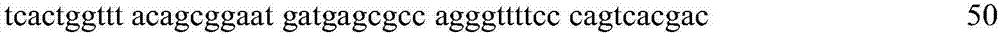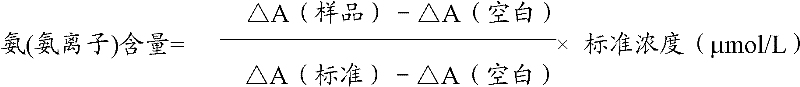Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30 results about "Glutamate kinase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Recombinant corynebacterium crenatum for over expression of N-acetylglutamate kinase and application thereof
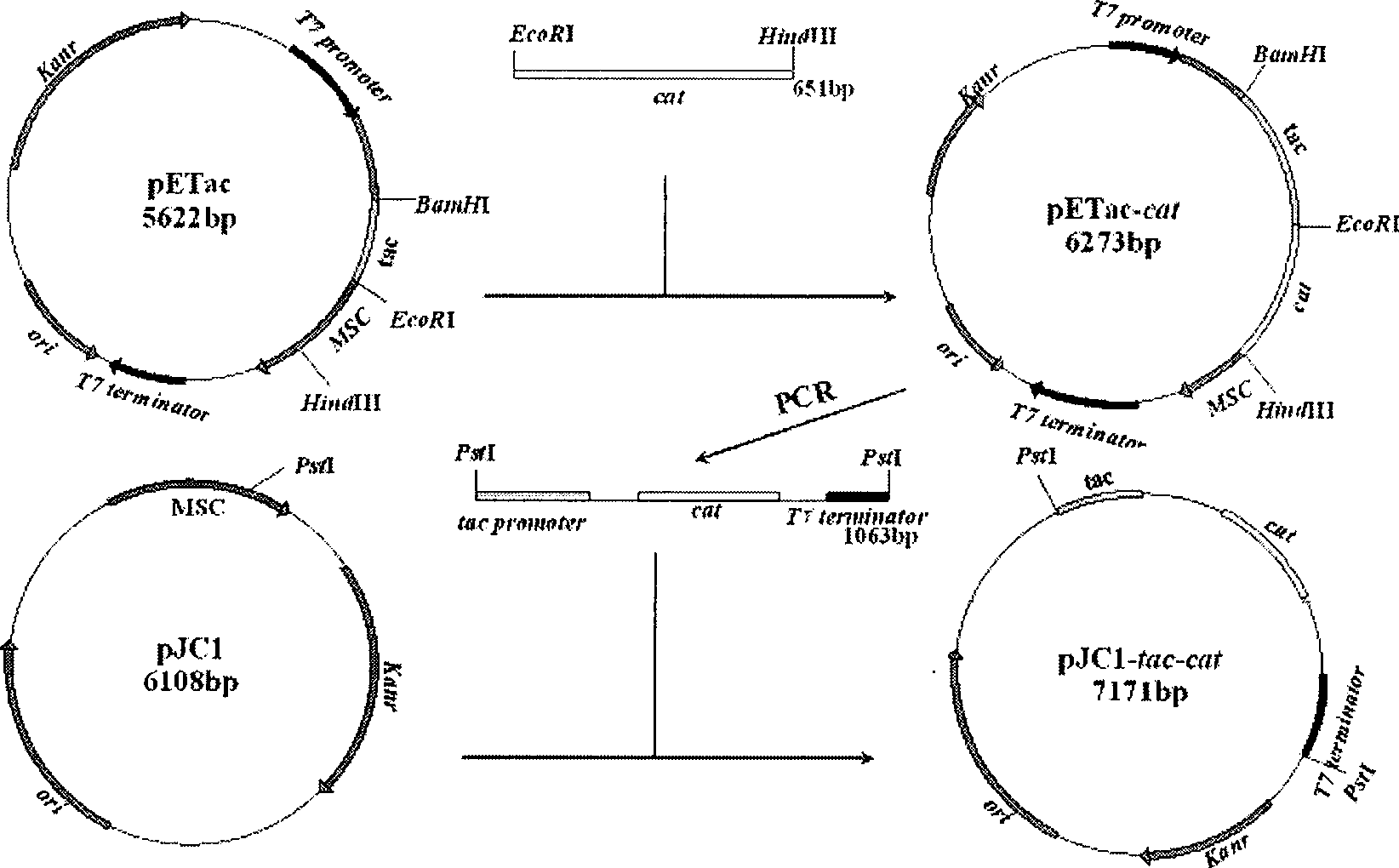
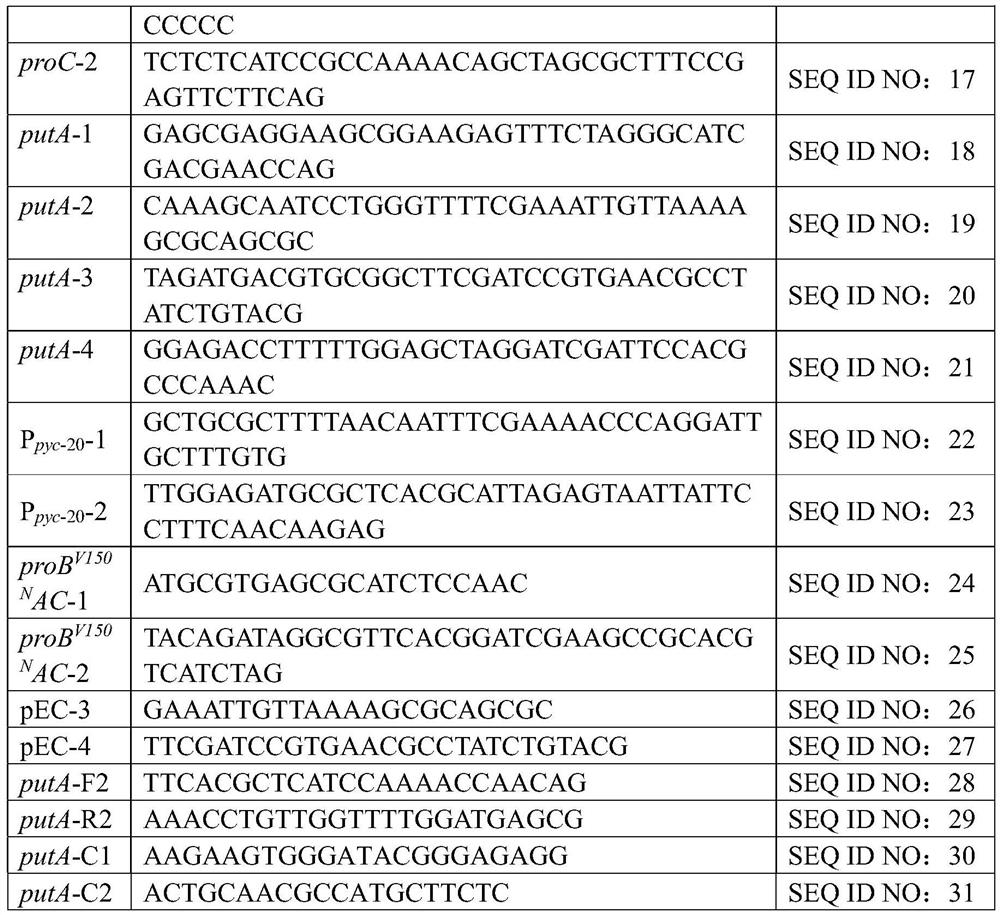
The invention relates to a recombinant corynebacterium crenatum to enhance the expression of N-acetyl glutamic acid kinase and the application thereof, which belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. The classification and nomenclature of the recombinant corynebacterium crenatum to enhance the expression of N-acetyl glutamic acid kinase is corynebacterium crenatum SYPA / pJC1-tac-argB with an access number of CCTCC NO: M 208133; The application is as follows: using a key enzyme N-acetyl glutamic acid kinase from corynebacterium crenatum pathway arginine to construct a corynebacterium crenatum expression vector pJC1-tac-argB; introducing the corynebacterium crenatum expression vector pJC1-tac-argB into corynebacterium crenatum SYPA by electrotransformation to obtain the recombinant corynebacterium crenatum SYPA / pJC1-tac-argB; and excessively expressing N-acetyl glutamic acid kinase, which greatly enhances the utilization rate of a precursor glutamic acid and allows the metabolic flow to flow to the arginine synthesis pathway, weakens the synthesis of proline, achieves the purpose of improving the output of arginine and the output of arginine is increased by 23.4 percent than C. crenatum SYPA.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
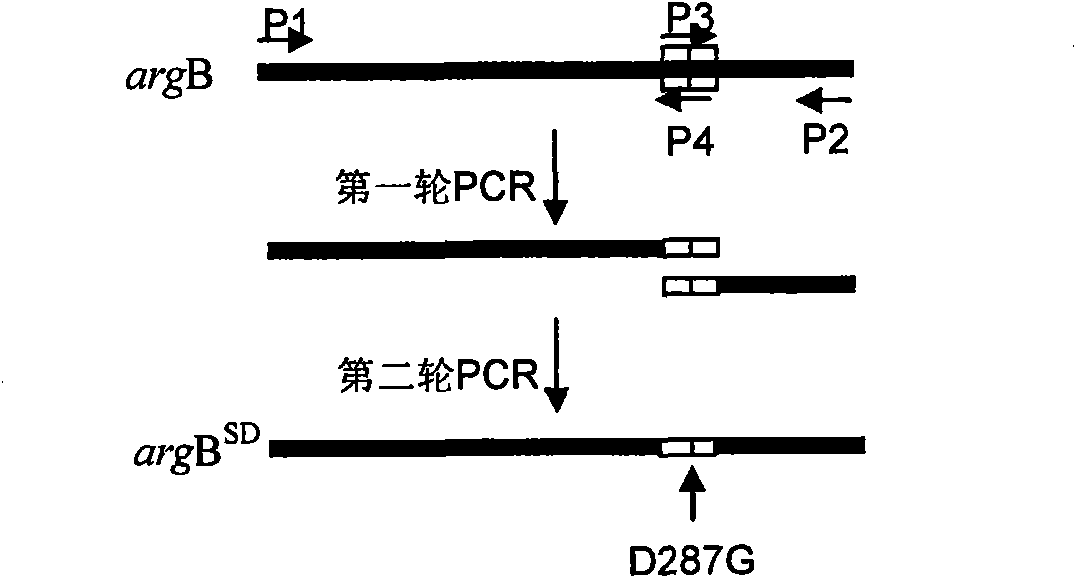
Method for improving yield of arginine by mutation of Corynebacterium crenatum N-acetyl glutamic acid kinase
The invention relates to a method for improving the yield of arginine by the mutation of Corynebacterium crenatum N-acetyl glutamic acid kinase. L-arginine is one of semi-essential basic amino acids for a human body, and has various particular physiology and pharmacology functions. High-yield arginine mutant strain C. crenatum SYPA5-5 is compounded into the arginine through a circulating way, and N-acetyl glutamic acid kinase (NAGK) is a key enzyme in the compounding way and is subject to the feedback inhibition of the product arginine. By using an overlapping PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) technique, a GAT (glycerol phosphate acyl transferase) codon used for coding aspartic acid is used for substituting a GGA (General Gonadotropic activity) codon used for coding glycine at the site 287 in the coding NAGK albumen, and the NAGK which has high activity and arginine with obviously reduced by the feedback inhibition can be obtained after the mutation. An argBSD gene is brought into the Corynebacterium crenatum of the high-yield arginine through pJCl-tac, and the expression volume of the key enzyme is further improved. The final acid yield is increased to 36.3g / L from original 28g / L, and the yield of the L-arginine is increased by 29.7 percent.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Preparation method of genetically engineered bacterium for synthesizing glutathione and product thereof
