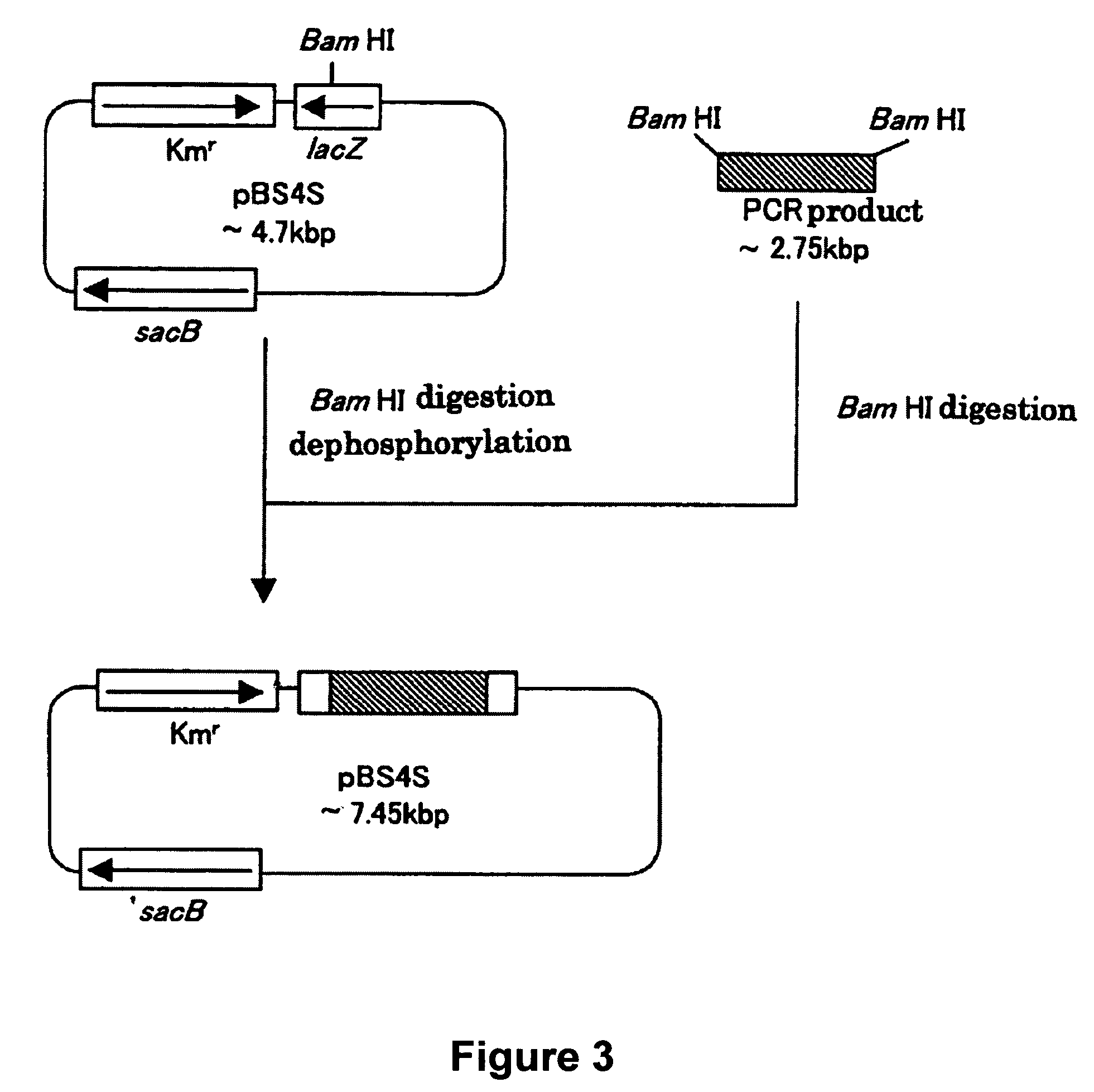
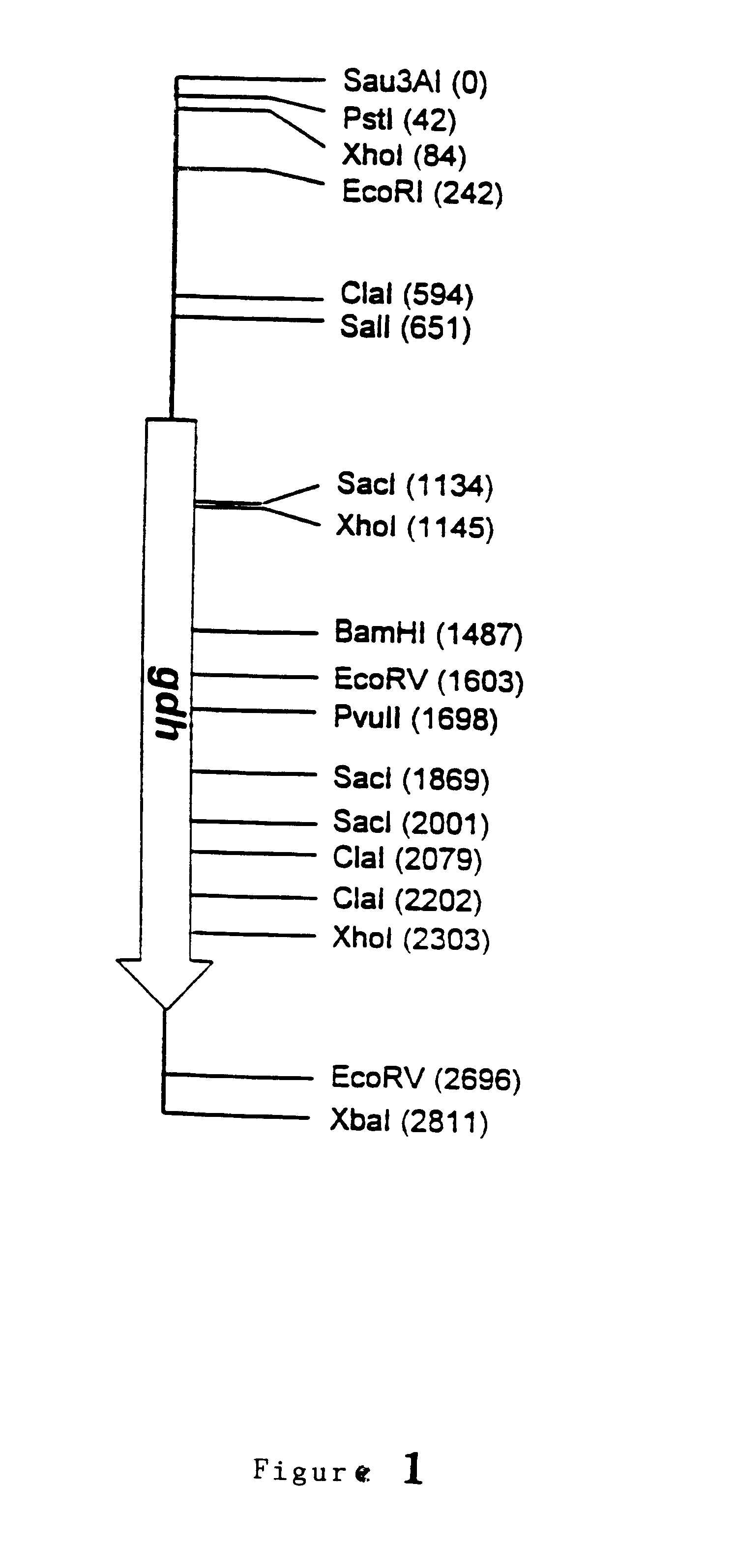
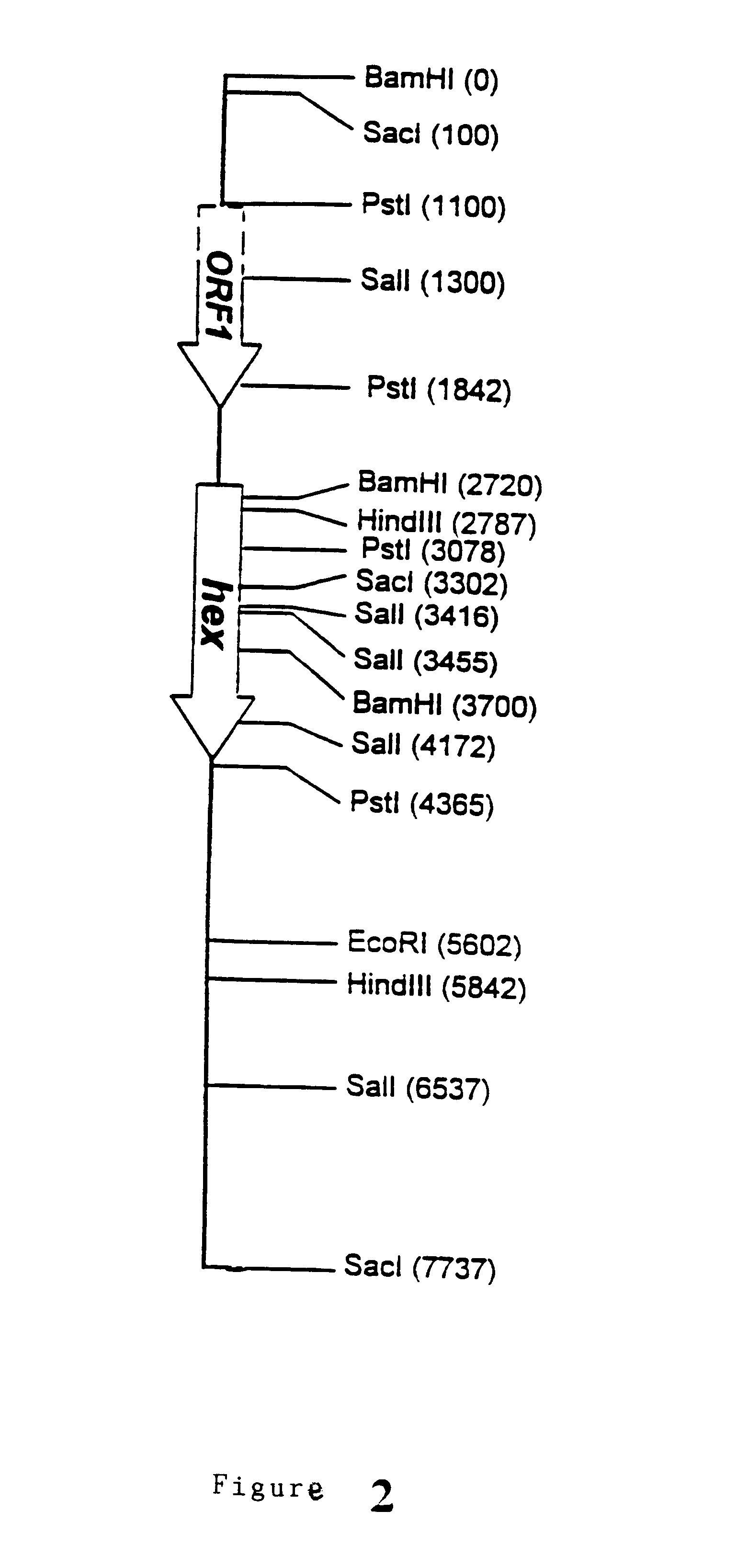
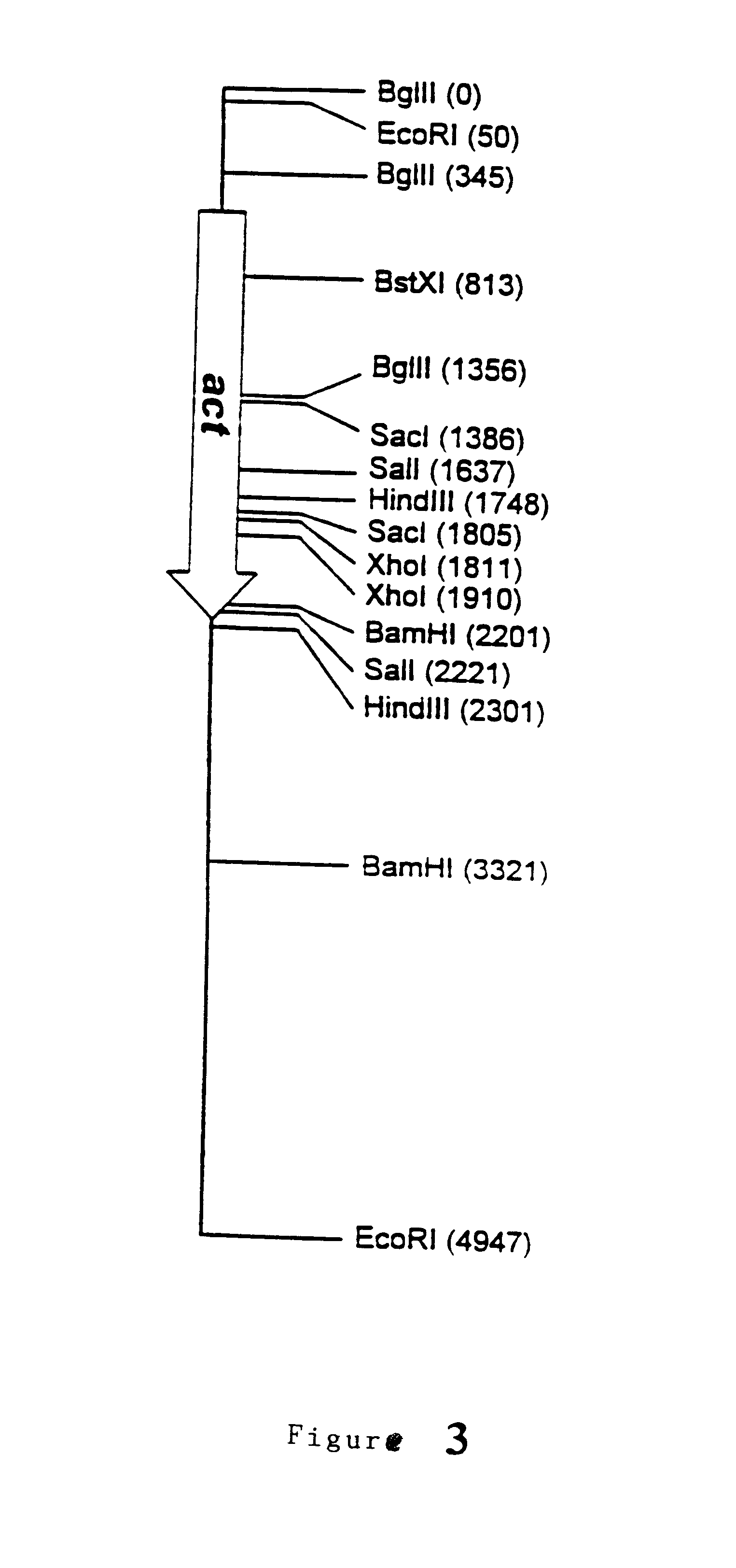
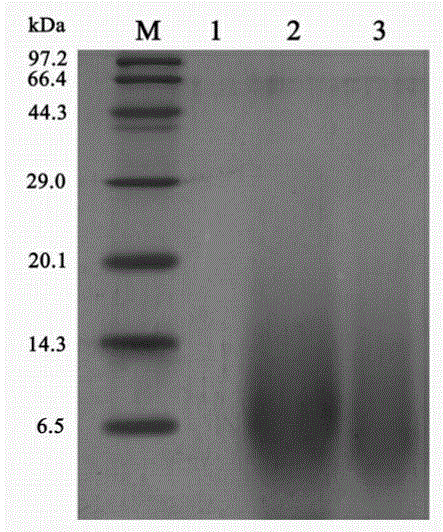
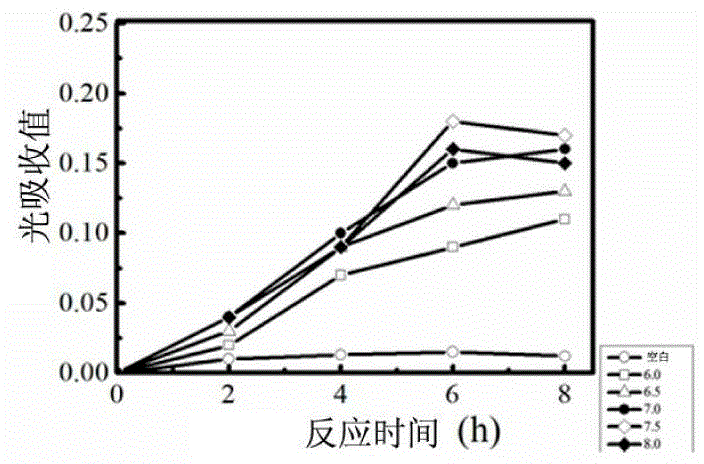
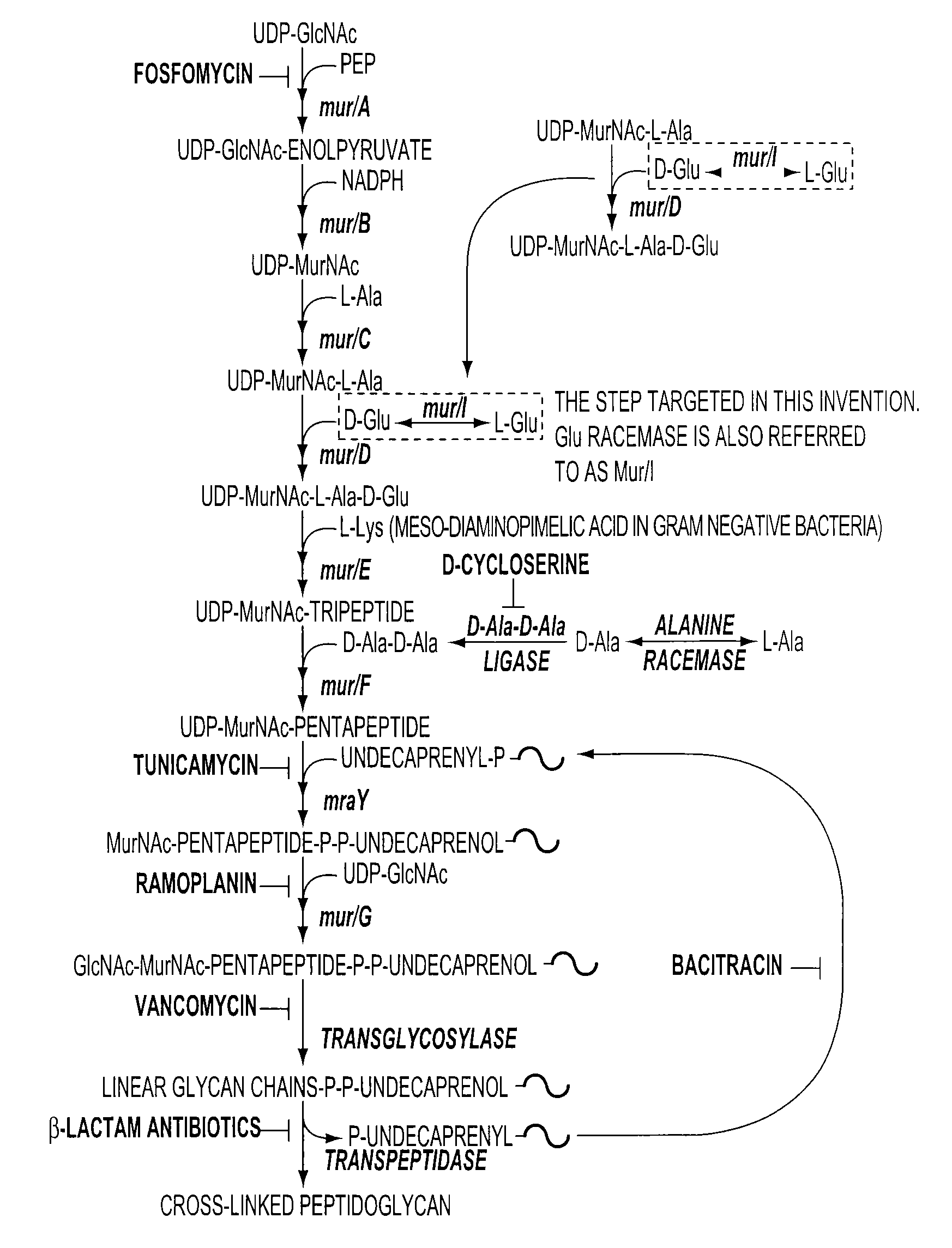
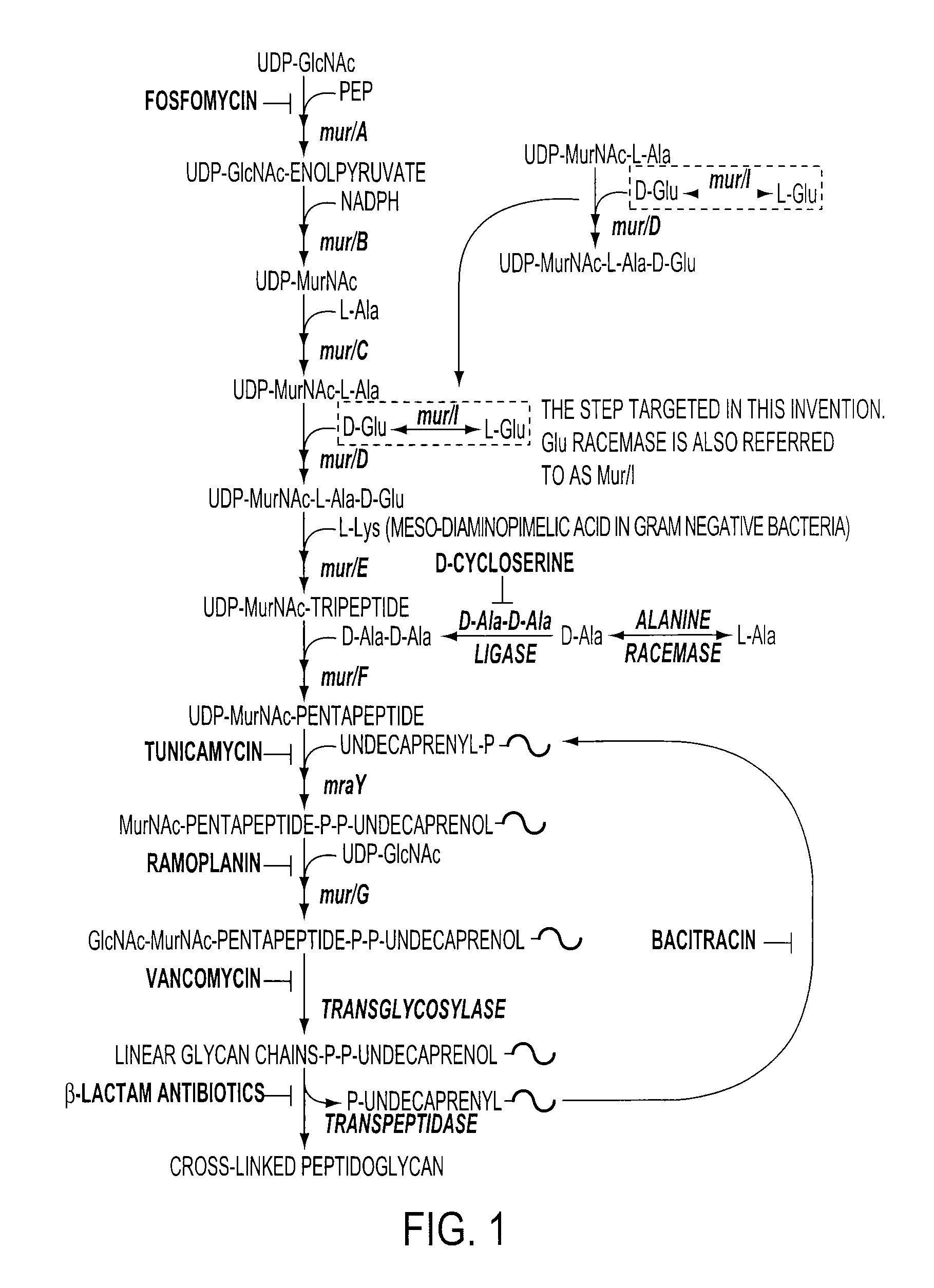
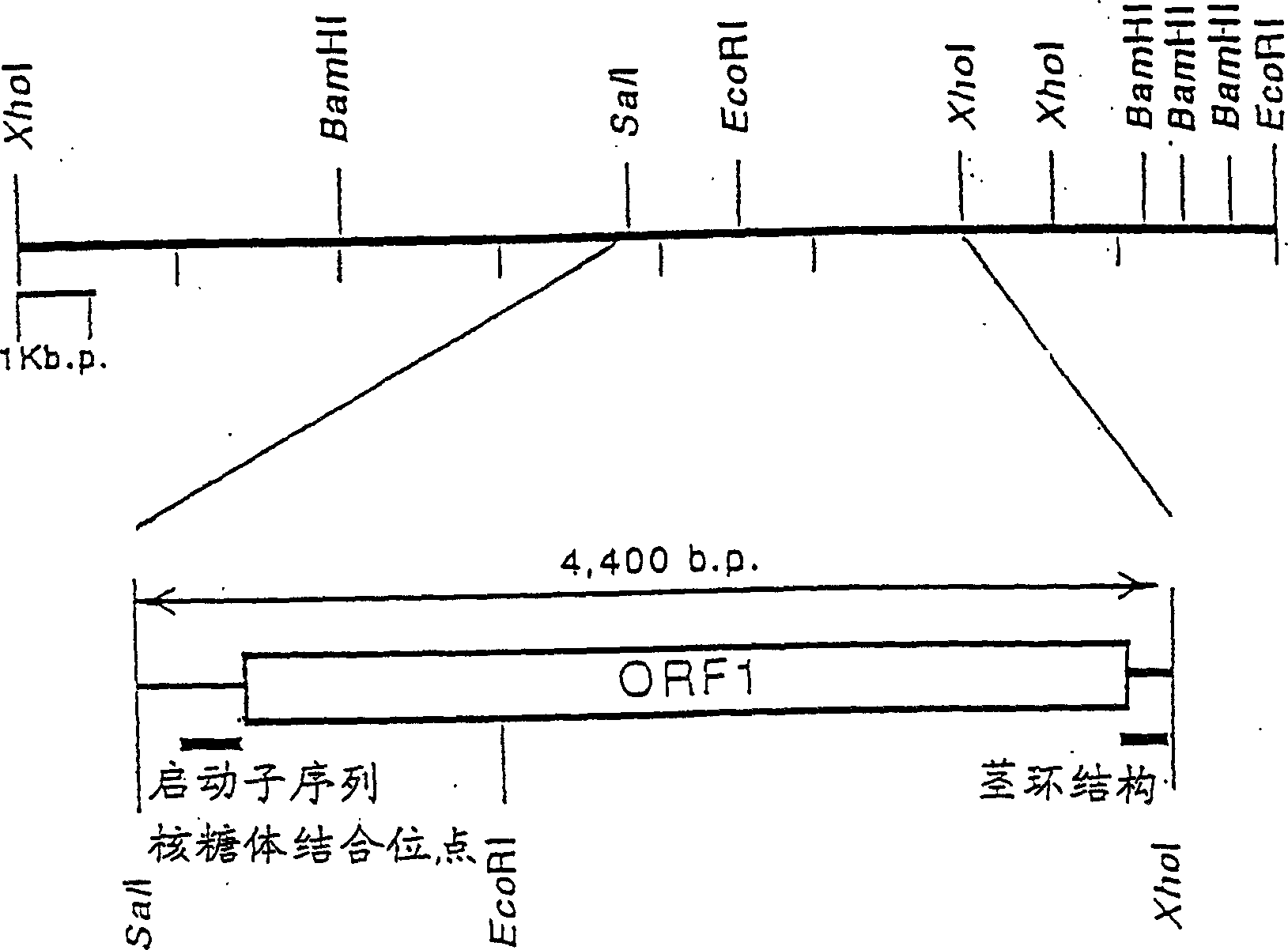
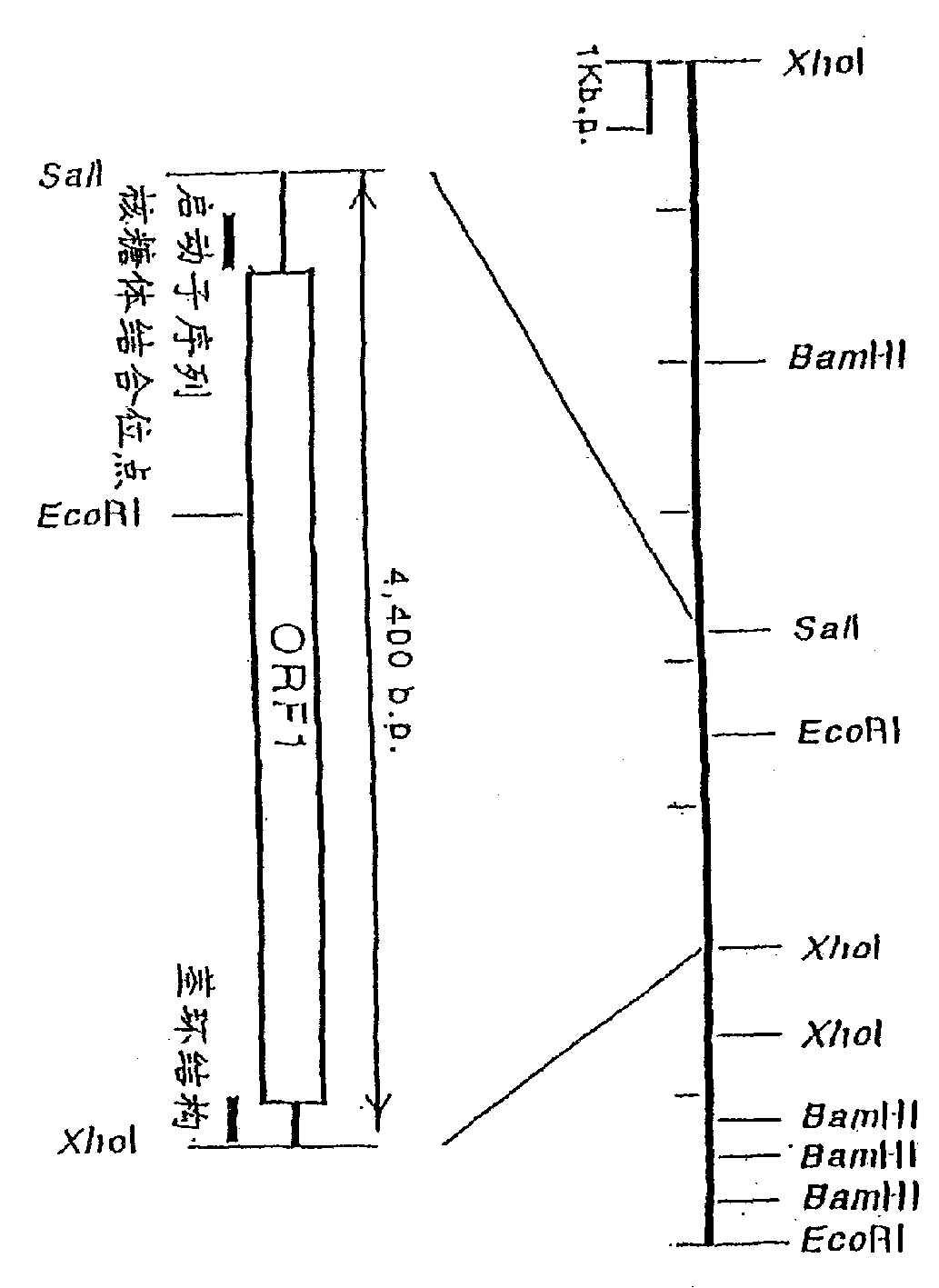
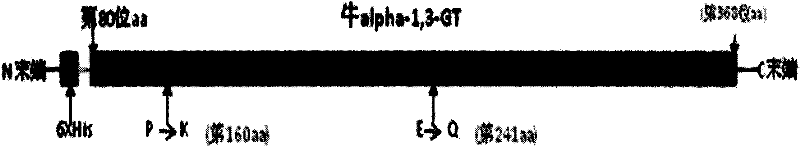Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
42 results about "GLYAT" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
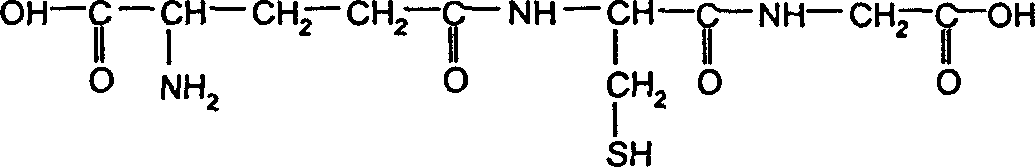
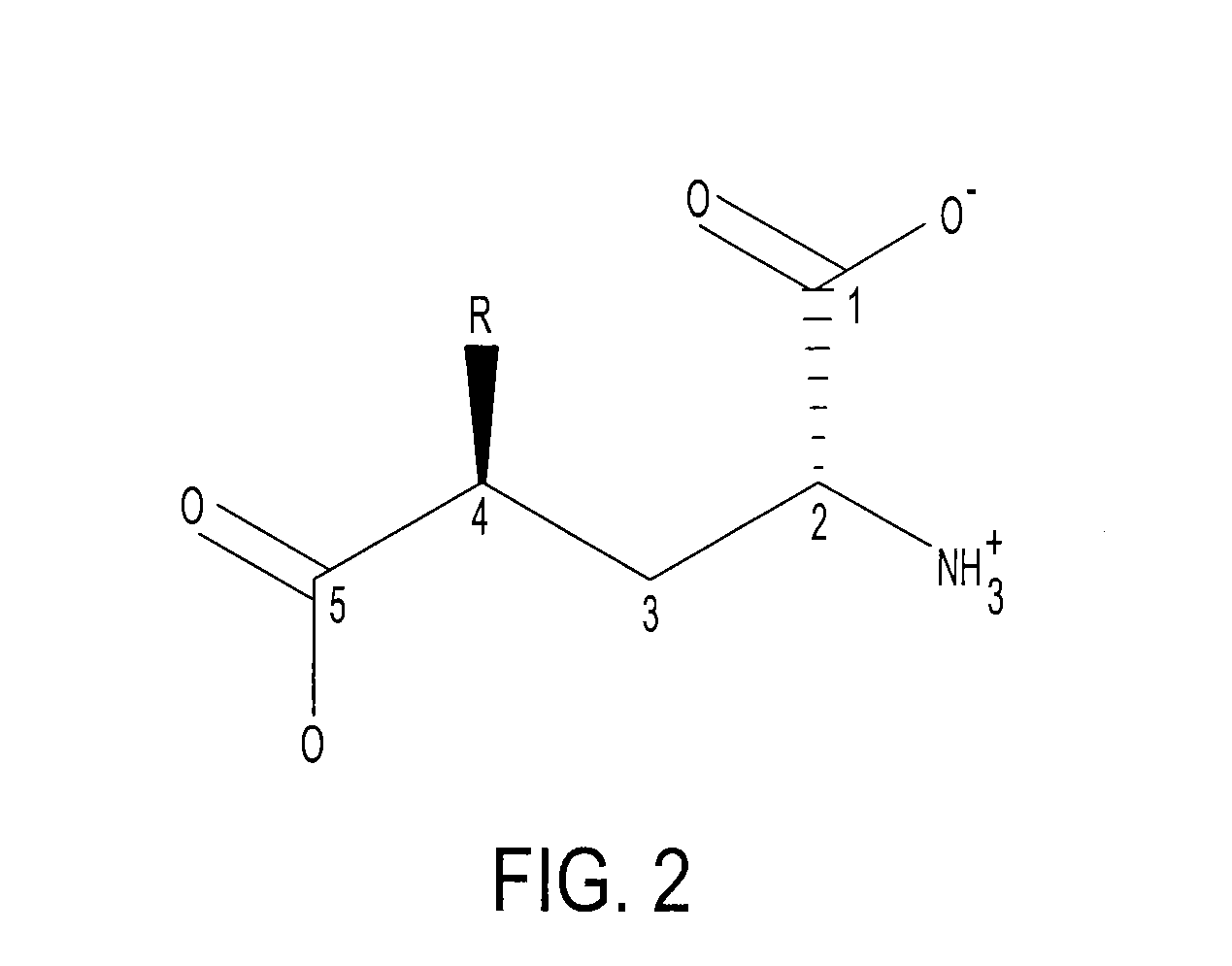
Glycine-N-acyltransferase, also known as GLYAT, is an enzyme which in humans is encoded by the GLYAT gene.
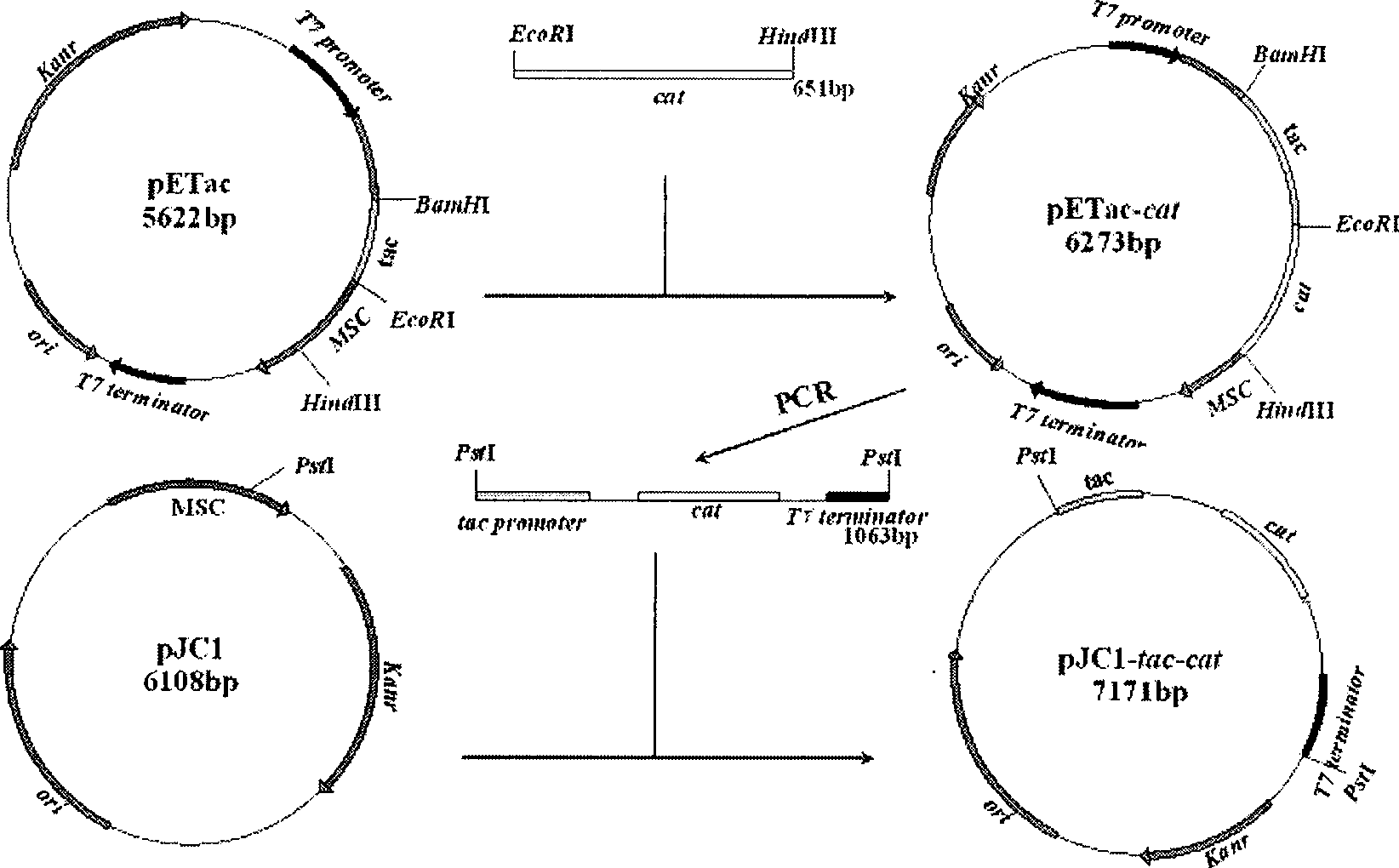
Recombinant corynebacterium crenatum for over expression of N-acetylglutamate kinase and application thereof
The invention relates to a recombinant corynebacterium crenatum to enhance the expression of N-acetyl glutamic acid kinase and the application thereof, which belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. The classification and nomenclature of the recombinant corynebacterium crenatum to enhance the expression of N-acetyl glutamic acid kinase is corynebacterium crenatum SYPA / pJC1-tac-argB with an access number of CCTCC NO: M 208133; The application is as follows: using a key enzyme N-acetyl glutamic acid kinase from corynebacterium crenatum pathway arginine to construct a corynebacterium crenatum expression vector pJC1-tac-argB; introducing the corynebacterium crenatum expression vector pJC1-tac-argB into corynebacterium crenatum SYPA by electrotransformation to obtain the recombinant corynebacterium crenatum SYPA / pJC1-tac-argB; and excessively expressing N-acetyl glutamic acid kinase, which greatly enhances the utilization rate of a precursor glutamic acid and allows the metabolic flow to flow to the arginine synthesis pathway, weakens the synthesis of proline, achieves the purpose of improving the output of arginine and the output of arginine is increased by 23.4 percent than C. crenatum SYPA.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
L-glutamic acid-producing microorganism and a method for producing L-glutamic acid
InactiveUS7205132B2Decreased ability to degrade L-glutamic acidReduced activityBacteriaSugar derivativesMicroorganismKetoglutarate dehydrogenase
A coryneform bacterium which has an L-glutamic acid-producing ability and grows at least at the same growth rate as a non-mutated strain or a wild-type strain and has intracellular α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase activity which is less than half that of the non-mutated or wild-type strain, and is obtained by introducing a mutation into a coding region or an expression control region of the chromosomal odhA gene encoding the E1o subunit of the α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Preparing gamma-poly glutamic acid, glutamate, glutathione and its precursor with bacillus subtilis NX-2
InactiveCN1425762AImprove protectionSimple process routeBacteriaFermentationProduction rateDipeptide
The bacillus subtilis NX-2, or CGMCC NO.0833 is one bacillus spawn obtained through screening and is used for the production of gamma-polyglutamic acid and its salt as well as glutathione and its precursor. In optimized condition, gamma-polyglutamic acid may be accumulated to 30-50 g / L and produced in the production efficinecy of 0.8-2.5 g / L. When bacillus subtilis NX-2 is used in fermenting to produce gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase in optimized condition, the fermented liquid may reach enzyme activity of 1-5 U / ml; and the fermented liquid or separation obtained enzyme or the immobilized enzyme is used in the production of glutathione and its precursor with substrate dipeptide or dipeptide precursor converting rate of 30-80% being reached.
