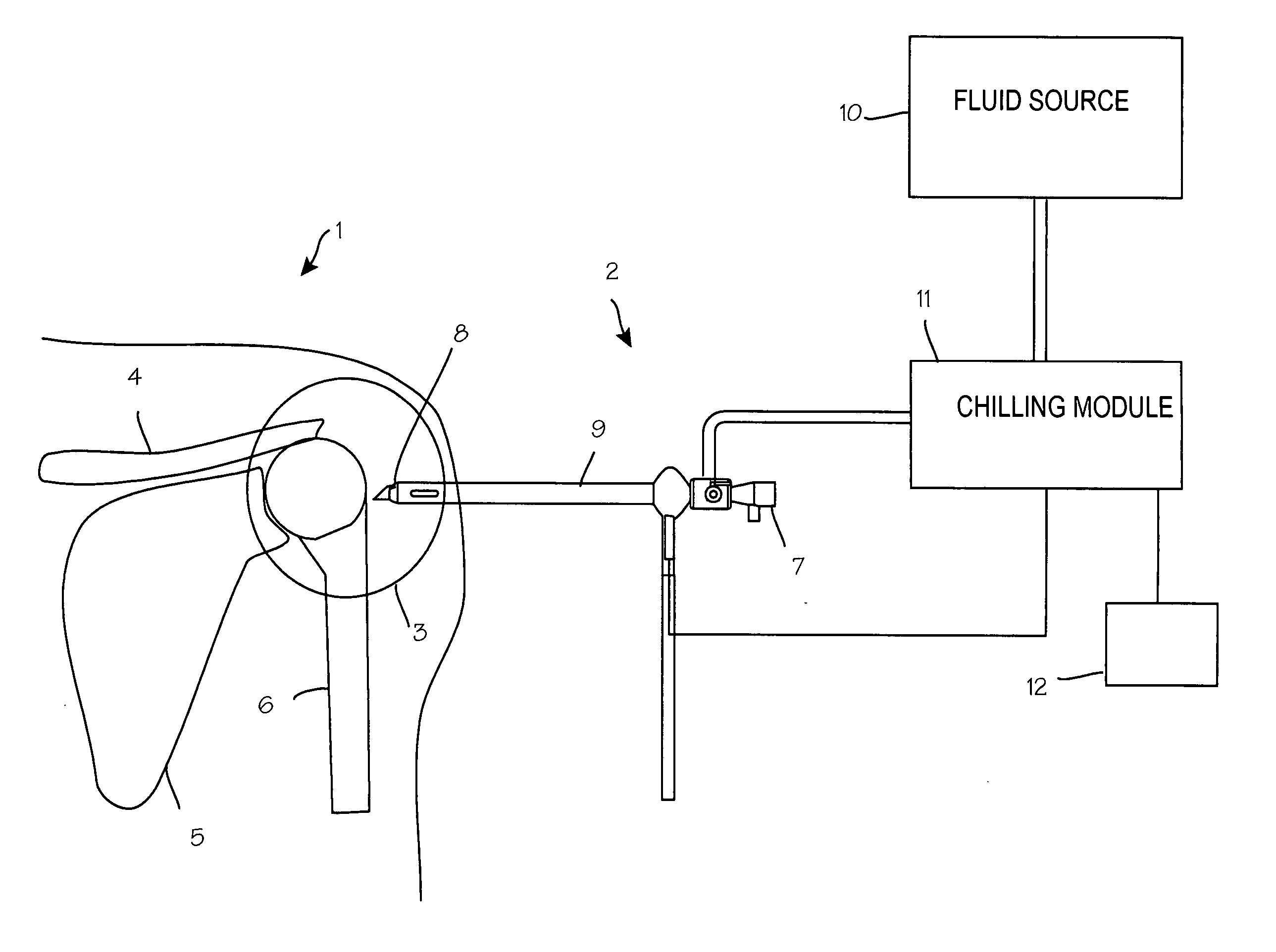
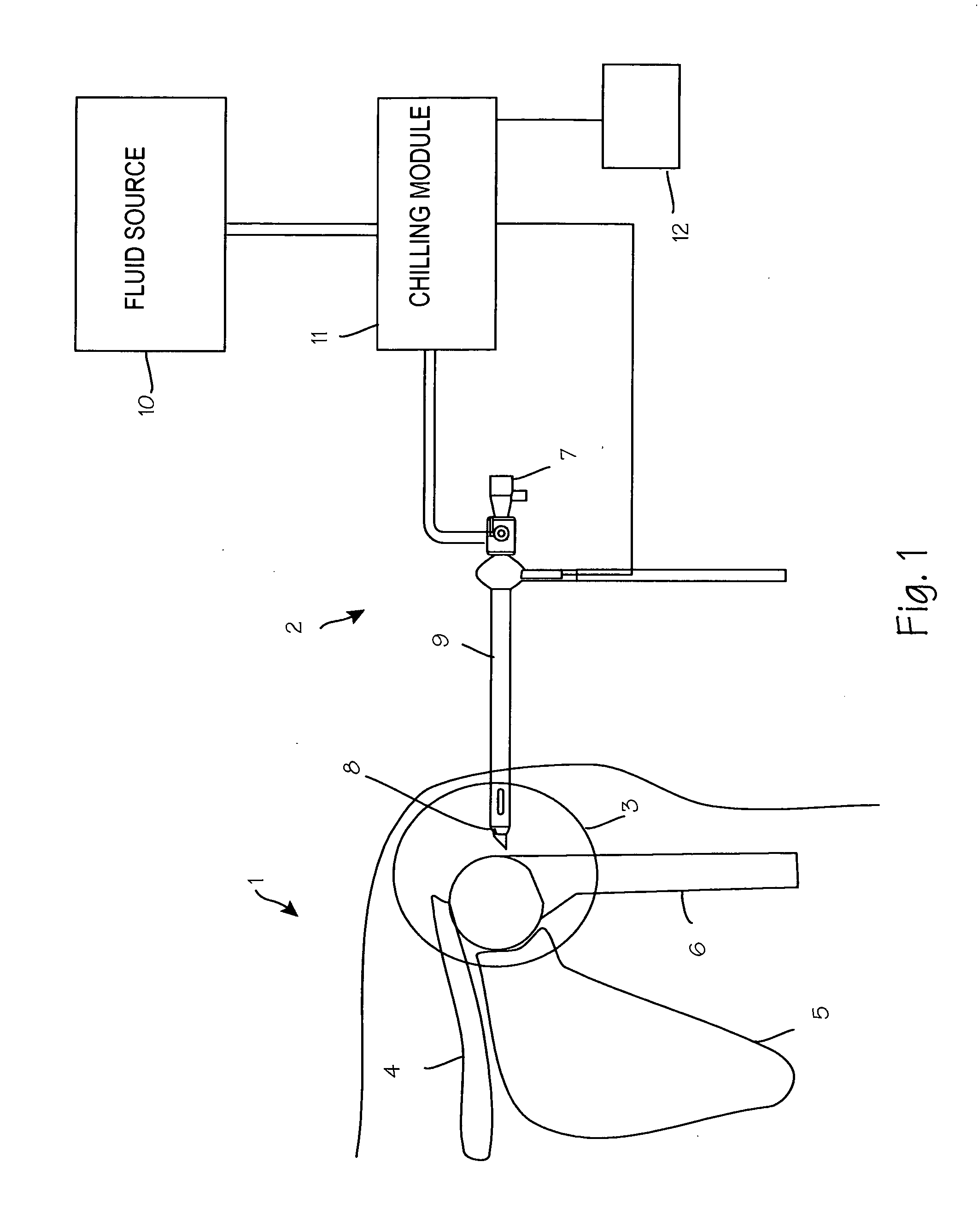
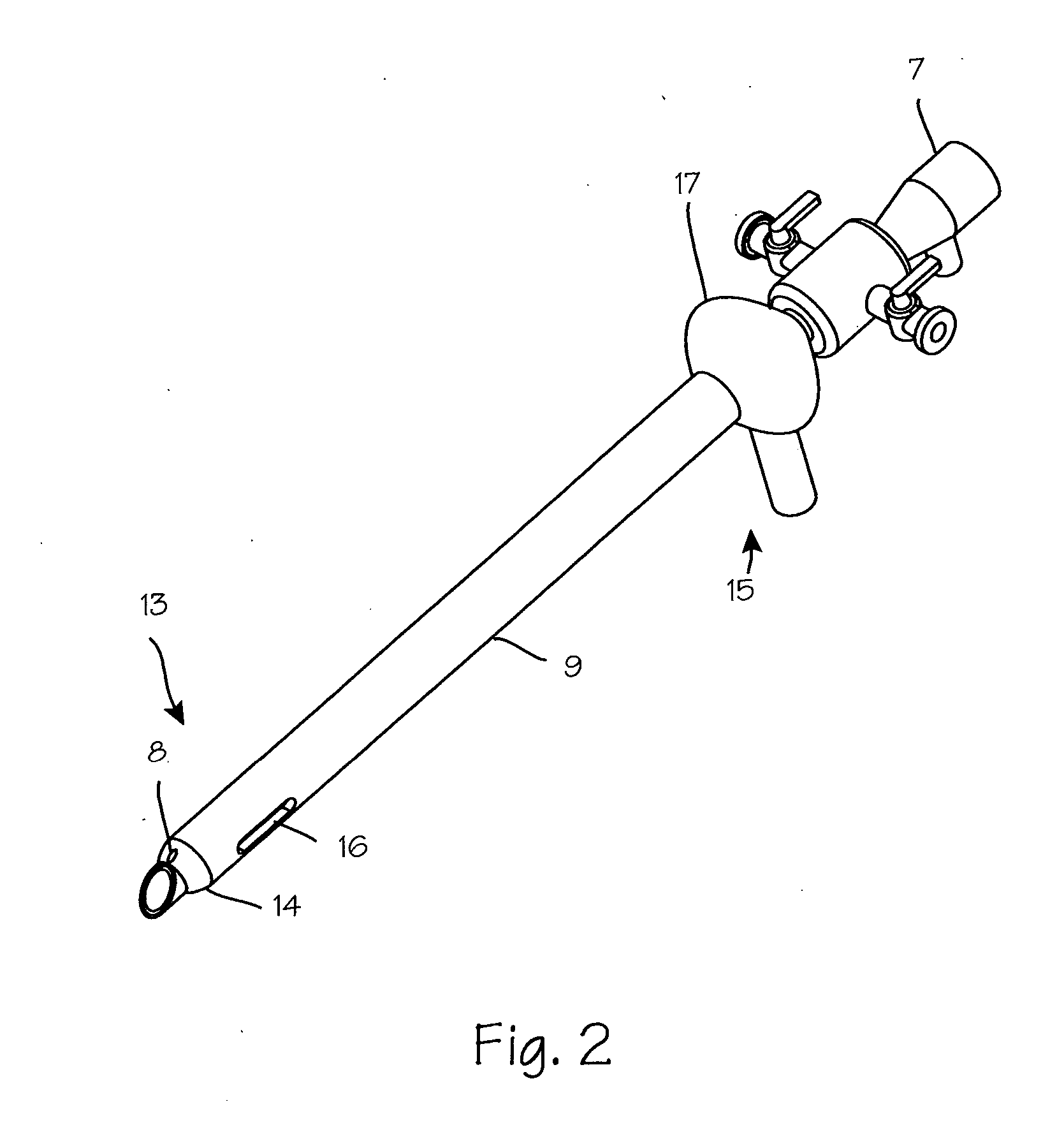
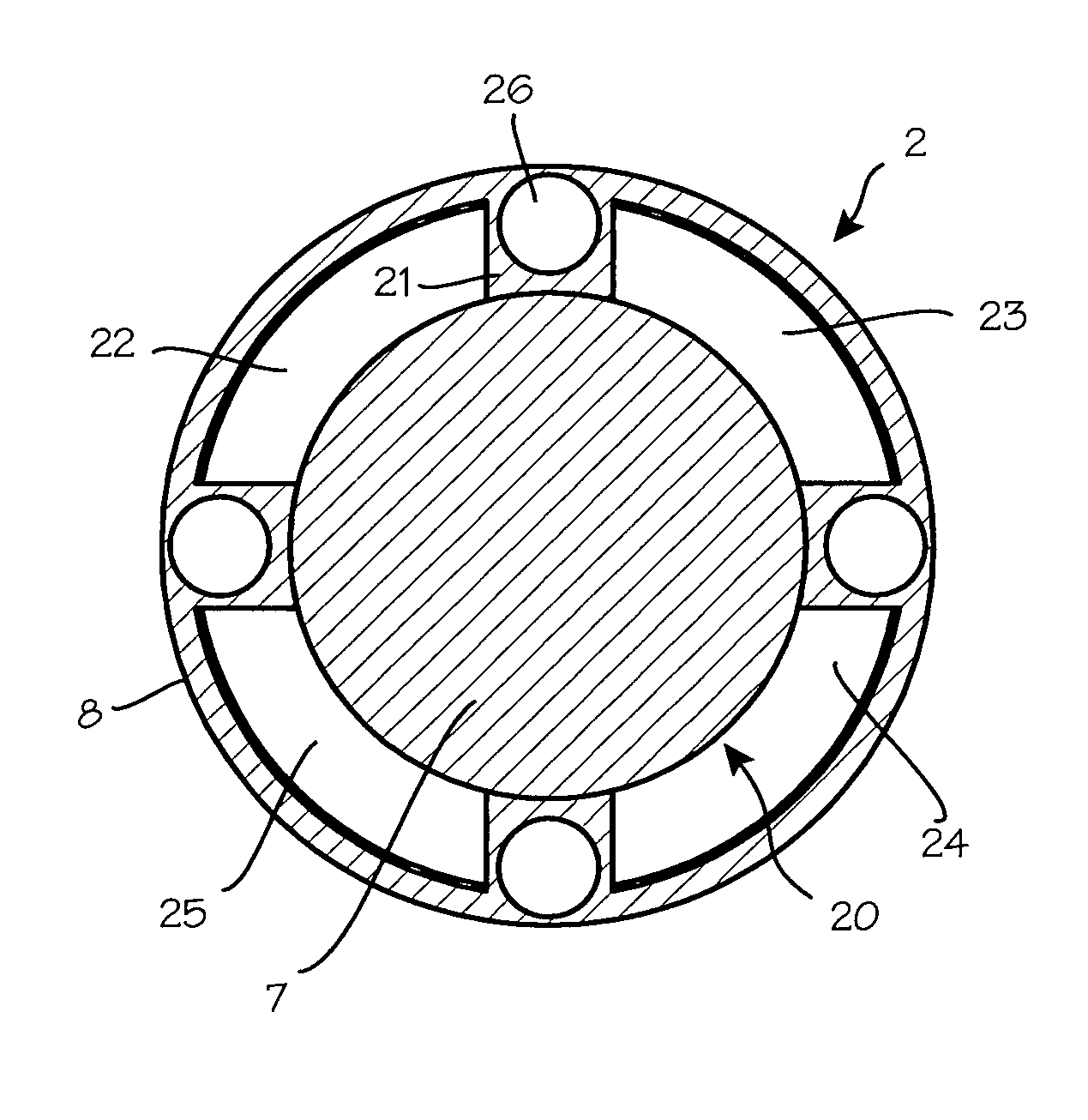
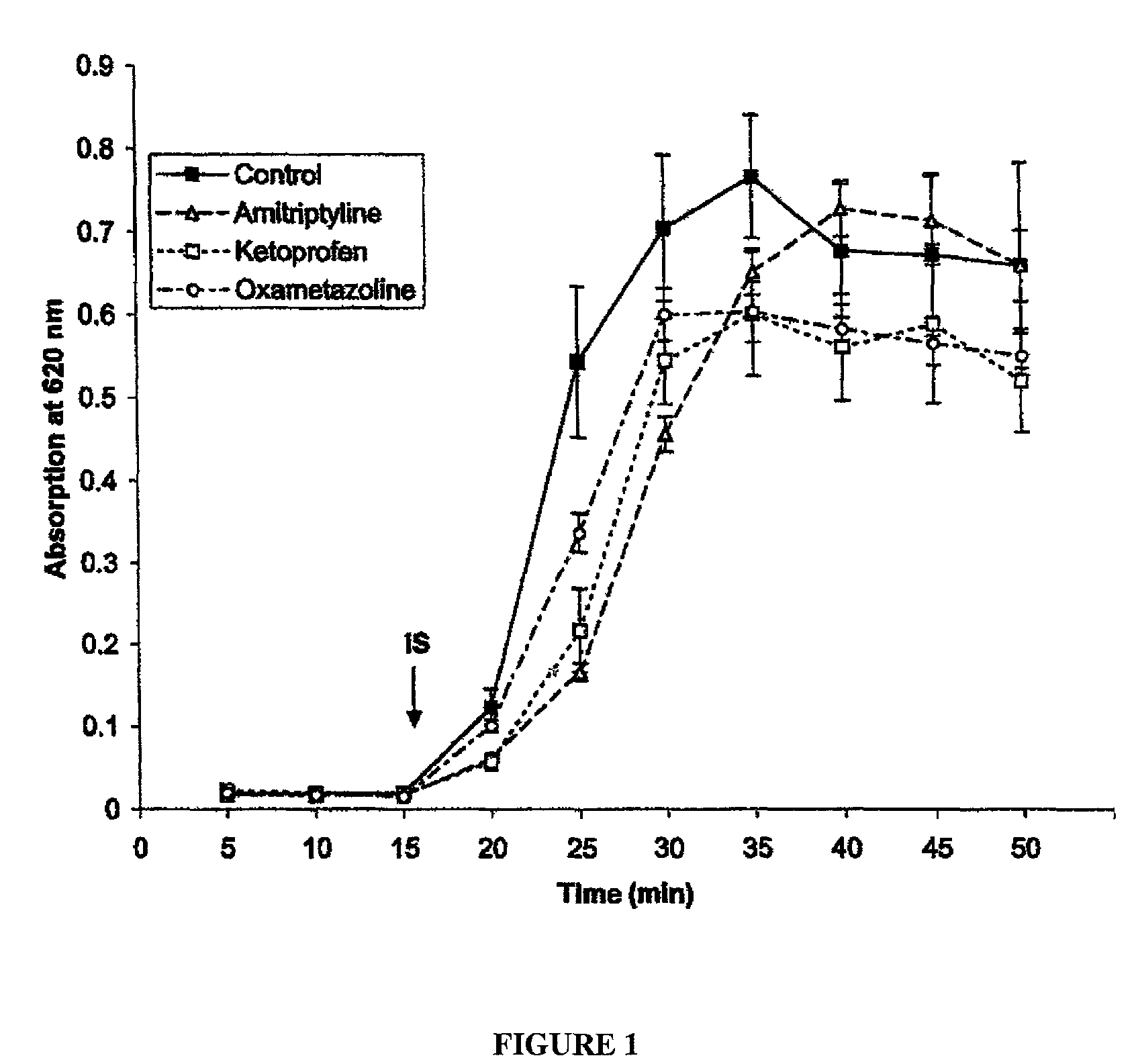
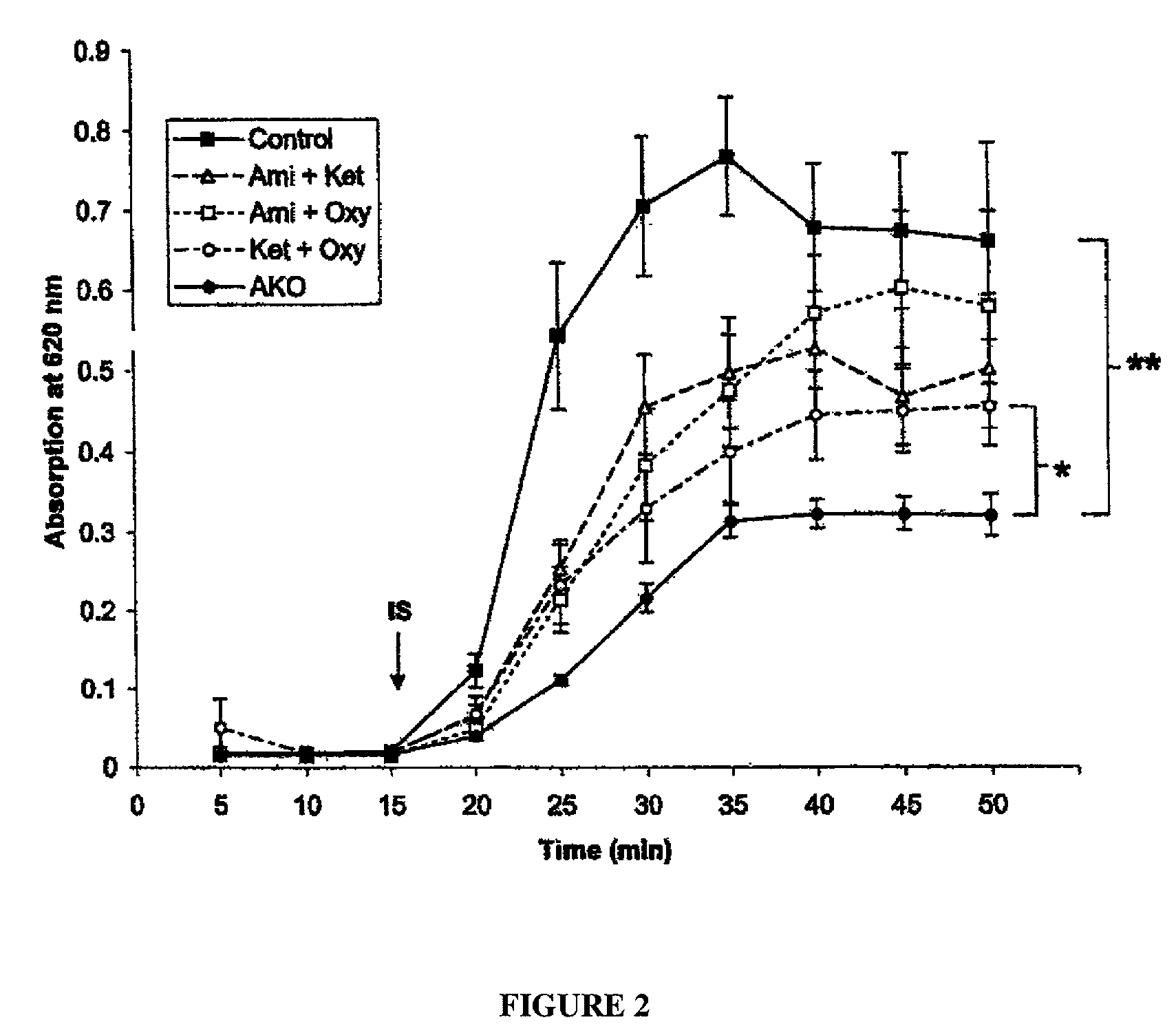
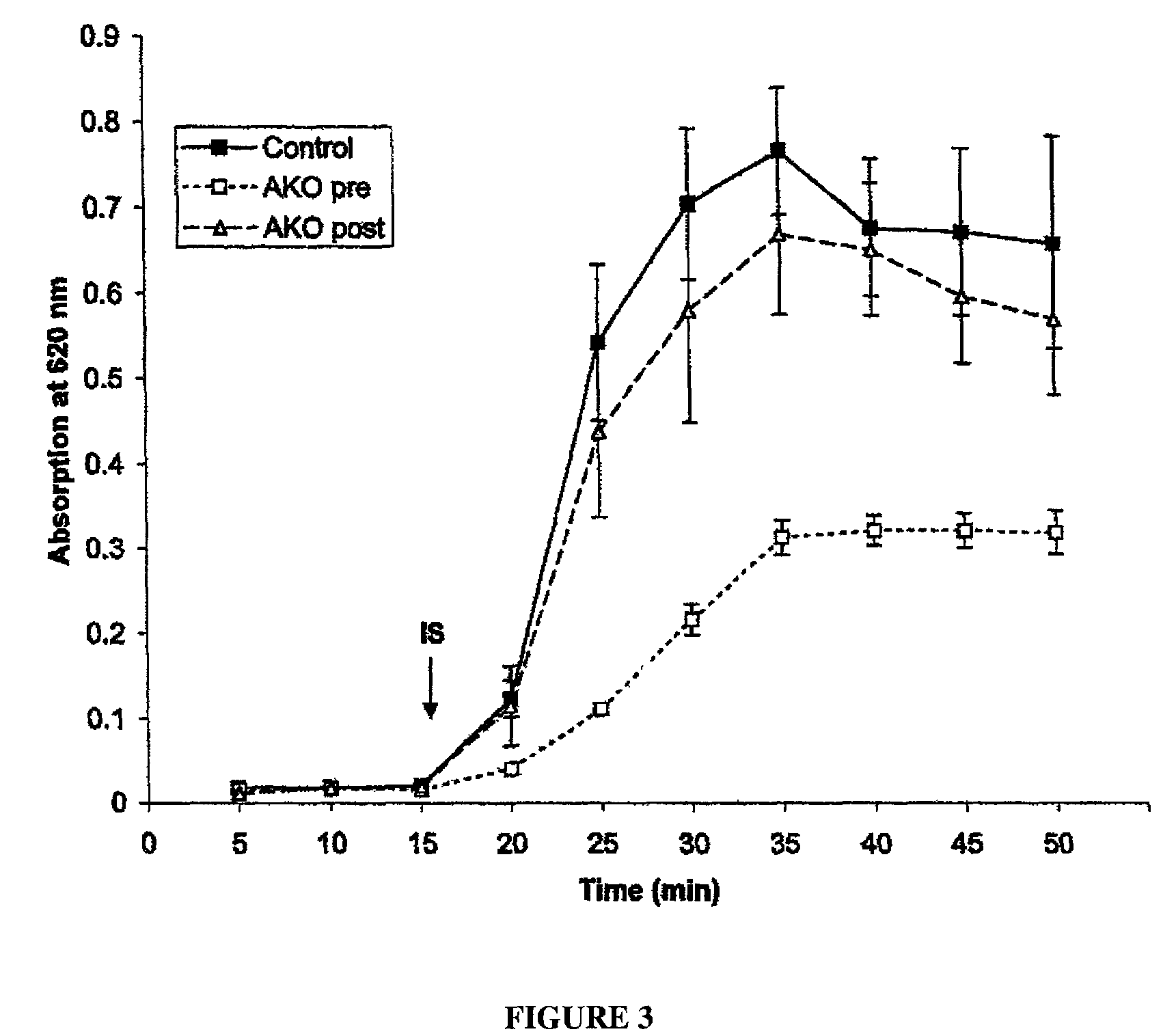
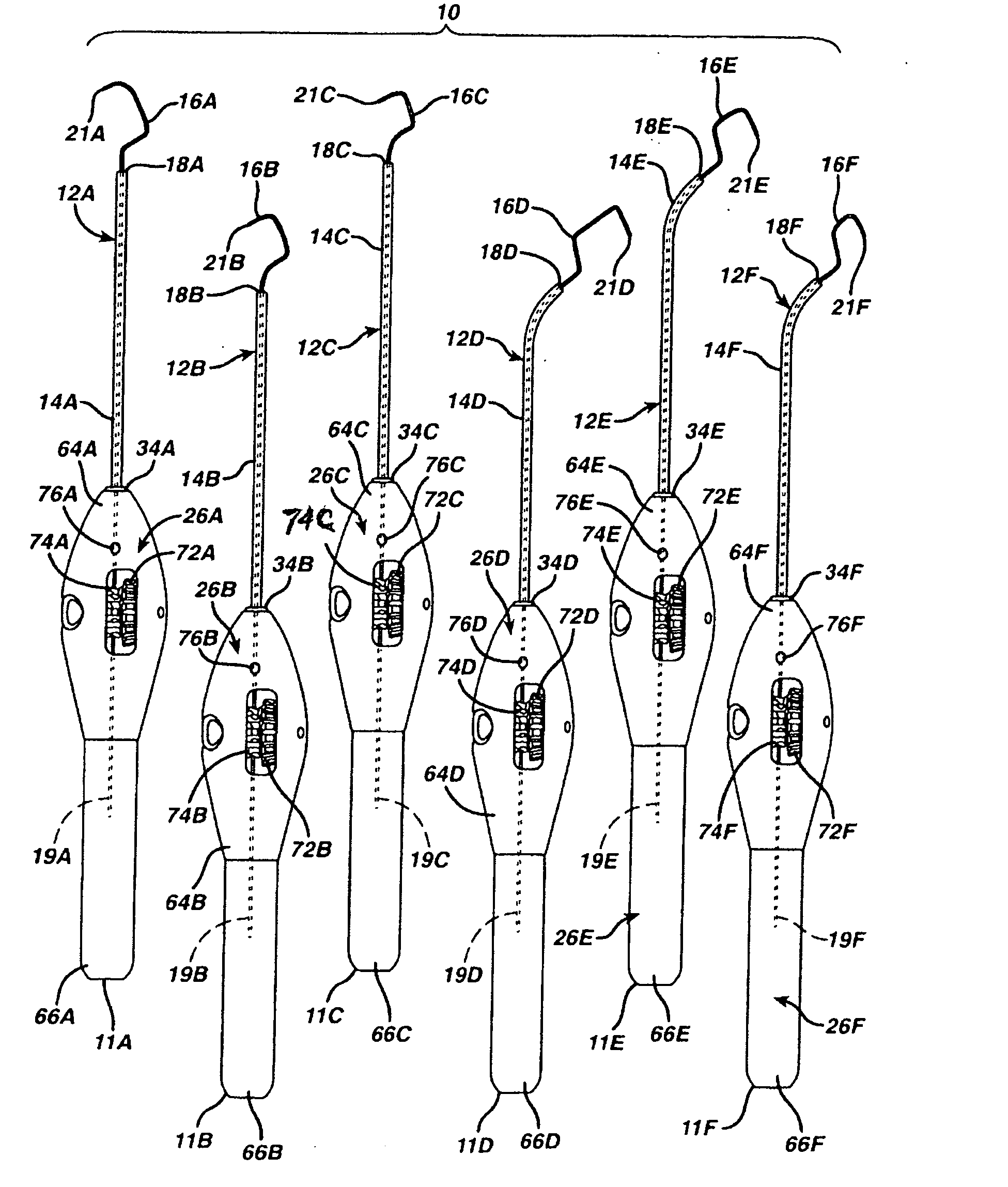
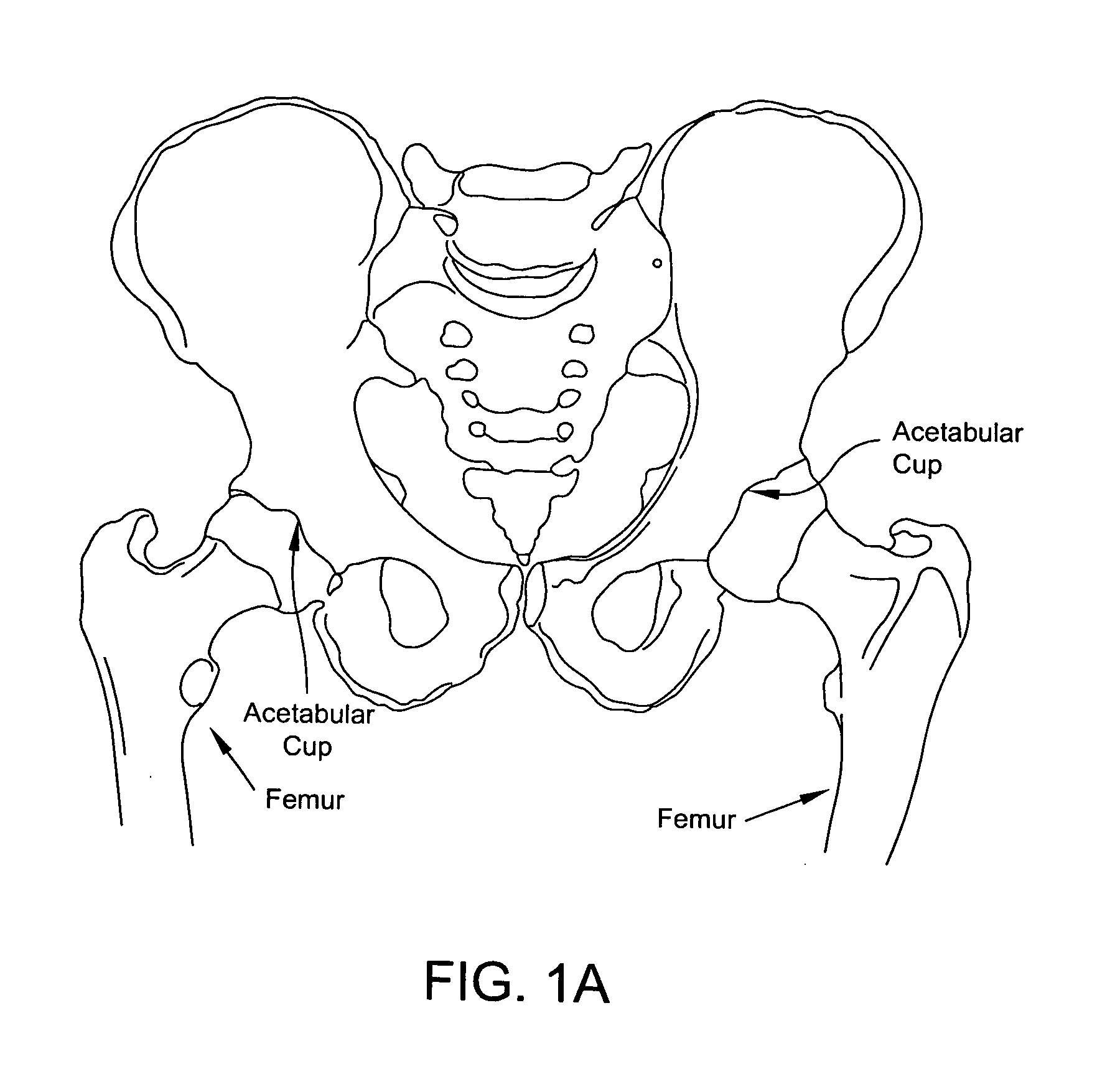
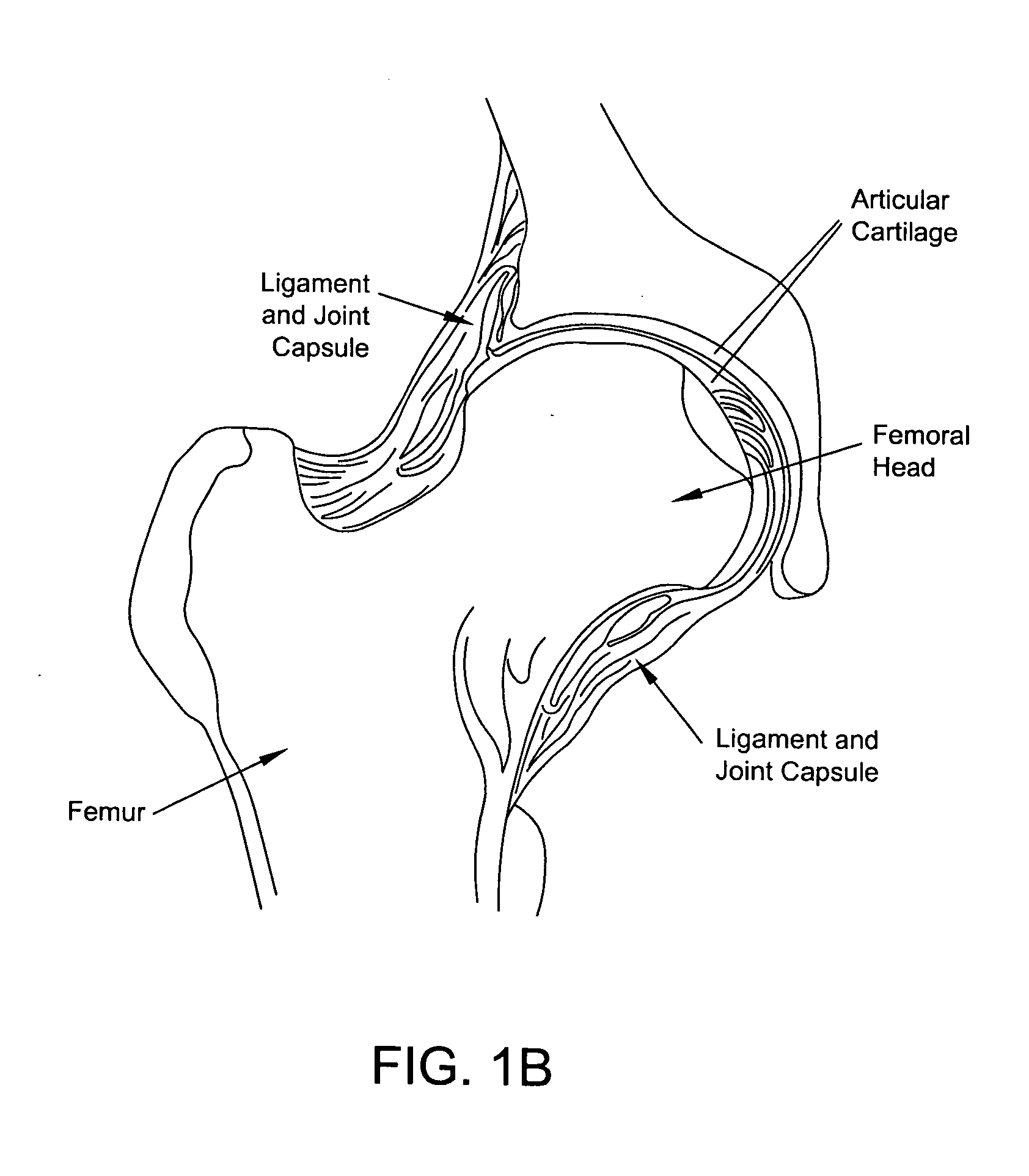
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
194 results about "Arthroscopic procedure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
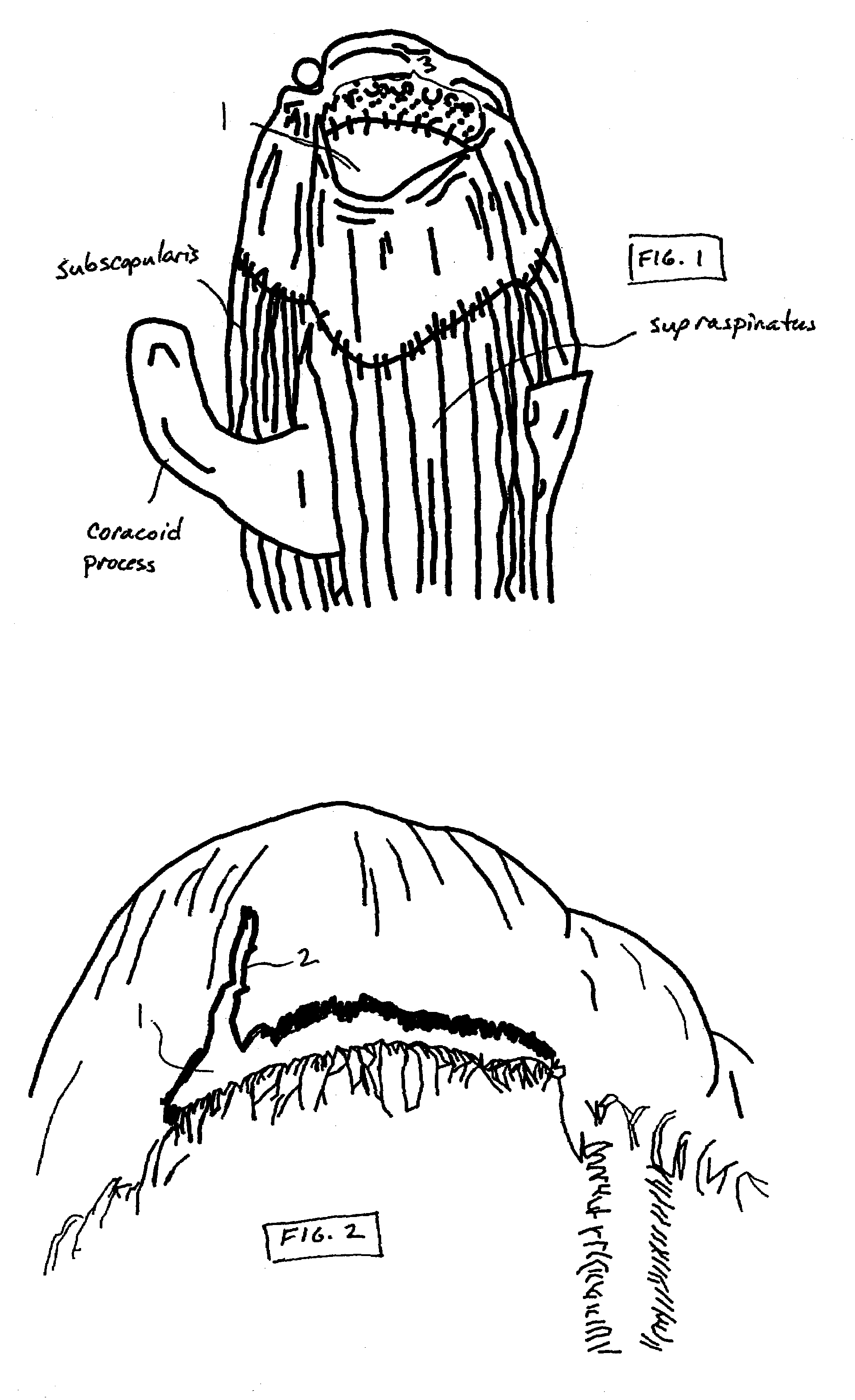
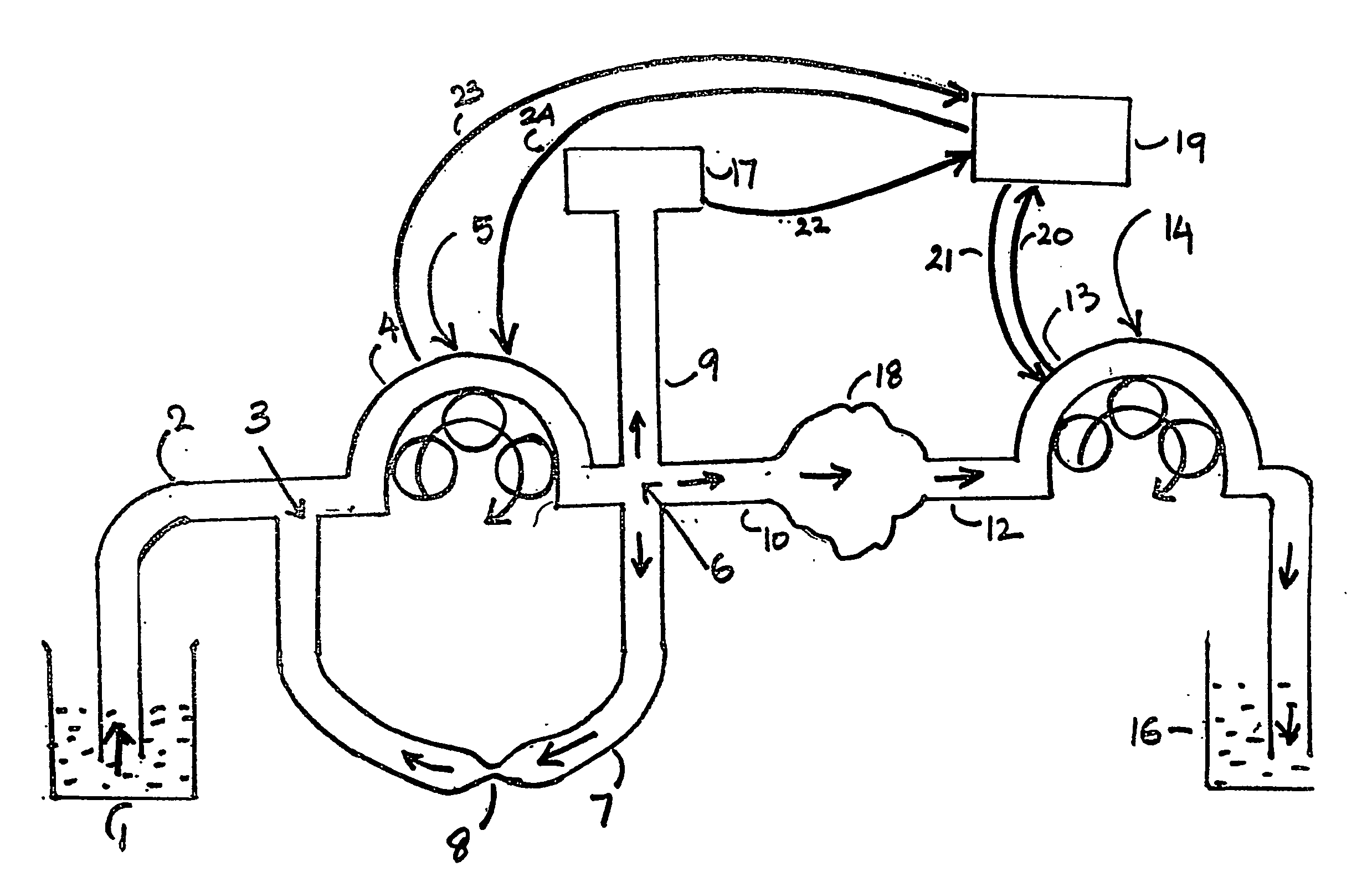
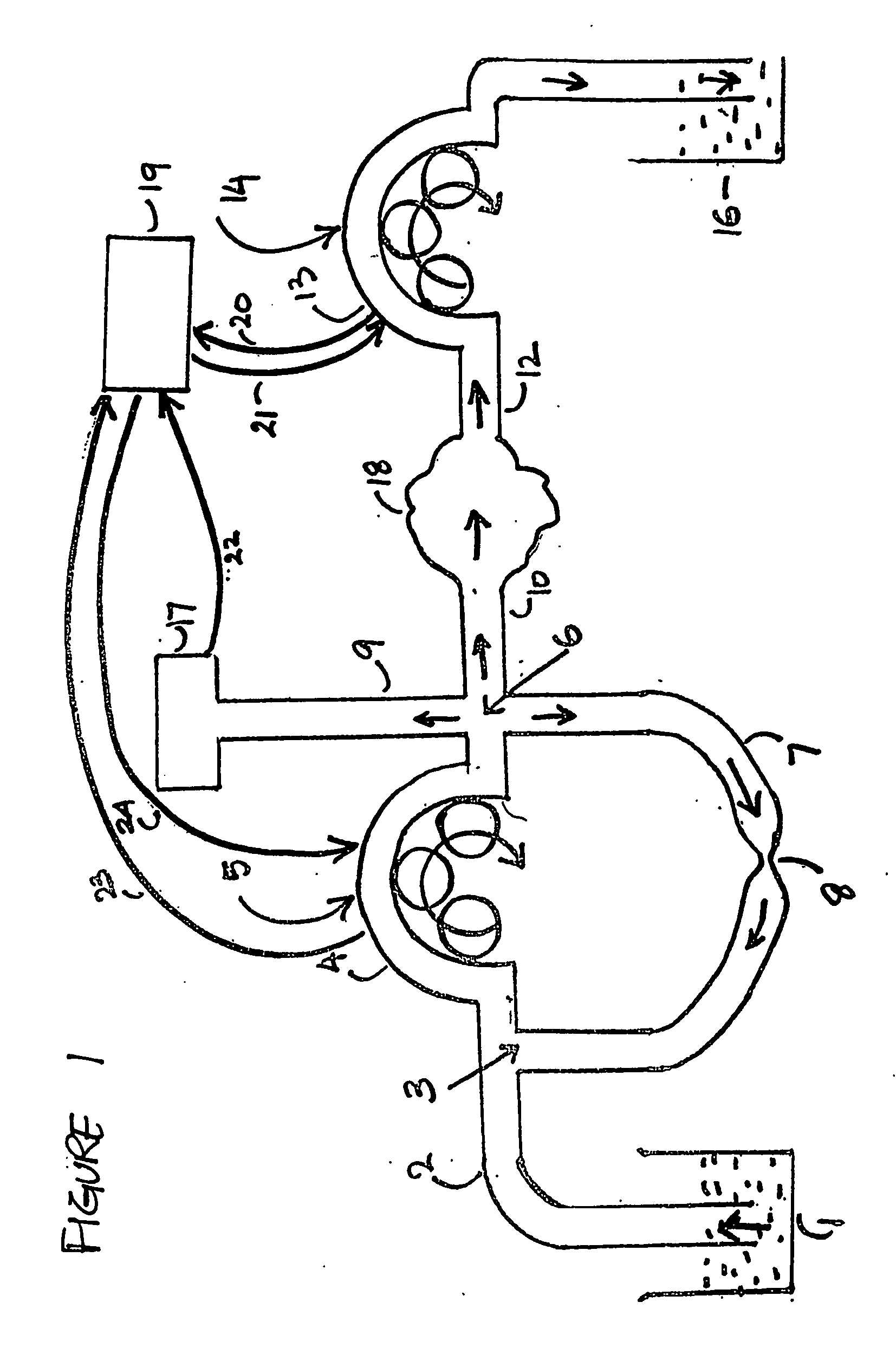
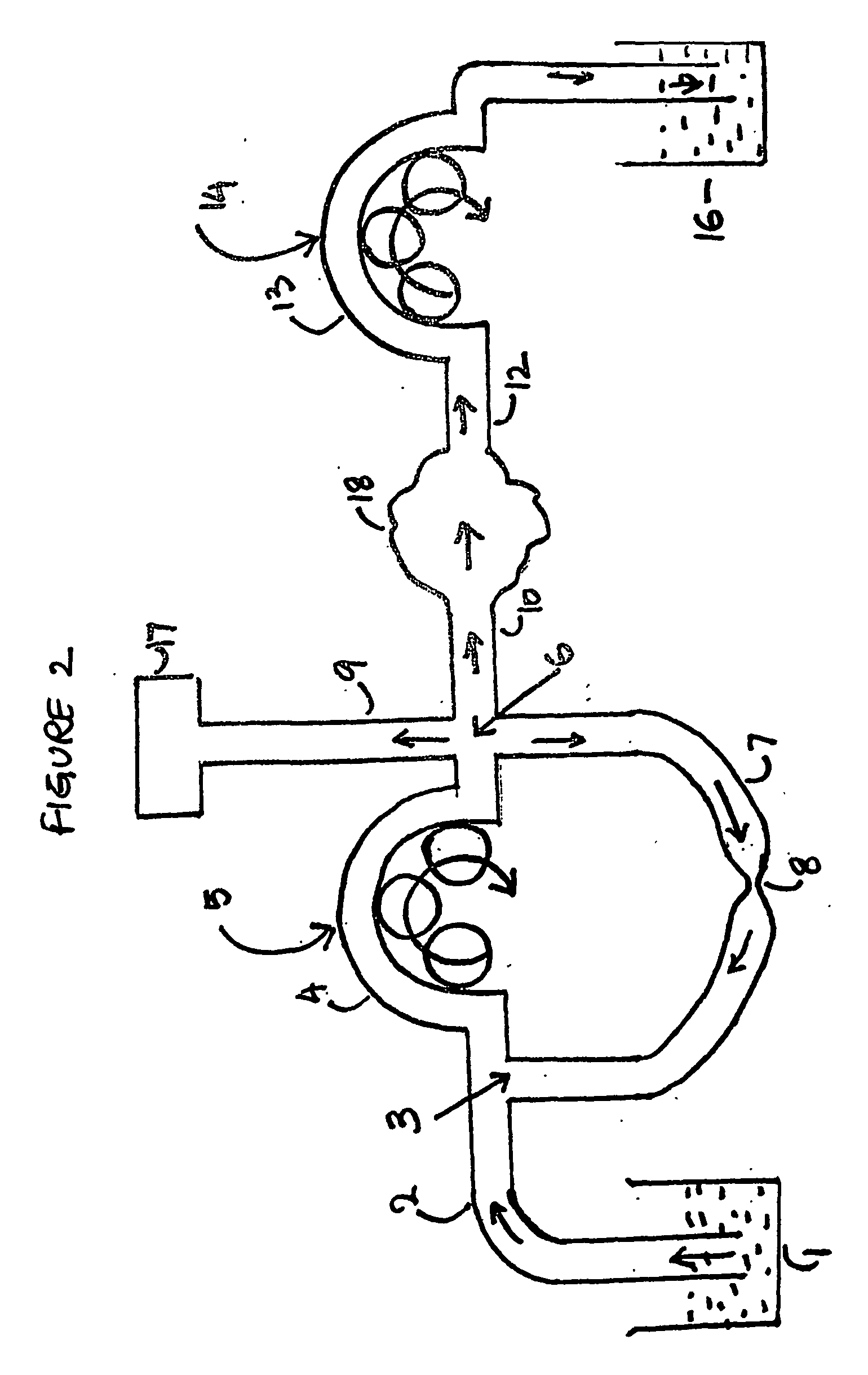
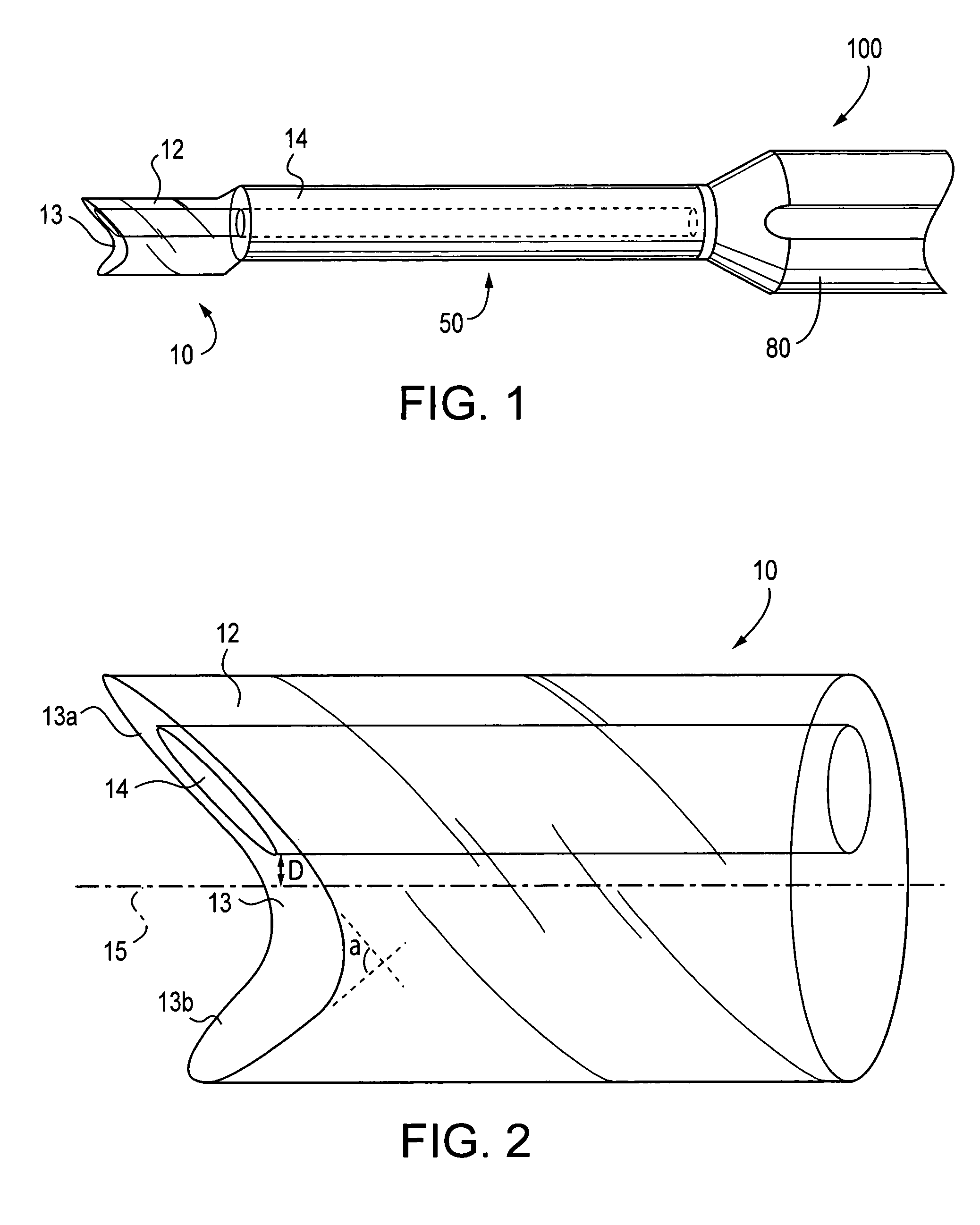
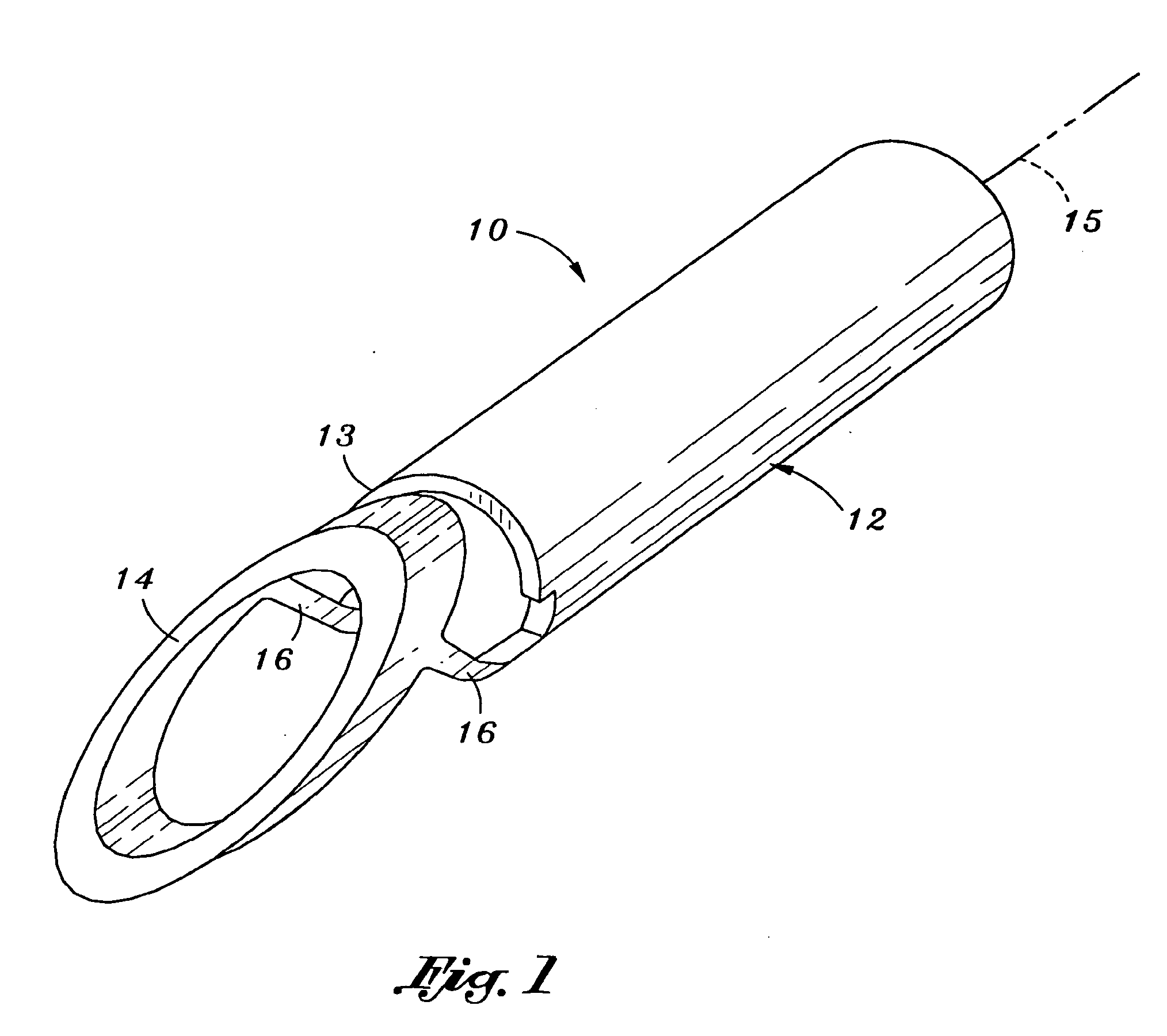
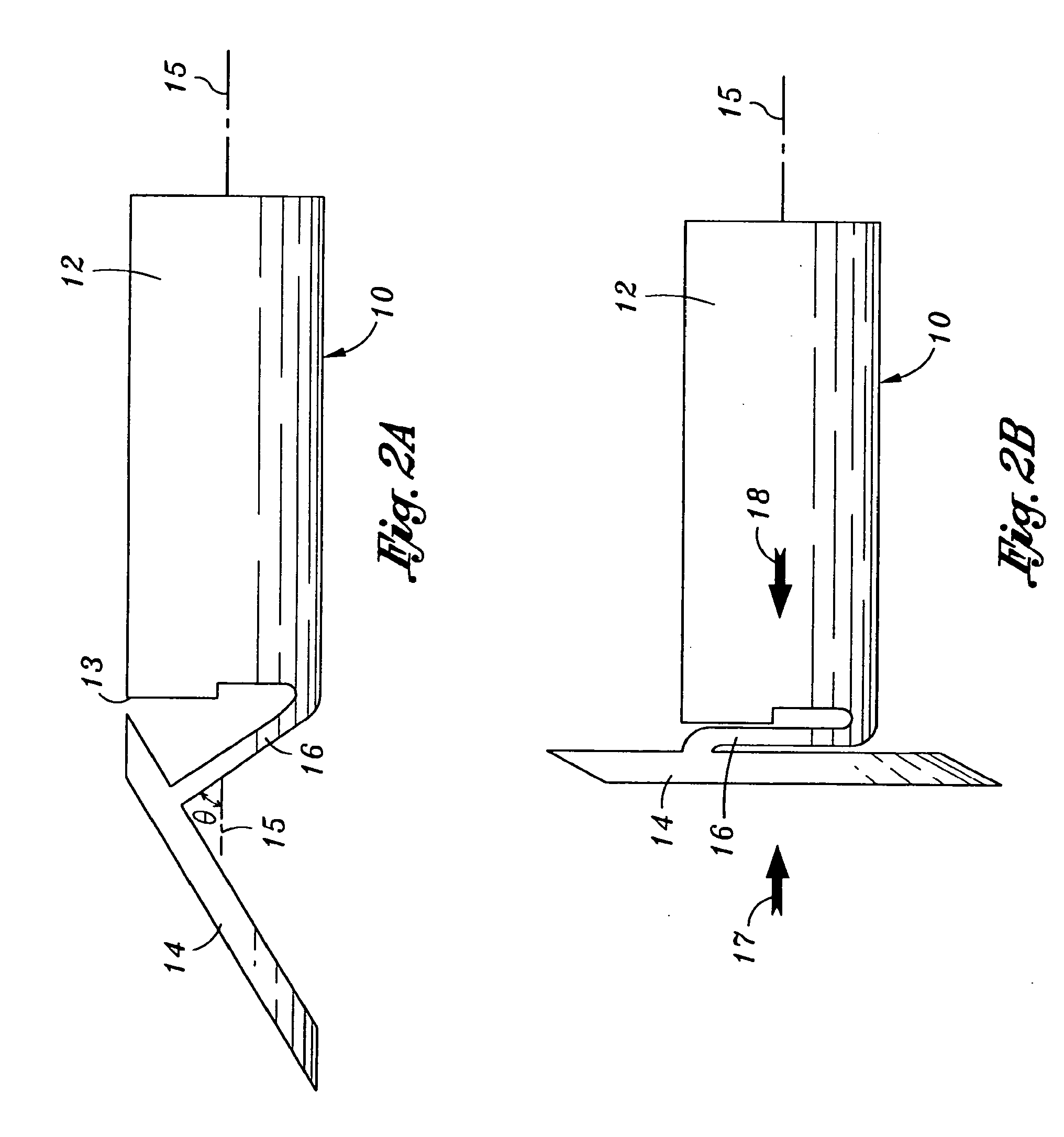
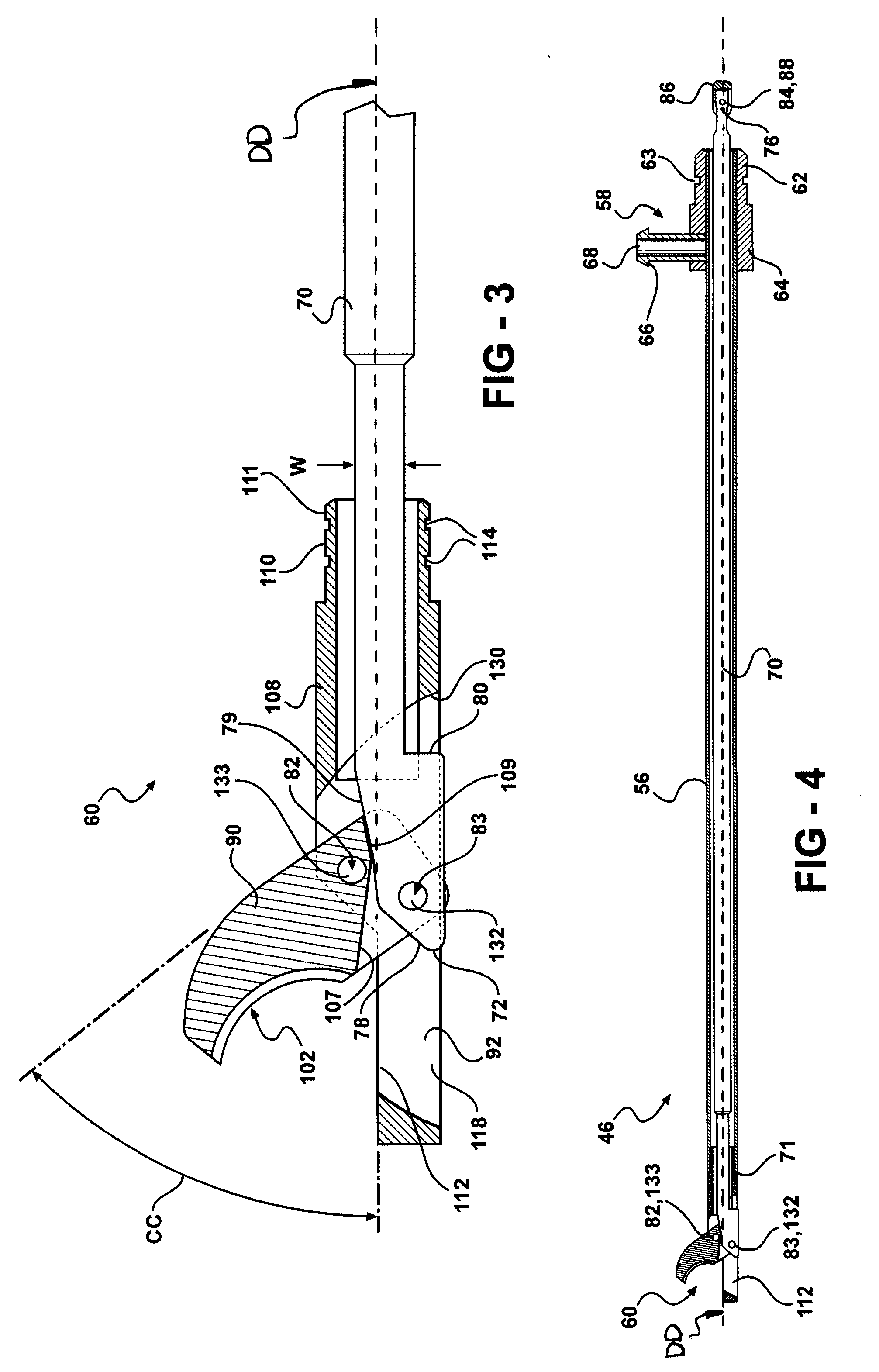
Concave probe for arthroscopic surgery
InactiveUS6135999AElectrotherapySurgical instruments for heatingThermal energyArthroscopic procedure
Disclosed herein is a new arthroscopic probe with a concave distal tip which simultaneously constrains and cuts tissue. It is particularly adapted to cutting ligaments and tendons. Also disclosed is a thermal energy delivery apparatus which includes (a) a probe means with a distal end and a proximal end, wherein the distal end has a concave tip; (b) a first electrode means positioned at the distal end of the probe means, wherein the first electrode means is configured to deliver sufficient thermal energy to cut ligaments or tendons; and (c) a cabling means coupled to the proximal end of the probe means. In another embodiment of the invention a controller for controlling the delivery of energy and liquid to a surgical instrument with a temperature sensor is disclosed. The energy is supplied by an energy source and the liquid is supplied by a pump. The controller includes a temperature and a flow regulator. The temperature regulator is coupled to the energy source and coupled to the pump. The temperature regulator is responsive to a first temperature indication from the temperature sensor to determine that the first temperature indication exceeds a setpoint and to reduce an energy level from the energy source. The flow regulator is coupled to the pump and coupled to the temperature regulator. The flow regulator includes responsiveness to the first temperature indication to increase a flow of the liquid from the pump.
