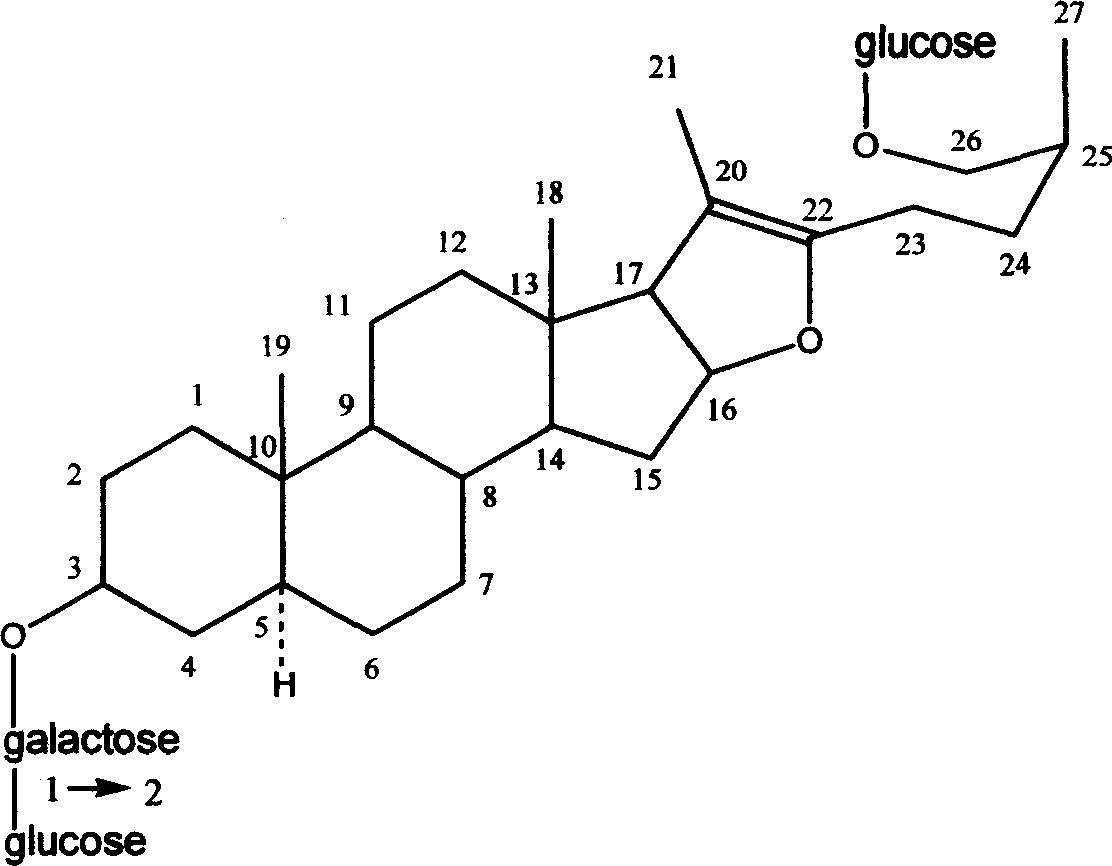
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
100results about How to "Reduced infarct volume" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method of reducing injury to mammalian cells
InactiveUS20050059597A1Attenuated downstream NMDAR signalingReduced infarct volumeNervous disorderCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsNR1 NMDA receptorN methyl D aspartate receptors
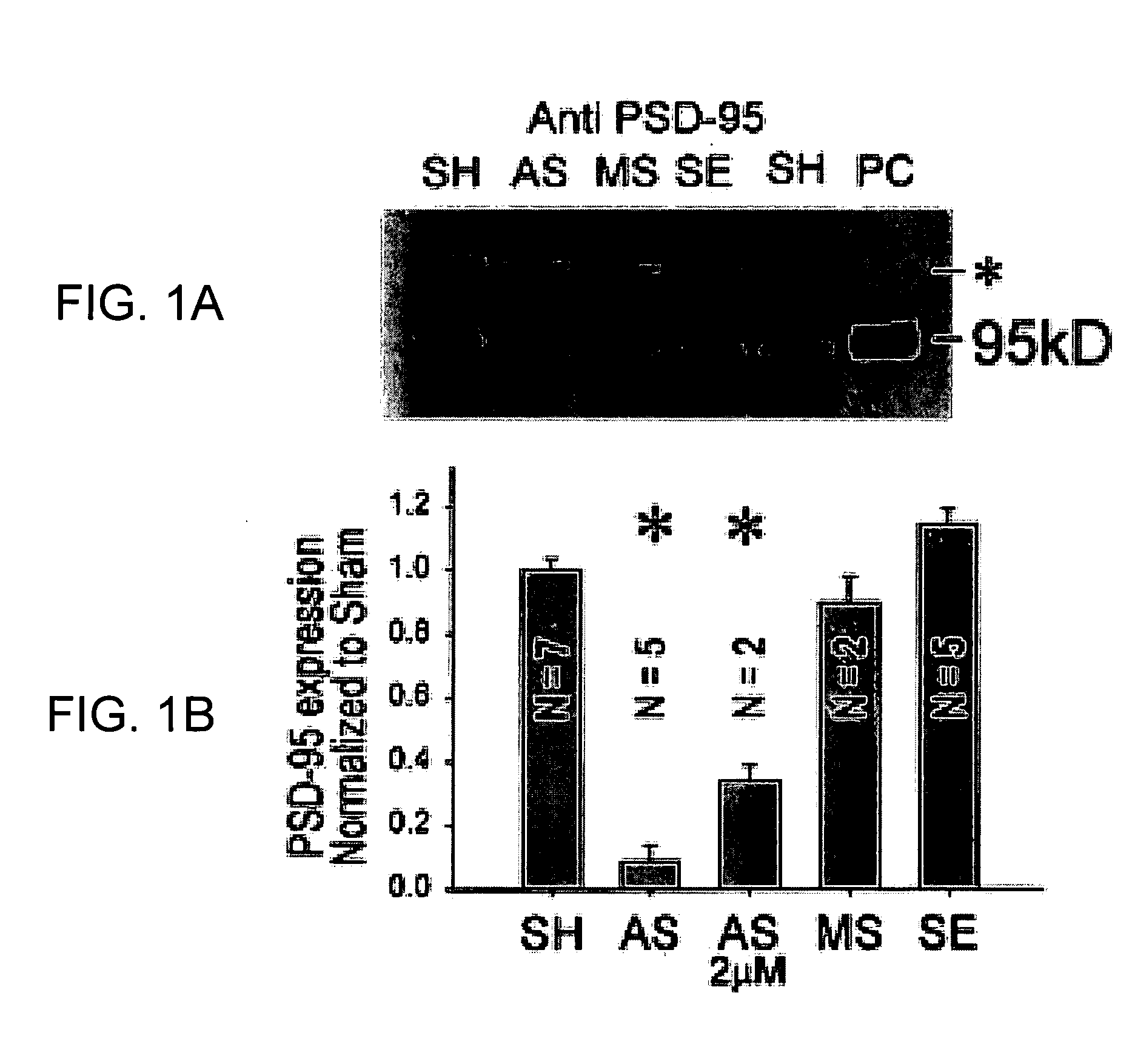
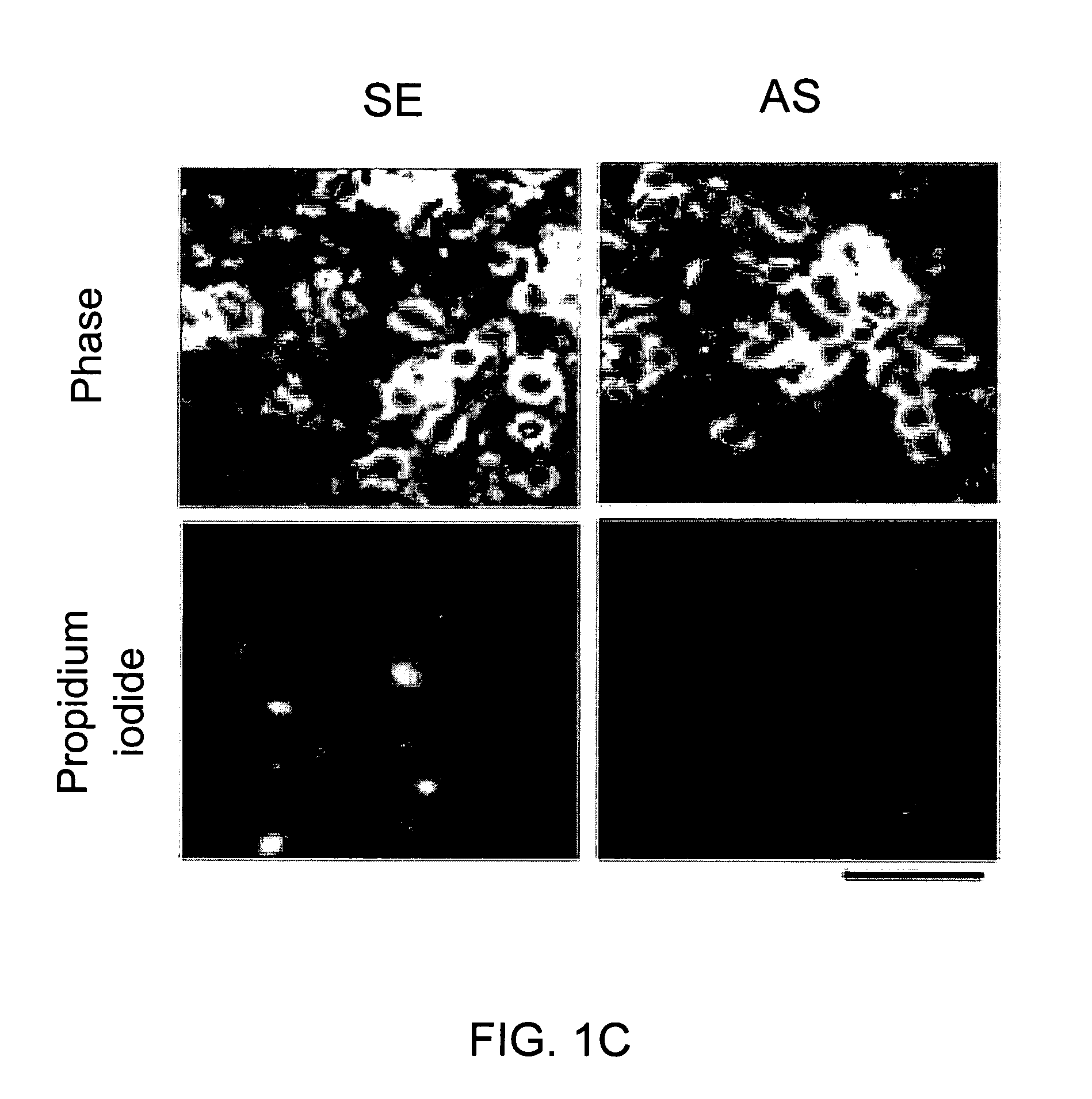
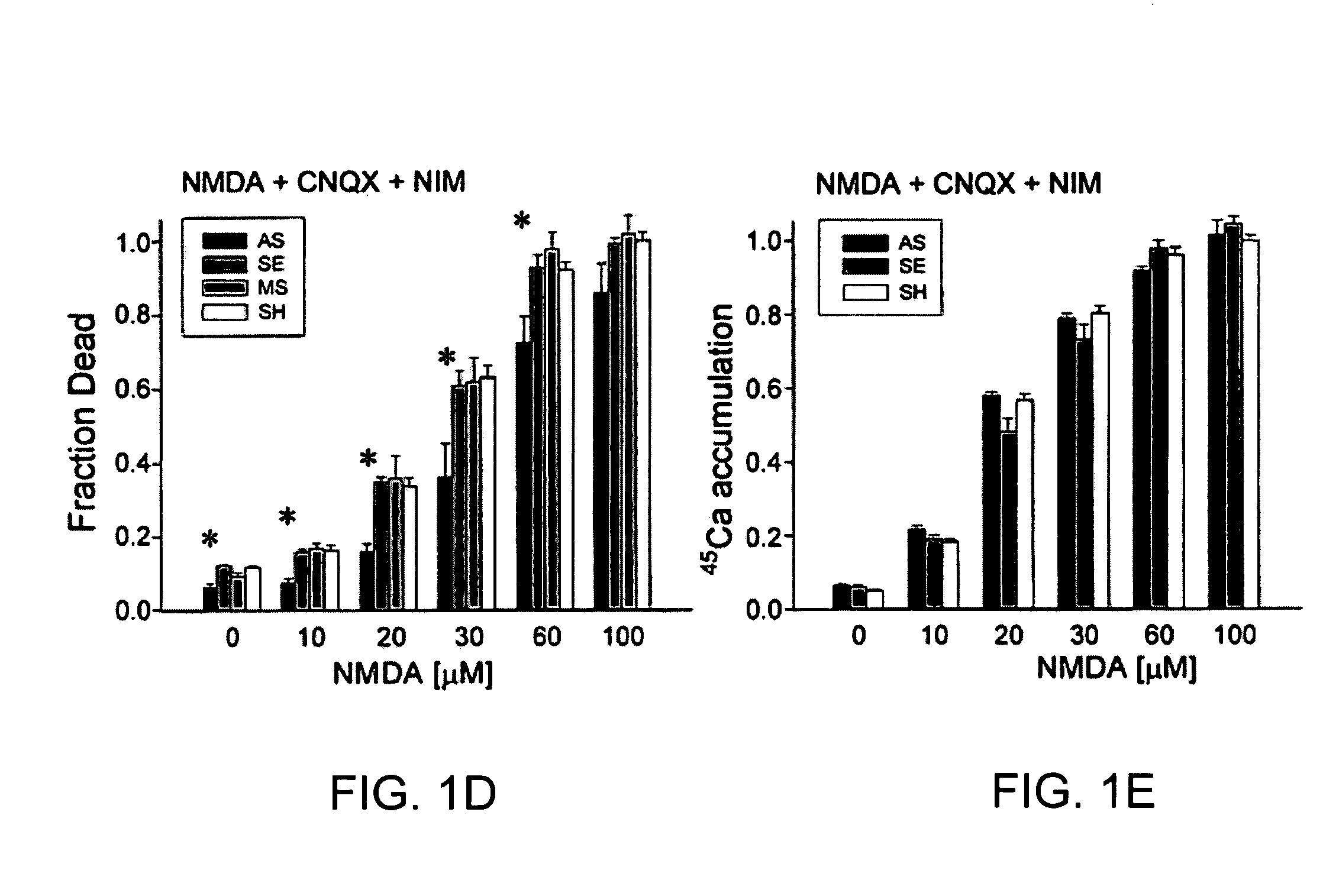
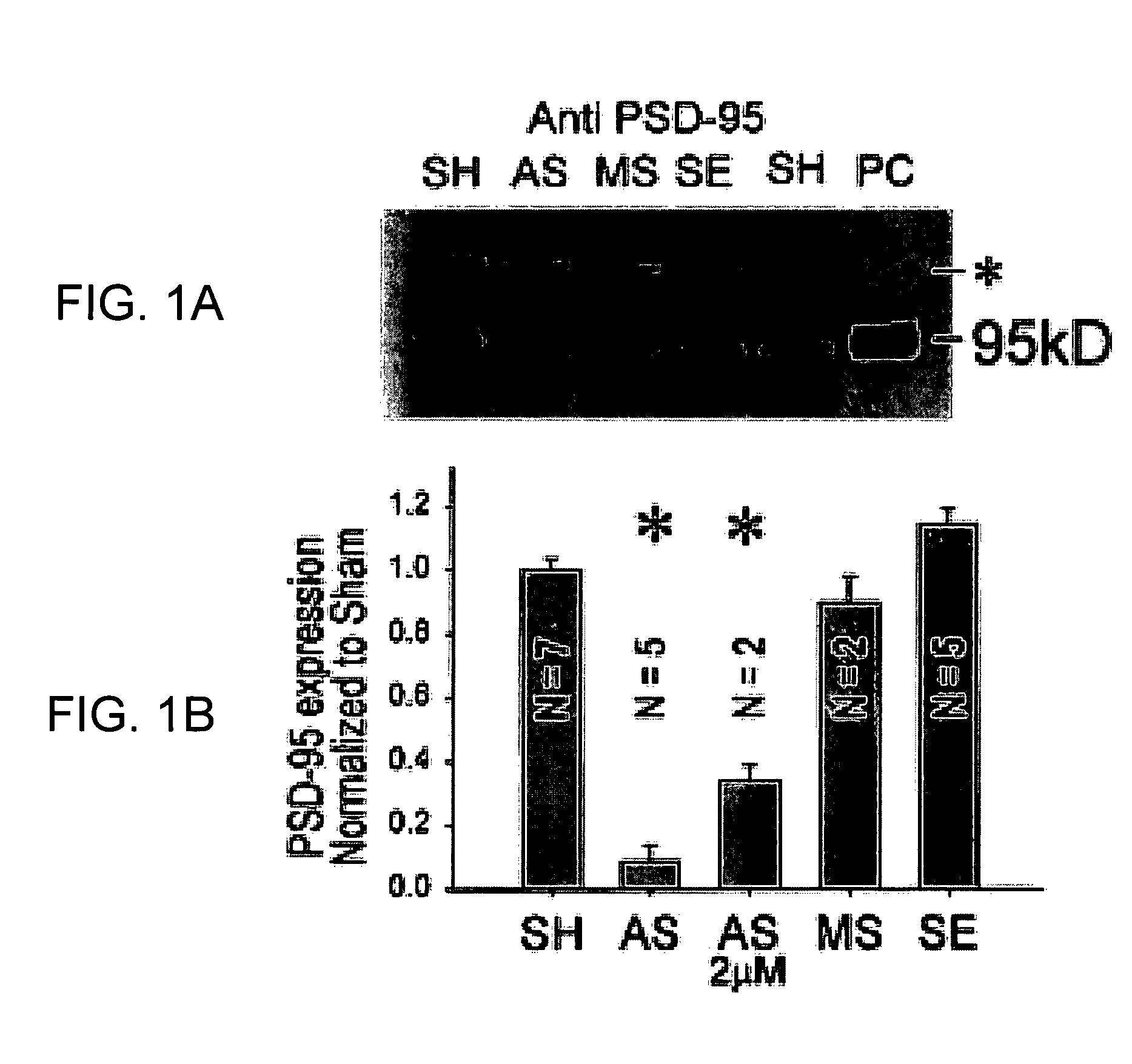
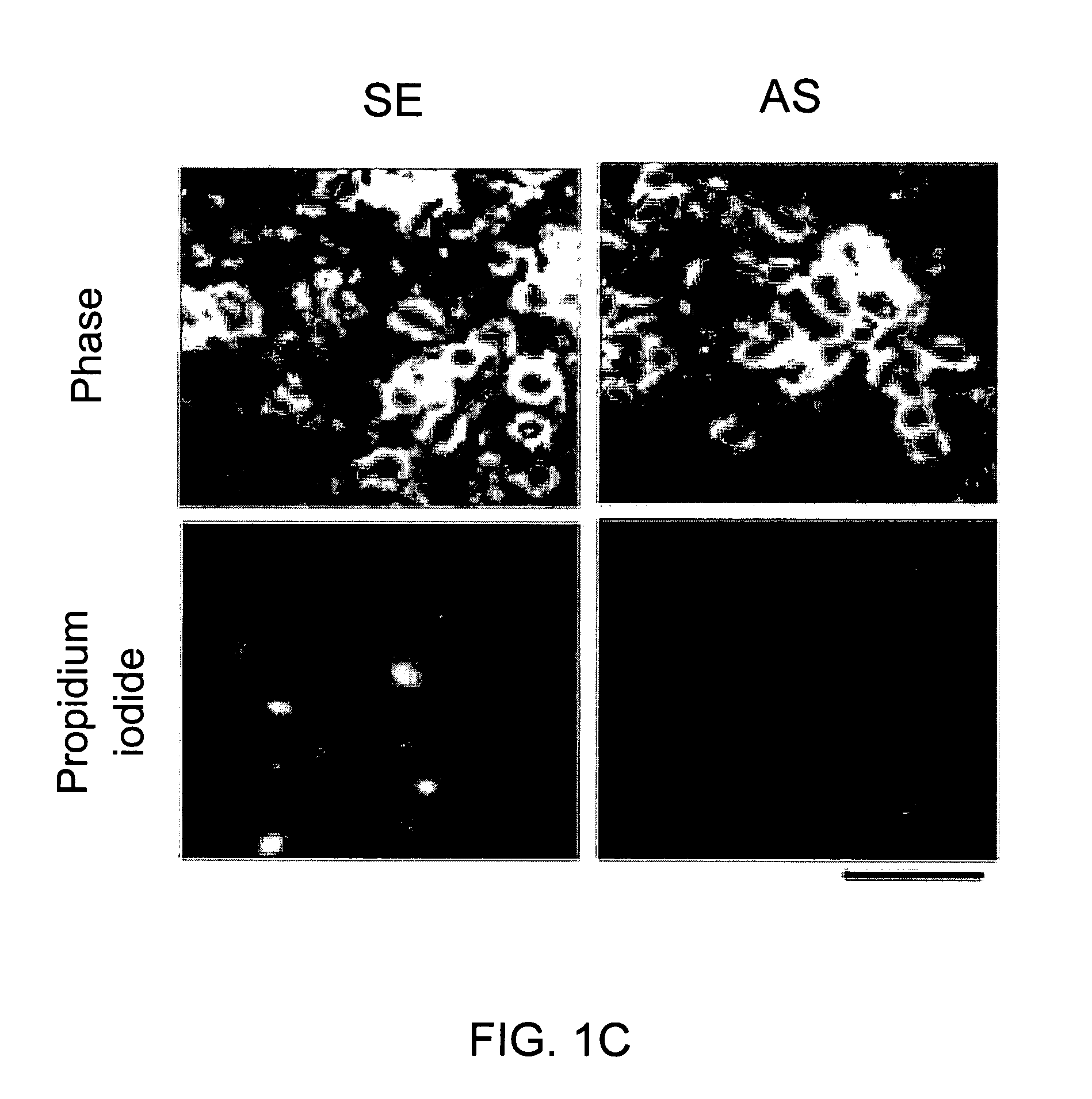
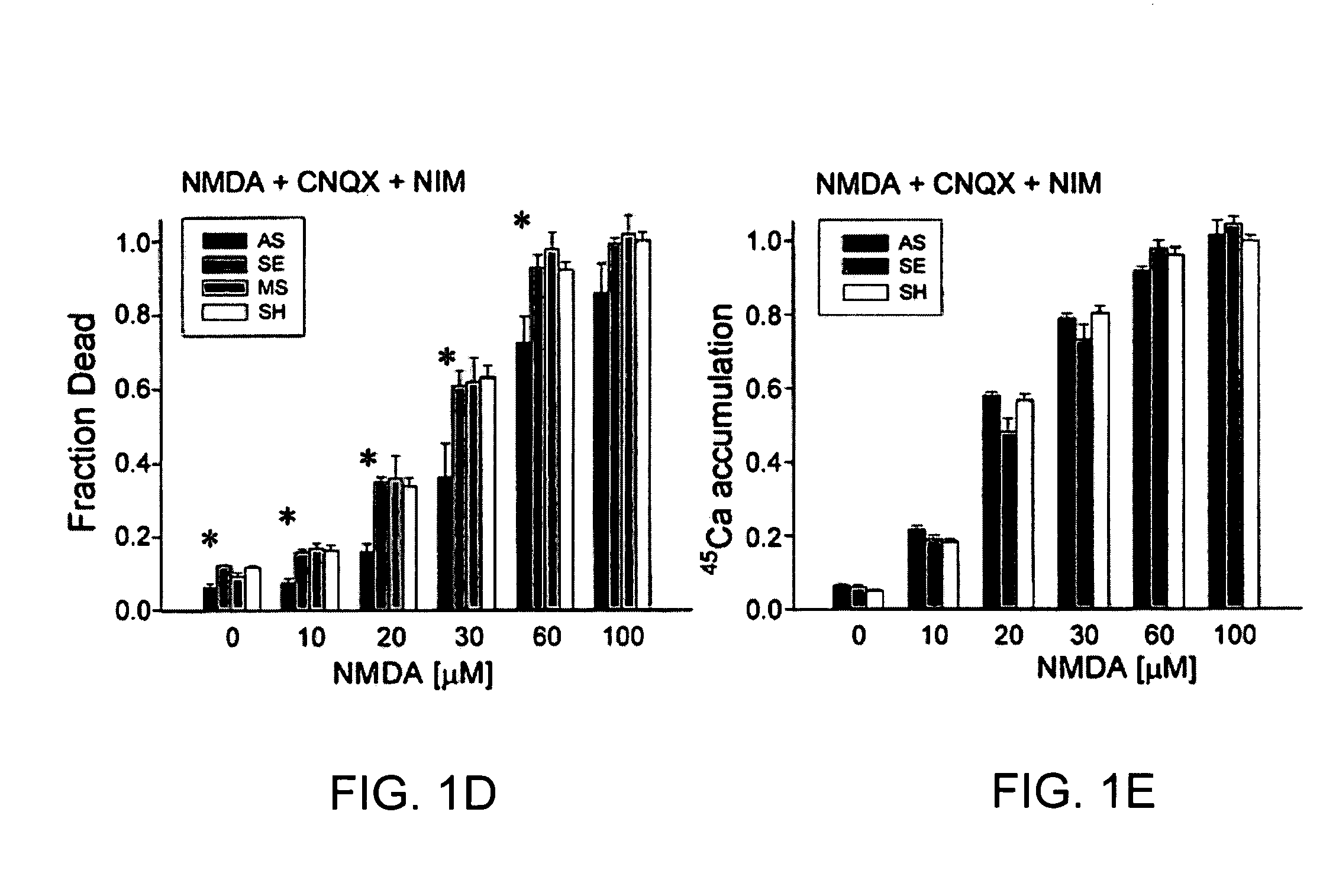
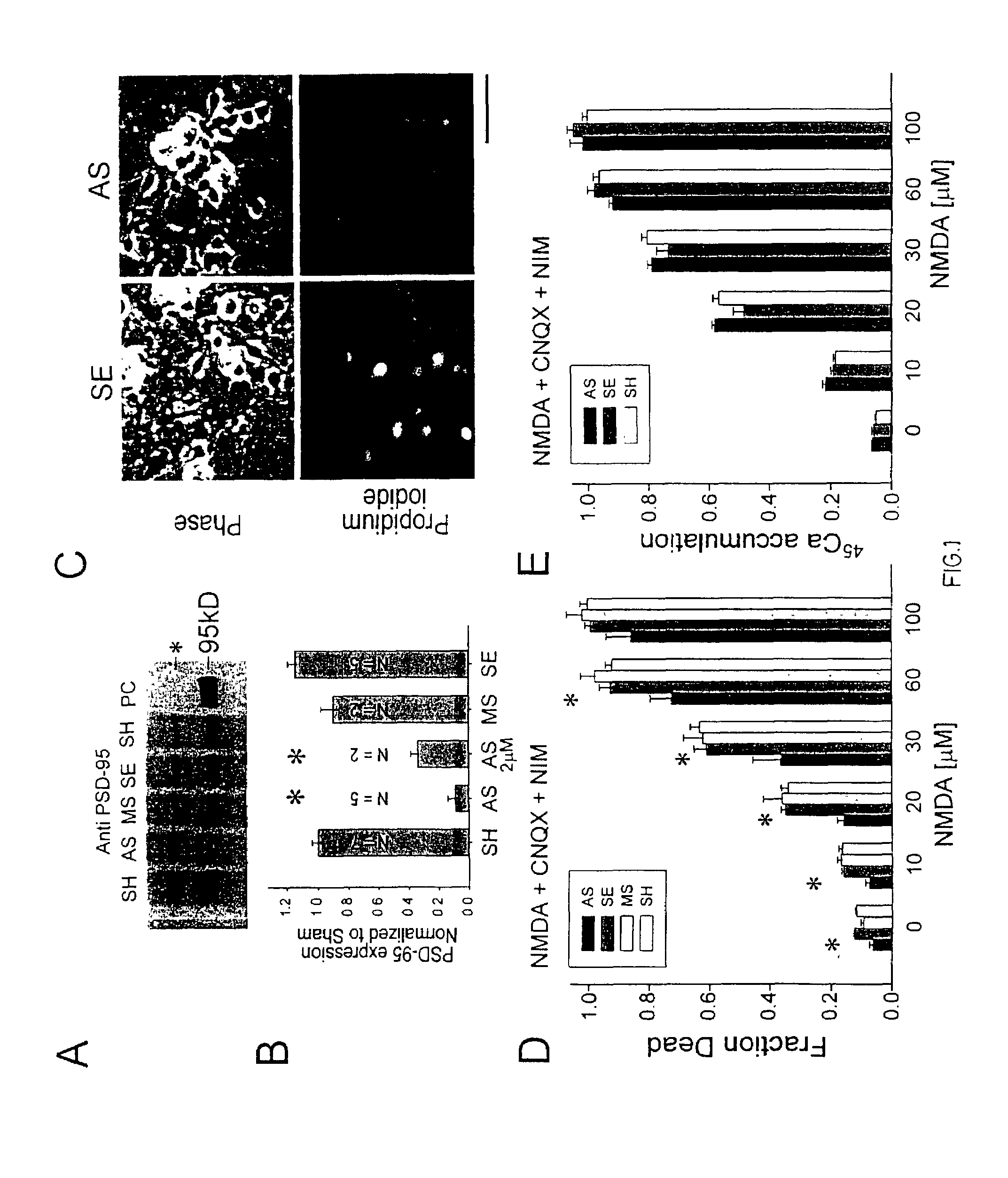
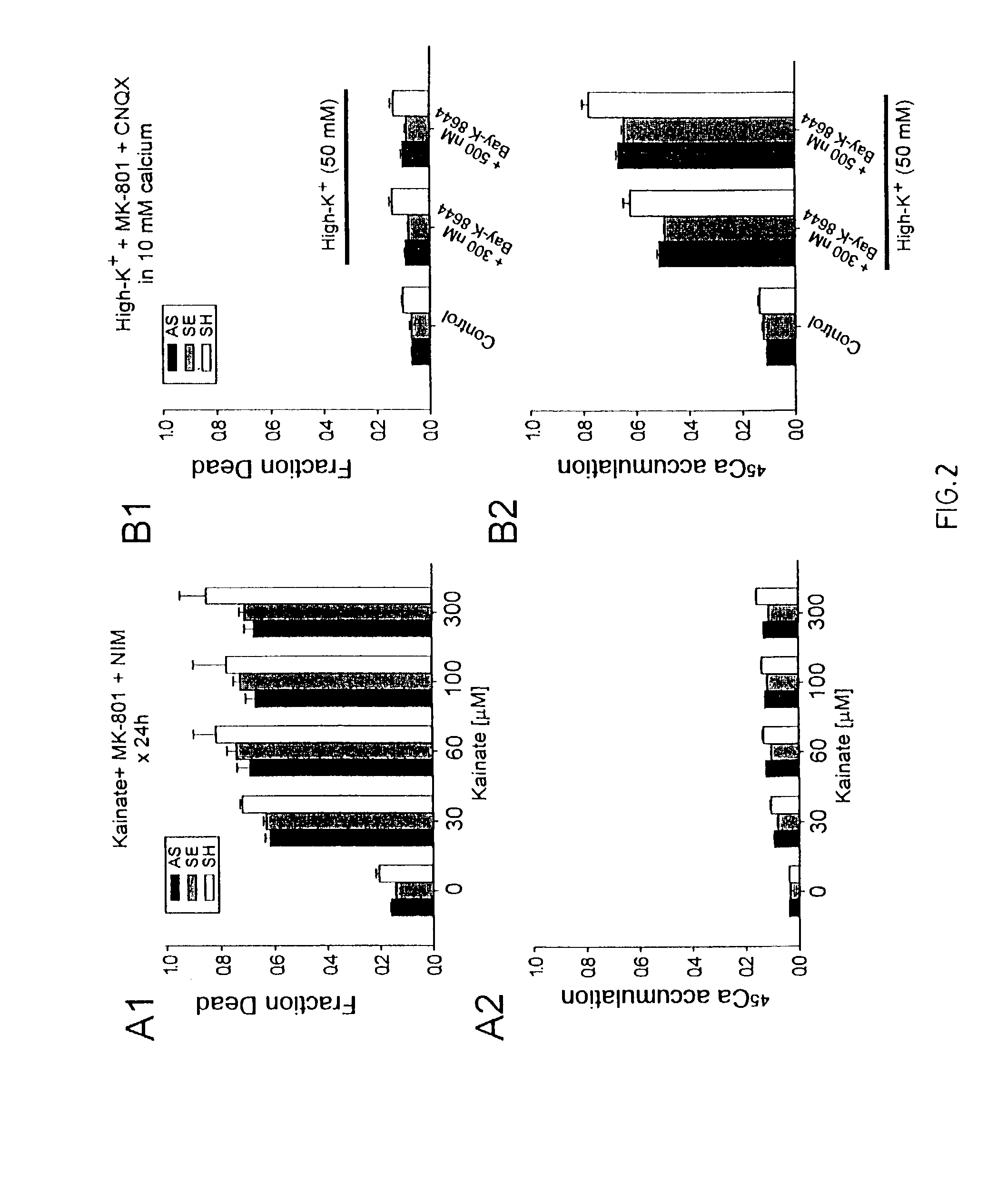
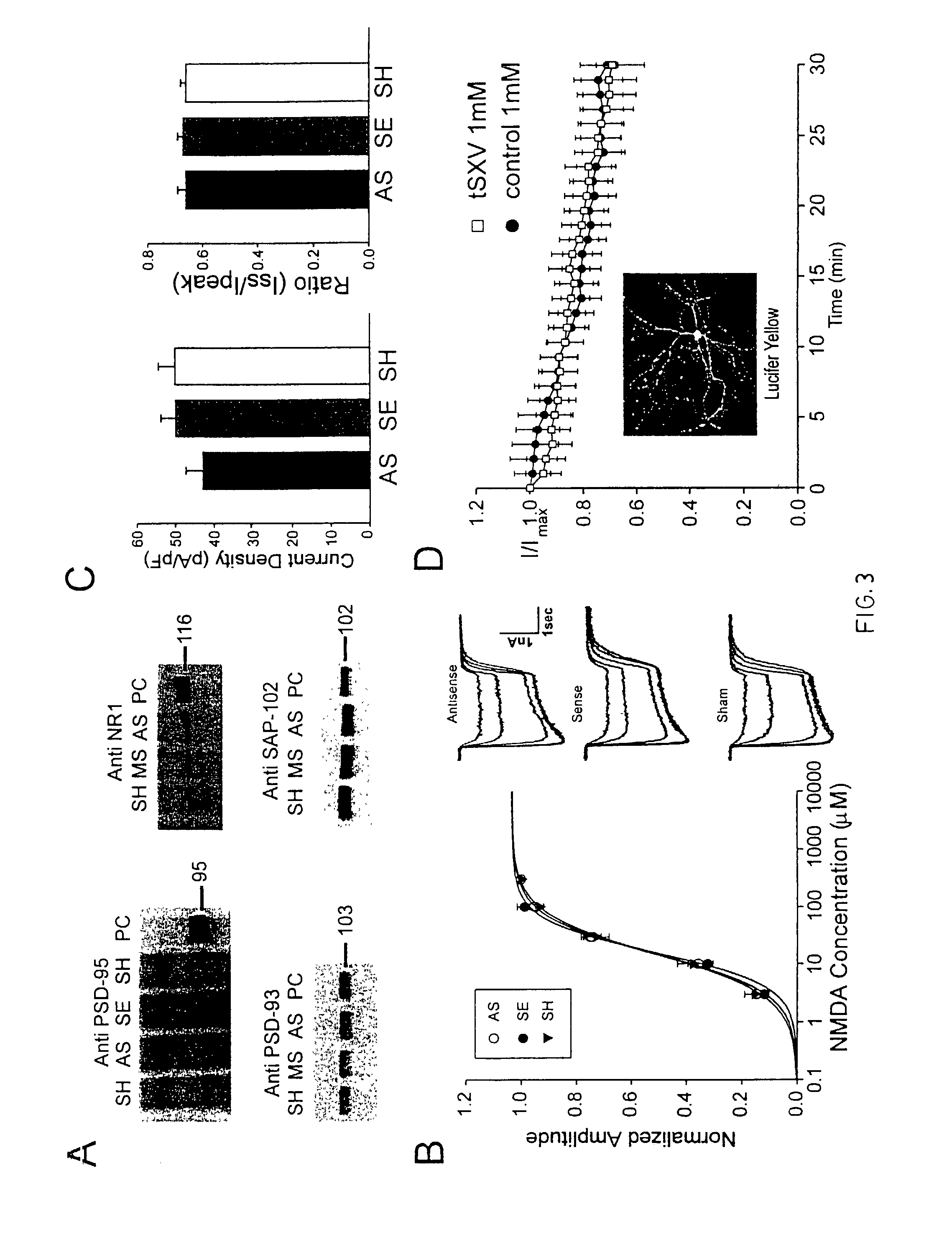
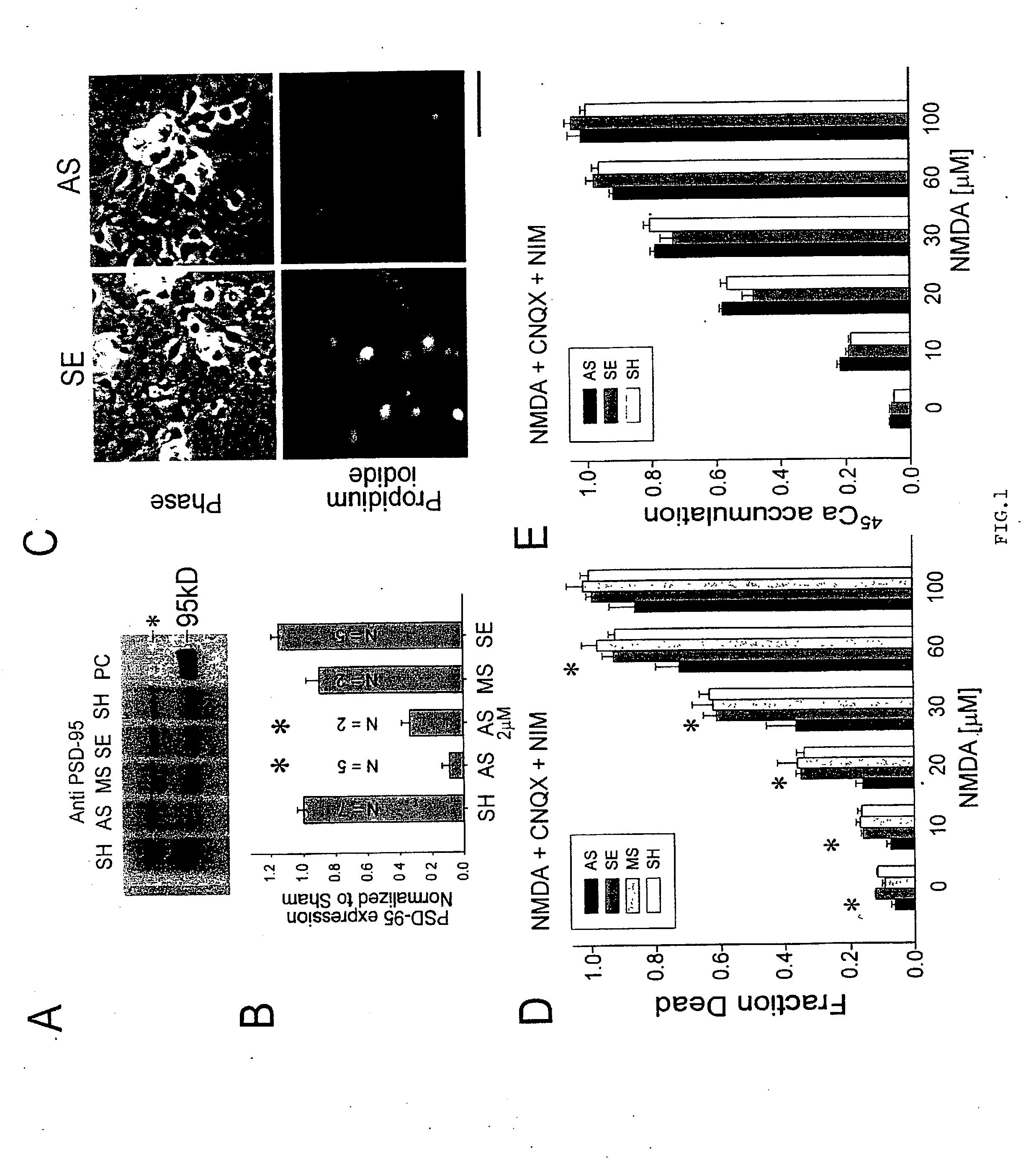
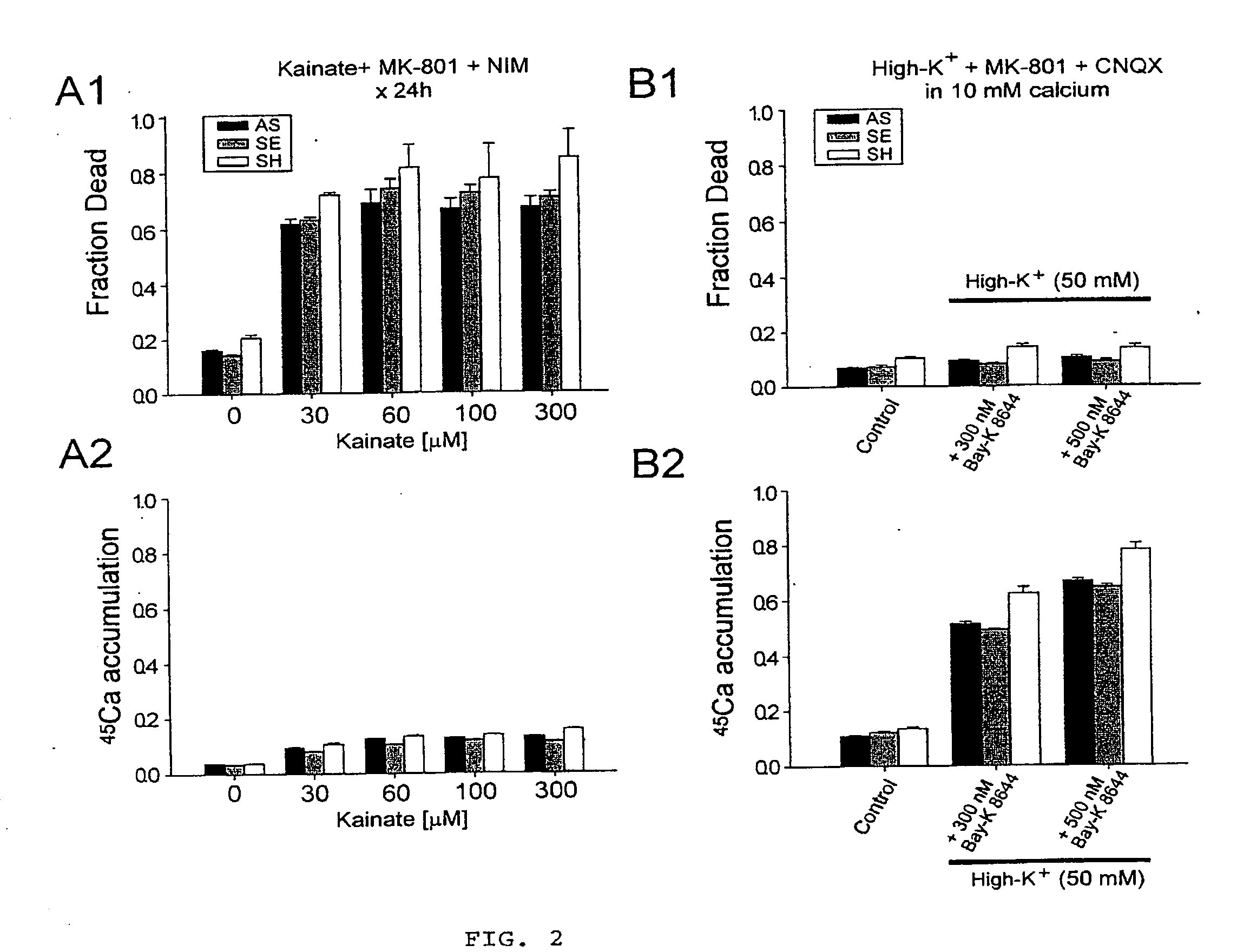
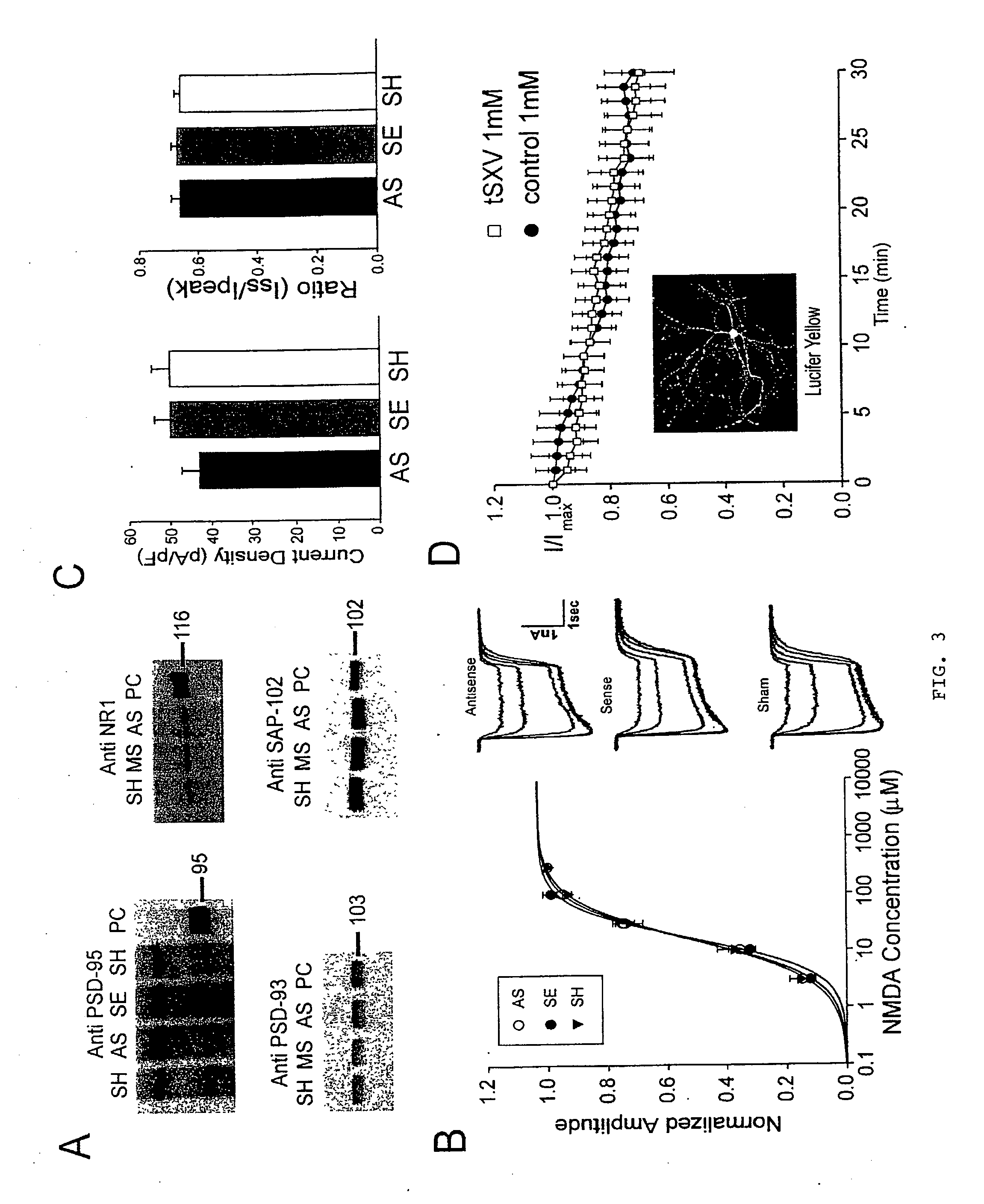
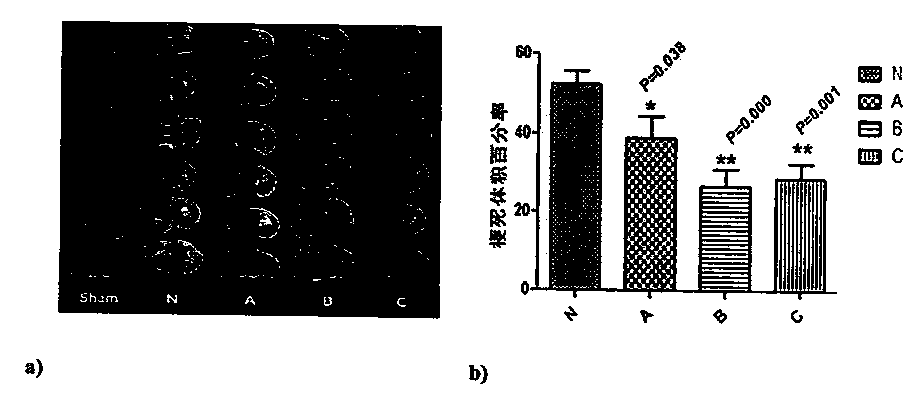
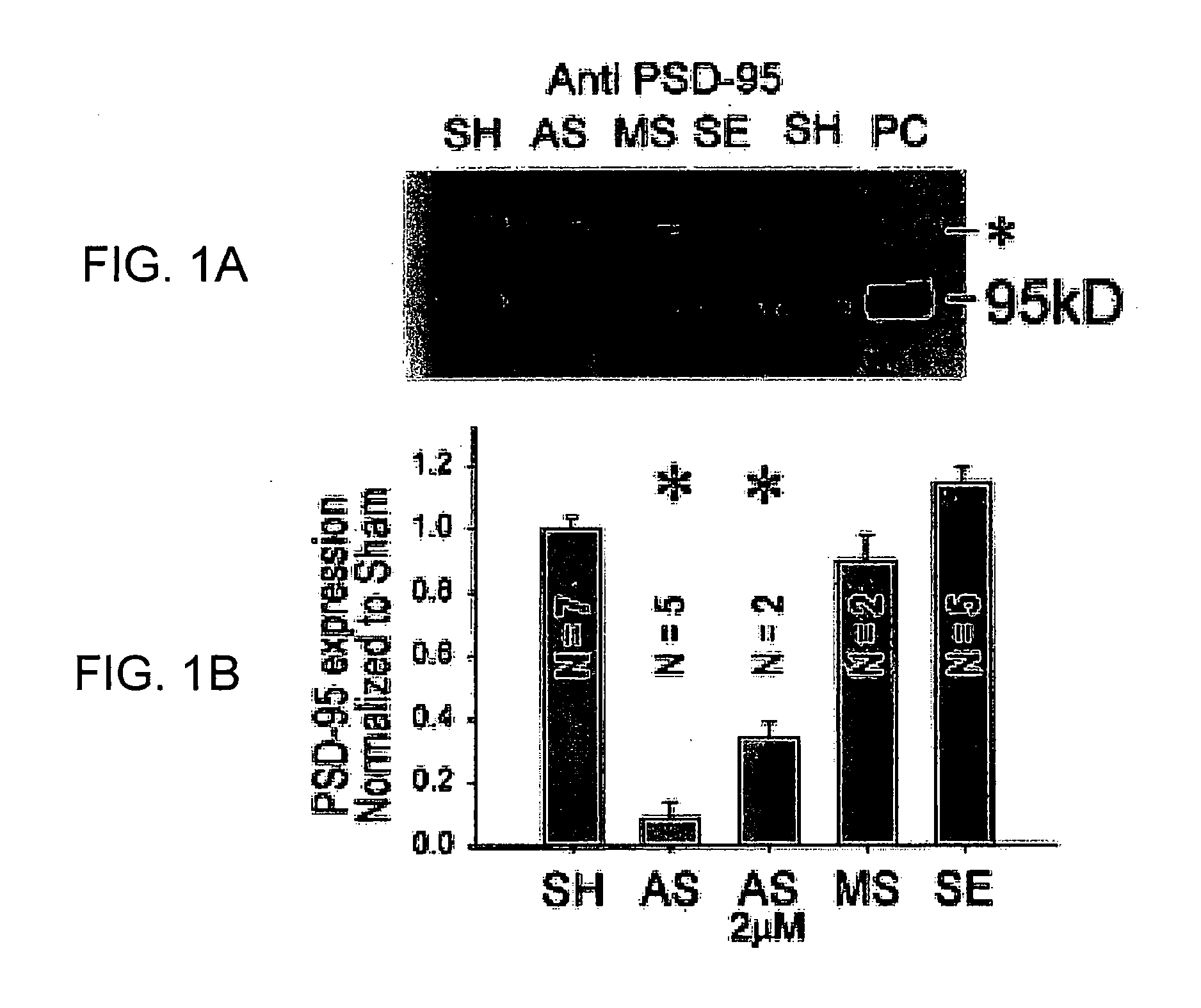
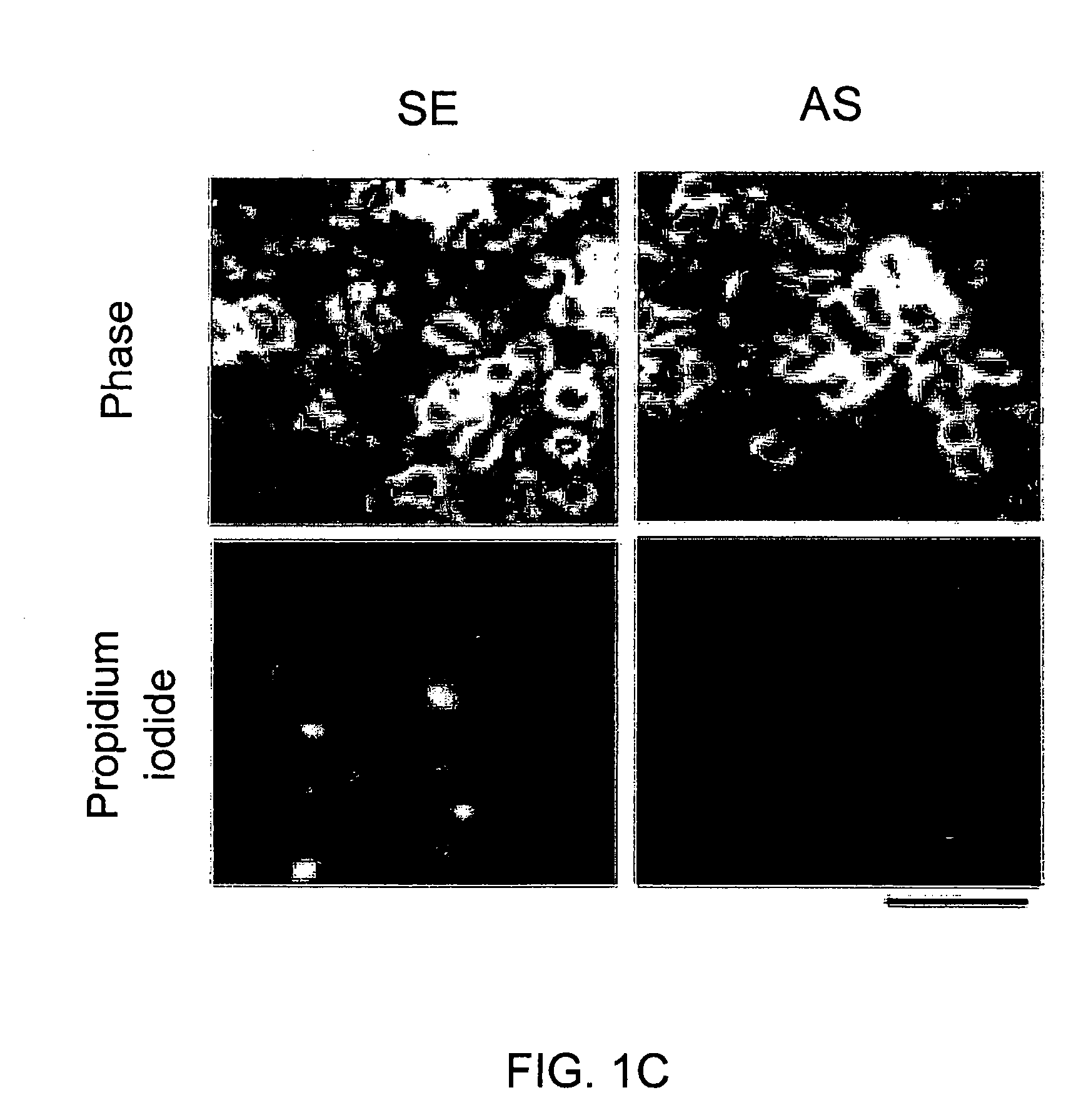
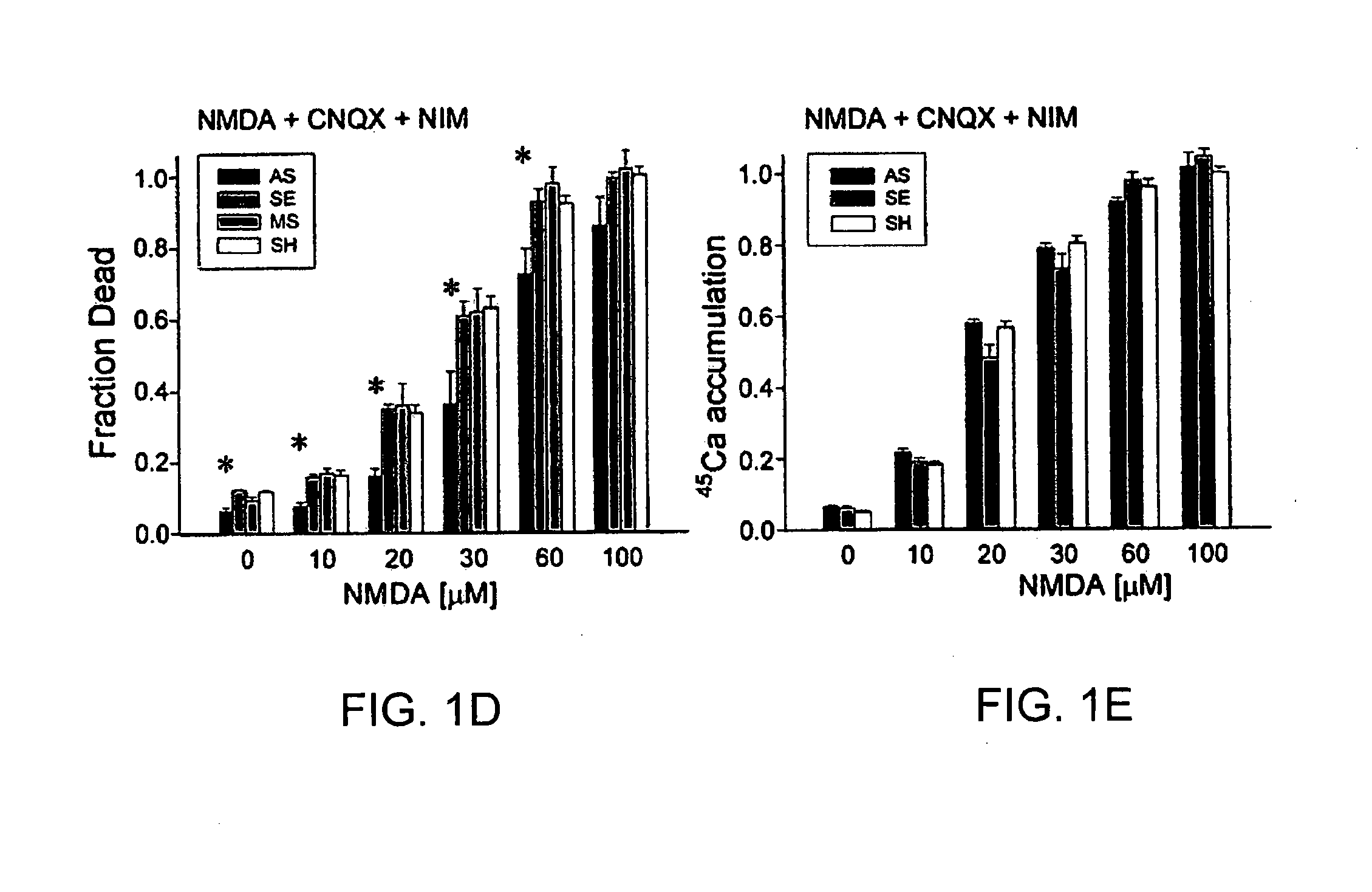
A method of inhibiting the binding between N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors and neuronal proteins in a neuron is disclosed. The method comprises administering to the neuron an effective inhibiting amount of a peptide replacement agent for the NMDA receptor or neuronal protein interaction domain that effect said inhibition of the NMDA receptor—neuronal protein interaction. The method is of value in reducing the damaging effect of injury to mammalian cells. Postsynaptic density-95 protein (PSD-95) couples neuronal N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) to pathways mediating excitotoxicity, ischemic and traumatic brain damage. This coupling was disrupted by transducing neurons with peptides that bind to modular domains on either side of the PSD-95 / NMDAR interaction complex. This treatment attenuated downstream NMDAR signaling without blocking NMDAR activity, protected cultured cortical neurons from excitotoxic insults, dramatically reduced cerebral infarction volume in rats subjected to transient focal cerebral ischemia, and traumatic brain injury (TBI) in rats.
