Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
40 results about "Excitatory amino-acid transporter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Glutamate transporters are a family of neurotransmitter transporter proteins that move glutamate – the principal excitatory neurotransmitter – across a membrane. The family of glutamate transporters is composed of two primary subclasses: the excitatory amino acid transporter (EAAT) family and vesicular glutamate transporter (VGLUT) family. In the brain, EAATs remove glutamate from the synaptic cleft and extrasynaptic sites via glutamate reuptake into glial cells and neurons, while VGLUTs move glutamate from the cell cytoplasm into synaptic vesicles. Glutamate transporters also transport aspartate and are present in virtually all peripheral tissues, including the heart, liver, testes, and bone. They exhibit stereoselectivity for L-glutamate but transport both L-aspartate and D-aspartate.
Methods for detecting neurological disorders
InactiveUS20060040315A1Reduce the amount requiredLower Level RequirementsMicrobiological testing/measurementAmyotrophic lateral sclerosisBiology
In one aspect, the present invention features methods for detecting at least one neurological disorder in a patient, the method comprising obtaining a biological sample from the patient; and detecting at least one aberrant human glutamate transporter 2 (EAAT 2) mRNA in the sample as being indicative of the neurological disorder in the patient. In a particular aspect, the invention is useful for detecting amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) in the patient.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Excitatory amino-acid transporter-3 gene cRNA in-situ hybridization probes and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102559904AClear specificityRealize the display effectMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationHybridization probeMicrobiology
