Gene directed molecular evolution system in vitro based on half-rational evolutionary design
An out-directed, gene-based technology, applied in organic chemistry, sugar derivatives, etc., can solve the problems of unclear genes, difficulties in gene expression and analysis, and lack of clarity of key sites.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] Embodiment 1: PCR amplification β-galactosidase gene (HLacZ)
[0053] (1) Test method:
[0054] 1. Synthesis of oligonucleotide primers
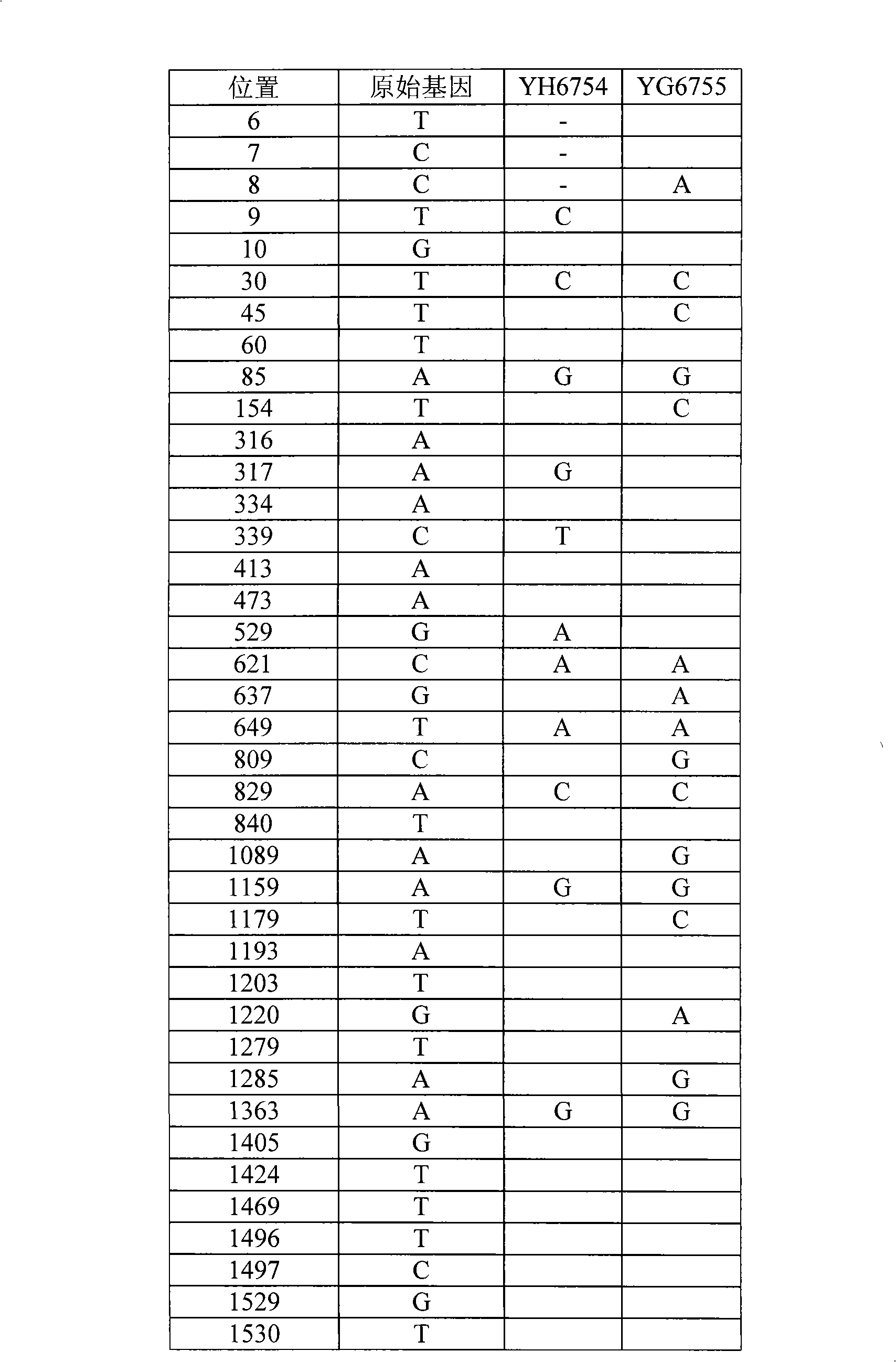
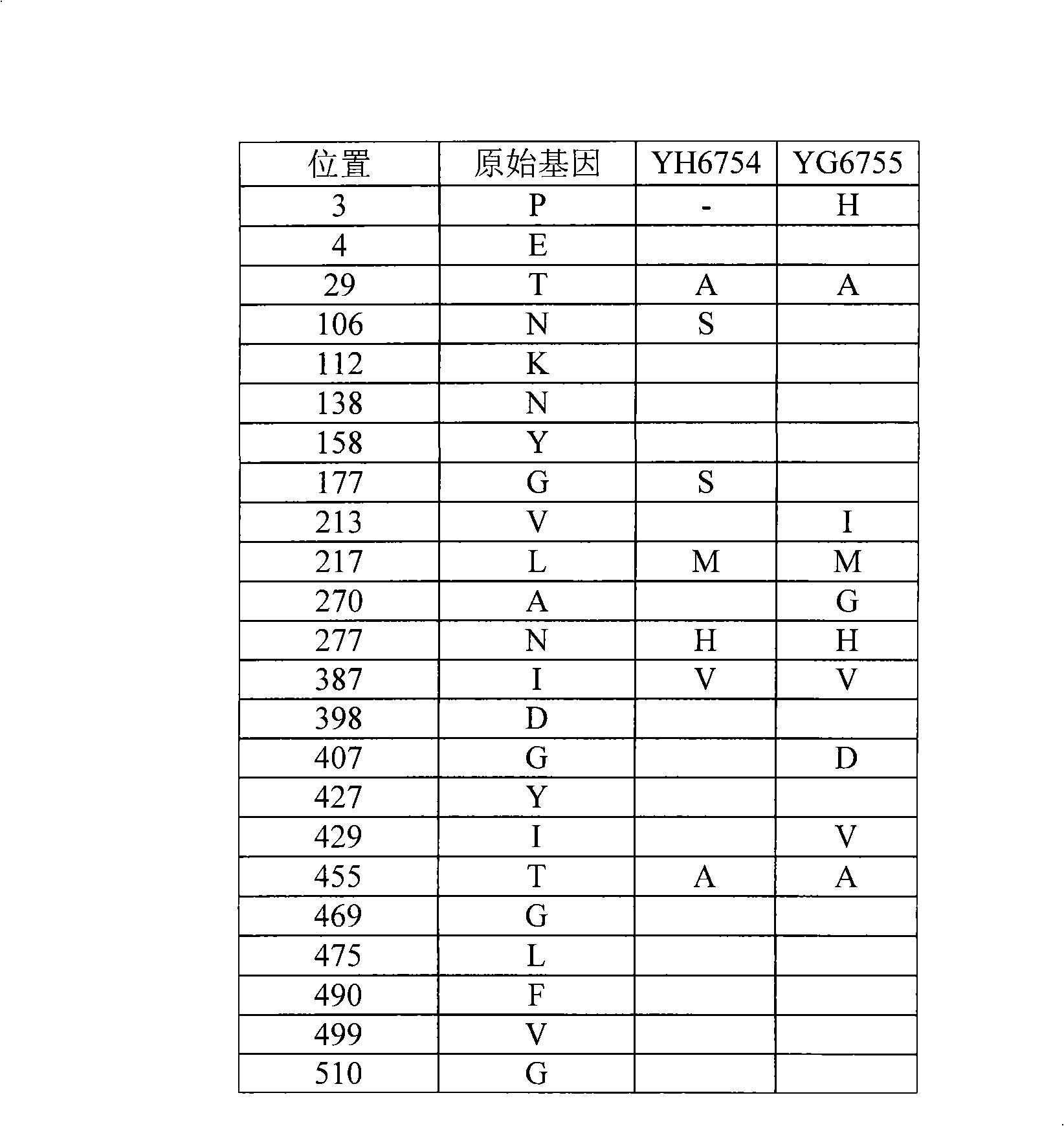
[0055] 1) According to the nucleotide sequence ( figure 1 ), design two oligonucleotide primers, respectively numbered as Hlacz-sh-S1 and Hlacz-sh-S2 primers. In order to facilitate cloning and construction, BamHI and SacI restriction site sequences were added to the 5' ends of the primers, respectively. For the designed primer sequences, see Figure 5 :
[0056] 2) Primer synthesis was completed by Shanghai Sangon Bioengineering Technology Service Co., Ltd.
[0057] 3) Purify by PAGE referring to the molecular cloning literature method.
[0058] 2. PCR amplification reaction:
[0059] HLacZ gene template: 1μl; Hlacz-sh-S1: 0.2ng; Hlacz-sh-S2: 0.2ng; 10×PCRbuffer: 5μl; dNTP (2.5mmol / L): 4μl; Taq polymerase: 2U; add ddH 2 O to a final volume of 50 μl.
[0060] The reaction program was 94°C, 10min pre-denaturation, 94°C denatur...
Embodiment 2
[0066] Embodiment 2: Construction of β-galactosidase gene (HLacZ) mutant library
[0067] (1) Test method:
[0068] 1. DNase I degradation and recovery of β-galactosidase gene (HLacZ) DNA fragment
[0069] 1) DNase I degradation:
[0070] Dissolve the β-galactosidase gene (HLacZ) DNA fragment recovered in Example 1 with 100 μl DNase I buffer, add 0.1 U DNase I, treat at 25° C. for 15 minutes, and then treat at 70° C. for 10 minutes (inactivation of DNase). The degradation products were identified by 10% acrylamide gel electrophoresis. In this step, the composition of DNase I buffer is: 50mmol / L Tris-C1pH7.4+1mmol / LMgCl 2 .
[0071] 2) Recovery of degradation products:
[0072] A small fragment of 50-100bp was recovered by the dialysis bag method. The precipitate was dissolved with 10 μl of 10× primer-free PCR buffer (50 mmol / L KCl+10 mmol / LTris-Cl pH9.0+1% Triton).
[0073] 2. Primer-free PCR amplification of degradation products:
[0074] reaction system:
[0075] De...
Embodiment 3
[0085] Embodiment 3: Construction and screening of the Escherichia coli transformant of the mutant library containing β-galactosidase gene (HLacZ) DNA fragment
[0086] 1. Construction of mutant library E. coli plasmid
[0087] According to the basic operation of Sambrook molecular biology (Sambrook J, Frets E F, Mannsdes Tet al. In: Molecular Cloning. 2nd ed. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 1989.), the expression vector pYPX251 was first digested with BamHI and SacI, and connected with T4DNA The enzyme ligation connects the β-galactosidase gene (HLacZ) DNA fragment, and the obtained connection product is the Escherichia coli expression plasmid containing the mutant library of the β-galactosidase gene (HLacZ) DNA fragment.
[0088] 2. Construction of mutant library transformants
[0089] The constructed Escherichia coli expression plasmid containing the mutant library of the β-galactosidase gene (HLacZ) DNA fragment was transformed into Escherichia coli strain DH5α by el...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com