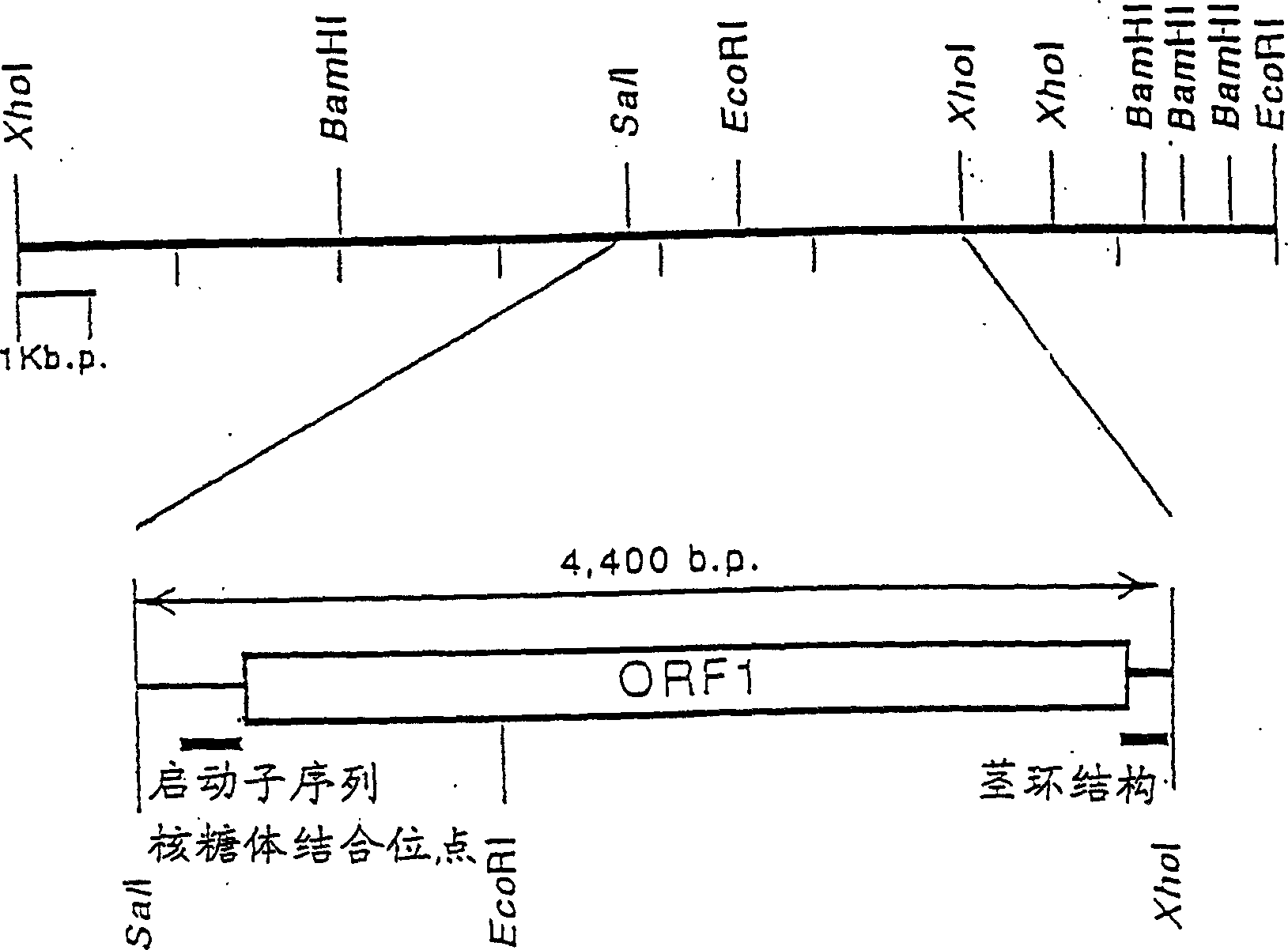
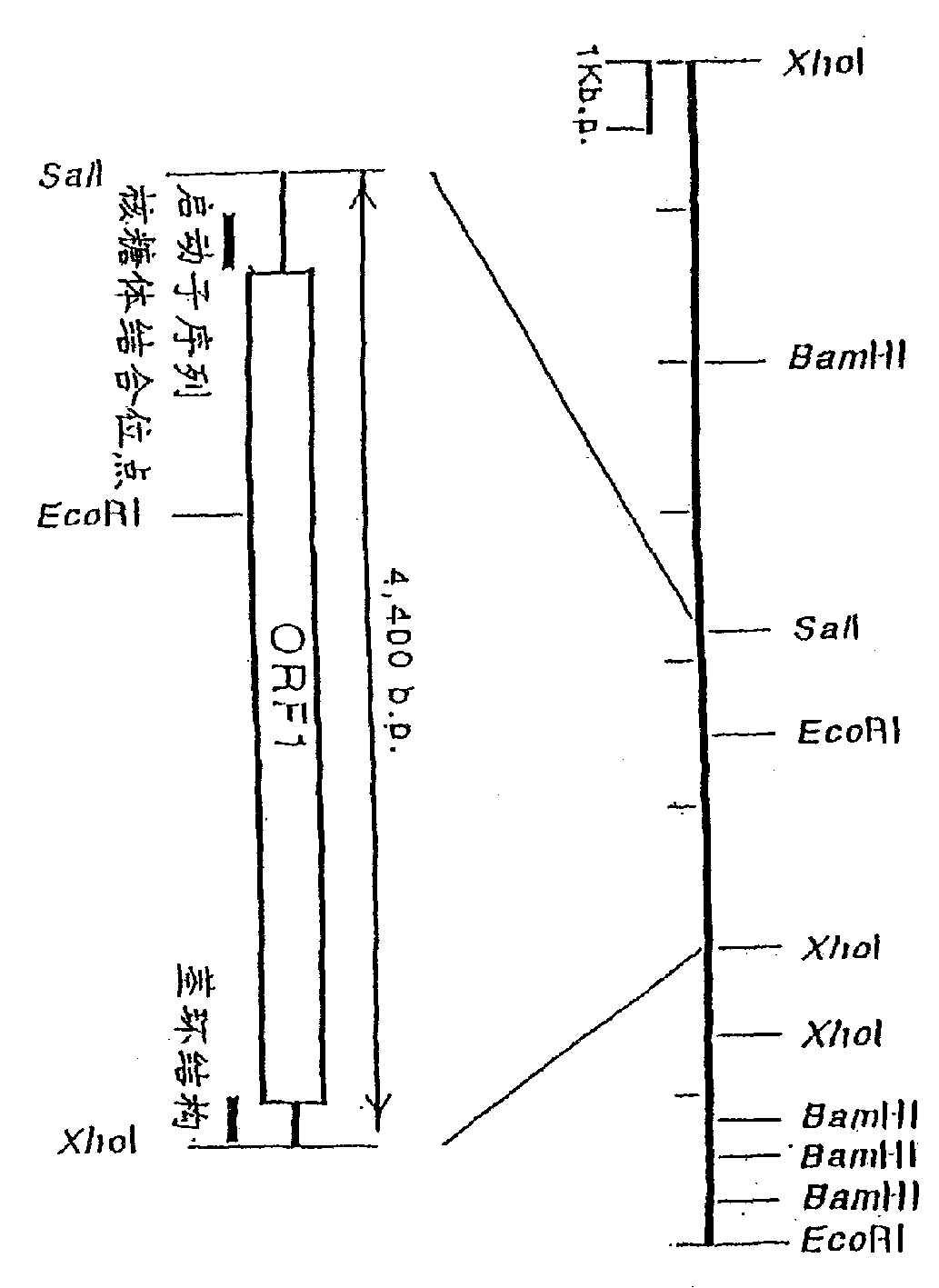
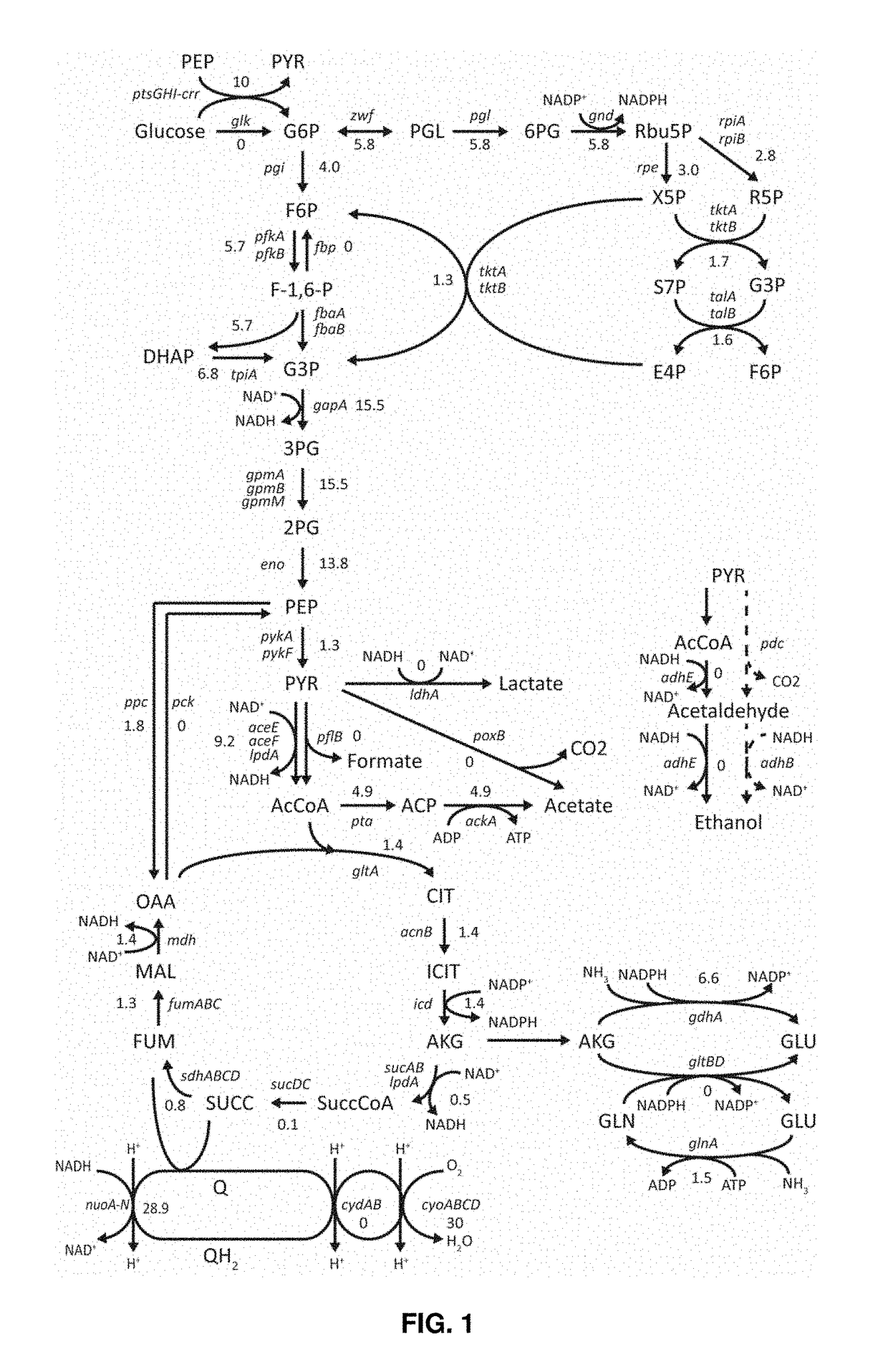
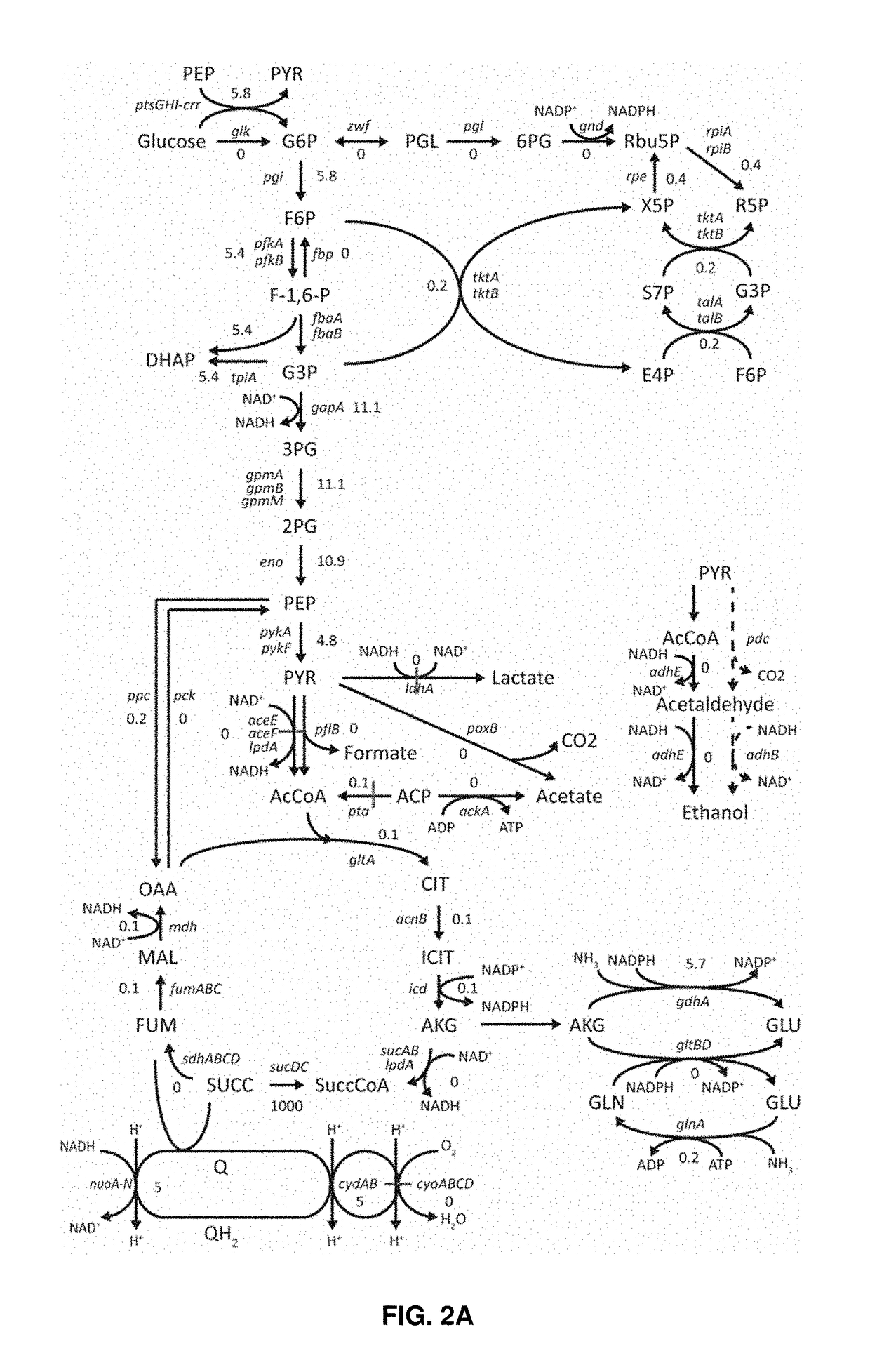
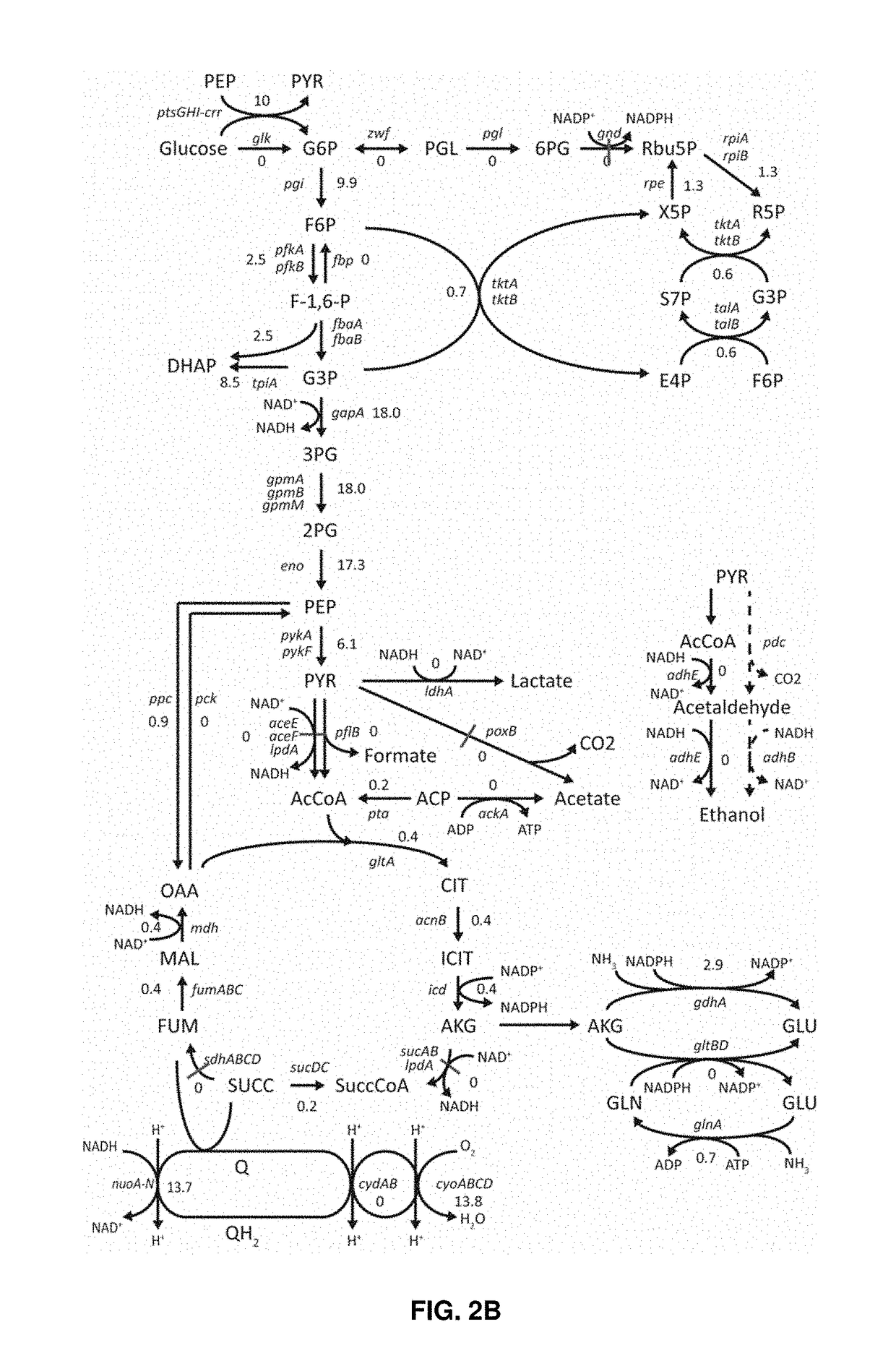
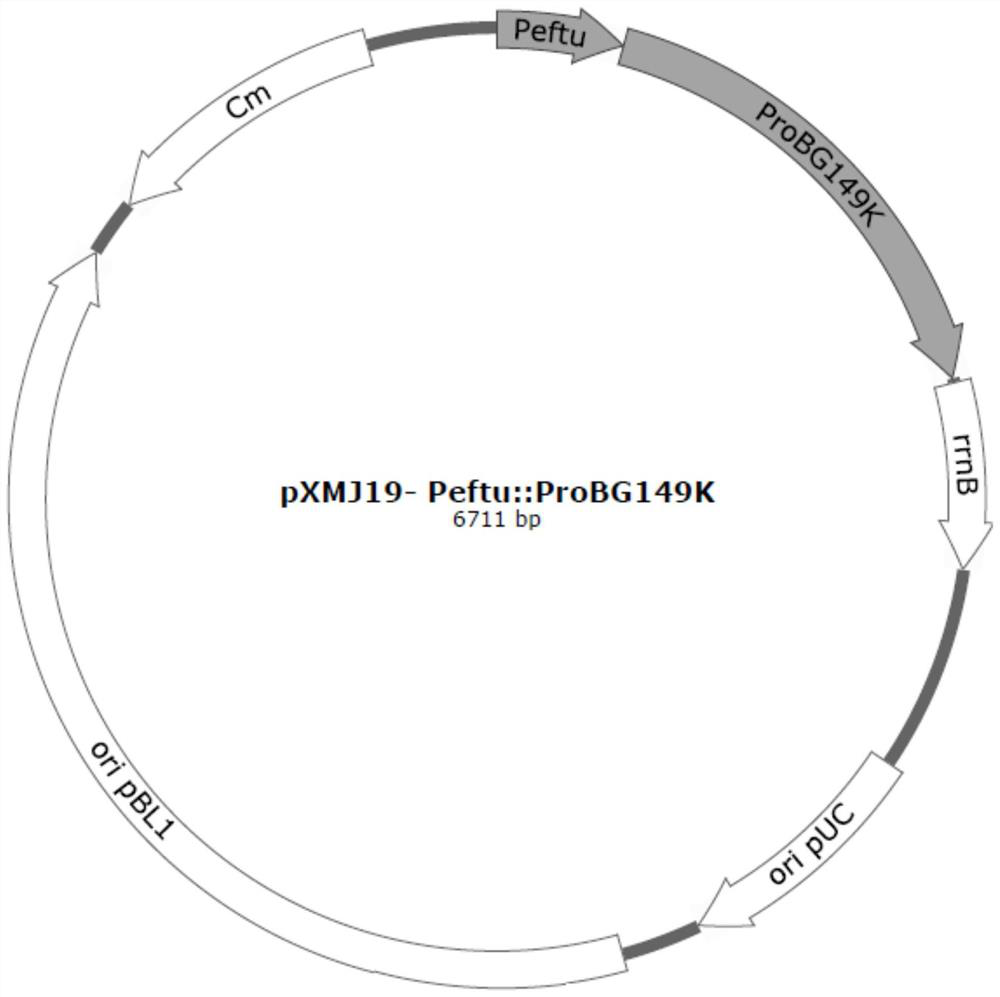
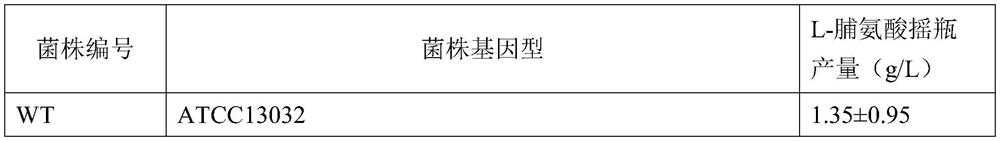
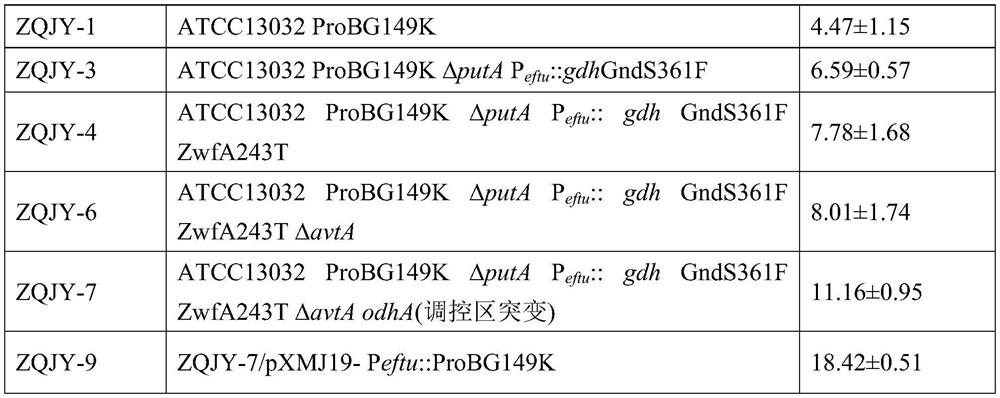
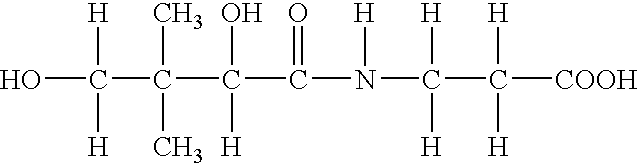Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34 results about "Ketoglutarate dehydrogenase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for producing an l-amino acid
ActiveUS20090286290A1Efficient productionEasy to useOxidoreductasesFermentationMicroorganismKetoglutarate dehydrogenase
A microorganism which has an L-amino acid producing ability and has been modified so that succinate dehydrogenase activity and α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase activity are decreased is cultured in a medium to produce and accumulate an L-amino acid in the medium or cells of the microorganism, and the L-amino acid is collected from the medium or cells to produce the L-amino acid.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
L-glutamic acid-producing microorganism and a method for producing L-glutamic acid
InactiveUS7205132B2Decreased ability to degrade L-glutamic acidReduced activityBacteriaSugar derivativesMicroorganismKetoglutarate dehydrogenase
A coryneform bacterium which has an L-glutamic acid-producing ability and grows at least at the same growth rate as a non-mutated strain or a wild-type strain and has intracellular α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase activity which is less than half that of the non-mutated or wild-type strain, and is obtained by introducing a mutation into a coding region or an expression control region of the chromosomal odhA gene encoding the E1o subunit of the α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Recombinant microorganism for generating terpenoid and construction method thereof
ActiveCN103087972AIncrease production capacityHigh strengthBacteriaOxidoreductasesEscherichia coliMicroorganism
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
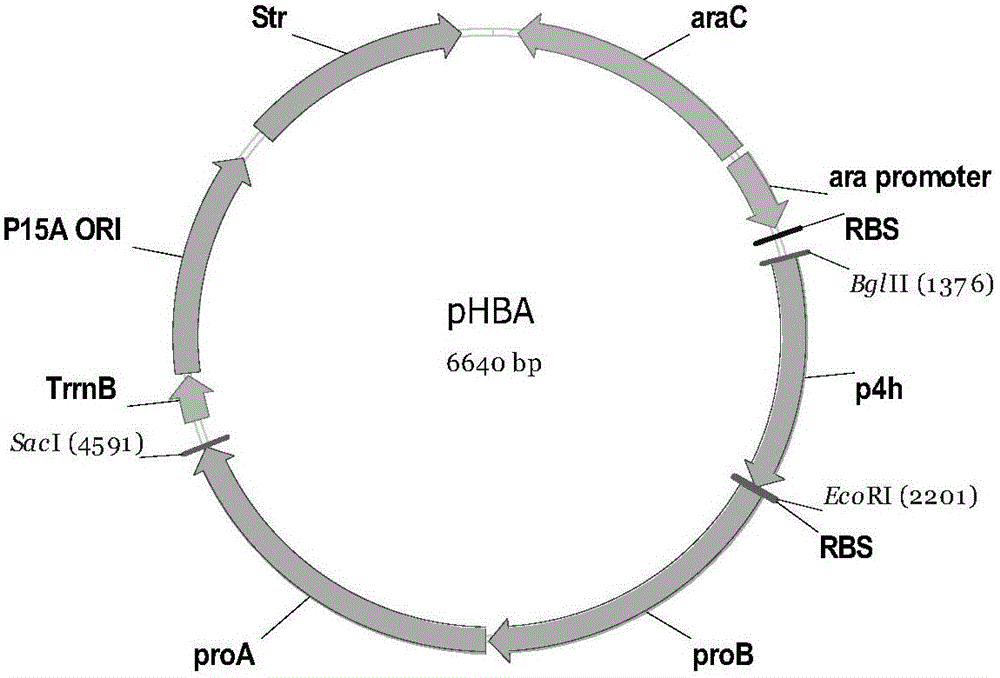
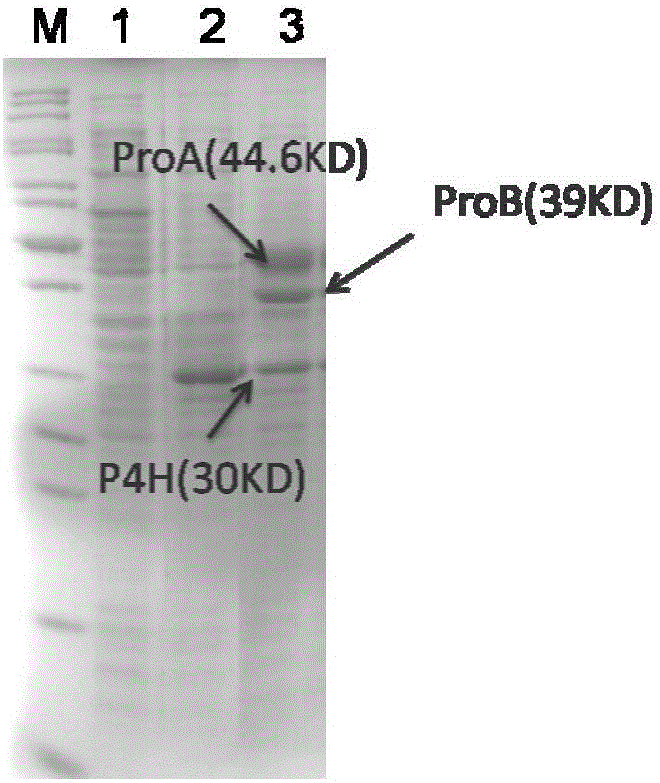
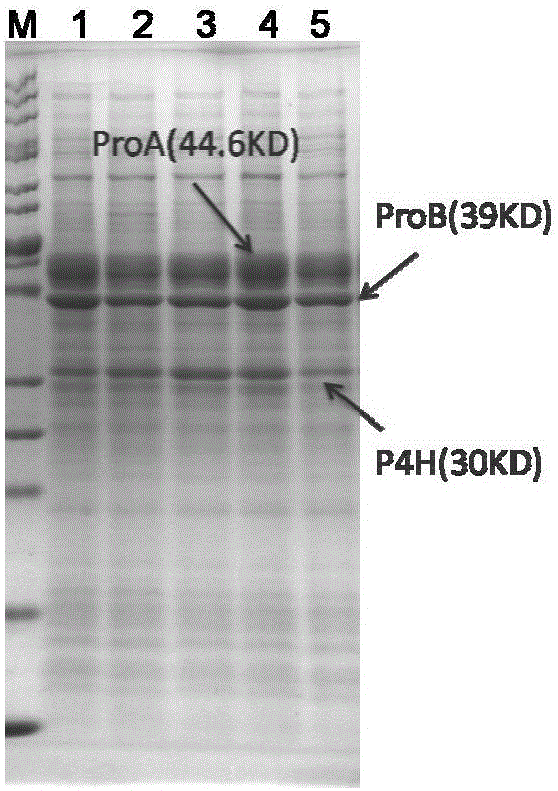
Engineering bacteria for producing trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN106086102AIncrease productionBacteriaTransferasesAcetyl Coenzyme A SynthetaseGlutamate 5-kinase