The invention discloses excitatory amino-acid transporter-3 (EAAT3) gene cRNA in-situ hybridization probes and a design method thereof. The method comprises the steps that: (1) specific primers of EAAT3 are designed according to a Gene bank sequence of EAAT3; an 292bp EAAT3 fragment is amplified by using the primers, and the fragment is adopted as a specific probe sequence of EAAT3; (2) EAAT3 cRNA in-situ hybridization probe plasmids are constructed; the probe plasmids are used for converting bacteria; the bacteria are cultivated; and the bacteria are sequenced; (3) EAAT3 cRNA in-situ hybridization probes are prepared; and (4) EAAT3 cRNA probe in-situ hybridization is detected.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
β-Benzyloxyaspartic acid derivatives having two substituents on their benzene rings
InactiveUS7670784B2Potent L-glutamate uptake inhibitory activityPotent L-glutamate uptake inhibitoryCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsDepsipeptidesL-glutamate uptakeBenzene
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
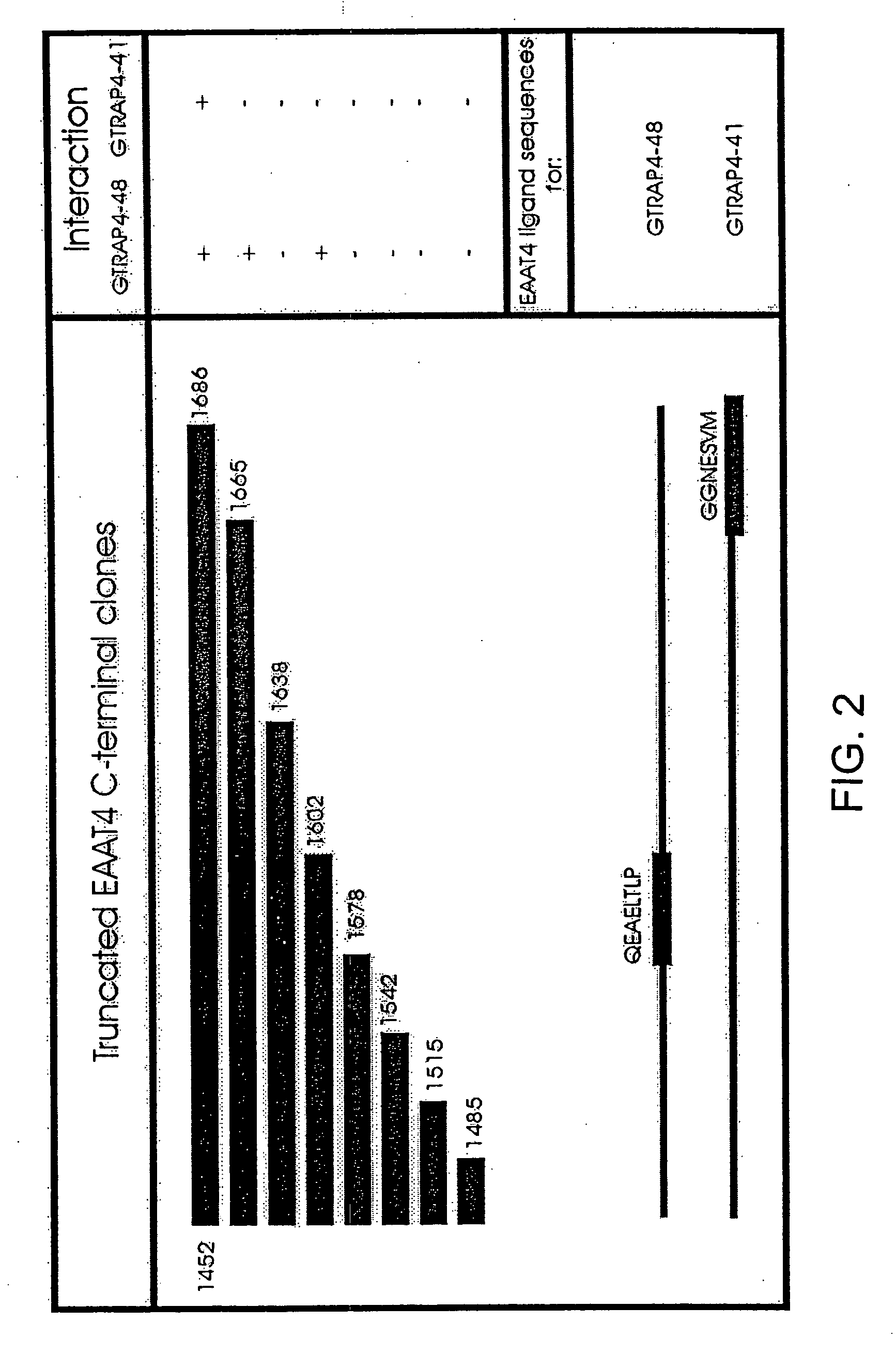
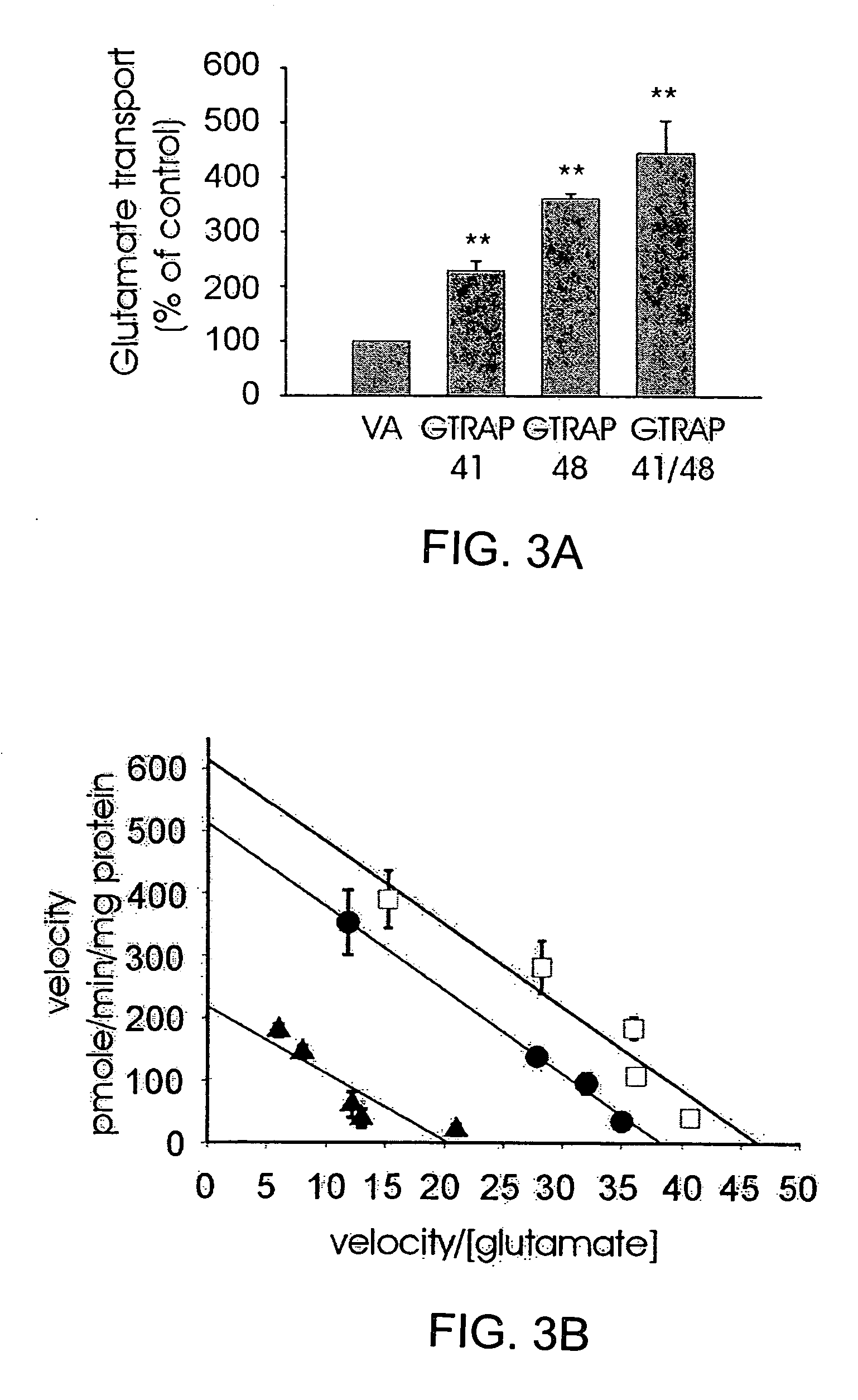
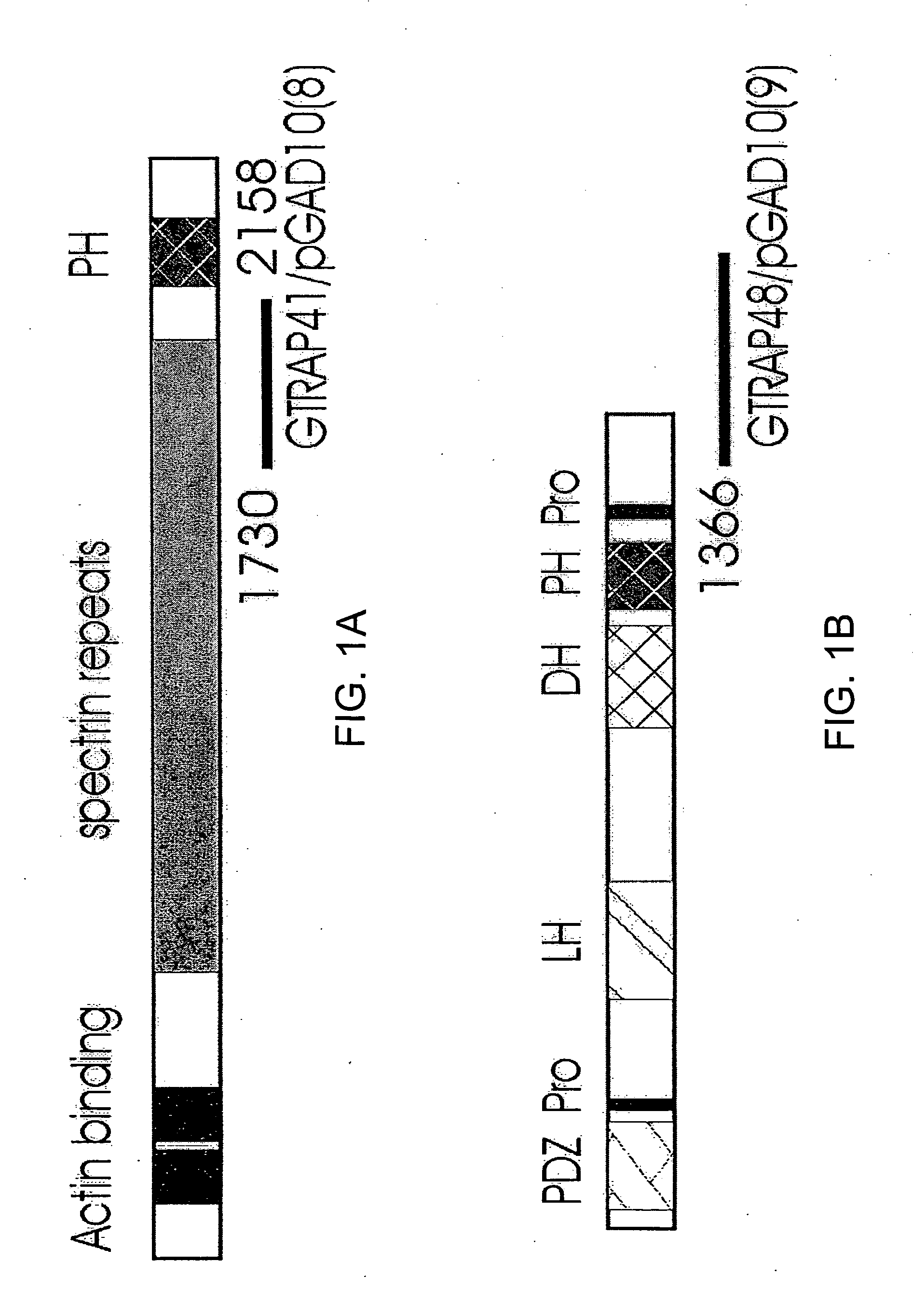
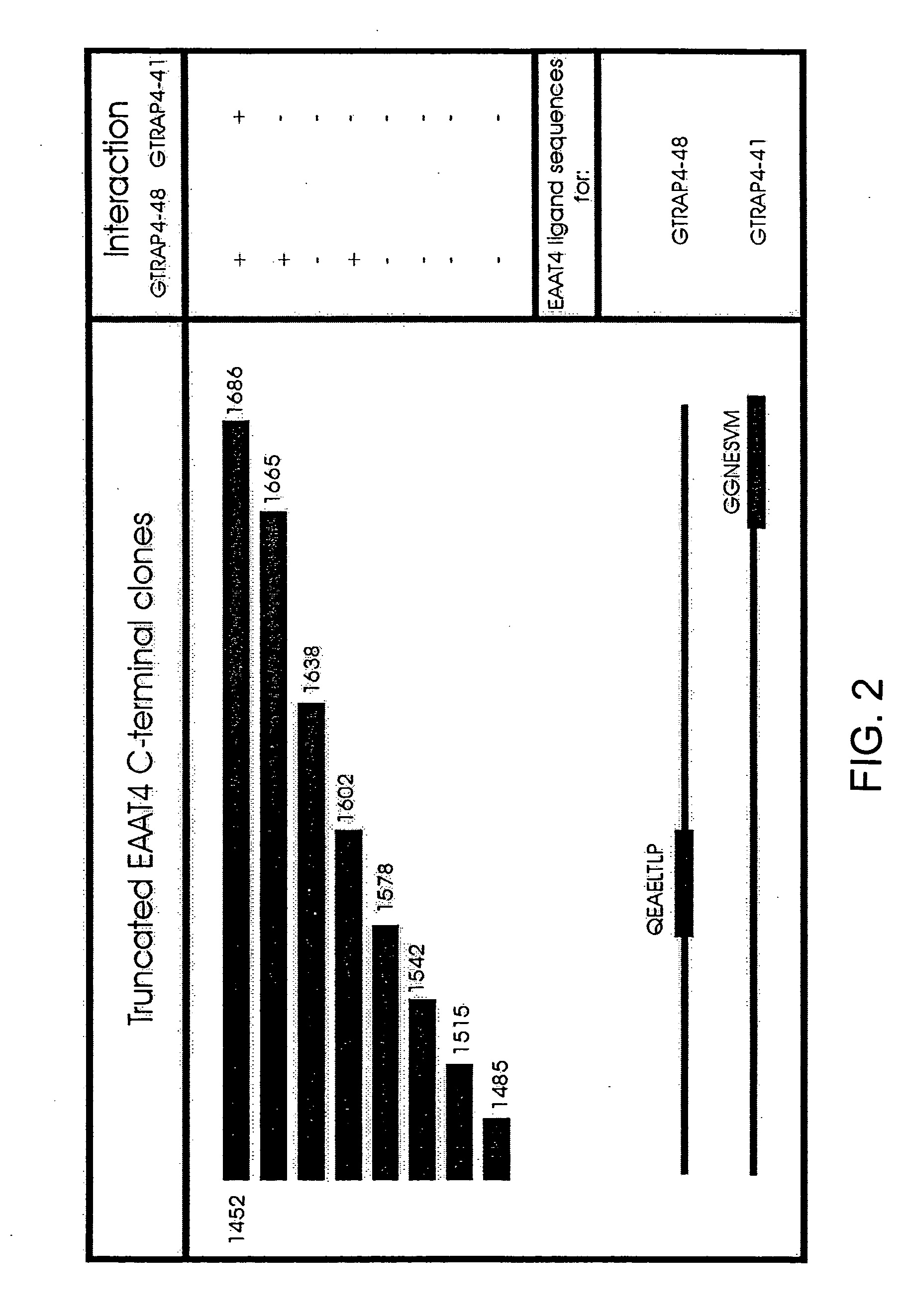
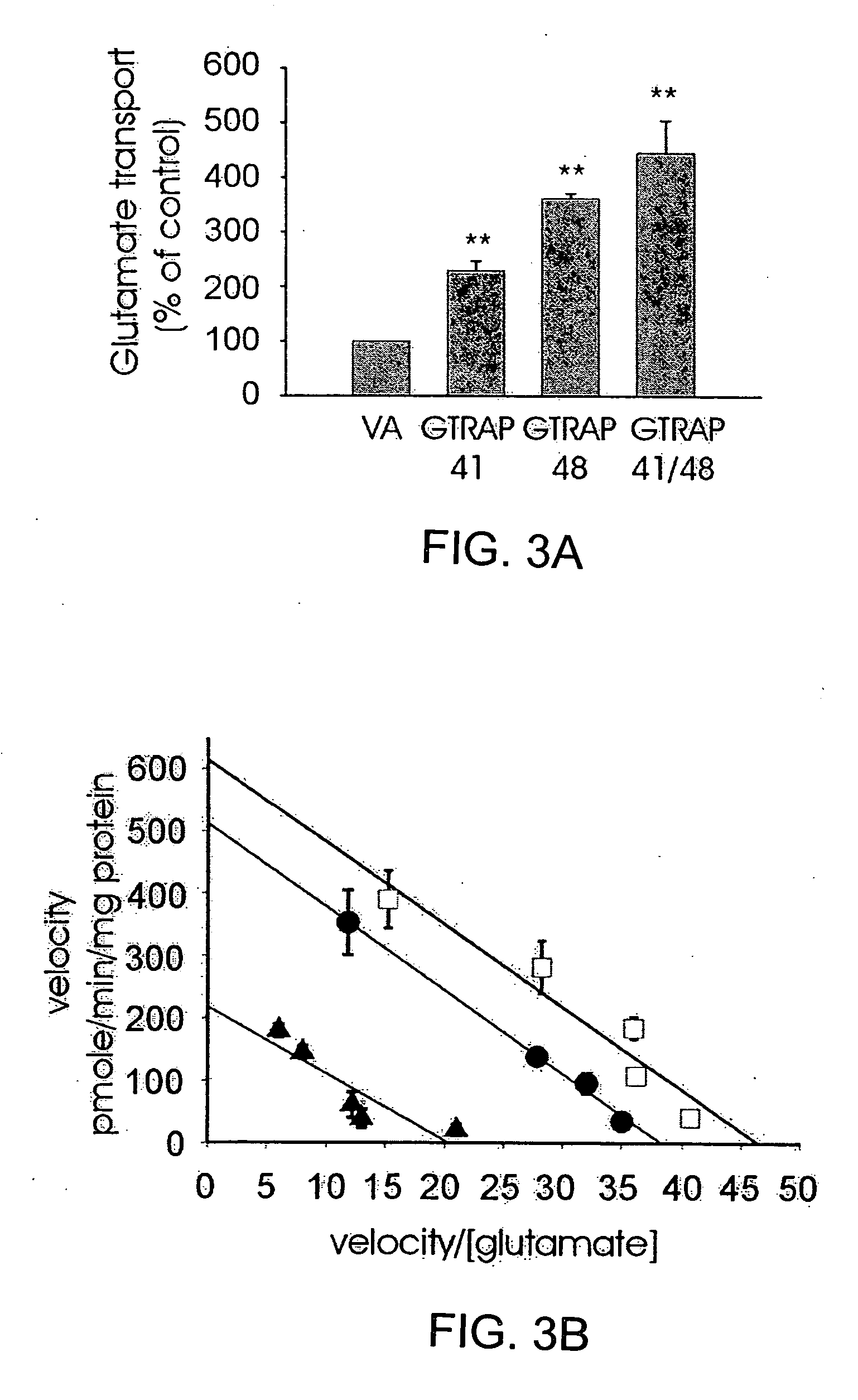
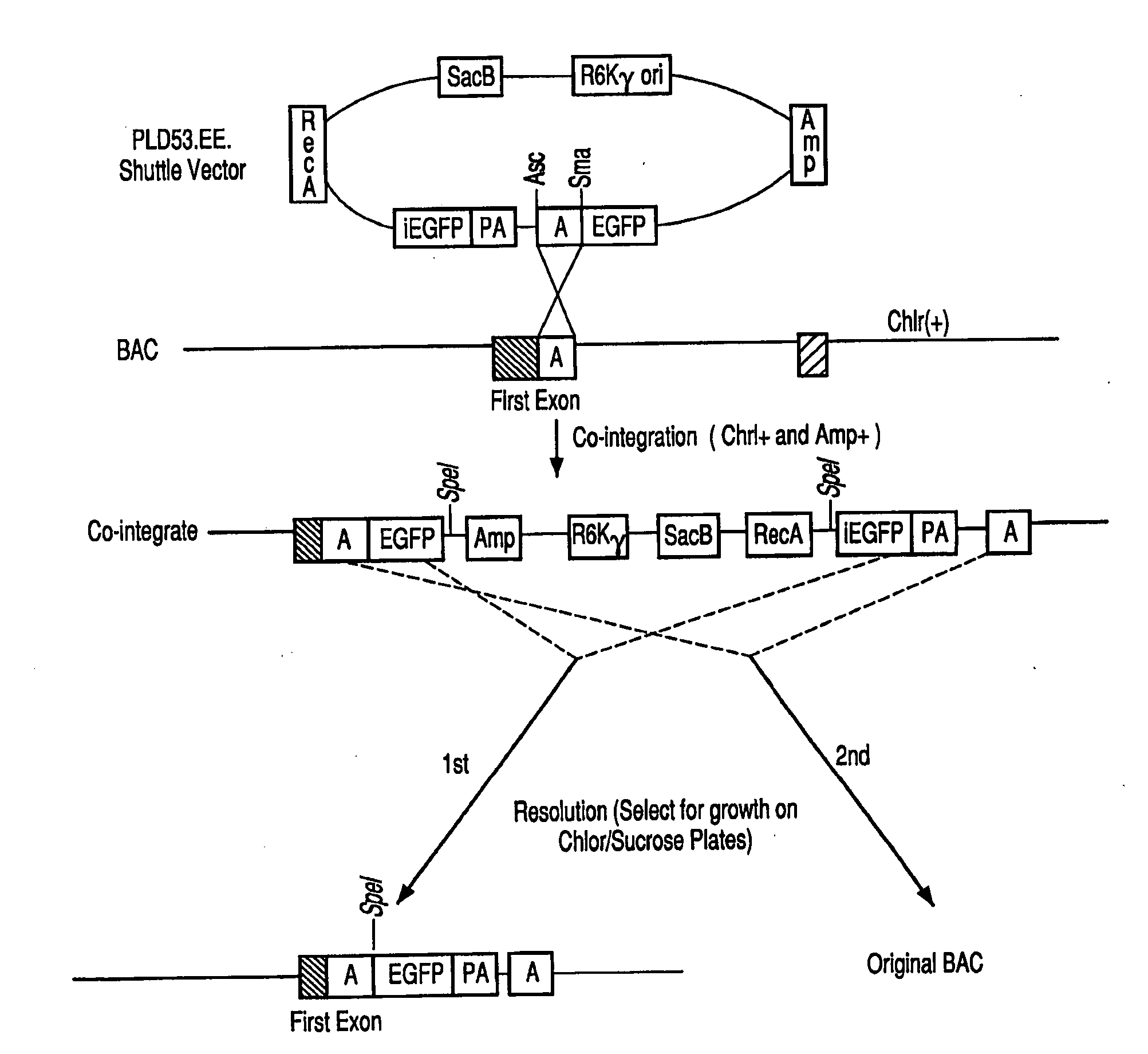
Glutamate transporter associated proteins and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20050106669A1Modulate transportGood effectCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesDiseaseL-glutamate transport
Glutamate Transporter Associated Proteins and nucleotide encoding Glutamate Transporter Associated Proteins are provided. Also provided is a method for identifying a compound that modulates a cellular response mediated by a Glutamate Transporter Associated Protein. A method is further provided for identifying a compound that inhibits an interaction between a Glutamate Transporter Associated Protein and a glutamate transporter protein. A method is provided for treating a disorder associated with glutamate transport.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Transgenic Mammals and Cell Lines for the Identification of Glutamate Transporter Modulators