ActiveCN104059936AIncrease productionEnhanced synthetase activityFungiMicroorganism based processesTransformation efficiencyInositol-3-phosphate synthase
The invention discloses a preparation method of a genetically engineered bacterium for synthesizing glutathione. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (i) converting a gene for encoding gamma-glutamoyl cysteine synthetase-linker peptide-glutathione synthetase fusion protein into a host bacterium cell, and highly expressing the gene; (ii) converting a gene for encoding gamma-glutamoyl cysteine synthetase-linker peptide-glutathione synthetase into the host bacterium cell, and highly expressing the gene; (iii) knocking off the gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase of the host bacterium cell; (iv) knocking off an inositol-3-phosphatep synthase gene of the host bacterium cell; and completing the steps (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv) in any sequence, thereby obtaining the genetically engineered bacterium for synthesizing glutathione. The invention further relates to the prepared genetically engineered bacterium. The genetically engineered bacterium for synthesizing glutathione, which is disclosed by the invention, is not only high in efficiency in synthesizing glutathione, but also can greatly improve the conversion efficiency of exogenous cysteine, and can be applied to glutathione production.
Owner:唐星
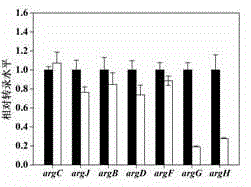
Metabolic transformation method for efficiently improving production capacity of corynebacterium crenatum SYPA5-5 L-arginine
The invention provides a metabolic transformation strategy for efficiently improving production capacity of corynebacterium crenatum SYPA5-5 L-arginine, and belongs to the biological technical field. Histidine at a site 268 in N-acetyl glutamatekinase, NAGK, argB of SYPA-5 is mutated into asparaginate, so that feedback inhibition effect of the L-arginine on NAGK can be effectively relived; a mutation site is precisely introduced to a corresponding position of SYPA5-5 genome, so that yield of the obtained feedback inhibition-preventing bacterial strain (H-7)L-arginine is lowered, and metabolic intermediate (L-ornithine and L-citrulline) is largely accumulated. Transcriptional analysis is carried out on an arg gene cluster of h-7 to find that arg GH transcriptional level is lowered. Arg GH reinforced expression is carried out in H-7, and production capacity of the obtained recombinant bacterial strain H-7-GH, L-arginine is improved by 99.0% in comparison with SYPA5-5. Preliminary