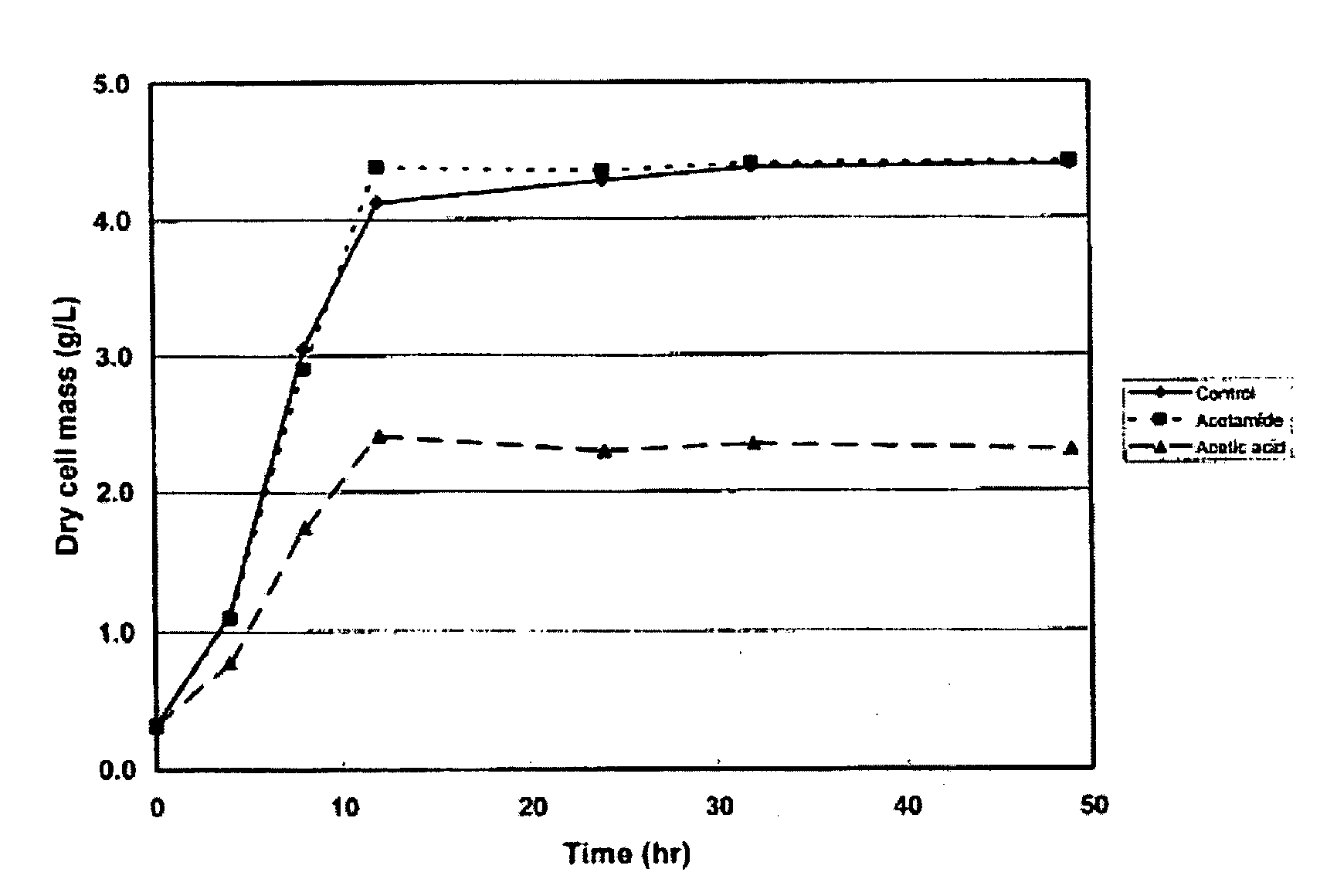
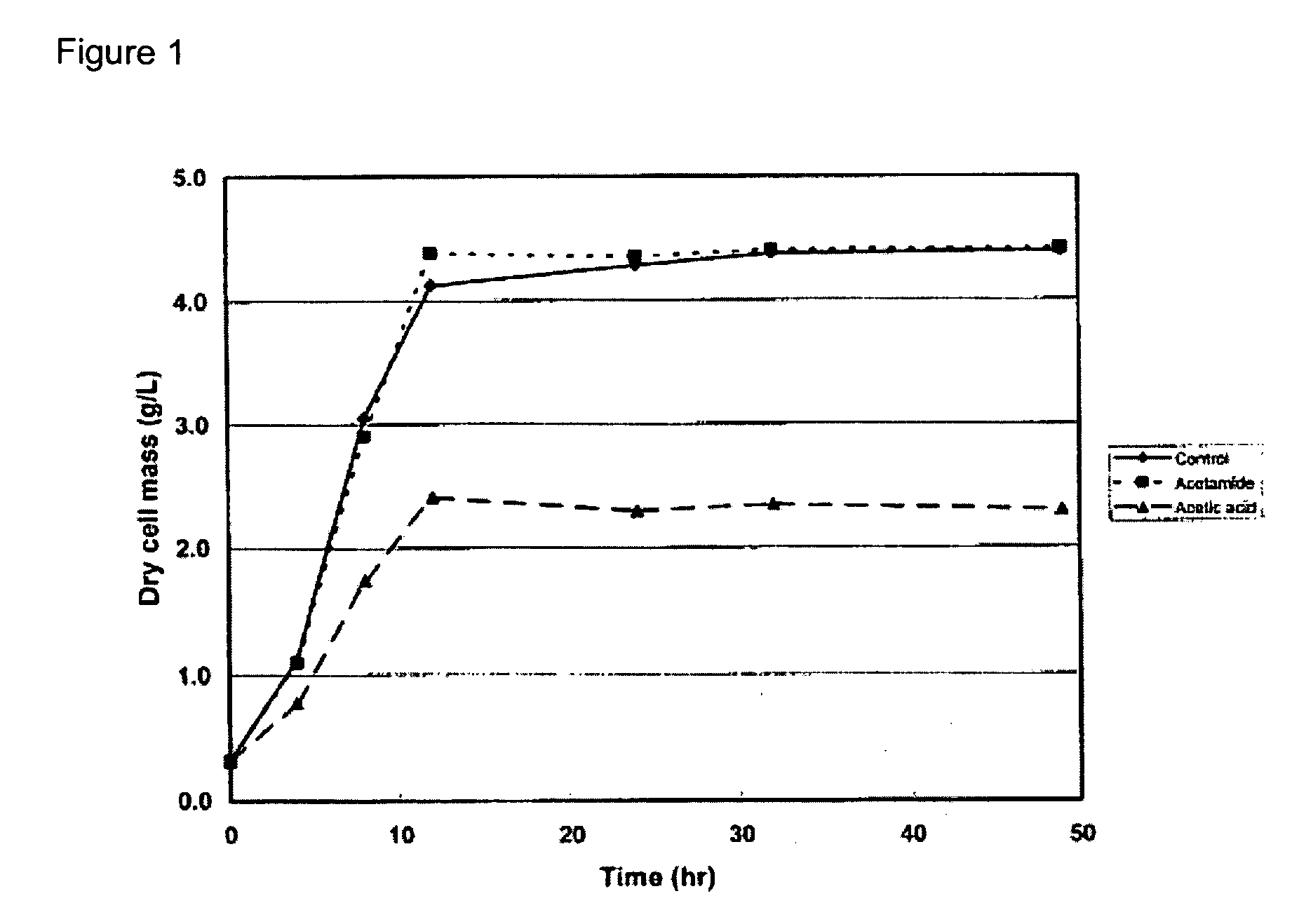
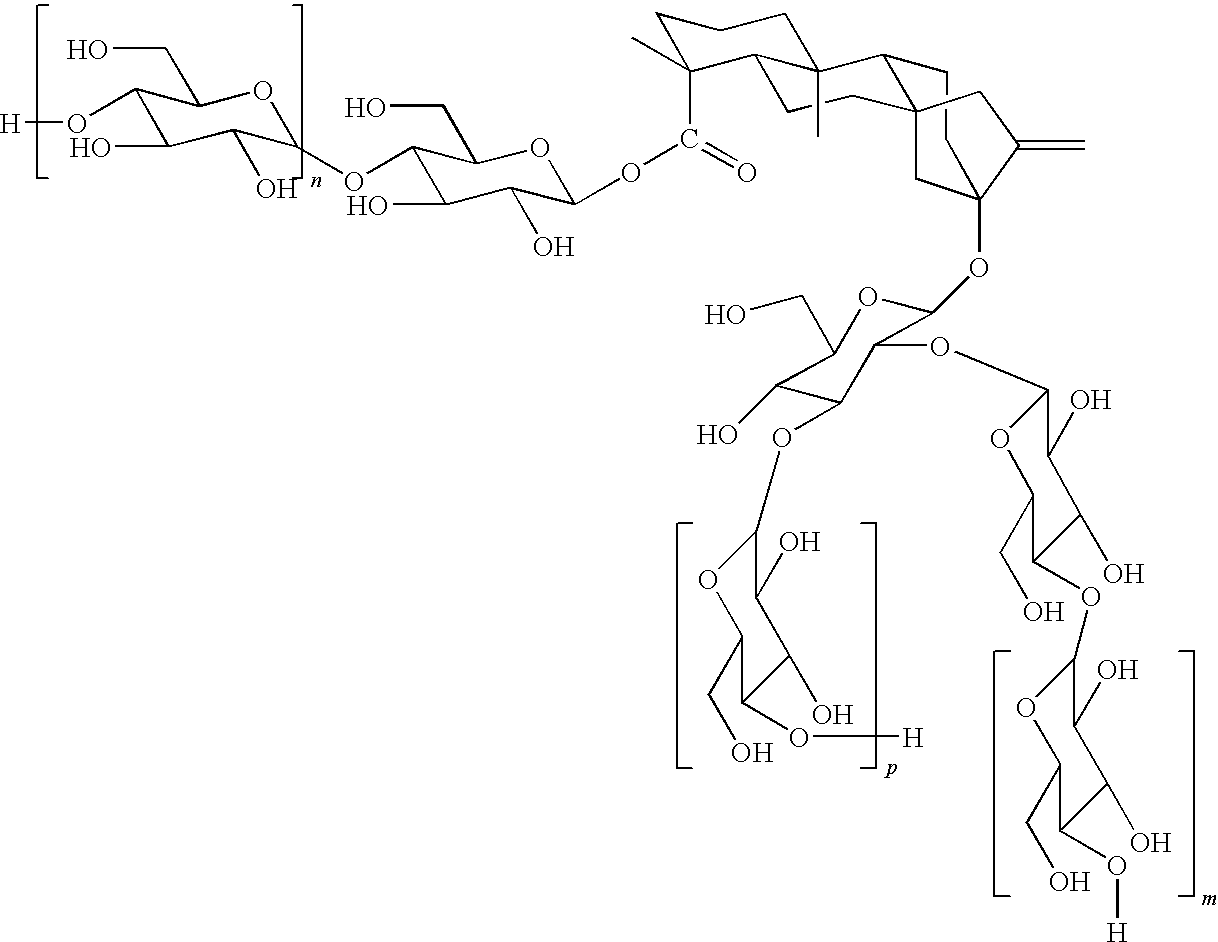
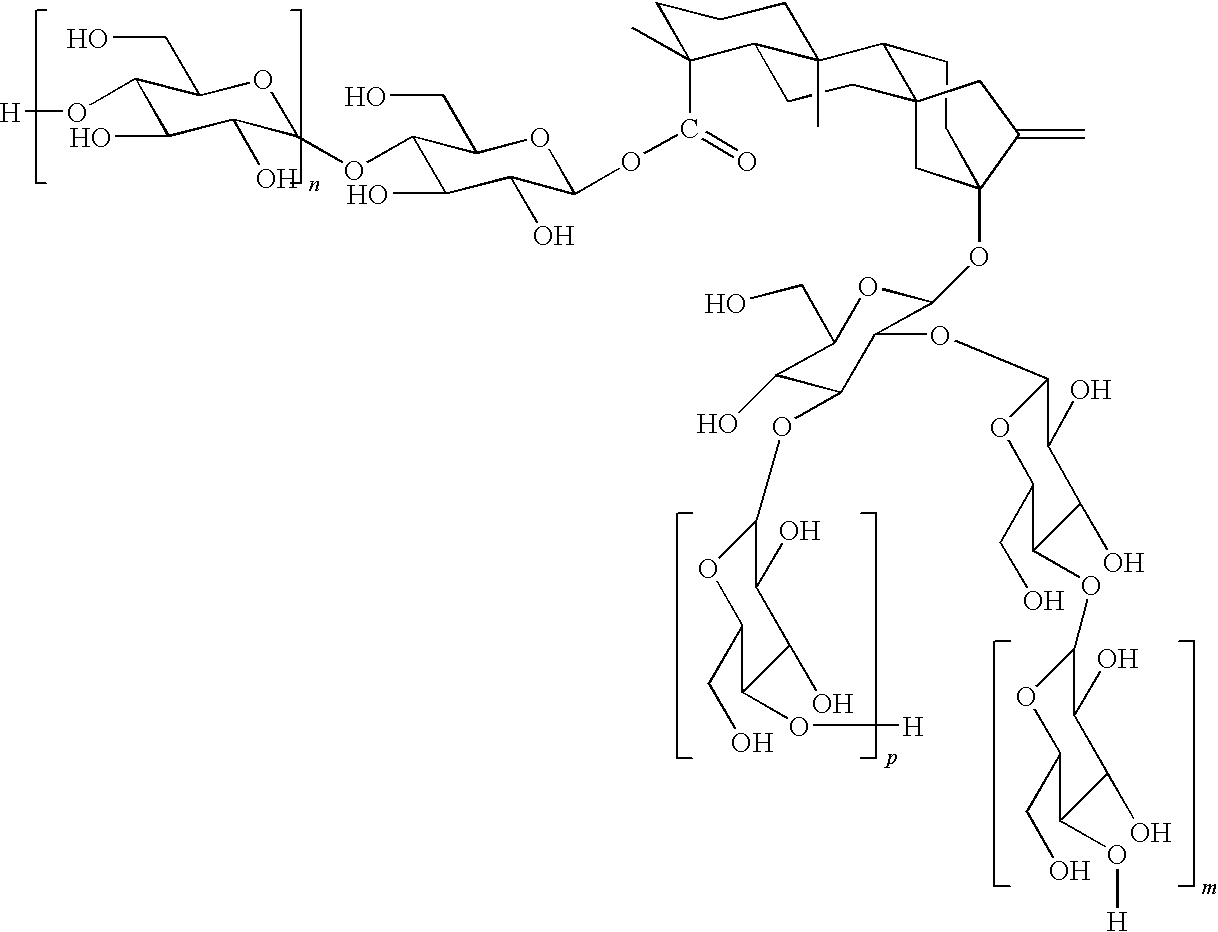
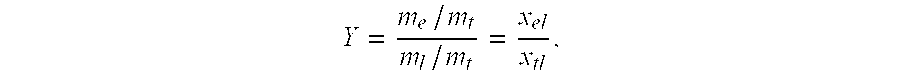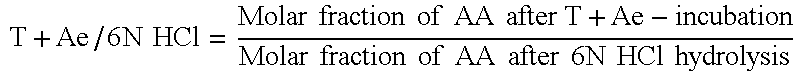Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1349results about "Protein foodstuffs working-up" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Treatment of biomass to obtain fermentable sugars
InactiveUS20070031918A1Toxic reductionReduce needBiological substance pretreatmentsByproduct vaporizationFermentable sugarCompound (substance)
Biomass is pretreated using a low concentration of aqueous ammonia at high biomass concentration. Pretreated biomass is further hydrolyzed with a saccharification enzyme consortium. Fermentable sugars released by saccharification may be utilized for the production of target chemicals by fermentation.
