Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
114 results about "Small intestinal submucosa" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
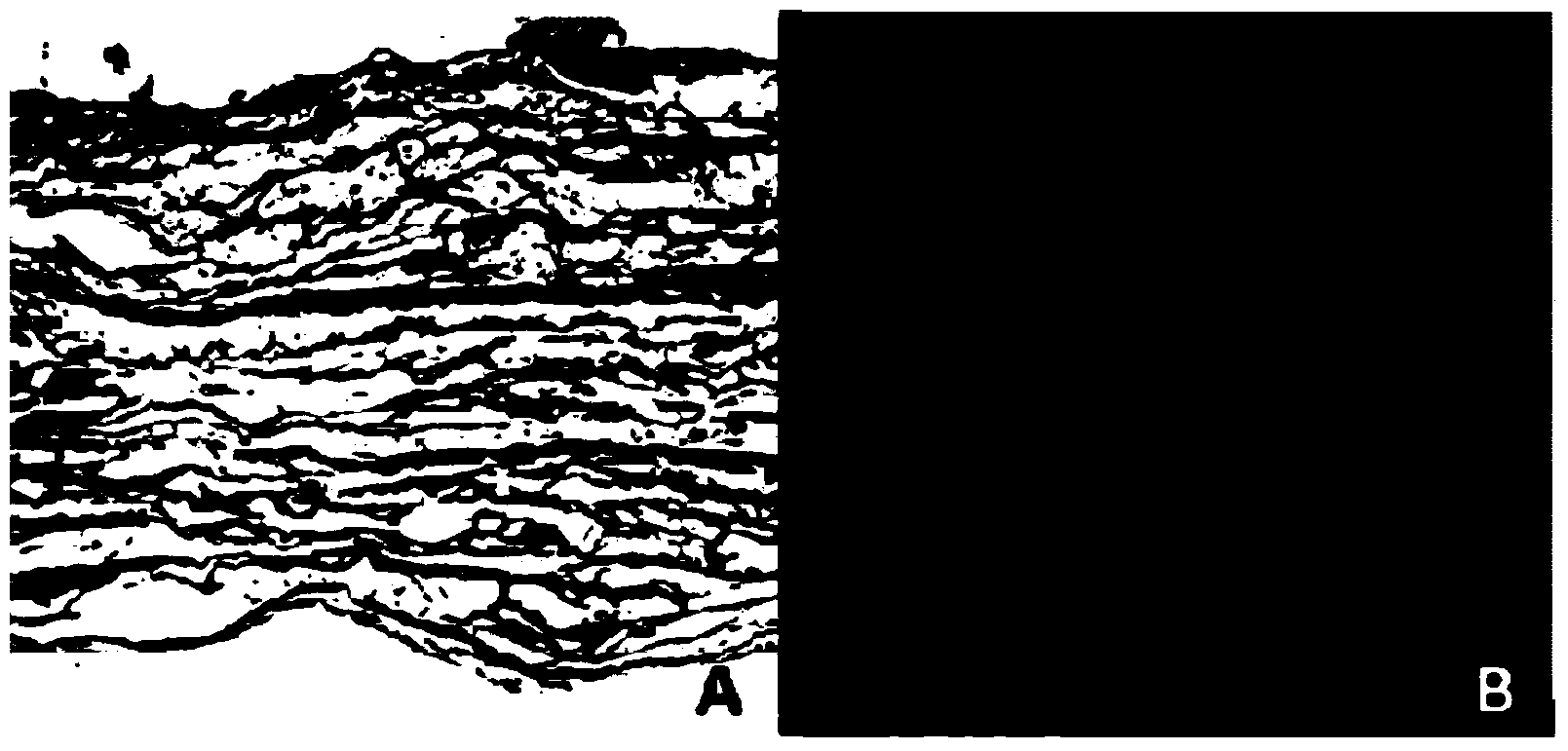
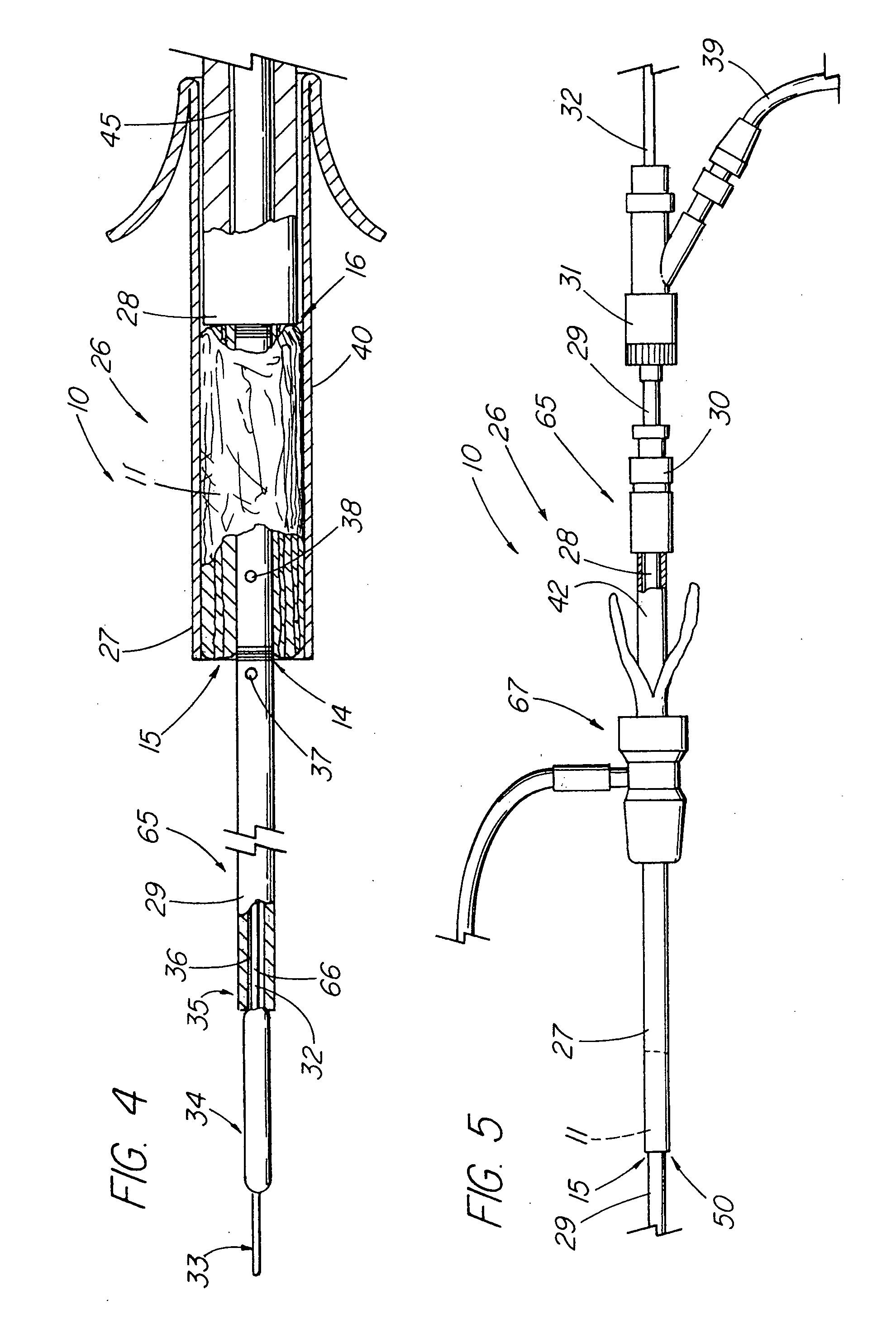
Small intestinal submucosa. Small intestinal submucosa (SIS) is submucosal tissue in the small intestines of vertebrates. SIS is harvested (typically from pigs) for transplanted structural material in several clinical applications, typically biologic meshes. They have low immunogenicity.
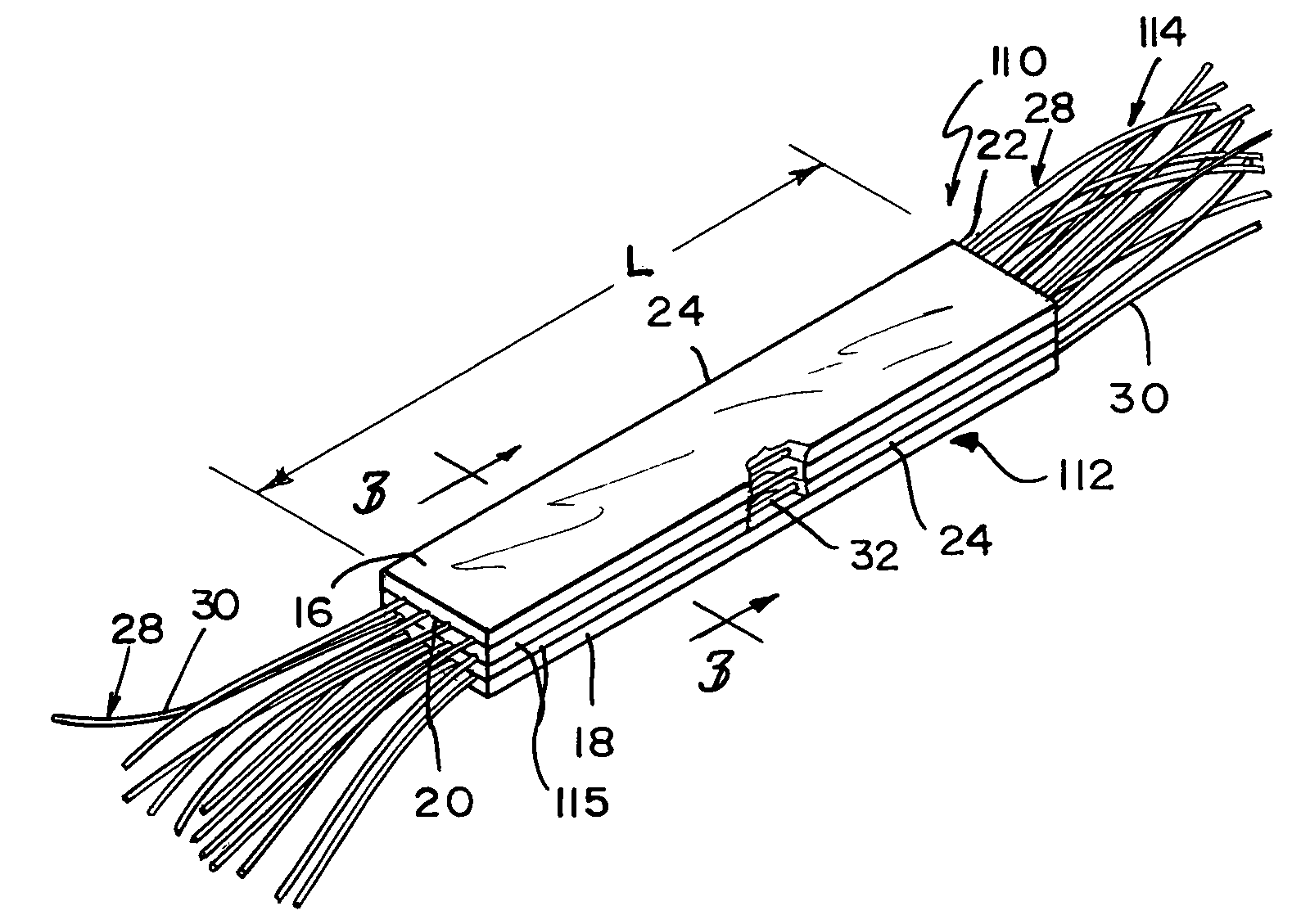
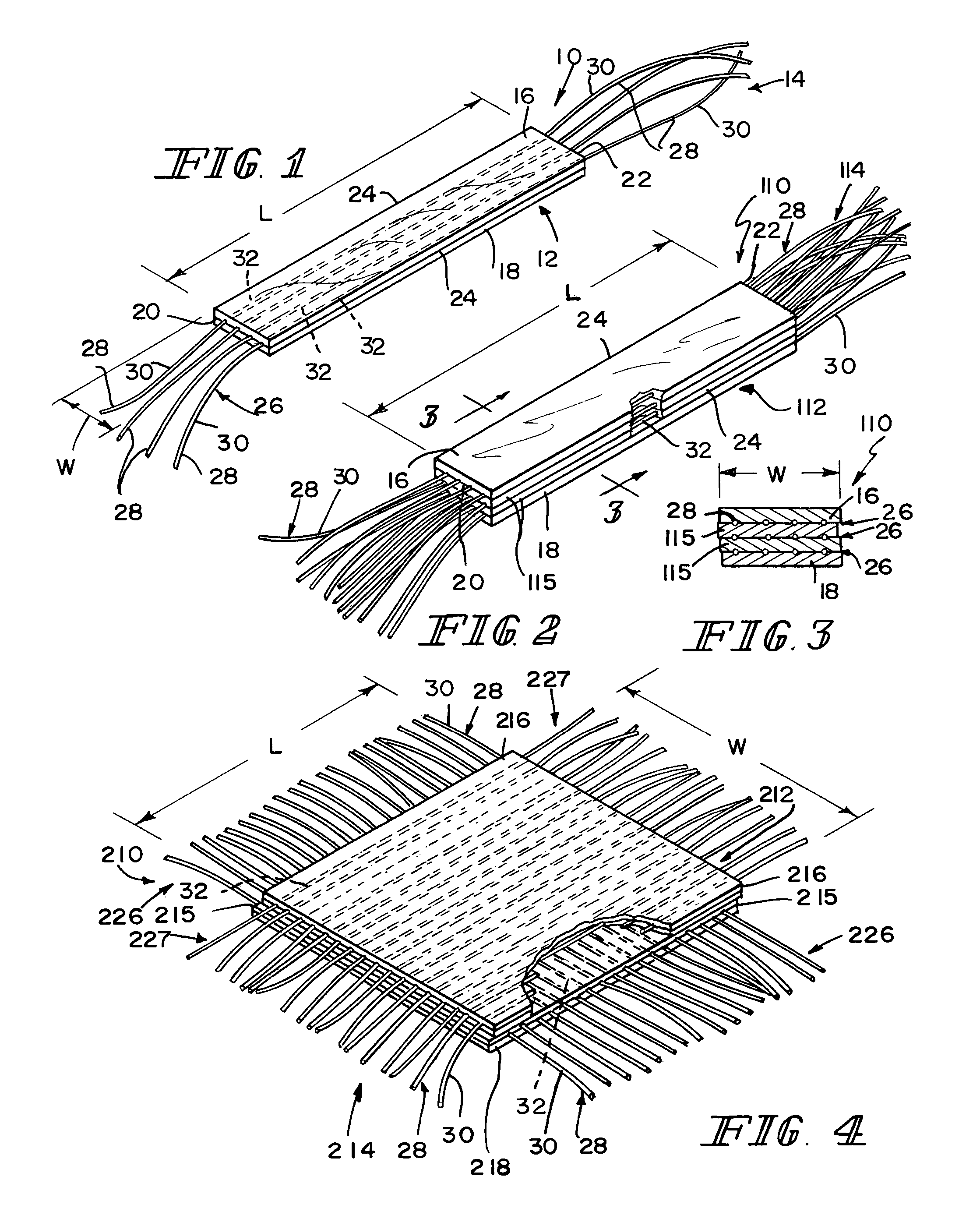
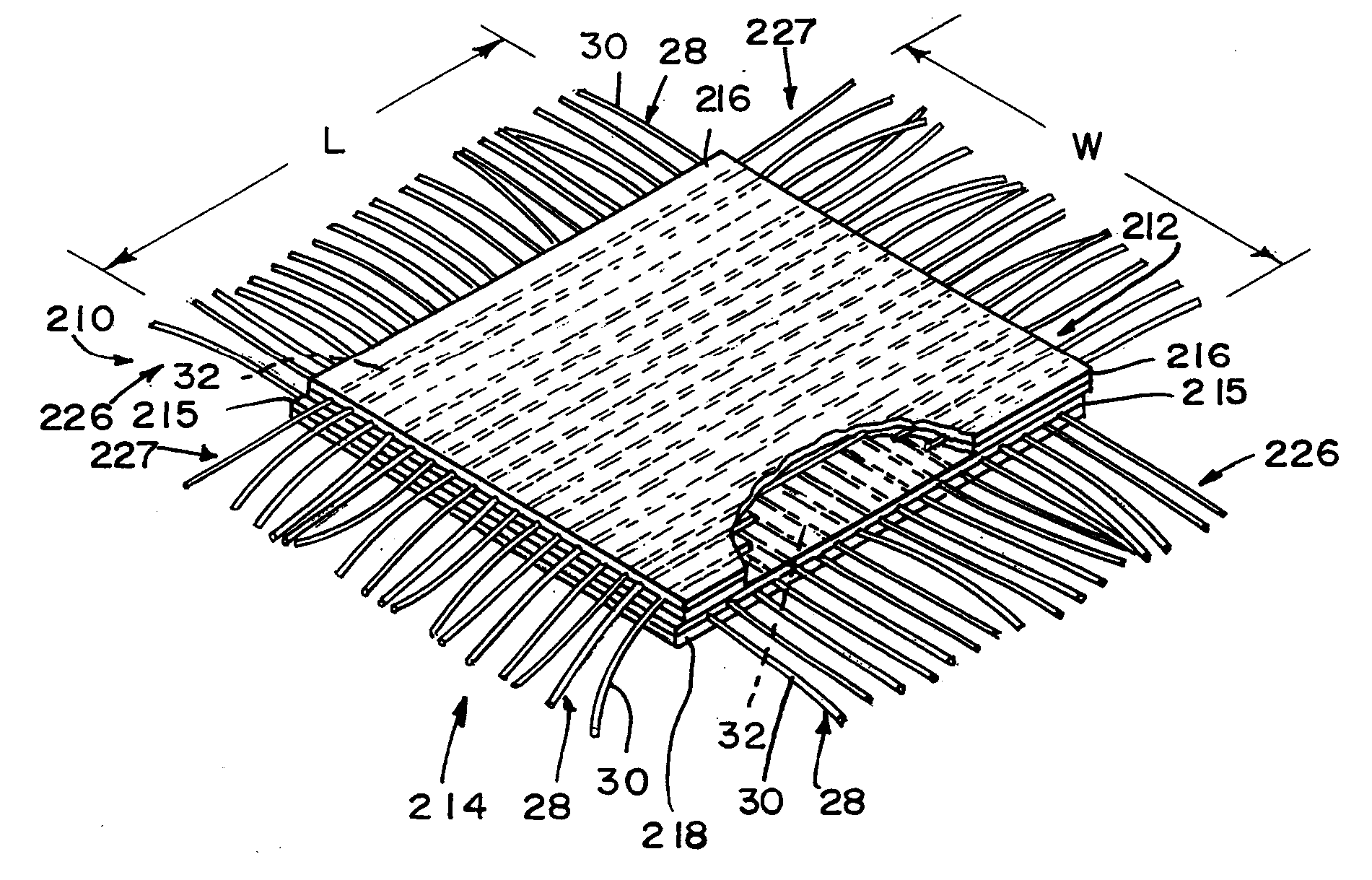
