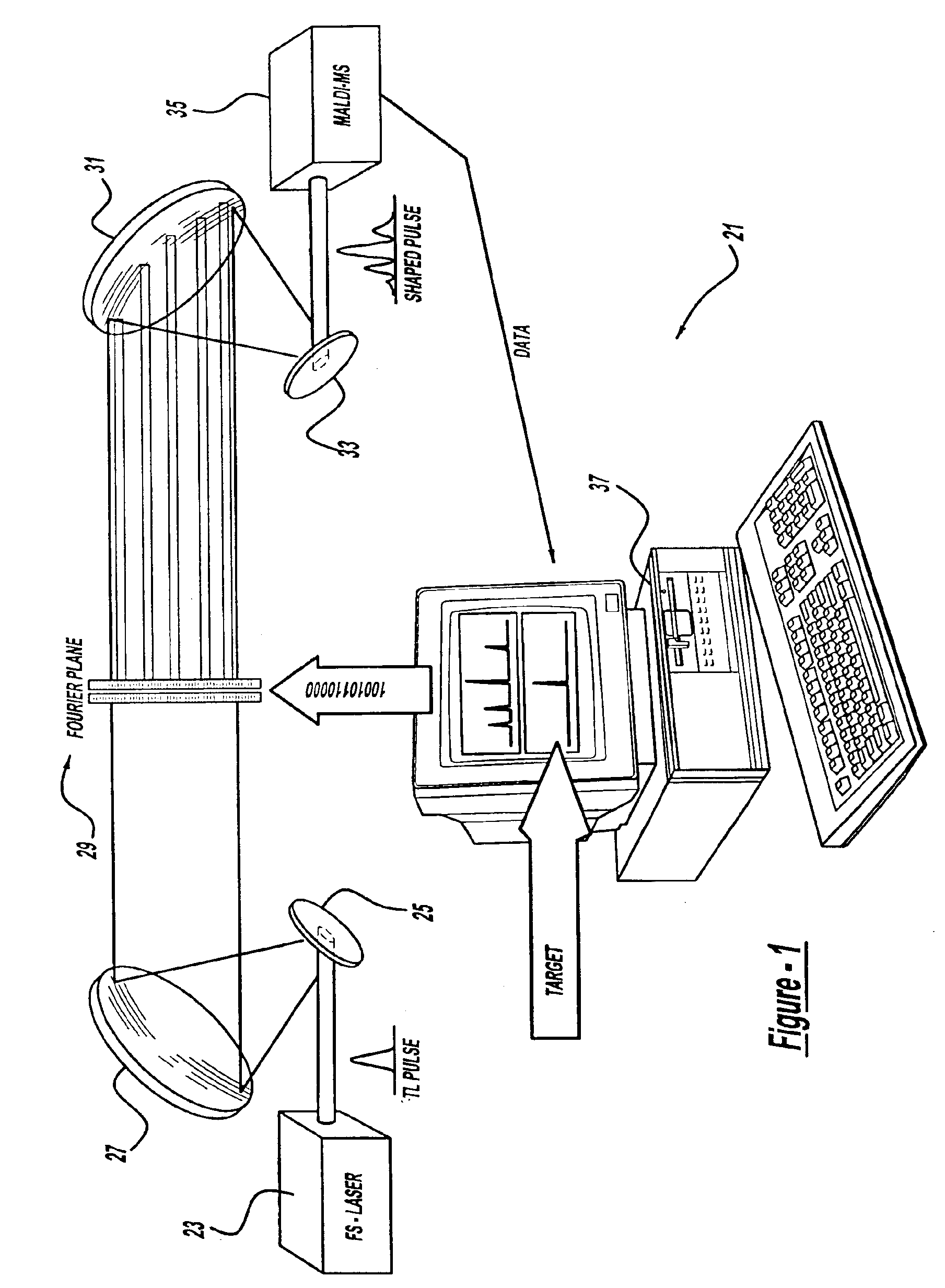
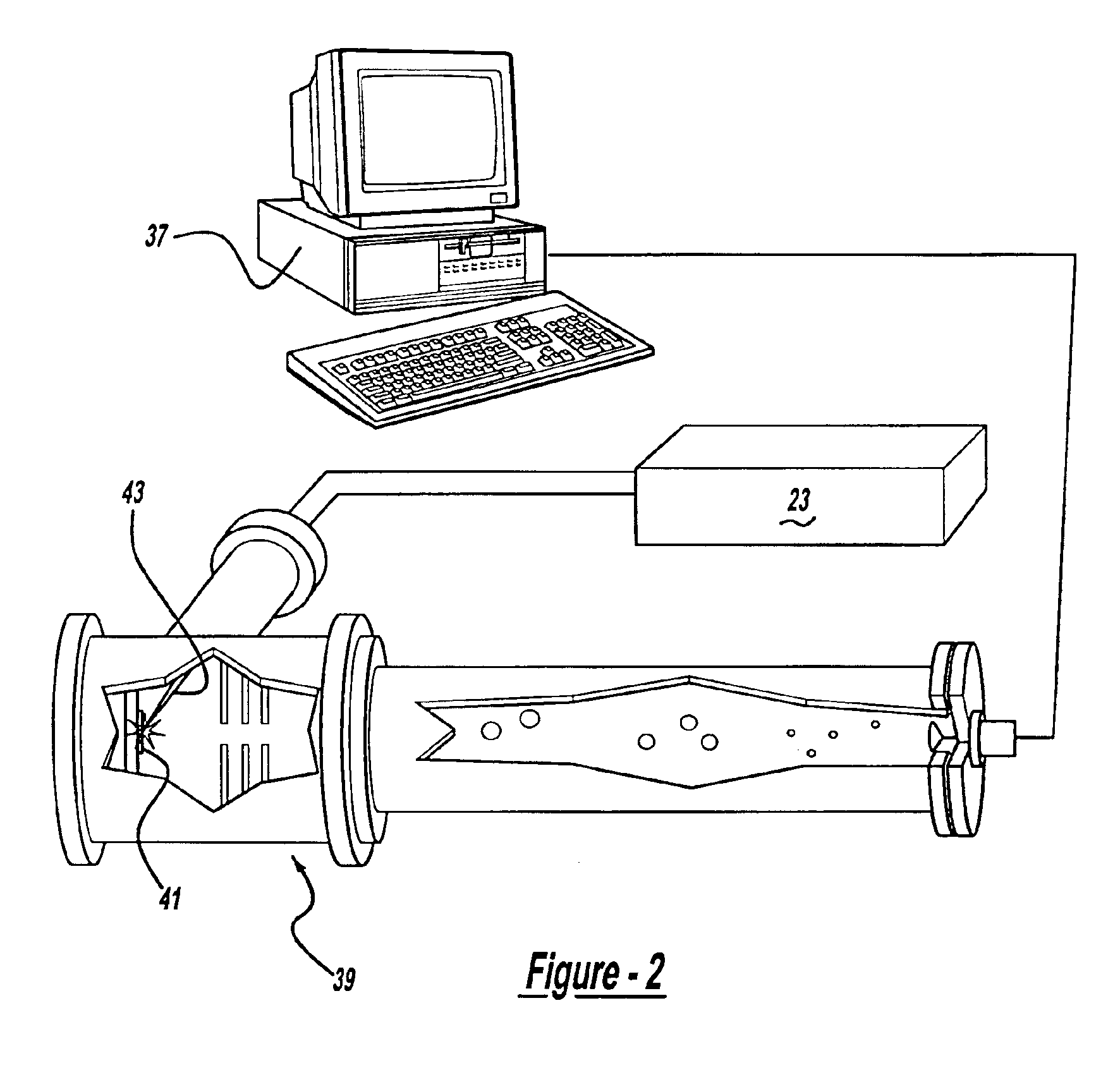
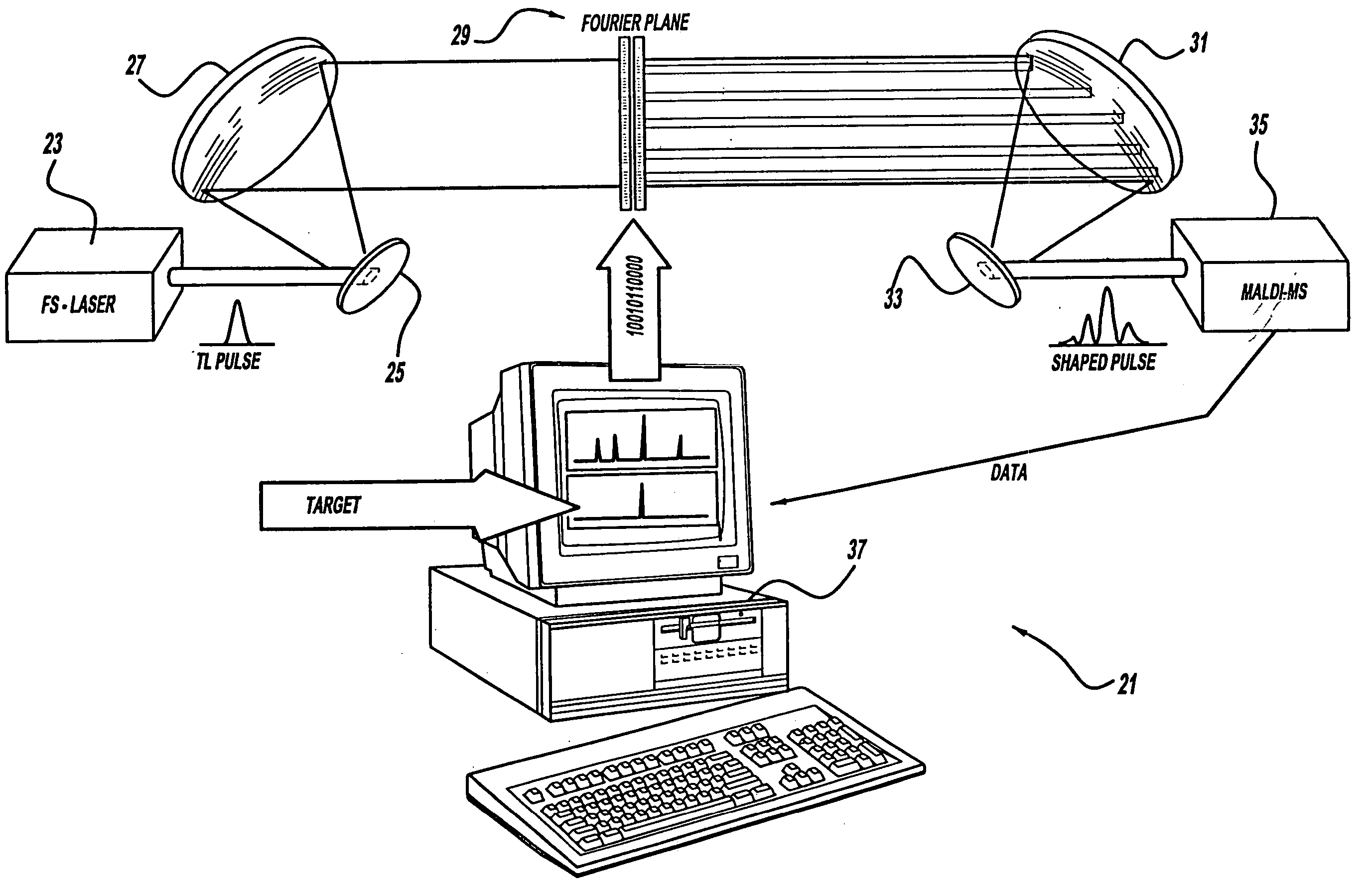
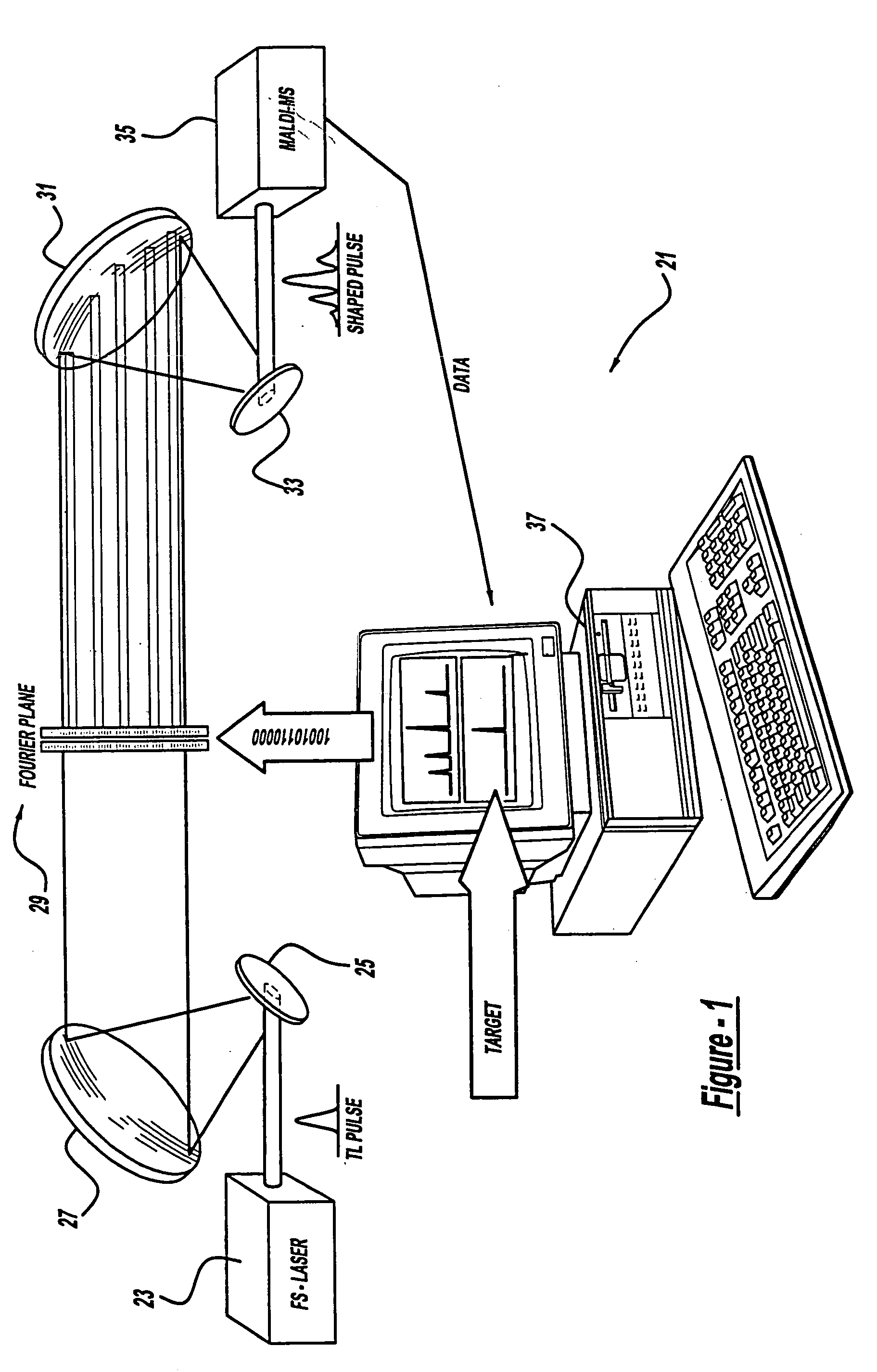
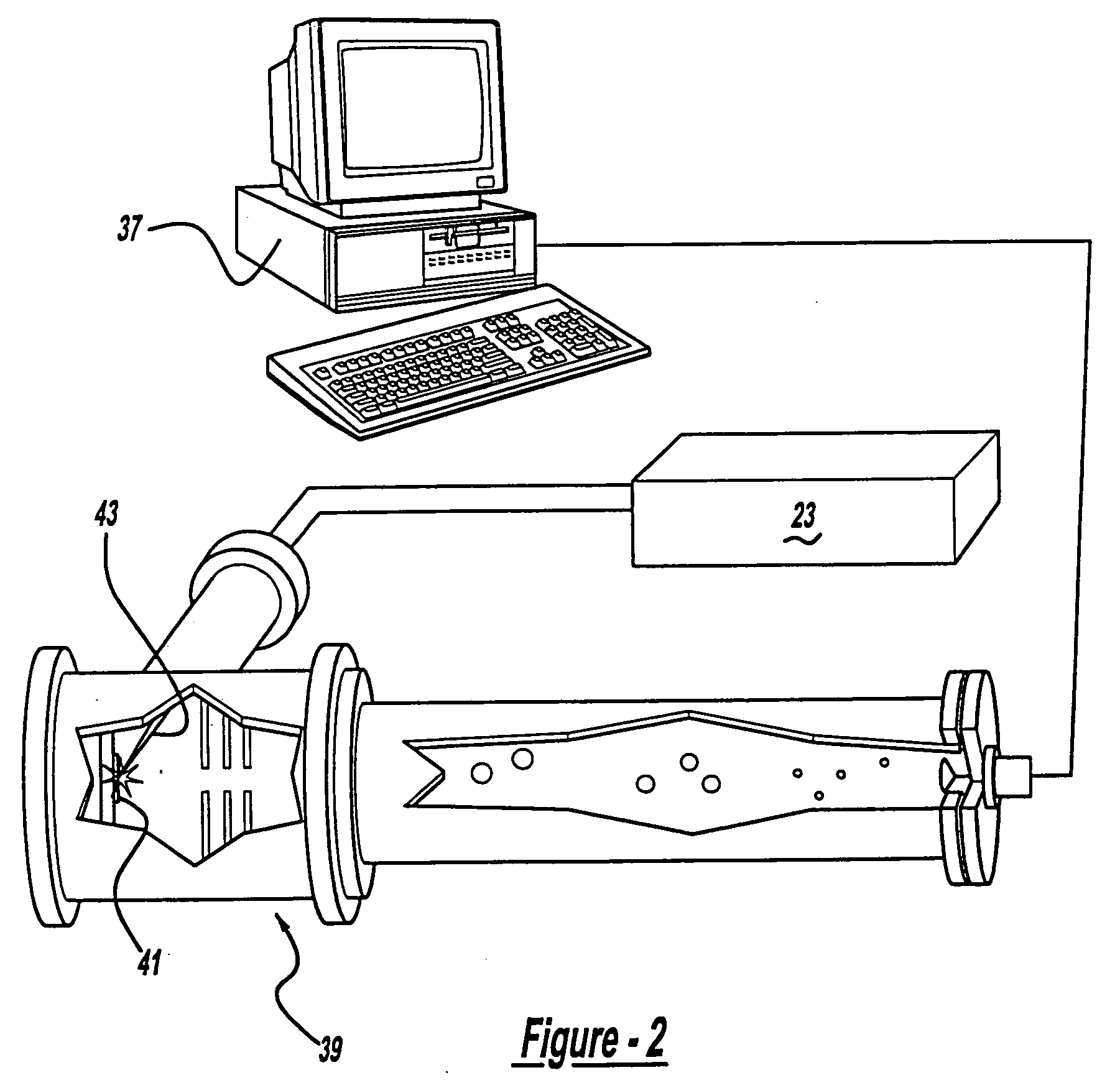
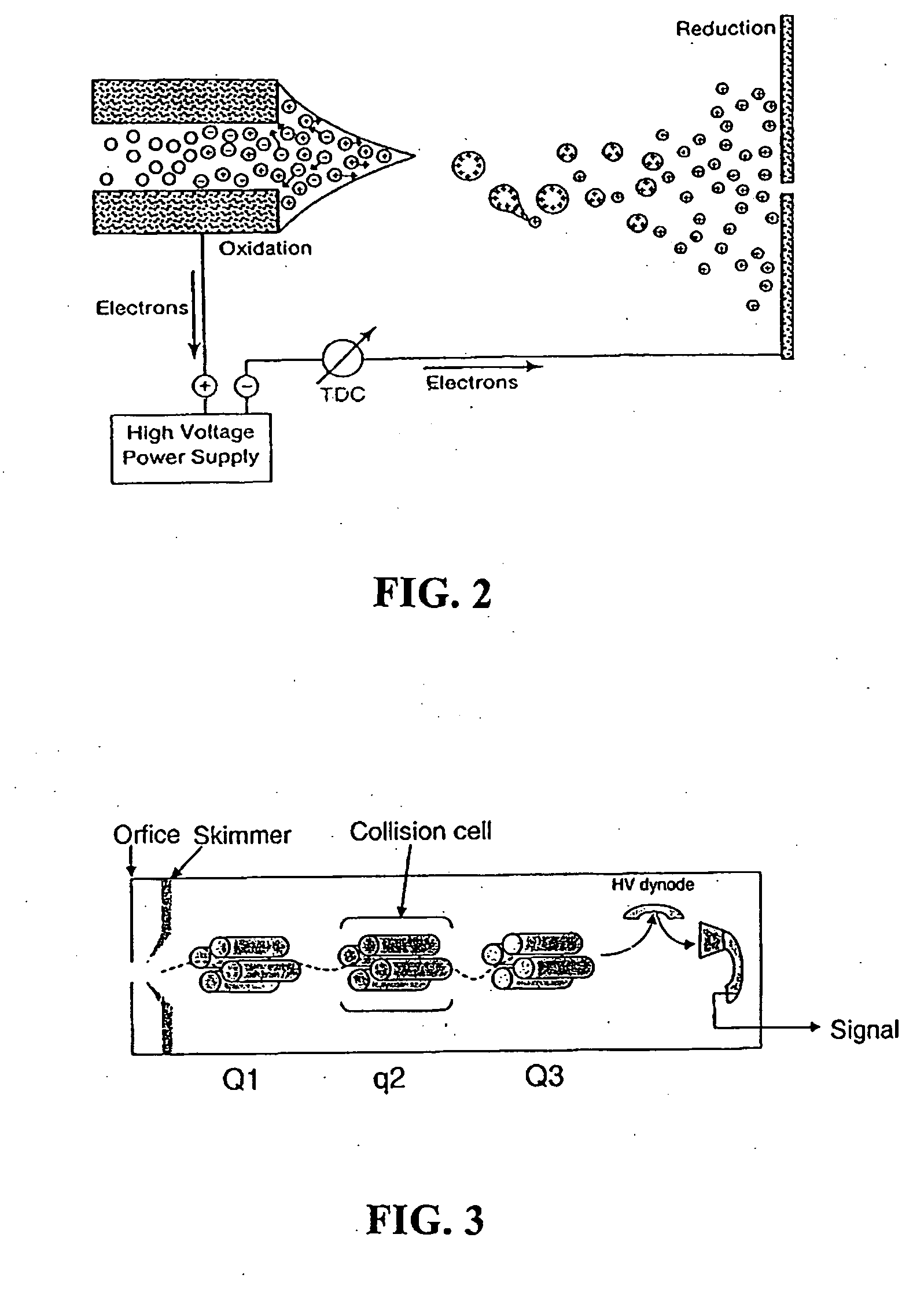
A control system and apparatus for use with laser ionization is provided. In another aspect of the present invention, the apparatus includes a laser, pulse shaper, detection device and control system. A further aspect of the present invention employs a femtosecond laser and a mass spectrometer. In yet other aspects of the present invention, the control system and apparatus are used in MALDI, chemical bond cleaving, protein sequencing, photodynamic therapy, optical coherence tomography and optical communications processes.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Methods and device for analyte characterization
ActiveUS8278055B2Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingAnalyteProtein Sequence Determination
Owner:INTEL CORP
Methods and device for analyte characterization
ActiveUS20050282229A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingAnalyteProtein Sequence Determination
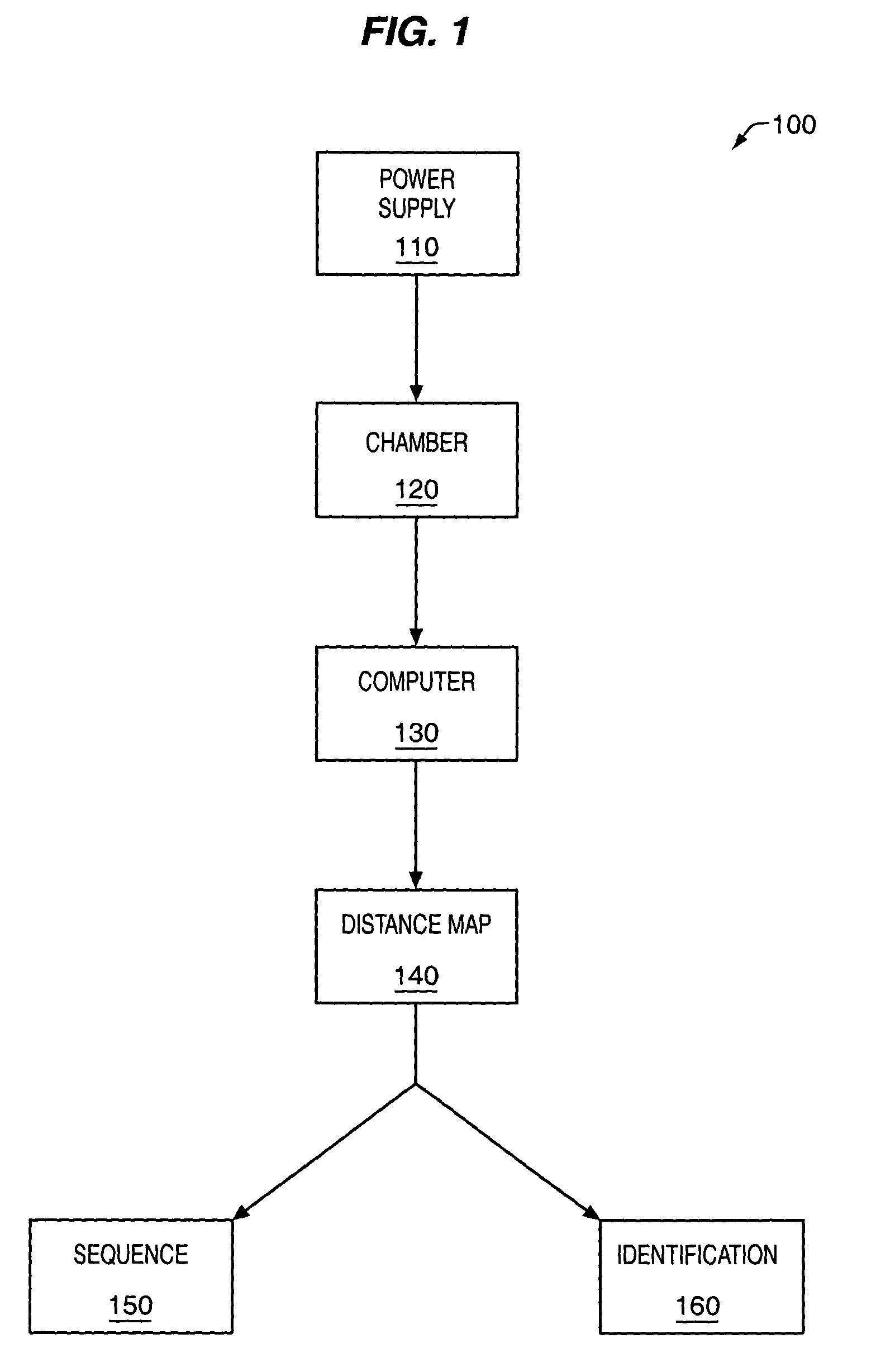
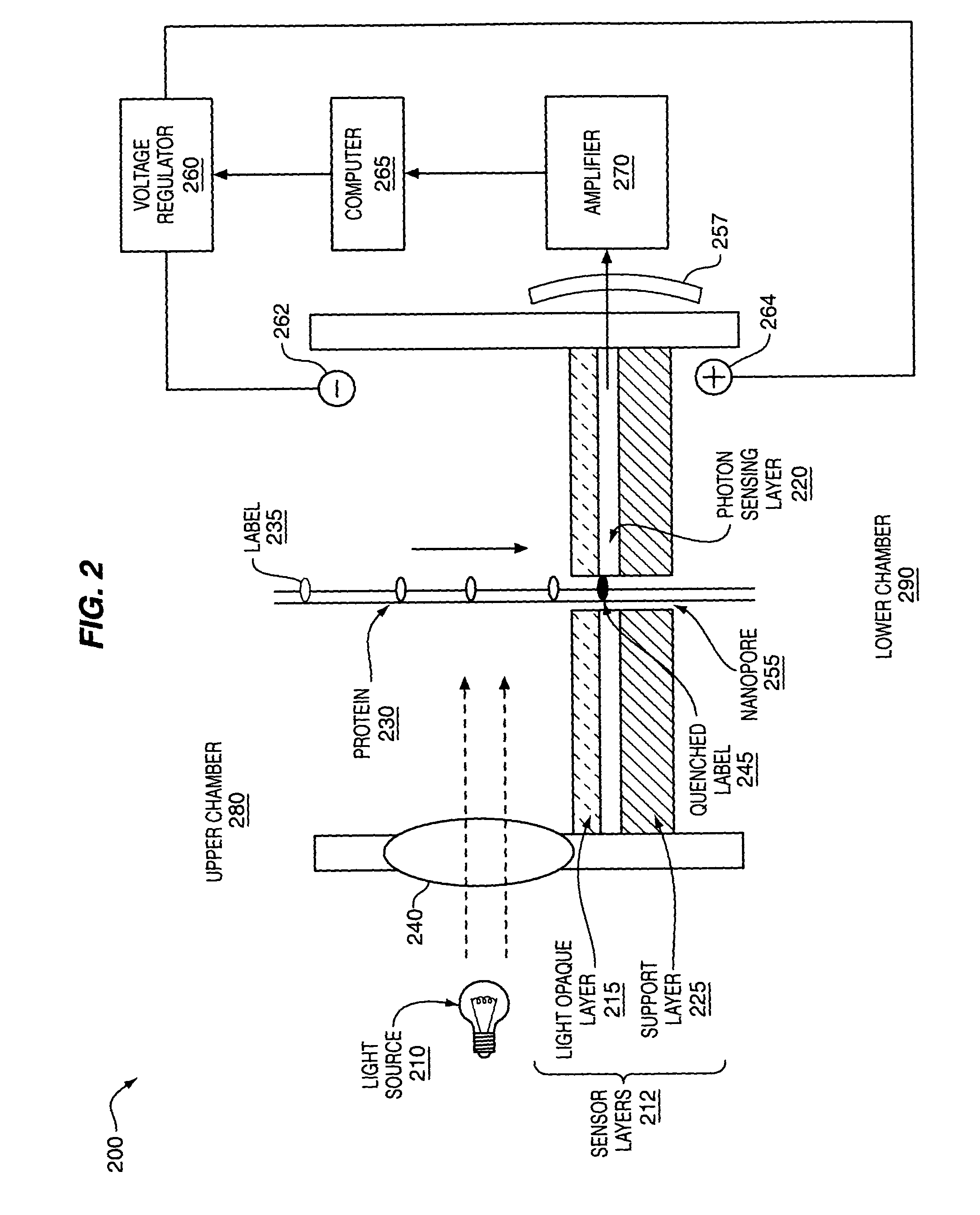
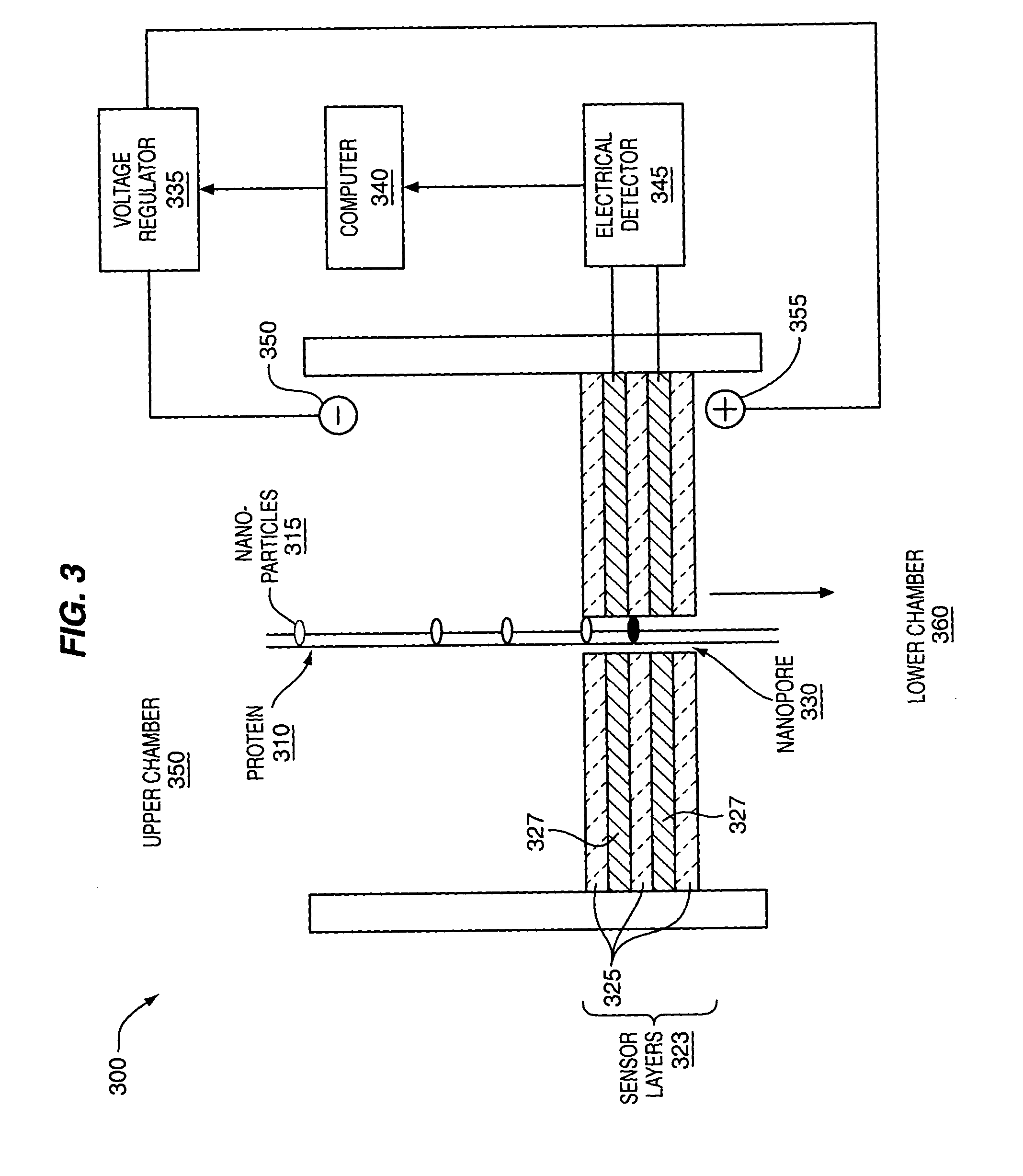
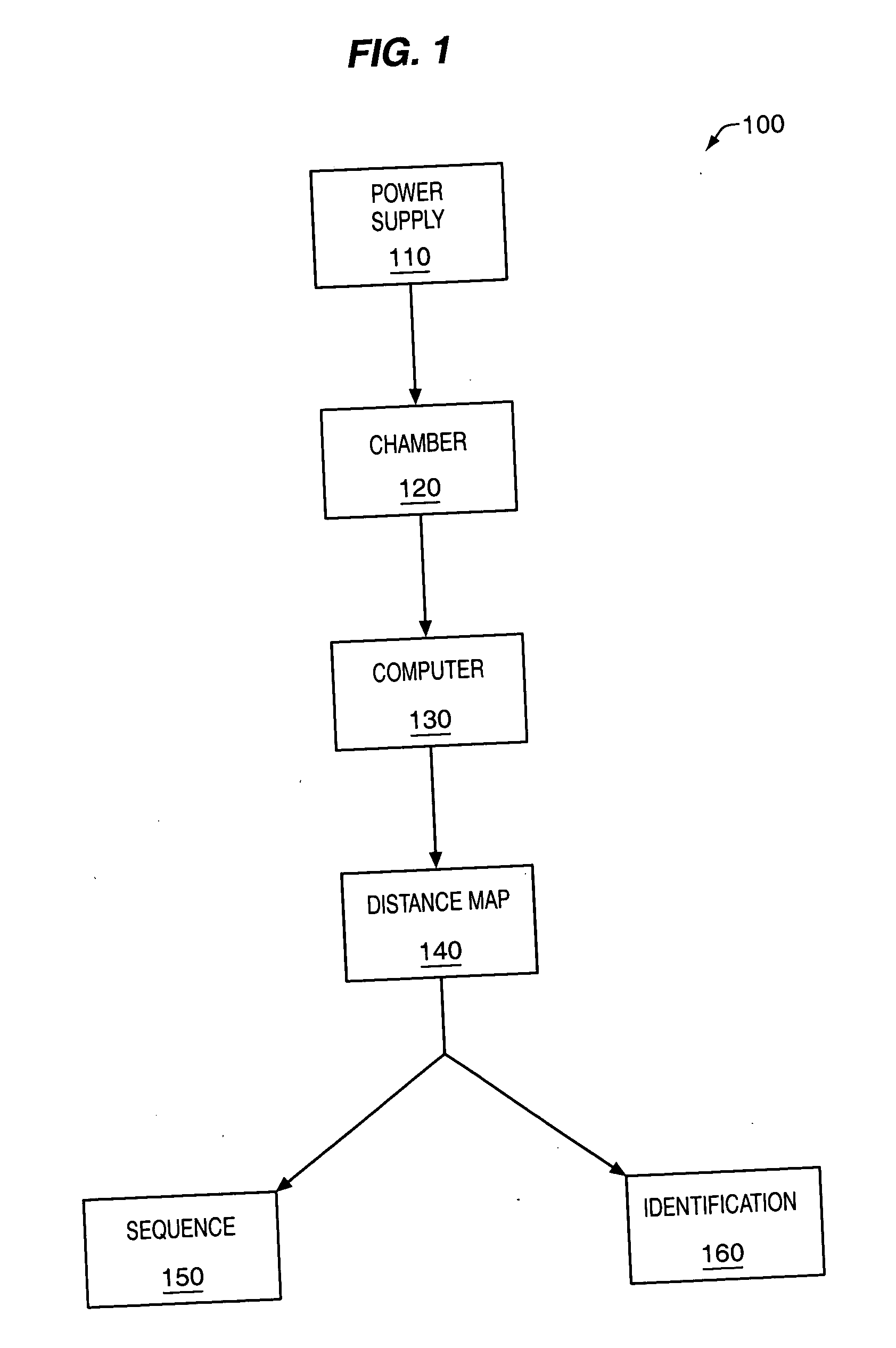
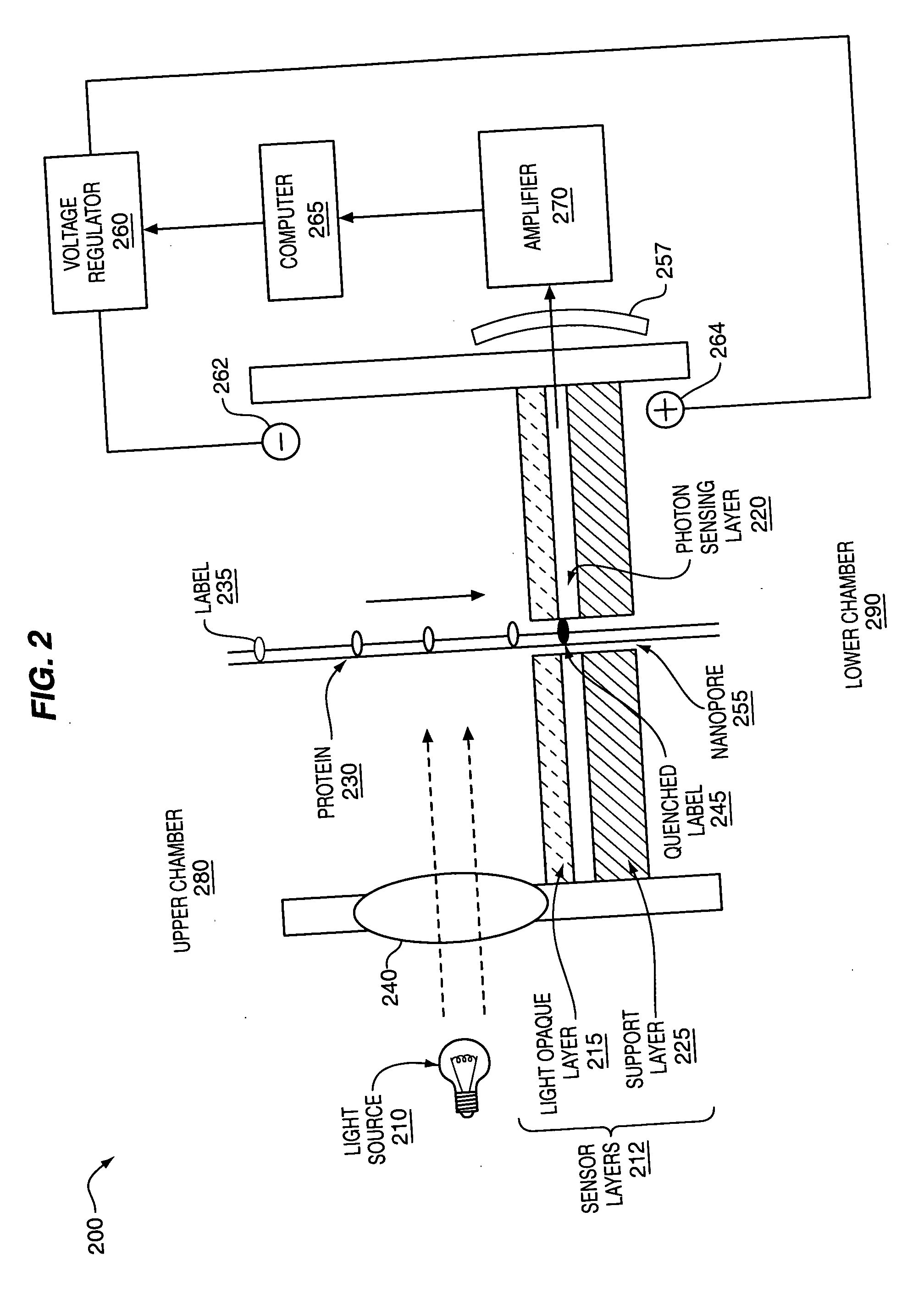
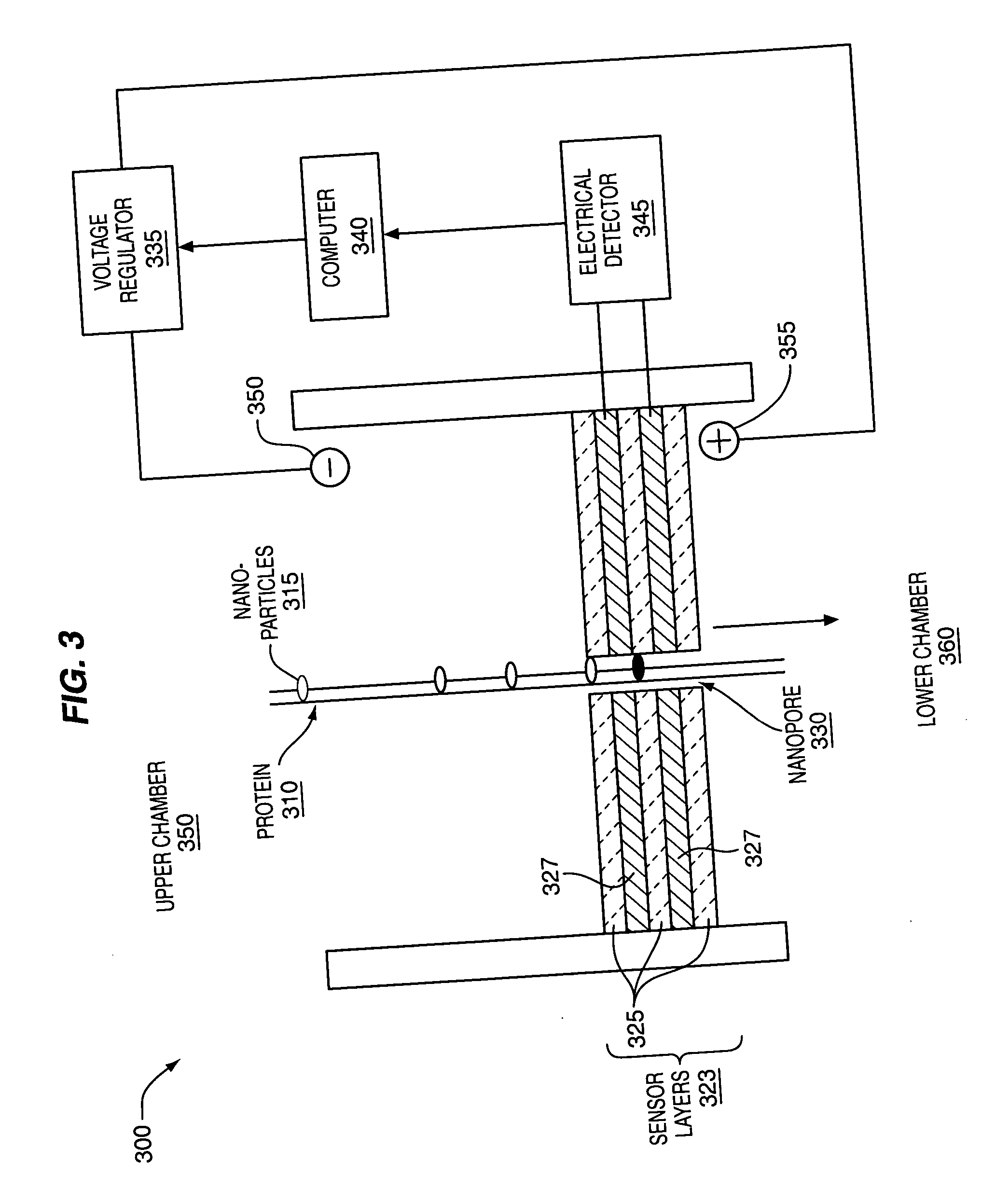
The methods and apparatus, disclosed herein are of use for sequencing and / or identifying proteins, polypeptides and / or peptides. Proteins containing labeled amino acid residues may be synthesized and passed through nanopores. A detector operably coupled to a nanopore may detect labeled amino acid residues as they pass through the nanopore. Distance maps for each type of labeled amino acid residue may be compiled. The distance maps may be used to sequence and / or identify the protein. Apparatus of use for protein sequencing and / or identification is also disclosed herein. In alternative methods, other types of analytes may be analyzed by the same techniques.
Owner:INTEL CORP
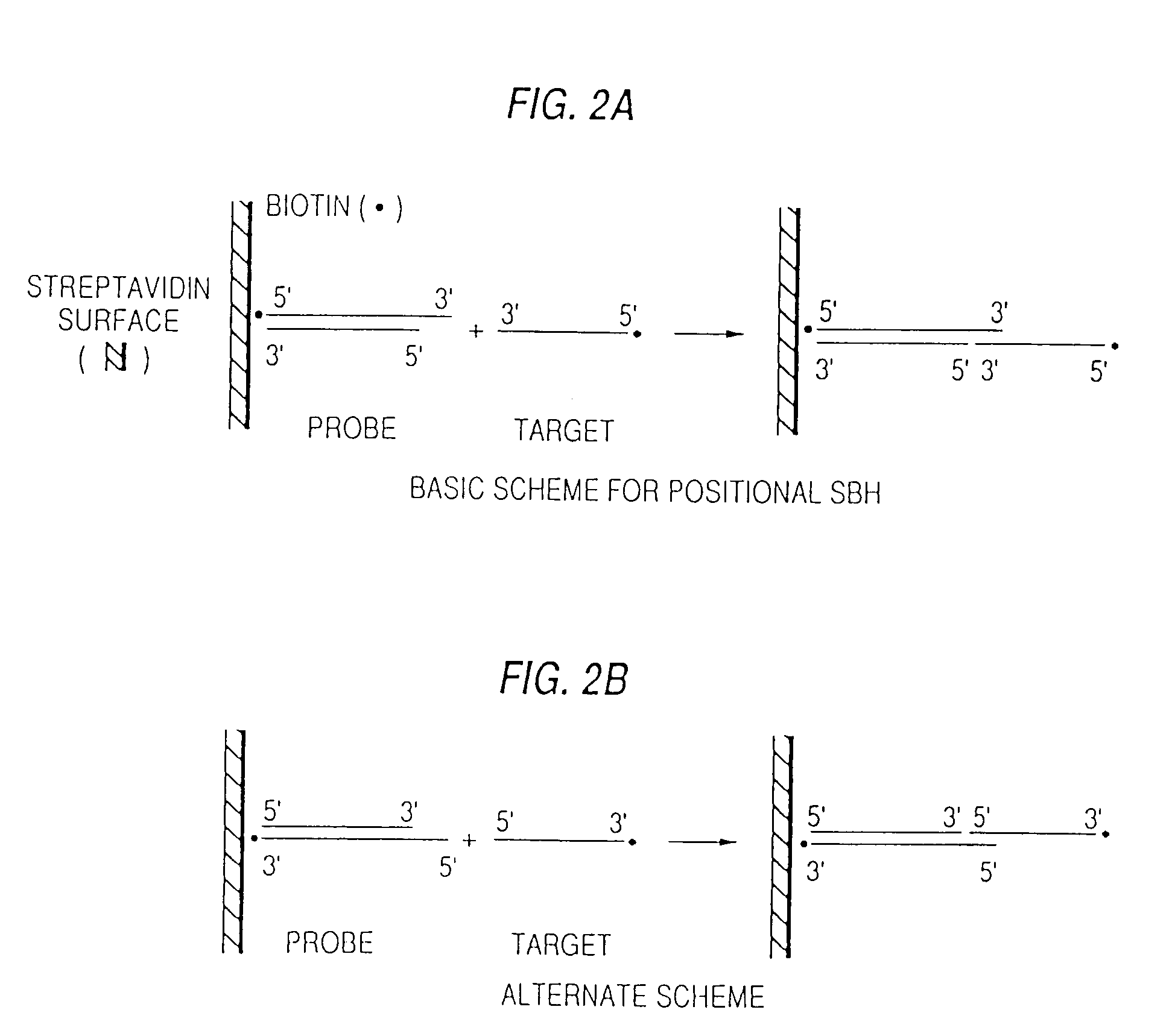
