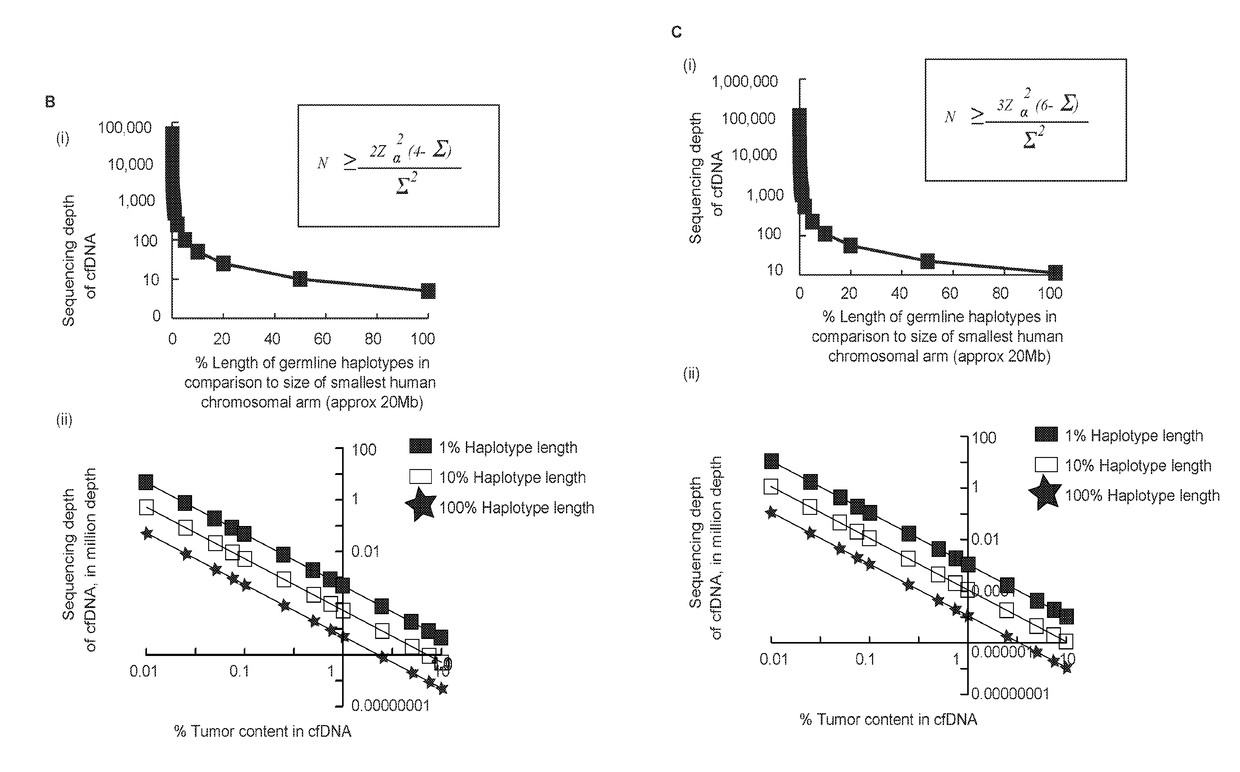
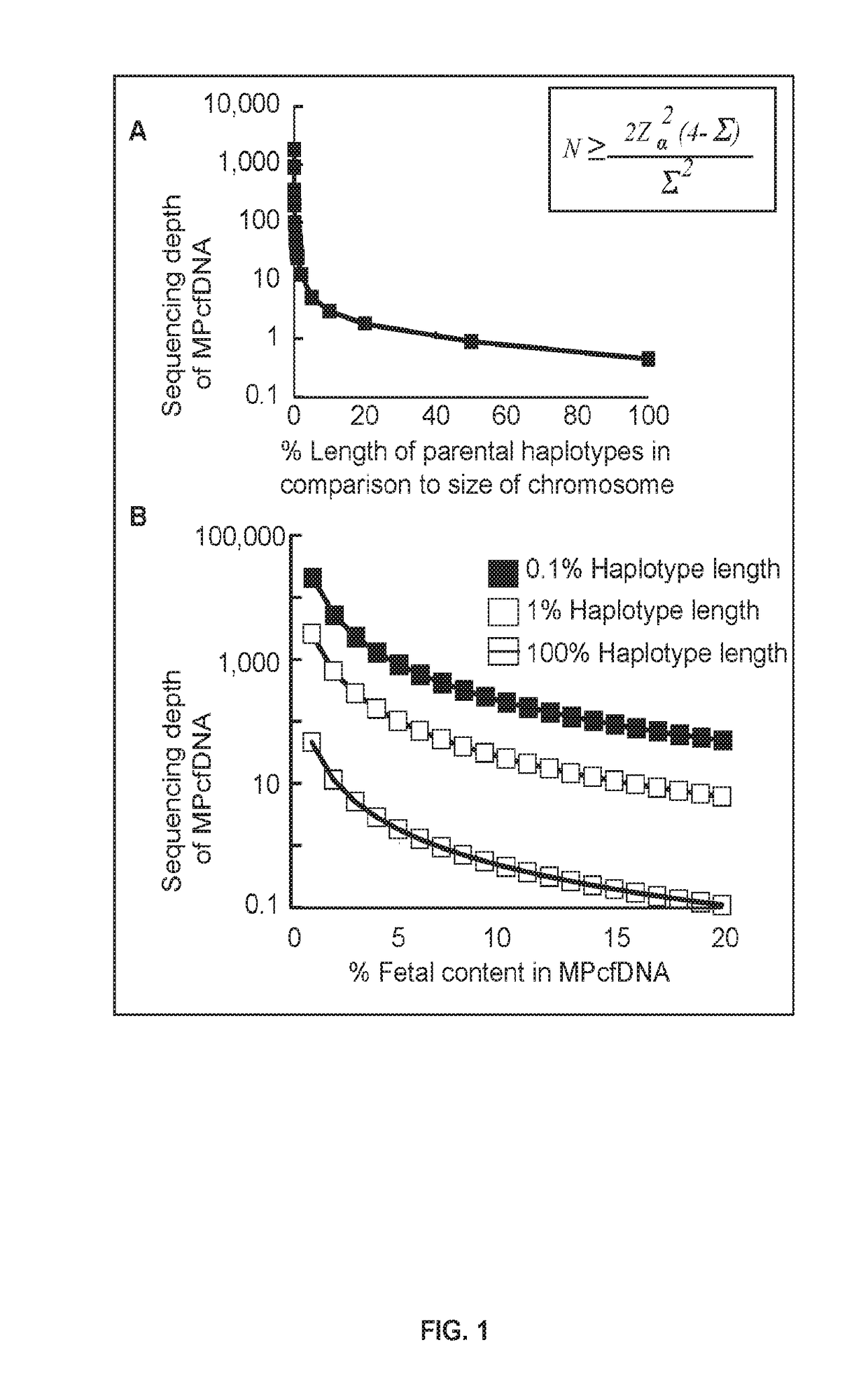
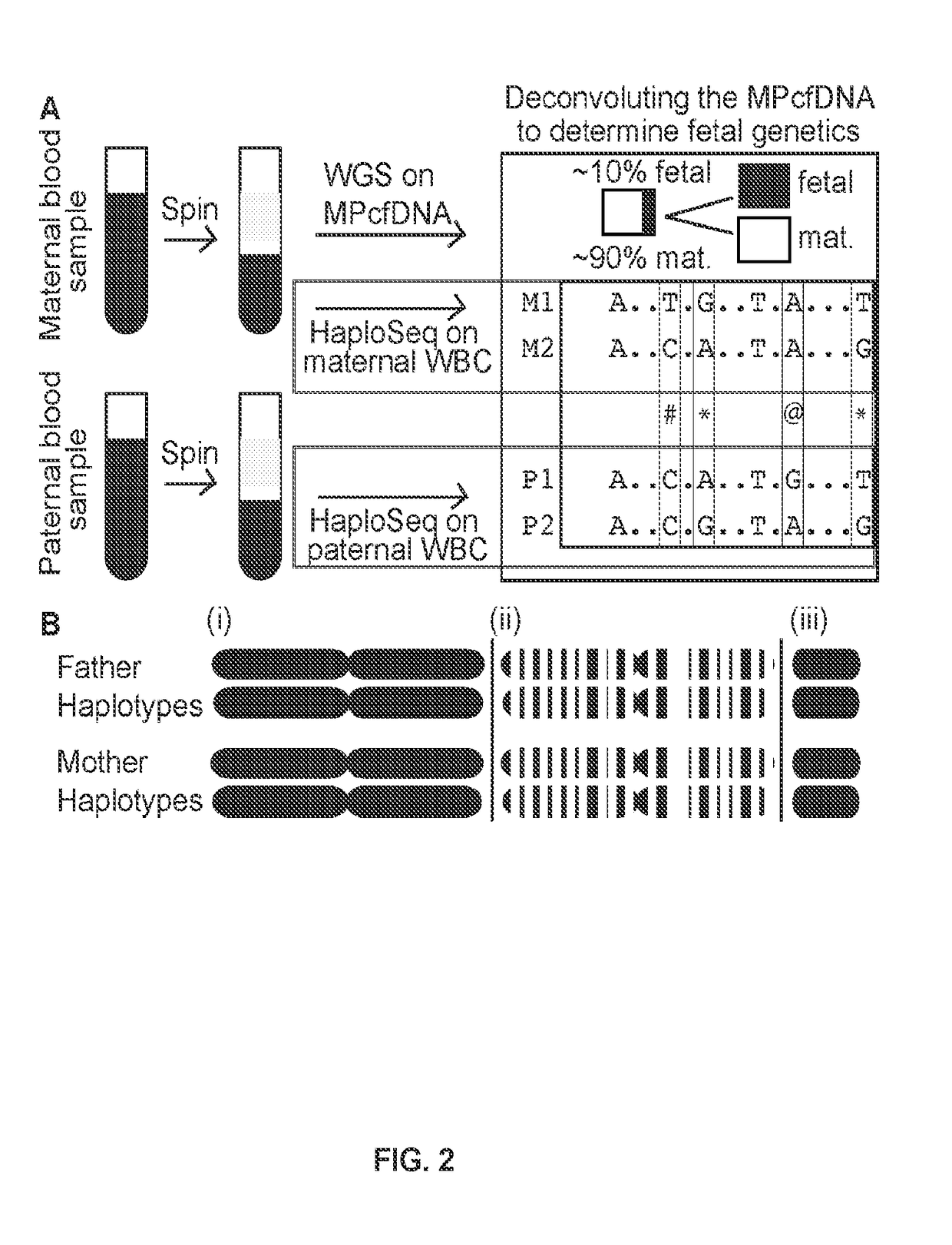
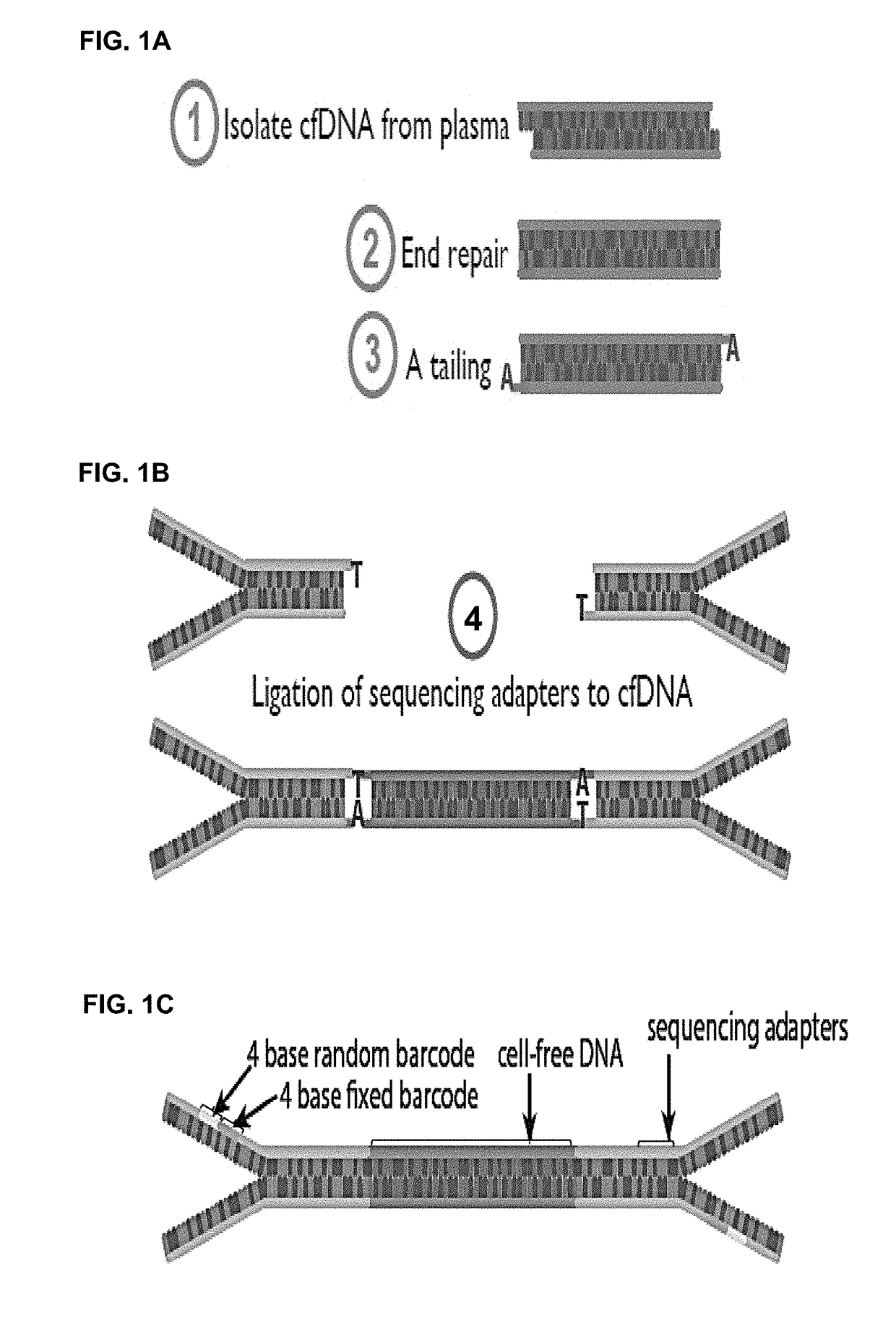
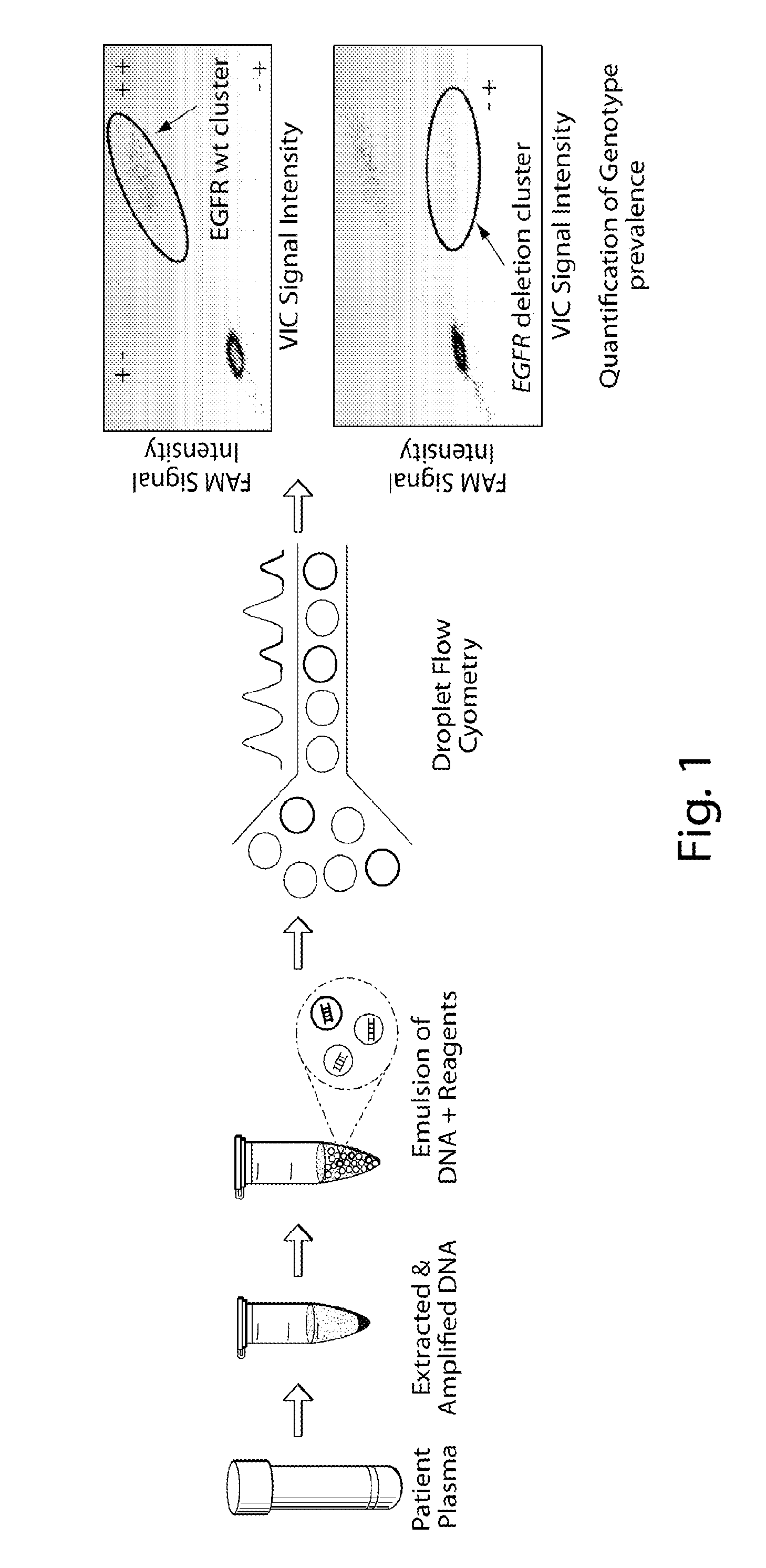
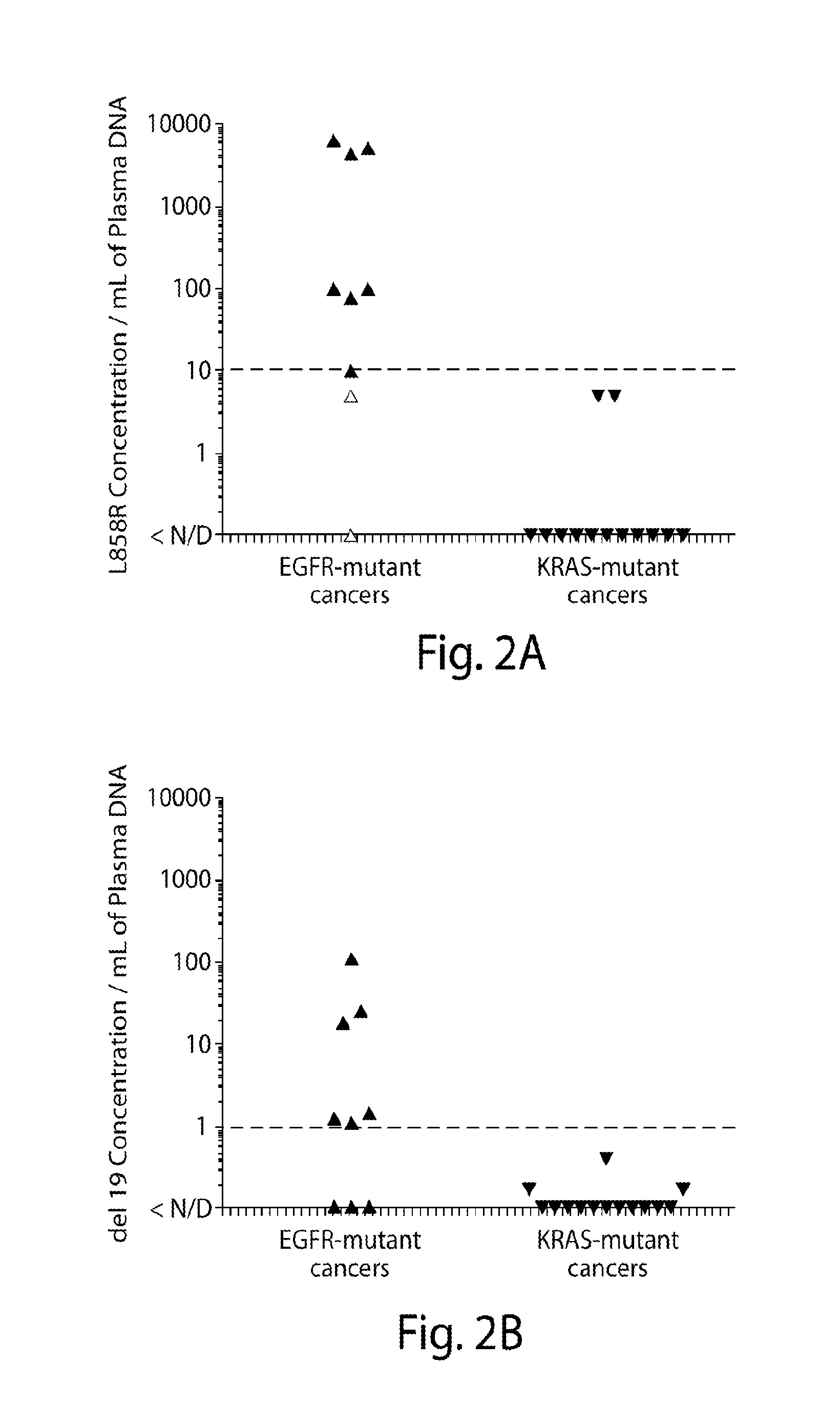
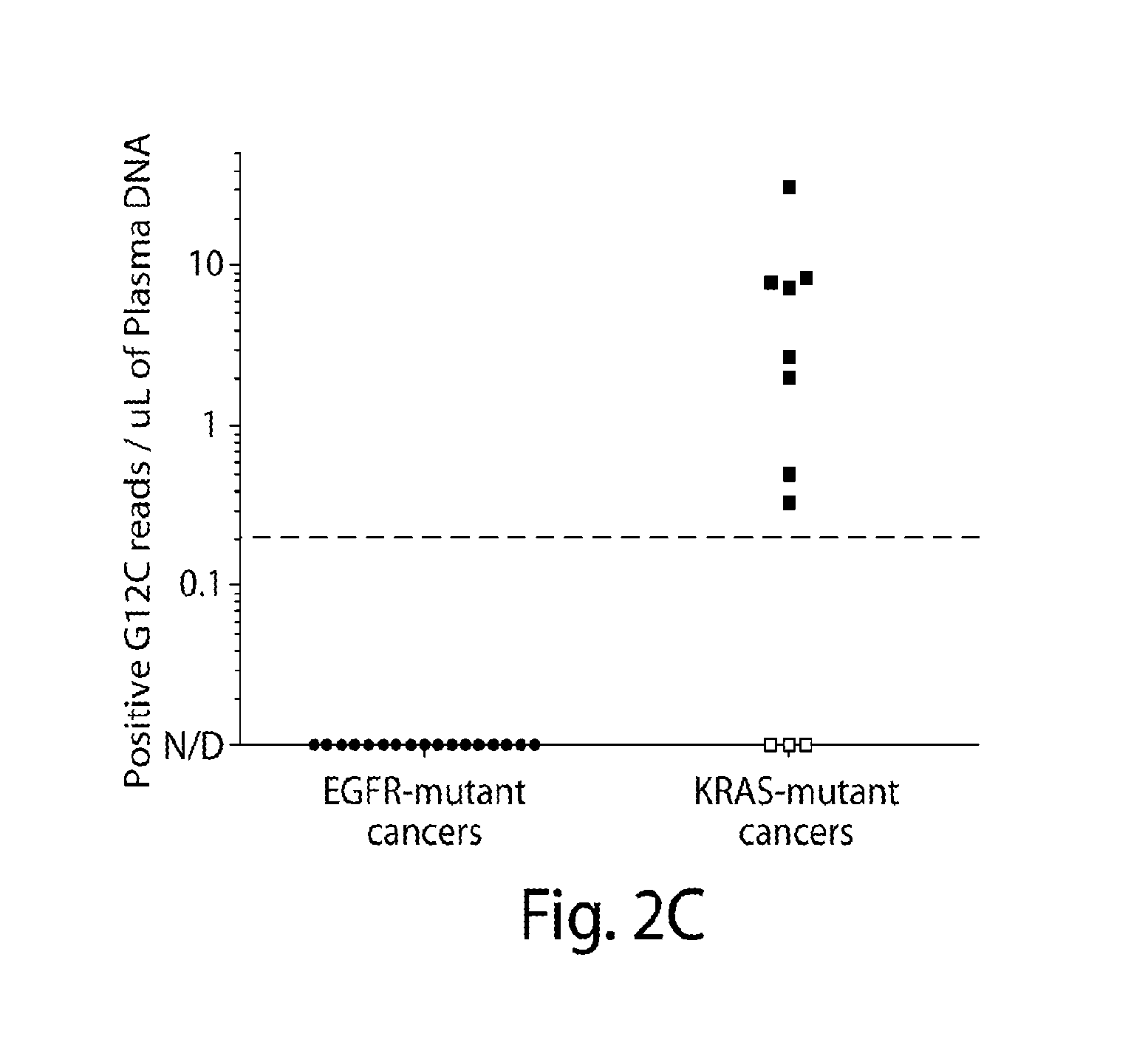
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
79 results about "Cell-Free Nucleic Acids" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Nucleic acids (DNA or RNA) found circulating in SERUM; PLASMA; or other BODY FLUIDS.
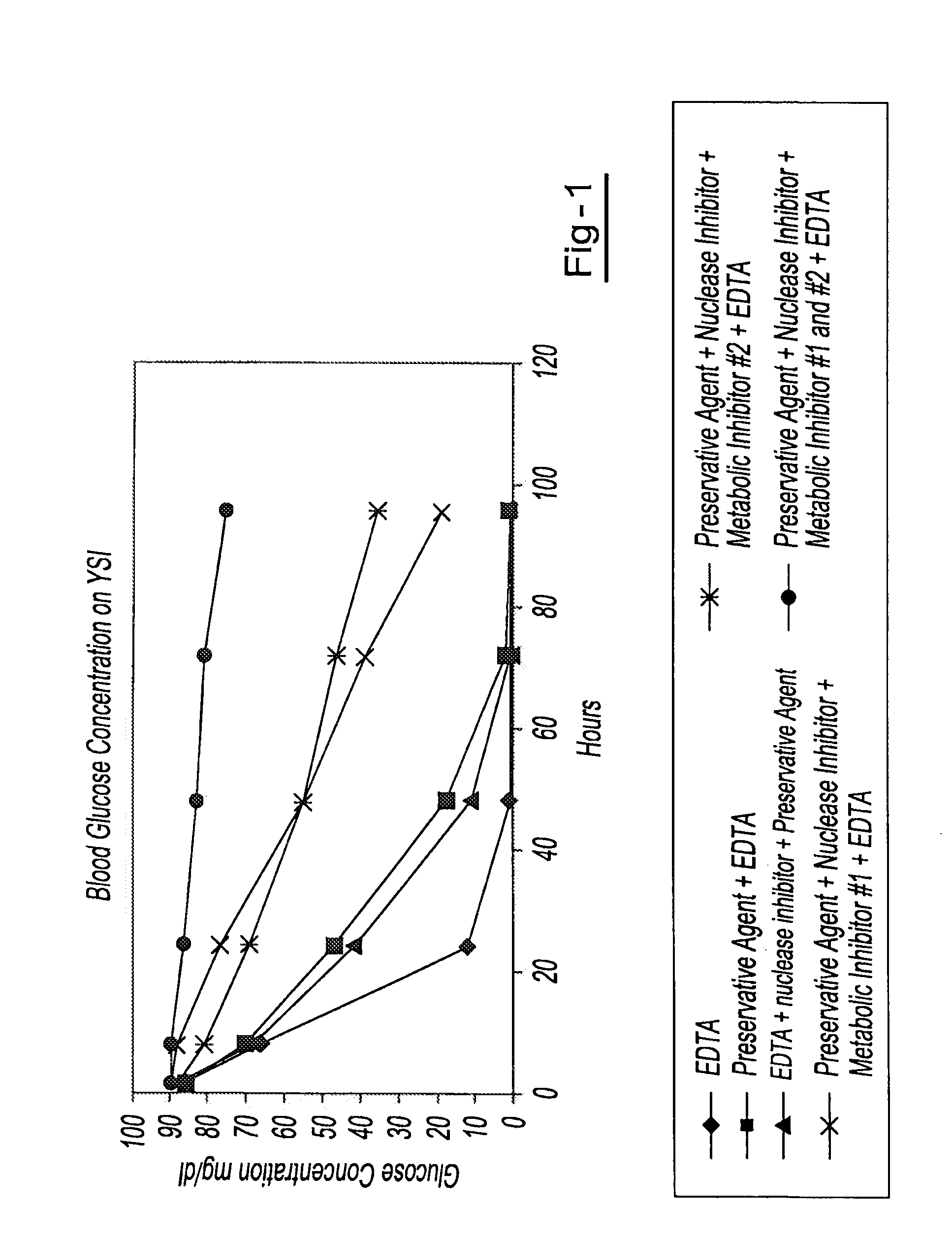
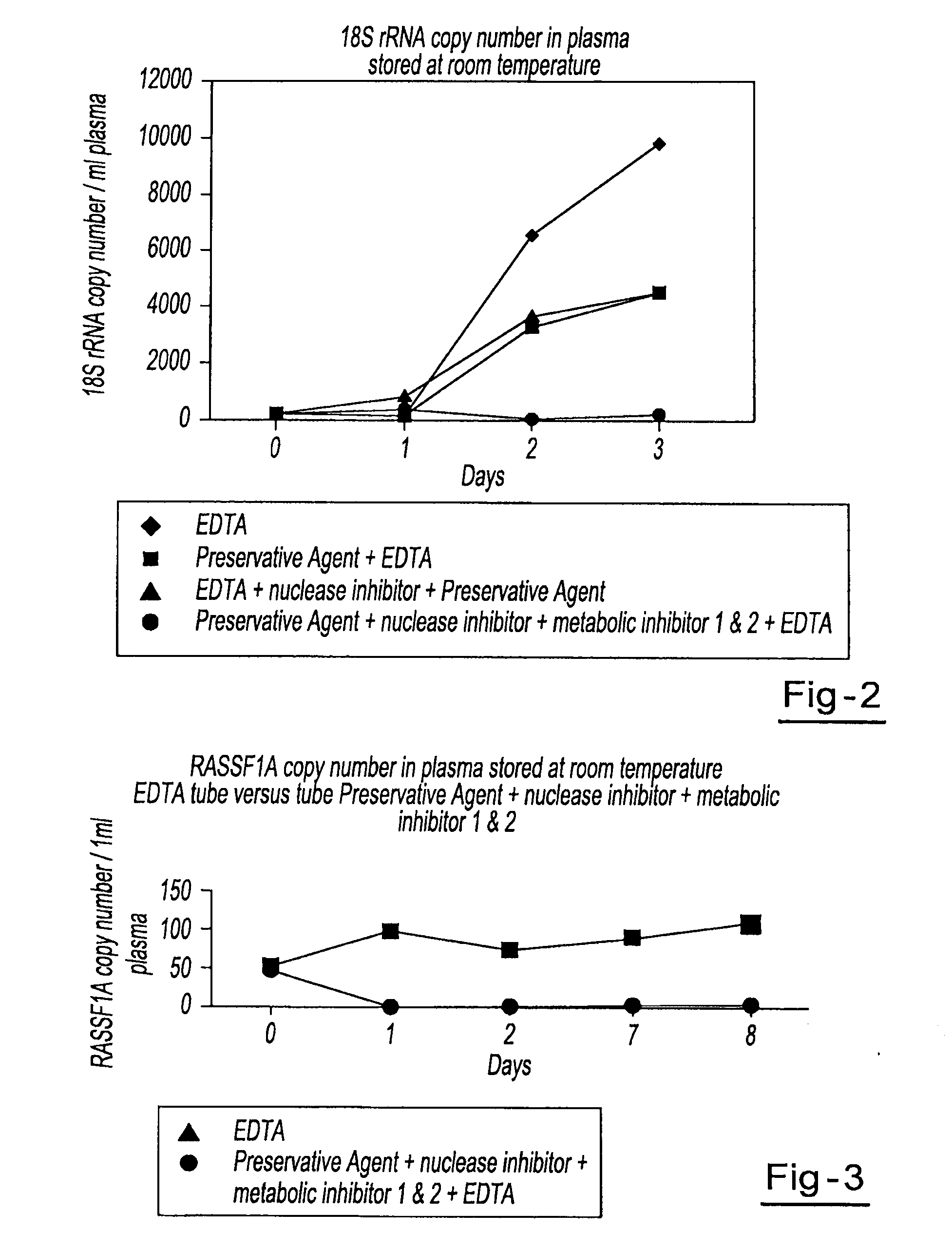
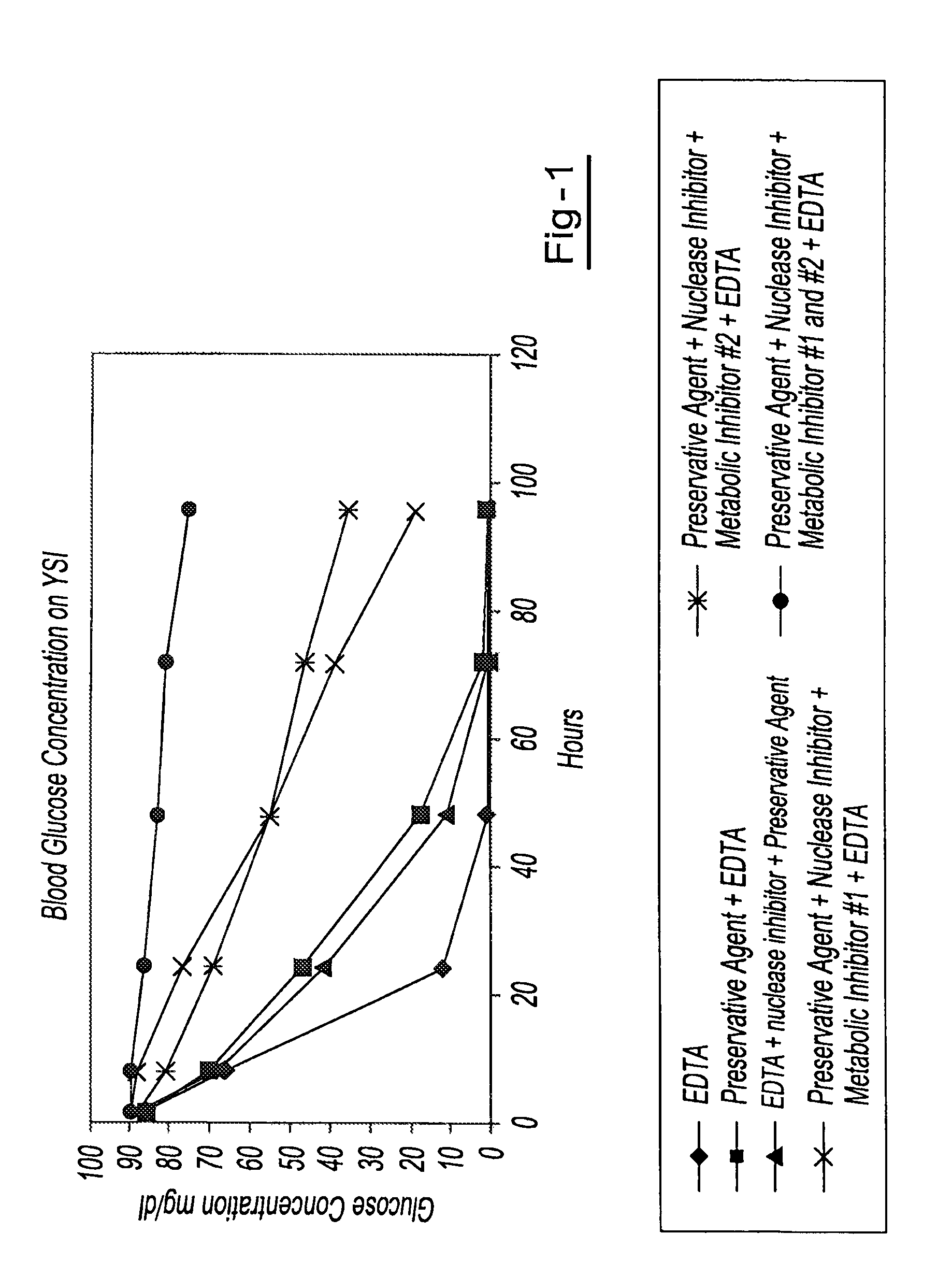
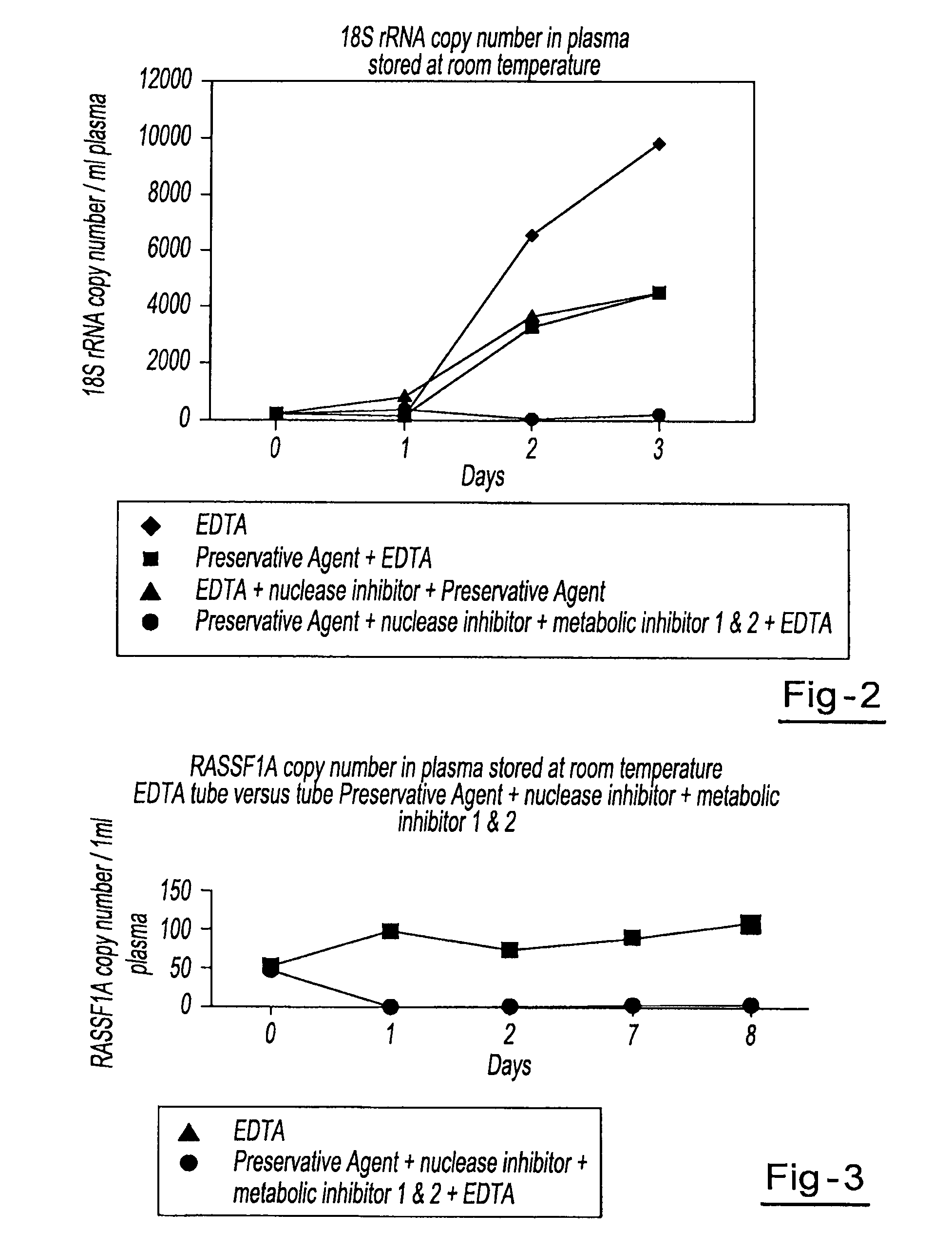
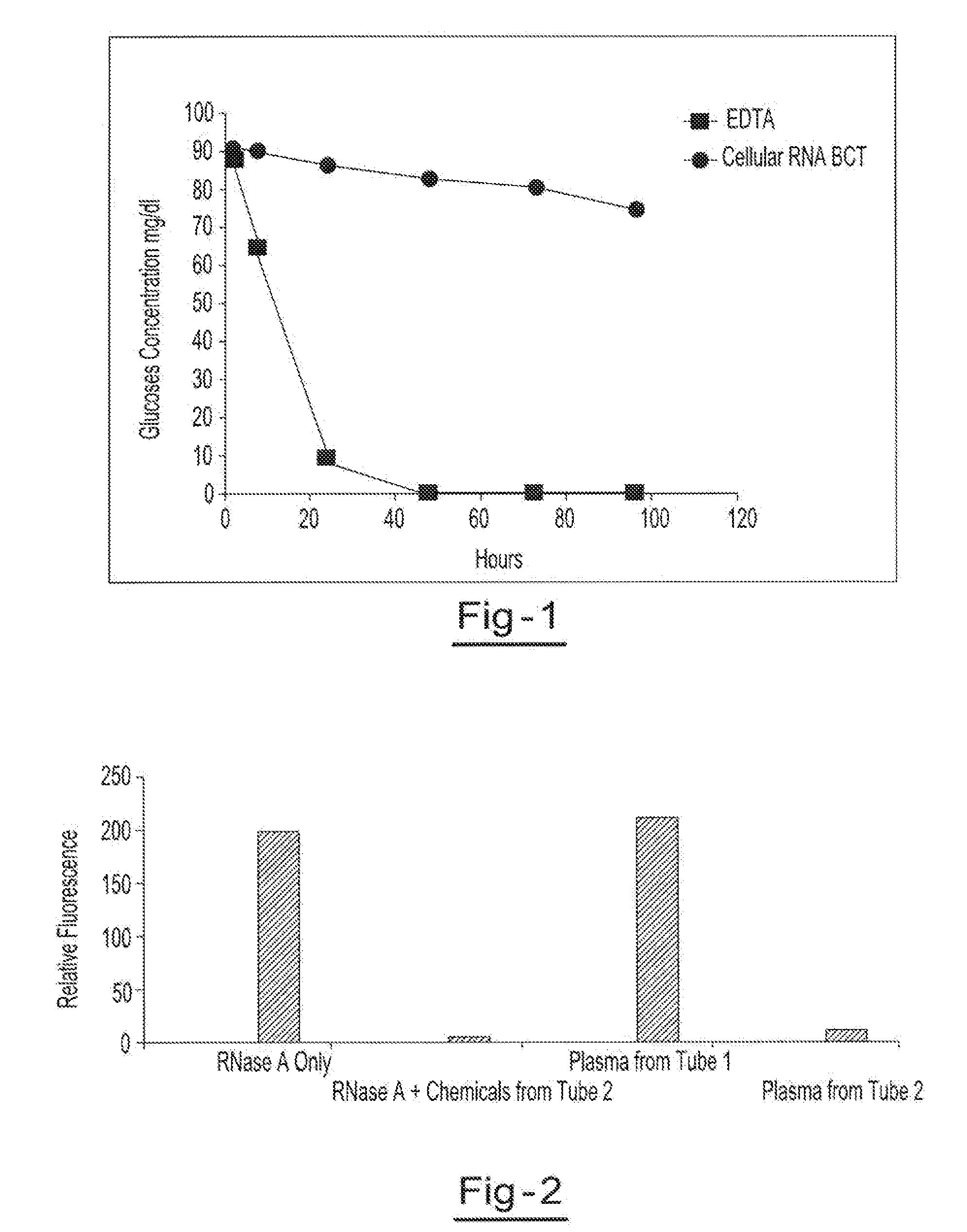
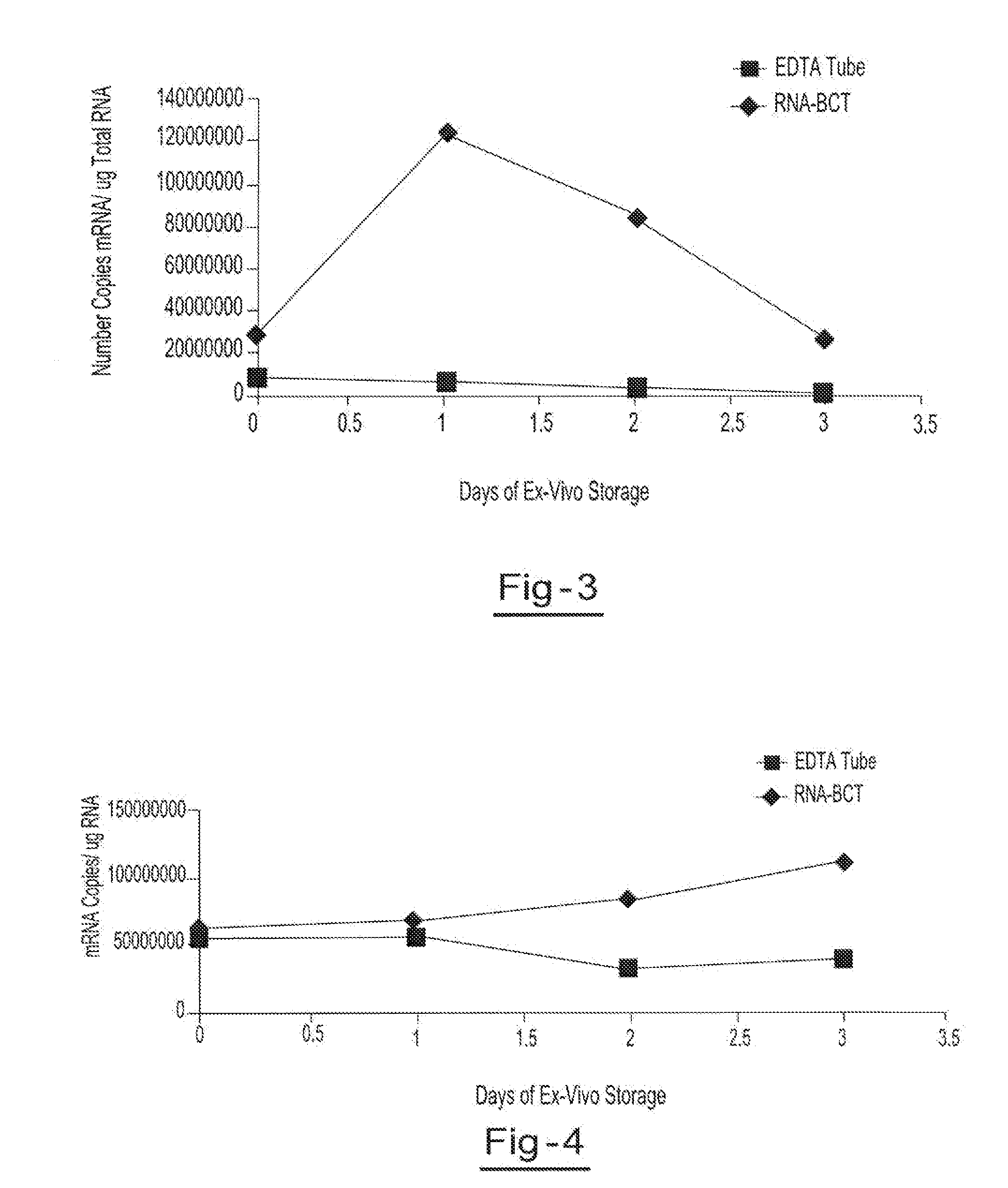
