Compositions and methods for detection of nucleic acid mutations
A technology of nucleotides and universal primers, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, combinatorial chemistry, nucleotide libraries, etc., can solve problems such as inability to apply plasma fusion detection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0165] Example 1. Identification of fusion gene breakpoints for tiling analysis
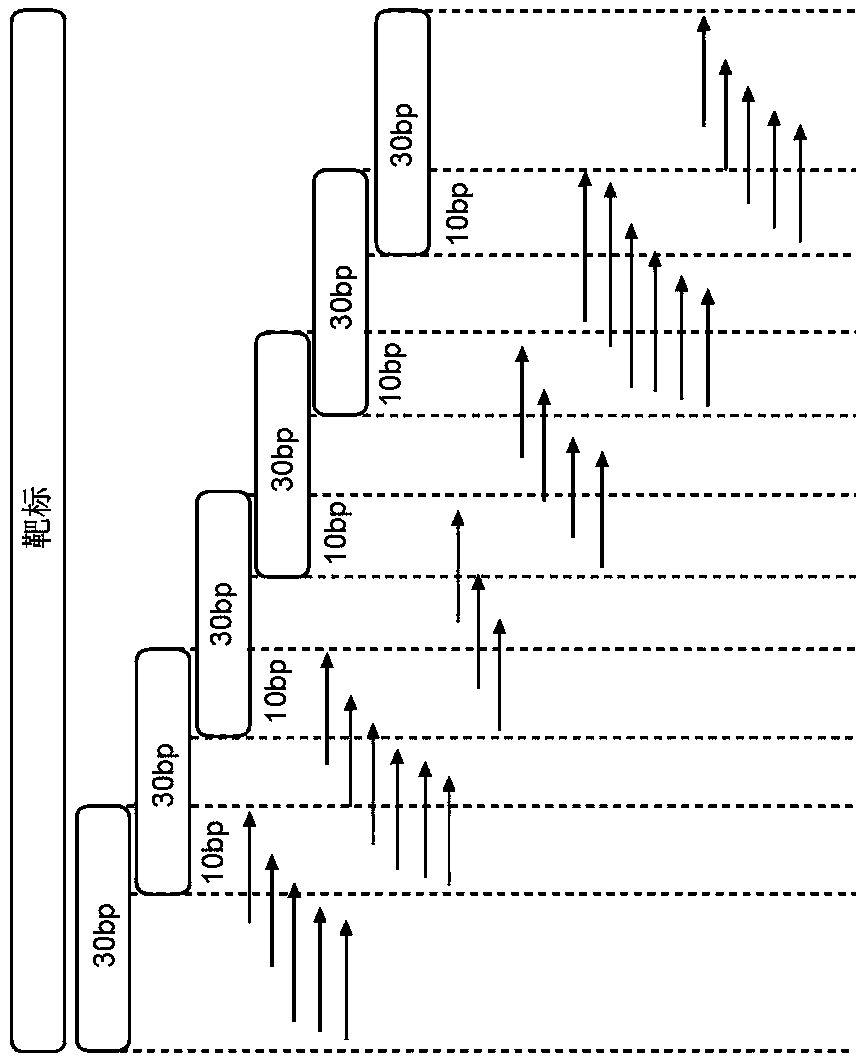
[0166] Provided herein are examples of how to design and select a series of tiling primers for use in the methods of the invention, particularly methods for detecting gene fusions using single-sided nested PCR reactions. Design of tiling primers for detection of gene fusions begins with mapping COSMIC fusion transcripts to genomic coordinates (ie, translocations). However, it was found that the use of transcript-level information caused uncertainty in breakpoint locations, as most were rearrangements of introns (and thus spliced out of transcripts). Therefore, it was necessary to cover a range of sequences for each reported fusion based on exon boundaries. Identification of molecular markers may aid in the development of cancer panels for the identification of gene fusions and may be applied to other cancers and diseases beyond lung cancer, eg ALK in hematopoietic, lymphoid tissue, RET in thyr...
