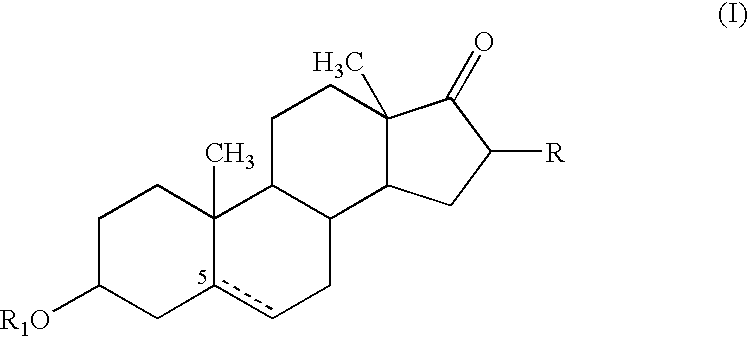
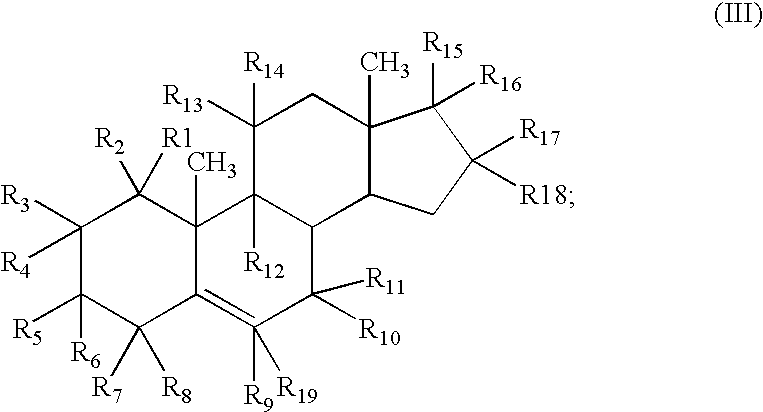
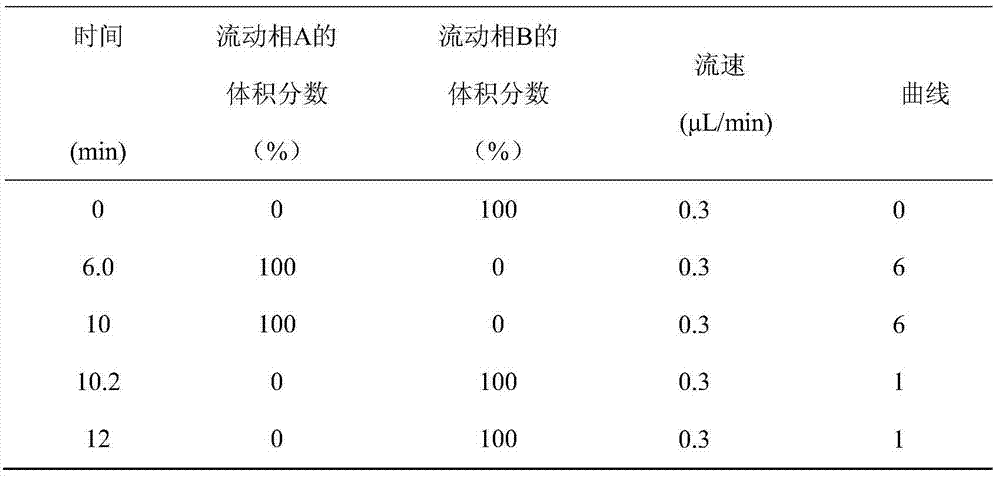
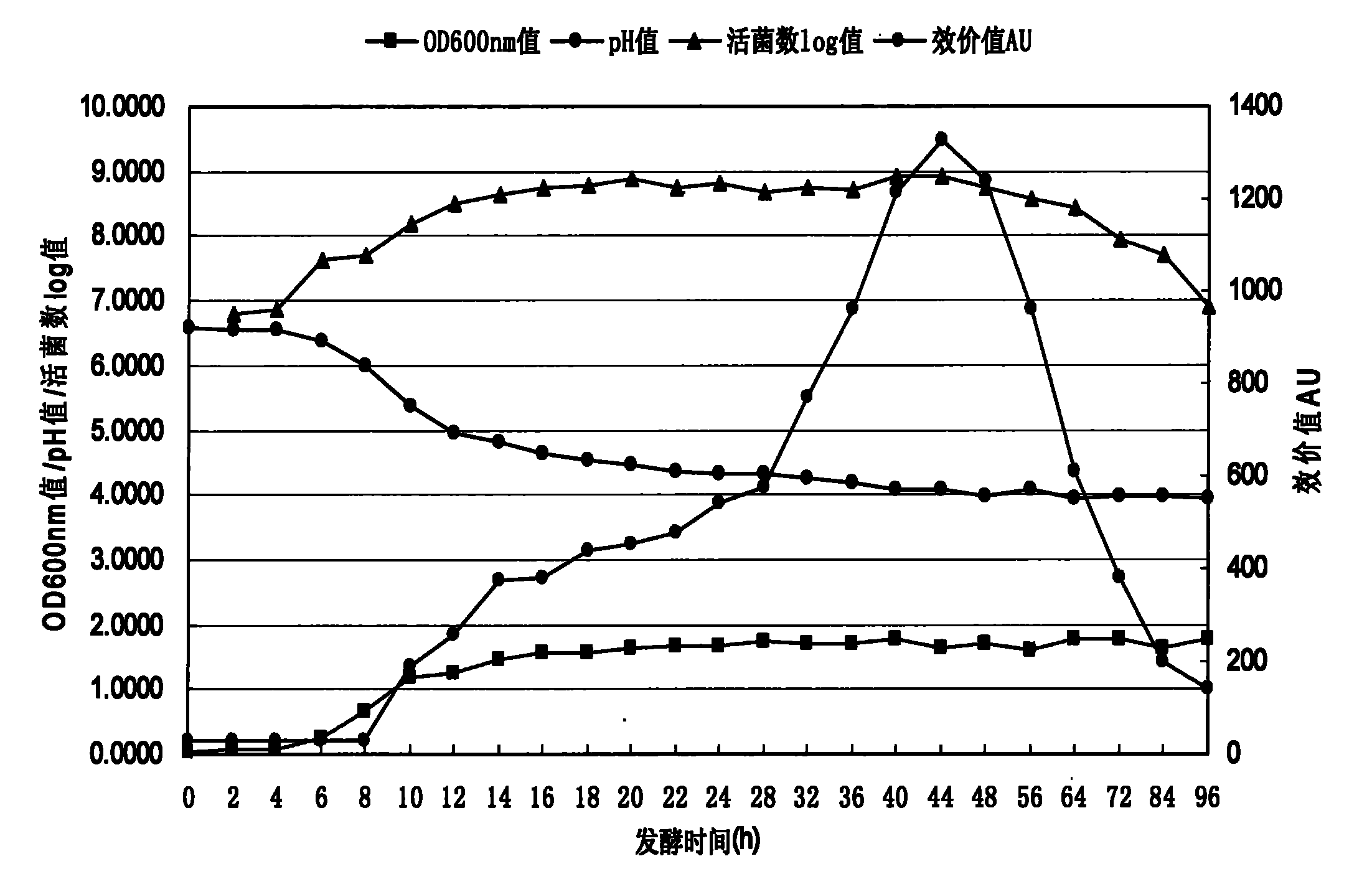
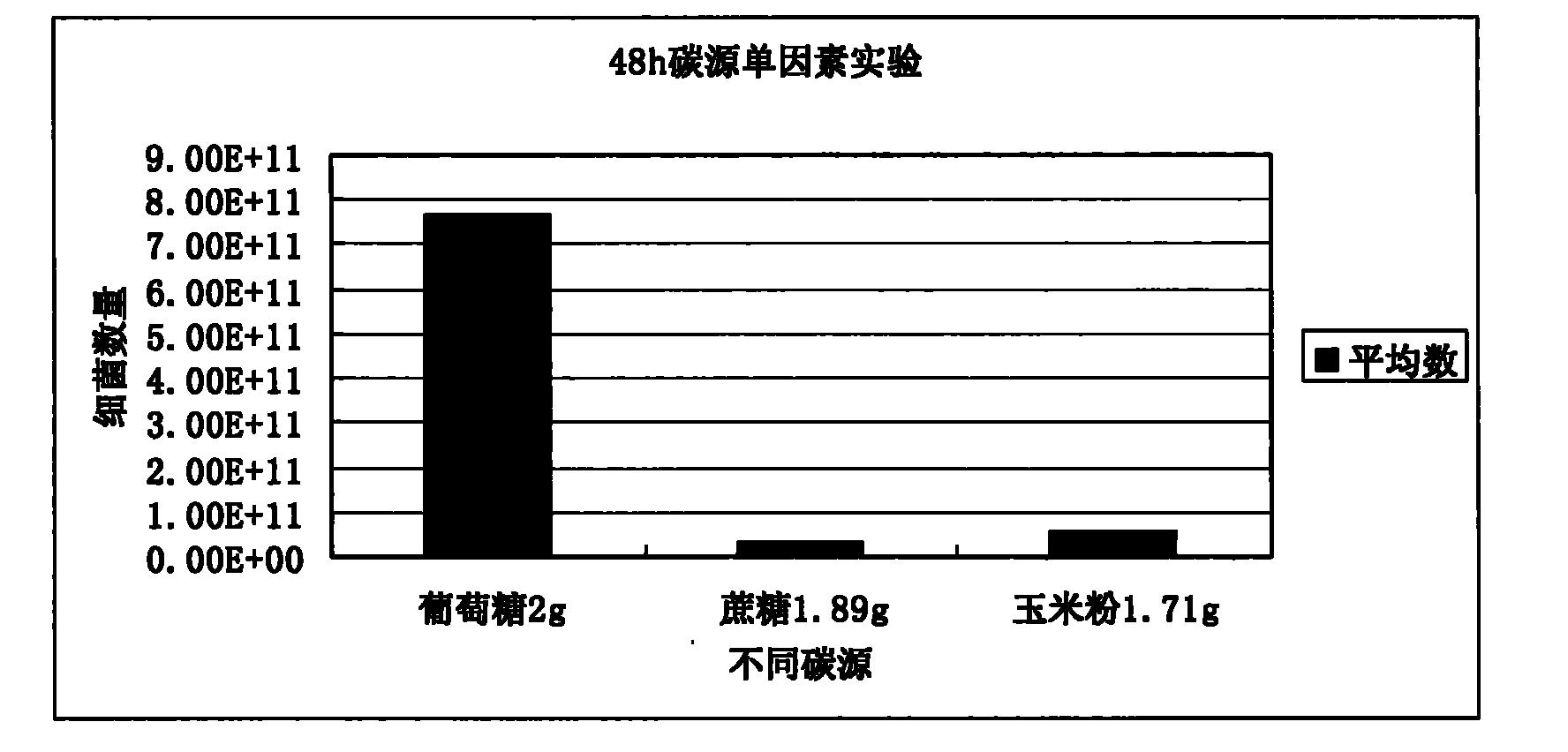
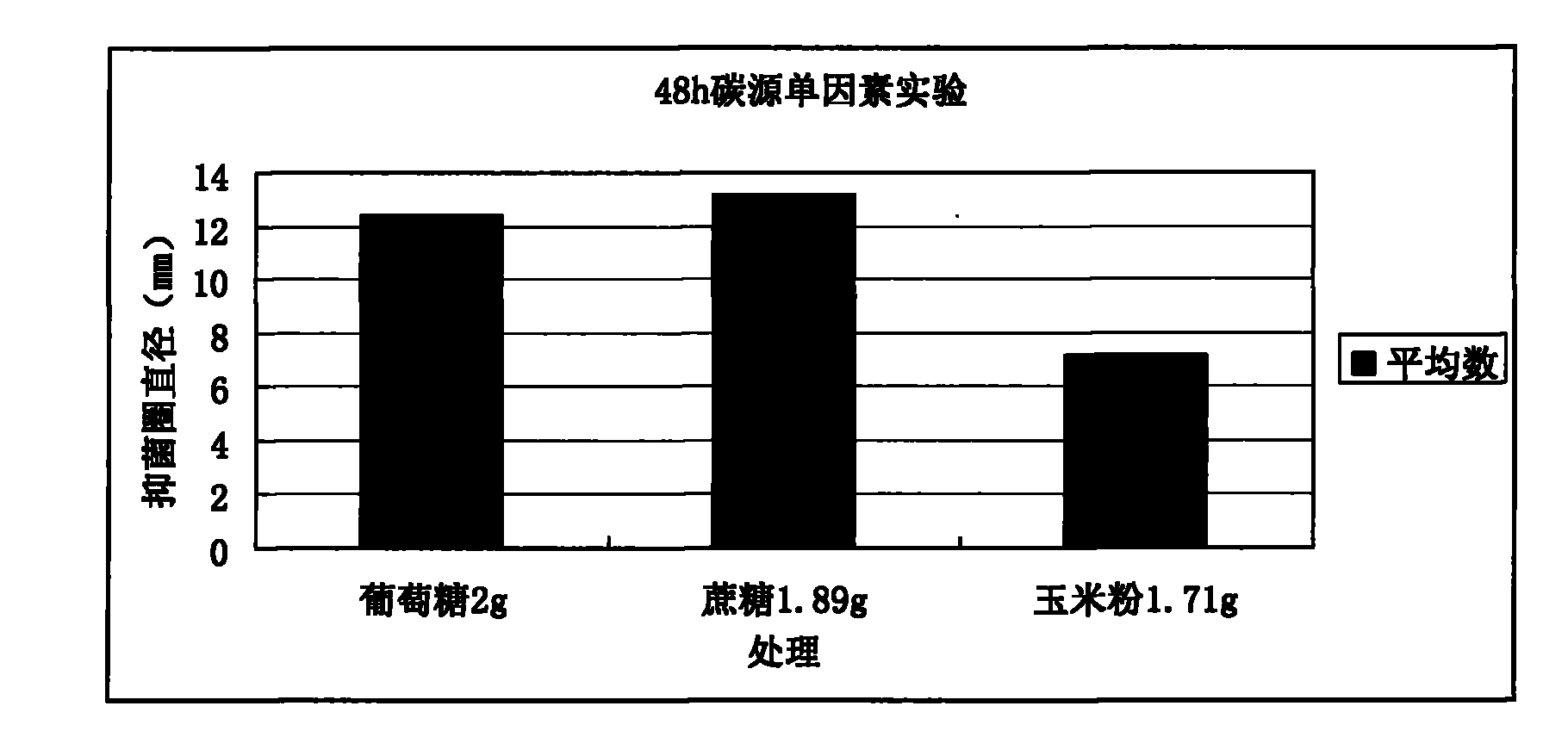
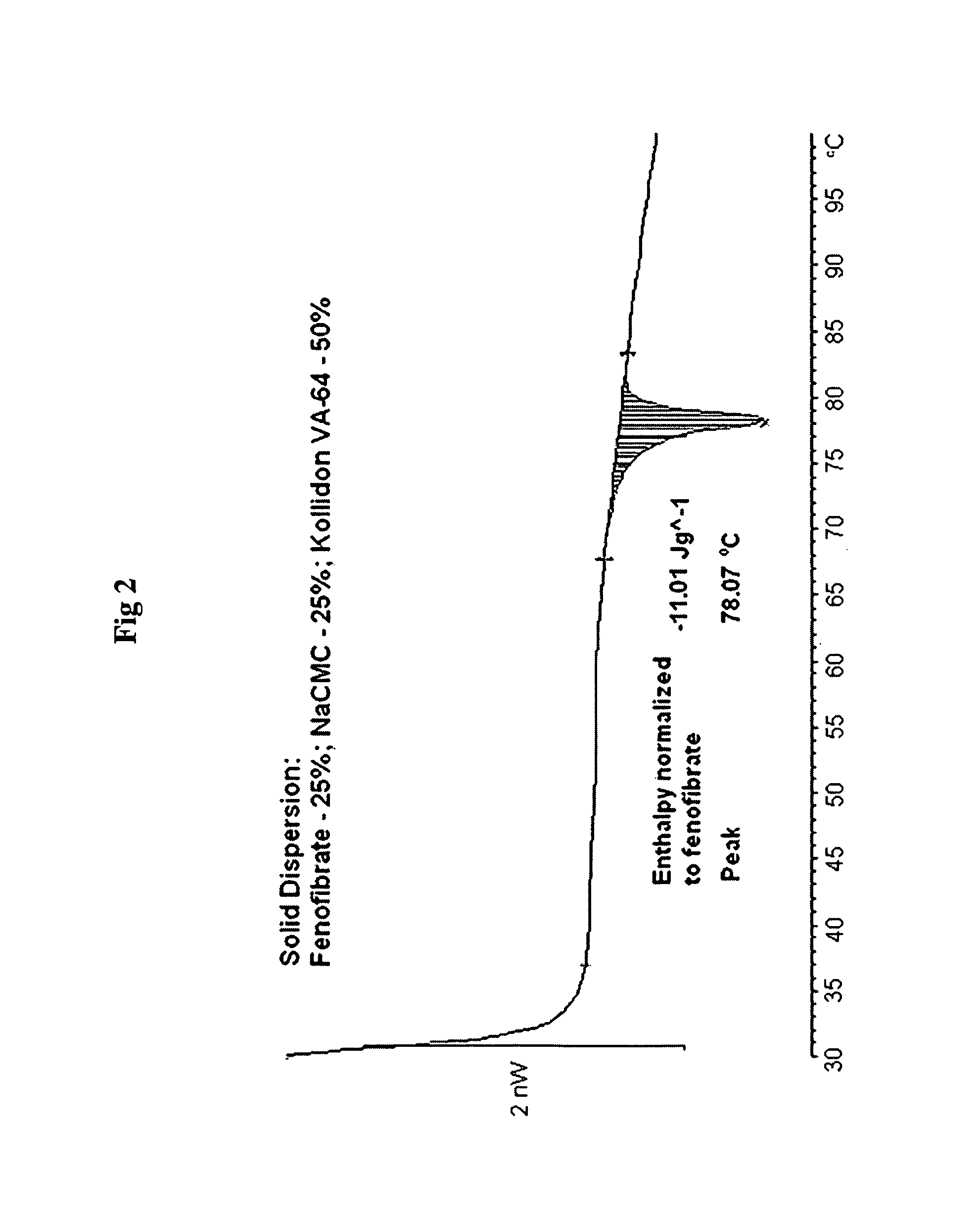
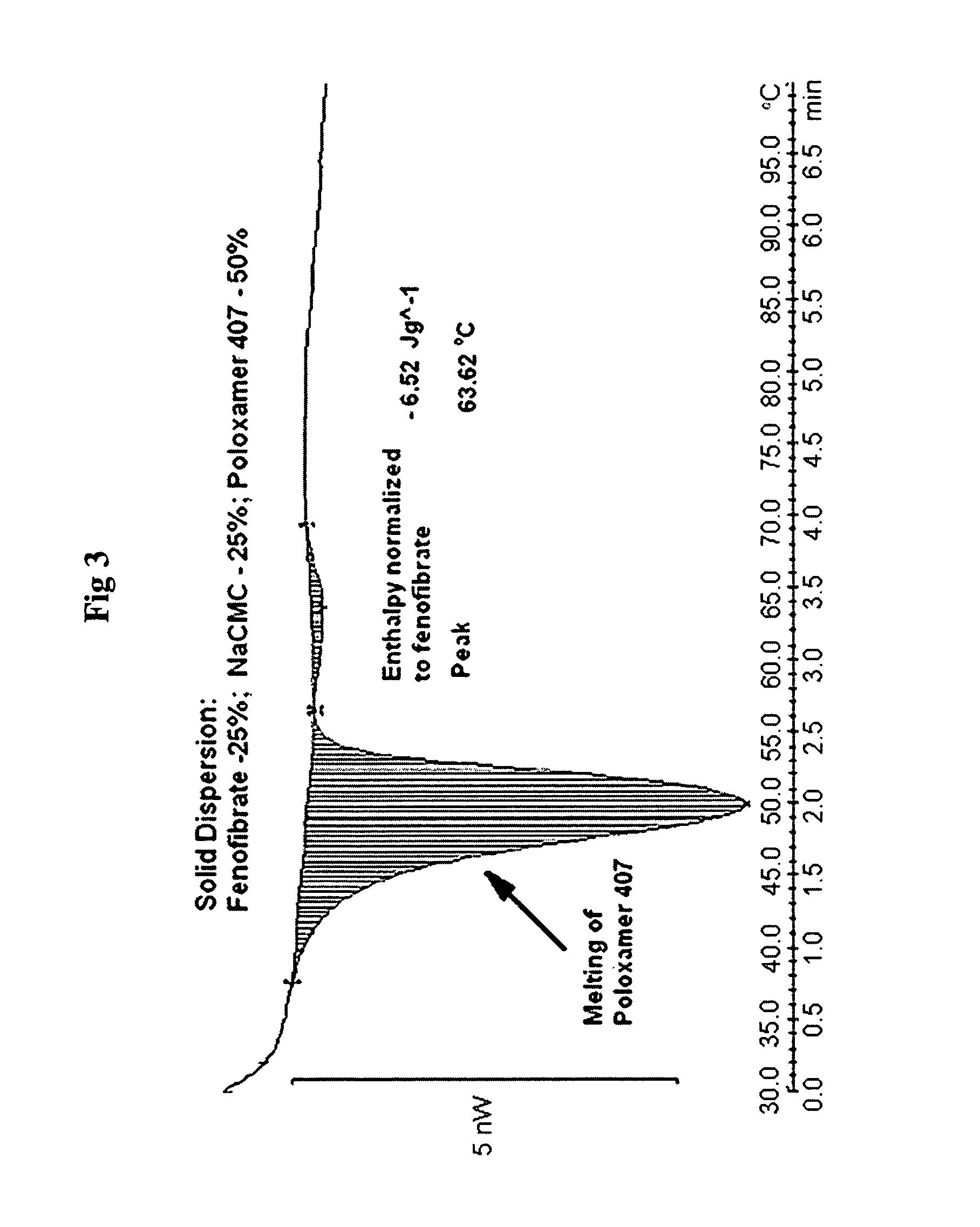
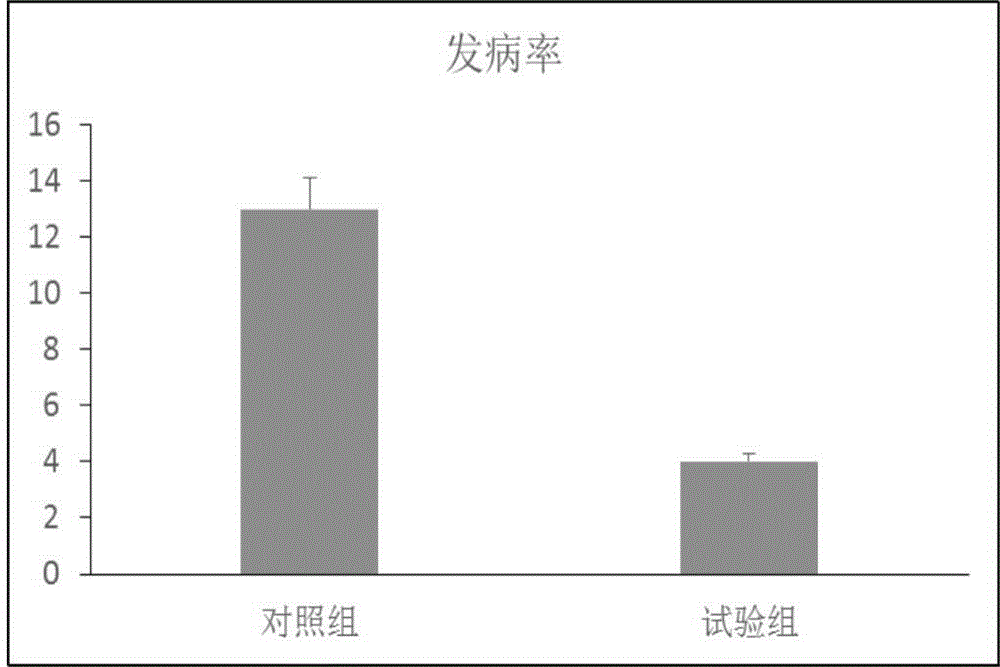
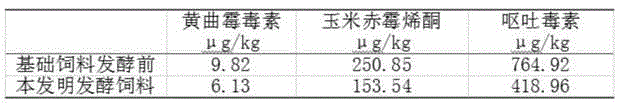
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2244 results about "Veterinary Drugs" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Drugs used by veterinarians in the treatment of animal diseases. The veterinarian's pharmacological armamentarium is the counterpart of drugs treating human diseases, with dosage and administration adjusted to the size, weight, disease, and idiosyncrasies of the species. In the United States most drugs are subject to federal regulations with special reference to the safety of drugs and residues in edible animal products.
