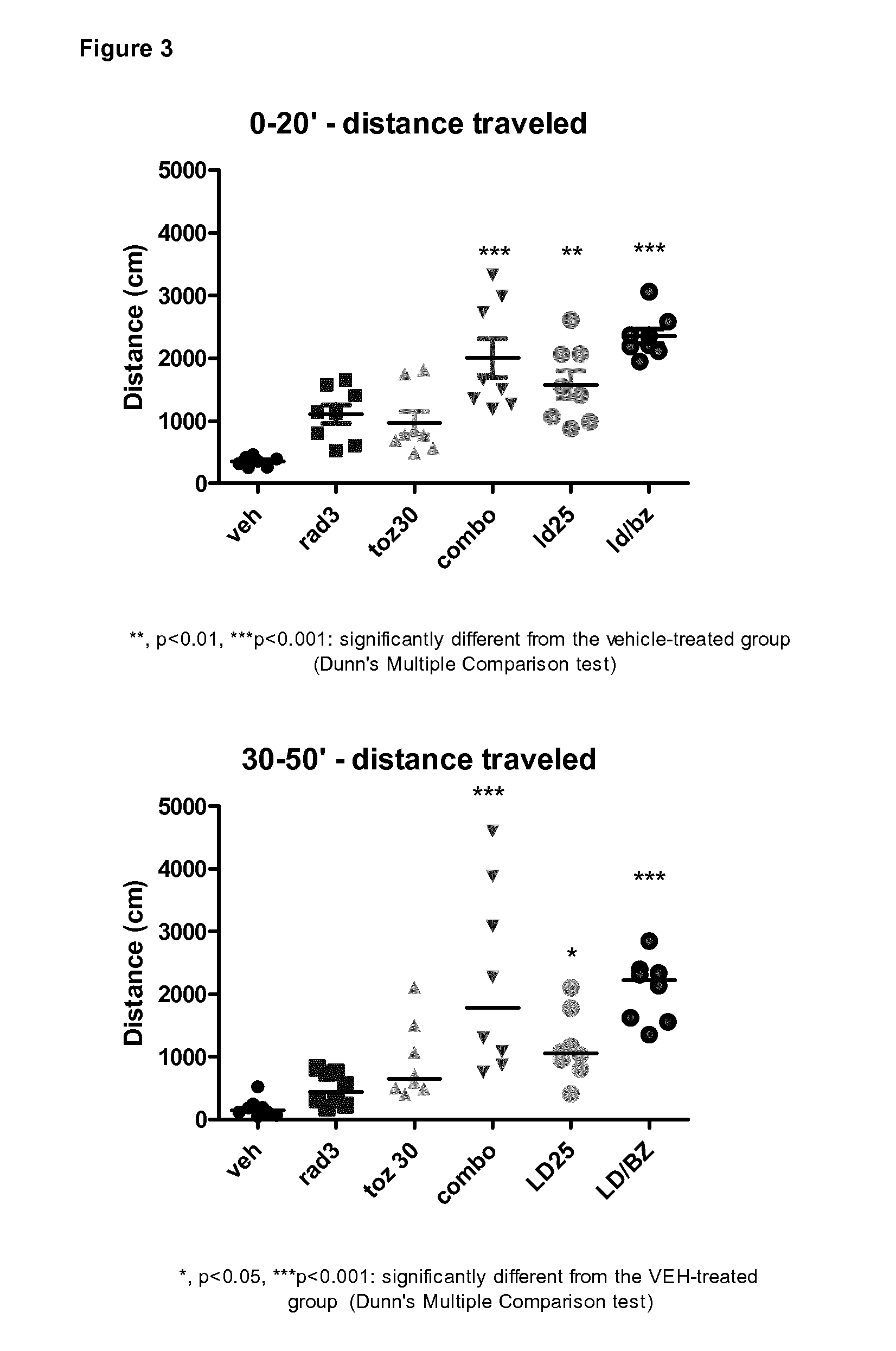
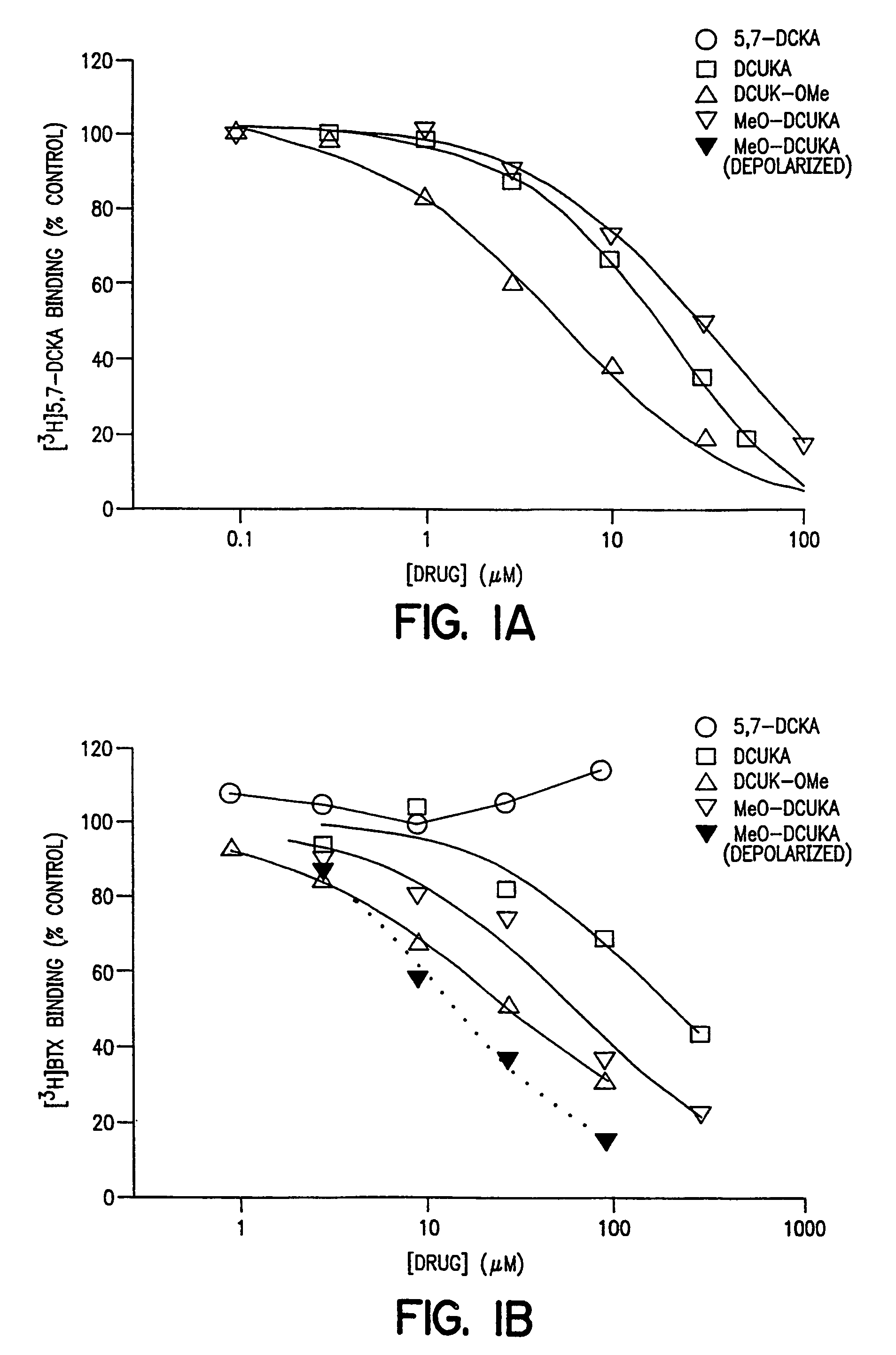
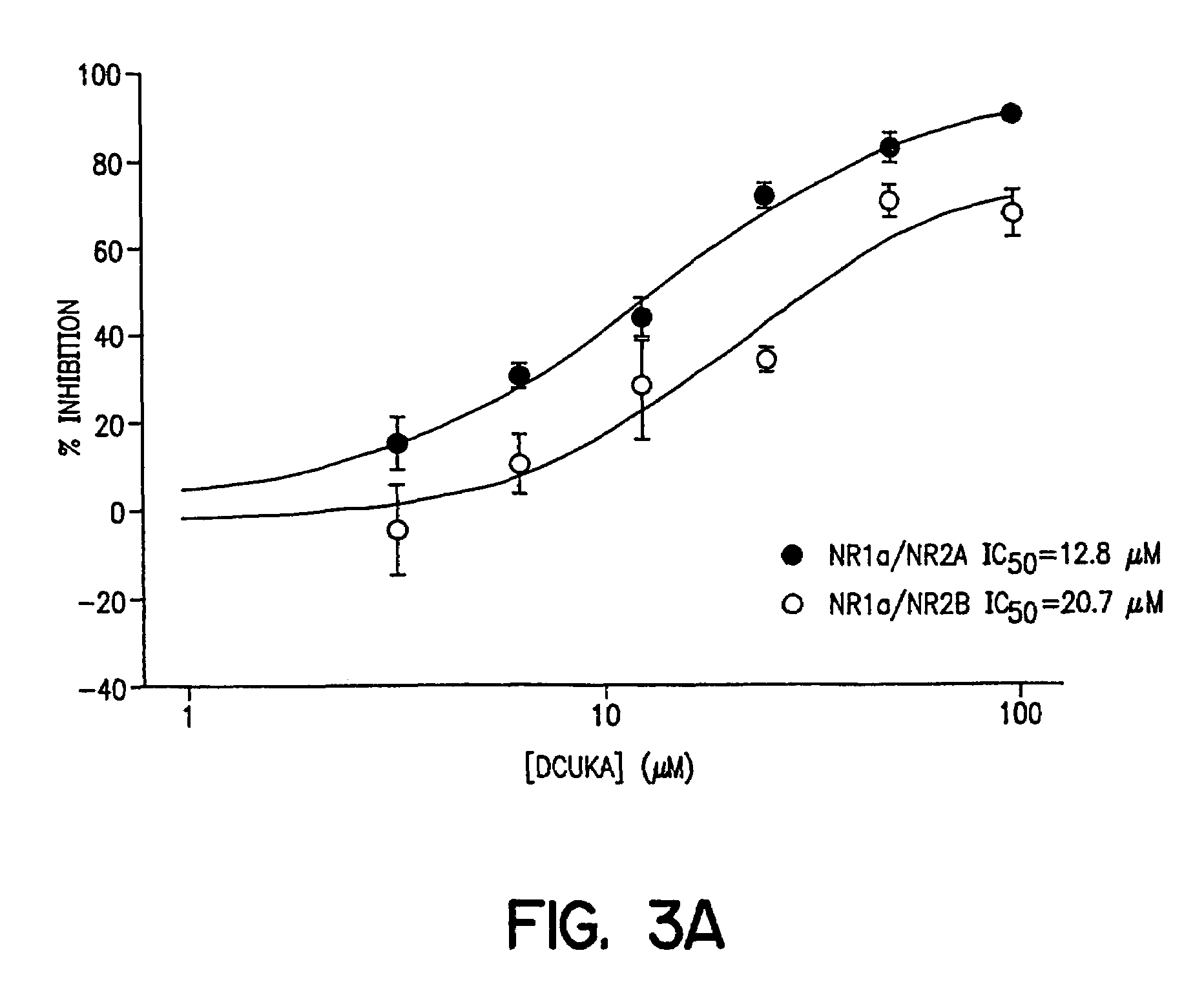
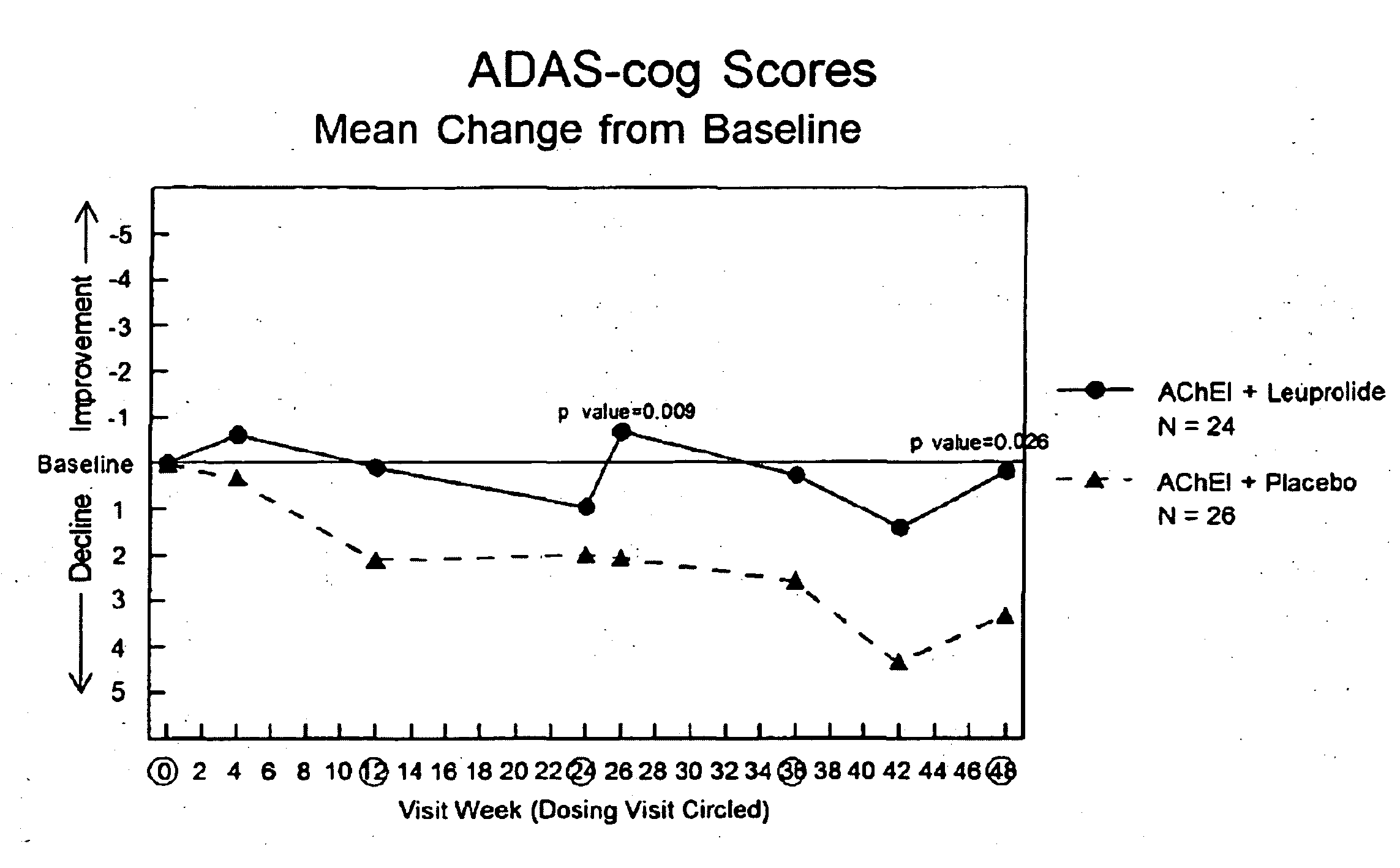
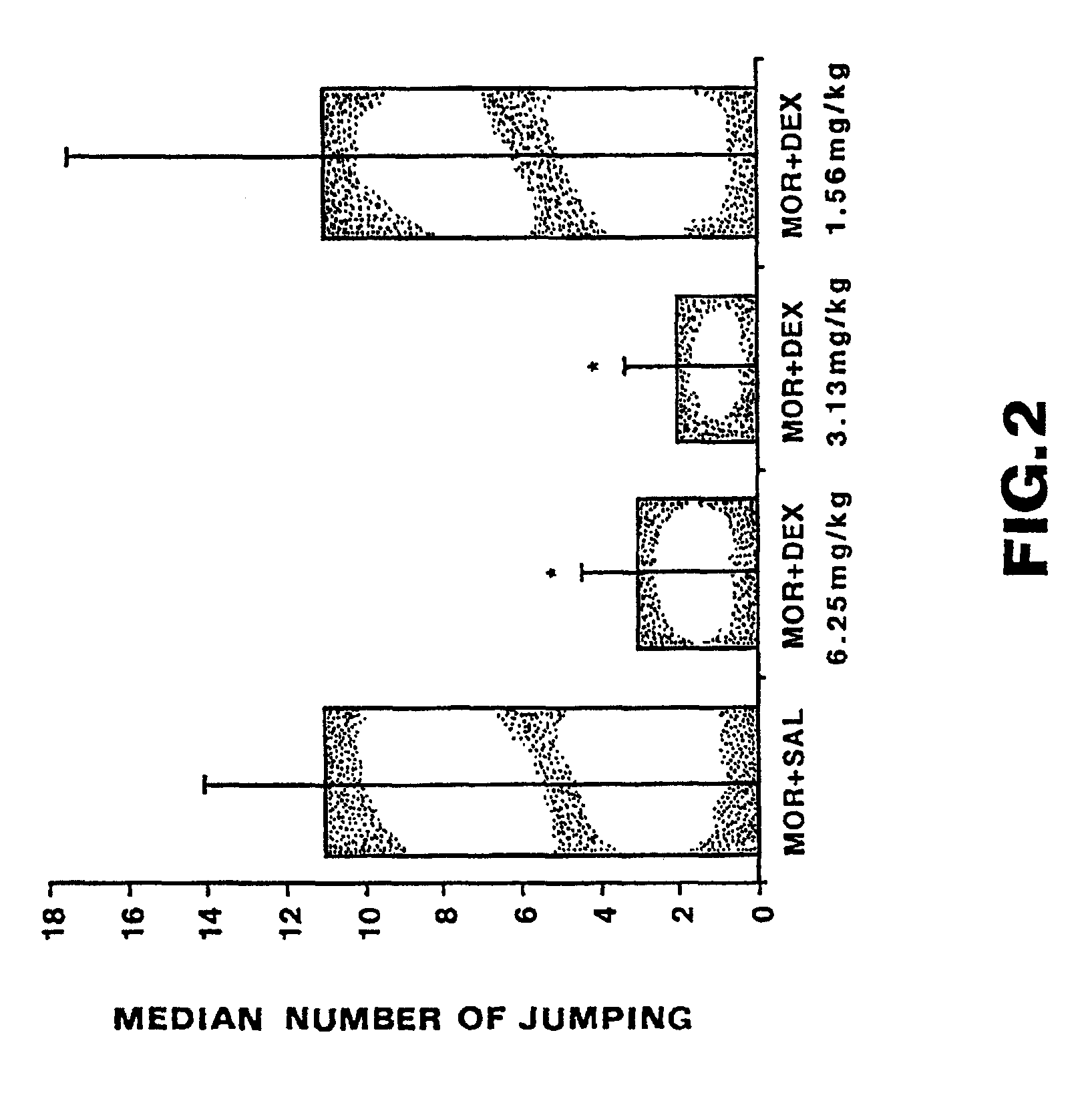
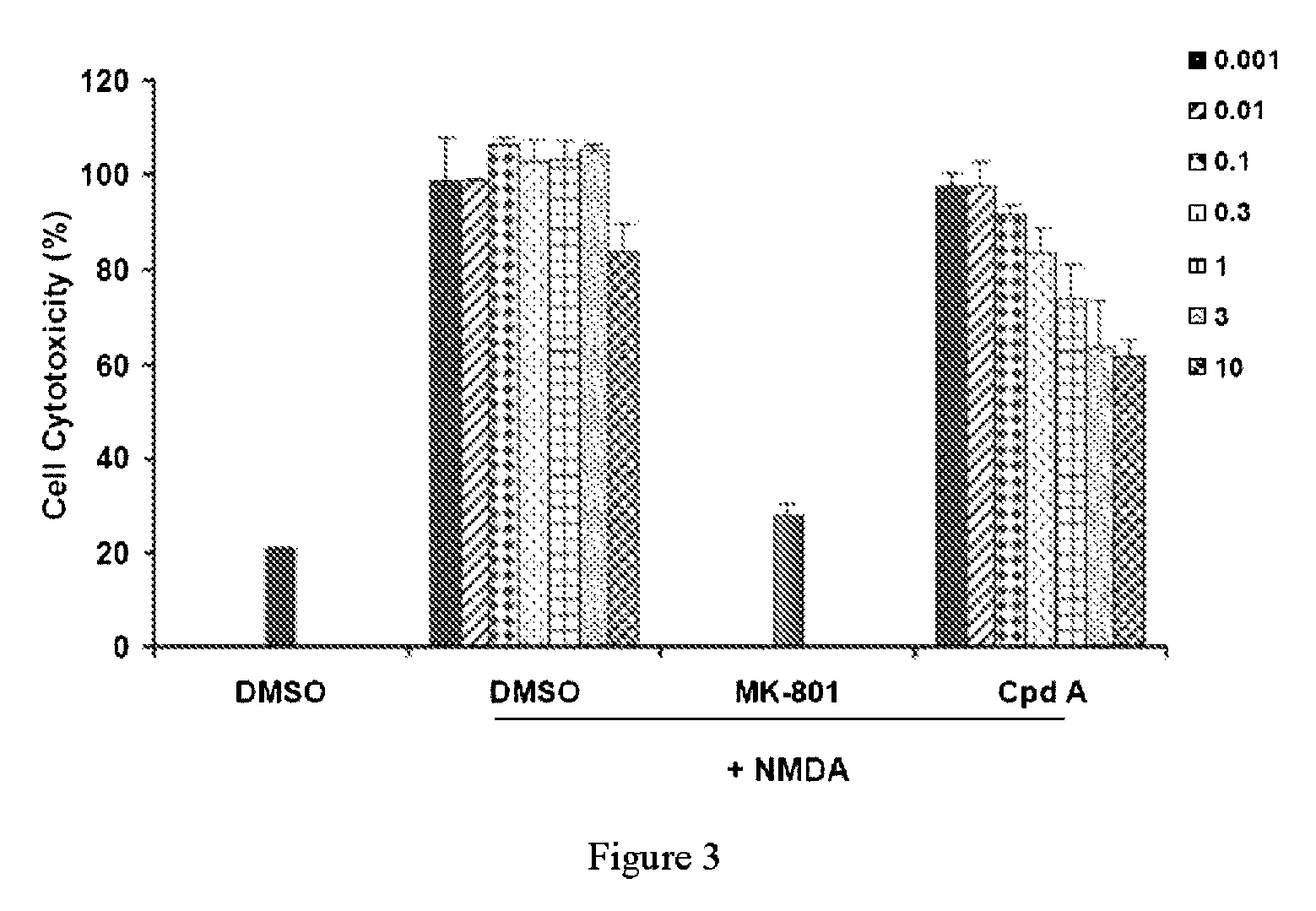
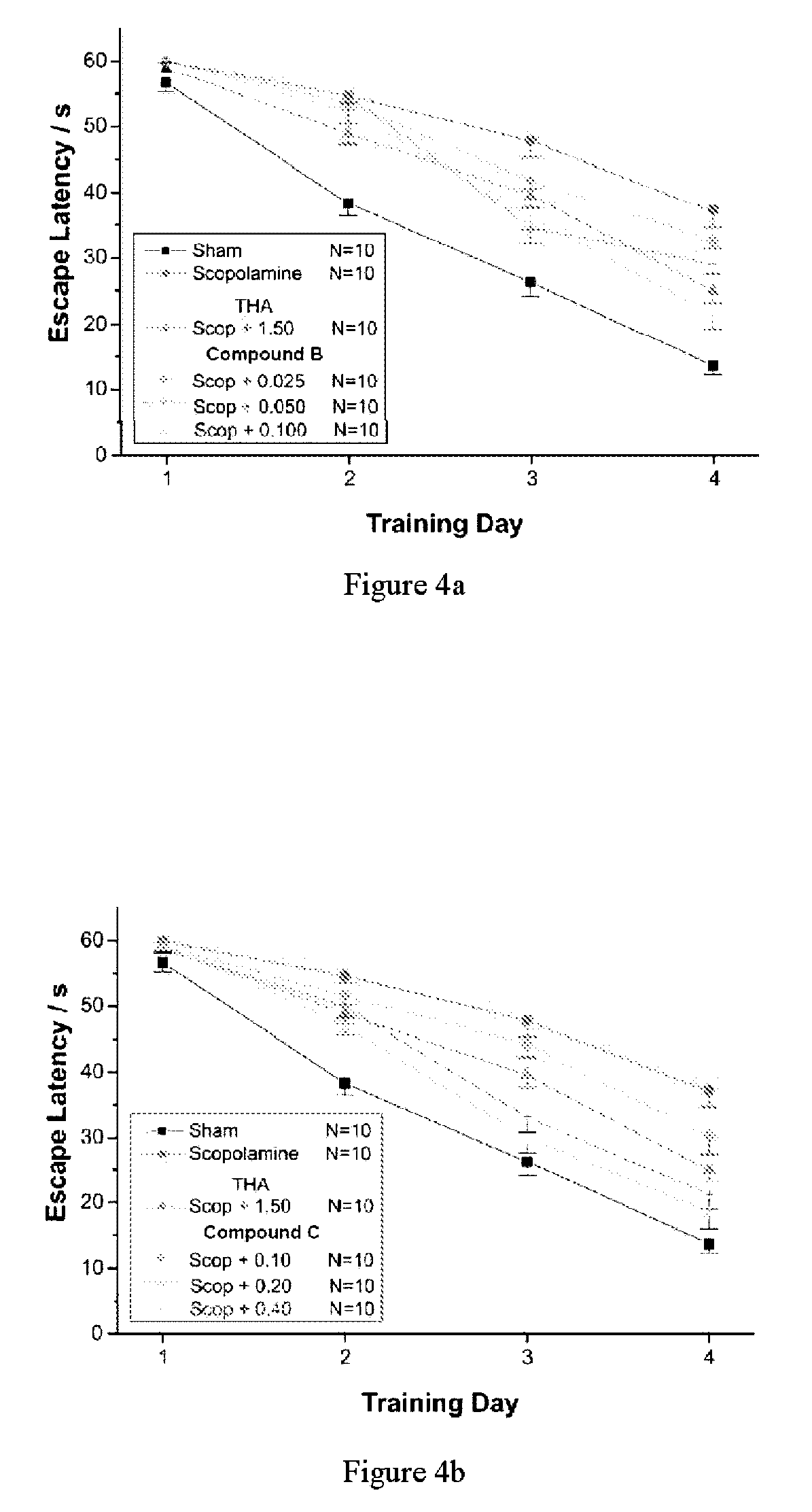
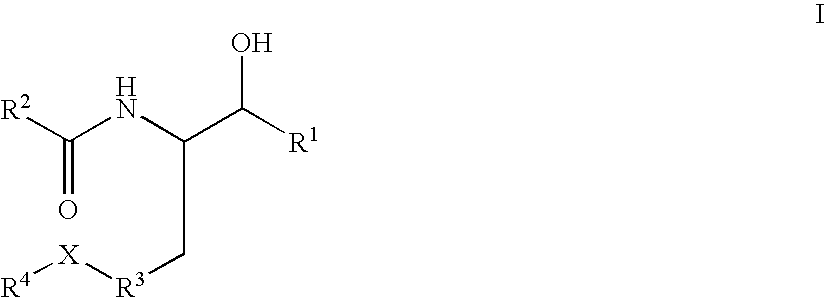
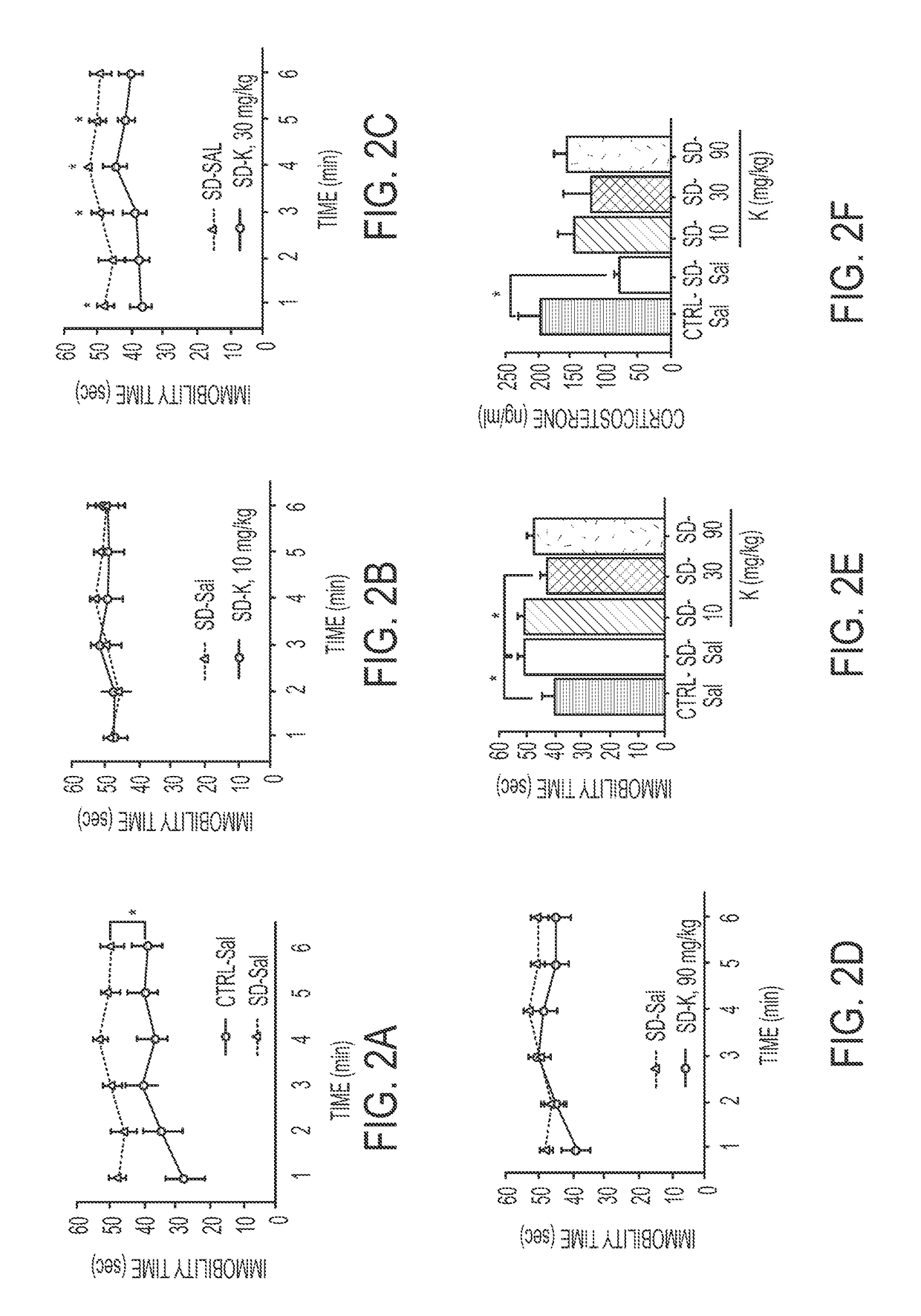
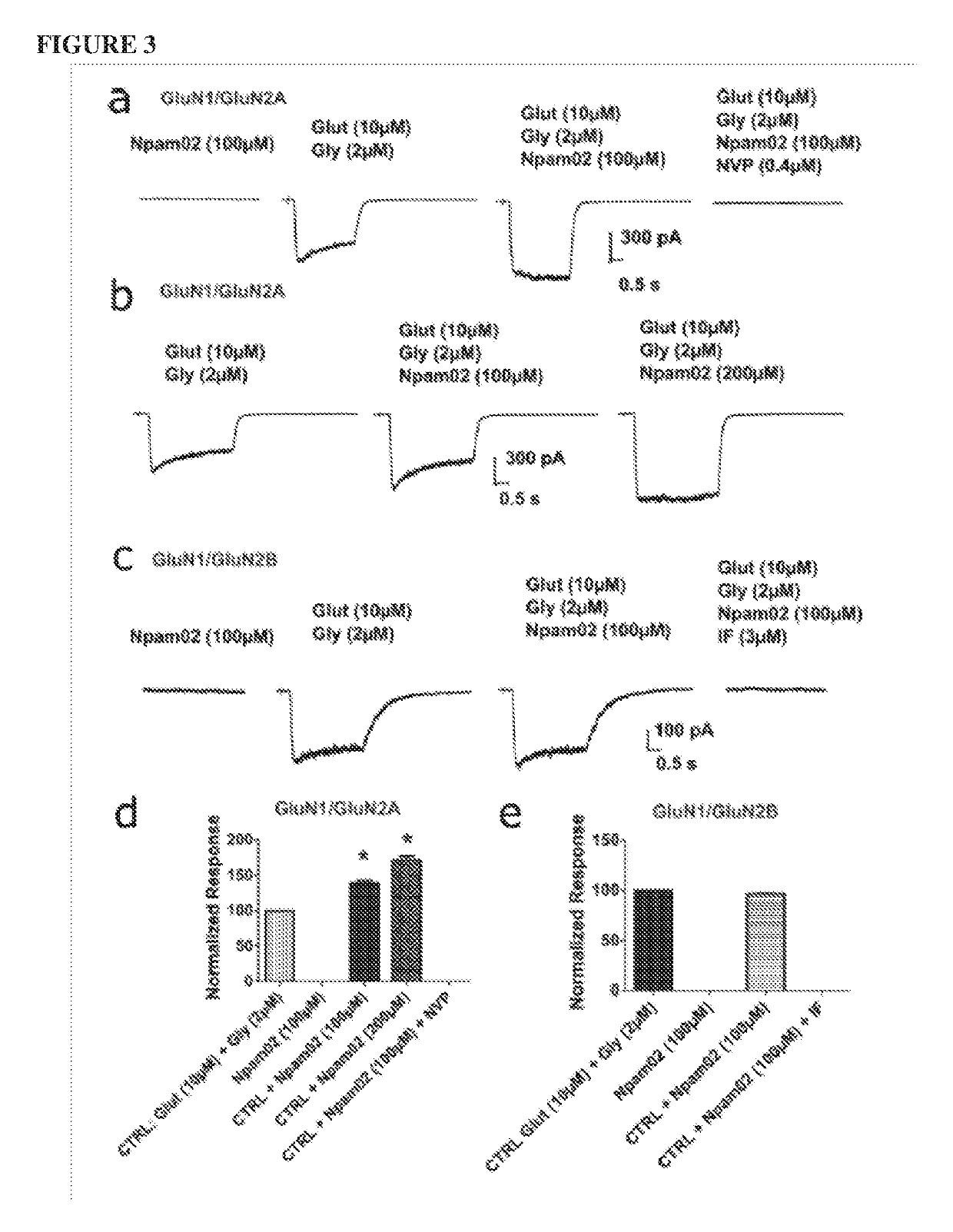
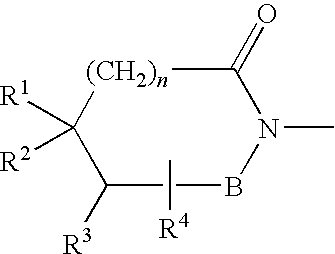
