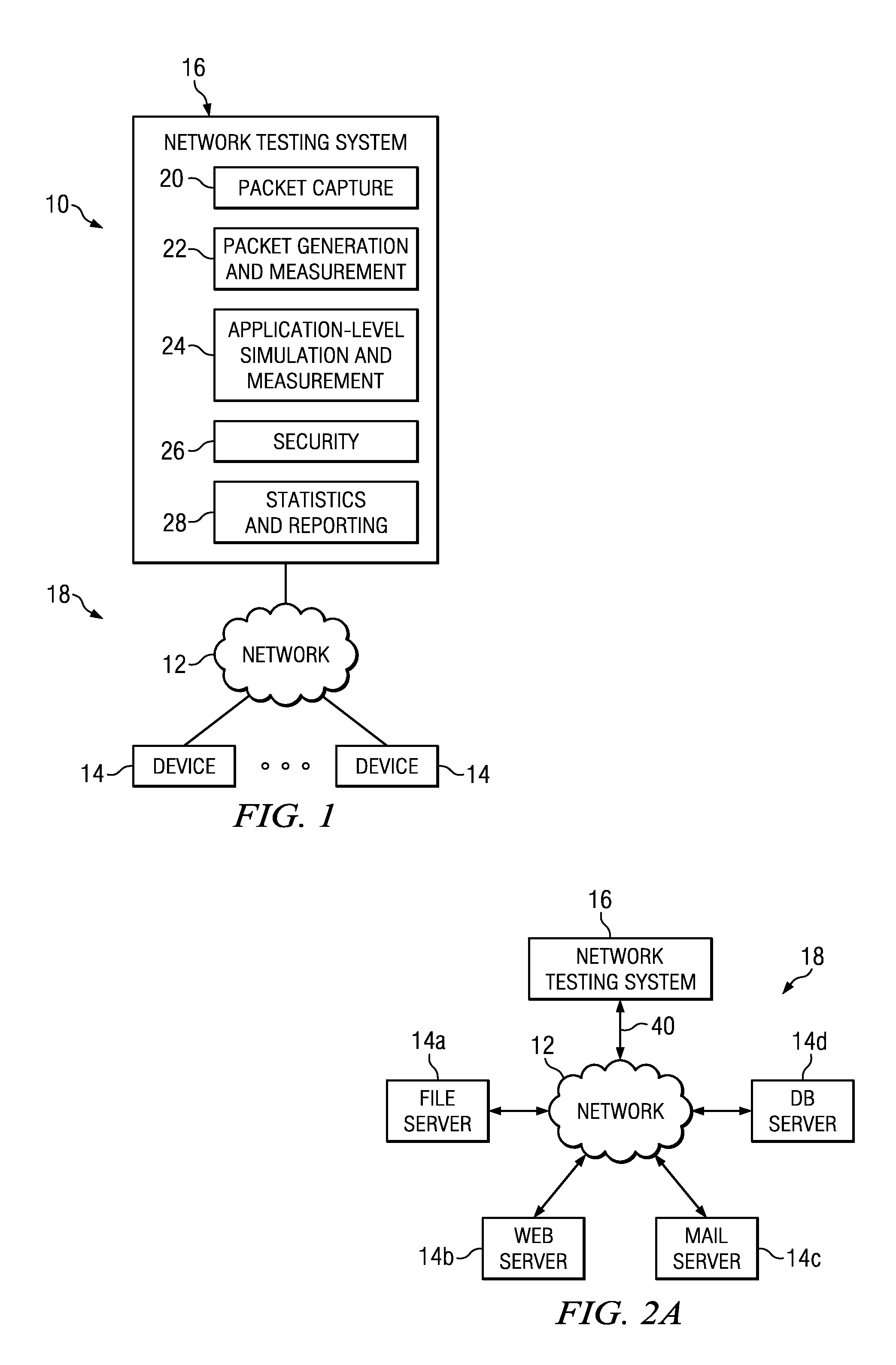
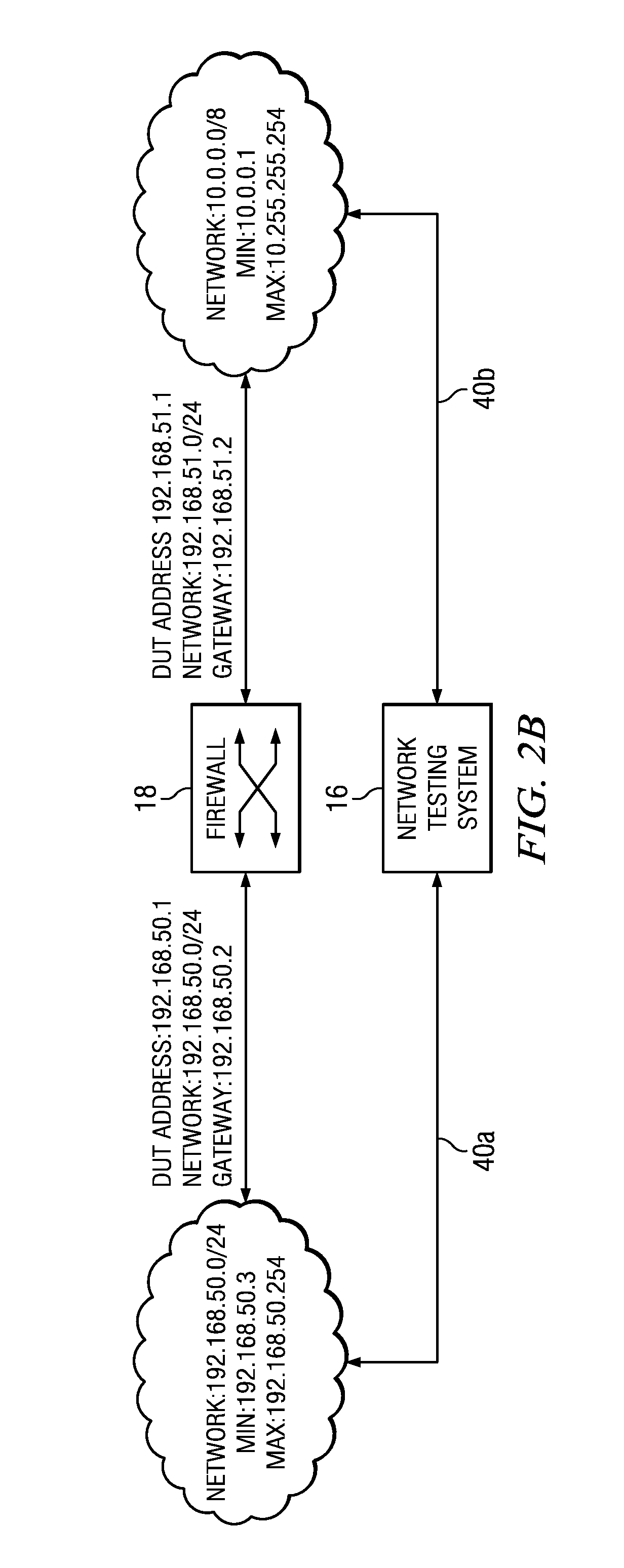
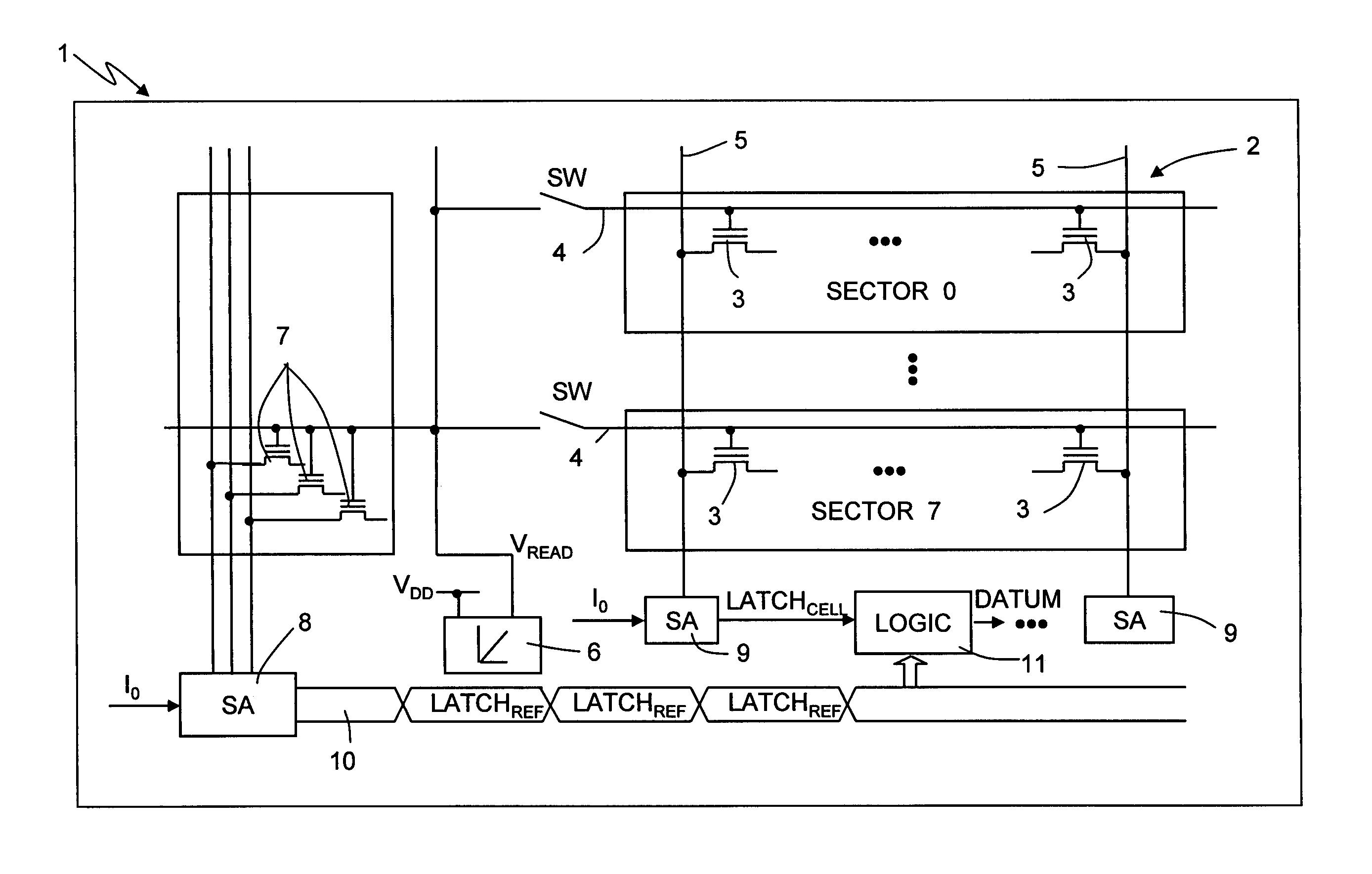
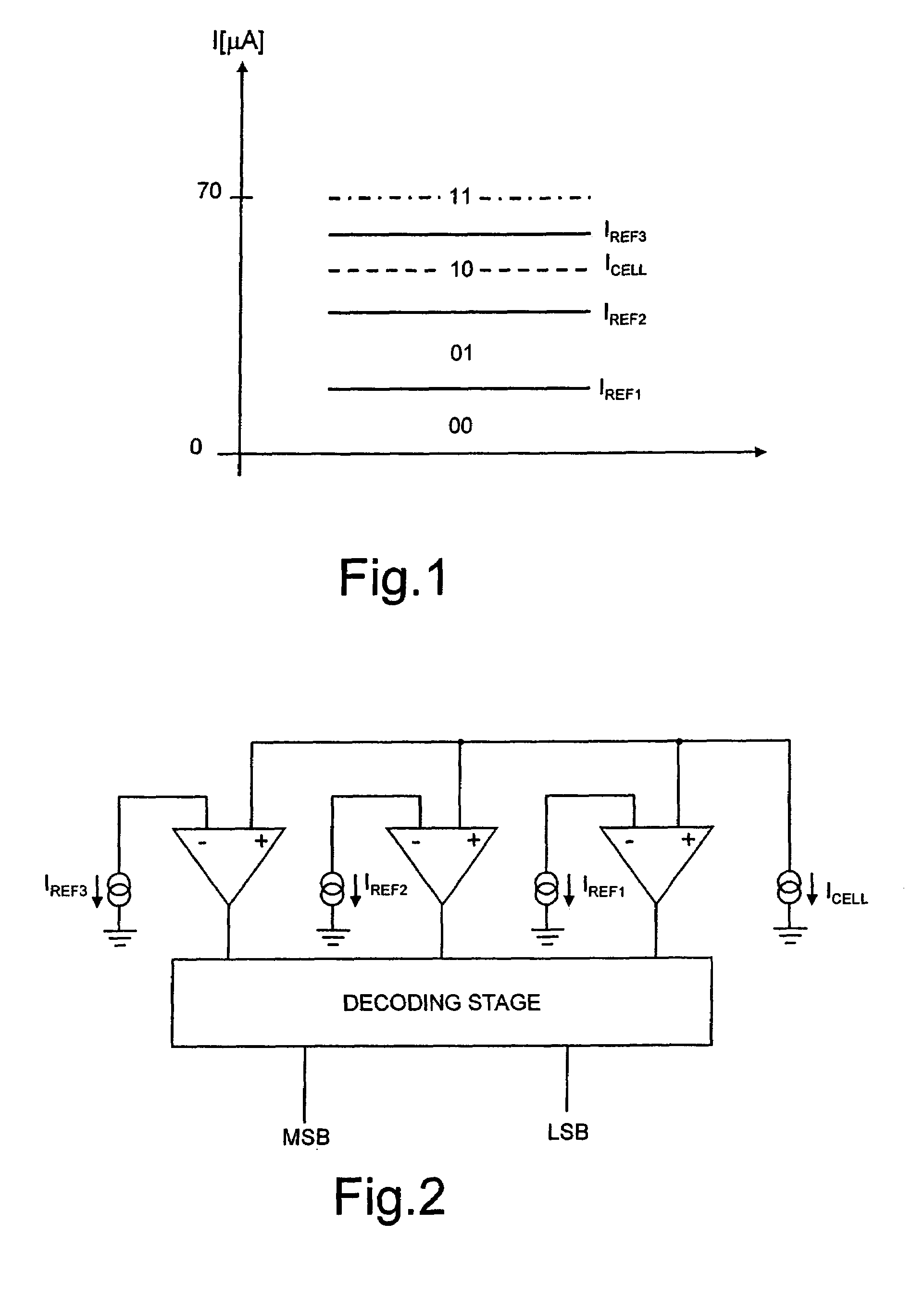
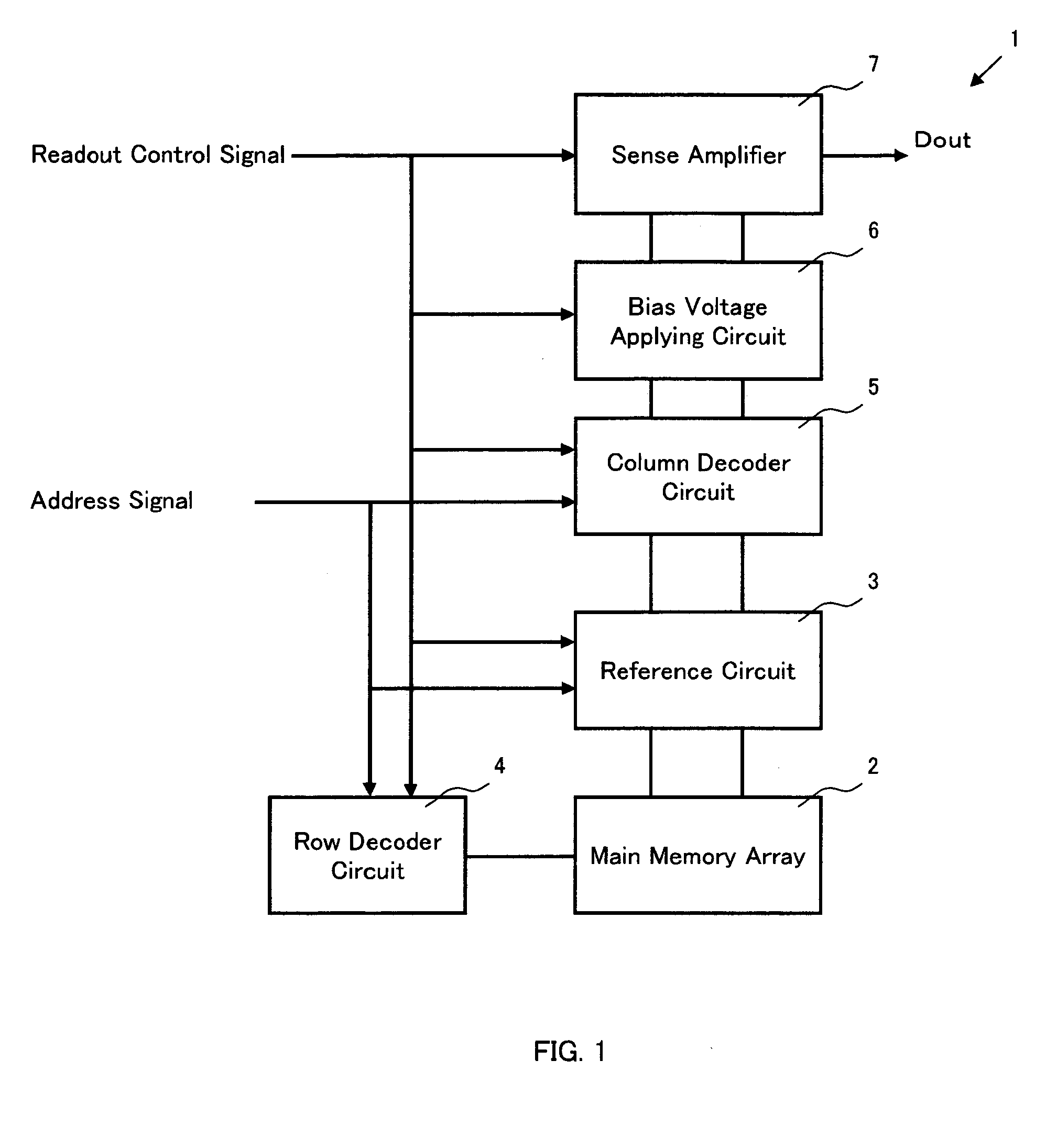
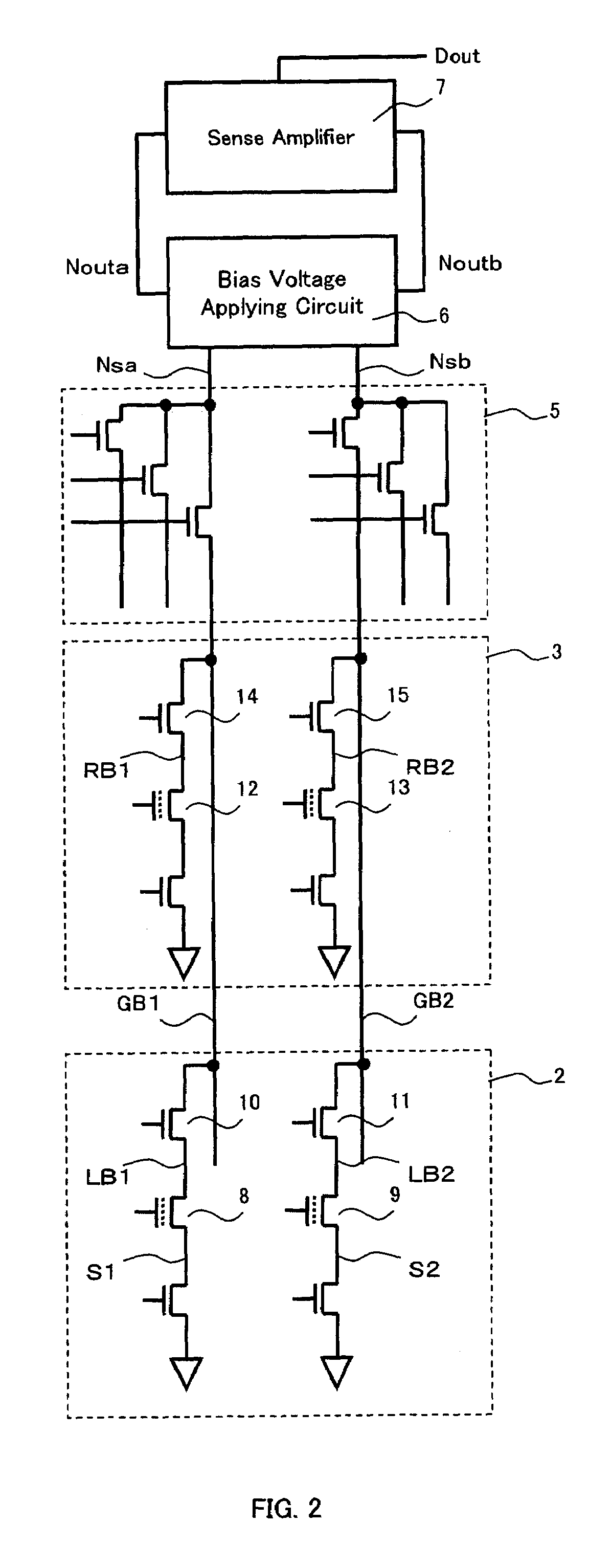
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
201 results about "Reference memory" patented technology
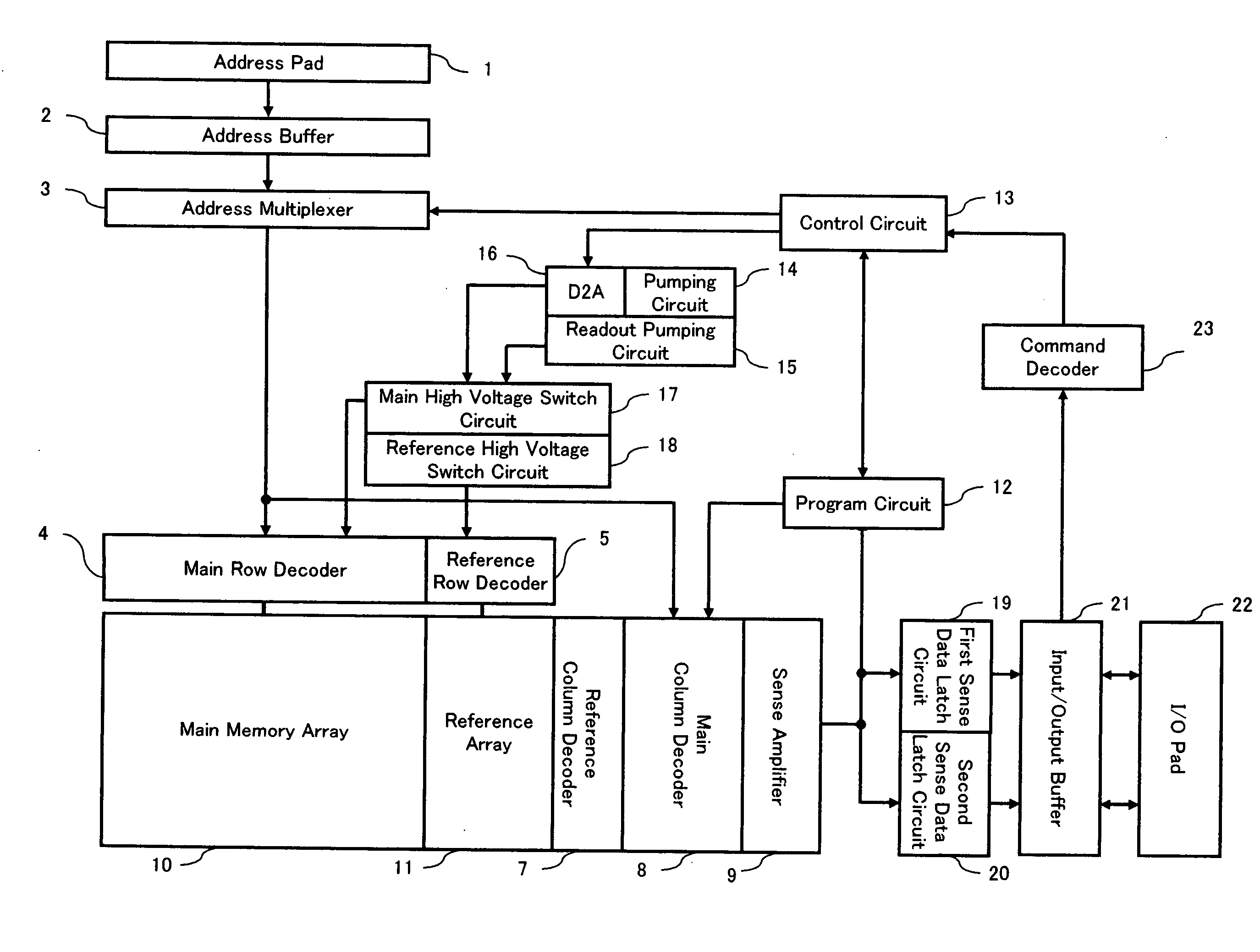
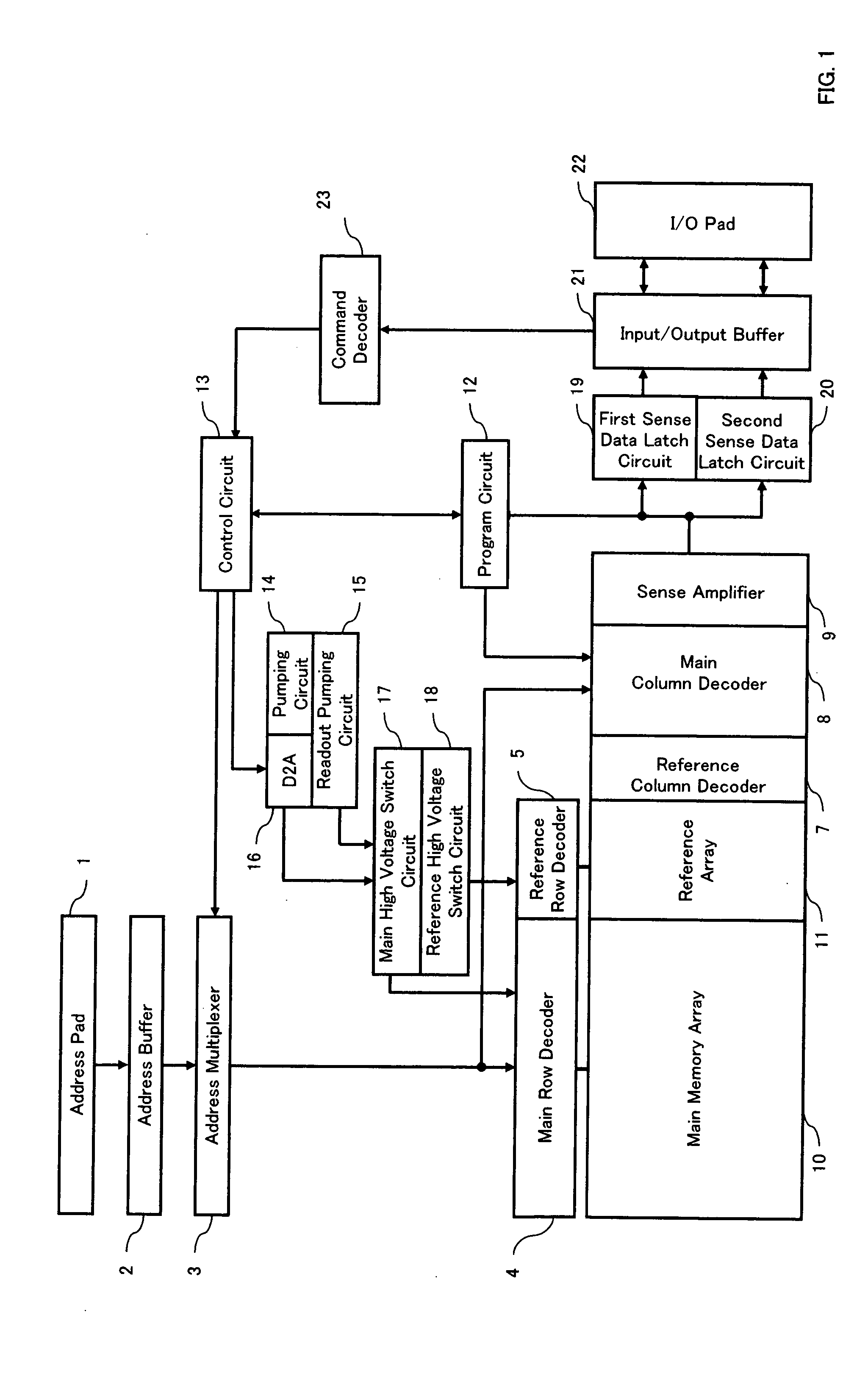
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
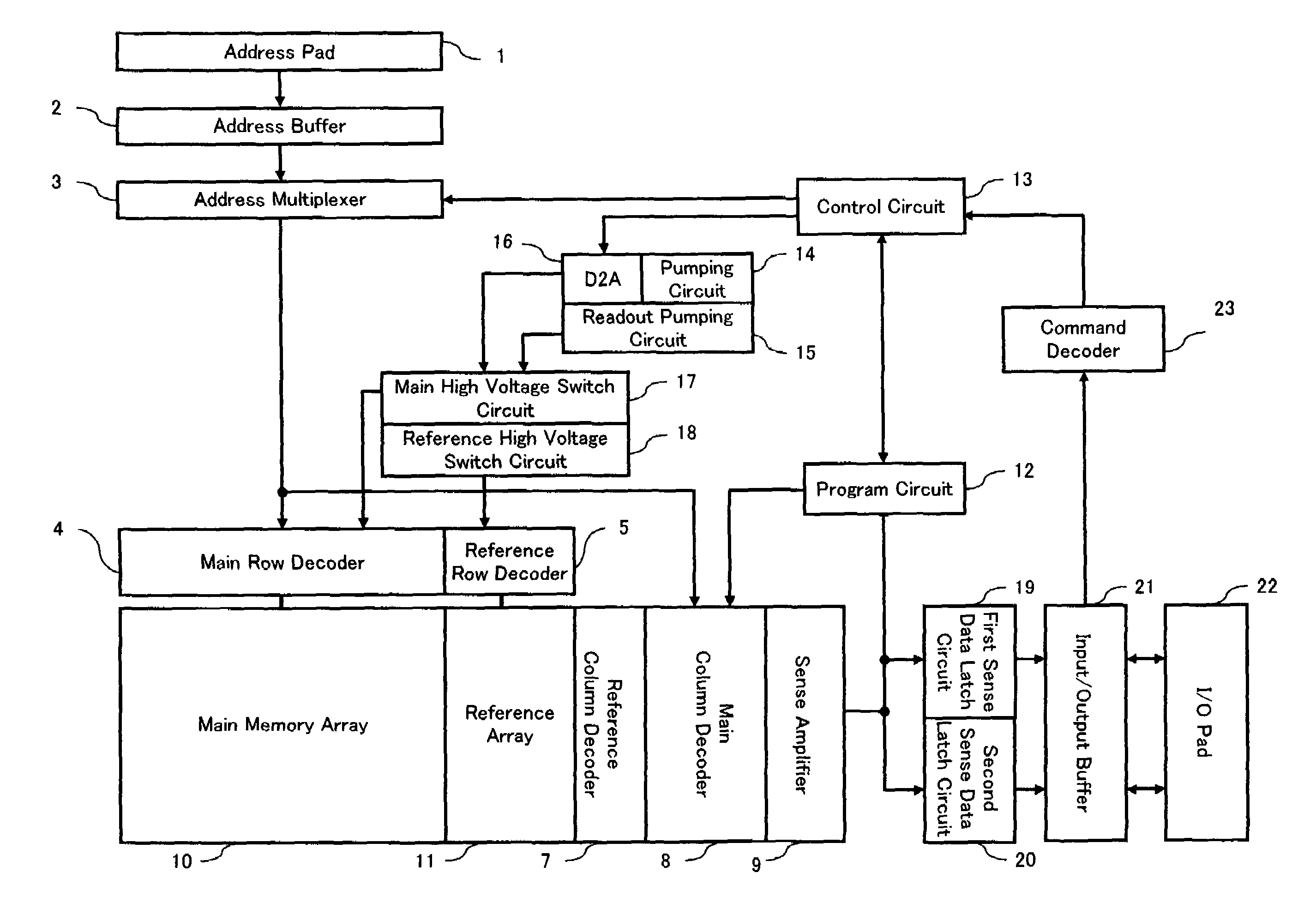
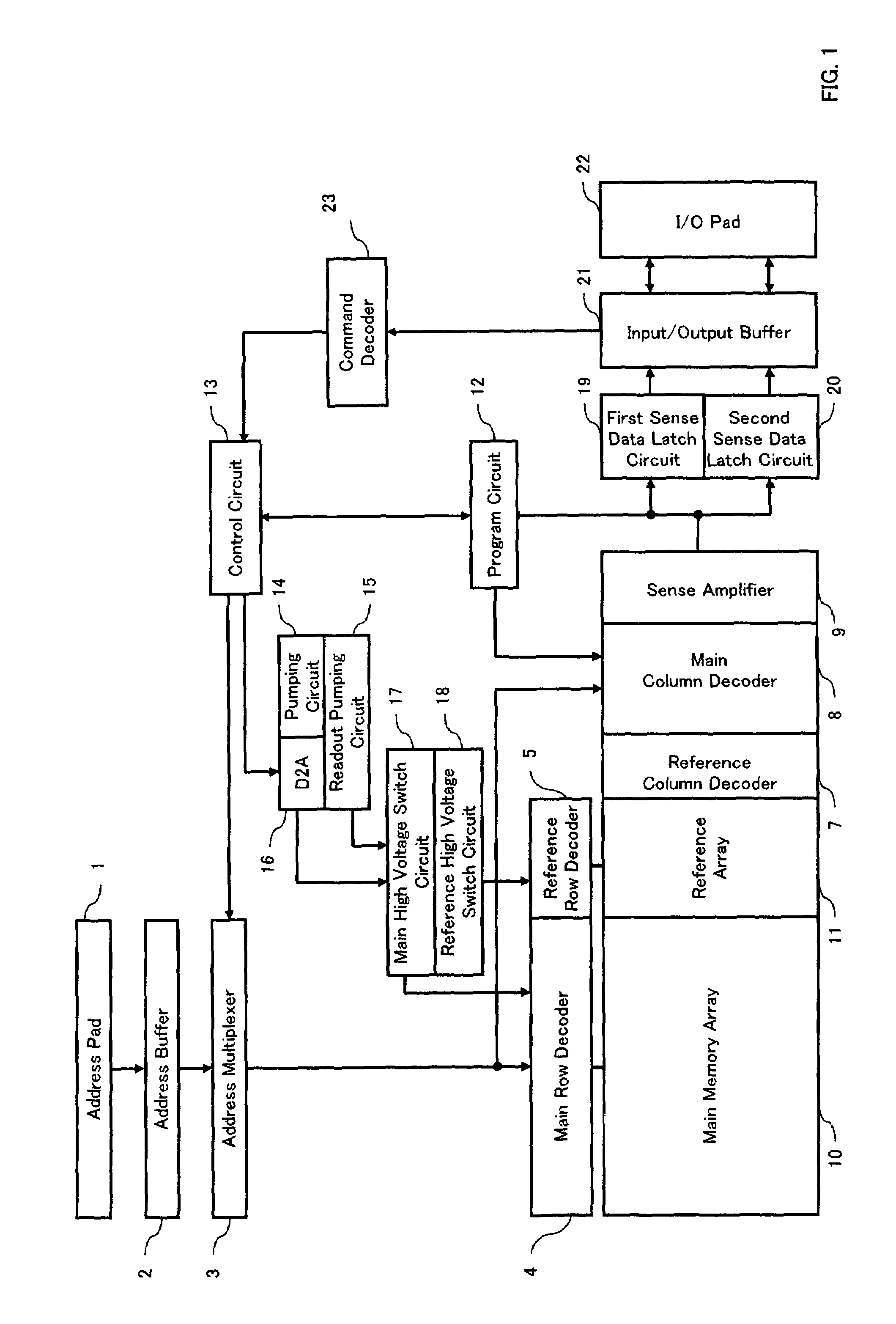
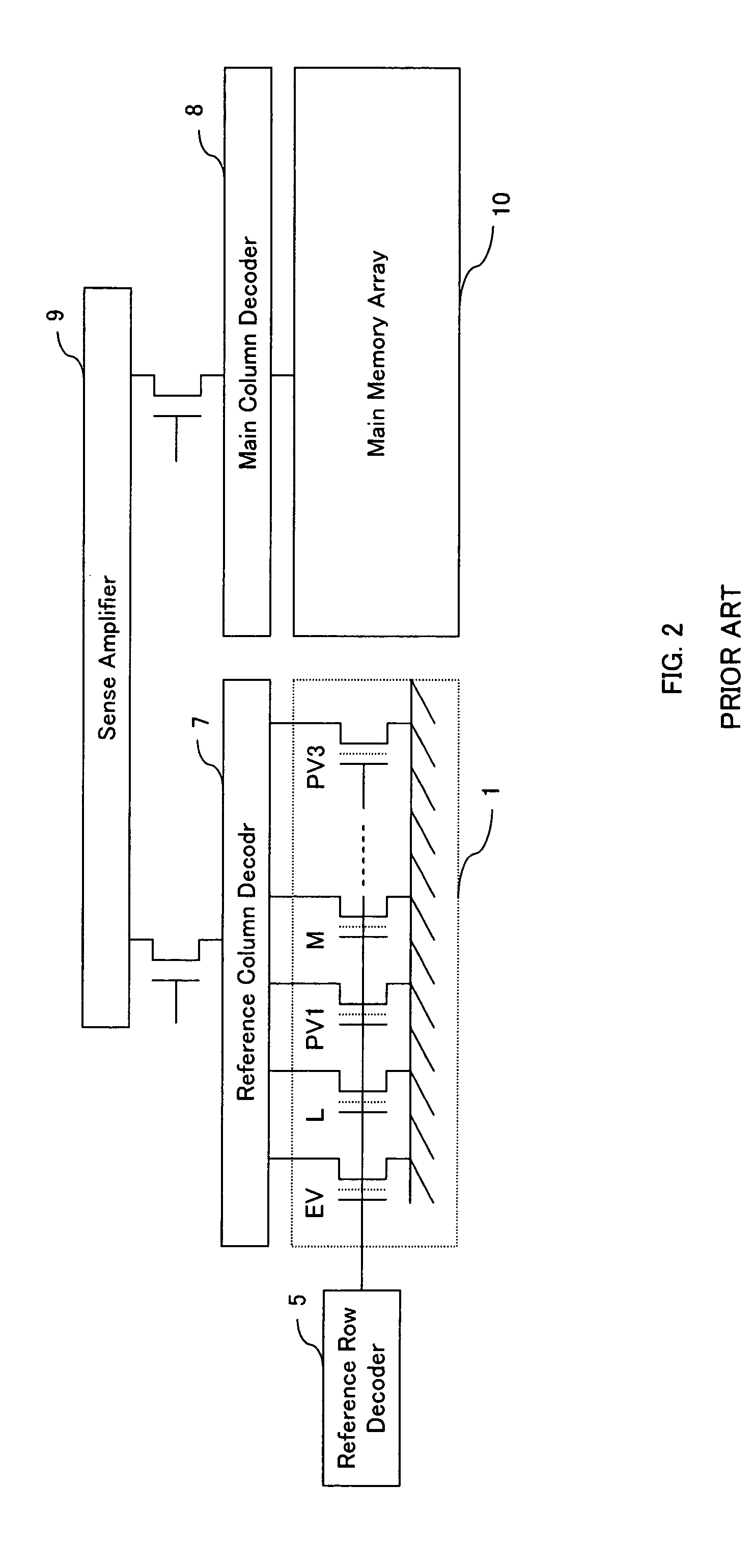
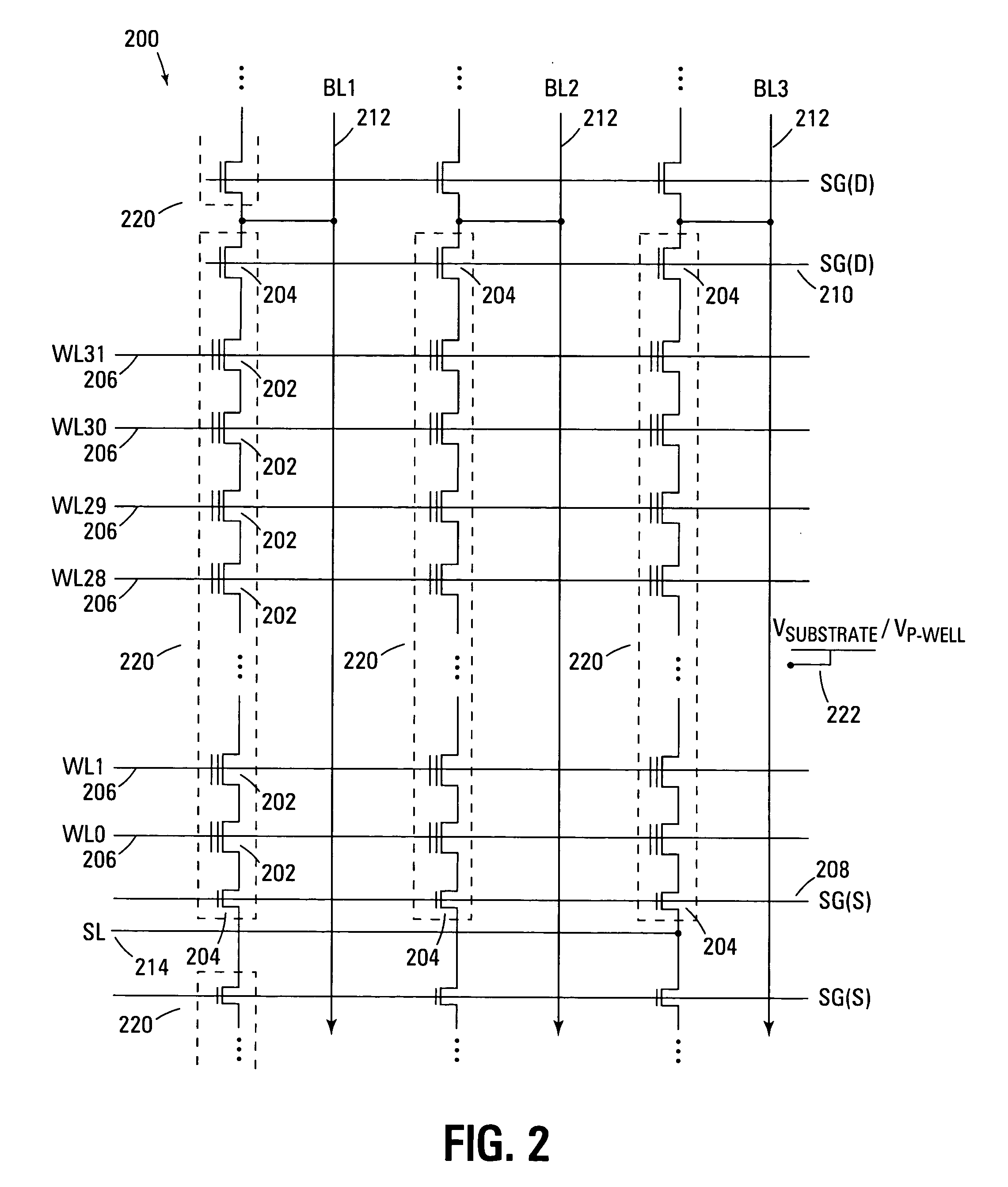
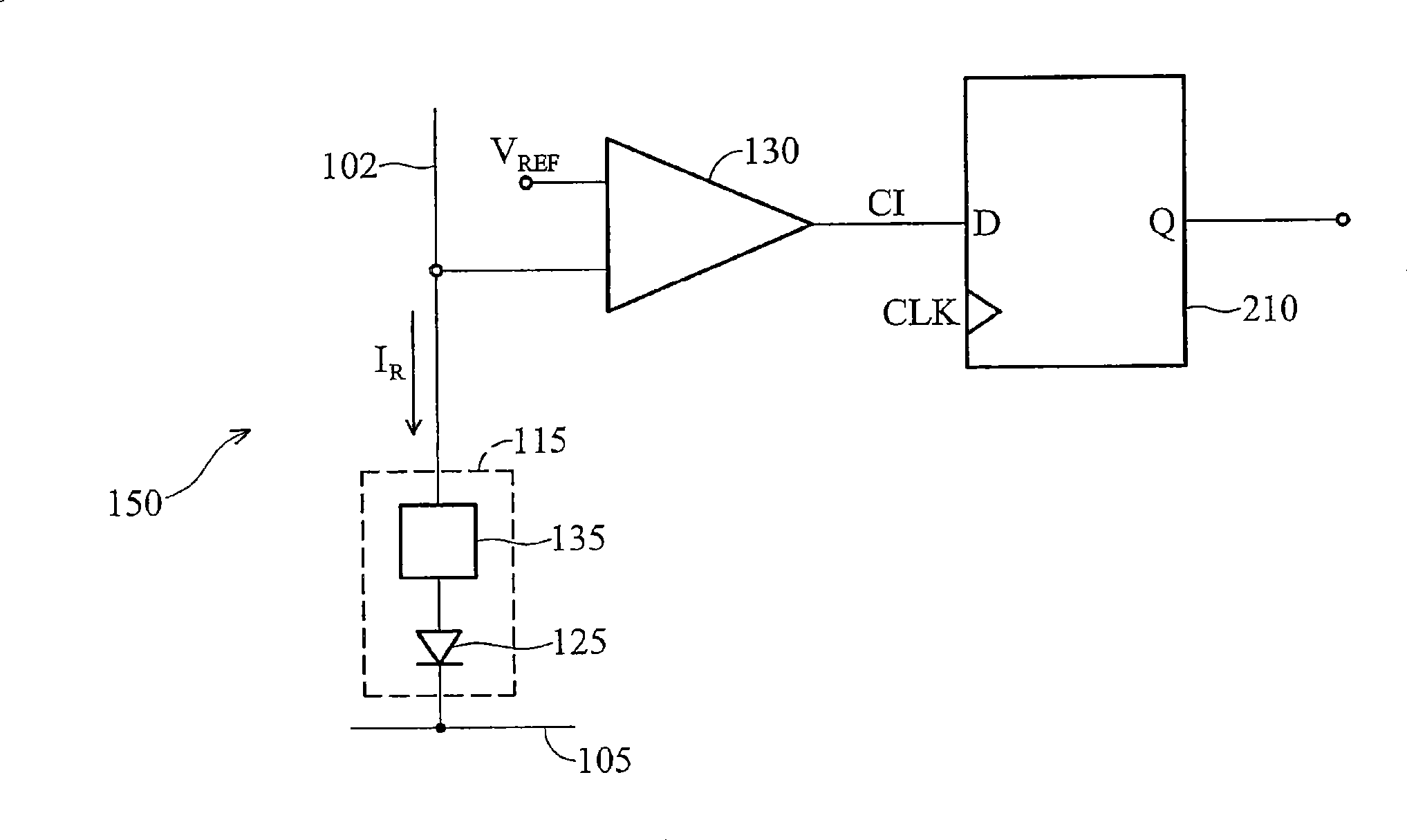
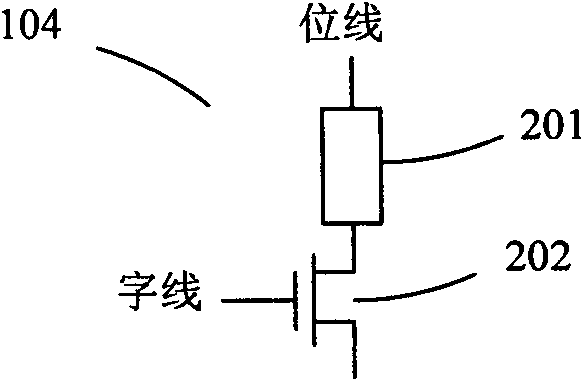
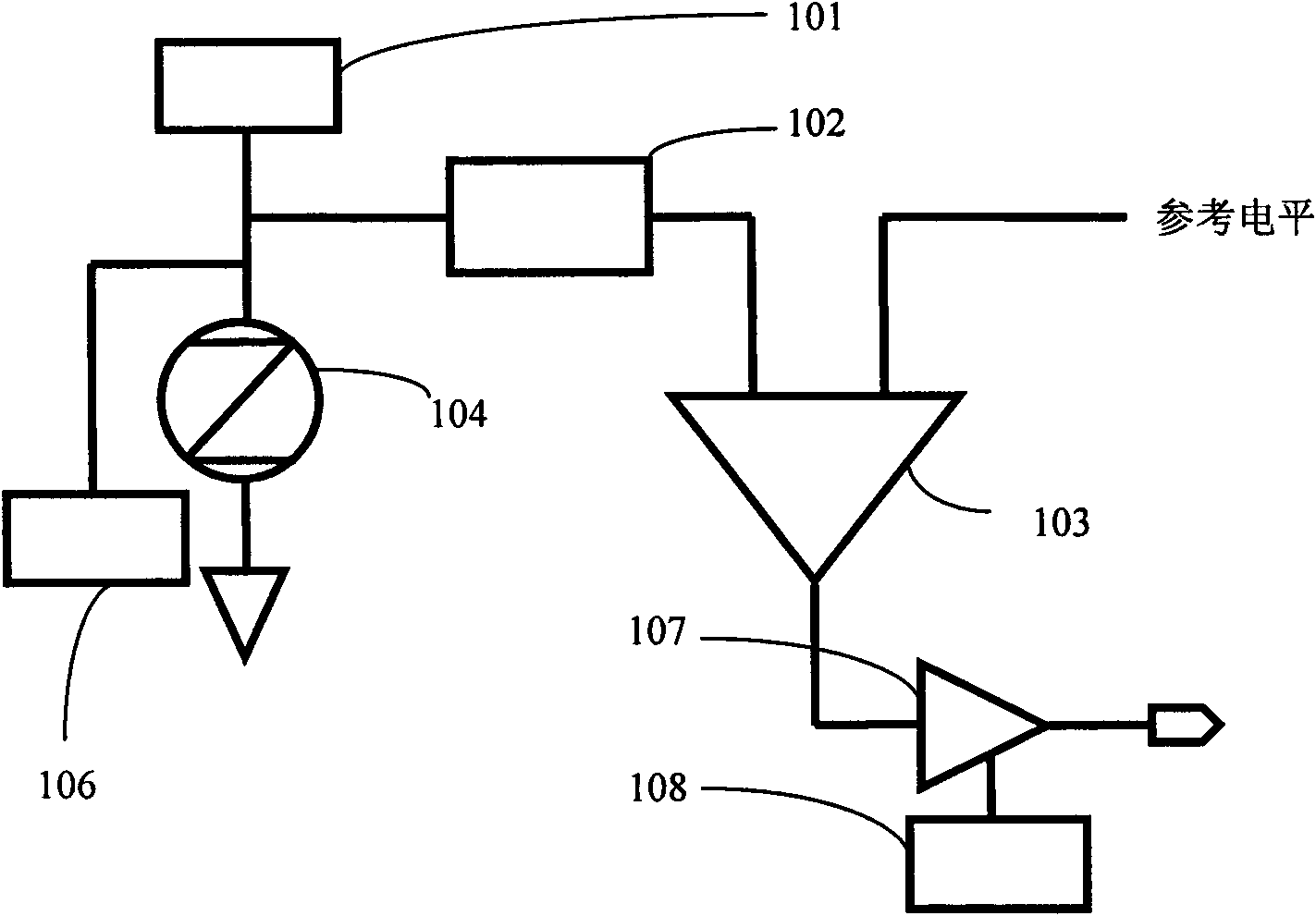
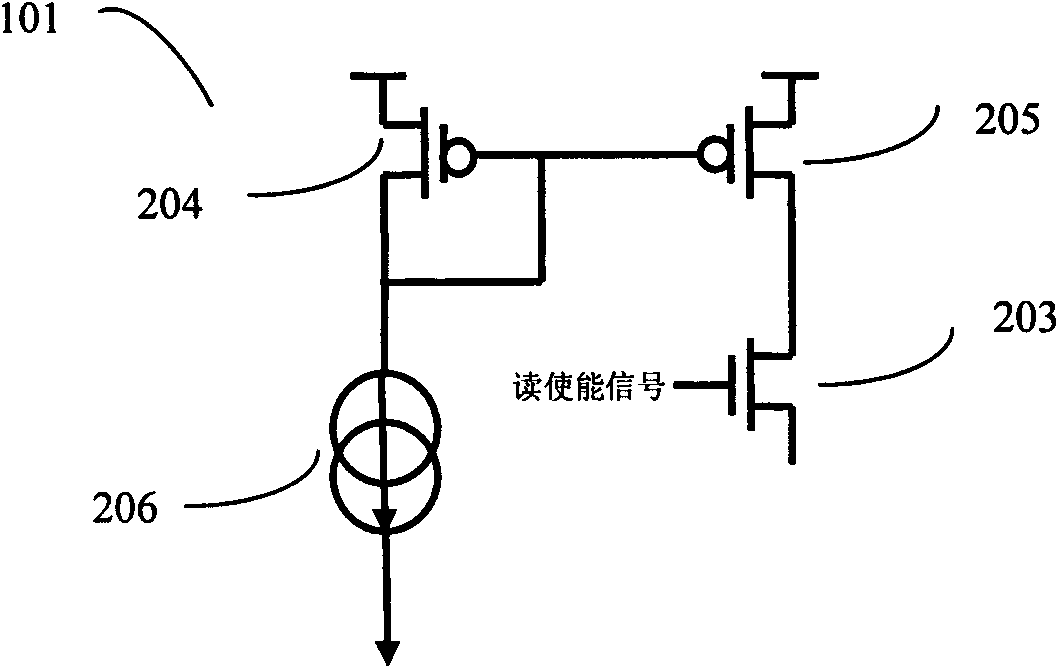
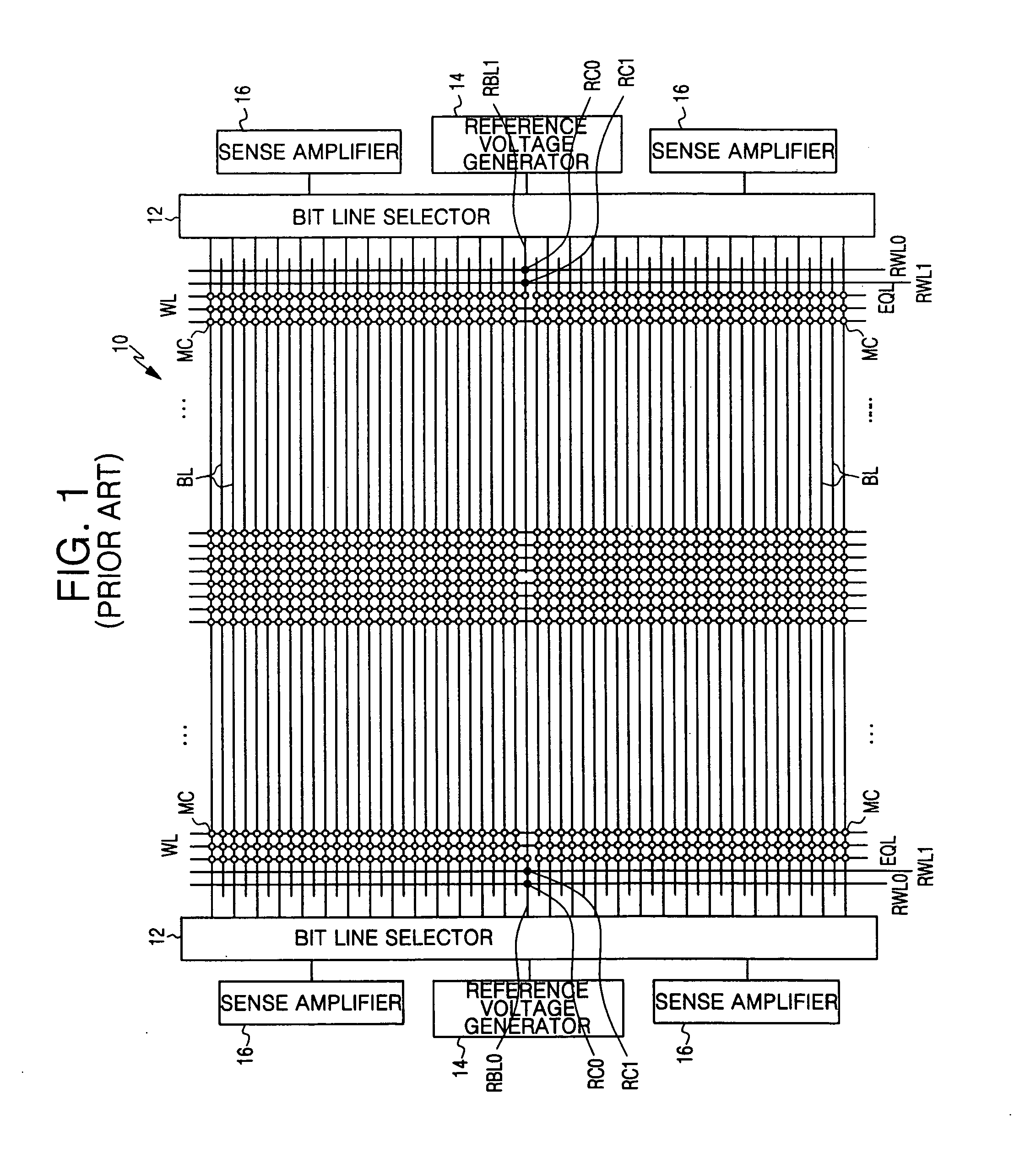
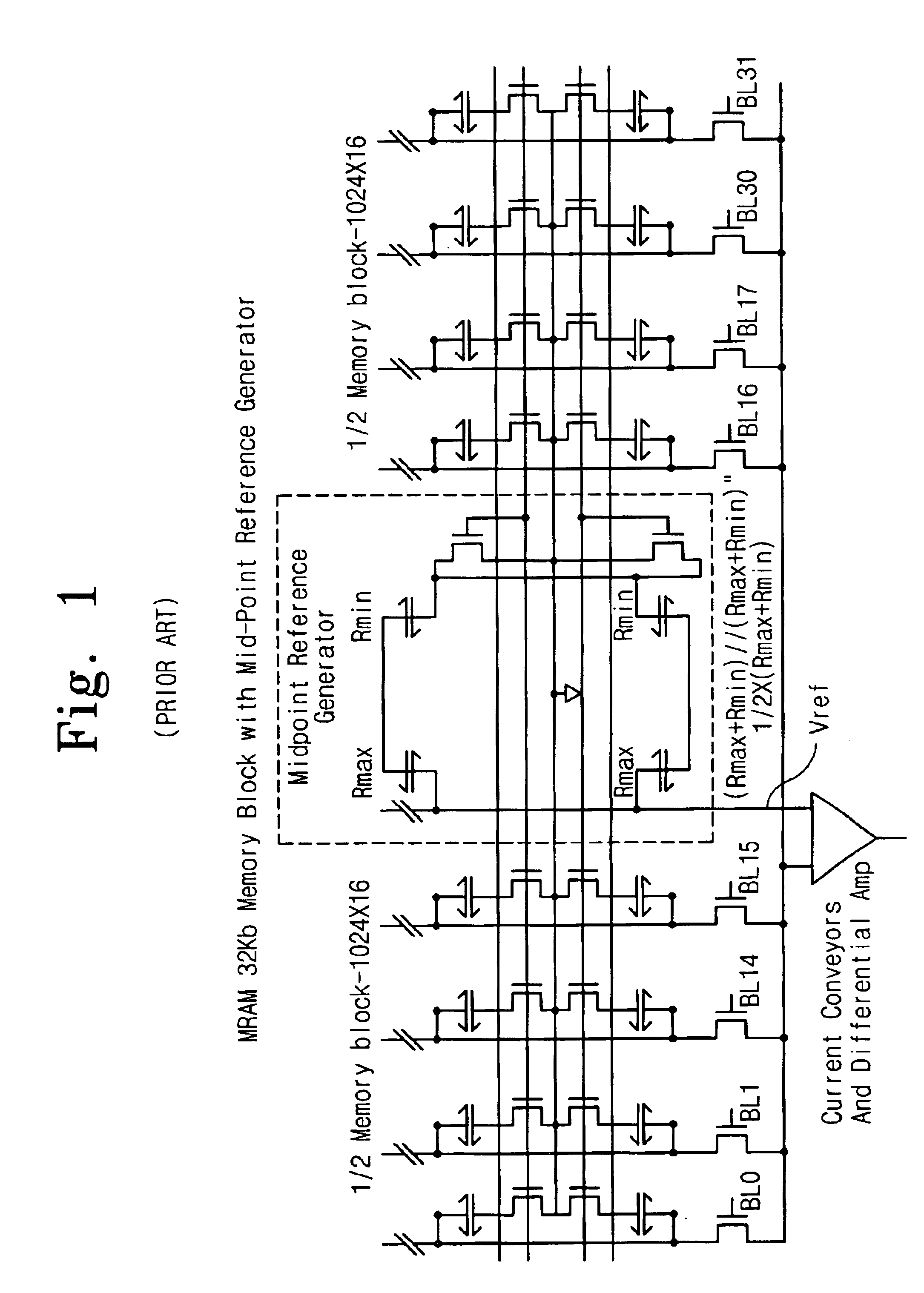