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY +1
Use
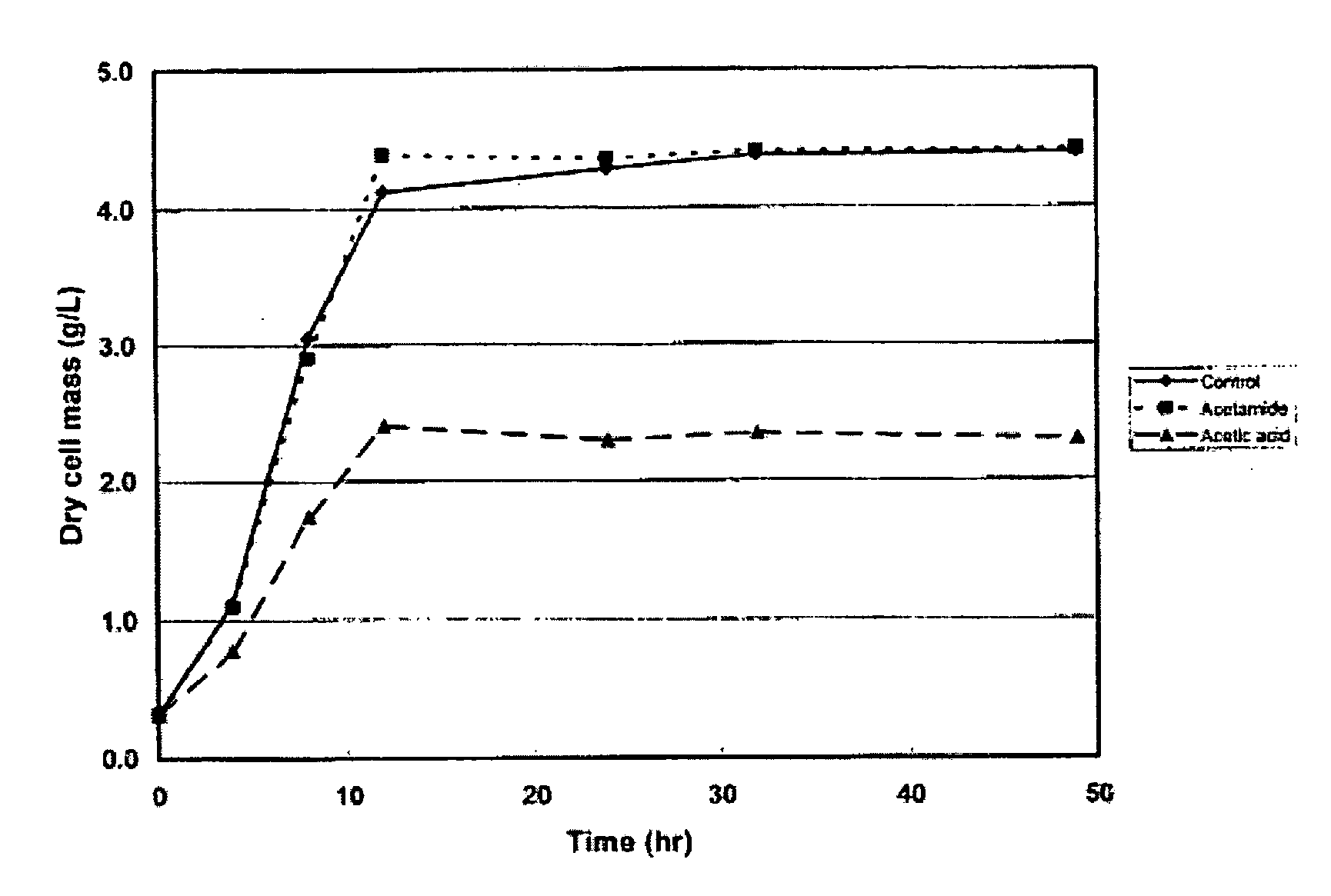
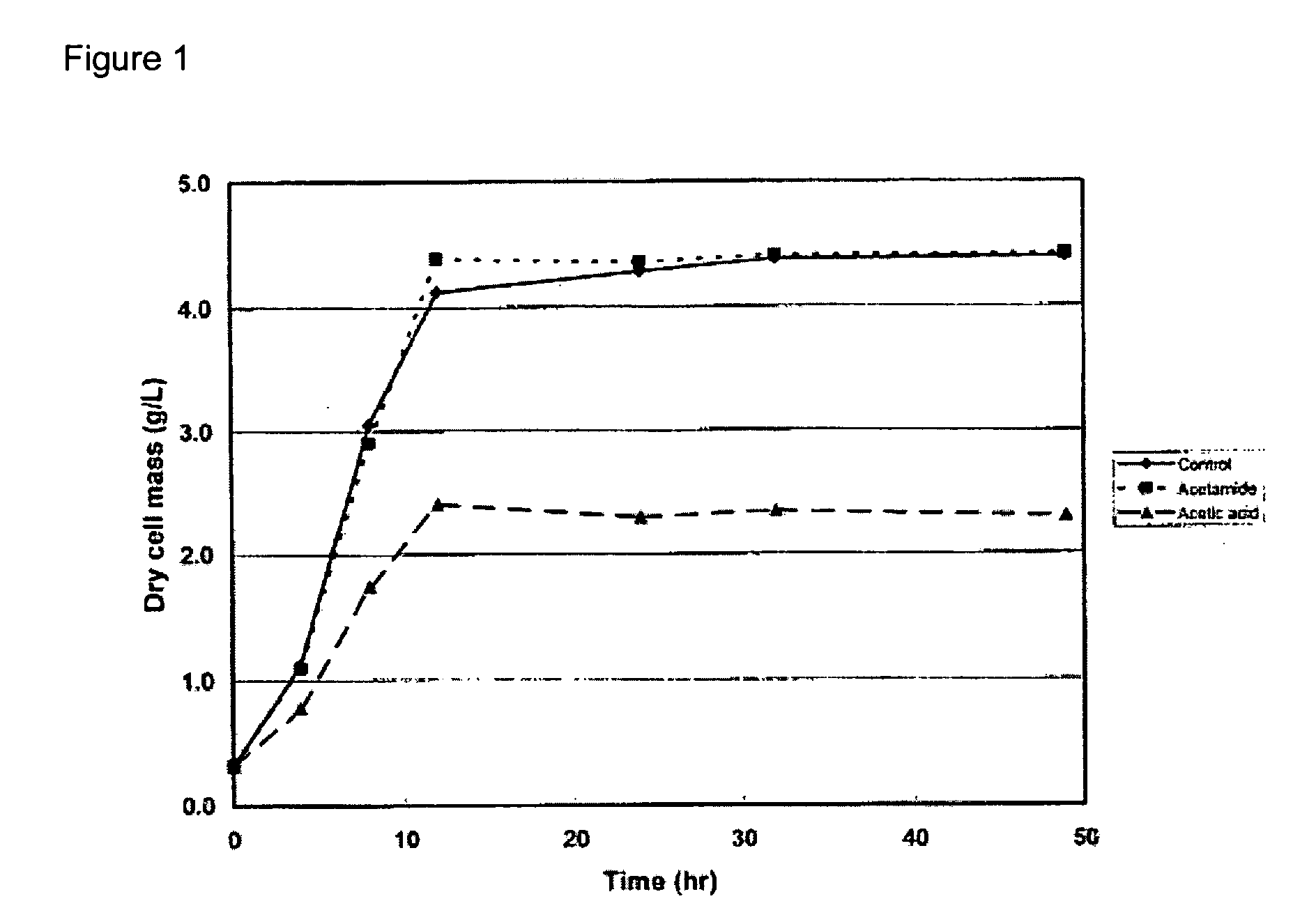
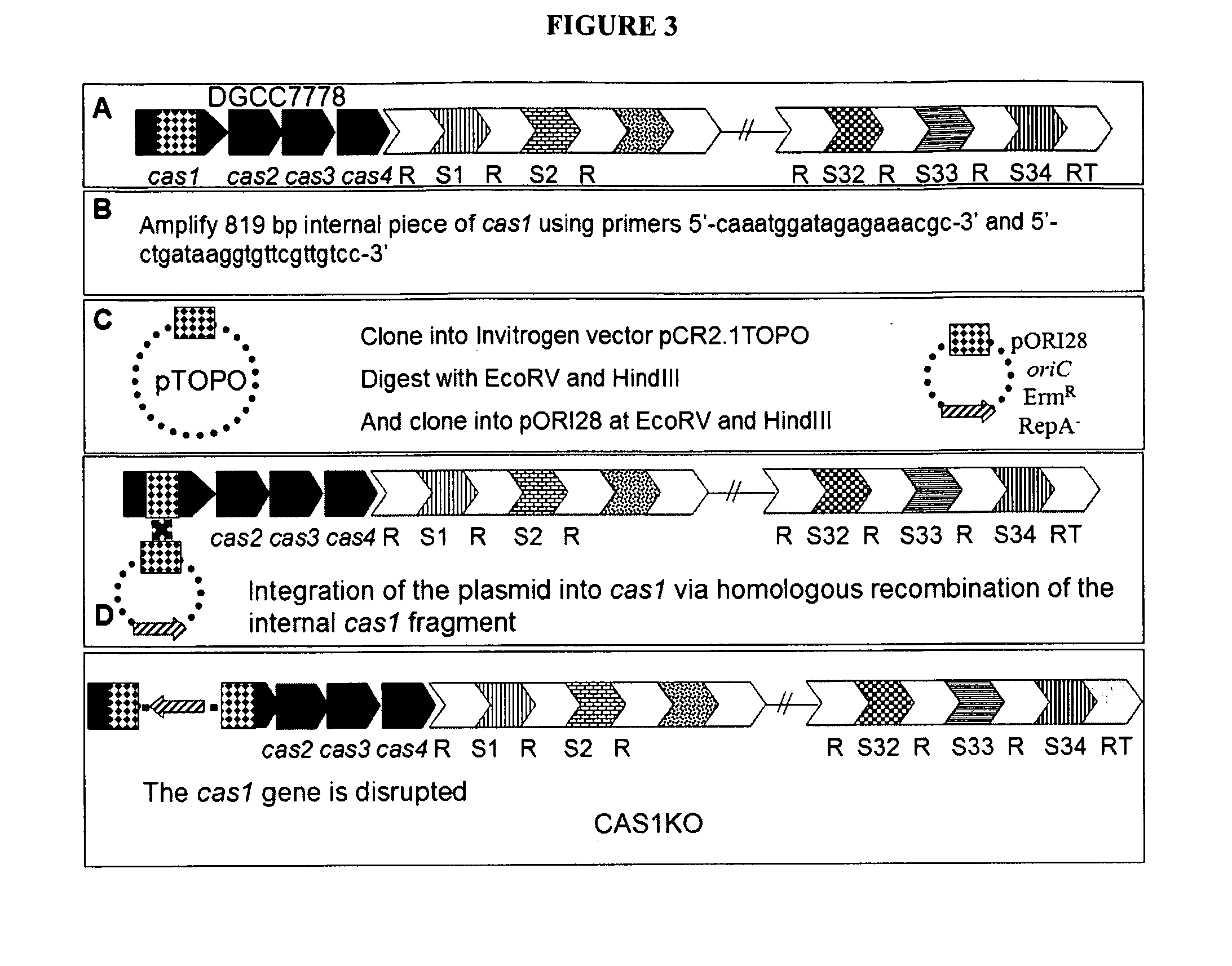
ActiveUS20130011828A1Modulate the resistance of a cellBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsGeneBioinformatics
The present invention relates to the use of one or more cas genes for modulating resistance in a cell against a target nucleic acid or a transcription product thereof.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
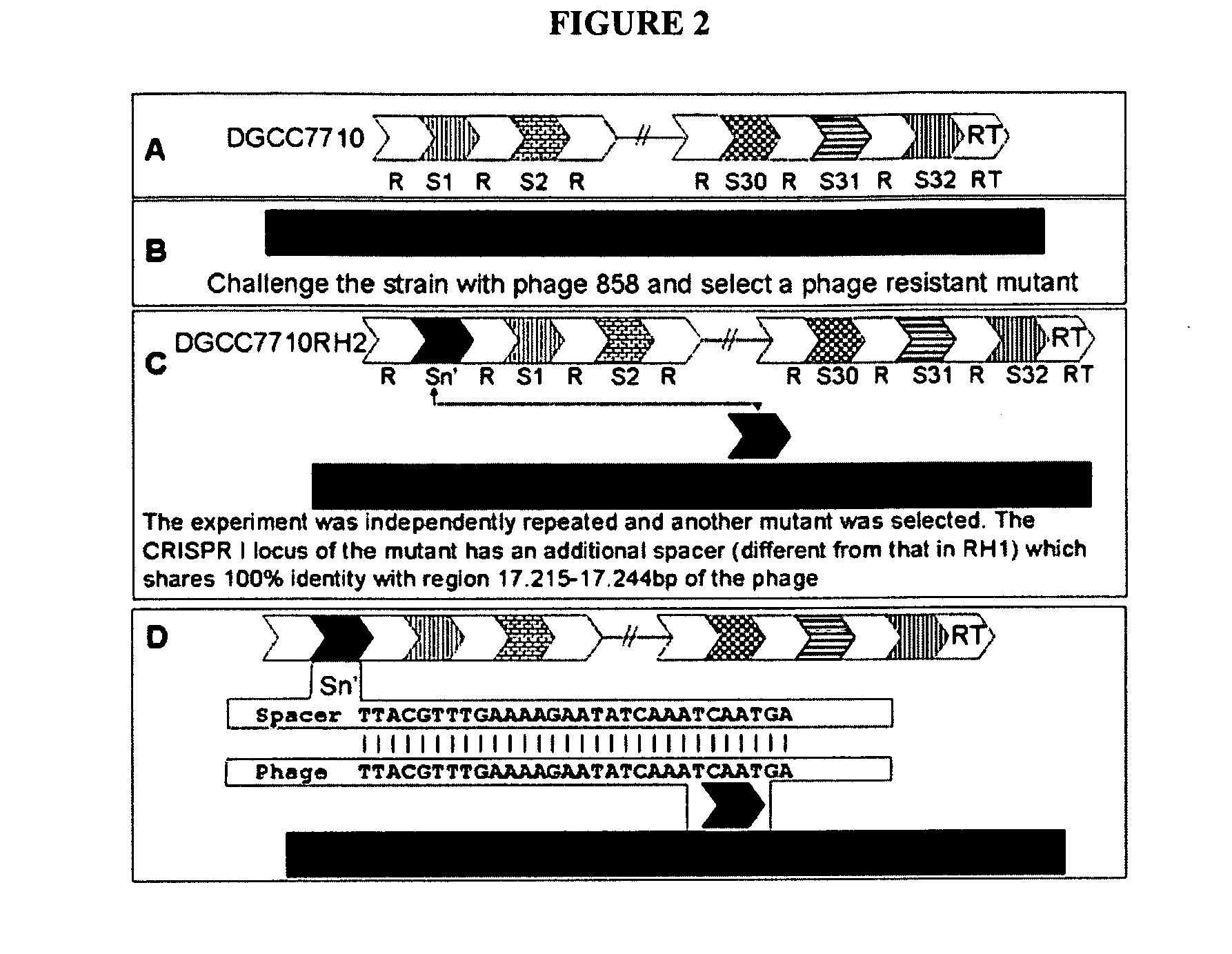
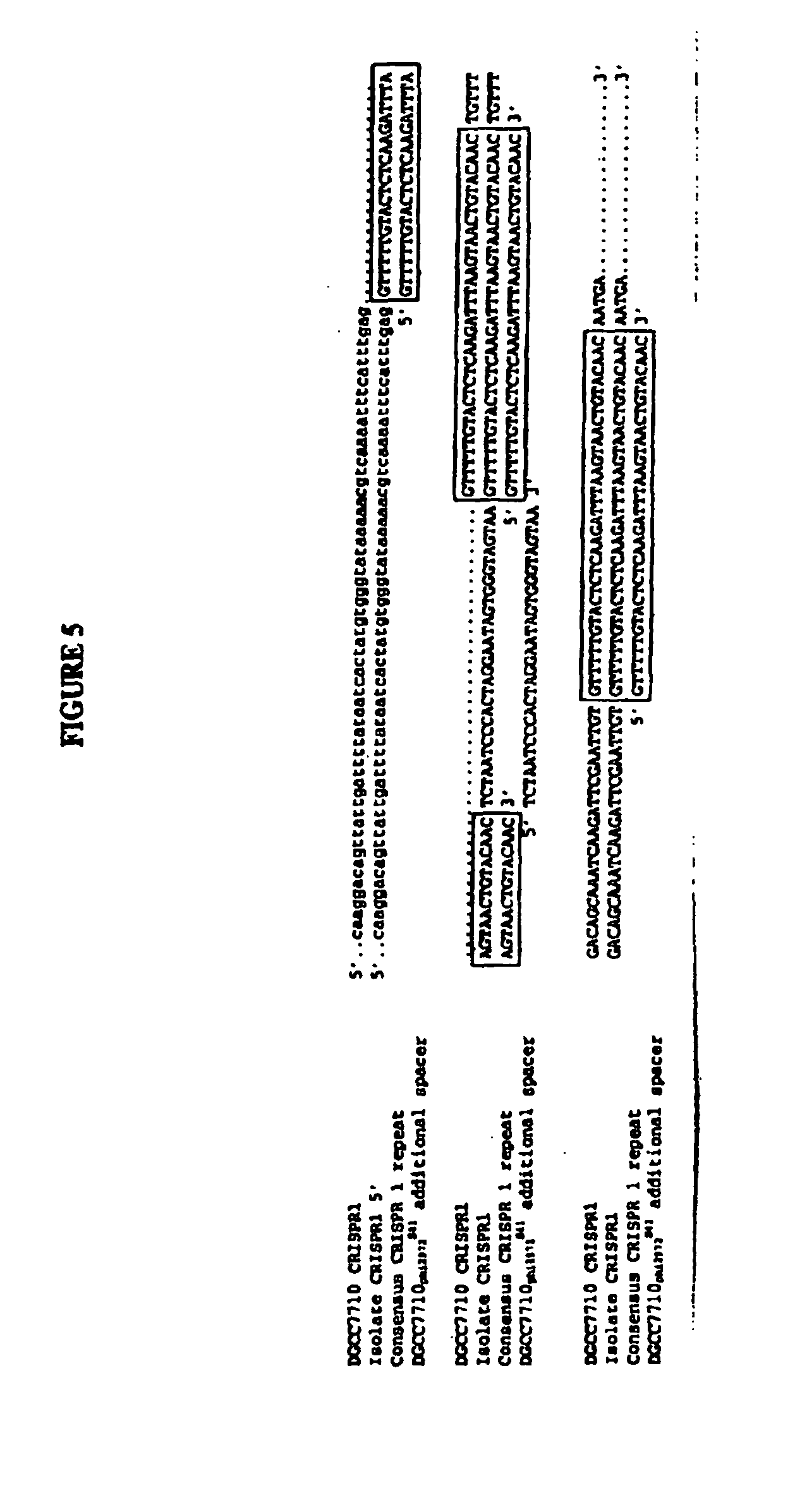
Cultures with Improved Phage Resistance
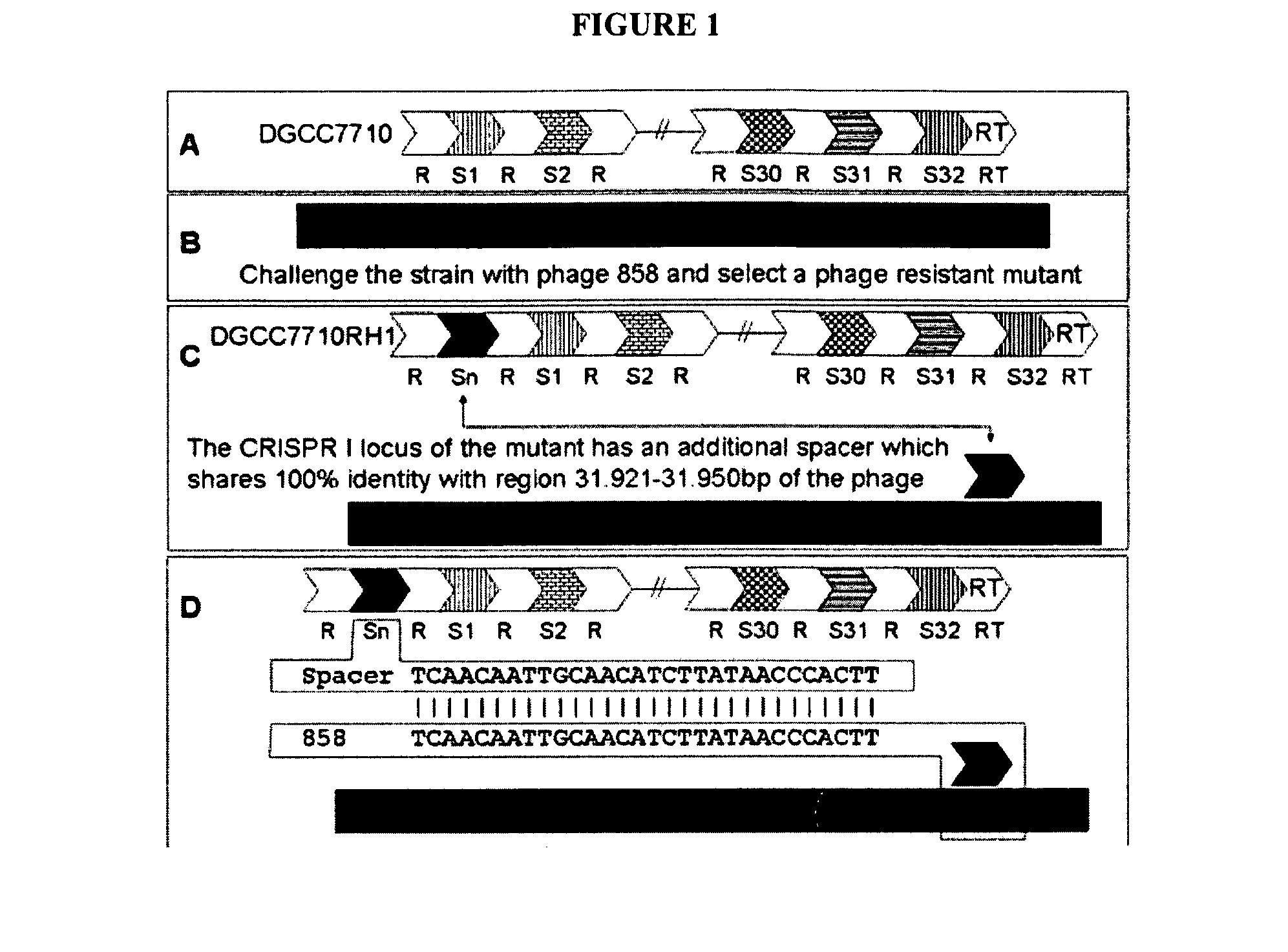
InactiveUS20110002889A1Reduced degree of homologyReduce decreaseBiocideBacteriaVirulent characteristicsBacteriophage
The present invention provides methods and compositions related to modulating the resistance of a cell against a target nucleic acid or a transcription product thereof. In some preferred embodiments, the present invention provides compositions and methods for the use of one or more cas genes or proteins for modulating the resistance of a cell against a target nucleic acid or a transcription product thereof. In some embodiments, the present invention provides methods and compositions that find use in the development and use of strain combinations and starter culture rotations. In additional embodiments, the present invention provides methods for labelling and / or identifying bacteria. In some preferred embodiments, the present invention provides methods for the use of CRISPR loci to determine the potential virulence of a phage against a cell and the use of CRISPR-cas to modulate the genetic sequence of a phage for increased virulence level. In still further embodiments, the present invention provides means and compositions for the development and use of phages as biocontrol agents.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Biomass hydrolysate and uses and production thereof
The present invention includes a palatable, stable composition comprising a biomass hydrolysate emulsion for incorporation, into, or used as, nutritional products, cosmetic products or pharmaceutical products. Preferred sources for biomass are microbial sources, plant sources and animal sources. The present invention also provides methods for making such compositions, specifically, a method for producing a product comprising a nutrient, particularly a long chain polyunsaturated fatty acid, comprising hydrolyzing a biomass comprising the nutrient and emulsifying the hydrolyzed biomass. Such compositions and methods are useful, for example, for increasing intake of nutrients such as omega-3 long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids having 18 or more carbons.
Owner:MARTEK BIOSCIENCES CORP
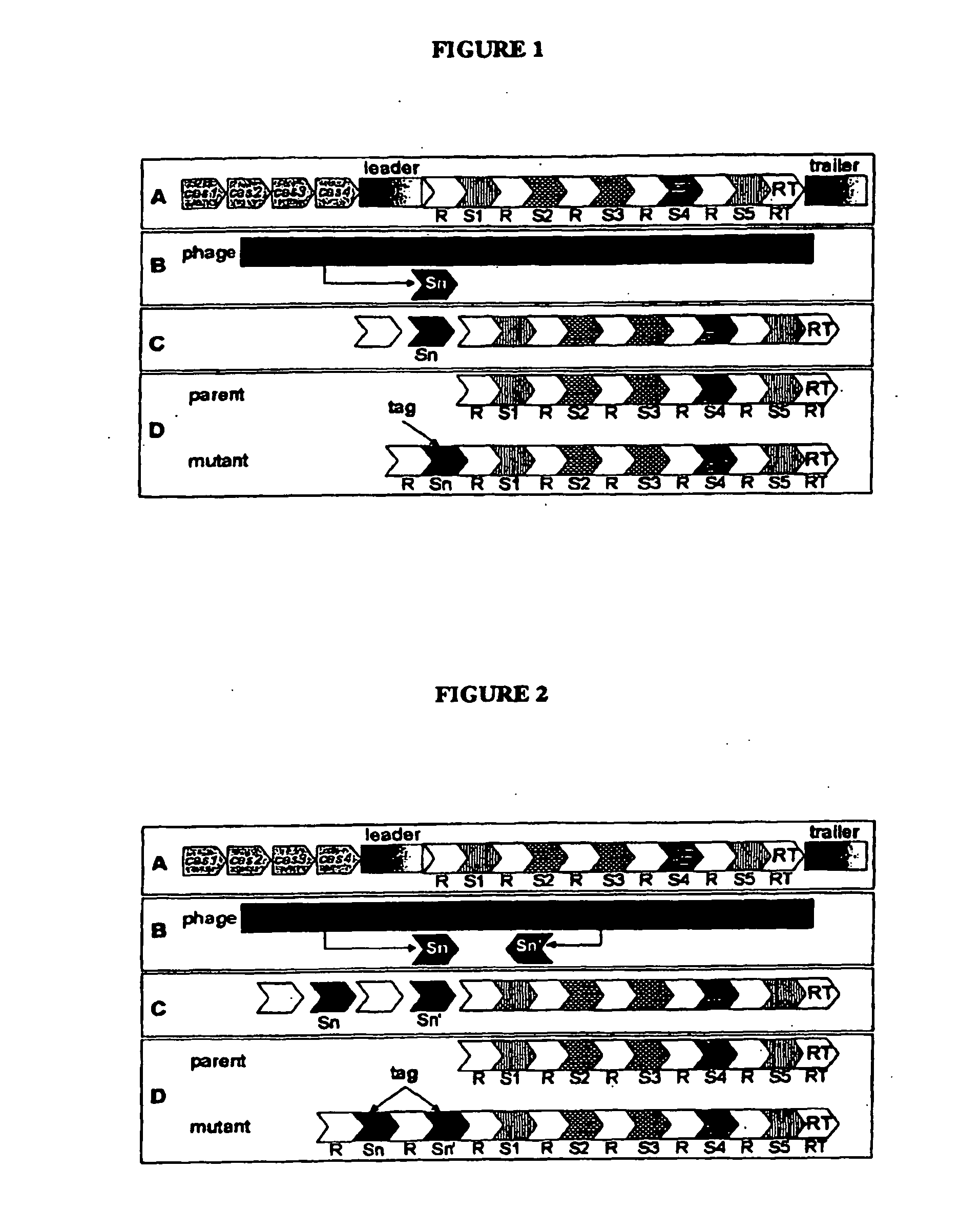