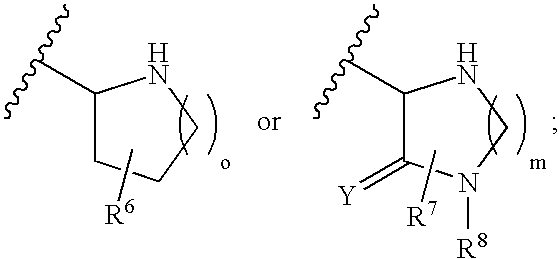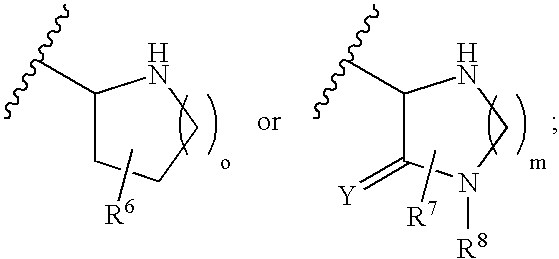Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
87 results about "N-Methyl-D-aspartic acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
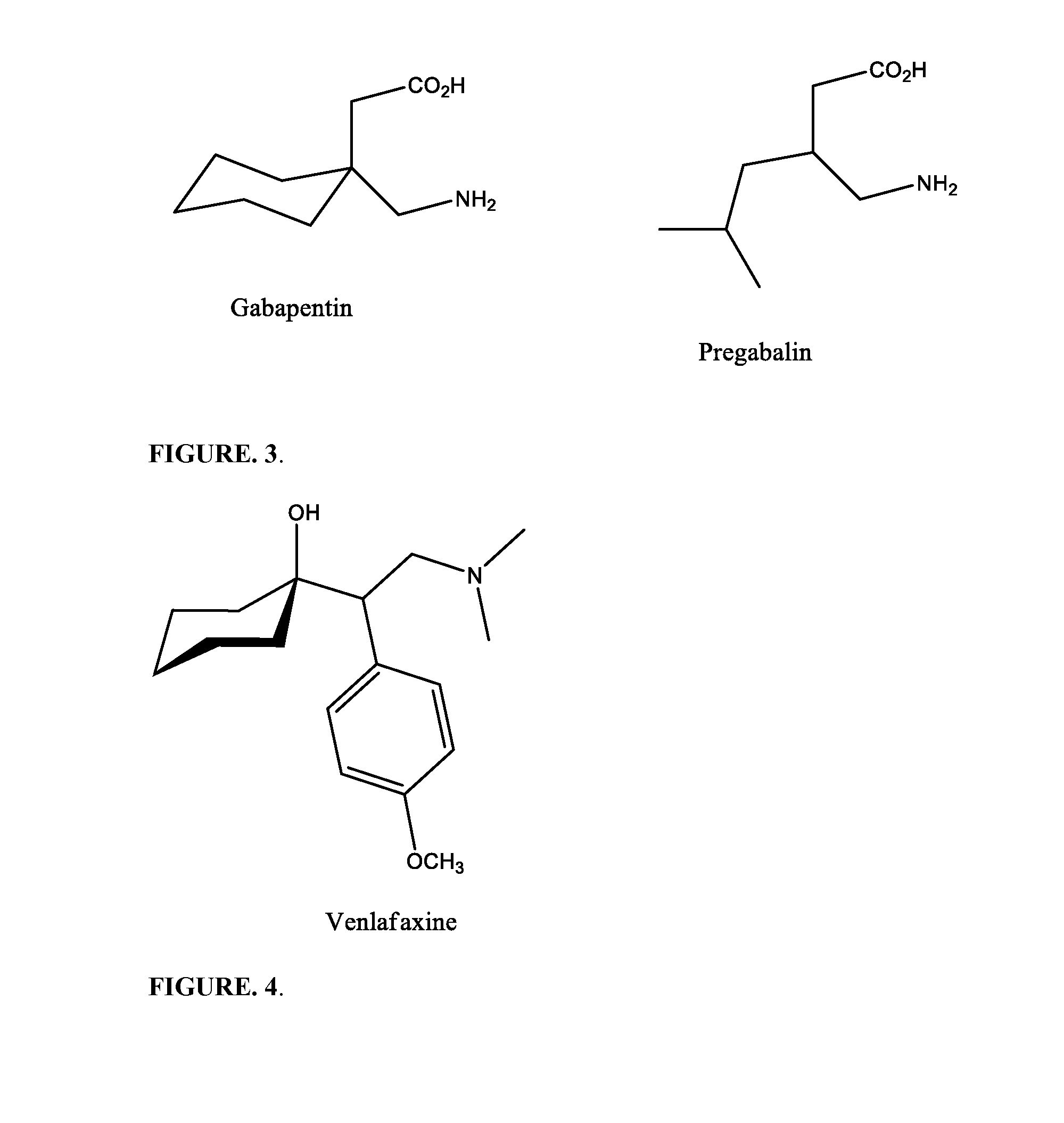
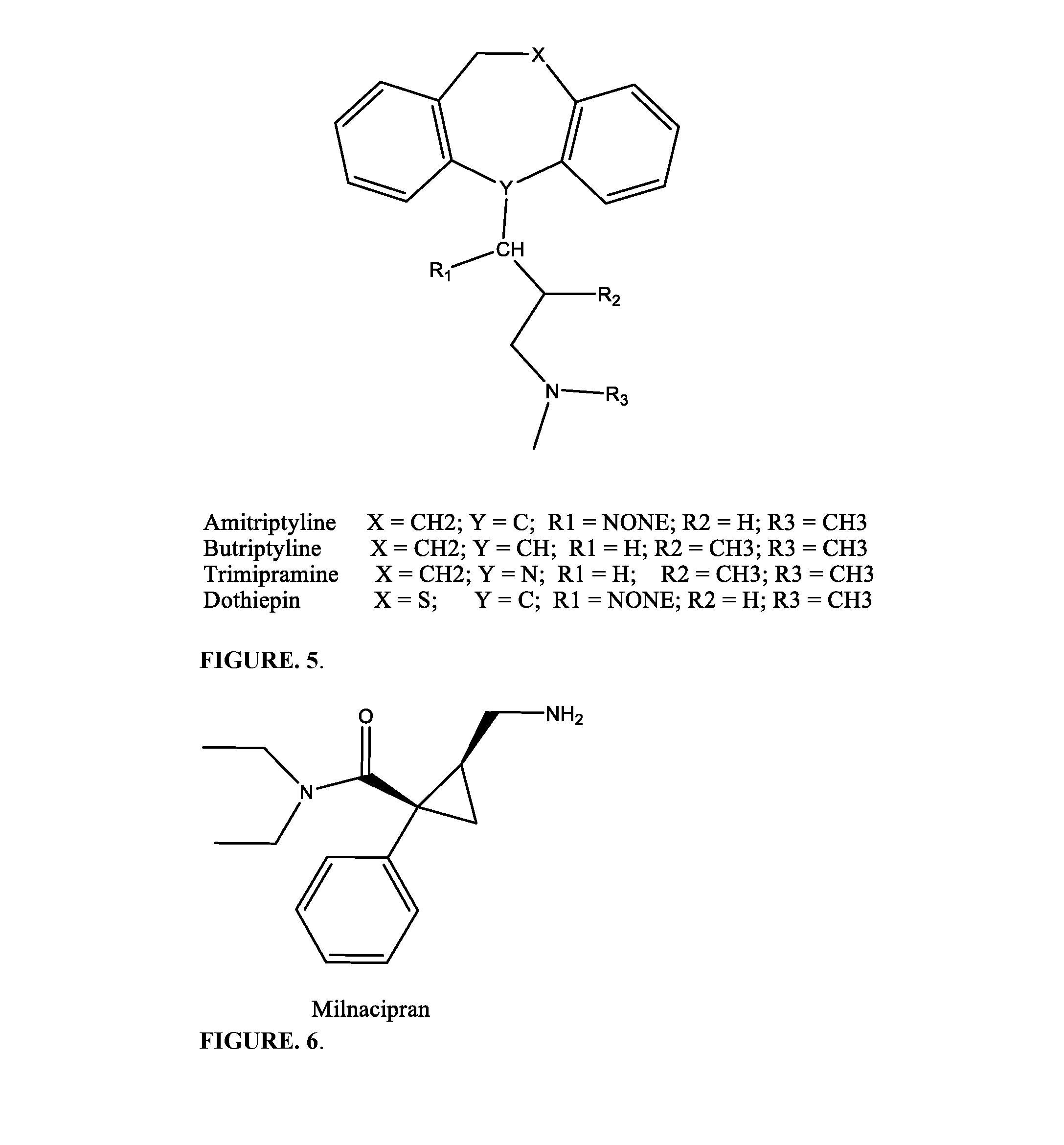
N-Methyl-d-aspartic acid or N-Methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) is an amino acid derivative that acts as a specific agonist at the NMDA receptor mimicking the action of glutamate, the neurotransmitter which normally acts at that receptor. Unlike glutamate, NMDA only binds to and regulates the NMDA receptor and has no effect on other glutamate receptors (such as those for AMPA and kainate). NMDA receptors are particularly important when they become overactive during withdrawal from alcohol as this causes symptoms such as agitation and, sometimes, epileptiform seizures.