Reference memory is a long-term memory. In a spatial task, it mimics two aspects of episodic memory, namely the “what” (content) and “where” (place) dimensions of an event. One of the tasks most frequently used to assess spatial reference memory in the rat is the Morris water maze. It is highly sensitive to hippocampal damage.
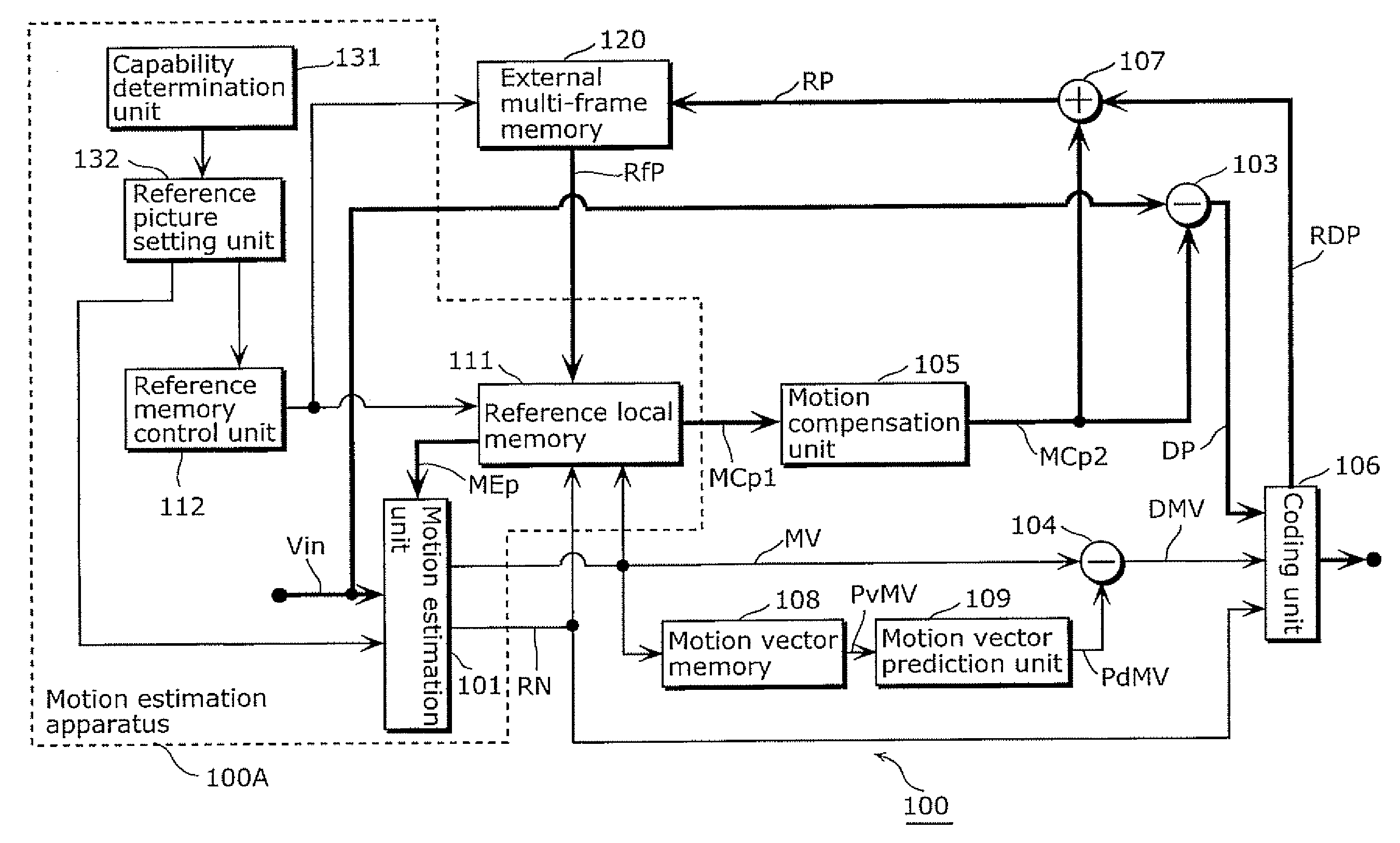
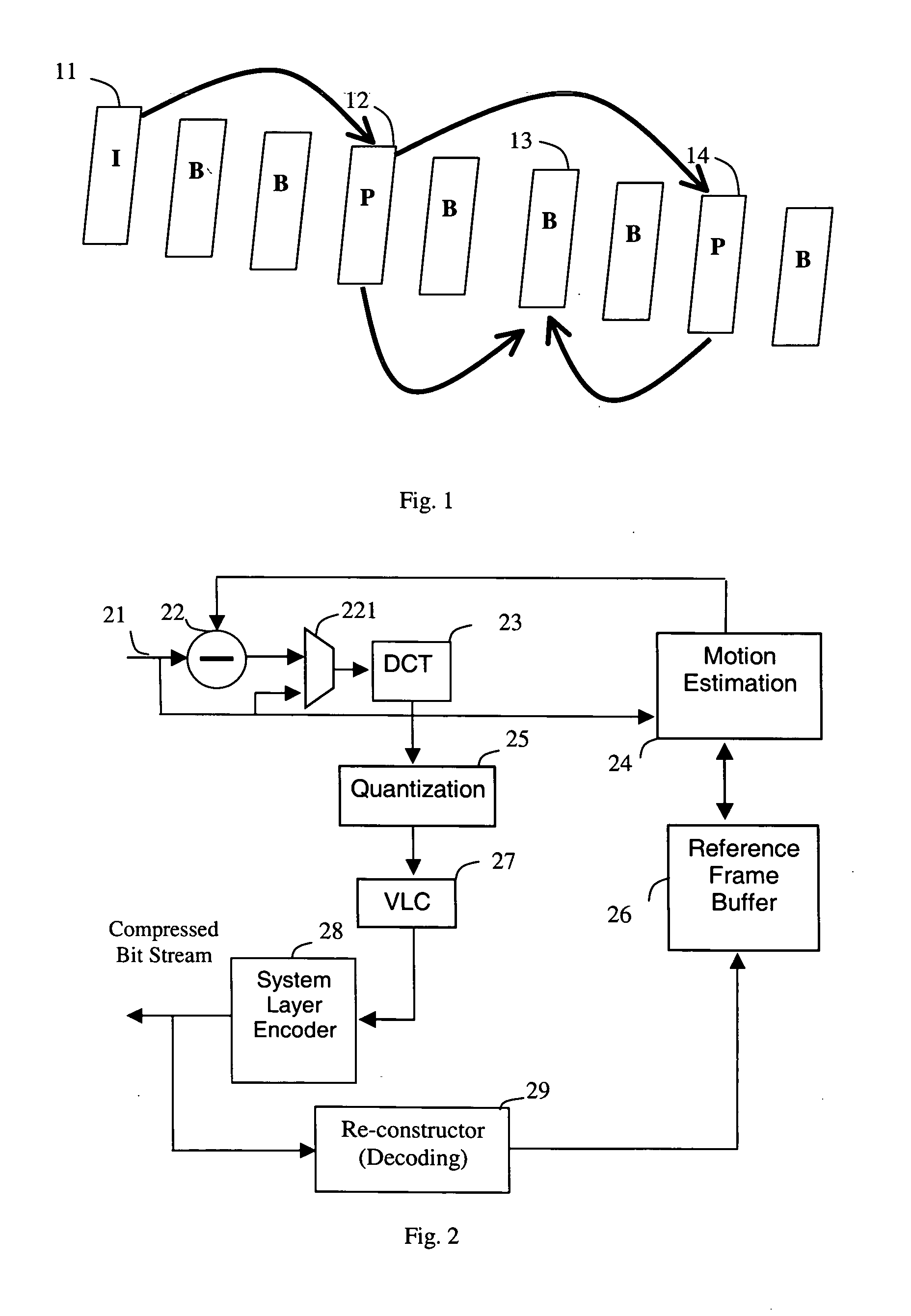
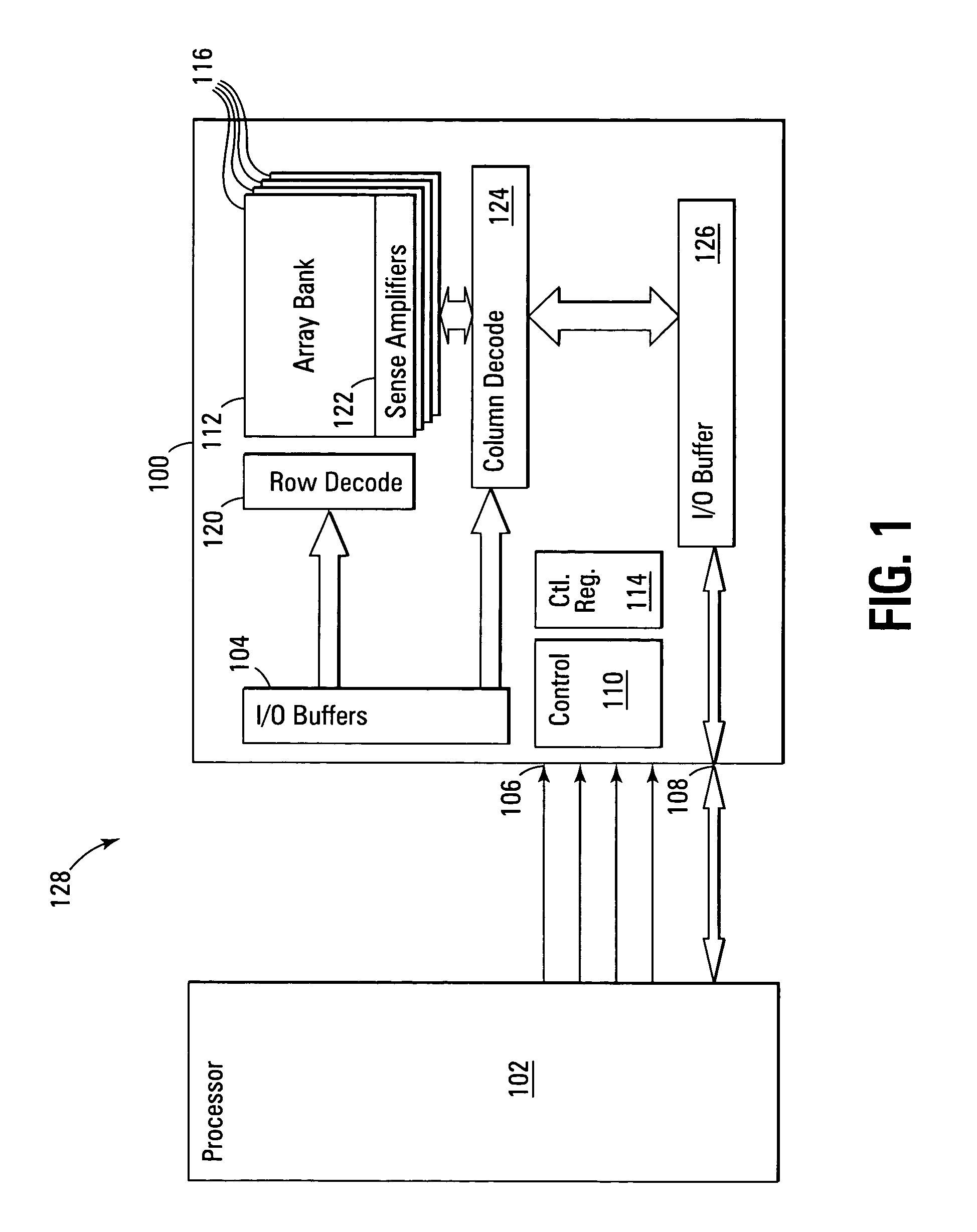
Motion estimation apparatus
InactiveUS20070030899A1Prevent system breakdownDecreasing quality of pictureColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMultiple frameReference image
A motion estimation apparatus, which can prevent a system breakdown without evenly lowering the quality of a picture to be decoded, includes: a reference picture setting unit which restricts a data transfer amount of image data to be transferred from an external multi-frame memory, in accordance with a data transfer capability of the external multi-frame memory for storing the image data; a reference local memory; a reference memory control unit which transfers, to the reference local memory, at least a portion of the image data stored in the external multi-frame memory, which is the data transfer amount restricted by the reference picture setting unit; and a motion estimation unit which performs motion estimation of the picture to be coded with reference to the at least the portion of the image data transferred to the reference local memory.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Systems and methods for efficient memory access
InactiveUS20130346719A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationProcessing coreProcessor register
A computer-implemented method of accessing data comprises resetting the value of a register of a first processing core of a multi-core processor, copying the bits of a compressed pointer into the lowest order bits of the register, left shifting the register a predetermined number of bits, and executing on the first processing core a first instruction referencing memory at a virtual address specified by the register.