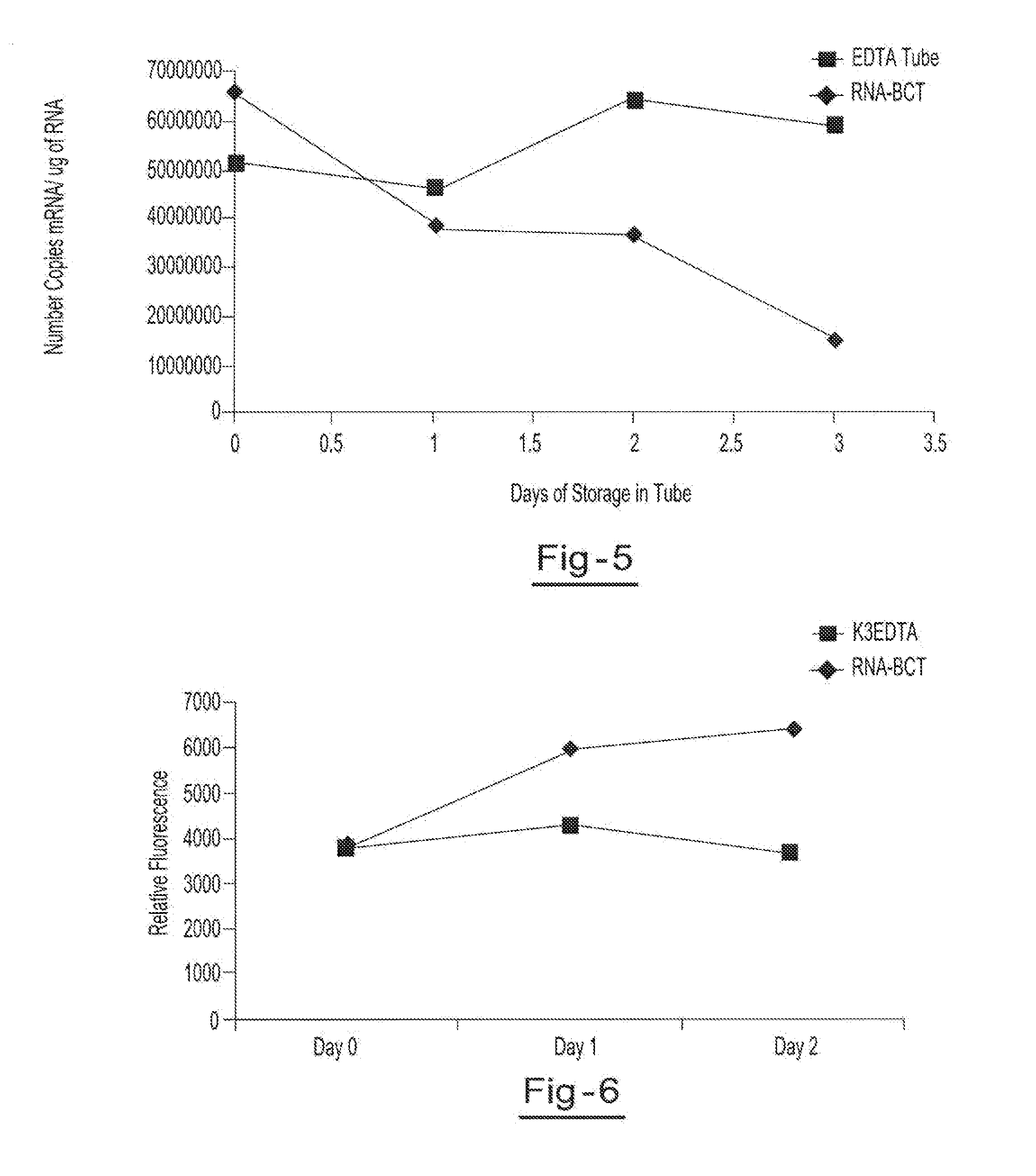
Preservation of cell-free nucleic acids
ActiveUS20100209930A1Prevent leakageInhibit synthesisMicrobiological testing/measurementChemical inhibitorsLysisNuclease
A method for preserving and processing cell-free nucleic acids located within a blood sample is disclosed, wherein a blood sample containing cell-free nucleic acids is treated to reduce both blood cell lysis and nuclease activity within the blood sample. The treatment of the sample aids in increasing the amount of cell-free nucleic acids that can be identified and tested while maintaining the structure and integrity of the nucleic acids.
Owner:STRECK LLC
Preservation of cell-free RNA in blood samples
ActiveUS8304187B2Prevent leakageInhibit synthesisSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementLysisNuclease
Owner:STRECK LLC
Stabilization of RNA in intact cells within a blood sample
InactiveUS20110111410A1Effective isolationEfficient testingMicrobiological testing/measurementTissue cultureLysisNuclease
A method for preserving and processing nucleic acids located within a blood sample is disclosed, wherein a blood sample containing nucleic acids is treated to reduce both blood cell lysis and nuclease activity within the blood sample. The treatment of the sample aids in increasing the integrity and amount of cellular nucleic acids that can be identified and tested while avoiding contamination of the isolated nucleic acids with cell-free nucleic acids.