The invention includes a transgenic, non-human mammal useful for identifying candidate compounds for treating neurological and / or psychiatric disorders. Incorporated into the genome of the transgenic mammal is a transgene comprising a glutamate transporter promoter operatively linked to a reporter gene. The transgenic non-human mammal and cells isolated therefrom can be used as an in vivo model for the identification of candidate compounds useful for the treatment of neurological and / or psychiatric disorders.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
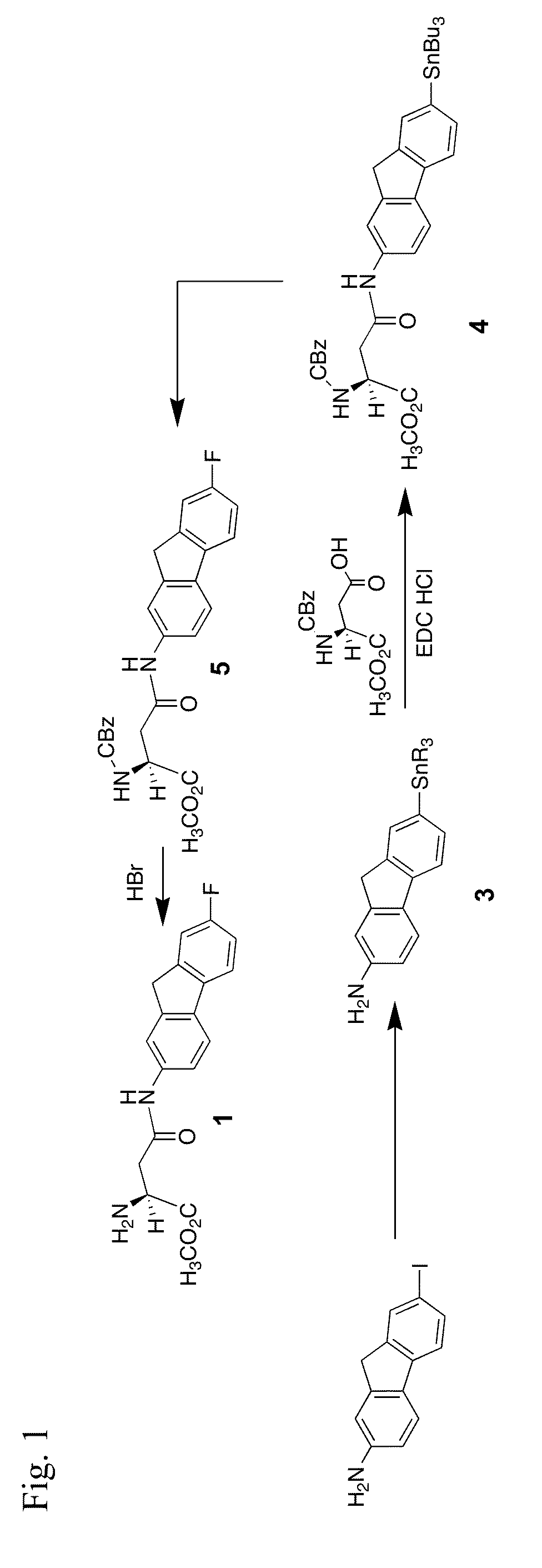
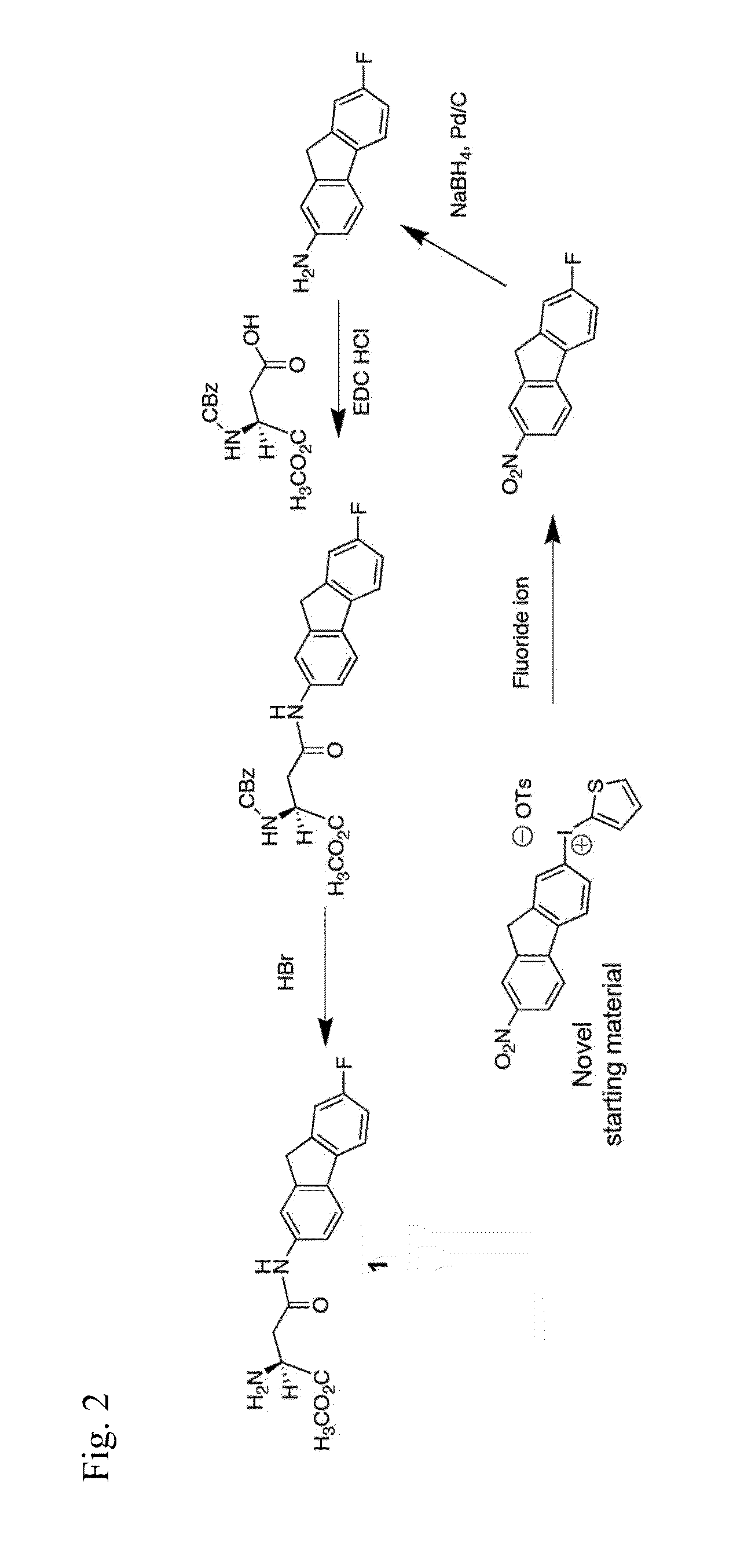
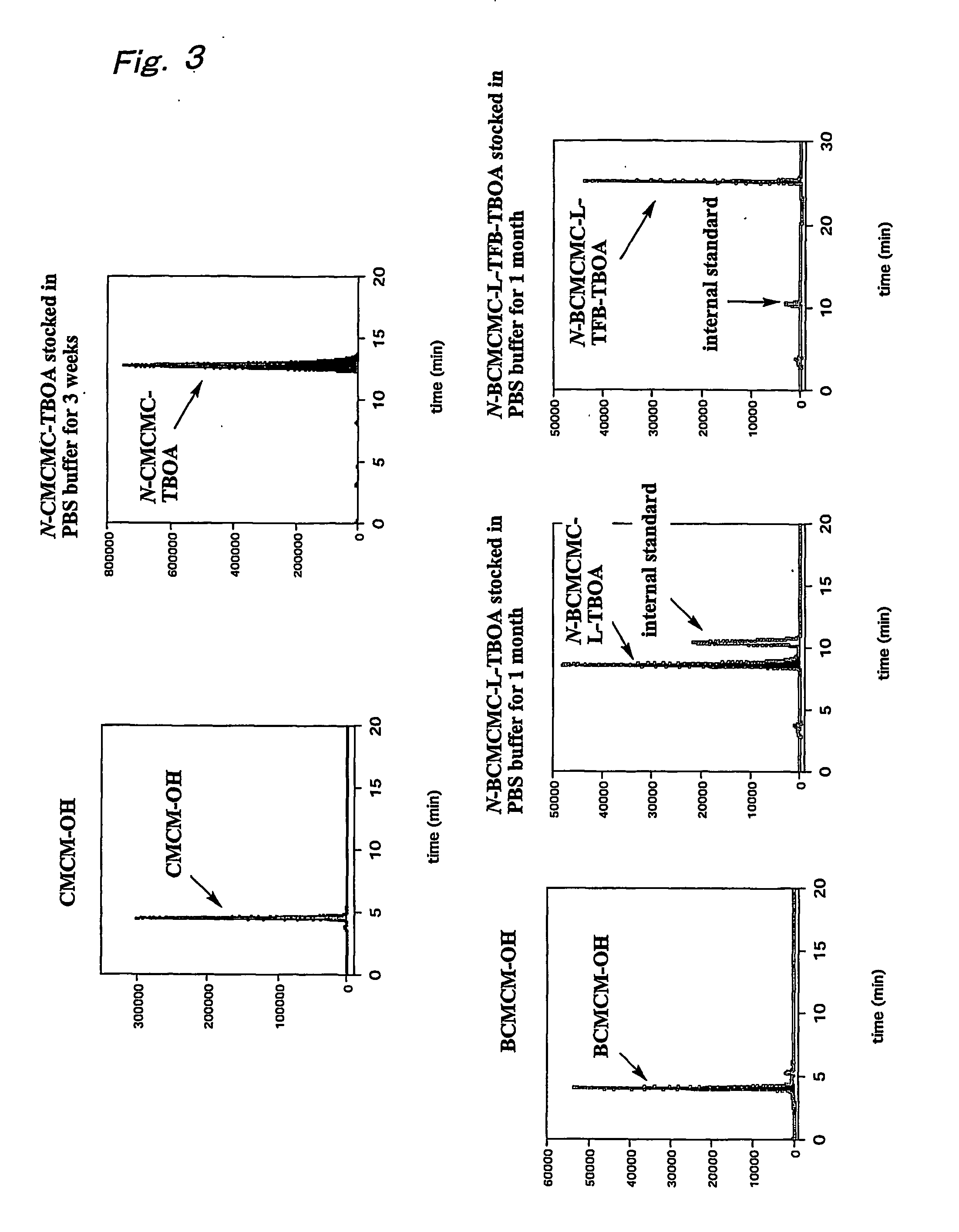
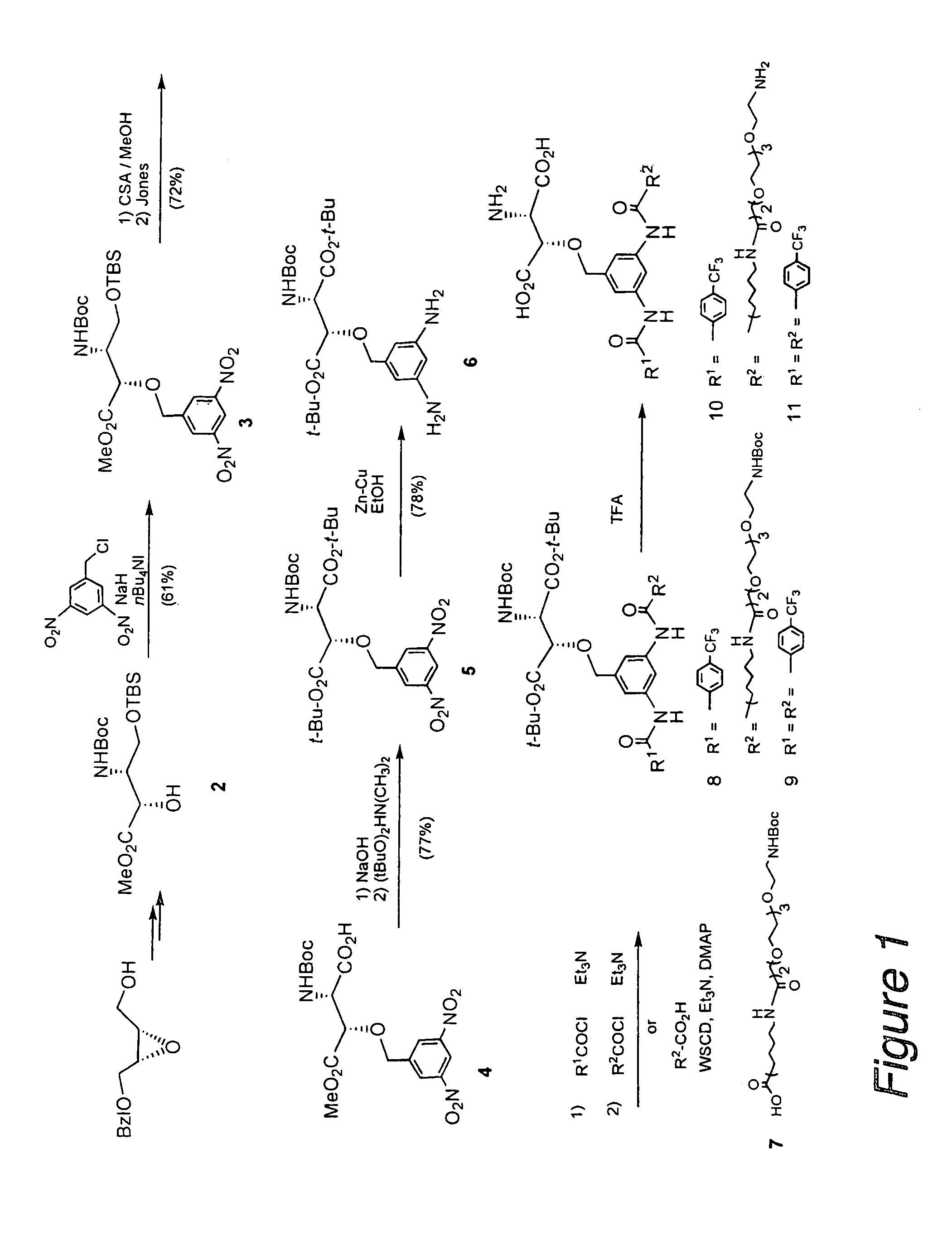
Radiolabeled 3-[3- (Benzoyl-Amido) Benzyloxy] Aspartic Acid Derivative and Method of Producing the Same
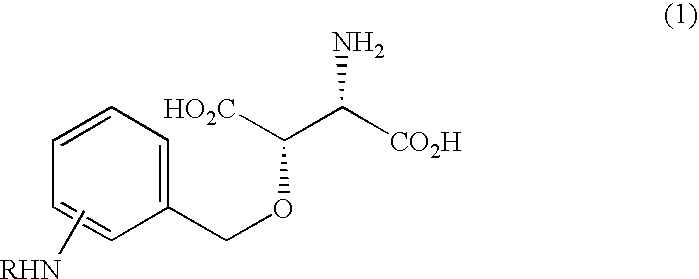
The present invention provides a radiolabeled ligand which is highly selective and potent for glutamate transporters and is usable in specifically detecting the glutamate transporter.Specifically, the present invention provides a 3-[3-(benzoylamido)benzyloxy]aspartic acid having a radioactive substituent on the benzoyl group which is represented by the following formula (1), or an ester or salt thereof:wherein X represents a substituent containing a radioactive atom(s) which is selected from a straight or branched lower aliphatic alkyl group, a hydroxyl group, a straight or branched lower aliphatic alkoxy group, an amino group, a straight or branched lower aliphatic acylamido group, a halogen atom and a straight or branched lower aliphatic haloalkyl group; and R1 and R2 each represents a hydrogen atom, a straight or branched lower aliphatic alkyl group or an acetoxymethyl group.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
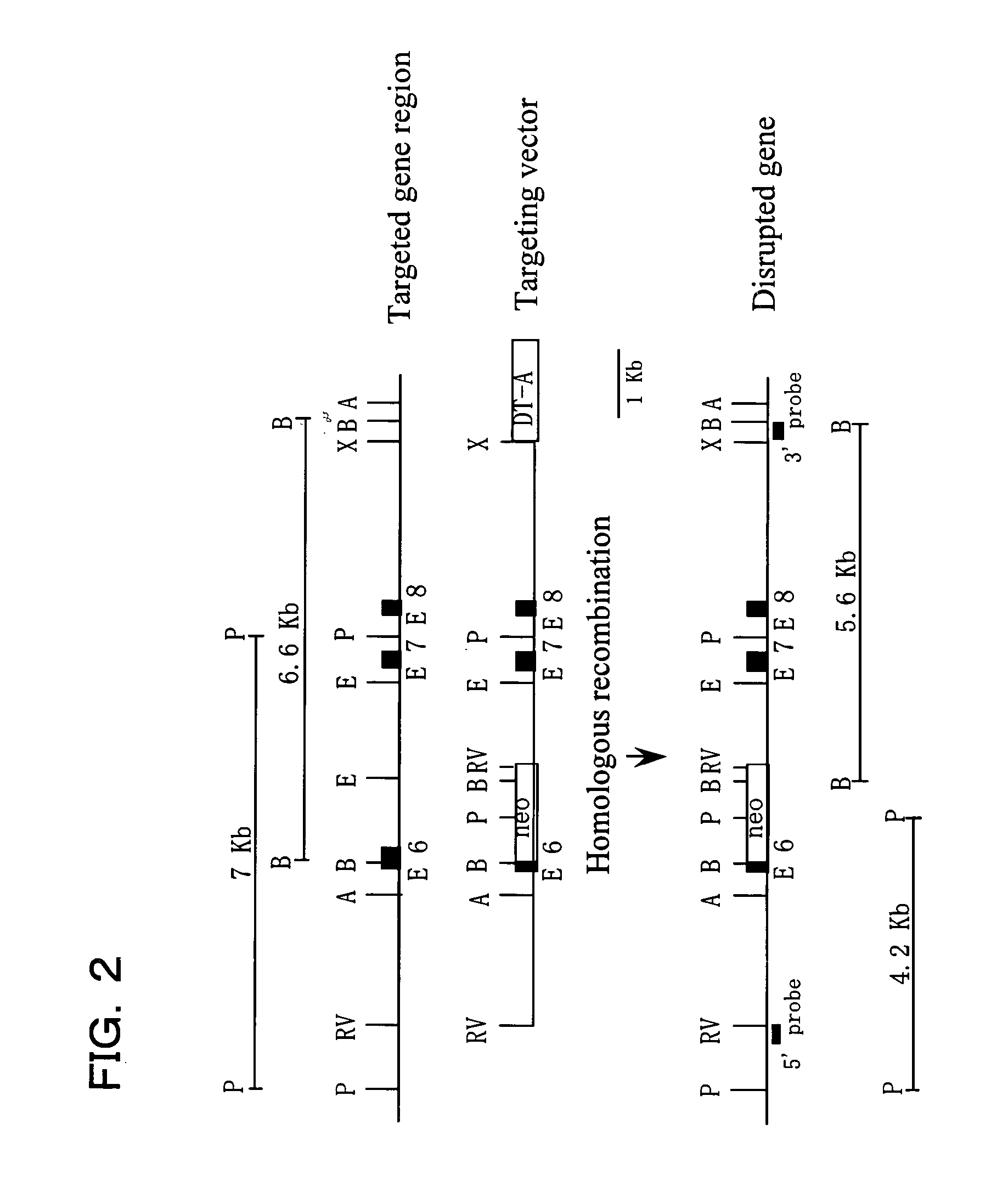
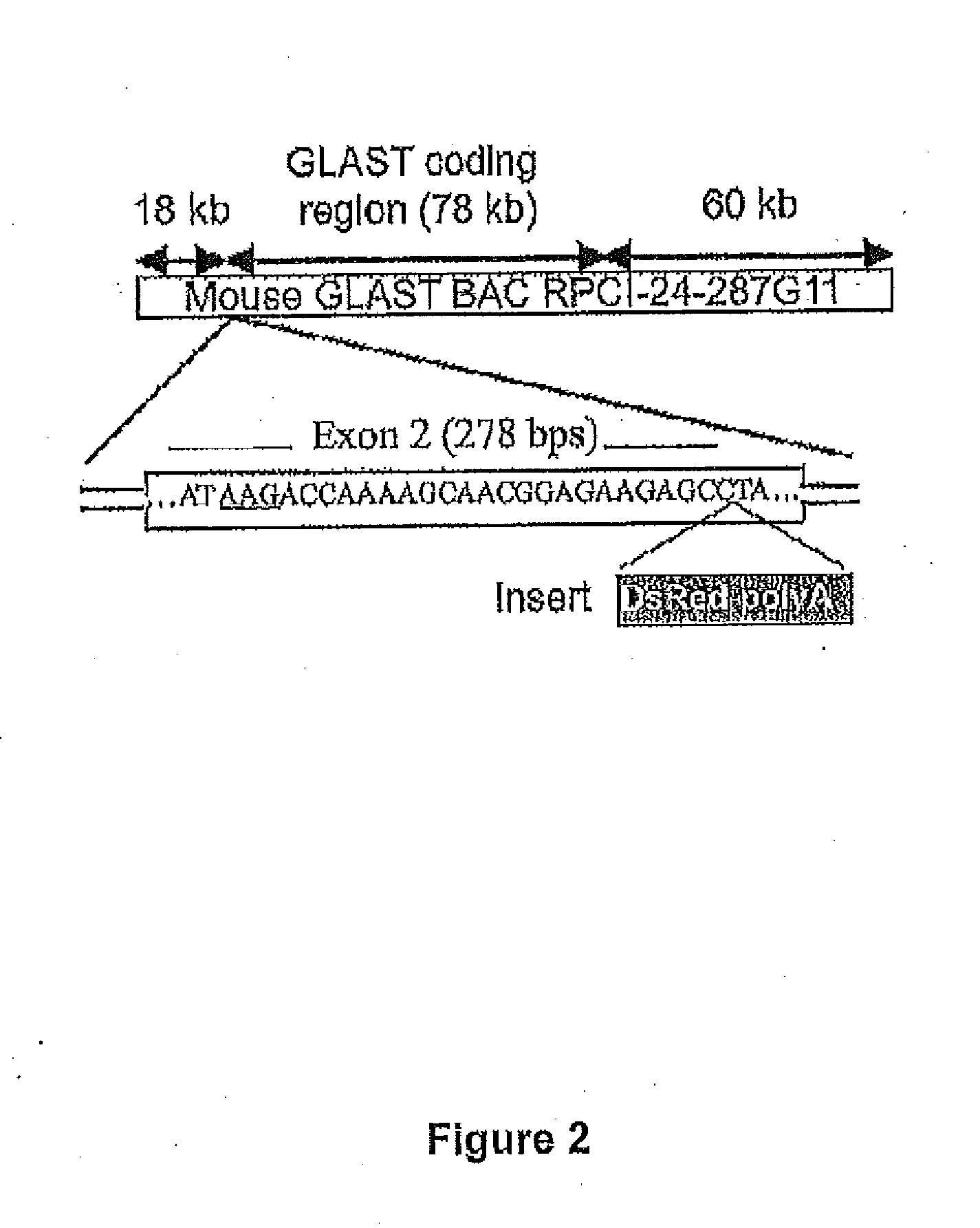
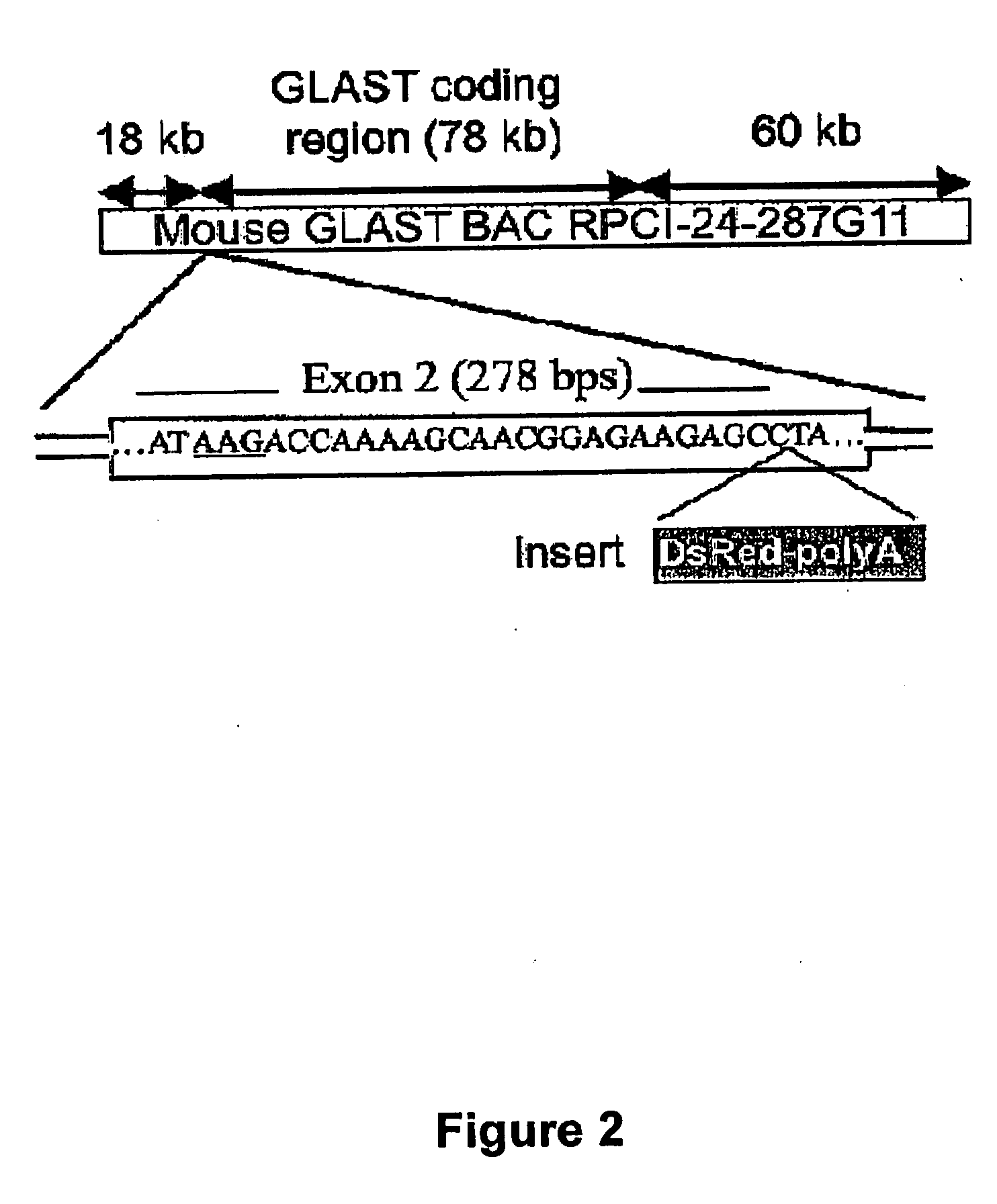
Mouse with deficiency of glutamate transporter glast function
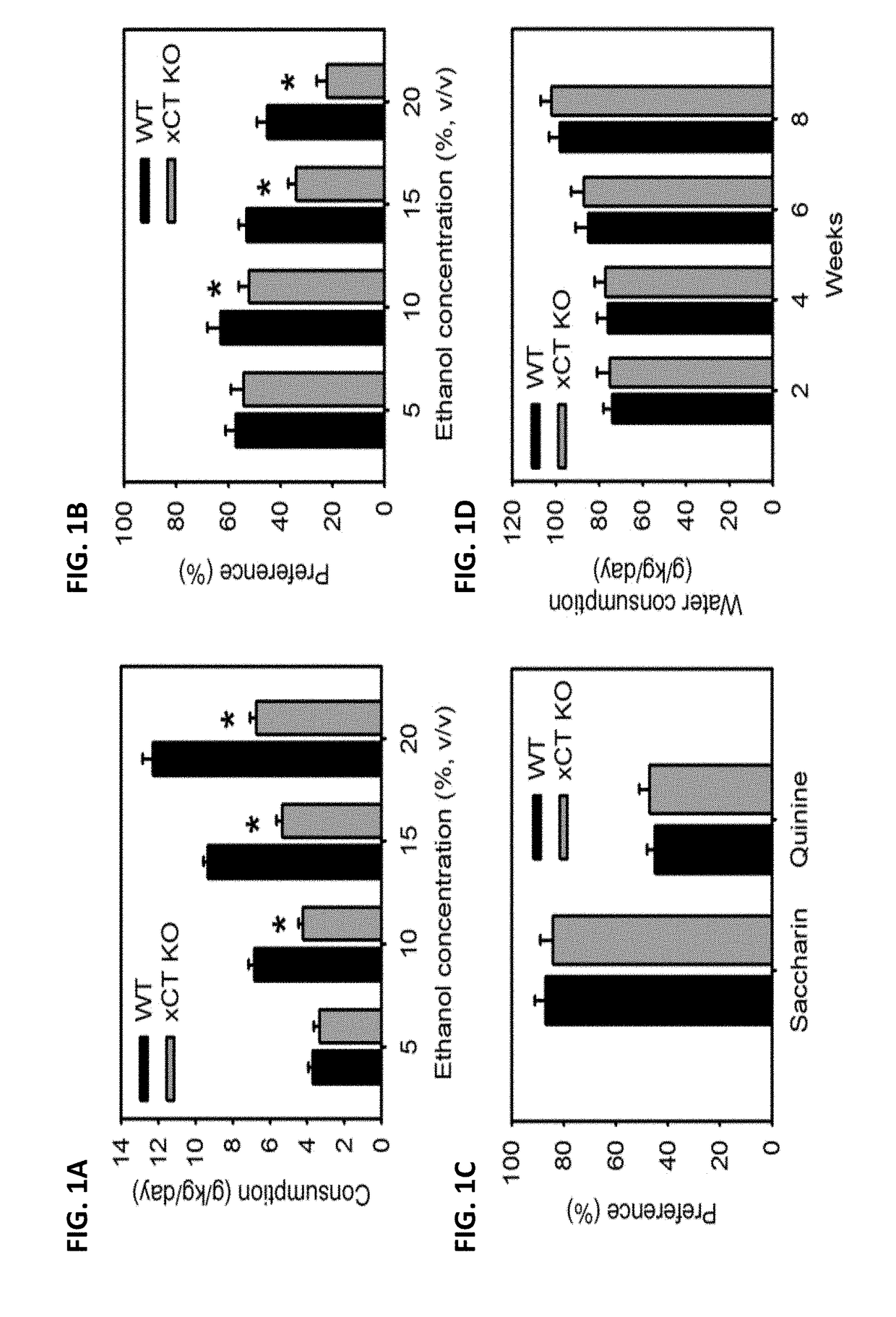
InactiveUS20070011758A1Reduce the number of cellsAnimal cellsBiological material analysisIntraocular pressureKnockout animal
