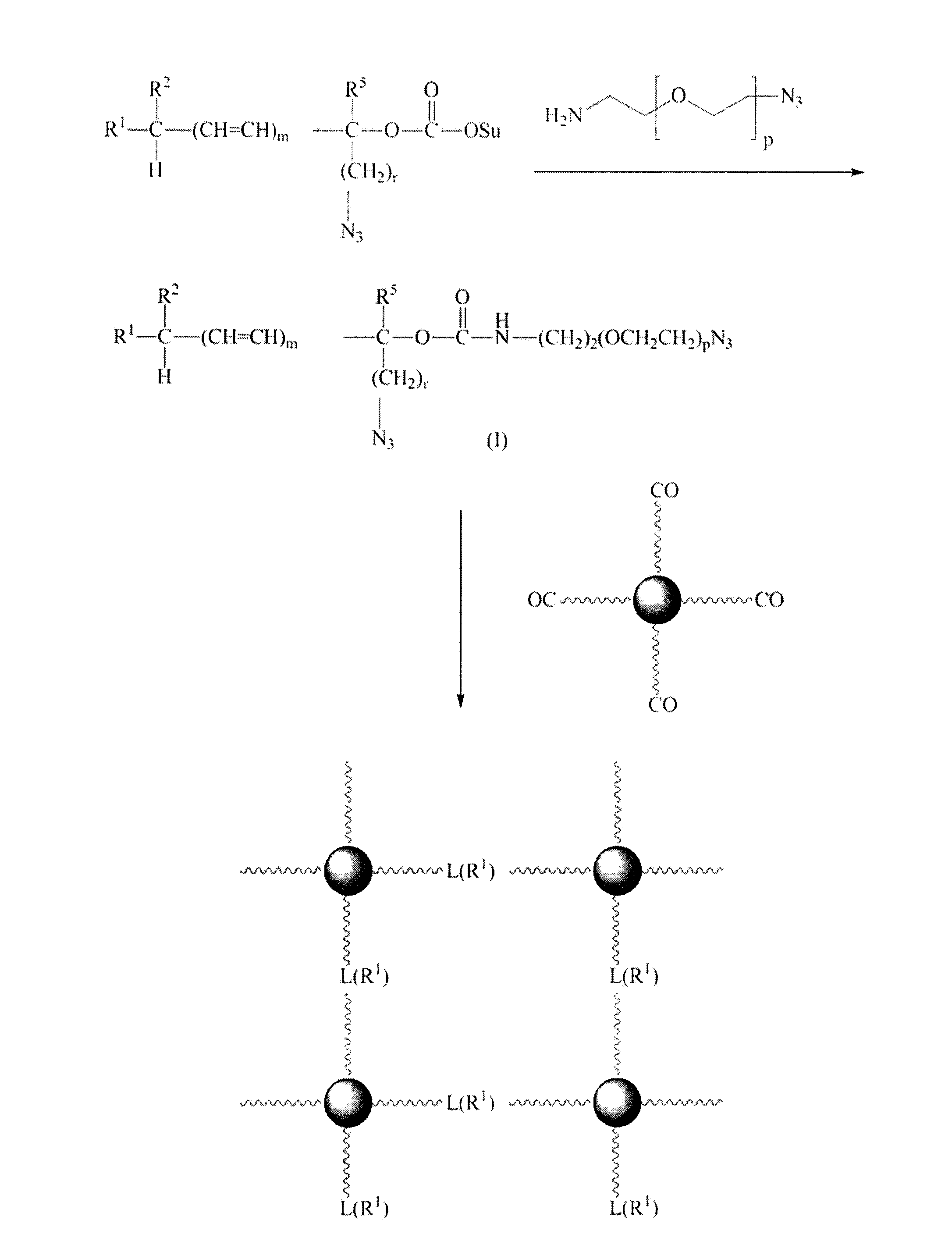
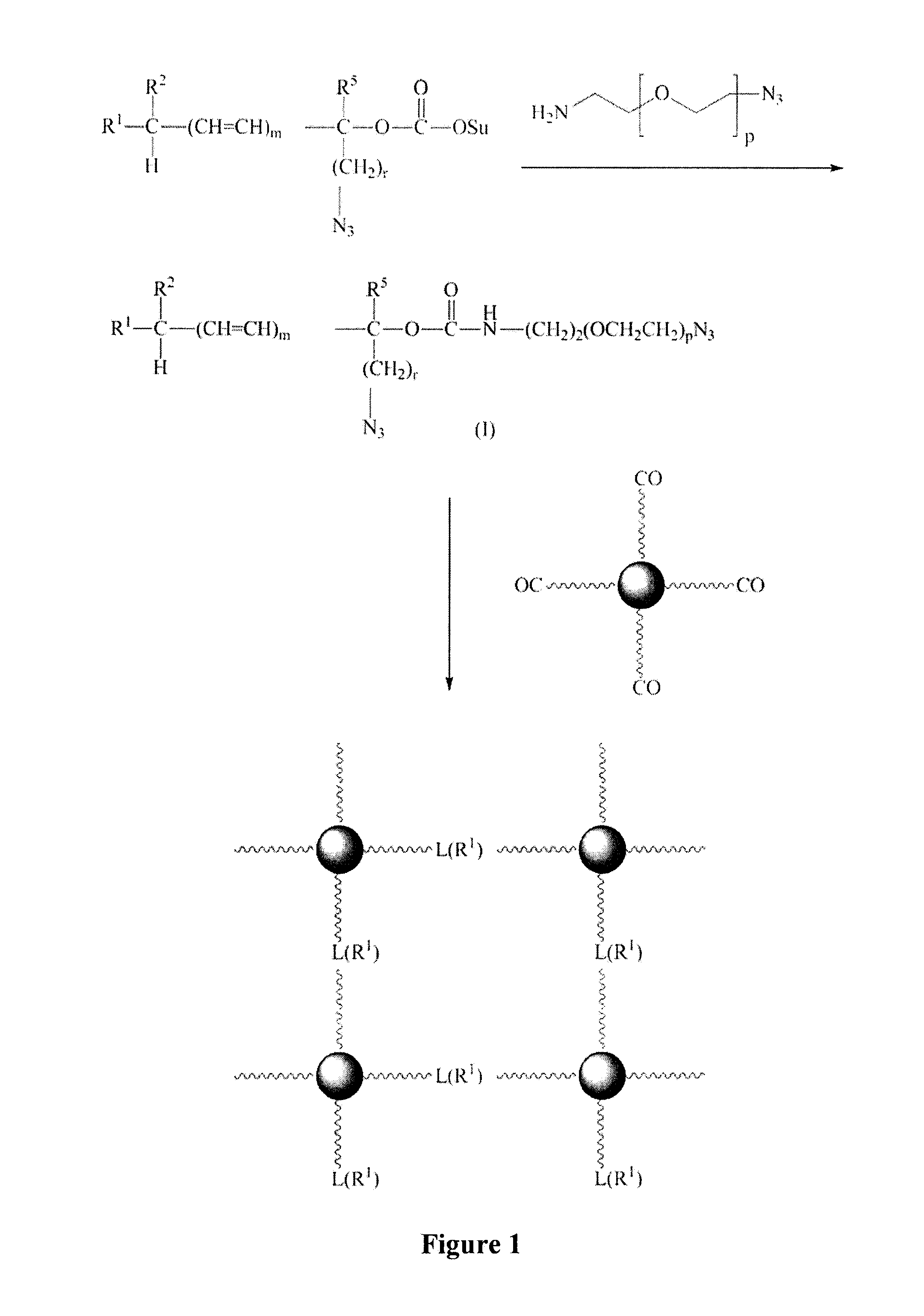
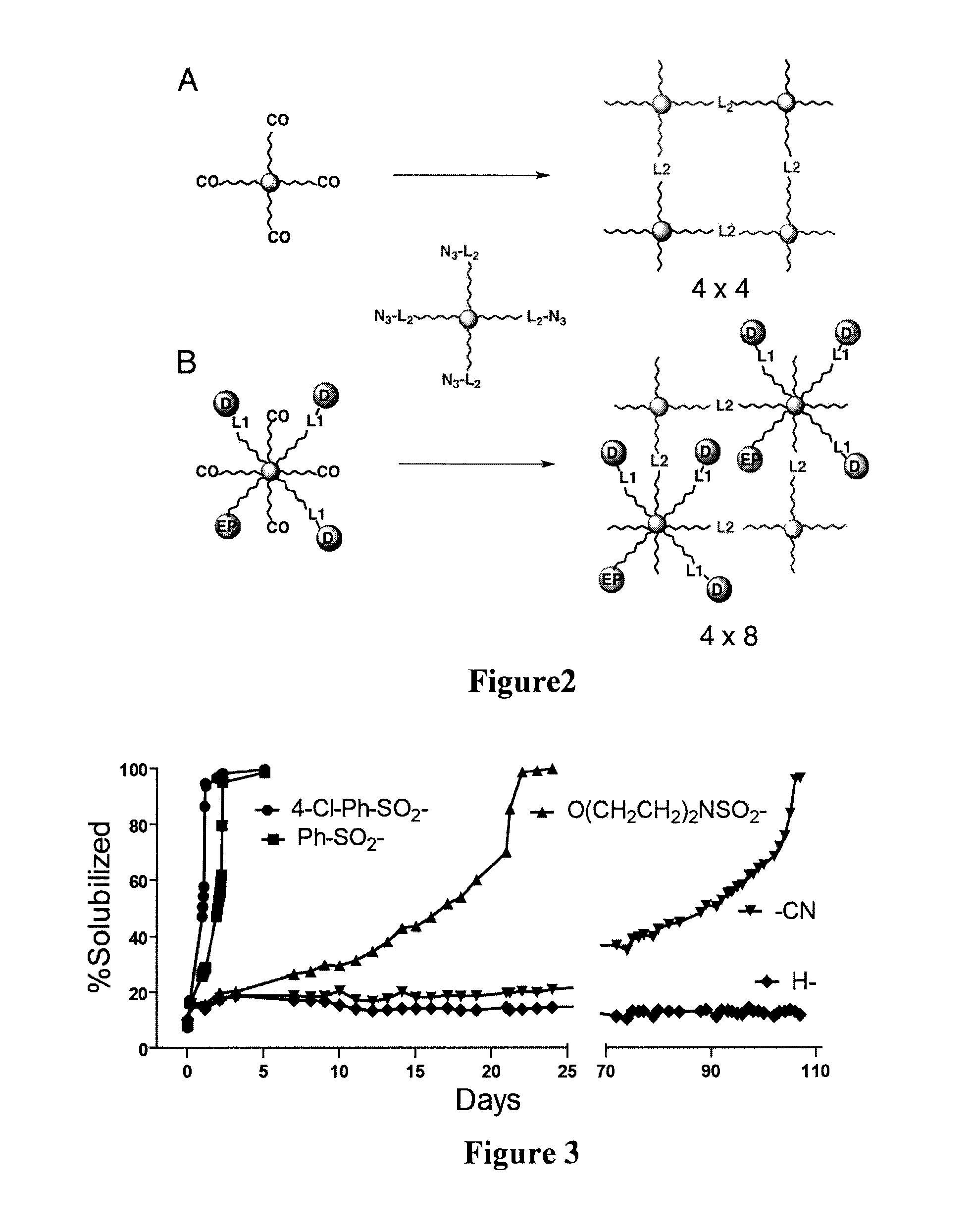
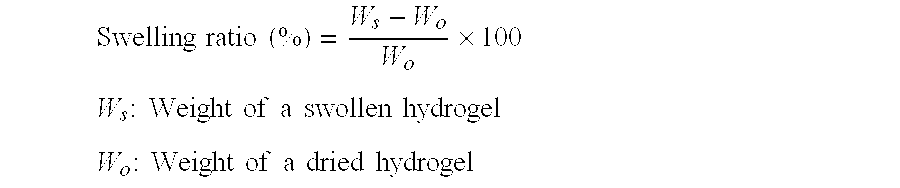Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
91 results about "Biodegradable hydrogels" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
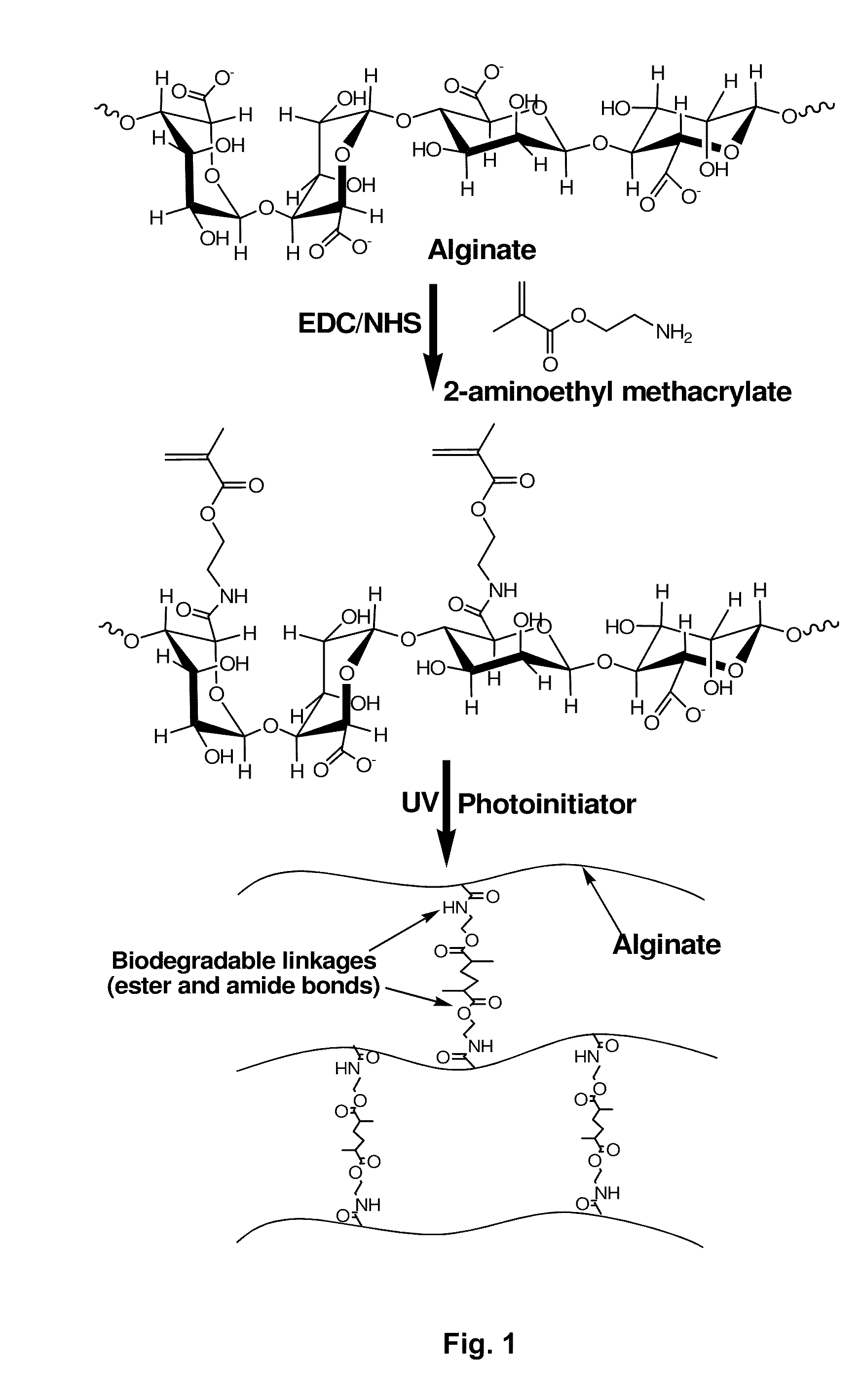
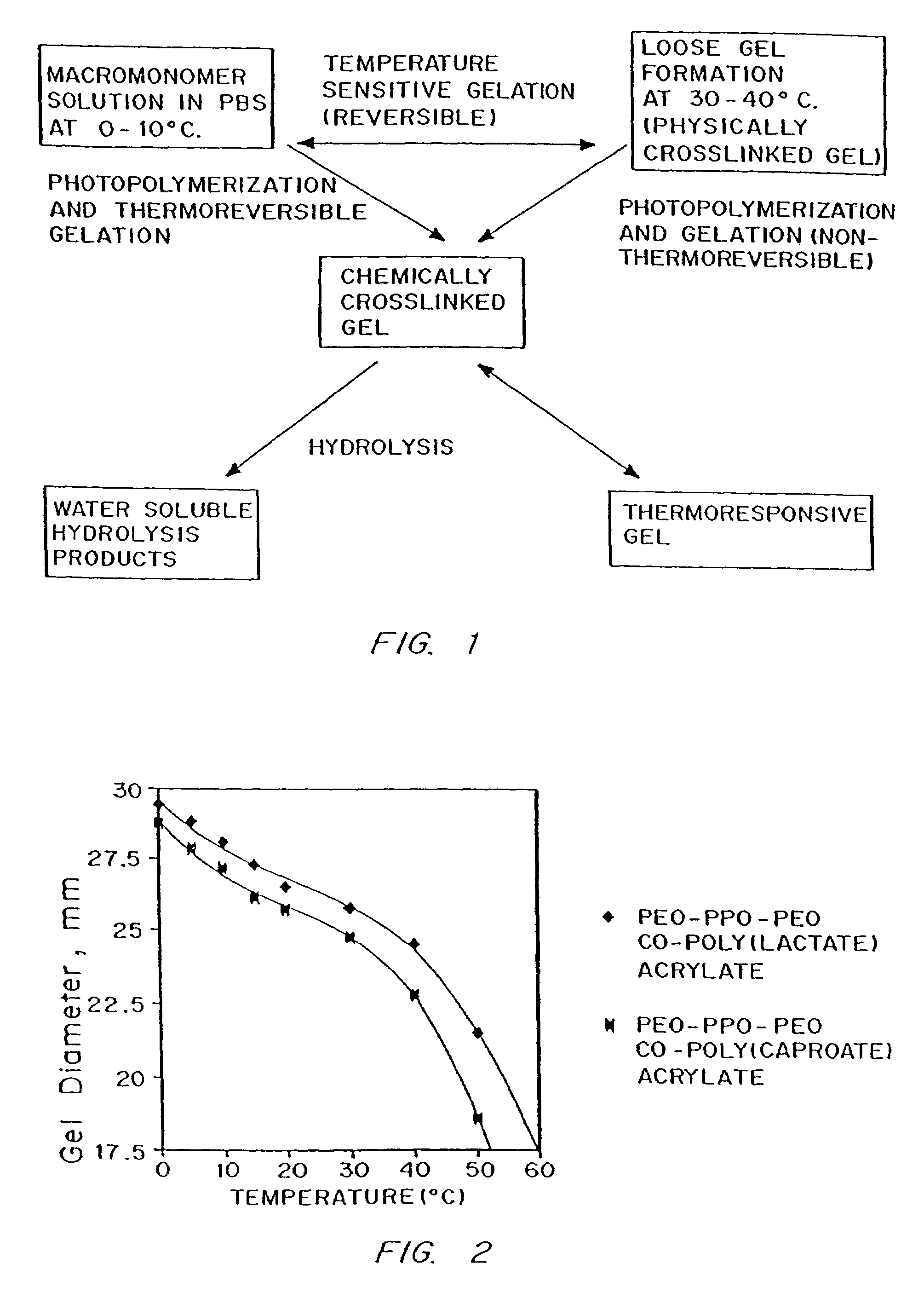
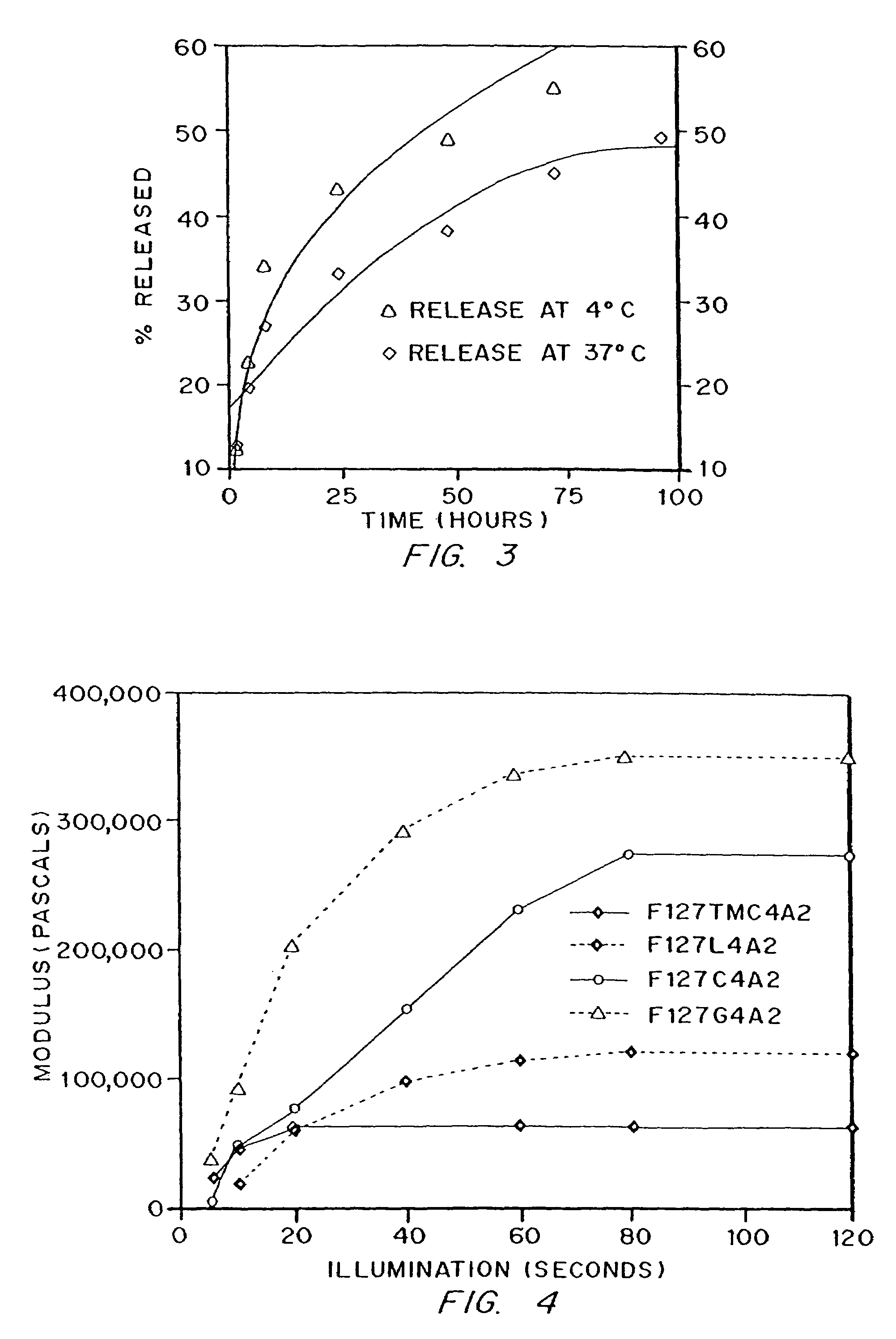
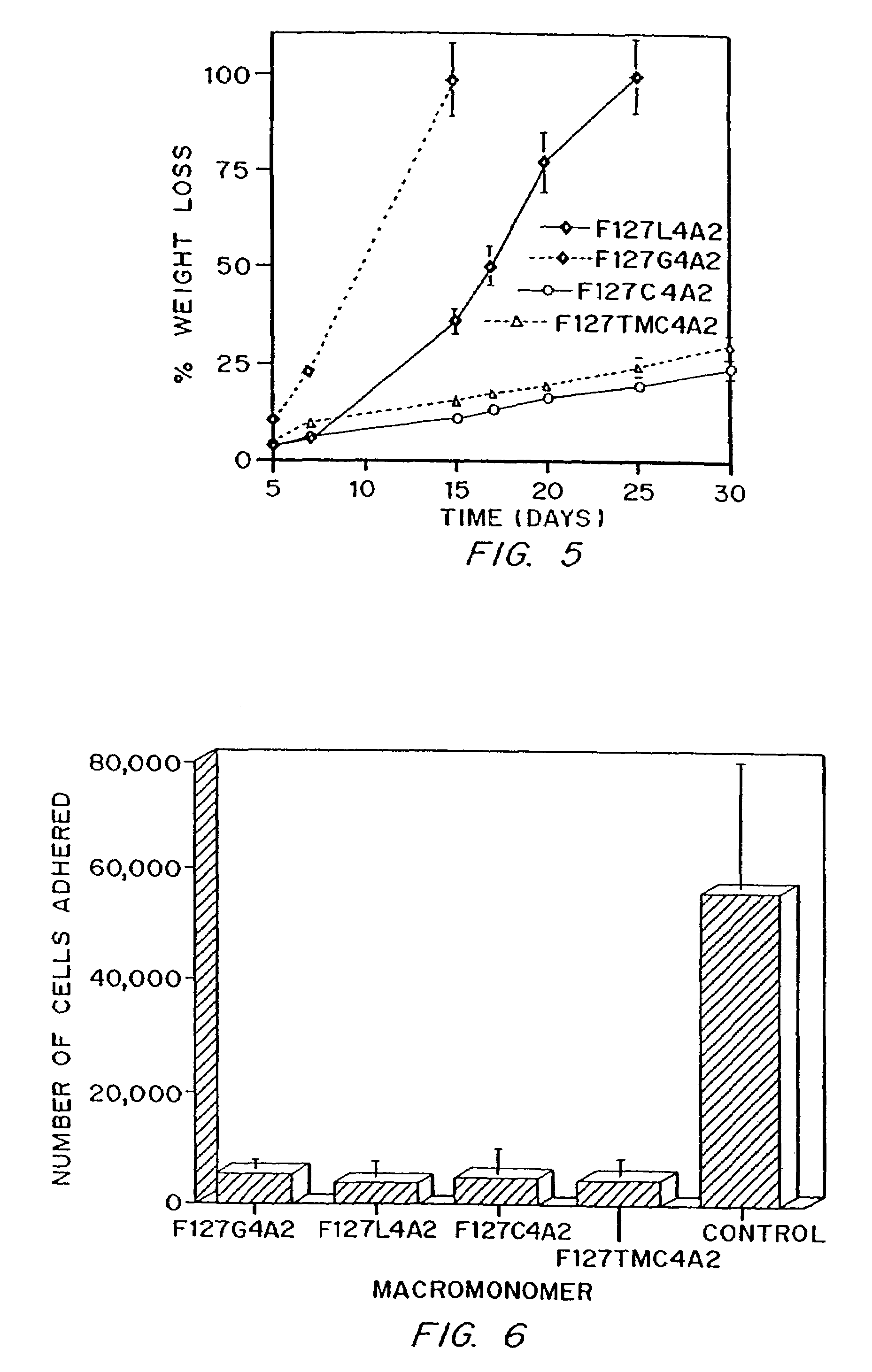
Photopolymerizable biodegradable hydrogels as tissue contacting materials and controlled-release carriers
InactiveUS6306922B1Fast gelationRapid polymerizationImmobilised enzymesPowder deliveryThermal energyUltraviolet lights
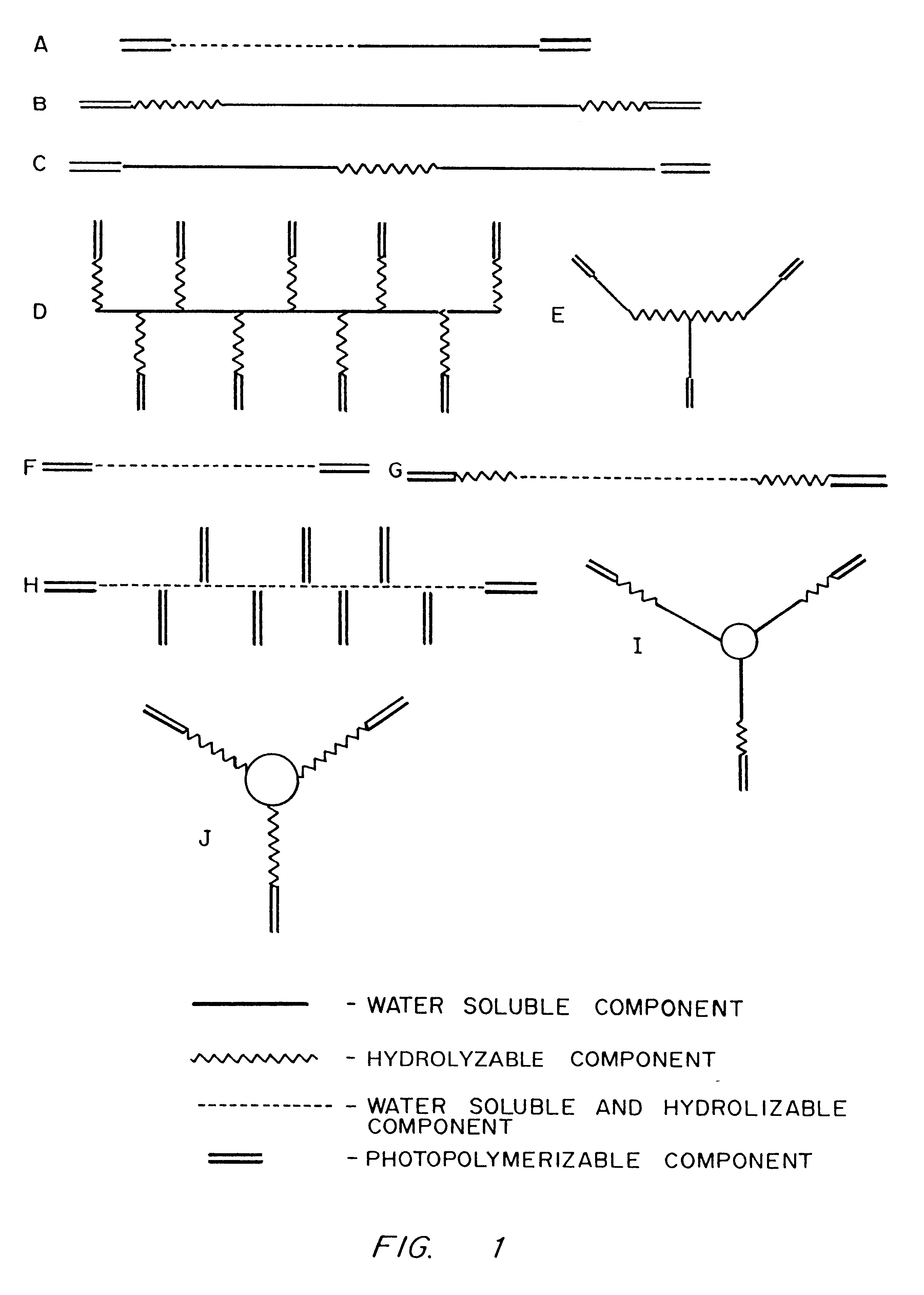
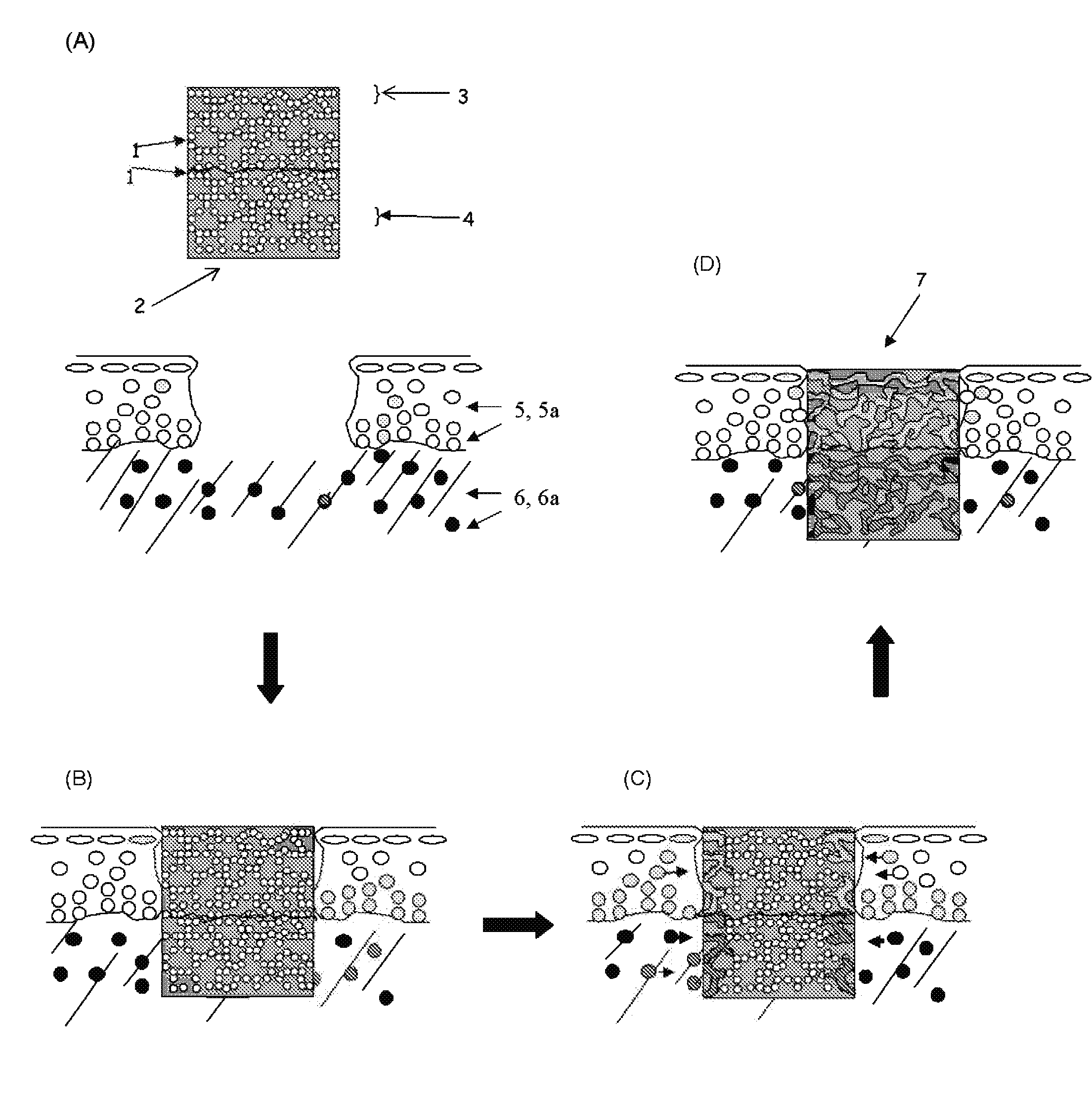
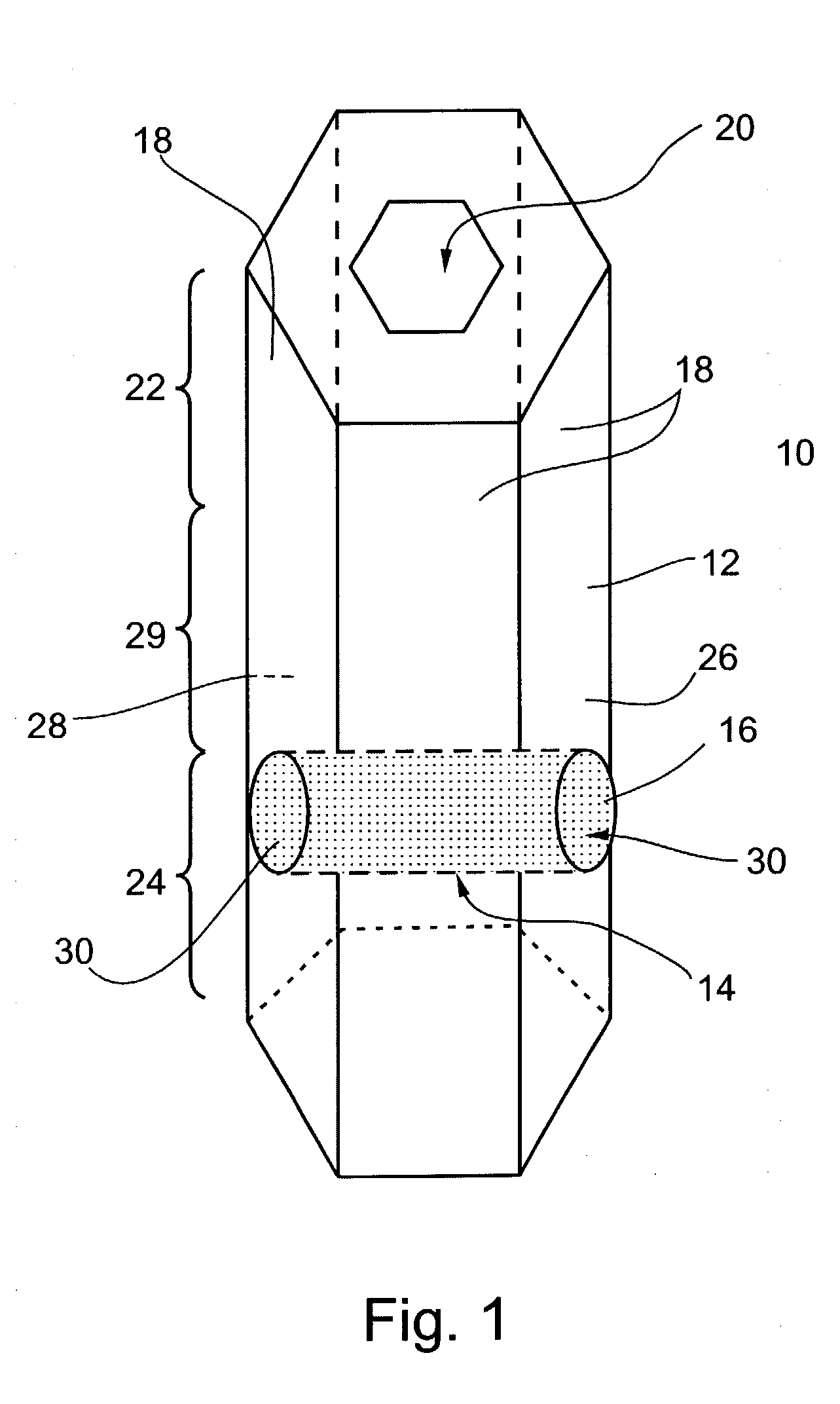
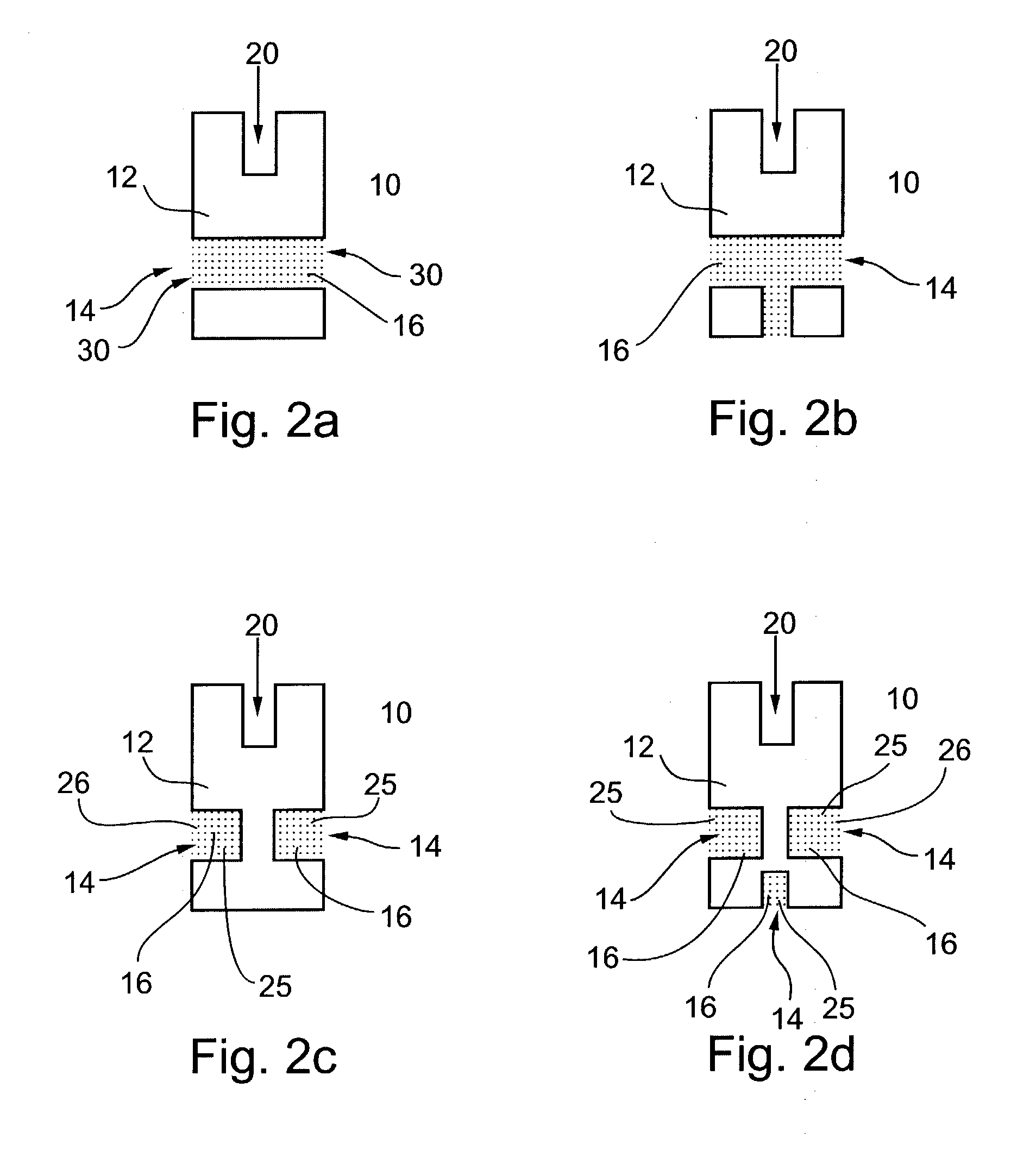
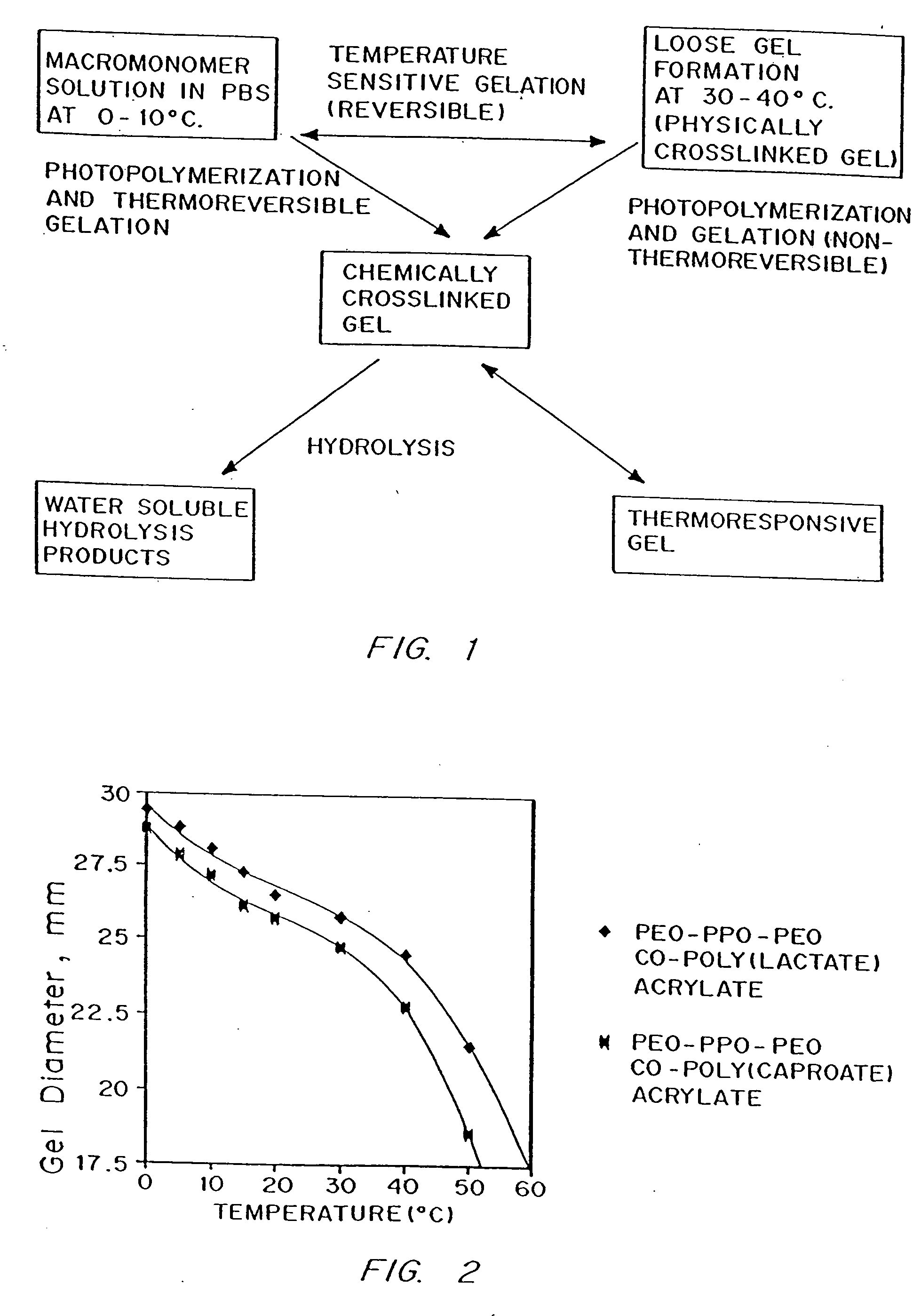
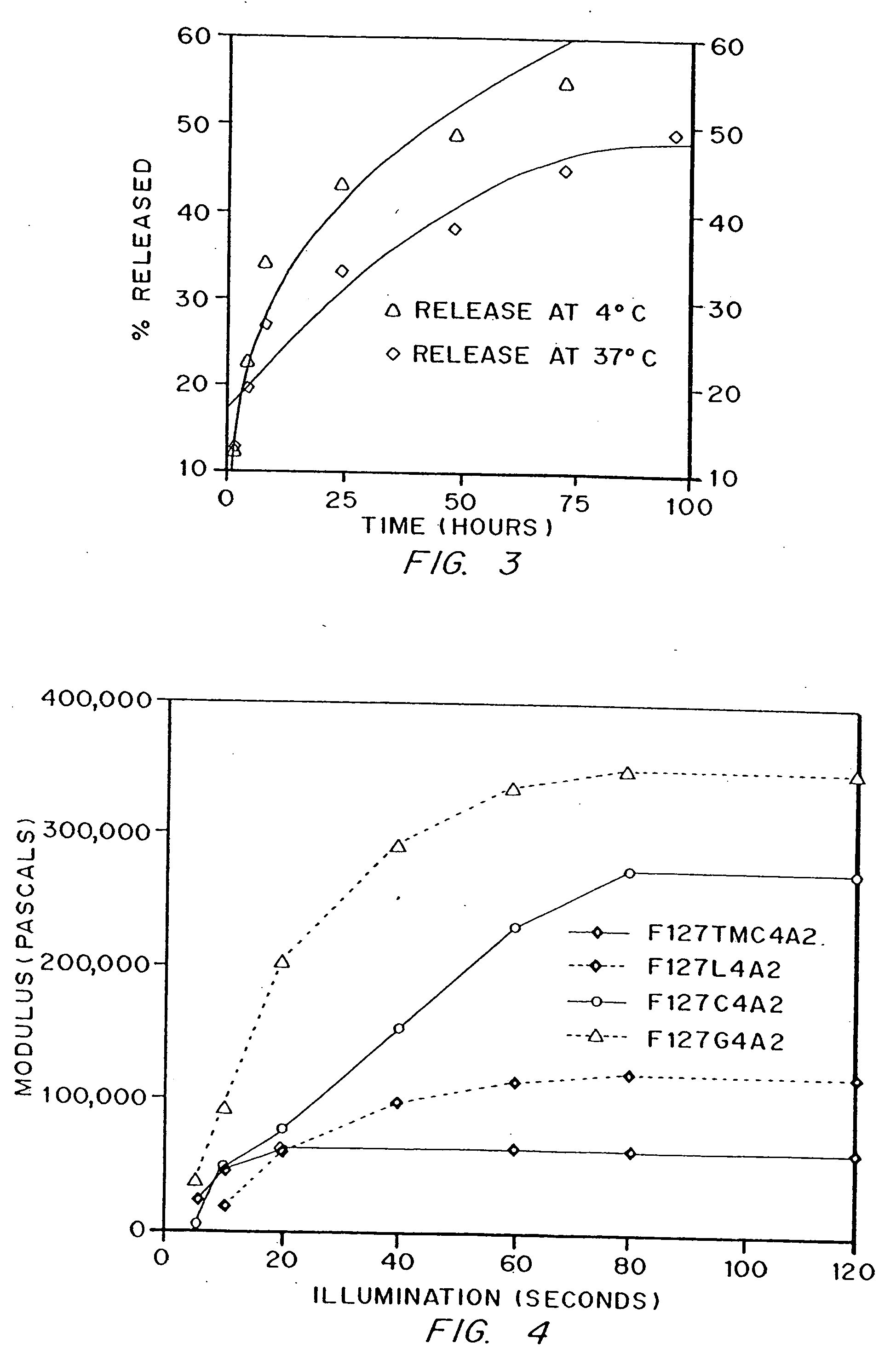
Hydrogels of polymerized and crosslinked macromers comprising hydrophilic oligomers having biodegradable monomeric or oligomeric extensions, which biodegradable extensions are terminated on free ends with end cap monomers or oligomers capable of polymerization and cross linking are described. The hydrophilic core itself may be