Arrays of probes for positional sequencing by hybridization
InactiveUS7319003B2Rapidly and accurately determining nucleotide sequenceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSequential/parallel process reactionsPcr ctppBiology
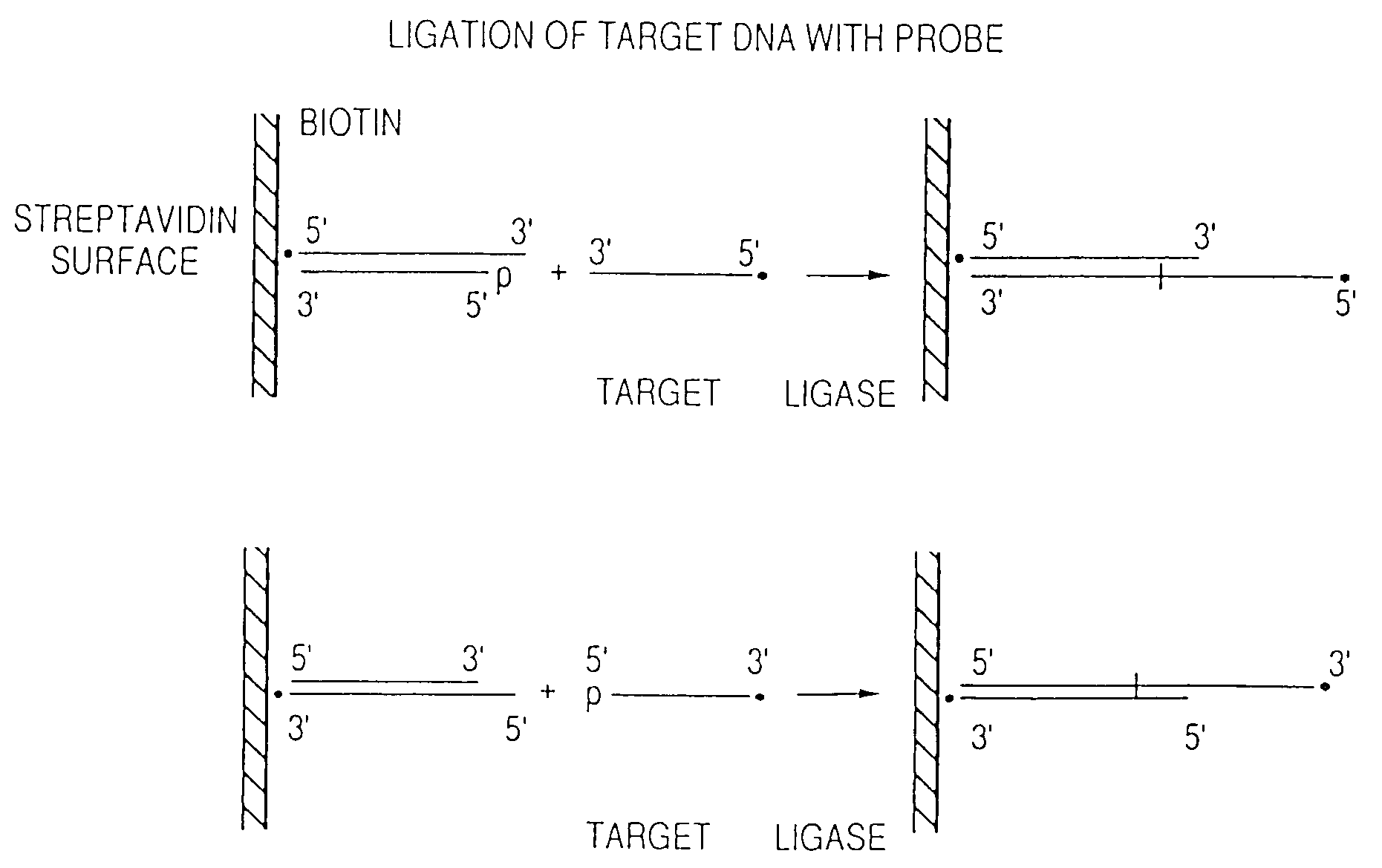
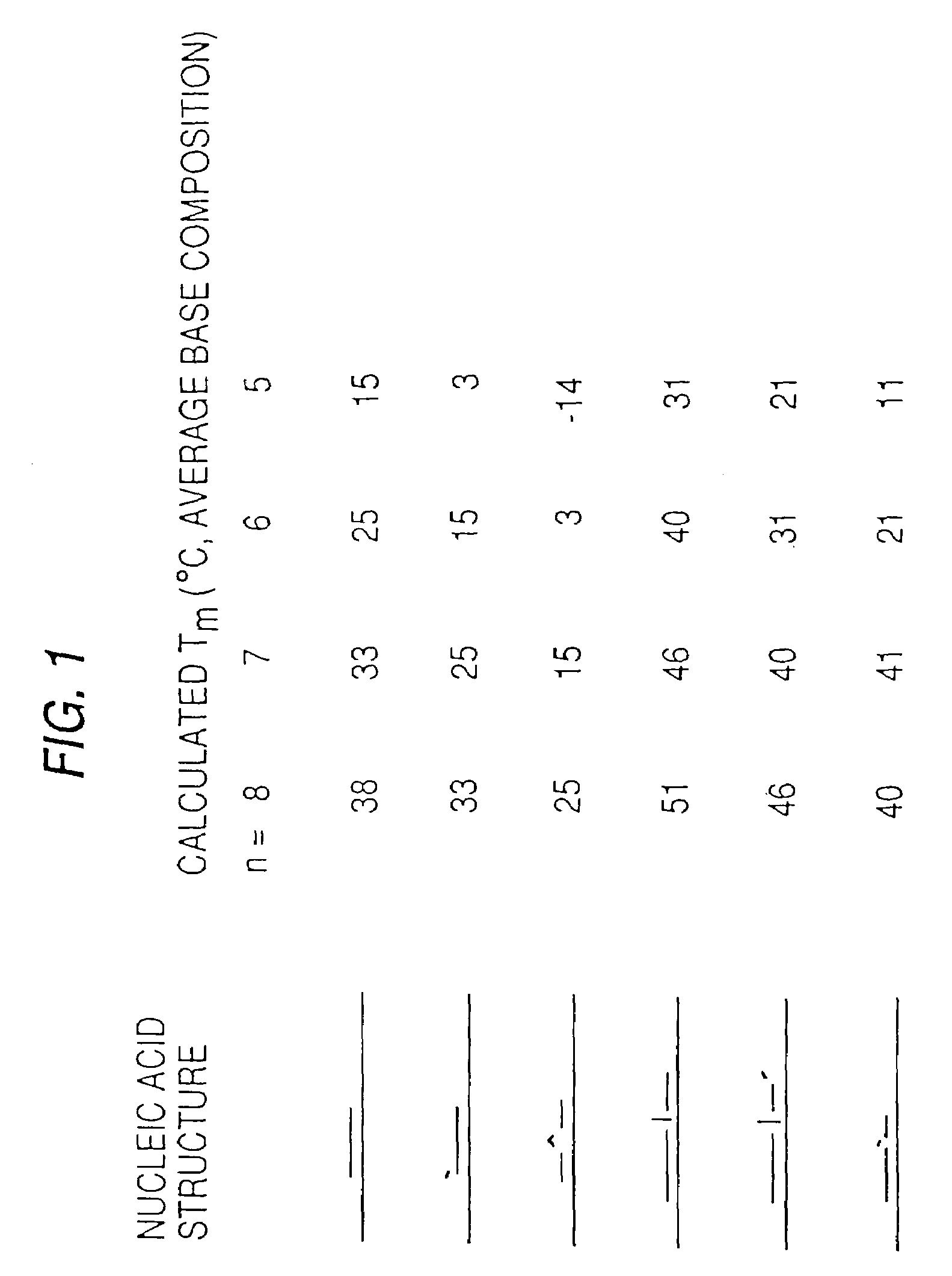
This invention is directed to methods and reagents useful for sequencing nucleic acid targets utilizing sequencing by hybridization technology comprising probes, arrays of probes and methods whereby sequence information is obtained rapidly and efficiently in discrete packages. That information can be used for the detection, identification, purification and complete or partial sequencing of a particular target nucleic acid. When coupled with a ligation step, these methods can be performed under a single set of hybridization conditions. The invention also relates to the replication of probe arrays and methods for making and replicating arrays of probes which are useful for the large scale manufacture of diagnostic aids used to screen biological samples for specific target sequences. Arrays created using PCR technology may comprise probes with 5′- and / or 3′-overhangs.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
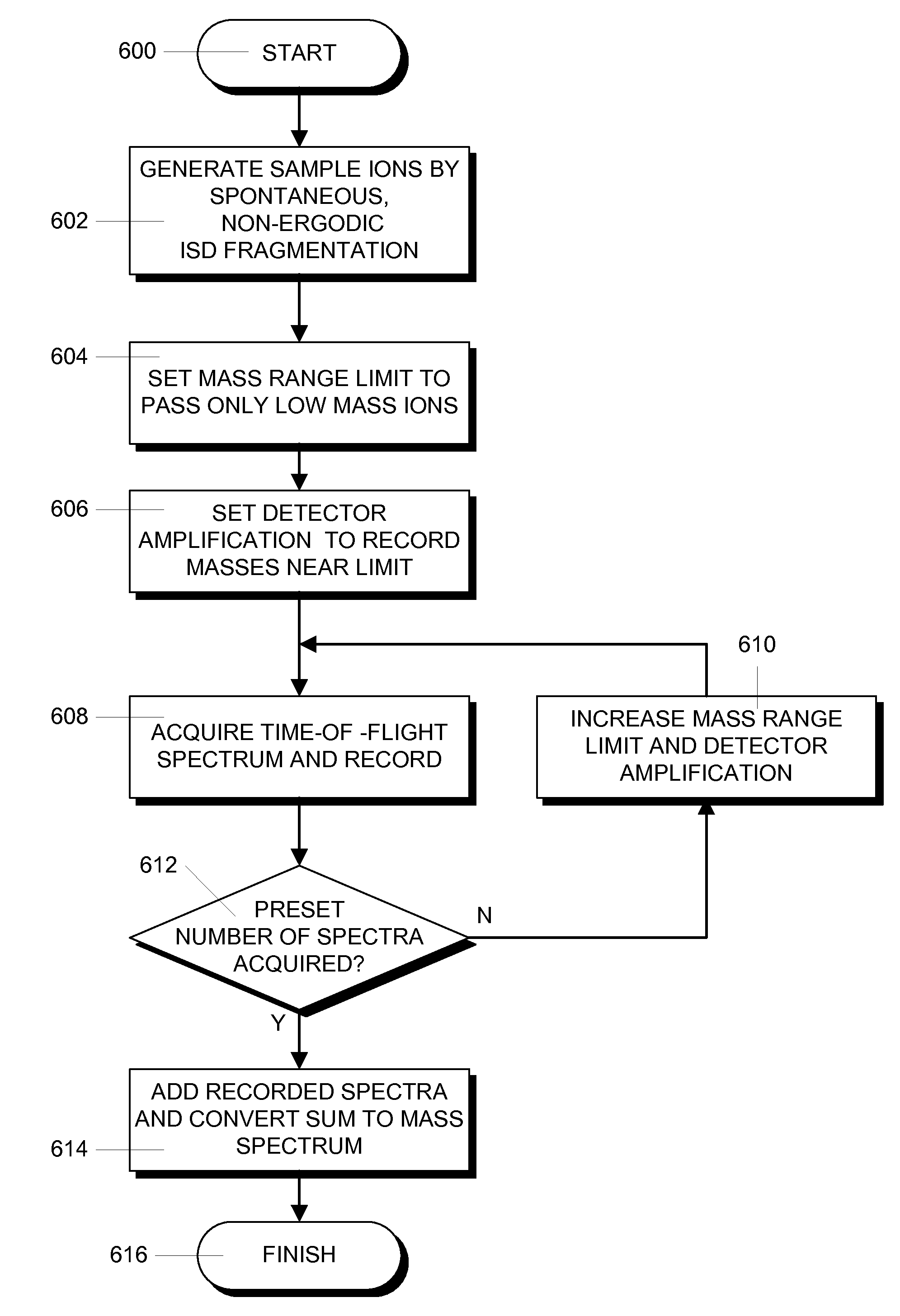
Protein sequencing with MALDI mass spectrometry
ActiveUS8581179B2Small amount of calculationIncrease productionTime-of-flight spectrometersSamples introduction/extractionDesorptionProtein Sequence Determination
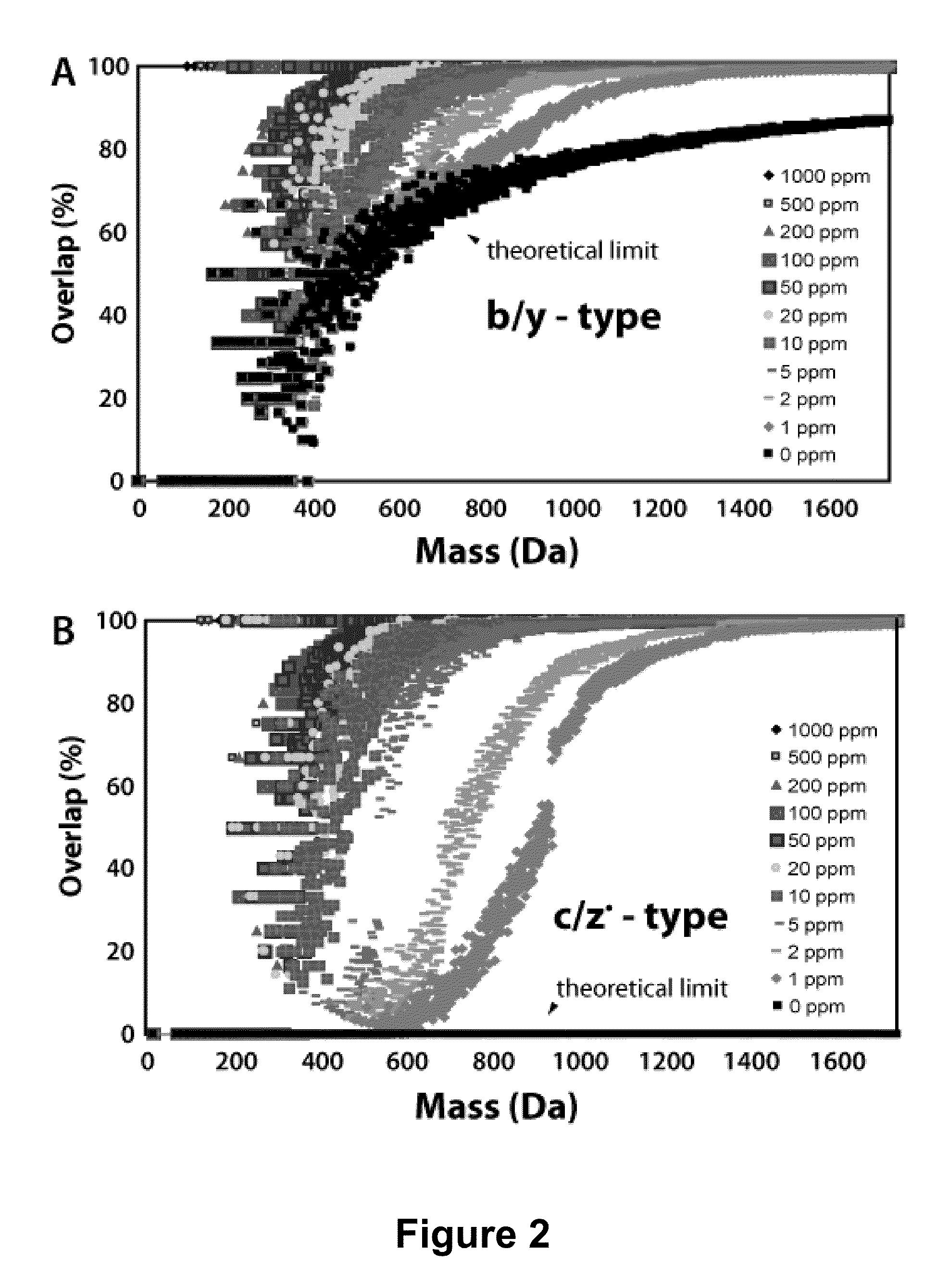
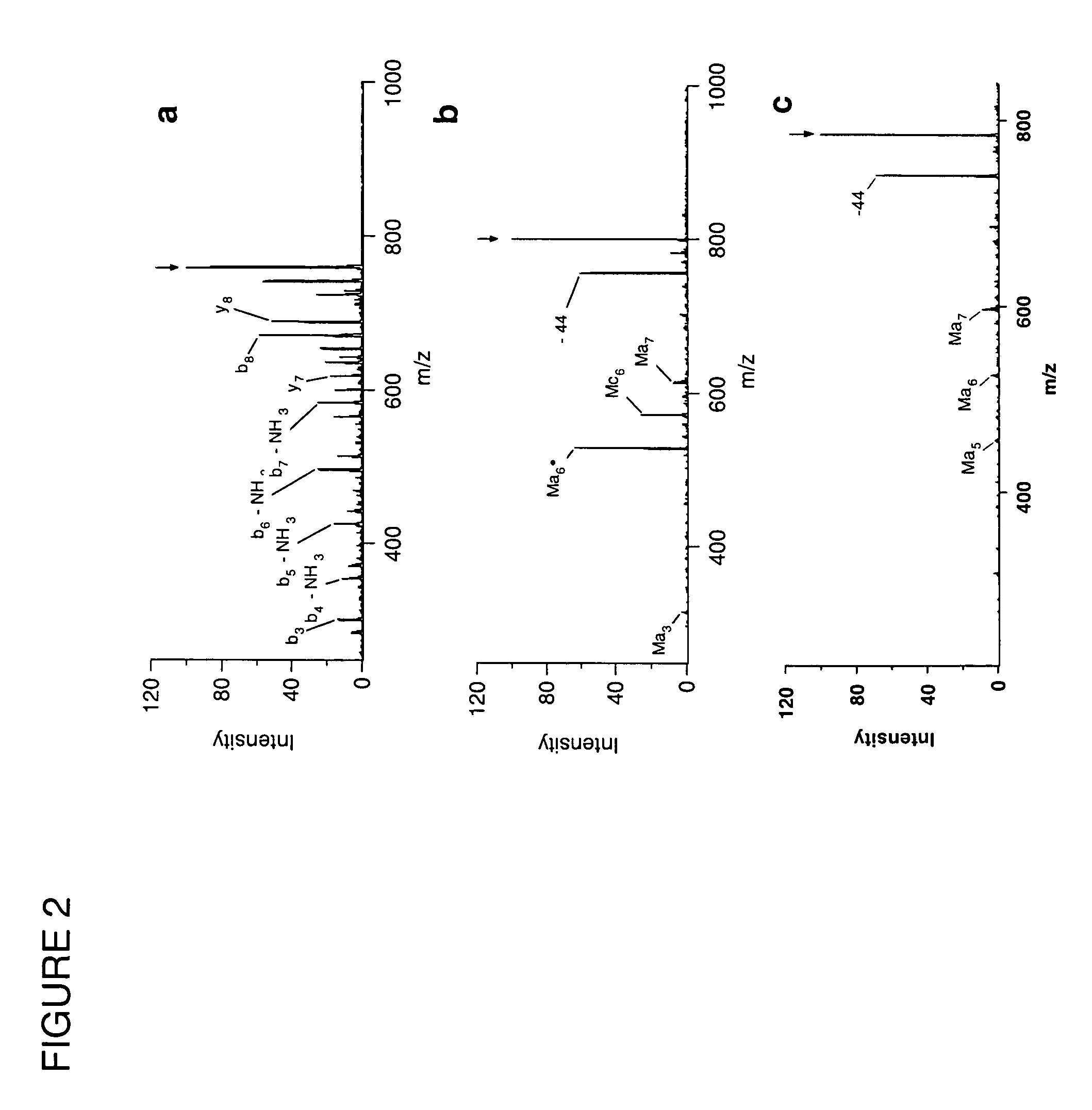
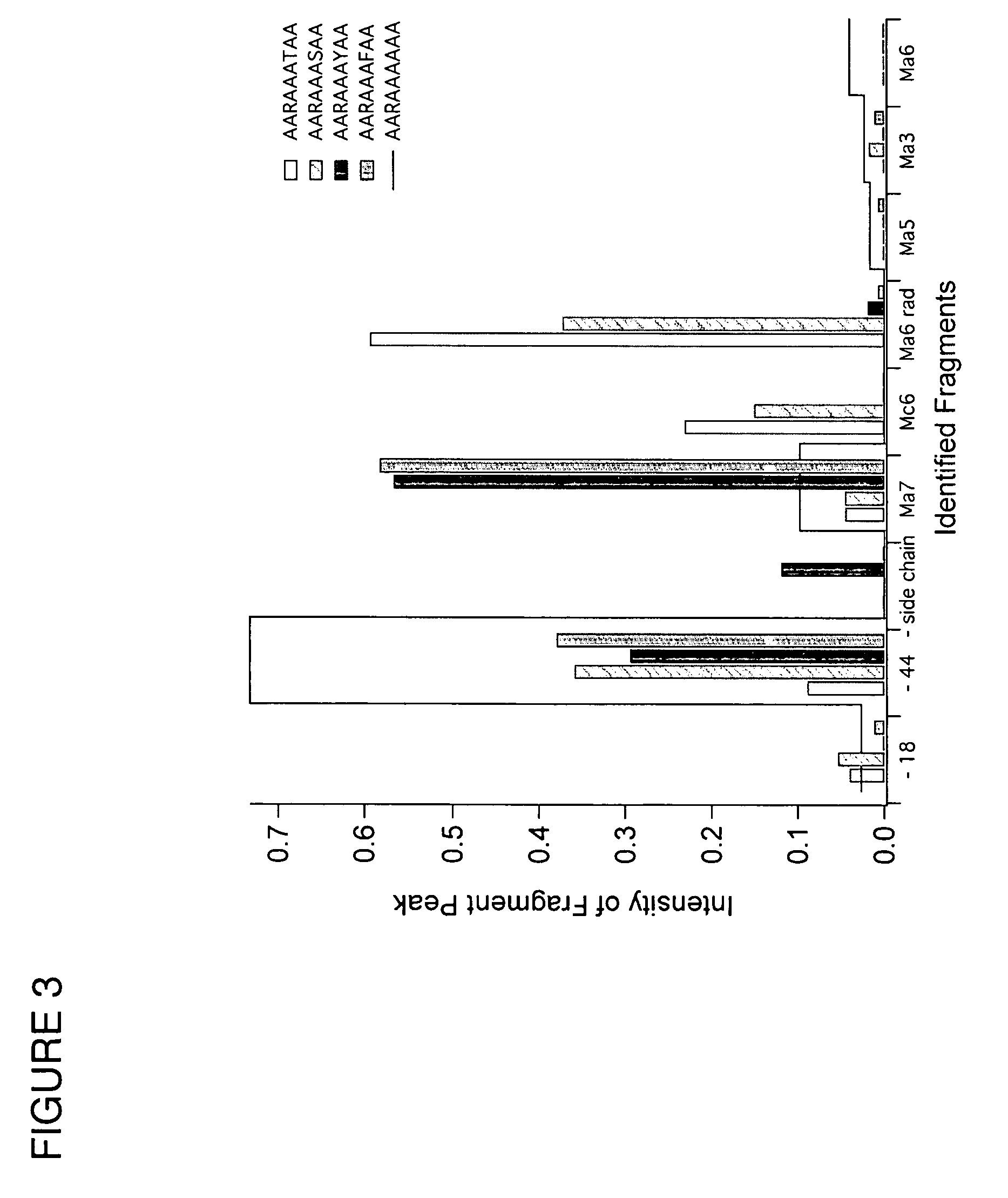
In a mass spectrometer, sample ions are produced by using matrix assisted laser desorption with a matrix substance that supports spontaneous, non-ergodic ISD fragmentation and a laser light source with nanosecond light pulses and a multiple spot beam profile. A plurality of individual time-of-flight spectra are recorded from the resulting ions in such a way that amplification of ion signals in the mass spectrometer detector is initially reduced so that only ions with masses near a mass range limit are initially recorded. During the repeated