Owner:KEYSIGHT TECH SINGAPORE (SALES) PTE LTD
Method for reading a nonvolatile memory device and nonvolatile memory device implementing the reading method
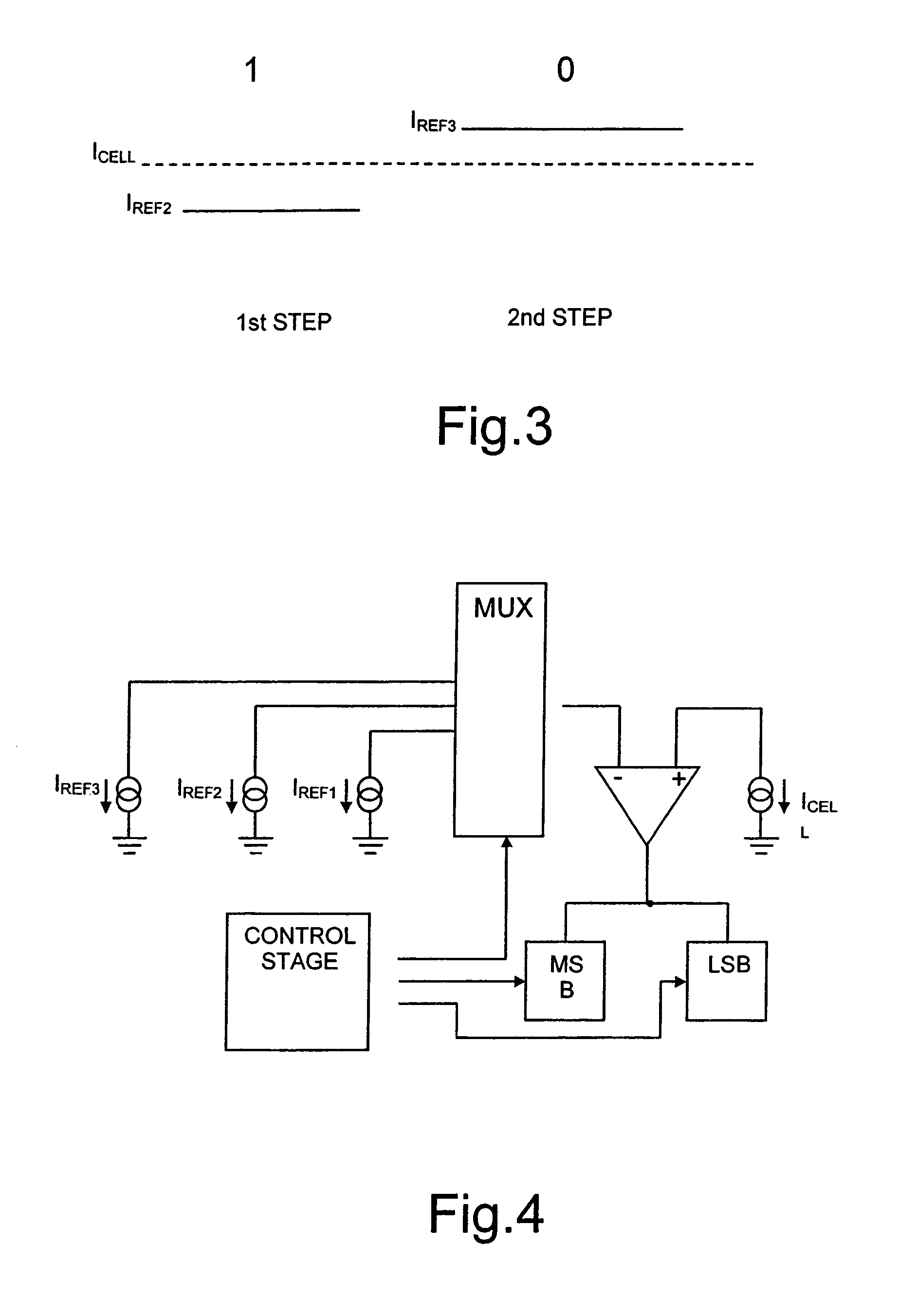
A reading method for a nonvolatile memory device, wherein the gate terminals of the array memory cell and of the reference memory cell are supplied with a same reading voltage having a ramp-like pattern, so as to modify their current-conduction states in successive times, and the contents of the array memory cell are determined on the basis of the modification order of the current-conduction states of the array memory cell and of the reference memory cell.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Packet data analysis with efficient and flexible parsing capabilities
ActiveUS6952425B1Optimize data processingOptimization mechanismData switching by path configurationStore-and-forward switching systemsState dependentData field
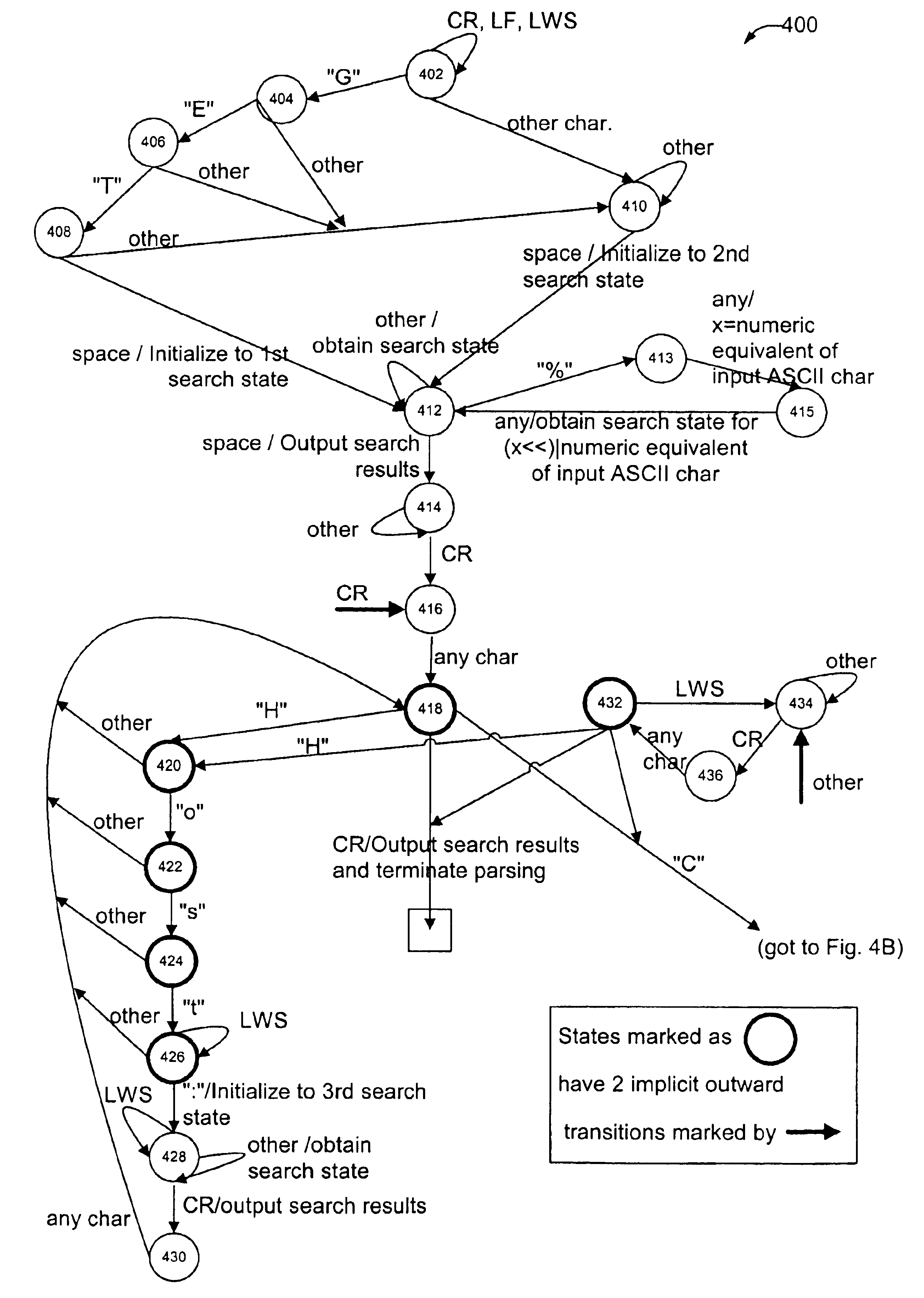
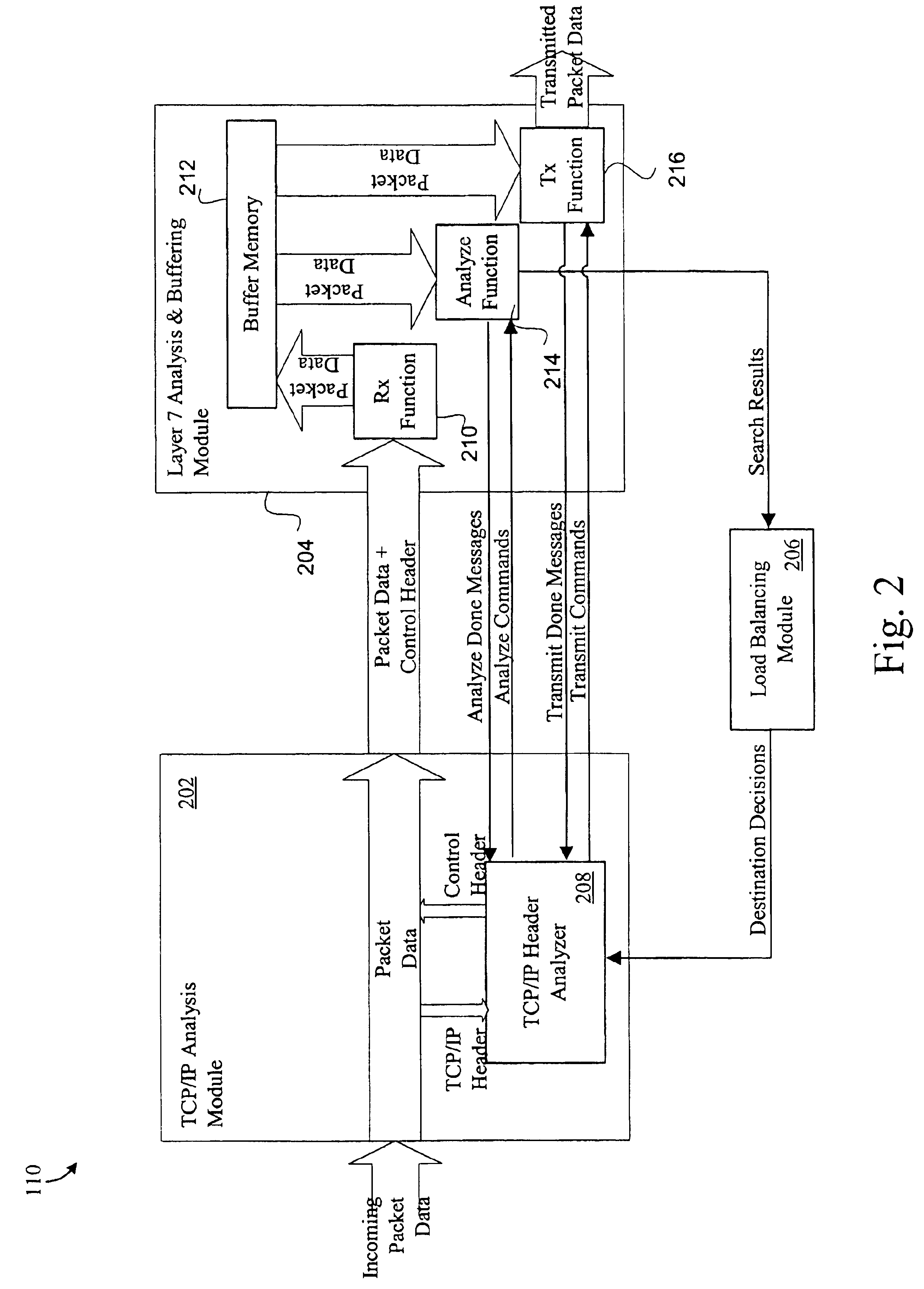
Methods and apparatus which facilitate the handling of data between platforms interconnected by any of a variety of network environments are disclosed. In general terms, the present invention represents an improvement over conventional packet parsing and searching mechanisms. The parse mechanism sequentially analyzes each character of the packet data and passes relevant characters to the search mechanism as soon as each character is reached. Preferably, the characters of each data field are parsed character-by-character. In one implementation, prior to searching a relevant data field, the parser initializes the appropriate search mechanism based on at least the data field type (e.g., the cookie field or URL field of an HTTP request). Each character of the relevant data is then passed sequentially to the search mechanism, where a search state are obtained for each passed character. Accordingly, the parser passes each character of the relevant data fields to the search mechanism. Since the parser passes the well-defined fields of standard protocols, such as HTTP and FTP, parsing may be efficiently performed without referencing memory (e.g., parsing is implemented in micro-code). When the parser reaches the end of the relevant data field, the parser may then cause the search mechanism to output search results associated with the search state of the last searched character. Alternatively, the parser may initiate another search for another data field, which is subsequently parsed and searched character-by-character as recited above for the first field.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Memory array with read reference voltage cells
InactiveUS20100067282A1Reliability of reference voltageElectric analogue storesRead-only memoriesHigh resistanceElectrical resistance and conductance
The present disclosure relates to memory arrays with read reference voltage cells. In particular the present disclosure relates to variable resistive memory cell apparatus and arrays that include a high resistance state reference memory cell and a low resistance state reference memory cell that provides a reliable average reference voltage on chip to compare to a read voltage of a selected memory cell and determine if the selected memory cell is in the high resistance state or low resistance state. These memory arrays are particularly suitable for use with spin-transfer torque memory cells and resolves many systematic issues related to generation of a reliable reference voltage.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
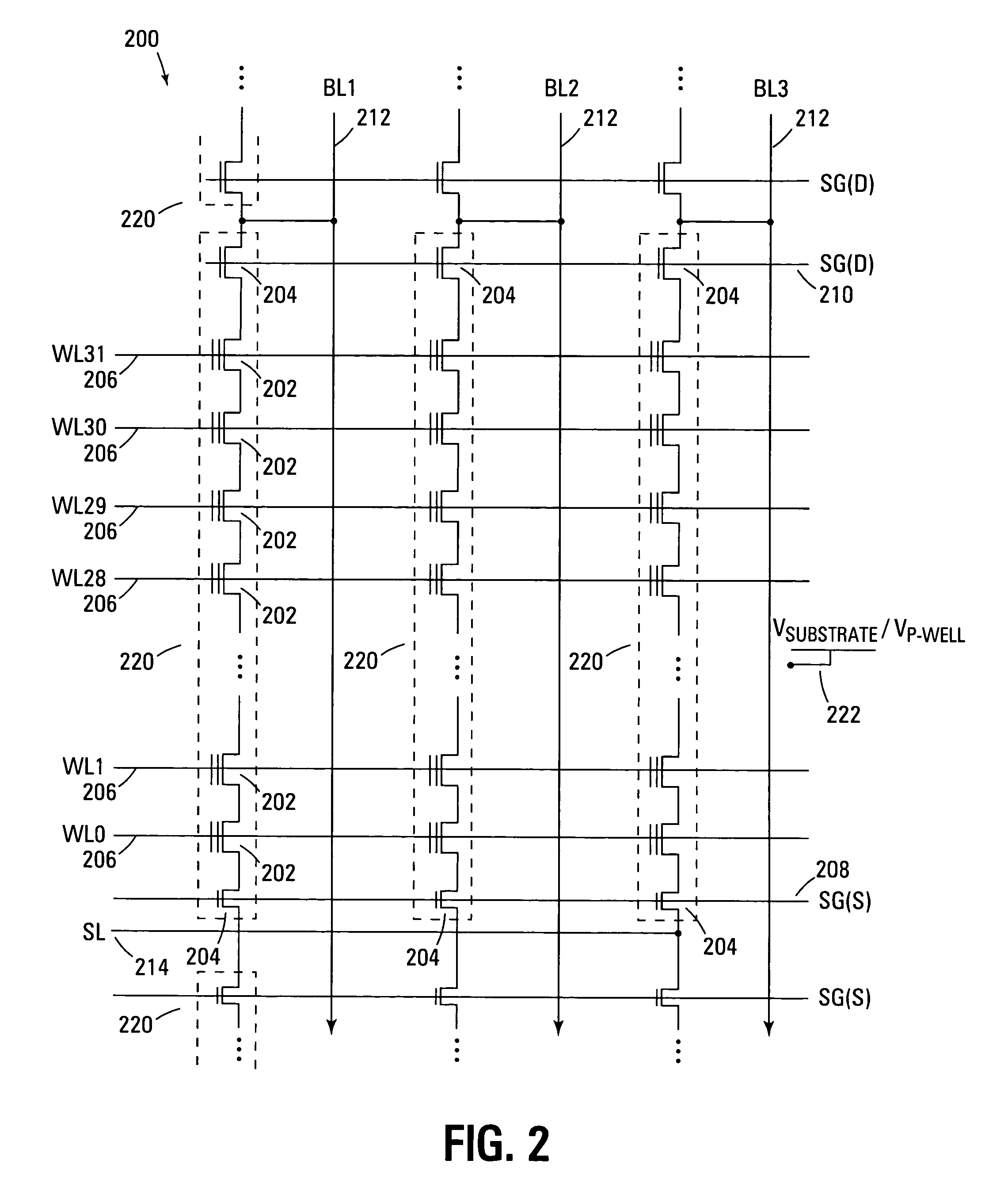
Non-volatile memory systems
InactiveUS20130058169A1Improve reliabilityImprove stabilityRead-only memoriesDigital storageBit lineComputer science
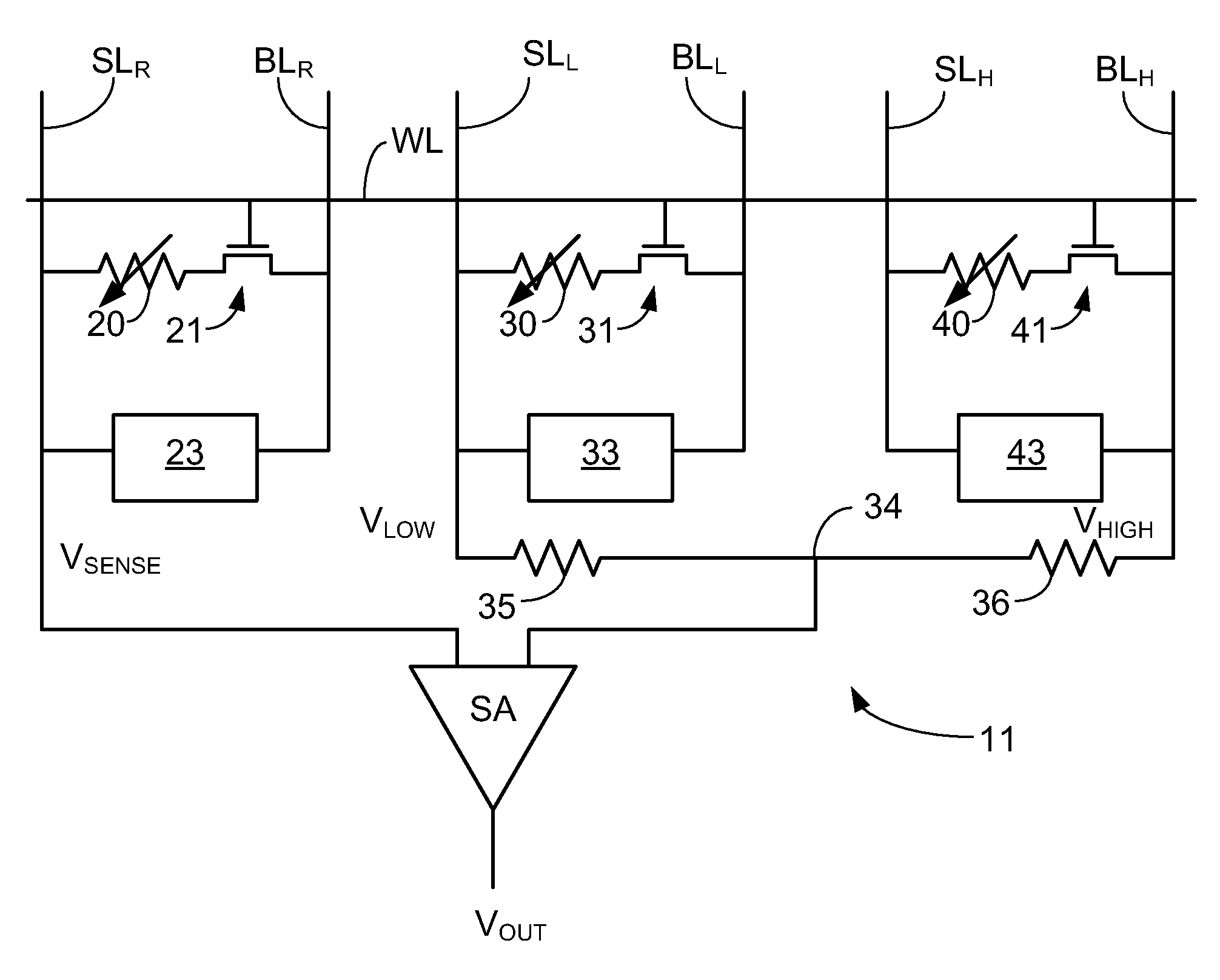
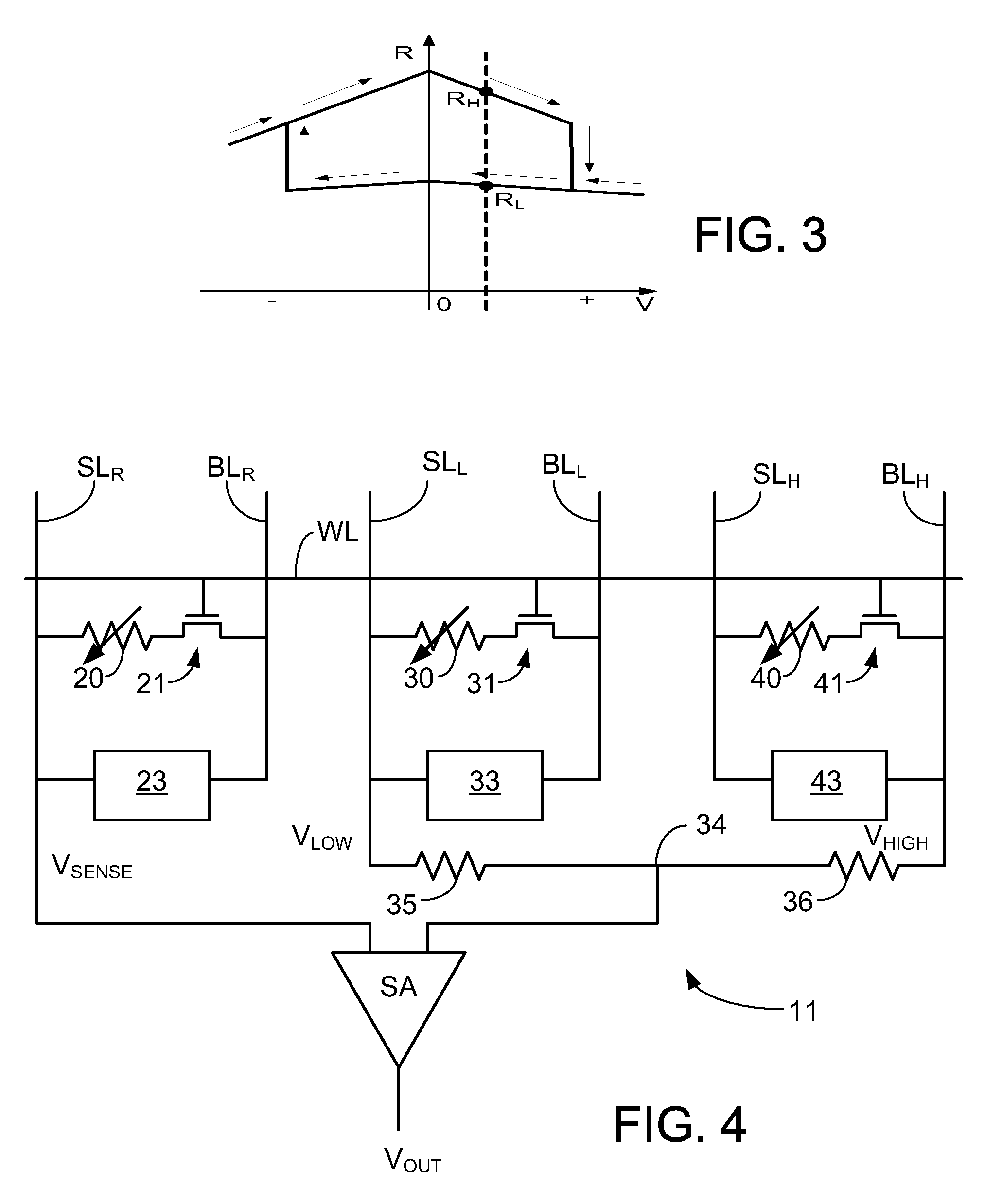
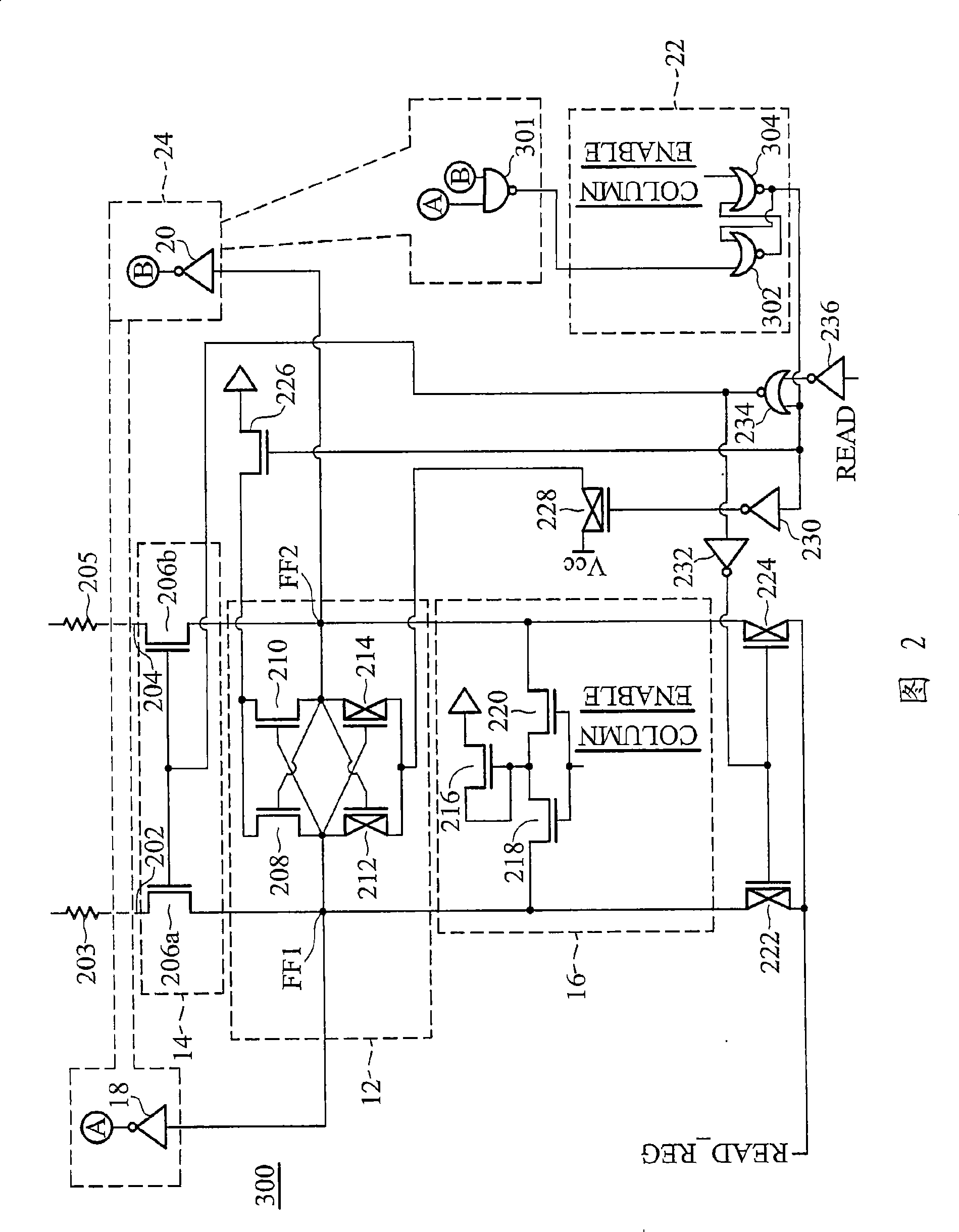
In a non-volatile memory system, a plurality of main memory cells for storing data is arranged in a data cell array and a plurality of reference memory cells is arranged in a reference cell array. The reference cell array includes first reference word lines connected to first reference memory cells and extending, second reference word lines connected to second reference memory cells and extending alternately with the first reference word lines, reference bit lines to which the first and the second reference memory cells are alternately connected in a line and a combined cell having a pair of the first and second reference memory cells and generating a reference signal for processing the data. The first and the second reference memory cells have different cell characteristics. The stability of the reference signal is improved irrespective of the differentiation of the first and the second reference memory cells.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
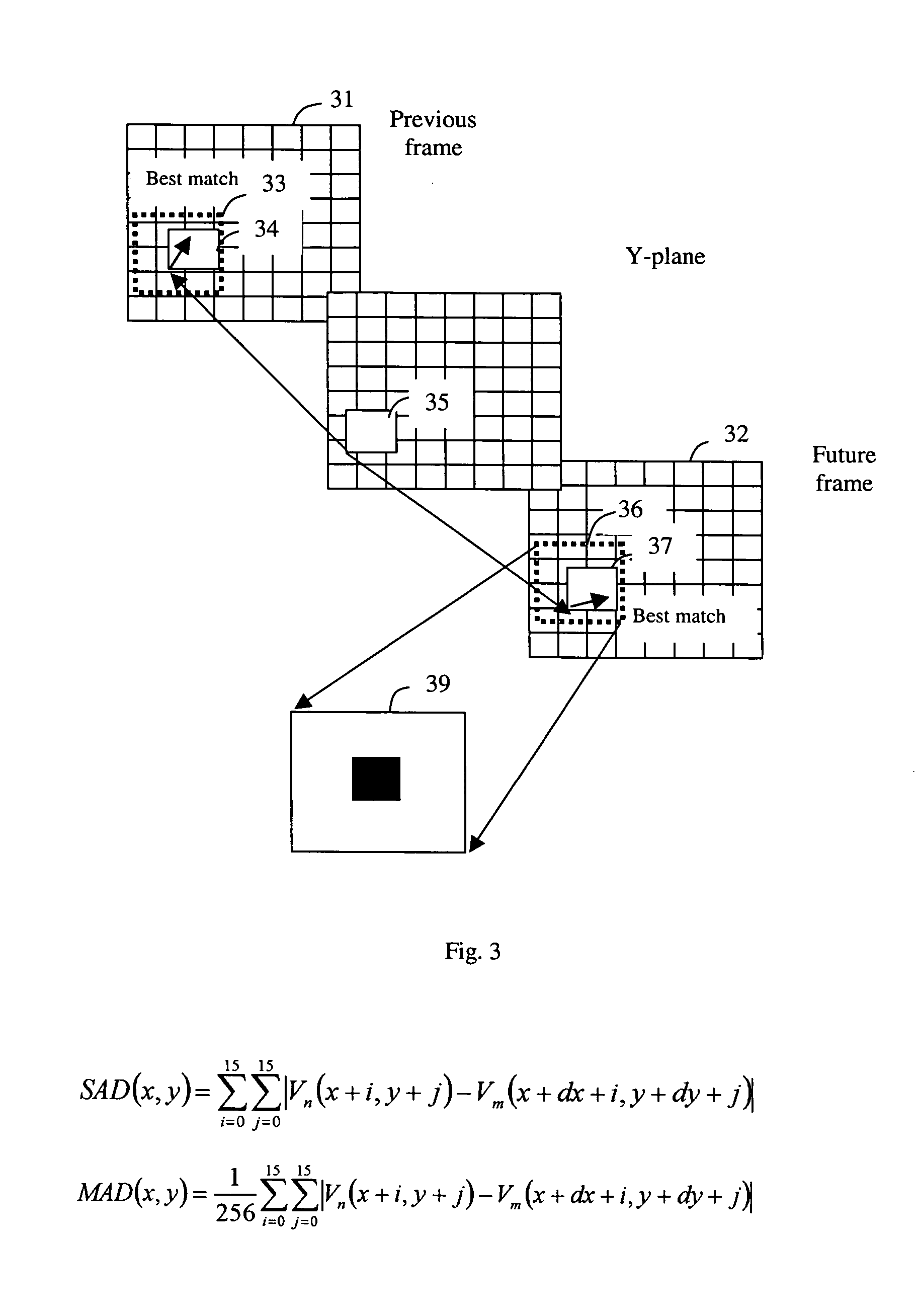
Reference picture loading cache for motion prediction
Video coders use motion prediction, where a reference frame is used to predict a current frame. Most video compression standards require reference frame buffering and accessing. Given the randomized memory accesses to store and access reference frames, there are substantial overlapped areas. Conventional techniques fail to recognize this overlap, and perform duplicate loading, thereby causing increased memory traffic. Techniques disclosed herein reduce the memory traffic by avoiding the duplicated loading of overlapped area, by using a reference cache that is interrogated for necessary reference data prior to accessing reference memory. If the reference data is not in the cache, then that data is loaded from the memory and saved into the cache. If the reference data is in the cache, then that data is used instead of loading it from memory again. Thus, memory traffic is reduced by avoiding duplicated memory access to overlapped areas.