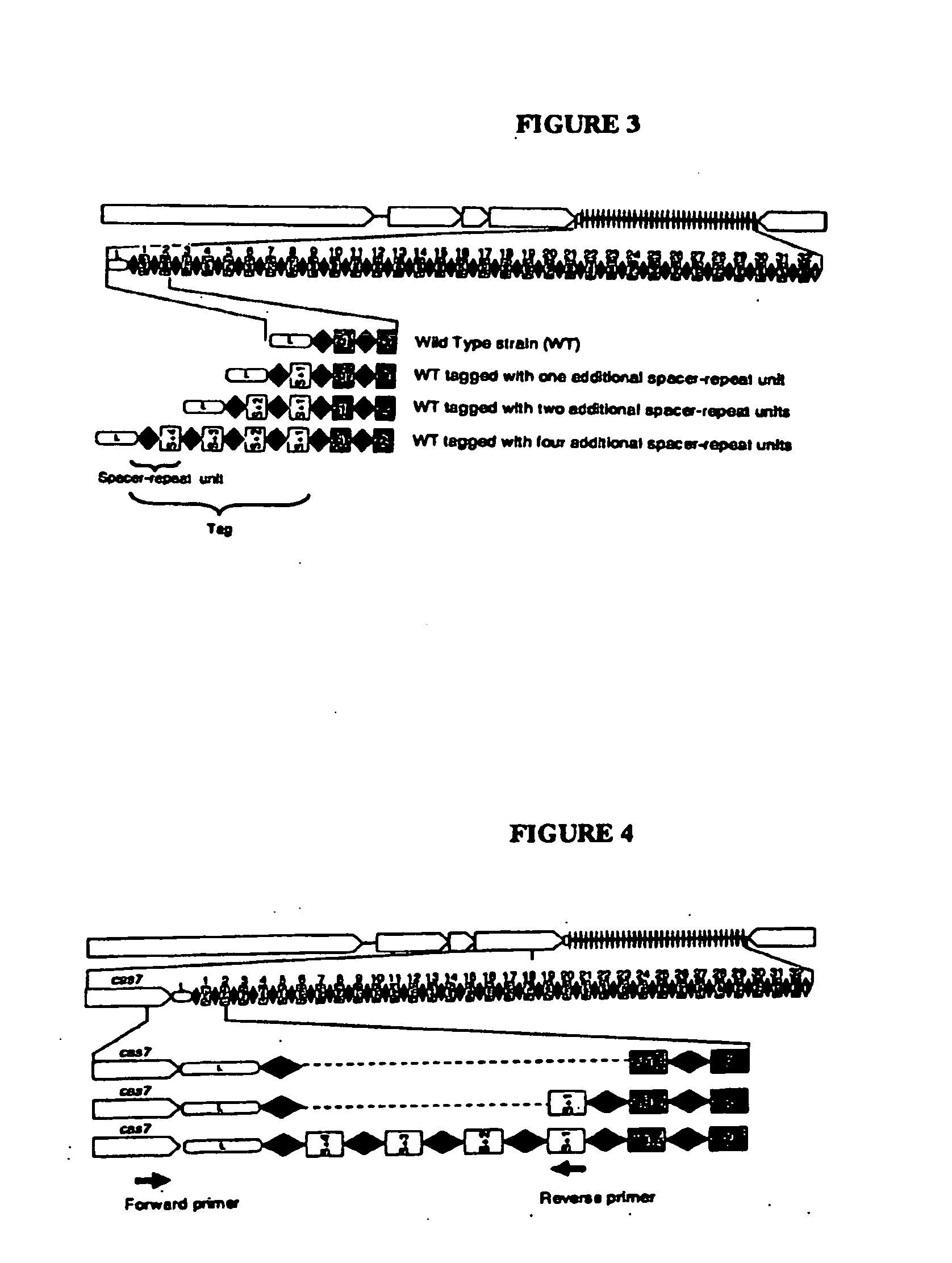
Tagged Microorganisms and Methods of Tagging
The present invention provides methods for tagging and / or identifying microorganisms. In some preferred embodiments, the microorganisms are bacteria. In some particularly preferred embodiments, the bacteria are members of the genus Streptococcus, while in other embodiments, the bacteria are members of other genera. The present invention also provides microorganisms tagged using the methods set forth herein. In some preferred embodiments, the tagged microorganisms are bacteria. In some particularly preferred embodiments, the tagged bacteria are members of the genus Streptococcus, while in other embodiments, the tagged bacteria are members of other genera.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Integration of alternative feedstreams for biomass treatment and utilization
InactiveUS20070037259A1High solid contentBiological substance pretreatmentsByproduct vaporizationHigh concentrationDry weight
The present invention provides a method for treating biomass composed of integrated feedstocks to produce fermentable sugars. One aspect of the methods described herein includes a pretreatment step wherein biomass is integrated with an alternative feedstream and the resulting integrated feedstock, at relatively high concentrations, is treated with a low concentration of ammonia relative to the dry weight of biomass. In another aspect, a high solids concentration of pretreated biomass is integrated with an alternative feedstream for saccharifiaction.
Owner:SUSTAINABLE TECH CORP +1
Confectionery compositions including an elastomeric component and a saccharide component
InactiveUS20080166449A1Center edible coresCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsElastomerChewing gum
The present invention relates to the confectionery compositions including a saccharide and a chewing gum base.
Owner:INTERCONTINENTAL GREAT BRANDS
Protein beverage and method of making the same
An improved protein beverage / drink composition which may provide a relatively high protein content, ranging from about 0.01% by weight to about 15% by weight, while optionally employing a carbonation concentration between about 0.1 volumes of carbonation (per volume of liquid drink solution or liquid drink suspension) to about 6 volumes of carbonation. Preferably the protein is a protein, such preferably as whey protein, or others. The protein beverage may contain juice and / or an additive which provides energy generation enhancement. The protein beverage may be heat treated to inactivate pathogenic microbes in the presence of the carbonation which may be used to provide taste and mouth feel for the drink. Typically, the treatment for pathogenic microbe inactivation is carried out in the individual package used for storage and handling of the protein drink.
