Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
204 results about "Human hepatocyte" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
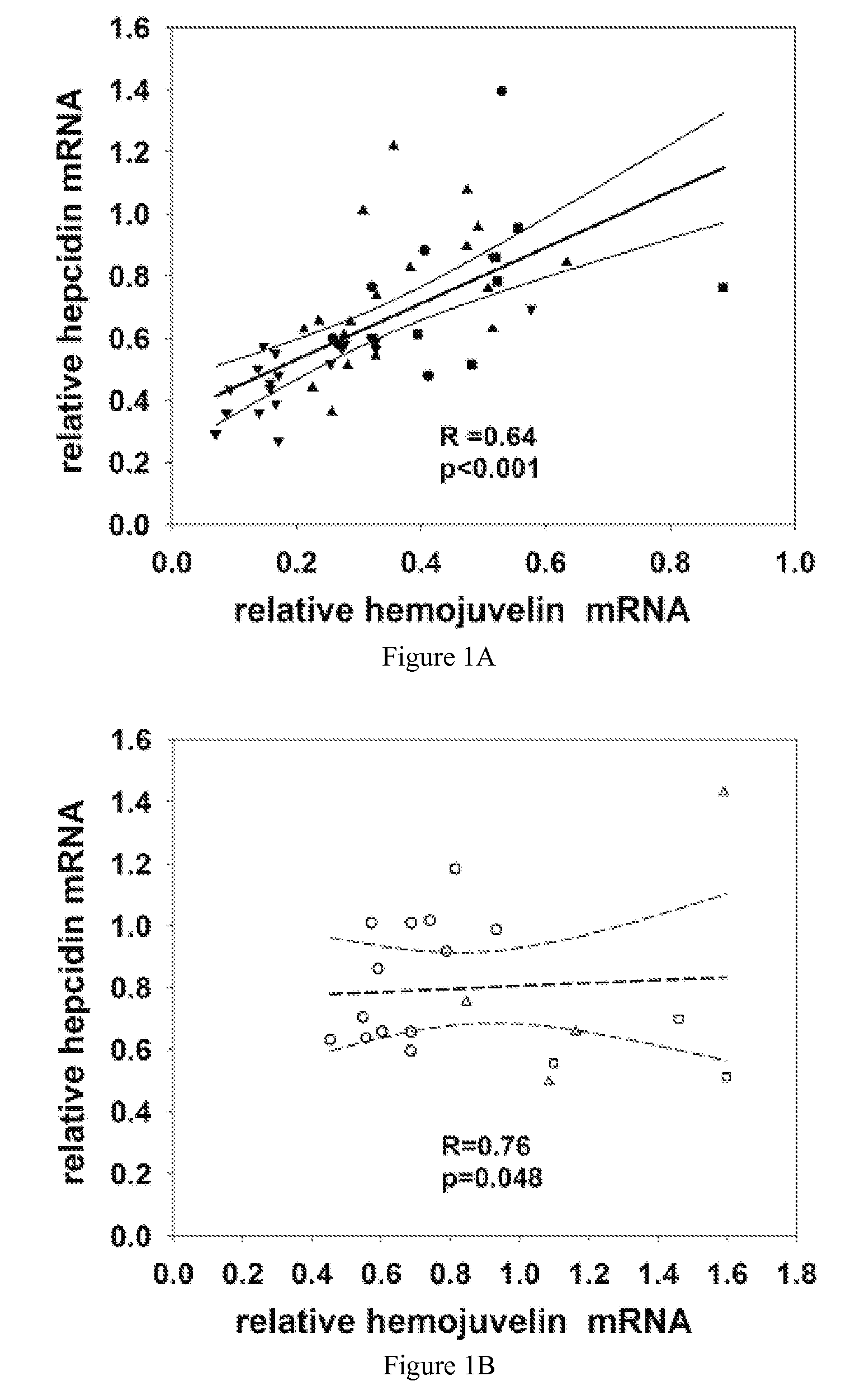
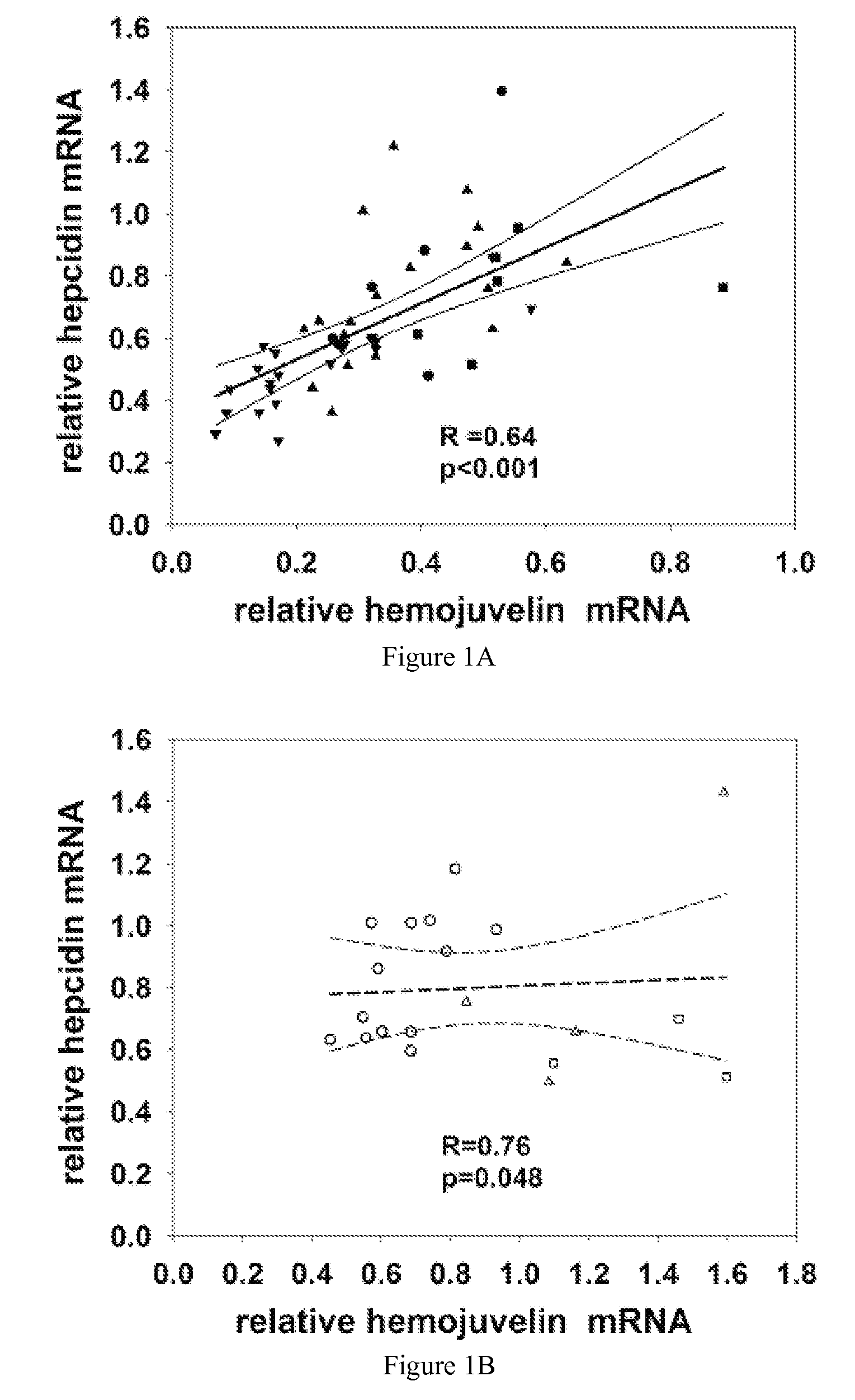
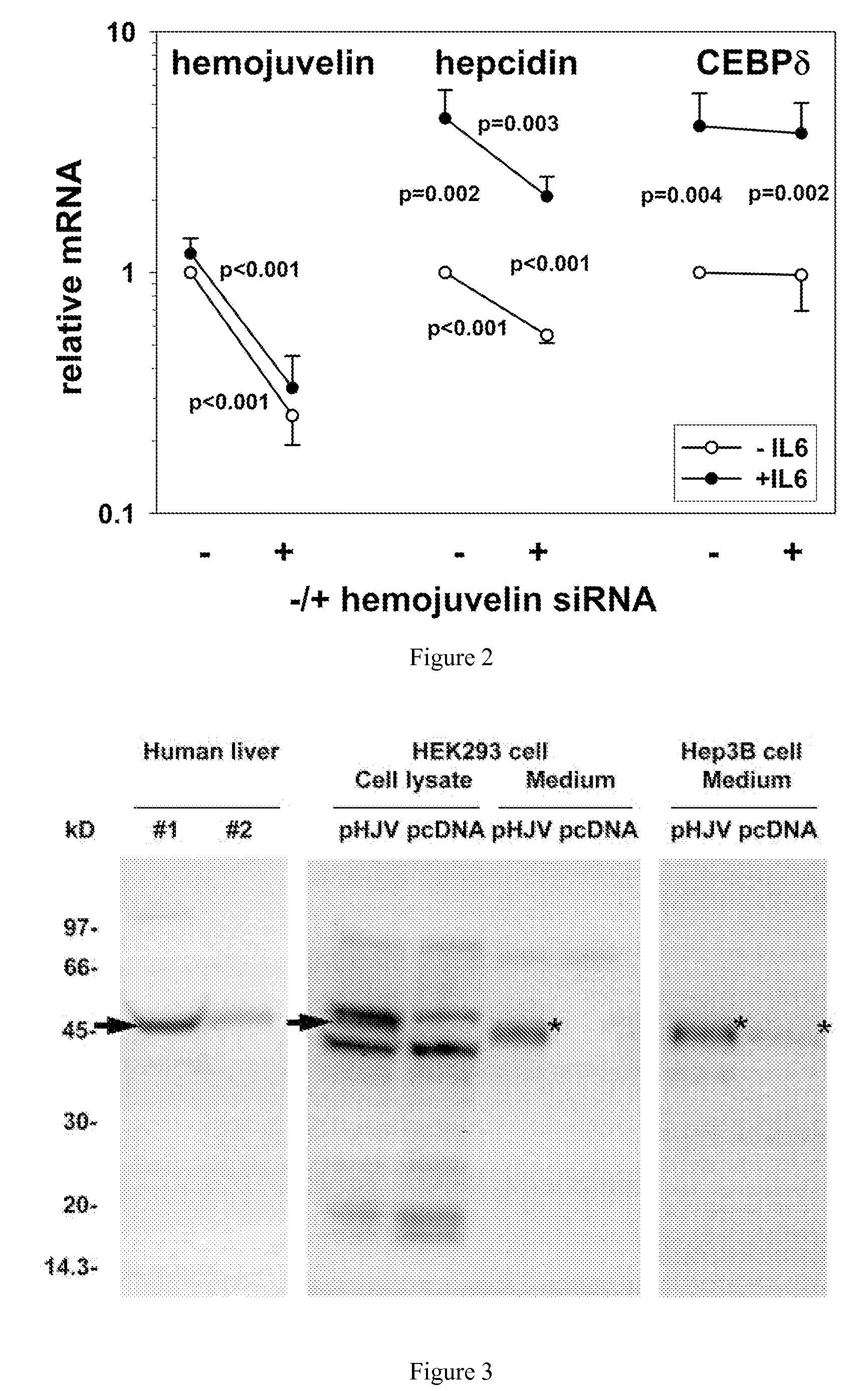
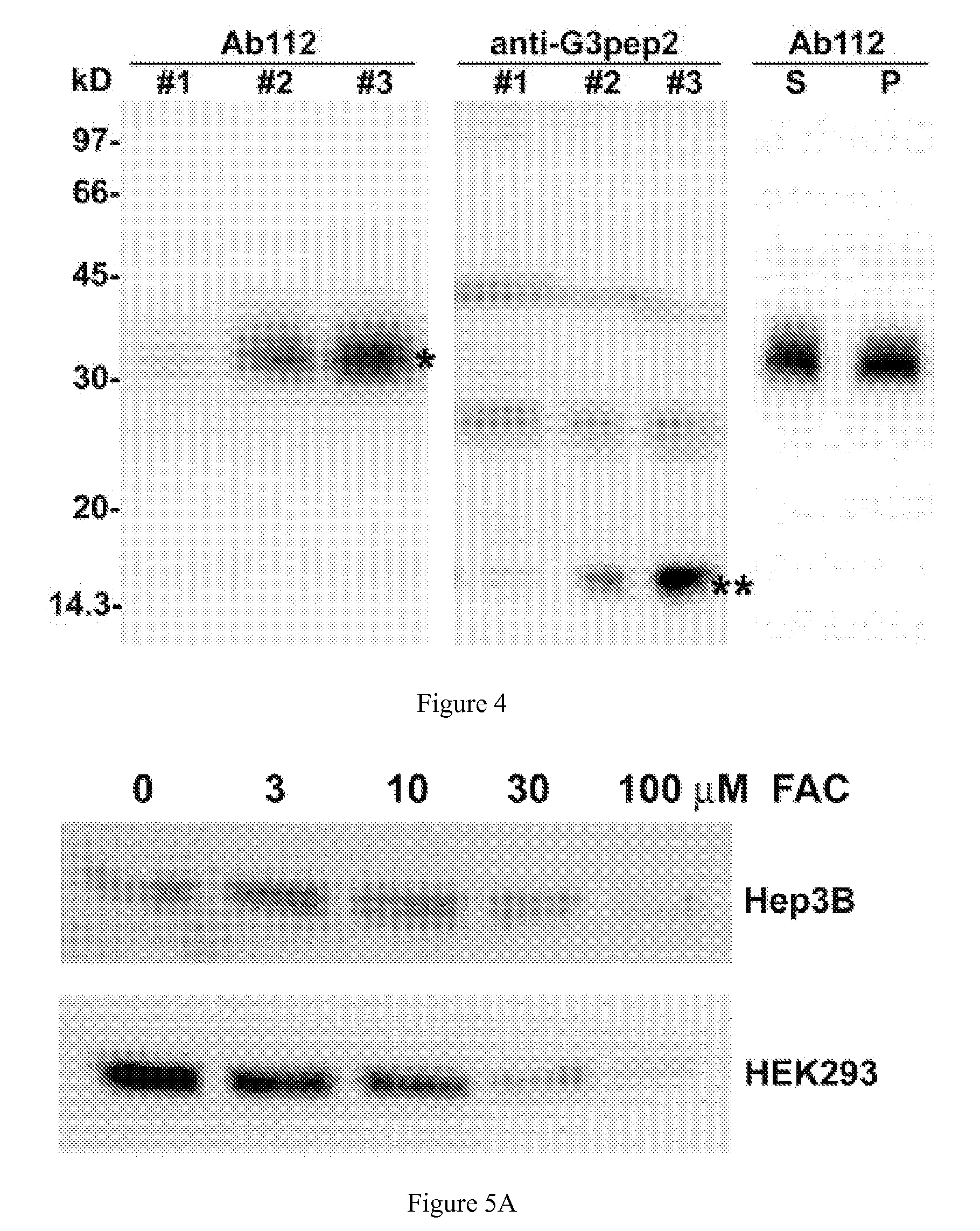
Competitive regulation of hepcidin mRNA by soluble and cell-associated hemojuvelin
InactiveUS7534764B2Increase productionReduce productionPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderDiseaseHemojuvelin
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