Owner:MICRONAS
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device
InactiveUS7020037B2Increase speedHigh-speed performanceFloating sedimentation devicesWater treatment parameter controlHemt circuitsData storing
A nonvolatile semiconductor memory device includes a readout circuit which reads data stored in a selected memory cell by applying predetermined voltage to the selected memory cell and a reference cell such that currents corresponding to the respective threshold voltage may flow, and comparing the current flowing in the selected memory cell with the current flowing in the reference cell. The readout circuit commonly uses the reference cell set in the same storage state for normal readout and for readout for program verification, and when the predetermined voltage is applied to the selected memory cell and the reference memory cell at the time of the readout for the program verification, it sets an applying condition to the reference memory cell such that its storage state may be shifted more in the program state direction than that in an applying condition at the time of the normal readout.
Owner:SHARP KK
Method and apparatus for decoding digital video stream
InactiveUS20070217702A1Accelerated programLess power consumptionCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationDigital videoMotion vector
The present invention provides method and apparatus of digital video stream decoding by calculating the complexity of the B-type coded frame or macro-block and decoding whether the motion compensation can be skipped to save the time of accessing the referencing memory. The block with the decompressed accumulative pixel difference is less than a predetermined threshold and the motion vector equals to (0,0) or “Frame movement”, the motion compensation is skipped and one of the P-Type or I-type referencing frames will be accessed as the reference for motion compensation.
Owner:TAIWAN IMAGINGTEK
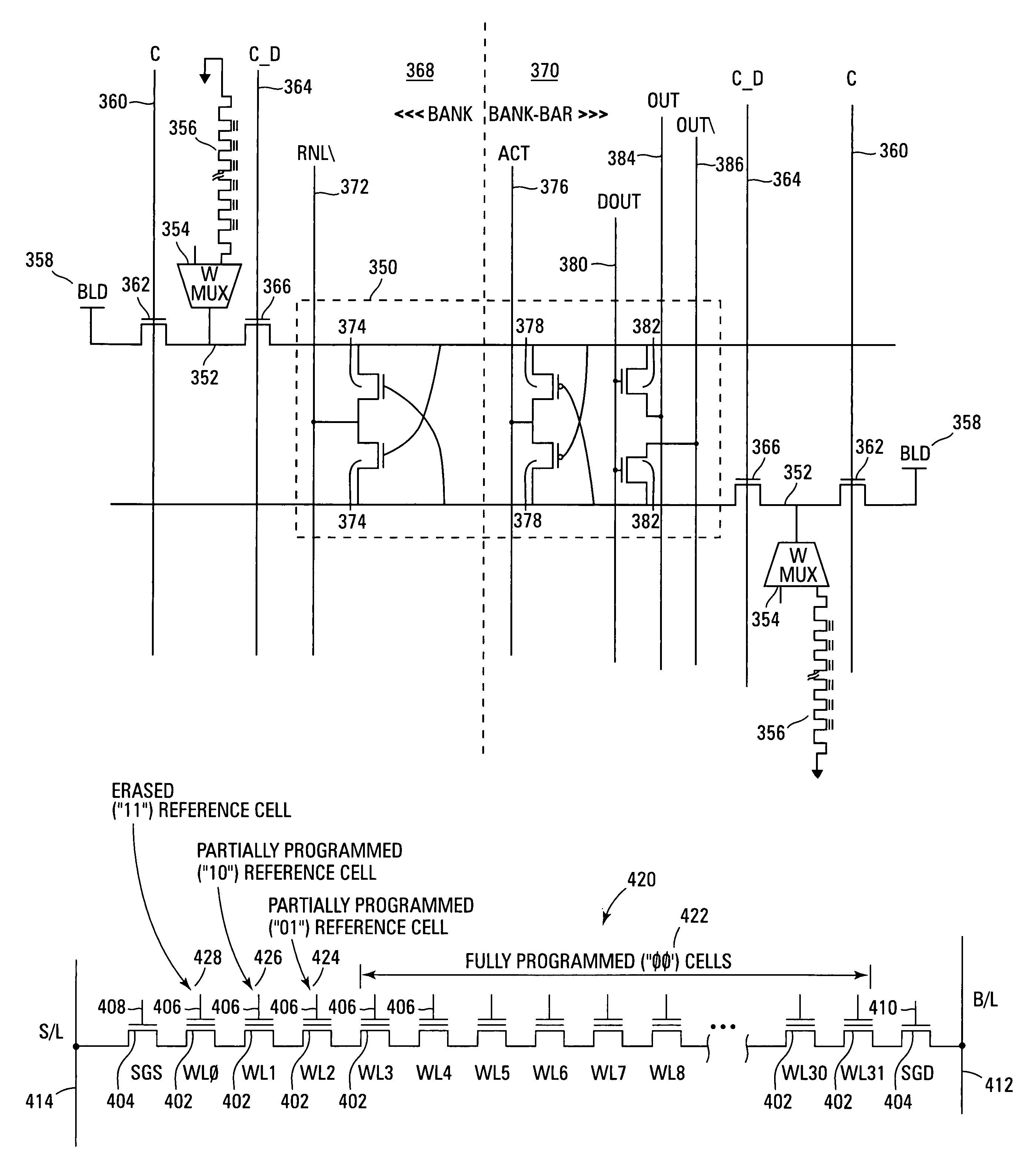
NAND architecture memory with voltage sensing
A NAND architecture non-volatile memory voltage sensing data read / verify process and sense amplifier has been described that senses data in floating gate or floating node field effect transistor memory cells using a voltage sensing data read / verify process. The voltage sensing process utilized a reference NAND string and reference memory cell that is coupled to a reference bit line. A voltage is precharged onto a bit line to be read and an associated reference bit line. The bit line is then coupled to a NAND string and selected memory cell while the reference bit line is coupled to a reference NAND string and selected reference memory cell. The relative voltage level of the bit line and reference bit line are then set by the relative currents flowing through the coupled NAND string and reference NAND string, and the voltage differential read by a coupled voltage sense amplifier.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Semiconductor memory
InactiveUS6275434B1Avoid yield lossData retention time is longTransistorSolid-state devicesBit lineRefresh cycle
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
System and method for memory allocation in embedded or wireless communication systems
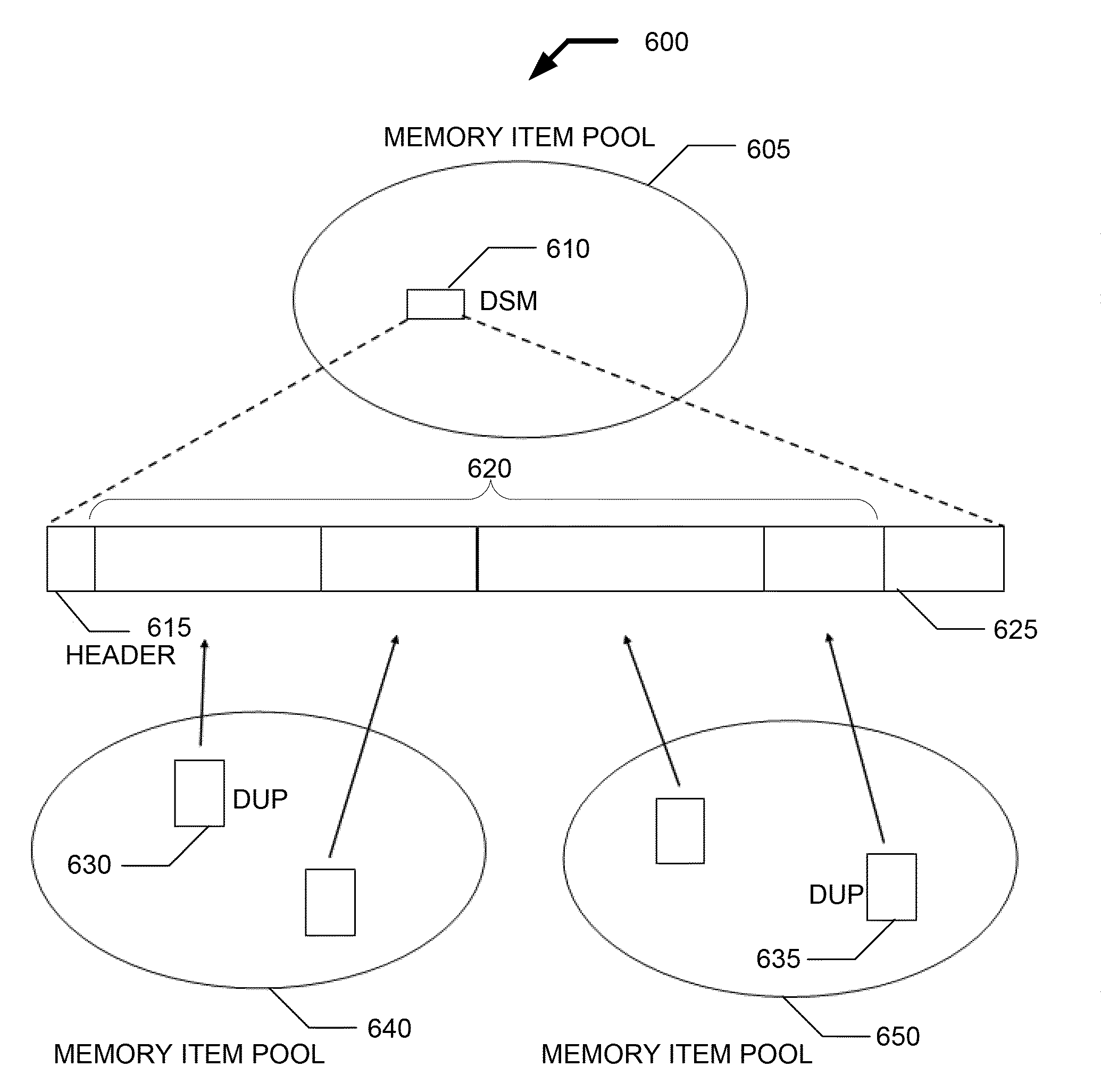
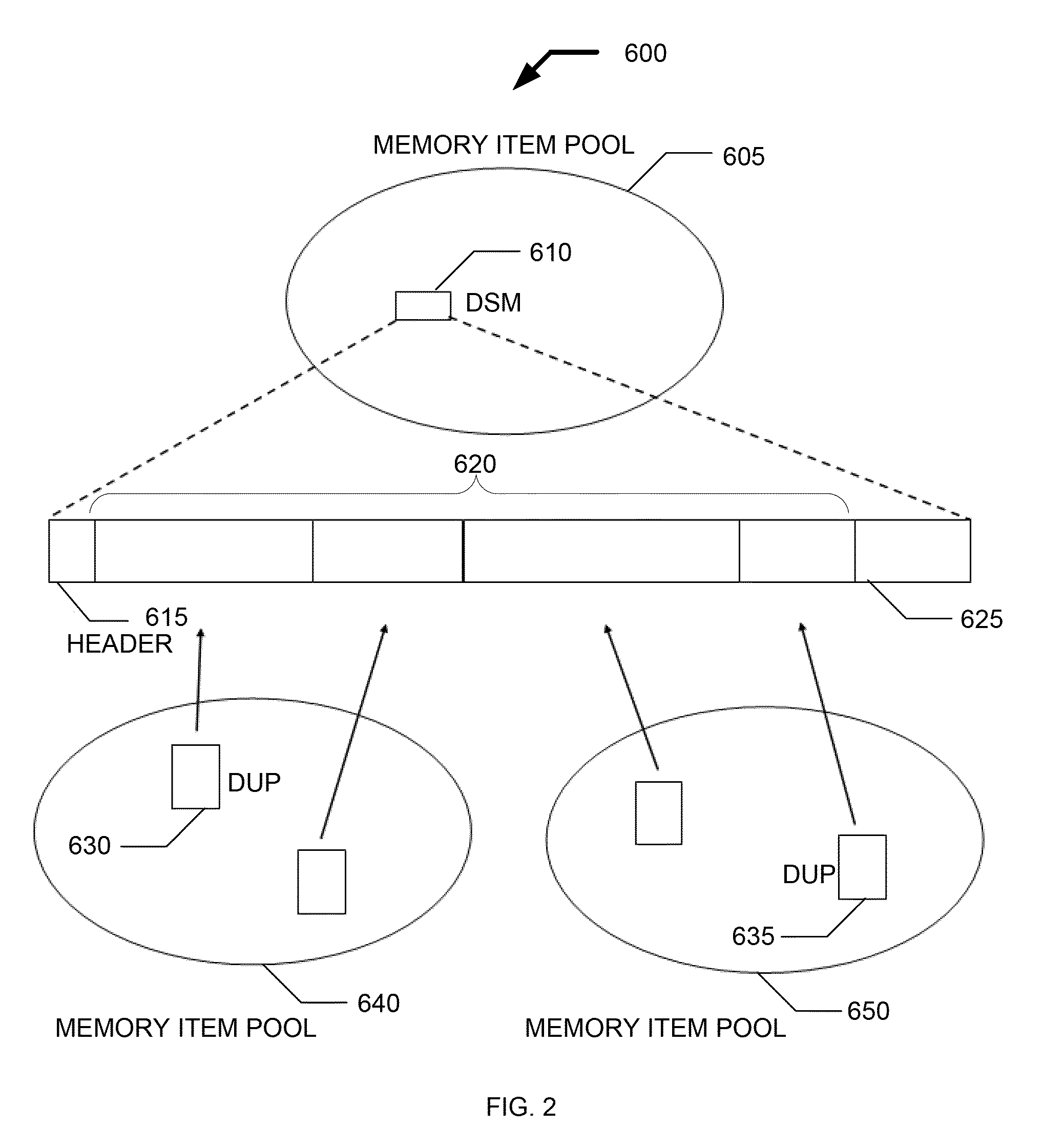
ActiveUS20090254731A1Reduce in quantityReduced checkMemory adressing/allocation/relocationTransmissionCommunications systemReference memory
Systems and methods for an improved memory allocation service in embedded or wireless devices. Memory is allocated using a combination of container memory items and referencing memory items.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
NAND architecture memory with voltage sensing
A NAND architecture non-volatile memory voltage sensing data read / verify process and sense amplifier has been described that senses data in floating gate or floating node field effect transistor memory cells using a voltage sensing data read / verify process. The voltage sensing process utilized a reference NAND string and reference memory cell that is coupled to a reference bit line. A voltage is precharged onto a bit line to be read and an associated reference bit line. The bit line is then coupled to a NAND string and selected memory cell while the reference bit line is coupled to a reference NAND string and selected reference memory cell. The relative voltage level of the bit line and reference bit line are then set by the relative currents flowing through the coupled NAND string and reference NAND string, and the voltage differential read by a coupled voltage sense amplifier.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
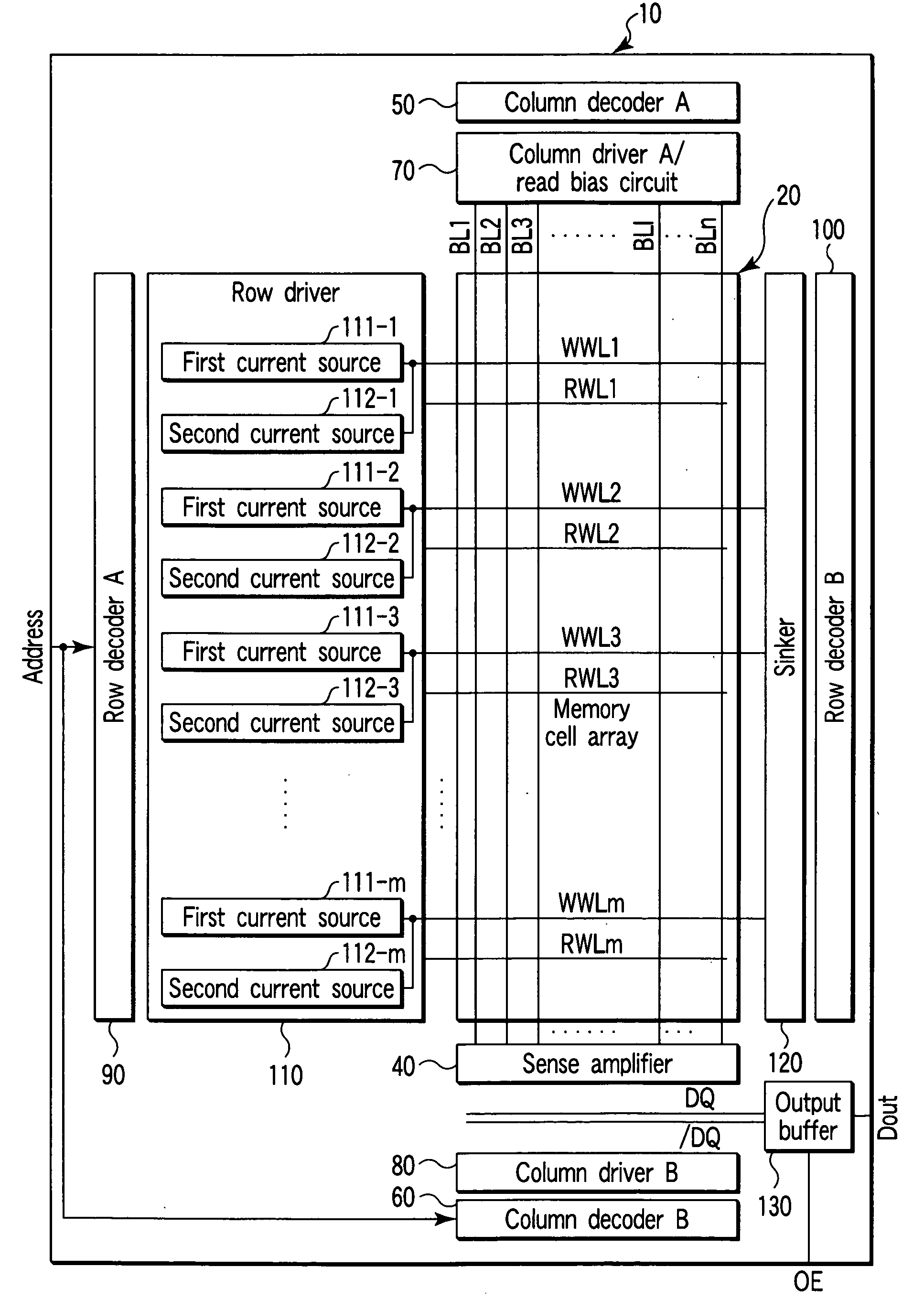
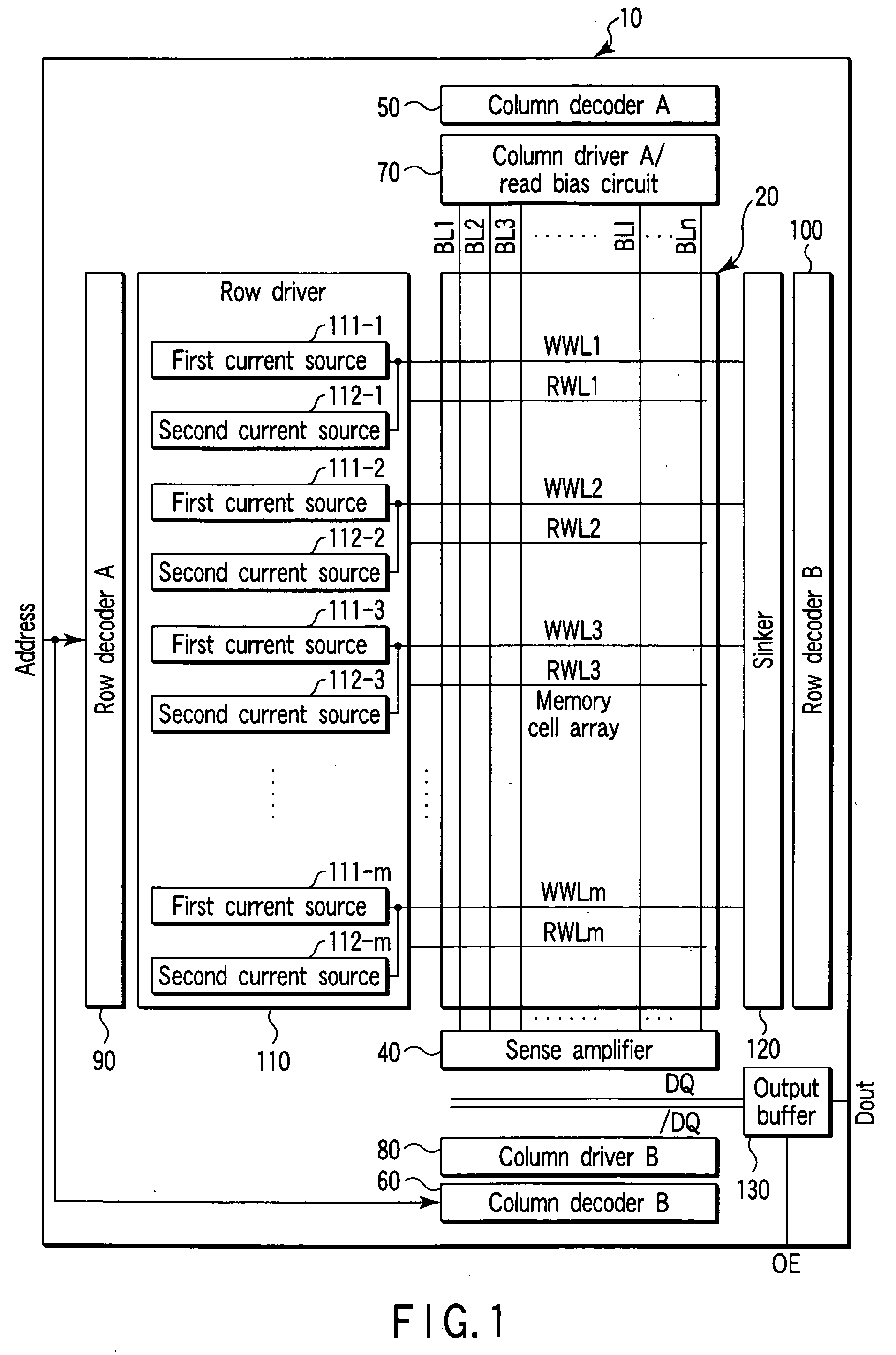
Semiconductor memory device including reference memory cell and control method
InactiveUS6999340B2Magnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesMagnetic reluctanceBit plane
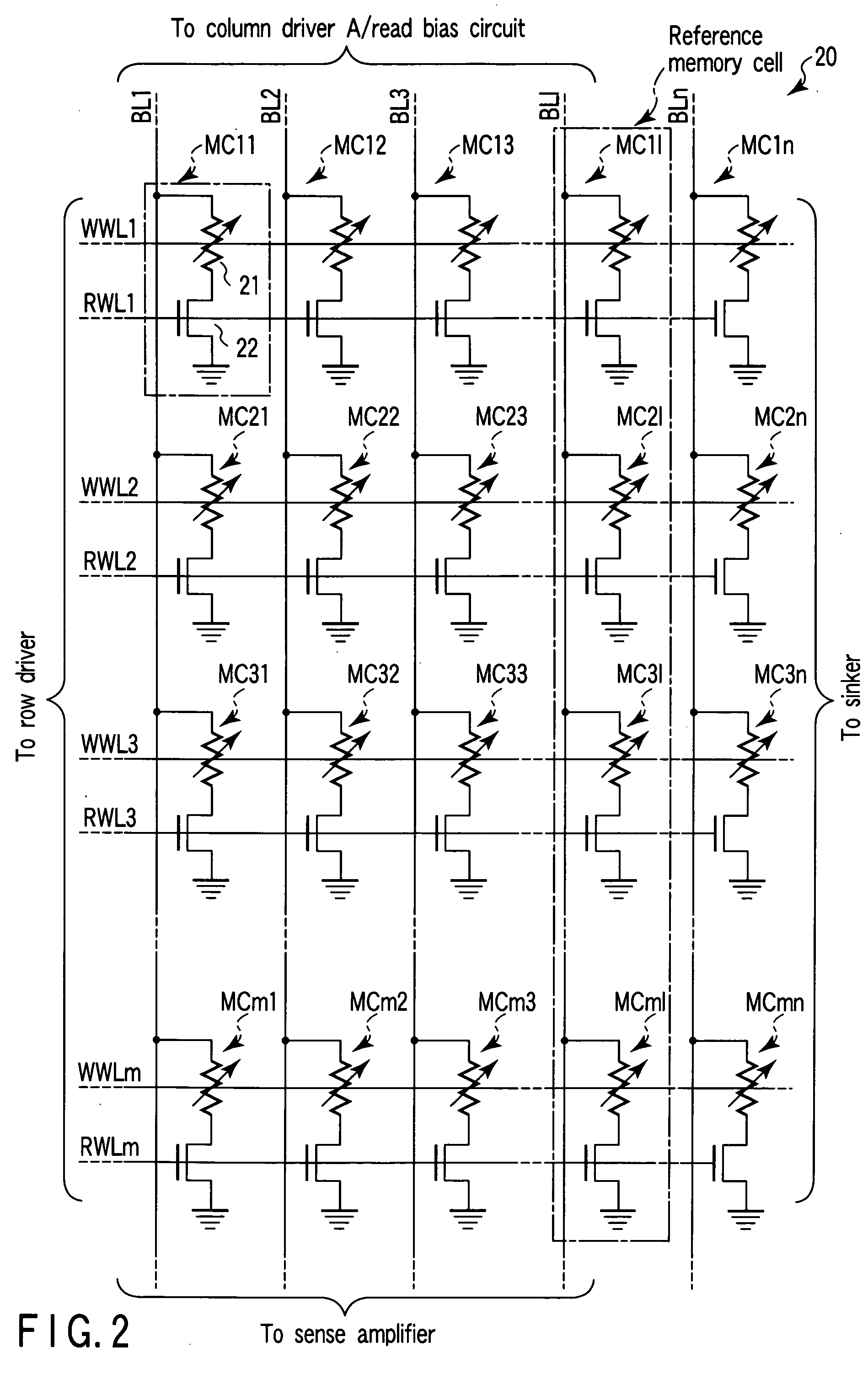
A semiconductor memory device includes word lines, bit lines, first memory cells, second memory cells, a memory cell array, a row decoder, a row driver, a column decoder, a column driver, and a sense amplifier. The first memory cell includes a magneto-resistive element which has either a first resistance or a second resistance smaller than the first resistance. The second memory cell includes a magneto-resistive element which has a resistance between the first and second resistances. The memory cell array includes the first and second memory cells disposed in intersections of the word line and bit line. The row driver supplies a first write current to the word line. The column driver supplies a second write current to the bit line. The sense amplifier amplifies data read from the first memory cell.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Semiconductor memory
InactiveUS6091655AAvoid yield lossData retention time is longTransistorSolid-state devicesBit lineRefresh cycle
A plurality of information memory cells and a single reference memory cell are coupled to a single word line. The reference memory cell stores reference information equivalent to a reference potential to information readout. Pieces of information, stored in the information memory cells, are fed, over respective bit lines, to first input terminals of sense amplifiers. The reference information, stored in the reference memory cell, is fed, over a bit line, to second input terminals of the sense amplifiers. When the potential of signal charges stored in the information memory cells falls due to leakage current, the potential of a signal charge stored in the reference memory cell correspondingly falls due to leakage current. This prolongs a length of time taken for a difference between these potentials to reach a sense limit, thereby achieving a longer data retention time. As a result of such arrangement, even when there occurs a small current leakage from memory cells, it is possible to secure a long data retention time thereby making it possible to obtain a long refresh cycle period.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Methods of program-verifying a multi-bit nonvolatile memory device and circuit thereof
