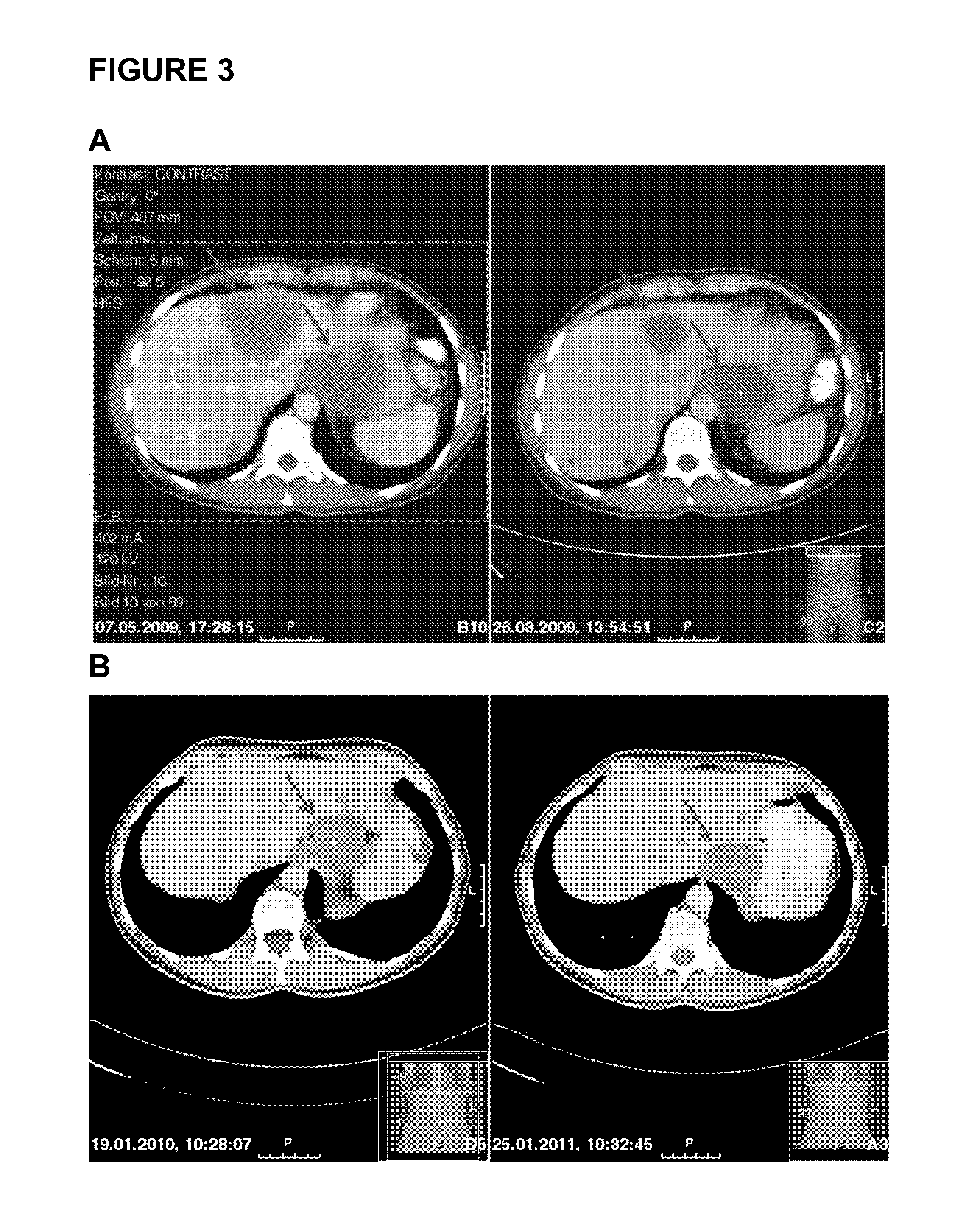
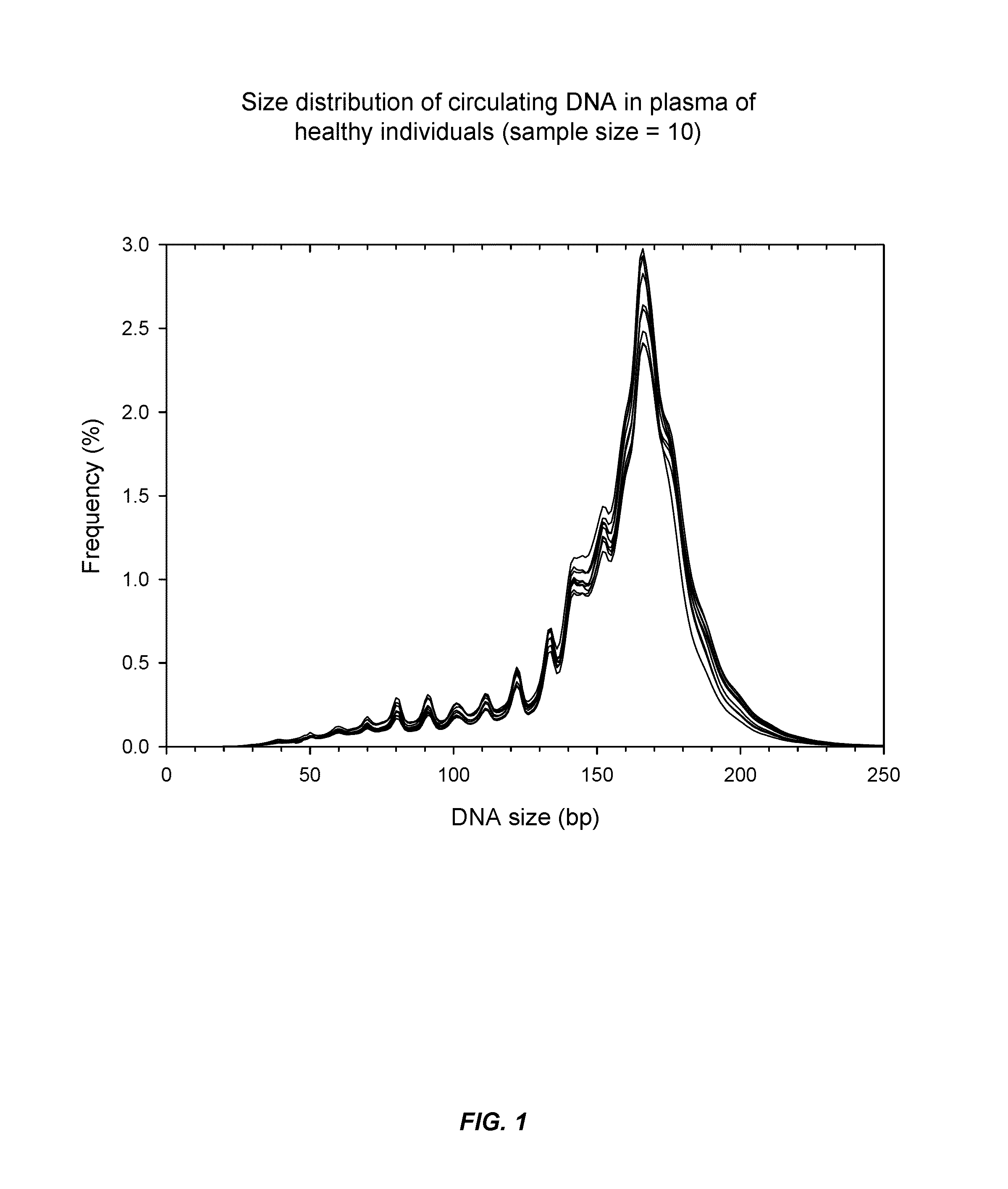
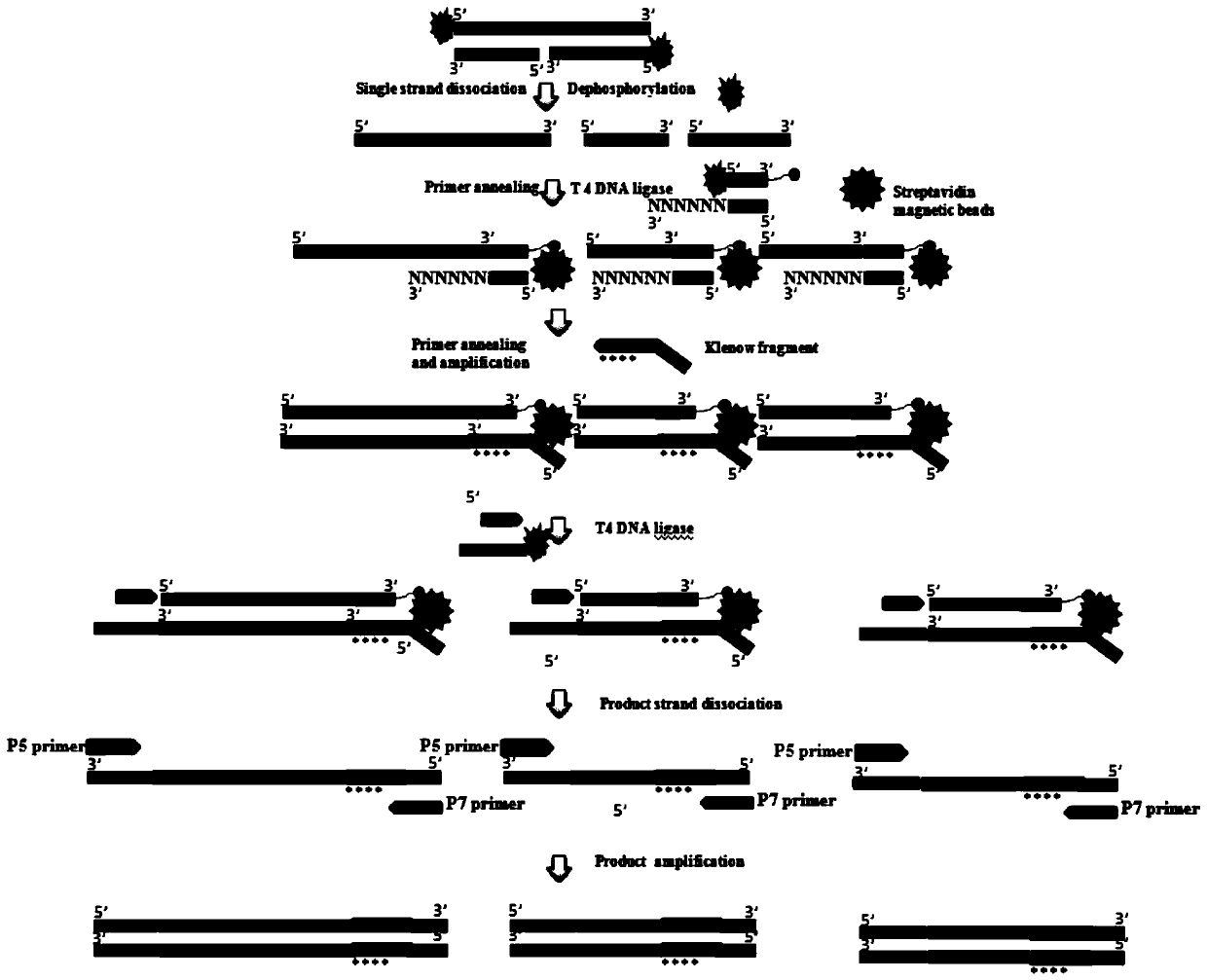
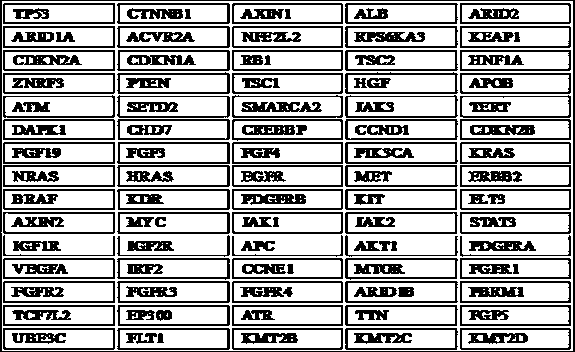
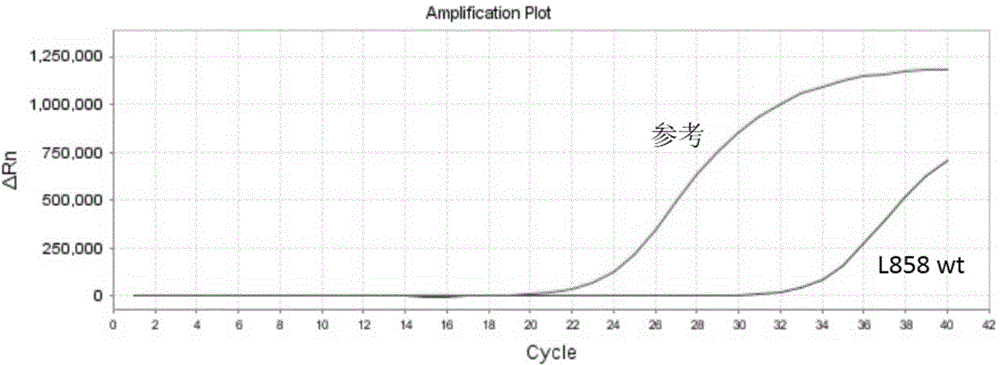
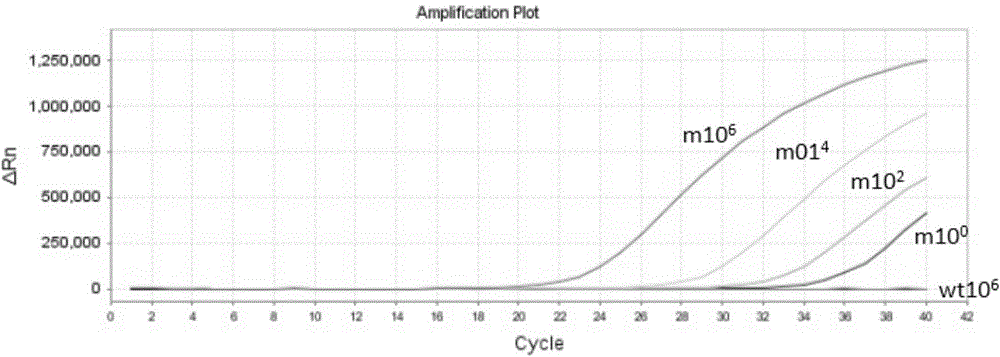
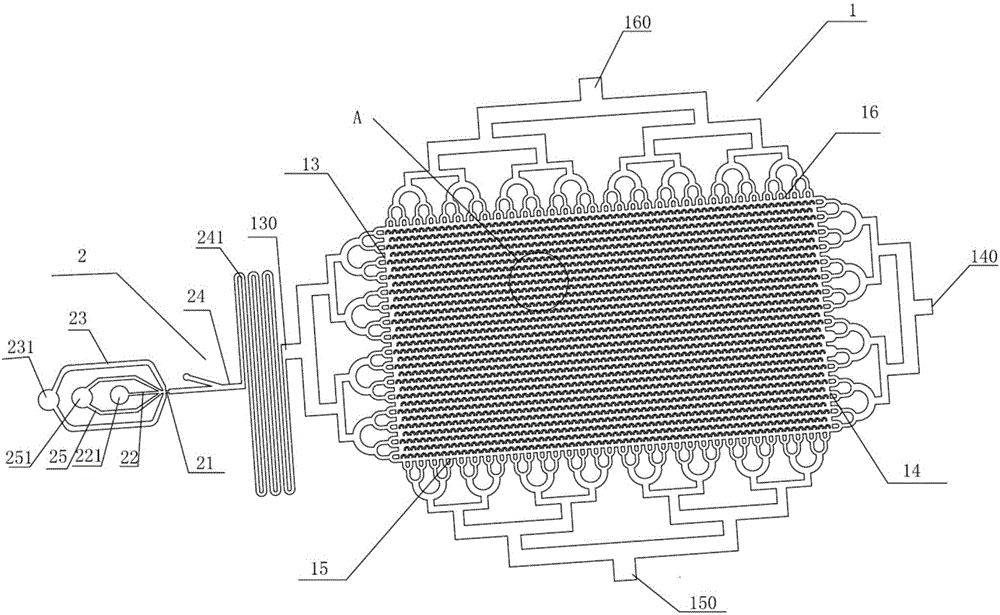
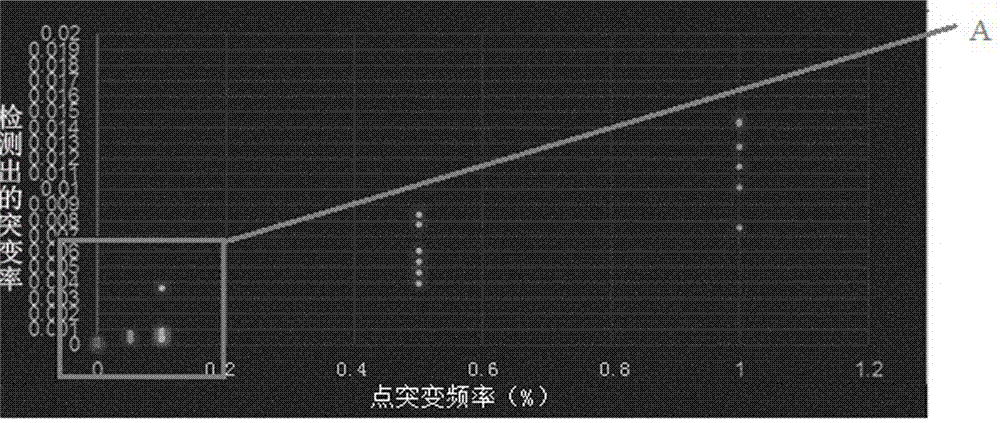
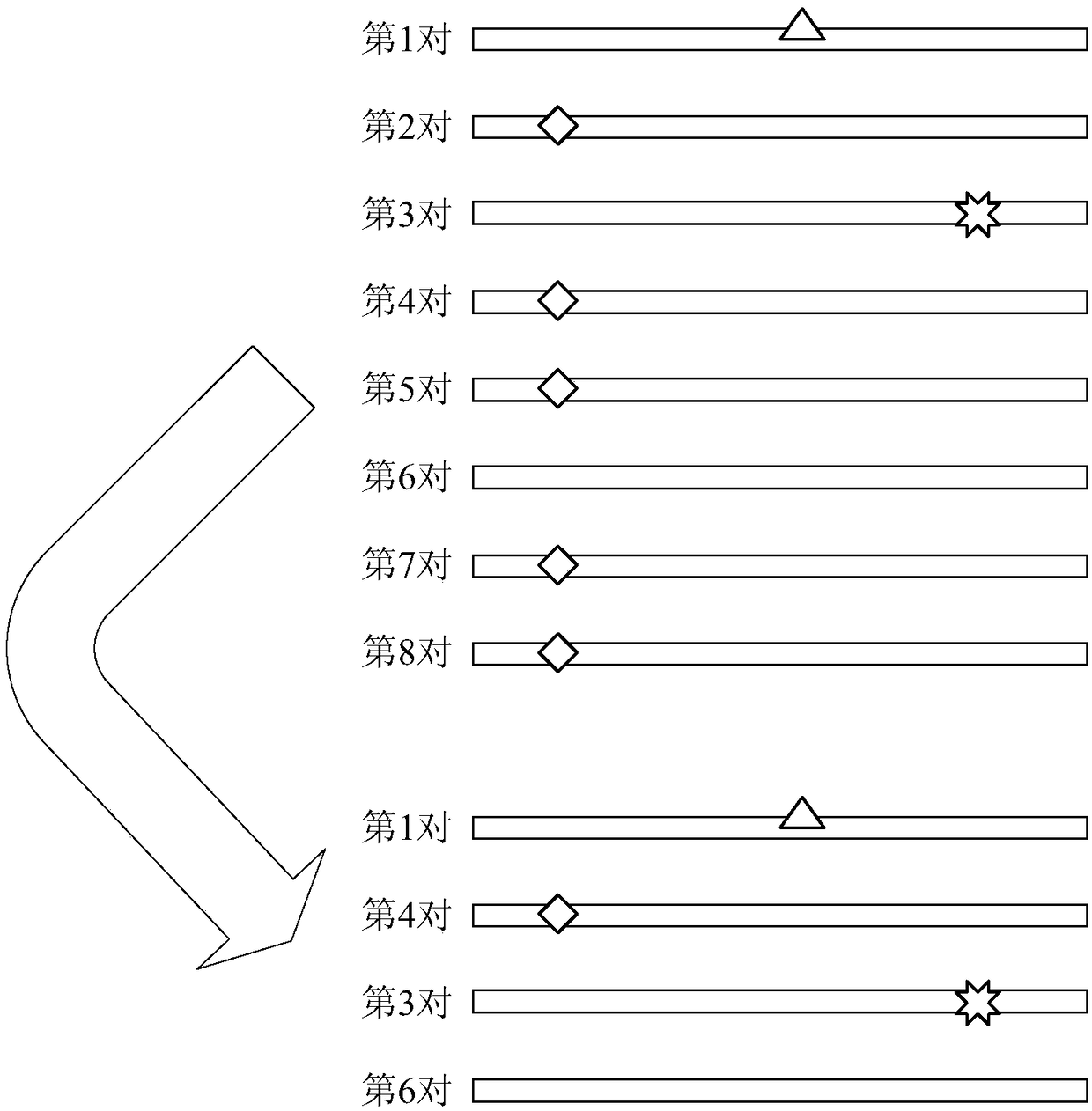
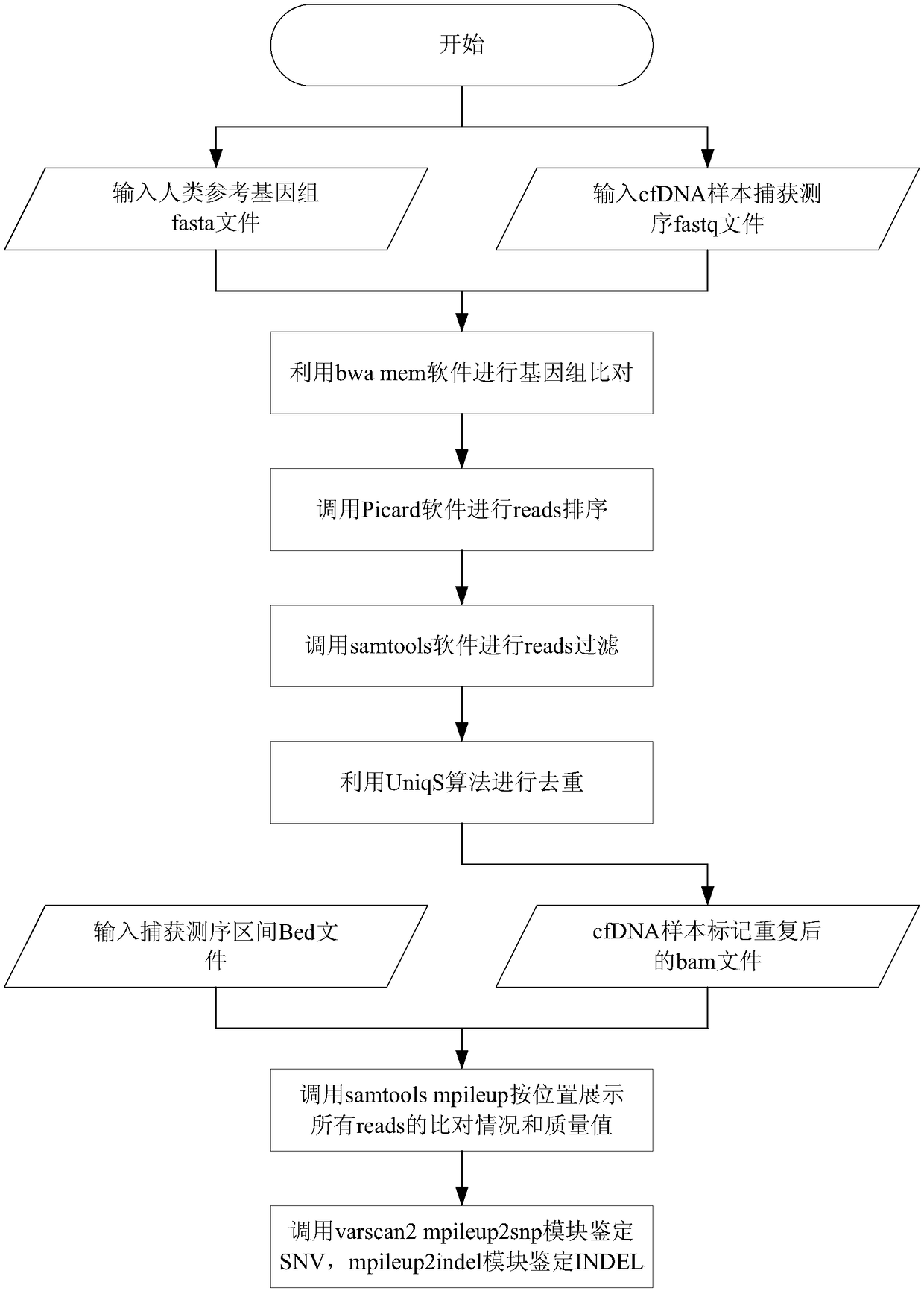
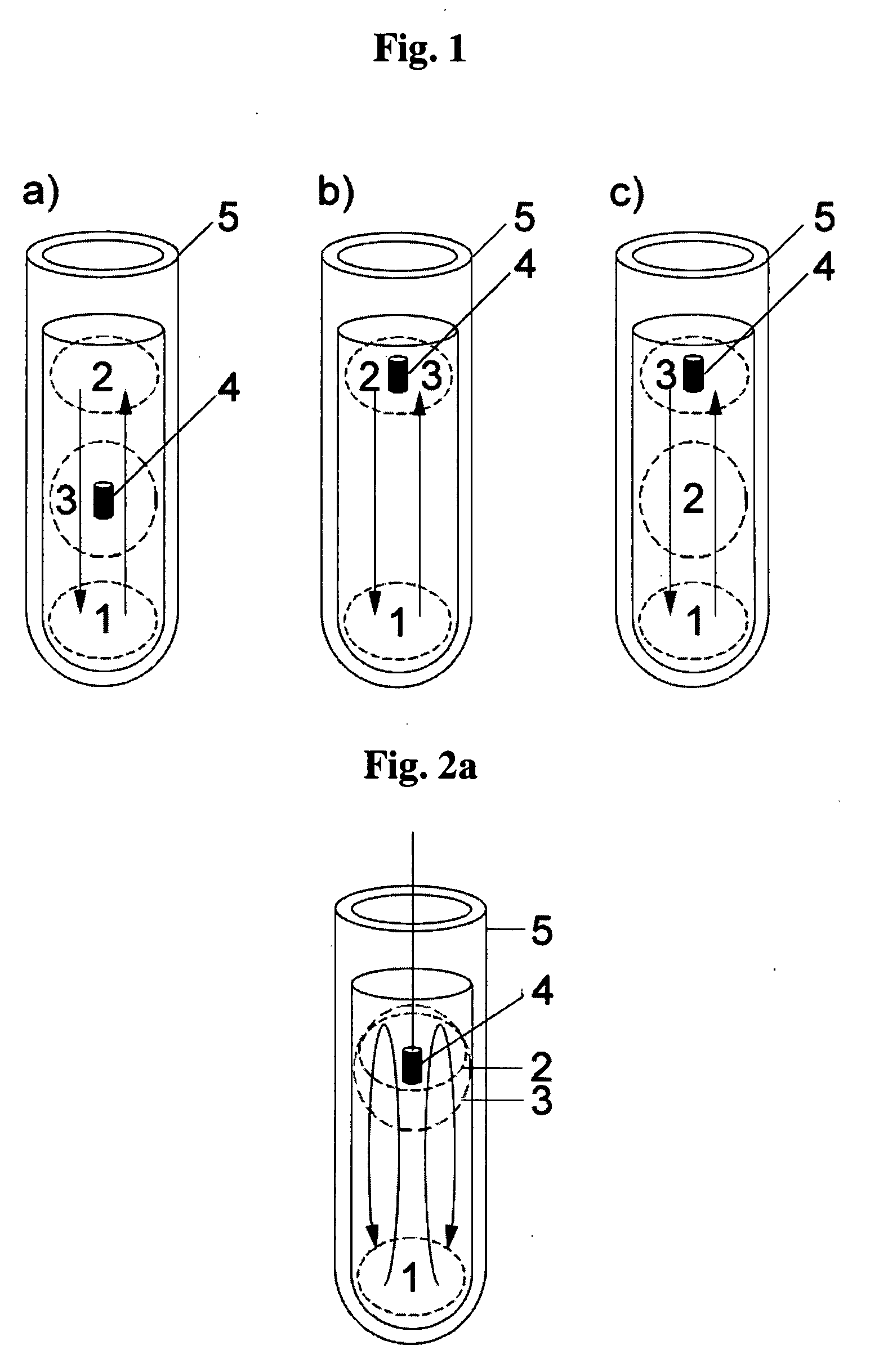
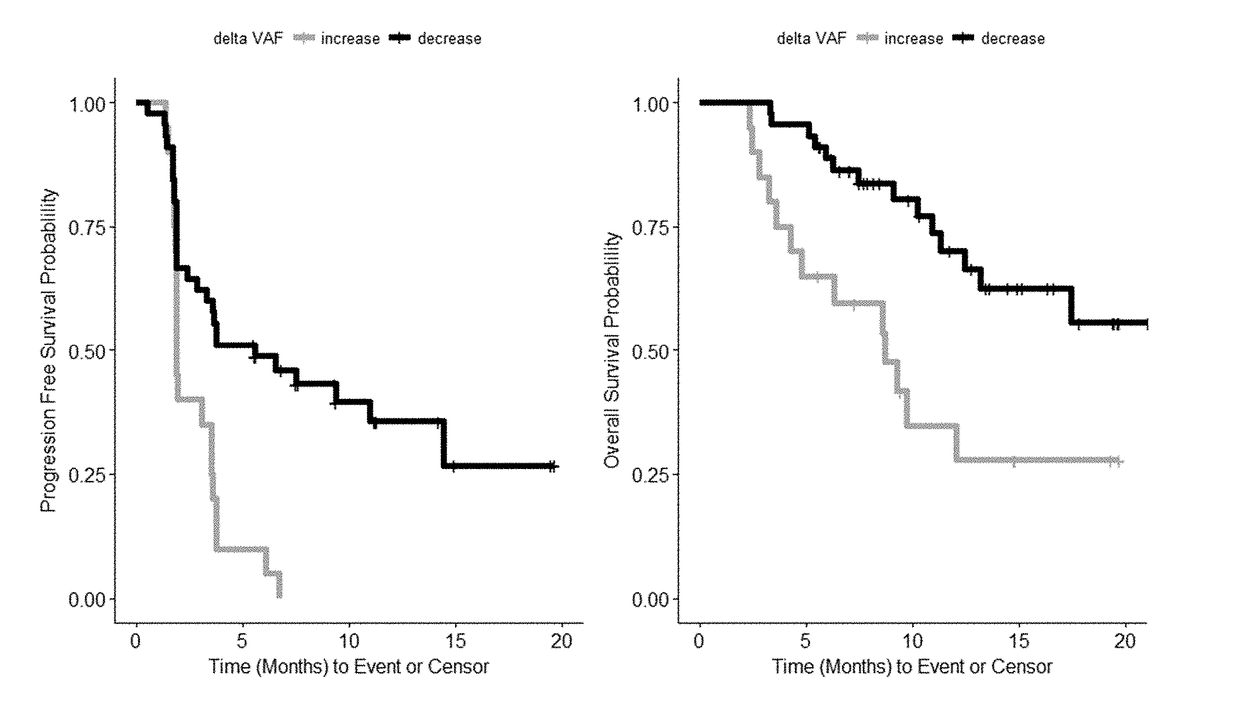
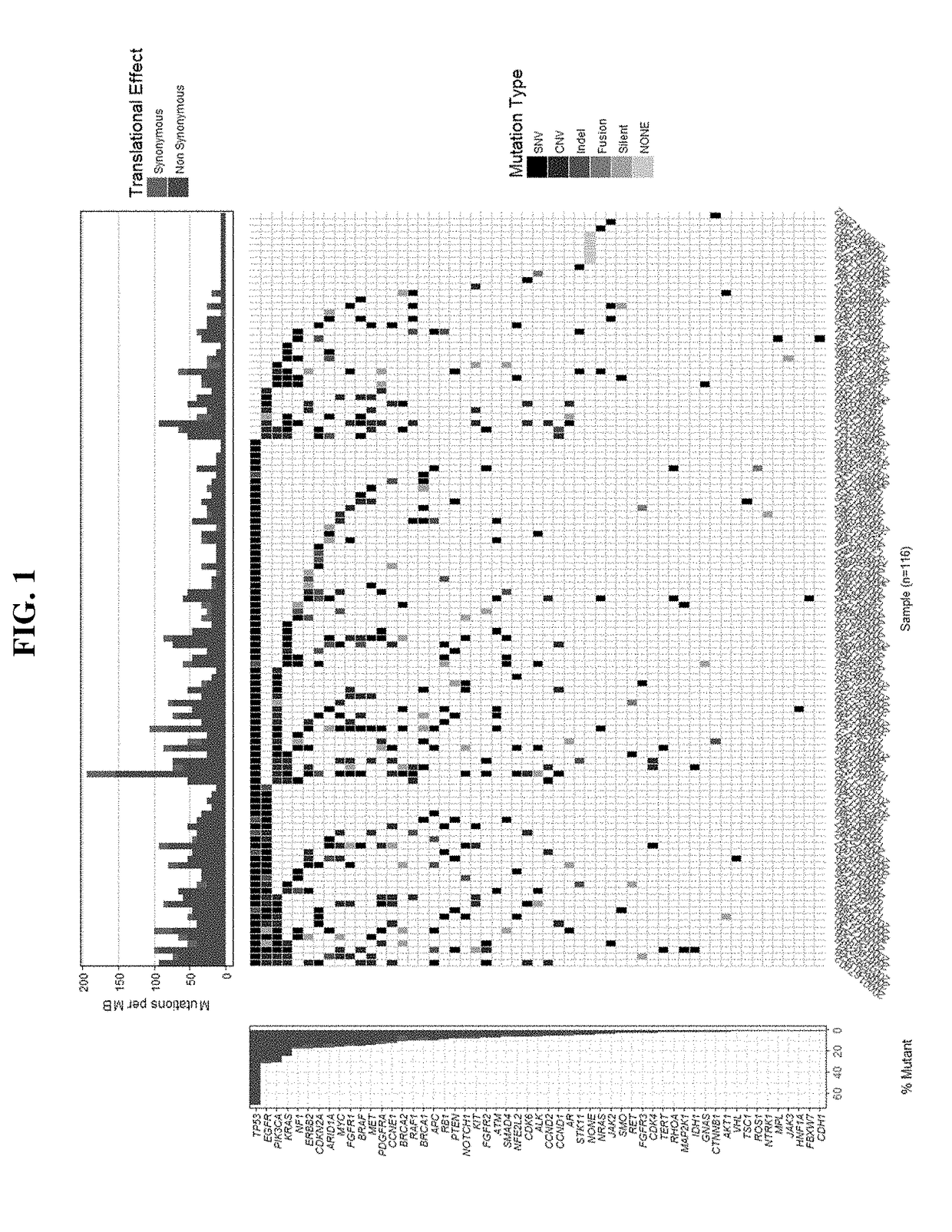
