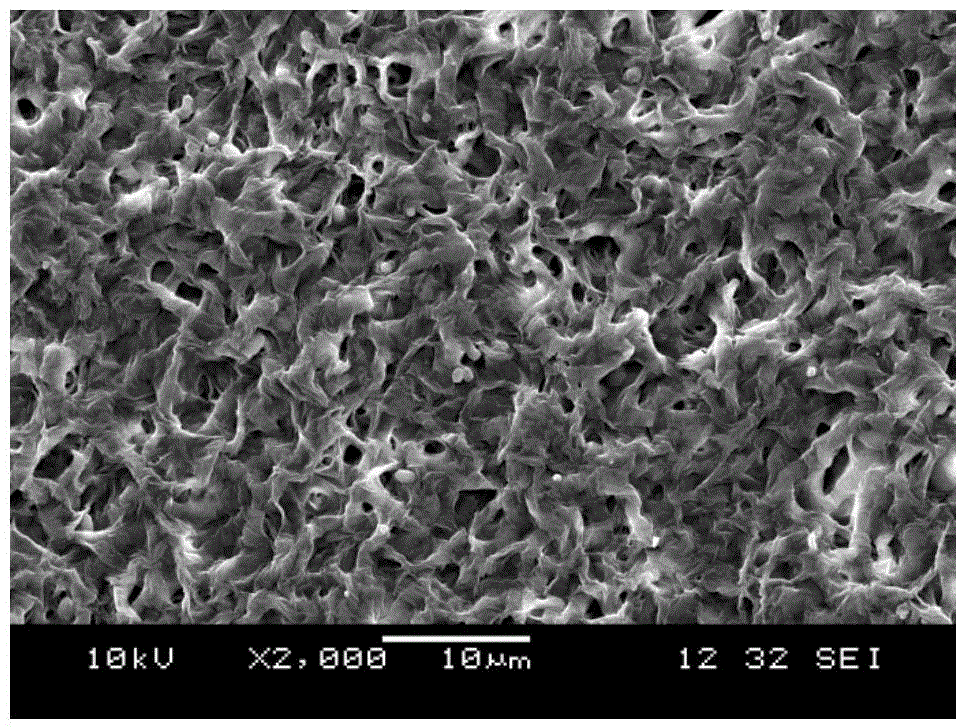
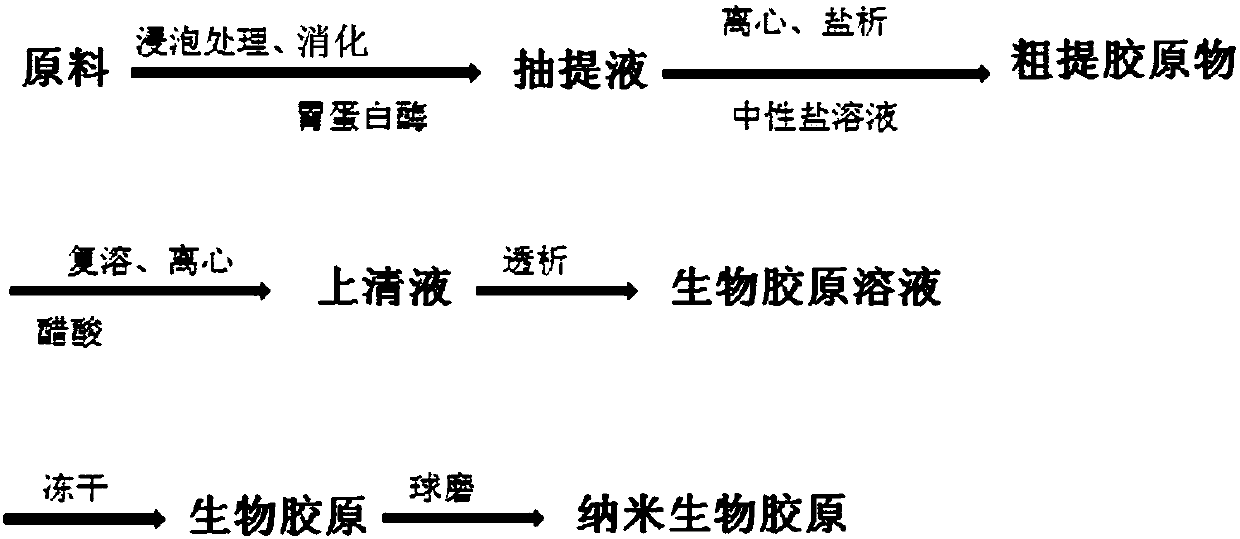
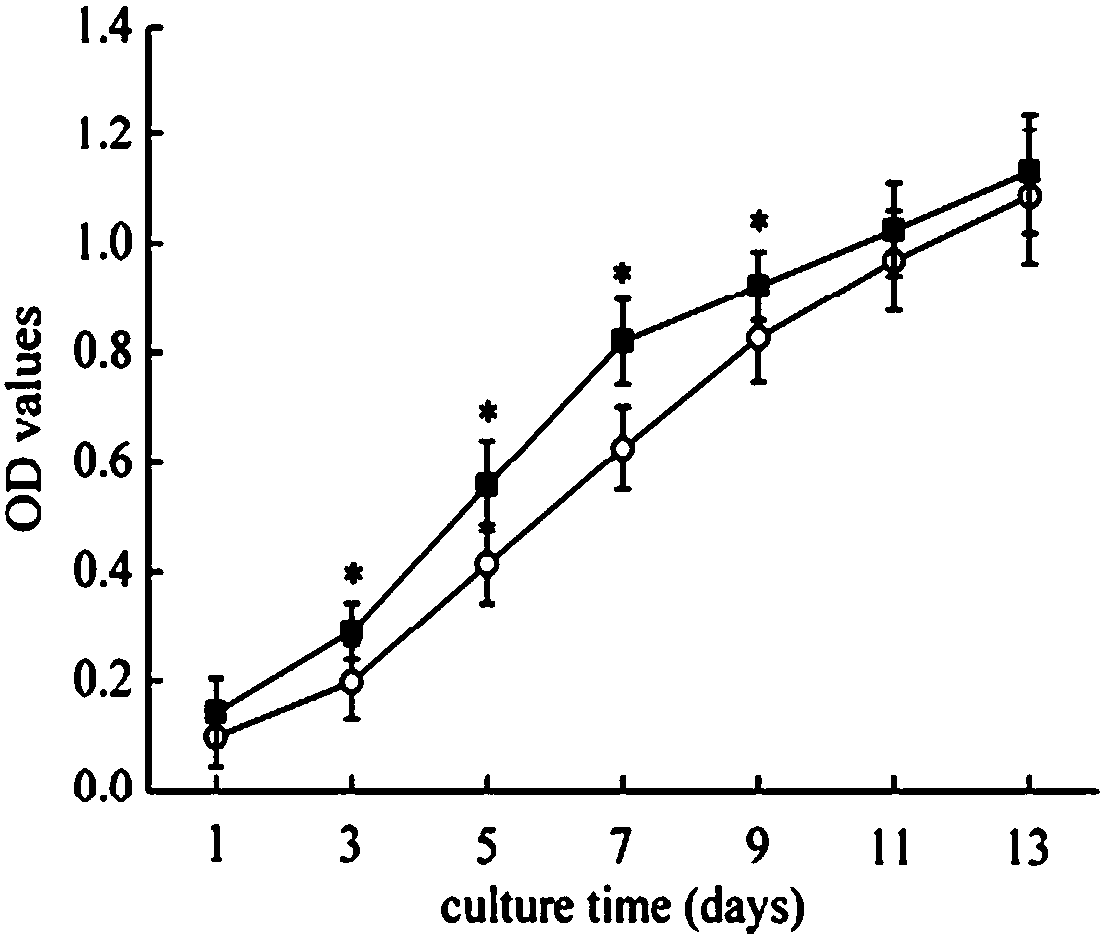
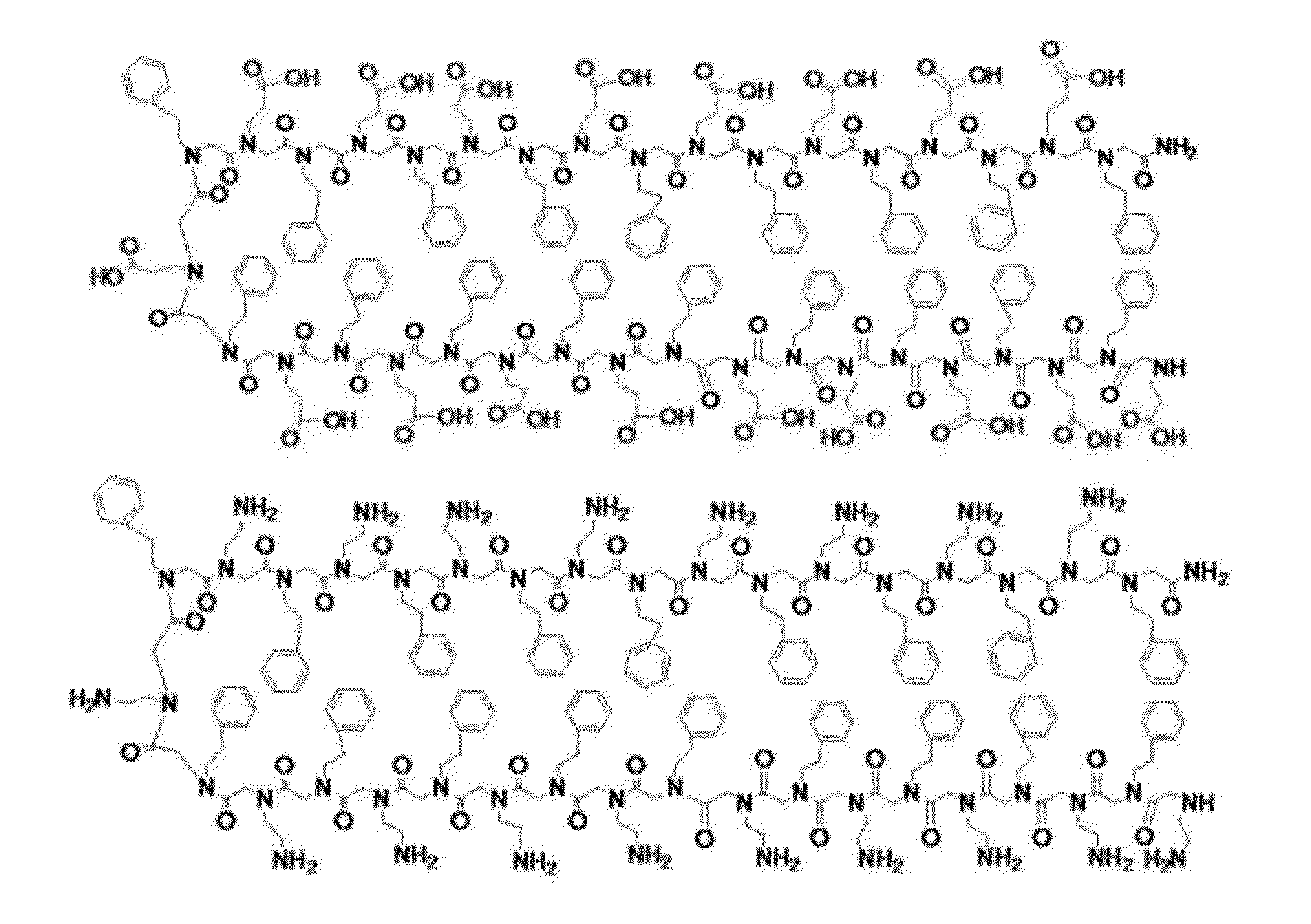Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
178 results about "Biologic scaffold" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Scaffolding in general means a structure providing support. The best example of scaffolding in biology is the repair of a broken bone (fracture). An initial temporary structure is made by the body called the pro callus. On this further growth takes place.