optimization is carried out on a fermentation culture medium of H-7-GH, so that yield of the L-arginine is 45.1g / L, which is improved by 49.8% in comparison with that before optimization, and improved by 1.13 times in comparison with SYPA5-5. Feedback inhibition of the L-arginine on NAGK is relieved, and metabolic transformation strategy of the arg GH gene is expressed in a strengthened manner at the same time, so that production capacity of the L-arginine of the SYPA 5-5 is effectively improved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
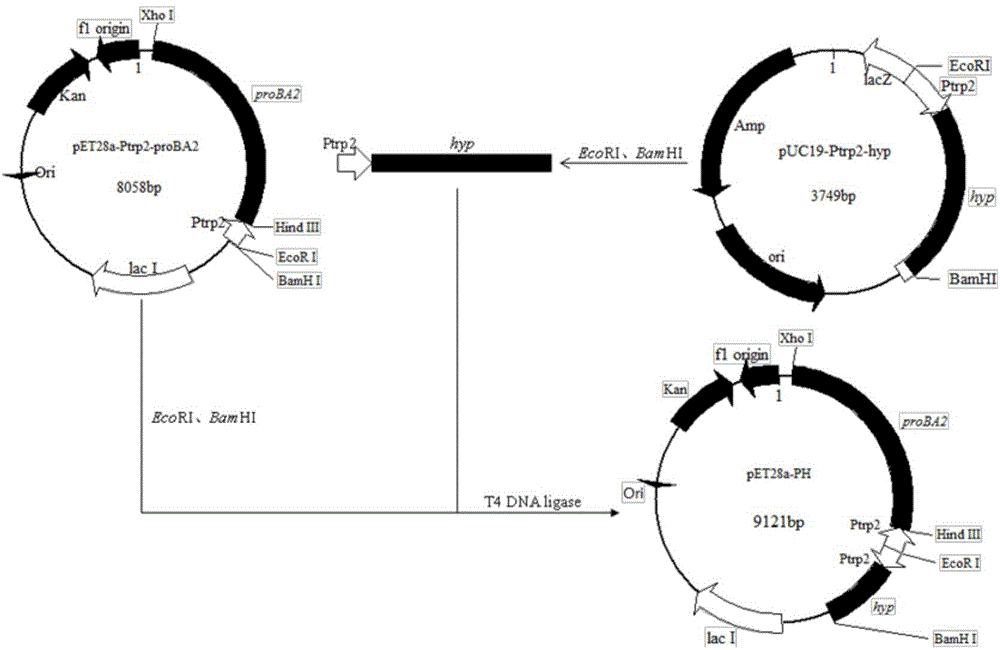
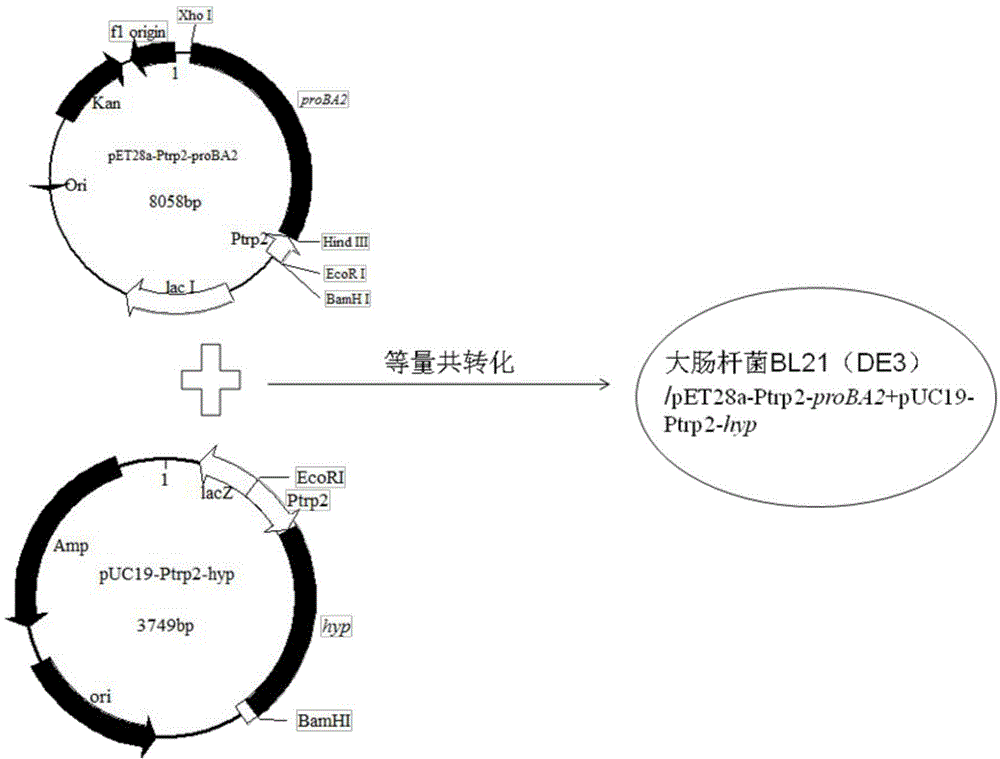
Method for producing trans-4-hydroxyproline from glucose in fermentation manner
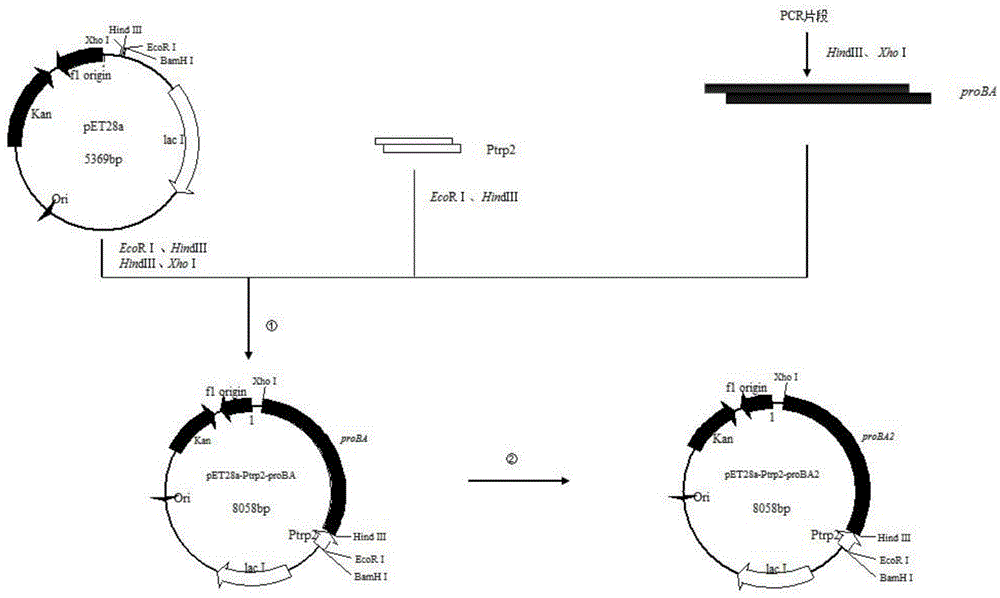
The invention discloses a method for producing trans-4-hydroxyproline from glucose in a fermentation manner by virtue of recombinant Escherichia coli without adding exogenous L-proline. A recombinant plasmid carried by the recombinant Escherichia coli has a mutant gene proBA2 and hyp (4-hydroxyproline), wherein proBA2 is mutated on a glutamyl kinase encoding gene proB, and the inhibition effect of L-proline on glutamyl kinase encoded by the mutated gene is remarkably reduced. proBA2 and hyp are co-expressed, and trans-4-hydroxyproline can be produced directly from glucose in the fermentation manner without adding exogenous L-proline. The recombinant plasmid is obtained by recombining proBA2 and hyp onto the same expression plasmid or by co-transforming recombinant plasmids which contain the two genes respectively and have different resistances. The invention further discloses the application of the Escherichia coli to the production of hydroxyproline.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
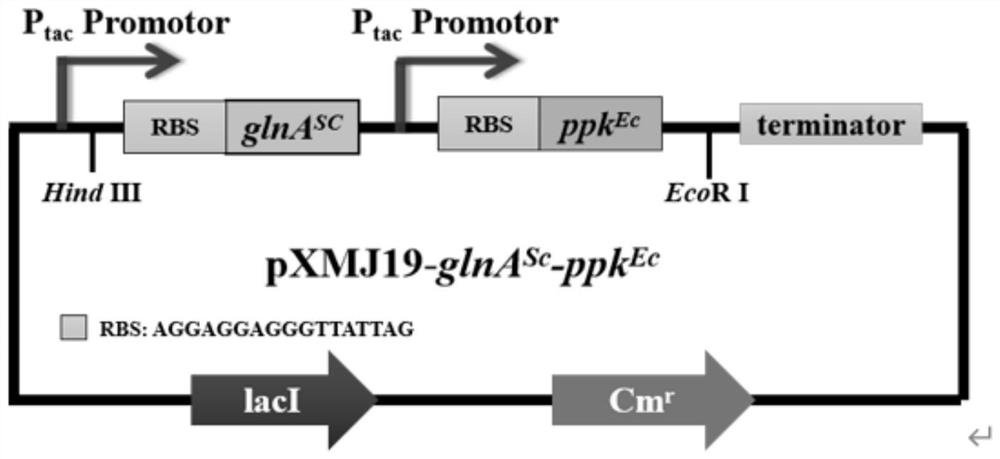
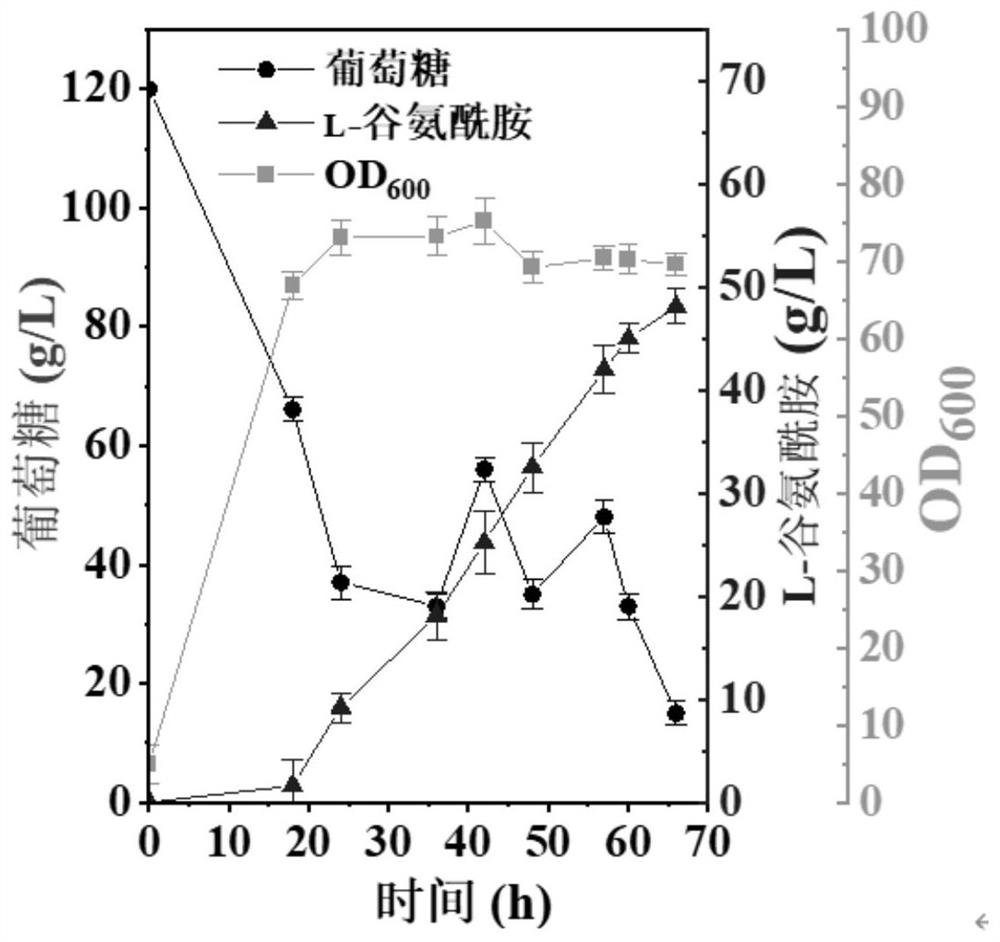
Recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum and application thereof in production of L-glutamine
ActiveCN113684165AIncrease productionHigh glycosamine conversion rateBacteriaTransferasesBacterosiraGlutamic acid
The invention discloses recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum and application thereof in production of L-glutamine, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The activity of gamma-glutamate kinase, glutamic acid secretion mechanical channel protein and adenosine acylase of glutamine synthetase in cells of the recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum is lost, and plasmid pXMJ19 is used for co-expressing the glutamine synthetase from saccharomyces cerevisiae and polyphosphate kinase from escherichia coli. The invention provides the recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum CGQ03 / pXMJ19-glnASc-ppkEc capable of producing the L-glutamine at high yield; the recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum is inoculated into a 5L fermentation tank and is fermented for 66h, so that the yield of the L-glutamine in fermentation liquid reaches 73.5 + / -3.1g / L and the conversion rate of glucosamine reaches 0.368 + / -0.034.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for improving acetylglucosamine yield of recombinant bacillus subtilis by knocking out argCJBD