The invention discloses engineering bacteria for producing trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline and a construction method and an application thereof. The construction method of the engineering bacteria provided by the invention includes the steps of A1) and A2): A1) introducing a L-proline-4-hydroxylase gene, a glutamate-5-kinase gene and a glutamate-5-semialdehyde dehydrogenase gene into a receptor cell; and A2) knocking an alpha-ketoglutaricdehydrogenase gene, an isocitratlyase gene or a proline dehydrogenase gene of the receptor cell out, or replacing a pyruvic oxidase gene of the receptor cell with an acetylcoenzyme A synthetase gene; and carrying out a reaction of the recombinant cell and a substrate to obtain the trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline. Experiments prove that the production method of the trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline can be used for production of the trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
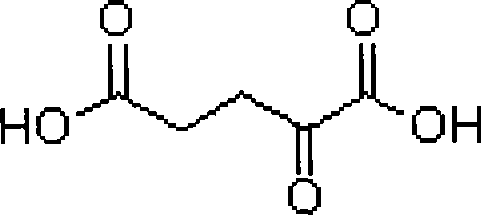
Method for realizing excessive accumulation of alpha-ketoglutarate acid by adding alpha-ketoglutarate acid dehydrogenase inhibitor
InactiveCN101250563AImproved compared to the controlMicroorganism based processesFermentationTorulopsis glabrataCarbon metabolism
The invention relates to a method for adding alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase inhibitor to realize excessive accumulation of alpha-ketoglutaric acid, which belongs to the technical field of the metabolic regulation optimized fermentation process of the protein level. The method of the invention comprises following steps: utilizing multi - vitamin - auxotrophic yeast of Torulopsis glabrata CCTCC M202019 as producing strains, regulating the activity of alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase through adding the alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase inhibitor: hydrogen peroxide, methotrexate, sodium hypochlorite or hydroxyamino in culture medium, purposively lowing the activity of the alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, reducing the degradation of the alpha-ketoglutaric acid in the metabolic process, and achieving the aim of the excessive accumulation of the alpha-ketoglutaric acid. The method of the invention cuts off carbon metabolism flow on a node of the alpha-ketoglutaric acid through regulating the stream distribution of carbon metabolism and the carbon metabolism flow, wherein the maximum output of the alpha-ketoglutaric acid reaches 23.2g / L, which is increased by 12.2% compared with the control. The invention provides a new thought for the fermentation research of TCA cycle intermediate metabolite.
Owner:GUANGDONG HUANXI BIOLOGICAL TECH
Method for synthesizing alpha-ketoglutaric acid by biological conversion method
ActiveCN105177065AGrow fastLow nutritional requirementsMicroorganism based processesFermentationKetoglutarate dehydrogenaseAlpha-Ketoglutaric acid
