Composite extracellular matrix ingredient biological material
A biomaterial and extracellular matrix technology, applied in the field of composite extracellular matrix component biomaterials, can solve the problems of insufficient mechanical strength, unstable repair area, difficulty in making products, etc., to promote adhesion and migration, low immunogenicity, Effect of reducing apoptosis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
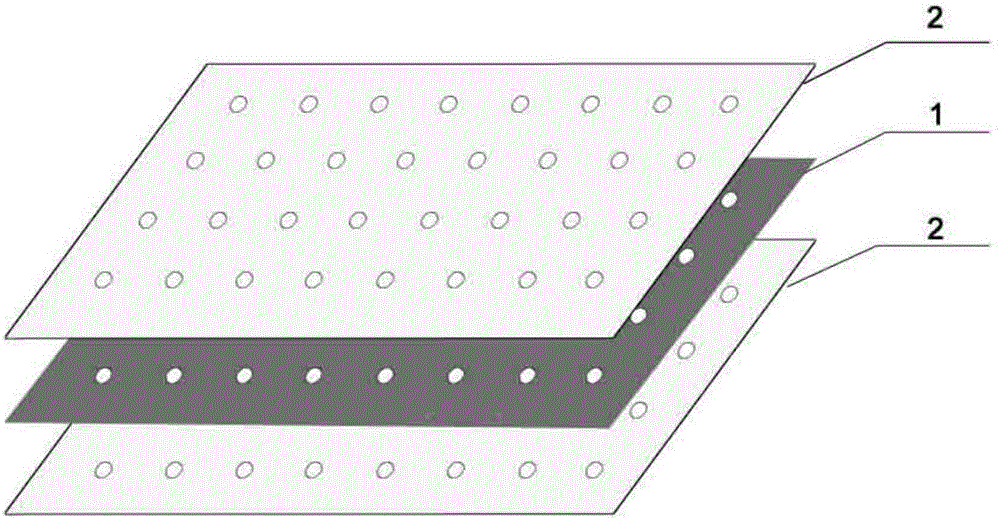
[0031] Porcine acellular bladder mucosal basement membrane (UBM) and acellular small intestinal submucosa (SIS) were prepared by Abraham's method. A layer of UBM is paved (smooth side down), and the single film-like SIS is spliced into independent sheets according to the interlayer misalignment of 50%, and it is tiled on the surface of the UBM, and the interlayer misalignment is 90°, and 4 layers are laid. A layer of UBM (smooth side up) is laid on it. Remove air bubbles, use medical chitosan adhesive to bond between layers, and then press them into one body with a pressure of -250mm Hg after 24 hours. The whole layer of the material is perforated, the hole spacing is 5mm, and the diameter is 1mm.
Embodiment 2
[0033] Porcine acellular bladder mucosal basement membrane (UBM) and acellular small intestinal submucosa (SIS) were prepared by Abraham's method. The two layers of UBM are paved (smooth side down), and the single film-like SIS is spliced into independent sheets according to the 50% misalignment between the layers, and spread on the surface of the UBM, and 6 layers are laid with a 90° misalignment between the layers. Lay two layers of UBM (smooth side up) on it. Remove the air bubbles, use medical collagen adhesive to bond the layers, and then press them into one body with a pressure of -300mm Hg after 36 hours. The whole layer of the material is perforated, the hole spacing is 8mm, and the diameter is 2mm.
Embodiment 3
[0035] According to GB / T528-2009, take 3 samples and make them into a 4cm×1cm dumbbell shape. After hydration, use a material mechanics testing machine to fix the two ends of the sample and stretch it at a speed of 10mm / min. The tensile strength of the material is measured to be 34±3N / cm.
[0036] Take 3 samples and make them 2cm×5cm, fix the two ends on the upper and lower holders of the tensile machine, and peel them off continuously at a stable speed of 10mm / min until the overlapping parts of the samples are delaminated. Measure the load force when delaminated. The peeling strength between SIS-SIS and UBM-SIS was 6±2N / cm, and the peeling strength was 1.5±0.5N / cm.
[0037] Evaluate the cytotoxicity of the material according to the method specified in GB / T 16886.5. NIH3T3 and L929 were used as model cells. The cells were cultured with the cell culture medium as the leaching medium, and the leaching liquid of gradient concentration was used to replace the culture medium, a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| peel strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com