ActiveCN105176879AEasy to buildIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesArginineAcetylornithine transaminase
The invention discloses a method for improving the acetylglucosamine yield of recombinant bacillus subtilis by knocking out argCJBD, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. Recombinant bacillus subtilis BSGN6-PxylA-glmS-P43-GNA1 serves as the original strain, acetyl glutamate glutamate-5-semialdehyde dehydrogenase coding gene (argC), ornithine acetyltransferase coding gene (argJ), acetyl glutamate kinase coding gene (argB) and acetyl ornithine aminotransferase coding gene (argD) are knocked out through homologous recombination, and therefore the approach of host bacteria for generating arginine from glutamic acid is stopped, and the reaction of converting glutamic acid into glutamine is promoted; glutamine serves as amino donors synthesized through acetylglucosamine, and therefore the yield of acetylglucosamine is improved. In the bottle shaking fermentation process through a semi-synthesized culture medium, the acetylglucosamine yield of recombinant bacillus subtilis reaches 6.4 g / L by knocking out argCJBD and is improved by 16.3% compared with the before-knockout yield. A foundation is laid for further producing glucosamine through bacillus subtilis transformed through metabolic engineering.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
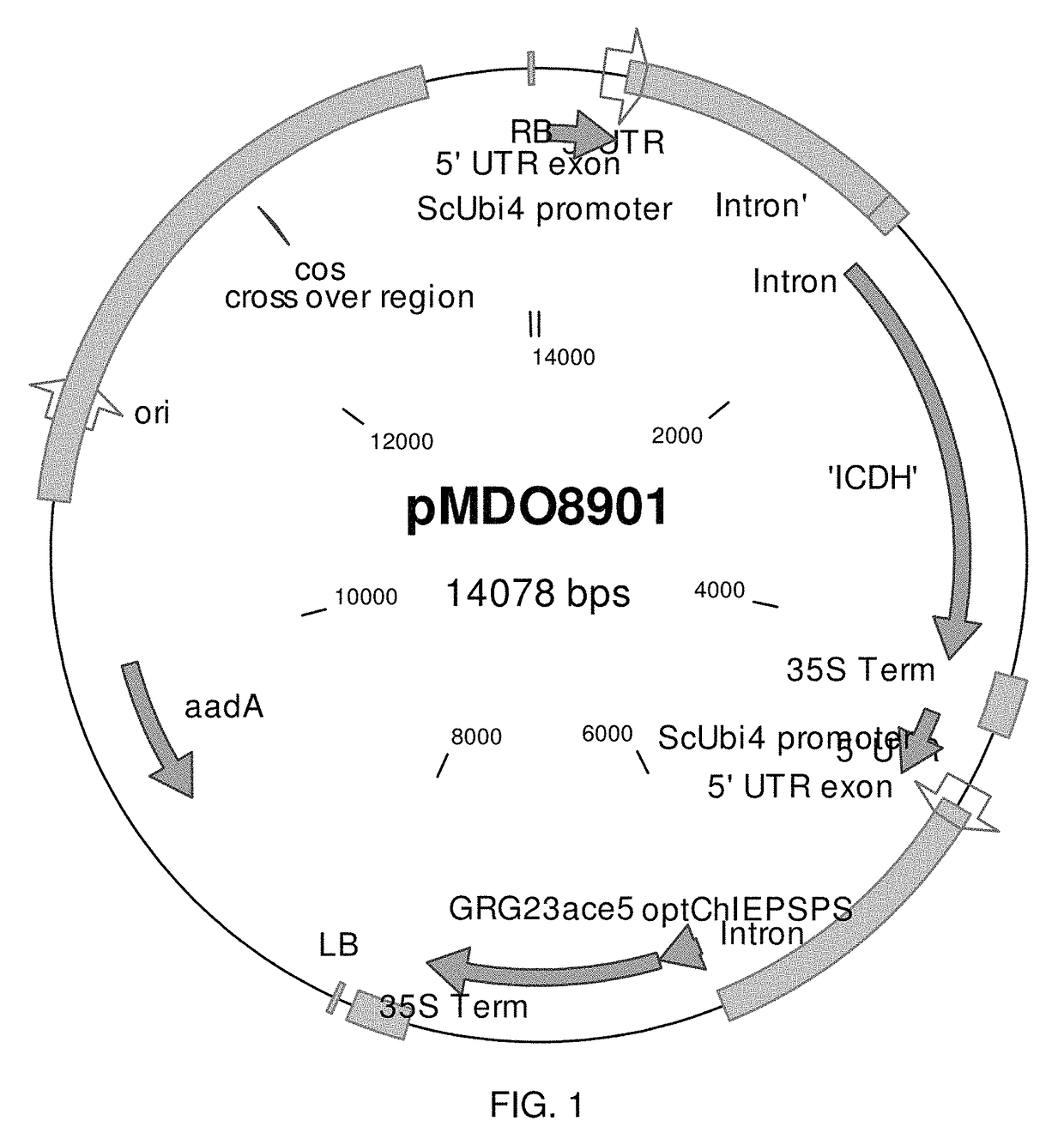
Plants With Improved Nitrogen Utilization and Stress Tolerance
InactiveUS20110252503A1Improve efficiencyIncrease productionSugar derivativesBacteriaTolerabilityArginine
The present invention relates to transgenic plants that have increased nitrogen use efficiency, stress tolerance, and / or alleviating a limitation such that yield is increased, or a combination of these and that have been transformed using a novel vector construct including a synthetic N-acetyl glutamate kinase (NAGK) gene that modulates nitrogen use in plants. The invention also includes the overexpression and enzymatic characterization of an arginine-insensitive NAGK isolated from a bacterial strain that improves stress tolerance and nitrogen uptake, metabolism or both. In various embodiments, the vector construct includes one or more nucleic acid sequences including SEQ ID NO: 1. The invention also relates to isolated vectors for transforming plants and to antibodies used for detecting transformed plants. The invention also relates to methods of expressing in plants the nucleic acid molecules corresponding to the nucleic acid sequences that modulate nitrogen use in plants or are modulated by nitrogen conditions.