The invention aims at providing a method for synthesizing alpha-ketoglutaric acid by a biological conversion method. According to the method, L-glutamic acid is used as a substrate; in a conversion culture solution obtained from kluyveromyces marxianus ATCC36534 through being cultured via a conversion culture substrate, alpha-ketoglutaricdehydrogenase inhibitors are added; the synthesis conversion culture is performed under the oscillation conditions of 25 to 30 DEG C and 200 to 250 r / min; after the synthesis conversion culture is completed, the alpha-ketoglutaric acid is obtained through separating and purifying the synthesis conversion solution; the L-glutamic acid is converted into alpha-ketoglutaric acid by yeast cells in the growth state; the alpha-ketoglutaricdehydrogenase inhibitors are added; the further metabolism consumption is blocked, so that a great amount of alpha-ketoglutaric acid is accumulated in the culture medium; when the feeing concentration of the substrate L-glutamic acid is 50g / L, the mol conversion rate can reach 83.2 percent. The low-value L-glutamic acid is converted into high-value alpha-ketoglutaric acid; the large-scale industrial application can be realized; a production process has the advantages of short period, high conversion rate, small environment pollution and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SHUREN UNIV
Corynebacterium glutamicum for high yield of L-glutamine as well as construction method and application thereof
PendingCN110951661AIncrease productionImprove conversion rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGlutaric acidKetoglutarate dehydrogenase
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering, and discloses corynebacterium glutamicum for high yield of L-glutamine as well as a construction method and an application of corynebacterium glutamicum. The activity of alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase and / or glutamic acid exporter protein in cells of the corynebacterium glutamicum for highly producing L-glutamine is lost, and adenylation modification of glutamine synthetase is removed. According to the corynebacterium glutamicum for highly producing L-glutamine disclosed by the invention, L-glutamine can be accumulated in a culture medium or cells, so that the yield of L-glutamine is increased to a great extent. The experiments show that the corynebacterium glutamicum disclosed by the invention is an L-glutamine high-yieldstrain; compared with an unmodified strain, the strain has the advantages that the capacity of producing L-glutamine is enhanced, L-glutamine can be effectively accumulated, the yield of L-glutamine is increased, the conversion rate is relatively high, a foundation is laid for industrial production of L-glutamine, and the strain has a wide industrial application prospect.