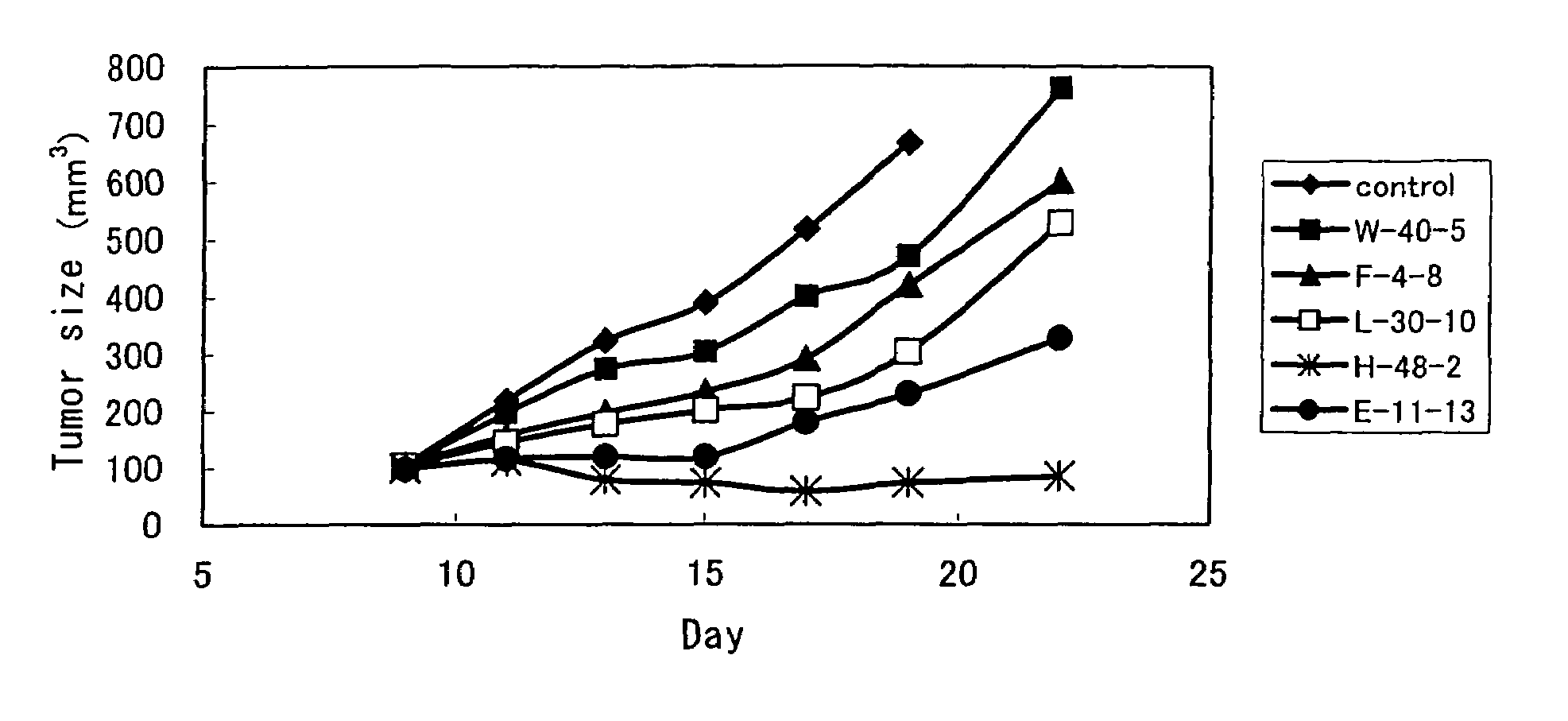
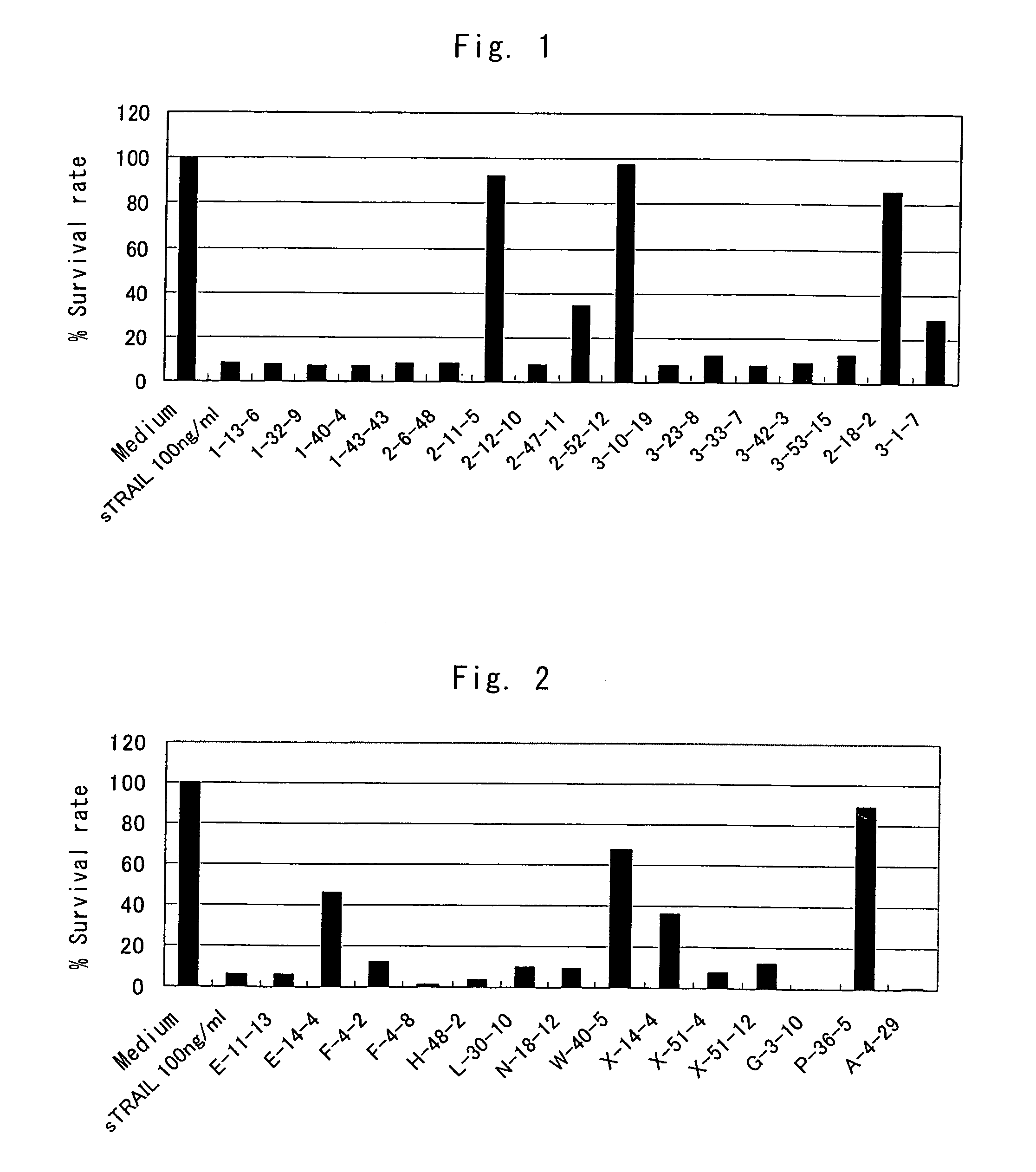
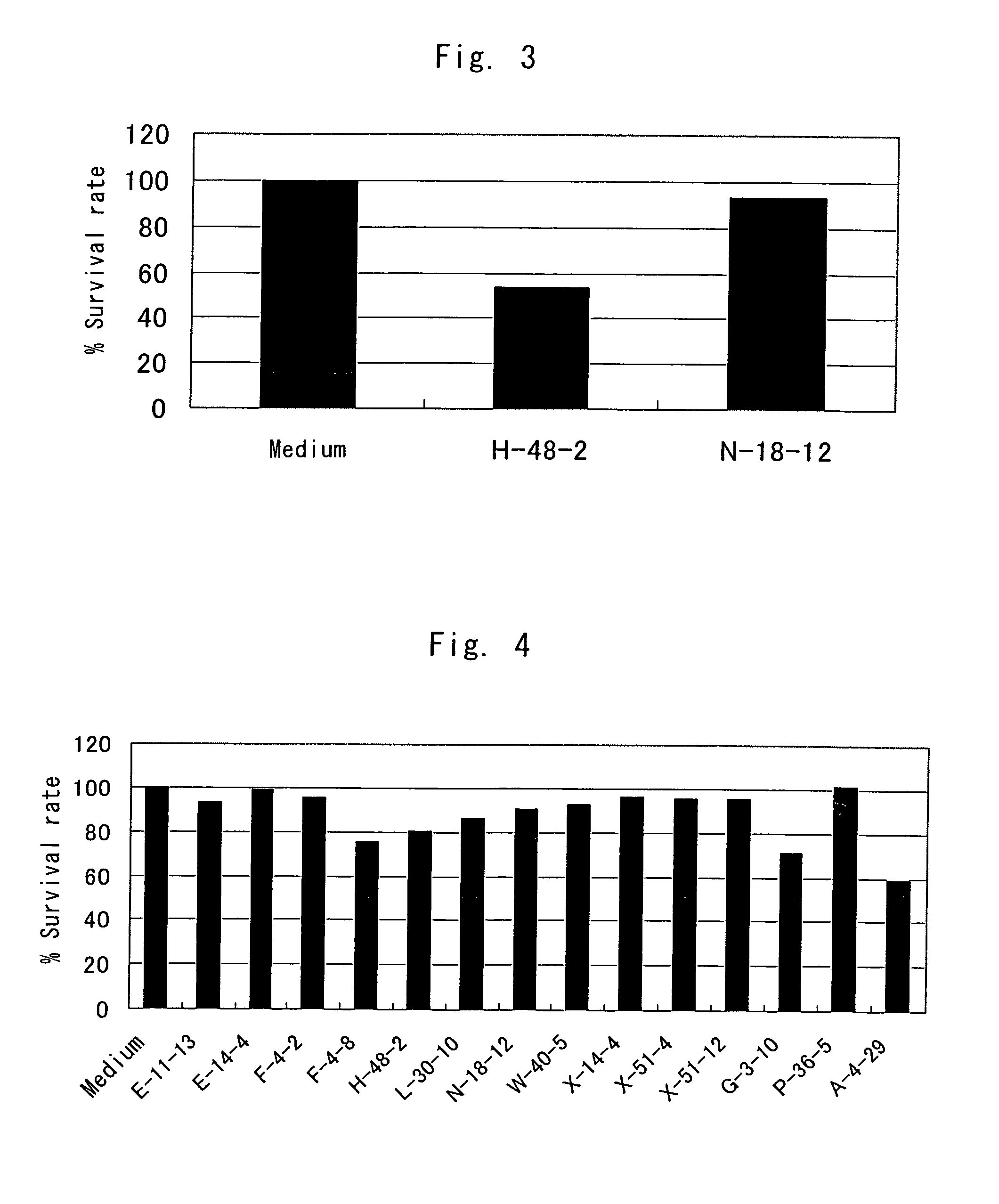
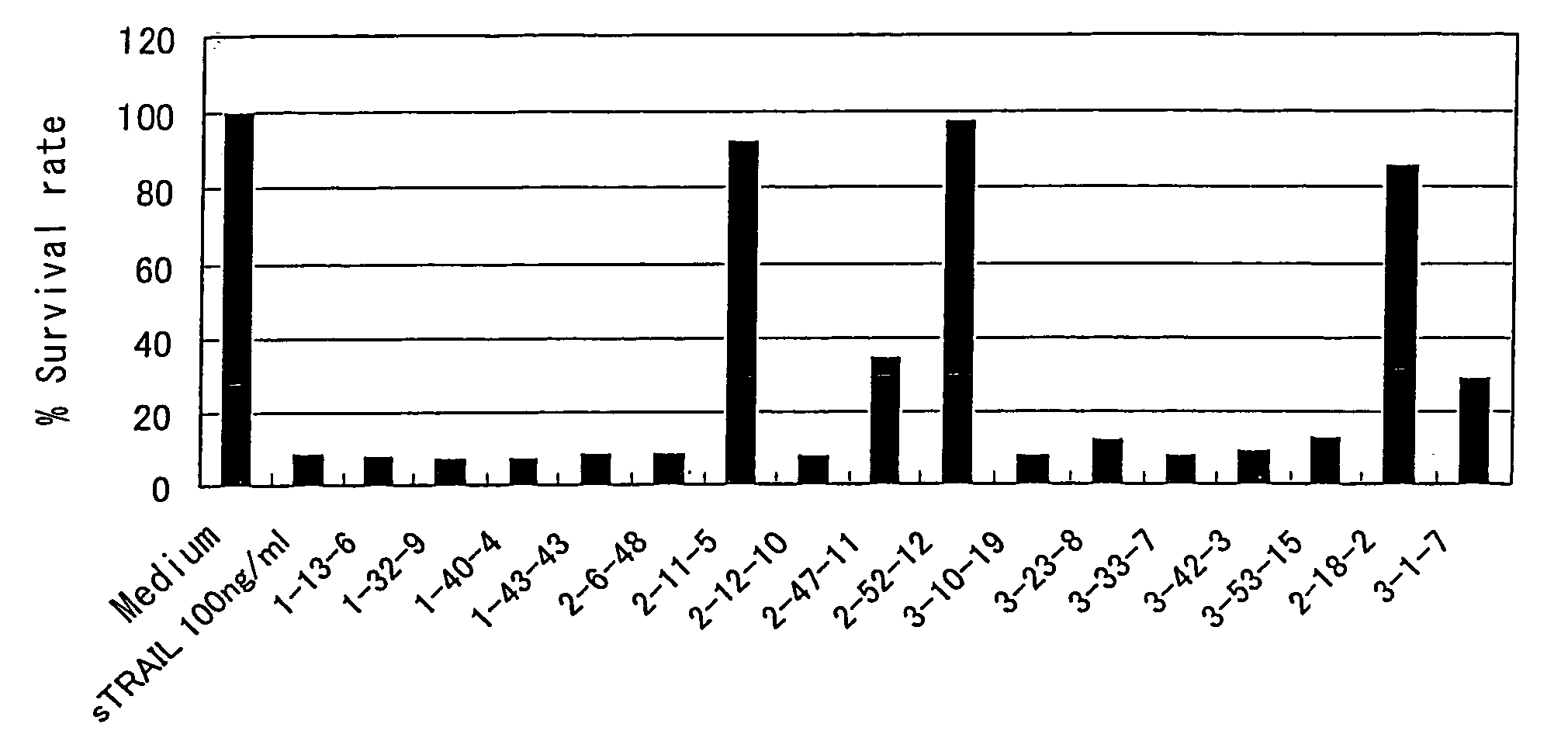
Anti-TRAIL-R antibodies
Anti-TRAIL-R1 and R2 antibodies or functional fragments thereof, having at least one property selected from the following (a) to (c) of:(a) having activity to induce apoptosis in carcinoma cells expressing TRAIL-R1 and / or TRAIL-R2;(b) not having effect on normal human cells expressing TRAIL-R1 and / or TRAIL-R2; and(c) not inducing human hepatocyte toxicity.