Owner:IOWA CORN PROMOTION BOARD
Method for fermentation production of L-proline by utilizing recombinant Escherichia coli
The invention discloses a method for fermentation production of L-proline by utilizing recombinant Escherichia coli. The recombinant Escherichia coli carries recombinant plasmid with gamma-glutamyl kinase genes with site mutagenesis and tryptophan series promoters, wherein the recombinant plasmid is obtained by connecting the cloned gamma-glutamyl kinase genes and the tryptophan series promoter in the lab to the same plasmid and performing whole plasmid PCR site-specific mutagenesis. The invention also discloses an application of the Escherichia coli in production of L-proline.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
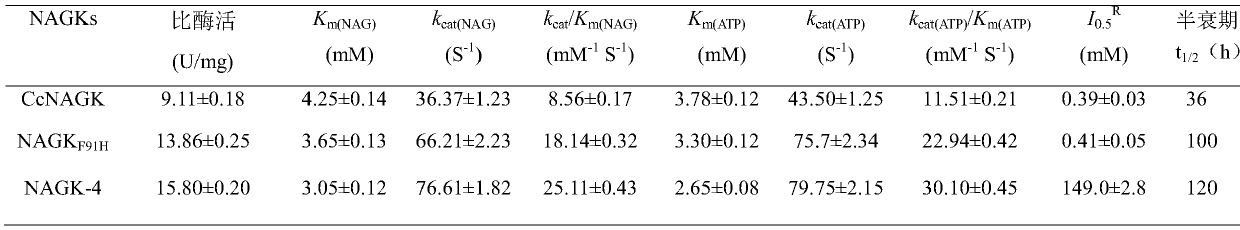
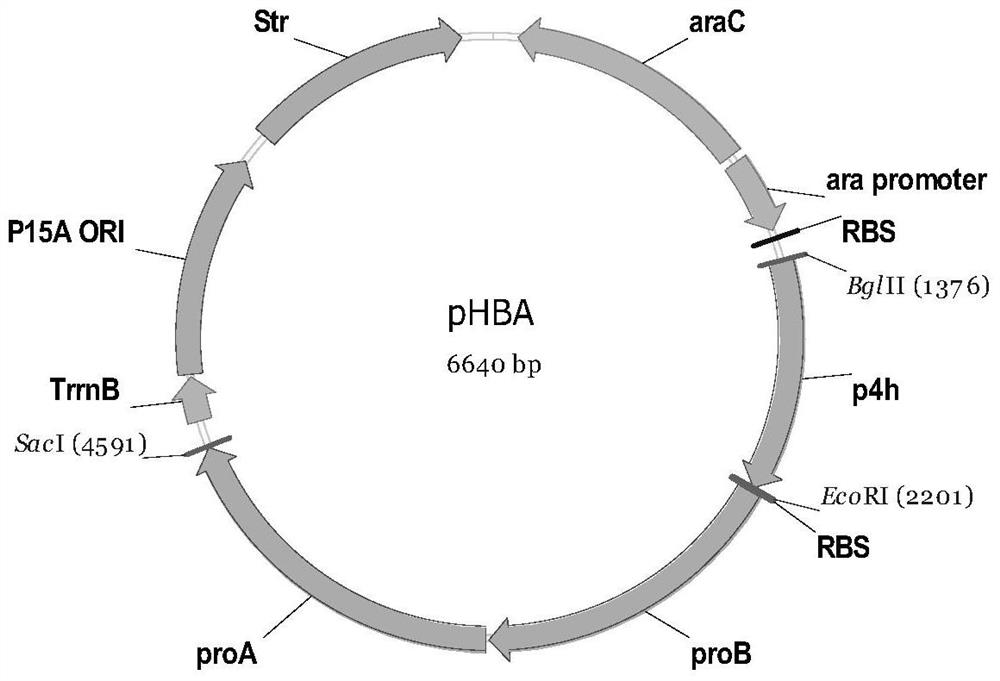
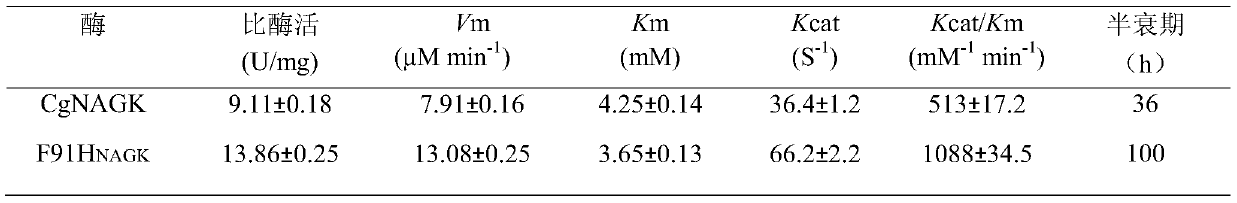
N-acetylgutamate kinase mutant with improved catalytic efficiency and thermal stability
ActiveCN105907735AHigh catalytic efficiencyImprove thermal stabilityTransferasesFermentationHalf-lifeArginine
The invention discloses an N-acetylgutamate kinase mutant with improved catalytic efficiency and thermal stability and belongs to the field of biological engineering. Gene of N-acetylgutamate kinase from Corynebacterium crenatum SYPA5-5 is subjected to site-specific mutagenesis so that coding amino acid sequence of this gene is mutated at 91-th site into histidine H by phenylalanine F. The N-acetylgutamate kinase mutant described herein is 2.12 times as high as a wild one in catalytic efficiency, and has half-life period that is 2.78 times as high as pre-mutation period. The N-acetylgutamate kinase mutant obtained herein is more satisfactory to the need for production of arginine and lays basis for efficient synthesis of L-arginine.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Prokarytoic-Type Isocitrate Dehydrogenase and Its Application for Improving Nitrogen Utilization in Transgenic Plants
ActiveUS20140283224A1Improve efficiencyIncrease productionSugar derivativesClimate change adaptationNitrogenNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention relates to transgenic plants that have increased nitrogen use efficiency, stress tolerance, and / or alleviating a limitation such that yield is increased, or a combination of these and that have been transformed using a novel vector construct including a synthetic isocitrate dehydrogenase (icdh) gene that modulates nitrogen use in plants. The invention also relates to stacking the icdh gene with other exogenous or heterologous genes that modulate nitrogen use in the plant, including a N-acetylglutamate kinase gene. The invention also relates to methods of expressing in plants the nucleic acid molecules corresponding to the nucleic acid sequences that modulate nitrogen use in plants or are modulated by nitrogen conditions.