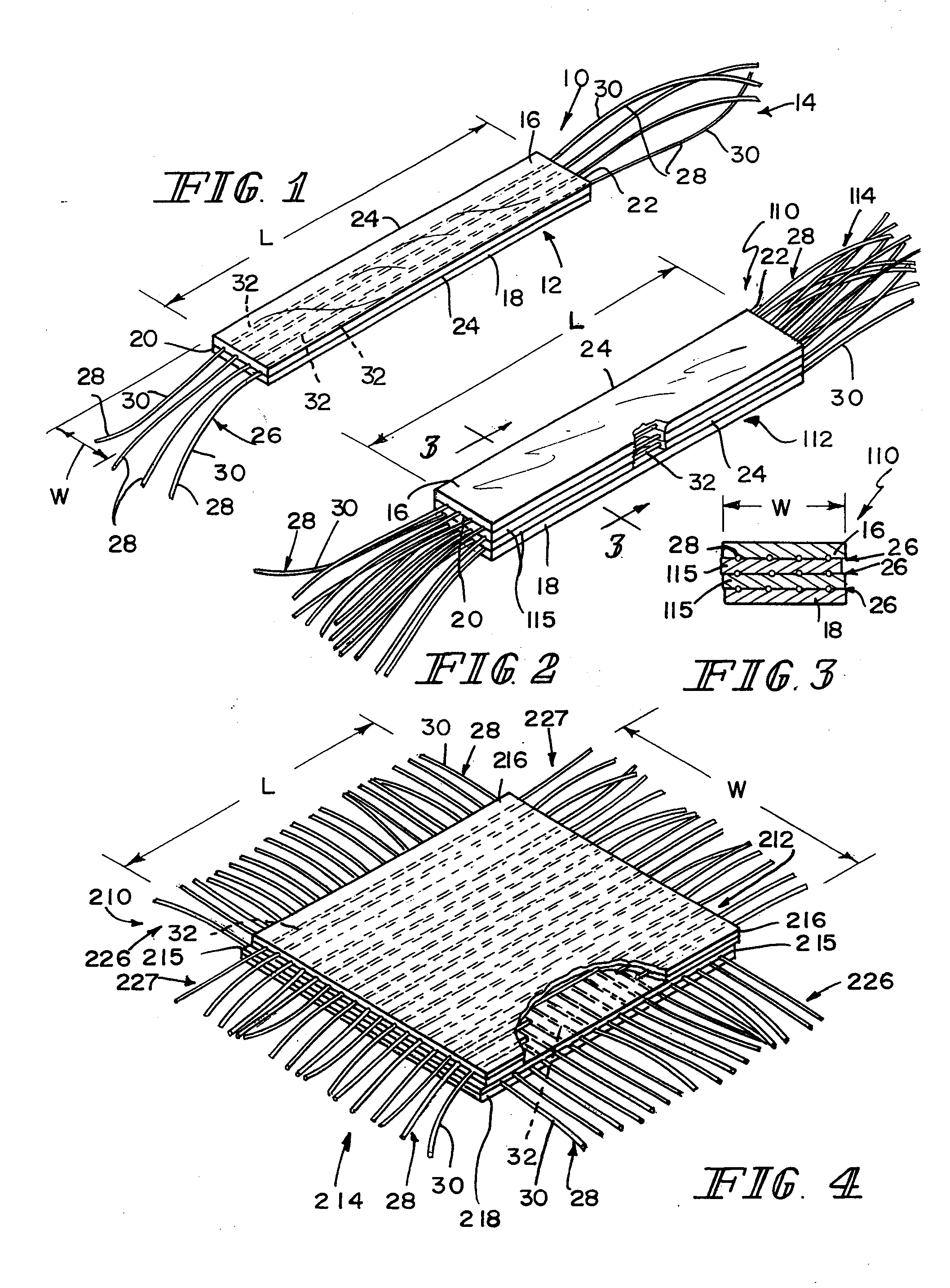
Reinforced small intestinal submucosa
InactiveUS7160333B2Improve mechanical propertiesEnhanced handling propertyBone implantSurgeryCell-Extracellular MatrixSmall intestine
Bioprosthetic devices for soft tissue attachment, reinforcement, or construction are provided. The devices comprise a sheet of naturally occurring extracellular matrix and a sheet of synthetic mesh coupled to the naturally occurring extracellular matrix portion.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Implantable vascular device
Owner:COOK BIOTECH +2
Bodily lumen closure apparatus and method