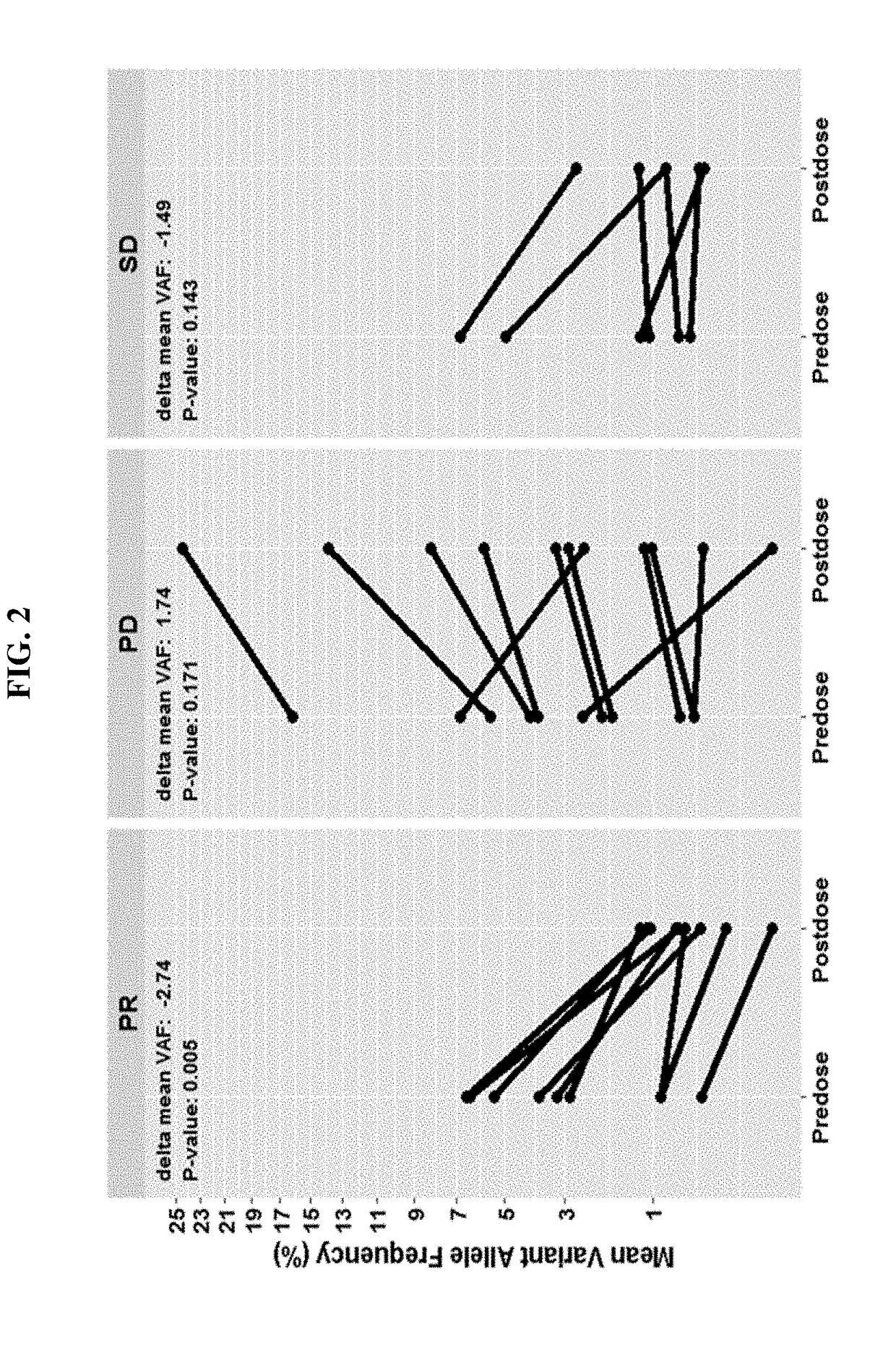
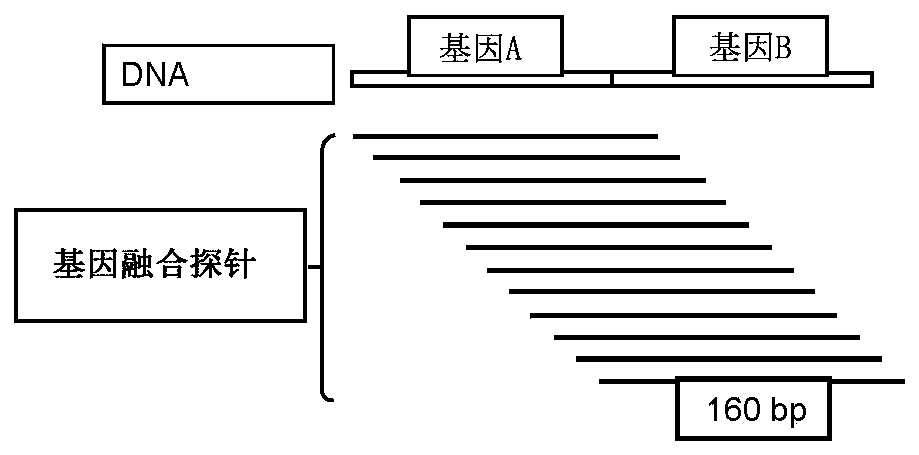
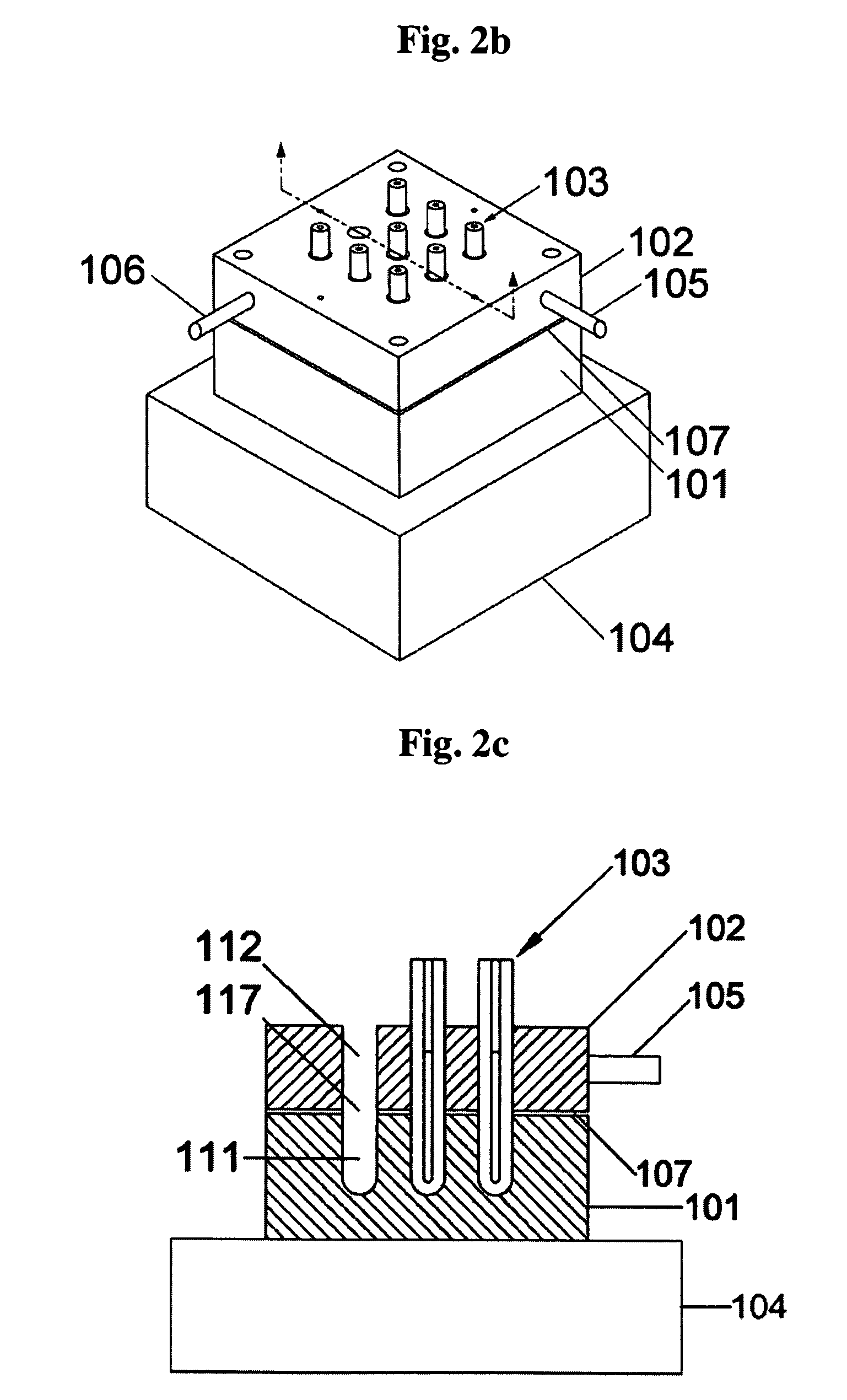
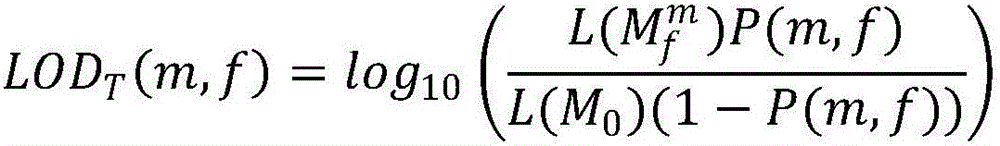Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
164 results about "Circulating DNA" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) is tumor-derived fragmented DNA in the bloodstream that is not associated with cells. ctDNA should not be confused with cell-free DNA (cfDNA), a broader term which describes DNA that is freely circulating in the bloodstream, but is not necessarily of tumor origin.