The present invention provides a GLAST knockout mouse lacking the function of an endogenous glutamate transporter GLAST gene, which shows: 1) an intraocular pressure within the normal range; and 2) a reduction in the number of cells in the retinal ganglions when compared with a wild-type normal mouse. Owing to the ocular properties, this knockout mouse is useful as a model for normal tension glaucoma. By using this knockout mouse, a compound useful for the treatment of normal tension glaucoma can be screened.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Application of miRNA-543-3p in diagnosis and treatment of Parkinson's disease
InactiveCN105617382ARemissionReduce neurotoxic effectsOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderNeurotoxicityGlutamic acid
The invention discloses an application of miRNA-543-3p in diagnosis and treatment of a Parkinson's disease. In the invention, it is screened and verified that the miRNA-543-3p has an effect of regulating expressions and functions of a glutamate transporter, and it is further verified that miRNA-543-5p directly acts on the glutamate transporter. It is discovered that miRNA-543-5p inhibitors can inhibit functions of the miRNA-543-5p, so that an inhibition effect of the miRNA-543-5p on mRNA translation of the glutamate transporter is reduced, and an expression level of a glutamate transporter protein is improved to some extent, thereby reducing a neurotoxicity effect of glutamic acid, relieving the state of the Parkinson's disease and providing a new target and a new way for clinical treatment of the Parkinson's disease.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Novel Aspartylamide Inhibitors of Excitatory Amino Acid Transporters
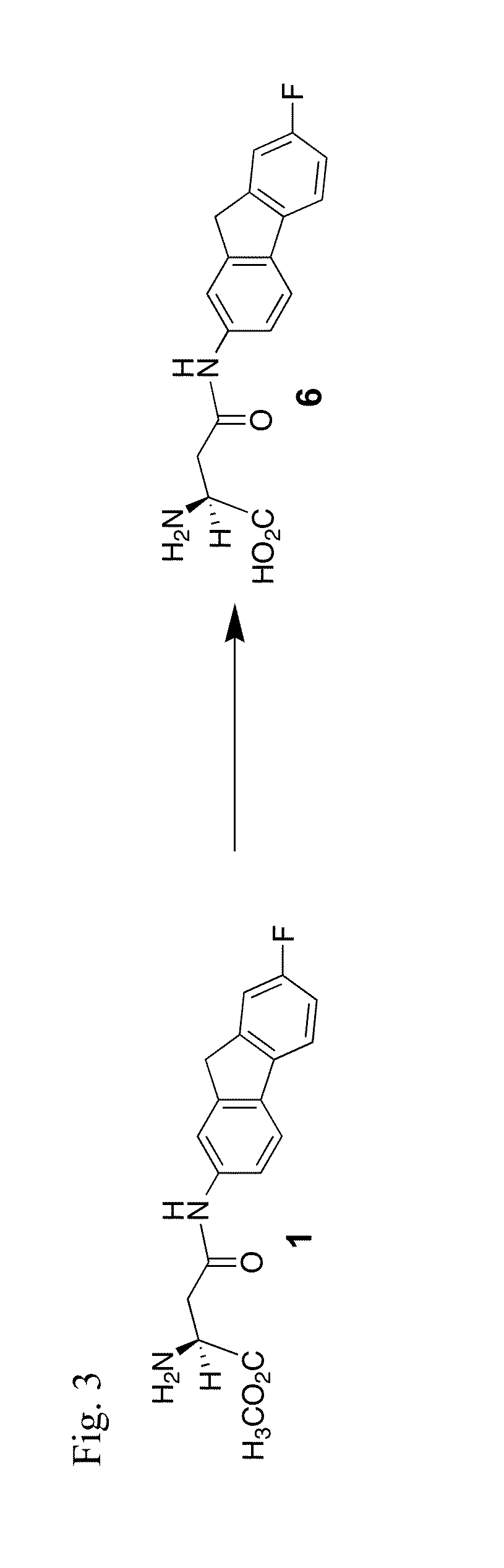