Owner:WUHAN ELITE CHEM FERTILIZER
Promoters of the genes glutamate dehydrogenase beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase and gamma-actin and their use in filamentous fungi expression, secretion and antisense systems
InactiveUS6300095B1Less efficiencyUndesirable enzyme activityFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyADAMTS Proteins
The invention relates to promoters of the genes glutamate dehydrogenase, beta-acetylhexosaminidase and gamma-actin and their use in systems of expression, secretion and anti-sense of filamentary fungi. The invention also relates to the use of the promoters of the genes which code: (I) glutamate dehydrogenase NADP depending (EC.1.4.1.4) of Penicillium chrysogenum, (II) gamma-N-actylhexosaminidase (EC.3.2.1.52) of Penicillium chrysogenum and (III) gamma-actin of Penicillium chrysogenum and Acrimonium chrysogenum, which can be used for the construction of potent vectors of expression and secretion useful both for P. chrysogenum and for A. chrysogenum and related species. These promoters can also be used for blocking the genic expression through anti-sense construction. Under the control of the above mentioned promoters, it is possible to conduct the expression of other genes in filamentary fungi, thereby increasing the production of antibiotics and / or proteins inherent to the same.
Owner:ANTIBIOTICOS SA
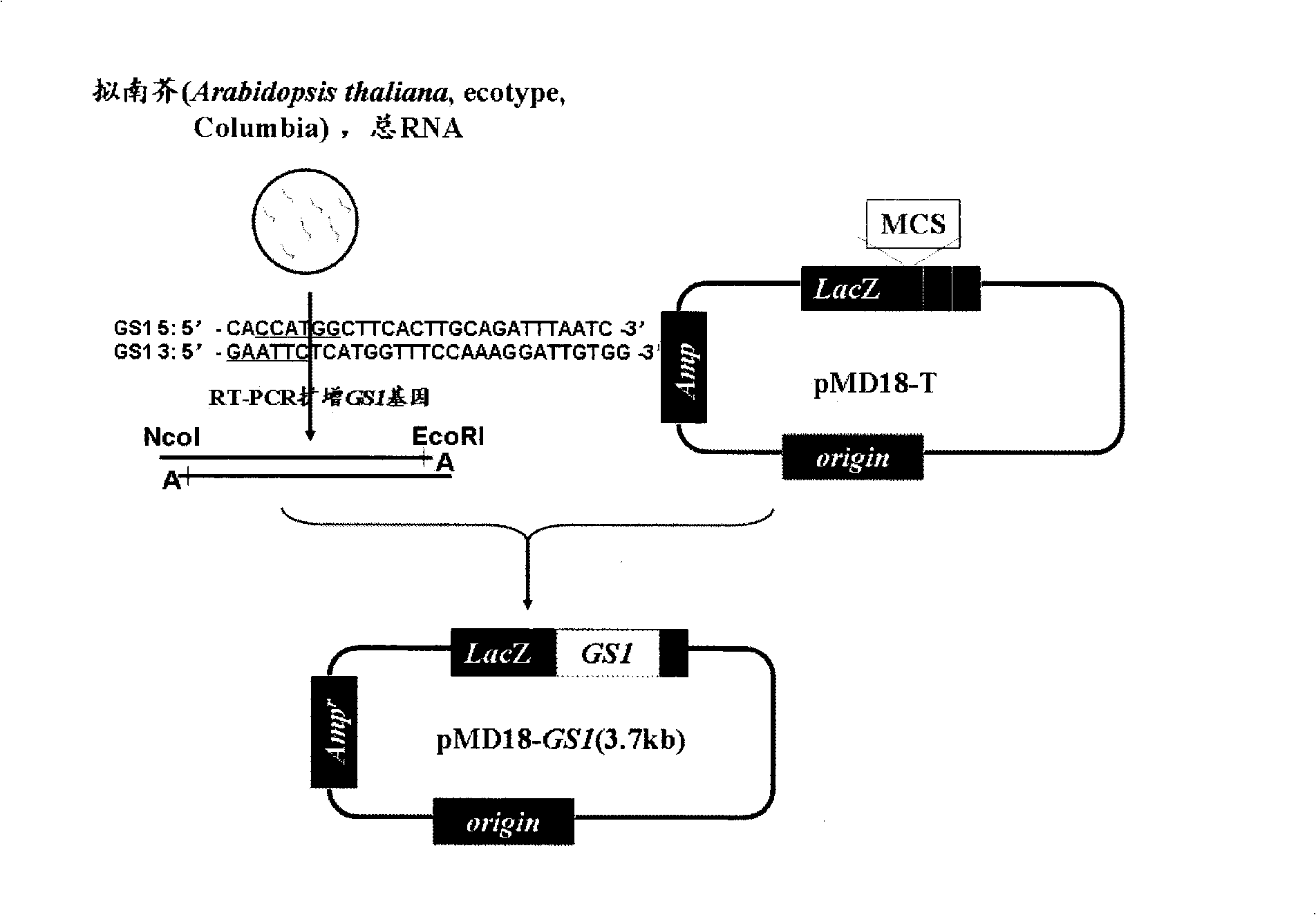
Construction and use of plant expression vector of Arabidopsis thaliana cytoplasm type glutamine synthetase gene
InactiveCN101407824AImprove nitrogen use efficiencyIncreased reassimilation capacityPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsNicotiana tabacumLow nitrogen
The invention relates to a special plant expression vector pH2-35S-PrbcS-GS1 which comprises an arabidopsis thaliana cytoplasm glutamine synthetase gene GS1 and can improve the utilization rate of a plant nitrogen element. A method of RT-PCR is used for cloning the GS1 gene from the arabidopsis thaliana of a model plant, a photoinduction type promotor (the promotor of a a small subunit Rubisco) is used for controlling the excessive expression of the GS1 gene in a plant leaf and a leaf disc conversion method is used for transferring the GS1 gene into a pPZP221-PrbcS-Dof1 type transgene tobacco. An experiment result shows that the GS1 gene can be normally transferred in the transgene tobacco; under the nutrition condition of low nitrogen and the growing conditions of indoor irradiation for 24 hours of 2000LUX and 25 DEG C, the growing situation of the plant transferred with the single gene of Dof1 is (the expression of the gene is controlled by the photoinduction type promotor Prbcs) is a little better than that of a contrast tobacco (a wild type without transgene); after being transferred under the natural growing condition of a green house, the growing situation of the tobacco which is simultaneously transferred with the GS1 gene and the Dof1 gene shows remarkable growing advantages than that of the contrast plant; and therefore, simultaneously and excessively expressing the GS1 gene and the Dof1 gene, can improve the efficiency of the GS / GOGAT (glutamine synthetase / glutamic acid synthetase) approaches in the leaf more extensively, thereby improving the utilization rate of the plant nitrogen element. The vector can be broadly applied to the molecule breeding of crops, improving the utilization rate of the plant nitrogen element thereof and the durability to the nutrition condition of low nitrogen and being capable of obtaining a higher yield under the conditions of applying less fertilizers and even not applying the fertilizers.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Mutations that confer genetic stability to additional genes in influenza viruses
ActiveUS10053671B2High genetic stabilityImprove stabilitySsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsVirus influenzaValine
The disclosure provides for an isolated recombinant influenza virus having at least one of: a PA gene segment encoding PA with a residue at position 443 that is not arginine, a PB1 gene segment encoding PB1 with a residue at position 737 that is not lysine, a PB2 gene segment encoding PB2 with a residue at position 25 that is not valine or a residue at position 712 that is not glutamic acid, a NS gene segment encoding a NS1 with a residue at position 167 that is not proline, a HA gene segment encoding a HA with a residue at position 380 that is not threonine, or any combination thereof, and methods of making and using the virus.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
High-specific activity L-glutamate oxidase gene multisite mutant, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106282205AHigh activityHigh specific activityMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzymesNucleotideMutant
The invention relates to a high-specific activity L-glutamate oxidase gene multisite mutant, and a preparation method and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the mutant is shown as SEQ ID No 64; the amino acid sequence of encoded protein is shown as SEQ ID No 65. A molecular in vitro recombination technique is used for screening high-specific activity L-glutamate oxidase gene; through vector building, enzyme activity screening, multisite mutation techniques and the like, the high-specific activity L-glutamate oxidase gene multisite mutant is obtained through preparation. The multisite mutant contains 9 different mutation sites on the same gene, so that the oxidation specificity and the specific activity of the multisite mutant on L-glutamic acid are greatly improved; the multisite mutant can be used for detecting the content of the L-glutamic acid in food.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
Further Improved AAV Vectors Produced in Insect Cells
ActiveUS20170356008A1Improve stabilityReduced expression levelVectorsVirus peptidesWild typeViral vector
The present invention relates to the production of adeno-associated viral vectors in insect cells. The insect cells therefore comprise a first nucleotide sequence encoding the adeno-associated virus (AAV) capsid proteins, whereby the initiation codon for translation of the AAV VP1 capsid protein is a non-ATG, suboptimal initiation codon and wherein the coding sequence for one or more amino acid residues have been inserted between the suboptimal translation initiation codon and the codon encoding the amino acid residue that corresponds to the amino acid residue at position 2 of the wild type capsid amino acid sequence of which the first amino acid residue is alanine, glycine valine, aspartic acid or glutamic acid. The insect cell further comprises a second nucleotide sequence comprising at least one AAV inverted terminal repeat (ITR) nucleotide sequence; a third nucleotide sequence comprising a Rep52 or a Rep40 coding sequence operably linked to expression control sequences for expression in an insect cell; and, a fourth nucleotide sequence comprising a Rep78 or a Rep68 coding sequence operably linked to expression control sequences for expression in an insect cell. The invention further relates to adeno-associated viral vectors with an altered ratio of the viral capsid proteins.
Owner:UNIQURE IP BV
One-step method for synthesizing gamma-aminobutyric acid by using recombinant corynebacterium crenatum and with glucose as substrate
ActiveCN103215198AReduce manufacturing costSimple preparation stepsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGlutamate decarboxylaseCorynebacterium crenatum
The invention belongs to the fields of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering, and relates to a one-step method for synthesizing gamma-aminobutyric acid by using recombinant corynebacterium crenatum (C.crenatum) and with glucose as a substrate. According to the method, a genetic engineering method is adopted, C.crenatum SYPA5-5 gene argB is knocked out, such that a safe strain C.crenatum E01 which can accumulate glutamic acid is obtained; a glutamic acid decarboxylase gene is cloned from L.Plantarum GB01-21 and is expressed in the C.crenatum E01, such that recombinant C.crenatum E01 / pGAD used for directly synthesizing gamma-aminobutyric acid with glucose as a substrate is obtained. A recombinant strain fermentation broth gamma-aminobutyric acid accumulation reaches 13.98g / L. According to the invention, glutamic acid and gamma-aminobutyric acid metabolic pathways are successfully integrated, such that one-step production from glucose to gamma-aminobutyric acid is realized. Therefore, preparation method is simplified, cost is reduced, safety is improved, and novel idea is provided for high-efficiency and low-cost amino acid preparation.