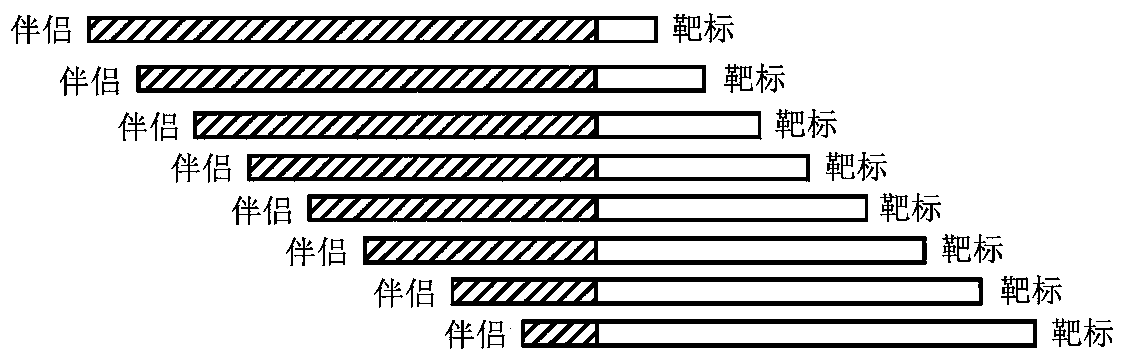
Circulating Mutant DNA to Assess Tumor Dynamics
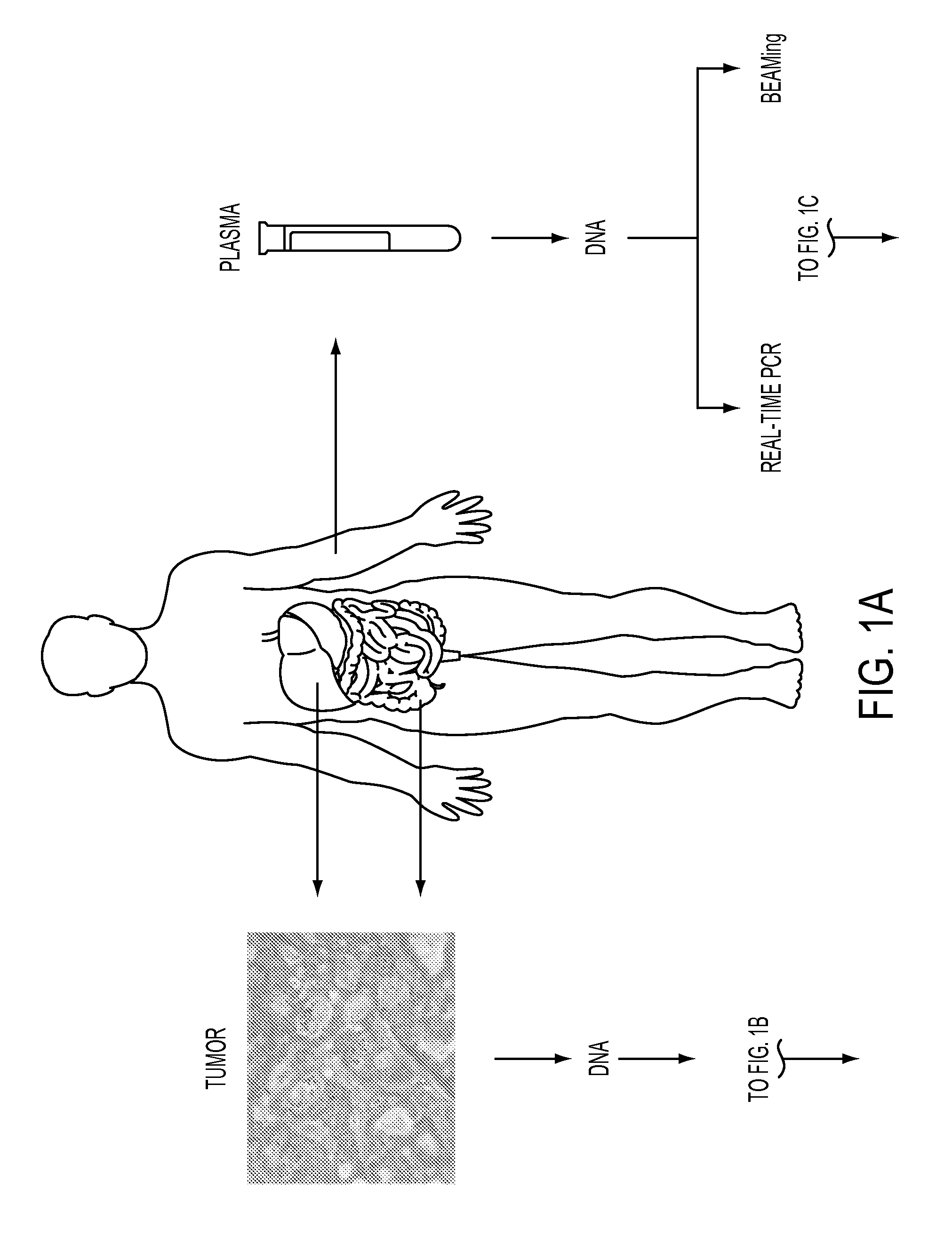
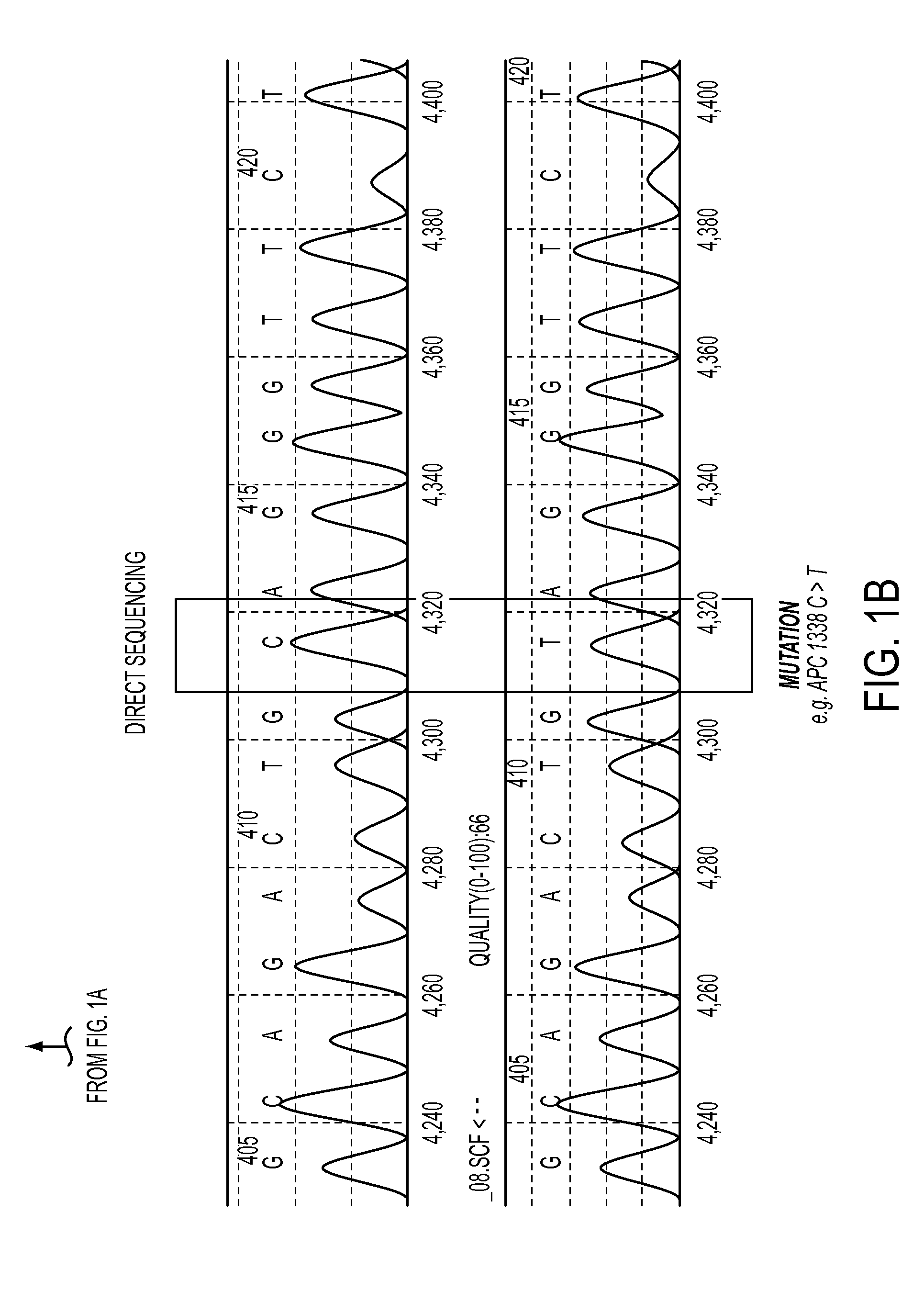
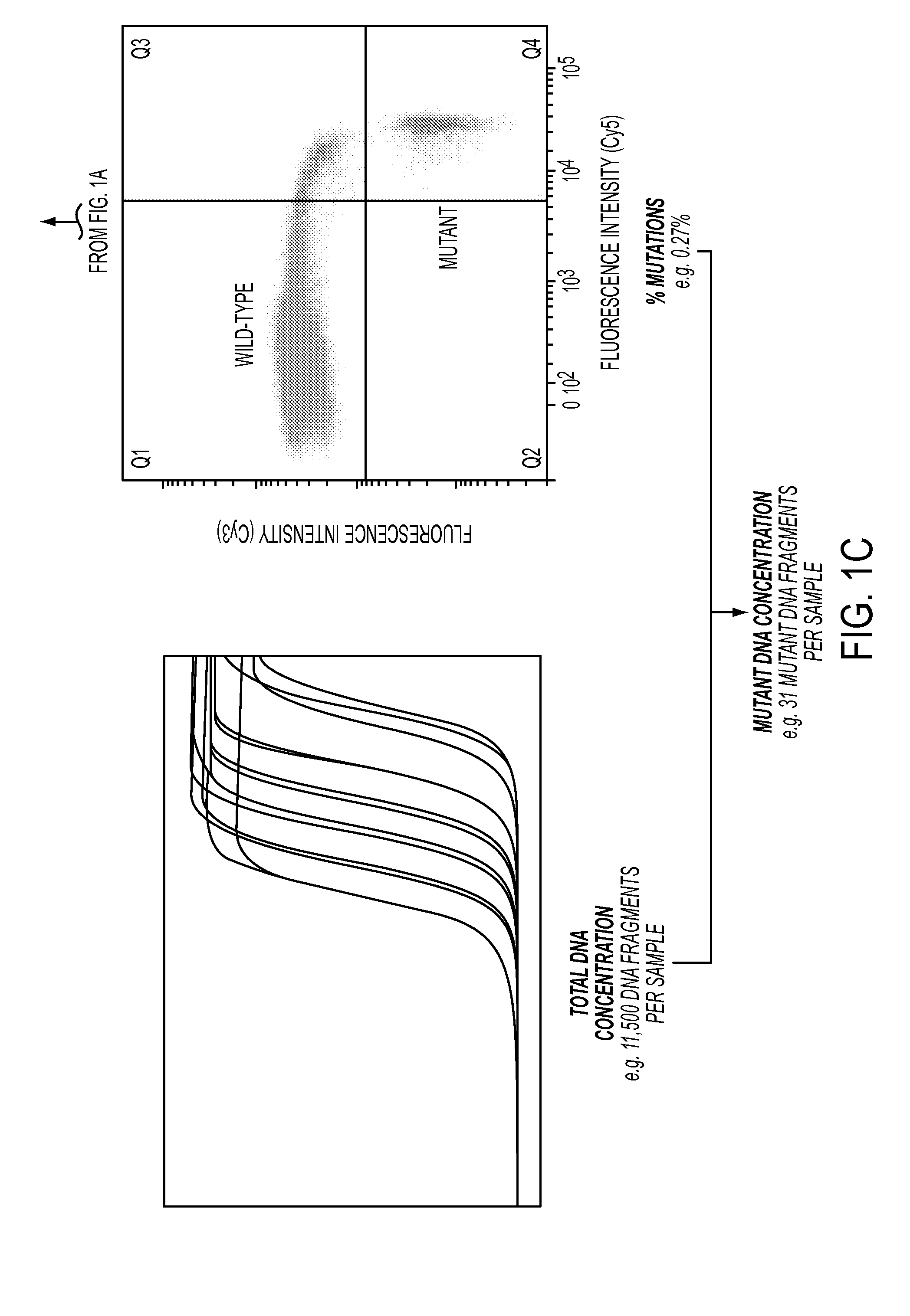
DNA containing somatic mutations is highly tumor specific and thus, in theory, can provide optimum markers. However, the number of circulating mutant gene fragments is small compared to the number of normal circulating DNA fragments, making it difficult to detect and quantify them with the sensitivity required for meaningful clinical use. We apply a highly sensitive approach to quantify circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) in body samples of patients. Measurements of ctDNA can be used to reliably monitor tumor dynamics in subjects with cancer, especially those who are undergoing surgery or chemotherapy. This personalized genetic approach can be generally applied.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Personalized Tumor Biomarkers
ActiveUS20150344970A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationBlood plasmaWilms' tumor
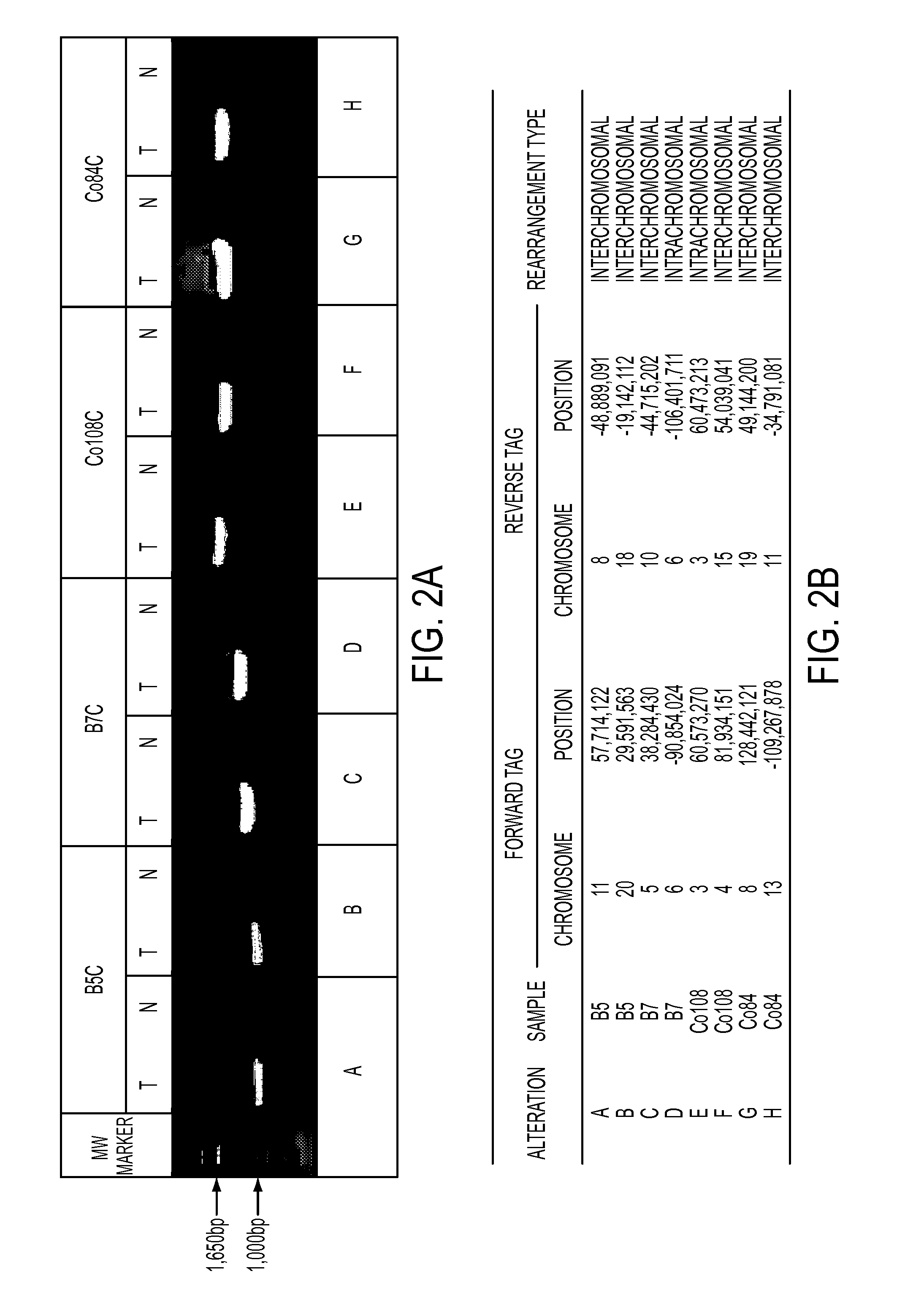
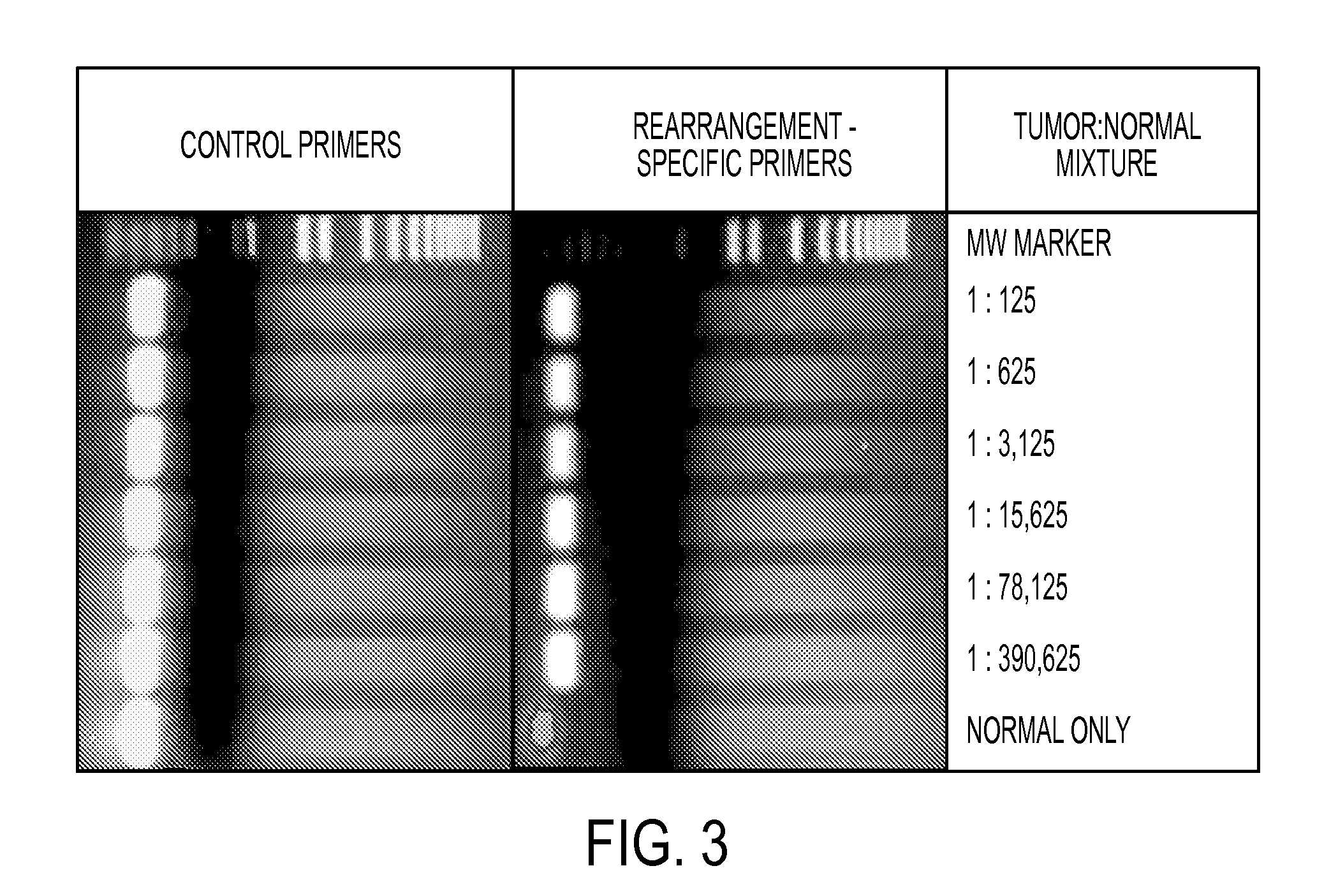
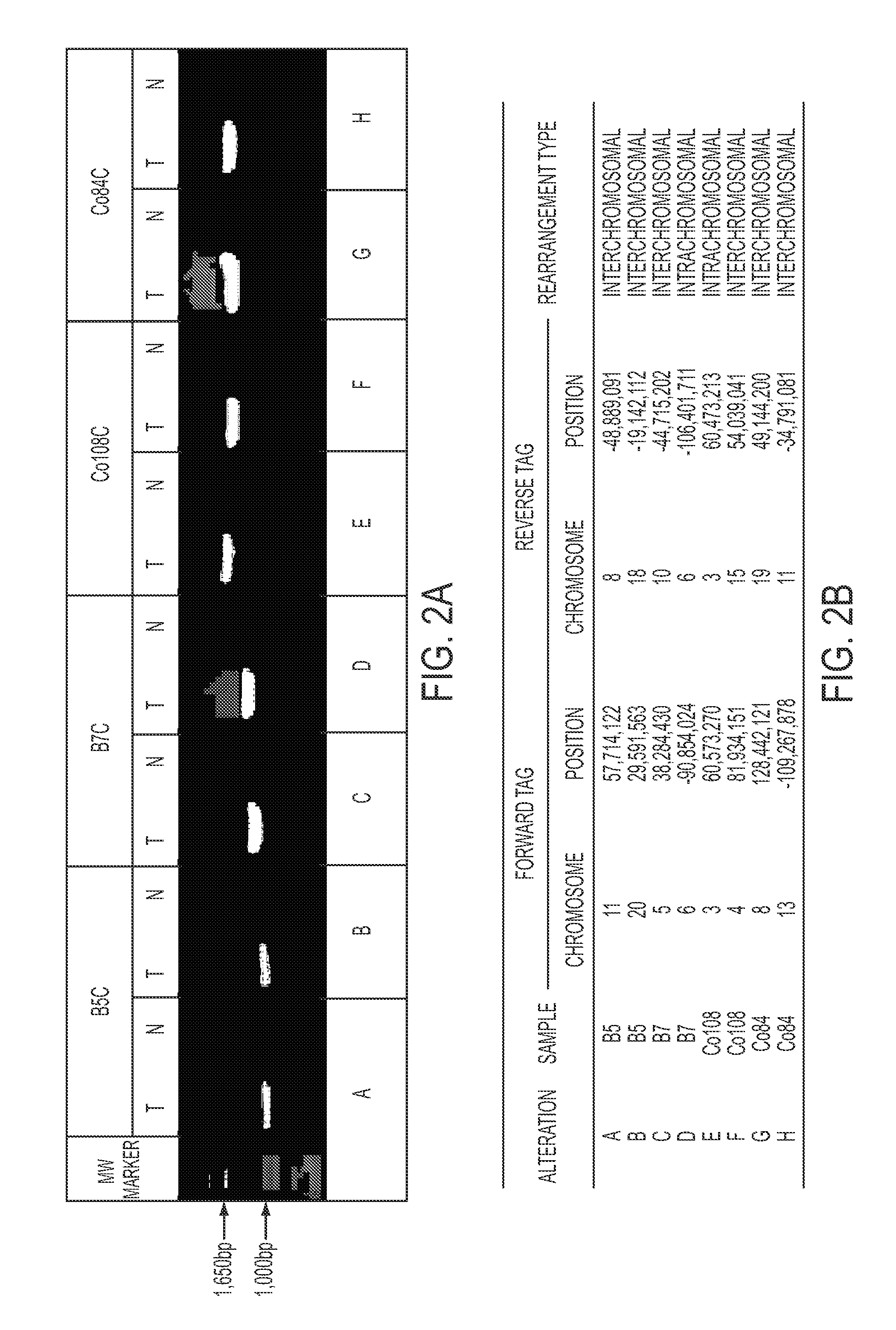
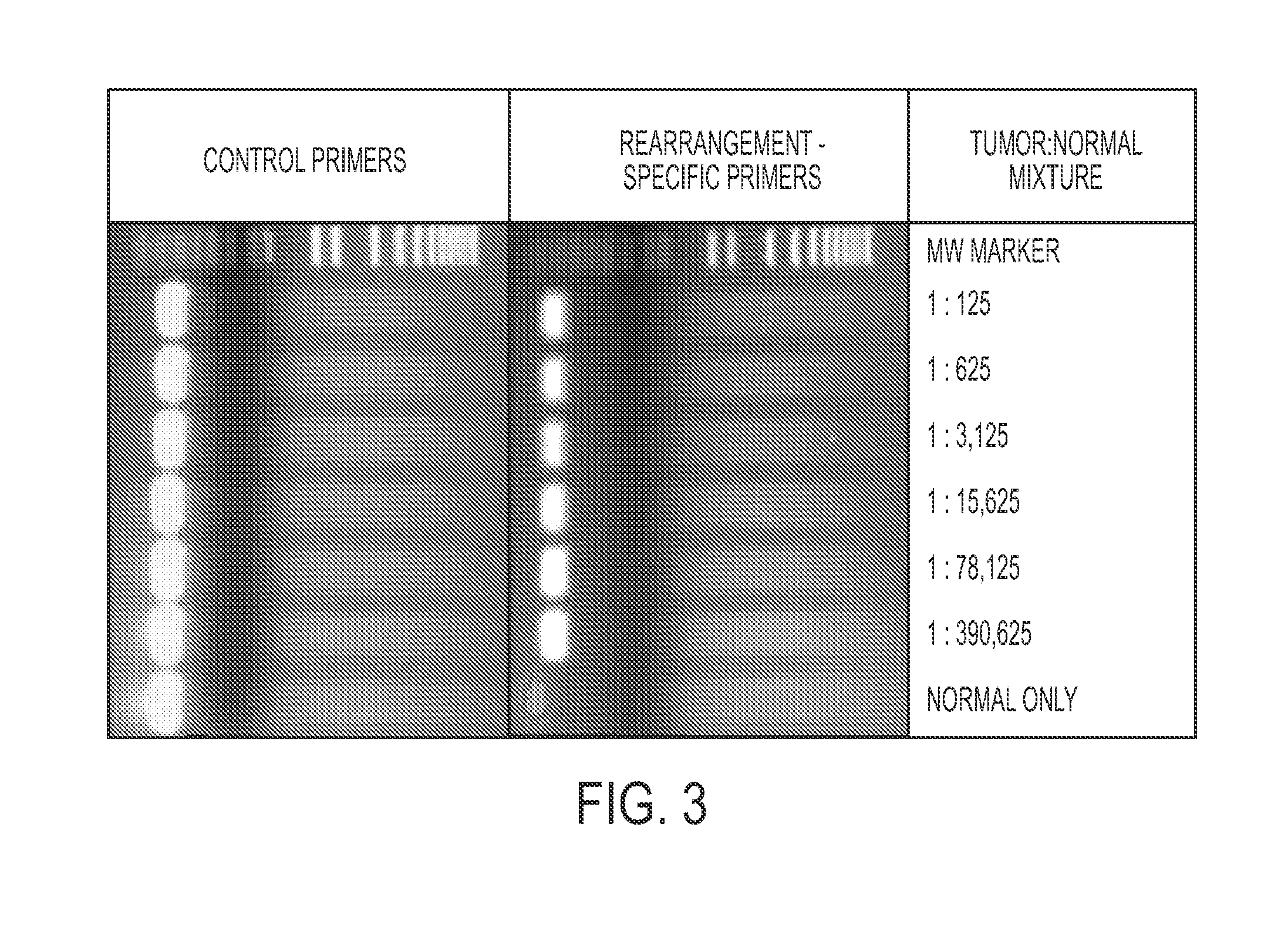
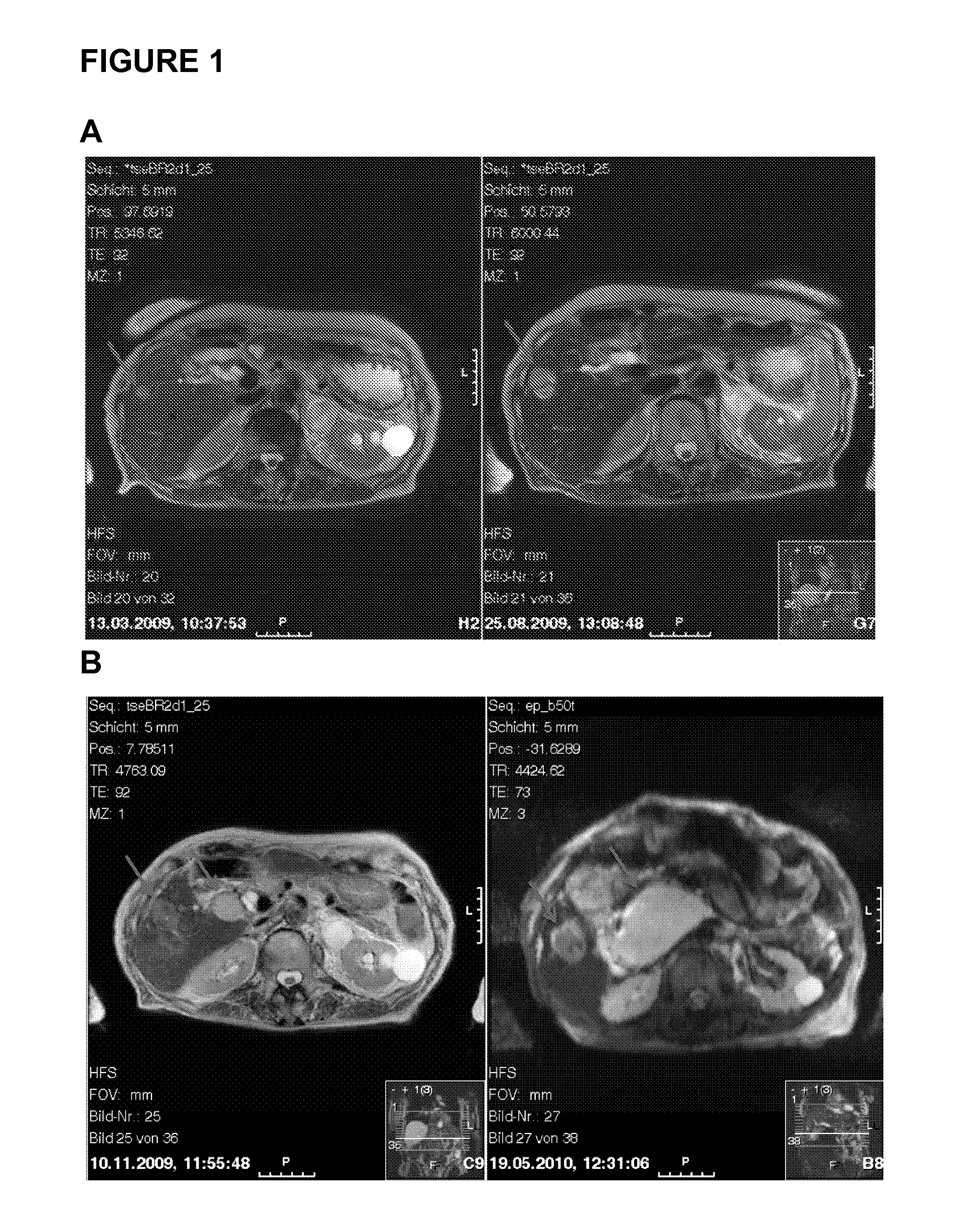
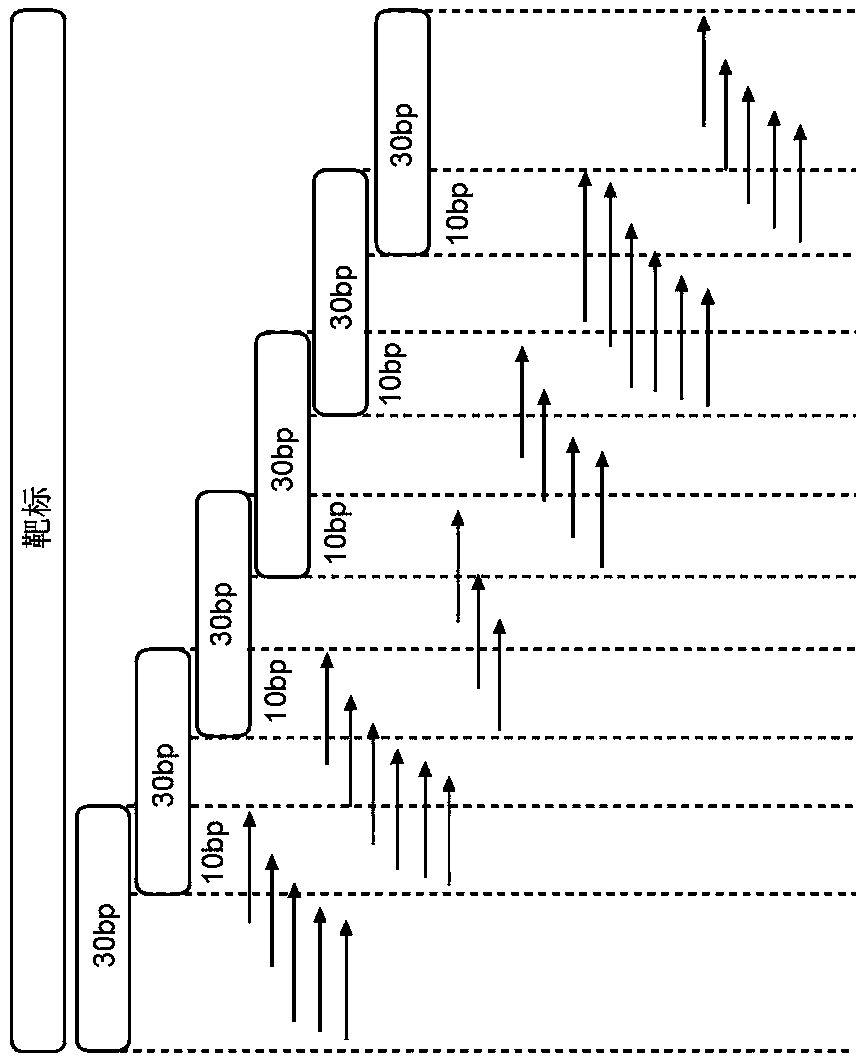