Pain relief lollipop compositions and methods
InactiveUS20090191257A1Without pain and invasivenessFast pain reliefOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderGabapentinOpioid Agonist
A pain relief lollipop comprises a candy matrix comprising (a) an opioid agonist, (b) an N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist different from the opioid agonist, (c) gabapentin, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, and, optionally, a muscle relaxant, sedative, anxiolytic, and / or antidepressant. A patient can self-administer small amounts of the pain relief drug as needed by simply licking or sucking on the lollipop in response to his subjective experience of pain.
Owner:INNOVATIVE PHARMA
Macrocyclic beta-secretase inhibitors
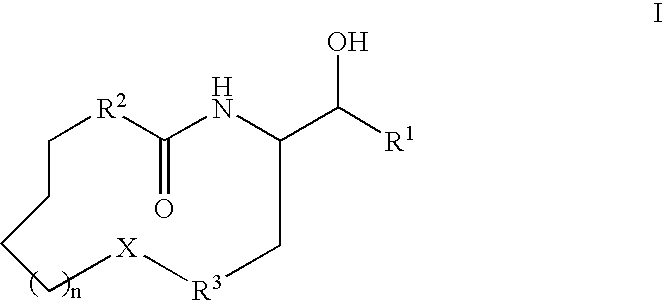
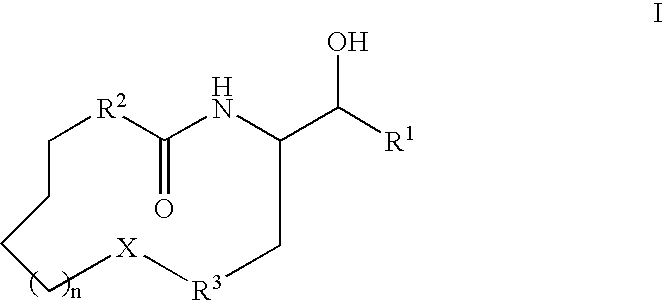
Disclosed are novel compounds of the formula or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof, wherein R1, R2, R3, n and X are as defined in the specification. Also disclosed are pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds of formula I. Also disclosed are methods of treating cognitive or neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease. Also disclosed are methods of treating a cognitive or neurodegenerative disease comprising administering to a patient I need of such treatment a combination of at least one compound of formula I and at least one compound selected from the group consisting of β-secretase inhibitors other than those of formula I, HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, gamma-secretase inhibitors, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents, N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists, cholinesterase inhibitors and anti-amyloid antibodies.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
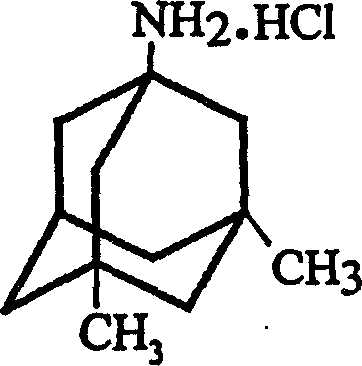
Preparation method of memantine hydrochloride
InactiveCN1400205AGet stableOperational securityNervous disorderOrganic compound preparationMemantine HydrochlorideSolvent
The preparation method of medicine for curing dementia, N-methyl-D-aspartic acid (NMDA) receptor antagonist memantine hydrochloride includes the following steps: using polybasic alcohol as solvent; making 1-bromo-3,5-dimethyl adamantane and urea according to the mole ratio of 1:0.25-10 react for 0.5-48 hr. at 20-200 deg.C; after the reaction is completed, adding sodium hydroxide into the reactionsolution according to that the mole ratio of 1-bromo-3,5-dimethyl adamantane and sodium hydroxide is 1:0.1-10, making alcoholysis at 50-200 deg.C, chloroform extraction, concentration, acidification with hydrochloric acid and salt-forming so as to obtain the invented menantine hydrochloride. It features safe and simple operation and low cost, etc.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF GEOCHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Pharmaceutical compositions for treating pain associated with dysmenorrhea
InactiveUS20150313892A1Reduced plasma concentrationEfficient managementBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsMolecular entityN-methyl-D-aspartate Receptor Antagonists
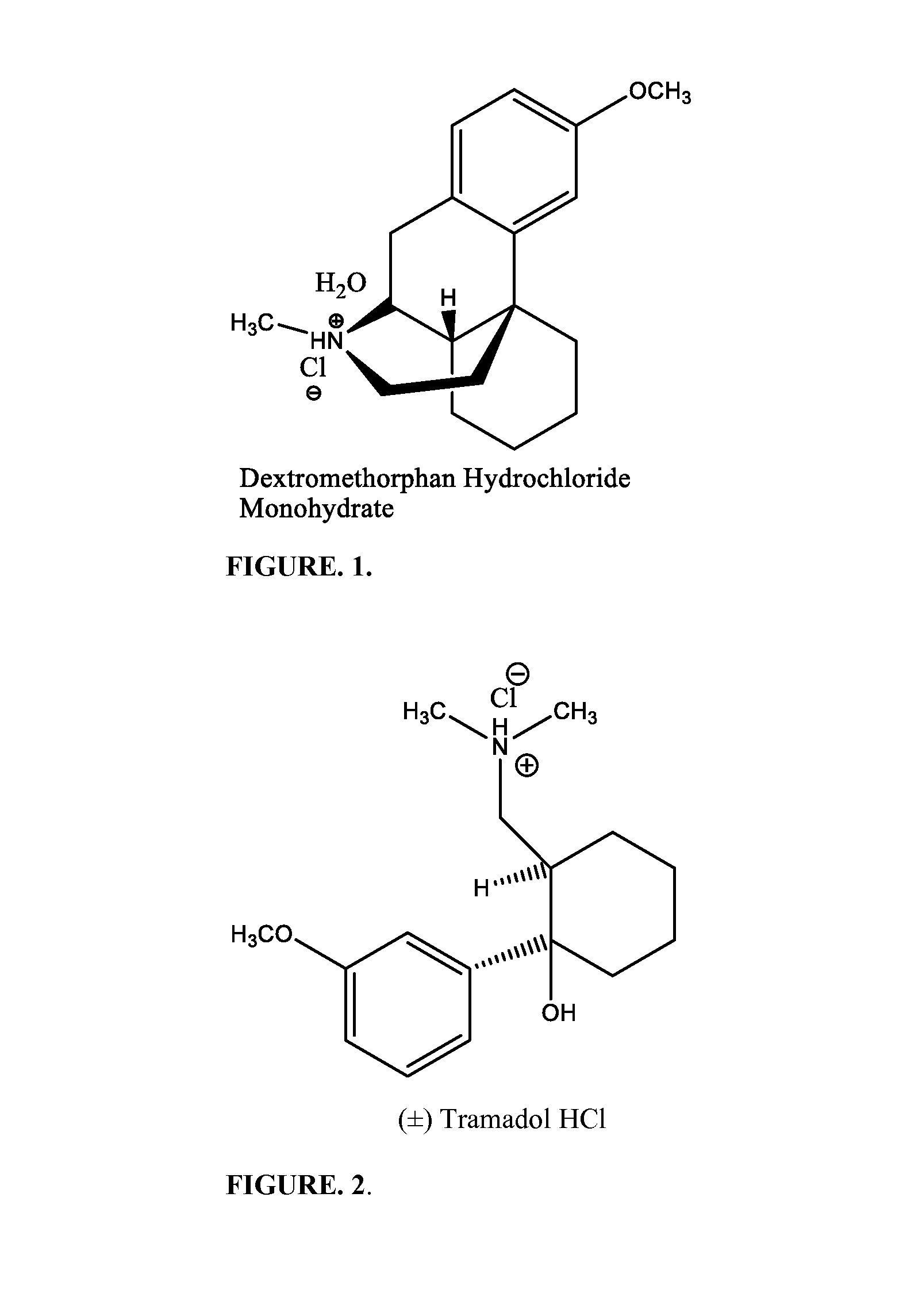
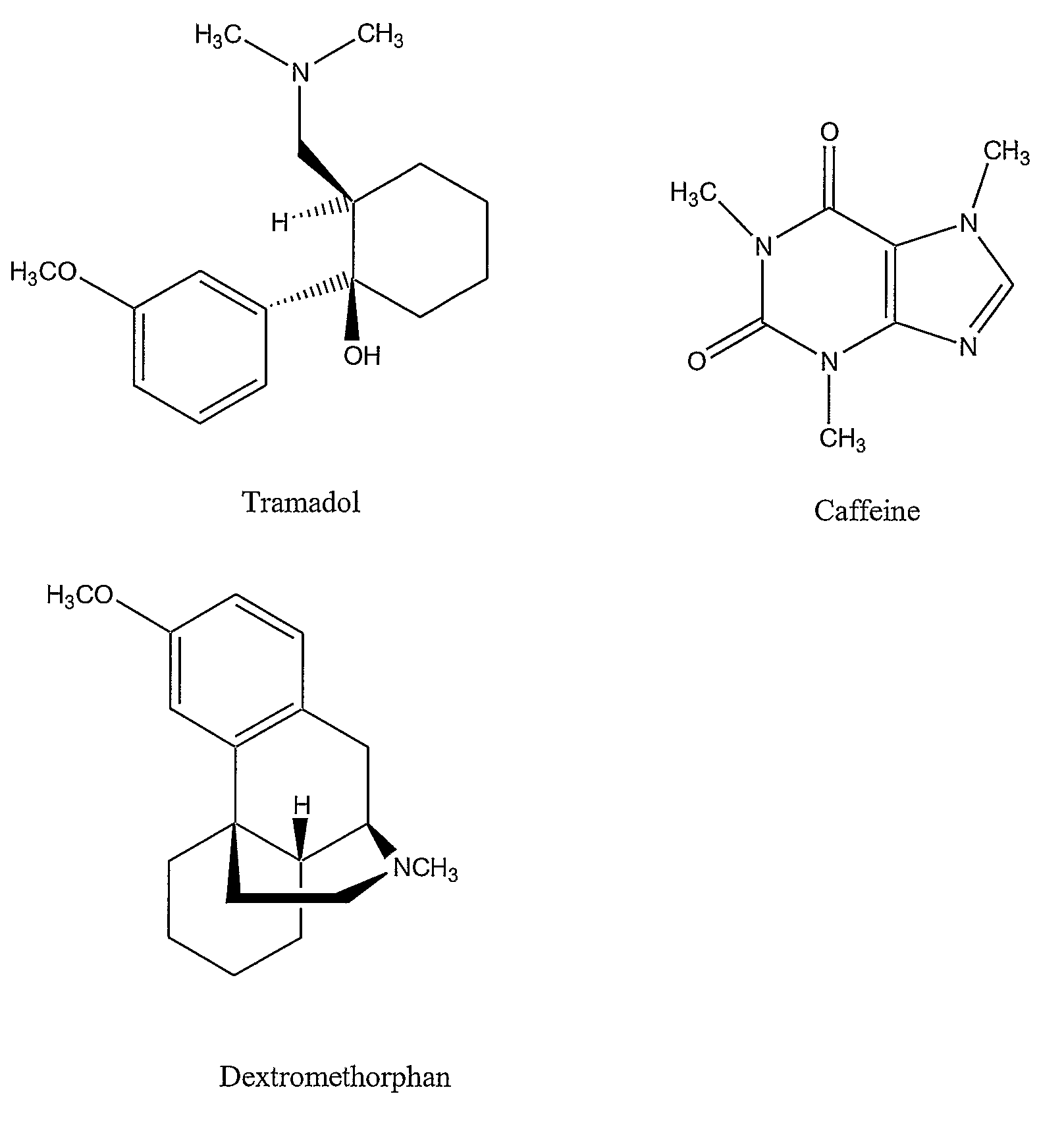
Pain associated with primary and secondary dysmenorrhea is relieved in a human suffering there from by administering to the human a pain relieving amount of a synergistically acting sub-therapeutic combination of a nontoxic N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist such as dextromethorphan, magnesium, dextrorphan, ketamine or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, tramadol or its analog such as recemic tramadol or an analogously acting molecular entity or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, and an anticonvulsant and / or a tricyclic anti-depressant or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, and optionally in sustained release dosage form.