Owner:南宁汉和生物科技股份有限公司
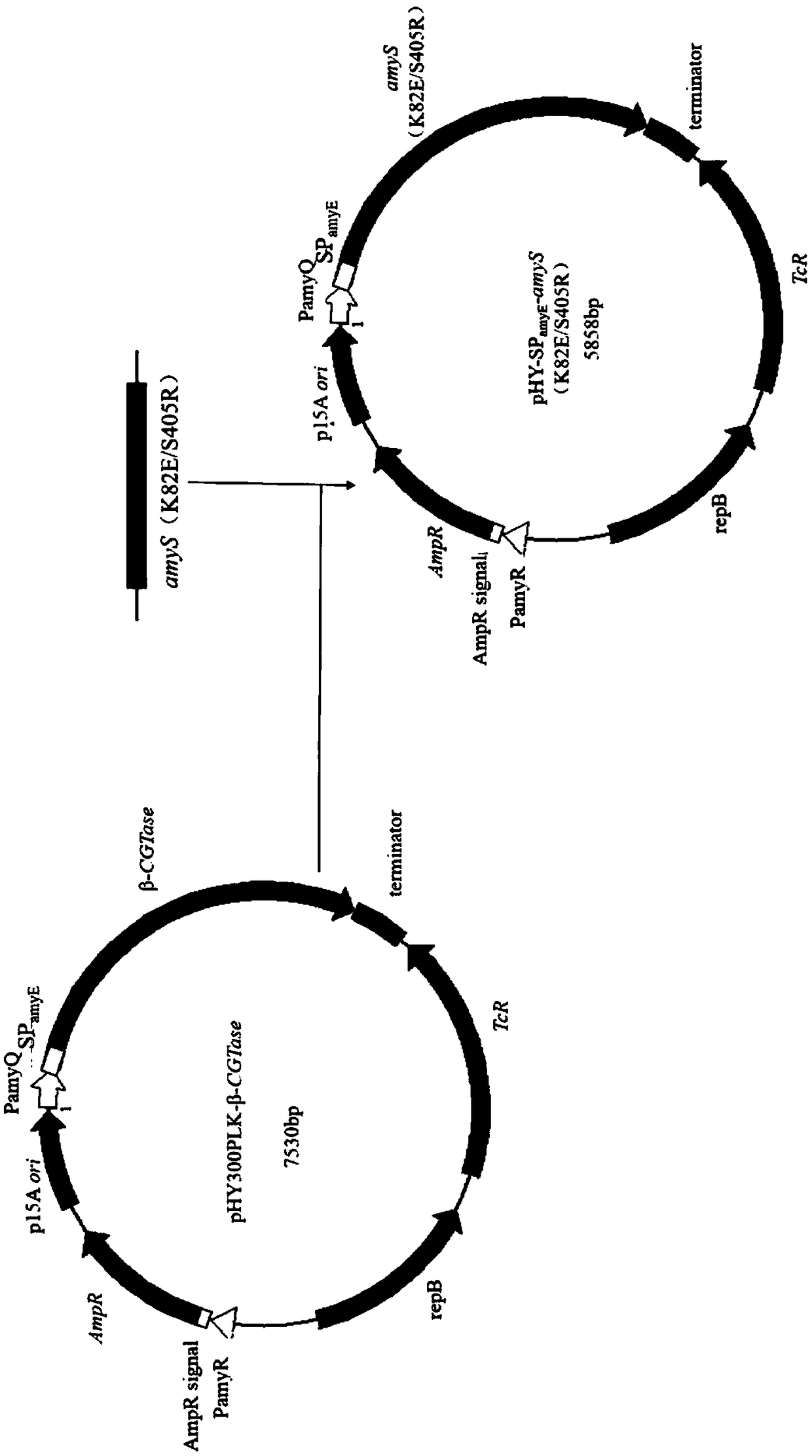
An alpha-amylase mutant with improved enzymatic activity and applications thereof
ActiveCN109022396AIncrease enzyme activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesArginineAlpha-amylase
An alpha-amylase mutant with improved enzymatic activity and applications thereof are disclosed and belong to the technical field of genetic engineering and microbial engineering. The mutant is obtained by mutating the amino acid at the number 82 site of alpha-amylase having an amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO.1 from lysine into glutamic acid or mutating the amino acid at the number 405 site of the alpha-amylase having an amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO.1 from serine into arginine or simultaneously mutating the amino acid at the number 82 site of the alpha-amylase having an amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO.1 from lysine into glutamic acid and mutating the amino acid at the number 405 site from serine into arginine. The enzymatic activity of alpha-amylase in a fermentation solution can beincreased to 474.7 U / mL by fermenting a recombinant Bacillus subtilis engineering bacterium for 48 h, with the recombinant Bacillus subtilis engineering bacterium being constructed by adopting a genecoding the mutant as a target gene, adopting pHY300PLK as an expression vector, and adopting Bacillus subtilis WS5 as an expression host.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Gene recombinant human cytomegalovirus fusion protein pp150/MDBP, preparation process and application thereof
InactiveCN1763203AHigh expressionHigh yieldPeptide/protein ingredientsBiological testingAntigenC-terminus
The present invention discloses one kind of gene recombinant human cytomegalovirus fusion protein pp150 / MDBP and its preparation process and application, and relates to gene engineering technology, preventing vaccine, diagnosis reagent and other technology. The recombinant fusion protein pp150 / MDBP is fusion protein formed through connecting serially the 197th amino acid in the 495-691 amino acid segment of human cytomegalovirus pp150 and the 64th amino acid in the 538-601 amino acid segment of MDBP protein. The 197th amino acid pp150 in the N-terminal of the fusion protein and the 64th amino acid of MDBP protein in the C-terminal of the fusion protein are connected through two amino acids including one Leu and one Glu, and the fusion protein has one increased Met and has whole length of 264 amino acids. The fusion protein is used in detecting human cytomegalovirus antibody and antigen, preparing antibody and protein chip, vaccine, ELISA detecting kit and other products.
Owner:SHANDONG MEDICAL BIO TECH RES CENT
D-carboxamide hydrolase mutant and its uses
InactiveCN1995336AIncrease enzyme activityShow potential application valueBacteriaHydrolasesTyrosineThreonine
The invention discloses four mutants of D-carbamoyl hydrolase and application to manufacture D-p-hydroxybenzene glycine in the biological engineering domain, which is characterized by the following: mutating the amino acid at 18th position of mutation enzyme 1 from alanine into threonine and tyrosine at 30th position of mutation enzyme 2 to asparagine; switching the lysine at 30th of mutation enzyme 2 into glutacid; overlapping three mutation positions; obtaining the mutation enzyme 4.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
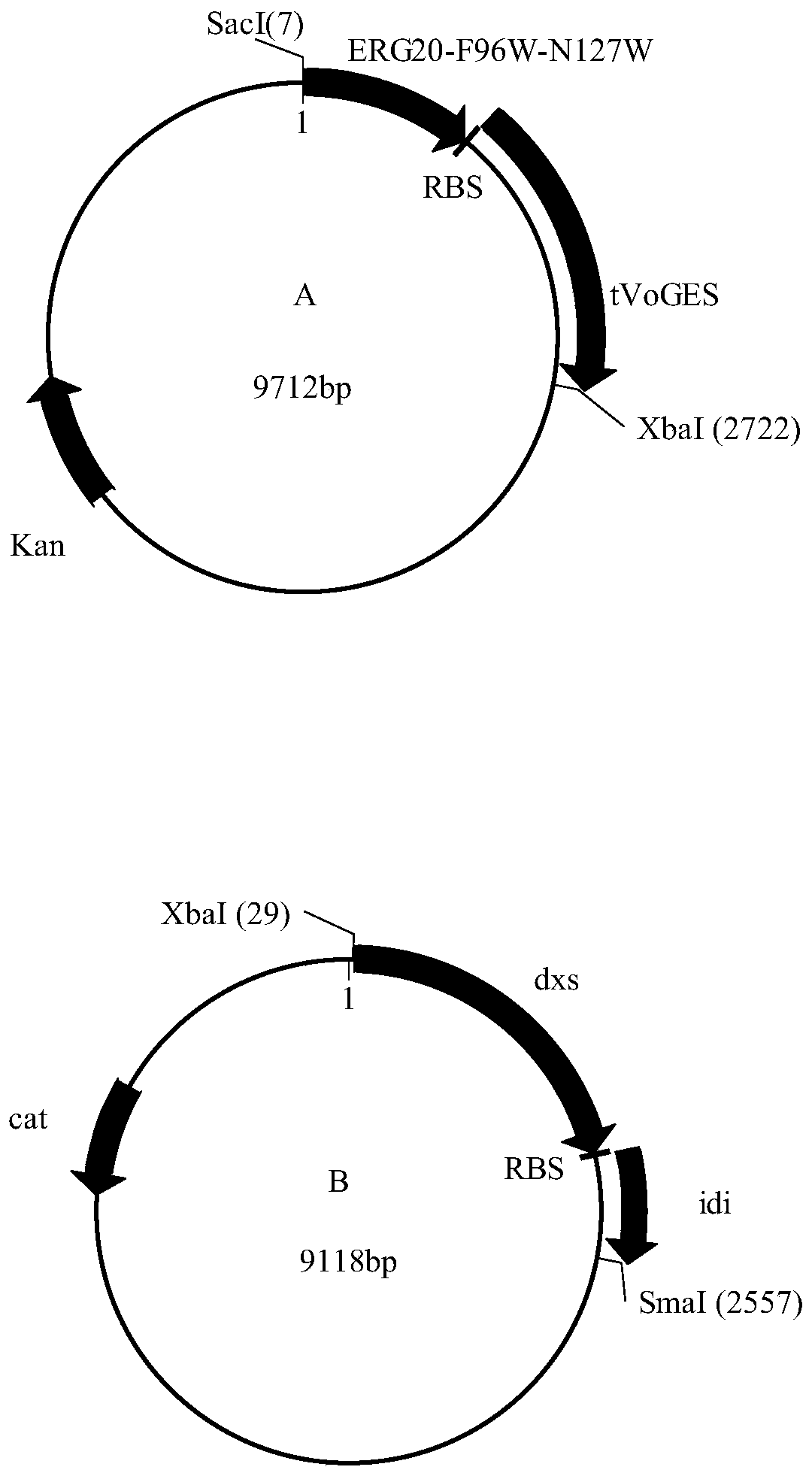
Corynebacterium glutamate for synthesizing geraniol and construction method and application of corynebacterium glutamate
InactiveCN110438145AShort fermentation timeBacteriaTransferasesCorynebacterium efficiensBinding site
The present invention discloses a corynebacterium glutamate for synthesizing geraniol and a construction method and application of corynebacterium glutamate. The construction method of corynebacteriumglutamate comprises the following steps: connecting a saccharomyces cerevisiae-derived mutant geranyl pyrophosphate synthase gene ERG20<F96W-N127W> and a valerian-derived geranol synthase gene tVoGEStruncated through cutting off of C-terminal 53 amino acid residues by fusion PCR, adding a ribosome binding site sequence to a homologous region, inserting SacI and XbaI enzyme cutting sites of a corynebacterium glutamate expression plasmid pEC-XK99E to obtain a plasmid 1; converting the plasmid 1 into corynebacterium glutamate to obtain corynebacterium glutamate 1 for synthesizing geraniol. Theconstruction method provides more precursors and short fermentation time (42 to 48 hours) for the synthesis of geraniol, and corresponding by-products are not detected out by GC-MS detection.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Cytochrome P450 BM-3 variant enzyme, coding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN102747053AImproved enzymatic parametersHigh catalytic activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesThreonineCytochrome P450
The invention discloses a cytochrome P450 BM-3 variant enzyme, a coding gene and application of the cytochrome P450 BM-3 variant enzyme. An amino acid sequence of the variant enzyme is shown in SEQ ID NO.1; three mutational sites are added on the basis of the cytochrome P450 BM-3 (F87 / A74G / L188Q) variant enzyme, namely aspartic acid (GAT) at the 168th site mutates into aminocaproic acid (CTT), glutamic acid (GAA) at the 435th site mutates into threonine (ACG), and valine (GTG) at the 445th site mutates into aminopropionic acid (GCG). Compared with male parent enzyme and protoenzyme, the variant enzyme disclosed by the invention has high affinity with substrate and the efficiency of catalyzing benzazole to generate indigo is higher.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF TECH ZHEJIANG UNIV ZHEJIANG
Preparing gamma-poly glutamic acid, glutamate, glutathione and its precursor with bacillus subtilis NX-2
InactiveCN1164737CImprove protectionSimple process routeBacteriaFermentationProduction rateDipeptide
The bacillus subtilis NX-2, or CGMCC NO.0833 is one bacillus spawn obtained through screening and is used for the production of gamma-polyglutamic acid and its salt as well as glutathione and its precursor. In optimized condition, gamma-polyglutamic acid may be accumulated to 30-50 g / L and produced in the production efficinecy of 0.8-2.5 g / L. When bacillus subtilis NX-2 is used in fermenting to produce gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase in optimized condition, the fermented liquid may reach enzyme activity of 1-5 U / ml; and the fermented liquid or separation obtained enzyme or the immobilized enzyme is used in the production of glutathione and its precursor with substrate dipeptide or dipeptide precursor converting rate of 30-80% being reached.