Clinical management of human cancer is dependent on the accurate monitoring of residual and recurrent tumors. We have developed a method, called personalized analysis of rearranged ends (PARE), which can identify translocations in solid tumors. Analysis of four colorectal and two breast cancers revealed an average of nine rearranged sequences (range 4 to 15) per tumor. Polymerase chain reaction with primers spanning the breakpoints were able to detect mutant DNA molecules present at levels lower than 0.001% and readily identified mutated circulating DNA in patient plasma samples. This approach provides an exquisitely sensitive and broadly applicable approach for the development of personalized biomarkers to enhance the clinical management of cancer patients.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Compositions and methods for detection of nucleic acid mutations
PendingUS20190185913A1Nucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementCirculating tumor DNAPcr method
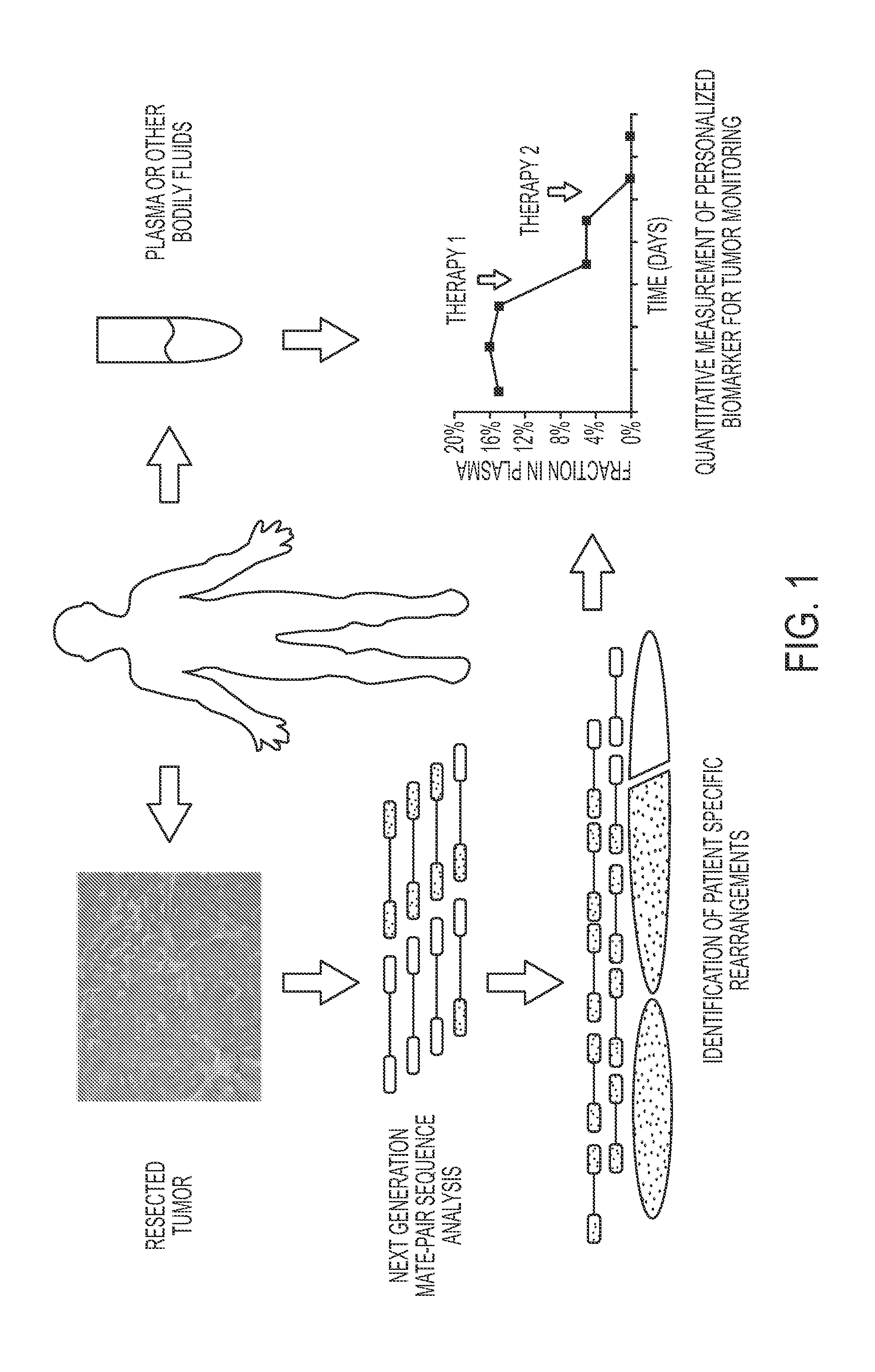
The invention provides methods and compositions for detecting a mutation in a target gene in a sample of blood or a fraction thereof, including in certain examples, a fraction that includes circulating tumor DNA. The methods can include a tiling PCR reaction, for example a one-sided multiplex tiling reaction. Virtually any type of mutation can be detected with the methods and compositions. In certain embodiments, gene fusions are detected. Improved PCR methods, especially for performing nested multiplex PCR reactions are provided.