Owner:新疆梅花氨基酸有限责任公司
Tomato bacterial wilt resistance gene Slalpha-KGDH E2 and application thereof
ActiveCN112626093AIdentification clearly distinguishesHigh expressionOxidoreductasesFermentationBiotechnologyNucleotide
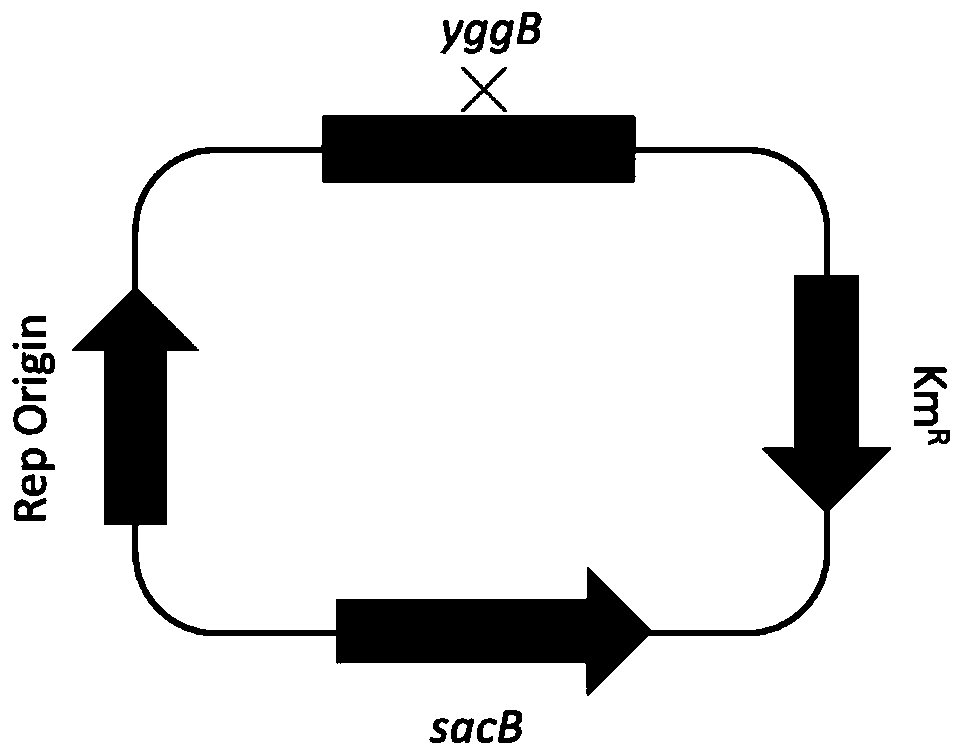
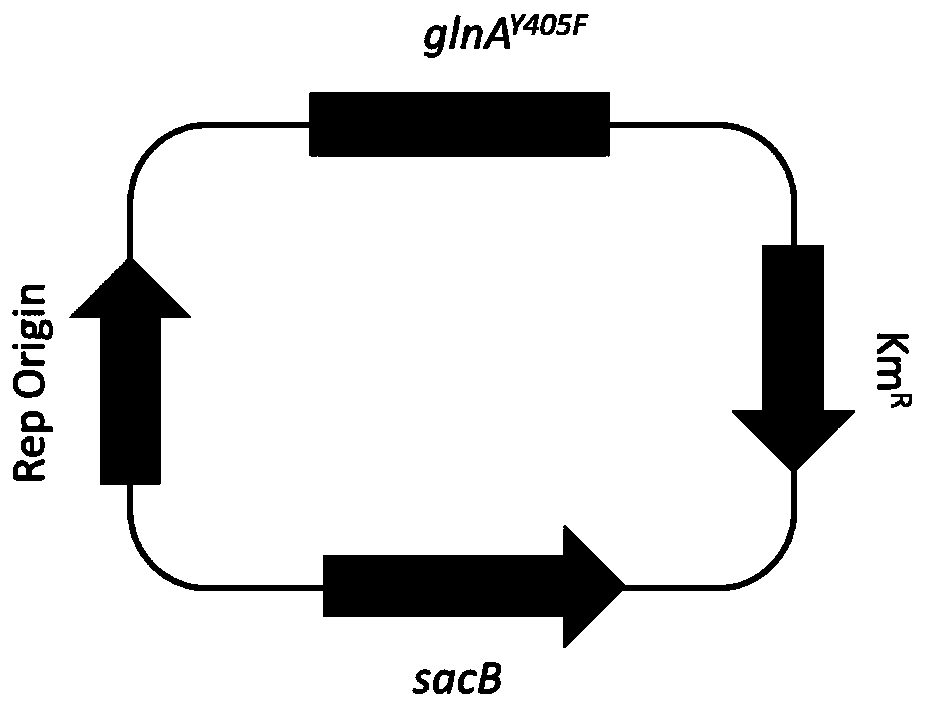
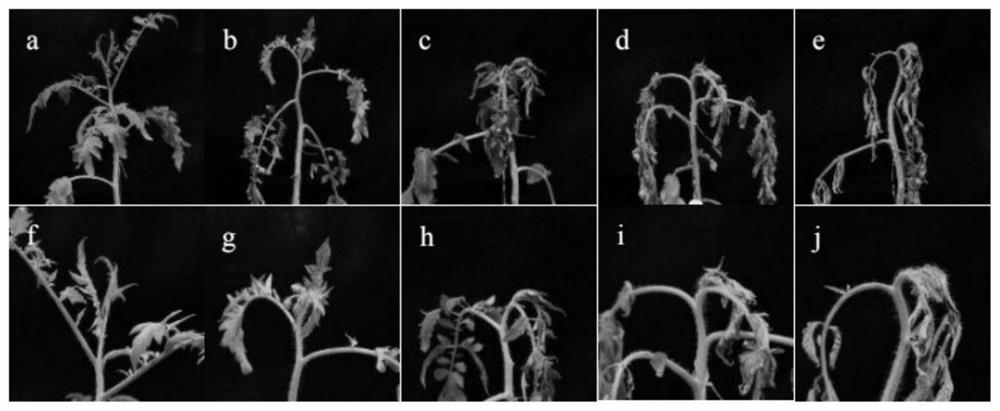
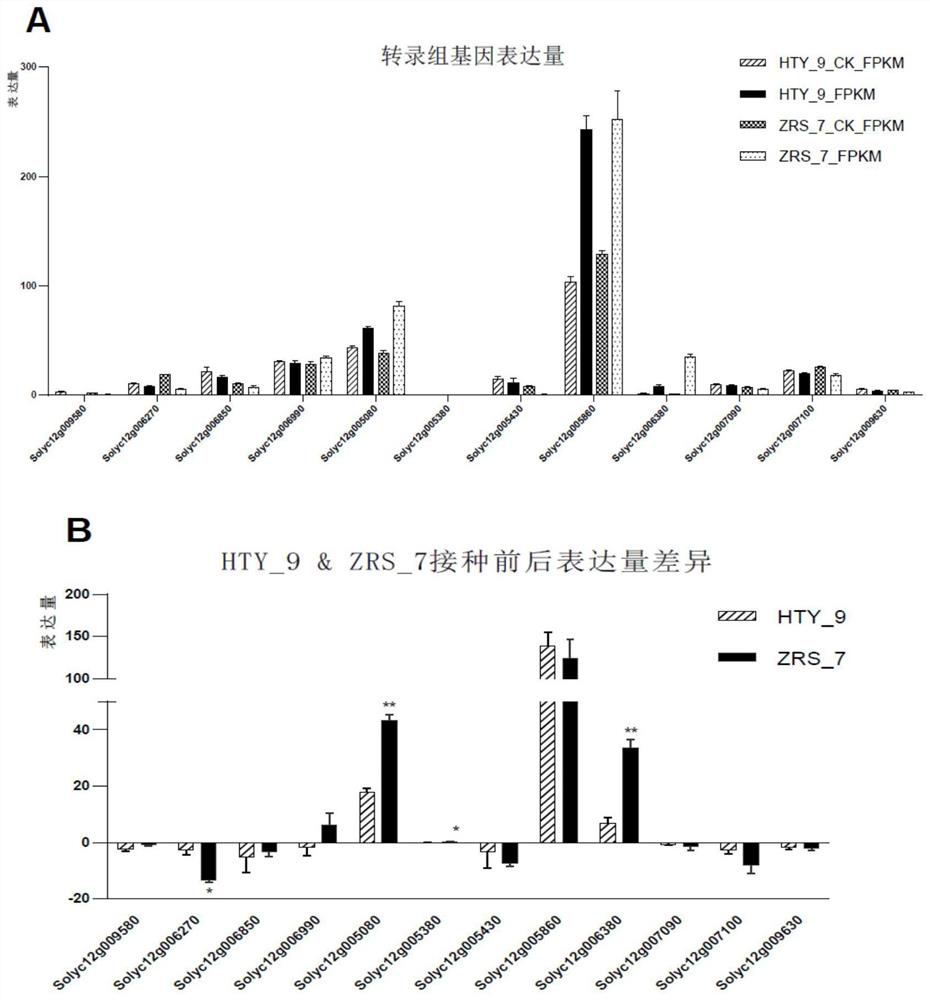
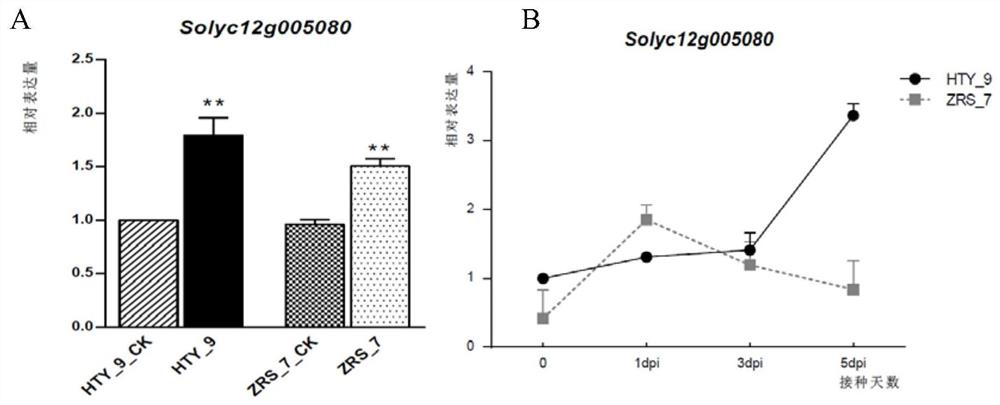
The invention discloses a tomato bacterial wilt resistance gene Slalpha-KGDH E2 and application thereof. The Slalpha-KGDH E2 codes an alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase E2 subunit, the nucleotide sequence of the gene is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1, and the protein sequence coded by the gene is shown as SEQ ID NO: 2. Reduction of the expression quantity of the gene or partial base mutation can enable tomato plants to lose resistance to tomato bacterial wilt. After ralstonia solanacearum is inoculated into disease-resistant plants, the expression quantity of the Slalpha-KGDH E2 gene is remarkably increased compared with that of a control group; and functional verification shows that the Slalpha-KGDH E2 gene has a key positive regulation effect on the resistance of tomatoes to ralstonia solanacearum, the resistance of tomatoes to bacterial wilt can be improved by overexpression of the Slalpha-KGDH E2 gene, and a new way is provided for breeding of new tomato disease-resistant varieties, so that the Slalpha-KGDH E2 gene has good application value.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Method for improving yield of arginine by utilizing corynebacterium glutamicum and corynebacterium crenatum
InactiveCN105018515AReduced transcript levelsIncrease supplyMicroorganism based processesFermentationArginineCarboxylic acid
The invention discloses corynebacterium glutamicum and corynebacterium crenatum, as well as a method for improving the yield of arginine by utilizing corynebacterium glutamicum and corynebacterium crenatum. According to the method, dtsR1 genes of corynebacterium glutamicum and corynebacterium crenatum are knocked out; then the transcriptional level of alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex (oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex, ODHC) regulated by the dtsR1 genes is greatly lowered, and alpha-ketoglutaric acid flows to arginine; meanwhile, Tween-80, oleic acid or a mixture of Tween-80 and oleic acid is added to a fermentation medium, so as to make up for nutrition loss caused by loss of the dtsR1 genes, and at the early logarithmic growth stage during the fermentation culturing, Tween-40 is added to induce the transcription level of the genes in the pentose phosphate pathway to be greatly improved. Thus, sufficient NADPH is provided for the synthesis of arginine, and other complicated molecular breeding methods for improving supply of NADPH and other accumulation methods for improving content of alpha-ketoglutaric acid in the tricarboxylic acid cycle pathway are eliminated.