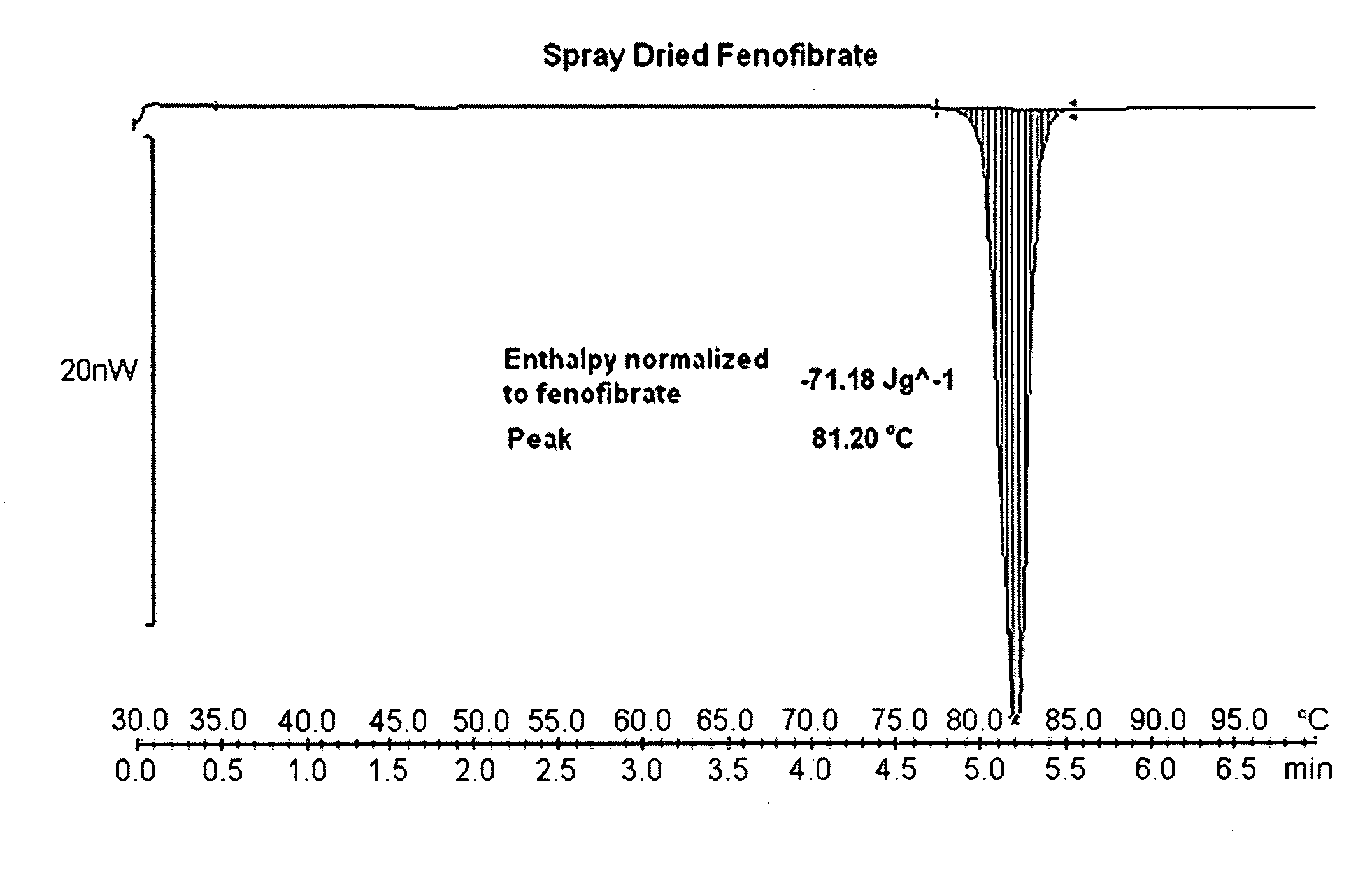
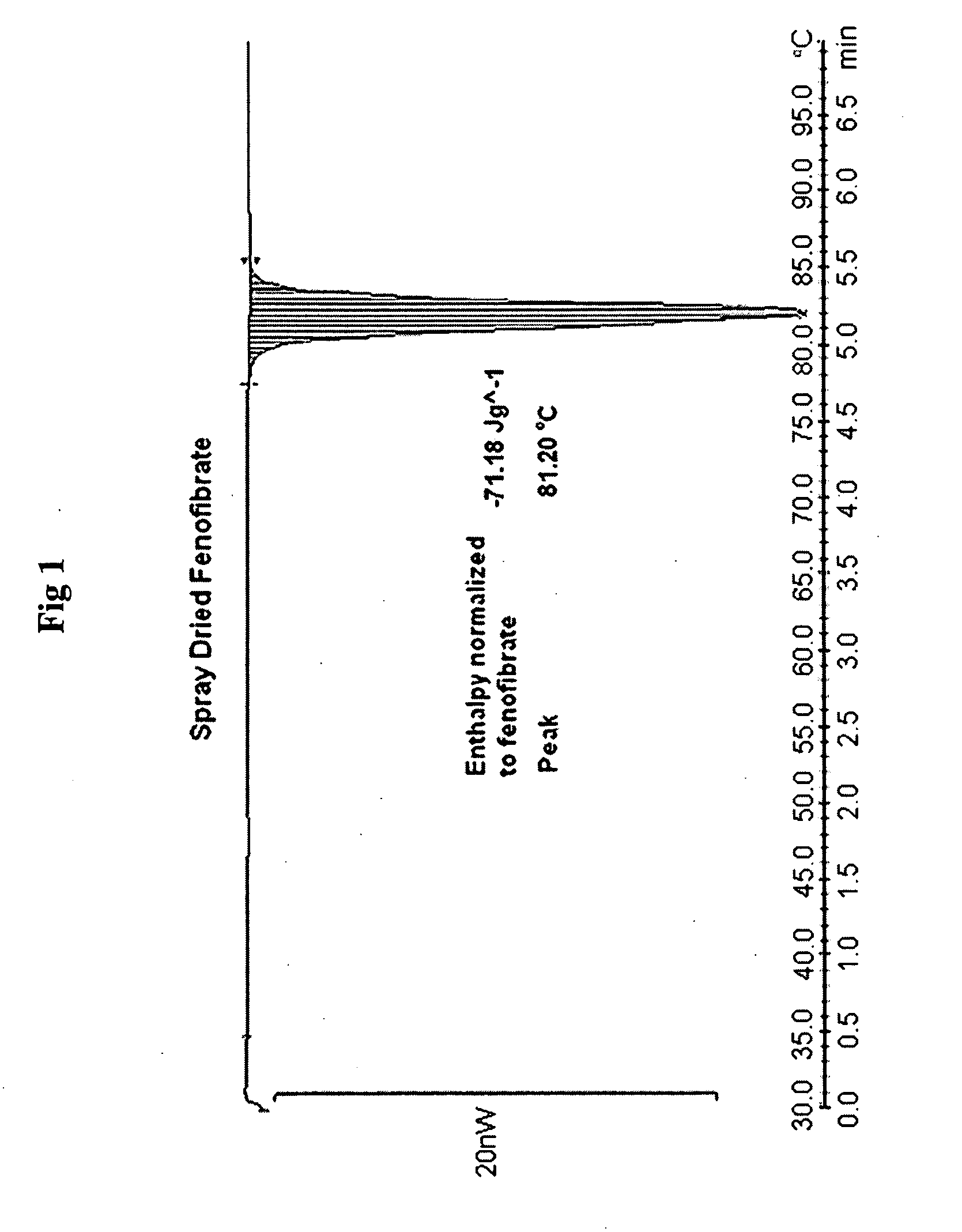
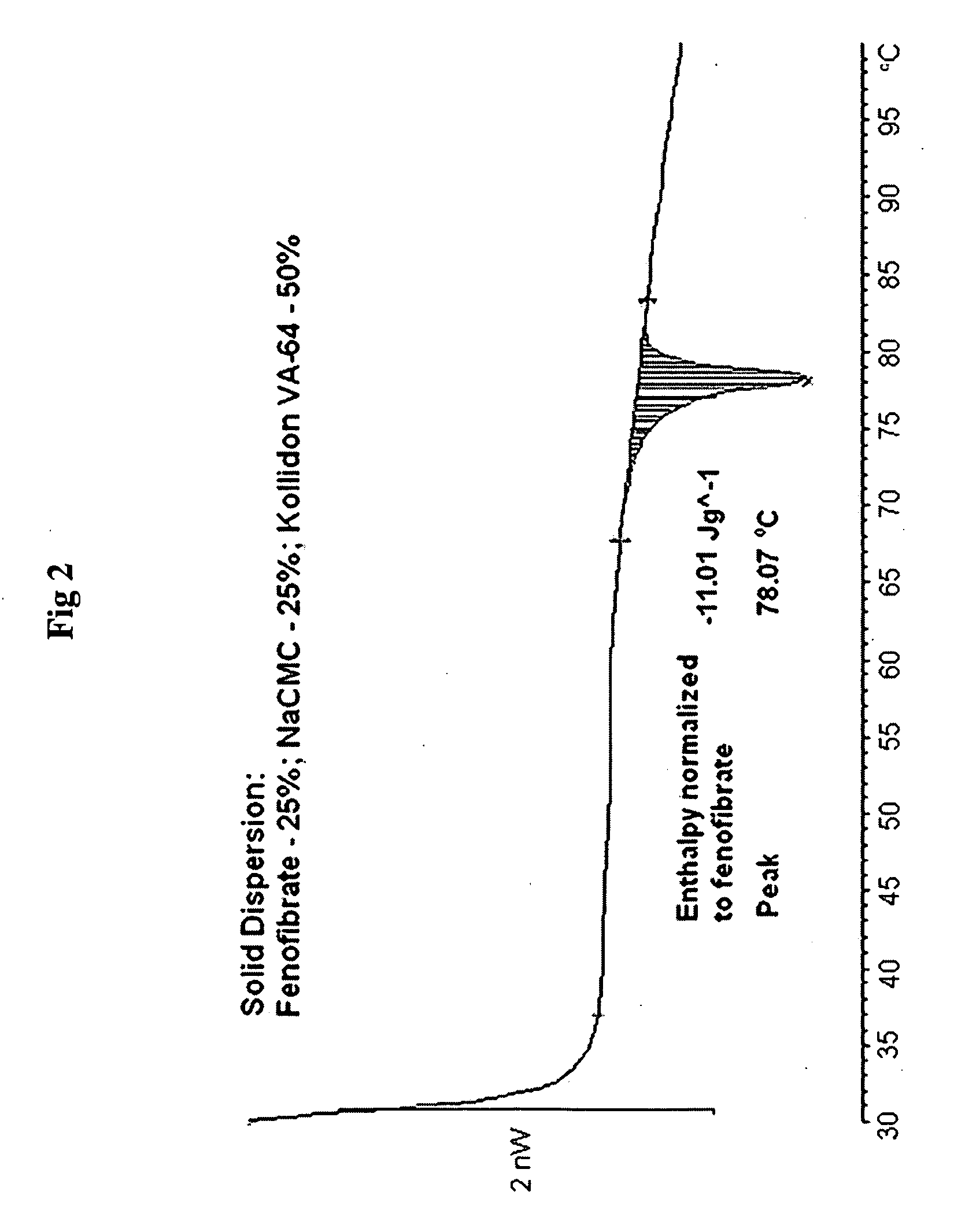
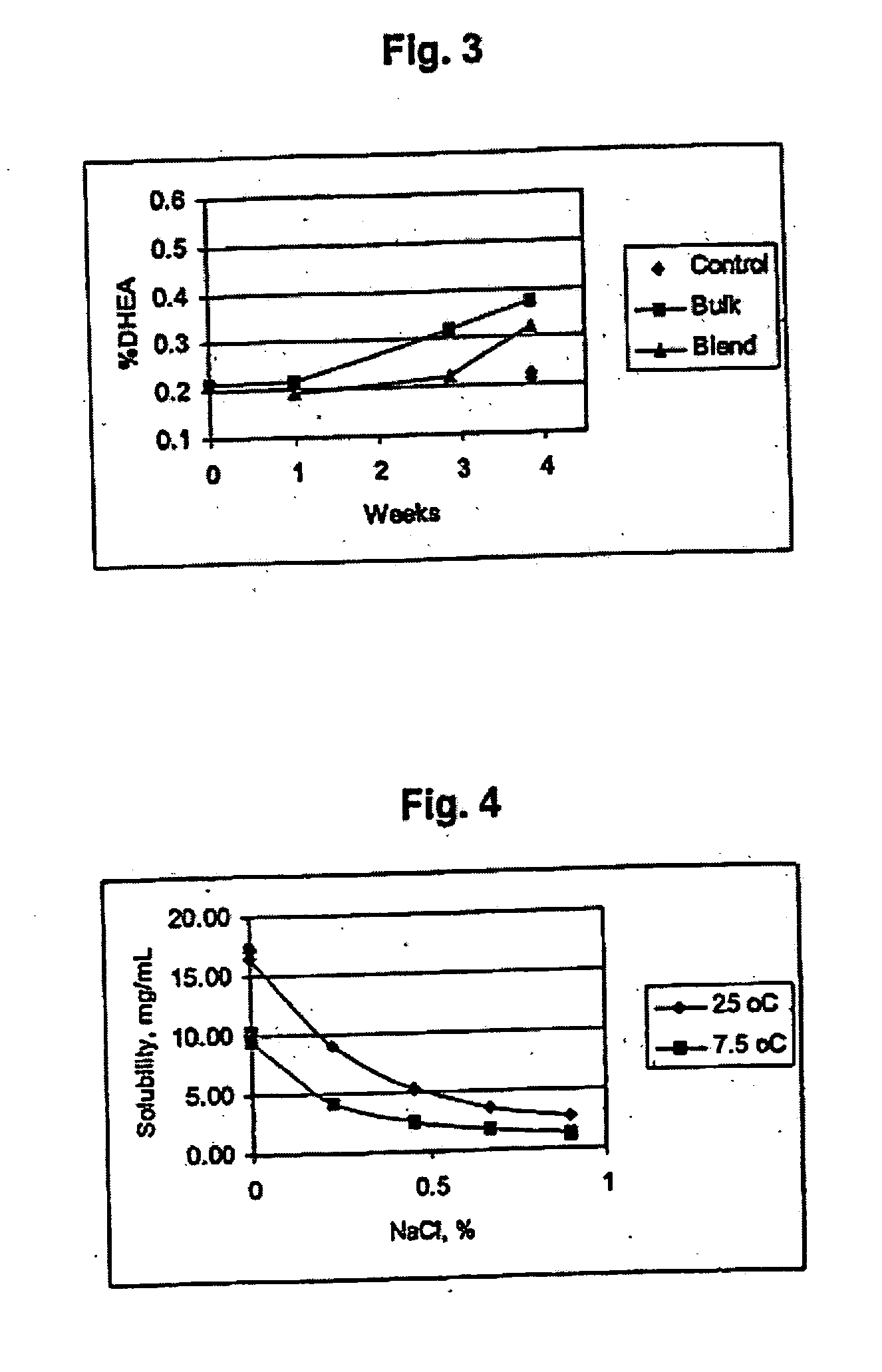
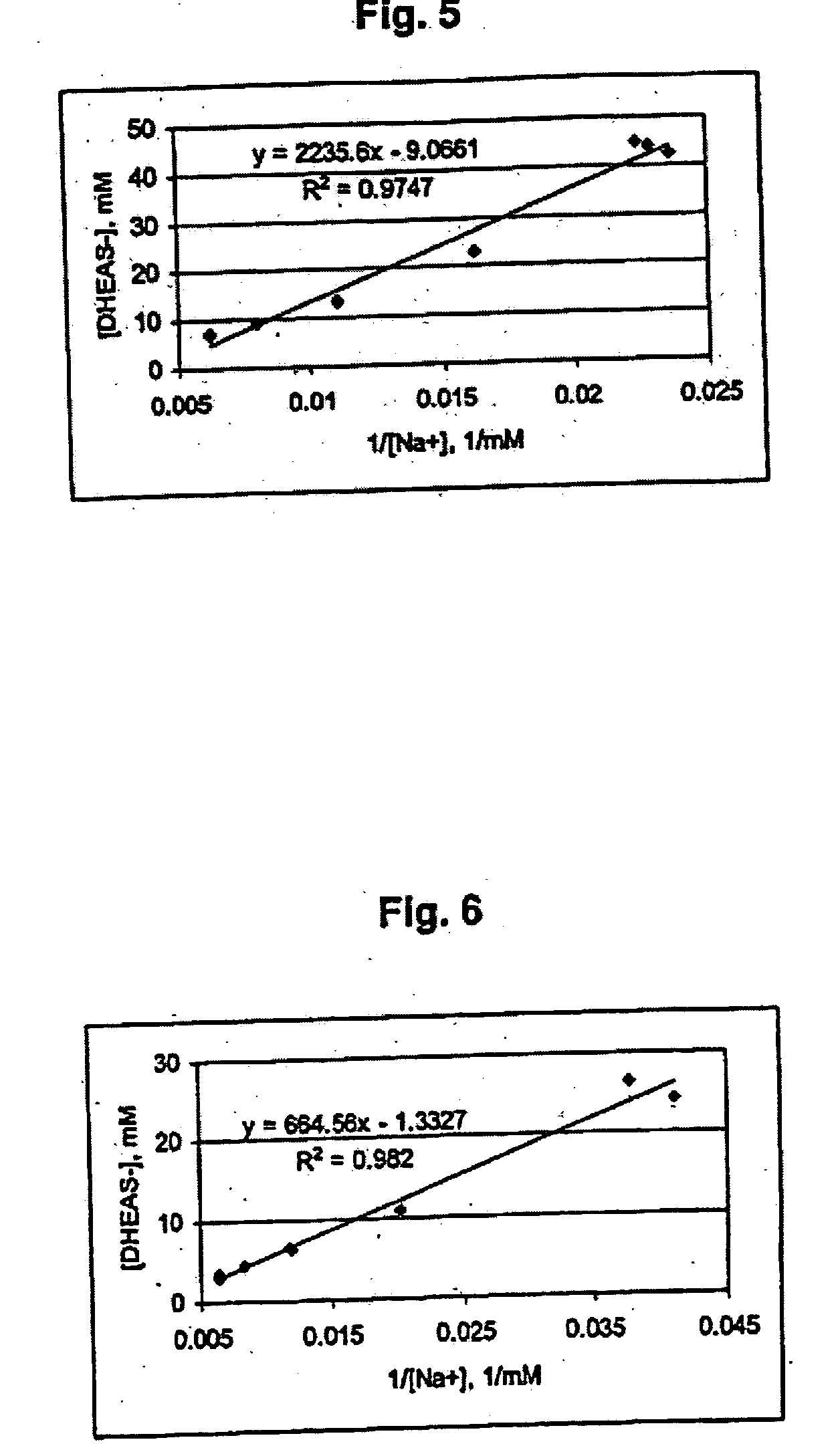
Compositions comprising lipophilic active compounds and method for their preparation
ActiveUS20090098200A1Quick releaseImprove bioavailabilityPowder deliveryBiocideHydrophilic polymersCompound (substance)
Compositions are provided comprising a lipophilic active compound, e.g., a human or veterinary drug or a nutraceutical, interwoven with a polymeric matrix formed by two or more polymers, wherein one of the polymers is an amphiphilic polymer and the other polymer is either an amphiphilic polymer with a different hydrophobic-hydrophilic balance or a hydrophilic polymer, and the active lipophilic compound has modified physicochemical properties. The composition forms colloidal nanodispersion upon contact with aqueous media.