acquisitions of the individual time-of-flight spectra, both the detector amplification and the mass range limit are increased. By these methods, it is possible to evaluate c and z fragment ions in lower mass ranges and to directly read N-terminal sequences from near terminus up to 80 amino acids and beyond, and C-terminal sequences up to more than 60 amino acids.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
Control system and apparatus for use with laser excitation and ionization
InactiveUS20050232317A1Way fastMaximize sensitivityLaser detailsIon sources/gunsProtein Sequence DeterminationOptical communication
A control system and apparatus for use with laser ionization is provided. In another aspect of the present invention, the apparatus includes a laser, pulse shaper, detection device and control system. A further aspect of the present invention employs a femtosecond laser and a mass spectrometer in yet other aspects of the present invention, the control system and apparatus are used in MALDI, chemical bond cleaving, protein sequencing, photodynamic therapy, optical coherence tomography and optical communications processes.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Method for predicting outer membrane protein of germs on basis of machine learning technique
InactiveCN108009405AQuick forecastEasy to identifyBiostatisticsCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorSupport vector machine
The invention discloses a method for using a machine learning technique for predicting outer membrane protein coded on genomes of germs. The method includes the steps of utilizing a PSI-BLAST algorithm to calculate a location specificity feature vector of the protein, adopting an autocorrelation function for conducting feature conversion, building a classification device based on a supporting vector machine, conducting classification on the outer membrane protein and non-outer membrane protein, receiving a protein sequence input by a user through a local computer program, and predicting whether or not the protein sequence belongs to the outer membrane protein. By means of the method, calculation prediction can be