Structurally modified acellular tissue engineering scaffolds and methods of production
ActiveUS20070248638A1Seed efficiency be facilitateImprove seeding efficiencyCell culture supports/coatingUnknown materialsBiomedical implantFreeze dry
Methods are provided for producing a bioscaffold from natural tissues by oxidizing a decellularized tissue to produce a bioscaffold having pores therein. The pore size and porosity is increased to better accommodate intact cells so that live cells can better infiltrate and inhabit the bioscaffold. The bioscaffold may be freeze-dried or lyophilized, sterilized and (optionally) aseptically packaged for subsequent use. A further aspect of the present invention is a bioscaffold produced by the processes described herein. Methods of treatment using the bioscaffold as a graft or as a biomedical implant for implantation are also provided. Also provided are methods of seeding a bioscaffold with mammalian cells, wherein the seeding carried out either in vitro or in vivo, and wherein a bioscaffold produced as described herein is utilized for said seeding.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIVERSITY
Preparation method for cellfree intestinum tenue submucosa biological material
ActiveCN101366975ARepair defectRepair membranous defectsProsthesisBiocompatibility TestingIntestinal submucosa
The invention relates to a method for preparing a biomaterial of acellular small intestinal submucosa, which comprises the steps of preposition treatment, acellular treatment, enzyme treatment, preparations of membranous products and particle products. Compared with the prior art, the biomaterial has higher bioactivity and biocompatibility, no obvious immune rejection and no toxic effect on cells; besides, the biomaterial has a certain mechanical strength and toughness, and variable shape, size and thickness, thereby being convenient for clinical suturing and fixing. At the same time, the preparation method has the advantages of unlimited raw material source, cell-free residues, no ethical issues and being capable of effectively inactivating virus. The prepared products are applicable to the biomedical engineering fields, such as repairing defections of body tissue, serving as tissue filling materials, repairing facial depression deformity, serving as tissue reinforcements to replace fascia, repairing membranous defections and malnourished and infected surfaces of wound, serving as materials for biodegradable stents, and serving as injectable filling materials.
Owner:SHAANXI RUISHENG BIOTECH
Double membrane tissue patching material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a double-layer membranous tissue repair material and a preparation method thereof, wherein, a cell-free membranous biological derivative material is used as a surface layer, and a fibroblast is compounded in the interior of a biological support material to form a substrate, and then the surface layer and the substrate are combined in a chimeric way to form the double-layer membranous tissue repair material; a compact surface layer structure can effectively reduce the loss of water, electrolytes and protein from surface of wound, avoid the invading and the reproduction of bacteria to the impaired surface of wound as well as prevent the infection of the surface of wound, thus being beneficial to epitheliosis and epithelial growth; the substrate can directly repair the surface of wound, promote the ingrowth of cells around the surface of wound and the angiogenesis, induce the differentiation from stem cells to skin cells and quicken wound healing; compared with the existing products, the tissue repair material has the advantages of being capable of promoting the regeneration of skin, improving the elasticity, the flexibility and the mechanical abrasion resistance of skin after the surface of wound is healed, reducing hyperplasia of scar tissues, controlling the contracture, having excellent biocompatibility, increasing the success rate of transplant and improving the quality of healing; the invention has wide material resources and simple production method; the double-layer membranous tissue repair material prepared is applicable to the clinical treatment of skin defect caused by inflammation, ulcer, thermal burns, iatrogenicity and the like.
Owner:SHAANXI RUISHENG BIOTECH
Dialdehyde carboxymethyl cellulose-collagen frozen gel and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101845226AHigh reactivityImprove mechanical propertiesSurgeryProsthesisBiologic scaffoldPorosity
The invention provides dialdehyde carboxymethyl cellulose-collagen frozen gel and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: first uniformly mixing 1 to 3 mass percent of the aqueous solution of collagen and 0.01 to 1 mass percent of the aqueous solution of dialdehyde carboxymethyl cellulose; then injecting the mixed solution into a mold and storing the mixed solution in a low-temperature reactor at the temperature of -40 to 0 DEG C for 1 to 7 days; and finally, taking the obtained product out and slowly unfreezing the obtained product to obtain the dialdehyde carboxymethyl cellulose-collagen frozen gel. The dialdehyde carboxymethyl cellulose-collagen freezing gel prepared by the method is improved in mechanical property, thermal stability and enzymatic degradation resistance at the same time of maintaining the biological activity of collagen gel per se, has the advantages of porosity, hydrophilicity, water absorbing and preserving property, good market application prospect and the like, and is widely used in biomedical fields, such as biologic scaffolds, cell culture, drug delivery, tissue engineering, wound and burning treatment and the like.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Double layer artificial skin and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a double-layer artificial skin and a preparation method thereof, wherein, cell-free membranous biological derivative material is used as a surface layer, and a fibroblast, extracellular matrix synthesized and secreted by the fibroblast and a cell growth factor are compounded in the interior of biological support material to form a dermis, and then the surface layer and the dermis are combined to form the double-layer artificial skin; a compact surface layer structure can effectively reduce the loss of water, electrolytes and protein from surface of wound, avoid the invading and the reproduction of bacteria to the impaired surface of wound as well as the infection of the surface of wound, and be beneficial to epitheliosis and epithelial growth; the dermis can directly repair the surface of wound, promote the ingrowth of cells around the surface of wound and the angiogenesis, induce the differentiation from stem cells to skin cells and quicken wound healing; the artificial skin has the advantages of being capable of promoting the regeneration of skin, improving the elasticity, the flexibility and the mechanical abrasion resistance of skin after the surface of wound is healed, reducing excess scar tissues, controlling the contracture, having excellent biocompatibility, increasing the success rate of transplant and improving the quality of healing; the double-layer artificial skin has wide material resources and simple production method, and is applicable to the clinical treatment of skin defect caused by inflammation, ulcer, thermal burns, iatrogenicity and the like.
Owner:SHAANXI RUISHENG BIOTECH
Compound platelet gel and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105030826APromote degradationMoisturizingAerosol deliveryOintment deliveryBiologic scaffoldCytokine
The invention discloses compound platelet gel and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method includes: taking chitosan which is a natural material high in biodegradability and biocompatibility as a biological scaffold and a drug delivery carrier; activating fibrinogen in PRP to be a fibrin netty structure to be connected to chitosan molecules to form a gel carrier scaffold; and enabling platelet-derived cytokines to be adhered and anchored in the gel carrier scaffold to form the compound platelet gel. The compound platelet gel has multiple functions of quickly promoting tissue regeneration, bleeding stopping, bacterium resisting, pain relieving and humidity maintaining, and is simple to prepare, convenient to use, capable of realizing slow release of platelet-derived growth factors and active substances, lasting in biological effect and suitable for application in restorative treatment of soft or hard tissue defect, skin or mucosa refractory damage or ulcer, articular cartilage degeneration and ischemic tissue necrosis.