Owner:NONO INC
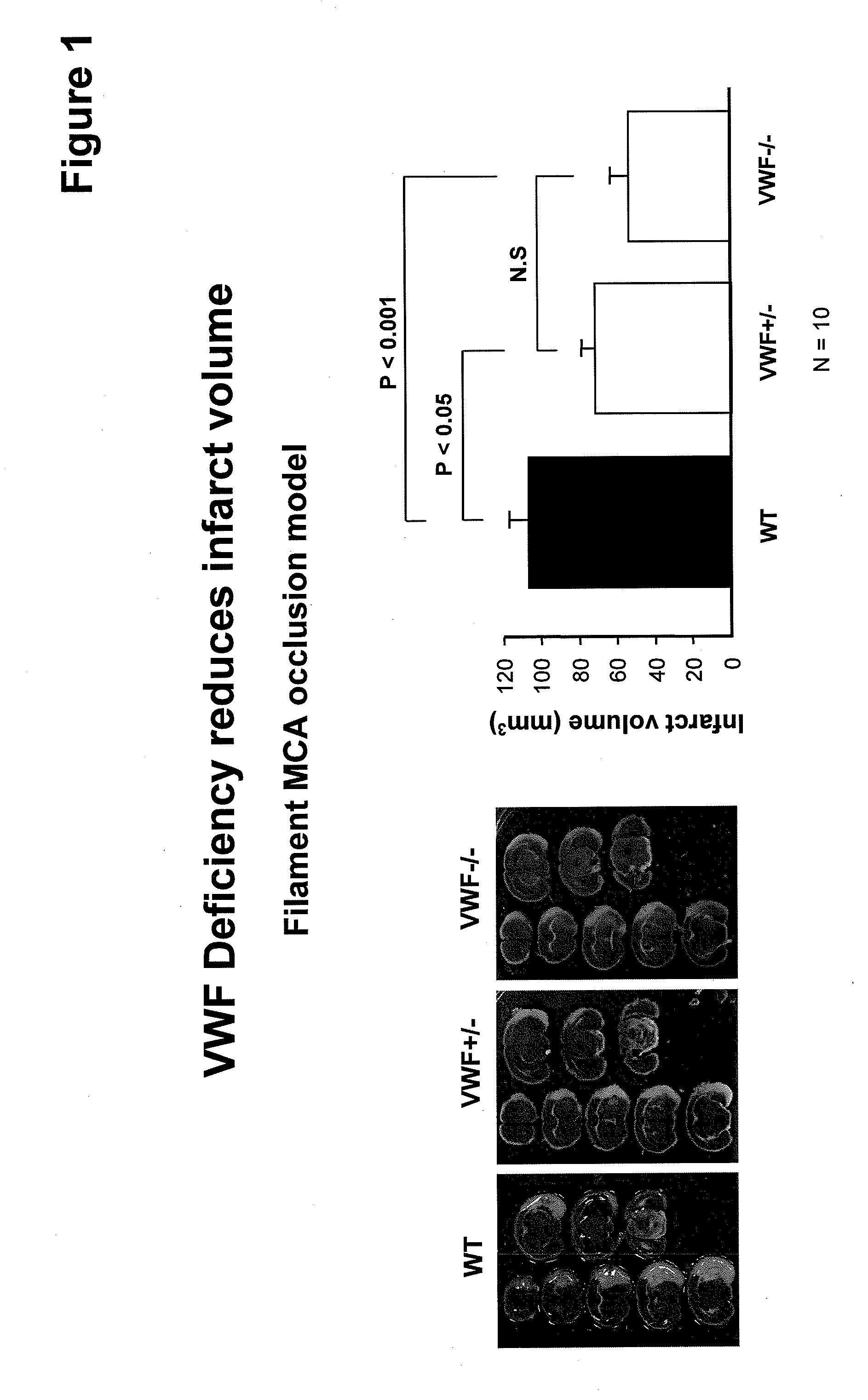
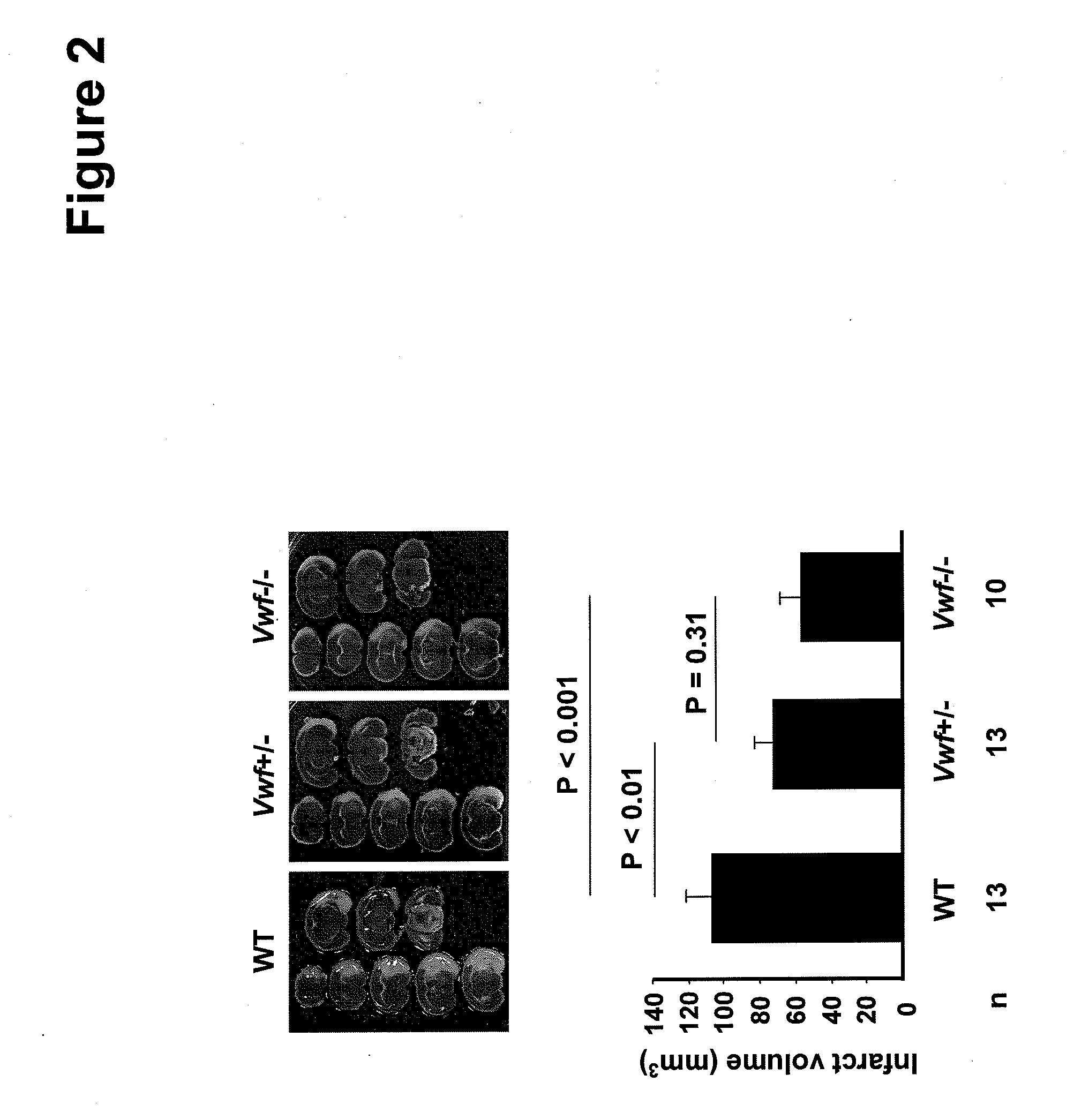
Von willebrand factor (VWF) inhibitors for treatment or prevention of infarction
InactiveUS20090317375A1Reduce capacitySuppress activityPeptide/protein ingredientsCardiovascular disorderFactor VIII vWFFactor ii
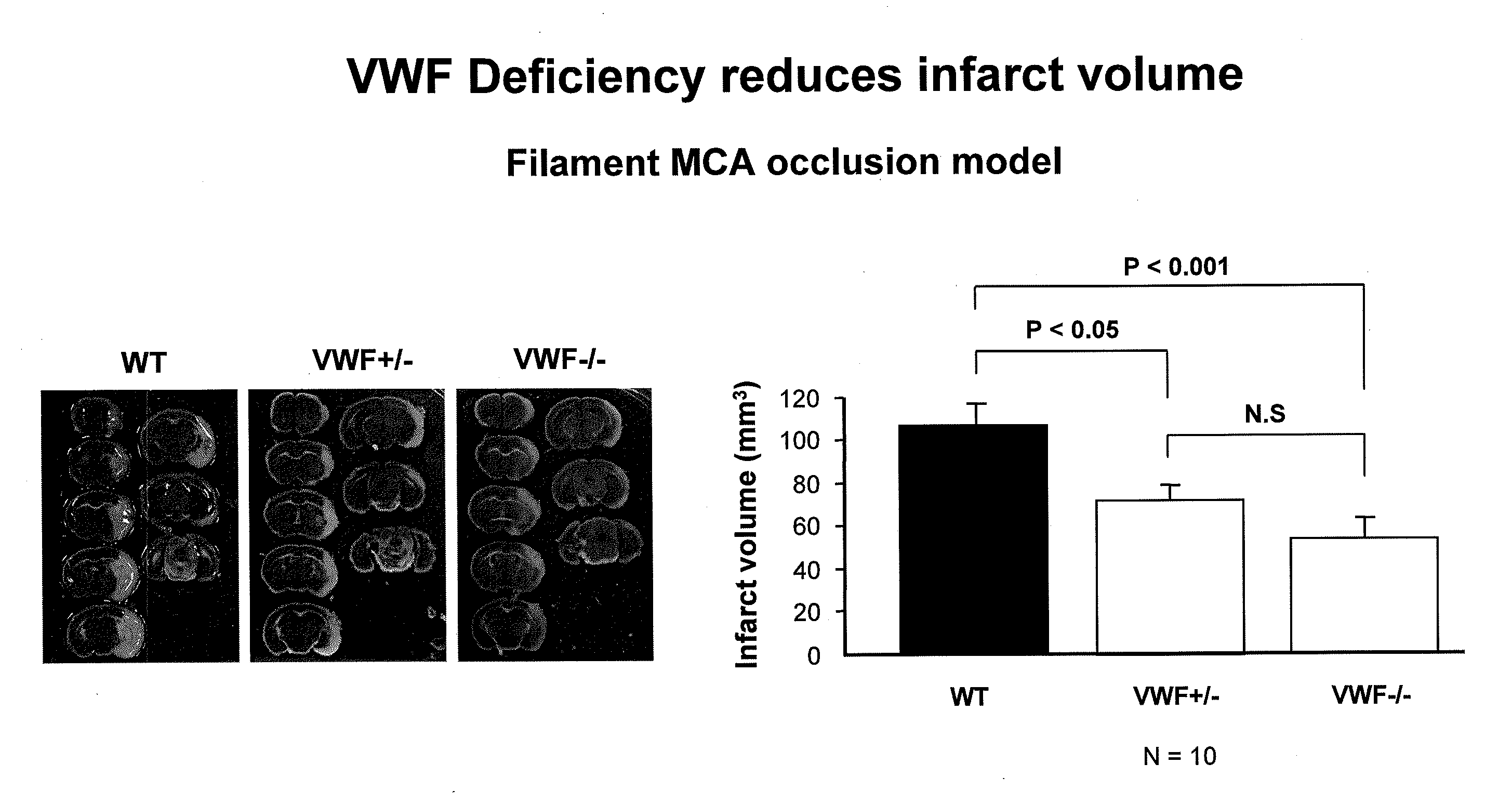
This invention relates to methods for treating or preventing an infarction by administering to a patient in need thereof a compound capable of suppressing the expression or activity of the von Willebrand Factor (VWF). Thus, the invention relates to the use of a pharmaceutically effective amount of a VWF inhibitor, such as ADAMTS13, for the preparation of a medicament for treating conditions known to involve infarction to reduce or eliminate the symptoms and effect of an infarction.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
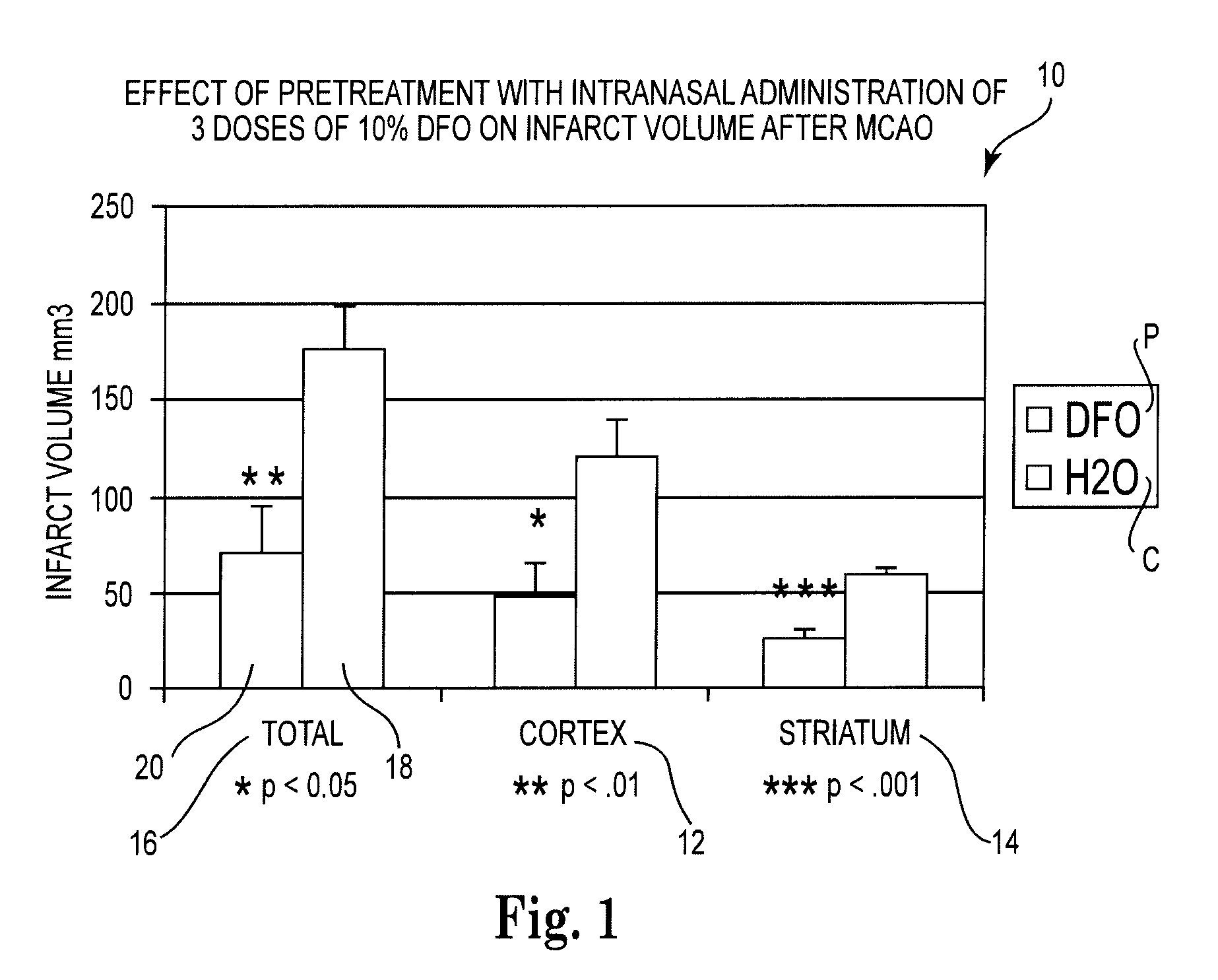
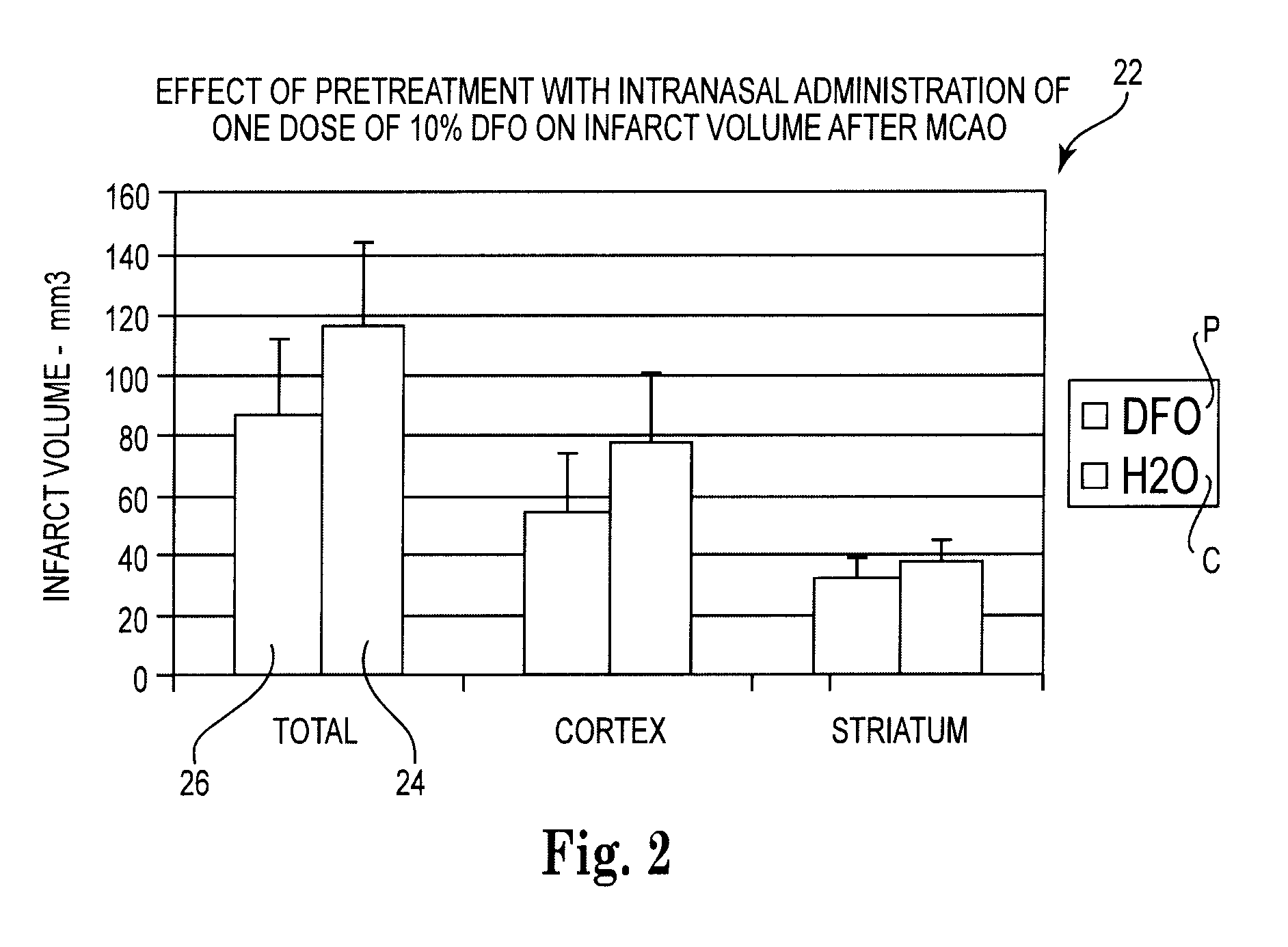
Methods for providing neuroprotection for the animal central nervous system against neurodegeneration caused by ischemia
ActiveUS7618615B2Minimize impactAvoid side effectsBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsNasal cavityNervous system
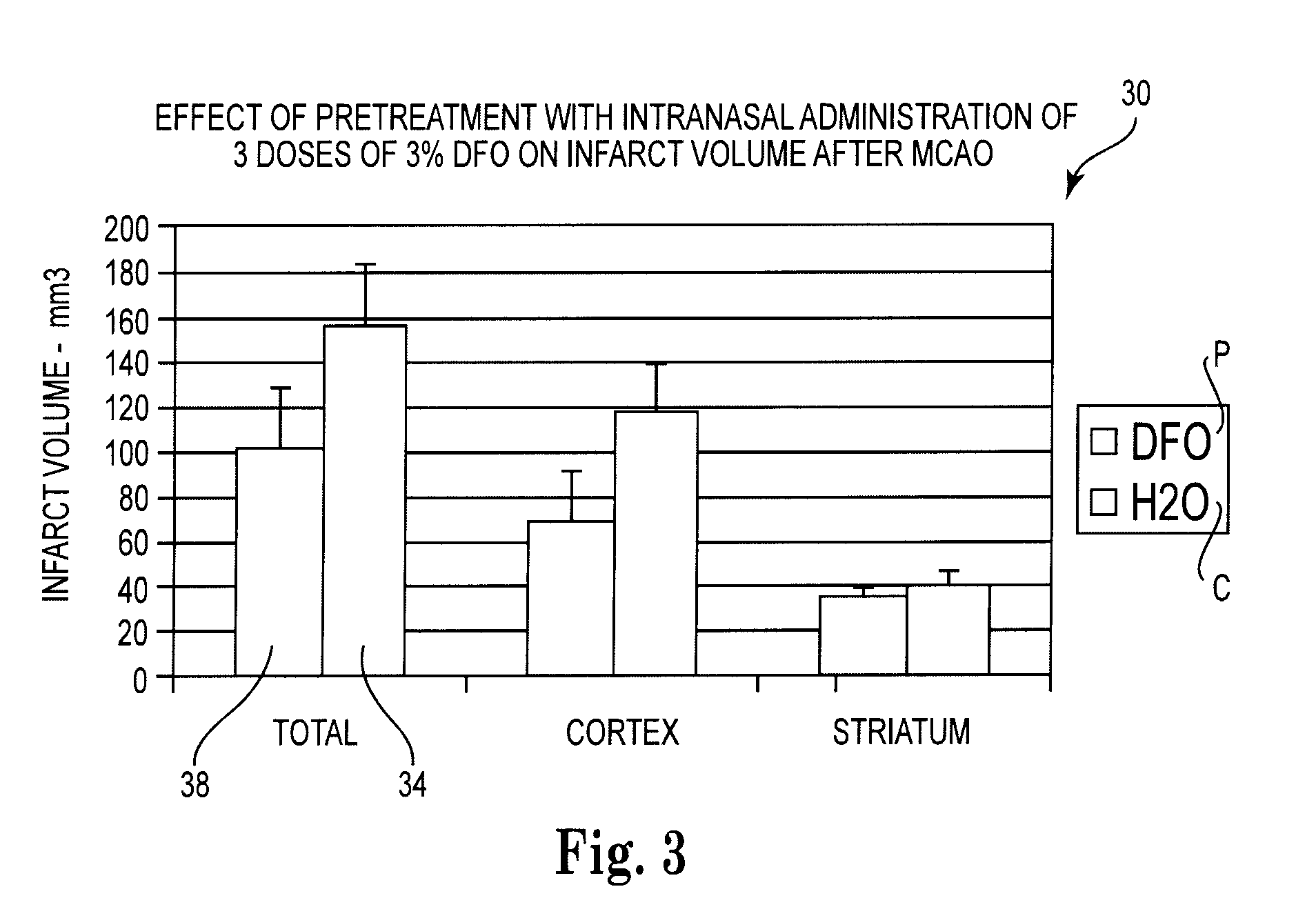
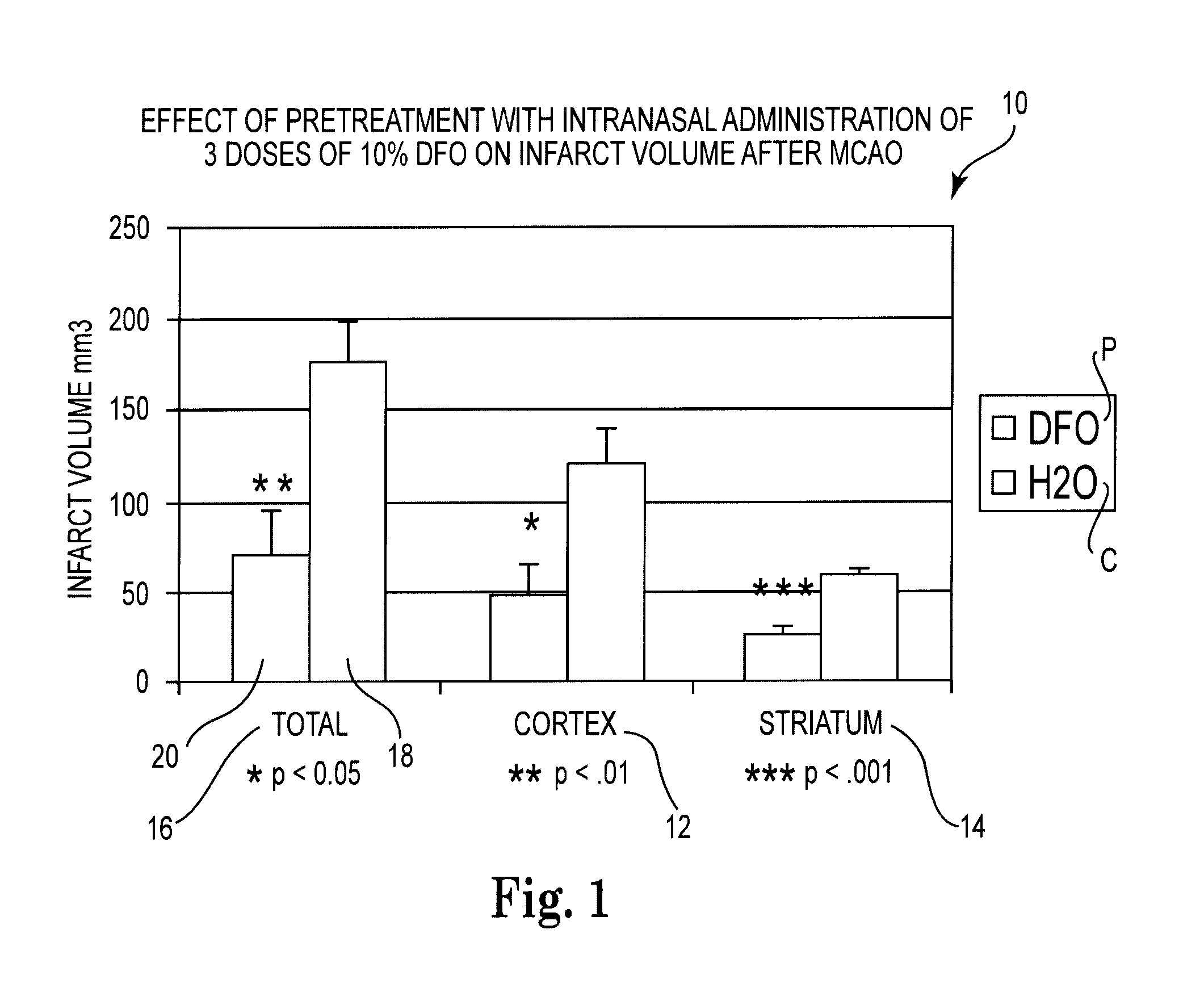
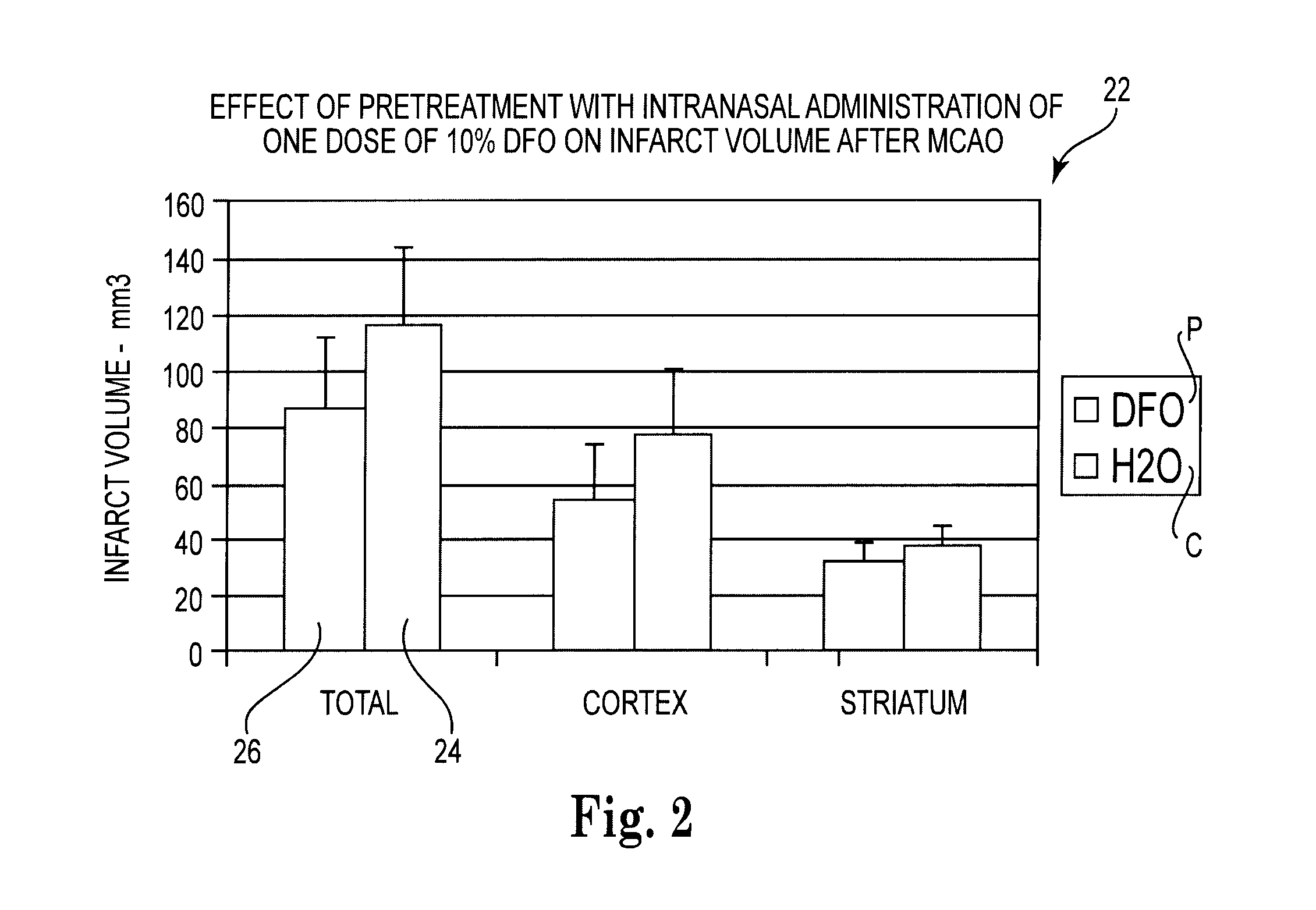
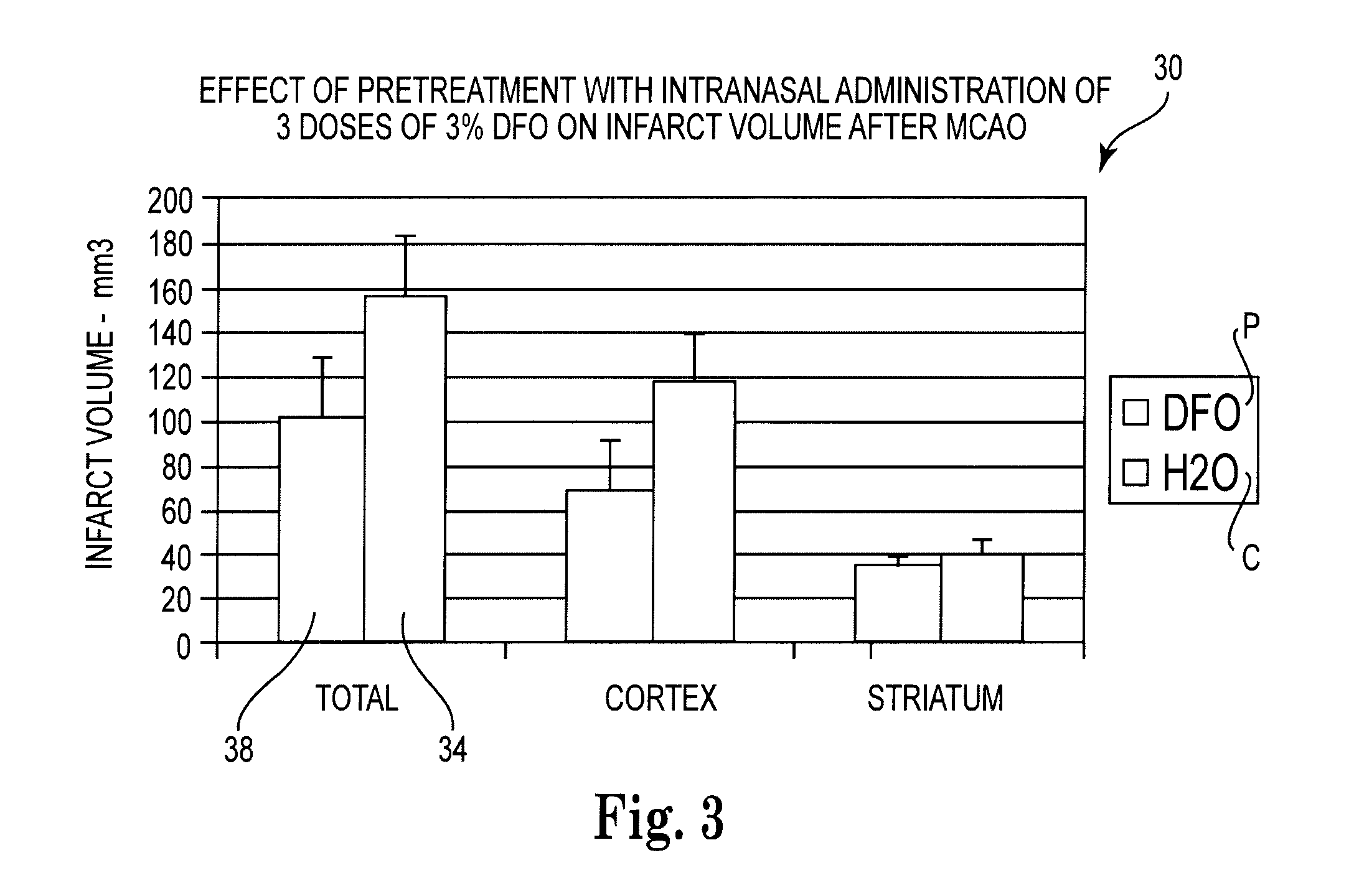
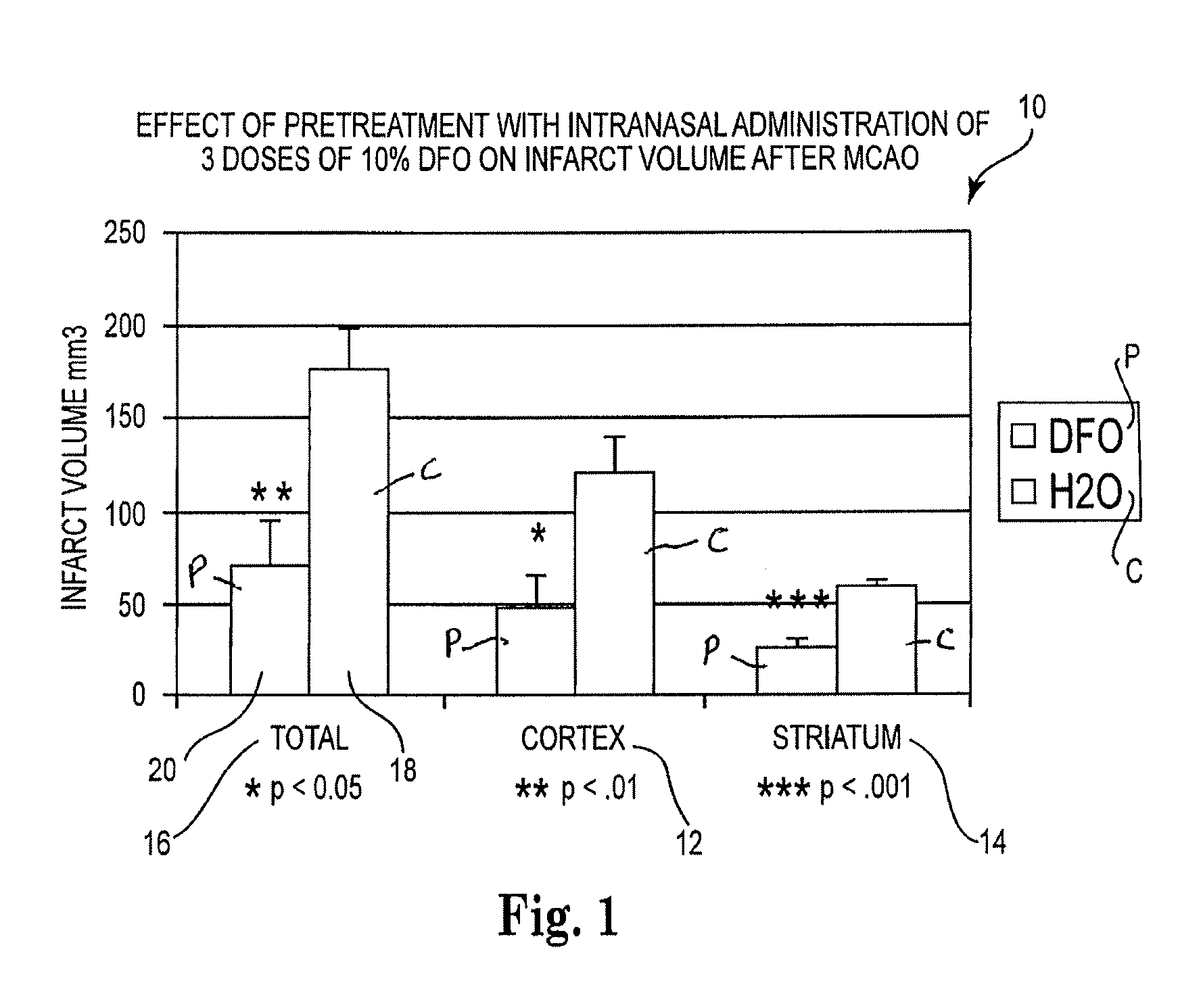
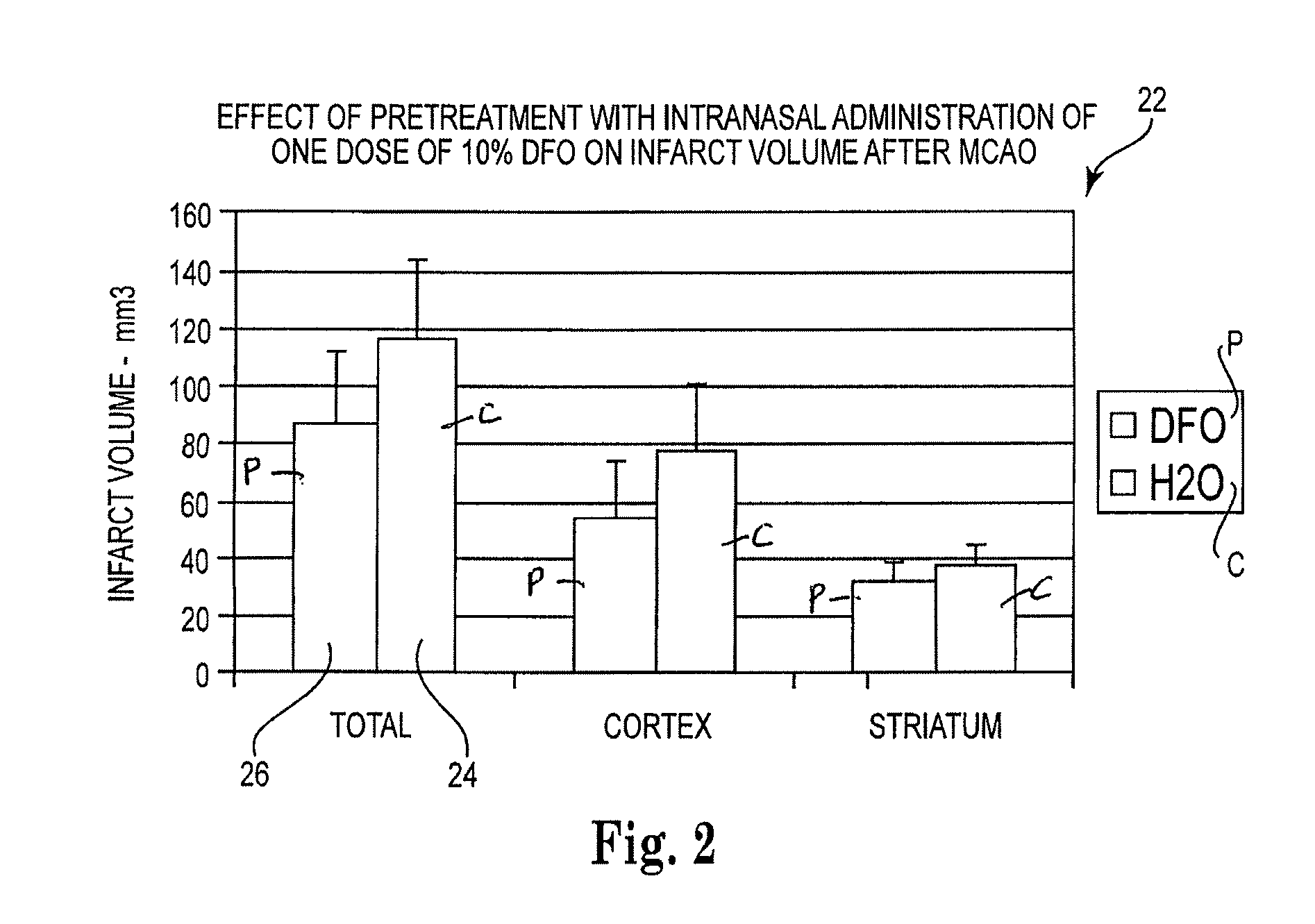
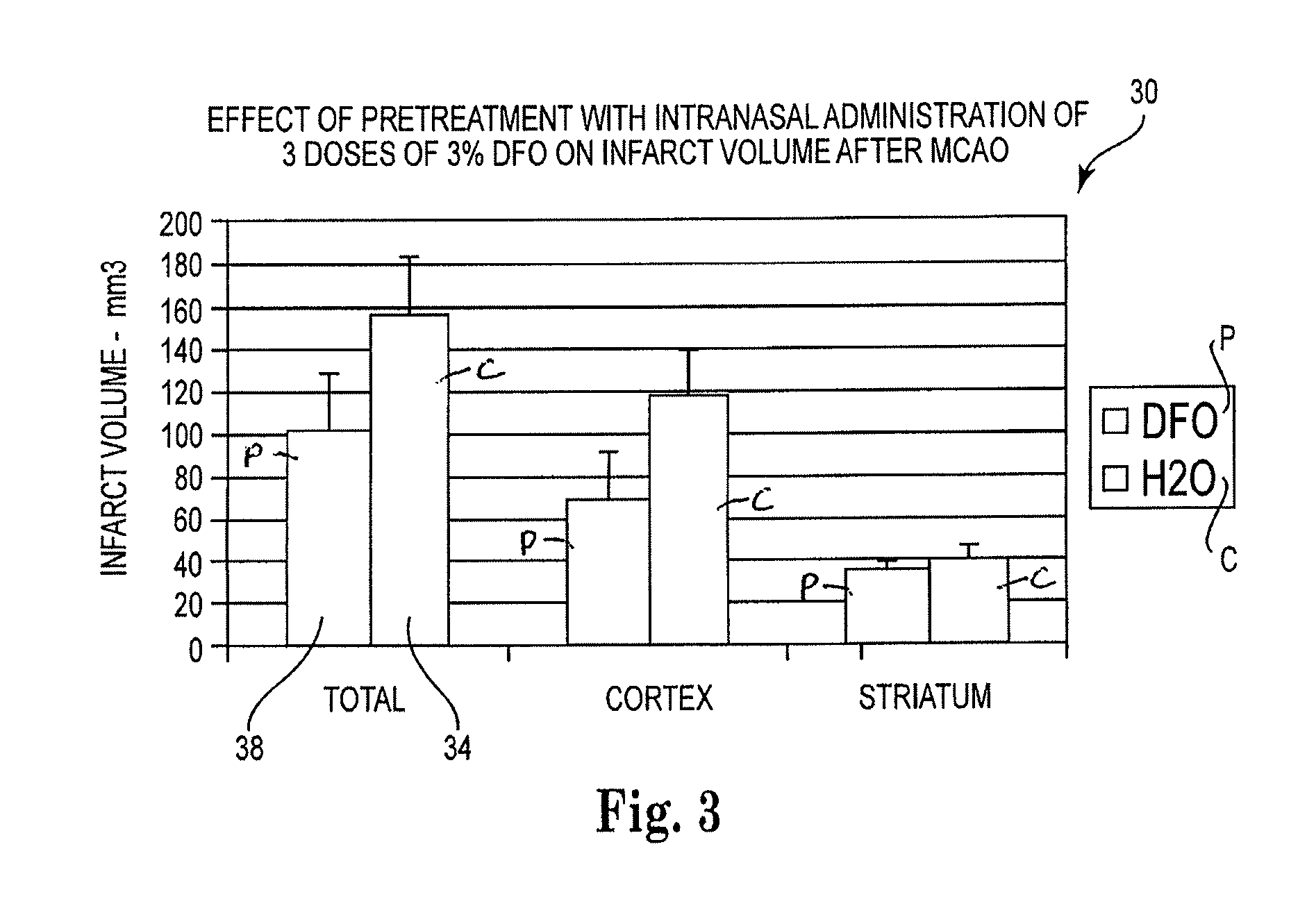