Owner:NATERA
Personalized tumor biomarkers
InactiveUS20130210645A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBlood plasmaRecurrent Tumor
Clinical management of human cancer is dependent on the accurate monitoring of residual and recurrent tumors. We have developed a method, called personalized analysis of rearranged ends (PARE), which can identify translocations in solid tumors. Analysis of four colorectal and two breast cancers revealed an average of nine rearranged sequences (range 4 to 15) per tumor. Polymerase chain reaction with primers spanning the breakpoints were able to detect mutant DNA molecules present at levels lower than 0.001% and readily identified mutated circulating DNA in patient plasma samples. This approach provides an exquisitely sensitive and broadly applicable approach for the development of personalized biomarkers to enhance the clinical management of cancer patients.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Methods and compositions for diagnosing gastrointestinal stromal tumors
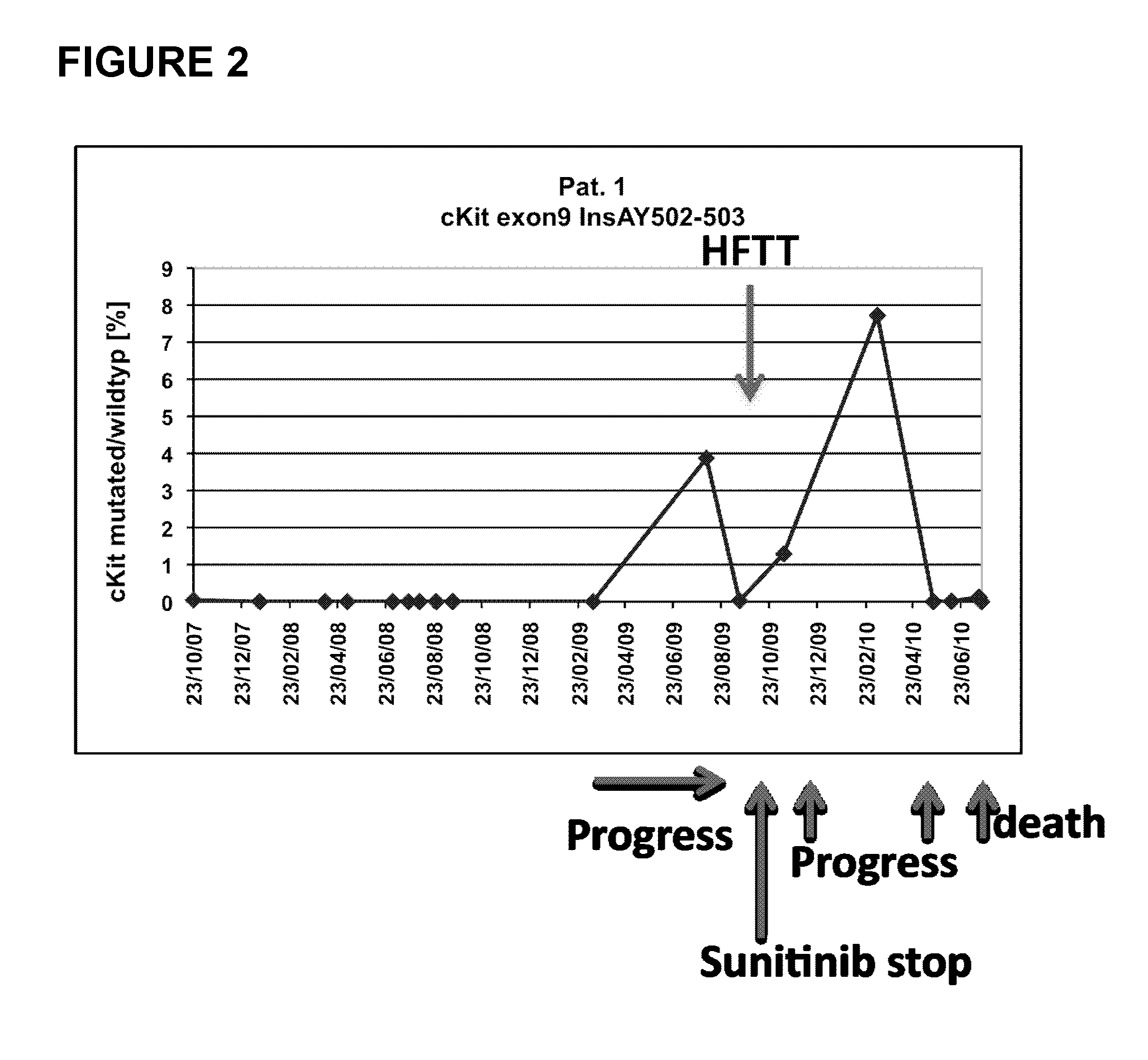
The present invention relates to an in vitro method for diagnosing and / or monitoring in a subject a gastrointestinal stromal tumor or a predisposition to develop a gastrointestinal stromal tumor, comprising detecting and / or analyzing in a test sample derived from the subject one or more mutations at the DNA level in any one or both of the marker genes cKIT (GenBank acc. no. NM_000222.2) and PDGFRA (GenBank acc. no. NM_006206.4), wherein the DNA is circulating DNA, and wherein the presence of any one of the mutations detected in the test sample is indicative of a gastrointestinal stromal tumor or a predisposition to develop a gastrointestinal stromal tumor in the subject. The present invention is also directed to a corresponding kit-of-parts for diagnosing and / or monitoring a gastrointestinal stromal tumor or a predisposition to develop a gastrointestinal stromal tumor, comprising means for detecting and / or analyzing one or more mutations as defined herein, as well as to the use of one or more mutations as defined herein as a panel of molecular markers for diagnosing and / or monitoring a gastrointestinal stromal tumor or a predisposition to develop a gastrointestinal stromal tumor.
Owner:ALBERT LUDWIGS UNIV FREIBURG
Method for measuring tumor burden in patient derived xenograft (PDX) mice
ActiveUS20180288982A1Easy to observeMicrobiological testing/measurementScreening processCirculating tumor DNAHuman patient
Kits and methods providing measurement of tumor burden in a patient derived xenograft (PDX) mouse are described. Exemplary embodiments contemplate taking a sample, typically a blood sample, from a PDX mouse and using a real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) system to quantitate both human patient circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) and mouse DNA. In preferred embodiments, both PCR amplifications are done simultaneously in a multiplex, and a highly polymorphic human DNA target sequence is amplified for high sensitivity, allowing for small volume samples, typically 50-100 μL, of mouse blood. Serial evaluations are possible because the mouse can survive withdrawal of these small volumes of blood. A related method allows for quantitation of ctDNA in the presence of human immune cells added to a “humanized” mouse. These relatively quick and easy methods of determining tumor burden in PDX mice can have predictive value for the efficacy of cancer treatments in human patients.
Owner:LIFE GENETICS LAB
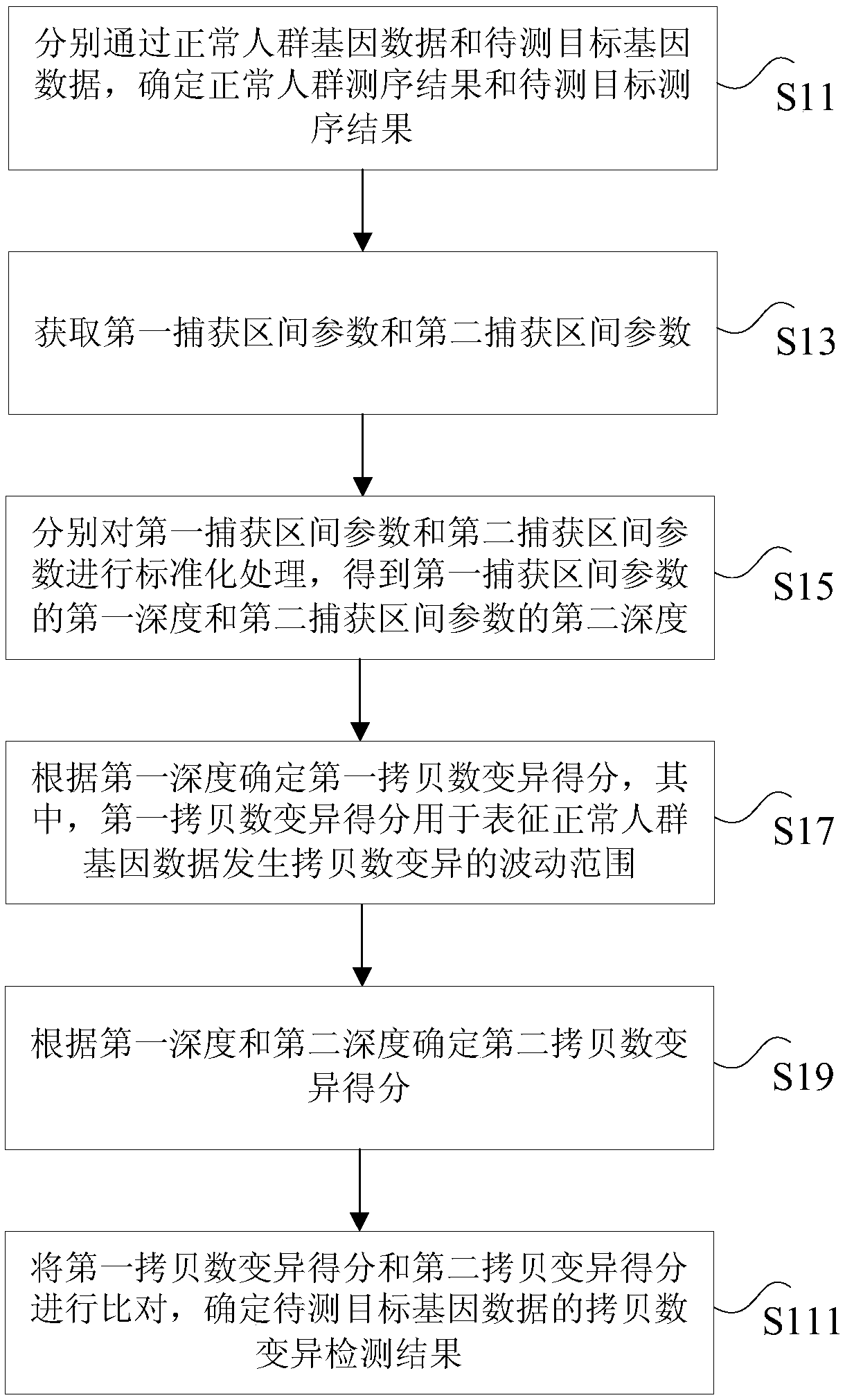
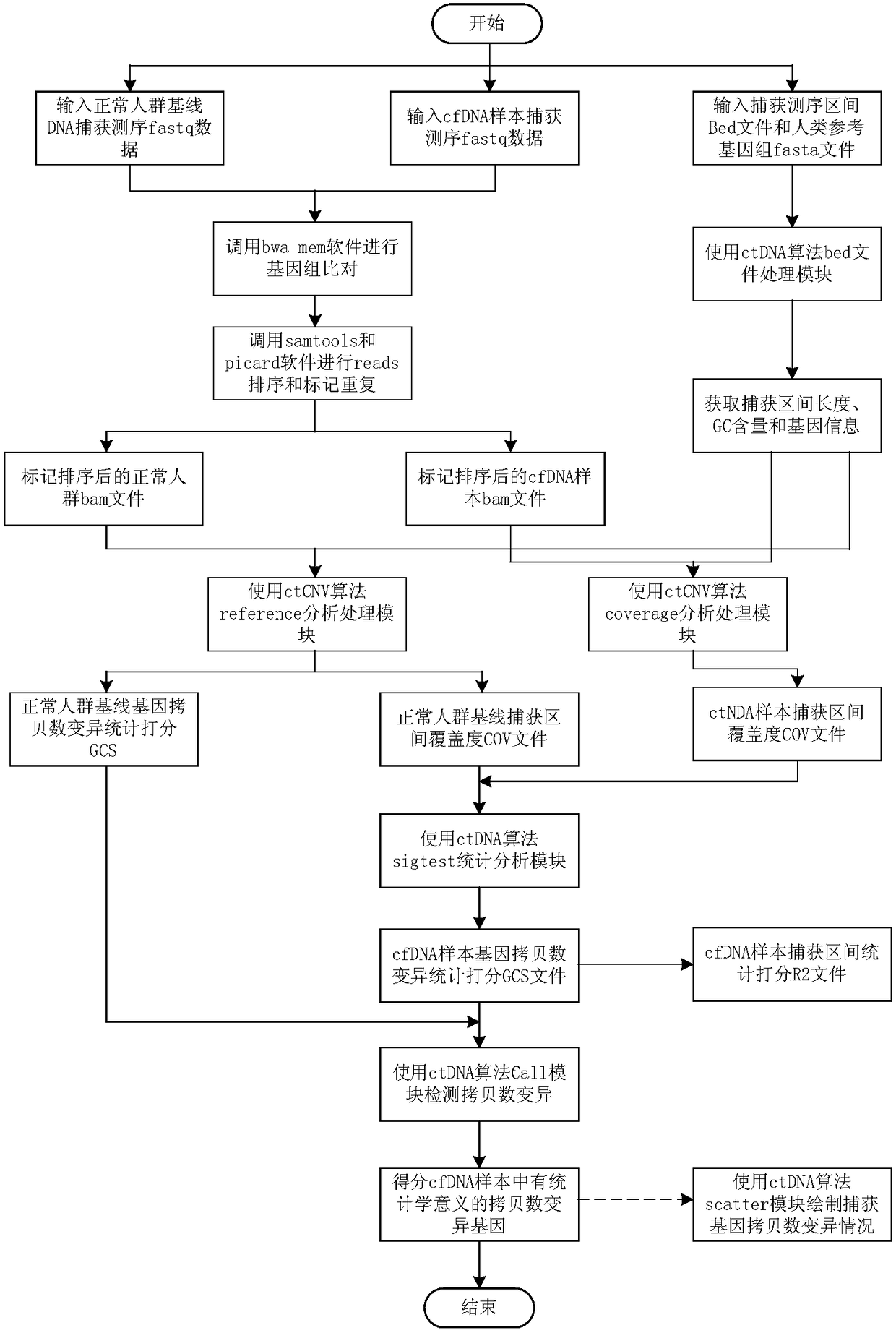
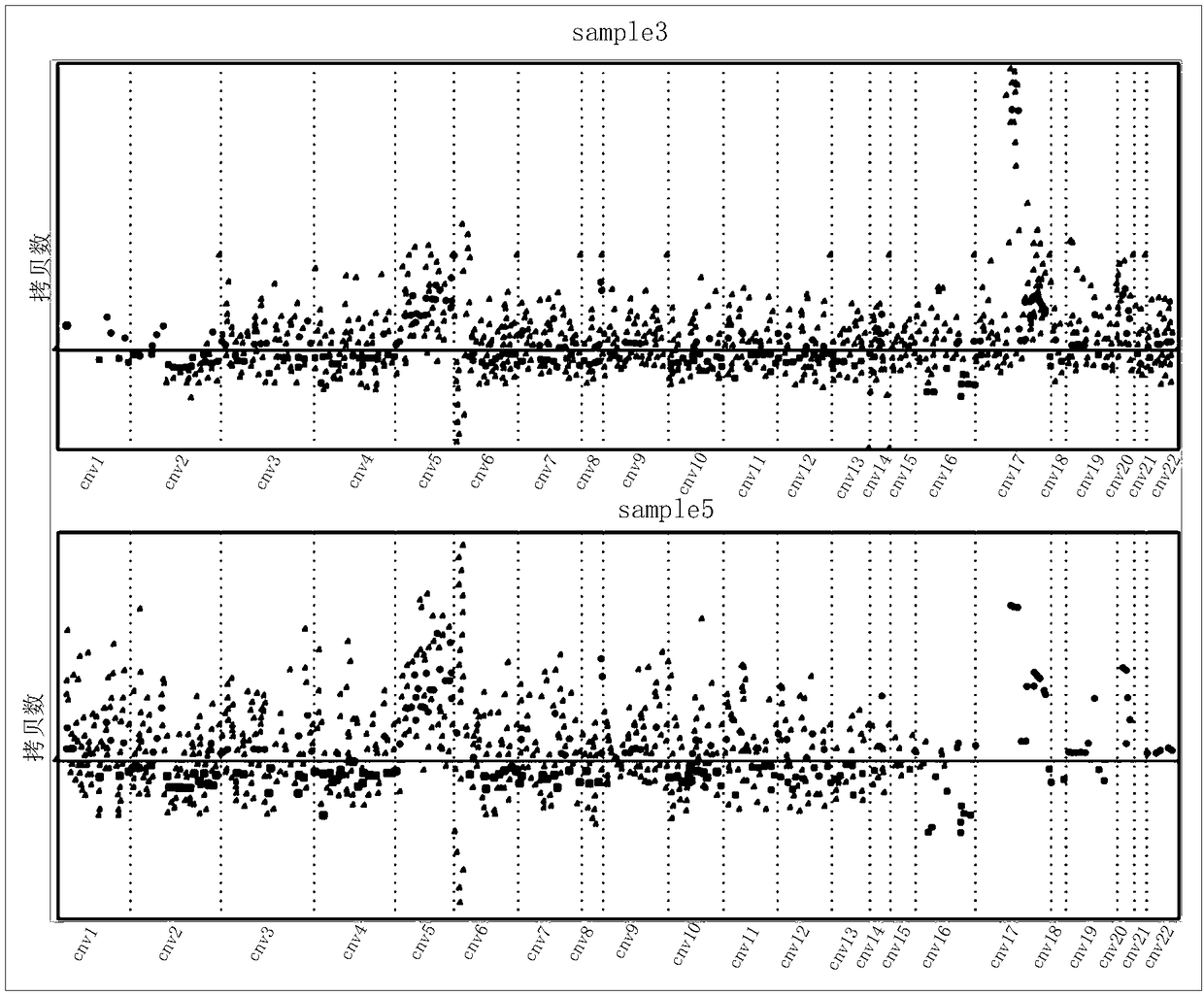
Circulating tumor DNA copy number variation detection method and apparatus
ActiveCN108319813ASolve the technical problem of poor accuracy of mutation detectionIncreased variant detection accuracyProteomicsGenomicsCirculating tumor DNACrowds
The invention discloses a circulating tumor DNA copy number variation detection method and apparatus. The method comprises the steps of determining a normal crowd sequencing result and a to-be-detected target sequencing result through normal crowd gene data and to-be-detected target gene data; obtaining a first capture interval parameter and a second capture interval parameter; performing standardization processing on the first capture interval parameter and the second capture interval parameter to obtain a first depth of the first capture interval parameter and a second depth of the second capture interval parameter; according to the first depth, determining a first copy number variation score; according to the first depth and the second depth, determining a second copy number variation score; and according to the first copy number variation score and the second copy number variation score, determining a copy number variation detection result of the to-be-detected target gene data. The technical problem of poor circulating tumor DNA copy number variation detection accuracy in the prior art is solved.