Owner:TRINITY LAB INC
Method of reducing injury to mammalian cells
InactiveUS7595297B2Prevent negative consequenceReduce signalingNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsNR1 NMDA receptorN methyl D aspartate receptors
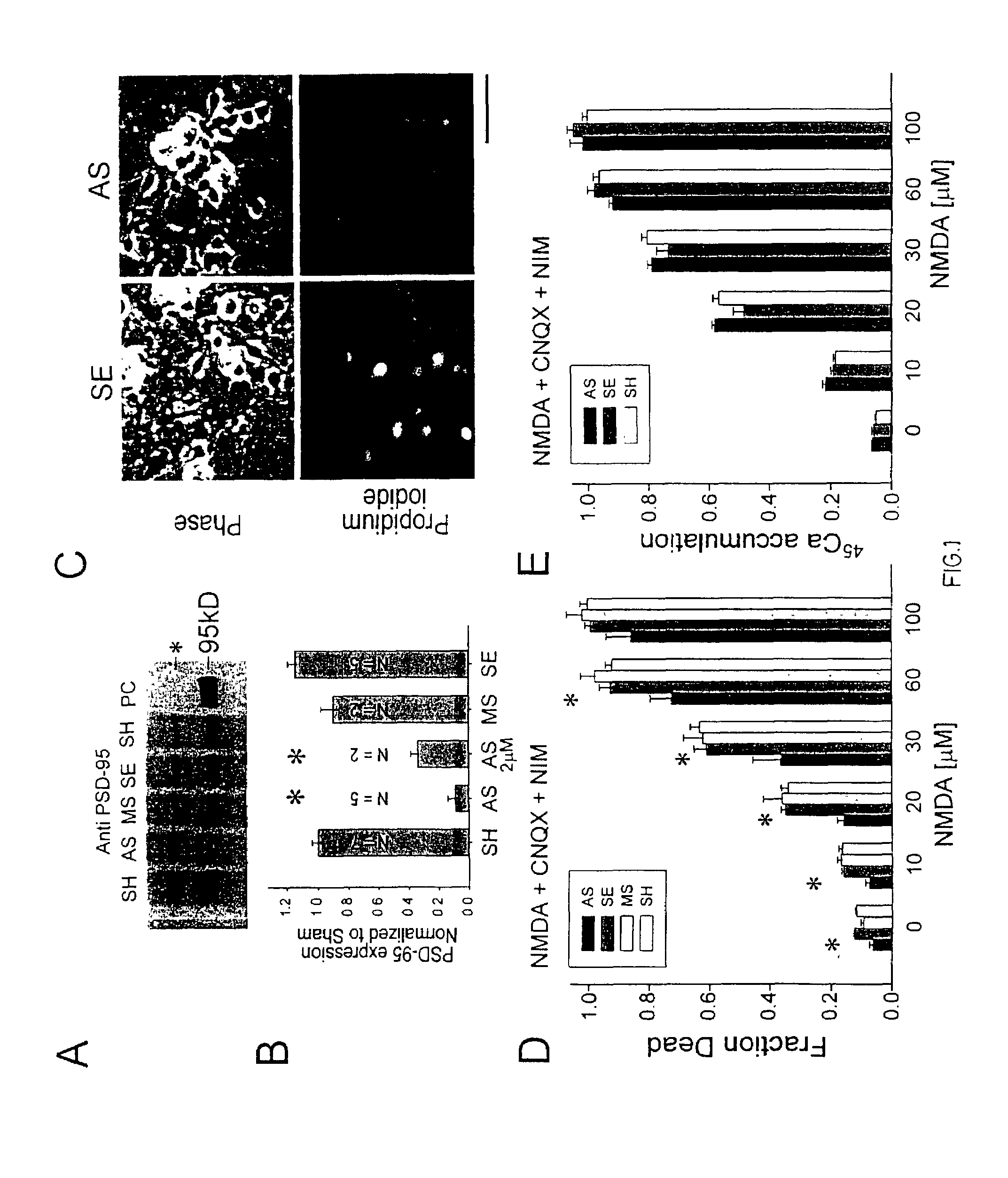
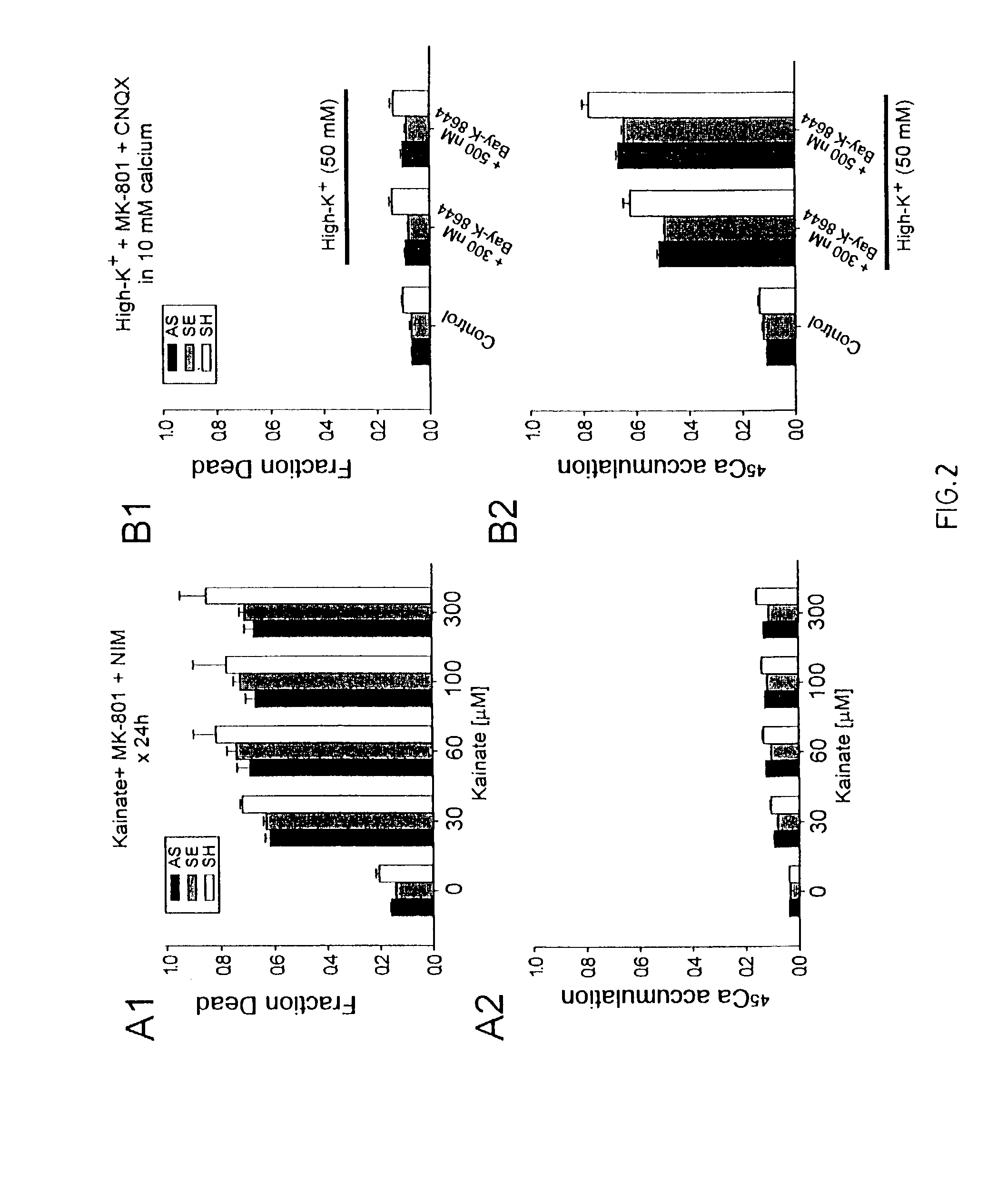
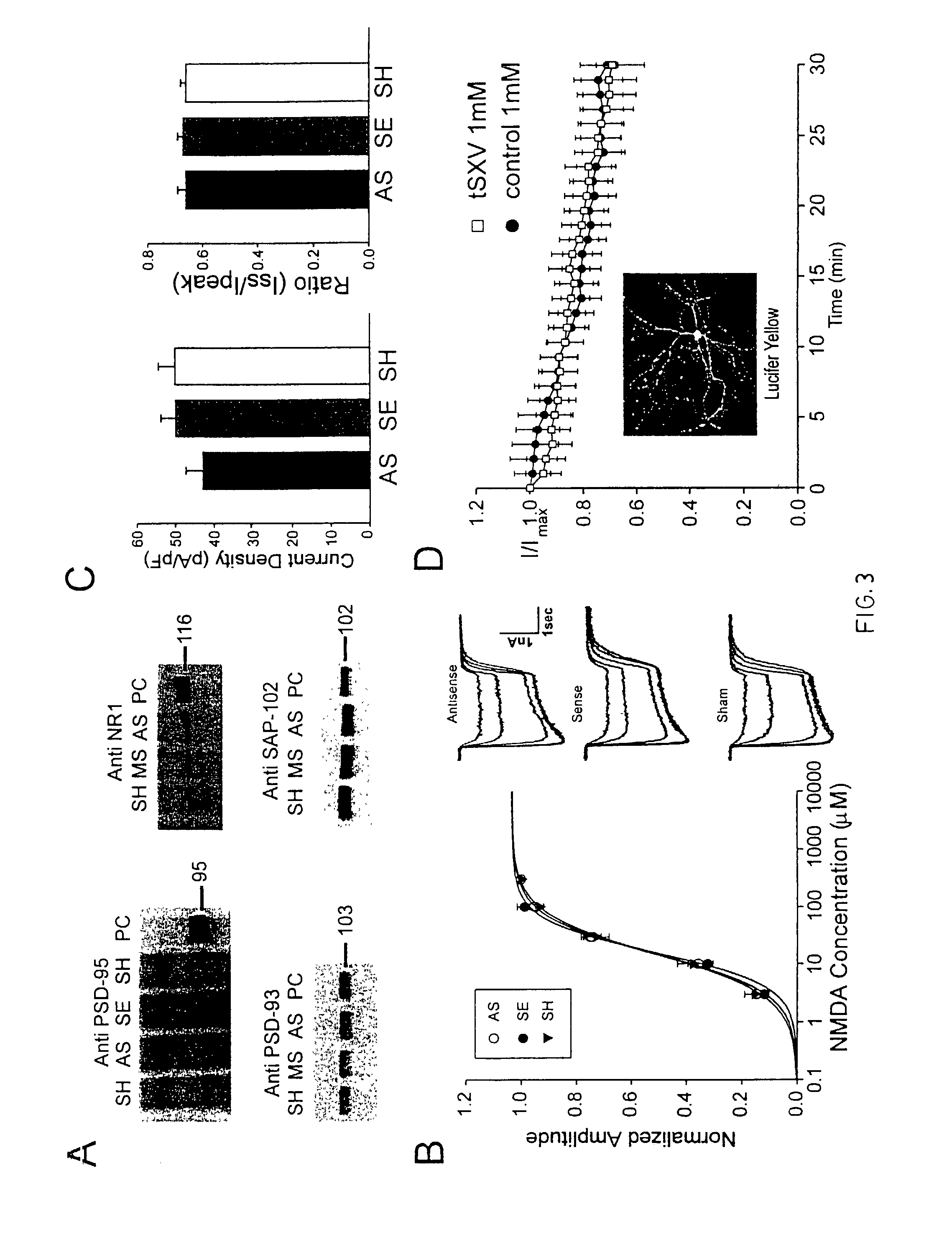
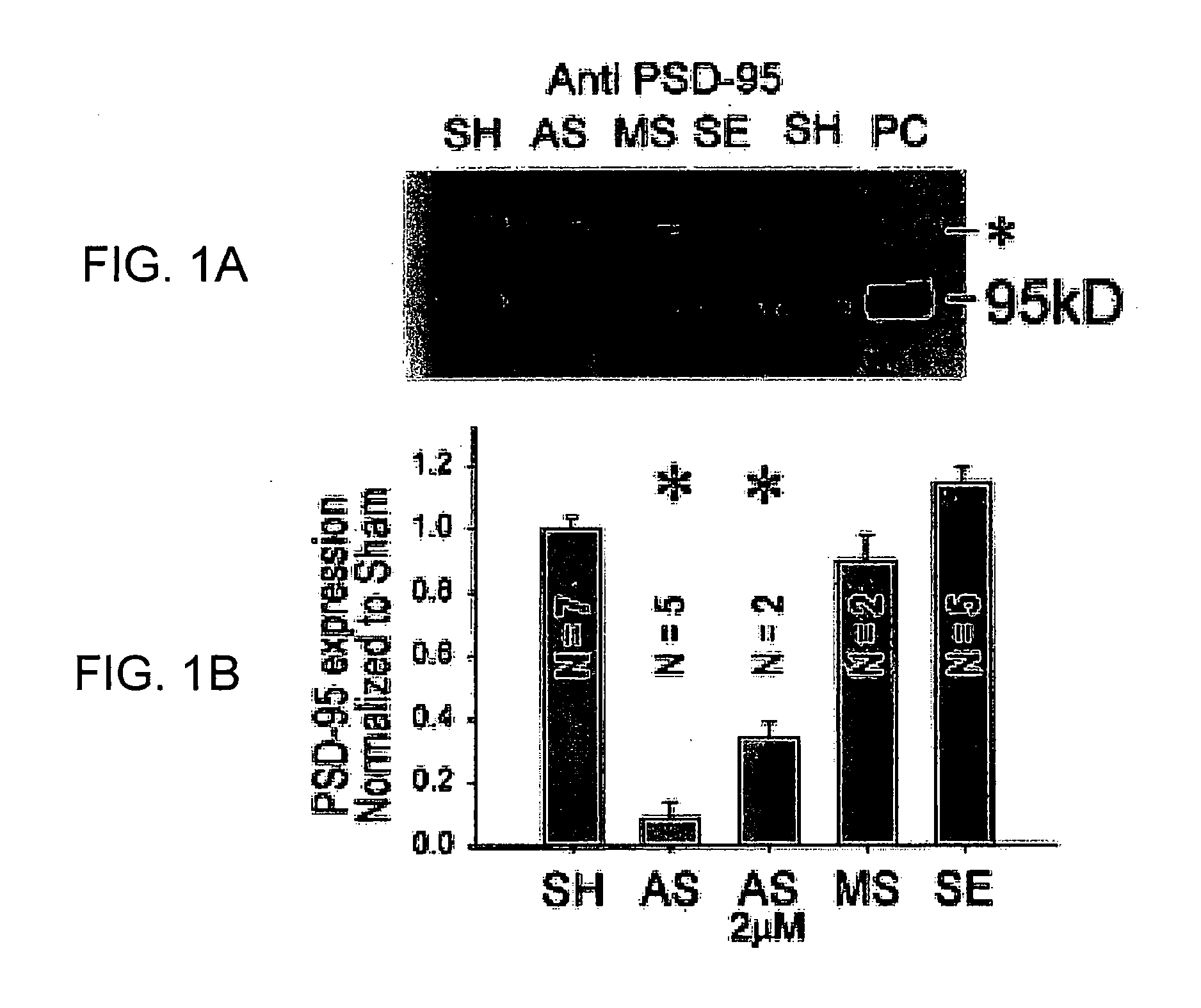
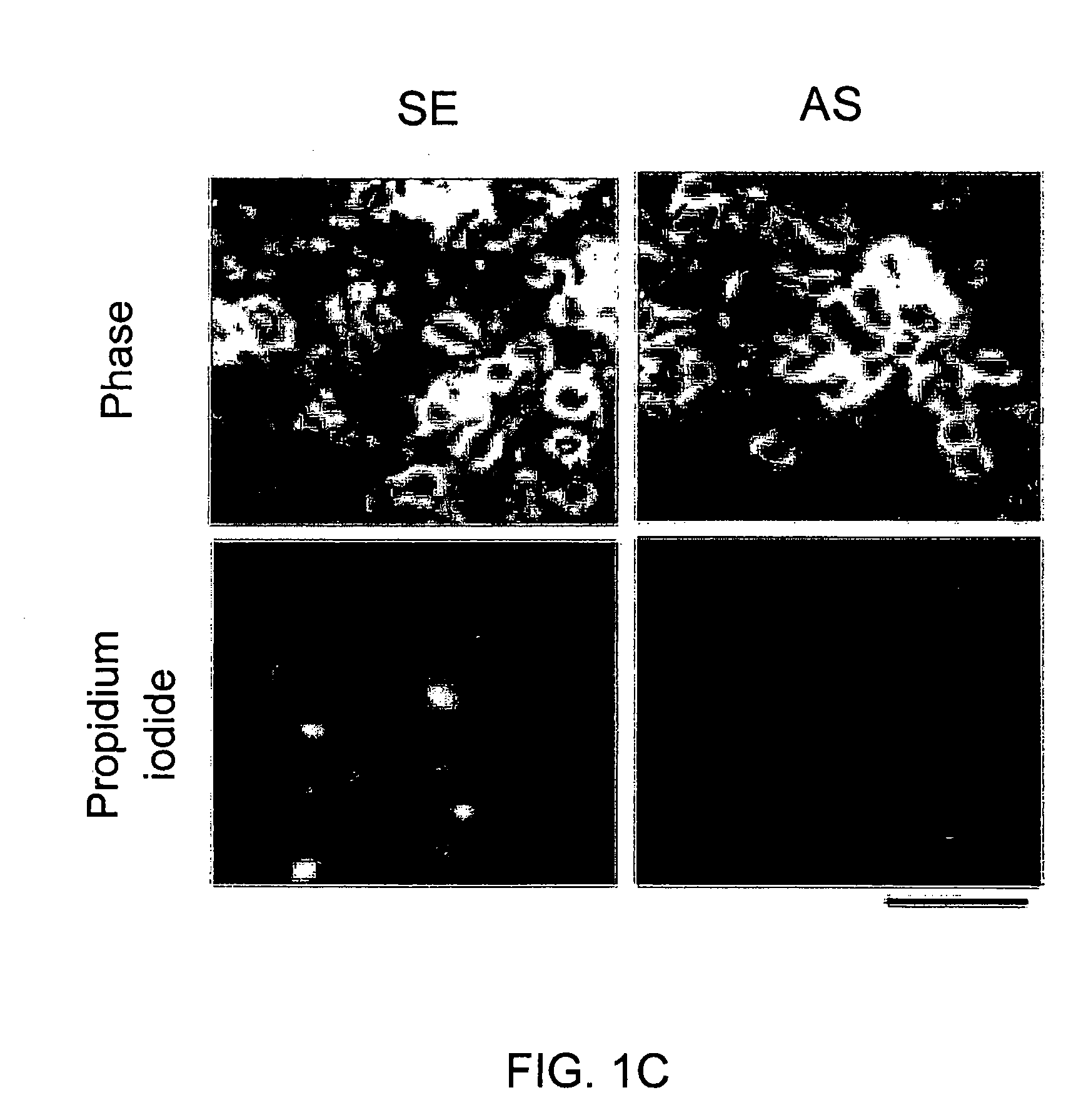
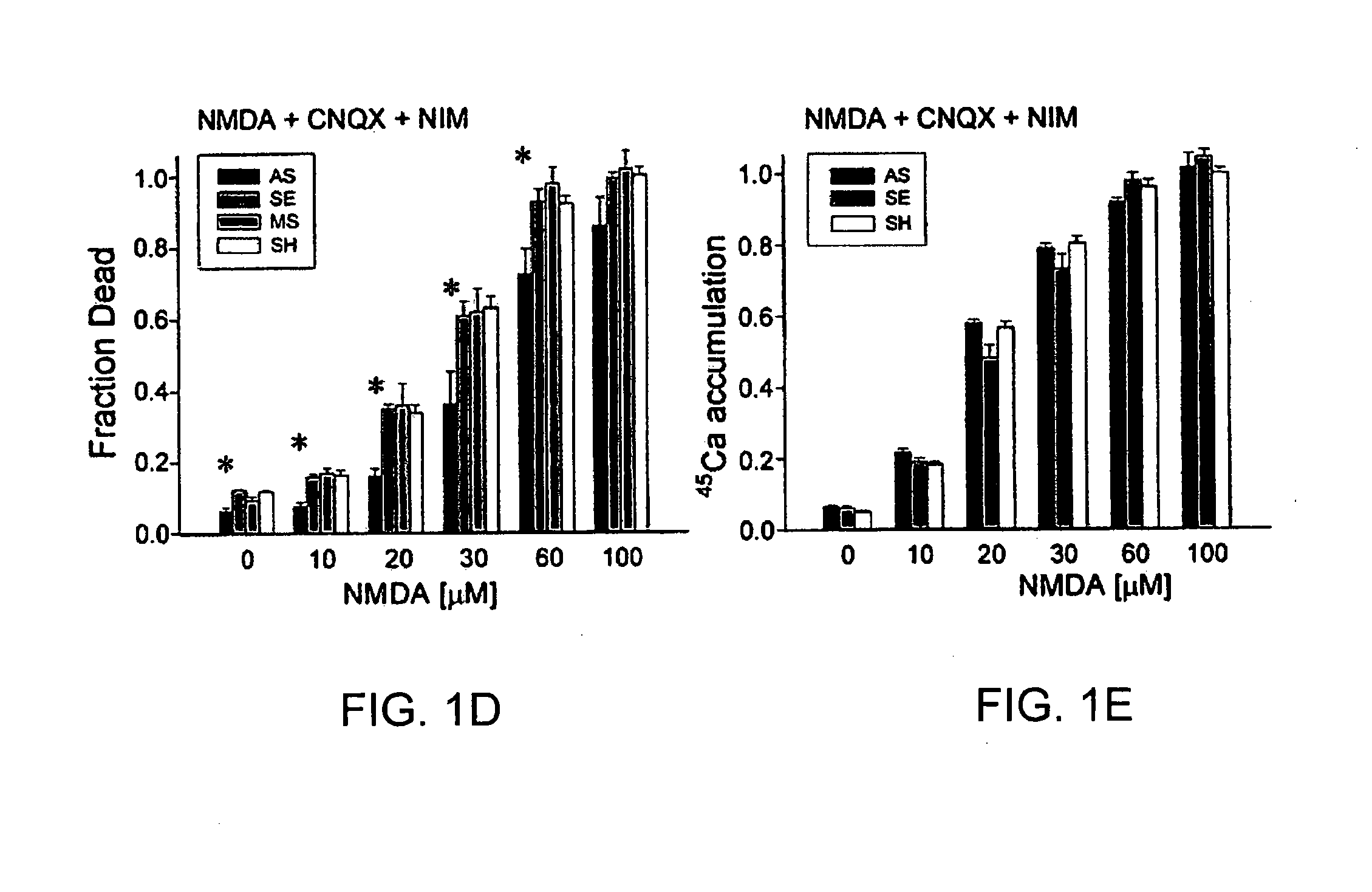
A method of inhibiting the binding between N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors and neuronal proteins in a neuron the method comprising administering to the neuron an effective inhibiting amount of a peptide replacement agent for the NMDA receptor or neuronal protein interaction domain that effect said inhibition of the NMDA receptor neuronal protein. The method is of value in reducing the damaging effect of injury to mammalian cells. Postsynaptic density-95 protein (PSD-95) couples neuronal N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) to pathways mediating excitotoxicity and ischemic brain damage. This coupling was disrupted by transducing neurons with peptides that bind to modular domains on either side of the PSD-95 / NMDAR interaction complex. This treatment attenuated downstream NMDAR signaling without blocking NMDAR activity, protected cultured cortical neurons from excitotoxic insults and dramatically reduced cerebral infarction volume in rats subjected to transient focal cerebral ischemia. The treatment was effective when applied either before, or one hour after, the onset of excitotoxicity in vitro and cerebral ischemia in vivo. This approach prevents negative consequences associated with blocking NMDAR activity and constitutes practical therapy for stroke.
Owner:NONO INC
In vivo screening method of therapeutic agent for memory/learning dysfunctions by schizophrenia
ActiveUS20090176800A1High activityImprove cognitive impairmentCompounds screening/testingNervous disorderPsychosis drugScreening method
Owner:SUMITOMO DAINIPPON PHARMA CO LTD
Composition Containing Anti-Dementia Drug
InactiveUS20090023778A1Improve complianceReduce the burden onBiocideNervous disorderCholinesteraseTreatment effect
An object of the present invention is to provide, for the case of implementing a therapeutic method in which at least two kinds of anti-dementia drugs are used together, a composition that has a good therapeutic effect on dementia, and also gives excellent compliance. Another object of the present invention is to provide a composition containing at least two kinds of anti-dementia drugs, in which release of the anti-dementia drugs from the composition is controlled, whereby a combined effect of the anti-dementia drugs can be achieved well. Still another object of the present invention is to provide a composition for which the frequency of administration and the amount taken are reduced and hence compliance can be improved, and a method of manufacturing such a composition. According to the present invention, there is provided a composition containing at least two kinds of anti-dementia drugs; such a composition containing at least one sustained-release portion containing an anti-dementia drug; and such a composition containing at least one cholinesterase inhibitor, and at least one N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist.
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Cyclic amine BACE-1 inhibitors having a benzamide substituent
Disclosed are compounds of the formulaor a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof, whereinR1 isR is —C(O)—N(R27)(R28) orand the remaining variables are as defined in the specification.Also disclosed are pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds of formula I.Also disclosed are methods of treating cognitive or neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease.Also disclosed are pharmaceutical compositions and methods of treating cognitive or neurodegenerative diseases comprising the compounds of formula I in combination with a β-secretase inhibitor other than those of formula I, an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, a gamma-secretase inhibitor, a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent, an N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist, a cholinesterase inhibitor or an anti-amyloid antibody.