The compounds of the invention are inhibitors of excitatory amino acid transporters (EAAT) that penetrate the blood-brain barrier to access the central nervous system. The compounds of the invention follow the structural formula:or a salt, ester or prodrug thereof, wherein X is a halogen, such as fluorine, or a radionuclide, such as fluorine-18. The compounds and methods described herein can be used for the treatment of, e.g., neurodegenerative disorders (e.g., amyotrophic lateral sclerosis), ischemia, spinal cord injury, and traumatic brain injury in a patient (e.g., a human). The invention further provides compounds and methods for the synthesis and use of radiographic tracers to diagnose and follow the progression of such disorders.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MONTANA
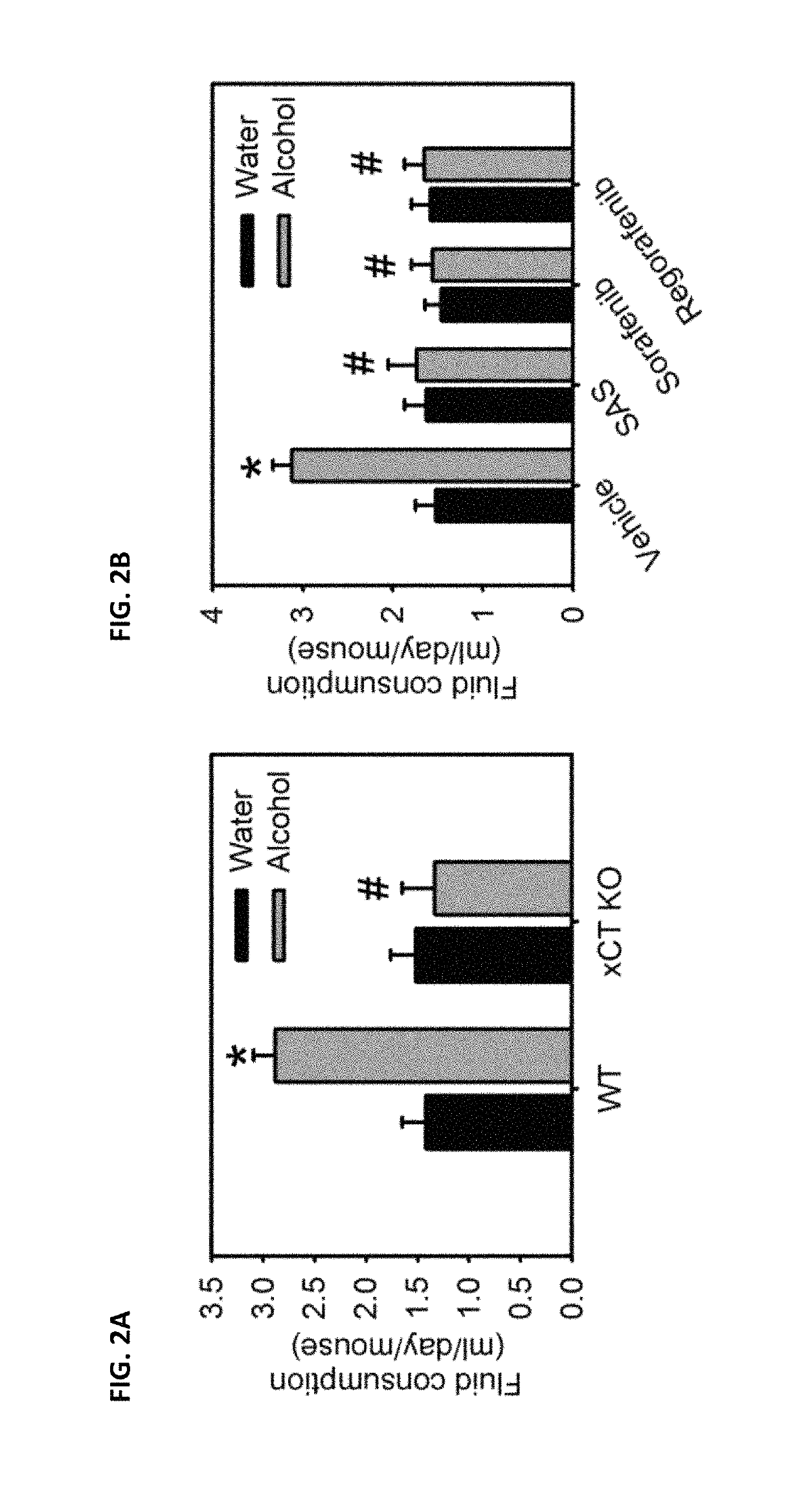
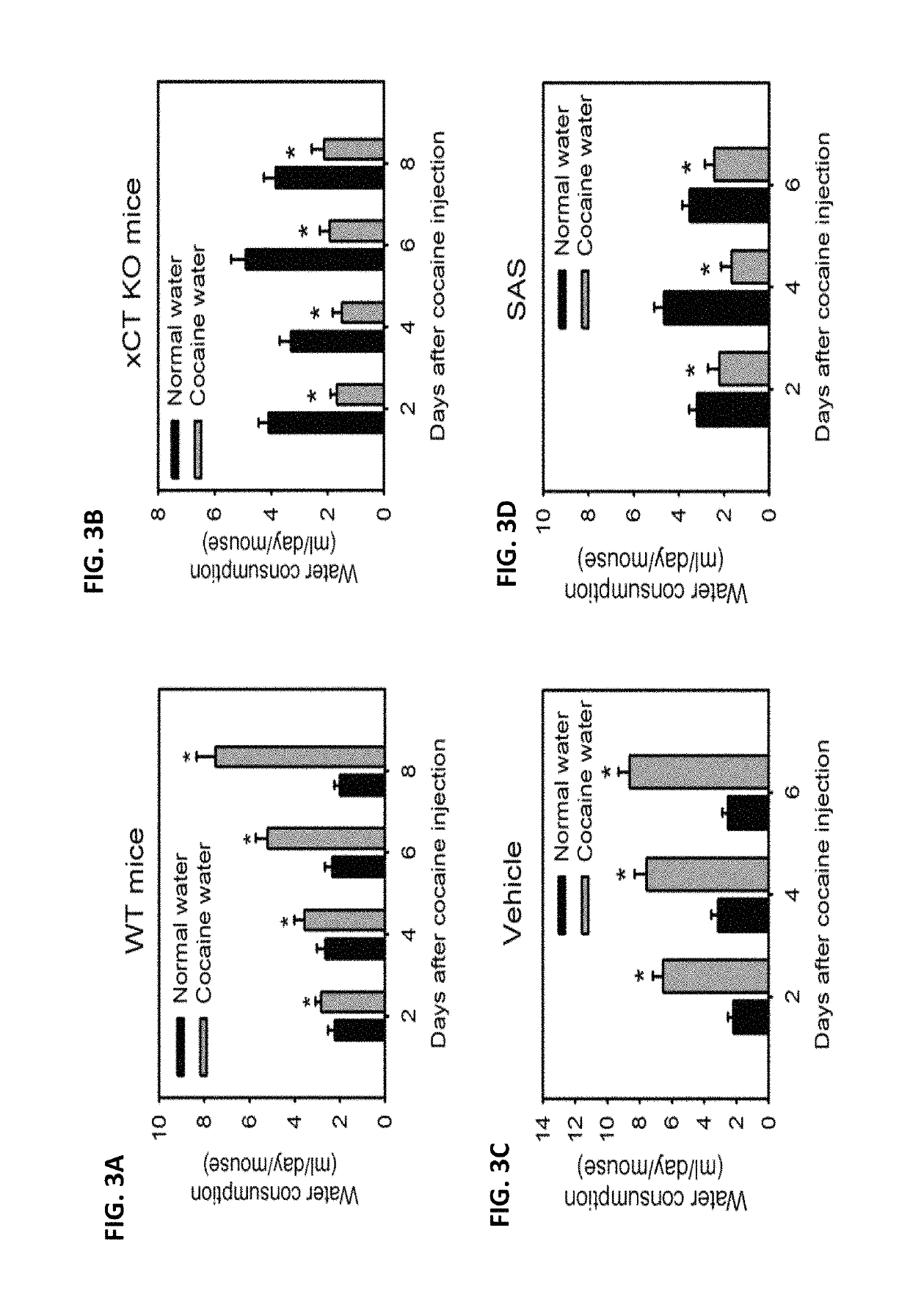
New use of inhibitor of cystine-glutamate transporter
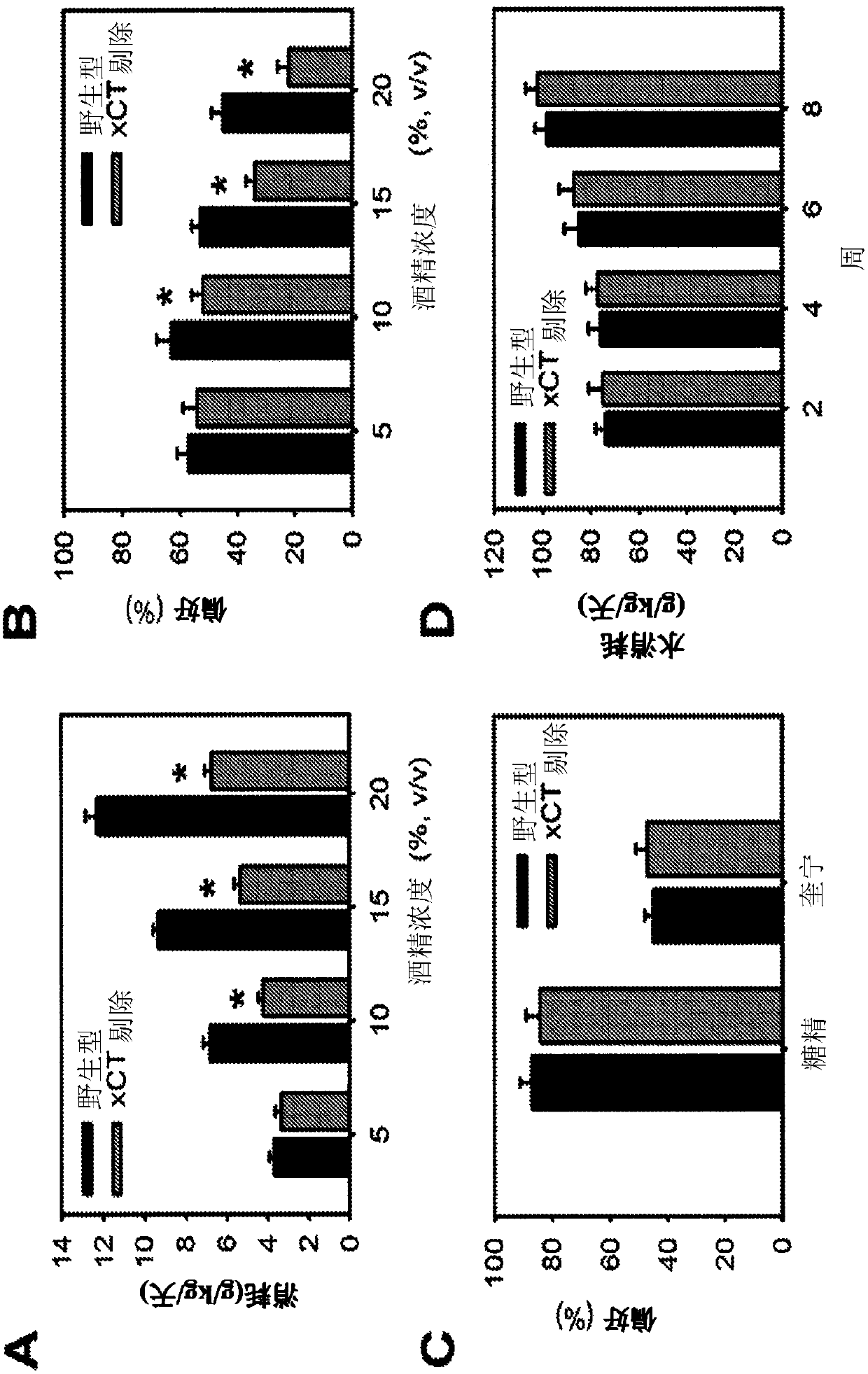
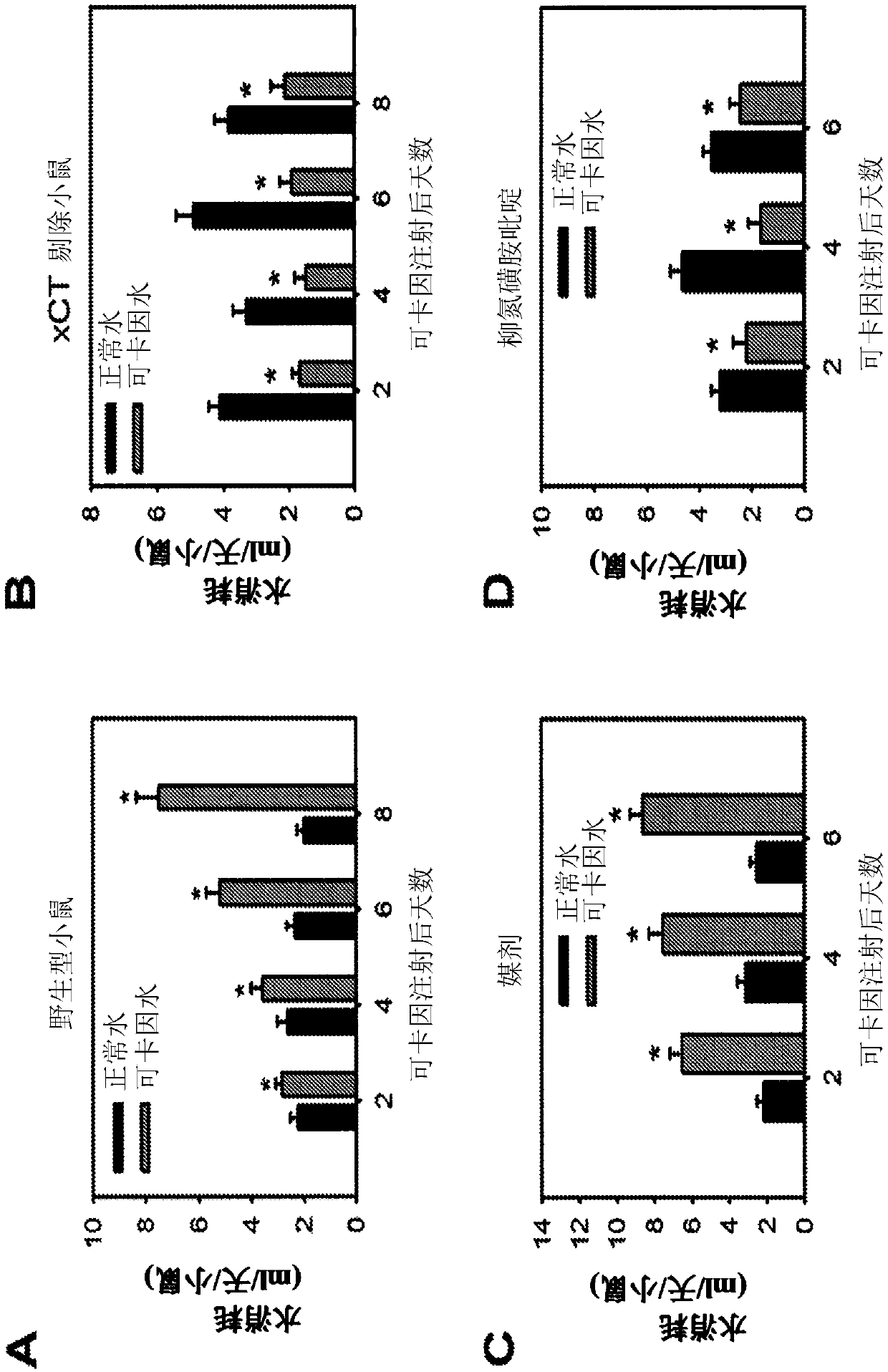
ActiveCN107735094ANervous disorderHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsSubstance inducedCystine/Glutamate Transporter
The agents that inhibit system x c - provide the therapeutic intervention in substance-related and addictive disorders and the treatment and / or prevention in substance-mediated brain damage, and confirm that system x c -is a promising therapeutic target for substance-induced addiction and brain damage.
Owner:CHINA MEDICAL UNIVERSITY(TW)
Glutamate transporter associated proteins and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20080057539A1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesNucleotideL-glutamate transport
Glutamate Transporter Associated Proteins and nucleotide encoding Glutamate Transporter Associated Proteins are provided. Also provided is a method for identifying a compound that modulates a cellular response mediated by a Glutamate Transporter Associated Protein. A method is further provided for identifying a compound that inhibits an interaction between a Glutamate Transporter Associated Protein and a glutamate transporter protein. A method is provided for treating a disorder associated with glutamate transport.
Owner:THE JOHNS HOPKINS UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Method of Treating Depression