Owner:SOLUBEST
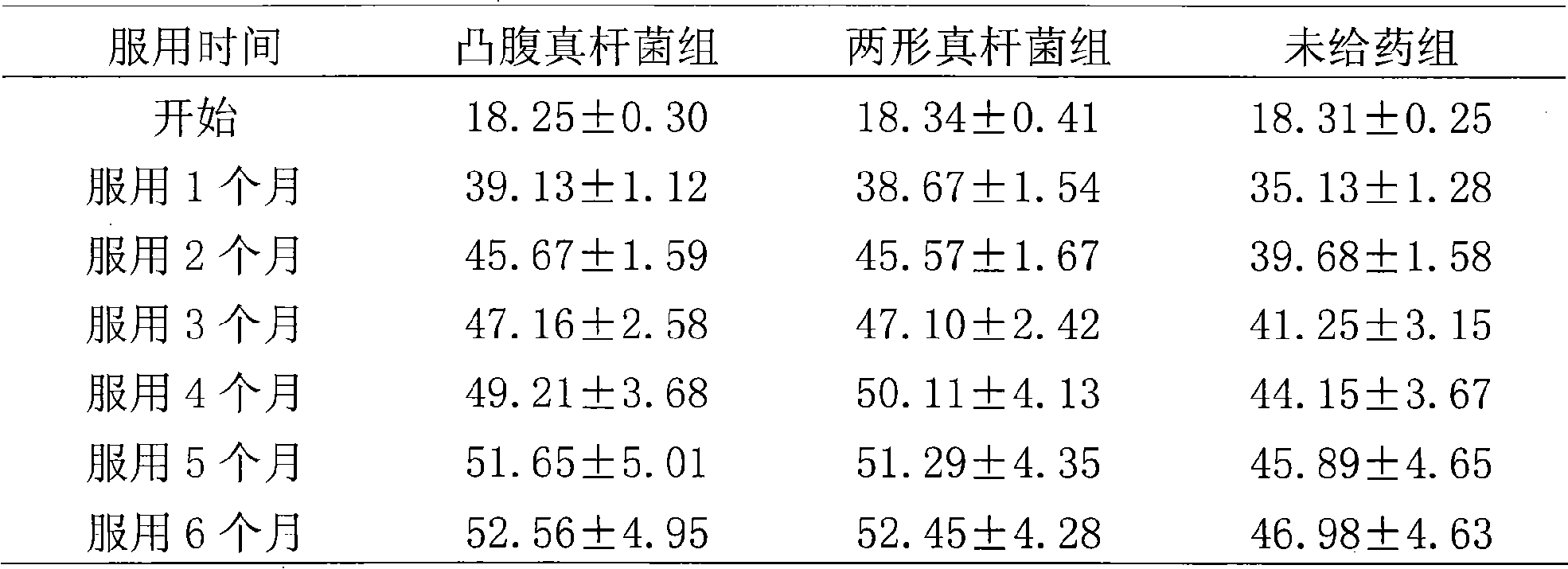
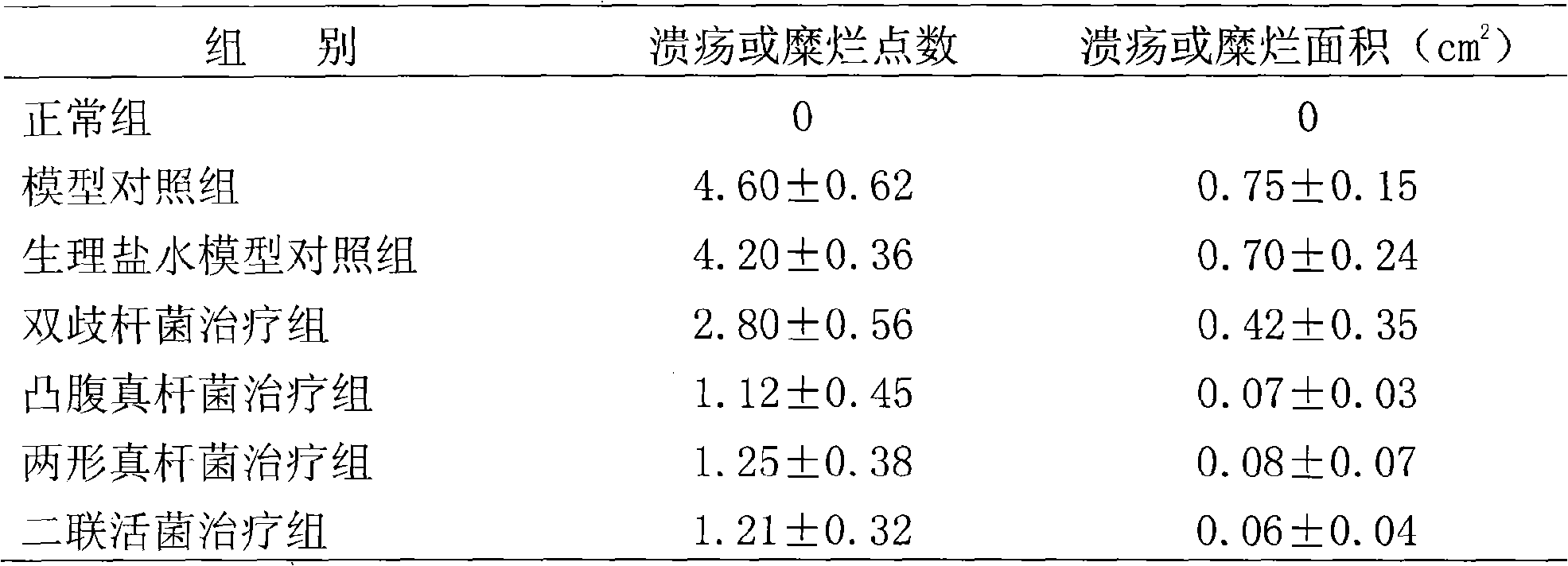
Eubacterium ventriosum and two-shape eubacterium preparation and application thereof
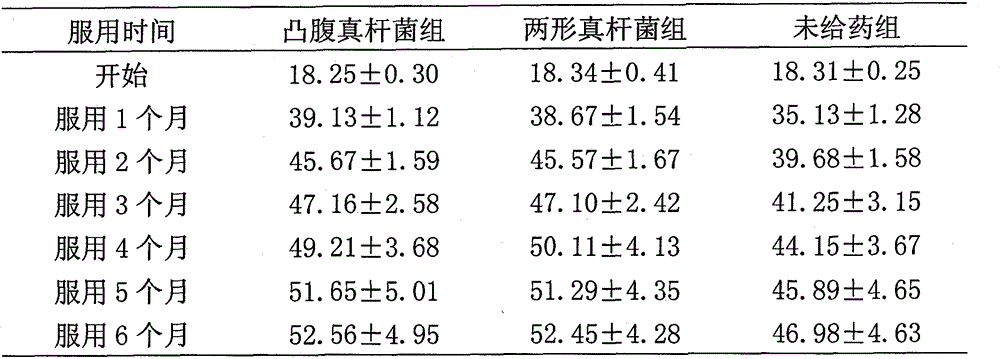
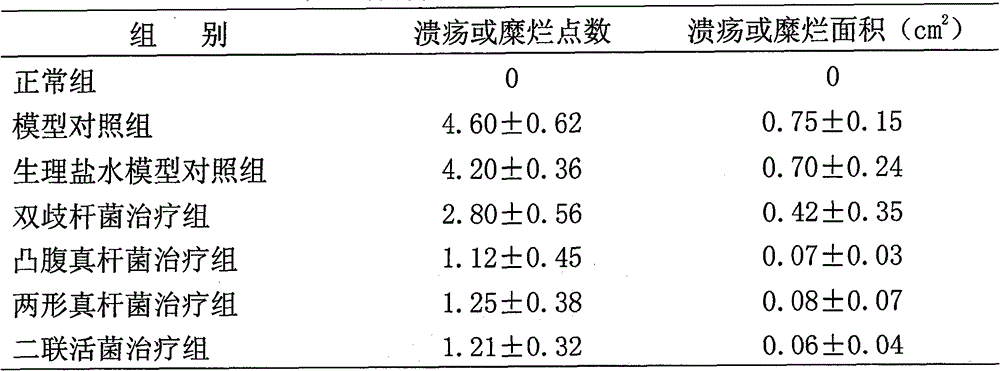
The invention relates to an eubacterium ventriosum and two-shape eubacterium preparation and application thereof, in particular to microbial ecological preparation prepared by using eubacterium ventriosum or / and two-shape eubacterium as main active ingredients, and application of the microbial ecological preparation for treating relative diseases. The microbial ecological preparation comprises medicine composition, health products, drinks, veterinary drug and feed additive.
Owner:QINGDAO EASTSEA PHARMA +1
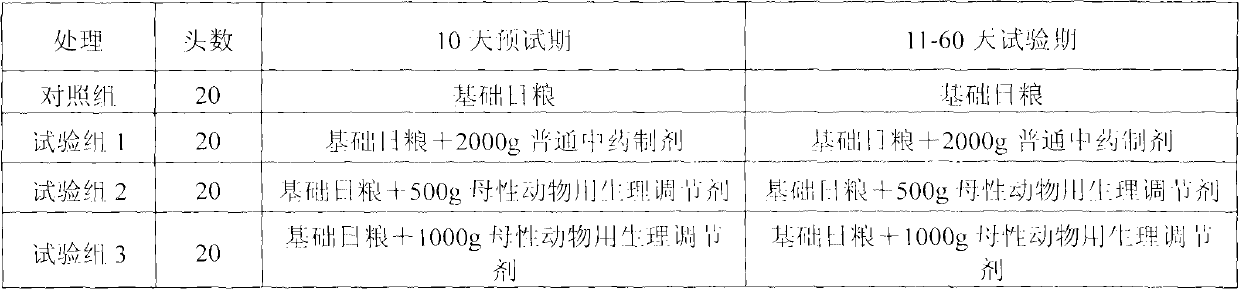
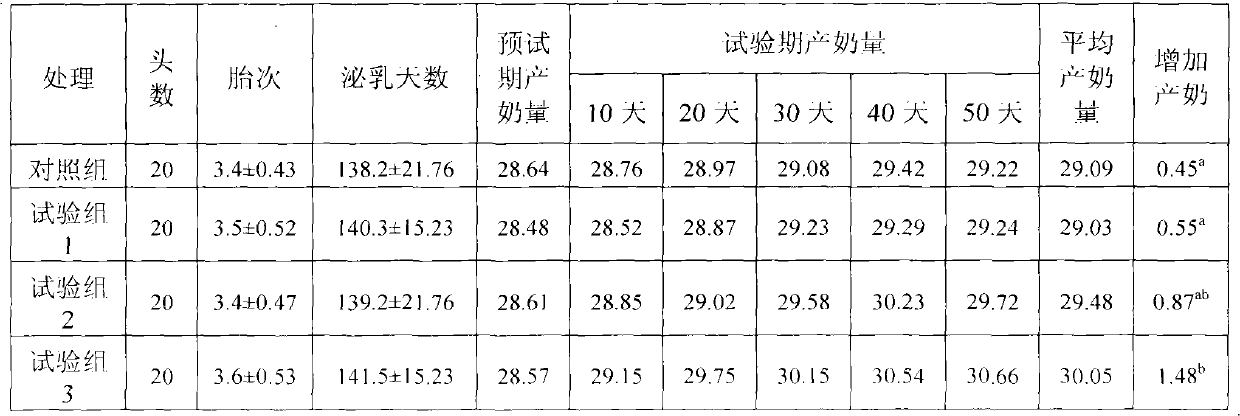
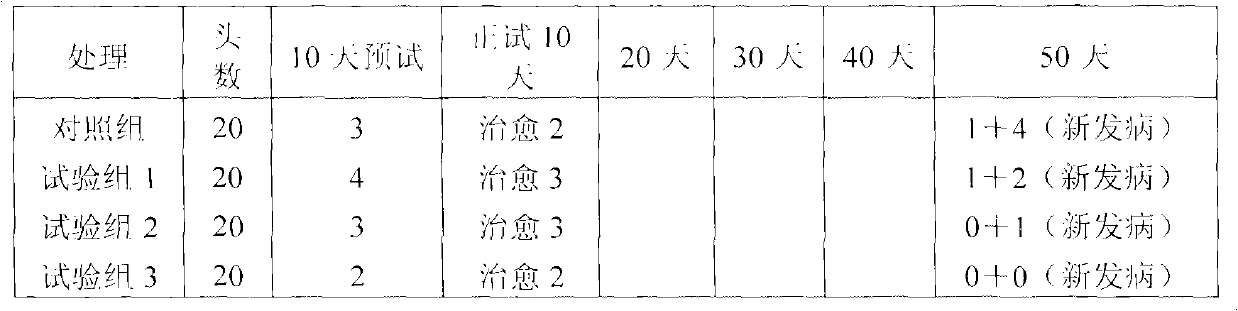
Physiological regulator for maternal animals, and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102232487AProtected from vandalismGood curative effectFood processingAnimal feeding stuffDiseaseFood additive
The invention discloses a special physiological regulator for maternal animals, and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of feed additive. A technical scheme of the physiological regulator comprises: carrying out crushing and screening for dandelion, leonurus, licorice root and angelica; adding soybean meal and / or wheat bran; adding water to carry out immersing; adjusting pH value of the resulting mixture; carrying out a sterilization; inoculating probiotics to carry out a fermentation after cooling, followed by stoving after completing the fermentation to obtain the physiological regulator. With the prepared physiological regulator for the maternal animals, immunity and disease resistance of the maternal animals are raised, incidence rate of genital system infection is effectively reduced, feed inversion rate is increased, mammogenesis is improved, milk yield is raised, incidence rate of mammitis is reduced, and milk quality is improved. The physiological regulator has characteristics of quick onset, stable and reliable effect, no toxic and side-effect, no pollution, no residue, and no drug resistance generating, and meets requirements of safe feed additive and assurance of foods of animal origin. In addition, the physiological regulator for the maternal animals can be adopted as a veterinary drug through raising using dosage of the physiological regulator, and provides a substantial curative effect for prevention and cure of the mammitis.
Owner:BEIJING KEEPYOUNG TECH
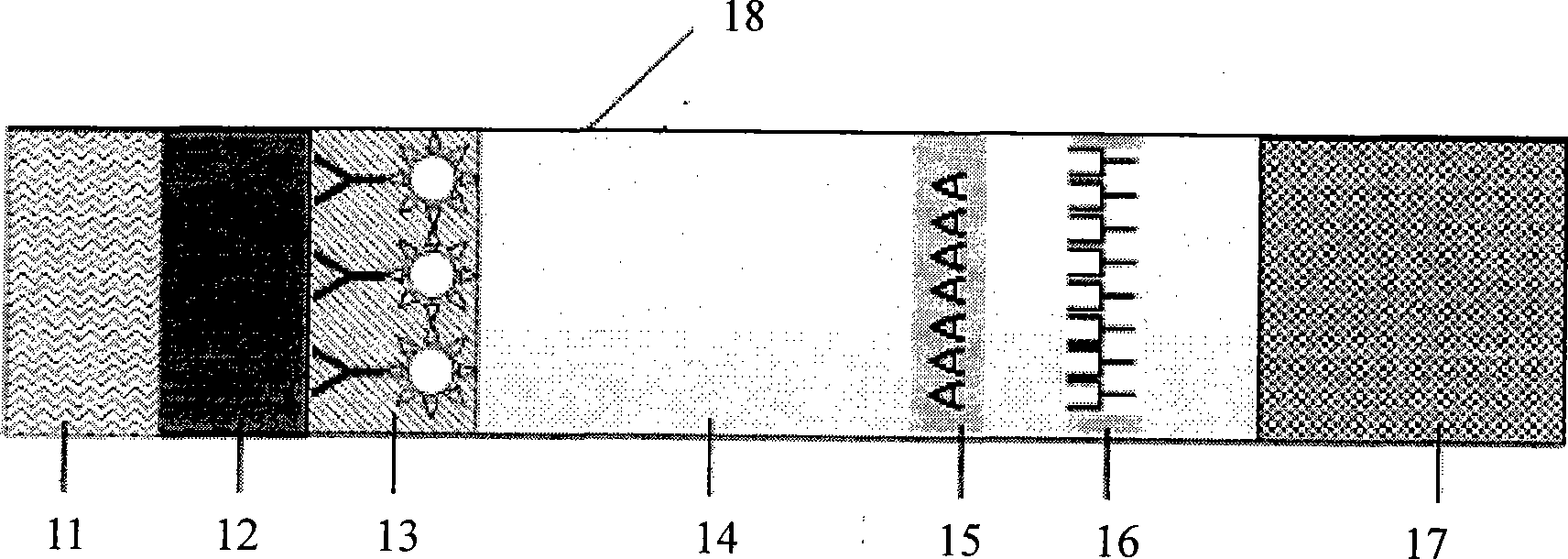
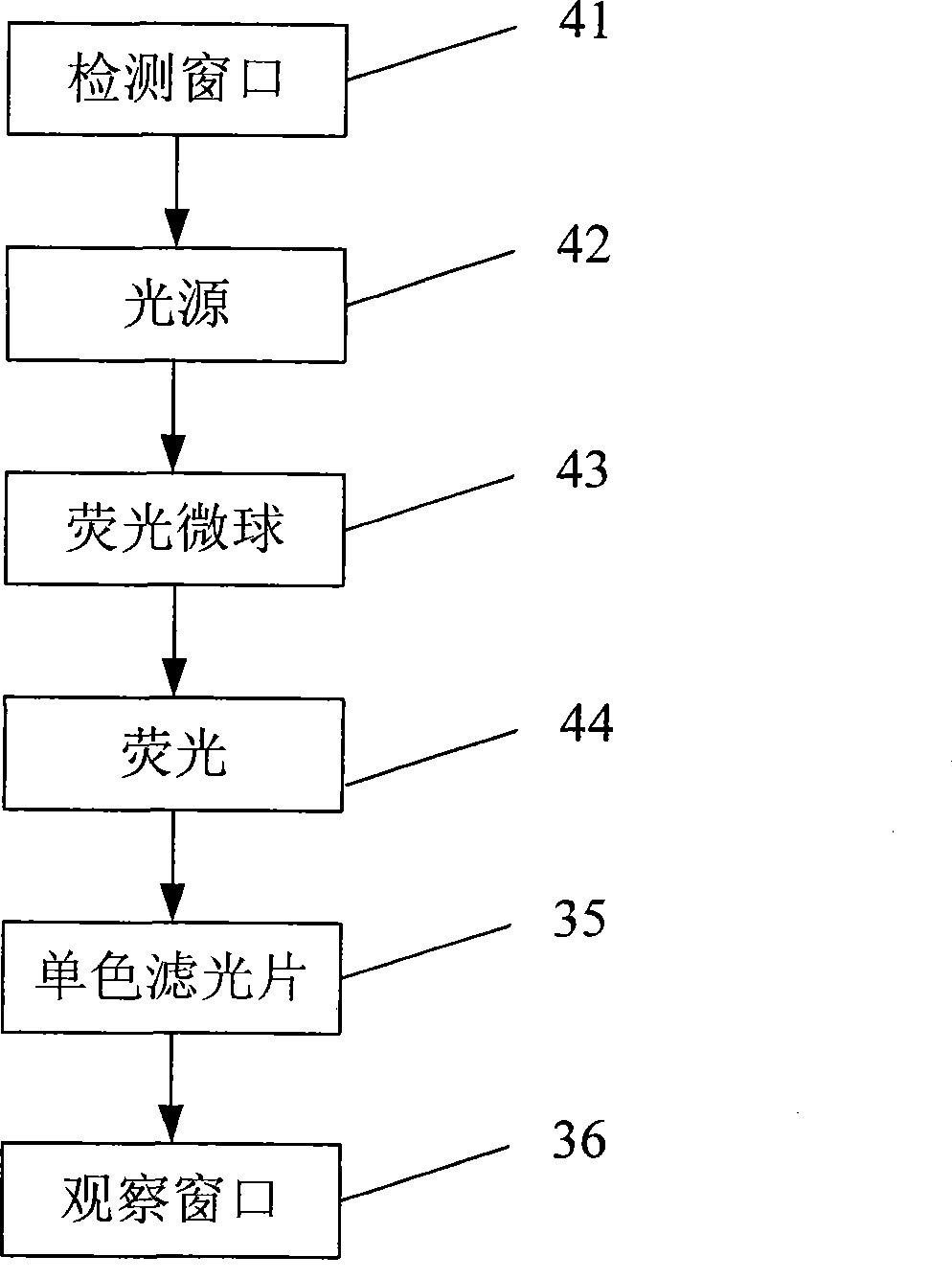
Fluorescent micro-ball immune chromatography test paper strip for detecting residual animal medicine and preparing method thereof
The invention discloses a test paper strip for the fluorescent bead immunochromatography of veterinary medicine remained in a detected sample and a preparation method thereof. A filter paper, a sample pad, a fiberglass membrane, a pyroxylin membrane and water sucking paper are sequentially stuck on a base plate in related joint; fluorescent beads are sprayed on the pyroxylin membrane for marking a veterinary medicine resistant molecule monoantibody; the pyroxylin membrane coated with a veterinary medicine molecule holoantigen is used as a detection region; the pyroxylin membrane coated with an anti-mouse antibody is used as a quality control region; and the test paper strip is prepared through the following steps: (1) the preparation of the pyroxylin membrane; (2) the preparation of a fluorescent bead pad; and (3) the assembling of the test paper strip. In the detecting process, emitted spectrums pass through a proper optical filter device; and all the emitted spectrums are collected through CCD scanning technology, are congregated, are multiplied and are analyzed through a fluorescence analyzer and relevant software to obtain a quantized fluorescence signal, thereby realizing quantitative detection. The test paper strip is mainly used for the qualitative detection and the quantitative detection of all the veterinary medicine classes in food safety detection.