InactiveUS7327609B2Easy to readReduce verification timeRead-only memoriesDigital storageComputer architectureHemt circuits
Methods of verifying a program state may be provided for a non-volatile memory device including a multi-bit memory cell transistor providing more than two different program states. More particularly, the multi-bit memory cell transistor may be programmed from a first program state to a second program state, and a reference memory cell corresponding to the second program state may be selected. After programming the multi-bit memory cell transistor to the second program state and after selecting the reference memory cell corresponding to the second program state, a current flowing through the multi-bit memory cell transistor programmed to the second memory state and a current flowing through the reference memory cell may be compared. Programming the multi-bit memory cell transistor to the second program state may then be verified responsive to comparing the currents flowing through the multi-bit memory cell and the reference memory cell.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Memory with resistance memory cell and evaluation circuit
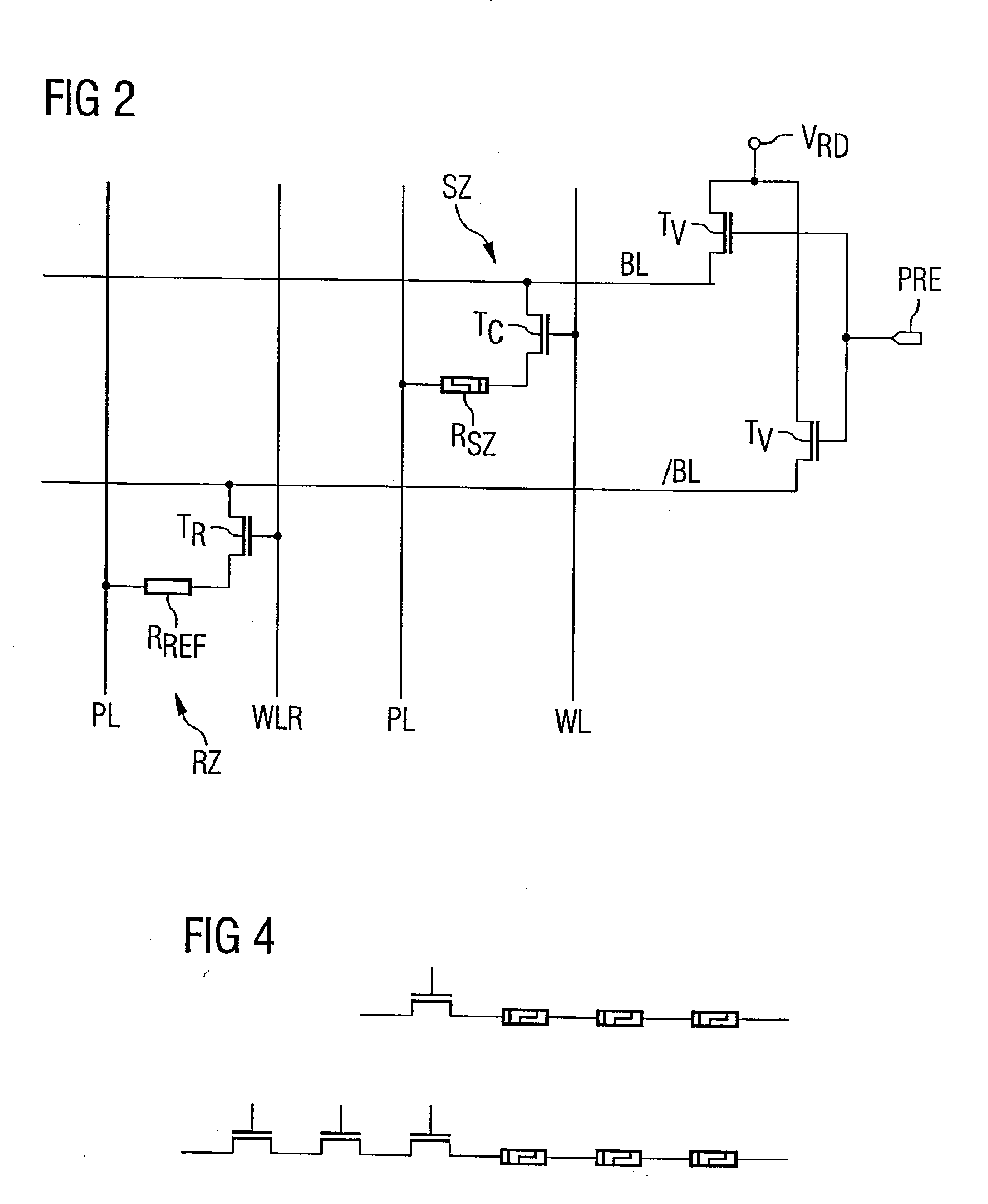
InactiveUS7499349B2Reliable compensationIncrease signal strengthRead-only memoriesDigital storageMemory circuitsReference memory
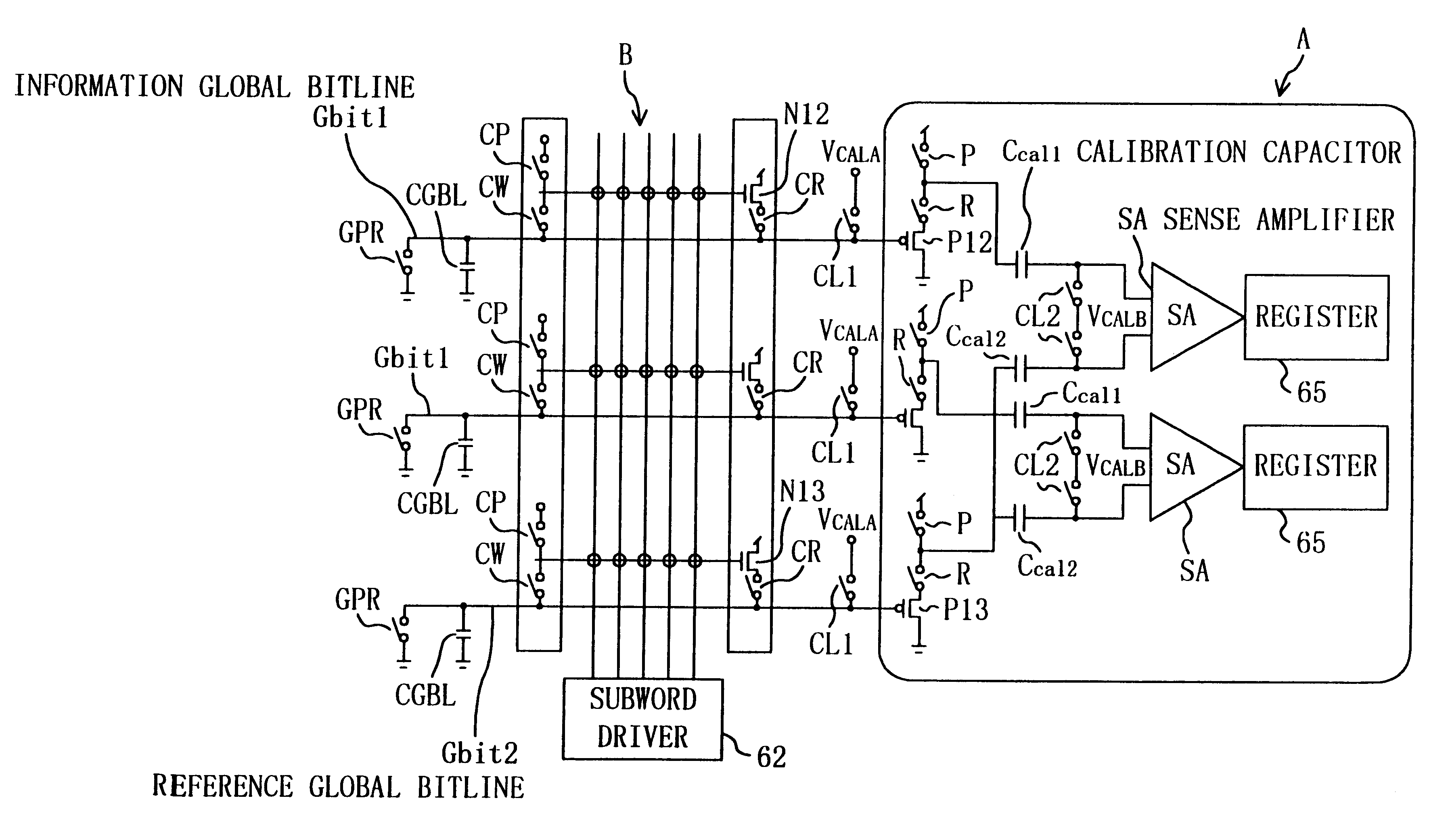
A memory circuit comprising a memory cell which has a resistance memory element and is connected between a ground terminal and a capacitor has a reference memory cell with a reference resistor which is connected between the ground terminal and a reference capacitor, in which case, during the reading operation of the memory cell, the memory cell and the reference memory cell are switched on in order to charge or discharge the capacitor and the reference capacitor, and an evaluation device evaluates the difference between the electrical potentials of the capacitor and the reference capacitor at a predetermined instant after the switching-on of the memory cell and the reference memory cell.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
Memory with resistance memory cell and evaluation circuit
InactiveUS20070147102A1Reliable compensationIncrease signal strengthRead-only memoriesDigital storageCapacitanceHemt circuits
A memory circuit comprising a memory cell which has a resistance memory element and is connected between a ground terminal and a capacitance has a reference memory cell with a reference resistance which is connected between the ground terminal and a reference capacitance, in which case, during the reading operation of the memory cell, the memory cell and the reference memory cell are switched on in order to charge or discharge the capacitance and the reference capacitance, and an evaluation device evaluates the difference between the electrical potentials of the capacitance and the reference capacitance at a predetermined instant after the switching-on of the memory cell and the reference memory cell.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
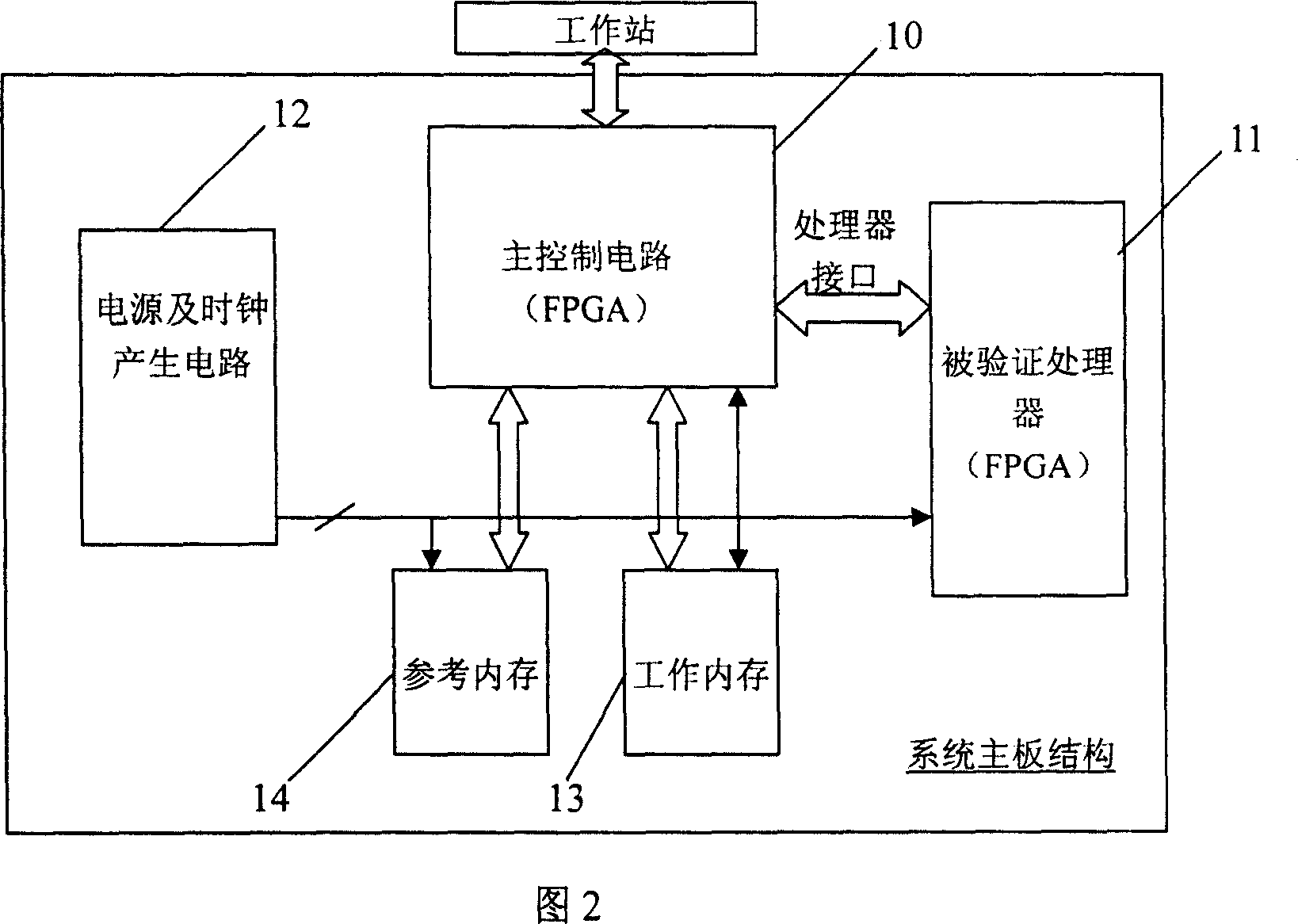
MPU FPGA verification device supporting stochastic instruction testing
ActiveCN101063979AFast testSoftware testing/debuggingSpecial data processing applicationsCommunication interfaceOperational system
This invention discloses one artificial valuation FPGA physical prototype validation device through micro processor design, wherein the device comprises the following parts: one main control circuit with one processor interface for connection with validation micro processor; one power and clock generation circuit connected with micro process to be tested; one work memory and one reference memory connected to main control circuit through main control circuit memory interface, wherein the main control circuit has one communication interface with one outer work station.
Owner:LOONGSON TECH CORP
Sensing circuit and method for phase-change memory
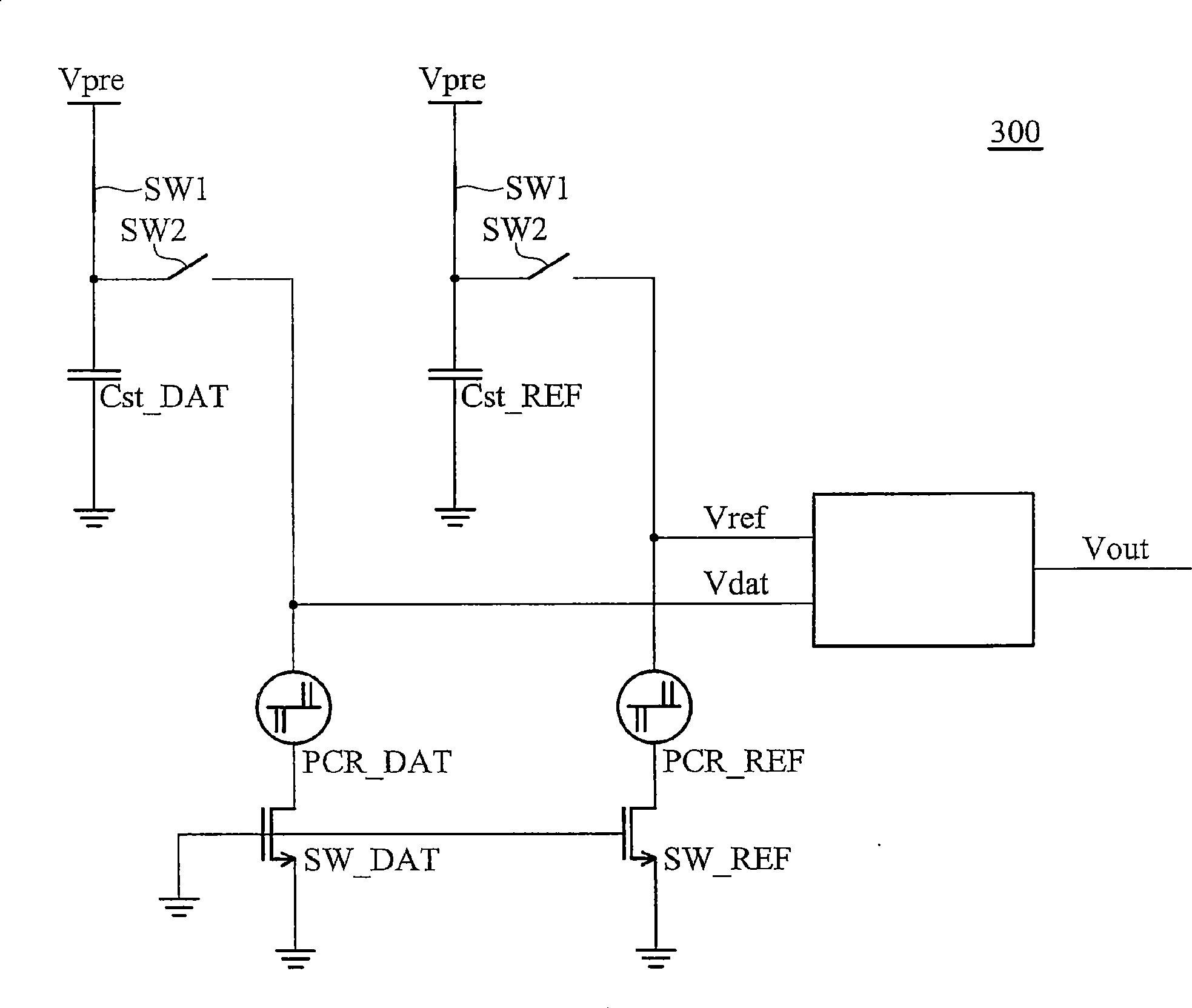
A sensing circuit for a phase change memory comprises a first storage capacitor and a reference capacitor, a storage memory element and a reference memory element, a storage discharge switch and a reference discharge switch, and a judgment device. The first ends of the storage capacitor and the reference capacitor are both coupled with a pre-charged voltage via a first switch, the first ends of the storage memory element and the reference memory element are respectively coupled with the first ends of the storage capacitor and the reference capacitor via a second switch, the storage discharge switch and the reference discharge switch are respectively coupled with the first ends of the storage memory element and the reference memory element, and the judgment device is coupled with the first ends of the storage memory element and the reference memory element and provides an output as the read result of the storage state of the storage memory element.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Memory cell shift estimation method and apparatus
Memory devices and methods are disclosed, such as those facilitating interpolation methods for reference memory cells based on their reference state and / or location in an array of memory cells. For example, a group of reference cells programmed to a subset of possible data states are utilized to interpolate for data states other than those in the subset. Such embodiments might be used to reduce the quantity of reference cells required.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
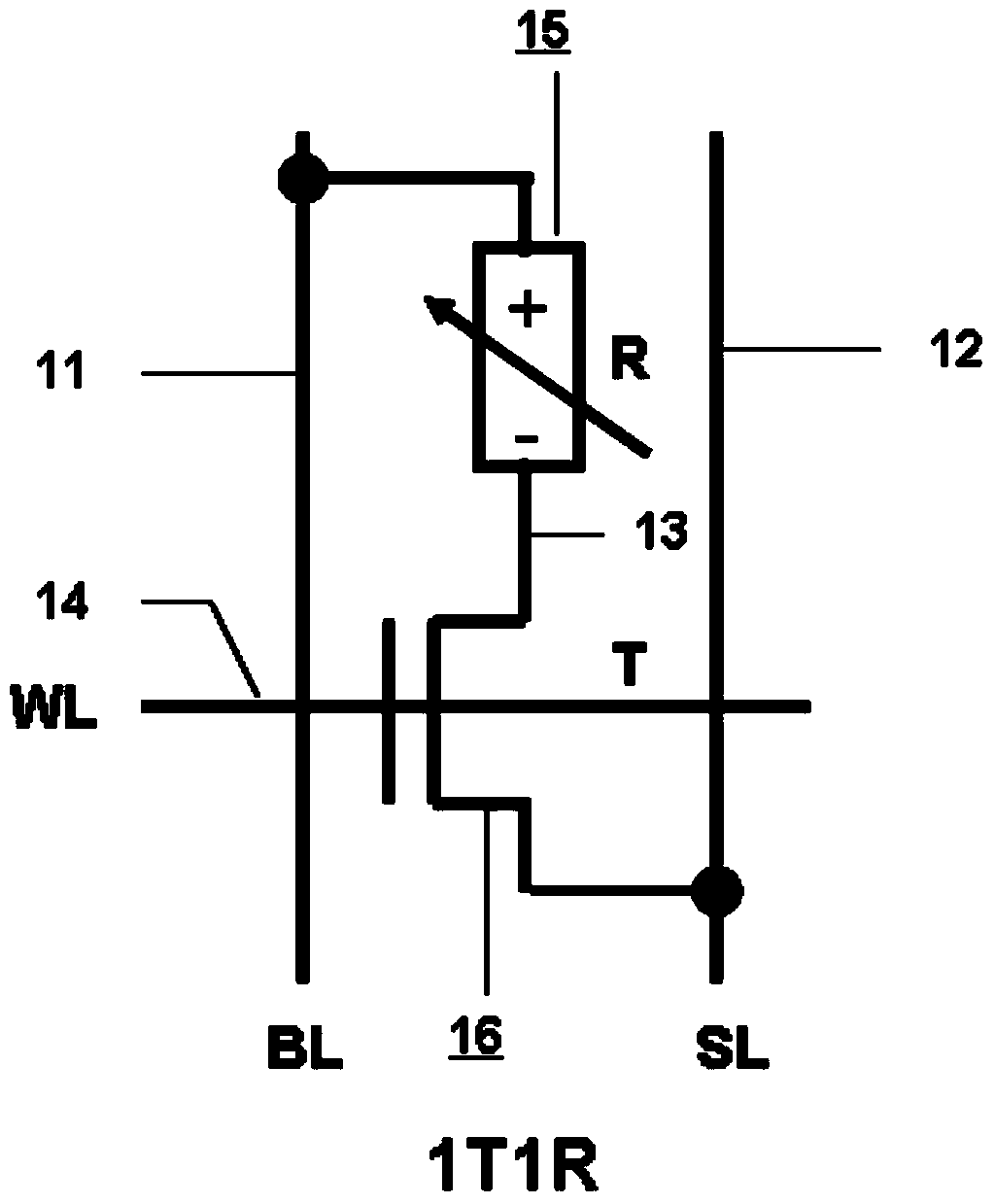
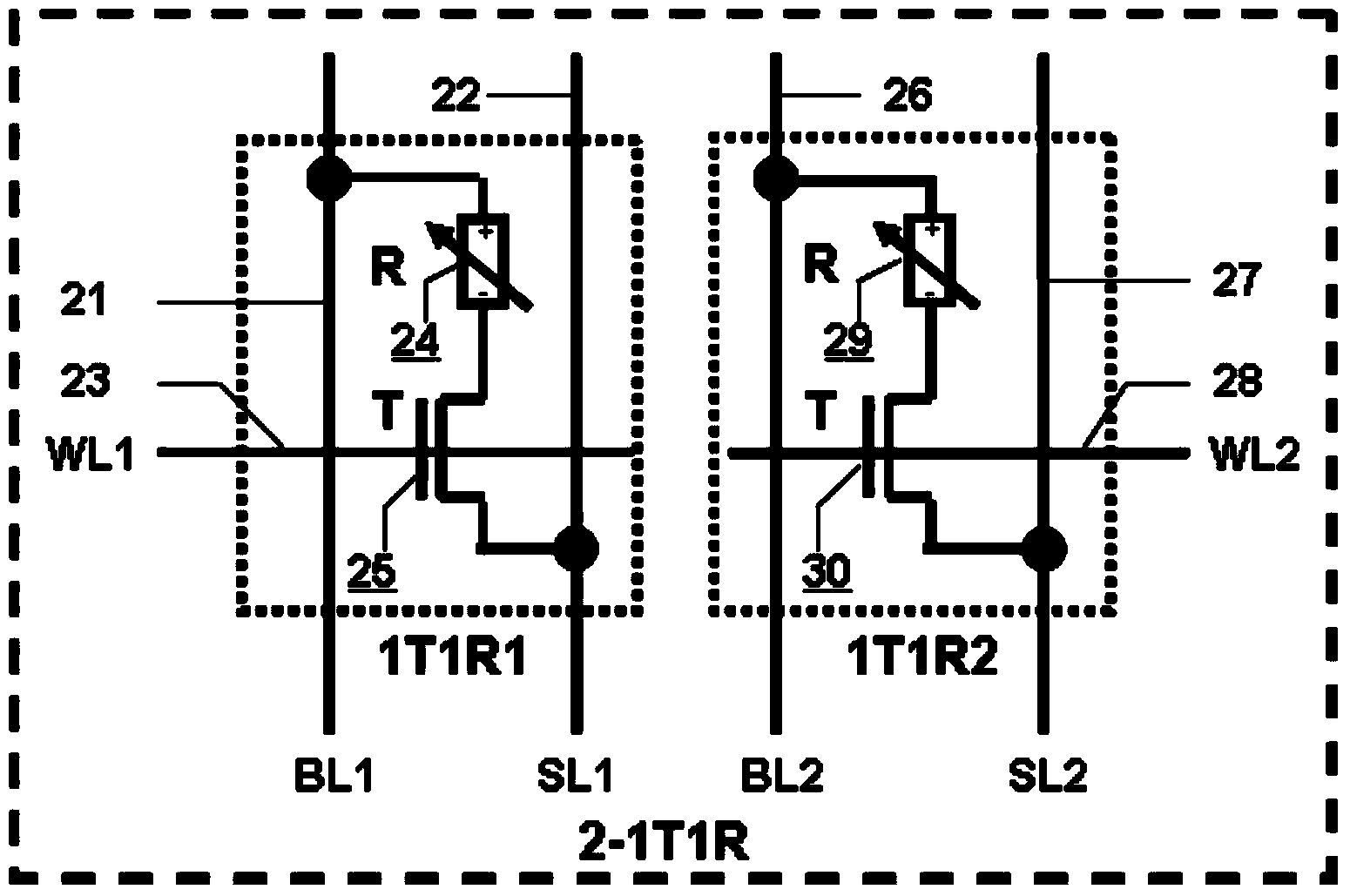
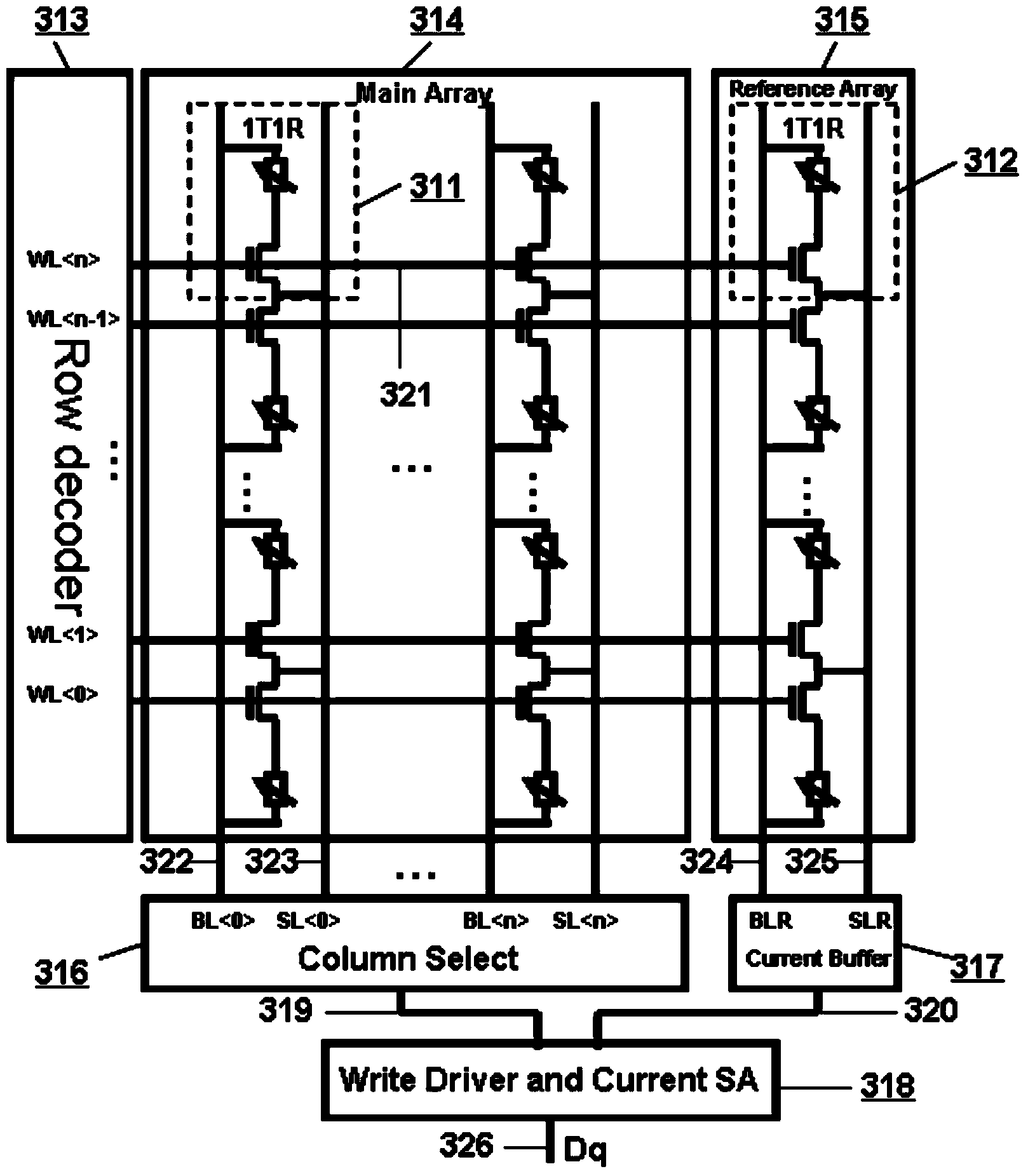
2-1T1R (2-1transistor1resistor) RRAM (resistive random access memory) unit with reading self-reference function
InactiveCN103839585AImprove reading speedIncrease success rateRead-only memoriesDigital storageComputer architecturePower flow
The invention provides a 2-1T1R (2-1transistor1resistor) RRAM (resistive random access memory) unit with a reading self-reference function. The 2-1T1R RRAM unit consists of two conventional RRAM 1T1R memory units, wherein one of the conventional RRAM 1T1R memory units is a main memory unit, and the other conventional RRAM 1T1R memory unit is a reference storage unit. During writing operation, the two 1T1R memory units are written as two opposite states respectively; if the main memory unit is written as '1' and the reference memory unit is written as '0', a 2-1T1R memory value is '1'; or if the main memory unit is written as '0' and the reference memory unit is written as '1', the 2-1T1R memory value is '0'. During reading operation, the reference memory unit serves as a reference unit for generating the reading reference current of the main memory unit. Compared with a conventional mode of using fixed reading reference current by a memory array or generating the reading reference current through a shared reference unit, the 2-1T1R RRAM unit has the advantages that the reading margin during the reading operation is doubled; the reading speed and the reading success rate are greatly improved.