Owner:GENE CRAB BIOTECH CO
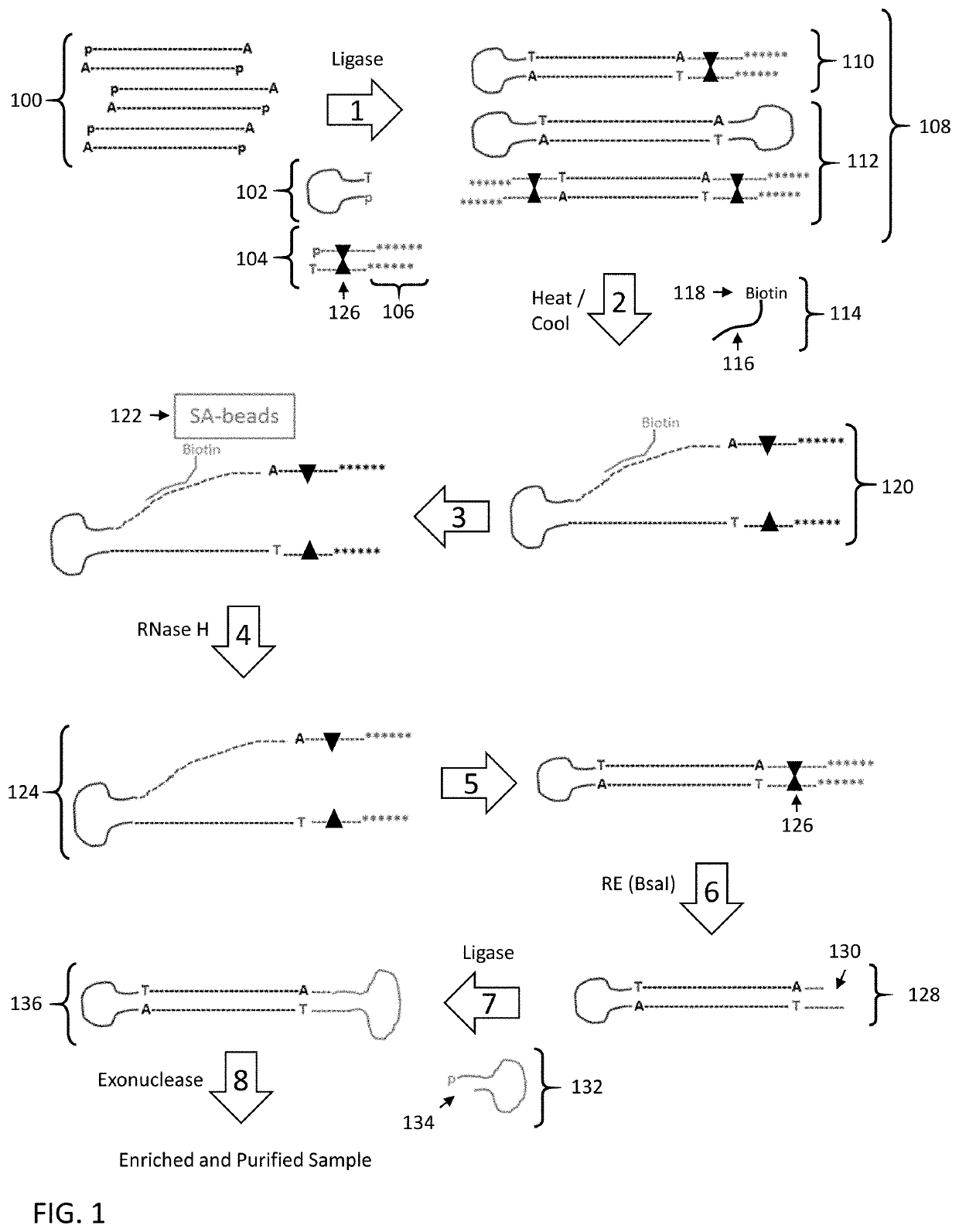
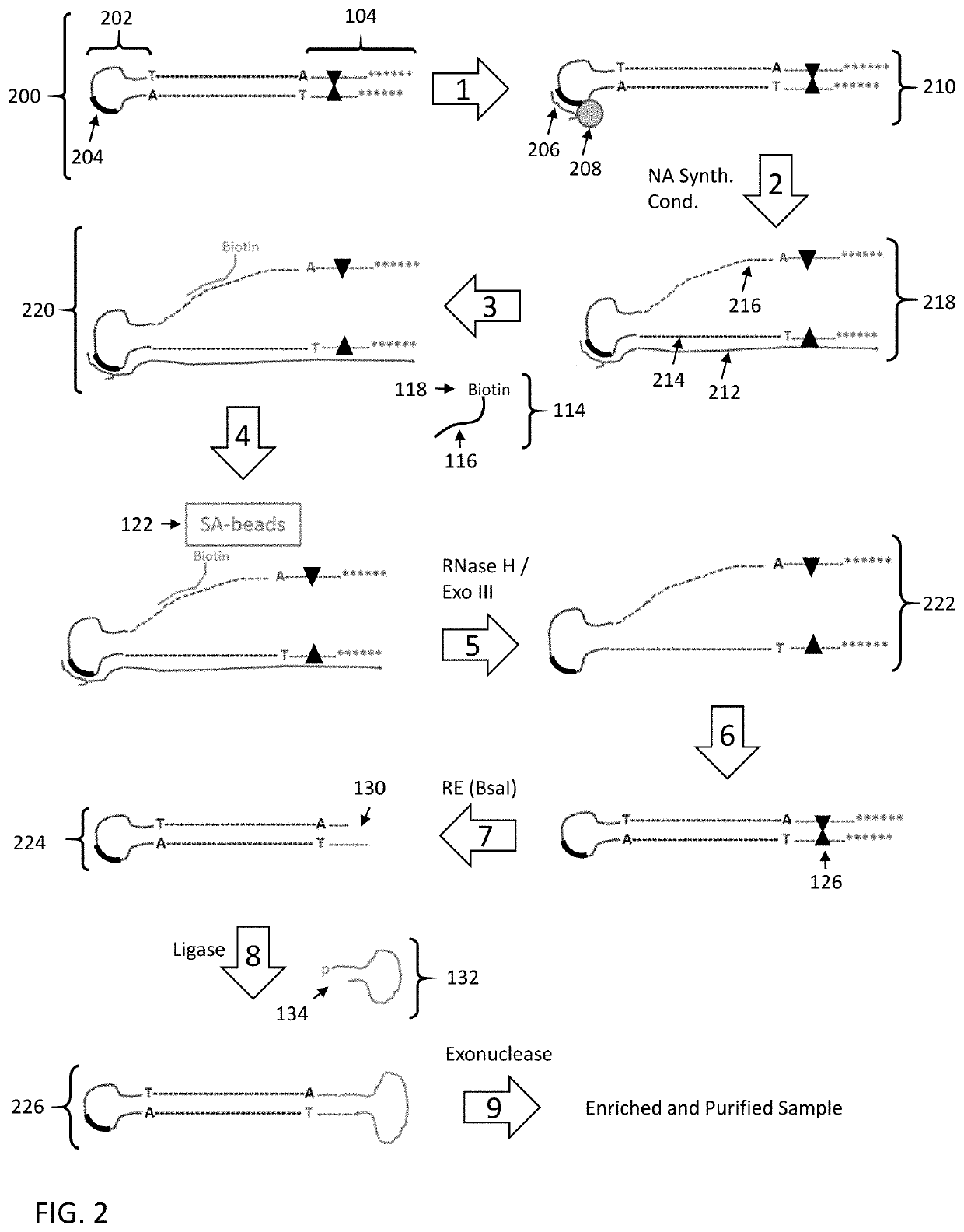
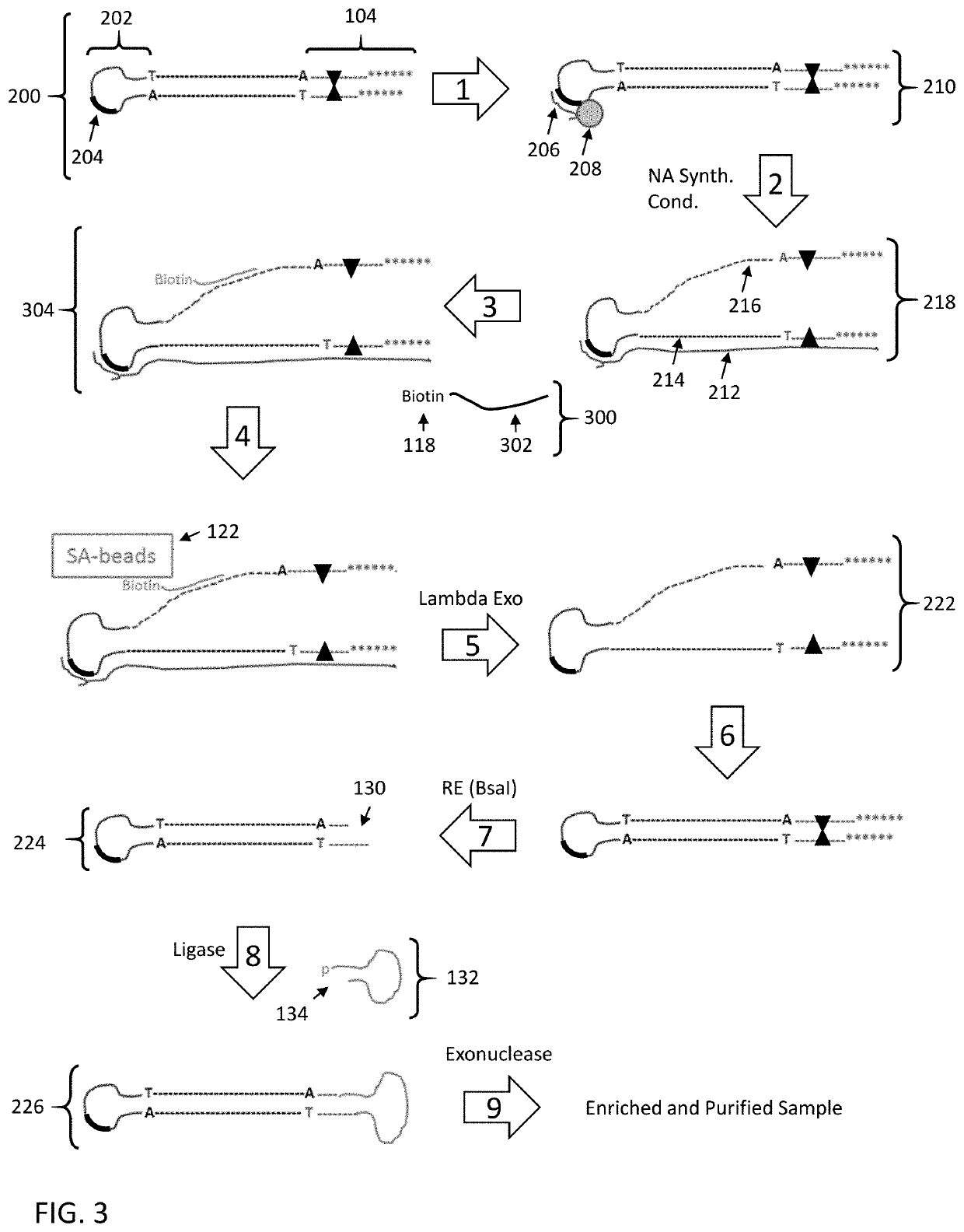
Enrichment of DNA comprising target sequence of interest
PendingUS20190360043A1Nucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementDownstream processingCell free
Disclosed are methods and compositions for enriching nucleic acid fragments from a sample that include one or more target region of interest. In certain aspects, a sample of double stranded nucleic acid fragments having a strand-linking adapter at one end and a non-strand-linking adapter at the other end are denatured and contacted with capture probes specific for a target sequence of interest. Capture probe-bound fragments are isolated from the sample, e.g., using a solid substrate specific for the binding moiety on the capture probes, and are renatured for downstream processing, thus maintaining the original double-stranded region. This enrichment process does not require amplification and as such maintains the nucleic acids in their native states. The disclosed enrichment process and compositions are suitable for analyzing nucleic acids that are fragmented and / or damaged, e.g., cell-free DNA such as circulating tumor DNA, as well as nucleic acids that are many kilobases in length.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
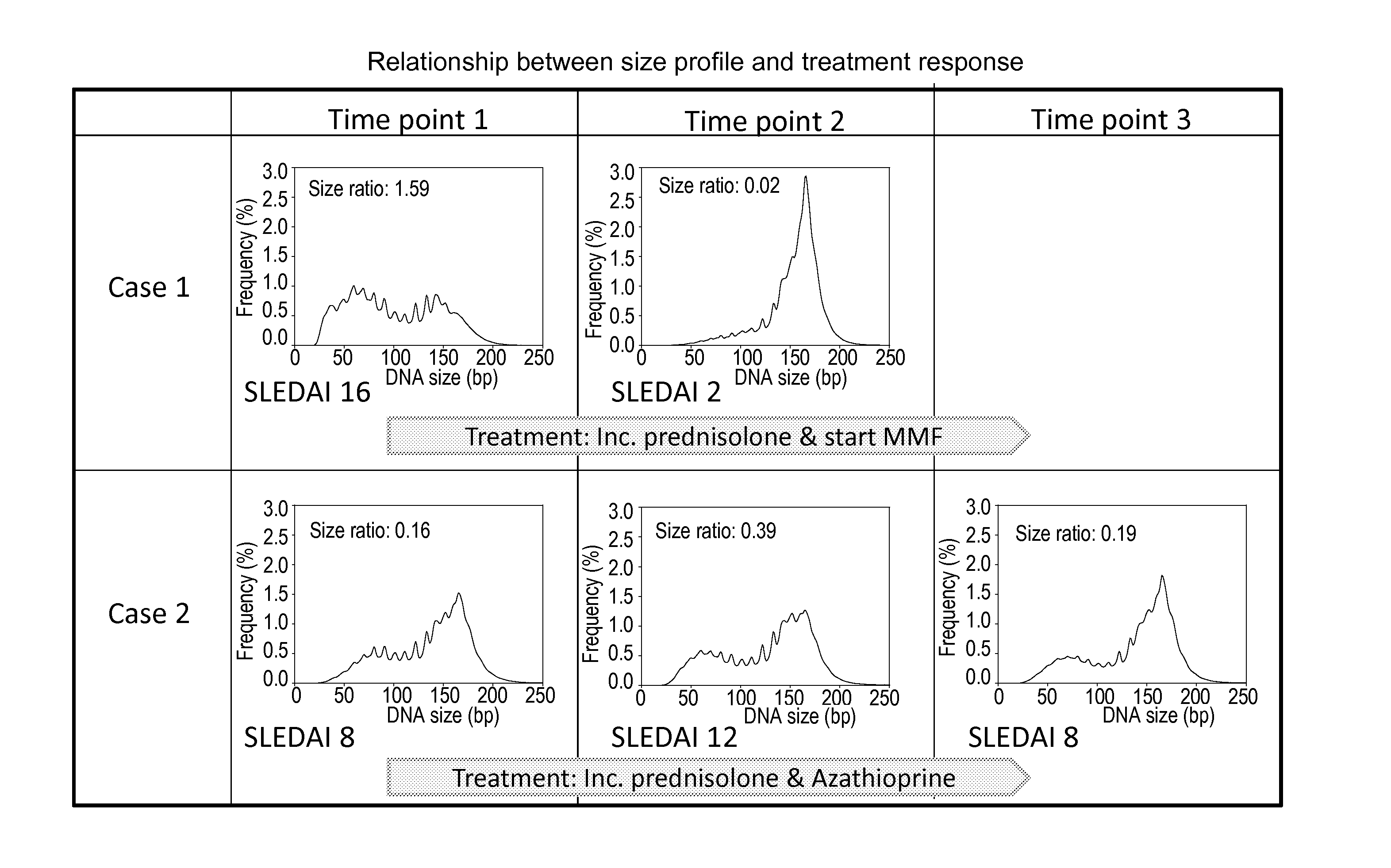
Sequencing analysis of circulating DNA to detect and monitor autoimmune diseases
ActiveUS20150087529A1Reducing methylationRaise the ratioHealth-index calculationMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisDisease
Systems, methods, and apparatuses are provided for diagnosing auto-immune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) based on the sizes, methylation levels, and / or genomic characteristics of circulating DNA molecules. Patients provide blood or other tissue samples containing cell-free nucleic molecules for analysis. Massively parallel and / or methylation-aware sequencing can be used to determine the sizes and methylation levels of individual DNA molecules and identify the number of molecules originating from different genomic regions. A level of SLE can be estimated based on: the amount of molecules having sizes below a threshold value; the methylation level(s) of the entire genome or portions of the genome; correlations between the sizes and methylation levels of DNA molecules; and / or comparing the representation of DNA molecules in each of a plurality of genomic regions with a reference value for that region, and determining an amount of genomic regions having increased or decreased measured genomic representation.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Single-chain molecular identifier adapter and single-chain DNA database creating method and application thereof to circulating tumor DNA detection
InactiveCN109797197AReduce dosageHigh-resolutionMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary linkersDNA databaseSingle strand dna
The invention discloses a single-chain molecular identifier adapter and a single-chain DNA database creating method and application thereof to circulating tumor DNA detection. The single-chain molecular identifier adapter comprises a stem structure formed by 14 base pairing, a sequencing primer sequence and a molecular identifier sequence formed by 8 random nucleotides, wherein a base 'U' is inserted between the sequencing primer sequence and a stem structure sequence, and a stem-loop structure can be formed by annealing denaturation of the single-chain nucleotide sequence. By single-chain DNAdatabase creating, technical problems of low sensitivity, fragmentation, low concentration and short ctDNA fragments in liquid biopsy in application of an existing detection technique are solved. Accurately distinguishing whether sequencing reads identical in genome coordinate beginning and end loci come from cfDNA released by the same one or multiple germinal cell is realized, sequencing reads derived from original positive and negative chains of the same cell are paired for analysis, and accordingly sequencing rehandling is reduced, and the distinguishing rate of false positive mutation isincreased.