Owner:WUXI ZODOLABS BIOTECH
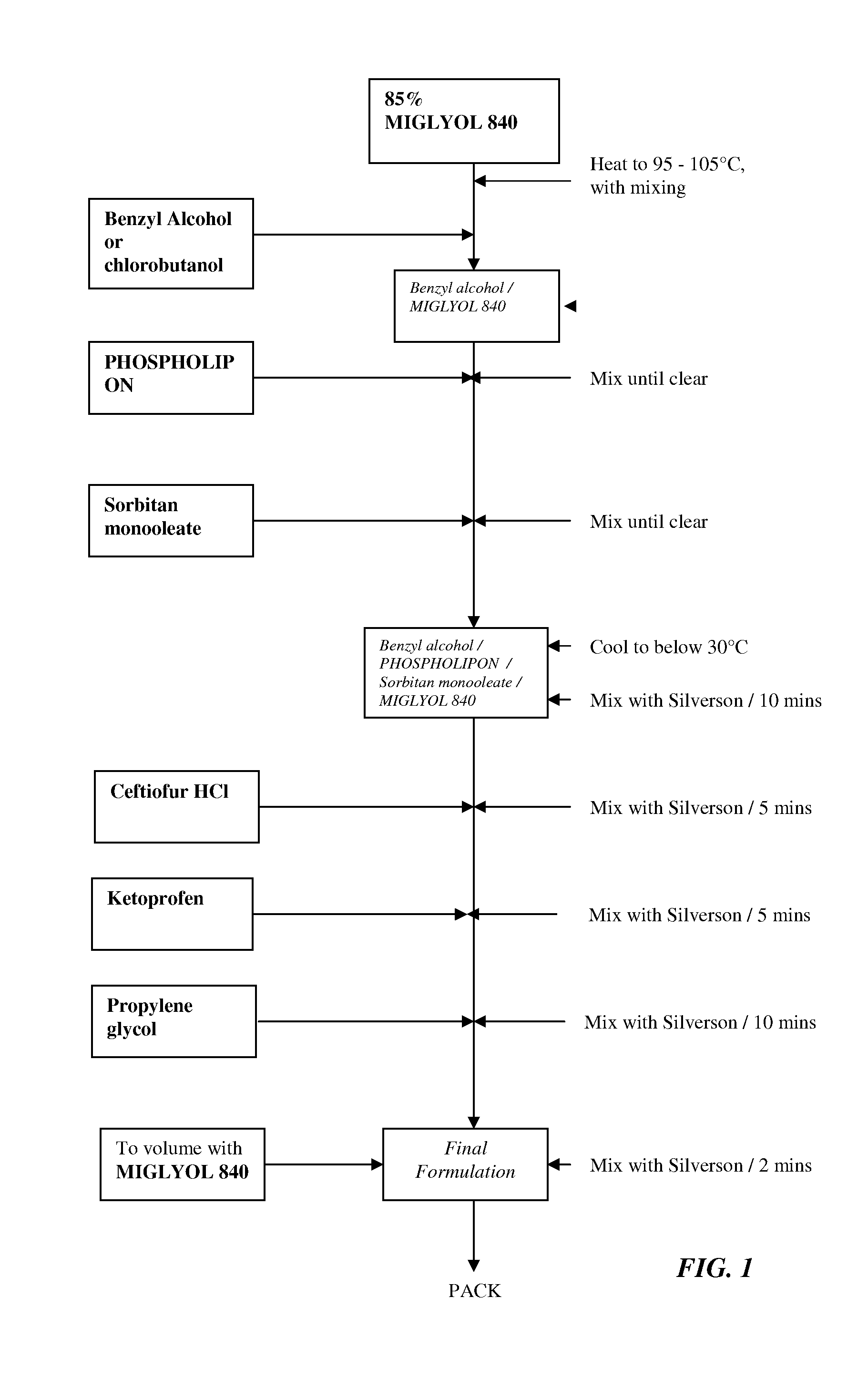
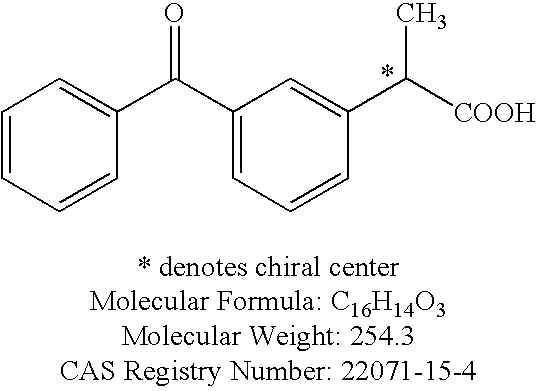
Formulations comprising ceftiofur and ketoprofen or ceftiofur and benzyl alcohol
InactiveUS20100125060A1Easily resuspendedTreating or preventing bovine respiratory disordersAntibacterial agentsBiocideDrugBovine respiratory disease
The present invention relates to veterinary or pharmaceutical formulations which may comprise ceftiofur, ketoprofen, benzyl alcohol, or effective combinations thereof. The formulations of the present invention may include a wetting or dispersing agent, a preservative, a flocculating agent or resuspendability enhancer, and / or a biocompatible oil vehicle. This invention also provides for, inter alia, formulations for the treating, controlling and preventing of respiratory disorders, particularly bovine respiratory disease (BRD), in warm-blooded animals, such as livestock,. This invention further provides for methods of increasing the resuspendability of an oily formulation which may comprise the addition.
Owner:MERIAL LTD
Eubacterium biforme preparation and use thereof
The invention relates to a eubacterium biforme preparation. The eubacterium biforme preparation is a microecological preparation adopting eubacterium biforme as a main active ingredient. The invention also relates to a use of the eubacterium biforme preparation in treatment on related diseases. The eubacterium biforme preparation can be prepared into a drug composition, a health care product, a drink, a veterinary drug and a feed additive.
Owner:QINGDAO EASTSEA PHARMA +1
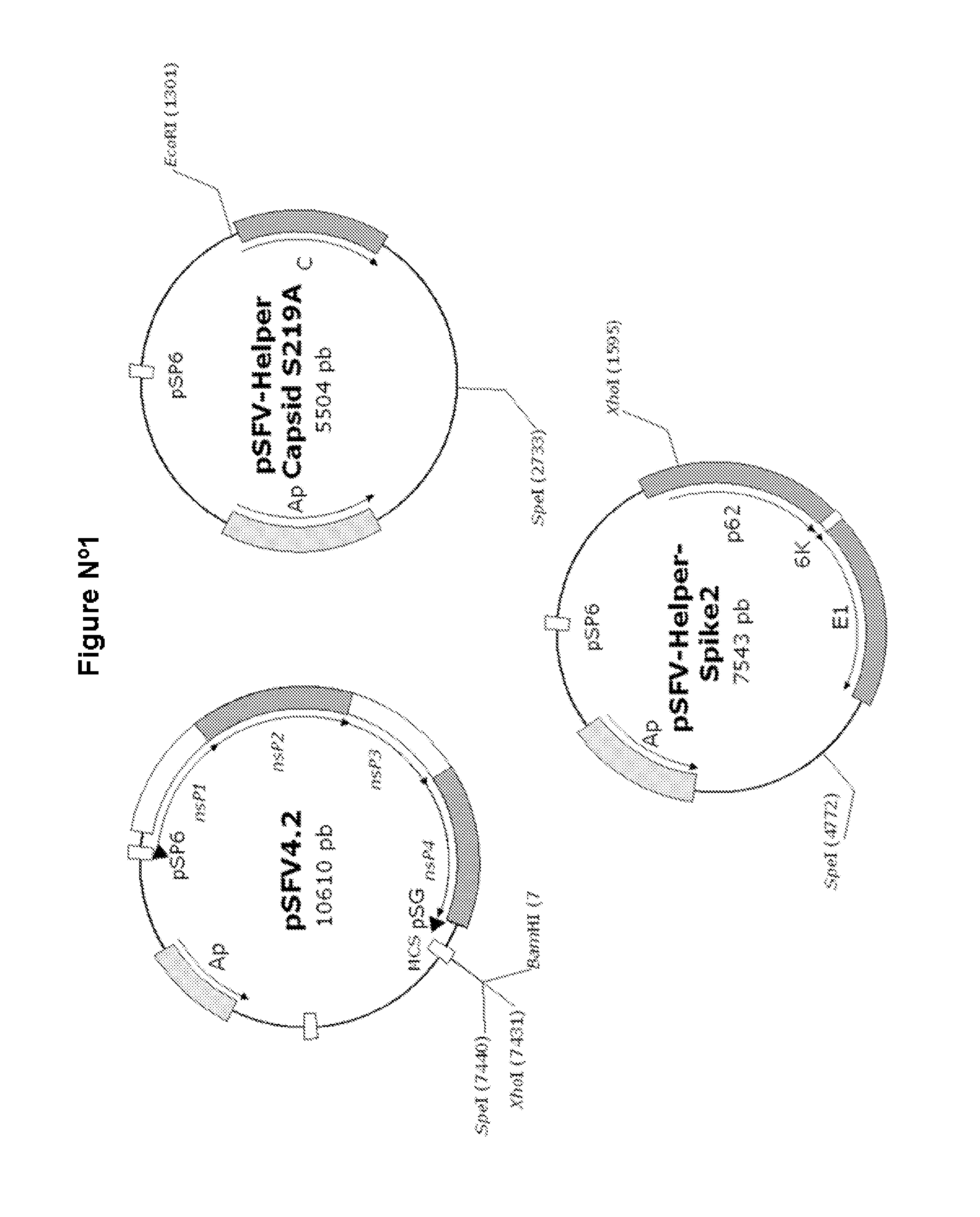
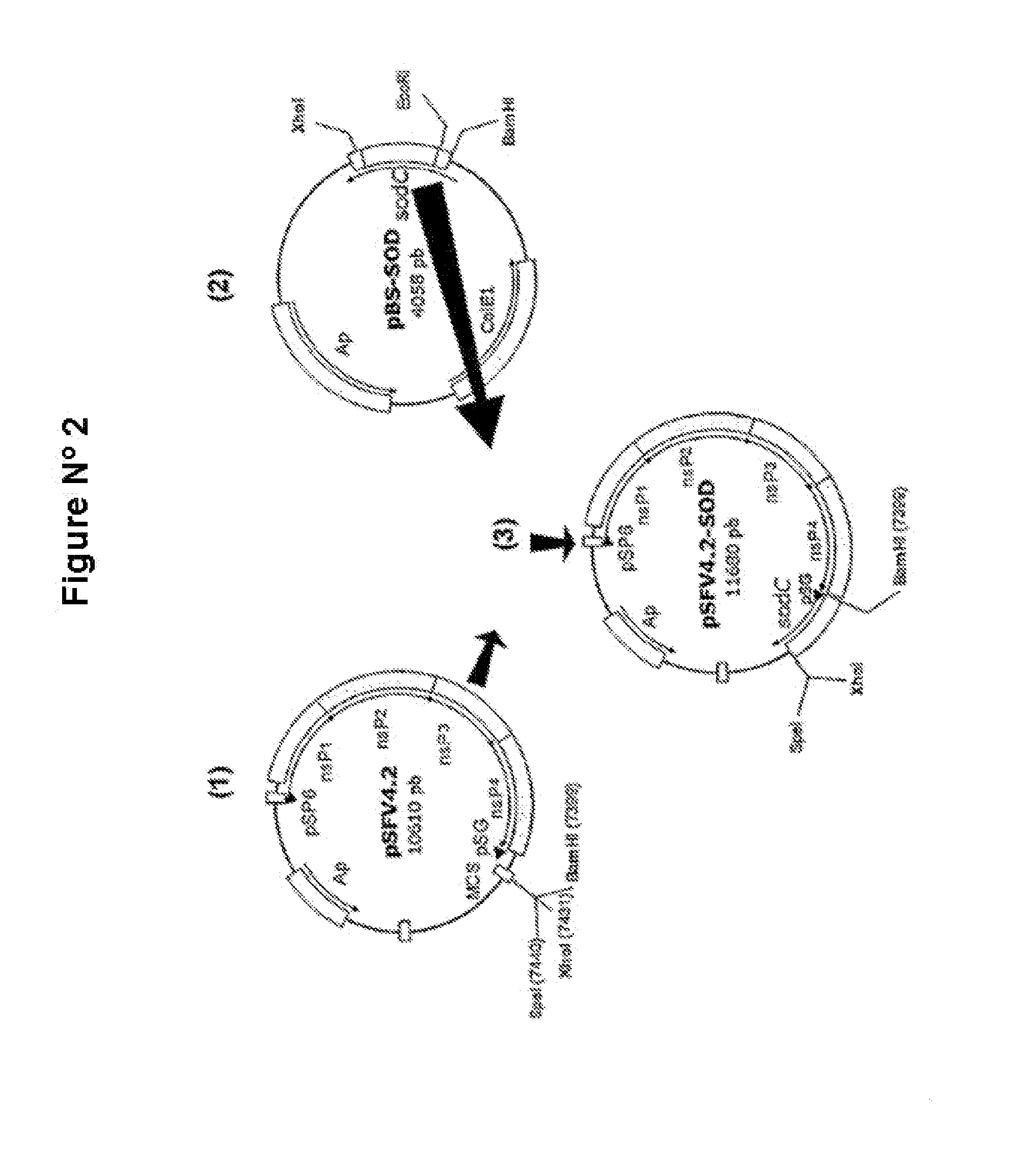
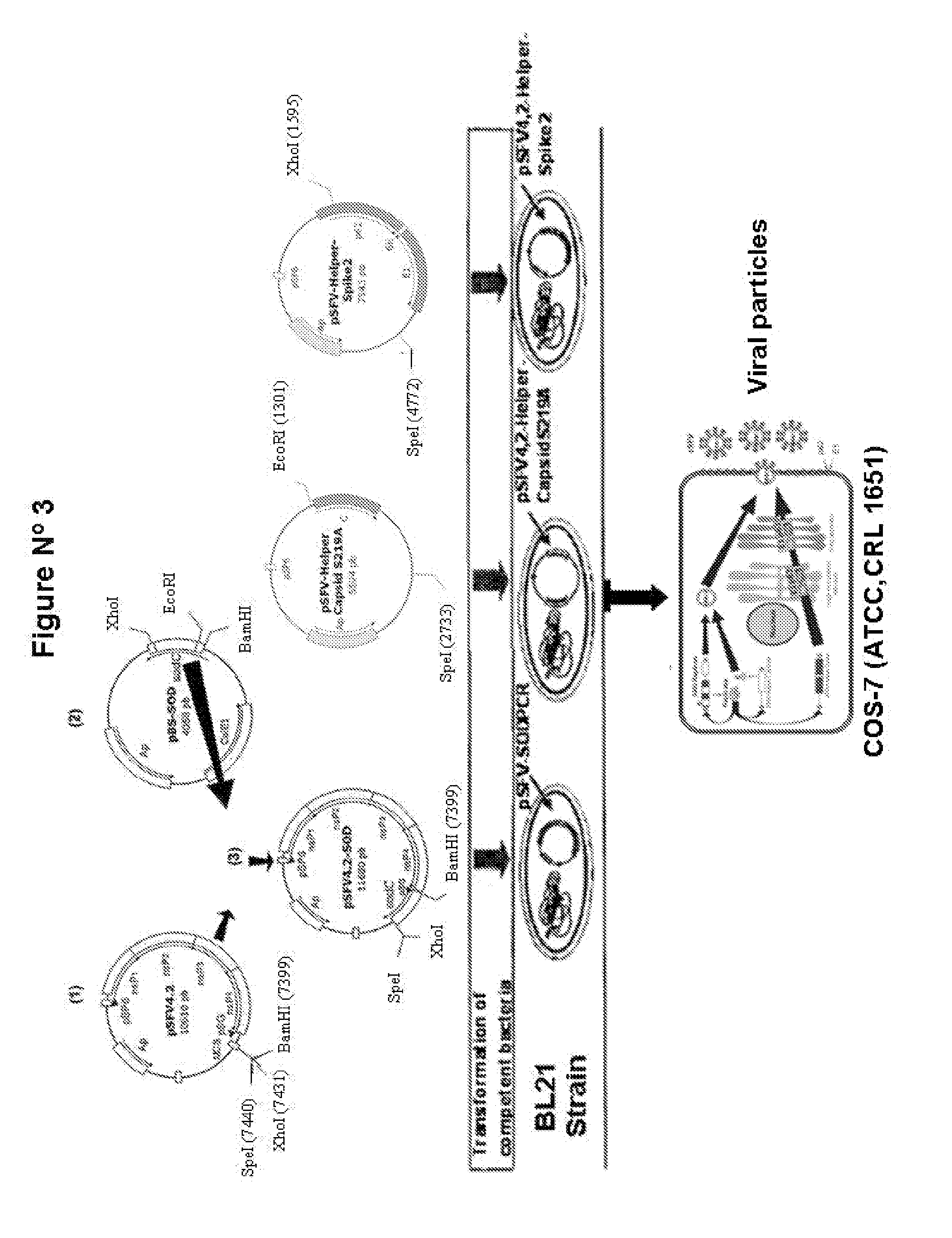
Veterinary pharmaceutical formulacion that comprises an RNA recombinant particle that encodes for a cu/zn superoxide dismutase protein of ruminant pathogenic bacteria and at least one RNA alphavirus belonging to the semliki forest virus family
InactiveUS20110200667A1Improve efficacyProtective efficacyAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsBrucella abortusZn superoxide dismutase
The technology is a veterinary pharmaceutical formulation of two vaccines, one from an RNA viral vector system constituted by an RNA recombinant particle that codifies for a Cu / Zn superoxide dismutase protein of Brucella abortus, and the other based on naked RNA constituted by a recombinant molecule of naked RNA that carries a sequence for the synthesis of at least one recombinant Cu / Zn superoxide dismutase protein of Brucella abortus and some Semliki Forest virus genes. An expression system based on the Semliki Forest virus and a use of this system, in addition to a method for the preparation of the pharmaceutical formulations.
Owner:UNIV DE CONCEPCION
Method for preparing and using reagent for simultaneously detecting multiple small molecular compounds
The present invention provides one kind of reagent for simultaneously detecting several kinds of small molecular compounds and its preparation process and usage. The preparation process includes the following steps: preparing coded microsphere reagent, and preparing one of the small molecular compound detecting antibody probes, including fluorescent quantum dot antibody probes, fluorescent quantum dot secondary antibody probes, fluorescent dye antibody probes and fluorescent dye secondary antibody probes. The method of detecting small molecular compounds with the antibody probe may be a direct antibody probe method or a indirect antibody probe method. The present invention may be used in detecting residual veterinary medicine, pesticide, banned drug, misused medicine and other small molecular compounds in food, agricultural product, living animal body and human body, and has the advantages of high sensitivity, high repeatability, etc.