Owner:PHARMACOPEIA DRUG DISCOVERY INC +1
Methods for treating Parkinson's disease
The invention pertains to a method of treating Parkinson's disease (PD) in a mammal, comprising administering a first pharmaceutical agent and a second pharmaceutical agent, wherein the first pharmaceutical agent is an antagonist of the adenosine receptor 2 (A2A) and the second pharmaceutical agent is an antagonist of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor subtype NR2B.
Owner:UCB PHARMA SRL +1
Compounds, compositions and method suitable for amelioration of withdrawal syndromes and withdrawal-induced brain damage
InactiveUS6962930B1Lack of unwanted stimulatory effectReduce and prevent in vitro measureBiocideNervous disorderVoltage-sensitive sodium channelN-Methyl-D-aspartic acid
Compounds, composition and method for ameliorating alcohol or drug dependency withdrawal syndromes and withdrawal-induced brain damage are disclosed. In particular, a series of N-substituted-4-uredo-5,7-dihalo-2-carboxy quinoline compounds are disclosed having combined properties as antagonists of voltage-sensitive sodium channels (VSNaC) and as selective competitive antagonists at the strychnine-intensive glycine site of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors. The disclosed compounds prevent or reduce the signs and symptoms of neurohyperexcitability and particularly the neurohyperexcitability associated with withdrawal syndrome manifested by patients upon withdrawal from chronic use of dependence inducing agents (e.g. ethanol, barbiturates, opiates etc.). The combined actions of the disclosed compound on VSNaC and NMDA receptors also impart properties to these compounds that are important in preventing and reducing excitotoxic neurodegeneration and reducing anxiety without the undesirable CNS depressant side-effects of agents hitherto employed for these purposes.
Owner:LOHOCLA RES CORP
Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease and Mild Cognitive impairment using GnRH-I analogs and one or more of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and NMDA receptor antagonists
InactiveUS20080171736A1Increase acetylcholine levelLower Level RequirementsBiocideNervous disorderNR1 NMDA receptorMild cognitive impairment (MCI)
Methods of treating, mitigating, slowing the progression of, or preventing Alzheimer's Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) include administration of gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogs in combination with acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and / or N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists.
Owner:VOYAGER PHARMA CORP
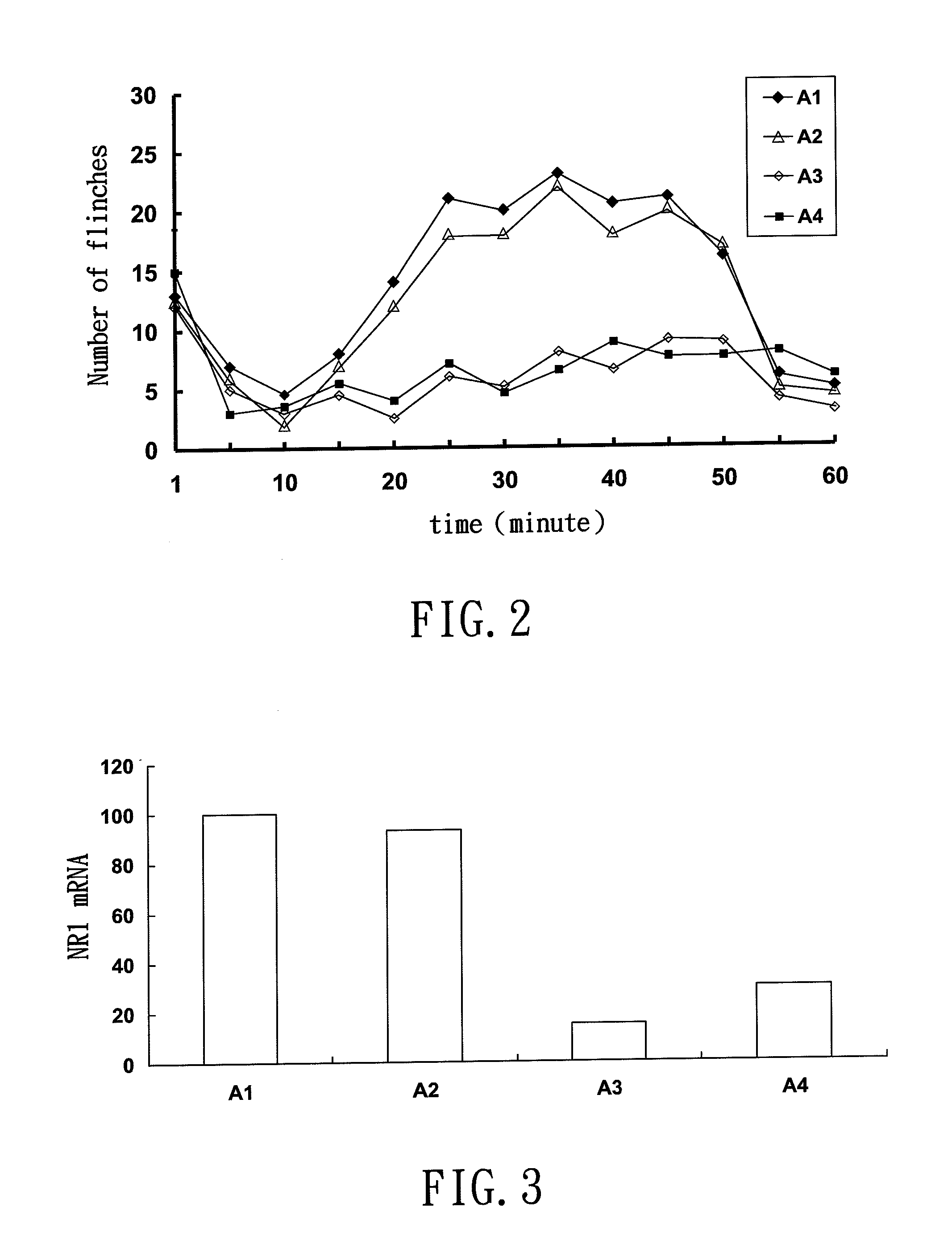
MicroRNA-based short hairpin RNA for gene knockdown of NR1 subunit of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor and its application on pharmaceutics
ActiveUS8575330B2Quick effectFrugal in costSugar derivativesAntipyreticSingle-Stranded RNAGene knockdown
The present invention relates to a microRNA-based short hairpin RNA for gene silencing the genetic expression of NR1 subunit of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor comprises a single strand RNA fragment comprising a first fragment, a second fragment and a connecting fragment, wherein the first fragment and the second fragment are complementary to each other, and are spaced and connected by the connecting fragment, with the connecting fragment being randomly arranged nucleotides, with the first fragment having a Drosha recognized cleavage site, a silencing site and a Dicer recognized cleavage site, with the Drosha recognized cleavage site and the Dicer recognized cleavage site being spaced and connected by the silencing site, with the silencing site encoding homologous nucleotides corresponding to NR1 subunit of subcutaneous N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor.