Owner:JIANGXI NORMAL UNIV
Application of Chinese yarn glycoprotein in improvement of activities of oxidative metabolism enzymes of mitochondria of brain cell
ActiveCN102920998AHigh activitySimple extraction methodNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsYarnKetoglutarate dehydrogenase
The invention relates to an application of Chinese yarn glycoprotein in improvement of the activities of an oxidative metabolism enzymes of mitochondria of a brain cell. Selection and verification are carried out by an animal test so as to prove that the Chinese yarn glycoprotein can obviously improve the activities of key enzymes namely pyruvate dehydrogenase and alpha-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase used for oxidative metabolism in the mitochondria of the brain cell, so that brain cell deterioration and damage diseases, such as senile dementia, vascular dementia, cerebral infarction and cerebral palsy, accompanying with oxidative metabolism efficiency reduction caused by reduction of the activities of the enzymes can be effectively treated.
Owner:新乡博凯生物技术有限公司
Enzyme cofactor combination for supplementing pyruvate dehydrogenase and alpha ketogluterate dehydrogenase complexes
The present invention provides a method and pharmaceutical composition for preventing or treating the development of syndromes related to dysfunctional energy metabolism, such as neuropathy, spontaneous nocturnal muscle cramps associated with neuropathy, seizuring, diabetes mellitus; pediatric hypoglycemia; myopathy; muscle fatigue; muscle spasms; somnolence; reduced mental acuity; exercise intolerance and myocardial insufficiency, which are due to cofactor deficiencies associated with the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex and the alpha-ketogluterate dehydrogenase (a-ketogluterate dehydrogenase) complex in humans or other mammals in need thereof. In particular, a method of preventing or treating at least one syndrome related to defective glucose metabolism in humans or other mammals is provided comprised of administering a combination of enzyme cofactors containing therapeutically effective amounts of thioctic acid, niacinamide, pantothenate, riboflavin and thiamine. Also provided is a pharmaceutical composition comprised of a carrier and the combination of cofactors.
Owner:HOWARD JAMES R
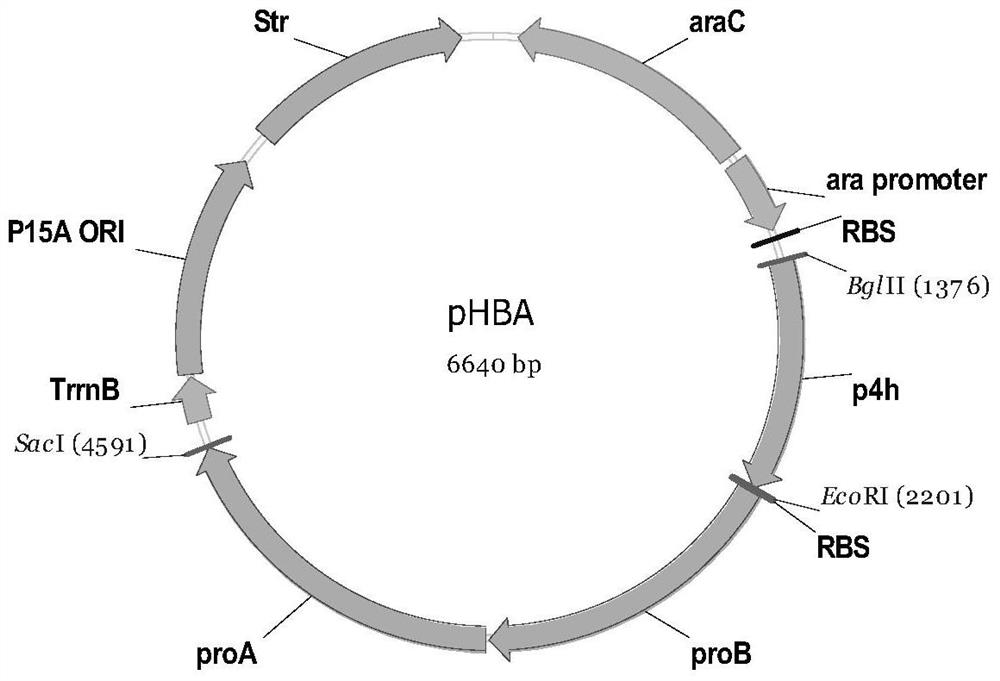
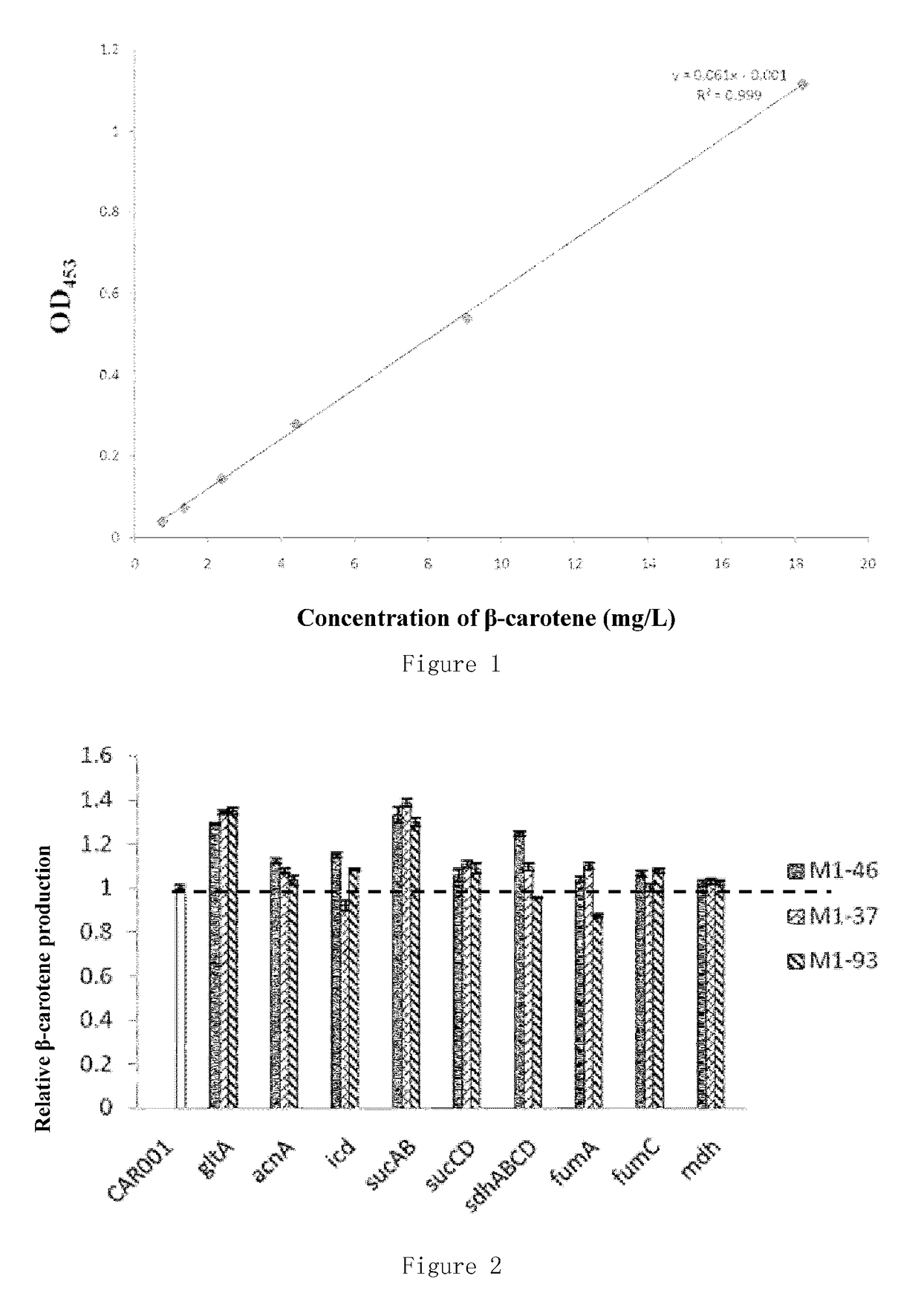
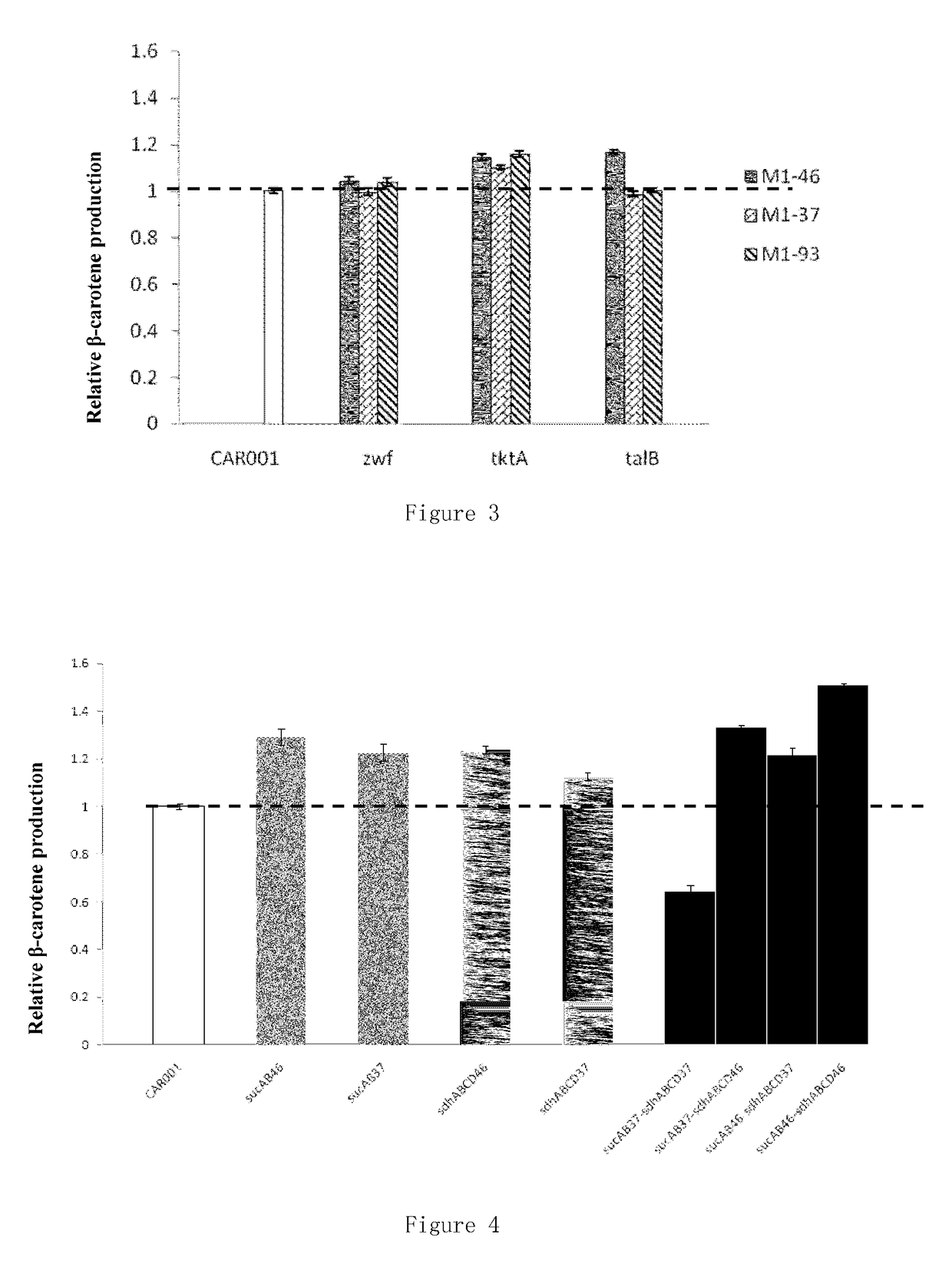
Recombinant microorganism for preparing terpenoid and method for constructing recombinant microorganism