Owner:邹明强
Nano-emulsion medicine for treating foot rot and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102552339AHigh thermodynamic stabilityEasy to operateAntibacterial agentsHydroxy compound active ingredientsPropanoic acidCutin
The invention discloses a nano-emulsion medicine for treating foot rot. The grain diameter of the nano-emulsion is in a range of 1-100 nanometers and the nano-emulsion is composed of the following raw materials: 0.1-10.0% of pine tar, 0.1-6.0% of cinnamyl aldehyde, 0.1-6.0% of carvacrol, 0.1-5.0% of camphor oil, 0.01-0.1% of clobetasol propionate, 18.0-35.0% of surfactant, 0-7.0% of co-surfactant and residual amount of distilled water; and the sum of the mass percentages of the components is 100%. The nano-emulsion disclosed by the invention has the functions of dissolving cutin, relieving itching, diminishing inflammation, restraining, partially disinfecting and resisting corrosion, accelerating absorption and the like, and is mainly used for treating animal foot rot. According to the nano-emulsion medicine for treating the foot rot, the solubility of the medicine is increased, the medicinal stability and the biological utilization rate are improved, the dosage of the medicine is reduced, the skin transmission rate is higher than that of common preparations including a medicinal extract and the like, and the cost is low, so that the nano-emulsion medicine has a wide market prospect in a veterinary medicine field.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Bacillus subtilis LFB112 as well as bacteriocin produced by same and application thereof
ActiveCN102071162ABenign sustainable developmentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAntibacterial activityBacterial strain
The invention provides bacillus subtilis LFB112 with the collection number of CGMCC No.2996. The bacterial strain has relatively high antibacterial activity and has antibacterial effect on various animal pathogenic bacteria and food pathogenic bacteria. The invention also provides bacteriocin produced by the bacterial strain, wherein the bacteriocin is relatively stable against heat and acid and has a broad-spectrum antibacterial effect without inhibiting beneficial bacteria. Experiments indicate that the bacterial strain LFB112 provided by the invention and the bacteriocin produced by the same can be used for improving the clinical symptoms of chicken and increasing the growth speed and feed price, and can be used in biological veterinary medicaments or feed additives.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
High-throughput detection method for 99 residual veterinary drugs in animal-derived food
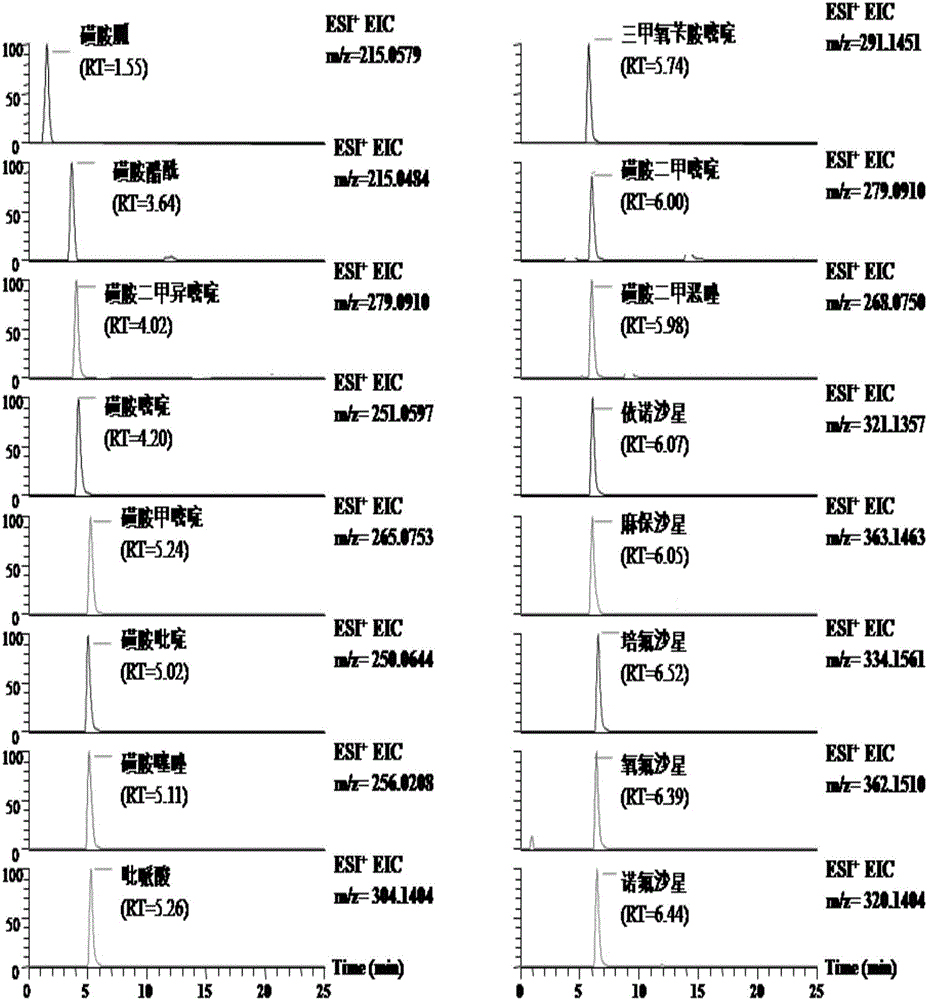
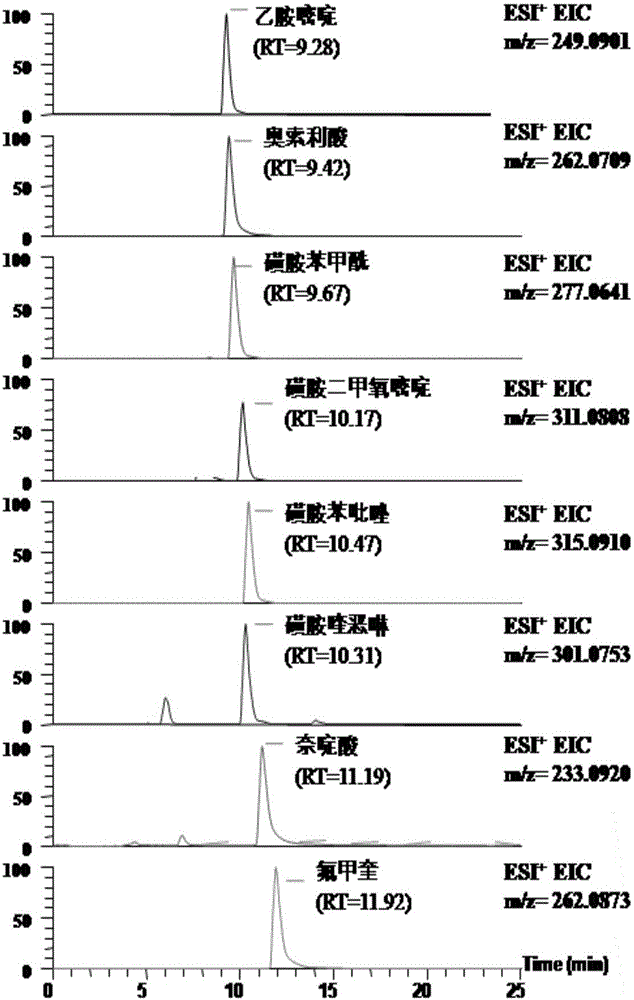
The invention discloses a high-throughput detection method for 99 residual veterinary drugs in animal-derived food. The detection method is characterized by comprising the following concrete steps: (1) carrying out extraction and purification on 99 residual veterinary drugs having substantially different physicochemical properties and belonging to eight kinds of common veterinary drugs through one-step pretreatment based on carrier-assisted liquid-liquid extraction technology; (2) preparation of a mixed standard solution and a matrix standard curve; and (3) determining the concentrations of 99 residual veterinary drugs in a to-be-detected solution by using ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry. According to the invention, the pretreatment and instrumental analysis process of the method is directed at compounds with different physicochemical properties, so the method has the advantages of good compatibility, high detection efficiency, good operability and low detection cost, and the detection limit of the method can meet requirements of all the test objects.
Owner:INSPECTION & QUARANTINE TECH CENT OF NINGBO ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
Disease-resistant growth promoter for aquatic animals and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102232474APromote growthImprove immunityClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffSide effectMicrobial transformation
The invention discloses a disease-resistant growth promoter for aquatic animals and a preparation method thereof. The disease-resistant growth promoter is characterized in that a novel environmentally-friendly feed additive is prepared by combining the traditional Chinese medicine with a modern microbial transformation technology. The preparation method comprises the following steps: mixing dandelion, licorice root, lightyellow sophora root, barberry root and the like after crushing and screening; adding bran, soybean meal, corn flour and water as a fermentation culture medium, regulating thepH value, sterilizing, cooling, adding a strain, and fermenting; and drying after the fermentation is finished. The disease-resistant growth promoter for the aquatic animals is formed by virtue of beneficial combination of the traditional Chinese medicine and probiotics, can be used for replacing antibiotics and has the effects of resisting bacteria, preventing verminosis, resisting virus, improving the immunity, promoting the growth of the aquatic animals and the like; no toxicity, no side effects, no pollution, no residue and no drug resistance are produced during the long-term use of the disease-resistant growth promoter; and the effects are stable and reliable, and the requirements of people on safe production of aquatic products can be met. The disease-resistant growth promoter for the aquatic animals can also be applied as a veterinary drug by improving the using dose.
Owner:BEIJING KEEPYOUNG TECH
Reagent for quantitative detection of Beta-receptor stimulant through Europium chelate latex time-resolved immunochromatographic assay
InactiveCN104090248AHigh sensitivityHigh quantitative sensitivityFluorescence/phosphorescenceMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsCelluloseReceptor
Disclosed is a reagent for quantitative detection of a Beta-receptor stimulant through Europium chelate latex time-resolved immunochromatographic assay. The reagent includes test card or test strip which includes a nitrocellulose membrane, absorbent paper, a sample pad and a PVC bottom plate, and a microporous container. A test sample firstly dissolves out Eu3+ fluorescent latex particles which are attached in the microporous container and marked with an anti-Beta-receptor-stimulant small-molecule antibody and after sufficient mixing, the test sample reacts completely with the marker and then a reaction liquid is dropped to the test card or test strip to carry out immunochromatography and at the same time, an immune competition reaction with a Beta-receptor-stimulant small molecule and BSA conjugate which envelopes the nitrocellulose membrane is carried out and five minutes later, the test card or the test strip is inserted into a fluorescent reading meter to measure a fluorescent value so as o obtain a test result. The method is high in sensitivity and quantitative and integrates the advantages of simple and convenient operation and rapidness, the method is applied to rapid detection of veterinary drug residuals such as the Beta-receptor stimulant and the like in food and raw materials on sites of production fields such as plantation, cultivation, animal husbandry and food processing and the like.
Owner:ROHI BIOTECH
Combination of dehydroepiandrosterone or dehydroepiandrosterone-sulfate with an anti-IgE antibody for treatment of asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
A pharmaceutical or veterinary composition, comprises a first active agent selected from a dehydroepiandrosterone and / or dehydroepiandrosterone-sulfate, or a salt thereof, and a second active agent comprising an anti-IgE antibody for the treatment of asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or any other respiratory disease. The composition is provided in various formulations and in the form of a kit. The products of this patent are applied to the prophylaxis and treatment of asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or any other respiratory disease.
Owner:EPIGENESIS PHARMA LLC
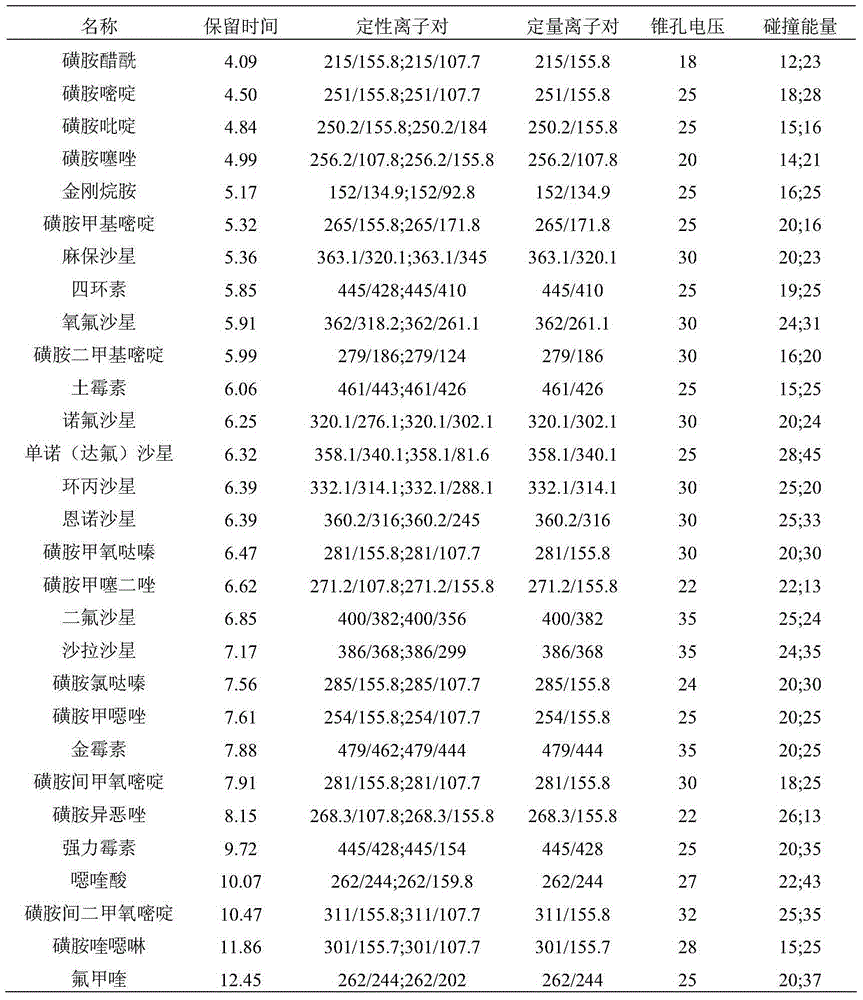
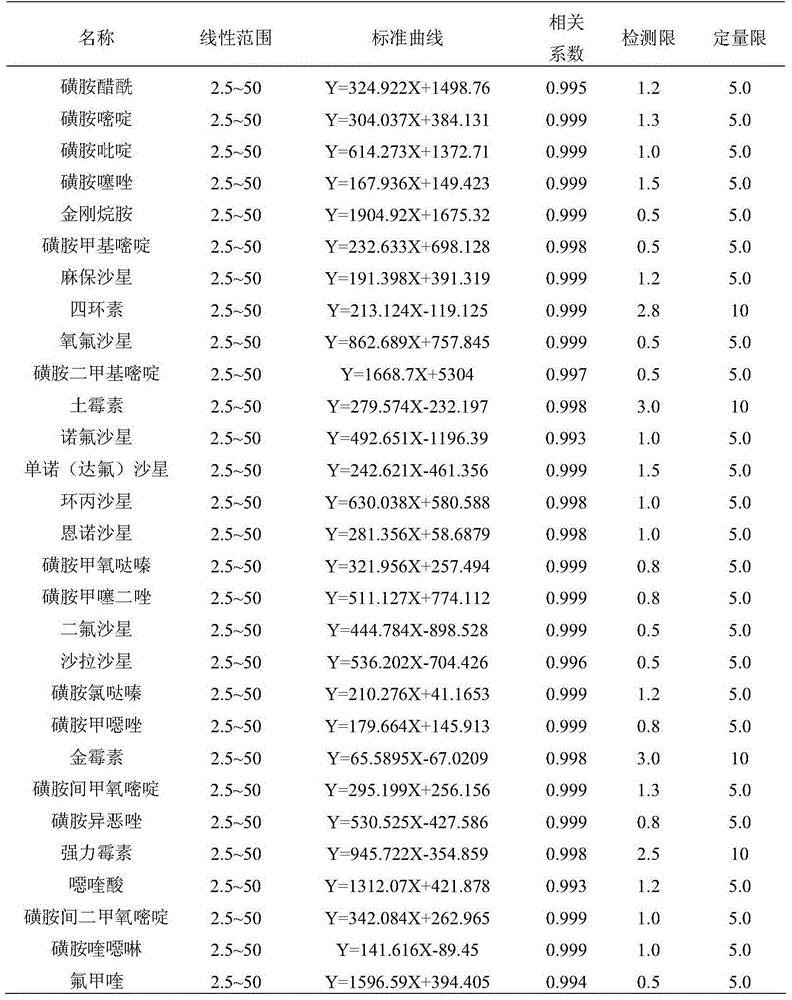
Method for simultaneously analyzing and detecting residual veterinary drug compositions in animal tissue
InactiveCN103713056AImprove linearitySimple processing and analysisComponent separationSulfur drugSulfanilamide
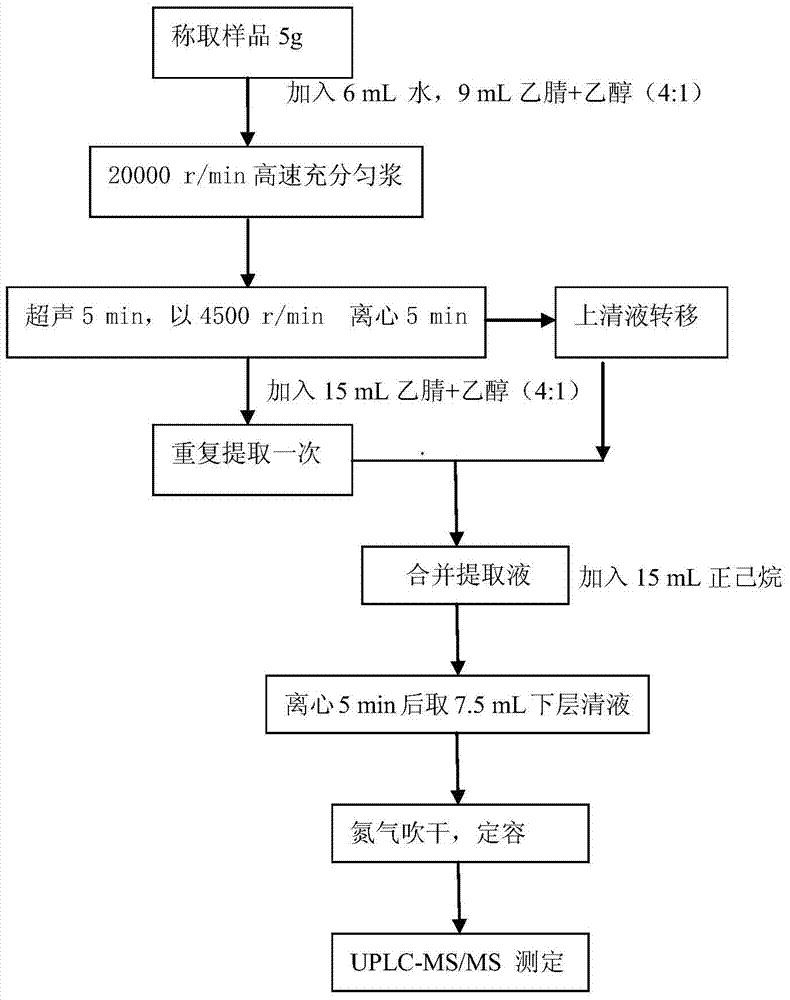
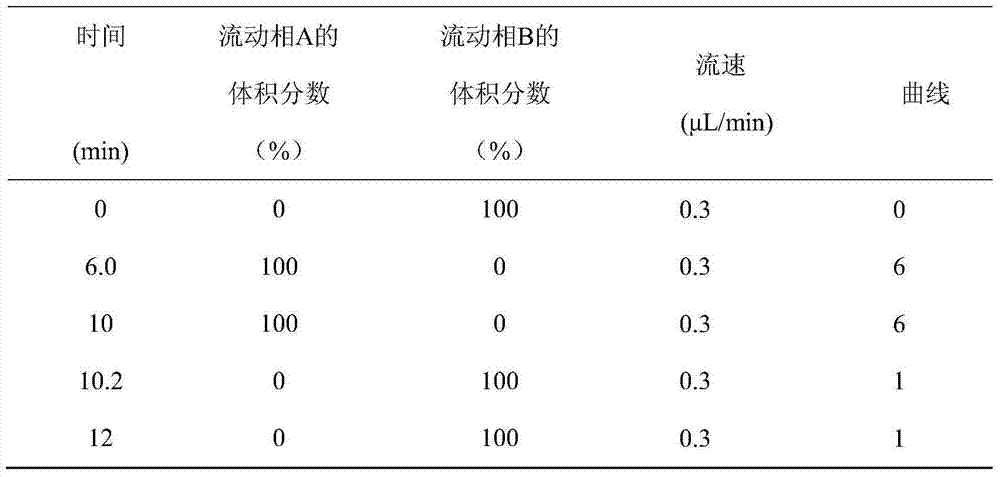
A disclosed method for simultaneously analyzing and detecting residual veterinary drug compositions in animal tissue comprises: performing homogenate on an animal tissue sample by 50% acetonitrile and ethanol, performing ultrasonic extraction and hexane purifying, and performing further precipitation by acetonitrile and ethanol, concentrating, utilizing UPLC-MS / MS to perform multi-reaction monitoring (MRM) determination under the negative ion mode, and quantifying according to a standard curve and an external standard method, detecting and calculating to obtain the content of 46 residual veterinary drug compositions in animal tissue. The method is applicable to present commonly-used veterinary drugs such as 18 kinds of quinolone drugs, 22 kinds of sulfanilamide drugs, dapsone, phenylethanolamine A, amoxicillin, adamantanamine, rimantadine, ethoxyquin and the like, and is capable of performing one-step simultaneous rapid accurate detection, and the application scope of the method is enlarged.