Methods and pharmaceutical compositions for preconditioning and / or providing neuroprotection to the animal central nervous system against the effects of ischemia, trauma, metal poisoning and neurodegeneration, including the associated cognitive, behavioral and physical impairments. In one embodiment, the method is accomplished by stimulating and stabilizing hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α). HIF-1α is known to provide a neuroprotective benefit under ischemic conditions. Patients at risk for certain diseases or disorders that are associated with risk for cerebral ischemia may benefit, e.g., those at risk for Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, Wilson's disease or stroke or those patients having head or spinal cord injury. Patients undergoing certain medical procedures that may result in ischemia may also benefit. Initially, the possibility of ischemia or neurodegeneration is recognized. Intranasal therapeutic agents are administered to the upper third of the nasal cavity to bypass the blood-brain barrier and access the central nervous system directly to avoid unwanted and potentially lethal side effects. Therapeutic agents include those substances that interact with iron and / or copper such as iron chelators, copper chelators, and antioxidants. A particular example of such therapeutic agents is the iron chelator deferoxamine (DFO). Intranasal administration of DFO is known to stimulate and / or stabilize HIF-1α and provides an efficient and safe method for pre-conditioning the brain to protect against cerebral ischemia. Moreover, DFO is shown to decrease weight loss in subjects when administered pre and / or post stroke.