conducted on the protein sequence coded by the whole genome of the germs, thesensitivity is high, the calculation speed is high, and an effective tool is provided for fast identification and screening of inner and outer membrane protein of the genomes of the germs. The methodis an accurate and effective screening method for the outer membrane protein and can be widely applied to identification of the outer membrane protein of new sequencing genomes of germs.
Owner:上海韦翰斯生物医药科技有限公司
Single molecule protein sequencing
InactiveUS20150185199A1Minimal ambiguityError minimizationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProtein insertionProtein Sequence Determination
The invention provides a device for determining the type of protein in a liquid, the device comprising (a) an immobilized ATP dependent protease based molecular transporter machine configured to guide a protein that is functionalized with labels through a detection area of a detector, (b) said detector, configured to detect a signal as function of the labels of the labelled amino acids, (c) a processor unit, configured to identify from the detector signal a sequence of amino acids of the functionalized protein, wherein the processor unit is further configured to compare the identified sequence of amino acids with the occurrence of such sequence in a database of proteins and to identify the type of protein.
Owner:TECH UNIV DELFT
Protein/Peptide Sequencing By Chemical Degradation in the Gas Phase
ActiveUS20080248585A1The parameters are accurate and reliableHigh performance resultIsotope separationRadio frequency spectrometersGas phaseMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
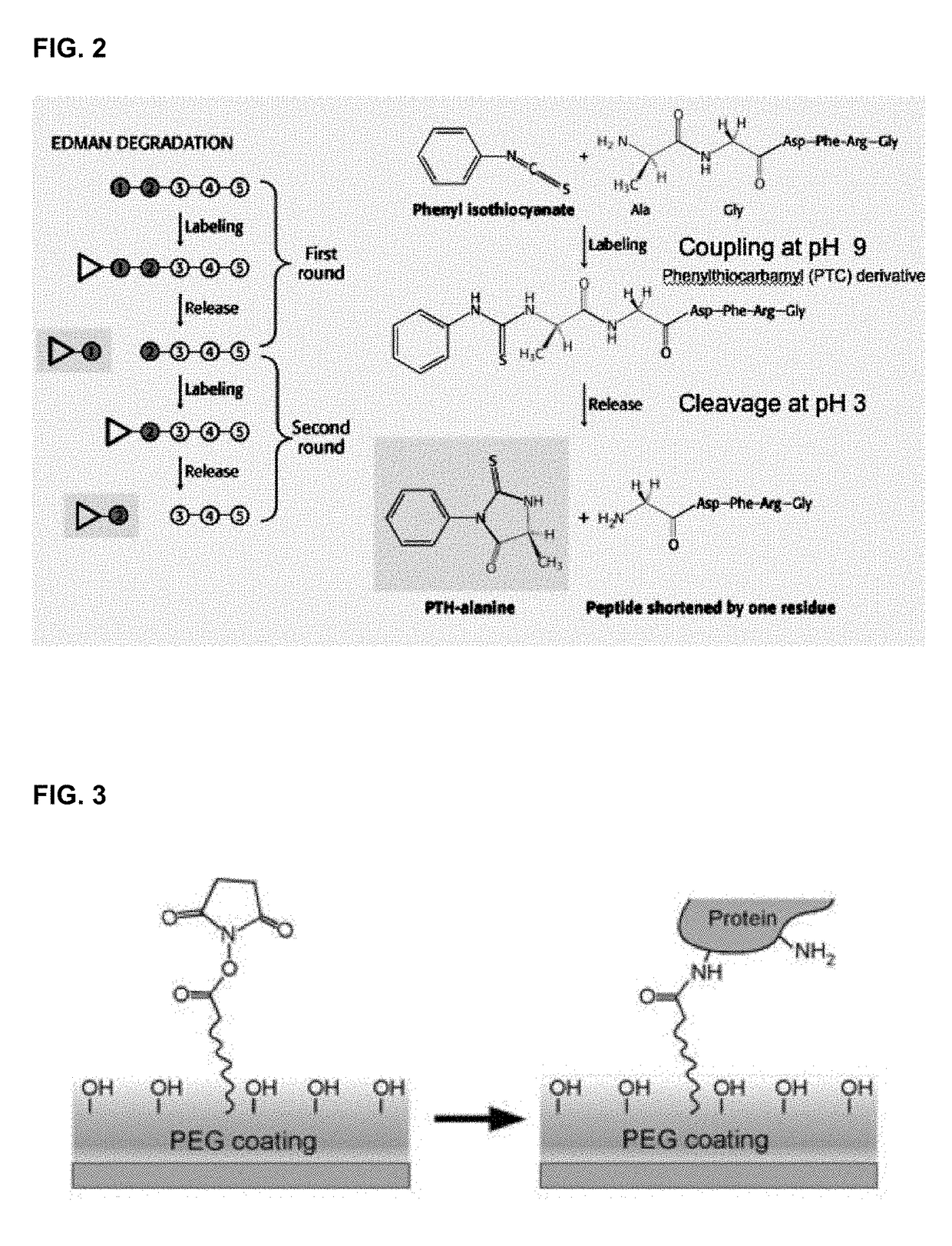
A fast and sensitive method and device for protein sequencing are disclosed. The method uses a combination of Edman degradation chemistry and mass spectrometry to sequence proteins and polypeptides. A peptide degradation reaction is performed on a polypeptide or protein ion reactant in the gas phase. The reaction yields a first ion product corresponding to a first amino acid residue of the polypeptide or protein reactant and a polypeptide or protein fragment ion. The mass-to-charge ratio for the first ion product, or the polypeptide or protein fragment ion, or both, is then determined. The first amino acid residue of the polypeptide or protein reactant is then identified from the mass-to-charge ratio so determined.