Owner:ORATEC INTERVENTIONS
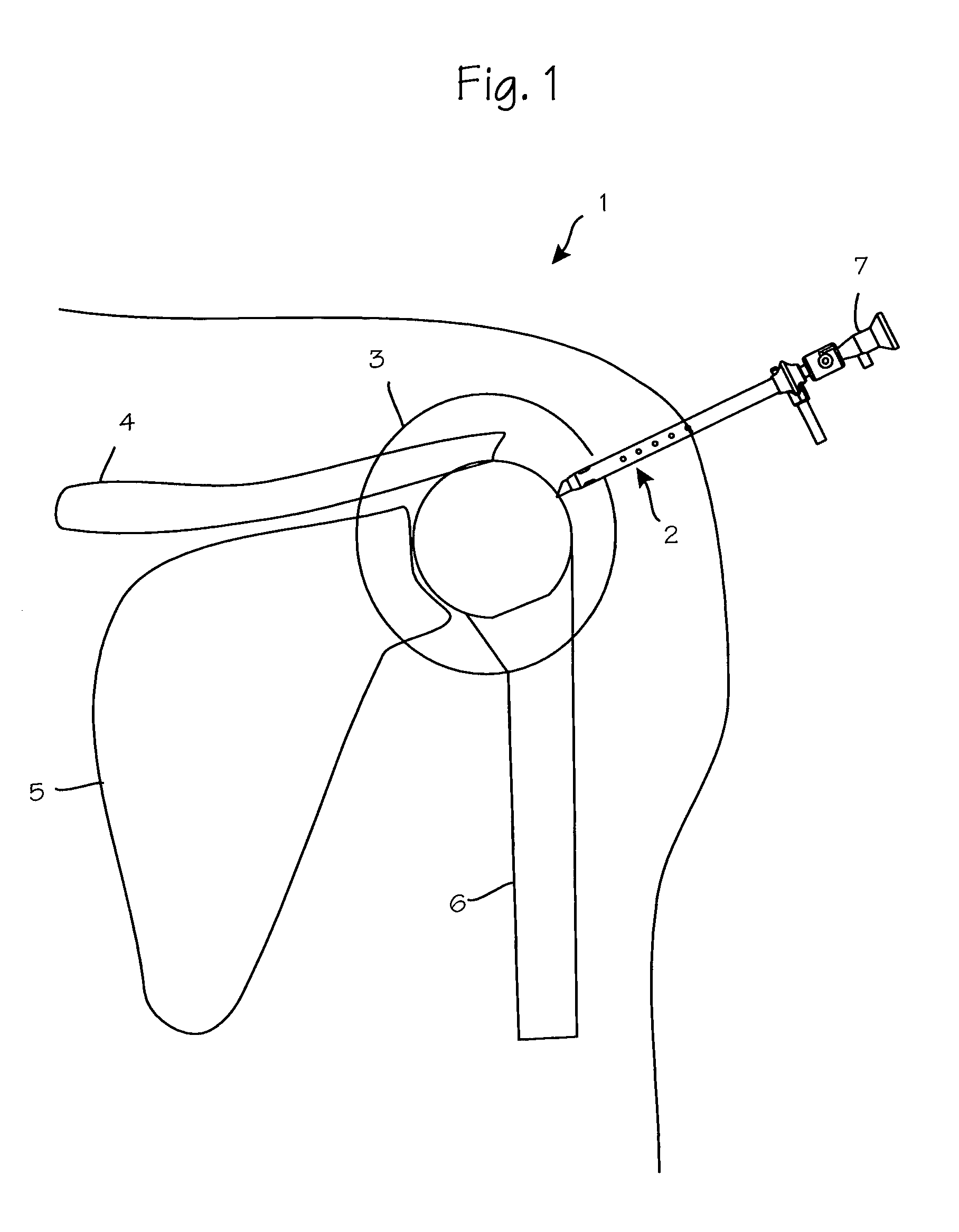
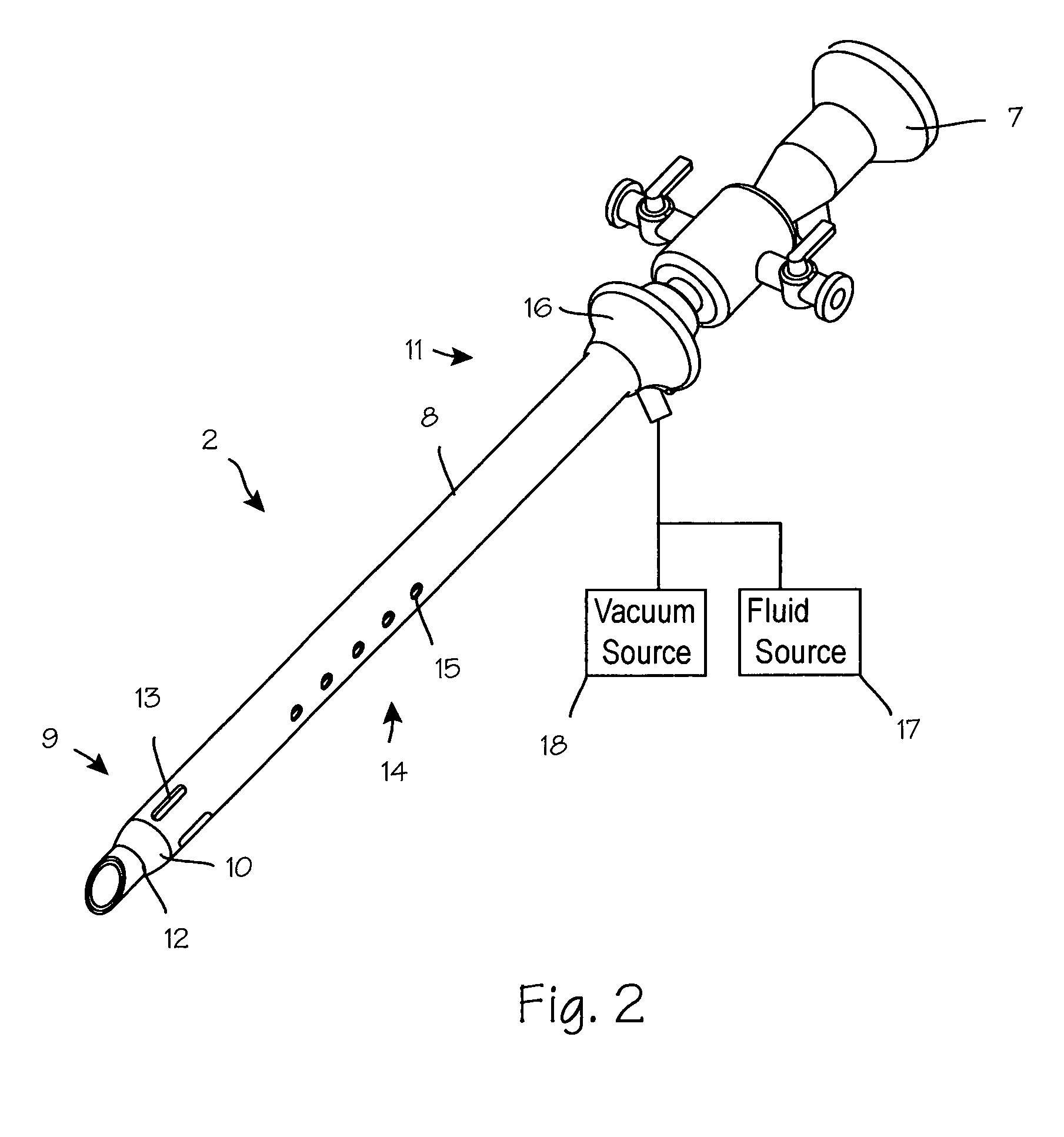
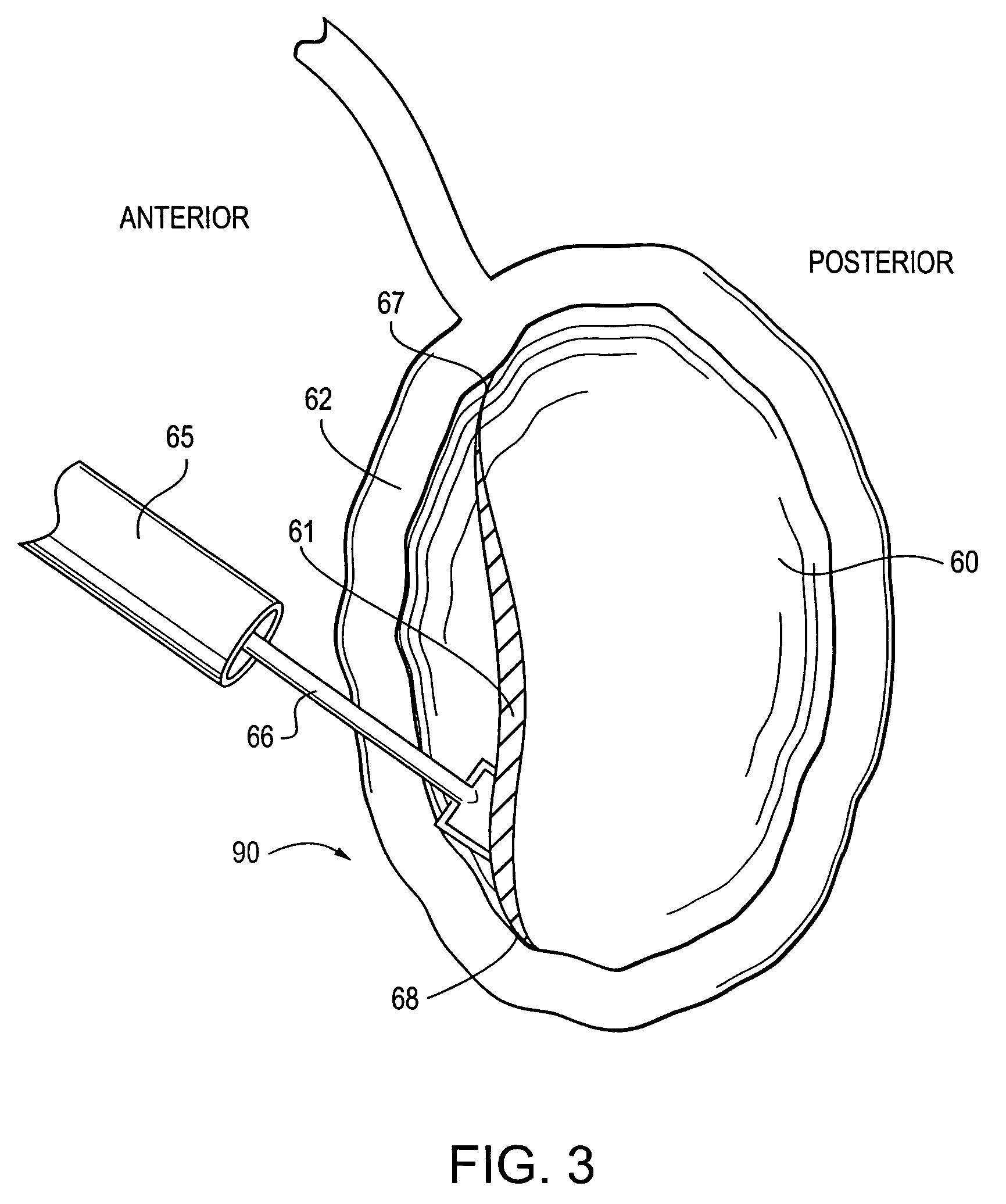
Anti-extravasation sheath and method
ActiveUS7503893B2Reduce extravasationClear surgical fieldCannulasSurgical needlesArthroscopic procedureArthroscopic Surgical Procedures
The methods shown provide for the minimization of extravasation during arthroscopic surgery. Use of an anti-extravasation sheath having at least one drainage aperture allows a surgeon to drain excess fluids from the tissue surrounding the surgical field during an arthroscopic surgical procedures when the drainage aperture is disposed within the tissue surrounding an arthroscopic surgical field outside of the joint capsule. The method of performing arthroscopic surgery may further include providing fluid inflow and outflow to the joint capsule through inflow / outflow holes in the anti-extravasation sheath.
Owner:CANNUFLOW INC
Apparatus and method for use in repairs of injured soft tissue
InactiveUS7303577B1Promote blood flowExtended range of motionSuture equipmentsLigamentsArthroscopic procedureSurgical repair
A method, system and apparatus for augmenting the surgical repair of soft tissue injuries, in which a first end of a bridge member attaches to a first portion of healthy tissue, and a second end of the bridge member attaches to a second portion of healthy tissue. The bridge member (or bridge members) used to augment the soft tissue repair may be interconnected or function independently. Flexibility and elasticity of the bridge member are determined by the situation and may be altered to improve healing. The device may be used in arthroscopic procedures, and may be manufactured in a variety of lengths, or may be manufactured one length and be cut to the desired length, or otherwise altered to provide an optimal length of the bridge member.
Owner:DEAN & WEBB
Arthroscopic surgical temperature control system
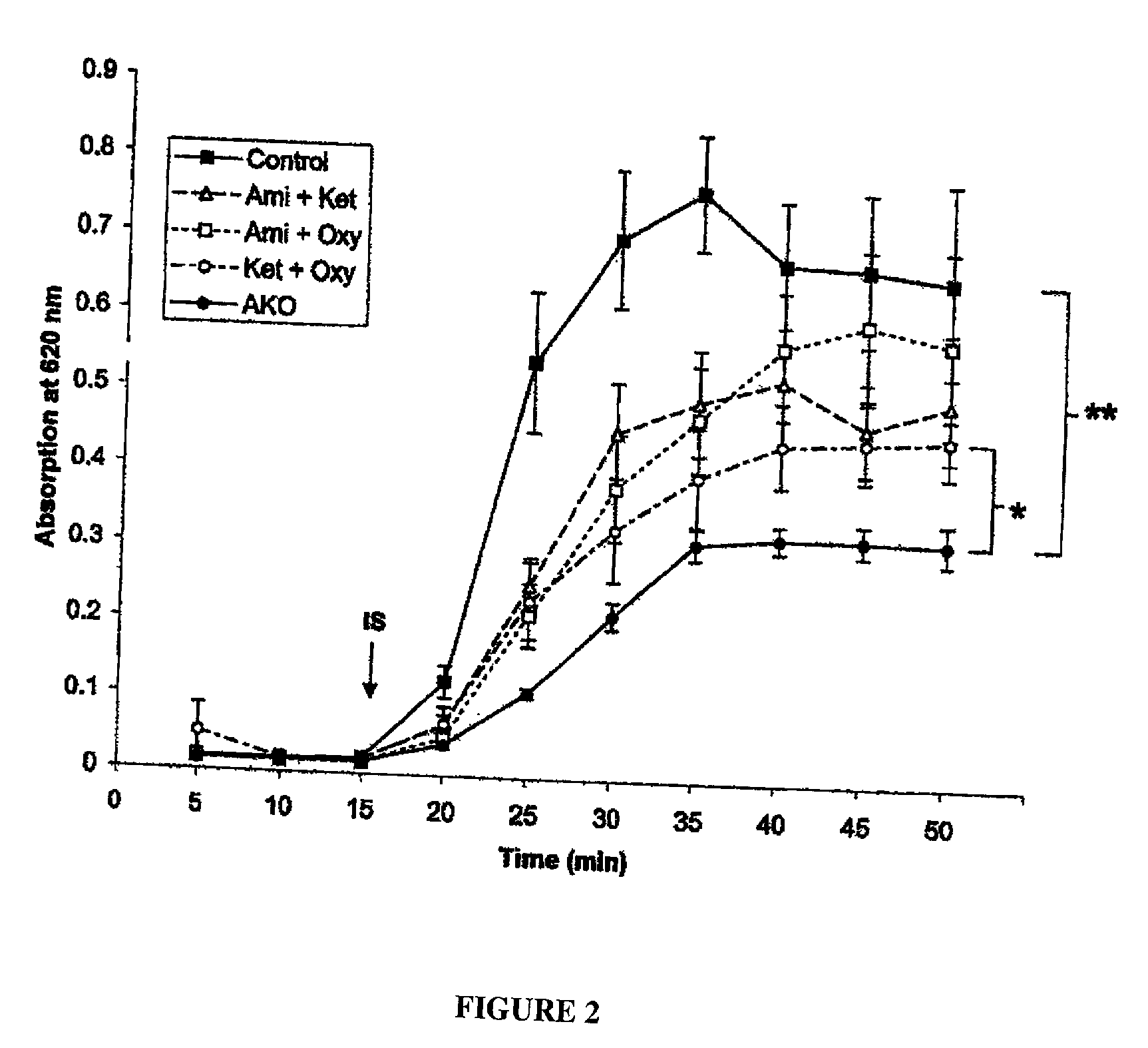
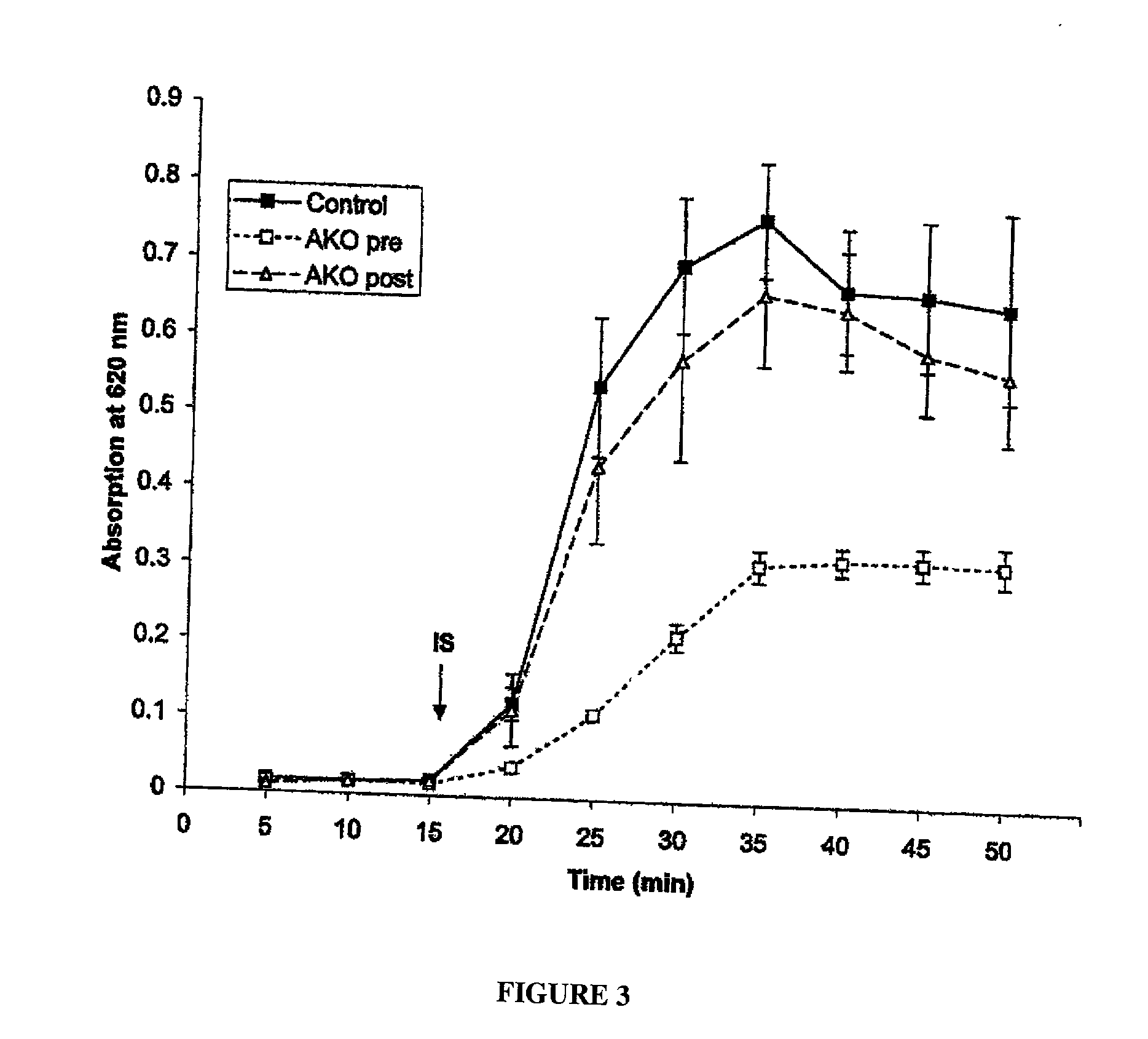
An arthroscopic surgical temperature control system and method able to monitor and control the temperature within a surgical site during arthroscopic ablation procedures in order to prevent tissue damage is provided.
Owner:CANNUFLOW INC
Chondroprotective/restorative compositions and methods of use thereof
The instant invention provides a method of treating or preventing osteoarthritis, joint effusion, joint inflammation and pain, synovitis, lameness, post operative arthroscopic surgery, deterioration of proper joint function including joint mobility, the reduction or inhibition of metabolic activity of chondrocytes, the activity of enzymes that degrade cartilage, the reduction or inhibition of the production of Hyaluronic acid, said method comprising orally administering to a mammalian species a therapeutically effective amount of Hyaluronic Acid or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof. Additionally, compositions containing hyaluronic acid; chondroitin sulfate, and glucosamine sulfate in a paste formulation are also disclosed which can be administered on their own or can be used as a feed additive.
Owner:PIERCE SCOTT W
Anti-extravasation sheath
ActiveUS20070185380A1ClearReduce extravasationCannulasSurgical needlesArthroscopic procedureArthroscopic Surgical Procedures
The devices and methods shown provide for the minimization of extravasation during arthroscopic surgery. The anti-extravasation sheath allows a surgeon to drain excess fluids from the soft tissue surrounding the surgical field during arthroscopic surgical procedures.