Owner:DAVINAS LLC
Lipid-Rich Microalgal Flour Food Compositions
InactiveUS20110256282A1Extended shelf lifeSimple compositionDough treatmentFrozen sweetsAlgaeBiology
Algal flour and algal biomass are disclosed. Food compositions comprising algal biomass or algal flour with a high lipid content are disclosed.
Owner:CORBION BIOTECH INC
Use of erythritol and D-tagatose in diet or reduced-calorie beverages and food products
A combination of one or more non-nutritive sweeteners, a sugar alcohol and D-tagatose are included in a reduced-calorie beverage or food product to achieve a taste substantially similar to that of a full-calorie beverage or food product. The combination is suitable for use in reduced-calorie frozen carbonated beverages. Preferably, the one or more non-nutritive sweeteners include one or more steviosides, a Stevia glycoside, a derivative of a Stevia glycoside, a glycoside of steviol, or a Lo Han Guo extract.
Owner:PEPSICO INC
High protein beverage and method of producing same
A high-protein beverage is made with a protein content of at least 15% of the total product content. At least 10% of the total product consists of hydrolyzed gelatin. A method of producing a high-protein beverage product via UHT processing comprising at least 15% total protein also is disclosed.
Owner:TETRA LAVAL HLDG & FINANCE SA
Reduced Pigmentation Microalgae Strains and Products Therefrom
InactiveUS20100297292A1Reduced colorationIncrease rangeMilk preparationDough treatmentHypopigmentationCarotenoid
The invention provides unique and novel strains of microalgae that have been subjected to non-transgenic methods of mutation sufficient to reduce the coloration of biomass produced by the strains. Biomass produced from such strains can be used in the manufacture of baked goods, gluten free foods, beverages, high lipid algal flours, and other foods. Pigments such as carotenoids and chlorophyll can be undesirable for consumer acceptance when incorporated into foods such as mayonnaise, yogurt, and white sauces that are not traditionally associated with colors such as yellow, red, orange and green. Some pigments, such as chlorophyll, can also create undesirable taste profiles. Use of reduced pigment microalgal biomass expands the range of food products that can be manufactured with healthy lipid profiles. High protein containing biomass of the invention, also reduced in pigmentation, is also incorporated into products such as meat analogues, nutritional bars and meal replacement beverages. The reduced pigmentation microalgae also allow for incorporation of higher amounts of biomass into certain food products that could otherwise be achieved using highly pigmented microalgal biomass. Methods of generating novel reduced pigment microalgae are disclosed herein. The strains provided by the invention are also useful in the manufacture of healthy, neutral colored extracted triglyceride oils.
Owner:TERRAVIA HLDG INC
Enrichment of process feedstock
InactiveUS20110124034A1Fit for consumptionUnicellular algaeBiomass after-treatmentMicroorganismBiofuel
The subject invention relates to novel methods for treating microbial biomass and uses thereof. In particular, this invention provides methods for production of lipids using ionic liquid solutions, and subsequent uses of biomass components in food, biofuels, and as chemical precursors. Further, this invention provides methods for recovering the ionic liquids using an antisolvent, thus enables subsequent reuse of the ionic liquids In addition, this invention provides practical methods for determining the lipid content of a biomass and screening potential lipid-producing microbial classes. This invention also provides a method of chemical dewatering the lipid-rich algae cells by ionic liquids with its subsequent reuse.
Owner:KUEHNLE AGROSYST
Fractionation of protein containing mixtures
InactiveUS7812138B2Easy to operatePeptide/protein ingredientsIon-exchanger regenerationHigh densitySorbent
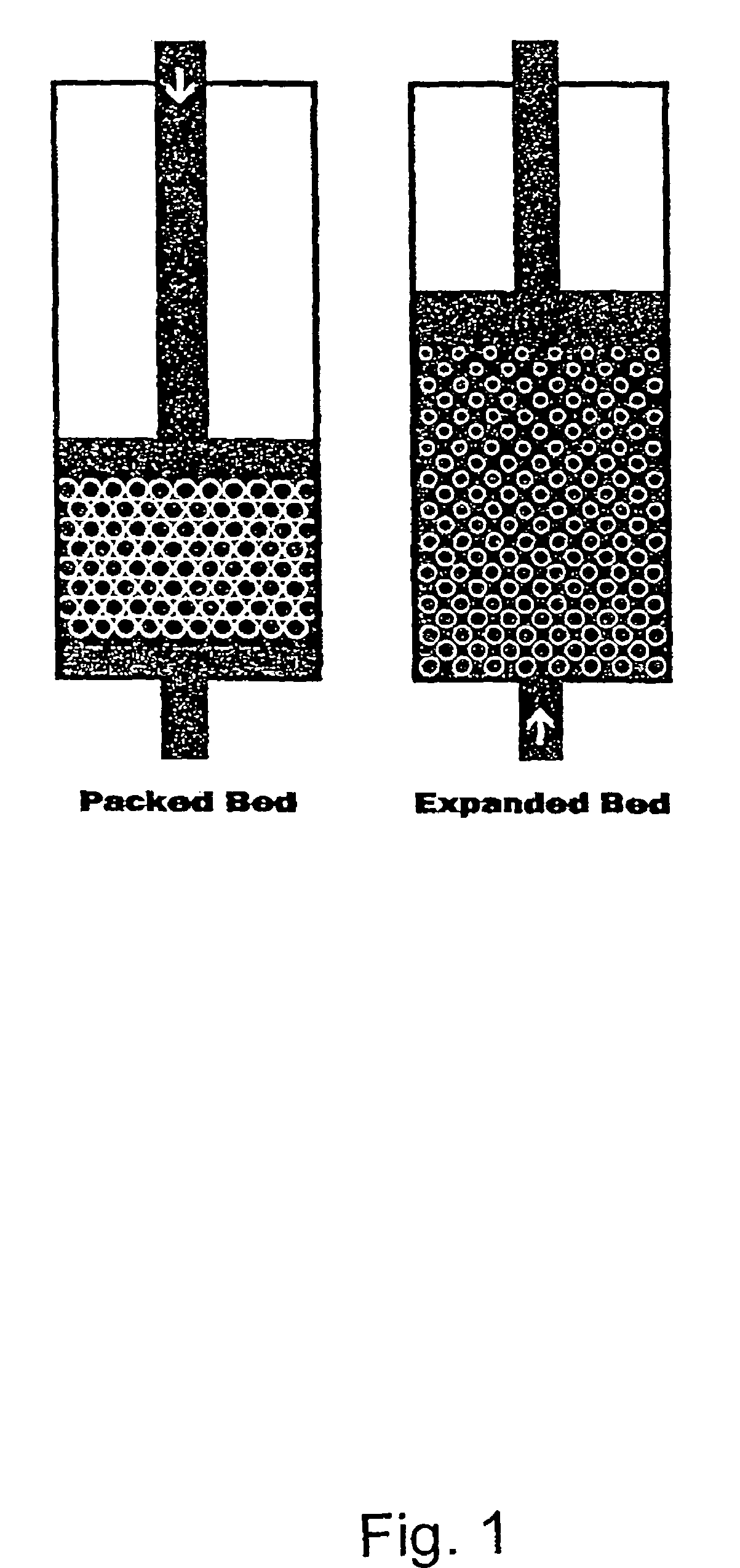
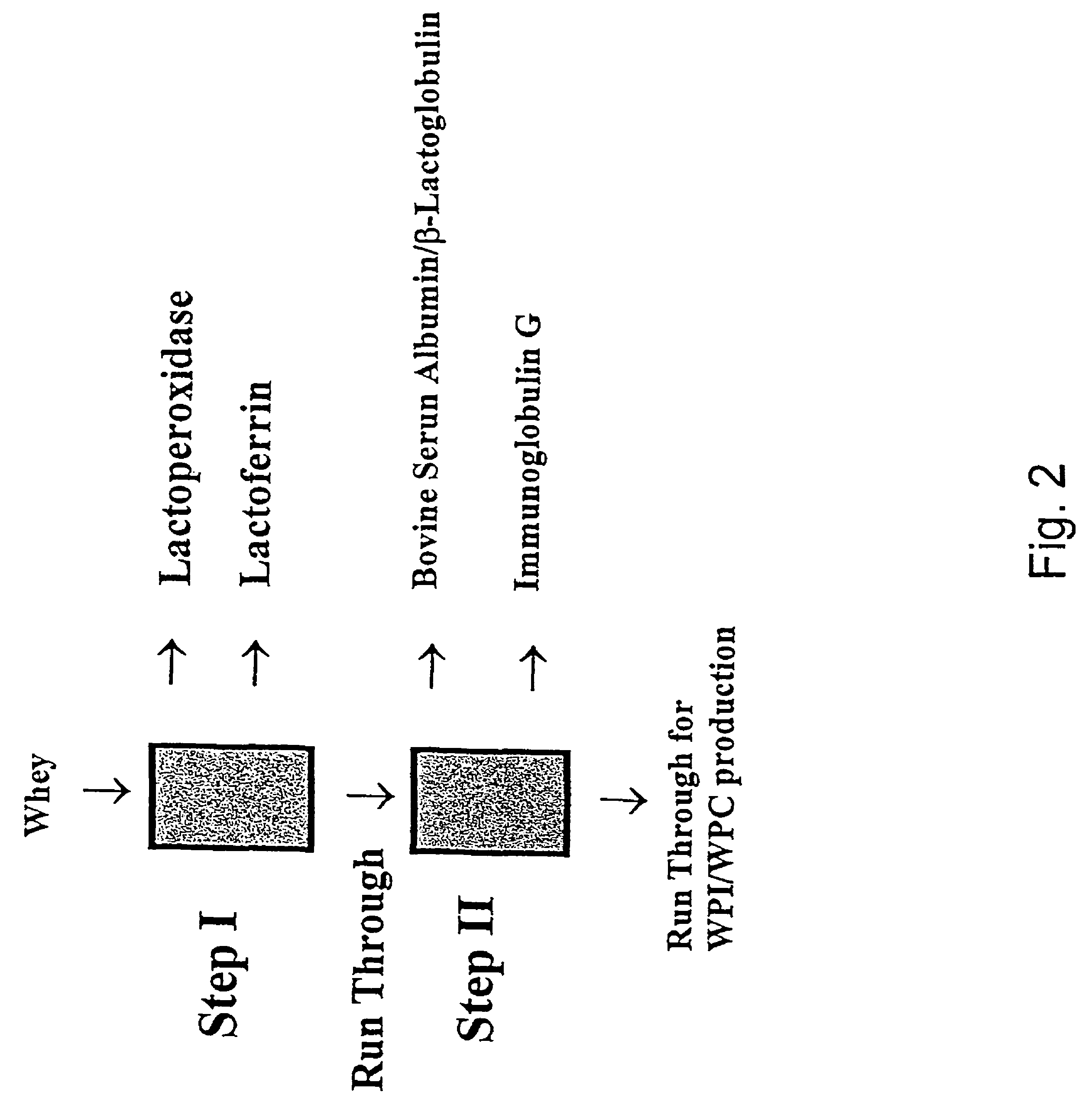
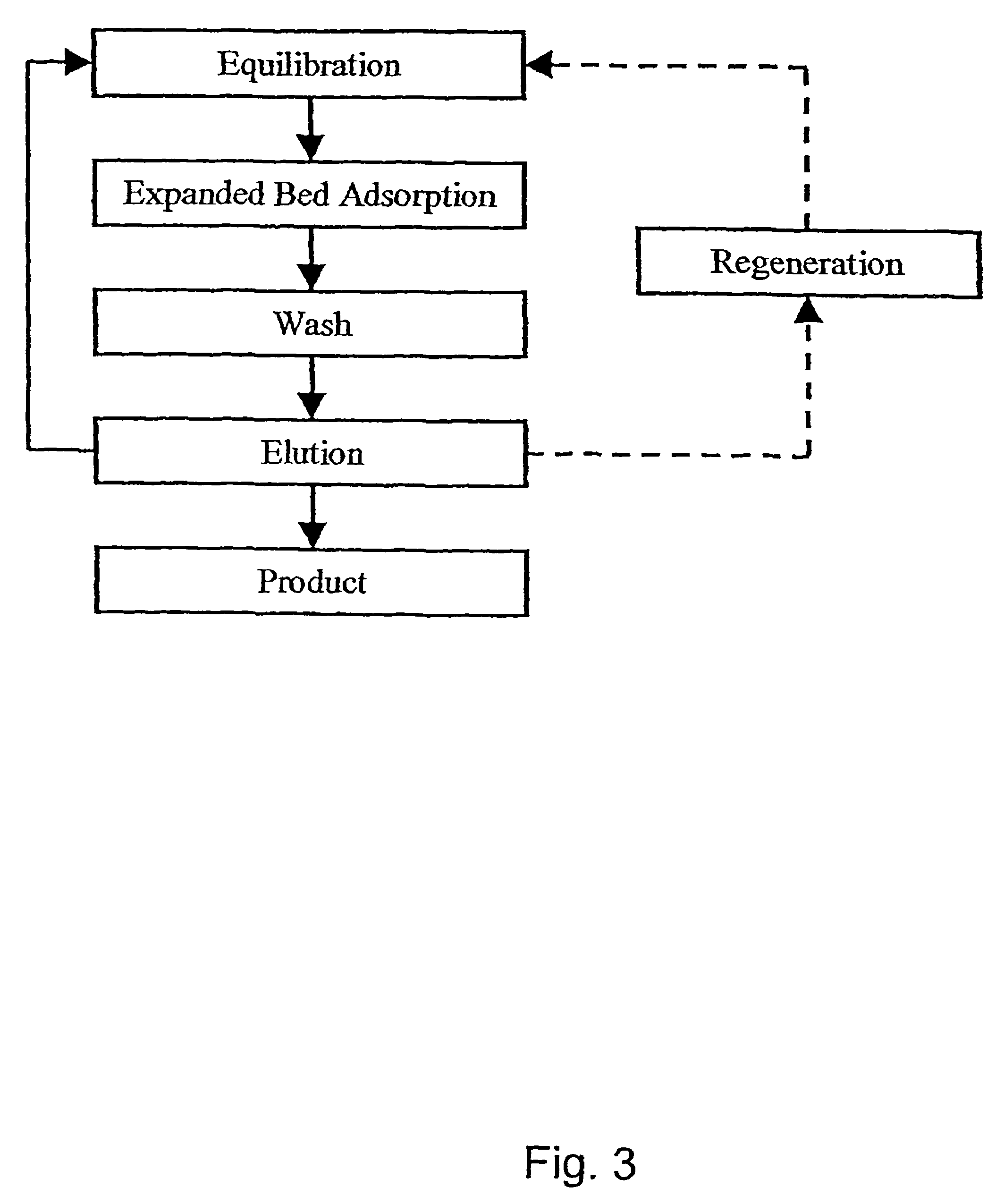
Thus, a primary aspect of the present invention relates to a method for the fractionation of a protein-containing mixture wherein the protein-containing mixture is selected from the group consisting of milk, milk derived products, milk derived raw materials, vegetable derived products, vegetable derived extracts, fruit derived products, fruit derived extracts, fish derived products, and fish derived extracts, the method comprising the steps of: a) optionally adjusting the pH of the mixture; b) applying the mixture to an adsorption column comprising an adsorbent, the adsorbent comprises a particle with at least one high density non-porous core, surrounded by a porous material, the adsorbent having a particle density of at least 1.5 g / ml and a mean particle size of at most 150 μm; c) optionally washing the column; d) eluting at least one protein from the adsorbent.