Owner:WUHAN ELITE CHEM FERTILIZER
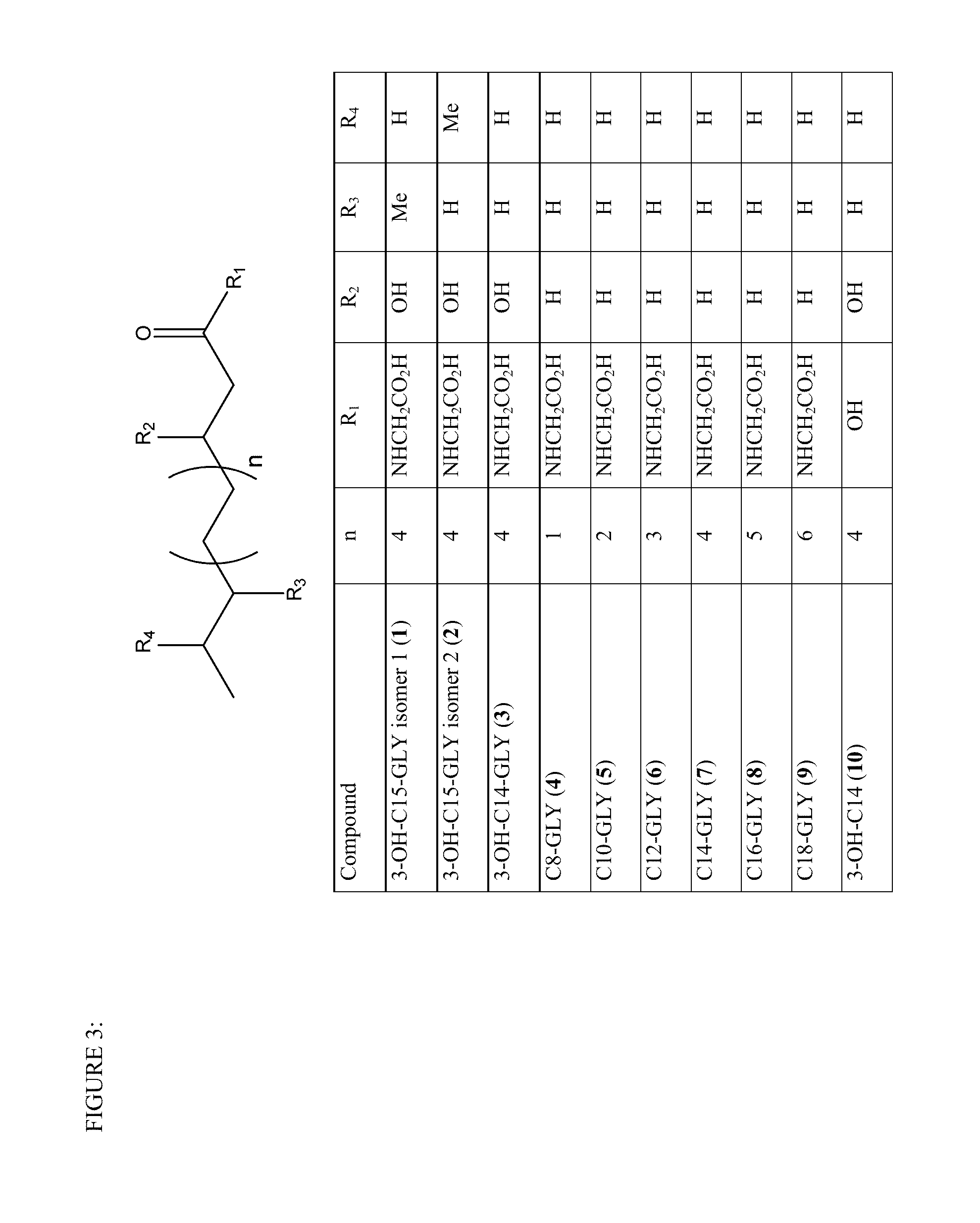
Heterologous expression of glycine n-acyltransferase proteins
The present disclosure provides novel compositions and methods for the production and use of polynucleotide sequences encoding a glycine N-acyltransferase protein (GLYAT, GLYATL 1, GLYATL 2, and GLYATL 3) for the biosynthesis of N-acylglycine biosurfactants within a heterologous expression system.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Glutamyltranspeptidase for synthesizing gamma-polyglutamic acid and coding gene thereof
The invention provides glutamyltranspeptidase for synthesizing gamma-polyglutamic acid and a coding gene thereof. The protein molecule of the glutamyltranspeptidase has the amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2; and the gene of the glutamyltranspeptidase has the nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1. The invention also discloses a method for synthesizing the gamma-polyglutamic acid by utilizing recombinant glutamyltranspeptidase. By adopting the method, the gamma-polyglutamic acid is synthesized by utilizing the recombinant glutamyltranspeptidase and taking glutamine monomers as raw materials. The glutamyltranspeptidase can be used for synthesizing the gamma-polyglutamic acid by taking the glutamine monomers as the raw materials, thus having importance significance in enriching glutamyltranspeptidase family members and developing a new gamma-polyglutamic acid synthesis route.
Owner:GUANGDONG IND TECHN COLLEGE
Heat-resistant beta-galactosidase mutant with transglycosylation and preparation method of mutant
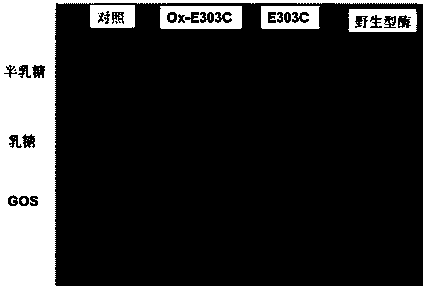
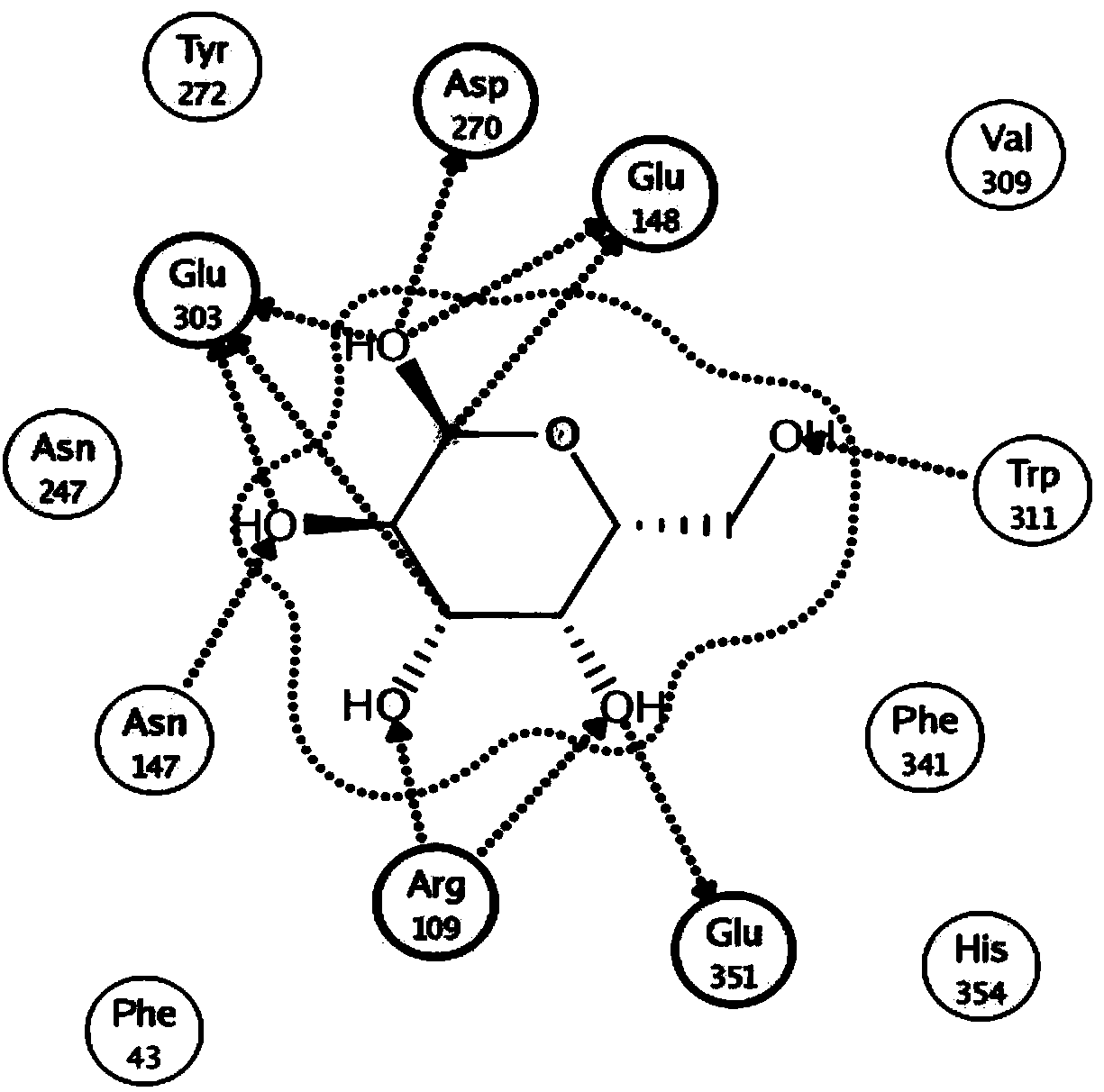
ActiveCN105950589ASpeed up the efficiency of functional evolutionIncrease synthesisNucleic acid vectorFermentationGalactooligosaccharideHydrolysis
The invention provides a heat-resistant beta-galactosidase mutant with transglycosylation. The mutant is obtained through the steps that beta-galactosidase (BgaB) catalyzes an amino acid site E303 to be mutated into cysteine (Cys) in a site-directed mode from original glutamic acid (Glu), and a cysteine sulfhydryl group is oxidized into -SOO<->. The invention further designs a preparation method and application of the mutant. Beta-galactosidase (BgaB) derived from bacillus stearothermophilus serves as an object, a method combining a site-directed mutant with chemical modification is adopted, the functional evolution efficiency of transglycosylation is significantly improved, the synthesis quantity of galactooligosaccharide is improved, the synthesis quantity of galactooligosaccharide is improved to 11.5% from 0% of wild-type enzyme under a medium temperature and neutral environment, limitation of reacting under an acid environment in the prior art is broken through, and meanwhile hydrolysis of a substrate or a product is avoided when galactooligosaccharide is synthesized.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Signal peptide and application thereof in recombinant bacteria for producing L-glutamic acid from konjaku flour
The present invention relates to a signal peptide and application thereof in recombinant bacteria for producing L-glutamic acid from konjaku flour, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering. The screened and codon-optimized signal peptide, namely SEQ ID No.1 is fused, by molecular cloning and genetic engineering techniques, with B. subtilis CCTCC M 209200-sourced beta-mannanase for construction of an expression vector for expressing in L-glutamic acid high-yield production bacterial stain. For the first time, the signal peptide is reported, wherein the signal peptide can be used for mediation of recombinant bacteria Brevibacterium tianjinese SW07-1 / pMSPman, which is capable of secreting the beta-mannanase, for producing the L-glutamic acid by fermentation of the chip konjaku flour, and the yield of a 5L fermentor is 65g / L under the condition of addition of an optimal carbon source.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Bacterium producing L-glutamic acid and method for producing L-glutamic acid
InactiveUS20100124777A1Increase productivityIncrease productionBacteriaSugar derivativesCorynebacterium efficiensBacteroides
L-Glutamic acid is produced by culturing a coryneform bacterium having L-glutamic acid producing ability, in which trehalose synthesis ability is decreased or deleted by, for example, disrupting a gene coding for trehalose-6-phosphate synthase, a gene coding for maltooligosyltrehalose synthase, or both of these genes to produce and accumulate L-glutamic acid in the medium, and collecting the L-glutamic acid from the medium.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Genetic medicine for treating cancer and other diseases characterized by run-off cell division and its prepn process
InactiveCN1416903ATo achieve the purpose of treatmentInhibition of divisionOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsNucleotideWild type
The genetic medicine for treating cancer and other diseases characterized by run-off cell division includes carrier and active component, and the active component contains mutant human alpha-tubulin gene with the nucleotide sequence encoding the 254 position amino acid Glu defected or displaced by nucleotide sequence of any other amino acid. The preparation process includes in vitro change of wild human alpha-tubulin gene or its fragment to displace or delete alpha-tubulin Glu 254 and obtain mutant alpha-tubulin gene; and implanting vector in expressable mode. When medicine is guided to the disease part, the expressed mutant alpha-tubulin and wild beta-tubulin are combined to form dimer and assemble microtubule. This will block disassembly of microtubule, break dynamic microtubule instability, disturb mitosis and treat cancer and other diseases characterized by run-off cell division.
Owner:王晓
Trail cell-penetrating peptide-like mutant mur6, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveUS20170247424A1Significant amplification potentialLow costPeptide/protein ingredientsTumor necrosis factorMutated proteinArginine
A TRAIL cell-penetrating peptide (CPPs)-like mutant MuR6 and a preparation method and the application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the mutant is SEQ ID NO: 2. The mutant selectively transforms the amino acid coding sequence of No. 114-119 of the outer fragment of the TRAIL wild-type protein cell membrane from VRERGP to RRRRRR, i.e., mutates valine into arginine on the 114th coding sequence, glutamic acid into arginine on the 116th coding sequence, glycine into arginine on the 118th coding sequence and proline into arginine on the 119th coding sequence, turning the coding sequence of N-terminal of the mutant protein into that of six arginines and making it a protein containing CPPs-like structure. Having a superior therapeutic effect on different types of tumor, the TRAIL mutant is a new generation of high-efficient drug for inducing tumor apoptosis of much potential.