Owner:CANNUFLOW INC
Arthroscopic surgical temperature control system
Owner:CANNUFLOW INC
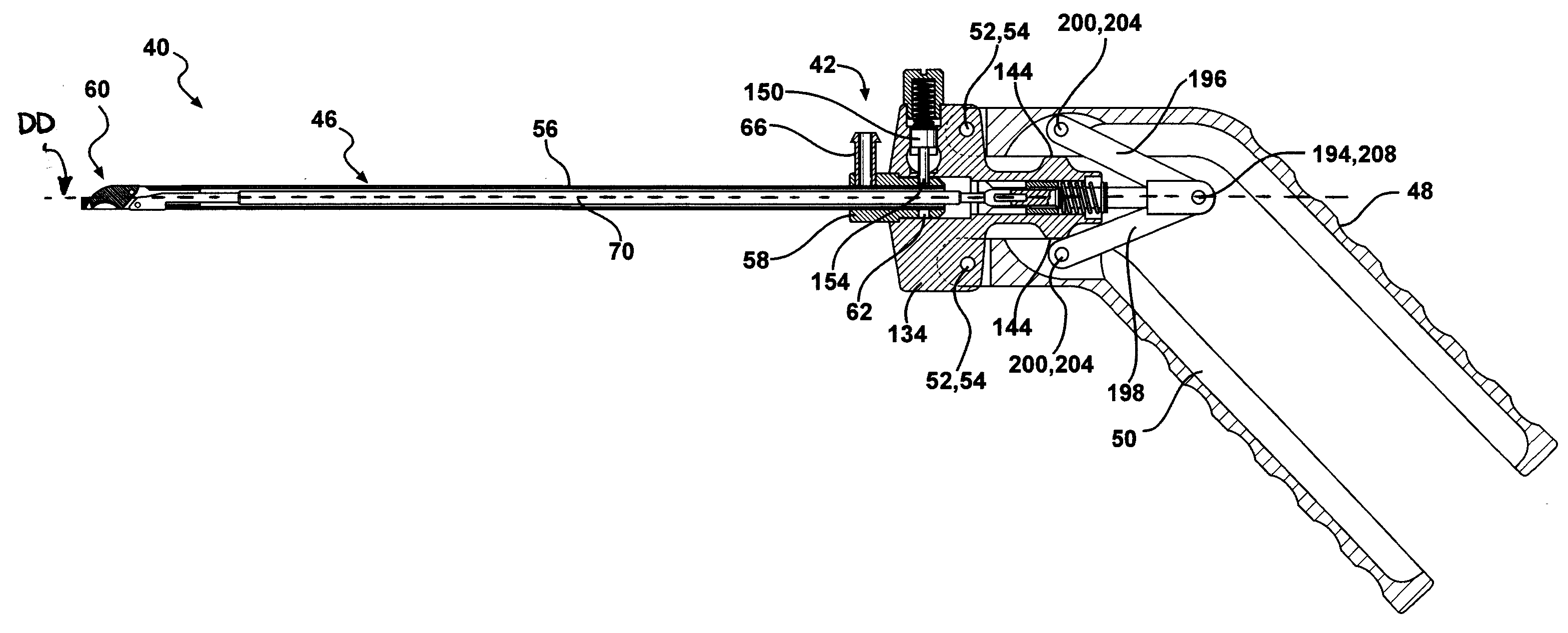
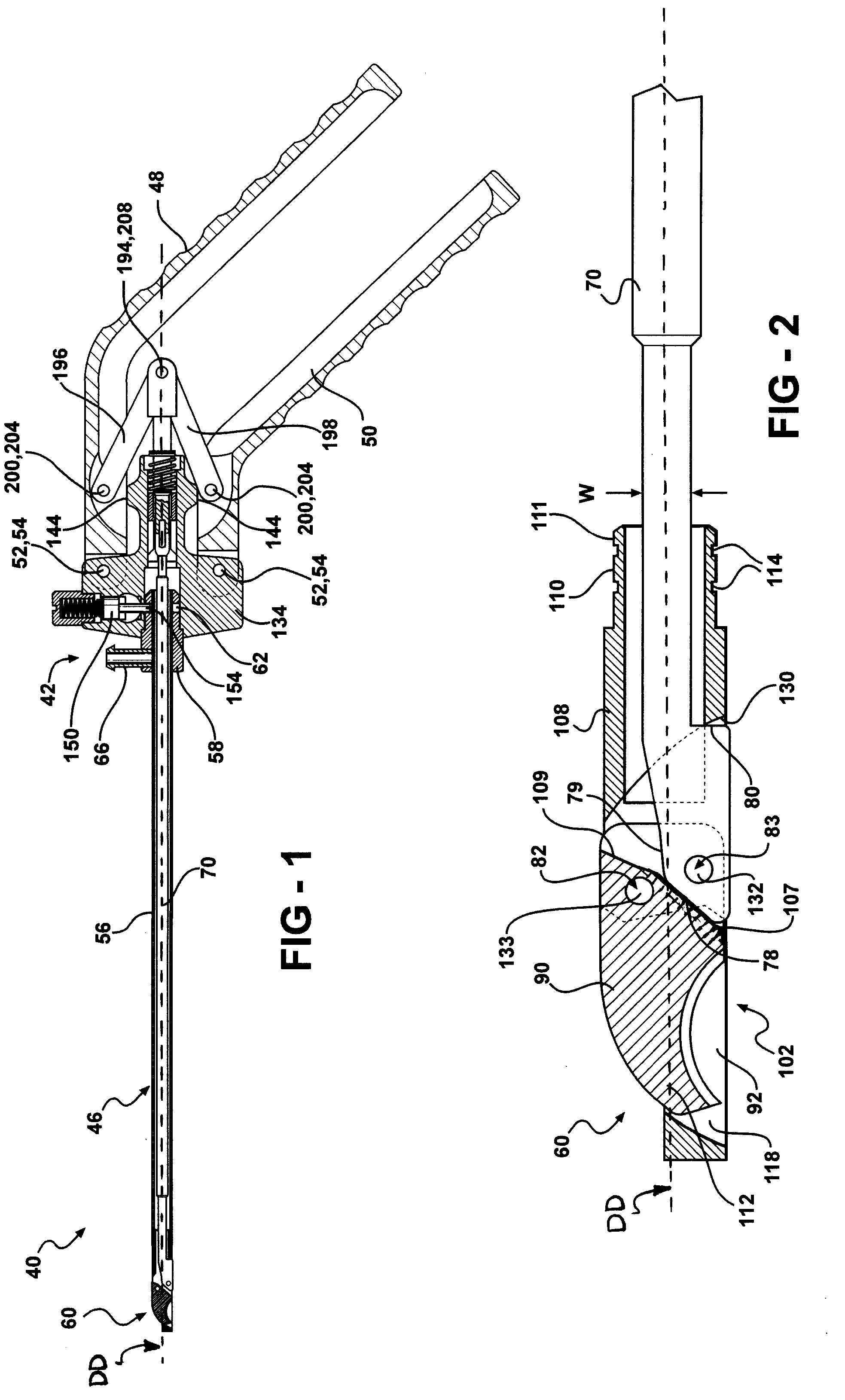
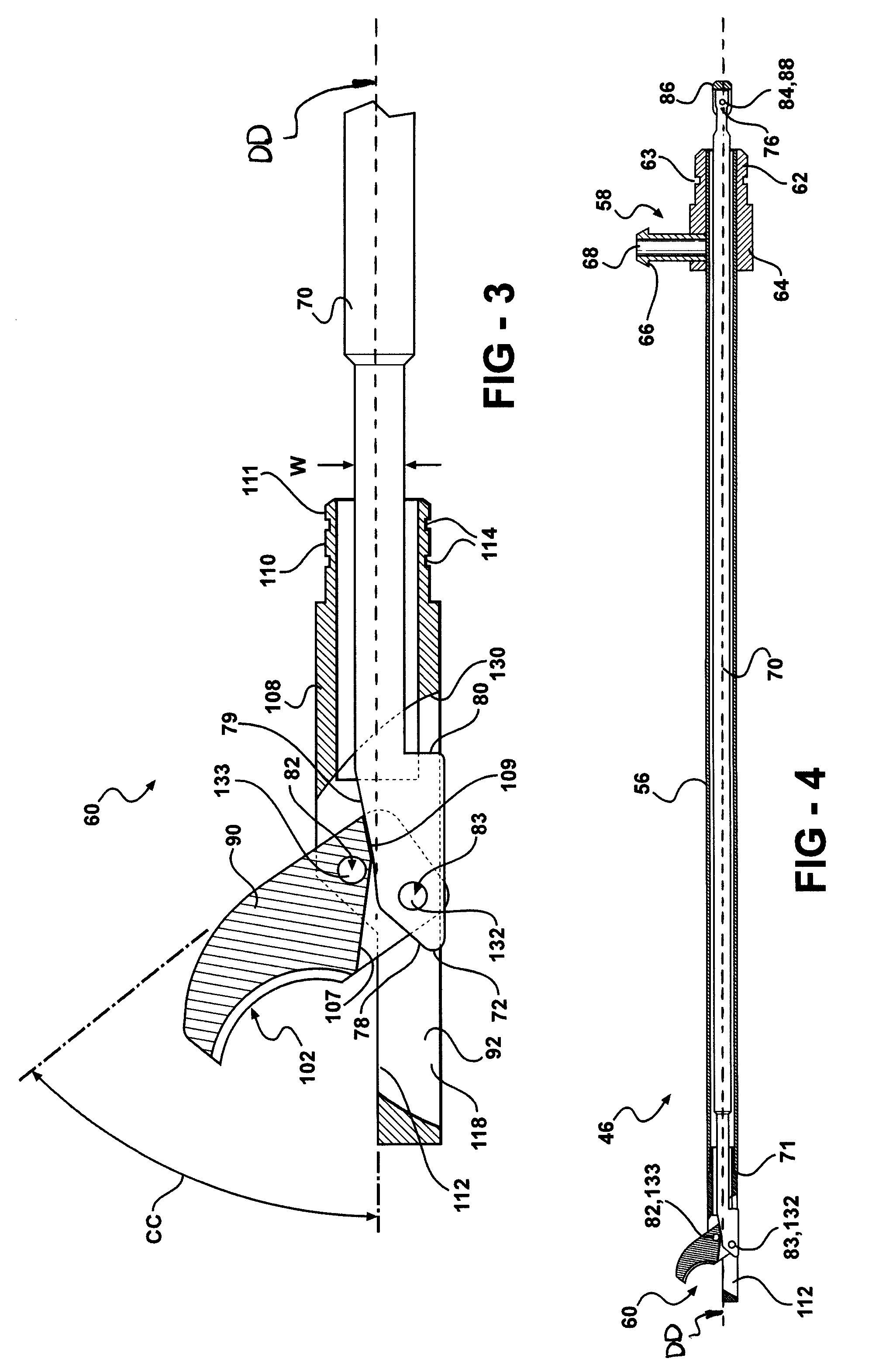
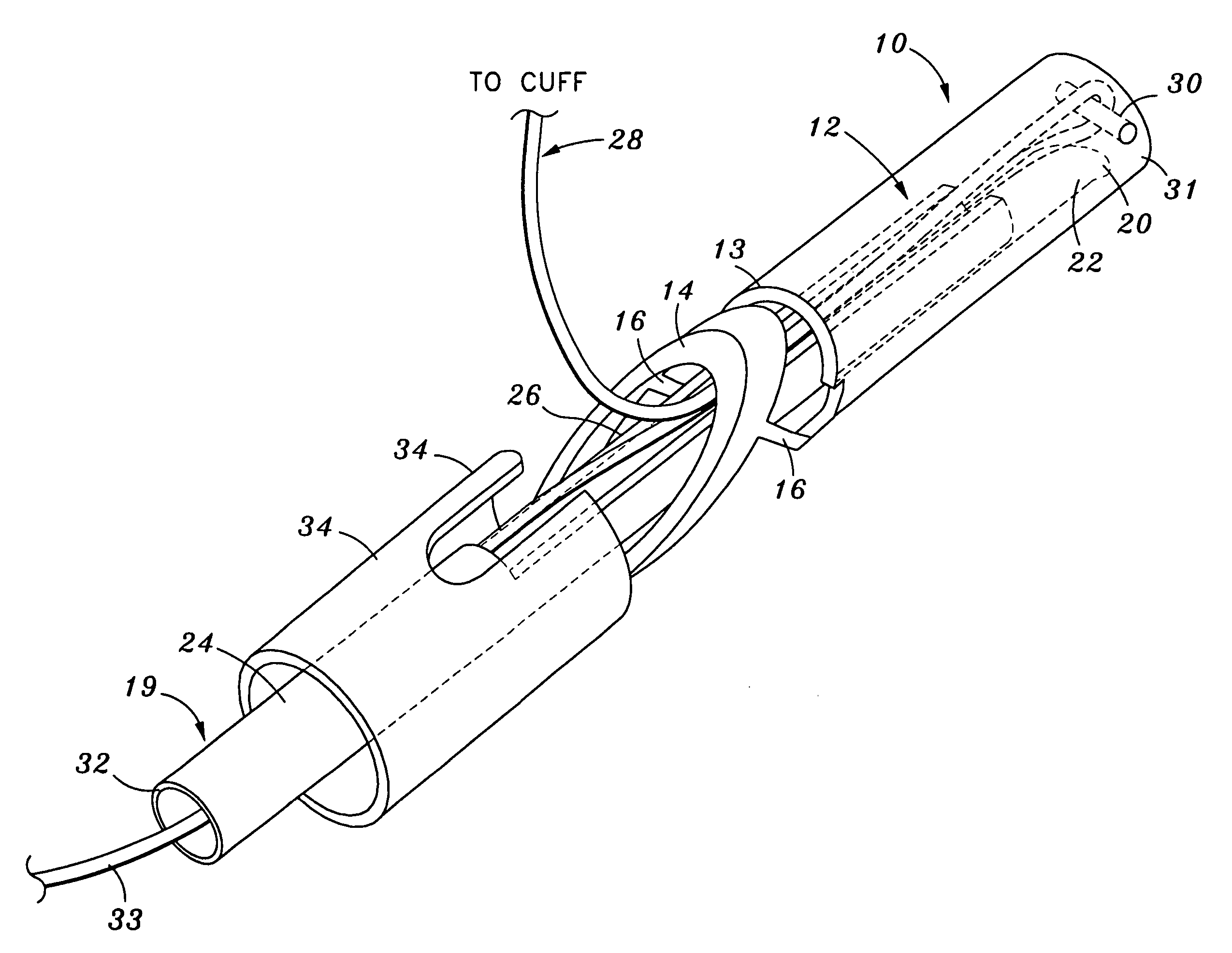
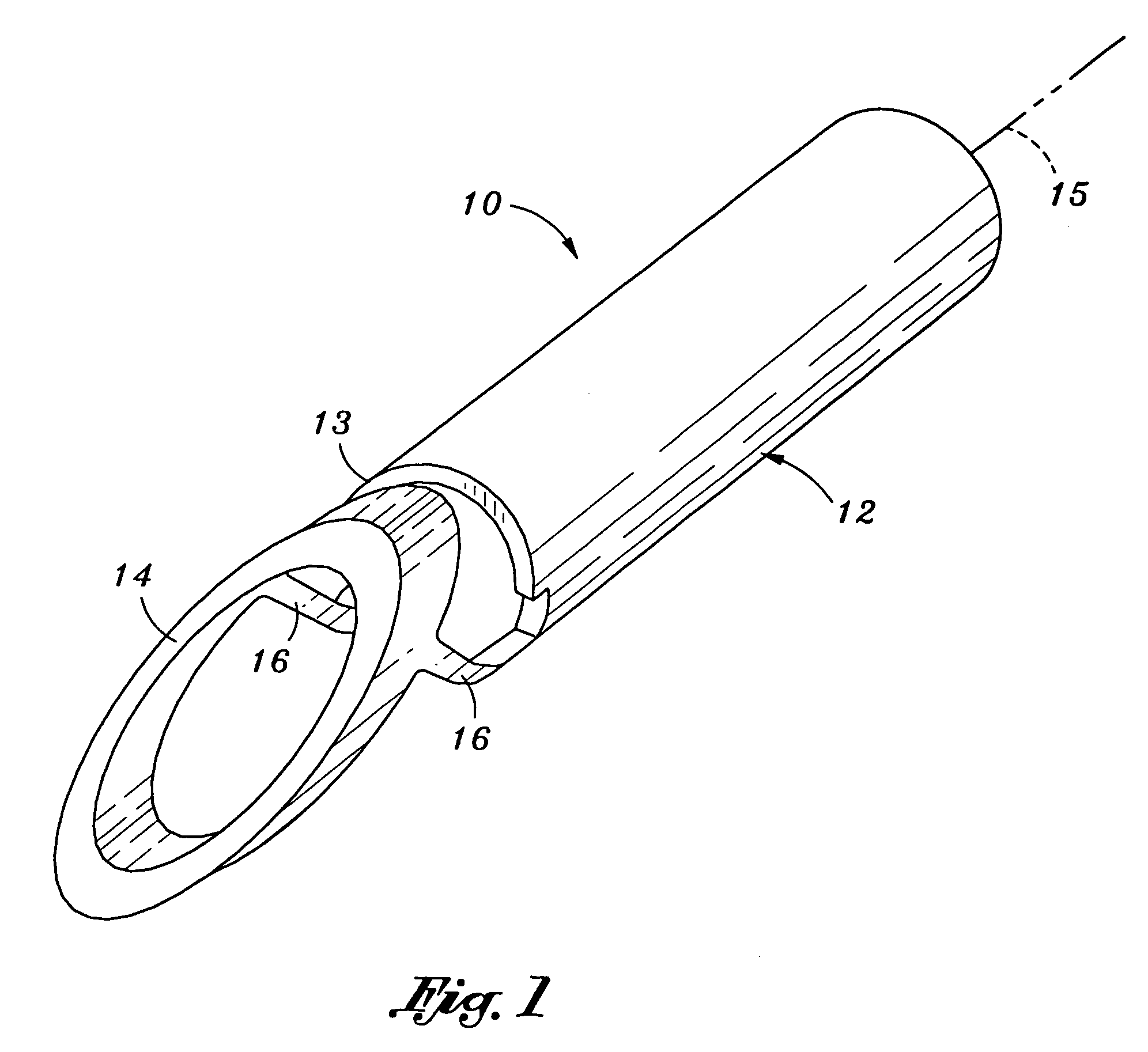
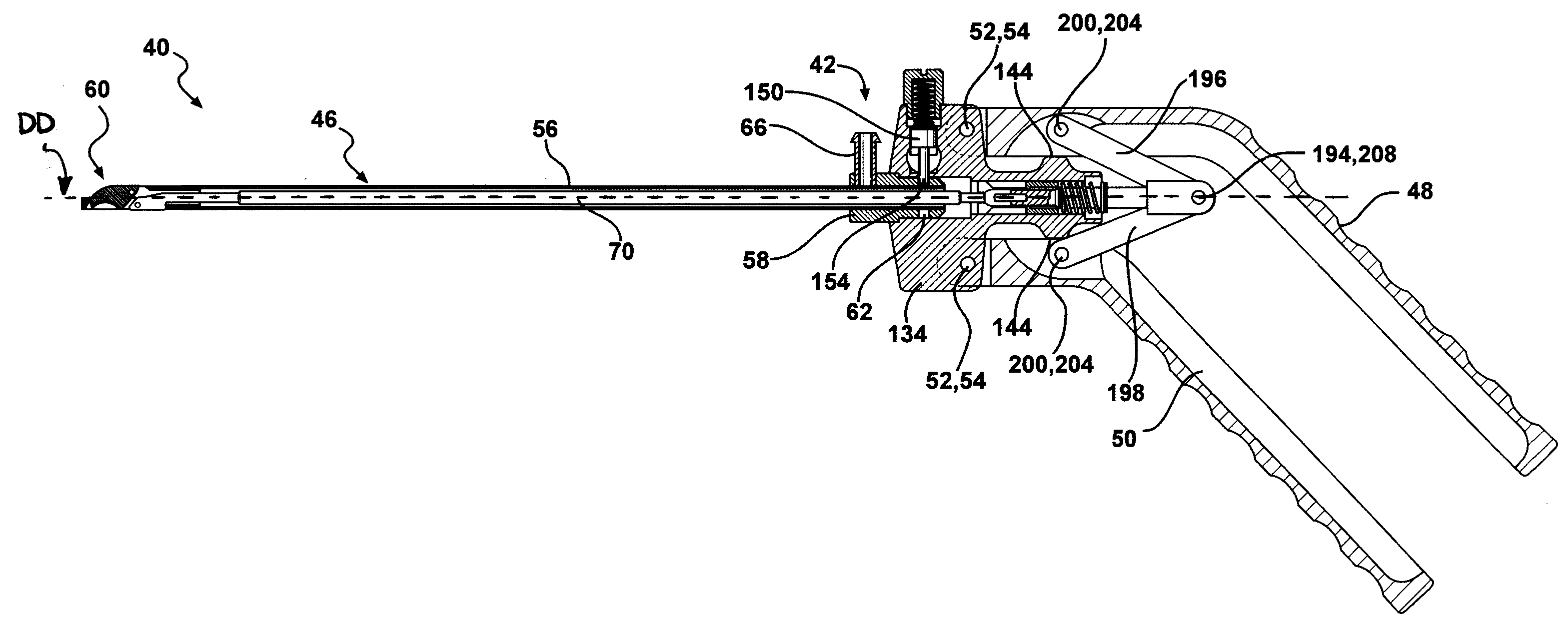
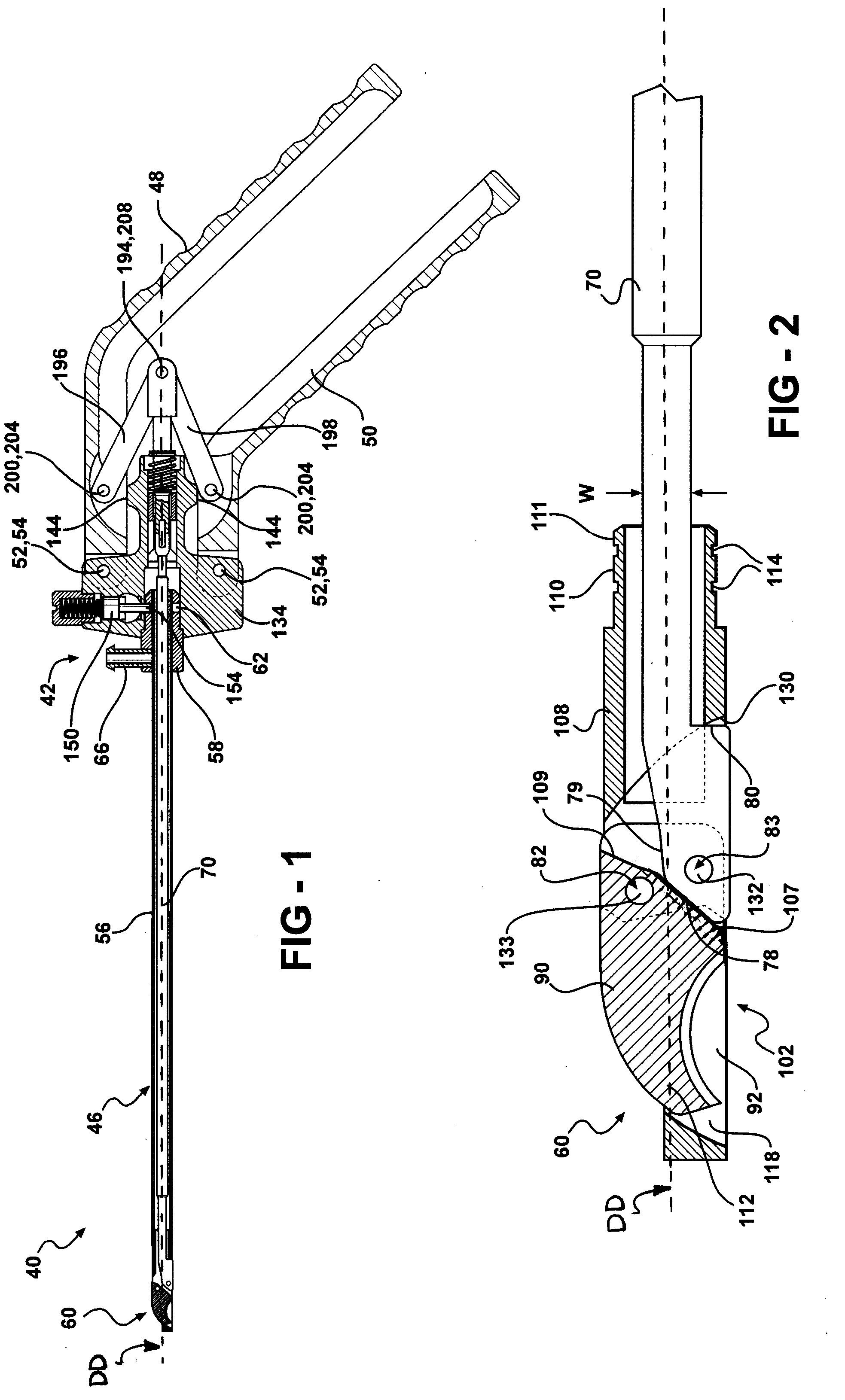
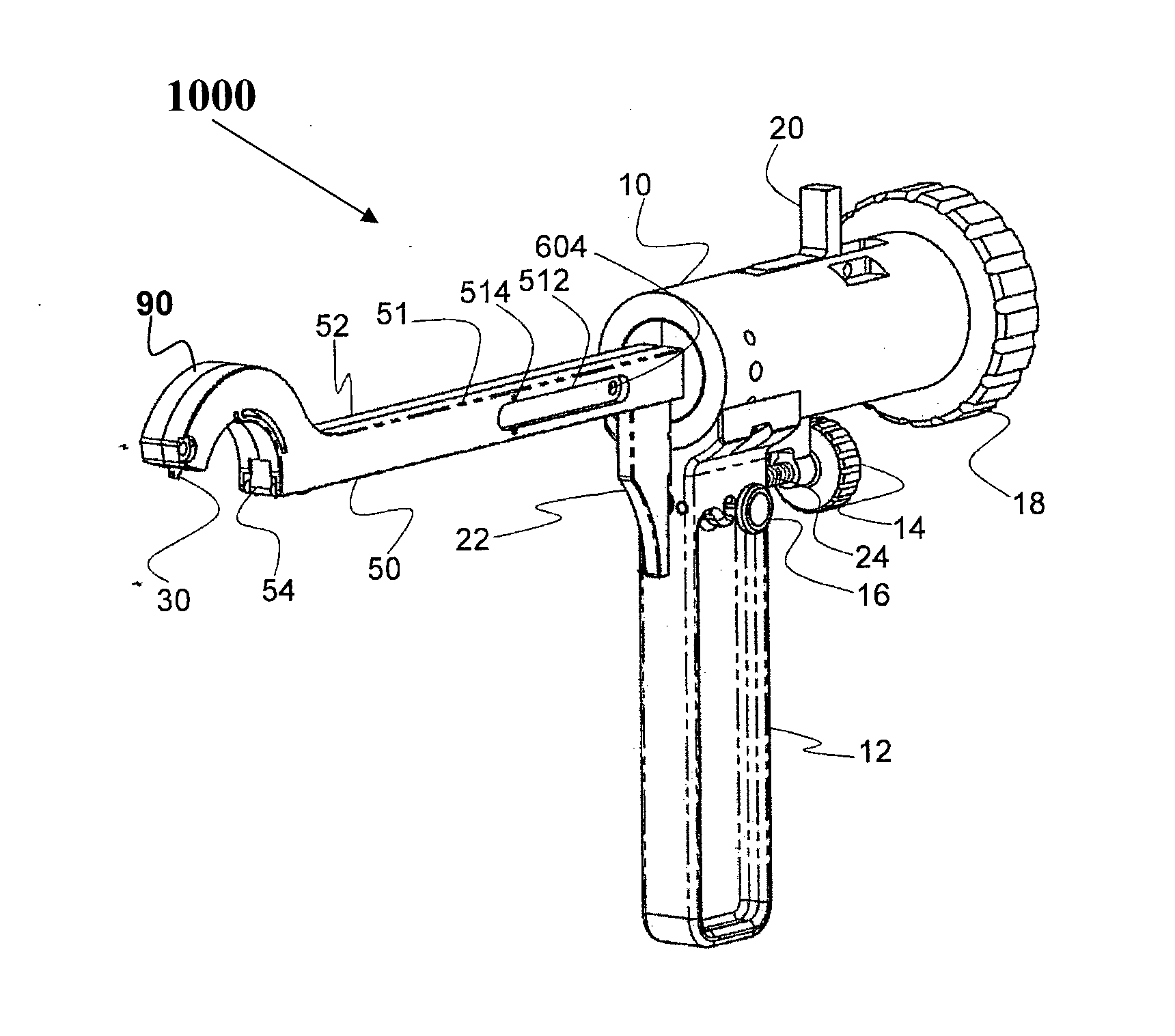
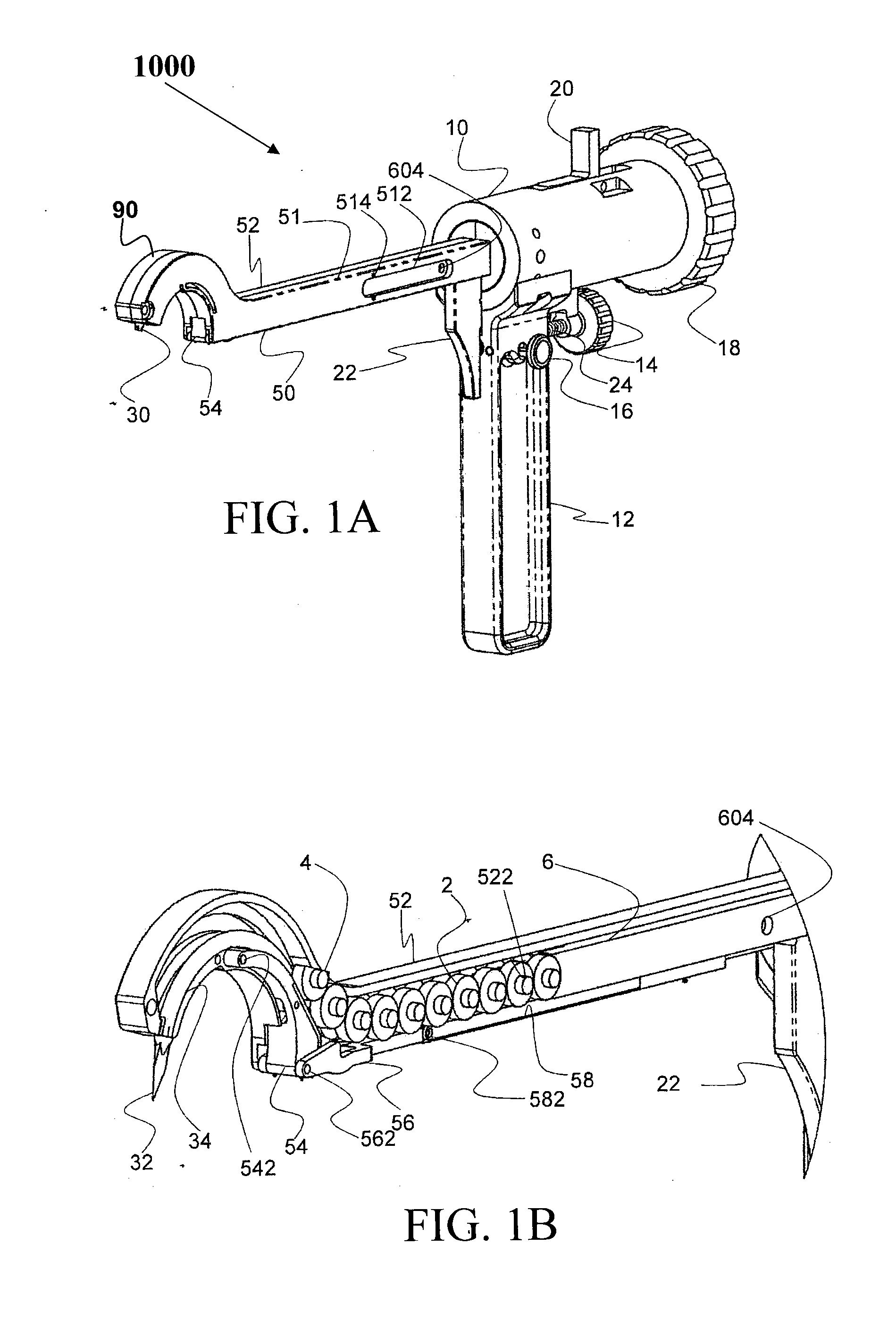
Forceps for performing endoscopic or arthroscopic surgery
Forceps for performing endoscopic or arthroscopic surgery include a body assembly, a tube assembly, and a pair of handles that pivot with respect to the body. The tube assembly is removably attached to the body assembly. The tube assembly includes a hollow tube and a tip assembly. The tip assembly includes an electrode or a blade for performing the surgery. The tip assembly and the blade are connected to the body and the handles by a cable. As the handles pivot, the cable slides within the tube to move the blade. When a different tube assembly (i.e., a bipolar or a monopolar electrode) or another style of tip assembly are desired, the installed one is removed and replaced by a new tube assembly or tip assembly as desired.
Owner:LIVNEH STEVE
System for distending body tissue cavities by continuous flow irrigation
ActiveUS20070021713A1Shorten the timeMinimize exposureEnemata/irrigatorsMedical devicesContinuous flowEndoscopic Procedure
The present invention provides a system and a method for distending a body tissue cavity of a subject by continuous flow irrigation such that minimal or negligible fluid turbulence is present inside the cavity, such that any desired cavity pressure can be created and maintained for any desired outflow rate. The present invention also provides a method for accurately determining the rate of fluid loss, into the subject's body system, during any endoscopic procedure without utilizing any deficit weight or fluid volume calculation or flow rate sensor. The system and the methods of the present invention described above can be used in any endoscopic procedure requiring continuous flow irrigation few examples of such endoscopic procedures being hysteroscopic surgery, arthroscopic surgery, trans uretheral surgery, endoscopic surgery of the brain and endoscopic surgery of the spine.
Owner:ARTHREX
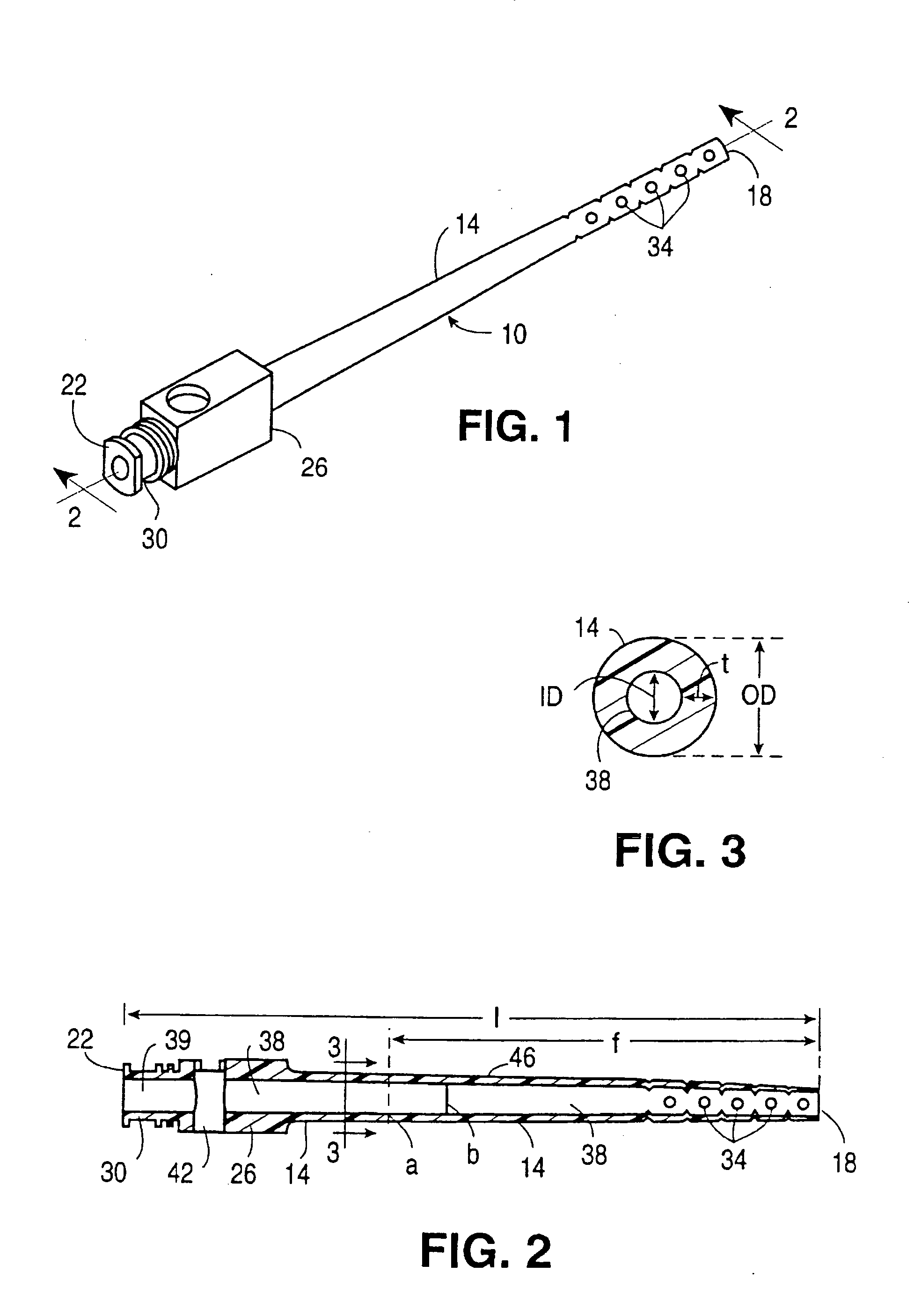
Method of using offset drill guide in arthroscopic surgery
ActiveUS7204839B2Avoid damageMinimal amountProsthesisOsteosynthesis devicesArthroscopic procedureSuture anchors
A cannulated offset drill guide and surgical methods for repairing Bankart lesions. The cannulated offset drill guide comprising a shaft which is offset from the guide center line by about 1 to 3 mm, more preferably of about 1.5 mm. The cannulated offset drill guide is provided at its proximal end with a concave clear tip which allows a surgeon to visualize the drill and the insertion of an anchoring device, for example a suture anchor. The concave clear tip has beveled, smooth edges to prevent damage to adjacent bone and tissue, and to avoid damage to the rubber dam of the cannula through which the offset drill guide is inserted. The configuration of the concave clear tip is designed to engage and match the generally convex-curve articulating face of the glenoid, and to precisely aligning the offset drill guide with the glenoid face. The clear tip may also be employed in a standard drill guide having a shaft which is not offset from the center line of the guide.