degradable, thus combining the core and extension functions. Macromers are polymerized using free radical initiators under the influence of long wavelength ultraviolet light, visible light excitation or thermal energy. Biodegradation occurs at the linkages within the extension oligomers and results in fragments which are non-toxic and easily removed from the body. Preferred applications for the hydrogels include prevention of adhesion formation after surgical procedures, controlled release of drugs and other bioactive species, temporary protection or separation of tissue surfaces, adhering of sealing tissues together, and preventing the attachment of cells to tissue surfaces.
Owner:BOARD OF REGENTS
Hydrogel Porogents for Fabricating Biodegradable Scaffolds
InactiveUS20080206308A1Rheologic propertyElimination of porogen leaching stepPowder deliveryBiocideBiodegradable scaffoldBiodegradable hydrogels
Hydrogel microparticles with entrapped liquid are used as the porogen to reproducibly form interconnected pore networks in a porous scaffold. In one embodiment, a biodegradable unsaturated polymer, a crosslinking agent, and a porogen comprising biodegradable hydrogel microparticles are mixed together and allowed to form a porous scaffold in an mold or in a body cavity. Example biodegradable unsaturated polymers include poly(propylene fumarate) and poly(e-caprolactone-fumarate). The cosslinking agent may be a free radical initiator, or may include a free radical initiator and a monomer capable of addition polymerization. Example hydrogel microparticles include uncrosslinked or crosslinked collagen , an uncrosslinked or crosslinked collagen derivative, and an uncrosslinked or crosslinked synthetic biodegradable polymer such as oligo(poly(ethylene glycol) fumarate).
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Porous non-biodegradable hydrogel admixed with a chemoattractant for tissue replacement
InactiveUS20090017096A1Facilitate in vivo tissue ingrowthEasy to integrateBone implantPolyesterTissue defect
A non-biodegradable hydrogel matrix containing microspheres of a biodegradable polymer for the purpose of treating, repairing, or replacing damaged biological tissue is described. The biodegradable phase can be admixed with a chemoattractant. Examples of degradable polymers include degradable polyesters such as 50:50 PLA:PGA, the degradation profiles of which are well characterized. The matrix is permanently inserted into a tissue defect to provide mechanical support before, during, and after tissue ingrowth.