ActiveUS20050155608A1Improve sealingPrevent leakageStentsFallopian occludersCell-Extracellular MatrixSource material
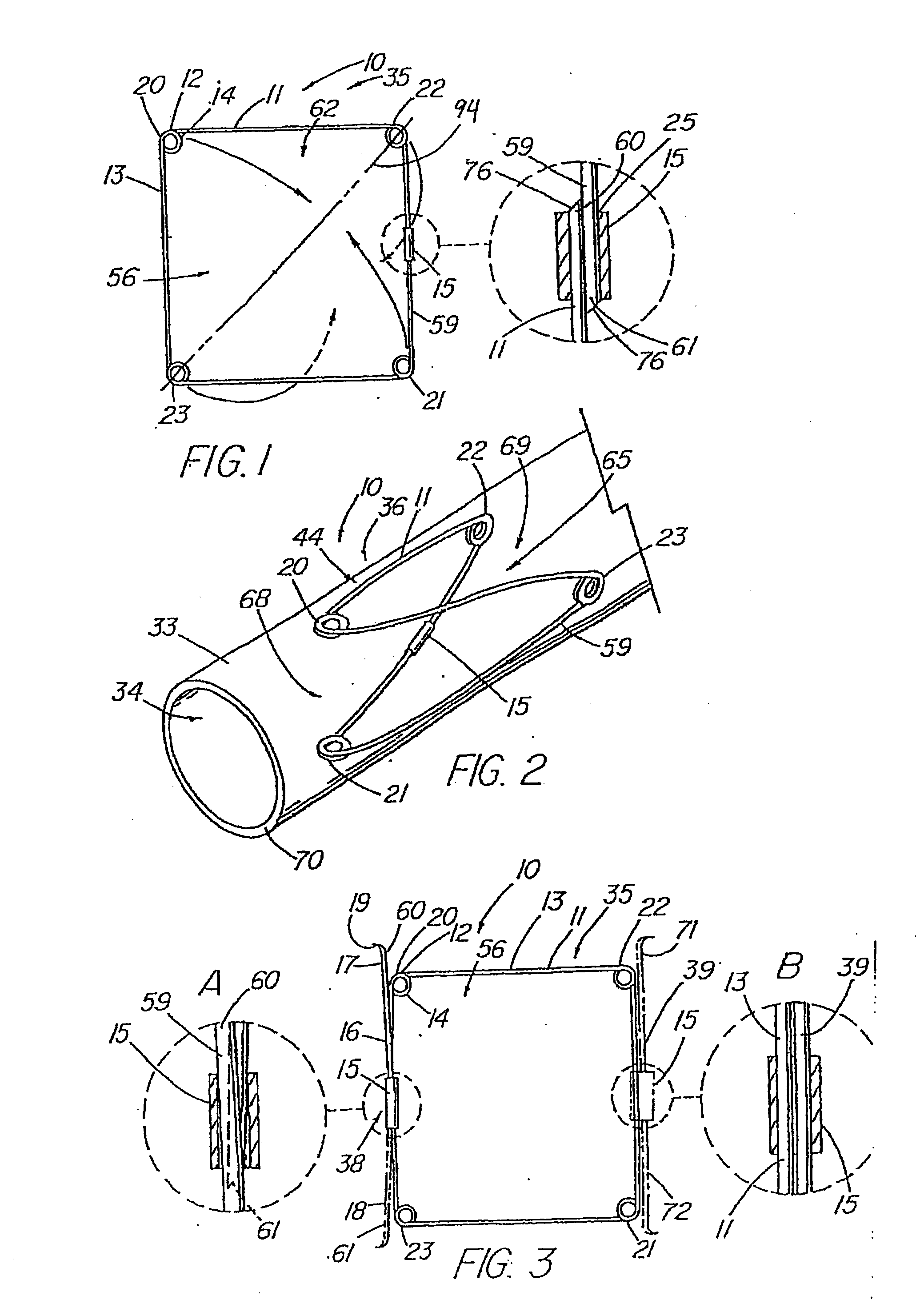
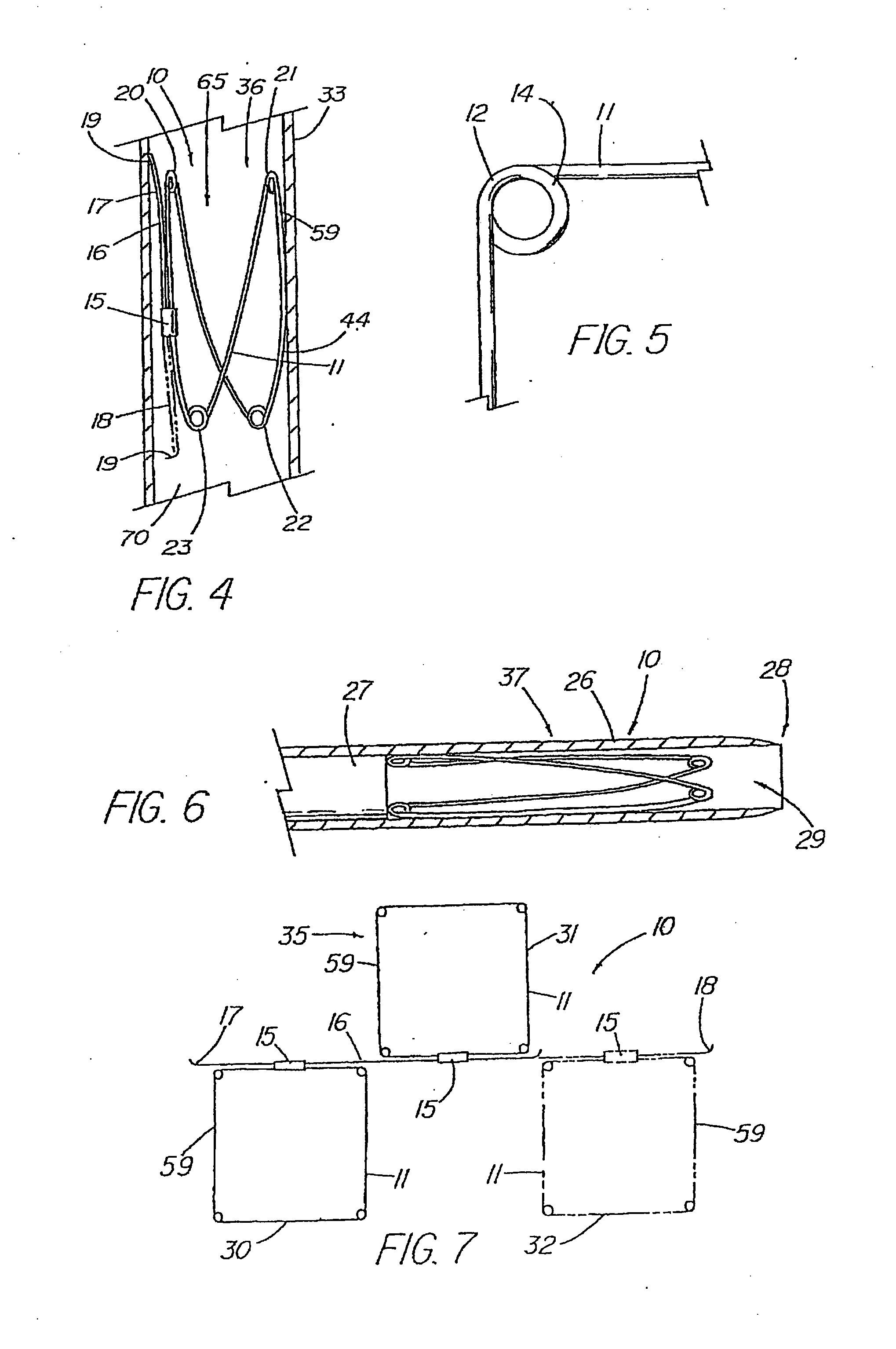
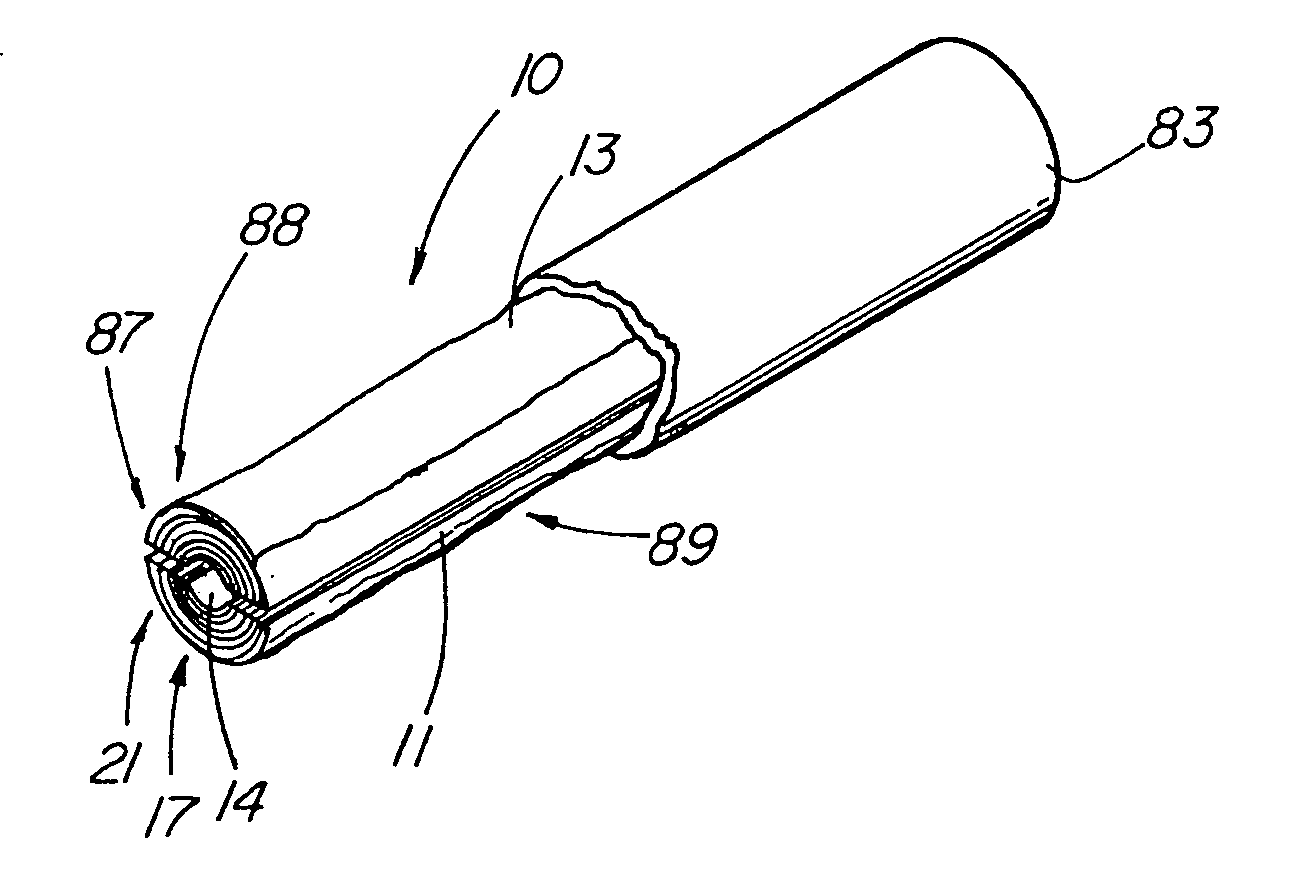
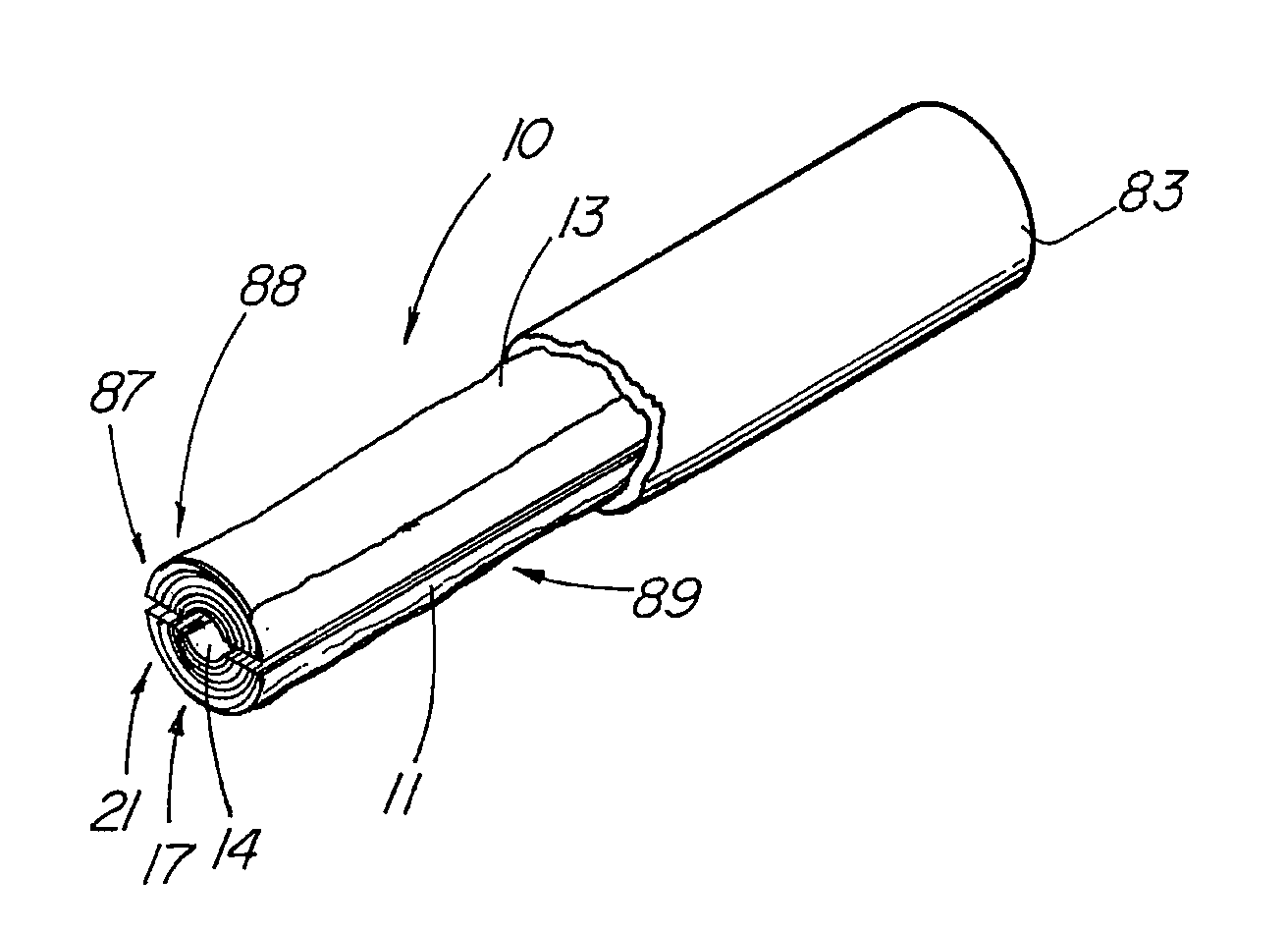
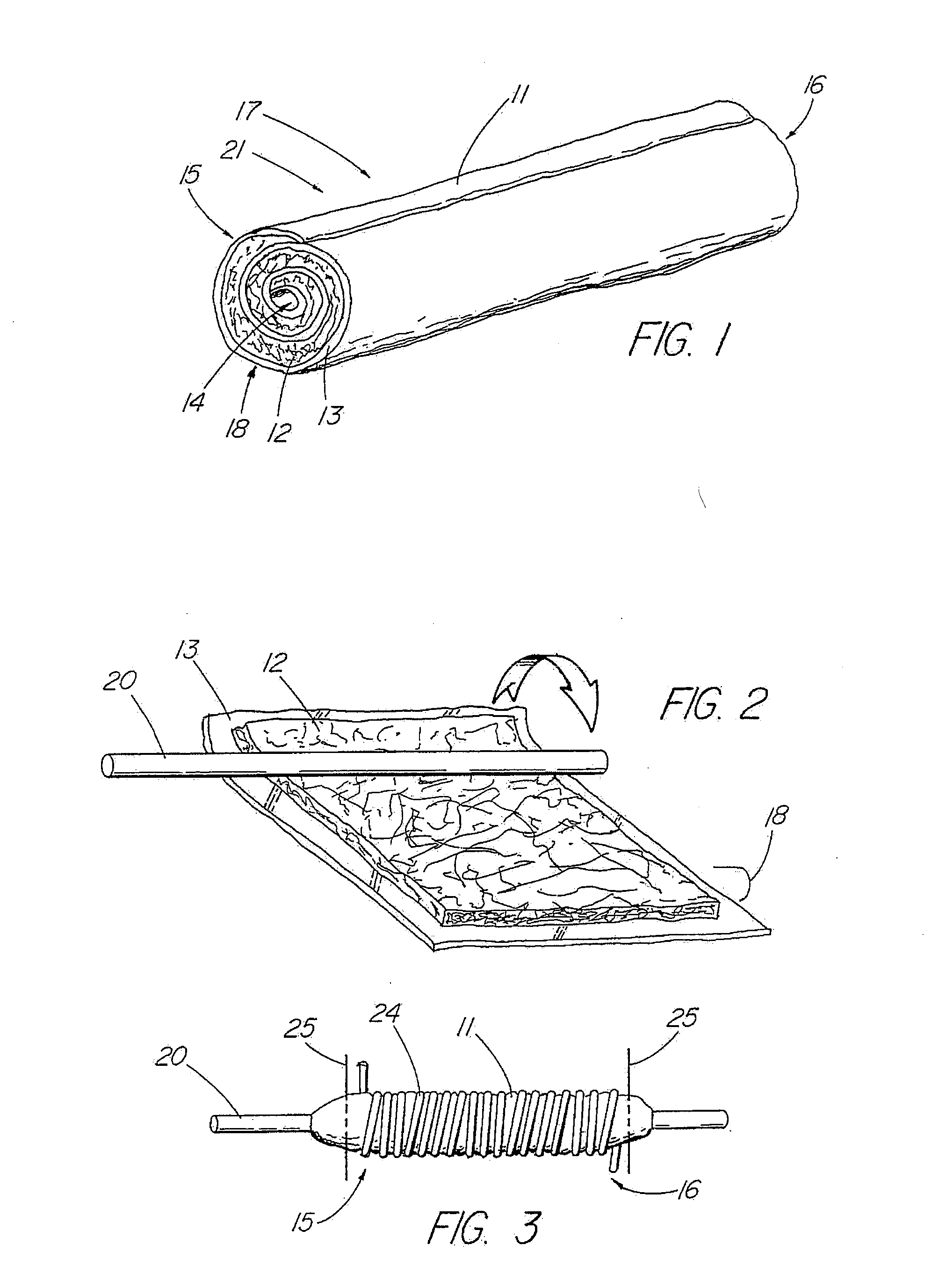
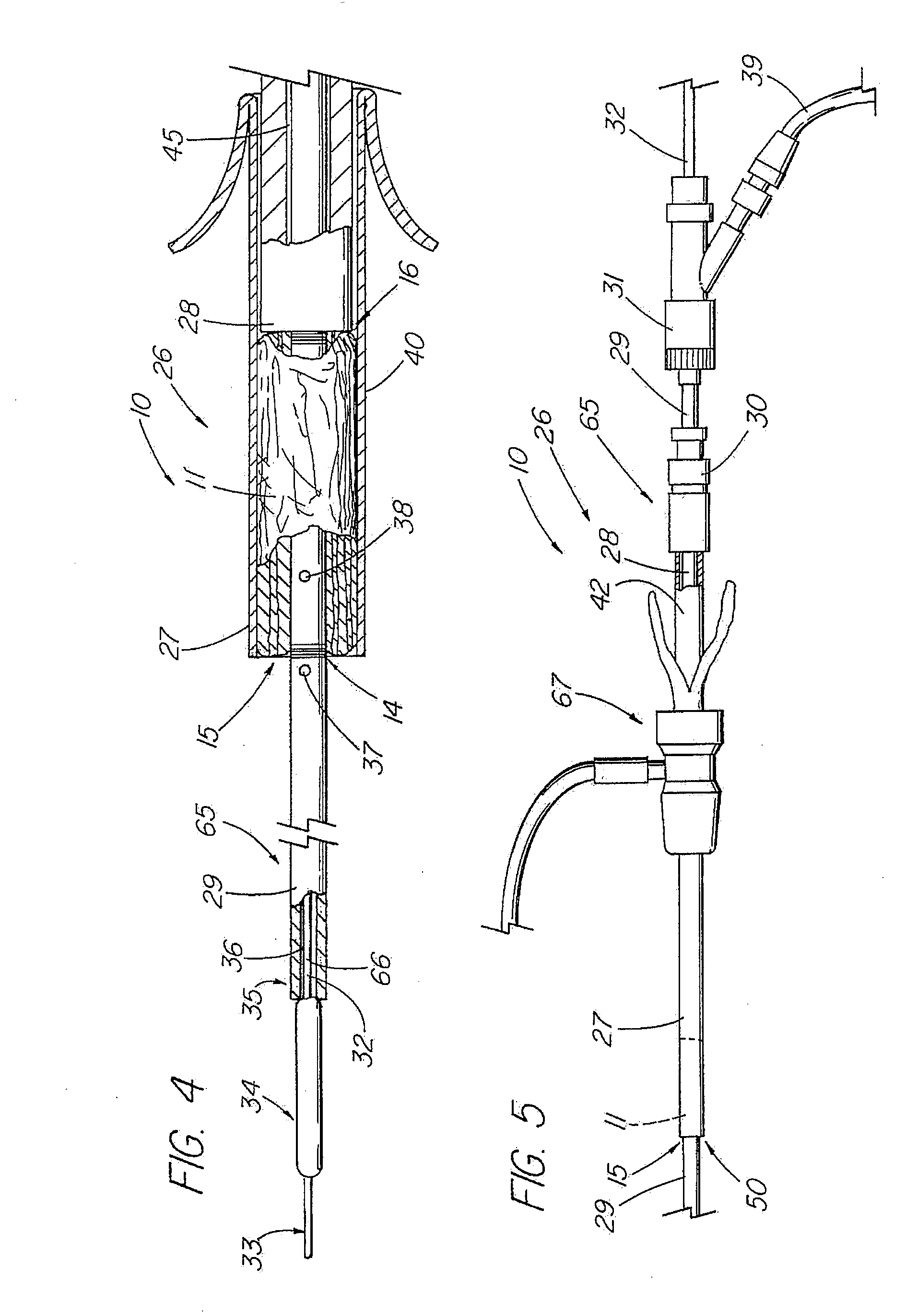
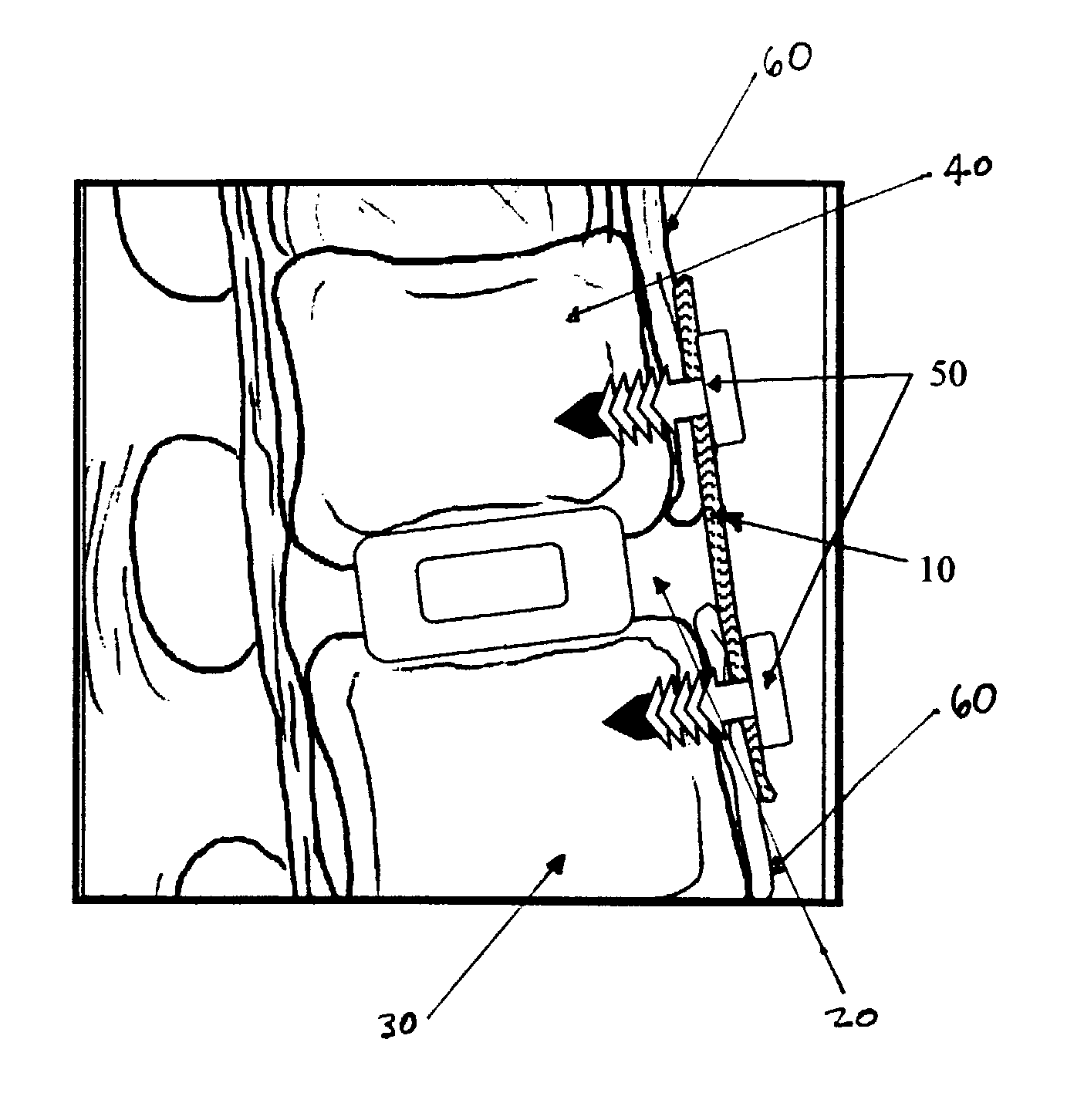
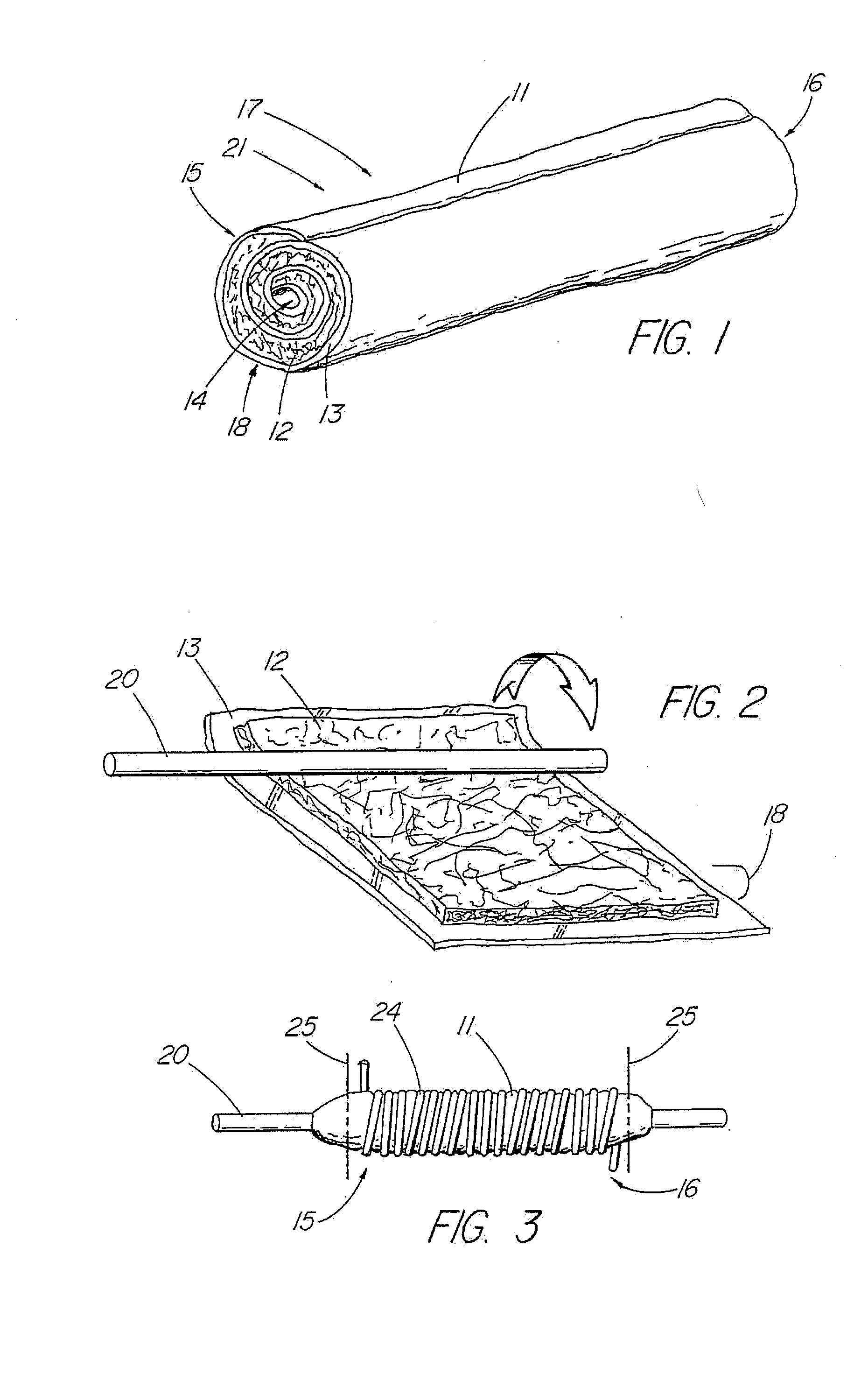
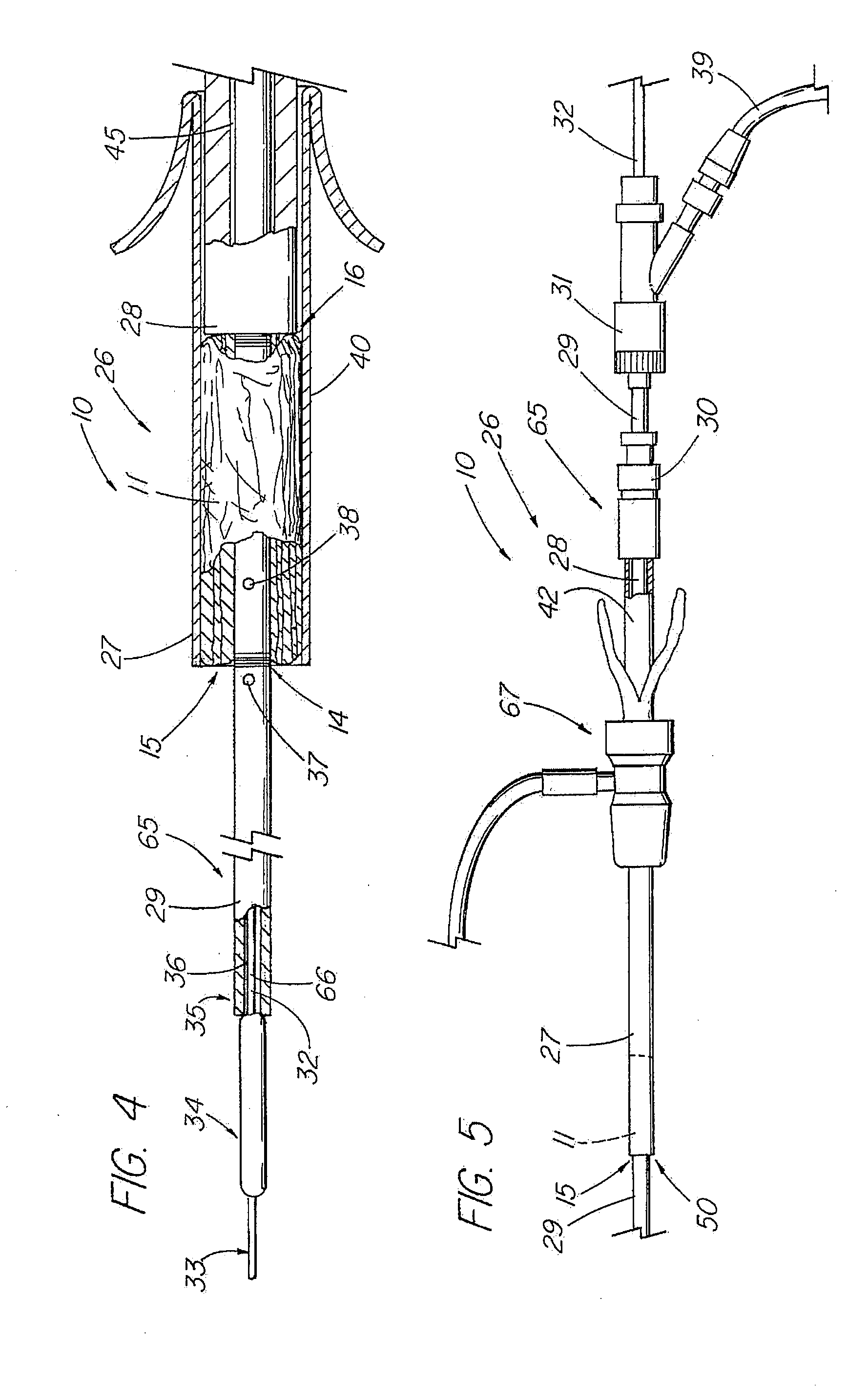
An absorbable and expandable closure member used to occlude or exclude a body lumen or cavity, such as a blood vessel, fallopian tube, duct, aneurysmal sac, etc., comprising a closure member comprising one of more sheets of a biomaterial that are rolled, stacked, or folded to form a multilayer construct of a generally cylindrical configuration for deployment through a delivery system, either as a singularly or part of a multiplicity of closure members. The biomaterial is derived from a source material, such as small intestinal submucosa or another remodelable material (e.g., an extracellular matrix) having properties for stimulating ingrowth of adjacent tissue into the biomaterial deployed within the bodily lumen. The closure member is deployed to the bodily lumen from a delivery sheath, cartridge, and / or over a inner guiding member, such as a wire guide or catheter.