Owner:ARTHREX
Chondroprotective/restorative compositions and methods of use thereof
The instant invention provides a method of treating or preventing osteoarthritis, joint effusion, joint inflammation and pain, synovitis, lameness, post operative arthroscopic surgery, deterioration of proper joint function including joint mobility, the reduction or inhibition of metabolic activity of chondrocytes, the activity of enzymes that degrade cartilage, the reduction or inhibition of the production of Hyaluronic acid, said method comprising orally administering to a mammalian species a therapeutically effective amount of Hyaluronic Acid or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof. Additionally, compositions containing hyaluronic acid; chondroitin sulfate, and glucosamine sulfate in a paste formulation are also disclosed which can be administered on their own or can be used as a feed additive.
Owner:PIERCE SCOTT W
Flexible inflow/outflow cannula and flexible instrument port
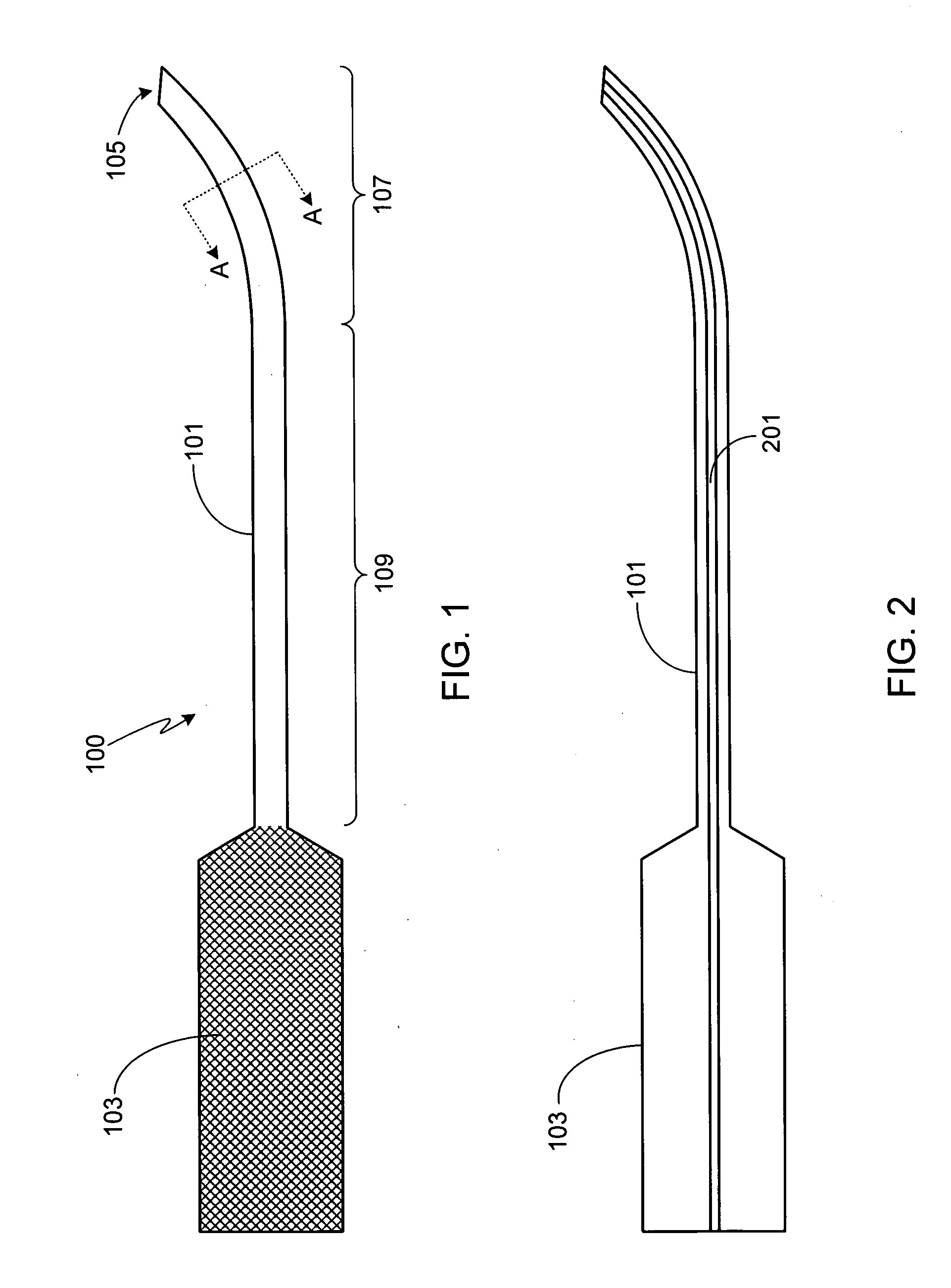
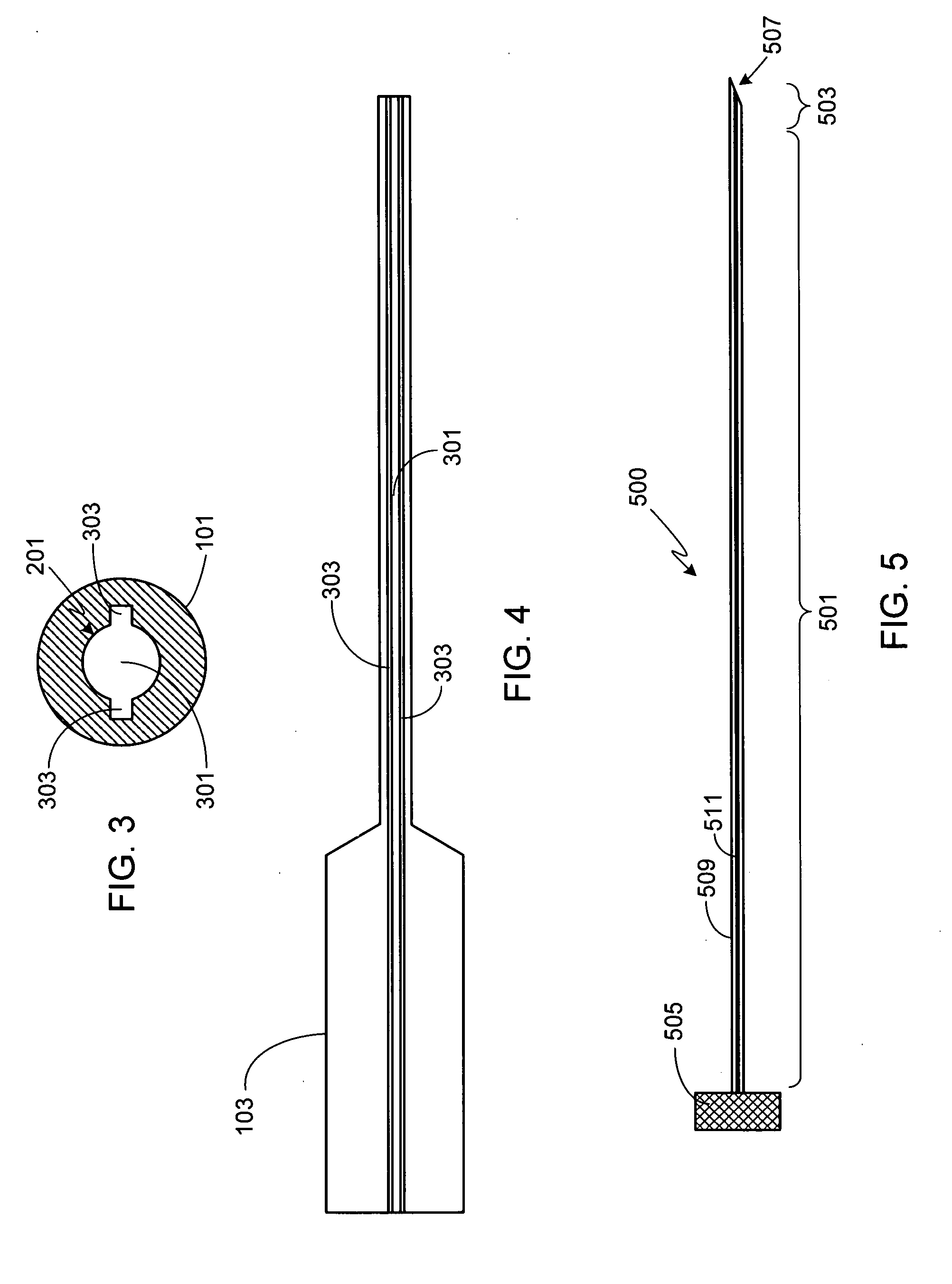
InactiveUS20050043682A1Avoid flowIncrease flexibilityEar treatmentCannulasArthroscopic procedureSacroiliac joint
A flexible plastic cannula for use during arthroscopic surgery. The cannula is a flexible elongated tube having longitudinally staggered slots disposed on the distal end of the tube. The tube is tapered along its length so that the proximal portion of the tube is relatively rigid, while the distal end is narrower and more flexible. The tube is sufficiently flexible to allow the tube to bend with a joint during arthroscopic surgery.
Owner:CANNUFLOW INC
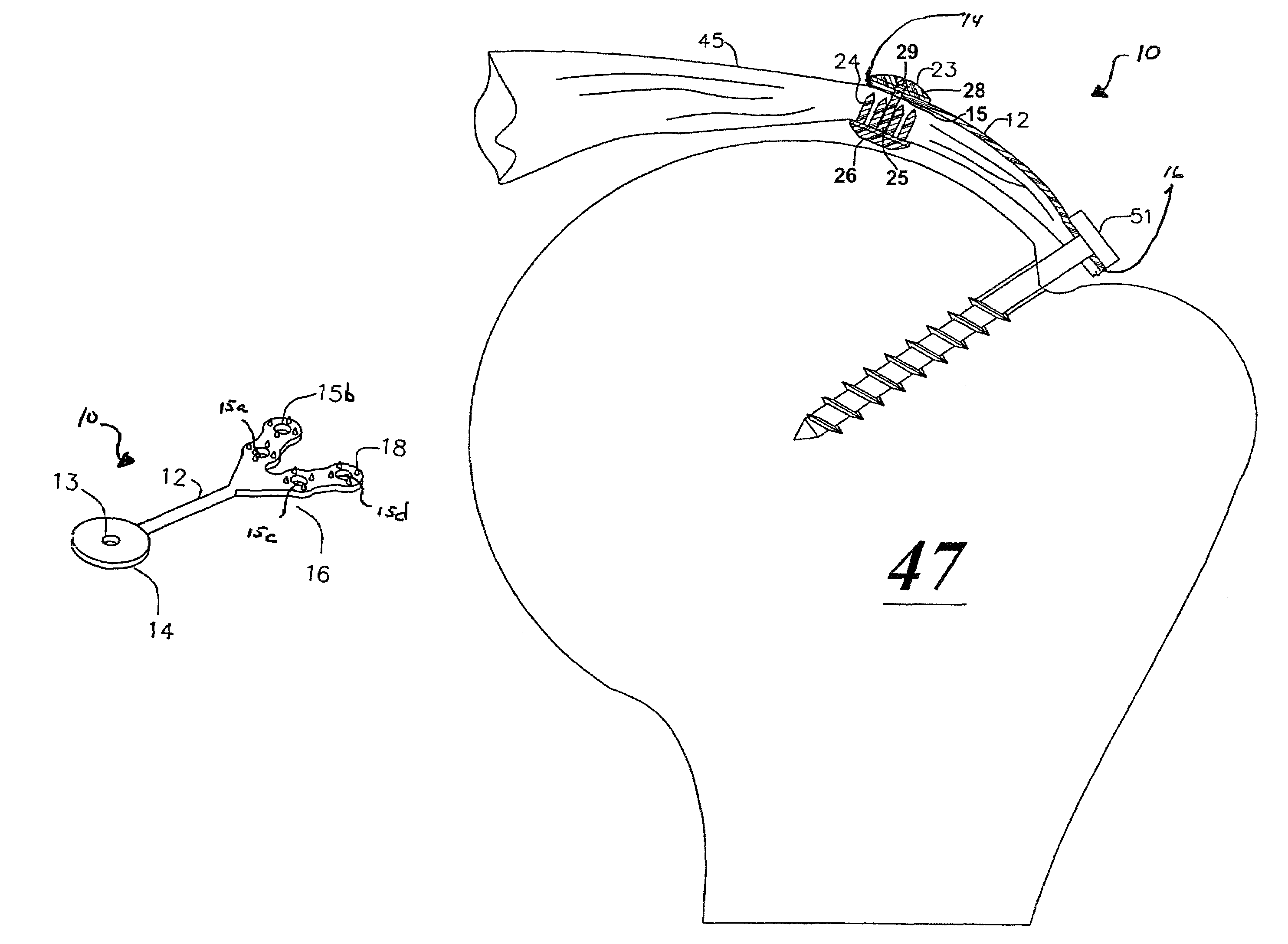
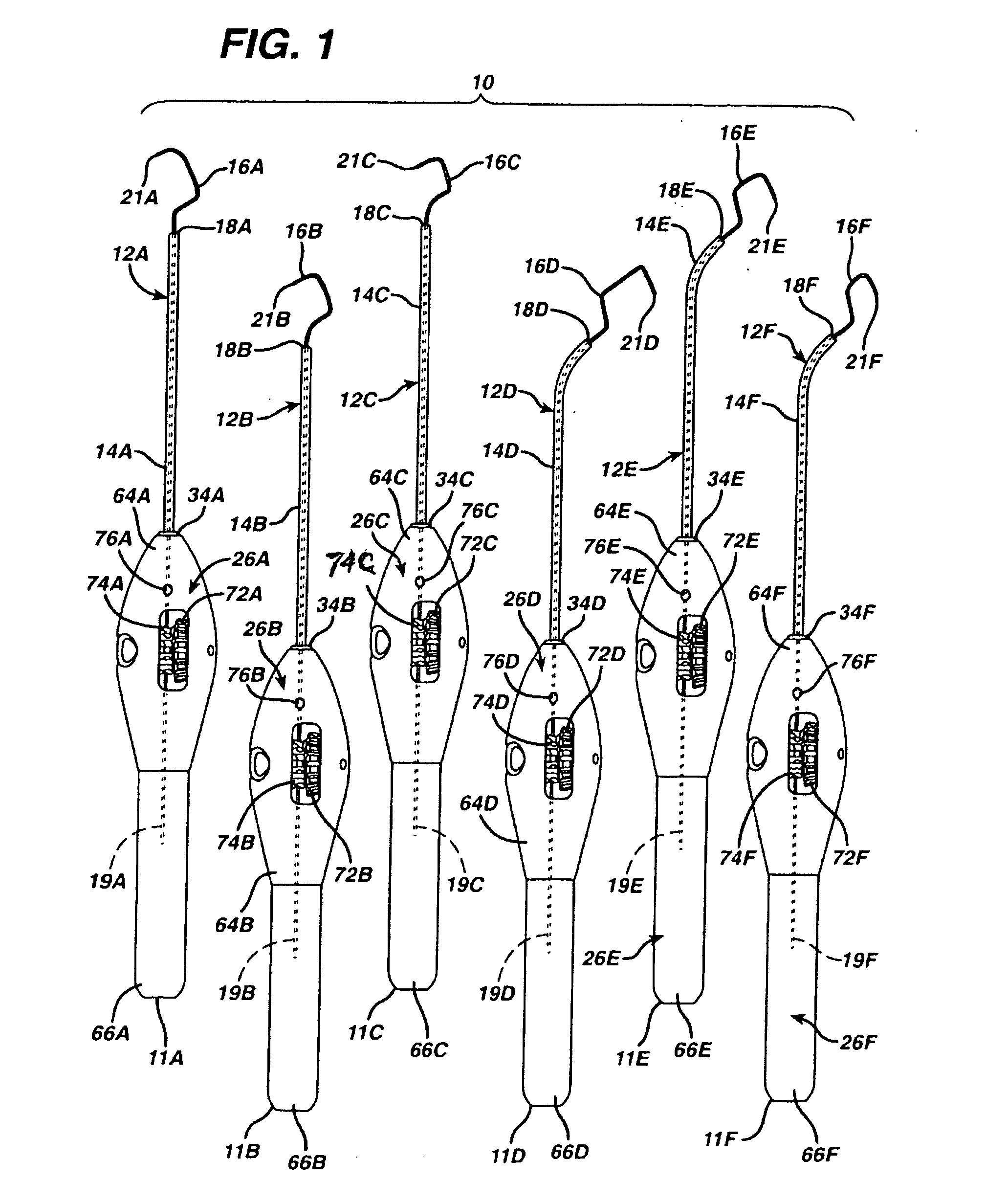
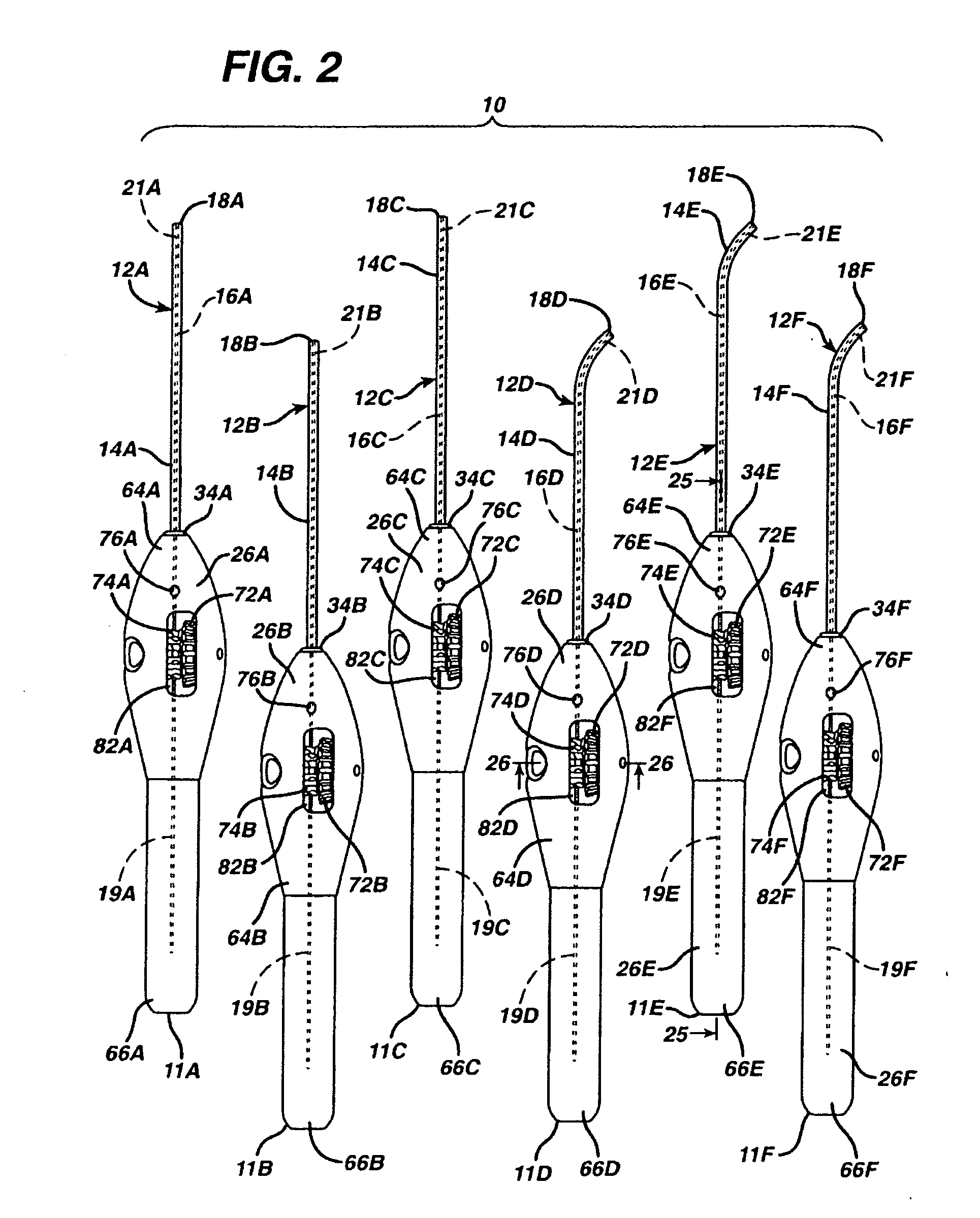
Bone anchor device having toggle member for attaching connective tissues to bone
A device for attaching connective tissue to bone has a longitudinal axis and comprises an annular toggle member and a body member disposed distally of the toggle member, such that there is an axial space between the toggle member and the body member. The toggle member is movable between an undeployed position wherein the toggle member has a smaller profile in a direction transverse to the axis and a deployed position wherein the toggle member has a larger profile in the direction transverse to the axis. When installed in a desired procedural site, in suitable bone, suturing material extends axially through a center aperture in the annular toggle member, without being secured to or contacting the toggle member. This approach permits a suture attachment which lies entirely beneath the cortical bone surface, and which further permit the attachment of suture to the bone anchor without the necessity for tying knots, which is particularly arduous and technically demanding in the case of arthroscopic procedures.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Button cannula
ActiveUS8038652B2Improve stabilityPrevent insertionCannulasInfusion syringesArthroscopic procedureSurgery
Owner:ARTHREX
Arthroscopic irrigation solution and method for peripheral vasoconstriction and inhibition of pain and inflammation
InactiveUS20030087962A1Control inflammationPain controlBiocideKallidin/bradykinin ingredientsArteriolar VasoconstrictionInflammation Process
A method and solution for perioperatively inhibiting a variety of pain and inflammation processes during arthroscopic procedures. The solution preferably includes a vasoconstrictor that demonstrates substantial agonist activity at alpha adrenergic receptors and that is selected for peripheral (local) vasoconstriction and one or more additional pain and inflammation inhibitory agents at dilute concentration in a physiologic carrier, such as saline or lactated Ringer's solution. The solution is applied by continuous irrigation of a wound during a surgical procedure for peripheral vasoconstriction and inhibition of pain and / or inflammation while avoiding undesirable side effects associated with systemic application of larger doses of the agents.
Owner:OMEROS CORP
Method and apparatus for arthroscopic bone preparation
InactiveUS20050216023A1Shorten the timeReduce the risk of infectionJoint implantsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesArthroscopic procedurePlane of reference
A guide system for resecting a bone through incisions of the type utilized for arthroscopic procedures is provided. The guide system comprises a first alignment pin, a second alignment pin and a wire saw. The first alignment pin is configured to be inserted through a first incision into a bone in a first orientation. The second alignment pin is configured to inserted through a second incision into the bone in a second orientation. The first alignment pin and the second alignment pin are configured and oriented to define a resection plane of reference through which the bone is to be resected and the wire saw is configured to be inserted through the first and second incisions to be guided by the first and second alignment pins while being moved to resect the bone.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
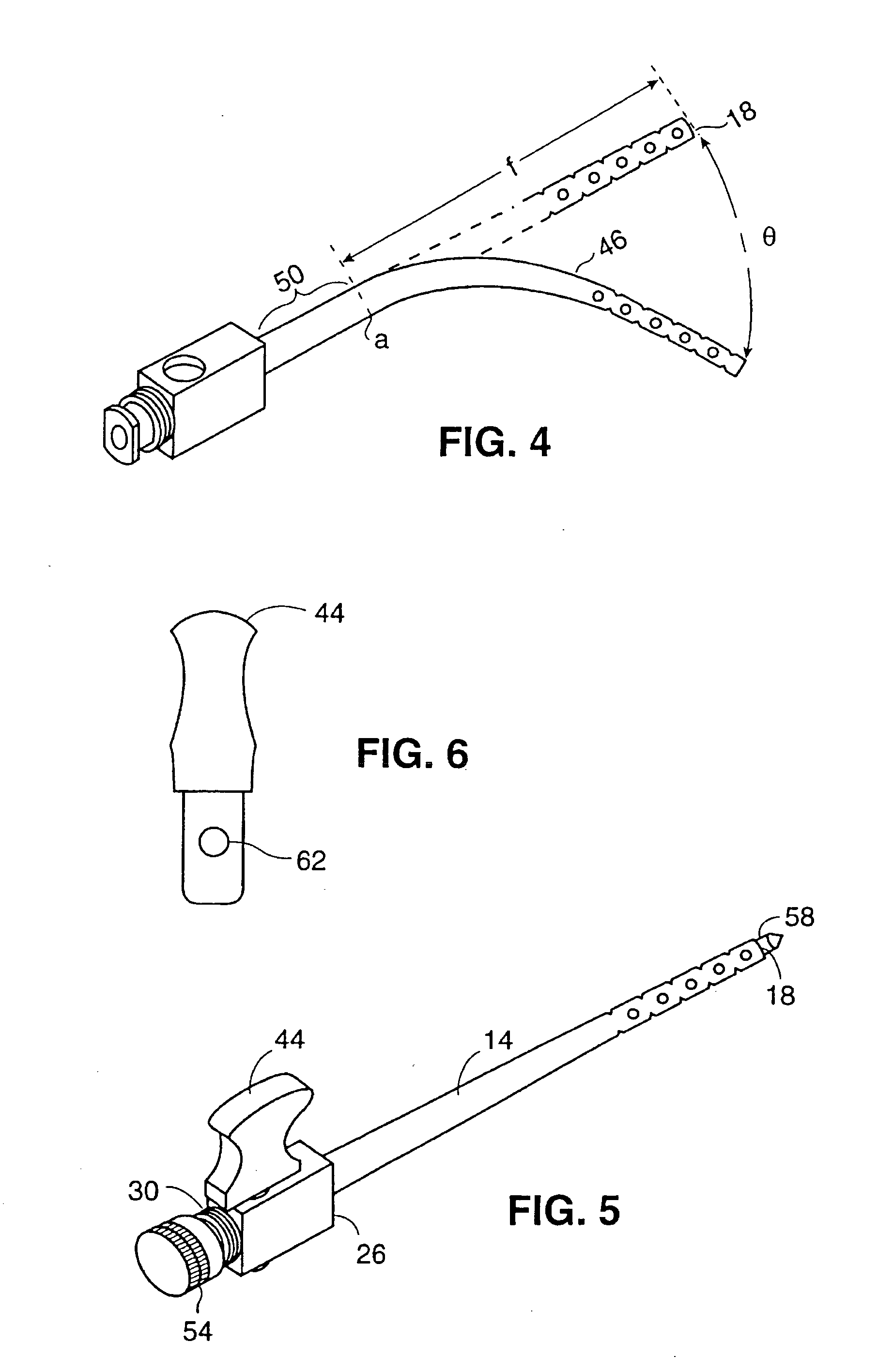