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Protein sequencing methods and reagents
ActiveUS20180299460A1Facilitates chemical cleavage of N-terminalOrganic chemistryLibrary member identificationProtein Sequence DeterminationComputational chemistry
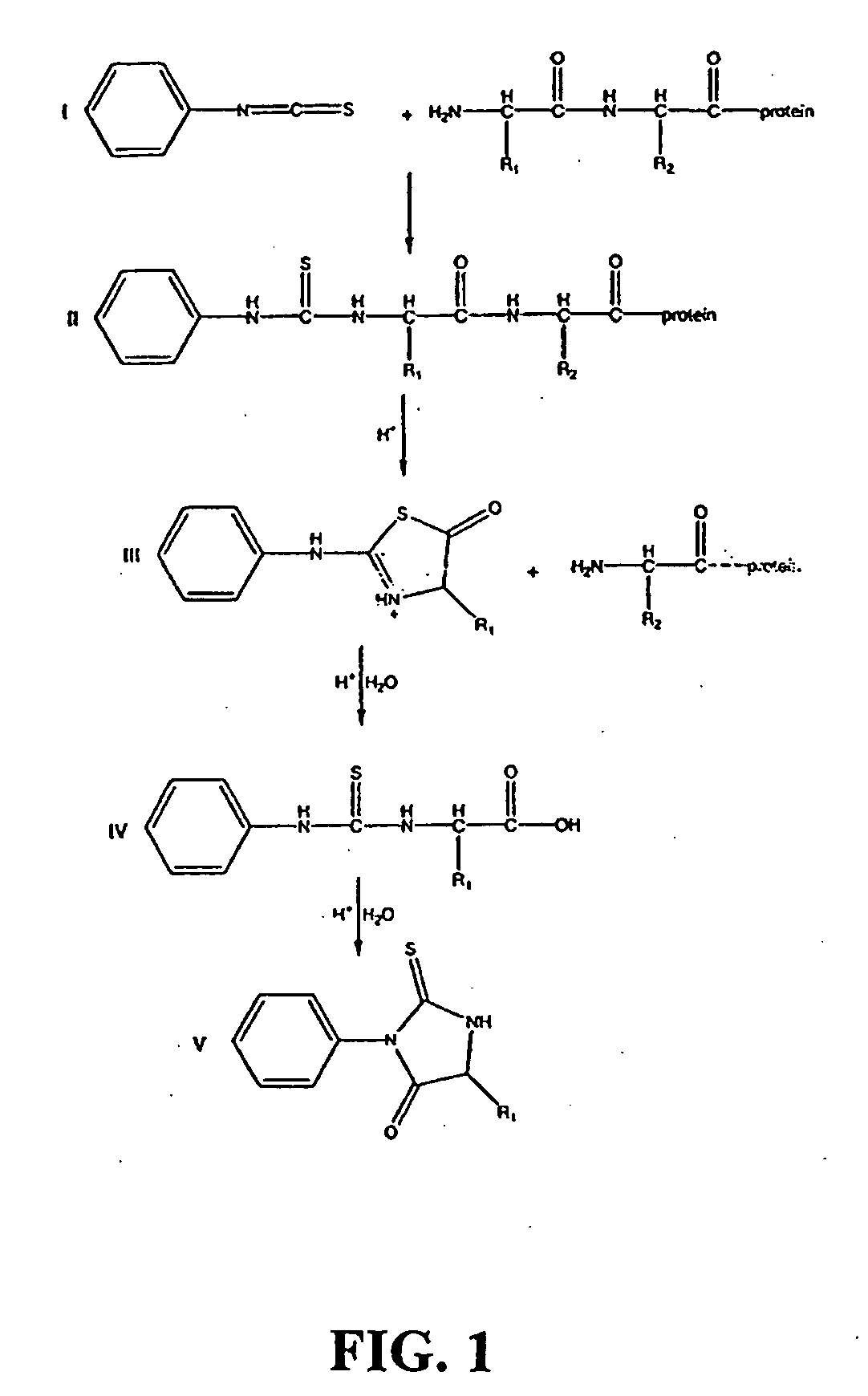
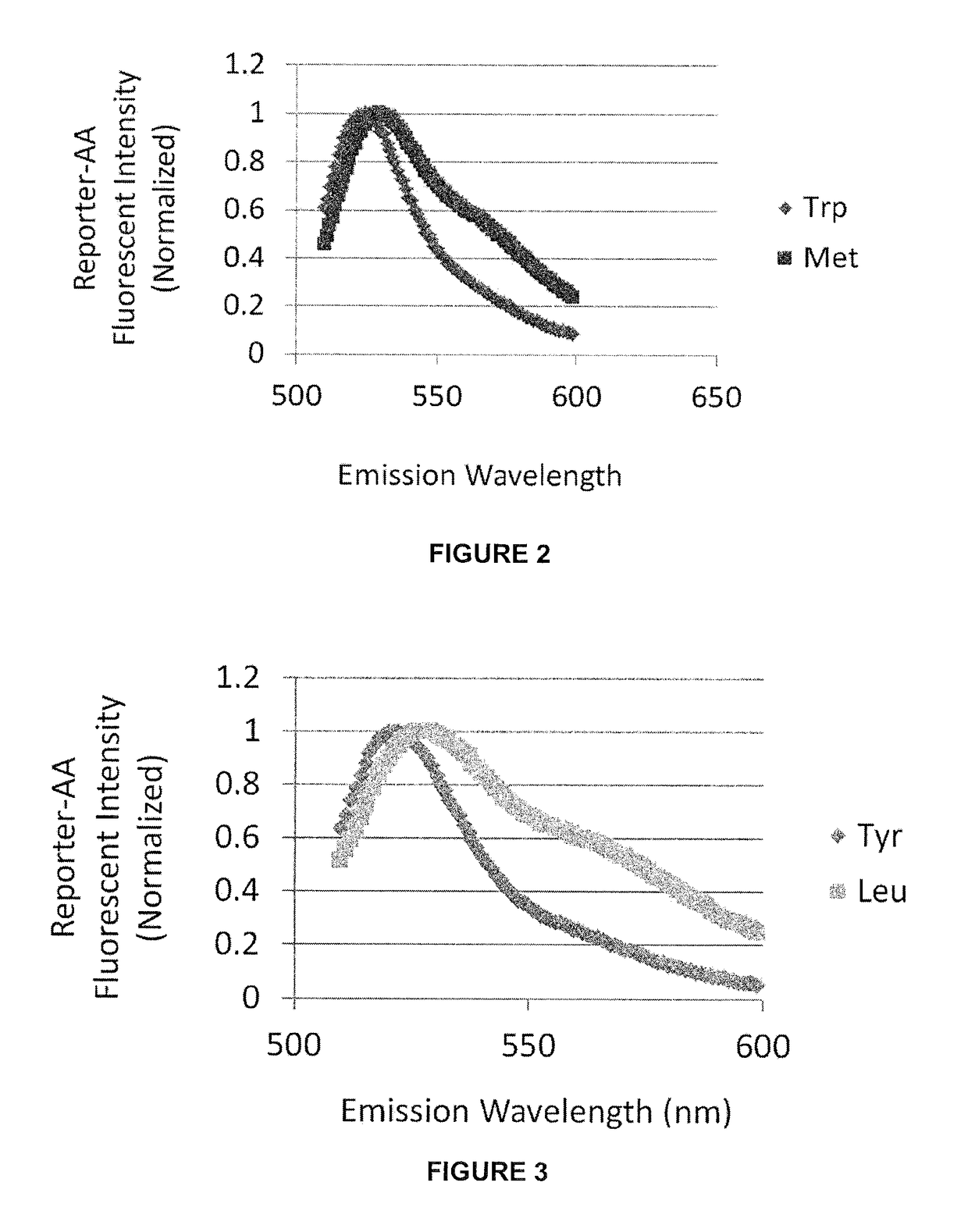
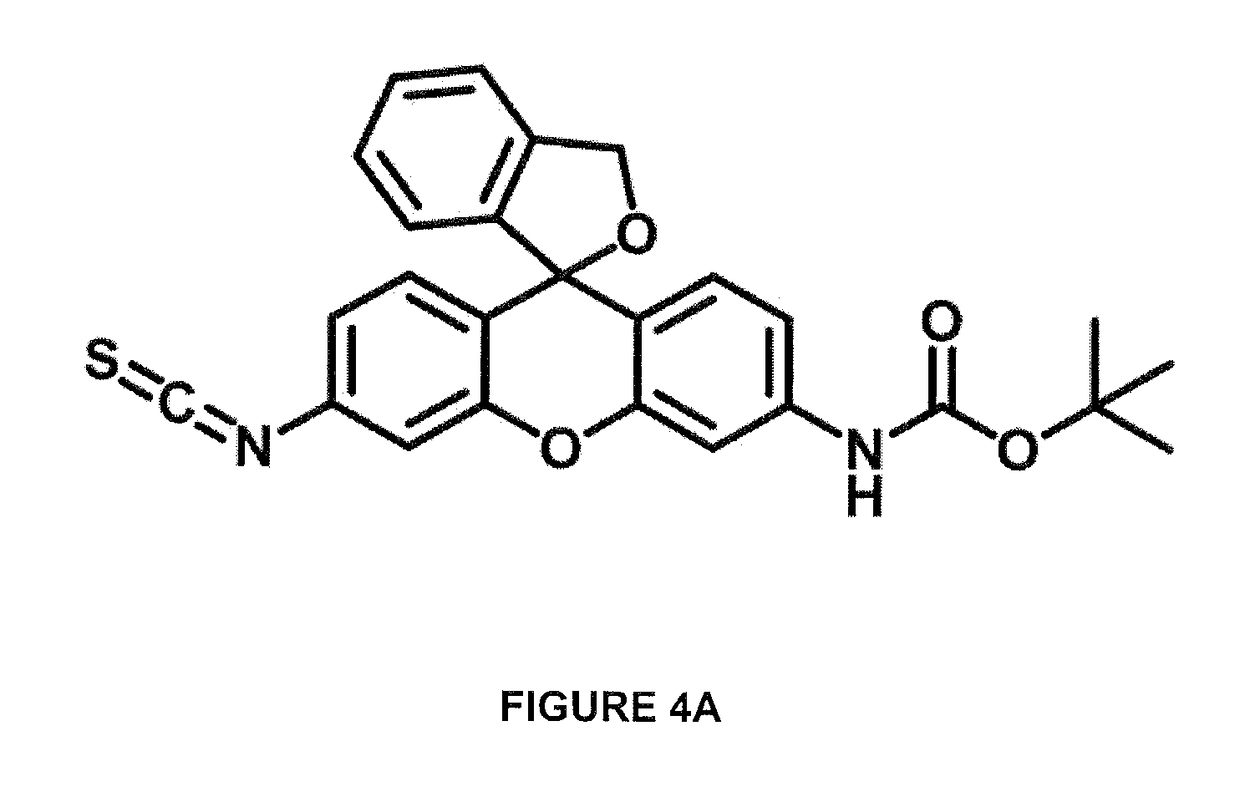
Described are optical methods and reagents for sequencing polypeptides. A probe that exhibits different spectral properties when conjugated to different N-terminal amino acids is conjugated to the N-terminal amino acid of a polypeptide. Sequentially detecting one or more spectral properties of the probe conjugated to the N-terminal amino acid and cleaving the N-terminal amino acid produces sequence information of the polypeptide. The use of super-resolution microscopy allows for the massively parallel sequencing of individual polypeptide molecules in situ such as within a cell. Also described are probes comprising hydroxymethyl rhodamine green, an isothiocyanate group and a protecting group.
Owner:THE GOVERNINIG COUNCIL OF THE UNIV OF TORANTO
Methods for Processing Tandem Mass Spectral Data for Protein Sequence Analysis
ActiveUS20090173878A1Reliably and uniquely identifying and classifyingThe composition is uniqueParticle separator tubesCalibration apparatusFrequency spectrumProtein sequence analysis
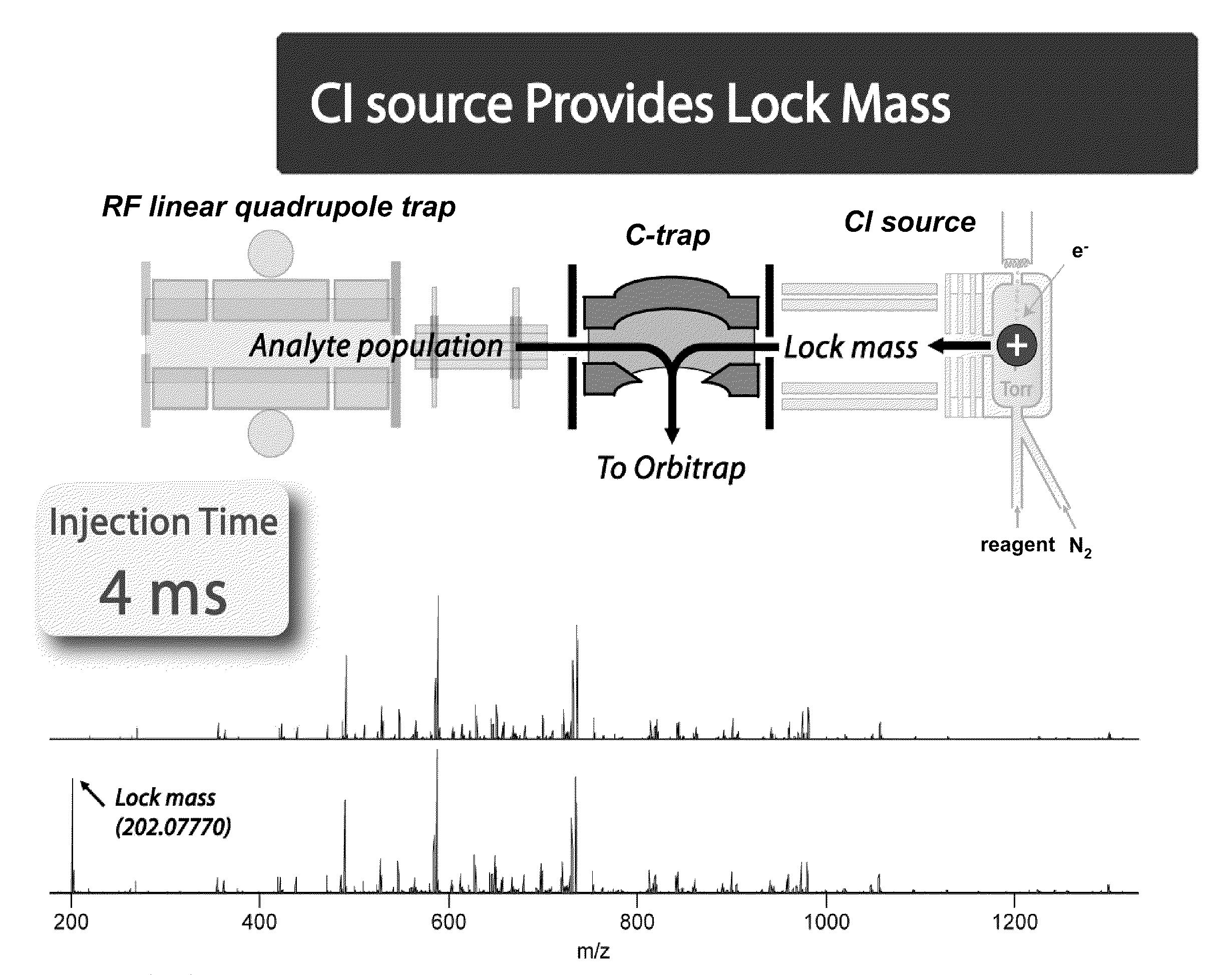
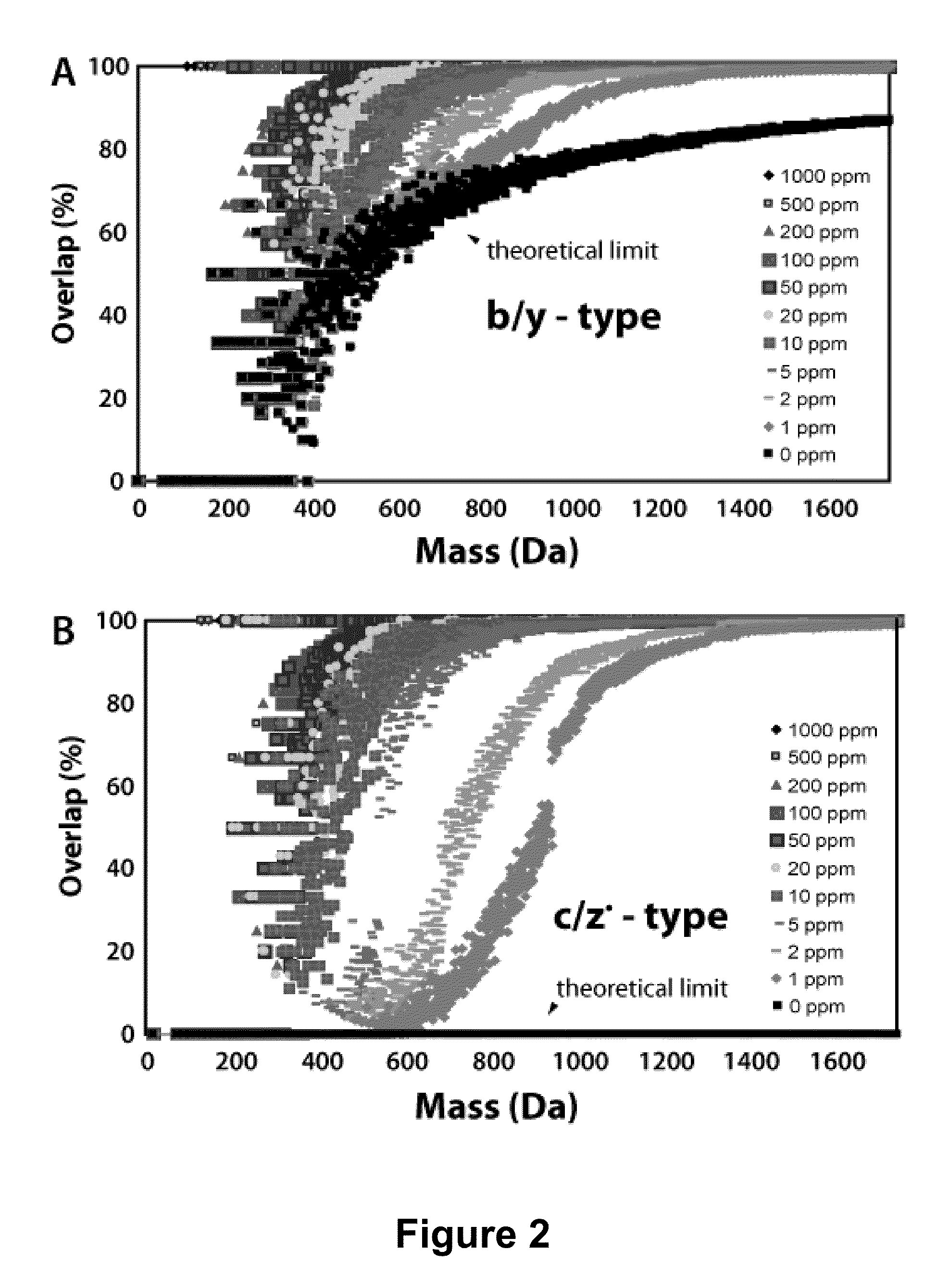
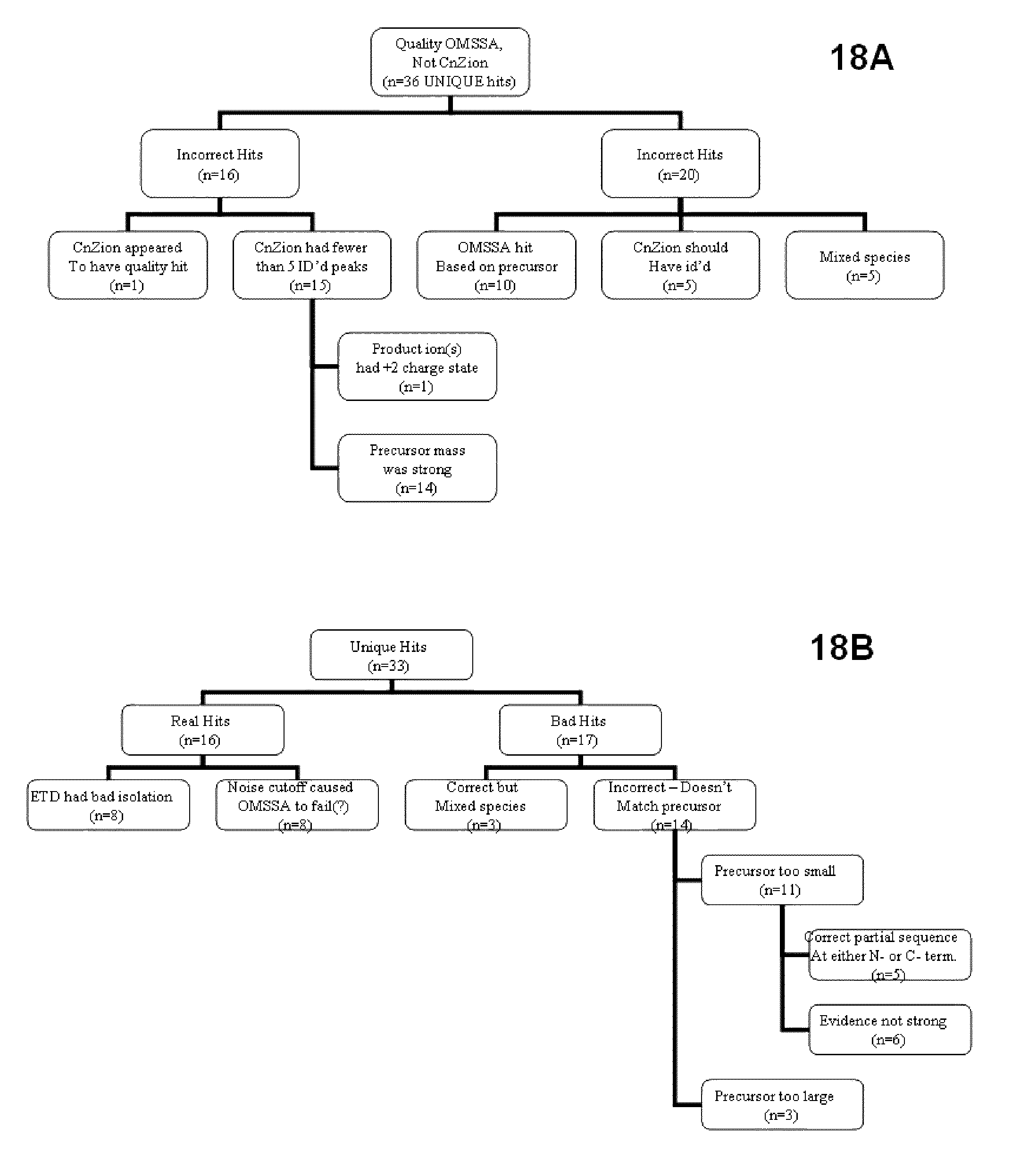
Various mass spectroscopy-based methods are provided to improve protein sequencing by detecting z-type product ions generated from the protein. A polypeptide is introduced to a mass spectrometer, and in particular c- and z-type product ions that are generated by selectively fragmenting the polypeptide. The z-type product ions are distinguished from the c-type