Owner:I-SHOU UNIVERSITY
Synthesis of N-methyl-D-aspartic acid
InactiveCN103159638ASolve the problem of dimethylationSolve the problem of racemizationOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationDimethyl sulfateN-Methyl-D-aspartic acid
The invention relates to an N-methyl-D-aspartic acid preparation method. The N-methyl-D-aspartic acid preparation method comprises the following steps of: carrying out amino protection reaction by taking D-aspartic acid as a starting raw material to obtain amino protected D-aspartic acid, then carrying out Leuchart Wallanch reaction to obtain an N-methyl product, and then removing protecting groups with strong acid to obtain the N-methyl-D-aspartic acid in the end. The N-methyl-D-aspartic acid preparation method is mainly characterized in that the amino protection is carried out before amino methylation to solve the dimethylation problem, oxalaldehydic acid is used as a methylation reagent, the use of toxic and expensive reagents such as methyl iodide and dimethyl sulfate is avoided, and the high-purity product can be obtained without needing the complex purification process under the condition that the technology is safe, environment-friendly and inexpensive and has good yield.
Owner:ZHANG JIA GANG VINSCE BIO PHARM
Preparation method of medicament-carrying biological membrane
ActiveCN102091057AControl release speedWith repair and rebuild functionNervous disorderMetabolism disorderNR1 NMDA receptorEpoxy
The invention discloses a preparation method of a medicament-carrying biological membrane, which comprises the following steps: preparing type I collagen into a porous and degradable collagen spongy carrier by a freeze-drying process by temperature cross-linking; according to the pharmacokinetics of the selected medicaments, adding medicaments with a certain concentration, such as antibiotics, antiepileptic medicaments, nerve growth factors, NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartic acid) receptor stimulants, NMDA receptor antagonists and the like, into the liquid medicine slowly in the preparation process of slurry, or soaking a biological membrane into the liquid medicine with a certain concentration; adsorbing the medicaments for a period of time; freeze-drying; packaging; and sterilizing in a proper sterilizing mode (gamma rays or epoxy ethane) according to the properties of the medicaments to form a medicament-carrying preparation with a slow-release effect. The invention has wide application prospects in the technical fields of infection prevention, nerve growth promotion, NMDA metabolism, epileptic prevention and the like.
Owner:TIANXINFU (BEIJING) MEDICAL APPLIANCE CO LTD
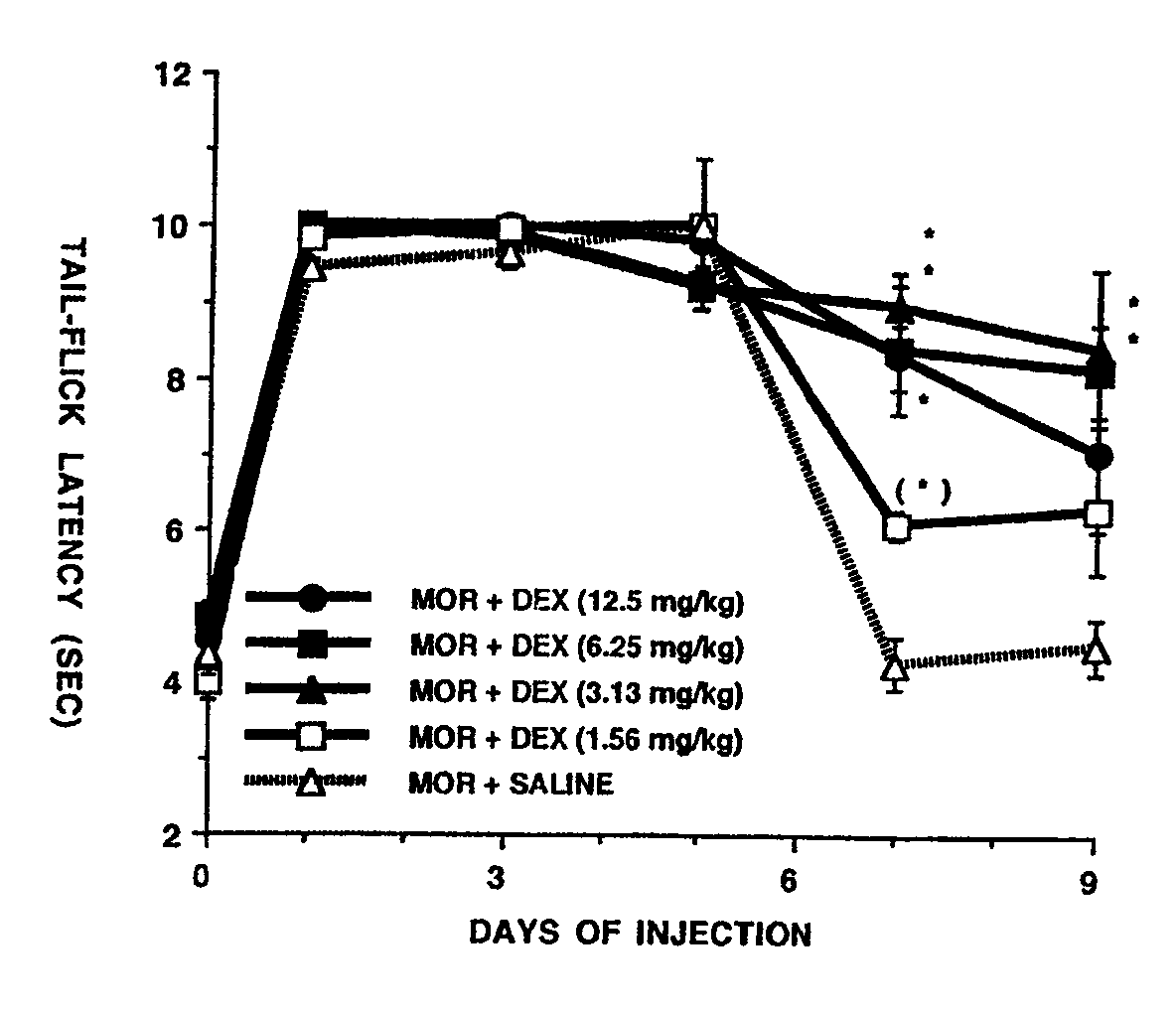
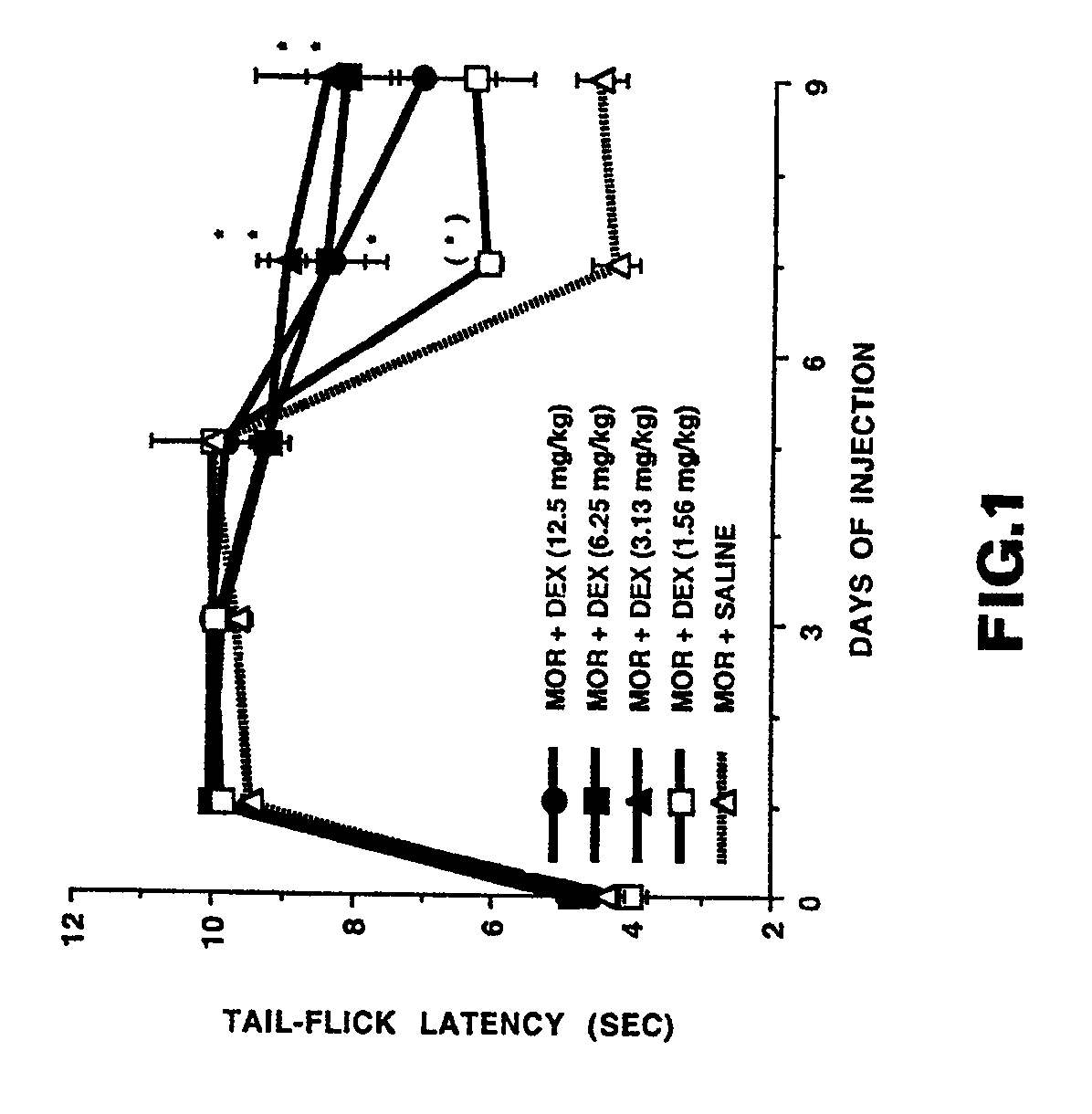
Inhibiting the development of tolerance to and/or dependence on an addictive substance
InactiveUSRE39300E1Alleviate withdrawal symptomsRelieve symptomsBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsNR1 NMDA receptorTolerability
Nontoxic substances that block the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor, e.g., a morphinan such as dextromethorphan or dextrorphan, or that block a major intracellular consequence of NMDA-receptor activation, e.g., a ganglioside such as GM1 or GT1b, a phenothiazine such as trifluoperazine or a naphthalenesulfonamide such as N-(6-aminohexyl)-5-chloro-1-naphthalenesulfonamide, inhibit the development of tolerance to and / or dependence on addictive drugs, e.g., narcotic analgesics such as morphine, codeine, etc.
Owner:VIRGINIA COMMONWEALTH UNIV MEDICAL COLLEGE
Compositions and methods for modulating nicotinic/nmda receptor function
InactiveUS20110097324A1Reduce developmentOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderNR1 NMDA receptorN methyl D aspartate receptors
The present invention provides a method for modulating nicotinic / NMDA receptor function in a mammal in need of such treatment comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of an agent that disrupts heterodimerization of α7 neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and N-methyl-D-asparate glutamate receptor. A polypeptide and fragments thereof comprising an amino acid sequence selected from the second intracellular loop of the α7 nAchR and carboxyl tail of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor are also provided, which are able to inhibit the heterodimerization. Also disclosed are nucleotide sequences encoding the polypeptides, and methods of inhibiting the heterodimerization of α7 nAchR and NMDAR using the polypeptides and nucleic acids.
Owner:CENT FOR ADDICTION & MENTAL HEALTH
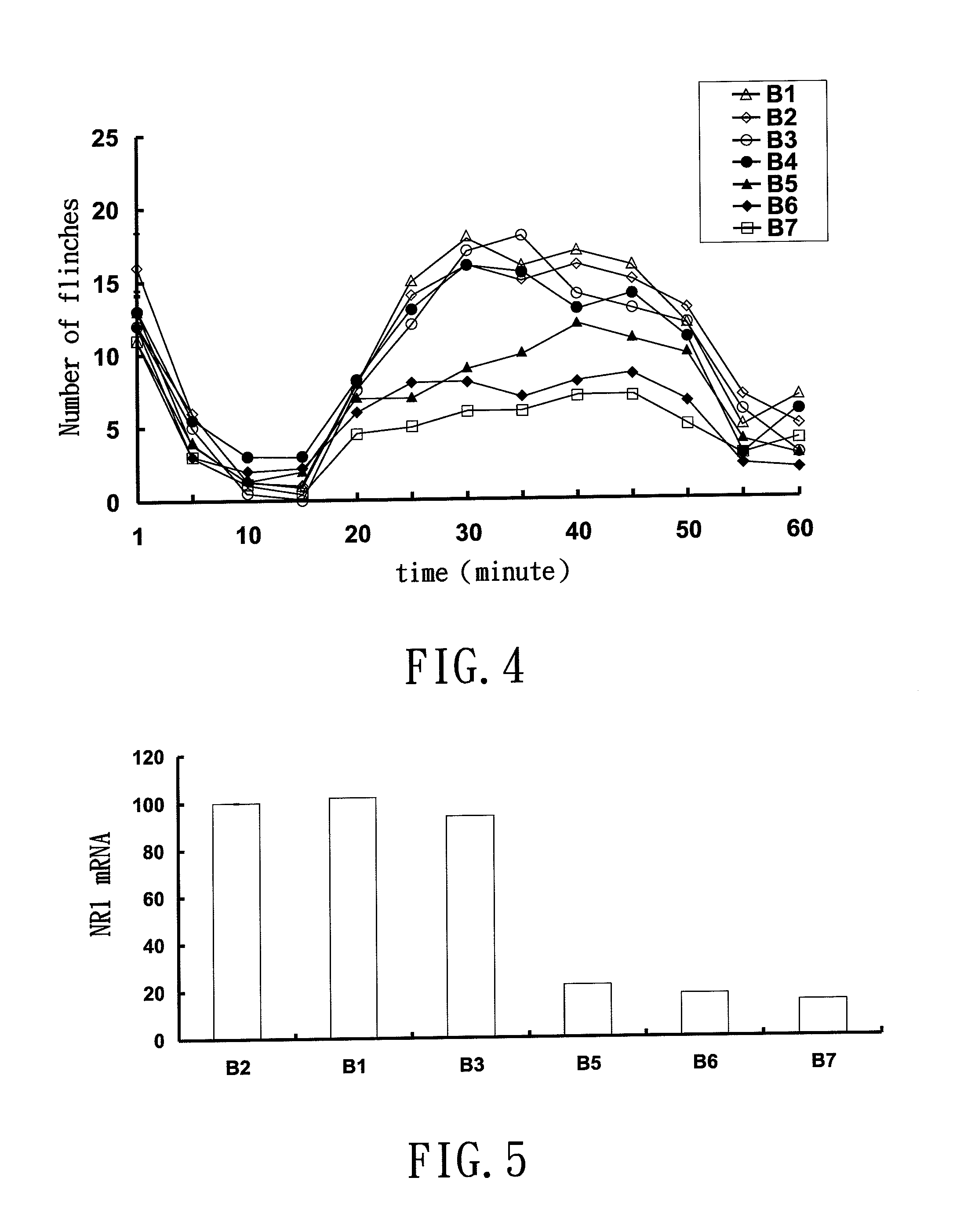
Small interfering RNA for gene knockdown of the subcutaneous N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor NR1 subunit, and it's application on pharmaceutics
ActiveUS8372817B2Avoid side effectsImprove efficiencyBiocideAntipyreticNR1 NMDA receptorN methyl D aspartate receptors
A small interfering RNA for gene knockdown of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor NR1 subunit comprises 21 to 25 ribonucleic acids, which are homologous to the RNA sequence of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor NR1 subunit. A method of using the small interfering RNA, applying the small interfering RNA on subcutaneous tissues temporary interfere with the genetic expression of the NMDA receptor NR1 subunit in hypoderm. A use of the small interfering RNA on pharmaceutics, applying the small interfering RNA manufacture into new analgesic drugs for moderating the inflammatory pain or intolerable chronic pain, especially on clinical chronic pain and burn pain patients. An analgesic drug for skin inflammatory pain comprising: the small interfering RNA and a siRNA acceptable vehicle.