Owner:NEW YORK SOC FOR THE RUPTURED & CRIPPLED MAINTAINING THE HOSPITAL FOR SPECIAL SURGERY +1
Hydrogel incorporated with bone growth promoting agents for dental and oral surgery
A dental implant that comprises a generally rod-like article formed with one or more hollow(s) therein and a biodegradable hydrogel containing one or more bone growth-promoting agent(s) in the hollow(s) is disclosed. A method of implanting the dental implant and a method of sinus augmentation prior to implanting a dental implant are further disclosed.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Multiblock biodegradable hydrogels for drug delivery and tissue treatment
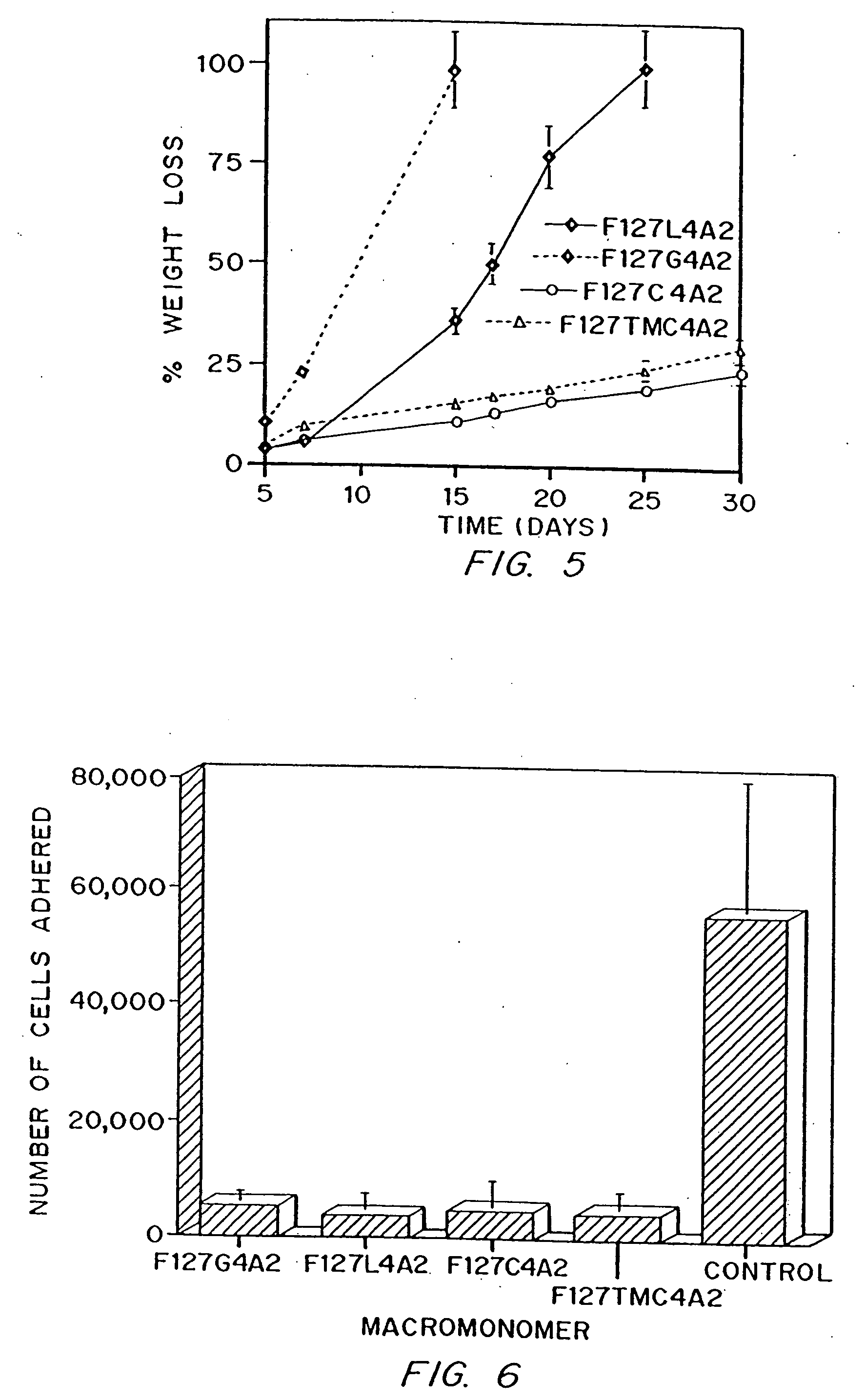
Gel-forming macromers including at least four polymeric blocks, at least two of which are hydrophobic and at least one of which is hydrophilic, and including a crosslinkable group are provided. The macromers can be covalently crosslinked to form a gel on a tissue surface in vivo. The gels formed from the macromers have a combination of properties including thermosensitivity and lipophilicity, and are useful in a variety of medical applications including drug delivery and tissue coating.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Hydrolysable hydrogels for controlled release
InactiveUS7060296B2Poorly controllable release behaviourImprove applicabilityPowder deliverySolution deliveryCross-linkControlled release
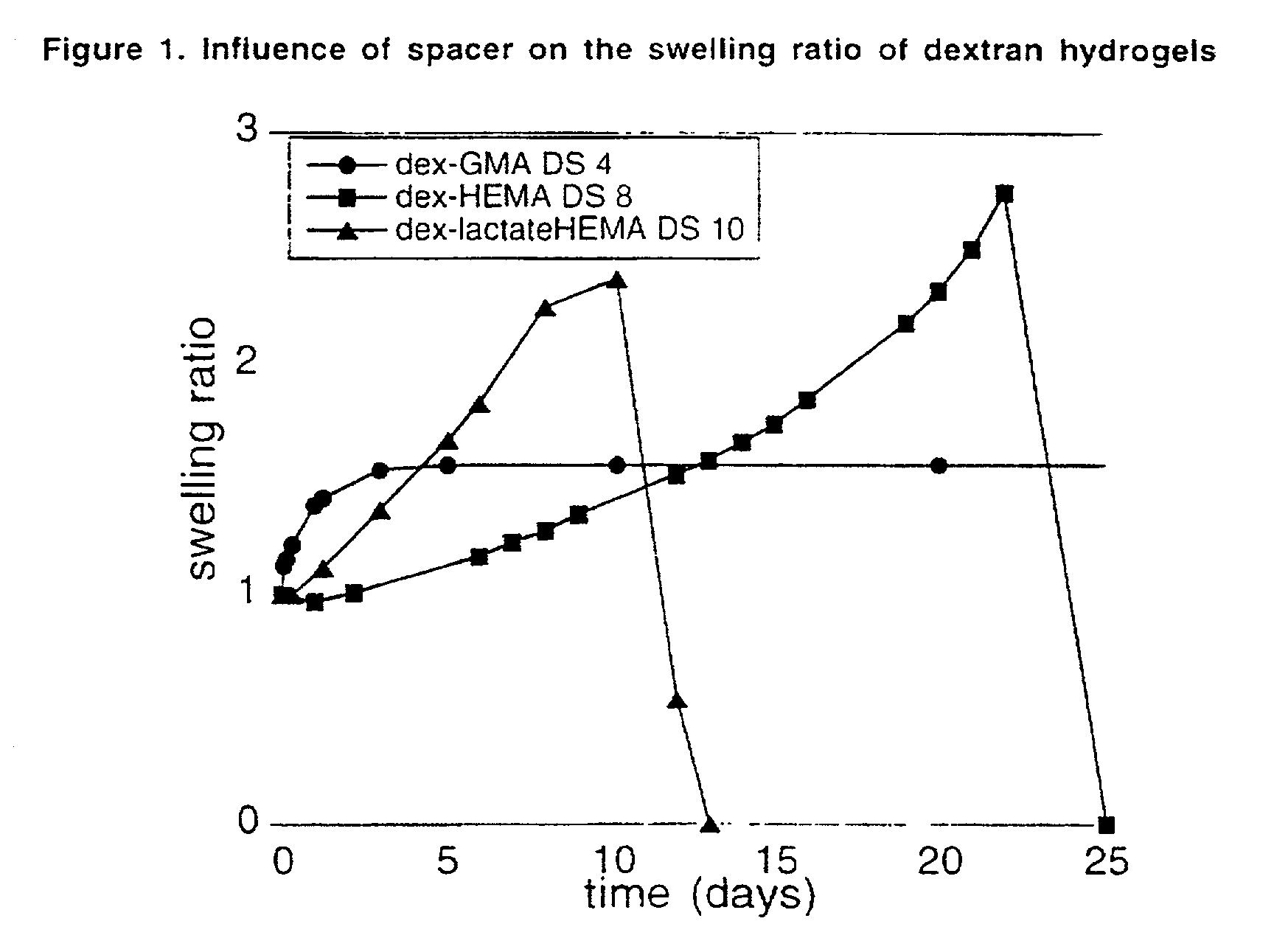
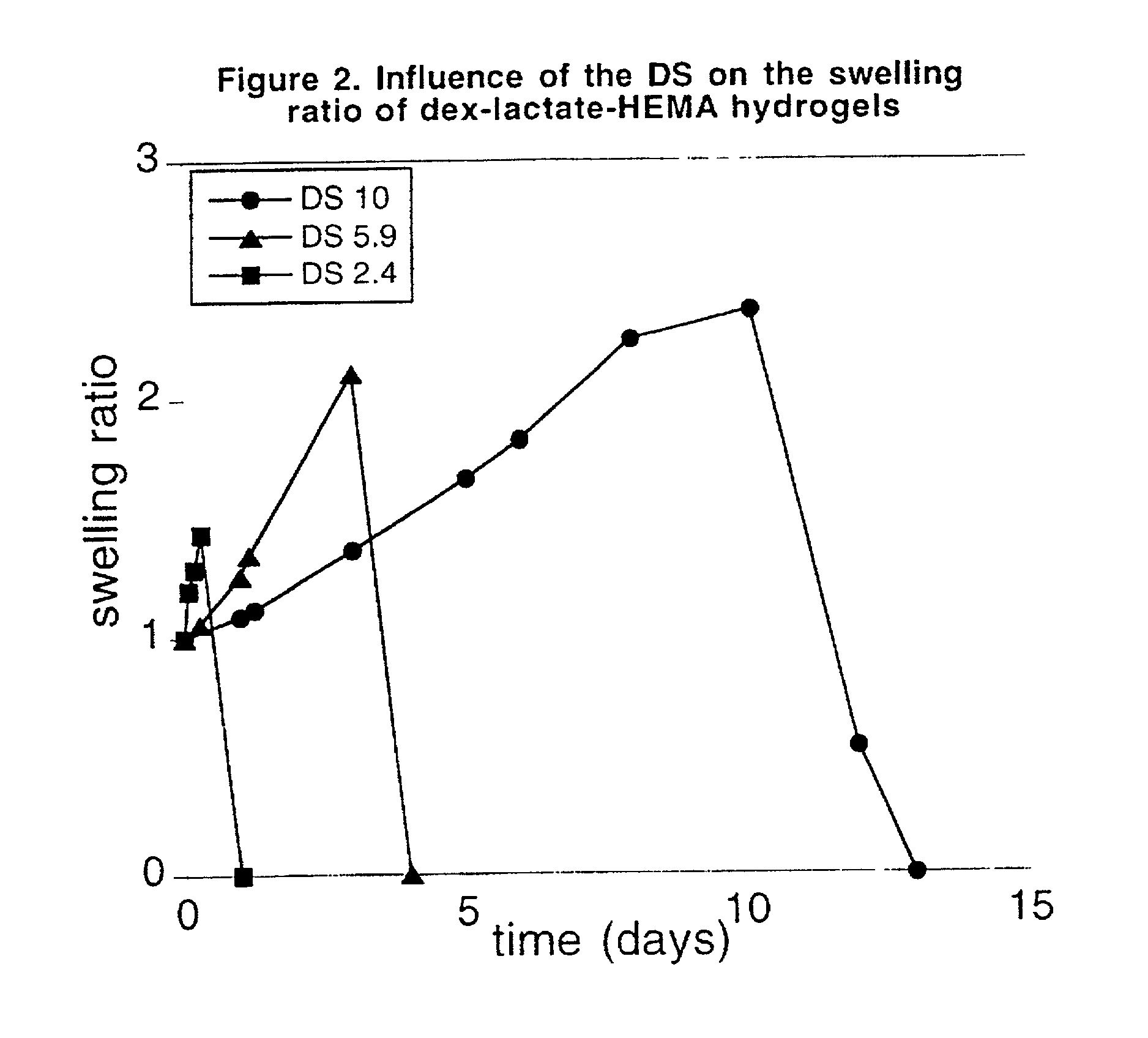
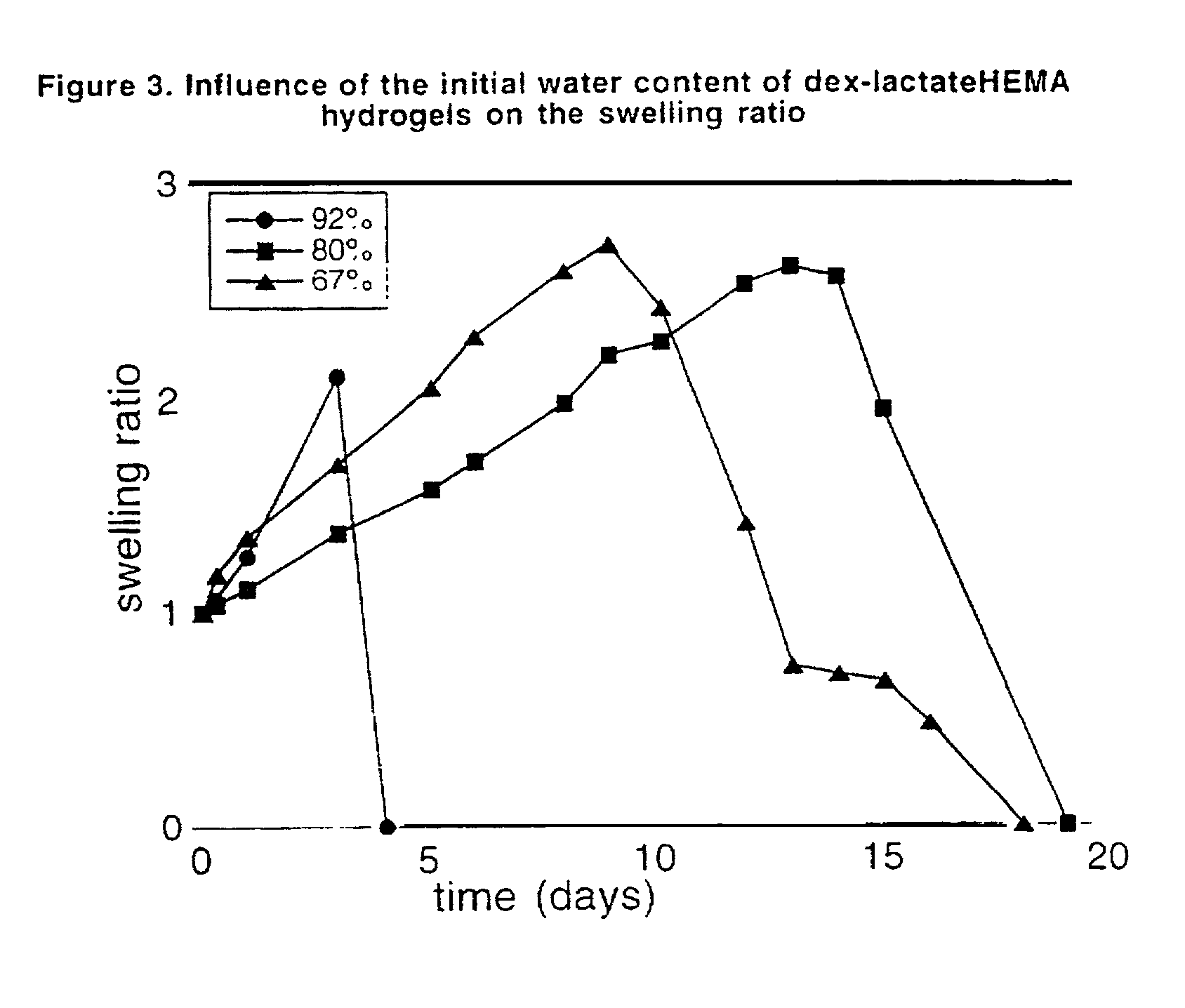
The present invention relates to a biodegradable hydrogel comprising bonds which are hydrolyzable under physiological conditions. More particularly, the hydrogel consists of two interpenetrating polymer networks interconnected to one another through hydrolyzable spacers. In addition, the invention relates to a method for the preparation of a hydrogel, wherein macromolecules, e.g., polymers which contain bonds which are hydrolyzable under physiological conditions, are cross-linked in an aqueous solution.