Owner:KIRIN BEER KABUSHIKI KAISHI KAISHA
Competitive Regulation of Hepcidin mRNA by Soluble and Cell-Associated Hemojuvelin
InactiveUS20070004618A1Increase productionReduce productionPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderHemeHemojuvelin
Disclosed herein are hemojuvelin-specific siRNAs that vary hemojuvelin mRNA concentration. Also disclosed herein, GPI-hemojuvelin positively regulated hepcidin mRNA expression, independently of the IL-6 pathway, whereas soluble hemojuvelin (s-hemojuvelin) suppressed hepcidin mRNA expression in primary human hepatocytes in a log-linear dosedependent manner. Disclosed are compositions and methods for modulating diseases of iron metabolism and hepcidin expression or hepcidin levels.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Methods of using farnesoid x receptor (frx) agonists
InactiveUS20050107475A1Increasing leptin releaseFacilitated releaseBiocideAnimal repellantsFarnesoid X receptorAgonist
Treatment of human hepatocytes with farnesoid X receptor (FXR) agonists resulted in increased expression of FGF-19. Methods of using FXR agonists to alter cell metabolism, and in pharmaceutical weight loss methods, are described.
Owner:CURAGEN CORP +1
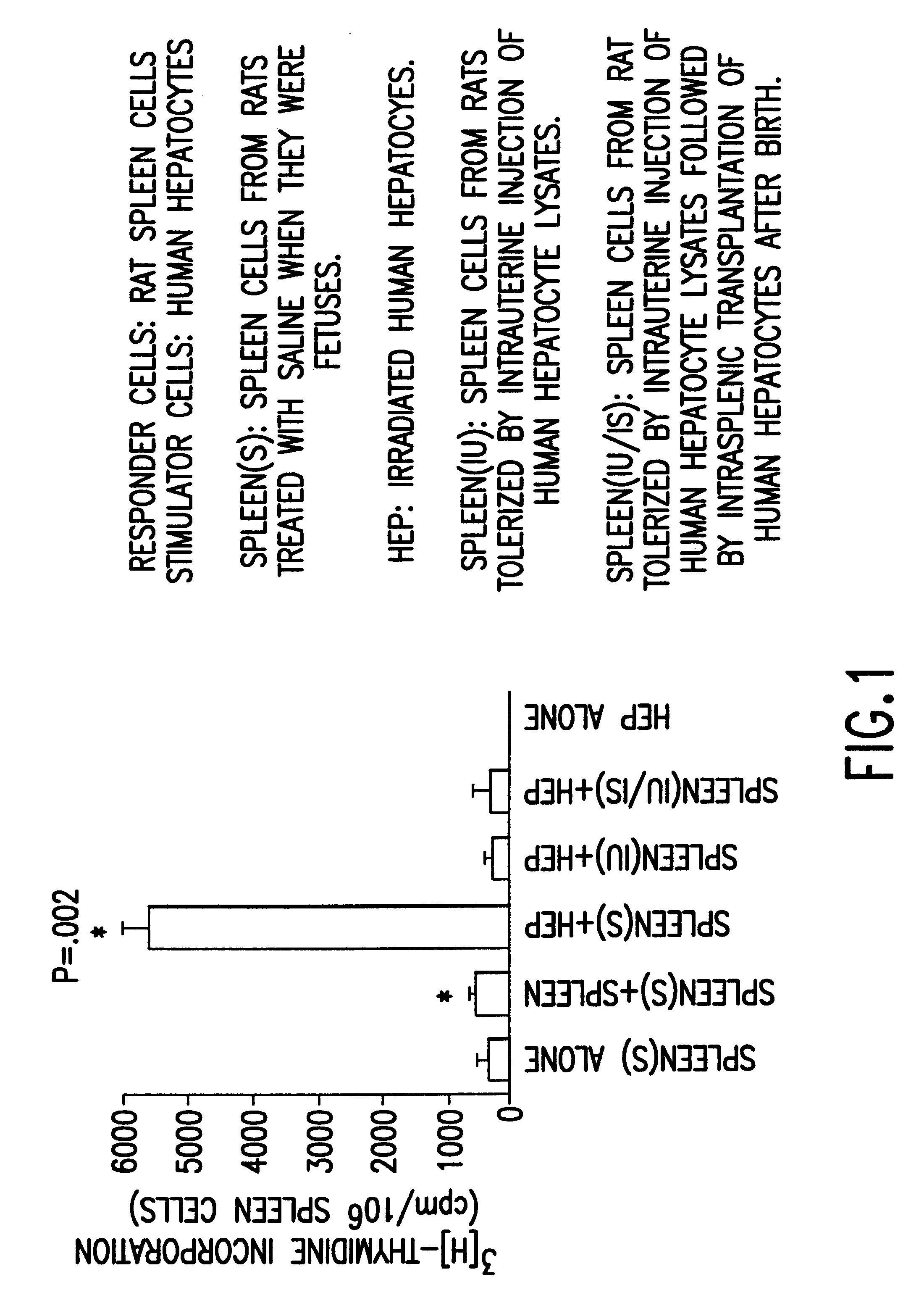
Propagation of human hepatocytes in non-human mammals
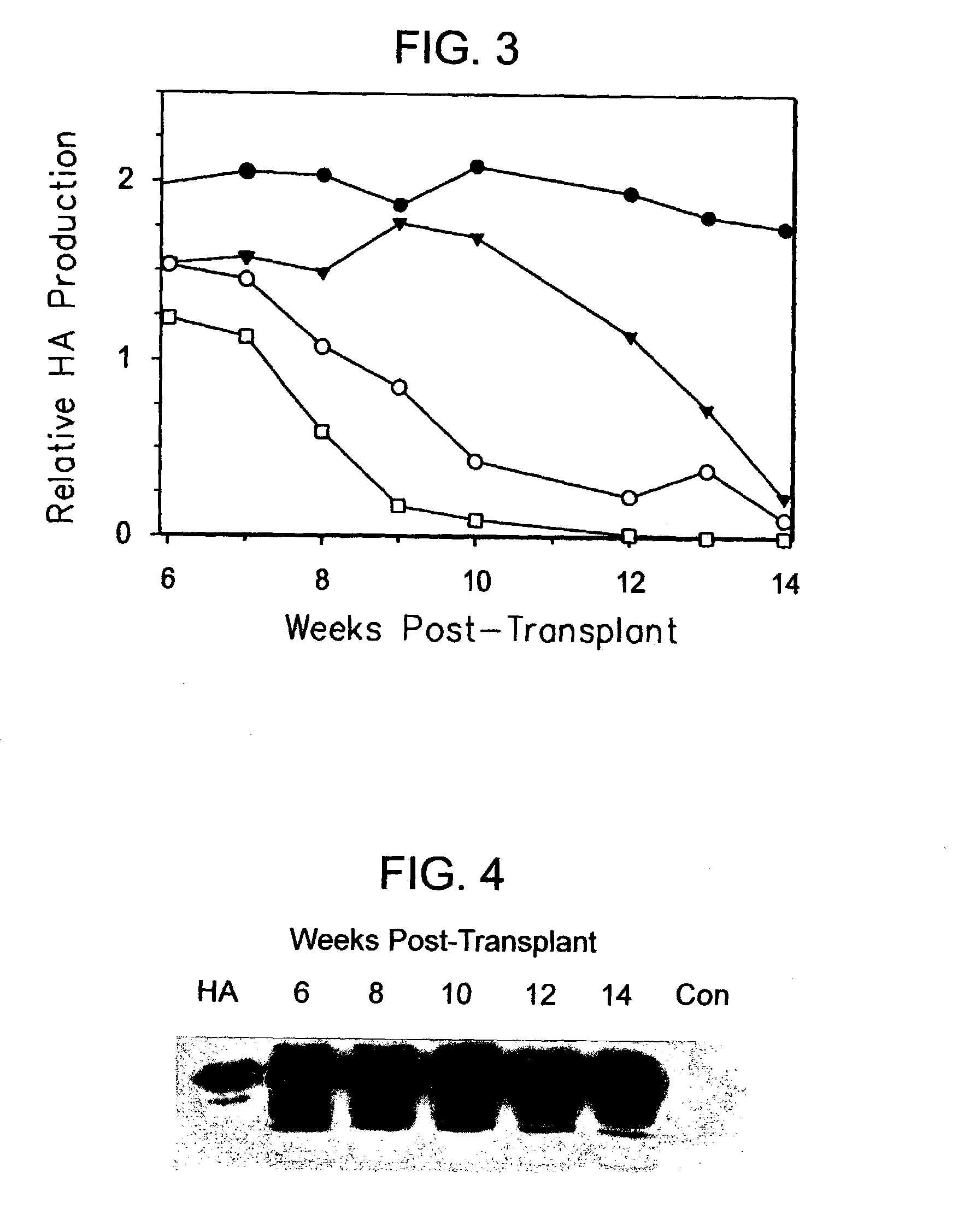
The present invention relates to the preparation of non-human animals having chimeric livers, whereby some or substantially all of the hepatocytes present are human hepatocytes. It is based, at least in part, on the discovery that rats, tolerized in utero against human hepatocytes, were found to serve as long-term hosts for human hepatocytes introduced post-natally, and the introduced hepatocytes maintained their differentiated phenotype, as evidenced by continued production of human albumin.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
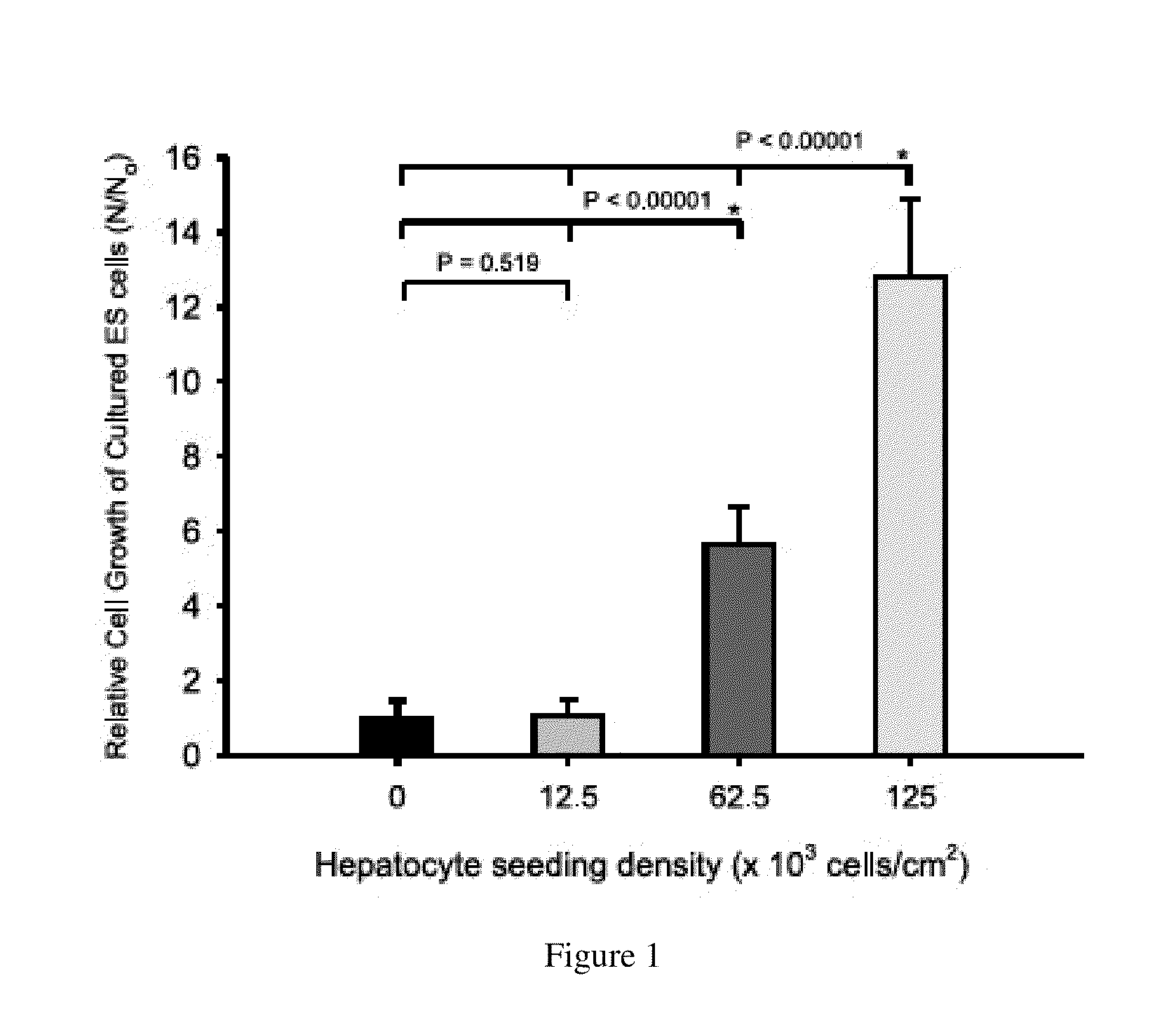
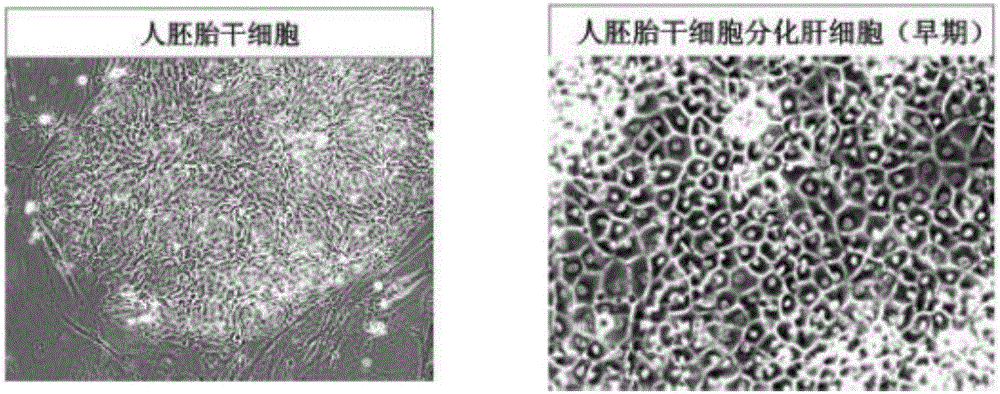
Homogeneous differentiation of hepatocyte-like cells from embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS20100143313A1Rapid and direct differentiationImprove survivalBiocideHepatocytesLiver morphologyBioartificial liver device