Provided are a recombinant strain for preparing a terpenoid, and method for constructing the recombinant strain. Also provided is a recombinant bacterium 1, the recombinant bacterium 1 being a recombinant bacterium obtained in order to improve the enzymatic activity of α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase in escherichia coli or the mutant thereof. The method for improving the enzymatic activity of α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase in escherichia coli or the mutant thereof is replacing the original regulating element of the ketoglutarate dehydrogenase gene (sucAB) in escherichia coli or the mutant thereof with any of the following regulating elements: artificial regulating element M1-46, M1-37, and M1-93. Also provided are a plurality of recombinant bacteria. By improving the enzymatic activity of α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, succinic acid dehydrogenase and transaldolase therein and improving the ability of a cell to synthesize NADPH and ATP, the efficiency of the MEP pathway and the production capacity of terpenoid are improved.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
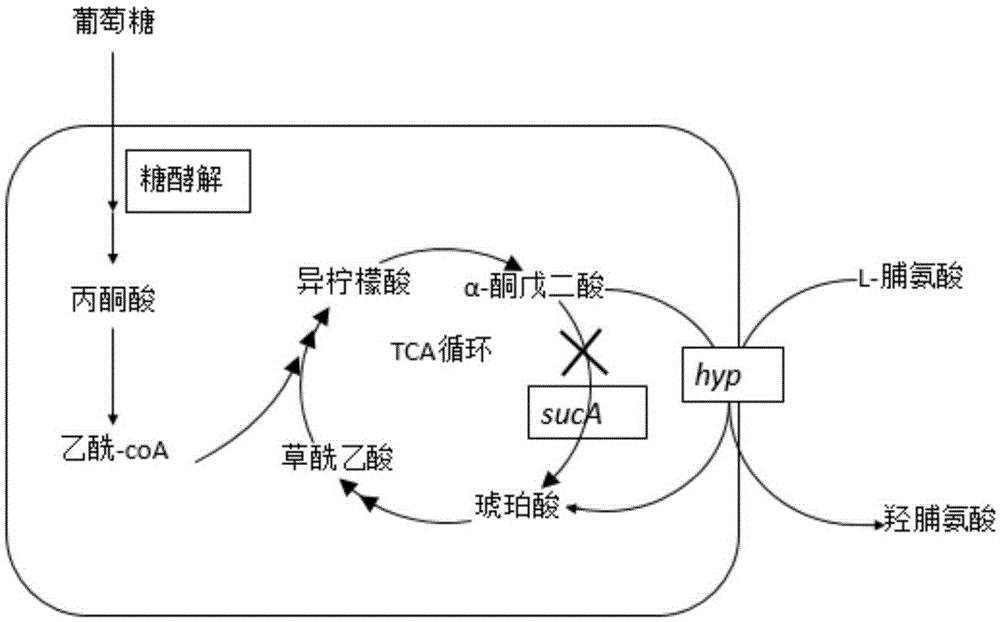
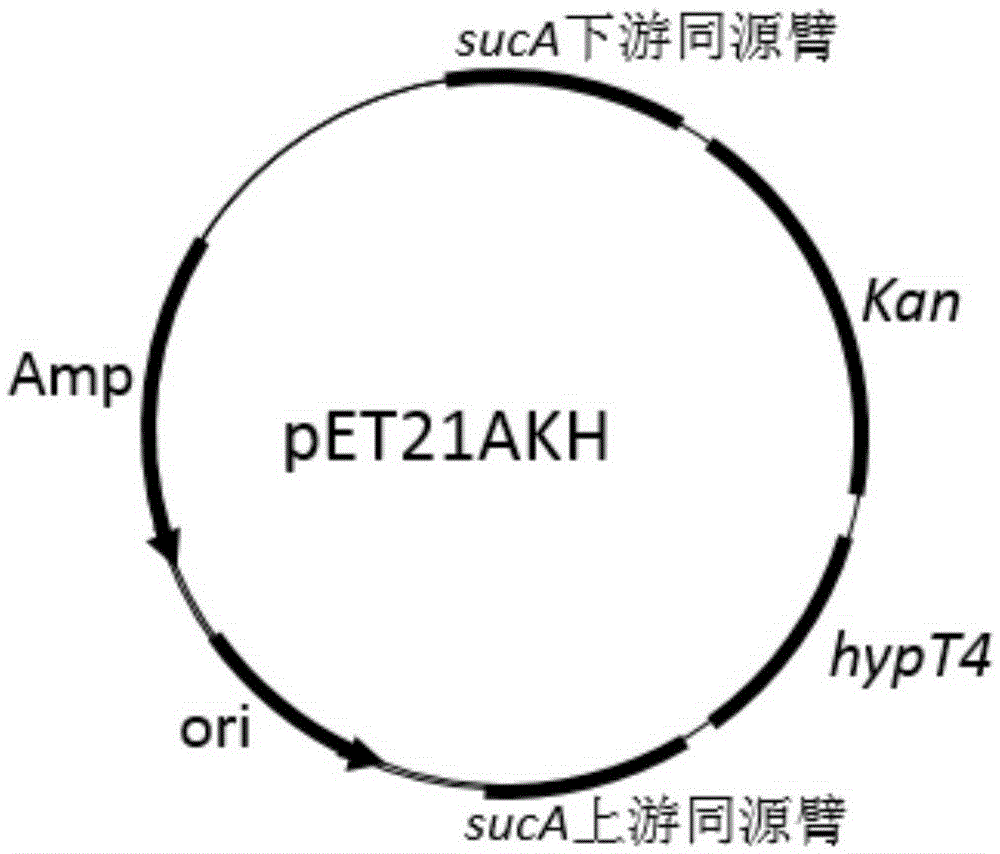
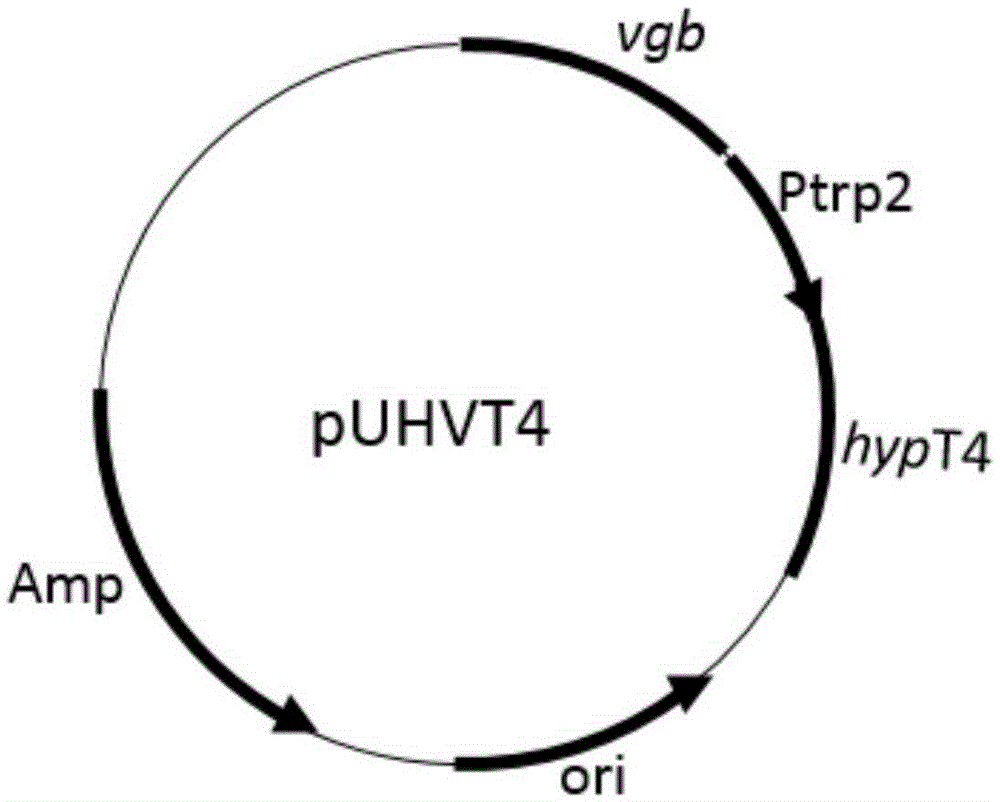
Construction of high-yield trans-4-hydroxyproline sucA gene knockout bacteria
The invention provides construction of high-yield trans-4-hydroxyproline sucA gene knockout bacteria and discloses a biosynthesis method of trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline through gene knockout. According to the method, the gene suc A is knocked out on the basis of escherichia coli BL21(DE3) delta put A, the process that alpha-oxoglutarate generates succinic acid or an alpha-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex is utilized for catalyzing in the TCA circulation process is disturbed, meanwhile, the trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline hydroxylase gene (hyp) is inserted, and then plasmid pUC19-Ptrp2-hyp-vgb is converted; hydroxylase replaces functions of alpha-ketoglutaricdehydrogenase, 'anaplerosis' is conducted on the TCA circulation process, and it is guaranteed that hydroxyproline is generated while the TCA circulation is conducted. The invention further discloses application of recombinant escherichia coli to production of trans-4- hydroxyproline, it is indicated by the flask shaking fermentation result that the yield of hydroxyproline obtained after mediumoptimization is 1344.1 mg / L and is about 5.53 times that before optimization; compared with original bacteria which are converted into the plasmid pUC19-Ptrp2-hyp-vgb in the same mode, advantages are achieved on the aspect of production of hydroxyproline.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for stick bacteria capable of producing L-glutaminic acid and producing 1-glutaminc acid
Disclosed are Corynebacterium L-glutamic acid producing L-glutamic acid deficient in α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, a method for producing L-glutamic acid by using the bacterium, coding derived from Corynebacterium L-glutamic acid producing A gene for an enzyme with KGDH activity, a recombinant DNA containing the gene, a coryneform bacterium carrying the recombinant DNA, and a method for producing L-lysine using a bacterium carrying the recombinant DNA and having the ability to produce L-lysine .