Owner:UTRECHT UNIVERSITY
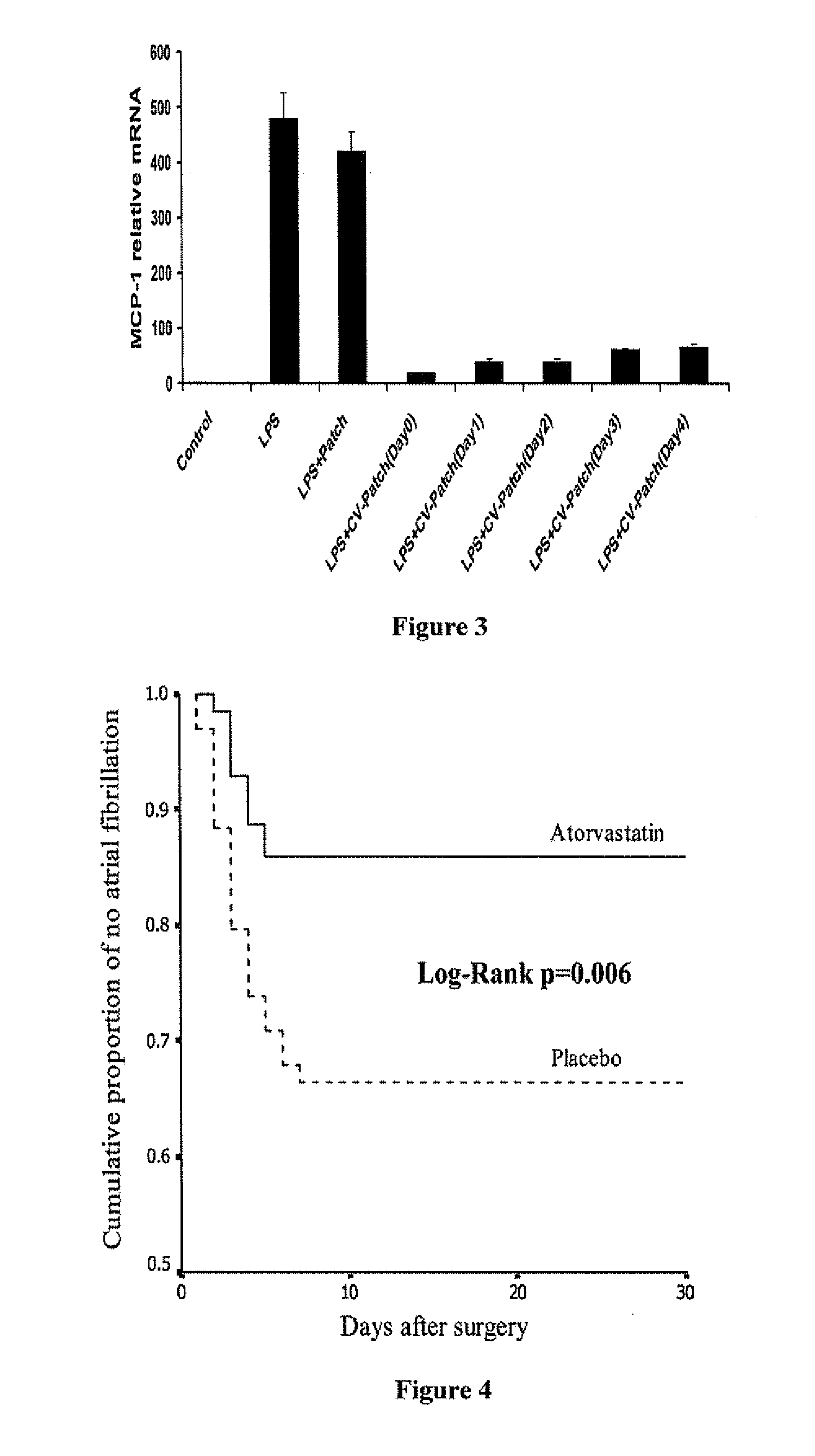
Drug eluting patch for the treatment of localized tissue disease or defect
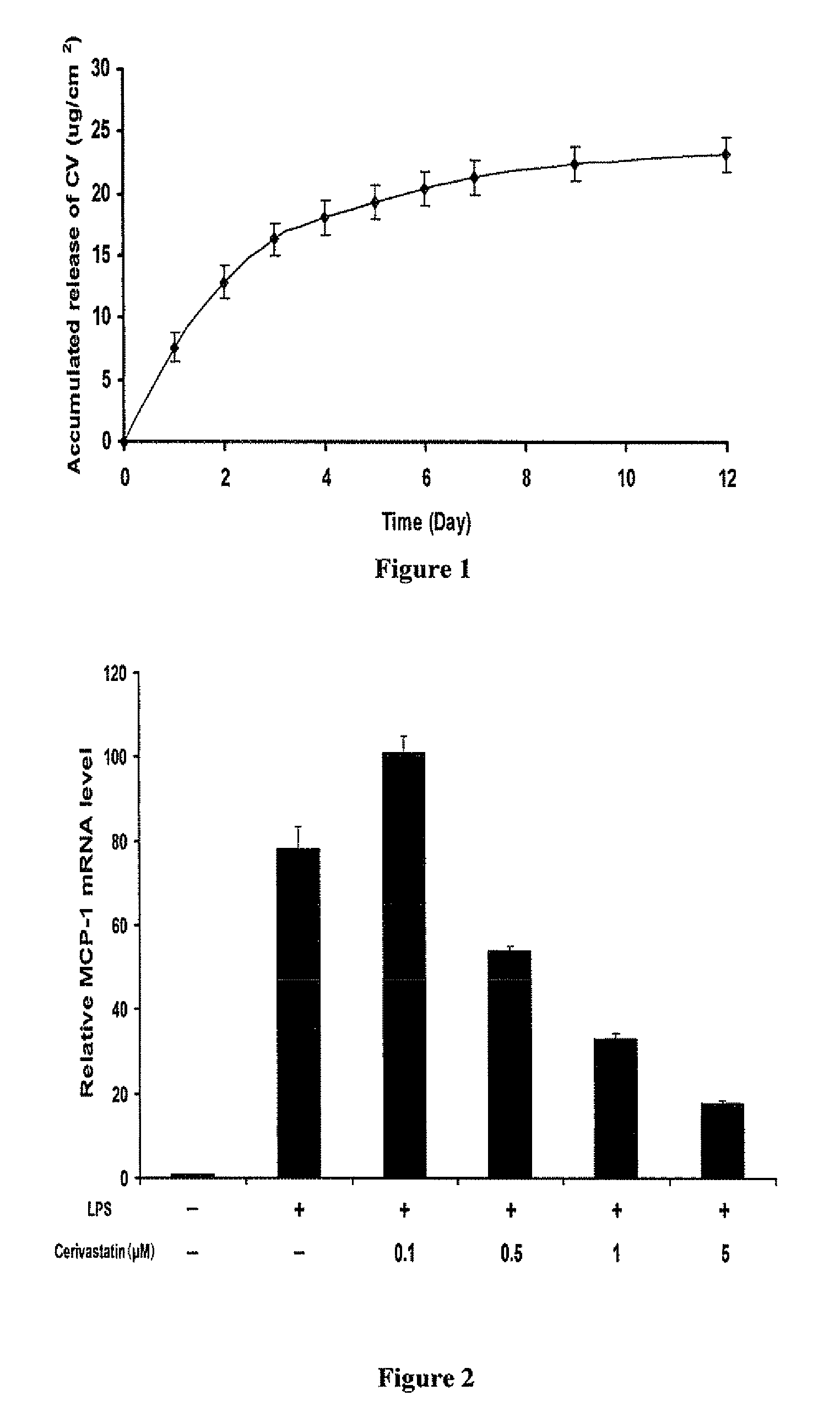
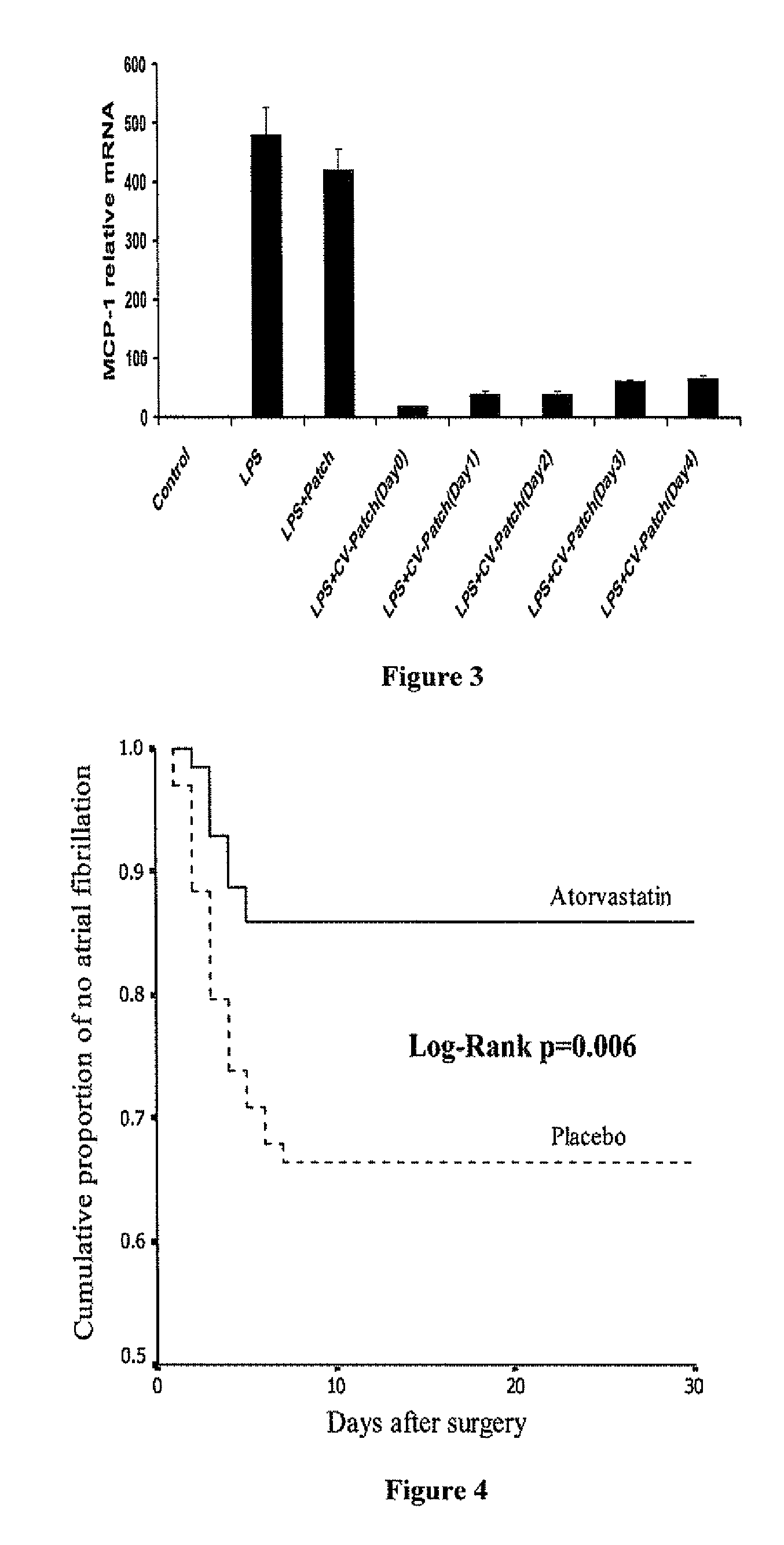
A polymeric matrix for delivery of an HMG CoA reductase inhibitor such as a statin to tissue such as cardiac tissue in need thereof for the treatment or prevention of a disease or defect such as atrial fibrillation has been developed. In the preferred embodiment, a statin is delivered by means of a patch sutured to cardiac tissue at the time of cardiothoracic surgery. In the most preferred embodiment, the patch is a biodegradable material providing controlled or sustained release over a prolonged period of time, such as a week. Suitable materials include extracellular matrix, or other biodegradable hydrogels or polymeric materials providing sustained or controlled release of statin at the site of application.
Owner:MIDCAP FINANCIAL TRUST AS AGENT
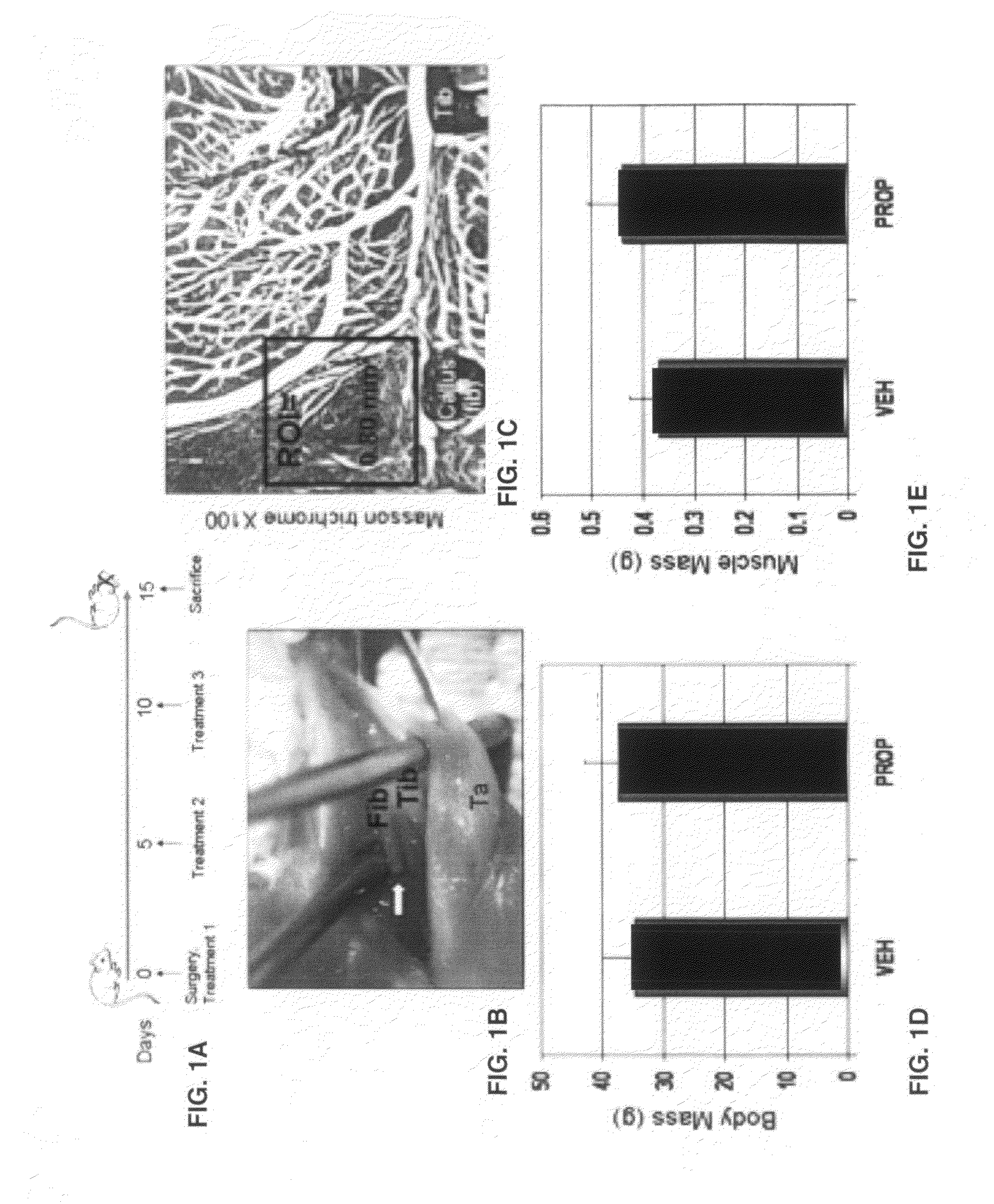
Myostatin inhibitor enhancement of musculoskeletal repair
InactiveUS20100331252A1Promote repairPromote regenerationPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsMyostatinNon union
The methods and compositions of this invention provide a means of regenerating injured musculoskeletal tissue by inhibition of myostatin function. The invention provides methods of treating a nonunion fracture in an individual comprising delivering to the fracture via a delivery system comprising biodegradable hydrogel, a pharmacological amount of myostatin propeptide effective to inhibit myostatin function. The invention also teaches compositions useful for the treatment of non-union fracture in an individual, said compositions comprising a pharmacological amount of myostatin propeptide effective to inhibit myostatin function; and a delivery system for delivering said myostatin propeptide to said fracture, wherein the delivery system comprises a biodegradable hydrogel or biodegradable nanobeads.
Owner:GEORGIA HEALTH SCI UNIV RES INST
Optimally expanded, collagen sealed ePTFE graft with improved tissue ingrowth
Owner:LIFESHIELD SCI +1
Low-swelling biocompatible hydrogels
Some aspects of the present disclosure relate to methods for treating a tissue by forming a low-swelling biodegradable hydrogel in situ adherent to the tissue. In embodiments the hydrogel exhibits negative swelling, i.e., shrinking. Such treatments may be utilized to in cosmetic or reconstructive surgery, in sphincter augmentation, treating nerve inflammation, and the like.
Owner:CONFLUENT SURGICAL
Drug eluting patch for the treatment of localized tissue disease or defect
A polymeric matrix for delivery of an HMG CoA reductase inhibitor such as a statin to tissue such as cardiac tissue in need thereof for the treatment or prevention of a disease or defect such as atrial fibrillation has been developed. In the preferred embodiment, a statin is delivered by means of a patch sutured to cardiac tissue at the time of cardiothoracic surgery. In the most preferred embodiment, the patch is a biodegradable material providing controlled or sustained release over a prolonged period of time, such as a week. Suitable materials include extracellular matrix, or other biodegradable hydrogels or polymeric materials providing sustained or controlled release of statin at the site of application.
Owner:MIDCAP FINANCIAL TRUST AS AGENT
Low swelling biocompatibility hydrogel
Owner:CONFLUENT SURGICAL
Sterilization of biodegradable hydrogels
ActiveUS20120253071A1Good pharmacokinetic propertiesImproved physicochemicalOrganic chemistryEnergy modified materialsBiodegradable hydrogelsSolvent
The present invention relates to a terminal sterilization process for biodegradable PEG-based insoluble hydrogels using irradiation. The presence of a protective solvent ensures that the hydrogel remains intact with functionally preserved three-dimensional and physicochemical properties.
Owner:ASCENDIS PHARM AS
Hydrogels with biodegradable crosslinking
ActiveUS20140288190A1Small degradationCosmetic preparationsImpression capsBiodegradable hydrogelsAbsorbent material
Hydrogels that degrade under appropriate conditions of pH and temperature by virtue of crosslinking compounds that cleave through an elimination reaction are described. The hydrogels may be used for delivery of various agents, such as pharmaceuticals. This invention provides hydrogels that degrade to smaller, soluble components in a non-enzymatic process upon exposure to physiological conditions and to methods to prepare them. The hydrogels are prepared from crosslinking agents that undergo elimination reactions under physiological conditions, thus cleaving the crosslinking agent from the backbone of the hydrogel. The invention also relates to the crosslinking agents themselves and intermediates in forming the hydro gels of the invention. The biodegradable hydro gels prepared according to the methods of the invention may be of use in diverse fields, including biomedical engineering, absorbent materials, and as carriers for drug delivery.