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV +2
Small intestinal submucosa (SIS) soft tissue repair patch and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102462561AImprove surface porosityImprove biological activityProsthesisTissue repairSoft tissue.FNA
The invention relates to a method for preparing a small intestinal submucosa (SIS) soft tissue repair patch, and the soft tissue repair patch prepared by the method. The invention also relates to application of the soft tissue repair path to tissue repair.
Owner:BEIJING MED ZENITH MEDICAL SCI CORP LTD
Preparation method for cellfree intestinum tenue submucosa biological material
ActiveCN101366975ARepair defectRepair membranous defectsProsthesisBiocompatibility TestingIntestinal submucosa
The invention relates to a method for preparing a biomaterial of acellular small intestinal submucosa, which comprises the steps of preposition treatment, acellular treatment, enzyme treatment, preparations of membranous products and particle products. Compared with the prior art, the biomaterial has higher bioactivity and biocompatibility, no obvious immune rejection and no toxic effect on cells; besides, the biomaterial has a certain mechanical strength and toughness, and variable shape, size and thickness, thereby being convenient for clinical suturing and fixing. At the same time, the preparation method has the advantages of unlimited raw material source, cell-free residues, no ethical issues and being capable of effectively inactivating virus. The prepared products are applicable to the biomedical engineering fields, such as repairing defections of body tissue, serving as tissue filling materials, repairing facial depression deformity, serving as tissue reinforcements to replace fascia, repairing membranous defections and malnourished and infected surfaces of wound, serving as materials for biodegradable stents, and serving as injectable filling materials.
Owner:SHAANXI RUISHENG BIOTECH
Bodily lumen closure apparatus and method
InactiveUS20080215087A1Improve sealingPrevent leakageStentsMale contraceptivesCell-Extracellular MatrixSource material
An absorbable and expandable closure member used to occlude or exclude a body lumen or cavity, such as a blood vessel, fallopian tube, duct, aneurysmal sac, etc., comprising a closure member comprising one of more sheets of a biomaterial that are rolled, stacked, or folded to form a multilayer construct of a generally cylindrical configuration for deployment through a delivery system, either as a singularly or part of a multiplicity of closure members. The biomaterial is derived from a source material, such as small intestinal submucosa or another remodelable material (e.g., an extracellular matrix) having properties for stimulating ingrowth of adjacent tissue into the biomaterial deployed within the bodily lumen. The closure member is deployed to the bodily lumen from a delivery sheath, cartridge, and / or over a inner guiding member, such as a wire guide or catheter.
Owner:COOK BIOTECH +1
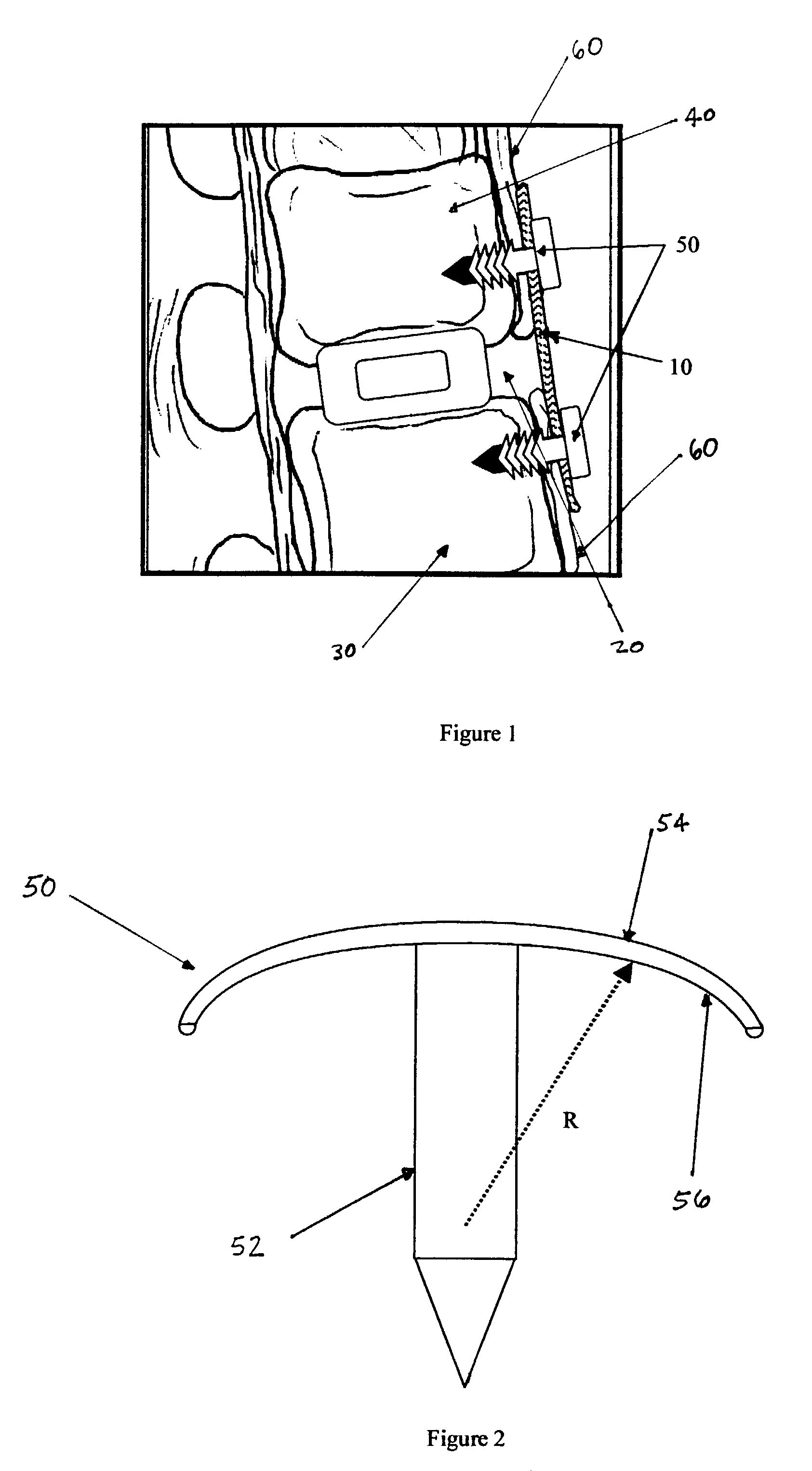
Regenerative implants for stabilizing the spine and devices for attachment of said implants
The invention comprises flat, porous, bioabsorbable implants that are conducive to tissue ingrowth at spinal implantation site, and once absorbed, leave behind a functional ligamentous structure. A preferred material is small intestinal submucosa. Also disclosed are anchoring devices for attaching said implants to the vertebral bodies.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Reinforced small intestinal submucosa
Bioprosthetic devices for soft tissue attachment, reinforcement, or construction are provided. The devices comprise a sheet of naturally occurring extracellular matrix and a sheet of synthetic mesh coupled to the naturally occurring extracellular matrix portion.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Biological tissue matrix material, and preparation method and purpose thereof
ActiveCN107007886AImprove processing efficiencyHigh bonding strengthTissue regenerationProsthesisFiberCell-Extracellular Matrix
The invention provides a biological tissue matrix material, and a preparation method and a purpose thereof. The biological tissue matrix material is characterized by comprising an extracellular matrix, wherein the extracellular matrix comprises collagenous fiber, growth factors and fibronectin. The biological tissue matrix material is prepared from small intestinal submucosa matrix materials. The preparation method is characterized by comprising the following steps that decellularization is performed: decellularized liquid contains trypsin and PBS solution, and also contains EDTA, EDTA-2Na or EDTA-4Na; the decellularized liquid is used for treatment in multi-frequency ultrasonic environment for decellularization; the dual-frequency ultrasound at least contains two ultrasonic frequencies with different frequencies. The decellularization process technology is improved; the DNA residual quantity of the obtained product is lower; the immunogenicity is lower; the anti-infection capability is higher; the restoration capability is higher.
Owner:BEIJING BIOSIS HEALING BIOLOGICAL TECH
Tissue patch and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101366979AImprove biological activityGood biocompatibilityProsthesisCell freeBiocompatibility Testing
The invention provides a tissue patch and a preparation method thereof. The tissue patch uses an acellular small intestinal submucosa as an inner layer, the two sides of the tissue patch are covered with acellular amniotic membranes; the prepared tissue patch isolates from immunotoxicity of the acellular small intestinal submucosa, and the acellular small intestinal submucosa compensates for the deficiencies of a mechanical strength of the acellular amniotic membrane. Compared with the prior art, the tissue patch has higher biological activity and biocompatibility, no obvious immune rejection and no toxic effect on cells; and the preparation method has the advantages of unlimited raw materials source, cell-free residues, no ethical issues and capability of effectively inactivating virus. The prepared product is applicable to serving as a tissue reinforcement to repair a shortcoming or a defect of a strength of a body soft tissue; the prepared product is used as a tissue filling material and is applicable to the repair of facial depression deformity.