Owner:CHENGDU HUACHUANG BIOTECH CO LTD
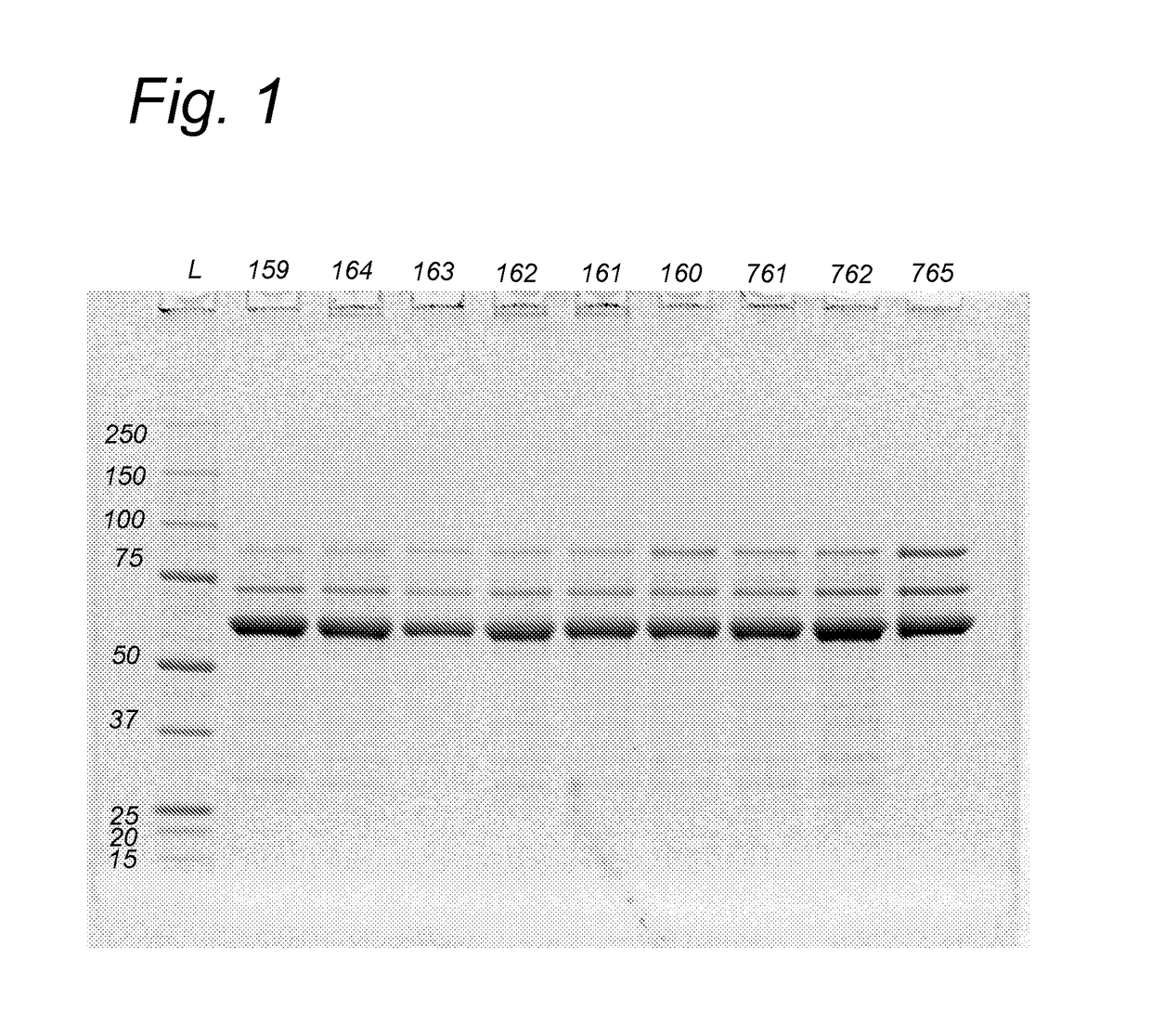
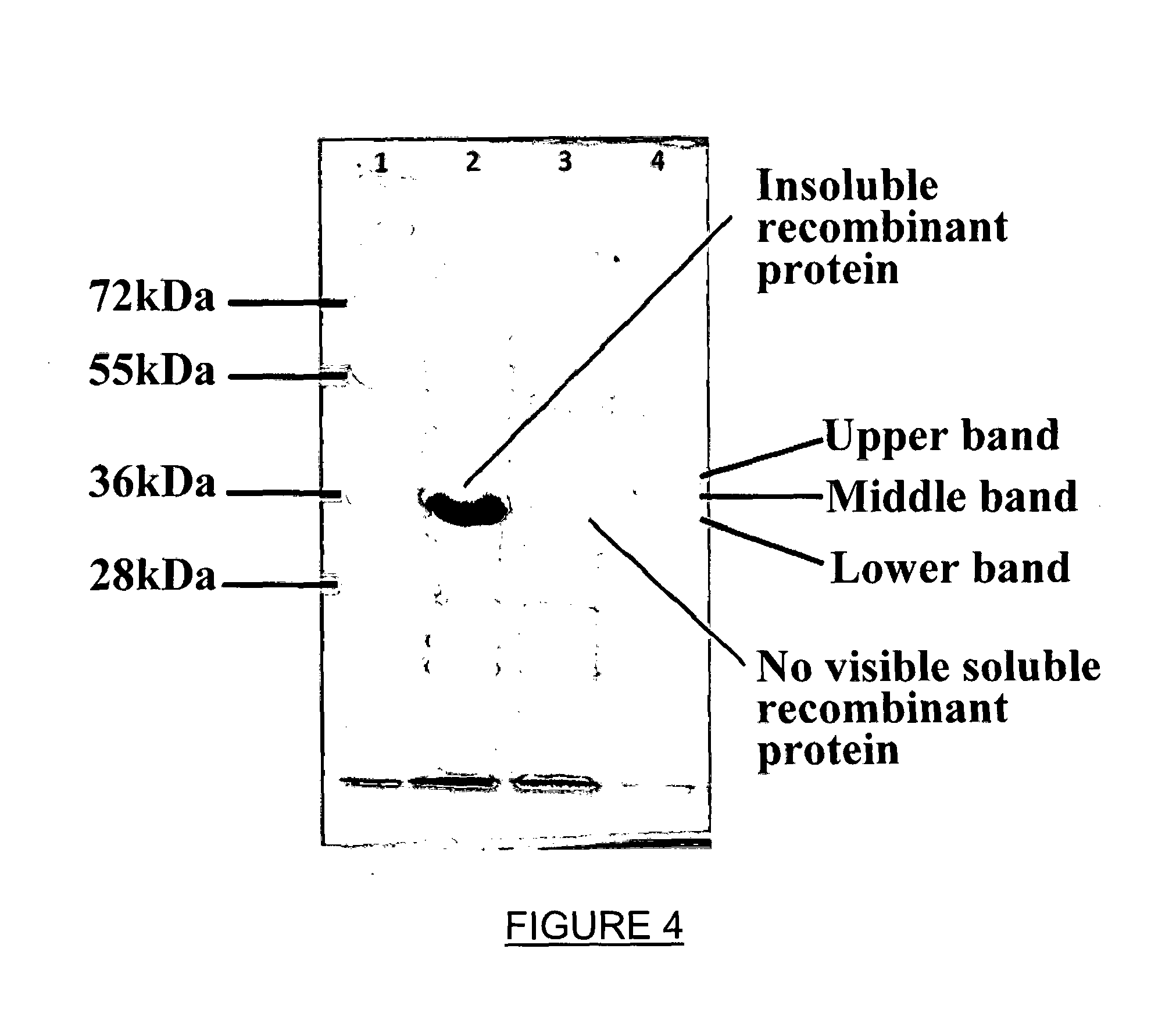
Recombinant therapeutic glycine n-acyltransferase
This invention relates to a method of producing a recombinant enzyme, more particularly, this invention relates to a method of producing water soluble enzymatically active recombinant glycine N-acyltransferase (GLYAT (E.G. 2.1.3.13)), including the steps of providing a suitable expression host; preparing a vector including a gene for expressing GLYAT in the expression host to form an expression piasmid; transforming the host with the expression piasmid to form an expression system; expressing the GLYAT gene in the expression system; and separating the expressed GLYAT from the expression system.
Owner:NORTH WEST UNIV (ZA)
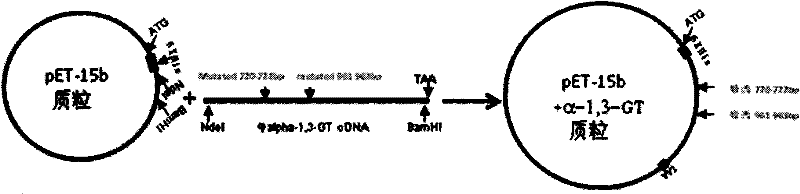
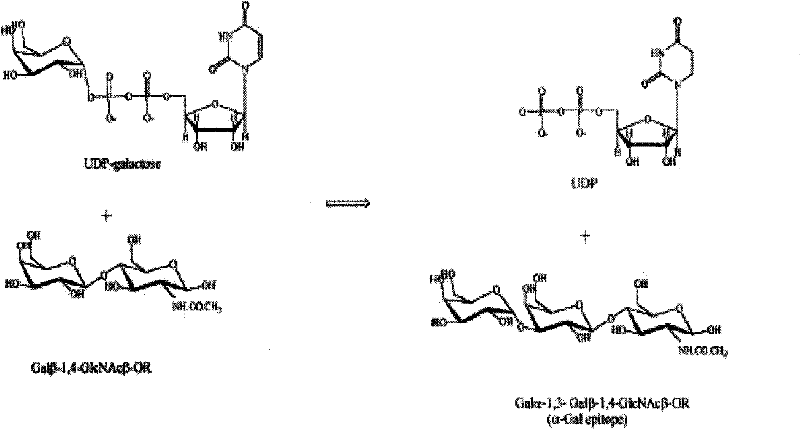
Clone and expression of bovine recombinant alpha-1,3-galactoside transferase (GT)
The invention relates to a recombinant zymoprotein having high activity and specific GT. According to the invention, the 80th to 368th amino acids of Inner Mongolia cow thymus GT proteins, the smallest water-soluble part with activity of GT, are employed. To further improve water-solubility and enzyme reaction activity of recombinant GT, through molecular designing and gene engineering reconstruction of natural proteins, the 160th amino acid of GT proline is modified to be lysine, the 241st amino acid of GT glutamic acid is modified to be glutamine, and therefore, recombinant zymoprotein withstronger enzymatic activity is obtained; the obtained recombinant zymoprotein has enzymatic activity 8 to 10 times that of existing zymoprotein and is applicable to the medical field of tumor treatment.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA MEDICAL COLLEGE
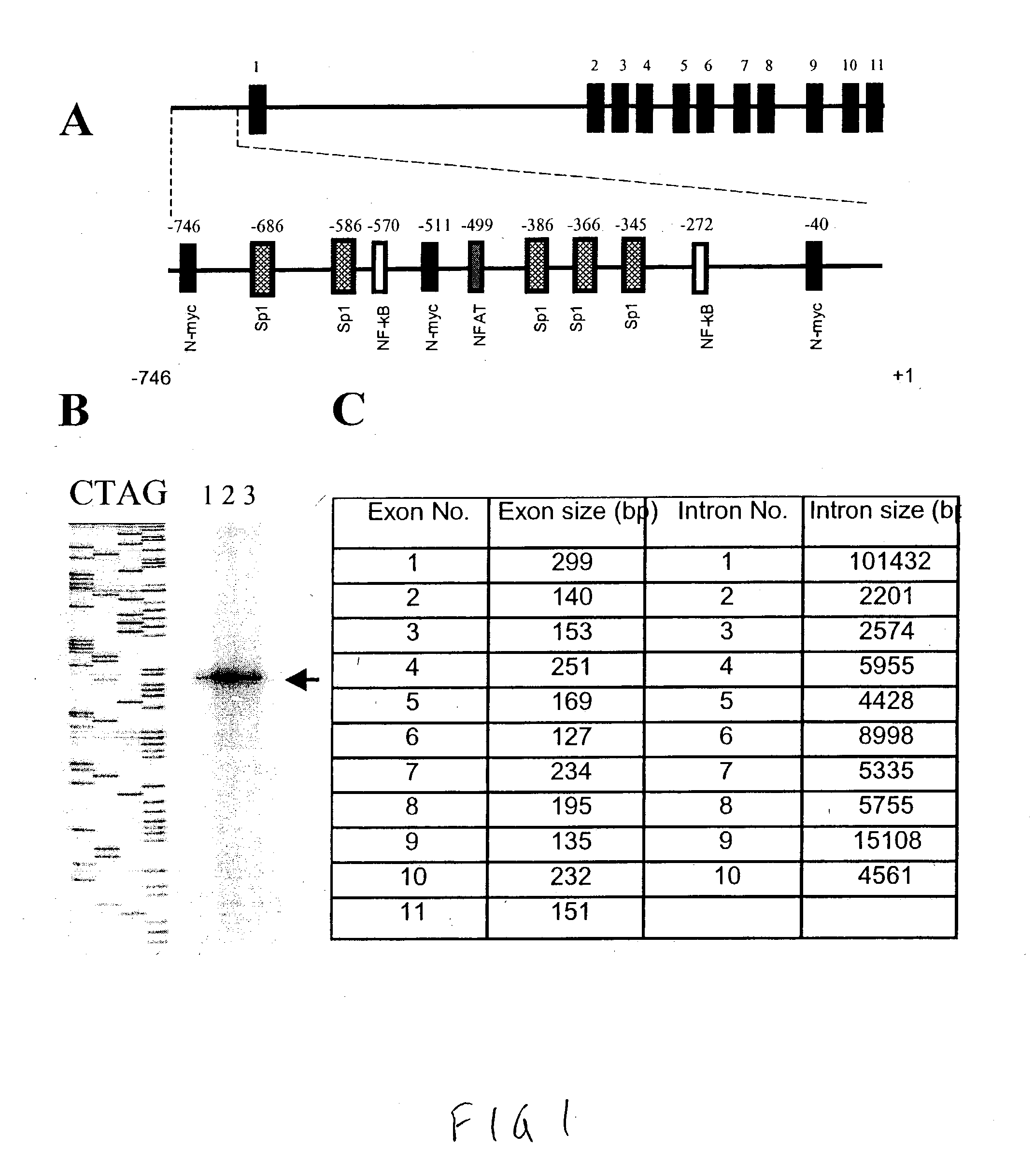
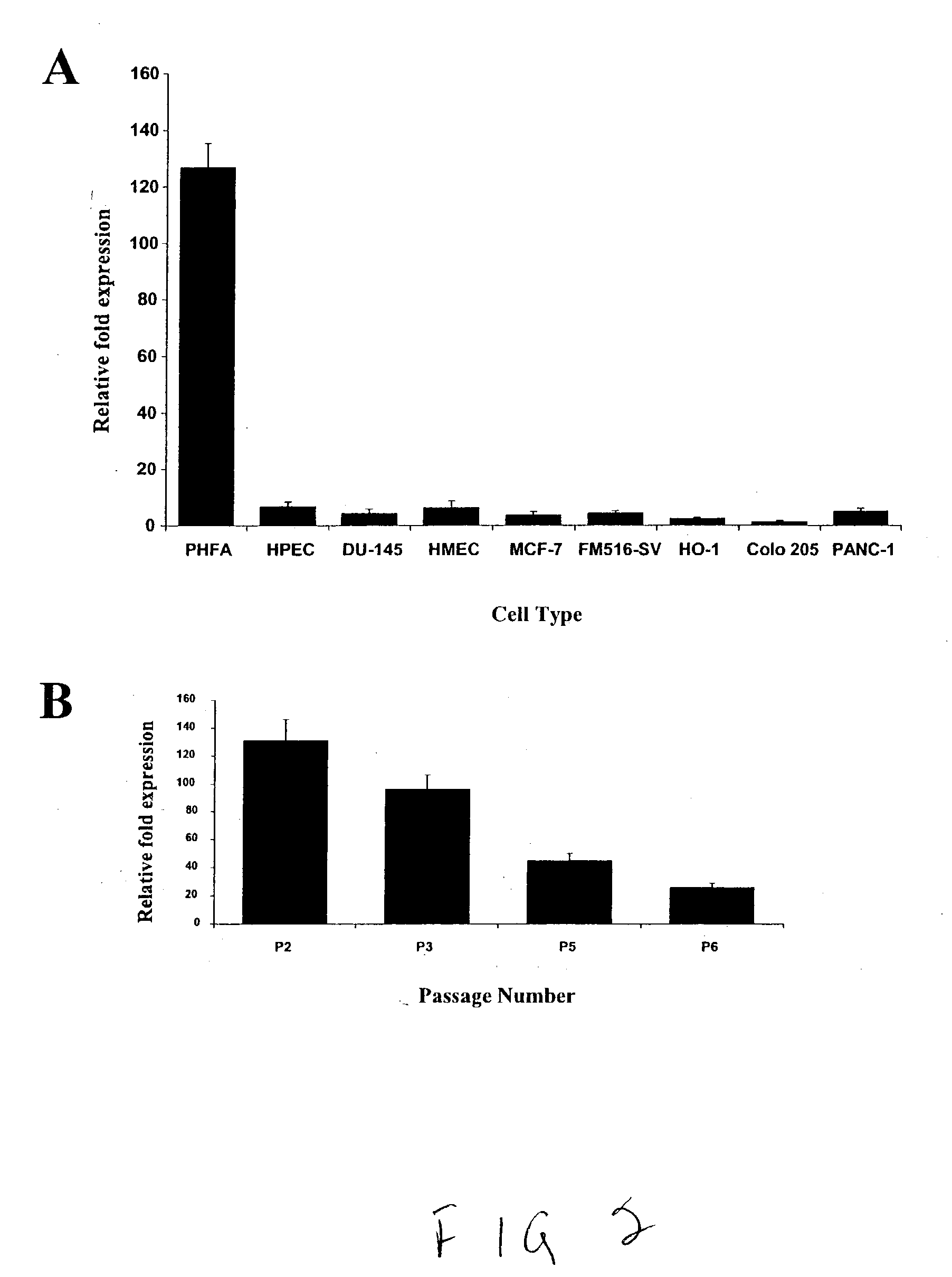
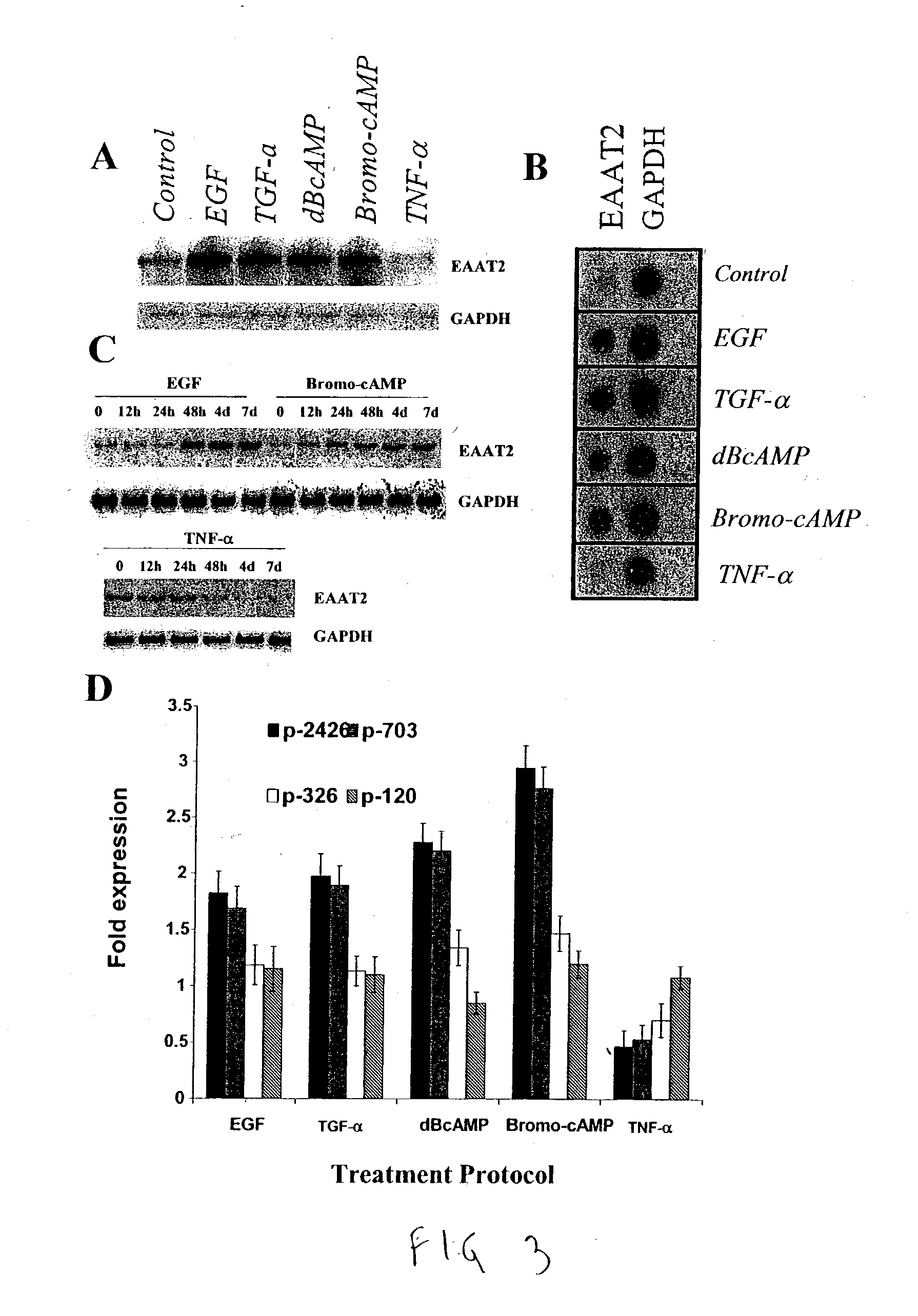
Human excitatory amino acid transporter-2 gene promoter and uses thereof
The nucleic acid sequence of the human Excitatory Amino Acid Transporter-2 Gene (hEAAT2) promoter, a nucleic acid sequence that hybridizes to the hEAAT2 promoter nucleic acid sequence under stringent hybridization conditions, and a nucleic acid sequence that is functionally equivalent to the hEAAT2 promoter sequence are provided, as are vectors containing these nucleic acid sequences. In addition, methods for the use of these nucleic acids to achieve tissues- or cell-specific gene expression are provided, as are methods for the use of these hEAAT2 promoter nucleic acids to identify agents that can modulate glutamate transport or the activity of the glutamate promoter. Such agents may be useful in the prevention, palliation or treatment of neurodegenerative and / or cerebrovascular diseases.
Owner:FISHER PAUL B +1
Method for producing gamma-aminobutyric acid by using recombinant Bacillus subtilis
ActiveCN105936923AIncreased relative conversion efficiencyMicroorganism based processesFermentationEscherichia coliGamma-Aminobutyric acid
The invention relates to a method for producing gamma-aminobutyric acid by using recombinant Bacillus subtilis. The method uses Bacillus subtilis as the host cells to conduct expression of Escherichia coli decarboxylase gene (gadA) or co-expression of regeneration gene of coenzyme pyridoxal phosphate (pdxH); the conditions for transformation of glutamic acid for synthesis of gamma-aminobutyric acid by using recombinant B.subtilis 168 / pHT01-gadA-pdxH whole cells are further optimized, and the optimal conditions are as below: a transformation buffer system is 0.1MTris-HCl with pH value of 6.5, the transformation temperature is 35 DEG C, and an activator is 5mmol / LCa<2+> and 5 mmol / L Mg<2+>. Under the above conditions, the transformation is carried out for 24h, and the generated GABA reaches a concentration of 327g / L; and the residual L-glutamate in the transformation system is less than 1%. The recombinant strain obtained by the invention has high conversion efficiency, and has certain industrialization prospect.
Owner:常州科畅生物科技有限公司
Glutamyltranspeptidase for synthesizing gamma-polyglutamic acid and coding gene thereof
InactiveCN103232980BEfficient synthesisSynthesis fastTransferasesFermentationNucleotideProtein molecules