Owner:UPFRONT CHROMATOGRAPHY
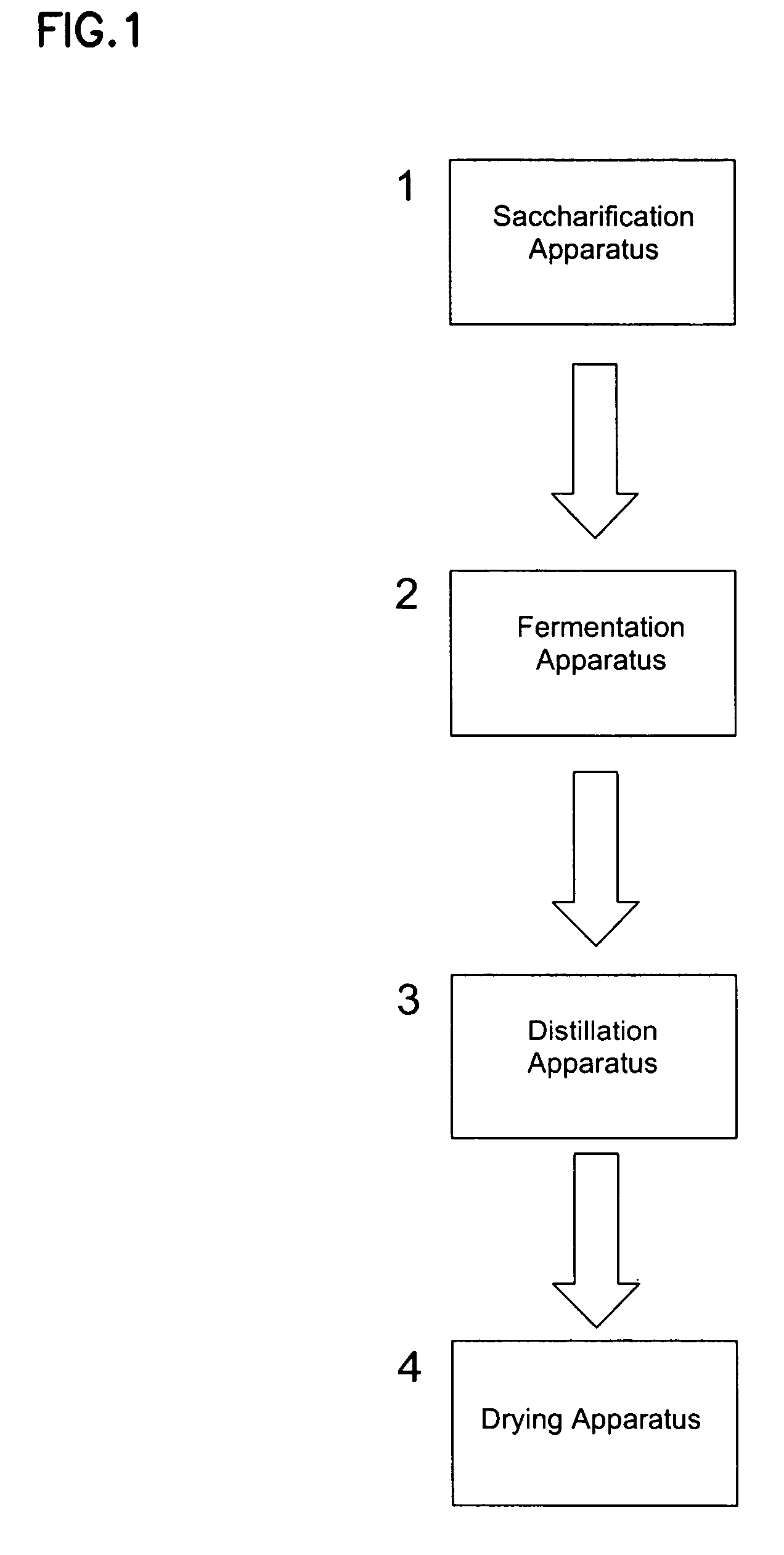
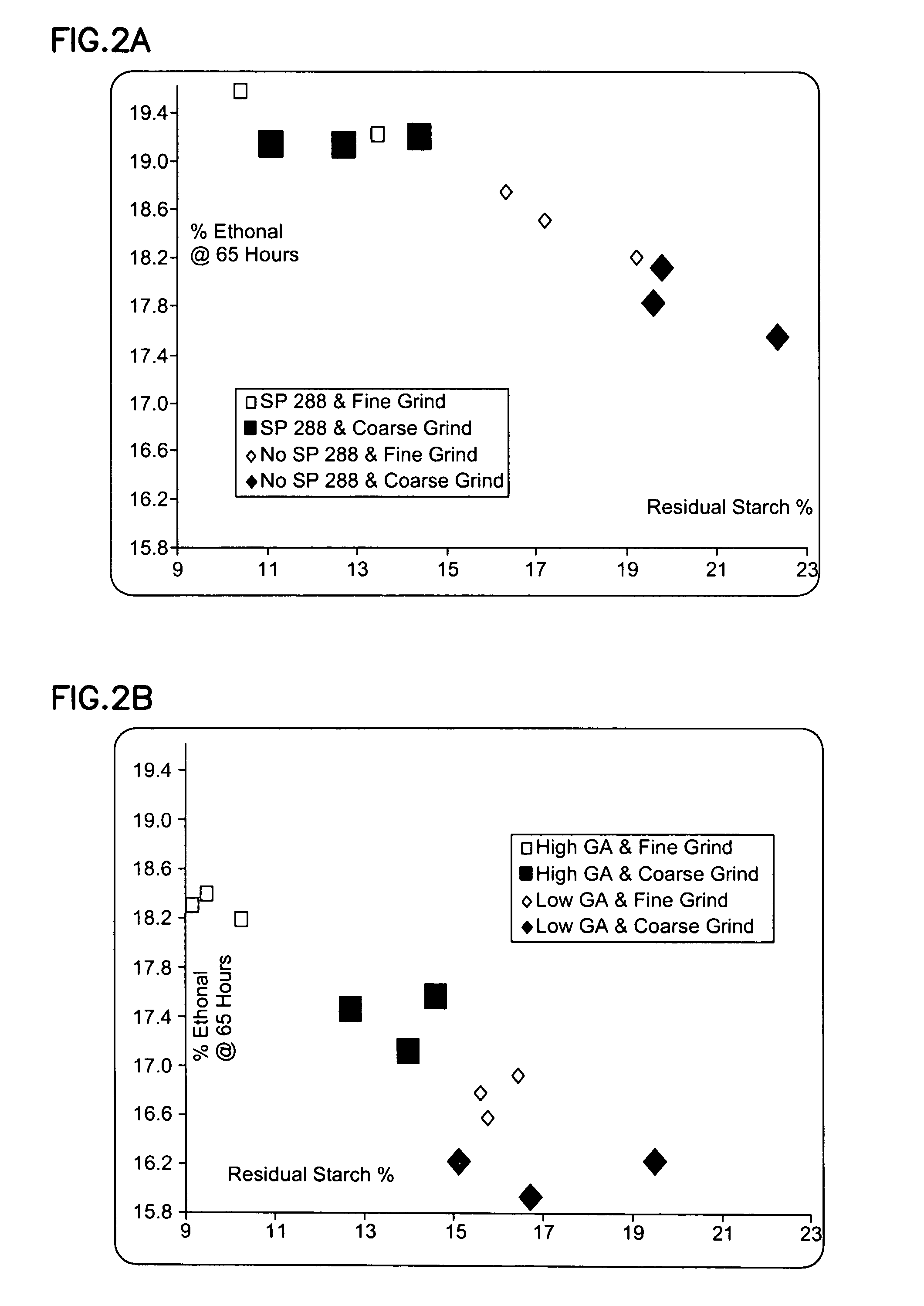
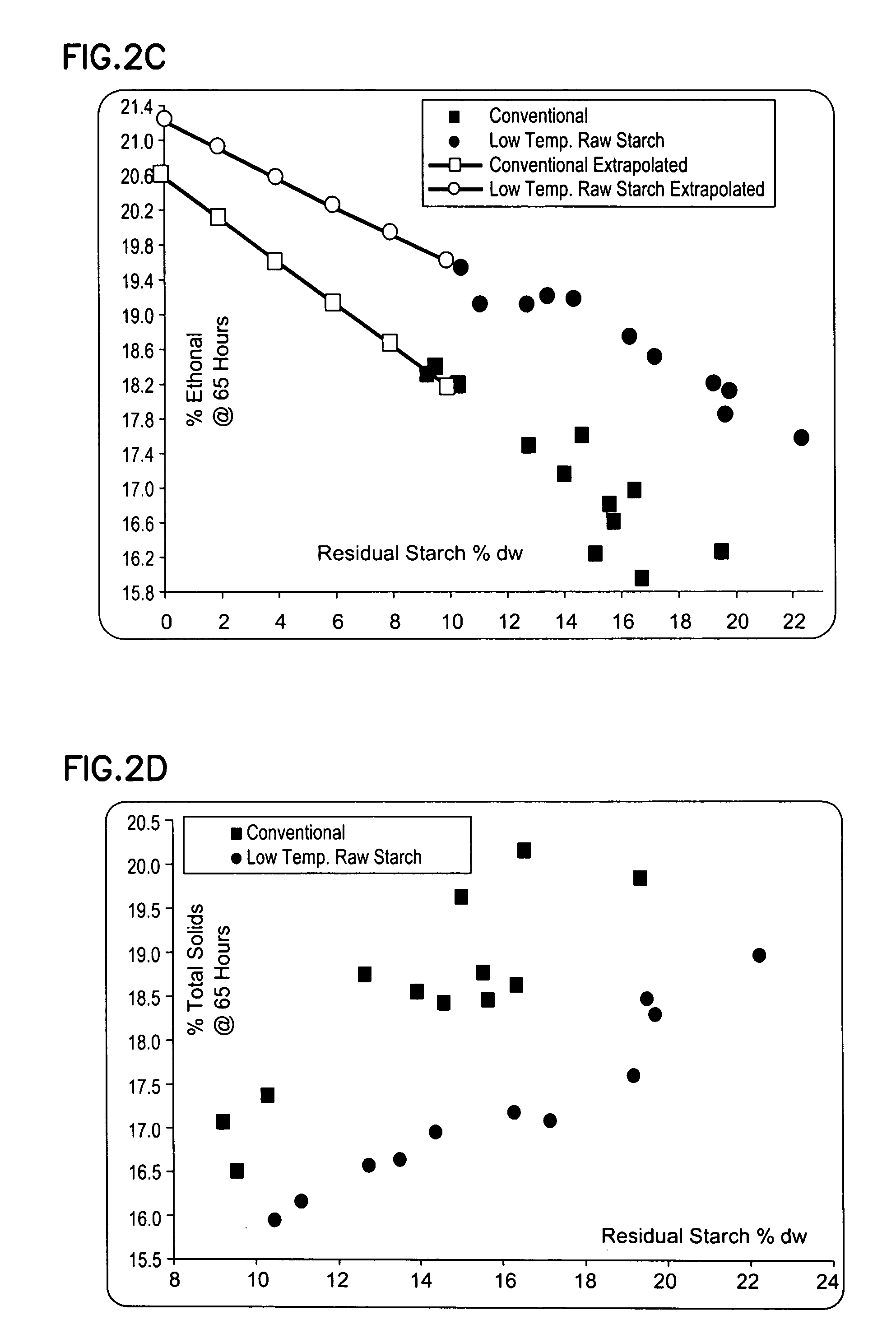
Methods and systems for producing ethanol using raw starch and selecting plant material
ActiveUS20070178567A1Improve the level ofDough treatmentWort preparationHigh alcohol beerStarch production
The present invention relates to methods for producing high levels of alcohol during fermentation of plant material, and to the high alcohol beer produced. The method can include selecting plant material. Selecting can include excluding plant material that has been exposed to high temperatures or that has had high moisture content.
Owner:POET RES INC
Method for preparing a slurried confection
InactiveUS6068875AMinimize storageImprove accessibilityMeat/fish preservationRotary stirring mixersFreezing Point TemperatureFlavor
A method for preparing a flavored slurried confection includes the use of a disposable serving container holding an individual serving of a neutral flavored mix which has a freezing point temperature lower than normally found for that of water. A large supply of the mix filled containers is stored in a storage freezer for maintaining the neutral flavored mix at a storage temperature, such as is typical of a food storage freezer for a restaurant. A desired quantity of the mix filled containers is then transferred from the storage freezer to a tempering freezer, generally close to a preparation and serving area, for maintaining the neutral flavored mix at a desirable blending temperature. The mix filled container is then removed from the tempering freezer for preparation of a flavored confection, such as a flavored shake. In preparing the flavored confection, a small quantity of a selected syrup is pumped from a selected bag-in-the-box styled carton into the mix filled container for blending the selected syrup with the neutral flavored mix while the mix remains chilled at the blending temperature. The small quantity of syrup adds provides the selected flavor to the neutral flavored mix for forming the flavored slurried confection which is then served within the disposable serving container.
Owner:ARCHIBALD BROS FINE BEVERAINC
Instant particulate dry mix composition for producing a cappuccino beverage having a marbled foam
An instant particulate dry mix composition produces a cappuccino beverage having surface foam with a marbled appearance upon reconstitution in water. The dry mix composition is made by freeze drying the coffee extract to produce granules having an outer surface layer which is rapidly soluble and a larger inner core layer which is slowly soluble.