Owner:AFFILIATED HOSPITAL CHINA ACADEMY OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI
Assembling type cell-derived extracellular matrix membrane compound bone repairing material as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108310467AEnhance bone regeneration abilityGood osteoinductivityTissue regenerationProsthesisHuman bodyCell-Extracellular Matrix
The invention provides an assembling type cell-derived extracellular matrix membrane (ECM) compound bone repairing material as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The bone repairingmaterial is prepared by the following steps: completely covering a three-dimensional degradable biological scaffold with a sheet-shaped acellular matrix membrane under sterile conditions and then freezing the three-dimensional degradable biological scaffold for 24 to 48h under the condition of -20 to -80 DEG C; then carrying out freeze drying treatment to obtain the ECM membrane compound bone repairing material, wherein the sheet-shaped acellular matrix membrane is a cell-derived extracellular matrix which is generated by in-vitro culture of cells, is subjected to decellularization treatment and has certain bone induction activity, and the three-dimensional degradable biological scaffold is a biological scaffold which is prepared from natural polymers, has a three-dimensional porous microscopic structure and can be completely degraded and absorbed in human bodies. The assembling type cell-derived extracellular matrix membrane compound bone repairing material has a good bone induction capability; furthermore, the bone regeneration capability of the compound material is strengthened; a construction method is simple and feasible and the material can be stored for a long time and has awide clinical application potential.
Owner:XIEHE HOSPITAL ATTACHED TO TONGJI MEDICAL COLLEGE HUAZHONG SCI & TECH UNIV
Tissue engineering corium and its preparation method
A tissue-engineered epidermis is prepared from skin fibroblasts through obtaining the skin fibroblasts, preparing culture medium, amplifying culture, preparing extocytic matrix compound, preparing biologic scaffold, compounding the skin fibroblasts on the surface of biologic scaffold, and 3D culture. Its advantages are a certain elasticity and toughness, short culture time, and no obvious immunorejection reaction.
Owner:陕西艾尔肤组织工程有限公司
Pearl powder artificial bone supporting material with multi-stage micro-nano structure and technique for producing the same
The invention relates to a novel biological scaffold material for bone repair and a preparation method thereof. PLGA and PLA with a mass ratio of 1: 1-10: 1 are dissolved into chloroform, dimethyl sulfoxide, 1, 4-dioxane or a mixed liquid of the 1, 4-dioxane and ultrapure water, and then pearl powder which is subjected to partial or complete deproteinization treatment is added into the obtained product according to the proportion of the PLGA / a PLA mixture to the pearl powder (mass ratio) is 1: 1-10: 1 to obtain forming slurry. A three-dimensional scaffold with high porosity and connectivity rate is designed through a 3D software, and then a low-temperature rapid forming system is utilized to ensure that the three-dimensional scaffold is formed to obtain a scaffold with a microporous structure. An artificial bone biological scaffold material prepared by the method has a three-dimensional scaffold structure that a macroscopic structure has aperture channels with diameters of between 100 and 500mu m and a microstructure has micropores with diameters of between 10 and 20mu m, wherein micron pearl powder is dispersedly distributed on walls of the micropores. The porosity is between 60 and 90 percent, and a macroporous structure is perforated in three directions of X axis, Y axis and Z axis, and has 100 percent of connectivity.
Owner:REGENOVO BIOTECH
Porous biological material using modified gelatin as crosslinking agent and preparation method of porous biological material
The invention provides a porous biological material using modified gelatin as a crosslinking agent and a preparation method of the porous biological material. The preparation method specially comprises the following steps: dissolving an acrylamide monomer, methacrylamide modified gelatin and inorganic nano-clay in deionized water, and stirring for 10 to 30 minutes in an inert atmosphere; adding a catalyst, stirring for 5 to 10 minutes in the inert atmosphere, and then adding an initiator; performing radical polymerization for 12 to 48 hours at the temperature of -30 DEG C to 30 DEG C; soaking the reaction product in the deionized water at 20 DEG C for 48 to 72 hours, and replacing the deionized water every 5 to 8 hours, and finally performing freeze-drying on the reaction product for 24 to 48 hours to obtain the porous biological material using modified gelatin as the crosslinking agent. The preparation method is simple in preparation process, the condition can be controlled, and the prepared porous biological material has the characteristics of good biocompatibility, mechanical property, macroporous property, quick swelling property and the like at the same time, and can be widely applied in the fields of biological scaffolds, cell culture, drug controlled release, tissue engineering, trauma and burn treatment and other biomedical materials.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
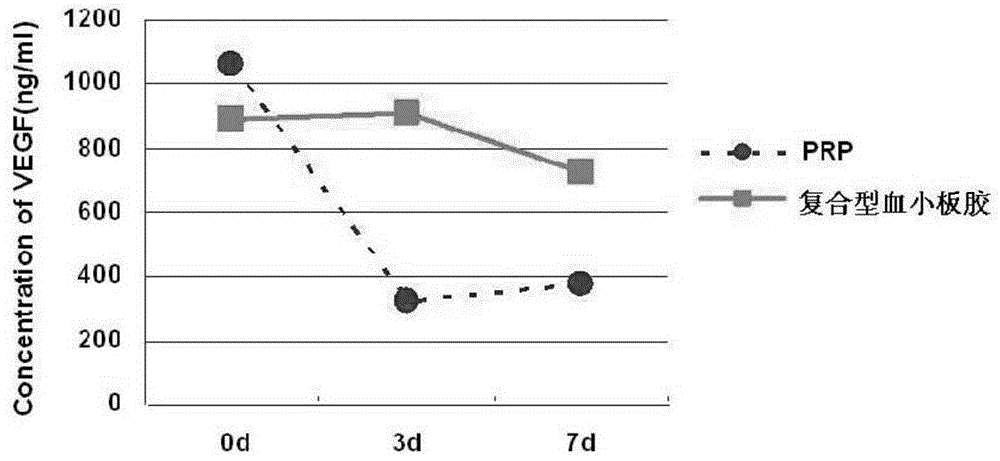
Preparation method of autologous platelet-factor-rich plasma (PFRP) preparation
The invention discloses a preparation method of an autologous platelet-factor-rich plasma (PFRP) preparation. The preparation method is characterized by comprising the steps of: A, preparation of autologous PFRP, to be specific, collecting autologous whole blood, and preparing the autologous PFRP in a centrifuging and freeze-thawing manner; and B, preparation of the PFRP preparation, to be specific, mixing the obtained PFRP with a biological scaffold / autologous somatic cells according to a volume ratio of (3:1)-(1:1) to obtain the PFRP preparation. By means of specially processing the autologous whole blood to obtain the autologous PFRP, pollution risks caused by adding an activating agent are reduced, and the immune risks of a membrane antigen during heterogenous usage are avoided. The autologous PFRP preparation prepared according to the method not only has a good effect of repairing damaged tissues such as meniscus, but also has very good anti-wrinkle, filling and lifting effects.
Owner:CHENGDU QINGKE BIOTECH
Organic composite hydrogel cross-linked by modified gelatin nano-microsphere and preparation method of organic composite hydrogel
ActiveCN104448161AImprove mechanical propertiesGood swelling propertiesBiologic scaffoldPtru catalyst
The invention provides an organic composite hydrogel cross-linked by a modified gelatin nano-microsphere and a preparation method of the organic composite hydrogel. Specifically, the preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing a modified gelatin nano-microsphere by virtue of a two-step solvent removal process, then respectively dissolving an acrylamide monomer and the modified gelatin nano-microsphere in de-ionized water and stirring in an inert atmosphere for 5-30min; adding a catalyst, stirring in the inert atmosphere for 5-10min, and adding an initiator; carrying out a free radical polymerization reaction at minus 40-40 DEG C for 12-48hr; and soaking a reactant in de-ionized water at 20 DEG C, replacing the de-ionized water once every other 5-8hr, and keeping for 48-72hr to obtain the organic composite hydrogel. The method disclosed by the invention is simple in process and controllable in condition, and the prepared organic composite hydrogel integrates the characteristics of a nano composite material and covalent cross-linking and has the characteristics of being good in biocompatibility, mechanical property, macro-porous property, rapid swelling property and the like; and the organic composite hydrogel can be widely applied to the biomedical materials of biological scaffold, cell culture, medicine controlled release, tissue engineering and the like.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Exosome targeted slow-release microsphere biological stent and preparation method and use thereof
ActiveCN107582567ASlow-release controllableImprove targeted repairNervous disorderSkeletal disorderTreatment effectMicrosphere
The invention provides an exosome targeted slow-release microsphere biological stent and a preparation method and a use thereof; the biological stent includes collagen, degradable microspheres dispersed in the collagen, and an exosome combined on the microspheres. The preparation method comprises the steps: separating collagen from animal tissues; separating an exosome from a culture substance ofbone marrow or umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells; preparing microspheres combined with the exosome by an emulsification-crosslinking method; and mixing the microspheres with the collagen, and freeze-drying. Chitosan and other high molecular materials are combined with the exosome by a microsphere structure, the microsphere structure is dispersed to the collagen, a biological stent material having a function of directional release of the exosome is formed, the exosome targeted repairing and treatment effects can be significantly improved, and the microsphere structure makes the release of the exosome have slow-release controllable characteristics, accords with development trend of accurate drug diversity, has diverse dosage forms, and has broad clinical application value.