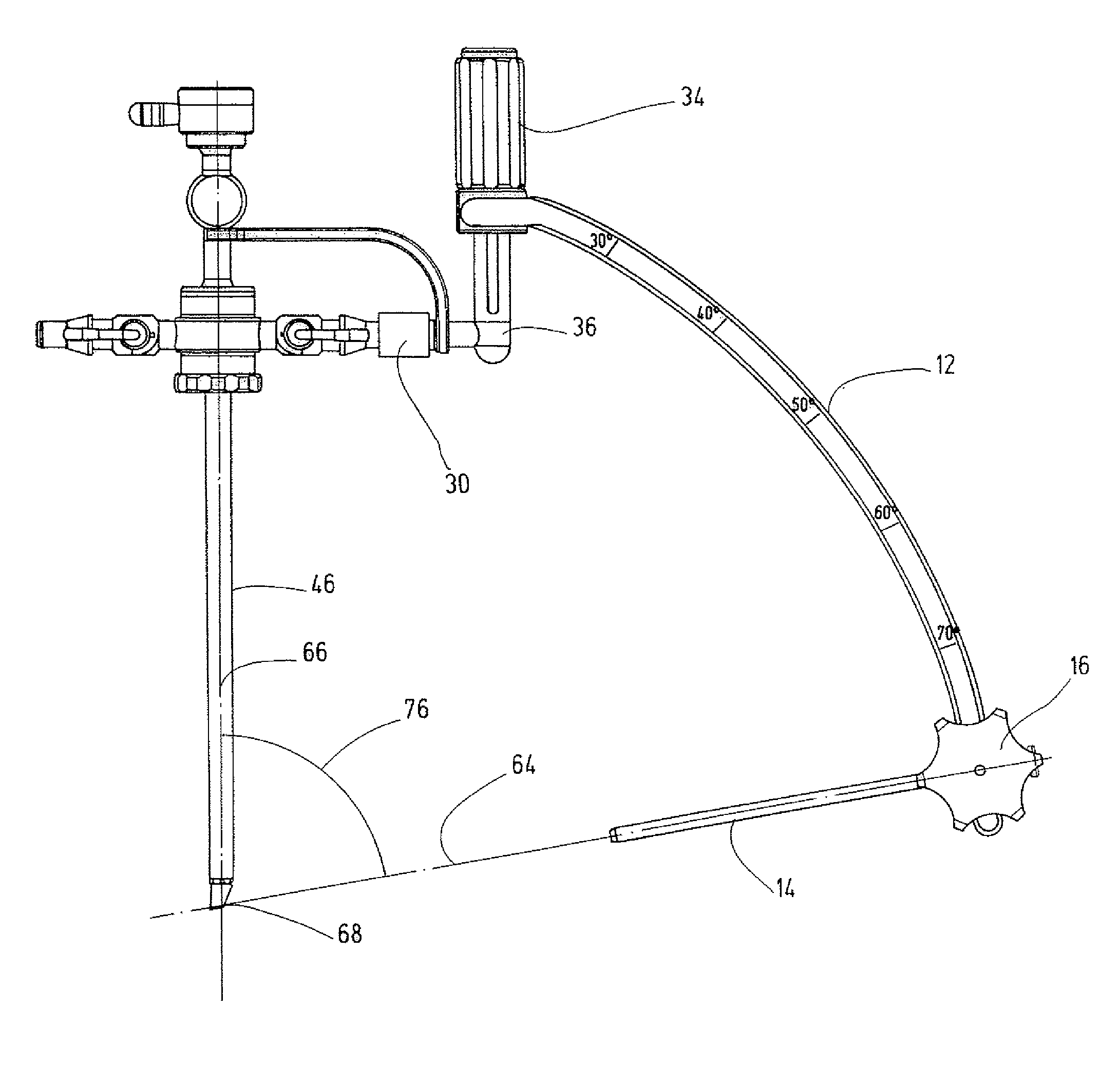
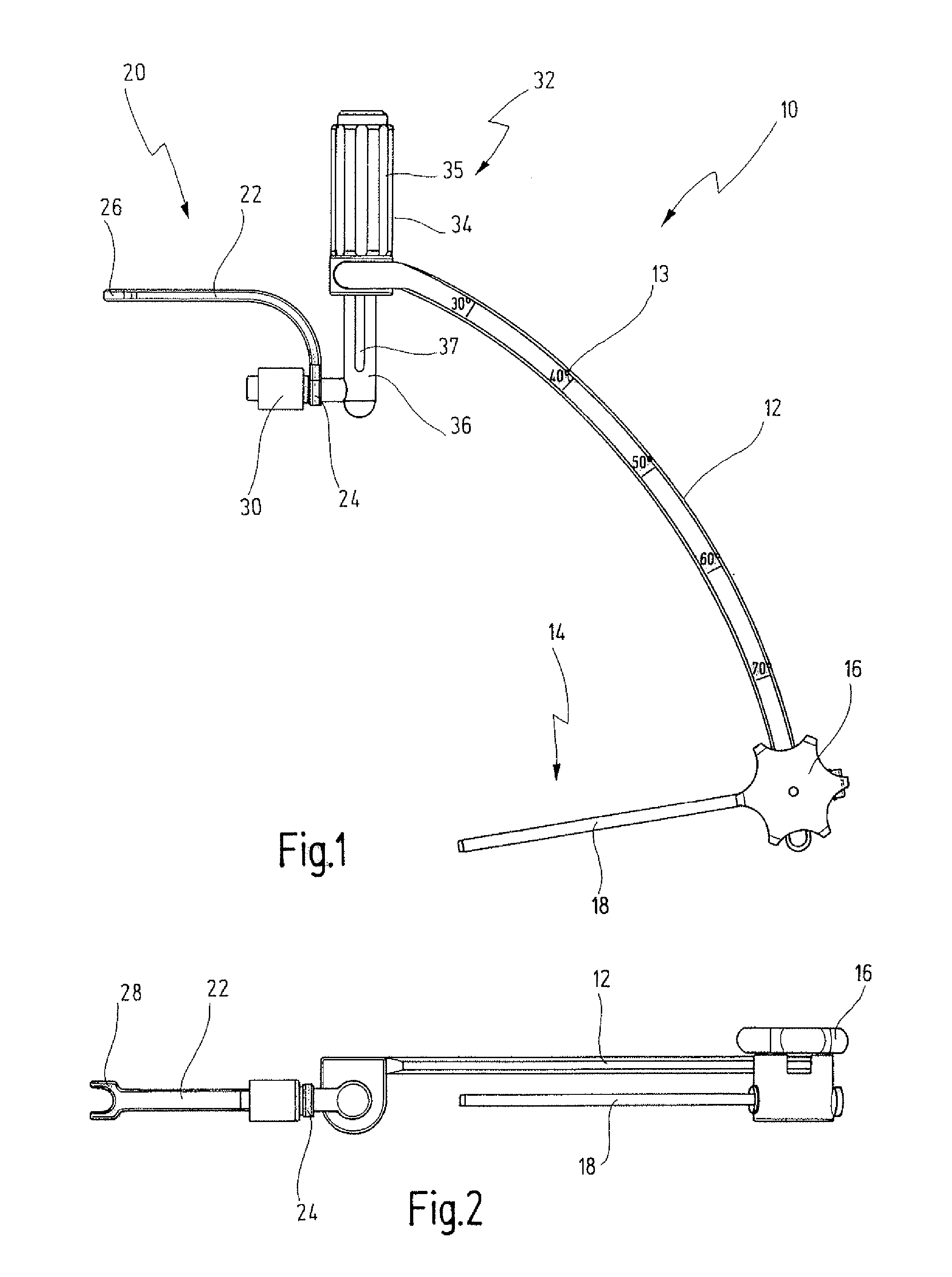
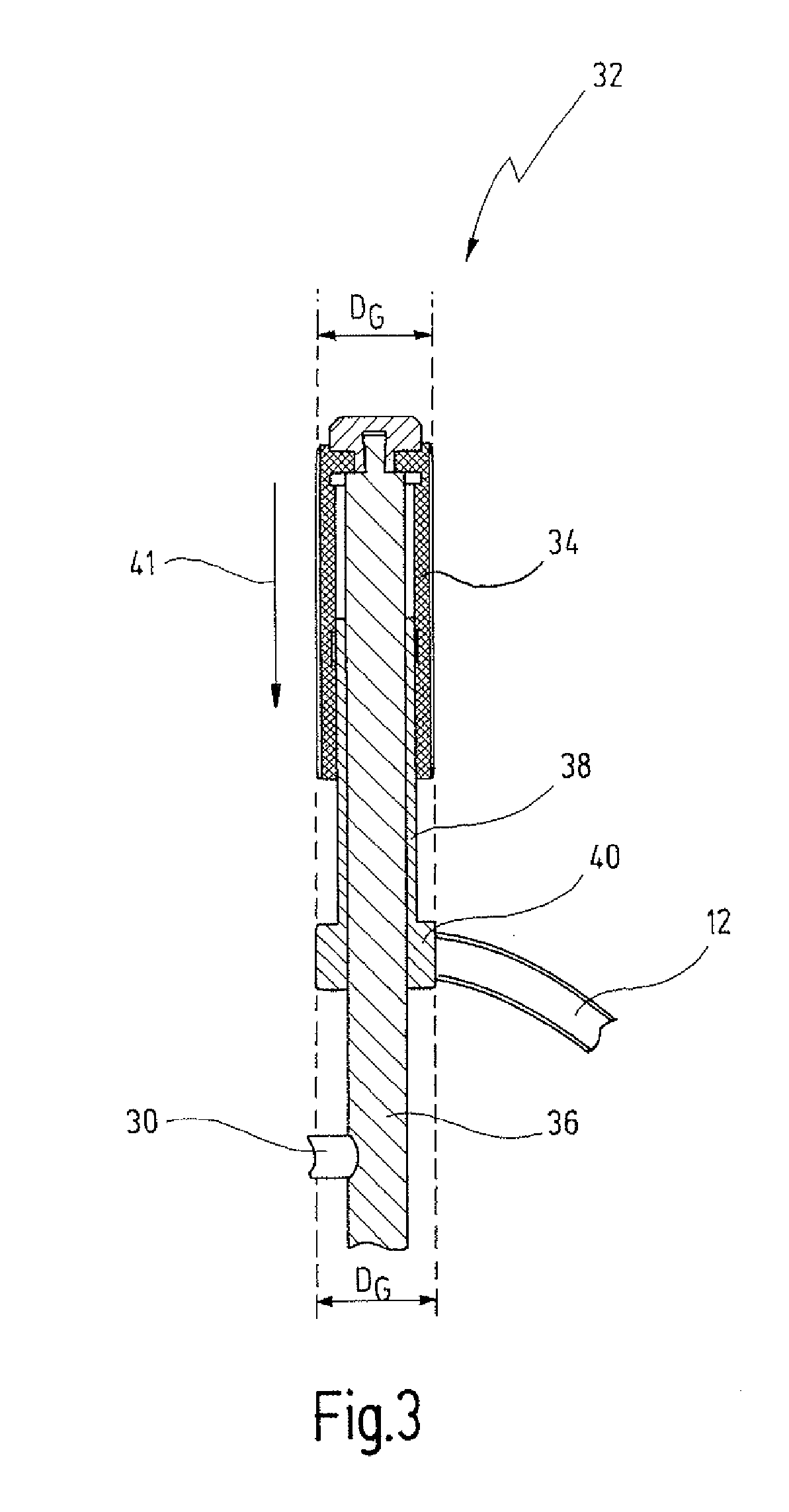
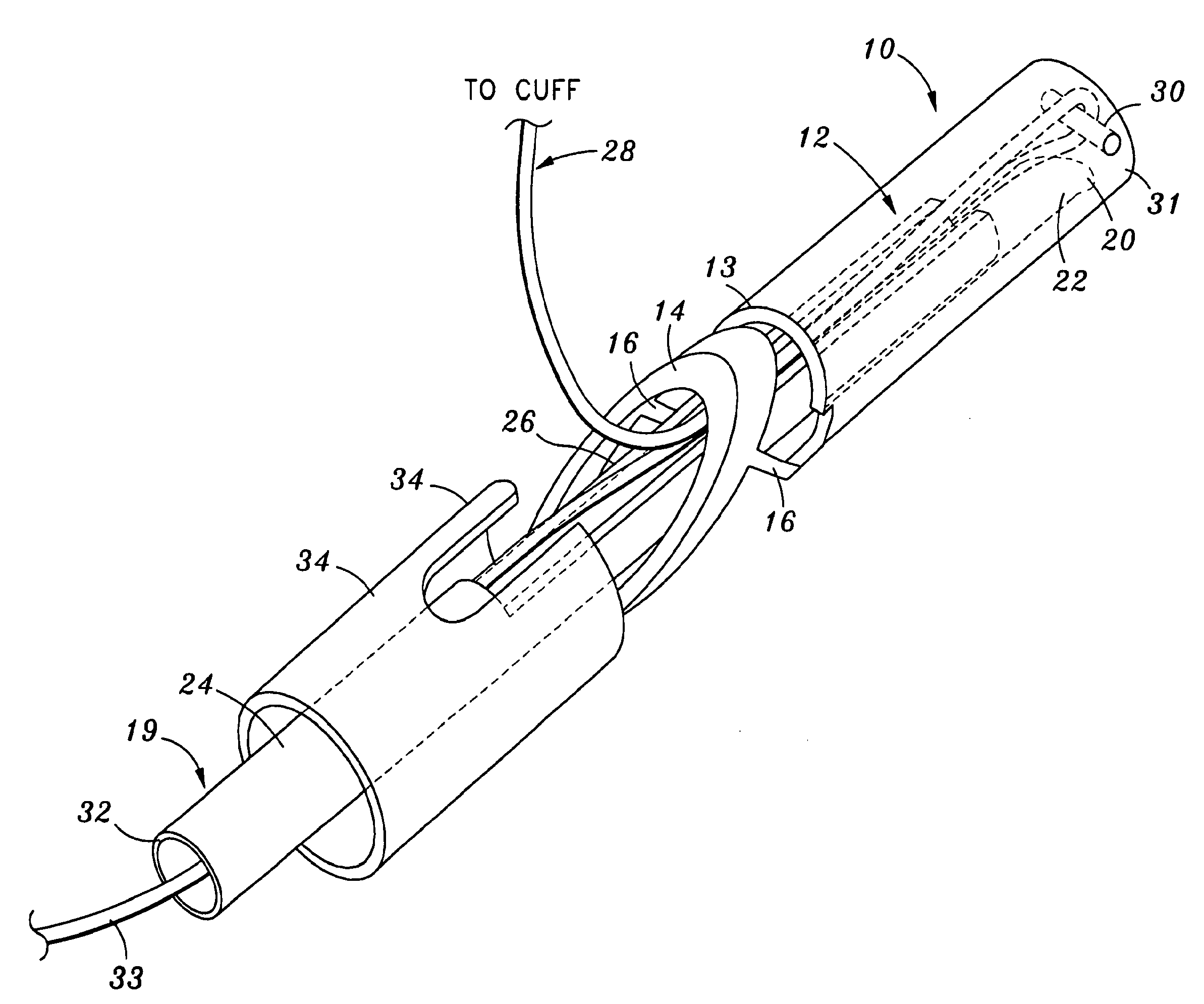
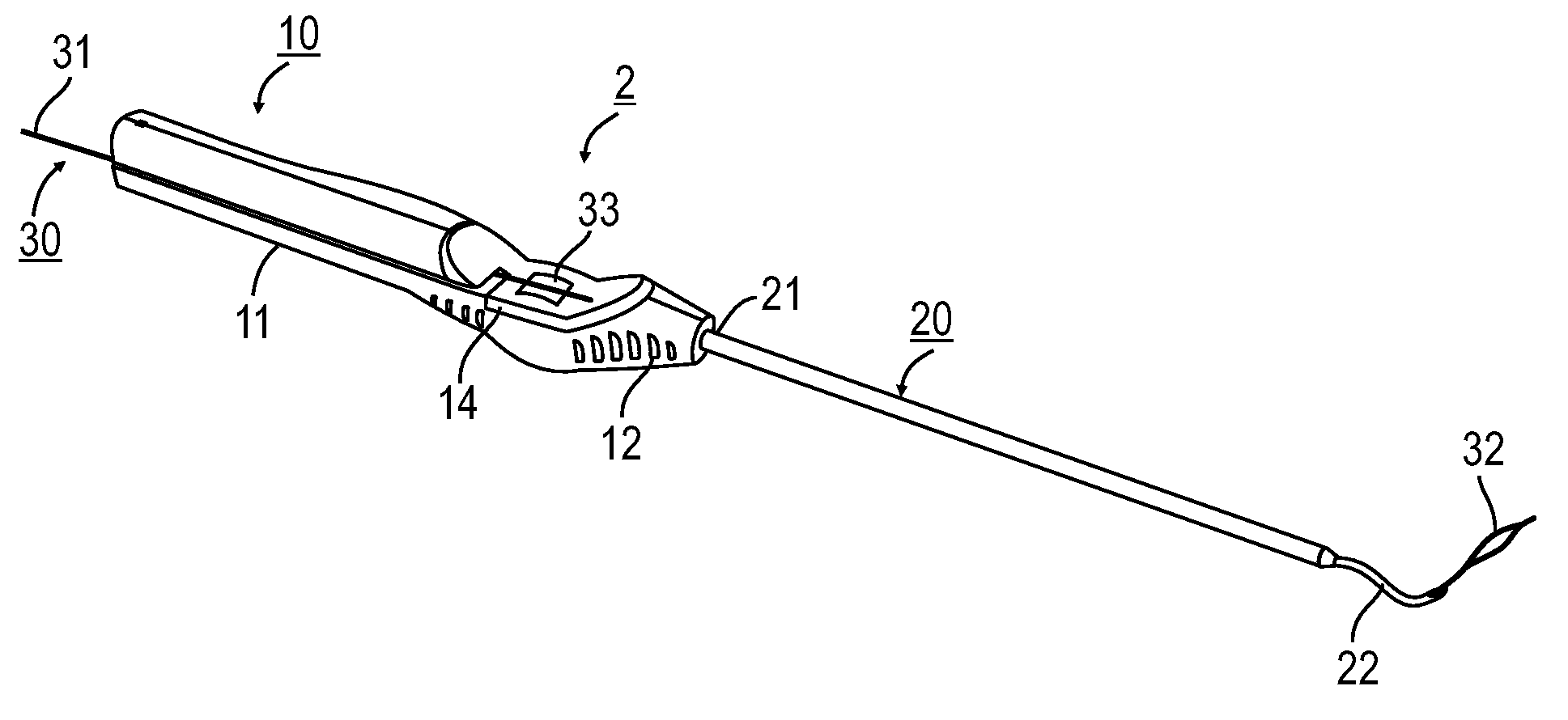
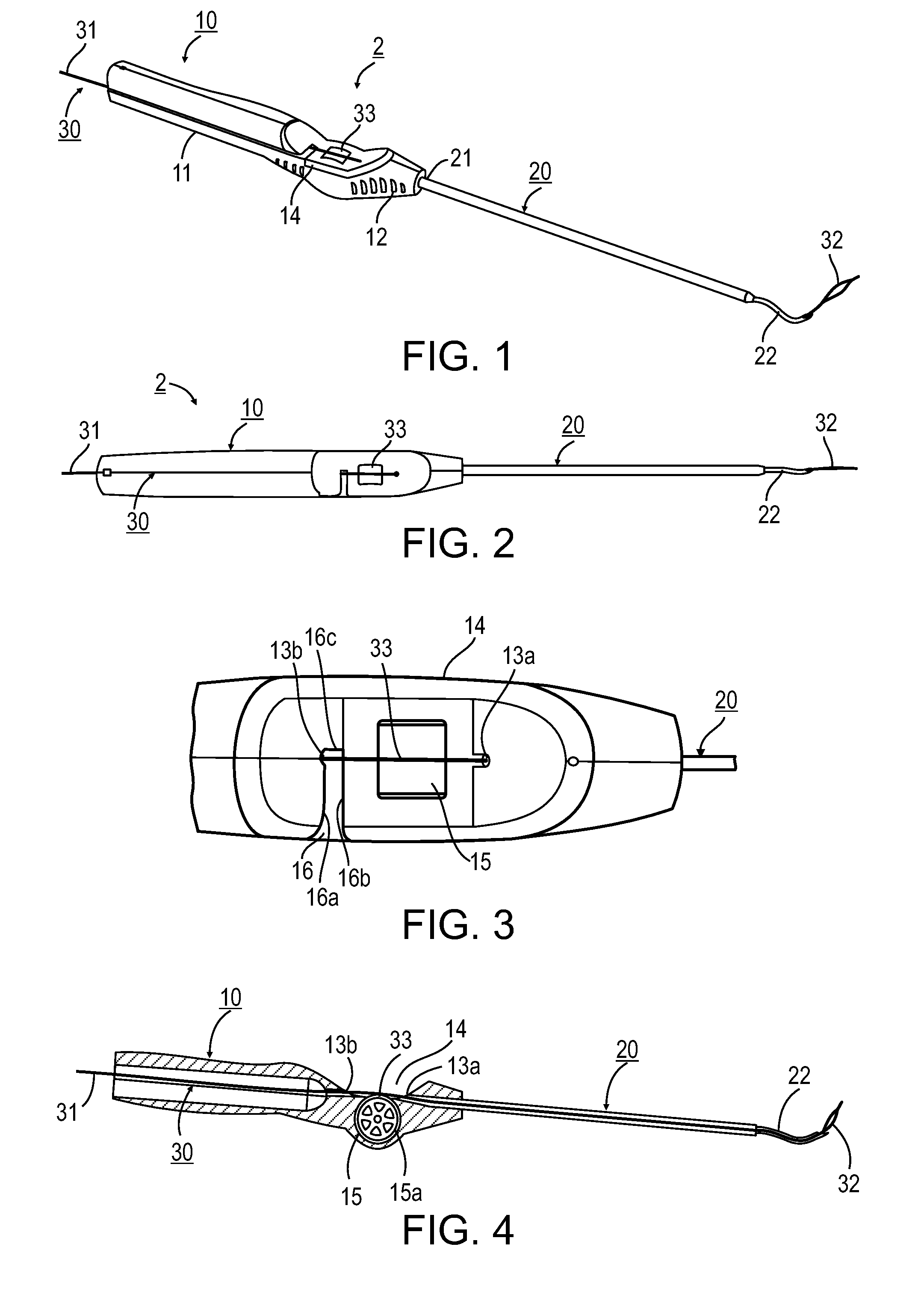
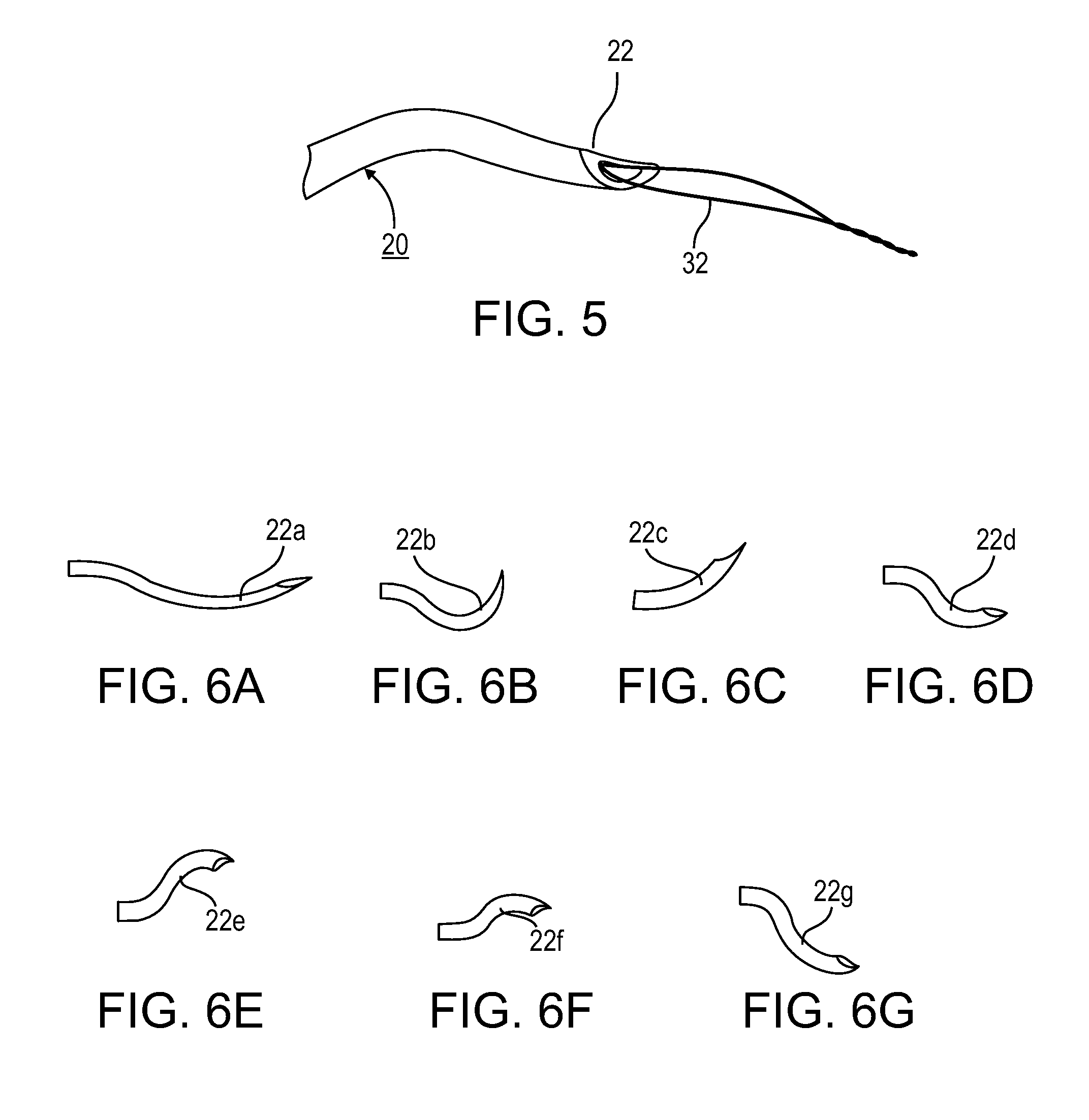
Method and Devices for Minimally Invasive Arthroscopic Procedures
A surgical device is provided, the device having a tubular outer body member with a handle at its proximal end and a flexible distal end segment extending from its distal end. The surgical device also has an operable end extending from the distal end of the flexible distal end segment. The device is configured for selectively causing the flexible end segment to bend to adopt a desired curvature and for selectively rotating the operable end relative to the flexible distal end segment about an axis of the flexible distal end segment.
Owner:ORTHODYNAMIX
Arthroscopic irrigation solution and method for peripheral vasoconstriction and inhibition of pain and inflammation
InactiveUS7973068B2Control inflammationPain controlKallidin/bradykinin ingredientsBiocideInflammation ProcessSide effect
A method and solution for perioperatively inhibiting a variety of pain and inflammation processes during arthroscopic procedures. The solution preferably includes a vasoconstrictor that exhibits alpha-adrenergic activity and one or more additional pain and inflammation inhibitory agents at dilute concentration in a physiologic carrier, such as saline or lactated Ringer's solution. The solution is applied by continuous irrigation of a wound during a surgical procedure for peripheral vasoconstriction and inhibition of pain and / or inflammation while avoiding undesirable side effects associated with systemic application of larger doses of the agents.
Owner:OMEROS CORP
Implant system with sizing templates
Surgical instruments for use in sizing tissue defects and selecting an appropriate implant for the defect include sizing templates. The sizing templates are sized and shaped to correspond to the size and shape of the implants. The sizing templates may be retractable into a tube for use in arthroscopic surgery. The retractable sizing templates are resilient to allow them to be retracted into a small diameter tube, and to expand on release from the tube to the desired size and shape. The method of using the instrument set is also described.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Button cannula
ActiveUS20090221968A1Improve stabilityPrevent insertionCannulasInfusion syringesArthroscopic procedureSurgery
Flexible button cannulas for arthroscopic surgery made from silicone, or a similar flexible material. Exemplary embodiments of the button cannula have large inner and outer flanges for improved stability when installed into the body. Exemplary embodiments of the button cannula include two fluid dams. A first dam is located within the cannula elongated portal between the inner and outer flanges and prevents fluid from squirting out of the body when instruments are being inserted through the cannula. A second dam is located at the outer, or top, flange (i.e., the flange that remains outside of the body) to prevent fluid from squirting when the cannula itself is being inserted within the body. Exemplary embodiments of the button cannula also include an outer, or top, flange that is thicker than the inner, or bottom, flange, to prevent the over insertion of the cannula into the body.
Owner:ARTHREX
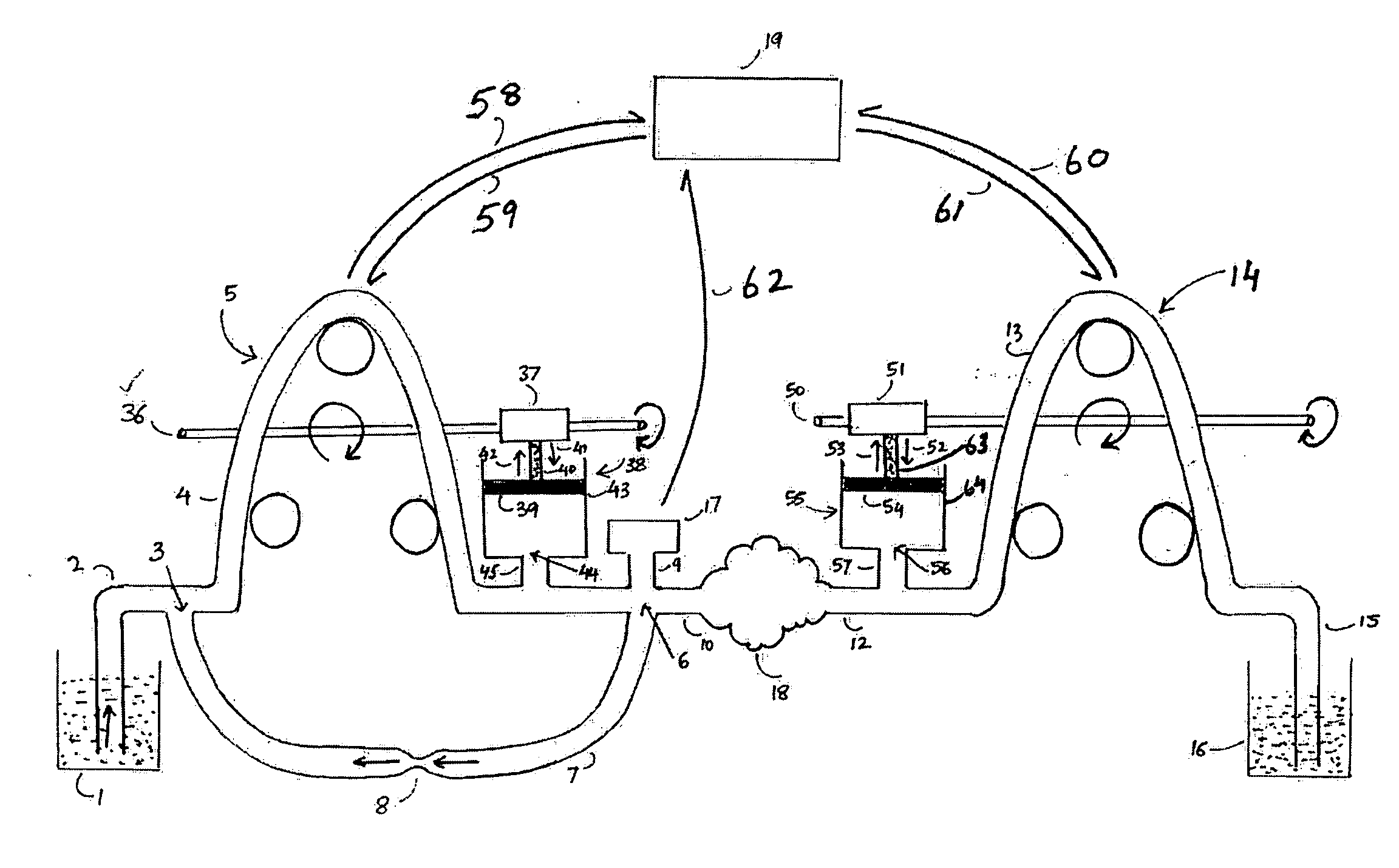
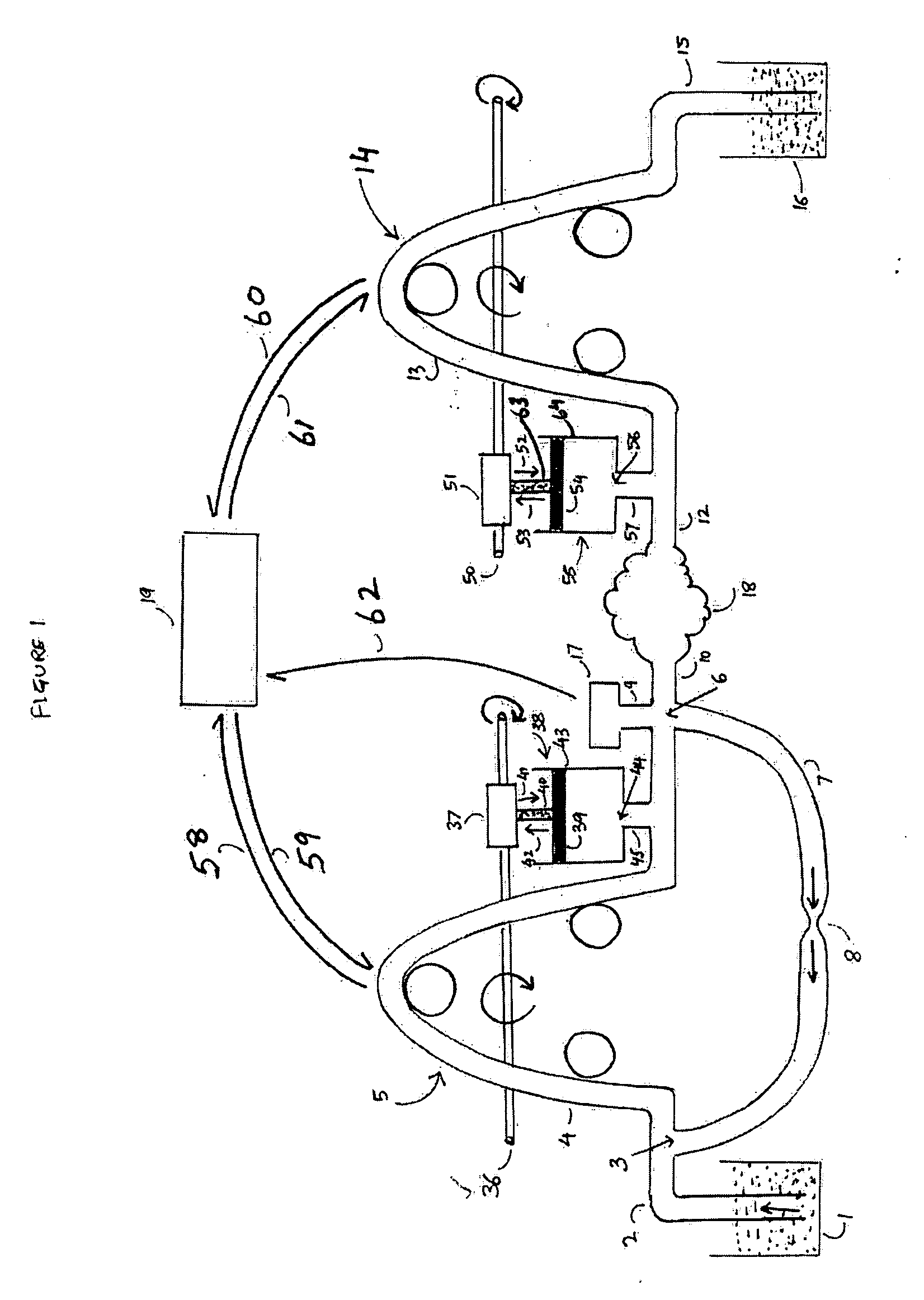
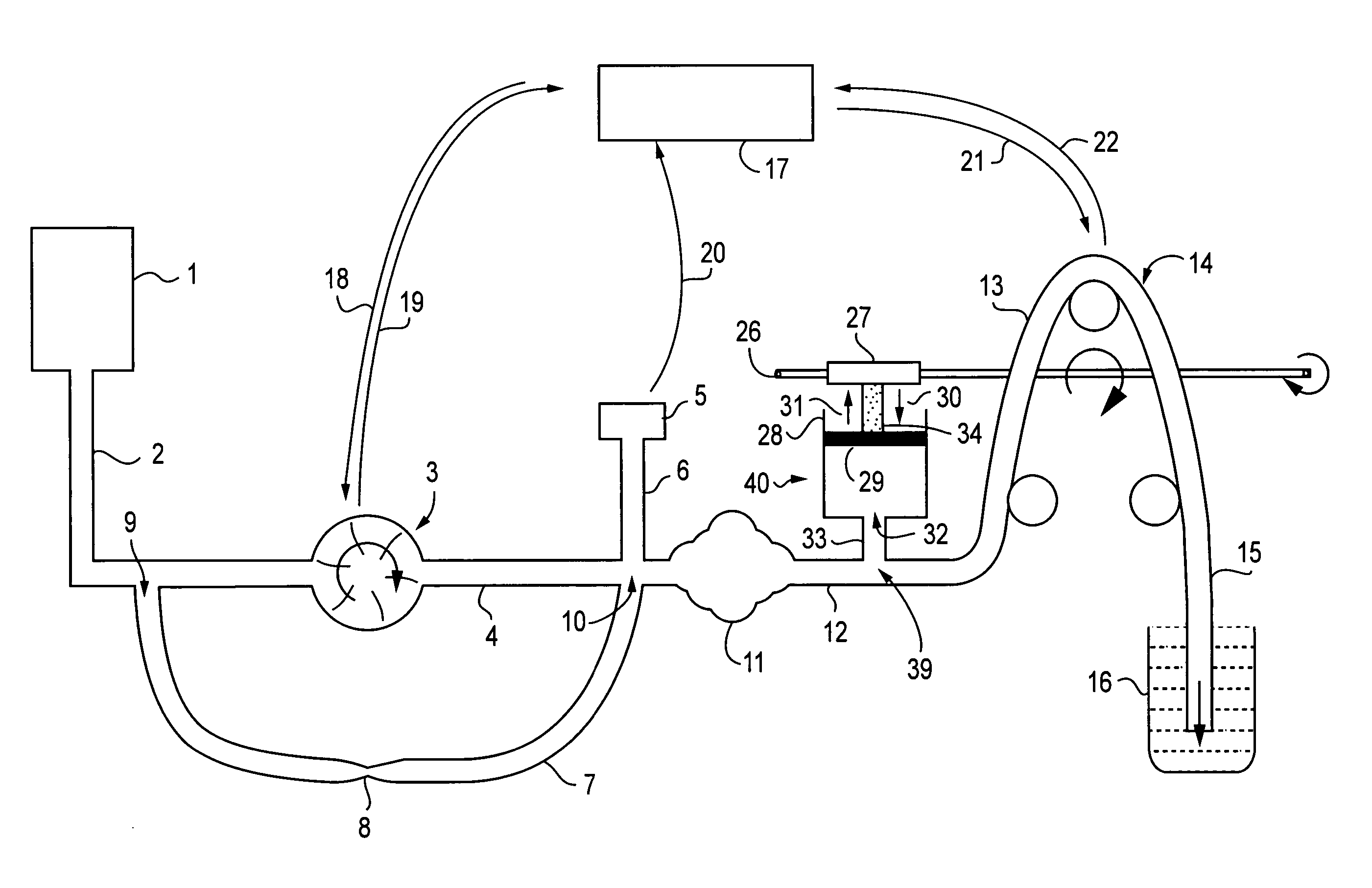
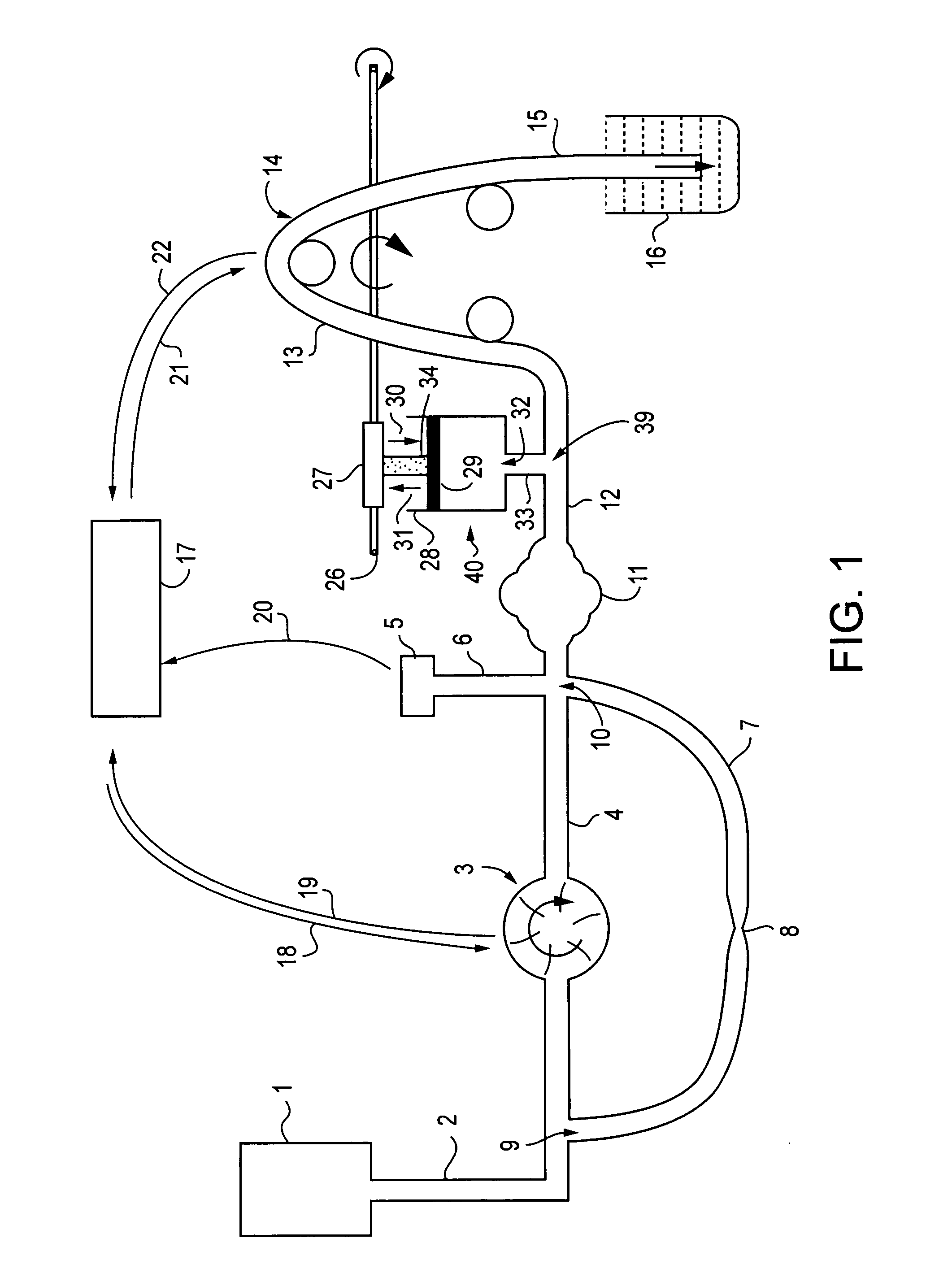
Low turbulence fluid management system for endoscopic procedures
ActiveUS20060122556A1Reduce cavity filling timeMinimize such riseEndoscopesMedical devicesPeristaltic pumpEndoscopic Procedure
The present invention provides a system and a method for distending a body tissue cavity of a subject by continuous flow irrigation by using two positive displacement pumps, such as peristaltic pumps, one pump on the inflow side and another pump on the outflow side, such that the amplitude of the pressure pulsations created by a the said positive displacement pumps inside the tissue cavity is substantially dampened to almost negligible levels. The present invention also provides a method of reducing the frequency of the said pressure pulsations. The present invention also provides a method for accurately determining the rate of fluid loss, into the subject's body system, during any endoscopic procedure without utilizing any deficit weight or fluid volume calculation, the same being accomplished by using two fluid flow rate sensors. The present invention also provides a system of creating and maintaining any desired pressure in a body tissue cavity for any desired cavity outflow rate. The system and the methods of the present invention described above can be used in any endoscopic procedure requiring continuous flow irrigation few examples of such endoscopic procedures being hysteroscopic surgery, arthroscopic surgery, trans uretheral surgery, endoscopic surgery of the brain and endoscopic surgery of the spine.