product ions and the mass-to-charge ratio of at least a portion of the z-type product ions are determined. From the mass of the z-type product ions, a putative chemical composition is identified for at least a portion of the z-type product ions, c-type product ions, or both, which is used to determine polypeptide compositions. Further provided are various methods for reducing spectral noise, instrument calibration and database searching and verification.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Methods for processing tandem mass spectral data for protein sequence analysis
ActiveUS8278115B2Reliably and uniquely identifying and classifyingThe composition is uniqueParticle separator tubesIsotope separationSequence analysisFrequency spectrum
Various mass spectroscopy-based methods are provided to improve protein sequencing by detecting z-type product ions generated from the protein. A polypeptide is introduced to a mass spectrometer, and in particular c- and z-type product ions that are generated by selectively fragmenting the polypeptide. The z-type product ions are distinguished from the c-type product ions and the mass-to-charge ratio of at least a portion of the z-type product ions are determined. From the mass of the z-type product ions, a putative chemical composition is identified for at least a portion of the z-type product ions, c-type product ions, or both, which is used to determine polypeptide compositions. Further provided are various methods for reducing spectral noise, instrument calibration and database searching and verification.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Paired end sequencing
InactiveCN101351552AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationDNA constructProtein sequencing
The present invention provides for a method of preparing a target nucleic acid fragments to produce a smaller nucleic acid which comprises the two ends of the target nucleic acid. Specifically, the invention provides cloning and DNA manipulation strategies to isolate the two ends of a large target nucleic acid into a single small DNA construct for rapid cloning, sequencing, or amplification.