Owner:李征宇 +1
Mesenchymal stem cell biological winkle removing agent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101785853AEliminate wrinklesAnti agingOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsBiologic scaffoldSkin texture
The invention discloses a mesenchymal stem cell biological winkle removing agent and a preparation method thereof. The winkle removing agent is prepared by uniformly mixing mesenchymal stem cells, recipient blood plasma, growth factors, insulin and hyaluronic acid. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: (1) collecting and culturing the mesenchymal stem cells to prepare cell concentrated solution; (2) collecting the recipient blood plasma; (3) adding the growth factors and the insulin into the recipient blood plasma; and (4) using the hyaluronic acid as a biologic scaffold, and repeatedly sucking and uniformly mixing 2 percent hyaluronic acid, the blood plasma into which the growth factors and the insulin are added and the mesenchymal stem cell concentrated solution in aninjector to obtain a mesenchymal stem cell preparation. The winkle removing agent prepared by the method is used for removing and preventing skin winkles and has the advantages of quick response, long maintenance time, non-stiff facial expression, unobvious hardening of hyperplastic tissues and skin texture accordant with normal skin.
Owner:晏泽
Collagen-based biomedical material by taking dialdehyde polyethylene glycol as cross-linking agent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104262648ANon-irritatingAvoid Metabolic Toxic PhenomenaAbsorbent padsProsthesisBiologic scaffoldPolymer science
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Collagen scaffold for cell growth and a method for producing same
InactiveUS20120093877A1Improve propertiesHigh mechanical strengthWarp knittingPharmaceutical delivery mechanismBiologic scaffoldFiber
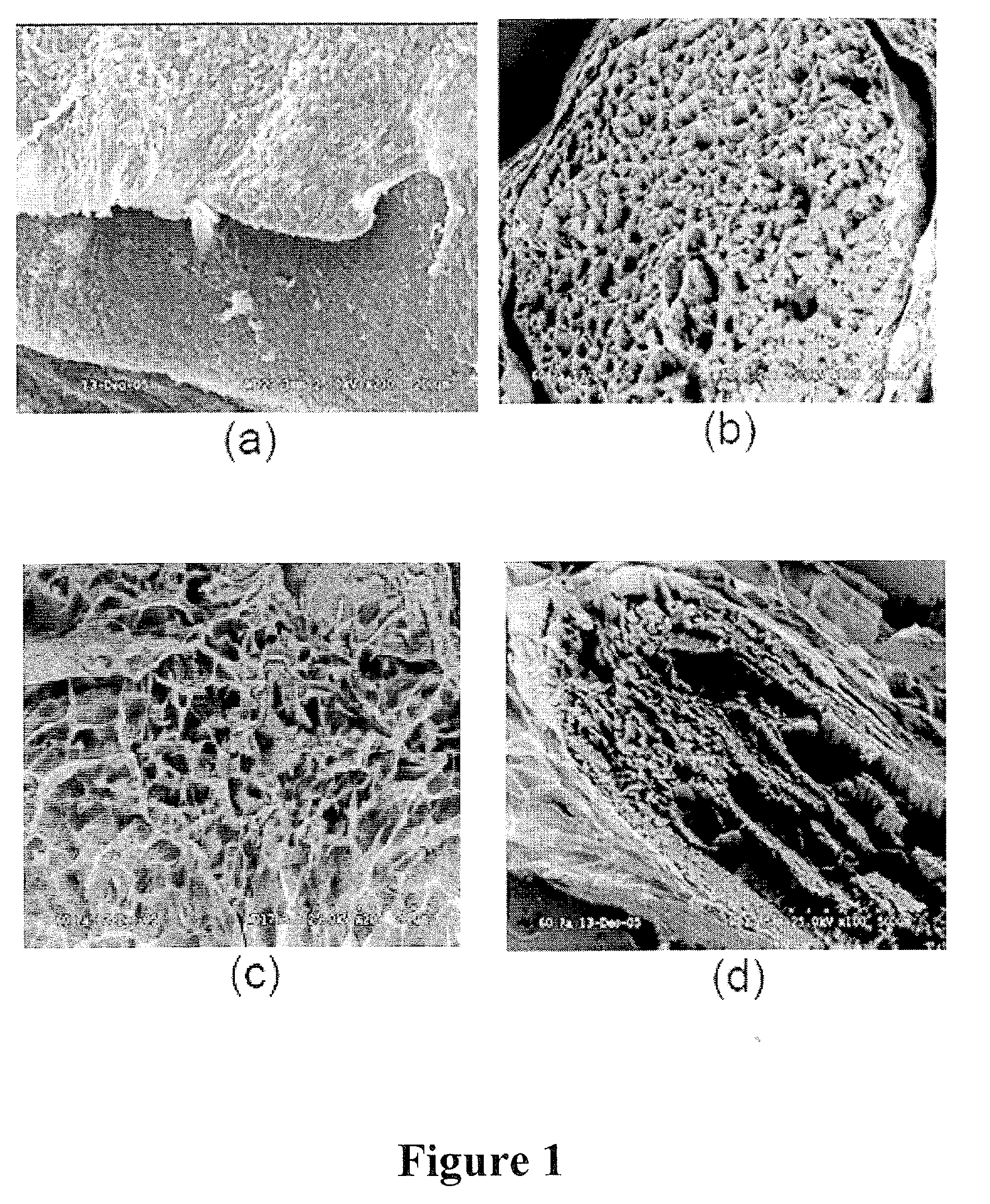
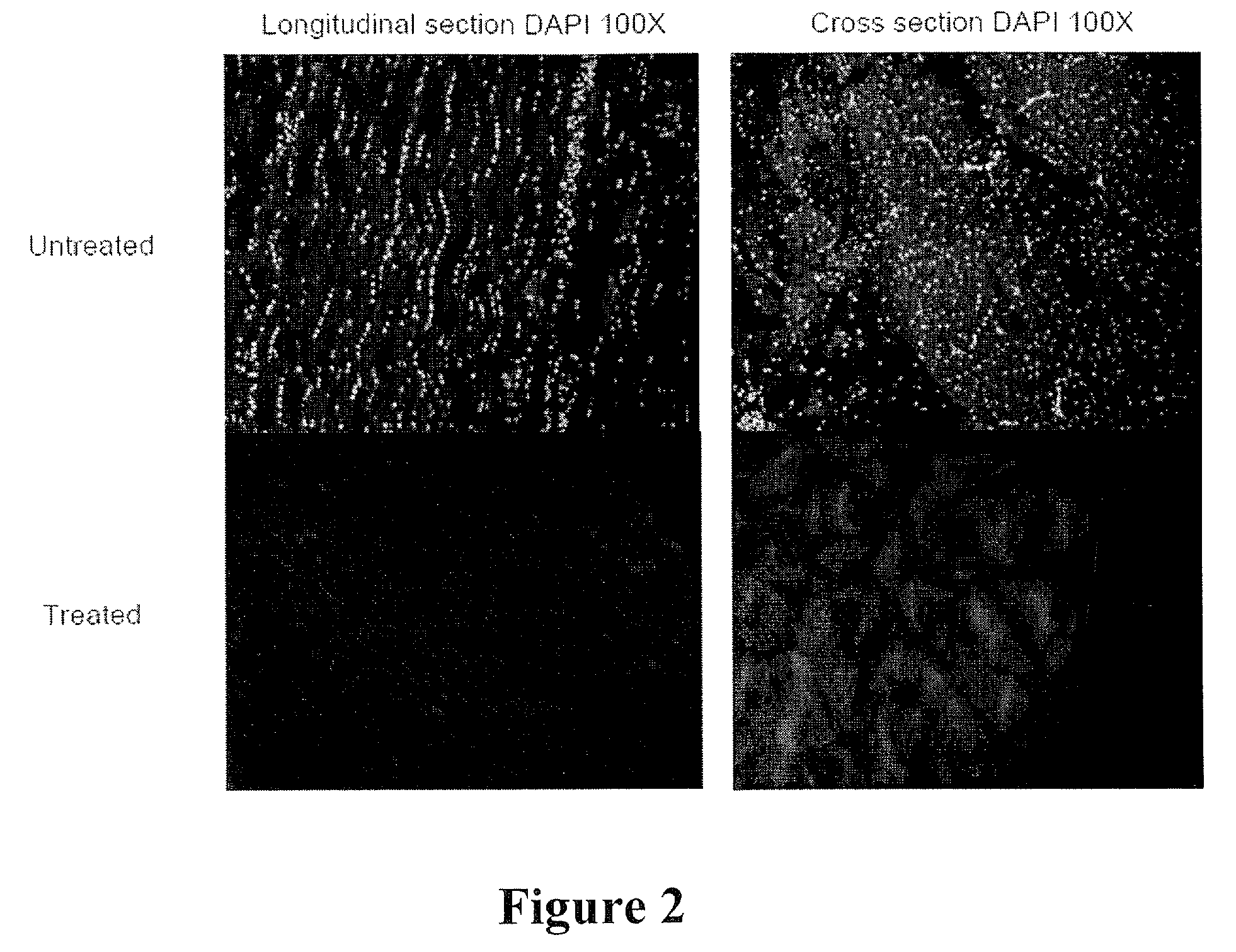
A bioscaffold and method of manufacture is described. The bioscaffold comprised greater than 80% type I collagen fibers or bundles having a knitted structure providing tensile load strength. The method of manufacture comprises the steps of: (a) isolating collagen fibers or bundles; (b) incubating said fibers or bundles in a mixture of NaOH, alcohol, acetone, HC; and ascorbic acid; and (c) mechanical manipulation of said fibers or bundles to produce a knitted structure.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN AUSTRALIA
Method for preparing biological scaffold by 3D printing
InactiveCN105903078AGood biocompatibilityNo toxicityAdditive manufacturing apparatusProsthesisBiologic scaffoldNormal bone
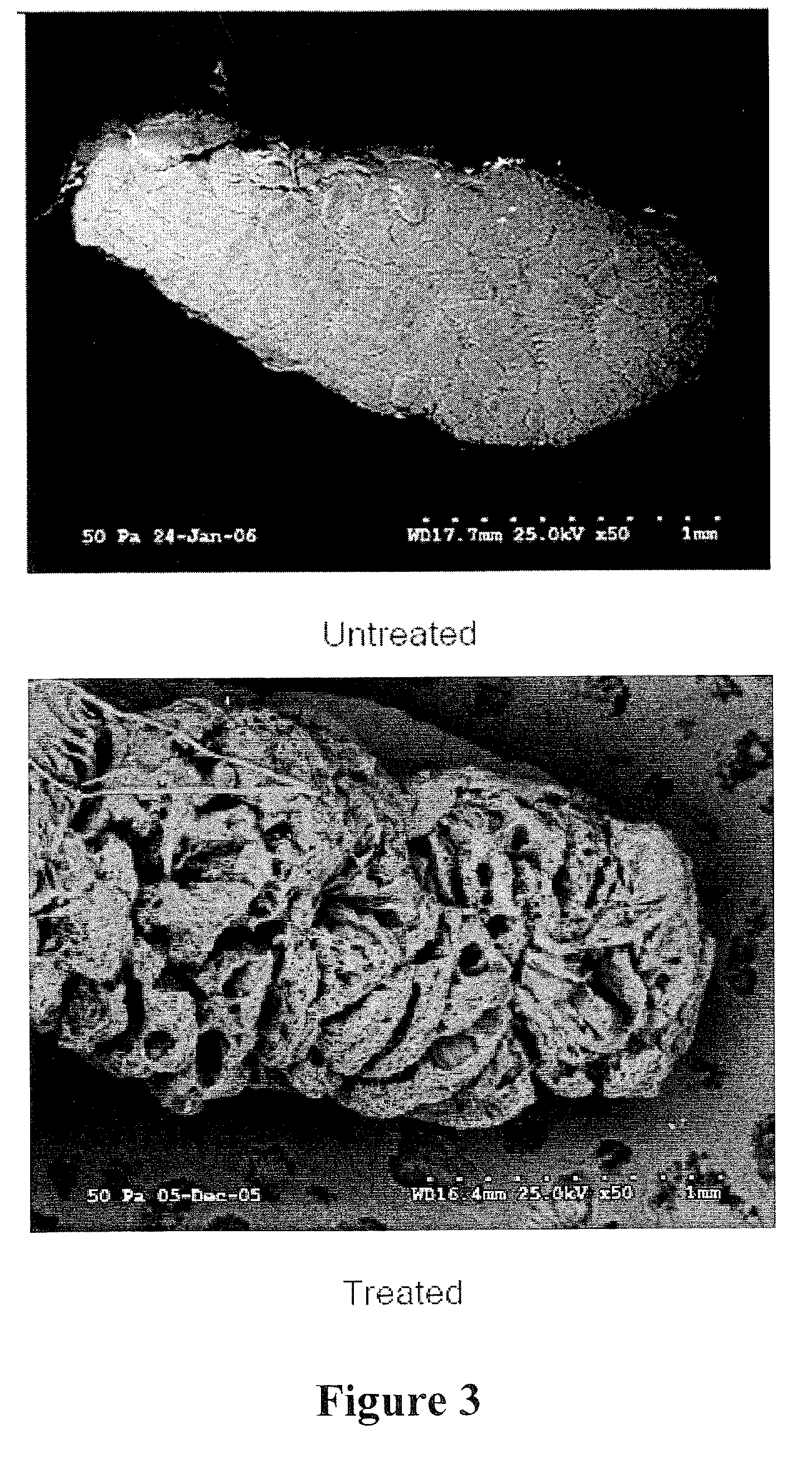
The invention provides a method for preparing a biological scaffold by 3D printing. The method comprises the steps of grinding allogeneic bones or heterogeneous bones at a low temperature in a freezing grinder to obtain a printing material, modeling 3D printing with the aid of a computer, and then performing post treatment in a genipin solution. The prepared biological scaffold has good biological compatibility, and the bone graft material does not have toxicity, rejection, mutagenicity or antigenicity in vivo, and does not disturb bone and tissue regeneration; the prepared biological scaffold can be gradually degraded and absorbed and replaced by autologous bone tissues, can bear the pressure close to 20MPa with normal bone cortex, and has good initial mechanical properties; and the elastic modulus is gradually reduced, stress shielding is avoided, fracture, collapse and loosening of implants in the long-term healing process are avoided, bone fusion can be accelerated, and the implants can be finally completely converted into autologous bone tissues.
Owner:THE THIRD AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF PLA
Method for constructing tissue engineering skin