Owner:I-SHOU UNIVERSITY
Heterodimers and methods of using them
Novel heterodimers of tetrahydroacridines and tetrahydroquinolinones are disclosed. The heterodimers are capable of acting as both acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonists. The heterodimers may be used to improve cognitive defects via treatment or prevention in both humans and non-humans.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Substituted amide beta secretase inhibitors
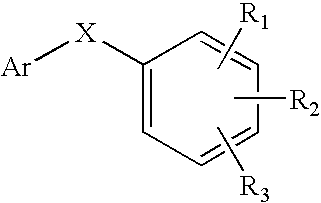
Disclosed are novel compounds of the formulaor a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof, whereinR1, R2, R3, R4 and X are as defined in the specification.Also disclosed are pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds of formula I.Also disclosed are methods of treating cognitive or neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease.Also disclosed are methods of treating a cognitive or neurodegenerative disease comprising administering to a patient I need of such treatment a combination of at least one compound of formula I and at least one compound selected from the group consisting of β-secretase inhibitors other than those of formula I, HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, gamma-secretase inhibitors, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents, N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists, cholinesterase inhibitors and anti-amyloid antibodies.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Macrocyclic .beta.-secretase inhibitors
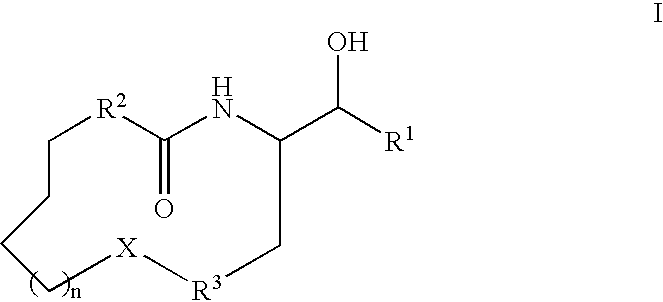
Disclosed are novel compounds of the formulaor a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof, whereinR1, R2, R3, n and X are as defined in the specification.Also disclosed are pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds of formula I.Also disclosed are methods of treating cognitive or neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease.Also disclosed are methods of treating a cognitive or neurodegenerative disease comprising administering to a patient I need of such treatment a combination of at least one compound of formula I and at least one compound selected from the group consisting of β-secretase inhibitors other than those of formula I, HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, gamma-secretase inhibitors, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents, N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists, cholinesterase inhibitors and anti-amyloid antibodies.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Heterodimers and Methods of Using Them
ActiveUS20080176308A1Stroke preventionImprove cognitive abilityBiocideNervous disorderCholinesterase inhibitionCognitive defects
Novel heterodimers of tetrahydroacridines and tetrahydroquinolinones are disclosed. The heterodimers are capable of acting as both acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonists. The heterodimers may be used to improve cognitive defects via treatment or prevention in both humans and non-humans.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Novel Pharmaceutical Compositions for Treating Acquired Chronic Pain and Associated Dysphoria
InactiveUS20080176873A1Good analgesic effectEffective pain managementBiocideNervous disorderDextrorphanSustained release drug
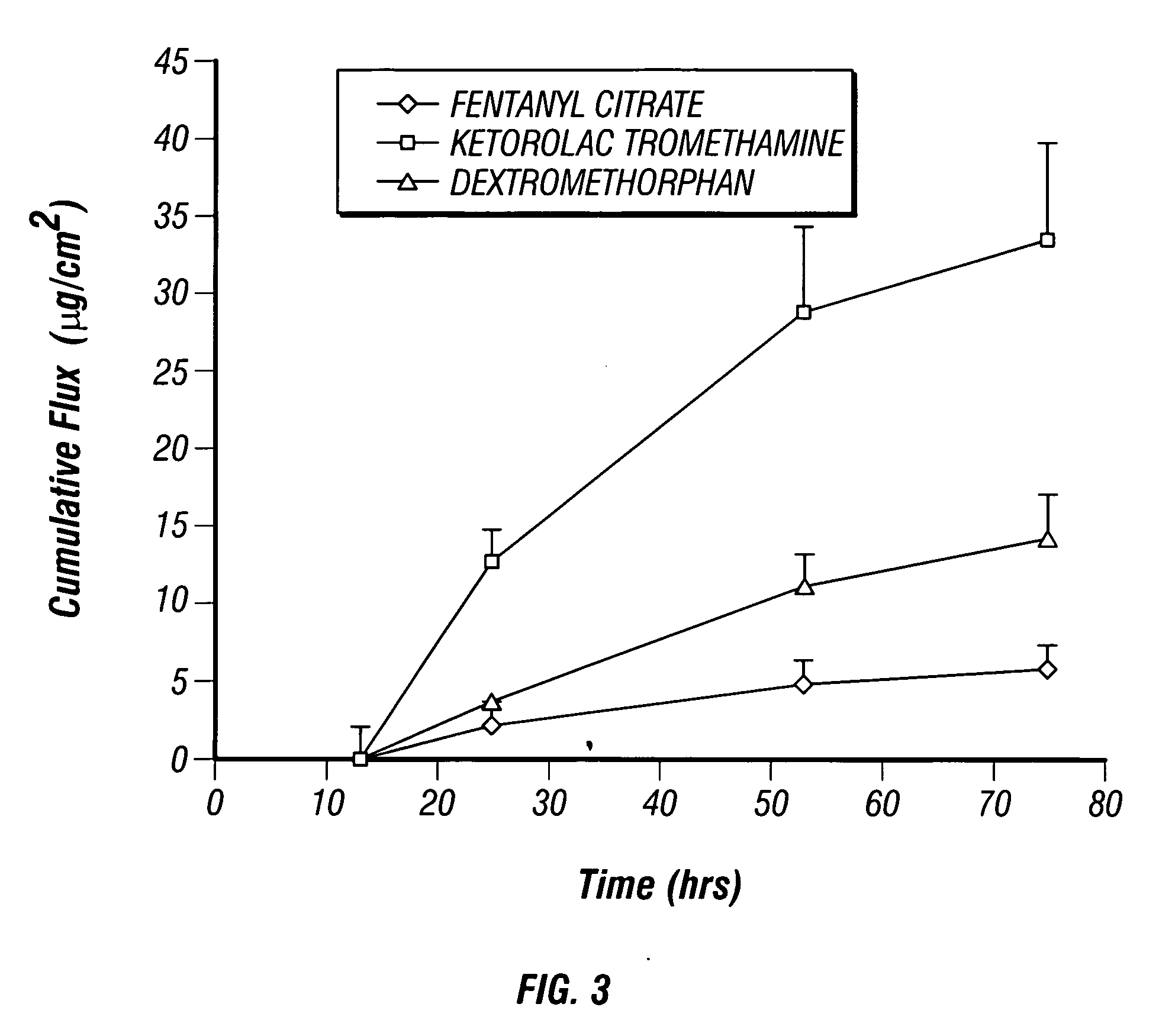
Chronic pain is alleviated in a mammal suffering there from by administering to the mammal a chronic pain alleviating amount of a nontoxic N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist such as dextromethorphan, dextrorphan, ketamine or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, in combination with a μ-opiate analgesic such as tramadol or an analogously acting molecular entity, and a methylxanthine such as caffeine, and optionally in sustained release dosage form.
Owner:TRINITY LAB INC
Transdermal pain control method and device
Compositions comprising skin-permeable pharmaceutically effective amounts of an opioid agonist; an N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist and an anti-inflammatory may be incorporated into formulations and devices suitable for transdermal delivery of the active ingredients to alleviate pain.
Owner:INNOVATIVE PHARMA
Pharmacological prophylactics against stress-induced affective disorders and their associated symptoms
ActiveUS20180325844A1Preventing and delaying stress-induced cognitive impairmentPreventing and delaying and declineNervous disorderInorganic active ingredientsStress inducedPsychopathology
Methods for prophylactically treating a stress-induced affective disorder or stress-induced psychopathology in a subject are provided. Also provided are methods for inducing and / or enhancing stress resilience in a subject. In certain embodiments, an effective amount, of an antagonist of the glutamate N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor, such as ketamine, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or derivative thereof, is administered to a subject prior to a stressor.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Method for preparing memantine hydrochloride
InactiveCN1193981CGood crystal formHigh purityNervous disorderPreparation by rearrangement reactionsMemantine HydrochlorideTert-Butyl chloride
The invention is a manufacturing method of diamante amine hydrochlorate. The invention adopts 1, 3-dimethyl adamantine to reacts with tert-butylchlorine and gets 1-chlorine-3, 5-dimethyl adamantine; then reacts with acetamide directly, the educt from water reacts with sodium hydroxide in ethanediol or glycerine solvent, extracts by acetic ester, condenses, and blow in dry hydrochloride gas and gets the coarse product. There gets the pure product through alcohol-acetic ester recrystallization.
Owner:JIANGSU INST OF NUCLEAR MEDICINE
N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor allosteric modulators and methods for their use
ActiveUS20190216753A1Organic active ingredientsNervous disorderN methyl D aspartate receptorsAllosteric modulator
This invention relates to therapeutic compounds and compositions, and methods for their use in the prevention or treatment of neurological disorders. In particular, the invention relates to N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) allosteric modulators and methods for their use in the prevention or treatment of disorders or conditions caused by or related to NMDAR dysfunctions. The invention also relates to a method for identifying NMDAR allosteric modulators.
Owner:QINGDAO PRIMEDICINE PHARMA CO LTD
Method of treating memory/learning dysfunctions caused by schizophrenia with lurasidone
ActiveUS8835438B2High activityImprove cognitive impairmentCompounds screening/testingNervous disorderPsychosis drugTypical antipsychotic
A method of evaluating memory / learning functions with the use of a model with glutamic acid N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) type receptor hypofunction as an animal model for schizophrenia and with the use of reference memory task, wherein there has been found concrete means for detecting any differences in activity between typical anti-psychosis drugs and atypical anti-psychosis drugs is found.An in vivo animal model for screening of a therapeutic agent for improving cognitive dysfunction by schizophrenia is provided.
Owner:SUMITOMO PHARMA CO LTD
Method of Reducing Injury to Mammalian Cells
InactiveUS20090281037A1Prevent negative consequenceReduce signalingNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsNR1 NMDA receptorN methyl D aspartate receptors
A method of inhibiting the binding between N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors and neuronal proteins in a neuron is disclosed. The method comprises administering to the neuron an effective inhibiting amount of a peptide replacement agent for the NMDA receptor or neuronal protein interaction domain that effect said inhibition of the NMDA receptor-neuronal protein interaction. The method is of value in reducing the damaging effect of injury to mammalian cells. Postsynaptic density-95 protein (PSD-95) couples neuronal N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARS) to pathways mediating excitotoxicity, ischemic and traumatic brain damage. This coupling was disrupted by transducing neurons with peptides that bind to modular domains on either side of the PSD-95 / NMDAR interaction complex. This treatment attenuated downstream NMDAR signaling without blocking NMDAR activity, protected cultured cortical neurons from excitotoxic insults, dramatically reduced cerebral infarction volume in rats subjected to transient focal cerebral ischemia, and traumatic brain injury (TBI) in rats.
Owner:NONO INC
Piperidine derivatives
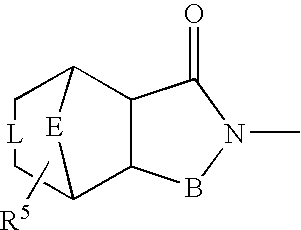
For example, a piperidine derivative represented by following formula (I) (wherein, —C(═O)-Z- represents —C(═O)—CH2—, —C(═O)—C(CH3)2—, —C(═O)—NH—, —C(═O)—O—, —C(═O)—S—, —C(═O)—CH2CH2—, —C(═O)—CH═CH—, —C(═O)—CH2O—, —C(═O)—CH2S—, —C(═O)—CH2CH2CH2— or —C(═O)—NR8CH2—; R1 represents a hydrogen atom, substituted or unsubstituted lower alkyl, or the like; R2 represents a hydrogen atom or hydroxy; R3 represents a hydrogen atom, substituted or unsubstituted lower alkyl, or the like; R5 represents a hydrogen atom, hydroxy, or the like; R6 represents a hydrogen atom, hydroxy, substituted or unsubstituted lower alkyl, or the like, etc.; R7 represents a hydrogen atom, halogen, substituted or unsubstituted lower alkyl, or the like; n and k each independently represents an integer of 0 to 2; and ---- represents a single bond, or a double bond together with R4, where in case ---- is a single bond, R4 represents a hydrogen atom, hydroxy, or the like) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof and the like having an antagonistic activity for a glutamic acid receptor (NR2B / NMDA receptor) of an N-methyl-D-aspartic acid (NMDA) type containing an NR2B subunit are provided.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KOGYO CO LTD
Substituted Aryl-Indole Compounds and Their Kynurenine/Kynuramine-Like Metabolites As Therapeutic Agents
This invention is directed to substituted aryl compounds, which are linked to a substituted indole moiety by various linkers, and the kynurenine / kynuramine-like metabolites of these agents, their preparation and pharmaceutical compositions containing these compounds. This invention further is directed to the pharmaceutical use of the compounds for inhibiting GSK3β kinase and / or modulating N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) channel activities for the treatment of neurodegenerative and other disorders.
Owner:NEURIM PHARMA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com