Embodiment 2A
[0178] Example 2A. Development of synthetic fusion standards
[0179] Design of Gene Fusion Probes
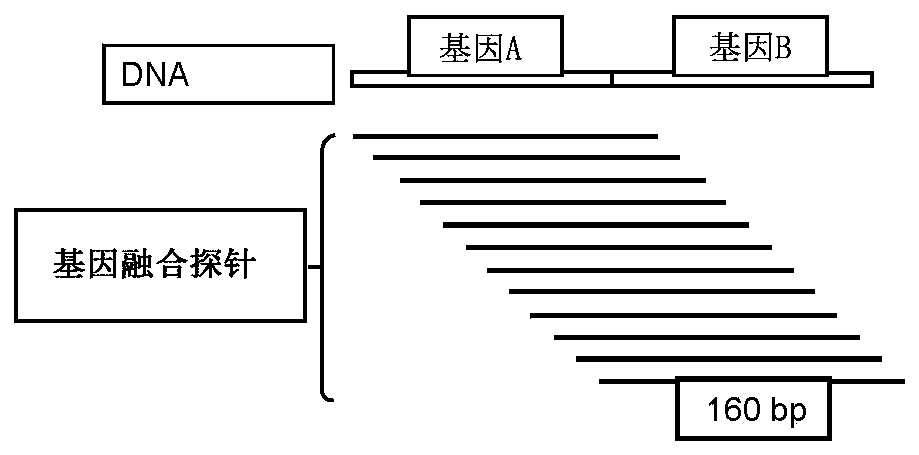
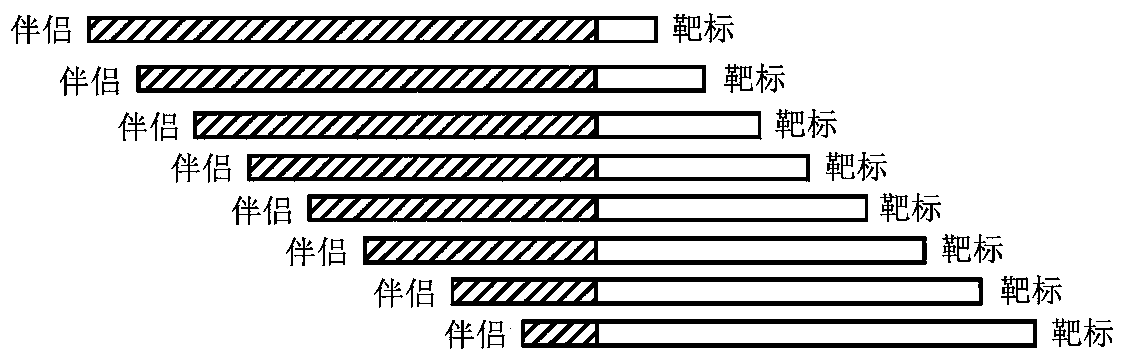
[0180] As used herein, fusion probes refer to synthetic gene fusions such as CD74:Ros1, NMP1:Alk1(x2) and TPM4:Alk1. The first genes are partners (such as CD74, NMP1 and TPM4) and the latter are targets (Ros1, ALK1 (both groups) and Alk1). Fusion probes were designed to correspond to the average length of cfDNA, a length of 160 bp was chosen. Such as figure 1 As shown in , the design utilizes nine tiling primers spanning the 160 fusion probe "target".
[0181] As used herein, fusion probes are designed to span a "junction," which can refer to a fusion break between two fusion partners. To illustrate, consider the following example, there are two genes A and B consisting of the sequences {a_i} and {b_i} between which a fusion occurs. To generate fusion probes, we first identified the location of the breakpoint in each gene and then constructed probe S:
[0182] S=a_{i-m},....
Embodiment 2B
[0184] Example 2B. Development of synthetic fusion standards
[0185] The design of synthetic fusion probes is done to develop a system that allows detection of gene fusion profiles. Identification of gene fusion profiles can aid in the identification of fusion genomic sequences for rearrangement following sequencing of the fusion genomic DNA. Genomic sequences (suspected to have gene fusions) were used to construct tiling primer template synthetic oligonucleotides tiling across each target sequence containing breakpoints as tiling fusion probes, each 160 bp in length . figure 1 The tiling of these synthetic oligonucleotides for construction of fusion probes is illustrated.
[0186] A literature review of published translocation genome sequences to identify gene fusion products. This led to the selection of six regions (5 ALK, 1 ROS) containing gene fusions, followed by bioinformatics calculations to identify the corresponding genomic positions to unify the results.
[018...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com