Owner:KUMAR BV
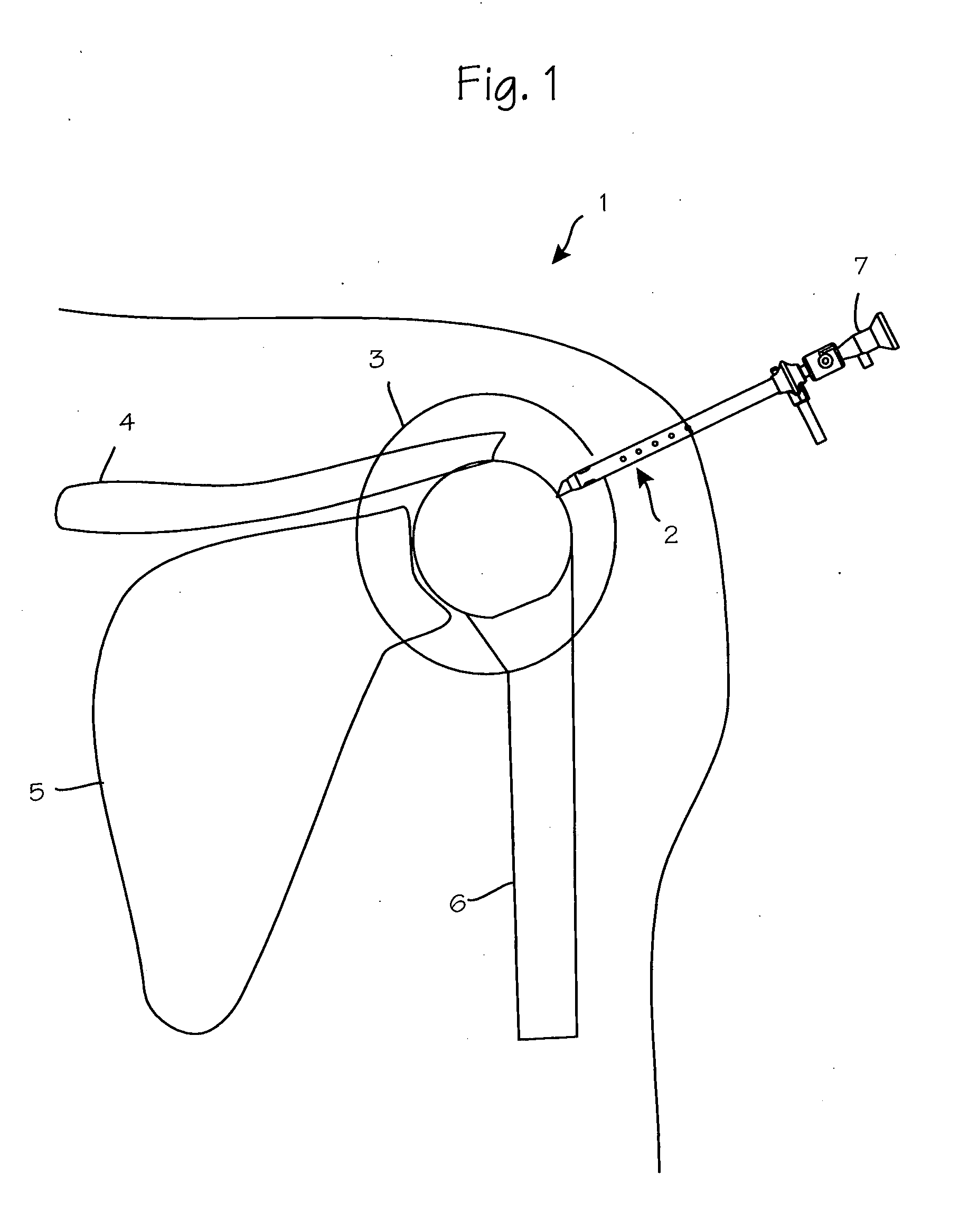
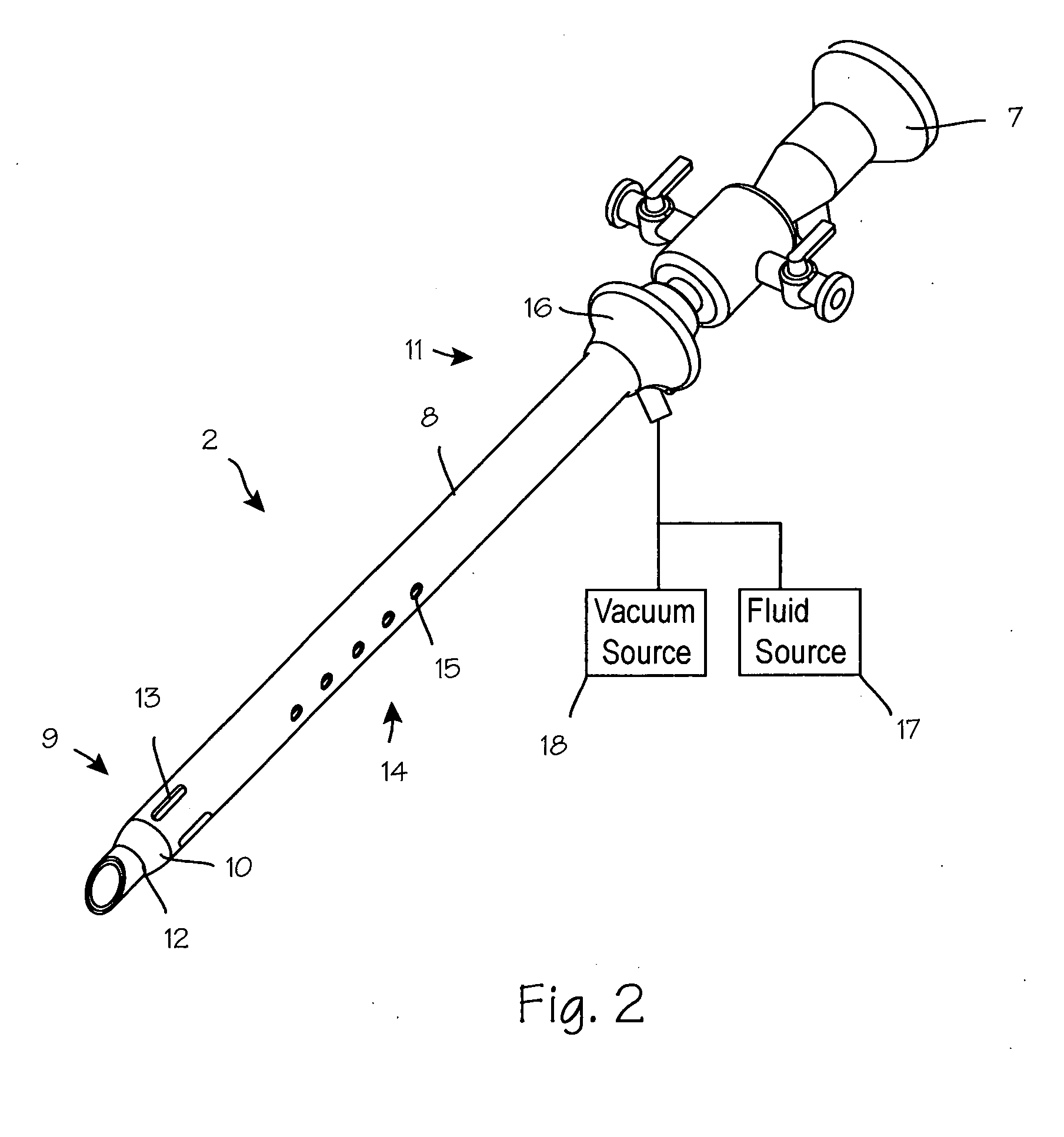
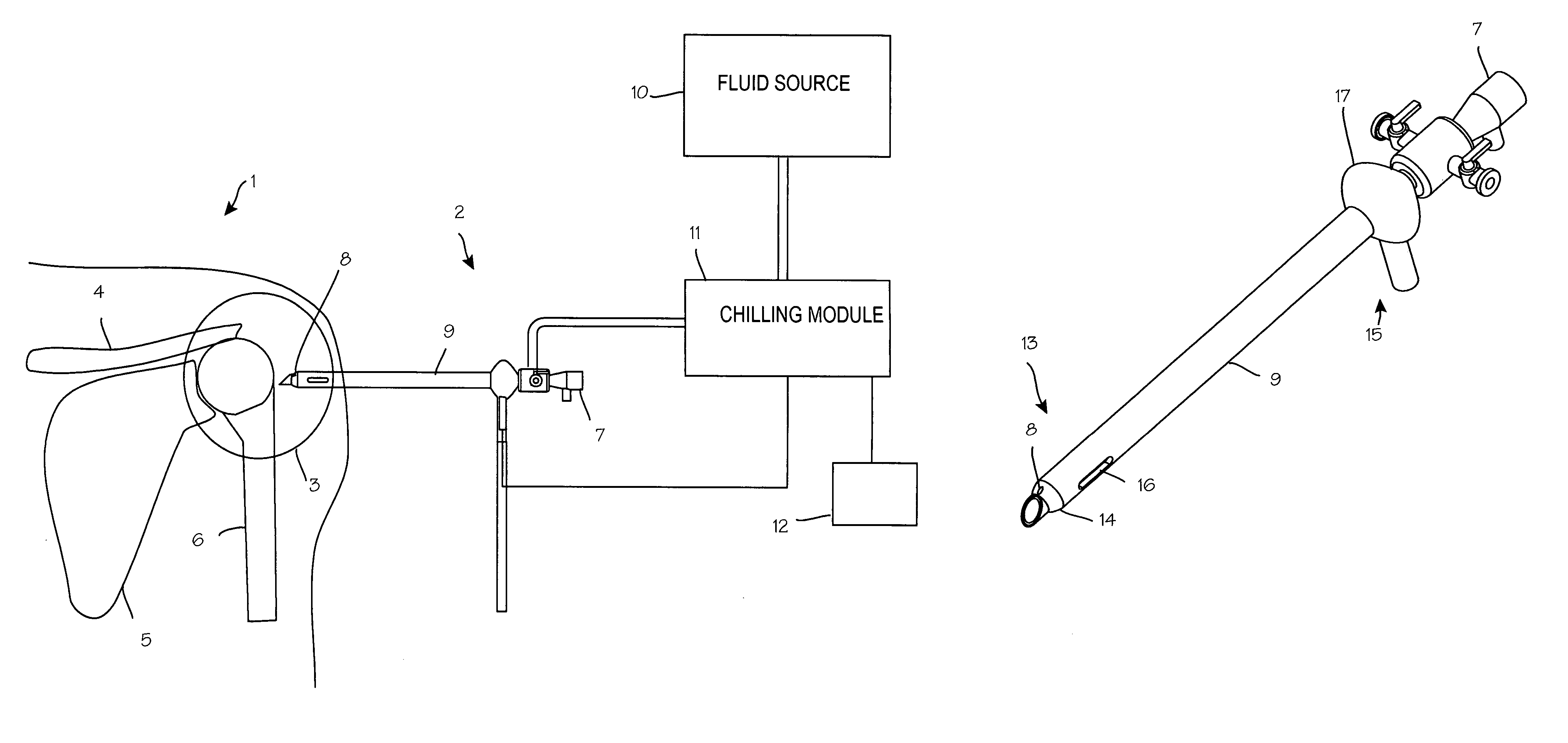
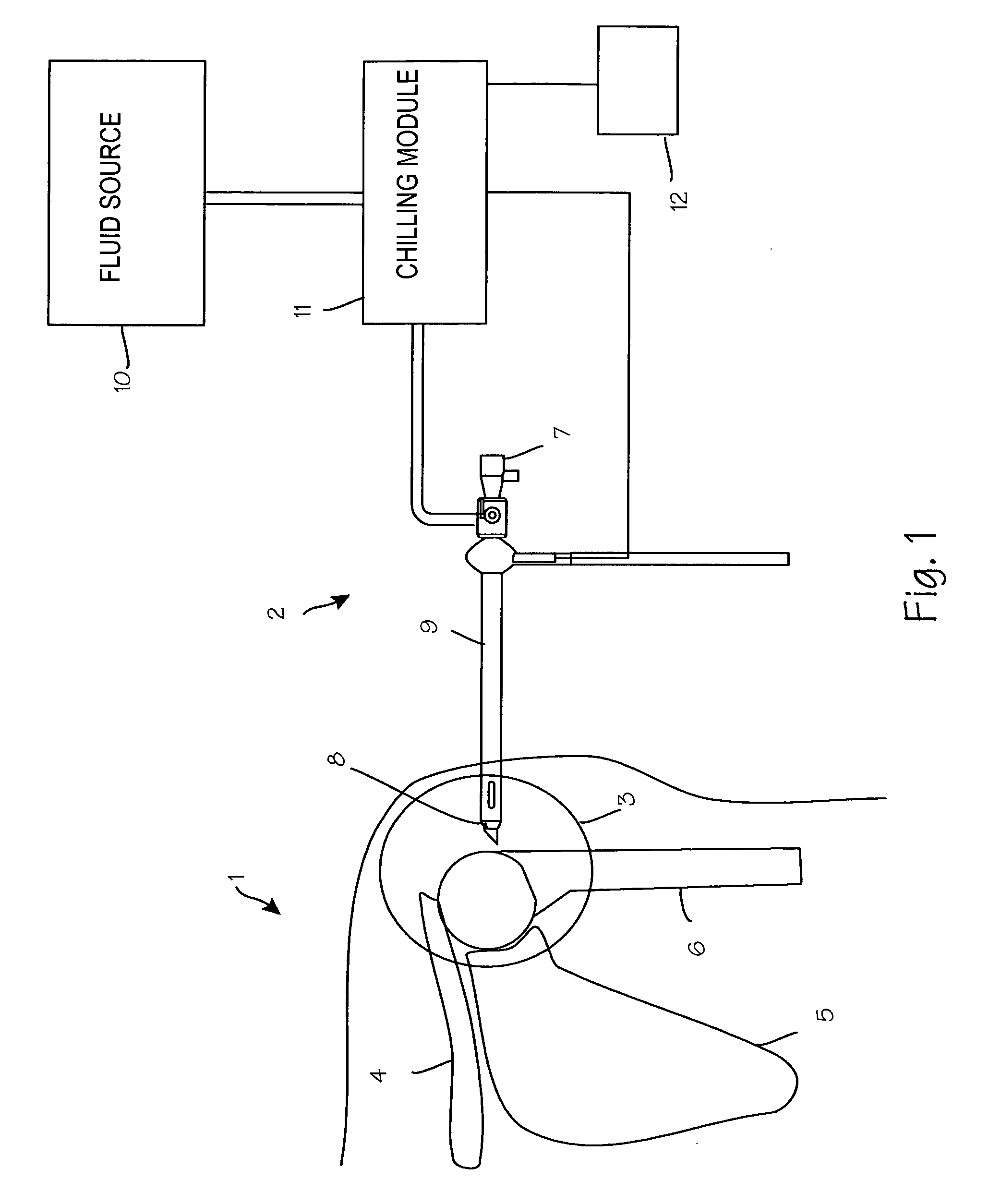
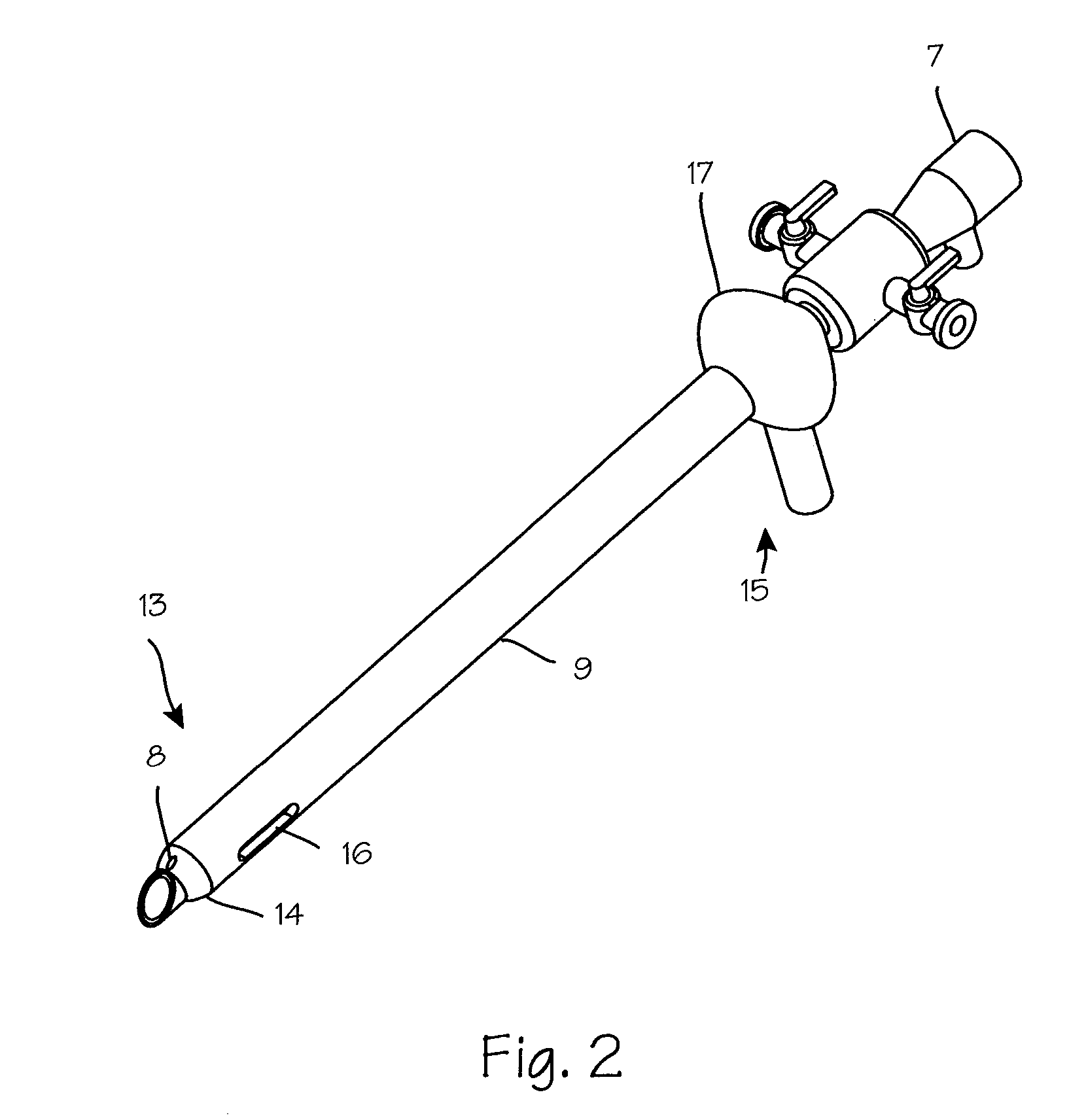
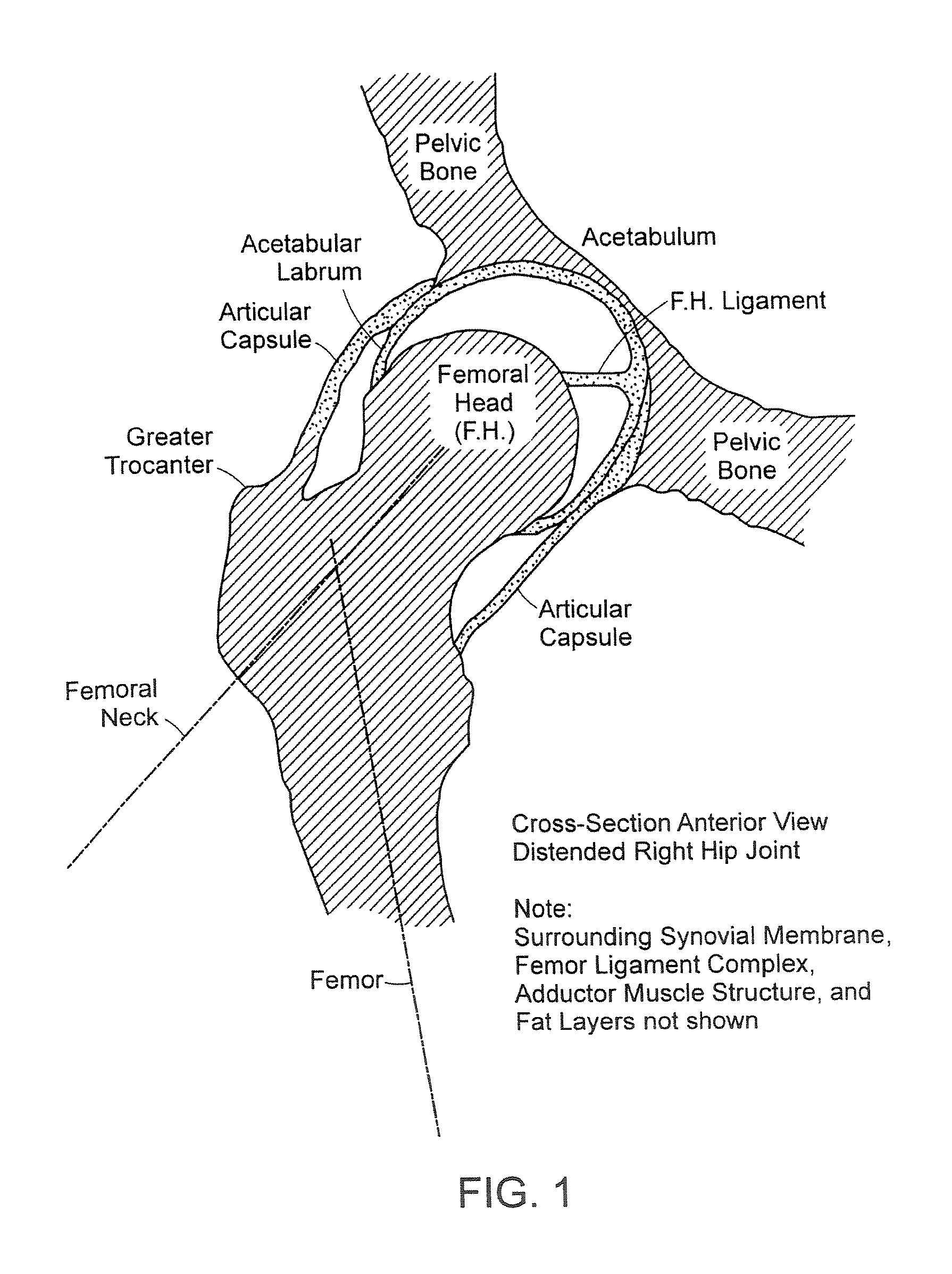
Partial Aiming Device For Targeting An Arthroscopic Operation Site For A Medical Intervention
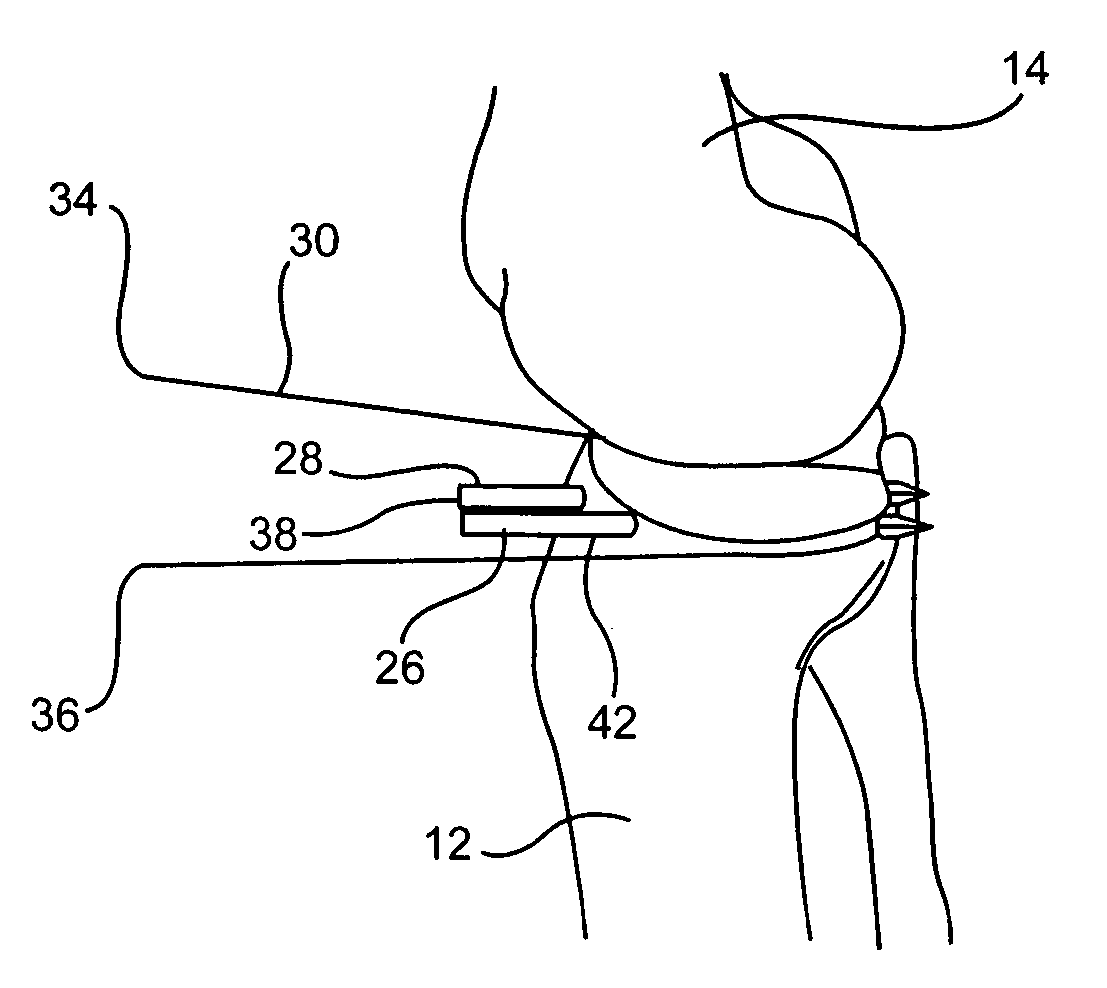
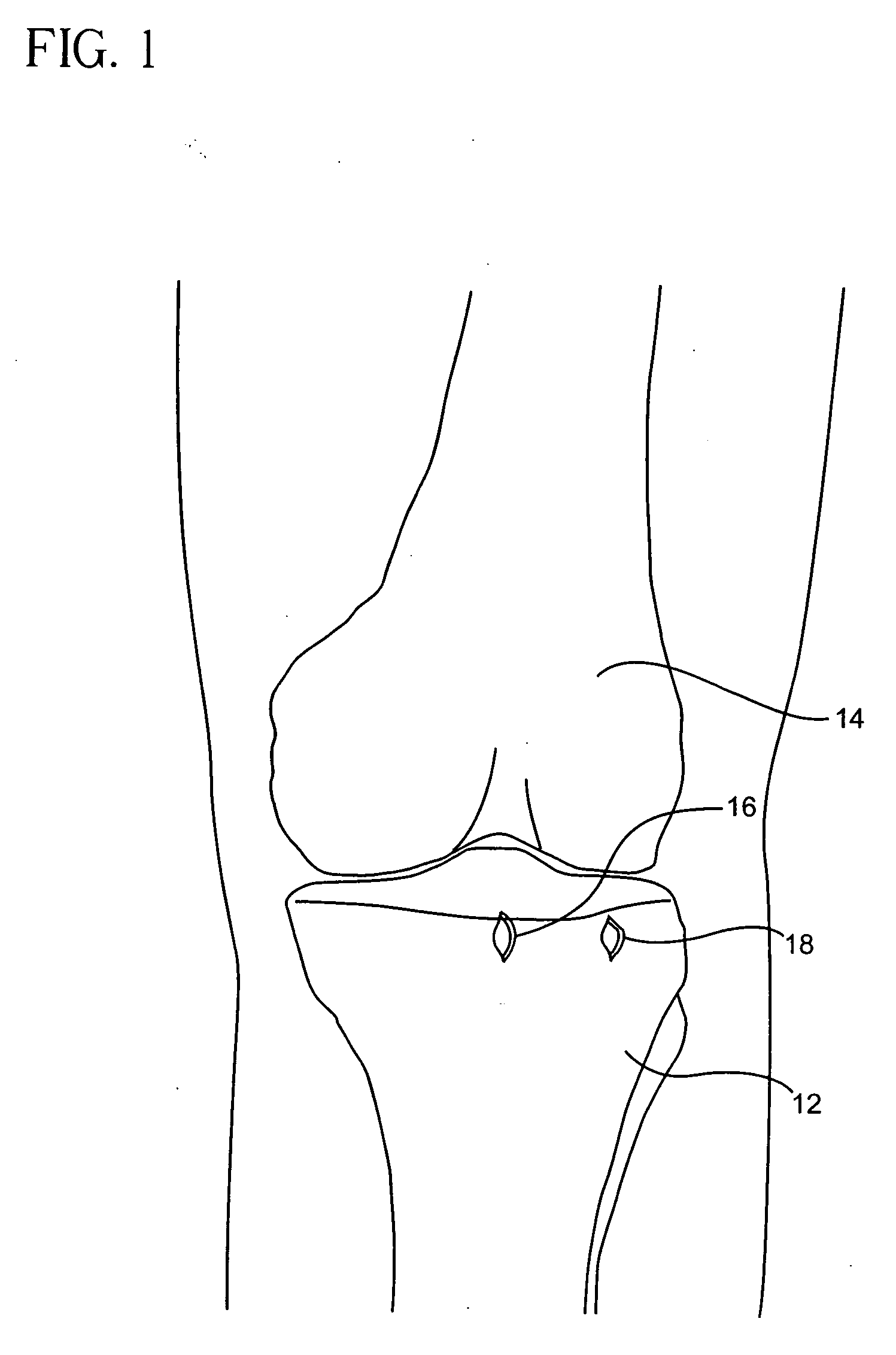
ActiveUS20080027457A1Intuitive effectFirmly connectedDiagnosticsSurgical needlesArthroscopic procedureEngineering
Owner:KARL STORZ GMBH & CO KG
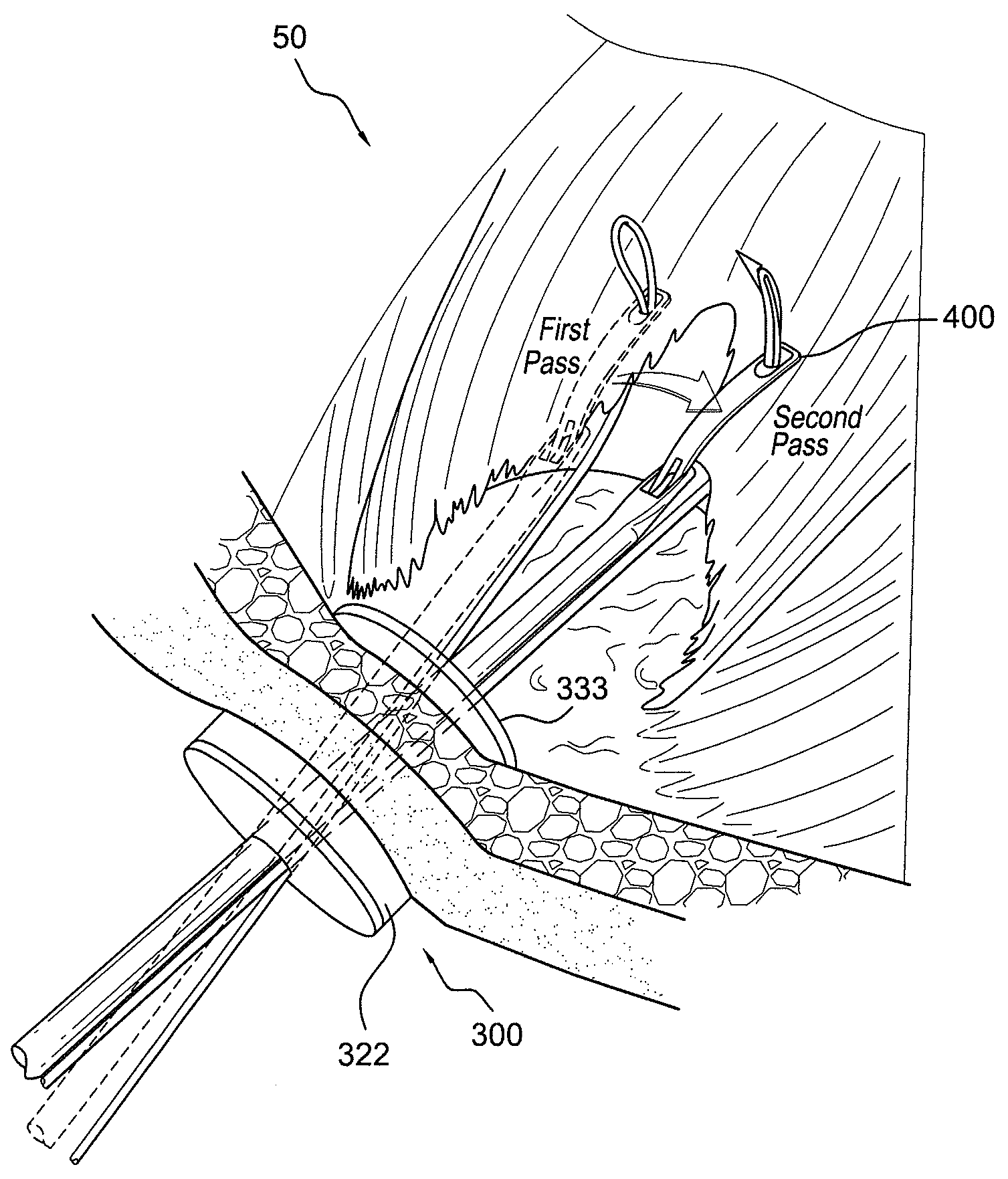
Methods and devices for attaching connective tissues to bone using a knotless suture anchoring device
InactiveUS20090222041A1Prevent removalSuture equipmentsLigamentsArthroscopic procedureSuture anchors
Owner:ARTHROCARE
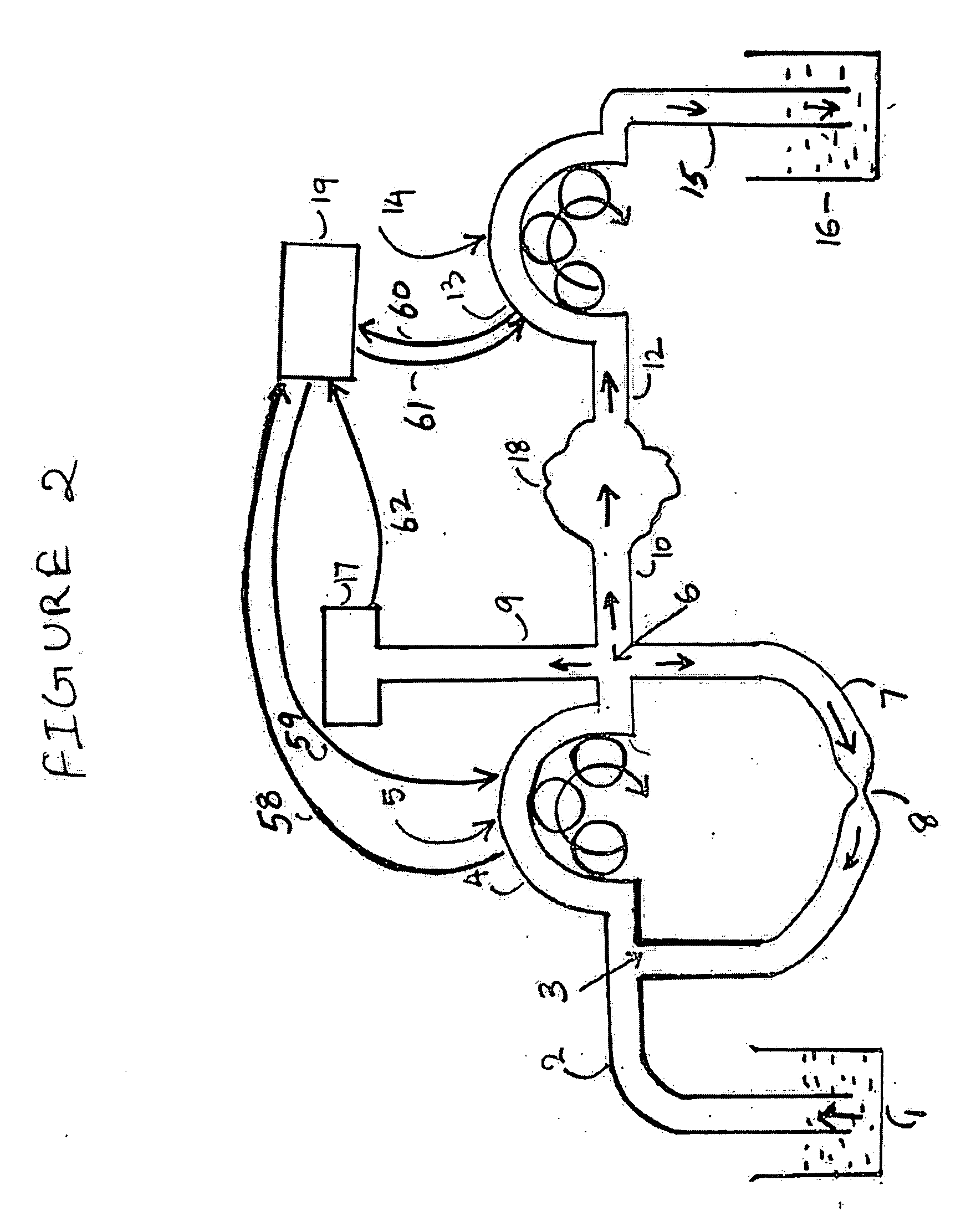
Controlled tissue cavity distending system with minimal turbulence
ActiveUS20060047240A1Safe and efficient and turbulenceSafe and efficient and turbulence free systemElectrotherapyMedical devicesPeristaltic pumpEngineering
The present invention provides a system and a method for distending a body tissue cavity of a subject by continuous flow irrigation by using a dynamic pump, such as a centrifugal pump, on the inflow side and a positive displacement pump, such as a peristaltic pump, on the outflow side, such that the amplitude of the pressure pulsations created by a the said outflow positive displacement pump inside the said tissue cavity is substantially dampened to almost negligible levels. The present invention also provides a method for accurately determining the rate of fluid loss, into the subject's body system, during any endoscopic procedure without utilizing any deficit weight or fluid volume calculation, the same being accomplished by using two fluid flow rate sensors. The present invention also provides a system of creating and maintaining any desired pressure in a body tissue cavity for any desired cavity outflow rate. The system and the methods of the present invention described above can be used in any endoscopic procedure requiring continuous flow irrigation few examples of such endoscopic procedures being hysteroscopic surgery, arthroscopic surgery, trans uretheral surgery, endoscopic surgery of the brain and endoscopic surgery of the spine.
Owner:KUMAR BV
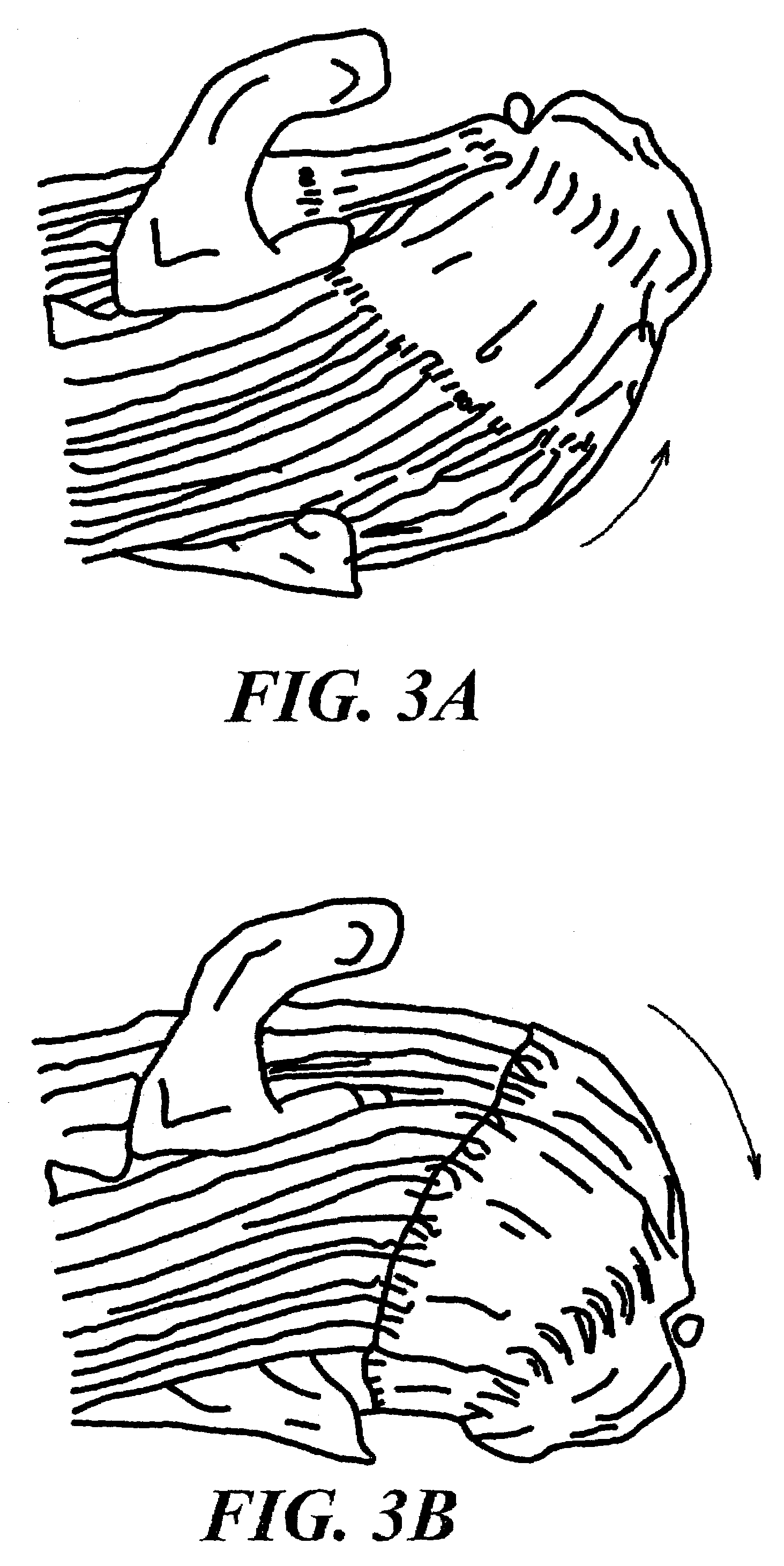
Tissue manipulation
InactiveUSRE43143E1Minimally interferesOvercome problemsSuture equipmentsLigamentsArthroscopic procedureSacroiliac joint
An apparatus and method for manipulating and anchoring tissue is provided. The invention is directed to solving the problem of manipulating and anchoring tissue within a joint when access to that tissue is limited, for example, during arthroscopic surgery.
Owner:HAYHURST JOHN O
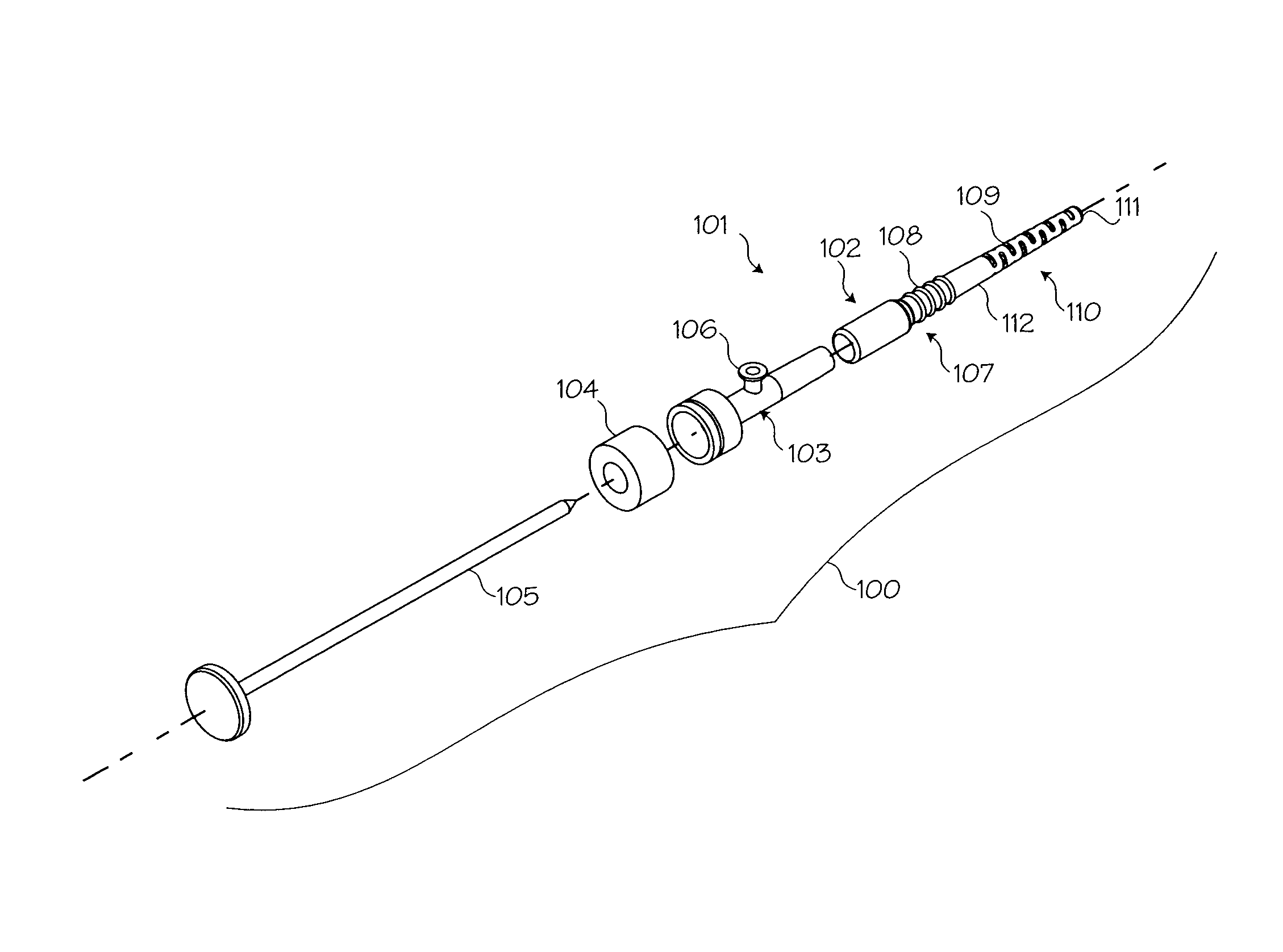
Medical implement for manipulating sutures particularly useful in arthroscopic surgery
ActiveUS20110301622A1Effective centeringSuture equipmentsExcision instrumentsArthroscopic procedureTarsal Joint