Owner:IOWA CORN PROMOTION BOARD
Plants with improved nitrogen utilization and stress tolerance
InactiveUS8692070B2Increasing nitrogen uptakeImprove efficiencyBacteriaSugar derivativesArginineNitrogen
The present invention relates to transgenic plants that have increased nitrogen use efficiency, stress tolerance, and / or alleviating a limitation such that yield is increased, or a combination of these and that have been transformed using a novel vector construct including a synthetic N-acetyl glutamate kinase (NAGK) gene that modulates nitrogen use in plants. The invention also includes the overexpression and enzymatic characterization of an arginine-insensitive NAGK isolated from a bacterial strain that improves stress tolerance and nitrogen uptake, metabolism or both. In various embodiments, the vector construct includes one or more nucleic acid sequences including SEQ ID NO: 1. The invention also relates to isolated vectors for transforming plants and to antibodies used for detecting transformed plants. The invention also relates to methods of expressing in plants the nucleic acid molecules corresponding to the nucleic acid sequences that modulate nitrogen use in plants or are modulated by nitrogen conditions.
Owner:IOWA CORN PROMOTION BOARD
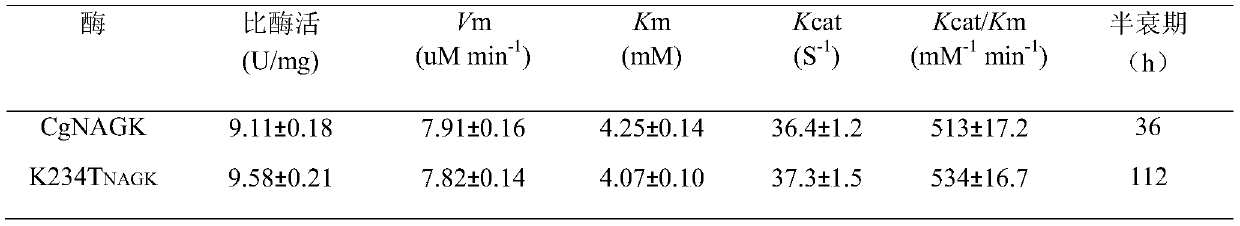
N-acetylgutamate kinase mutant with heat stability improved remarkably
The invention discloses an N-acetylgutamate kinase mutant with heat stability improved remarkably and belongs to the field of bioengineering .The gene of N-acetylgutamate kinase from Corynebacterium crenatum SYPA5-5 is subjected to site-specific mutagenesis, so that lysine K at the site 234 of the encoded amino acid sequence is mutated into threonine T .the half-life period of the N-acetylgutamate kinase mutant at 37 DEG C is prolonged to be 112 h from 36 h of a wild type N-acetylgutamate kinase mutant, which is 3.11 times of the length before mutation .The N-acetylgutamate kinase mutant can better meet the production requirement of arginine, and lays a foundation for efficient synthesis of L-arginine.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Corynebacterium glutamicum high-producing l-proline and method for high-producing l-proline
ActiveCN114107141BIncrease productionImprove conversion rateBacteriaTransferasesPyruvate synthesisGlyceraldehyde
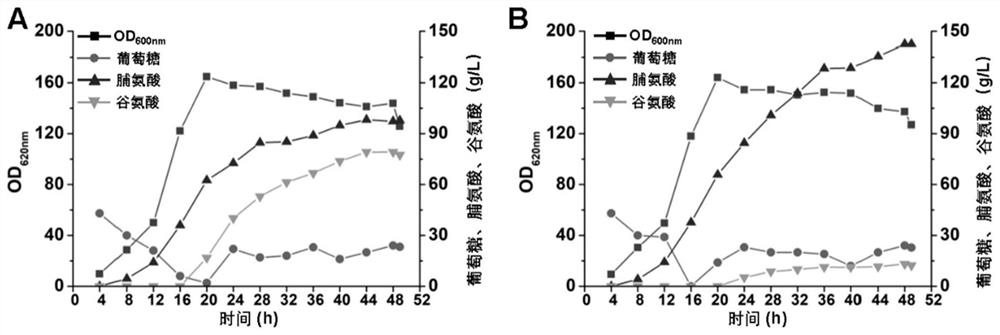
The invention provides a Corynebacterium glutamicum for producing L-proline, and a method for producing L-proline by using the strain. The L-proline-producing Corynebacterium glutamicum constructed by the present invention, wherein proline dehydrogenase / pyrrole-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase PutA is inactivated, glutamate kinase ProB, glutamate-5- Enhanced activity of semialdehyde dehydrogenase ProA, pyrrole-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase ProC, pyruvate carboxylase Pyc, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase GapN, L-proline efflux protein ThrE or SerE, The L-glutamate efflux protein MscCG is inactivated, and the L-proline yield, transformation rate and production intensity of the obtained strain are significantly improved compared with the starting strain, which can reduce the production cost of L-proline.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
N-acetylgutamate kinase mutant with improved catalysis efficiency
The invention discloses an N-acetylgutamate kinase mutant with improved catalysis efficiency and belongs to the field of biological engineering .A gene of N-acetylgutamate kinase coming from Corynebacteriaum crenatum SYPA5-5 is subjected to site-directed mutation, so that the amino acid sequence encoded by the gene is mutated from isoleucine I to valine V at the 74th site .Catalysis efficiency (Kcat / Km) of the N-acetylgutamate kinase mutant is improved to 843 mM<-1>min<-1> from 513 mM<-1>min<-1> of a wild type, and is 1.64 times of the catalysis efficiency before mutation .Heat stability of the mutant is also improved .The N-acetylgutamate kinase mutant better meets production requirements of arginine, and a foundation is laid for efficient synthesis of L-arginine.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Corynebacterium glutamicum for high yield of L-proline and method for high yield of L-proline
ActiveCN114107141AIncrease productionImprove conversion rateBacteriaTransferasesPyruvate synthesisCarboxylic acid
The invention provides corynebacterium glutamicum for producing L-proline and a method for producing the L-proline by using the strain. According to the corynebacterium glutamicum for producing the L-proline, proline dehydrogenase / pyrrole-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase PutA is inactivated, activity of glutamate kinase ProB, glutamic acid-5-semialdehyde dehydrogenase ProA, pyrrole-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase ProC, pyruvate carboxylase Pyc, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase GapN, L-proline efflux protein ThrE or SerE is enhanced, and activity of L-proline is enhanced. The L-glutamic acid efflux protein MscCG is inactivated, the L-proline yield, the conversion rate and the production intensity of the obtained strain are remarkably improved compared with those of an original strain, and the production cost of the L-proline can be reduced.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Ammonia (ammonia ion) determination method, ammonia (ammonia ion) diagnosis/determination kit
InactiveCN102466708AMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsGlutamate kinaseIon
The invention relates to an ammonia (ammonia ion) content determination method by using an enzyme colorimetric method and an enzyme coupled reaction method, a reagent composition and components. The technical principle of the determination method is that a series of catalytic reactions can be carried out according to ammonia kinases, glutamine kinases and glutamine synthetase. The invention also relates to an ammonia (ammonia ion) diagnosis / determination kit. The determination method of invention has the advantages of high sensitivity and small error. The determination method and the kit of the present invention can be widely used for clinical medicine / food examination.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
High-yield strain and construction method of cyclic lipopeptide antibiotics hemastatin
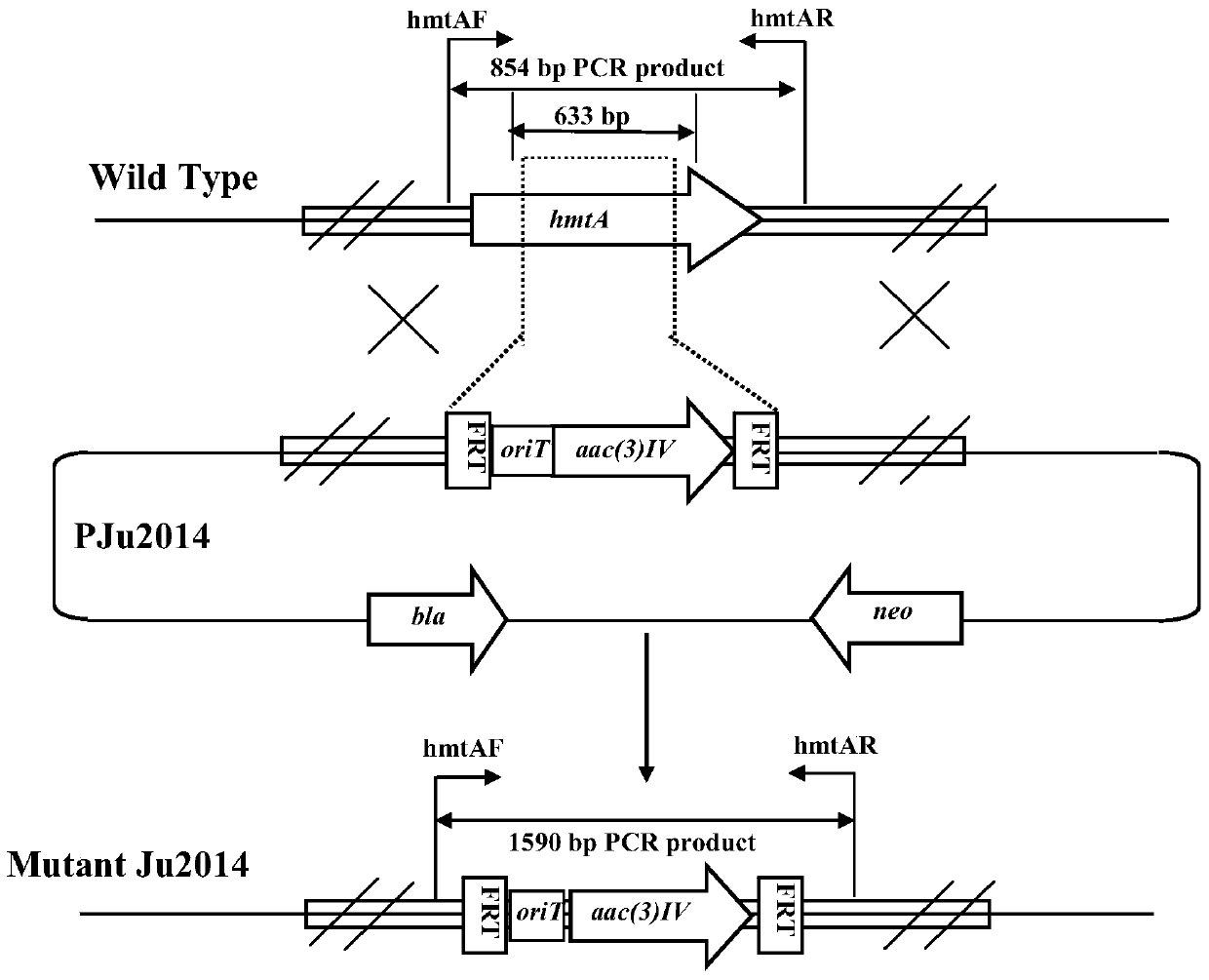