Owner:HEALTHPARTNERS RESEACH FOUND
Compounds and compositions for treating neuronal death or neurological dysfunction
InactiveUS20070298129A1Avoid necrosisReduced infarct volumeBiocideSalicyclic acid active ingredientsDiabetic retinopathyBenzoic acid
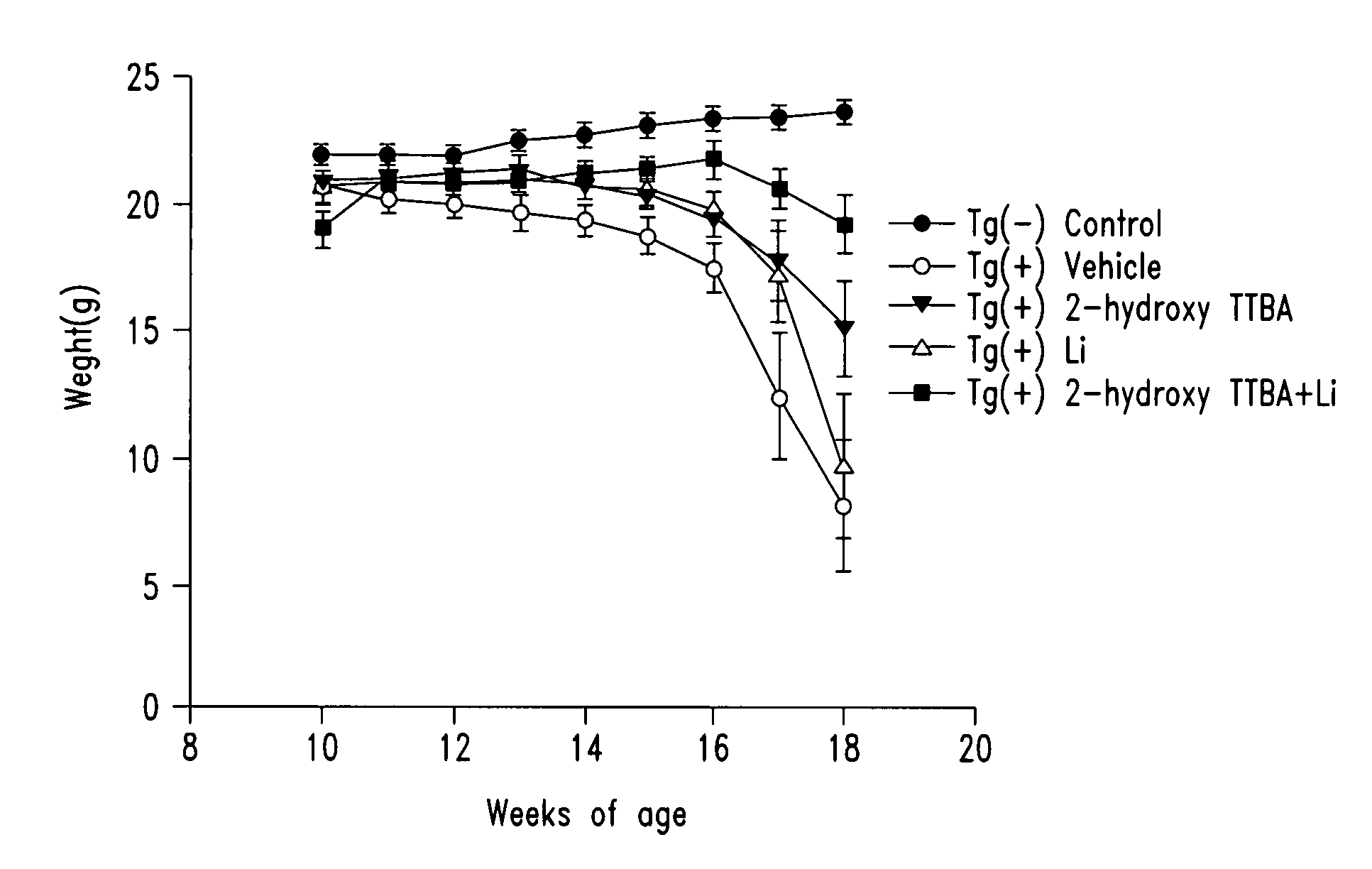
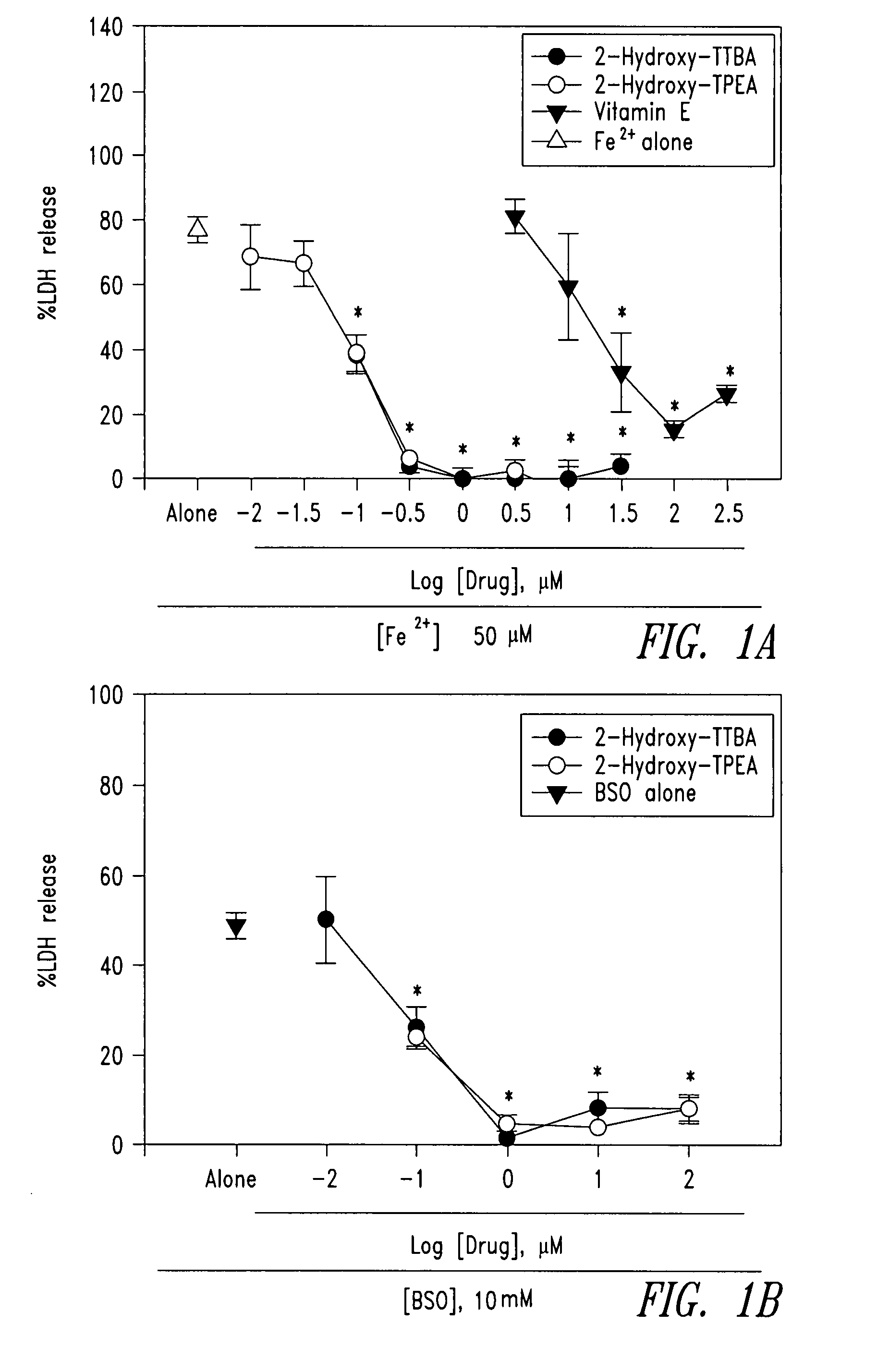
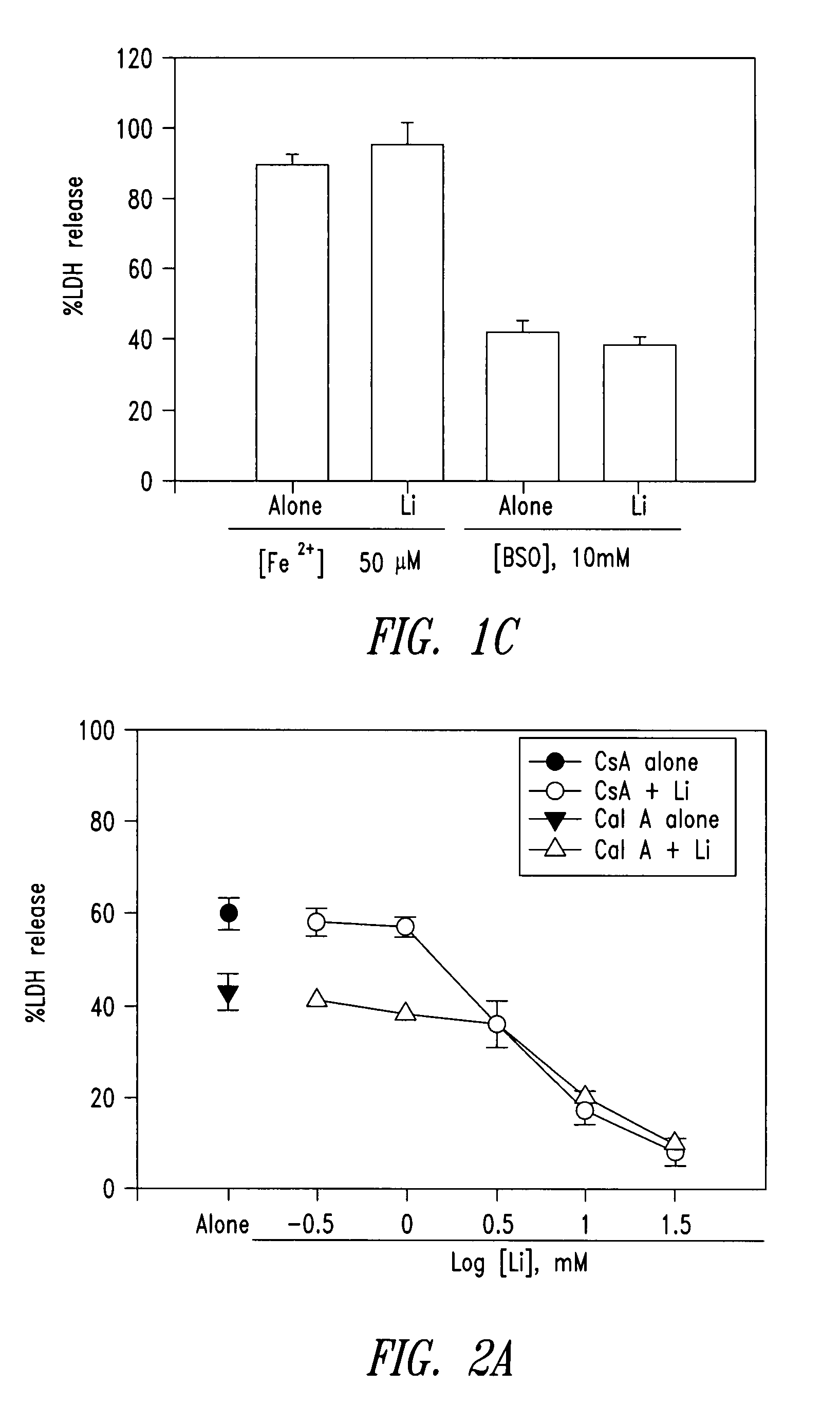
The present invention relates to 2-hydroxy-alkylamino-benzoic acid derivatives and to a combination of cell necrosis inhibitor and lithium, process for the preparation of the derivatives or the combination, pharmaceutical formulation containing the derivatives or the combination, and use of the derivatives or the combination by either concomitant or sequential administration for improvement of treatment of neuronal death or neurological dysfunction. The derivatives and the combination of the present invention are useful for treating neurological diseases, such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS, Lou Gehrig's disease), spinal muscular atrophy, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, Huntington's disease, stroke, traumatic brain injury or spinal cord injury; and for treating ocular diseases such as glaucoma, diabetic retinopathy or macular degeneration.
Owner:NEUROTECH PHARMA
Method of screening peptides useful in treating traumatic injury to the brain or spinal cord
InactiveUS7510824B2Prevent negative consequenceReduce signalingNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsInjury causeMedicine
A method of screening peptides which bind to at least one PDZ domain and comprise a cell-membrane transduction domain for use in treating traumatic injury to the brain or spinal cord by deforming neurons on a flexible substrate with sublethal stretch, then inflicting a secondary injury, and determining survival of the stretched neurons in the absence or presence of the peptide which is being screened.
Owner:NONO INC
Method of reducing injury to mammalian cells
InactiveUS7595297B2Prevent negative consequenceReduce signalingNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsNR1 NMDA receptorN methyl D aspartate receptors
A method of inhibiting the binding between N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors and neuronal proteins in a neuron the method comprising administering to the neuron an effective inhibiting amount of a peptide replacement agent for the NMDA receptor or neuronal protein interaction domain that effect said inhibition of the NMDA receptor neuronal protein. The method is of value in reducing the damaging effect of injury to mammalian cells. Postsynaptic density-95 protein (PSD-95) couples neuronal N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) to pathways mediating excitotoxicity and ischemic brain damage. This coupling was disrupted by transducing neurons with peptides that bind to modular domains on either side of the PSD-95 / NMDAR interaction complex. This treatment attenuated downstream NMDAR signaling without blocking NMDAR activity, protected cultured cortical neurons from excitotoxic insults and dramatically reduced cerebral infarction volume in rats subjected to transient focal cerebral ischemia. The treatment was effective when applied either before, or one hour after, the onset of excitotoxicity in vitro and cerebral ischemia in vivo. This approach prevents negative consequences associated with blocking NMDAR activity and constitutes practical therapy for stroke.
Owner:NONO INC
Methods for the treatment of brain edema
InactiveUS20090286799A1Reduced infarct volumeReduce mortalityBiocideAnimal repellantsMortality rateCalcium influx
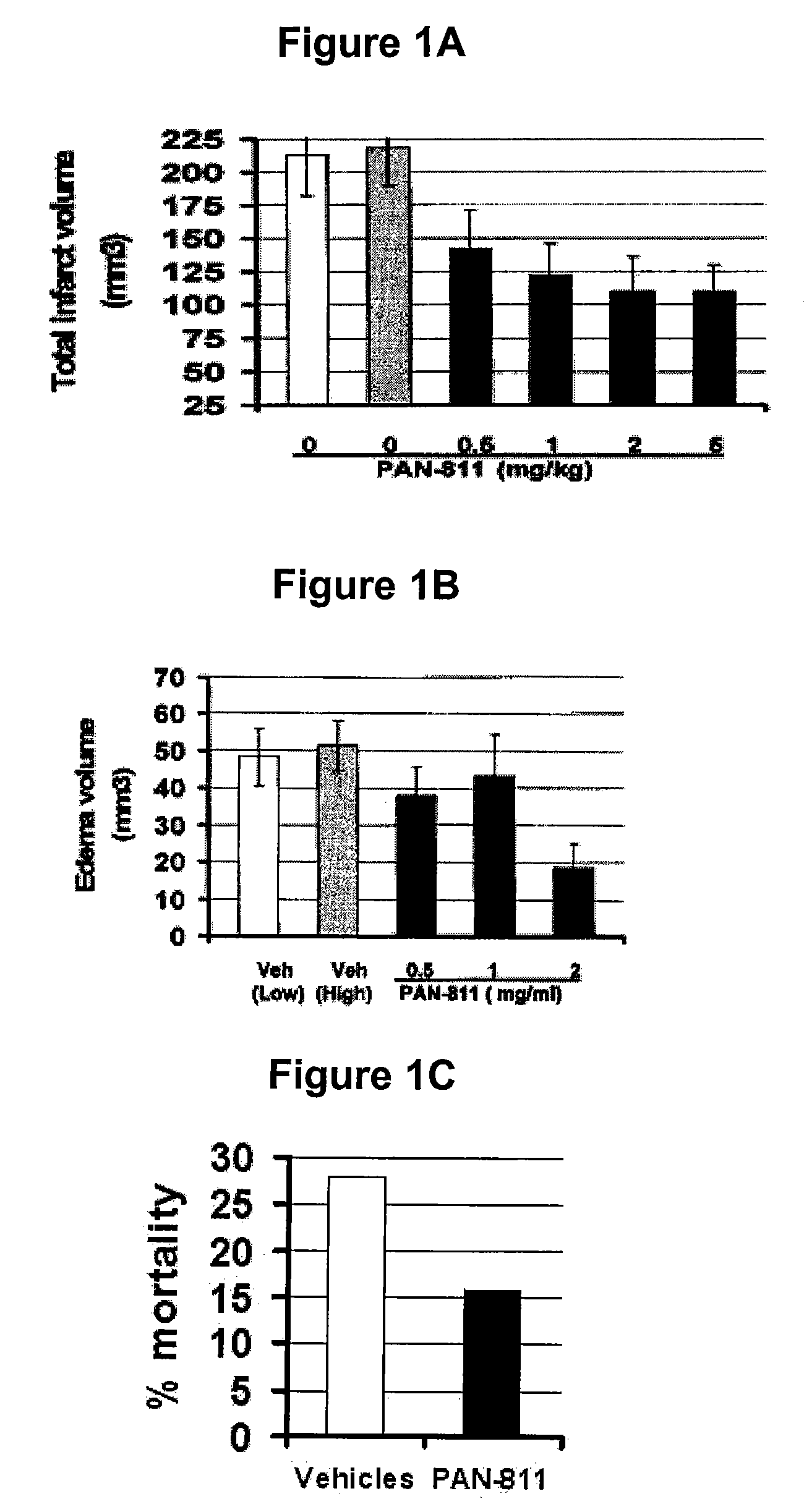
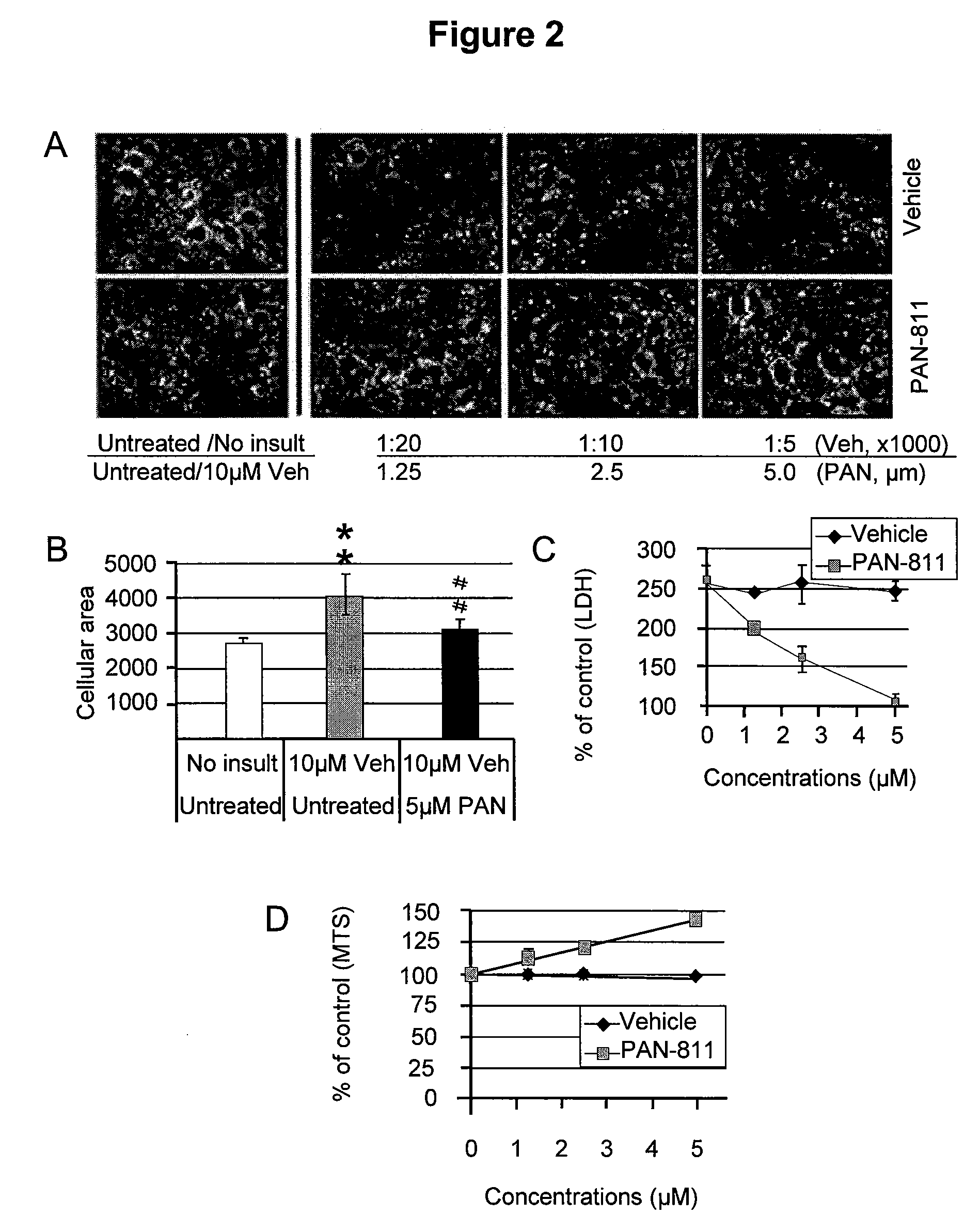
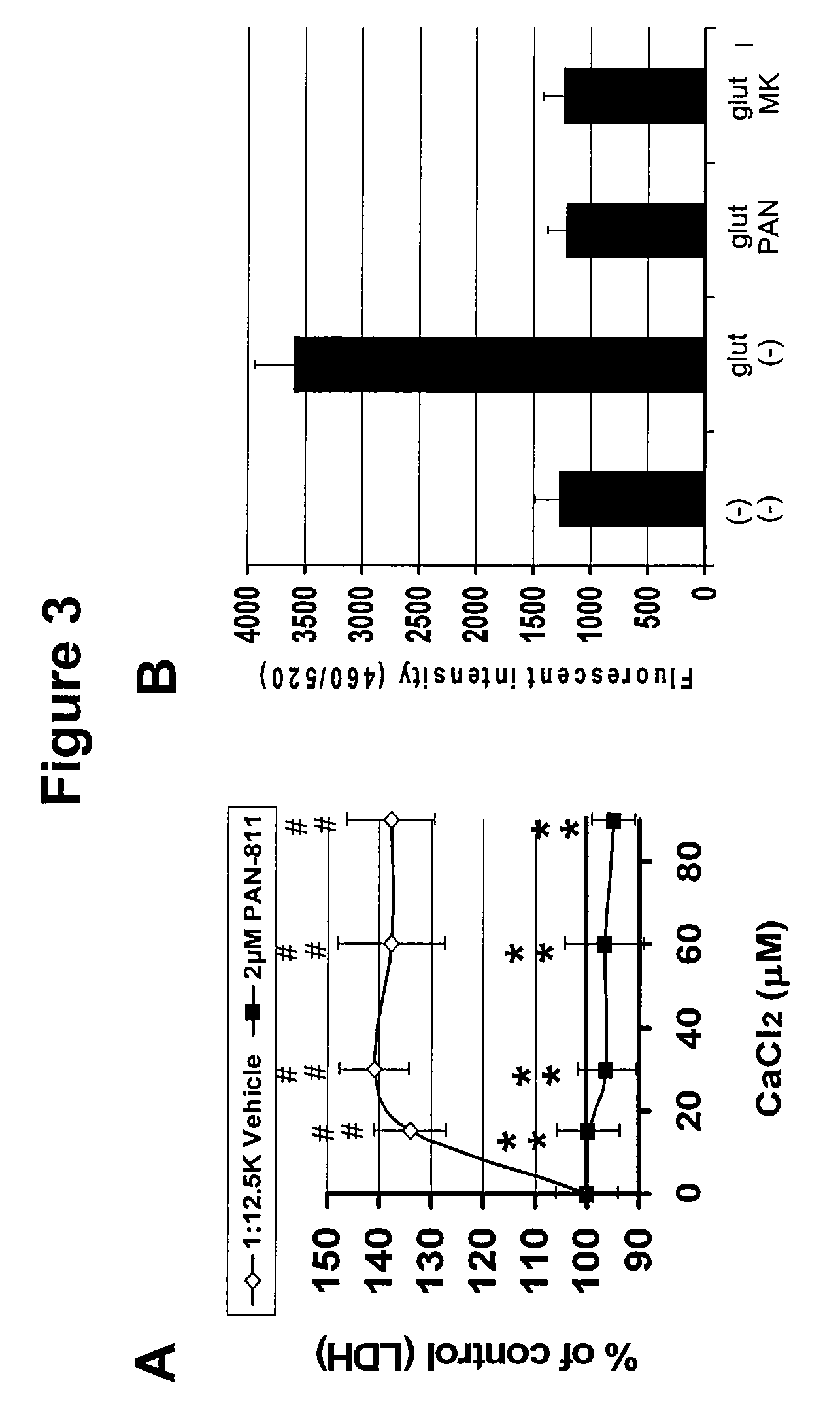
The present invention is based on the discoveries that PAN-811 (1) reduces infarct volume, suppresses brain edema and decreases mortality associated with ischemia; (2) blocks veratridine-induced swelling and neuronal cell death; (3) chelates free calcium and inhibits MMP-9 activity; and (4) blocks calcium-induced neuronal cell death and suppresses glutamate-induced calcium influx into neuronal cells. More particularly, the present invention relates to methods for treating, ameliorating or preventing vasogenic and / or cytotoxic brain edema, by administering to a subject in need thereof certain thiosemicarbazone compounds or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof. An example of such a thiosemicarbazone is 3-aminopyridine-2-carboxaldehyde thiosemicarbazone (PAN-811).
Owner:PANACEA PHARMA
Methods for providing neuroprotection for the animal central nervous system against the effects of ischemia, neurodegeneration, trauma, and metal poisoning
ActiveUS20100061959A1Minimize impactAvoid side effectsBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsNasal cavityNervous system
Methods and pharmaceutical compositions for providing neuroprotection to the animal central nervous system against the effects of ischemia, and neurodegeneration. Patients at risk for certain diseases or disorders that are associated with cerebral ischemia may benefit, e.g., those at risk for Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, Wilson's disease or stroke or those patients having head or spinal cord injury. Patients undergoing certain medical procedures that may result in ischemia may also benefit. Initially, the possibility of ischemia or neurodegeneration is recognized. Intranasal therapeutic agents are administered to the upper third of the nasal cavity to bypass the blood-brain barrier and access the central nervous system directly to avoid unwanted and potentially lethal side effects. Therapeutic agents include those substances that interact with iron and / or copper such as iron chelators and copper chelators. A particular example of such therapeutic agents is the iron chelator deferoxamine (DFO). Intranasal administration of DFO provides an effective method for pre-conditioning the brain to protect against cerebral ischemia.