One of the major hurdles of cellular therapies for the treatment of liver failure is the low availability of functional human hepatocytes. Although embryonic stem (ES) cells represent a potential cell source for therapy, current methods for differentiation result in mixed cell populations or low yields of the cells of interest. The present invention provides for a rapid, direct differentiation method that yields a homogeneous population of endoderm-like cells with 95% purity. In one embodiment, mouse ES cells cultured on top of collagen-sandwiched hepatocytes differentiate and proliferate into a uniform and homogeneous cell population of endoderm-like cells. The endoderm-like cell population was positive for Foxa2, Sox17 and AFP, and could further differentiate into hepatocyte-like cells that demonstrate hepatic morphology, functionality, and gene and protein expression. Incorporating the hepatocyte-like cells into a bioartificial liver device to treat fulminant hepatic failure improved animal survival, thereby underscoring the therapeutic potential of these cells.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
In vivo, animal model for expression of hepatitis C virus
Disclosed is a method for expressing hepatitis C virus in an in vivo, animal model. Viable, hepatitis C virus-infected, human hepatocytes are transplanted into a liver parenchyma of a scid / scid mouse host. The scid / scid mouse host is then maintained in a viable state, for up to five days or greater, whereby viable, morphologically intact human hepatocytes persist in the donor tissue and hepatitis C virus is replicated in the persisting human hepatocytes.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Animal model having a chimeric human liver
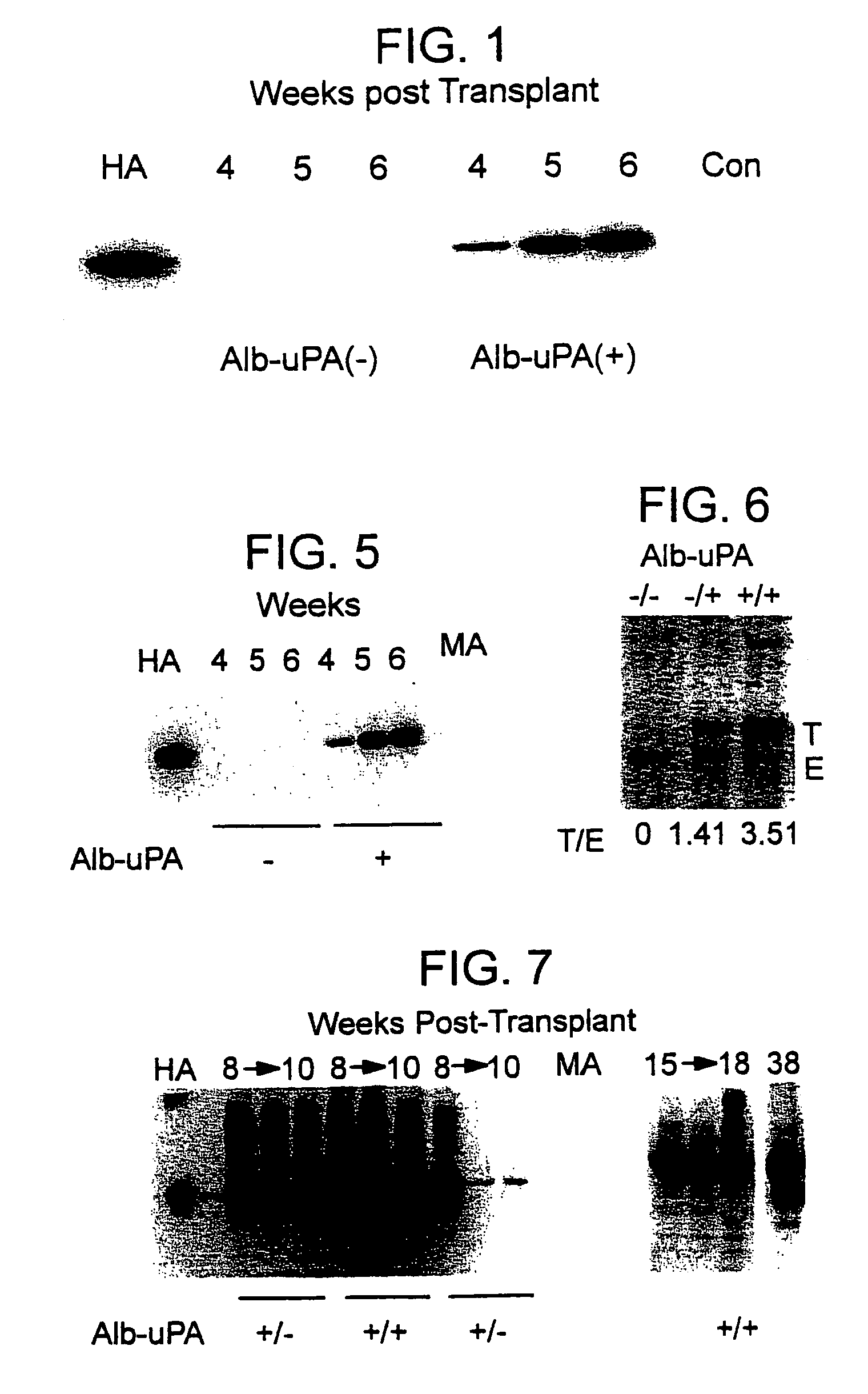
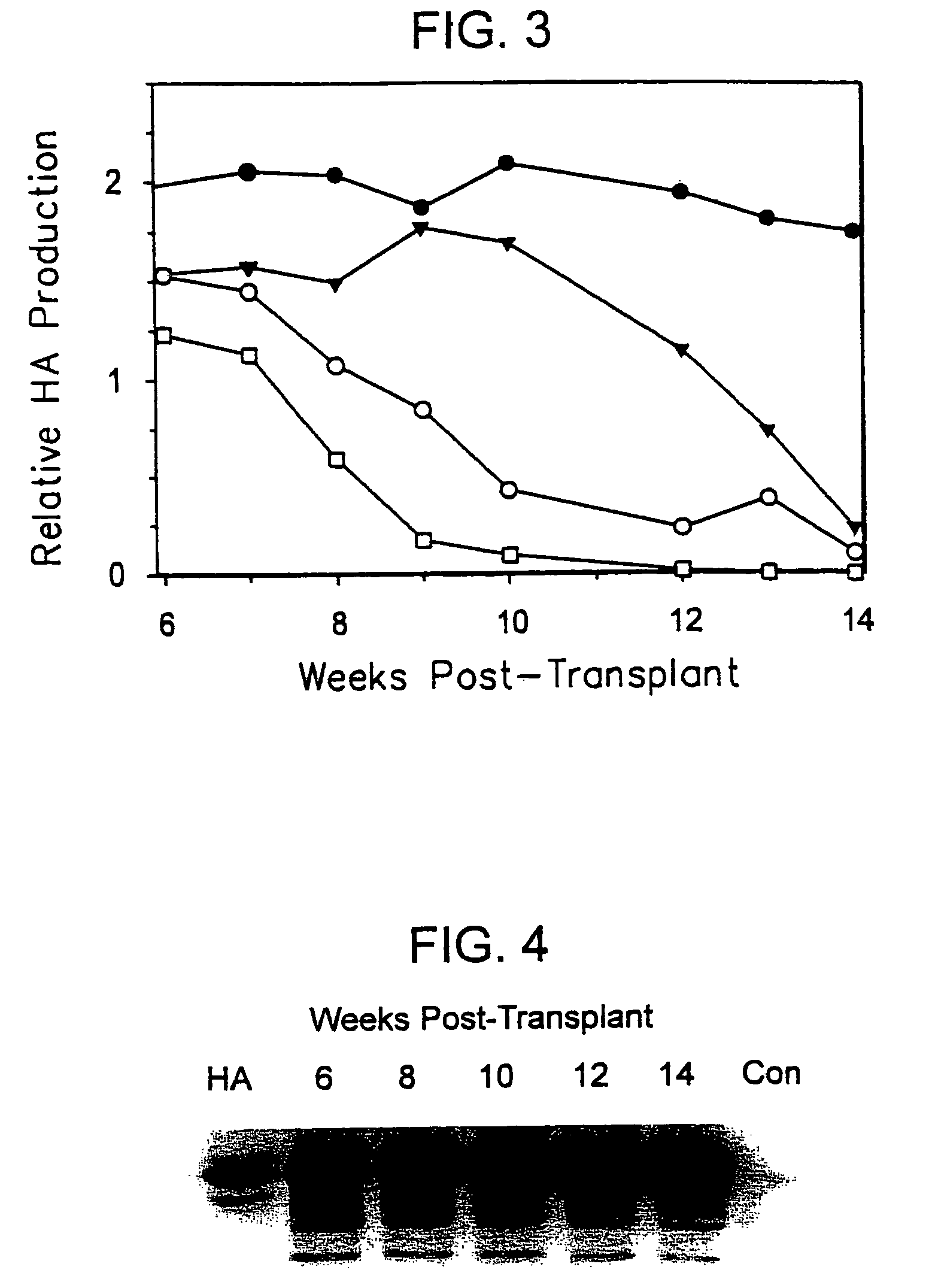
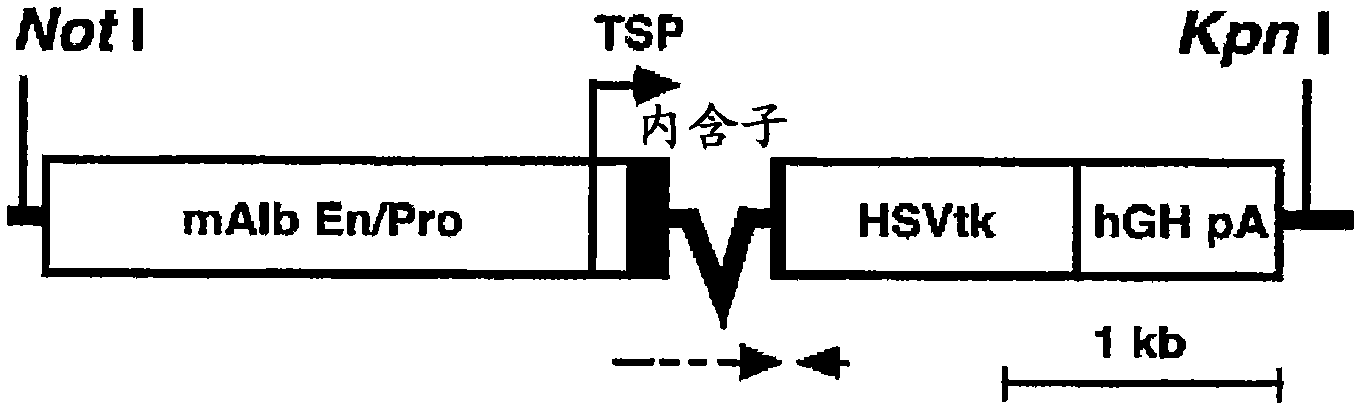
The present invention features a non-human animal model that is susceptible to infection by human hepatotrophic pathogens, particularly human hepatitis C virus (HCV). The model is based on a non-human, immunocompromised transgenic animal having a human-mouse chimeric liver, where the transgene provides for expression of a urokinase-type plasminogen activator in the liver. The invention also features methods for identifying candidate therapeutic agents, e.g., agents having antiviral activity against HCV infection. The animals of the invention are also useful in assessing toxicity of various agents, as well as the activity of agents in decreasing blood lipids.