The invention relates to a method for constructing tissue-engineering skin. The construction method adopts an autocrine extracellular matrix of fibroblast as a biological scaffold of the tissue-engineering skin. The method utilizes the extracellular matrix excreted by the cultured fibroblast as the biological scaffold and human epidermal cells as seed cells, and the cultured tissue-engineering skin is closer to the structure of natural skin. The method has the advantages that: firstly, the method is simple and convenient, and favorable for synthesis and mass production of products because thematerials take the form of liquid; secondly, the obtained product has the structure which is closer to the natural skin, and the method is favorable for improving the sensibility and the precision ofprediction of the toxicity of compounds; thirdly, the product does not contain additional biomaterials, so that the risk of cross infection of zoonosis cannot occur; and fourthly, the obtained product is convenient for quality control, so that the variation between batches is reduced.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF INSPECTION & QUARANTINE
Blank PLGA microspheres and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104448356ANo toxicityDoes not affect growth activityProsthesisBiologic scaffoldPolyvinyl alcohol
The invention provides blank polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer microspheres which are prepared by a water-oil-water emulsion process. The PLGA microspheres are prepared from PLGA powder by using excellent dissolving capacity of dichloromethane and emulsification of polyvinyl alcohol. Through representation observation and particle size determination of the microspheres, the diameter and the surface sign of a biological scaffold material are obtained; and the diameters of the PLGA blank microspheres accord with the injection size. Through CCK-8 determination and lactic dehydrogenase determination, the microspheres have no toxicity on attached mesenchymal stem cells, and do not affect the growth activity. Compared with chitosan particles, the microspheres are simple in preparation method, high in repetitive rate, clear structure, and easy to degrade in a living body, do not affect microenvironment metabolism, and can used as good cell carriers for different treatment targets in tissue regeneration engineering.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
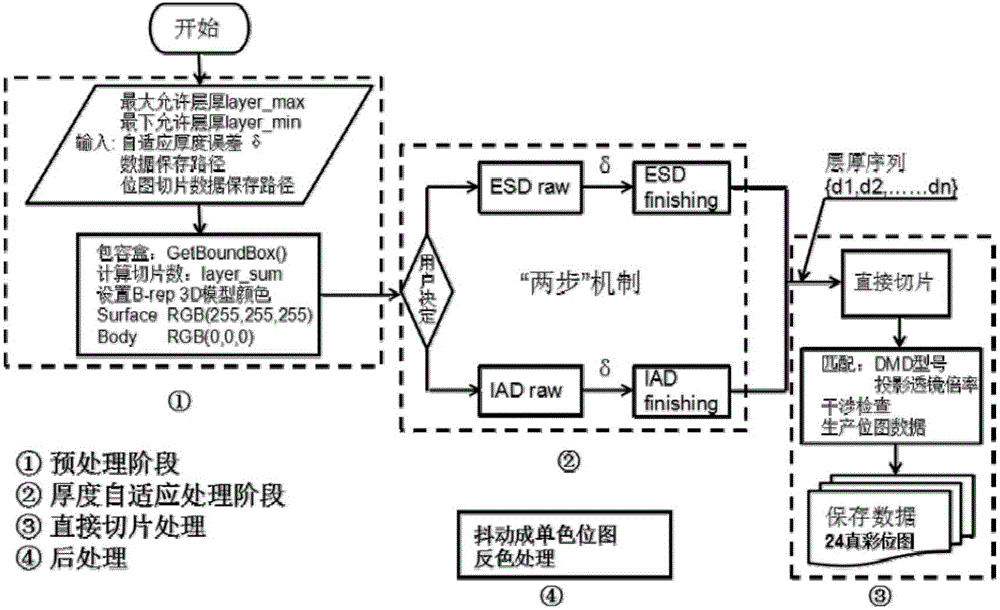
Self-adaptive direct slicing method for preparing biological scaffold
ActiveCN106671422AGuaranteed accuracyReduce the number of slicesMedical simulationAdditive manufacturing apparatusBiologic scaffoldOperand
The invention discloses a self-adaptive direct slicing method for a preparing biological scaffold. The method is secondary development using VC++ and conducted on a SolidWorks2011 platform, and the core concept provided by the method and a special treatment mechanism adopted by aiming at the three-dimensional mold characteristics of the biological scaffold can be particularly achieved by relying on other software and hardware platforms. The self-adaptive direct slicing method for the preparing biological scaffold is mainly divided into four parts including pre-treatment, thickness self-adaptive treatment, direct slicing and post-treatment. Two constituent parts, namely an ESD substep and an IAD substep, of the thickness self-adaptive treatment are two completely independent steps and are not overlapped on operand and operational objects. Algorithm or operation which wastes system resources and spends a lot of time during the preparation process is effectively avoided, efficiency can be improved, and precision can be guaranteed.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Tissue engineering skin containing appendage and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107217028AEasy accessImprove efficiencyEpidermal cells/skin cellsArtificial cell constructsFiberBiologic scaffold
The invention belongs to the biotechnical field and in particular to tissue engineering skin containing appendage and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: performing transfection of a urine cell to induce to generate a multifunctional stem cell; continuously inducing the multifunctional stem cell to generate a mesenchymal stem cell; differentiating the mesenchymal stem cell to form an epidermis cell, a fibroblast and a hair follicle cell; and constructing tissue engineering double-layered skin containing the appendage with a biological stent material amniotic membrane. The seed cell of the tissue engineering skin prepared by the preparation method is the urine cell which is convenient to obtain and short in cultivation period. The hair follicle structure which is contains facilitates union of a wound, and the tissue engineering skin containing the appendage provided by the invention lays a foundation for follow-up development of the tissue engineering skin containing the appendage.