Owner:HANGZHOU NEOANTIGEN THERAPEUTICS CO LTD
Device for detecting DNA copy number variation of circulating tumor
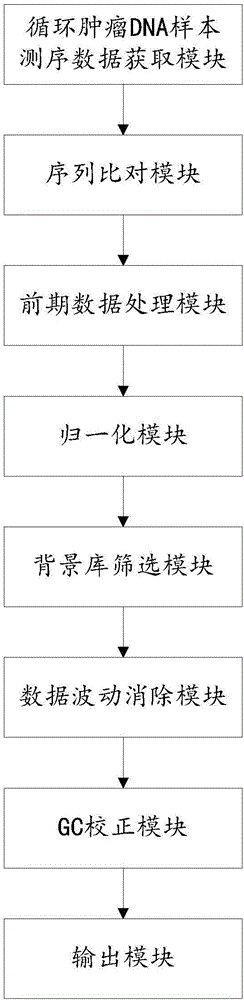
ActiveCN106650312AHybridisationSpecial data processing applicationsAbnormal tissue growthData acquisition
The invention relates to a device for detecting DNA copy number variation of circulating tumor, which has high detection sensitivity. The device provided by the invention comprises a sequencing data acquisition module, a sequence matching module, an early data processing module, a normalization module, a background library screening module, a data fluctuation eliminating module, a GC correction module and an output module.
Owner:ANNOROAD GENE TECH BEIJING +2
Biological information processing method for analyzing circulating tumor DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
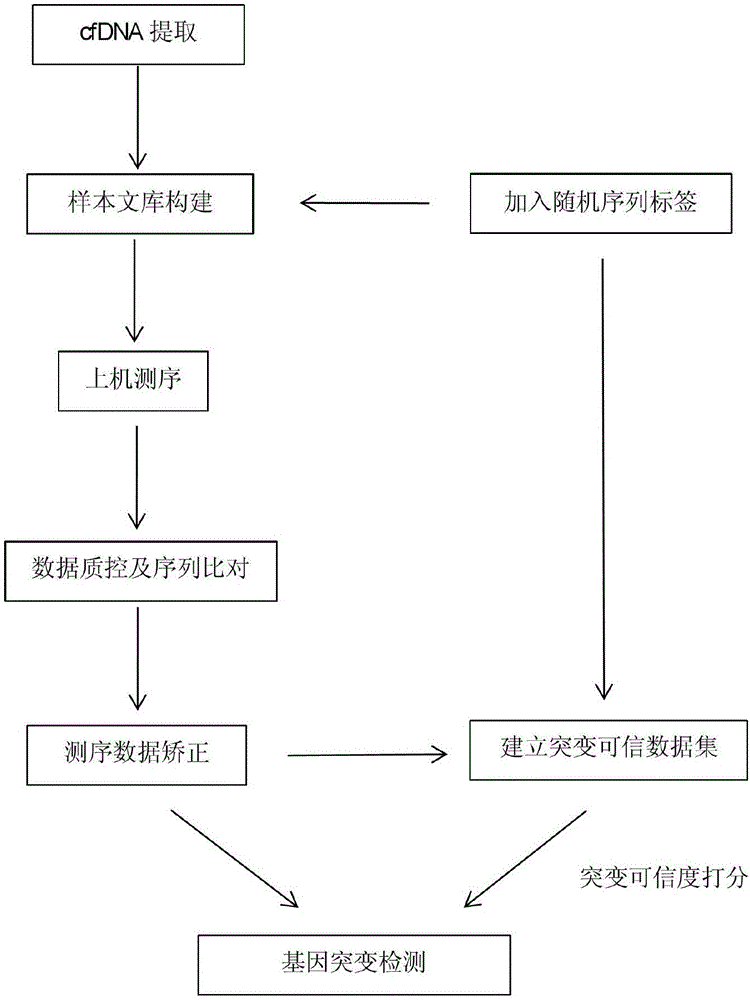
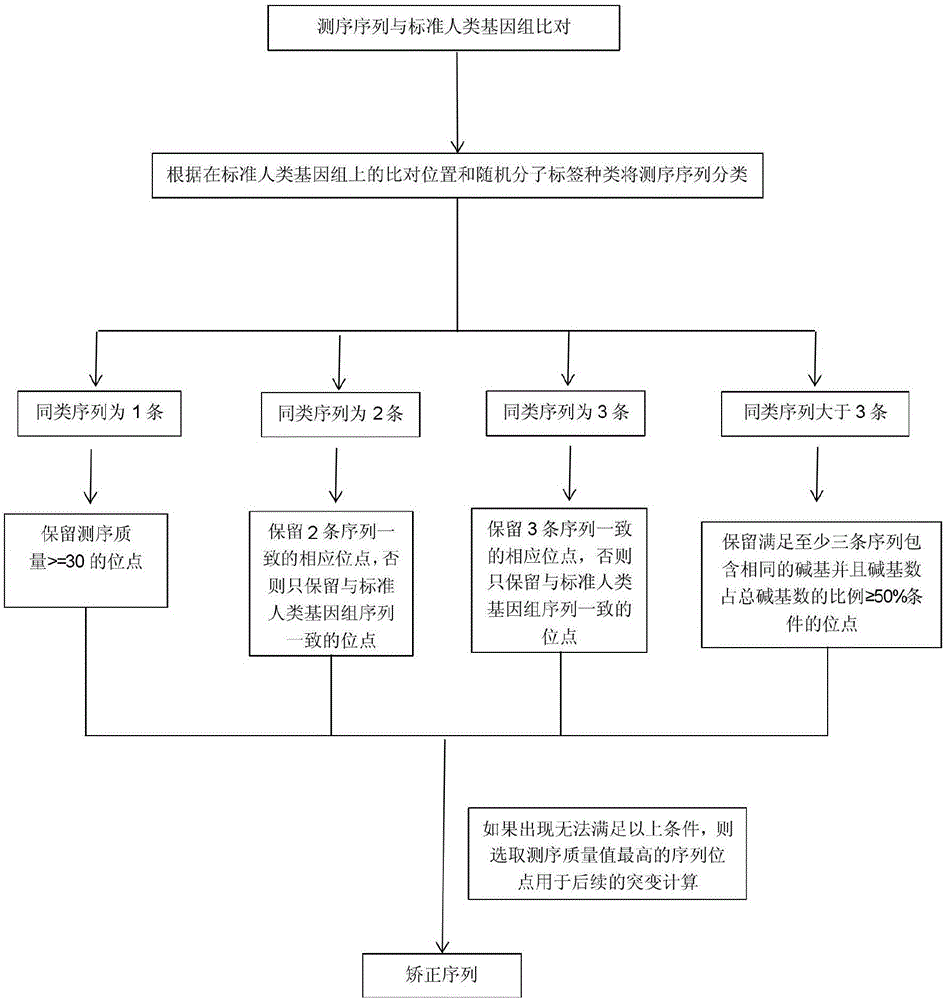
InactiveCN107523563ASample collection is simple and convenientKeep valid dataMicrobiological testing/measurementHybridisationData setData quality
The invention provides a biological information processing method for analyzing circulating tumor DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). The method includes 1), performing cfDNA extraction, database creating and sequencing; 2), performing sequencing-data quality control and sequencing comparison; 3), performing sequencing data correction; 4), using two pieces of software to simultaneously perform gene mutation detection on the sequencing data corrected in the step 3) and summing and integrating analysis results of the software; 5), establishing a mutant trusted data set by the aid of a sequence corrected in the step 3) and using the data set to provide credibility support to a mutation result acquired in the step 4). The ctDNA in the cfDNA is taken as a detection object, detection can be performed by only collecting a small amount of peripheral blood of a subject, and conciseness and convenience in sample collection are achieved.
Owner:HANGZHOU HEYI GENE TECH
High-flux detection method of circulating DNA liver cancer driver gene
PendingCN107723352AGuaranteed catchHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementBlood plasmaExon
The invention discloses a high-flux detection method of a circulating DNA liver cancer driver gene. According to the method, a mutant gene which is the most common of the existing liver cancer is selected and combined with a second-generation high-flux sequencing technology to more comprehensively detect a gene mutant condition of the liver cancer. Since a blood plasma sample of a patient is adopted, the method can greatly reduce the detection injury of a patient; secondly, the whole-exome detection is performed on 75 liver cancer genes, the method is more comprehensive compared to the detection method based on real-time PCR and first-generation Sanger sequencing technology; and since only 75 genes are detected, the sample can be detected in a greater sequencing depth, so that the detection precision can reach 0.1 percent. Therefore, a reference can be provided for more and better individual precision therapeutic schemes of the patient.
Owner:JIAXING YUNYING MEDICAL INSPECTION CO LTD
Library for performing high-throughput detection on circulating tumor DNA target genes, as well as detection method and application of library
InactiveCN107447258AImprove detection efficiencyReduce testing costsMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationNon invasiveExon
The invention relates to the field of genomic high-throughput sequencing, in particular to a library for performing high-throughput detection on circulating tumor DNA target genes, as well as a detection method and application of the library. Circulating body fluid of a tumor patient is used as a biological sample, low-concentration free nucleic acid is extracted, the low-concentration free nucleic acid of the biological sample is used as a sample template, target gene exons of the sample template are amplified in a multiplex PCR form, then the tail ends of obtained amplicons are repaired and the 3' ends of the amplicons are connected with A basic groups, the modified amplicons are connected to Illumina sequencing adapters, and then library PCR is carried out by using an index-containing primer, and an amplified product is the library for detecting mutation diversity of the circulating tumor DNA target genes. The in-vitro circulating body fluid of the tumor patient is used as the biological sample for achieving non-invasive detection; the low-concentration free nucleic acid is used as the template for highly-sensitive detection; multiple target gene exons are amplified in a multiplex PCR form at the same time so as to improve the detection efficiency; via establishment of an amplicon library, high-throughput sequencing and data analysis, the detection cost can be greatly reduced.
Owner:DALIAN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Device for detecting somatic cell mutation by circulating tumor DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) samples
PendingCN106845153AAccurate distinctionHigh sensitivitySequence analysisSpecial data processing applicationsMutation frequencyCirculating tumor DNA
The invention relates to a device for detecting somatic cell mutation by circulating tumor DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) samples. The device comprises a data acquisition module, a mutation frequency statistics module, a comparison module, a judgment module and a detection result output module. The device for detecting the somatic cell mutation by the aid of the circulating tumor DNA samples has the advantages that system errors can be accurately differentiated from the real somatic cell mutation by the device, accordingly, the sensitivity can be improved, and false positive and false negative can be reduced.
Owner:ANNOROAD GENE TECH BEIJING +2
Circulating tumor DNA EGFR detecting technology and reagent kit thereof
InactiveCN104789677AHigh sensitivityEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementWild typeCirculating tumor DNA
The invention discloses a circulating tumor DNA EGFR (Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor) detecting technology and a reagent kit thereof. The circulating tumor DNA EGFR detecting technology comprises the following steps: step 1, designing a synthetic primer, a closed probe and a detecting probe for a mutation site; step 2, processing a sample and extracting DNA; step 3, applying the circulating tumor DNA EGFR detecting technology to the reagent kit, and establishing a PCR amplified reaction system. According to the circulating tumor DNA EGFR detecting technology disclosed by the invention, the specific MGB Blocker probe, the EGFR specific probe and the primer are adopted to detect the EGFR mutation in the circulating tumor DNA; the MGB Blocker probe is utilized to retard nonspecific amplification of the EGFR wild type genome and improves the sensitivity; the circulating tumor DNA EGFR detecting technology can be used for detecting the EGFR mutation in the circulating tumor DNA, is simple to operate, cheap in detection, capable of being popularized at a large scale and high in detection speed; the detecting process can be completed for about 2 hours.
Owner:张道允 +1
Digital PCR chip based on seaweed gel liquid drop and application thereof
ActiveCN106754245AImprove stabilityFusion does not occurBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPcr chipCirculating tumor DNA
The invention discloses a liquid drop capturing chip. The liquid drop capturing chip comprises a plurality of fluid micro channels arranged in parallel, wherein a plurality of liquid drop capturing structures are formed along the fluid micro channels at intervals; the liquid drop capturing structures comprise liquid drop entering ends and inhibition liquid drop flowing-out ends; and the inhibition liquid drop flowing-out ends are communicated with the adjacent fluid micro channels. The invention further discloses a fully integrated digital PCR chip based on a seaweed gel liquid drop and application thereof. The digital PCR chip based on the seaweed gel liquid drop, disclosed by the invention, can finish the full process from the generation of liquid drops to capture of the liquid drops and to the detection of the liquid drops. And moreover, seaweed gels are introduced; after the seaweed gels are solidified, the seaweed gel liquid drops are stable, cannot be fused and cannot affect the PCR amplification efficiency; and the method can be applied to the detection of circulating tumor DNA in the blood and other related biology and medical sciences; and due to the introduction of the seaweed gels, the application can be further expanded to single cell analysis and so on.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method of detecting circular tumor DNA in free DNA of peripheral blood, kit and analytic method of sequencing result thereof
InactiveCN107475403AHigh sensitivityAvoid interferenceMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisAbnormal tissue growthTail
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method of detecting circular tumor DNA in free DNA of peripheral blood, a kit and an analytic method of a sequencing result thereof. The method of detecting circular tumor DNA comprises the following steps: S1, filling the tail end of cfDNA, and adding a basic group A into 3' of cfDNA; S2, connecting a joint to the tail end of the cfDNA treated in the S1 to obtain a connecting product, wherein the joint contains a molecular tag sequence and an Index sequence; S3, amplifying the connecting product with universal primers Primer 1.0 and Primer7; S4, capturing and enriching the amplified product obtained in the S3 by means of a probe; and S5, amplifying the enriched product obtained in the S4 by using the Primer 7 and Primer 5 and performing sequencing. The system error induced by PCR and sequencing can be removed effectively, so that the sequencing sensitivity of ctDNA is improved effectively.
Owner:深圳因和生物科技有限公司
Method and device for processing circulating tumor DNA repetitive sequence
ActiveCN108229103AImprove processing accuracySequence analysisSpecial data processing applicationsReference genome sequenceCirculating tumor DNA
The invention discloses a method and device for processing a circulating tumor DNA repetitive sequence. The method comprises the steps that sequencing data and a reference genome sequence of to-be-detected circulating tumor DNA are obtained, wherein the sequencing data is obtained by carrying out high-throughput sequencing on the to-be-detected circulating tumor DNA and comprises a plurality of pairs of double-ended sequences; the sequencing data is compared with the reference genome sequence to obtain a first comparison result, wherein the first comparison result at least comprises genome positions, base sequences and corresponding base quality value sequences of the double-ended sequences; the type of each pair of double-ended sequences is determined on the basis of the first comparisonresult, wherein the types comprise independent sequences and repeated sequences. The method and the device solve the problem that a sequencing data processing method in the prior art is used for sequencing samples to delete or mark repetitive sequences and accordingly the accuracy is low.
Owner:GENE CRAB BIOTECH CO
Method and apparatus for amplification of nucleic acid sequences using immobilized DNA polymerase
InactiveUS20040191830A1Easy to separatePromote recoveryBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLab-on-a-chipPolymerase L
The present invention generally relates to methods and apparatuses for amplifying nucleic acid sequences using immobilized DNA polymerase. More particularly, it relates to methods and apparatuses useful for amplifying target nucleic acid sequences by forming a plurality of reaction regions in which polymerase chain reaction (PCR) can occur, positioning immobilized DNA polymerase in a specific reaction region, and circulating DNA through the reaction regions. The present invention provides those methods and apparatuses that allow simple separation and recovery of the DNA polymerase after the amplification, that can be operated not only with thermostable DNA polymerases but also with non-thermostable DNA polymerases, and that are simpler in their designs and processes so that they can be readily integrated into complex devices such as Lab-on-a-chip.
Owner:AHRAM BIOSYST
Probe for detecting circulating tumor DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) of human breast cancer and application of probe
InactiveCN105950739AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDiseaseIndividualized treatment
The invention discloses a probe for detecting a circulating tumor DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) of a human breast cancer and application of the probe, belonging to the field of diagnosis and prevention of diseases. The invention designs a breast cancer selector which consists of DNA segments in mutation regions of related genes of the breast cancer. The circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) of a breast cancer patient is subjected to liquid-phase hybridization capture by using the probe designed by the selector; after high-throughput sequencing, specific cancer gene variation of a patient is found, and a tumor load is monitored. Compared with a conventional detection means, the probe and the application thereof disclosed by the invention have the characteristics of no invasiveness, high throughout, good sensitivity and specificity, and the like; the probe and the application thereof can be used for better screening and early-stage diagnosis of the human breast cancer and are applied to individualized treatment of cancer.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Tumor burden as measured by cell free DNA
InactiveUS20180282417A1Good chanceLong survivalMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsCell freeAllele frequency
Disclosed are methods for treating cancer (e.g., solid tumor cancers, lung cancer, bladder head and neck cancer) with an anti-PD-L1 antibody in a patient identified as being responsive to anti-PD-L1 antibody therapy by detecting a mutation in one or more disclosed circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) markers. Also disclosed are methods for determining the efficacy of anti-PD-L1 therapeutic antibody treatment in a patient having lung cancer or bladder cancer comprising detecting variant allele frequency in ctDNA in plasma samples and determining the difference of the variant allele frequency in ctDNA between the first and at least second plasma samples, wherein a decrease in the variant allele frequency in the at least second plasma sample relative to the first plasma sample identifies the anti-PD-L1 antibody treatment as effective. The disclosure also provides methods of identifying a subject having a cancer responsive to a therapy comprising an anti-PD-L1 antibody by detecting the expression of a mutation in one or more circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) markers.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
Compositions and methods for detection of nucleic acid mutations
InactiveCN109415764ANucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementMultiplexCirculating tumor DNA
The invention provides methods and compositions for detecting a mutation in a target gene in a sample of blood or a fraction thereof, including in certain examples, a fraction that includes circulating tumor DNA. The methods can include a tiling PCR reaction, for example a one-sided multiplex tiling reaction. Virtually any type of mutation can be detected with the methods and compositions. In certain embodiments, gene fusions are detected. Improved PCR methods, especially for performing nested multiplex PCR reactions are provided.