Owner:STRECK INC
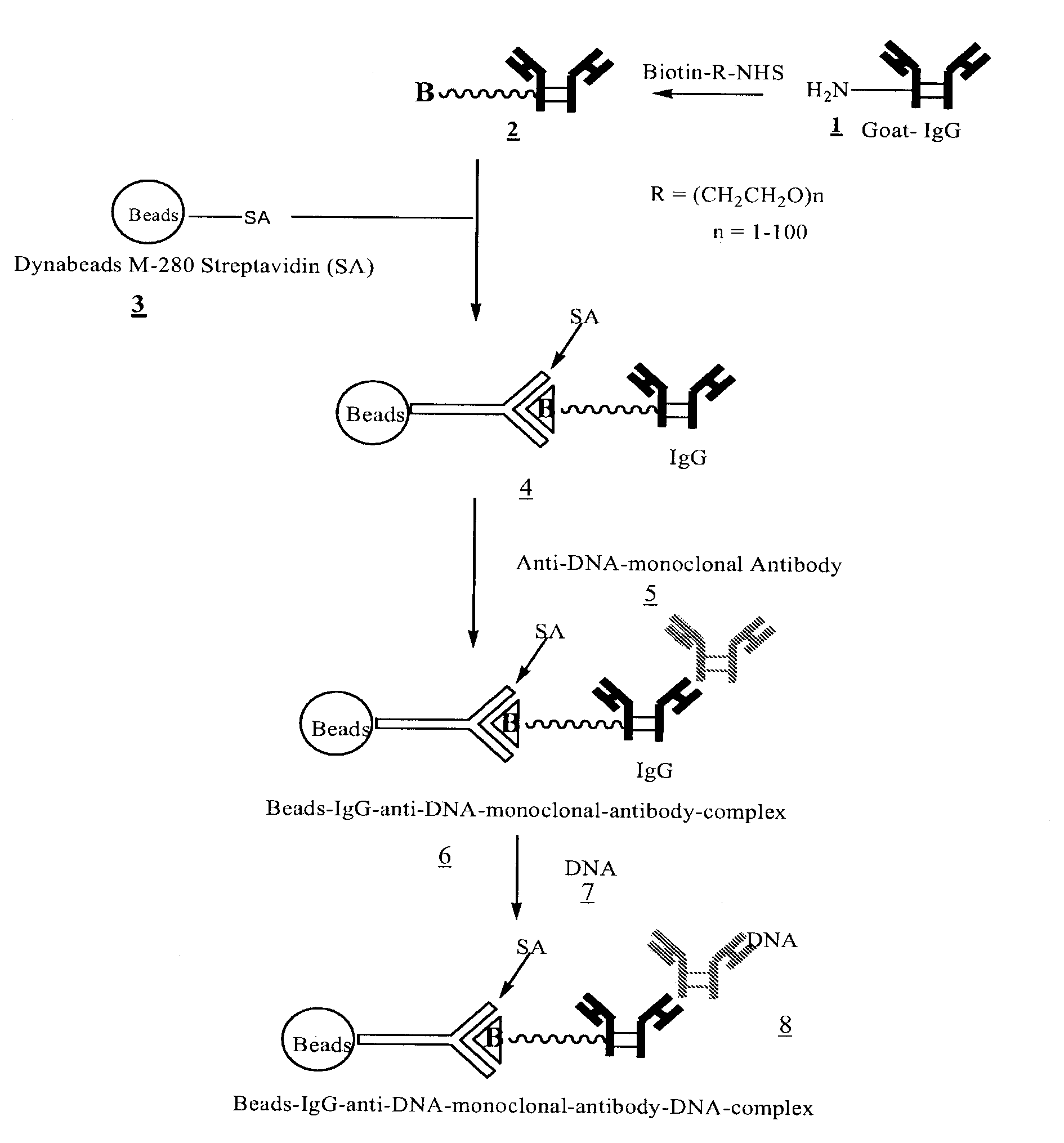
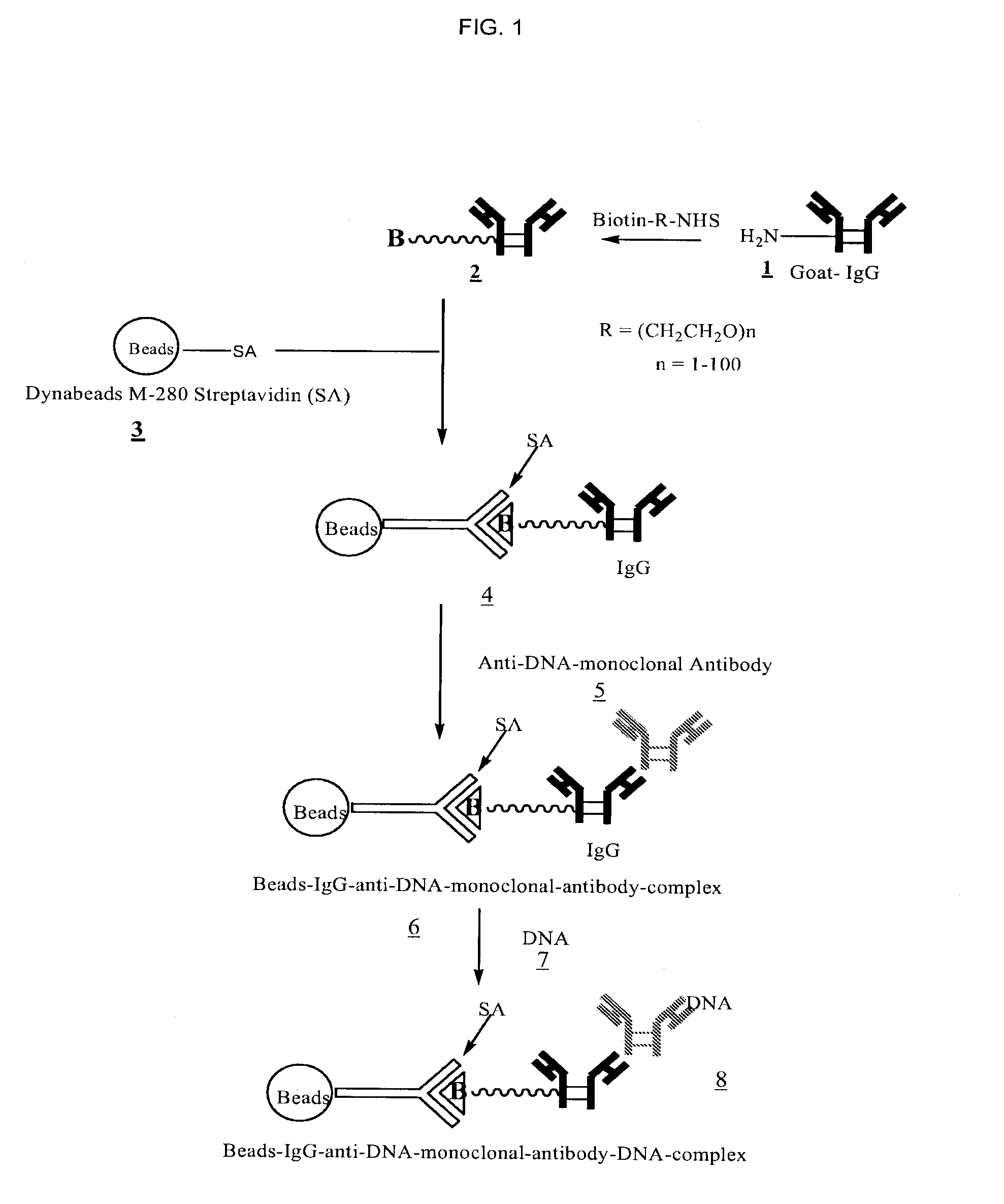
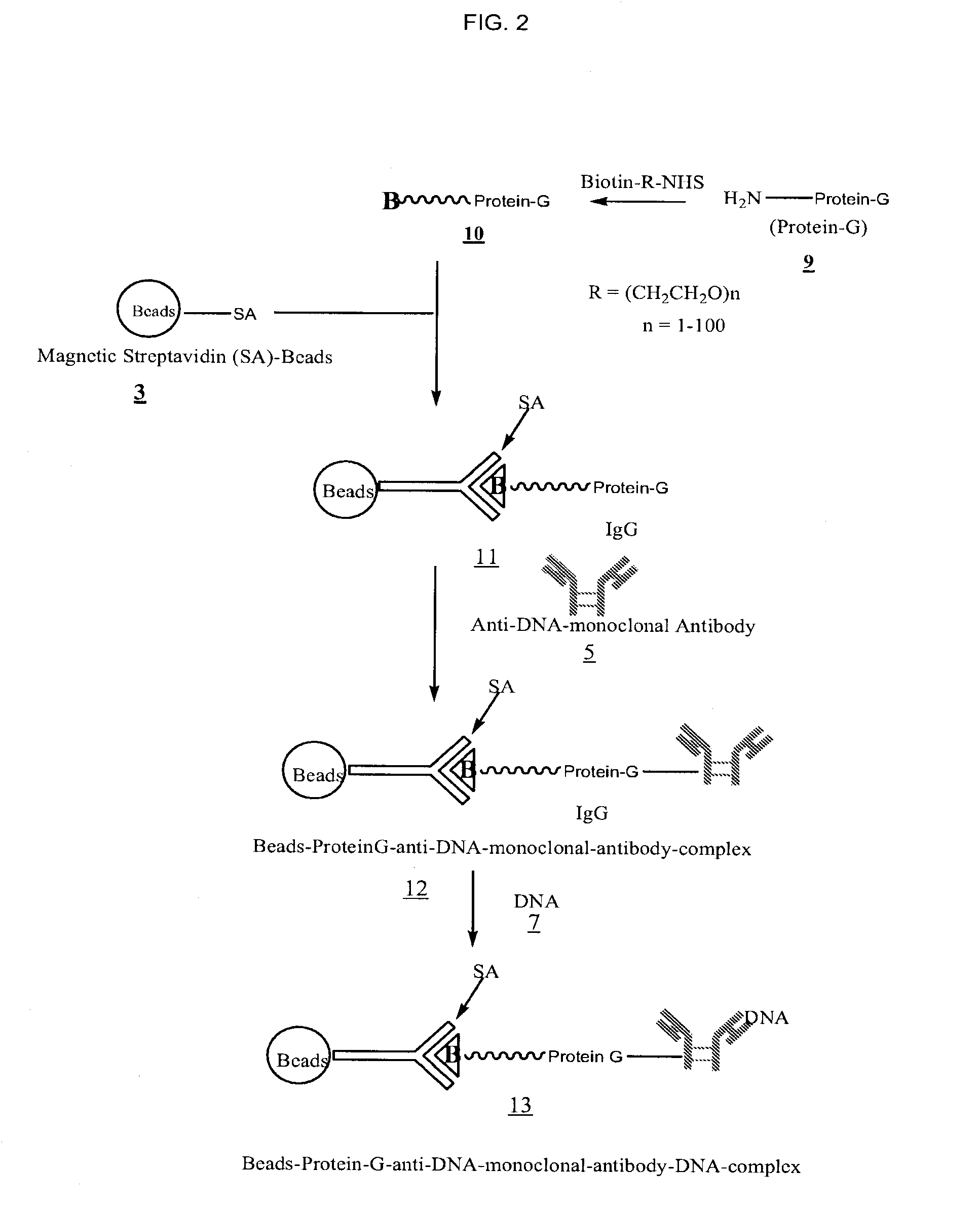
Method for isolating cell free apoptotic or fetal nucleic acids
The present invention provides methods for isolating cell free nucleic acid, e.g., apoptotic or fetal nucleic acids and methods of detecting neoplastic cells or identifying the genetic composition of a fetus. The invention also provides magnetic particles comprising an anti-DNA antibody, and kits comprising the magnetic particles.
Owner:NOVARTIS VACCINES & DIAGNOSTICS INC
Single molecule spectroscopy for analysis of cell-free nucleic acid biomarkers
InactiveUS20120135874A1Quick analysisHinder acceptanceMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningFluorescent lightFluorescent labelling
The present invention relates, e.g., to a method for detecting a nucleic acid molecule of interest in a sample comprising cell-free nucleic acids, comprising fluorescently labeling the nucleic acid molecule of interest, by specifically binding a fluorescently labeled nanosensor or probe to the nucleic acid of interest, or by enzymatically incorporating a fluorescent probe or dye into the nucleic acid of interest, illuminating the fluorescently labeled nucleic acid molecule, causing it to emit fluorescent light, and measuring the level of fluorescence by single molecule spectroscopy, wherein the detection of a fluorescent signal is indicative of the presence of the nucleic acid of interest in the sample.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Methods for multi-resolution analysis of cell-free nucleic acids
ActiveUS9850523B1Improve capture efficiencyImprove detection accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementHybridisationDiseaseMulti resolution analysis
The present disclosure provides a method for enriching for multiple genomic regions using a first bait set that selectively hybridizes to a first set of genomic regions of a nucleic acid sample and a second bait set that selectively hybridizes to a second set of genomic regions of the nucleic acid sample. These bait set panels can selectively enrich for one or more nucleosome-associated regions of a genome, said nucleosome-associated regions comprising genomic regions having one or more genomic base positions with differential nucleosomal occupancy, wherein the differential nucleosomal occupancy is characteristic of a cell or tissue type of origin or disease state.
Owner:GUARDANT HEALTH
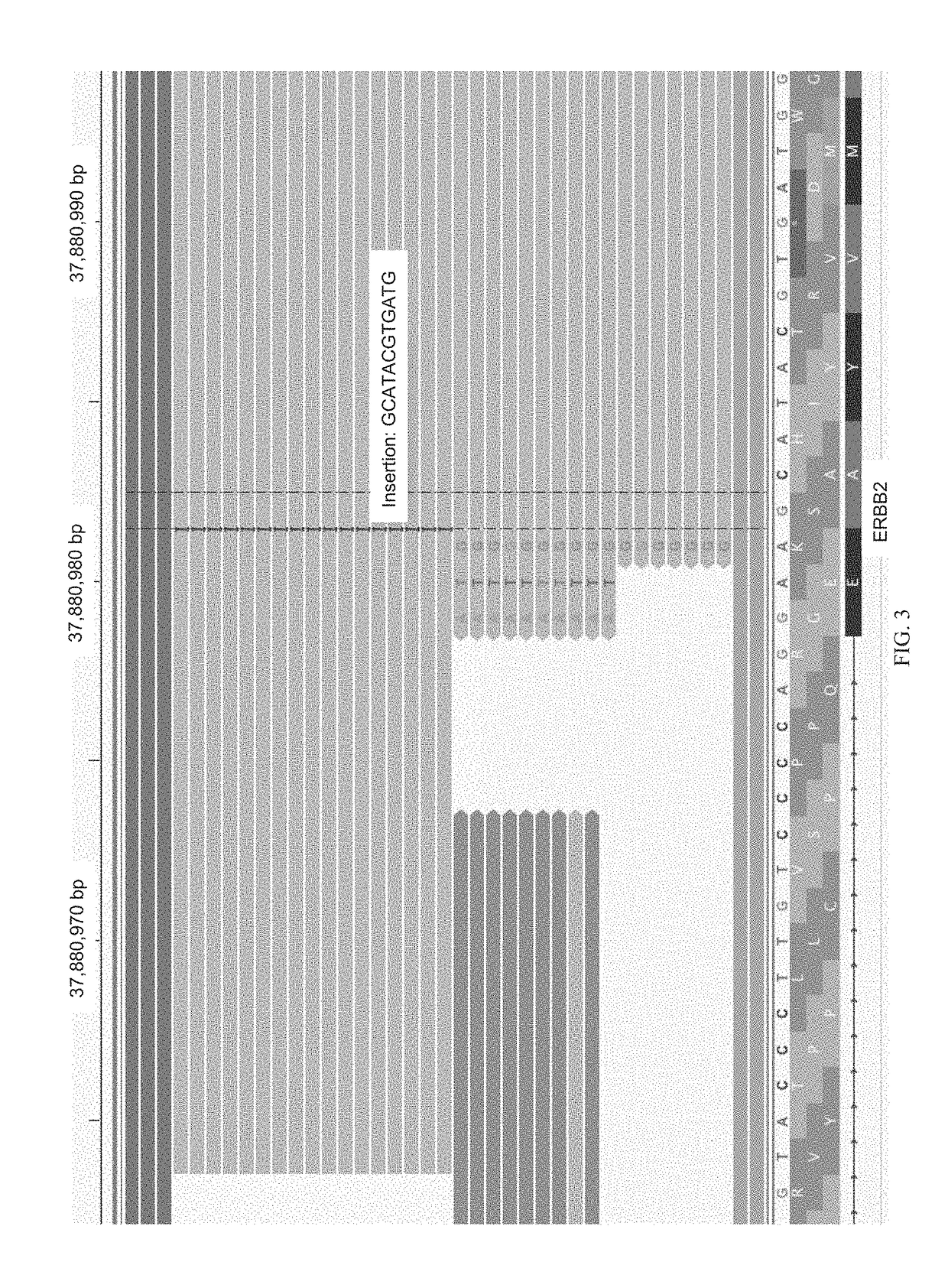
Identification and use of circulating nucleic acid tumor markers
ActiveCN105518151AMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisCancers diagnosisCancer therapy
Methods for creating a selector of mutated genomic regions and for using the selector set to analyze genetic alterations in a cell-free nucleic acid sample are provided. The methods can be used to measure tumor-derived nucleic acids in a blood sample from a subject and thus to monitor the progression of disease in the subject. The methods can also be used for cancer screening, cancer diagnosis, cancer prognosis, and cancer therapy designation.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Accurate molecular deconvolution of mixture samples
PendingUS20180187241A1Reduce varianceAccurate deconvolutionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsNon invasiveBlood plasma