Owner:SHAANXI RUISHENG BIOTECH
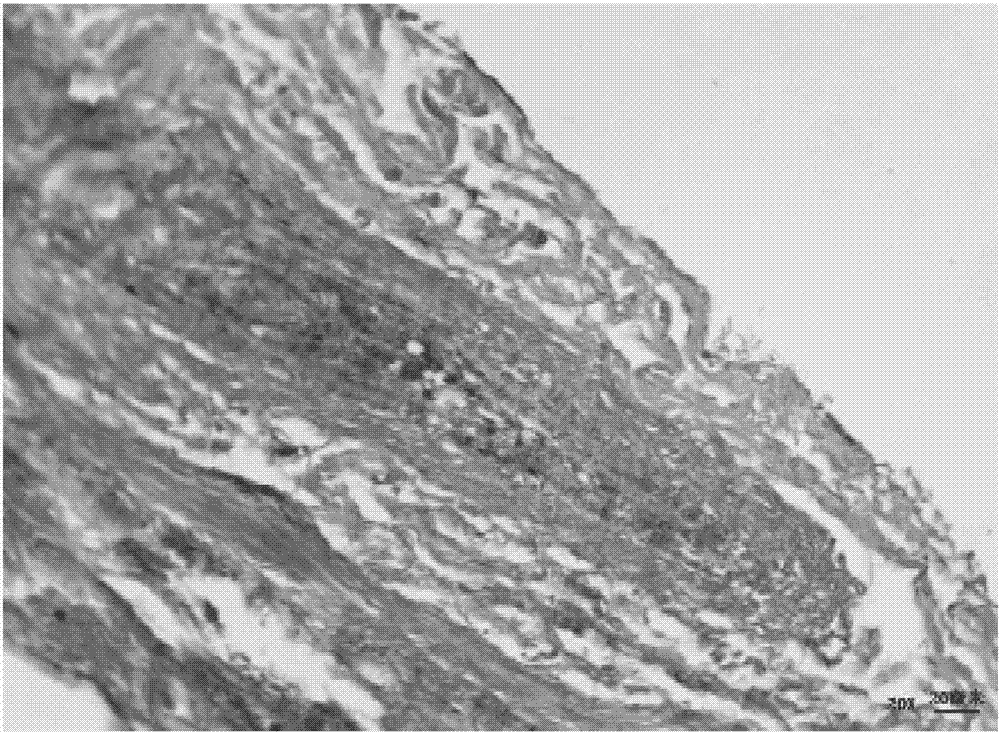
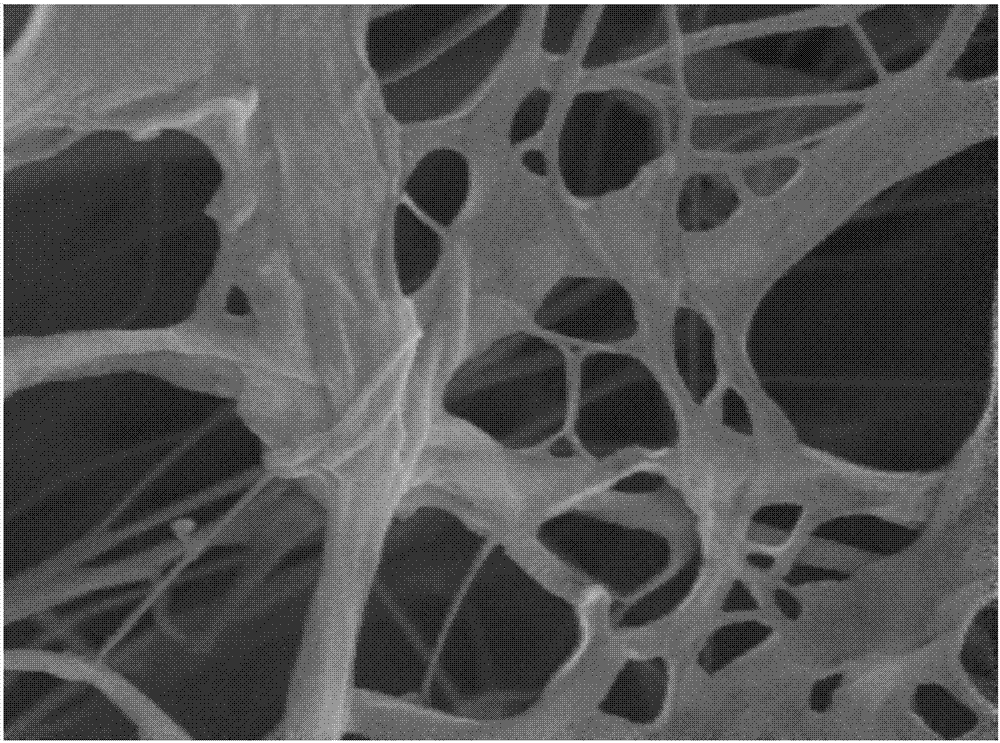
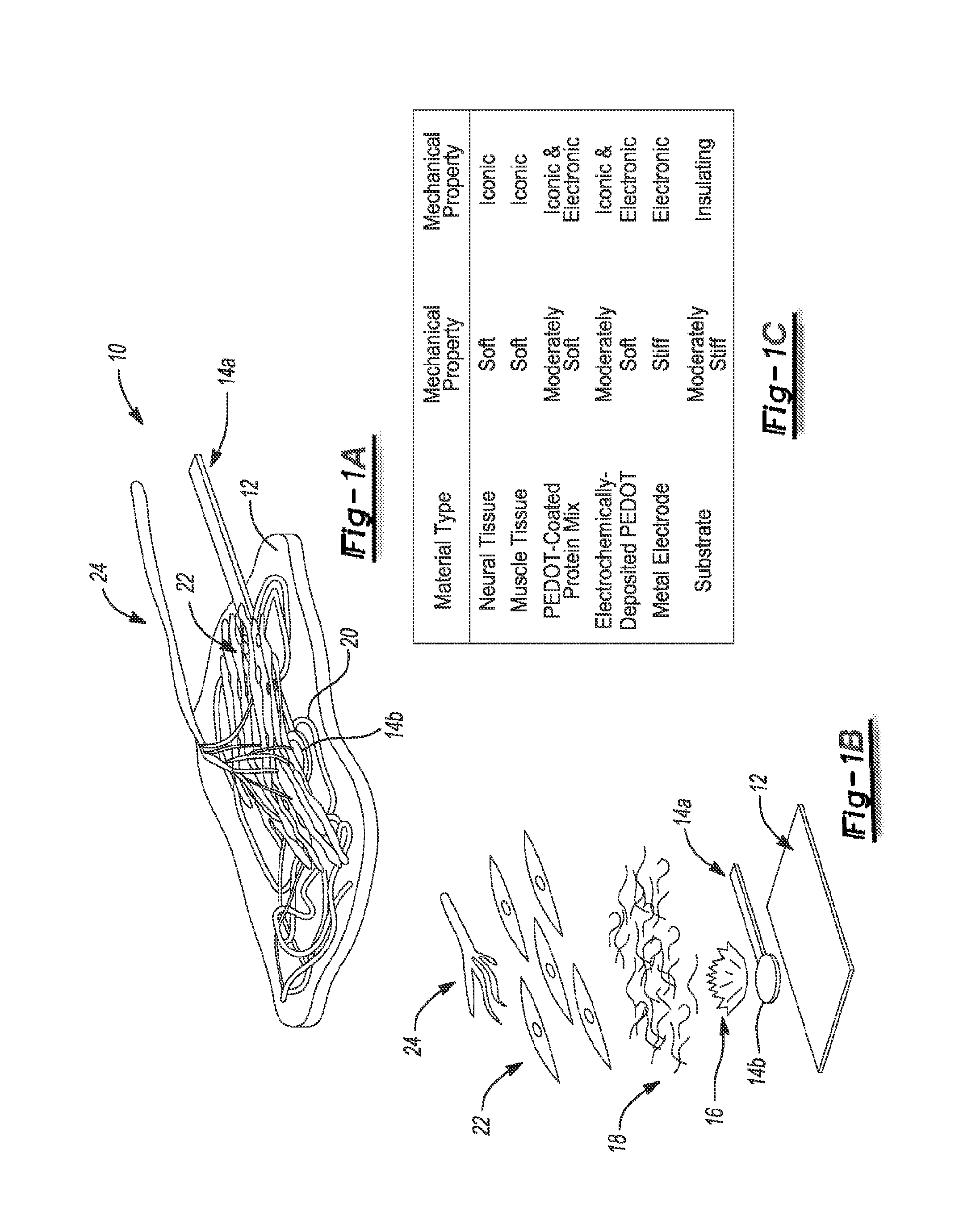
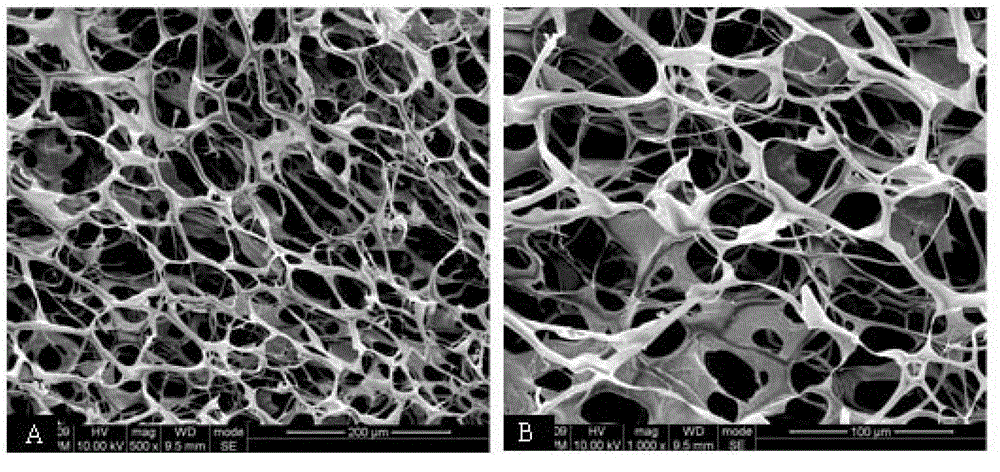
Regenerative peripheral nerve interface
The present disclosure provides a regenerative peripheral nerve interface (RPNI) for a subject comprising an insulating substrate, at least one metallic electrode deposited onto the insulating substrate forming a thin-film array; a portion of the at least one metallic electrode surface having a layer of a first conductive polymer and a layer of decellularized small intestinal submucosa (SIS) coating a portion of the electrode, wherein a second conductive polymer is electrochemically polymerized through the SIS to form the regenerative peripheral nerve interface. The present disclosure also provides that a layer of muscle tissue contacts the regenerative peripheral nerve interface.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN +1
Novel composite biological dura mater
The invention discloses a novel composite biological dura mater. According to the dura mater, a dura mater substitute is prepared by compounding SIS (small intestinal submucosa) and collagen sponge, is relatively close to a natural dura mater, has the characteristics of being degradable, plastic and modifiable and does not need stitching. The product is relatively substantially improved in performances, mechanical strength and safety. An innovative crosslinking manner enables the product degradation time to be consistent with newborn tissue growth time, and the product is better than clinical a same kind of products. The state of the artificial dura mater patch is innovatively designed according to the thickness difference of different parts of human dura mater, and defects of conventional clinical dura mater products are effectively solved.
Owner:王伟
Dura-mater biological patch and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107320777ALow content of related substancesReduce immune rejectionTissue regenerationProsthesisLipid formationCell-Extracellular Matrix
The invention discloses a dura-mater biological patch and a preparation method thereof. The dura-mater biological patch adopts a process of using small intestinal submucosa tissues as materials and systemically removing immunogenic substances. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: using alcohol to treat and remove lipids, using trypsin and alkali solution to treat and remove cells, using DNA enzyme to treat and remove DNA, and using alpha-galactosidase to treat and remove alpha-Gal antigens and the like. The dura-mater biological patch and the preparation method disclosed by the invention have the advantages that not only can the immunogenic substances be effectively removed, but also the normal structure of extracellular matrix can not be damaged; and when the dura-mater biological patch is clinically applied in repairing dura-mater defects, the leakage of cerebrospinal fluid can be effectively prevented, the tissue can be guided for ingrowth, the tissue growing speed is matched with the patch decomposing speed, the immunological rejection is low and the biocompatibility is good.
Owner:上海白衣缘生物工程有限公司
Tissue repair material, preparation method thereof and application
ActiveCN102743791AProlong the action timeIncrease proliferative activityProsthesisTissue repairMedicine
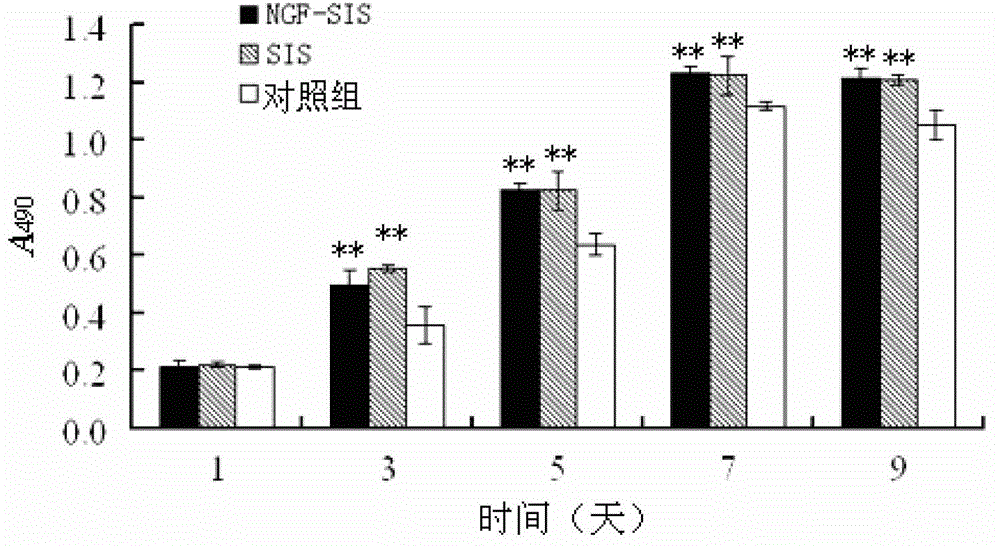
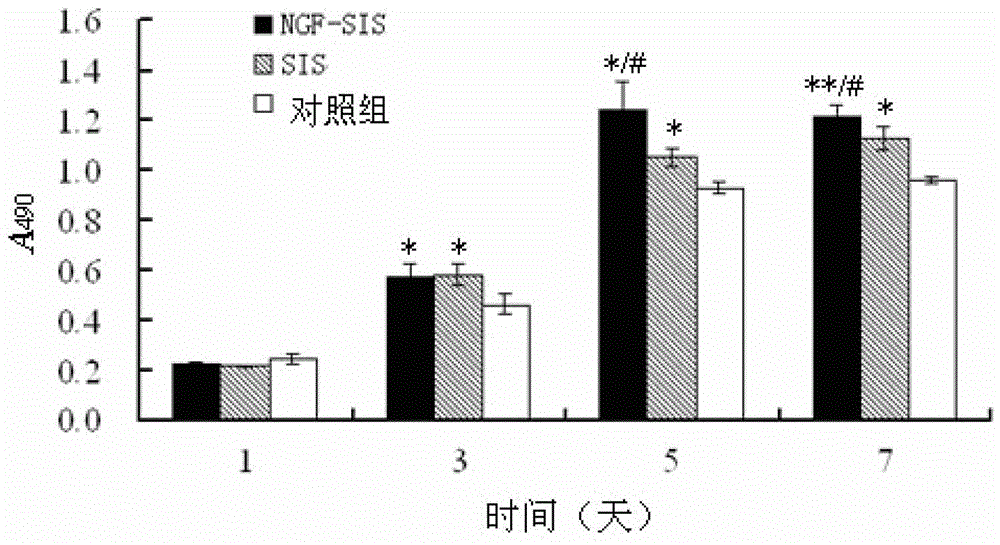
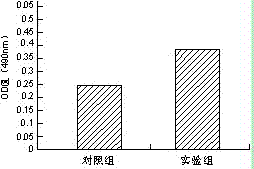
The invention discloses a tissue repair material which comprises an SIS (small intestinal submucosa) and an NGF (nerve growth factor). When the NGF is individually used or simply mixed with the SIS in use, the NGF is rapidly inactivated and is unfavorable for wound repair. However, after the composite material is prepared with the NGF and the SIS according to the specific method, the action time of the NGF can be effectively prolonged, the cell proliferation activity of the NGF-SIS composite material is remarkably enhanced as compared with that of the individually used SIS, and the NGF-SIS composite material plays a role in synergy.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
Preparation method for biomimetic matrix type biological wound healing material
ActiveCN102526803AReduce functionReduce the situationProsthesisCell-Extracellular MatrixPlatelets blood
The invention provides a preparation method for a novel biomimetic matrix type biological wound healing material. According to the method, small intestinal submucosa with a three-dimensional scaffold structure is compounded with platelet-rich blood plasma containing a specific proportion of bioactive factors, and a specific process is adopted to carry out modification to form the novel material containing biological induction factors, wherein the novel material has a three-dimensional biomimetic structure. With the biomimetic matrix type biological wound healing material prepared by the method of the present invention, the healing can be promoted, the physiological repair can be promoted, the pathological repair can be inhibited, and the regeneration repair efficiency and the repair quality of the damaged tissue can be improved. The novel biological wound healing material of the present invention can be used for repairs of various human soft tissues, membranous tissues or cavity walls, and for cavity filling, and can be used as the ideal extracellular matrix biomimetic material and the cell scaffold material for wound repairs of the tissues and the organs, promotion of wound healing, prevention of adhesion and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI SIXTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Composite biological patch based on pig small intestinal submucosa and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN107233630AEffective repair effectGood biocompatibilityProsthesisBiotechnologySmall intestine
The invention discloses a composite biological patch based on pig small intestinal submucosa and a preparation method and application thereof. The composite biological patch is characterized in that the accellular pig small intestinal submucosa is compounded with an additive so as to obtain the composite biological patch based on the pig small intestinal submucos; the additive is selected from one or two of growth factors and medicines. The composite biological patch based on the pig small intestinal submucos has the advantages that the composite biological patch is a good biological stent material, the structure component and the space three-dimensional structure are very similar, the good biological compatibility is presented in the clinical experiment, the healing of wounds is promoted, and various tissues are regenerated and remolded; the biological stent material has effective restoration effect on the healing of skin wounds, and has important meaning on the regeneration of the skins.
