Novel lactic acid bacteria and compositions containing them
A composition, lactic acid bacteria technology, applied in detergent compositions, medical preparations containing active ingredients, drug combinations, etc., can solve the problem of not describing the use of microorganisms and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0152] In order to identify and select the microorganisms of the present invention, various strains from the Lactobacillus strain library were tested by a 4-step screening method, wherein they were first tested for their ability to micro-bind with pathogenic skin microorganisms (hereinafter also referred to as "target microorganisms") They (binding assay), and subsequently, the strains identified in the first step were tested on a microtiter plate scale in a coagglutination assay, in which coagglutination with the corresponding target organisms was qualitatively measured using a binocular stereomicroscope. In addition, coagulation was studied The strength of agglutination and the stability of binding to target microorganisms and the ability to prevent biofilms, which ultimately lead to the exemplary microorganisms (Lactobacilli) identified according to the present invention.
[0153] Combined analysis
[0154] In order to be able to quantify the binding activity of selected ...
Embodiment 2
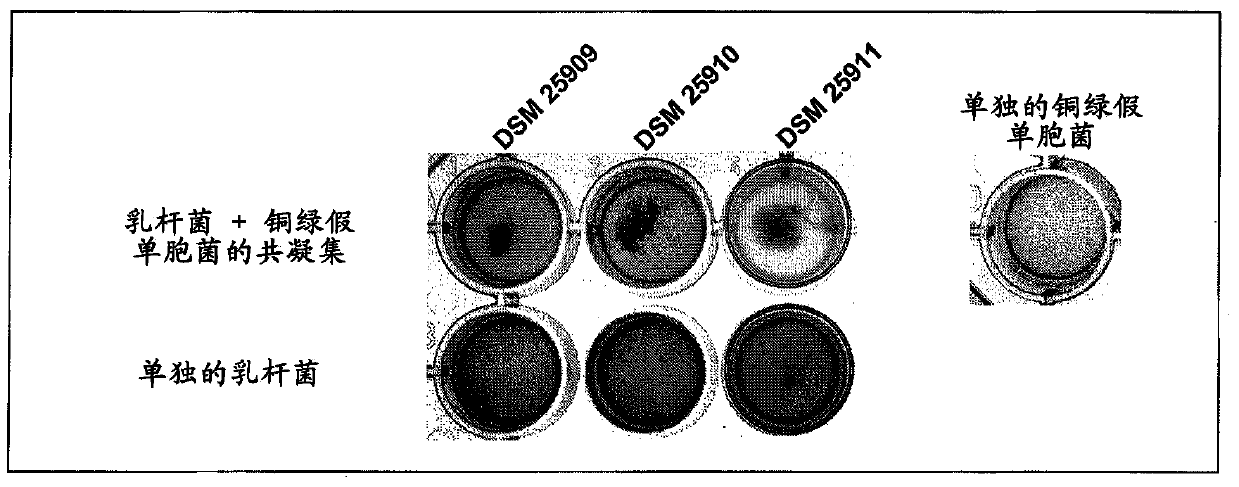
[0165] coagglutination assay
[0166] The following validations in a volume of 0.8 mL and / or in 24-well plates were used to show the co-agglutination activity of the selected Lactobacillus strains.
[0167]In this method, the coagglutination behavior of the lactobacillus and the coagglutination behavior of the target strain are considered separately, and finally the coagulation action of the lactobacillus and the target strain mixed together is considered. This analysis was performed macroscopically and microscopically by using photographs of 24-well plates.
[0168] For these experiments, the target microorganism - Pseudomonas aeruginosa Monascus (DSMZ22644) and Staphylococcus aureus (DSMZ18587).
[0169] Lactobacillus strains were grown anaerobically in MRS medium at base 37 (deMan et al., 1960).
[0170] To make target microorganisms, after 16 hours, cells were harvested, washed 3 times with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS, pH 7.4) and adjusted to OD 600 =4.
[0171] ...
Embodiment 3
[0179] In addition, experiments were performed to show the effect of proteases on the Lactobacillus strains of the invention and their agglutination properties on target microorganisms.
[0180] The Lactobacillus strains and target strains of the invention were thus treated as described in Example 2.
[0181] The Lactobacillus strains of the invention were trypsinized with a protease (examples of proteases shown here). After treatment of the Lactobacillus strains, they were trypsinized at 37 for 60 minutes (12.4 units / mg, Sigma). Subsequently, the cells were washed twice again with PBS and the agglutination properties were quantified as described in Example 2.
[0182] These experiments have shown that after protease treatment, the Lactobacillus strains of the present invention have 50-76% of the target microorganism bacteria / target strain Pseudomonas aeruginosa and / or Staphylococcus aureus in a coagglutination assay of the target microorganisms. Agglutination. As examples ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com