Methods for treatment of depression-related mood disorders in mammals, particularly humans are disclosed. The methods of the invention include administration of compounds capable of enhancing glutamate transporter activity in the brain of mammals suffering from depression. ATP-sensitive K+ channel openers and β-lactam antibiotics are used to enhance glutamate transport and to treat depression-related mood disorders and depressive symptoms.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
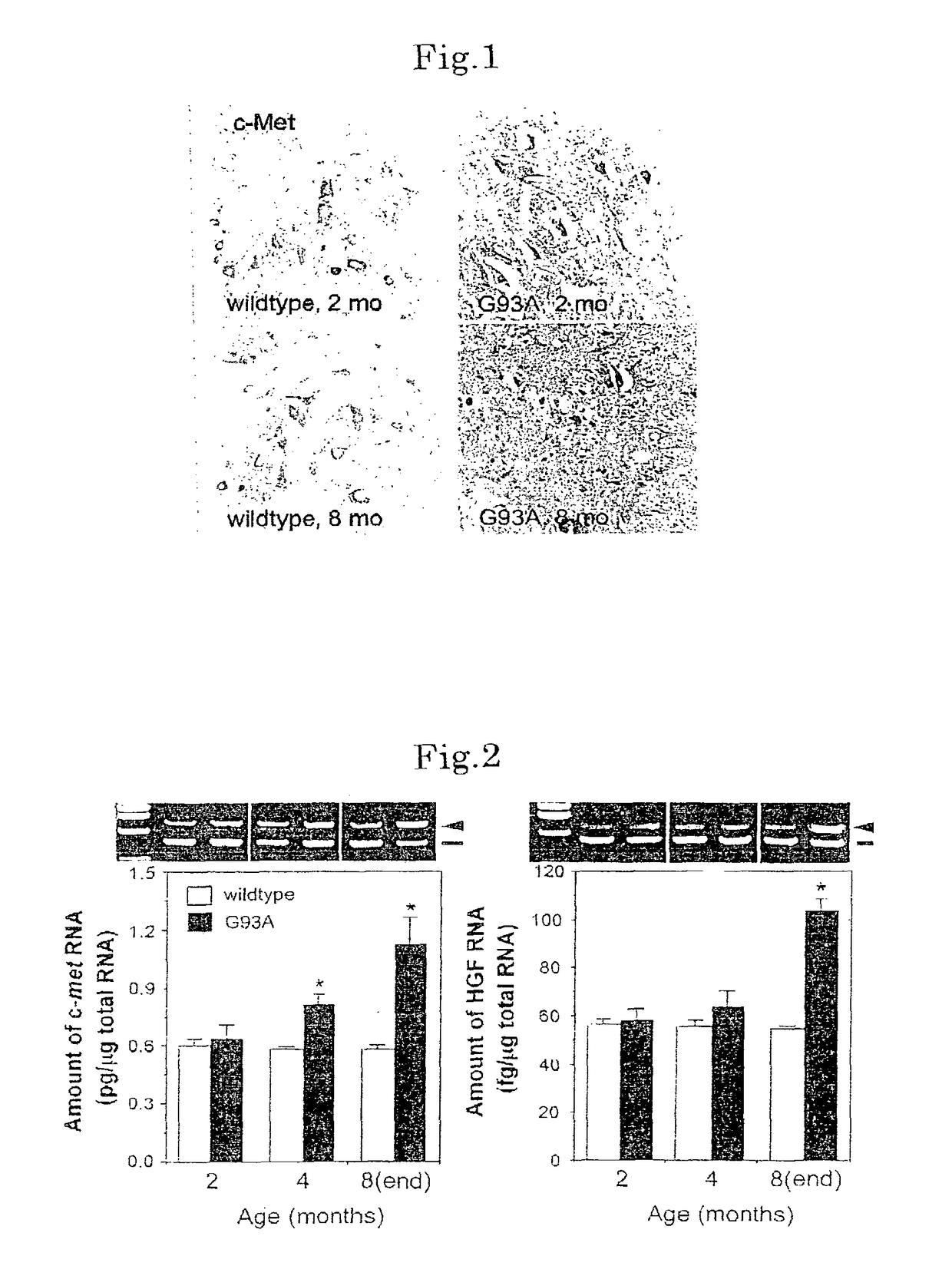
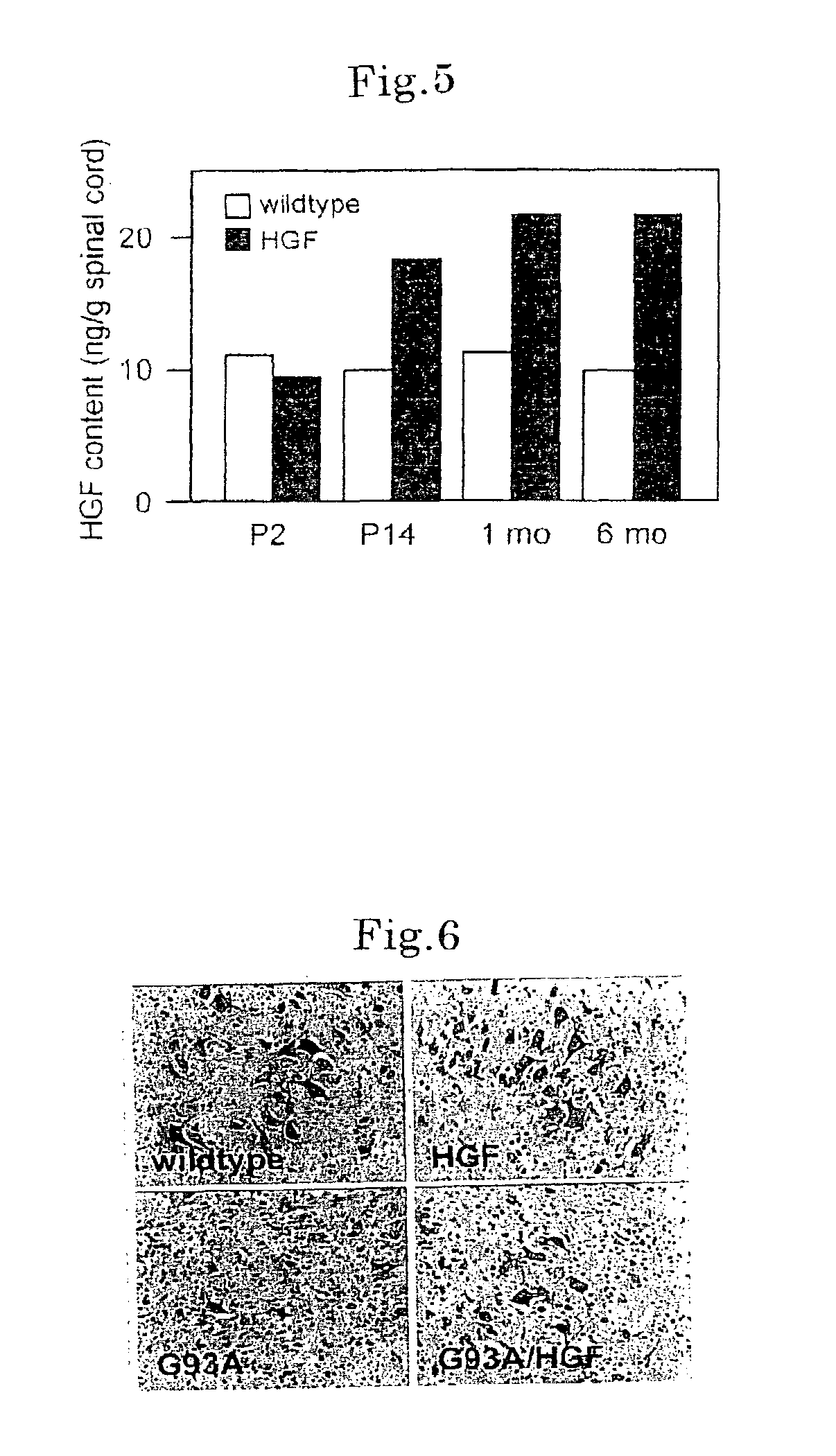
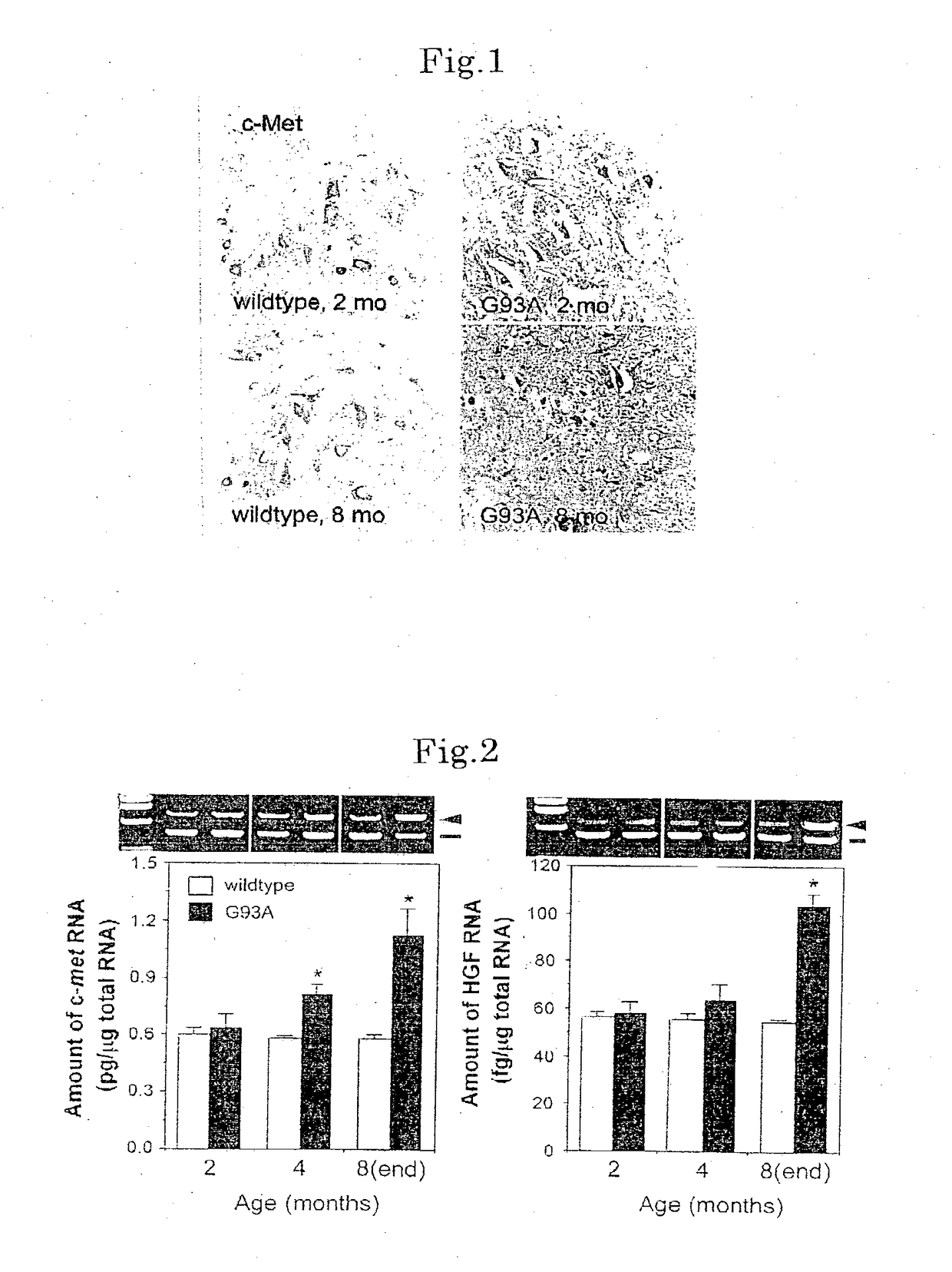
Methods of treating amyotrophic lateral sclerosis by HGF
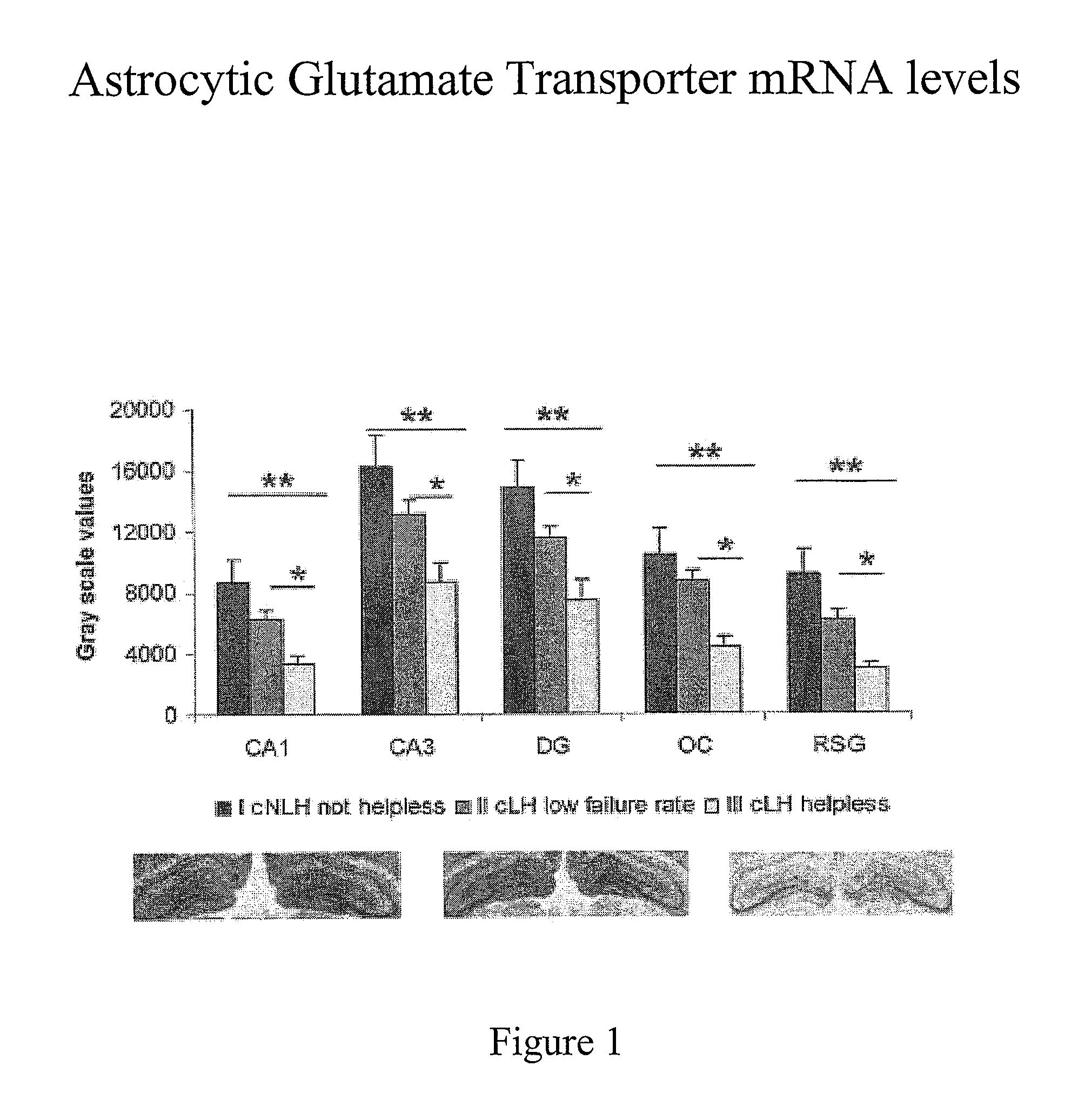
The invention presents a therapeutic agent (and progress suppressant) for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) containing HGF and / or HGF gene as active ingredient. HGF has an effect of improving the motor function of ALS and life span through two actions, that is, direct neuronutrient factor activity on motoneurons, and indirect improving action of glutamate cytotoxicity on motoneurons by maintaining the level of glutamate transporter in astrocytes. Hence, HGF and / or HGF gene can be used as an effective therapeutic agent not known in the past.
Owner:NAKAMURA TOSHIKAZU
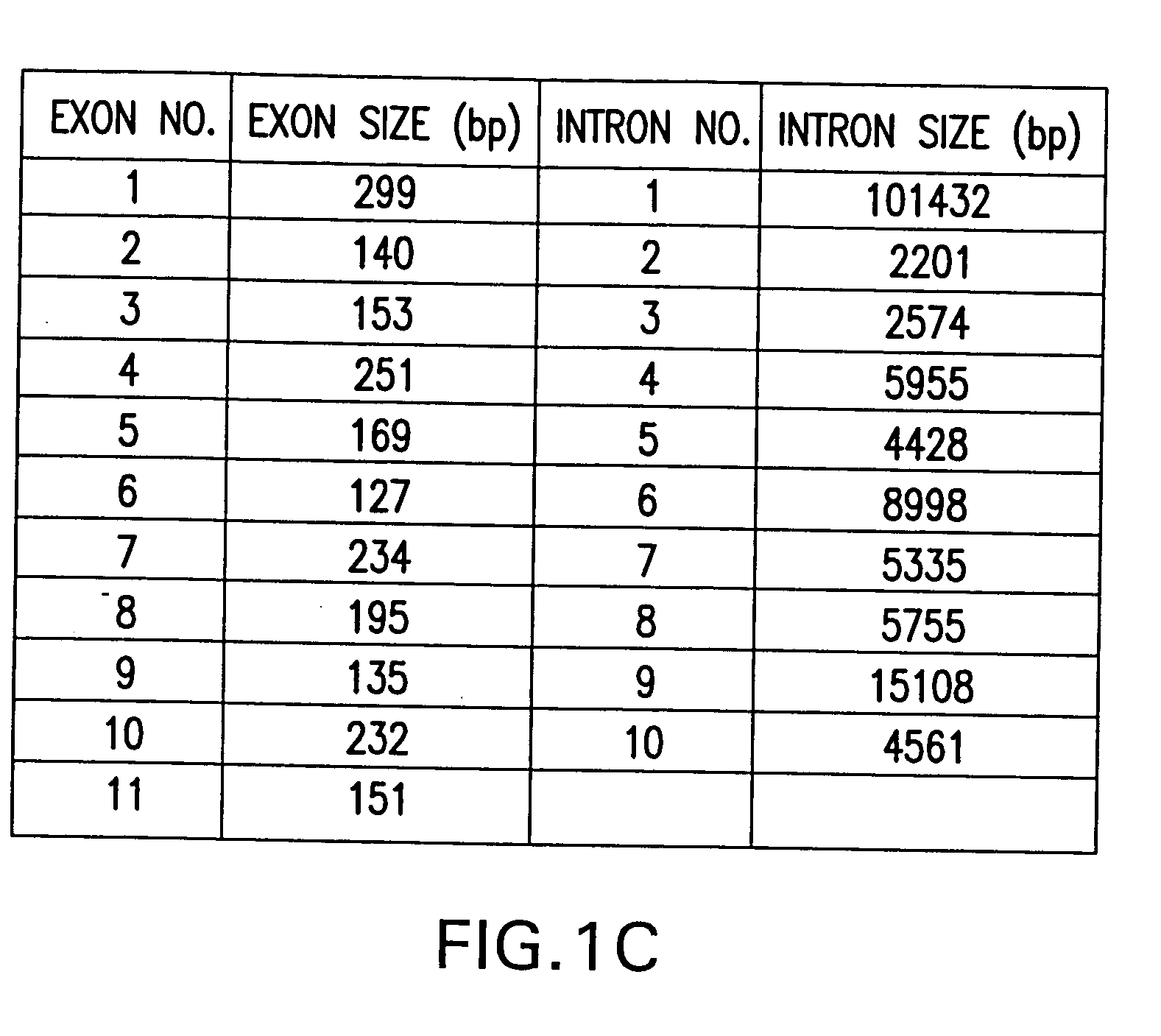
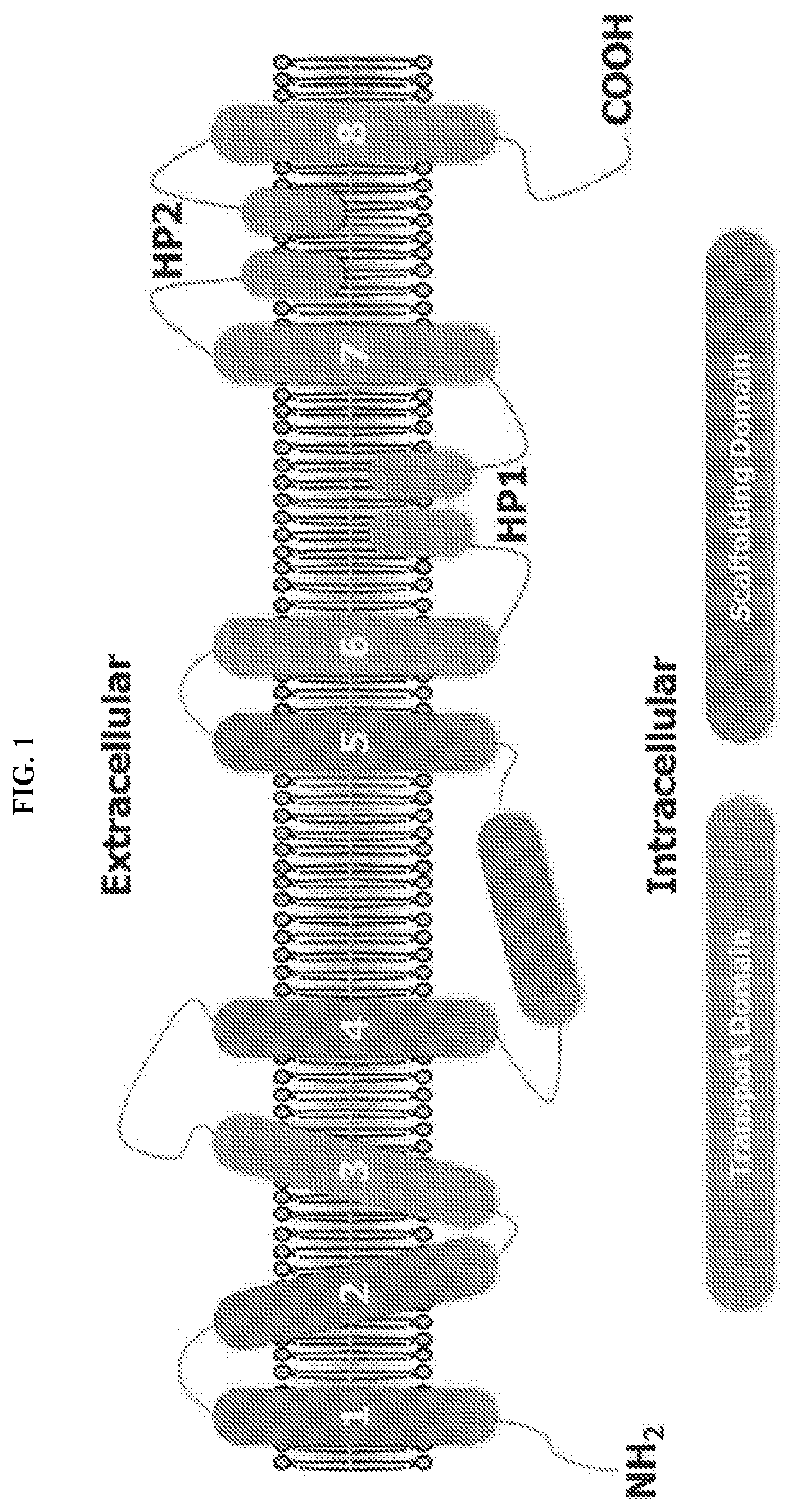
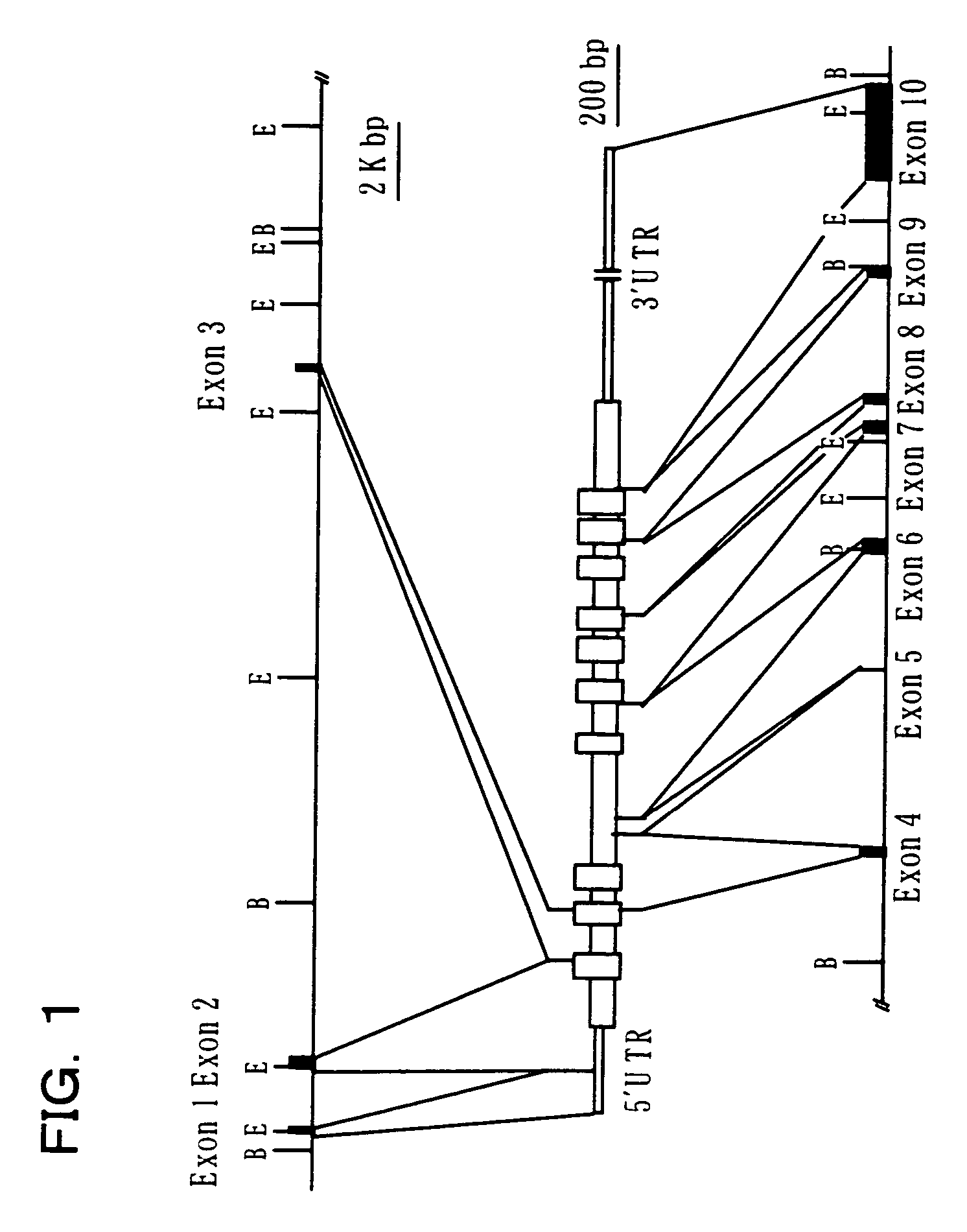
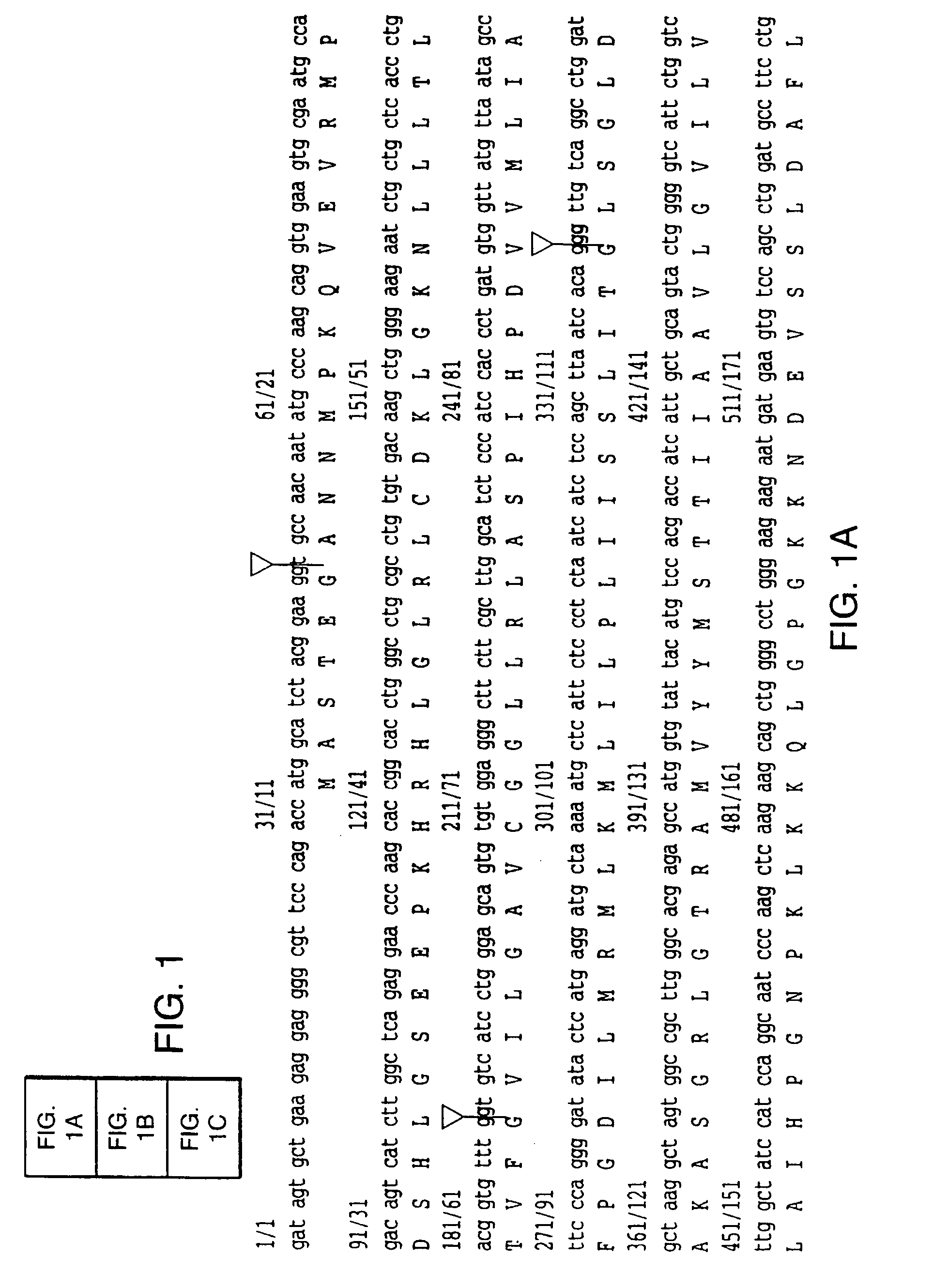
Human excitatory amino acid transporter-2 gene promoter and uses thereof
The nucleic acid sequence of the human Excitatory Amino Acid Transporter-2 Gene (hEAAT2) promoter, a nucleic acid sequence that hybridizes to the hEAAT2 promoter nucleic acid sequence under stringent hybridization conditions, and a nucleic acid sequence that is functionally equivalent to the hEAAT2 promoter sequence are provided, as are vectors containing these nucleic acid sequences. In addition, methods for the use of these nucleic acids to achieve tissue- or cell-specific gene expression are provided, as are methods for the use of these hEAAT2 promoter nucleic acids to identify agents that can modulate glutamate transport or the activity of the glutamate promoter. Such agents may be useful in the prevention, palliation or treatment of neurodegenerative and / or cerebrovascular diseases.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Oligopeptide and application thereof