Owner:苏州期佰生物技术有限公司
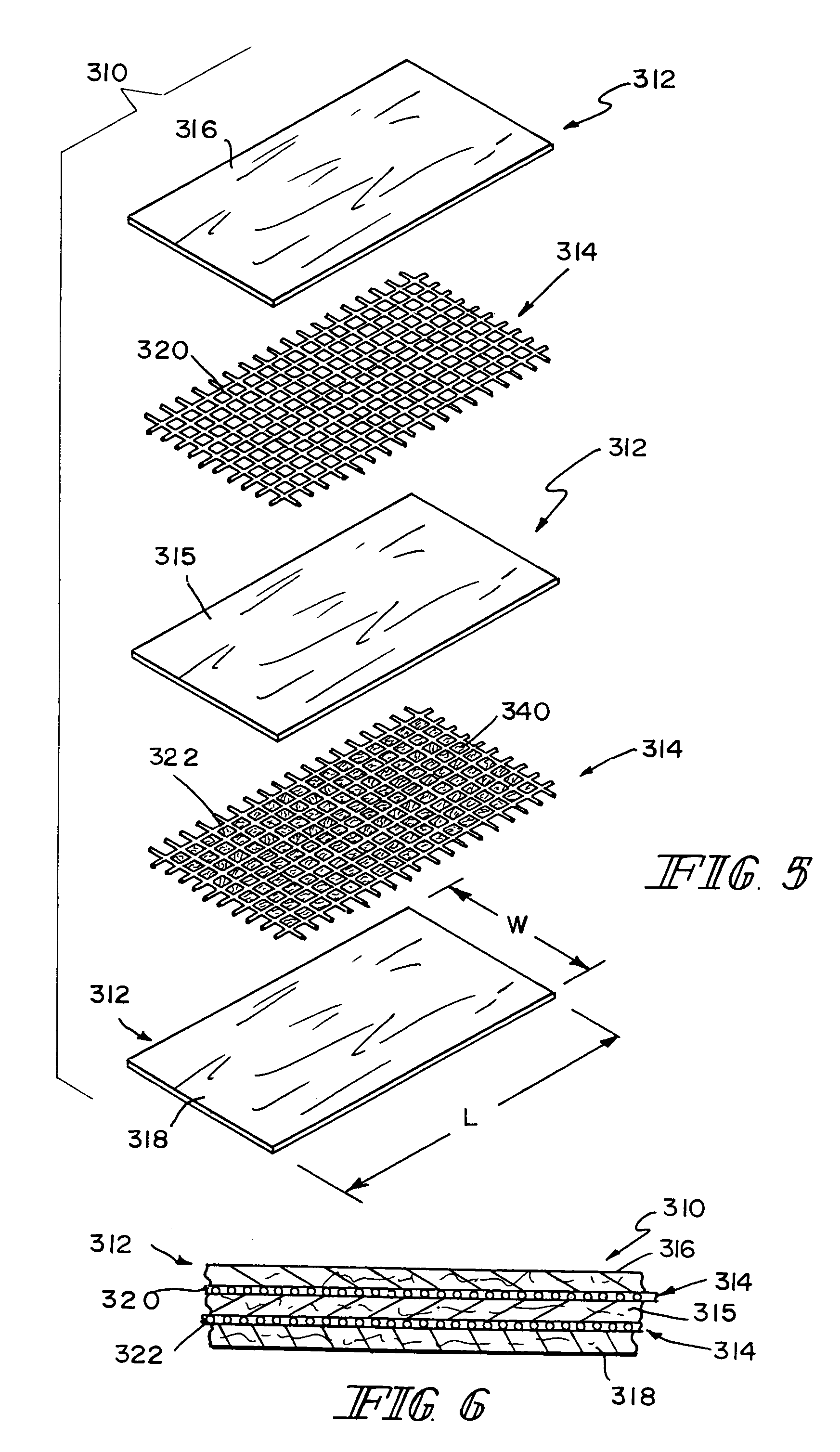
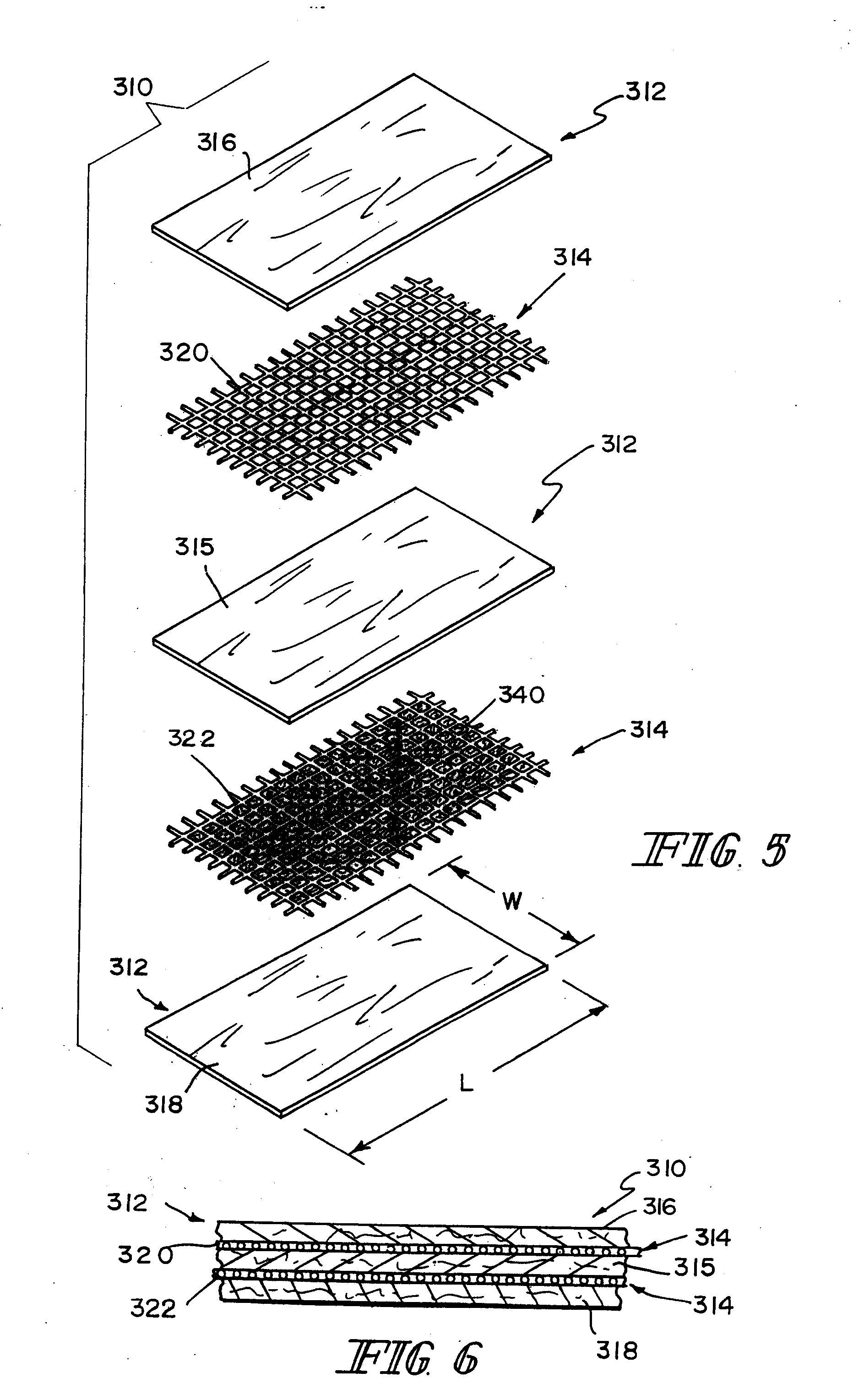
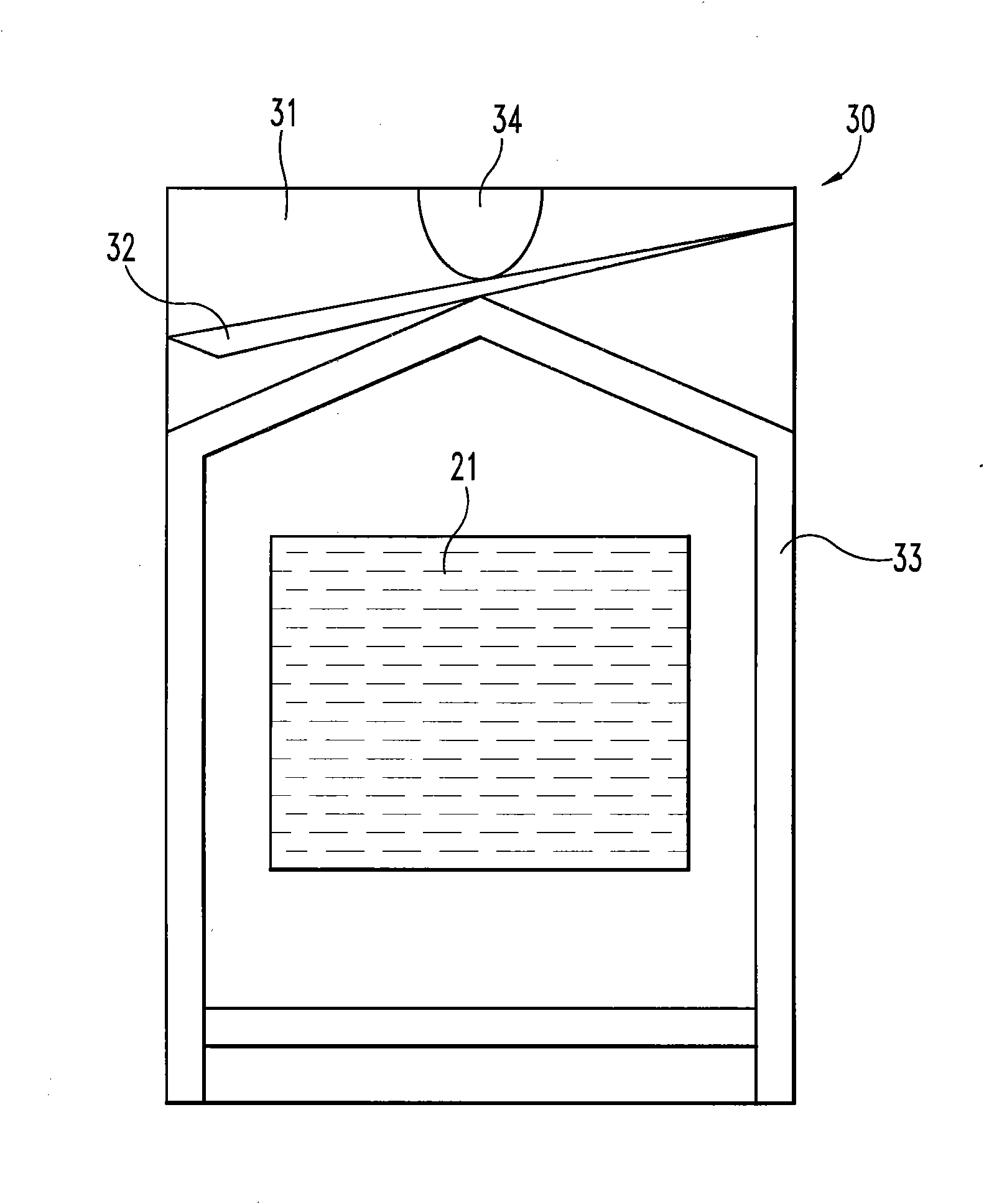
Graft materials and methods for staged delivery of bioactive components
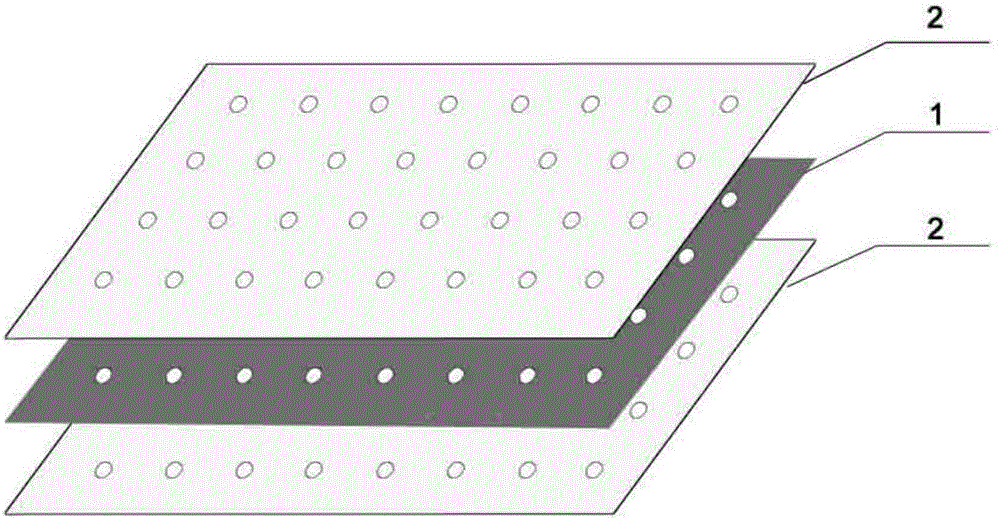
Described, in certain aspects of the invention, are multilaminate medical graft products, as well as methods for preparing and using the same. An illustrative multilaminate medical graft product of the invention comprises a first layer of remodelable extracellular matrix (ECM) material bonded to a second layer of remodelable ECM material, wherein the first material layer is enriched with a growth factor relative to the second material layer. Such a remodelable ECM material may be comprised of submucosa from a warm-blooded vertebrate, for example, porcine small intestinal submucosa (SIS).