Owner:INSPECTION & QUARANTINE TECH CENT OF NINGBO ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
Lactobacillus plantarum, method for fermenting and preparing bacteriocin of Lactobacillus plantarum, and application of Lactobacillus plantarum and bacteriocin
The invention provides a new Lactobacillus plantarum bacterial strain YJG which was preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGNCC) with the collection number of CGMCC No. 2994 on march, 30th, 2009. The Lactobacillus plantarum bacterial strain YJG can produce broad-spectrum bacteriostatic activity bacteriocin with high yield, and can express bacteriostasis for staphylococcus aureus, salmonella and E.coli of gram-negative bacterium, L. plantarum, L.brevis, Streptococcus and Bacillus of gram-positive bacterium, and the like. A virus attacking tests with high dosage proves that the Lactobacillus plantarum bacterial strain YJG is safe to animal bodies. The Lactobacillus plantarum bacterial strain YJG and a zymophyte liquid thereof can be used for preparing additives of green animal feeds, and the bacteriocin of the Lactobacillus plantarum bacterial strain YJG can be used for preparing green biological veterinary drugs, environmental-friendly biopreservatives, biocontrol drugs and the like.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
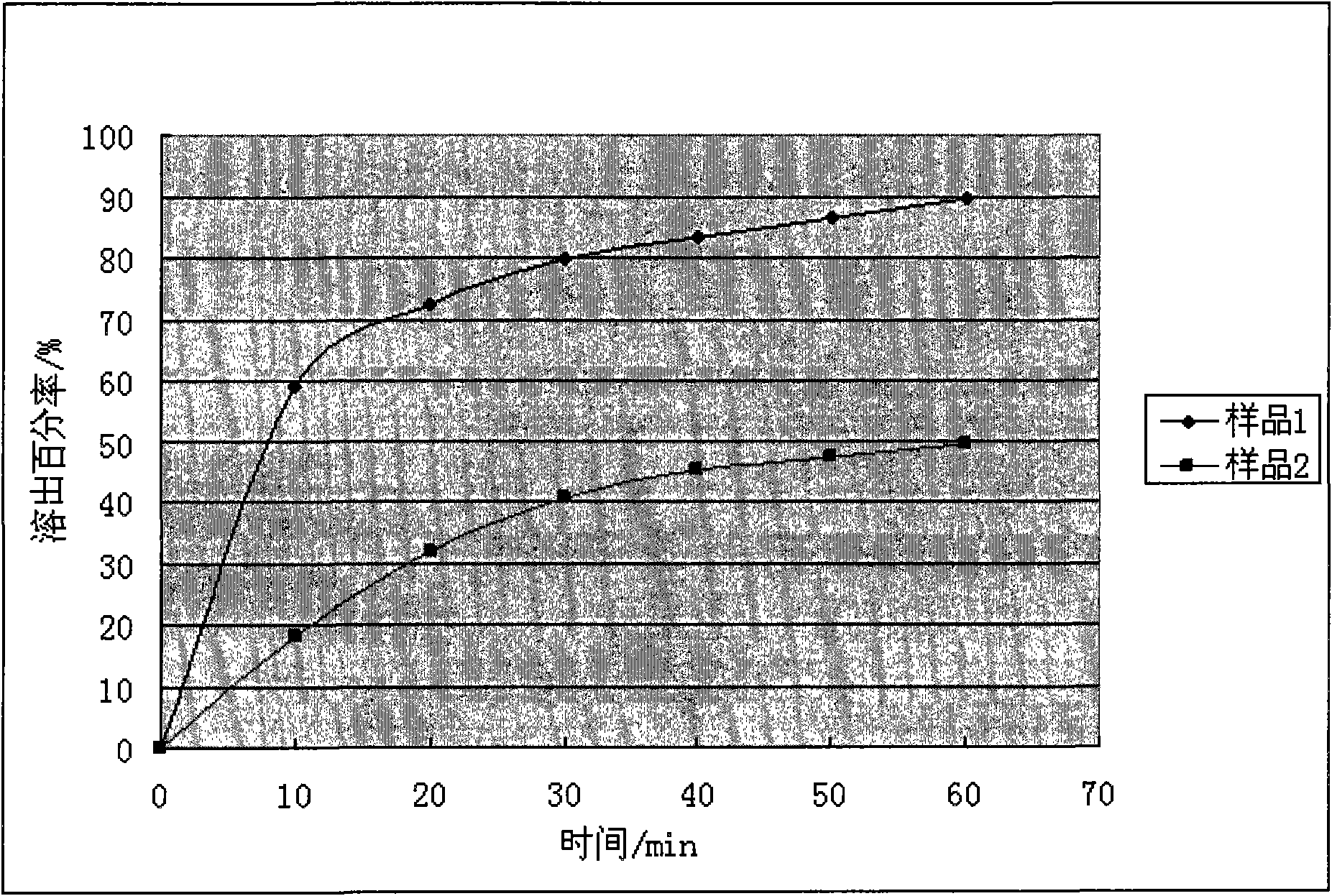
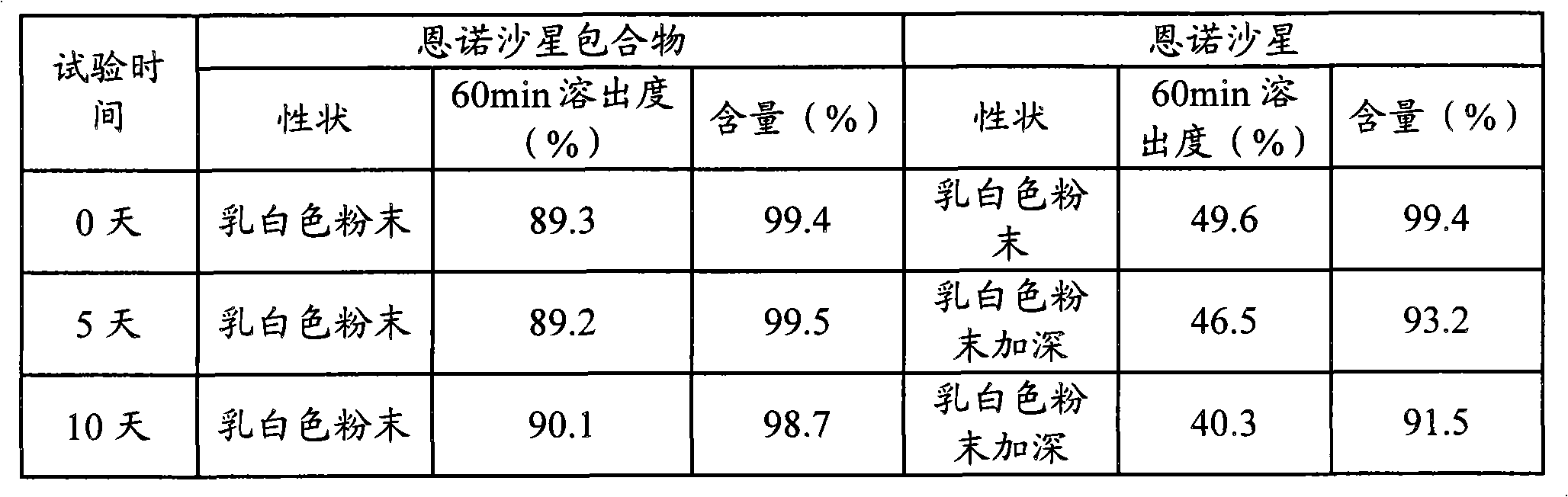
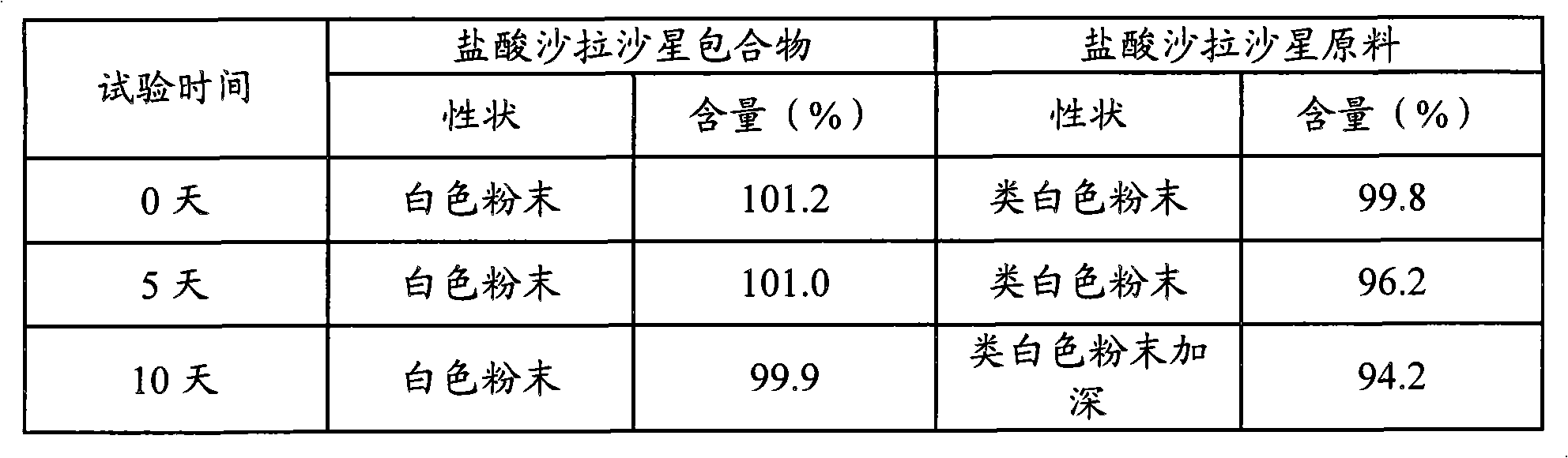
Animal medicine inclusion compound, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101954089AImprove solubilityImprove stabilityPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSolubilityOrganic solvent
The invention discloses application of an inclusion technology in preparing animal medicines, and an animal medicine inclusion compound. The animal medicine inclusion compound can increase the dissolution velocity and the solubility of indissolvable medicines, improve the stability of the medicines which are changeable in the presence of lights or moistures and the like, and facilitate the storage of medicines. The invention also provides a method for preparing the animal medicine inclusion compound, and the method is simple in operation, can reduce the use of organic solvent, lower the cost, reduce the poisonous side effects of the medicines, and can be applied to the preparation of animal medicines.
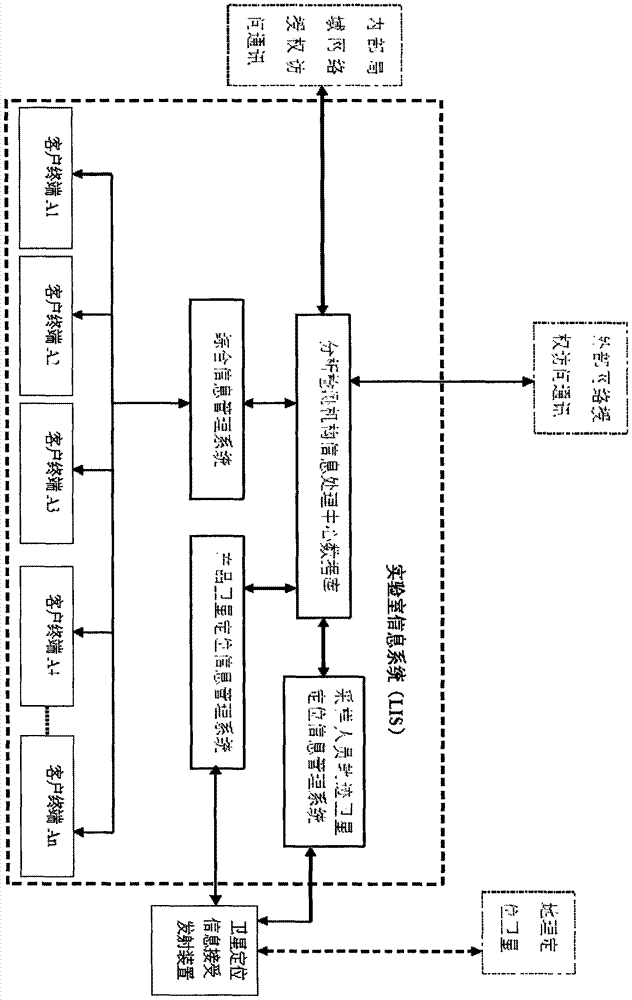
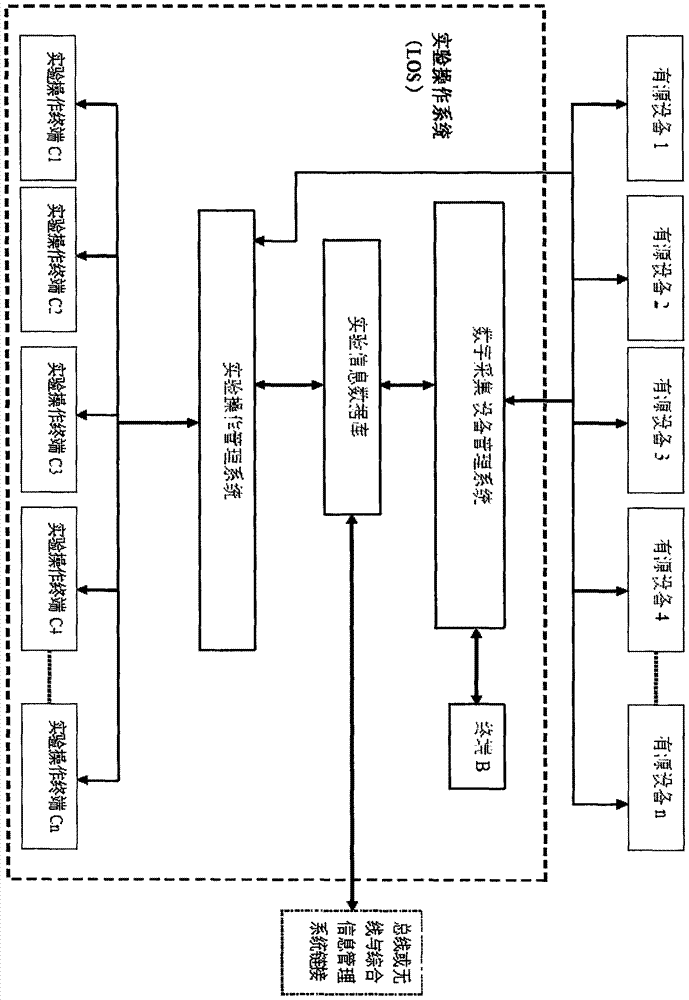
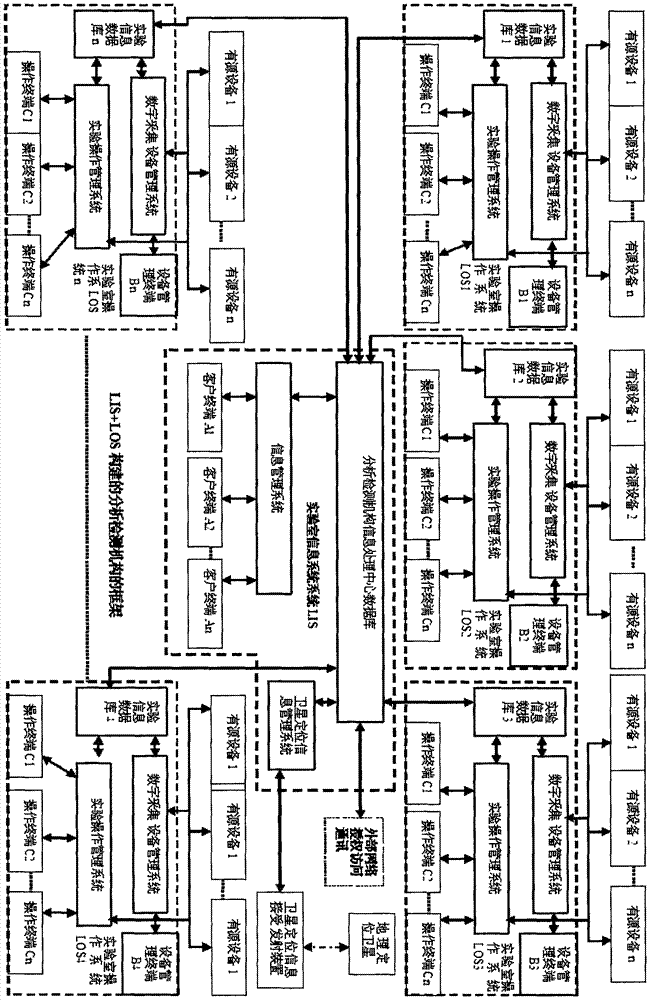
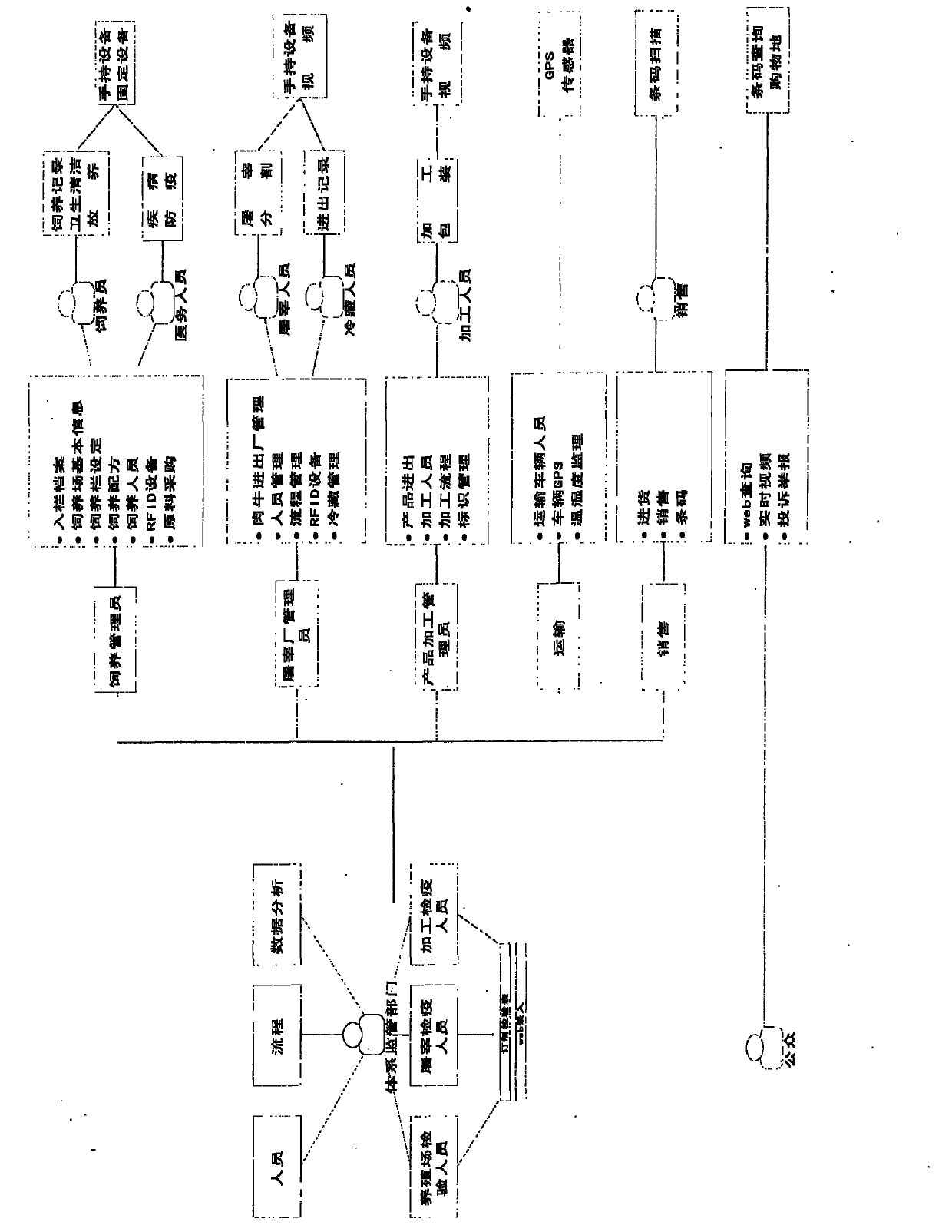
Detection and supervision information management system architecture and program design method
PendingCN107274326ATo achieve a strong governmentBoost credibilityResourcesEffective solutionOriginal data
The invention provides a simple and standardized package solution for information management system architecture and program design when the information management system architecture and program design of an analysis detection laboratory (analysis detection mechanism) of food, medicine, cosmetics, health care products, veterinary drugs, pesticides, chemical fertilizers, chemical reagents and environmental protection detection samples is carried out. The core element of the package solution is the standardization of the physical (hardware) environmental architecture of the information management system of the analysis detection mechanism and a supervision management mechanism and the standardization of an information data structure, and is an effective solution for the physical architecture and program design of the information management system used for original data tracing of the government supervision, analysis and detection mechanisms.
Owner:高华 +1
Combination of dehydroepiandrosterone or dehydroepiandrosterone-sulfate with a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, delta opioid receptor antagonist, neurokinin receptor antagonist, or VCAM inhibitor for treatment of asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
InactiveUS20050026850A1Alleviate different aspectConvenient treatmentBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseActive agent
A pharmaceutical or veterinary composition, comprises a first active agent selected from a dehydroepiandrosterone and / or dehydroepiandrosterone-sulfate, or a salt thereof, and a second active agent comprising a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, delta opioid receptor antagonist, neurokinin receptor antagonist, or VCAM inhibitor for the treatment of asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or other respiratory diseases. The composition is provided in various formulations and in the form of a kit. The products of this patent are applied to the prophylaxis and treatment of asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or other respiratory diseases.
Owner:EPIGENESIS PHARMA LLC
Screening method of 79 antibacterial agents in animal foods
InactiveCN107228912APromote healthy developmentReduce testing costsComponent separationHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsScreening method
The invention discloses a screening method of 79 antibacterial agents in animal foods. The screening method comprises preparation of a standard working solution, analysis pretreatment on a sample to be tested, drawing of a standard curve, qualitative analysis and quantitative analysis. A high throughput screening and quantitative detection platform is built so that the detection of a single compound is developed into the simultaneous detection of a plurality of compounds in the field. Compared with the prior art, the screening method realizes a detection cost about 1 / 2 the original cost, shortens a sample detection period by 1 / 2 and greatly improves work efficiency. The screening method plays an effective role in the veterinary drug residue monitoring program, the pollution-free animal product testing program and the national animal product routine testing program implemented by the Ministry of Agriculture.