Owner:PROLYNX LLC
Biodegradable hydrogel and method for preparing same
The invention discloses a biodegradable hydrogel and method for preparing same which consists of, preparing microporous konjak gluglucosan aqueous gel, preparing refined konjaku flour, dissolving in distilled water, agitating, charging inorganic solvent, adjusting pH, carrying out crossbridging under a controlled temperature and time, water scrubbing the product yield, repeated frost thawing, freeze-drying, then swelling the konjak gluglucosan gel into the aqueous solution of acroleic acid, cross linking agent, and initiating agent, carrying out polymerization under a controlled temperature and time, and water scrubbing the obtained outcome yield.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Biodegradability hydrogel controlled-release preparation and its preparation method and application
InactiveCN101283966ASimple manufacturing methodControl release speedPharmaceutical delivery mechanismLactidePLA-PEG-PLA
The invention relates to a biodegradable hydrogel controlled release preparation and a preparation and an application thereof, belonging to the technology field of medicines. The preparation method comprises the steps of: synthesizing poly(lactic acid)-polyethylene glycol-poly(lactic acid) (PLA-PEG-PLA) triblock copolymer by inducing L-lactide and D-lactide to respectively conduct ring-expansion polymerization by using zinc powder, zinc lactate or stannous octoate as catalyst and polyethylene glycol (PEG) 2,000-20,000; respectively dissolving poly-L-lactic acid-polyethylene glycol-poly-L-lactic acid and poly-D-lactic acid-polyethylene glycol-poly-D-lactic acid in water to obtain solutions with concentration of 0.05-0.5g / mL, swelling, mixing, and allowing gelatinization under constant temperature to obtain PLA-PEG-PLA triblock copolymer hydrogel for injection by complexing reaction. The hydrogel has good biological compatibility and biodegradability, can be used for embedding water-soluble drugs, and is an ideal drug controlled release carrier.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Preparing biodegradable hydrogel for biomedical application
Biodegradable dextran based hydrogel suitable for biomedical application is produced by subjecting polysaccharide substituted with unsaturated moiety, e.g. dextran methacrylate, in aqueous medium to UV or visible light irradiation in the precense of riboflavin / L-arginine or riboflavin / chitosan to cause photocrosslinking of polysaccharide substituted with unsaturated moiety.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Light-curable bone growth material for treating dental bone defects
InactiveUS20070269518A1High viscosityGood handling propertyPowder deliveryImpression capsCross-linkParticulates
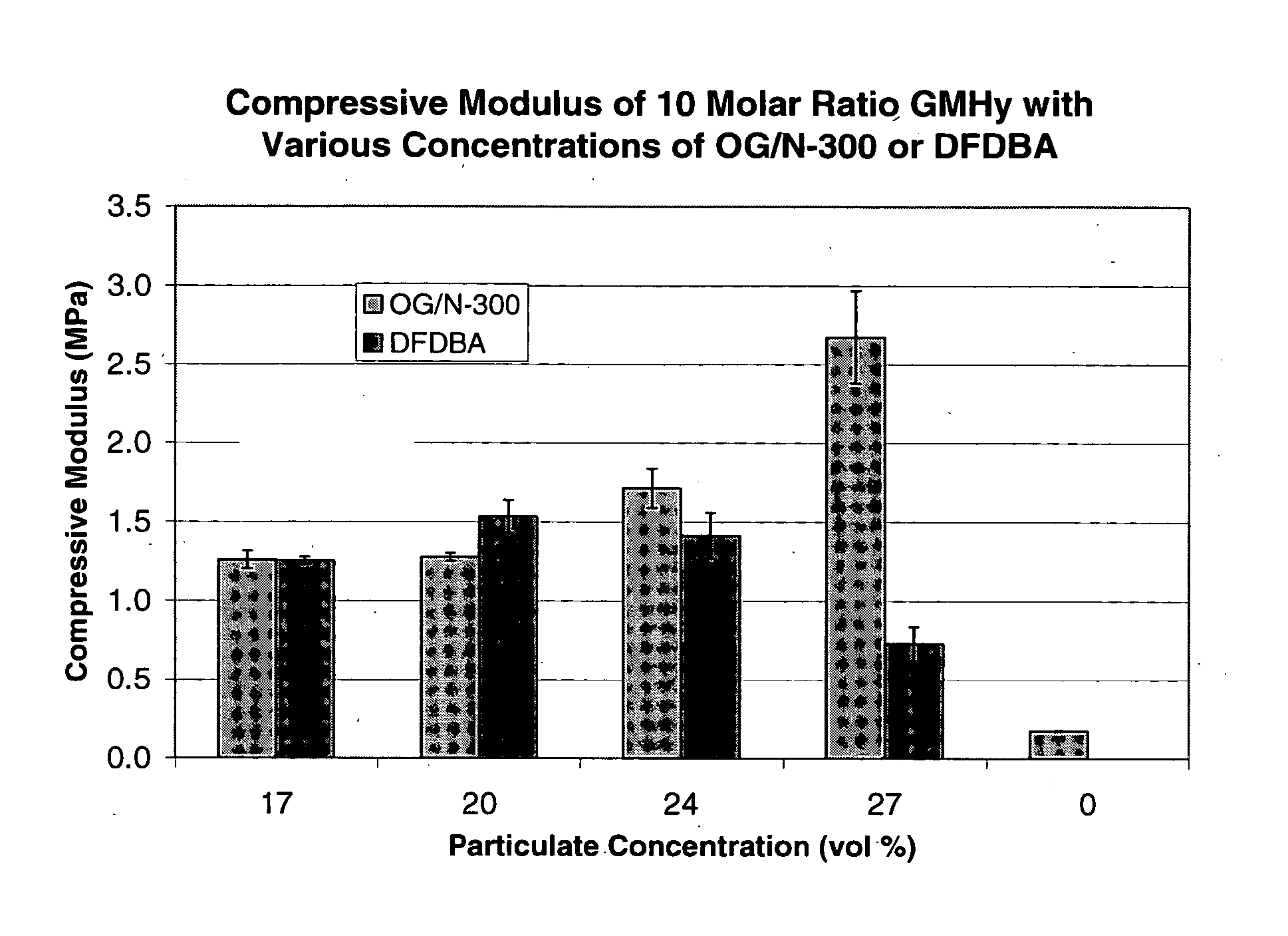
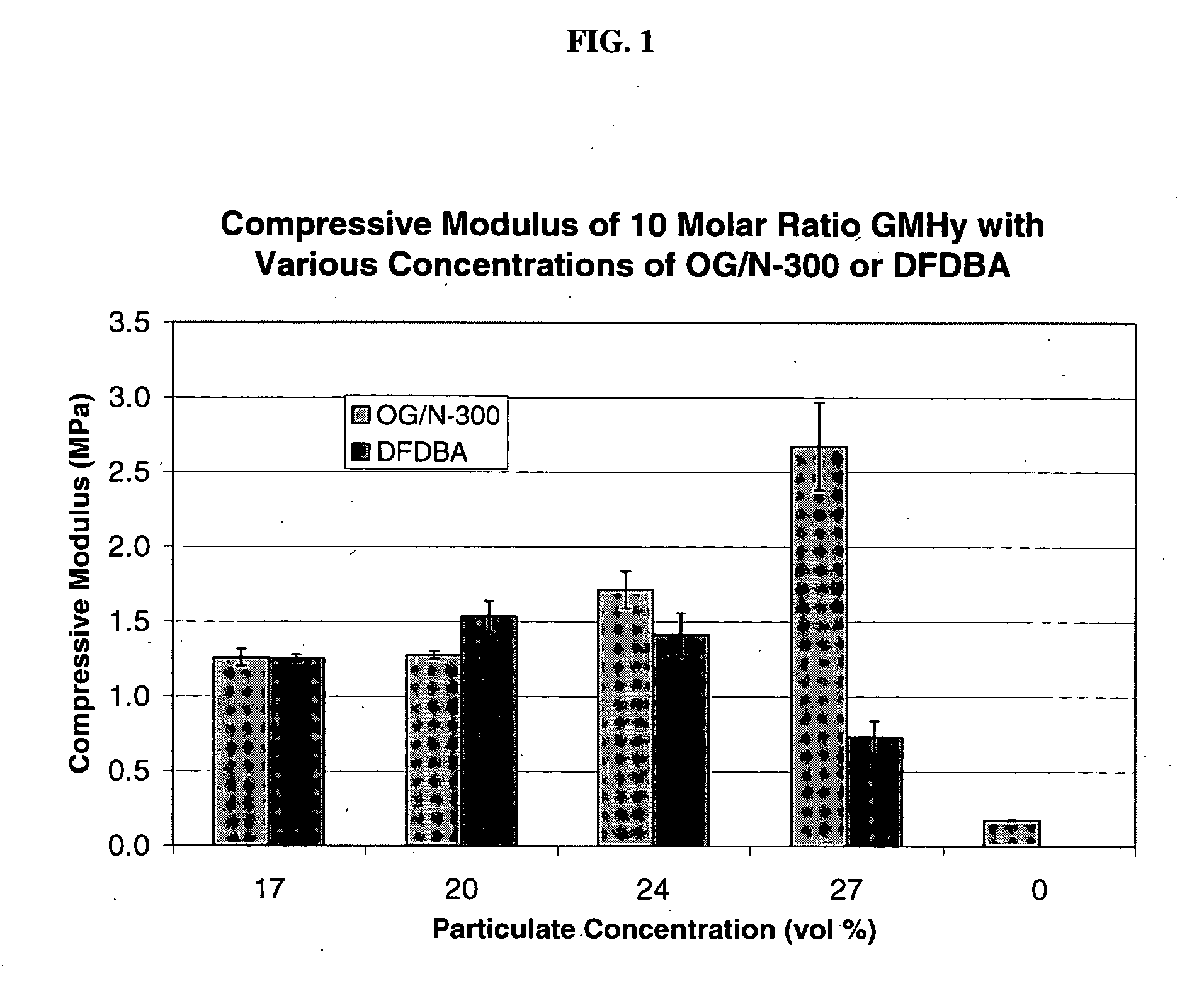
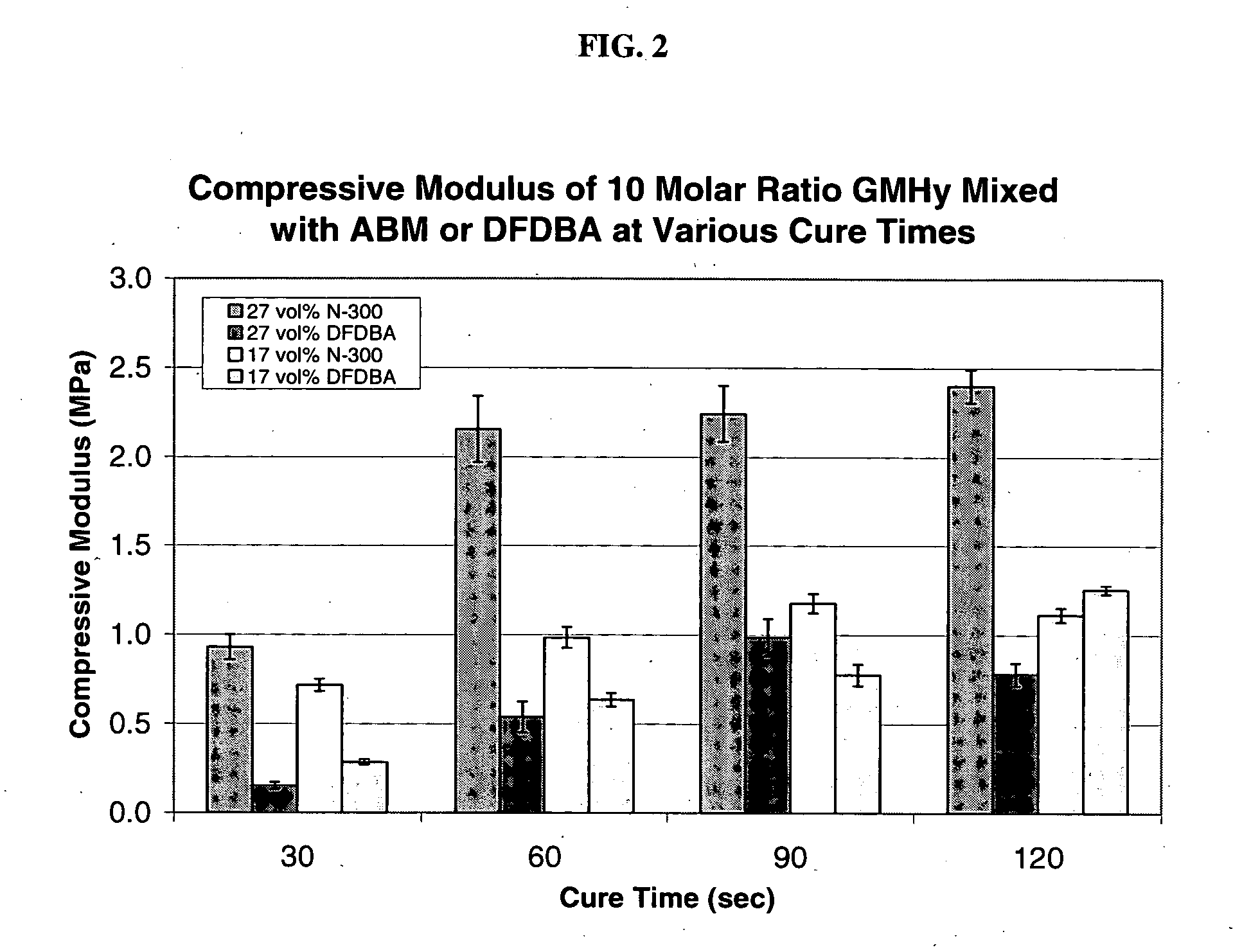
Improved compositions comprising a mixture of particulate bone growth material and polymeric carrier are provided. The particulate is preferably porous, resorbable, anorganic bone material. The polymeric carrier can be light-cured to form a cross-linked, biodegradable hydrogel. In one version, the bone growth material is a synthetic peptide bound to anorganic bone matrix particles and the carrier is methacrylated sodium hyaluronate (MHy) or methacrylated hydroxyethylcellulose (MHEC). The composition is particularly suitable for repairing defective dental and orthopedic bone tissue. The particulate and hydrogel carrier are biodegradable so the composition can be replaced by new bone formation over time.
Owner:WALLINE KATHERINE SUZANNE +1
Controlled release formulations
ActiveUS20090110735A1Extension of timeExtended stayPowder deliveryBiocideMedicineBiodegradable hydrogels
The present invention provides stable, self-assembling, biocompatible and biodegradable hydrogel formulations, into which one or more compounds may be incorporated allowing for delayed release or controlled release of the incorporated compounds as the hydrogel is degraded in the body.