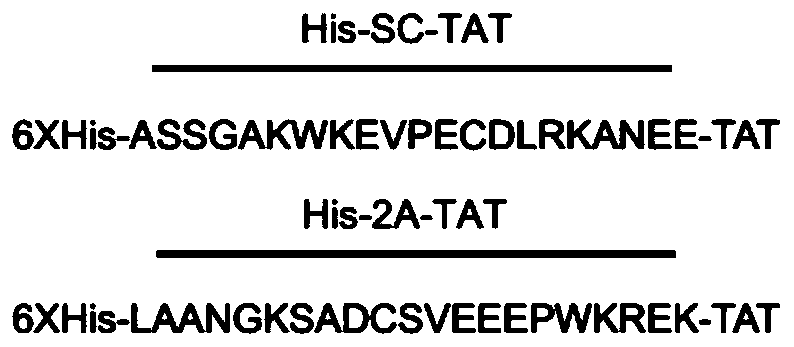
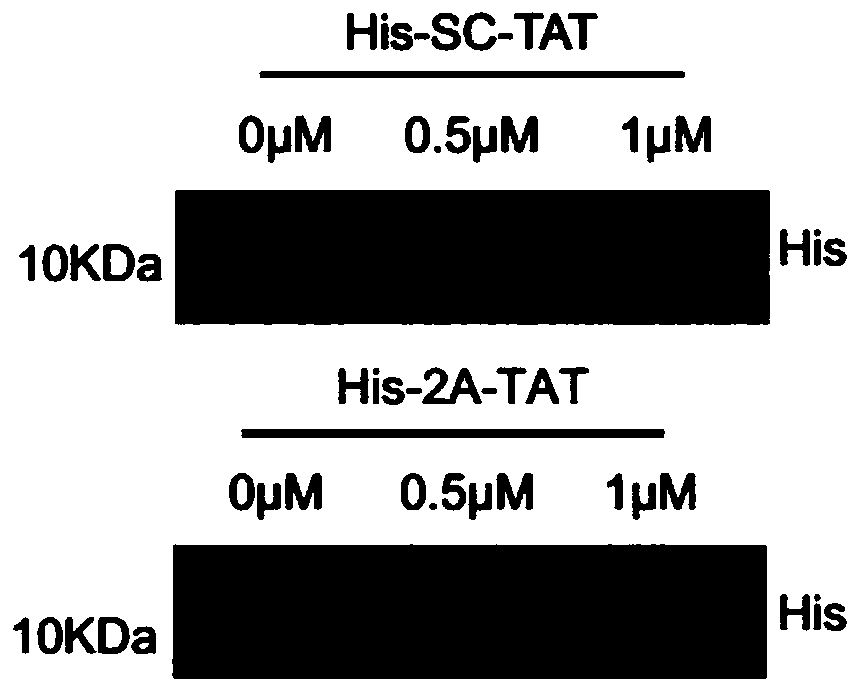
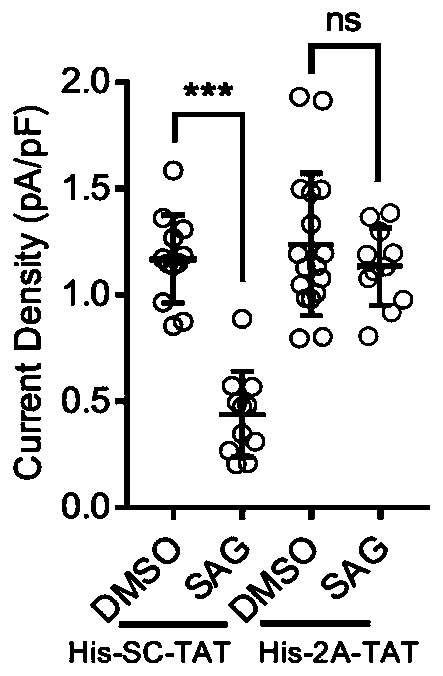
ActiveCN110669143AReduced activityPlay a neuroprotective rolePolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifPeptide-nucleic acidsCell membraneOligopeptide
The invention discloses oligopeptide and application thereof, and belongs to the field of biomedicine. The amino acid sequence of the oligopeptide is as shown in the sequence listing SEQ ID NO.1 or anamino acid sequence with the same function formed by replacing, deleting or adding one or several amino acids to the sequence. An SHH signaling pathway can rapidly regulate and control the activity of glutamate transporter GLT-1 in ischemic stroke, that is, by reducing the amount of glutamate transporter GLT-1 protein on a cell membrane, the activity of the glutamate transporter GLT-1 is reduced.His-2A-TAT can effectively prevent the reduction of the activity of the glutamate transporter GLT-1 caused by SHH, and thus a neuroprotective role in the ischemic stroke is played.
Owner:ACADEMY OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI
Methods of treating brain ischemia or hypoxia
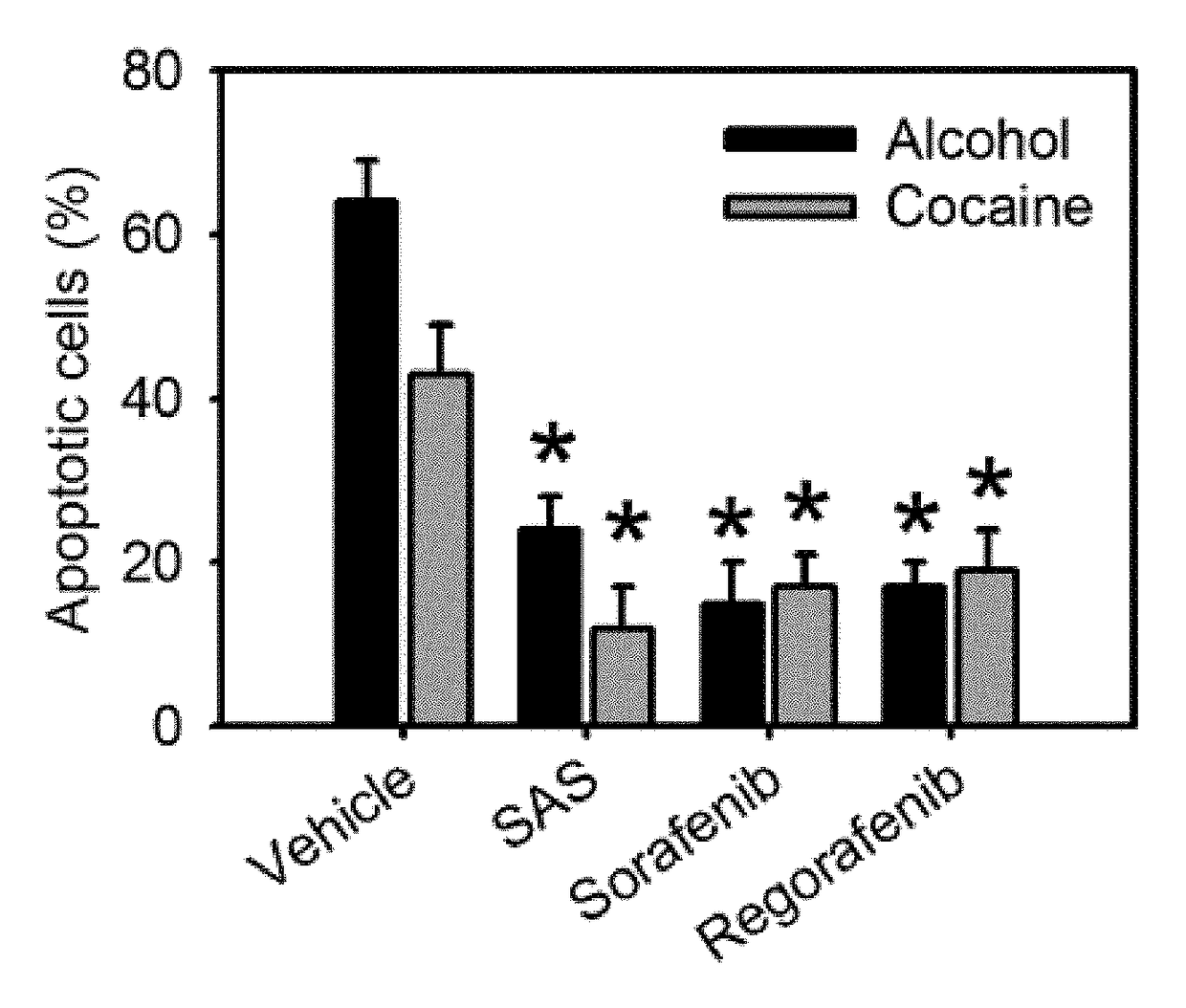
InactiveUS20160199393A1Improve and even treat ischemic brain damageReduced infarct volumeBiocideNervous disorderCysteine thiolateExcitotoxicity
Methods of treating brain ischema or hypoxia by using an inhibitor of cysteine-glutamate transporter (i.e. system xc−) is provided. The inhibitor includes sorafenib and a derivative thereof, erastin, and suifasalazine. These inhibitors can effectively decrease a concentration of extracellular glutamate, so that excitotoxicity to central nervous system (CNS) and a cortical infarct volume in brains can be reduced.