Owner:SHANDONG SINOCHIP SEMICON
Fast reading device and method of phase change memory
ActiveCN102013271AAvoid destructionImprove read rateRead-only memoriesDigital storageCapacitanceParasitic capacitor
The invention relates to a fast reading device of a phase change memory, which comprises a phase change memory cell to be read, a charging circuit, an overshoot recovery rate detecting circuit, a sensitive amplifier circuit and a reference level or a reference memory cell. On one hand, the phase change memory cell (which can be abstracted as a resistor in the circuit) and a parasitic capacitor ona digit line form a resistor-capacitor (RC) circuit, and on the other hand, a gated metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) pipe instantly enters a linear region from a saturation region when being switched on / of, thereby causing an overshoot phenomenon. For phase change resistors of different states, the corresponding recovery rates after the overshoot are different. By reading the recovery rate of the digit-line level after the overshoot and fast reading the state of the phase change memory cell, the reading rate of the whole memory is accelerated. In addition, fast reading is beneficial to avoiding the damage caused by reading operation to the phase change cell, thereby achieving the purpose of reducing reading interference.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Semiconductor memory device including memory cell without capacitor
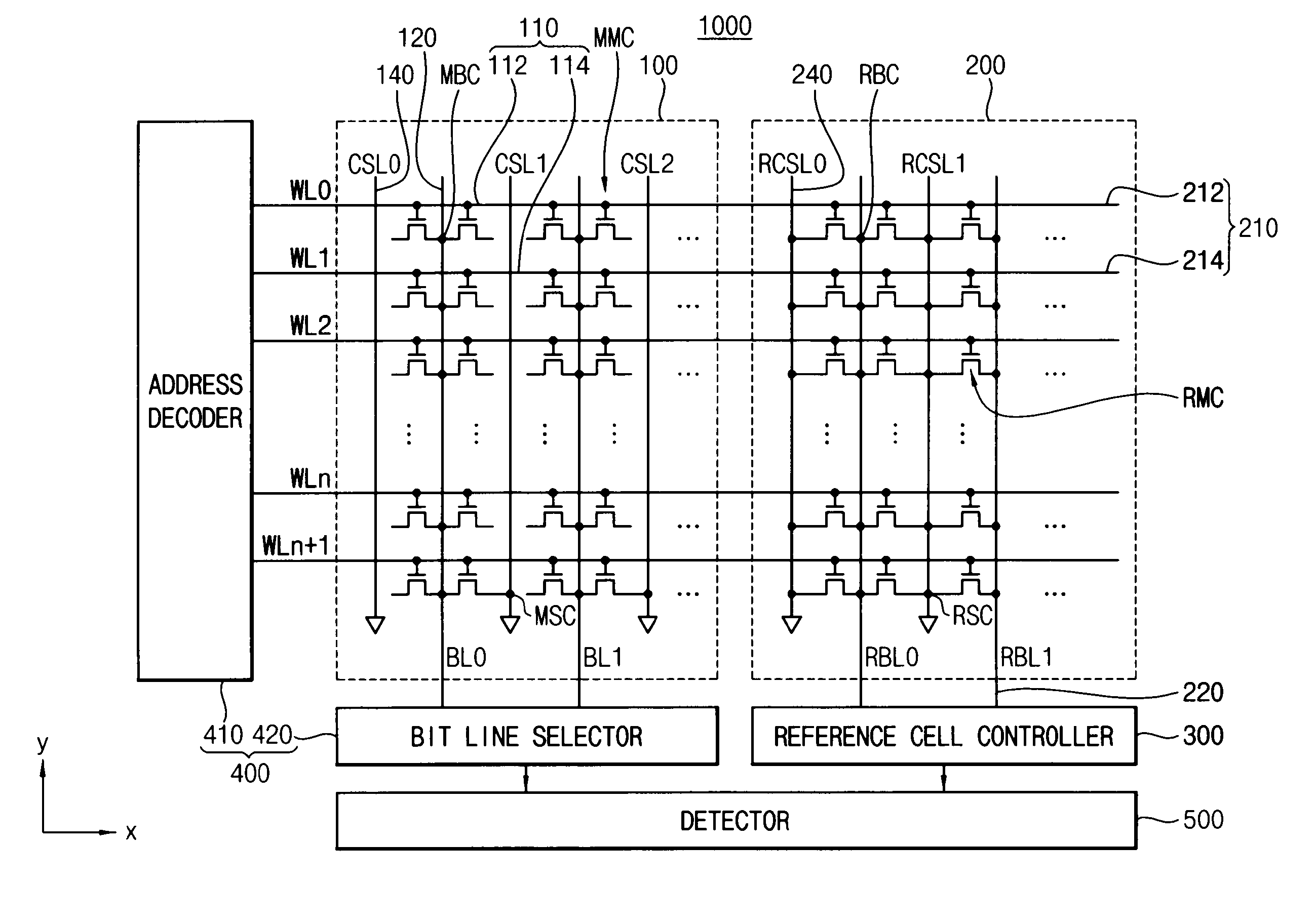
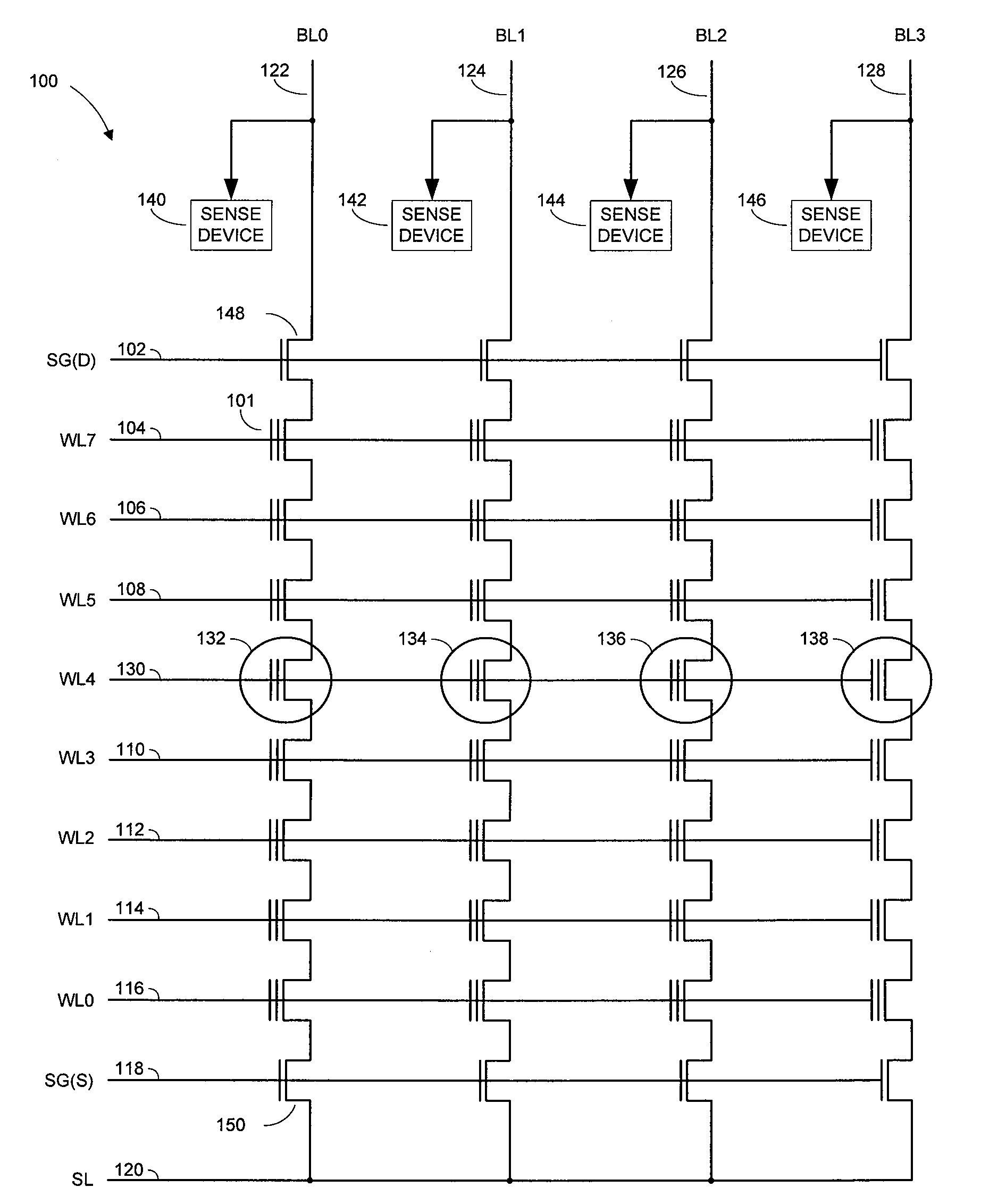
A semiconductor memory device including a memory cell without a capacitor includes: a memory cell array block including first memory cells connected between a first bit line and first word lines and second memory cells connected between a second bit line and second word lines; and a reference memory cell array block including first reference memory cells connected between a first reference bit line connected to the first bit line and a first reference word line and second reference memory cells connected between a second reference bit line connected to the second bit line and a second reference word line. When the first word lines are selected, the second reference memory cells are selected, and when the second word lines are selected, the first reference memory cells are selected. Thus, each bit line includes a reference memory cell and outputs reference signal from the reference memory cell so that data can be precisely sensed during a read operation.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Read-out circuit in semiconductor memory device
InactiveUS20070019469A1Large actionSpeeding up the read-out actionRead-only memoriesDigital storageLoad circuitVoltage generator
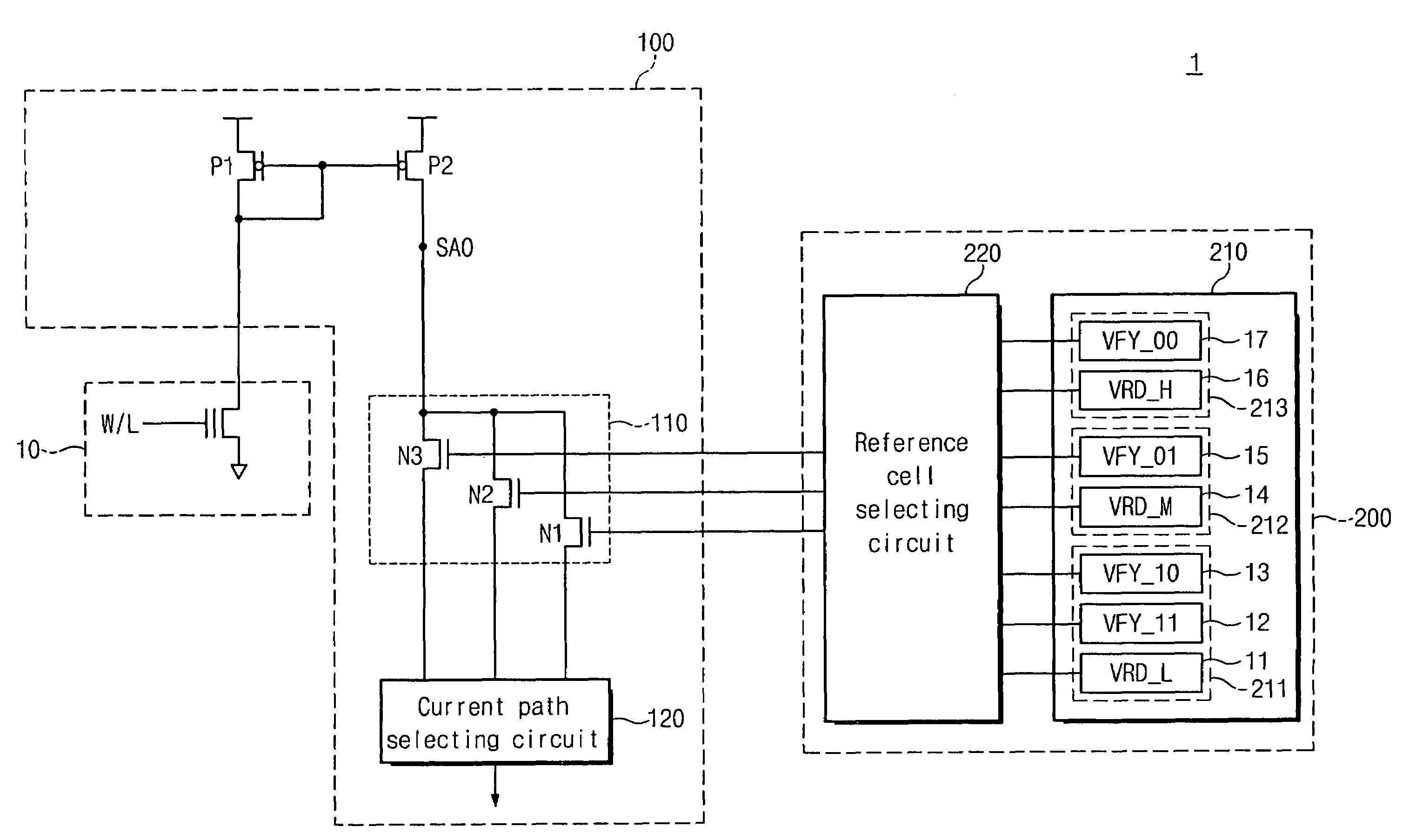
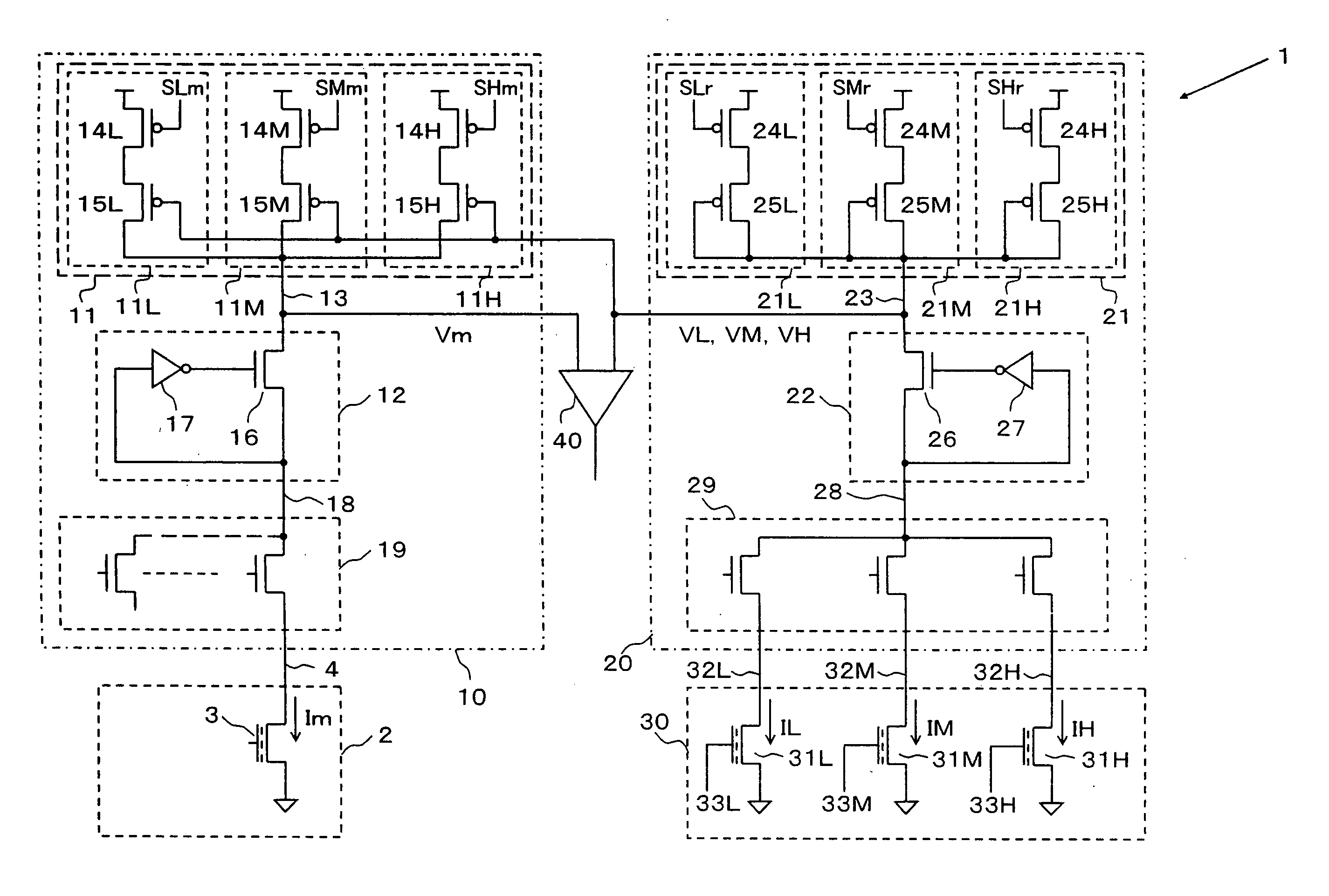
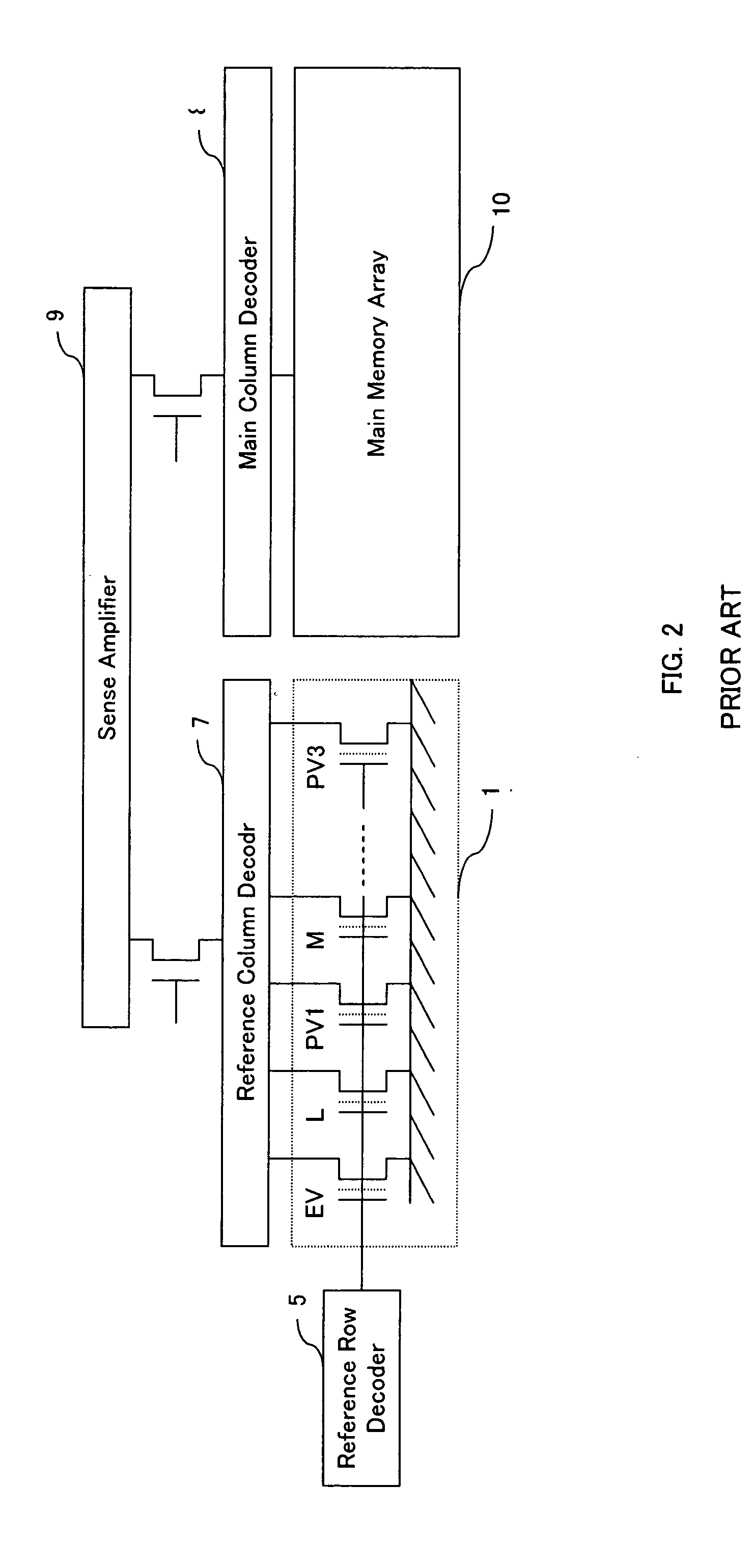
A read-out circuit comprises a read-out voltage generator circuit converting a memory cell current into a read-out voltage, a reference voltage generator circuit supplying a reference memory cell corresponding to each memory state intermediate between multilevel data with a reference current from a reference loading circuit and converting the reference current flowing through the reference memory cell sequentially selected into a reference voltage. The reference voltage generator circuit modifies the current supply capability of the reference loading circuit corresponding to a change in the selection of the reference memory cell to suppress a change in the reference voltage derived from a change in the reference current and the read-out voltage generator circuit modifies the current supply capability of the main loading circuit corresponding to a change in the selection of the reference memory cell to increase or decrease in proportion to the current supply capability of the reference loading circuit.