Owner:454 LIFE SCIENCES CORP
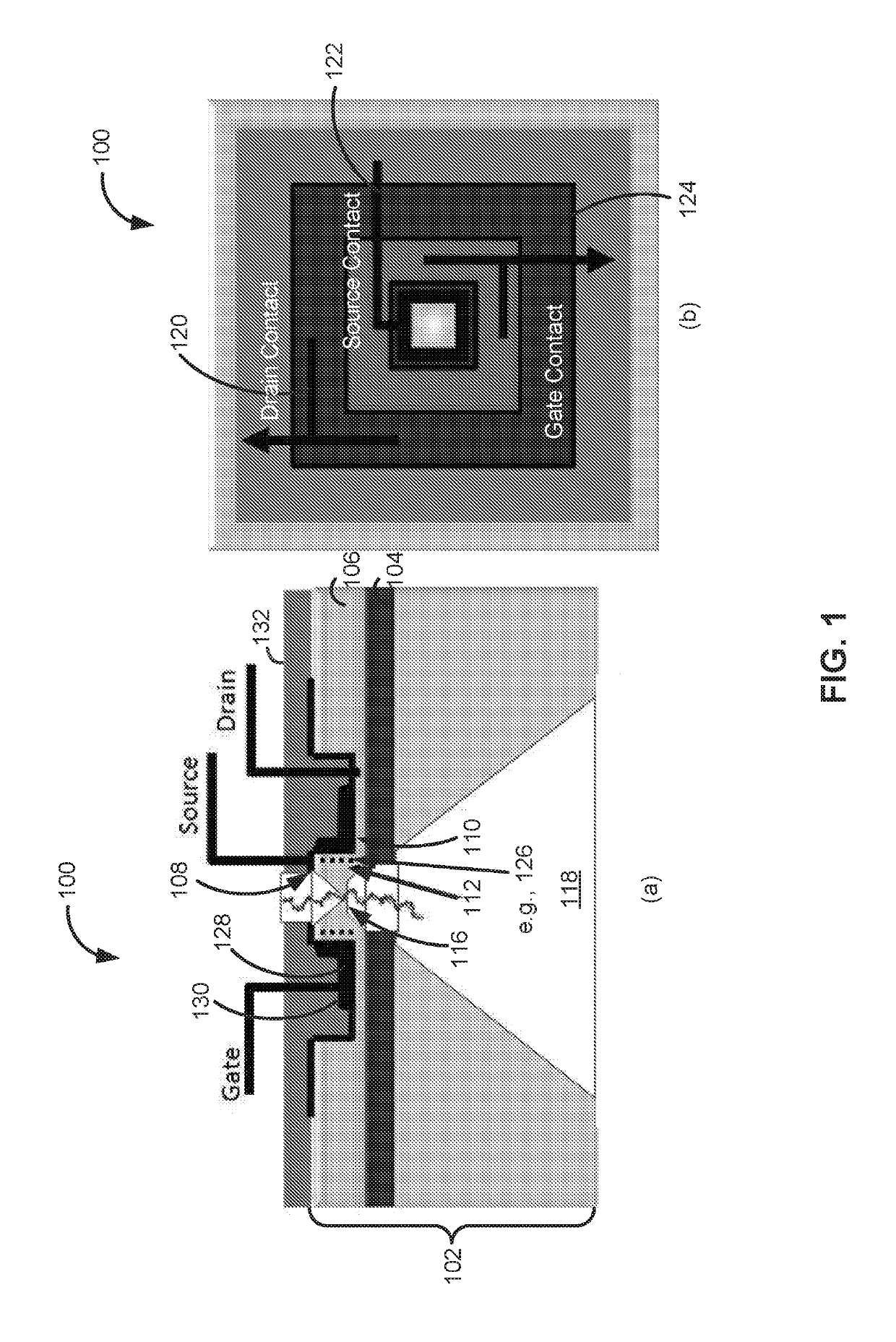
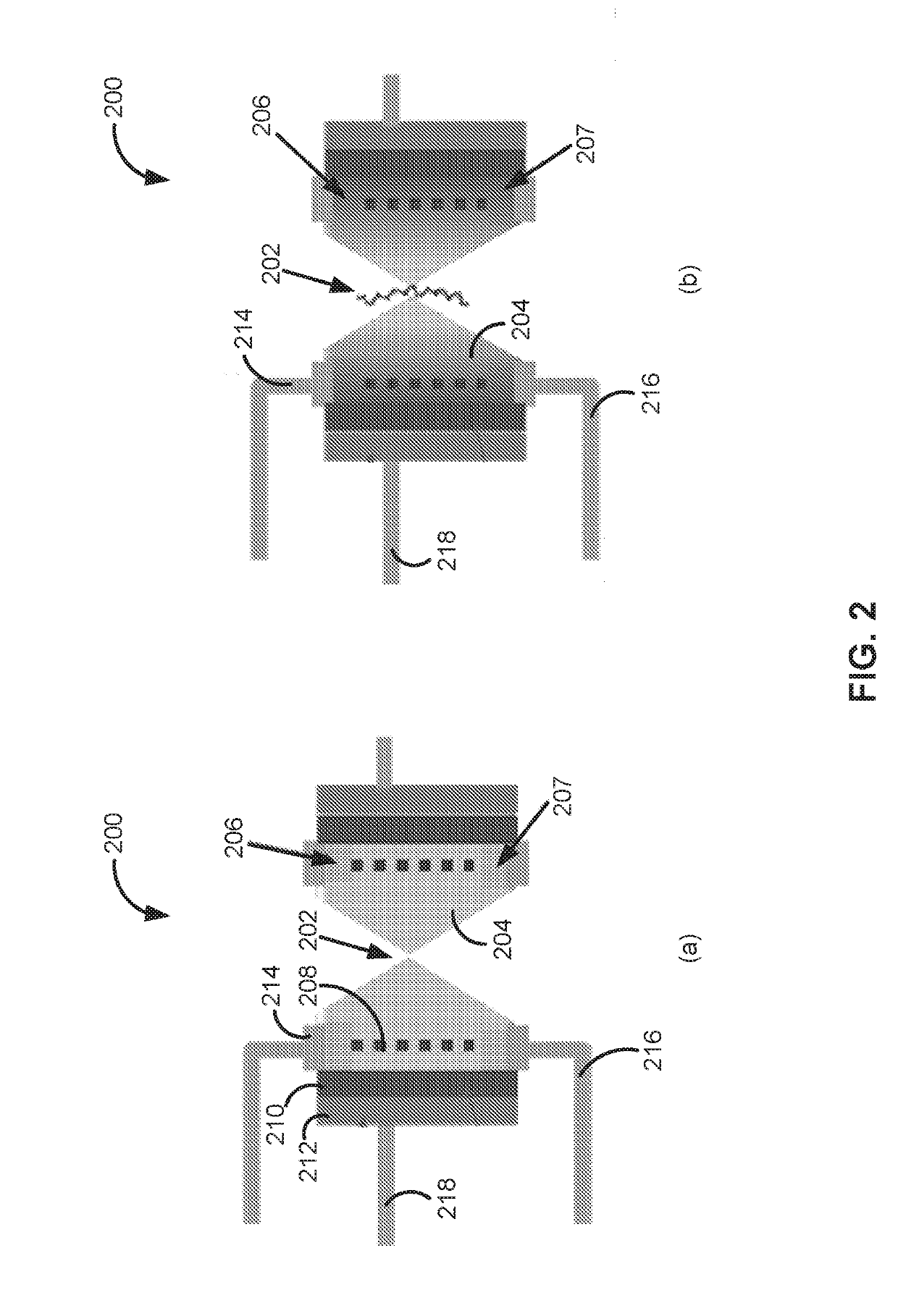
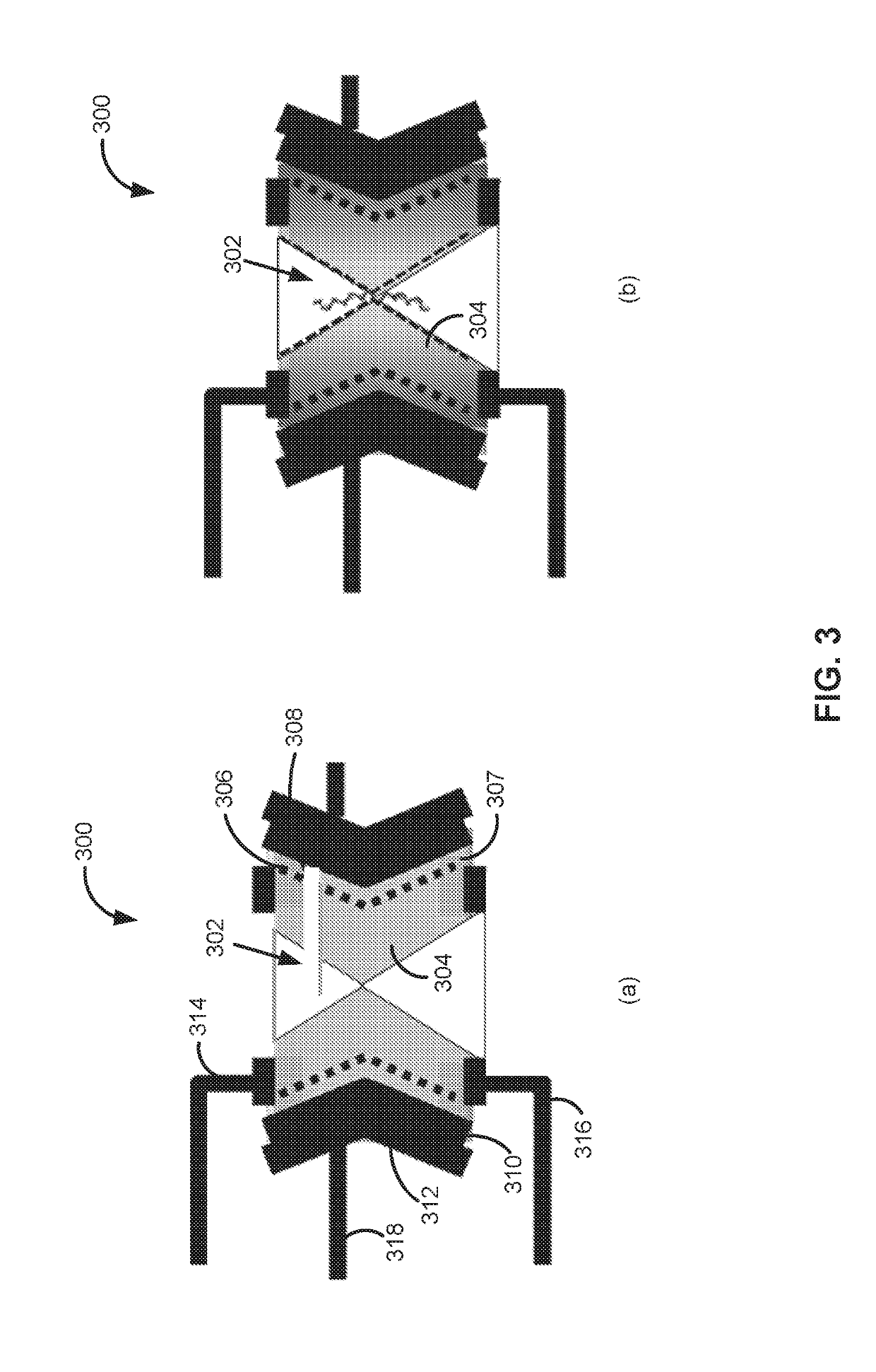
Field effect transistor, device including the transistor, and methods of forming and using same
ActiveUS20150060952A1Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansGenomic sequencingOrganic field-effect transistor
The present disclosure provides an improved field effect transistor and device that can be used to sense and characterize a variety of materials. The field effect transistor and / or device including the transistor may be used for a variety of applications, including genome sequencing, protein sequencing, biomolecular sequencing, and detection of ions, molecules, chemicals, biomolecules, metal atoms, polymers, nanoparticles and the like.
Owner:INANOBIO
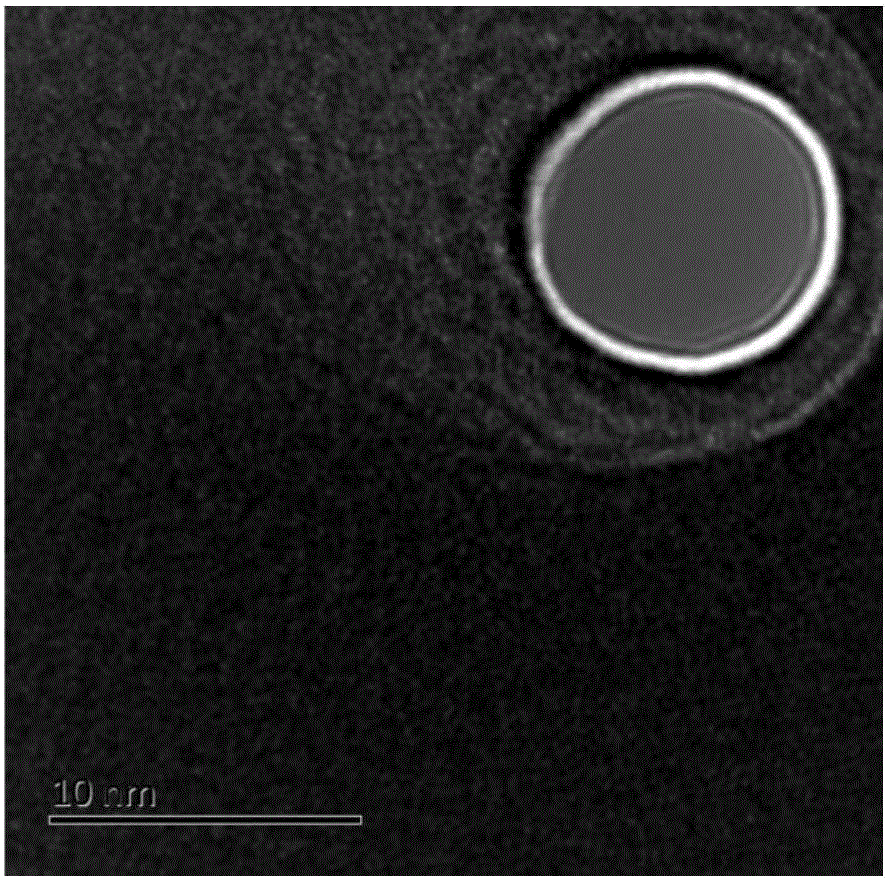
Single-layer mica sheet and preparation method and application of nanopore electronic device thereof
ActiveCN105883838AAchieve single layer cleavage effectRealize identificationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProtein moleculesHigh energy
The invention discloses a single-layer mica sheet and a preparation method and application of a nanopore electronic device thereof. The method comprises the steps that an ultrathin single mica layer is prepared and coats a proper supporting substrate, and a high-energy focusing electronic beam or an ion beam is used for preparing nanopores of the specification being 1-5 nm in the single-layer mica sheet to obtain a solid-state nanopore electronic device based on the single-layer mica sheet. Single-stranded nucleic acid or protein molecules are driven by an electric field to penetrate through the nanopores in the electronic device, and a basic group on the single-stranded nucleic acid penetrating through the pores or amino acid on the single-stranded protein is recognized by detecting changes of via-pore current in real time. A high throughput parallel molecular device can be prepared from the electronic device, and rapid and ultralow cost nucleic acid / protein sequencing can be achieved.