Owner:INTERCONTINENTAL GREAT BRANDS LLC
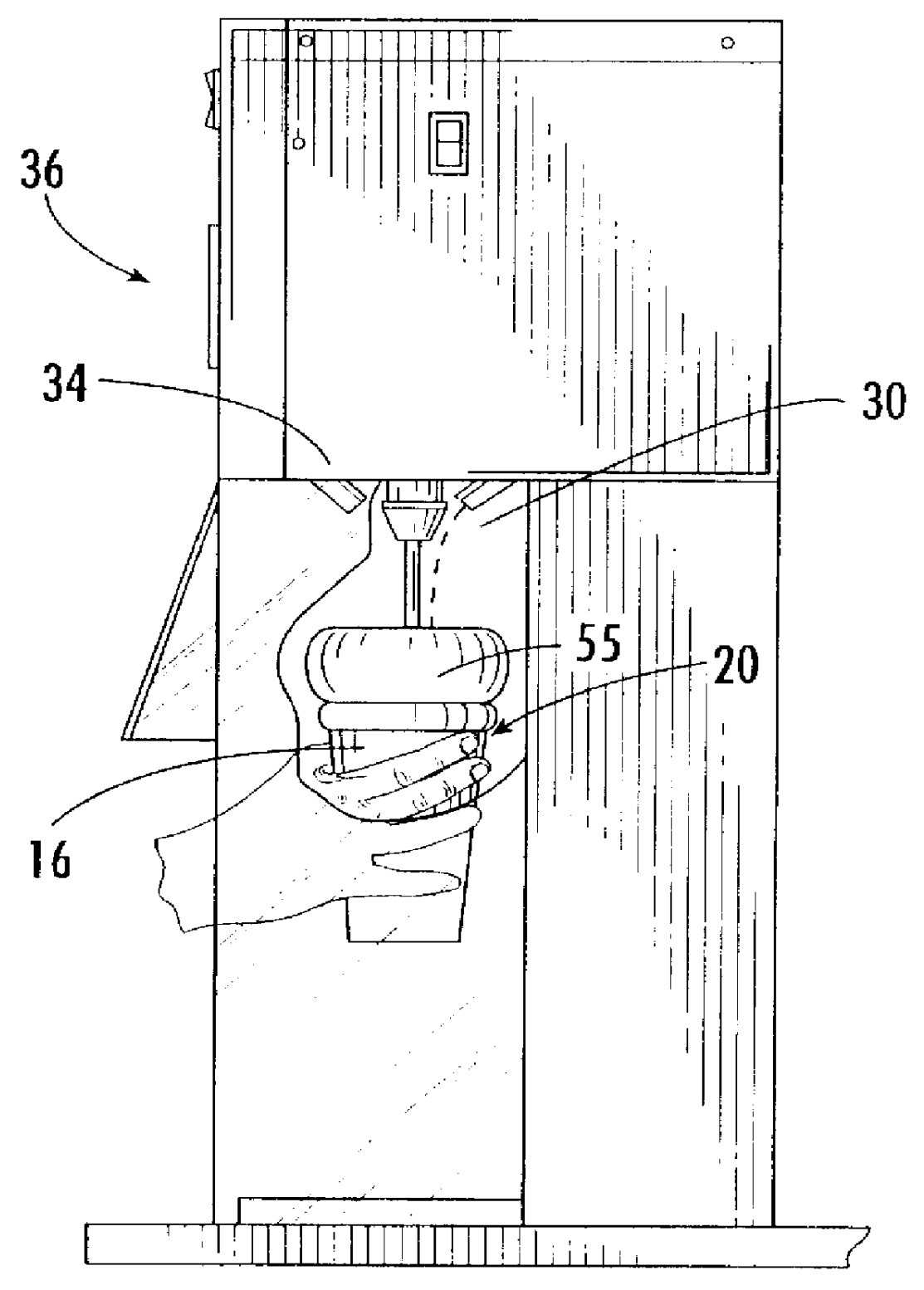
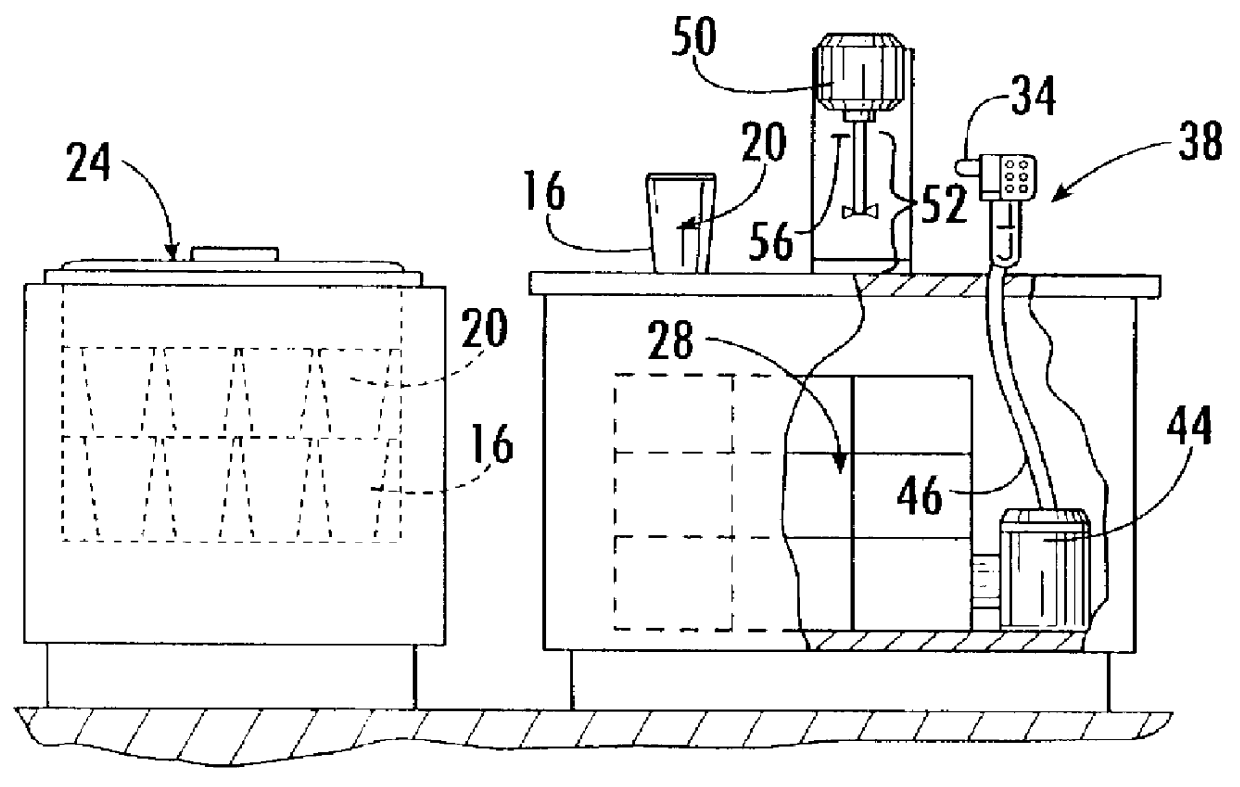
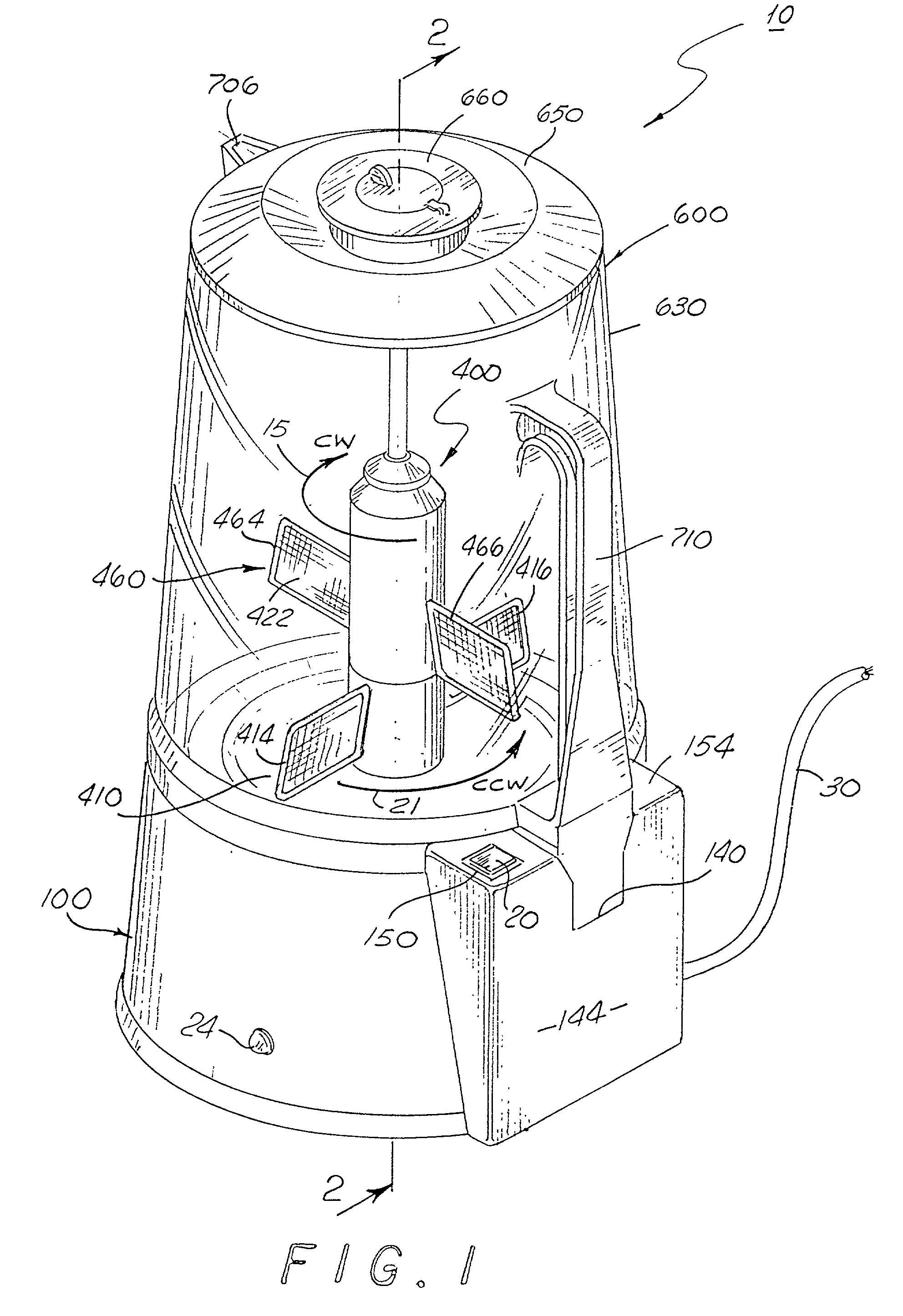
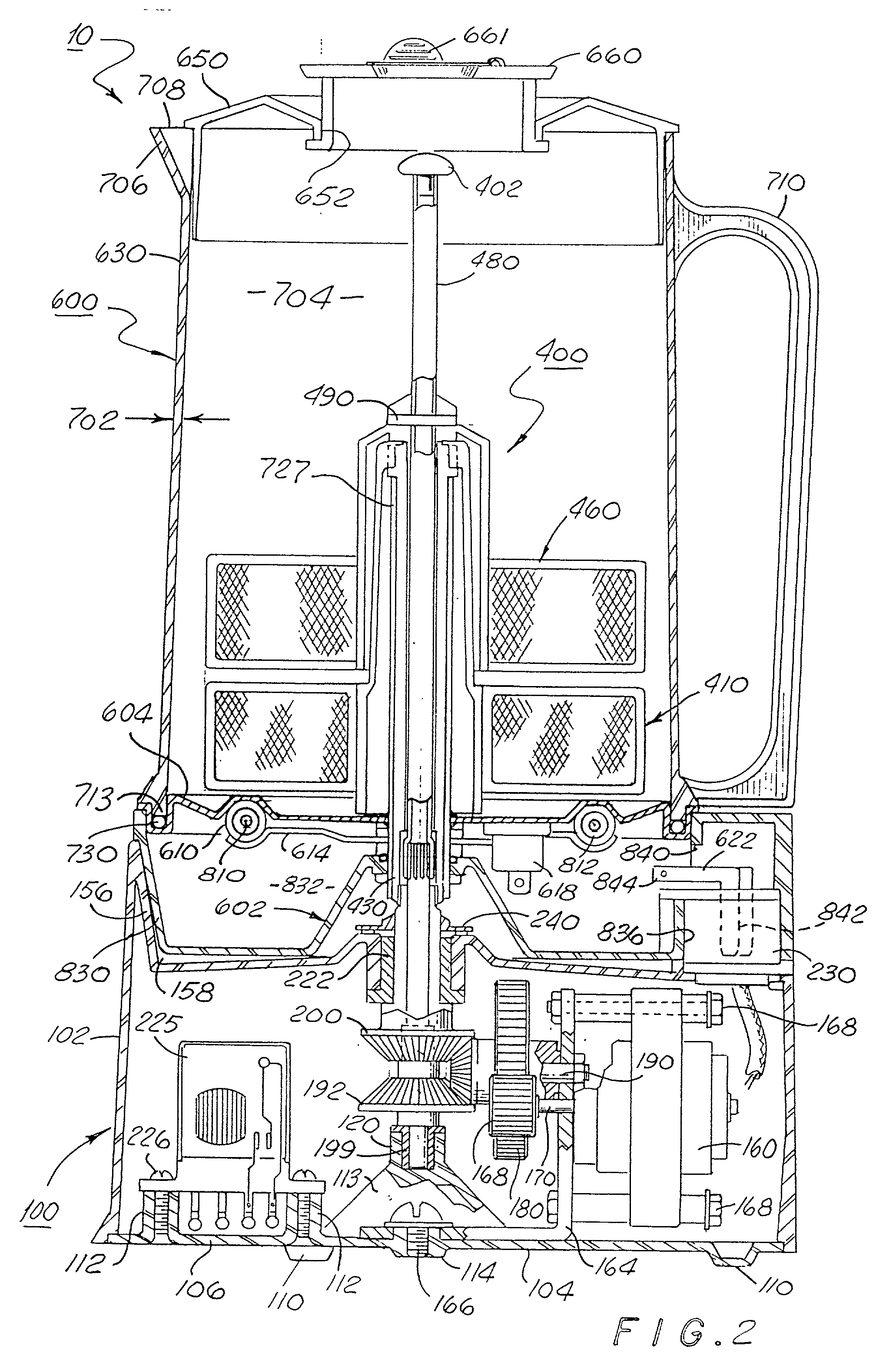
Method and apparatus to automatically heat and froth milk for beverages
The invention relates to an automatic beverage frother. The beverage frother includes a lower housing assembly having a motor coupled to a gear train. The gear train may be removeably coupled to an upper paddle group and a lower paddle group disposed within a container. Each paddle group rotates about the longitudinal axis of the container in opposite directions. Within each paddle group is at least one paddle where each paddle is formed of a frame having mesh disposed within the frame. Other embodiments are disclosed.
Owner:FREL STEPHEN W
Aqueous process for preparing protein isolate and hydrolyzed protein from an oilseed
InactiveUS20120252065A1Peptide/protein ingredientsProtein composition from vegetable seedsProtein solutionPhytase
The present disclosure relates to an aqueous process for the preparation of a protein isolate and a hydrolyzed protein concentrate from an oilseed meal, optionally comprising:mixing an oilseed meal with an aqueous solvent to form a slurry;optionally treating the slurry with phytase y;separating the slurry with a solid / liquid separation to form:a liquid phase, comprising the aqueous solvent, soluble protein and oil; anda solid phase comprising insoluble protein;separating the liquid phase to form:an oil phase; andan aqueous protein phase;subjecting the aqueous protein phase to membrane filtration to obtain a protein solution; and drying the protein solution to obtain the protein isolatesubjecting the insoluble protein to enzymatic hydrolysis, andsubjecting the hydrolyzed protein to membrane filtration to obtain an amino acid and peptide solution; and drying the amino acid and peptide solution to obtain the hydrolyzed protein concentrate.
Owner:POS PILOT PLANT CORP +1
Protein hydrolysates
The present invention describes protein hydrolysates: obtainable by the hydrolysis of a protein containing substrate; comprising free amino acids and peptides; and wherein the molar fraction of at least one free amino acid, present in the protein hydrolysate is at least a factor 2.5, preferably at least a factor 3, more preferably at least a factor 3.5 times higher than in a hydrolysate of the same protein containing substrate which has been completely hydrolysed to free amino acids, wherein the molar fraction of the at least one free amino acid in the protein hydrolysate is at least 25%; and wherein the Amino Acid Quotient (AAQ) in the protein hydrolysate is at least 10%. These protein hydrolysates can be used in the preparation of food compositions, wherein these protein hydrolysates provide for novel and unexpected flavours. Moreover these protein hydrolysates are applicable in personal care applications.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Method of preparing a multi-flavored shake
InactiveUS6126983AEfficiently and effectively preparingMinimize storageRotary stirring mixersFrozen sweetsEngineeringFood flavor
A flavored shake drink is prepared from a prepackaged neutral flavored mix stored within a serving cup. A flavored syrup is selected and dispensed through a dedicated nozzle carried by a housing. Each of a plurality of nozzles is in fluid communication with a corresponding solenoid control valve which controls the flow of the selected syrup pumped from a bag-in-the-box styled reservoir. One reservoir is provided for each of the selected flavors. A manually activated programmable timer controls the length of time that the solenoid activated valve remains opened thus providing a preselected amount of syrup into the cup. Switches are provided for doubling and halving the amount of the preselected quantity of syrup when creating varying single flavored and combination flavored shakes. In addition to shielding provided around the blender spindle carried by the housing for maintaining the surrounding area in a clean condition, a protective sleeve is placed within the cup for limiting the amount of mix splashed from the cup during blending of the selected syrup and neutral flavored mix. Prior to adding a selected syrup, the cup of unflavored mix is stored in a tempering freezer where it is maintained at a pre-selected temperature suitable for providing desirable blending of the syrups with the mix.
Owner:ARCHIBALD BROS FINE BEVERAINC
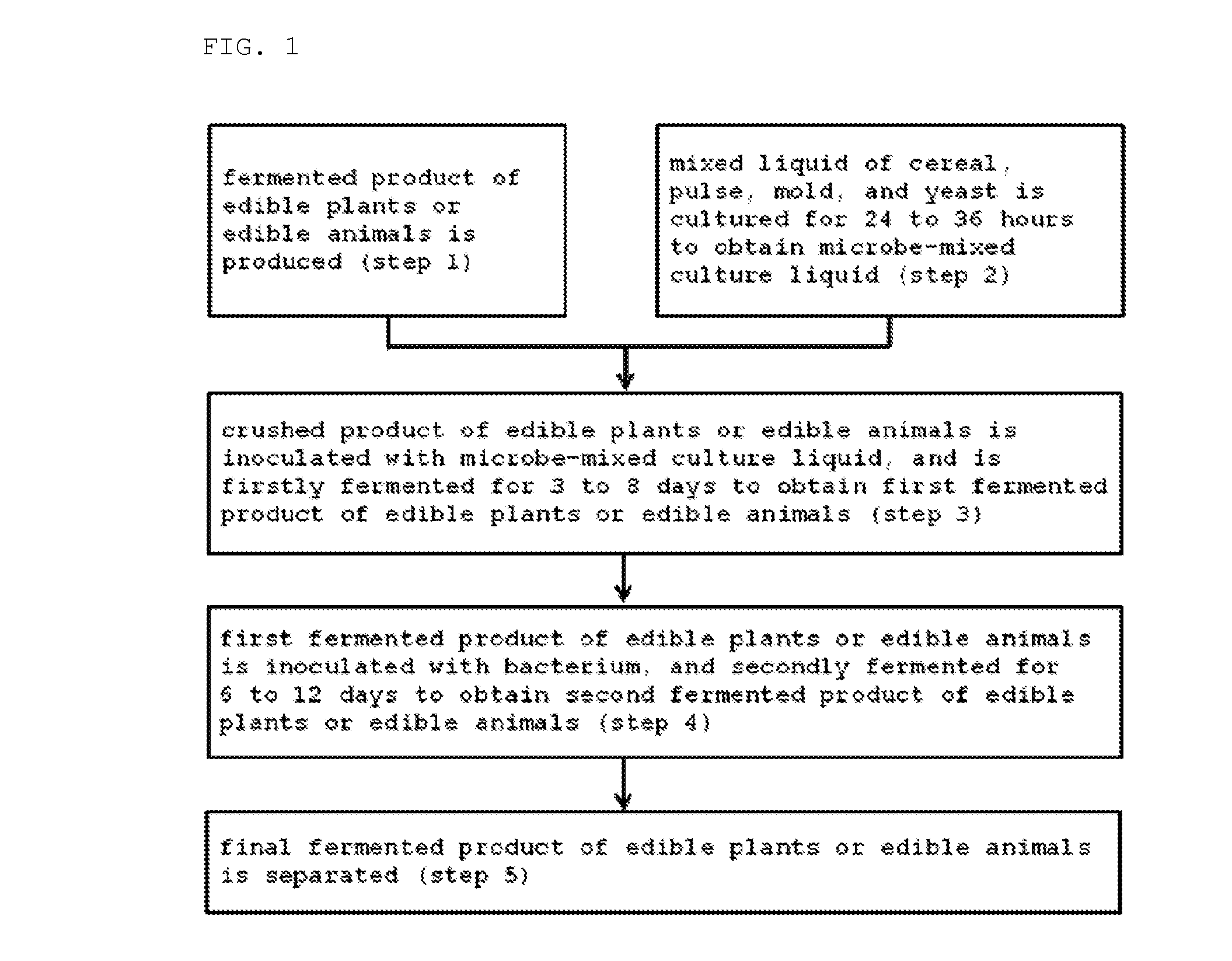
Method for producing fermented edible plants or edible animal/plants, fermented edible plants or edible animal/plants produced by same, and foods containing same
ActiveUS20100316763A1Increase heightPrevent invasionDough treatmentEdible seed preservationFood flavorOrganism
The present invention relates to a method for producing fermented edible plants or edible animal / plants, to fermented edible plants or edible animal / plants produced by same, and to foods containing same. The method for producing fermented edible plants or edible animal / plants includes the steps of: producing crushed edible plants or edible animal / plants; culturing a liquid mixture of grains, saccharides, filamentous fungi, and yeast for 24 to 36 hours to produce a mixed microbial broth; inoculating the edible plants or edible animal / plants with the mixed microbial broth, and firstly fermenting the edible plants or edible animal / plants for 3 to 8 days to produce first fermented edible plants or edible animal / plants; and inoculating the first fermented edible plants or edible animal / plants with bacteria, and secondly fermenting the first fermented edible plants or edible animal / plants for 6 to 12 days to produce second fermented edible plants or edible animal / plants. Whereby, a fermentation period can be shortened, and food deterioration and the growth of pathogenic microorganisms can be suppressed. Further, adding the fermented edible plants or edible animal / plants produced by the above-described method into foods can provide storage stability, increase bioavailability, and improve flavor.