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
L-glutamic acid-producing microorganism and a method for producing L-glutamic acid
InactiveUS20060057686A1Decreased ability to degrade L-glutamic acidEfficient productionBacteriaSugar derivativesMicroorganismKetoglutarate dehydrogenase
A coryneform bacterium which has an L-glutamic acid-producing ability and grows at least at the same growth rate as a non-mutated strain or a wild-type strain and has intracellular α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase activity which is less than half that of the non-mutated or wild-type strain, and is obtained by introducing a mutation into a coding region or an expression control region of the chromosomal odhA gene encoding the E1o subunit of the α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Construction method of synthetic path for generating glutamic acid by utilizing xylose in corynebacterium glutamicum
The invention belongs to the field of gene engineering, and discloses a construction method of a synthetic path for generating glutamic acid by utilizing xylose in corynebacterium glutamicum. The construction method comprises the following steps of (1) expressing heterogenous pentose transport protein in the corynebacterium glutamicum; (2) expressing heterogenous xylose isomerase and xylulokinasein the corynebacterium glutamicum; (3) generating alpha-ketoglutarate from generated 5-xylulosephosphate through a phosphopentose pathway and a glycolysis pathway, and carrying out weakened expressionon alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, so that more alpha-ketoglutarate flows to the synthesis of glutamic acid; and (4) modifying glutamic acid secretory protein to ensure that the corynebacterium glutamicum does not respond to external biotin pressure any more, and continuously secreting the glutamic acid out of cells. According to the constructed synthetic path from the xylose to the glutamic acid, the corynebacterium glutamicum can utilize the xylose to produce the glutamic acid in a conventional synthetic culture medium, and the synthesis from the xylose to the glutamic acid can also be conducted in a high-biotin environment such as lignocellulose.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for producing an L-amino acid
ActiveUS8058035B2Efficient productionEasy to useOxidoreductasesFermentationKetoglutarate dehydrogenaseSuccinate dehydrogenase
A microorganism which has an L-amino acid producing ability and has been modified so that succinate dehydrogenase activity and α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase activity are decreased is cultured in a medium to produce and accumulate an L-amino acid in the medium or cells of the microorganism, and the L-amino acid is collected from the medium or cells to produce the L-amino acid.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Glutamic acid production strain and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN111925953APromotes interpenetrating healingGrow fastBacteriaMicroorganism lysisStainingKetoglutarate dehydrogenase
The invention discloses a glutamic acid production strain ands a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the field of bioengineering. The method comprises the following steps: fusing protoplast between corynebacterium glutamicum A (the preservation number is CGMCC NO.1. 10760) and corynebacterium glutamicum B (the preservation number is CGMCC NO.1. 1735), and performing mutationand regeneration so that the FM19-007 strain (CGMCC No. 18678) is obtained. The strain is characterized in that the strain is short-rod-shaped, spore-free and flagellate-free when observed under a microscope, gram staining is positive, the cell size is 0.7-1 * 1.2-3 [mu] m, and alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase is lost; the glutamate dehydrogenase activity is high; glutamic acid is not used, glutamic acid feedback inhibition is relieved, and the capacity of secreting glutamic acid to the outside is achieved; in the fermentation process, obvious morphological change and cell membrane permeability change (forming cell leakage) occur at the decay stage. The mutant strain is fermented to produce glutamic acid, the yield of glutamic acid is 22%, the yield is increased by 51.72%, and the yieldof glutamic acid is remarkably increased.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY +1
Escherichia coli strain for producing succinic acid with glycerol as well as construction method and use
ActiveCN103436477AImprove throughputEfficient use ofBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseEscherichia coli
The invention discloses an Escherichia coli strain for producing succinic acid with glycerol as well as a construction method and use. The Escherichia coli strain for producing succinic acid with glycerol has the preservation number of CGMCC No. 7999. The construction method comprises the following steps: knocking out the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase gene of Escherichia coli, and performing over-expression of key enzymes (isocitrate lyase and malate synthetase) of the glyoxylate cycle to obtain an evolved starting strain; by virtue of evolution, obtaining an evolved strain which can grow in an M9 basic salt medium with glycerol as unique carbon source and has enhanced glyoxylate cycle flux; knocking out the succinate dehydrogenase gene, and performing over-expression of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase and alpha-ketoglutaric dehydrogenase systems to obtain an Escherichia coli strain for producing succinic acid by using glycerol. The strain grows rapidly and has a high cell density, so that the rate of producing succinic acid with glycerol is increased.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Alph-ketoglutaric acid dehydrase gene
A coryneform L-glutamate producing bacterium deficient in alpha -ketoglutaric dehydrogenase activity; a process for producing L-glutamic acid by using the bacterium; a gene coding for an enzyme having an alpha -KGDH activity originating in the coryneform L-glutamate producing bacterium; a recombinant DNA containing the above gene; a coryneform bacterium holding the above DNA; and a process for producing L-lysine by using an L-lysine producing bacterium holding the recombinant DNA.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Microorganisms and methods for producing pyruvate, ethanol, and other compounds
Microorganisms comprising modifications for producing pyruvate, ethanol, and other compounds. The microorganisms comprise modifications that reduce or ablate activity of one or more of pyruvate dehydrogenase, 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase, phosphate acetyltransferase, acetate kinase, pyruvate oxidase, lactate dehydrogenase, cytochrome terminal oxidase, succinate dehydrogenase, 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase, glutamate dehydrogenase, pyruvate formate lyase, pyruvate formate lyase activating enzyme, and isocitrate lyase. The microorganisms optionally comprise modifications that enhance expression or activity of pyruvate decarboxylase and alcohol dehydrogenase. The microorganisms are optionally evolved in defined media to enhance specific production of one or more compounds. Methods of producing compounds with the microorganisms are provided.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Method for improving production capacity of amino acid producing strain
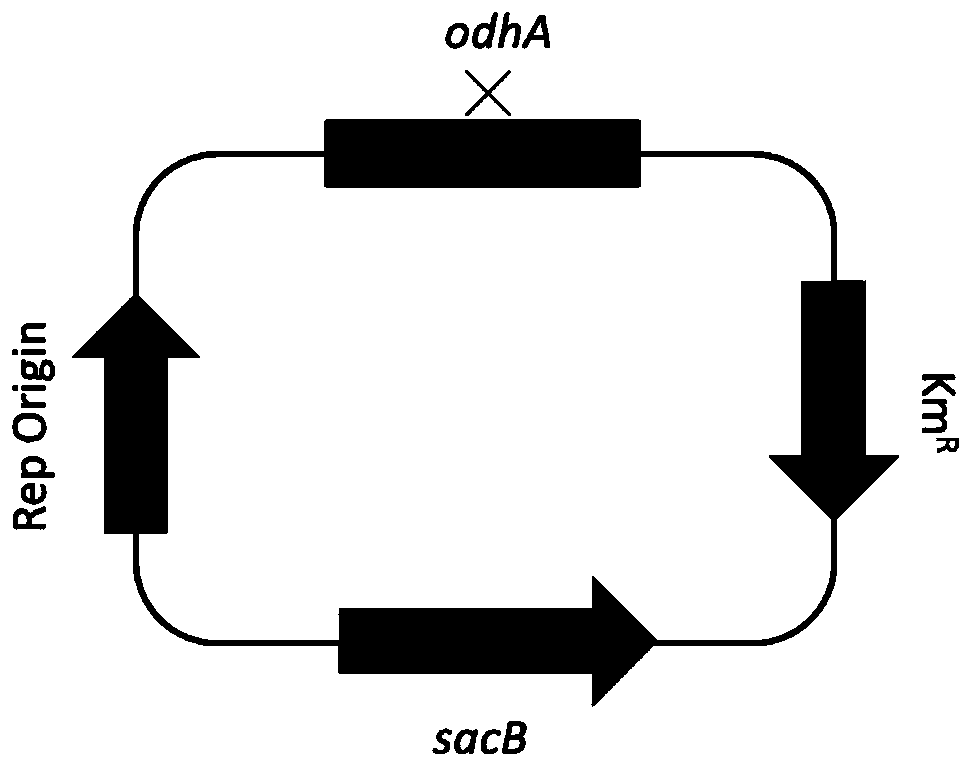
ActiveCN113637699ABacteriaStable introduction of DNAKetoglutarate dehydrogenaseKetoglutarate Dehydrogenase Complex
The invention discloses a method for improving the production capacity of an amino acid producing strain. The method comprises the step of mutating and / or deleting a regulatory region of an odhA gene of an Elo subunit for encoding an alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase compound on a chromosome. By means of the method, the L-proline production capacity of an L-proline production strain can be improved by at least three times, the yield of L-proline produced through fermentation of the constructed engineering strain CCTCC NO: M 2020060 reaches up to 119.90 g / L, and industrial application prospects are achieved.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
Screening method for Fe<2+> and alpha-ketoglutaric acid-dependent hydroxylase and isoleucine hydroxylase
InactiveCN108517328AHigh affinityHigh catalytic efficiencyVectorsHydrolasesHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsScreening method
The invention relates to a screening method of high-activity Fe<2+> and alpha-ketoglutaric acid-dependent hydroxylase. The method includes the steps of: constructing a bacterial strain with deletion of alpha-ketoglutaric acid dehydrogenase encoding gene and isocitric acid lyase encoding gene; amplifying Fe<2+> and alpha-ketoglutaric acid-dependent hydroxylase encoding gene through error-prone PCRto obtain a mutant thereof, and connecting the mutant to an expression vector; and converting the expression vector to the bacterial strain with deletion of alpha-ketoglutaric acid dehydrogenase encoding gene and isocitric acid lyase encoding gene and screening a bacterial strain, having high growth speed, on a culture medium containing alpha-ketoglutaric acid and corresponding substrates; extracting a plasmid therefrom, and amplifying a hydroxylase encoding gene mutant. The method achieves high-throughput screening on the high-activity Fe<2+> and alpha-ketoglutaric acid-dependent hydroxylaseand accelerates application process of the enzyme.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Recombinant microorganism capable of efficiently utilizing methanol and application thereof
PendingCN114134092AIncrease biomassReduce accumulationBacteriaTransferasesEscherichia coliEnzyme Gene
The invention relates to the technical field of genetic engineering and biological fermentation, and particularly discloses a recombinant microorganism capable of efficiently utilizing methanol and application of the recombinant microorganism. The invention provides a recombinant microorganism which has increased expression and / or enzymatic activity of methanol dehydrogenase and dihydroxyacetone synthetase and reduced expression quantity of a formaldehyde dissimilatory gene frmAB and expression and / or enzymatic activity of 6-phosphofructokinase compared with an original strain, and the recombinant microorganism has the advantages that the expression quantity of the methanol dehydrogenase and the dihydroxyacetone synthetase is increased, and the expression quantity of the formaldehyde dissimilatory gene frmAB and the expression quantity of 6-phosphofructokinase are reduced; the starting strain is escherichia coli. Specifically, after a formaldehyde dissimilatory gene frmAB, a 6-phosphofructokinase gene pfkAB and an alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase gene sucA are knocked out at the same time, and a 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde dehydrogenase gene gapA is inhibited, the utilization rate of methanol can be further improved, and accumulation of intermediate formaldehyde is reduced.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
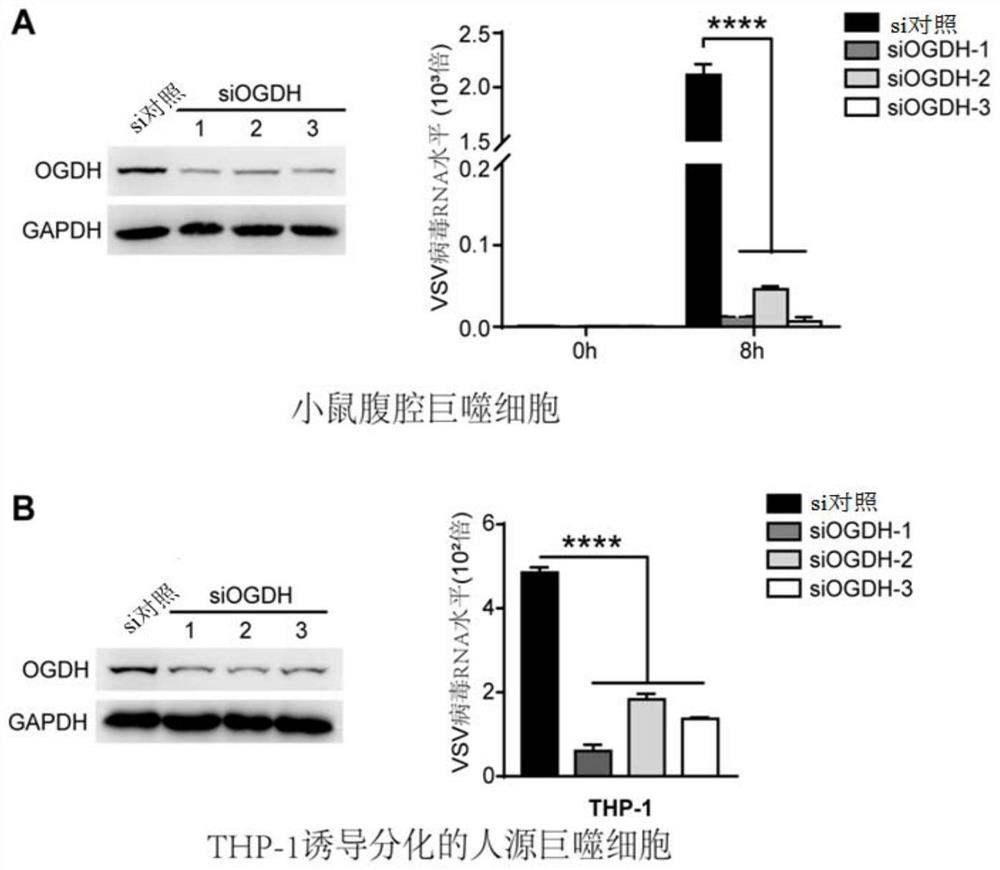
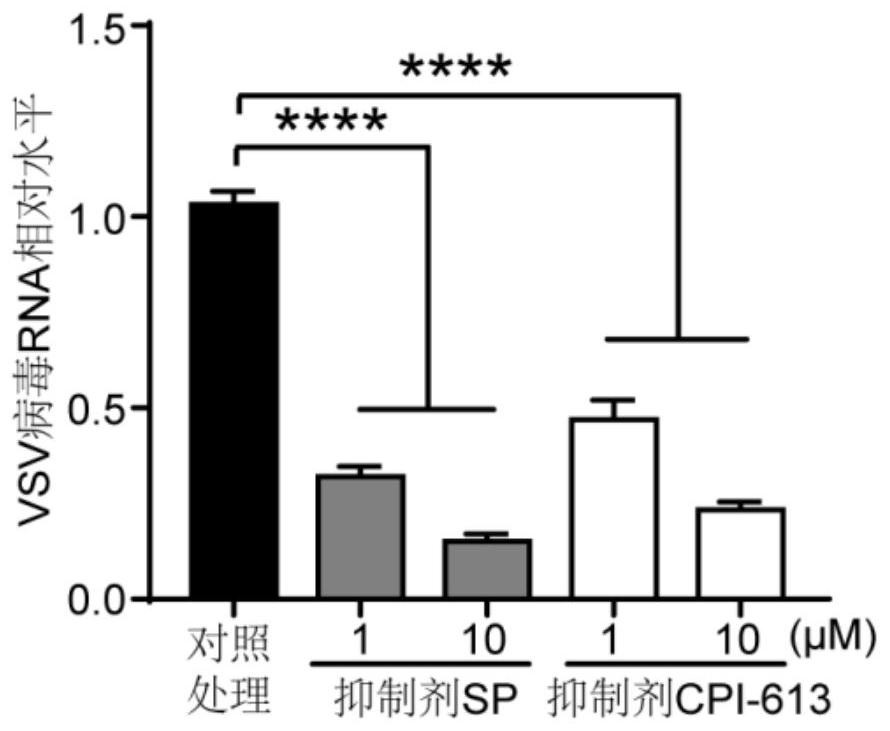
Application of ogdh inhibitors in the treatment of viral infectious diseases
ActiveCN110404074BAntiviralsPharmaceutical active ingredientsPharmaceutical drugViral infectious disease
The present disclosure relates to the application of inhibitors of α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase (OGDH) in the treatment of viral infectious diseases. Specifically, the present disclosure relates to the use of OGDH inhibitors in the preparation of products for the treatment of viral infectious diseases and / or diseases and / or symptoms associated with viral infections, and corresponding pharmaceutical compositions or kits thereof . The present disclosure can be used for suppressing and treating virus infection, especially for objects with abnormal natural immune function, and has broad application prospects.