The present disclosure relates to methods to deconvolute a mixture sample of genetic material from different origins or sources. The disclosed methods can be used in various applications, including, the non-invasive determination of a fetal genome, a fetal -ome (e.g. exome). or other targeted fetal locus from cell-free nucleic acids in maternal plasma or other body fluids; the de-termination of cancer-associated mutations from cell-free nucleic acids in a body fluid sample that contains a mixture of nucleic acids from normal cells and tumor cells; and quantification of donor cell contamination using a body fluid from a transplantation recipient to monitor and / or predict the outcome of a transplantation procedure.
Owner:ARIMA GENOMICS INC
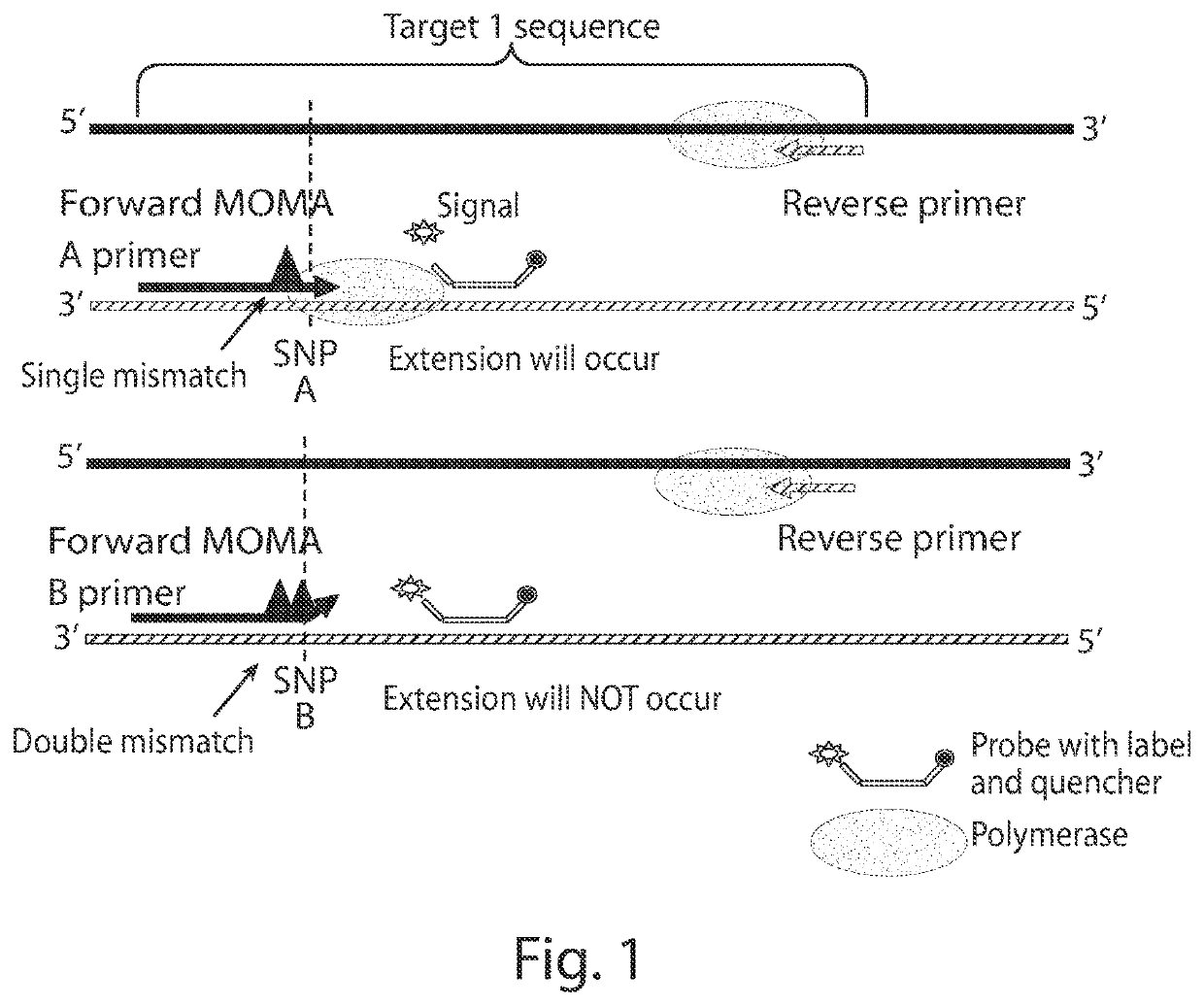
Identification and use of circulating nucleic acids
ActiveUS20180251848A1Nucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementPolynucleotideCell-Free Nucleic Acids
Disclosed herein are polynucleotide adaptors and methods of use thereof for identifying and analyzing nucleic acids, including cell-free nucleic acids from a patient sample. Also disclosed herein are methods of using the adaptors to detect, diagnose, or determine prognosis of cancers.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
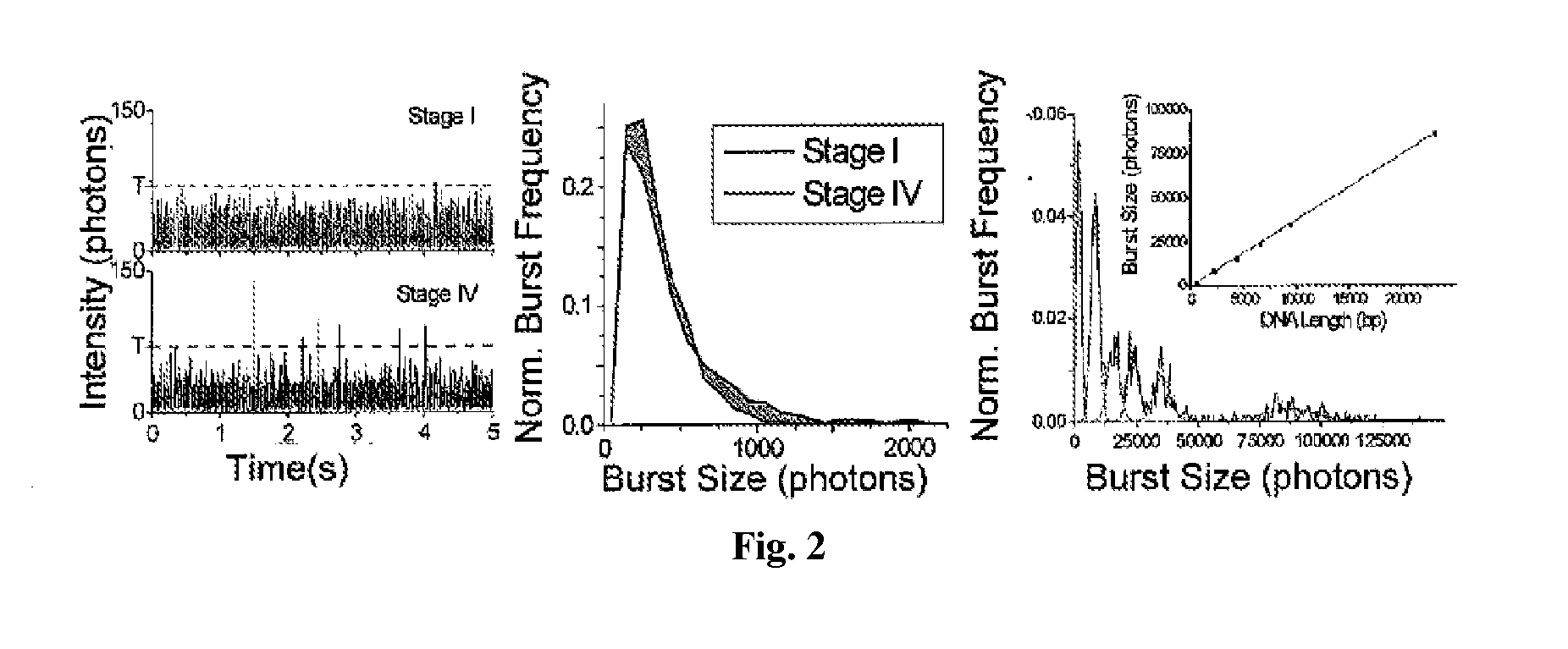
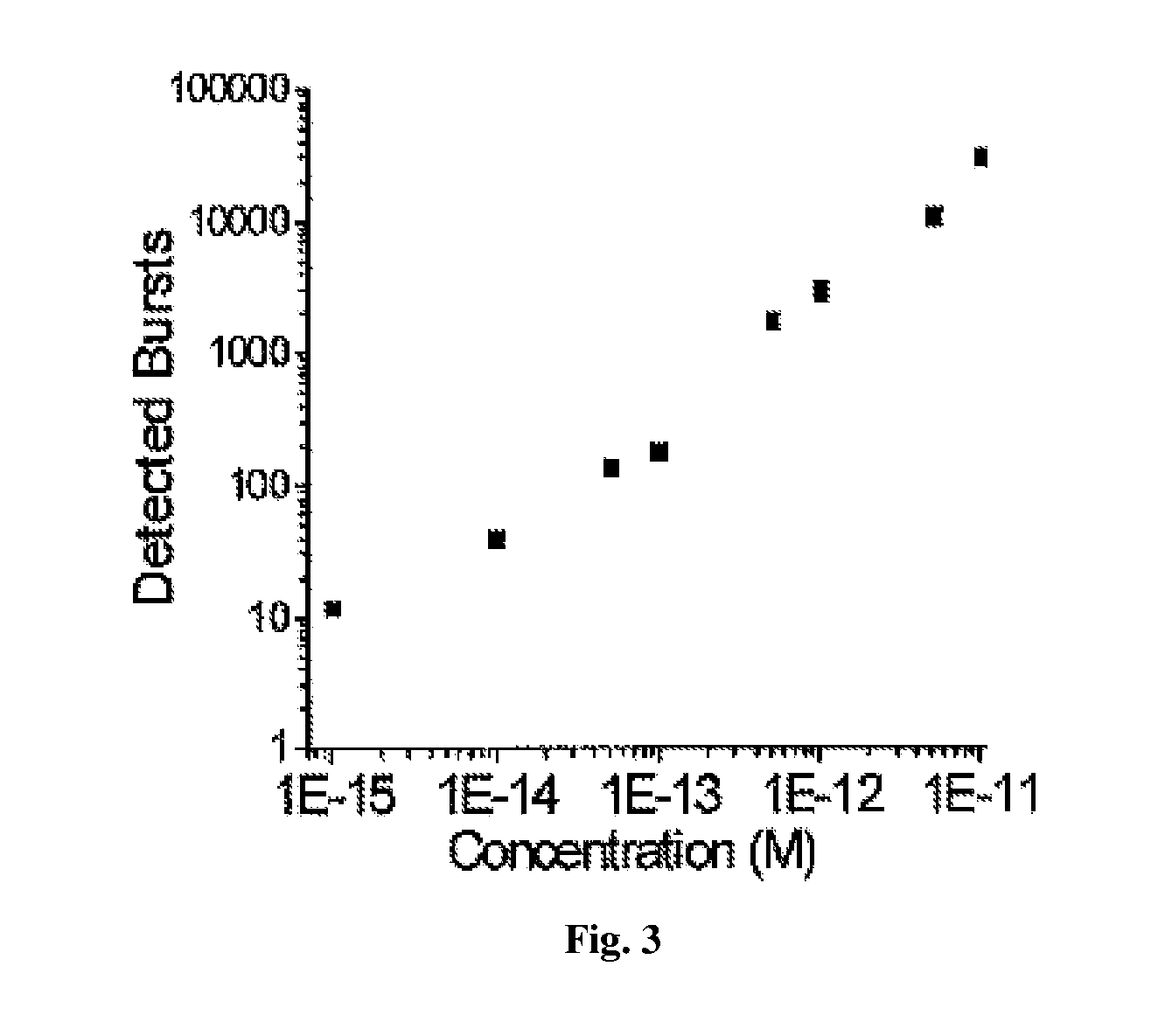
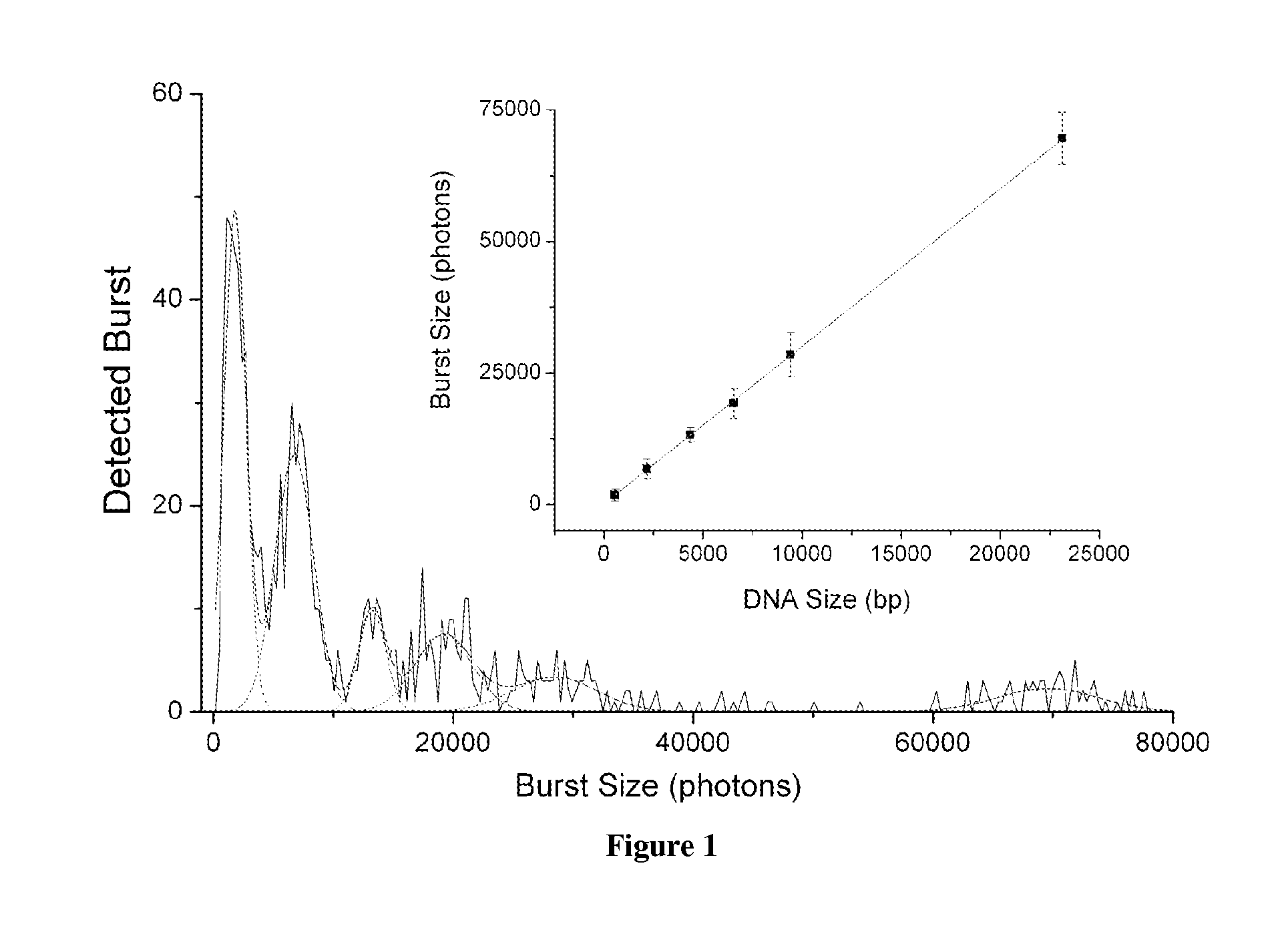
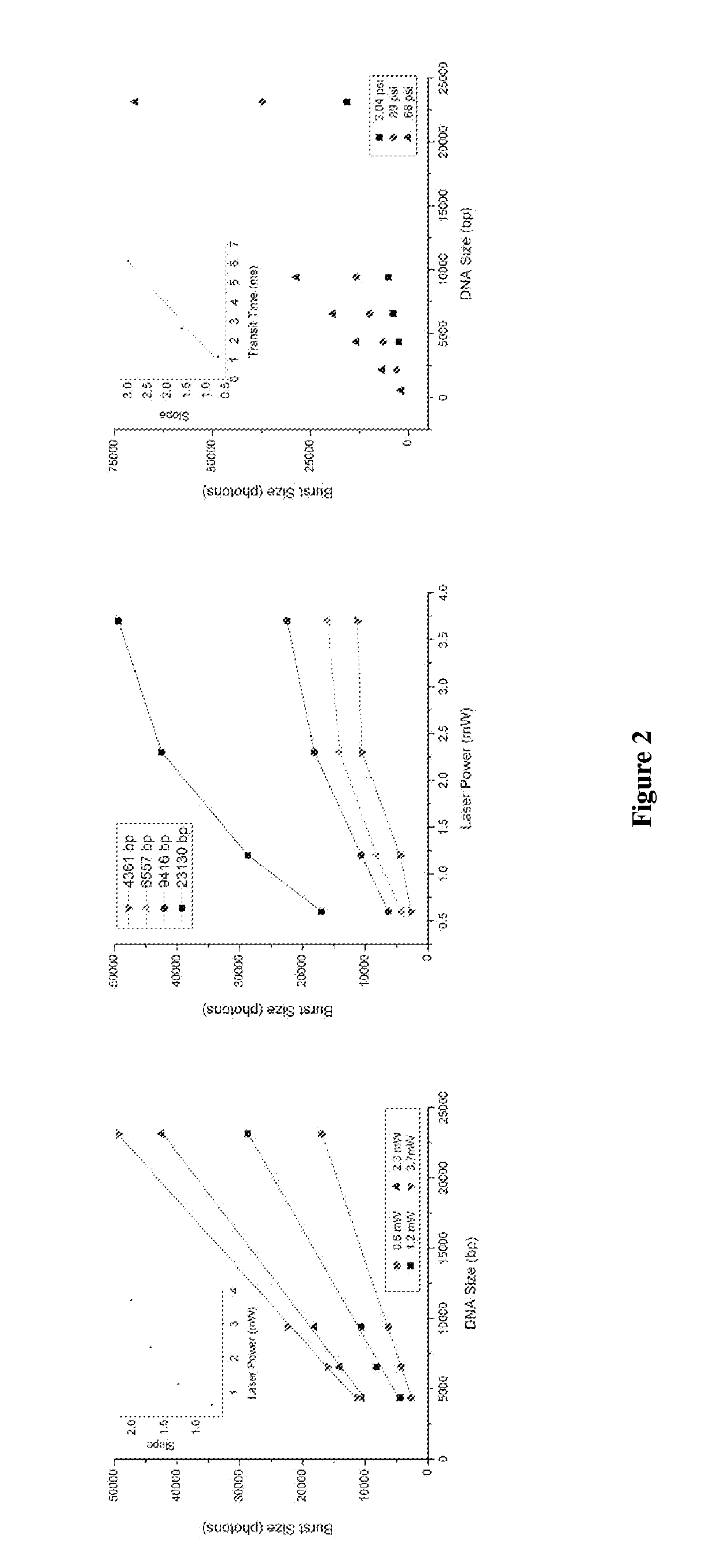
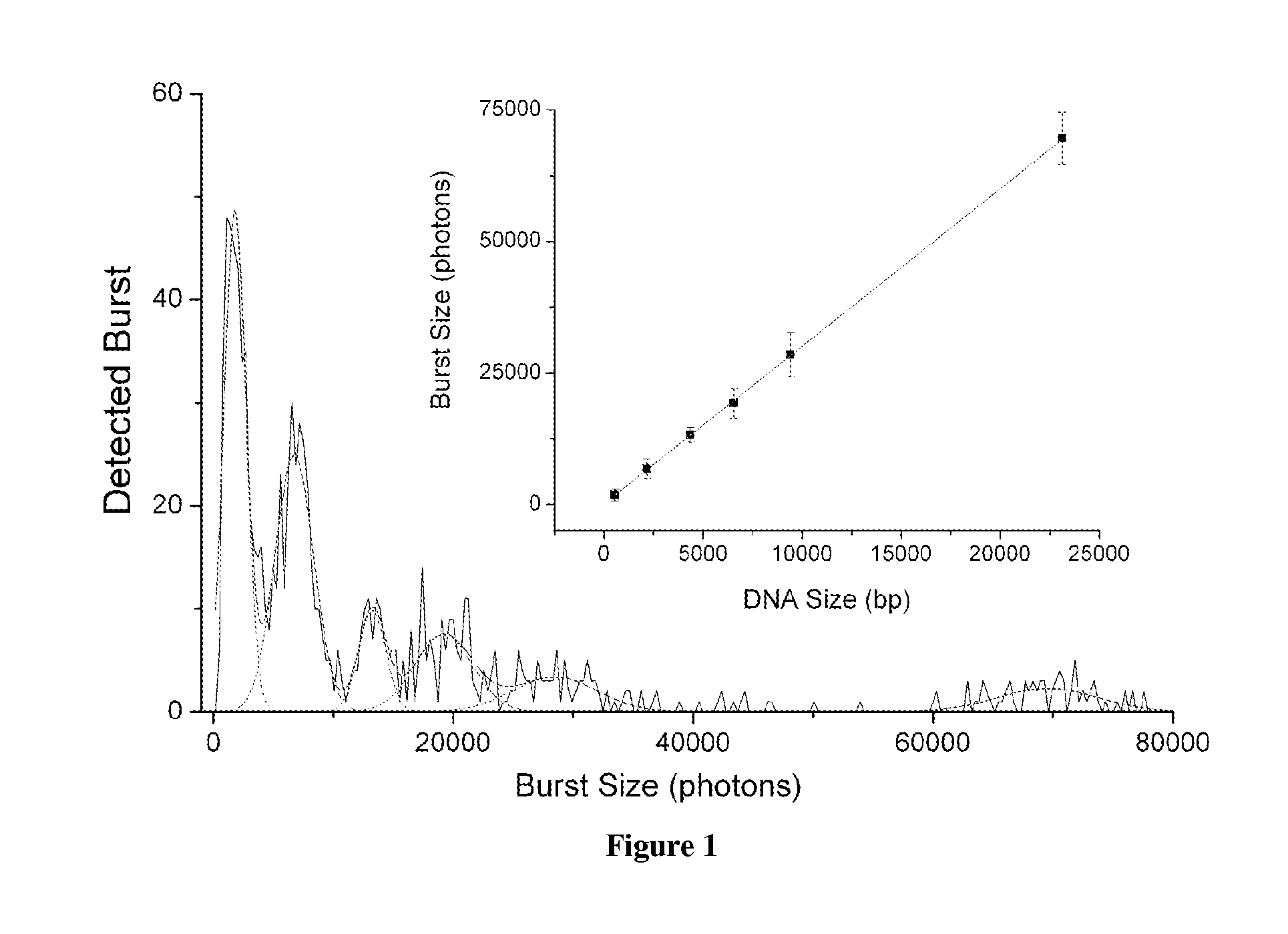
DNA integrity assay (DIA) for cancer diagnostics, using confocal fluorescence spectroscopy
The present invention relates, e.g., to a method for determining the size distribution of DNA molecules in a sample comprising cell-free nucleic acid, comprising labeling the DNA with a fluorescent dye in a stoichiometric manner, subjecting the DNA to molecular spectroscopy (e.g., cylindrical illumination confocal spectroscopy), analyzing suitable fluorescent burst parameters of the labeled DNA, and conducting single molecule DNA integrity analysis of the labeled DNA molecules in the sample. In one embodiment of the invention, the method is used as a diagnostic method for detecting cancer.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
DNA integrity assay (DIA) for cancer diagnostics, using confocal fluorescence spectroscopy
ActiveUS20110171741A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingFluorescence spectrometryMolecular spectroscopy
The present invention relates, e.g., to a method for determining the size distribution of DNA molecules in a sample comprising cell-free nucleic acid, comprising labeling the DNA with a fluorescent dye in a stoichiometric manner, subjecting the DNA to molecular spectroscopy (e.g., cylindrical illumination confocal spectroscopy), analyzing suitable fluorescent burst parameters of the labeled DNA, and conducting single molecule DNA integrity analysis of the labeled DNA molecules in the sample. In one embodiment of the invention, the method is used as a diagnostic method for detecting cancer.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
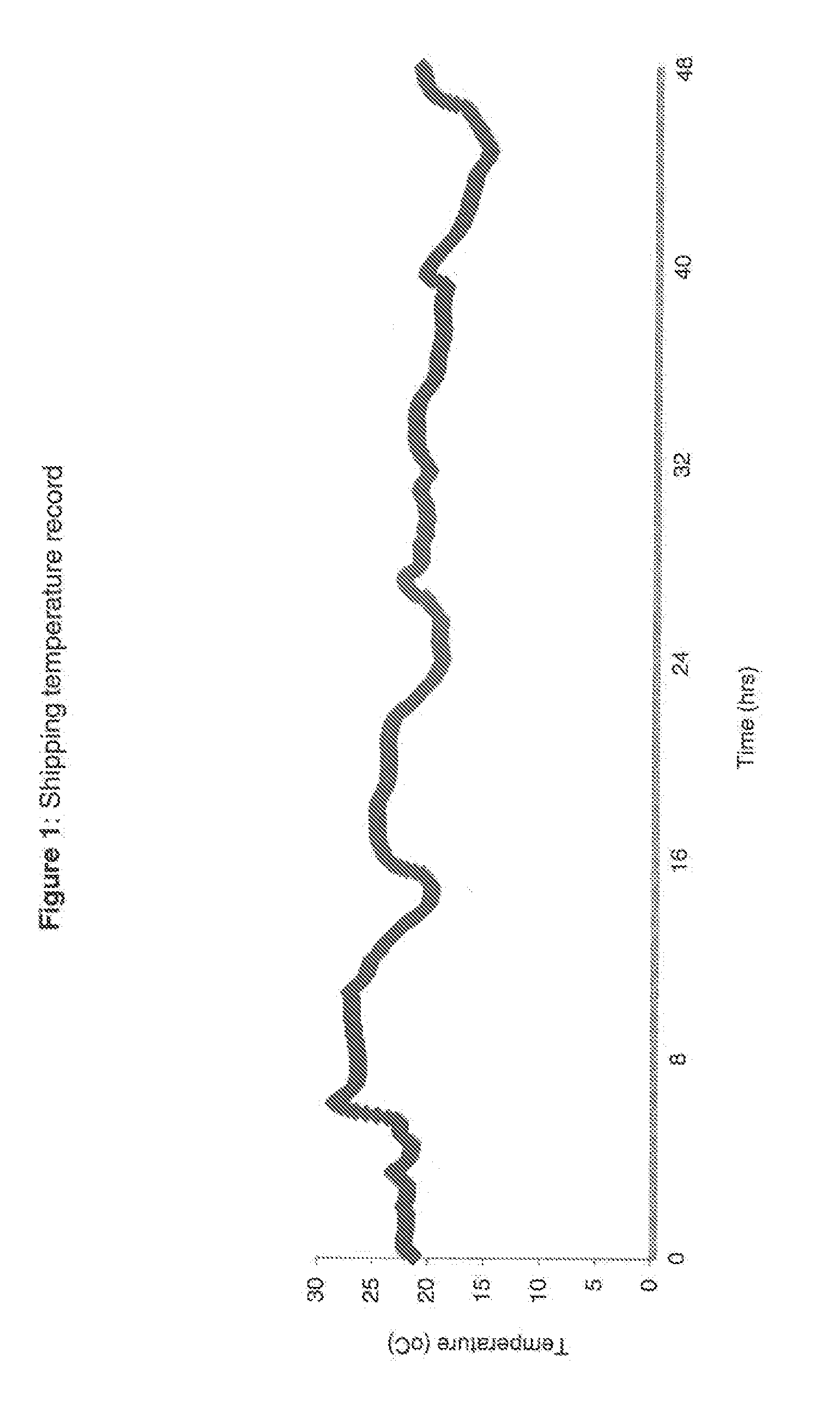
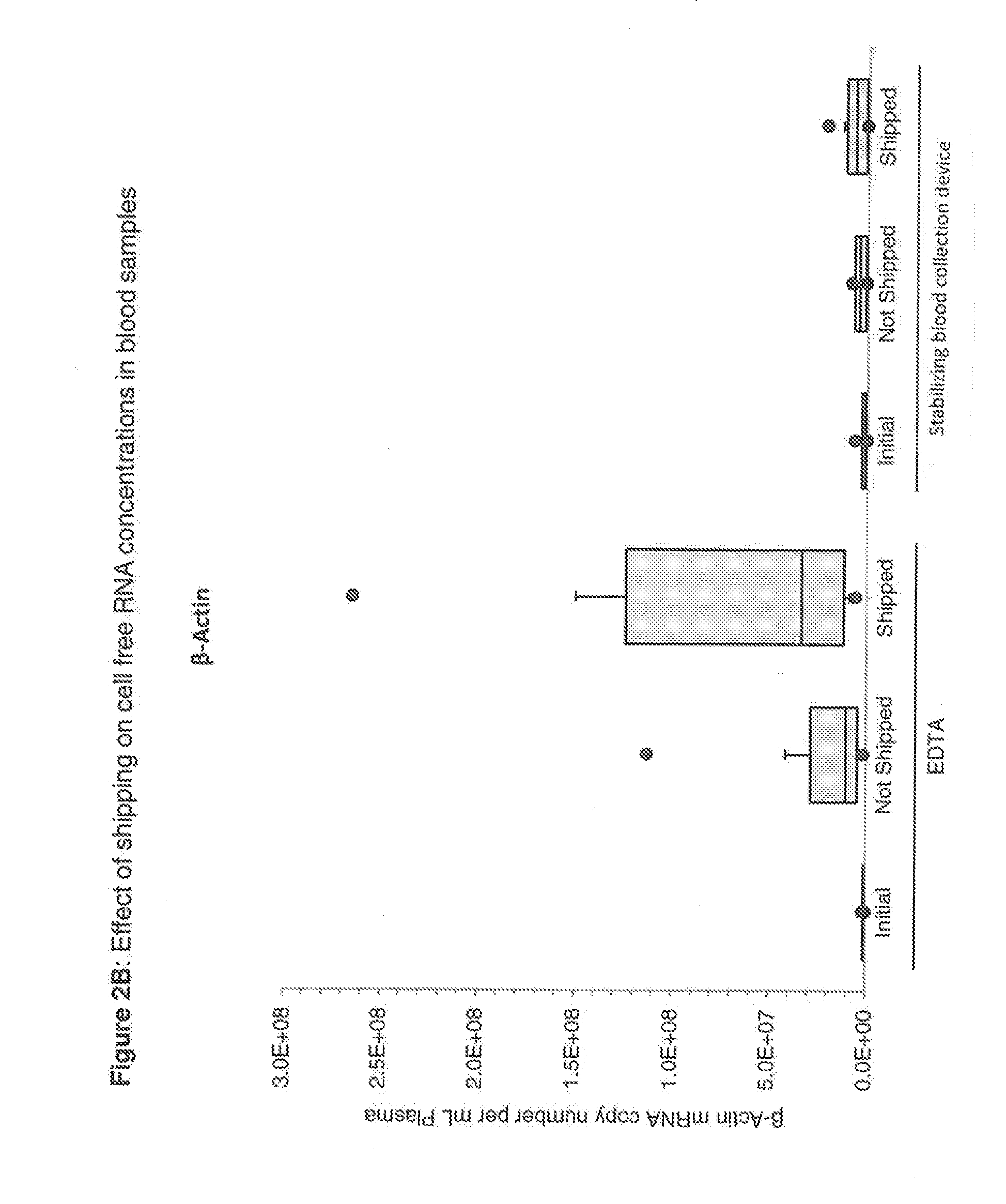
Blood collection device for stabilizing cell-free RNA in blood during sample shipping and storage
InactiveUS20140199681A1Prevent increase in RNA levelQuality improvementMicrobiological testing/measurementDead animal preservationBlood collectionBlood plasma
A method for preserving and protecting cell-free nucleic acids located within blood plasma samples is disclosed, wherein a sample of blood containing nucleic acids is treated to reduce deleterious effects of storage and transport.