Owner:河南省兽药饲料监察所
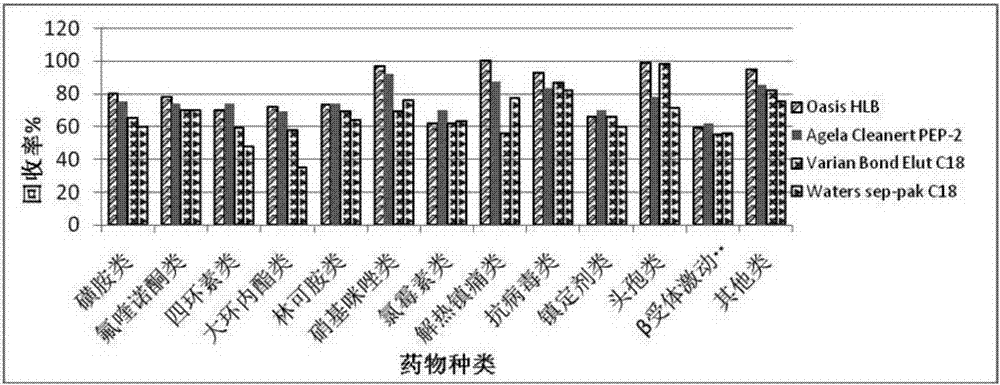
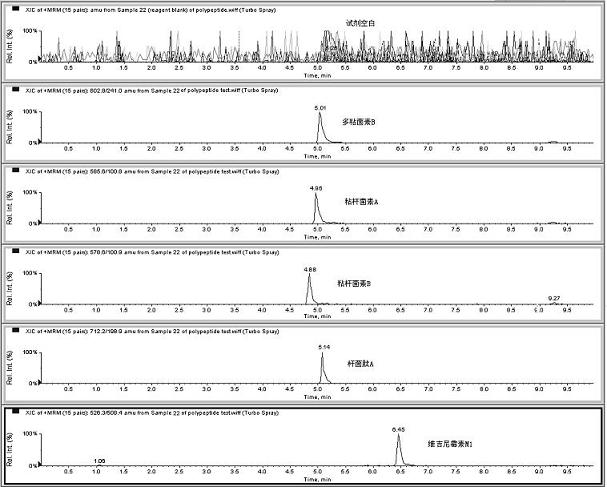
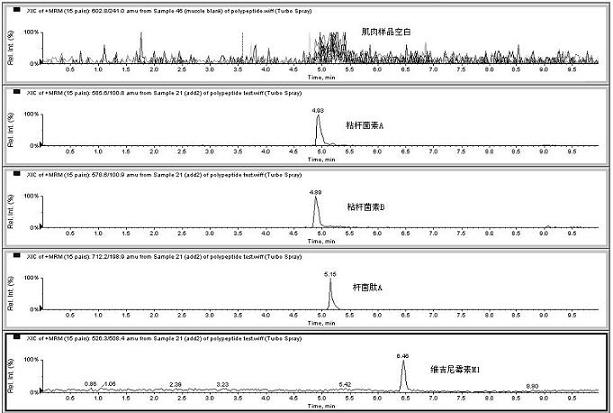
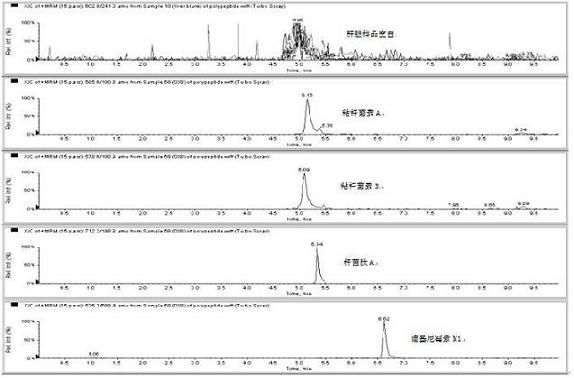
Method for detecting residual quantity of multiple polypeptidepolypeptide veterinary drugs in animal-derived food
InactiveCN102236005AAchieving Simultaneous DetectionReduce dissolutionComponent separationVirginiamycinVeterinary Drugs
The invention relates to the fields of analytical chemistry and food safety, particular to a method for detecting the residual quantity of multiple polypeptide veterinary drugs in animal-derived foods. The method comprises the following steps of: processing a sample with a TCA(trichloroacetic acid) and acetonitrile system for depositing proteins; extracting with a carbinol and 0.1% formic acid aqueous solution system; purifying with a Oasis HLB solid phase extraction column; performing gradient elution with an Eclipse XDB-C18 analytical column in the presence of an acetonitrile and 0.1% formic acid aqueous solution used as a mobile phase; and then performing electrospray and positive ion scanning mode separation for finally detecting four polypeptides. The limits of the four polypeptides, namely colistin, bacitracin A, polymyxin B and virginiamycin M, are 25 micrograms / kilogram, 100 micrograms / kilogram, 250 micrograms / kilogram and 120 micrograms / kilogram respectively; the recovery rates of colistin, bacitracin A, polymyxin B and virginiamycin M are 74.9-88.1%, 76.2-89.0%, 76.6-81.2% and 77.3-86.9% respectively; and the coefficients of variation (CV%) of colistin, bacitracin A, polymyxin B and virginiamycin M are 5.7-15.1%, 7.2-15.7%, 6.0-8.0% and 9.5-18.6% respectively. The detection limit, the recovery rate, the accuracy and other technical indexes all meet related detection requirements at home and aboard.
Owner:林维宣
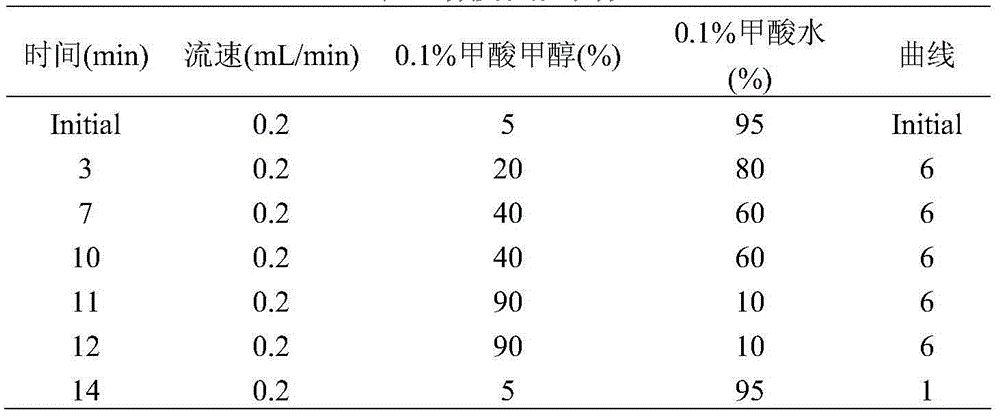
UPLC-MS/MS method for analyzing four categories and 29 types of restricted veterinary drug residues in animal foodstuff
InactiveCN105319292ASimplified processing stepsHigh sensitivityComponent separationVeterinary DrugsSolid phase extraction
The invention provides an UPLC-MS / MS method for analyzing four categories and 29 types of restricted veterinary drug residues in animal foodstuff. The method is characterized in that an advanced QuEChERS method is adopted for conducting sample preprocessing, a sample is subjected to McIlvaine buffering liquid-acetonitrile extraction, an extracting solution is subjected to acidification and salting out, a small amount of acetonitrile phase is taken, a C18 and NH2 adsorbing agent is utilized for conducting dispersive solid-phase extraction and purification, after purification liquid is subjected to concentration and volume setting, an ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometer (UPLC-MS / MS) is adopted to conduct detection. The problem that it is difficult for tetracycline class veterinary drug to be extracted and purified along with other types of veterinary drugs is solved, meanwhile the sample processing steps are simplified, the UPLC-MS / MS method has the advantages of being efficient, rapid, low in cost, simple and convenient to operate, good in purification effect and high in sensitivity, and the accuracy and precision both meet the requirement of a multi-residue analysis method.
Owner:TIANJIN INSTITUE OF QUALITY STANDARD & TESTING OF AGRICULTUAL PRODS
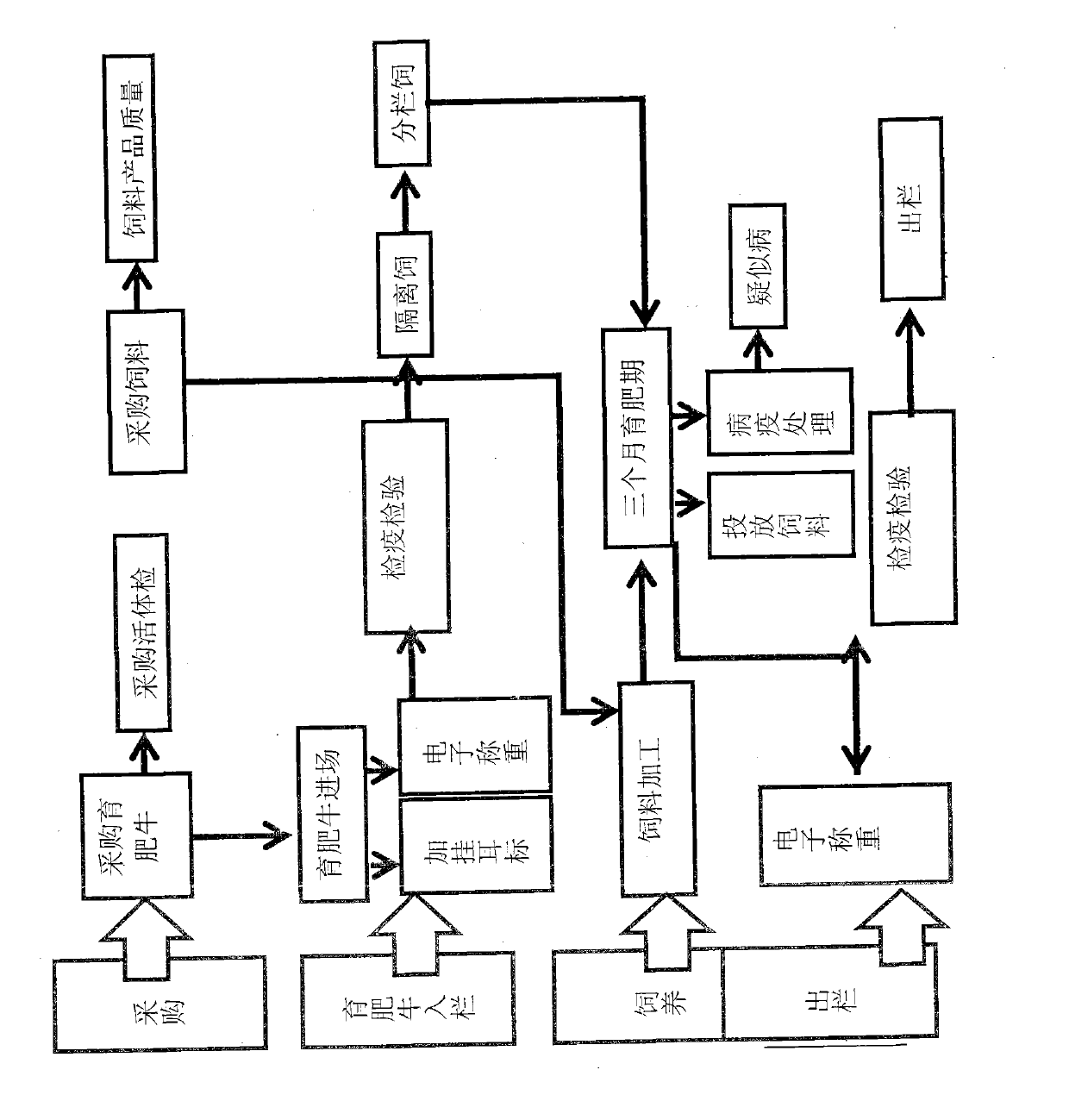
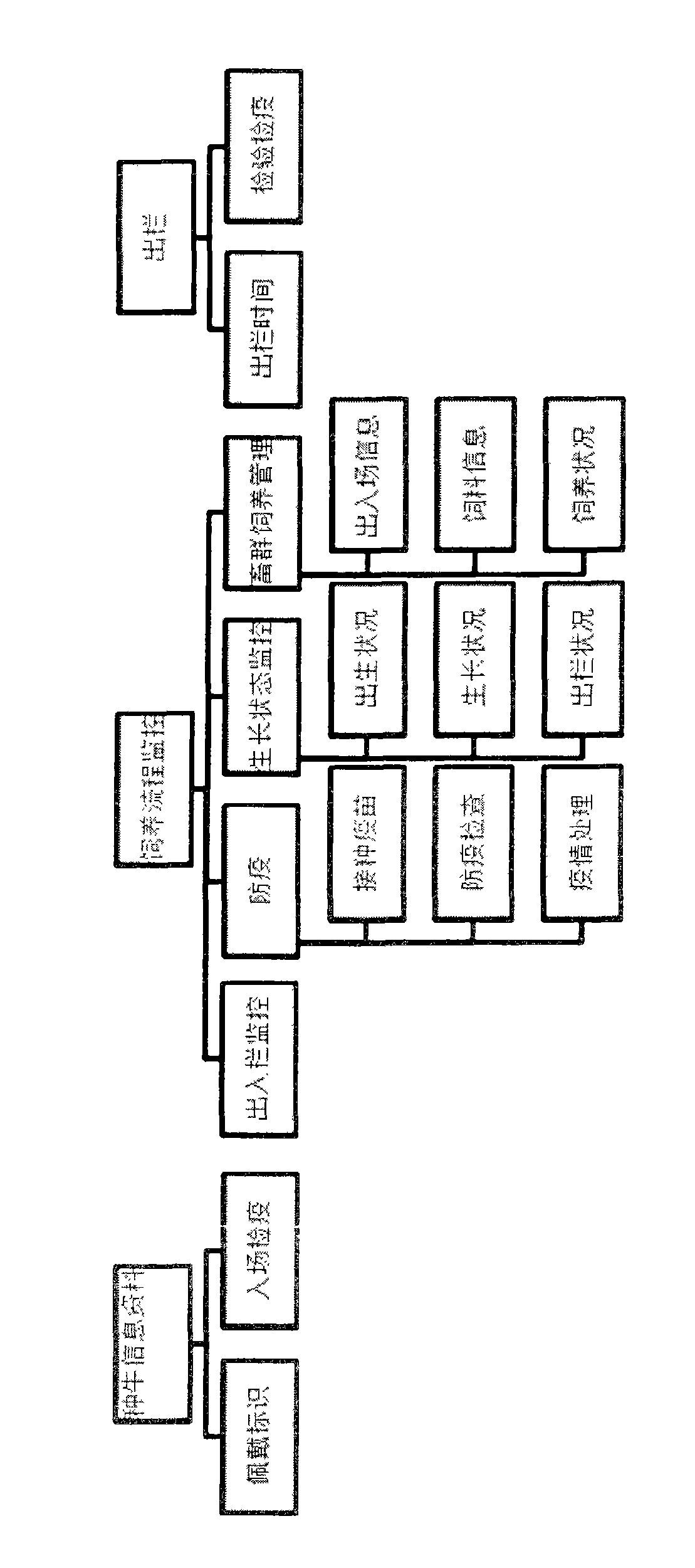
Finished cattle quality safety feeding and management method and system which are based on radio frequency identification devices (RFID) technology
ActiveCN103106564AFully documentedAdequate Breeding InformationCo-operative working arrangementsResourcesEar tagVeterinary Drugs
The invention relates to a finished cattle quality safety feeding and management method and a system which are based on radio frequency identification devices (RFID) technology. Cattle ear tags are knocked in ears of finished cattle, a feeding process of the finished cattle is tracked, using conditions of feed, health cleaning, epidemic prevention and immunization, feeding environment, inspection and quarantine and veterinary drug used in the feeding process are recorded through an RFID data reading and writing technology. The whole process of feeding of the finished cattle is comprehensively and truly recorded, and therefore adequate feeding information is provided for future quality and safety tracing.
Owner:内蒙古自治区科学技术信息研究院 +1
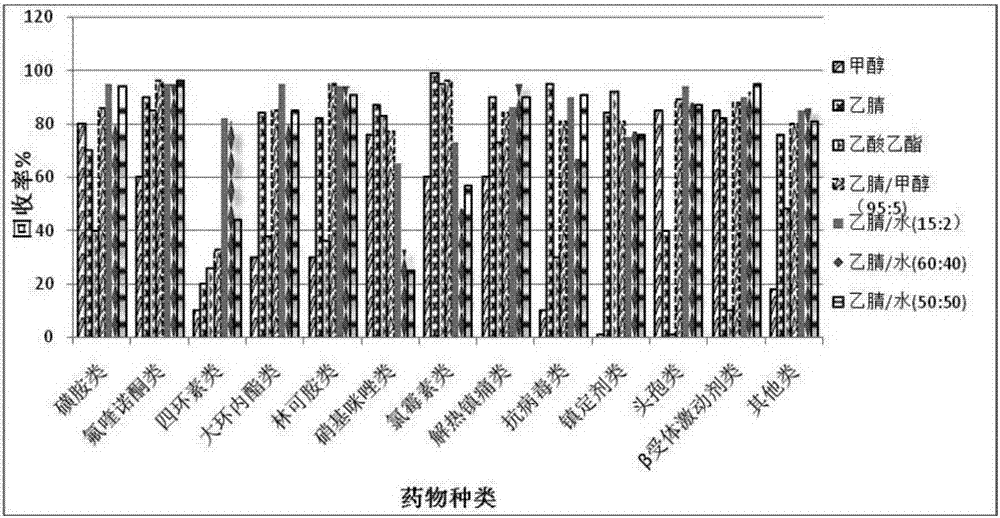
Method for analyzing residual veterinary drugs in mutton
The invention relates to the field of analysis and testing and particularly relates to a method for analyzing residual veterinary drugs in mutton. The method at least comprises sample pretreatment, enzymatic hydrolysis, extraction, purification and on-machine testing. Compared with the existing detection method, the method provided by the invention has higher accuracy, extracts, purifies and testsa variety of veterinary drugs, and is fast and efficient. The method utilizes a multi-extraction method using three different solvents, fully extracts the veterinary drugs in mutton as many as possible, improves the detection accuracy and reduces the influence caused by the base on the veterinary drugs. In gradient elution, three mobile phases are used so that it is solved that the original two mobile phases with solubility under action of an adsorbent in a chromatographic column are layered so that the target drugs are respectively dissolved in two solvents, the characteristic peak detectedby the detector splits into a primary characteristic peak and a secondary characteristic peak, the drug content capable of being detected is reduced and the determination of other drugs is influenced.