Owner:KMT HEPATECH
In vitro culture-amplified human liver progenitor cell and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101275121AAccelerate self-renewalConvenient sourceArtificially induced pluripotent cellsNon-embryonic pluripotent stem cellsCell-Extracellular MatrixECM Protein
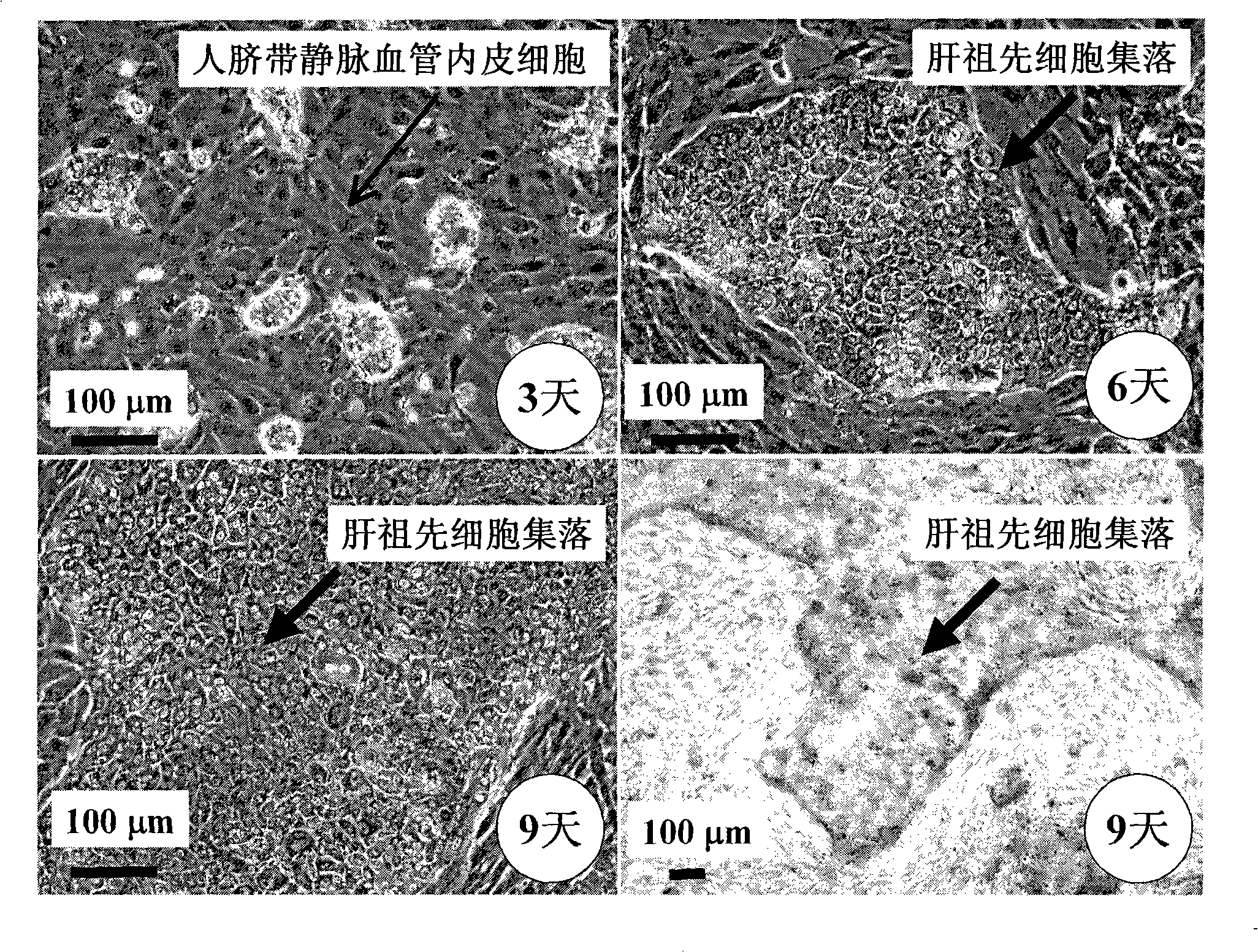
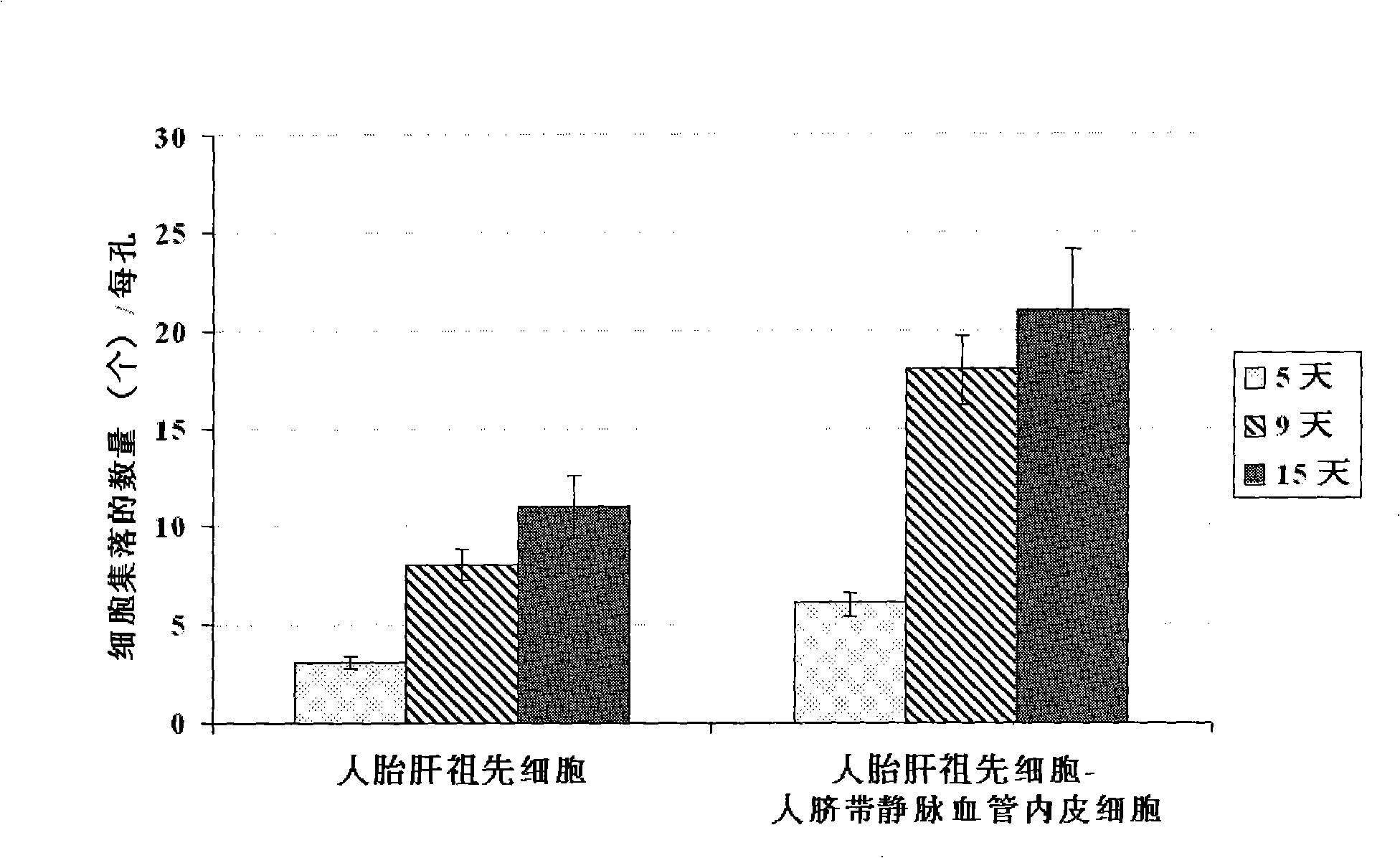
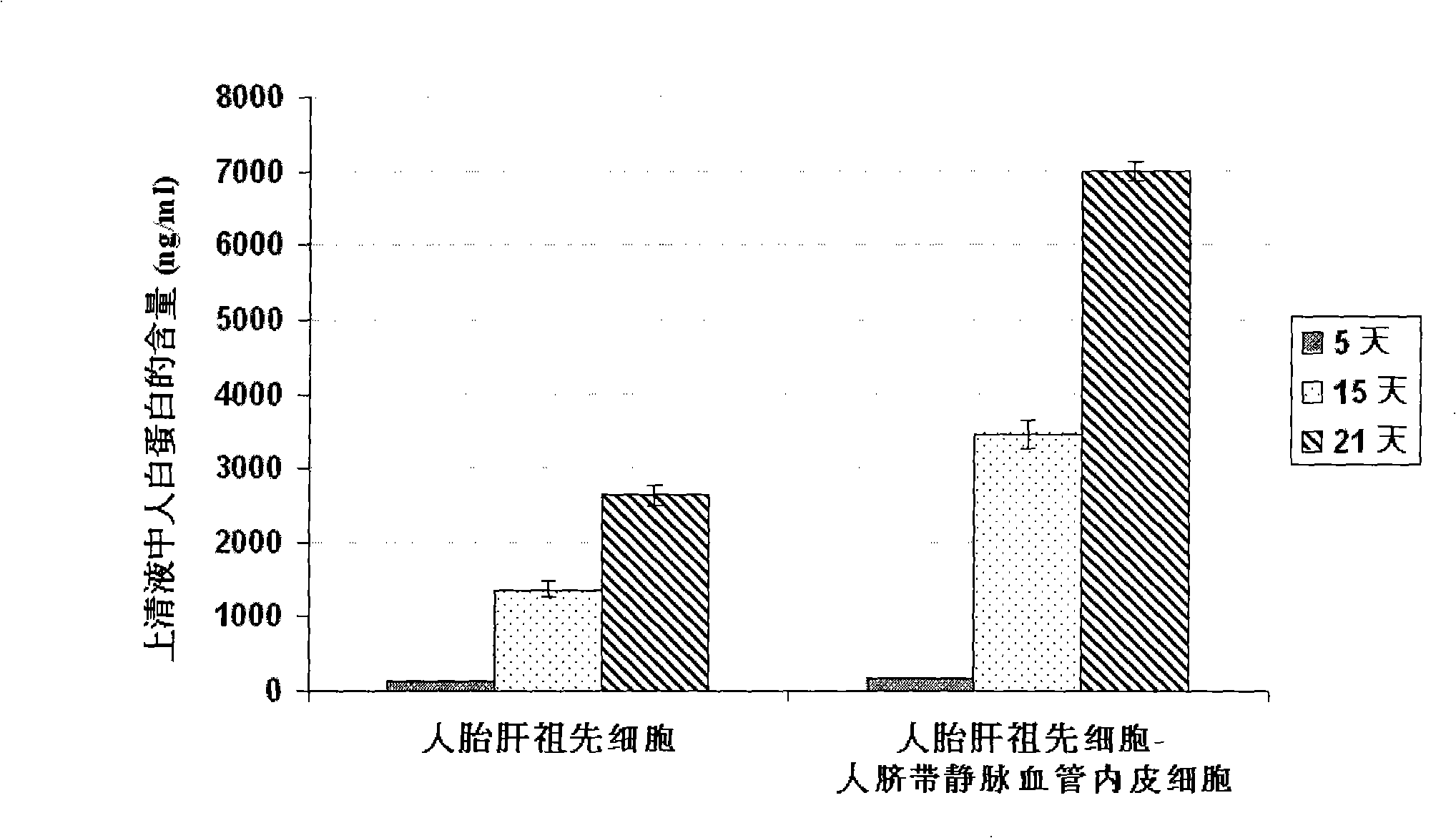
The present invention provides a preparing method of a human hepatic progenitor cell which is amplified and cultivated in vitro, including: a. separating the human hepatic progenitor cell; b. co-cultivating a feeder cell and the human hepatic progenitor cell separated from the step a by a medium having no serum on an extracellular matrix containing human fibrin sealant or other analogues, obtaining a human hepatic progenitor cell colony by amplification. The human hepatic progenitor cell colony is easy to separate from the surface of human fibrin sealant by the simple gelatinolytic band process, purified or / and subcultured by further single cell preparation technology process such as enzymatic degradation etc. The human hepatic progenitor cell prepared by the method is hepatic progenitor cell treatment, including a cell transplantation and a bioartificial liver support system, providing excellent human hepatocyte source for cytotoxicity test platform in the drug screening, virus infection and drug screening platform etc.
Owner:芦银雪
Human liver cell line
In this application is described the establishment and maintanence of a normal human hepatocyte cell line able to support complete development of malaria parasite development in vitro. Advantages and uses of the cell line are also described.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
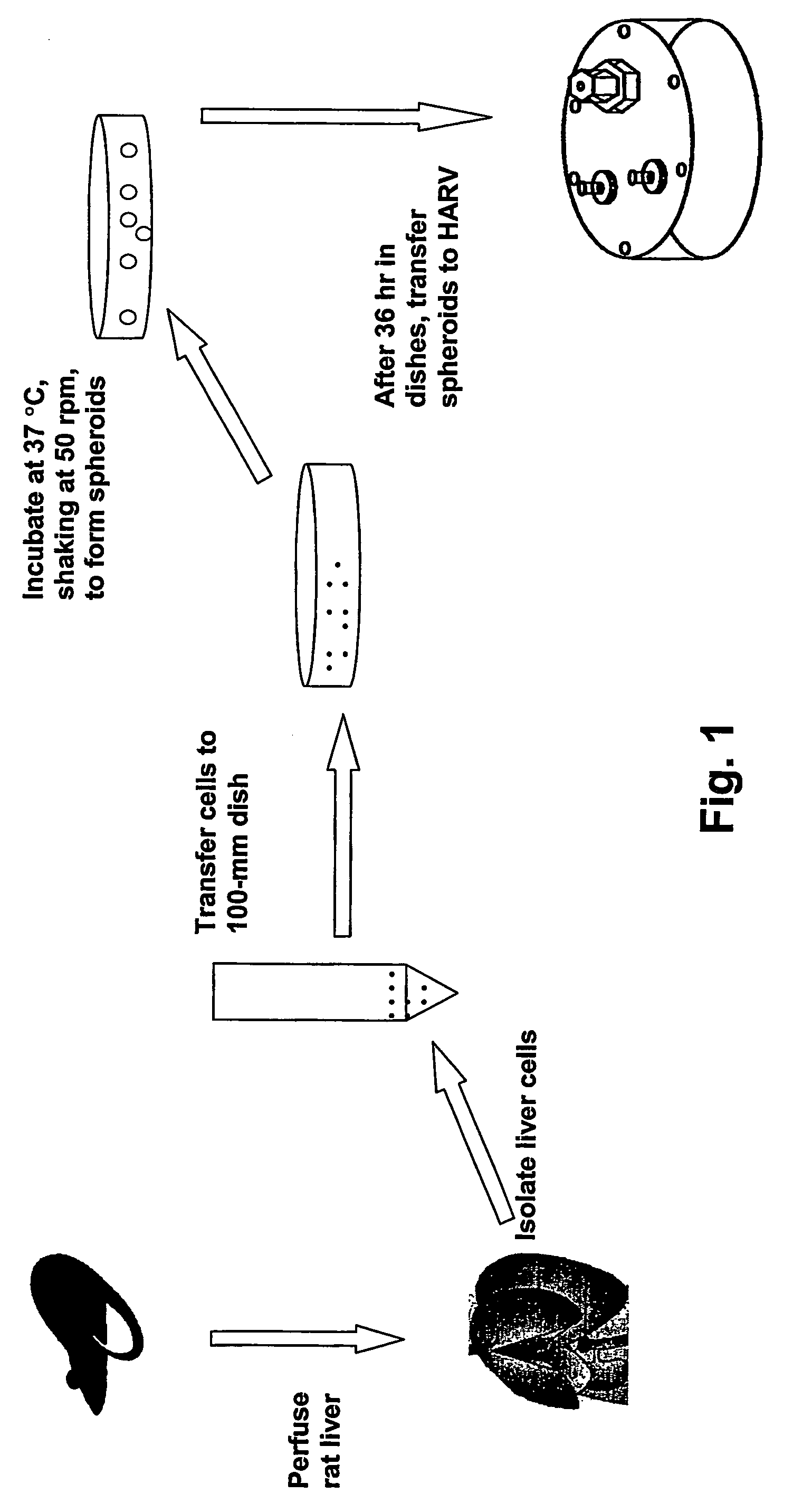
Hepatocyte bioreactor system for long term culture of functional hepatocyte spheroids
A rotating wall vessel is used as a culture vessel and bioreactor for the cultivation of hepatocytes in the form of spheroids to generate a culture with many properties of the intact liver. These properties include enzyme activity comparable to fresh cells and long-term maintenance of viability and cellular function for periods on the order of months. The cultures may be used to produce hepatocyte products, evaluate metabolism of an agent, propagate Hepatitis C virus and test agents as inhibitors of this virus. Thus, the culture system disclosed herein makes long term functional cultivation of human hepatocytes feasible.
Owner:IN VITRO TECH
Anti-TRAIL-R antibody
Anti-TRAIL-R1 and R2 antibodies or functional fragments thereof, having at least one property selected from the following (a) to (c) of: (a) having activity to induce apoptosis in carcinoma cells expressing TRAIL-R1 and / or TRAIL-R2; (b) not having effect on normal human cells expressing TRAIL-R1 and / or TRAIL-R2; and (c) not inducing human hepatocyte toxicity, and an anti-TRAIL-R1 and R2 antibodies or functional fragments thereof, having the following properties: having activity to induce apoptosis in carcinoma cells independently of exogenous factors and as a monomer of an antibody.