Owner:STRECK INC
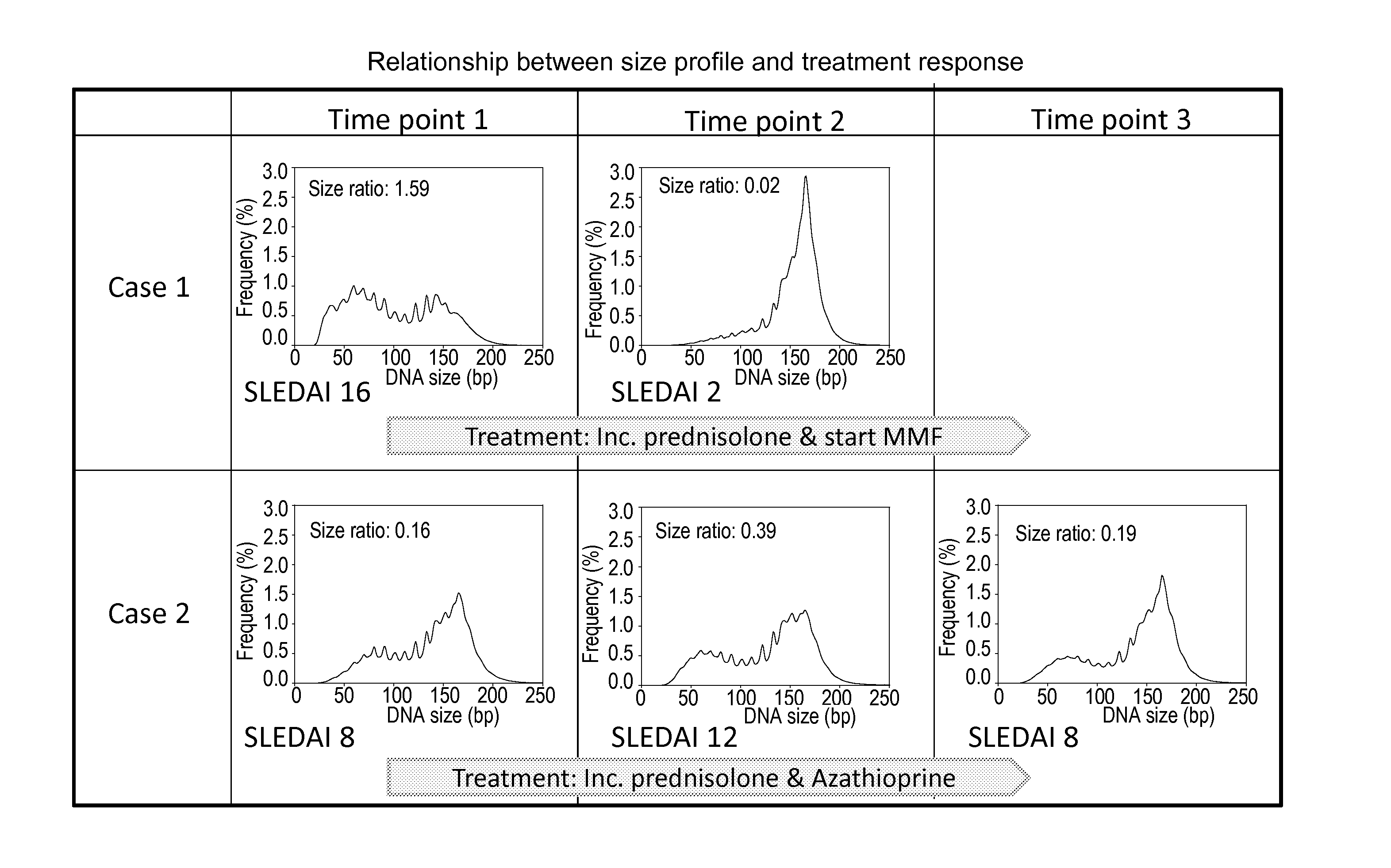
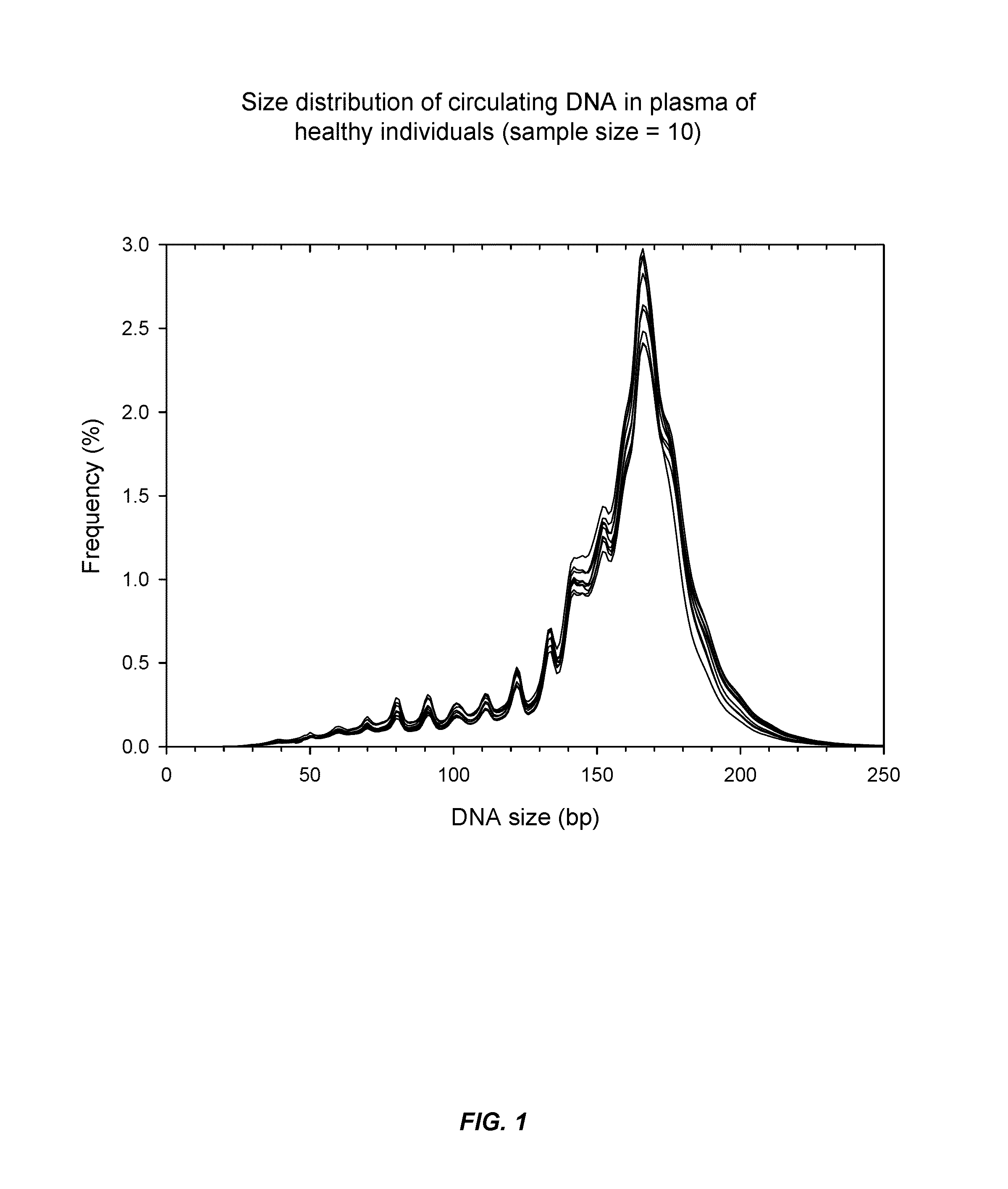
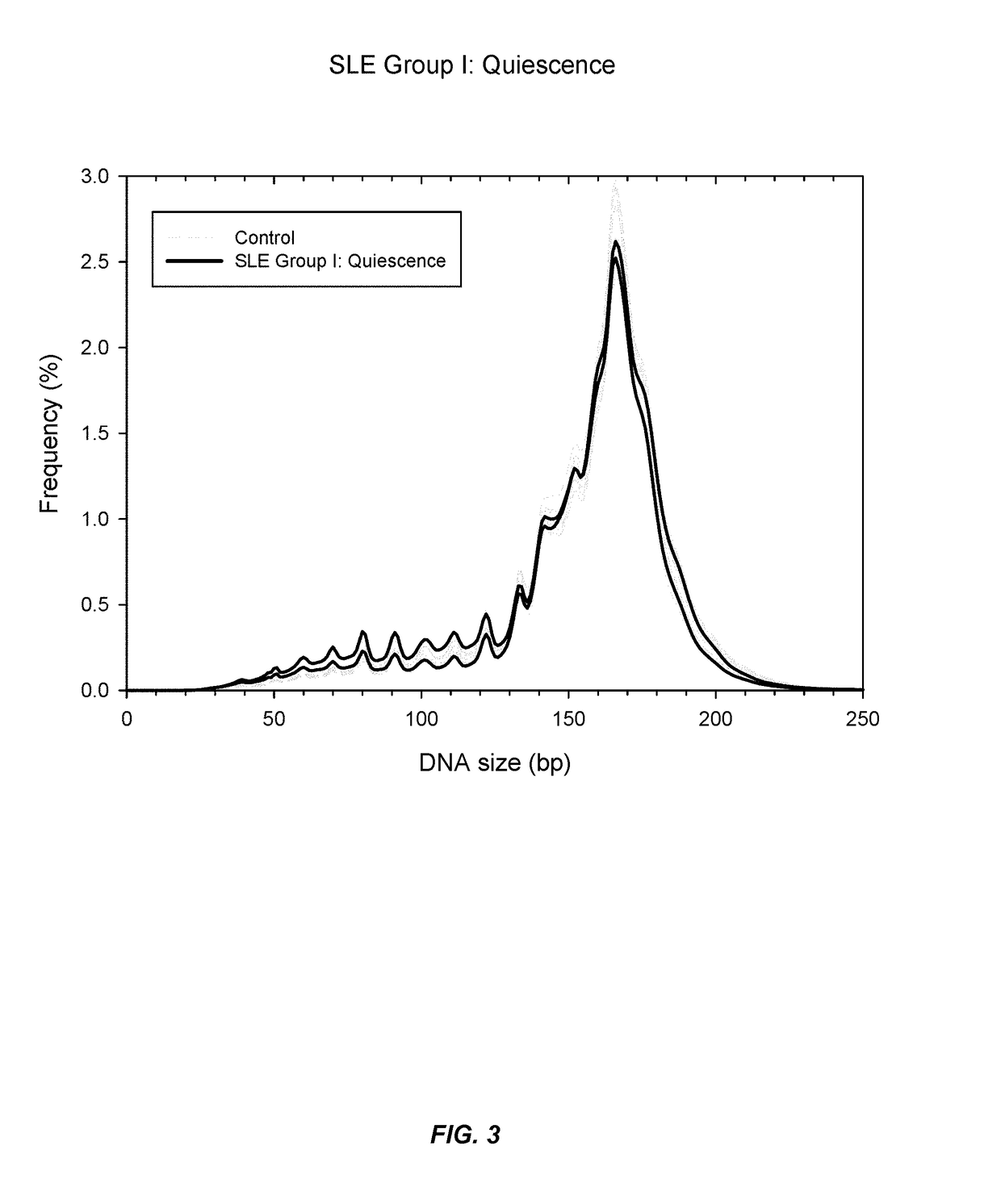
Sequencing analysis of circulating DNA to detect and monitor autoimmune diseases
ActiveUS20150087529A1Reducing methylationRaise the ratioHealth-index calculationMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisDisease
Systems, methods, and apparatuses are provided for diagnosing auto-immune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) based on the sizes, methylation levels, and / or genomic characteristics of circulating DNA molecules. Patients provide blood or other tissue samples containing cell-free nucleic molecules for analysis. Massively parallel and / or methylation-aware sequencing can be used to determine the sizes and methylation levels of individual DNA molecules and identify the number of molecules originating from different genomic regions. A level of SLE can be estimated based on: the amount of molecules having sizes below a threshold value; the methylation level(s) of the entire genome or portions of the genome; correlations between the sizes and methylation levels of DNA molecules; and / or comparing the representation of DNA molecules in each of a plurality of genomic regions with a reference value for that region, and determining an amount of genomic regions having increased or decreased measured genomic representation.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Monitoring mantle cell lymphoma clonotypes in peripheral blood after immunotransplant
InactiveUS20150299800A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningDiseaseAutologous T-cells
The invention is directed to a method of monitoring a mantle cell lymphoma residual disease in an immunotransplant patient by post-treatment analysis of clonotype profiles from patient blood samples. In some embodiments, methods of the invention comprising steps of (a) treating a patient by immunotransplanting the patient with vaccine-primed autologous T cells; (b) obtaining a peripheral blood sample from the patient comprising B-cells and / or cell-free nucleic acids; (c) amplifying molecules of nucleic acid from the B-cells of the sample and / or cell-free nucleic acids in the sample, the molecules of nucleic acid comprising recombined DNA sequences from immunoglobulin genes; (d) sequencing the amplified molecules of nucleic acid to form a clonotype profile; and (e) determining from the clonotype profile a presence, absence and / or level of the one or more patient-specific clonotypes correlated with the mantle cell lymphoma, including phylogenic clonotypes thereof.