Owner:GUANGZHOU RAINHOME PHARM&TECH CO LTD
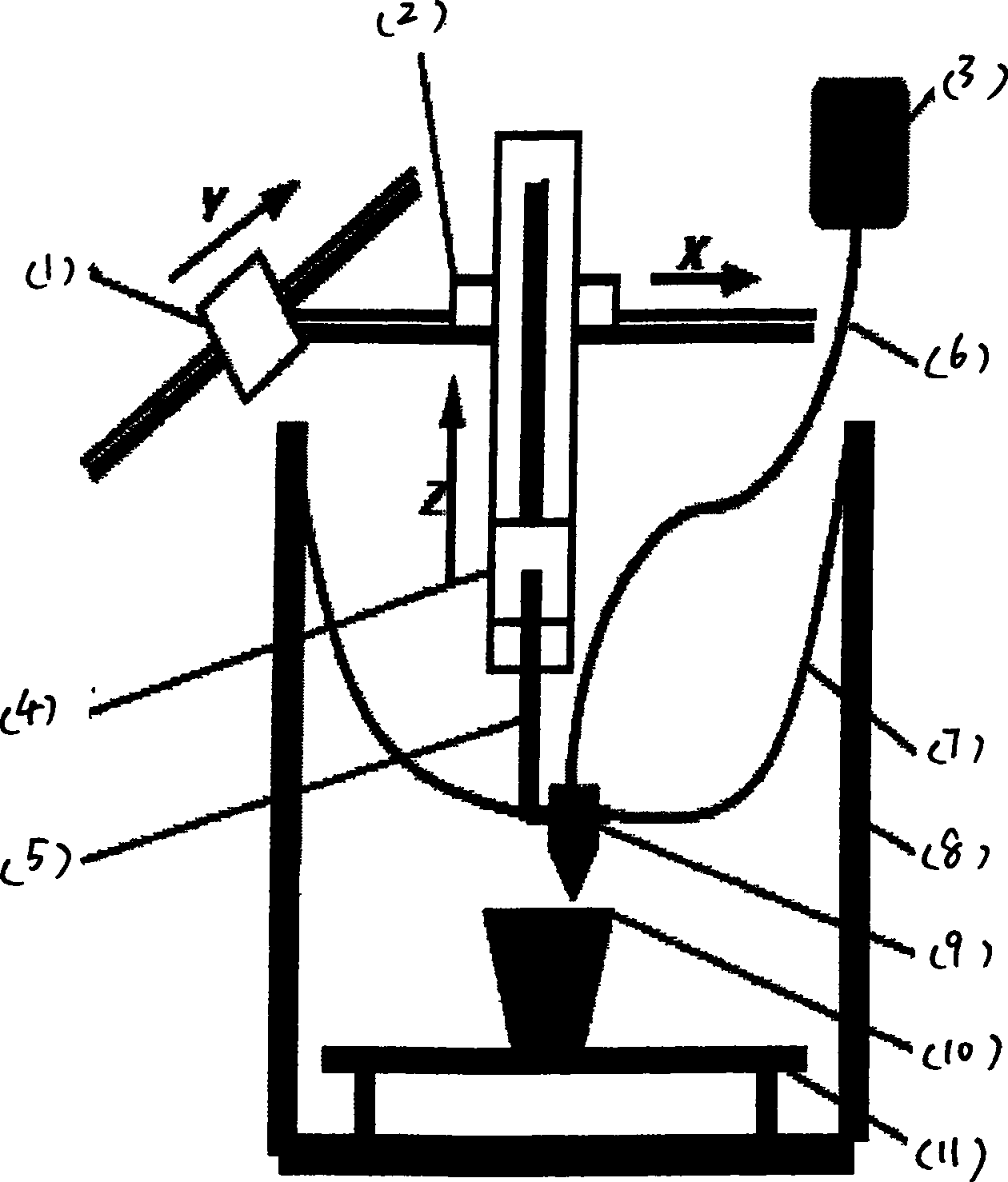
3-dimensional bioscaffolds
InactiveCN105813602AHigh resolutionManufacturing platforms/substratesManufacturing enclosuresMeniscal injuryBiologic scaffold
The invention concerns an apparatus and a method for the manufacture of a three-dimensional (3D) bioscaffold; a 3D bioscaffold made using same; and the use of said 3D bioscaffold in the manufacture of an implant to treat injuries such as, but not limited to, meniscal injuries.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Scaffold containing platelets and hyaluronic acid and preparation method of scaffold
InactiveCN104587525AGood biocompatibilityExtended shelf lifeProsthesisBiologic scaffoldPlatelets blood
The invention is suitable for the technical field of biomedicine materials and provides a biological scaffold containing platelets and hyaluronic acid which are mixed uniformly, wherein the platelets are activated by calcium ions before being mixed with hyaluronic acid. The invention also provides a preparation method of the biological scaffold. The preparation method comprises the following steps: obtaining platelet-rich plasma (PRP); adding calcium ions into the PRP; and uniformly mixing the obtained PRP with hyaluronic acid. The biological scaffold provided by the invention has good biological compatibility and more pore structures and can ensure that the platelets slowly release growth factors.
Owner:SHENZHEN CHINA CAPTICAL BIOMEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Exosome-compounded collagen biological scaffold with directional releasing function as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107550933AStrong combinationGood targetingNervous disorderSkeletal disorderBone marrowNanoscopic scale
The invention provides an exosome-compounded collagen biological scaffold with a directional releasing function as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The exosome-compounded collagenbiological scaffold comprises nano collagen and exosomes dispersed in the nano-collagen. The preparation method of the biological scaffold comprises the following steps: separating collagen from animal tissue, carrying out ball milling till the collagen is nanoscale collagen; separating exosomes from culture of bone marrow or umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells; mixing the exosomes with the collagen, freezing and drying. The preparation method of the biological scaffold is used for dispersing the exosomes in the nanoscale collagen to form a biological scaffold material with a function of directionally releasing exosomes; the targeted repairing and treating effects of the exosomes can be obviously improved; the development tendency of accurate drug administration can be met; the dosage forms are various; the biological scaffold has extensive clinical application values.