The invention discloses a high-producing strain for the cyclic lipopeptide antibiotic--himastatin and a construction method thereof. The high-producing strain for himastatin is constructed by inactivating the hmtA gene or hmtB gene of S. himastatinicus sp.Nov, so the high-producing mutant strain S. himastatinicus sp.Nov for himastatin is obtained, wherein the nucleotide sequence of the hmtA gene is as shown in SEQ ID No. 1 and the nucleotide sequence of the hmtB gene is as shown in SEQ ID No. 3. According to the invention, the hmtA-inactivated mutant strain S. himastatinicus sp.Nov Ju2014 and the hmtB-inactivated mutant strain S. himastatinicus sp.Nov Ju2015 are respectively obtained by inactivating the Mer-family transcriptional regulation gene hmtA and the acetyl glutamic acid kinase gene hmtB at the upper stream of the biosynthesis gene cluster of the cyclic lipopeptide antibiotic--himastatin of S. himastatinicus sp.Nov. The himastatin output of the mutant strain S. himastatinicus sp.Nov Ju2014 and the mutant strain S. himastatinicus sp.Nov Ju2015 is more than 10 times that of a wild strain S. himastatinicus sp.Nov. Thus, successful construction of the two high-producing mutant strains for the cyclic lipopeptide antibiotic--himastatin enables acceleration of the industrialization process of himastatin to be possible and hopeful.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A method for knocking out argcjbd to improve the production of acetylglucosamine in recombinant Bacillus subtilis
ActiveCN105176879BEasy to buildIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAcetylornithine transaminaseAcetylglutamate kinase
The invention discloses a method for knocking out argCJBD to increase the yield of acetylglucosamine of recombinant Bacillus subtilis, belonging to the field of genetic engineering. The invention uses the recombinant Bacillus subtilis BSGN6-PxylA-glmS-P43-GNA1 as the starting strain, and knocks out the gene encoding acetylglutamate semialdehyde dehydrogenase (argC) and the gene encoding ornithine acetyltransferase through homologous recombination (argJ), acetylglutamate kinase encoding gene (argB) and acetylornithine transaminase encoding gene (argD), block the pathway of host bacteria producing arginine from glutamic acid, and promote the conversion of glutamic acid into glutamic acid The reaction of amide, and glutamine is the amino donor for the synthesis of acetylglucosamine, thereby increasing the production of acetylglucosamine. During the shake flask fermentation process using semi-synthetic medium, the yield of acetylglucosamine of the recombinant Bacillus subtilis with knockout of argCJBD reached 6.4 g / L, which was 16.3% higher than that before knockout. It laid the foundation for further metabolic engineering of Bacillus subtilis to produce glucosamine.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
N-acetyl glutamic acid kinase mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN106434594AIncrease productionIncrease synthesis rateBacteriaTransferasesStructure analysisArginine
The invention provides an N-acetyl glutamic acid kinase mutant capable of relieving the feedback inhibition effect of L-arginine and obviously increasing the catalytic activity and thermal stability and belongs to the field of bioengineering. A molecular docking technique and the structure analysis for N-acetyl glutamic acid kinase (CcNAGK) from corynebacterium crenatum CGMCC NO:0890 are firstly adopted for confirming that the E19 locus plays an important role in inhibiting the feedback of arginine and three key amino residue loci I74, F91 and K234 located on a substrate combining bag have significant impacts on enzymatic catalytic activity and heat stability; the encoded amino acid is replaced and the gene argB4 after compound mutation is introduced into the corynebacterium crenatum highly yielding arginine through pDXW10, so that the compounding rate of the arginine in corynebacterium crenatum can be obviously increased; lastly, after fermentation for 98h in a 5L fermentation tank, the yield of arginine is increased to 61.2g / L from original 43.2g / L, and the yield of the L-arginine is increased by 41.8%.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for producing L-arginine, L-ornithine or L-citrulline
It is intended to provide a polypeptide having (i) an amino acid sequence derived from the amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO:1 by substitution of one or more amino acids in the amino acid sequences of from the 20- to the 38-th positions from the N end, or (ii) an amino acid sequence derived from the amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO:1 by substitution of one or more amino acids in the amino acid sequences of from the 20- to the 38-th positions from the N end and deletion, substitution or addition of one or more amino acids in the amino acid sequence of from the first to the 19-th positions or from the 39-th to the 294-th positions, and having an N-acetylglutamate kinase activity.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO BIO CO LTD
Method for improving yield of arginine by mutation of Corynebacterium crenatum N-acetyl glutamic acid kinase
The invention relates to a method for improving the yield of arginine by the mutation of Corynebacterium crenatum N-acetyl glutamic acid kinase. L-arginine is one of semi-essential basic amino acids for a human body, and has various particular physiology and pharmacology functions. High-yield arginine mutant strain C. crenatum SYPA5-5 is compounded into the arginine through a circulating way, andN-acetyl glutamic acid kinase (NAGK) is a key enzyme in the compounding way and is subject to the feedback inhibition of the product arginine. By using an overlapping PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) technique, a GAT (glycerol phosphate acyl transferase) codon used for coding aspartic acid is used for substituting a GGA (General Gonadotropic activity) codon used for coding glycine at the site 287 in the coding NAGK albumen, and the NAGK which has high activity and arginine with obviously reduced by the feedback inhibition can be obtained after the mutation. An argBSD gene is brought into the Corynebacterium crenatum of the high-yield arginine through pJCl-tac, and the expression volume of the key enzyme is further improved. The final acid yield is increased to 36.3g / L from original 28g / L, and the yield of the L-arginine is increased by 29.7 percent.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
A recombinant strain producing trans-4-hydroxy-l-proline and its construction and application
ActiveCN105483069BIncrease productionYield has no effectBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliHydroxyproline
The invention relates to a recombination strain for producing trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline and building and application of the recombination strain and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. The recombination strain for producing the trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline is identified as escherichia coli HJ which is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection on September 17th, 2015, and the preservation number of the escherichia coli HJ is CCTCC No. M2015550. The recombination strain has the advantages that wild glutamate kinase controlled by feedback regulation is used to enhance expression, three to-be-expressed genes and expression elements such as related initiators are integrated to the chromosome of the escherichia coli, the to-be-expressed genes can be constantly replicated along with the replication of the chromosome, extremely-high genetic stability is kept, the problem of plasmid loss is solved, effective fermentation cycle is prolonged, and the yield of hydroxyproline is increased.
Owner:ZHEJIANG LVCHUANG BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
A kind of n-acetyl glutamate kinase mutant and its application
ActiveCN106434594BIncrease productionIncrease synthesis rateBacteriaTransferasesArginineAcetylglutamate kinase
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Determination method of ammonia (ammonium ion) and diagnosis/determination reagent kit of ammonia (ammonium ion)
InactiveCN102539694AMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsEnzymatic ColorimetryCoupling reaction
The invention relates to a determination method for determining ammonia (ammonium ion) content by utilizing an enzymatic cycling amplification method, an enzymatic colorimetric method and enzyme couple reaction technology, and composition and components of a reagent. The technology principle for the determination is that the determination is finished according to series catalytic reactions of ammonia kinase, glutamic kinase and glutamic dehydrogenase. The invention further relates to a diagnosis / determination reagent kit of ammonia (an ammonium ion). The determination method is high in sensitivity and small in errors, and accordingly the determination method and the reagent kit can be widely applied to clinical medicine / food inspection.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
An N-acetylglutamate kinase mutant with significantly improved thermostability
The invention discloses an N-acetylgutamate kinase mutant with heat stability improved remarkably and belongs to the field of bioengineering .The gene of N-acetylgutamate kinase from Corynebacterium crenatum SYPA5-5 is subjected to site-specific mutagenesis, so that lysine K at the site 234 of the encoded amino acid sequence is mutated into threonine T .the half-life period of the N-acetylgutamate kinase mutant at 37 DEG C is prolonged to be 112 h from 36 h of a wild type N-acetylgutamate kinase mutant, which is 3.11 times of the length before mutation .The N-acetylgutamate kinase mutant can better meet the production requirement of arginine, and lays a foundation for efficient synthesis of L-arginine.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Prokarytoic-type isocitrate dehydrogenase and its application for improving nitrogen utilization in transgenic plants
ActiveUS9725701B2Increasing nitrogen uptakeImprove efficiencyClimate change adaptationOxidoreductasesNitrogenNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention relates to transgenic plants that have increased nitrogen use efficiency, stress tolerance, and / or alleviating a limitation such that yield is increased, or a combination of these and that have been transformed using a novel vector construct including a synthetic isocitrate dehydrogenase (icdh) gene that modulates nitrogen use in plants. The invention also relates to stacking the icdh gene with other exogenous or heterologous genes that modulate nitrogen use in the plant, including a N-acetylglutamate kinase gene. The invention also relates to methods of expressing in plants the nucleic acid molecules corresponding to the nucleic acid sequences that modulate nitrogen use in plants or are modulated by nitrogen conditions.
Owner:IOWA CORN PROMOTION BOARD
A kind of engineering bacteria producing trans-4-hydroxy-l-proline and its construction method and application
The invention discloses engineering bacteria for producing trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline and a construction method and an application thereof. The construction method of the engineering bacteria provided by the invention includes the steps of A1) and A2): A1) introducing a L-proline-4-hydroxylase gene, a glutamate-5-kinase gene and a glutamate-5-semialdehyde dehydrogenase gene into a receptor cell; and A2) knocking an alpha-ketoglutaricdehydrogenase gene, an isocitratlyase gene or a proline dehydrogenase gene of the receptor cell out, or replacing a pyruvic oxidase gene of the receptor cell with an acetylcoenzyme A synthetase gene; and carrying out a reaction of the recombinant cell and a substrate to obtain the trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline. Experiments prove that the production method of the trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline can be used for production of the trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A N-acetylglutamate kinase mutant with improved catalytic efficiency and thermal stability
ActiveCN105907735BHigh catalytic efficiencyImprove thermal stabilityTransferasesFermentationHalf-lifeWild type
The invention discloses an N-acetylgutamate kinase mutant with improved catalytic efficiency and thermal stability and belongs to the field of biological engineering. Gene of N-acetylgutamate kinase from Corynebacterium crenatum SYPA5-5 is subjected to site-specific mutagenesis so that coding amino acid sequence of this gene is mutated at 91-th site into histidine H by phenylalanine F. The N-acetylgutamate kinase mutant described herein is 2.12 times as high as a wild one in catalytic efficiency, and has half-life period that is 2.78 times as high as pre-mutation period. The N-acetylgutamate kinase mutant obtained herein is more satisfactory to the need for production of arginine and lays basis for efficient synthesis of L-arginine.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
An N-acetylglutamate kinase mutant with improved catalytic efficiency
The invention discloses an N-acetylgutamate kinase mutant with improved catalysis efficiency and belongs to the field of biological engineering .A gene of N-acetylgutamate kinase coming from Corynebacteriaum crenatum SYPA5-5 is subjected to site-directed mutation, so that the amino acid sequence encoded by the gene is mutated from isoleucine I to valine V at the 74th site .Catalysis efficiency (Kcat / Km) of the N-acetylgutamate kinase mutant is improved to 843 mM<-1>min<-1> from 513 mM<-1>min<-1> of a wild type, and is 1.64 times of the catalysis efficiency before mutation .Heat stability of the mutant is also improved .The N-acetylgutamate kinase mutant better meets production requirements of arginine, and a foundation is laid for efficient synthesis of L-arginine.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com