Owner:ADAPTIVE BIOTECH
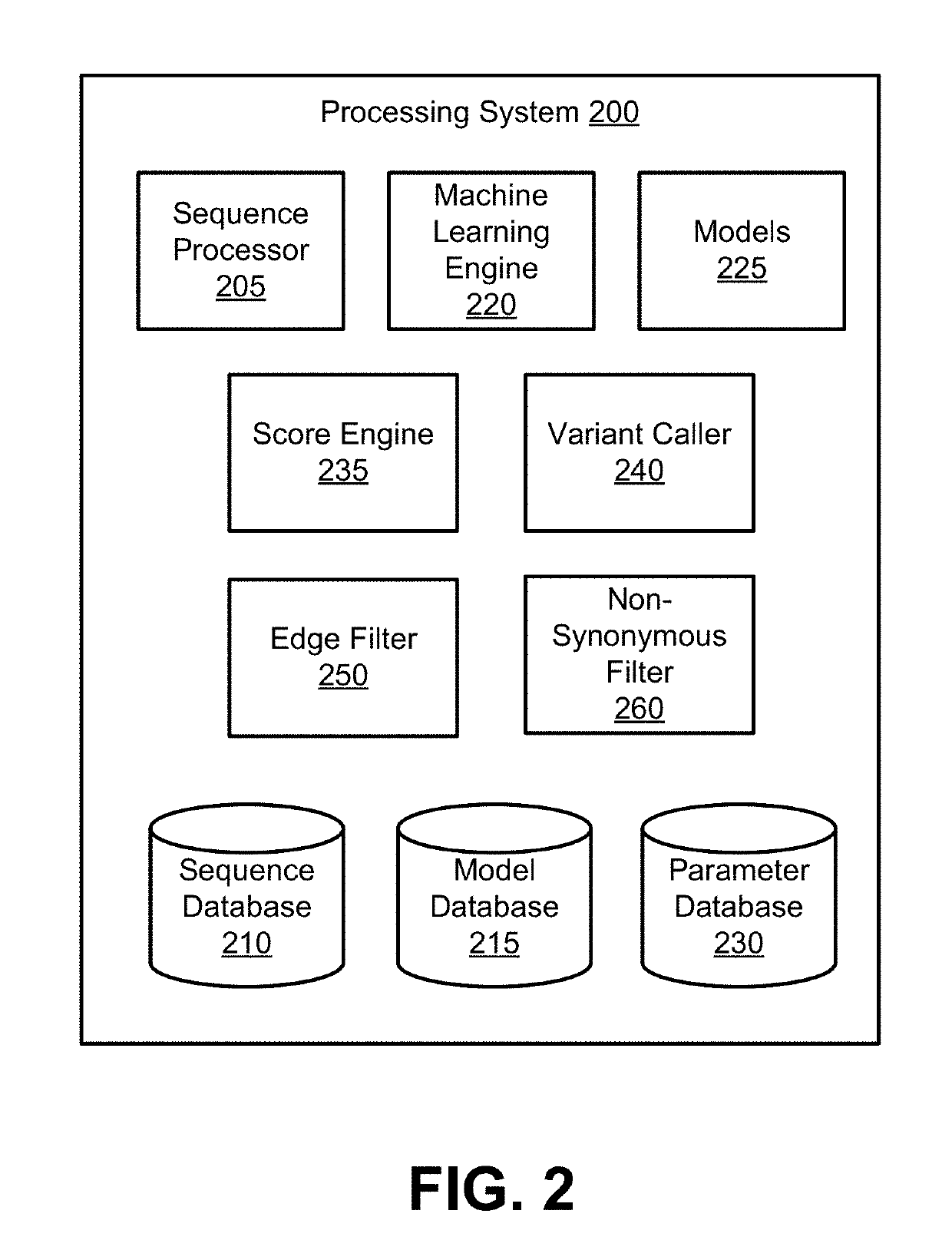
Models for Targeted Sequencing
PendingUS20190164627A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsDiseaseCell-Free Nucleic Acids
A processing system uses a Bayesian inference based model for targeted sequencing or variant calling. In an embodiment, the processing system generates candidate variants of a cell free nucleic acid sample. The processing system determines likelihoods of true alternate frequencies for each of the candidate variants in the cell free nucleic acid sample and in a corresponding genomic nucleic acid sample. The processing system filters or scores the candidate variants by the model using at least the likelihoods of true alternate frequencies. The processing system outputs the filtered candidate variants, which may be used to generate features for a predictive cancer or disease model.
Owner:GRAIL LLC
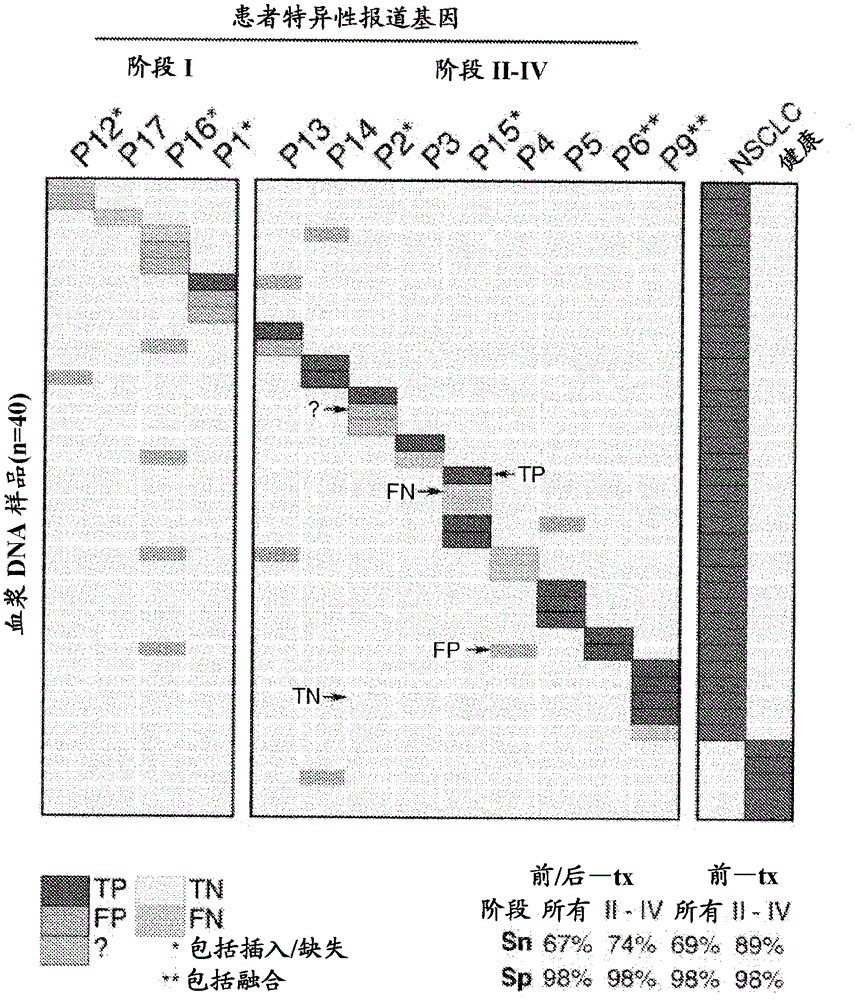
Detecting somatic single nucleotide variants from cell-free nucleic acid with application to minimal residual disease monitoring
The present disclosure provides a probabilistic model for accurate and sensitive somatic single nucleotide variant (SNV) detection in cell-free nucleic acid samples comprising a set of sequence data.A joint genotype may be determined for each locus in the set of sequence data, and germline mutations may be intrinsically removed. A set of filtrations can be applied to eliminate low quality somaticvariant calls. Further, a global tumor cell-free deoxyribonucleic acid (cfDNA) fraction and overlapping read mates can be considered, thereby enabling accurate SNV detection and variant allele frequency estimation from samples with low tumor cfDNA fraction. A sensitive early detection of minimal residual disease (MRD) is designed by using the probabilistic model and the machine learning model fordistinguishing true variants from sequencing errors.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Alignment free filtering for identifying fusions
ActiveUS20180355423A1Efficient and scalableReduce computing costData visualisationBiostatisticsTest sampleNucleic acid sequencing
Cell free nucleic acids from a test sample obtained from an individual are analyzed to identify possible fusion events. Cell free nucleic acids are sequenced and processed to generate fragments. Fragments are decomposed into kmers and the kmers are either analyzed de novo or compared to targeted nucleic acid sequences that are known to be associated with fusion gene pairs of interest. Thus, kmers that may have originated from a fusion event can be identified. These kmers are consolidated to generate gene ranges from various genes that match sequences in the fragment. A candidate fusion event can be called given the spanning of one or more gene ranges across the fragment.
Owner:GRAIL LLC
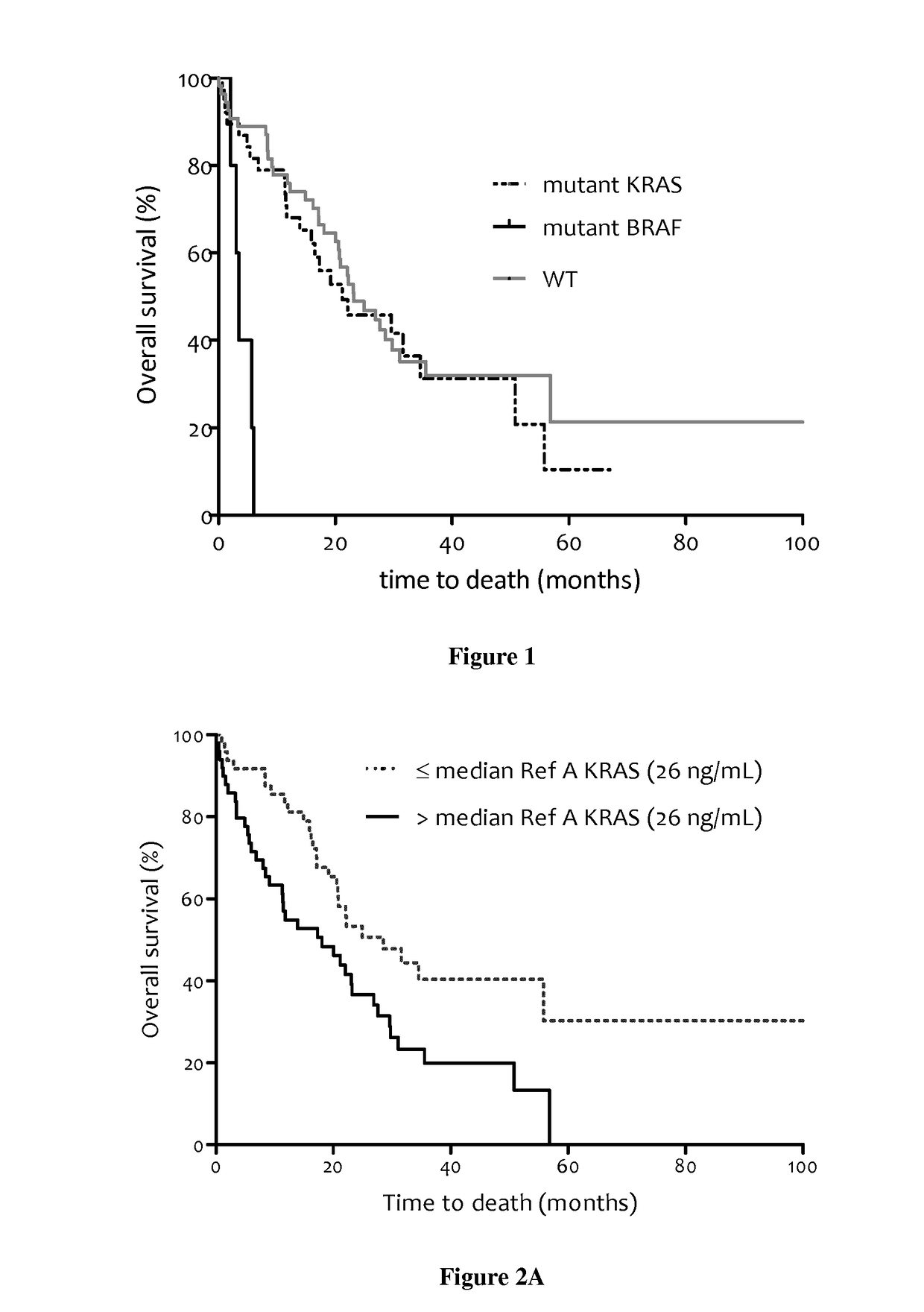
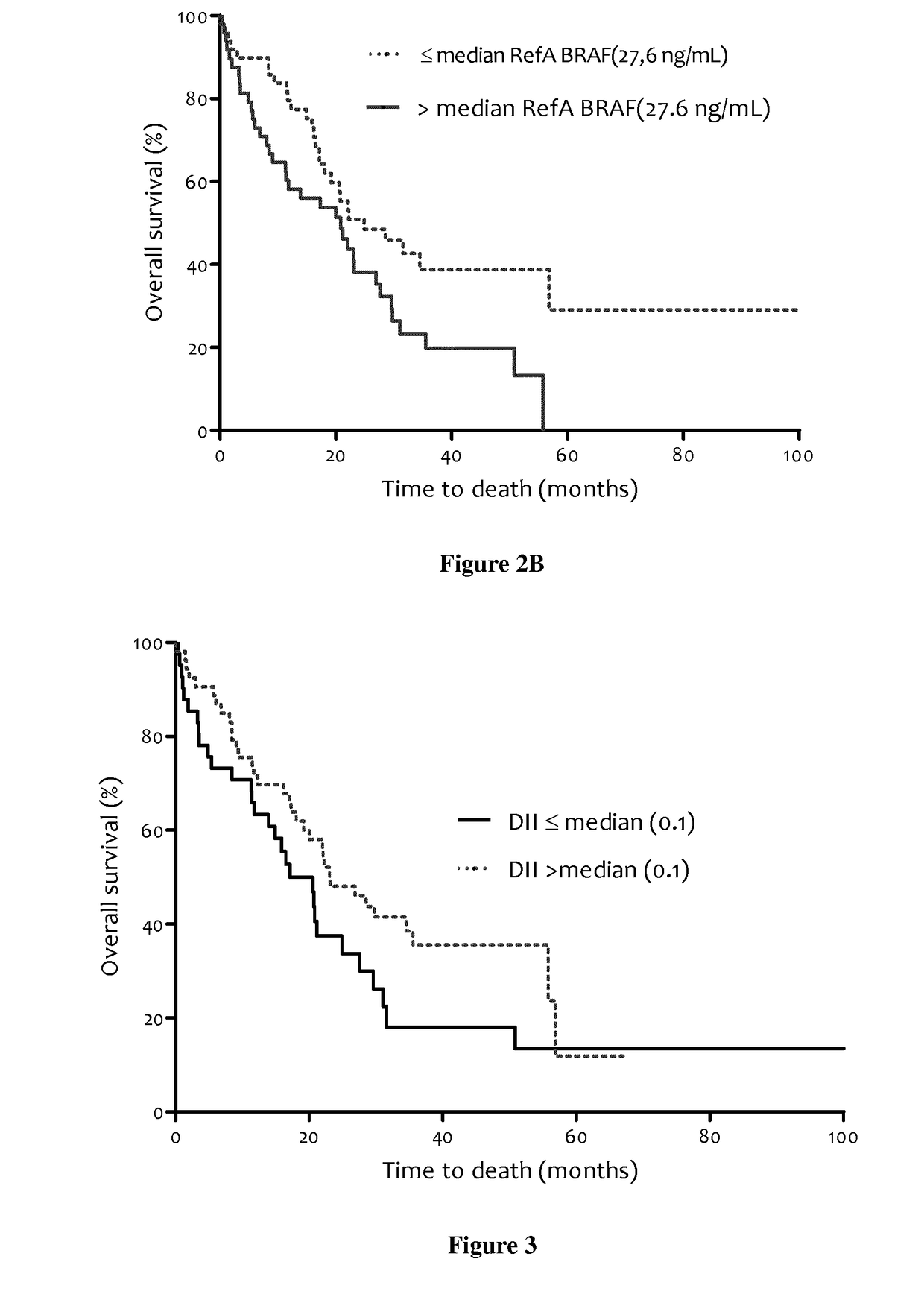
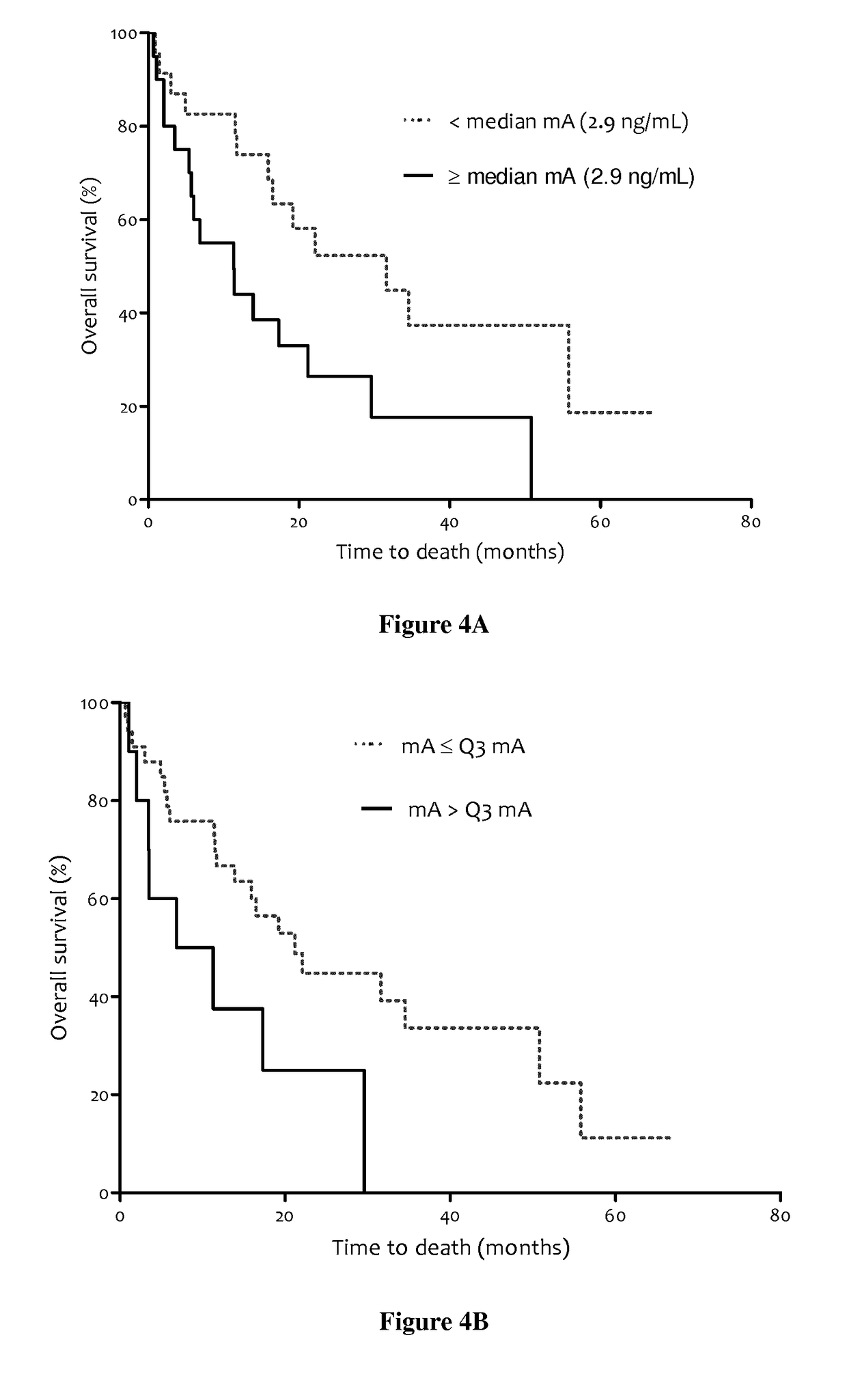
Methods for predicting the survival time of patients suffering from cancer
InactiveUS20170183742A1Short survival timeKeep for a long timeMicrobiological testing/measurementPatient survivalBiology
The present invention relates to methods for predicting the survival time of patients suffering from cancer. Said methods are based on the quantification and analysis of the cell free nucleic acids that are present in a sample from the patient and typically include the determination of the level of the mutant nucleic acid which contains a mutation of interest, the calculation of the mutation load for said mutation of interest, the calculation of the DNA integrity index or a combination thereof.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +2
Non-invasive blood based monitoring of genomic alterations in cancer
ActiveUS20160138112A1Diagnostic and prognostic utilityAccurate measurementBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementControl subjectsHousekeeping gene
The invention provides methods to monitor cell free nucleic acids. The method comprises obtaining a plasma sample from a subject known to have a cancer characterized by a pair of mutually exclusive mutations specific to the cancer; isolating cell free nucleic acids from the plasma sample obtained from the subject; measuring the amount a housekeeping gene and / or total DNA in the cell free nucleic acids isolated from the plasma sample to confirm that the amount of housekeeping gene and / or total DNA in the sample is within a selected range; measuring the amount of a first of the pair of mutually exclusive mutations specific to the cancer in the cell free nucleic acids isolated from the plasma sample; and indicating in a report that the subject has the first mutation when (a) the amount of the housekeeping gene and / or total DNA in the cell free nucleic acids isolated from the plasma sample is within the selected range and (b) the amount of the first mutation is increased as compared to a control amount, wherein the control amount is determined by measuring the apparent amount of the first mutation in control cell free nucleic acids isolated from plasma samples obtained from control subjects known to have the second of the pair of mutually exclusive mutations specific to the cancer using measuring conditions substantially the same as those used to measure the amount of the first mutation in the cell free nucleic acids isolated from the plasma sample from the subject.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
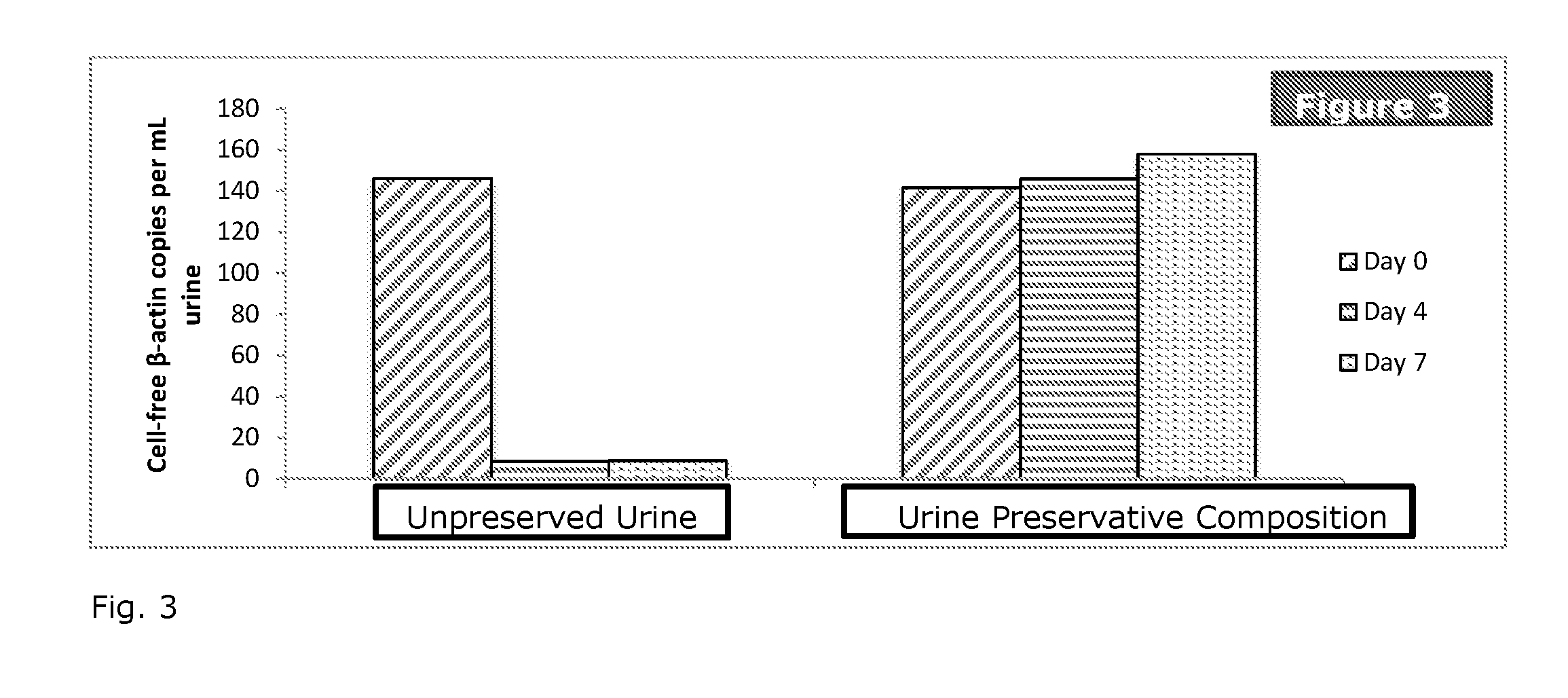
Stabilization of nucleic acids in urine
ActiveUS20160257995A1Preserve integrityMinimize the post-sampling urinary DNA backgroundMicrobiological testing/measurementPreservativeBiology
A composition and method for preserving a urine sample and a preservative delivery vessel are disclosed wherein treatment of the urine sample aids in preserving circulating cell-free nucleic acids in urine over a wide range of dilution ratios within temperature fluctuations that can occur during urine sample handling, storage and transportation. The urine sample preservation composition and method and preservative delivery vessel provide a method for obtaining high quality stabilized urinary cell-free nucleic acids for clinical diagnostics development and application.