Owner:KIRIN BREWERY CO LTD
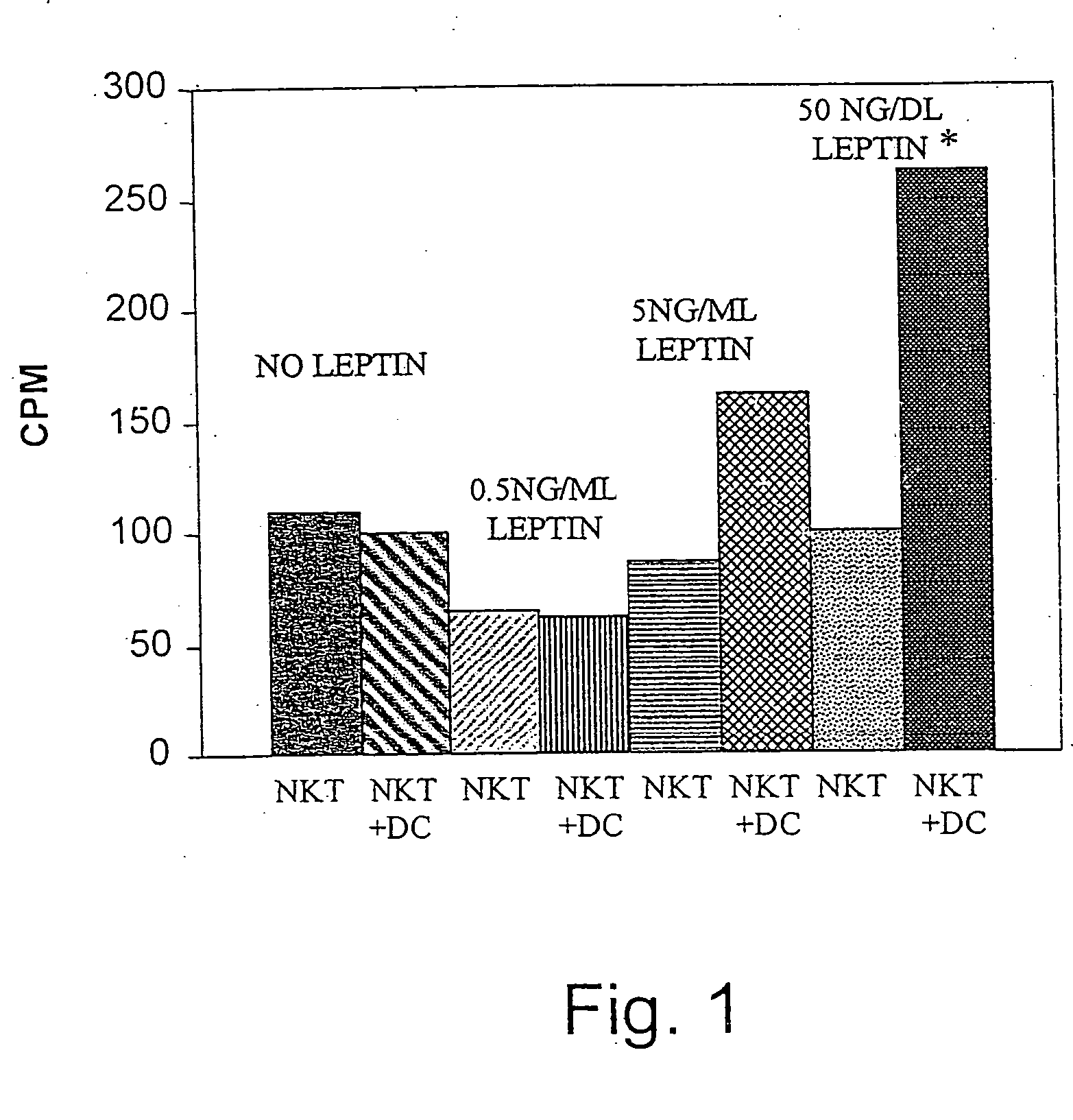
Methods and uses of leptin in immune modulation and hepatocellular carcinoma
Leptin was previously demonstrated to exert potent immune modulatory properties in several immune mediated disorders. The aim of the study was to determine leptin's anti-tumor effect in a murine model of human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). In vivo, Athymic T cell deficient (nude) mice transplanted with 1×106 human Hep3B cells, followed by administration of two daily intraperitoneal doses of 0.5 mg / gram leptin for 6 weeks. Leptin administration induced a significant reduction in tumor size and improved survival in nude mice. Histologically, tumors of leptin-administered mice featured increased inflammatory exudate in interphase areas. Leptin-induced tumor suppression was associated with a significant increase in peripheral natural killer (NK) cell number. Splenocytes from leptin-treated mice featured decreased expression of CIS mRNA. To determine which lymphocyte subset is a prerequisite for the anti tumor effect of leptin, T&B cell deficient (Scid) mice and T,B& NK deficient (Scid-Beige) mice were subcutaneously implanted with Hep3B tumor cells, with and without the daily intraperitoneal administration of 0.5 mg / gram leptin for 6 weeks. SCID mice featured leptin-associated tumor suppression similar to those of nude mice. In contrast, NK-deficient SCID-Beige mice developed larger tumors. To further establish natural killer cell's central role in mediation of leptin's anti-tumor effect, NK cells were incubated in vitro with increasing doses of leptin, demonstrating a dose-dependent increase in cytotoxic activity. Incubation of leptin with hepatoma cell line was found to induce a dose-dependent reduction in hepatoma cell proliferation, suggesting an additive direct anti-tumor effect. Further synergism in inhibition of hepatoma cell proliferation in vitro was achieved following addition of natural killer cells. HCC cells expressed leptin receptor mRNA, while addition of leptin induced increased mRMA expression of STAT2 and SOCS1 on tumor cell lines. Leptin administration induces a significant suppression of human HCC. This effect is mediated by induction of natural killer cell proliferation and activation, and by direct inhibition of tumor growth. Decreased natural killer cell expression of inhibitory CIS protein and over expression of the anti-proliferative STAT2 and SOCS1 proteins in HCC lines may underline both anti cancerous effects of leptin.
Owner:ENZO THERAPEUTICS
Animals comprising human hepatocellular tissue.
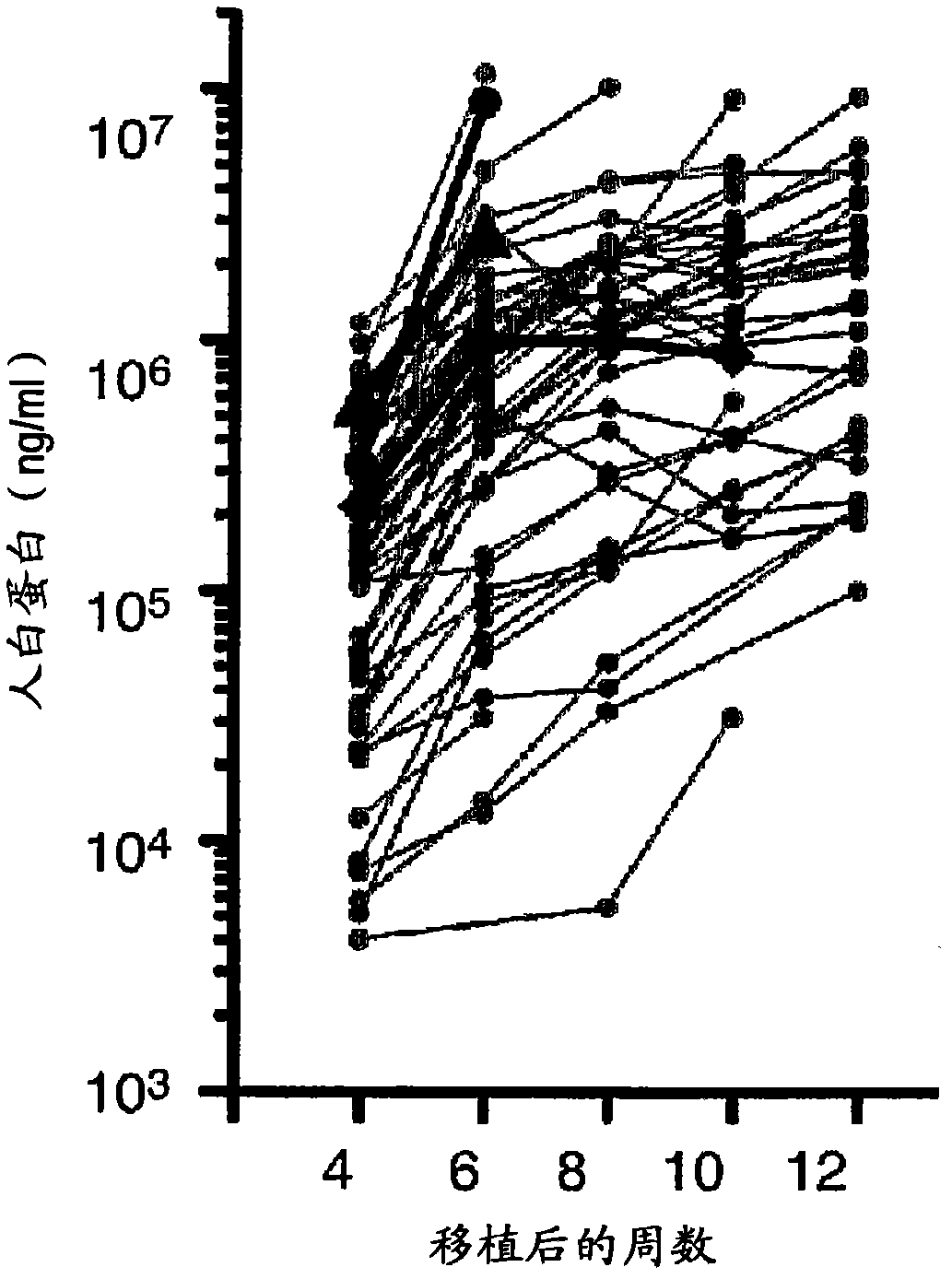
Non-human mammalian hosts are provided, comprising functional human hepatocytes. Isolated human hepatocytes or fragments of human hepatic tissue are introduced into the xenogeneic host in conjunction with one or more agent that stimulates human hepatocyte growth factor receptor. The human hepatocytes are maintained in the host by administration of one or more agent that stimulates human hepatocyte growth factor receptor, either continuously (e.g., via an implanted catheter or intravenous apparatus) or in discrete, regular dosages of the agent (e.g., via intravenous injections or oral dosages). The human hepatocytes are able to survive and function in the host animal for a period of at least 5 months.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Human hepatocyte-like cells and uses thereof
InactiveUS20060154235A1Improve efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsCytochrome P450Culture mediums
The present invention provides modified methods of producing human hepatocyte-like cells which exhibit phenotypes more similar to those of human hepatocytes. The present invention also provides the human hepatocyte-like cells and uses thereof. The methods of the present invention comprises a prolonged incubation period and addition of dexamethasone to the culture medium. The methods of the inventors produce human hepatocyte-like cells whose morphology is more similar to that of human hepatocytes, compared with the conventional system. The cells produced have both morphological and functional features of primary culture cells from normal human liver, including cytochrome P450 (CYP), multi-drug resistance-associated protein (MRP), and multi-drug protein (MDR). The use of human hepatocyte-like cells of the present invention enables, without using any animal model, assessment of metabolism and hepatotoxicity of test compounds, which are drug candidates, and screening for therapeutic agents for hepatic diseases, inhibitors to hepatitis virus infection, and therapeutic agents for viral hepatitis.
Owner:EFFECTOR CELL INST
Method for separating primary adult hepatocytes, and special sterile apparatus box thereof
InactiveCN102220278AGuaranteed sterilityFor long-term storageBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSerum freeType IV collagen
The invention discloses a method for separating primary adult hepatocytes. The method comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out multi-point puncture on surface of isolated adult hepatic tissue through a needle syringe, and injecting a preperfusate, wherein connective tissues are removed from the isolated adult hepatic tissue; (2) carrying out the multi-point puncture on the surface of the isolated adult hepatic tissue through the needle syringe again, and injecting a IV collagenase solution; (3) separating the isolated adult hepatic tissue, followed by adding the IV collagenase solution and carrying out digesting through vibration at a temperature of 37 DEG C to obtain digest; (4) carrying out filtering for the digest, followed by centrifuging and collecting cell aggregate in the underlayer, then resuspending the adult hepatocyte aggregate through a hepatocyte wash buffer, followed by filtering and centrifuging, then abandoning supernatant and collecting the adult hepatocyte aggregate in the underlayer; (5) washing the adult hepatocyte aggregate in the underlayer from the step (4) through a serum-free DMEM medium to obtain the primary adult hepatocytes. The invention further discloses a disposable special sterile apparatus box for separating the primary adult hepatocytes. With the present invention, the disposable special sterile apparatus box is adopted, the primary adult hepatocytes are separated through the multi-point puncture on the surface of the tissue and the injection, such that operation is simplified, cost is reduced, and the method and the apparatus box are applicable for extracting the hepatocytes from small pieces of the irregular isolated adult hepatic tissues of recovery of liver resection.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
New method for inducing directional differentiation of human stem cells into hepatocytes
ActiveCN106554936AArtificial cell constructsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsInduced pluripotent stem cellMature cell
Owner:TRANSCEND CYTOTHERAPY CO LTD
Animal model having a chimeric human liver
The present invention features a non-human animal model that is susceptible to infection by human hepatotrophic pathogens, particularly human hepatitis C virus (HCV). The model is based on a non-human, immunocompromised transgenic animal having a human-mouse chimeric liver, where the transgene provides for expression of a urokinase-type plasminogen activator in the liver. The invention also features methods for identifying candidate therapeutic agents, e.g., agents having antiviral activity against HCV infection. The animals of the invention are also useful in assessing toxicity of various agents, as well as the activity of agents in decreasing blood lipids.
Owner:KMT HEPATECH
Hepatocyte bioreactor system for long term culture of functional hepatocyte spheroids
A rotating wall vessel is used as a culture vessel and bioreactor for the cultivation of hepatocytes in the form of spheroids to generate a culture with many properties of the intact liver. These properties include enzyme activity comparable to fresh cells and long-term maintenance of viability and cellular function for periods on the order of months. The cultures may be used to produce hepatocyte products, evaluate metabolism of an agent, propagate Hepatitis C virus and test agents as inhibitors of this virus. Thus, the culture system disclosed herein makes long term functional cultivation of human hepatocytes feasible.
Owner:IN VITRO TECH
Differentiated human liver cell cultures and their use in bioartificial liver systems
InactiveUS20120111795A1Function increaseBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLiver failureOrganism
The present invention concerns human hepatocyte cell line cultures and their use in bioartificial liver (BAL) systems. These systems are used to treat subjects suffering from liver failure to temporarily compensate for loss of hepatocellular function and generally comprise a bioreactor loaded with functional liver cells. Until now, it has been problematic to acquire cells with a broad spectrum metabolic functionality, resembling that of freshly isolated human hepatocytes, to the extent that they are in fact suitable for successful clinical BAL application The present inventors have managed to develop human hepatocyte cell line cultures that display broad-spectrum metabolic functionality such as to render them particularly suitable for effective clinical BAL application.
Owner:ACADEMISCH ZIEKENHUIS BIJ DE UNIV VAN AMSTERDAM ACADEMISCH MEDISCH CENT
Method of expanding human hepatocytes in vivo
Described herein is a method of expanding human hepatocytes in vivo using an immunodeficient mouse which is further deficient in fumarylacetoacetate hydrolase (Fah). The method comprises transplanting human hepatocytes into the immunodeficient and Fan-deficient mice, administering an IL-IR antagonist to the mouse and allowing the hepatocytes to expand. Alternatively, the method includes transplanting human hepatocytes into the immunodeficient and Fah-deficient mice, wherein the mouse is further deficient for IL-IR and allowing the hepatocytes to expand. The method also allows serial transplantation of the human hepatocytes into secondary, tertiary, quaternary or additional mice.