Owner:SHARP KK
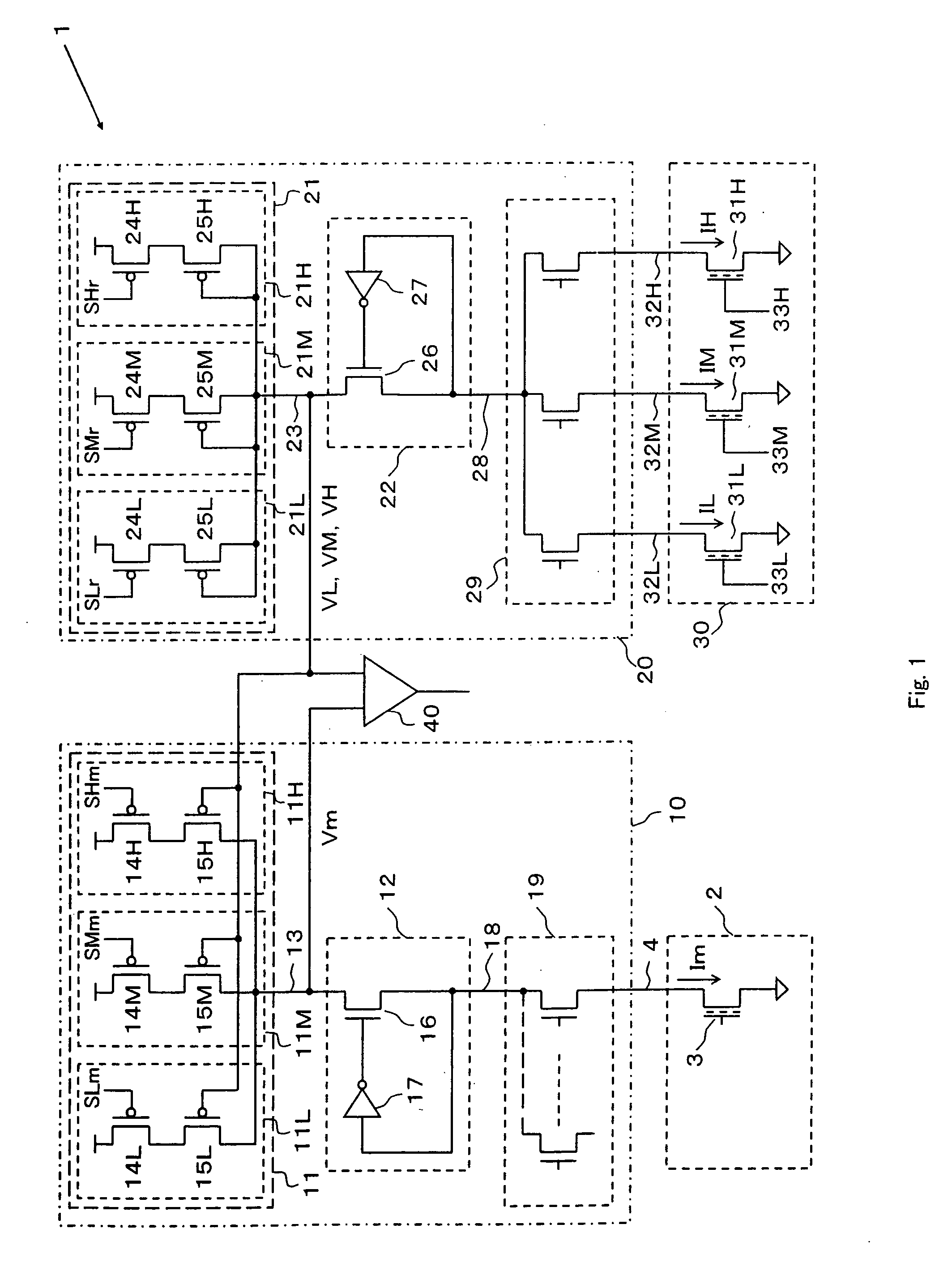
Magnetic memory device implementing read operation tolerant to bitline clamp voltage (VREF)
ActiveUS6853599B2Stable read operationGuaranteed uptimeMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsDigital storageBit lineAudio power amplifier
A magnetic memory device includes a memory cell array block and a reference memory cell array block having a plurality of magnetic memory cells arranged, respectively, at intersections of wordlines, digit lines, and bitlines, and reference wordlines, the digit lines, and a reference bitline, a first bitline clamp circuit coupled to a bitline to which a first selected magnetic memory cell is connected and supplying a first current to the first selected magnetic memory cell through the bitline, second and third bitline clamp circuits coupled to respective upper and lower ends of the reference bitline, for supplying a second current to selected magnetic memory cells in the reference memory cell array block through the reference bitline, and a sense amplifier for sensing and amplifying currents on first and second data lines, respectively connected to the bitline and the reference bitline, to judge data of the first selected magnetic memory cell.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
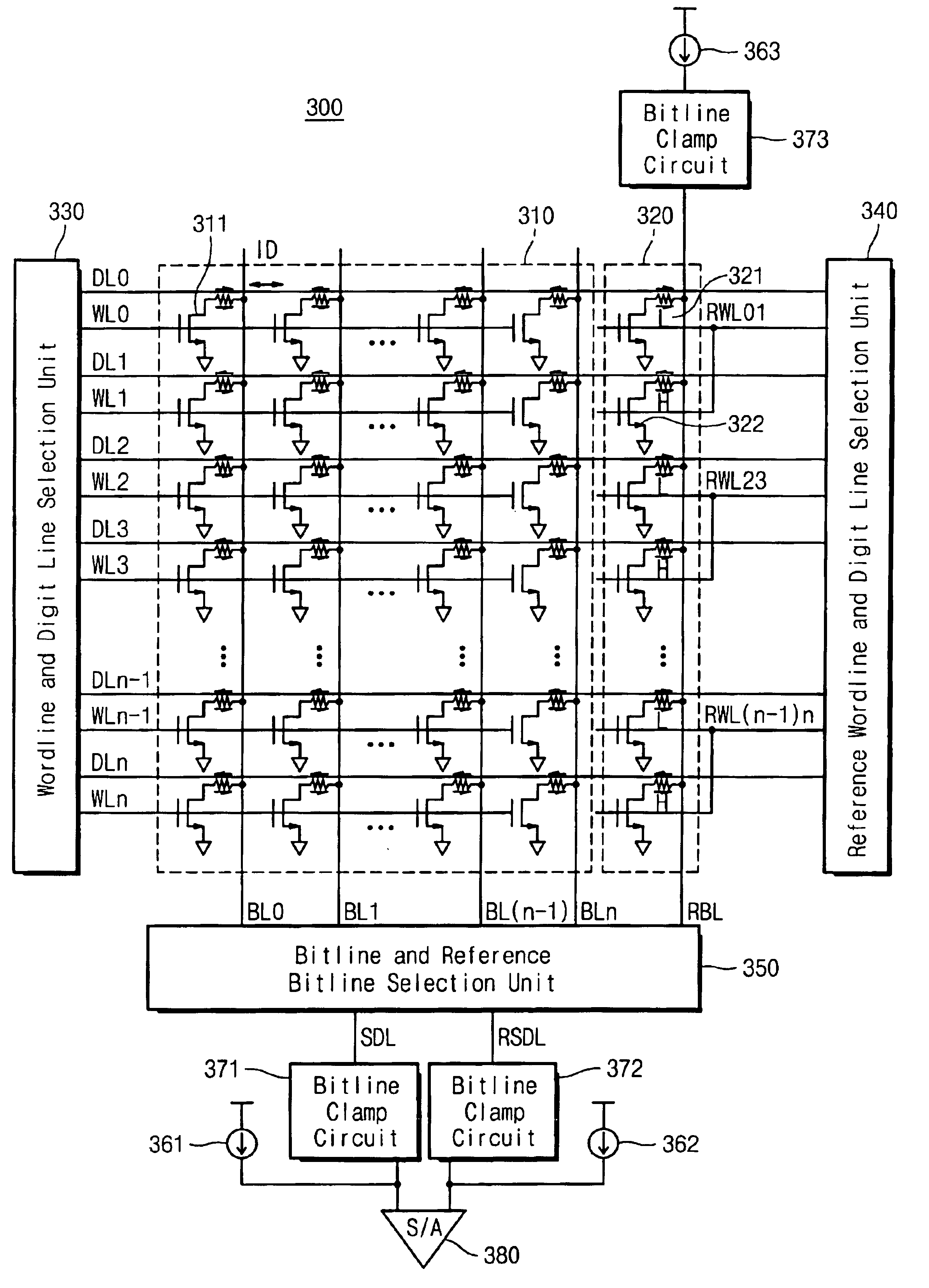
Dynamic semiconductor storage device and method for operating same
InactiveUS20080117700A1High speedShorten the overall cycleDigital storageBit lineAudio power amplifier
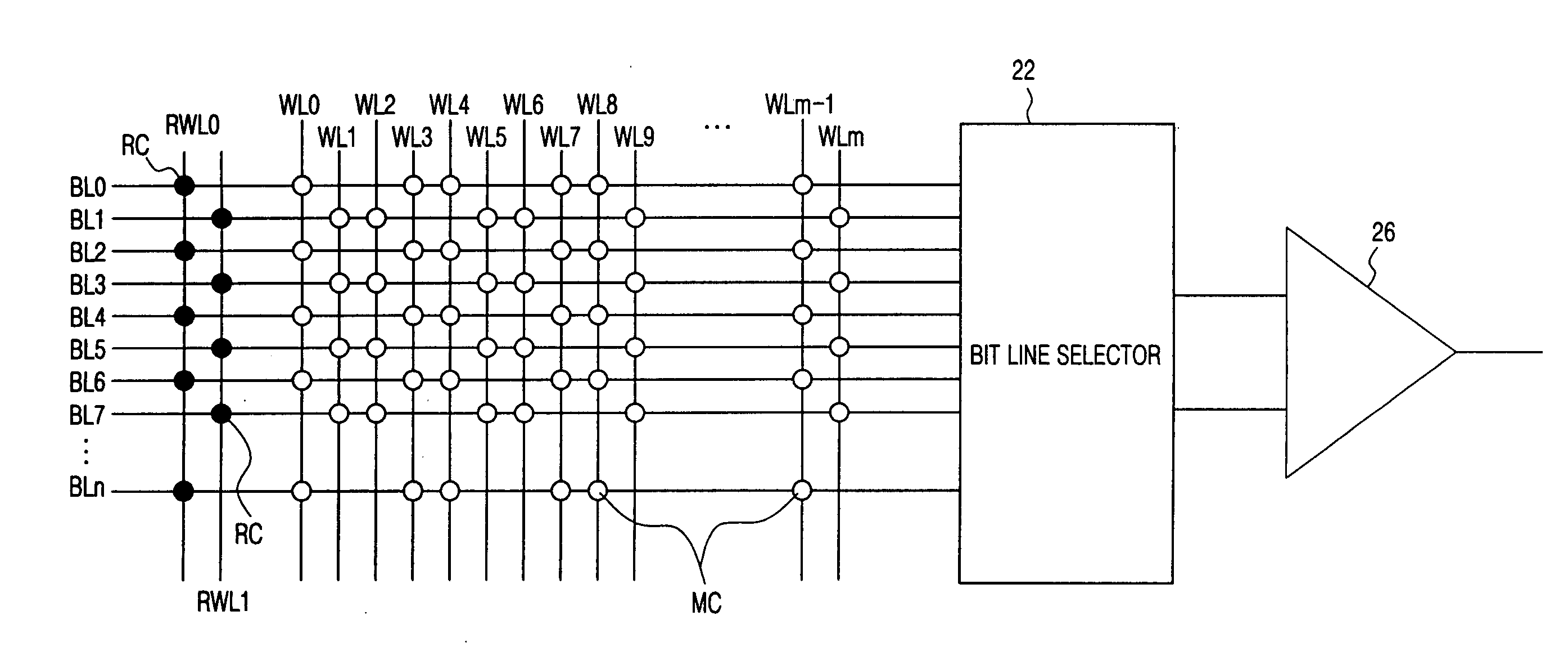
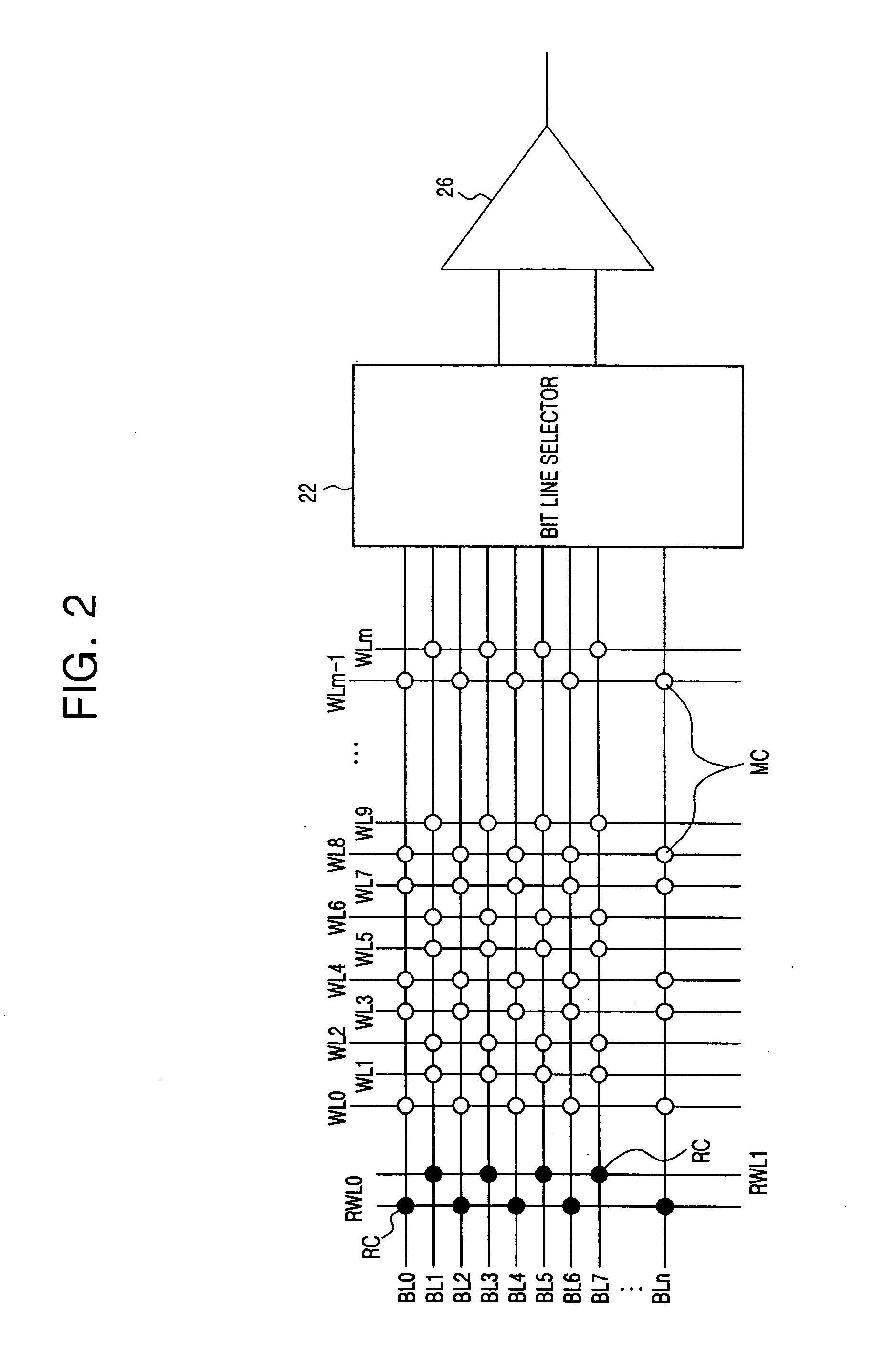
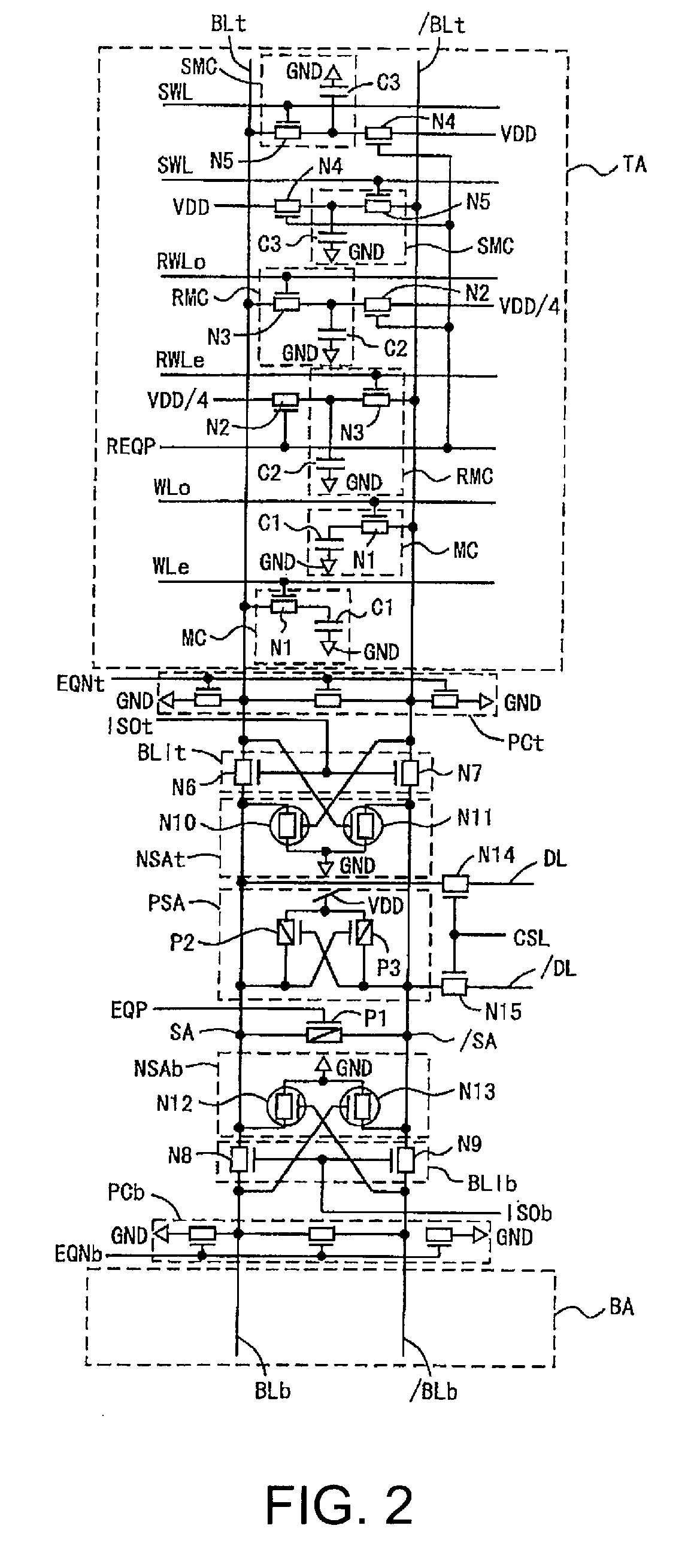
The object of the present invention is to provide a DRAM, in which the operation speed for a sense amplifier can be increased. Bit line precharging circuits PCt and PCb are arranged to precharge bit lines BLt and / BLt to a ground voltage GND, and reference word lines RWLo and RWLe and reference memory cells RMC are arranged, so that when a word line WL is activated, a potential difference is always generated between the bit lines BLt and / BLt. The sources of transistors N10 and N11 of an N-type sense amplifier NSAt are connected directly to a ground terminal GND, and the sources of transistors P2 and P3 of a P-type sense amplifier PSA are connected directly to a power source VDD. The gates of the transistors N10 and N11 are connected to the bit lines / BLt and BLt, and the drains are connected to the bit lines BLt and / BLt, respectively. Shift word lines SWL and shift memory cells SMC are arranged, so that the N sense amplifier NSAt can amplify the potential difference between the bit lines BLt and / BLt.
Owner:IBM CORP
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device
InactiveUS20050174868A1Increase speedHigh-speed performanceFloating sedimentation devicesWater treatment parameter controlHemt circuitsData storing
A nonvolatile semiconductor memory device comprises a readout circuit which reads data stored in a selected memory cell by applying predetermined voltage to the selected memory cell and a reference cell such that currents corresponding to the respective threshold voltage may flow, and comparing the current flowing in the selected memory cell with the current flowing in the reference cell. The readout circuit commonly uses the reference cell set in the same storage state for normal readout and for readout for program verification, and when the predetermined voltage is applied to the selected memory cell and the reference memory cell at the time of the readout for the program verification, it sets an applying condition to the reference memory cell such that its storage state may be shifted more in the program state direction than that in an applying condition at the time of the normal readout.
Owner:SHARP KK
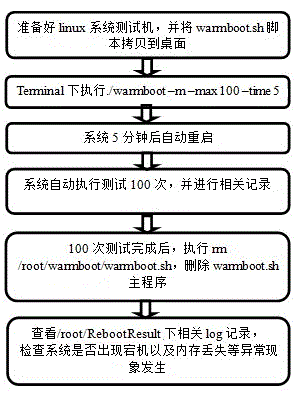
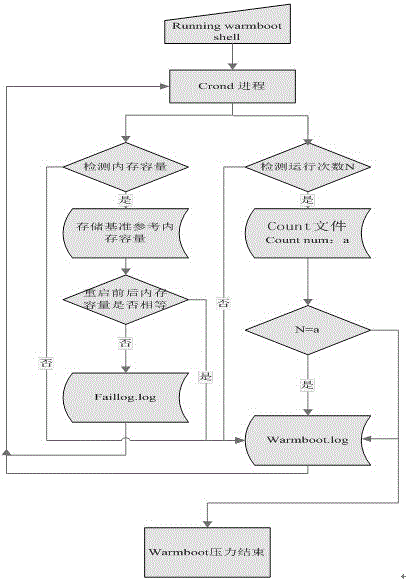
Memory monitoring achievement method based on startup and shutdown of Linux system
The invention discloses a memory monitoring achievement method based on startup and shutdown of a Linux system, and belongs to the technical field of memory monitoring. The memory monitoring achievement method comprises the following specific steps: (1) ensuring that the Linux system is arranged on a to-be-tested main machine, enabling a user to log in, coping a warmboot script to a desktop, opening linux system termination program, switching a current directory into the desktop, executing the following operations as shown in the specification; (2) after the command is executed, capturing memory capacity under / proc / meminfo by a script as reference memory capacity; (3) generating a RebootResult file folder on the desktop, and recording the memory test condition by a sub-file holder under the file holder; (4) restarting the system according to the set time interval; (5) counting by reading a RebootResult / count file, capturing the memory capacity in the / proc / meminfo and comparing with the reference capacity; and (6) automatically carrying out the test frequency set by restart by the system until execution is ended. According to the memory monitoring achievement method, unattended operation and automatic test are achieved; the test is counted; the memory capacity is monitored; and the stability of the overall machine in a tester restart pressure test is evaluated.
Owner:LANGCHAO ELECTRONIC INFORMATION IND CO LTD
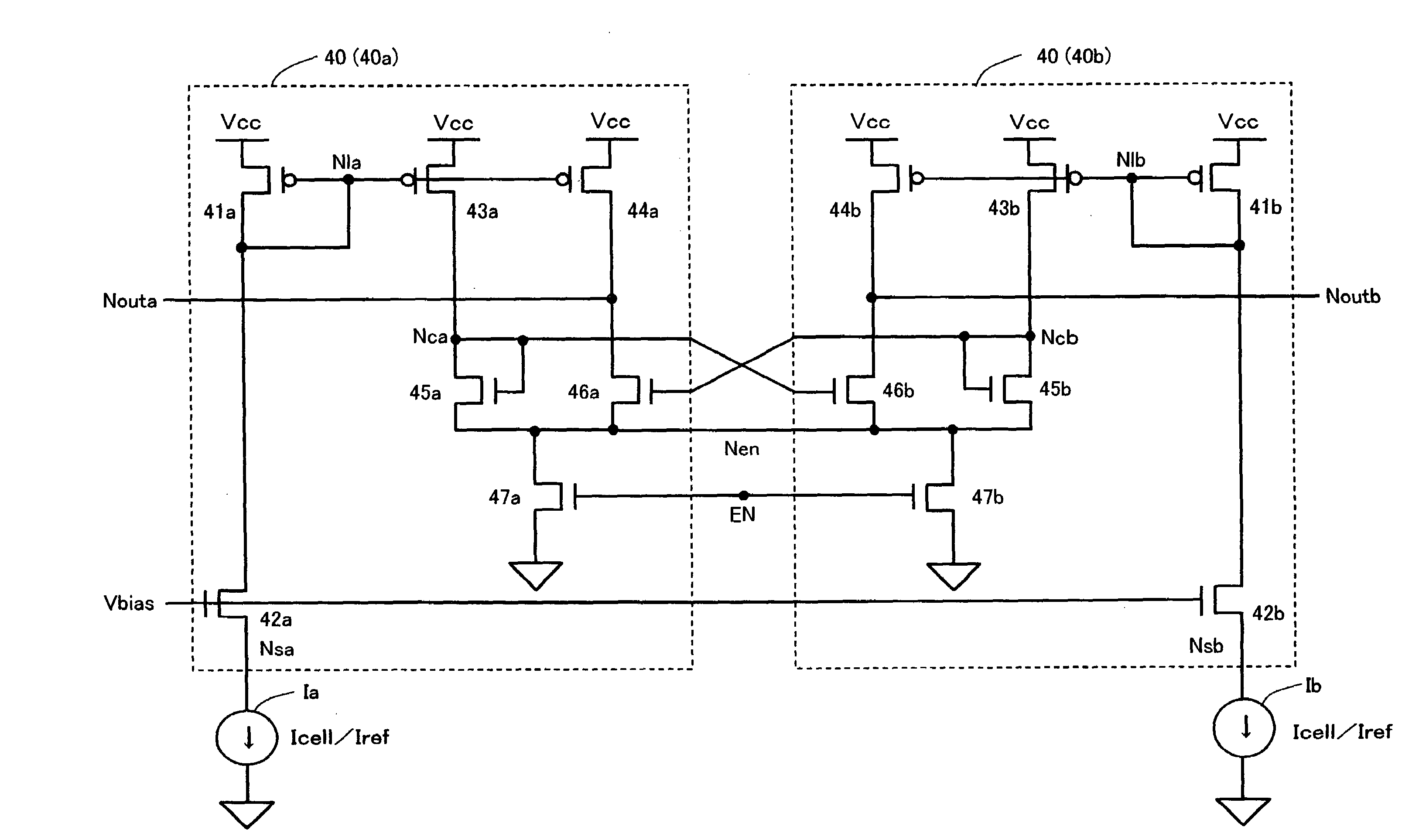
Bias voltage applying circuit and semiconductor memory device
Two bias circuits which supply a current to a selected memory cell and a reference memory cell have the same circuit constitution. Each bias circuit includes a first active element between a power supply node and a junction node, where a current is controlled to prevent a voltage level at the junction node from fluctuating, a second active element between the power supply node and an output node, where a current is controlled such that a voltage level at the output node is changed in direction opposite to a voltage level at the junction node in other bias circuit, a third active element and a fourth active element between the junction node and a current supply node and between the output node and the current supply node, respectively, where a bias voltage is adjusted.
Owner:SHARP KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com