Owner:STRECK LLC
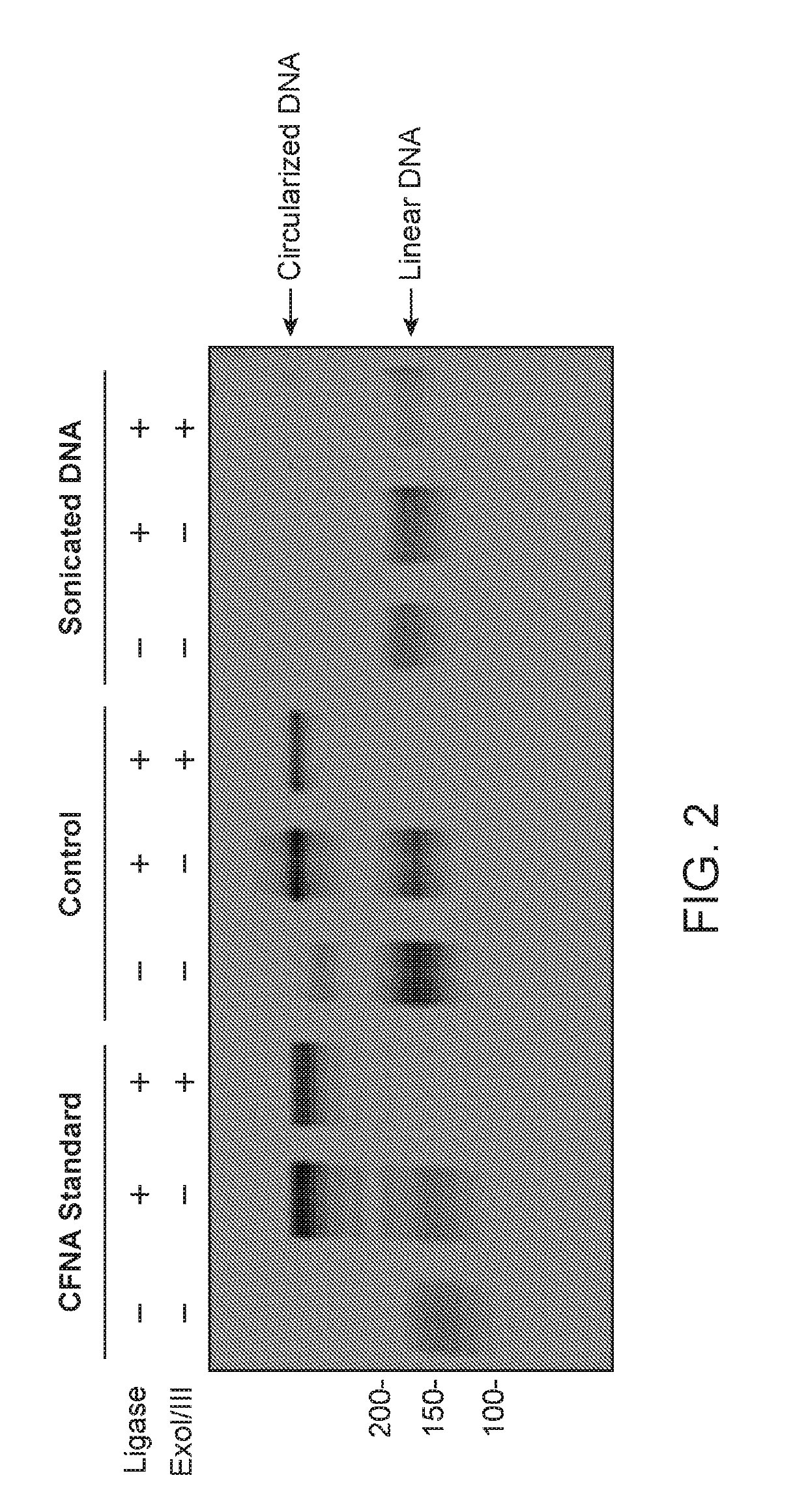
Cell-free nucleic acid standards and uses thereof
The present disclosure provides cell-free nucleic acid standards comprising genomic polynucleotides and methods of using cell-free nucleic acid standards comprising genomic polynucleotides for developing, optimizing, and validating cell-free nucleic acid assays.
Owner:ACCURAGEN HLDG LTD
Sequencing analysis of circulating DNA to detect and monitor autoimmune diseases
Systems, methods, and apparatuses are provided for diagnosing auto-immune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) based on the sizes, methylation levels, and / or genomic characteristics of circulating DNA molecules. Patients provide blood or other tissue samples containing cell-free nucleic molecules for analysis. Massively parallel and / or methylation-aware sequencing can be used to determine the sizes and methylation levels of individual DNA molecules and identify the number of molecules originating from different genomic regions. A level of SLE can be estimated based on: the amount of molecules having sizes below a threshold value; the methylation level(s) of the entire genome or portions of the genome; correlations between the sizes and methylation levels of DNA molecules; and / or comparing the representation of DNA molecules in each of a plurality of genomic regions with a reference value for that region, and determining an amount of genomic regions having increased or decreased measured genomic representation.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Methods for fragmentome profiling of cell-free nucleic acids
The present disclosure contemplates various uses of cell-free DNA. Methods provided herein may use sequence information in a macroscale and global manner, with or without somatic variant information, to assess a fragmentome profile that can be representative of a tissue of origin, disease, progression, etc. In an aspect, disclosed herein is a method for determining a presence or absence of a genetic aberration in deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) fragments from cell-free DNA obtained from a subject, the method comprising: (a) constructing a multi-parametric distribution of the DNA fragments over a plurality of base positions in a genome; and (b) without taking into account a base identity of each base position in a first locus, using the multi-parametric distribution to determine the presence or absence of the genetic aberration in the first locus in the subject.
Owner:GUARDANT HEALTH
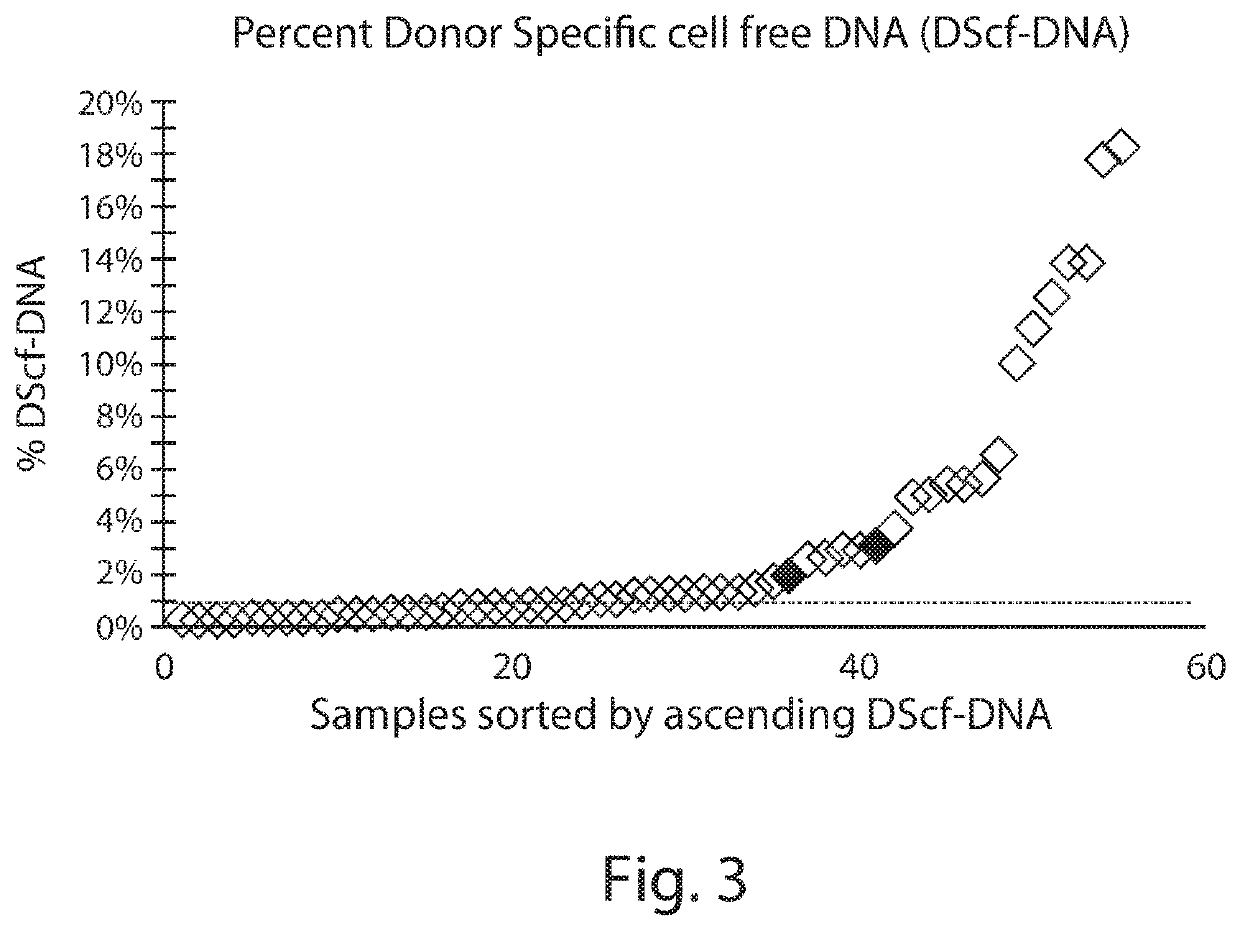
Methods for assessing risk using total and specific cell-free DNA
This invention relates to methods and compositions for assessing risk by measuring total and specific cell-free nucleic acids (such as DNA) in a subject. The methods and compositions provided herein can be used to determine risk of a condition, such as transplant rejection.
Owner:THE MEDICAL COLLEGE OF WISCONSIN INC
Models for targeted sequencing
A processing system uses a Bayesian inference based model for targeted sequencing or variant calling. In an embodiment, the processing system generates candidate variants of a cell free nucleic acid sample. The processing system determines likelihoods of true alternate frequencies for each of the candidate variants in the cell free nucleic acid sample and in a corresponding genomic nucleic acid sample. The processing system filters or scores the candidate variants by the model using at least the likelihoods of true alternate frequencies. The processing system outputs the filtered candidate variants, which may be used to generate features for a predictive cancer or disease model.
Owner:GRAIL LLC
Methods and systems for analyzing microbiota
Systems, media, methods, and kits disclosed herein can be used to analyze human microbiota for the detection of a condition (e.g., a disease or condition). Further, the systems, media, methods, and kits disclosed herein can utilize machine learning algorithms to analyze samples with high accuracy. In an aspect, a classifier capable of distinguishing a population of subjects based on microbiome composition may comprise: a plurality of microbiome-associated features associated with two or more classes of subjects inputted into a machine learning model, wherein the features comprise the microbiome species and abundance of microbiome elements, wherein the features are derived from a taxonomic community composition analysis of a cell-free nucleic acid sample in a population of subjects; wherein the features contribute to a classifier sensitivity of greater than 50% and a classifier specificity of greater than 85% to distinguish the population of subjects into two or more classes.
Owner:FREENOME HLDG INC
Hydroxymethylation analysis of cell-free nucleic acid samples for assigning tissue of origin, and related methods of use
PendingCN112534067AHealth-index calculationMicrobiological testing/measurementReference genesCell free
A method is provided for probabilistically assigning a tissue of origin to a nucleic acid in a sample, e.g., DNA in a cell-free fluid sample obtained from a human subject. A hydroxymethylation profileis generated for the sample DNA and then compared across a reference data set of hydroxymethylation profile vectors, where each hydroxymethylation profile vector identifies the hydroxymethylation profile at a specific reference locus, the tissue-specific gene associated with the reference locus, and the tissue with which the gene and reference locus are associated. A tissue of origin can be probabilistically assigned to the sample nucleic acid using the results of the comparison. Other methods of use are also provided.
Owner:蓝星基因组股份有限公司
Methods for screening a subject for a cancer
ActiveUS20170240975A1Improve filtering effectEnhance immune responseMicrobiological testing/measurementAnucleated cellOncology
The present invention relates to methods for screening a subject for a cancer. In particular, the present invention relates to a method (A) for screening a subject for a cancer comprising the steps of i) extracting the cell free nucleic acids from a sample obtained from the subject, ii) determining the total concentration of mitochondrial cell free nucleic acids, ii) determining the total concentration of nuclear cell free nucleic acids iv) calculating the ratio of the level determined at step ii) to the concentration determined at step iii), v) comparing ratio determined at step iv) with a predetermined corresponding reference value and vi) concluding that the subject suffers from a cancer when the ratio determined at step iv) is lower than the predetermined corresponding reference value or concluding that the subject does not suffer from a cancer when the ratio determined at step iv) is higher than the predetermined corresponding reference value.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +2
Hydroxymethylation analysis of cell-free nucleic acid samples for assigning tissue of origin, and related methods of use
InactiveUS20200010880A1Health-index calculationMicrobiological testing/measurementReference genesCell free
A method is provided for probabilistically assigning a tissue of origin to a nucleic acid in a sample, e.g., DNA in a cell-free fluid sample obtained from a human subject. A hydroxymethylation profile is generated for the sample DNA and then compared across a reference data set of hydroxymethylation profile vectors, where each hydroxymethylation profile vector identifies the hydroxymethylation profile at a specific reference locus, the tissue-specific gene associated with the reference locus, and the tissue with which the gene and reference locus are associated. A tissue of origin can be probabilistically assigned to the sample nucleic acid using the results of the comparison. Other methods of use are also provided.
Owner:CLEARNOTE HEALTH INC
Site-specific noise model for targeted sequencing
A processing system uses a Bayesian inference based model for targeted sequencing or variant calling. In an embodiment, the processing system determines first depths and first alternate depths of first sequence reads from a cell free nucleic acid sample of a subject. The processing system determines second depths and second alternate depths of second sequence reads from a genomic nucleic acid sample of the subject. The processing system determines likelihoods of true alternate frequency of the cell free nucleic acid sample and of the genomic nucleic acid sample. Using the first likelihood, the second likelihood, and one or more parameters, the processing system determines a probability that the true alternate frequency of the cell free nucleic acid sample is greater than a function of the true alternate frequency of the genomic nucleic acid sample.
Owner:GRAIL LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com