Owner:HEALTHPARTNERS RESEACH FOUND
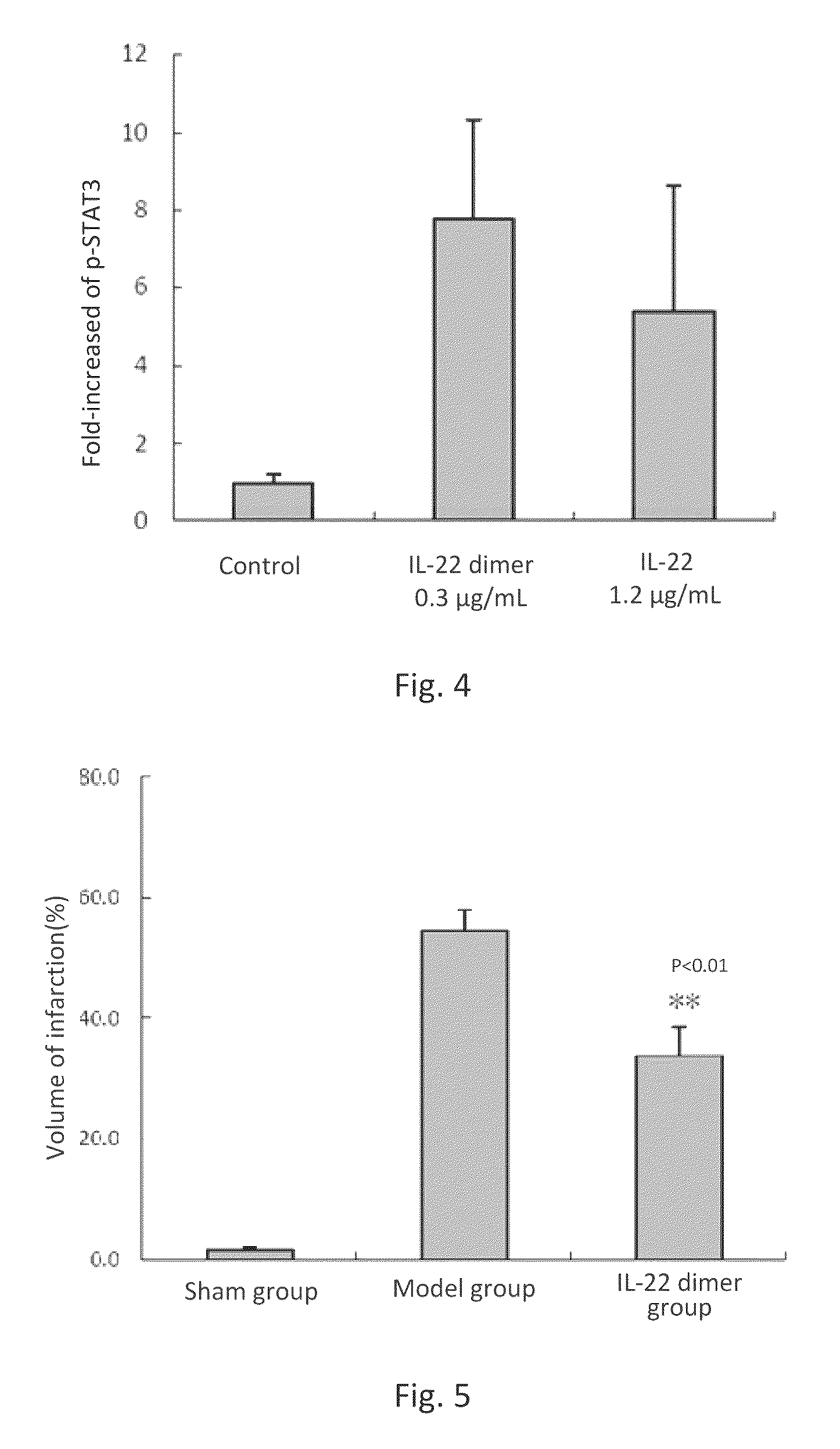
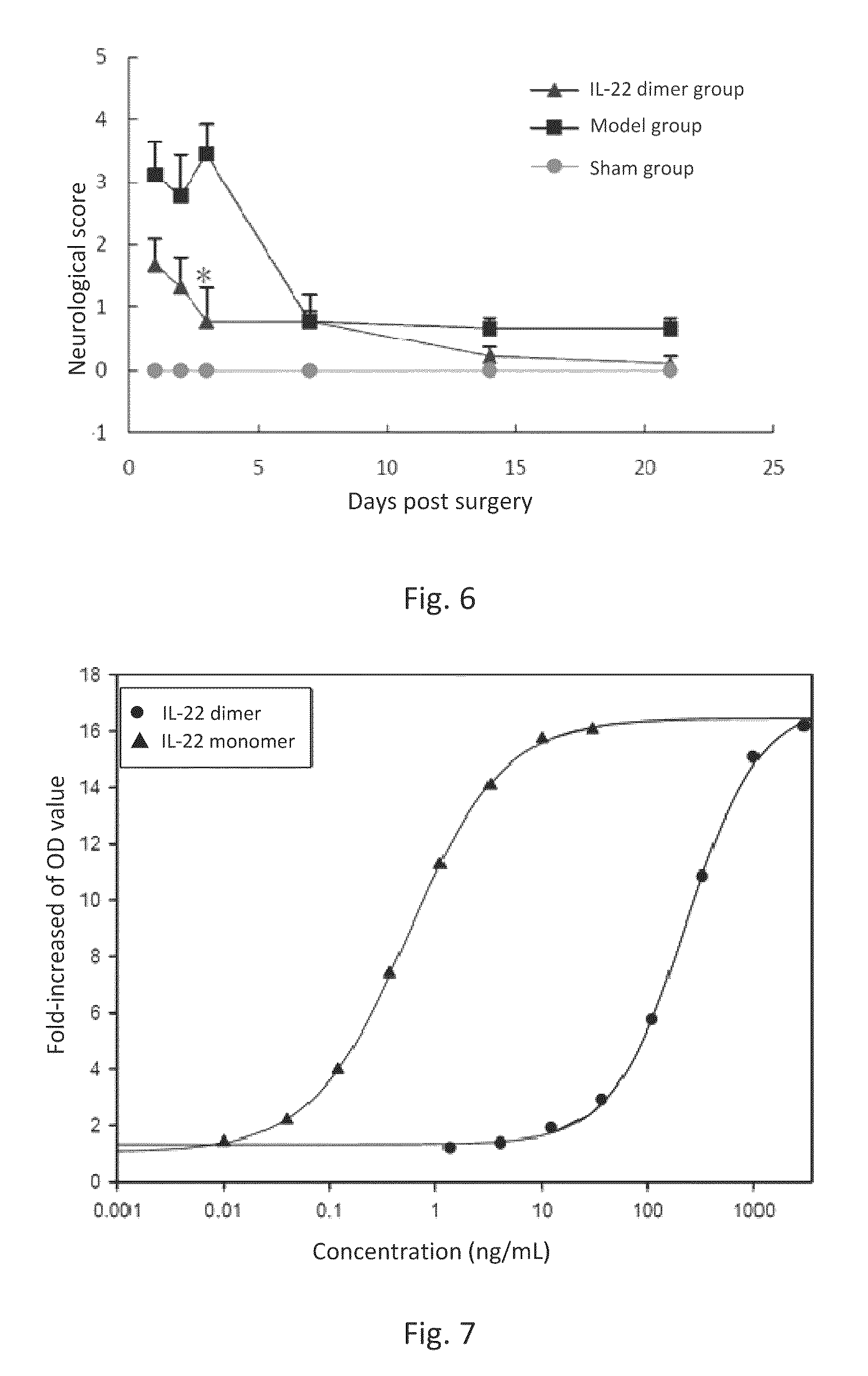
Uses of interleukin-22(il-22) in treating and preventing nerve damage diseases or neurodegenerative diseases
ActiveUS20150147293A1Enabling recoveryFunction increaseNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsIn vivoDisease cause
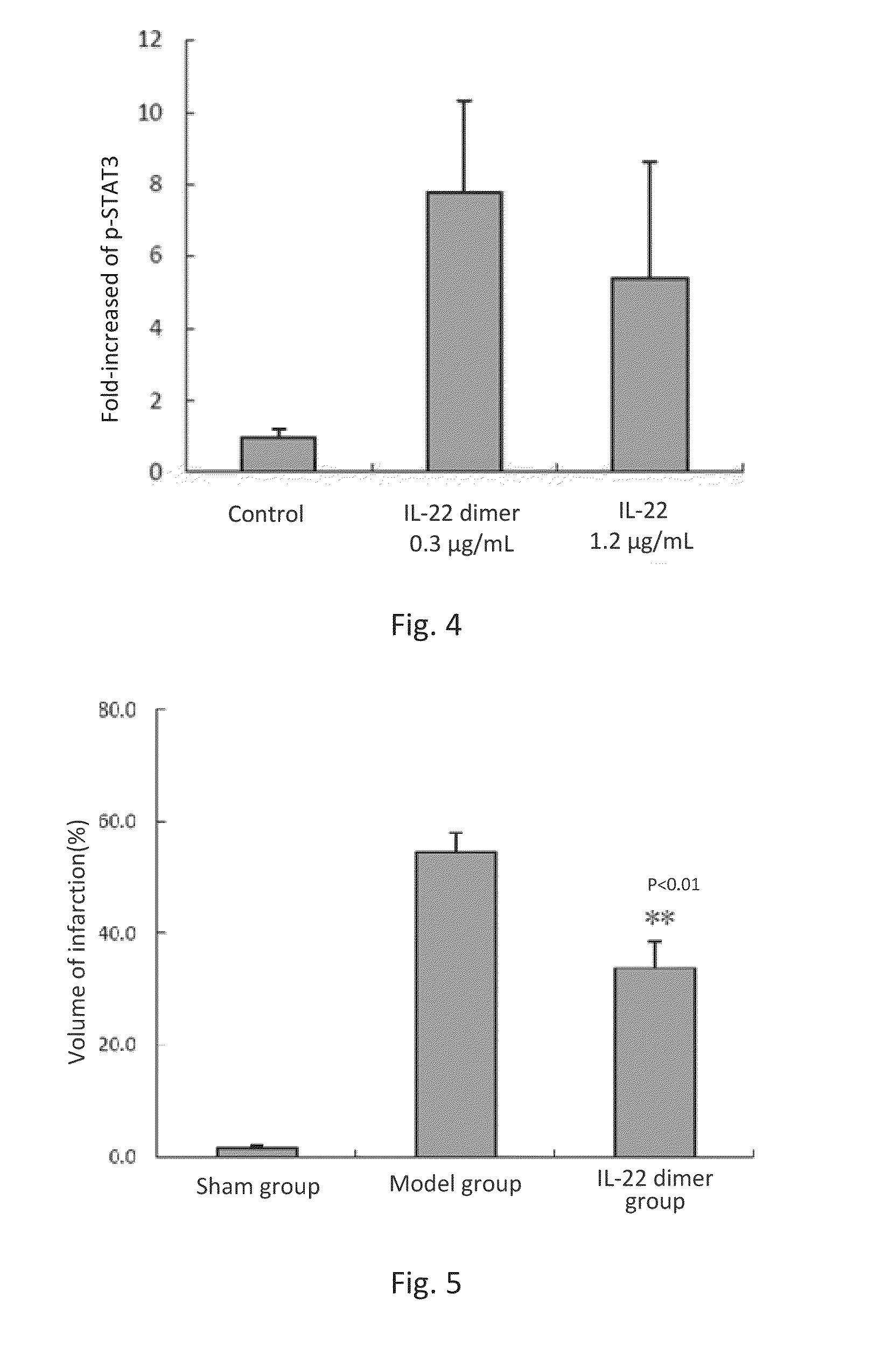
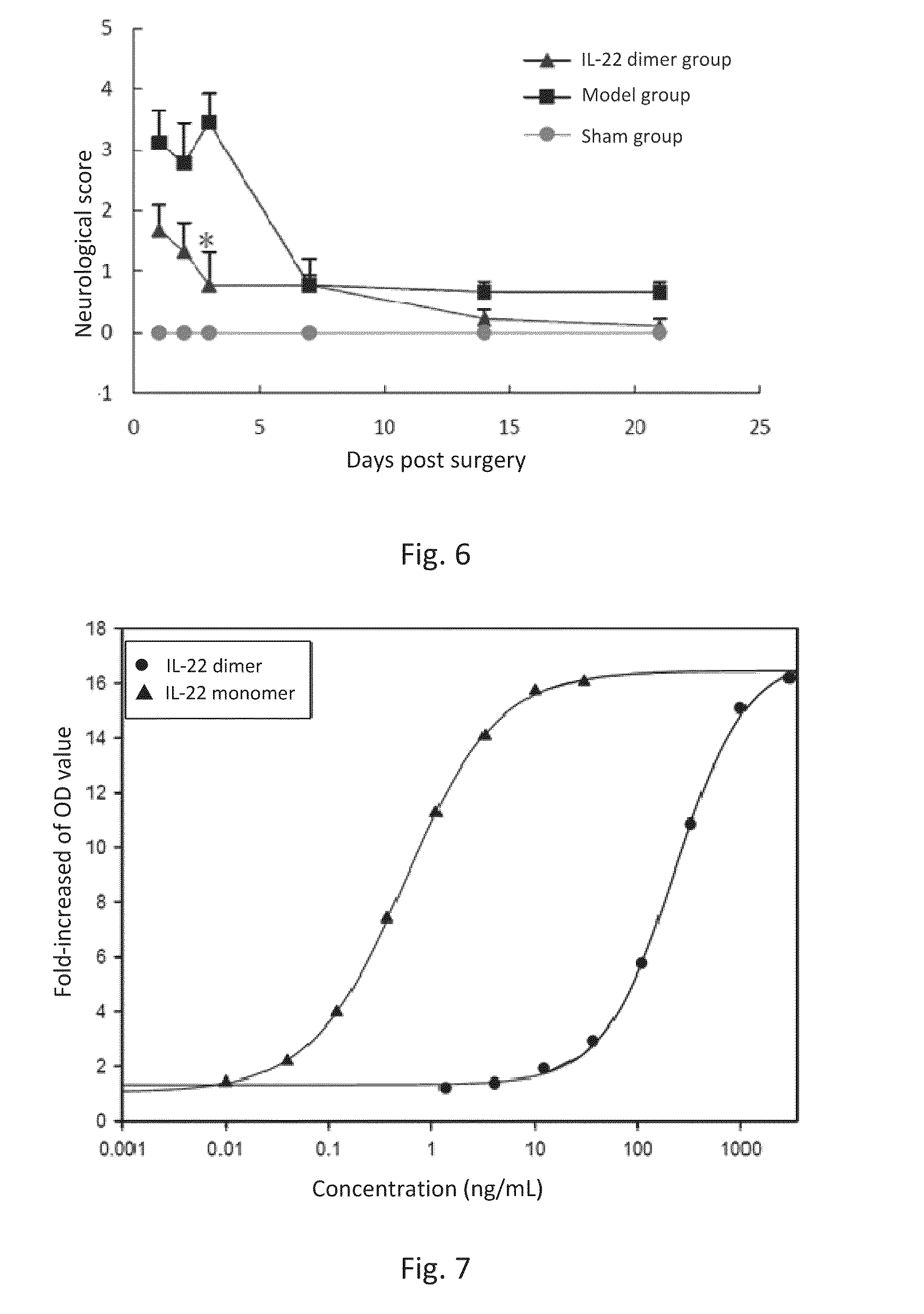
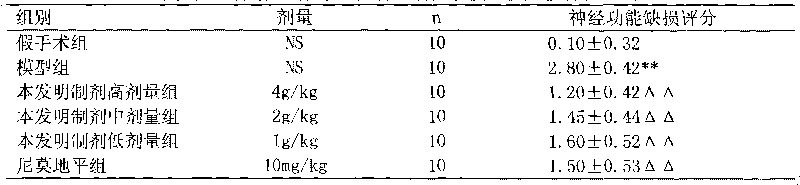
This invention discloses the uses of IL-22 in the treatment and prevention of a nerve damage disease or a neurodegenerative disease. In particular, the invention discloses the uses of IL-22 or IL-22 dimers as follows: (i) can protect neurons to recover the functions of injured neurons after ischemic nerve damage in animals in vivo, thus enabling effective treatment of nerve damage diseases, (ii) can significantly inhibit the loss of dopaminergic neurons in substantia nigra in PD model animal, enhance the functions of dopaminergic neurons, significantly reduce neuronal apoptosis in hippocampus, improve learning and memory capacity of AD model rats, and effectively prevent neuronal loss, thereby enabling more effective treatment of neurodegenerative diseases.
Owner:EVIVE BIOTECHNOLOGY (SHANGHAI) LTD
Medicament for preventing and treating ischemic brain injury, and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101732402AGood treatment effectOpen up treatment ideasCardiovascular disorderPlant ingredientsClinical manifestationTherapeutic effect
The invention relates to the field of Chinese medicaments, in particular to a Chinese medicinal composition for preventing and treating ischemic brain injury, and a preparation method thereof. The Chinese medicinal composition for preventing and treating ischemic brain injury is an orally taken preparation prepared from extracts of raw astragalus roots, panax notoginseng, kudzuvine roots, baikal skullcap roots and gardenia serving as main active components, as well as pharmaceutical auxiliary materials. The preparation has obvious therapeutic effects on cerebral infarction convalescent symptoms of which the clinical manifestations are eye-mouth distortion, glossolalia, slobbering or hemiplegia, dark red tongue or yellow greasy tongue coating, weak or uneven pulse and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CHINESE MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Injecta of anemarrhena extractive
InactiveCN1628790AReduce edemaReduce blood viscosityPowder deliveryUnknown materialsFluid infusionMedicine
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Application of curcumin to preparation of drugs for treating cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injuries
InactiveCN102652741AWide variety of sourcesEasy to getNervous disorderDigestive systemDiseaseReperfusion injury
The invention discloses application of curcumin to preparation of drugs for treating cerebral ischemia / reperfusion injuries, belonging to the technical field of drug preparation. A cerebral ischemia / reperfusion injury model is prepared and curcumin-PVP (polyvinylpyrrolidone) solid dispersions are used for treating the disease model after being dissolved with the saline for injection. Results show that curcumin can obviously improve the injuries of vital organs such as distant livers and kidneys caused by cerebral tissue injuries and cerebral ischemia / reperfusion injuries and can control the expression levels of several factors related to apoptosis, inflammations and oxidation, control further aggravation of the injuries and protect the vital organs such as cerebral tissues and livers and kidneys.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
Method of reducing injury to mammalian cells
InactiveUS20090131321A1Signal attenuationPrevent negative consequenceHormone peptidesNervous disorderN-Methyl-D-aspartic acidNeuron
A method of inhibiting the binding between N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors and neuronal proteins in a neuron the method comprising administering to the neuron an effective inhibiting amount of a peptide replacement agent for the NMDA receptor or neuronal protein interaction domain that effect said inhibition of the NMDA receptor neuronal protein. The method is of value in reducing the damaging effect of injury to mammalian cells. Postsynaptic density-95 protein (PSD-95) couples neuronal N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) to pathways mediating excitotoxicity and ischemic brain damage. This coupling was disrupted by transducing neurons with peptides that bind to modular domains on either side of the PSD-95 / NMDAR interaction complex. This treatment attenuated downstream NMDAR signaling without blocking NMDAR activity, protected cultured cortical neurons from excitotoxic insults and dramatically reduced cerebral infarction volume in rats subjected to transient focal cerebral ischemia. The treatment was effective when applied either before, or one hour after, the onset of excitotoxicity in vitro and cerebral ischemia in vivo. This approach prevents negative consequences associated with blocking NMDAR activity and constitutes practical therapy for stroke.
Owner:TYMIANSKI MICHAEL
Use of methylene blue in prevention of acute cerebral ischemia damage
InactiveCN104027338AImprove performanceReduced infarct volumeOrganic active ingredientsFood preparationIntraperitoneal routeModerate-Dose
The invention relates to novel use of methylene blue (MB) in prevention of acute cerebral ischemia. MB can remarkably reduce cerebral ischemia infarction caused by permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion (middle cerebral artery occlusion MCAO) and alleviate damage of neurological function. The inventors of the invention permanently occlude middle cerebral artery of a mouse by adopting a suture method and after intraperitoneal injection of MB at the moment and at different time points after cerebral ischemia, changes on degree and ethology of permanent cerebral ischemia infarction of the mouse are observed. Researches discover that MB can remarkably reduce infarct volume caused by cerebral ischemia and improve the active ability of the mouse after cerebral ischemia. Through the method provided by the invention, moderate doses of MB are delivered for many times after cerebral ischemia can remarkably alleviate damage degree after permanent cerebral ischemia of the mouse so as to improve the active ability of the mouse after cerebral ischemia. The use of MB is expected to provide a rescue therapeutic measure to cerebral apoplexy and alleviate permanent neurological function deficit after golden treatment period.
Owner:INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF PLA
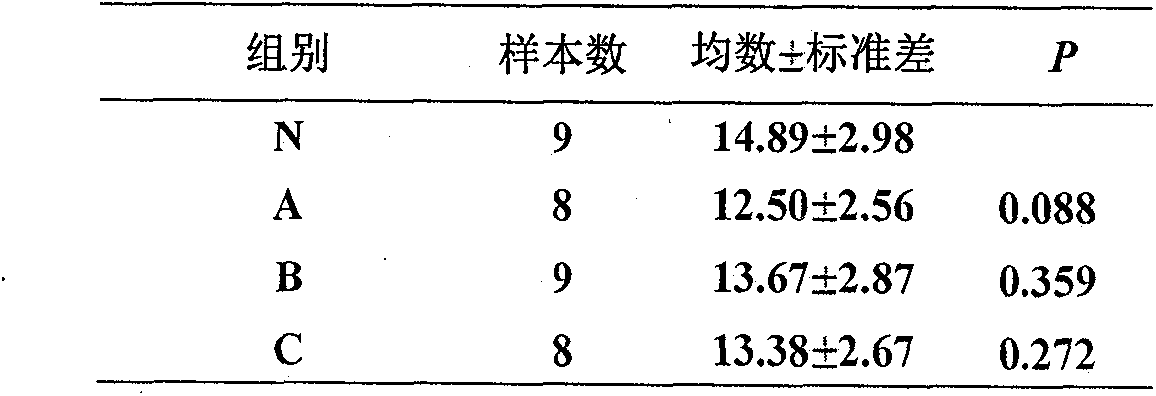
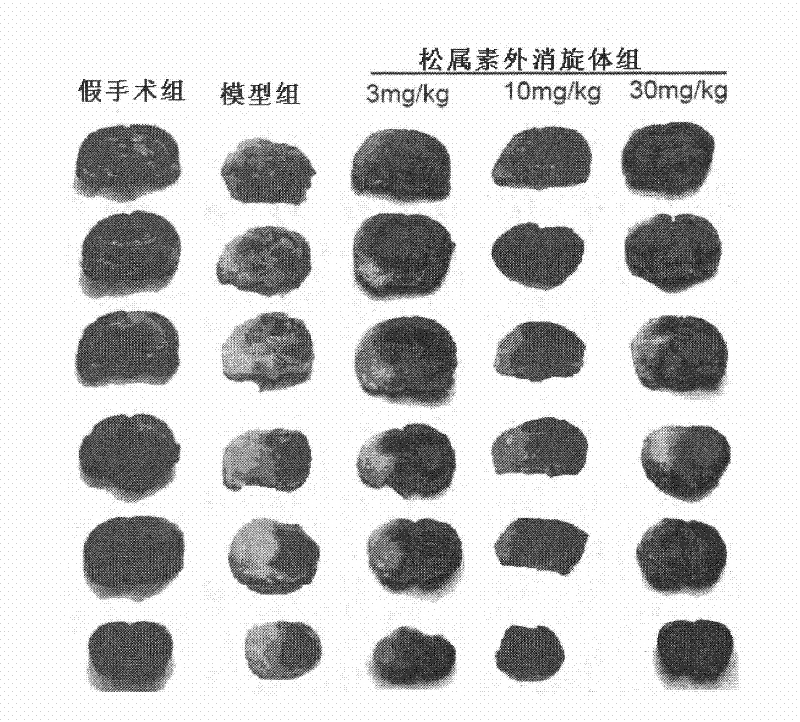
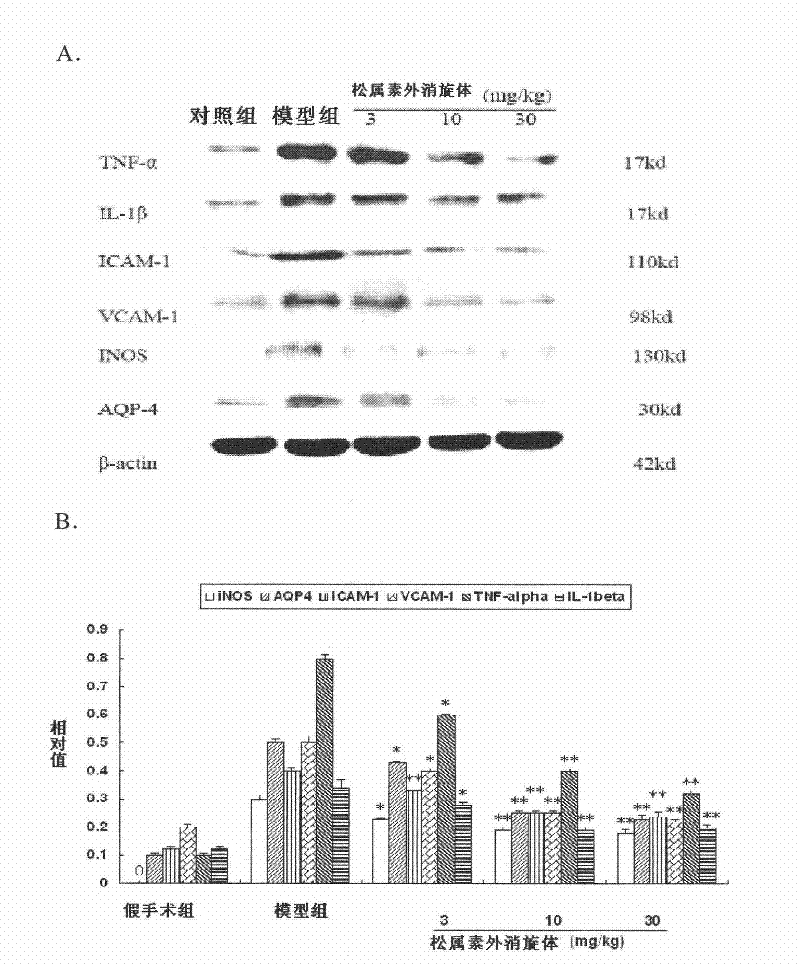
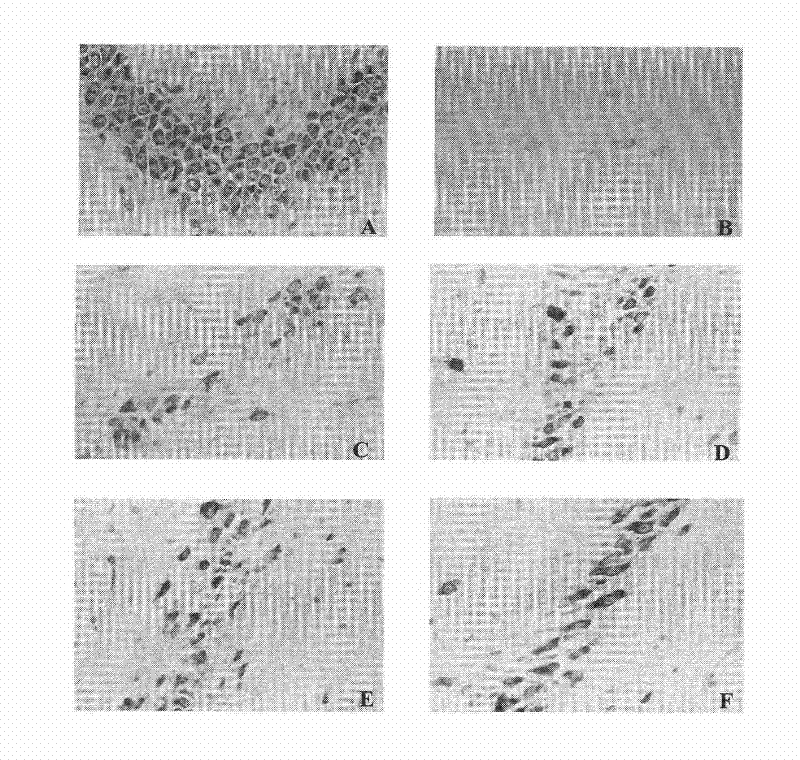
Application of pinocembrin raceme in preparation of medicals for cerebral apoplexy
ActiveCN101744806AImprove behavioral changesDecreased cerebral blood flowOrganic active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderMedicinePinocembrin
The invention relates to the medical field, discloses applications of racemes of pinocembrin, racemes of pinocembrin salt, racemes of pinocembrin precursors or racemes of pinocembrin hydrate in preparation of medicals for preventing and treating cerebral apoplexy, and further discloses the application of racemes of pinocembrin in prevention and treatment of acute ischemic stroke.