Owner:PHARVIS R&D KOREA
Algal culture production, harvesting , and processing
InactiveUS20110138682A1Maintaining culture selectivityLoss of selectivityAlgae productsUnicellular algaeAlgaenanLipid formation
Materials and methods are provided for growing algae while maintaining culture selectivity. Algae that can be grown include, for example, green algae such as those of the genus Scenedesmus. Lipid obtained from the algae can be used to produce biofuels such as biodiesel or polyunsaturated fatty acids such as omega-3 fatty acids. Feedstocks such as animal feed and aquaculture feed can also be produced as can phytonutrients such as asataxanthin and beta-carotene.
Owner:AQUATIC ENERGY LLC
Protein Hydrolysate Compositions Having Improved Sensory Characteristics and Physical Properties
InactiveUS20080305212A1Fatty substance preservation using additivesCocoaArginineProtein hydrolysates
The present invention provides protein hydrolysate compositions, processes for making protein hydrolysate compositions, and food products comprising protein hydrolysate compositions. The protein hydrolysate compositions generally comprise polypeptide fragments having primarily either an arginine residue or a lysine residue at each carboxyl terminus.
Owner:SOLAE LLC
Food compositions having a realistic meat-like appearance, feel, and texture
InactiveUS20100233347A1Improve palatabilityHighly palatableAnimal feeding stuffWorking-up animal fodderBiotechnologyPlasticizer
The invention provides novel food compositions having a realistic meat-like appearance, feel, and texture. The compositions comprise from about 40 to about 90% functional proteins, from about 0.05 to about 2% of one or more cross-linking agents, and from about 60 to about 10% of a meat slurry, wherein the meat slurry comprises meat and one or more humectant plasticizers in a meat:humectant plasticizer ratio of from about 20:80 to about 80:20. The compositions are produced by heating a preconditioned mixture of the food components under pressure and then expanding the heated composition to form the food composition.
Owner:NESTEC SA
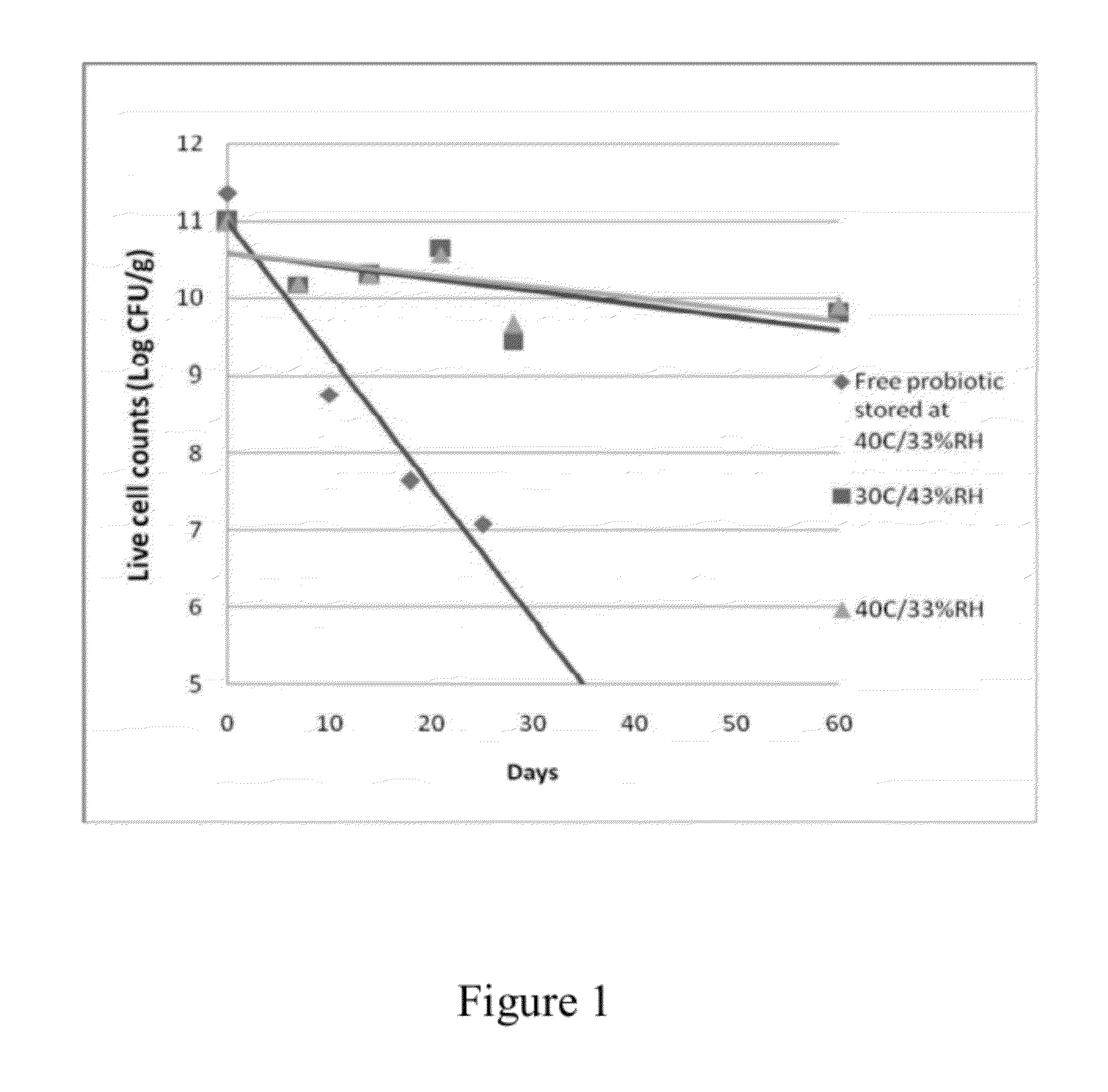
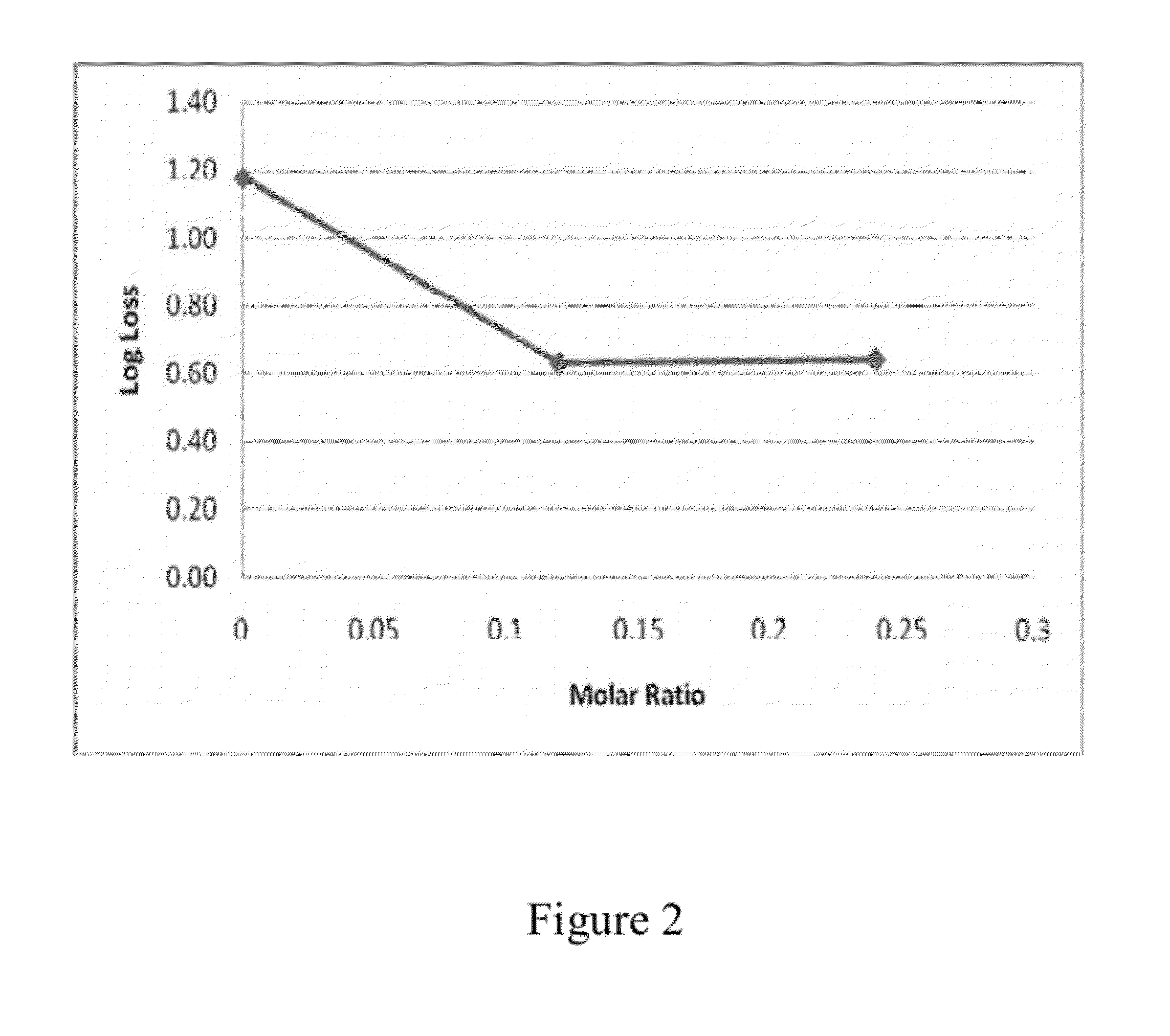
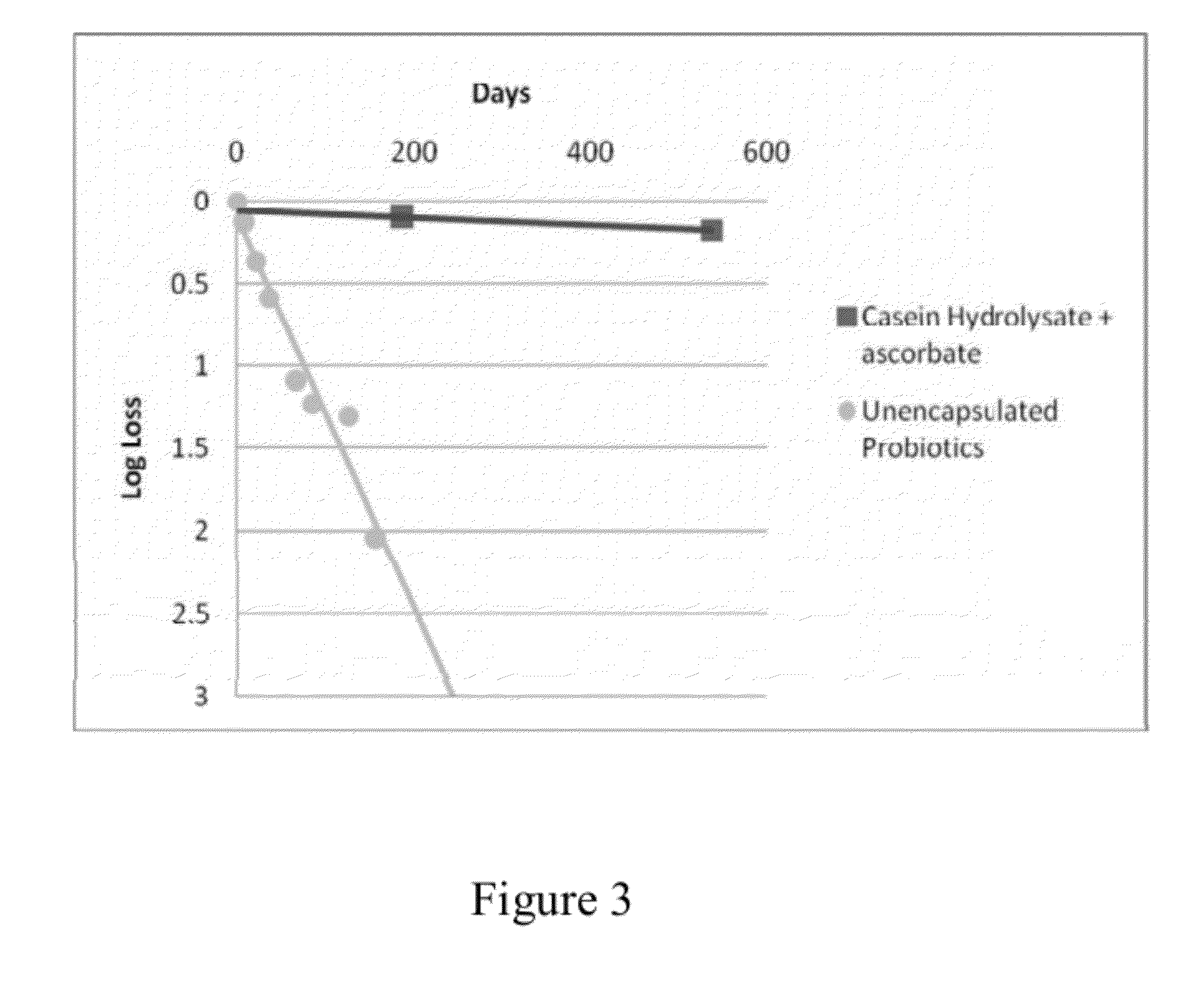
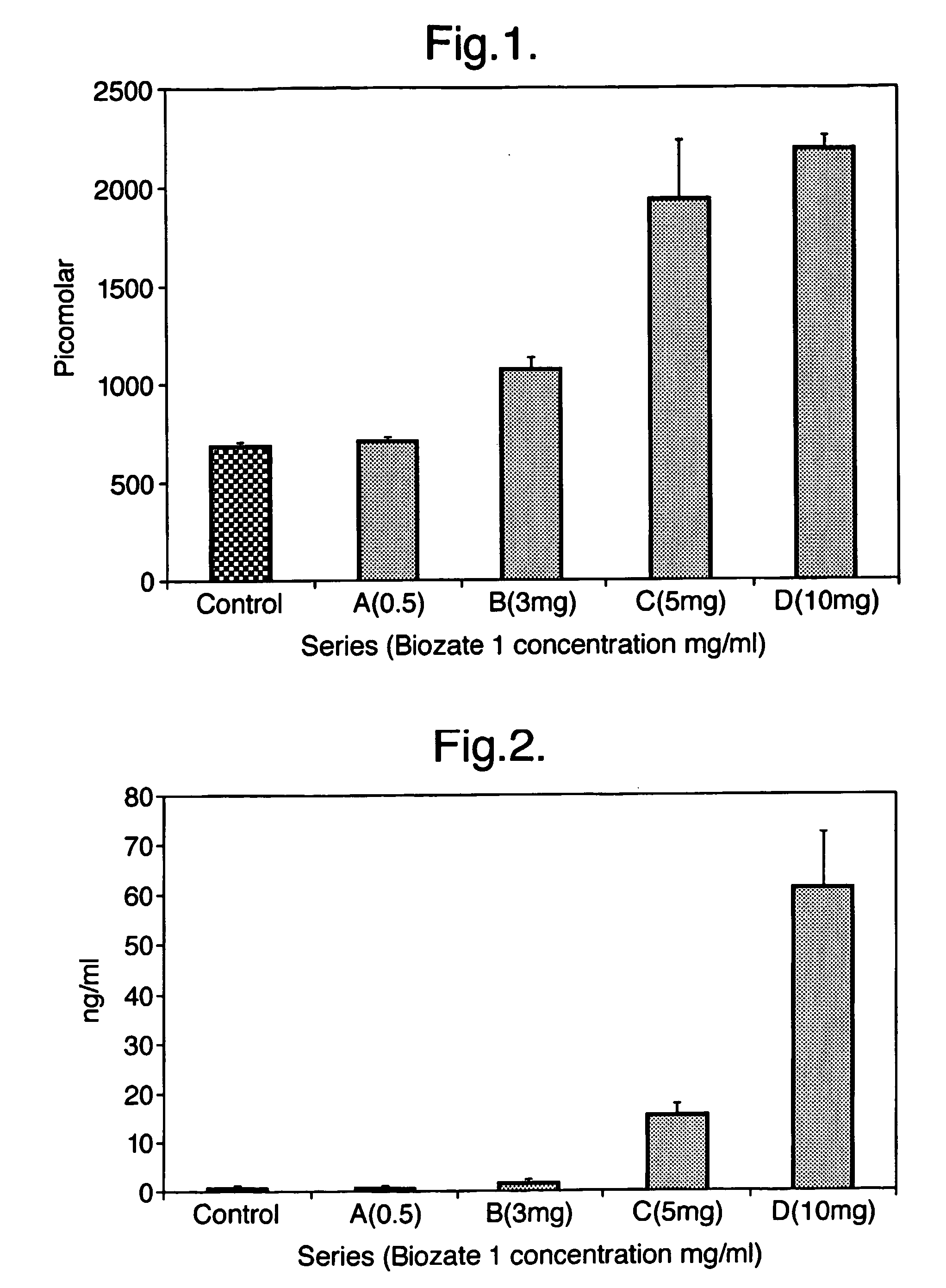
Dry storage stabilizing composition for biological materials
ActiveUS20120039956A1Improve biostabilityBenefit of stabilizingPowder deliveryVirusesBiotechnologyBiological materials
The present invention includes compositions and drying methods for preserving sensitive bioactive materials, such as peptides, proteins, hormones, nucleic acids, antibodies, drugs vaccines, yeast, bacteria (probiotic or otherwise), viruses and / or cell suspensions, in storage. The compositions include a carbohydrates component and a glass enhancer component, wherein the carbohydrate component includes a mixture of di-, oligo- and polysaccharides and the glass enhancer includes ions of organic acid and protein hydrolysates. The composition is prepared by dispersing all the solid components in a solution and then snap-frozen to form small beads, strings or droplets. The preferred drying method of the frozen beads, strings or droplets is initiated by a short purging and structure stabilizing step of the frozen particles under a vacuum pressure of less than <2000 mTORR followed by a primary drying step under vacuum pressure of more than >2000 mTORR and at a desired temperature. During the secondary and final drying step of the material a full vacuum pressure and elevated temperature are applied, to achieve a final desirable water activity of the dry material.