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV
Method of proliferating human hepatocytes and method for obtaining human hepatocytes
InactiveUS20050255591A1Genetically modified cellsArtificial cell constructsImmunodeficiencyLiver disease
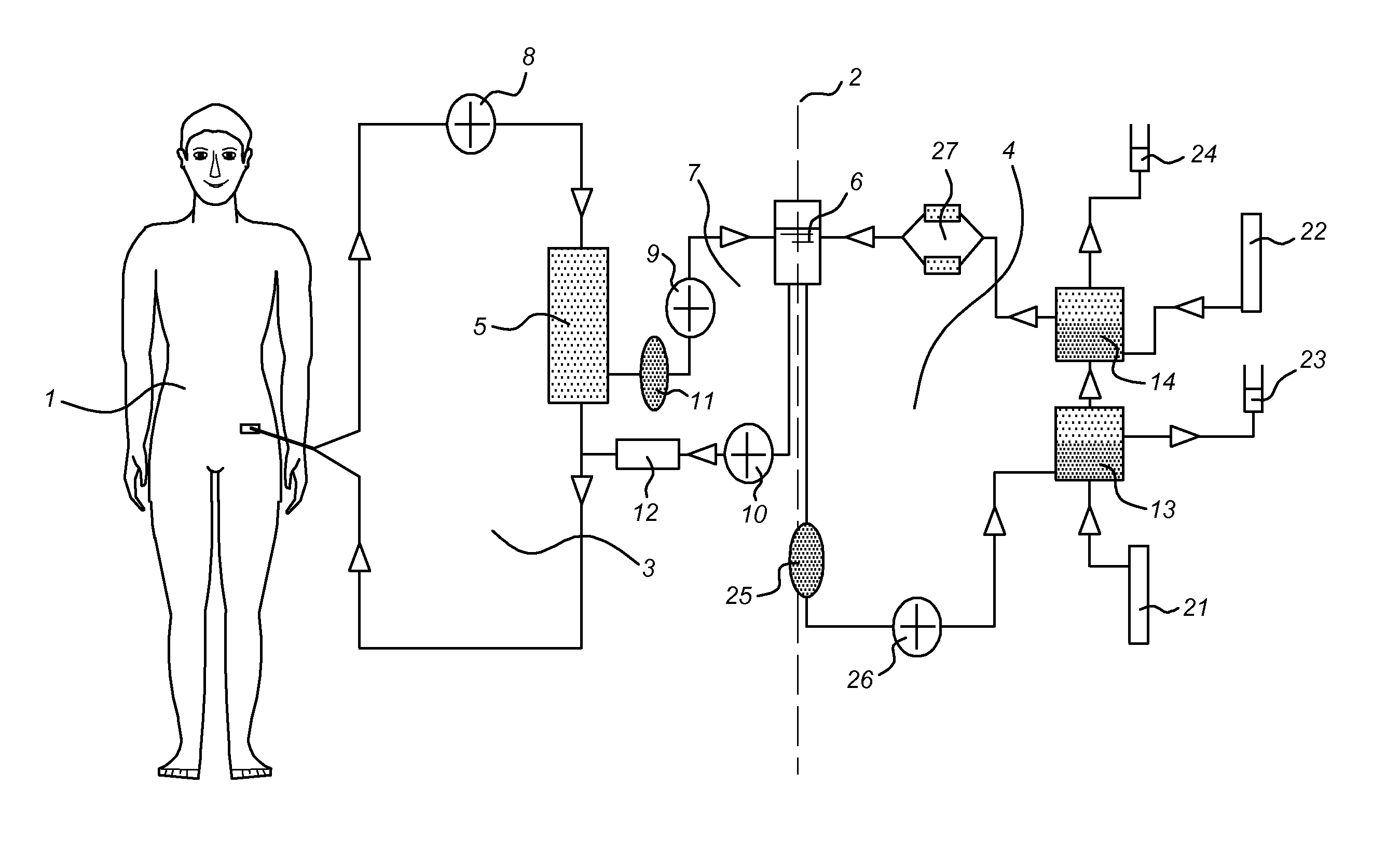
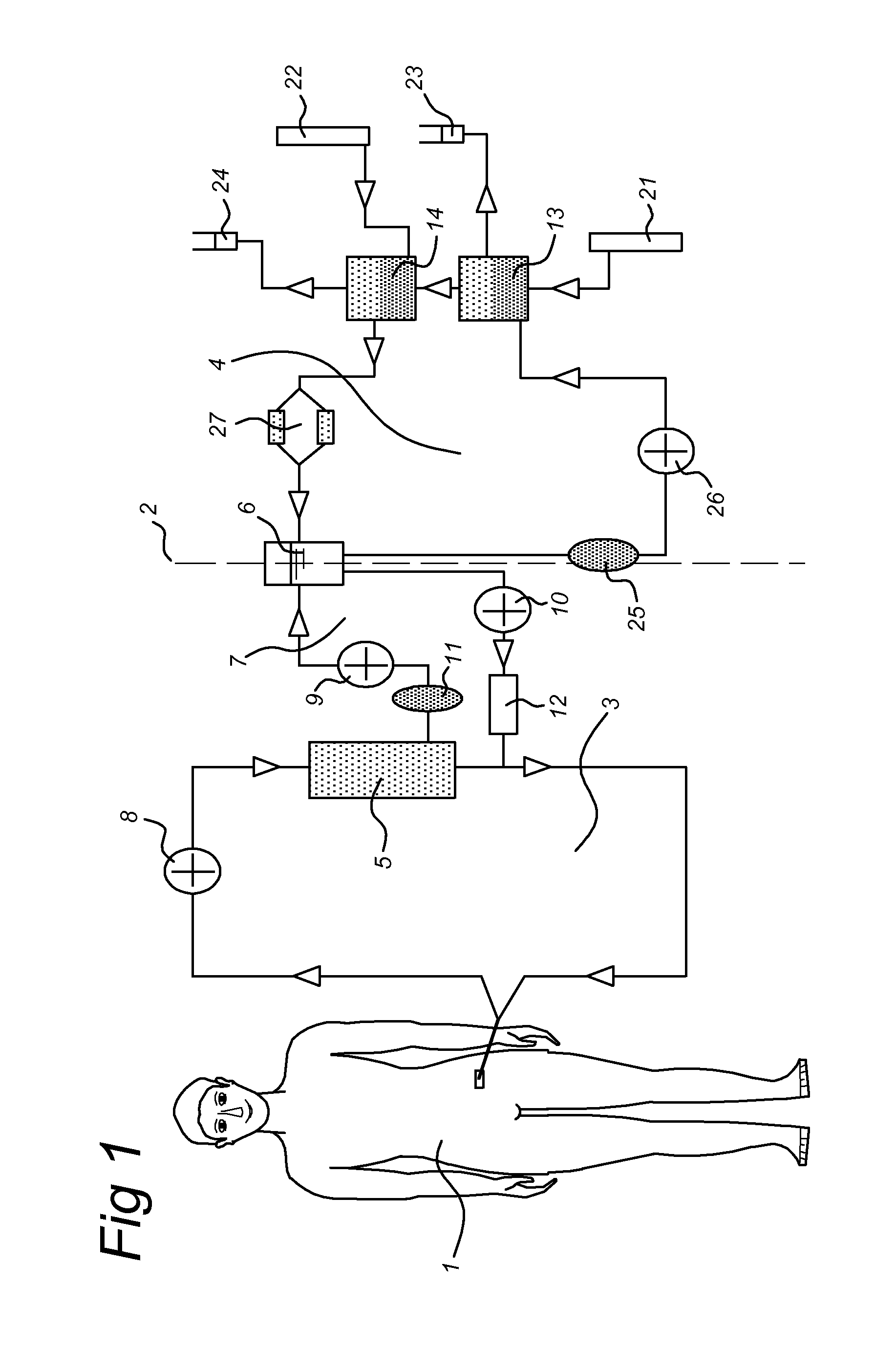
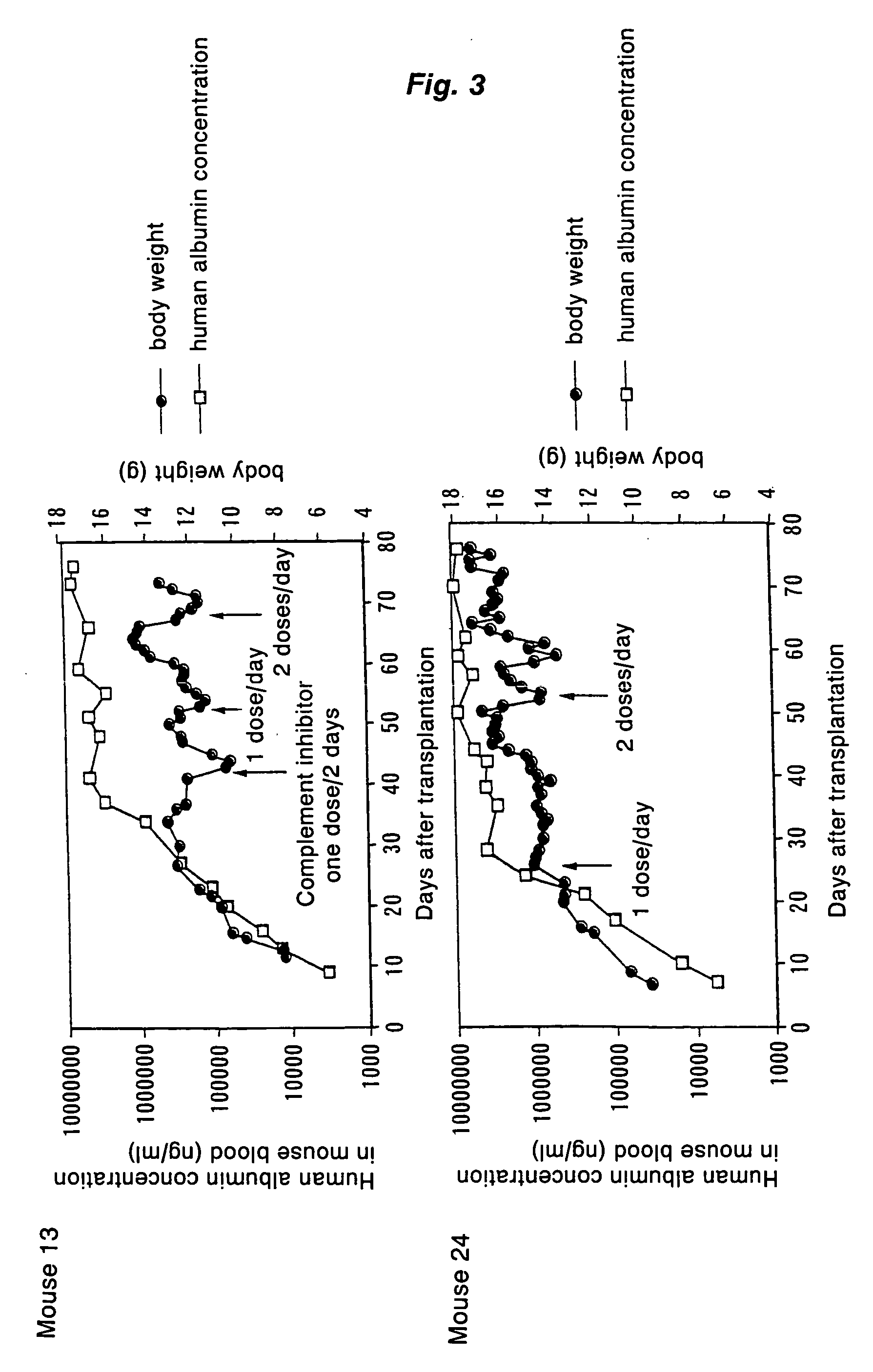
Transplanting human hepatocytes into a liver of an immunodeficient hepatopathy mouse, and then feeding the mouse transplanted with the human hepatocytes under such a condition as being protected from the attack by human complement produced by the human hepatocytes thereby proliferating the transplanted human hepatocytes in the mouse liver. Further, Obtaining human hepatocytes in large scale by repeating the above steps using the proliferated human hepatocytes.
Owner:HIROSHIMA IND PROMOTION ORG 80
Preparation and application of morinda root water extract, oligosaccharides and polysaccharides
ActiveCN108752497APromote proliferationPromote secretionSugar derivativesDigestive systemLiver and kidneyOrganism
The invention relates to a morinda root water extract, coarse polysaccharides and oligosaccharide and polysaccharide components and preparation methods and application thereof. The morinda root waterextract and the coarse polysaccharides are extracted from morinda roots by a mode of water extraction, then the coarse polysaccharides are separated to obtain the oligosaccharide and polysaccharide components in the coarse polysaccharides, and properties are measured. Experiments show that both the morinda root water extract and the coarse polysaccharides provided by the invention can promote theproliferation of spleen cells and the secretion of cell factors in mice, promote the proliferation of human liver cells, reduce the damage of toxic agents on cells, inhibit the expression of hepatitisB surface antigens and core antigens, inhibit the proliferation of liver cancer cells as well as inhibit the damage of ConA to the livers and kidneys of the mice, have obviously better biological activity than that of the morinda root oligosaccharides, polysaccharides or morinda root polysaccharide components prepared by other methods, and have the prospect of being developed into immunomodulators, anti-liver injury and anti-tumor drugs or health-care food. Preparation steps are simple, and preparation processes have less pollution to the environment and are suitable for industrial production.
Owner:SHUGUANG HOSPITAL AFFILIATED WITH SHANGHAI UNIV OF T C M +2
Inula wissmannian extract and preparation thereof and application in preparation of antitumor drug
The invention provides an inula wissmannian extract and preparation thereof and application in preparation of an antitumor drug. The extract is gemma alkane type sesquiterpene lactone inula wissmannian lactone methyl, ethyl, propyl, butyl and amyl or sheepear inula herb lactone. The extract has the following chemical structural formula and absolute configuration that: due to the toxicity killing function experiment of inula wissmannian lactone methyl, ethyl, propyl, butyl and amyl or sheepear inula herb lactone on human hepatoma cells HepG2, human prostatic cancer cells PC-3, human gastric carcinoma cells MGC-803, human leukemia cells K562, human nasopharynx cancer cells KB and normal human hepatocytes LO2, the result shows that the gemma alkane type sesquiterpene lactone has strong tumor cell killing function, and proliferation of tumor cells can be inhibited, so that the tumor cells are killed. The animal in-vivo experiment proves that the inula wissmannian plant extract and monomeric compounds have the anti-tumor effect and can serve as active ingredients for preparing the antitumor drug. A novel cancer treatment medicine is provided clinically, and high clinical application values and social benefits are generated.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Mice transplanted with human hepatocytes
Disclosed is a mouse having human hepatocytes transplanted therein. Specifically disclosed is a mouse having human hepatocytes transplanted therein. In the mouse, a foreign thymidine kinase gene or an urokinase-type plasminogen activator gene is retained so that the gene can be expressed specifically in the liver of the mouse, and hepatocytes of the mouse are substituted by human hepatocytes.