The invention provides glutamyltranspeptidase for synthesizing gamma-polyglutamic acid and a coding gene thereof. The protein molecule of the glutamyltranspeptidase has the amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2; and the gene of the glutamyltranspeptidase has the nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1. The invention also discloses a method for synthesizing the gamma-polyglutamic acid by utilizing recombinant glutamyltranspeptidase. By adopting the method, the gamma-polyglutamic acid is synthesized by utilizing the recombinant glutamyltranspeptidase and taking glutamine monomers as raw materials. The glutamyltranspeptidase can be used for synthesizing the gamma-polyglutamic acid by taking the glutamine monomers as the raw materials, thus having importance significance in enriching glutamyltranspeptidase family members and developing a new gamma-polyglutamic acid synthesis route.
Owner:GUANGDONG IND TECHN COLLEGE
Model for Glutamate Racemase Inhibitors and Glutamate Racemase Antibacterial Agents
ActiveUS20100240727A1Easy to identifyImproved pharmacokinetic propertiesBiocideMolecular designPeptidoglycan biosynthesisGLYAT
The increase in antibacterial resistance has created the demand for new antibiotics. The present invention relates to a more potent antibiotic that targets the enzyme glutamate racemase from known glutamate racemase inhibitors. Glutamate racemase catalyses the interconversion of L-glutamate to D-glutamate, making D-glutamate available, which is required for bacterial peptidoglycan biosynthesis. Knockout mutations have shown glutamate racemase to be necessary for bacterial cell survival and, before the present invention, no antibiotic on the market targeted this enzyme. The present invention relates to new, ligand based glutamate racemase inhibitors, developed using software to extract a pharmacophore model from a group of known glutamate racemase inhibitors. Forty-seven (47) known inhibitors were collected from the literature and several pharmacophore models were extracted therefrom. The functional groups common to all the known inhibitors were included in a pharmacophore model that described the requirements for glutamate racemase inhibition with 82% accuracy. Of these models, one was found to describe the requirements for glutamate racemase inhibition with 82% accuracy. The model was used to search databases of commercially available chemical compounds and 2-(2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethylamino)-4-oxo-4-p-tolylbutanoic acid and 2-(2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethylamino)-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-4-oxobutanoic acid were identified as showing antibacterial activity. These compounds were assayed against S. pneumoniae and were shown to have antibacterial activity against the non-virulent strain R6 and against a multidrug resistant strain.
Owner:OHIO NORTHERN UNIVERSITY
Trail cell-penetrating peptide-like mutant mur5, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveUS20170247427A1Significant amplification potentialLow costPeptide/protein ingredientsTumor necrosis factorMutated proteinArginine
A TRAIL cell-penetrating peptide (CPPs)-like mutant MuR5 and a preparation method and the application thereof. The amino acid sequence of said mutant is SEQ ID NO: 2. The TRAIL CPPs-like mutant selectively transforms the amino acid coding sequence of No. 114-118 of the outer fragment of the TRAIL wild-type protein cell membrane from VRERG to RRRRR, i.e., mutates valine into arginine on the 114th coding sequence, glutamic acid into arginine on the 116th coding sequence and glycine into arginine on the 118th coding sequence, turning the coding sequence of N-terminal of the mutant protein into that of five arginines and making it a protein containing CPPs-like structure. Having a superior therapeutic effect on different types of tumor, the TRAIL CPPs-like mutant is a new generation of high-efficient drug for inducing tumor apoptosis of much potential.
Owner:CHENGDU HUACHUANG BIOTECH CO LTD
Alph-ketoglutaric acid dehydrase gene
A coryneform L-glutamate producing bacterium deficient in alpha -ketoglutaric dehydrogenase activity; a process for producing L-glutamic acid by using the bacterium; a gene coding for an enzyme having an alpha -KGDH activity originating in the coryneform L-glutamate producing bacterium; a recombinant DNA containing the above gene; a coryneform bacterium holding the above DNA; and a process for producing L-lysine by using an L-lysine producing bacterium holding the recombinant DNA.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com