Owner:ADVANCED BIONUTRITION CORP
Satiety inducing composition
InactiveUS20050238694A1Good effectIncrease satietyPeptide/protein ingredientsWhey manufactureBiotechnologyLactalbumin hydrolysate
The invention provides the use of a whey protein and / or whey protein hydrolysate which stimulate the cellular release of the satiety peptides choleocystokinin and glucagon-like-peptide in the preparation of edible compositions. The edible compositions can be used to control body weight and have beneficial effects on satiety. Edible compositions are also provided.
Owner:KSF ACQUISITION
Bone health compositions derived from milk
InactiveUS20040052860A1Reducing net bone lossMetabolism disorderProtein composition from milkHydrolysatePhysiology
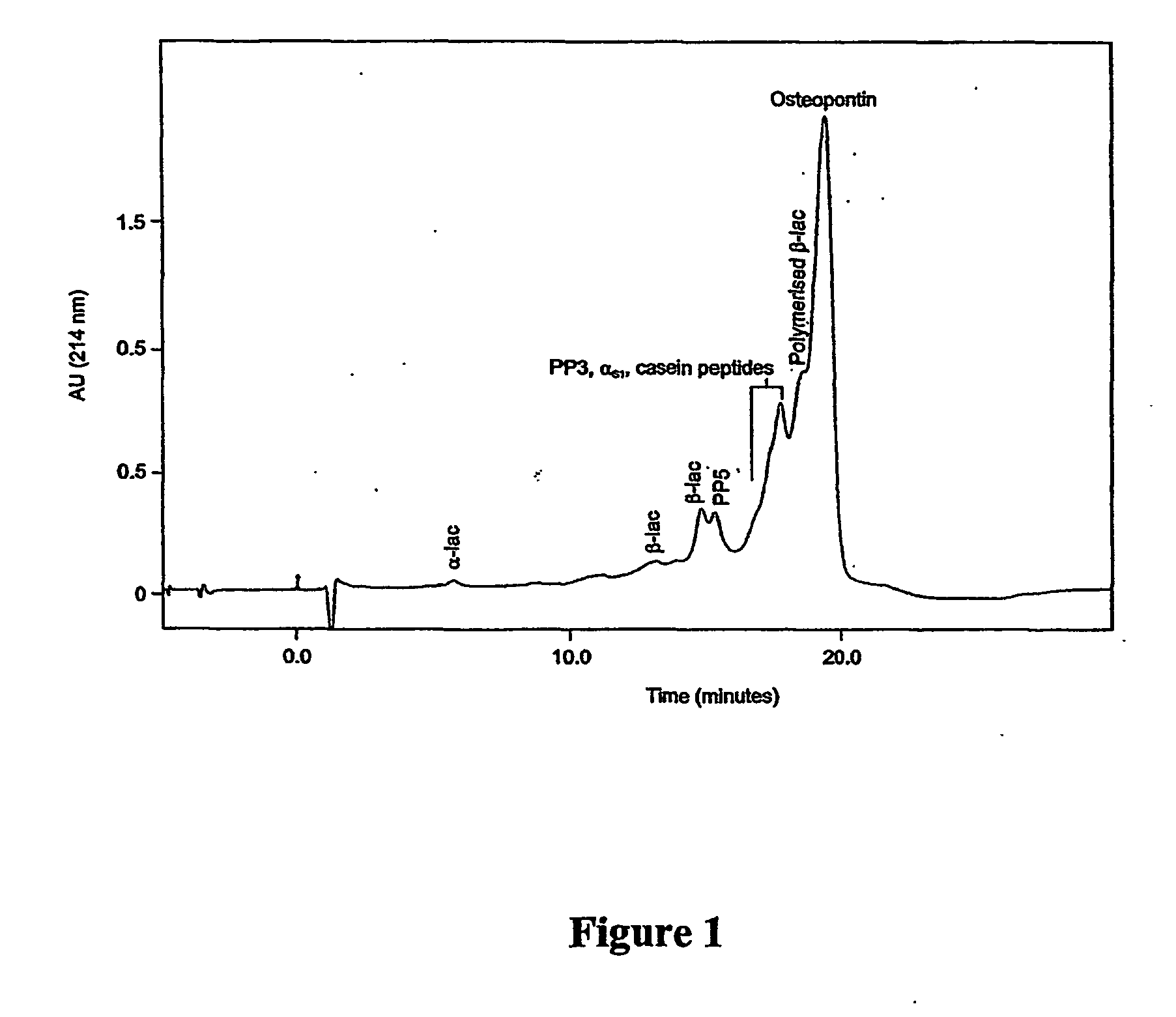
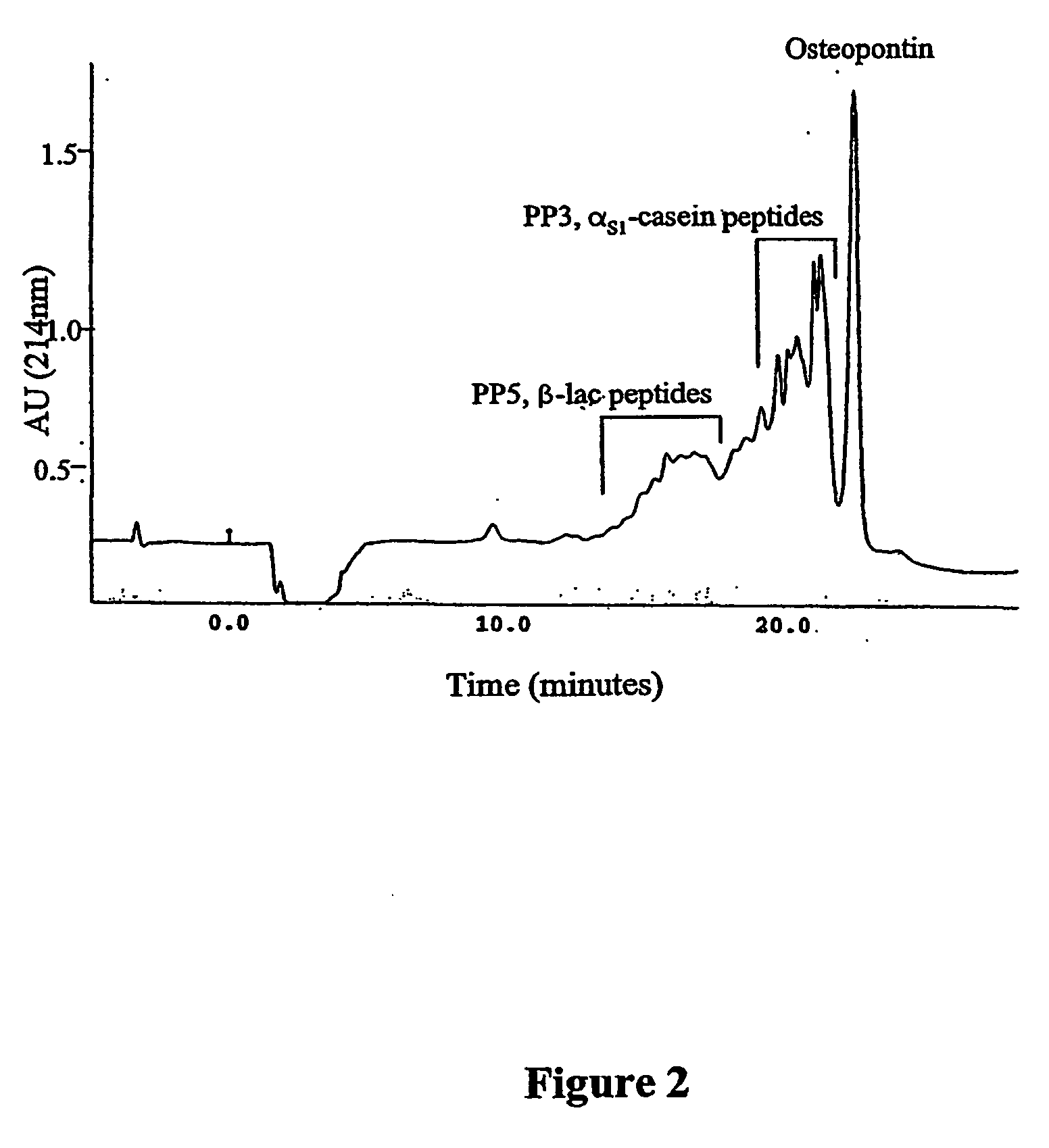
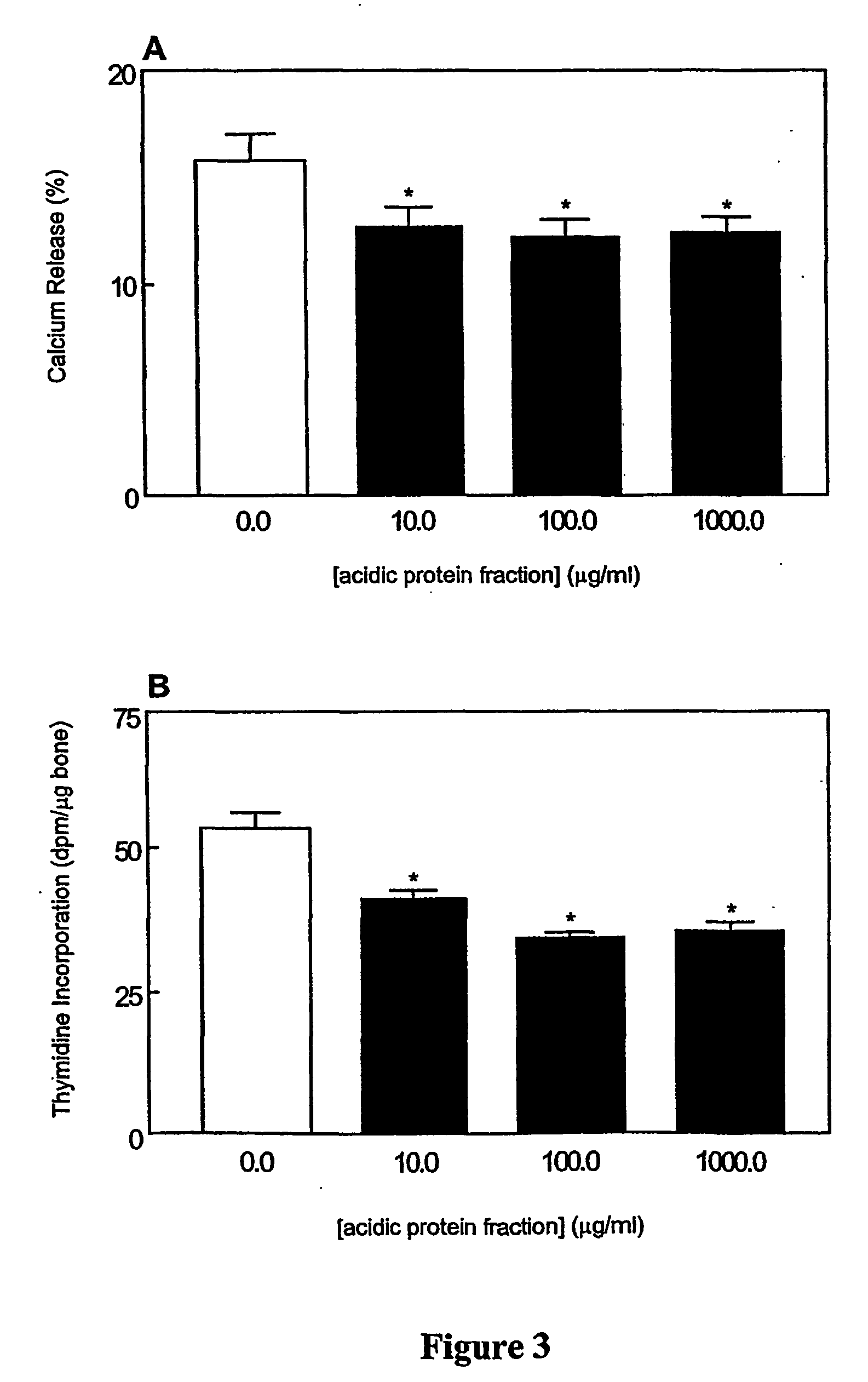
The invention relates to bone health compositions comprising an acidic protein fraction of milk, to a method of producing said bone health composition, to methods of treatment comprising said bone health compositions and to medicinal uses of said bone health compositions. One broad aspect of the invention provides a bone health composition comprising an acidic protein fraction derived from milk, from a component of milk, from whey, from hydrolysates thereof, or from a combination thereof, or from a combination thereof wherein the composition does not comprise caseinoglycomacropeptide (CGMP). Another broad aspect provides a method of manufacturing the composition of the invention using anion exchange chromatography.
Owner:NEW ZEALAND DAIRY BOARD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com