Owner:XINJIANG ACADEMY OF ANIMAL SCI QUALITY STANDARDS INST OF ANIMAL HUSBANDRY XINJIANG UYGUR AUTONOMOUS REGION SHEEP & WOOL CASHMERE QUALITY SAFETY SUPERVISION & INSPECTION CENT
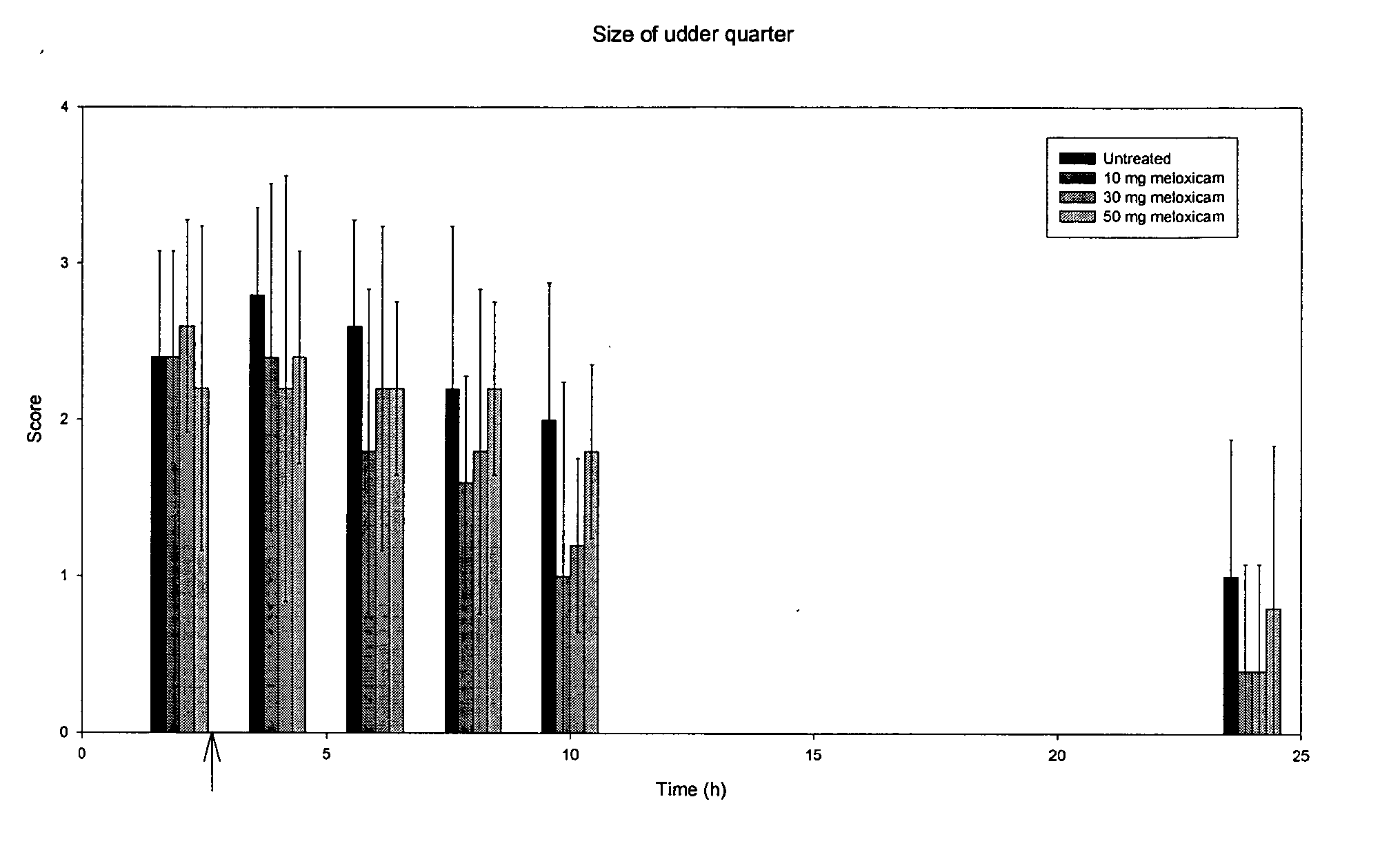
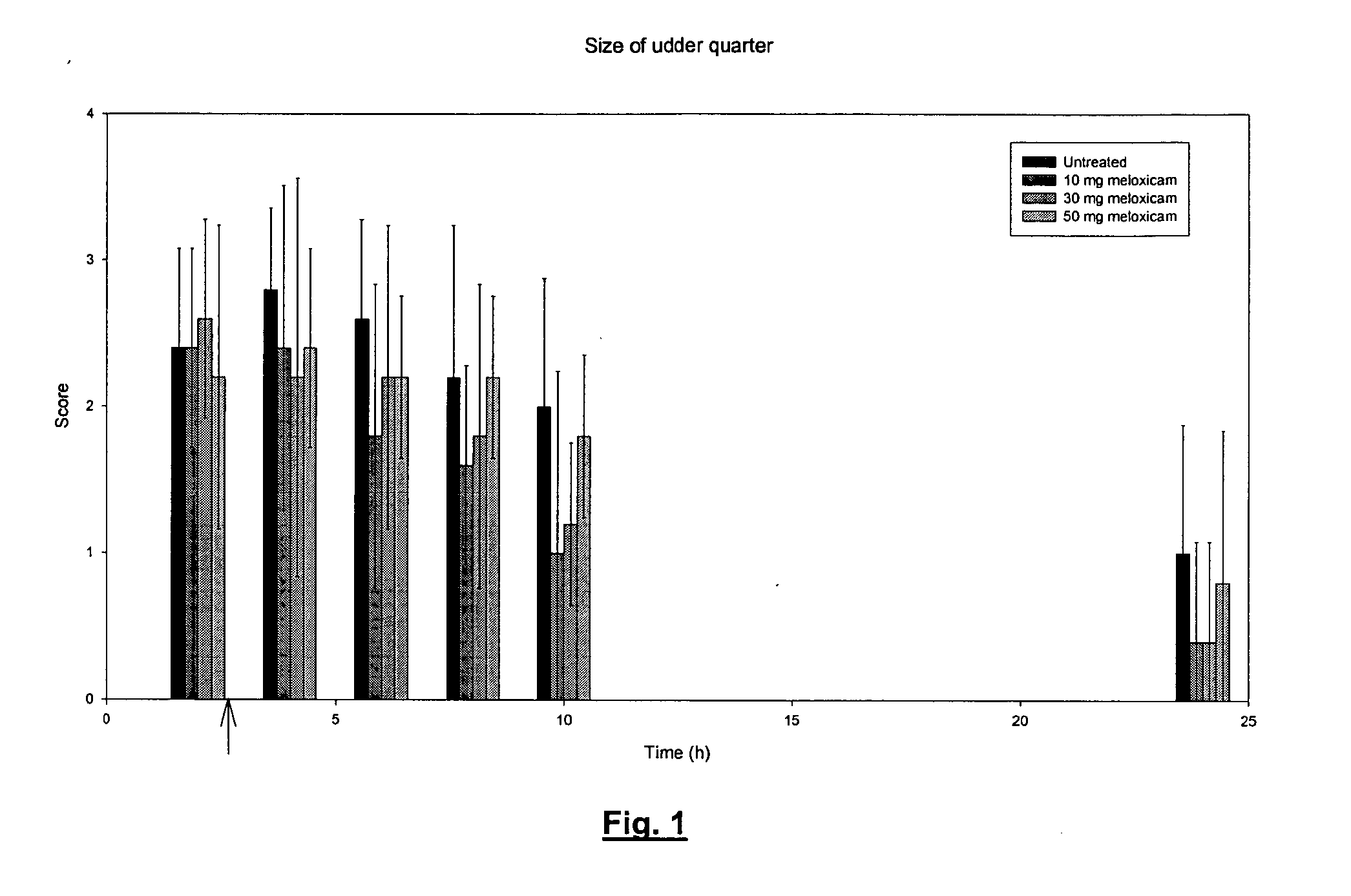
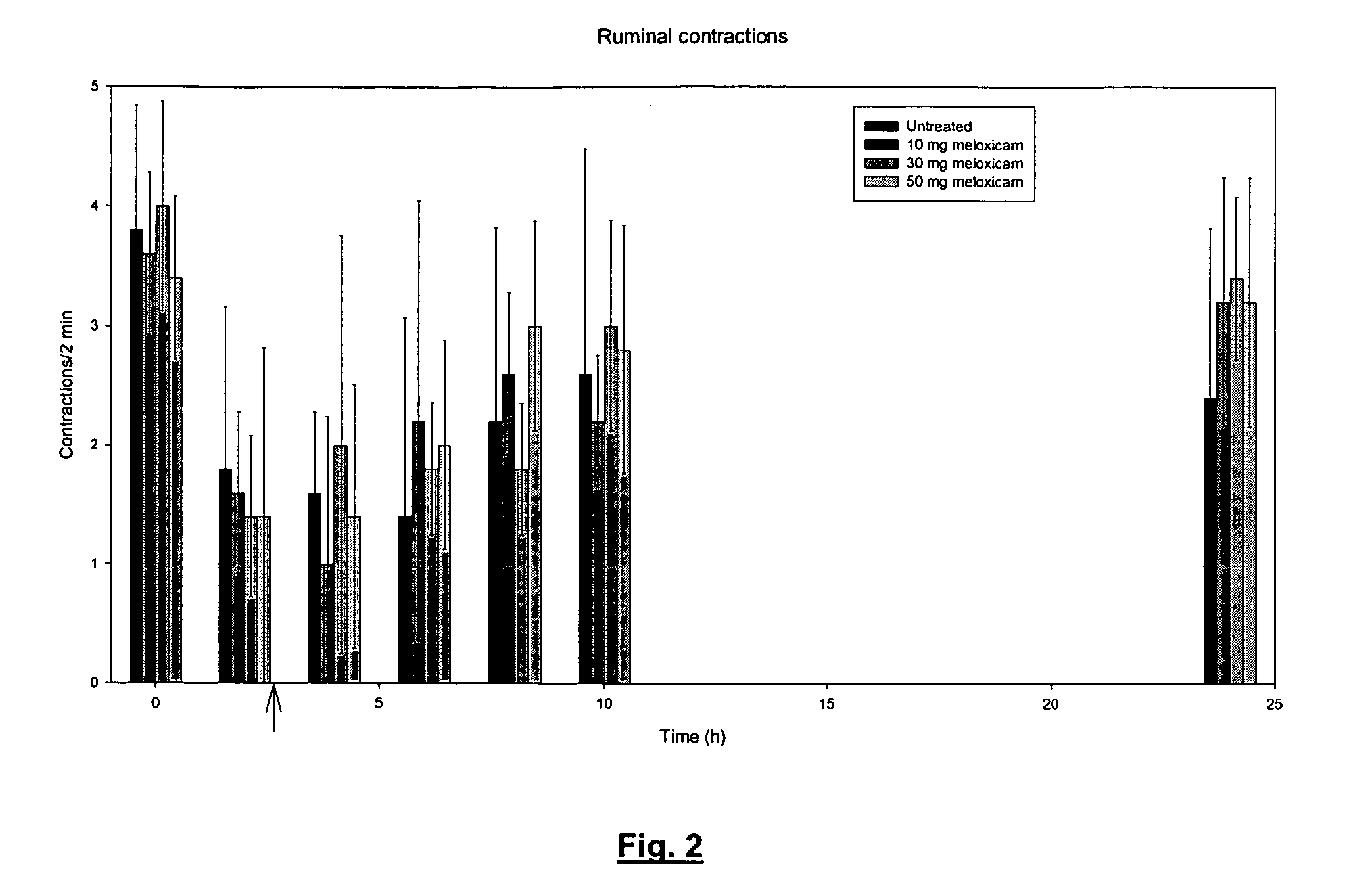
Use of meloxicam formulations in veterinary medicine
The invention is directed to the use of a formulation containing meloxicam or a pharmacologically acceptable meloxicam salt of an organic or inorganic base, one or more vehicles and one or more suitable additives for preparing a veterinary medical composition for intramammary treatment of inflammatory diseases in mammals, particularly mastitis. The intramammary administration leads to an effective concentration in the target tissue, which is achieved very quickly.
Owner:BOEHRINGER LNGELHEIM VETMEDICA GMBH
Antibacterial agents
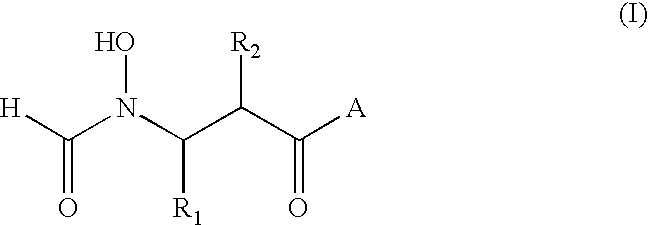
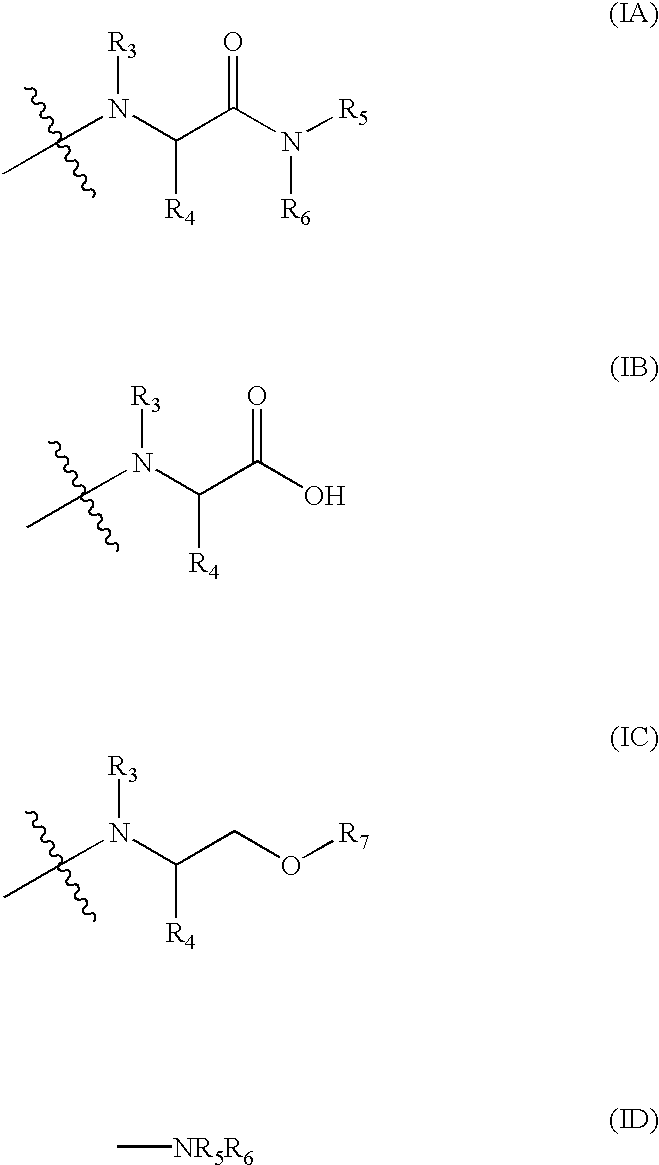
A method for the treatment of bacterial infections in humans and non-human mammals, which comprises administering to a subject suffering such infection an antibacterially effective dose of a compound of formula (I) or a pharmaceutically or veterinarily acceptable salt thereof:wherein:R1 represents hydrogen, or C1-C6 alkyl or C1-C6 alkyl substituted by one or more halogen atoms; R2 represents a group R10-(X)n-(ALK)m- wherein R10 represents hydrogen, or a C1-C6 alkyl, C2-C6 alkenyl, C2-C6 alkynyl, cycloalkyl, aryl, or heterocyclyl group, any of which may be unsubstituted or substituted by (C1-C6)alkyl, (C1-C6)alkoxy, hydroxy, mercapto, (C1-C6)alkylthio, amino, halo (including fluoro, chloro, bromo and iodo), trifluoromethyl, cyano, nitro, -COOH, -CONH2, -COORA, -NHCORA, -CONHRA, NHRA, -NRARB, or -CONRARB wherein RA and RB are independently a (C1-C6)alkyl group, and ALK represents a straight or branched divalent C1-C6 alkylene, C2-C6 alkenylene, or C2-C6 alkynylene radical, and may be interrupted by one or more non-adjacent -NH-, -O- or -S-linkages, X represents -NH-, -O- or -S-, and m and n are independently 0 or 1; and A represents a group as defined in the specification.
Owner:BRITISH BIOTECH PHARMA LTD
Staged beef cattle breeding method
The invention discloses a staged beef cattle breeding method. The staged beef cattle breeding method includes a lactation stage, a nursing stage, a stocking stage and a sty return fattening stage. Aiming at the growth physiological characteristics of beef cattle, the beef cattle are bred through the scientific staged breeding method, calves out of the lactation period are nursed and then put on a mountain to be stocked, the calves are made to freely move and take food to the maximum degree in the high-speed growth period of the calves, skeleton growth is promoted, a good foundation is laid for later-period fattening, and meanwhile the quality of beef can be greatly improved through field free pollution-free stocking; special feed formulas are adopted at all the stages so as to guarantee sufficient nutrients for the beef cattle, the physiological functions of the beef cattle are adjusted by creatively adding Chinese herbal medicine, metabolism is promoted, the effects of improving anti-stress capacity, resisting bacteria, diminishing inflammation, repelling insects and boosting immunity are achieved, and therefore the purposes of improving the resistance of the beef cattle and preventing and treating diseases are achieved; the defect that a large number of veterinary drugs and antibiotics are used in beef cattle large-scale breeding at the present stage is overcome.
Owner:LUOPING HENGXIN ANIMAL HUSBANDRY
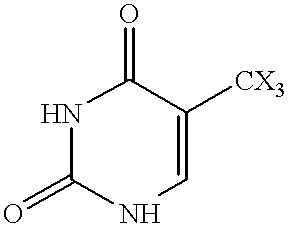
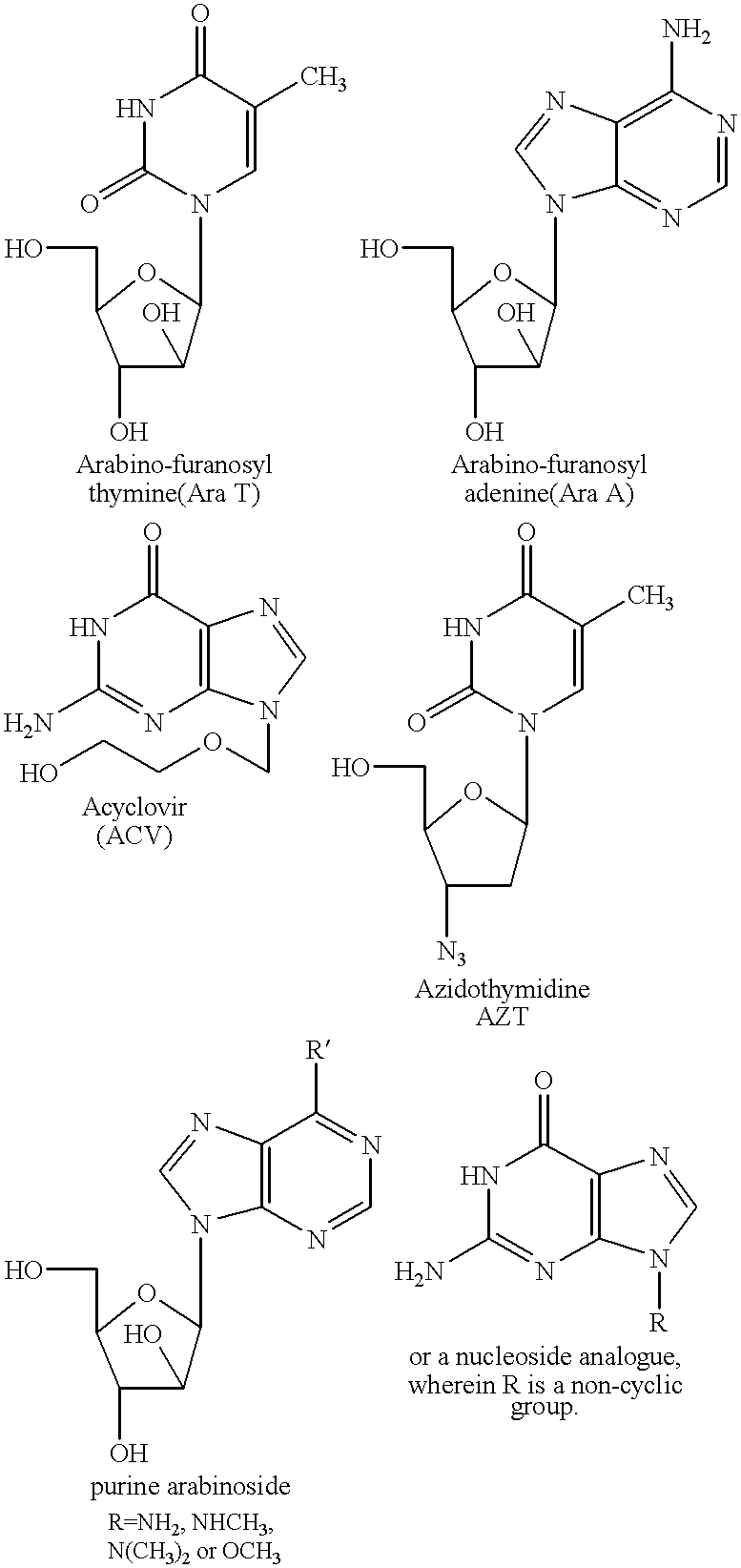
Fatty acid esters of nucleoside analogs
New compounds of the general formula (I): Nu-O-Fa, wherein O represents an oxygen, Nu is a nucleoside or nucleoside analogue, and Fa is an acyl group of a mono-unsaturated C18 or 20 fatty acid. The invention also concerns anti viral pharmaceutical and veterinary compositions comprising a compound of formula (I) alone in a combination with a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
Owner:NORSK HYDRO ASA
Compositions comprising lipophilic active compounds and method for their preparation
ActiveUS9254268B2Quick releaseImprove bioavailabilityPowder deliveryDispersion deliveryHydrophilic polymersVeterinary Drugs
Owner:SOLUBEST
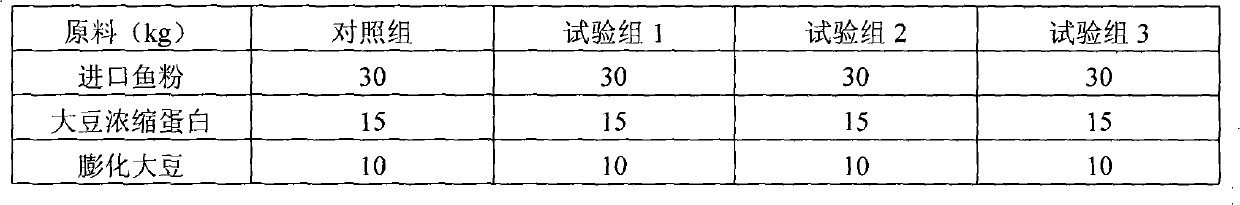
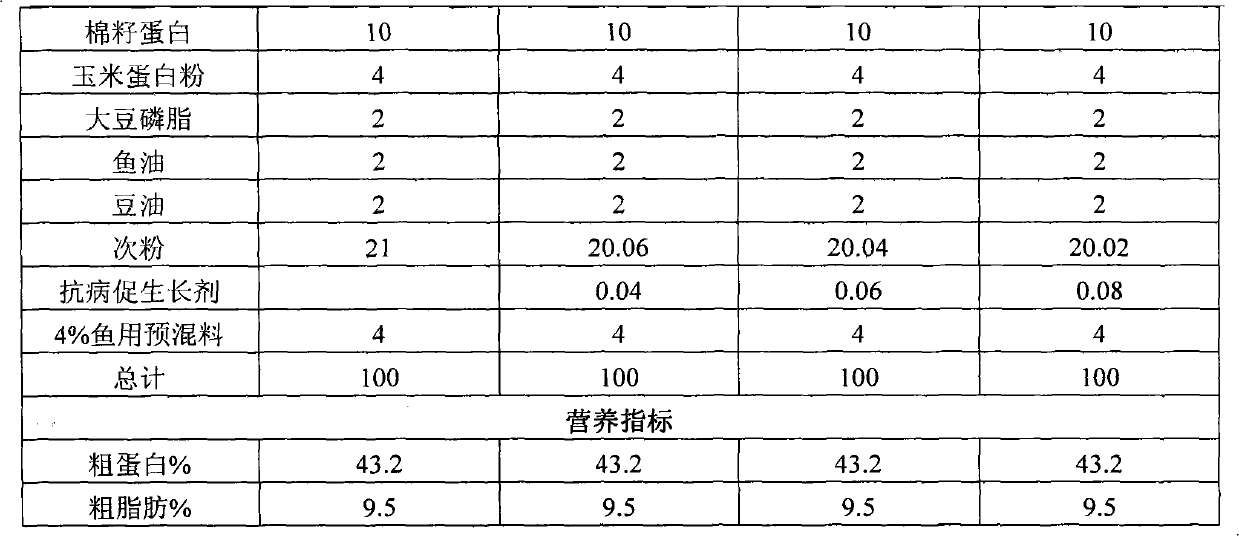
Pig complete fermented feed and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105410410AEasy to operateReduce morbidityAnimal feeding stuffNutritive valuesAnimal science
The invention discloses a pig complete fermented feed preparation method and an application thereof. A pig complete fermented feed comprises the following main components: 60-70.5% of corn, 13-27% of soybean meal and the balance of wheat bran. The strain is composed of mixed lactic acid bacteria, saccharomyces and bacillus according to a ratio of (2-3):(1):(1). The fermented feed is prepared by performing solid state fermentation on a low-nutrition complete feed, molasses and multiple strains, can be used for feeding and nursing, pigs at multiple phases such as growth and pregnancy. The feed combines multi-phase physiological characteristics of pigs and aims at problems of component, nutrition and production of the pig feed at a current specific phase, the pig complete fermented feed can be prepared by using combination fermentation of the specific strains, nutrition value of the feed with low cost is increased, mycotoxin and antinutritional factors are reduced, usage of veterinary drug is reduced, culture cost is reduced, and animal health and production performance can be increased.
Owner:CHUYING AGRO PASTORAL GRP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com