Owner:CENT INST FOR EXPERIMENTAL ANIMALS +1
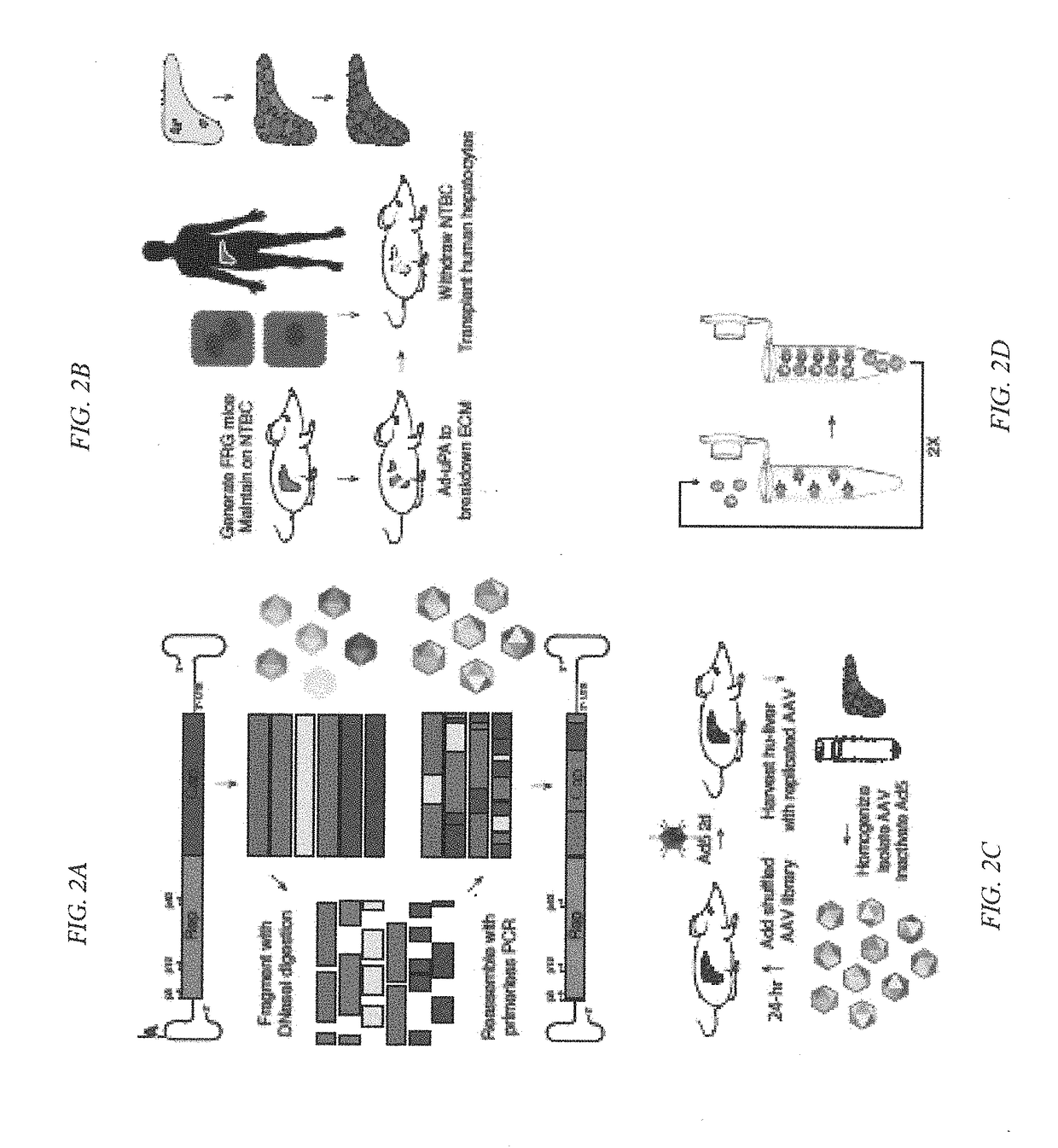
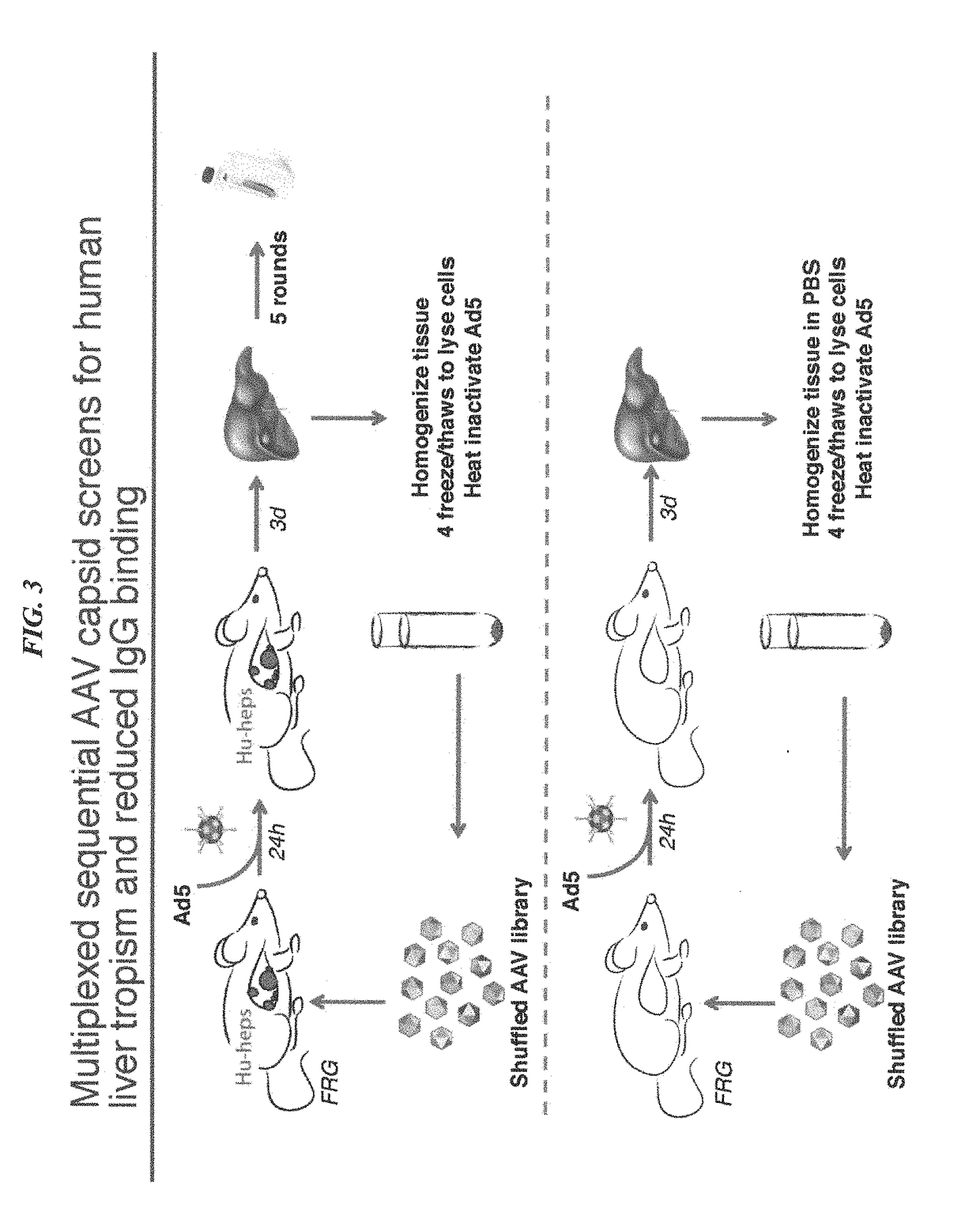
Novel recombinant adeno-associated virus capsids resistant to pre-existing human neutralizing antibodies
ActiveUS20170360962A1Improved profileEnhanced transductionGenetic material ingredientsDigestive systemHepaticaTropism
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Special culture medium and culture method for long-term maintenance, propagation, and subcultring of human hepatocyte
The invention discloses a special culture medium and culture method for long-term maintenance, propagation, and subcultring of human hepatocyte. The optimized culture medium for long-term culture of hepatocyte is disclosed for the first time. By using the culture medium, long-term propagation, subcultring and maintenance of the human hepatocyte can be performed, and forms and functions of the hepatocyte can be maintained. The culture medium is applied to culture hepatocyte, and the culture method is simple to operate and low in cost, and is safe and stable. The human hepatocyte obtained from culture, propagation and subcultring is applicable to clinical cell transplantation for treating liver diseases, is used for mechanism research related to liver diseases and for bioartificial liver construction, and is used as a hepatocyte source or a cell model for basic research relative to medicine hepatotoxicity, detection of medical efficacy and medical target, and the like. The culture medium and culture method has a bright application prospect.
Owner:HEPATOBILIARY SURGERY HOSPITAL SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV
Use of recombined adenovirus carrying hepatocyte growth factor gene
InactiveCN1142272CReach scientificImprove scienceHepatocyte-growth/scatter/tumor-cytotoxic factorDigestive systemDiseaseFactor ii
The present invention relates to biomedicine. Human hepatocyte growth factor full-length code area cDNA is inserted to defect duplicated adenovirus vector GT4050 to obtain recombinant adenovirus with carried human hepatocyte growth factor. When it is injected to rat body, the recombinant adenovirus has treating effect on rat's liver fibrillation. When it is applied to wound, the recombinant adenovirus can prevent scar.
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE PLA
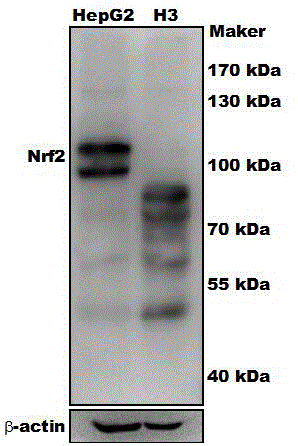
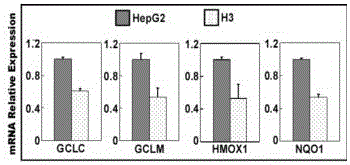
sgRNA and vector pair for orientated knockout of nrf2 gene in human hepatocyte and application
InactiveCN106520772AEasy to editExcellent gene editing effectPeptidesNucleic acid vectorCancer researchHuman hepatocyte
The invention provides sgRNA and a vector pair for orientated knockout of an Nrf2 gene in human hepatocyte and application. The sgRNA consists of sgRNA1 for specifically recognizing the Nrf2 gene and sgRNA2 for specifically recognizing the Nrf2 gene; the vector pair consists of an Nrf2-CAS9-1 vector and an Nrf2-CAS9-2 vector; the Nrf2-CAS9-1 vector is a vector containing an sgNRA1 fragment; the Nrf2-CAS9-2 vector is a vector containing an sgRNA2 fragment; the vector pair can be applied to orientated knockout of the Nrf2 gene in the human hepatocyte and establishment of an Nrf2 gene knockout type human hepatocyte. By adopting the sgRNA, the vector pair and the application, the purpose of completely knocking out the Nrf2 gene at the genetic background that the length of a genome is not greatly changed can be achieved, and thus no Nrf2 protein can be retained in liver cells.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
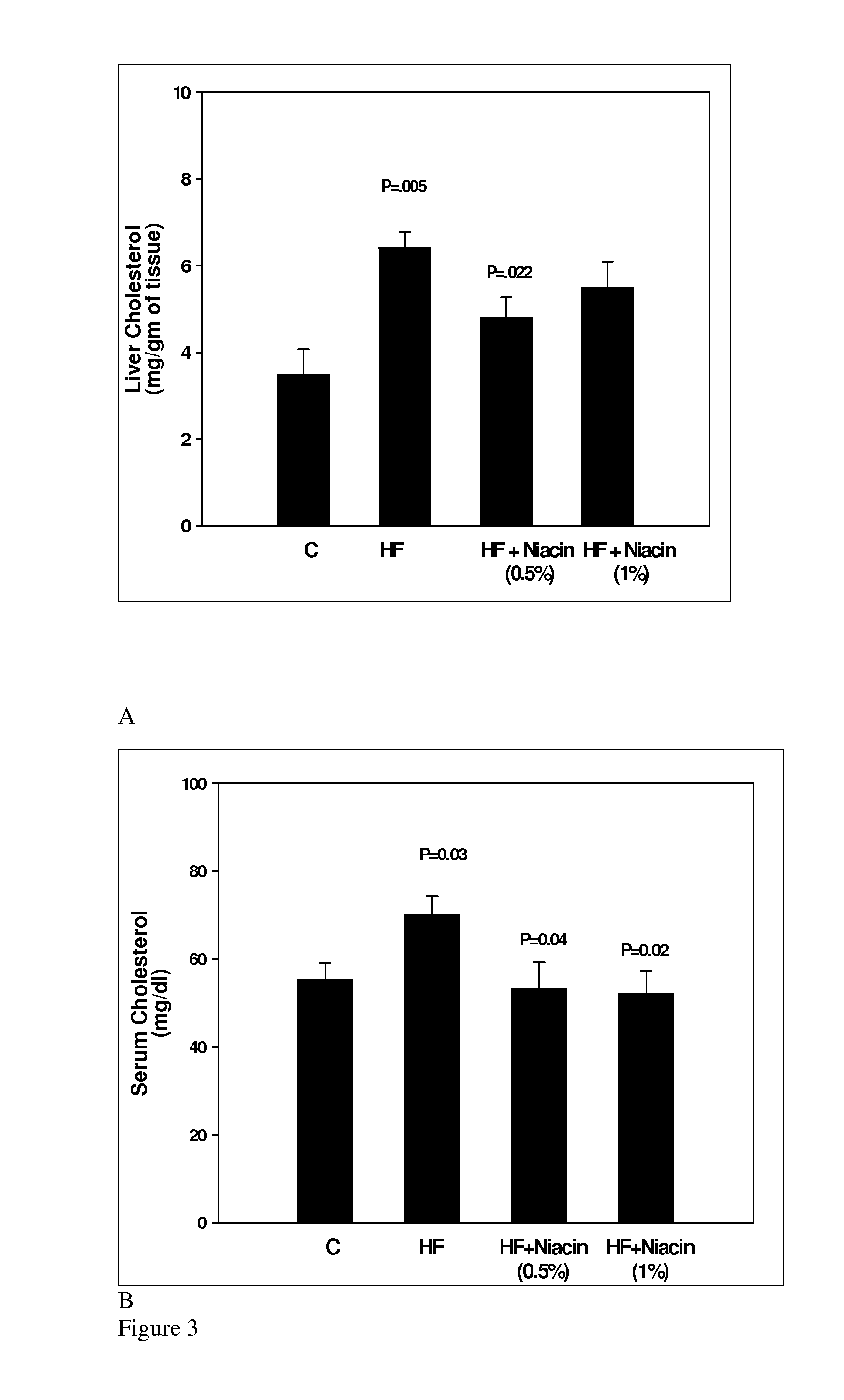
Indication for use of niacin (nicotinic acid) for treatment, prevention and reversal of fatty liver disease
Niacin prevents and / or reverses the development of experimental hepatic steatosis, deposition of triglycerides in liver and serum of individuals, deposition of total cholesterol in liver and serum in individuals, and inhibit liver lipid peroxidation and oxidative stress in individuals at risk of developing fatty liver disease or NAFLD. In cultured human hepatocytes, niacin inhibits alcohol-induced fat accumulation.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com