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA AN INST OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Application of serine in preparing medication for treating cerebral ischemia
InactiveCN101049295AGood anti-ischemic brain injury effectInhibit excitotoxicityOrganic active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderL serinePharmaceutical formulation
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
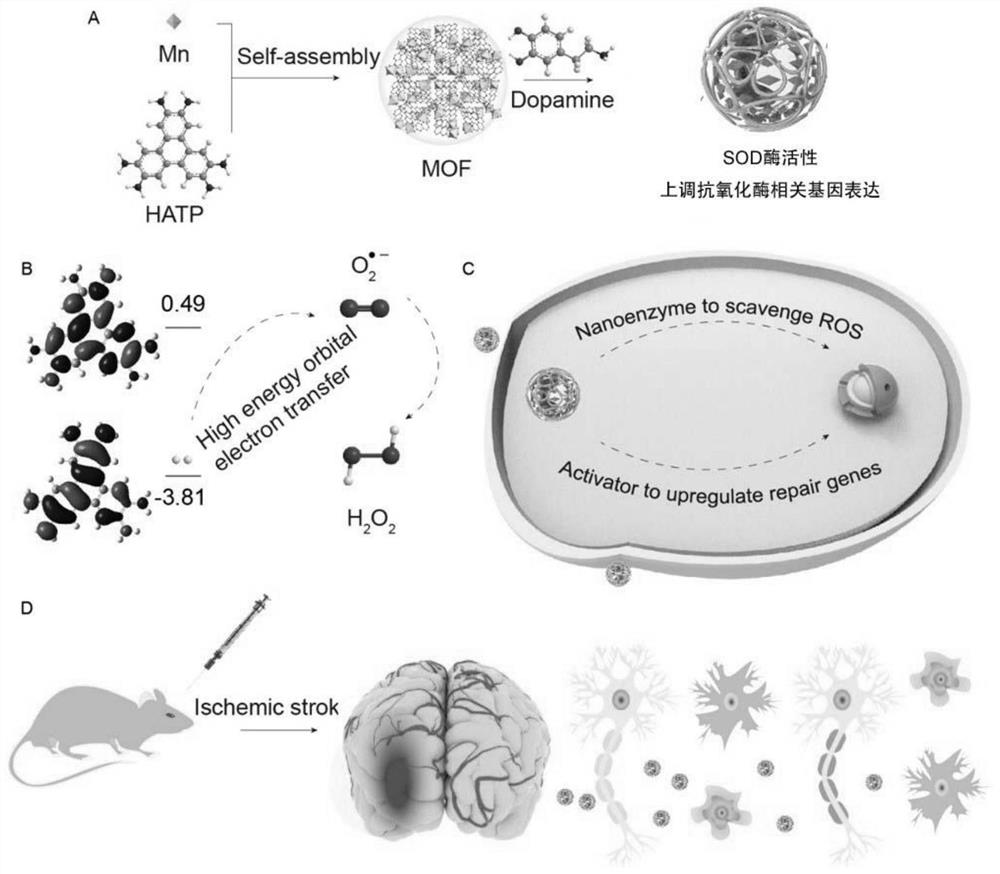
Preparation method of metal organic framework material for treating cerebral arterial thrombosis
ActiveCN113061259AImprovement of the microenvironment of the lesionReduced neuronal deathCardiovascular disorderBiophysicsBiomedical engineering
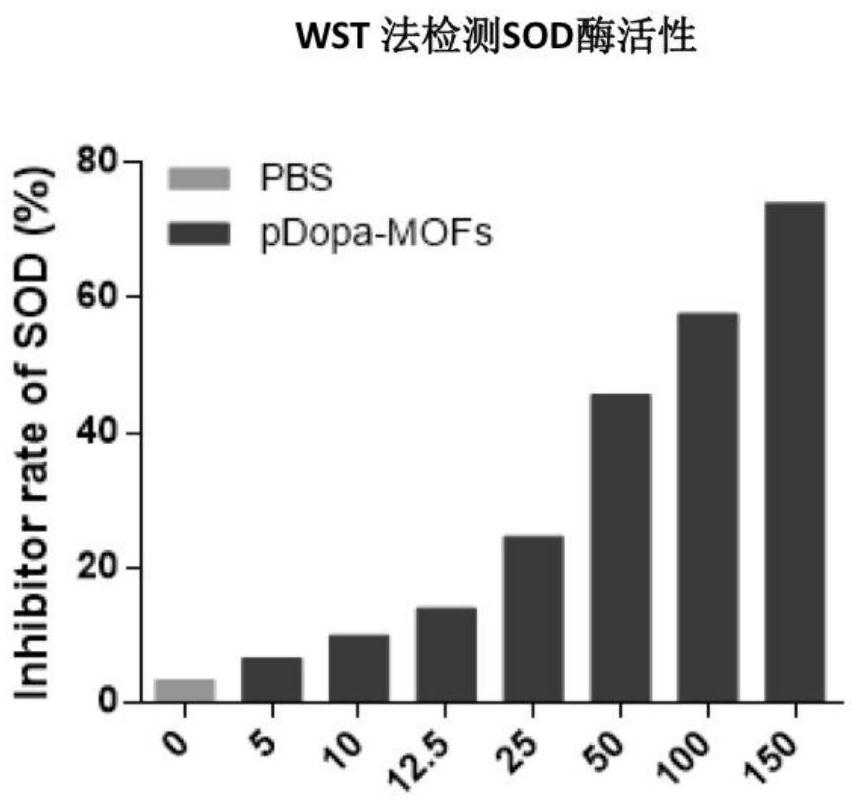
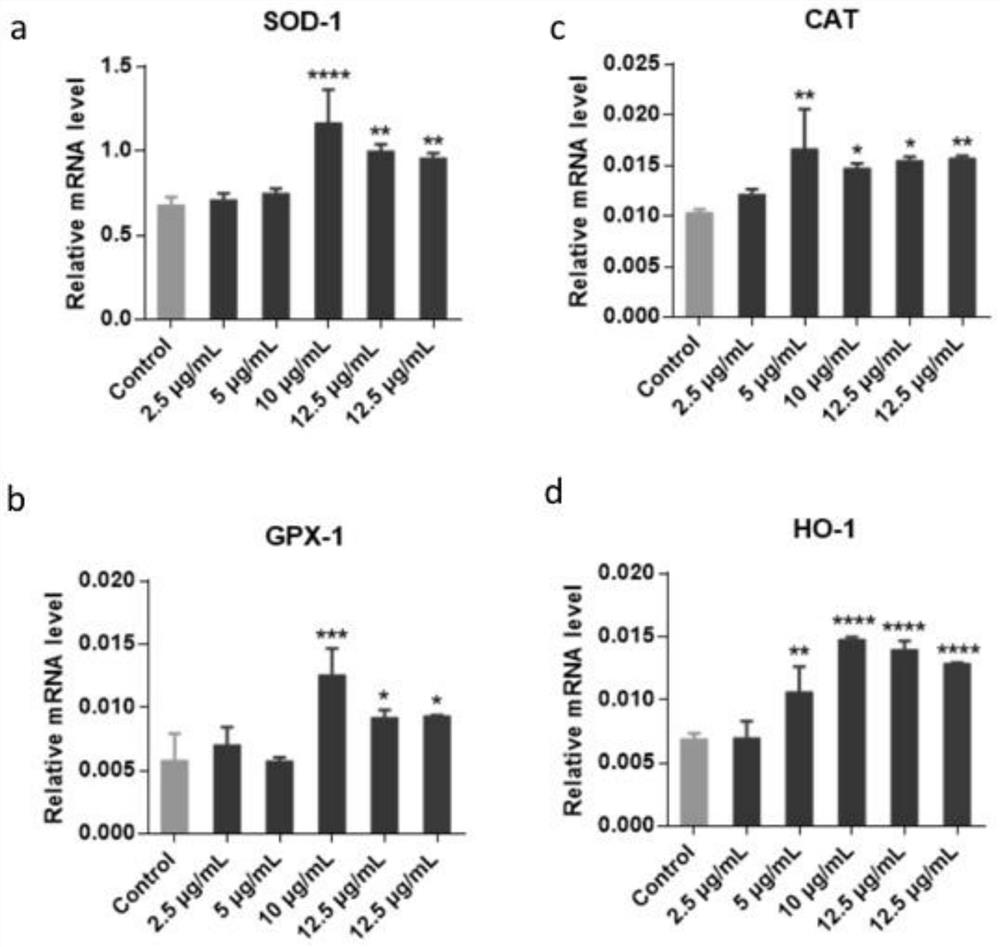
The invention discloses a preparation method of a metal organic framework material for treating cerebral arterial thrombosis. The preparation method comprises the following steps: step 1, preparing the metal organic framework material; step 2, removing unreacted raw materials and solvent molecules in the metal organic framework material, and activating the metal organic framework material; and step 3, carrying out dopamine modification on the obtained metal organic framework material. The metal organic framework material has superoxide dismutase (SOD), oxygen free radicals can be effectively converted into water and oxygen, meanwhile, the novel metal organic framework material can up-regulate the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzyme of nerve cells, and free radicals are further removed. The metal organic framework material is delivered in the stroke mouse in a lateral ventricle injection mode, the focus microenvironment is improved, the nerve cell death rate is reduced, the infarct volume is reduced, and the mouse postoperative behavioral function is effectively recovered.
Owner:XIEHE HOSPITAL ATTACHED TO TONGJI MEDICAL COLLEGE HUAZHONG SCI & TECH UNIV
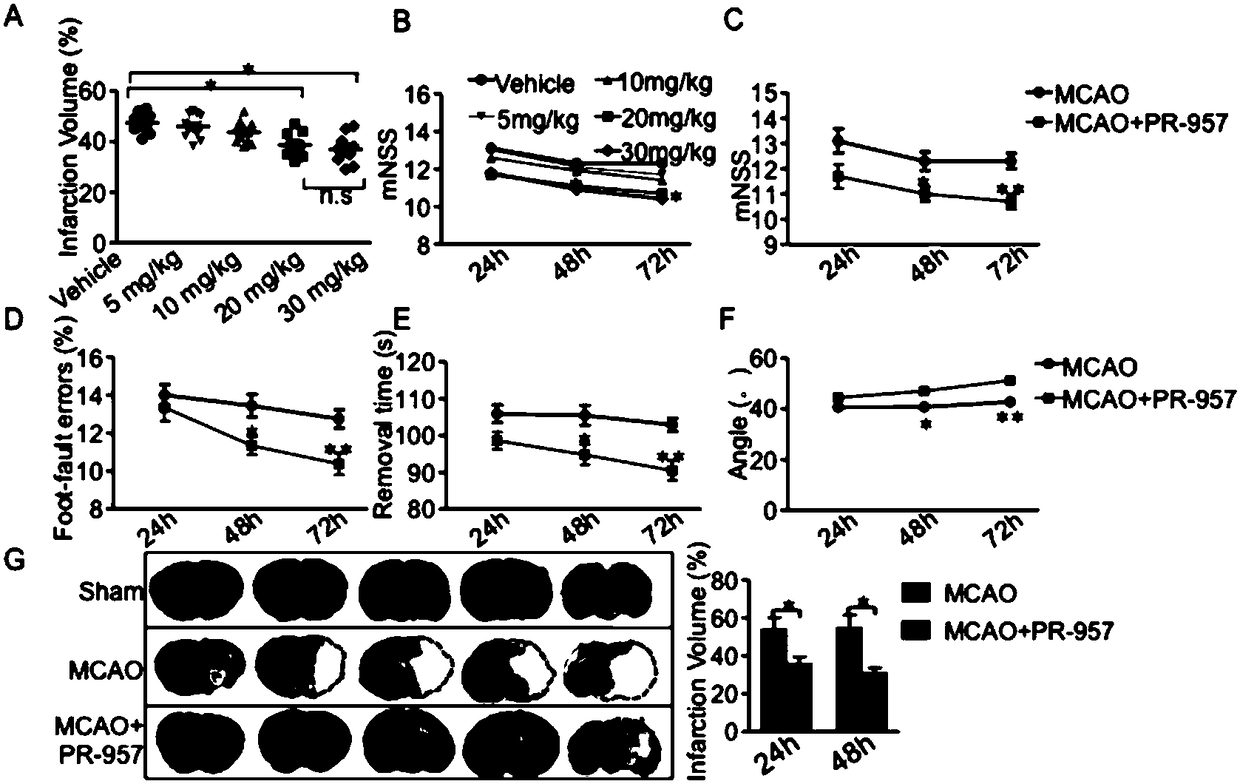
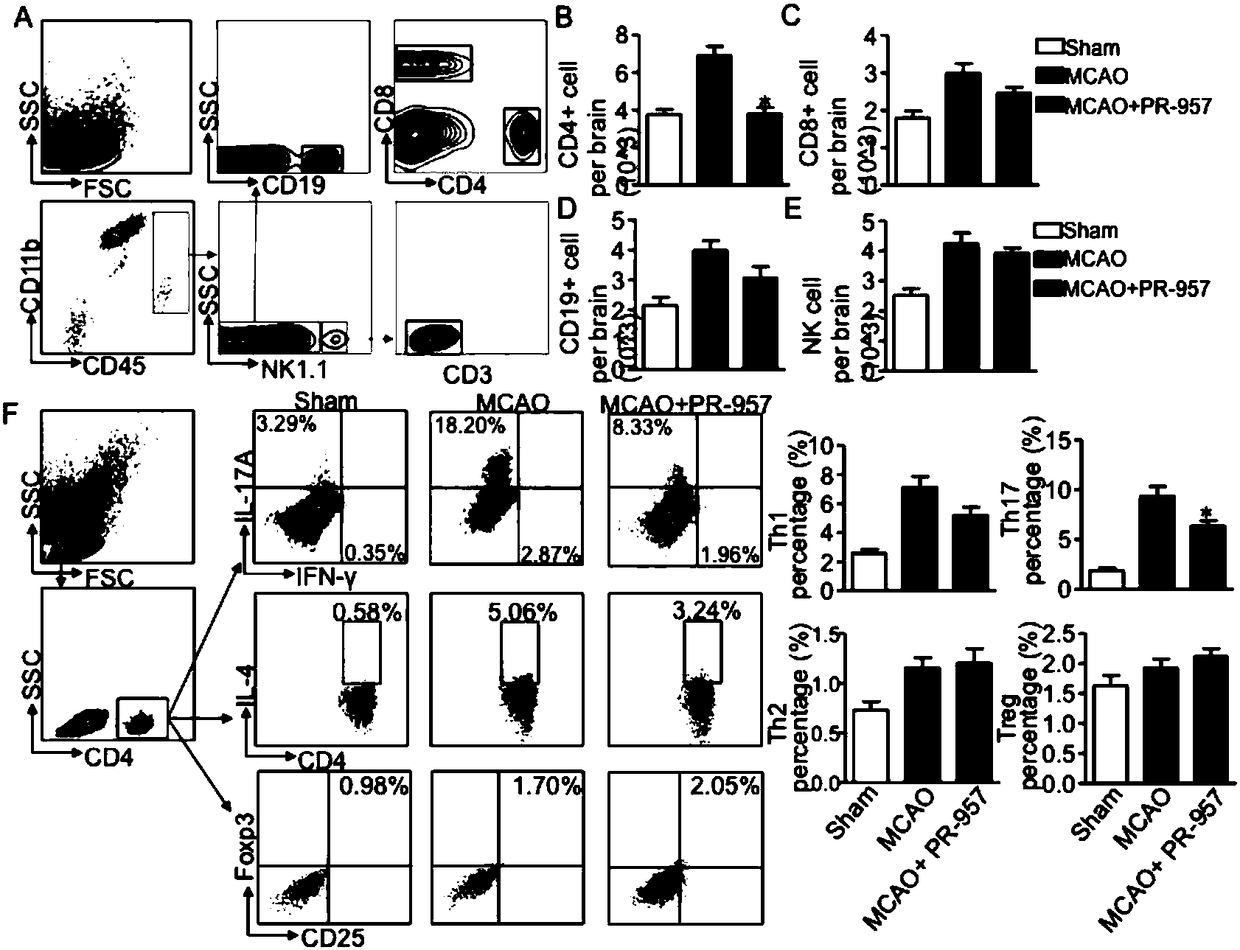
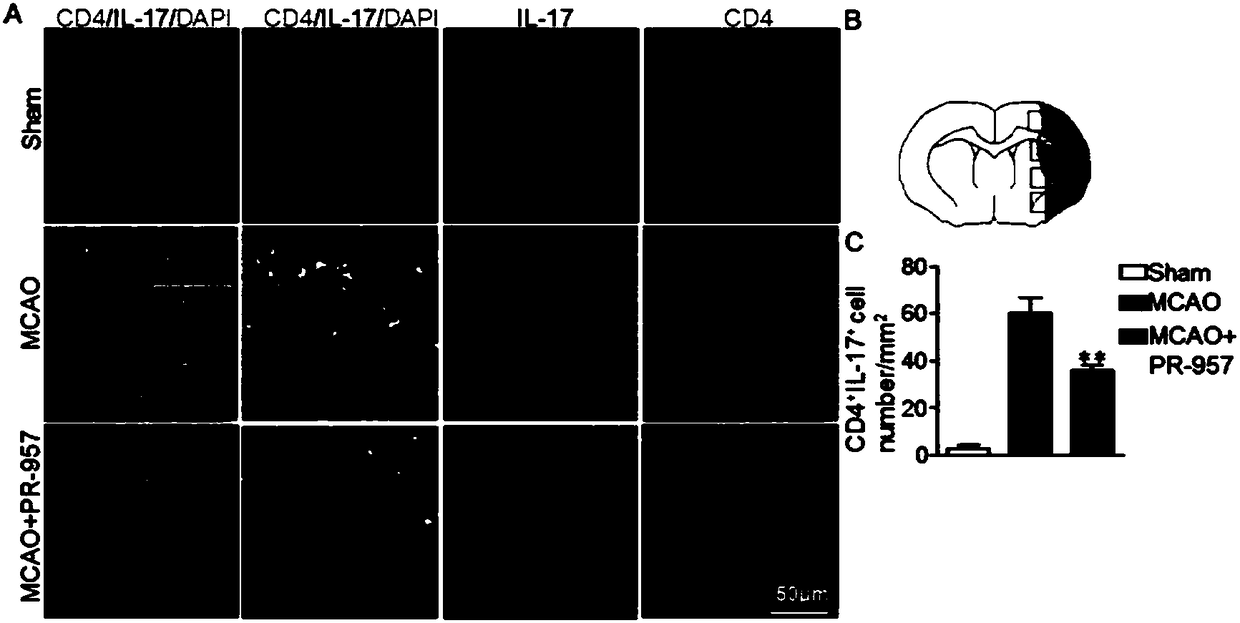
Application of PR-957 in preparing drugs for treating cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury
ActiveCN108159394AImproved neuroprotectionAnti-inflammatoryNervous disorderAntipyreticInjury brainReperfusion injury
The invention provides application of PR-957 in preparing drugs for treating cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. The technical scheme is that an MCAO animal model is taken as an experimental subjectand the role of immune proteasome in cerebral ischemic stroke is investigated by using the PR-957. The experimental results show that PR-957 therapy leads to lowering transcription level in ROR gammat and IL-17 by reducing the phosphorylation level of STAT3, so that Th17 differentiation is inhibited, cerebral inflammatory response is reduced, cerebral infarction volume is reduced and neurological dysfunction is alleviated. Therefore, the PR-957 plays a key role in regulating the inflammatory state of helper T cells of the cerebral ischemic stroke in mice and can be used as a therapeutic means of relieving brain injury of the cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF TIANJIN MEDICAL UNIV
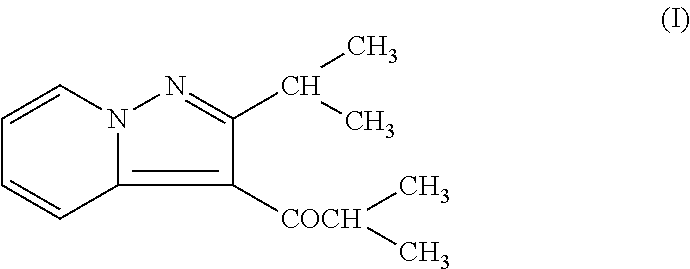
Combination of ibudilast and riluzole and methods of using same
The present disclosure relates generally to methods for treating neurodegenerative diseases, including their progressive forms. In particular, the present disclosure pertains to methods of treating or preventing neurodegenerative diseases, including their progressive forms and their associated symptoms by administering a combination of ibudilast (3-isobutyryl-2-isopropylpyrazolo[1,5-a]pyridine) and riluzole, or pharmaceutically acceptable salts of one or both thereof.
Owner:MEDICINOVA INC
Salvia miltiorrhiza bge.f.alba functional beverage and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102326813AEnsure maximum efficacyReasonable formulaFood preparationSalvia miltiorrhizaFlavor
The invention relates to healthcare beverage and a preparation method thereof. The healthcare beverage has functions on assisting the adjustment of blood fat and blood pressure. Salvia miltiorrhiza bge.f.alba and hawthorn are adopted as raw materials, and the beverage comprises the following compositions by weight ratio: 10 parts of salvia miltiorrhiza bge.f.alba, 5 parts of hawthorn, 1 part of crystal sugar, 1 part of honey, 100 parts of purified water and 0.02 percent of p-hydroxybenzoate (g.ml<-1>). The healthcare beverage has simple formula, is convenient to take, has a remarkable effect, and is suitable for the flavor of a particular group of people and satisfies the requirement on adjusting the function of the human body.
Owner:孟国良
Uses of interleukin-22(IL-22) in treating and preventing nerve damage diseases or neurodegenerative diseases
ActiveUS9352024B2Reduced infarct volumeInhibiting the loss of dopaminergic neuronsNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsIn vivoDisease cause
This invention discloses the uses of IL-22 in the treatment and prevention of a nerve damage disease or a neurodegenerative disease. In particular, the invention discloses the uses of IL-22 or IL-22 dimers as follows: (i) can protect neurons to recover the functions of injured neurons after ischemic nerve damage in animals in vivo, thus enabling effective treatment of nerve damage diseases, (ii) can significantly inhibit the loss of dopaminergic neurons in substantia nigra in PD model animal, enhance the functions of dopaminergic neurons, significantly reduce neuronal apoptosis in hippocampus, improve learning and memory capacity of AD model rats, and effectively prevent neuronal loss, thereby enabling more effective treatment of neurodegenerative diseases.