Owner:COOK BIOTECH
Composite extracellular matrix ingredient biological material
ActiveCN105920669ALight adhesionImprove adhesionTissue regenerationProsthesisCell-Extracellular MatrixAdditive ingredient
Owner:SHANGHAI EXCELLENCE MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Bodily Lumen Closure Apparatus and Method
InactiveUS20140148839A1Avoid blood leakagePrevent leakageStentsFallopian occludersSource materialSmall intestine
An absorbable and expandable closure member used to occlude or exclude a body lumen or cavity, such as a blood vessel, fallopian tube, duct, aneurysmal sac, etc., comprising a closure member comprising one of more sheets of a biomaterial that are rolled, stacked, or folded to form a multilayer construct of a generally cylindrical configuration for deployment through a delivery system, either as a singularly or part of a multiplicity of closure members. The biomaterial is derived from a source material, such as small intestinal submucosa or another remodelable material (e.g., an extracellular matrix) having properties for stimulating ingrowth of adjacent tissue into the biomaterial deployed within the bodily lumen. The closure member is deployed to the bodily lumen from a delivery sheath, cartridge, and / or over a inner guiding member, such as a wire guide or catheter.
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV
Dura mater biopatch and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108478870ALow content of related substancesReduce immune rejectionTissue regenerationProsthesisAntigenCell-Extracellular Matrix
Owner:上海白衣缘生物工程有限公司
Tissue graft compositions and methods for producing same
A tissue graft composition is described herein that includes a segment of small intestinal submucosa having at least one nanoparticle incorporated therein such that the permeability of the segment of small intestinal submucosa is altered, thereby providing the segment of small intestinal submucosa with a more substantially uniform structure for cell migration and proliferation. The tissue graft composition may further comprise at least one macromolecule incorporated into the nanoparticle. The tissue graft composition may be utilized in seeded or unseeded methods of tissue repair.
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA
Neural restoration promoting material as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102861360AImprove efficacyGood effectPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderMedicineSmall intestinal submucosa
The invention discloses a material for promoting neural restoration. The material comprises a small intestinal submucosa and a nerve growth factor of which the content is 1 to 500pg / cm<2>. The invention also discloses a preparation method and application of the neural restoration promoting material. According to the material for promoting neural restoration, the nerve growth factor can be slowly released at (42.01+ / -1.43)-(82.43+ / -1.89)pg / cm<2> each day, so that the shortcoming caused by directly adding the growth factor can be overcome; and the preparation method is simple, the cost is low, and the material has good application prospect.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
Small intestinal submucosa-based vascularization promoting thermosensitive material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104189009AGood injectabilityPromotes vascularizationAerosol deliveryOintment deliveryCross-linkFreeze-drying
The invention provides a small intestinal submucosa-based vascularization promoting thermosensitive material. The small intestinal submucosa-based vascularization promoting thermosensitive material is prepared by packaging a small intestinal submucosa matrix and a dissolving solution, respectively, wherein the small intestinal submucosa matrix is obtained through the following steps: performing enzymatic hydrolysis, acid dissolution and freeze-drying on the small intestinal submucosa, and then crushing and sterilizing the small intestinal submucosa to obtain a sterile powdery or flocculent small intestinal submucosa matrix material; the dissolving solution consists of phosphate buffer containing NaOH or normal saline. According to the invention, the two matrixes of the small intestinal submucosa-based vascularization promoting thermosensitive material both can be preserved for a long time and are mixed in an appropriate ratio before in use; the thermosensitive material has excellent injectability and is capable of forming a stable gel at 37 DEG C without cross-linking polymerization; the thermosensitive material is proven to have the effect of promoting vascularization by both experiments in vitro and vivo.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
Biological anti-adhesion material, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106983918AGood biocompatibilityGood tissue adhesionSurgeryTissue regenerationTissue materialWound surface
The invention provides a biological anti-adhesion material, a preparation method and application thereof. The biological anti-adhesion material is characterized in that the biological anti-adhesion material is prepared by using a small intestinal submucosa tissue material of an animal as a raw material, eliminating immunogenicity and retaining complete extracellular matrix ingredients and comprises a first surface, a second surface and a degradable absorbing structure positioned therebetween, the first surface is a smooth surface, the second surface is a coarse surface, and the degradable absorbing structure is in gradually-varied connection. The coarse surface of the biological anti-adhesion material is conducive to guiding growth of wound surface tissue cells so as to repair the wound surface; the smooth surface is conducive to stopping the cells to be adhered to other tissue so as to effectively prevent adhesion. The biological anti-adhesion material can be used for anti-adhesion treatment of the wound surface in enterocoelia, thorax or pelvic cavity.
Owner:BEIJING BIOSIS HEALING BIOLOGICAL TECH
Temperature-sensitive composite as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103599567APreserved ultrastructureGood restorativeProsthesisDisodium glycerophosphateBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a temperature-sensitive composite matrix compound which comprises the following components in parts by weight: 80-200 parts of chlorinated chitosan, 200-260 parts of beta-disodium glycerophosphate, 37.5-87.5 parts of hydroxyethyl cellulose and 125-375 parts of small intestinal submucosa micropowder. The invention further discloses a temperature-sensitive composite material as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The temperature-sensitive composite has a favorable temperature-sensitive property and intrinsic bioactivity, can sustainably release a plurality of growth factors and has favorable biocompatibility and a good clinical application prospect.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
Anal fistula plug which is insusceptible to dropping
The invention relates to an anal fistula plug which is insusceptible to dropping. The anal fistula plug comprises a circular table body implanting section, wherein the large end face of the implanting section is connected with one end of a plug body section; the other end of the plug body section is connected with a bottom surface of a cylindrical stitching area; the plug body section is formed by connecting more than two oblate spheroids; and the stitching area and the plug body section are made of a small intestinal submucosa or an allogenic biological material. According to the anal fistula plug, a plug body consists of a plurality of oblate spheroids, and the axial self-balancing of uniformly-distributed acting force to which the single oblate spheroid is subjected can be realized, so axial force generated by deformation stretching is generated on the integral plug body section only, and is balanced with 'rectal resting pressure' which acts on the large-end face side of the implanting section to avoid operation failure caused by the dropping of the implanting section. Numerical simulation indicates that the axial component force of the anal fistula plug under weight pressure can be reduced greatly, so that the anal fistula plug is prevented from dropping.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Gel biological material having shape memory function and preparation method of gel biological material
InactiveCN105126171AImprove adhesionPromote growthProsthesisCell-Extracellular MatrixAdditive ingredient
The invention provides a gel biological material, wherein the gel biological material is prepared from a small intestinal submucosa extracellular matrix; the gel biological material is characterized in that the gel biological material is of a porous structure that pores are mutually communicated; and the gel biological material can recover to original form when the volume is compressed by more than 85%. The major ingredient of the gel biological material disclosed by the invention is close to a natural extracellular matrix ingredient in structure; the gel biological material has an elastic deformation capacity and a shape memory function, and has a good mechanical performance; and meanwhile, the gel biological material is relatively good in biocompatibility and is suitable to be used as a tissue regenerating repair material in clinical field.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Method for establishing three-dimensional tissue in vitro
The invention provides a method for establishing a three-dimensional tissue in vitro. The method comprises the steps of separately culturing epithelial cells and muscle cells; implanting a small intestinal submucosa acellular matrix stent into a muscle cell suspension; continuing to culture after finishing oscillating and compounding operations; and dropwise adding an epithelial cell suspension on a muscle cell layer of the stent treated in the step 2, and continuing to culture to obtain the three-dimensional tissue. According to the method, the epithelial cells and the muscle cells of tongue mucosa are used as seed cells, so that materials are conveniently obtained, the cells can be increased to the relatively high quantity within relatively short time, and therefore, the application requirement is met; the muscle cells are compounded with the small intestinal submucosa acellular matrix stent by using an oscillating method, so that a plurality of muscle cells can be soaked into the stent and can be relatively uniformly distributed; meanwhile, the stent can be loosened as much as possible on the premise that the stent is not obviously damaged, so that nutrient permeation and neovascularization can be favorably realized; and the three-dimensional tissue which can be used for tissue engineering urethra can be established.
Owner:SHANGHAI SIXTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Development of a tissue - engineered scaffold for nerve regeneration using a biocompatible and injectable hydrogel
The present invention relates to a tissue-engineered scaffold prepared by using a biocompatible and injectable hydrogel, and particularly to a tissue-engineered scaffold capable of regenerating or recovering an injured spinal nerve for central nervous system after being implanted to connect neurons, prepared by combining an adult stem cell or a nerve cell with a physiologically active material on tissue-engineered carriers comprising biocompatible and temperature-sensitive polyethylene glycol / polyester block copolymer or biocompatible and injectable hydrogel made of small intestinal submucosa tissue powder with sol-gel phase transition behavior.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF CHEM TECH
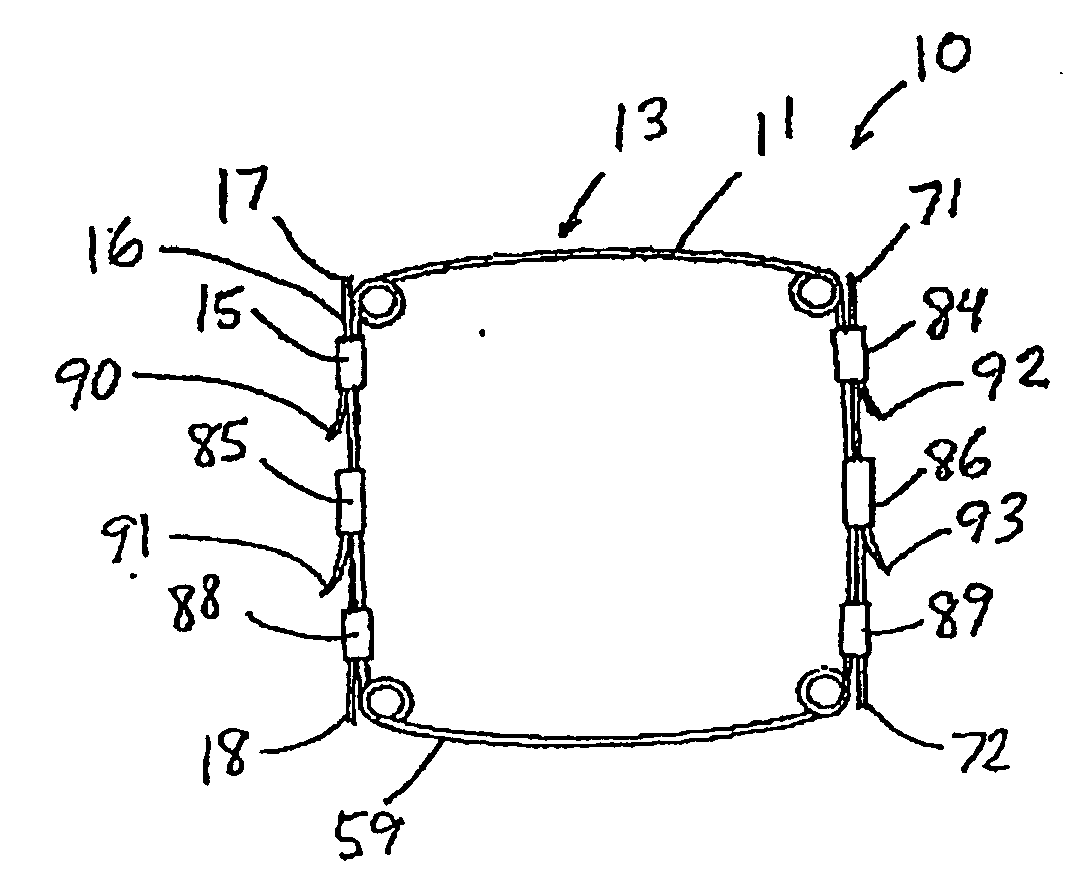
Vitro engineered, regenerated urinary tract tissue compositions and methods for producing same
A method for providing a urinary tract tissue graft composition includes providing a tissue culture frame and a segment of small intestinal submucosa and positioning the segment of small intestinal submucosa in the tissue culture frame such that the segment of small intestinal submucosa is suspended and held in a taut position by the tissue culture frame. Smooth muscle and urothelial cells are isolated from a tissue specimen of a subject and cultured, and then seeded upon the segment of small intestinal submucosa, thereby forming a urinary tract tissue graft. A tissue culture frame in which such a urinary tract tissue graft may be formed is also disclosed.
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com