Owner:NATERA
Substance, kit and method used for detecting systemic infection
ActiveCN107312839AEasy to detectImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesIn vivo
The invention relates to a substance, a kit and a method used for detecting systemic infection. The substance is a circulating DNA disintegrated and released in vivo from a pathogenic bacterium. The substance provided by the invention is based on the detection of DNA degraded by the pathogenic bacterium of peripheral blood, objectively reflects that whether the pathogenic bacterium invades into blood circulation, and better helps to distinguish the systemic infection and non-infective diseases. The substance does not depend on the separation and identification of a living bacterium thallus, is not affected by the content of the living bacterium in a blood specimen, is not affected by the influences of the contaminated bacterium in specimen collection process, and is higher in detection sensitivity and specificity. The provided detection kit comprises a capture probe for 16 S rDNA of 662 pathogenic bacteria, and can better identify the species of the pathogenic bacterium. The provided detection method better reflects the severity of the infection as well as the course and the condition of the disease through the semi-quantitative analysis of the circulating DNA from the bacterium in the peripheral blood, so as to guide treatment and evaluate prognosis.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV CANCER CENT
Method and apparatus for amplification of nucleic acid sequences using immobilized DNA polymerase
InactiveUS7488595B2Readily separated and recoveredImprove purification effectBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusPolymerase LLab-on-a-chip
Owner:AHRAM BIOSYST INC
Ultra-sensitive detection of circulating tumor DNA through genome-wide integration
PendingCN112601826AMedical simulationMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseCirculating tumor DNA
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY +1
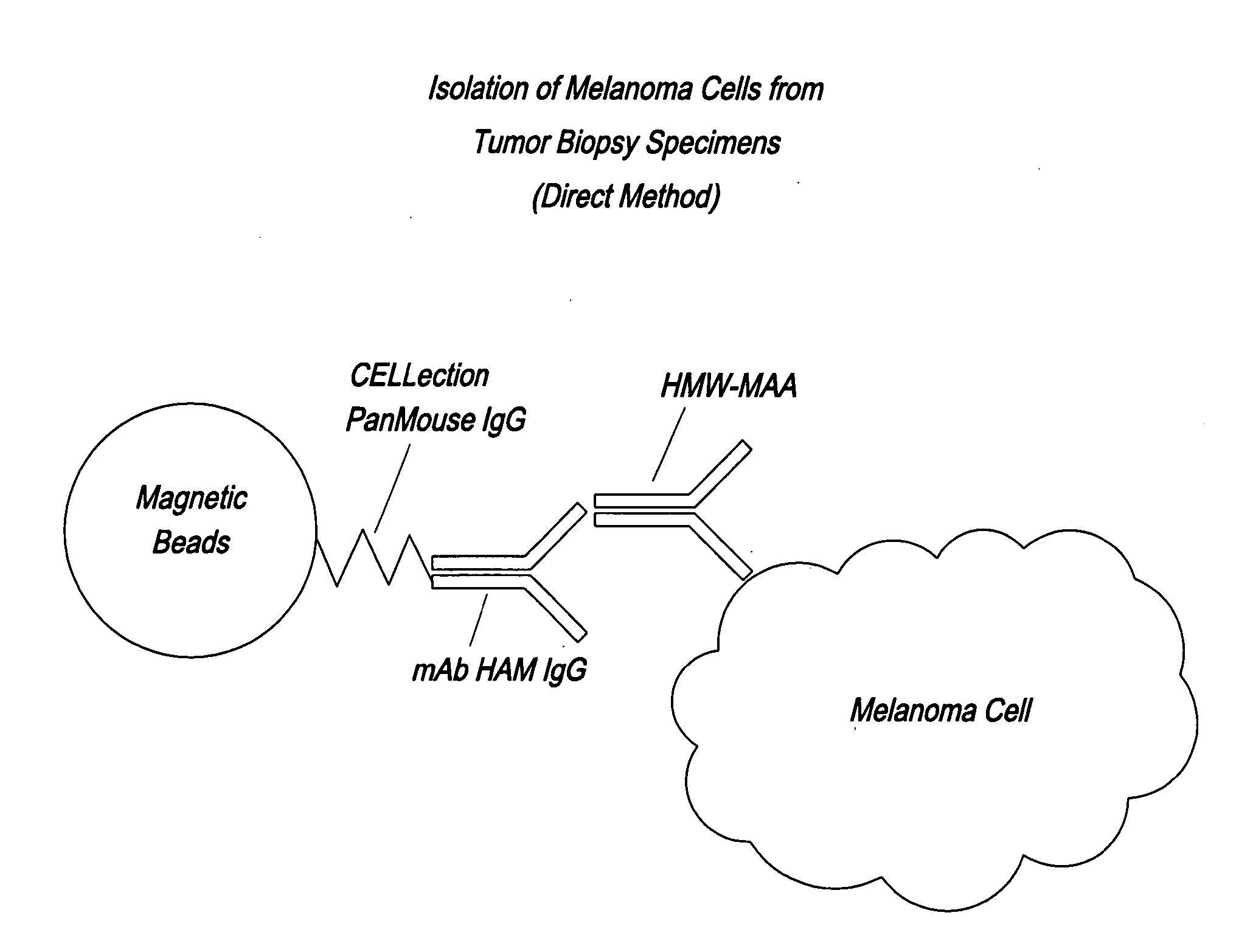
Utility of high molecular weight melanoma associated antigen in diagnosis and treatment of cancer
InactiveUS20080076727A1Strong specificityHigh sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAntigenCancer cell
HMW-MAA antibody cocktails and their uses in detecting cancer and isolating cancer cells are disclosed. Also disclosed are methods of detecting cancer based on the presence of an HMW-MAA genomic sequence in circulating DNA, as well as the increased expression of the HMW-MAA gene and the reduced methylation of the HMW-MAA gene promoter in tissues and circulating cells.
Owner:JOHN WAYNE CANCER INST
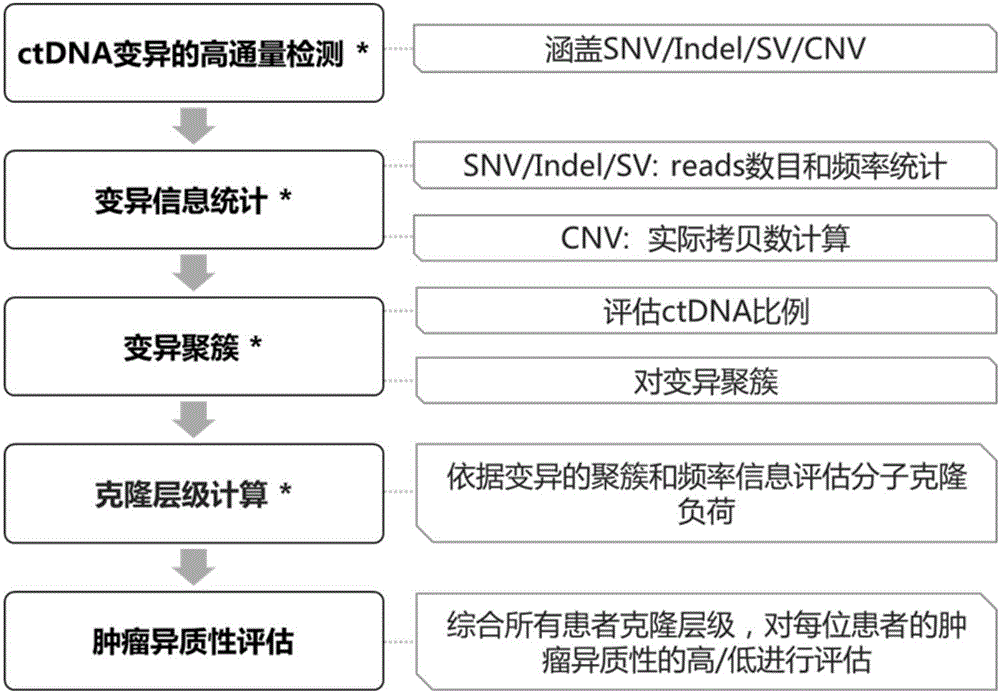
System and method for tumor heterogeneity assessment
ActiveCN106676178ARich in featuresAccurate and Reasonable AssessmentMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsCirculating tumor DNATumor heterogeneity
The invention discloses a system and a method for tumor heterogeneity assessment and particularly provides a molecular clone analysis method. On the basis of various types of variation detection results of high-throughput sequencing in circulating tumor DNA, all variations are divided into different molecular clones to realize tumor heterogeneity assessment by molecular clone levels. By adoption of the method, tumor heterogeneity assessment based on ctDNA high-throughput variation detection is realized to effectively assist in making of tumor prognosis and treatment schemes.
Owner:BEIJING GENEPLUS TECH +1
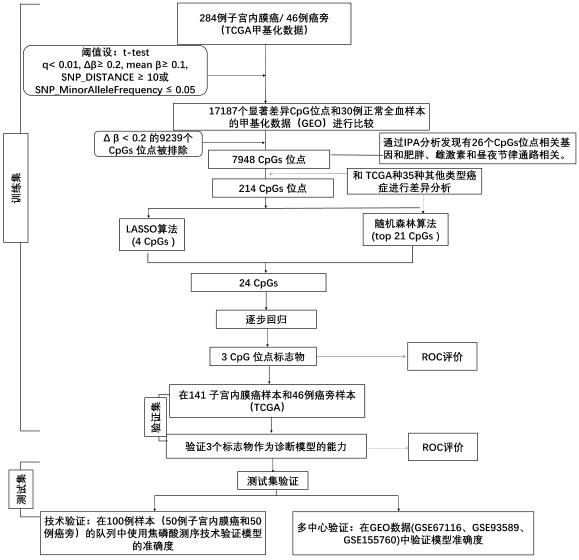
Detection kit for TMEM101 gene methylation in human peripheral blood circulating tumor DNA for early screening of endometrial cancer
ActiveCN113215264AImprove complianceSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsOncologyGene targeting
The invention discloses a detection kit for TMEM101 gene methylation in human peripheral blood circulating tumor DNA for early screening of endometrial cancer. The detection kit is applied to early screening of endometrial cancer and comprises a methylation specific primer of a TMEM101 gene target site, a hydrolysis probe which is specific to the TMEM101 gene, and a primer of a reference gene and a hydrolysis probe of the reference gene, wherein the target site of the TMEM101 gene is at least one CpG site in an upstream and downstream 2000bp interval of a transcription start site of the TMEM101 gene; the reference gene is one or more of GAPDH and beta-actin; and the kit comprises a PCR pre-amplification reaction system and a PCR amplification reaction system. According to the provided detection kit for TMEM101 gene methylation in human peripheral blood circulating tumor DNA for early screening of endometrial cancer, the technical defects that in the prior art, the process is tedious, the detection time is long, the false positive is high, and the early screening of the endometrial cancer blood cannot be traced are overcome.
Owner:上海伯豪生物技术有限公司
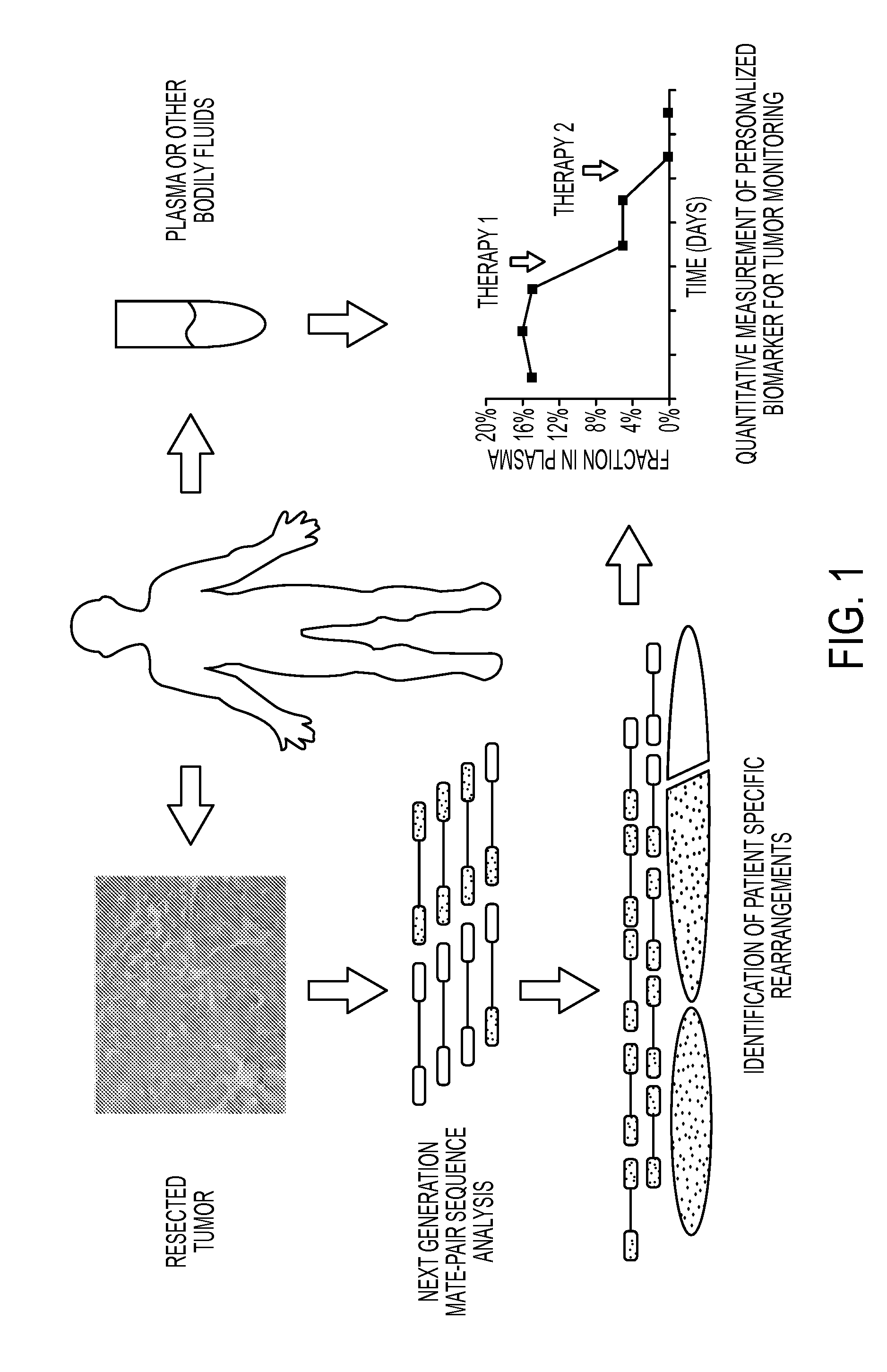
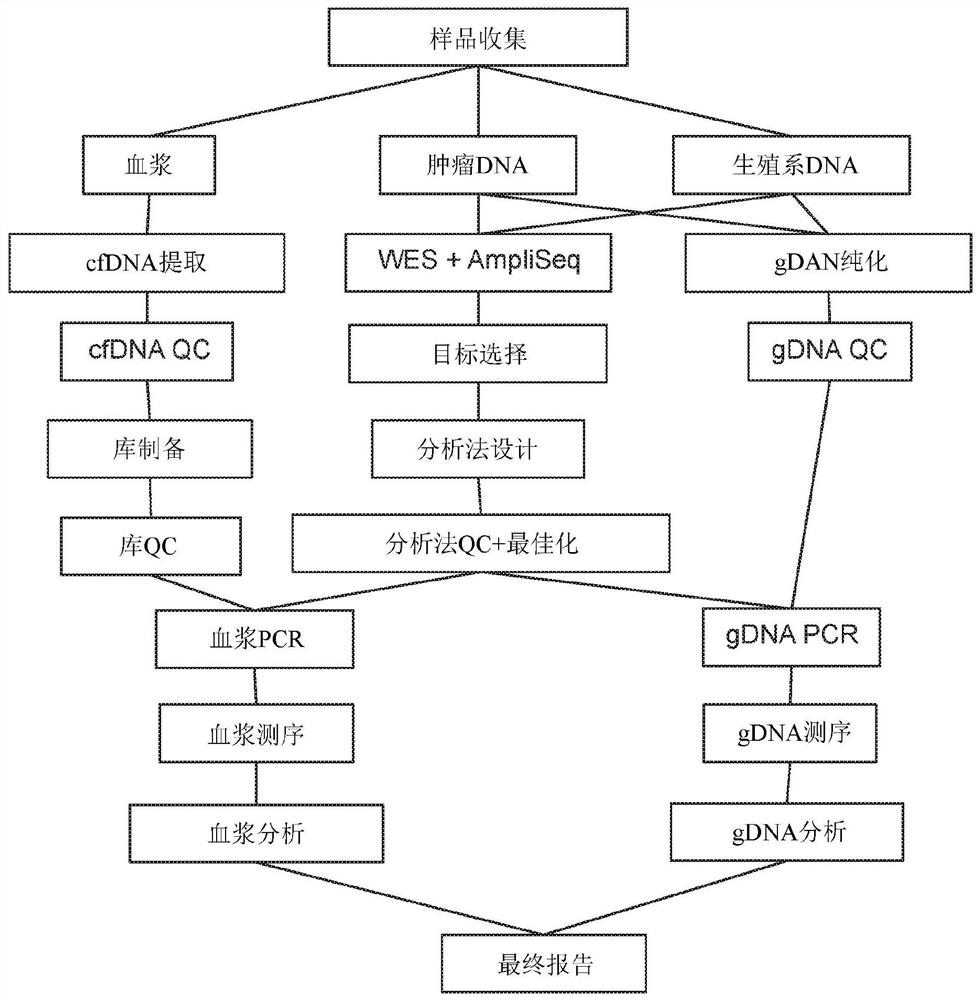
Methods for cancer detection and monitoring by means of personalized detection of circulating tumor DNA
The invention provides methods for detecting single nucleotide variants in breast cancer, bladder cancer, or colorectal cancer. Additional methods and compositions, such as reaction mixtures and solidsupports comprising clonal populations of nucleic acids, are provided. For example, provided here is a method for monitoring and detection of early relapse or metastasis of breast cancer, bladder cancer, or colorectal cancer, comprising generating a set of amplicons by performing a multiplex amplification reaction on nucleic acids isolated from a sample of blood or urine or a fraction thereof from a patient who has been treated for a breast cancer, bladder cancer, or colorectal cancer, wherein each amplicon of the set of amplicons spans at least one single nucleotide variant locus of a set ofpatient-specific single nucleotide variant loci associated with the breast cancer, bladder cancer, or colorectal cancer; and determining the sequence of at least a segment of each amplicon of the setof amplicons that comprises a patient-specific single nucleotide variant locus, wherein detection of one or more patient-specific single nucleotide variants is indicative of early relapse or metastasis of breast cancer, bladder cancer, or colorectal cancer.
Owner:NATERA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com