Owner:龙乾发 +1
Novel biomimetic peptoid polymers
The present invention provides for novel peptoid oligomers that are capable of self-assembling into two-dimensional sheet structures. The peptoid oligomers can have alternately hydrophilic or polar side-chains and hydrophobic or apolar side-chains. The peptoid oligomers, and the two-dimensional sheet structures, can be applied to biological applications where the peptoid plays a role as a biological scaffold or building block. Also, the two-dimensional sheet structures of the present invention can be used as two-dimensional nanostructures in device applications.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
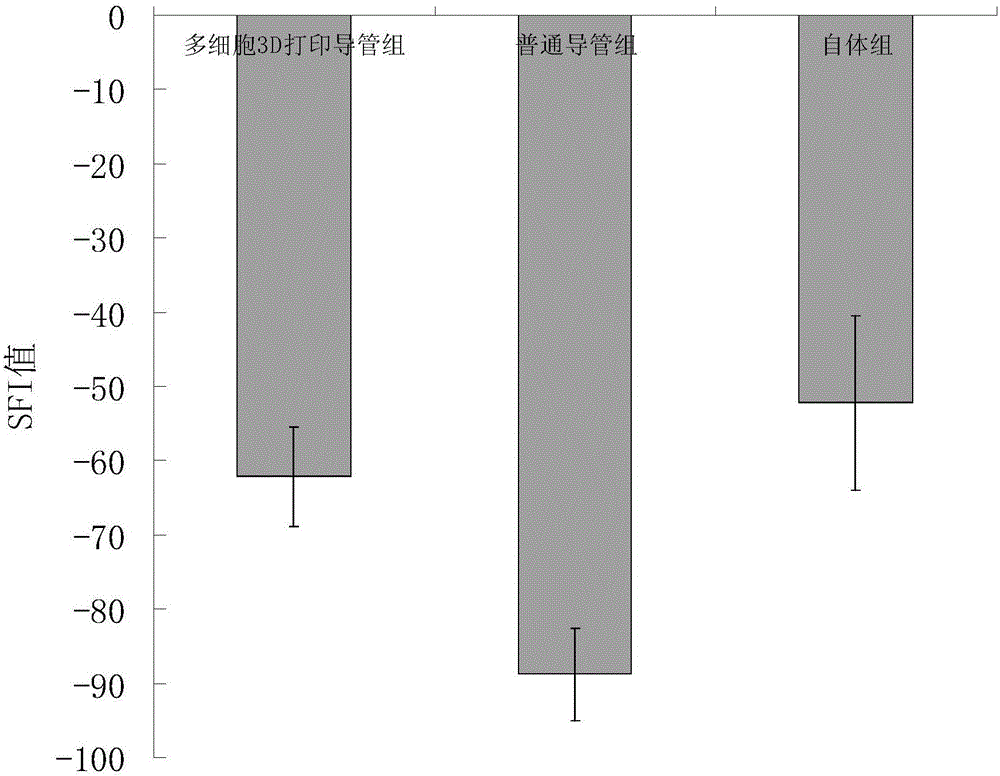
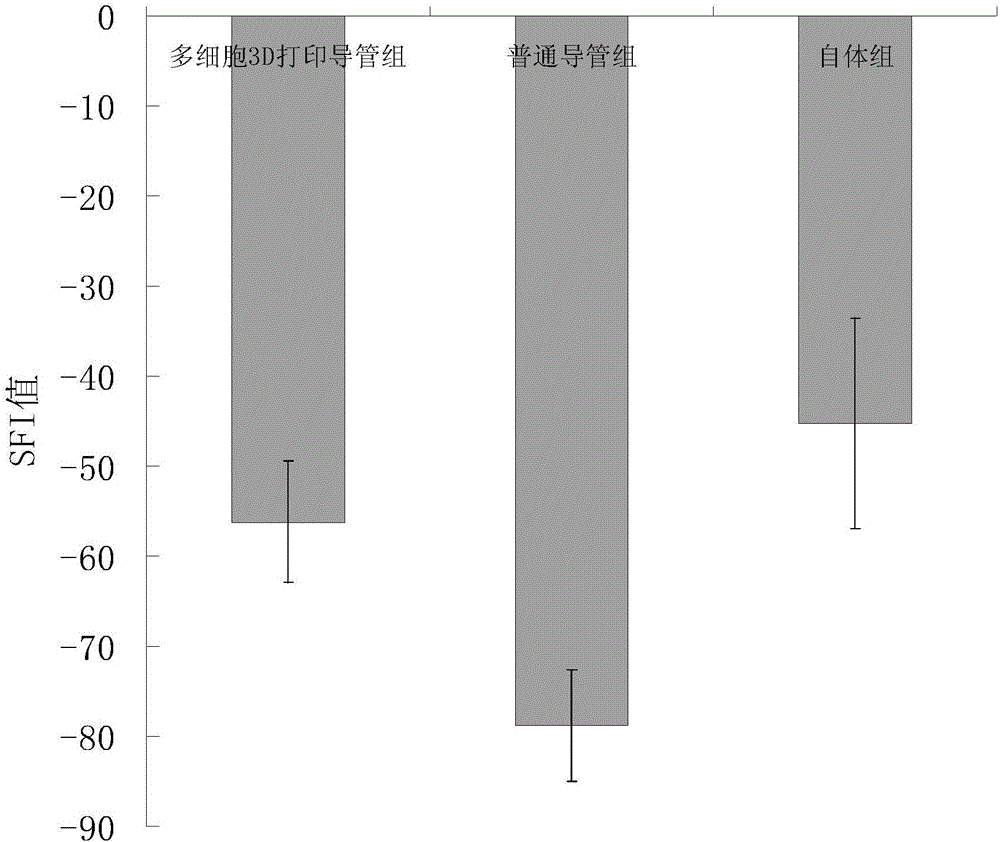
Nerve conduits based on three-dimension printing of multiple types of cells and producing method thereof
InactiveCN106215241AImprove hydrophilicityAdjust the density and loosenessAdditive manufacturing apparatusTissue regenerationBiologic scaffoldMolecular materials
The invention relates to a method for producing nerve conduits based on three-dimension printing of multiple types of cells. The method comprises the following steps: a high-molecular material is used for producing filaments, the filaments are assembled into braided lines, and the braided lines are produced into tubular external layered braided supports and internal braided supports of nerve conduits; a normal pressure plasma is used for carrying out surface treatment for the tubular external layered braided supports and internal braided supports; multiple types of cells are obtained, each type of cell is respectively dissolved into biological solvents in order to produce biological ink, and the ink is placed into different printing ink cartridges; biological printing parameters are adjusted, the biological ink is printed on external surfaces of the braiding type tubular internal and external layered biological supports; the tubular external layered braided supports and the internal braided supports are assembled, and high-molecular glue is used for carrying out adhesion and fixation of two ends of nerve conduits. The method has the following characteristics and beneficial effects: the nerve conduits employ the high-molecular degradable material as the material, the material is easily available, and the material has certain strength and good biological compatibility.
Owner:ZHEJIANG PROVINCIAL PEOPLES HOSPITAL
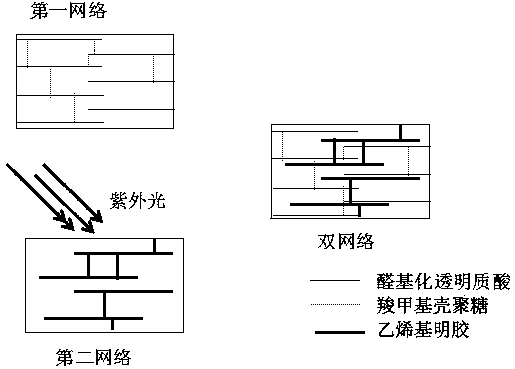
Dual-network hydrogel composition, dual-network hydrogel biological scaffold, preparation method of scaffold, and application of composition
The invention discloses a dual-network hydrogel composition, a dual-network hydrogel biological scaffold, a preparation method of the scaffold, and an application of the composition. The double-network hydrogel composition comprises aldehyde hyaluronic acid, carboxymethyl chitosan, vinyl gelatin and a photo-crosslinking initiator, wherein a mass ratio of the aldehyde hyaluronic acid to the carboxymethyl chitosan is 1:1 to 5:1, and a mass ratio of the vinyl gelatin to the carboxymethyl chitosan is 1:2 to 5:1. The aldehyde hyaluronic acid and carboxymethyl chitosan in the composition are reactedto obtain a first network, the vinyl gelatin photo-initiates free radical polymerization to prepare a second network structure, the formed double-network hydrogel biological scaffold has good structural stability, good cell compatibility, good biological safety and excellent structural fidelity, and the compression modulus of the hydrogel biological scaffold can be adjusted to 10-100 KPa by controlling the proportions of all the components, so the hydrogel biological scaffold is suitable for printing various tissue bodies, and the activity of printed cells is 80% or above, thereby the application of the cell biological scaffold material is further expanded.
Owner:MEDPRIN REGENERATIVE MEDICAL TECH
Preparation method of biological scaffold material and SVF assistant adipose tissue
The invention discloses a preparation method and an application of a biological scaffold material and SVF assistant adipose tissue. Under an aseptic condition, the biological scaffold material, a stromal vascular fraction (SVF) prepared by digesting purified adipose granules with a medical-graded collagenase, and the purified adipose particles are evenly mixed according to a certain proportion to prepare an adipose graft for filling. The SVF is a mixture of adipose mesenchymal stem cells and various cells, is transplanted after being mixed with autogenous adipose particles, and can be continued to be developed into a mature adipose tissue in vivo; the biological scaffold material can provide a support for transplanted adipose, allows the transplanted tissue to be prone to revascularization, and improves the survival rate of the transplanted tissue; the transplanted tissue is suitable for being injected with a 16 G or 18 G needle, facilitates clinical application, and can be used for repairing of concave deformity (such as tempora and cheek concave), beautifying packing of faces and chests, soft tissue function reconstruction and the like; and especially in the beautifying packing, the prepared transplanted adipose tissue can promote shape recovery and prevent liquefactive necrosis.