Owner:CHINA MEDICAL UNIVERSITY(TW)
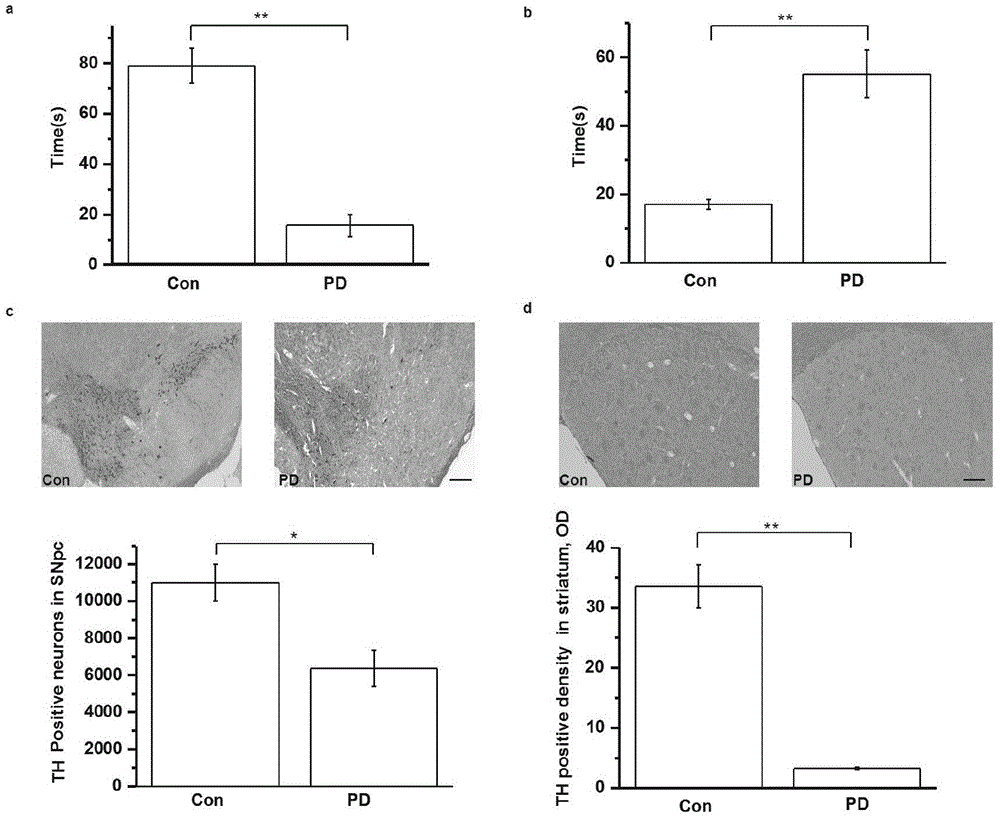
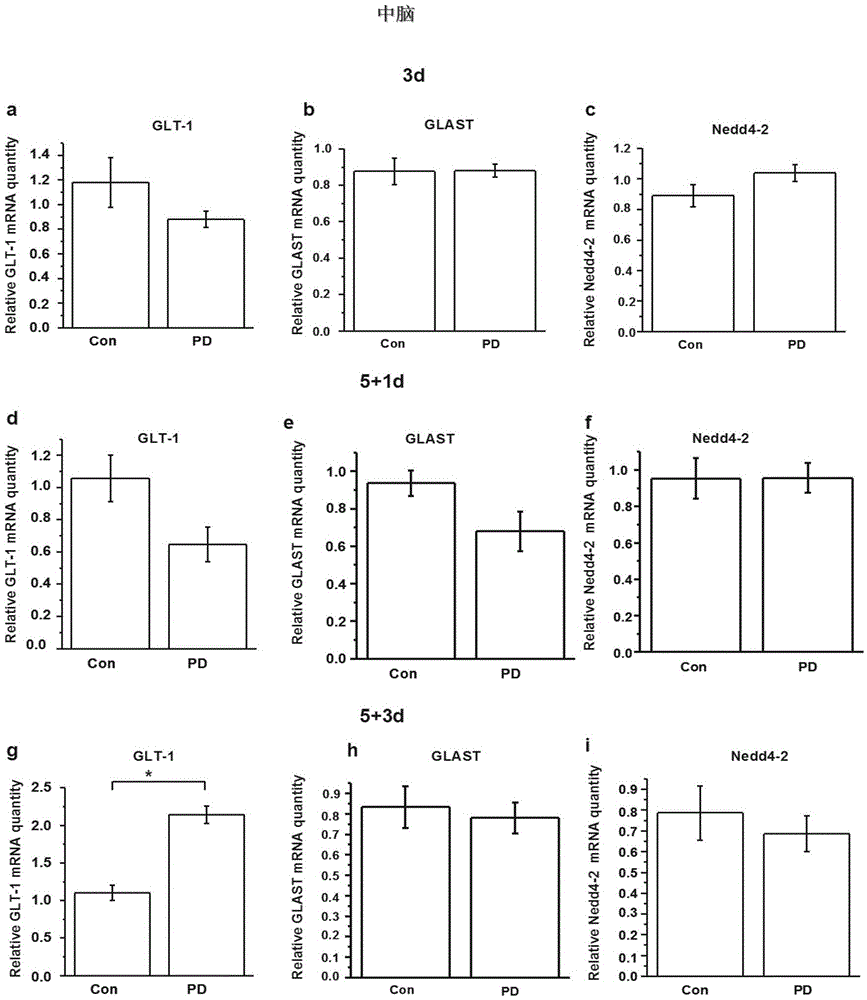
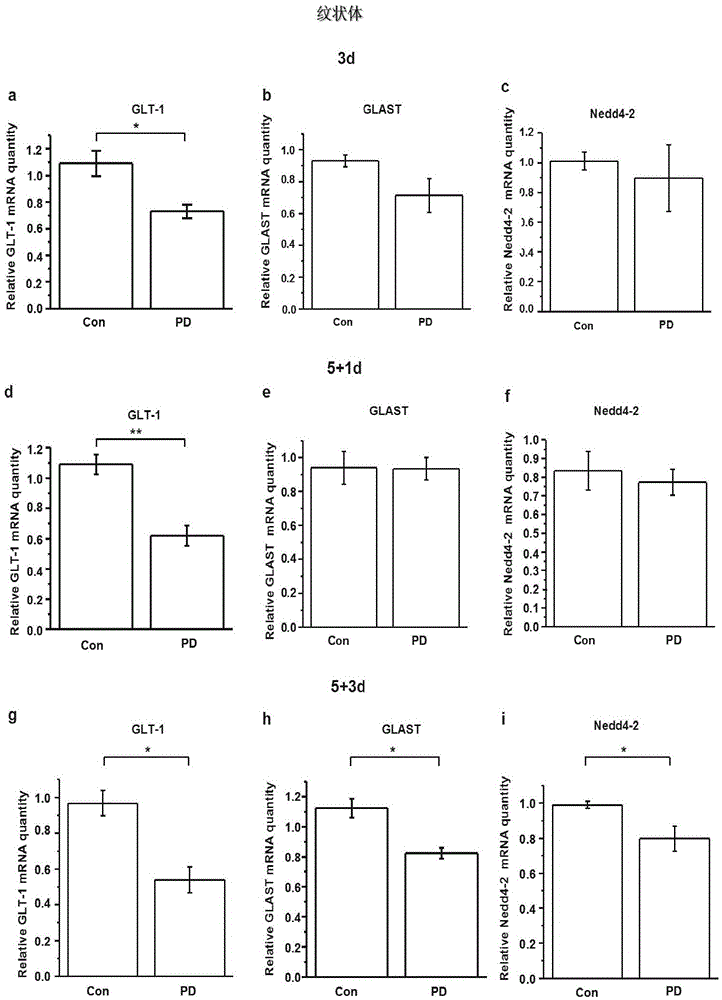
Application of Nedd4-2 to parkinson's disease treatment
InactiveCN105535977AHigh expressionReduce excitotoxic effectsOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderLife qualityNEDD4
The invention discloses application of Nedd4-2 to parkinson's disease treatment. It is found that the regulation effect on glutamate transporter from Nedd4-2 participates in attack of PD, significance of regulation abnormity of Nedd4-2 to the glutamate transporter in the PD attack process is focused on, interaction between Nedd4-2 and the glutamate transporter and the influence on the expression and the function of the glutamate transporter from the concentration and activity of N2dd4-2 are discussed at the animal model and cell experiment level, the molecule mechanism for adjusting the glutamate transporter by Nedd4-2 is analyzed, and it is approved that Nedd4-2 can serve as a target for treating PD. Gene treatment on parkinson's disease is directed, parkinson's disease resistant drugs are effectively screened, and Nedd4-2 has great significance in the life quality improvement of parkinson's disease patients.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Transgenic mammals and cell lines for the identification of glutamate transporter modulators
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Method of treating depression
Methods for treatment of depression-related mood disorders in mammals, particularly humans are disclosed. The methods of the invention include administration of compounds capable of enhancing glutamate transporter activity in the brain of mammals suffering from depression. ATP-sensitive K+ channel openers and β-lactam antibiotics are used to enhance glutamate transport and to treat depression-related mood disorders and depressive symptoms.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
B-benzyloxyaspartate derivatives with photosensitive groups
The present invention relates to photosensitive derivatives of optically active L-threo-β-benzyloxyaspartate or its benzene ring-substituted analogs, represented by the following formula (1) or (2): (1) (2) wherein R1 represents hydrogen atom, amino group, straight or branched lower aliphatic acylamino group optionally substituted at the acyl group portion, alicyclic acylamino group or aromatic acylamino group optionally having a substituent on the aromatic ring, R2 represents hydrogen atom or one or more straight or branched optionally substituted lower aliphatic alkyloxy groups on the benzene ring, R3 represents hydrogen atom, methyl group or carboxyl group, and R4 and R5 each represent hydrogen atom, hydroxyl group, straight or branched lower alkyloxy group optionally substituted at the alkyl portion, amino group, straight or branched lower alkyl-substituted amino group, or a halogen atom, which upon photoirradiation can produce compounds exhibiting a function of suppressing the glutamate uptake activity of L-glutamate transporters.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
Use of inhibitor of cystine-glutamate transporter
The invention surprisingly found that agents that inhibit system xc− provide the therapeutic intervention in substance-related and addictive disorders and the treatment and / or prevention in substance-mediated brain damage and confirms that system xc− is a promising therapeutic target for substance-induced addiction and brain damage.
Owner:CHINA MEDICAL UNIVERSITY(TW)
Remedies for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
The invention presents a therapeutic agent (and progress suppressant) for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) containing HGF and / or HGF gene as active ingredient. HGF has an effect of improving the motor function of ALS and life span through two actions, that is, direct neuronutrient factor activity on motoneurons, and indirect improving action of glutamate cytotoxicity on motoneurons by maintaining the level of glutamate transporter in astrocytes. Hence, HGF and / or HGF gene can be used as an effective therapeutic agent not known in the past.
Owner:NAKAMURA TOSHIKAZU
Application of bakuchiol compound
InactiveCN101088498BGood antidepressantsNo toxicityNervous disorderHydroxy compound active ingredientsDiseaseCytotoxicity
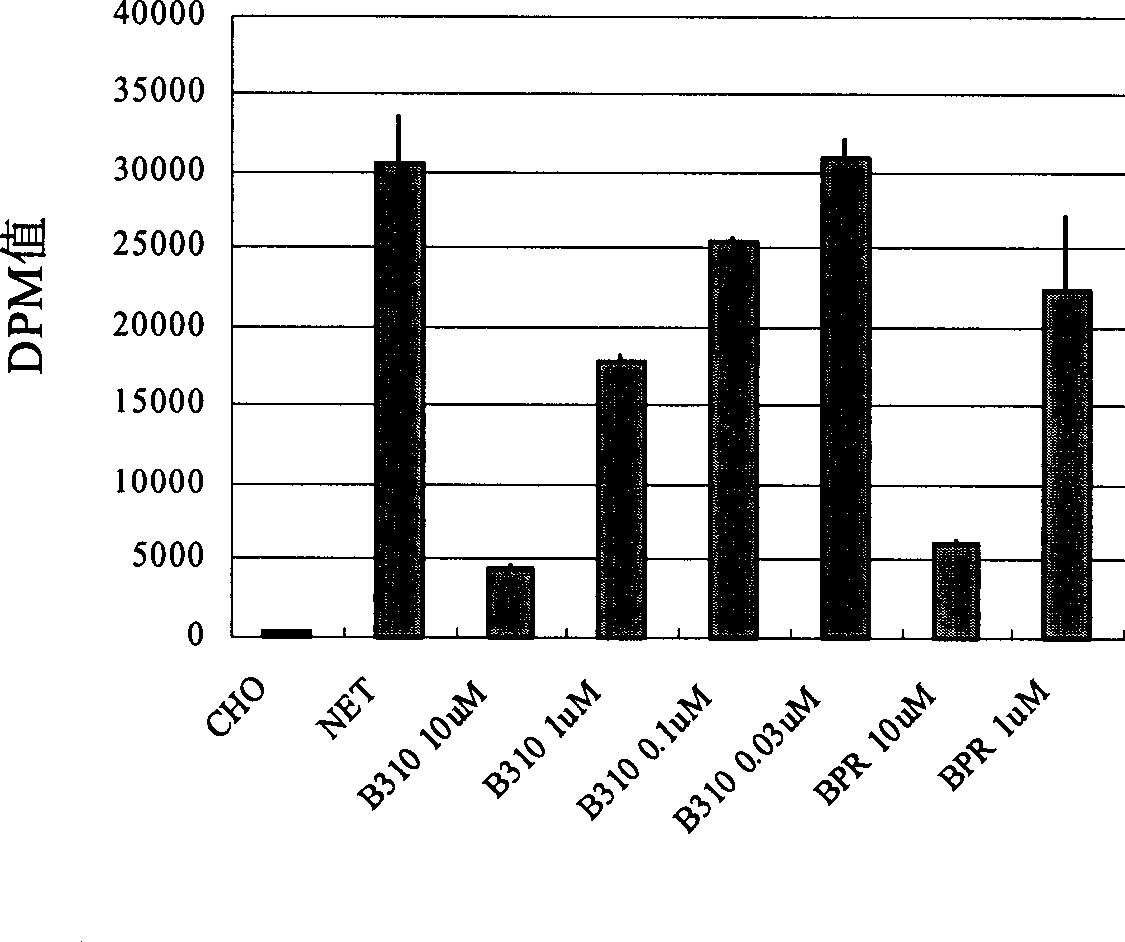
The present invention discloses the application of bakuchiol compound in preparing medicine for treating psychogenic diseases and neurogenic diseases. Extracorporeal experiment and animal experiment show that the bakuchiol compound can suppressing dopamine transport protein, noradrenalin transport protein and 5-hydroxy tryptamine transport protein selectively, and no influence on gamma-aminobutyric acid transport protein and L-glytamic acid transport protein, no cytotoxicity, and antidepressant effect higher than available antidepressant medicine amfebutamoe hydrochloride. Therefore, the bakuchiol compound has excellent marketability in preparing medicine for treating psychogenic diseases and neurogenic diseases.
Owner:上海国联干细胞技术有限公司
Modulators of Excitatory Amino Acid Transporters and Methods Using Same
The present disclosure provides in one aspect compounds of Formula I. In certain embodiments, the compounds of the disclosure are useful for treating, ameliorating or preventing a disease or disorder that is caused, induced or characterized by abnormal reduction in glutamate transporter activity or abnormal increase in extracellular CNS glutamate concentration in a subject. In certain embodiments, the compounds of the disclosure stimulate a glutamate transporter.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV +1
Beta-benzyloxyaspartate derivatives with amino group on benzene ring
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
Excitatory amino-acid transporter-3 gene cRNA in-situ hybridization probes and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102559904BClear specificityRealize the display effectMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationHybridization probeMicrobiology
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
New use of inhibitor of cystine-glutamate transporter
ActiveUS20180153865A1Improve substance seekingImprove craving behaviourNervous disorderHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsDiseaseSubstance induced
The invention surprisingly found that agents that inhibit system xc− provide the therapeutic intervention in substance-related and addictive disorders and the treatment and / or prevention in substance-mediated brain damage and confirms that system xc− is a promising therapeutic target for substance-induced addiction and brain damage.
Owner:CHINA MEDICAL UNIVERSITY(TW)
Glutamate transporter activators and methods using same
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
Glutamate transporter associated proteins and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS7252970B2Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesNucleotideTranslocator protein
Glutamate Transporter Associated Proteins and nucleotide encoding Glutamate Transporter Associated Proteins are provided. Also provided is a method for identifying a compound that modulates a cellular response mediated by a Glutamate Transporter Associated Protein. A method is further provided for identifying a compound that inhibits an interaction between a Glutamate Transporter Associated Protein and a glutamate transporter protein. A method is provided for treating a disorder associated with glutamate transport.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Mouse with deficiency of glutamate transporter GLAST function
InactiveUS7642399B2Reduce the number of cellsReduce in quantityAnimal cellsBiological material analysisKnockout animalIntraocular pressure
The present invention provides a GLAST knockout mouse lacking the function of an endogenous glutamate transporter GLAST gene, which shows: 1) an intraocular pressure within the normal range; and 2) a reduction in the number of cells in the retinal ganglions when compared with a wild-type normal mouse. Owing to the ocular properties, this knockout mouse is useful as a model for normal tension glaucoma. By using this knockout mouse, a compound useful for the treatment of normal tension glaucoma can be screened.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com






![Radiolabeled 3-[3- (Benzoyl-Amido) Benzyloxy] Aspartic Acid Derivative and Method of Producing the Same Radiolabeled 3-[3- (Benzoyl-Amido) Benzyloxy] Aspartic Acid Derivative and Method of Producing the Same](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/61874a74-67ee-4621-88dd-d6d77df96b62/US20080248485A1-20081009-D00001.png)
![Radiolabeled 3-[3- (Benzoyl-Amido) Benzyloxy] Aspartic Acid Derivative and Method of Producing the Same Radiolabeled 3-[3- (Benzoyl-Amido) Benzyloxy] Aspartic Acid Derivative and Method of Producing the Same](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/61874a74-67ee-4621-88dd-d6d77df96b62/US20080248485A1-20081009-D00002.png)
![Radiolabeled 3-[3- (Benzoyl-Amido) Benzyloxy] Aspartic Acid Derivative and Method of Producing the Same Radiolabeled 3-[3- (Benzoyl-Amido) Benzyloxy] Aspartic Acid Derivative and Method of Producing the Same](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/61874a74-67ee-4621-88dd-d6d77df96b62/US20080248485A1-20081009-D00003.png)