Owner:PEKING UNIV +1
Characteristic extraction and classification method and device for DNA (Deoxyribo-Nucleic Acid) binding protein sequence information
InactiveCN108875310AImplement function annotationsAchieve classification goalsSpecial data processing applicationsData setProtein insertion
The invention relates to a characteristic extraction and classification method and device for DNA (Deoxyribo-Nucleic Acid) binding protein sequence information. The method comprises the following steps that: firstly, carrying out theory argumentation, and analyzing and arranging collected data to obtain a reliable dataset with a biological meaning and a statistical meaning; then, extracting effective protein sequence data characteristic parameters from a complex protein three-dimensional structure as a key link which is a way of converting sequence character information into digital characteristic information, designing a reasonable classification algorithm for extracted characteristic data, and screening the characteristics favorable for classification for realizing target classification;and finally, adopting a reasonable and fair evaluation system, including testing methods, checking means, evaluation index selection and the like, for classification performance. By use of the method, requirements on high-flux protein sequencing function annotation can be met, automated DNA binding protein sequence function annotation can be realized, and meanwhile, the characteristics which areput forward can assist biologists in carrying out experimental analysis and research on the DNA binding protein sequence.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
Field effect transistor, device including the transistor, and methods of forming and using same
ActiveUS9341592B2Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansGenomic sequencingNanoparticle
The present disclosure provides an improved field effect transistor and device that can be used to sense and characterize a variety of materials. The field effect transistor and / or device including the transistor may be used for a variety of applications, including genome sequencing, protein sequencing, biomolecular sequencing, and detection of ions, molecules, chemicals, biomolecules, metal atoms, polymers, nanoparticles and the like.
Owner:INANOBIO
Primer design developing method of length polymorphism sign based on restriction enzyme digestion database-establishing pair-end sequencing
ActiveCN102831331ASimplify complexityLower Sequencing CostsSpecial data processing applicationsRestriction enzyme digestionRestriction site
The invention discloses a primer design developing method of a length polymorphism sign based on restriction enzyme digestion database-establishing pair-end sequencing. Sequencing data of RAD (restriction site associated DNA) pair-end sequencing is processed by adopting a bioinformatics analysis method, therefore, Indel locus information on an RAD sequencing segment is searched, the bottleneck of being lack of a reference sequence in a model organism is broken through, the complexity of a genome is simplified, and the sequencing cost is reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI MAJORBIO BIO PHARM TECH
Labidura japonica de haan antimicrobial peptide DEI and application thereof in duck feed
InactiveCN108503702AStrong toleranceGrow fastAccessory food factorsAnimals/human peptidesEscherichia coliPichia pastoris
The invention discloses a labidura japonica de haan antimicrobial peptide DEI and application thereof in duck feed, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The labidura japonica de haanantimicrobial peptide DEI is prepared by acquiring an antimicrobial peptide DEI of labidura japonica de haan, testing an amino acid sequence of the antimicrobial peptide DEI by using an automatic protein sequencing instrument, further by means of genetic engineering, designing a cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) fragment of the amino acid sequence, establishing cloning plasmid pUC57-TM, converting escherichia coli DH 5alpha, performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) and sequencing to carry out further identification, establishing a recombinant expression vector pPICZaC-TM, performinglinearization on the recombinant expression vector, performing electric conversion into pichia pastoris SMD1168, screening to obtain a high-copy recombinant yeast conversion factor, and culturing a single colony of the recombinant yeast conversion factor, thereby obtaining the labidura japonica de haan antimicrobial peptide DEI. The labidura japonica de haan antimicrobial peptide DEI can be applied to duck feed, then the immunity of ducks can be improved, the morbidity of the ducks can be greatly reduced, the survival rate of the ducks can be increased, and thus the feeding cost of duck farmers can be reduced.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
System and method of free radical initiated protein sequencing
A method for the selective fragmentation of peptides using free radical initiator-peptide conjugates is provided. Free radical initiated peptide sequencing, or FRIPS, consists of covalently attaching a free radical initiator to a peptide and collisionally activating this conjugate. This results in fragment formation. Subsequent collision-activated dissociation further dissociates the fragments, producing a group of ions based on the interaction of the free radical initiator and the target molecule. The methodology is applied to the fundamental study of biologically relevant reactions of free radicals with peptides and proteins in the gas phase, as well as to a completely gas-phase approach to protein sequencing.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Method for separating and purifying glutamine transaminase activation proteinase inhibitor
InactiveCN101121747ASimple separation processShort cyclePeptide preparation methodsProtease inhibitorsPurification methodsStreptomyces hygroscopicus
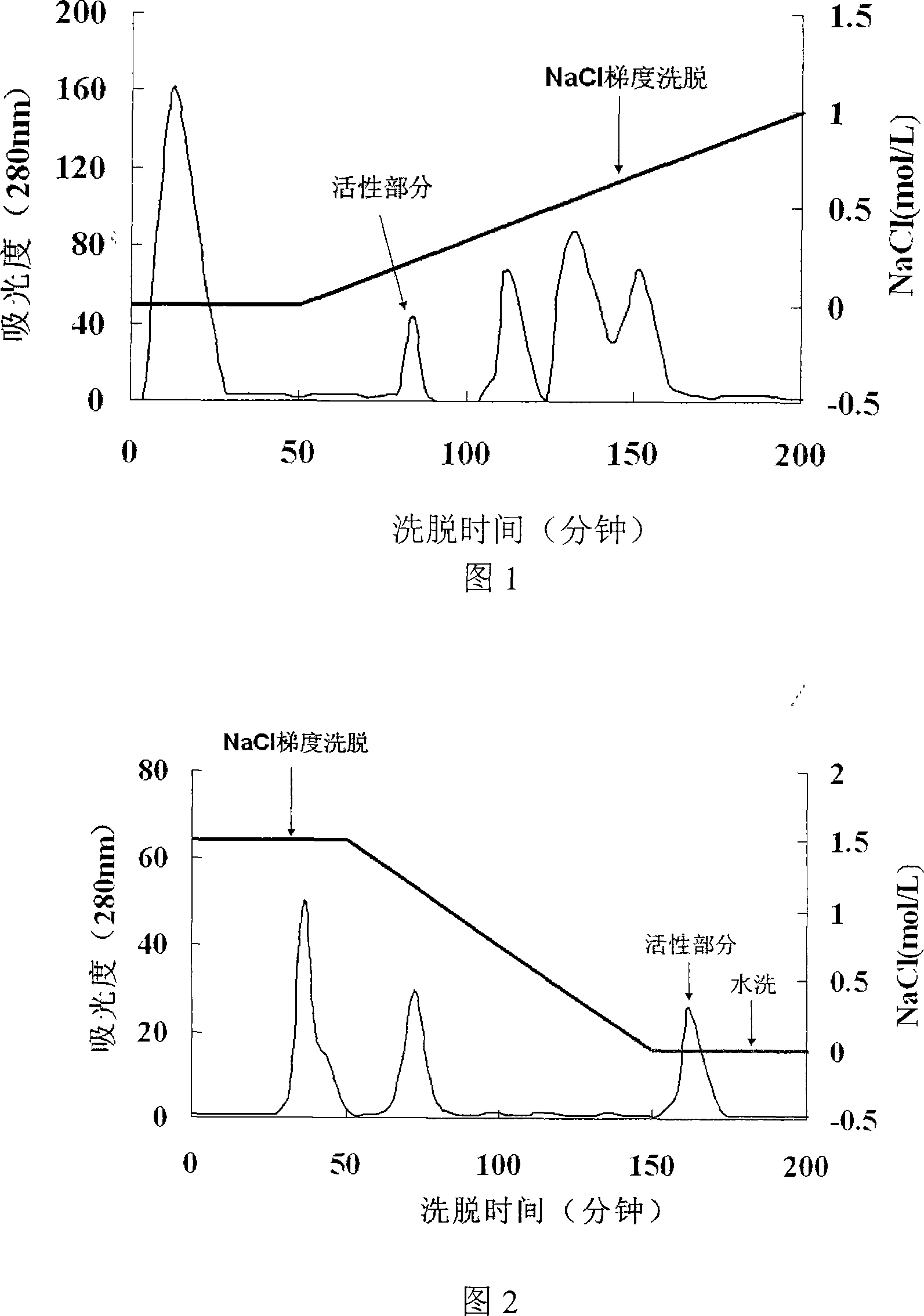
The invention discloses a method for separating and purifying a transglutaminase-activating protease inhibitor, which belongs to the technical field of separation and purification of biological products. The present invention uses Streptomyces hygroscopicus as the starting strain, and the transglutaminase activating protease inhibitory factor prepared by liquid submerged fermentation obtains electrophoretic pure transglutaminase after ethanol precipitation, cation exchange chromatography and hydrophobic chromatography Enzyme-activating protease inhibitor solution for subsequent protein sequencing and characterization studies. The method has simple steps and high enzyme purity, and is a simple and effective enzyme separation and purification method.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Protein sequencing method and reagents
InactiveUS20170212126A1Biological material analysisDepsipeptidesAcid derivativeProtein Sequence Determination
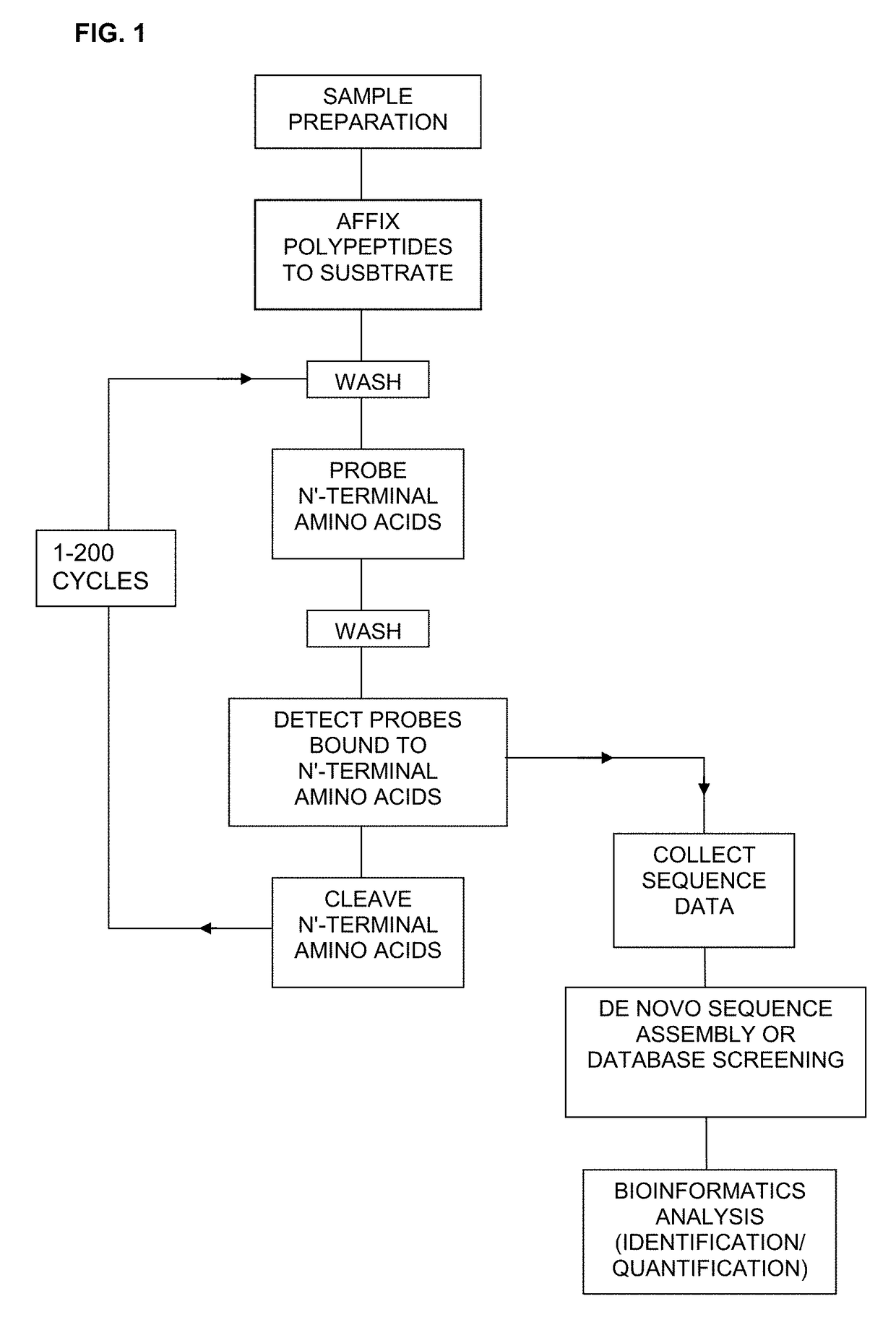
The invention describes methods and reagents useful for sequencing polypeptide molecules. The method comprises affixing a polypeptide to a substrate and contacting the polypeptide with a plurality of probes. Each probe selectively binds to an N-terminal amino acid or an N-terminal amino acid derivative. Probes bound to the polypeptide molecule are then identified before cleaving the N-terminal amino acid or N-terminal amino acid derivative of the polypeptide. Also provided are methods for the sequencing a plurality of polypeptide molecules in a sample and probes specific for N-terminal amino acids or N-terminal amino acid derivatives.
Owner:THE GOVERNING COUNCIL OF THE UNIV OF TORONTO
Method for Isolating and Purifying Immuno-Modulating Polypeptide from Cow Placenta
InactiveUS20080319163A1High purityPeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsAnion-exchange chromatographyProtein Sequence Determination
The present invention provides a method for isolating and purifying immuno-modulating polypeptide from cow placenta, which is characterized by using the steps of anion-exchange chromatography, gel exclusion chromatography and reverse-phase high performance liquid chromatography to isolate and purify immuno-modulating polypeptide from cow placenta, identifying its activity of stimulating lymphocyte proliferation in vitro by MTT method, then determining its molecular weight by MALDI-TOF-MS, its isoelectric point by CIEF and its amino acid sequence with analyzer for protein sequencing. Since the obtained immuno-modulating polypeptide by the method according to the present invention has more than 90% purity, its bioactivity can reach medicinal standards.
Owner:SHI JIA ZHUANG SANLU GRP
Nanopore sensor, structure and device including the sensor, and methods of forming and using same
PendingUS20190145950A1Increase interaction distanceImprove accuracyMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansLaboratory glasswaresGenomic sequencingNanoparticle
The present disclosure provides an improved device that can be used to sense and characterize a variety of materials. The device may be used for a variety of applications, including genome sequencing, protein sequencing, biomolecular sequencing, and detection of ions, molecules, chemicals, biomolecules, metal atoms, polymers, nanoparticles and the like.
Owner:TAKULAPALLI BHARATH
Amplitude-modulated laser
PendingUS20210218218A1Fluorescence enhancementExtension of timeFluorescence/phosphorescenceSolid state laser constructional detailsFluorescenceEngineering
Systems and methods are described for producing an amplitude-modulated laser pulse train. The laser pulse train can be used to cause fluorescence in materials at which the pulse trains are directed. The parameters of the laser pulse train are selected to increase fluorescence relative to a constant-amplitude laser pulse train. The amplitude-modulated laser pulse trains produced using the teachings of this invention can be used to enable detection of specific molecules in applications such as gene or protein sequencing.
Owner:QUANTUM SI
Constructing method of amplification sublibrary for precise sequencing of ctDNA
InactiveCN107523640AEasy to operateSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationNatural abundanceNon targeted
The invention discloses a constructing method of an amplification sublibrary for precise sequencing of ctDNA. The constructing method comprises the following steps: S01, randomized ligation and randomized fragmentation of cfDNA, adaptor adding and library building; and S02, non-targeted / targeted library amplification of the cfDNA. According to the constructing method disclosed by the invention, firstly, the problem that a large amount of tag sequences need to be synthesized by adopting an exogenous tag method, so that the cost is relatively-high is solved; secondly, the problems that low-abundance cfDNA fragments are small, and characteristic primers for designing a target gene often cannot amplify out a target sequence under the condition that broken sites are randomly distributed are solved.
Owner:厦门燕旭安生物科技有限公司
Single molecule peptide sequencing
ActiveUS20200018768A1OmicsCarrier-bound/immobilised peptidesLarge-Scale SequencingProtein Sequence Determination
Identifying proteins and peptides, and more specifically large-scale sequencing of single peptides in a mixture of diverse peptides at the single molecule level is an unmet challenge in the field of protein sequencing. Herein are methods for identifying amino acids in peptides, including peptides comprising unnatural amino acids. In one embodiment, the N-terminal amino acid is labeled with a first label and an internal amino acid is labeled with a second label. In some embodiments, the labels are fluorescent labels. In other embodiments, the internal amino acid is Lysine. In other embodiments, amino acids in peptides are identified based on the fluorescent signature for each peptide at the single molecule level.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com