Owner:EVIVE BIOTECHNOLOGY (SHANGHAI) LTD
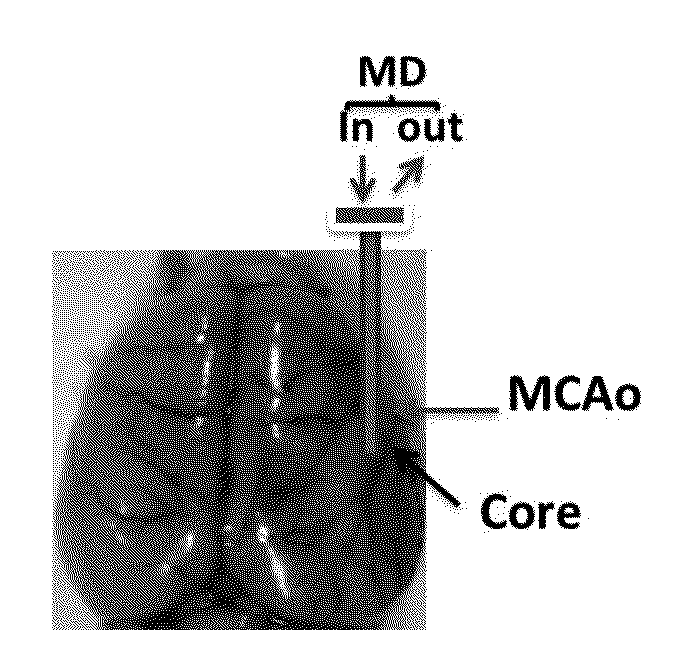
Method for treating brain injury or stroke
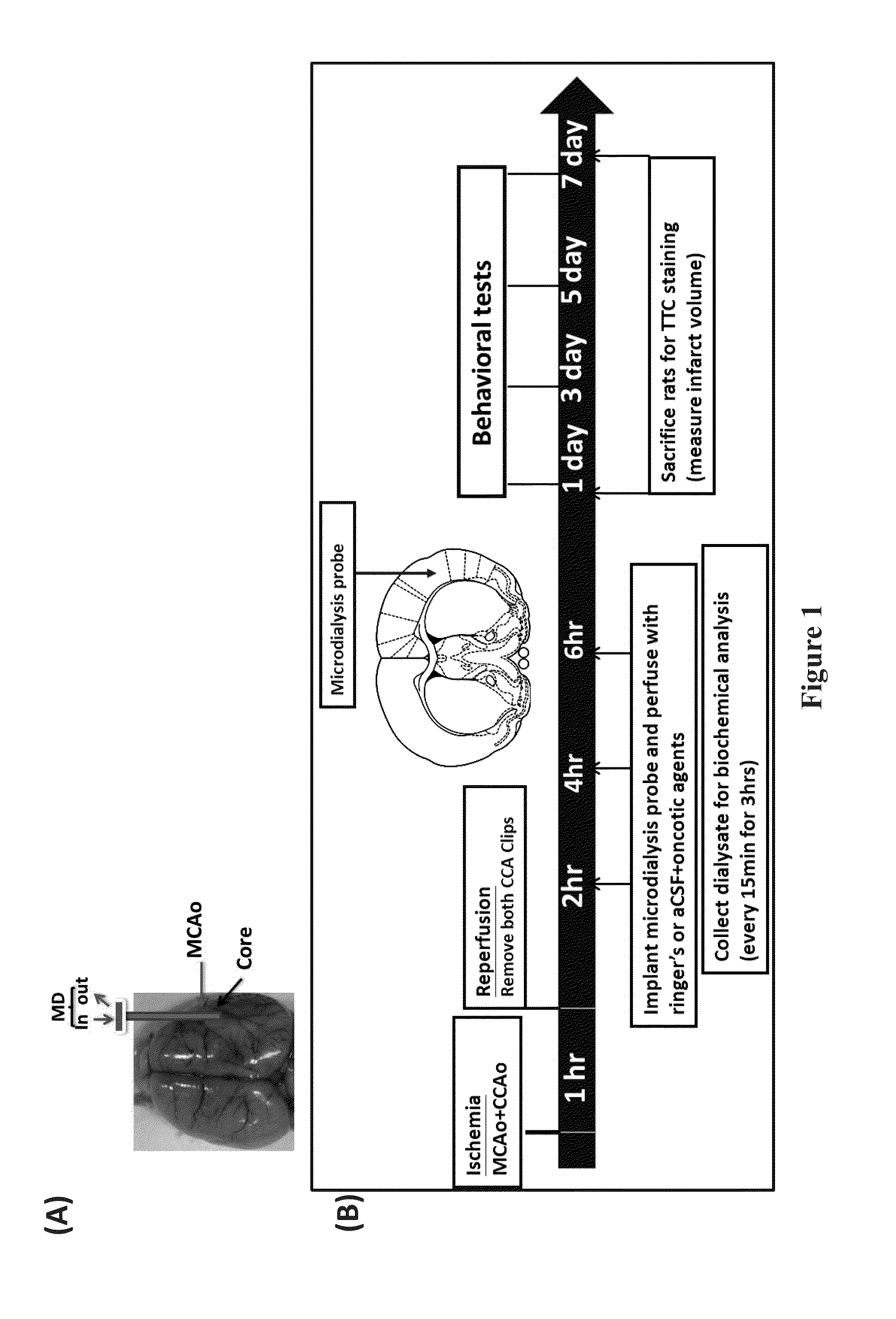
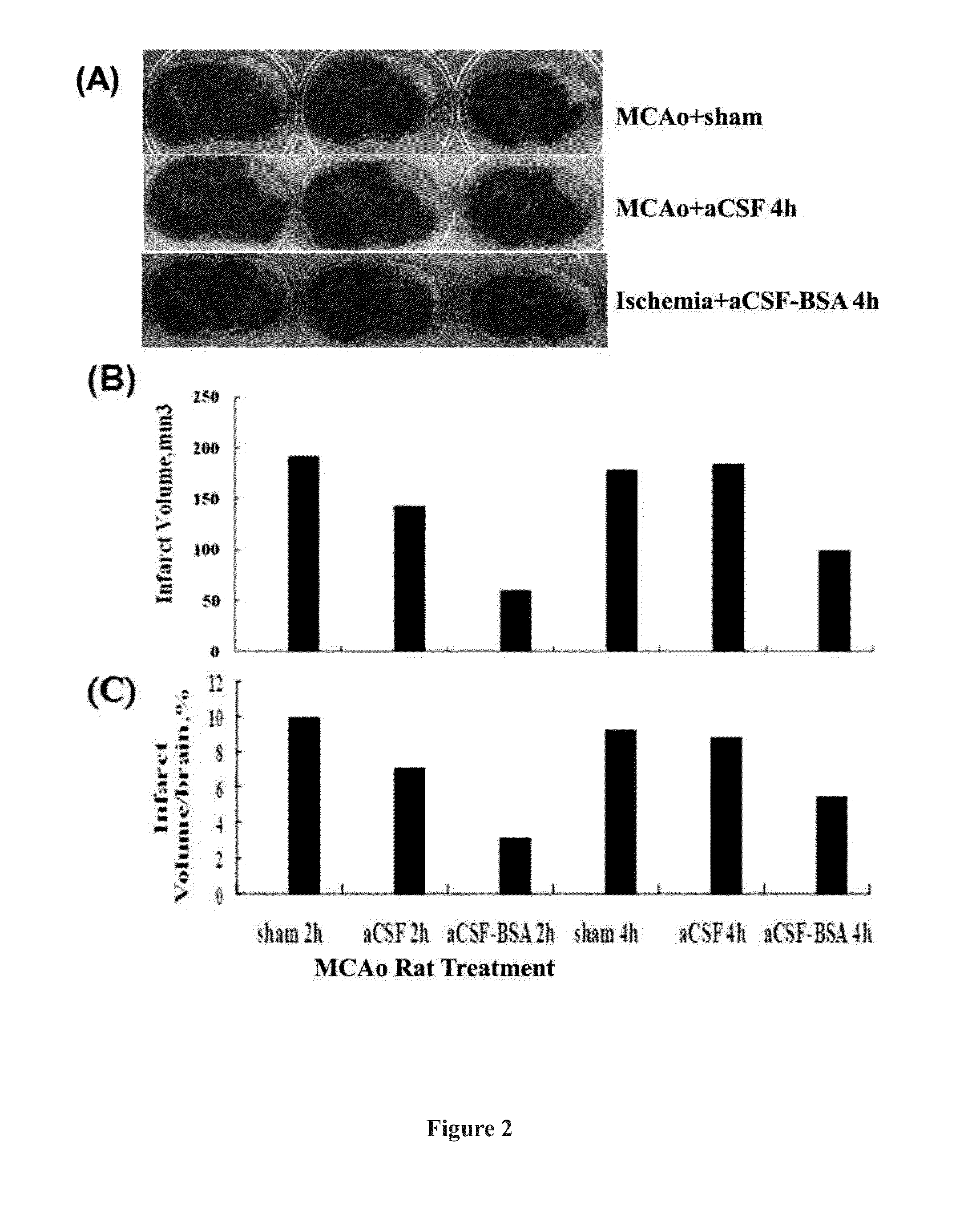
InactiveUS20140155816A1Reduce infarct volumePromote recoveryNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsBrain damageDialysis membranes
The present invention provides a method for treating brain injury or stroke in a subject in need thereof, comprising implanting a microdialysis probe into the injury or insult core of the subject and perfusing the probe with an oncotic agent dissolved in a physiologically acceptable buffer, wherein the microdialysis probe comprises a dialysis membrane with a molecular weight cutoff less than the molecular weight of the oncotic agent.
Owner:EU SOL BIOTECH
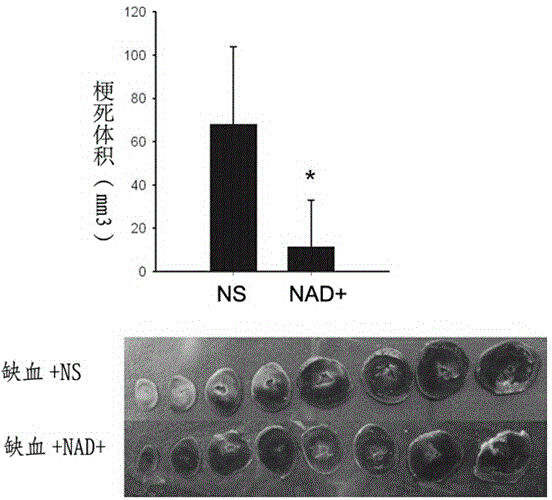
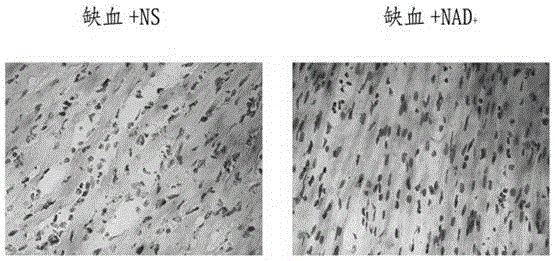
Application of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide in preparation of drug for preventing and treating heart ischemic injuries
InactiveCN105168236AProtectiveReduced infarct volumeOrganic active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderCardiac ischaemiaAdditive ingredient
The invention relates to application of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide as an active ingredient in preparation of a drug for preventing or treating heart ischemic injuries. In experiments, caudal vein normal saline injection and a heart ischemia operation are carried out on rats in a control group, it is found through research results that a great number of apoptosis signals (TUNEL positive signals) appear on the hearts, while apoptosis signals of rats, on which caudal vein NAD+solution injection is carried out, in an experiment group can be effectively reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHEST HOSPITAL
Application of oxymatrine in medicines for treating neonatal hypoxic ischemic brain damages
InactiveCN104739830AReduce apoptosis rateReduced infarct volumeOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderPreventing injuryCerebral infarction
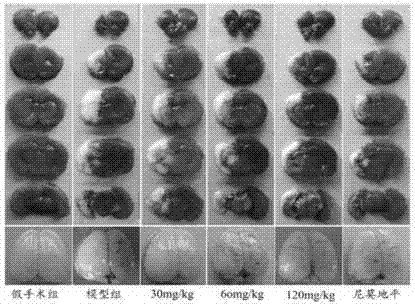
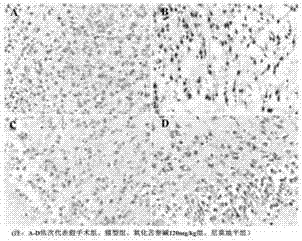
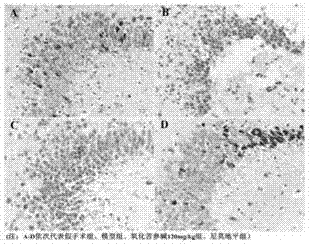
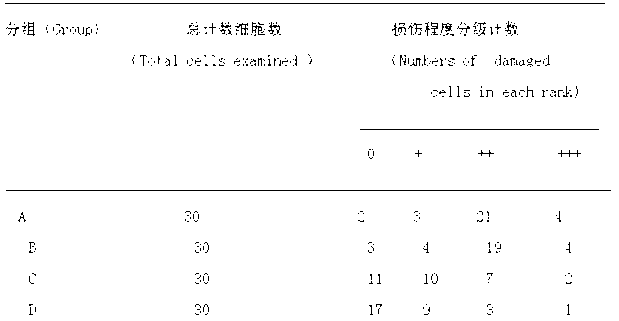
The invention discloses an application of oxymatrine in medicines for treating neonatal hypoxic ischemic brain damages. An experiment result shows that oxymatrine has a certain dose-effect correlation when used in a safe dose range; when the dose is 120mg / kg of body weight, the volume of ischemia area cerebral infarction and neuron apoptosis rate can be reduced; pathological damages to brain tissues can be relieved; the activity of antioxidase in the brain tissues can be improved; and the content of malondialdehyde is lowered. The oxymatrine has the effects of preventing injuries and deaths caused by neonatal hypoxic ischemic brain damages and promoting neural functional recovery.
Owner:NINGXIA MEDICAL UNIV
Edaravone composition for injection
InactiveCN103301119AGood treatment effectReduce dosePowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsSide effectHalf-life
The invention provides an edaravone composition for injection, and relates to the technical field of medicine manufacturing. The main medicine of the composition comprises edaravone and melatonin, wherein the melatonin comprises a quick release part and a cyclodextrin-included slow release part. According to the edaravone composition for injection provided by the invention, the therapeutic effect of edaravone is improved, instability caused by oral administration of MT (Melatonin) is avoided and MT is quick to distribute and eliminate and the like, and the first pass effect of MT is reduced. The dosage of edaravone is reduced, and the side effect of edaravone is reduced. The design of dosage combining quick release and slow release is in accordance with secretion characteristic of MT, so that the problem of half-life period of MT is solved and the bioavailability of a product is improved. The melatonin combined with edaravone acted on nerve cells has the synergistic effect of preventing encephaledema, reducing the infarct volume and improving the neurological function.
Owner:HAINAN WEI KANG PHARMA QIANSHAN
Method of Reducing Injury to Mammalian Cells
InactiveUS20090281037A1Prevent negative consequenceReduce signalingNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsNR1 NMDA receptorN methyl D aspartate receptors
A method of inhibiting the binding between N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors and neuronal proteins in a neuron is disclosed. The method comprises administering to the neuron an effective inhibiting amount of a peptide replacement agent for the NMDA receptor or neuronal protein interaction domain that effect said inhibition of the NMDA receptor-neuronal protein interaction. The method is of value in reducing the damaging effect of injury to mammalian cells. Postsynaptic density-95 protein (PSD-95) couples neuronal N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARS) to pathways mediating excitotoxicity, ischemic and traumatic brain damage. This coupling was disrupted by transducing neurons with peptides that bind to modular domains on either side of the PSD-95 / NMDAR interaction complex. This treatment attenuated downstream NMDAR signaling without blocking NMDAR activity, protected cultured cortical neurons from excitotoxic insults, dramatically reduced cerebral infarction volume in rats subjected to transient focal cerebral ischemia, and traumatic brain injury (TBI) in rats.
Owner:NONO INC
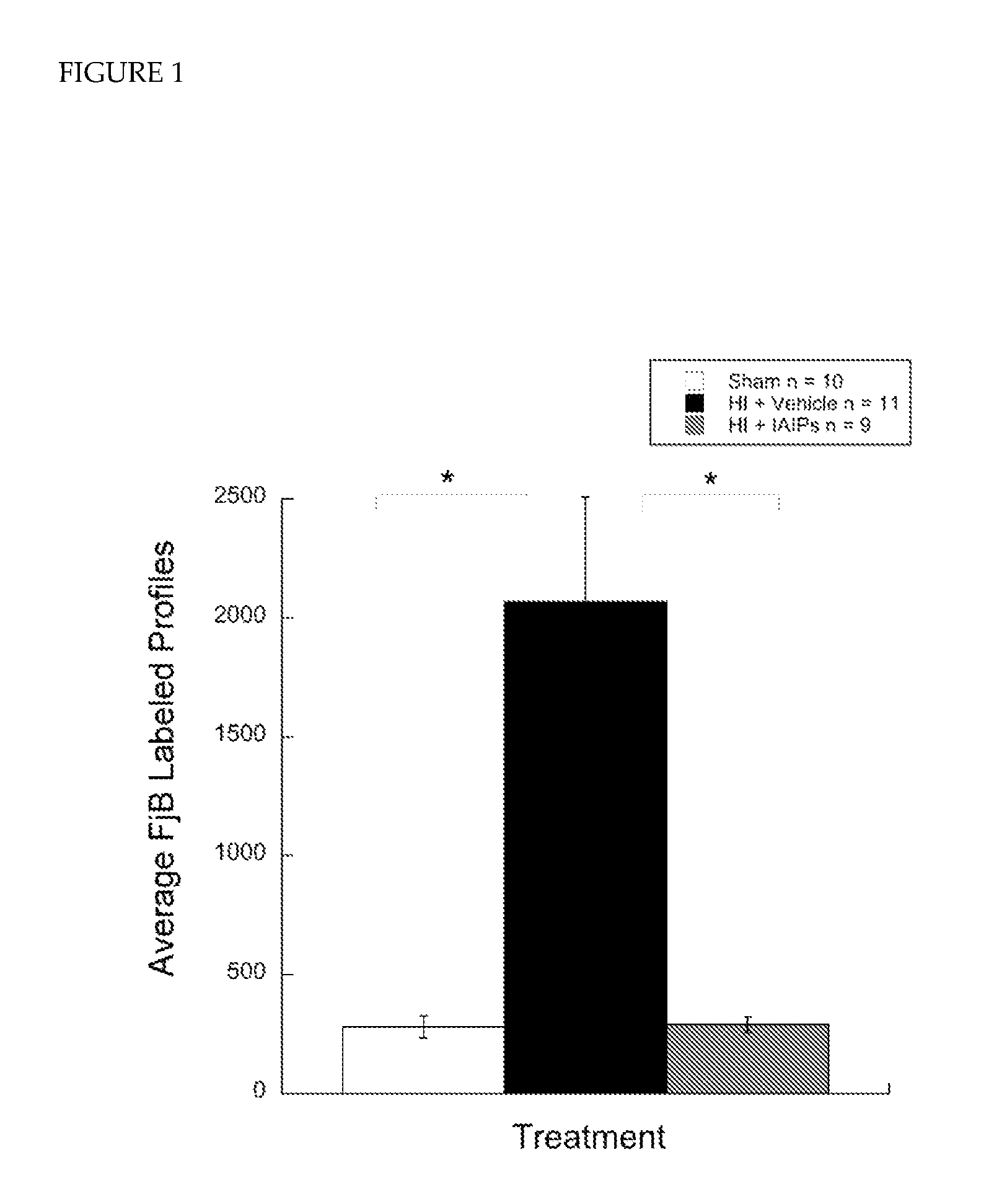
Treatment of disease using inter-alpha inhibitor proteins
ActiveUS9572872B2Reduced likelihoodReduce riskPeptide/protein ingredientsCardiovascular disorderDiseaseViral infection
The invention relates to methods of treatment of medical conditions (e.g., diseases and injuries) in a mammal (e.g., a human), such as hypoxia / ischemia, burns, and viral infections (e.g., influenza, West Nile virus, and Dengue fever), in adults and in children (e.g., neonates) by administering a composition that includes an IAIP.
Owner:WOMEN & INFANTS HOSPITAL OF RHODE ISLAND +1
Preparation and applications of phenylquinolinone-based and flavone-based derivative
ActiveCN109111400ARestore nerve functionReduced infarct volumeNervous disorderOrganic chemistryDiseaseNervous system
The present invention relates to a phenylquinolinone-based and flavone-based derivative and a preparation method thereof, wherein the derivative is a histamine H3 receptor antagonist, can protect andrestore the normal function of central nervous system, especially can be used in neurodegenerative diseases and ischemic brain injury, and has great clinical application value.
Owner:HANGZHOU BIO SINCERITY PHARMA TECH CO LTD
Methods of treating huntington's disease comprising administering metal chelators to the upper one-third of the nasal cavity
ActiveUS20140179789A1Preventing and minimizing and treating neurologic complicationReduce weight lossBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsHuntingtons choreaNasal cavity
Methods for preconditioning and / or providing neuroprotection to the animal central nervous system against the effects of Huntington's disease. Therapeutic agents are administered to the upper third of the nasal cavity to bypass the blood-brain barrier and access the central nervous system directly to avoid unwanted and potentially lethal side effects. Therapeutic agents include those substances that interact with iron and / or copper such as iron chelators, copper chelators, and antioxidants. A particular example of such therapeutic agents is the iron chelator deferoxamine (DFO). An effective amount of DFO may be administered to the upper third of the nasal cavity of a patient at risk for, or diagnosed with Huntington's disease. The effective amount of DFO is delivered directly to the patient's central nervous system for preconditioning, preventing and / or treating Huntingon's disease.
Owner:HEALTHPARTNERS RESEACH FOUND
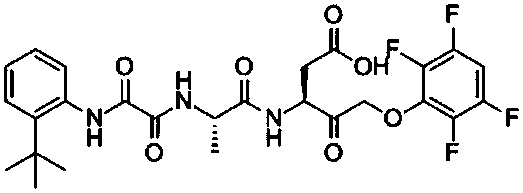
Application of emricasan in preparation of medicine for treating ischemia/reperfusion injury
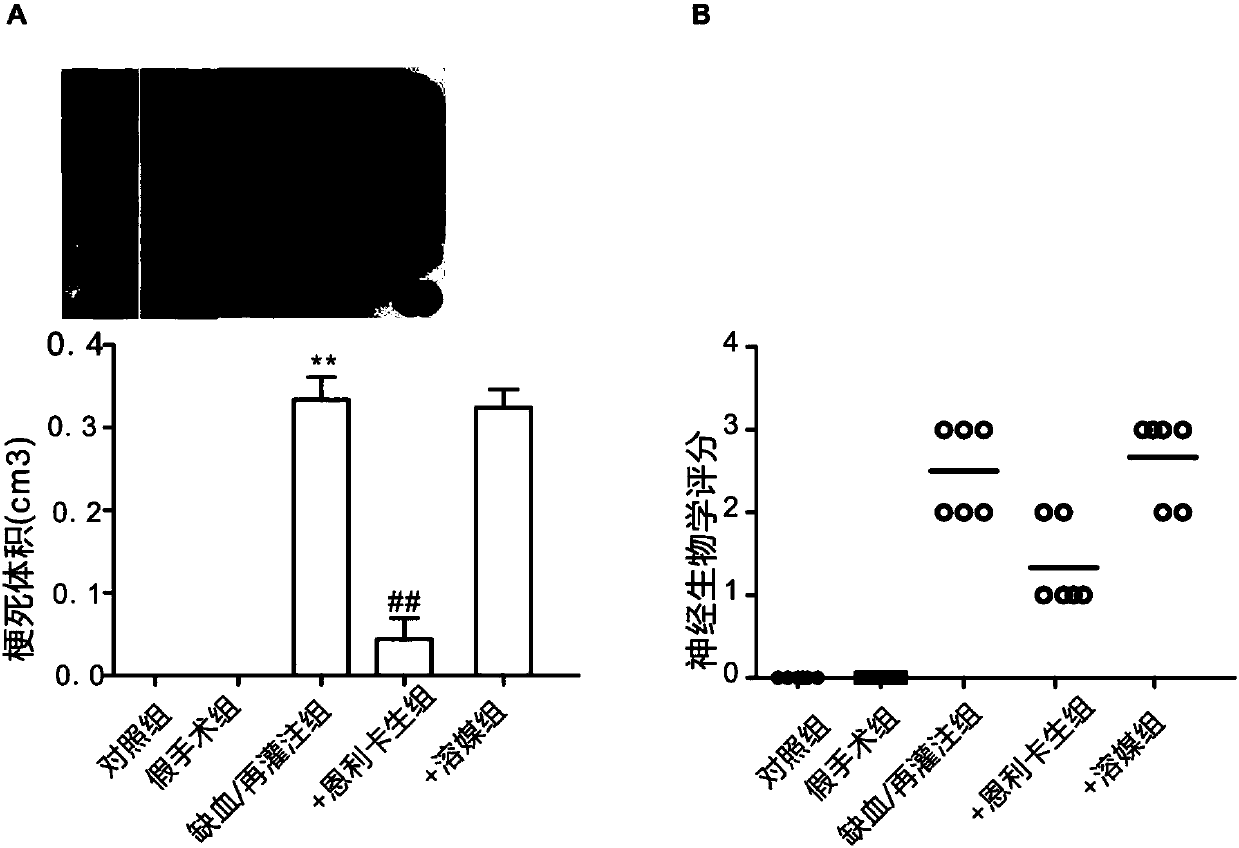
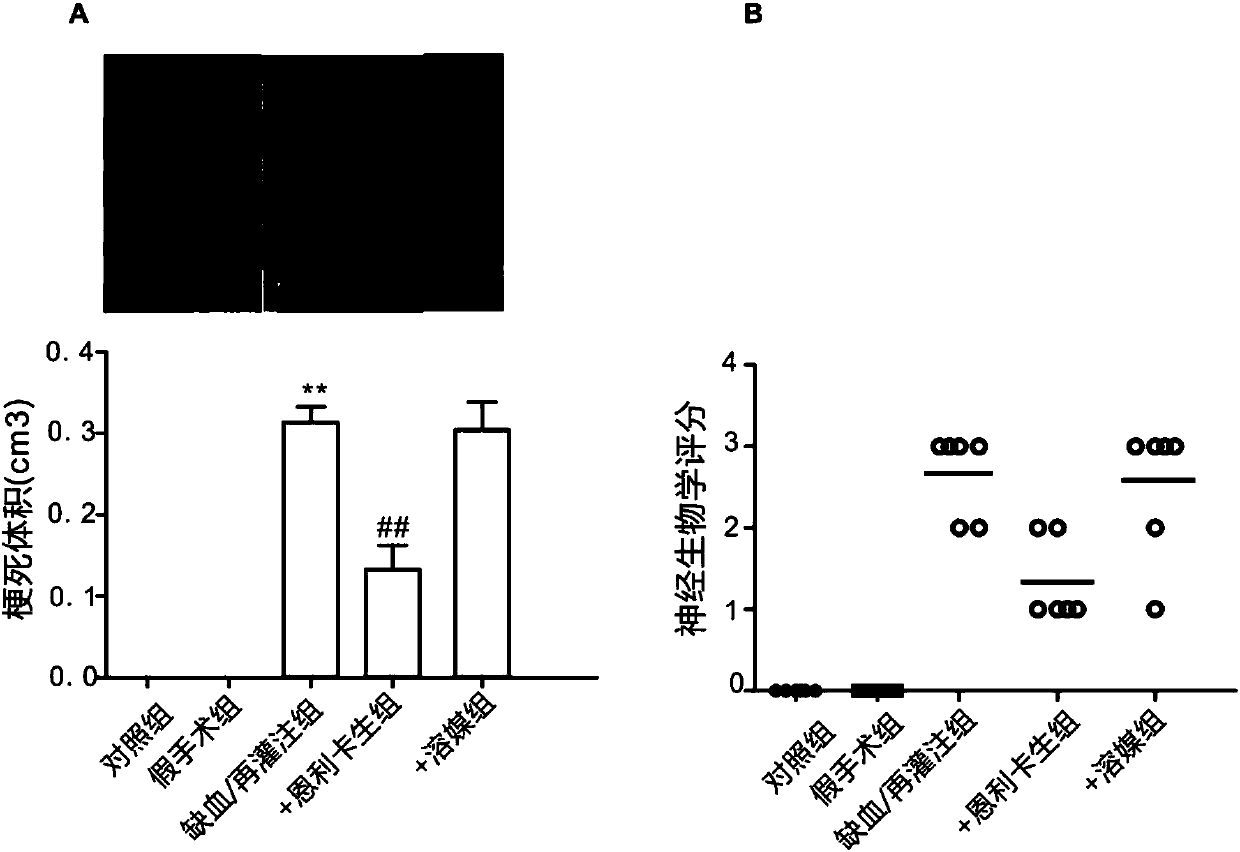
ActiveCN107648213AReduce apoptosisReduced infarct volumeOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderReperfusion injuryCerebral arterial thrombosis
The invention discloses application of emricasan in the preparation of a medicine for treating ischemia / reperfusion injury. By using emricasan in treatment of ischemia / reperfusion injury, especially treatment of brain tissue neuropathy and even especially protective effect of cerebral ischemia / reperfusion (cerebral arterial thrombosis), cerebral ischemia / reperfusion injury can be remarkably mitigated.
Owner:湖南恒兴医药科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com