A medical implement particularly useful in arthroscopic sutures, includes: a handle having a proximal end configured for manual gripping by a user, a distal end, an internal passageway extending between the proximal end and the distal end, and an intermediate portion formed with a recess extending from the outer surface to the internal passageway. A shuttle is movable through the passageway and has an intermediate portion exposed within the recess for manipulation by a user gripping the handle, and a suture-receiving-element at its distal movable axially through the distal end of the handle. A roller is rotatably mounted to the handle to underlie the exposed portion of the shuttle such that, after a suture has been received by the suture-receiving-element of the shuttle, a user, gripping the handle, may manipulate the shuttle with respect to the distal end of the handle by thumb-pressing the exposed portion of the shuttle against the roller and rotating the roller.
Owner:T MEDICAL DEVICES AGRI COOP
Curved arthroscopic guide
InactiveUS20090198258A1Easy accessLess tissue damageSuture equipmentsCannulasArthroscopic procedureEngineering
Owner:WORKMAN WILLIAM BUCHANAN
Forceps for performing endoscopic or arthroscopic surgery
Forceps for performing endoscopic or arthroscopic surgery include a body assembly, a tube assembly, and a pair of handles that pivot with respect to the body. The tube assembly is removably attached to the body assembly. The tube assembly includes a hollow tube and a tip assembly. The tip assembly includes an electrode or a blade for performing the surgery. The tip assembly and the blade are connected to the body and the handles by a cable. As the handles pivot, the cable slides within the tube to move the blade. When a different tube assembly (i.e., a bipolar or a monopolar electrode) or another style of tip assembly are desired, the installed one is removed and replaced by a new tube assembly or tip assembly as desired.
Owner:LIVNEH STEVE
Circular bone tunneling device
InactiveUS20130178854A1Improve stabilitySuture equipmentsSurgical needlesArthroscopic procedureAdjustable suture
An adjustable suture passer for use in arthroscopic surgery is disclosed. In a preferred embodiment, the adjustable suture passer comprises a head that describes a semicircular arc, an elongate body, a support element, and driving and control mechanisms. The head is adapted to accommodate a surgical needle and a guide wire. When the adjustable suture passer is activated, the needle is driven with sufficient force to penetrate bone. Use of the adjustable suture passer thus enables surgical attachment of soft tissue to bone without any necessity for a separate anchor.
Owner:MININVASIVE
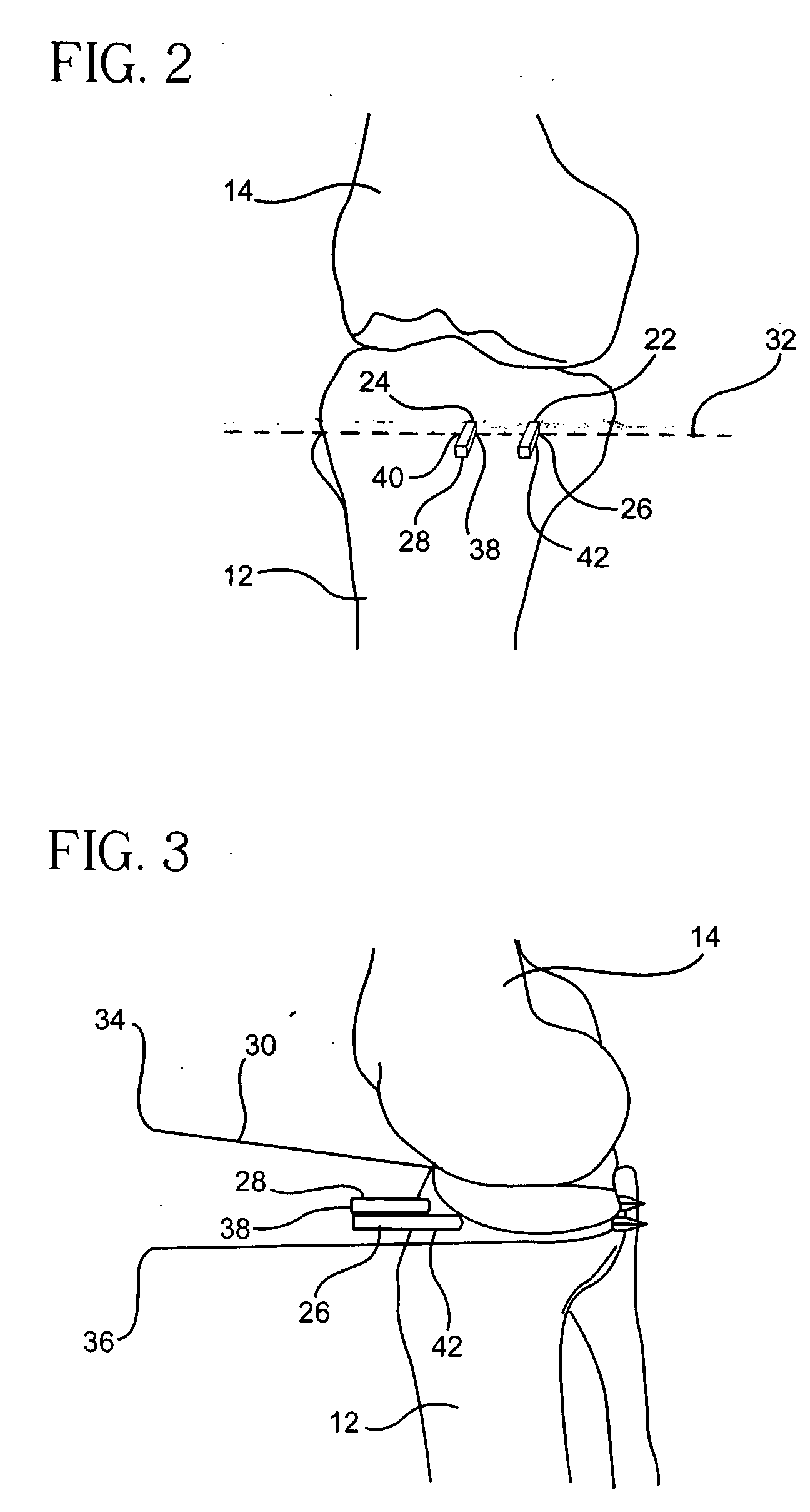
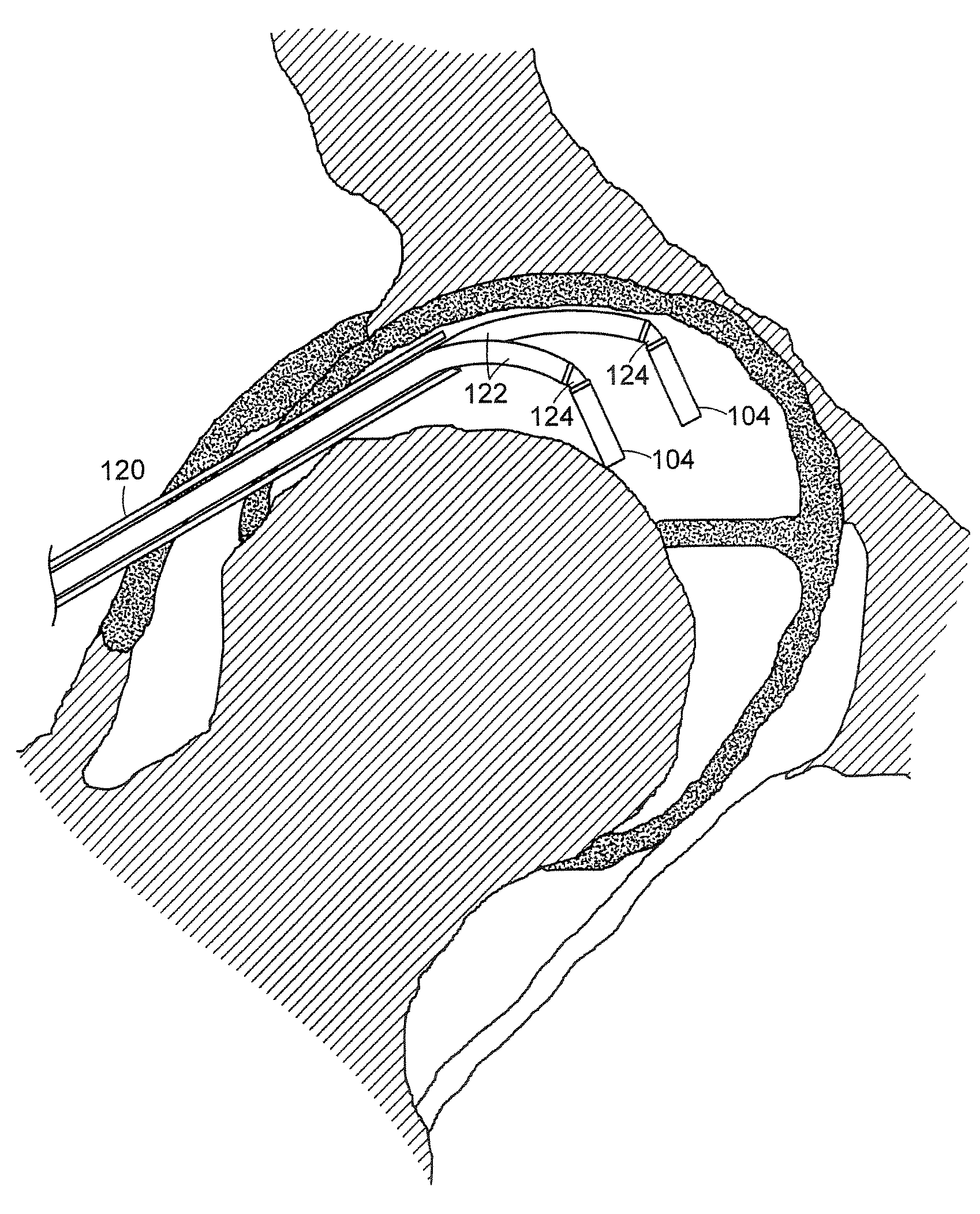
Methods and apparatus for performing an arthroscopic procedure using surgical navigation
InactiveUS20110190774A1Sufficient amountAvoid damageDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsArthroscopic procedureSacroiliac joint
The method for performing an arthroscopic procedure on a joint using surgical navigation. A 3-D virtual model of the anatomy is created from a scan of the anatomy. The 3-D virtual model is then used to reproduce motion of the joint and plan the arthroscopic procedure. The 3-D virtual model is placed into registration with the real-world anatomy, so that a virtual image generated by the 3-D virtual model may be placed into registration with an arthroscopic image of the real-world anatomy. Preferably, arthroscopic registration markers, positioned prior to scanning, are used to place the 3-D virtual model in registration with the real-world anatomy. The arthroscopic registration markers may be placed either percutaneously or arthroscopically. At the conclusion of the procedure, the registration markers may be left in place, removed arthroscopically or allowed to biodegrade.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com