Owner:UAB RES FOUND +1
Biodegradable hydrogels
InactiveUS20080131512A1Poorly release behaviorImprove the usefulnessBiocidePowder deliveryBiodegradable hydrogelsPolysaccharide
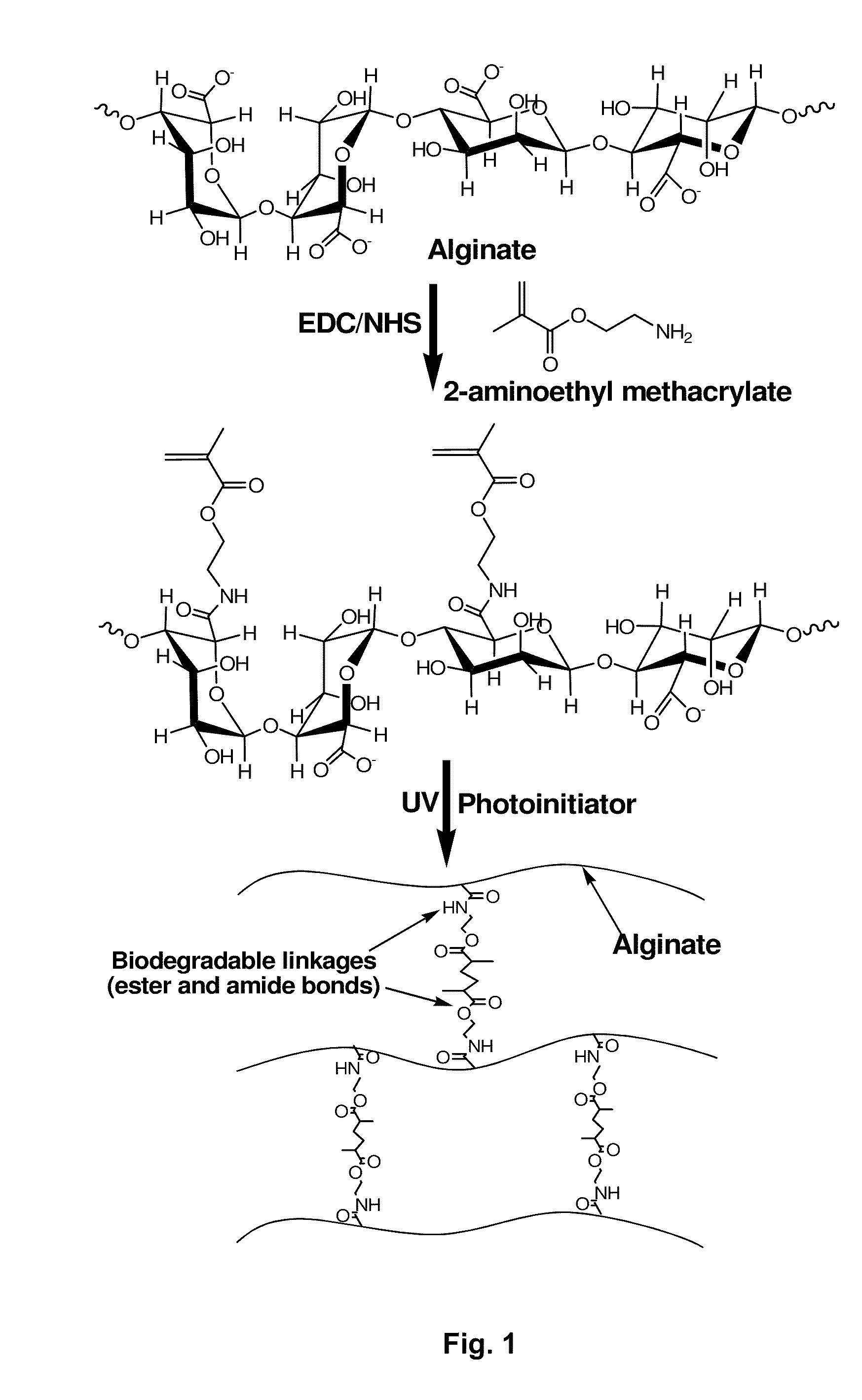
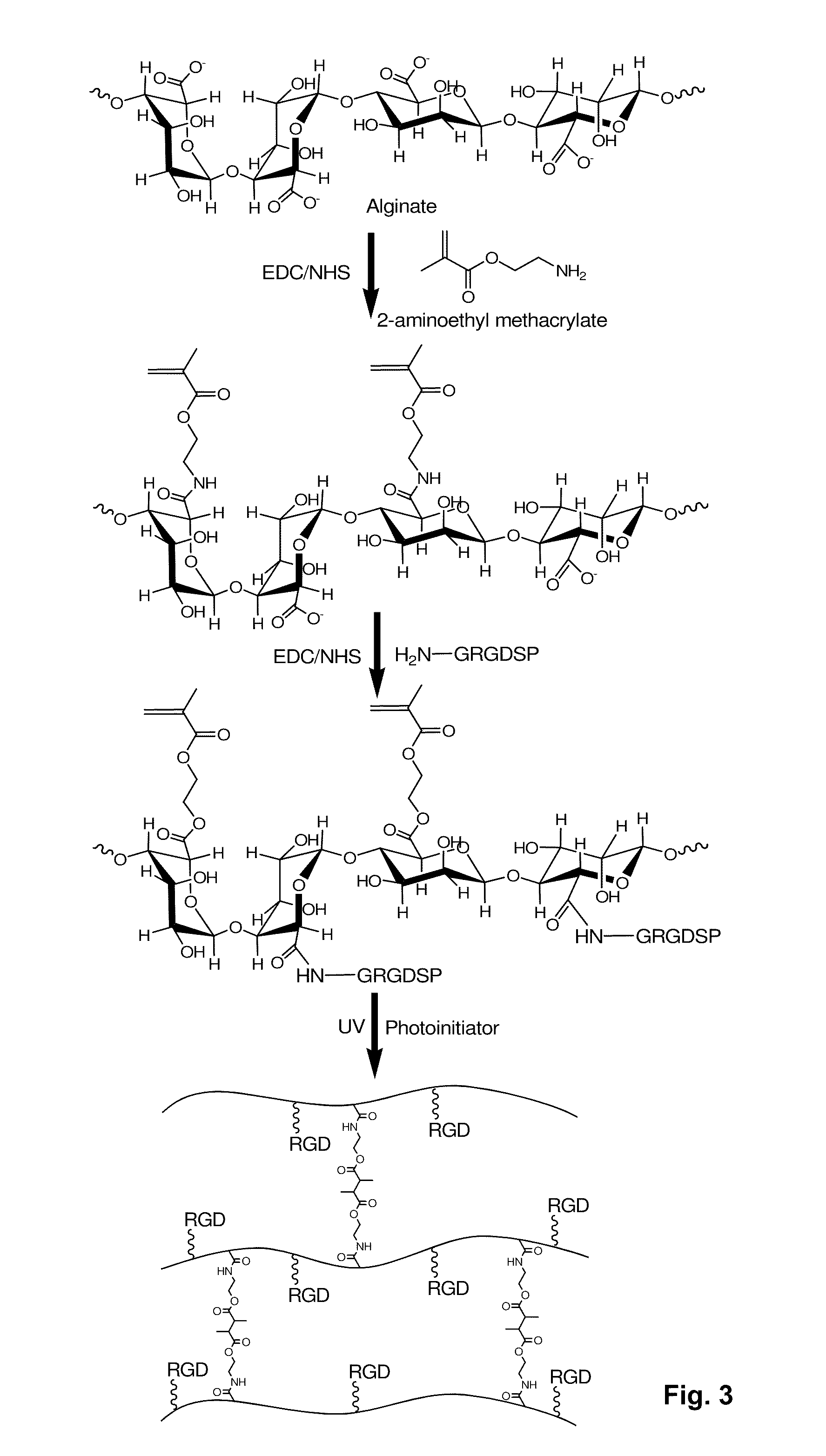
A prepolymer comprises polymerisable macromolecules, each polymerisable macromolecule comprises a polysaccharide backbone and at least two side units, wherein each of the at least two side units comprises a polymerisable group which is connected to the backbone via at least one group which is hydrolysable under physiological conditions; wherein the polymerisable group of each of the side units is independently selected from optionally alkylated and / or hydroxyalkylated acrylates and acrylamides; and wherein the at least one group which is hydrolysable under physiological conditions is selected from carbonate, lactate, glycolate, and succinate. The invention is also directed to biodegradable hydrogels useful in pharmaceutical compositions, comprising polymerized or co-polymerized prepolymers.
Owner:UTRECHT UNIVERSITY
Biodegradable hydrogel with temperature sensitivity and production method and use thereof
InactiveCN101371933ASensitive to temperatureBiodegradableSurgeryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsPhosphorous acid(Hydroxyethyl)methacrylate
The invention relates to a hydrogel which is temperature-sensitive and biodegradable simultaneously, the hydrogel is prepared by the following method: hydroxyethyl methacrylate-polycaprolactone is obtained by the reaction of hydroxyethyl methacrylate and epsilon-caprolactone; the hydroxyethyl methacrylate-polycaprolactone reacts with carbonyldiimidazole, hydroxyethyl methacrylate-polycaprolactone-imidazole is obtained by rotary evaporation; the hydroxyethyl methacrylate-polycaprolactone-imidazole and Alpha-(1->6)-D-glucan are dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide, p-dimethylaminopyridine is added, mixture which is obtained by the reaction at room temperature is settled in isopropyl alcohol, hydroxyethyl methacrylate-polycaprolactone-g-Alpha-(1->6)-D-glucan is obtained by vacuum drying; N-isopropylacrylamide and the hydroxyethyl methacrylate-polycaprolactone-g-Alpha-(1->6)-D-glucan are dissolved in phosphorous acid buffer solution with pH of 7.4, then ammonium persulfate and N,N,N',N'-tetramethylethylenediamine are added, the hydrogel is obtained by the reaction at room temperature; dialysis is carried out on the obtained hydrogel by phosphorous acid buffer solution, thereby obtaining the temperature-sensitive and biodegradable hydrogel.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Biodegradable multiple targeting hydrogel orientated to eolon as well as its preparation and application
InactiveCN1480219AIncrease drug release rateOvercome the shortcoming of slow single enzymatic hydrolysis ratePharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCross-linkBiodegradable hydrogels
A biodegradable hydrogel with multiple target location function in colon is prepared from the aqueous solution of konjak glucomannan and acrylic through graft copolymerizing under the action of redox trigger and azo compound as cross-linking agent. It can be used as the carrier of protein polypeptide medicine for locating in the colon and releasing the medicine.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Biodegradable composite for internal local radiotherapy
InactiveUS20090304587A1Remove of complexity and discomfortEliminate needRadioactive preparation carriersAntineoplastic agentsLocal radiotherapySimple Organic Compounds
The present invention discloses composites which generally comprise a polymeric matrix and a hydrophobic organic compound which is associated with a radioisotope. The composites are biocompatible and biodegradable hydrogels suitable for use in internal local radiation therapy
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD +1
Whey Protein Isolate Hydrogels and Their Uses
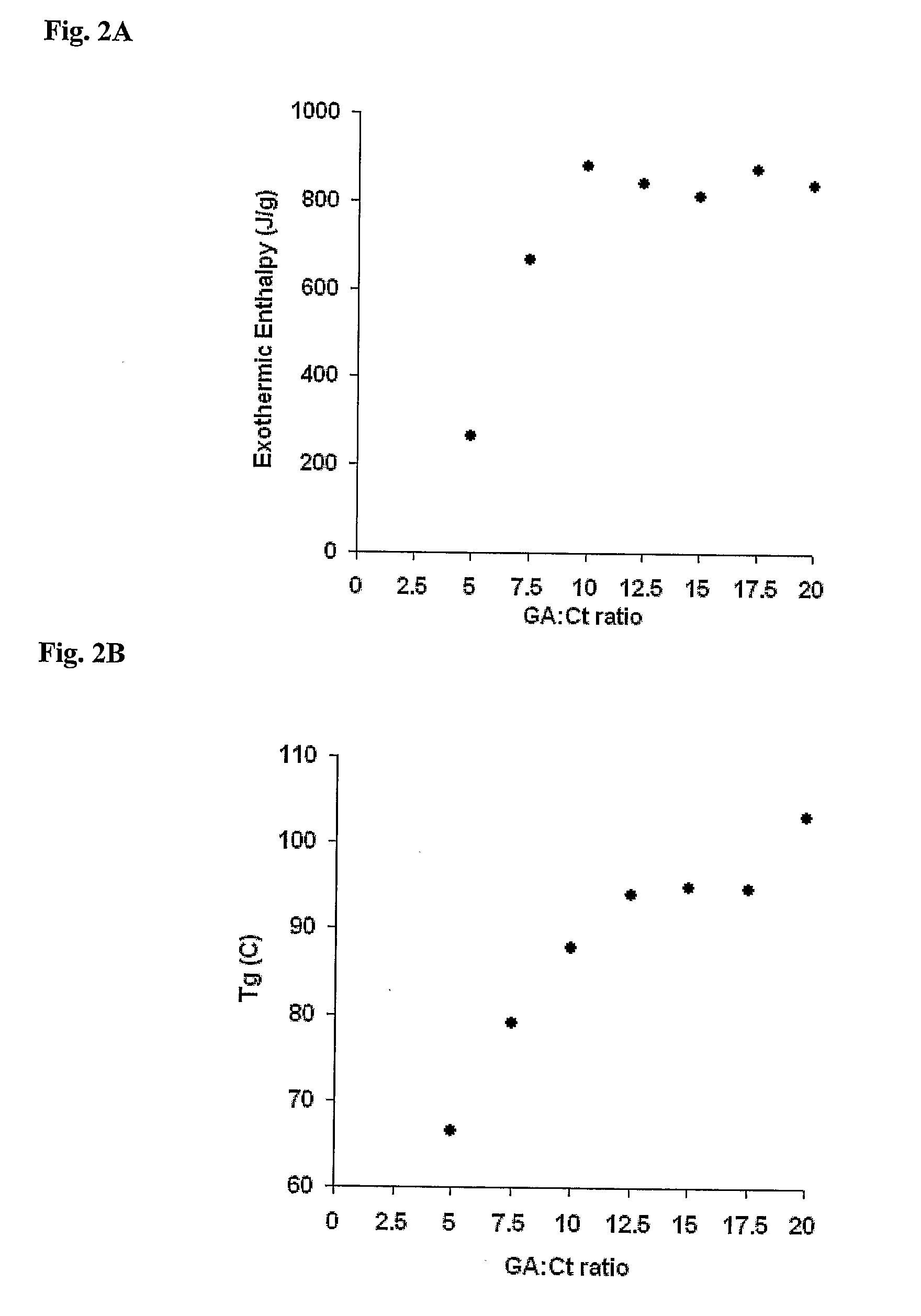
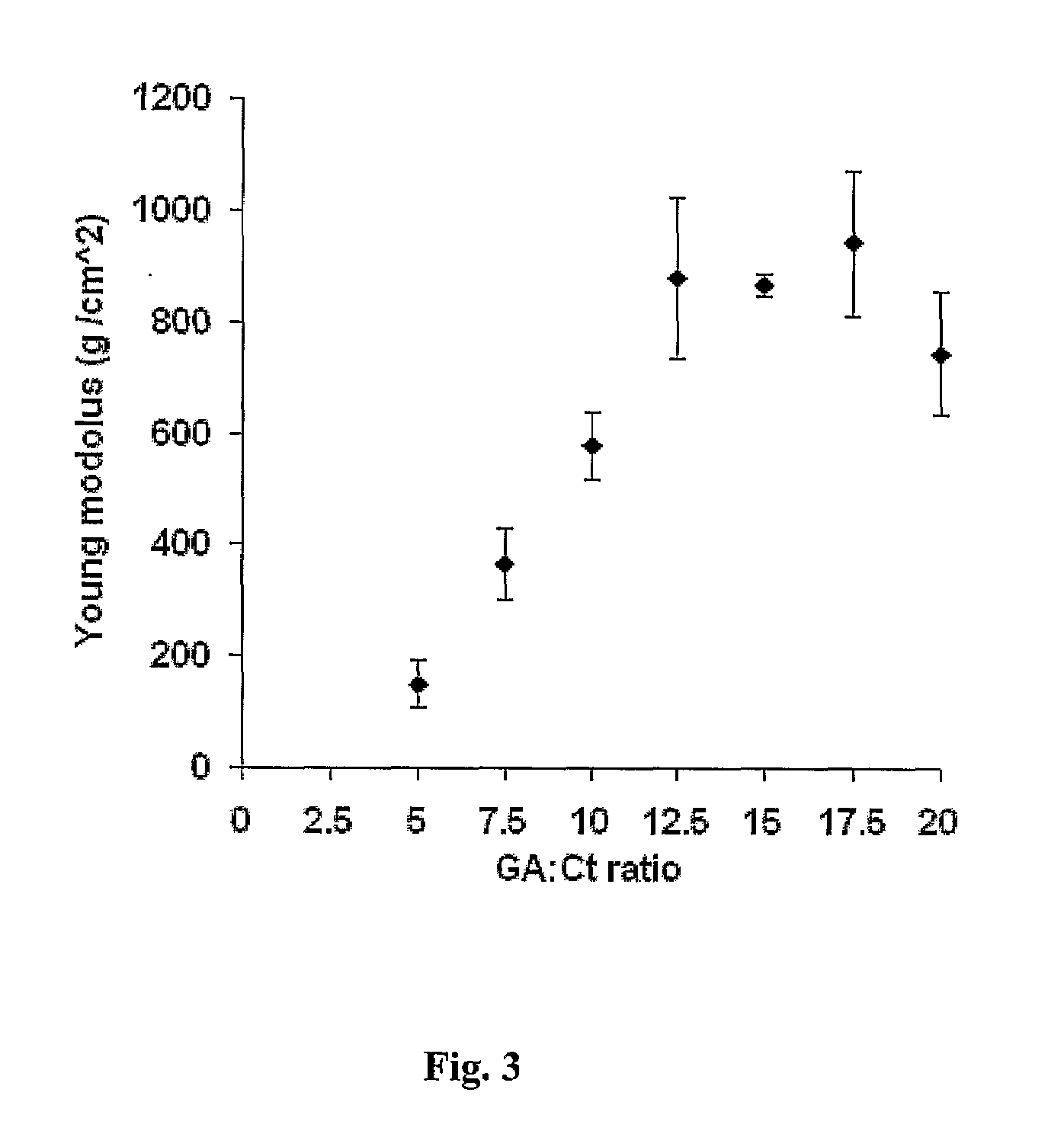
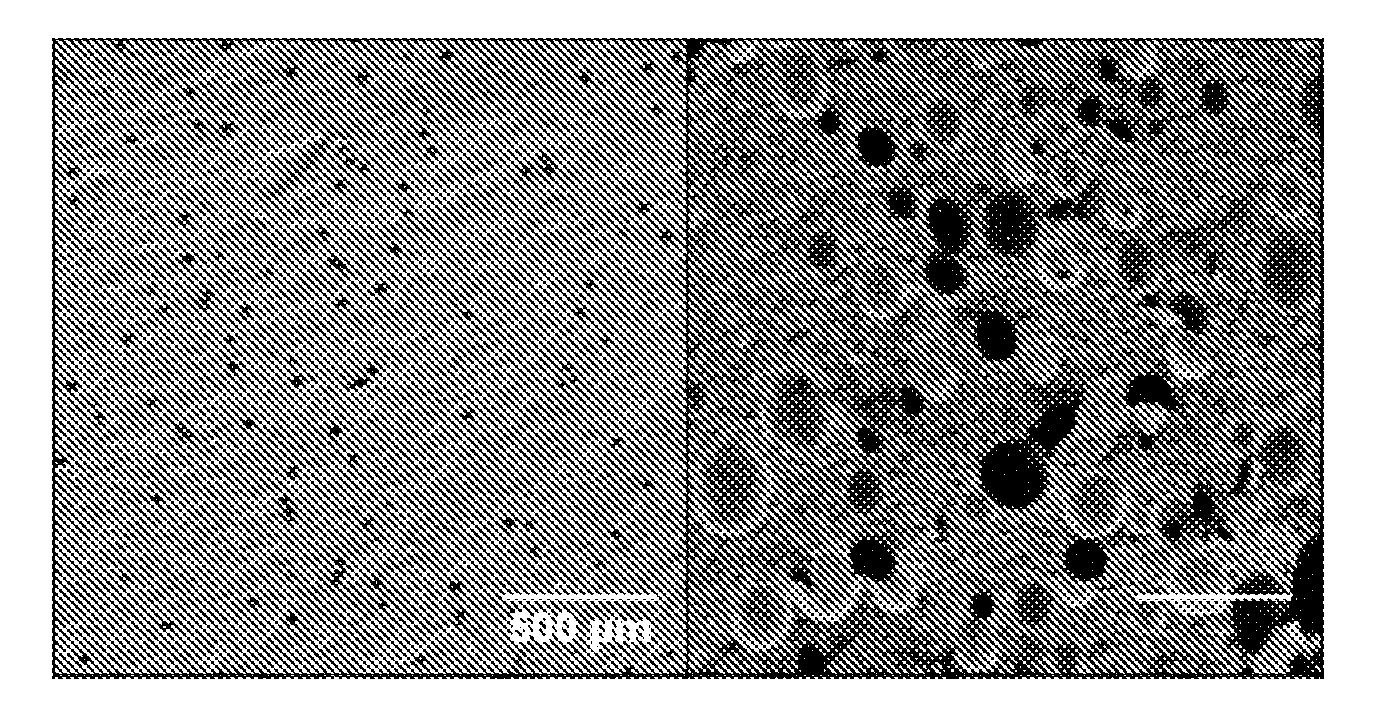
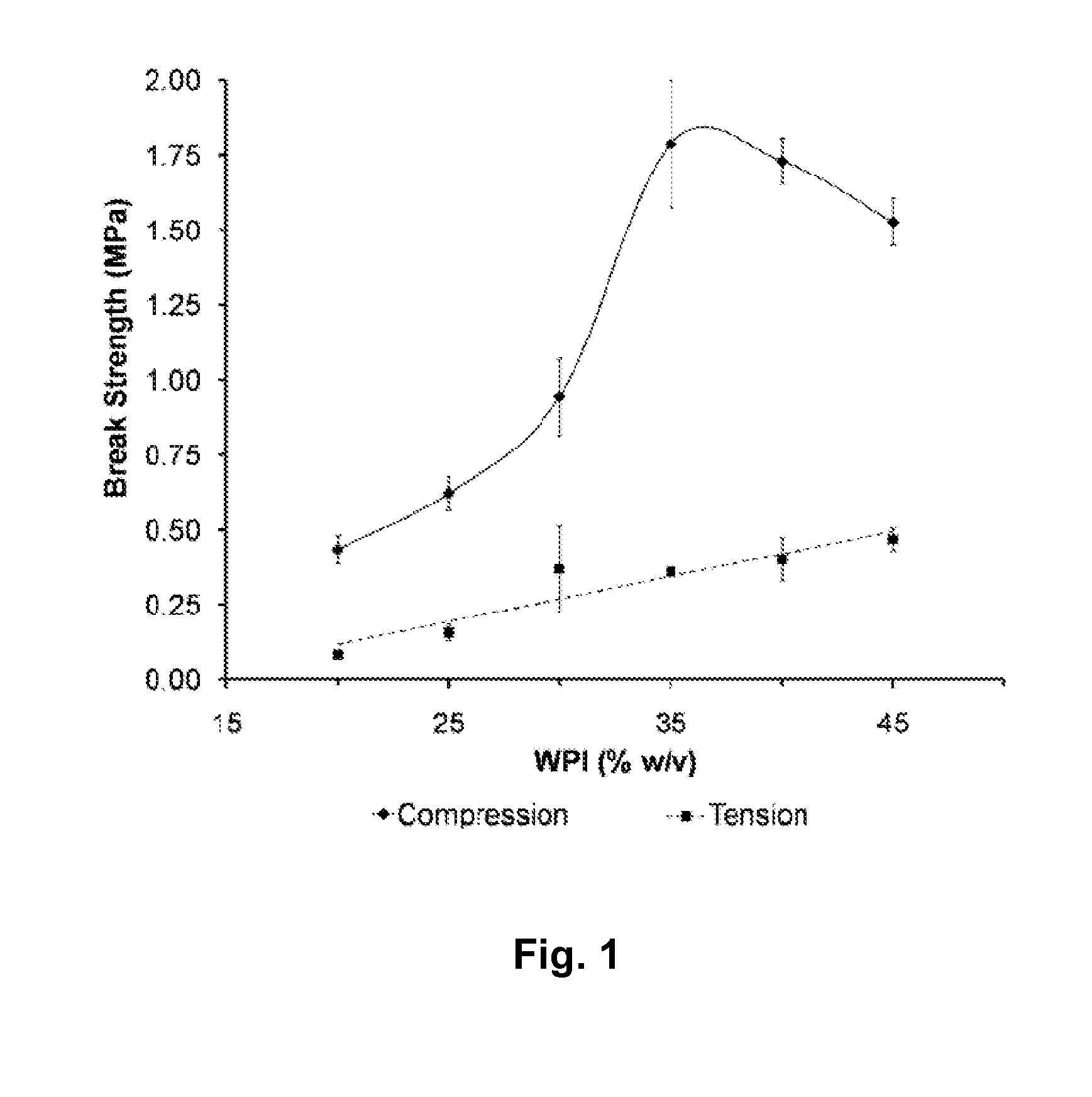
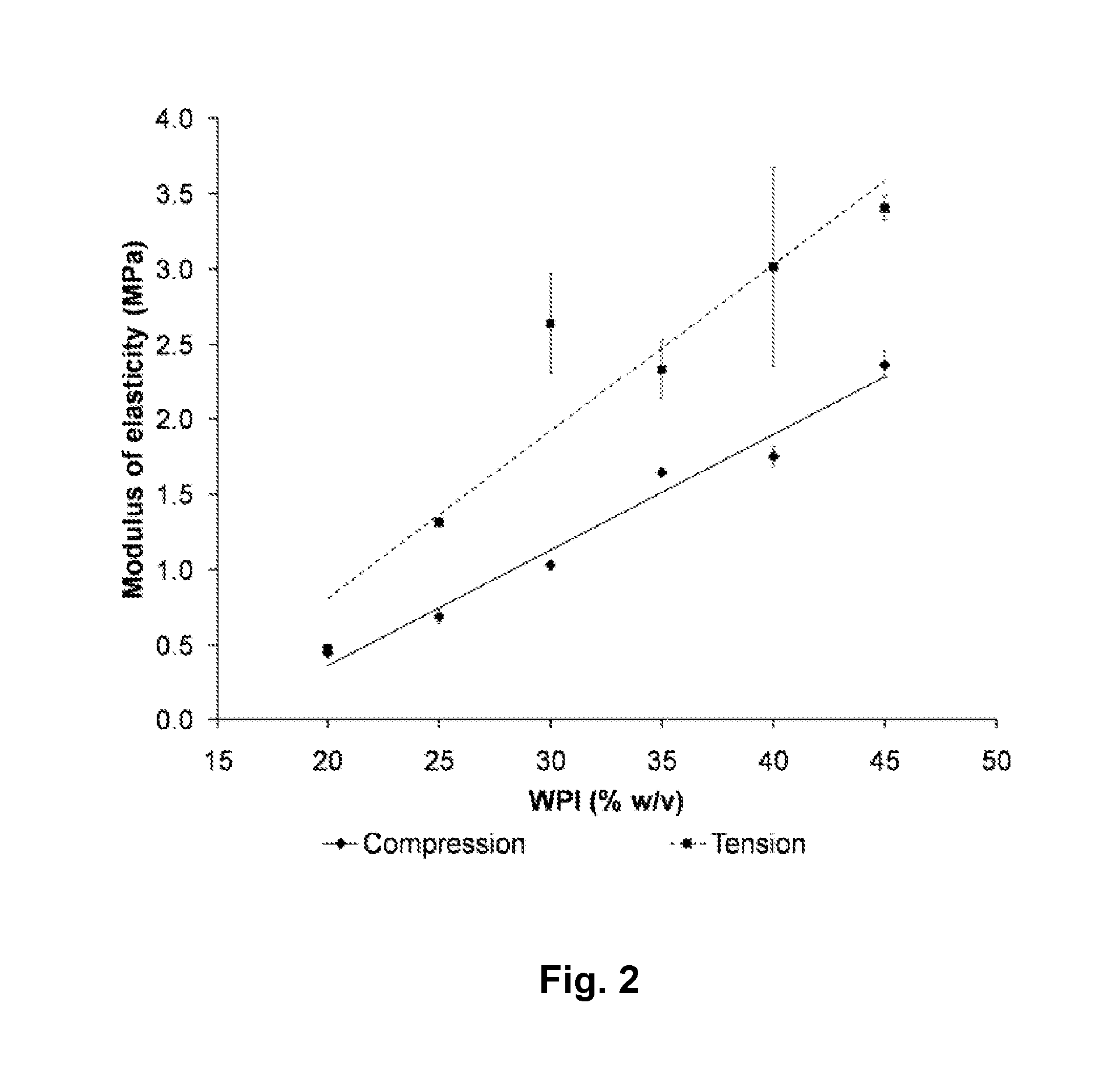
A biodegradable hydrogel has been made based on high concentrations of whey protein isolate (WP1). WP1 gels of different compositions were fabricated by thermally inducing gelation of high-concentration suspensions of protein, and characterized for compressive strength and modulus, hydration swelling and drying properties, mechanical behavior change due to polysaccharide additives, and intrinsic pore network structure. The gels were shown to be compatible with bone cells and could be used as bone tissue scaffolds. In addition, WP1 fibers were produced by electrospinning. Several additives could be incorporated into the WPI gels, including structural additives, growth factors, amino acids, etc. The WP1 hydrogels can be made with glycerol to increase flexibility and stability. The hydrogels could be used for tissue regeneration, food protection, controlled-release applications (including drug encapsulation, dietary supplement release, attractant release in lures, nutrient release to plants (fertilizers), column packing for compound separation, and membrane development.