Owner:THE INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Escherichia coli strain for producing succinic acid with glycerol as well as construction method and use
ActiveCN103436477BImprove throughputEfficient use ofBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
A kind of engineering bacteria producing trans-4-hydroxy-l-proline and its construction method and application
The invention discloses engineering bacteria for producing trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline and a construction method and an application thereof. The construction method of the engineering bacteria provided by the invention includes the steps of A1) and A2): A1) introducing a L-proline-4-hydroxylase gene, a glutamate-5-kinase gene and a glutamate-5-semialdehyde dehydrogenase gene into a receptor cell; and A2) knocking an alpha-ketoglutaricdehydrogenase gene, an isocitratlyase gene or a proline dehydrogenase gene of the receptor cell out, or replacing a pyruvic oxidase gene of the receptor cell with an acetylcoenzyme A synthetase gene; and carrying out a reaction of the recombinant cell and a substrate to obtain the trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline. Experiments prove that the production method of the trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline can be used for production of the trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for realizing excessive accumulation of alpha-ketoglutarate acid by adding alpha-ketoglutarate acid dehydrogenase inhibitor
InactiveCN101250563BImproved compared to the controlMicroorganism based processesFermentationTorulopsis glabrataMetabolite
Owner:GUANGDONG HUANXI BIOLOGICAL TECH
Recombinant microorganism for preparing terpenoid and method for constructing recombinant microorganism
Provided are a recombinant strain for preparing a terpenoid, and method for constructing the recombinant strain. Also provided is a recombinant bacterium 1, the recombinant bacterium 1 being a recombinant bacterium obtained in order to improve the enzymatic activity of α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase in escherichia coli or the mutant thereof. The method for improving the enzymatic activity of α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase in escherichia coli or the mutant thereof is replacing the original regulating element of the ketoglutarate dehydrogenase gene (sucAB) in escherichia coli or the mutant thereof with any of the following regulating elements: artificial regulating element M1-46, M1-37, and M1-93. Also provided are a plurality of recombinant bacteria. By improving the enzymatic activity of α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, succinic acid dehydrogenase and transaldolase therein and improving the ability of a cell to synthesize NADPH and ATP, the efficiency of the MEP pathway and the production capacity of terpenoid are improved.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
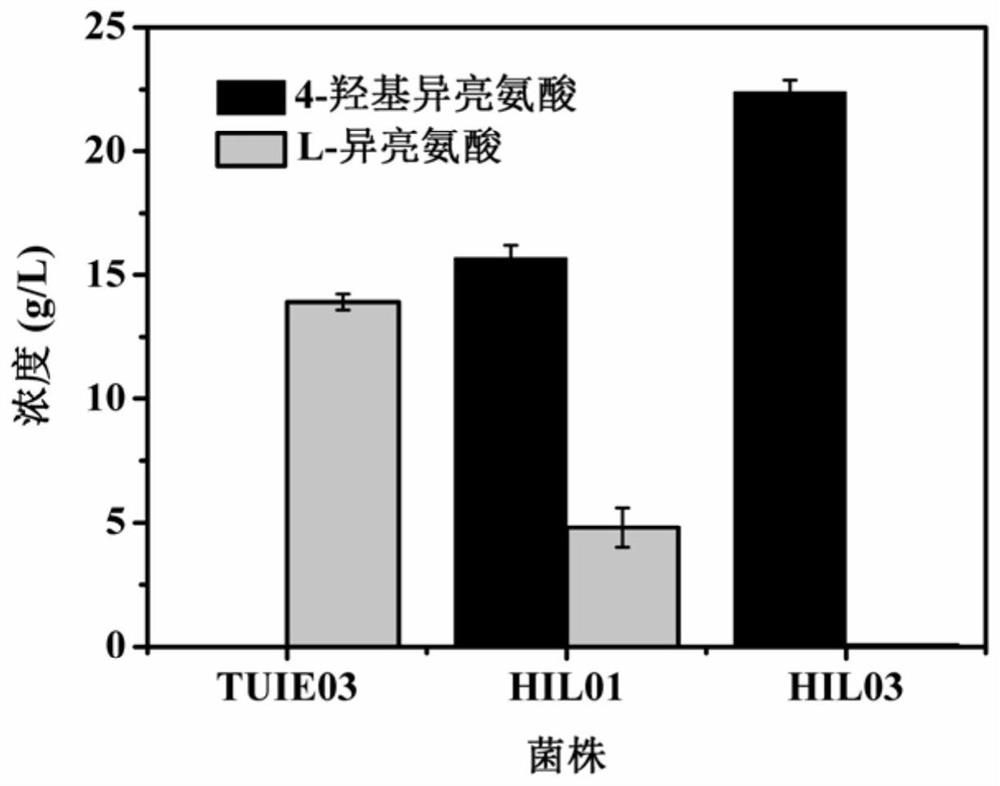
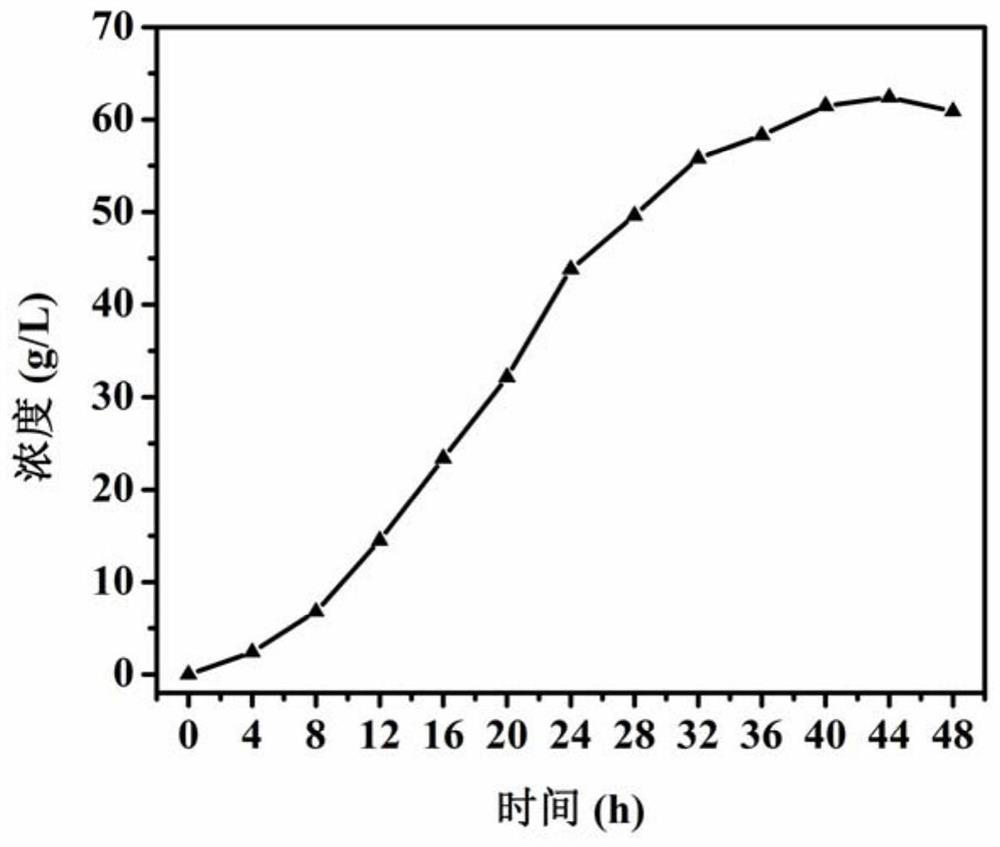
Genetically engineered bacterium for producing 4-hydroxyisoleucine and application of genetically engineered bacterium
ActiveCN112481186AIncrease productionIncrease fermentation intensityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesOxygenaseKetoglutarate dehydrogenase
The invention relates to a genetically engineered bacterium for producing 4-hydroxyisoleucine and application of the genetically engineered bacterium, and belongs to the field of metabolic engineering. According to the strain, TUIE03 is taken as a host, and expression of an alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase E1 subunit encoding gene sucA is weakened while an isoleucine dioxygenase encoding gene idois overexpressed. After the strain is fermented for 24-48h, the yield of the 4-hydroxyisoleucine reaches 32.5-62.4 g / L, and the L-isoleucine is not detected in the whole fermentation process, which indicates that the L-isoleucine is completely converted. The fermentation process adopted by the method is simple, precursors L-isoleucine and alpha-ketoglutaric acid do not need to be added, and the method is easy to control, low in production cost and beneficial to popularization and application of industrial production.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com