Owner:广东佰鸿干细胞再生医学有限公司
Tissue engineering full-layer skin and preparing method thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of tissue engineering and discloses tissue engineering full-layer skin and a preparing method thereof. The tissue engineering full-layer skin comprises epidermal cells, dermal cells and a biological scaffold material. The skin is obtained by compounding the dermal cells in the biological scaffold material, inoculating the surface with the epidermal cells and carrying out culturing and preparing. The tissue engineering full-layer skin is provided with a dermis layer and an epidermal layer which are provided with activity cells, the epidermal layer contains stratum corneum and is approximate to the normal skin, after transplanting is carried out, complete human skin with a function can be regenerated, the regenerated skin has skin appendant organs such as hair and the sebaceous gland, and the skin can be used for treating skin defects caused by inflammation, ulcer, burns, scalds and the like, and can also be used for preparing a skin model for disease study, medicine testing and screening, cosmetic testing and the like.
Owner:JINAN PANSHENG BIOTECH
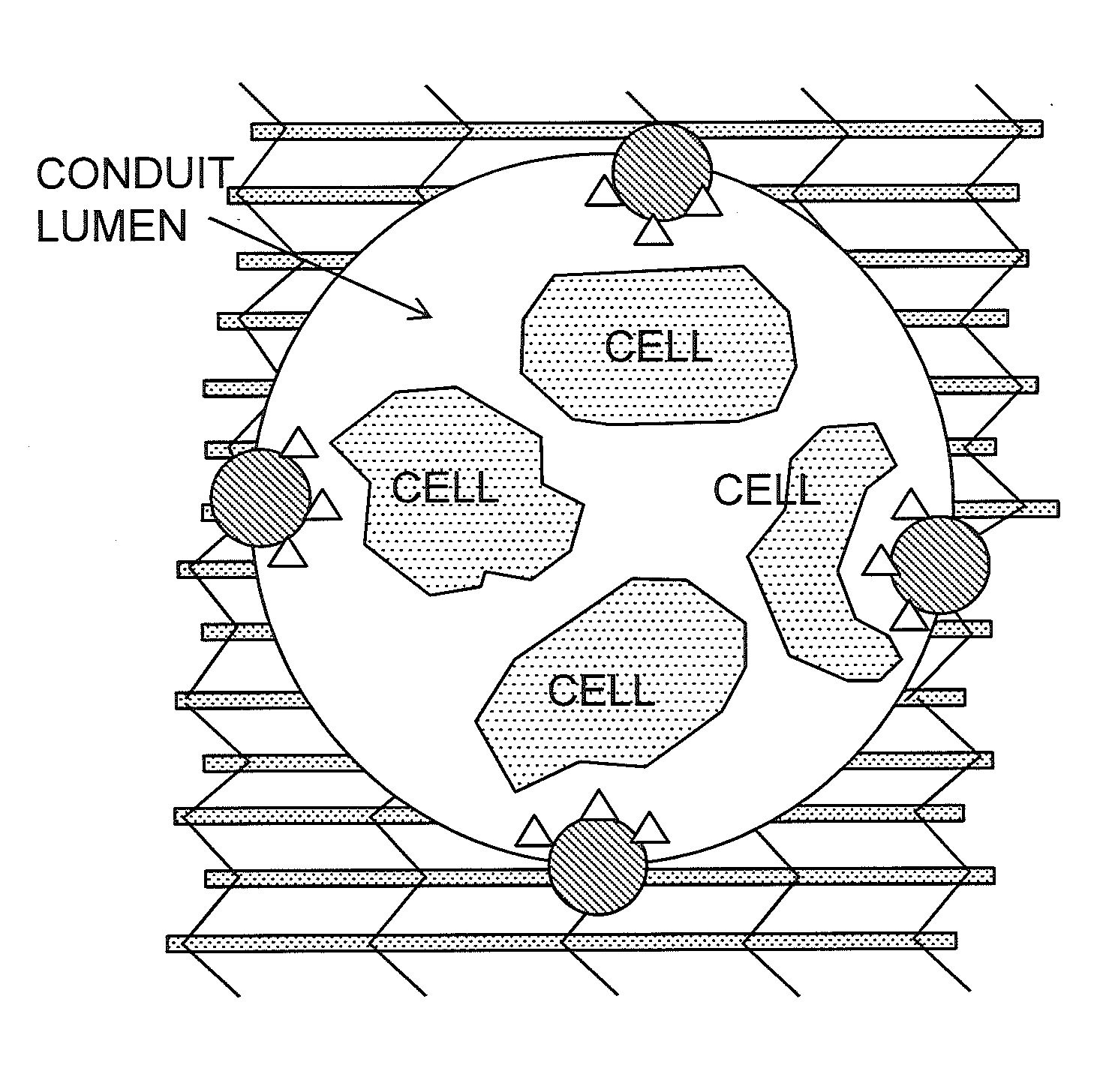
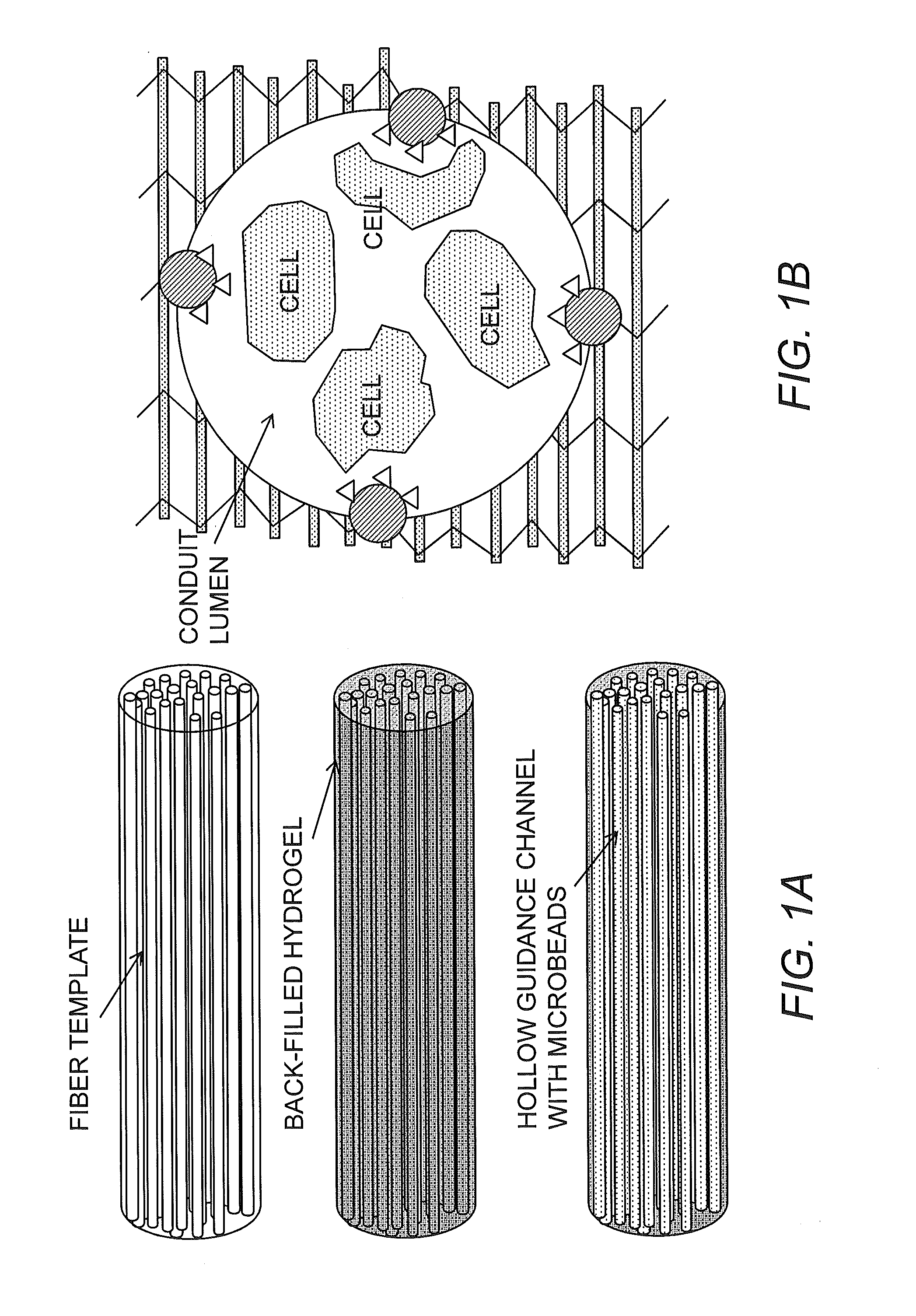
Bioscaffolds for formation of motor endplates and other specialized tissue structures
ActiveUS20140234388A1Promote formationFunction increaseHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideBiologic scaffoldTissue architecture
Provided herein are scaffolds and methods useful to promote the formation of functional clusters on a tissue, for example, motor endplates (MEPs) or a component thereof on skeletal muscle cells or tissue, as well as the use of scaffolds so produced for repairing a tissue injury or defect.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com