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE
Dextran-chitosan based in-situ gelling hydrogels for biomedical applications
InactiveUS20110076332A1Reduce the possibilityPromote host integrationOrganic active ingredientsBiocideCross-linkBiofilm growth
A biodegradable hydrogel comprises a water-soluble dextran having aldehyde groups cross-linked with a water-soluble chitosan. Various chemical agents may be encapsulated in the hydrogel or bonded thereto for controlled release. The hydrogel may be applied as a coating to reduce the likelihood of bacterial attachment and biofilm growth; used in tissue engineering applications to prevent tissue ingrowth; or used as a matrix in which cells may proliferate. The components of the hydrogel can be applied sequentially as a spray or by immersion and will gel spontaneously at environmental or physiological temperatures.
Owner:STEVENS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Water-soluble and degradable cross-linking agent, preparation method of gamma-polyglutamic acid water absorbing material using cross-linking agent
The invention discloses a preparation method of gamma-polyglutamic acid water absorbing material. Gamma-polyglutamic acid is used as a main raw material, chitosan oligosaccharide-graft-acrylic acid is used as a biodegradable cross-linking agent, and the gamma-polyglutamic acid hydrogel water absorbing material is obtained after preparation in an aqueous solution. The biodegradable cross-linking agent replaces a common chemical cross-linking agent for preparing the hydrogel, the reaction medium is free of toxic organic solvents, gamma-polyglutamic acid which is safe and nontoxic is used as the main raw material, the water-soluble and degradable chitosan oligosaccharide-graft-acrylic acid is used as a cross-linking agent, and the gamma-polyglutamic acid water absorbing material is prepared in the aqueous solution. The raw materials and mediums do not have harmful substances for human body, the safe, nontoxic and biodegradable hydrogel is obtained, and the hydrogel can be applied to disposable hygiene products, drug carriers, medical articles, etc.
Owner:新疆康润洁环保科技股份有限公司
Multiblock biodegradable hydrogels for drug delivery and tissue treatment
Gel-forming macromers including at least four polymeric blocks, at least two of which are hydrophobic and at least one of which is hydrophilic, and including a crosslinkable group are provided. The macromers can be covalently crosslinked to form a gel on a tissue surface in vivo. The gels formed from the macromers have a combination of properties including thermosensitivity and lipophilicity, and are useful in a variety of medical applications including drug delivery and tissue coating.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
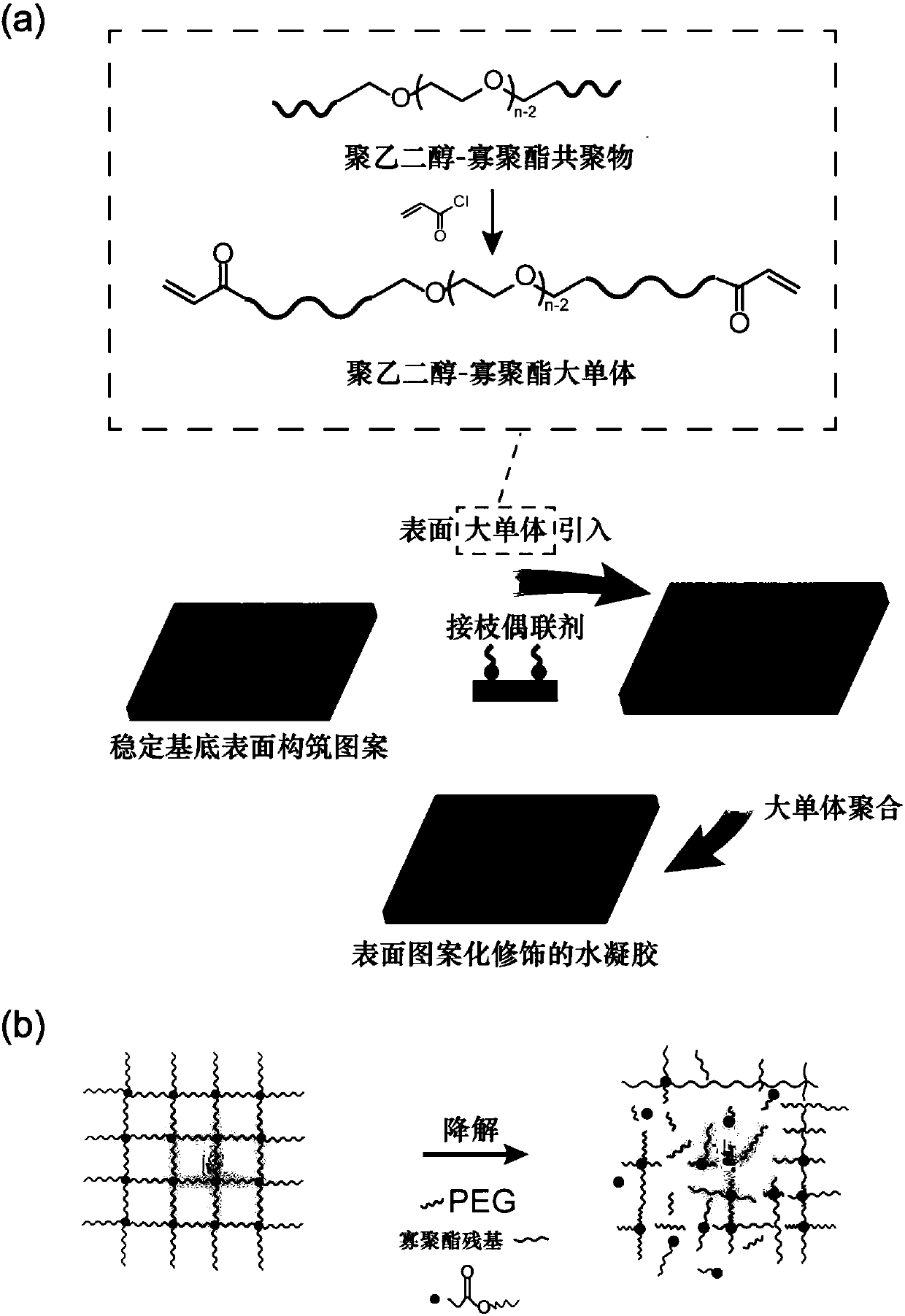
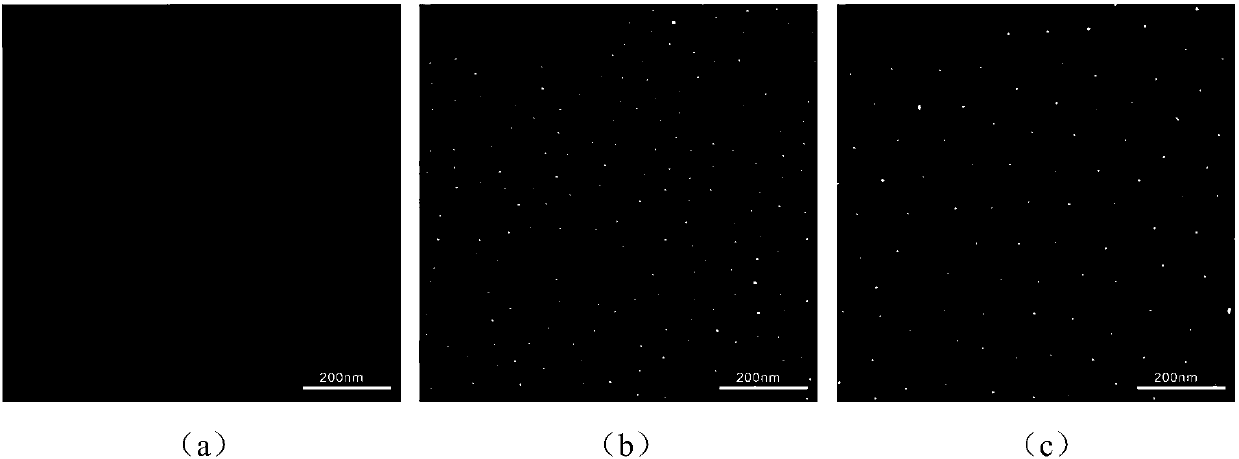
Degradable high polymer material with patterned surface as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN108484956AGood biocompatibilityEasy to operateBiocompatibility TestingBiodegradable hydrogels
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological materials, and particularly relates to a degradable high polymer material with a patterned surface as well as a preparation method and application thereof. According to the degradable high polymer material, biodegradable hydrogel is used as a matrix, and the surface of the matrix is modified with a pattern composed of active substances; the patterned surface means that the matrix material surface is modified to form a pattern array. The patterned shape constructed on the hydrogel surface is stable in structure, and compositions can beindependent from the matrix material component. The obtained material has good biocompatibility and controllable degradability, and the patterned shape can be used for further modifying sites which have the responsiveness and biological activity; by introducing the dynamic degradability, the material has functions which confirm to the real physiological environment more; the material can be applied to the fields of stem cell culture, tissue engineering, biological diagnosis, biological recognition, biomimetic material design and the like.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com